Patents
Literature
124 results about "Surgical training" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
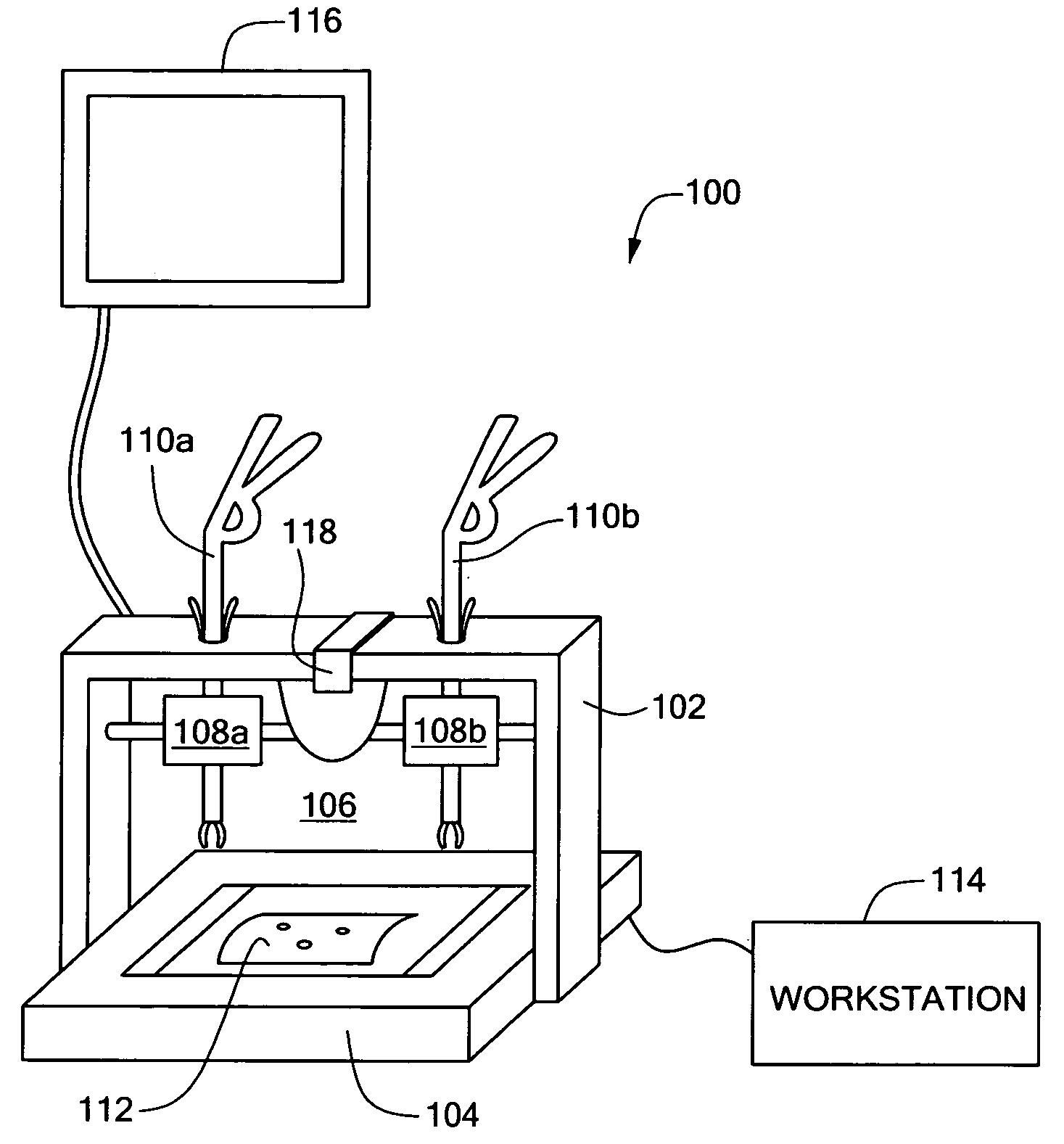
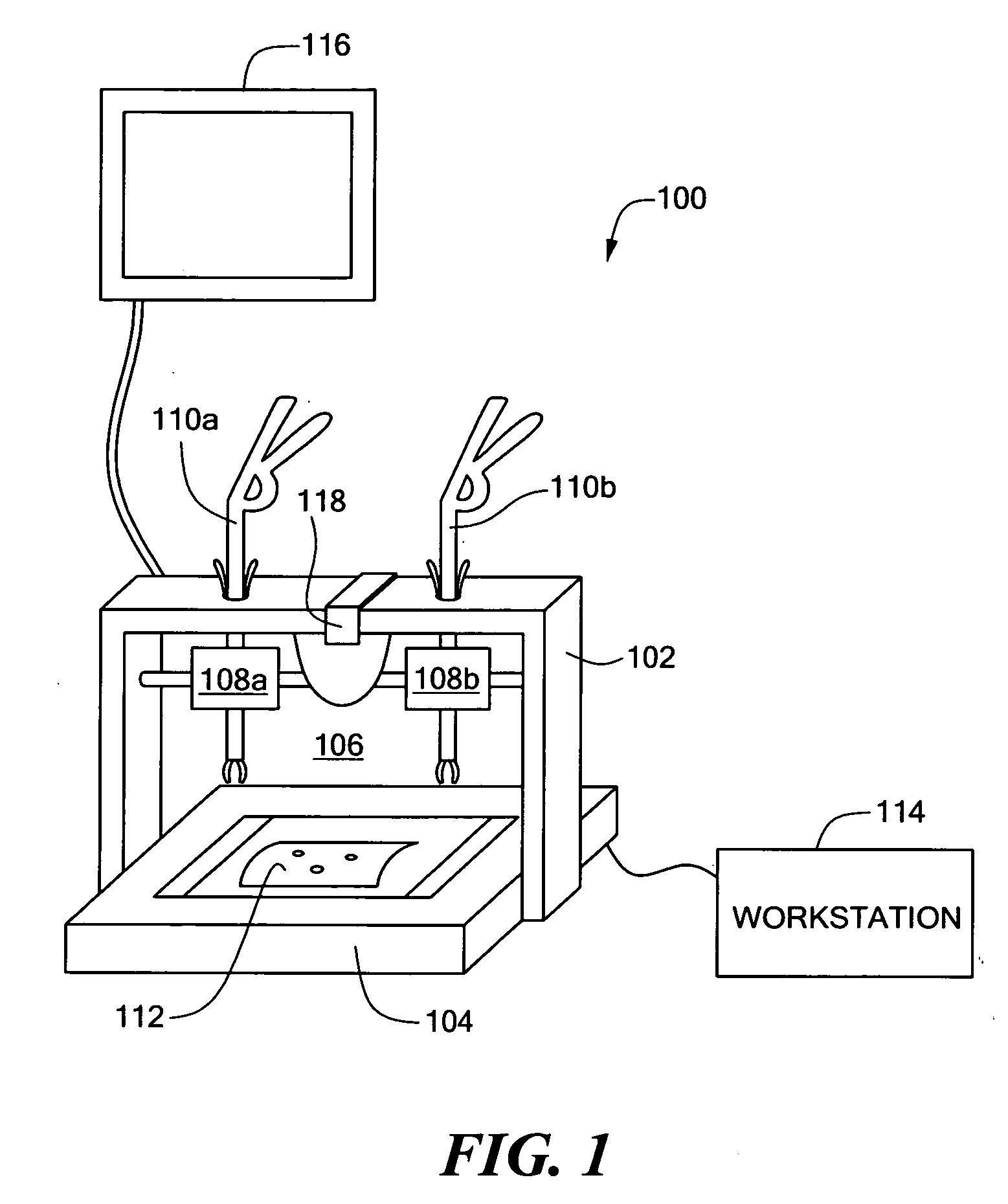
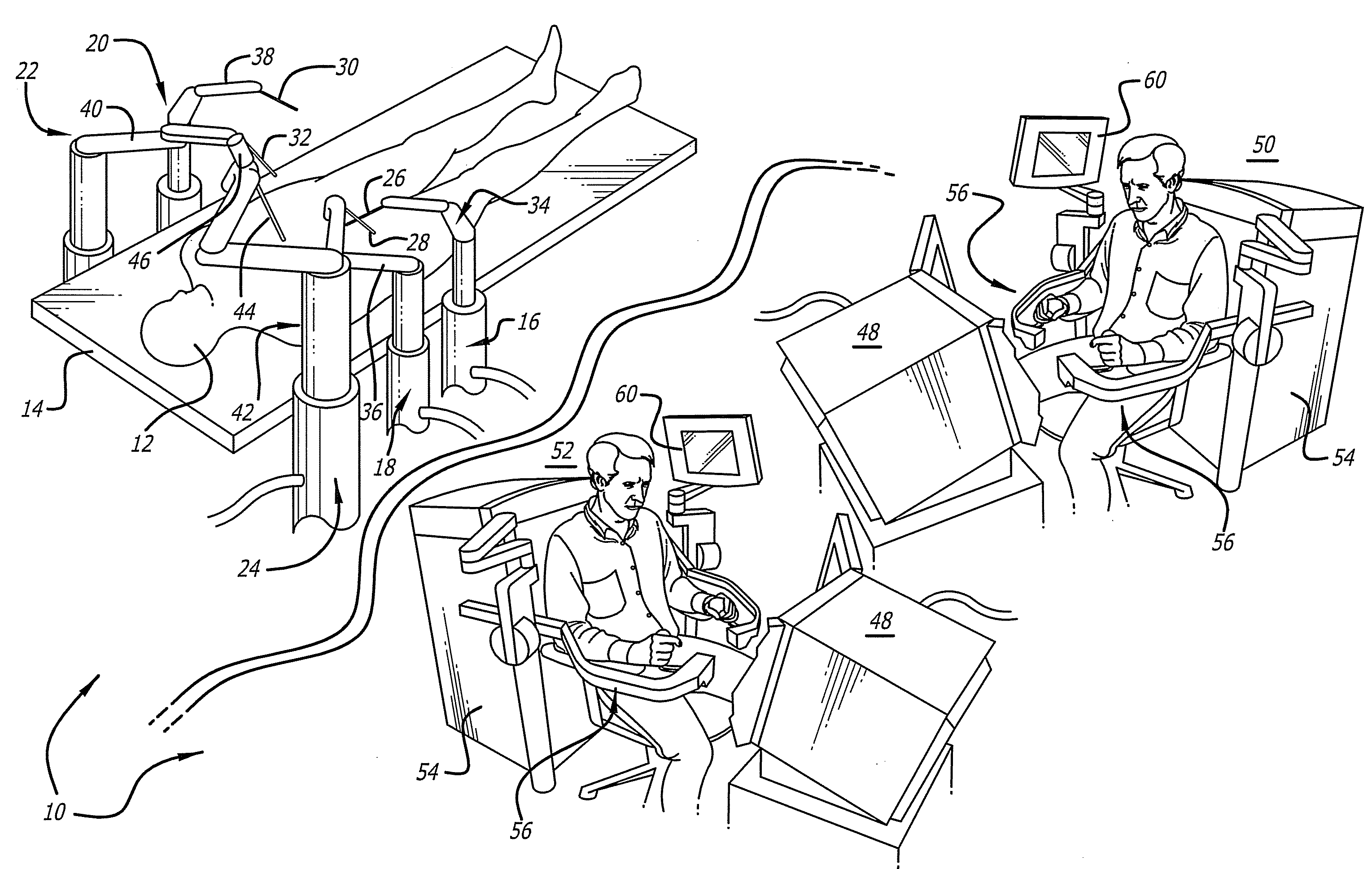
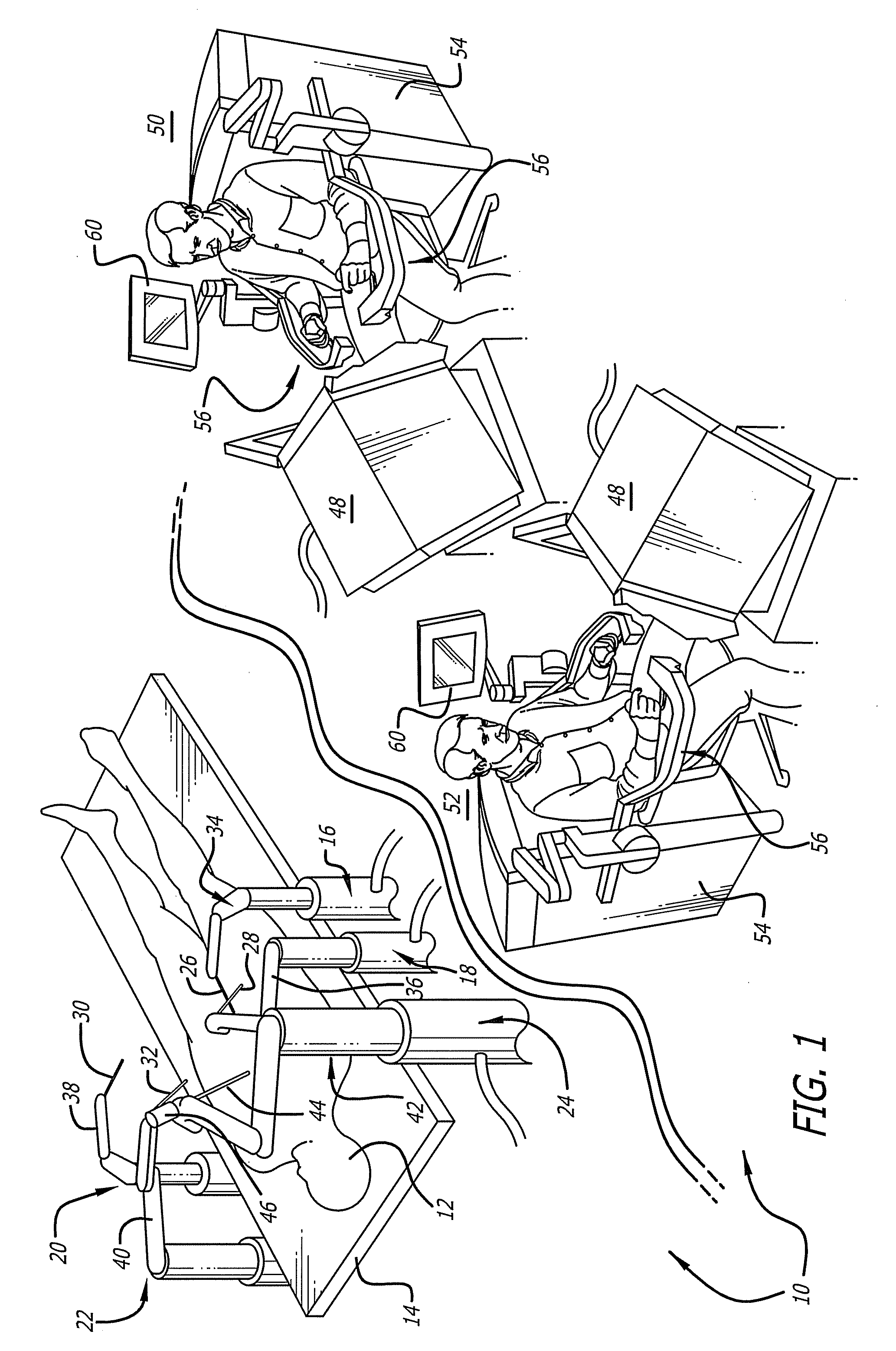
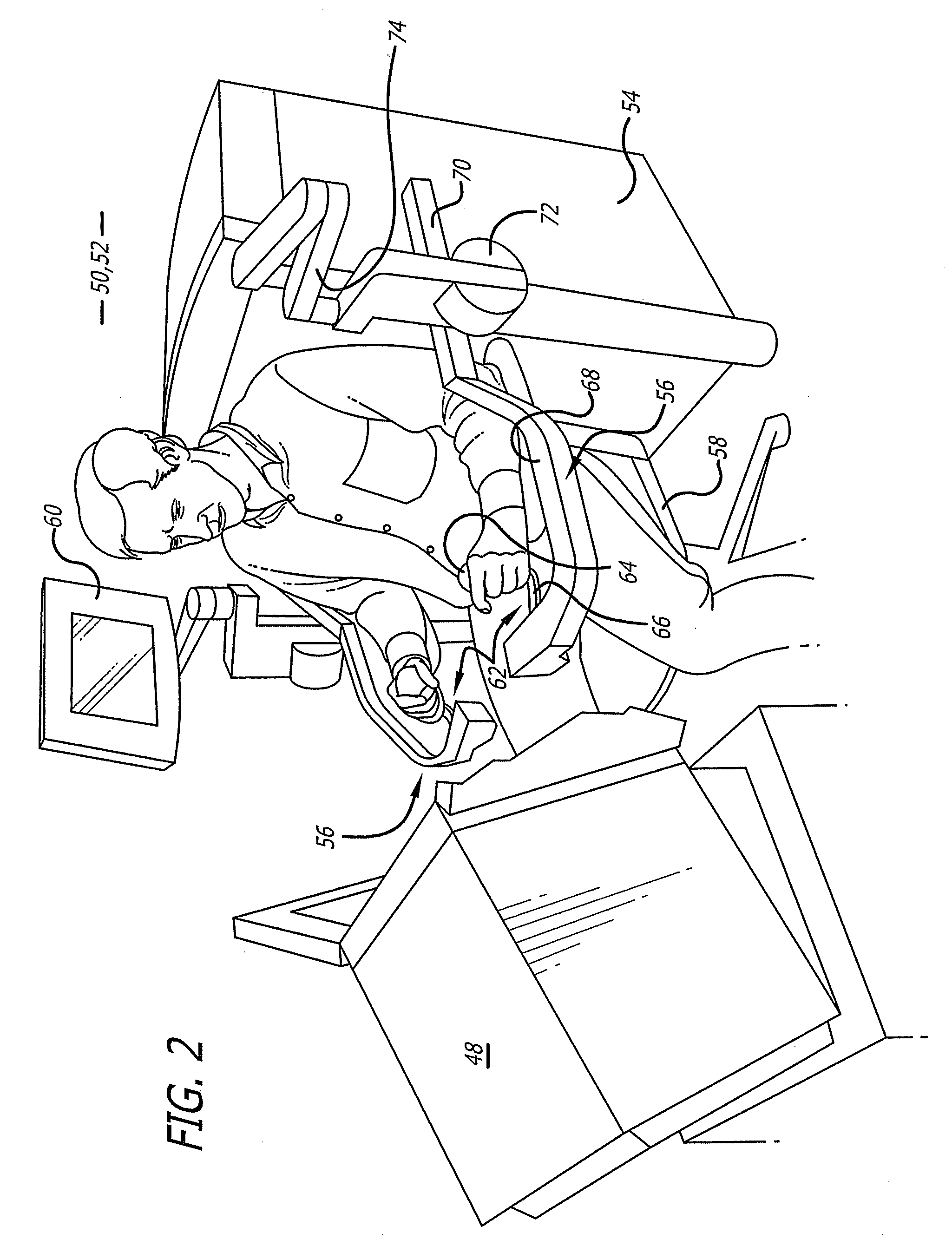
Minimally invasive surgical training using robotics and tele-collaboration
InactiveUS6852107B2Cosmonautic condition simulationsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMini invasive surgeryEngineering
A medical system that allows a mentor to teach a pupil how to use a robotically controlled medical instrument. The system may include a first handle that can be controlled by a mentor to move the medical instrument. The system may further have a second handle that can be moved by a pupil to control the same instrument. Deviations between movement of the handles by the mentor and the pupil can be provided as force feedback to the pupil and mentor handles. The force feedback pushes the pupil's hand to correspond with the mentor's handle movement. The force feedback will also push the mentor's hand to provide information to the mentor on pupil's movements. The mentor is thus able to guide the pupil's hands through force feedback of the pupil handles to teach the pupil how to use the system.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Computer-based training methods for surgical procedures
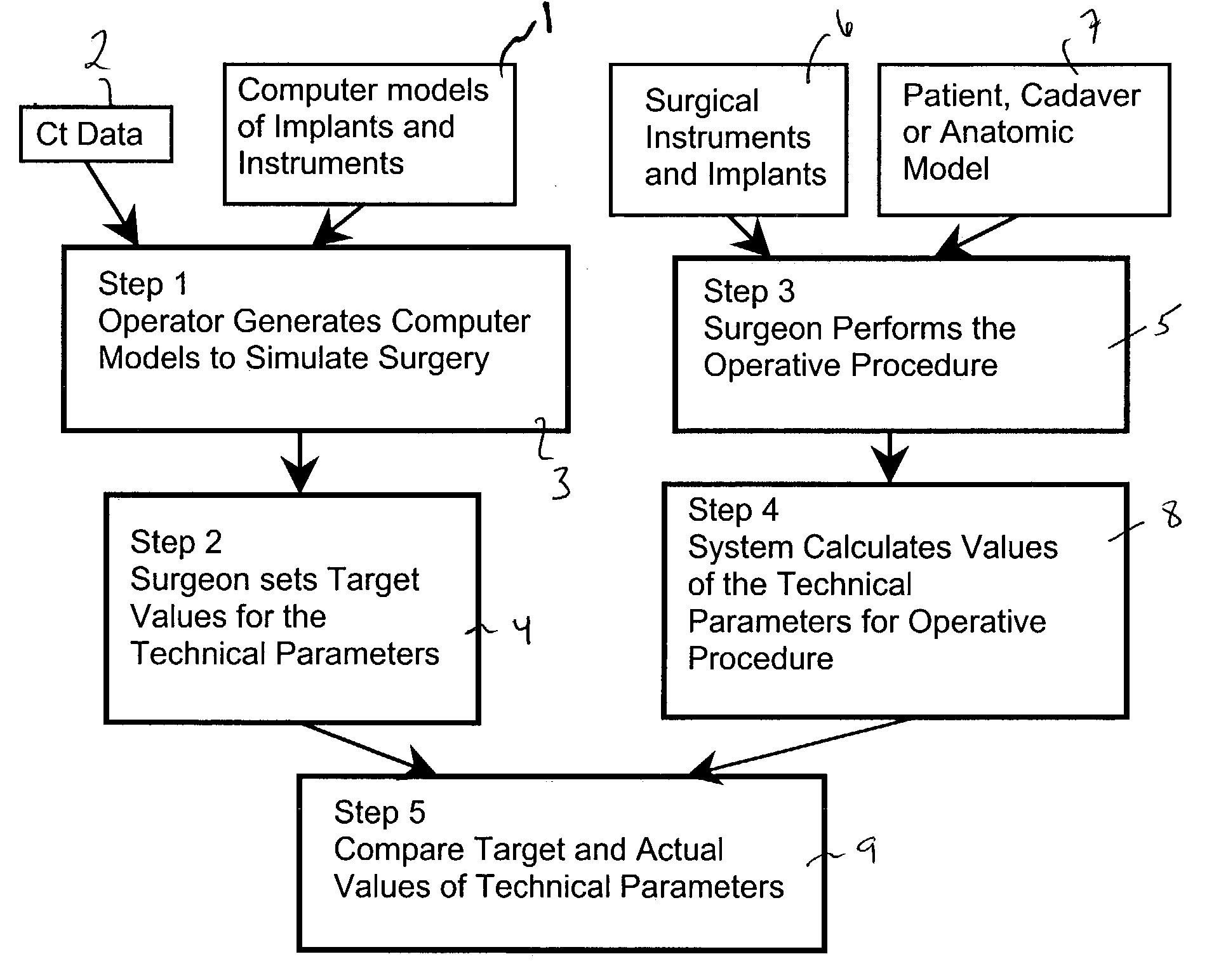
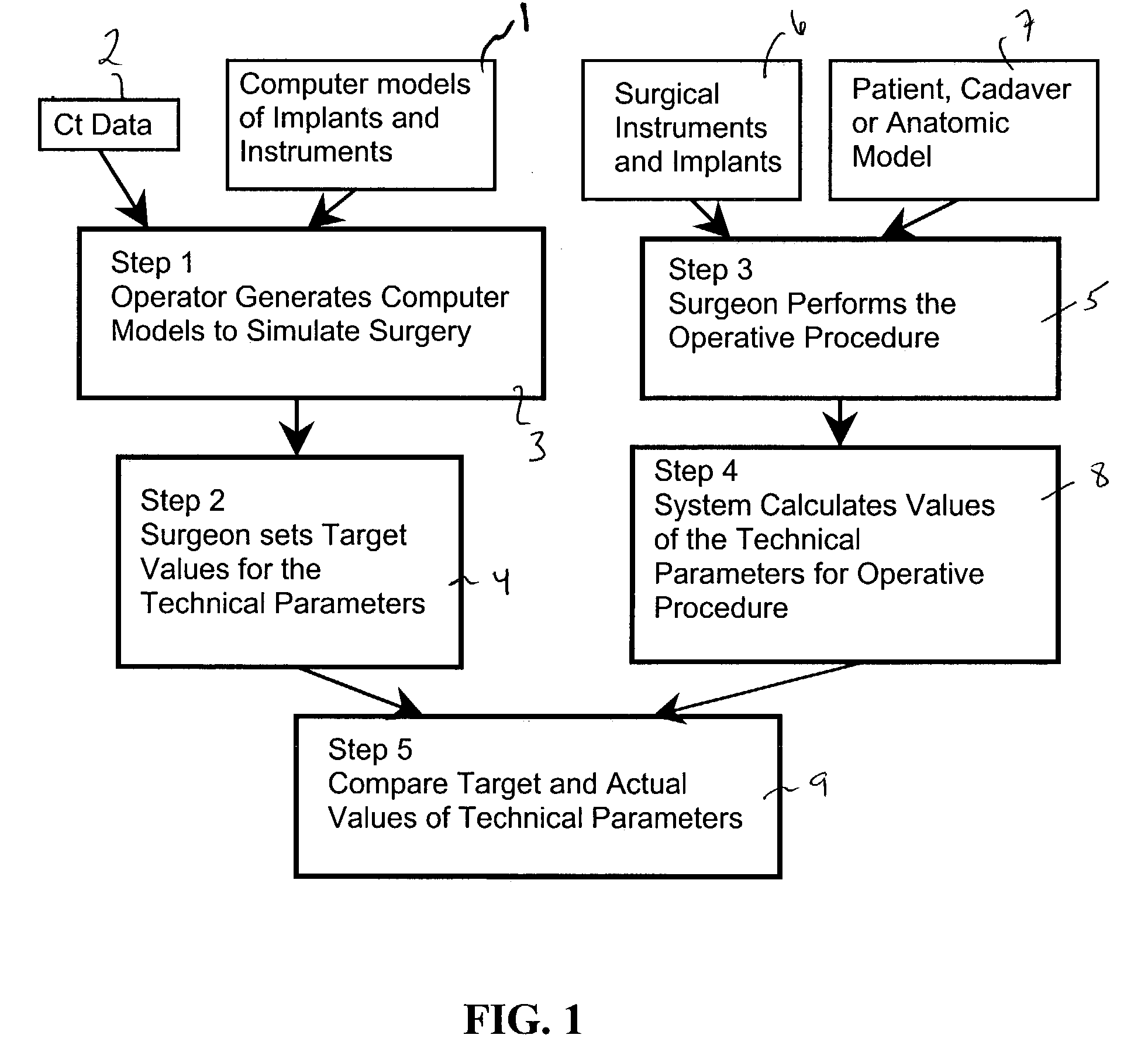
ActiveUS7427200B2Without expenseMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSystems analysisTechnical success
A method is disclosed for analyzing surgical techniques using a computer system for gathering and analyzing surgical data acquired during a surgical procedure on a body portion and comparing that data to pre-selected target values for the particular surgical procedure. The inventive method allows the surgeon, for example, to measure the technical success of a surgical procedure in terms of quantifiable geometric, spatial, kinematic or kinetic parameters. The method comprises calculation of these parameters from data collected during a surgical procedure and then comparing these results with values of the same parameters derived from target values defined by the surgeon, surgical convention, or computer simulation of the same procedure prior to the operation itself.
Owner:NOBLE PHILIP C +1
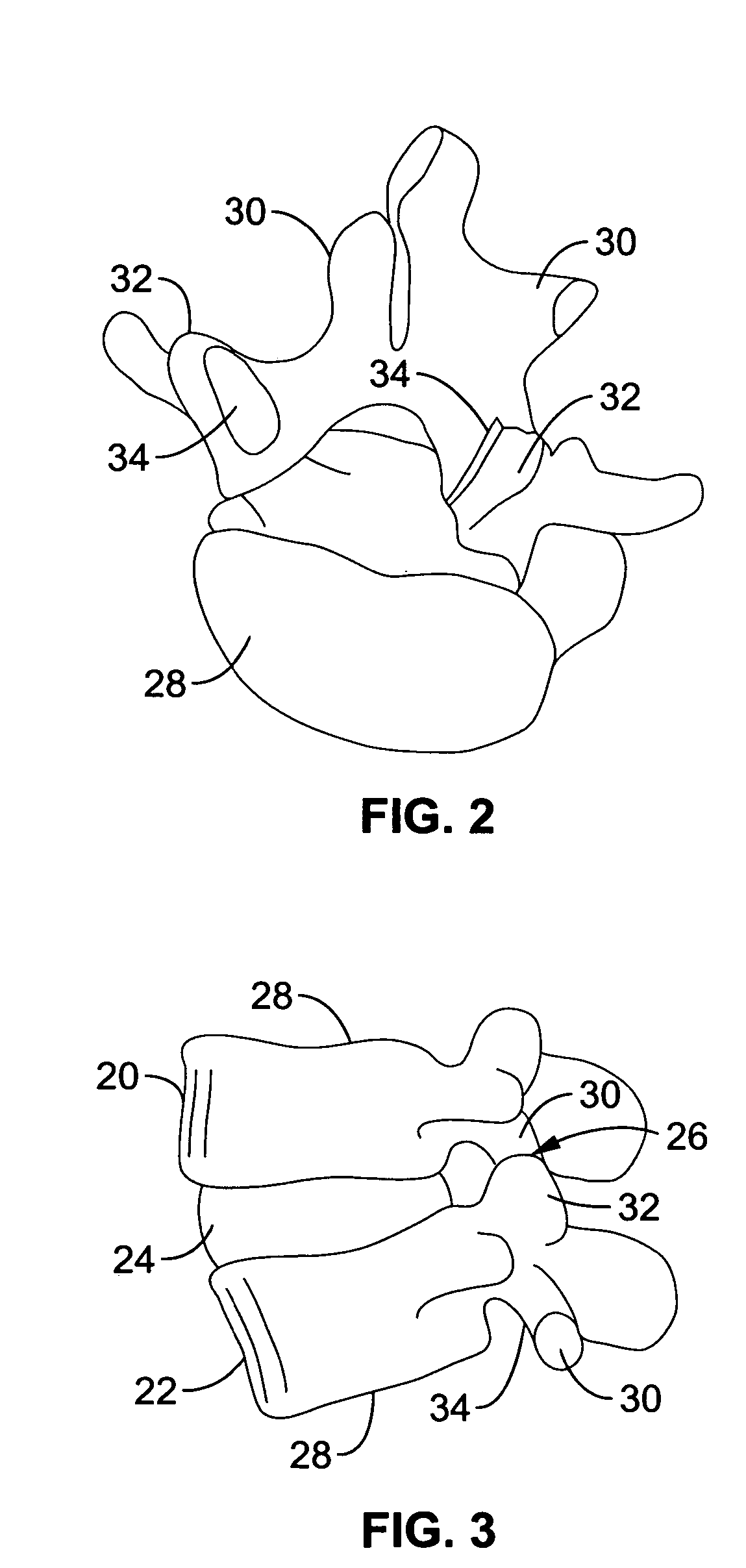
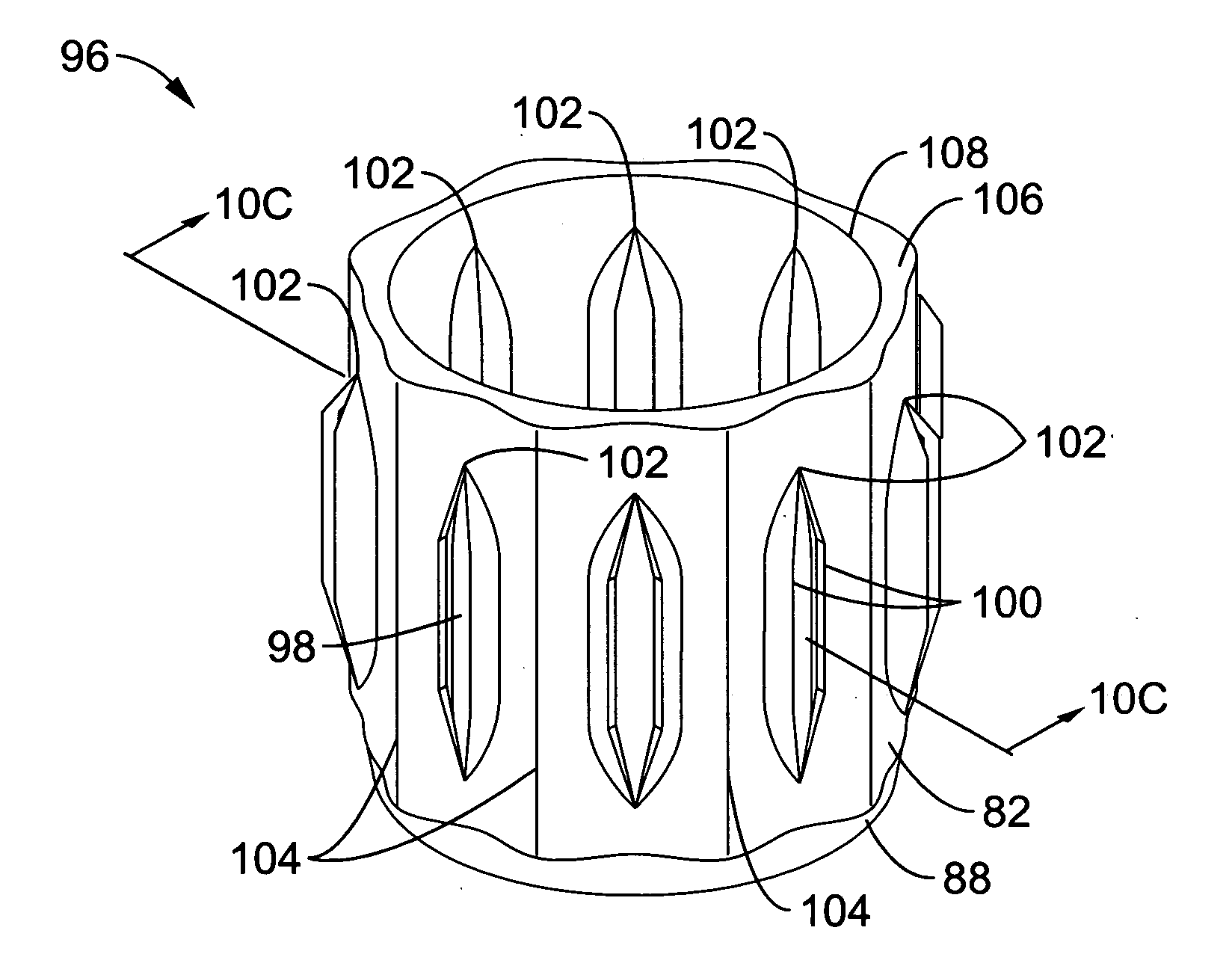
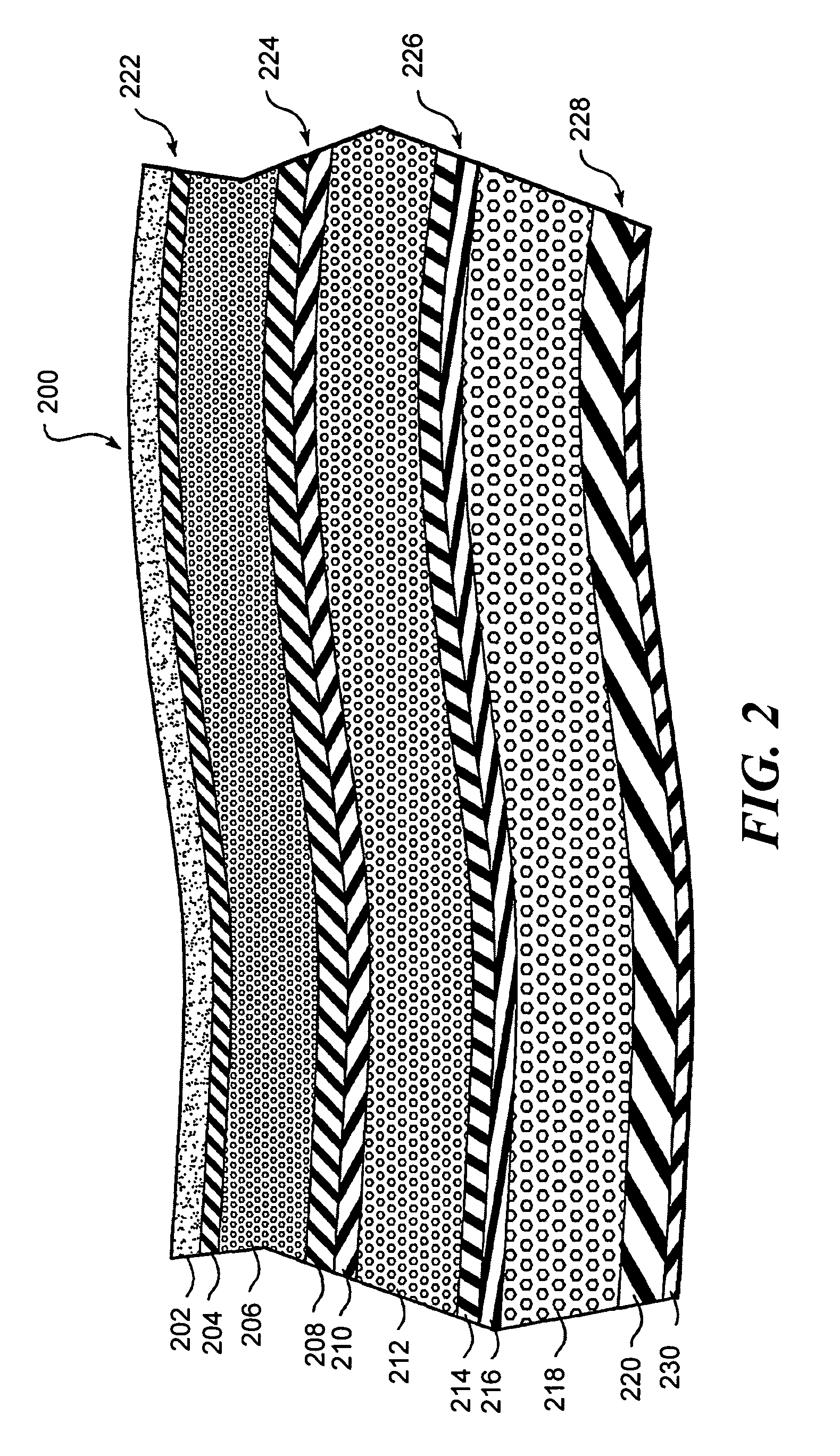
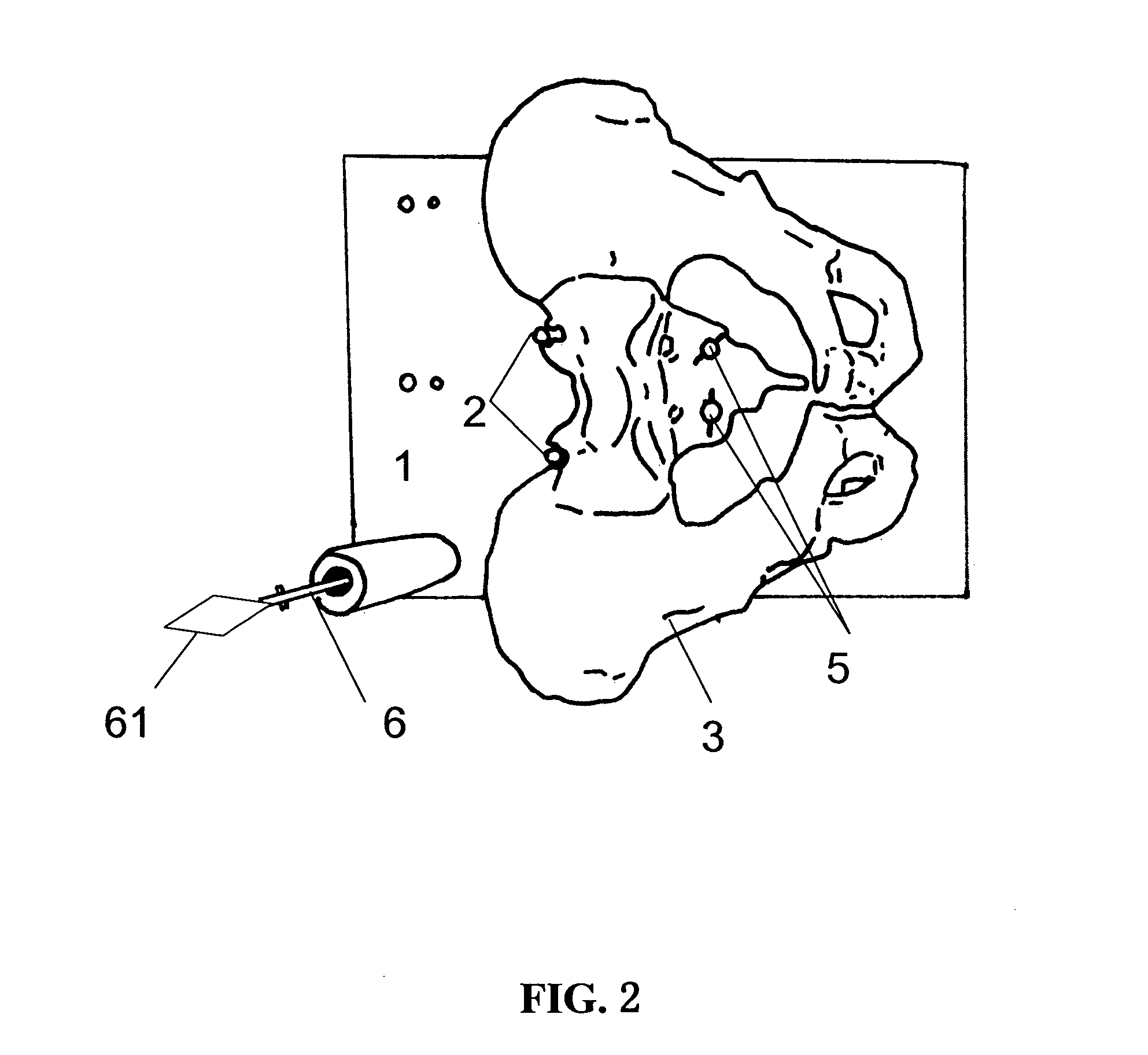
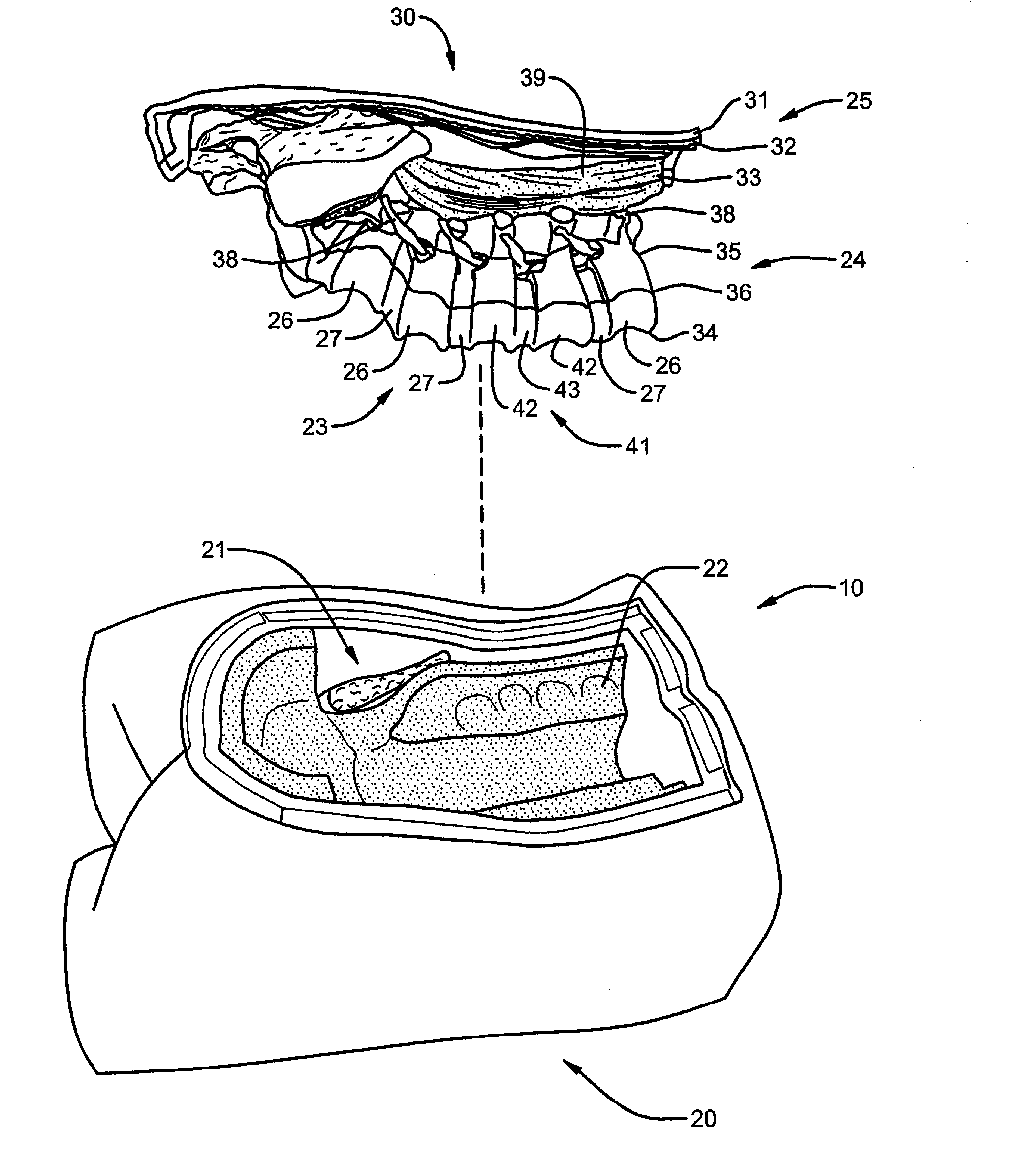
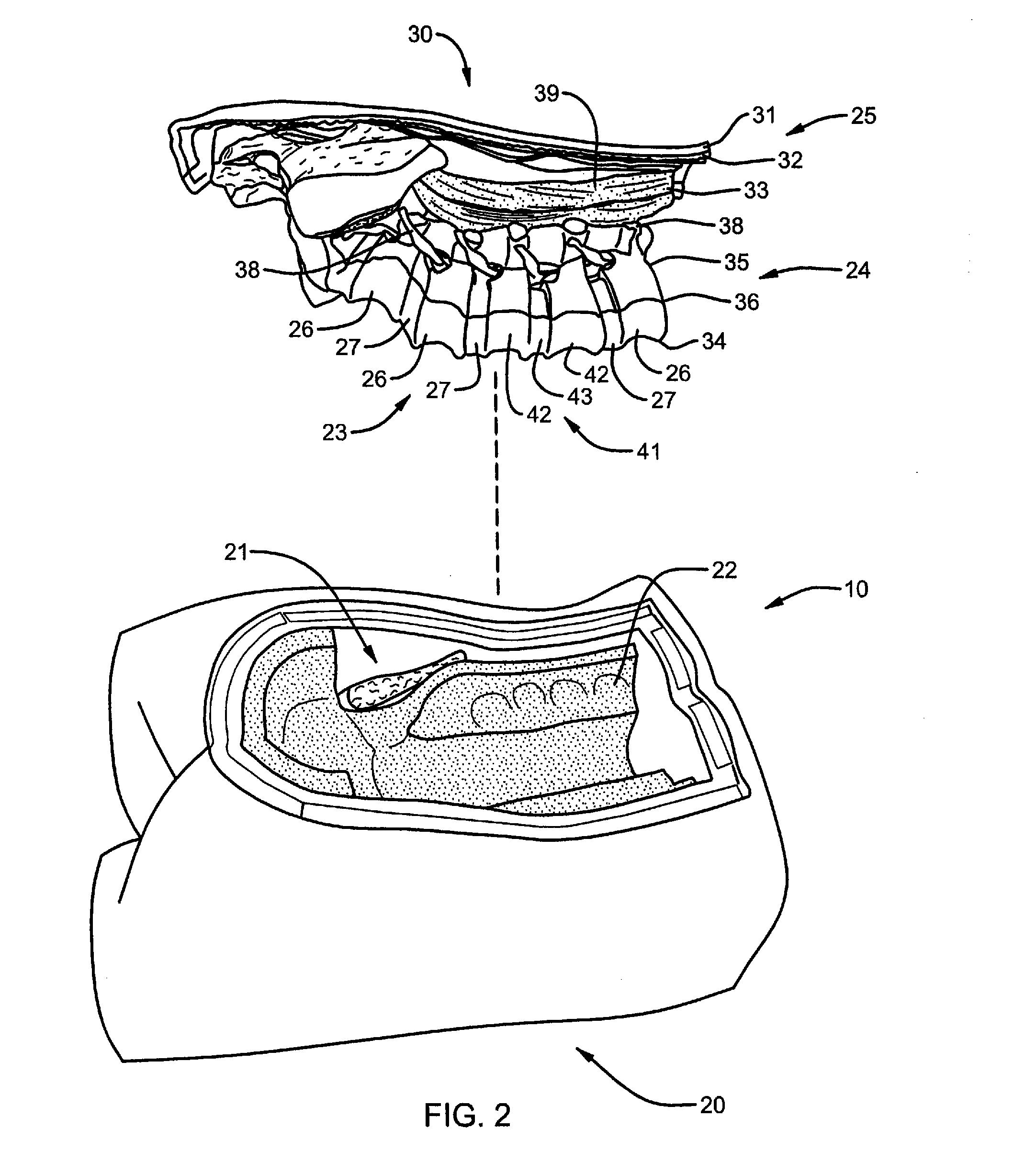
Spine microsurgery techniques, training aids and implants
InactiveUS7452369B2Improve securityWide range of usesInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsAnatomical structuresArticular facet
Owner:BARRY RICHARD J
Surgical training system for laparoscopic procedures
InactiveUS20050142525A1Objectively assessPerformance evaluation enhancedMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesEducational modelsSurgical departmentComputer science
A surgical training system includes a tracking system for tracking the position of one or more instruments during a training procedure and objectively evaluating trainee performance based upon one or more metrics using the instrument position information. Instrument position information for the training procedure can be compared against instrument position information for an expert group to generate standardized scores. Various training object can provide realistic haptic feedback during the training procedures.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Spine microsurgery techniques, training aids and implants
InactiveUS20060085068A1Improve securityBroad utilityInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSpinal columnArticular facet
A minimally invasive, fluoroscopically guided system is disclosed for stabilizing the articular facet joints of adjacent vertebrae. Ring and dowel implants are disclosed for installation into the facet joint. The invention includes a novel spine surgical training aid used in the initial surgeon training process for refreshing the surgeon's perspective of the critical three dimensional anatomy of the vertebrae. The invention also includes a surgical kit having a range of size-specific drills, inserters, impactors and custom-length long k-wires matched to the internal diameter of the instrumentation system.
Owner:BARRY RICHARD J
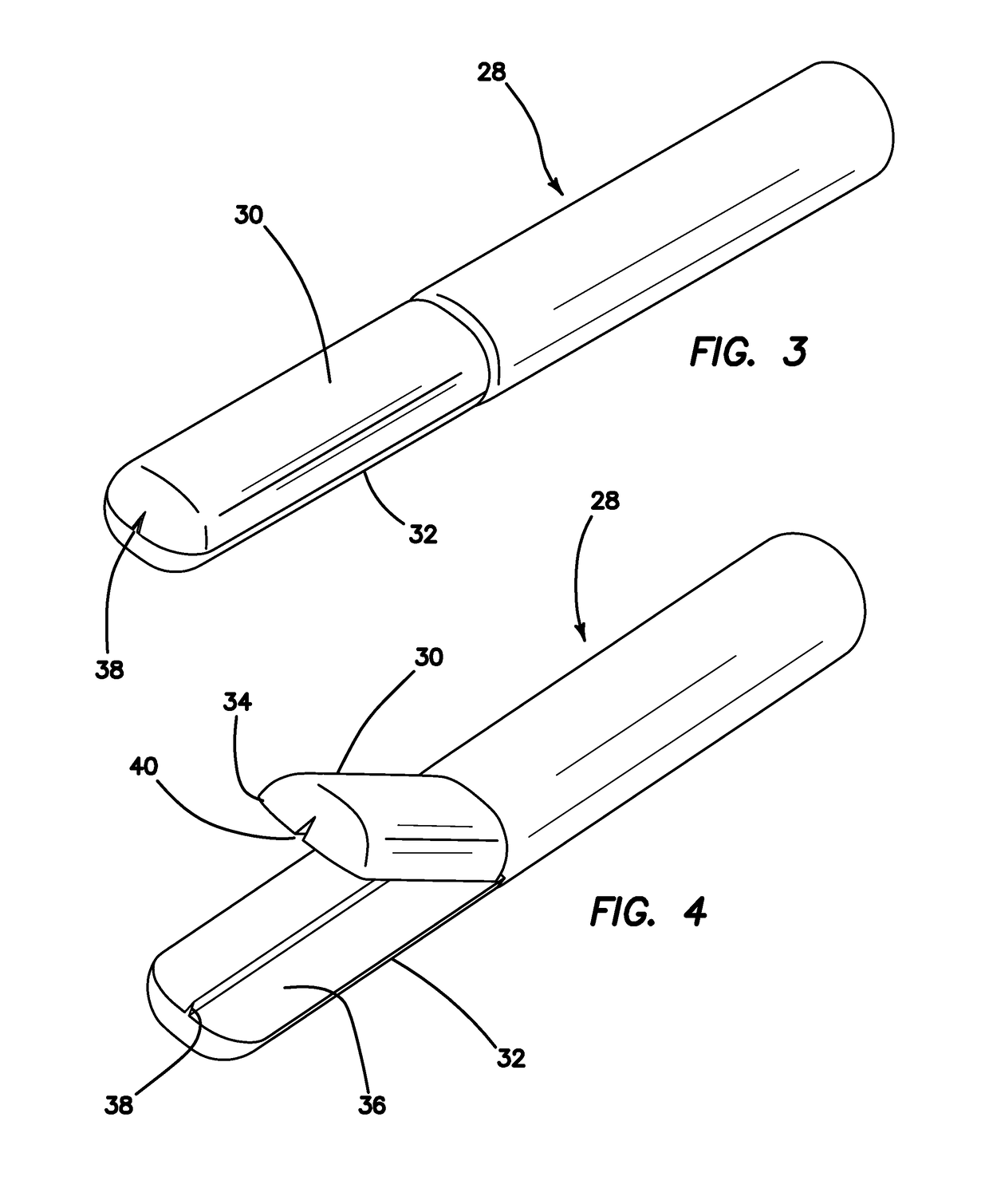
Simulated stapling and energy based ligation for surgical training
InactiveUS10198965B2Surgical instruments for heatingEducational modelsSurgical instrumentationEnergy based
An inexpensive and practical surgical training system to train practitioners in the use of surgical stapling and energy-based ligation instruments and procedures is provided. The system comprises a modified or simulated surgical instrument such as linear surgical stapling device having a fixed anvil and an opposed, movable jaw sized and configured to be closed upon a simulated tissue structure. A marking or inking element is associated with the jaw and anvil of the stapling device and configured to impose a visible pattern on the surfaces of simulated tissue placed between the anvil and jaw. A pressure sensitive adhesive or other adhesive is associated with the inner surfaces of the simulated tissue that is activated upon compression between the anvil and jaw to simulate surgical occlusion.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
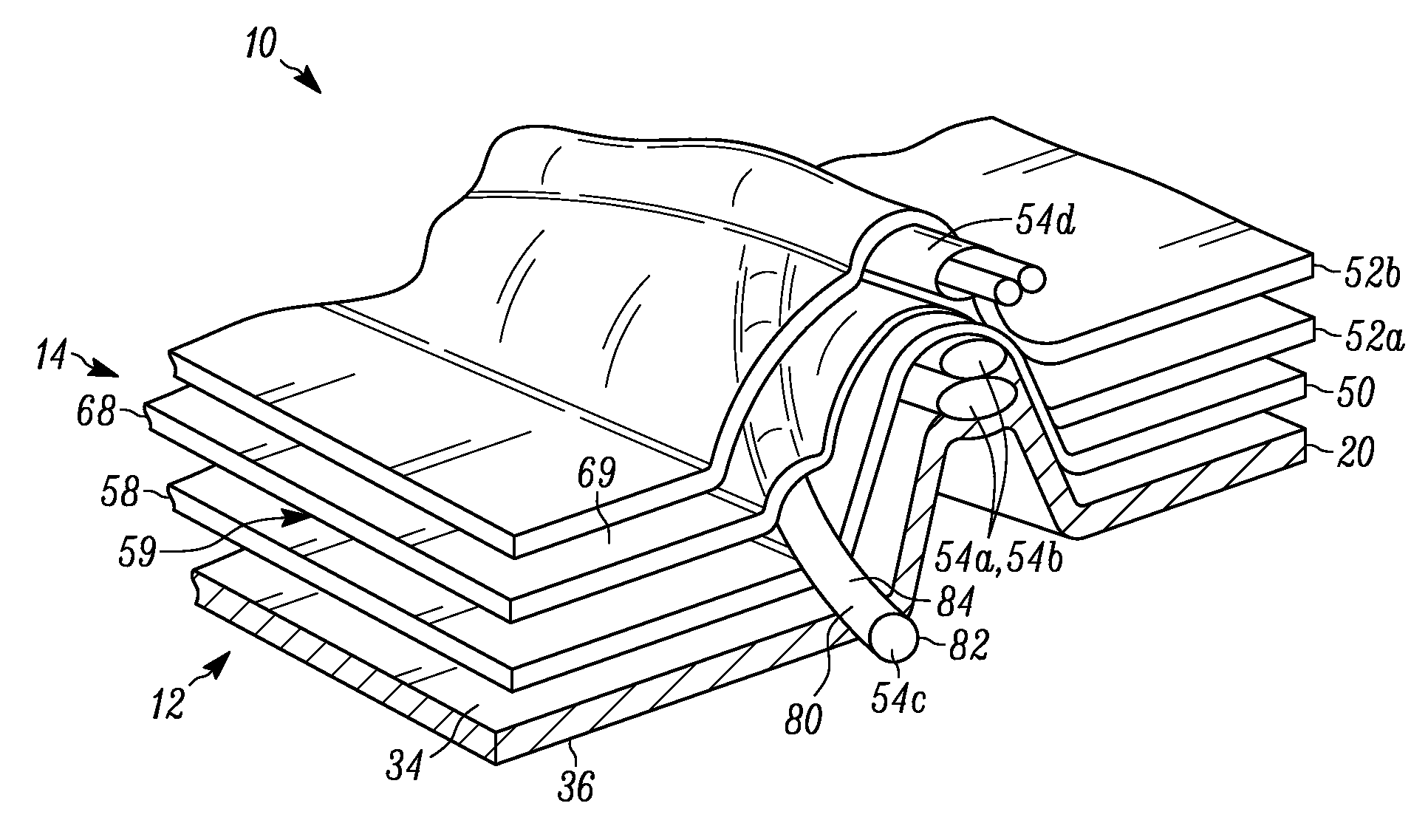
Medical physiological simulator including a conductive elastomer layer
Conductive elastomeric circuits are used in various simulated physiological structures such as tissues and organs, enabling feedback to be provided indicating whether a simulated task is being performed correctly. For example, a surgical trainer has a simulated human tissue structure made of an elastomeric composition, at least one reinforcing layer of a fibrous material, and at least one flexible electrical circuit. The surgical trainer preferably includes multiple areas for practicing surgical skills, each with evaluation circuits for providing feedback regarding that skill. Conductive elastomers are also incorporated into other types of medical training simulators, to similarly provide feedback. In another embodiment, a simulated organ has a conductive elastomeric circuit in the periphery of the simulated organ, enabling feedback to be provided to evaluate whether a person is properly manipulating the organ in response to a manual applied pressure.
Owner:TOLY CHRISTOPHER C
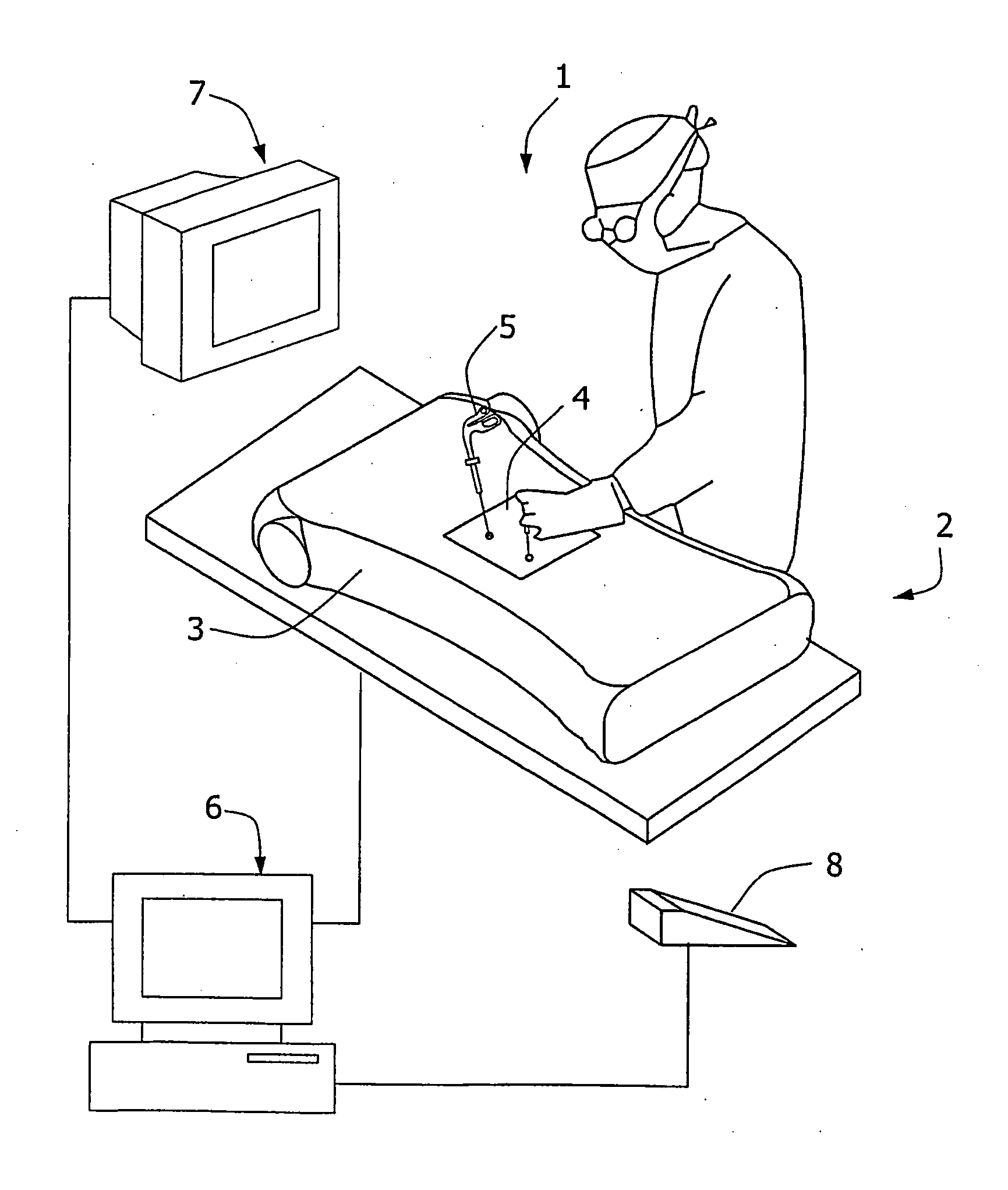
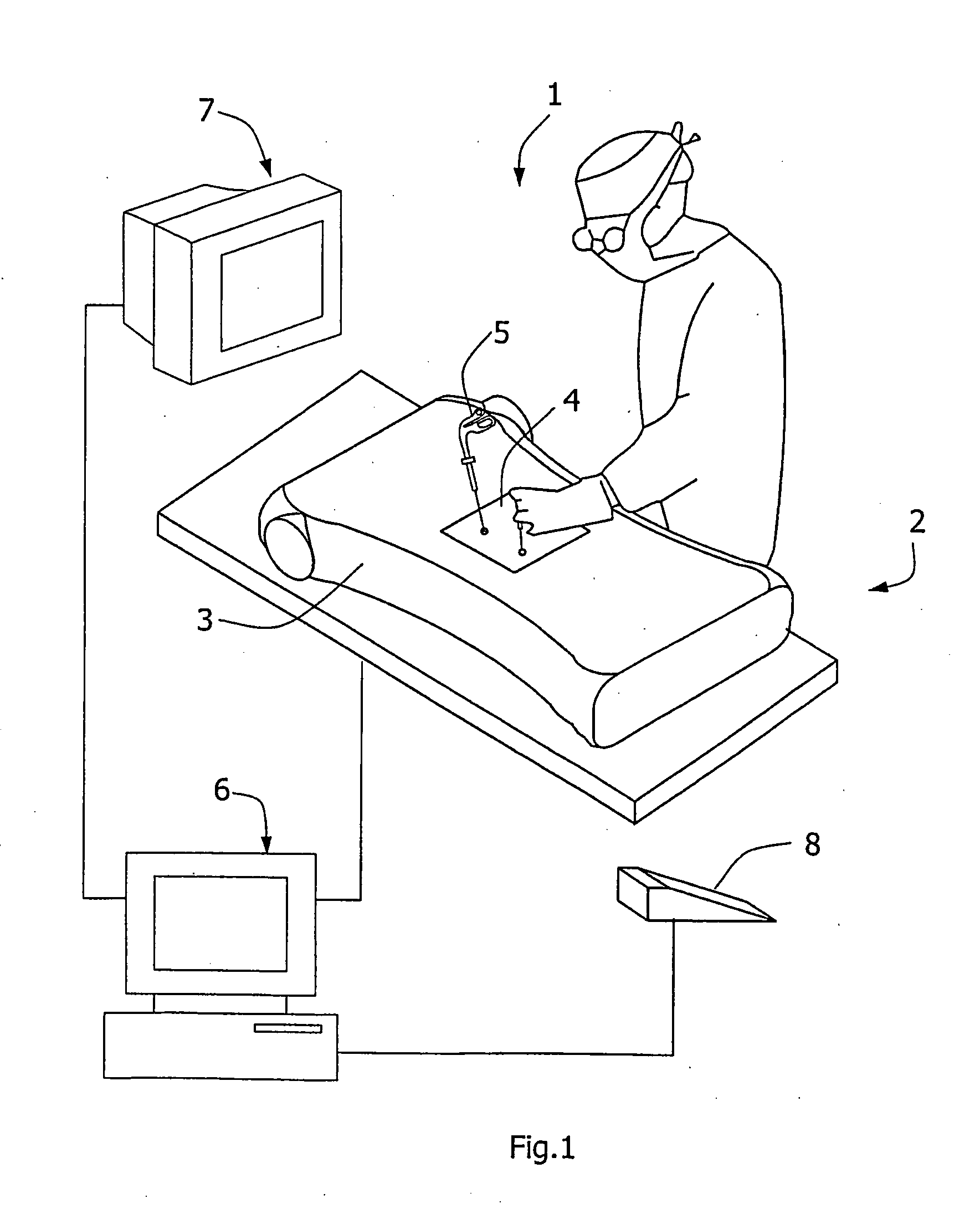
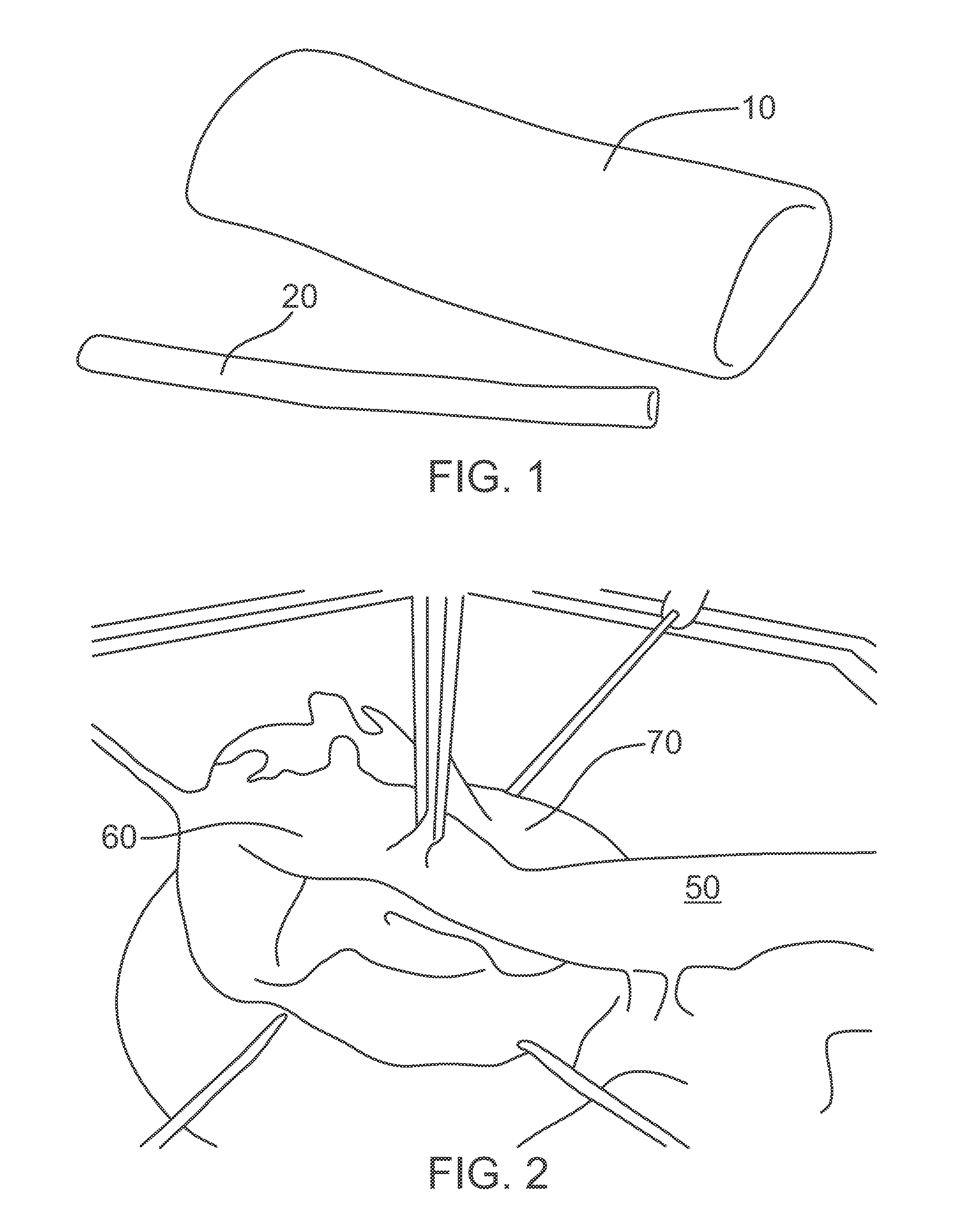
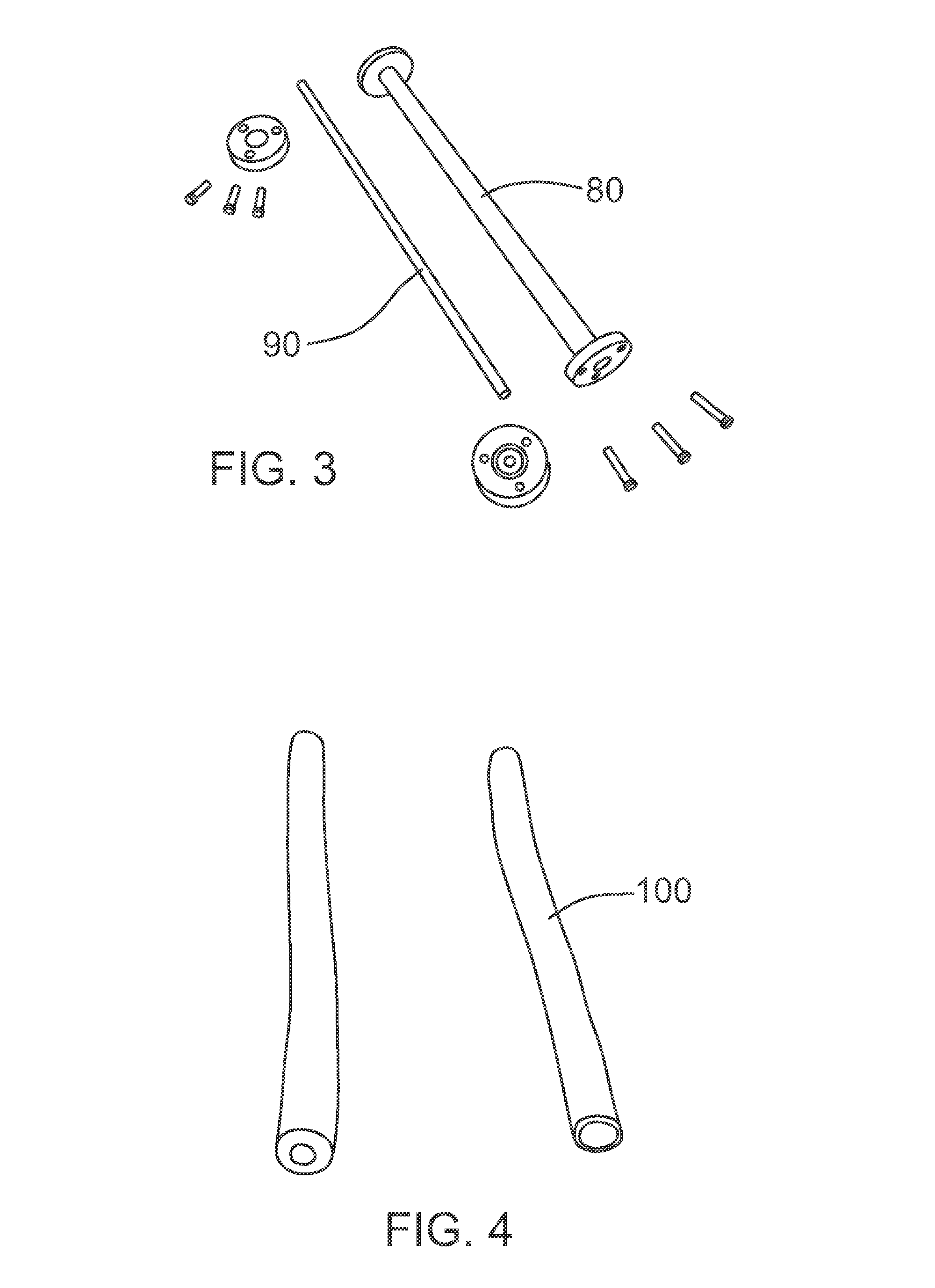
Surgical training simulator
A simulator (1) has a body form apparatus (2) with a skin-like panel (4) through which laproscopic instruments (5) are inserted. Cameras (10) capture video images of internal movement of the instruments (5) and a computer (6) processes them. 3D positional data is generated using stereo triangulation and is linked with the associated video images. A graphics engine (60) uses the 3D data to generate graphical representations of internal scenes. A blending function (70) blends real and recorded images, or real and simulated images to allow demonstration of effects such as internal bleeding or suturing.
Owner:CAE HEALTHCARE
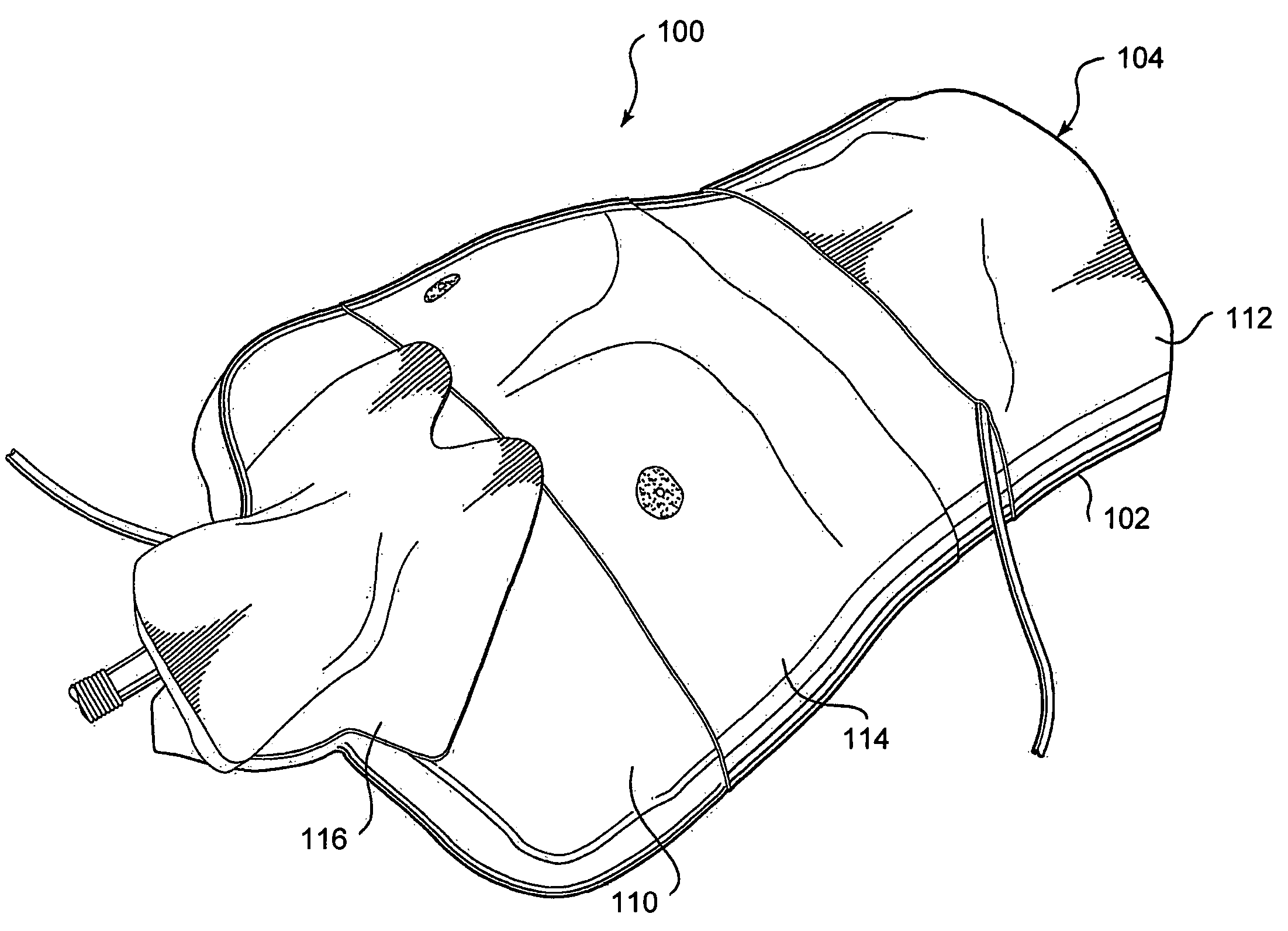
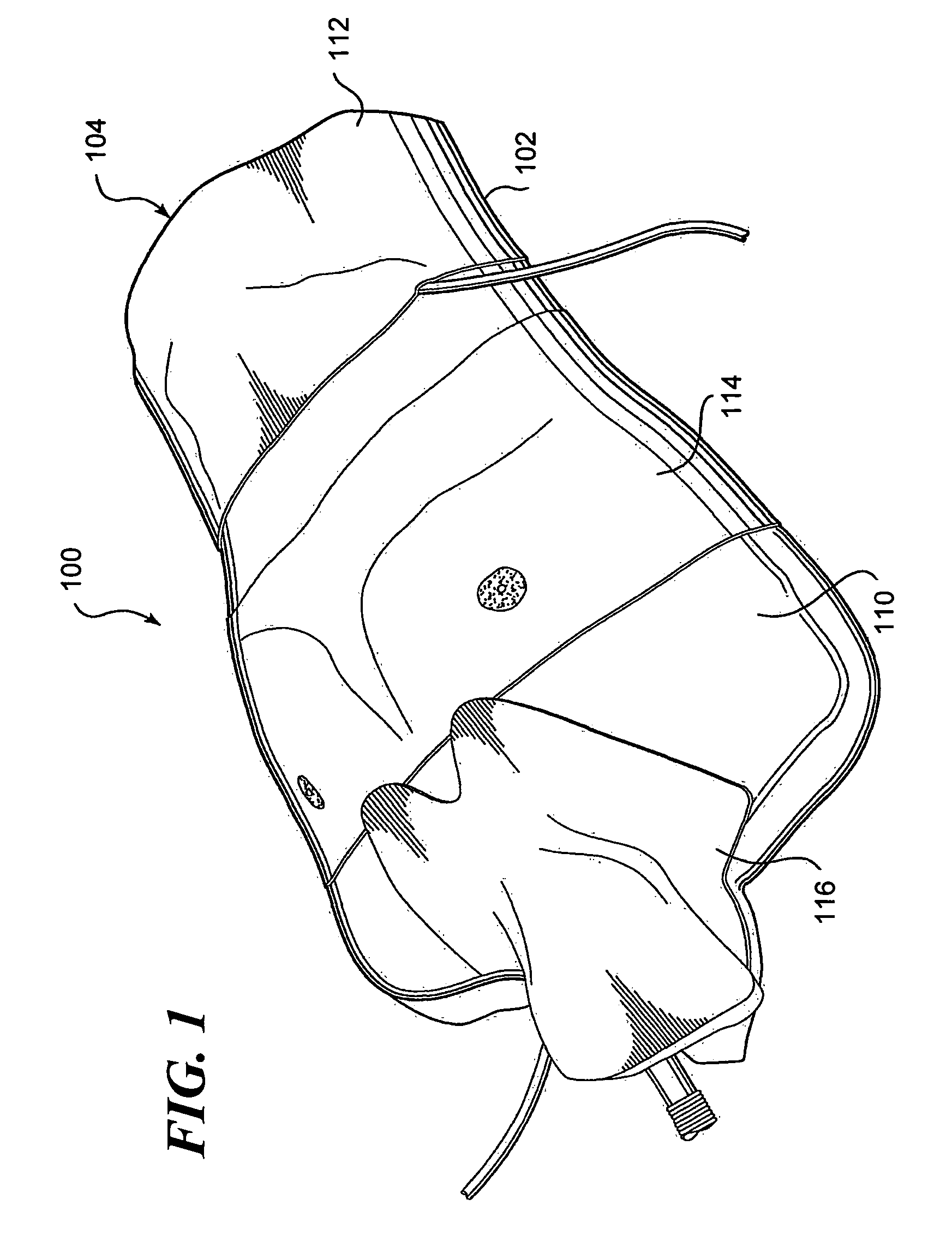
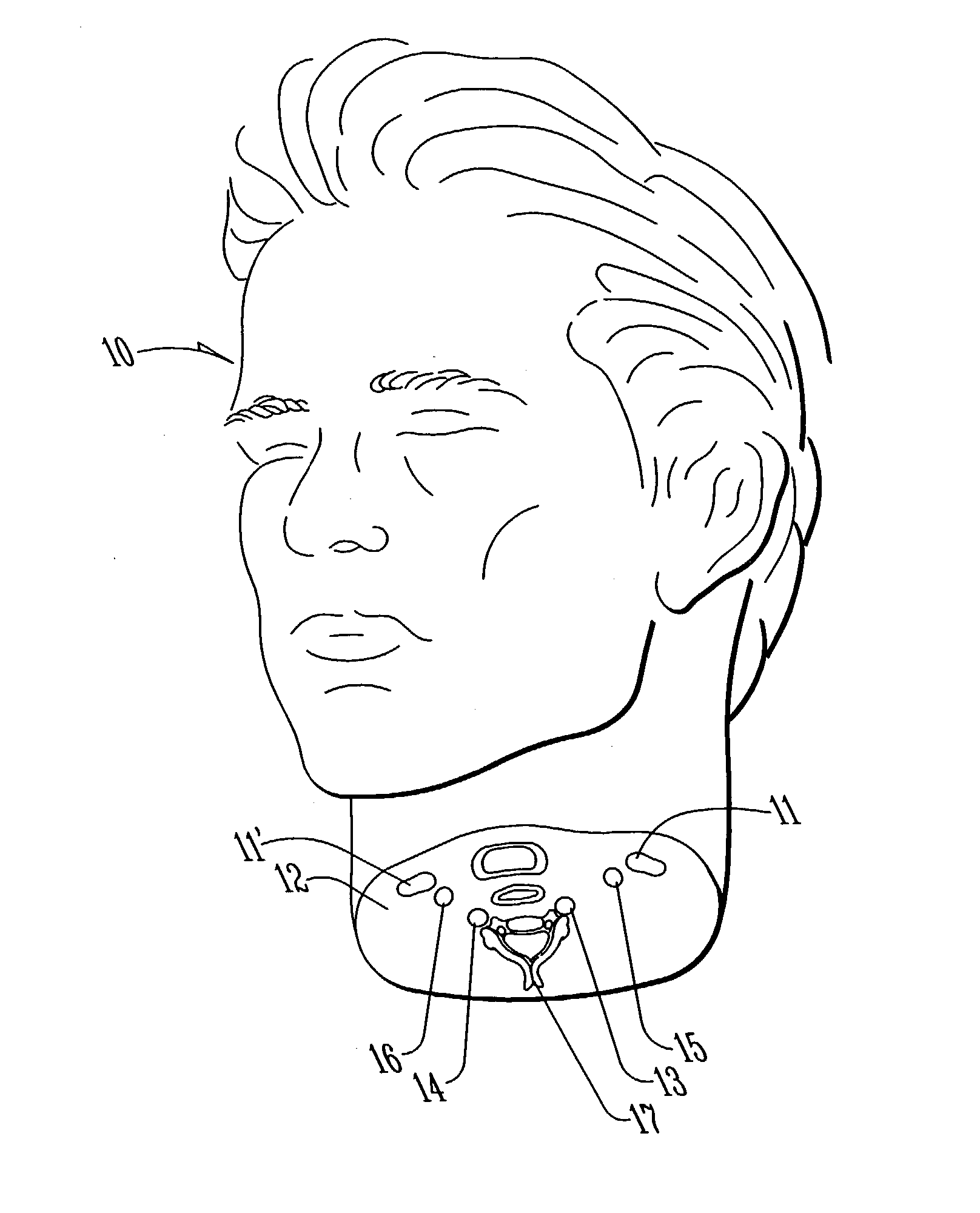
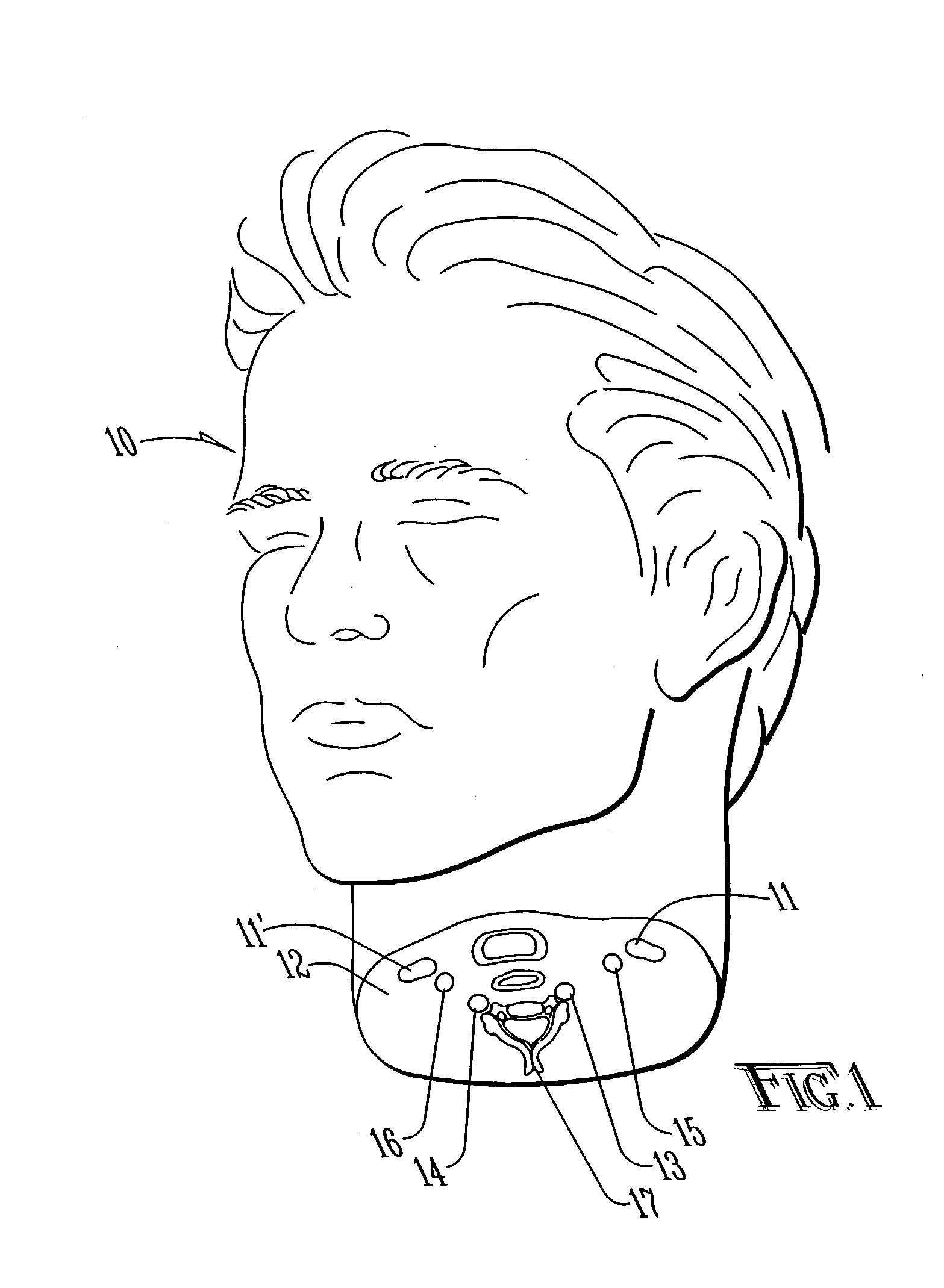
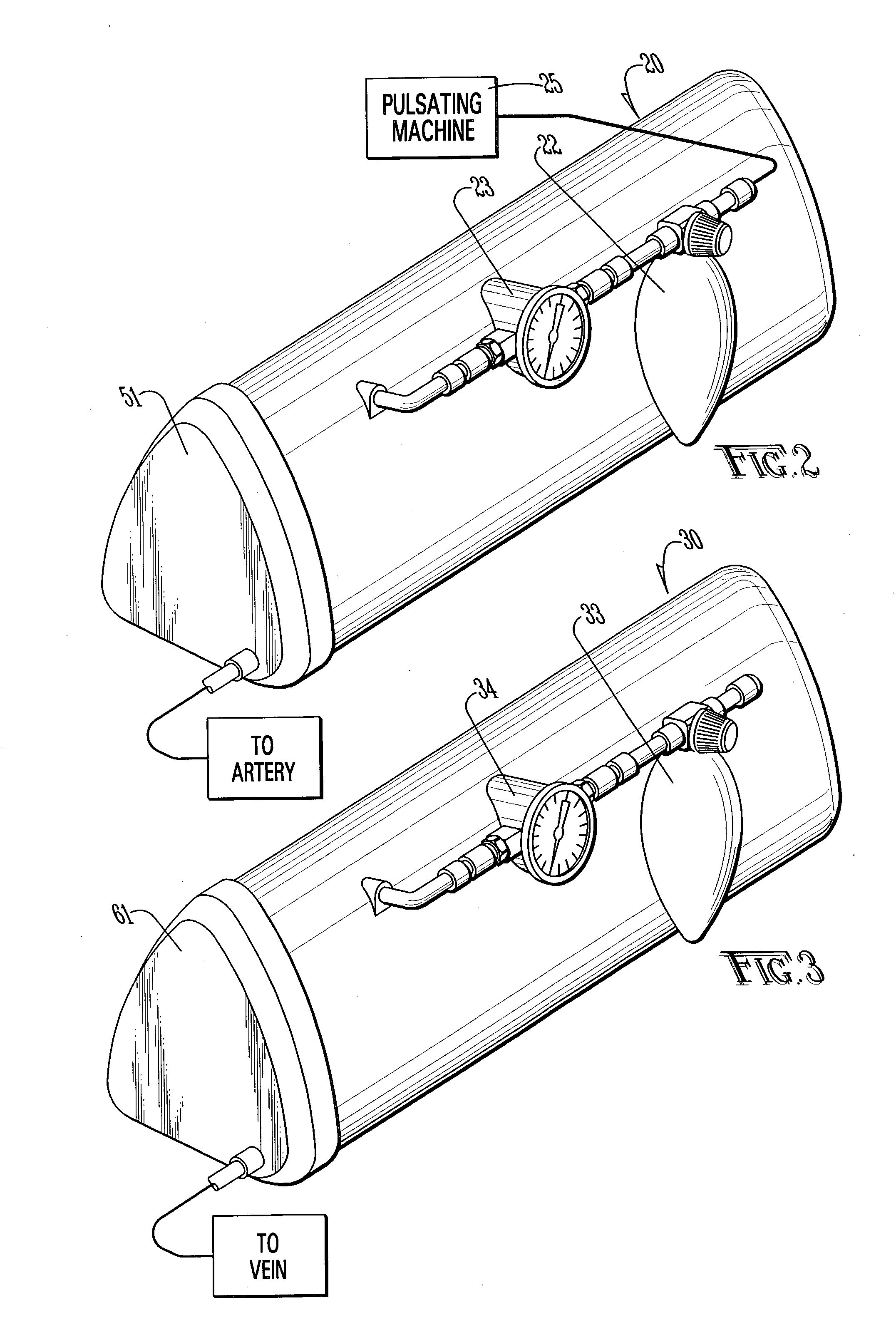
Method and apparatus for surgical training
An apparatus and method for microsurgical training using cadaveric anatomy with filling of the vascular system by fluids under pressure to simulate the appearance and function of live surgery. One or more arteries on the specimen of cadaveric anatomy are cannulated and connected to an arterial reservoir having a flexible container holding an arterial fluid simulating the appearance of blood circulating in the arteries of the living organism from which the cadaveric anatomy is derived. Suitable static pressure simulating the arterial pressure appropriate to that of the living organism is applied to the air in an air-tight space surrounding the flexible container in the arterial reservoir. A pulsating machine provides air pulsations to the space surrounding the flexible fluid container to simulate the normal pulsations of the arterial system. One or more veins on the specimen are also cannulated and connected to a venous reservoir having a flexible container holding a venous fluid simulating the appearance of blood circulating in the veins of the living organism. Suitable static pressure simulating the venous pressure appropriate to that of the living organism is applied to the air in an air-tight space surrounding the flexible container in the venous reservoir. Optionally, if the specimen includes at least a portion of spinal canal, a clear fluid reservoir can be connected to the specimen through the spinal canal to simulate cerebrospinal fluid.
Owner:ABOUD GHAITH +1
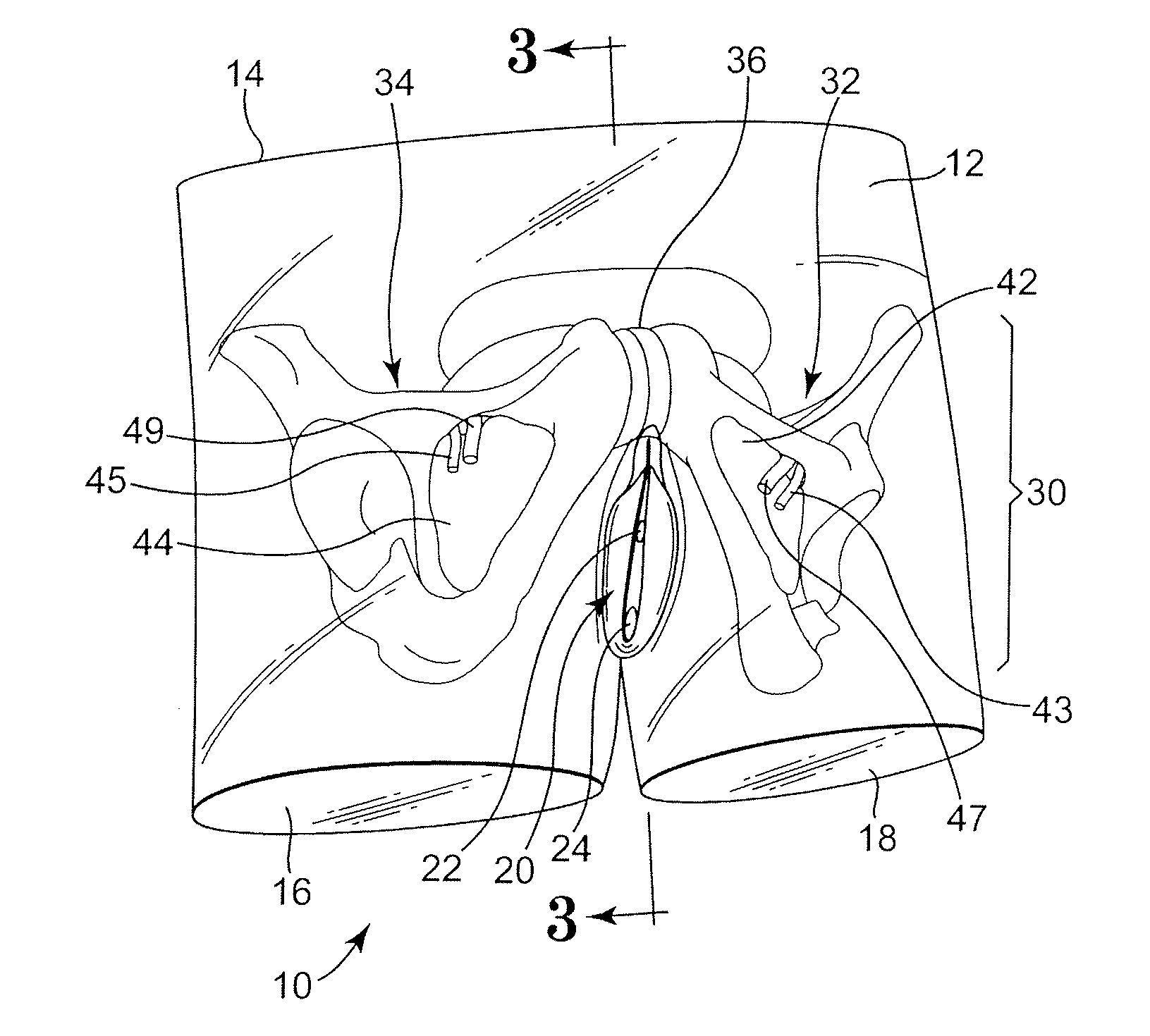
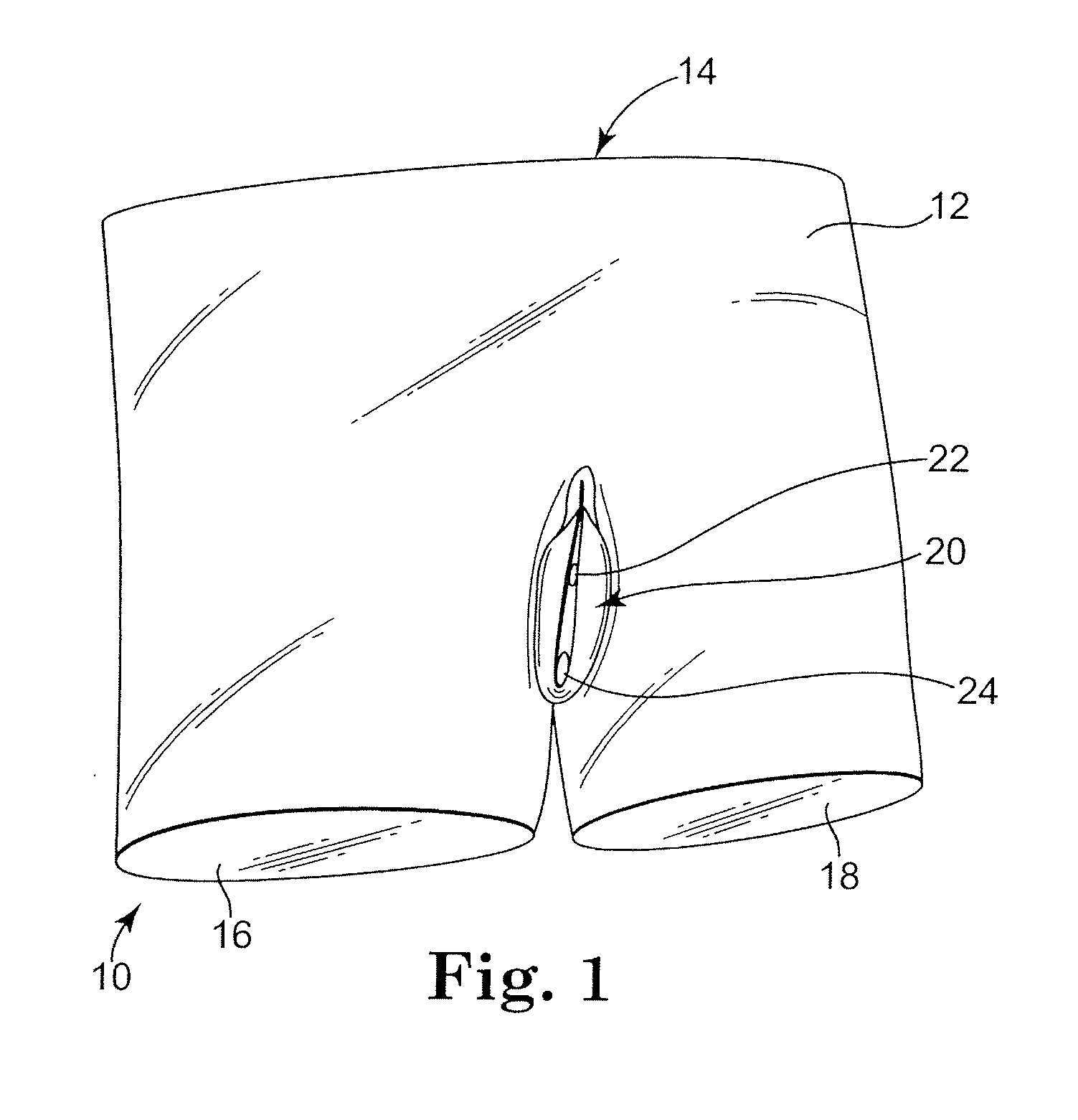
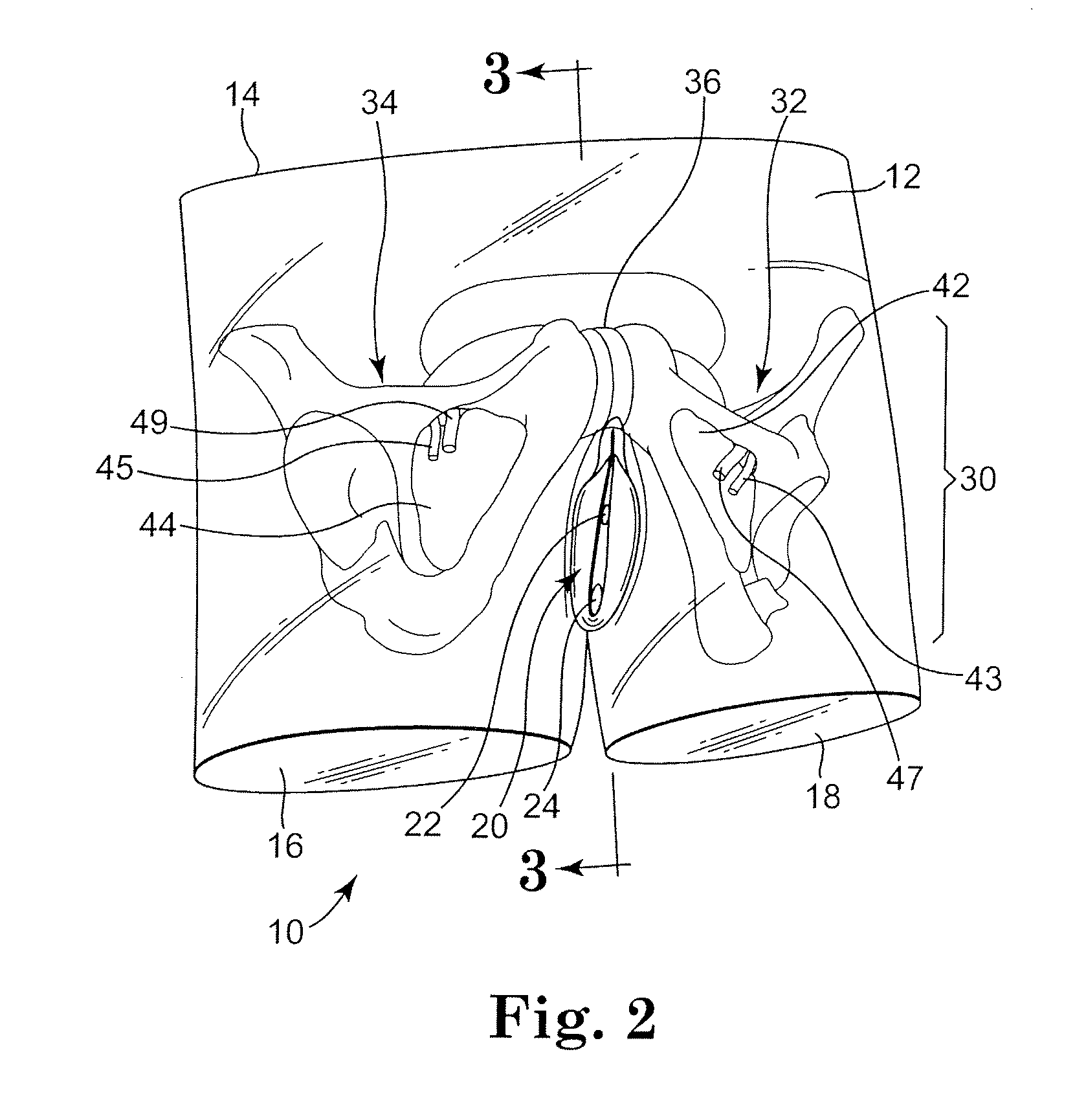
Abdominopelvic region surgical training model
Surgical training models of the abdominopelvic region of male and female human patient's bodies to assist in training an operator in microsurgical techniques are disclosed. The surgical training models may be used in training in implantation of implantable medical devices, e.g., in the performance of surgical procedures using particular sling implantation tools to implant a urethral sling to support the urethra or bladder to treat incontinence.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
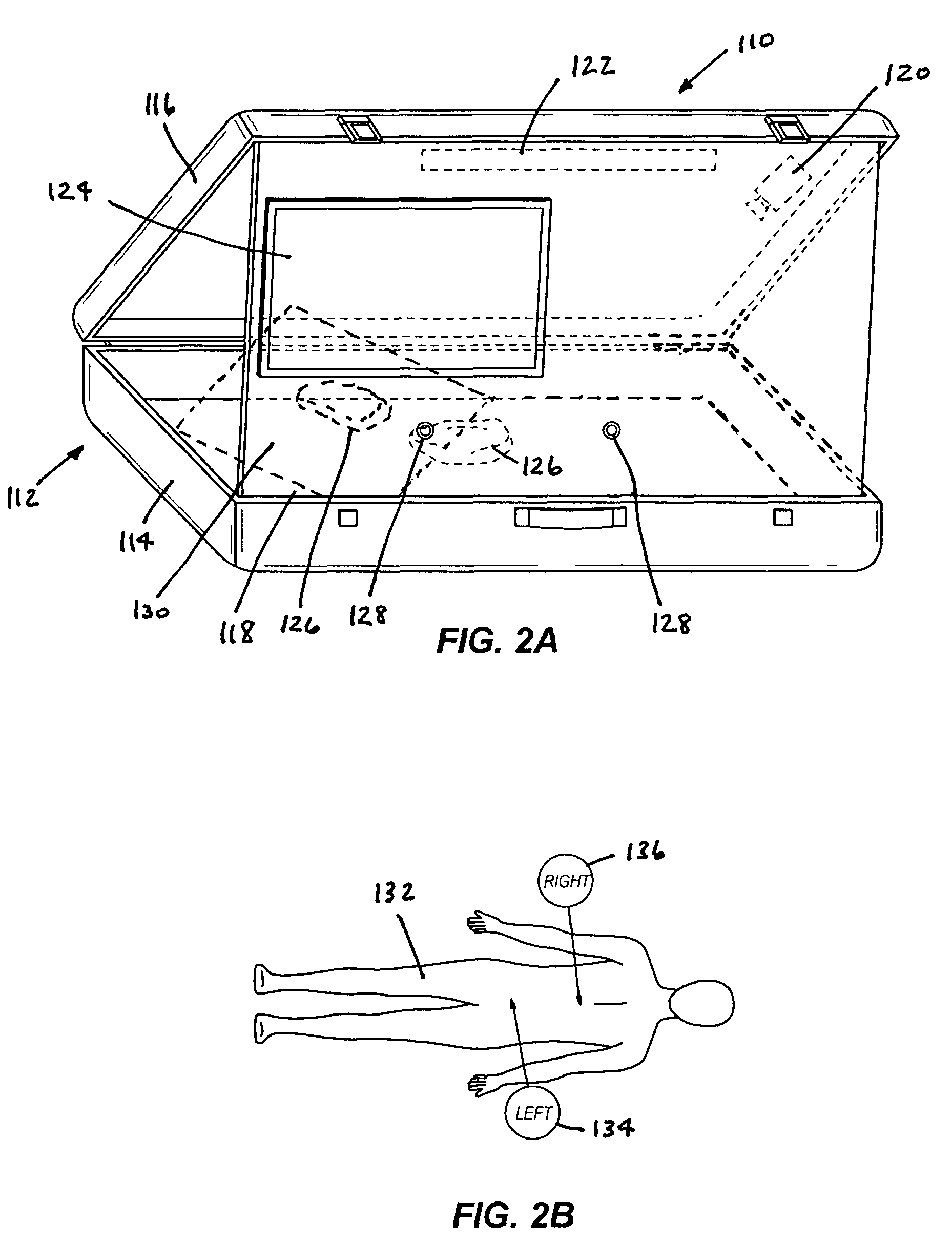
Surgical training simulator having multiple tracking systems
A surgical training device, includes a body form, at least two cameras configured to obtain image data of at least one implement located within the body form, and a magnetic tracking system operative to transmit signals, the signals corresponding to position and alignment information of the at least one implement. The surgical training device also includes a computer configured to receive the image data from the at least two cameras, receive the signals from the magnetic tracking system, and generate position and alignment data of the at least one implement from the image data and the signals. A display is operatively coupled to the computer and operative to display at least one image of the at least one implement and a virtual background, the virtual background depicting a portion of a body cavity.
Owner:CAE HEALTHCARE
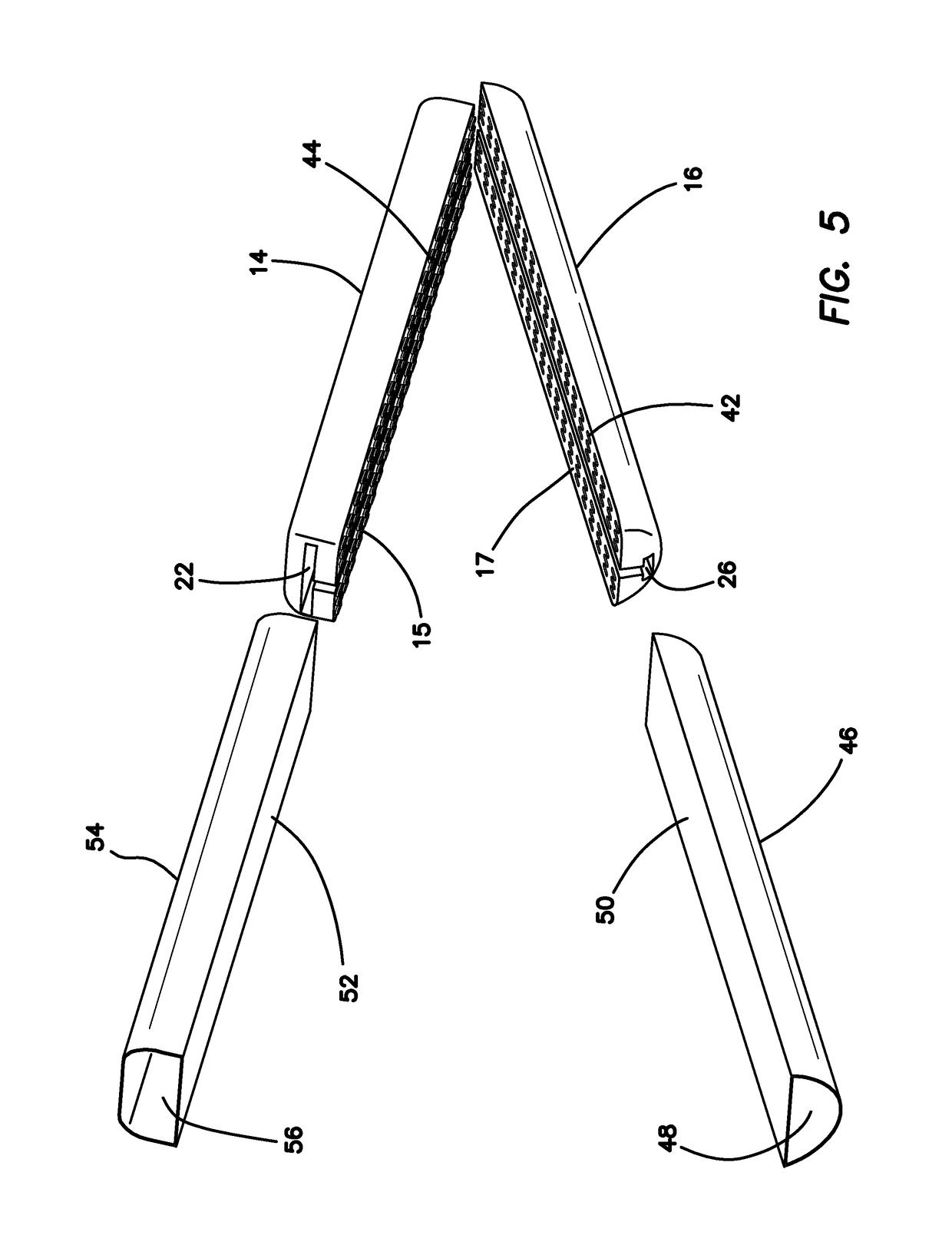
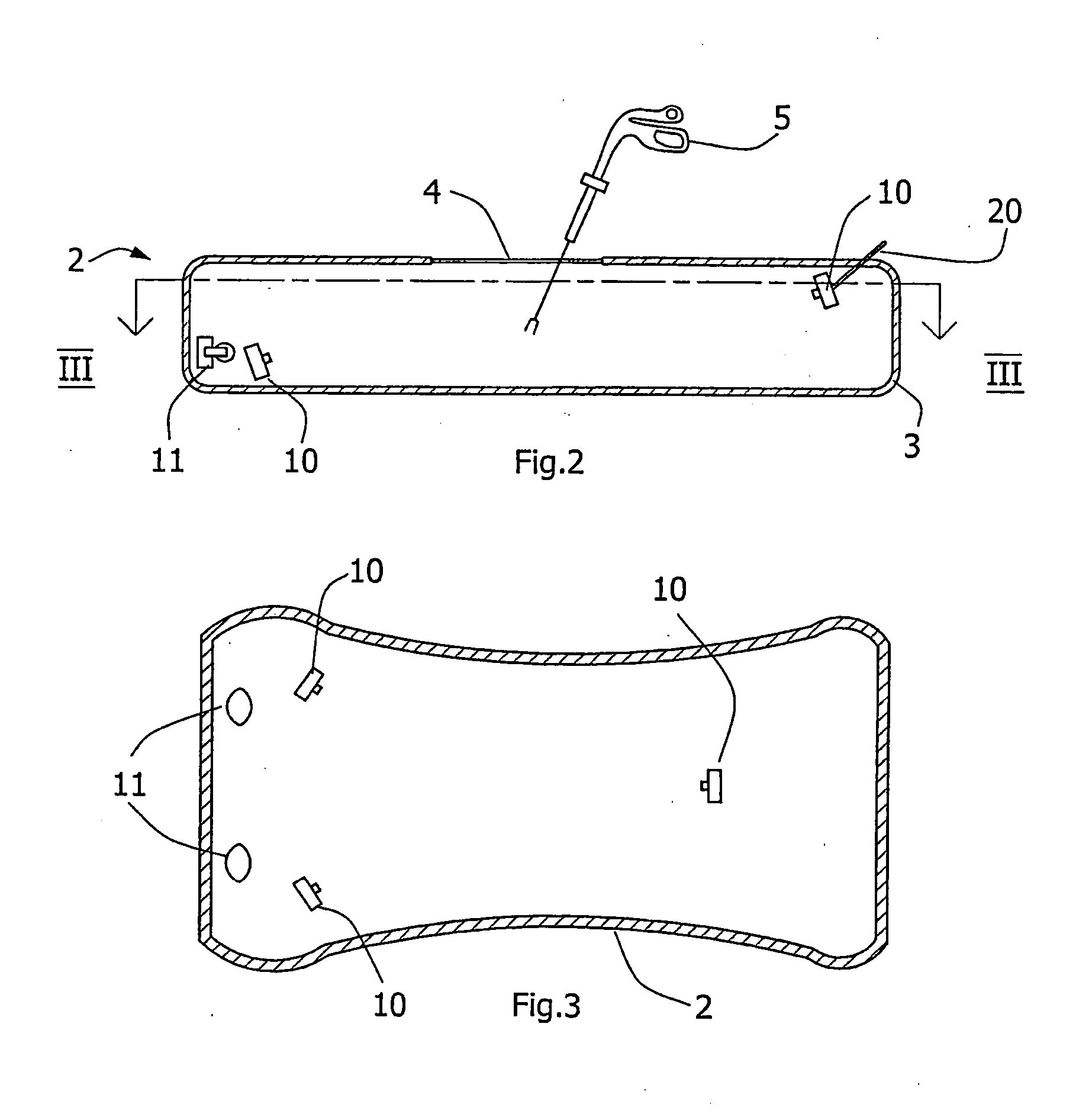
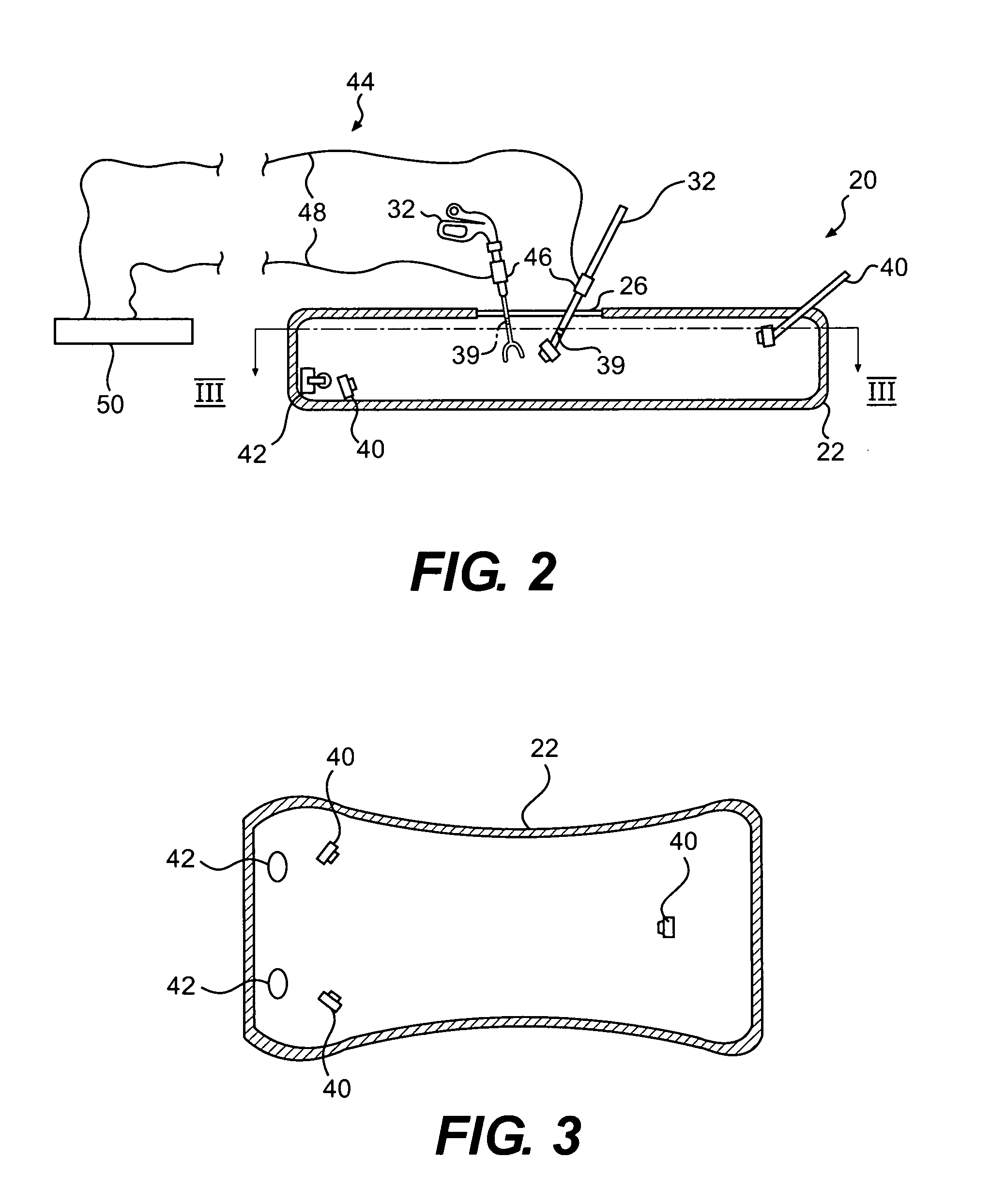
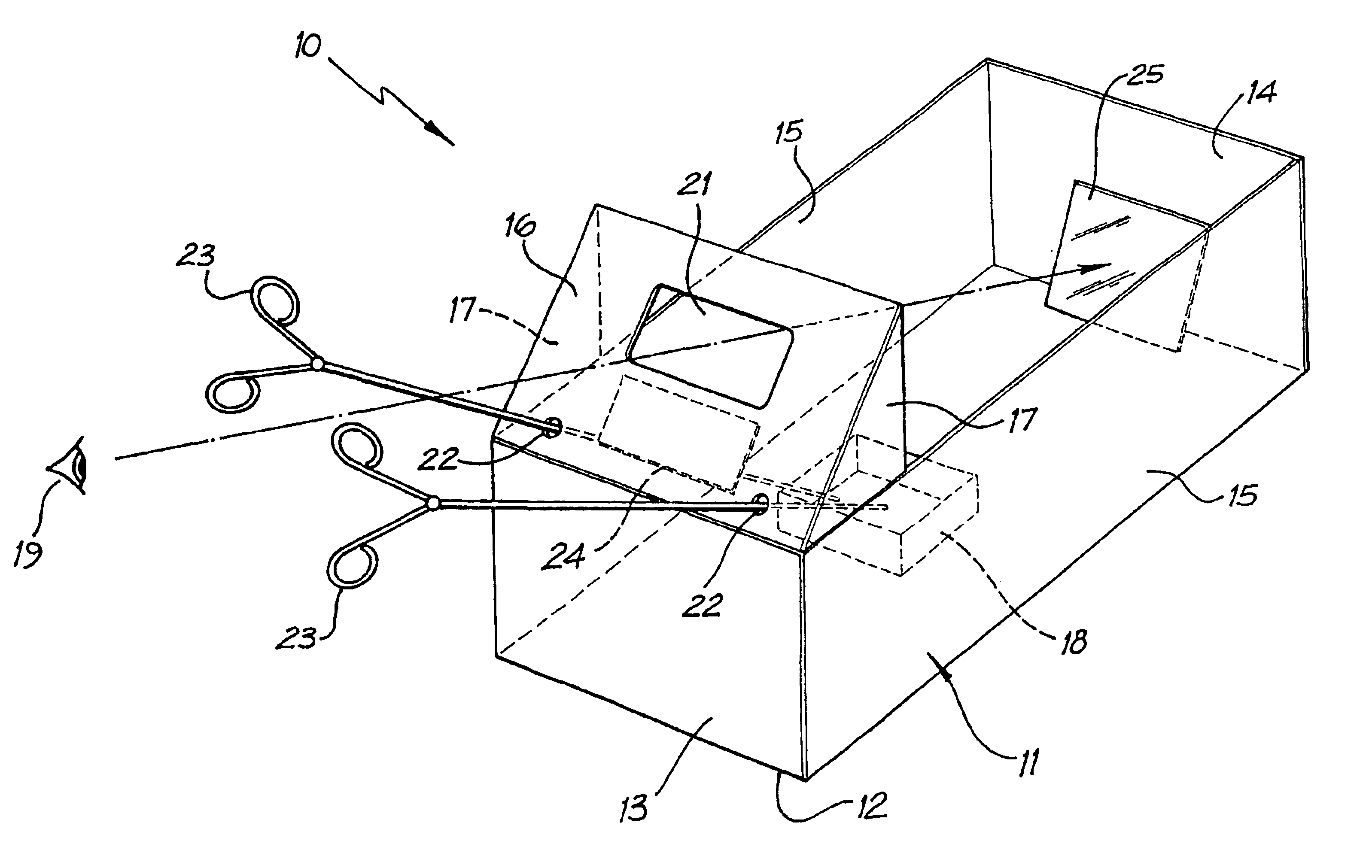
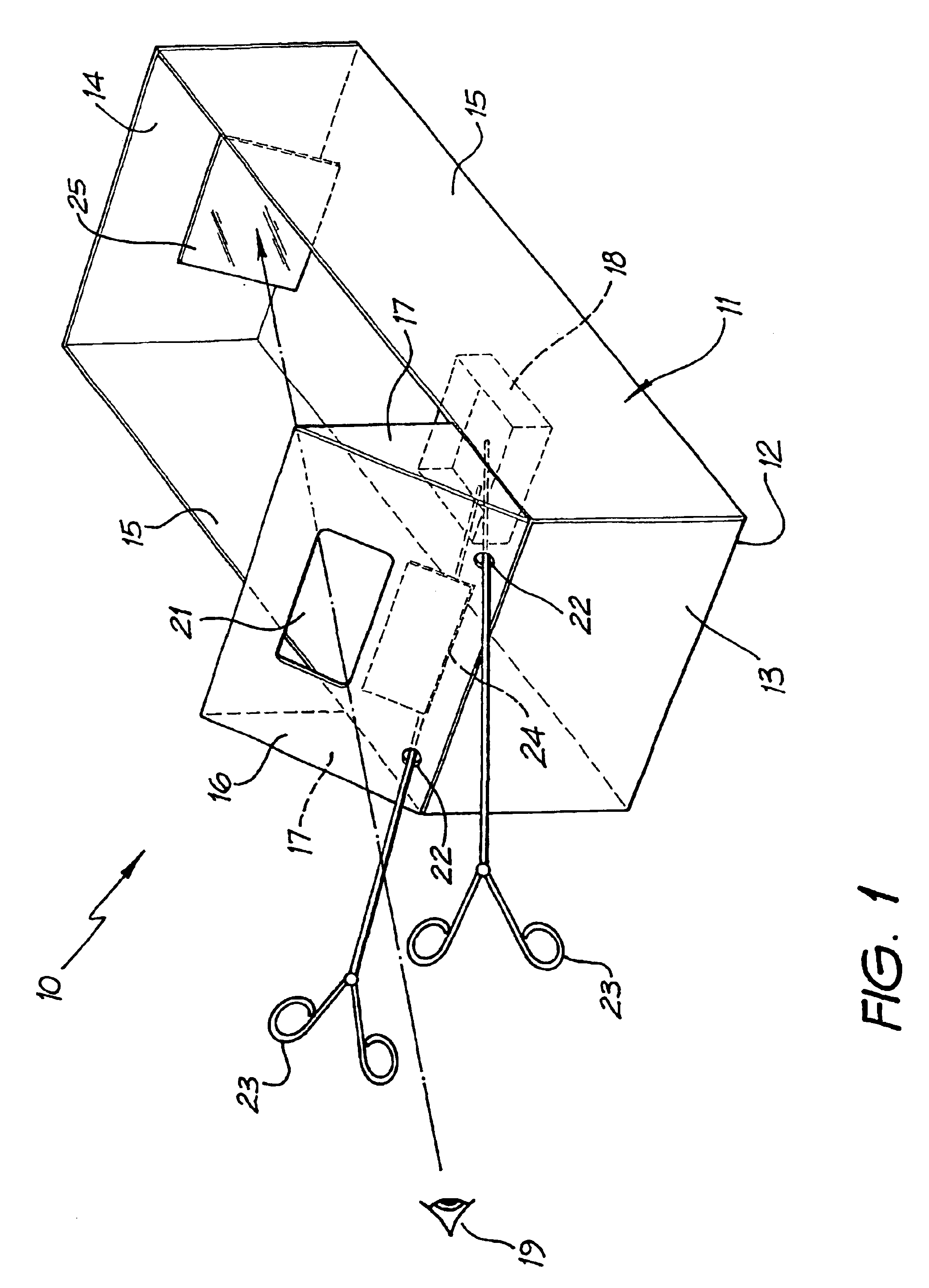
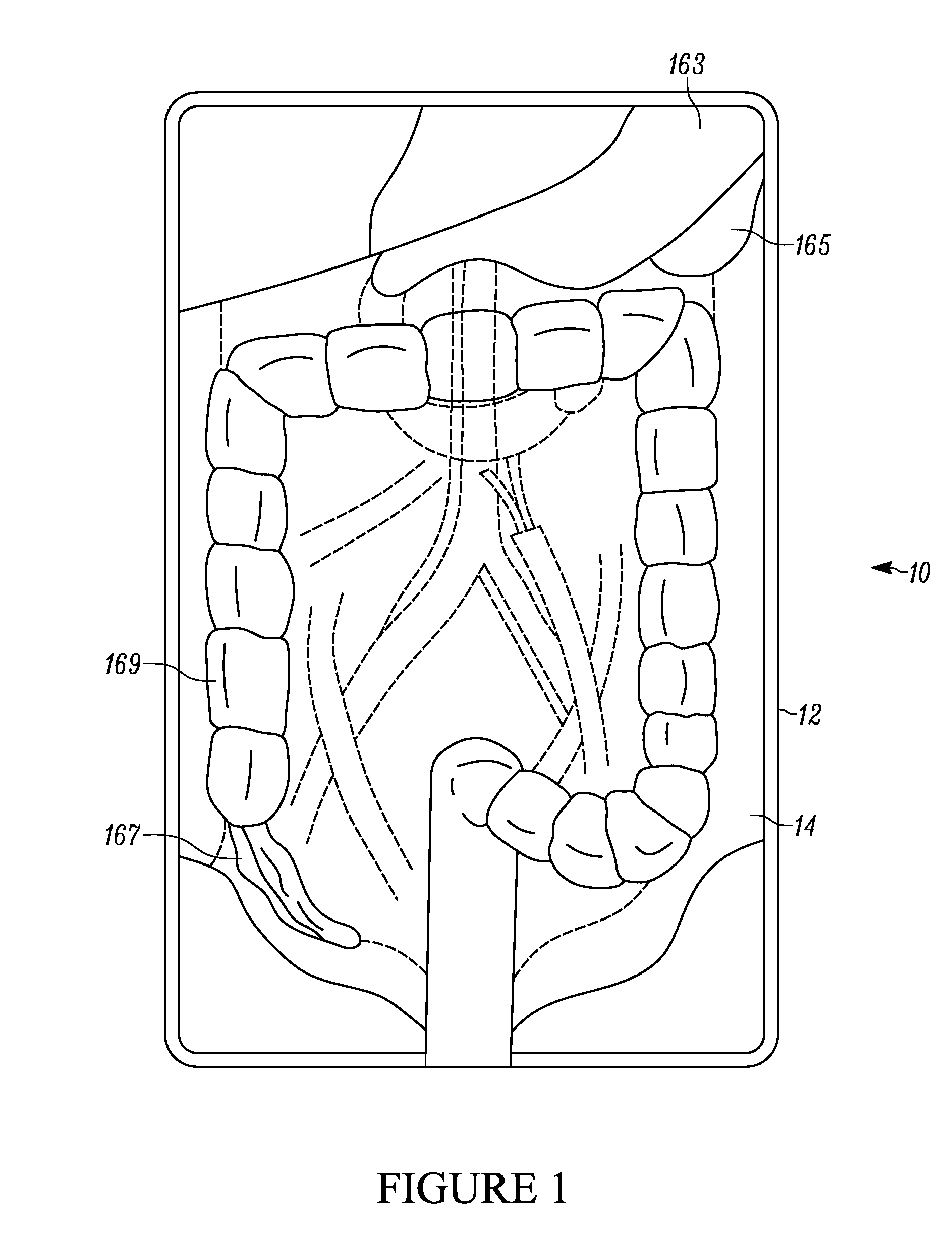
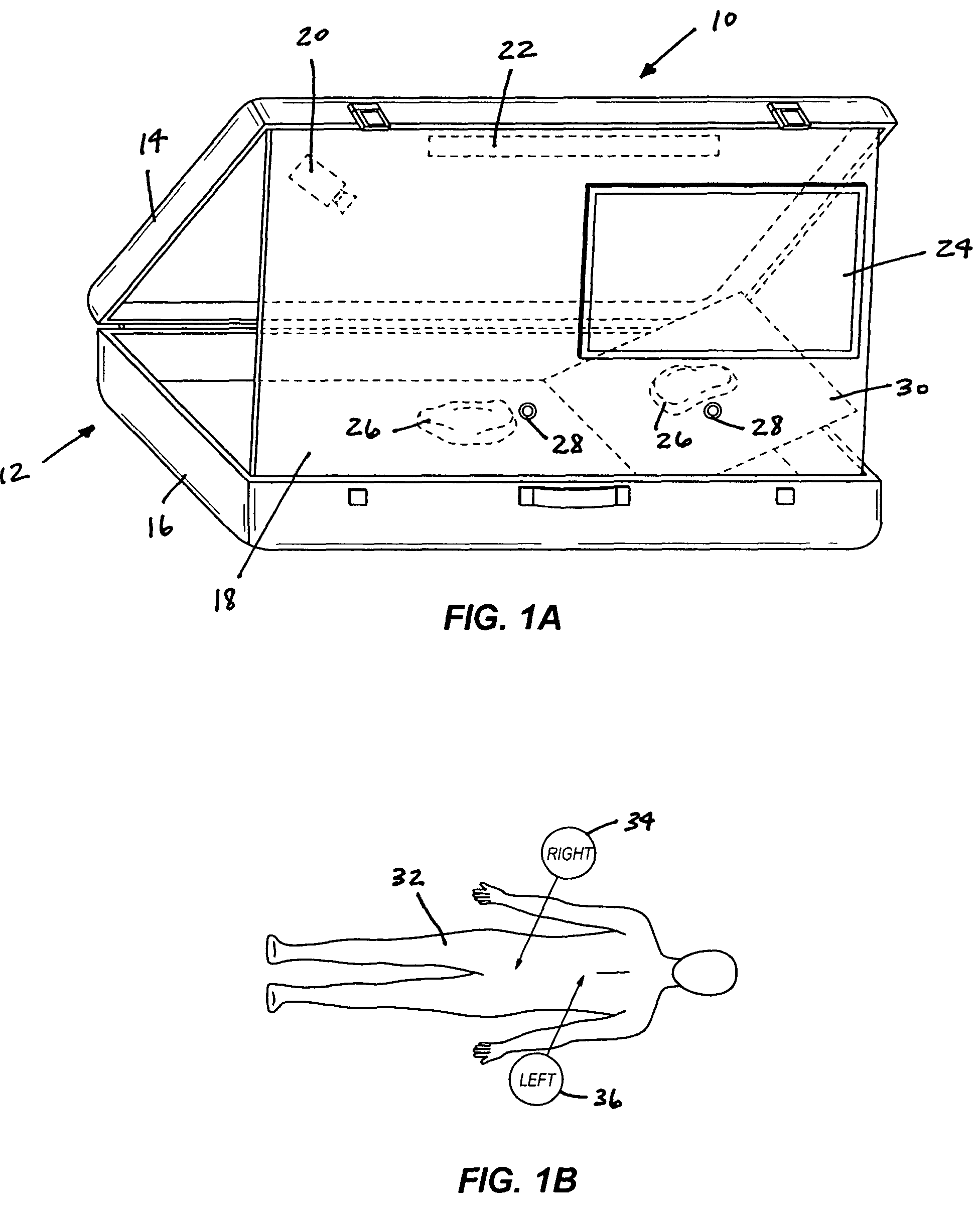
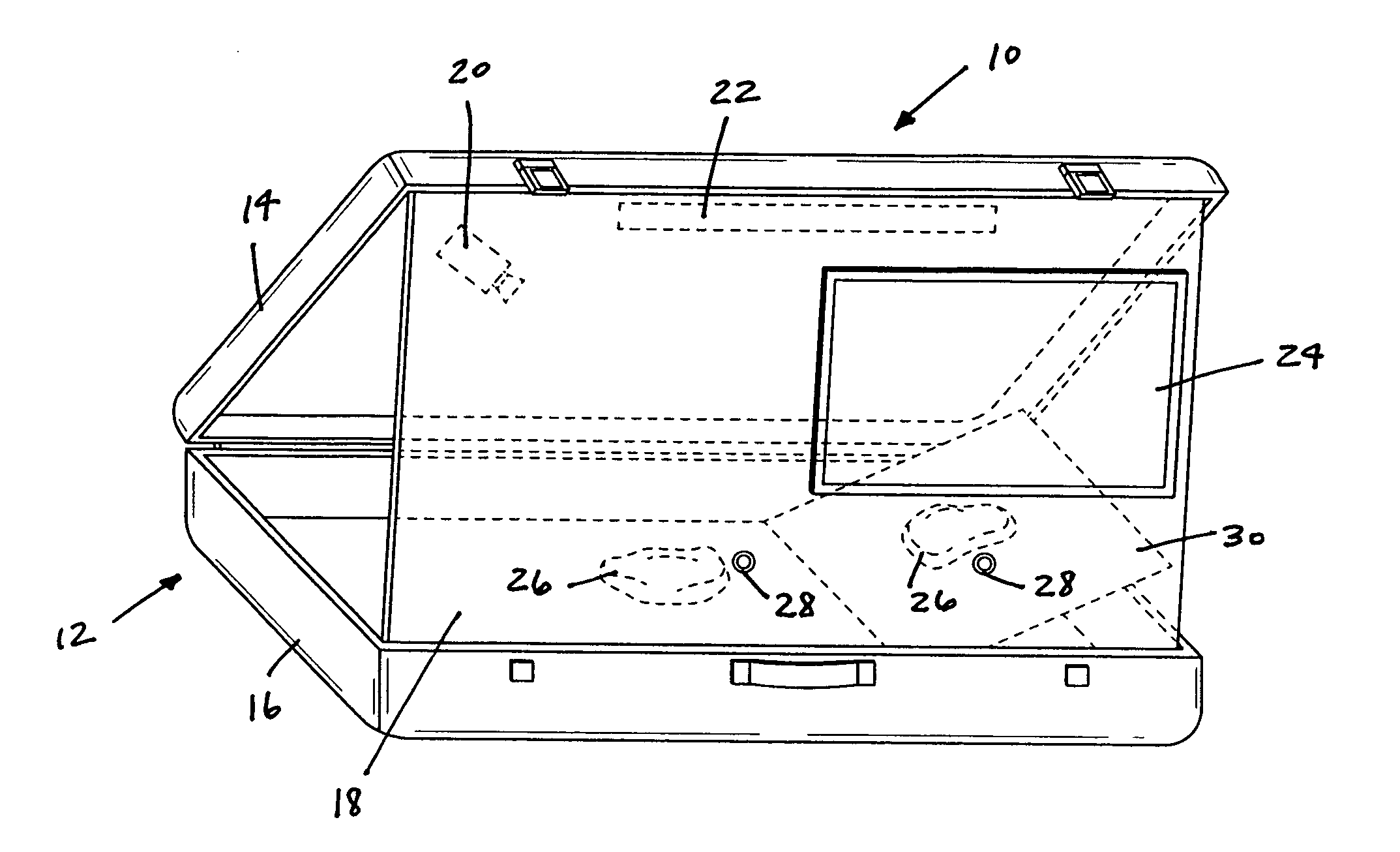
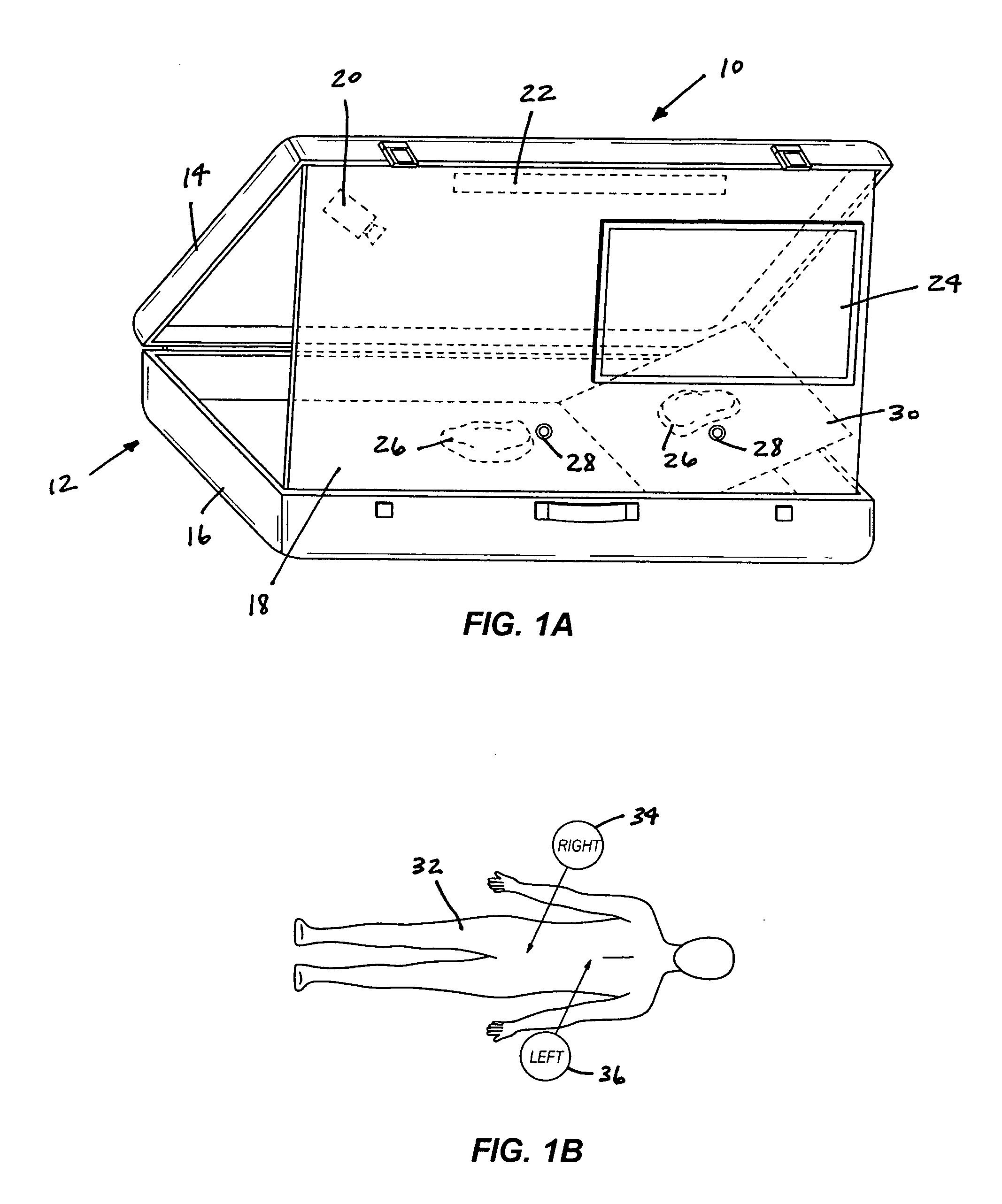
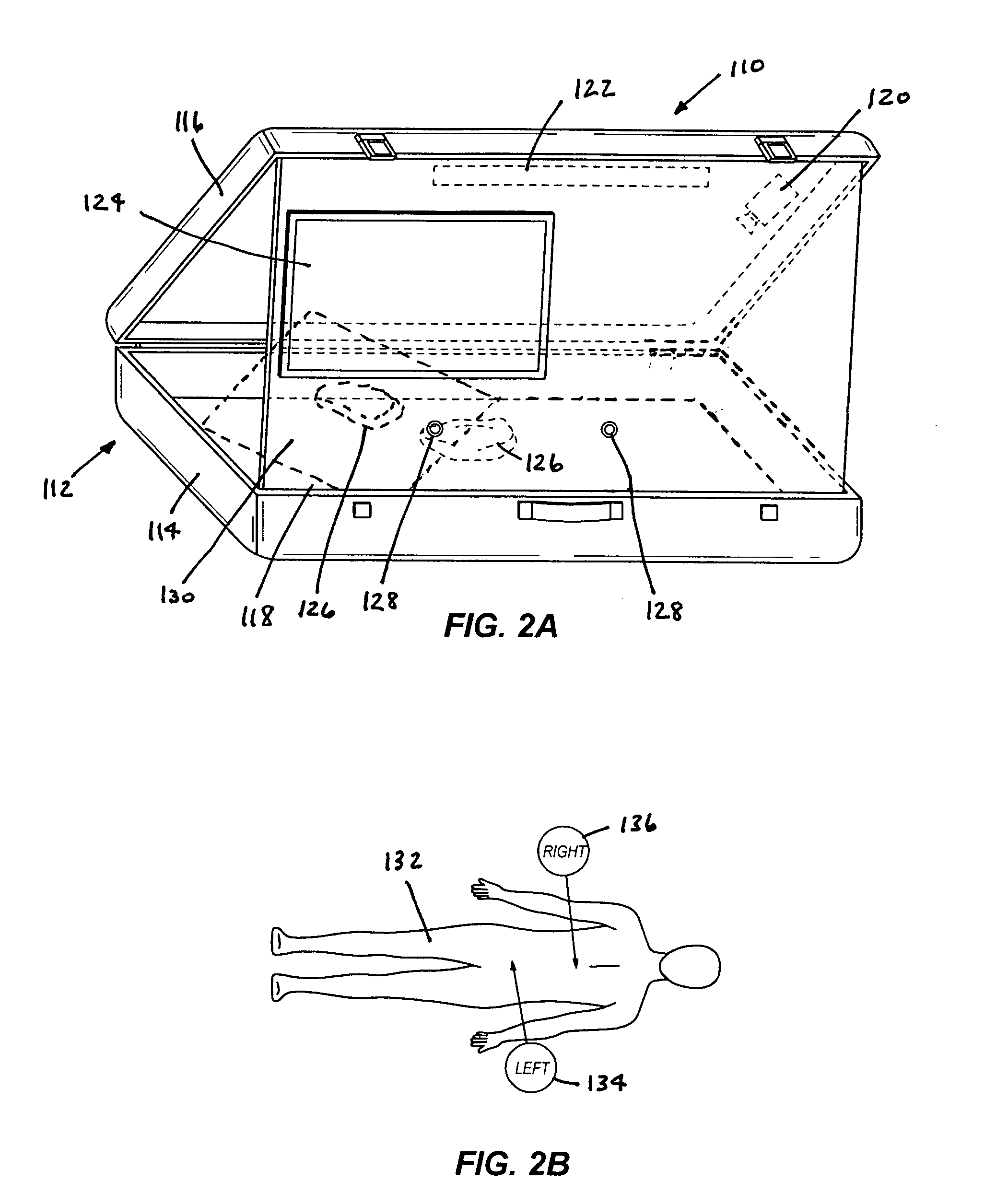
Laparoscopic trainer
InactiveUS6887082B2Easy to transportSmall and portableDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPERITONEOSCOPEEngineering
A surgical training device (10) for the practice of surgical techniques. The device (10) comprises an operation area (18) arranged to receive an operable structure and a screening wall (13) having an aperture (21). The wall (13) is positioned relative to the operation area (18) such that the wall prevents direct viewing of the operation area (18) from at least one position (19) external the wall (18). The device further includes an optical system comprising a first mirror (24) and a second mirror (25). The first mirror (24) is arranged to reflect a primary image of the operation area (18) to the second mirror (25) which in turn is arranged to reflect a secondary image of the operation area (18) that is visible from the external position (19). The position and orientation of the mirrors and the aperture (21) is such that only the secondary image of the operation area (18) is visible from the external position (19).
Owner:THE SYDNEY CHILDRENS HOSPITALS NETWORK RANDWICK & WESTMEAD
Surgical training aid apparatus
A surgical training aid apparatus for facilitating the training of medical procedures comprising a housing and an anatomical replicating assembly. The housing includes a tray having a bottom surface and a top surface opposite the bottom surface. The anatomical replicating assembly is positioned upon the top surface of the tray of the housing, and includes a base layer and at least one body component. The base layer has a bottom surface and a top surface, and, overlays a portion of the top surface of the tray of the housing. The base layer further includes a tackiness. The body component is positioned between the top surface of the housing and the bottom surface of the base layer or on the base layer. The body component likewise includes a tackiness. The body component is releasably coupled to the base layer due to the tackiness of the two components, wherein the tackiness is overcome so as to separate the at least one body component relative to the base layer.
Owner:SENAGORE ANTHONY +1
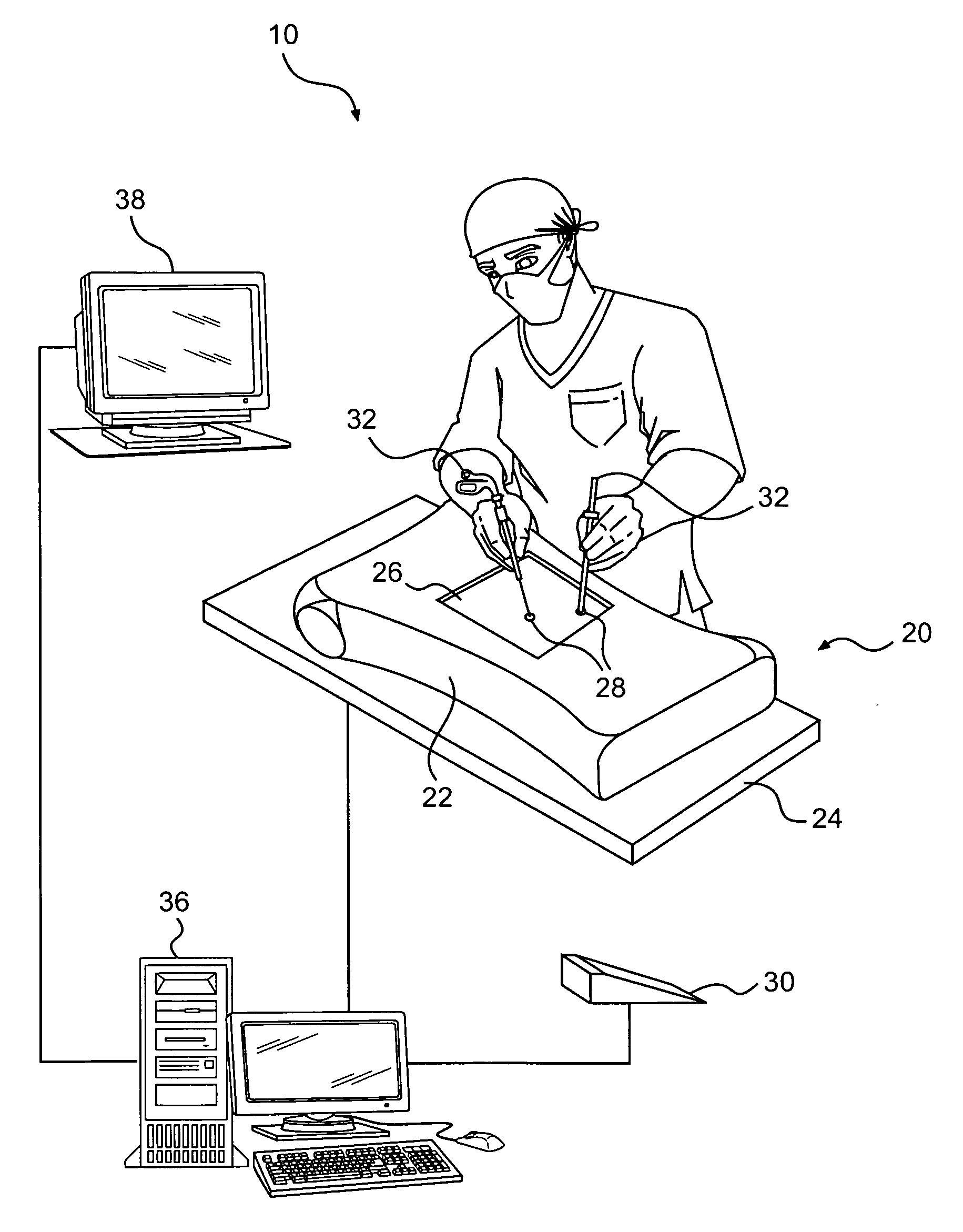
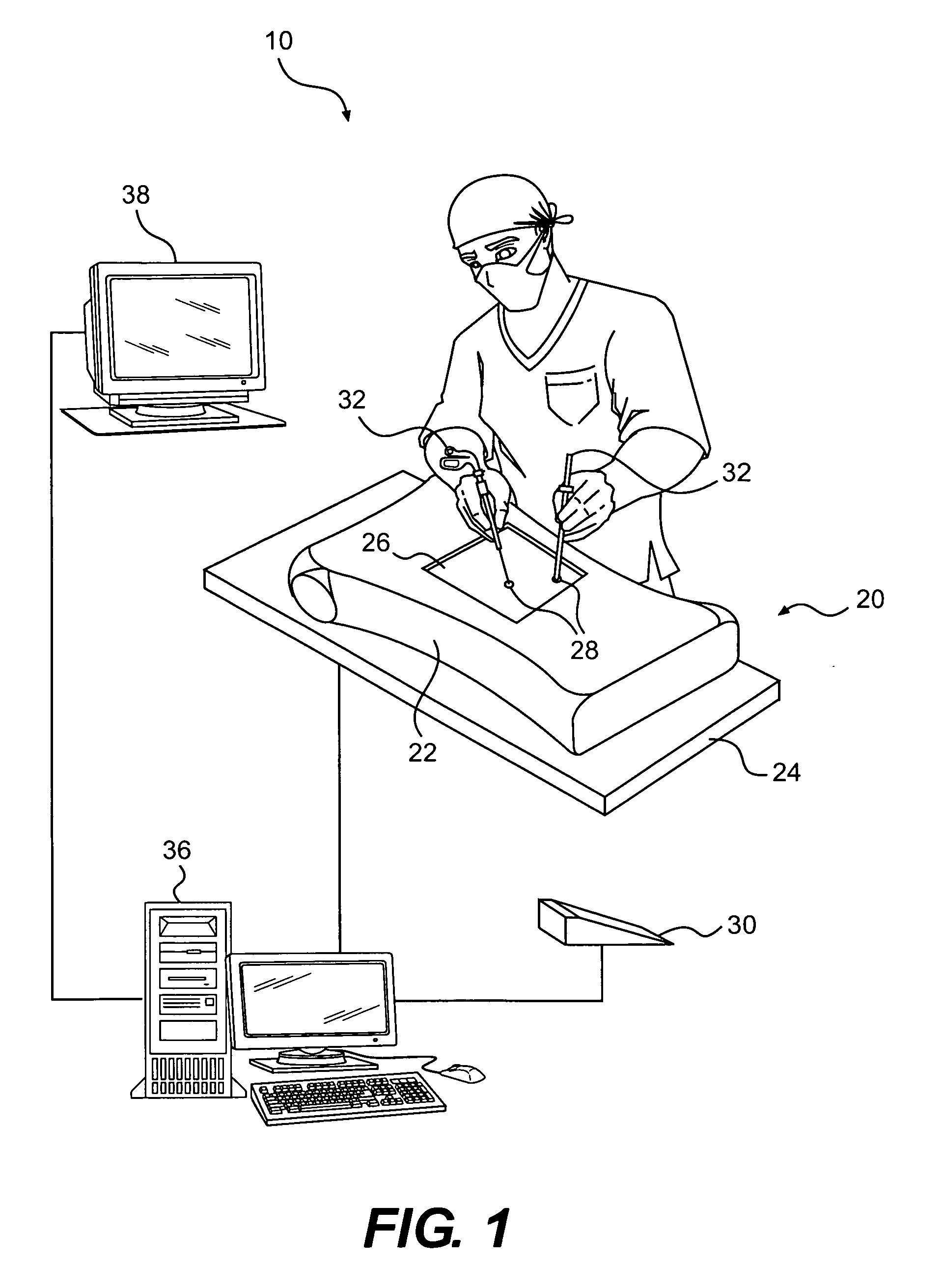
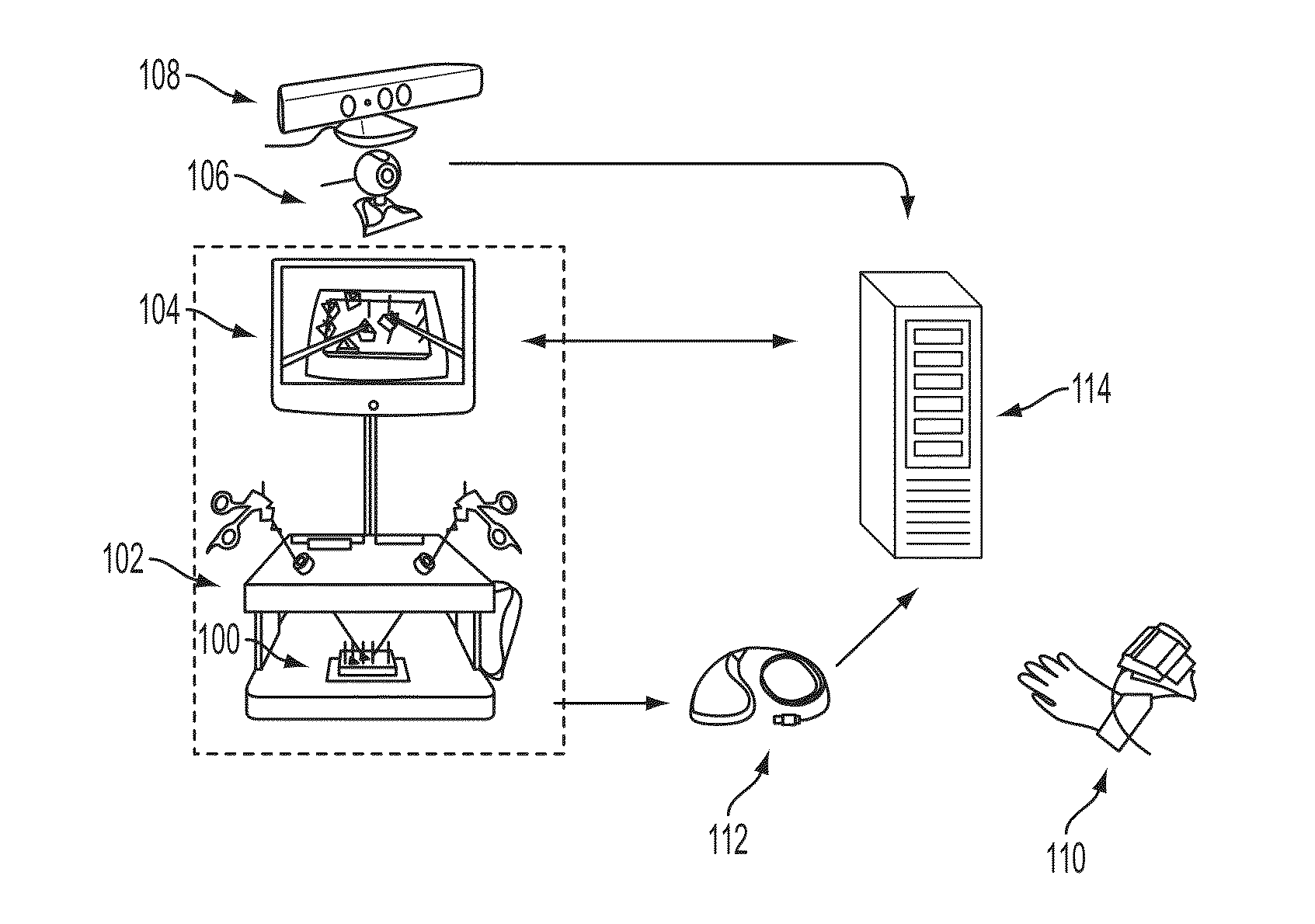
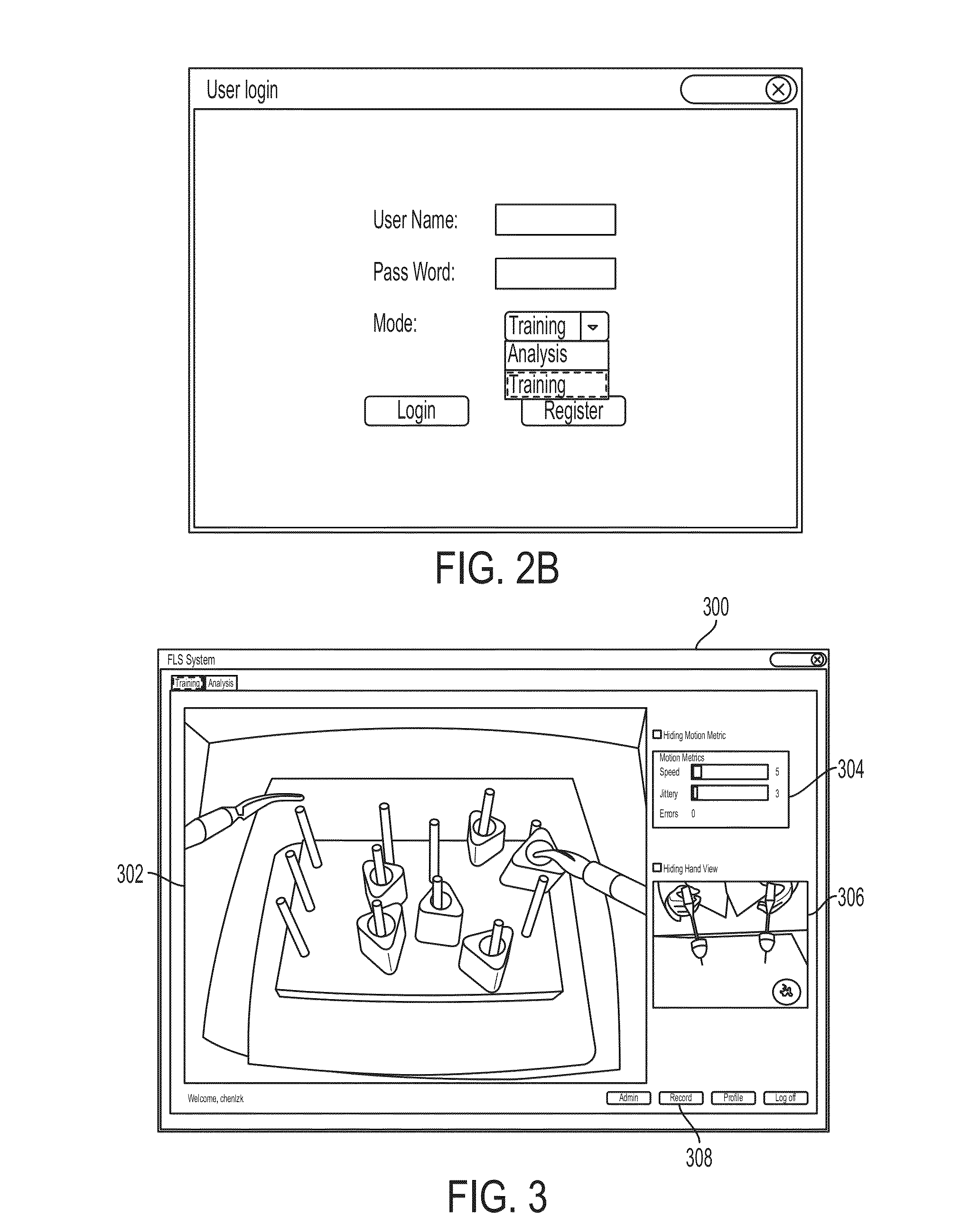
Video-Based System for Improving Surgical Training by Providing Corrective Feedback on a Trainee's Movement
An intelligent system that supports real-time and offline feedback based on automated analysis of a trainee's performance using data streams captured in the training process is disclosed.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Surgical training device and method
Owner:KOH CHARLES H
Surgical training aids and methods of fabrication thereof
The present invention provides surgical training aids formed from hydrogels and adapted to exhibit realistic mechanical properties mimicking those of real organs. Surgical training aids are preferably fabricated by subjecting a concentration of polyvinyl alcohol to freeze-thaw cycles in a mold designed to approximate the shape of an organ, and process parameters are selected to tailor the mechanical properties of the formed hydrogel to those of the organ simulated by the surgical aid. The mechanical properties of the hydrogel forming the surgical training aid may be tailored by incorporating bacterial cellulose and by applying strain during hydrogel formation, thereby producing controlled anisotropy.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
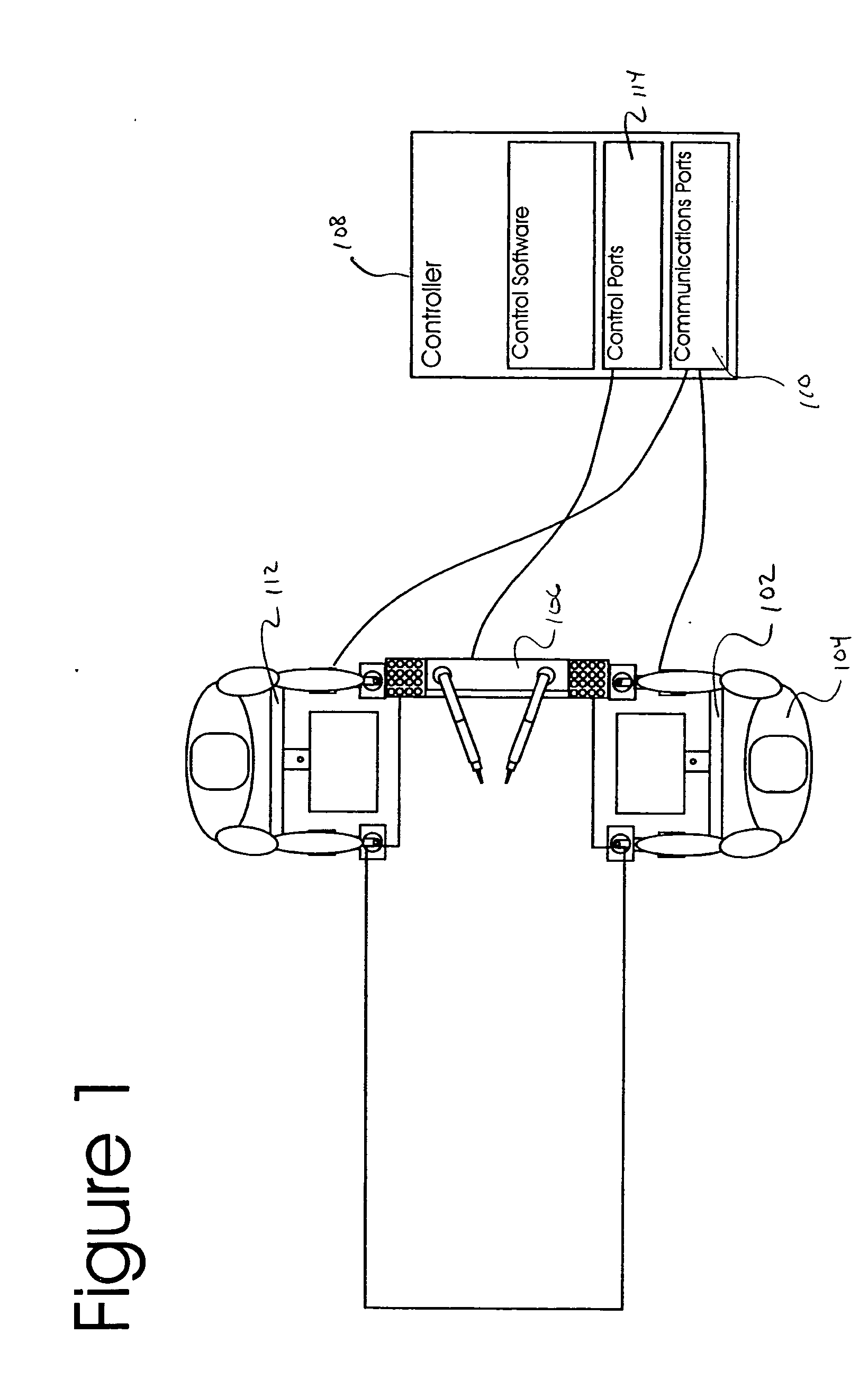
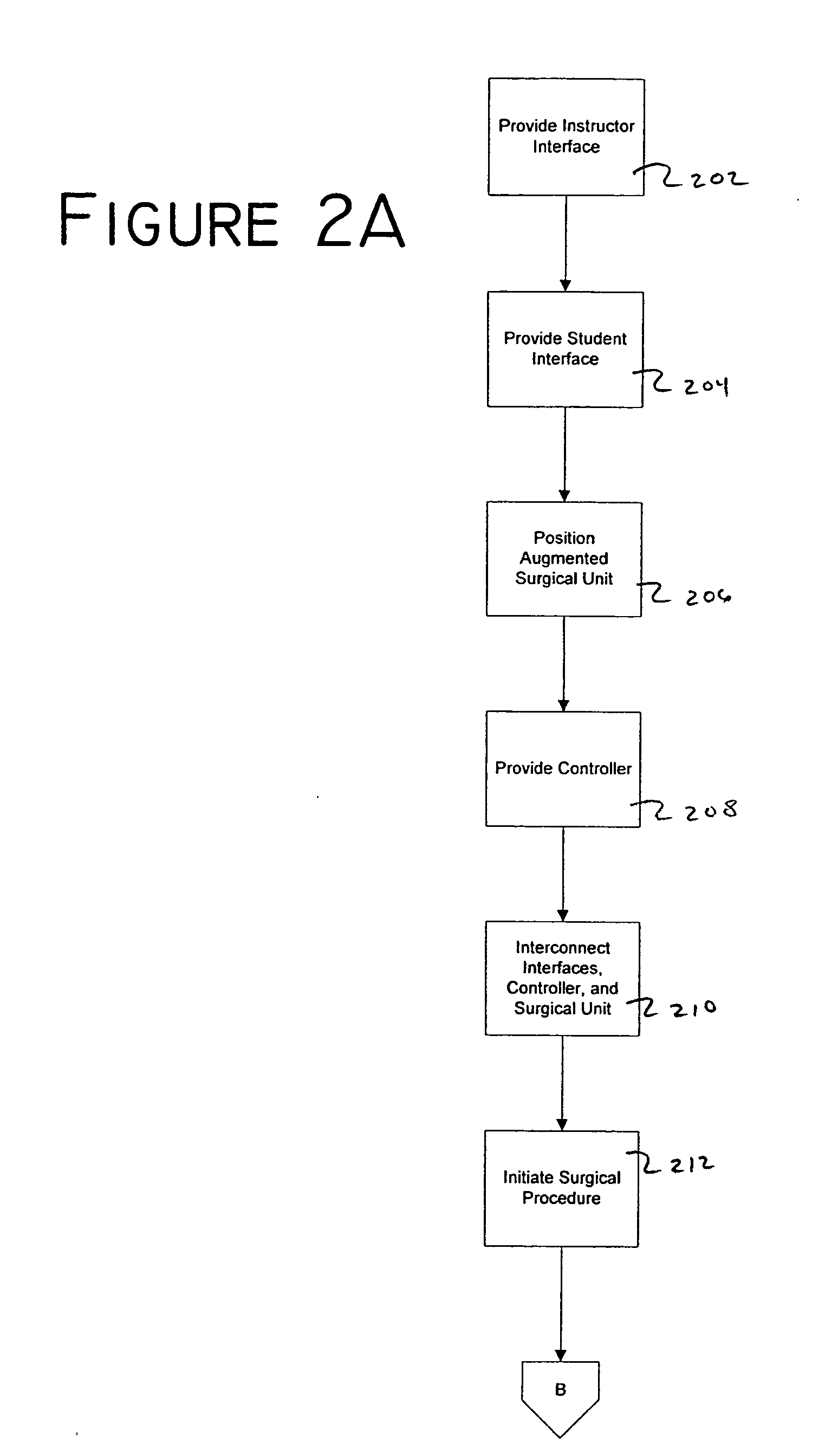
Augmented surgical interface
The present invention is a system comprising surgical units and operator interface units configured to provide multiple capabilities within a surgical environment, or within a surgical training environment. The system may provide such capabilities in a modular fashion, such that various functions may be accomplished through the addition or deletion of modules to the system to allow core components to be used to accomplish more than one function.
Owner:LIPOW KENNETH I
Surgical training aids and methods of fabrication thereof
The present invention provides surgical training aids formed from hydrogels and adapted to exhibit realistic mechanical properties mimicking those of real organs. Surgical training aids are preferably fabricated by subjecting a concentration of polyvinyl alcohol to freeze-thaw cycles in a mold designed to approximate the shape of an organ, and process parameters are selected to tailor the mechanical properties of the formed hydrogel to those of the organ simulated by the surgical aid. The mechanical properties of the hydrogel forming the surgical training aid may be tailored by incorporating bacterial cellulose and by applying strain during hydrogel formation, thereby producing controlled anisotropy.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Laparoscopic trainer and method of training
Owner:WANG SHYH JEN +1
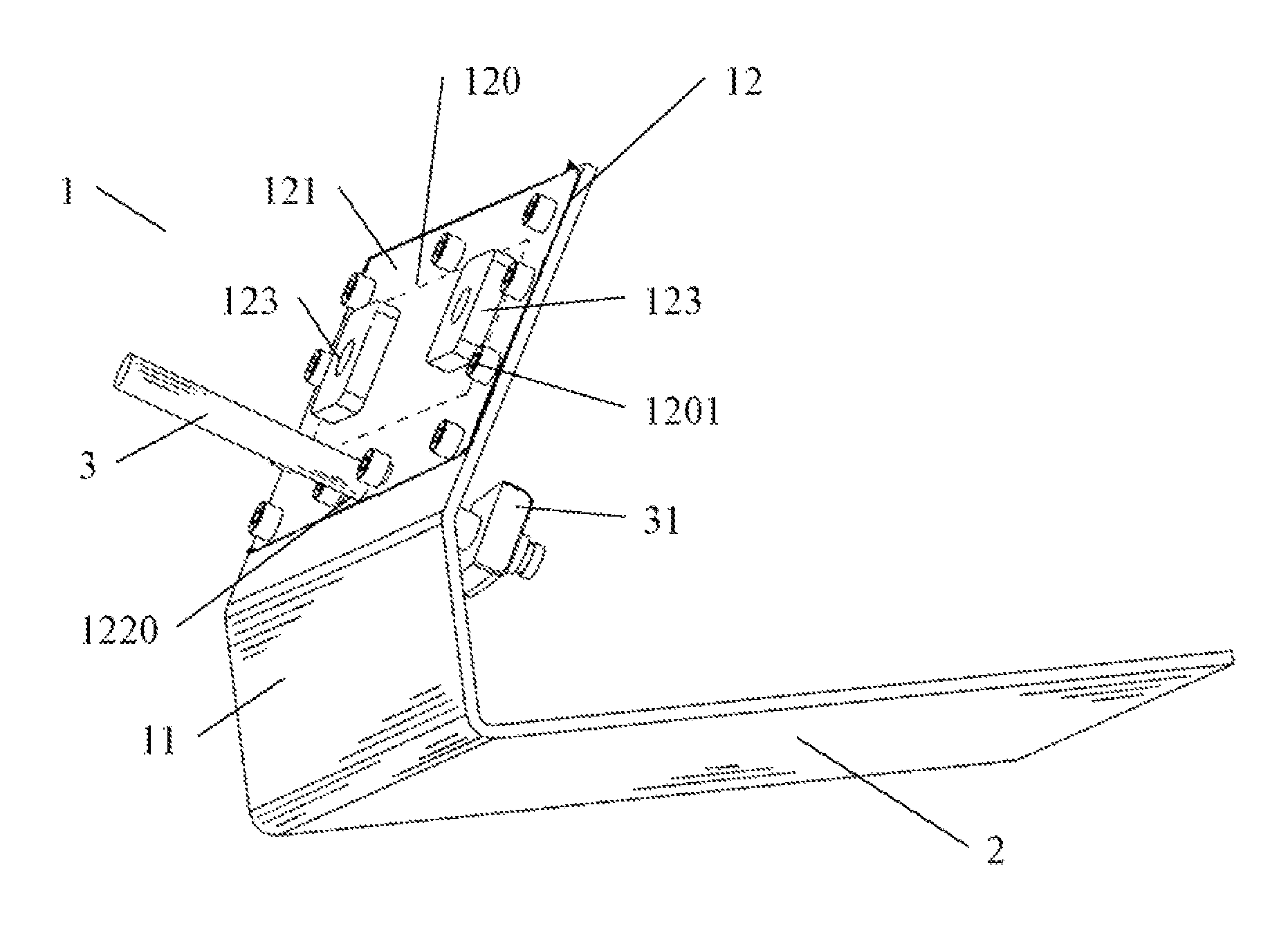
Navigation surgical training model, apparatus having the same and method thereof
InactiveUS8021162B2Reduce X-ray exposureEffective and inexpensive and extensive trainingUsing mechanical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical operationFluoroscopic image
Disclosed is a navigation-training model comprises a base, a holding device for securing a surgical practice model bone to the base in a predetermined position, and a support for fixing a patient tracker onto the base at a predetermined orientation. With the fixed relative positions of the support and the holding device, constant orientation of the patient tracker and the surgical practice model bone is achieved each time they are placed on the navigation-training model. A navigation-training apparatus having the navigation-training model is also disclosed, which includes a navigation system and a surgical tool with a tool tracker. Fluoroscopic images of the surgical practice model bone are captured once and uploaded into a computer of the navigation system. The practice of the fluoroscopic images-guided orthopedic surgery can thus be carried out with the fluoroscopic images loaded onto the navigation system without the need for further fluoroscopy. This eliminates X-ray exposure and standardizes the procedures of navigation-training.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
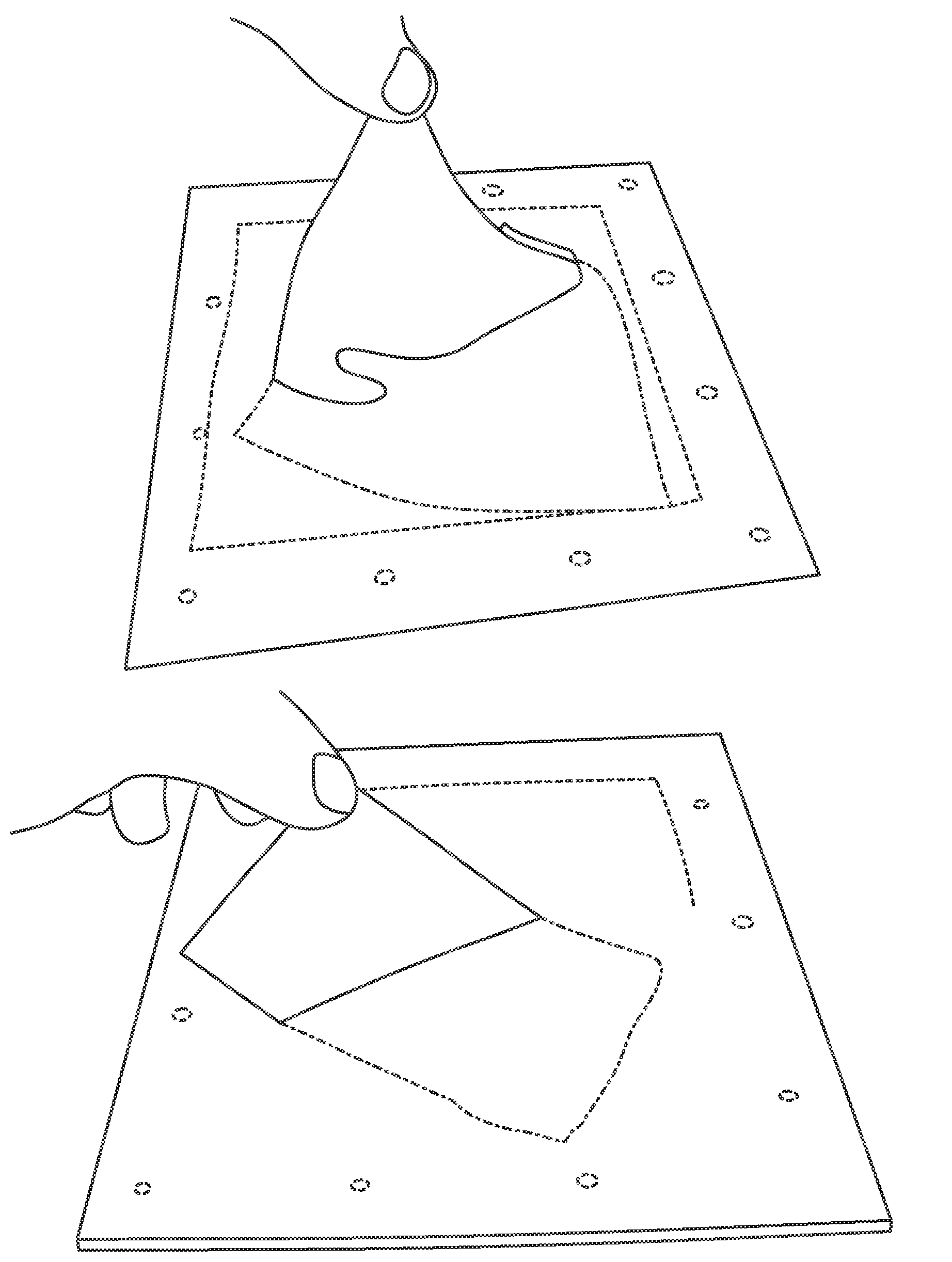
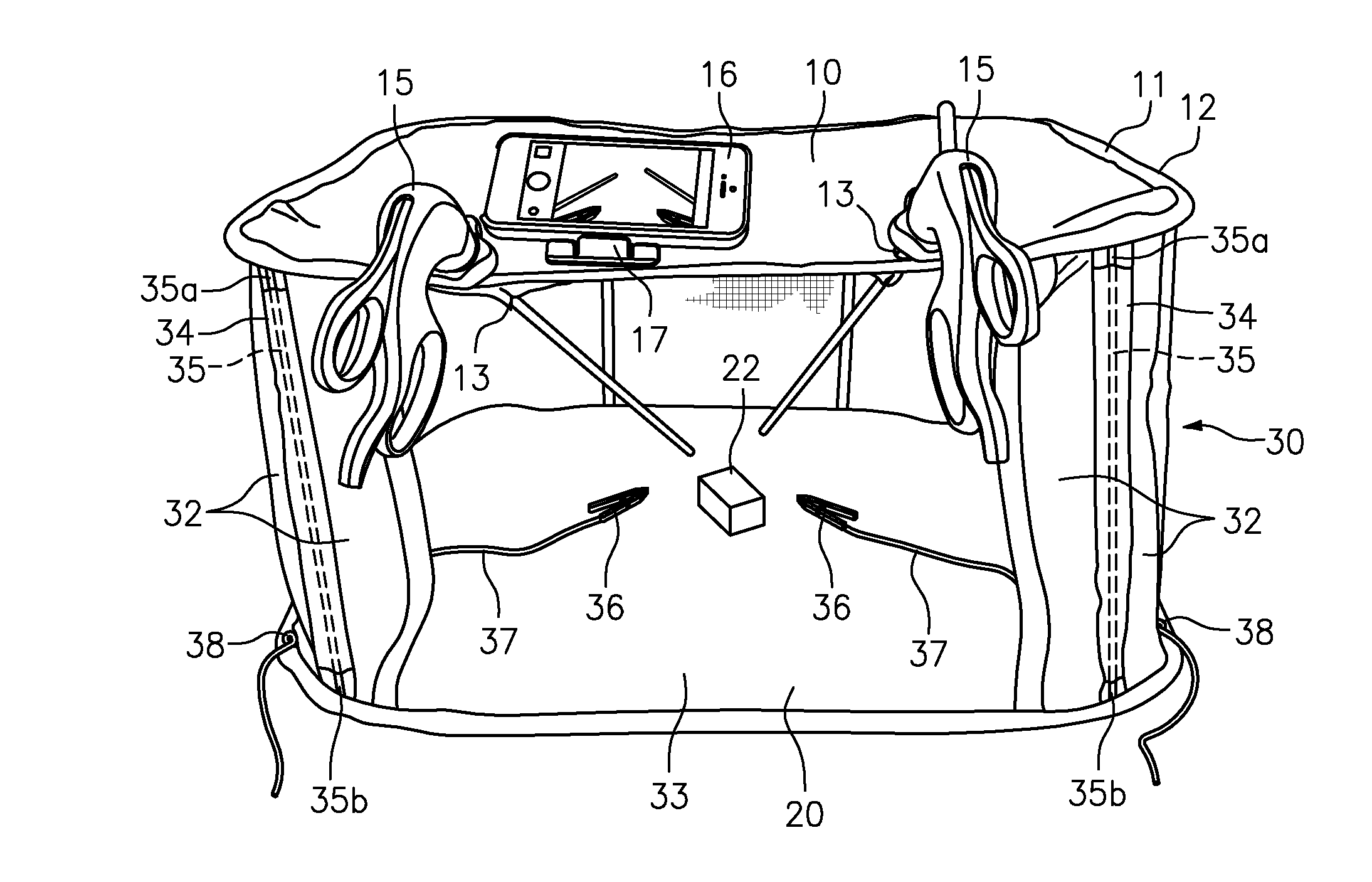
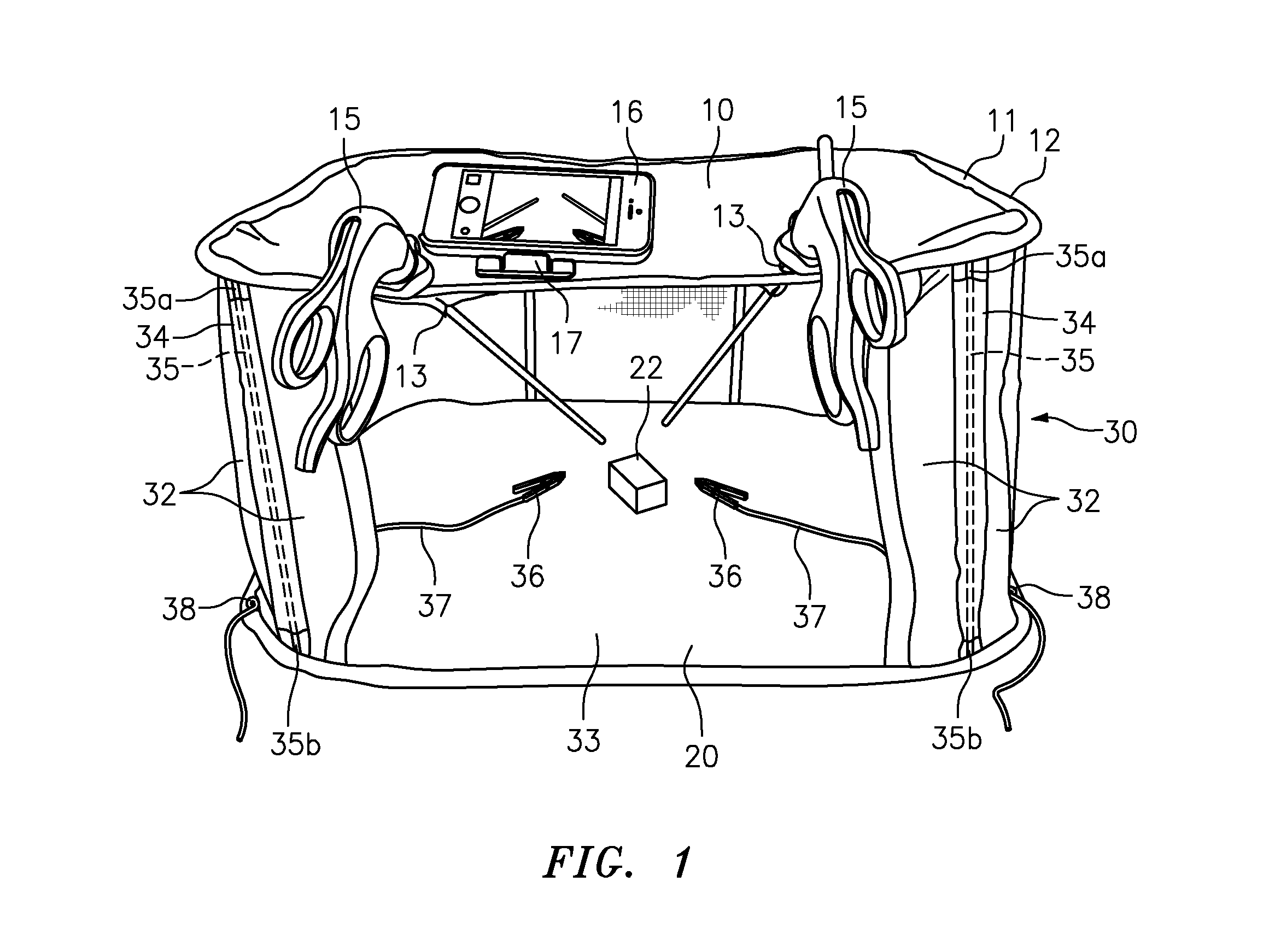
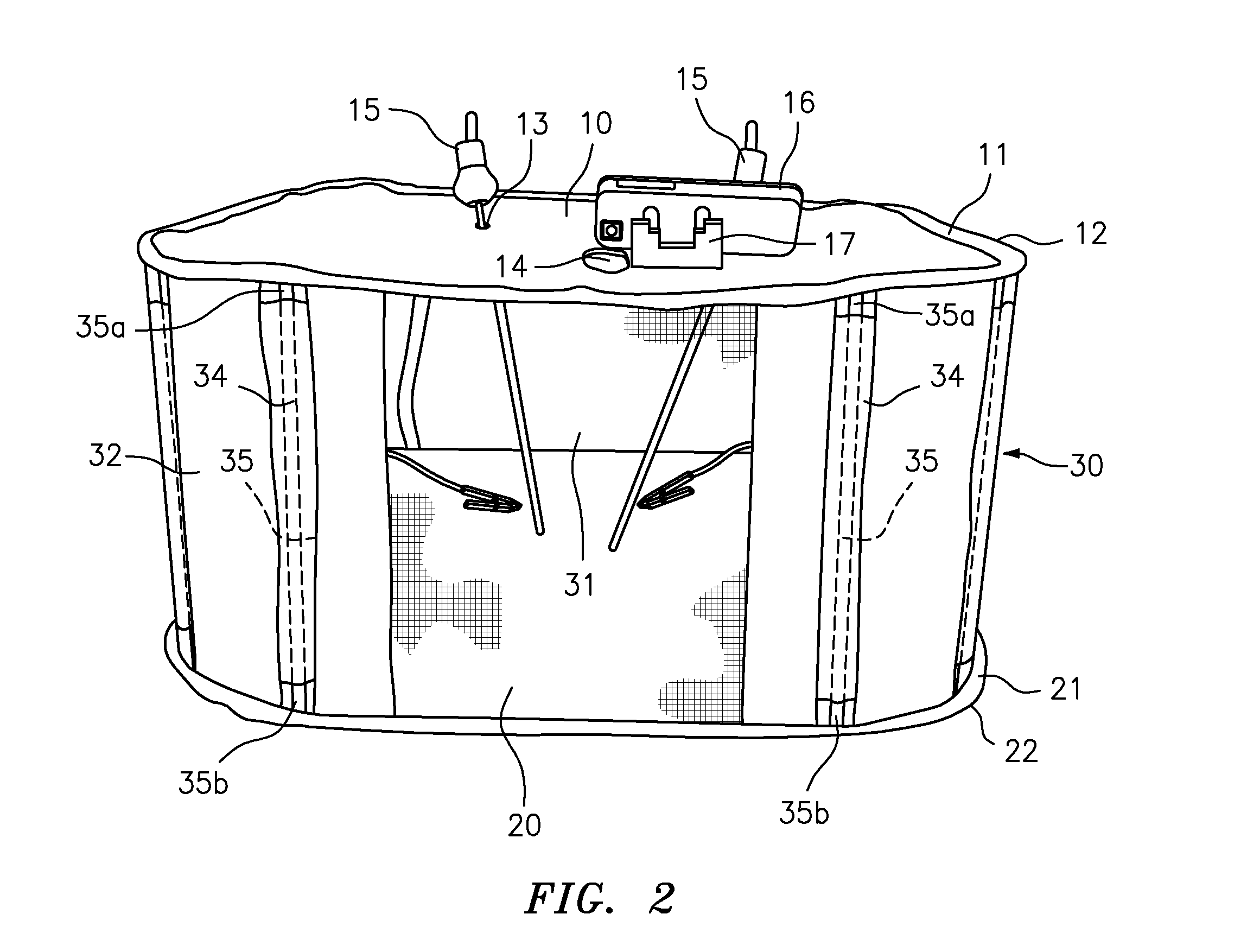
Collapsible Surgical Training Apparatus and Method for Laparoscopic Procedures
A laparoscopic surgery training kit and method is disclosed. The laparoscopic surgery training kit has improved portability and storability because it is collapsible and foldable. The laparoscopic surgery training kit is assembled by unfolding it into a taut condition and inserting a plurality of rods into a plurality of sleeves on a side panel arrangement to place the laparoscopic surgery training kit into its expanded condition. Holes or slits are provided, which are configured to allow insertion of surgical instruments, such as graspers, and / or configured to allow a camera to view the interior of the laparoscopic surgery training kit. In a preferred embodiment, the camera of a smartphone or tablet device is used, which is placed on the laparoscopic surgery training kit using a stand. The image viewed by the camera is shown to the trainee or examinee as a real-time display, preferably at eye-level. The trainee or examinee uses the one or more surgical instruments to manipulate one or more objects contained within the laparoscopic surgery training kit while viewing the real-time display.
Owner:JABBOUR IBRAHIM IHSAN +1
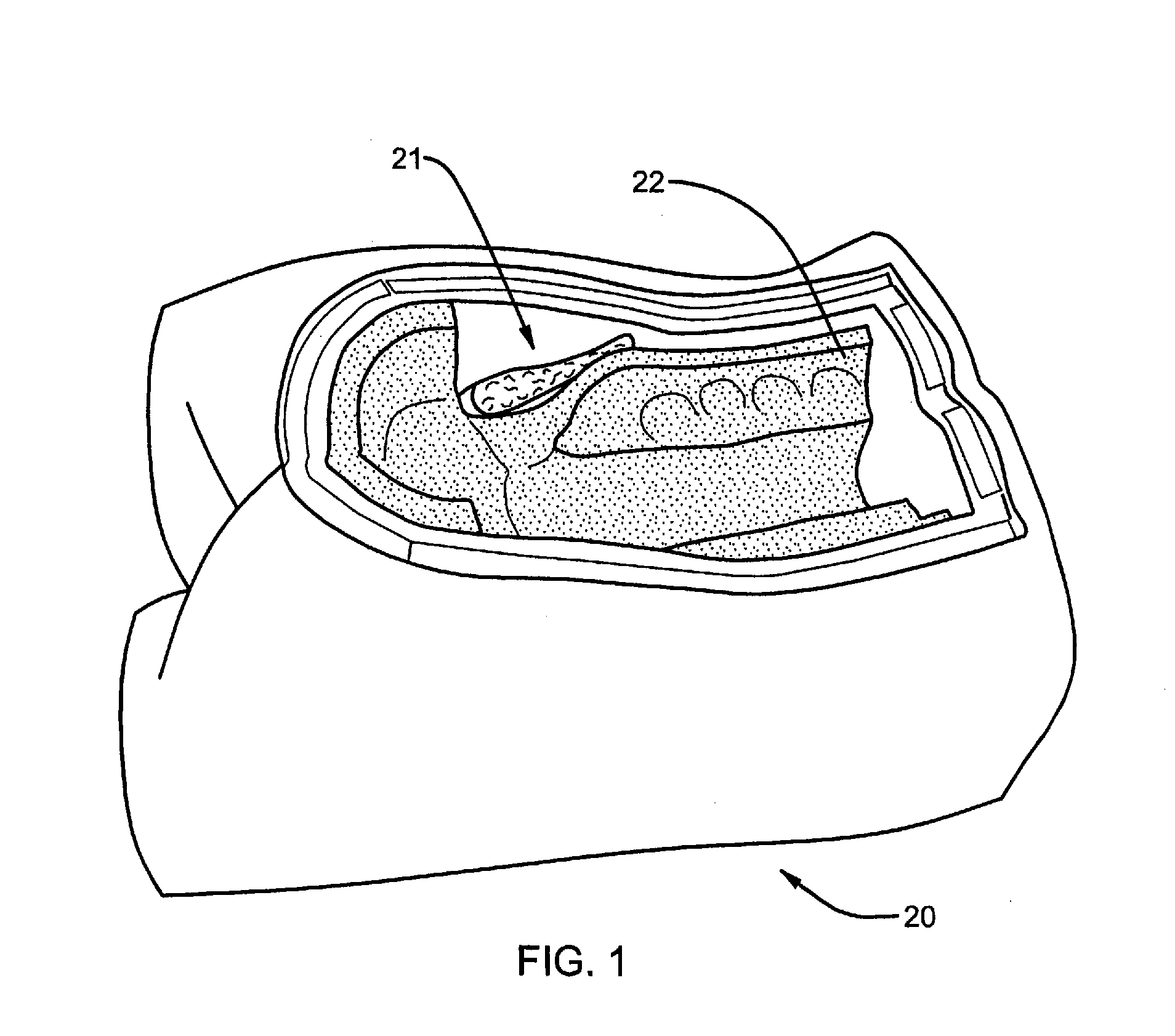
Surgical training model and method for use in facilitating training of a surgical procedure
InactiveUS20080138781A1Reduce use costIncrease flexibilityEducational modelsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityDisease
A surgical training model for use in facilitating training a user of a surgical procedure. The model includes a holder member with a receptacle and an insert member configured for placement within the receptacle of the holder member. The insert member is modular relative to the holder member, thereby allowing a user of the model to dispose of the insert member following the performance of a surgical procedure. The insert member includes a portion of a human vertebral column, with the human vertebral column having an artificial bone portion and artificial soft tissue portion. The artificial bone portion and the artificial soft tissue portion are positioned proximate relative to each other to substantially mimic resistance of human vertebral bone and surrounding soft tissue. The insert member also includes a pathology structure that replicates certain disease or structural modalities. A method for manufacturing a surgical training model is also disclosed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Simulated stapling and energy based ligation for surgical training
An inexpensive and practical surgical training system to train practitioners in the use of surgical stapling and energy-based ligation instruments and procedures is provided. The system comprises a modified or simulated surgical instrument such as linear surgical stapling device having a fixed anvil and an opposed, movable jaw sized and configured to be closed upon a simulated tissue structure. A marking or inking element is associated with the jaw and anvil of the stapling device and configured to impose a visible pattern on the surfaces of simulated tissue placed between the anvil and jaw. A pressure sensitive adhesive or other adhesive is associated with the inner surfaces of the simulated tissue that is activated upon compression between the anvil and jaw to simulate surgical occlusion.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
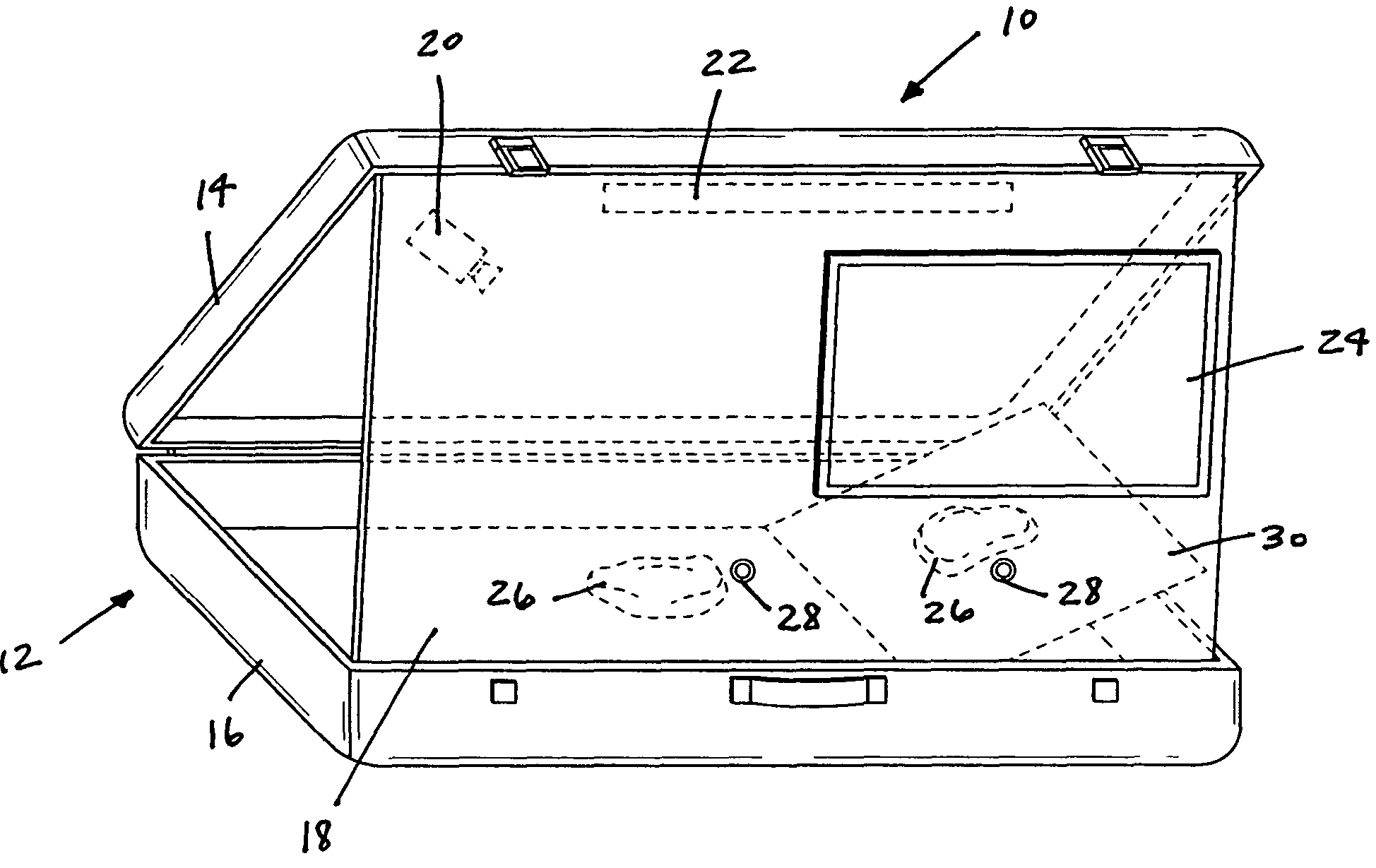
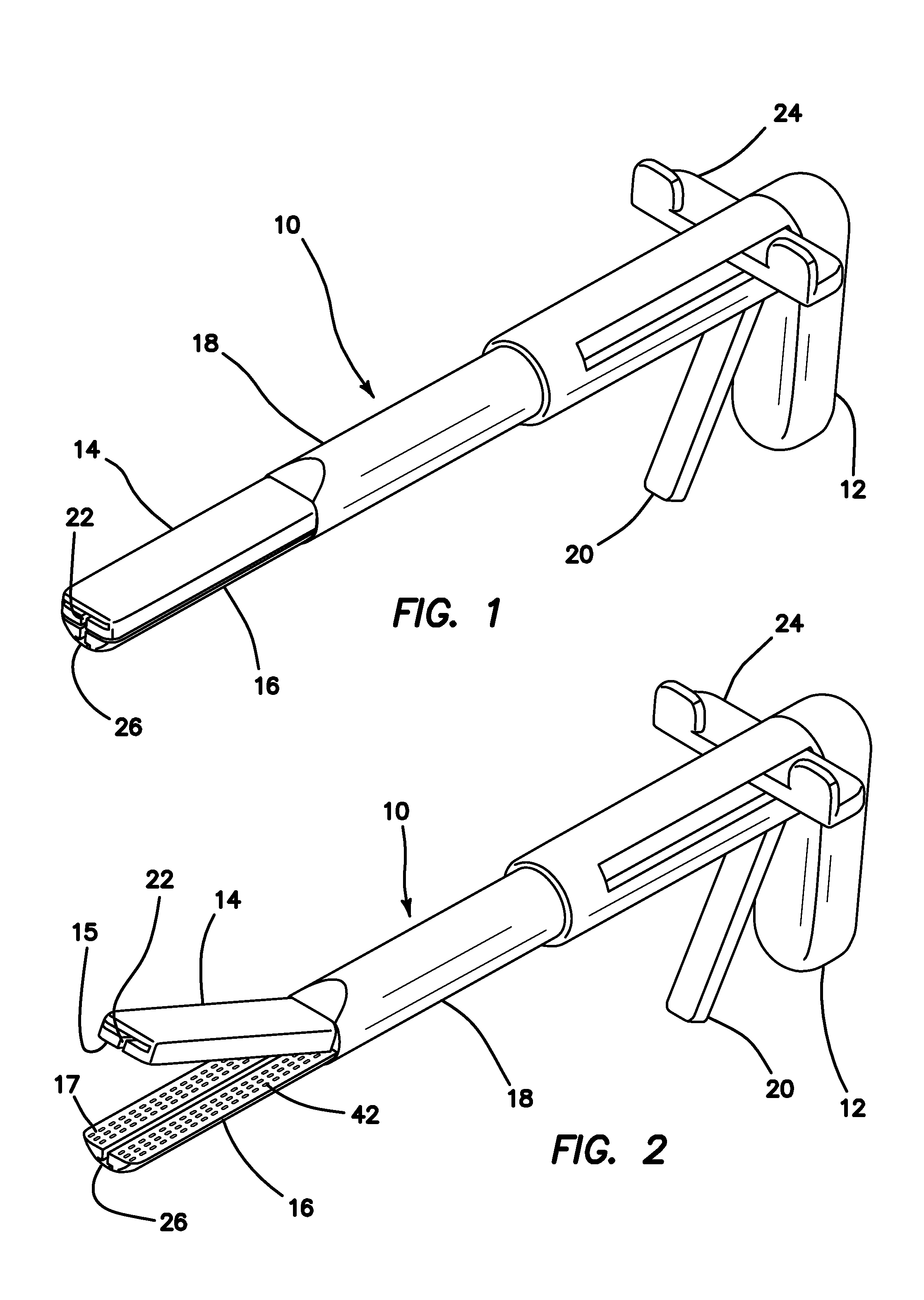
Surgical training device and method
A surgical training device and method. The surgical training device can include a portable case including a base and a lid. The surgical training device can include a support coupled to the base, and the support can be moveable from a first position stored within the base to a second position coupled to the lid. The support can include a plurality of ports positioned so that when the support is in the second position, the surgical instruments inserted into the plurality of ports are substantially horizontal and parallel to the base. The surgical training device can include a camera and a video monitor connected to the camera. The video monitor can display an output from the camera including the surgical instruments and / or simulated tissue.
Owner:KOH CHARLES H
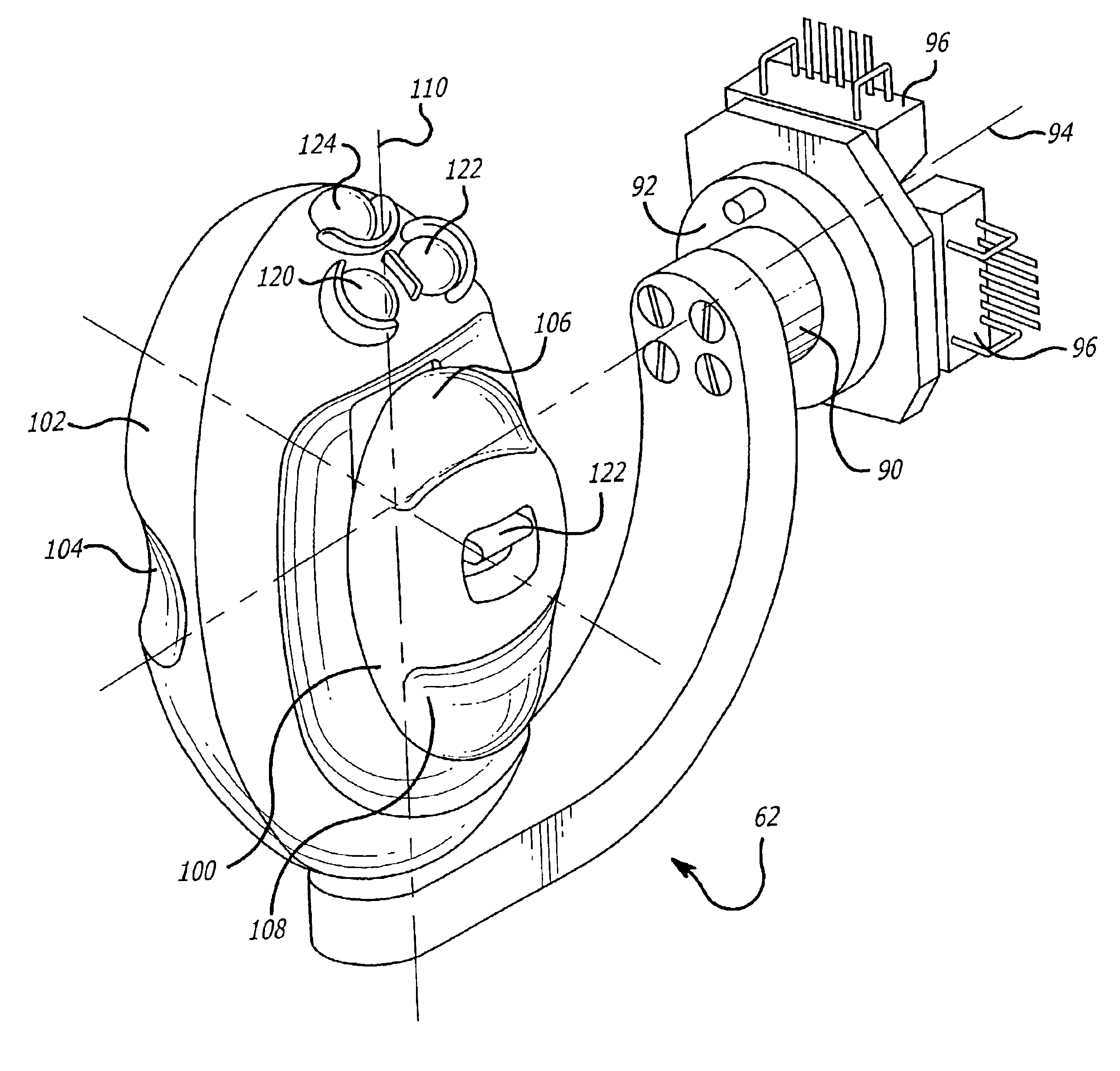
Minimally invasive surgical training using robotics and telecollaboration
InactiveUS20090099576A1Cosmonautic condition simulationsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLess invasive surgeryRobotics
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Multi-metric surgery simulator and methods
ActiveUS20180116724A1Improve performanceComputer-aided planning/modellingEducational modelsSurgery simulatorNavigation system
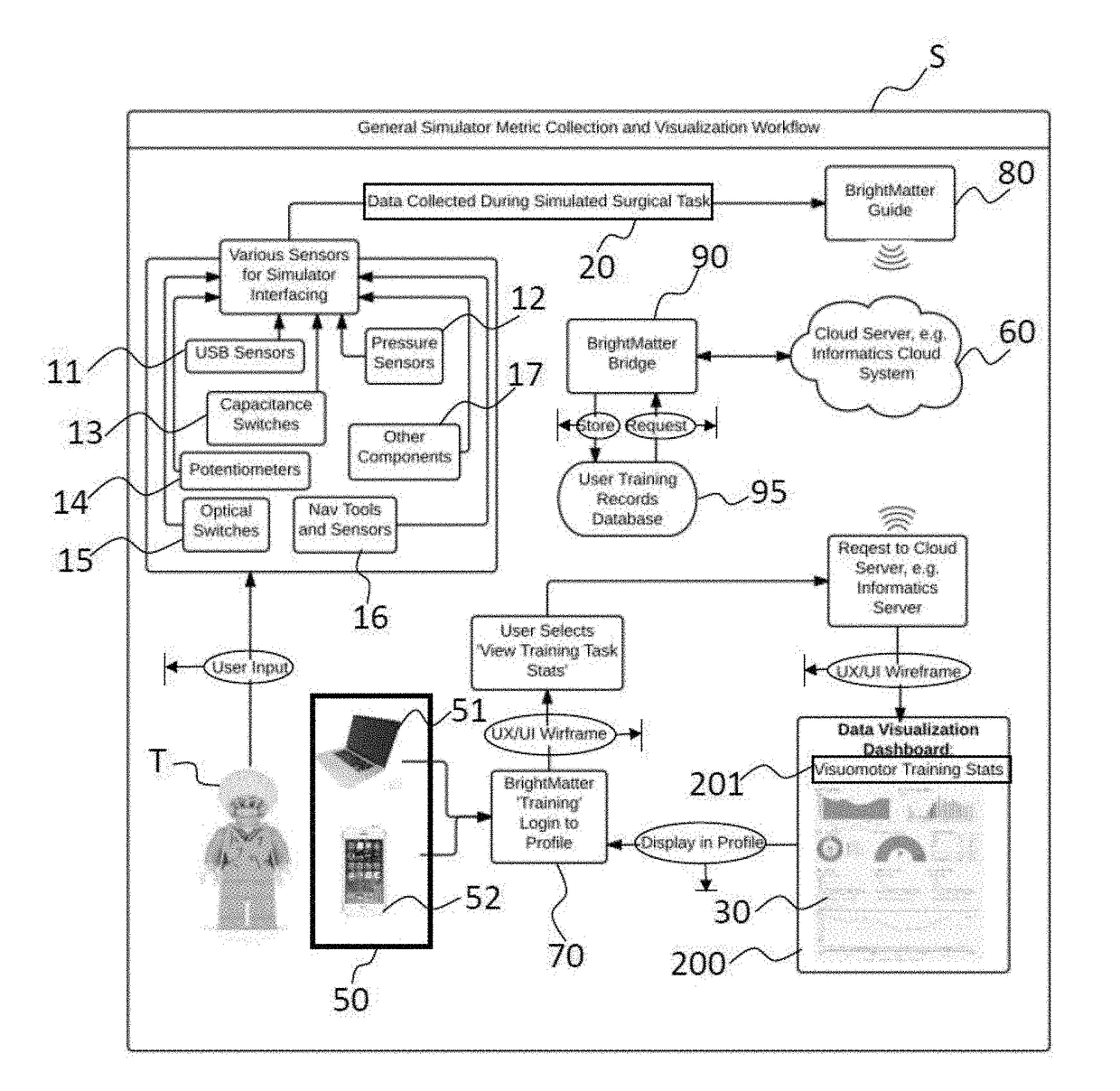
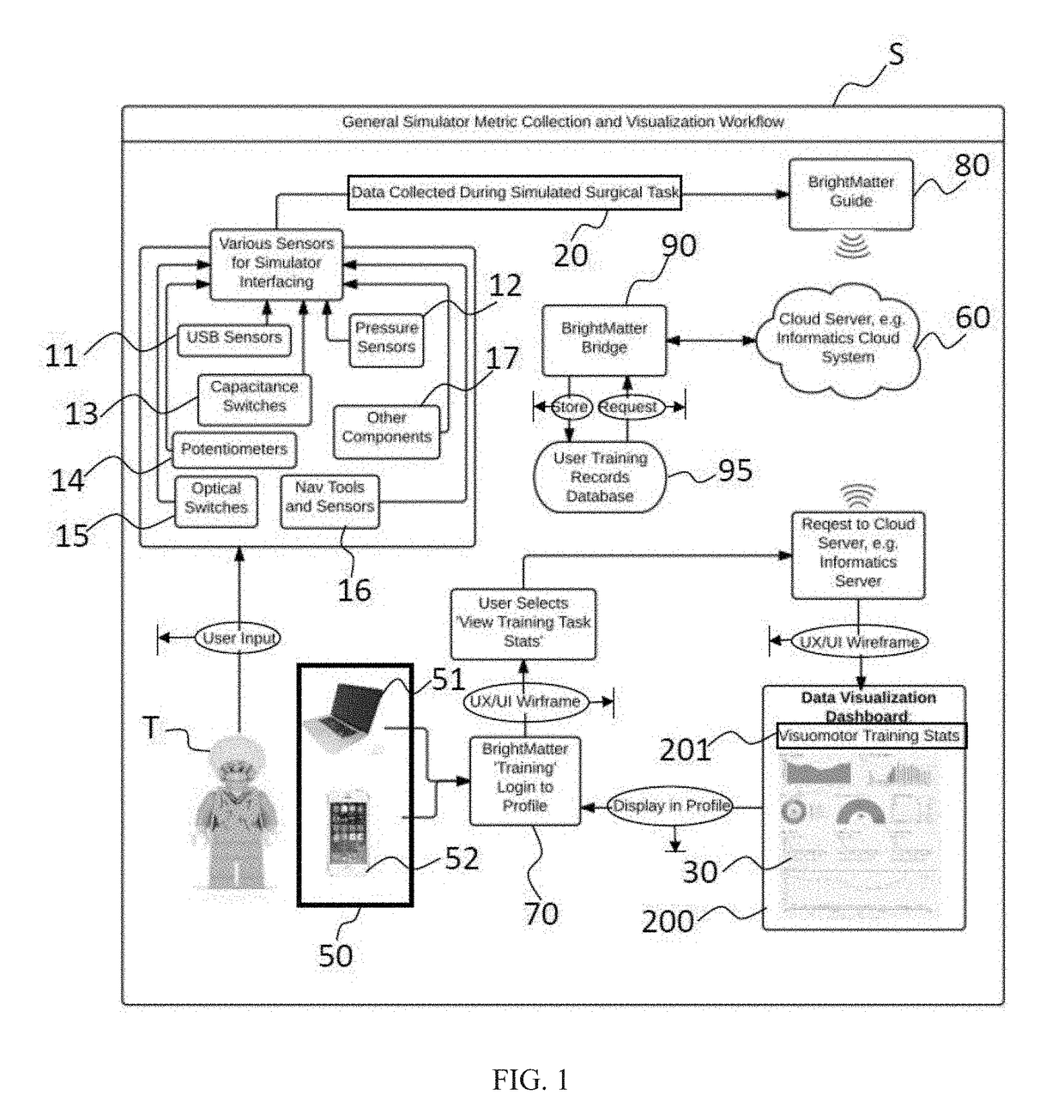
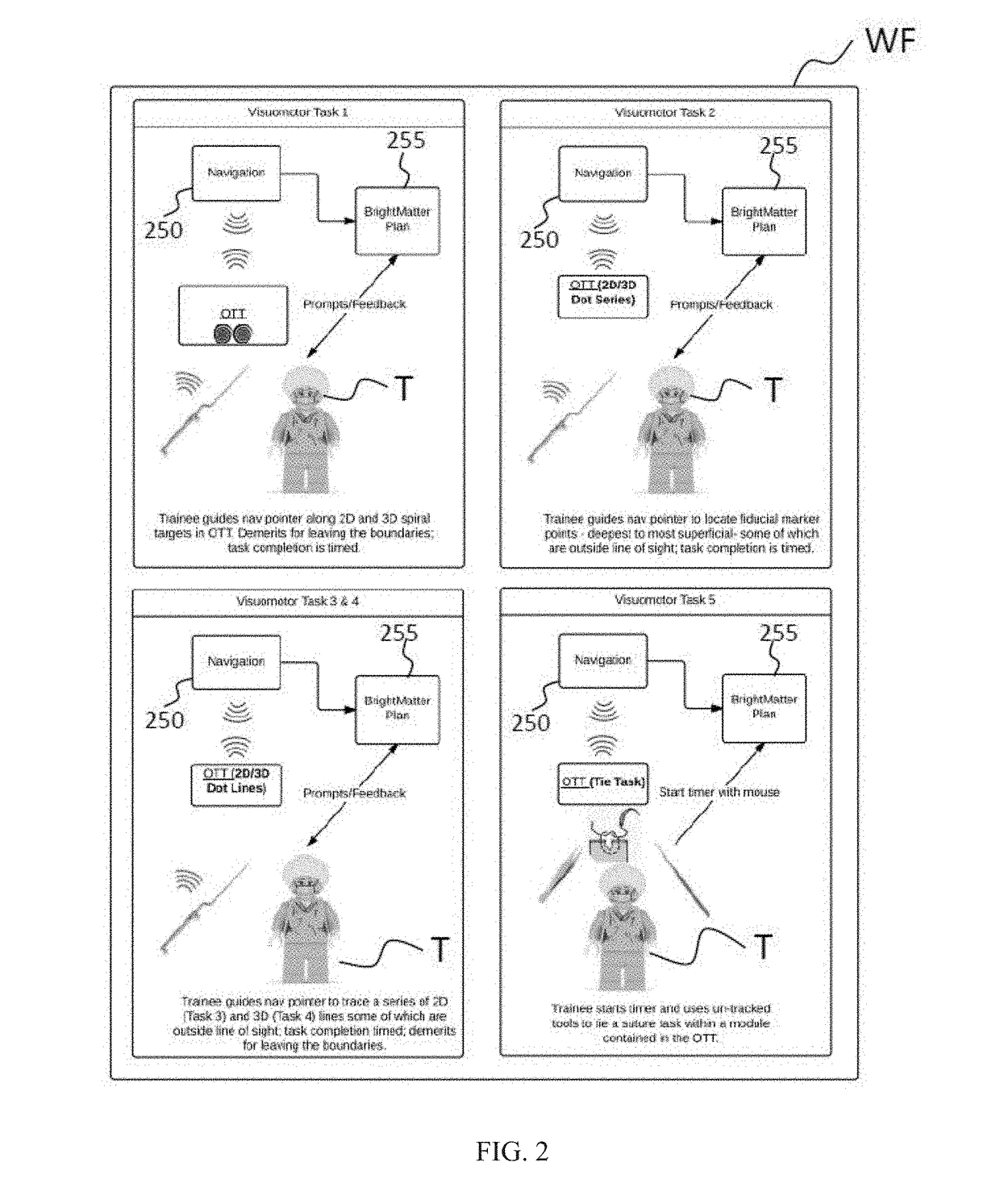
Multi-metric surgery simulator devices, systems, and methods, involving at least one sensor configured to collect surgical training performance data relevant to at least one surgical task, the at least one sensor configured to operate with a surgical navigation system comprising a processor, the processor configurable, by way of a set of executable instructions storable in relation to a non-transitory medium, to perform at least one of analyze collected data, transform the collected data, and provide feedback in relation thereto; and at least one surgery simulator apparatus operatively coupled with the at least one sensor, the at least one surgery simulator apparatus configured to operate with a tracking system, whereby collected data is obtainable and clinical performance in relation to the at least one surgical task is quantitatively evaluable and progressively improvable.
Owner:SYNAPTIVE MEDICAL INC
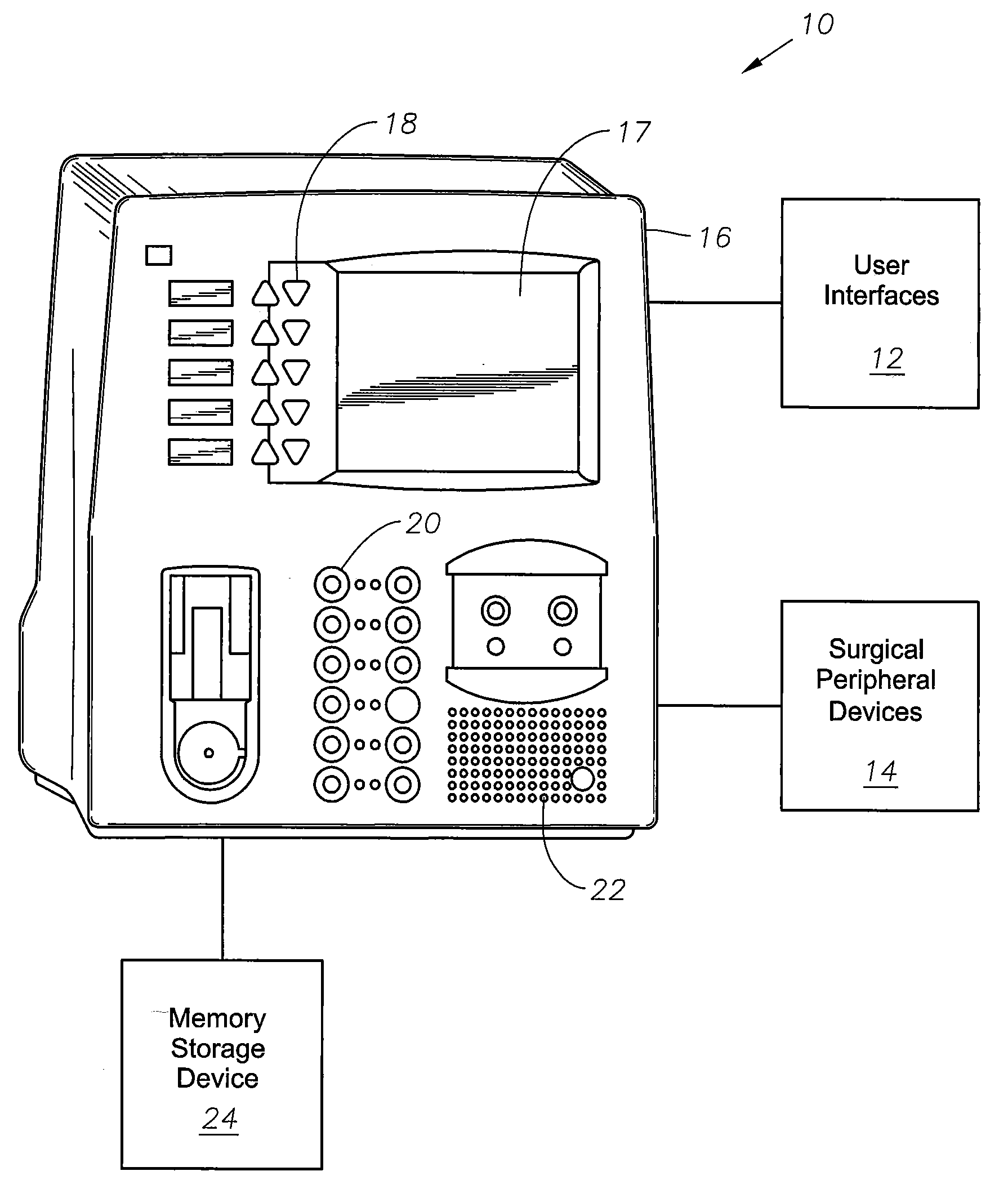
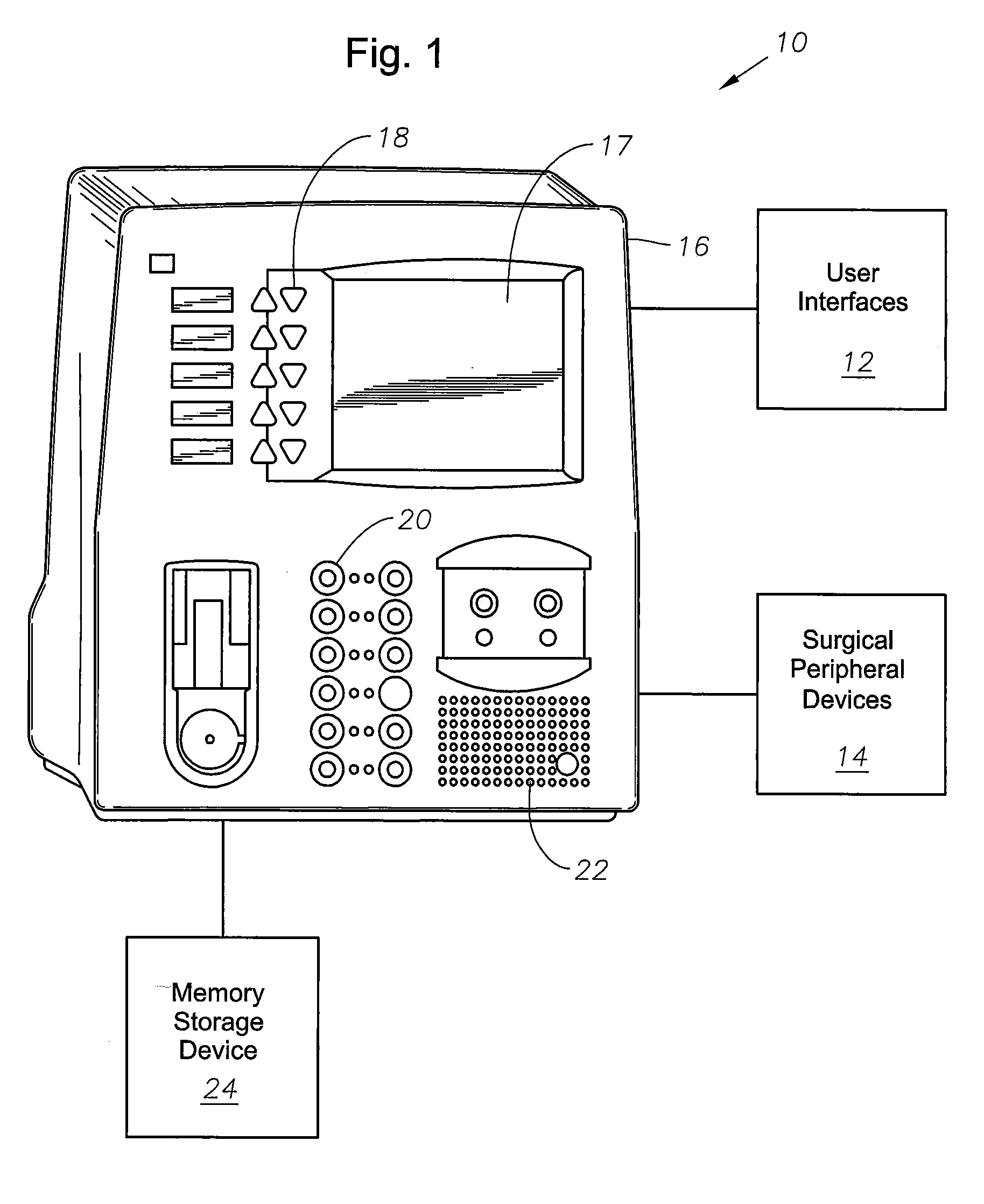
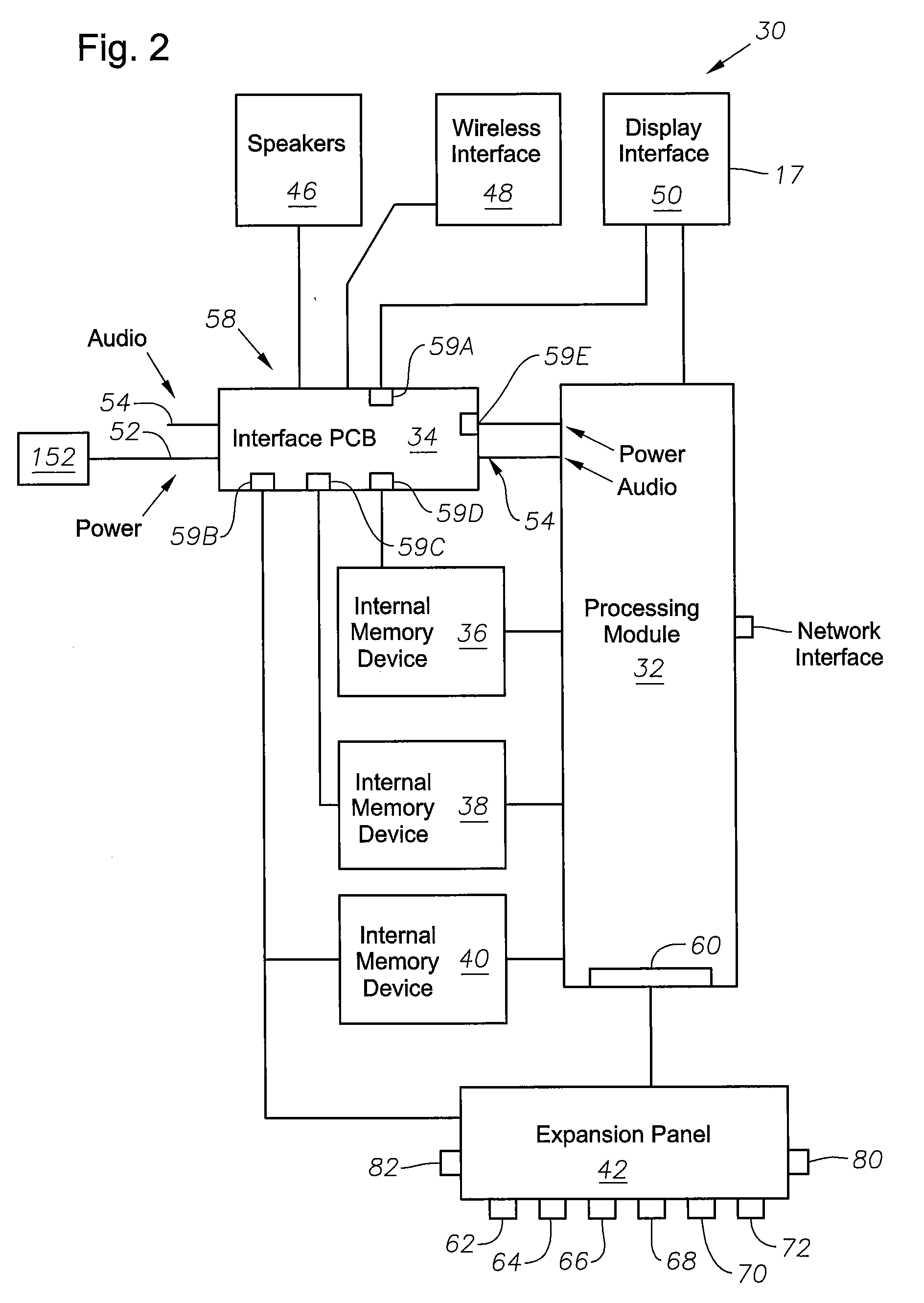
Surgical console operable to simulate surgical procedures
InactiveUS20080085499A1Without riskImprove familiarityEducational modelsSurgical instrumentationSurgical microscope
A surgical console is disclosed for simulating surgical procedures. Simulations can be directly integrated and supported by the surgical console and training surgical instruments. An operator may use actual control hardware to manipulate the surgical instruments that will be manipulated during actual surgical procedures to improve the operator's surgical dexterity. The surgical console can include a processing module, an external interface, simulation module, and a user interface. The processing module directs operation of peripheral devices coupled to the surgical console. The peripheral devices may include control devices, such as, but not limited to footswitches or other like control devices, surgical instruments such as, but not limited to, surgical microscopes, and other surgical training instruments, such as training surgical cutting tools. Additionally, the processing module may monitor the operating parameters and surgical modes associated with the training surgical procedure. The operator may receive feedback from the surgical console on his / her performance of the training surgical procedure.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Model for training of surgical operation of cataract
The present invention relates to a model for surgical operation for an eye with cataract comprising a pig's eye which is prepared by injecting self hardening type chemicals into a crystalline lens capsule or into an empty crystalline lens capsule of said pig's eye, further relates to a model for an enucleating operation of a fallen nucleus lens which is prepared by falling the hardened chemicals into corpus vitreum by breaking posterior capsule of crystalline lens consciously.
Owner:UMEYAMA HIDEKI +1
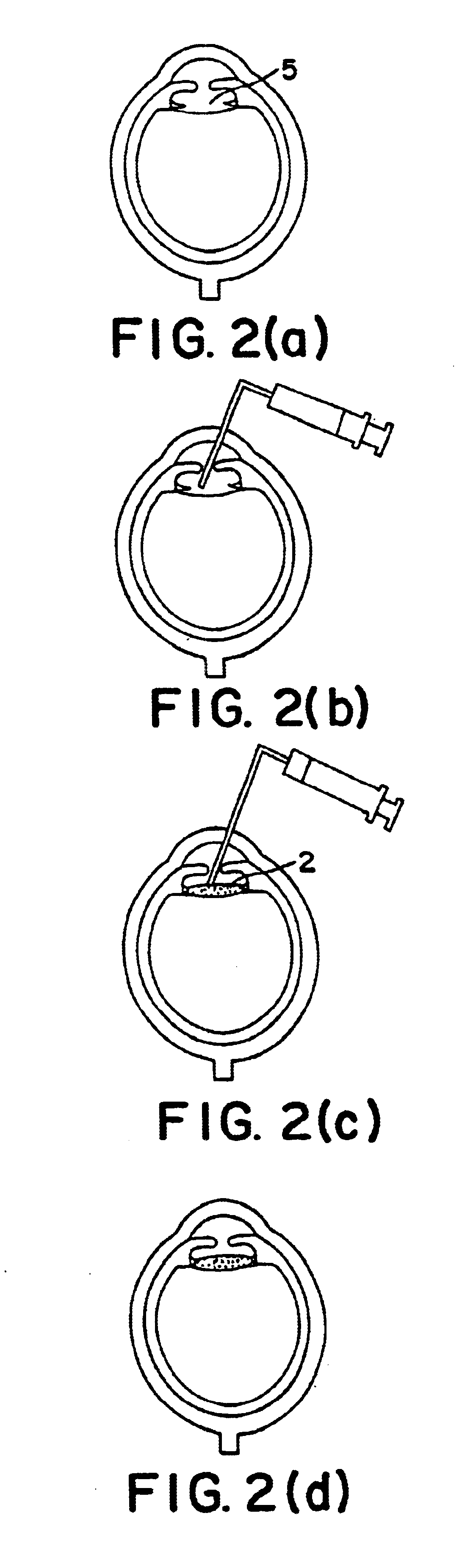
Heart model for training or demonstrating heart valve replacement or repair
The present invention relates to heart models for surgical training and / or demonstration. More particularly, the present invention relates to heart models, which incorporate features to simulate visual and manipulation of heart valves, to be used as training and / or demonstration subjects for heart valve replacement surgery. The simulated valves may be removable inserts, that are replaceable and disposable, attached to a support platform.
Owner:LOTANO VINCENT ERCOLE +1
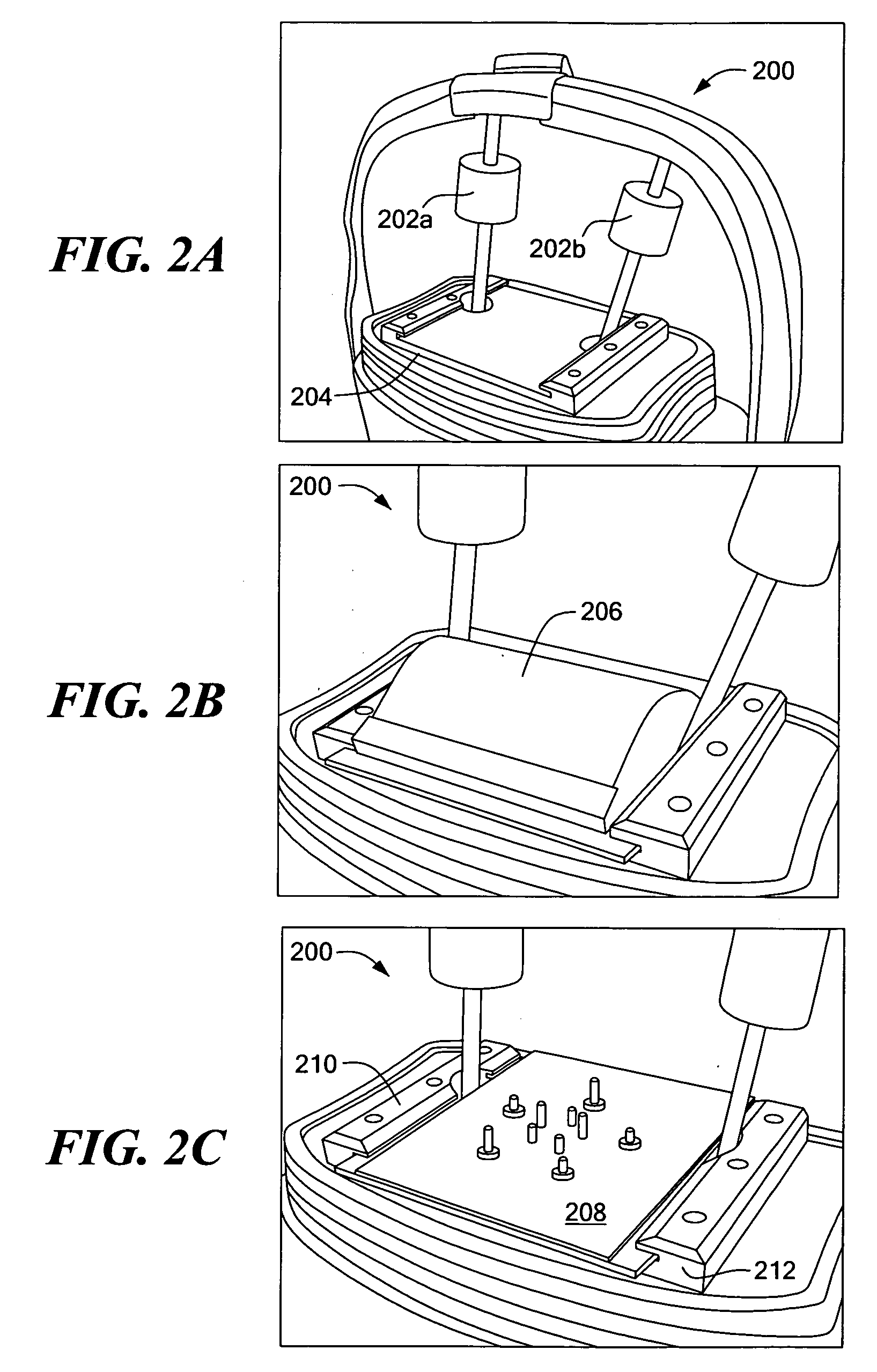
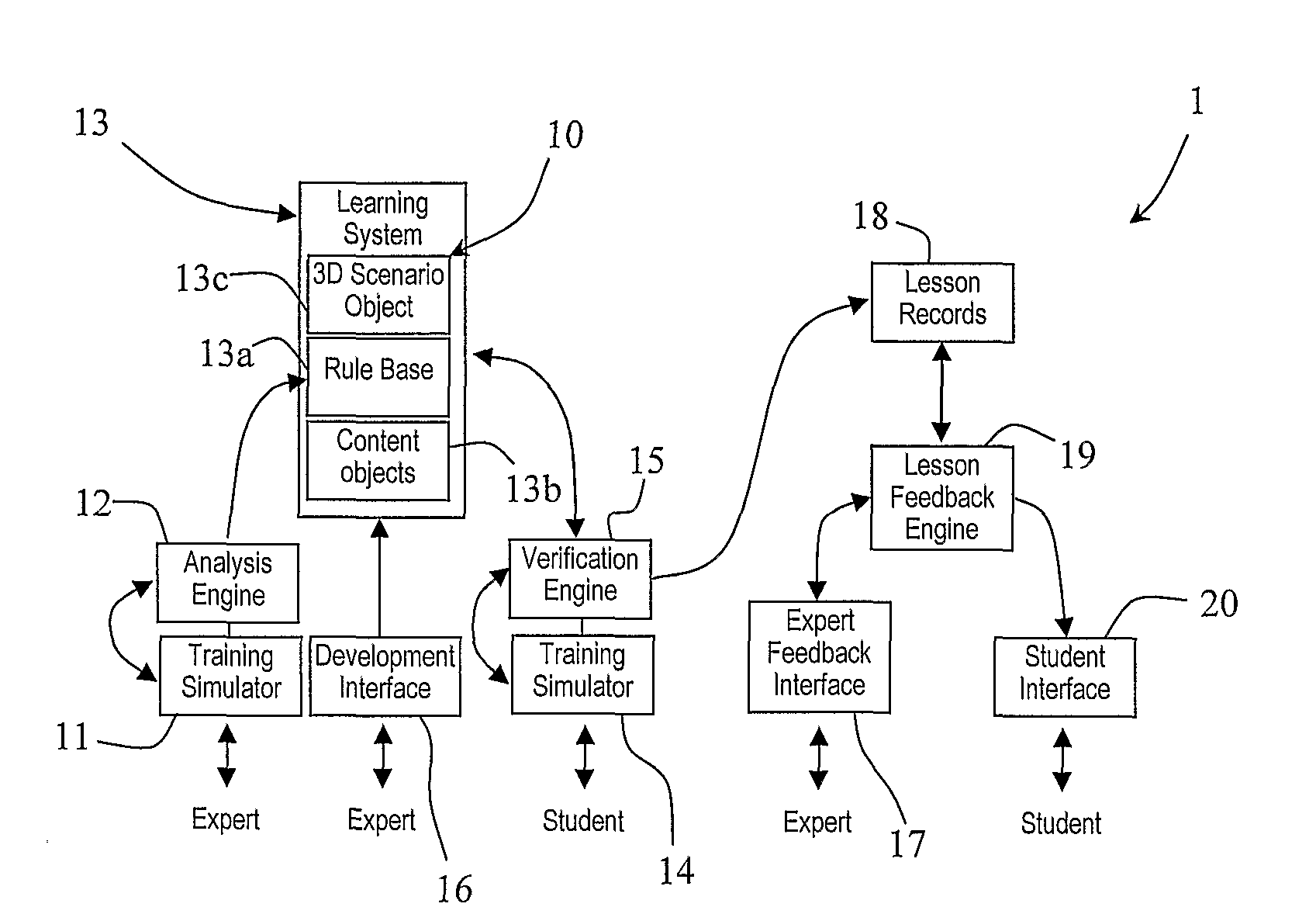
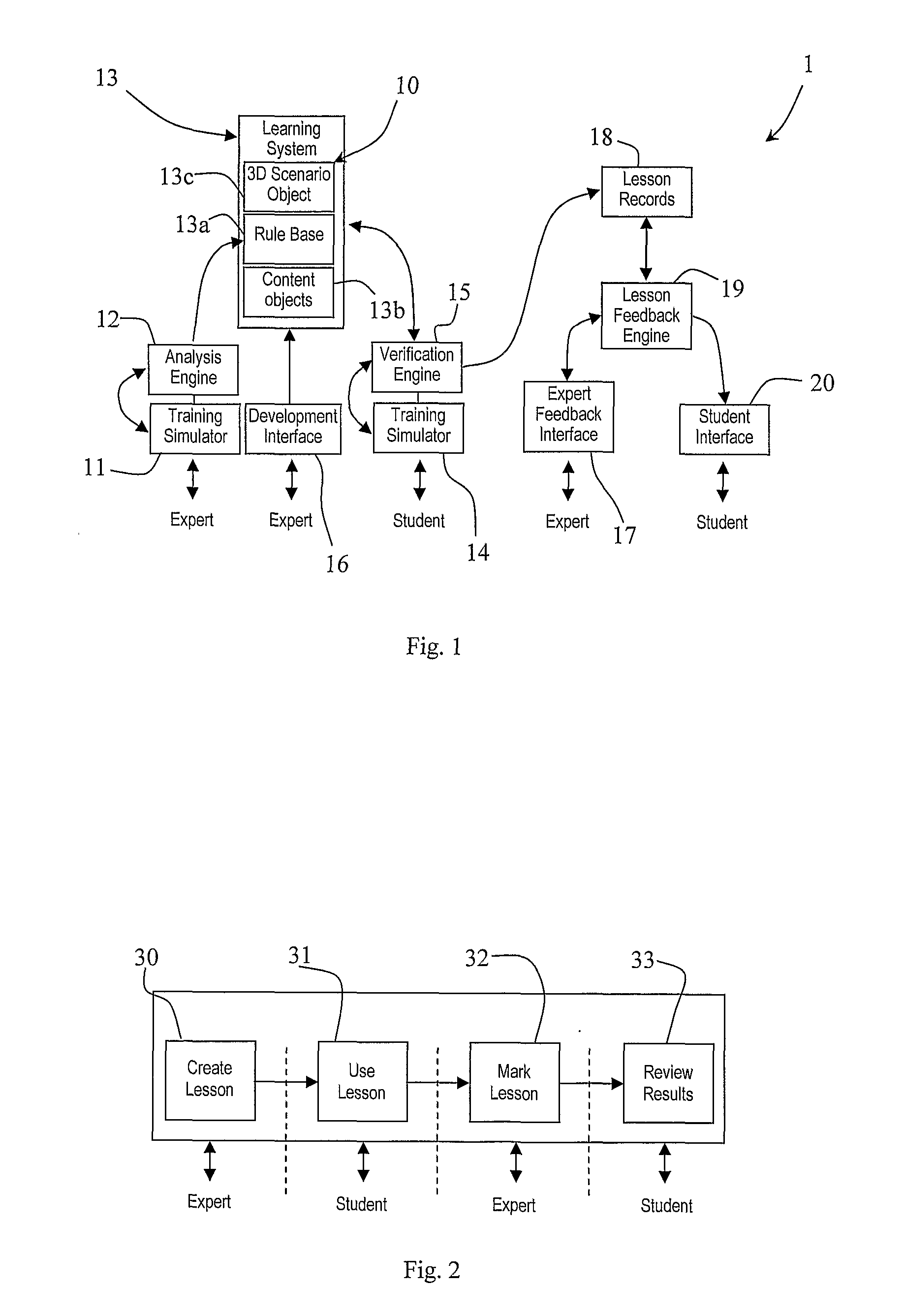
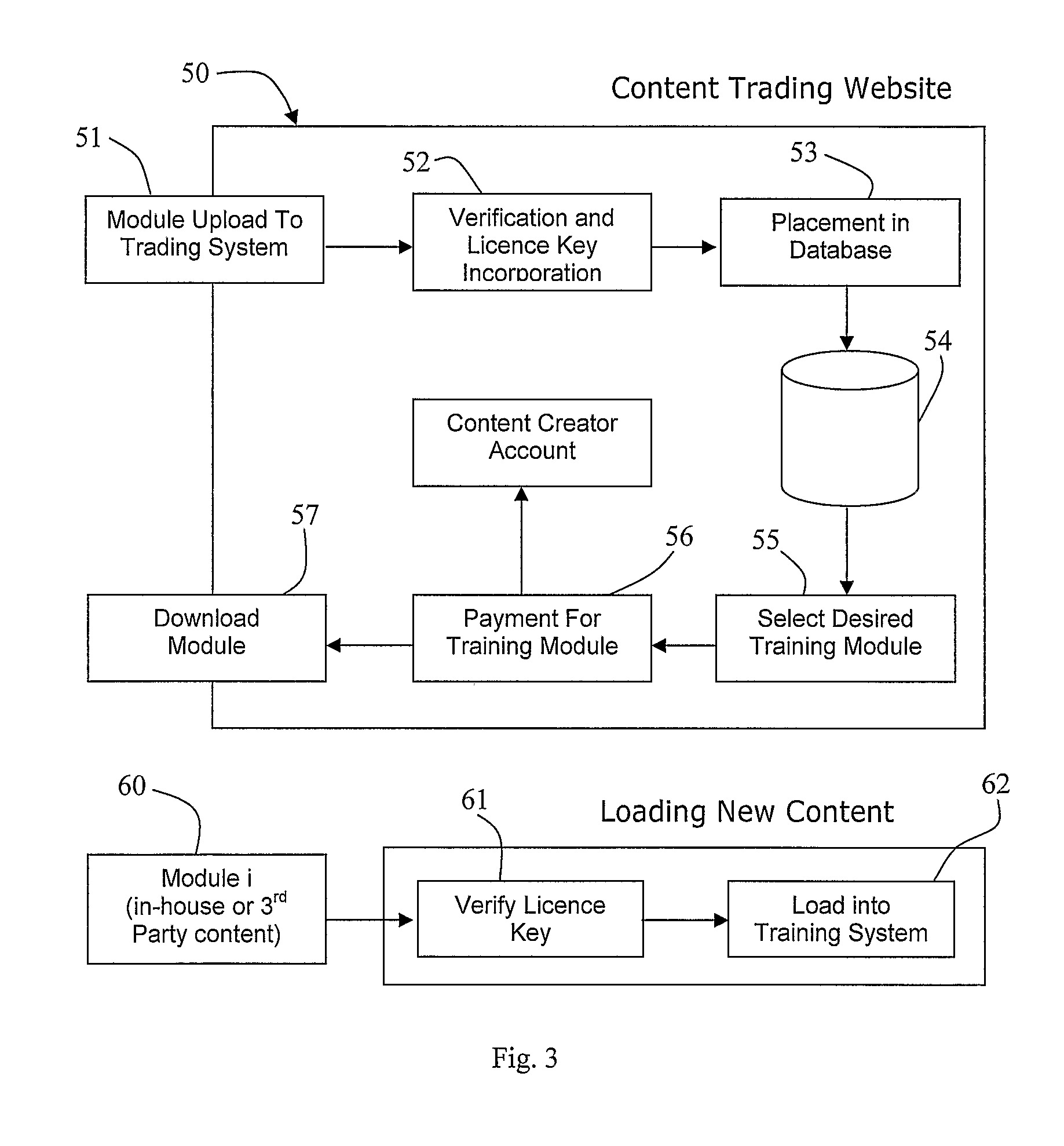
Method and System for Generating a Surgical Training Module
ActiveUS20080147585A1Improve versatilityEasy to trainEducational modelsKnowledge representationSimulationSurgical simulator
A system (1) comprises a physical surgical simulator (11) which transmits data concerning physical movement of training devices to an analysis engine (12). The engine (12) automatically generates rules for a rule base (13a) in a learning system (13). The learning system (13) also comprises content objects (13b) and 3D scenario objects (13c). A linked set of a 3D scenario object (13c), a rule base (13a), and a content object (13b) are together a lesson (10). Another simulator (14) is operated by a student. This transmits data concerning physical movement of training devices by a student to a verification engine (15). The verification engine (15) interfaces with the rule base (13a) to display the lesson in the manner defined by the lesson rule base (13a). It calculates performance measures defined in the lesson rule base (13a). It also records the performance measures into a lesson record (18) and it adapts the display of the lesson in line with the parameters defined in the lesson rule base (13a).
Owner:CAE HEALTHCARE CANADA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com