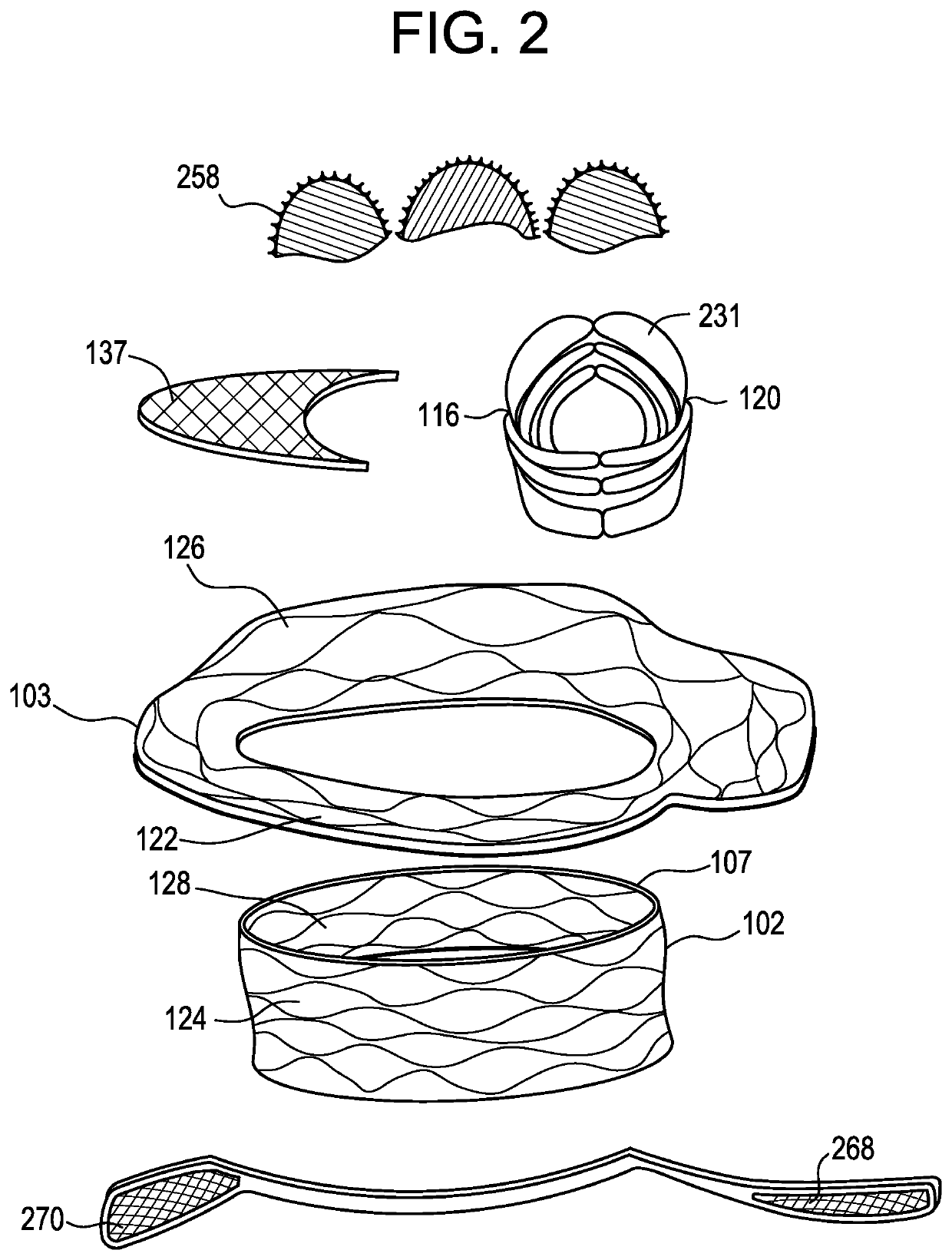
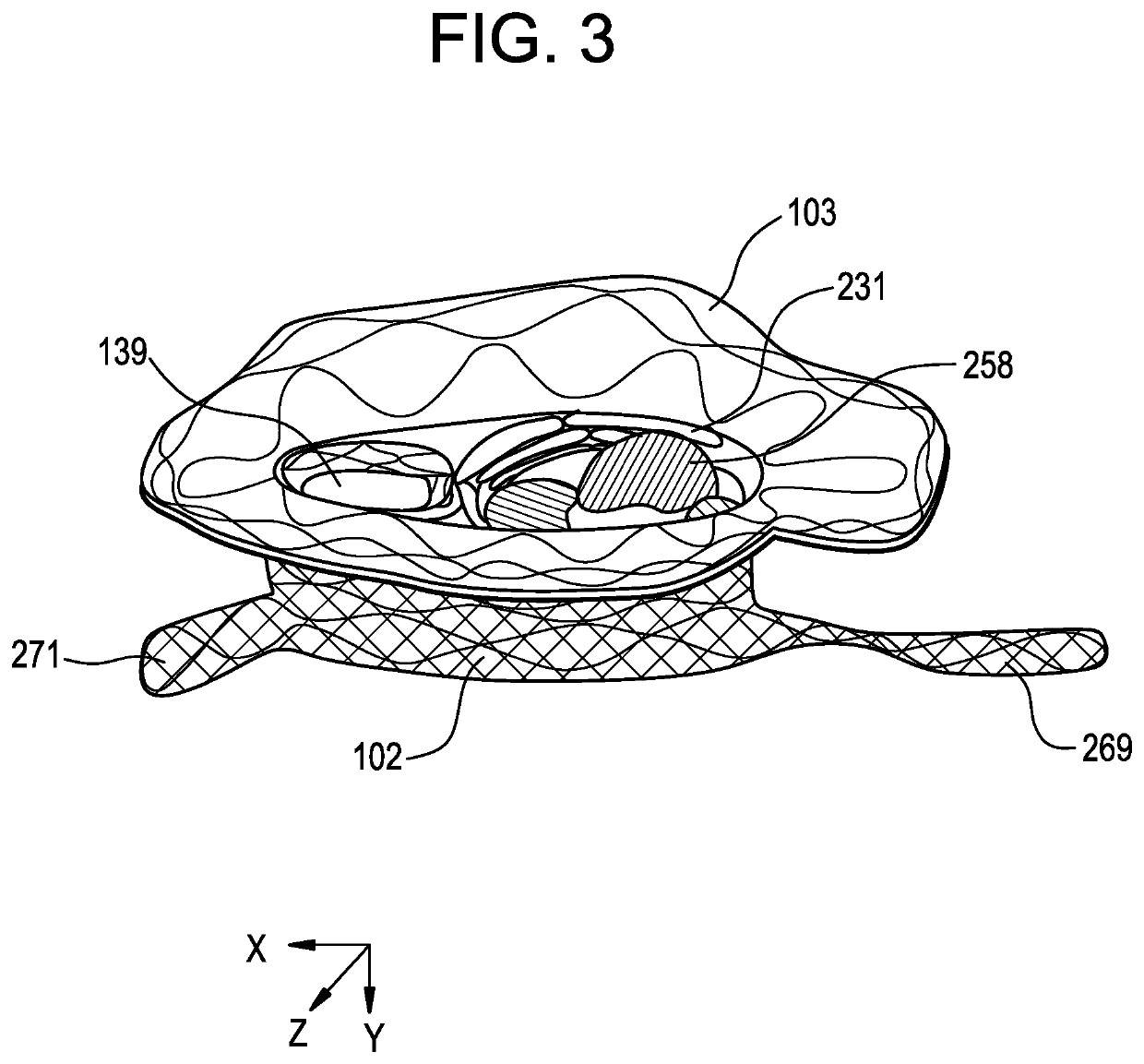
Patents
Literature
87 results about "Heart valve replacement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
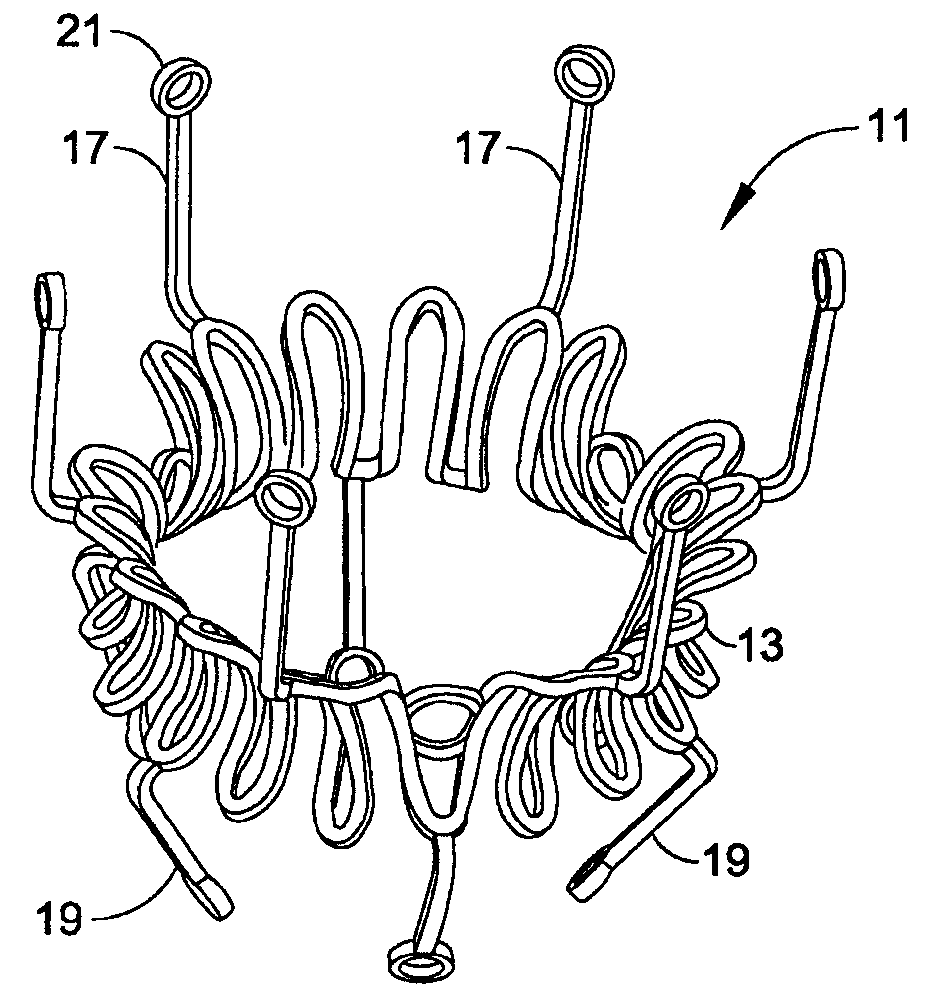
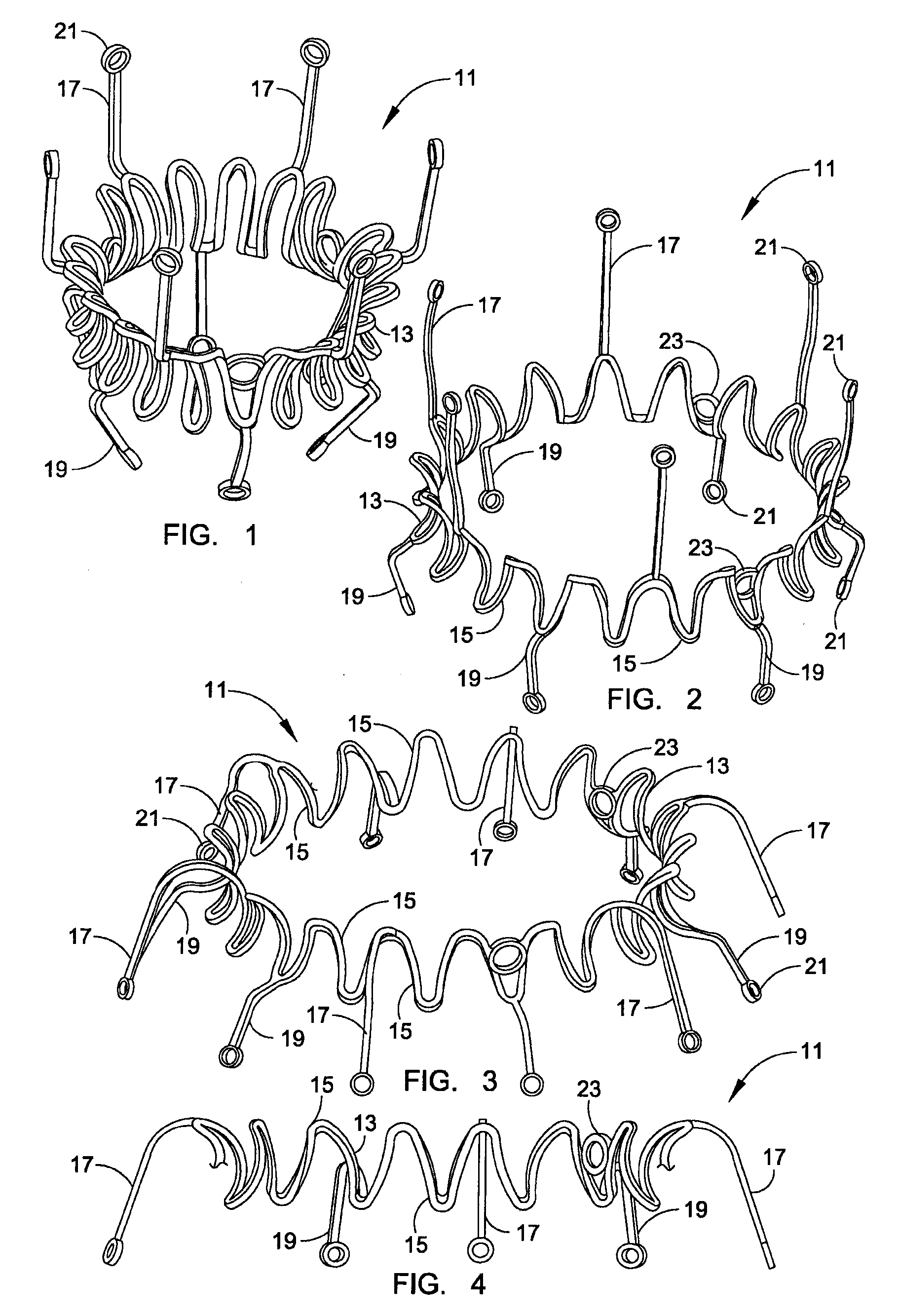
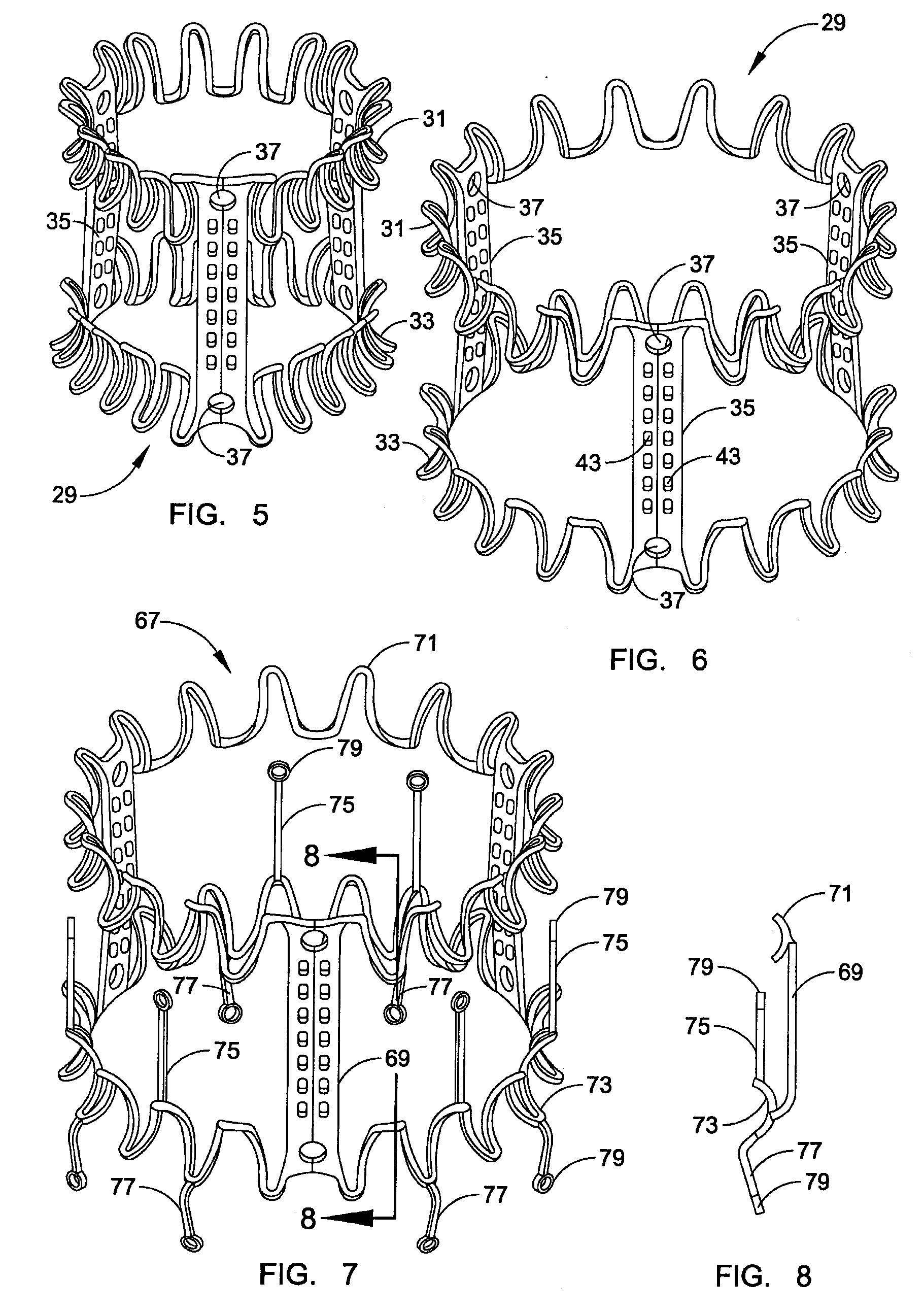
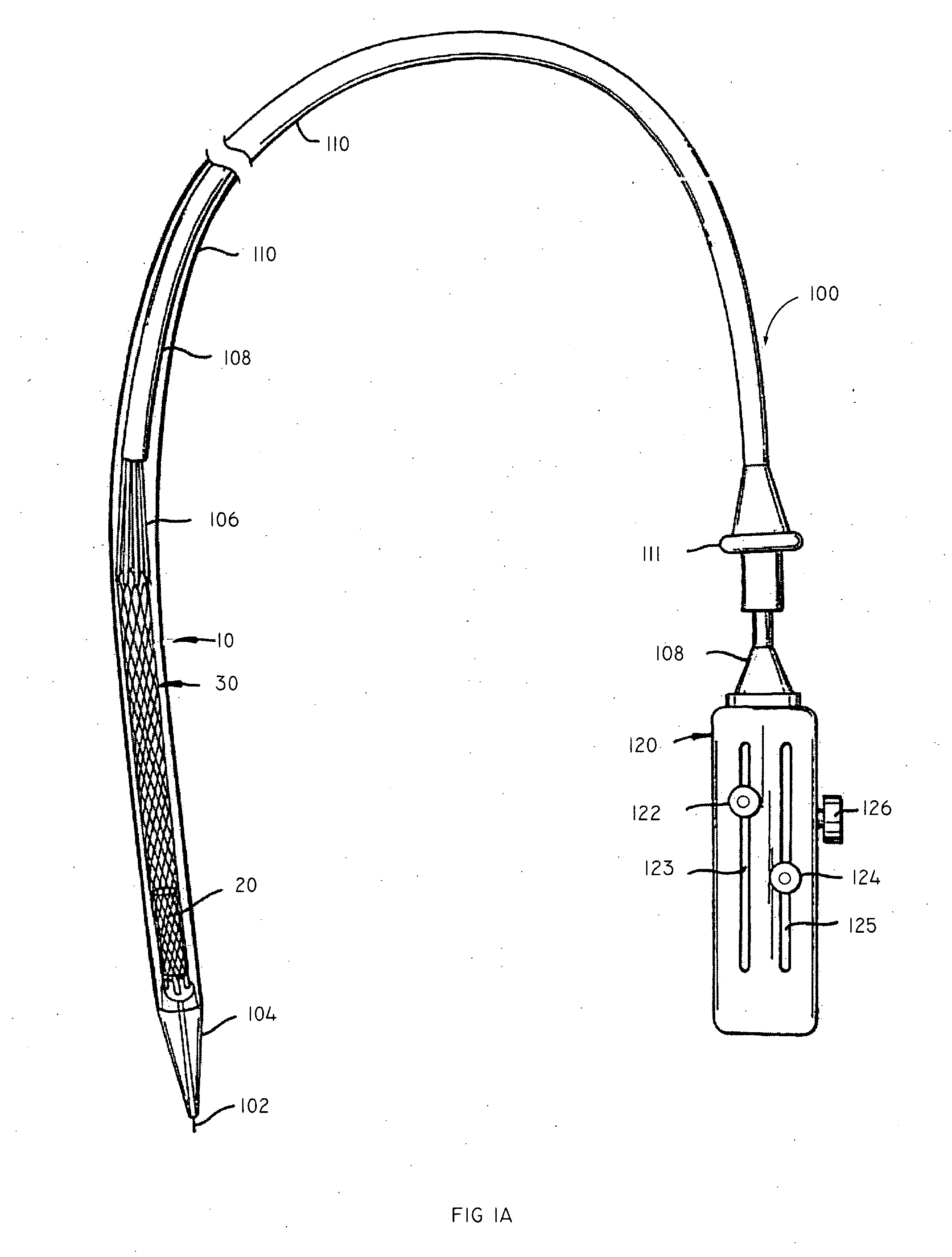
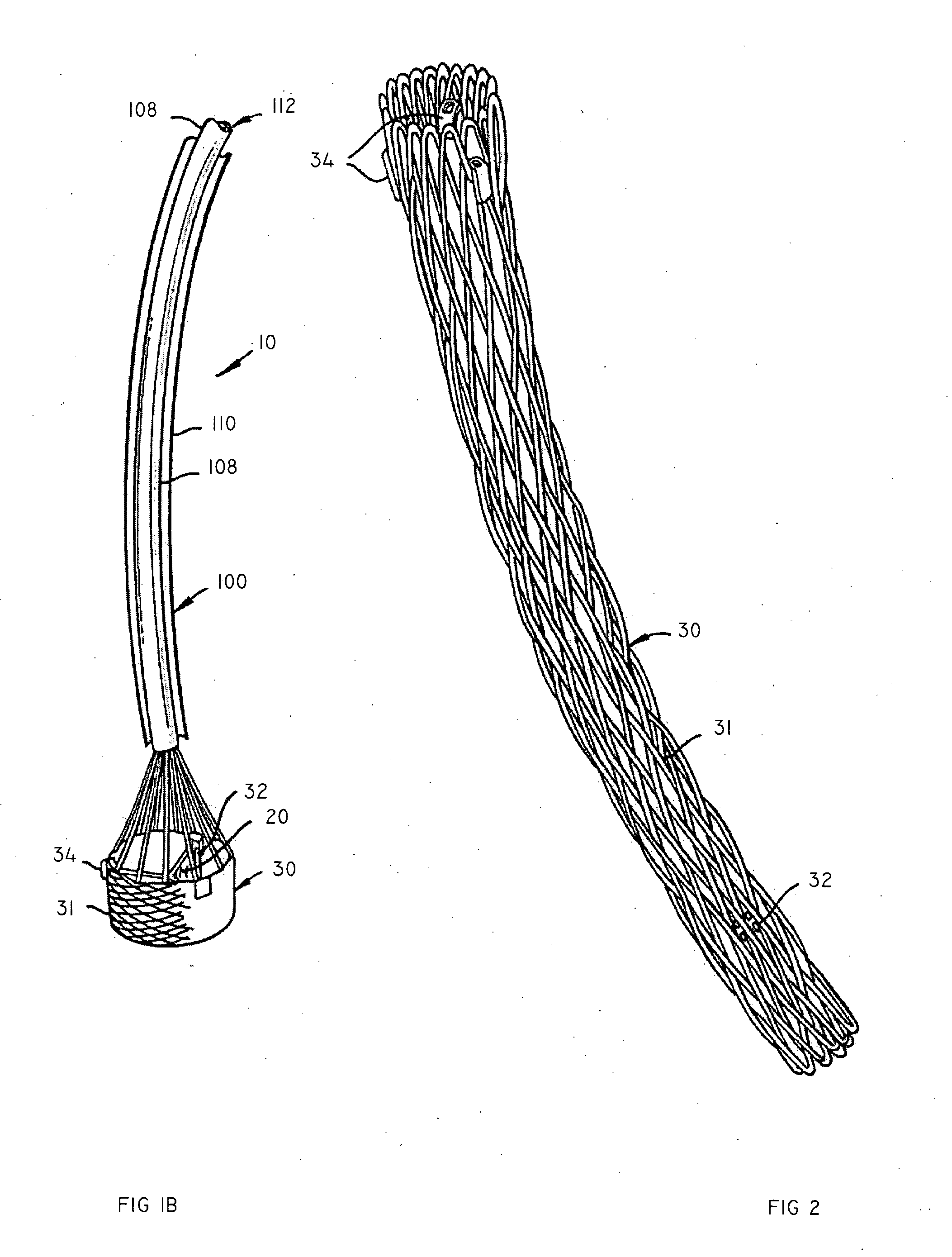
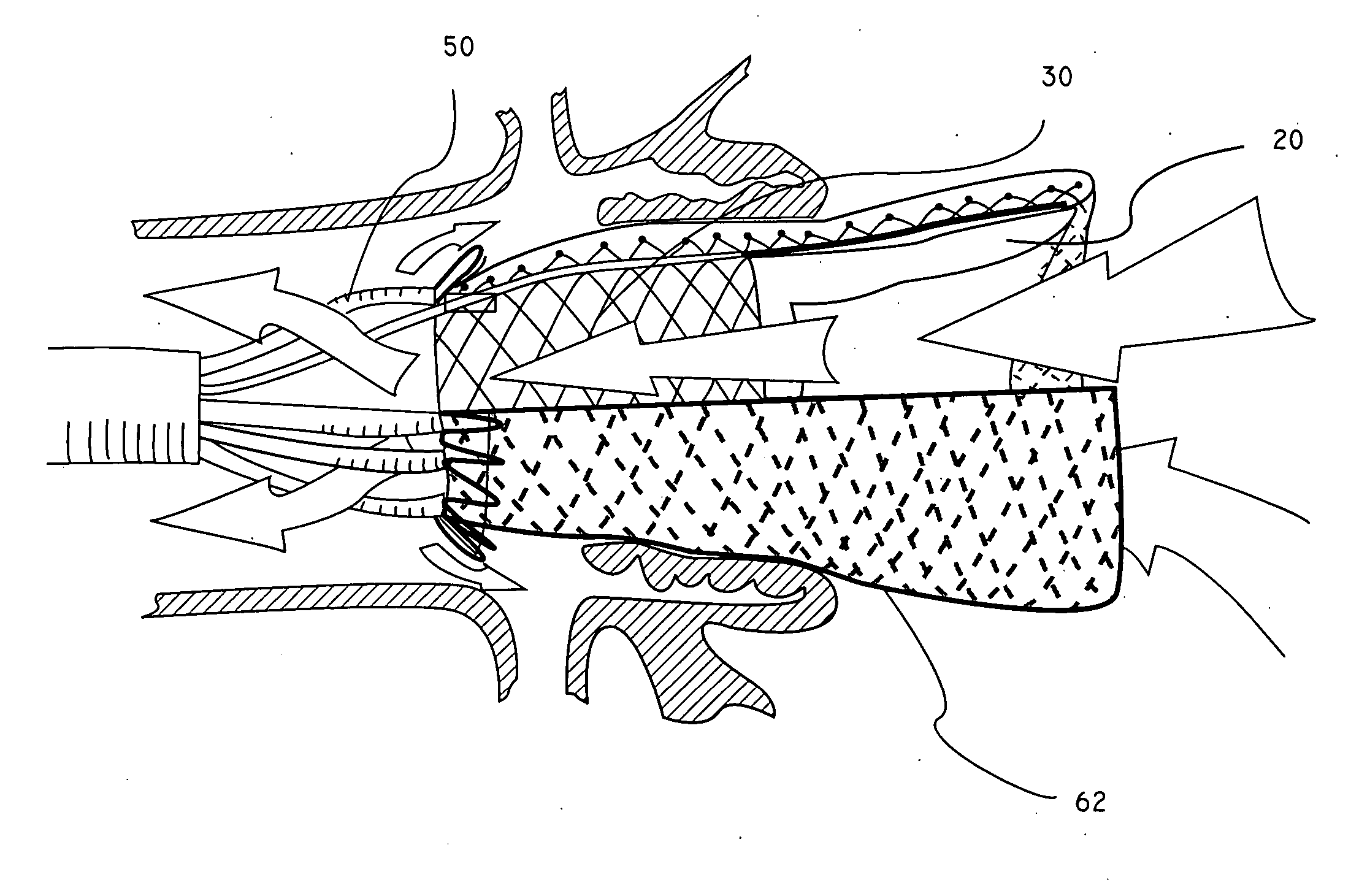
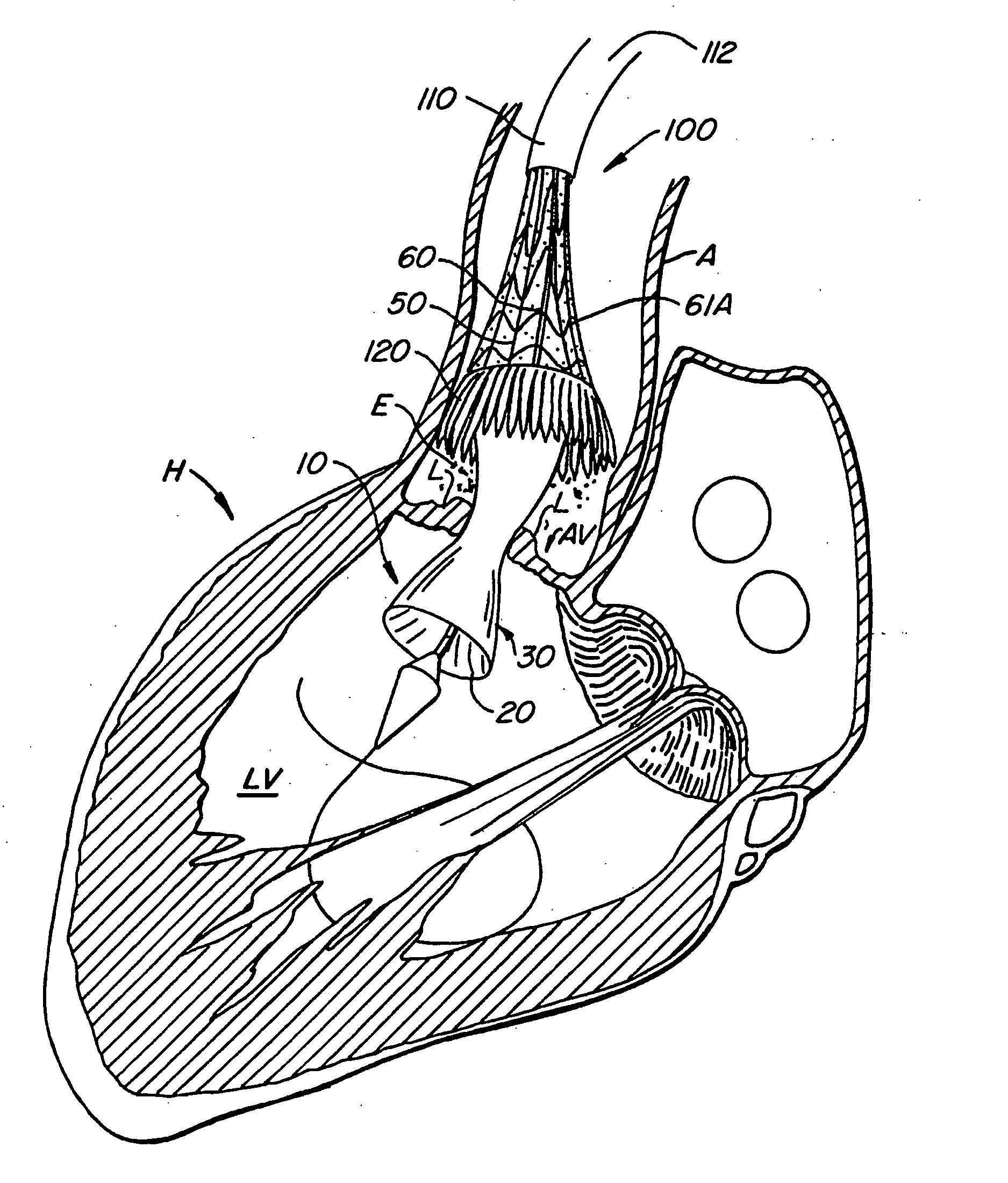
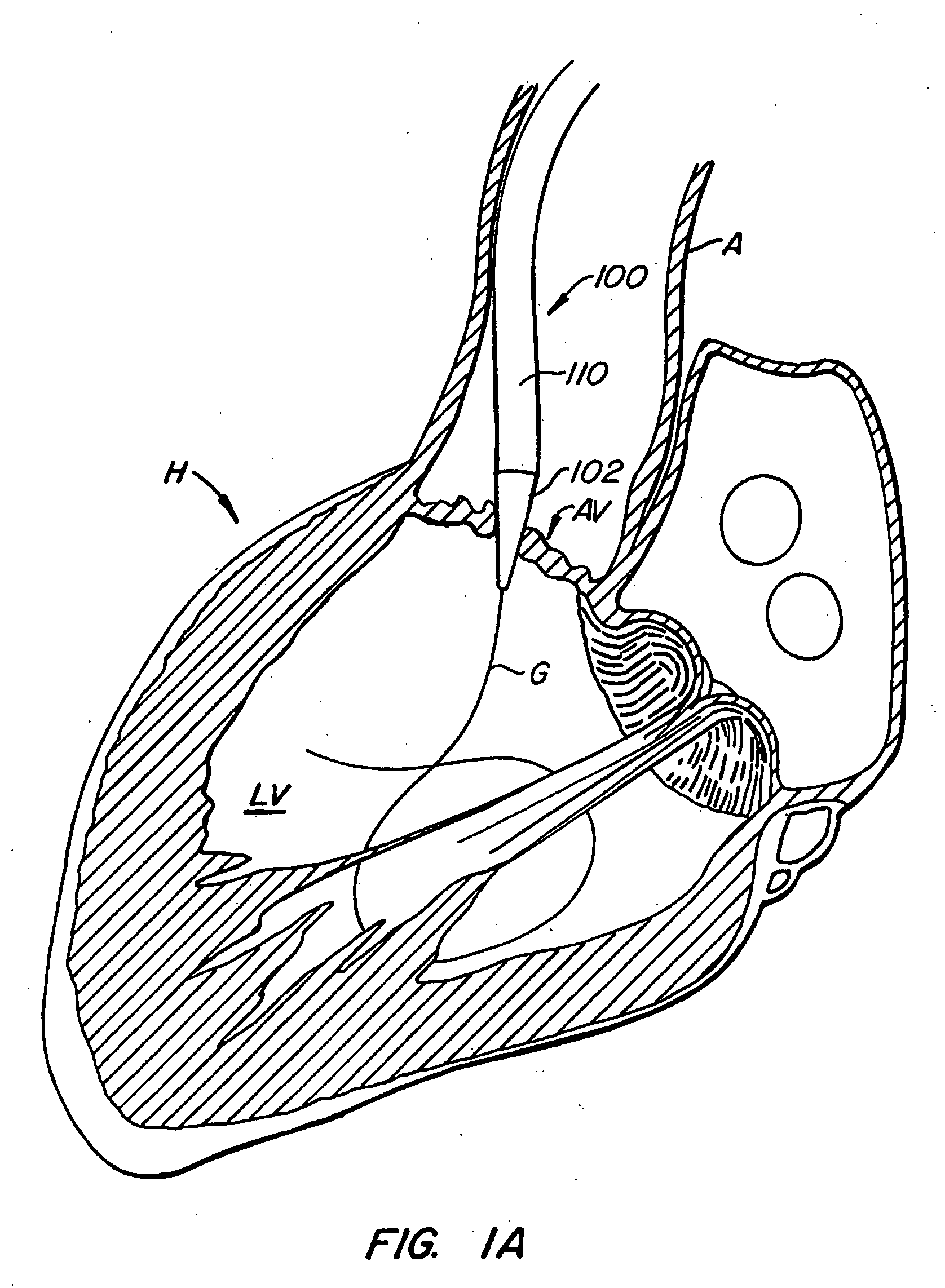
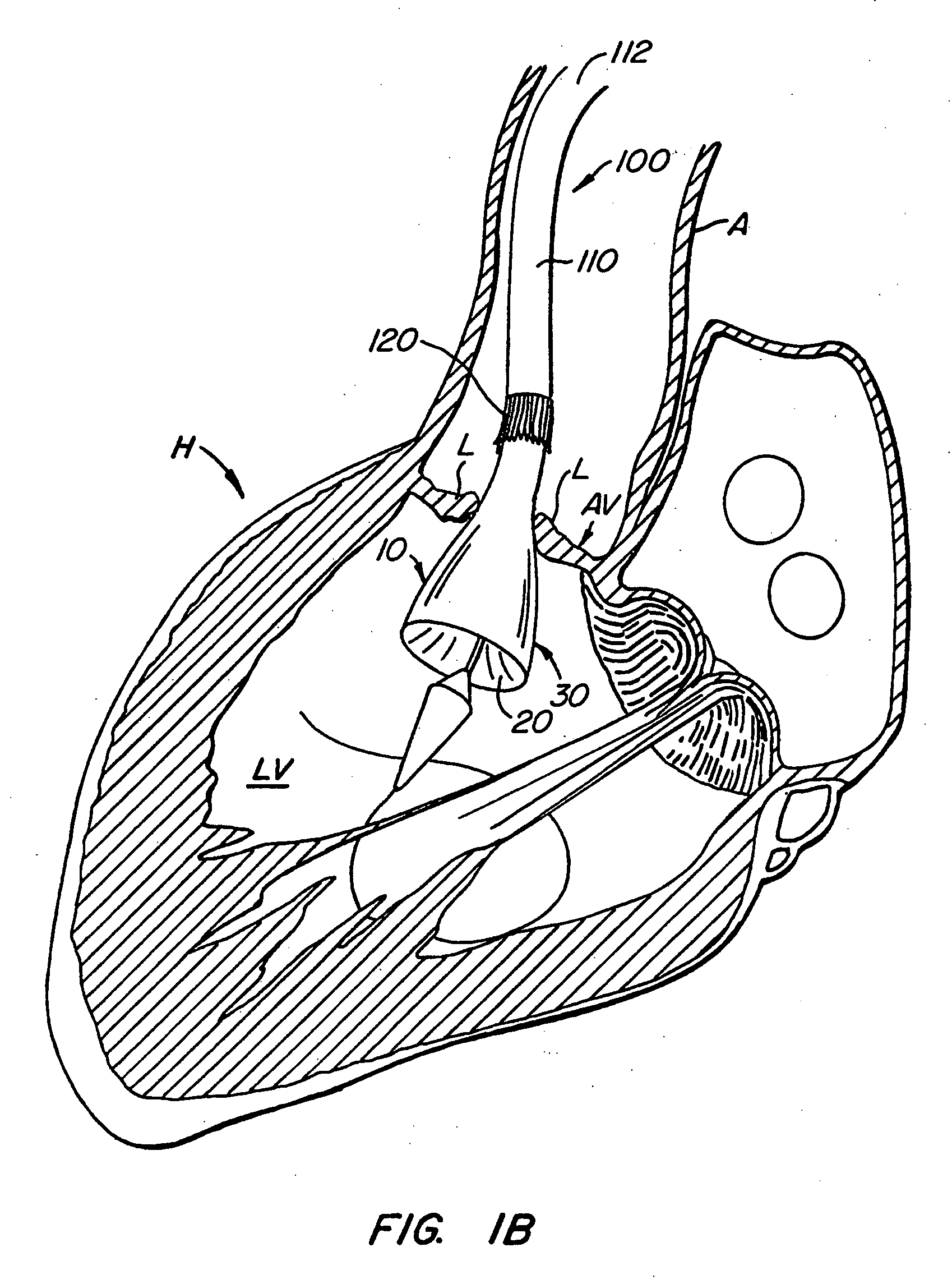
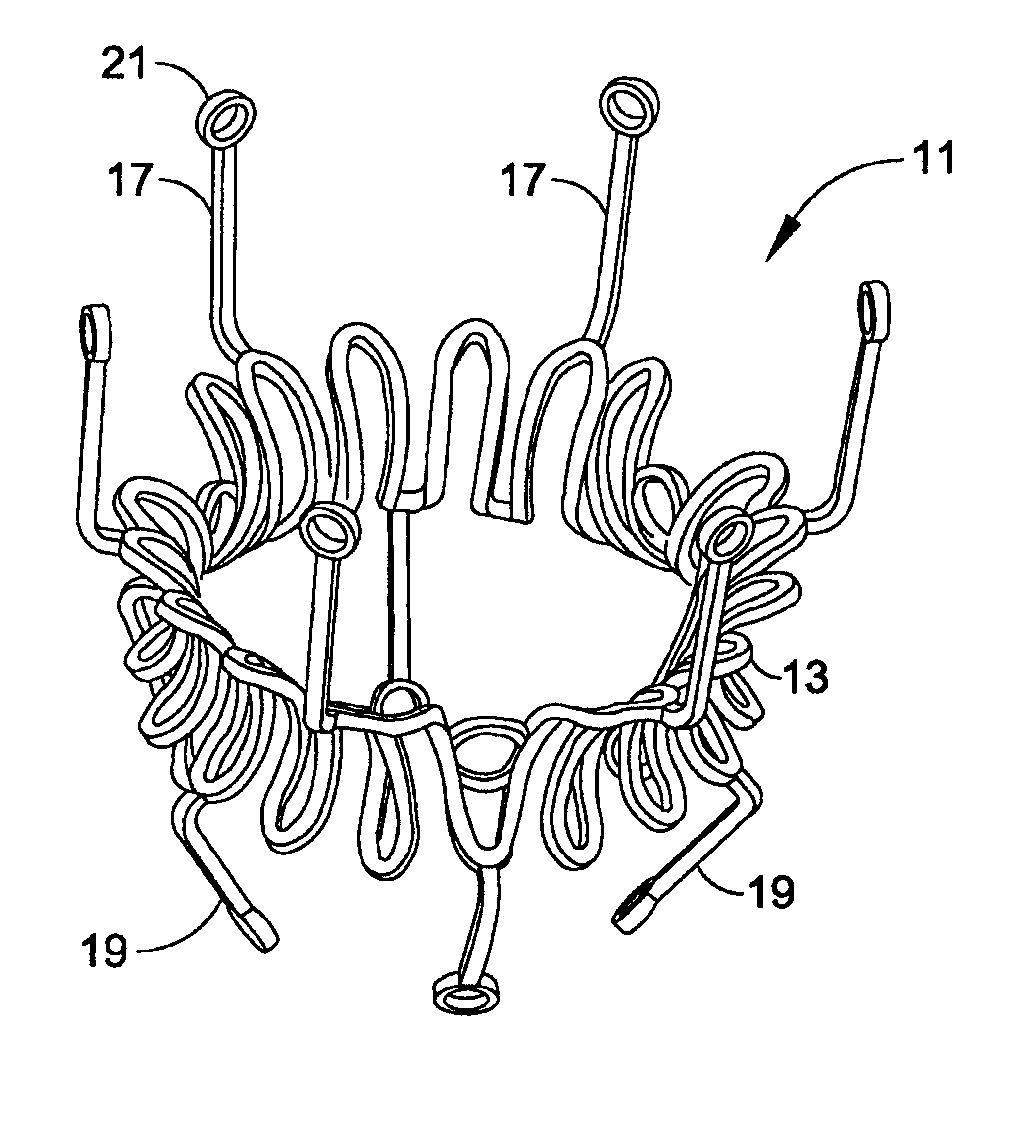
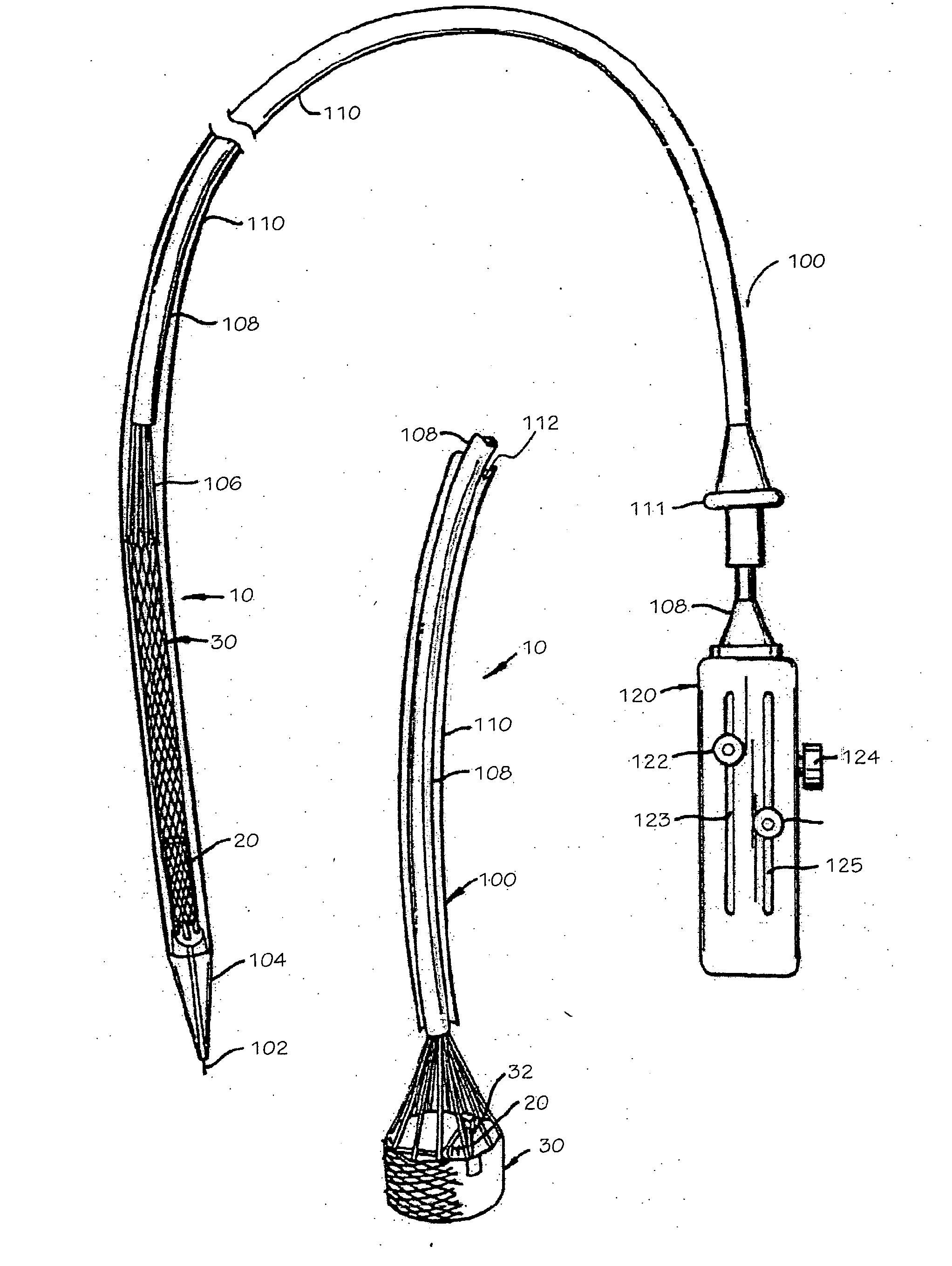
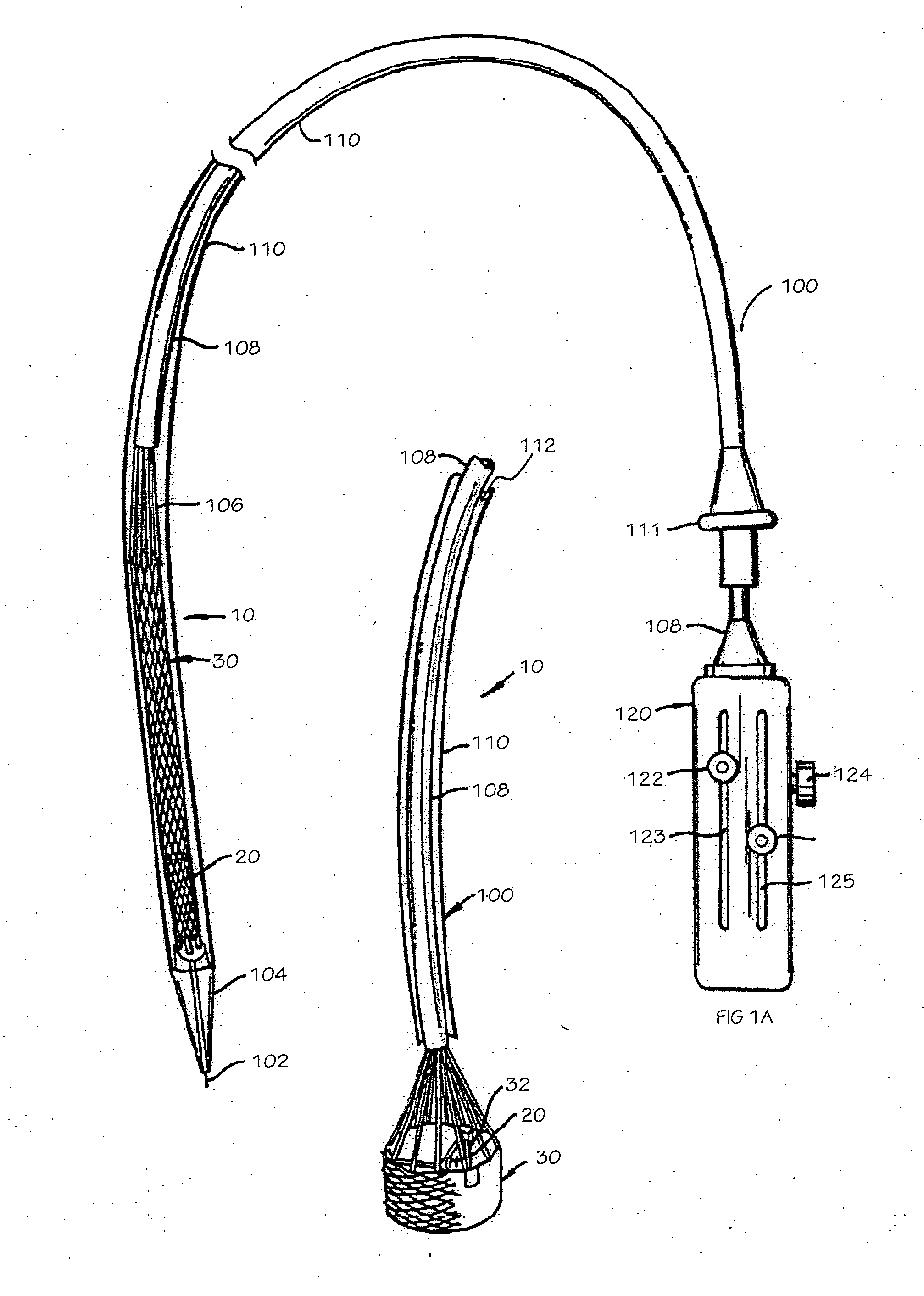
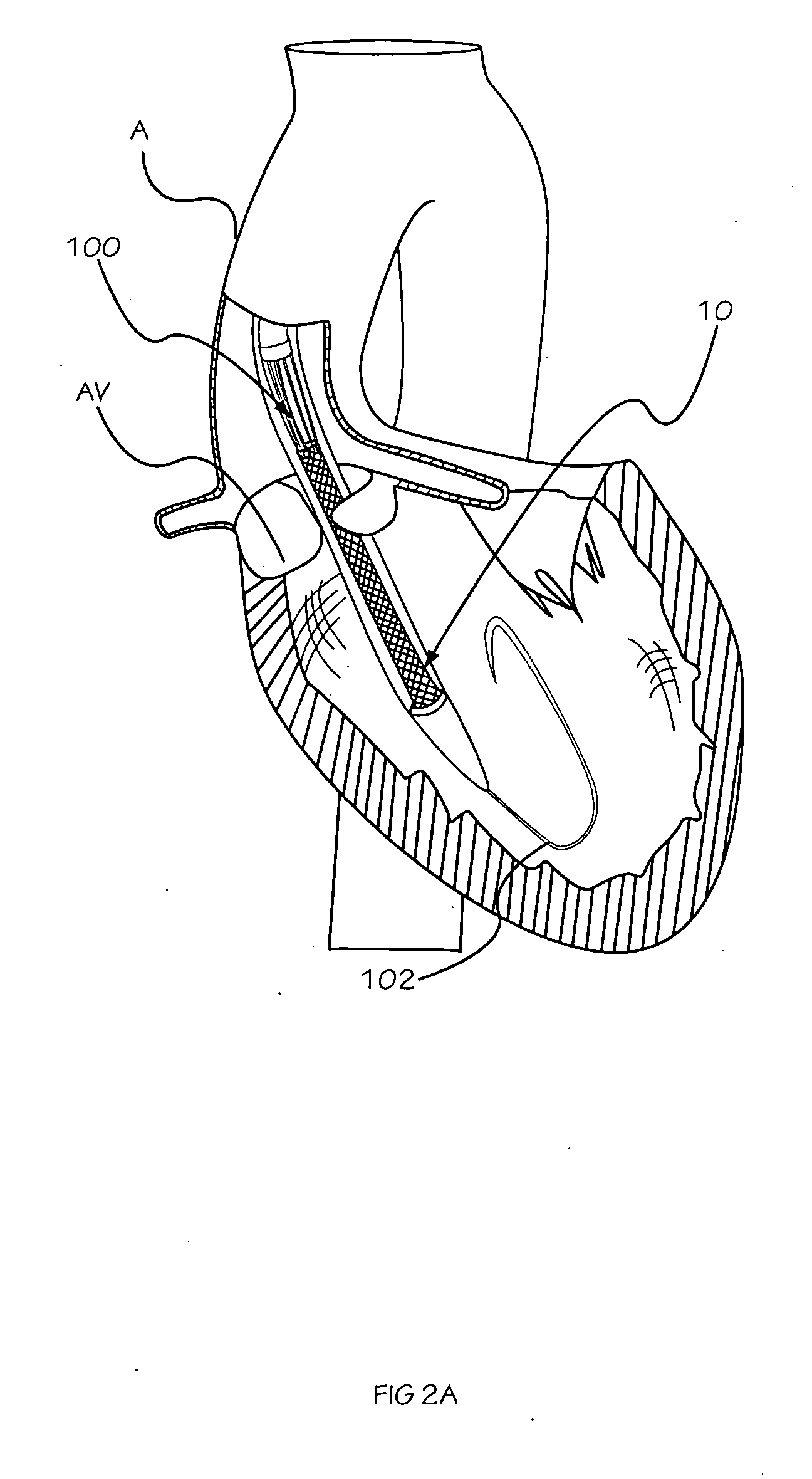
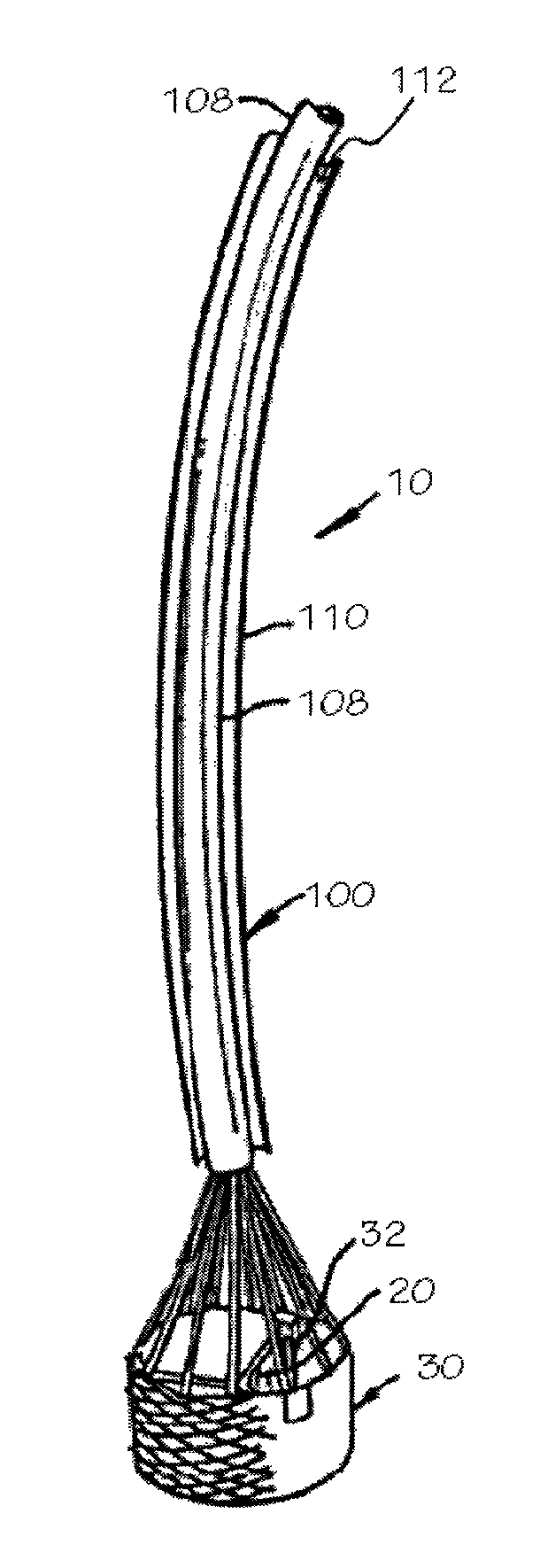
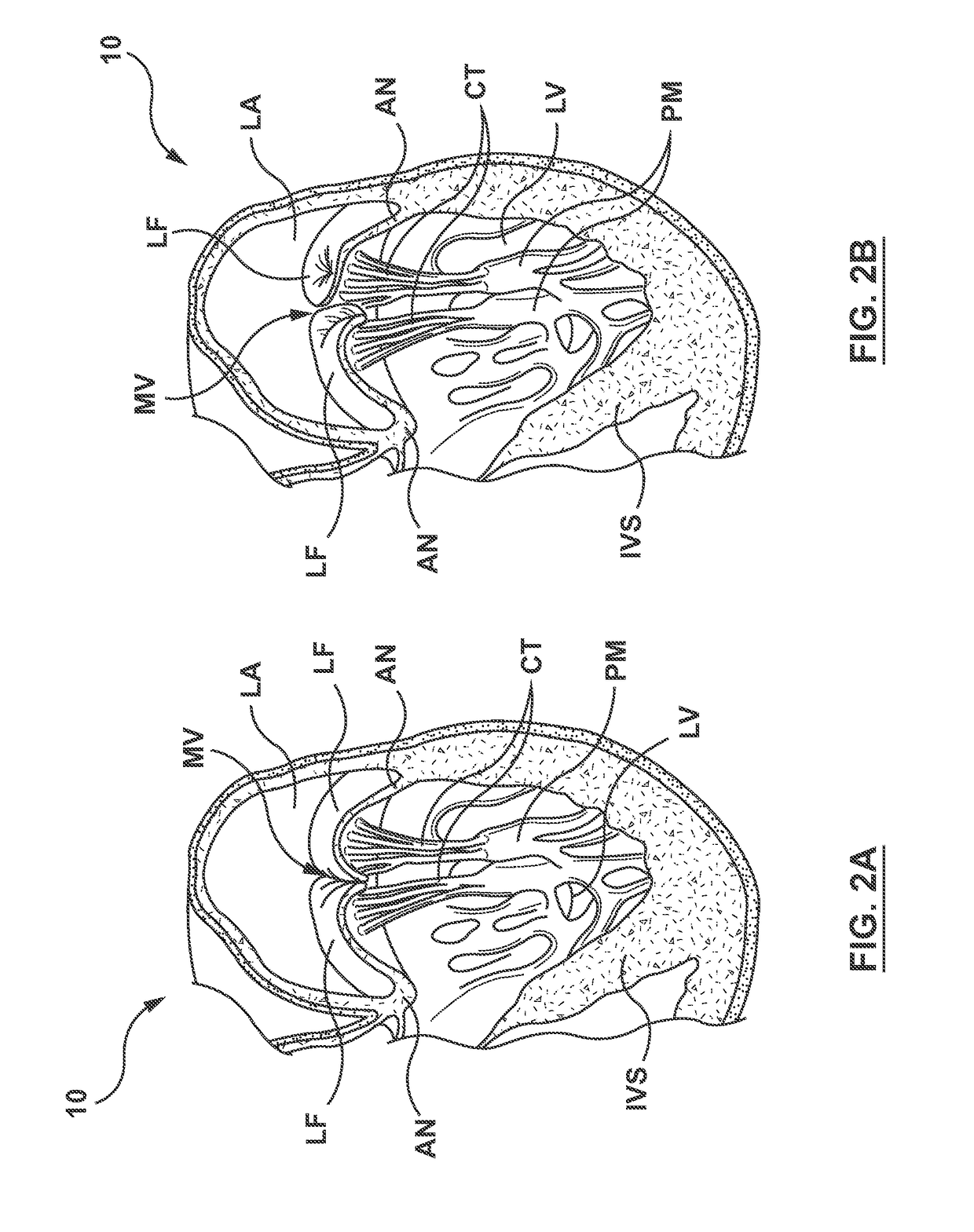
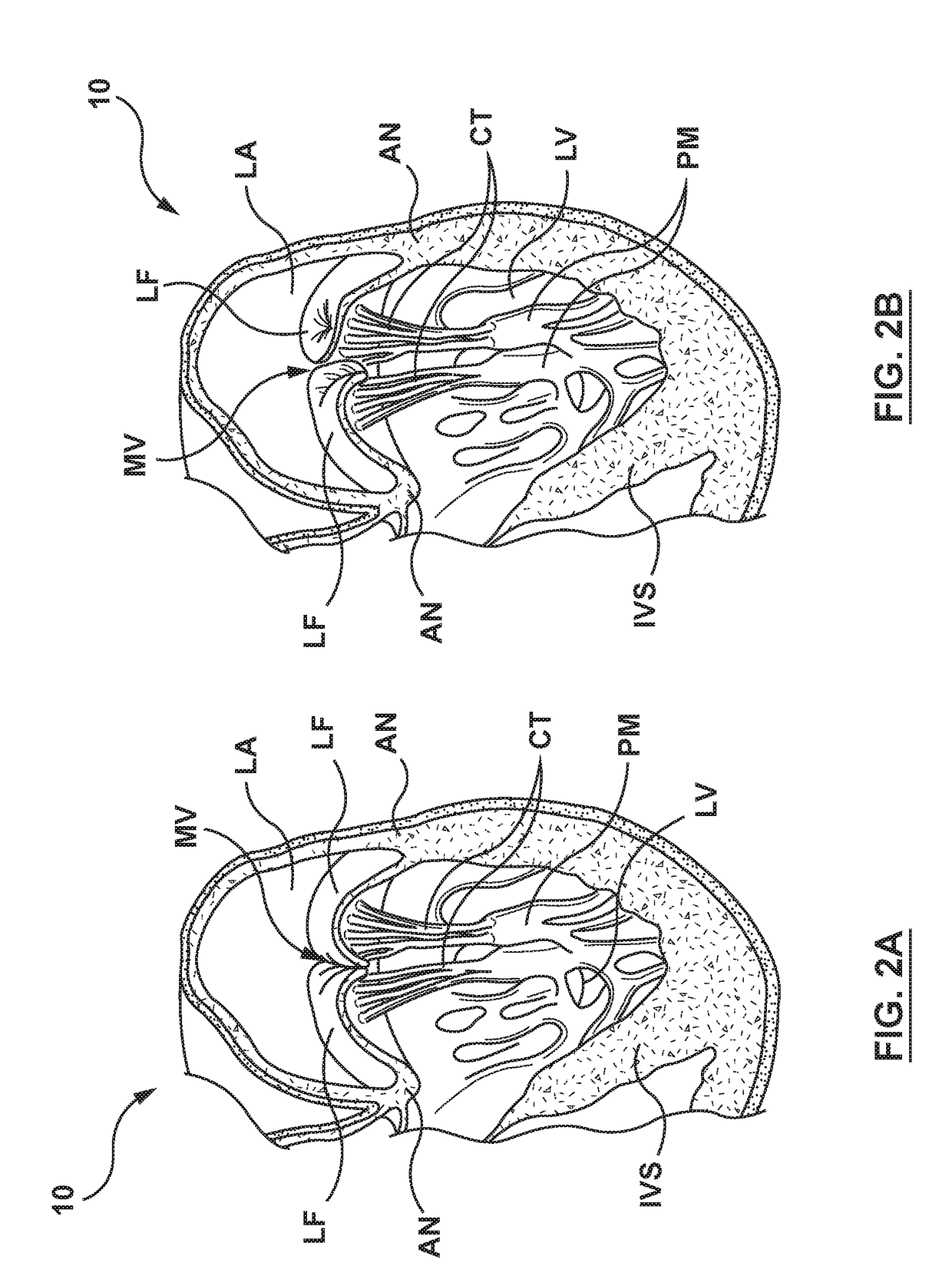
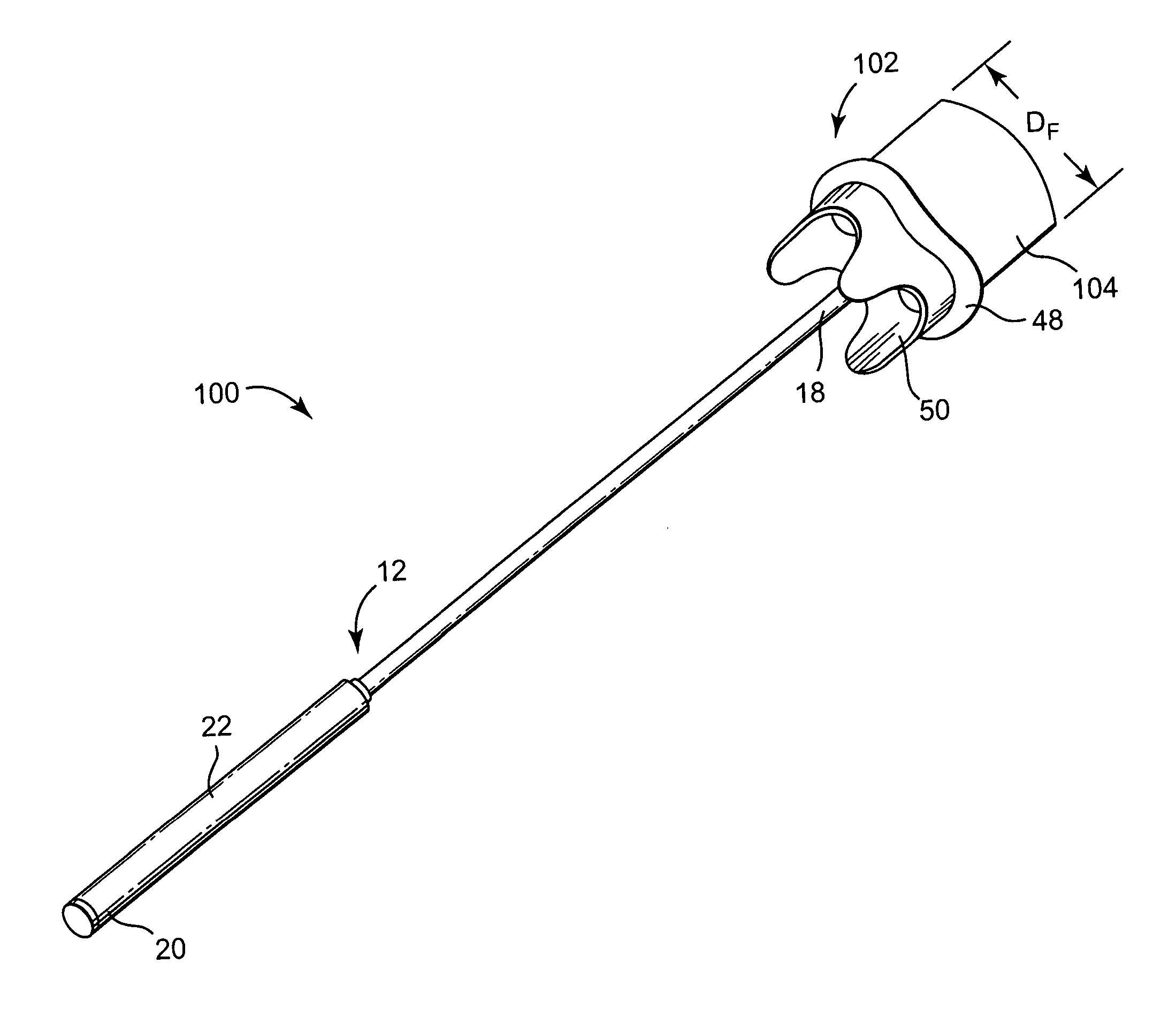
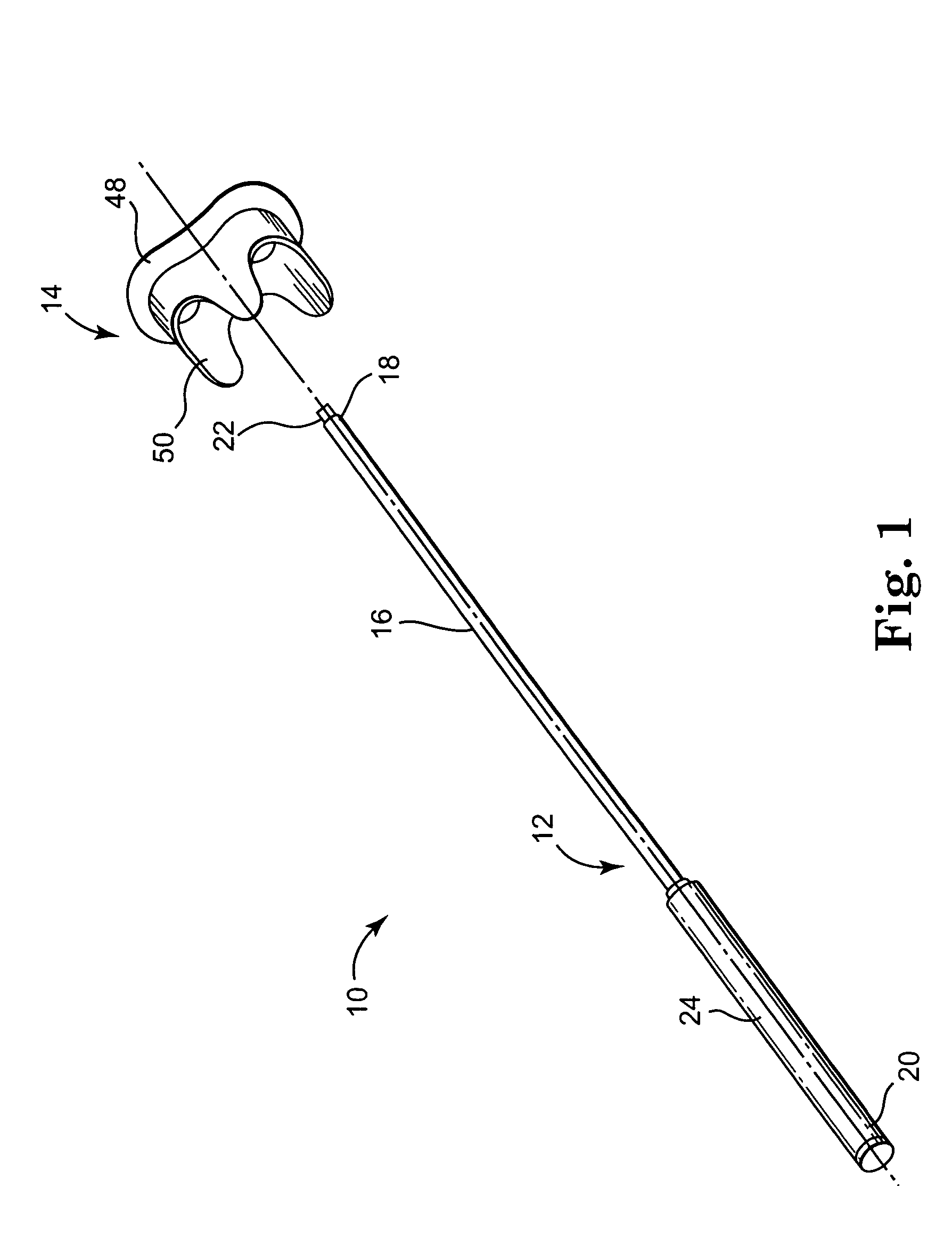
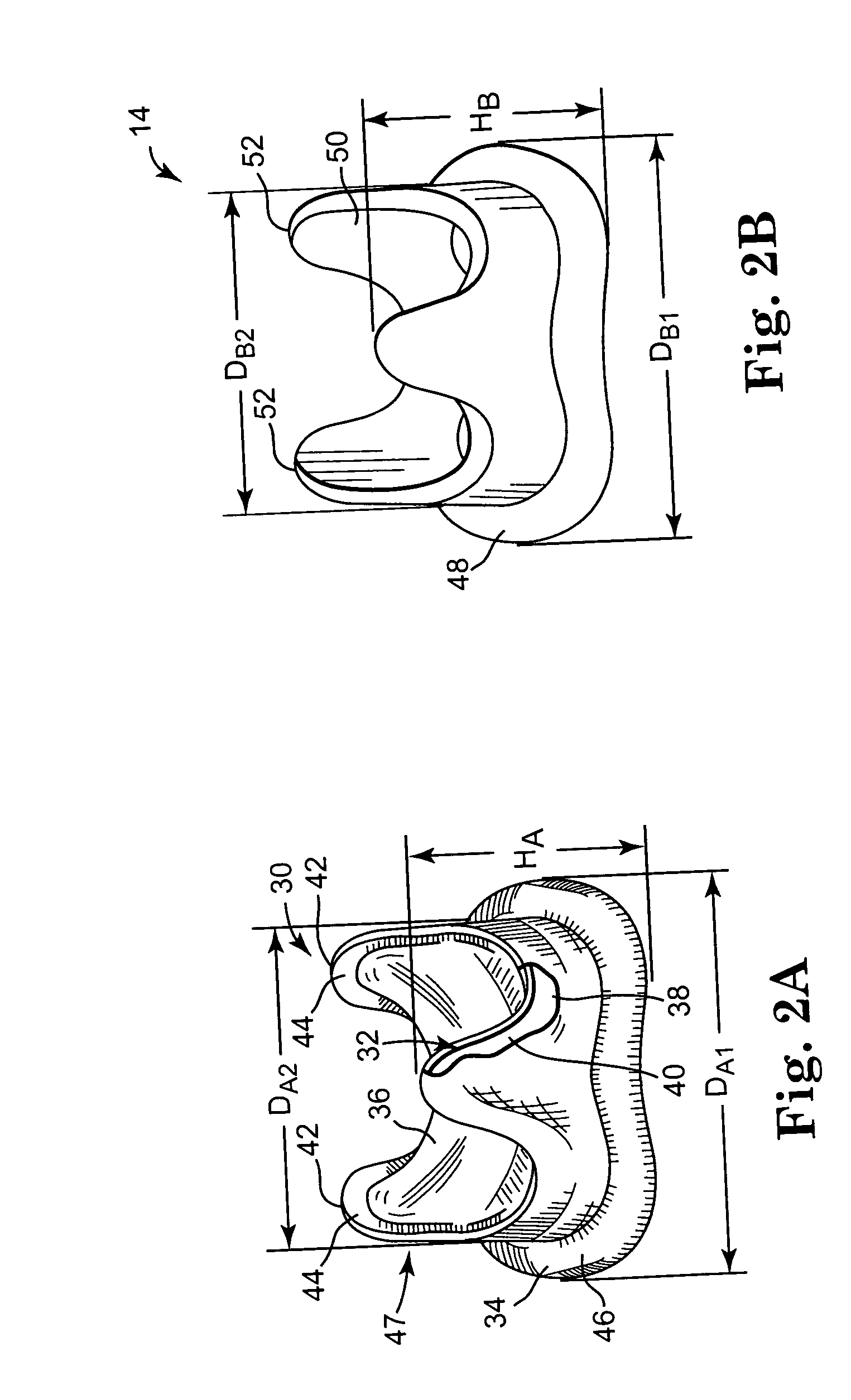
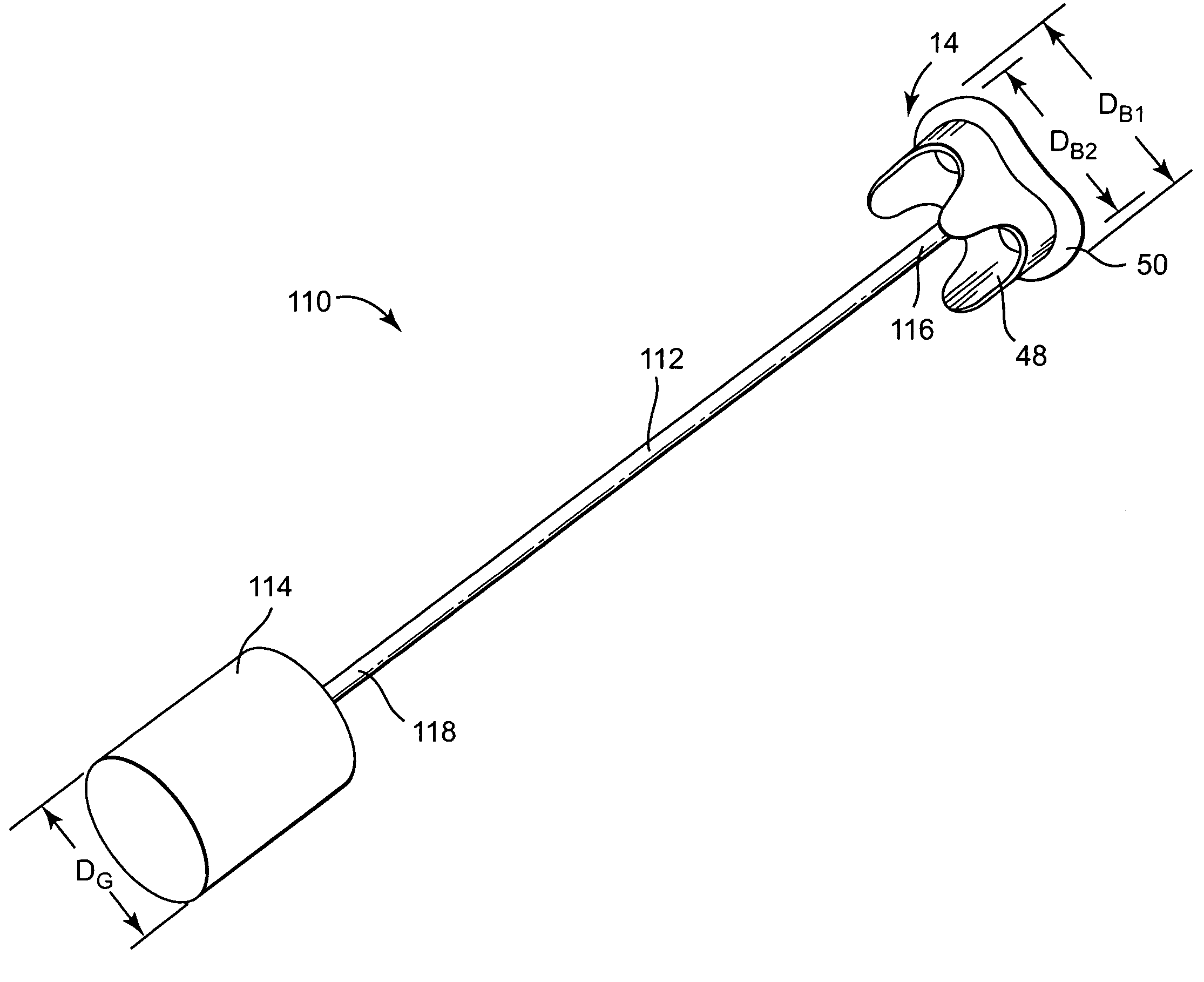
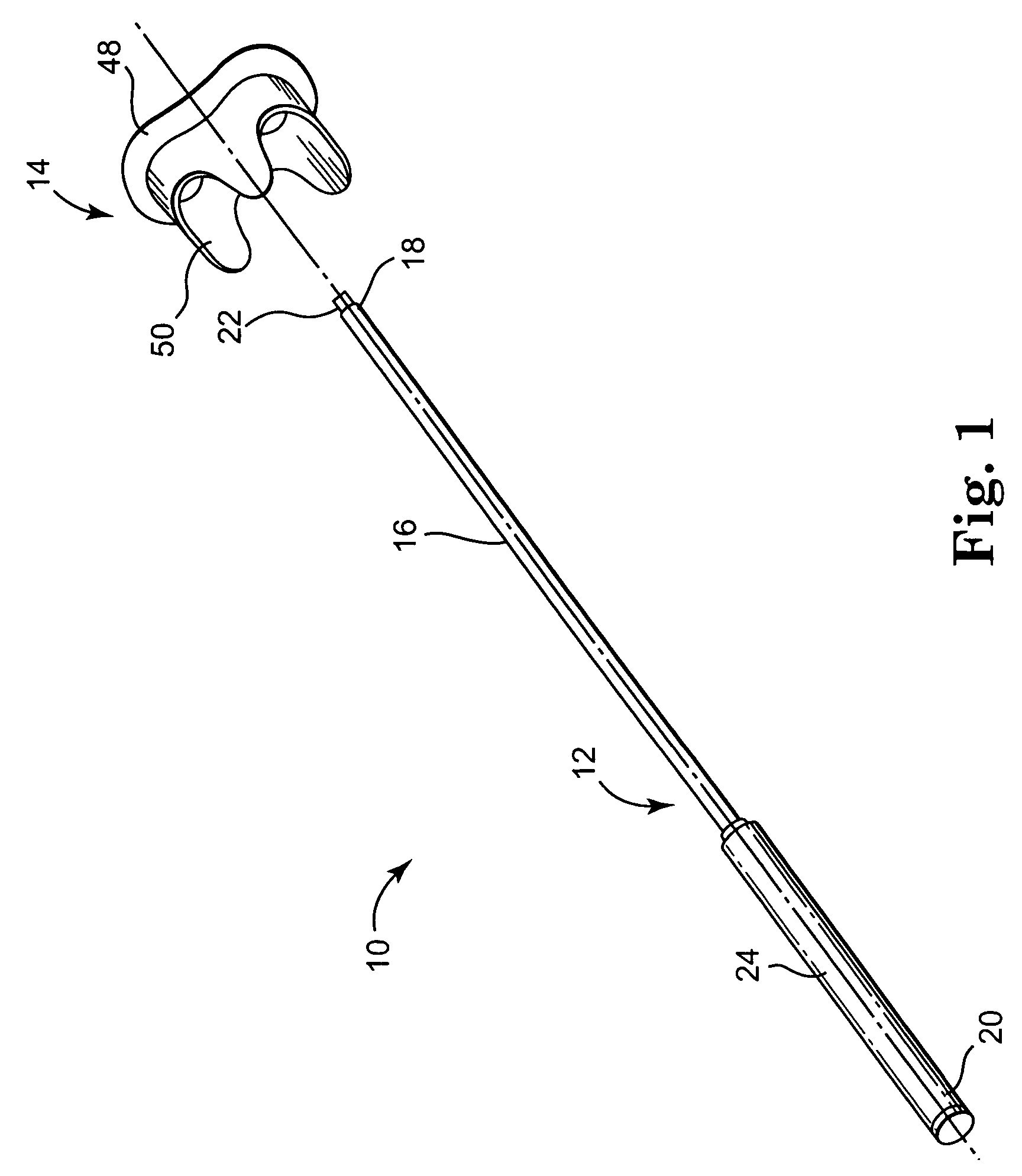
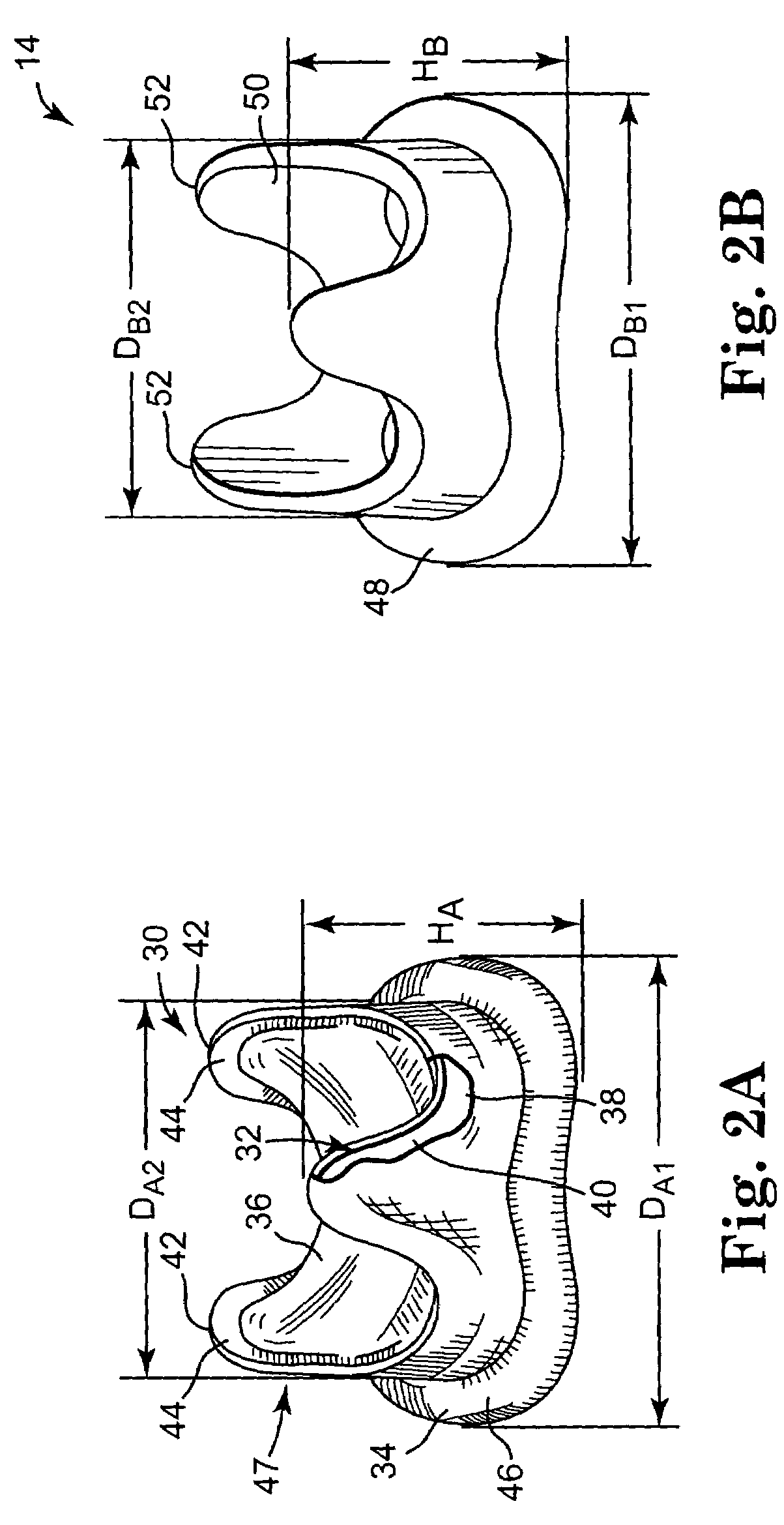
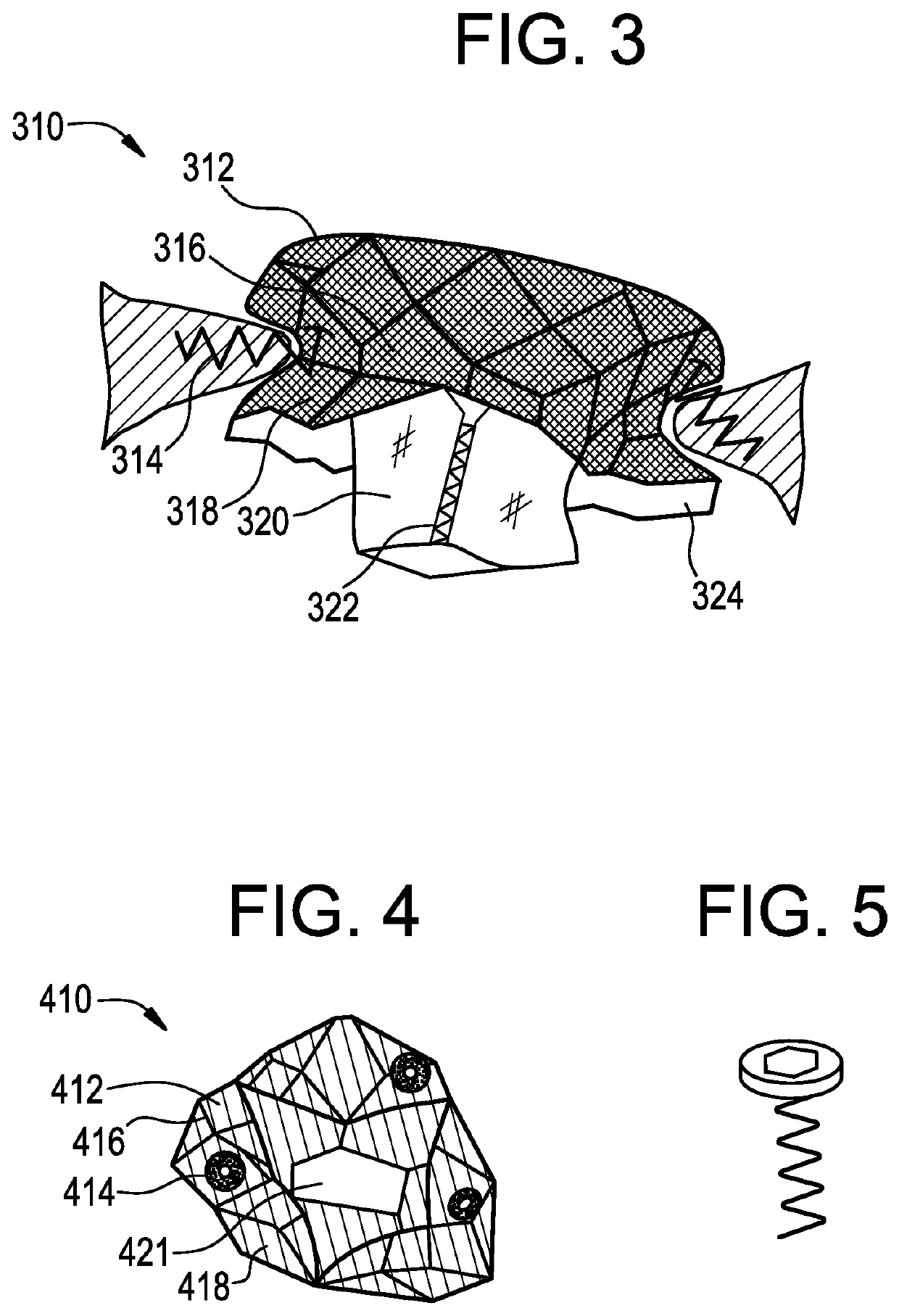
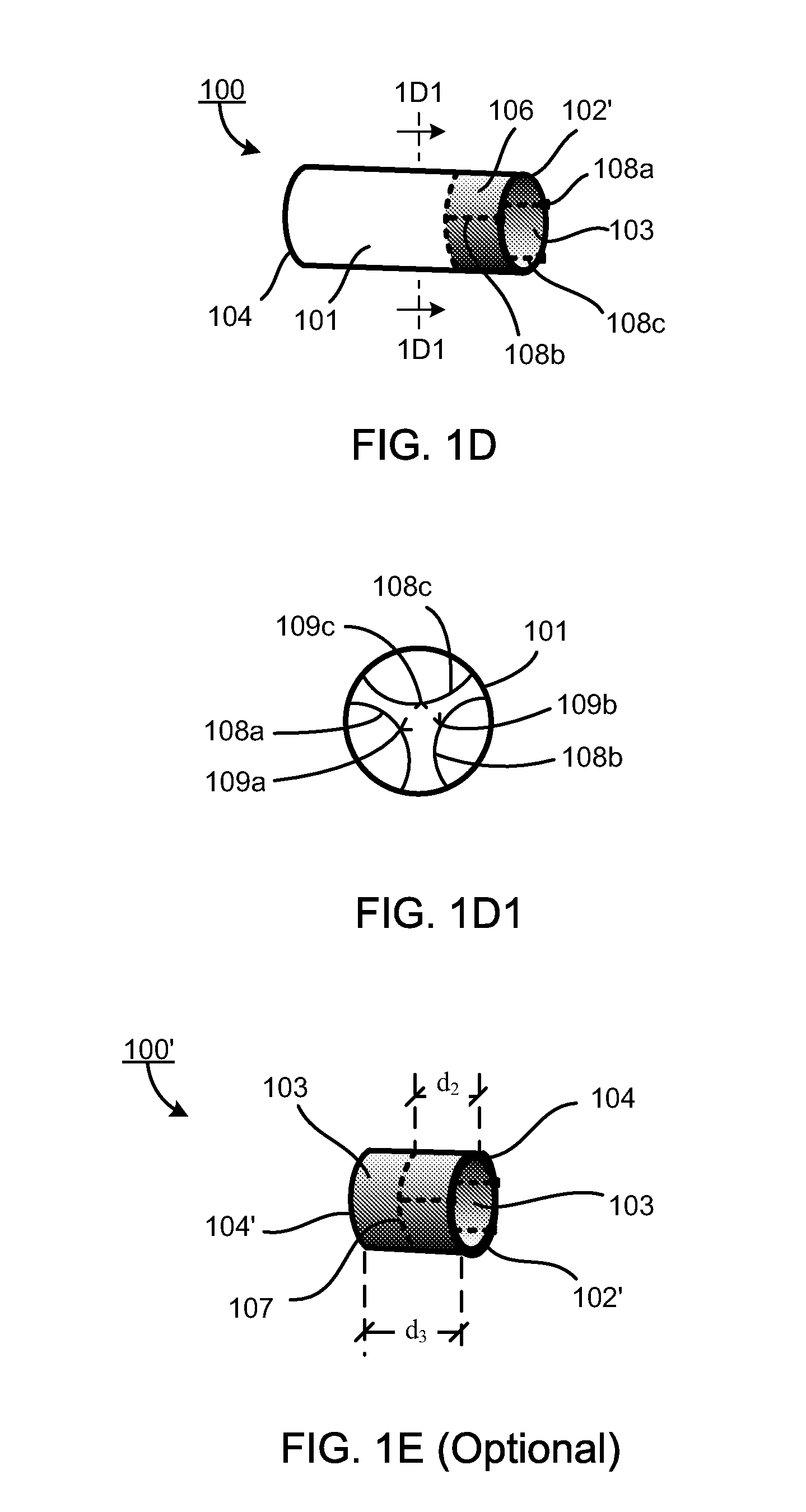
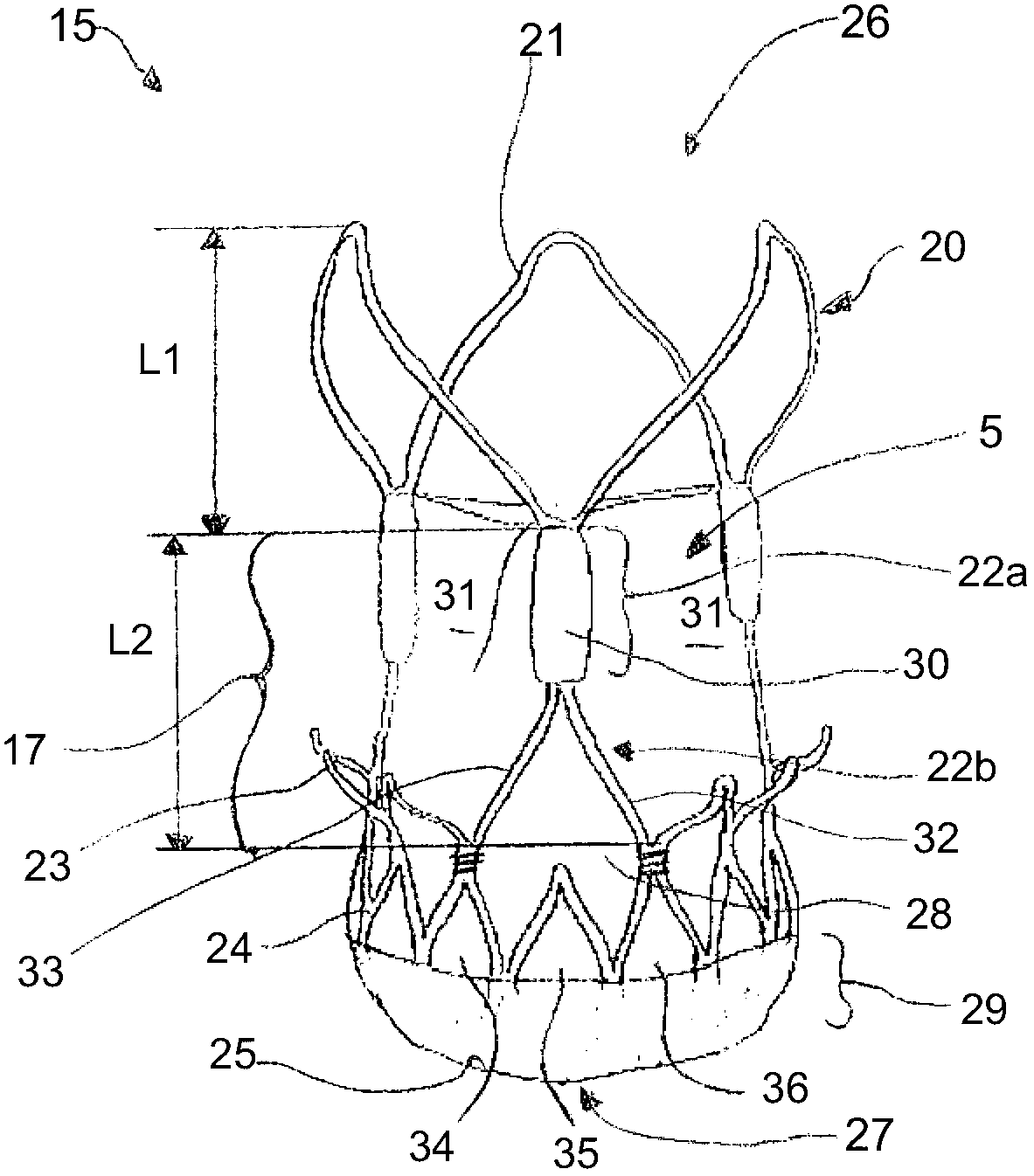
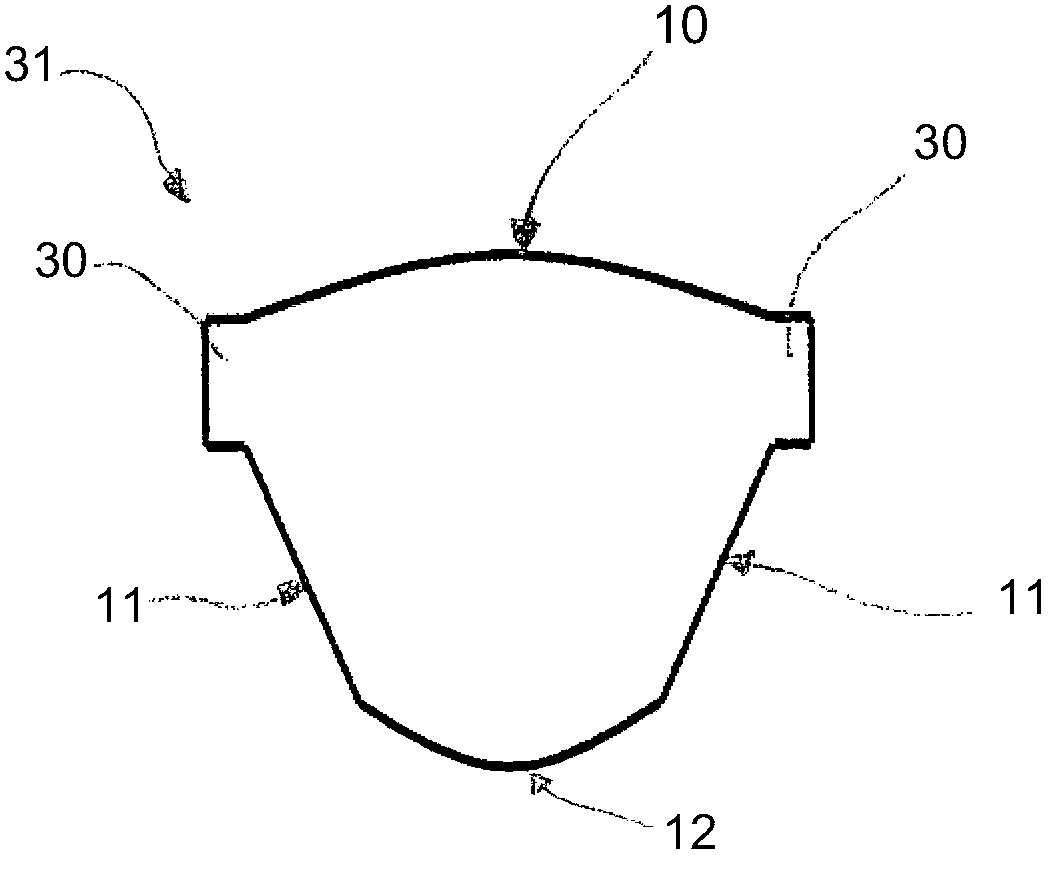
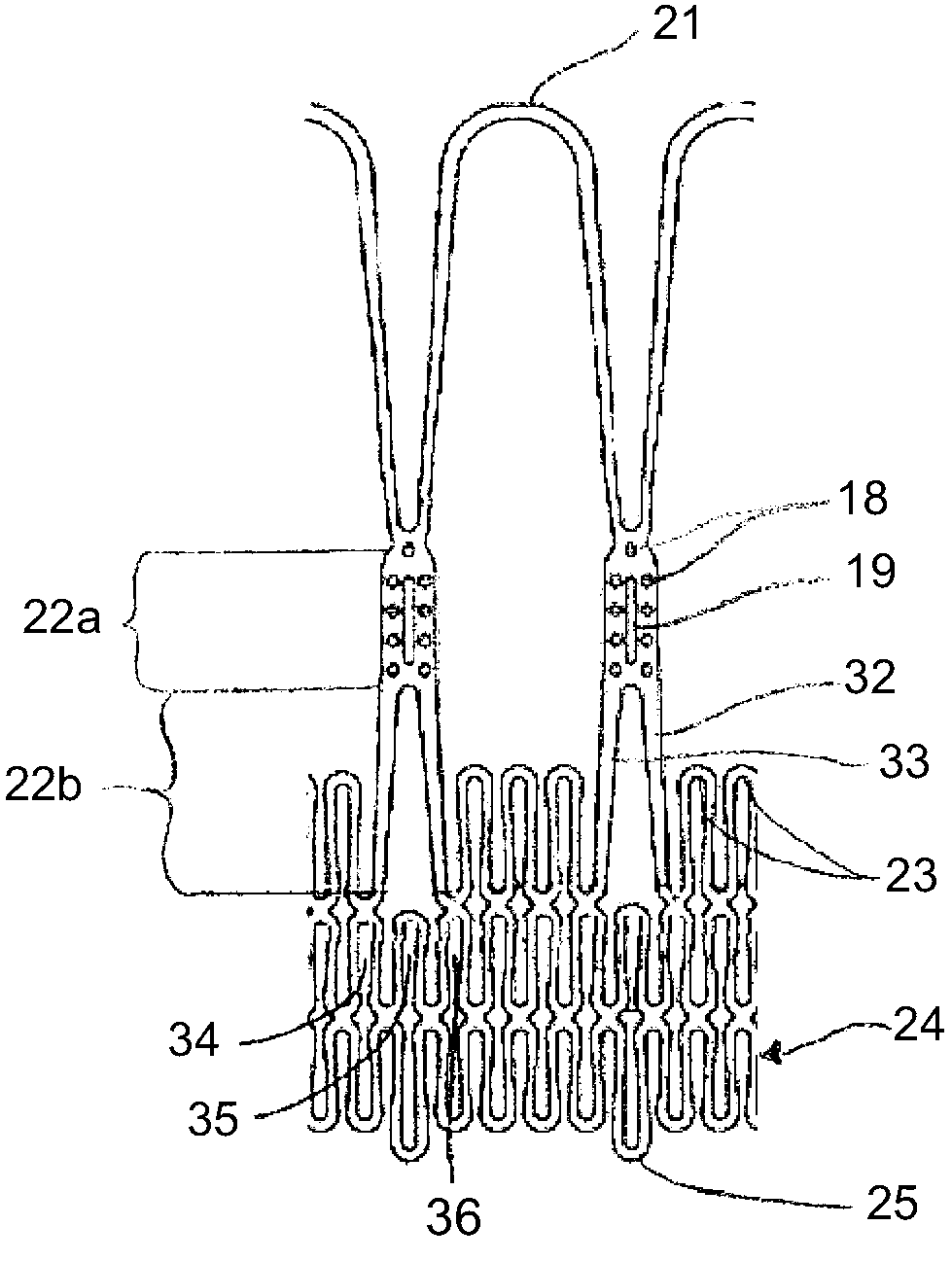
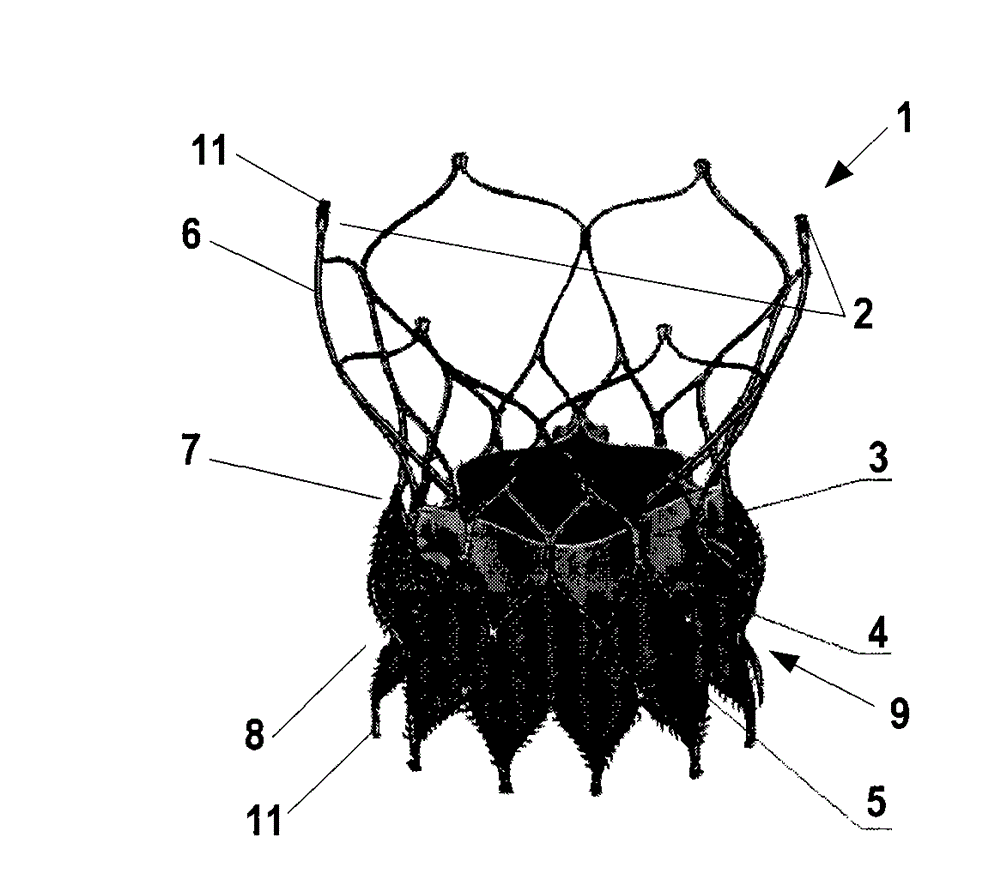
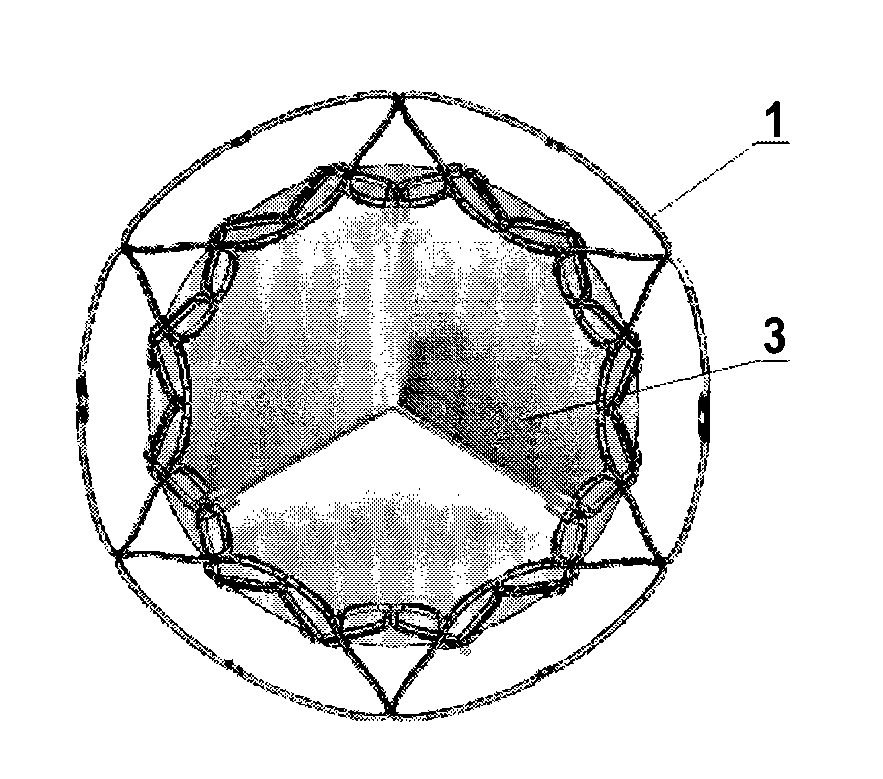
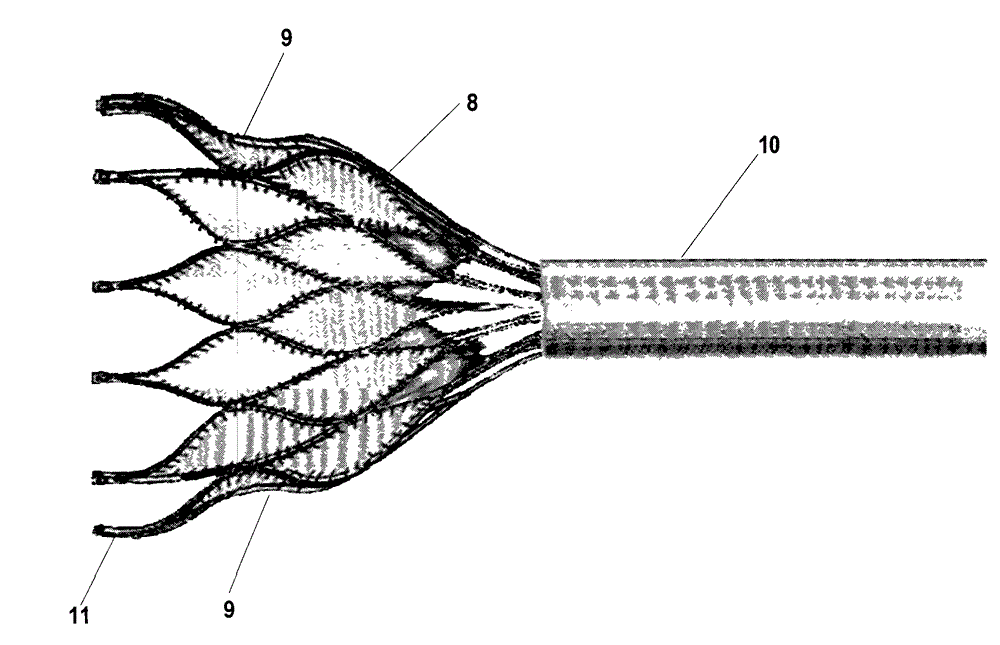
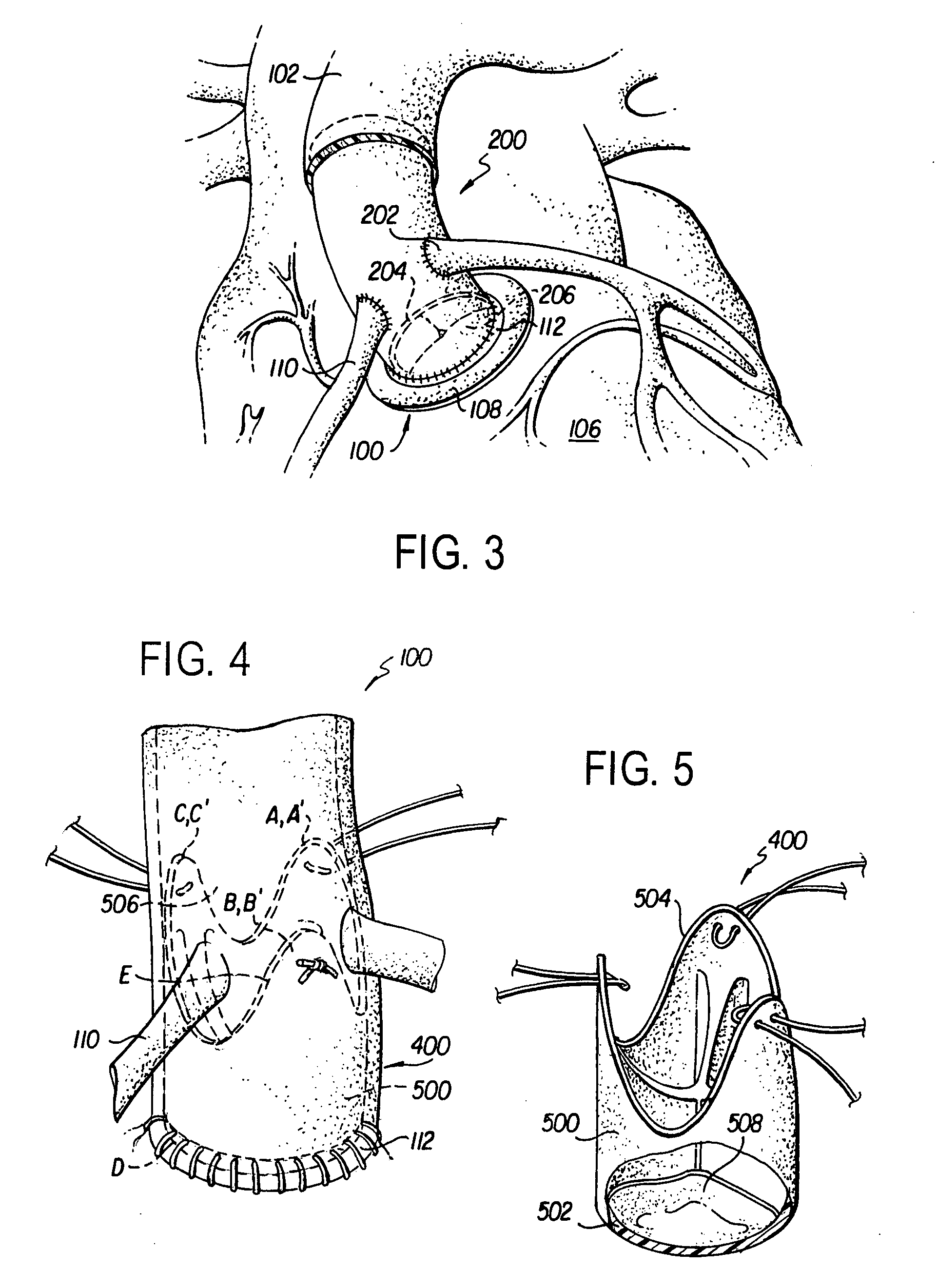
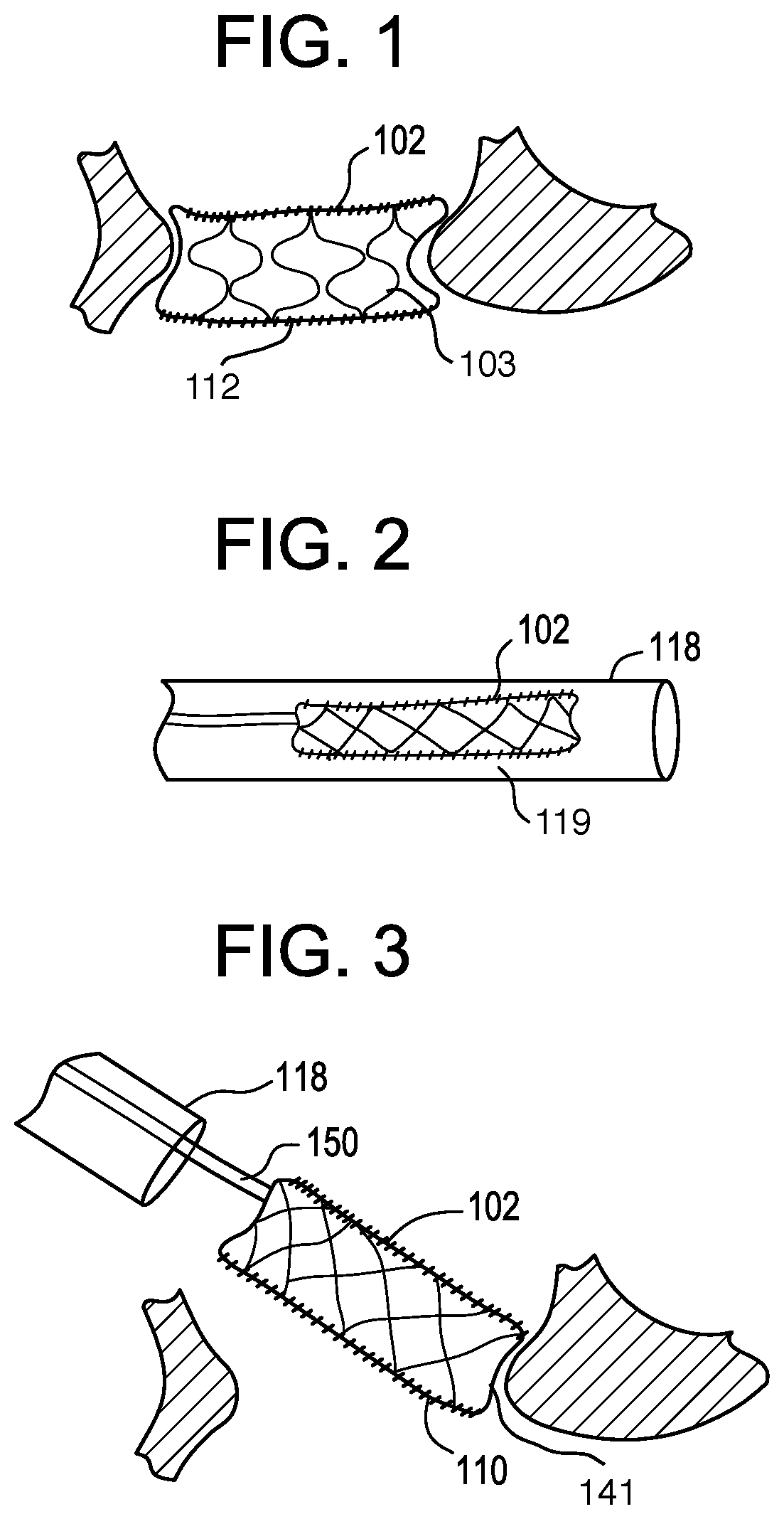
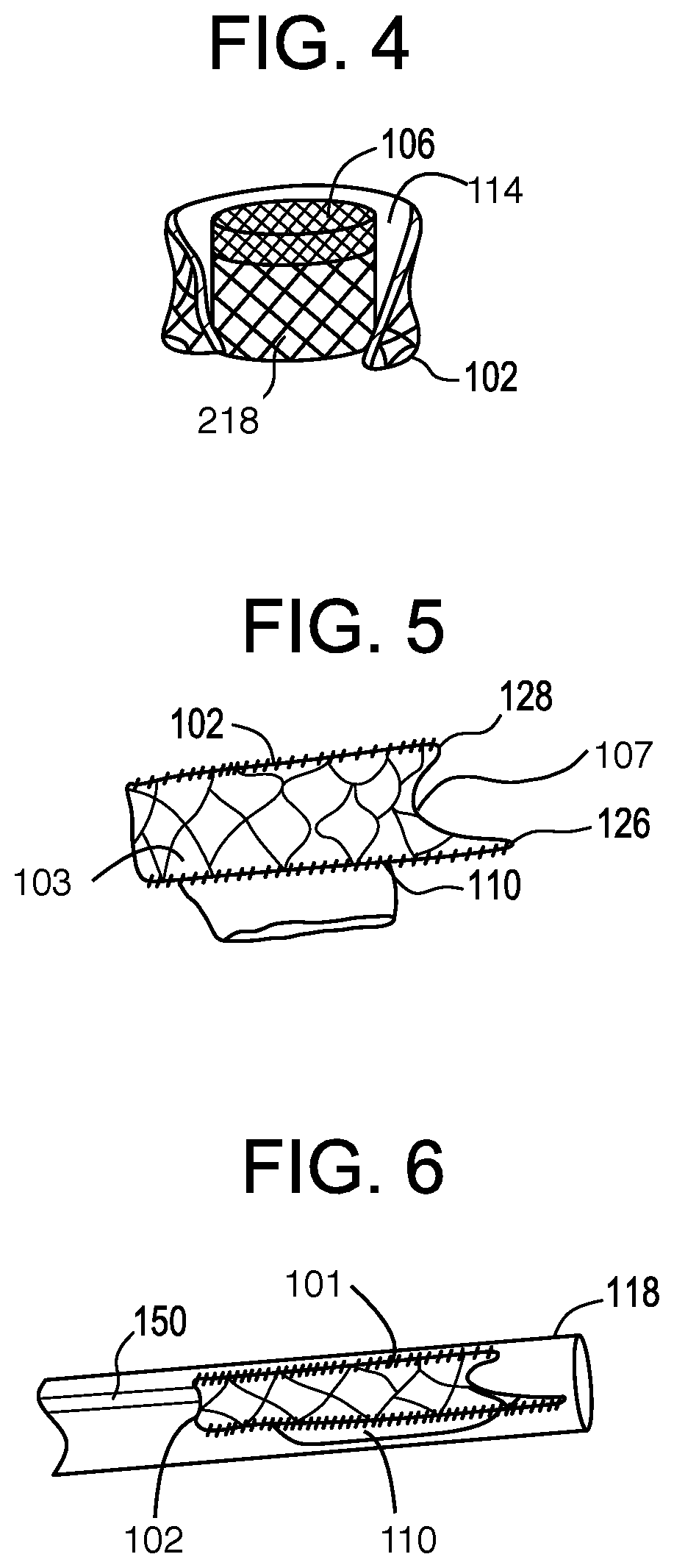
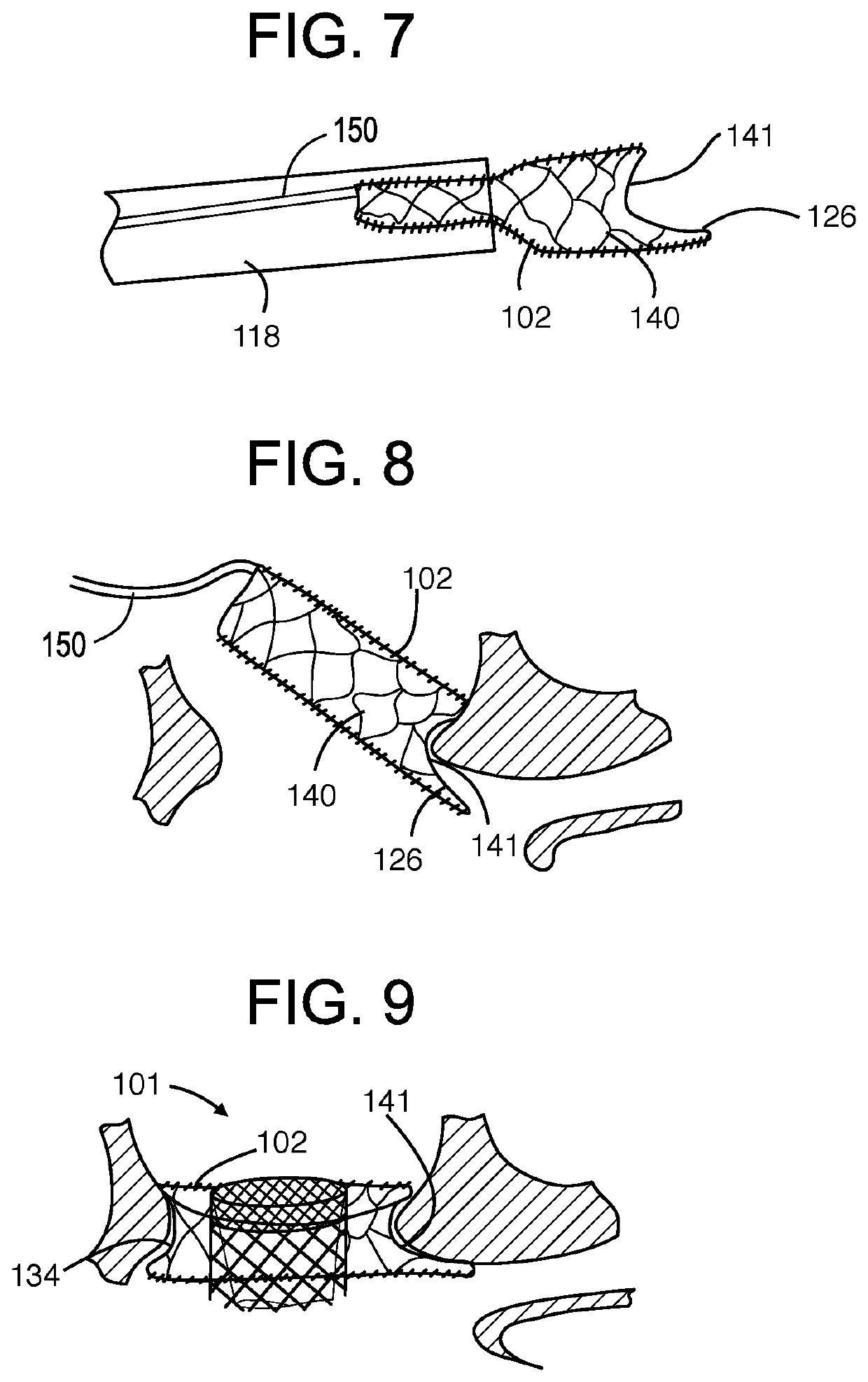
Minimally invasive heart valve replacement
ActiveUS20090005863A1Minimally invasiveSufficient flexibilityHeart valvesBlood vesselsHeart valve replacementThoracic cavity
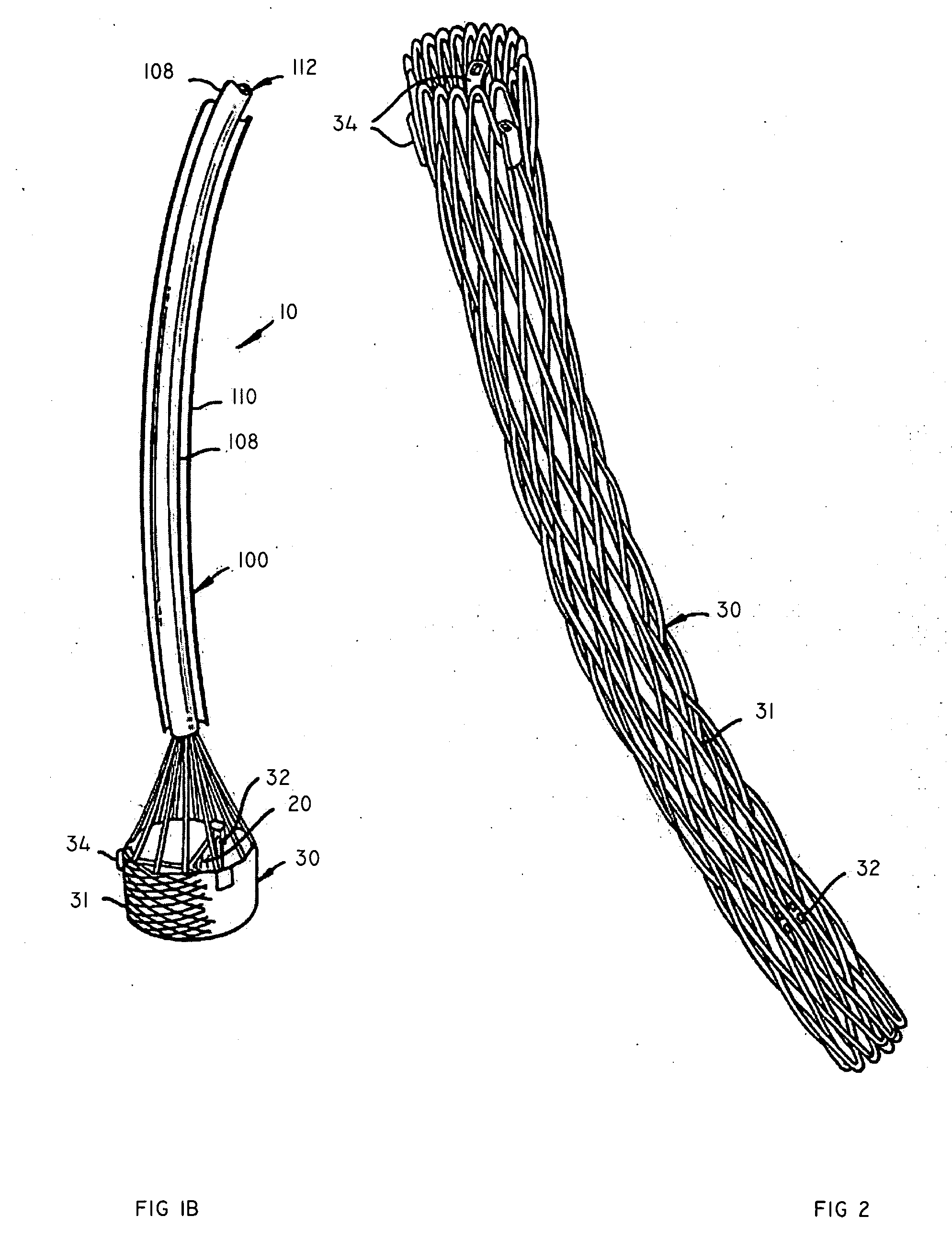
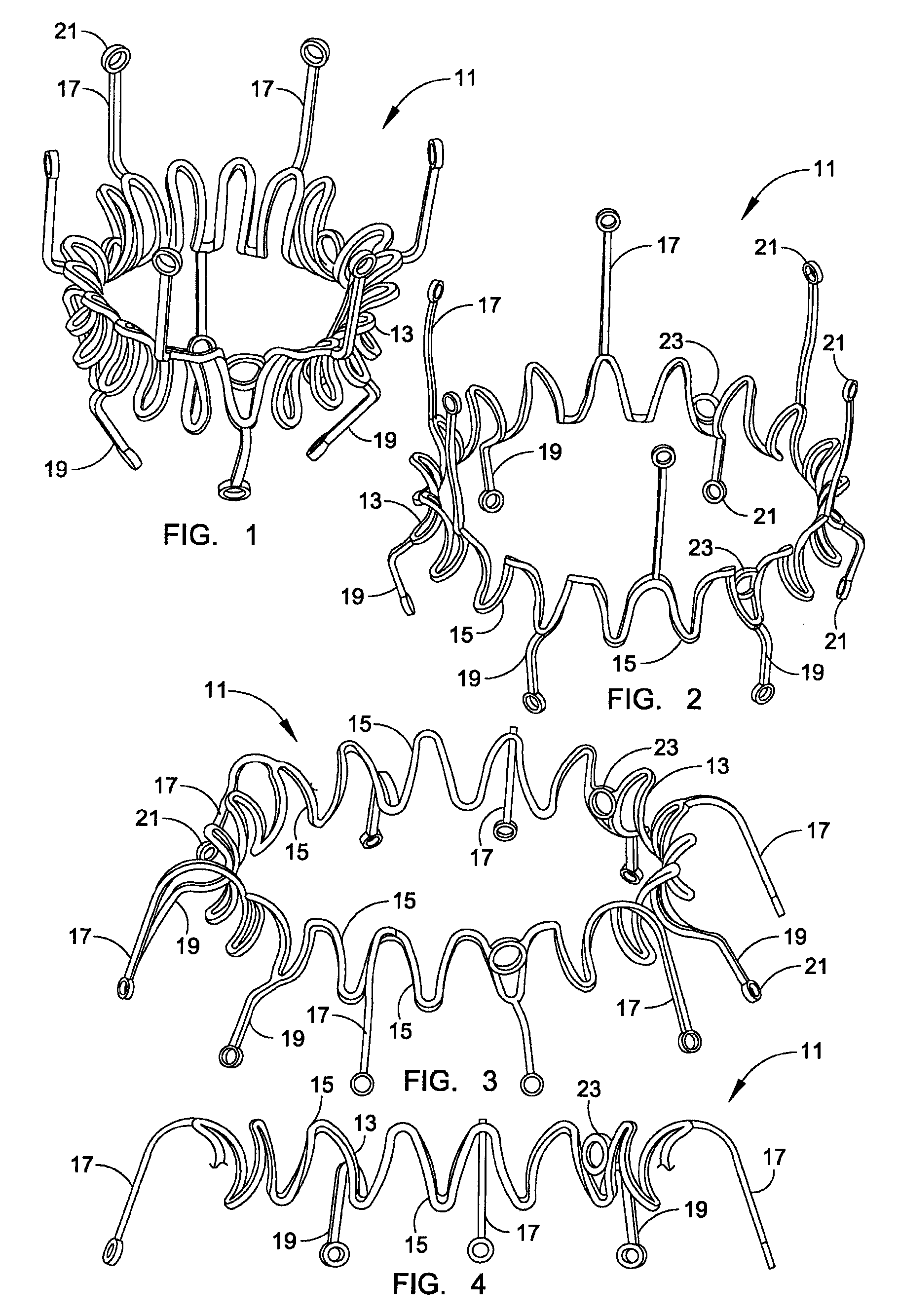
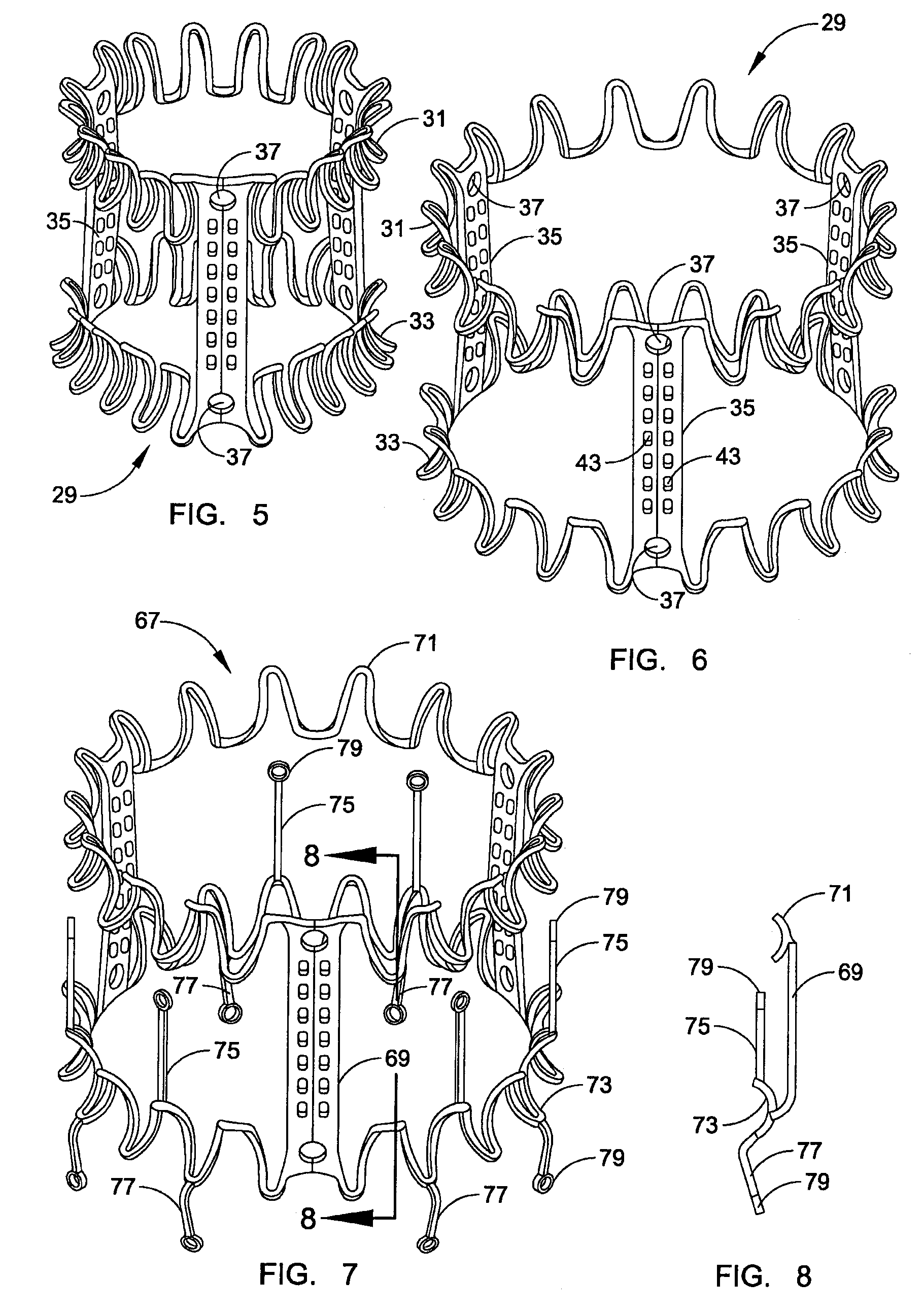
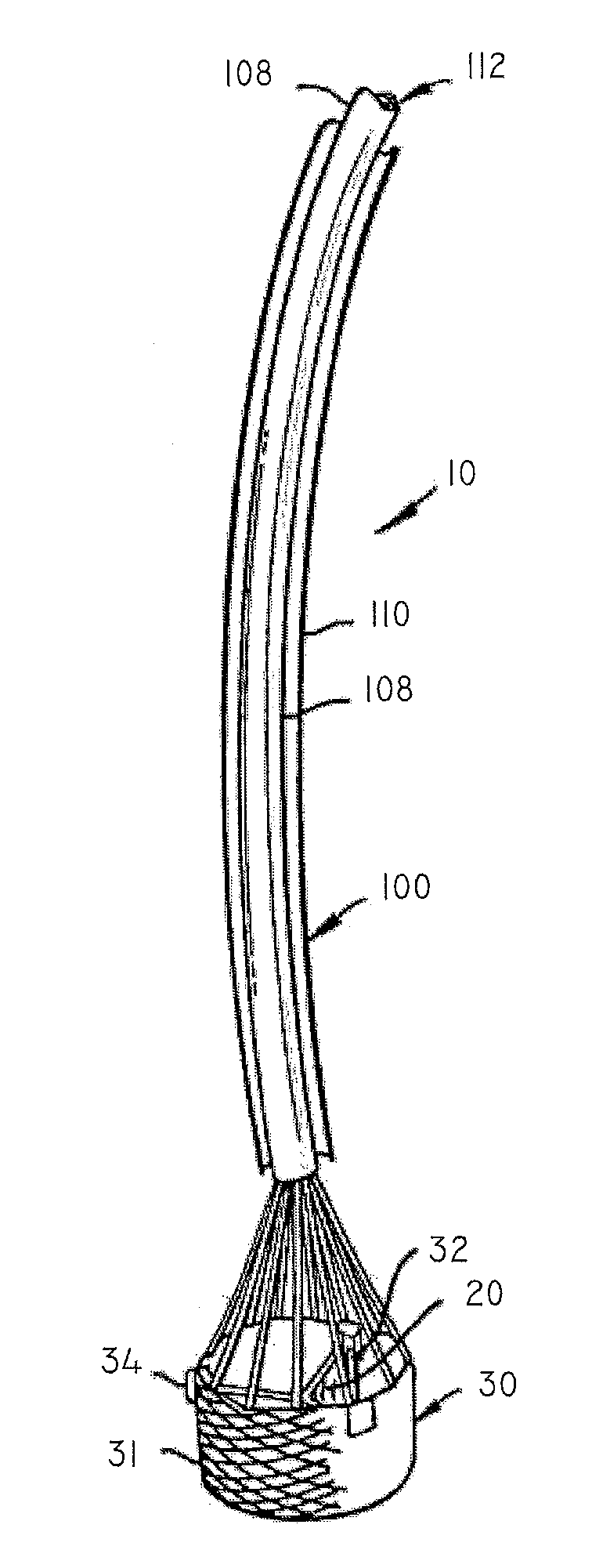
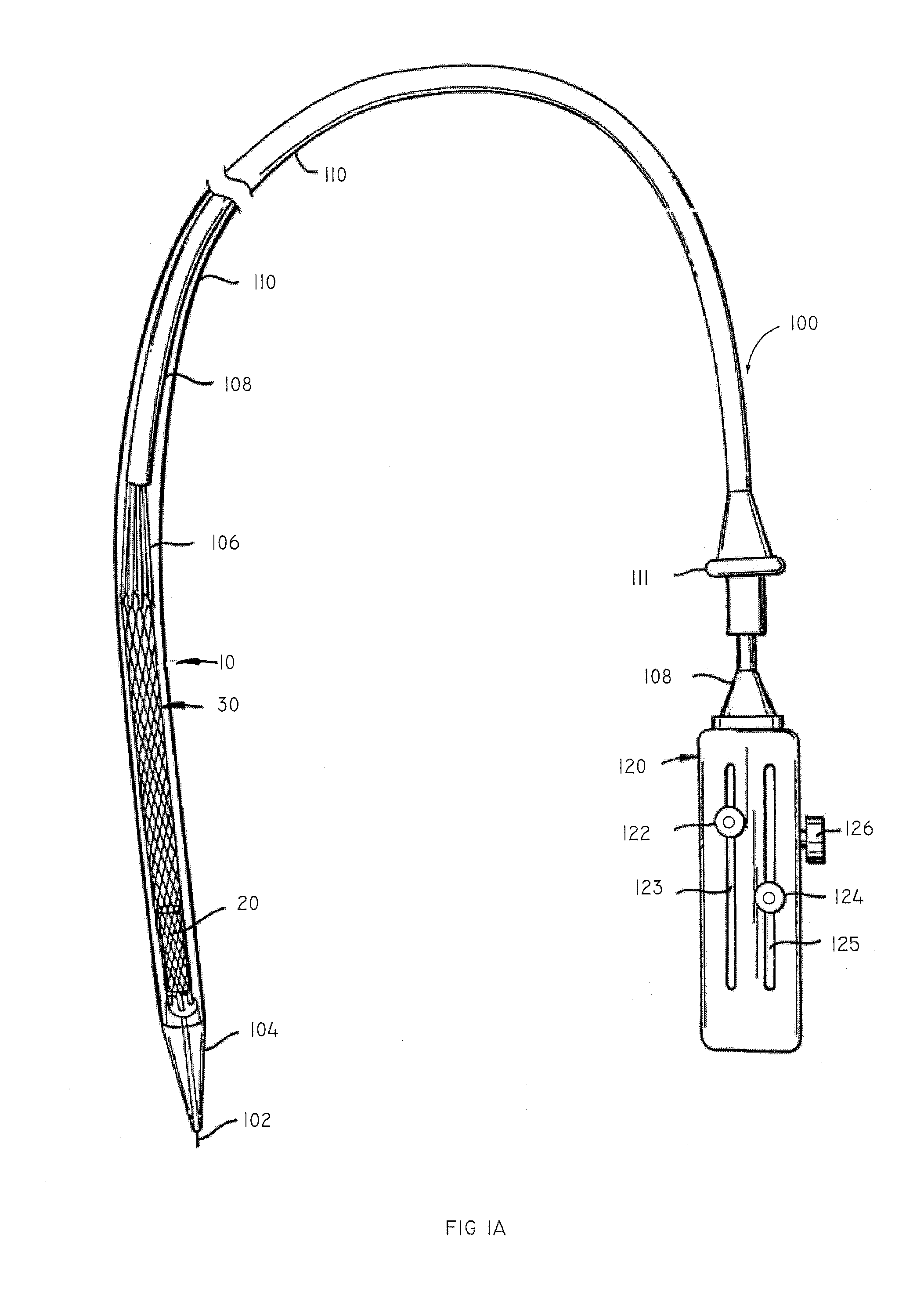
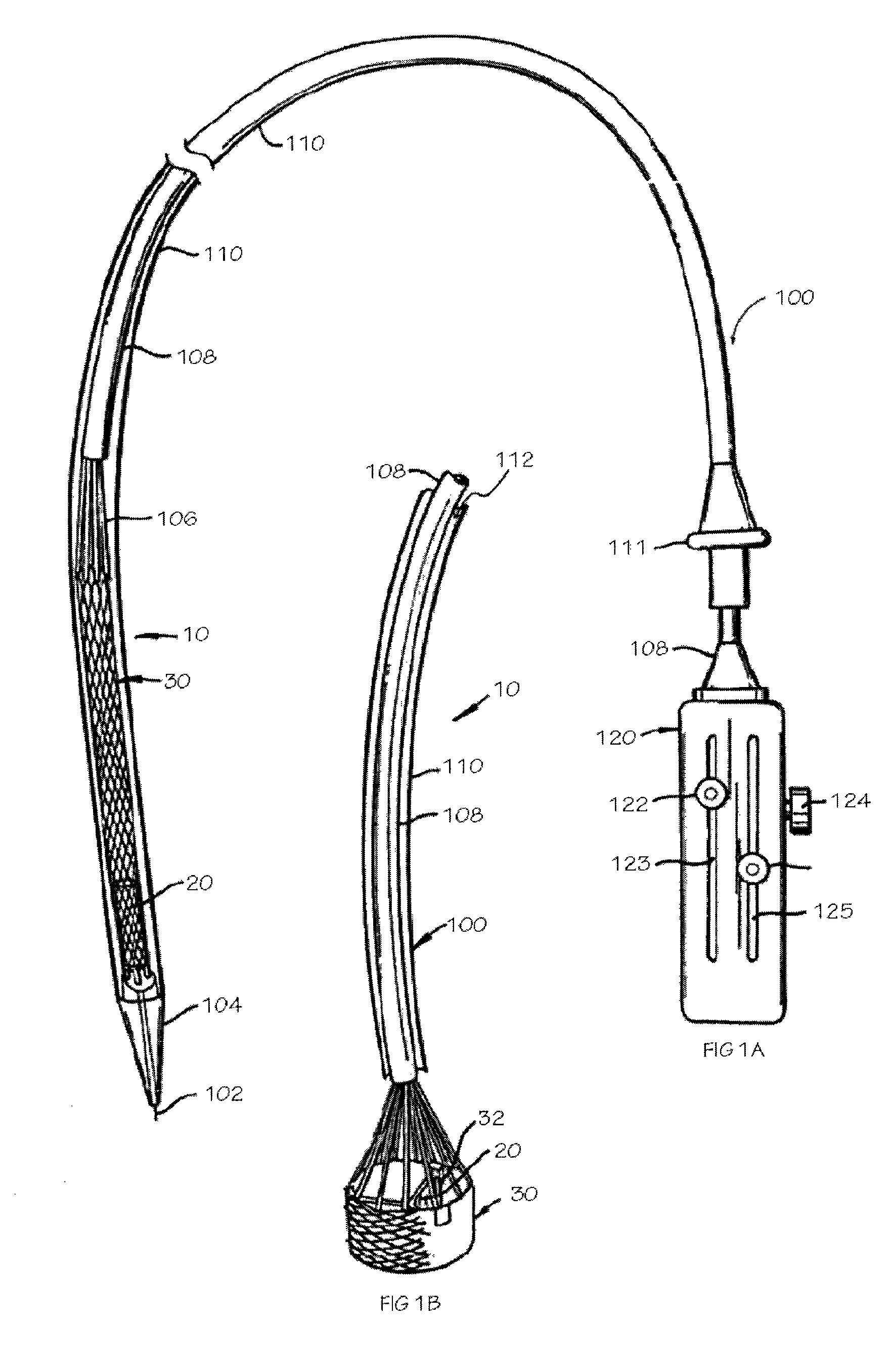
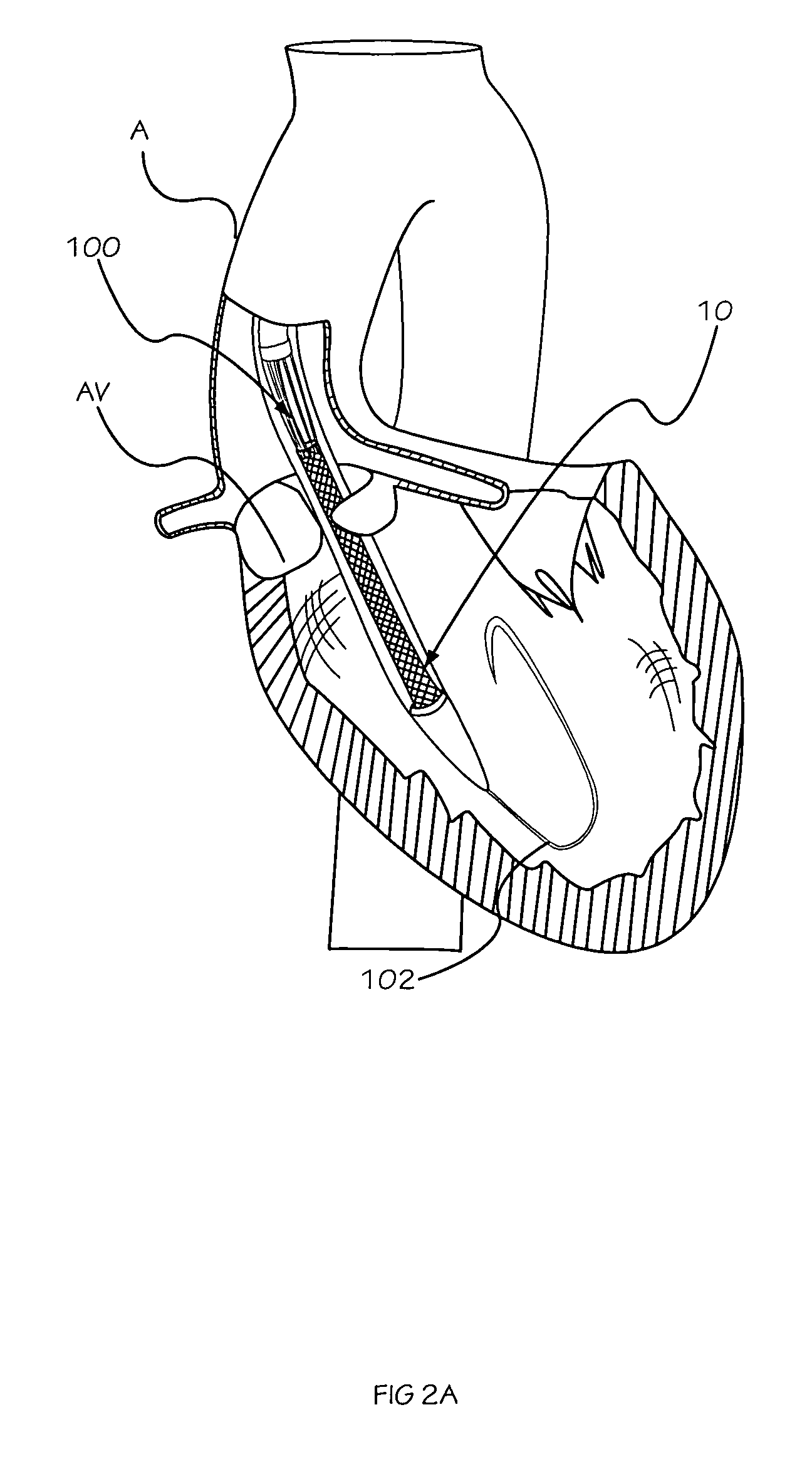
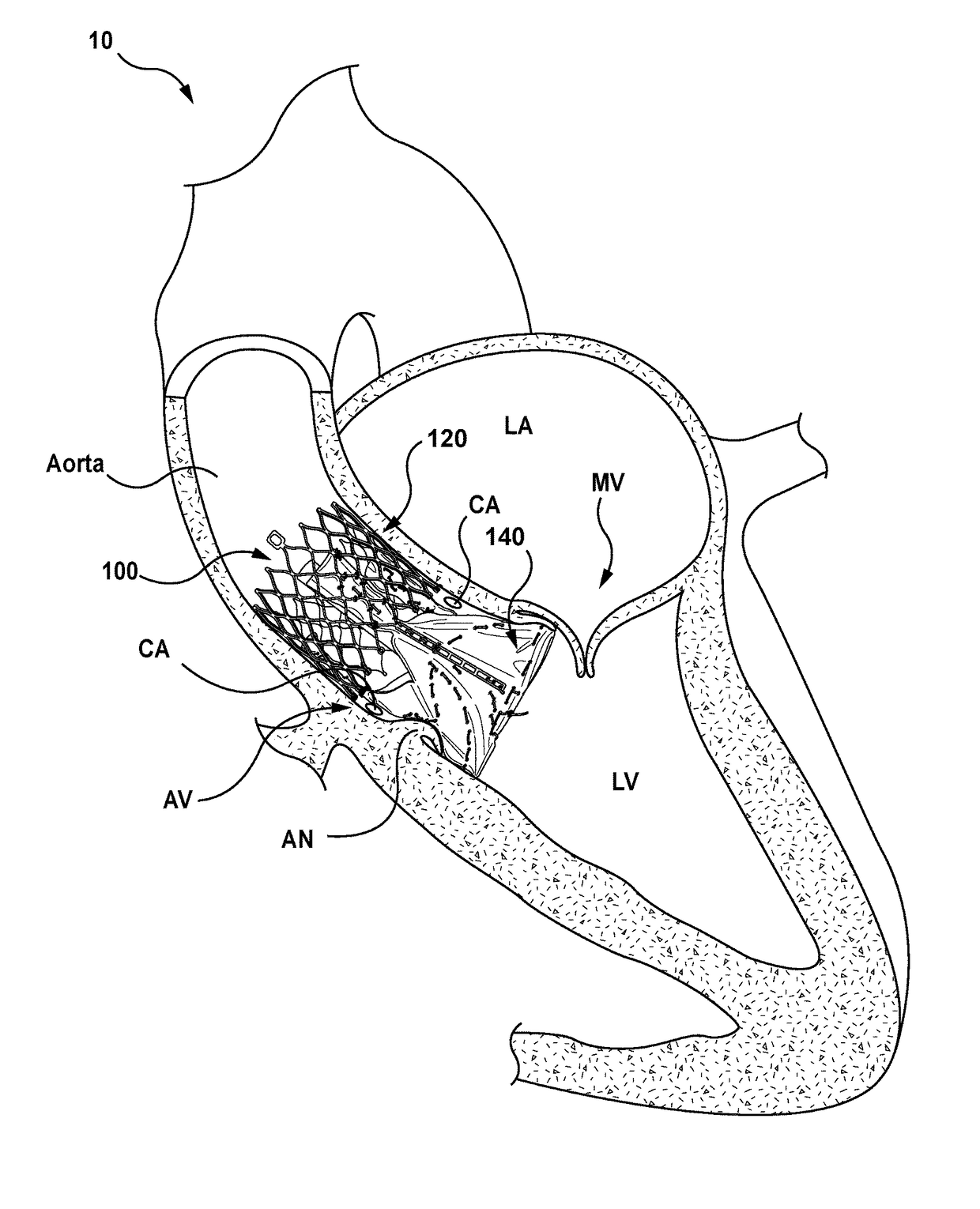
A replacement valve for implantation centrally within the orifice of a malfunctioning native heart valve. The valve is designed for minimally invasive entry through an intercostal opening in the chest of a patient and an opening in the apex of the human heart. The replacement valve includes either a separate anchor (11, 87, 111) or a combined anchor (67) that folds around the malfunctioning native valve leaflets, sandwiching them in a manner so as to securely anchor the replacement valve in a precise, desired location.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
Methods and apparatus for endovascular heart valve replacement comprising tissue grasping elements
ActiveUS20060058872A1Accurate placementPrevent blood backflowStentsBalloon catheterHeart valve replacementBlood vessel
The present invention provides an apparatus for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve. In some embodiments, the apparatus includes an expandable anchor supporting a replacement valve, the anchor and replacement valve being adapted for percutaneous delivery and deployment to replace the patient's heart valve, the anchor having a braid having atraumatic grasping elements adapted to grasp tissue in a vicinity of the patient's heart valve.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods and apparatus for endovascular heart valve replacement comprising tissue grasping elements
ActiveUS20060253191A1Accurate placementPermit blood flowStentsBalloon catheterHeart valve replacementBlood vessel
A method for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve including the following steps: endovascularly delivering an anchor and a replacement valve supported within the anchor to a vicinity of the heart valve in a collapsed delivery configuration, the anchor having grasping elements adapted to grasp tissue in a vicinity of the heart valve; expanding the anchor, thereby rotating the grasping elements; and grasping the tissue with the rotating grasping elements.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
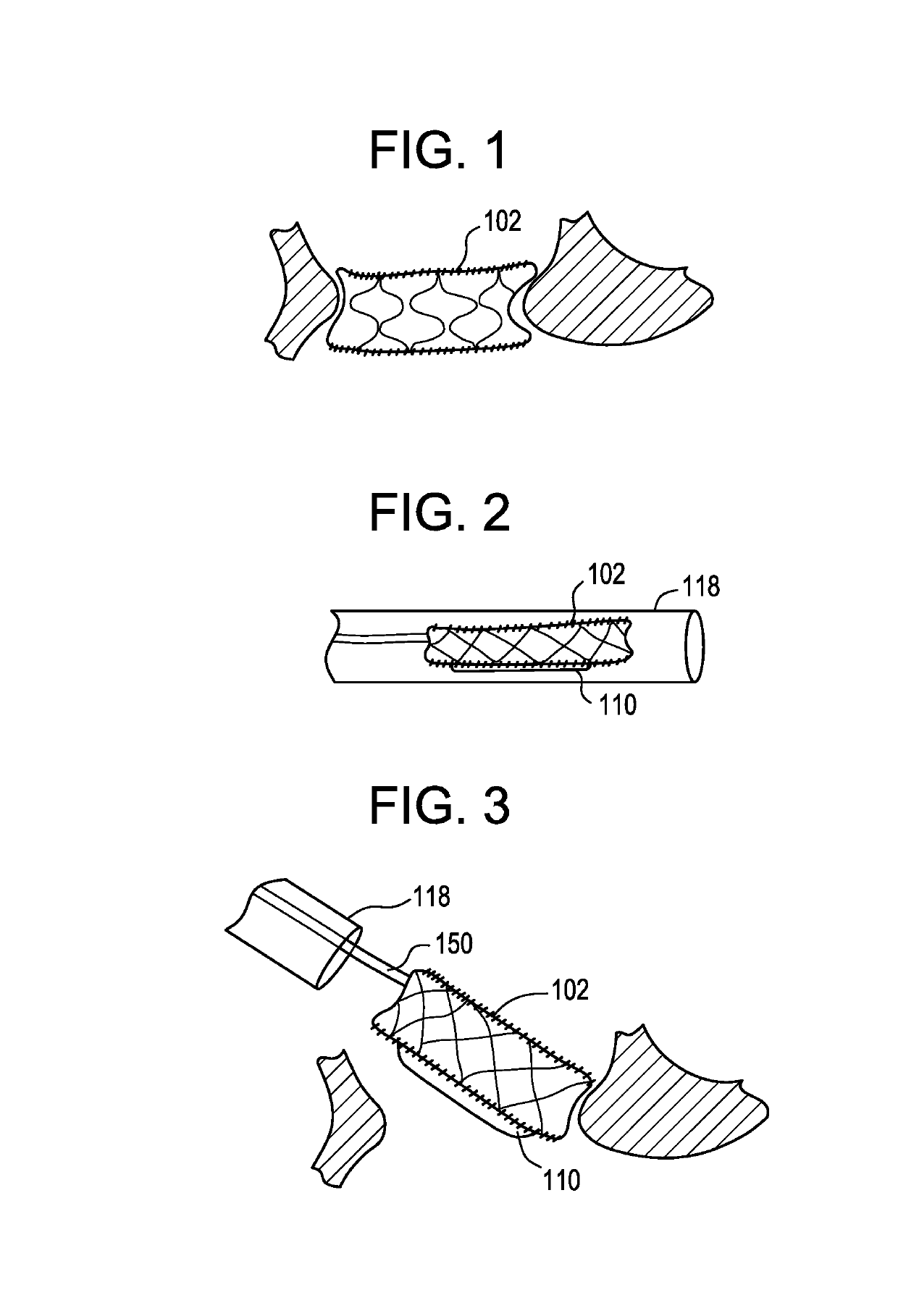
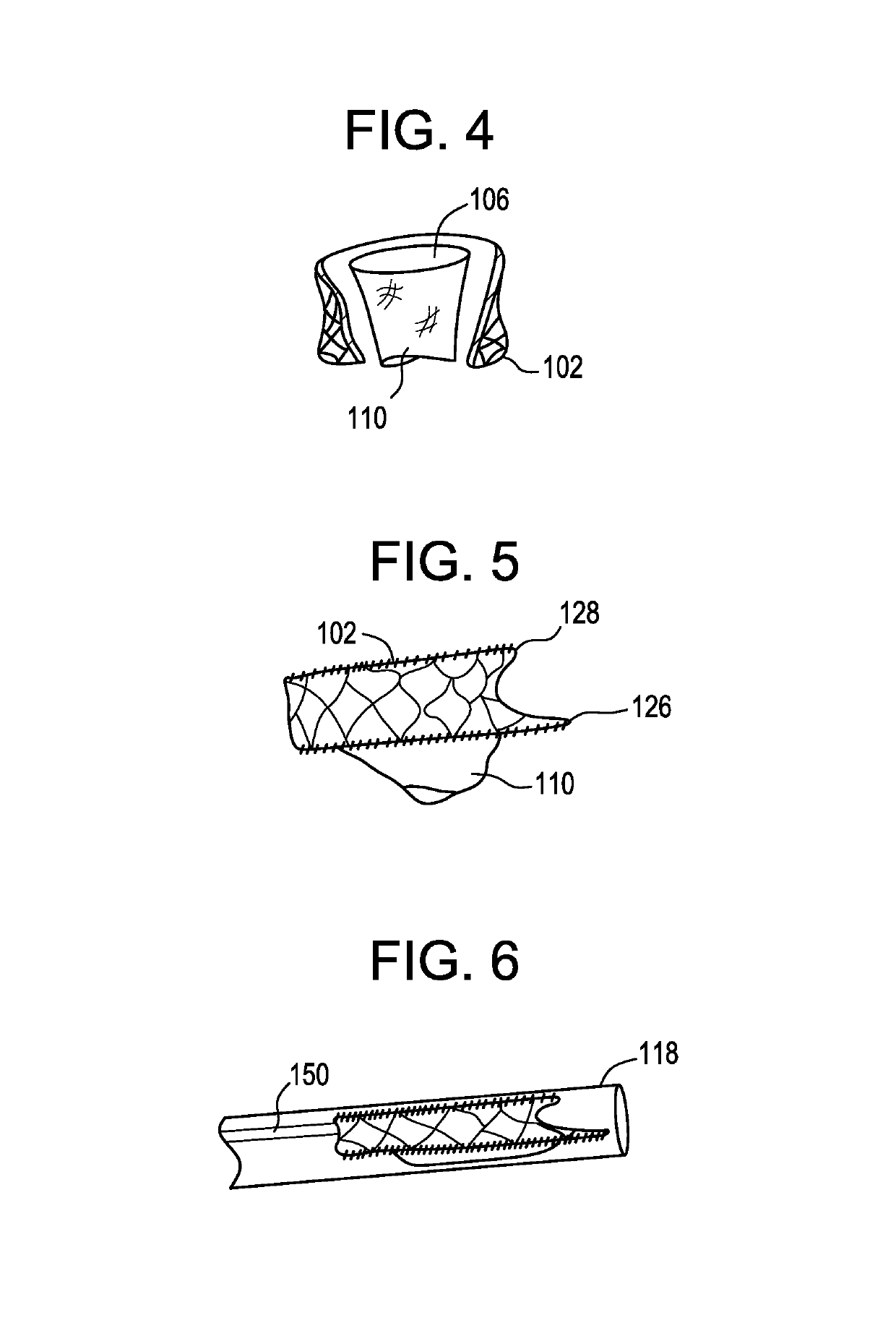
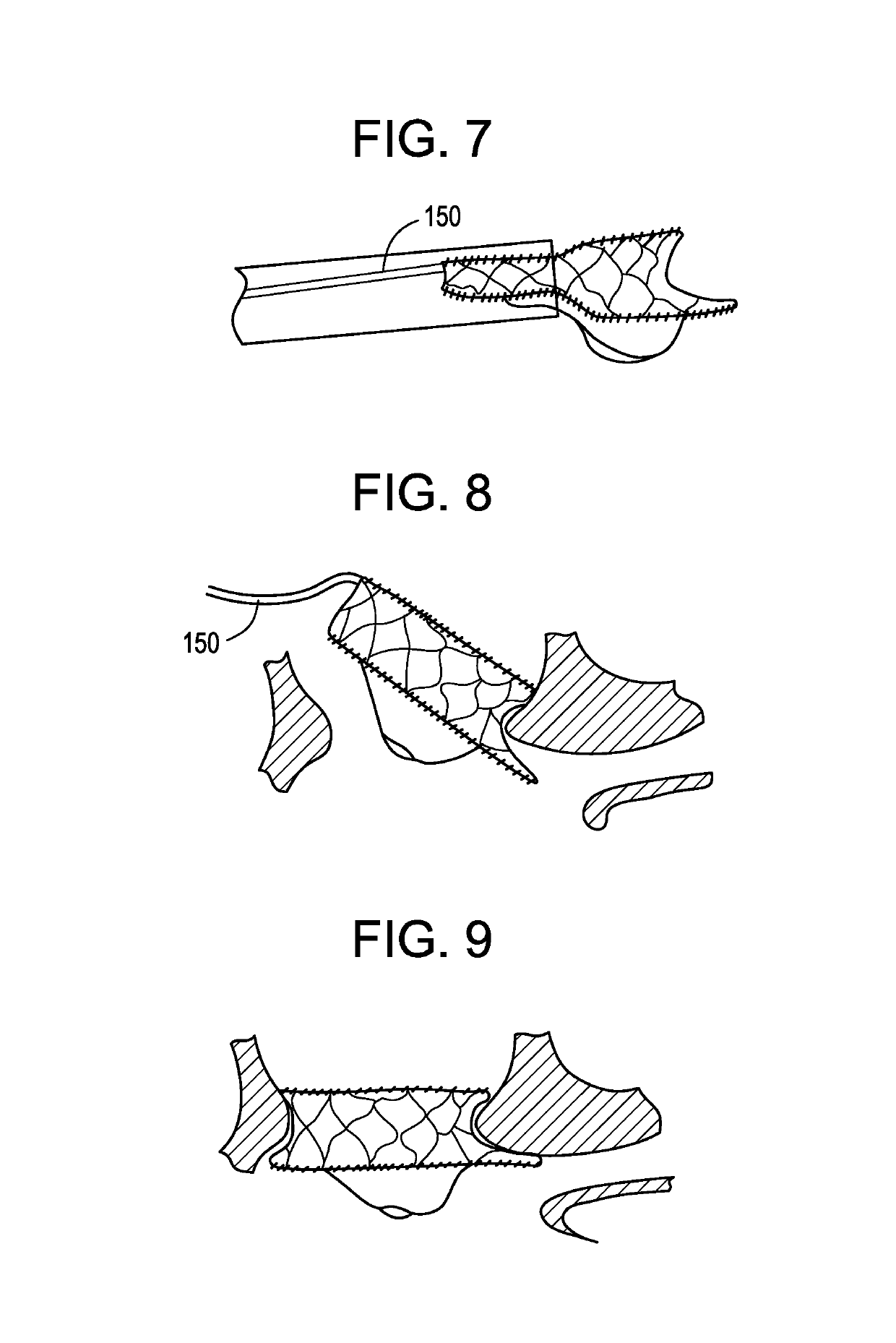
Stapling apparatus and method for heart valve replacement
A surgical stapler for securing a prosthetic heart valve within a patient generally includes a first cylindrical portion for carrying at least one staple assembly on a distal end thereof; a second cylindrical portion positioned concentrically about the first cylindrical portion and having a camming arm on a distal end thereof, the camming arm configured to cam the at least one staple assembly radially outward and drive the at least one staple assembly distally such that a first leg of the at least one staple assembly penetrates a cuff of the prosthetic heart valve and a second leg of the at least one staple assembly pierces a portion of heart tissue surrounding the prosthetic heart valve, as the second cylindrical portion is moved distally relative to the first cylindrical portion; and a third cylindrical portion positioned concentrically about the second cylindrical portion and having an anvil flange on a distal end thereof, the anvil flange configured to crimp the second leg of the at least one staple assembly toward the first leg of the at least one staple assembly to secure the prosthetic heart valve to the surrounding heart tissue as the third cylindrical portion is moved relative to the second cylindrical portion. A method of installing a heart valve within a patient which includes the steps of accessing a site within a heart from which a natural heart valve has been removed; lowering a prosthetic heart valve into position within the site in the heart; positioning a surgical stapler having at least one staple assembly removably held on a distal end thereof adjacent the prosthetic heart valve within the site in the heart; driving a first leg of the at least one staple assembly through a peripheral cuff of the prosthetic heart valve; and crimping a second leg of the at least one staple assembly in a direction toward the first leg such that the second leg pierces a portion of heart tissue surrounding the prosthetic heart valve, thereby securing the prosthetic heart valve to the surrounding heart tissue.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP
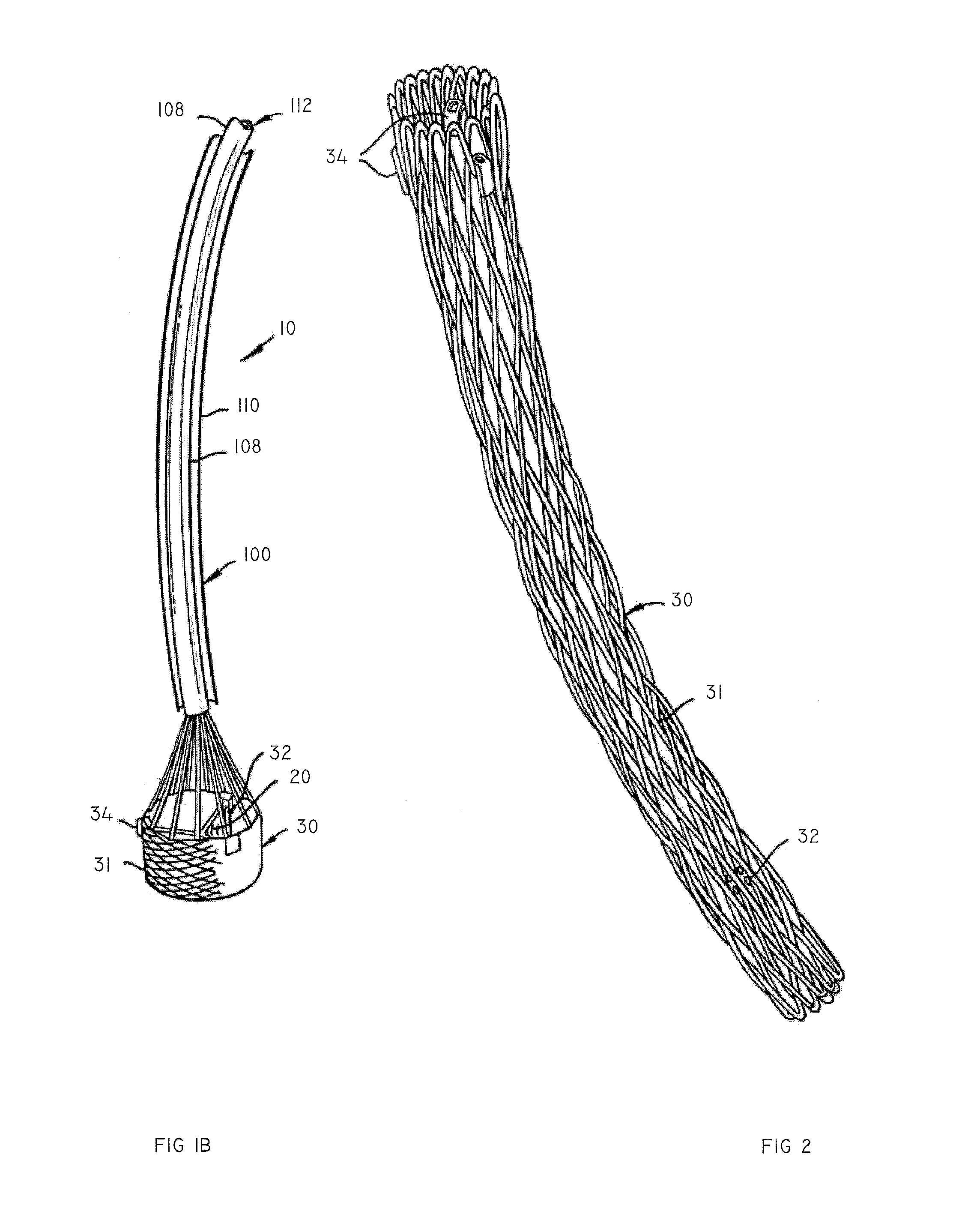
Apparatus and methods for protecting against embolization during endovascular heart valve replacement
Apparatus for protecting a patient against embolization during endovascular replacement of the patient's heart valve is provided, the apparatus including a replacement valve configured for endovascular delivery and deployment, and an embolic filter configured for disposal downstream of the replacement valve during deployment of the valve. Apparatus including a delivery catheter having an expandable replacement valve disposed therein, and an embolic filter advanceable along the delivery catheter for diverting emboli released during endovascular deployment of the replacement valve is also provided. Furthermore, methods for protecting a patient against embolization during endovascular replacement of the patient's heart valve are provided, the methods including the steps of endovascularly delivering a replacement valve to a vicinity of the patient's heart valve, endovascularly deploying an embolic filter downstream of the heart valve, and endovascularly deploying the replacement valve.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
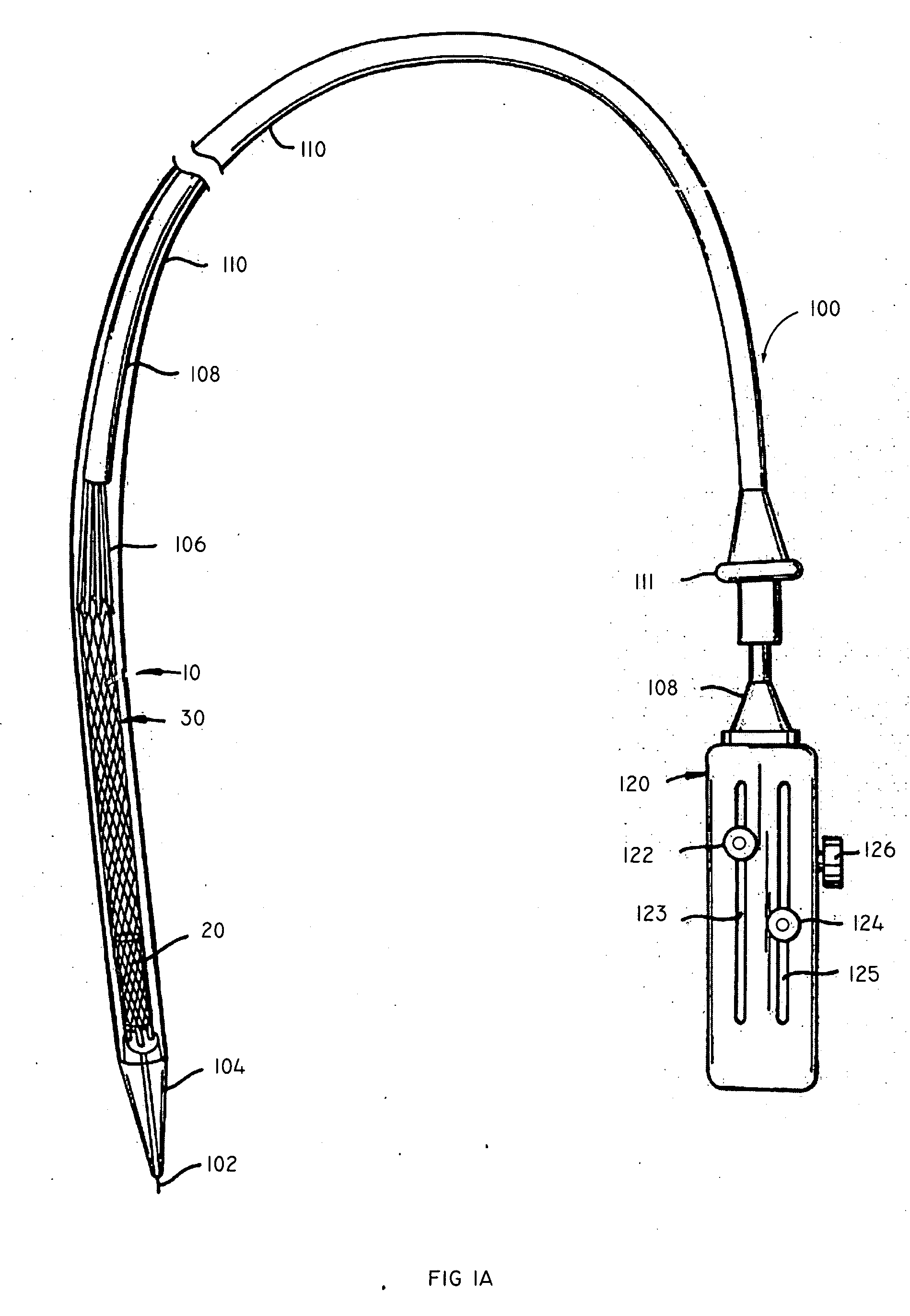
Minimally invasive heart valve replacement
ActiveUS7837727B2Sufficient flexibilitySevere size constraintHeart valvesBlood vesselsHeart valve replacementThoracic cavity
A replacement valve for implantation centrally within the orifice of a malfunctioning native heart valve. The valve is designed for minimally invasive entry through an intercostal opening in the chest of a patient and an opening in the apex of the human heart. The replacement valve includes either a separate anchor (11, 87, 111) or a combined anchor (67) that folds around the malfunctioning native valve leaflets, sandwiching them in a manner so as to securely anchor the replacement valve in a precise, desired location.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
Methods and Apparatus for Endovascular Heart Valve Replacement Comprising Tissue Grasping Elements
InactiveUS20120041550A1Accurate placementPermit blood flowStentsBalloon catheterHeart valve replacementBlood vessel
A method for endovascularly replacing a patient's heart valve including the following steps: endovascularly delivering an anchor and a replacement valve supported within the anchor to a vicinity of the heart valve in a collapsed delivery configuration, the anchor having grasping elements adapted to grasp tissue in a vicinity of the heart valve; expanding the anchor, thereby rotating the grasping elements; and grasping the tissue with the rotating grasping elements.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
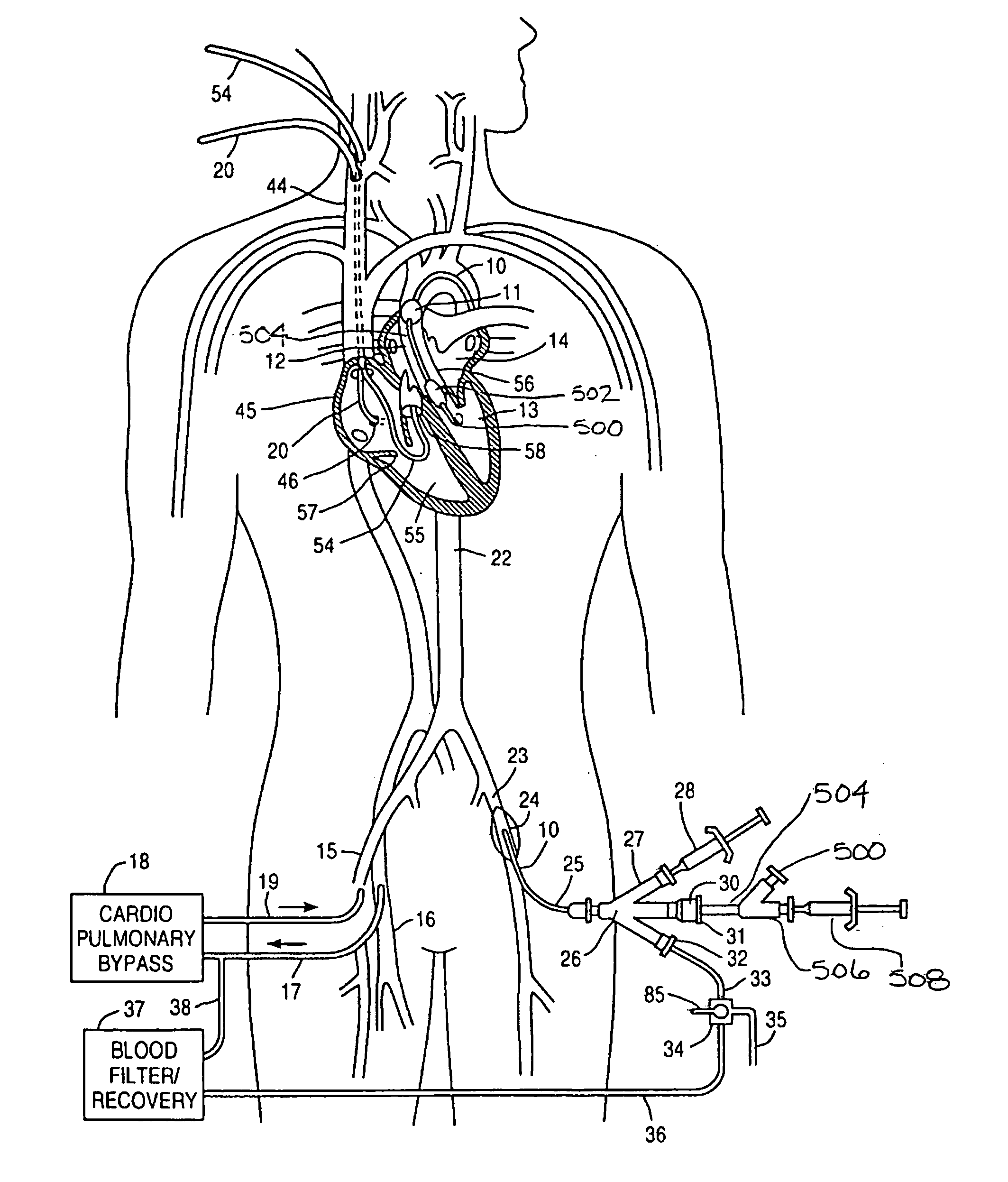
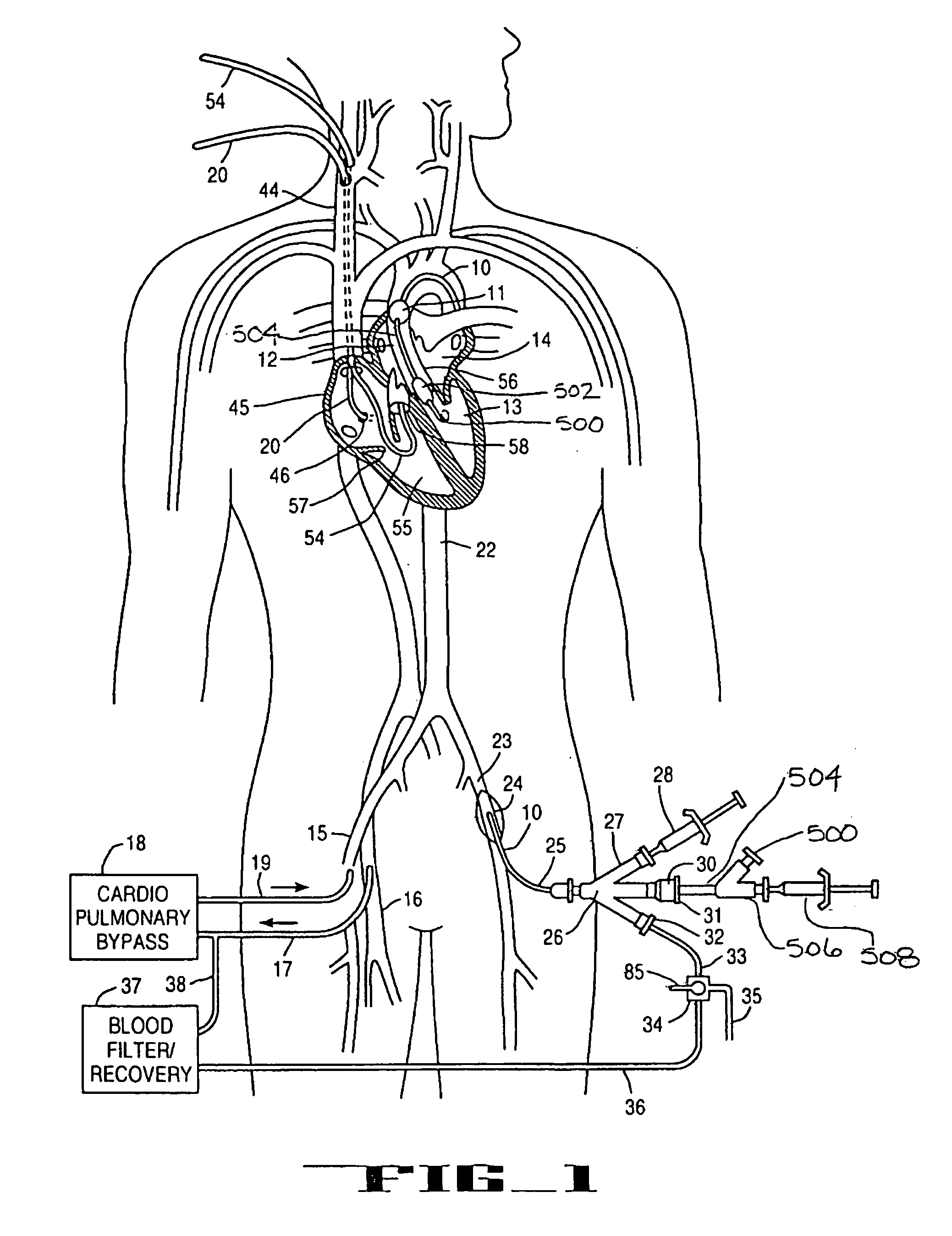
System and methods for performing endovascular procedures
InactiveUS20060058775A1Procedure is complicatedEasy to controlStentsGuide needlesExtracorporeal circulationAtherectomy
A system for inducing cardioplegic arrest and performing an endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of a patient. An endoaortic partitioning catheter has an inflatable balloon which occludes the ascending aorta when inflated. Cardioplegic fluid may be infused through a lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to stop the heart while the patient's circulatory system is supported on cardiopulmonary bypass. One or more endovascular devices are introduced through an internal lumen of the endoaortic partitioning catheter to perform a diagnostic or therapeutic endovascular procedure within the heart or blood vessels of the patient. Surgical procedures such as coronary artery bypass surgery or heart valve replacement may be performed in conjunction with the endovascular procedure while the heart is stopped. Embodiments of the system are described for performing: fiberoptic angioscopy of structures within the heart and its blood vessels, valvuloplasty for correction of valvular stenosis in the aortic or mitral valve of the heart, angioplasty for therapeutic dilatation of coronary artery stenoses, coronary stenting for dilatation and stenting of coronary artery stenoses, atherectomy or endarterectomy for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, intravascular ultrasonic imaging for observation of structures and diagnosis of disease conditions within the heart and its associated blood vessels, fiberoptic laser angioplasty for removal of atheromatous material from within coronary artery stenoses, transmyocardial revascularization using a side-firing fiberoptic laser catheter from within the chambers of the heart, and electrophysiological mapping and ablation for diagnosing and treating electrophysiological conditions of the heart.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
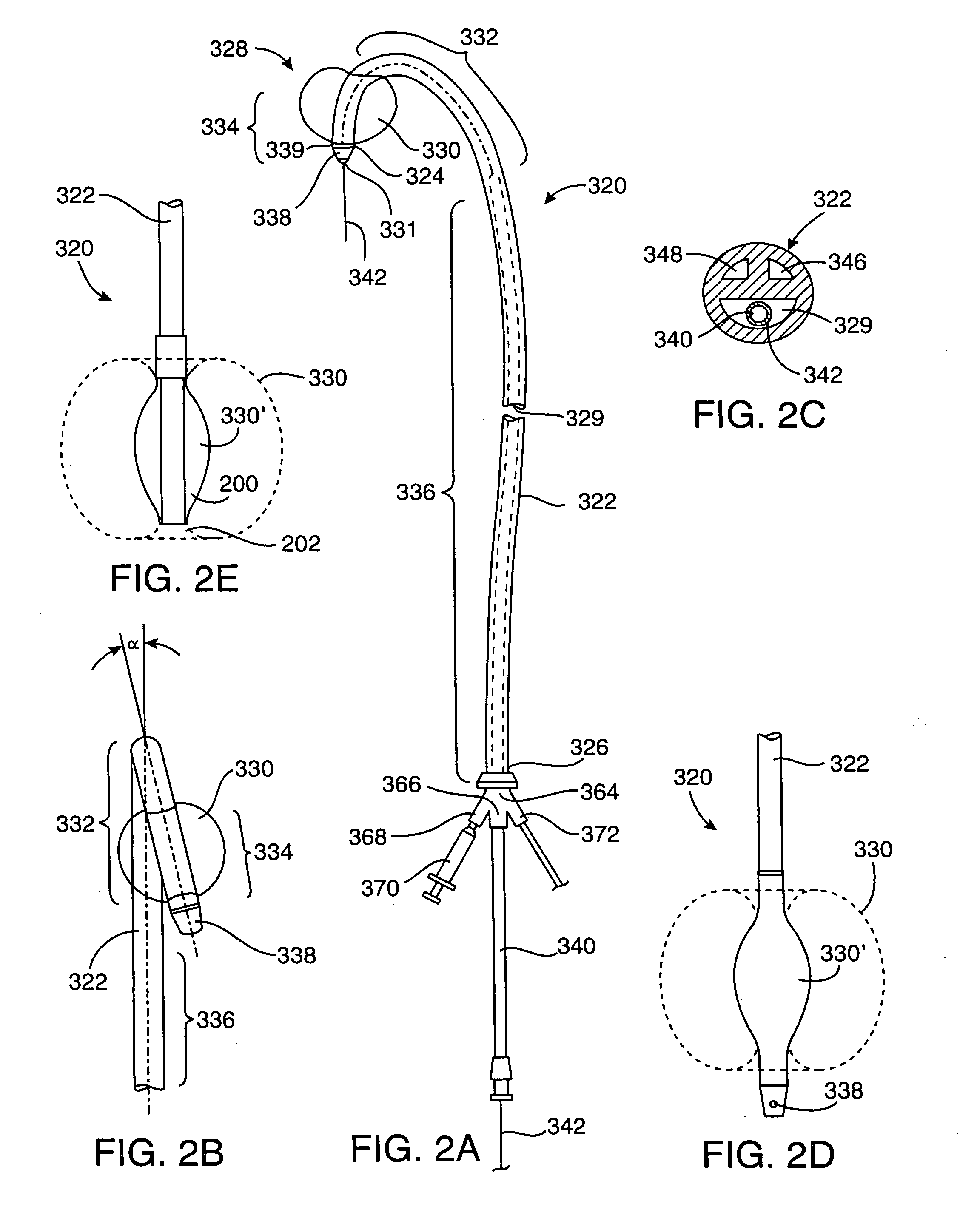
Methods and apparatus for performing valvuloplasty
The present invention relates to apparatus and methods for performing valvuloplasty. In some embodiments, the apparatus includes an expandable braid valvuloplasty device. In some embodiments, the methods and apparatus may be used as an adjunct to percutaneous heart valve replacement. In some embodiments, the apparatus and methods may provide a medical practitioner with feedback, monitoring or measurement information, e.g., information relevant to percutaneous transcatheter heart valve replacement.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods and apparatus for performing valvuloplasty
The present invention relates to apparatus and methods for performing valvuloplasty. In some embodiments, the apparatus includes an expandable braid valvuloplasty device. In some embodiments, the methods and apparatus may be used as an adjunct to percutaneous heart valve replacement. In some embodiments, the apparatus and methods may provide a medical practitioner with feedback, monitoring or measurement information, e.g., information relevant to percutaneous transcatheter heart valve replacement.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Heart Valves Prostheses and Methods for Percutaneous Heart Valve Replacement
ActiveUS20170100236A1Prevent retrograde blood flowHeart valvesHeart valve replacement (procedure)Heart valve replacement
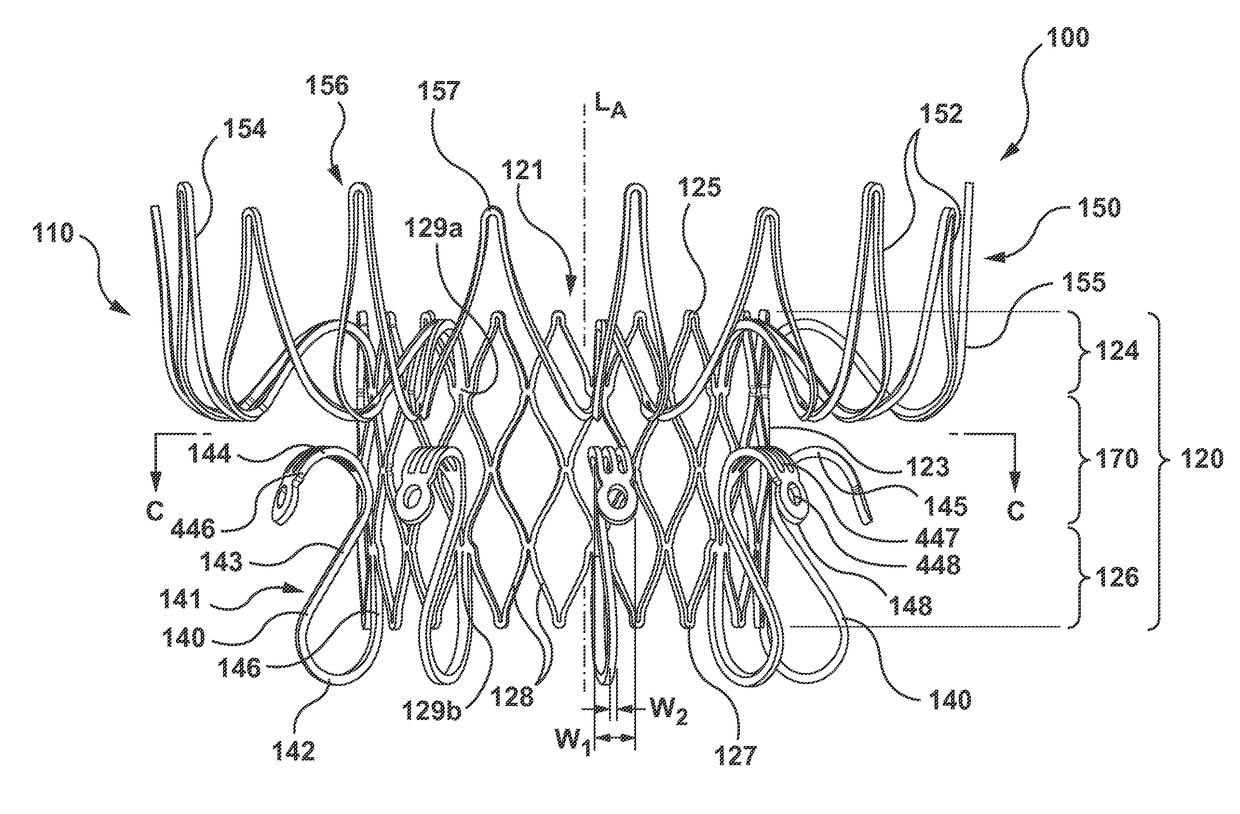
Prosthetic heart valve devices and associated methods for percutaneous heart valve replacement are disclosed herein. A transcatheter valve prosthesis configured in accordance herewith includes a frame having a valve support and one or more support arms coupled thereto. The one or more support arms are configured to extend from the second end of the valve support toward the first end when the valve prosthesis is in an expanded configuration. When deployed in the expanded configuration, the one or more support arms have a curvilinear shape, such as a substantially S-shape, that at least partially engages tissue at the native heart valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Heart valve prostheses having multiple support arms and methods for percutaneous heart valve replacement
Prosthetic heart valve devices and associated methods for percutaneous or transcatheter heart valve replacement are disclosed herein. A heart valve prosthesis configured in accordance herewith includes a frame having a valve support and a plurality of support arms extending therefrom. The plurality of support arms may include a main support arm configured to extend from the valve support for capturing at least a portion of a valve leaflet of a native heart valve therebetween when the valve prosthesis is in an expanded configuration and deployed within the native heart valve. In addition, the plurality of support arms may include multiple supplemental support arms disposed about the circumference of the valve support that when deployed in the expanded configuration are configured to at least partially engage subannular tissue at the native heart valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Systems and methods for enabling heart valve replacement
ActiveUS20090157174A1Increase heightEasy to optimizeStentsHeart valvesProsthesisHeart valve replacement
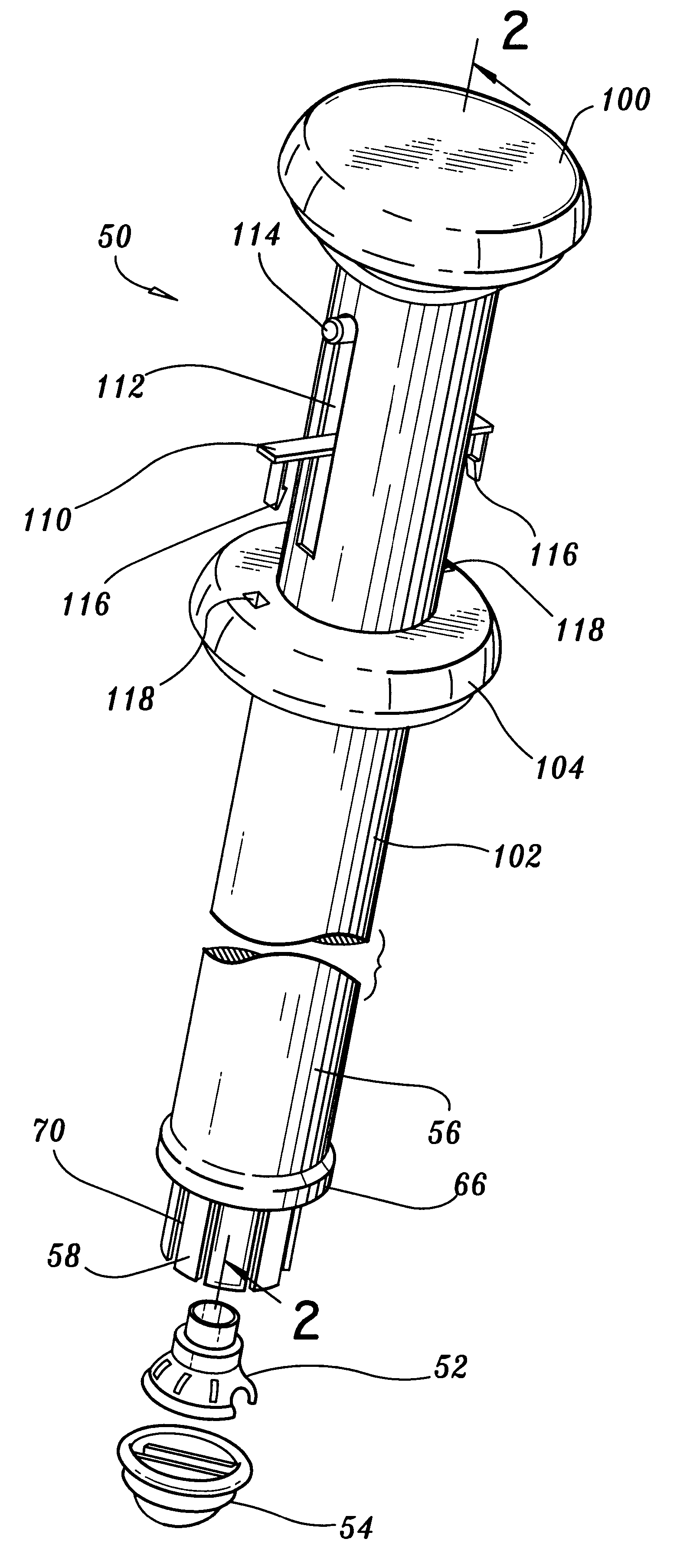
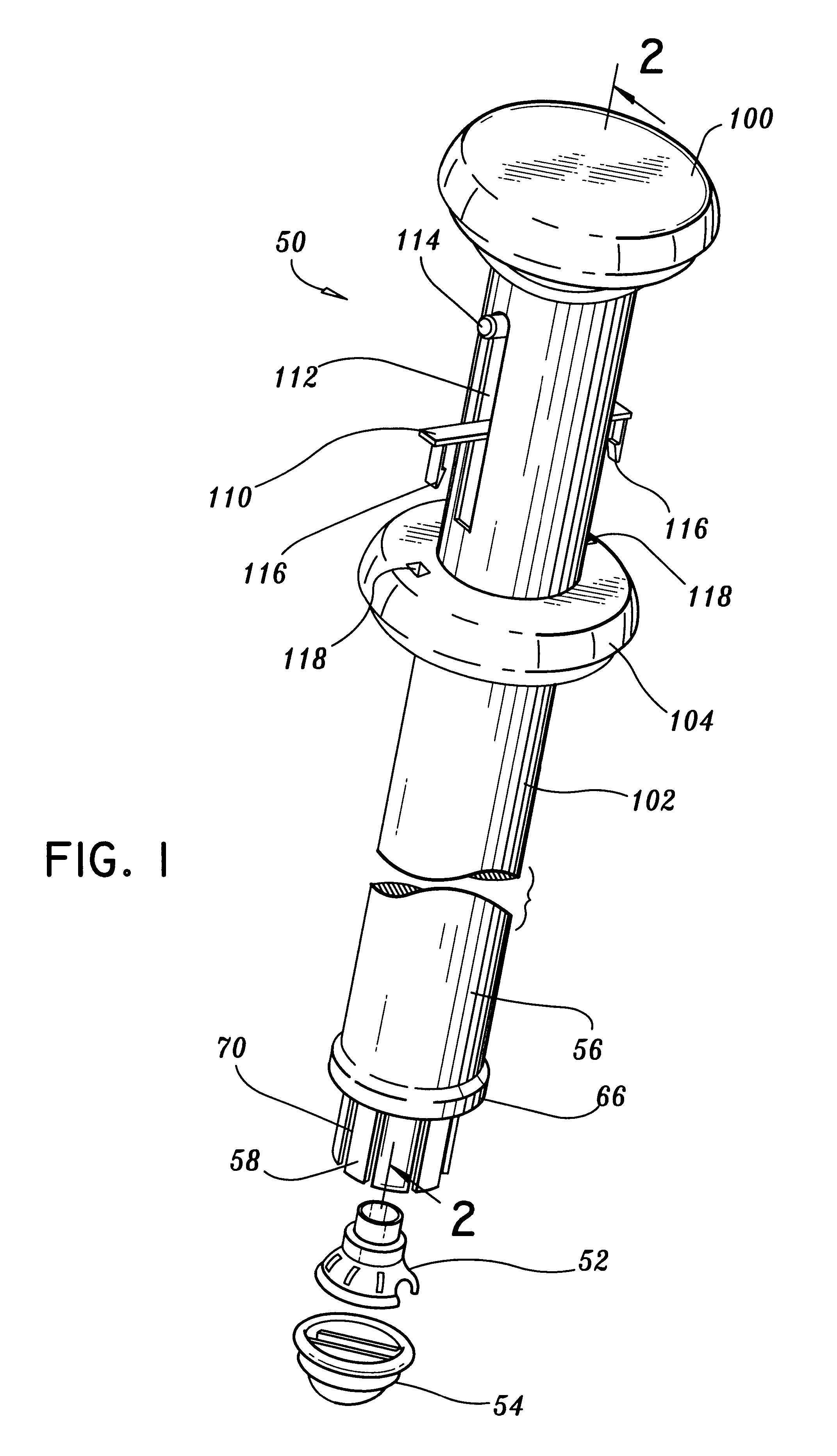
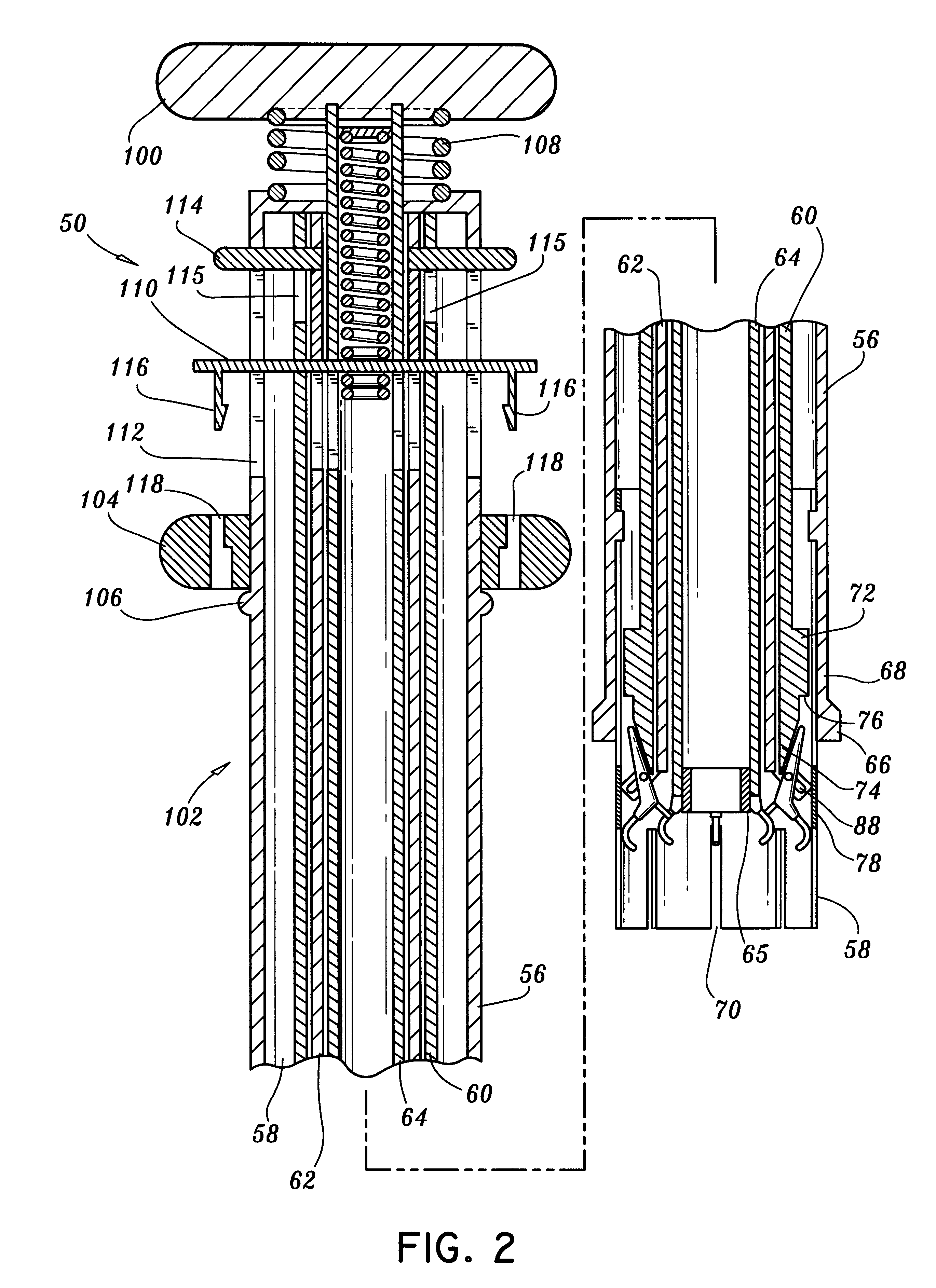
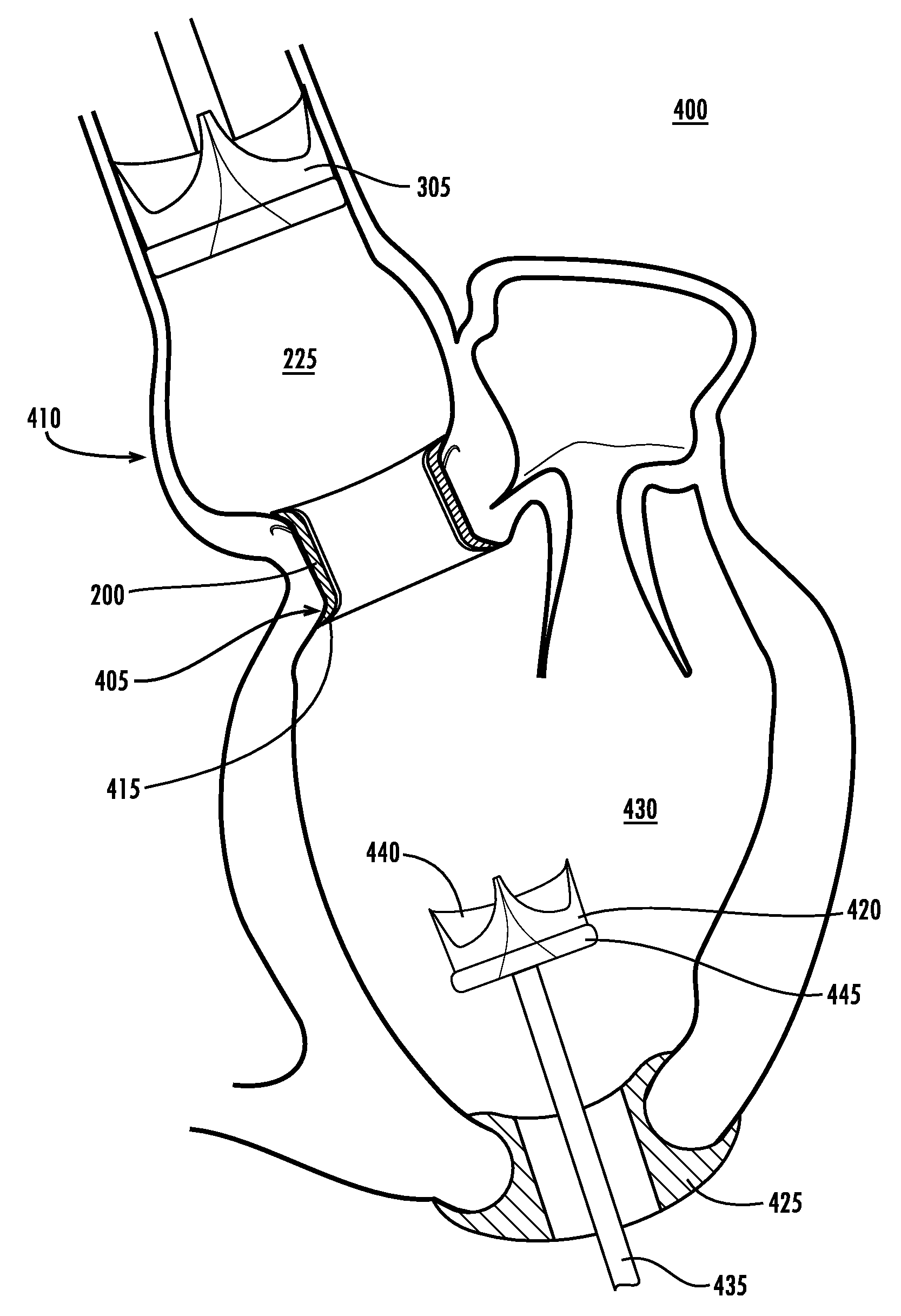
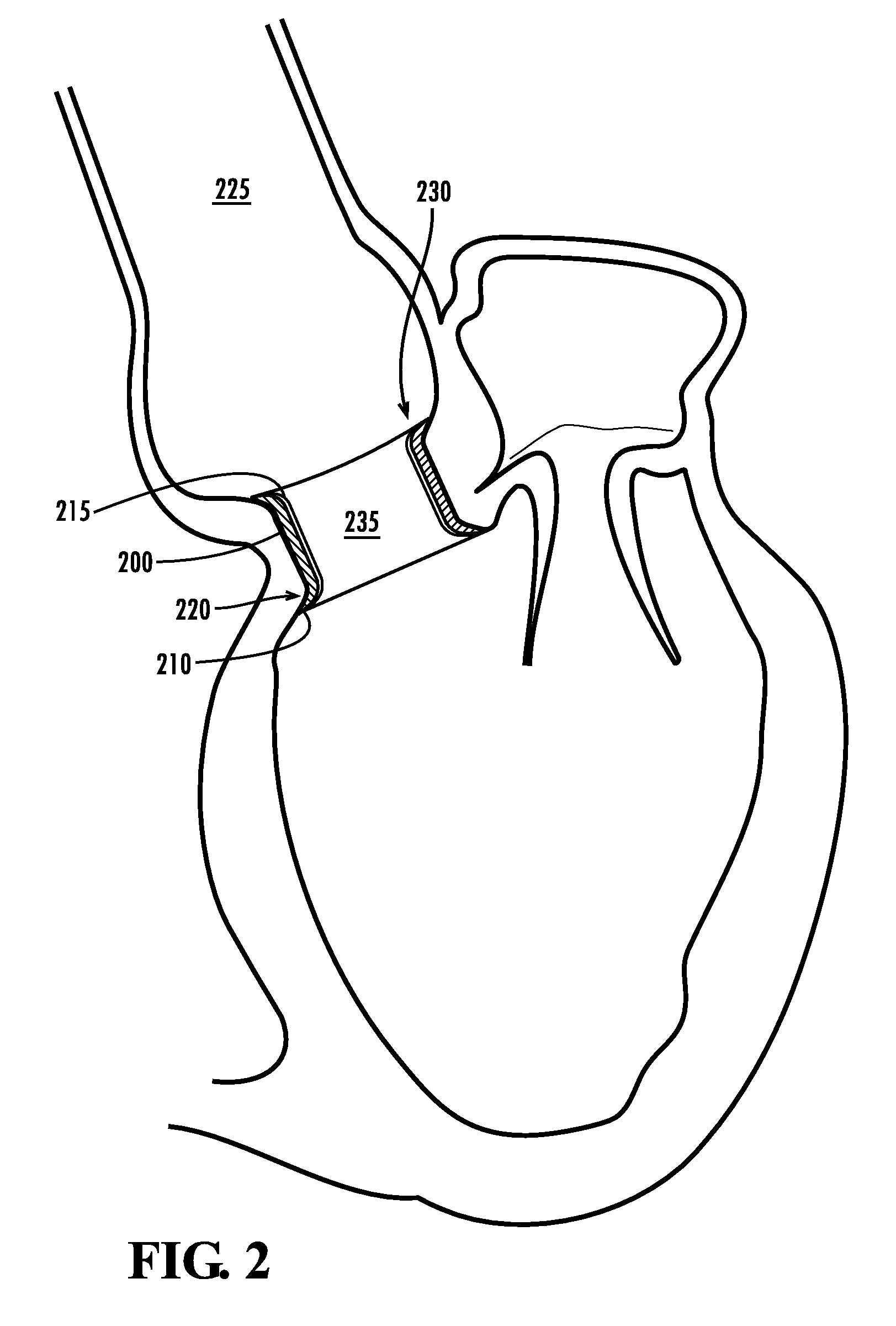
The present invention describes a cardiac prosthetic system (400) comprising: an anchoring conduit (200) having a harbour (415), the harbour including a first releasably engaging component (515); a temporary valve (305) and a heart valve prosthesis (420) having a second releasably engaging component (445) enabled to be securely coupled and uncoupled from the first releasably engaging component (515) of the harbour (415).
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Orthogonally delivered transcatheter heart valve replacement
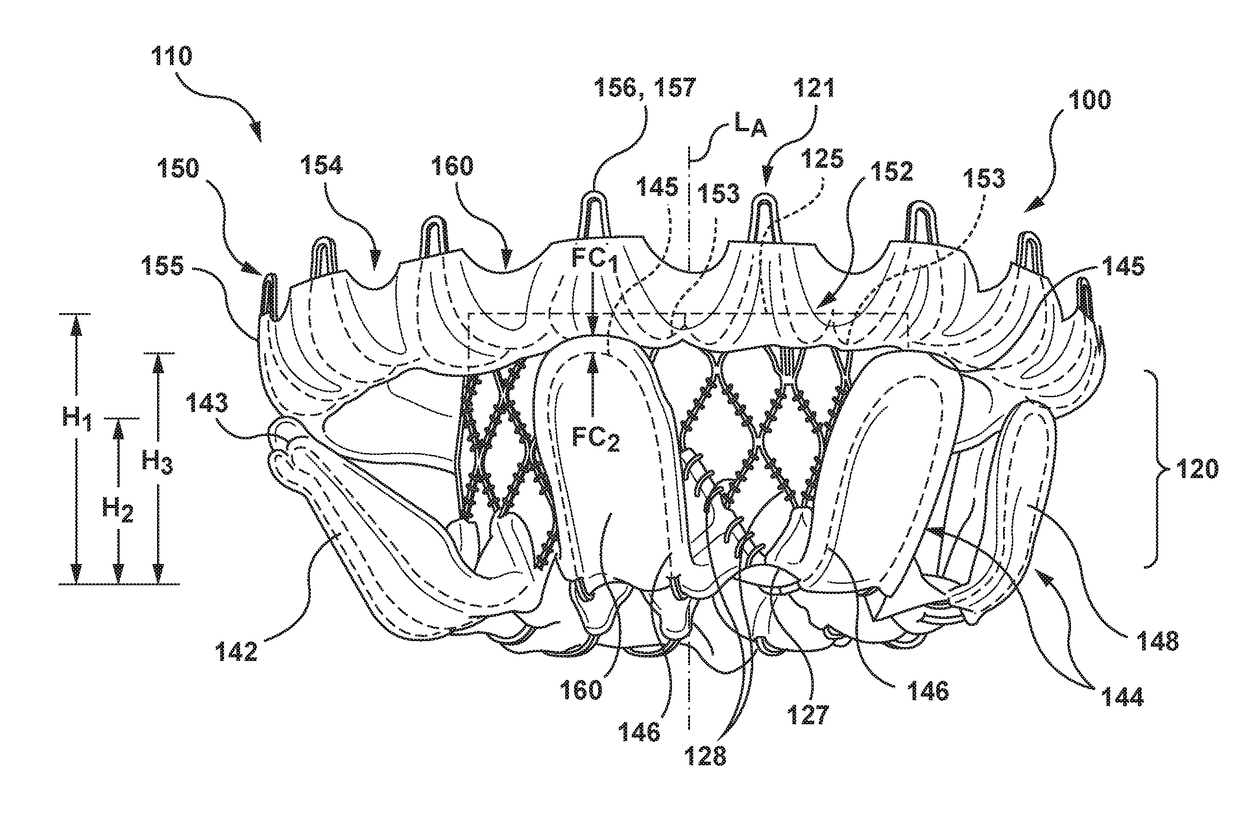
The invention relates to a transcatheter heart valve replacement (A61F2 / 2412), and in particular an orthogonally delivered transcatheter prosthetic valve having a tubular frame with a flow control component mounted within the tubular frame and configured to permit blood flow in a first direction through an inflow end of the valve and block blood flow in a second direction, opposite the first direction, through an outflow end of the valve, wherein the valve is compressible to a compressed configuration for introduction into the body using a delivery catheter for implanting at a desired location in the body, said compressed configuration having a long-axis oriented at an intersecting angle of between 45-135 degrees to the first direction, and expandable to an expanded configuration having a long-axis oriented at an intersecting angle of between 45-135 degrees to the first direction, wherein the long-axis of the compressed configuration of the valve is substantially parallel to a length-wise cylindrical axis of the delivery catheter, and wherein the valve has a height of about 5-60 mm and a diameter of about 25-80 mm.
Owner:VDYNE INC
Prosthetic heart valve sizer assembly with flexible sizer body
A flexible sizer body for evaluating a valve annulus to determine a size of a prosthetic heart valve to be sewn to the valve annulus during heart valve replacement surgery. The prosthetic heart valve includes an annular extension having a first flexibility and a sewing ring having a second flexibility. The flexible sizer body includes an outer ring and an annular wall coupled to and extending from the outer ring. The annular wall has a flexibility substantially similar to the first flexibility of the annular extension of the prosthetic heart valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
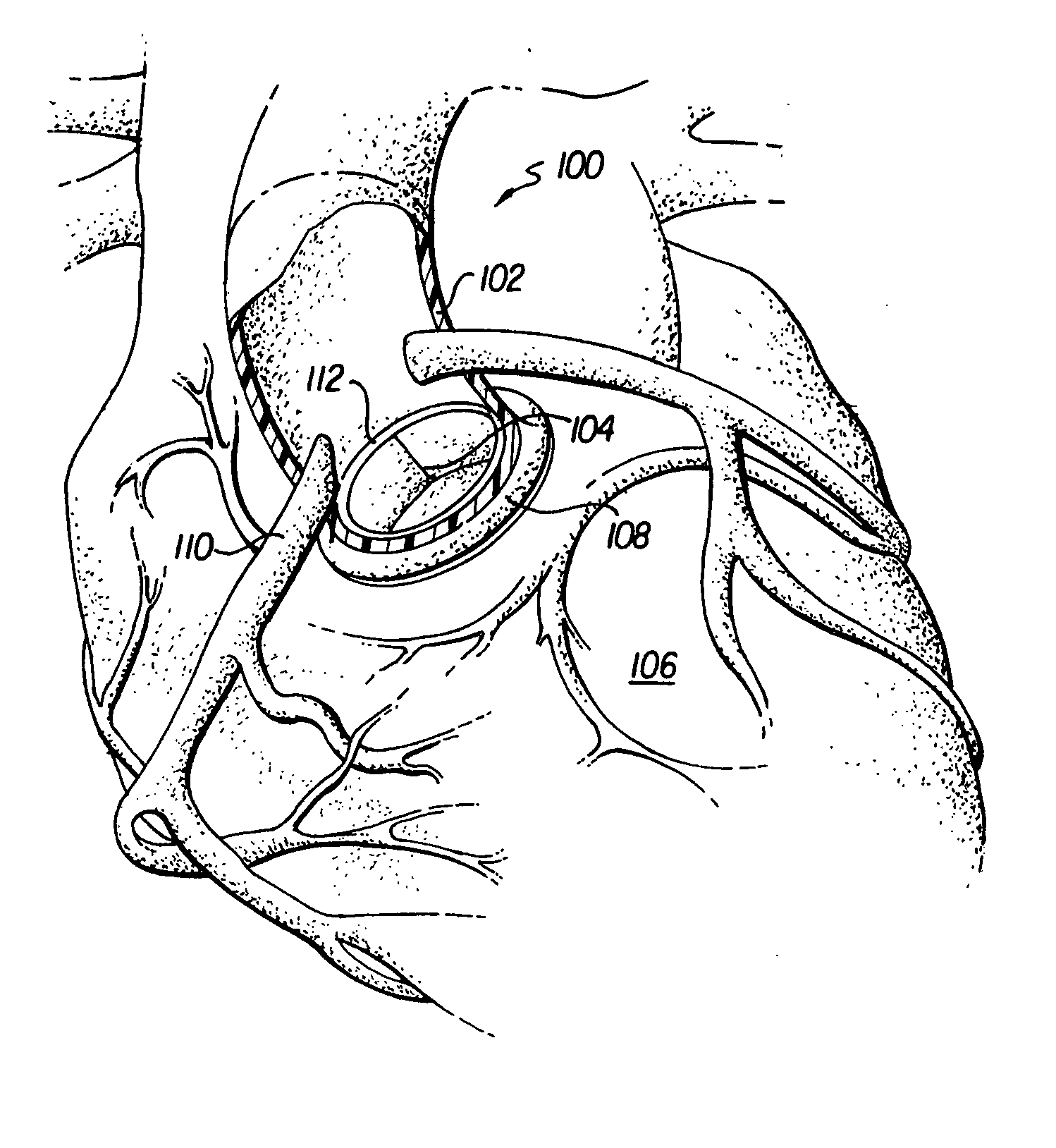
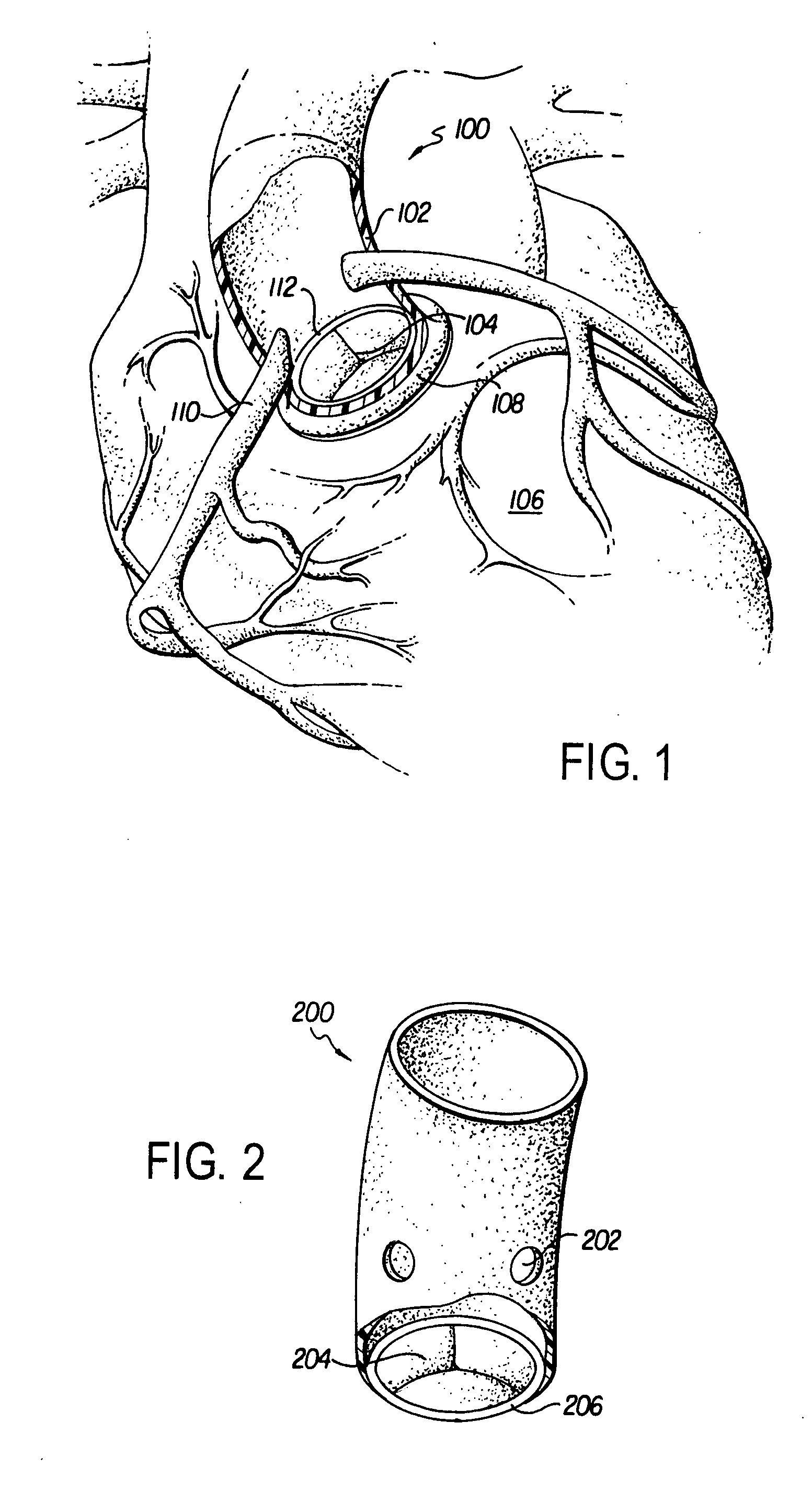
Device for the Deployment of a System of Guide Wires Within a Cardiac Chamber for Implanting a Prosthetic Heart Valve
A prosthetic system for heart valve replacement comprises an annular support structure within which a valved prosthetic body can be expanded until it meet opposition. The annular support is provided in two or more ring segments having terminal connection means for forming, in the condition of use of the prosthetic system, a stable and durable annular structural continuity capable of withstanding the opposition exerted by the valved prosthetic body. The prosthetic system is deployed using guide wires within a cardiac chamber guided through an introducer catheter having two or more through lumens, within which at least two first guide catheters are positioned. These guide catheters have respective deflected or deflectable distal ends adapted to emerge from the distal end of the introducer catheter to convey and direct the distal ends of respective guide wires, placed within the guide catheters, towards a capture member of a capture system which is provided within the introducer catheter.
Owner:INNOVHEART SRL
Prosthetic heart valve sizer assembly with flexible sizer body
A flexible sizer body for evaluating a valve annulus to determine a size of a prosthetic heart valve to be sewn to the valve annulus during heart valve replacement surgery. The prosthetic heart valve includes an annular extension having a first flexibility and a sewing ring having a second flexibility. The flexible sizer body includes an outer ring and an annular wall coupled to and extending from the outer ring. The annular wall has a flexibility substantially similar to the first flexibility of the annular extension of the prosthetic heart valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
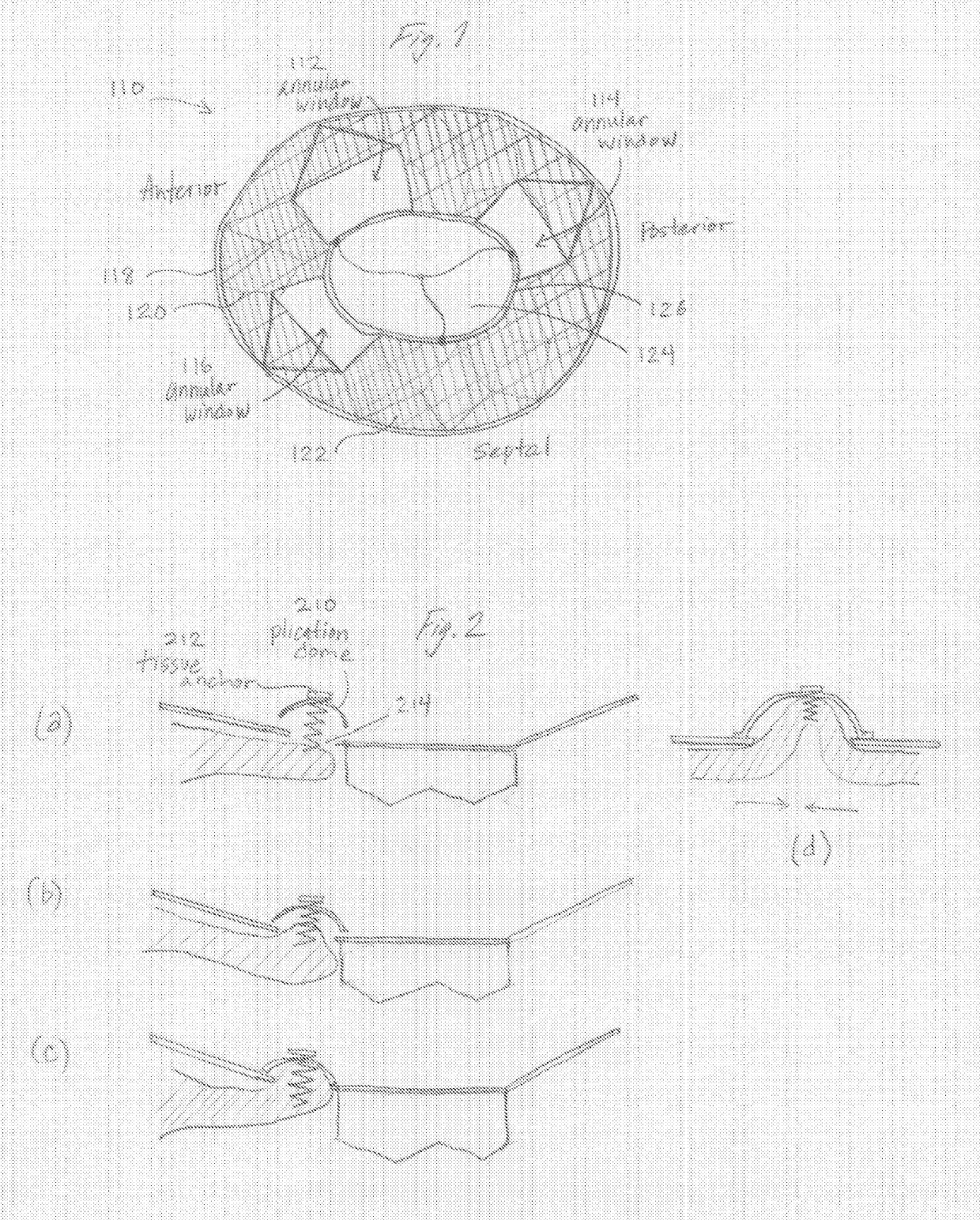
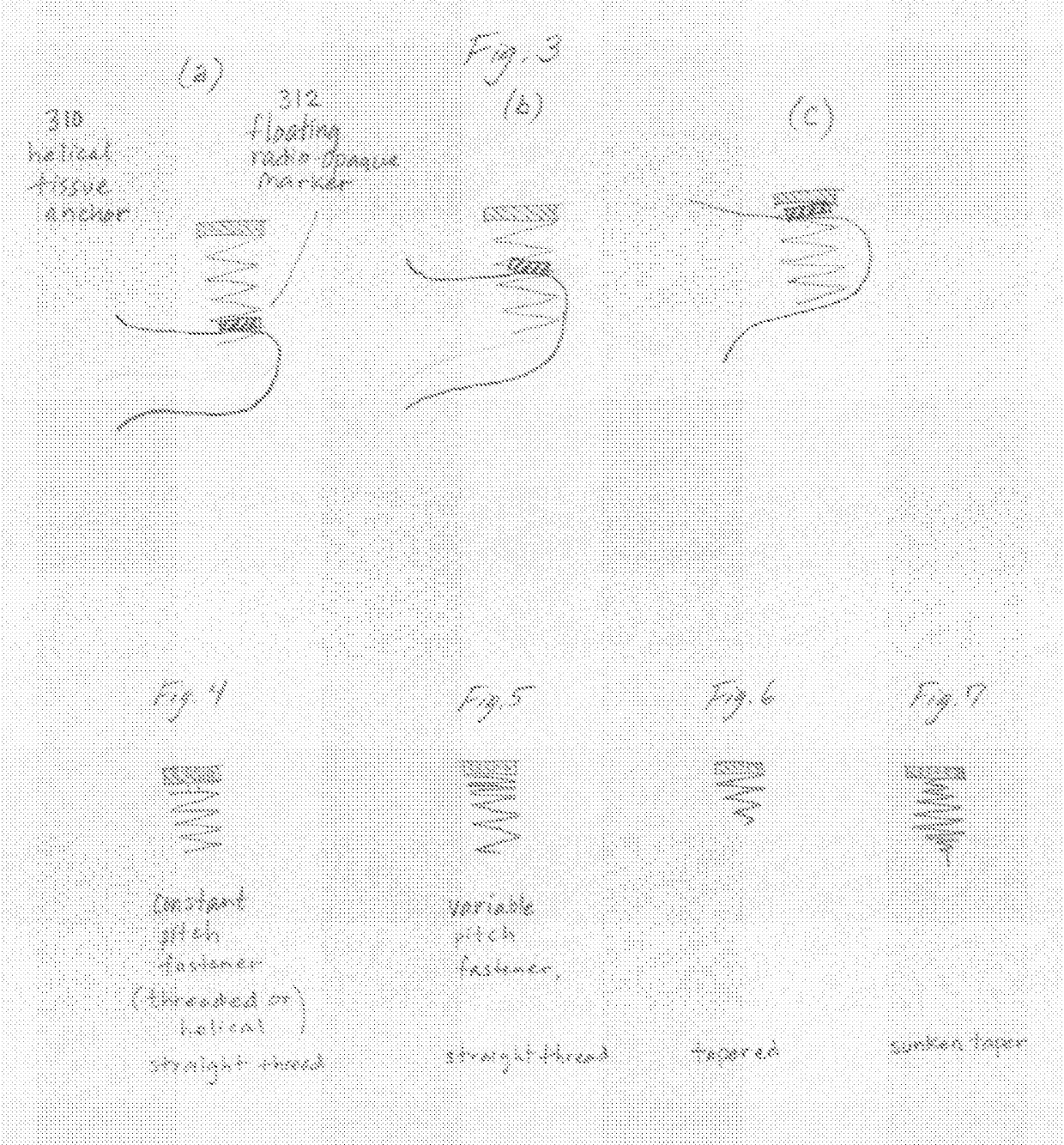
Transcatheter Heart Valve with Plication Tissue Anchors
The invention relates to a transcatheter heart valve replacement (A61F2 / 2412), and in particular a device and method for percutaneous annular plication and heart valve deployment for mounting a pressure actuated flow control sleeve, a pinch valve, as a replacement device for a heart valve, whereby the prosthesis has an atrial annular flange or cuff having one or more integral plication tissue anchors for engaging the valve annulus, wherein the is a reciprocating mechanical member that is compressed by pressurized working fluid within the heart during ventricular systole.
Owner:VDYNE INC
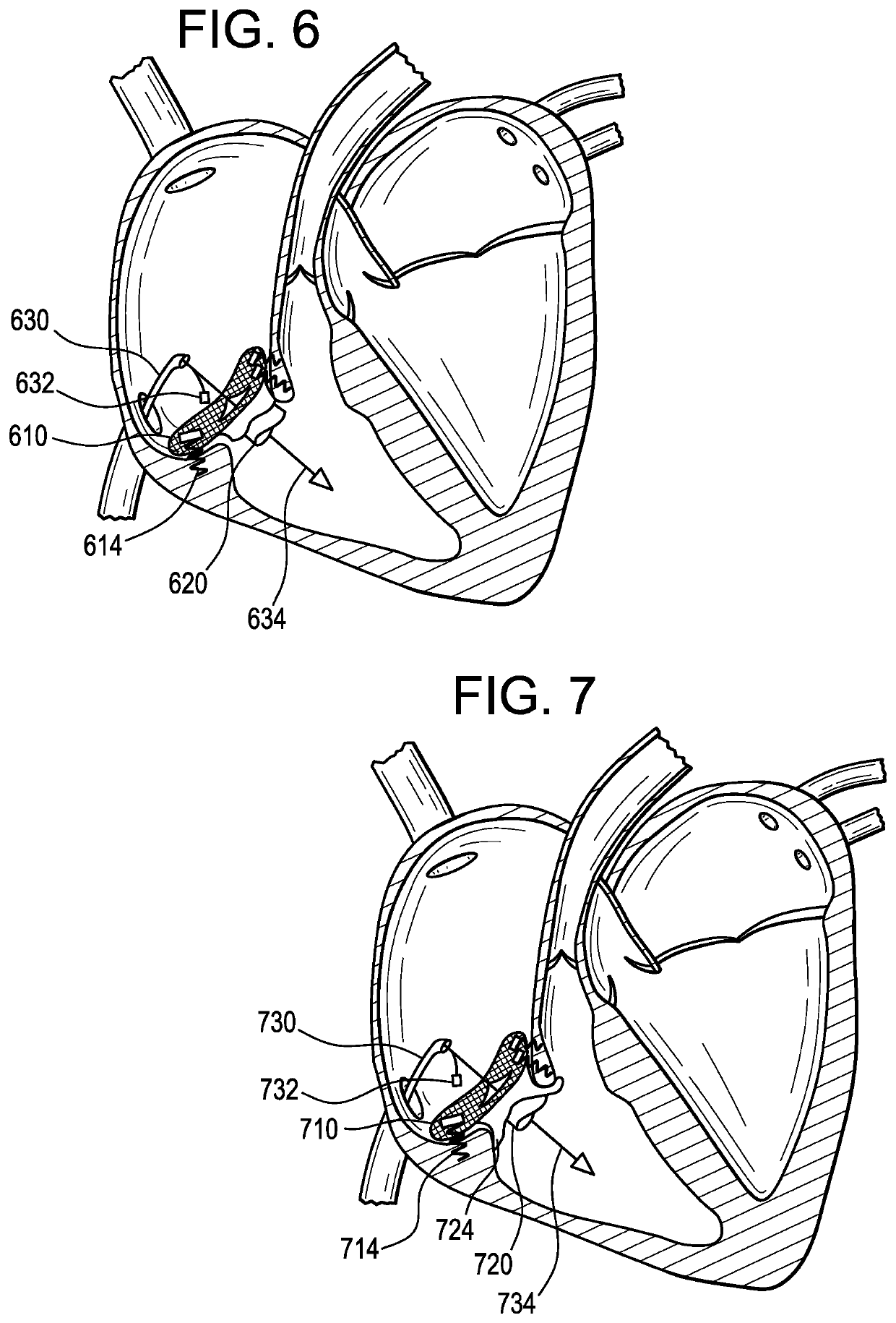
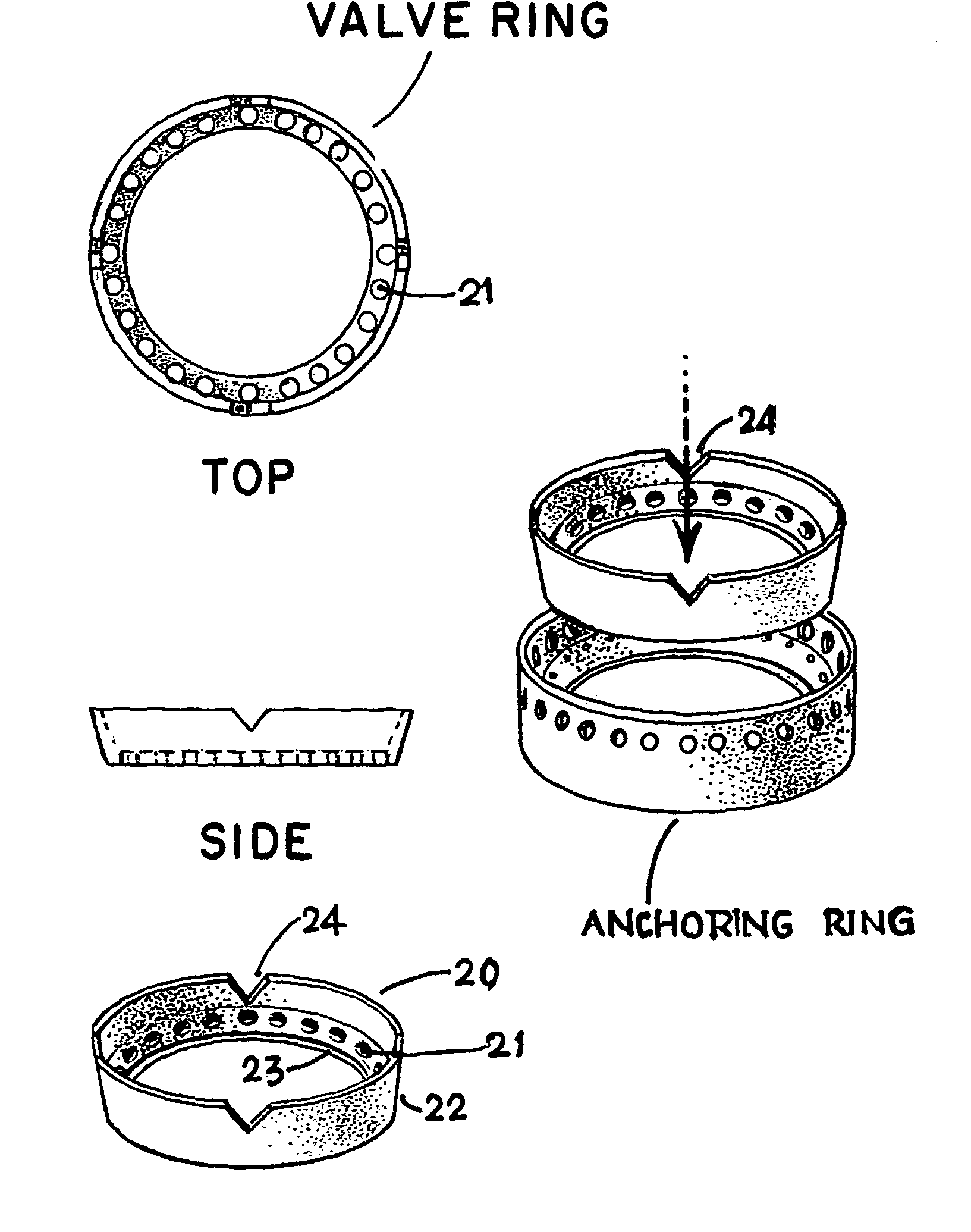
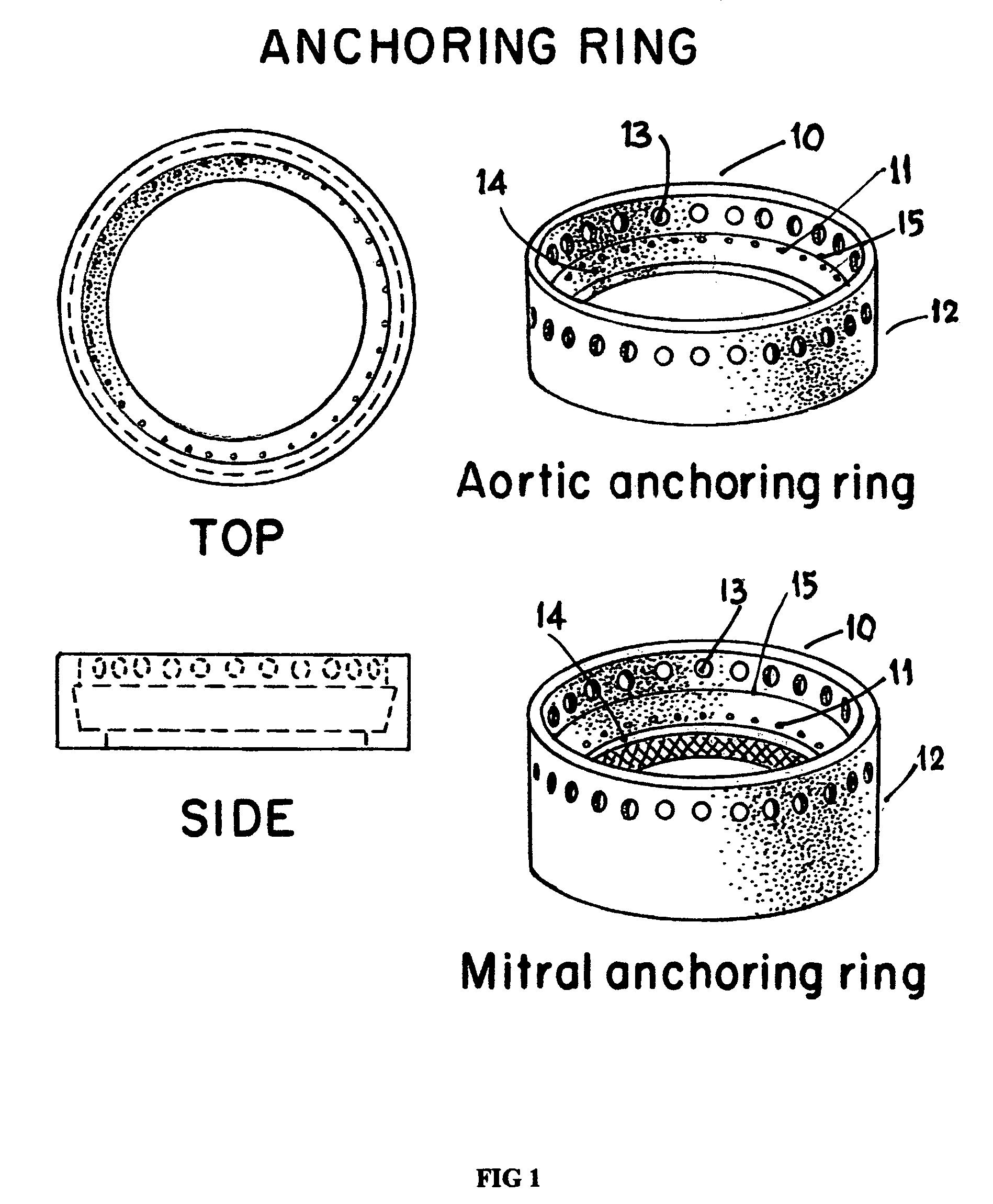
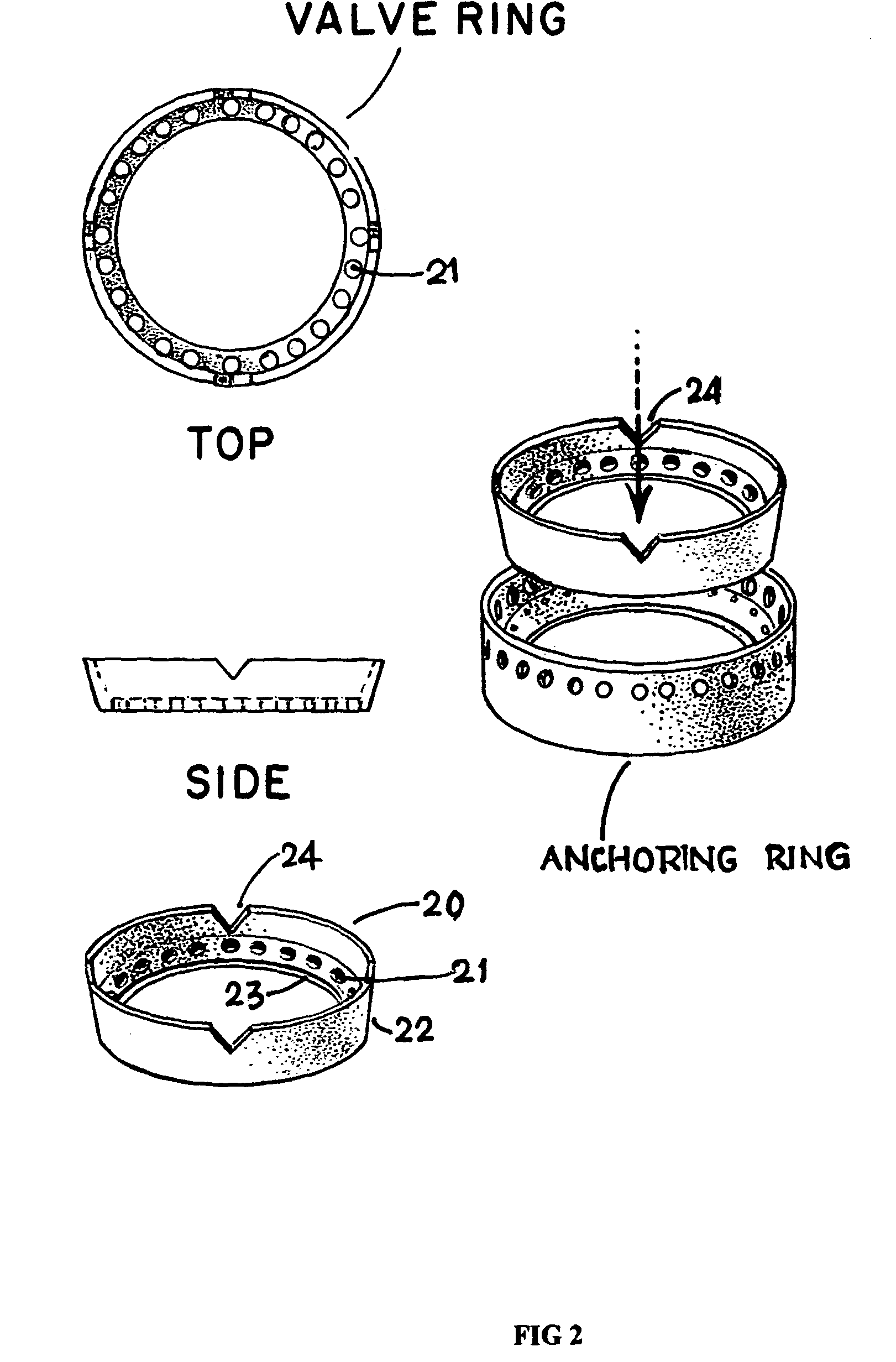
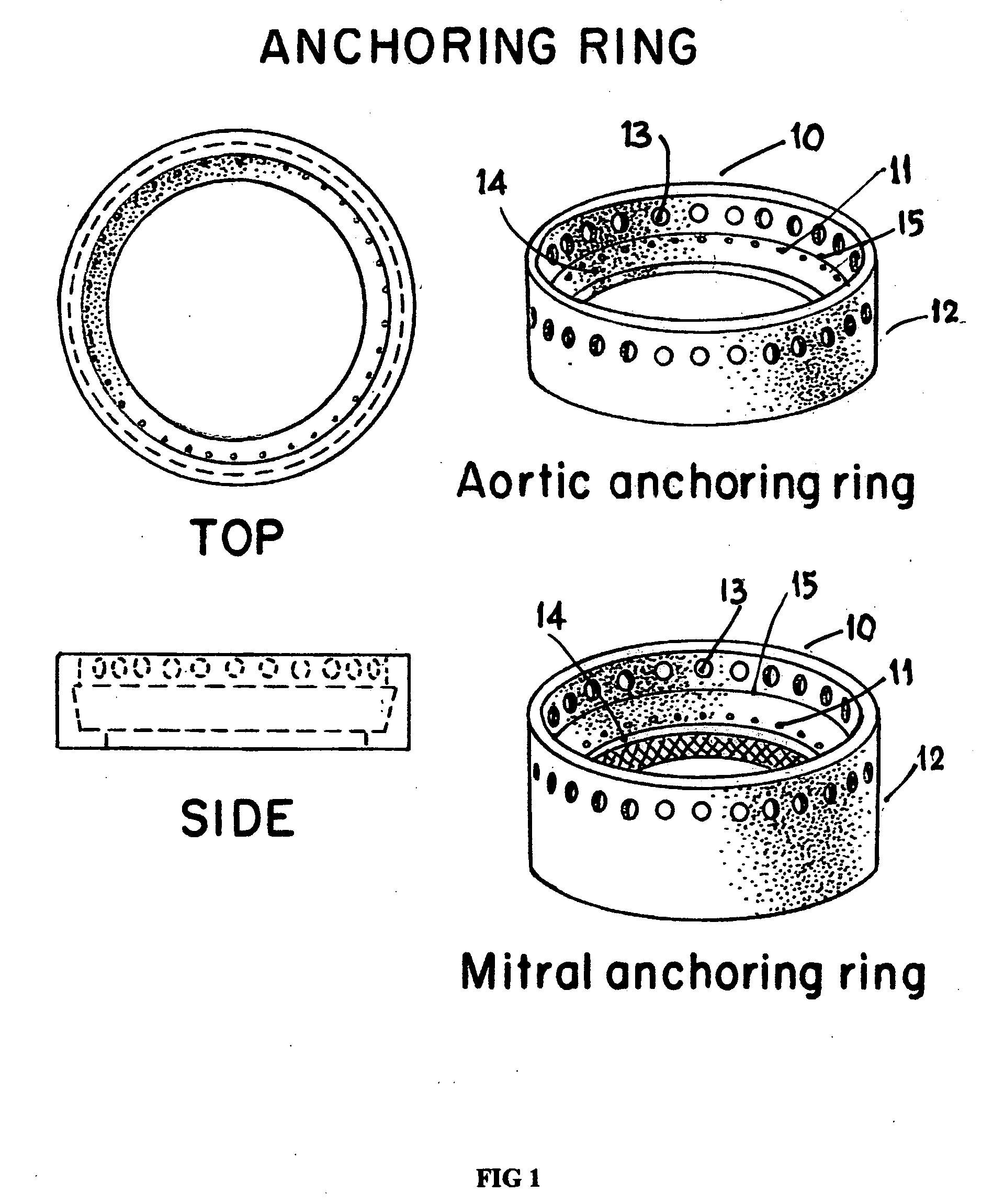
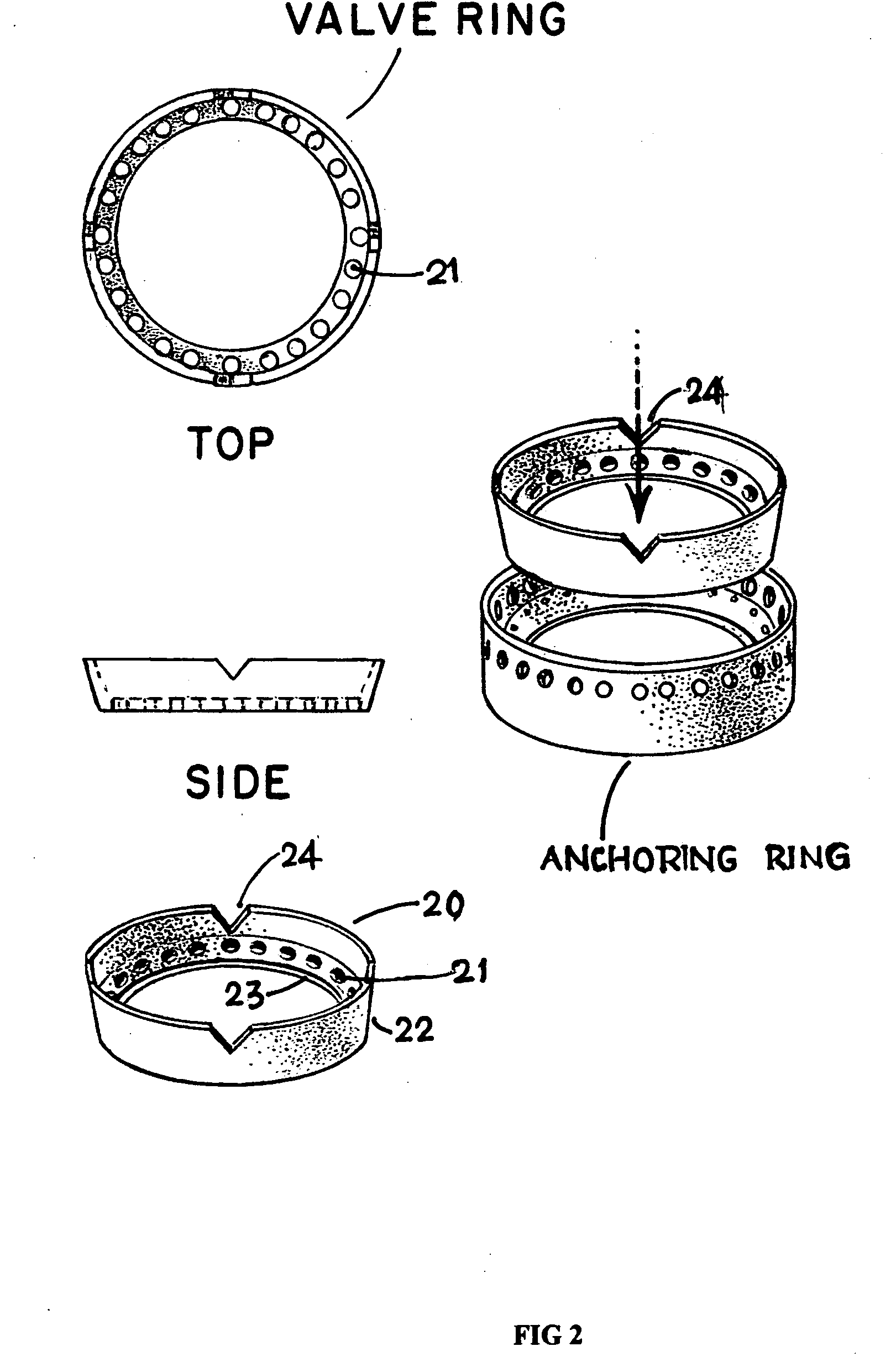
System and method for heart valve replacement
Owner:MACHIRAJU VENKAT R
System and method for heart valve replacement
A prosthetic heart valve replacement system and method aim to reduce the time duration of the patient on the heart-lung machine during surgery. In one embodiment, the invention uses a two rings (e.g., of Titanium) comprising a first outer anchoring ring installed in a first step in the patient annulus, e.g., by stapling (e.g., using Nitinol® staples), and a second inner valve ring which has apertures and to which the sewing cuff of prosthetic heart valve (e.g., of Dacron) is sutured around the sewing cuff. The suturing is expediently completed outside of the patient's body, parallel with the stapling of the anchoring ring in the patient annulus. The inner valve ring may have circumferential resiliency. The inner valve ring along with the fastened / sutured prosthetic valve is installed snugly (in a second step) to be captively retained concentrically within the already installed outer anchoring ring, to complete the heart valve replacement.
Owner:MACHIRAJU VENKAT R
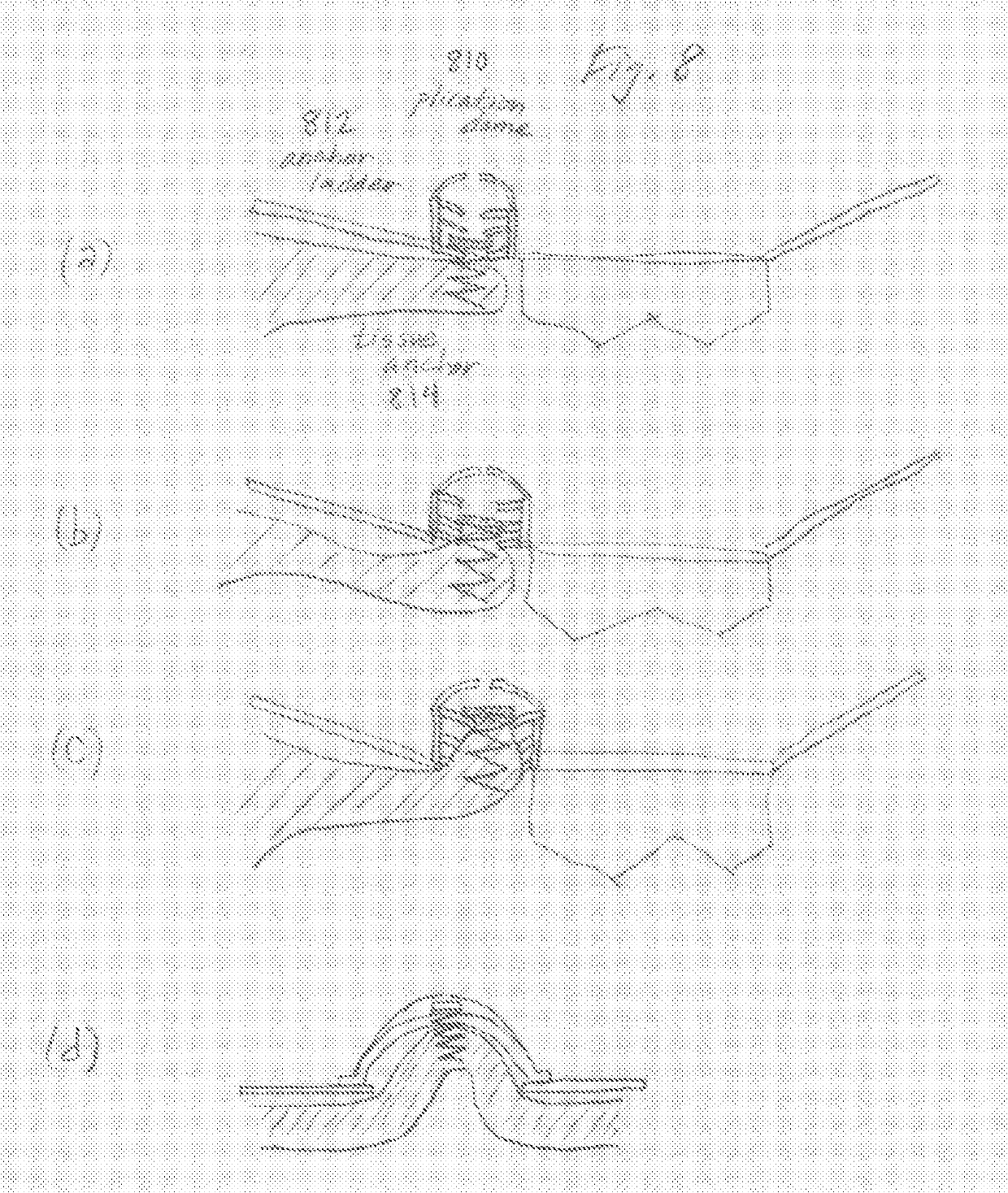
Transcatheter Heart Valve with Plication Window and Tissue Anchors
The invention relates to a transcatheter heart valve replacement (A61F2 / 2412), and in particular a device and method for percutaneous annular plication and heart valve deployment for mounting a pressure actuated flow control sleeve, a pinch valve, as a replacement device for a heart valve, whereby the prosthesis has an atrial annular flange or cuff having one or more integral plication windows connected to a pressure actuated flow control sleeve extending into the ventricle, wherein the is a reciprocating mechanical member that is compressed by pressurized working fluid within the heart during ventricular systole.
Owner:VDYNE INC
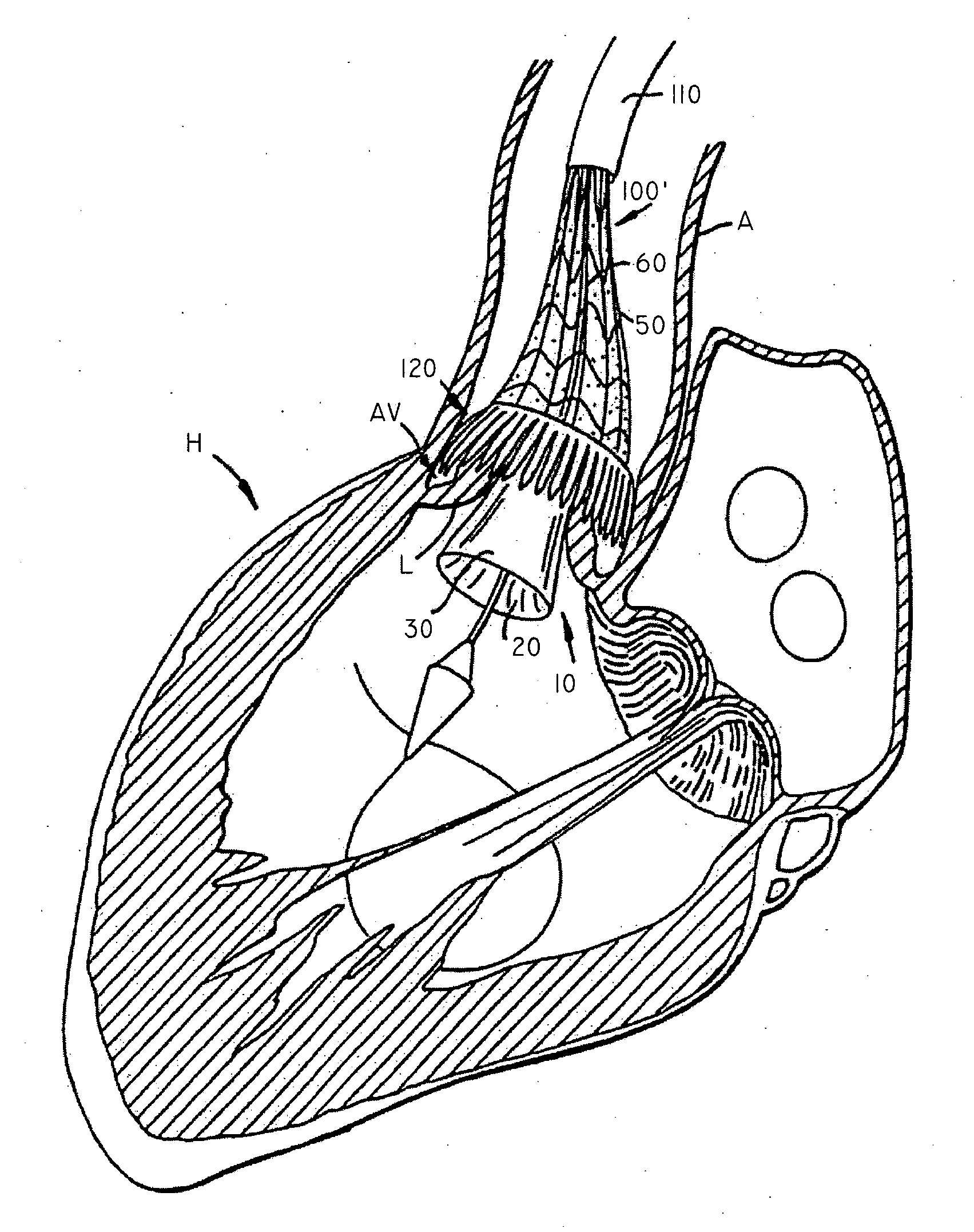
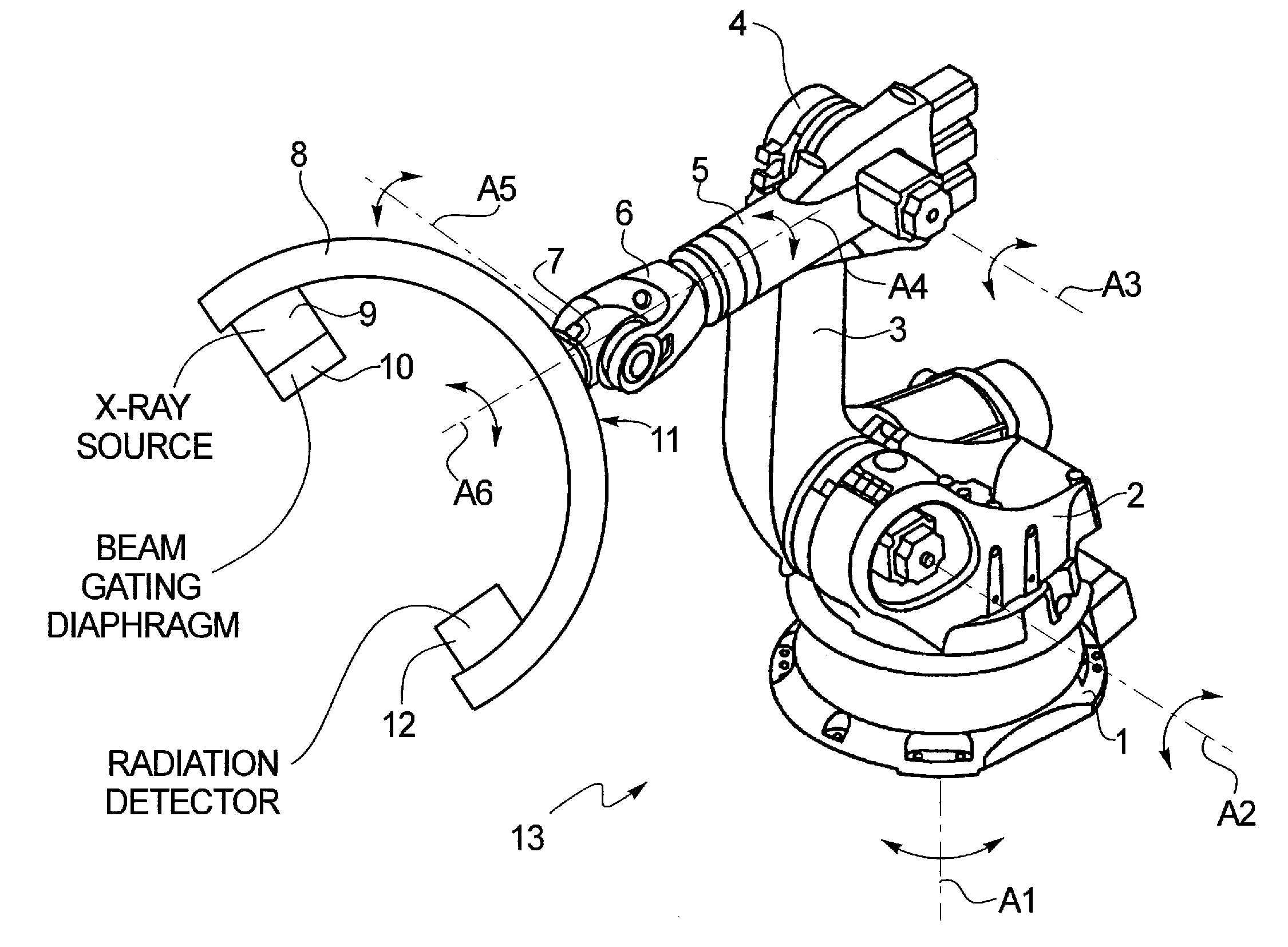
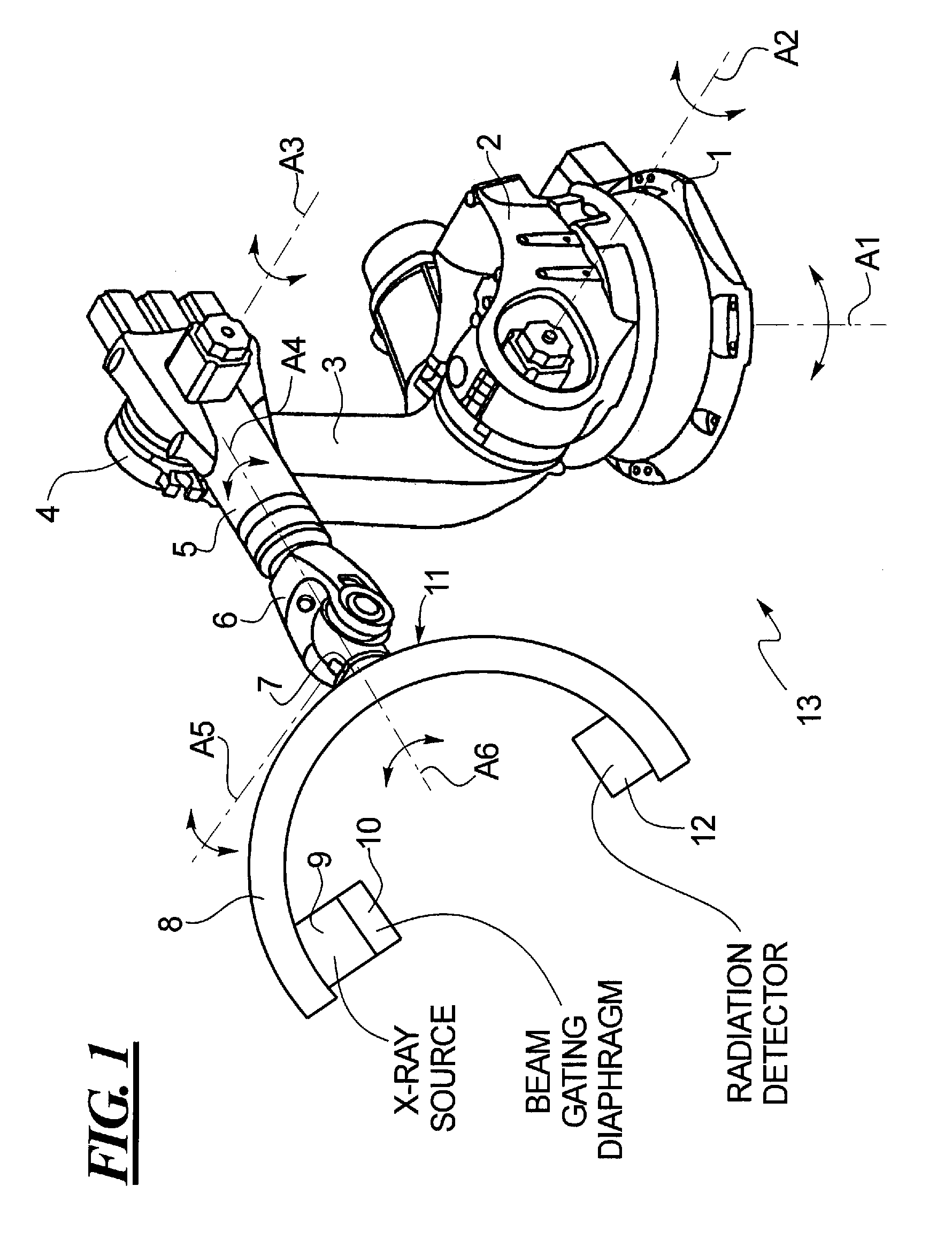
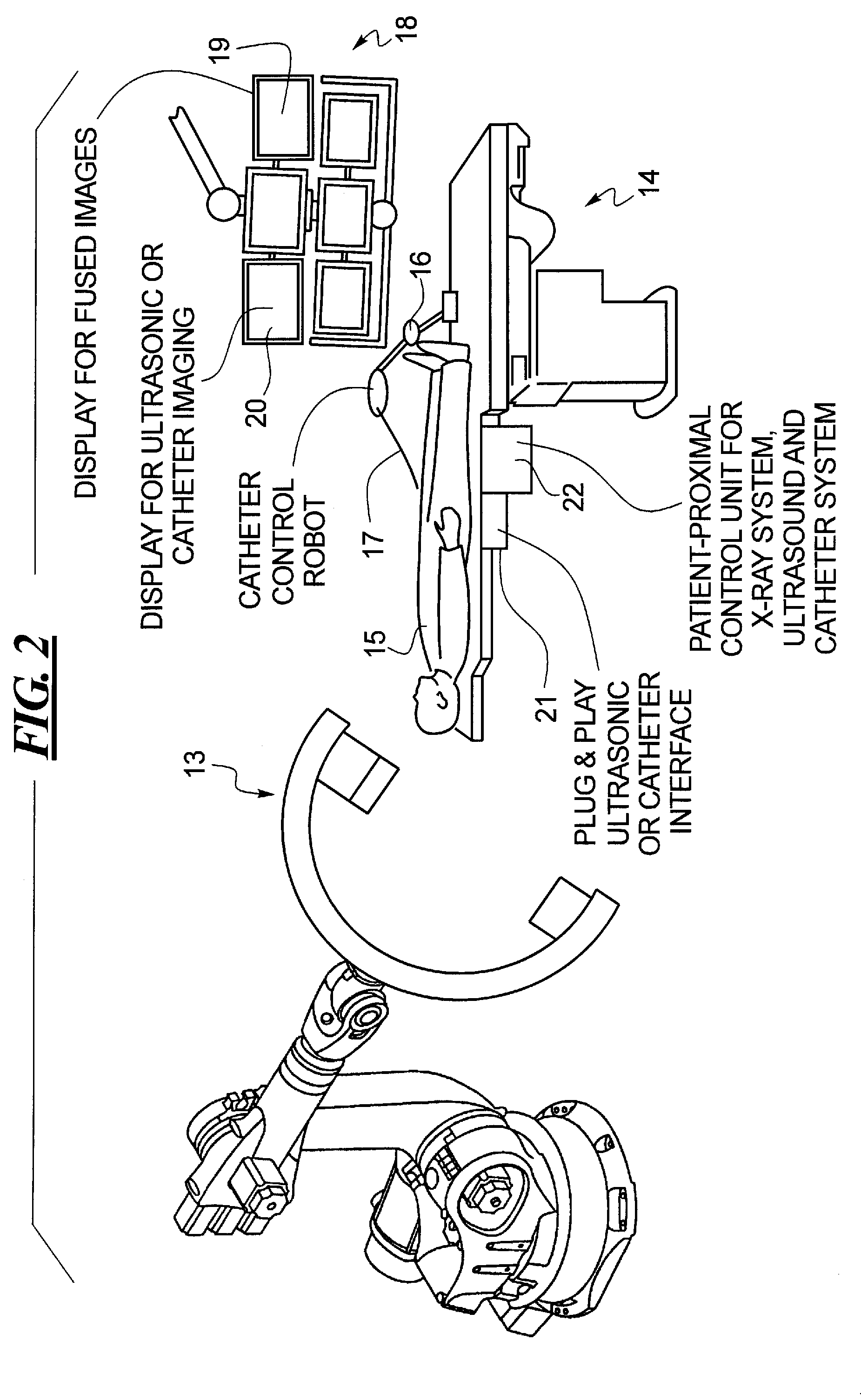
Method for therapy of heart valves with a robot-based x-ray device
InactiveUS20100114308A1High resolution imagePromote resultsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBalloon catheterMinimally invasive proceduresX-ray
A method or workflow for heart valve replacement, or more precisely emplacement of a prosthetic heart valve, using minimally invasive procedures includes imaging of the patient's heart during the procedure using a multi-access articulated x-ray imaging robot that allows a radiation detector carried by the robot to be moved in arbitrary paths around a patient in order to generate multiple projection exposures of the relevant region of the patient during the procedure. The imaging system is used to generate two dimensional image data during movement of the catheter and prosthetic heart valve into place and to generate three dimensional image data of the prosthetic heart valve within the patient's heart. The two dimensional image data and the three dimensional image data are registered and superimposed for use in positioning of the prosthetic heart valve. Additional imaging may be performed once the prosthetic heart valve is in position.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Replacement heart valve, valve holder and methods of making and using same
Owner:SAINT JOSEPHS TRANSLATIONAL RES INST +1
Transcatheter heart valve replacement systems, heart valve prostheses, and methods for percutaneous heart valve replacement
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
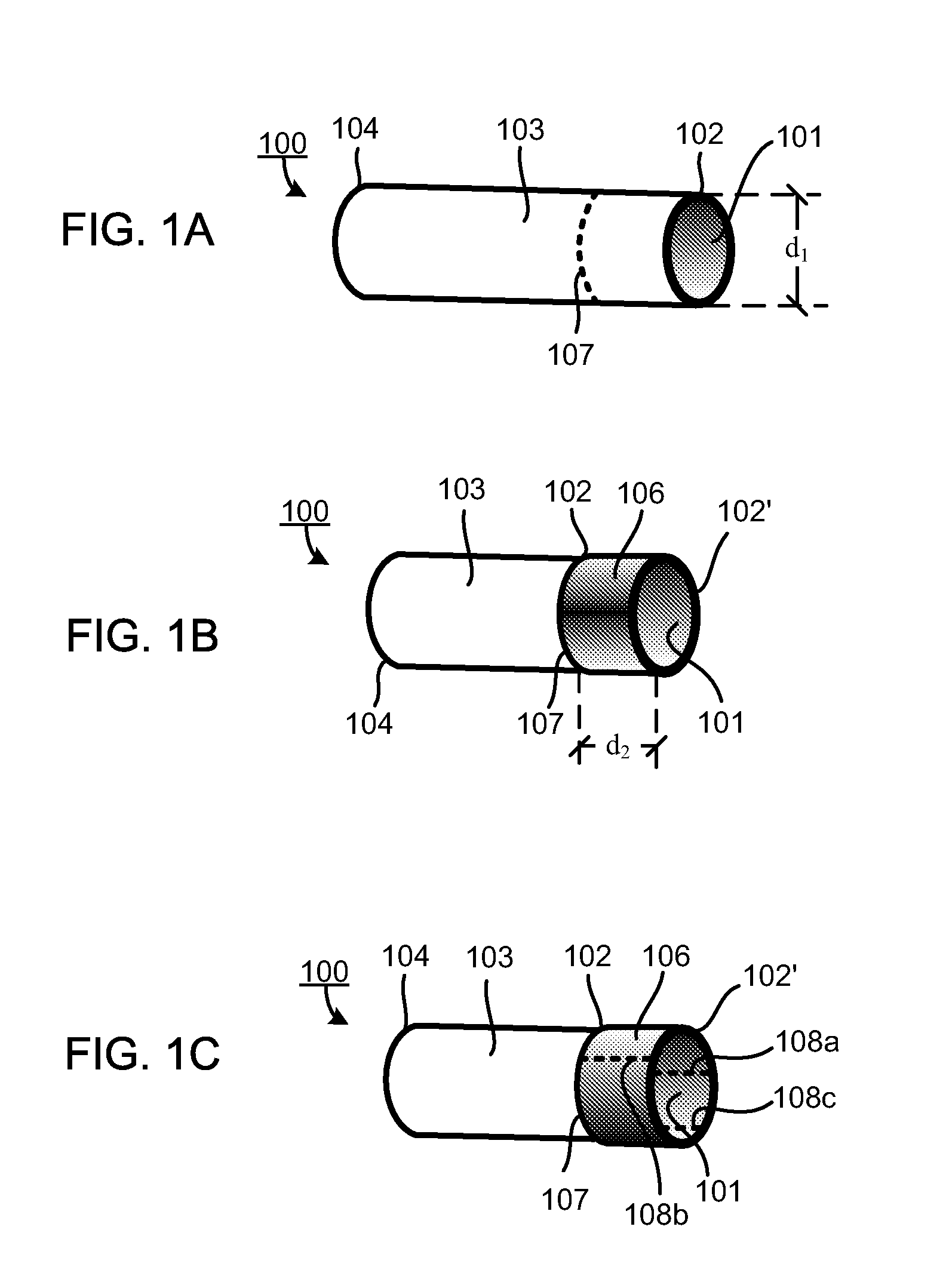
Valve replacement devices, delivery device for a valve replacement device and method of production of a valve replacement device
InactiveCN103108611ADoes not prevent compressionSmall sizeStentsHeart valvesPericardium tissueHeart valve replacement
A device for heart valve replacement comprises a valve component having at least two valve leaflets preferably made of pericardium tissue. Each valve leaflet includes at least two tabs. The device further includes a stent component configured to be radially compressible into a compressed state and expandable into a functional state. The stent component comprises a first end, a second end and at least one intermediate section arranged between said first and said second end. The intermediate section has at least two commissural posts generally aligned parallel to an axis spanning from the first end to the second end. The commissural posts are formed in the shape of a wishbone.
Owner:SYMETIS
Cardiac valve prostheses
ActiveCN104000672ARealize automatic positioningImprove accuracyHeart valvesHeart valve replacementSelf positioning
A stent (1) used for a heart valve prosthesis and the heart valve prosthesis that comprises the stent (1) and is used for heart valve replacement. The stent (1) is used for supporting the heart valve (3) and comprises, along a longitudinal axis, an inflow channel (8), an outflow channel (6) and a transition region (7) located between the inflow channel (8) and the outflow channel (6). The stent (1) is provided with a collapsed delivery configuration and an expanded deployment configuration. In the expanded configuration, the inflow channel (8) is provided with a concave structure that matches a petal ring primary structure. Through the concave structure, the stent (1) can implement a self-positioning function and be tightly attached after implantation, preventing a shift and perivalvular leakage from happening
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT CARDIOFLOW MEDTECH CO LTD
Heart model for training or demonstrating heart valve replacement or repair
The present invention relates to heart models for surgical training and / or demonstration. More particularly, the present invention relates to heart models, which incorporate features to simulate visual and manipulation of heart valves, to be used as training and / or demonstration subjects for heart valve replacement surgery. The simulated valves may be removable inserts, that are replaceable and disposable, attached to a support platform.
Owner:LOTANO VINCENT ERCOLE +1
Orthogonally Delivered Transcatheter Heart Valve Frame for Valve in Valve Prosthesis
The invention relates to a transcatheter heart valve replacement (A62F2 / 2412), and in particular an orthogonally delivered transcatheter prosthetic valve frame having a tubular frame for mounting a flow control component wherein the valve frame is compressible to a compressed configuration for sideways or lateral introduction into the body using a delivery catheter for implanting at a desired location in the body, where the compressed configuration has a long-axis oriented roughly perpendicular to the central axis of the native annulus, wherein the long-axis of the compressed configuration of the valve is substantially parallel to a length-wise cylindrical axis of the delivery catheter, and wherein the valve has a height of about 5-60 mm and a diameter of about 25-80 mm.
Owner:VDYNE INC
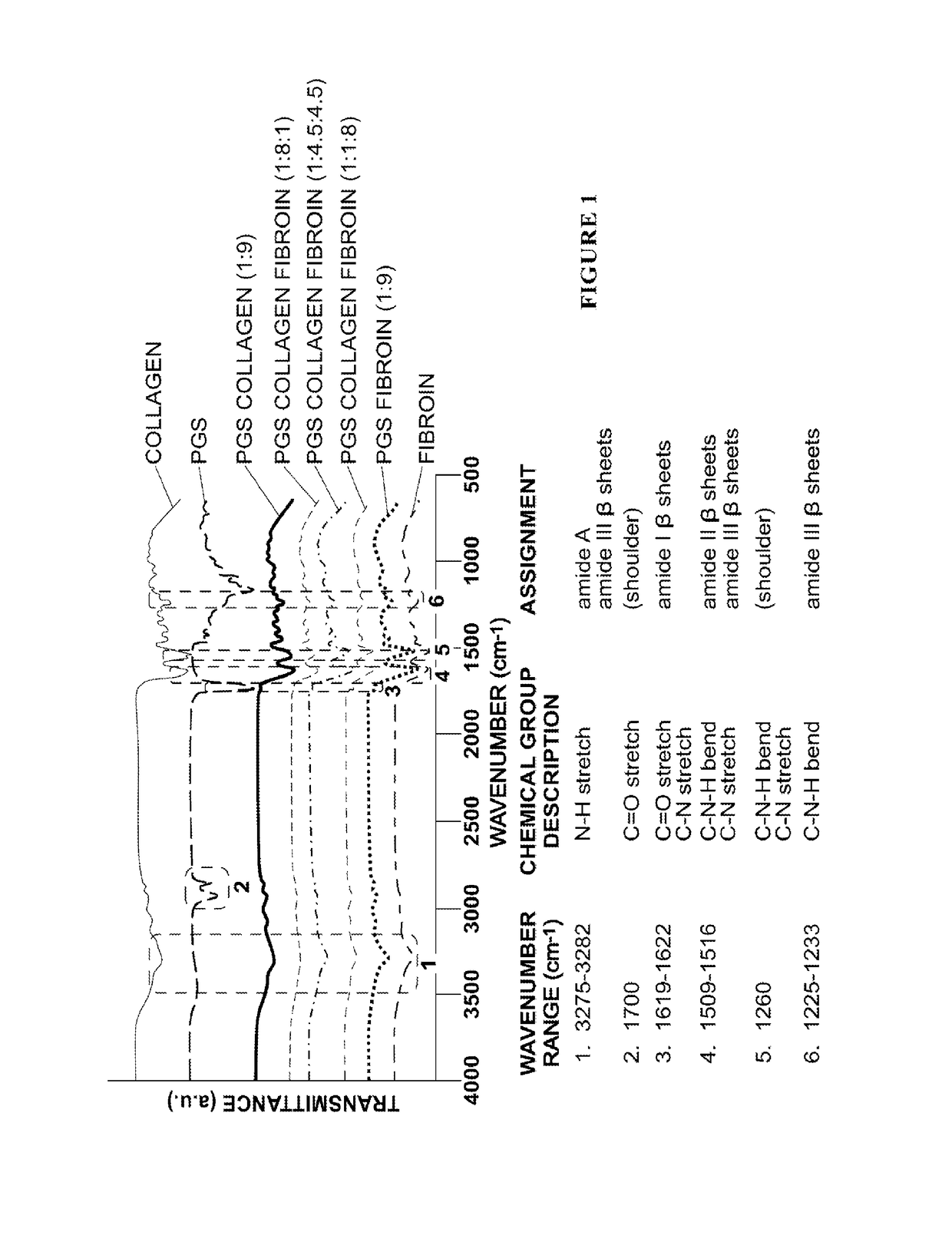
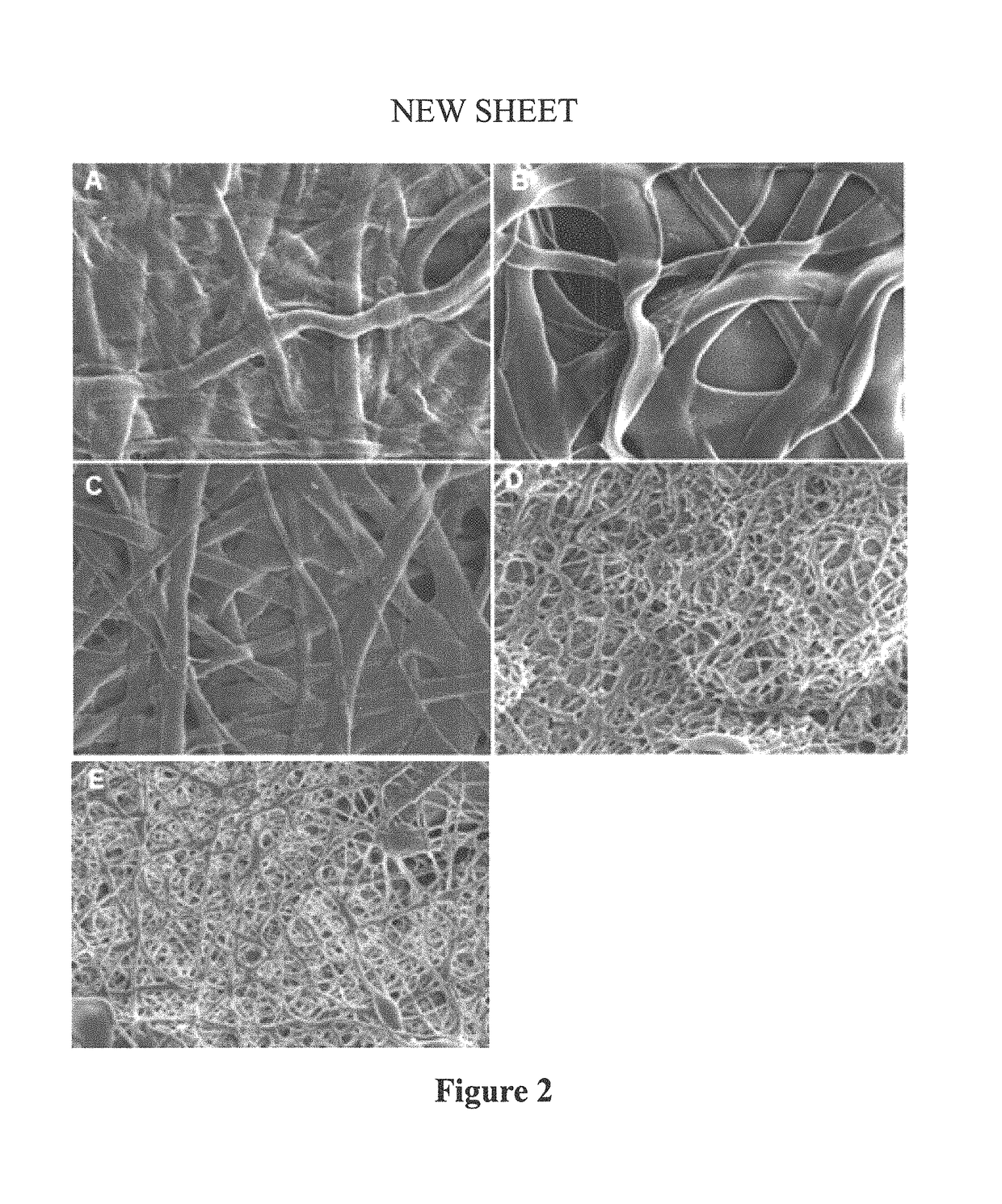
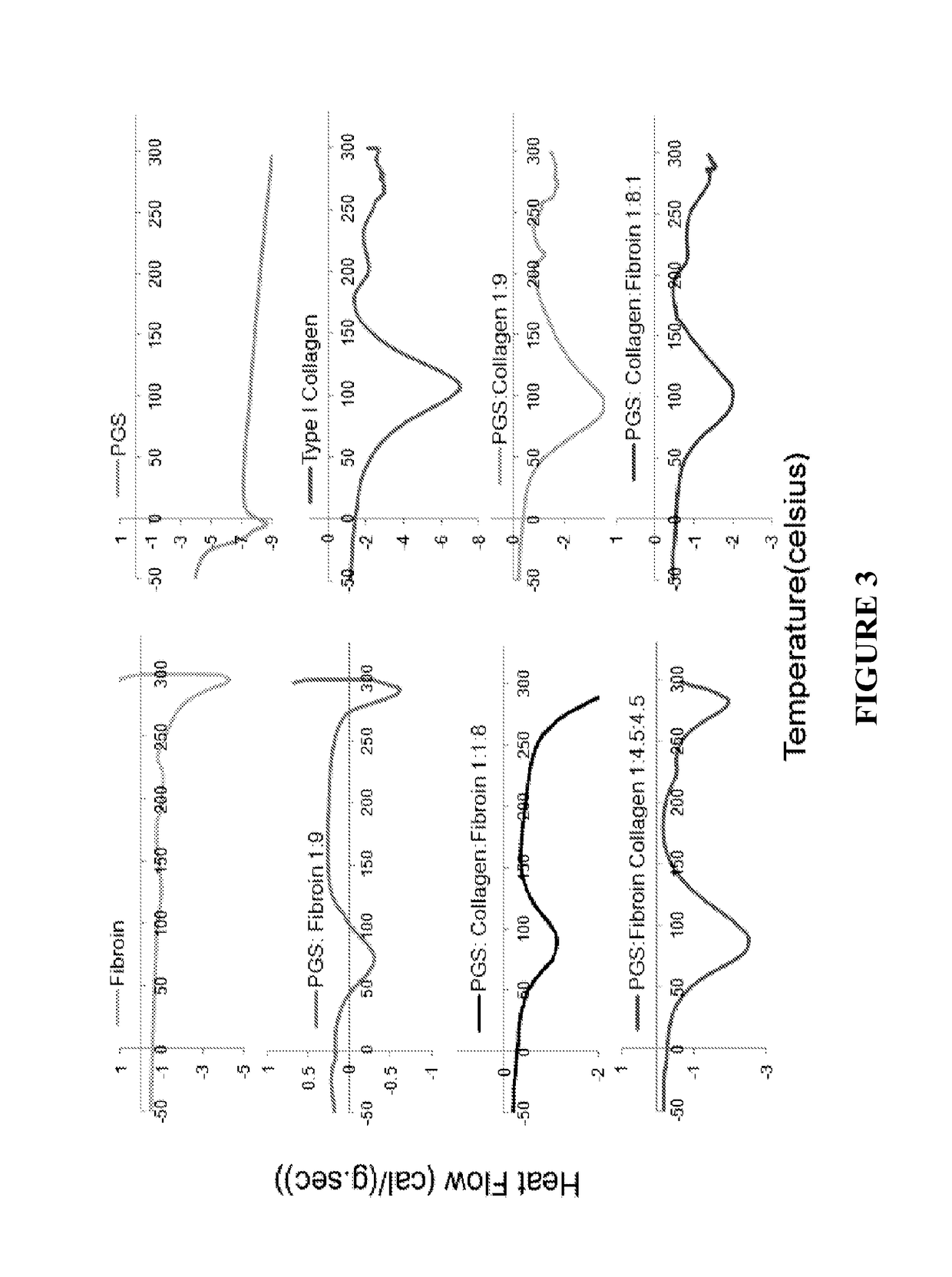
Nanofiber-based graft for heart valve replacement and methods of using the same
InactiveUS10219895B2OptimizationImprove mechanical propertiesStentsHeart valvesNanofiberHeart valve replacement
Nanofiber-based biomaterials containing fibroin for wound repair and tissue replacement and, more particularly, heart valve replacement.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Collapsible Inner Flow Control Component for Side-Delivered Transcatheter Heart Valve Prosthesis
ActiveUS20200237506A1Easy to rollEasy to foldAdditive manufacturing apparatusHeart valvesAcute angleProsthetic heart
The invention relates to a transcatheter heart valve replacement (A61F2 / 2412), and in particular a side delivered transcatheter prosthetic heart valve having a collapsible inner flow control component, and an outer annular support frame having compressible wire cells that facilitate folding flat along the z-axis and compressing the valve vertically along the y-axis, or orthogonally to the central axis of the flow control component, allowing a very large diameter valve to be delivered and deployed to the tricuspid valve from the inferior vena cava or superior vena cava, or trans-atrially to the mitral valve, the valve having a height of about 5-60 mm and a diameter of about 25-80 mm, without requiring an oversized diameter catheter and without requiring delivery and deployment from a catheter at an acute angle of approach.
Owner:VDYNE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com