Patents
Literature
31 results about "Surgical simulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
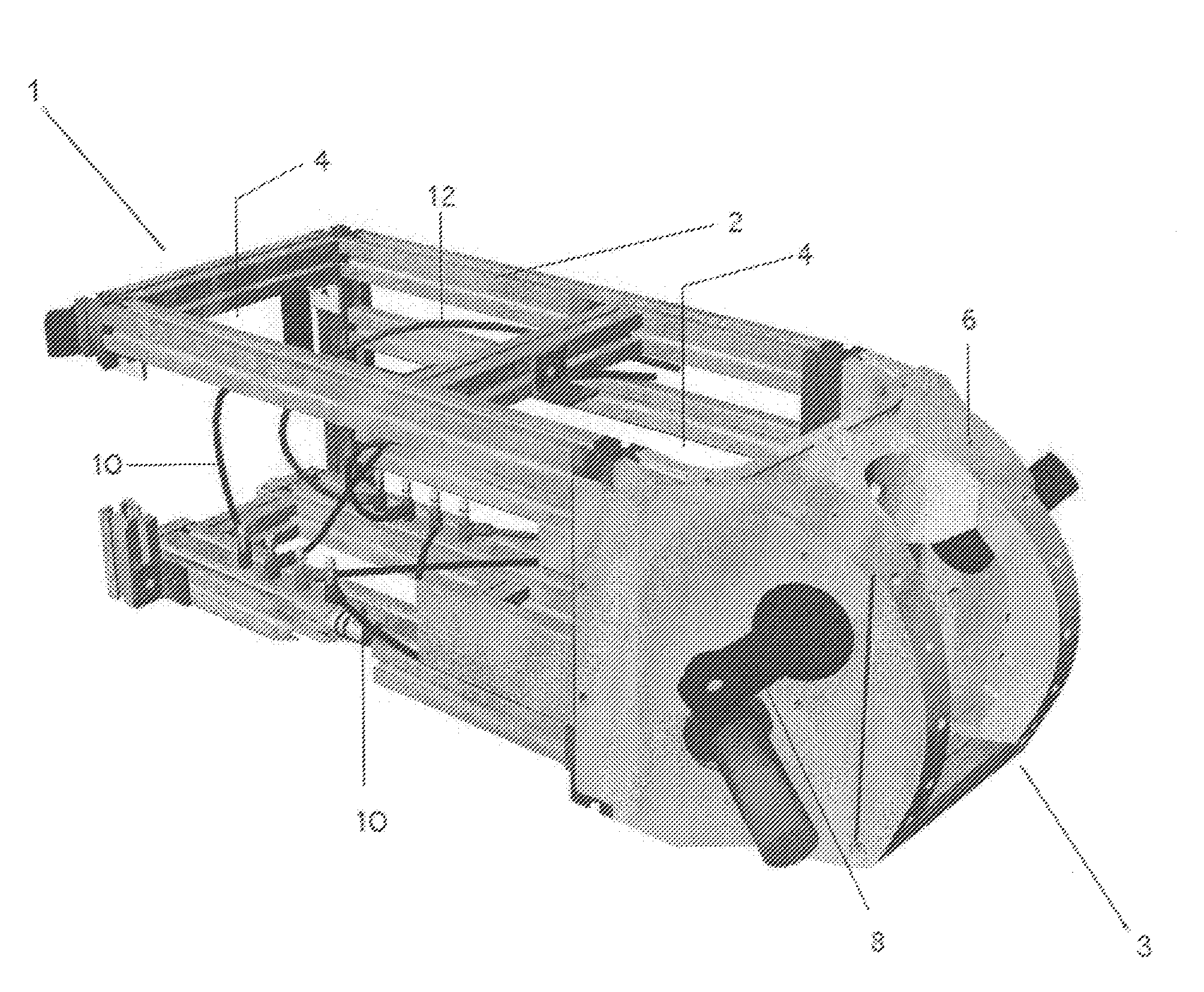
Surgical simulator system
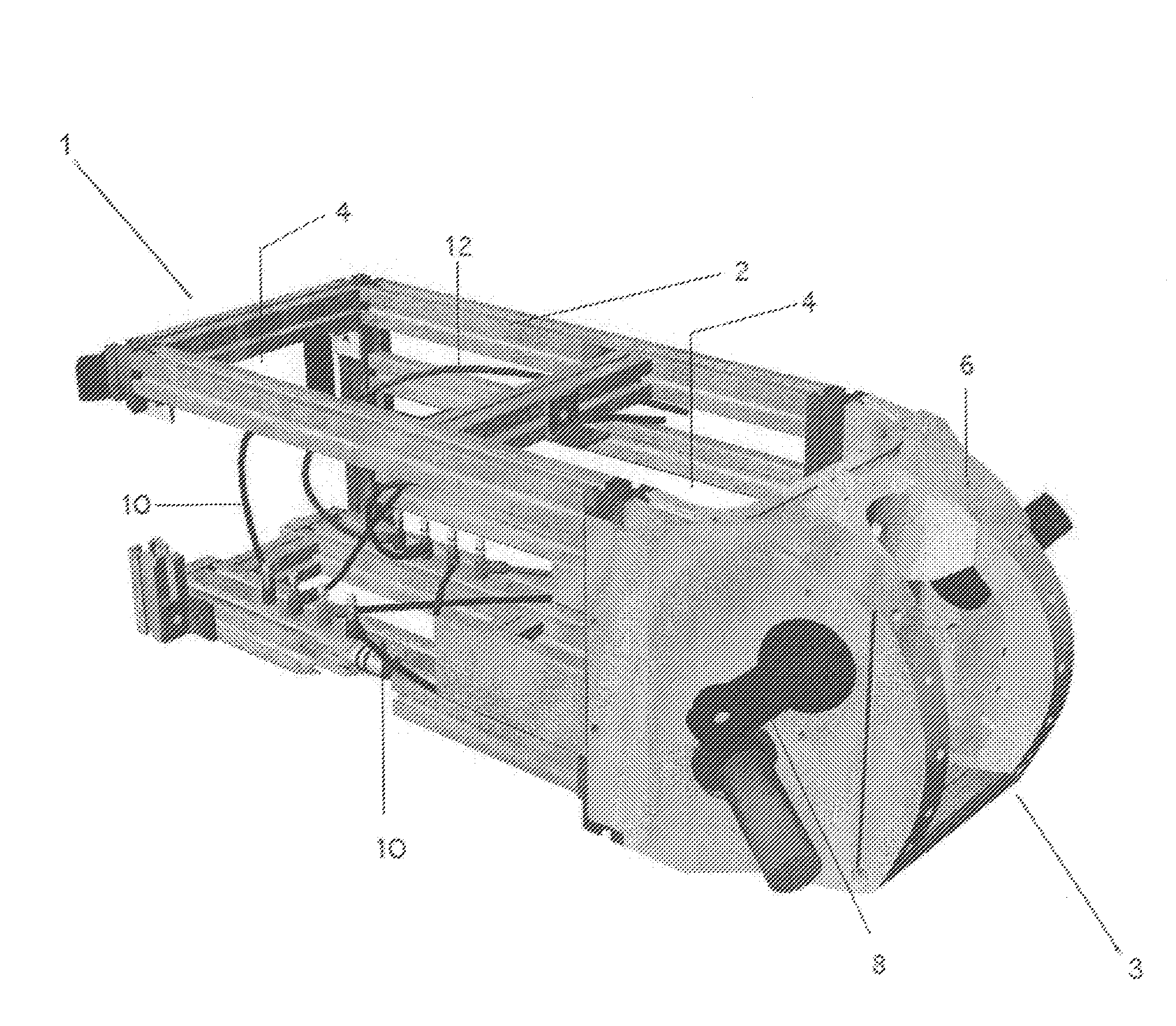
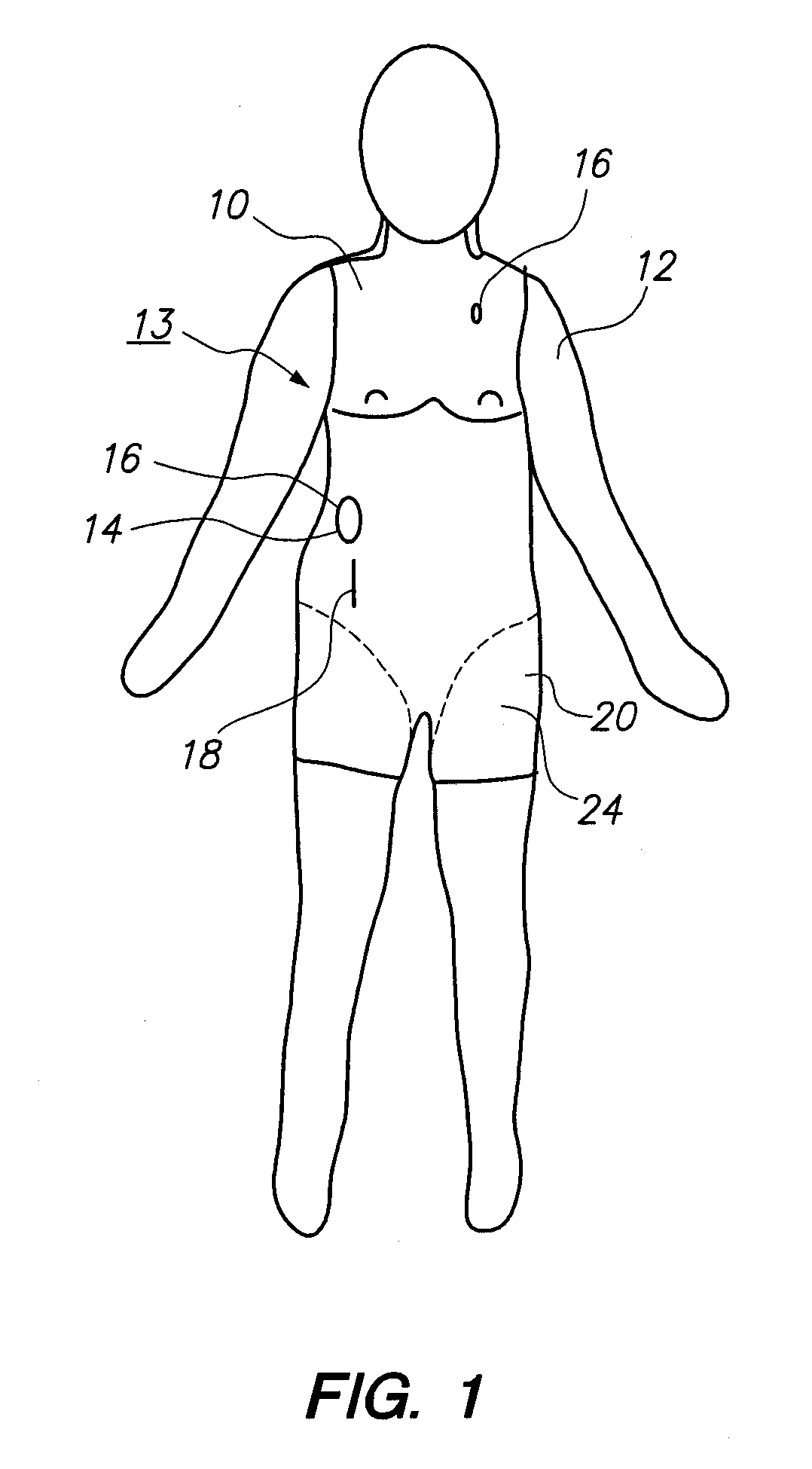
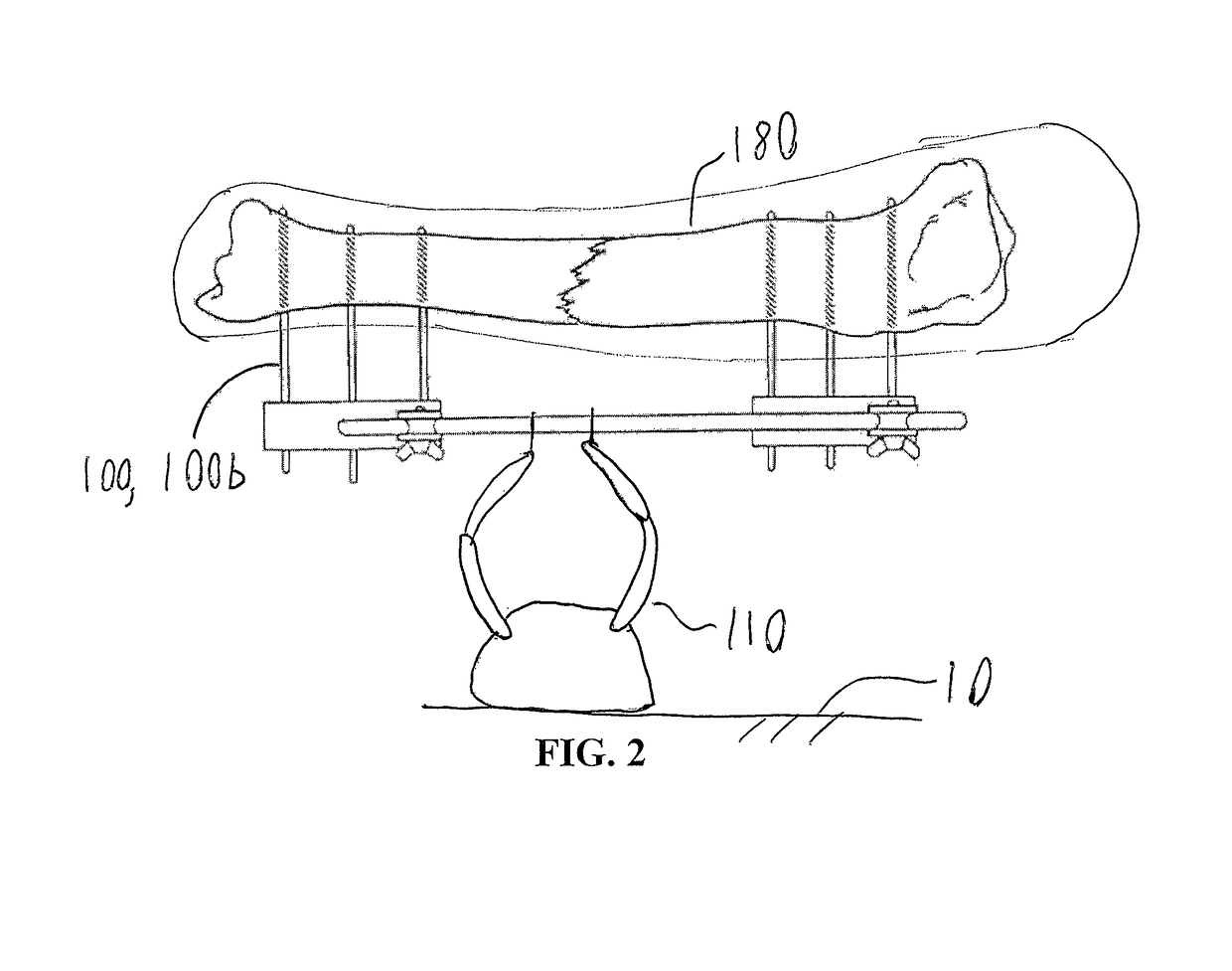
Disclosed is a surgical simulator for teaching, practicing, and evaluating surgical techniques. Such a simulator may comprise a cassette of organs, blood vessels, and tissues that may be disposable. The simulator also comprises a hemodynamic simulator and a frame assembly, the frame assembly providing support for the cassette of organs as well as a fluid conduit through which simulated blood flow from the hemodynamic simulator may be connected to the blood vessels of the organs and related tissues. The hemodynamic simulator provides adjustable and variable pressures to the arteries and veins, as well as variable pulse rates, which can be programmed at settings chosen by an instructor or user.
Owner:EAST TENNESSEE STATE UNIVERSITY
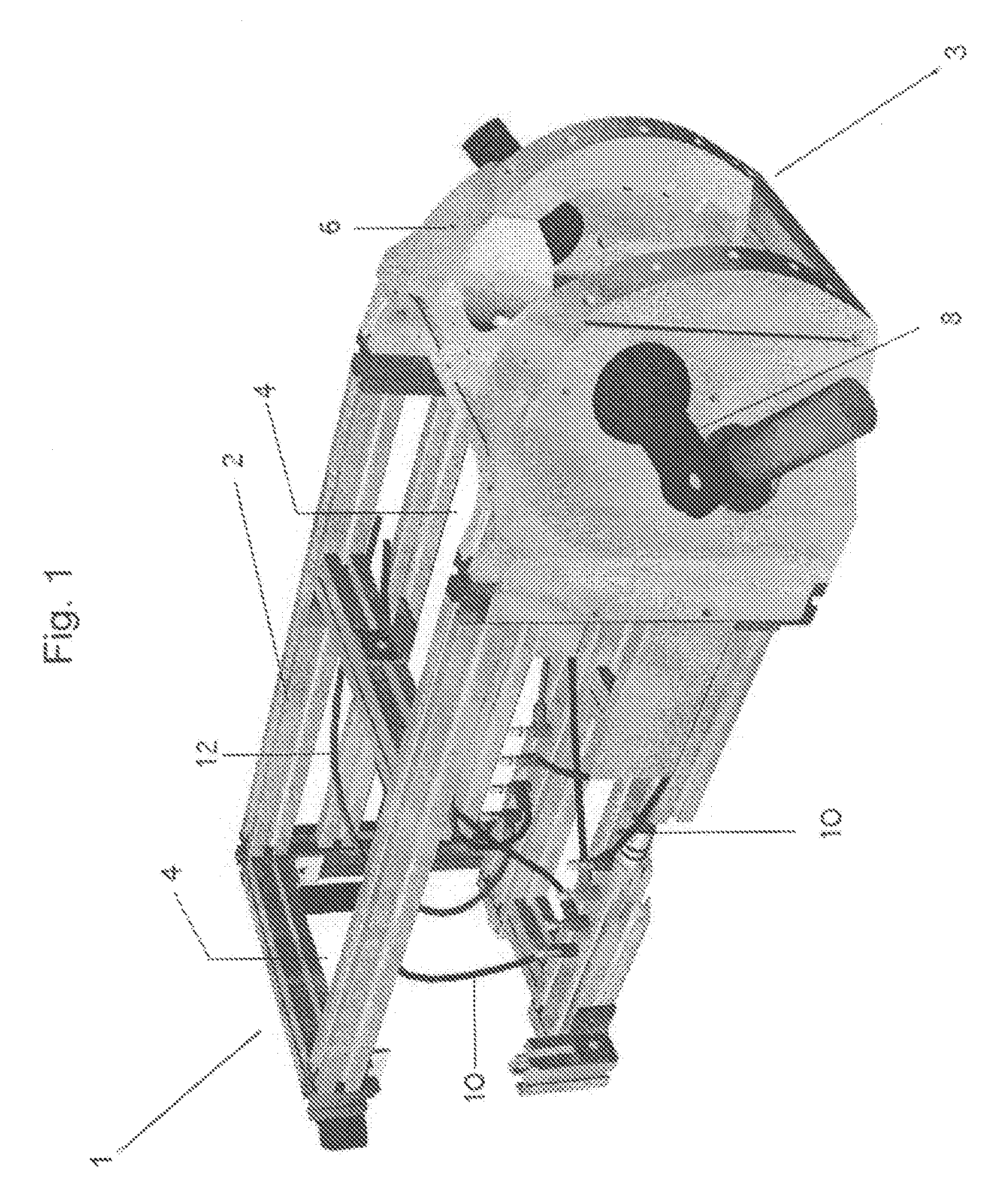
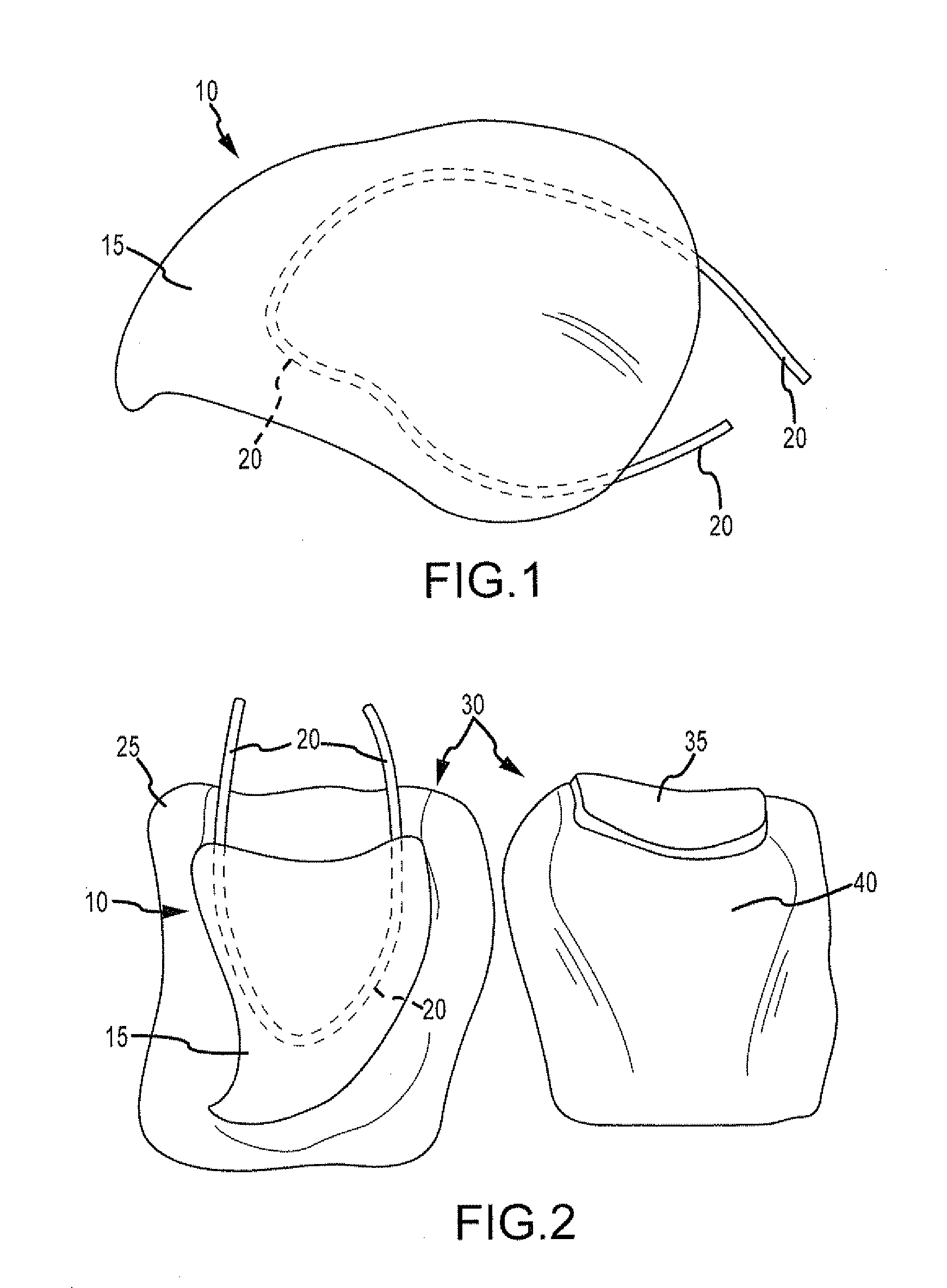
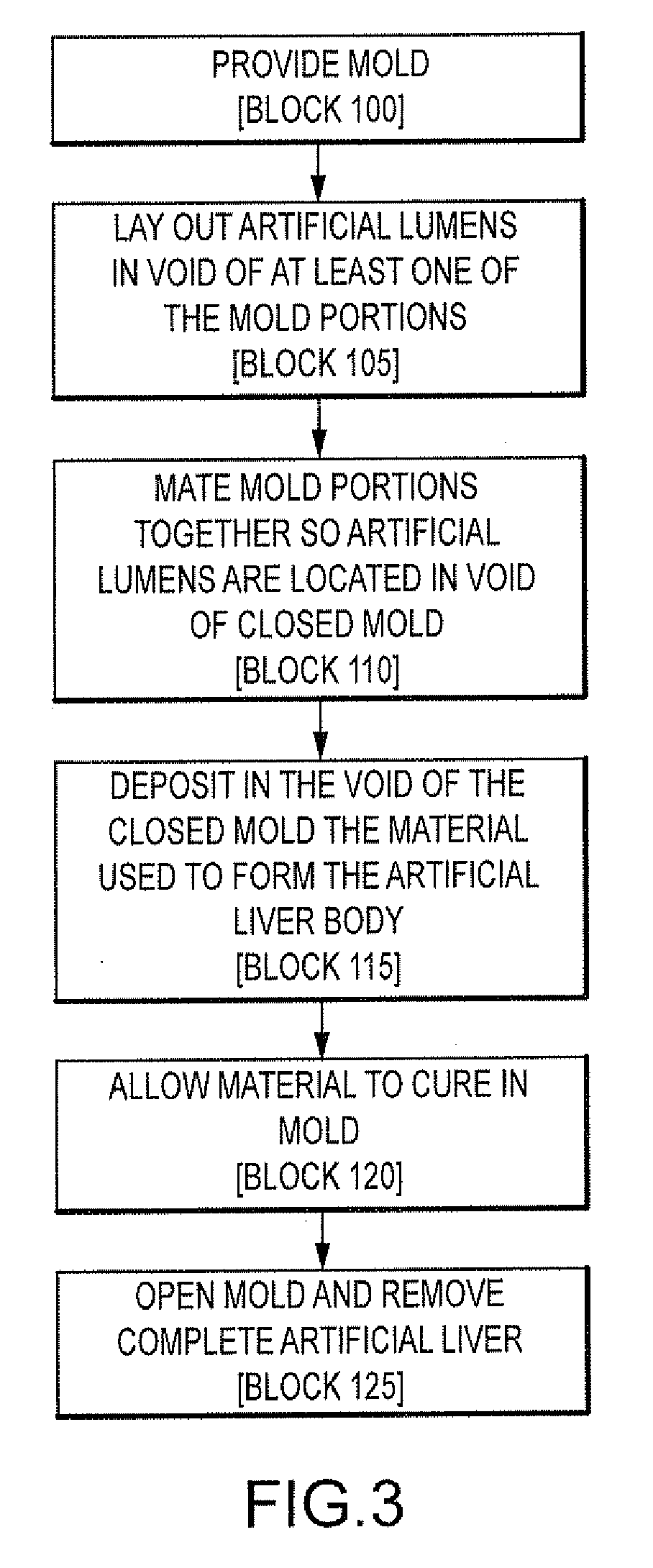
Surgical simulator, simulated organs and method of making same
A surgical simulator is disclosed herein. The surgical simulator includes an artificial organ and an enclosure substantially enclosing the artificial organ. The artificial organ is substantially formed of platinum cured room temperature vulcanization silicone rubber (“PCRTVS”).
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
Systems and methods for training one or more training users
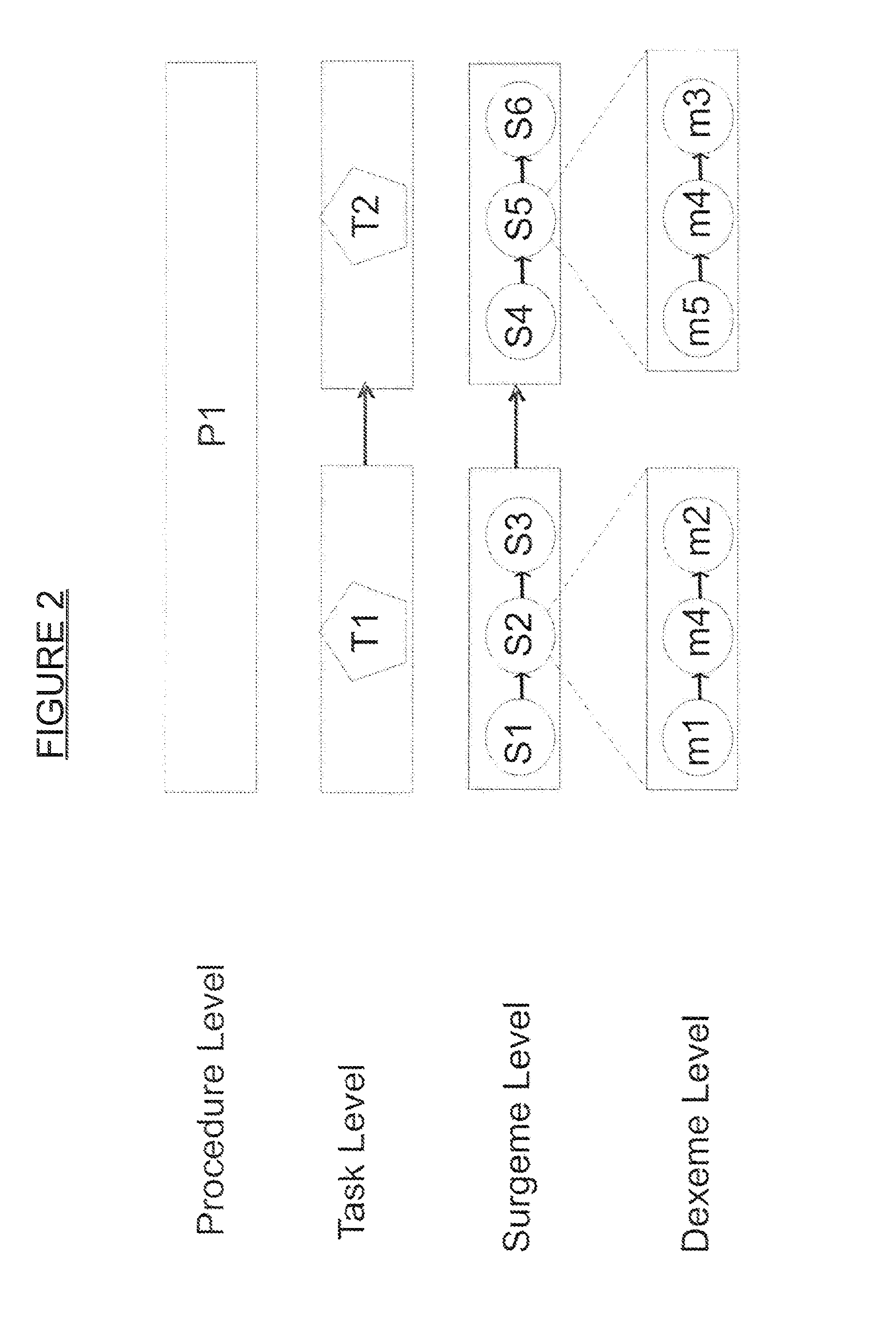
Systems and methods for training users. Surgical data related to surgical procedures done by expert level users is collected from surgical robots. The surgical data is segmented into surgemes and dexemes. The training users are trained at a level of the surgemes and / or a level of the dexemes by guiding the training users with surgical simulators to practice the surgemes and / or the dexemes, wherein the surgical simulators simulate surgery done by an expert level user.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
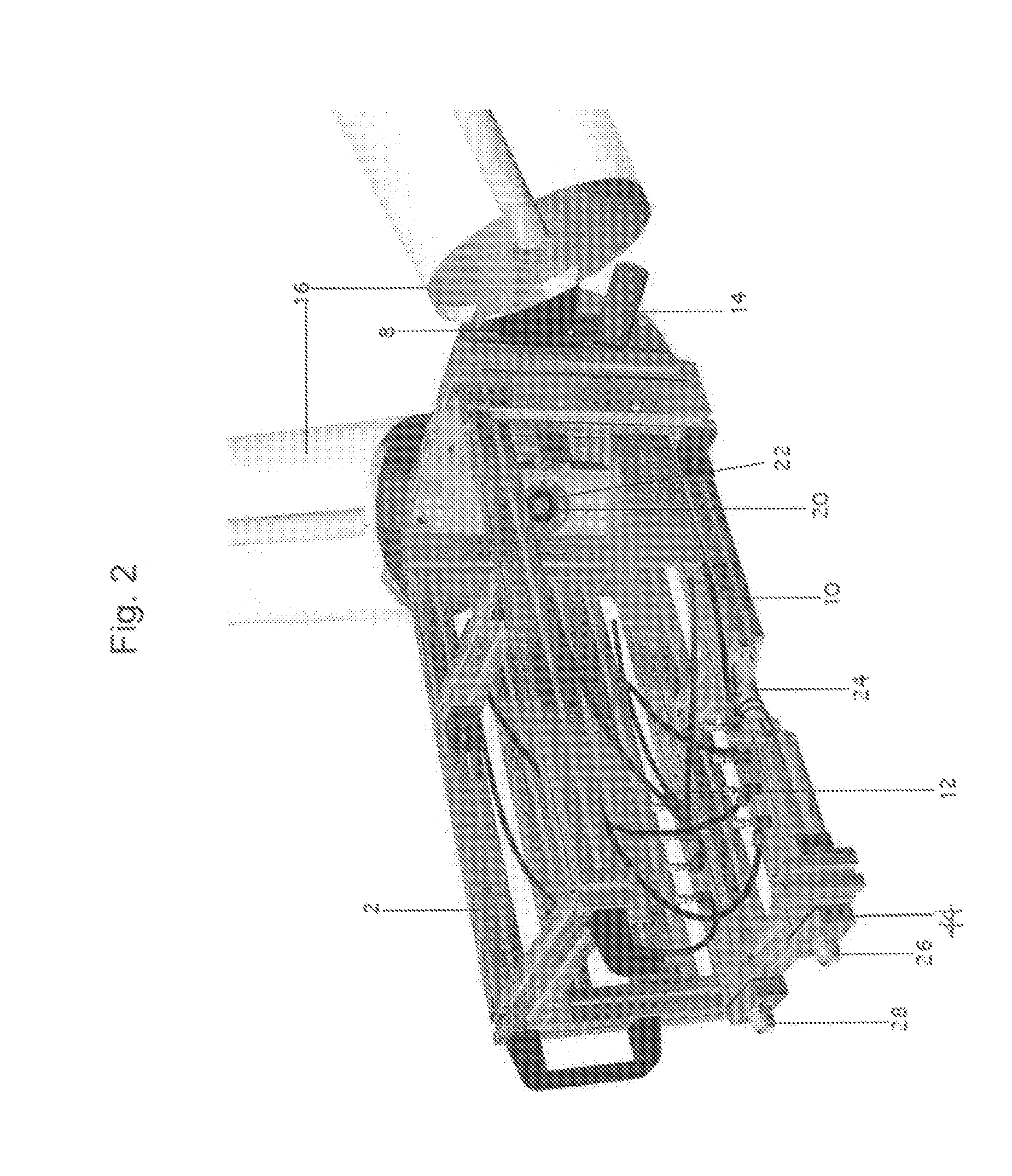
Combined soft tissue and bone surgical simulator
A surgery simulator includes a physical surrogate surgical interface that represents an interface between a user and a simulated patient in a simulated surgical scenario that involves manipulation of both simulated hard and soft tissue. Sensor(s) sense the user's manipulation of the surrogate surgical interface. A surgical simulation generator generates a real time 3D surgical simulation of the surgical scenario based on the manipulation sensed by the sensor(s). The real time 3D surgical simulation comprises real time simulation state data. The surgical simulation generator renders the real time simulation state data into a real time computer graphics generated video representation of the surgical simulation and provides the real time video representation to a display for real time viewing by the user. The surgical simulation generator simulates effects of the manipulation on both simulated hard tissue and simulated soft tissue of the simulated patient.
Owner:SIMQUEST
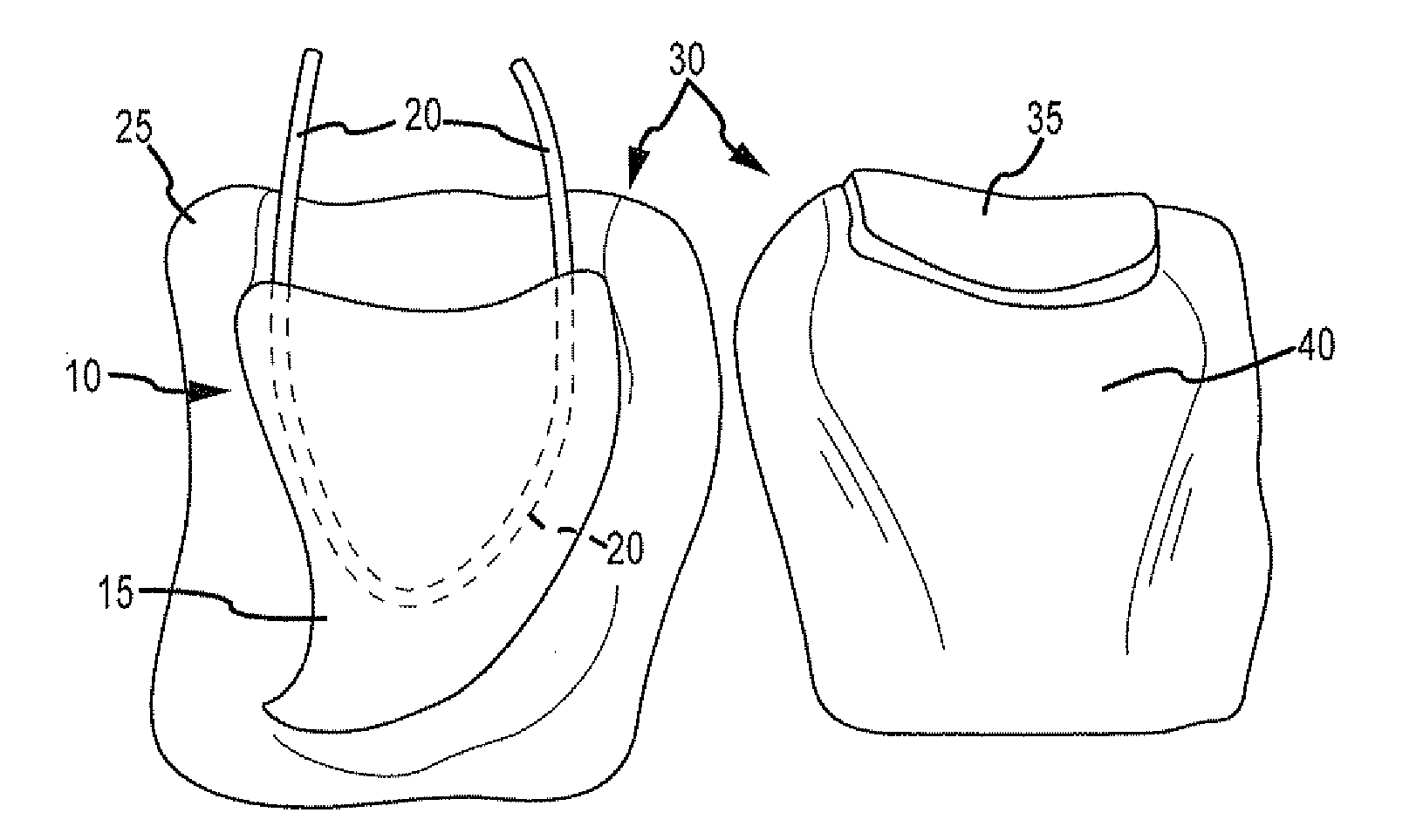
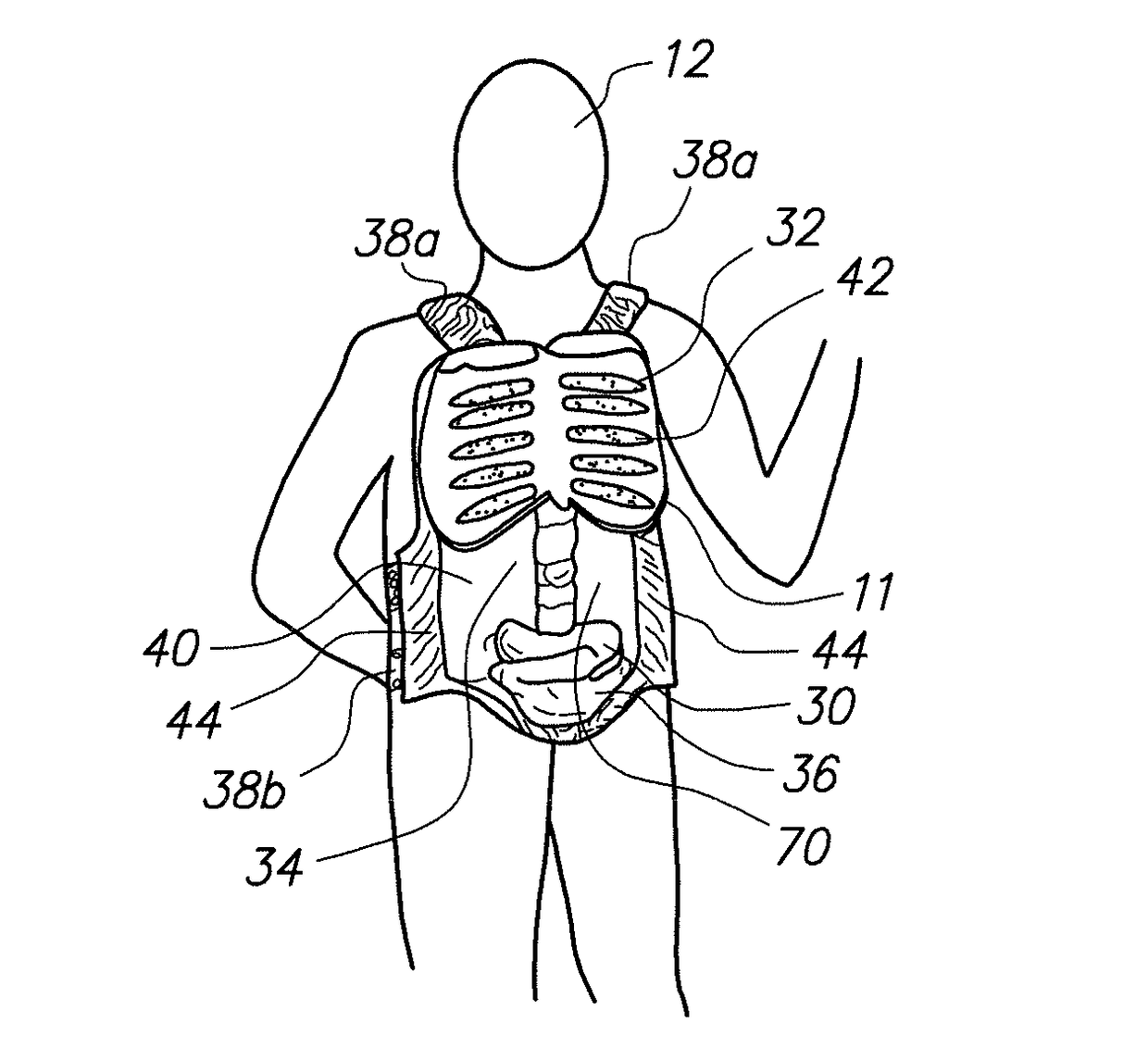
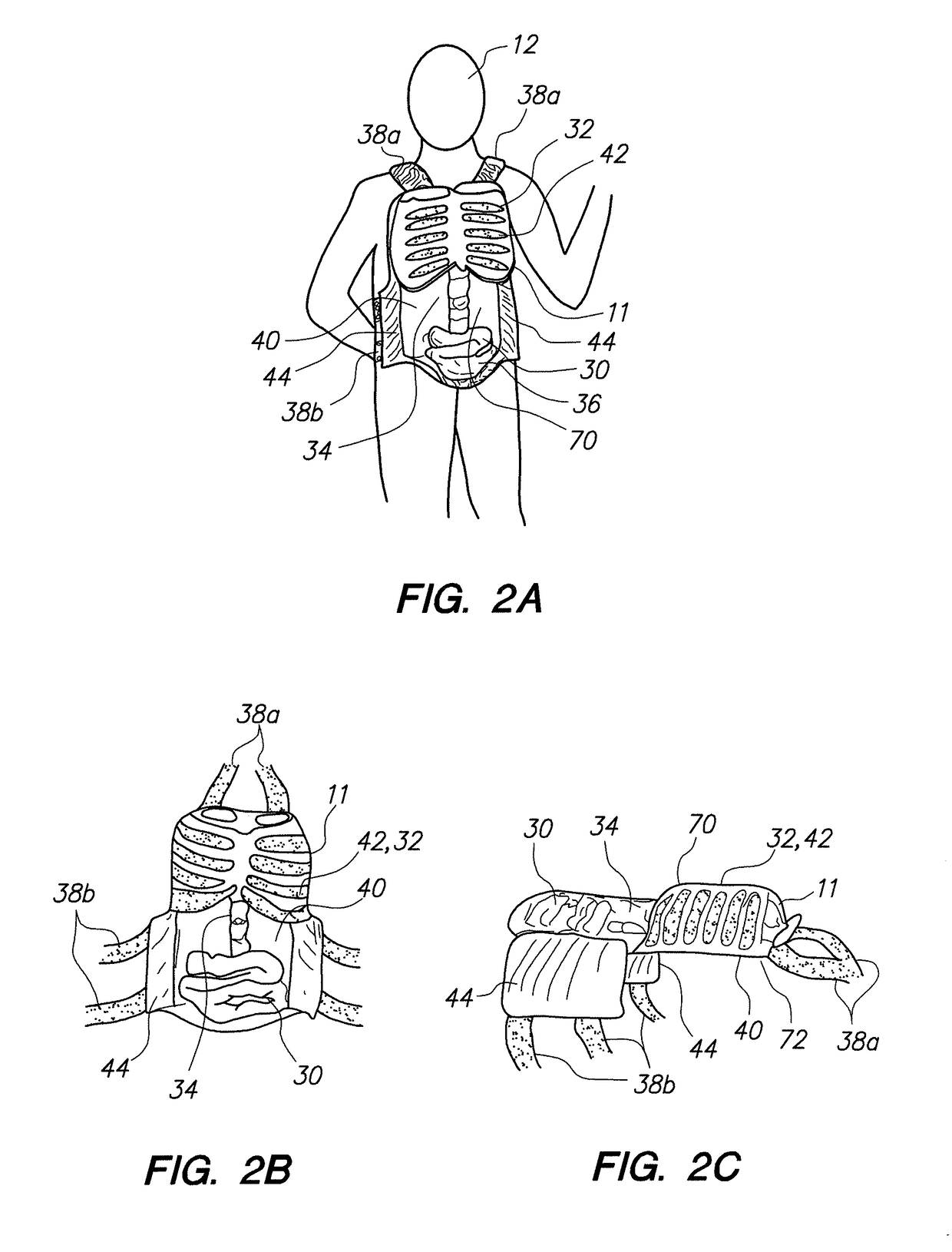
Wearable partial task surgical simulator
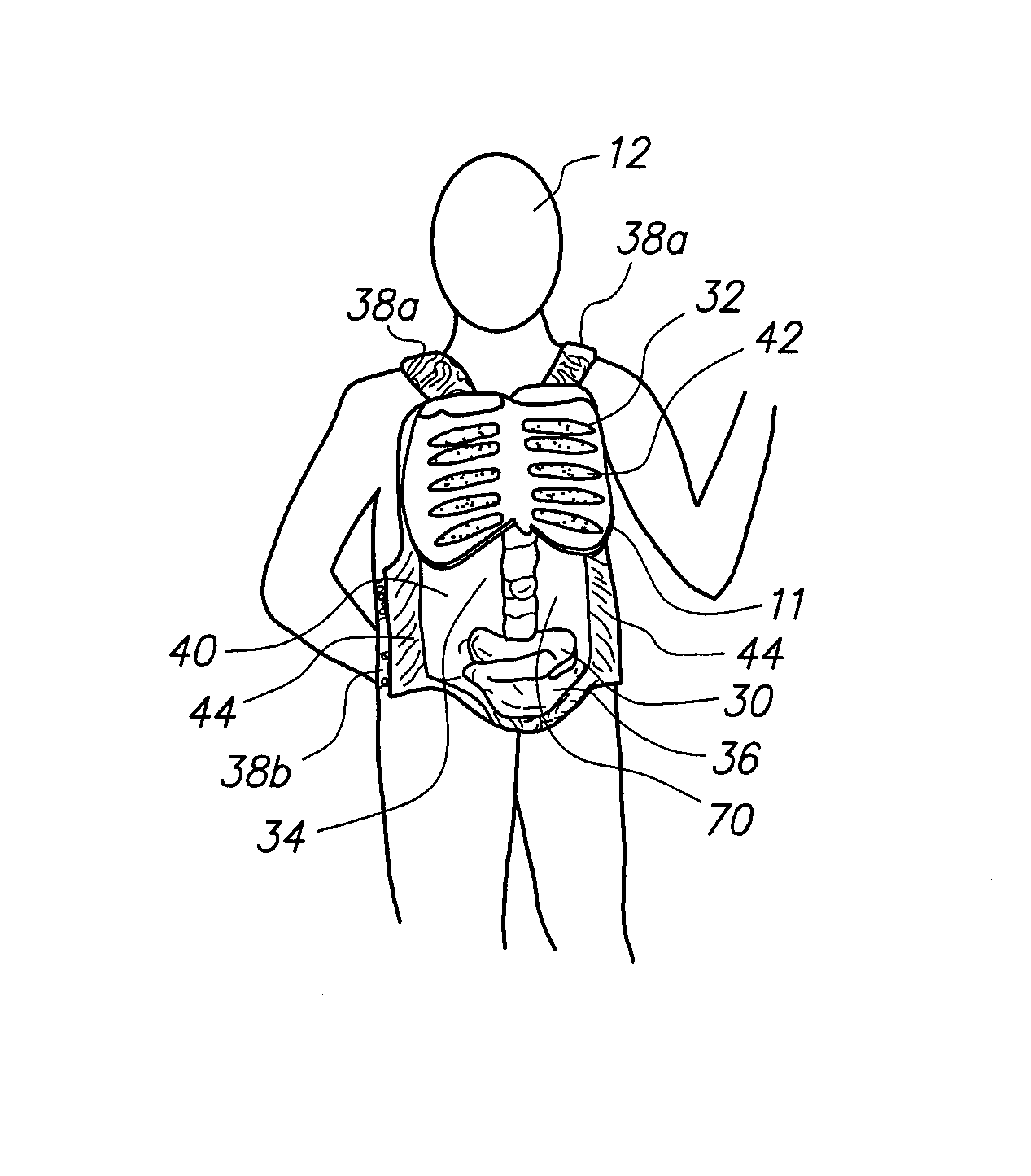
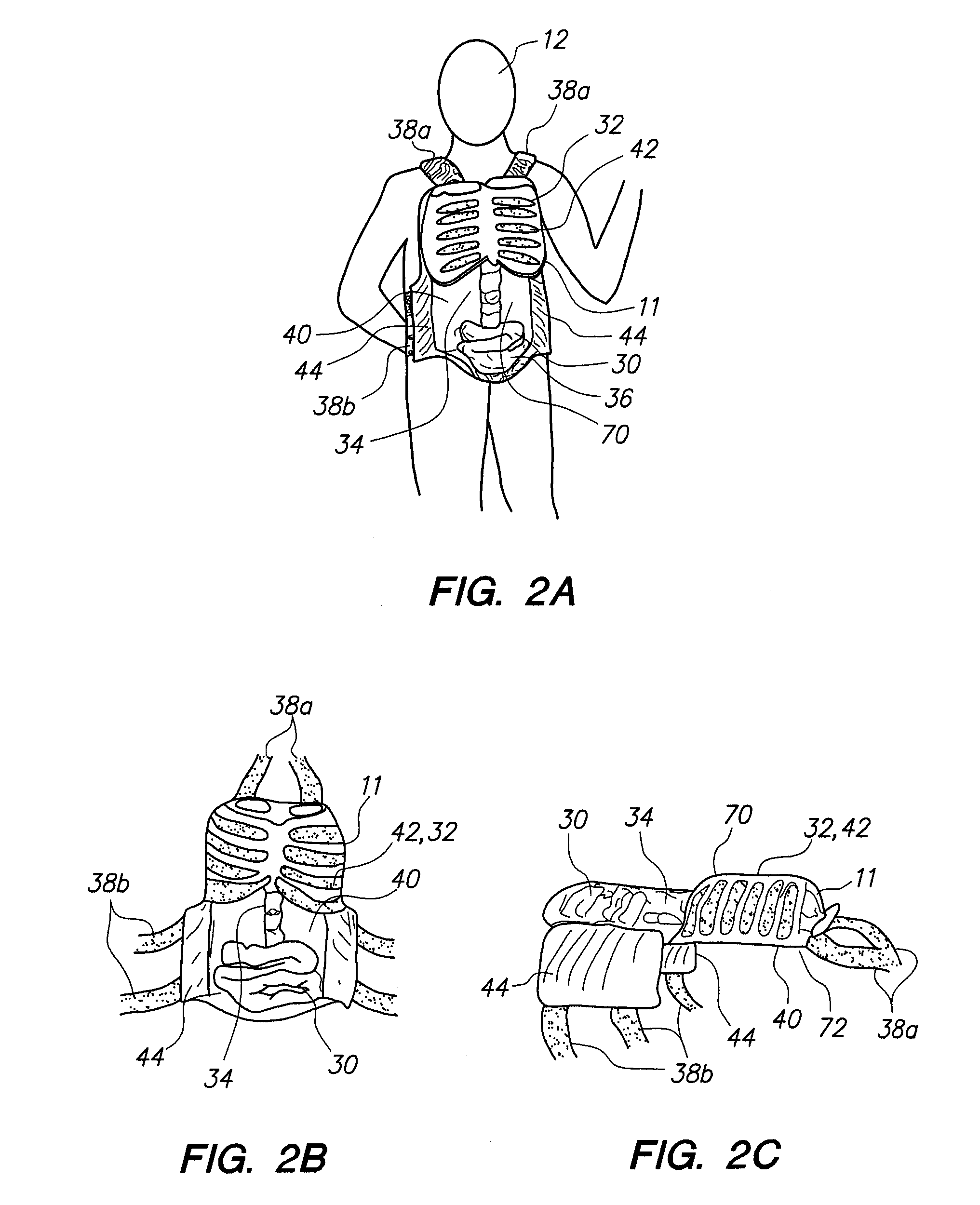
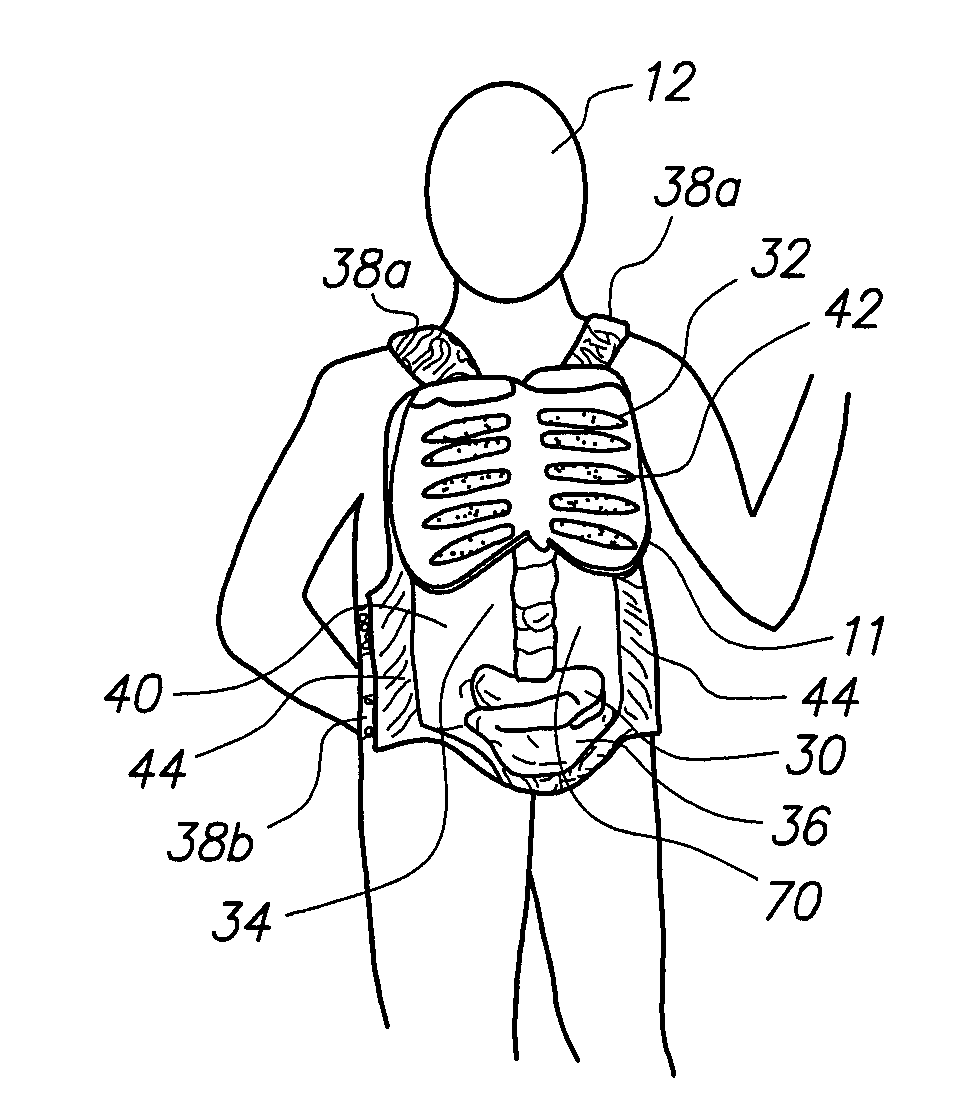
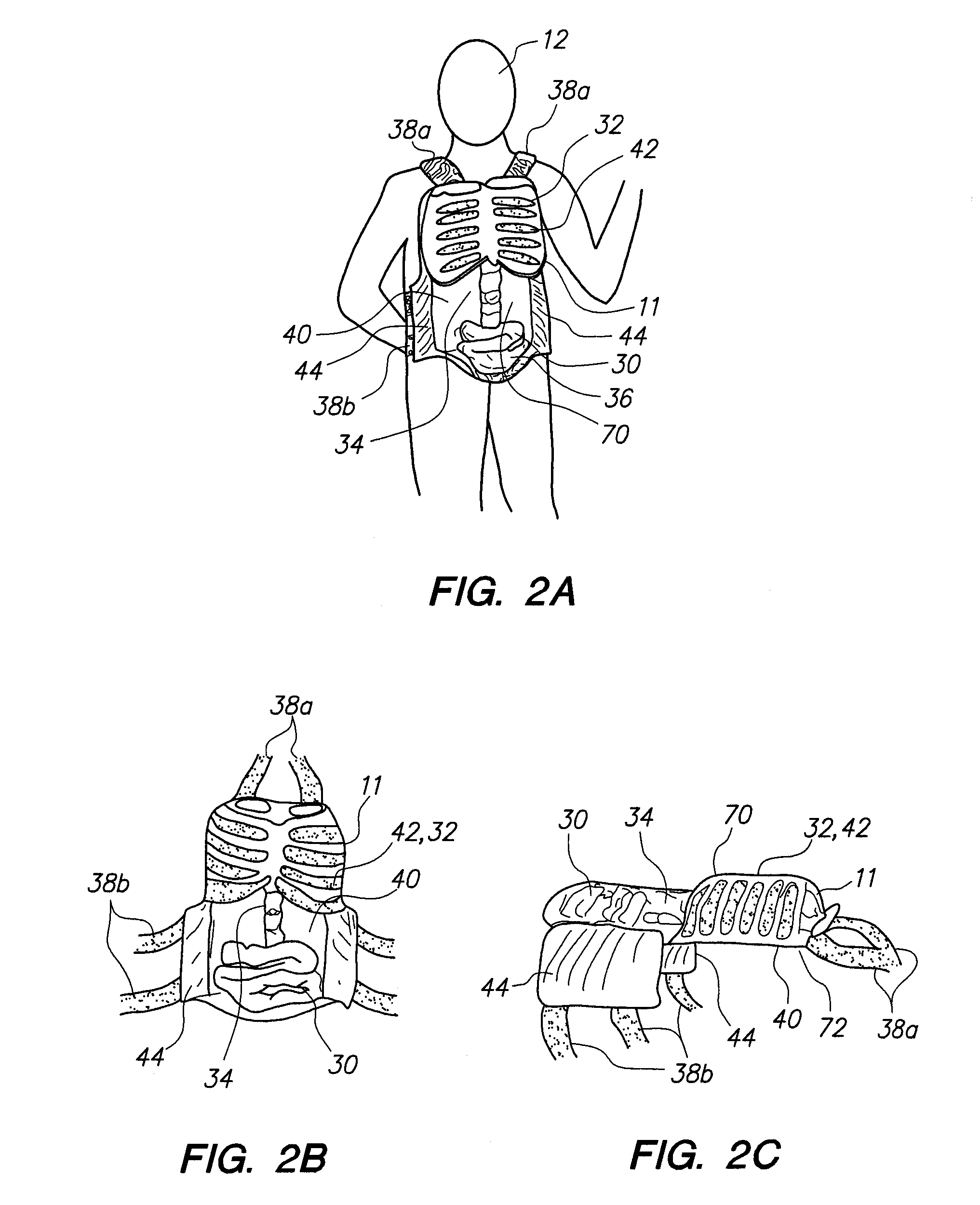
A wearable device for simulating wounds and injuries received during a trauma event includes a raiment and vest for covering the torso of a person. The raiment has an outer surface with a color and a texture comparable to human skin. Mounted on the outer surface is at least one wound simulator formed with an orifice that is in fluid communication with a fluid reservoir. Thus, the person can selectively expel a blood-like fluid from the reservoir, and through the wound simulator orifice, to simulate a trauma event. The vest includes an artificial rib cage and prosthetic internal organs juxtaposed with at least one wound simulator to simulate internal effects of a trauma event.
Owner:STRATEGIC OPERATIONS INC
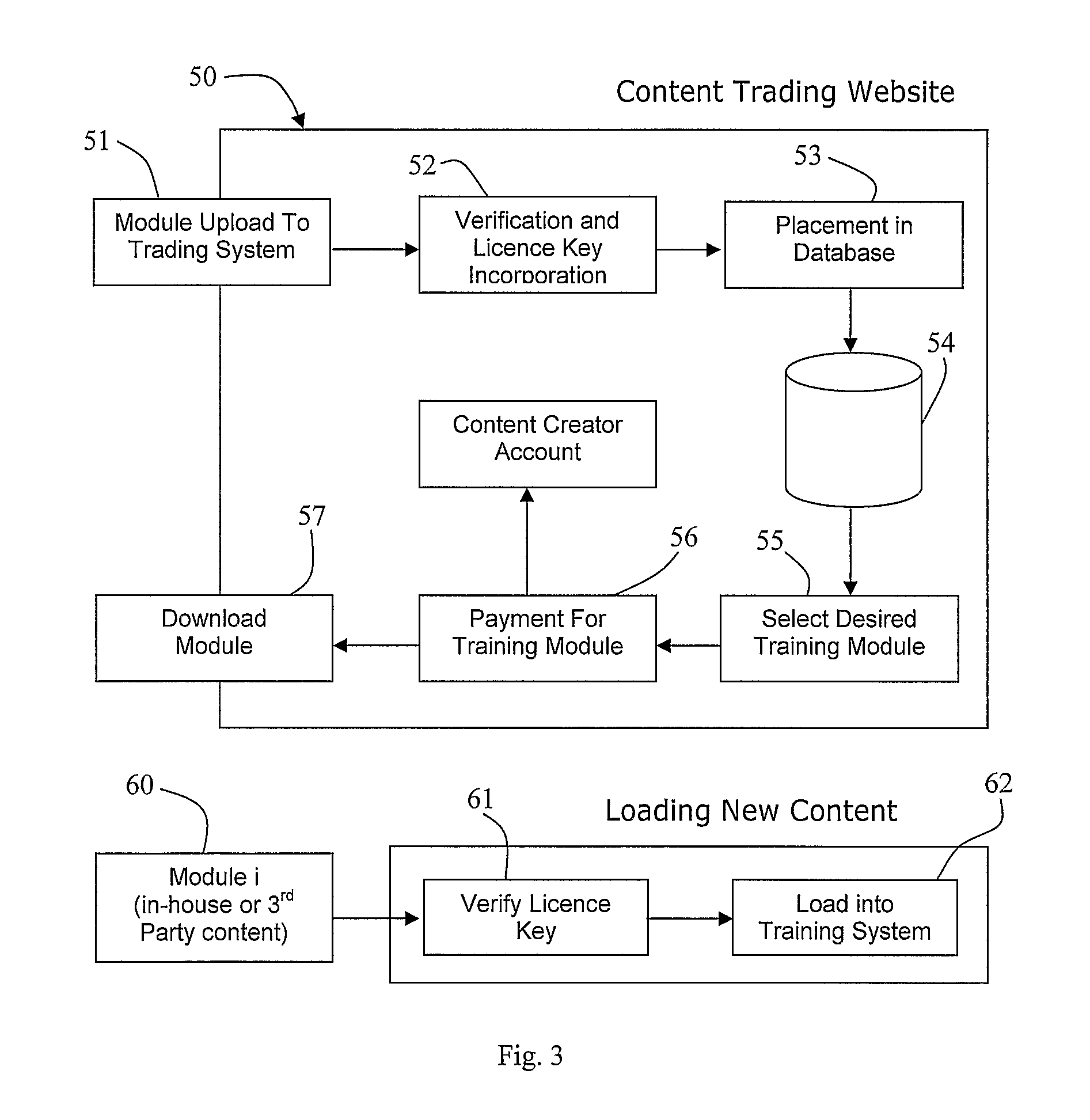
Method and System for Generating a Surgical Training Module
ActiveUS20080147585A1Improve versatilityEasy to trainEducational modelsKnowledge representationSimulationSurgical simulator
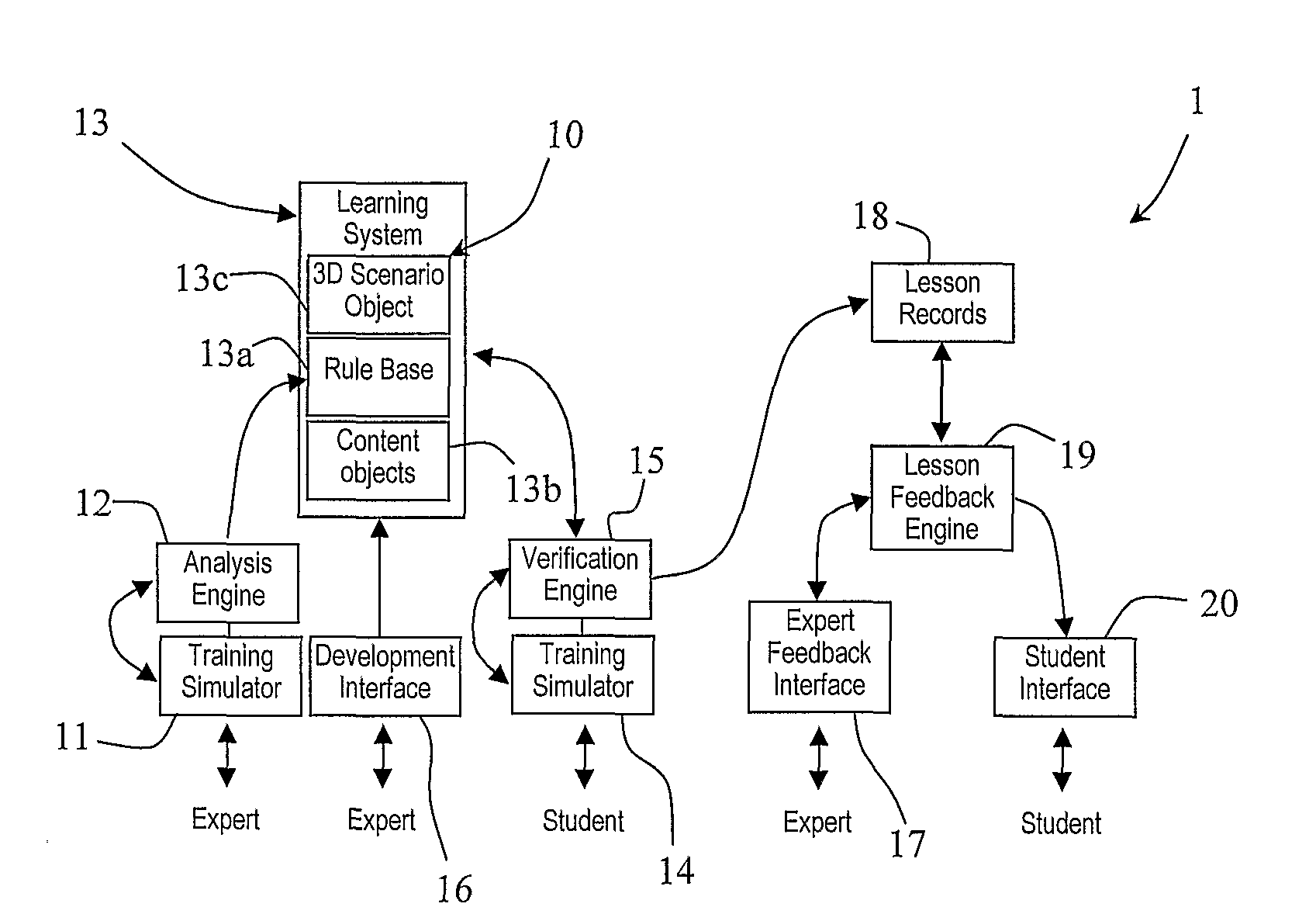
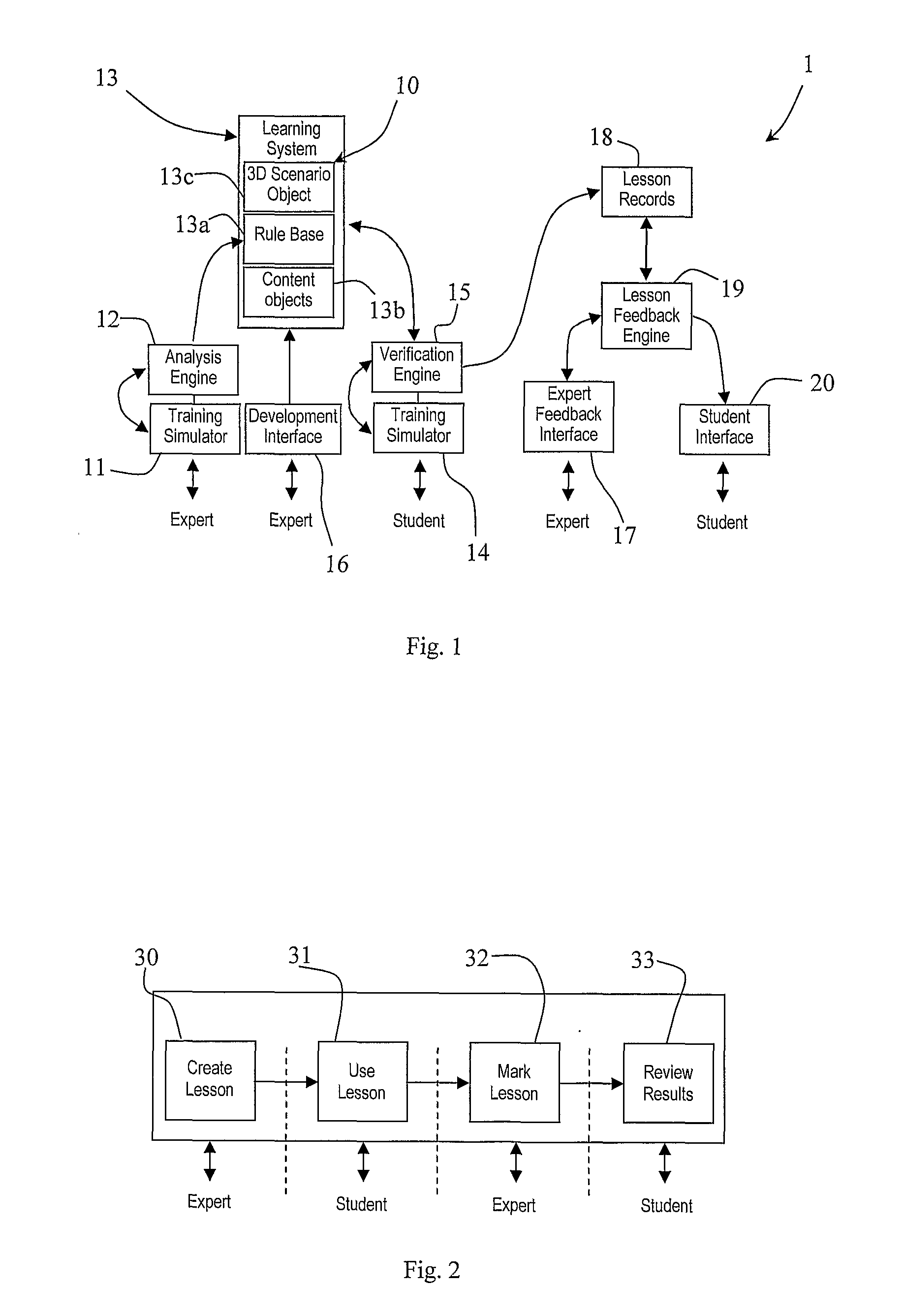
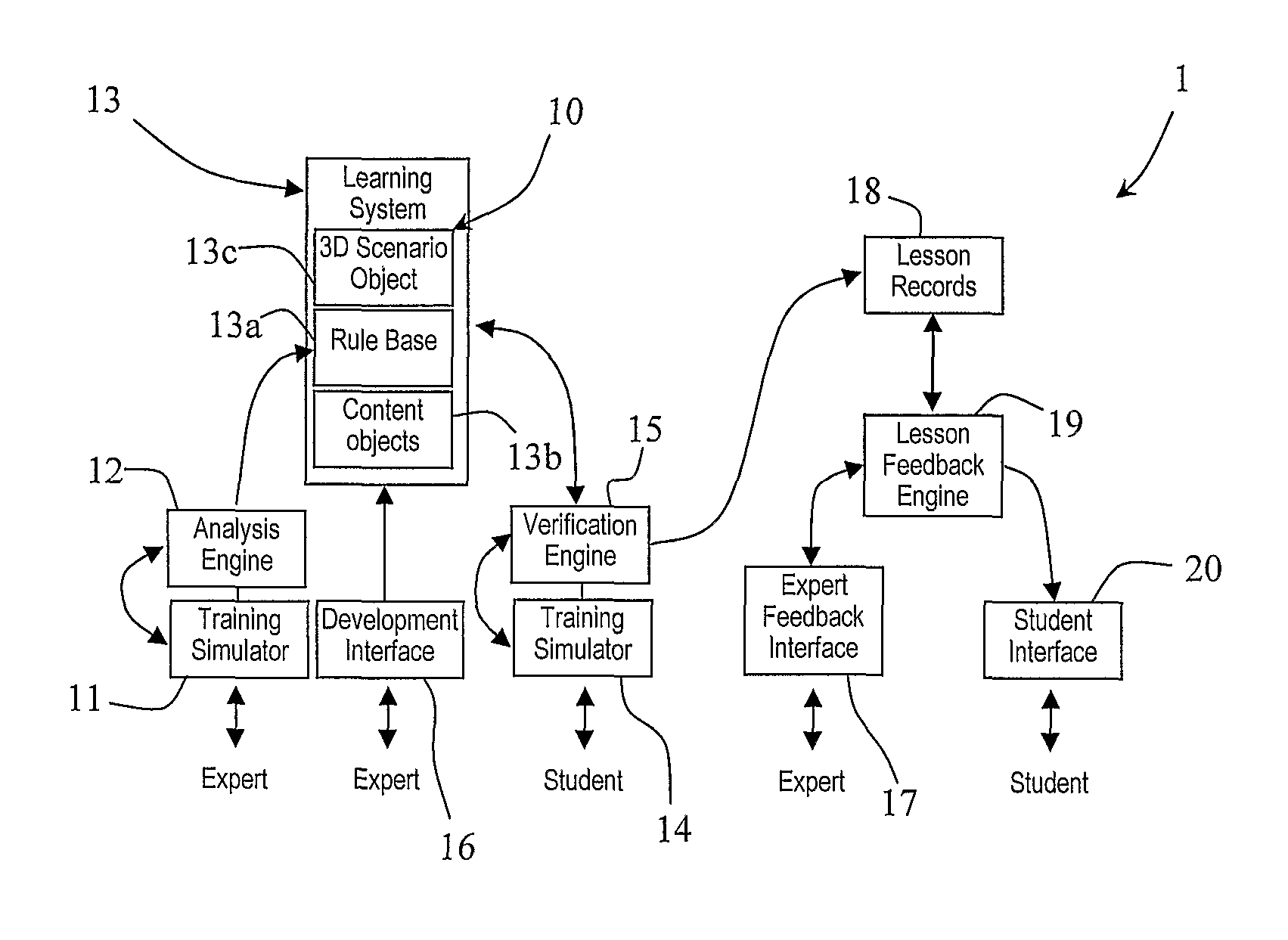
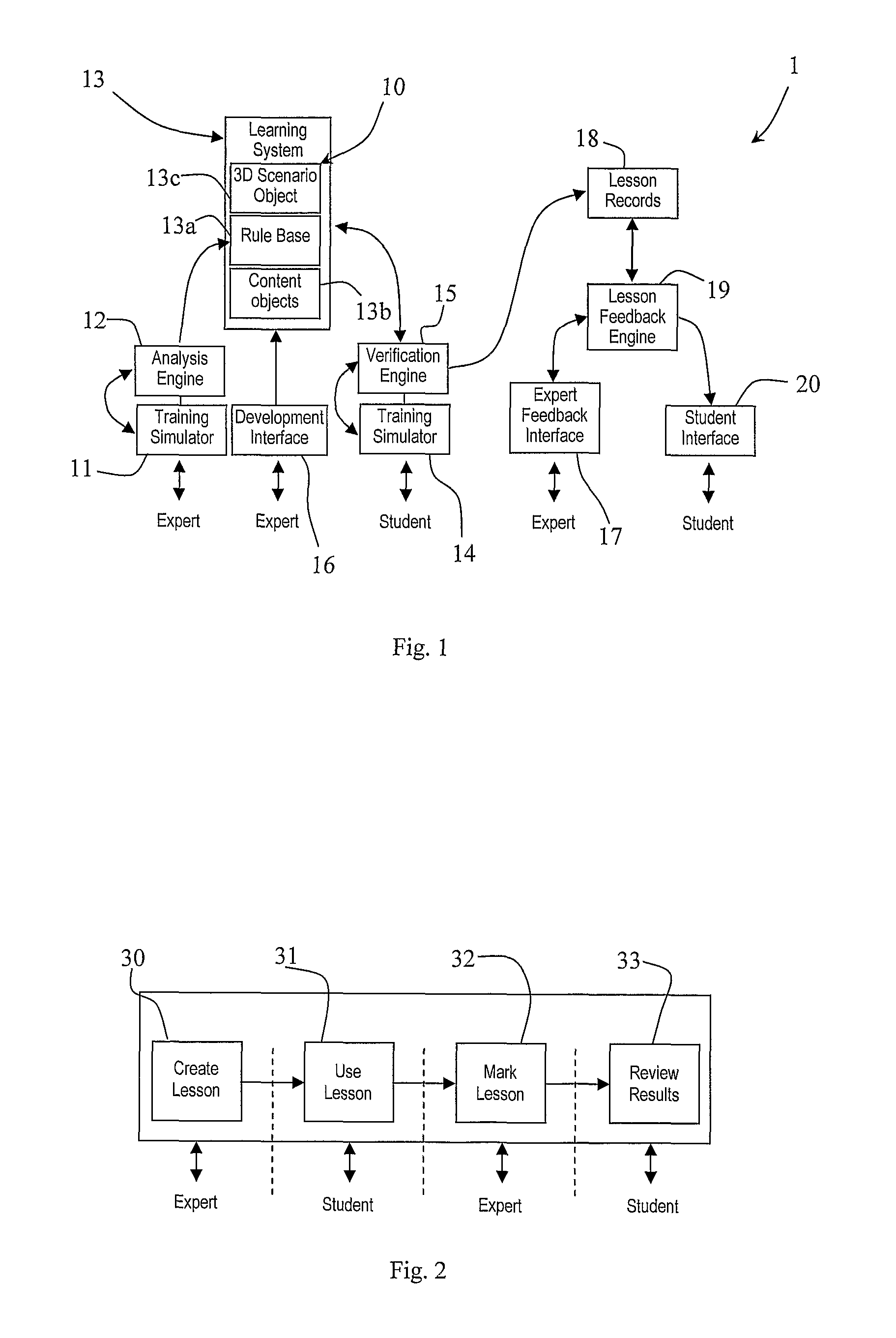
A system (1) comprises a physical surgical simulator (11) which transmits data concerning physical movement of training devices to an analysis engine (12). The engine (12) automatically generates rules for a rule base (13a) in a learning system (13). The learning system (13) also comprises content objects (13b) and 3D scenario objects (13c). A linked set of a 3D scenario object (13c), a rule base (13a), and a content object (13b) are together a lesson (10). Another simulator (14) is operated by a student. This transmits data concerning physical movement of training devices by a student to a verification engine (15). The verification engine (15) interfaces with the rule base (13a) to display the lesson in the manner defined by the lesson rule base (13a). It calculates performance measures defined in the lesson rule base (13a). It also records the performance measures into a lesson record (18) and it adapts the display of the lesson in line with the parameters defined in the lesson rule base (13a).
Owner:CAE HEALTHCARE CANADA
Computer-aided system of orthopedic surgery
InactiveUS7909610B1Promote formationAvoid difficultyEducational modelsComputer-aided surgerySurgical operationComputer-aided
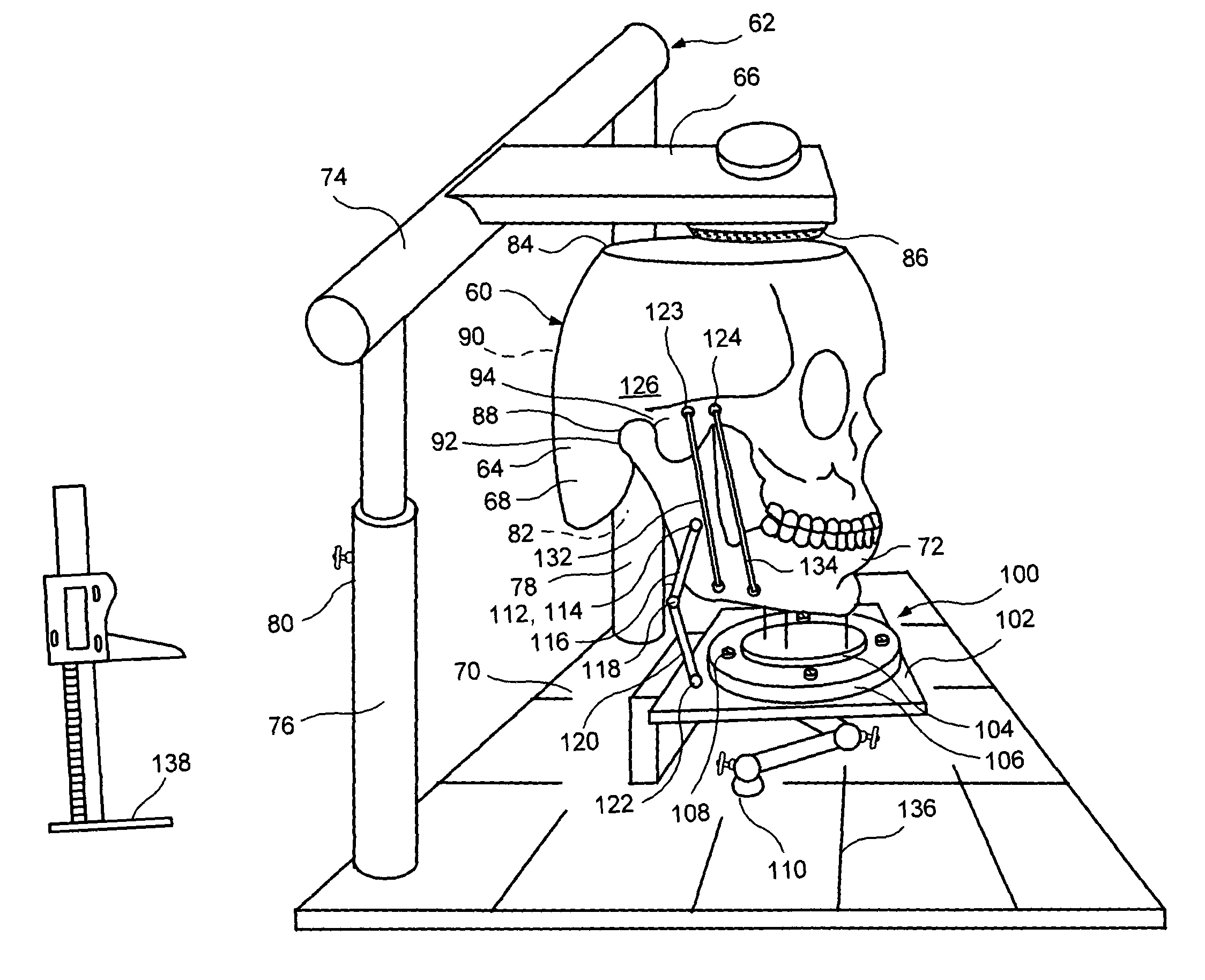
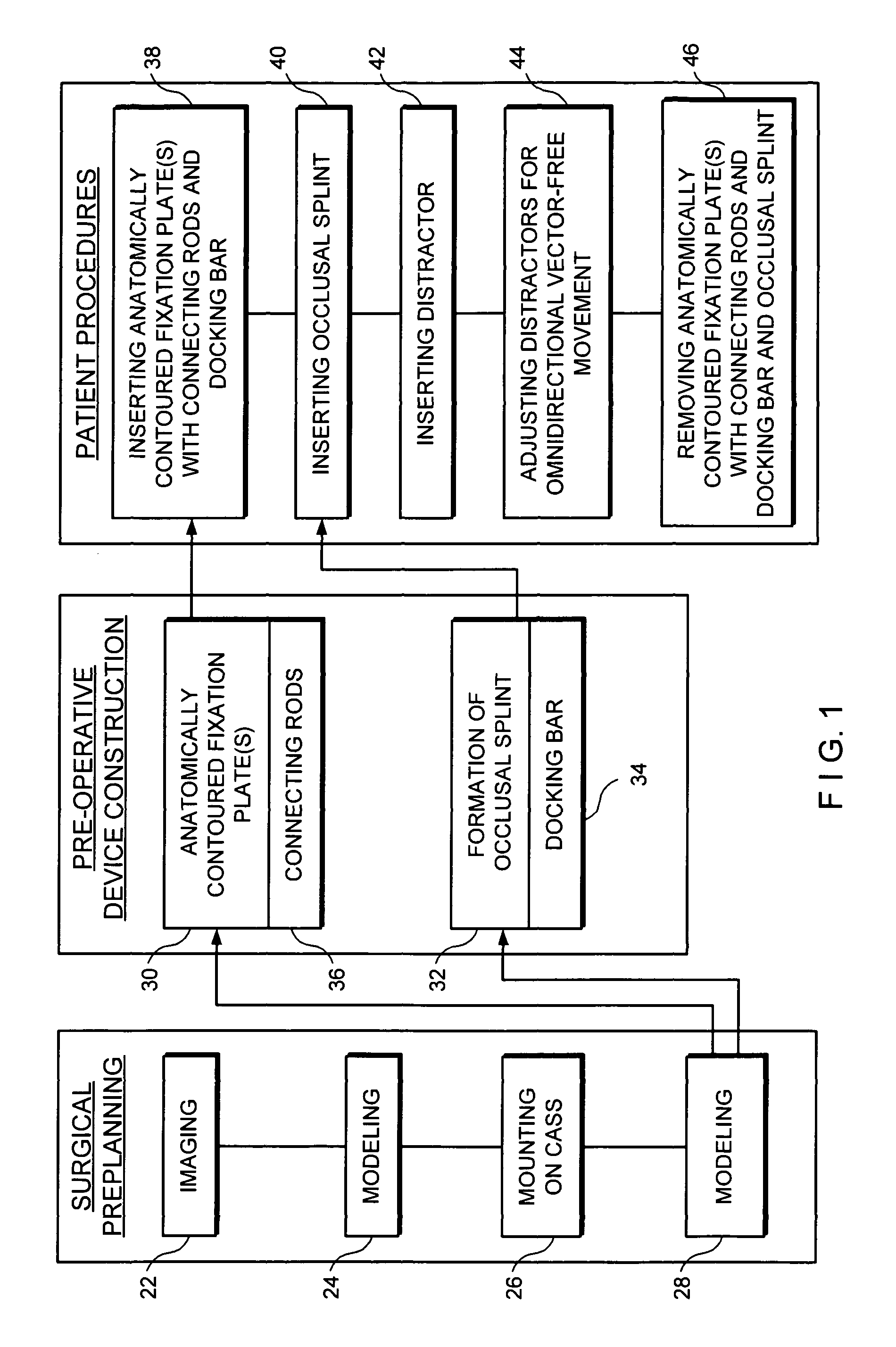
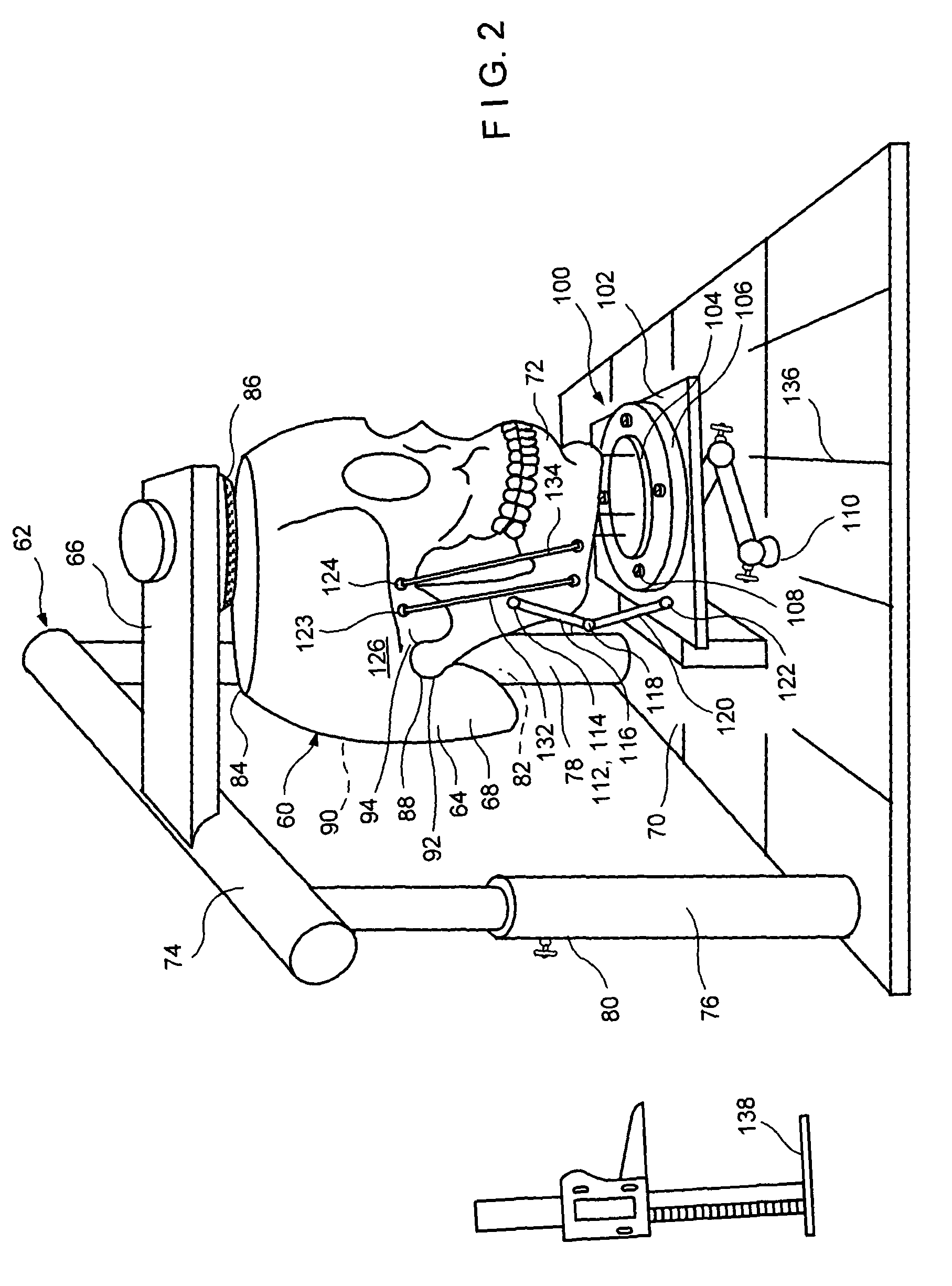
A computer aided system of orthopedic surgery is disclosed and omnidirectional osteogenesis is provided as an example thereof. To perform this surgery a craniofacial anatomic surgical simulator (CASS) is described, in which simulator a stereolithographic medical model is mounted. The medical model hereof is modified for this purpose so that pre-operative intra-oral devices, including custom-fitted fixation plates, can be crafted. An occlusal splint formed on the stereolithographic model acts as an armature for a docking bar which is, during the surgical operation, rigidly affixed to the fixation plate(s). The CASS, in one embodiment hereof, includes an indexing means for alignment of the stereolithographic model. The CASS also simulates the temporomandibular joint and fixedly mounts segments of the model in a post-operative condition.
Owner:AMATO CRANIOFACIAL ENG
Surgical simulator system and method
InactiveCN107205779AComputer-aided planning/modellingEducational modelsPhysics basedTouch Perception
Owner:HELP ME SEE INC
Surgical Simulator System
Disclosed is a surgical simulator for teaching, practicing, and evaluating surgical techniques. Such a simulator may comprise a cassette of organs, blood vessels, and tissues that may be disposable. The simulator also comprises a hemodynamic simulator and a frame assembly, the frame assembly providing support for the cassette of organs as well as a fluid conduit through which simulated blood flow from the hemodynamic simulator may be connected to the blood vessels of the organs and related tissues. The hemodynamic simulator provides adjustable and variable pressures to the arteries and veins, as well as variable pulse rates, which can be programmed at settings chosen by an instructor or user.
Owner:EAST TENNESSEE STATE UNIVERSITY
Wearable partial task surgical simulator
A wearable device for simulating wounds and injuries received during a trauma event includes a raiment and vest for covering the torso of a person. The raiment has an outer surface with a color and a texture comparable to human skin. Mounted on the outer surface is at least one wound simulator formed with an orifice that is in fluid communication with a fluid reservoir. Thus, the person can selectively expel a blood-like fluid from the reservoir, and through the wound simulator orifice, to simulate a trauma event. The vest includes an artificial rib cage and prosthetic internal organs juxtaposed with at least one wound simulator to simulate internal effects of a trauma event.
Owner:STRATEGIC OPERATIONS INC
Simulator for training medical personnel to perform uterine procedures
The surgical simulator contains a one-piece simulated uterus having a uterine fundus and body. A rigid hollow support base has a recess in its support surface that is complementary to the shape of at least a portion of the uterine fundus and body so that at least a posterior portion of the uterine fundus and body fit securely into the recess to retain the simulated uterus in position during use. Liquid can be introduced into the base to add weight, and the liquid can be heated to heat the simulated uterus to body temperature. The base can also provide a rigid hard tissue component that simulates the surface topography of the pelvic bone, portion of the spine, hip joints and heads of the femurs. The hard tissue component can be encased in an elastomeric material that simulates muscles and skin to practice obstetric procedures such as a C-section, insertion of an intrauterine tamponade balloon, insertion of an intrauterine contraceptive device, or insertion of compression sutures such as the B-Lynch suture.
Owner:SOUTER VIVIENNE +1
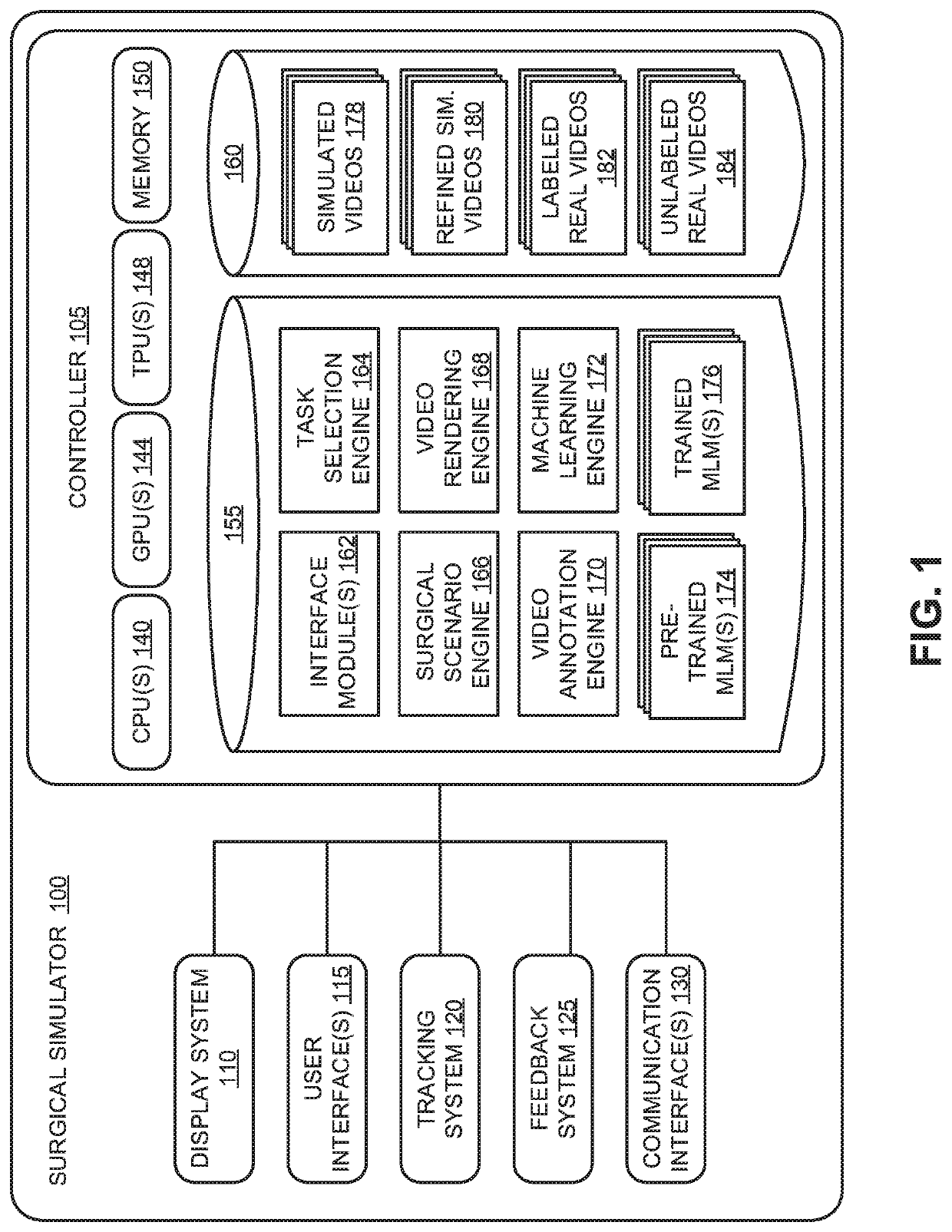
Surgical simulator providing labeled data
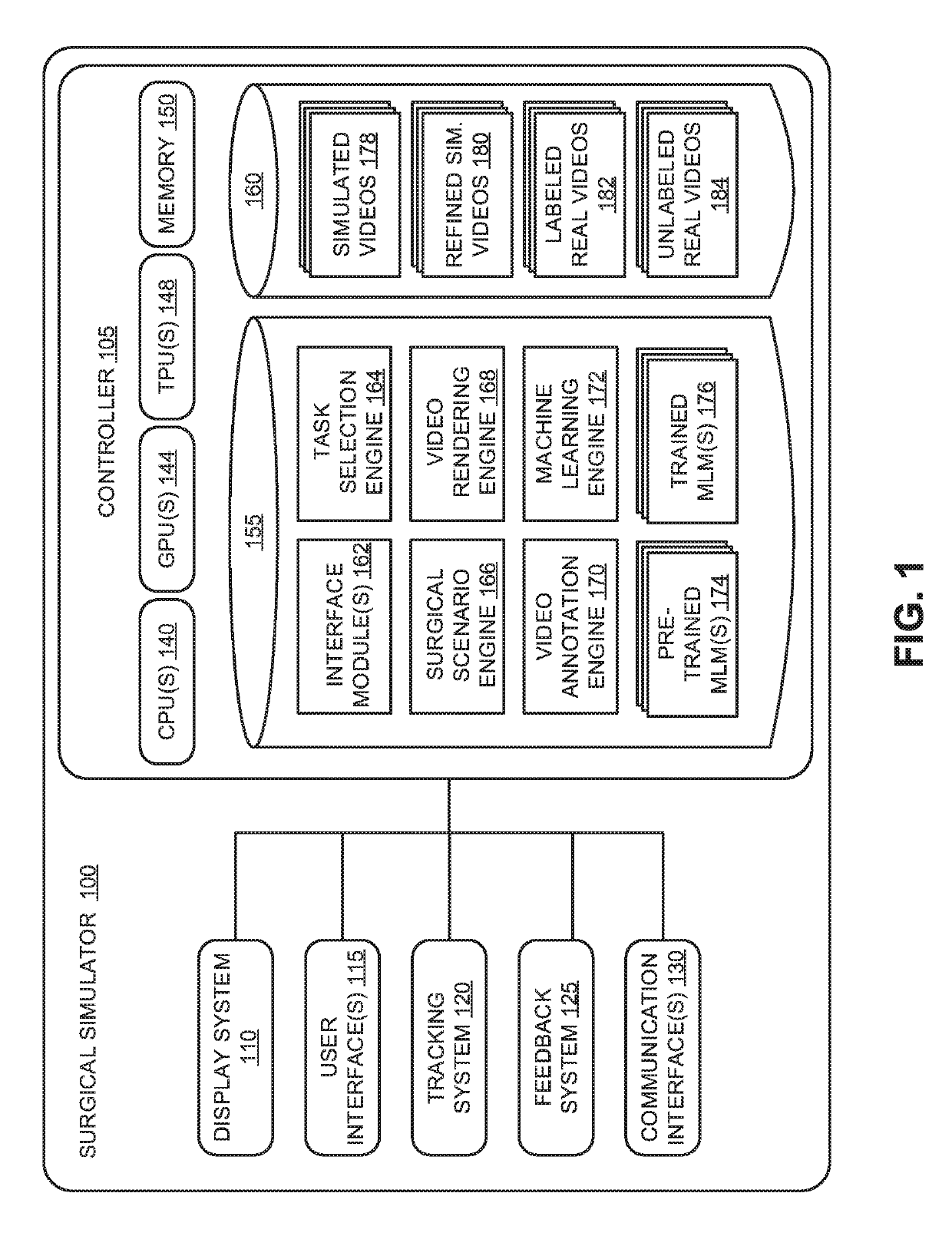
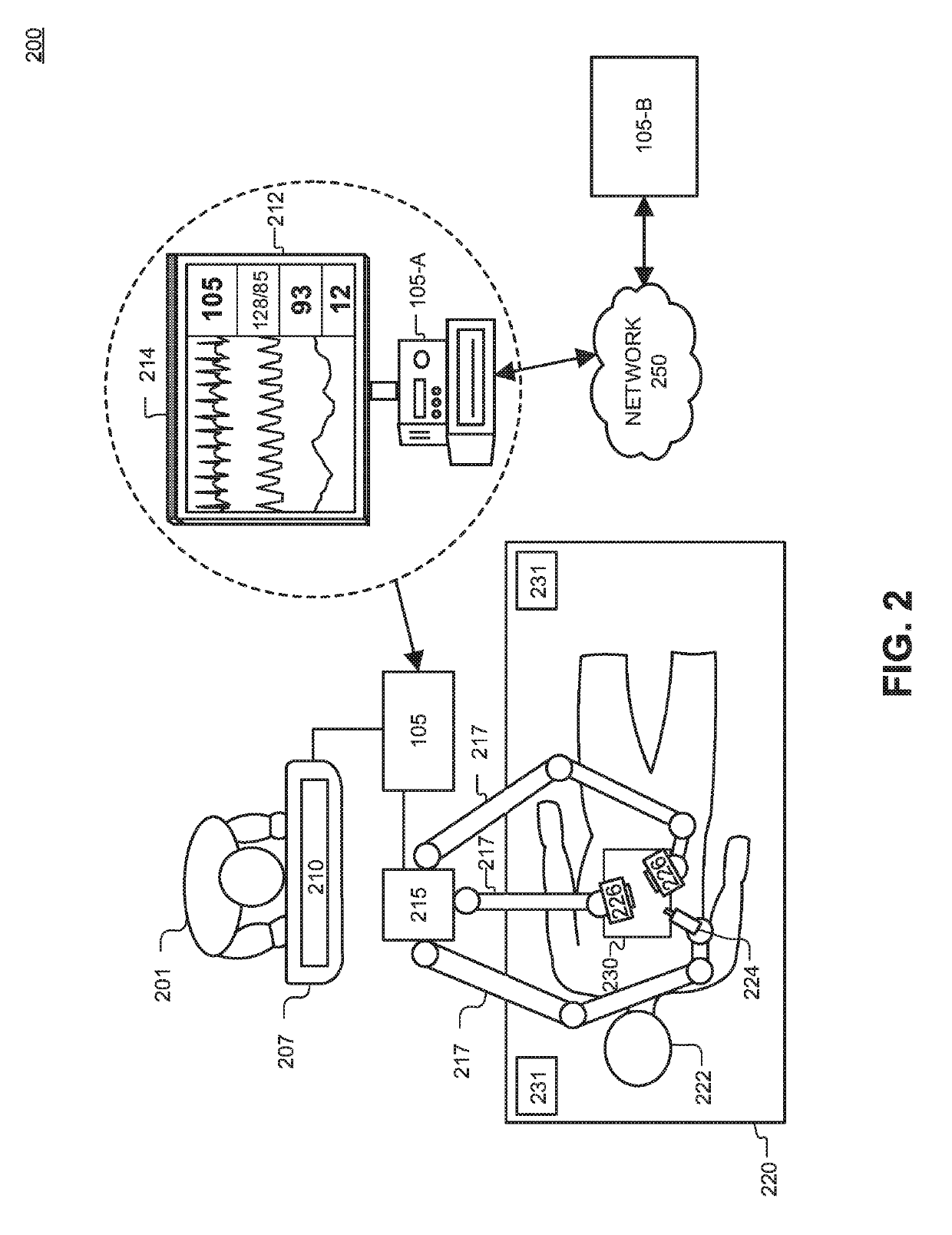
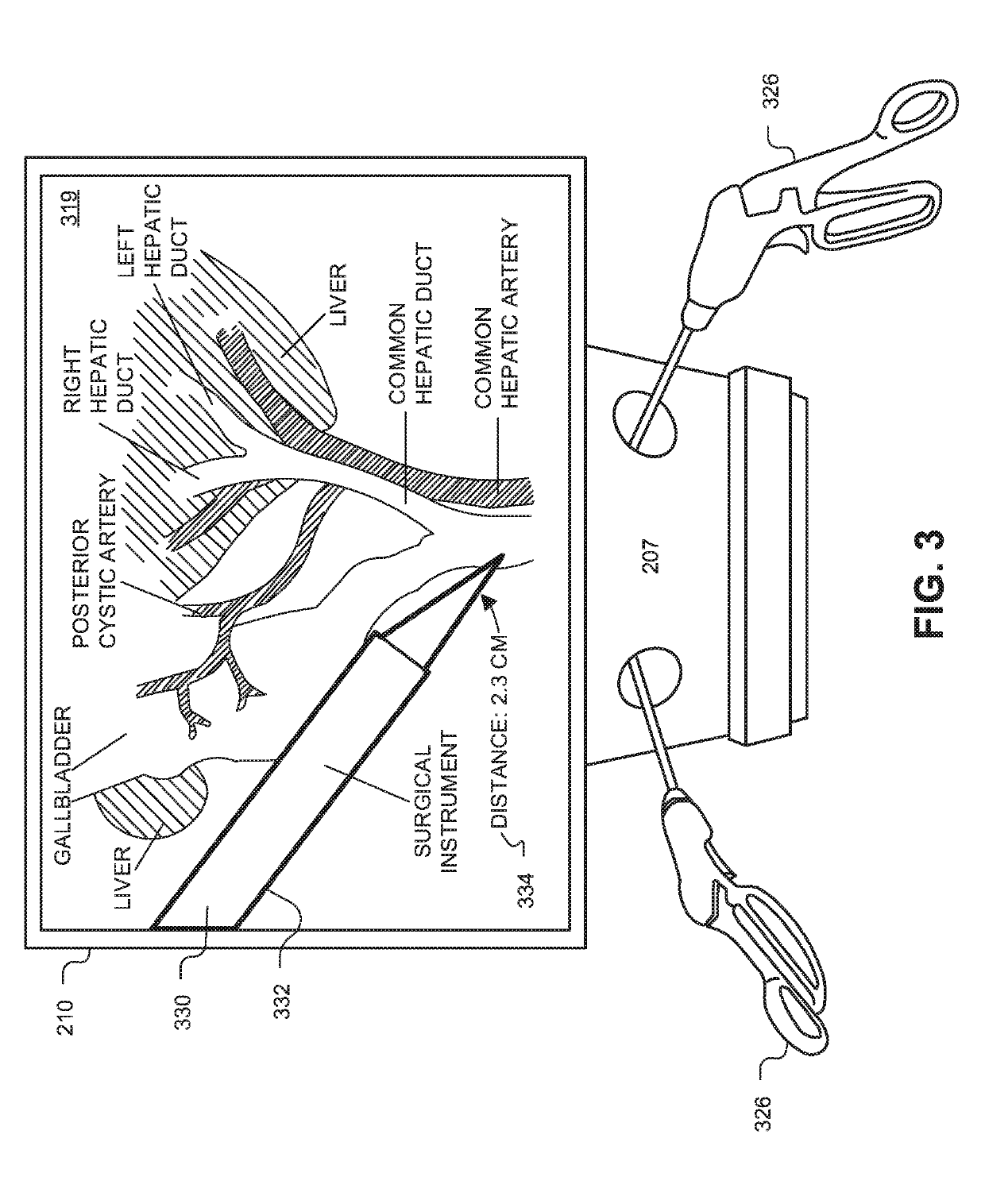
A surgical simulator for simulating a surgical scenario comprises a display system, a user interface, and a controller. The controller includes one or more processors coupled to memory that stores instructions that when executed cause the system to perform operations. The operations include generating simulated surgical videos, each representative of the surgical scenario. The operations further include associating simulated ground truth data from the simulation with the simulated surgical videos. The ground truth data corresponds to context information of at least one of a simulated surgical instrument, a simulated anatomical region, a simulated surgical task, or a simulated action. The operations further include annotating features of the simulated surgical videos based, at least in part, on the simulated ground truth data for training a machine learning model.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
Method and system for generating a surgical training module
ActiveUS8924334B2Improve versatilityEasy to trainCosmonautic condition simulationsDigital data processing detailsSimulationSurgical simulator
A system (1) comprises a physical surgical simulator (11) which transmits data concerning physical movement of training devices to an analysis engine (12). The engine (12) automatically generates rules for a rule base (13a) in a learning system (13). The learning system (13) also comprises content objects (13b) and 3D scenario objects (13c). A linked set of a 3D scenario object (13c), a rule base (13a), and a content object (13b) are together a lesson (10). Another simulator (14) is operated by a student. This transmits data concerning physical movement of training devices by a student to a verification engine (15). The verification engine (15) interfaces with the rule base (13a) to display the lesson in the manner defined by the lesson rule base (13a). It calculates performance measures defined in the lesson rule base (13a). It also records the performance measures into a lesson record (18) and it adapts the display of the lesson in line with the parameters defined in the lesson rule base (13a).
Owner:CAE HEALTHCARE CANADA
Hysterectomy model
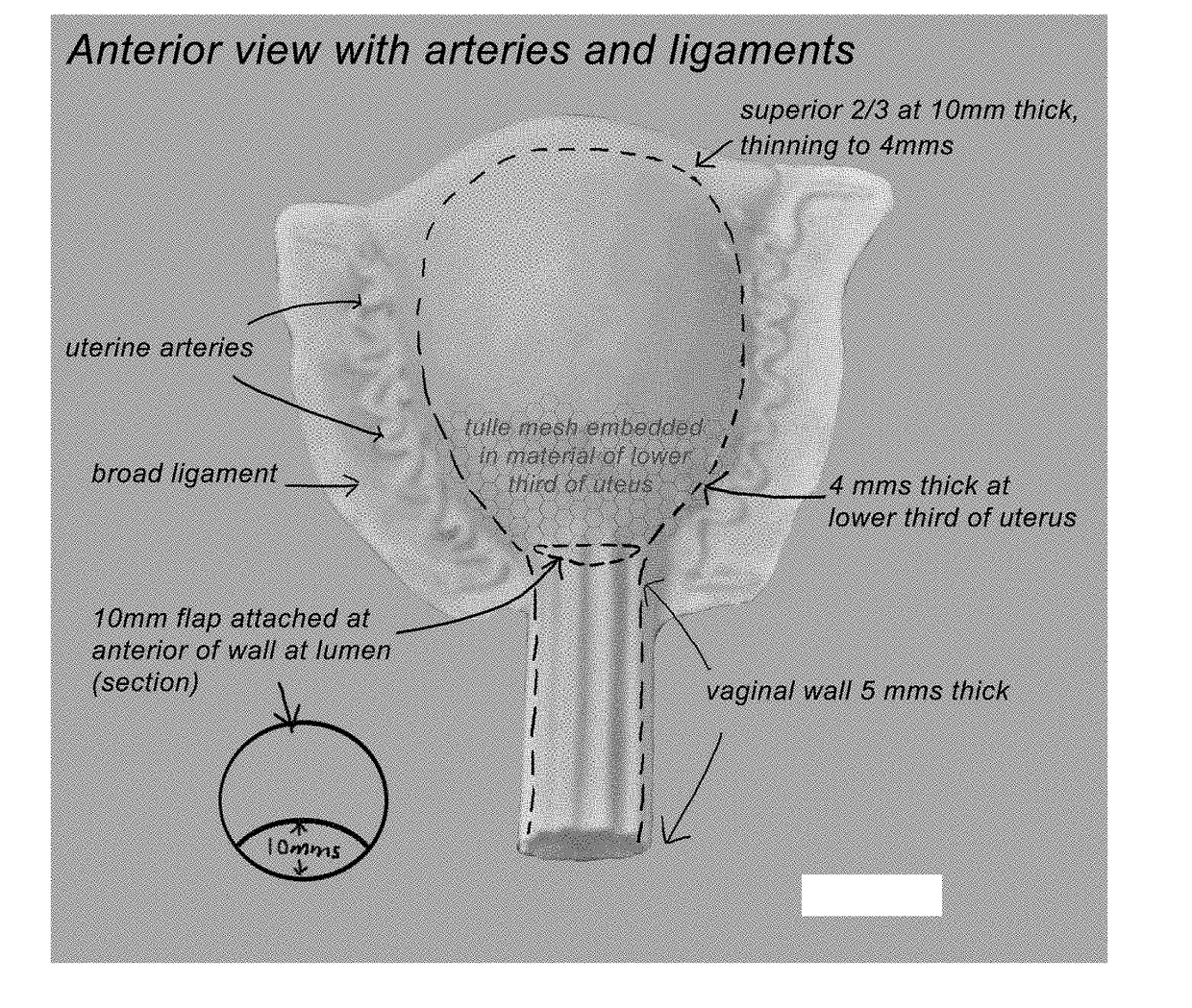
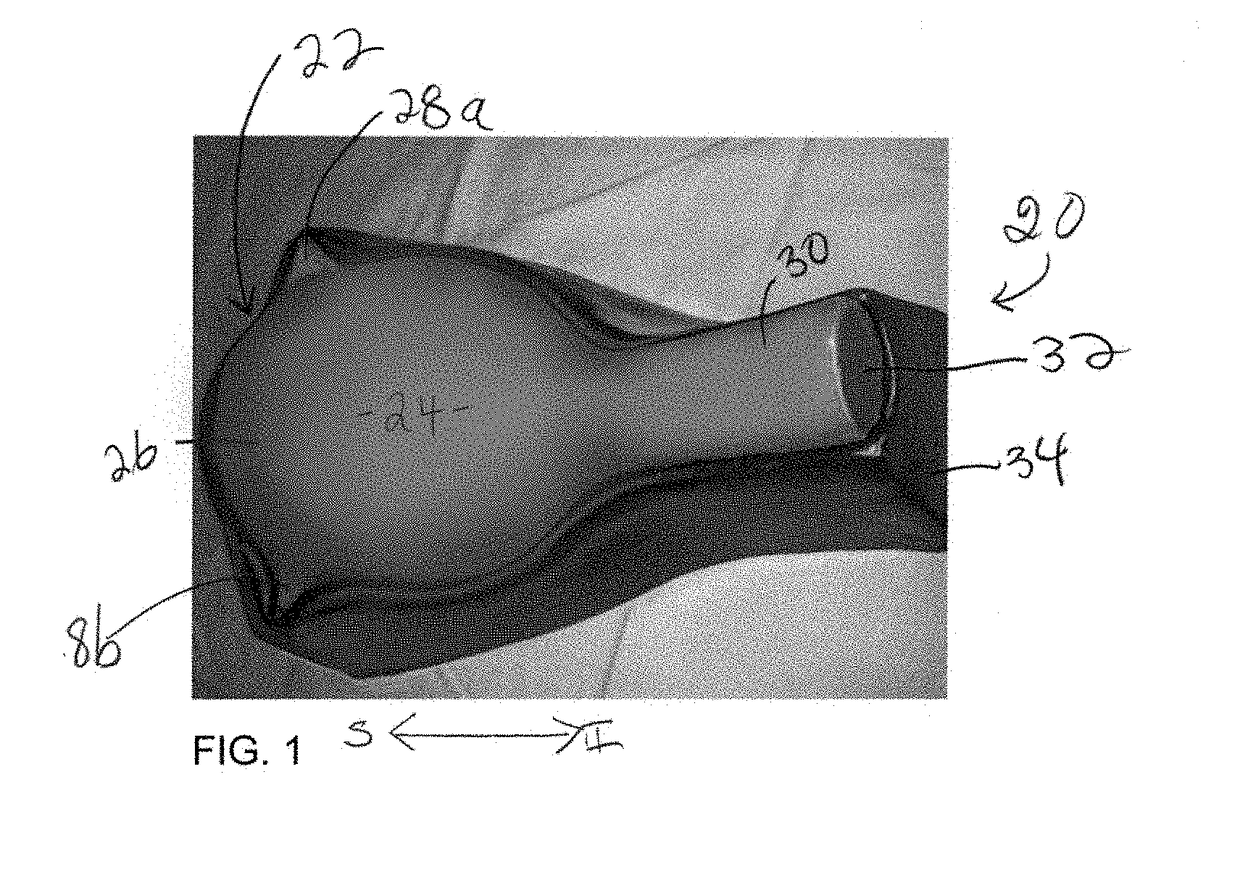
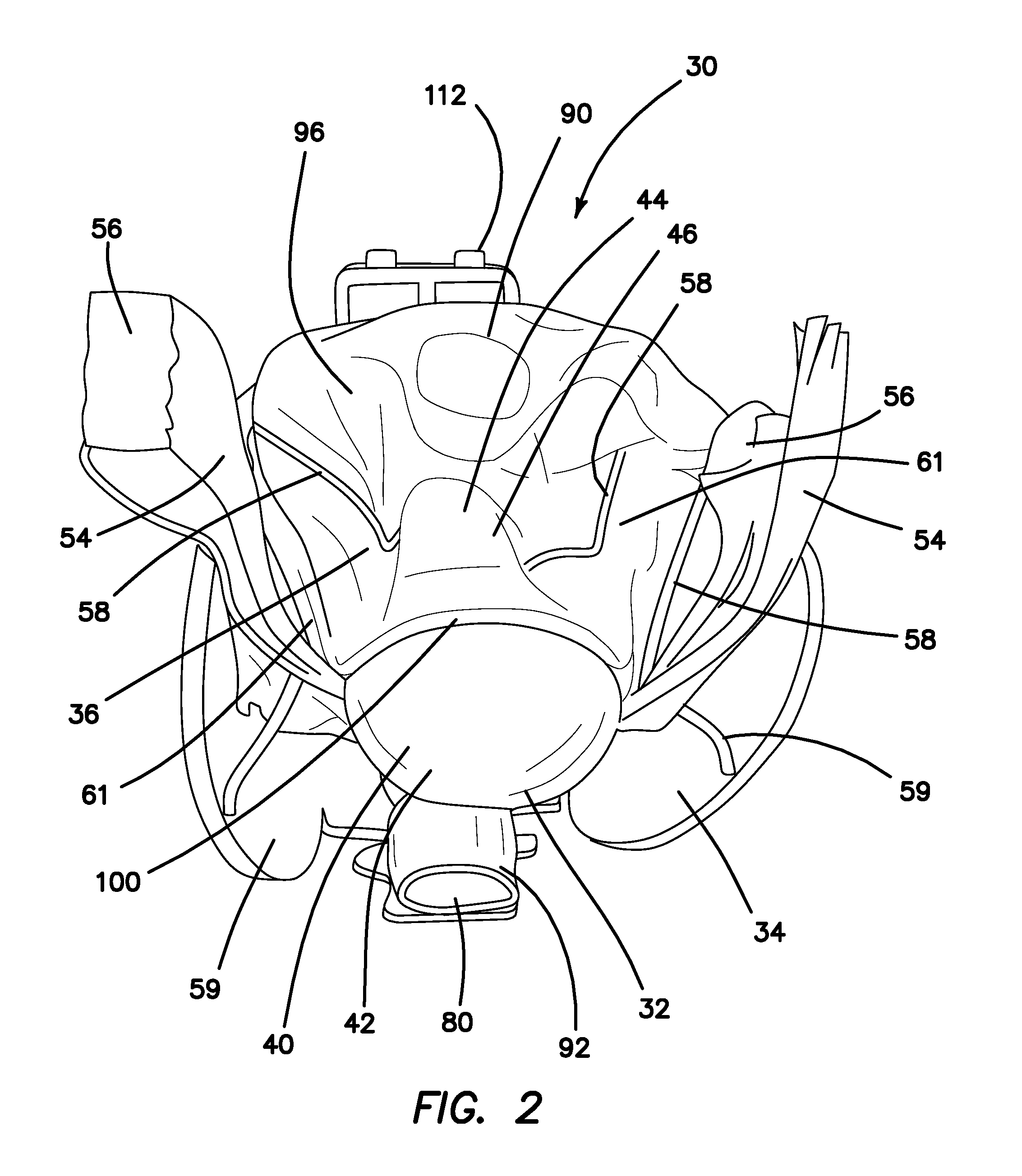
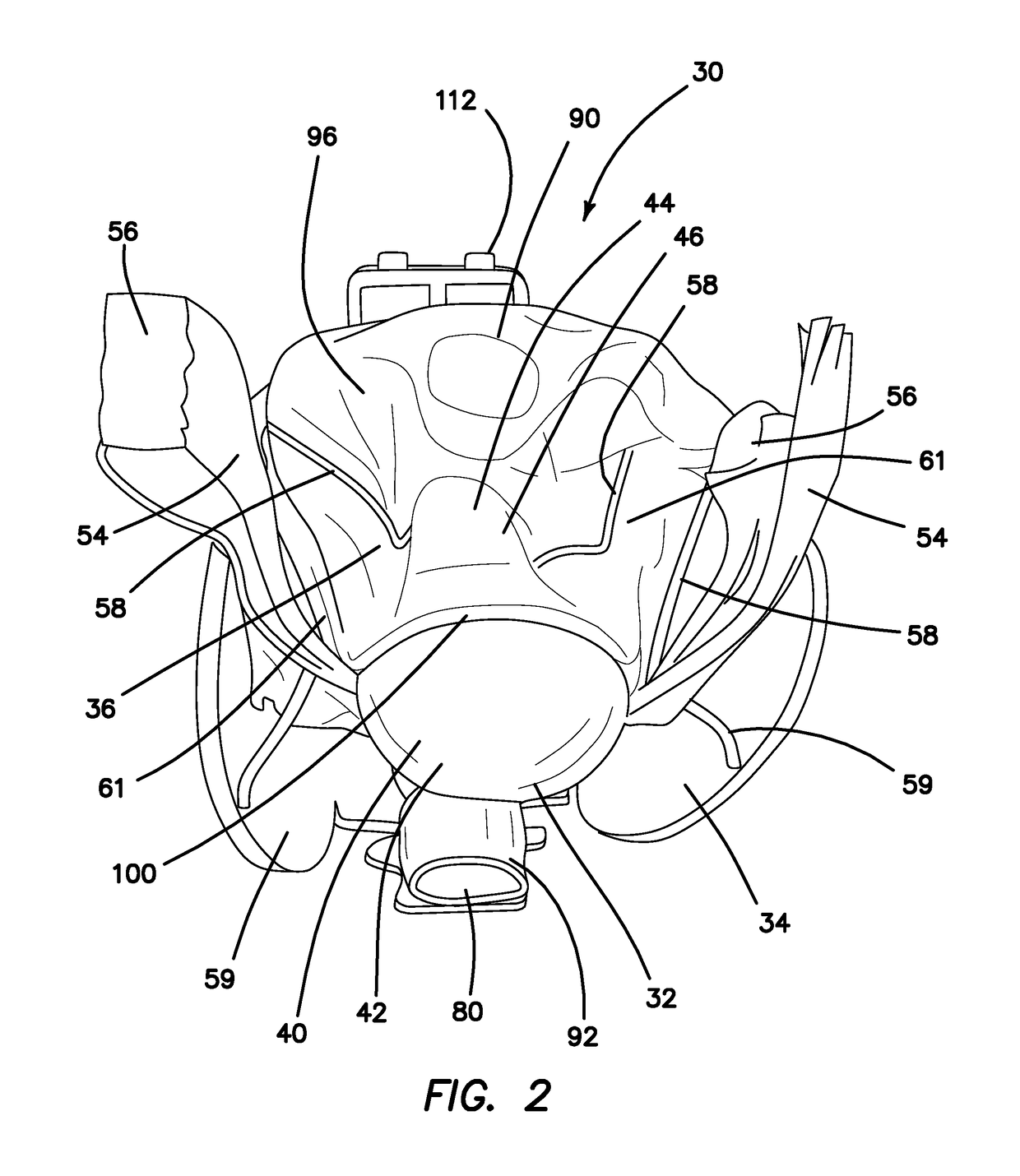
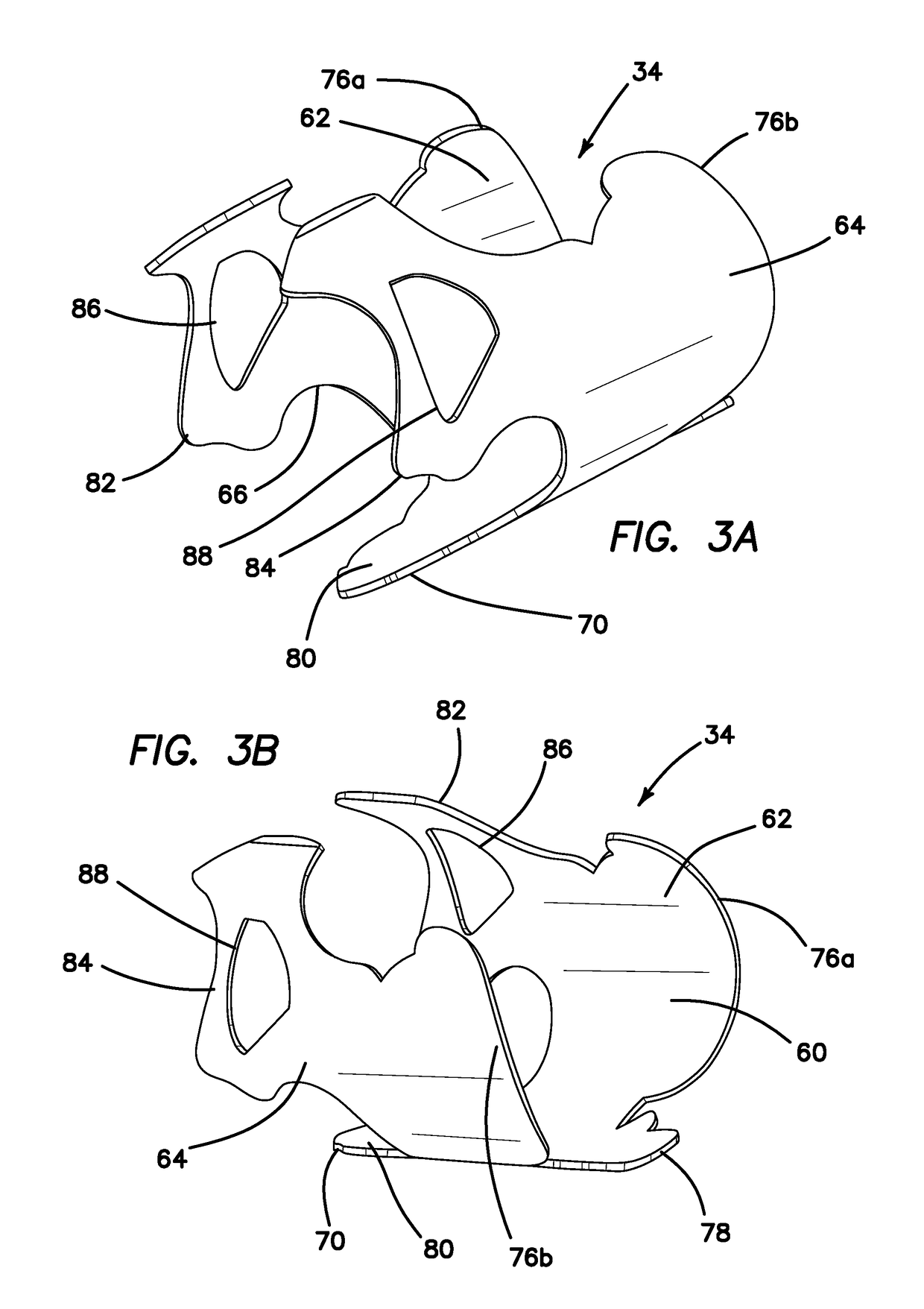
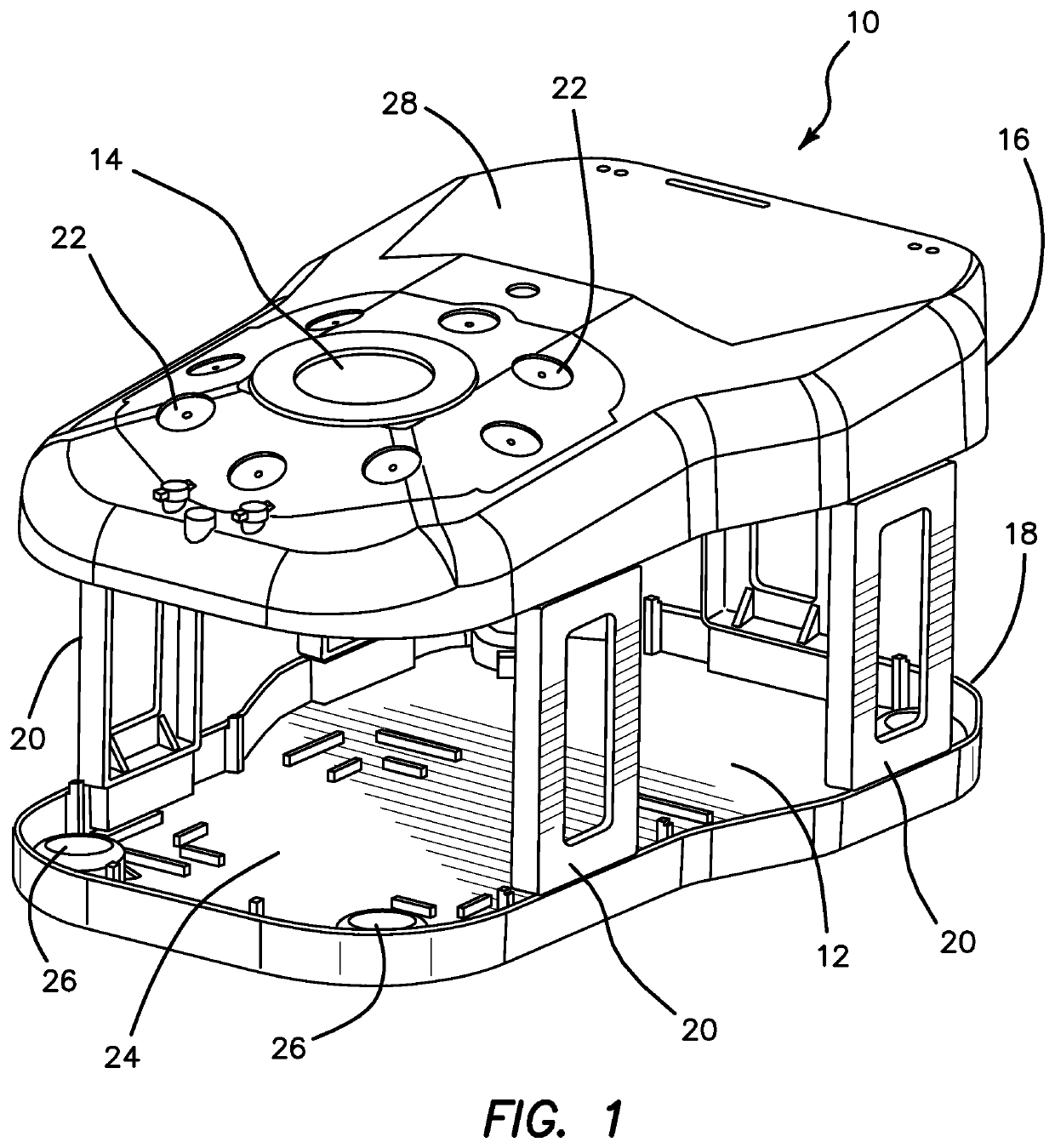
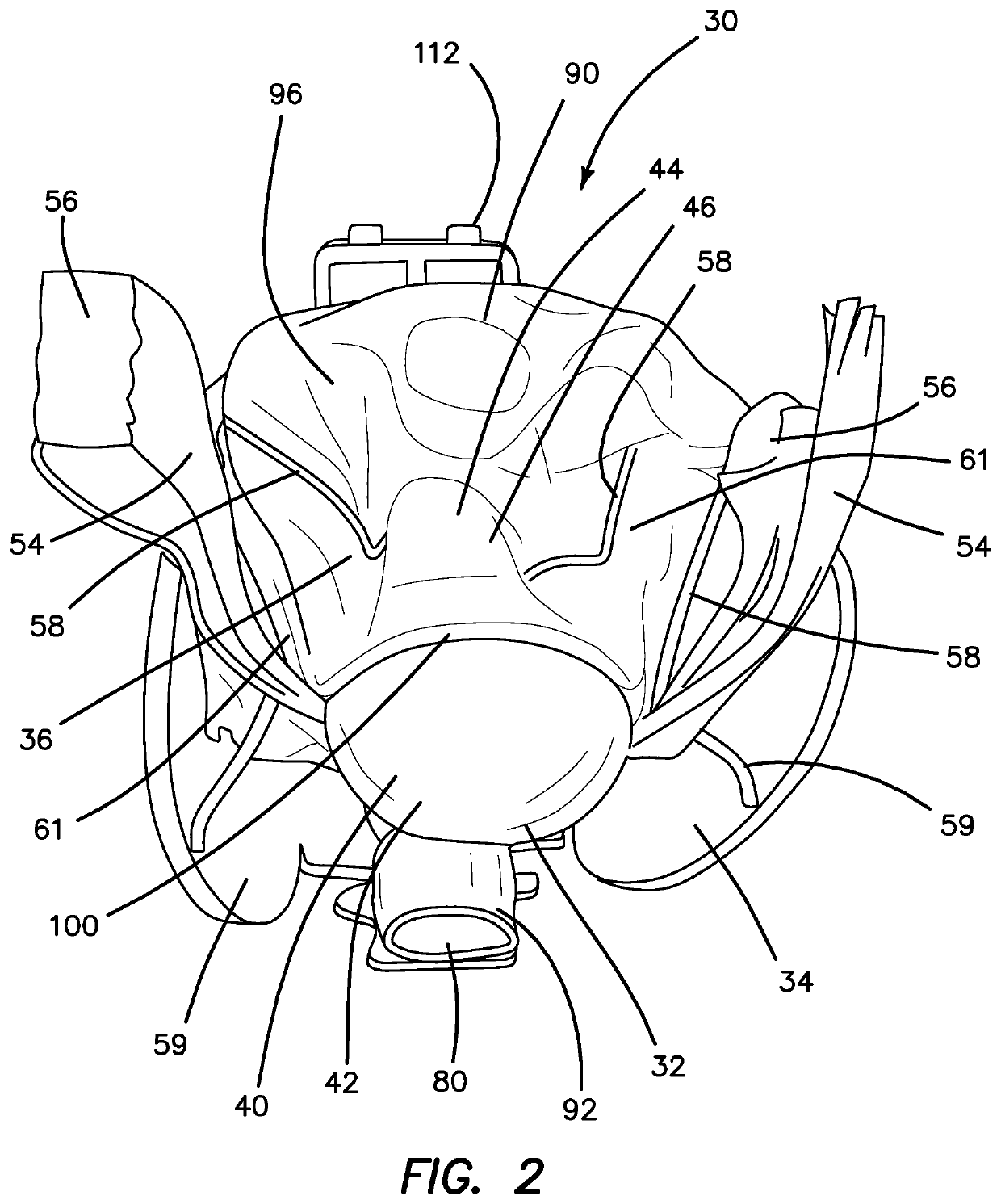
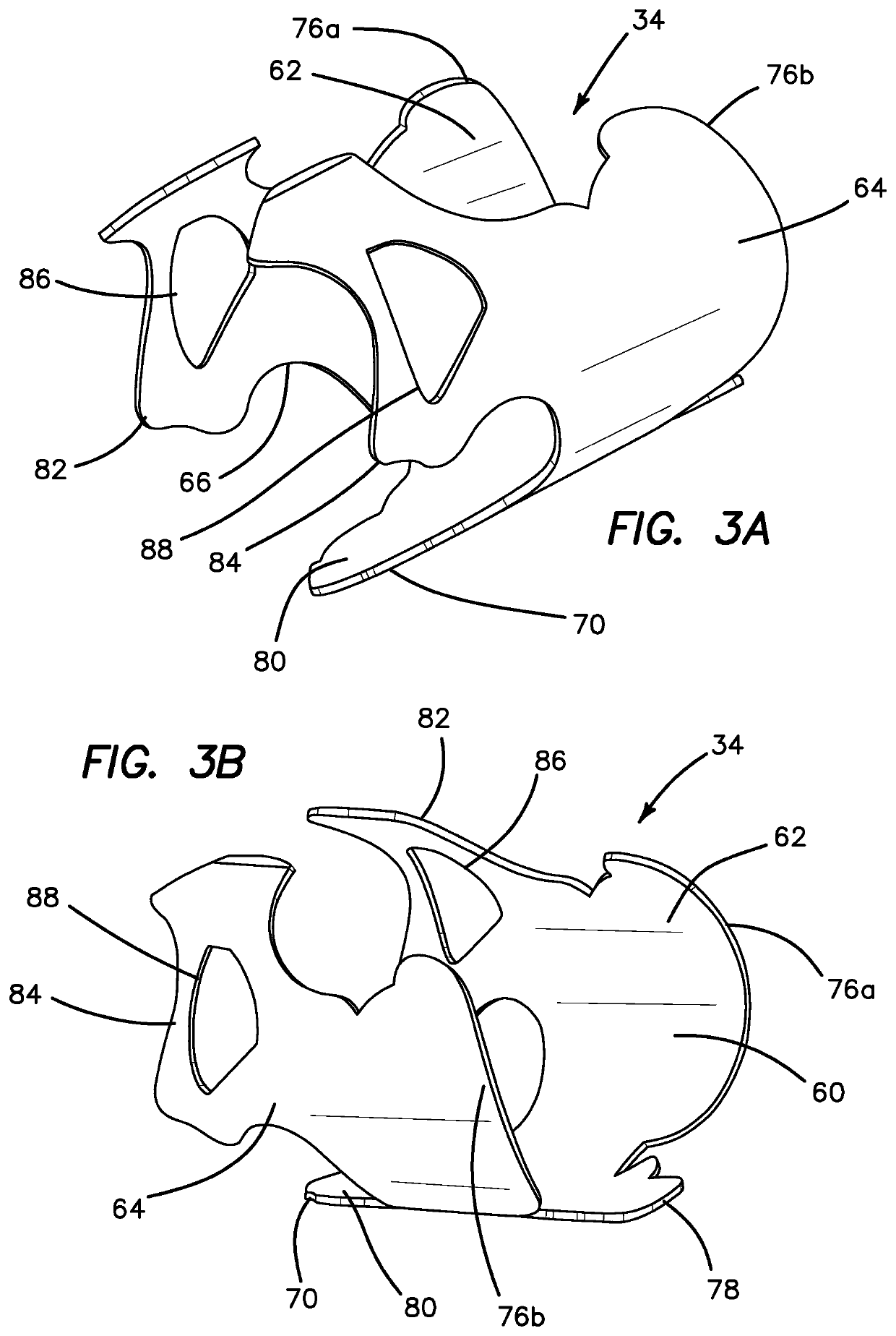
A surgical simulator for surgical training is provided. The simulator includes a frame defining an enclosure and a simulated tissue model located inside an enclosure. The simulated tissue model is adapted for practicing hysterectomies and includes at least a simulated uterus and a simulated vagina. The simulated tissue model is suspending inside the enclosure with two planar sheets of silicone such that the tissue model is located between the two sheets each of which form a fold and are in turn connected to the frame. The frame may be shaped like a cylinder and located inside a cavity of a larger laparoscopic trainer having a penetrable simulated abdominal wall. The tissue model is interchangeable and accessible laterally through an aperture provided in a support leg of the trainer.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Hysterectomy model
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Hysterectomy model
ActiveUS10720084B2Improve confinementReduce swingCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationPhysical therapy
A surgical simulator for surgical training is provided. The simulator includes a frame defining an enclosure and a simulated tissue model located inside the enclosure. The simulated tissue model is adapted for practicing a number of surgical procedures including but not limited to transanal excisions and transvaginal hysterectomies. The simulated tissue model includes one more components and is interchangeably connected to the frame with fasteners configured to pass through apertures in the frame to suspend the simulated tissue model within the frame. The enclosure of the frame is increasingly laterally constricted along the longitudinal axis to progressively increase the confinement of the components of the simulated tissue model.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
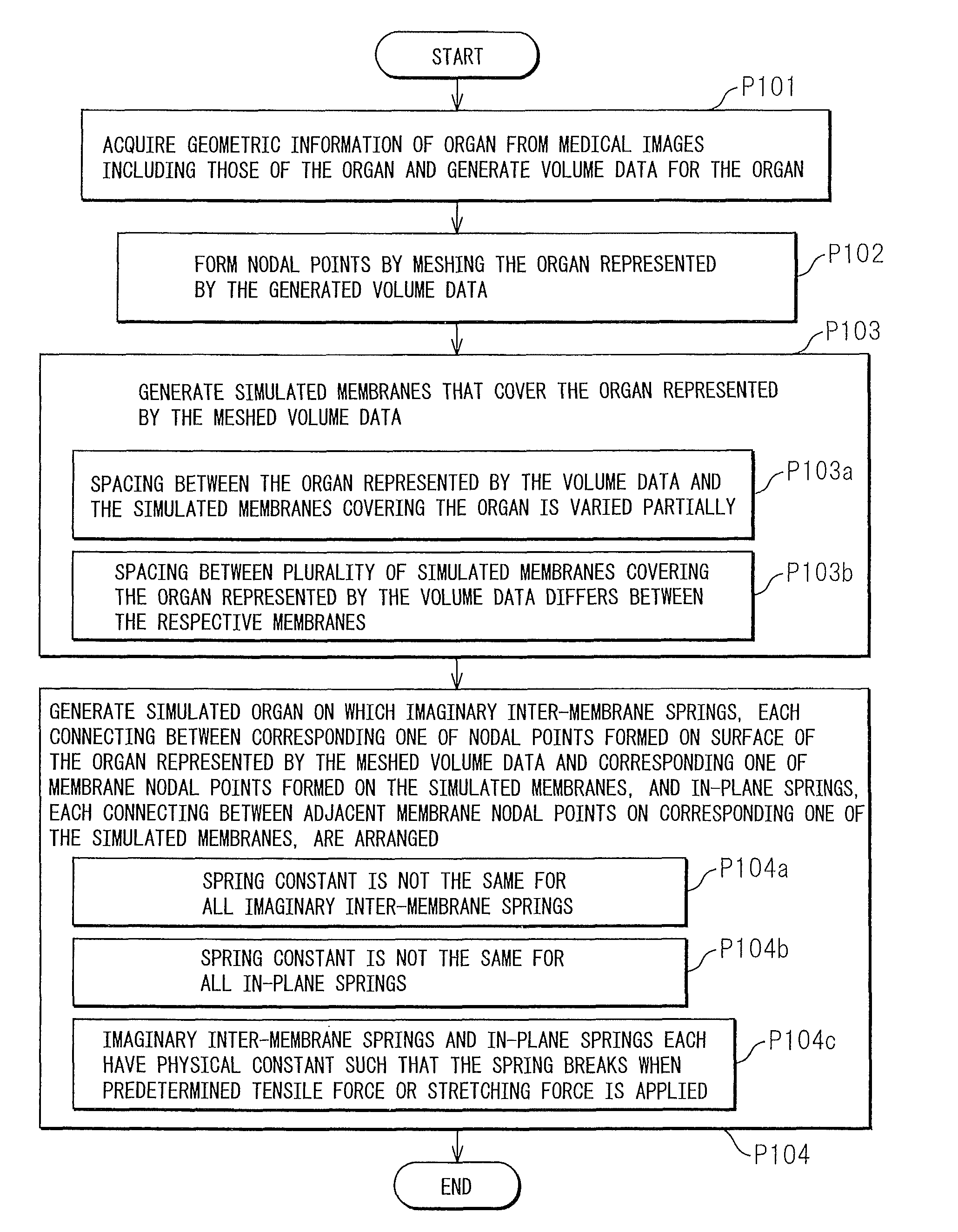
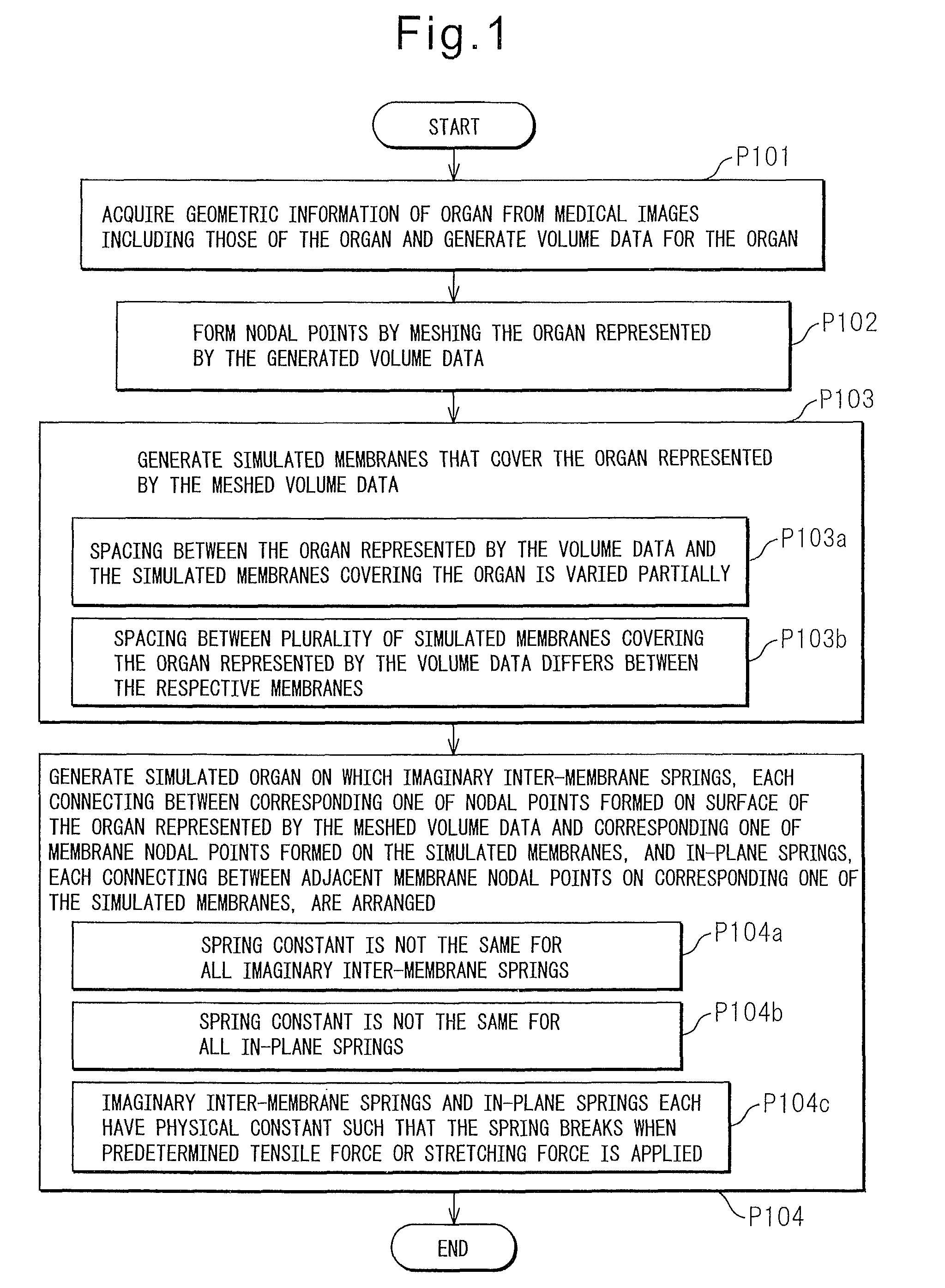
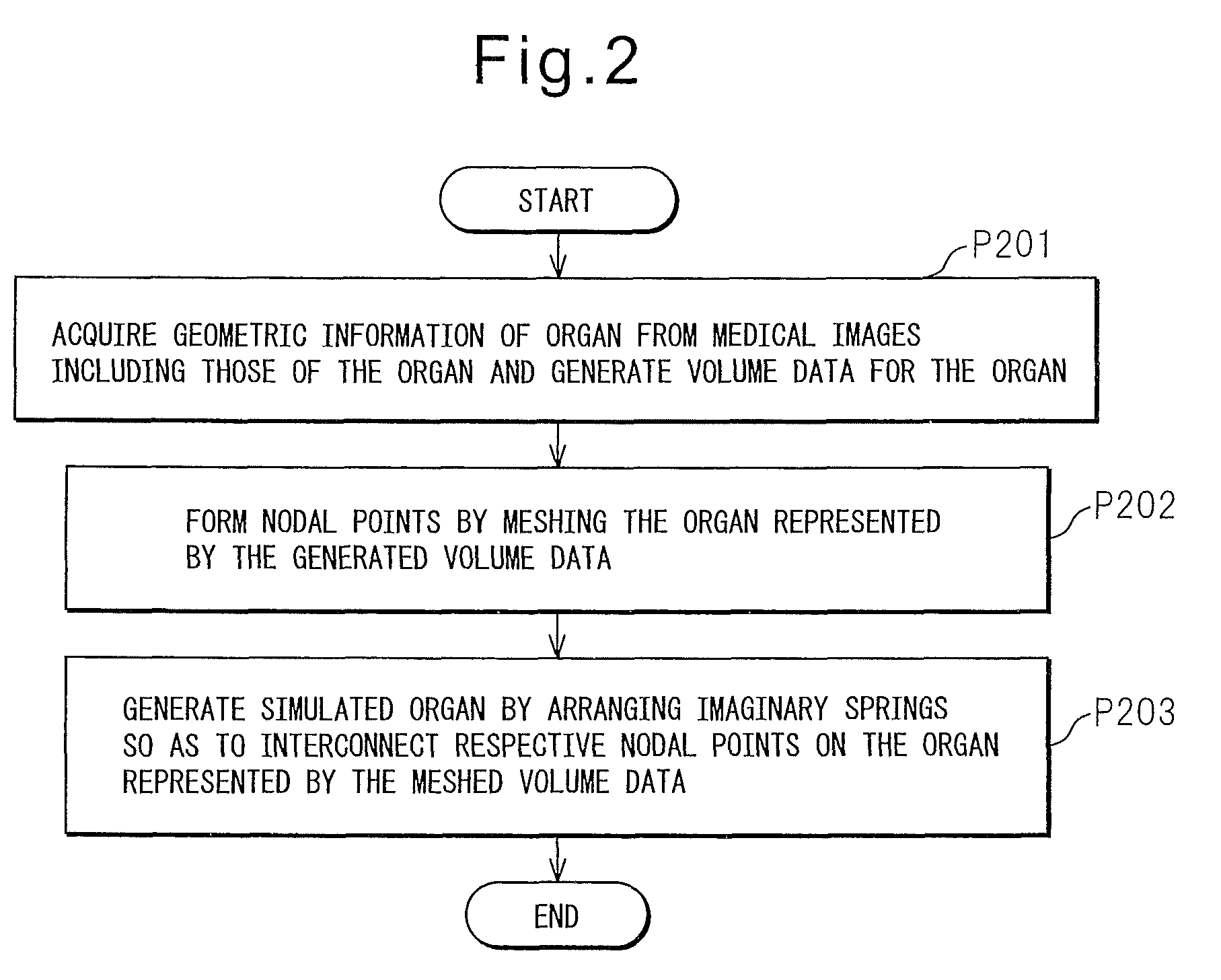
Surgical simulation model generating method, surgical simulation method, and surgical simulator
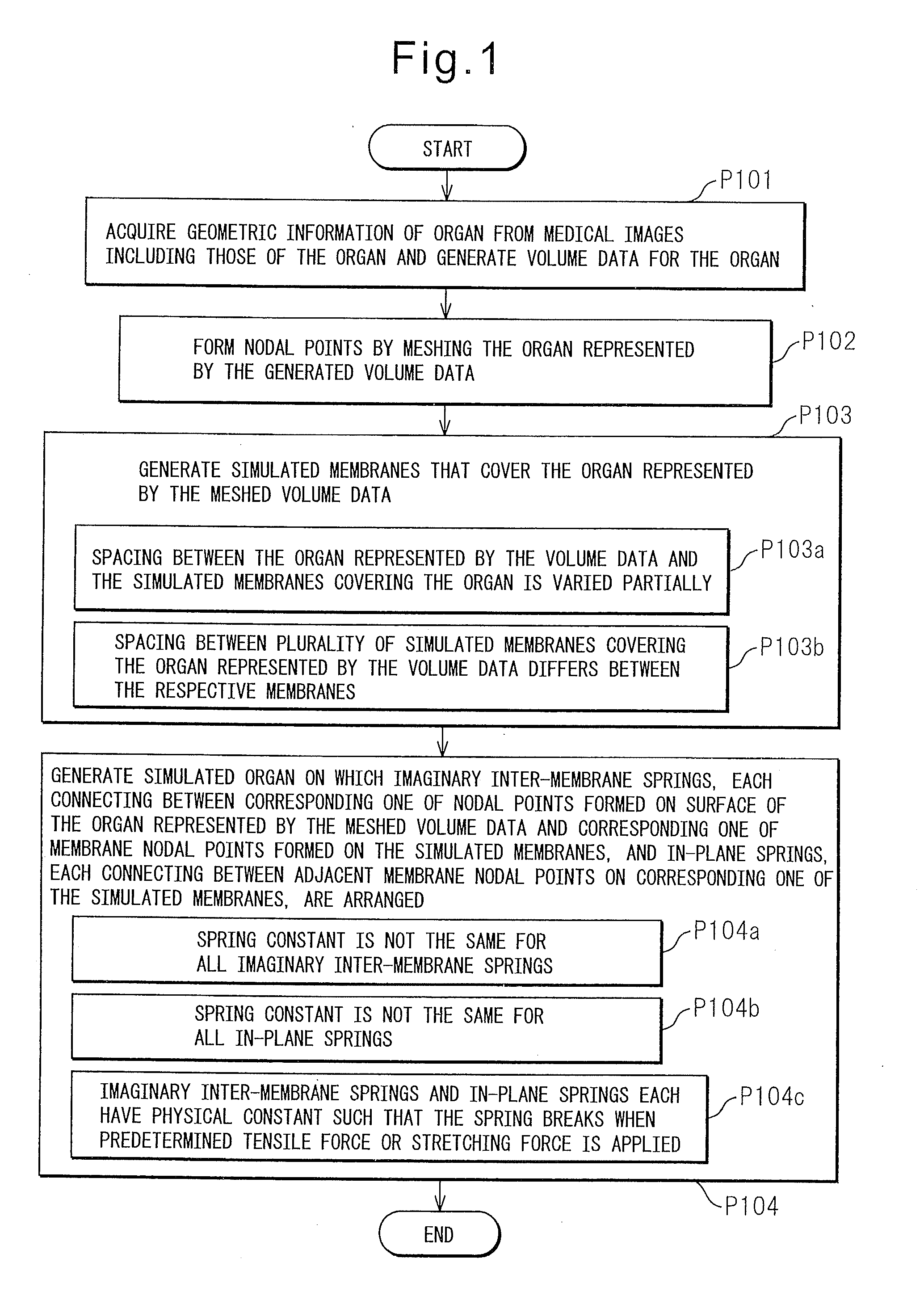
A surgical simulation model generating method includes: a first process in which a computing unit acquires geometrical information of an organ from a medical image stored in a storage unit, including an image of the organ, and generates volume data for the organ; a second process in which, after the first process, the computing unit forms nodal points by meshing the organ represented by the generated volume data; a third process in which the computing unit generates a simulated membrane that covers the organ represented by the volume data meshed in the second process; and a fourth process in which the computing unit generates a simulated organ by drawing an imaginary line so as to extend from each nodal point formed on a surface of the organ represented by the volume data meshed in the second process in a direction that intersects the simulated membrane and thereby forming a membrane nodal point at a point where the imaginary line intersects the simulated membrane generated in the third process, and by arranging on each imaginary line an imaginary inter-membrane spring that connects between the nodal point formed on the surface of the organ and the membrane nodal point, while also arranging an in-plane spring that connects between adjacent membrane nodal points on the simulated membrane.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PRECISION
Combined soft tissue and bone surgical simulator
A surgery simulator includes a physical surrogate surgical interface that represents an interface between a user and a simulated patient in a simulated surgical scenario that involves manipulation of both simulated hard and soft tissue. Sensor(s) sense the user's manipulation of the surrogate surgical interface. A surgical simulation generator generates a real time 3D surgical simulation of the surgical scenario based on the manipulation sensed by the sensor(s). The real time 3D surgical simulation comprises real time simulation state data. The surgical simulation generator renders the real time simulation state data into a real time computer graphics generated video representation of the surgical simulation and provides the real time video representation to a display for real time viewing by the user. The surgical simulation generator simulates effects of the manipulation on both simulated hard tissue and simulated soft tissue of the simulated patient.
Owner:SIMQUEST
Surgical simulation model generating method, surgical simulation method, and surgical simulator
A surgical simulation model generating method includes: a first process in which a computing unit acquires geometrical information of an organ from a medical image stored in a storage unit, including an image of the organ, and generates volume data for the organ; a second process in which, after the first process, the computing unit forms nodal points by meshing the organ represented by the generated volume data; a third process in which the computing unit generates a simulated membrane that covers the organ represented by the volume data meshed in the second process; and a fourth process in which the computing unit generates a simulated organ by drawing an imaginary line so as to extend from each nodal point formed on a surface of the organ represented by the volume data meshed in the second process in a direction that intersects the simulated membrane and thereby forming a membrane nodal point at a point where the imaginary line intersects the simulated membrane generated in the third process, and by arranging on each imaginary line an imaginary inter-membrane spring that connects between the nodal point formed on the surface of the organ and the membrane nodal point, while also arranging an in-plane spring that connects between adjacent membrane nodal points on the simulated membrane.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PRECISION
Wearable Partial Task Surgical Simulator
A wearable device for simulating wounds and injuries received during a trauma event includes a raiment and vest for covering the torso of a person. The raiment has an outer surface with a color and a texture comparable to human skin. Mounted on the outer surface is at least one wound simulator formed with an orifice that is in fluid communication with a fluid reservoir. Thus, the person can selectively expel a blood-like fluid from the reservoir, and through the wound simulator orifice, to simulate a trauma event. The vest includes an artificial rib cage and prosthetic internal organs juxtaposed with at least one wound simulator to simulate internal effects of a trauma event.
Owner:STRATEGIC OPERATIONS INC
Surgical simulator providing labeled data
A surgical simulator for simulating a surgical scenario comprises a display system, a user interface, and a controller. The controller includes one or more processors coupled to memory that stores instructions that when executed cause the system to perform operations. The operations include generating simulated surgical videos, each representative of the surgical scenario. The operations further include associating simulated ground truth data from the simulation with the simulated surgical videos. The ground truth data corresponds to context information of at least one of a simulated surgical instrument, a simulated anatomical region, a simulated surgical task, or a simulated action. The operations further include annotating features of the simulated surgical videos based, at least in part, on the simulated ground truth data for training a machine learning model.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
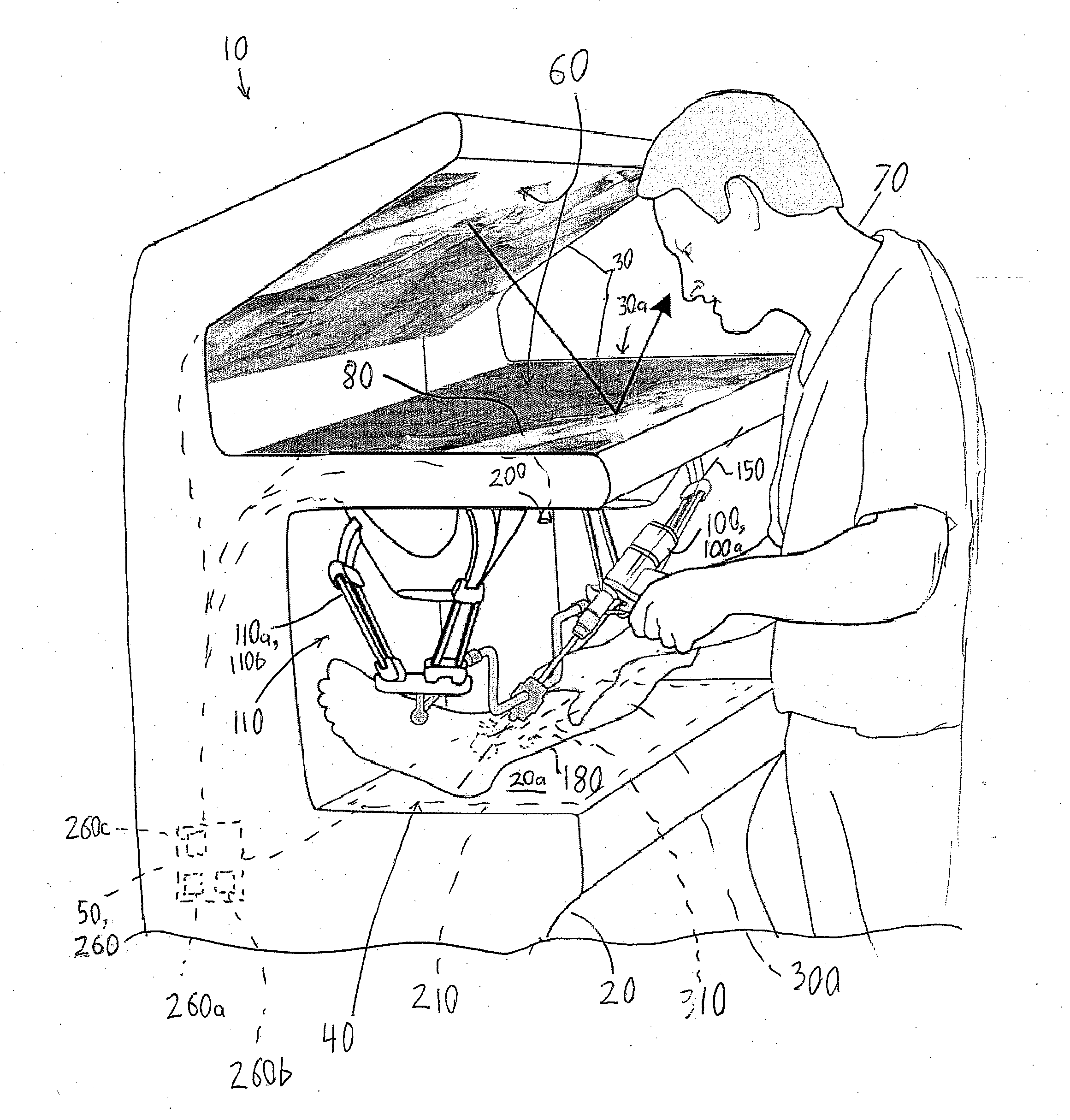
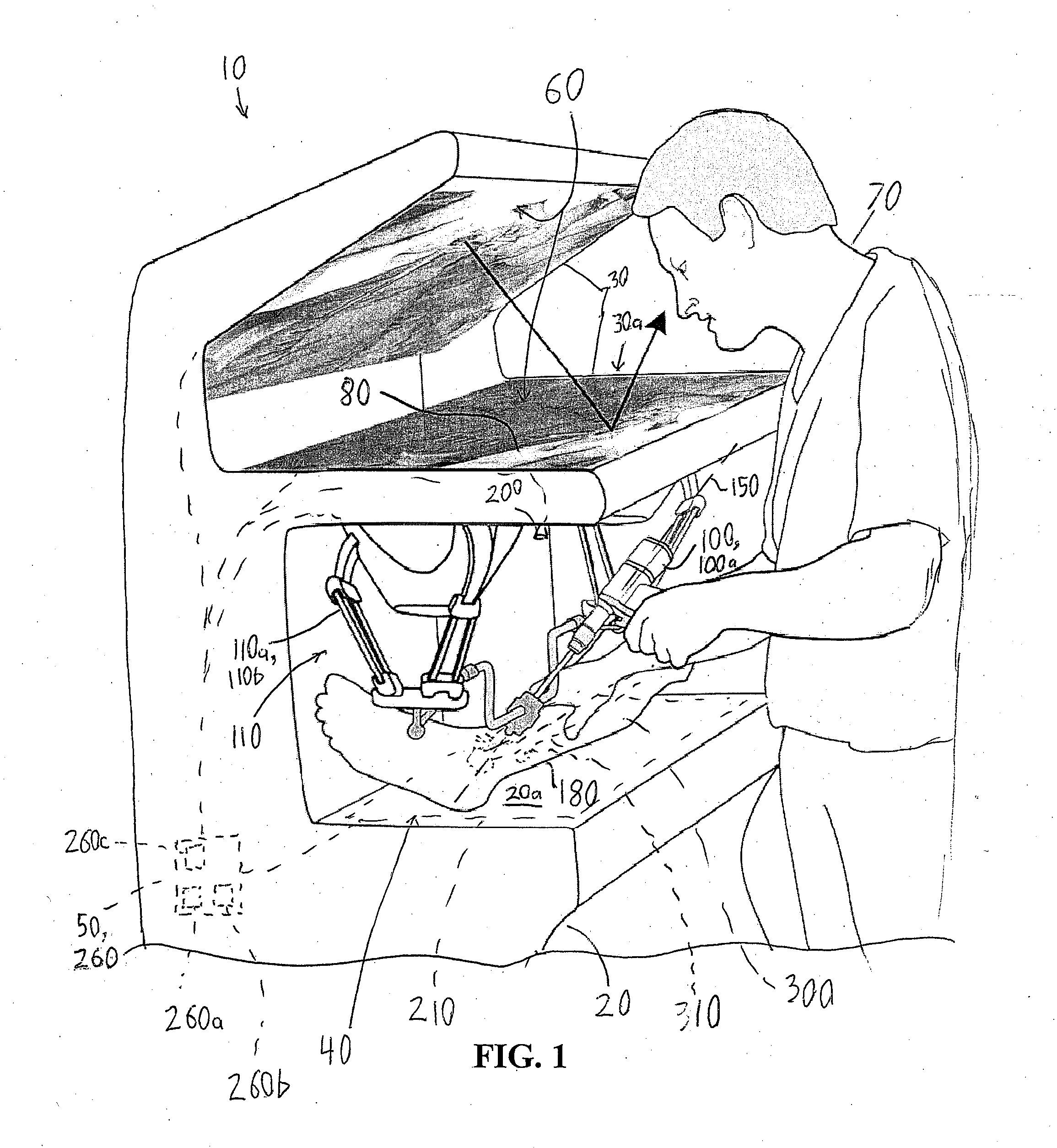
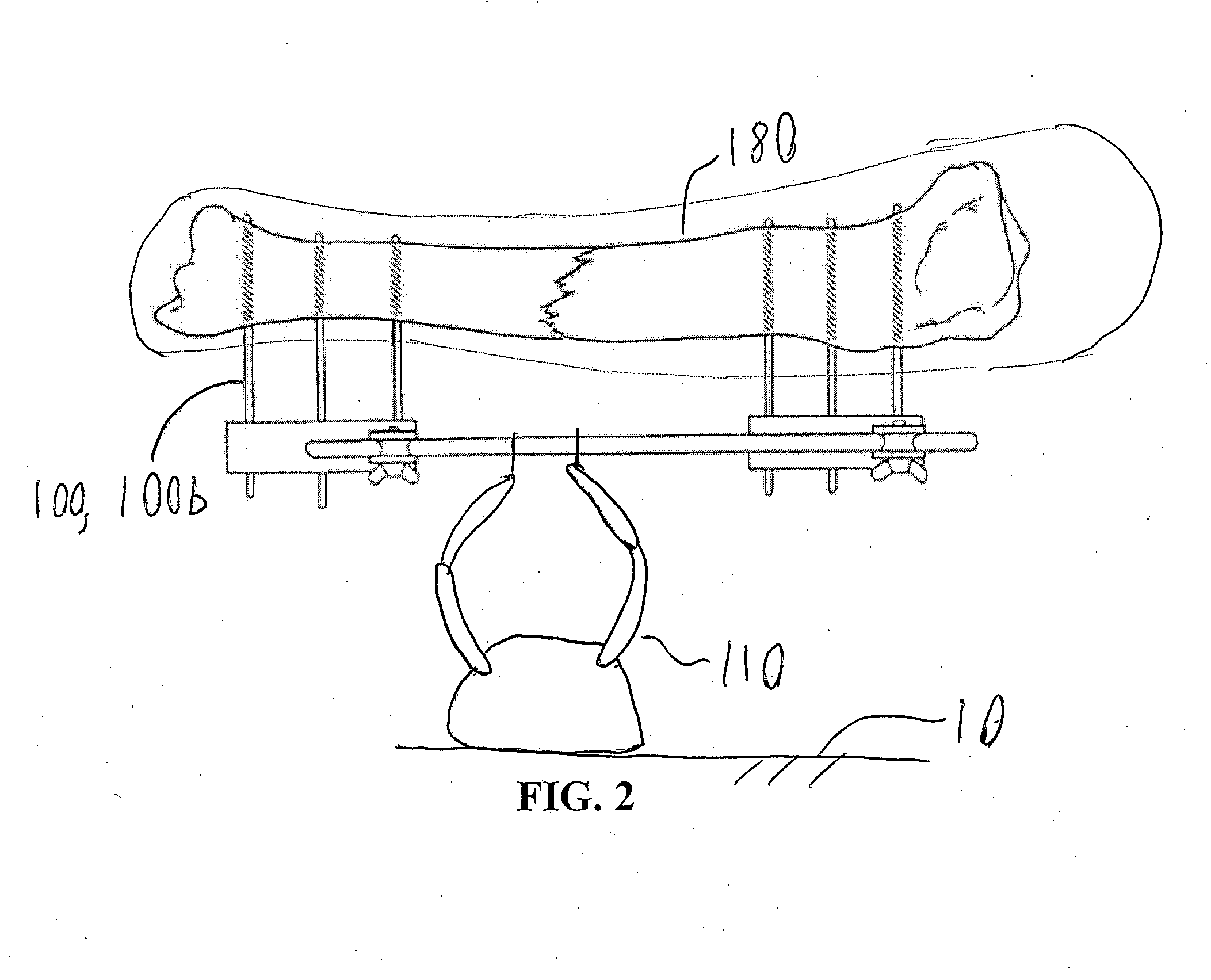
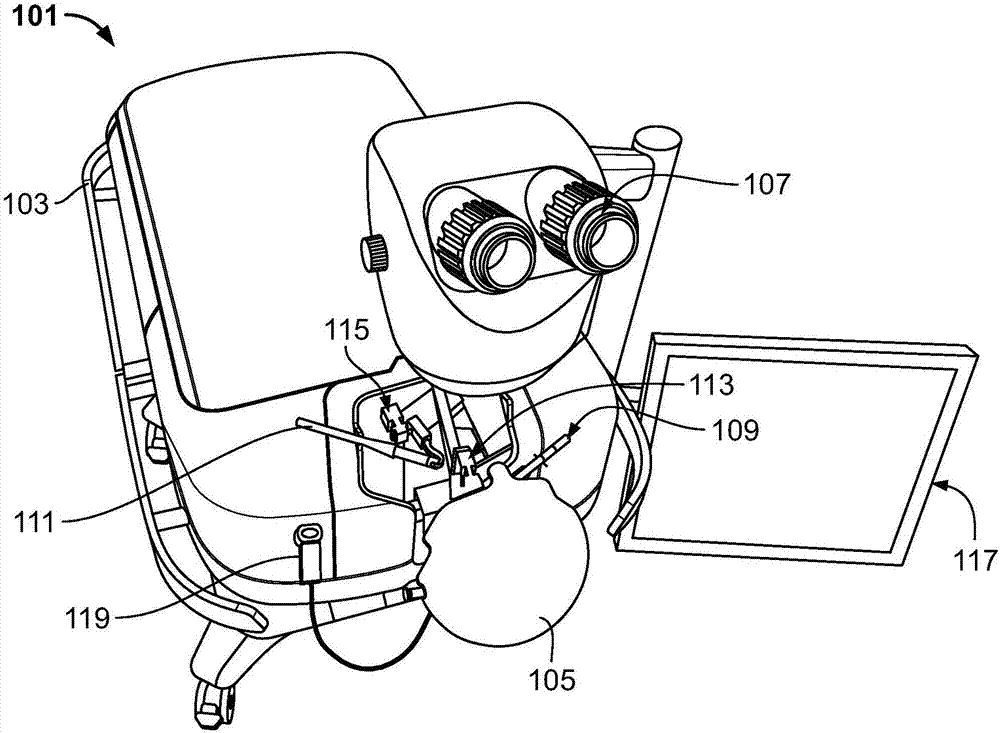
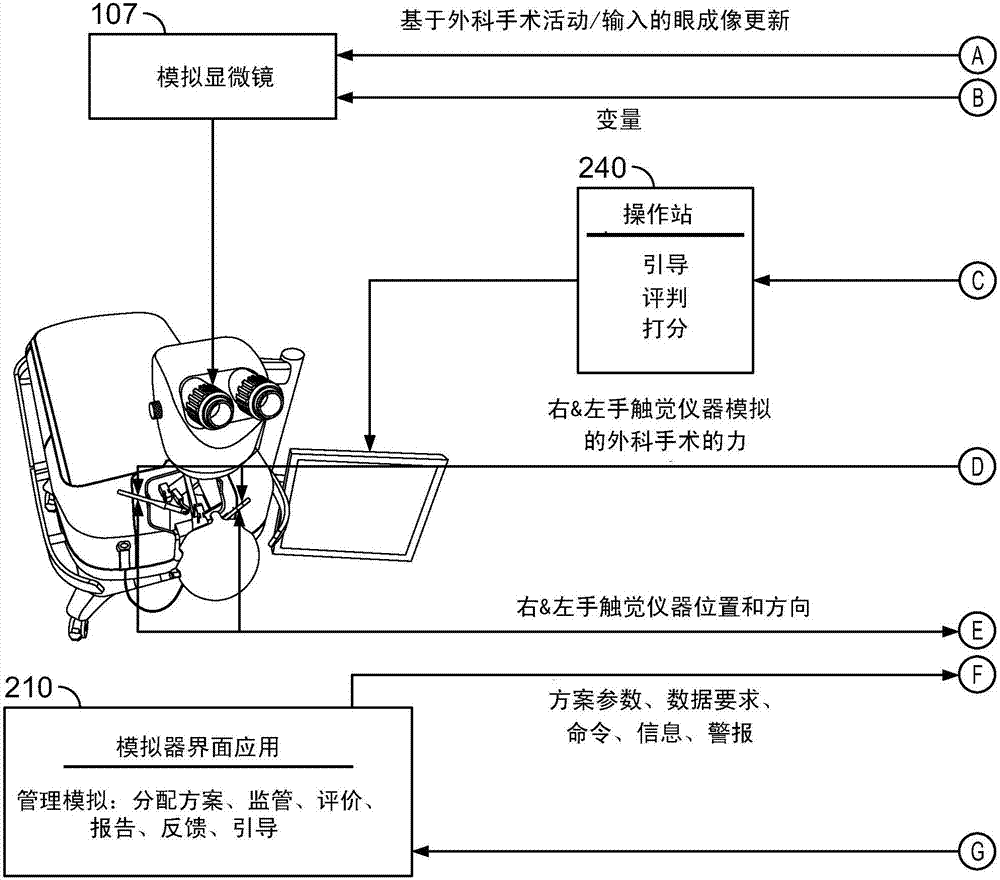
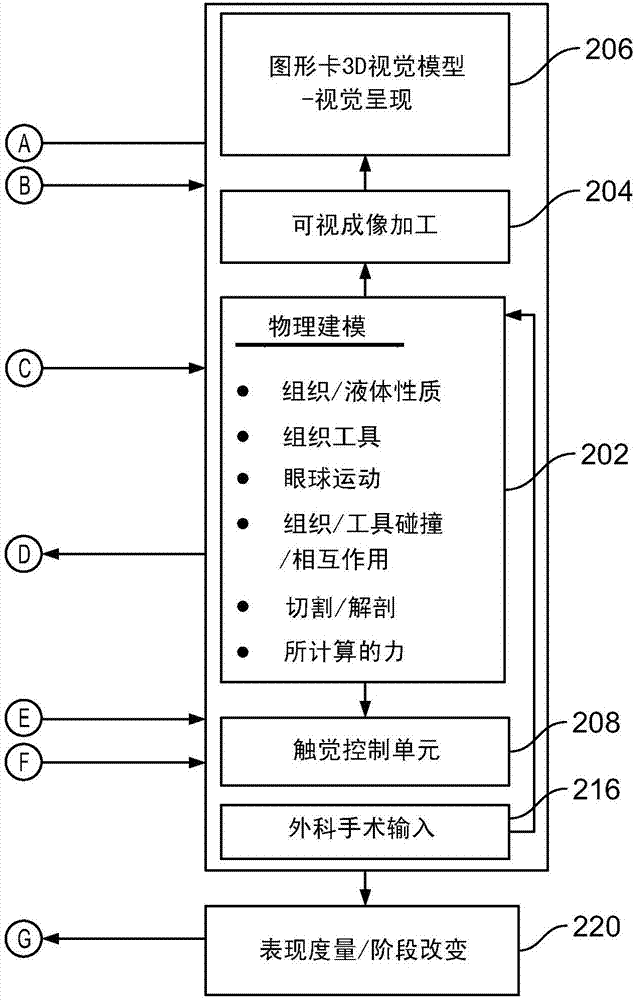
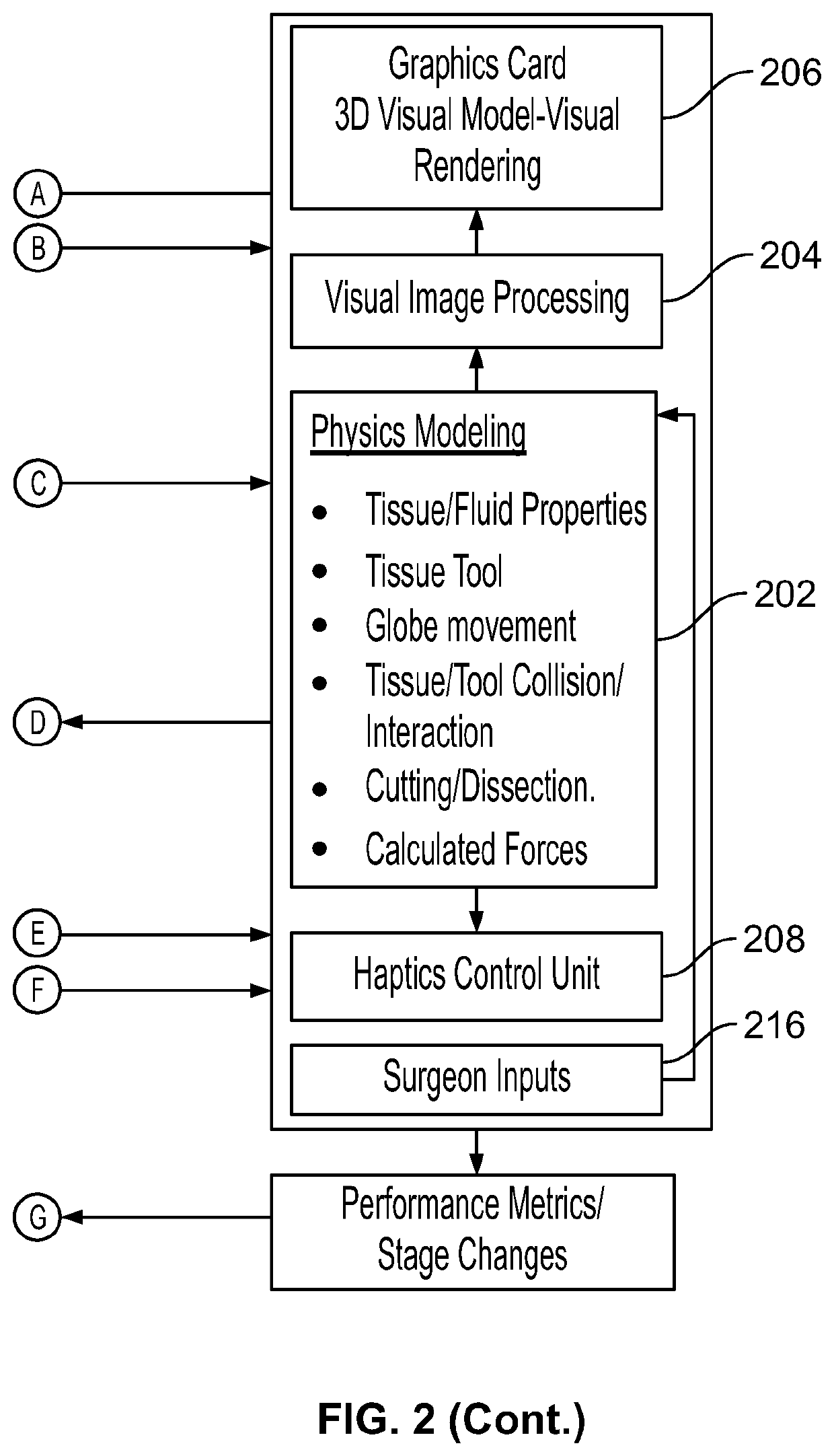
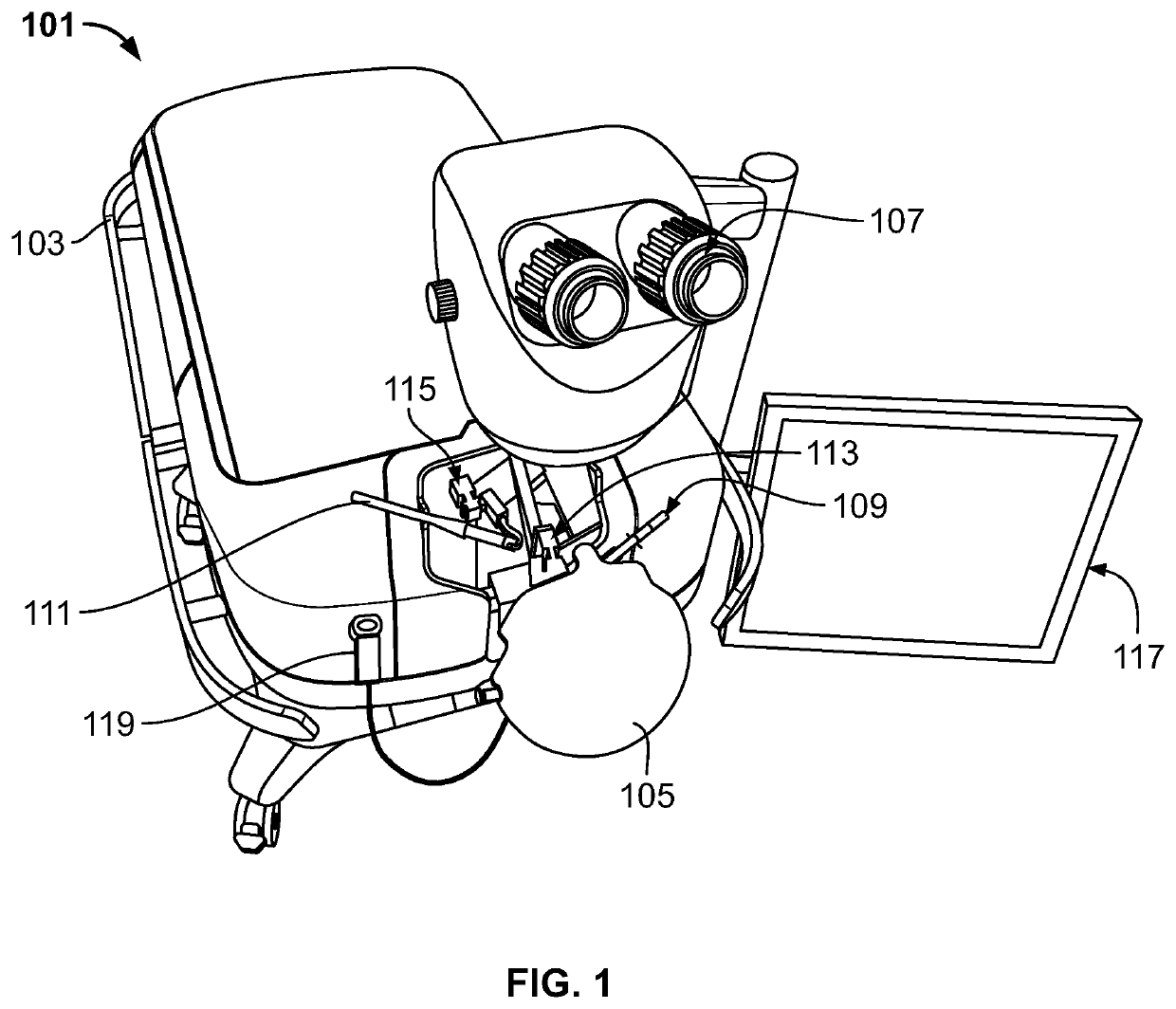
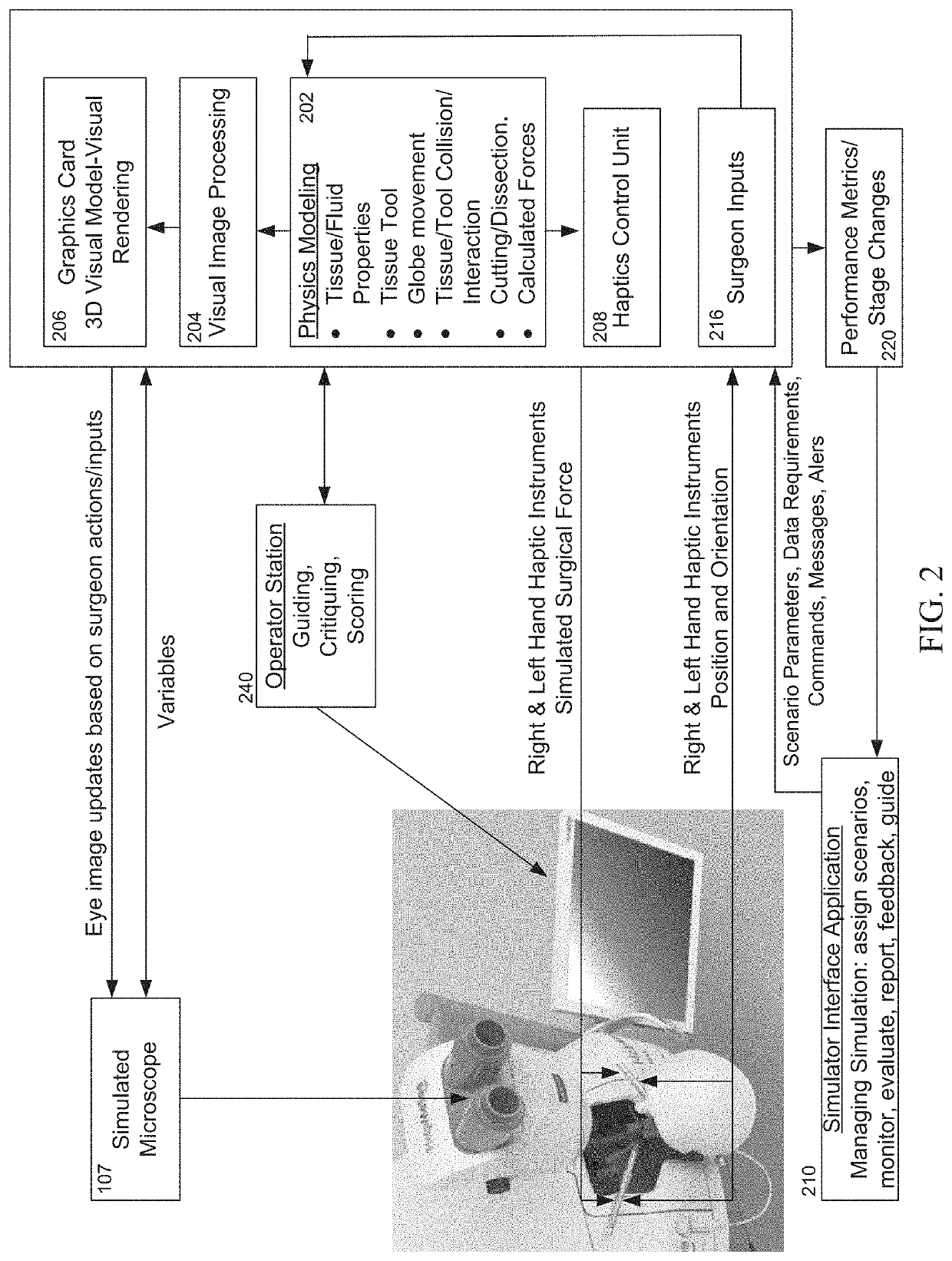
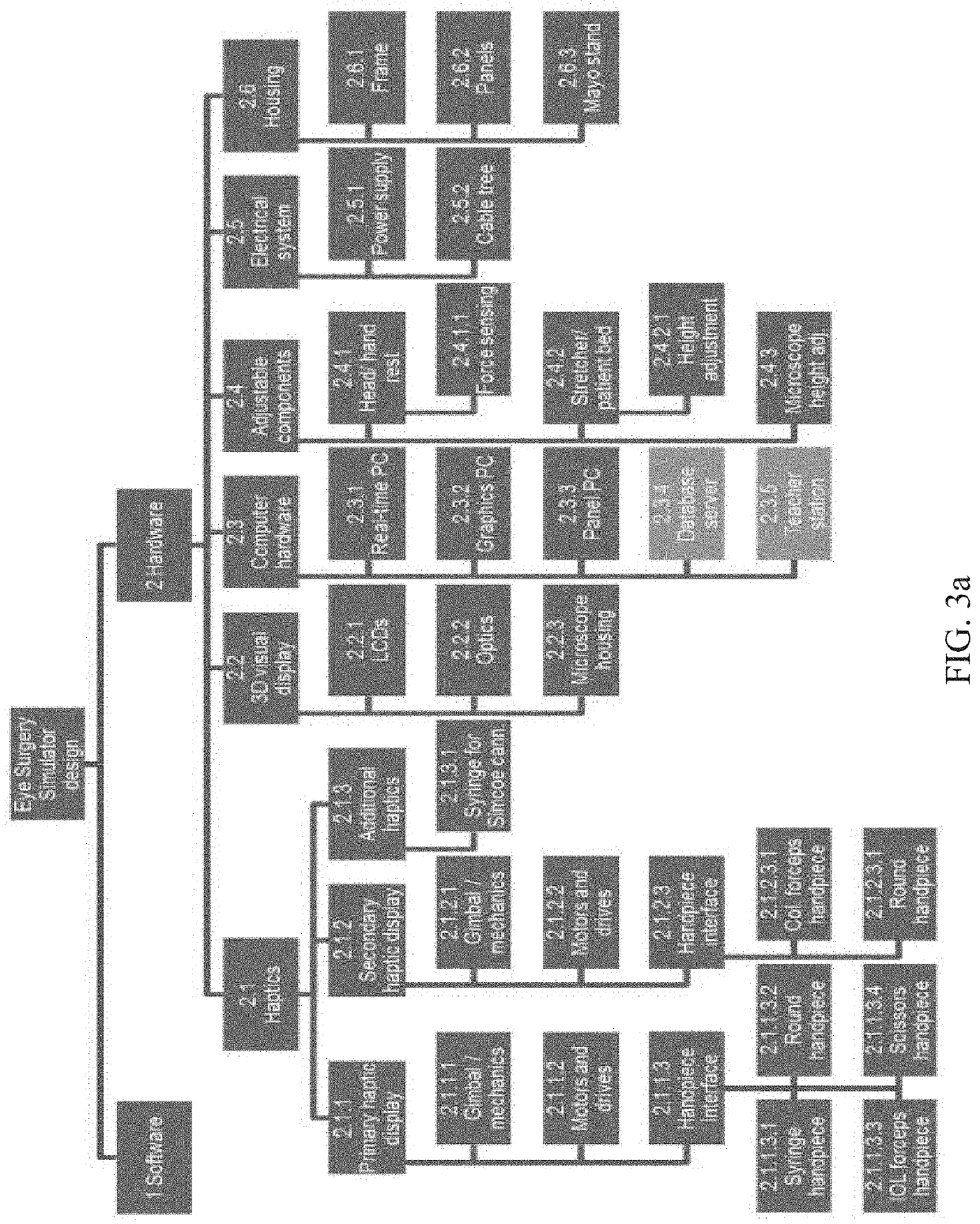
Surgical simulator systems and methods
A surgical simulator comprising a haptic arm capable of simulating forces generated during surgery from interactions between a surgical tool and tissue operated upon. The simulator further comprises a visual display capable of depicting a three-dimensional image of the simulated surgical tool and a physics-based computer model of the tissue. The haptic arm controls the movement and orientation of the simulated tool in the three-dimensional image, and provides haptic feedback forces to simulate forces experienced during surgery. Methods for simulating surgery and training users of the simulator are also described.
Owner:HELP ME SEE INC
Wearable partial task surgical simulator
Owner:STRATEGIC OPERATIONS INC
Surgical Simulator Systems and Methods
A surgical simulator comprising a haptic arm capable of simulating forces generated during surgery from interactions between a surgical tool and tissue operated upon. The simulator further comprises a visual display capable of depicting a three-dimensional image of the simulated surgical tool and a physics-based computer model of the tissue. The haptic arm controls the movement and orientation of the simulated tool in the three-dimensional image, and provides haptic feedback forces to simulate forces experienced during surgery. Methods for simulating surgery and training users of the simulator are also described.
Owner:HELP ME SEE INC
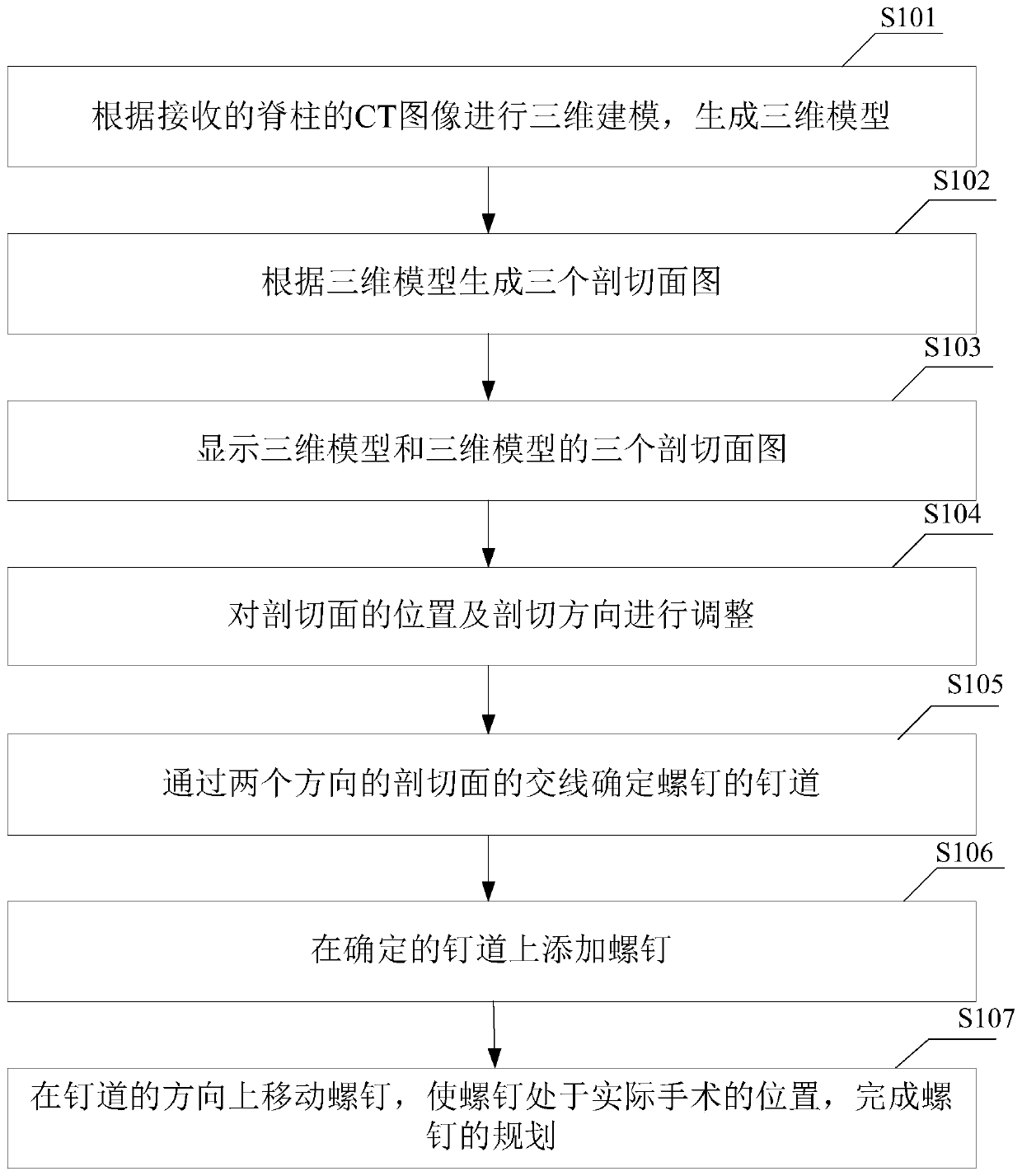
Three-dimensional simulated surgical nail planning method and surgical simulator
ActiveCN107260306BSimple and convenient planningAccurate planningComputer-aided planning/modellingSurgical operationThree dimensional simulation
The invention is applicable to the field of medical instruments, and provides a planning method for screw placement of three-dimensional simulated operation and a surgical operation simulator. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out three-dimensional modeling according to a received CT image of the spine, thus generating a three-dimensional model; generating drawings of three sectioning planes according to the three-dimensional model; displaying the three-dimensional model and the drawings of the three sectioning planes of the three-dimensional model; adjusting the positions and sectioning directions of the sectioning planes, so that the section condition of the spine can be intuitively observed; determining a screw channel of a screw through the intersecting line of the sectioning planes in two directions; adding the screw in the determined screw channel; and moving the screw in the direction of the screw channel, so that the screw is at the position of the actual operation, and thus the planning for the screw is completed. According to the technical scheme, the planning is concise and convenient, and the screw channel can be accurately planned, so that the screw placement is safe and reliable.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINJUNTE SMART MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Surgical simulator and methods of use
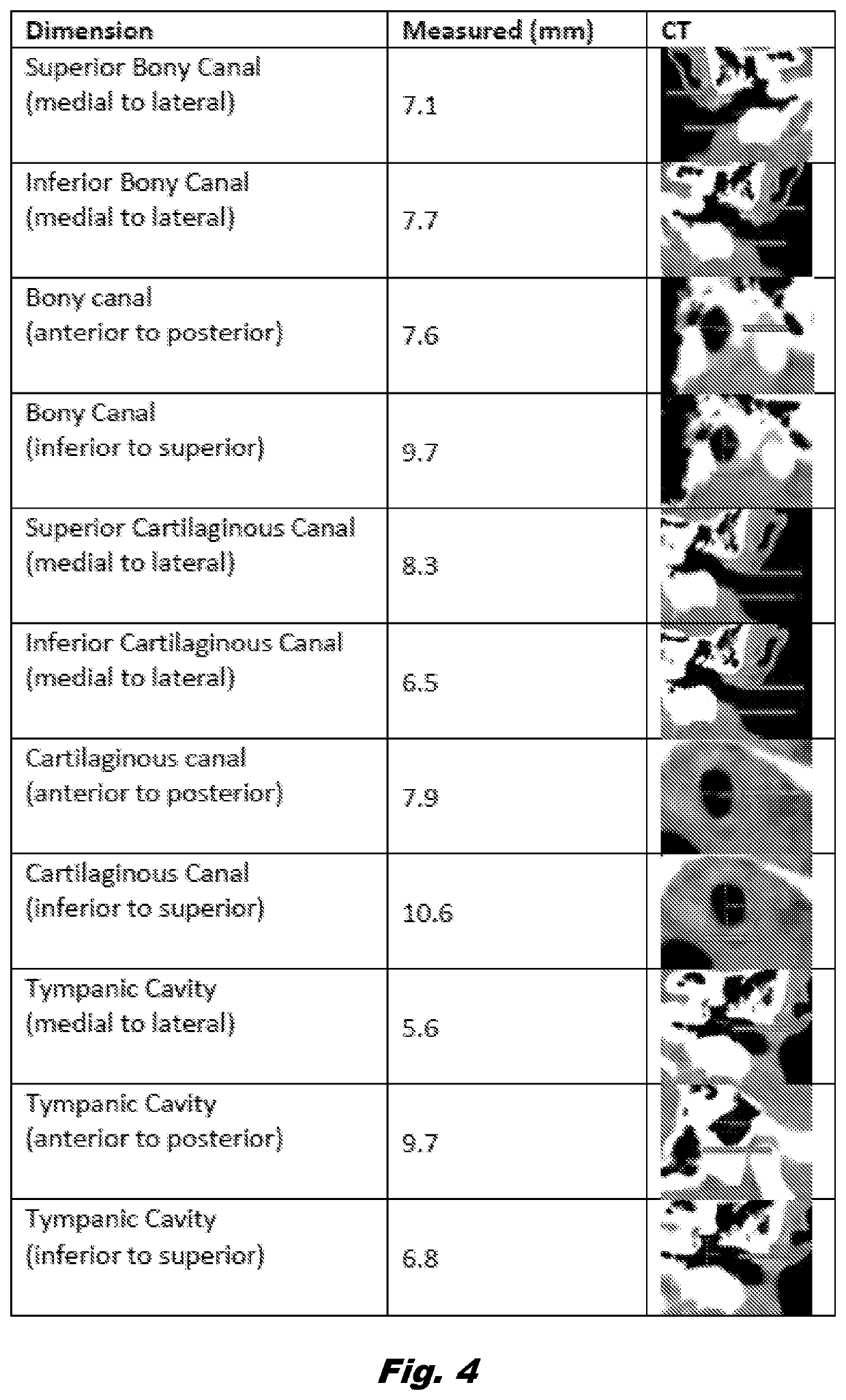
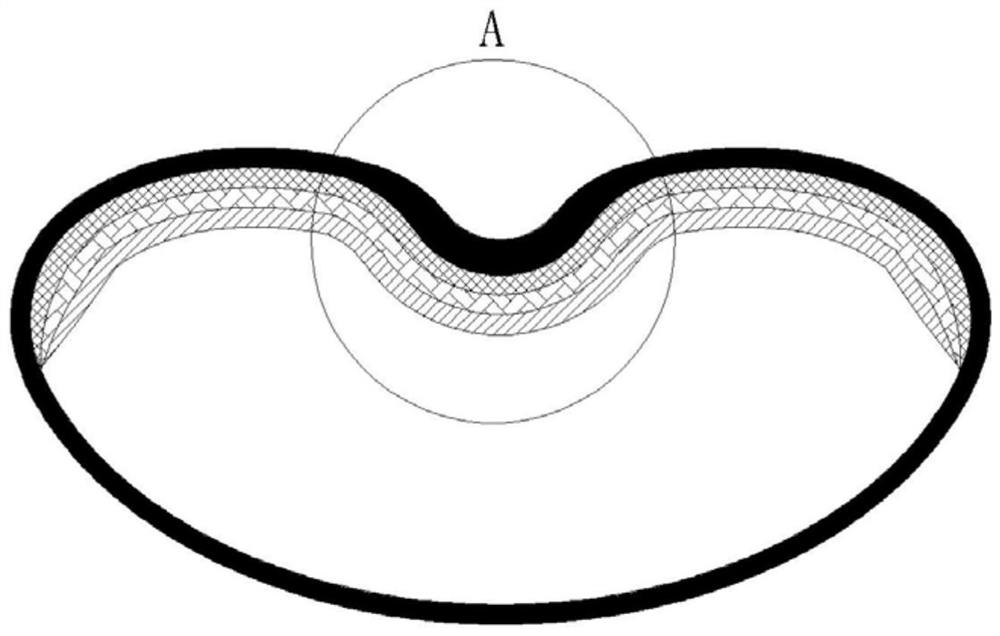
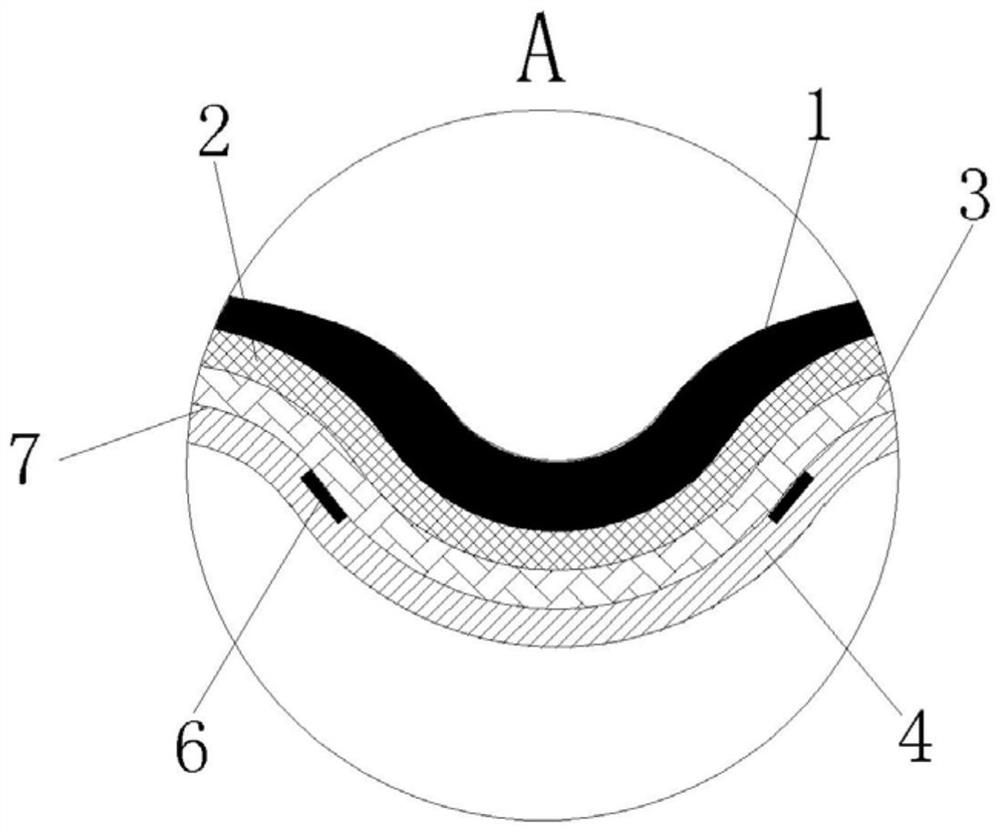
PendingUS20220139265A1Track accuracyCosmonautic condition simulationsEar treatmentCapacitancePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Provided are bench model surgical simulation devices that incorporate capacitance sensing technology. In embodiments, the surgical simulation devices objectively evaluate operator proficiency and improve trainee performance with regard to an underlying surgical procedure. This disclosure further provides for systems and methods of surgical simulation and evaluation of operator proficiency.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Operation simulation instrument capable of being repeatedly used and automatically repaired
ActiveCN113313988AAchieve reusePromote repairCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsHuman bodyMedical imaging
The invention provides an operation simulation instrument capable of being repeatedly used and repaired. An interventional surgery is a treatment mode between a conventional surgery and conservative treatment, and precision instruments such as specially-made catheters, guide wires and the like are introduced into a human body in a minimally invasive mode under the guidance of medical imaging equipment so that in-vivo pathological conditions are diagnosed and locally treated. Simulation training is generally carried out through a simple silica gel template in an existing interventional operation, however, puncture traces are left after the device is used, follow-up use is affected, or several puncture holes are preset, use is not flexible, and sufficient simulation cannot be achieved. The invention provides the operation simulation instrument capable of being repeatedly used and automatically repaired.
Owner:THE SECOND XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
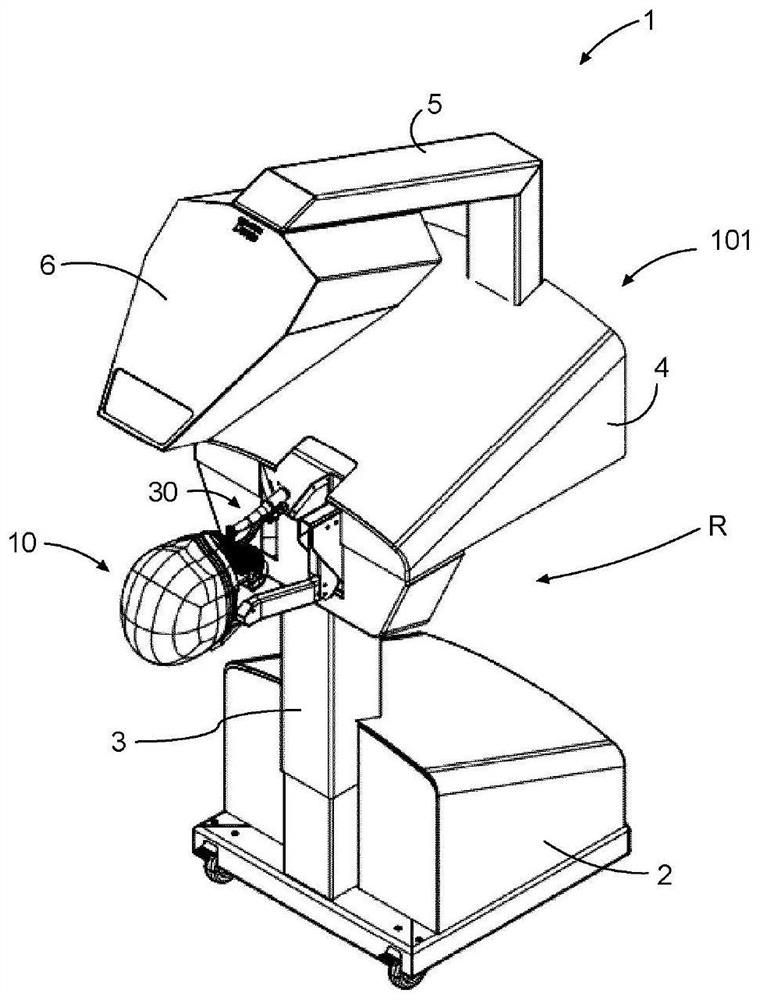
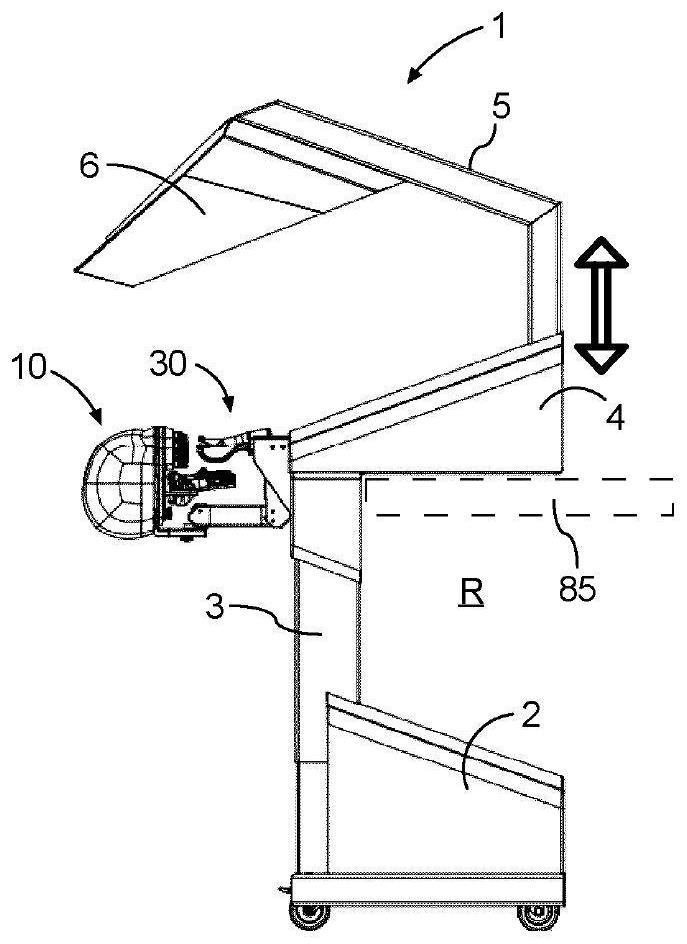
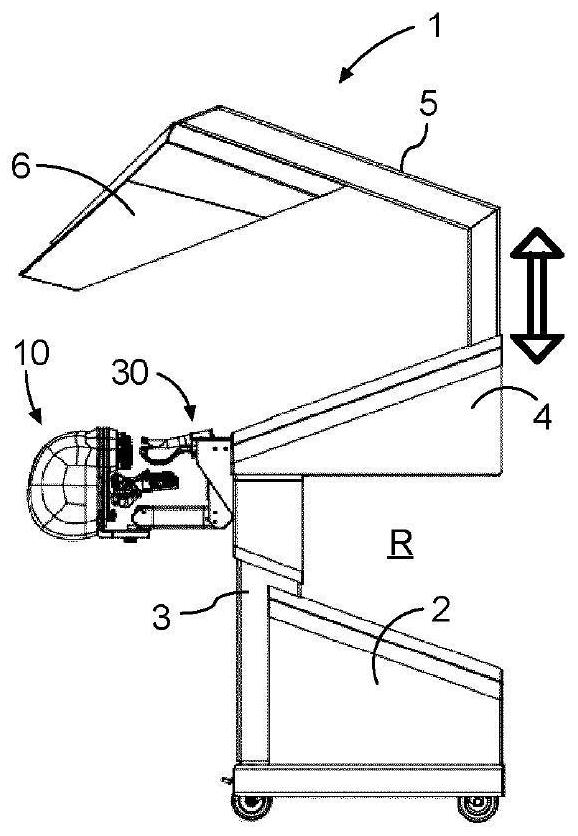
Apparatus and method for simulating dental surgery
A dental surgery simulator (1) comprises a support structure and a linkage (40) suspended from the support structure. The linkage (40) is controlled by a computer (80) configured to simulate a dental procedure or treatment. A handpiece (30) is coupled to the linkage (40) and is configured to be held in a hand of a user and manipulated by the user in a workspace (W) in a real space. A motif head (10) is provided with a motif upper jaw (13) and a motif lower jaw (14) and is supported by the support structure and arranged within the working space (W). The motif lower jaw (14) is arranged to be movable relative to the motif upper jaw (13).
Owner:SIMTOLIFE BV
A reusable and repairable surgical simulation device
ActiveCN113313988BAchieve reusePromote repairCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsHuman bodyEngineering
The present invention provides a repeated and repaired surgical simulation equipment.Interventional surgery is a treatment between conventional surgery and conservative treatment. Through the minimally invasive method, under the guidance of medical imaging equipment, special catheter, guide wires and other precision devices are introduced into the human body and performed the internal pathogenic state.Diagnosis and local treatment.Existing intervention surgery generally perform simulation training through simple silicone templates, but this kind of equipment will leave puncture marks after use, affect subsequent use, or set a few puncture in advance. It is not flexible and cannot achieve sufficient simulation.The invention provides a reusable and automatic surgical simulation equipment.
Owner:THE SECOND XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
Simulator for training medical personnel to perform uterine procedures
The surgical simulator contains a one-piece simulated uterus having a uterine fundus and body. A rigid hollow support base has a recess in its support surface that is complementary to the shape of at least a portion of the uterine fundus and body so that at least a posterior portion of the uterine fundus and body fit securely into the recess to retain the simulated uterus in position during use. Liquid can be introduced into the base to add weight, and the liquid can be heated to heat the simulated uterus to body temperature. The base can also provide a rigid hard tissue component that simulates the surface topography of the pelvic bone, portion of the spine, hip joints and heads of the femurs. The hard tissue component can be encased in an elastomeric material that simulates muscles and skin to practice obstetric procedures such as a C-section, insertion of an intrauterine tamponade balloon, insertion of an intrauterine contraceptive device, or insertion of compression sutures such as the B-Lynch suture.
Owner:SOUTER VIVIENNE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com