Patents
Literature
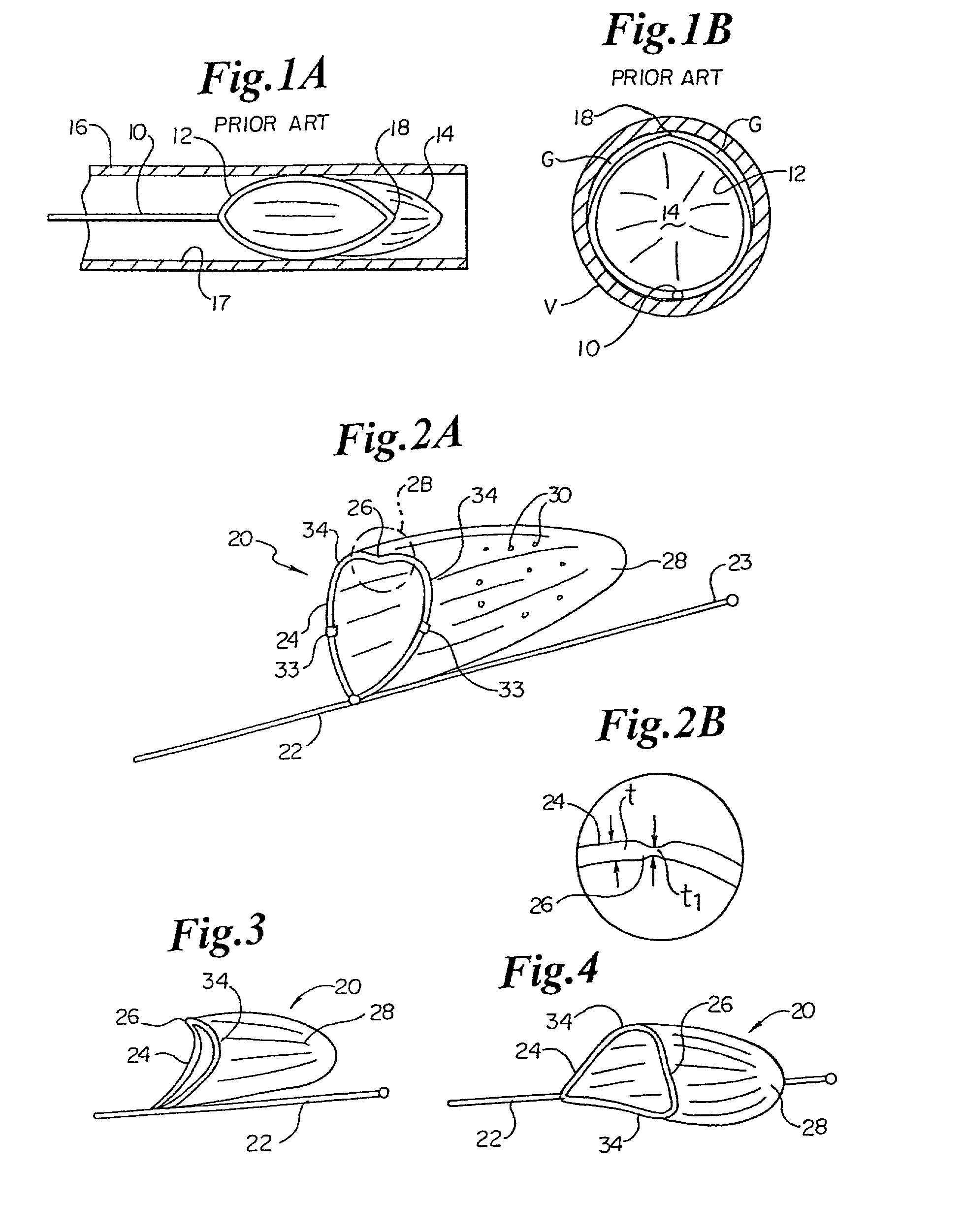
509 results about "Embolus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
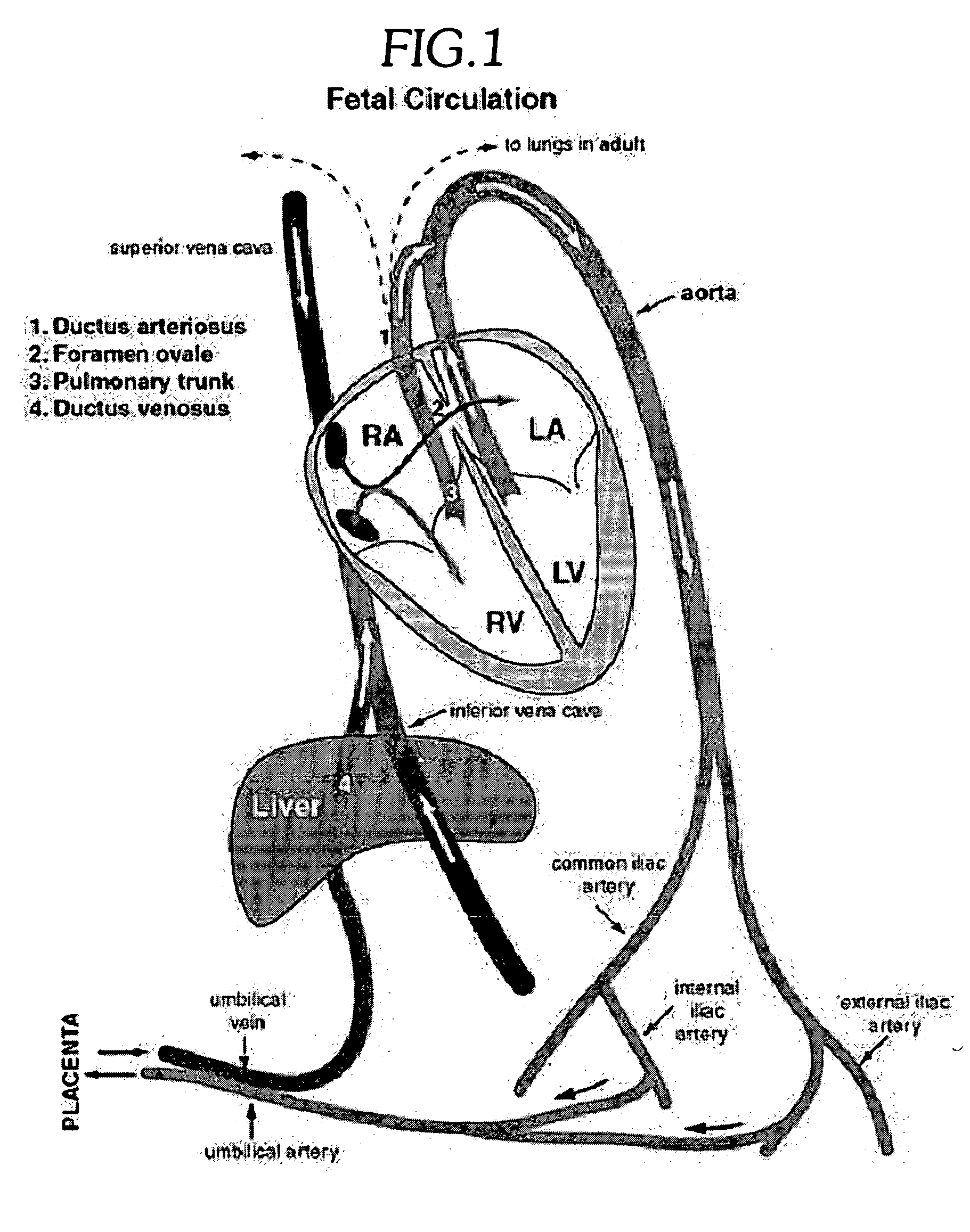
An embolus (/ˈɛmbələs/; plural emboli; from the Greek ἔμβολος "wedge", "plug") is an unattached mass that travels through the bloodstream and is capable of clogging arterial capillary beds (create an arterial occlusion) at a site distant from its point of origin. There are a number of different types of emboli, including blood clots, cholesterol plaque or crystals, fat globules, gas bubbles, and foreign bodies.
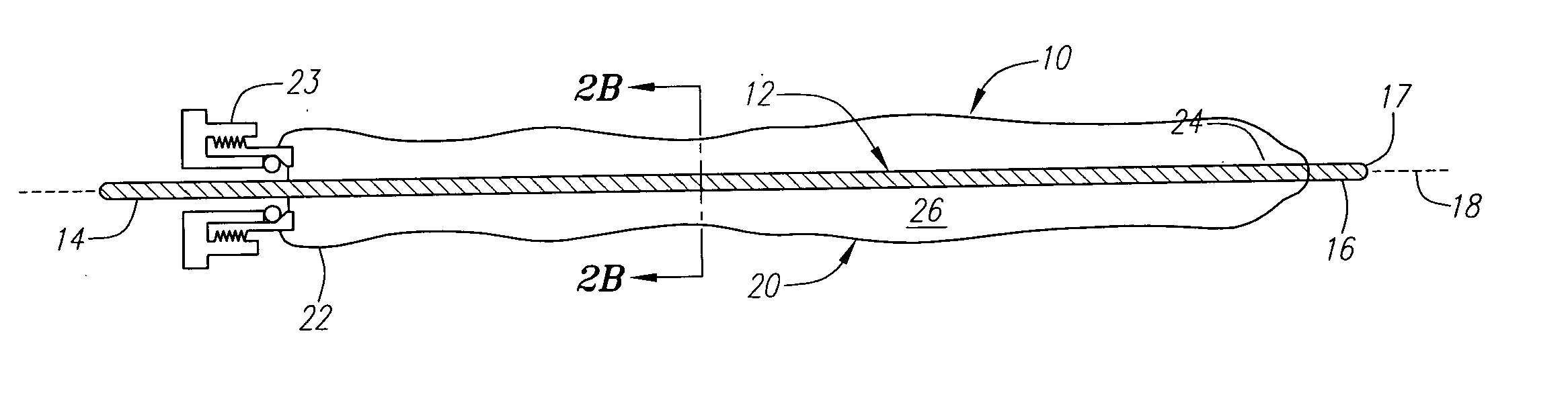
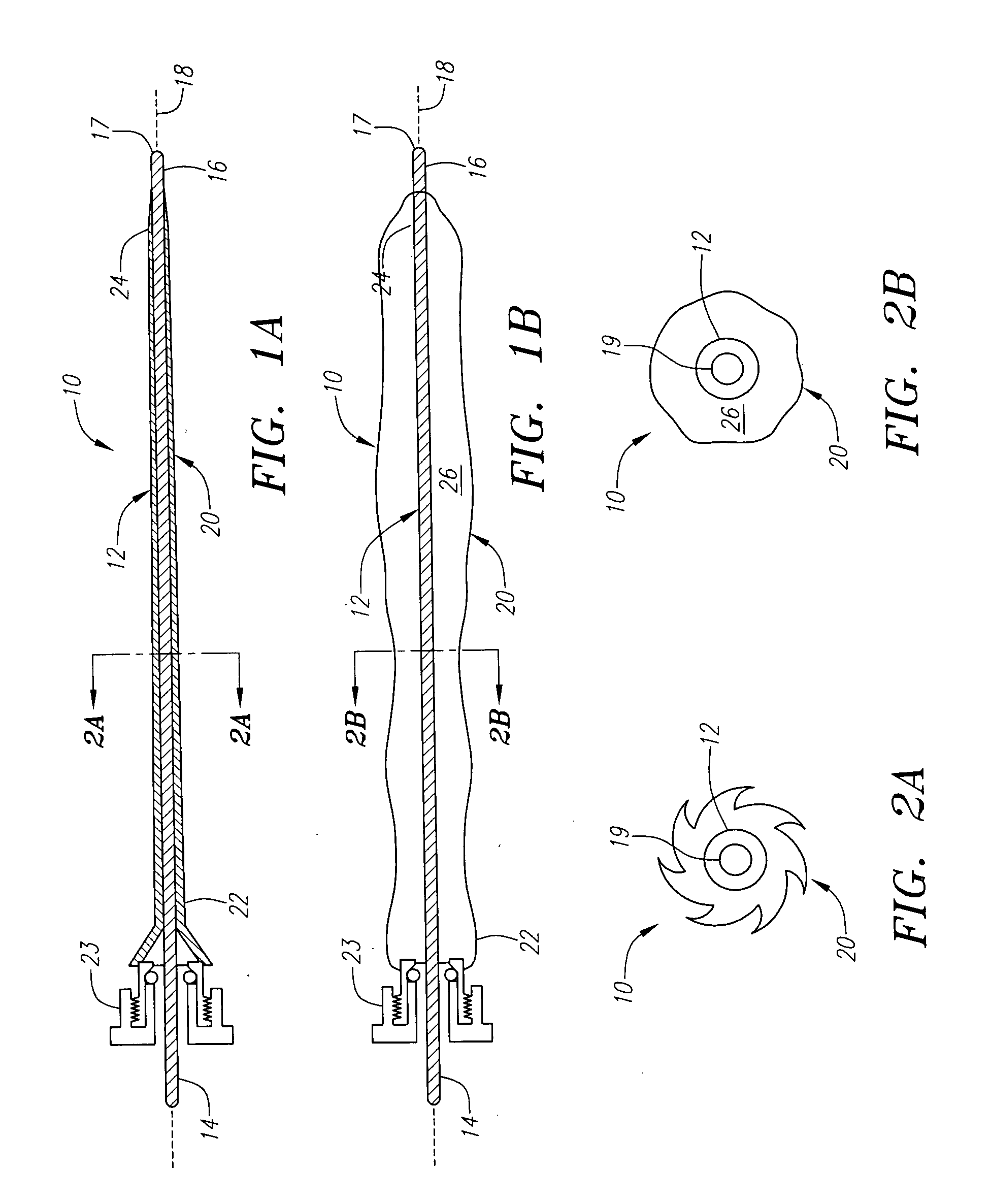
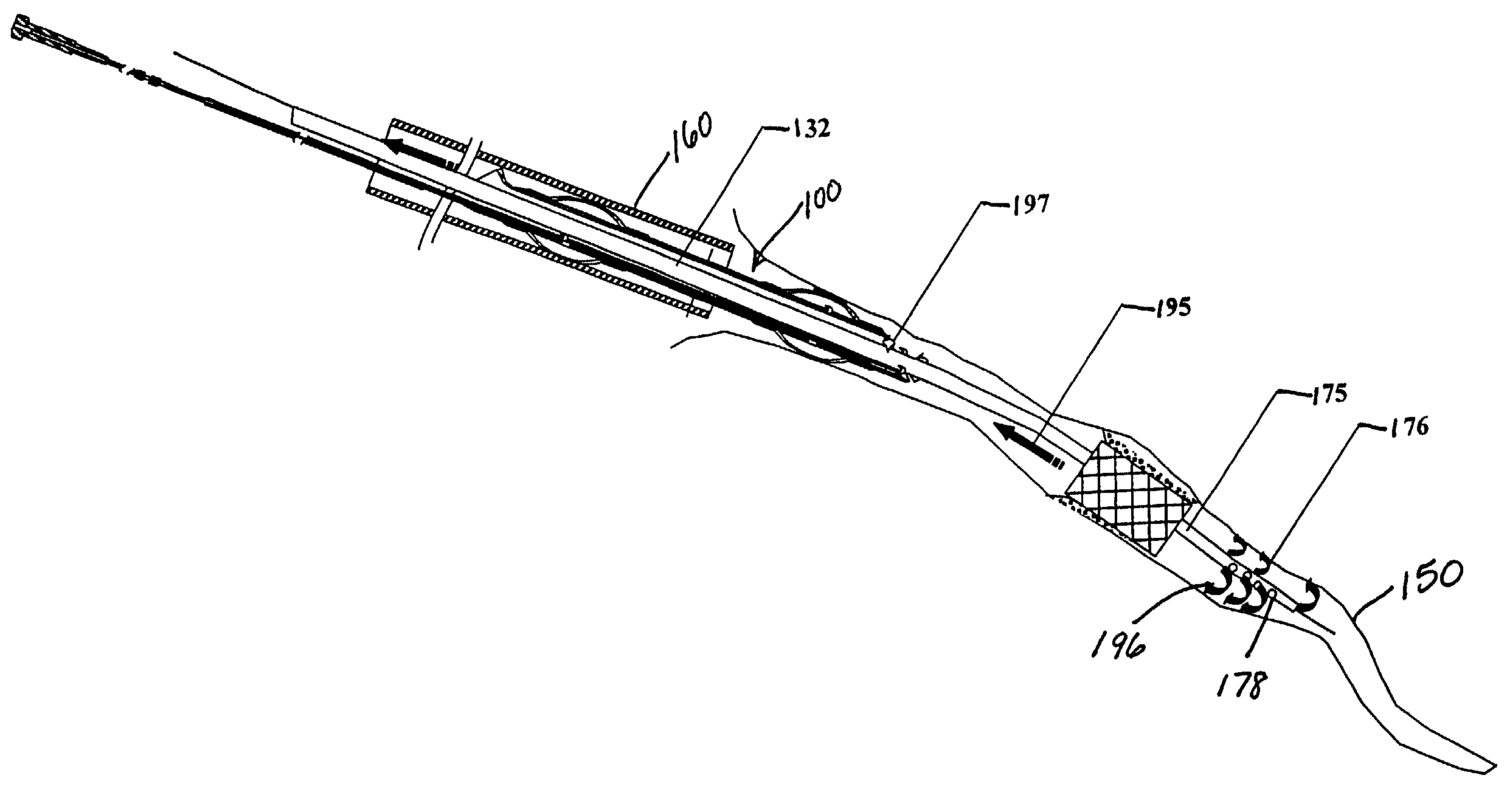
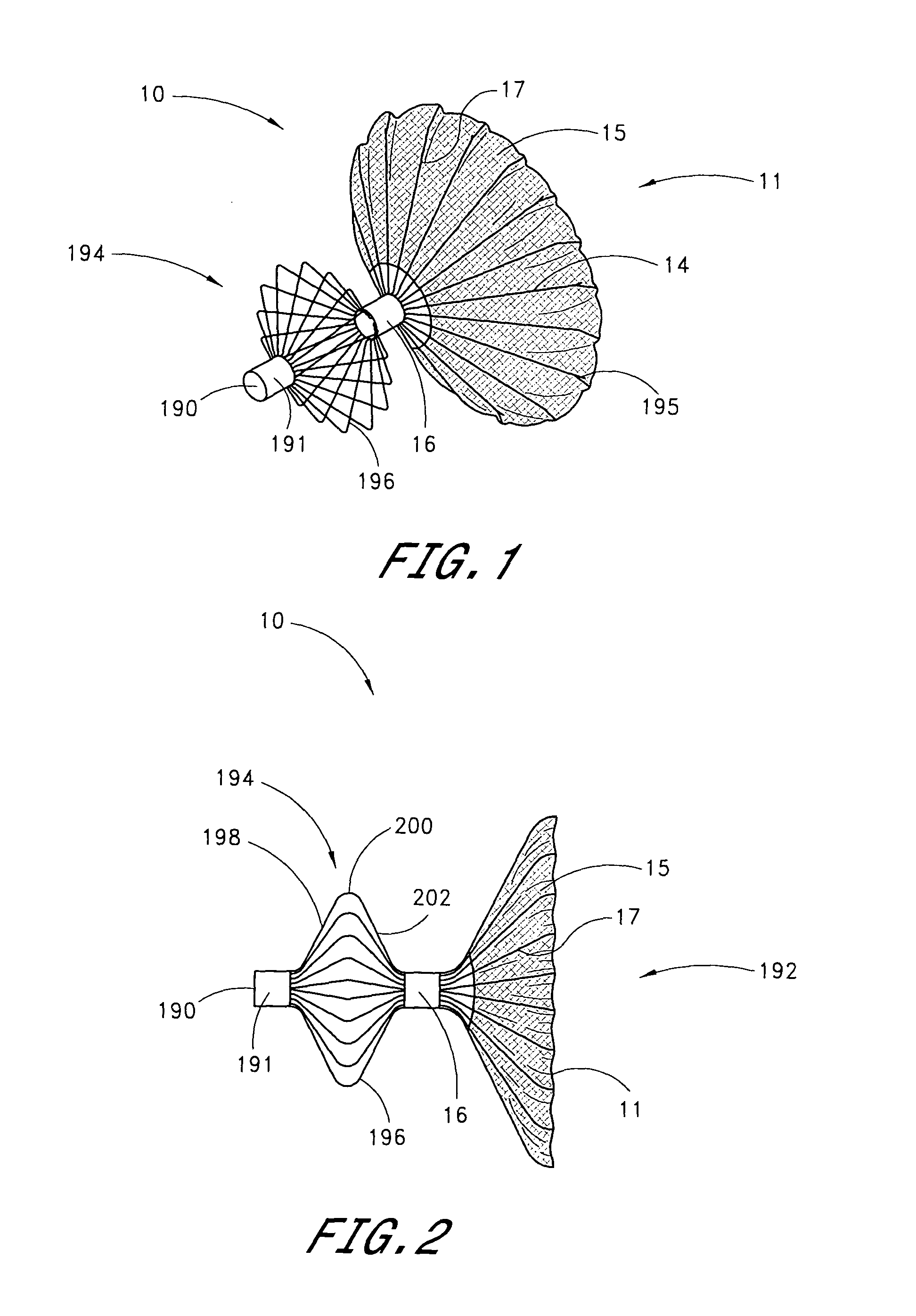
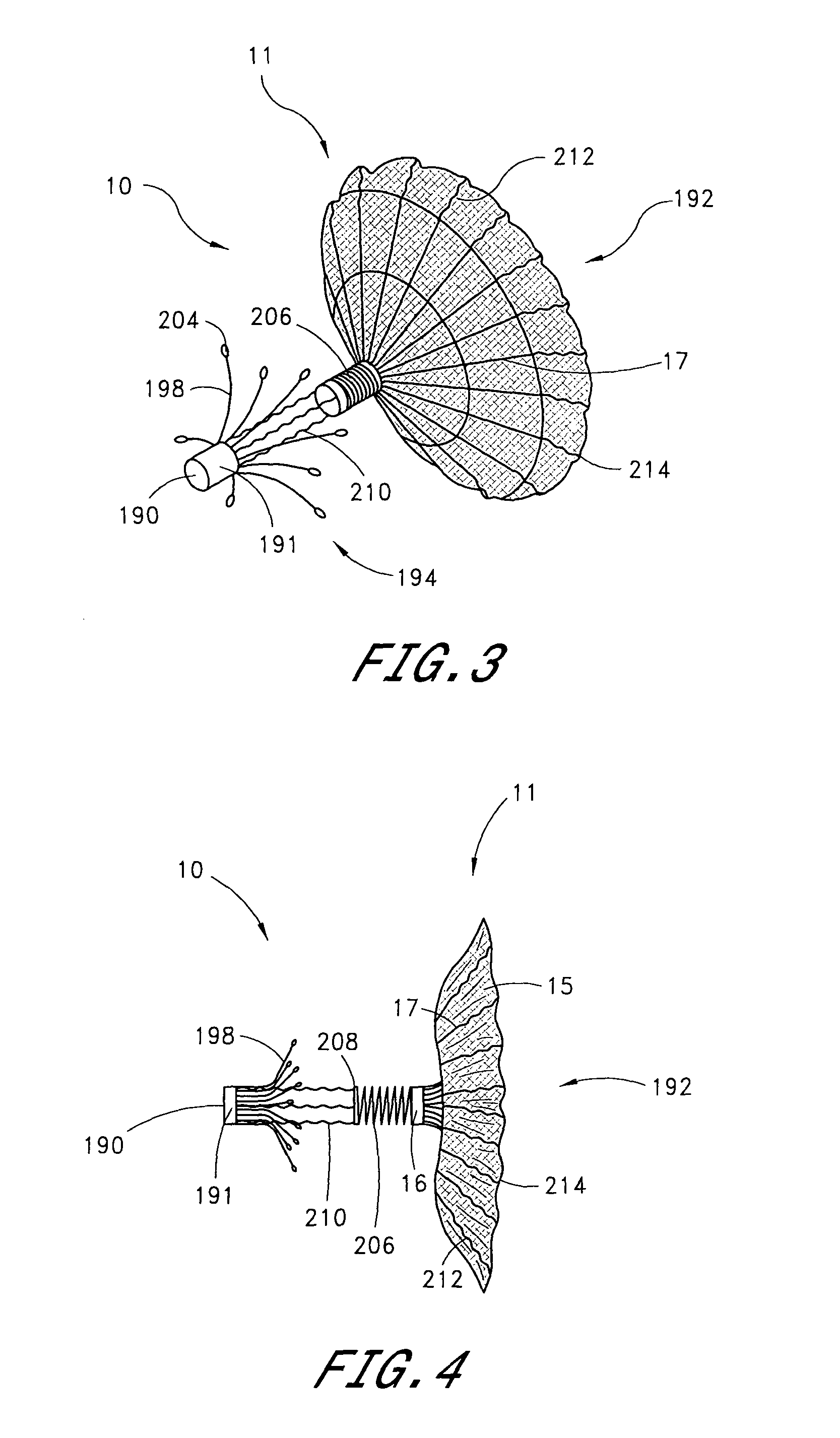
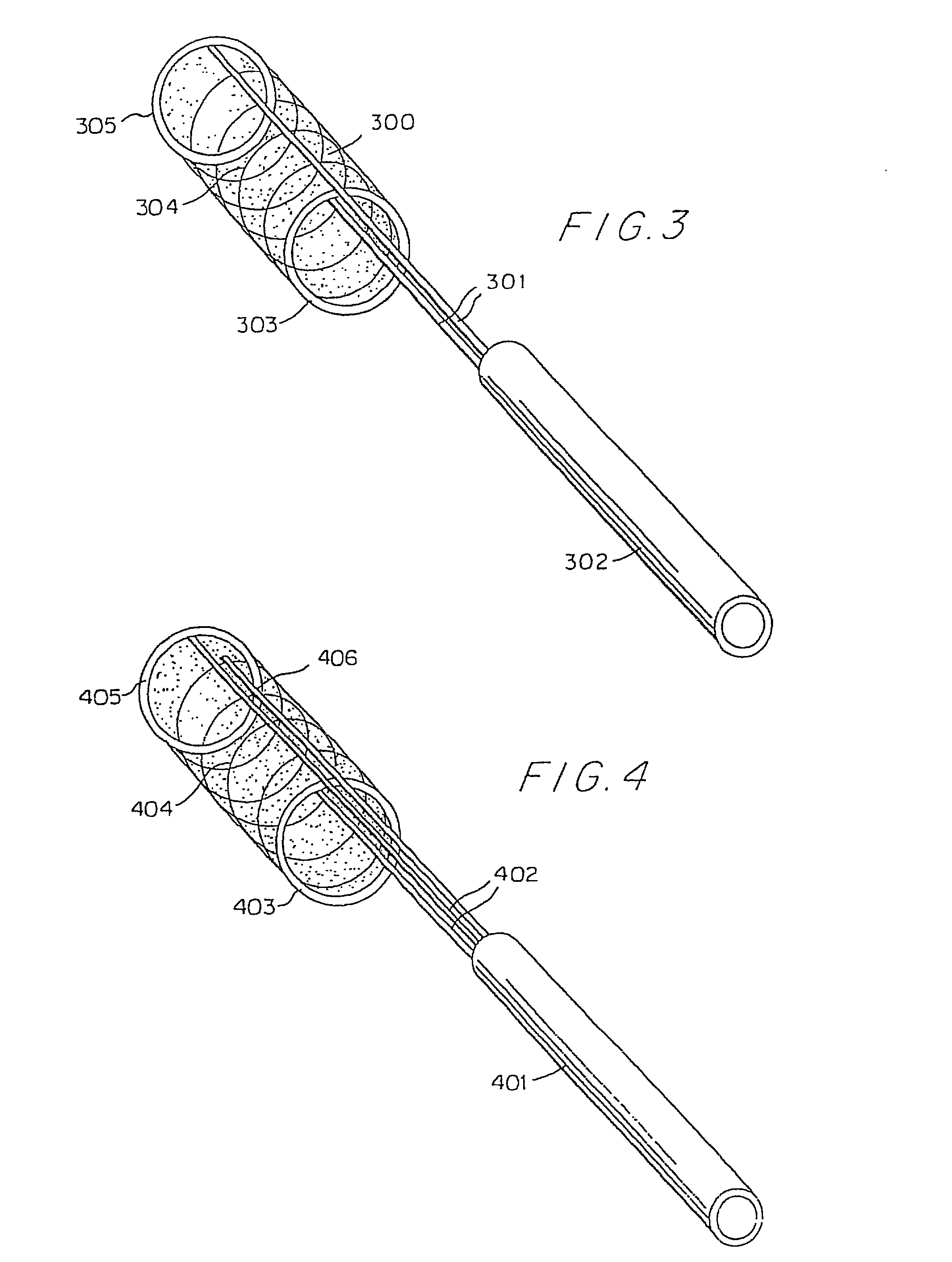
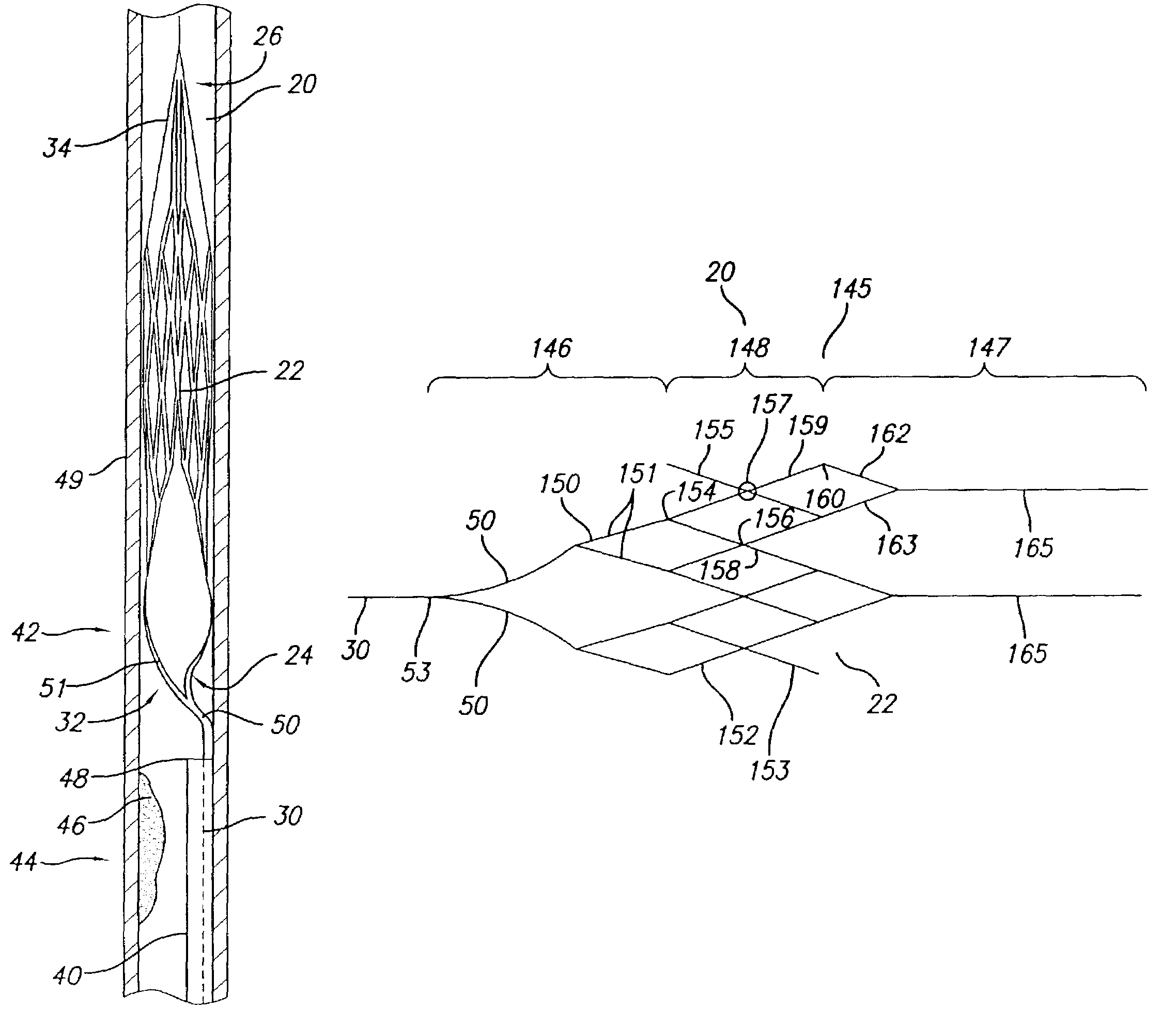
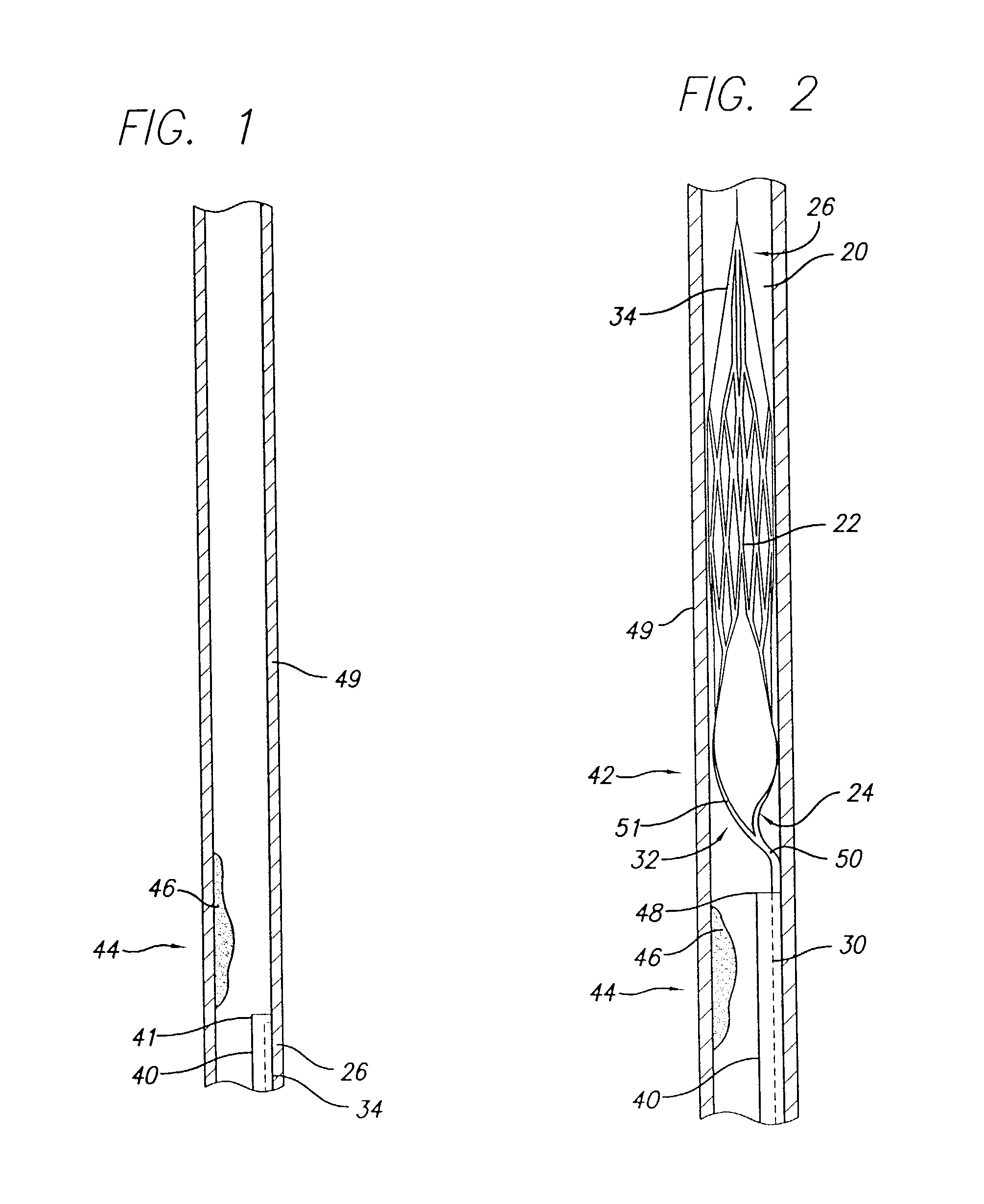
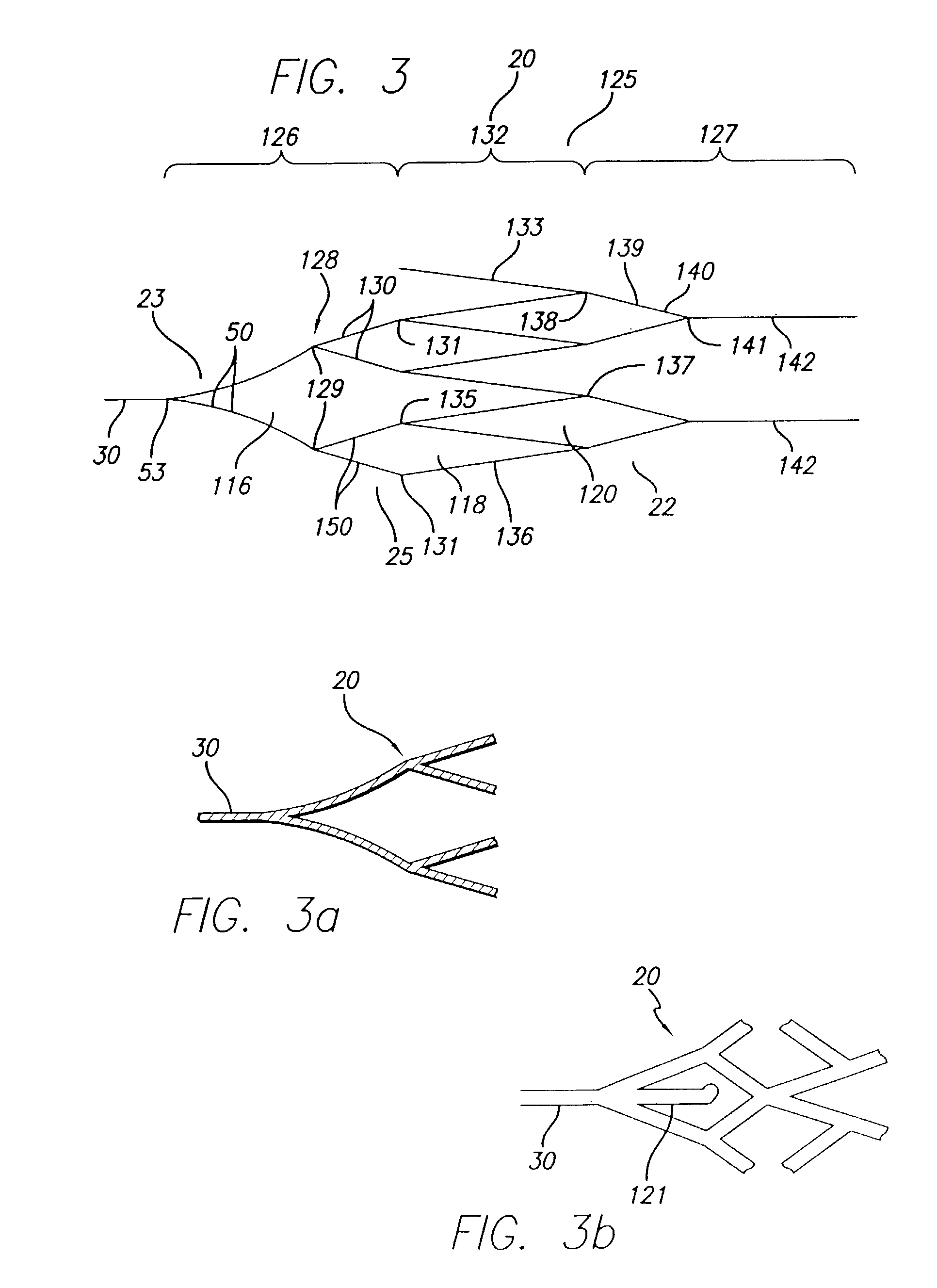
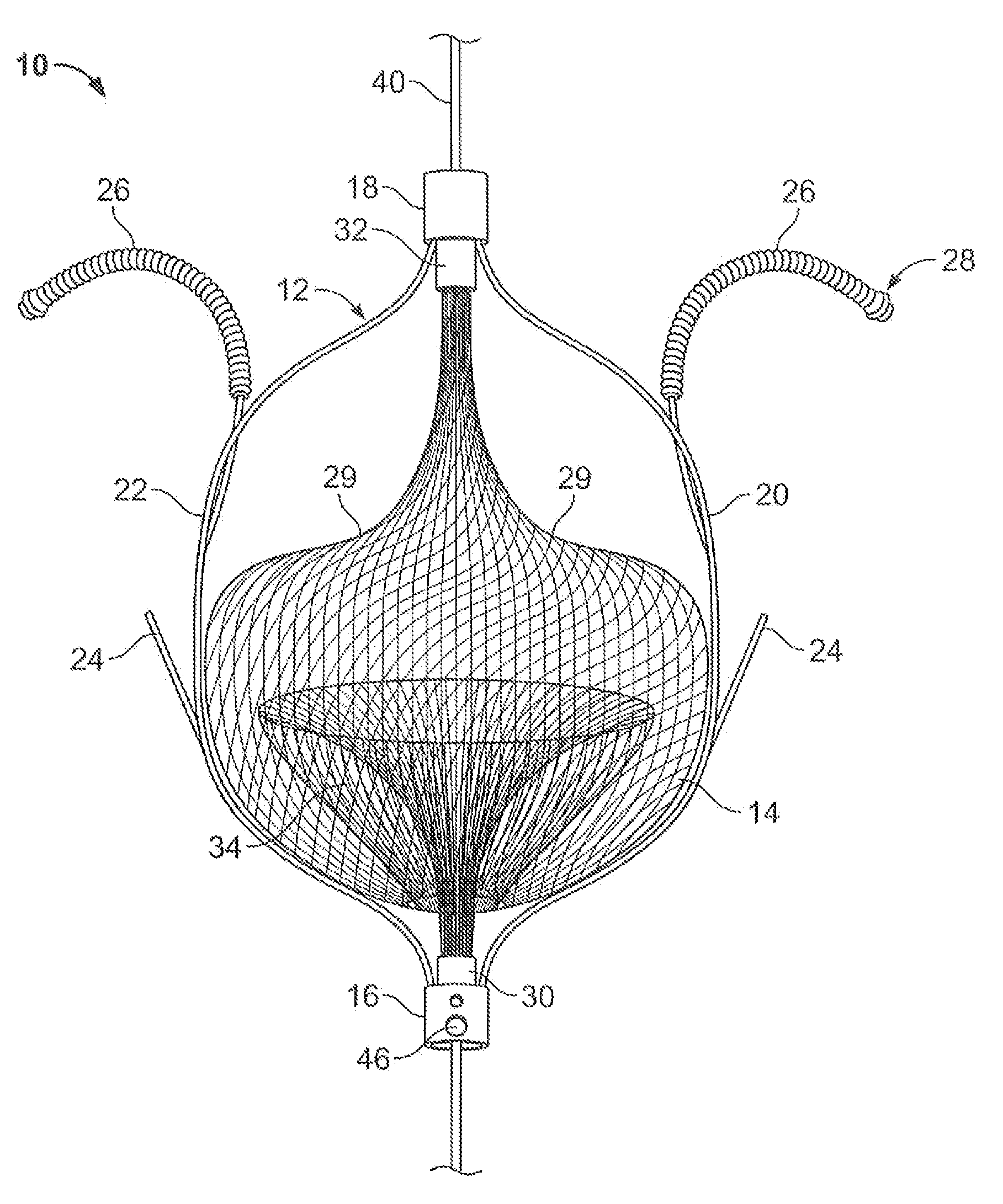
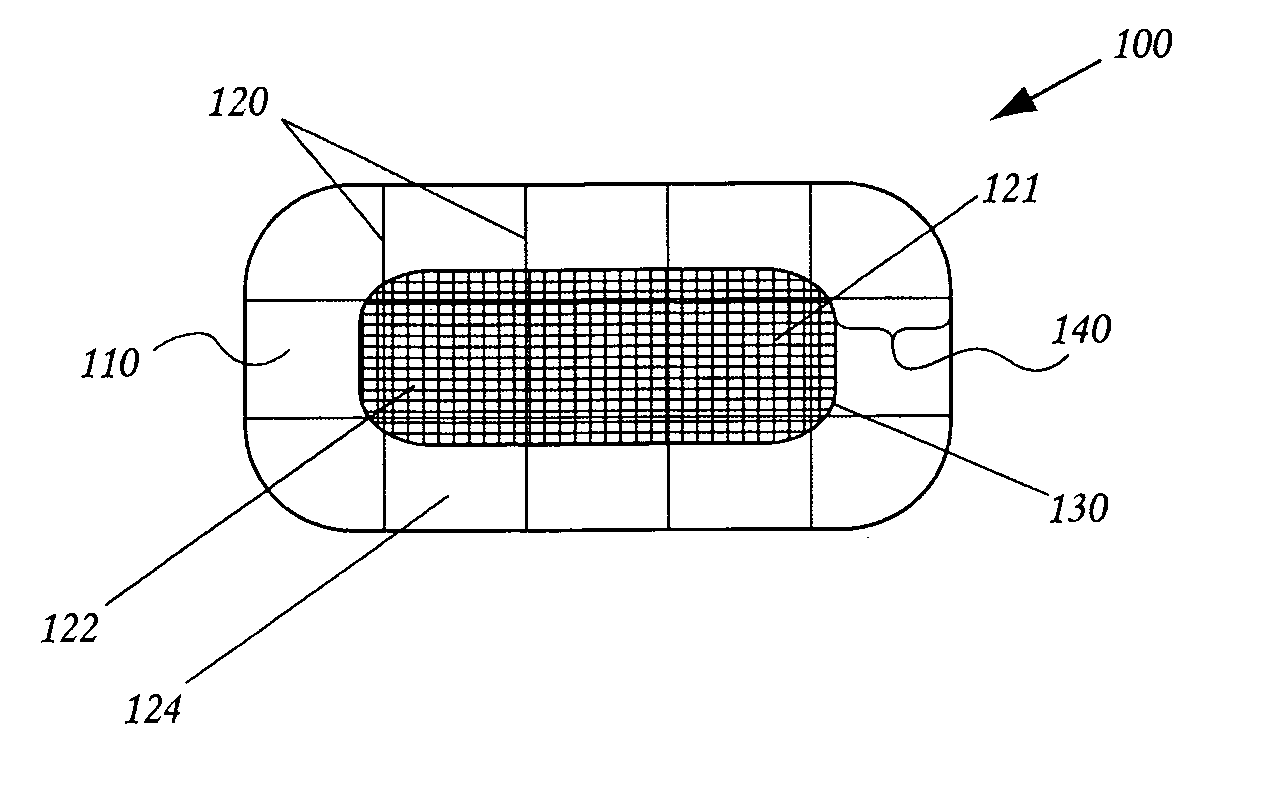
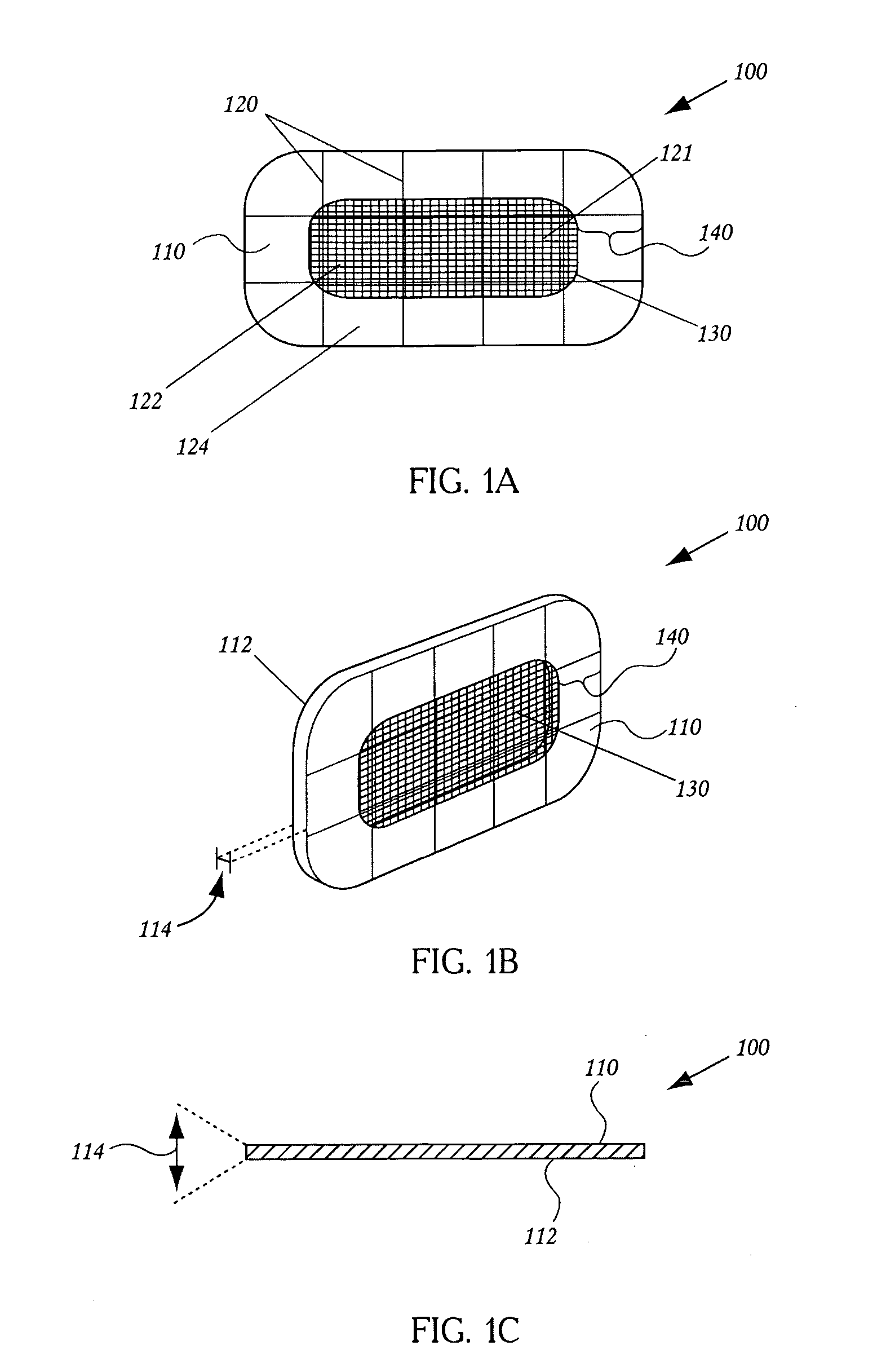
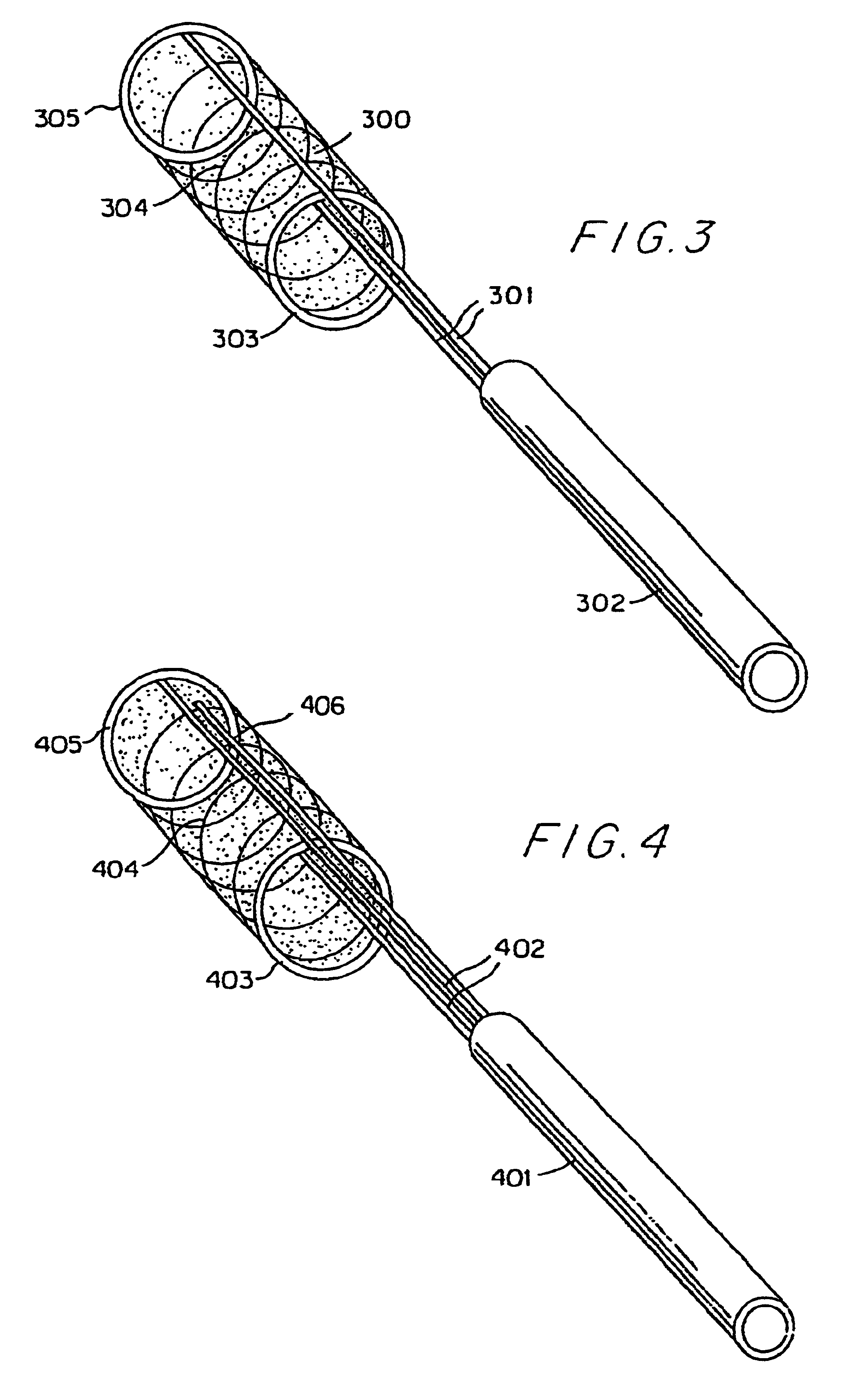
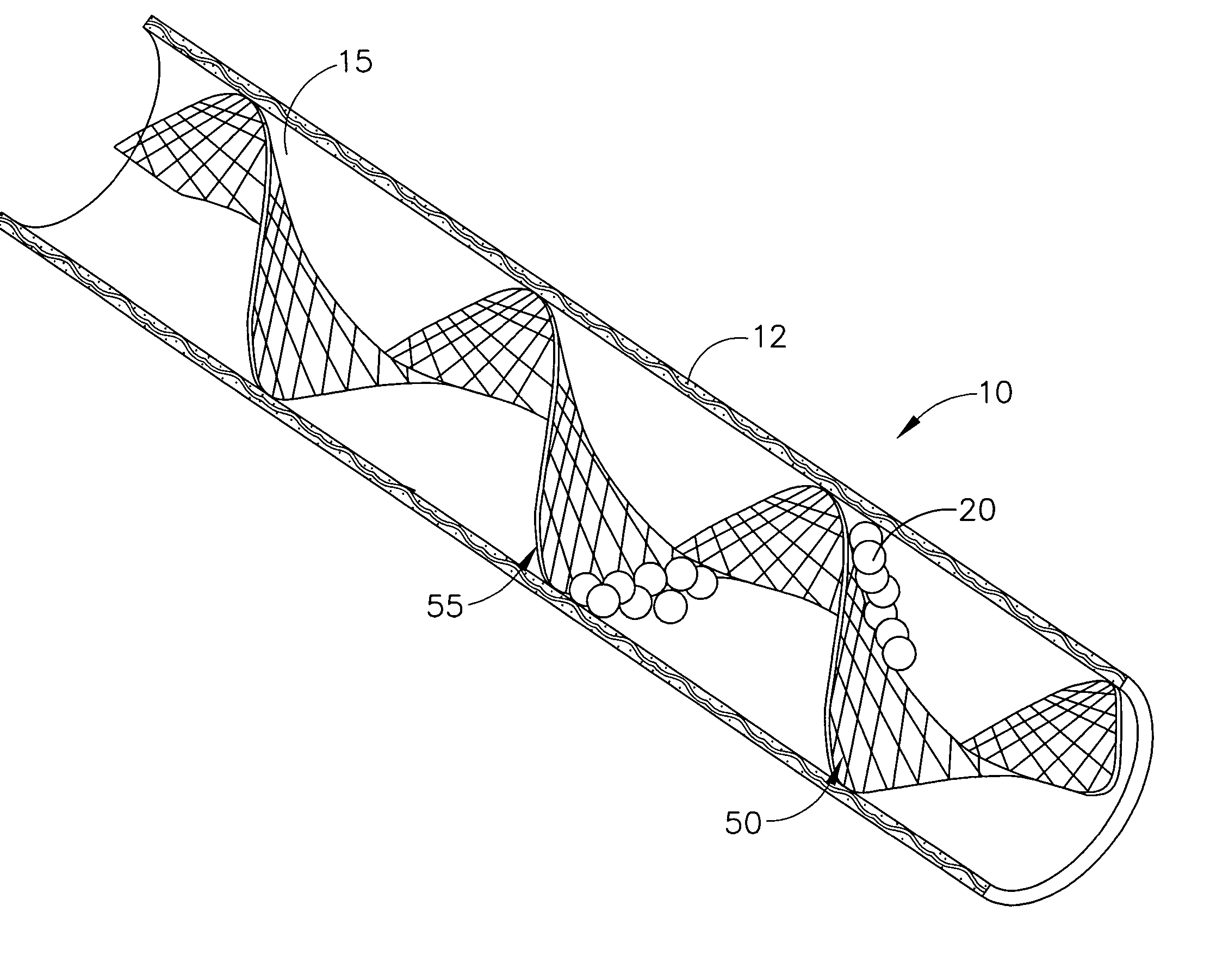
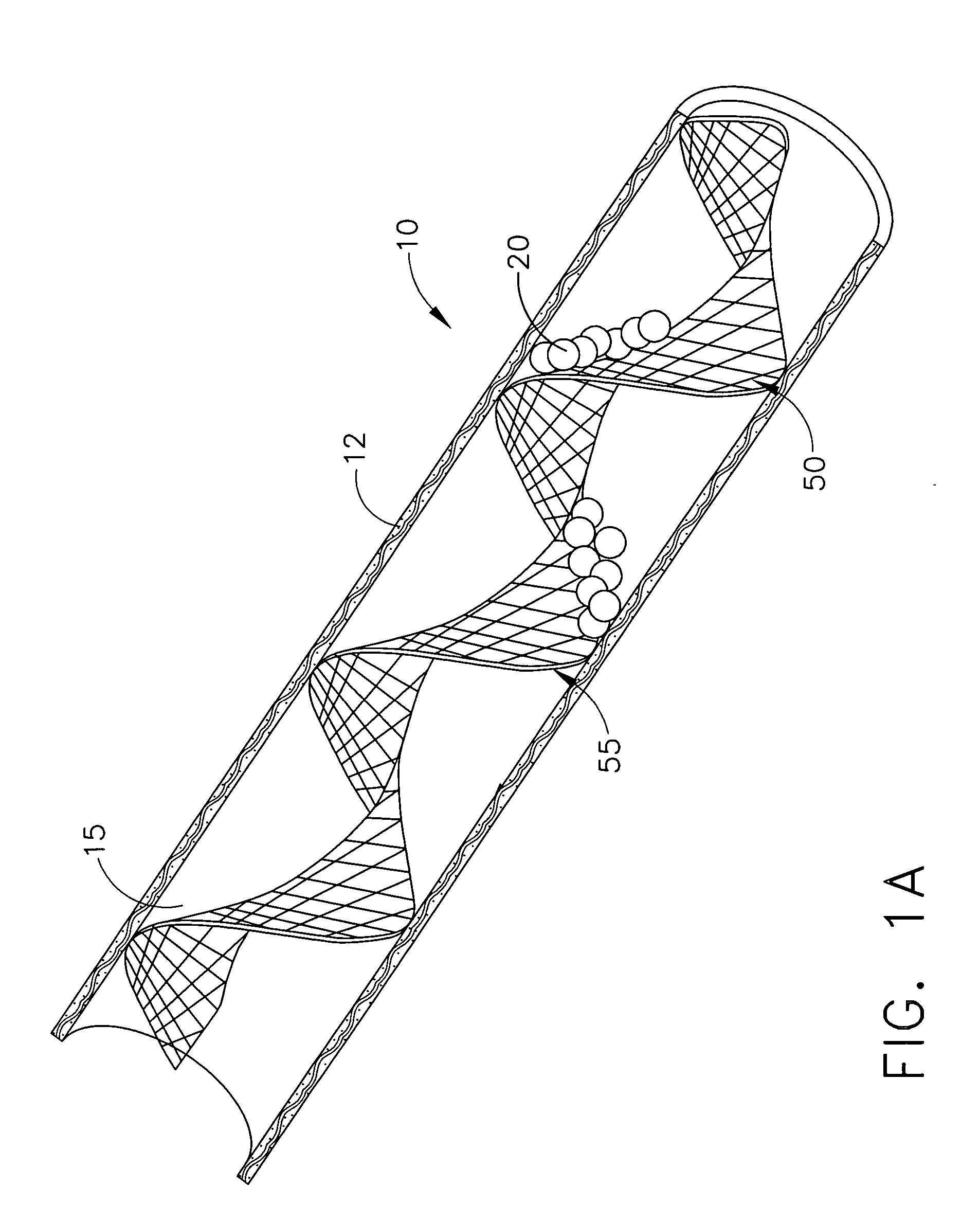
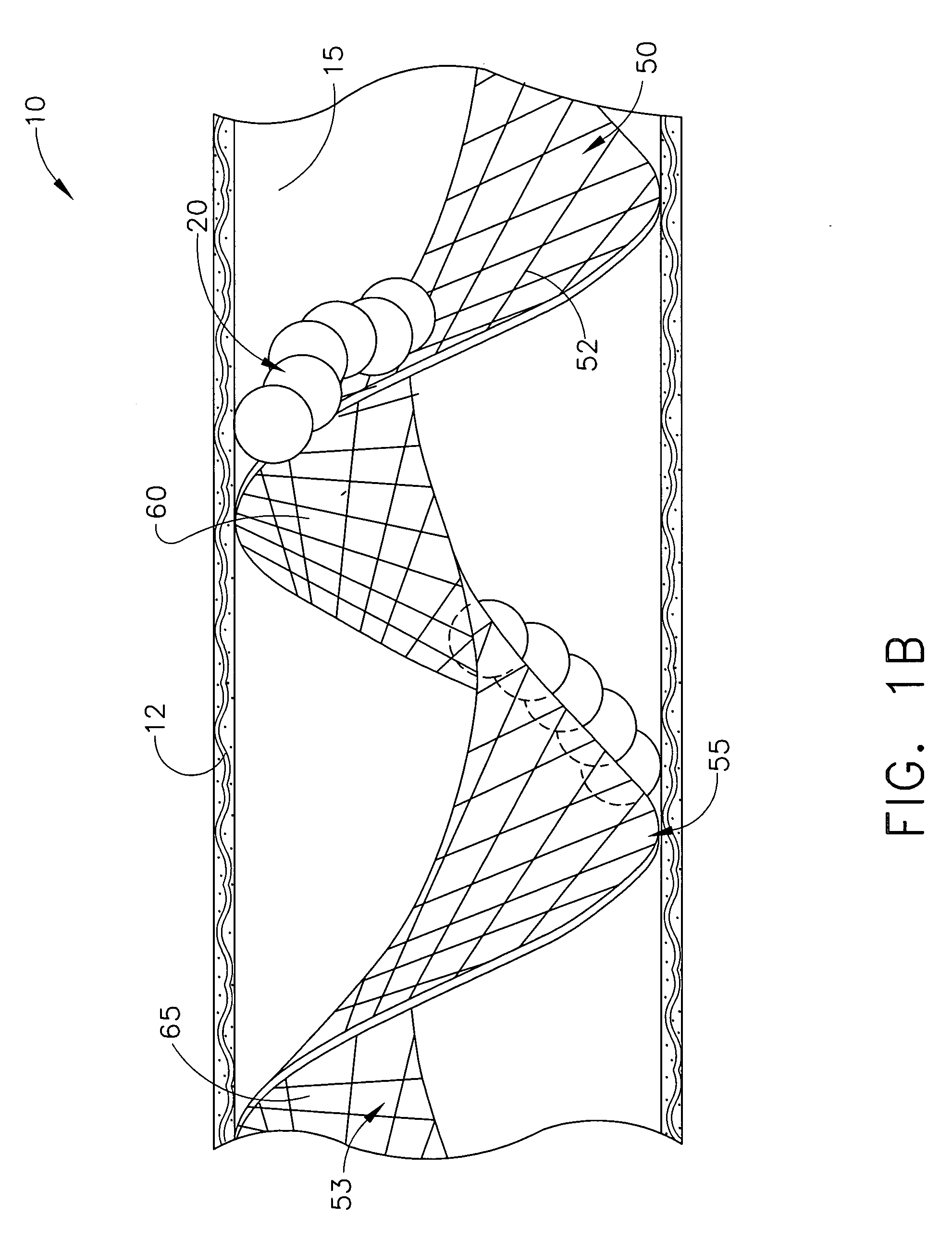
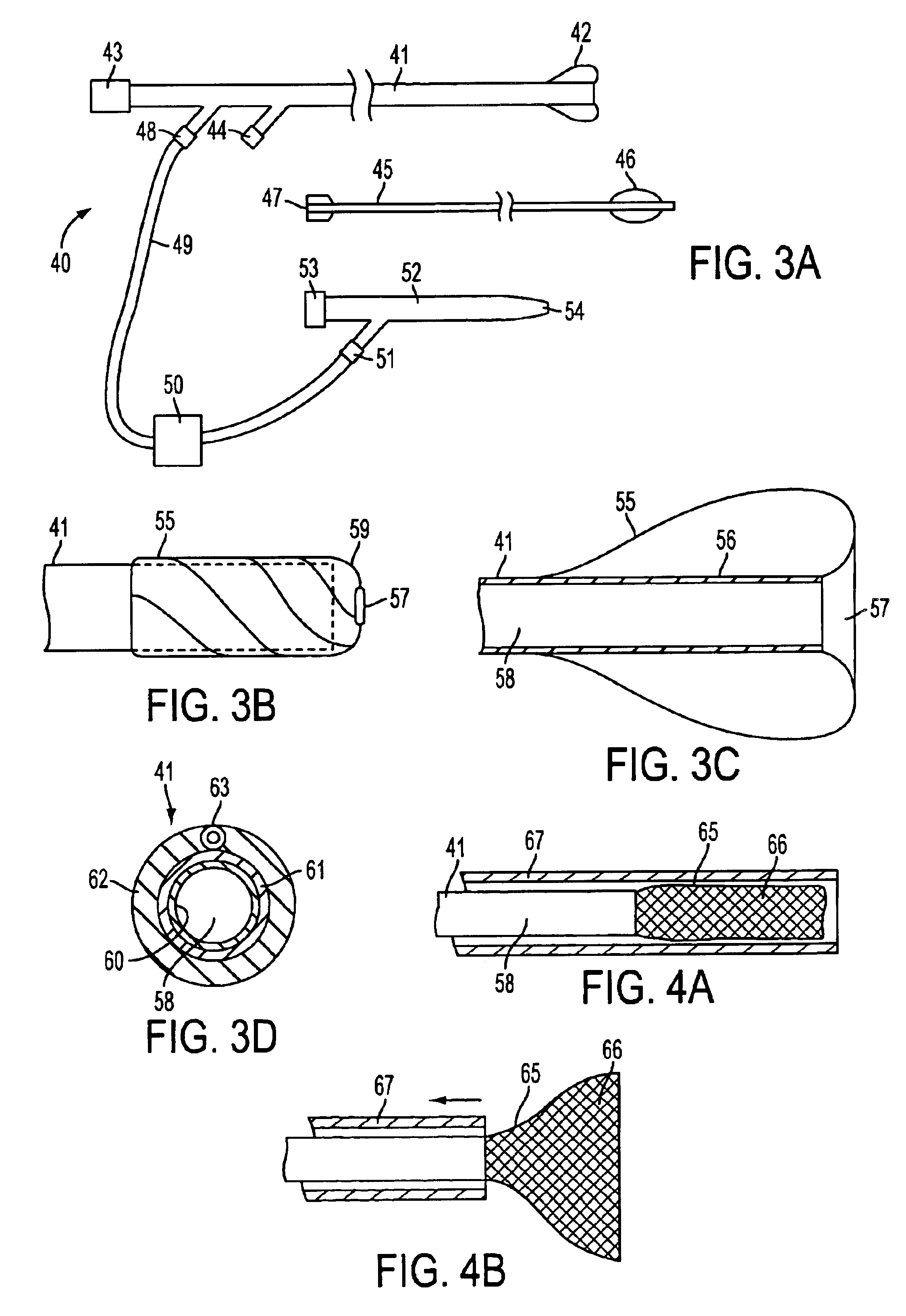
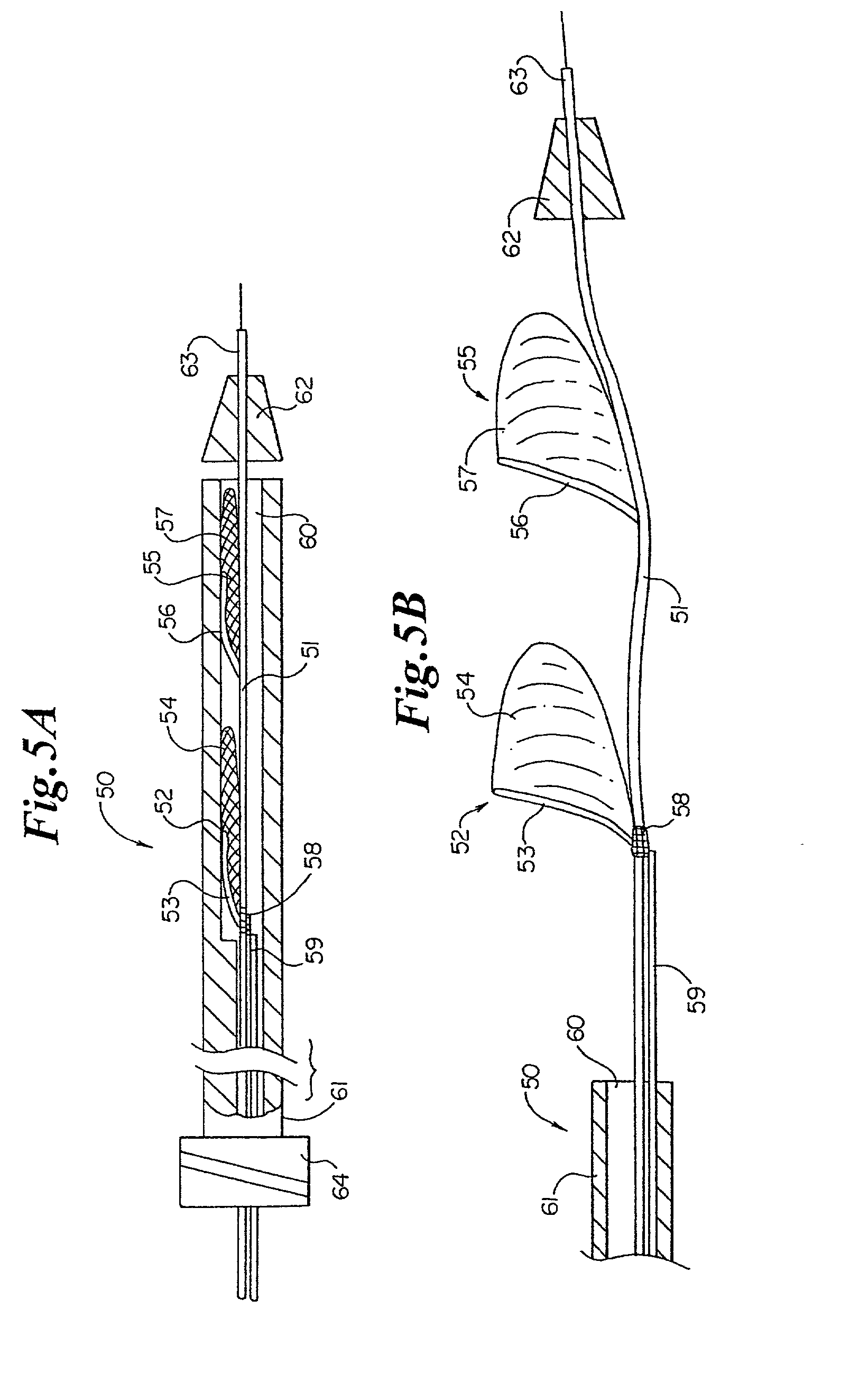
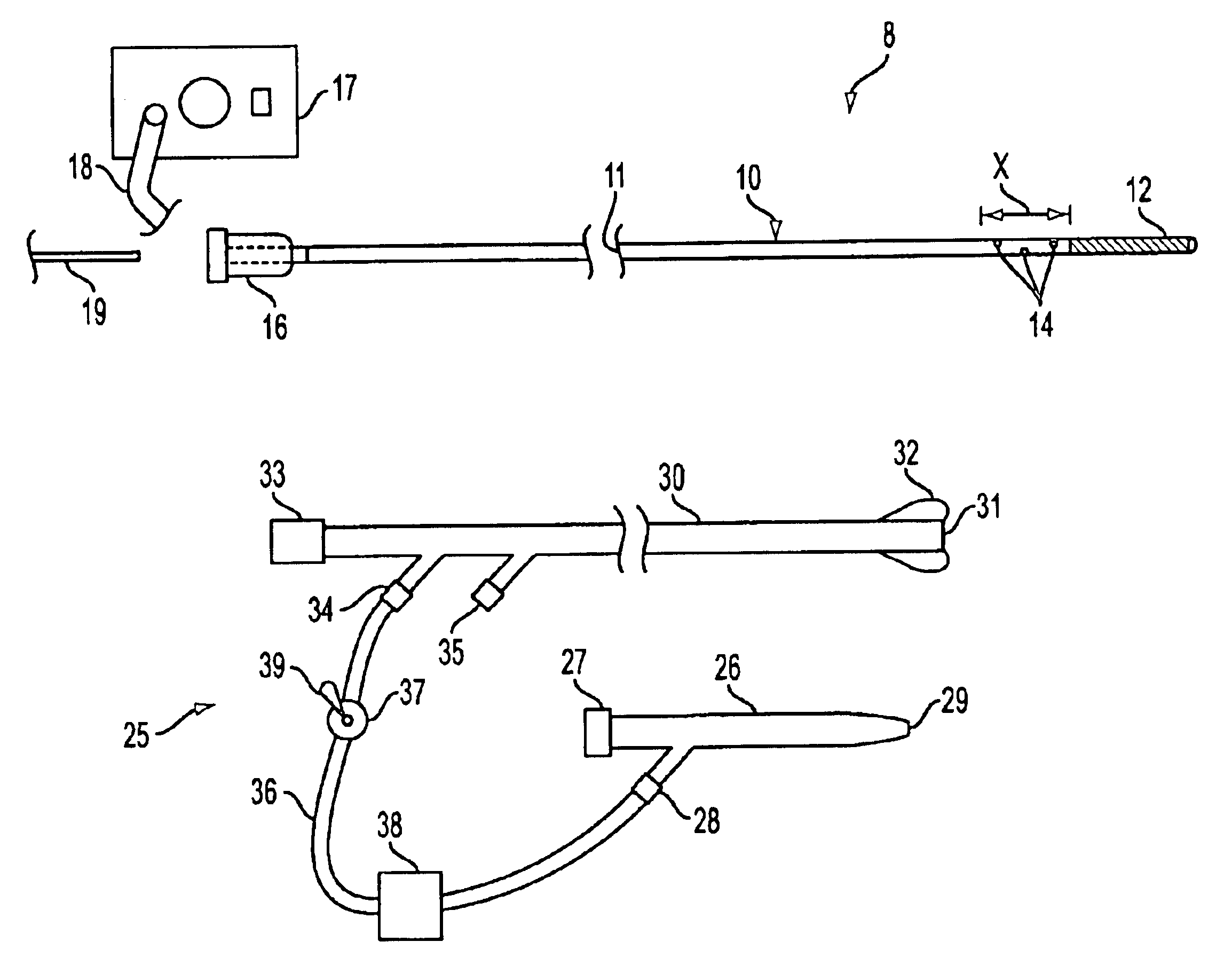
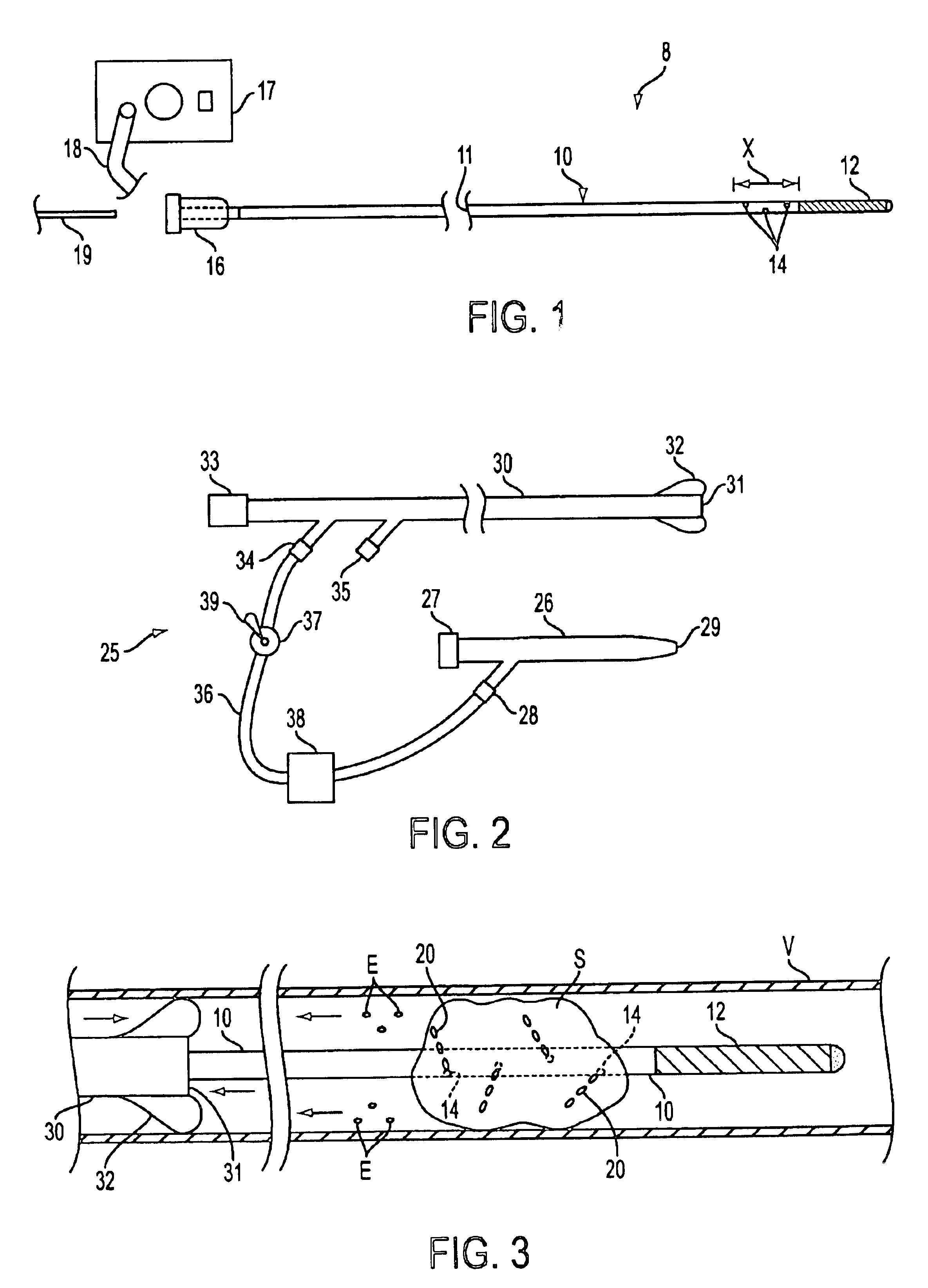
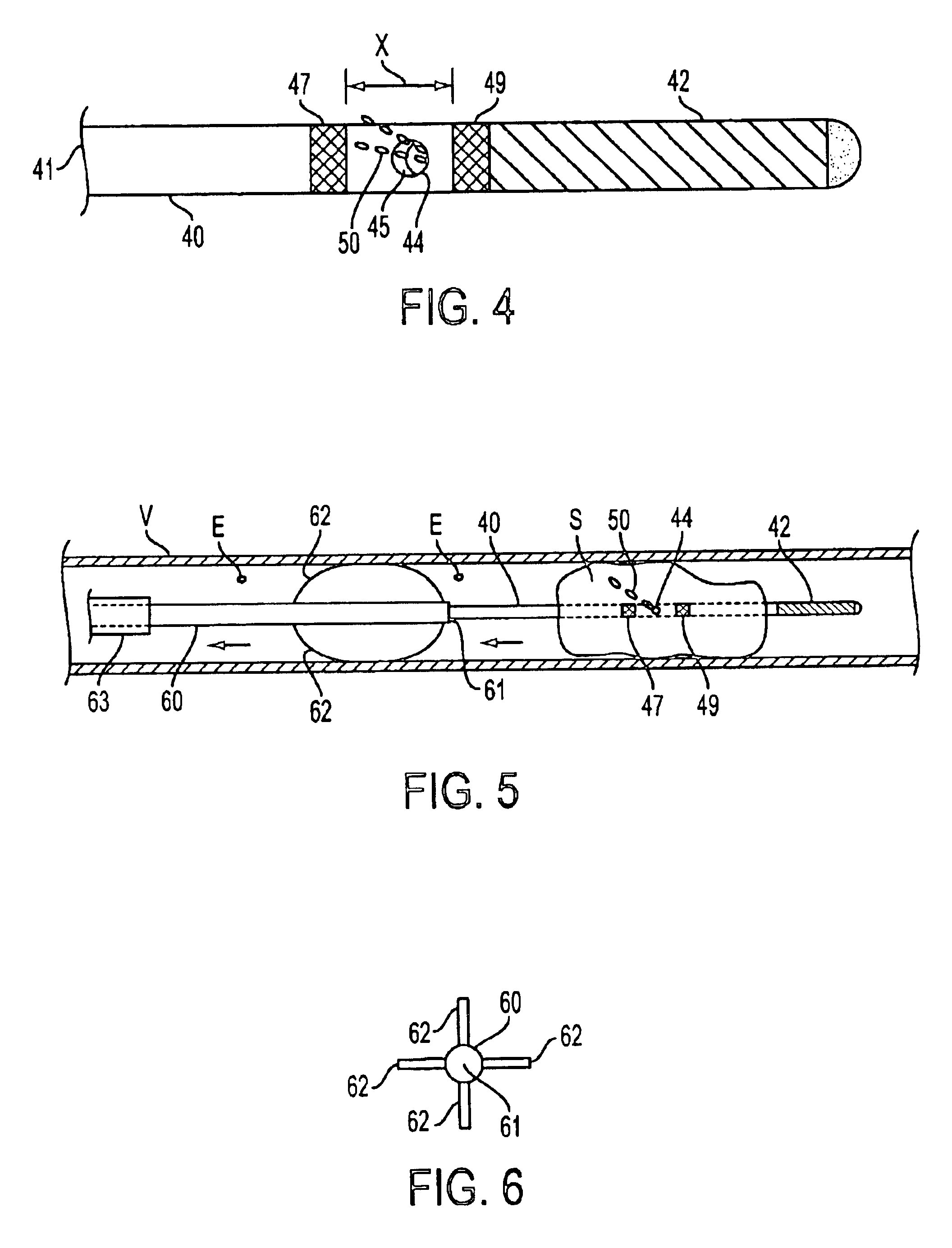
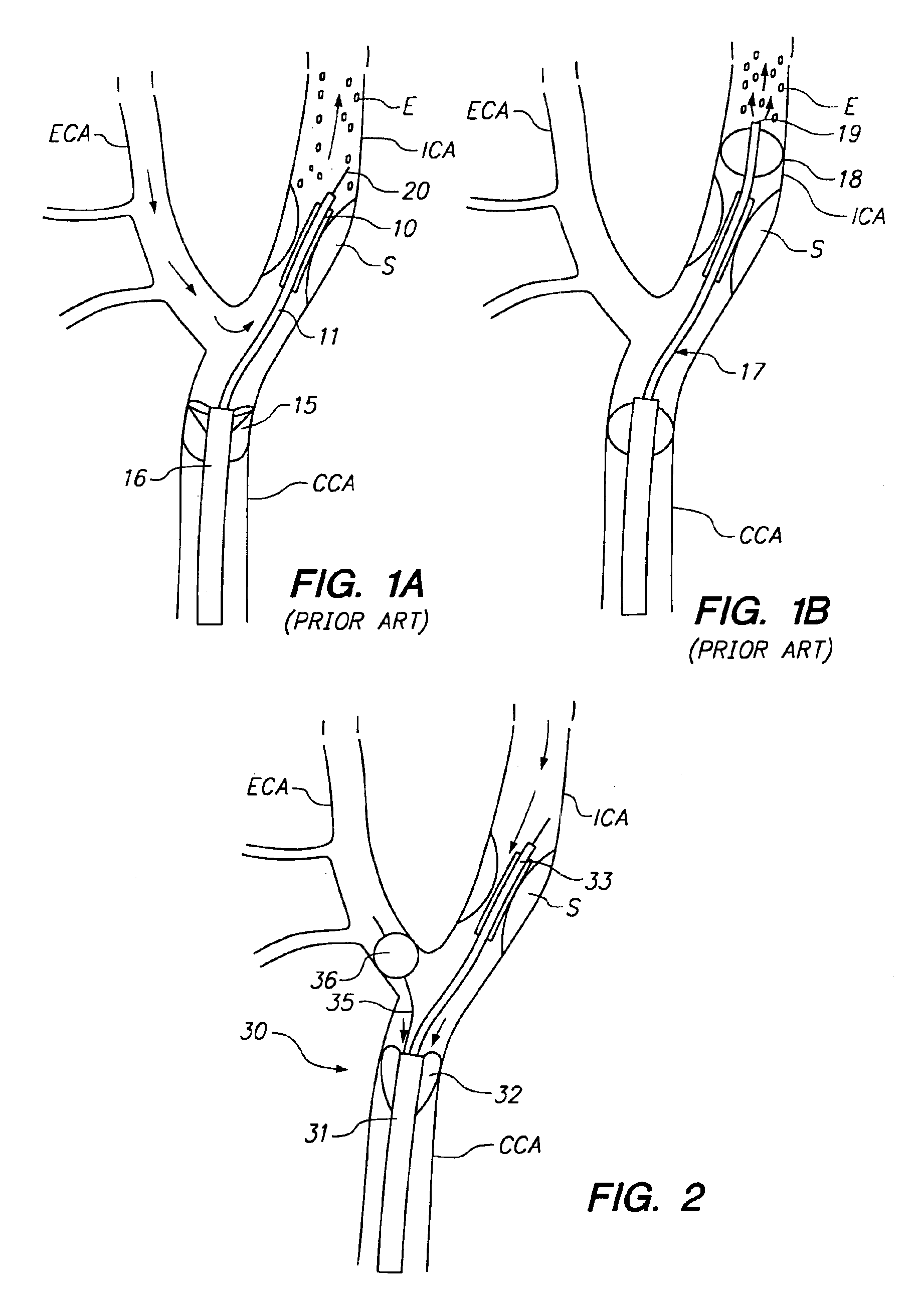
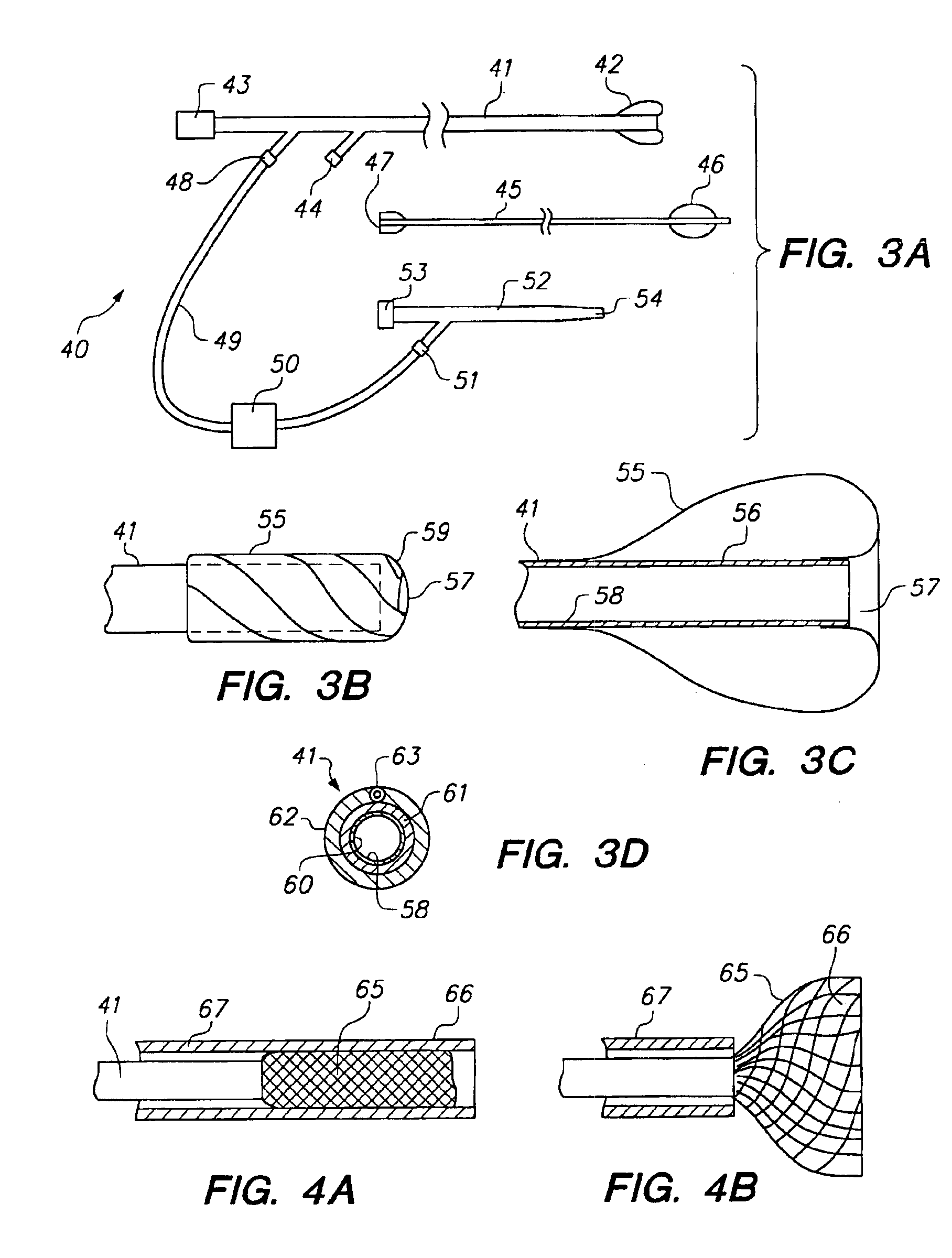
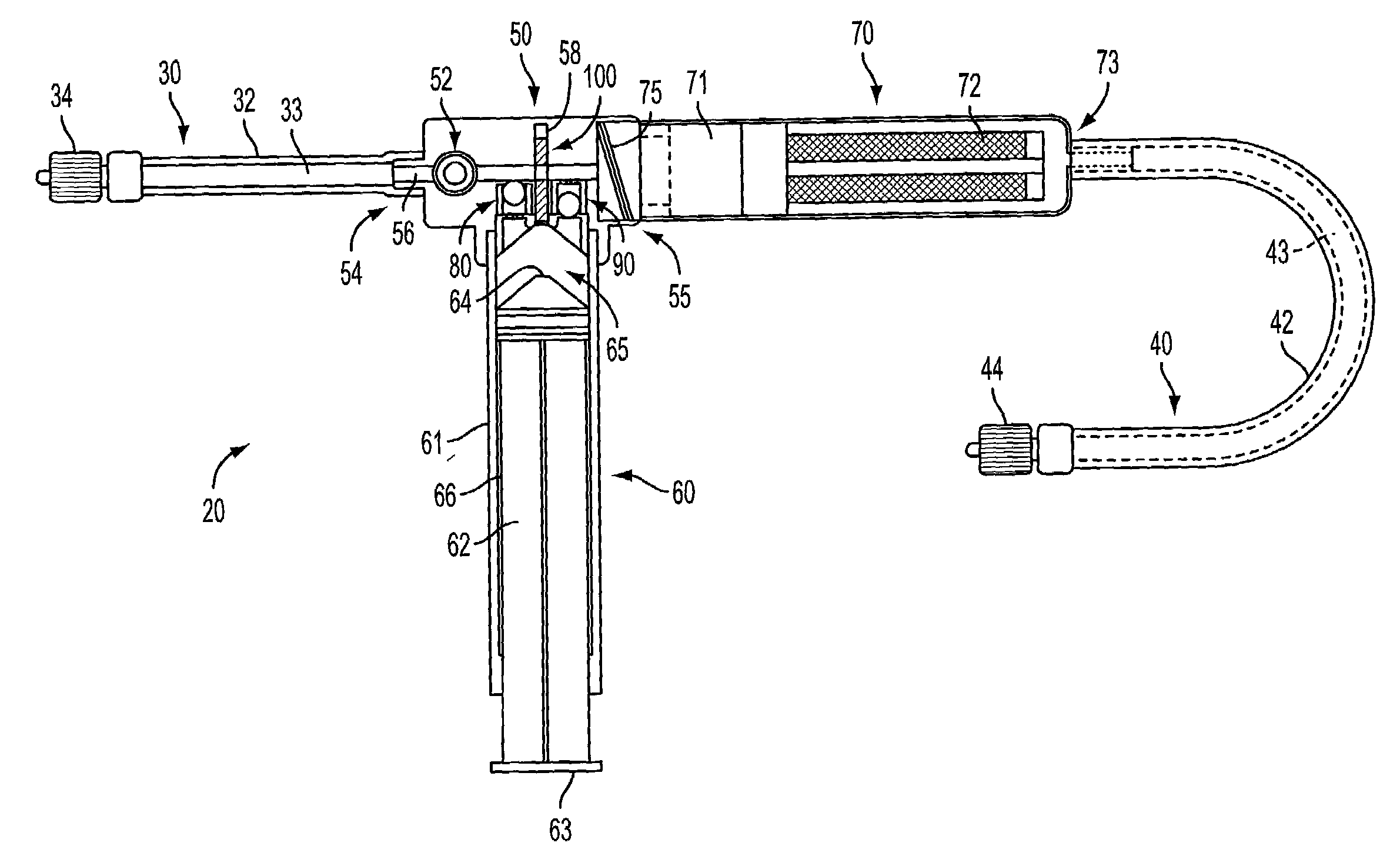
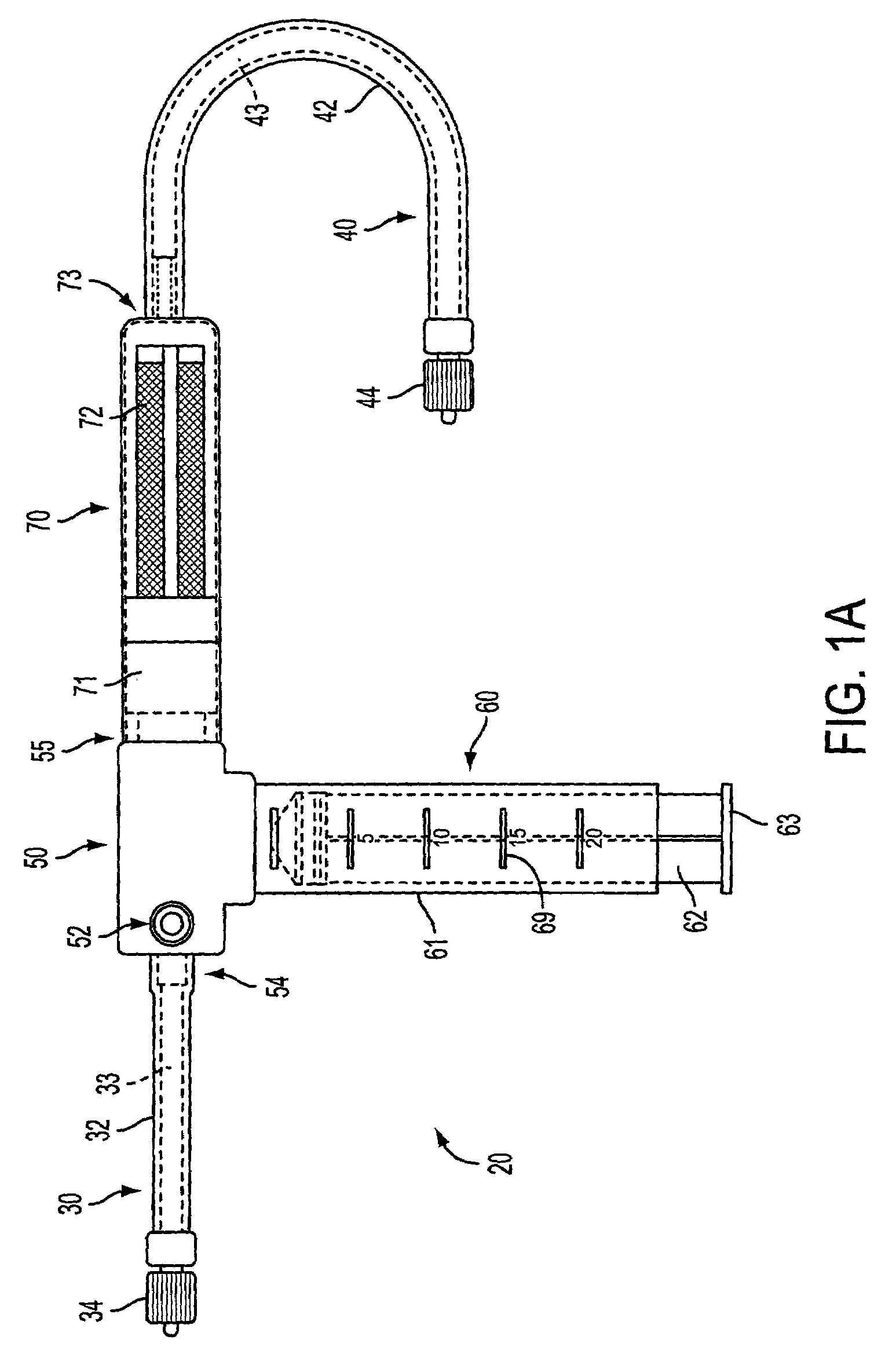
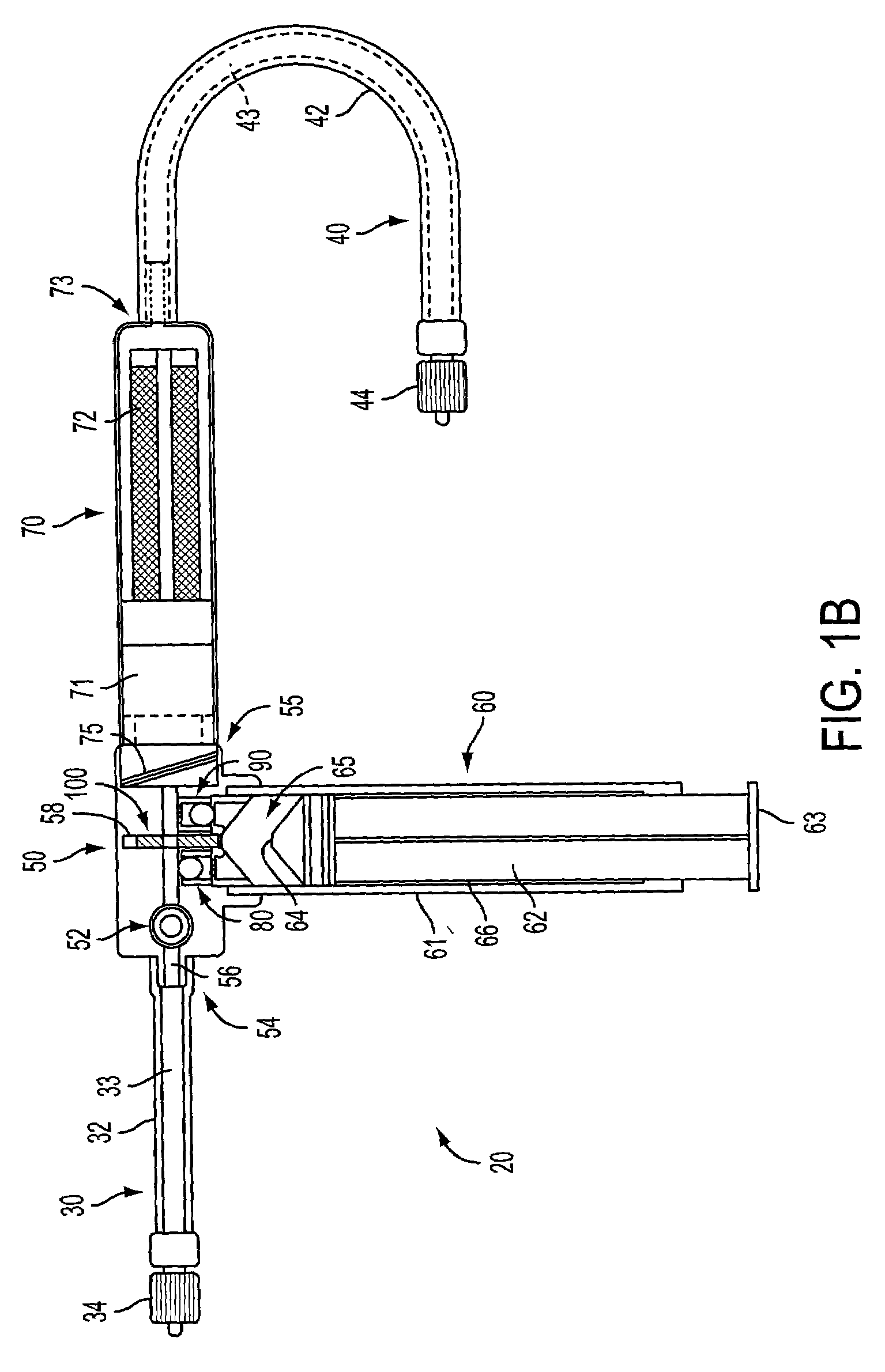
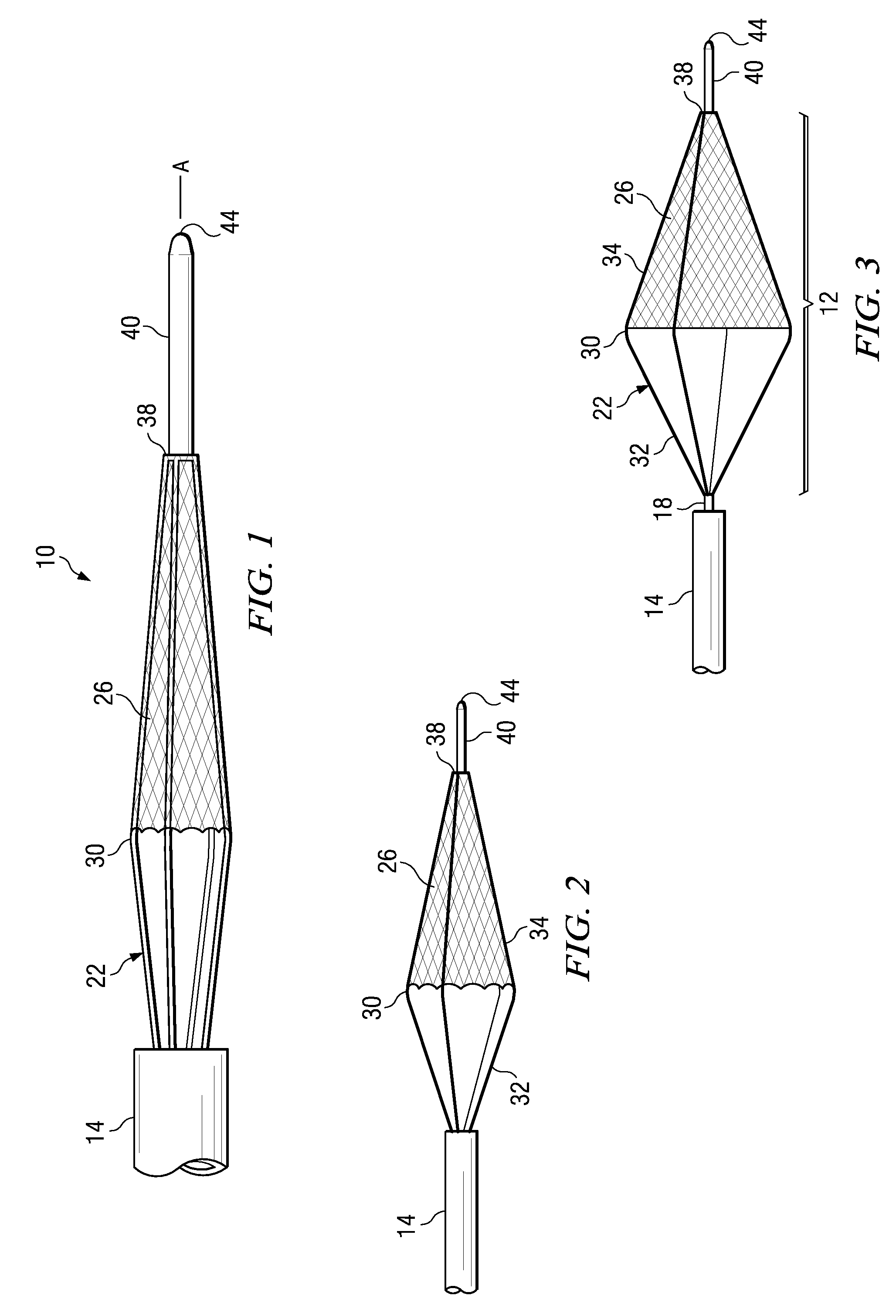
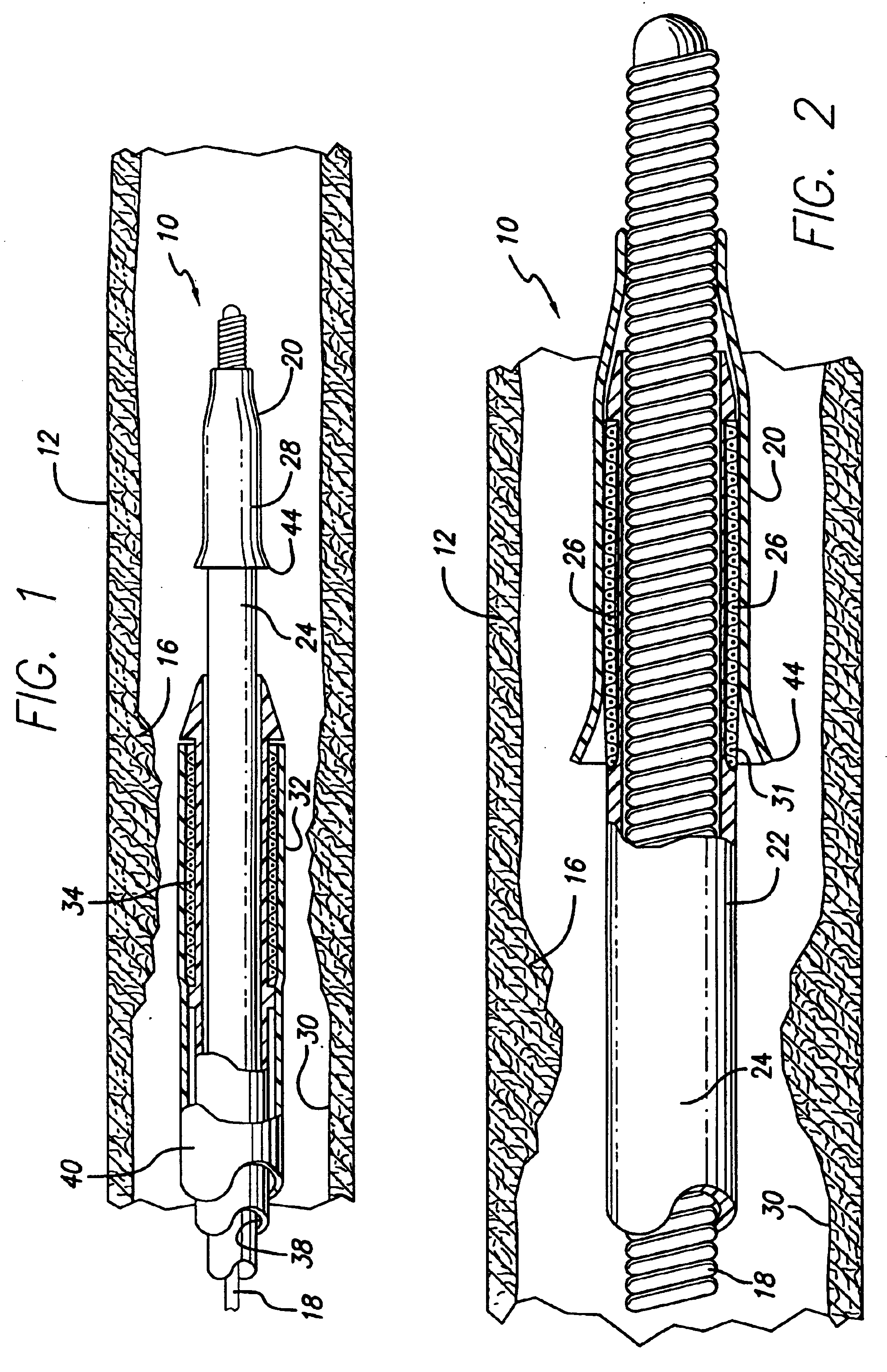
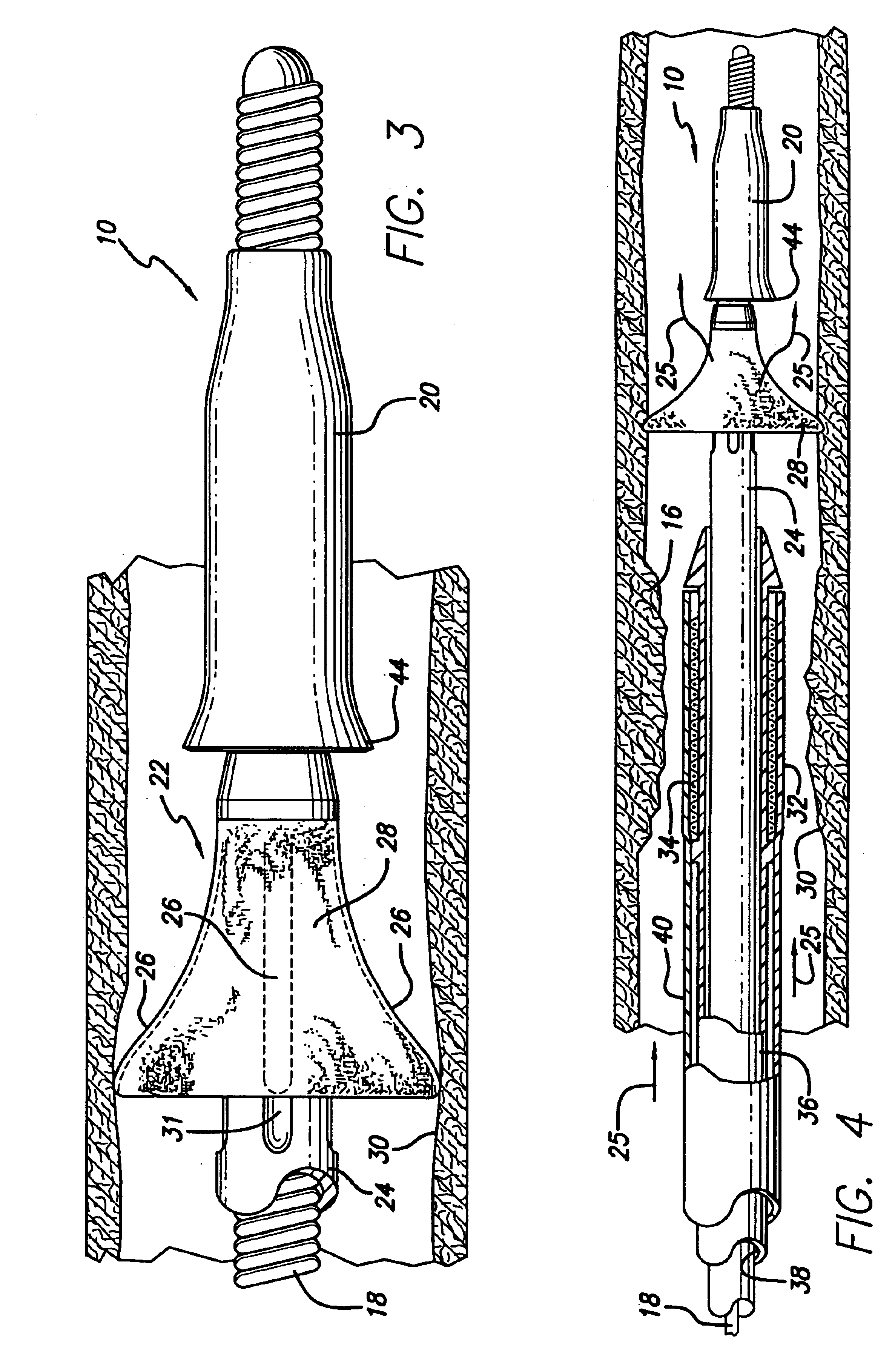
Expandable guide sheath and apparatus with distal protection and methods for use
Apparatus and methods provide distal protection while accessing blood vessels within a patient's vasculature. A flexible sheath and distal protection element, e.g., a balloon or filter, are carried by a stiffening member. The sheath is lubricious and has a relatively thin wall, thereby providing a collapsible / expandable guide for delivering fluids and / or instruments. The sheath is advanced into a blood vessel in a contracted condition, expanded to an enlarged condition to define a lumen, and the distal protection element is deployed within the vessel beyond the sheath. Fluids and / or instruments are introduced into the vessel via the sheath lumen, the distal protection element retaining the fluids and / or capturing emboli released by the instruments. Upon completing the procedure, the sheath, distal protection element, and stiffening member are removed from the vessel.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
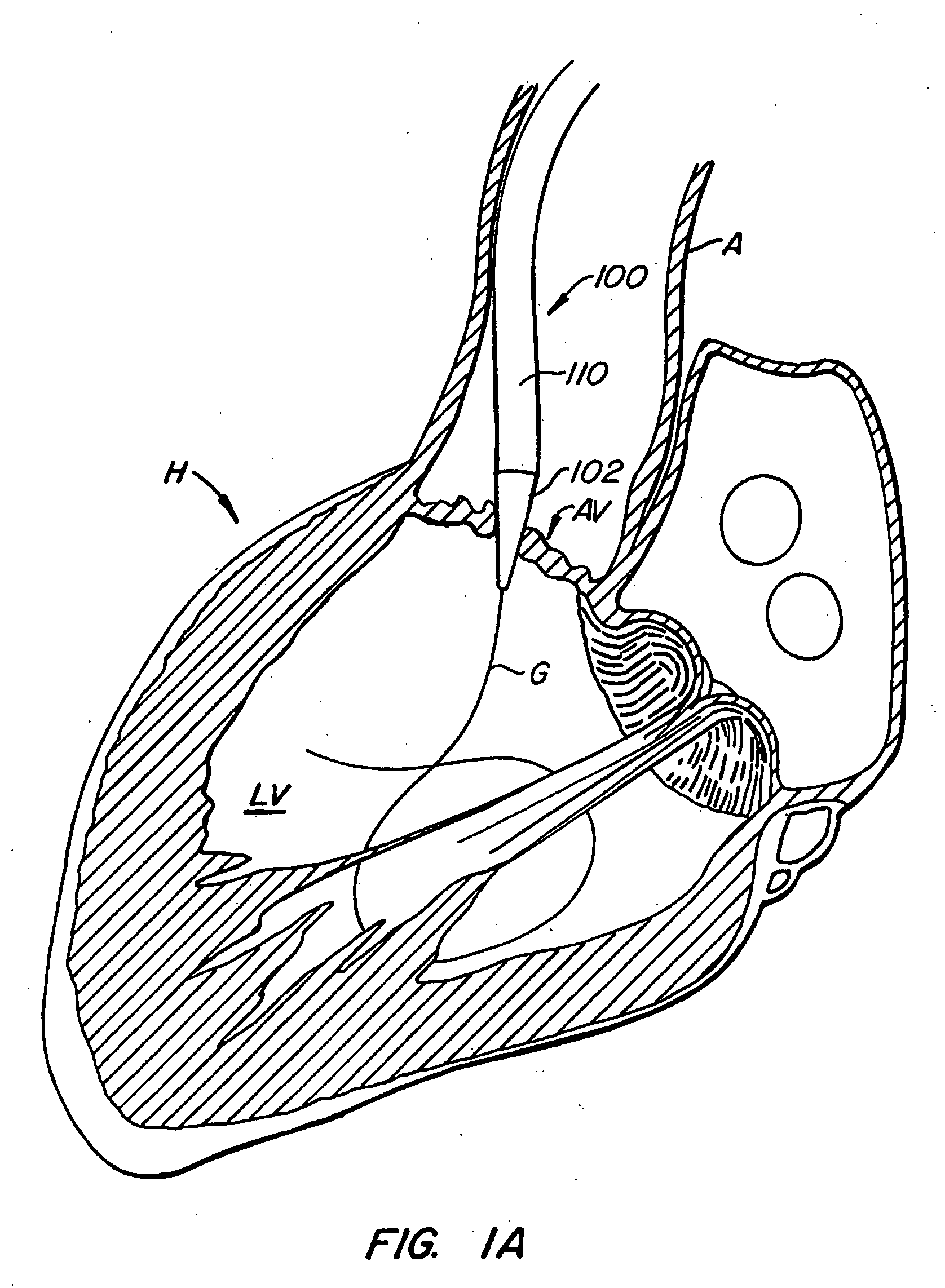
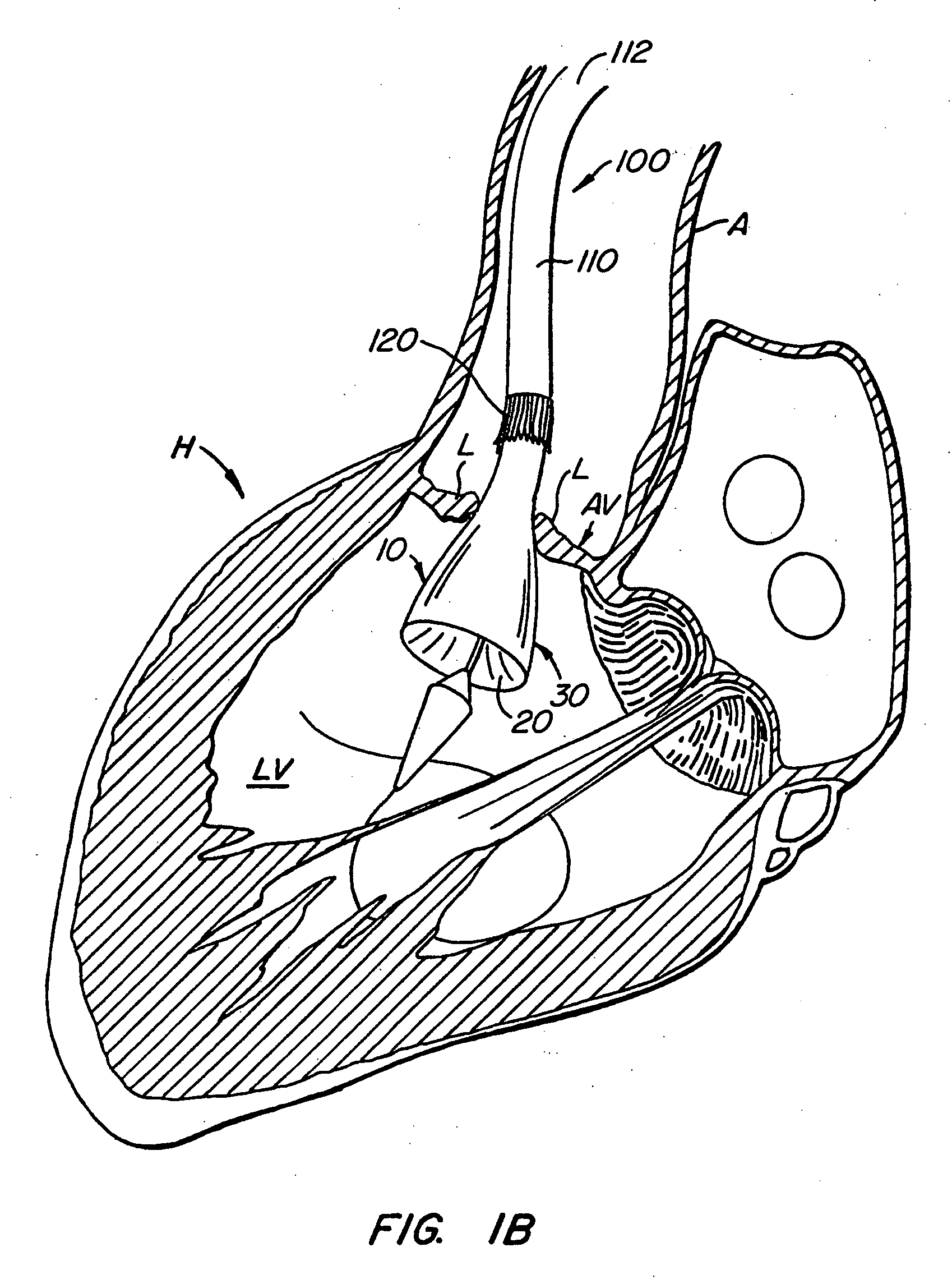
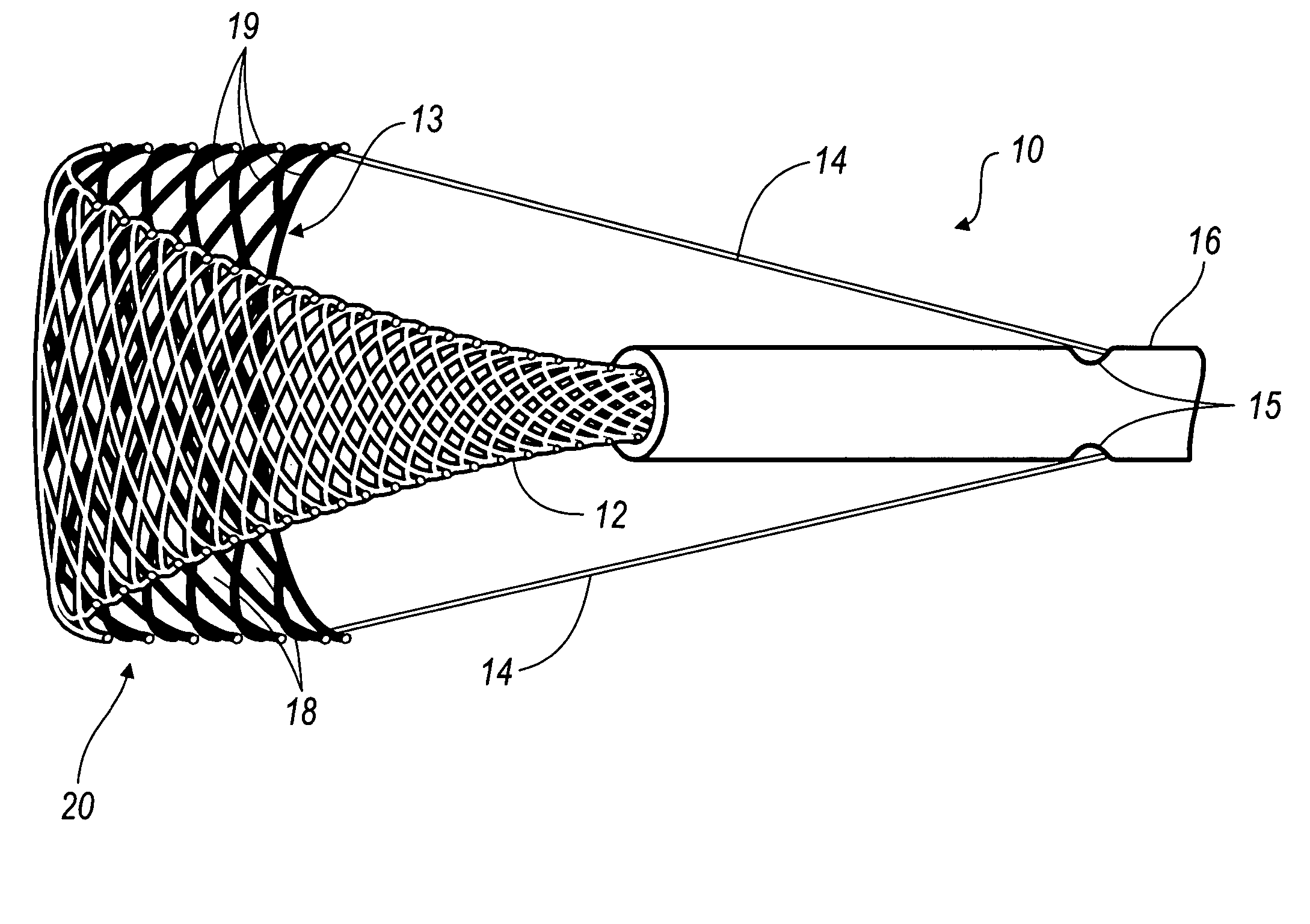
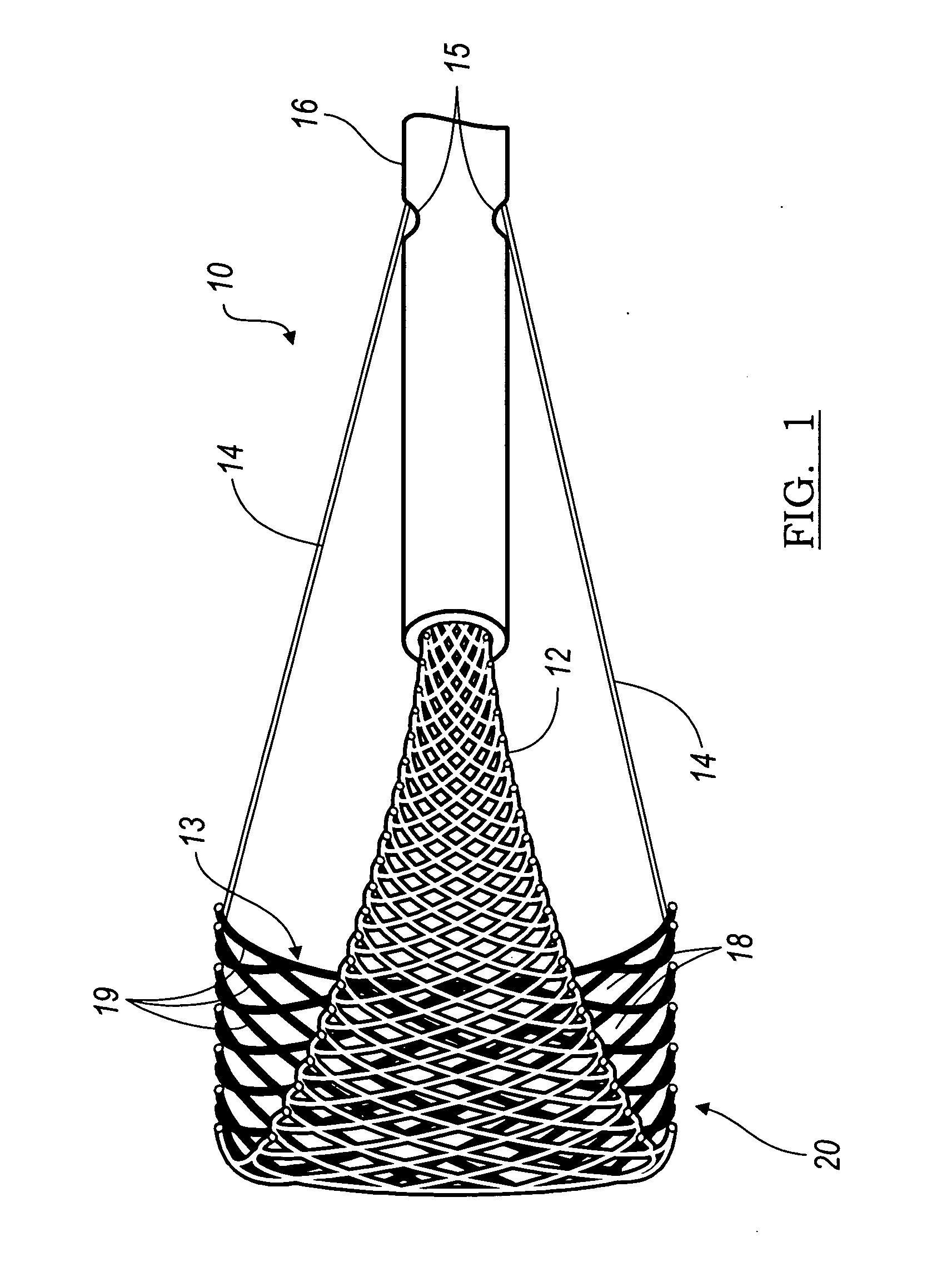
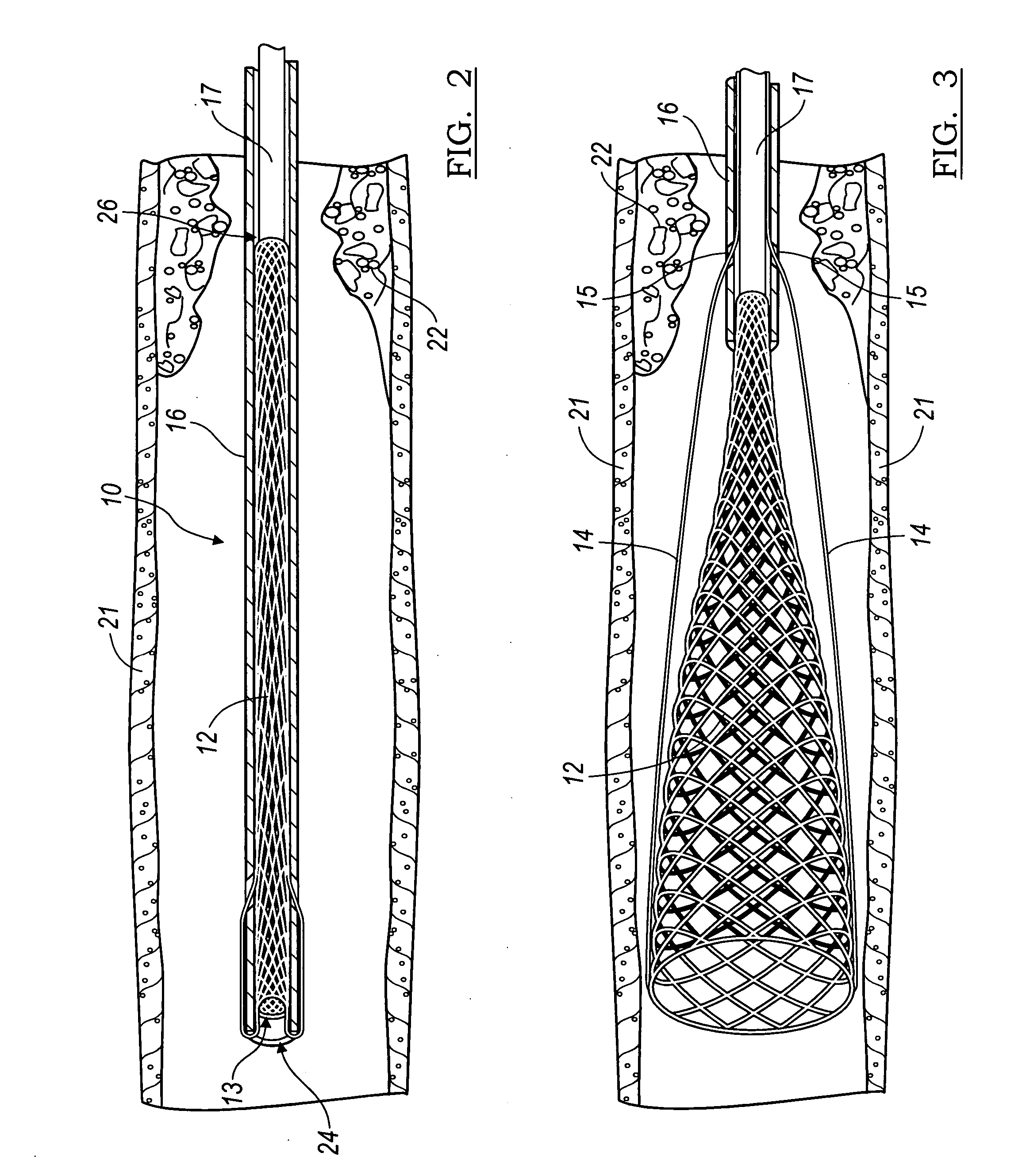
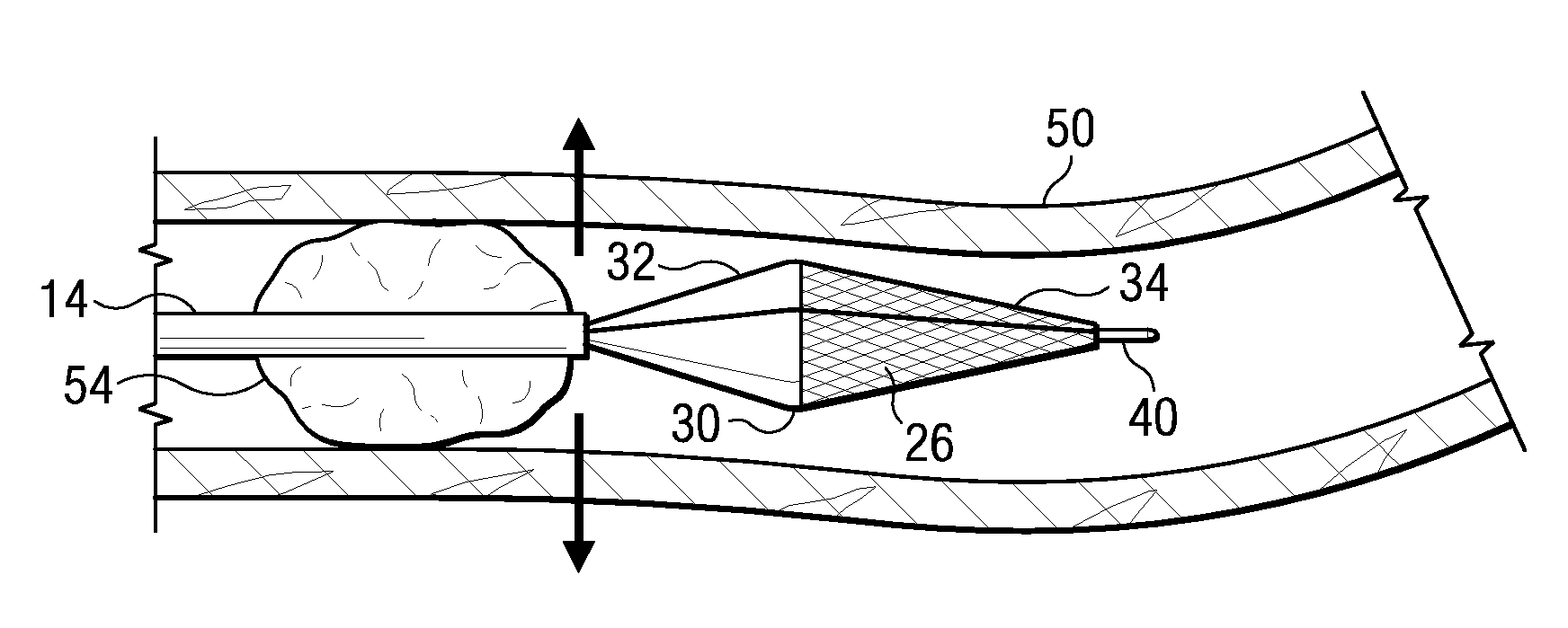
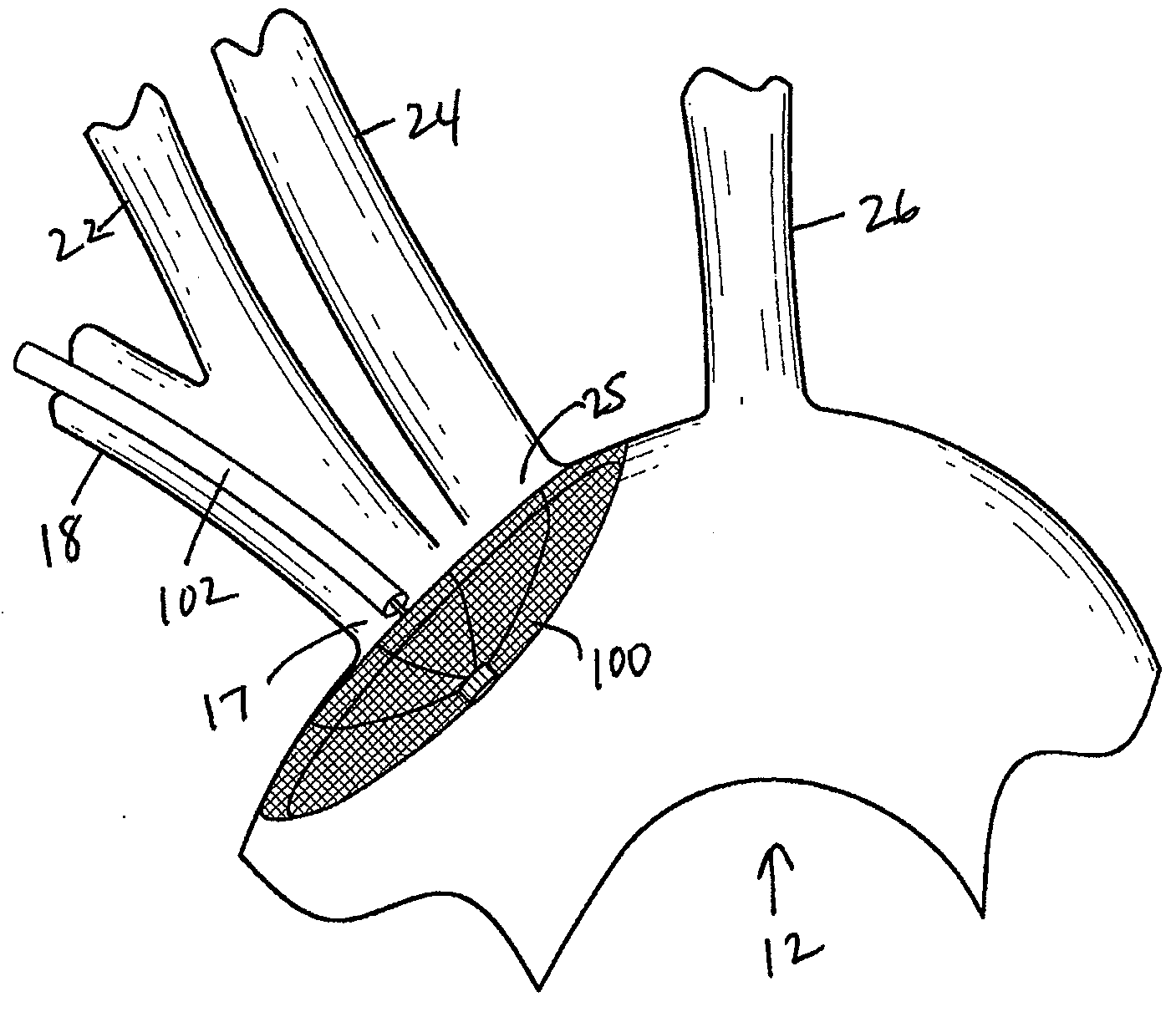
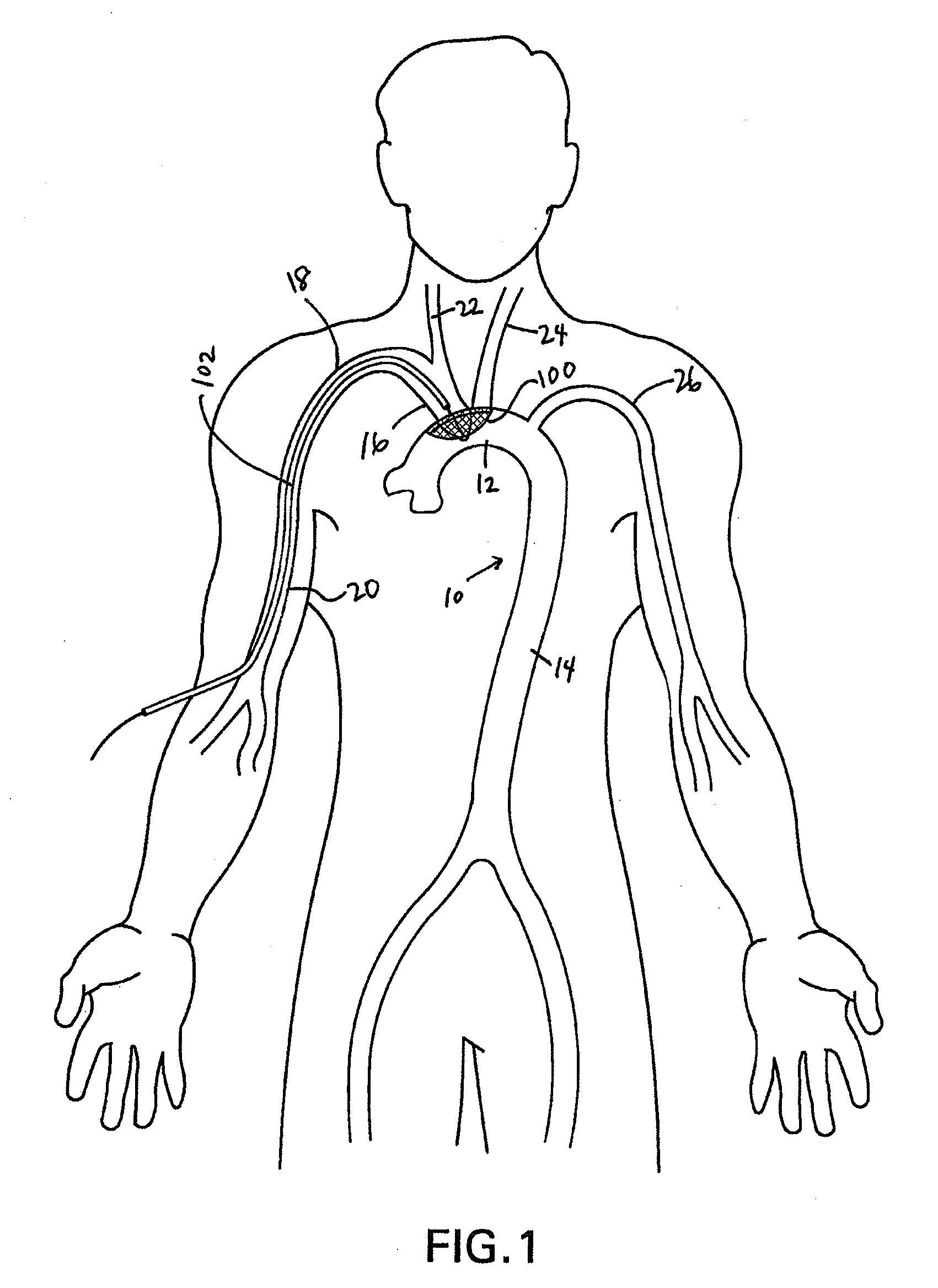
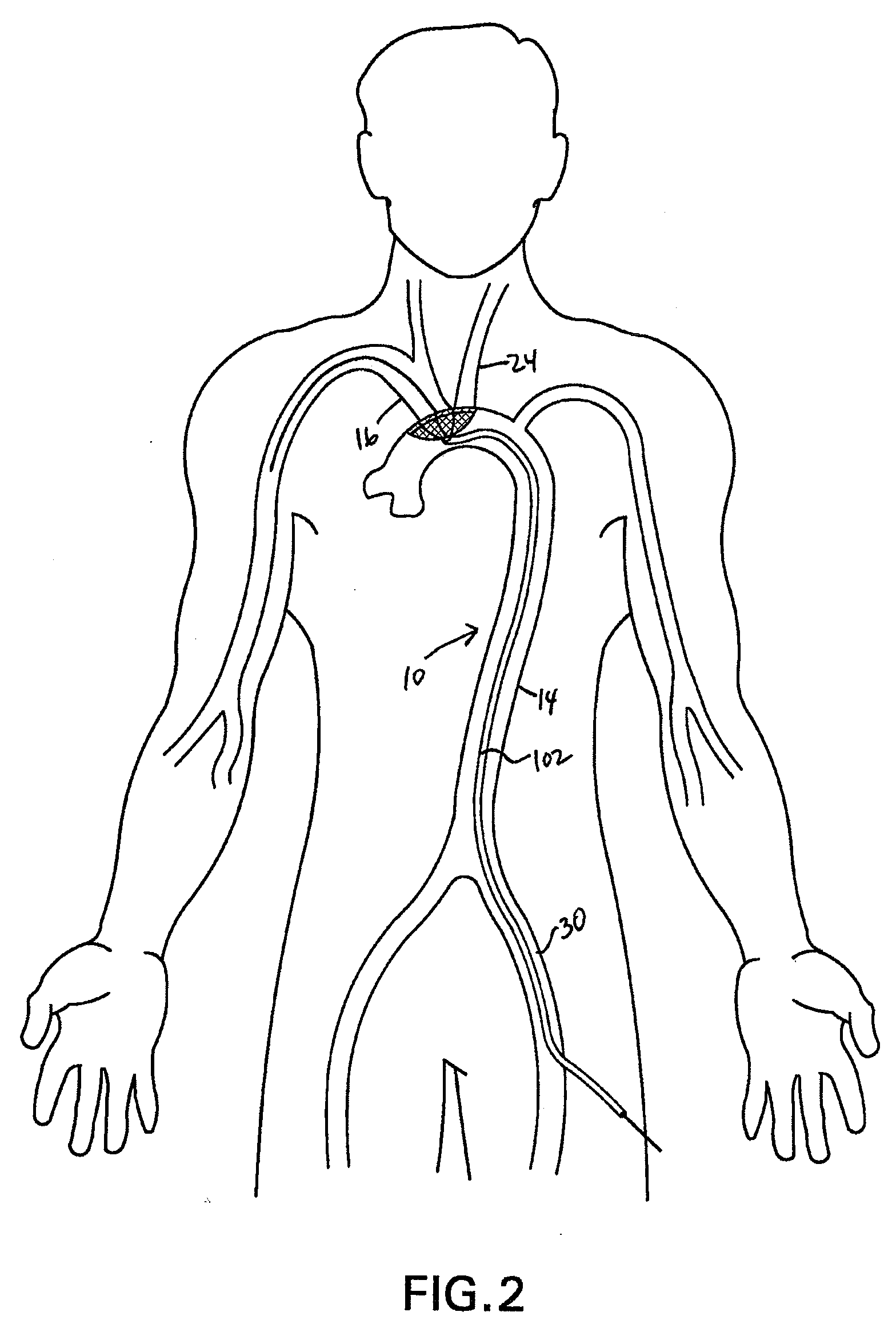
Apparatus and methods for protecting against embolization during endovascular heart valve replacement
Apparatus for protecting a patient against embolization during endovascular replacement of the patient's heart valve is provided, the apparatus including a replacement valve configured for endovascular delivery and deployment, and an embolic filter configured for disposal downstream of the replacement valve during deployment of the valve. Apparatus including a delivery catheter having an expandable replacement valve disposed therein, and an embolic filter advanceable along the delivery catheter for diverting emboli released during endovascular deployment of the replacement valve is also provided. Furthermore, methods for protecting a patient against embolization during endovascular replacement of the patient's heart valve are provided, the methods including the steps of endovascularly delivering a replacement valve to a vicinity of the patient's heart valve, endovascularly deploying an embolic filter downstream of the heart valve, and endovascularly deploying the replacement valve.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Endovascular thin film devices and methods for treating and preventing stroke
InactiveUS6605111B2Treating and preventing ischemic and hemorrhagic strokeInhibit migrationStentsCatheterIn situ polymerizationProsthesis
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Systems and methods for non-invasive detection and monitoring of cardiac and blood parameters
InactiveUS20060100530A1Easy to detectEffective assessmentBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterData acquisitionNon invasive
Methods and systems for long term monitoring of one or more physiological parameters such as respiration, heart rate, body temperature, electrical heart activity, blood oxygenation, blood flow velocity, blood pressure, intracranial pressure, the presence of emboli in the blood stream and electrical brain activity are provided. Data is acquired non-invasively using ambulatory data acquisition techniques.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
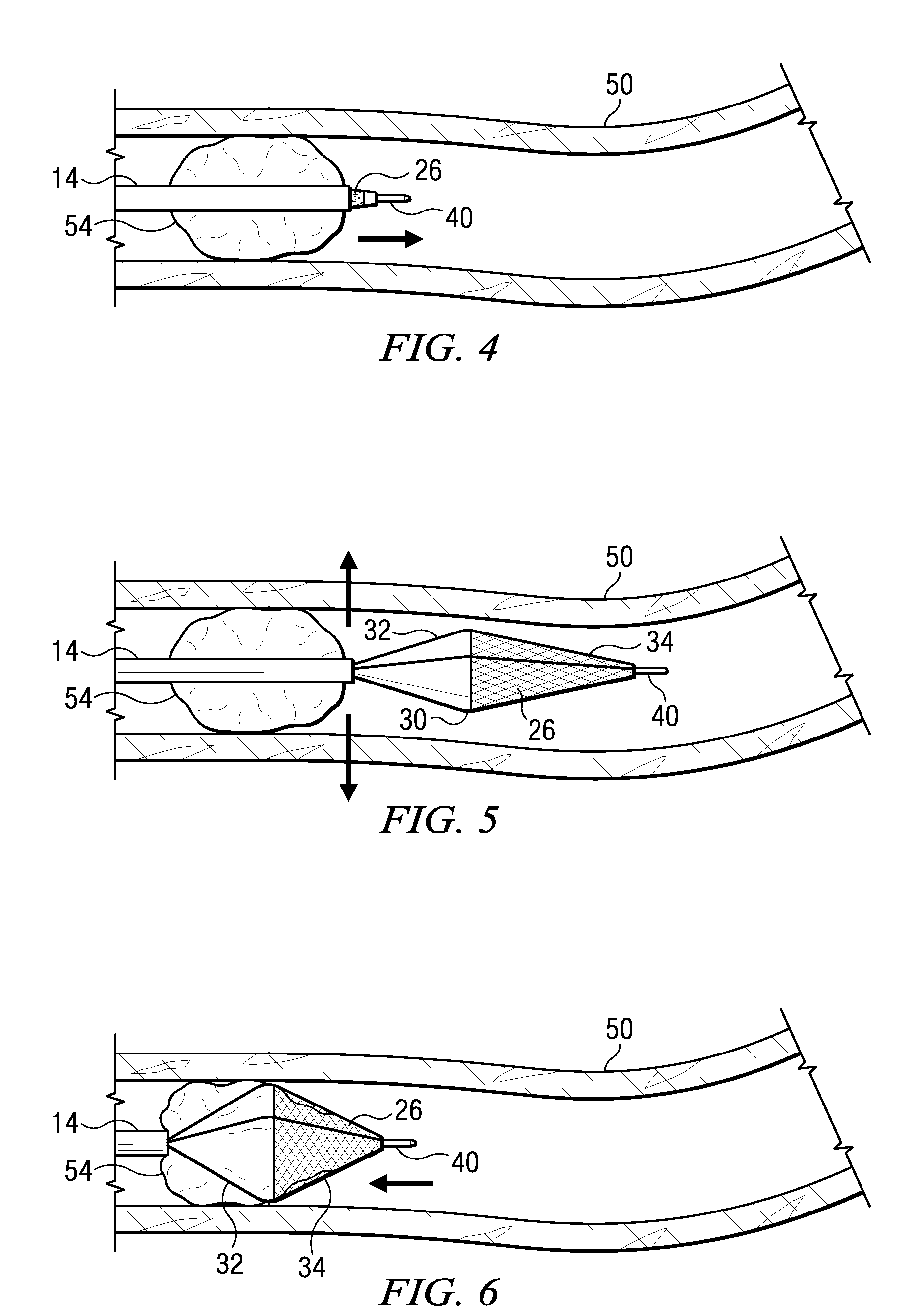
Emboli protection devices and related methods of use
ActiveUS7374560B2Improve visualizationStopping normal blood flowStentsDilatorsRetrograde FlowEmbolization material
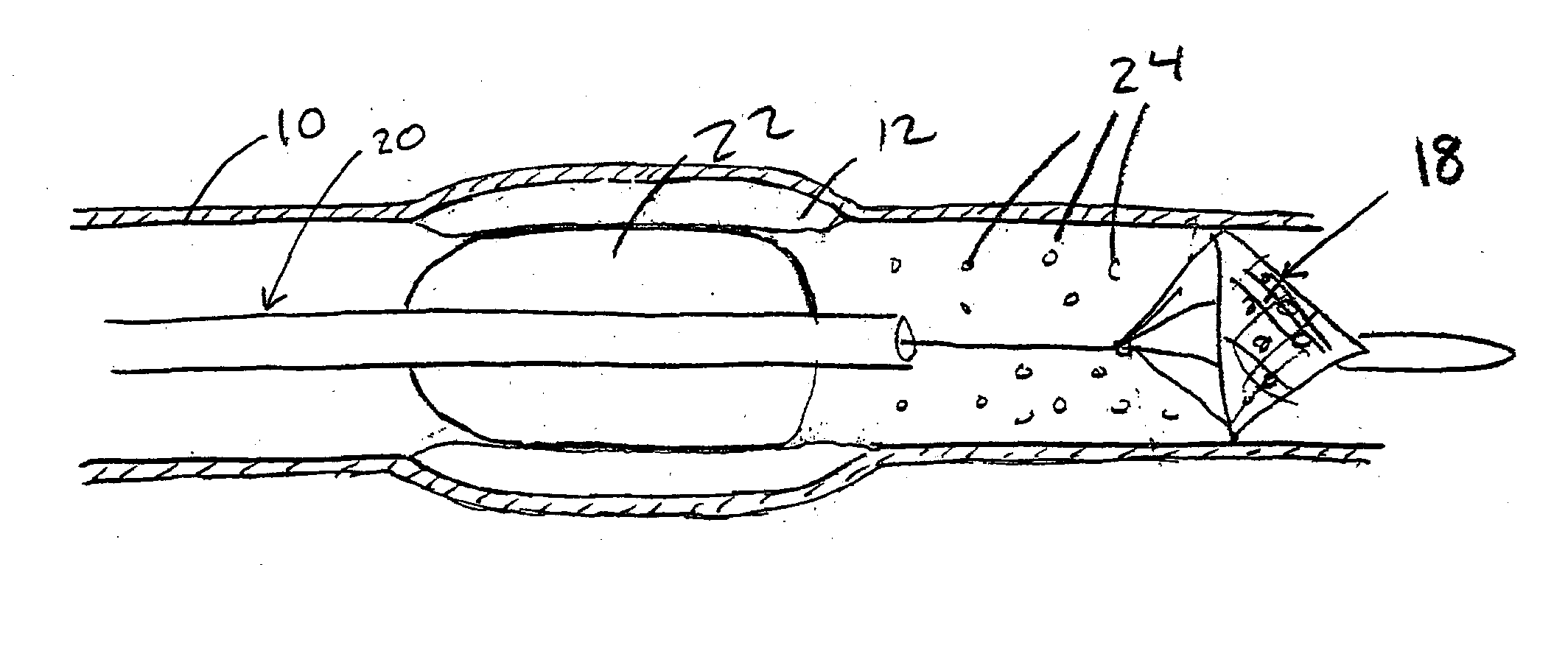
An evacuation sheath assembly and method of treating occluded vessels which reduces the risk of distal embolization during vascular interventions is provided. The evacuation sheath assembly includes an elongated tube defining an evacuation lumen having proximal and distal ends. A proximal sealing surface is provided on a proximal portion of the tube and is configured to form a seal with a lumen of a guided catheter. A distal sealing surface is provided on a distal portion of the tube and is configured to form a seal with a blood vessel. Obturator assemblies and infusion catheter assemblies are provided to be used with the evacuation sheath assembly. A method of treatment of a blood vessel using the evacuation sheath assembly includes advancing the evacuation sheath assembly into the blood vessel through a guide catheter. Normal antegrade blood flow in the blood vessel proximate to the stenosis is stopped and the stenosis is treated. Retrograde blood flow is induced within the blood vessel to carry embolic material dislodged during treating into the evacuation sheath assembly. If necessary to increase retrograde flow, the coronary sinus may be at least partially occluded. Alternatively, antegrade flow may be permitted while flow is occluded at the treatment site.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
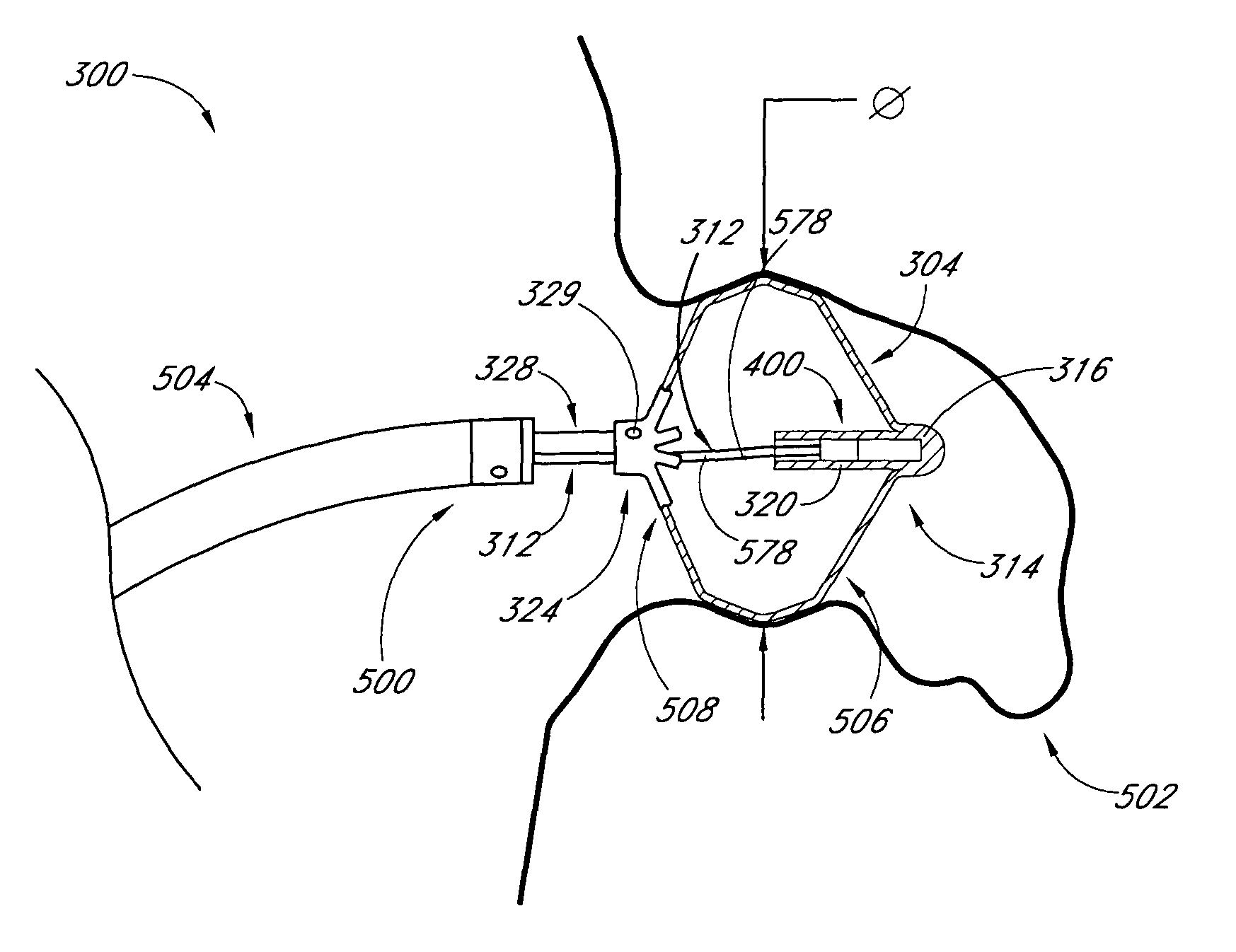
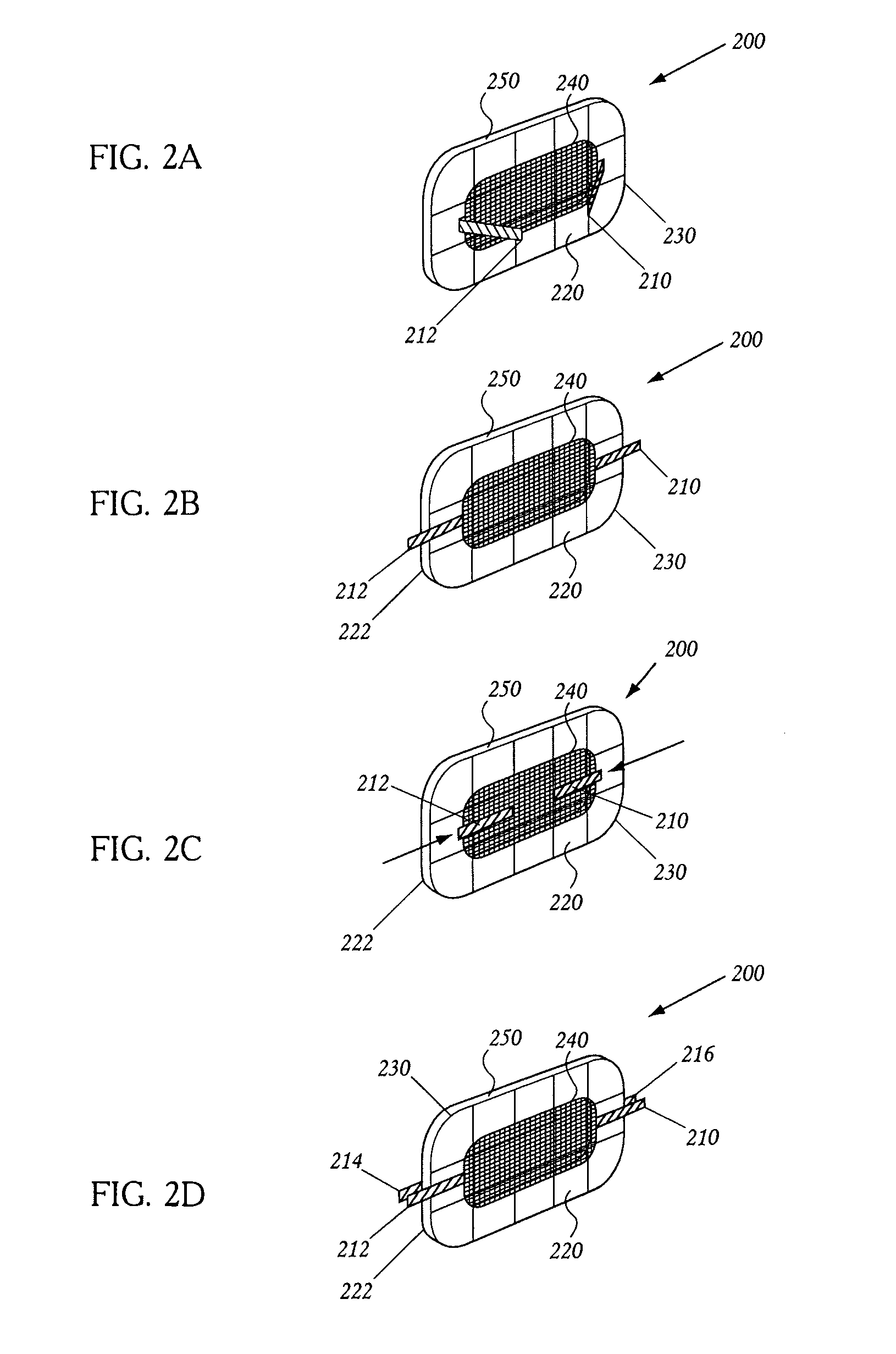
System and method for delivering a left atrial appendage containment device
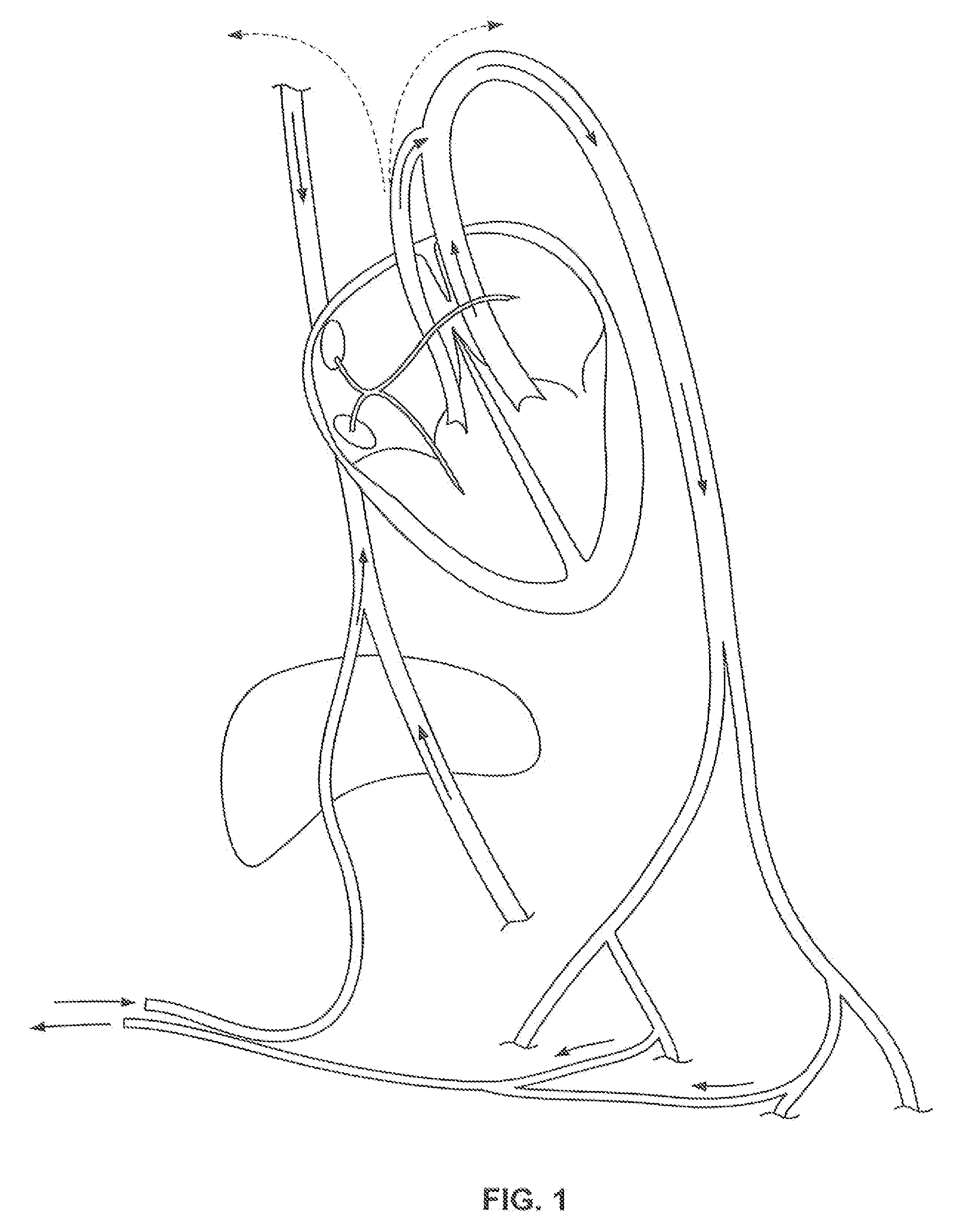
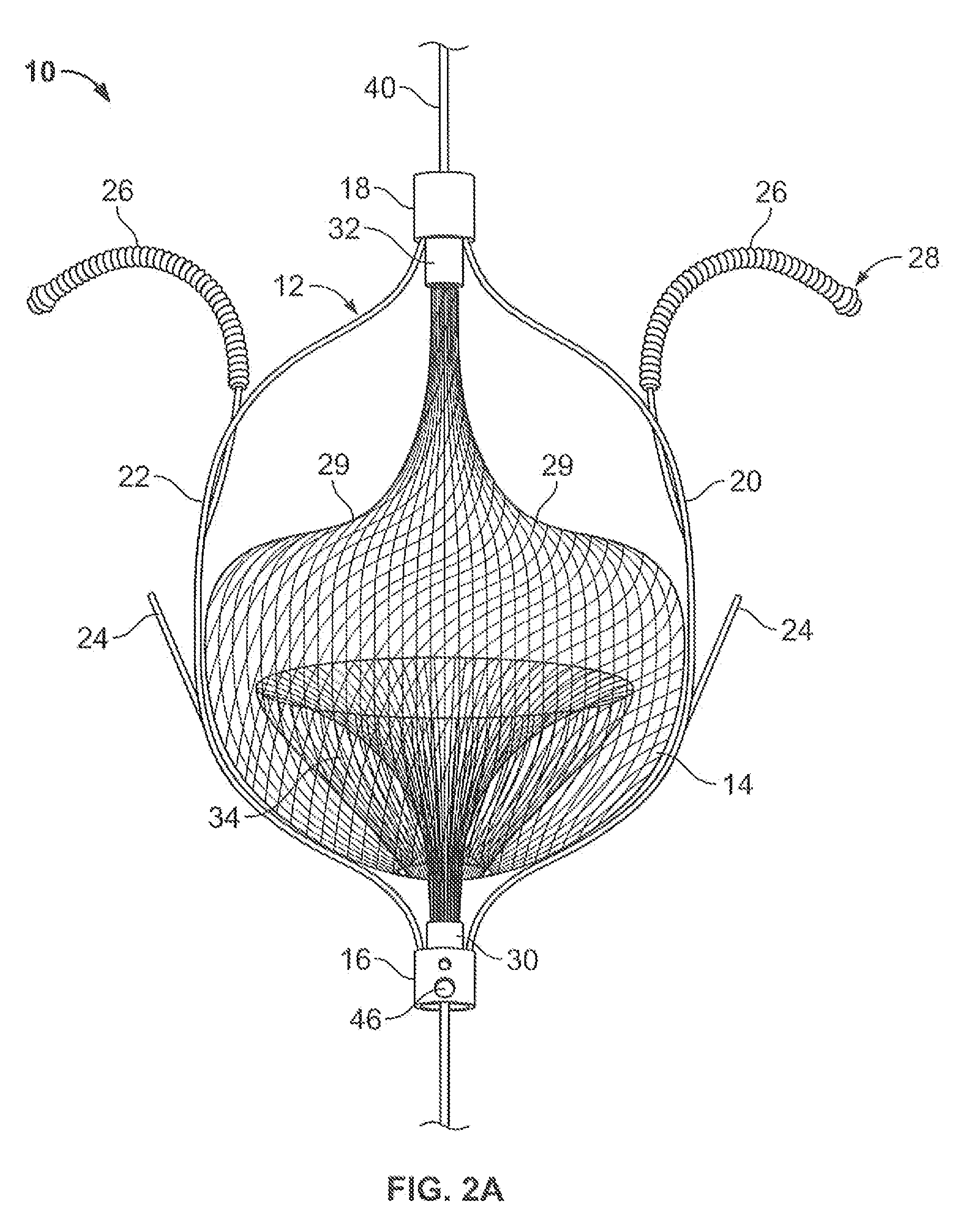
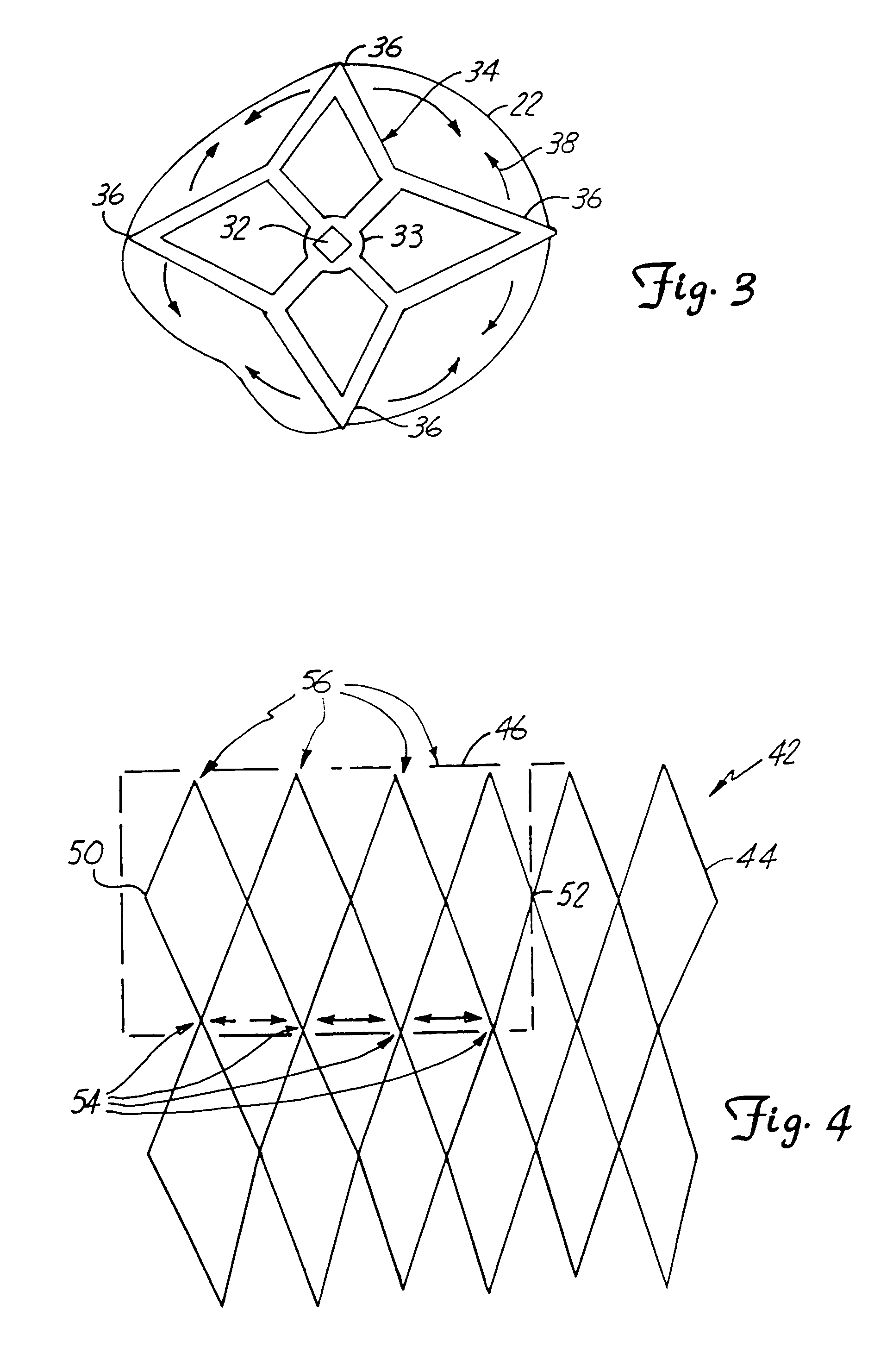
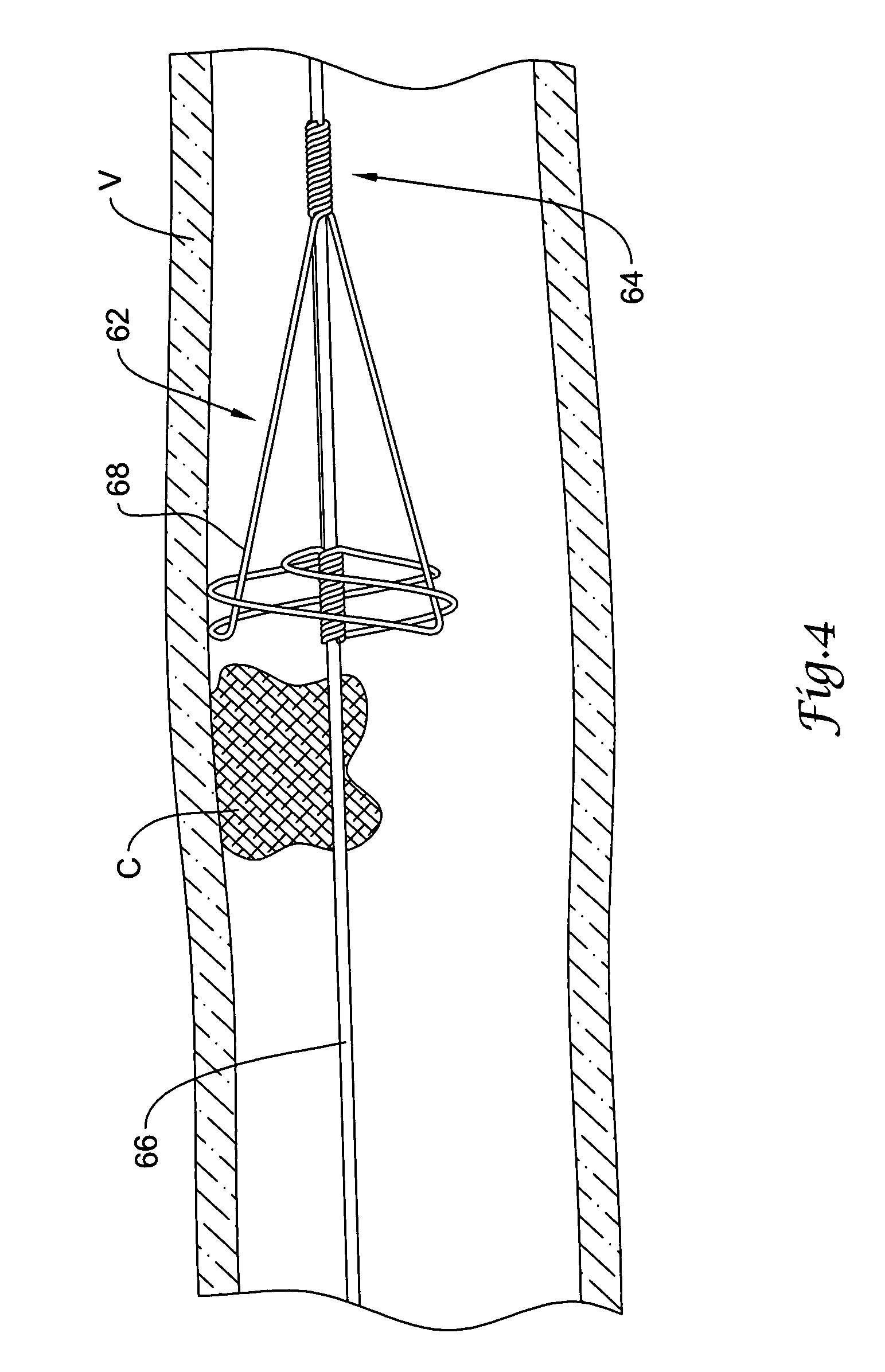
A device for containing emboli within a left atrial appendage of a patient includes a frame that is expandable from a reduced cross section to an enlarged cross section and a slider assembly. The frame extends between a proximal hub and a distal hub, and the slider assembly is coupled to the distal hub of the frame. The slider assembly includes a guide tube that has a channel extending proximally away from the distal hub, and a nut. The nut is longitudinally moveable within the channel of the guide tube over a predetermined distance relative to the guide tube. The nut is operable to be releasably coupled with an elongate core, and movement of the nut relative to the guide tube is at least partially limited by interference between a portion of the nut and a portion of the guide tube.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Endovascular thin film devices and methods for treating and preventing stroke
InactiveUS20030060782A1Safely and permanently excludingPreventing initial or recurrent aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhageStentsCatheterIn situ polymerizationProsthesis
Devices for excluding aneurysms and treating atherosclerotic disease, for intra-aneurysmal occlusion; and devices for preventing distal emboli. The devices are generally pliable and collapsible thin film devices which can be delivered via a microcatheter into the desired location where they are deployed and undergo either a shape memory phase transformation or in situ polymerization to assume the stable configuration of a permanent endoluminal prosthesis. Prior to being caused to assume their final shape, the devices remain soft, collapsible and pliable to ensure atraumatic delivery through the vascular system. Upon reaching the endoluminal defect in the vessel, the device is extruded from the microcatheter. Devices are also provided for retrieving clots.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Devices and methods for aspirating from filters
A method and apparatus for aspirating emboli and other particles from a vascular filter within a patient's vasculature. The aspiration catheter comprises an elongate body with an aspiration lumen having an aspiration port at the distal end and a guidewire lumen for receiving a guidewire. The aspiration lumen extends substantially beyond the distal end of the guidewire lumen such that the aspiration port may be,inserted into the interior volume of a filter. Accordingly, embolic particles may be aspirated from the interior volume of the filter. The aspiration port may have an oblique shape for increasing aspiration efficiency. The aspiration catheter may also have a therapy device mounted thereon, such as, for example, an inflatable balloon.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Embolic basket
Owner:ENDOVASCULAR TECH
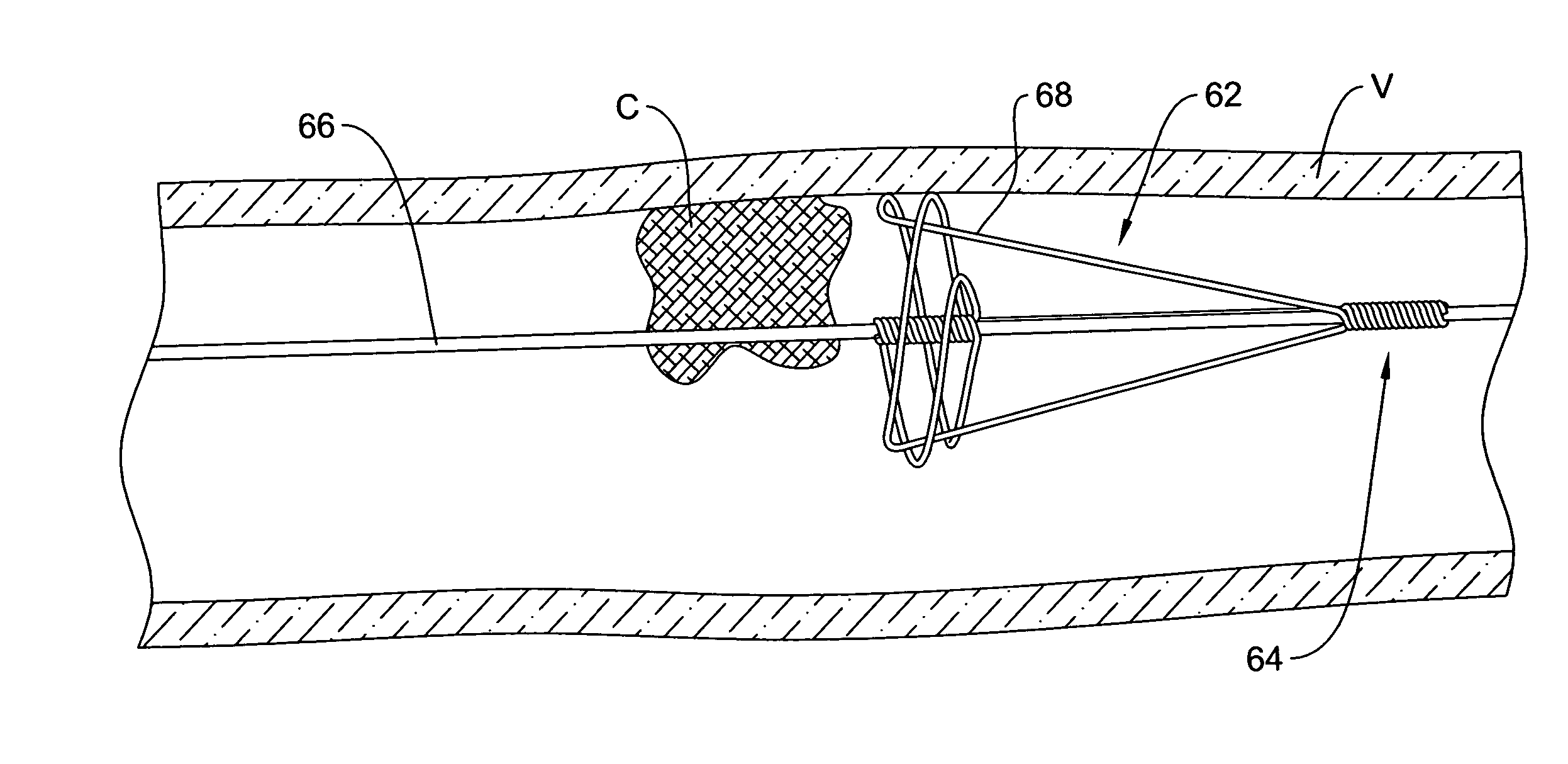
Mechanical tissue device and method
InactiveUS20080119886A1Rigid enoughLength of device being increasedDilatorsOcculdersVeinVenous blood
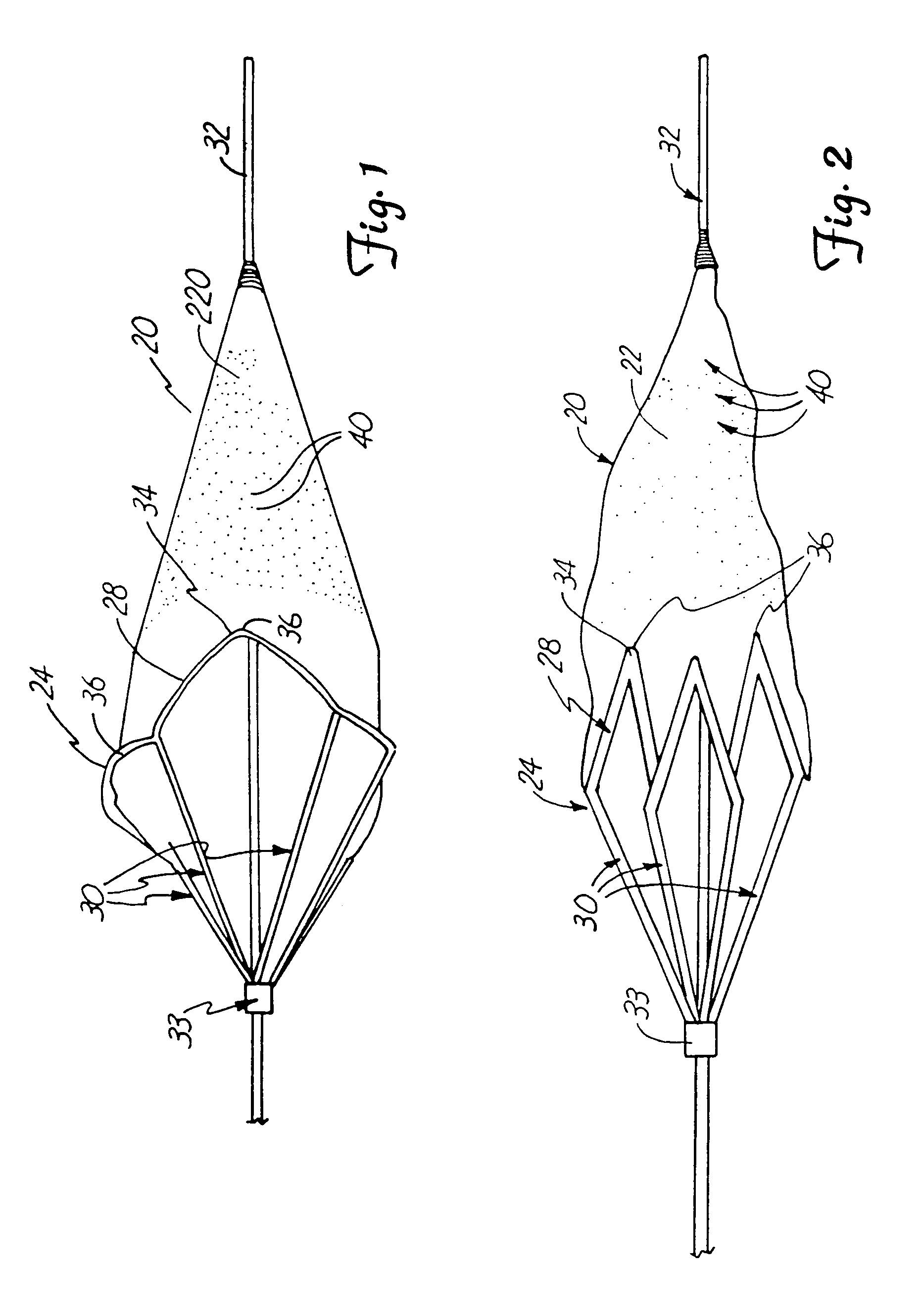
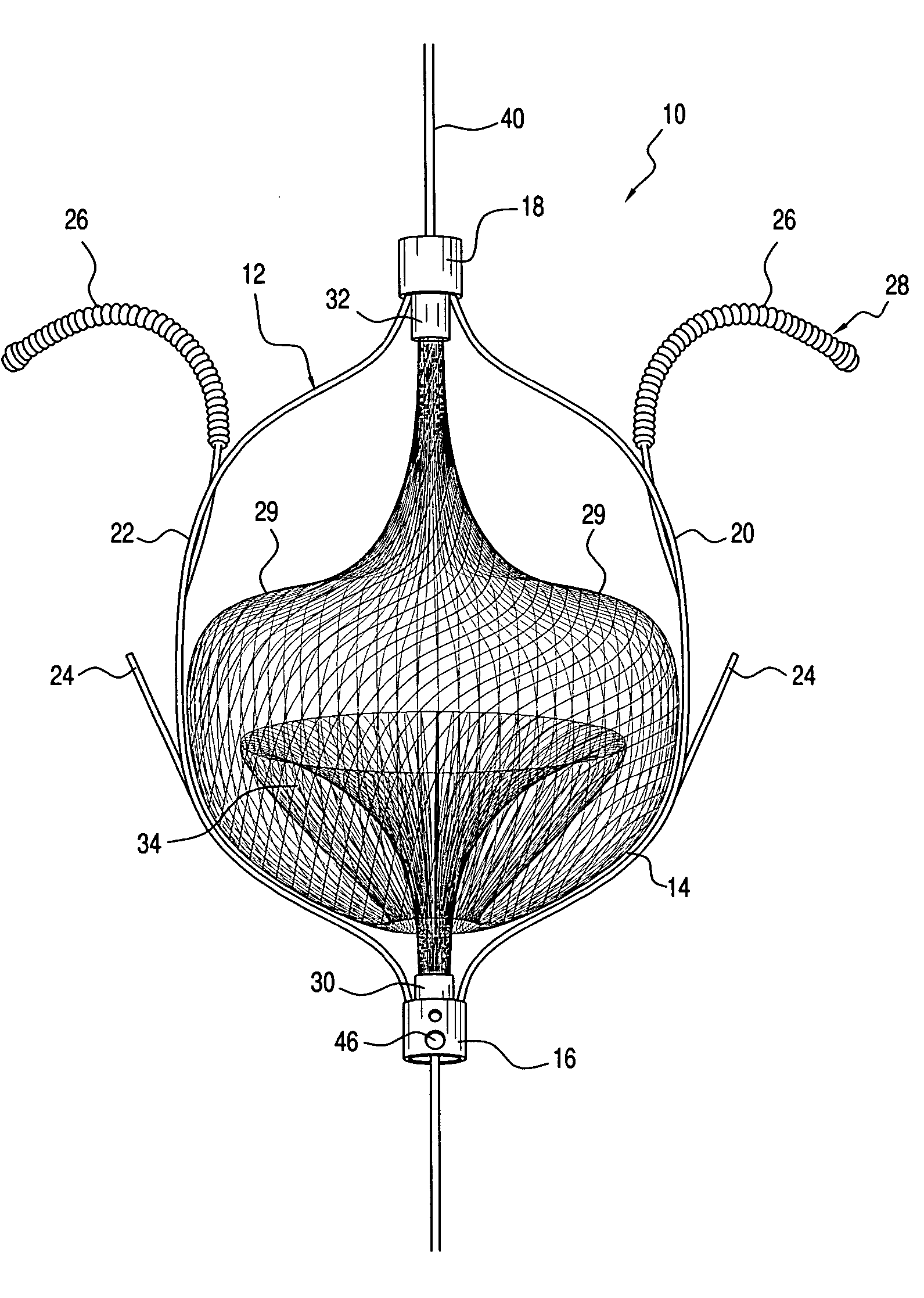
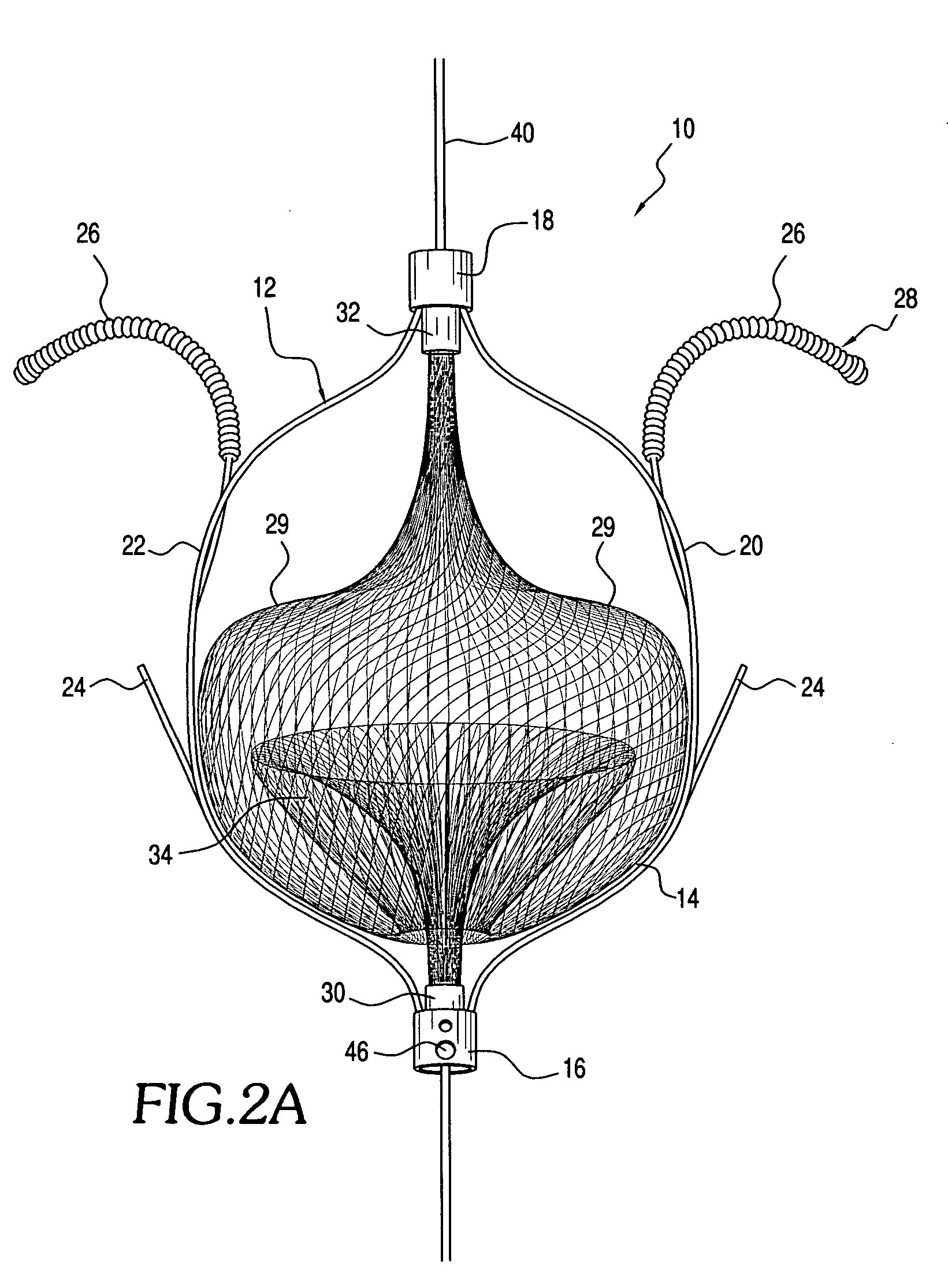
The present invention relates generally to a device and method for preventing the undesired passage of emboli from a venous blood pool to an arterial blood pool. The invention relates especially to a device and method for treating certain cardiac defects, especially patent foramen ovales and other septal defects, through the use of an embolic filtering device capable of instantaneously deterring the passage of emboli from the moment of implantation. The device consists of a frame, and a braided mesh of sufficient dimensions to prevent passage of emboli through the mesh. The device is preferably composed of shape memory allow, such as Nitinol, which conforms to the shape and dimension of the defect to be treated.
Owner:SEPTRX
Distal protection device and method
A device adapted for deployment in a body vessel for collecting floating debris and emboli in a filter. The device includes a collapsible proximally tapered frame for operably supporting the filter between a collapsed insertion profile and an expanded deployment profile. The tapered collapsible frame includes a mouth which is sized to extend to walls of the body vessel in the expanded deployed profile to seal the filter relative to the body vessel for collecting debris floating in the body vessel.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Embolic filtering method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060009799A1Obstruct passageEncourage and facilitate growth of tissueAnnuloplasty ringsDilatorsVenous bloodCardiac defects
The present invention relates generally to a device and method for preventing the undesired passage of emboli from a venous blood pool to an arterial blood pool. The invention relates especially to a device and method for treating certain cardiac defects, especially patent foramen ovales and other septal defects, through the use of an embolic filtering device capable of instantaneously deterring the passage of emboli from the moment of implantation. The device consists of a frame, and a braided mesh of sufficient dimensions to prevent passage of emboli through the mesh. The device is preferably composed of shape memory allow, such as nitinol, which conforms to the shape and dimension of the defect to be treated.
Owner:SEPTRX
Emboli diverting devices created by microfabricated means
A medical device for interposition between a first flow path and at least one second flow path is provided. The device includes a first surface facing toward the opening of at least one second flow path; and a second surface facing away from the opening of at least one second flow path. When the device is in the operative position, it extends less than the complete circumference of the first flow path and substantially covers the opening of at least one second flow path. The device contains one or more surface features to facilitate chronic implantation. The device further has one or more characteristic porosities. Different configurations are indicated depending on the pathophysiology being treated and dictate the characteristic porosity of the device. In some, cases blood is prevented from reaching the second flow path and in other cases, particulates traveling within the blood are prevented from reaching the second flow path. Methods of preventing emboli or blood flow into the second flow path are also provided. Methods and devices for delivery are also provided.
Owner:GERTNER MICHAEL
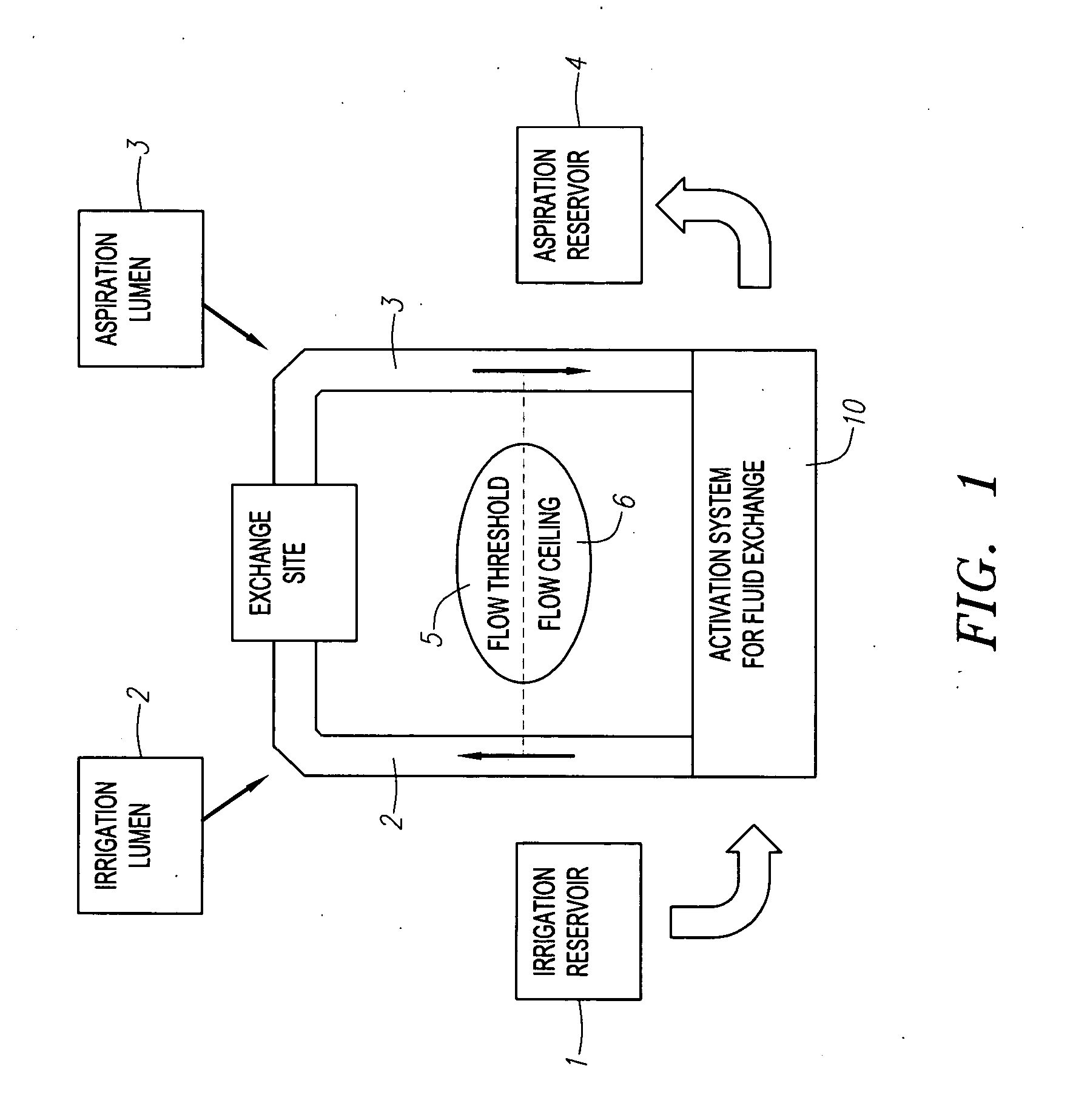
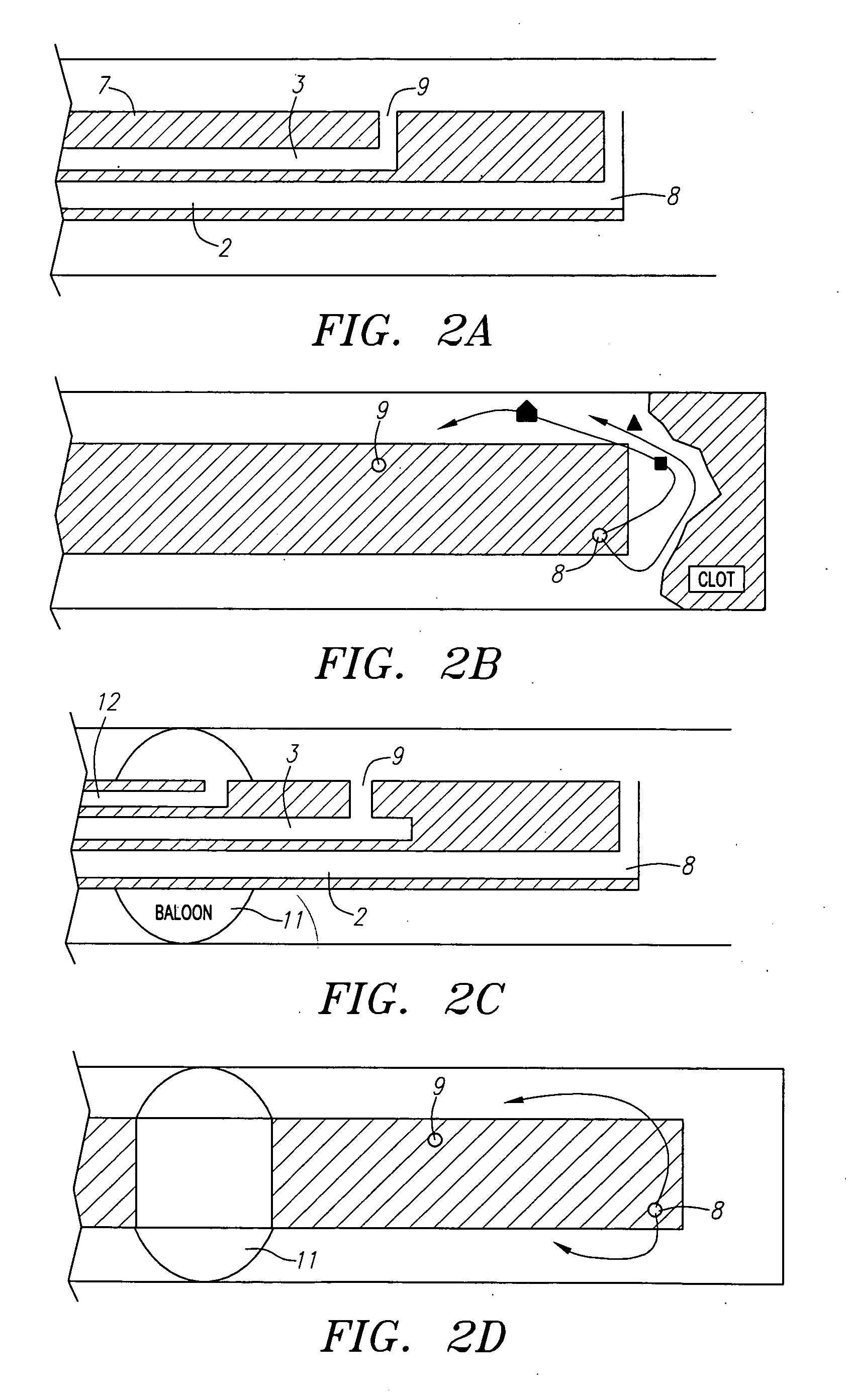
Fluid exchange system for controlled and localized irrigation and aspiration
InactiveUS20050085769A1Improved exchangeSpeed up the flowInfusion syringesSurgeryElectricityFluid management
The control of fluid introduction into and out of body conduits such as vessels, is of great concern in medicine. As the development of more particular treatments to vessels and organs continues it is apparent that controlled introduction and removal of fluids is necessary. Fluid delivery and removal from such sites, usually referred to as irrigation and aspiration, using fluid exchange devices that control also need to be considerate of potential volume and / or pressure in the vessel or organ are described together with catheter and lumen configurations to achieve the fluid exchange. The devices include several electrically or mechanically controlled embodiments and produce both controlled and localized flow with defined volume exchange ratios for fluid management. The applications in medicine include diagnostic, therapeutic, imaging, and uses for the introduction or removal of concentrations of emboli within body cavities.
Owner:FOX HOLLOW TECH
Endovascular thin film devices and methods for treating and preventing stroke
InactiveUS6666882B1Treating and preventing ischemic and hemorrhagic strokeInhibit migrationStentsOcculdersIn situ polymerizationDistal embolization
Devices for excluding aneurysms and treating atherosclerotic disease, for intra-aneurysmal occlusion, and devices for preventing distal emboli. The devices are generally pliable and collapsible thin film devices which can be delivered via a microcatheter into the desired location where they are deployed and undergo either a shape memory phase transformation or in situ polymerization to assume the stable configuration of a permanent endoluminal prosthesis. Prior to being caused to assume their final shape, the devices remain soft, collapsible and pliable to ensure atraumatic delivery through the vascular system. Upon reaching the endoluminal defect in the vessel, the device is extruded from the microcatheter. Devices are also provided for retrieving clots.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
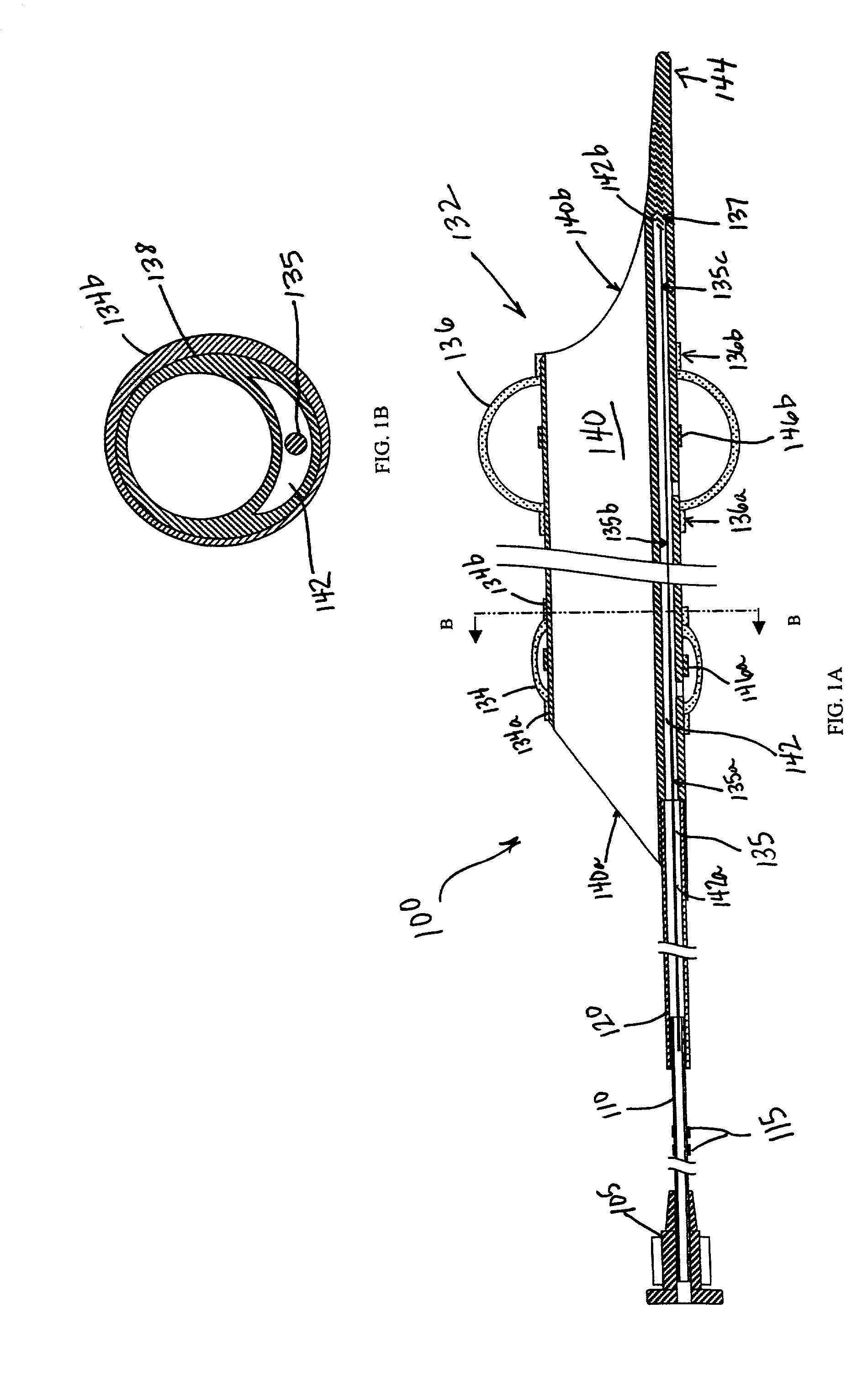
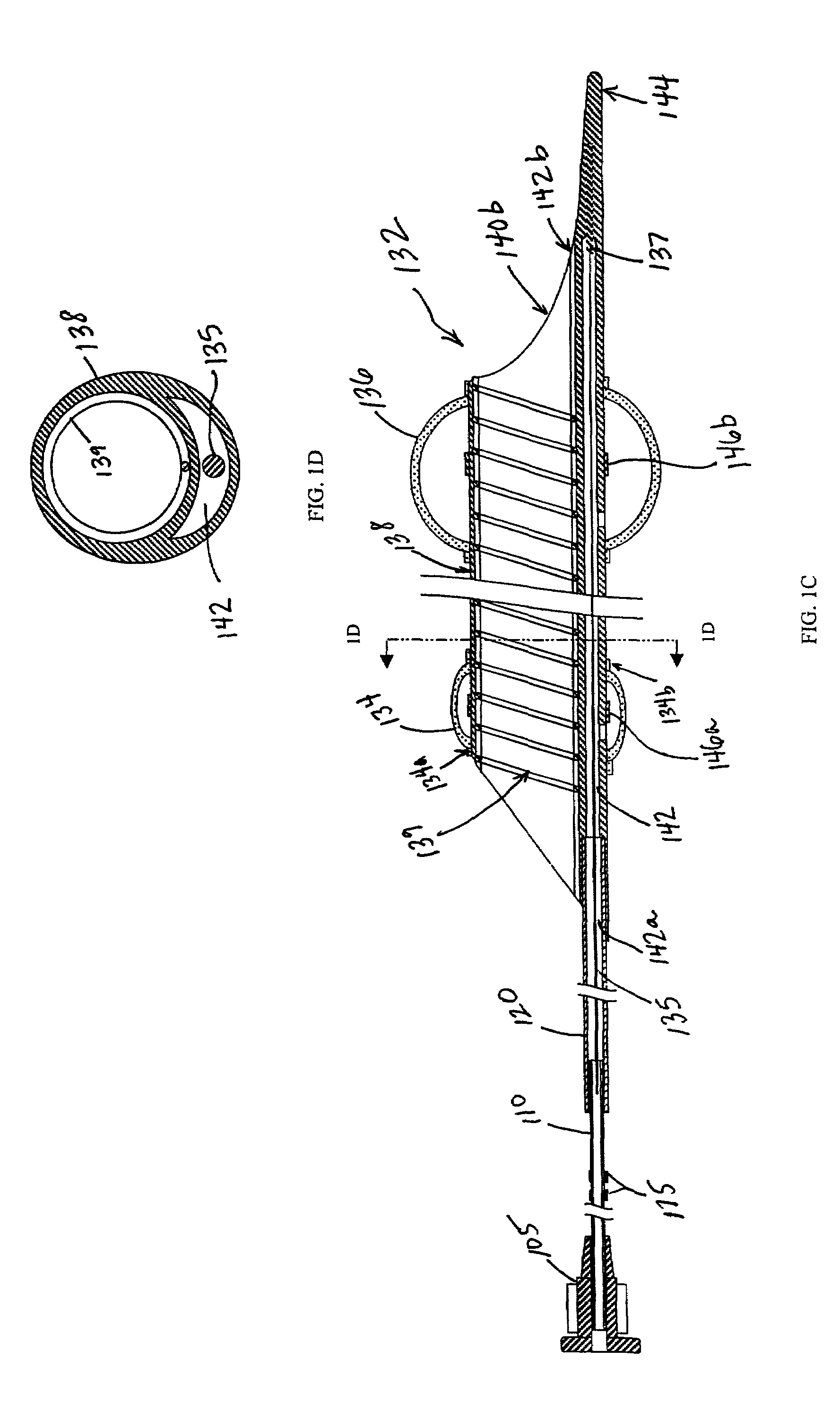
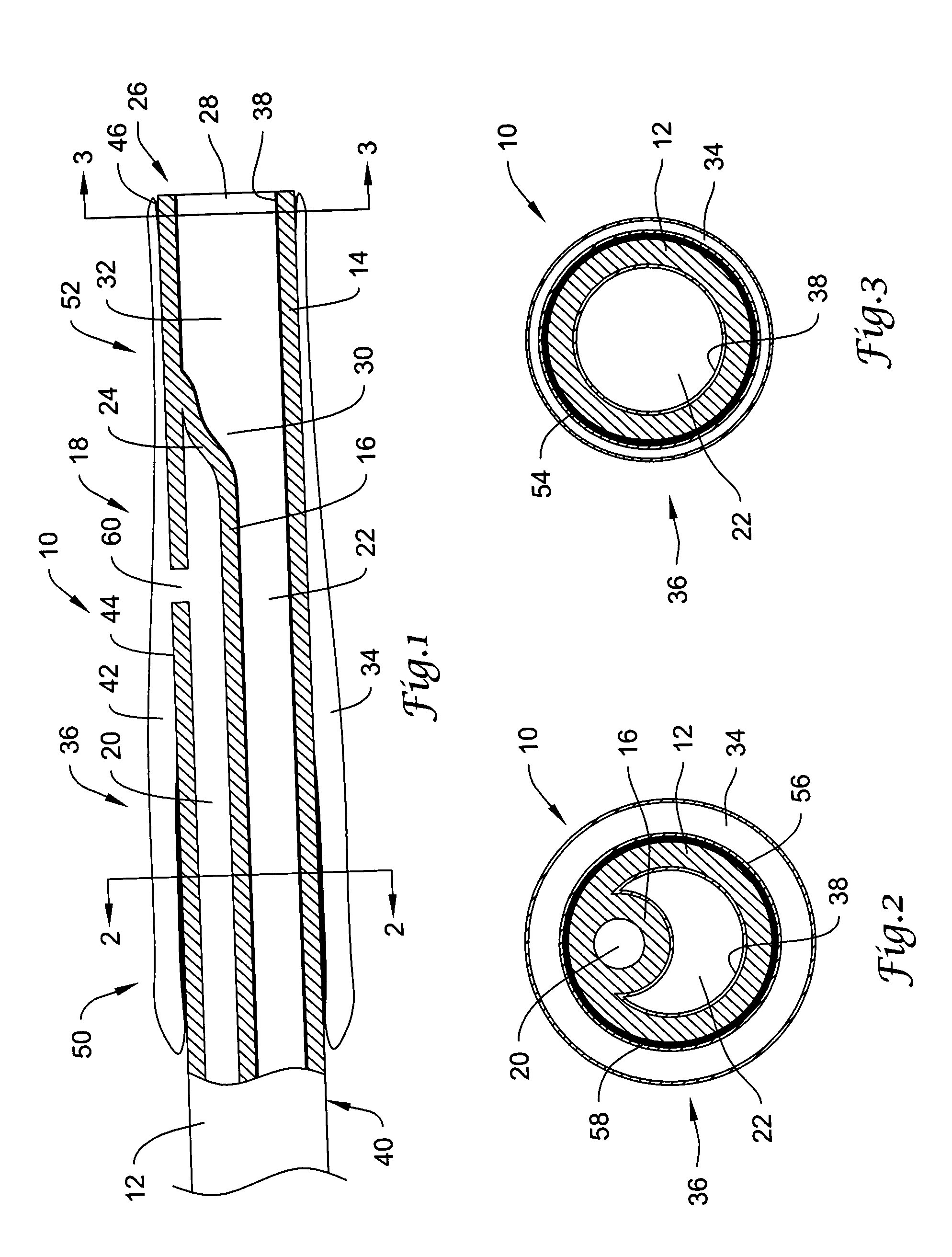
Embolic filters with controlled pore size
The invention provides a device for filtering emboli from blood flowing through a lumen defined by the walls of a vessel in a patient's body comprising a filter element. The filter is expandable from a collapsed configuration when the filter element is restrained to an expanded configuration when the filter element is unrestrained, and the filter element comprises a self-expanding material having pores. When the filter element is in the expanded configuration, the average pore size is from 30 to 300 microns and the standard deviation of the pore size is less than 20 percent of the average pore size.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Device for filtering blood in a vessel with helical elements
InactiveUS20060020286A1Efficient capturePreventing pulmonary embolismHaemofiltrationSurgeryMedicineEmbolus
A device for capturing an embolus within a vessel of a patient's body has at least one helix made of a mesh material. The at least one helix has a plurality of turns helically arranged around a longitudinal axis. The mesh material has a plurality of pores therein and the pores have a size ≧120 μm. The at least one helix includes a plurality of panels wherein the panels are movable from a collapsed state to an expanded state when placed within a vessel. The mesh material is made of a self-expanding material such as nickel titanium in one embodiment. In another embodiment, the device has a double helix arrangement.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
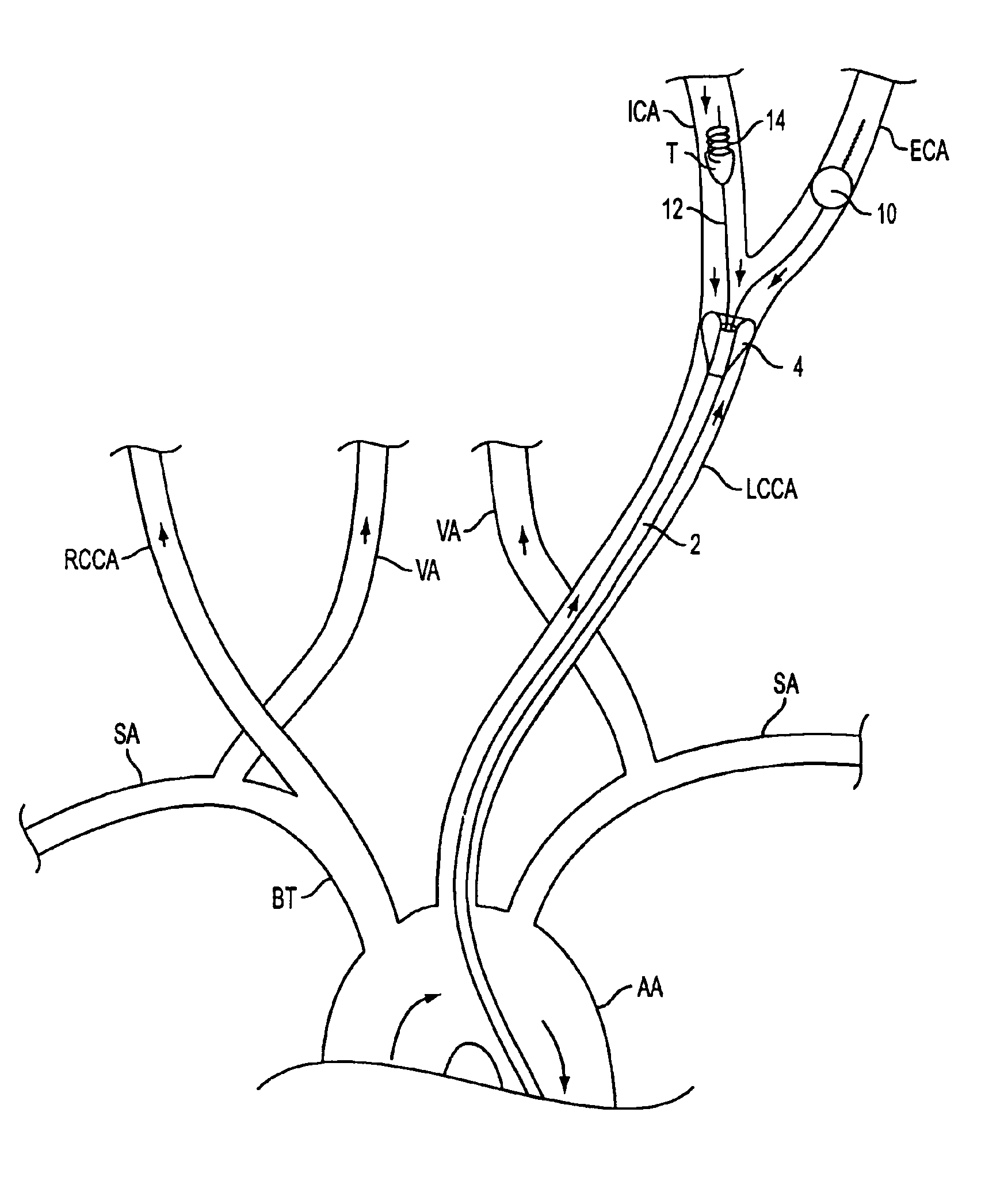
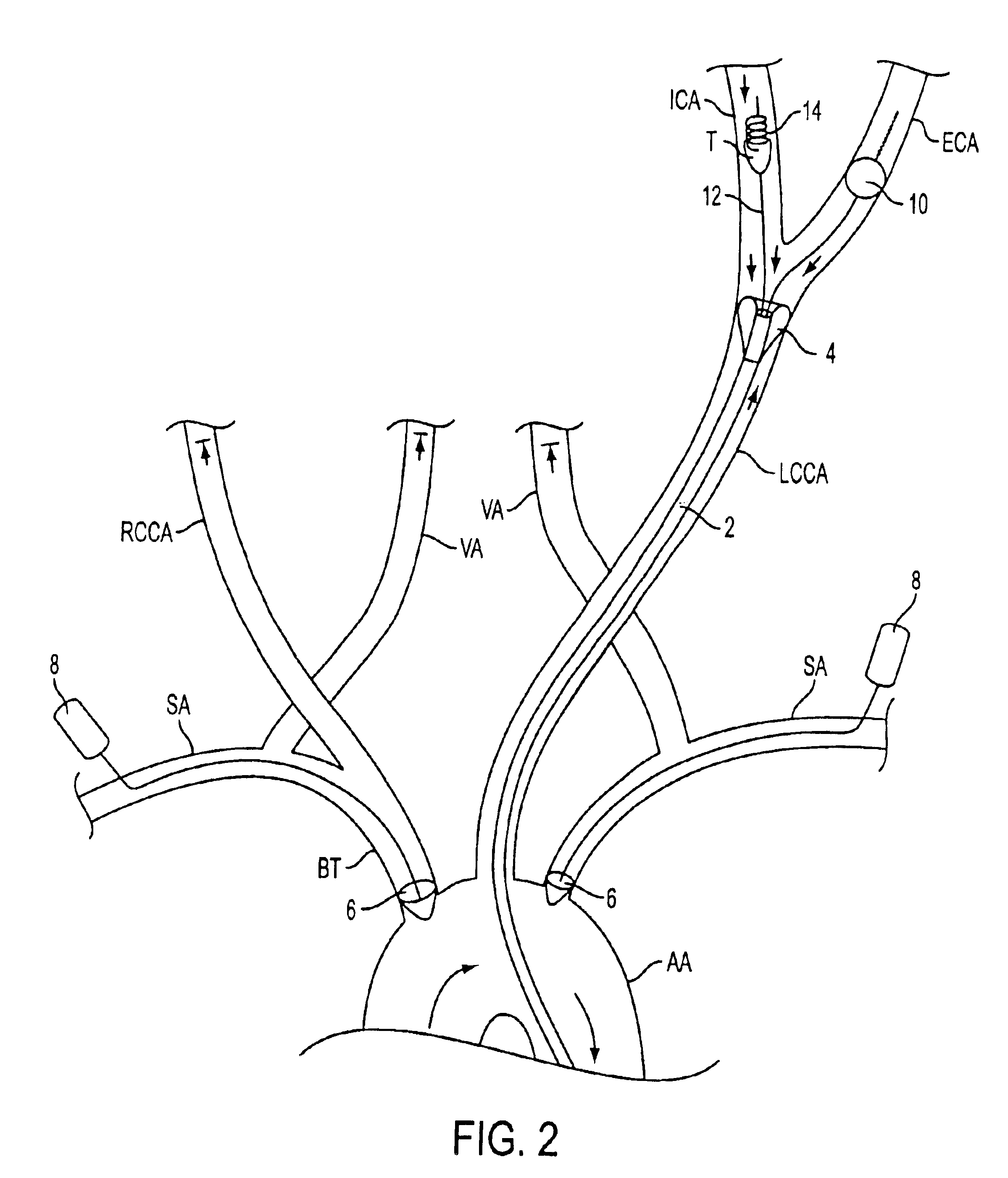
Apparatus and methods for treating stroke and controlling cerebral flow characteristics
InactiveUS6929634B2Quickly and efficiently treat cerebral occlusionConvenient introductionStentsBalloon catheterThrombusRetrograde Flow
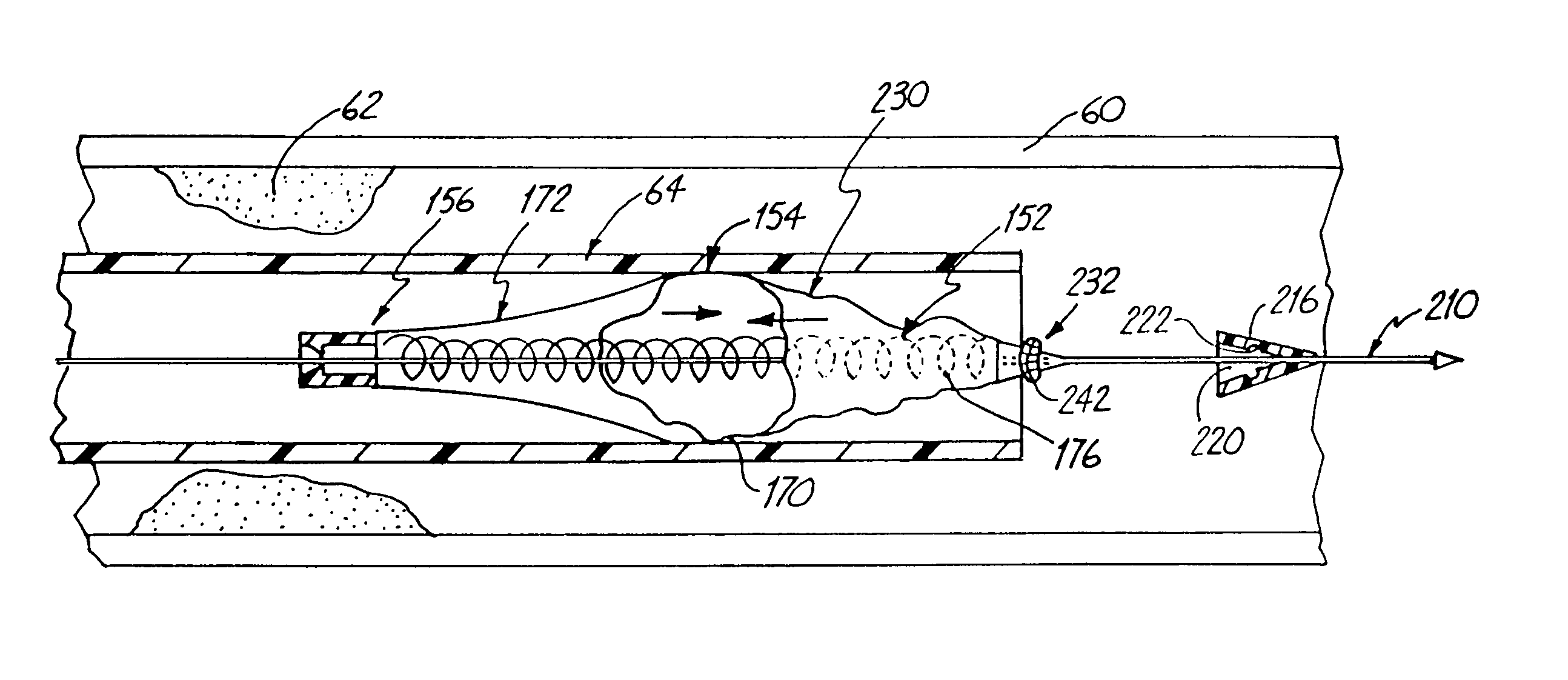
Apparatus and methods for treatment of stroke are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention disposes at least one catheter having a distal occlusive member in the common carotid artery of the hemisphere of the cerebral occlusion. Retrograde flow may be provided through the catheter to effectively control cerebral flow characteristics. Under such controlled flow conditions, a thrombectomy device may be used to treat the occlusion, and any emboli generated are directed into the catheter.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
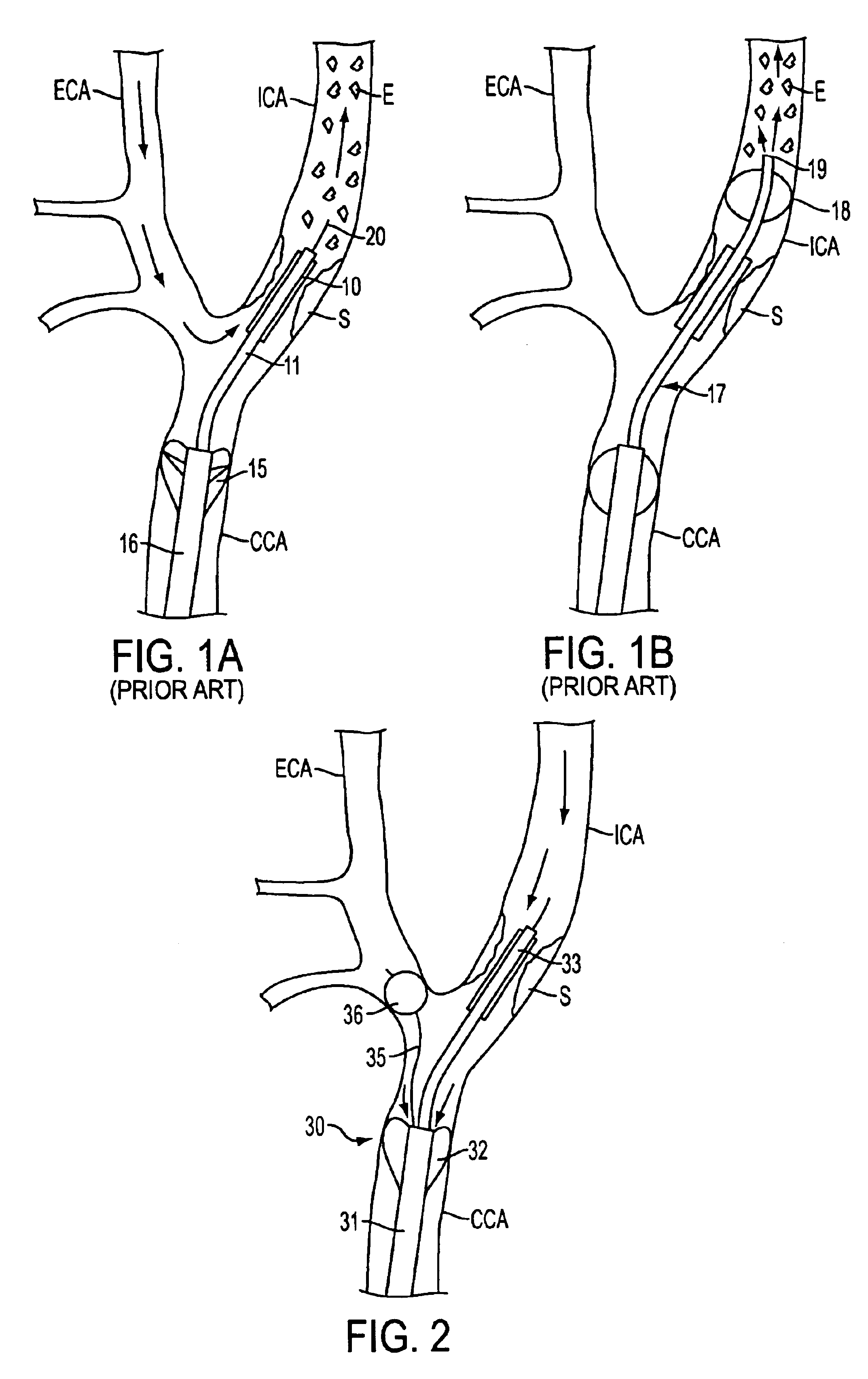
Apparatus and methods for reducing embolization during treatment of carotid artery disease
InactiveUS6908474B2Reduce riskAvoid developmentGuide needlesBalloon catheterPercutaneous angioplastyPressure difference
Methods and apparatus are provided for removing emboli during an angioplasty, stenting or surgical procedure comprising a catheter having an occlusion element, an aspiration lumen, and a blood outlet port in communication with the lumen, a guide wire having a balloon, a venous return sheath with a blood inlet port, and tubing that couples the blood outlet port to the blood inlet port. Apparatus is also provided for occluding the external carotid artery to prevent reversal of flow into the internal carotid artery. The pressure differential between the artery and the vein provides reverse flow through the artery, thereby flushing emboli. A blood filter may optionally be included in-line with the tubing to filter emboli from blood reperfused into the patient.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Vascular device for emboli and thrombi removal and methods of use
InactiveUS7306618B2Permit useFacilitate percutaneous introductionBalloon catheterInfusion syringesThrombusVascular device
Apparatus and methods are provided for use in filtering emboli from a vessel and / or performing thrombectomy and embolectomy, wherein a vascular device disposed on a guidewire comprises a support hoop disposed from a suspension strut. Alternately, a support hoop having an articulation region may be directly connected to a region proximate the distal end of the guidewire. A blood permeable sac is affixed to the support hoop to form a mouth of the blood permeable sac. The support hoop is disposed obliquely relative to the longitudinal axis of the guidewire and is capable of being properly used in a wide range of vessel diameters. The vascular device collapses during removal to prevent material from escaping from the sac. A delivery sheath and introducer sheath for use with the vascular device of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:INCEPT LLC
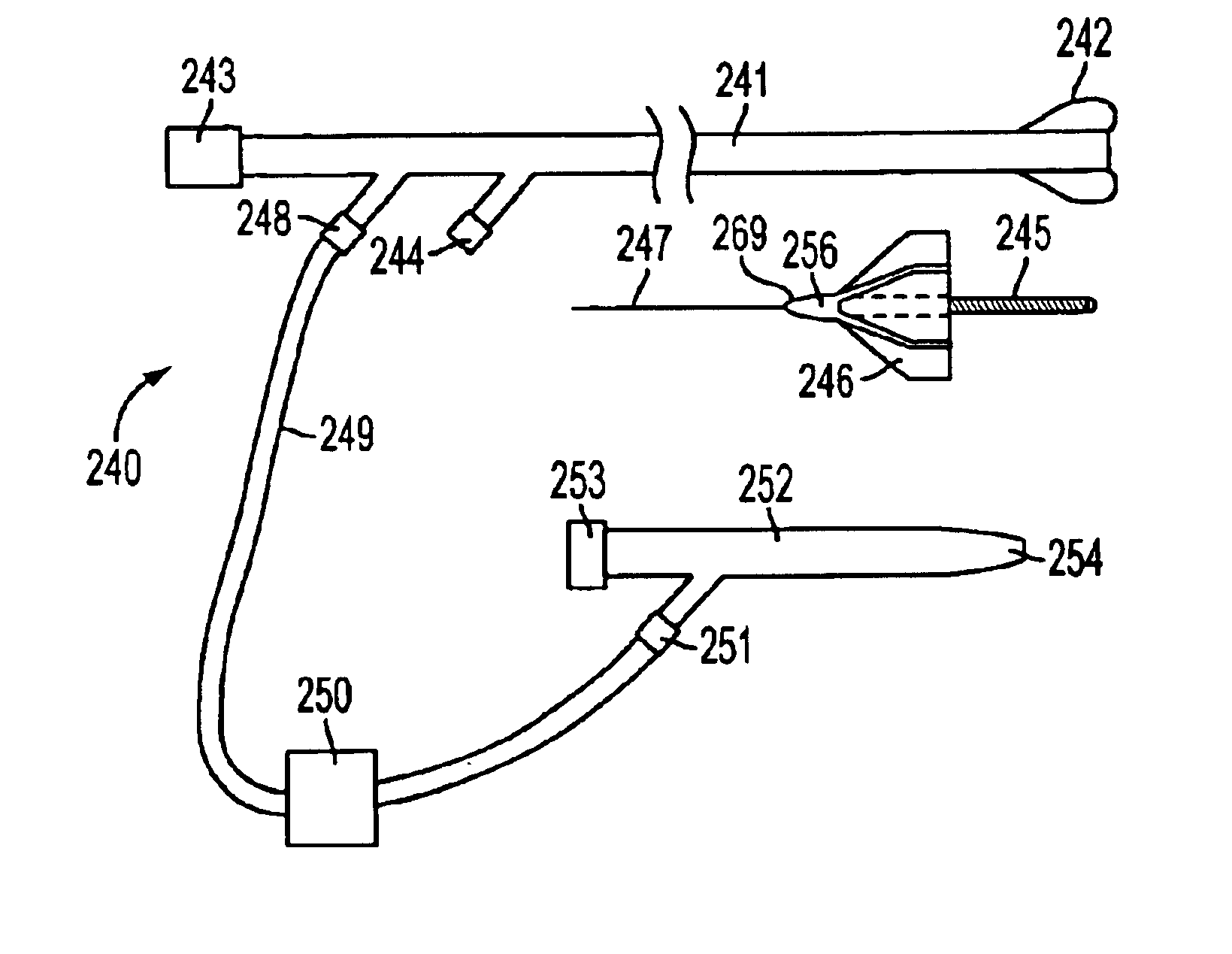
Infusion catheter having an atraumatic tip
The present invention is directed to apparatus and methods for treating a vascular occlusion by providing an infusion catheter having an atraumatic tip and at least one delivery port configured to infuse fluid into the occlusion. The fluid that is infused dilutes the occlusion and reduces adhesion of the occlusion to an intima of the vessel wall, thereby causing the occlusion to dislodge. Emboli generated in the process are directed into an emboli removal catheter for removal.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Apparatus and methods for treating stroke and controlling cerebral flow characteristics
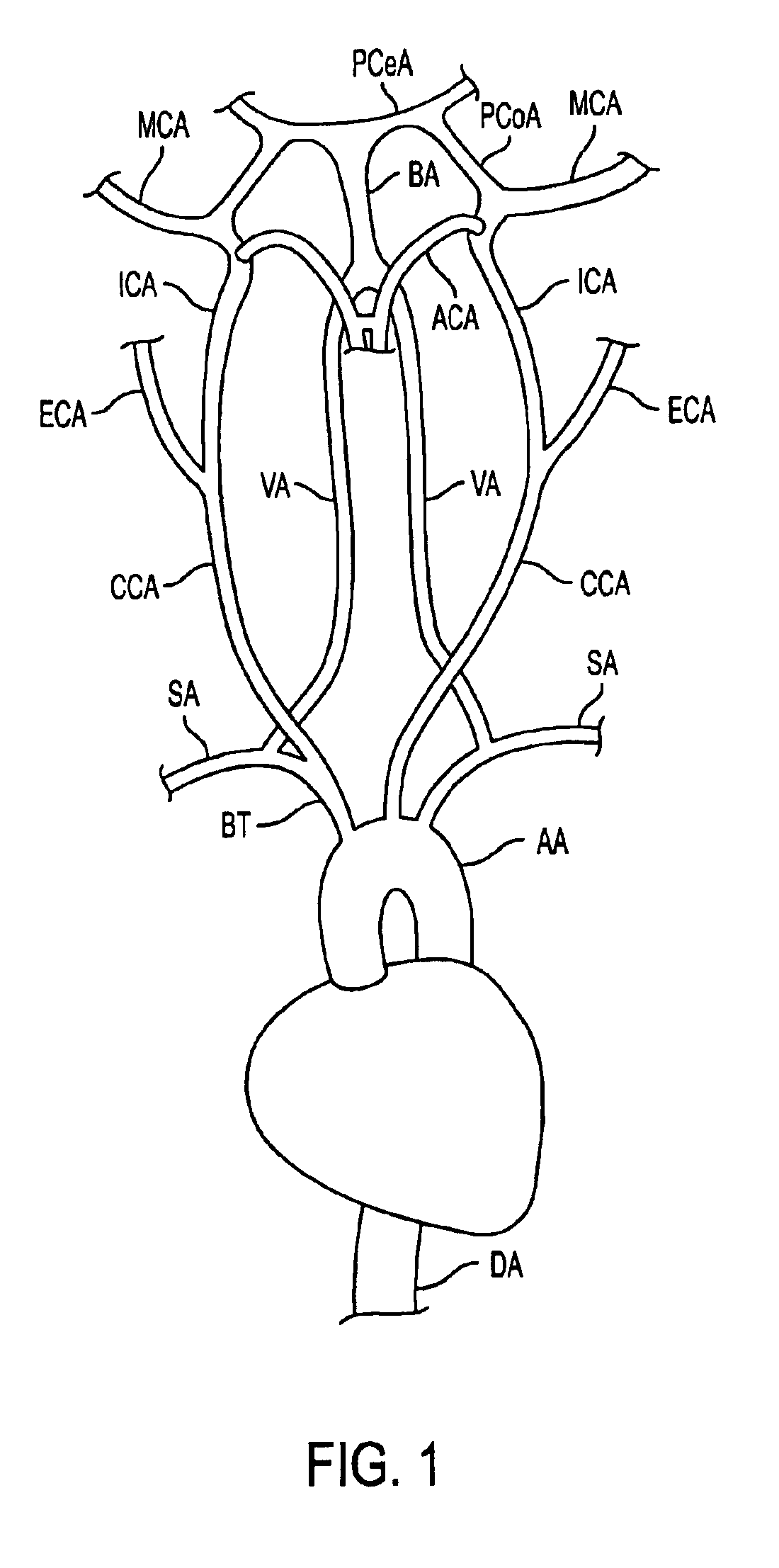
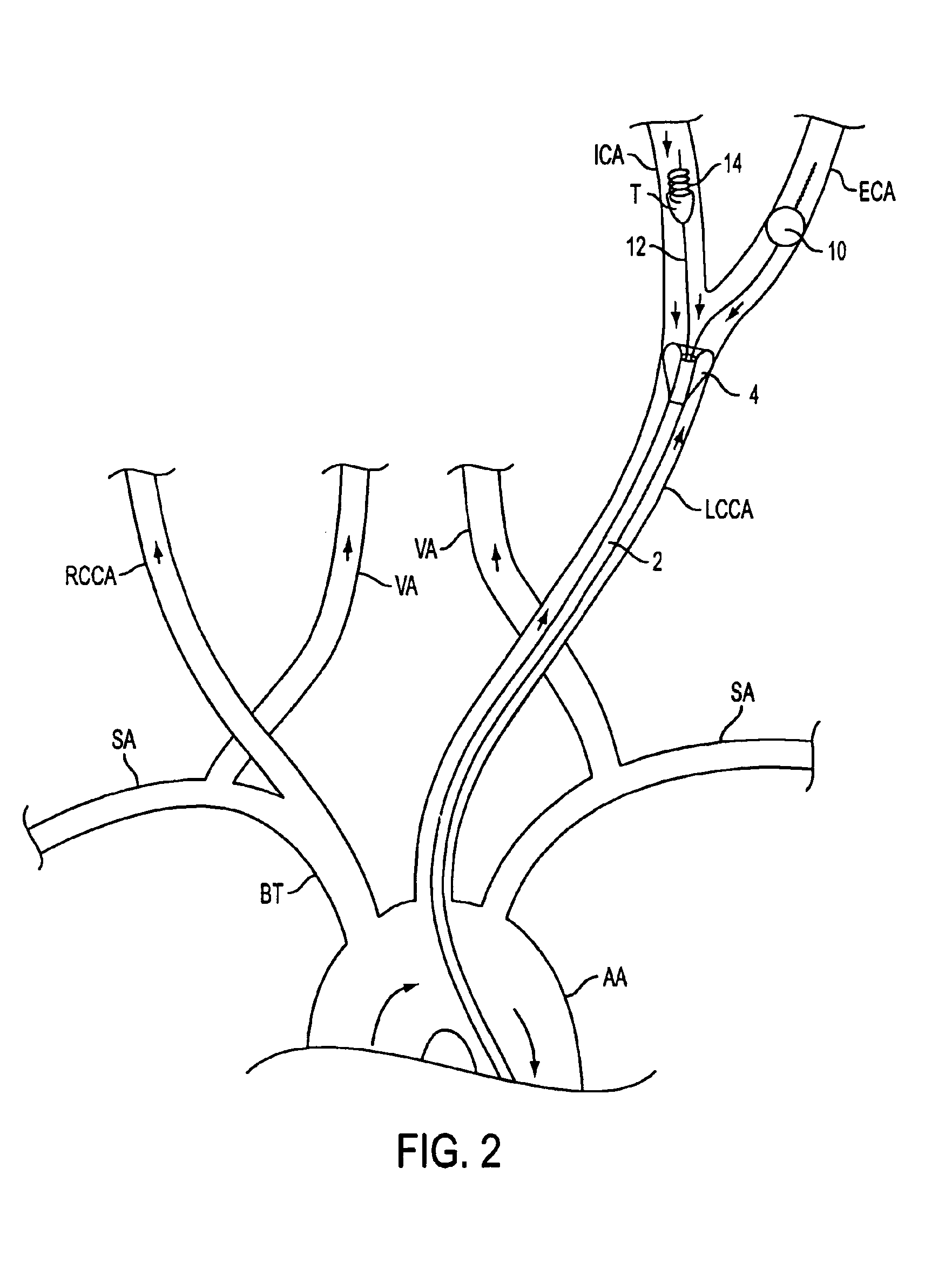
InactiveUS6902540B2Quickly and efficiently treat cerebral occlusionEfficient removalStentsBalloon catheterCarotid imtEmbolus
Apparatus and methods for treatment of stroke are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention disposes at least one catheter having a distal occlusive member in either the common carotid artery (CCA) or both the vertebral artery (VA) and the CCA on the hemisphere of the cerebral occlusion. Blood flow in the opposing carotid and / or vertebral arteries may be inhibited. Retrograde or antegrade flow may be provided through either catheter independently to effectively control cerebral flow characteristics. Under such controlled flow conditions, a thrombectomy device may be used to treat the occlusion, and any emboli generated are directed into the catheter(s).
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Apparatus and methods for reducing embolization during treatment of carotid artery disease
InactiveUS6905490B2Reduce riskAvoid developmentGuide needlesBalloon catheterPercutaneous angioplastyPressure difference
Methods and apparatus are provided for removing emboli during an angioplasty, stenting or surgical procedure comprising a catheter having an occlusion element, an aspiration lumen, and a blood outlet port in communication with the lumen, a guide wire having a balloon, a venous return catheter with a blood inlet port, and tubing that couples the blood outlet port to the blood inlet port. Apparatus is also provided for occluding the external carotid artery to prevent reversal of flow into the internal carotid artery. The pressure differential between the artery and the vein provides reverse flow through the artery, thereby flushing emboli. A blood filter may optionally be included in-line with the tubing to filter emboli from blood reperfused into the patient.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Blood aspiration system and methods of use
The present invention is directed to a blood aspiration system that is configured to enable various types of aspiration through a working lumen of a catheter. The blood aspiration system facilitates natural aspiration by providing a circuit between a patient's arterial and venous vasculature, and also comprises a manually actuated pump configured to selectively vary rates of aspiration in the working lumen. The blood aspiration system further comprises an external port that allows suction-assisted aspiration or infusion through the working lumen, and further comprises a detachable filter that removes emboli prior to reperfusing blood into a patient's venous vasculature.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Invertible filter for embolic protection
A medical device including a guiding member and a filter portion is disclosed. The guiding member includes a lumen configured to slidably engage the filter portion. The filter portion forms a tubular geometry that extends distally from the guiding member. The filter portion is configured to evert to form a proximally facing concave geometry for capturing emboli. Further, the filter portion includes filter openings that are sized to allow blood cells to pass therethrough while preventing the passage of emboli.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Mechanical embolectomy device and method
An embolectomy device includes a catheter and an elongated shaft positioned in and moveable within the catheter. The shaft has proximal and distal end portions, and a retrieval portion between the proximal and distal end portions. The retrieval portion has a plurality of legs having proximal and distal end portions. Portions of the legs are movable laterally outward from a long axis of the elongated shaft when the retrieval portion is at least partially moved out of the catheter. A retrieval net can be fixed to portions of the legs for engaging a clot or other occlusion within a body canal. An expander can be provided for moving portions of an occlusion toward canal walls to open a lumen. A method for removing clots and other occlusions from body canals is also disclosed.
Owner:RAZACK NASSER
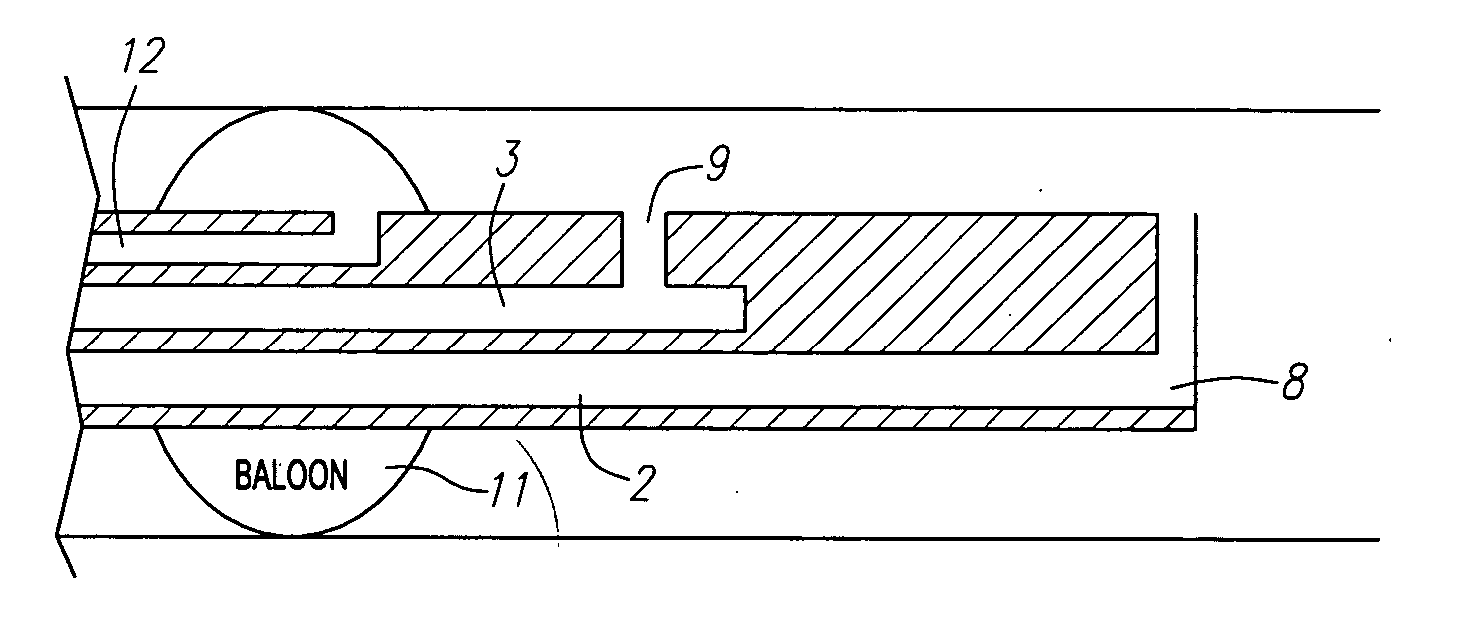
Unfolding balloon catheter for proximal embolus protection
Devices, systems and methods for removing foreign bodies within a body lumen are disclosed. An unfolding balloon catheter may include an elongated shaft having an intussuscepting balloon that can be actuated within a body lumen to capture and retrieve an intravascular device. The balloon may be configured to radially and / or axially expand when inflated, enveloping the intravascular device. In certain embodiments, the balloon may be formed by folding the ends of a distensible member inwardly, and then bonding the ends of the distensible member to the elongated shaft to form an expandable sleeve. An adhesive layer located along a portion of the elongated shaft may be used to temporarily secure the balloon to the elongated shaft.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Intravascular guidewire filter system for pulmonary embolism protection and embolism removal or maceration
An intravascular emboli capture and retrieval system for intravascular embolism protection and embolism removal or maceration. Guidewire mounted proximally and distally located multiple opening filters are deployed within the vasculature and used to part, divide and macerate embolic debris and to capture such embolic debris within the confines thereof. A deployable flexible preformed memory shaped capture sleeve is alternatively used to collapse one or more filters and embolic debris therein for subsequent proximal withdrawal from the vasculature.
Owner:SURMODICS MD LLC
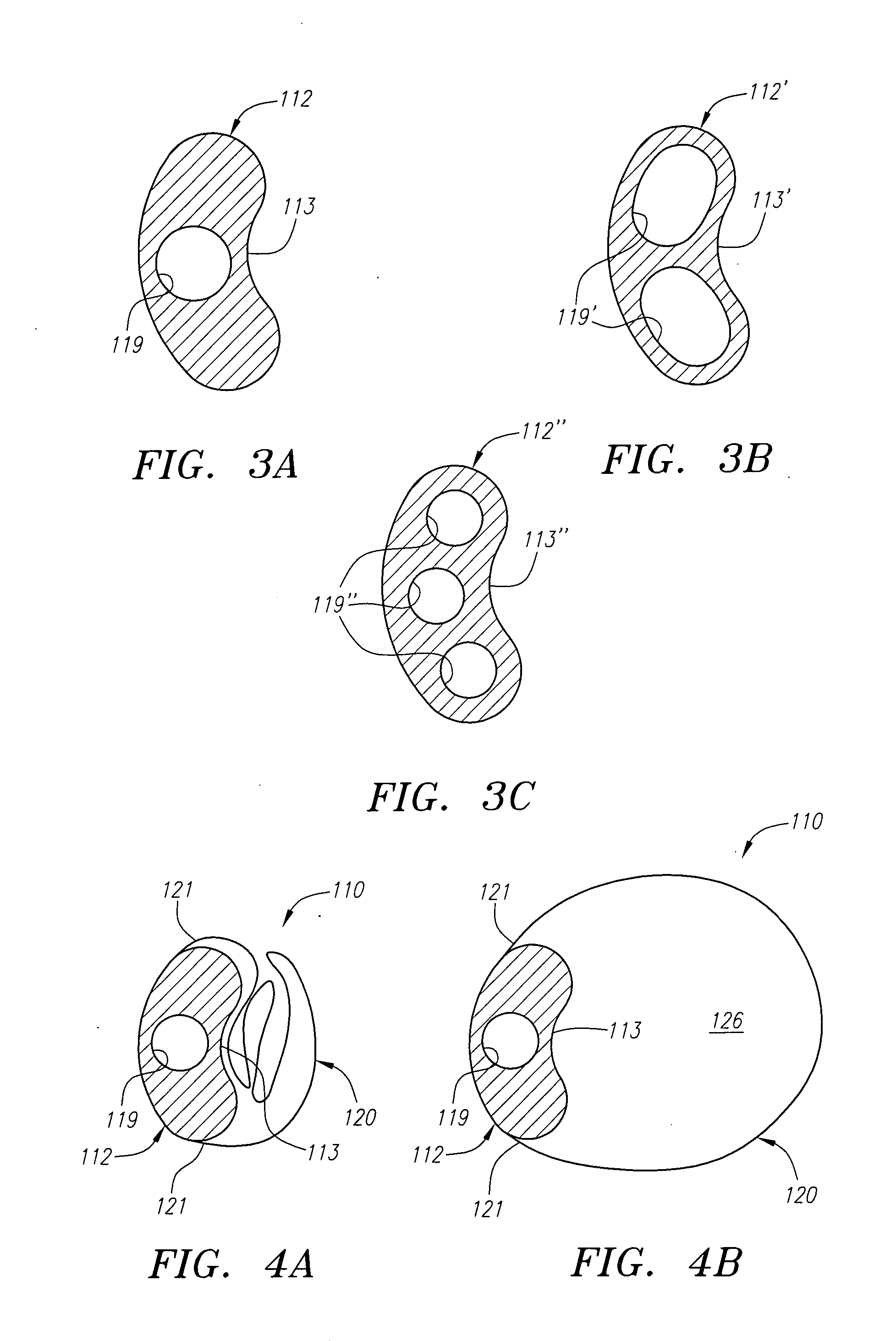
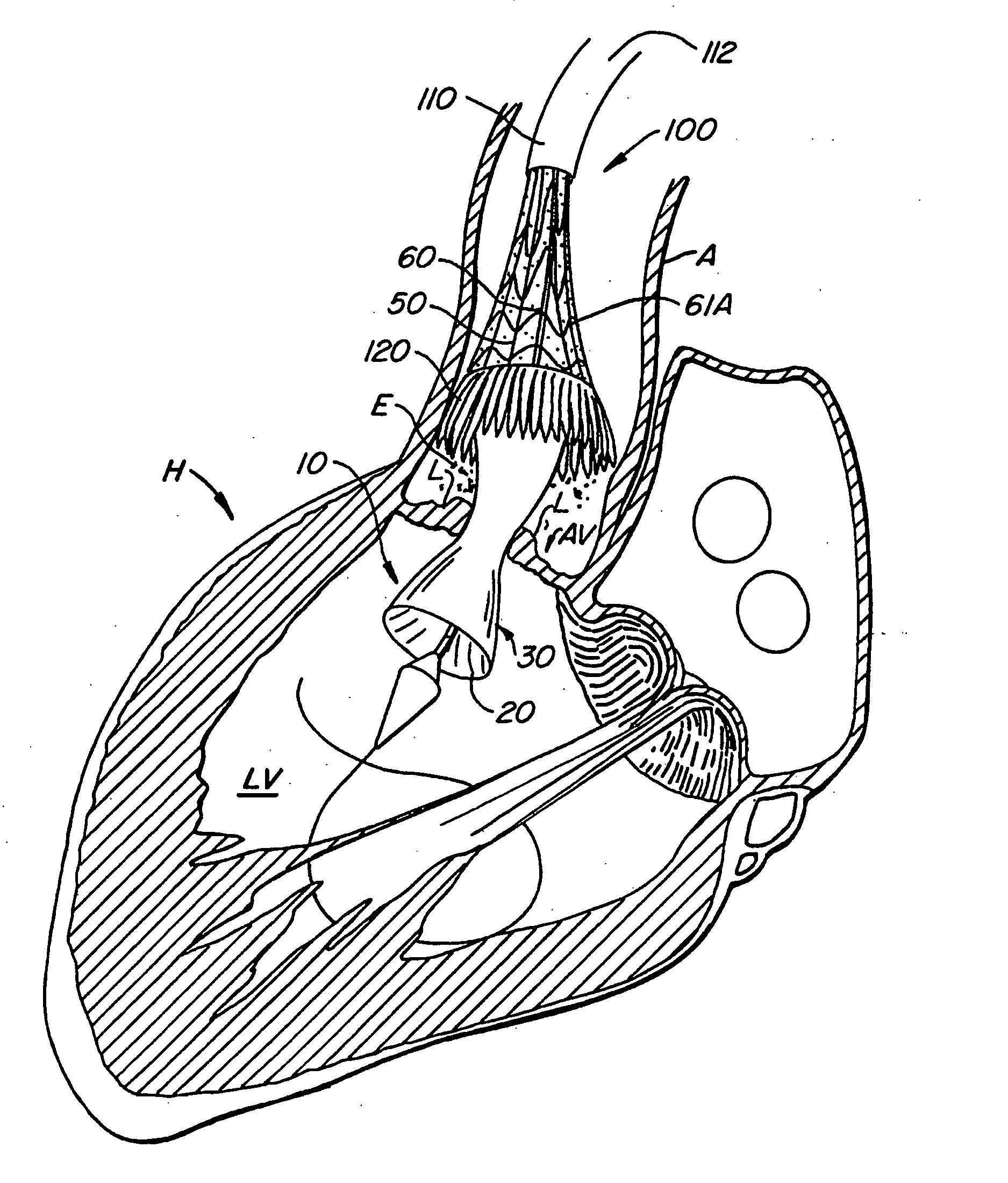
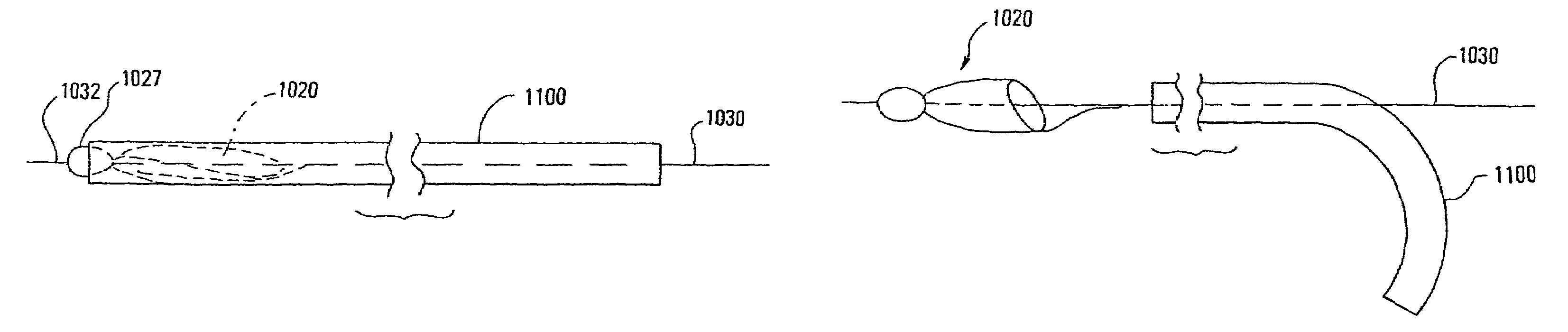
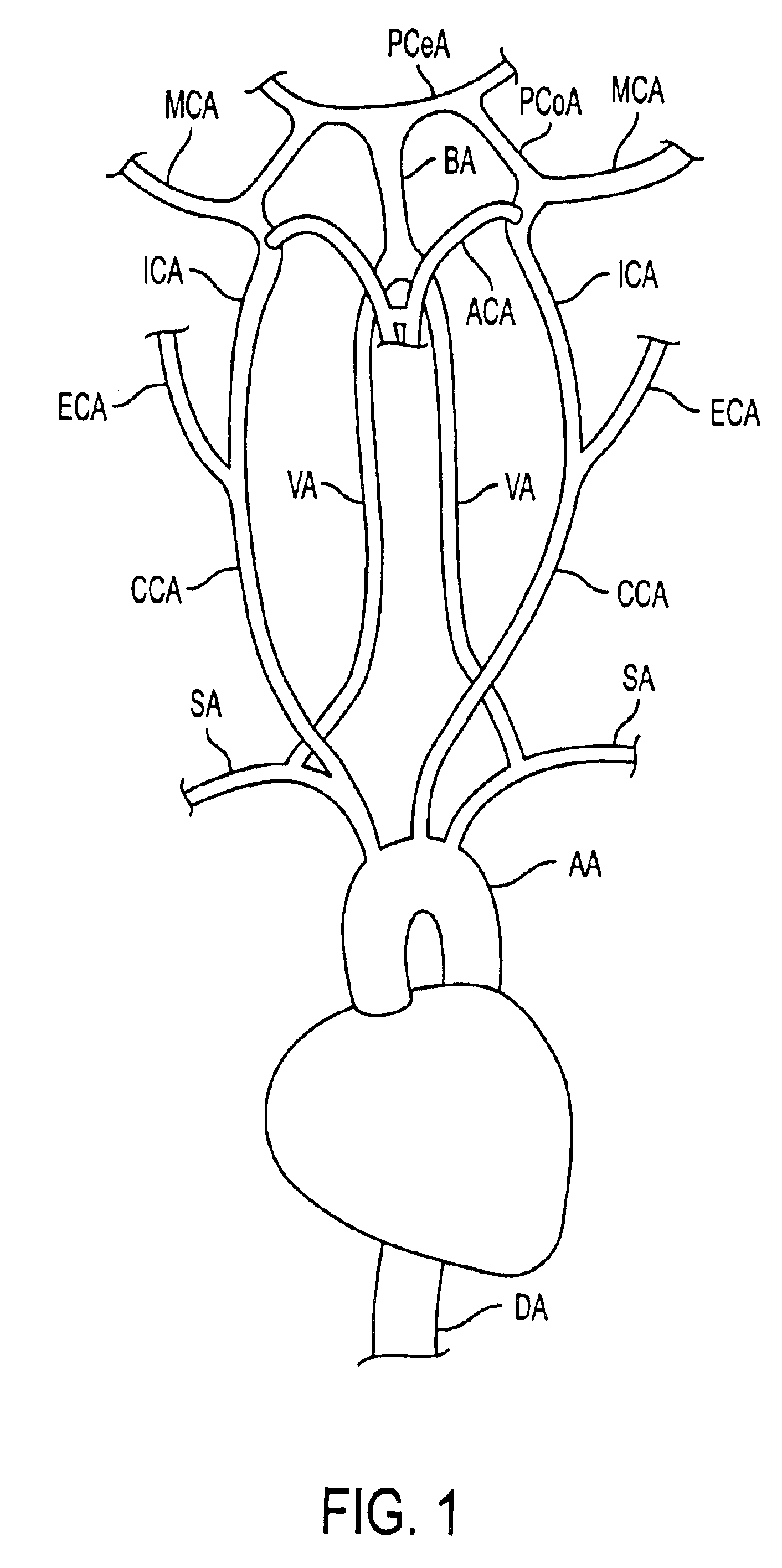
Methods of reducing embolism to cerebral circulation as a consequence of an index cardiac procedure
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (such as greater than 100 microns) from entering either the right or left common carotid arteries, and / or the right or left vertebral arteries by deflecting emboli downstream of these vessels. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The deflector has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the deflector.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Embolic protection guide wire
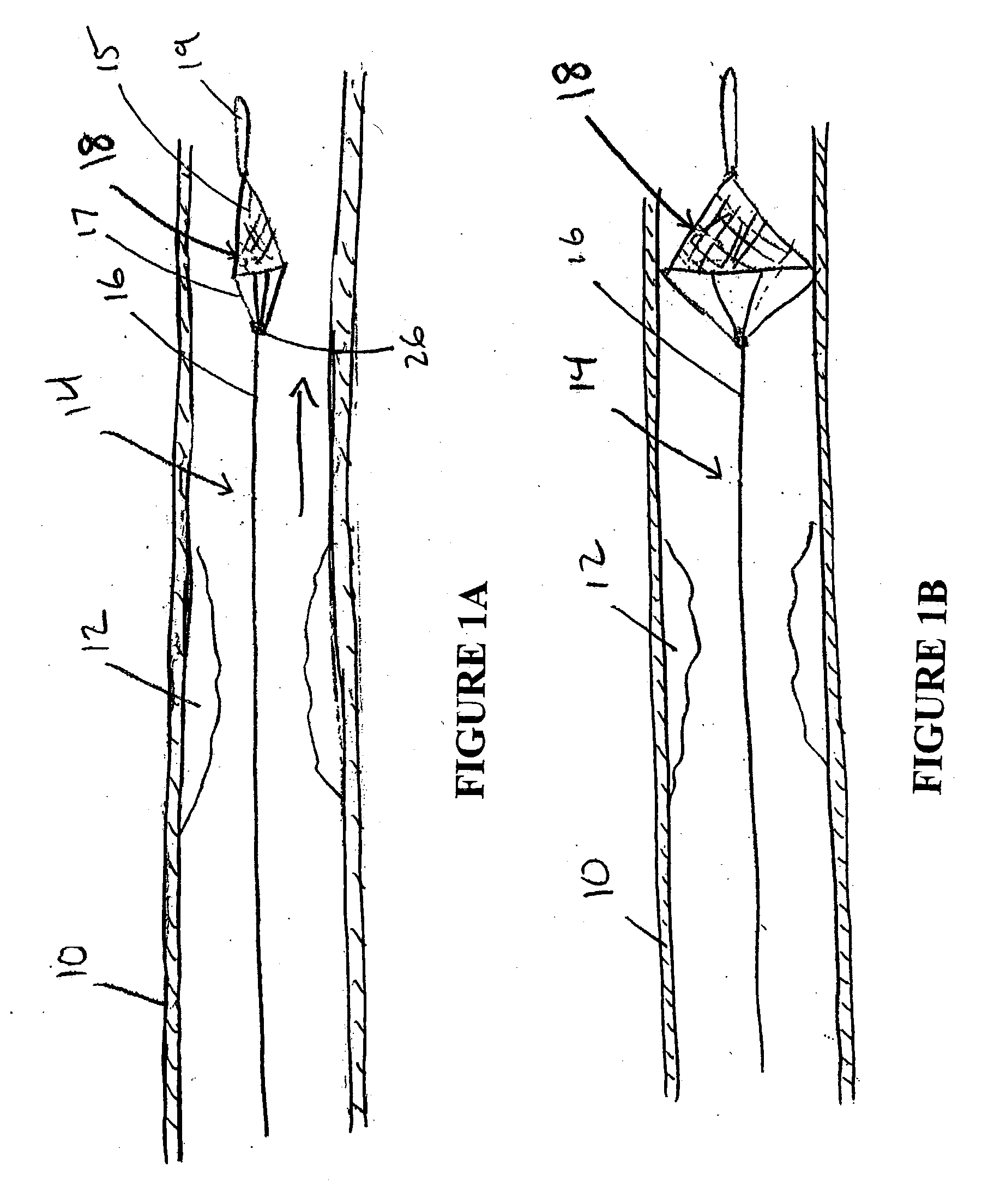
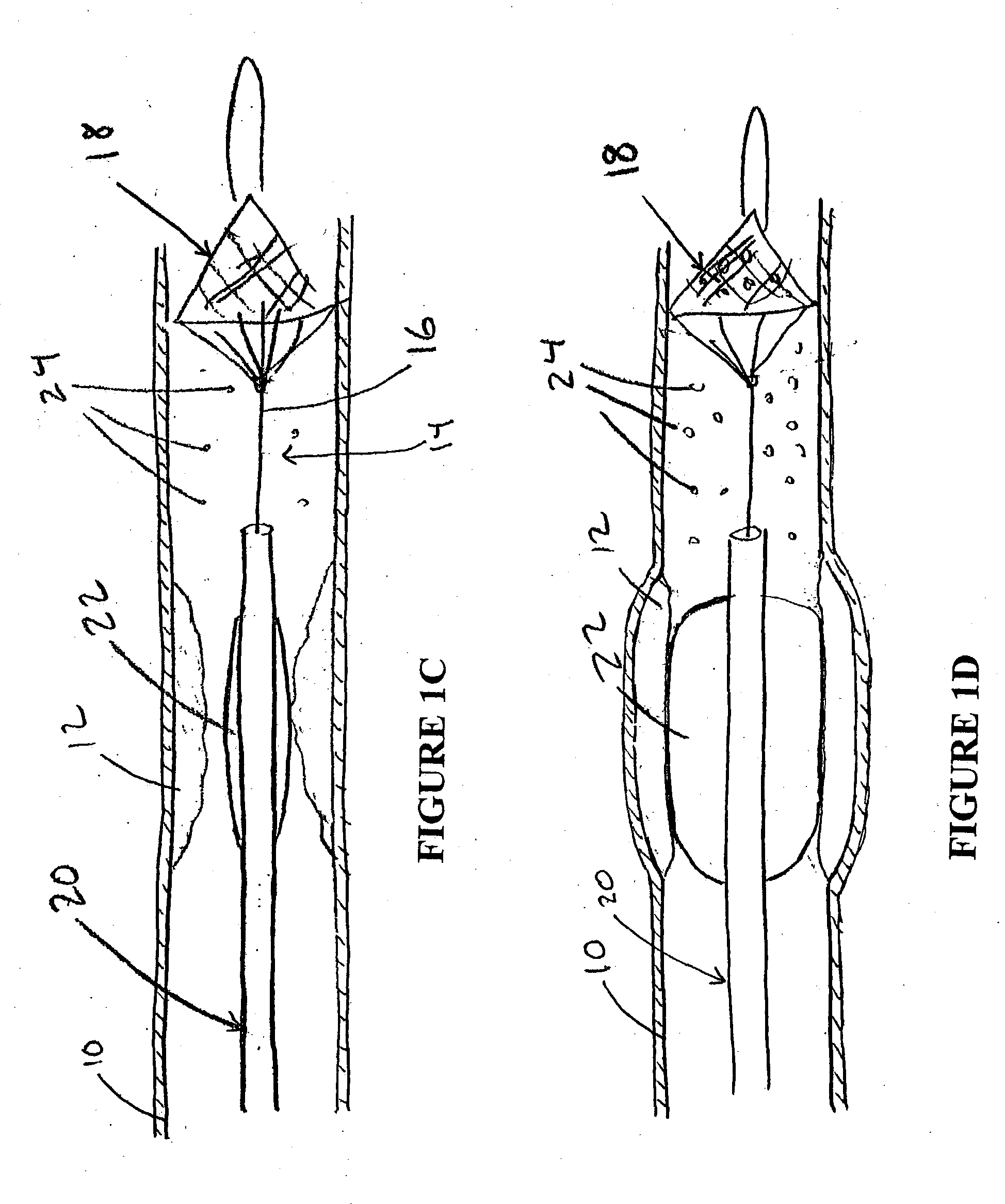
A sheath attached to a guide wire, a tubular shaft member slidable on the guide wire and a filtering assembly constricted within the sheath are movable in a vessel to a position distal to a lesion in the direction of fluid flow. The filtering assembly may be formed from a plurality of angularly spaced splines and a mesh disposed on the splines having properties of passing fluid in the vessel while blocking the passage of emboli in the fluid. The splines may be provided with shape memory for expanding against the wall of the vessel when released from constriction by the sheath. The sheath may be moved relative to the filtering assembly and the support member to release the filter for expansion against the vessel wall. An interventional device can be used to treat the lesion. Any emboli released into the vessel as a result of the interventional treatment are blocked by the filter member while fluid is allowed to pass there through.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com