Patents
Literature
901 results about "Spherical bearing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
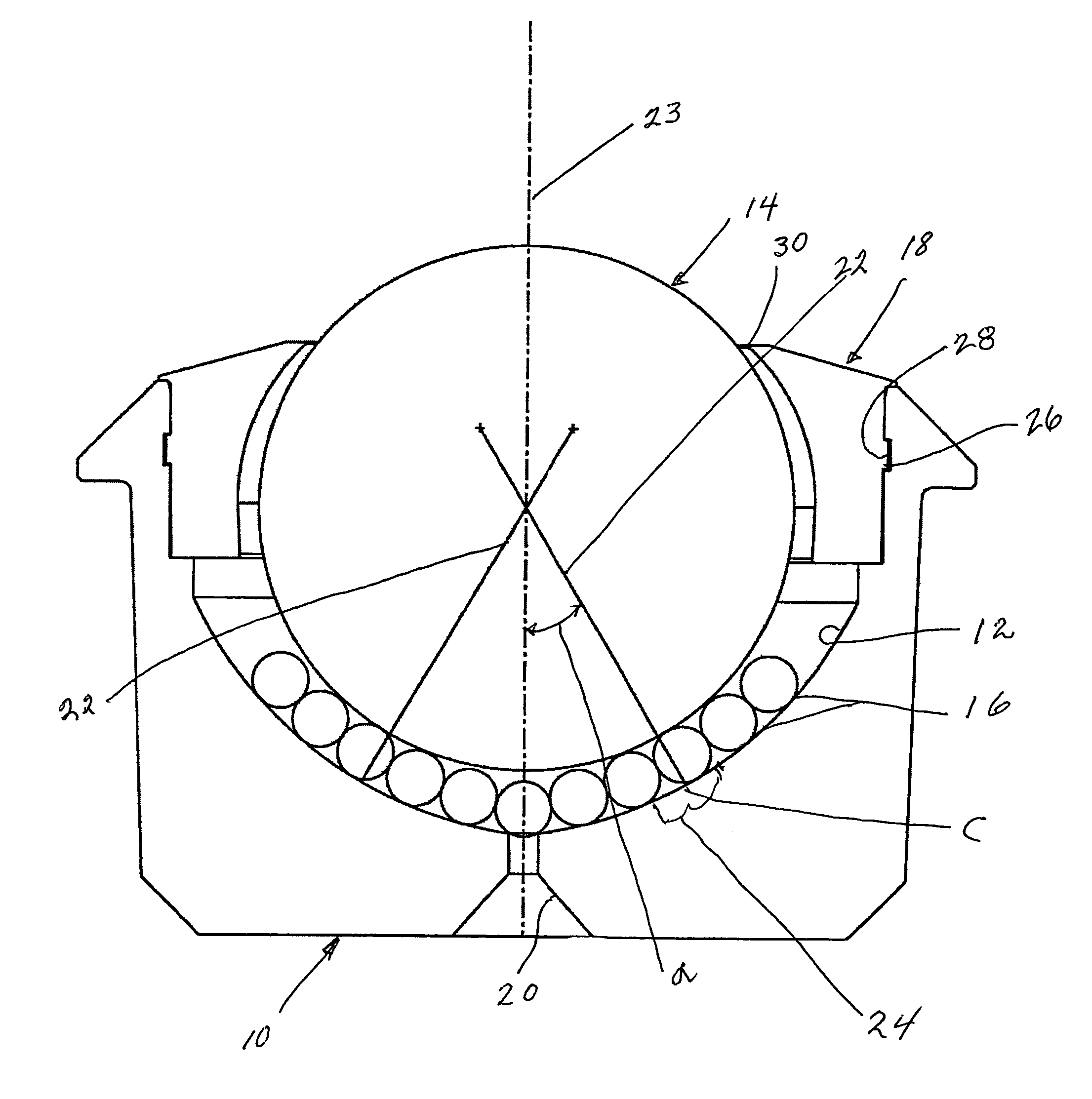
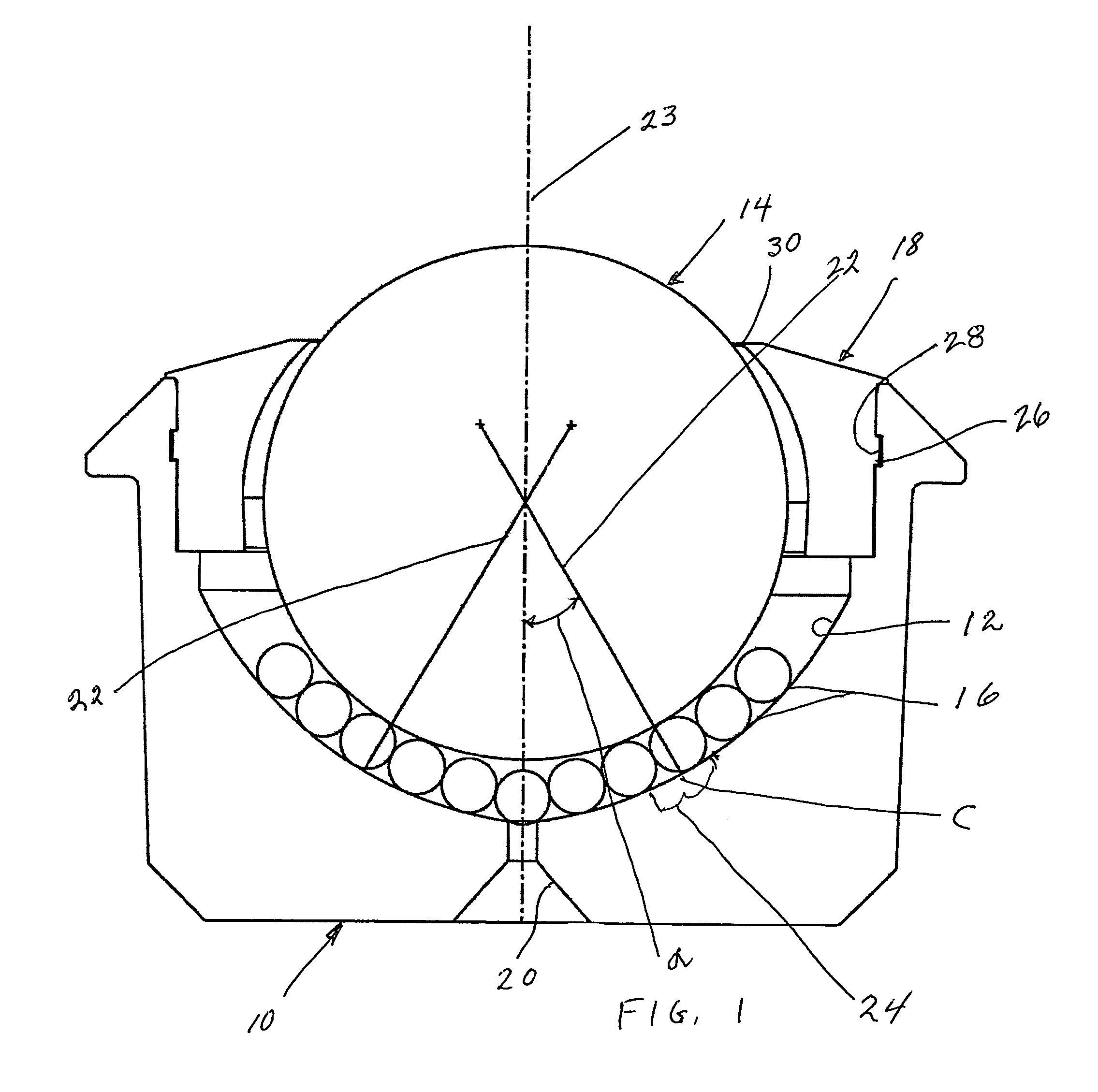
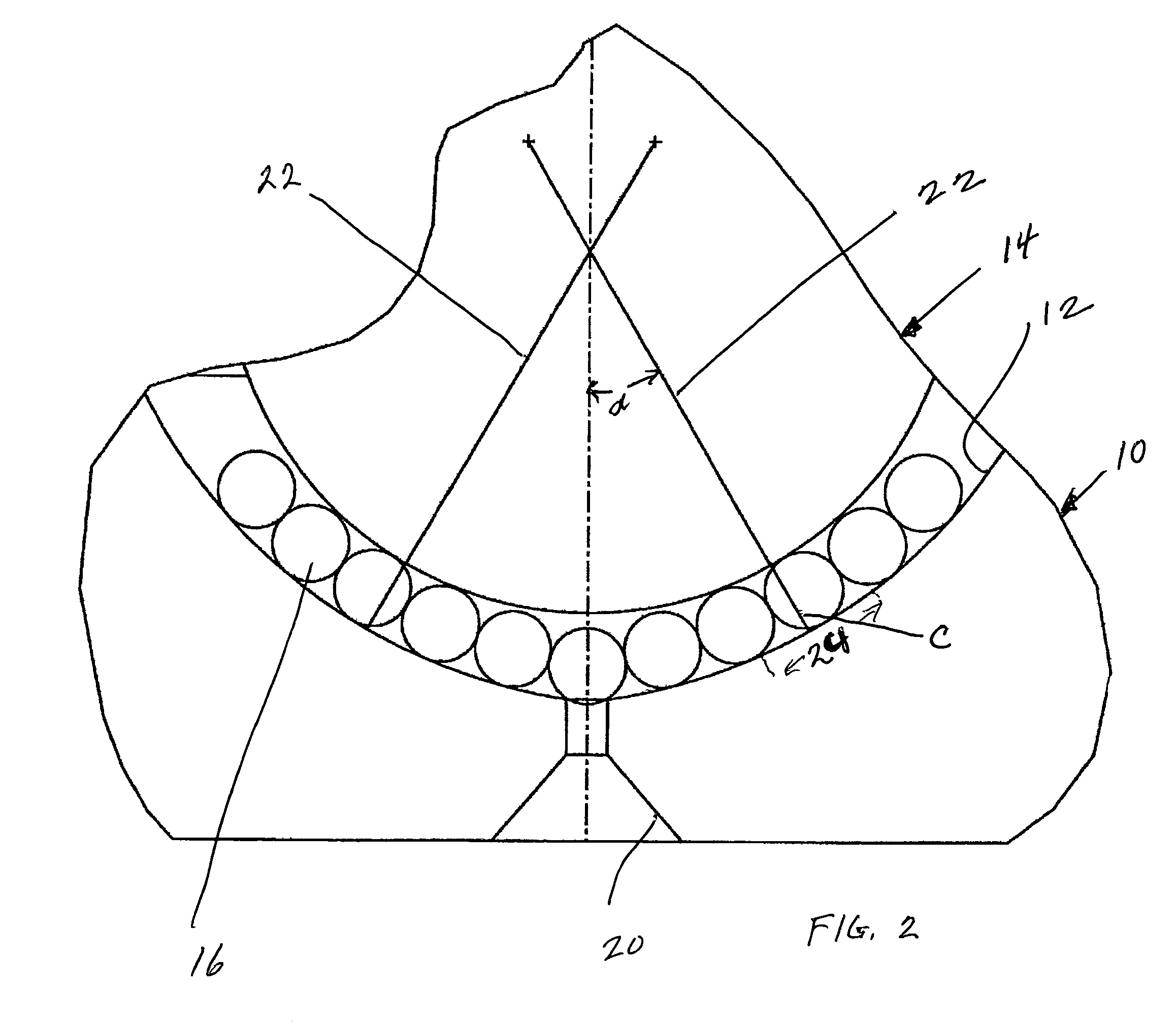
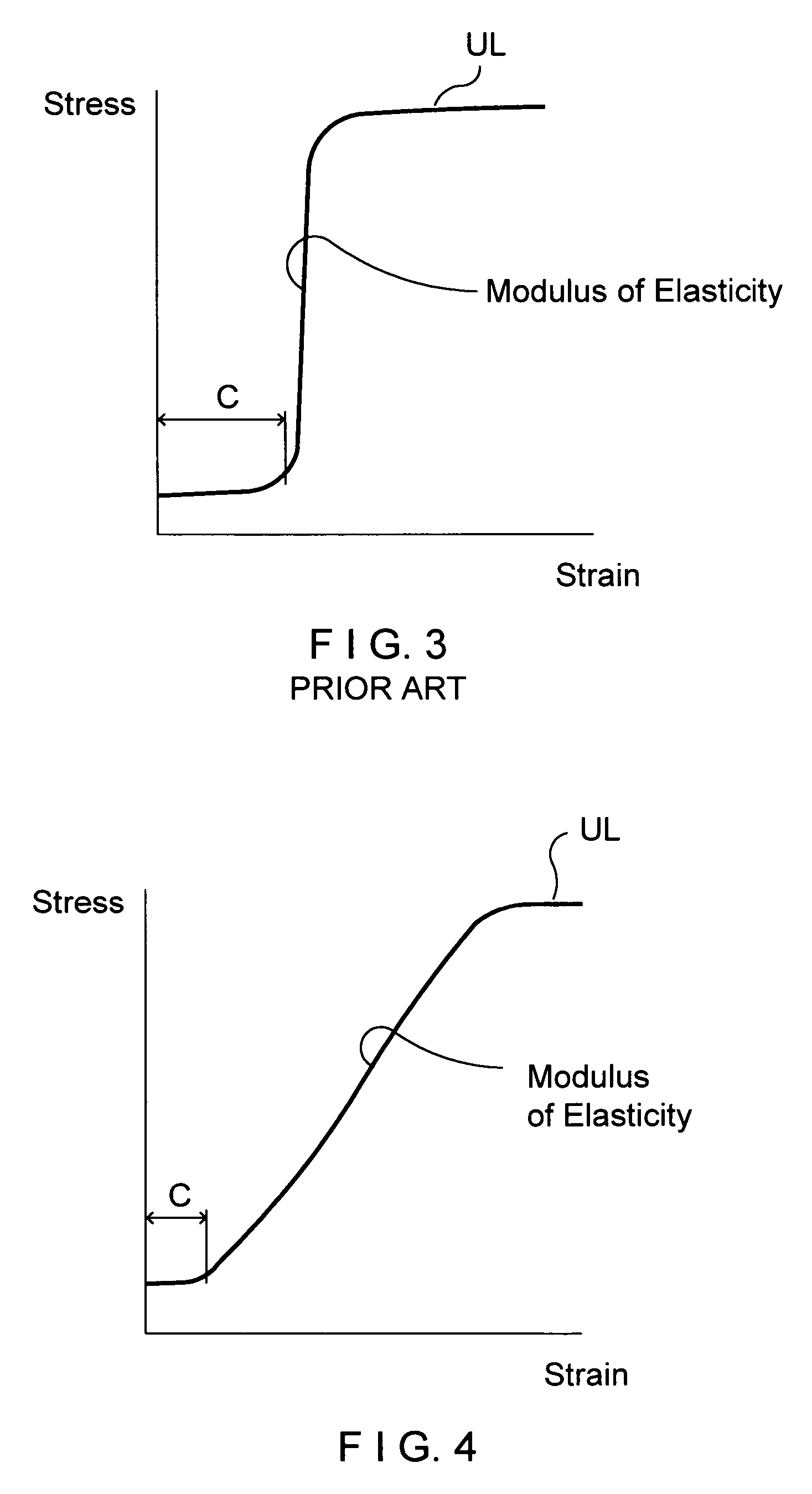
A spherical plain bearing is a bearing that permits angular rotation about a central point in two orthogonal directions (usually within a specified angular limit based on the bearing geometry). Typically these bearings support a rotating shaft in the bore of the inner ring that must move not only rotationally, but also at an angle.
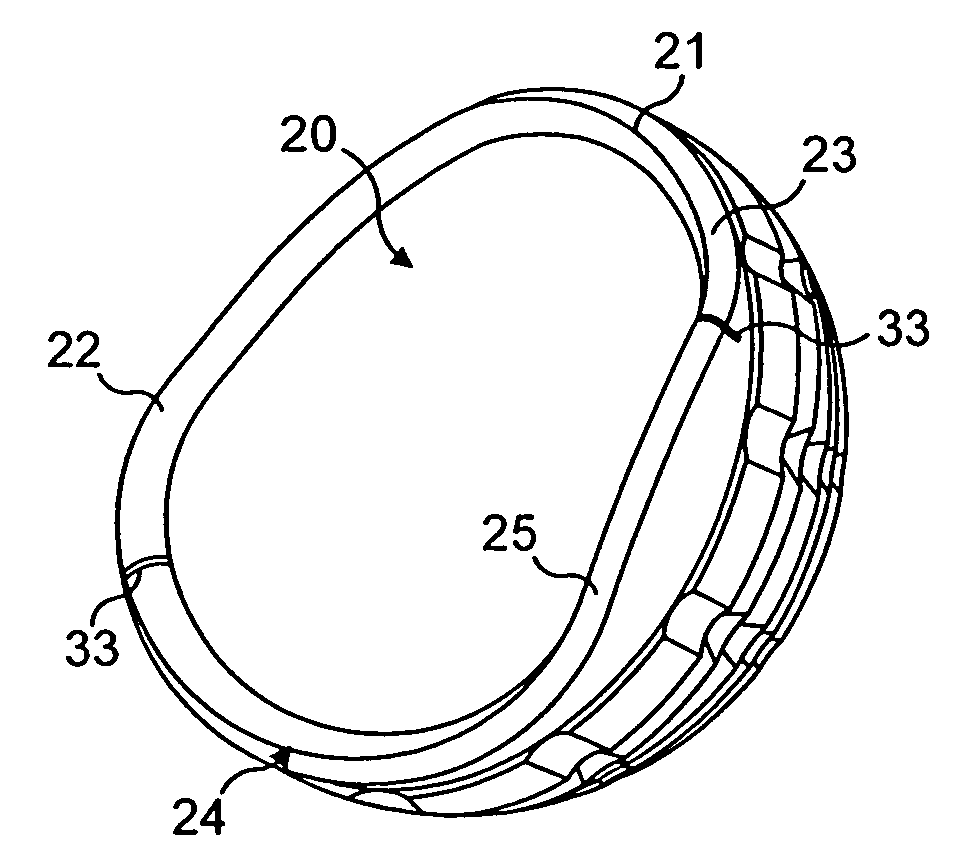
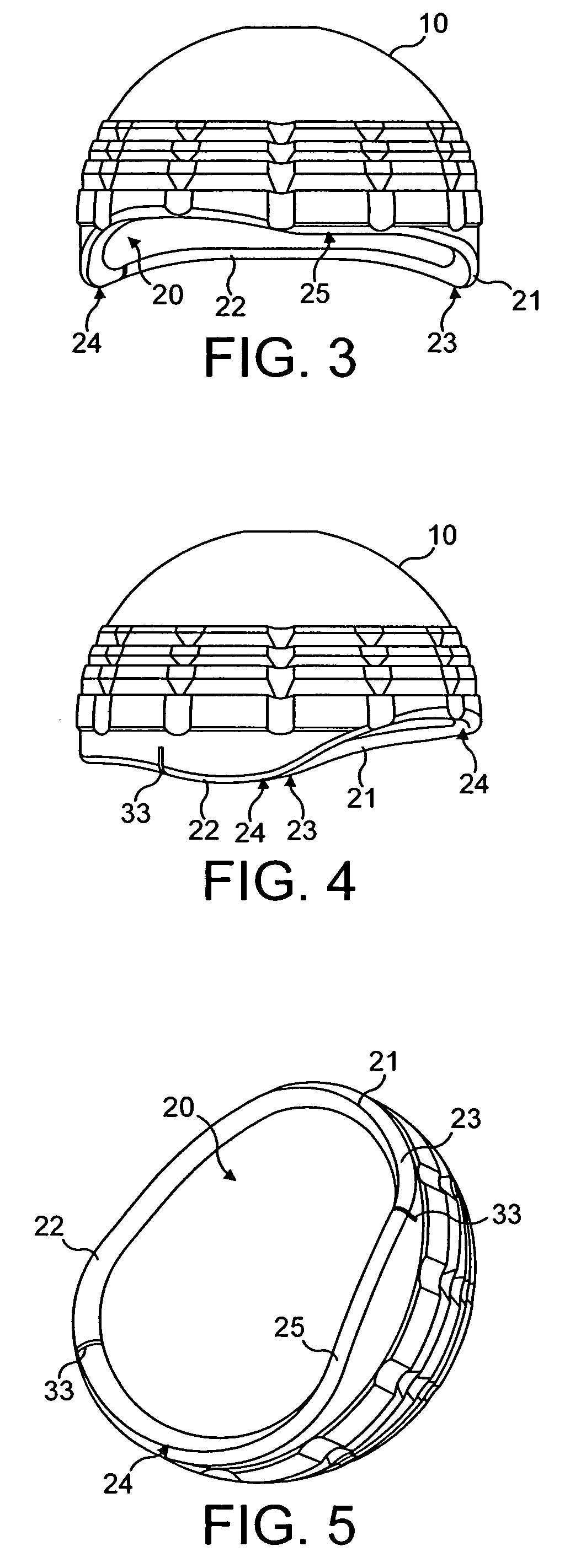
Prosthetic acetabular cup and prosthetic femoral joint incorporating such a cup
ActiveUS20050060040A1Natural angular movementReduce the possibility of misalignmentInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpherical bearingProsthesis
An acetabular prosthesis having an outer member for engaging the acetabulum. The outer member has a part-spherical bearing surface terminating in a distal rim. The rim has a contour such that the portion thereof to be located between the ischium and the pubis extends distally further from an equator of the bearing surface than the contour to be implanted between the pubis and the illium and between the ischium and the illium.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
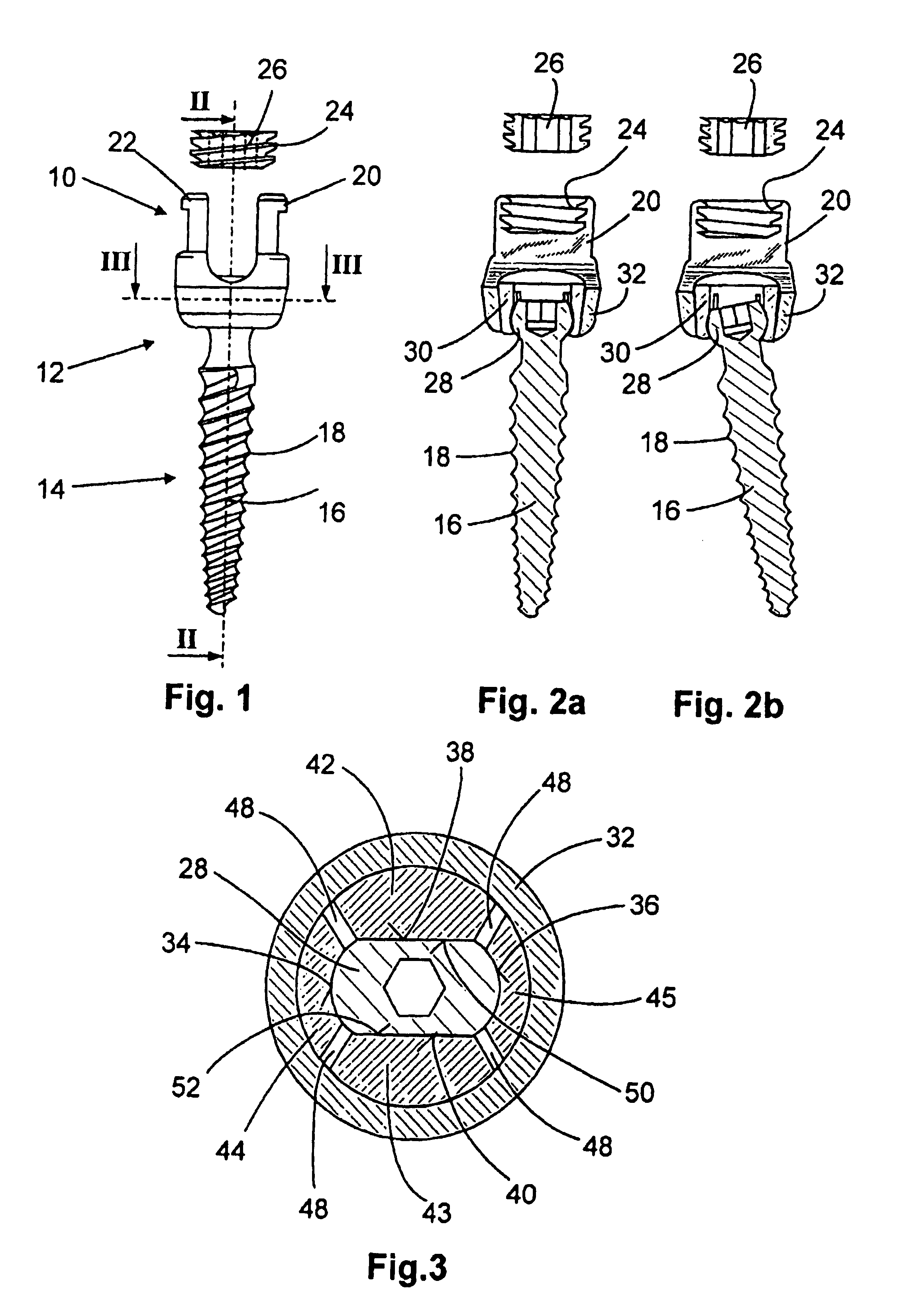
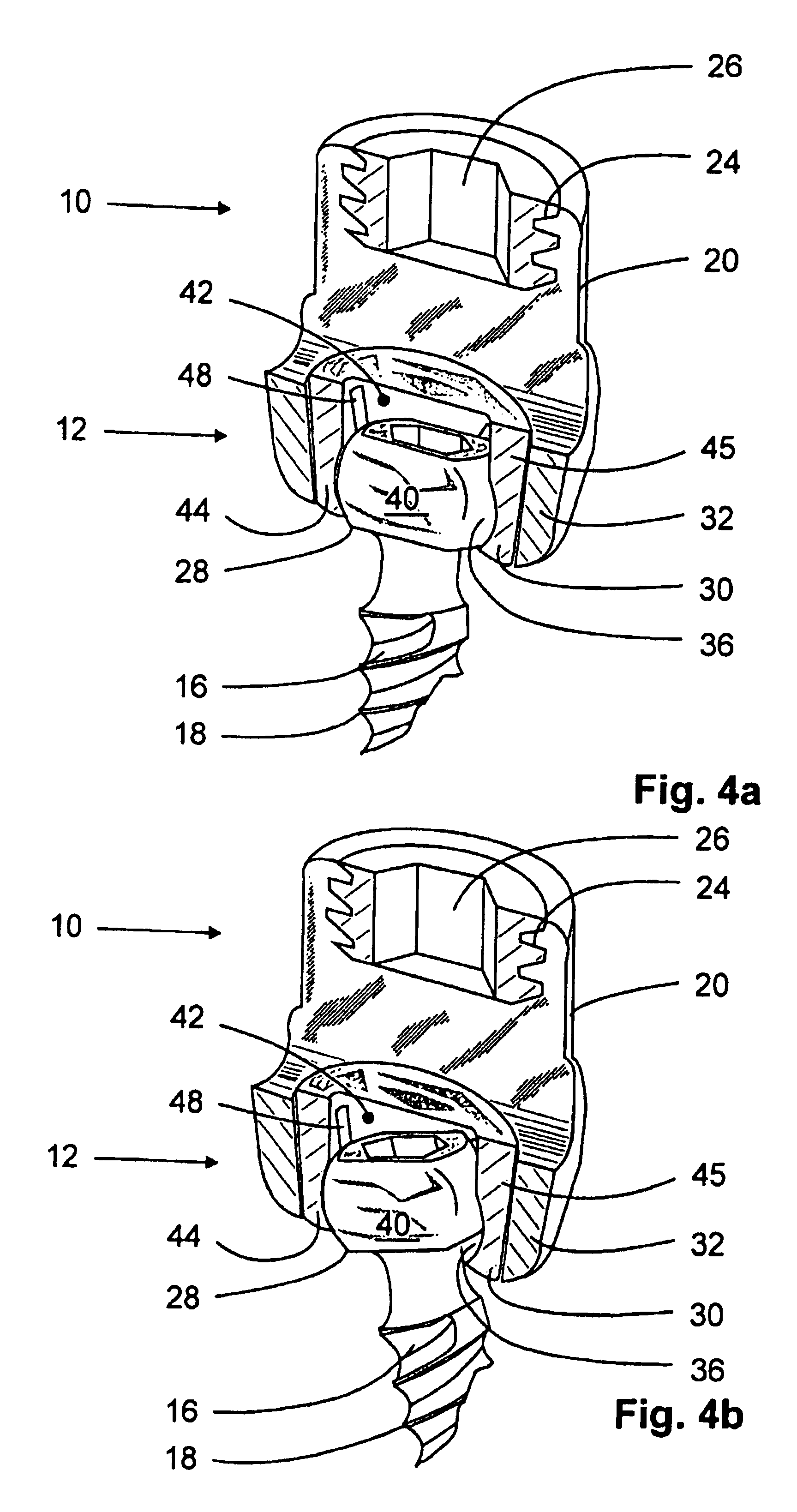
Anchoring element for fastening a rod of a device for adjusting a human or animal vertebral column on a vertebra
Owner:METZ STAVENHAGEN PETER
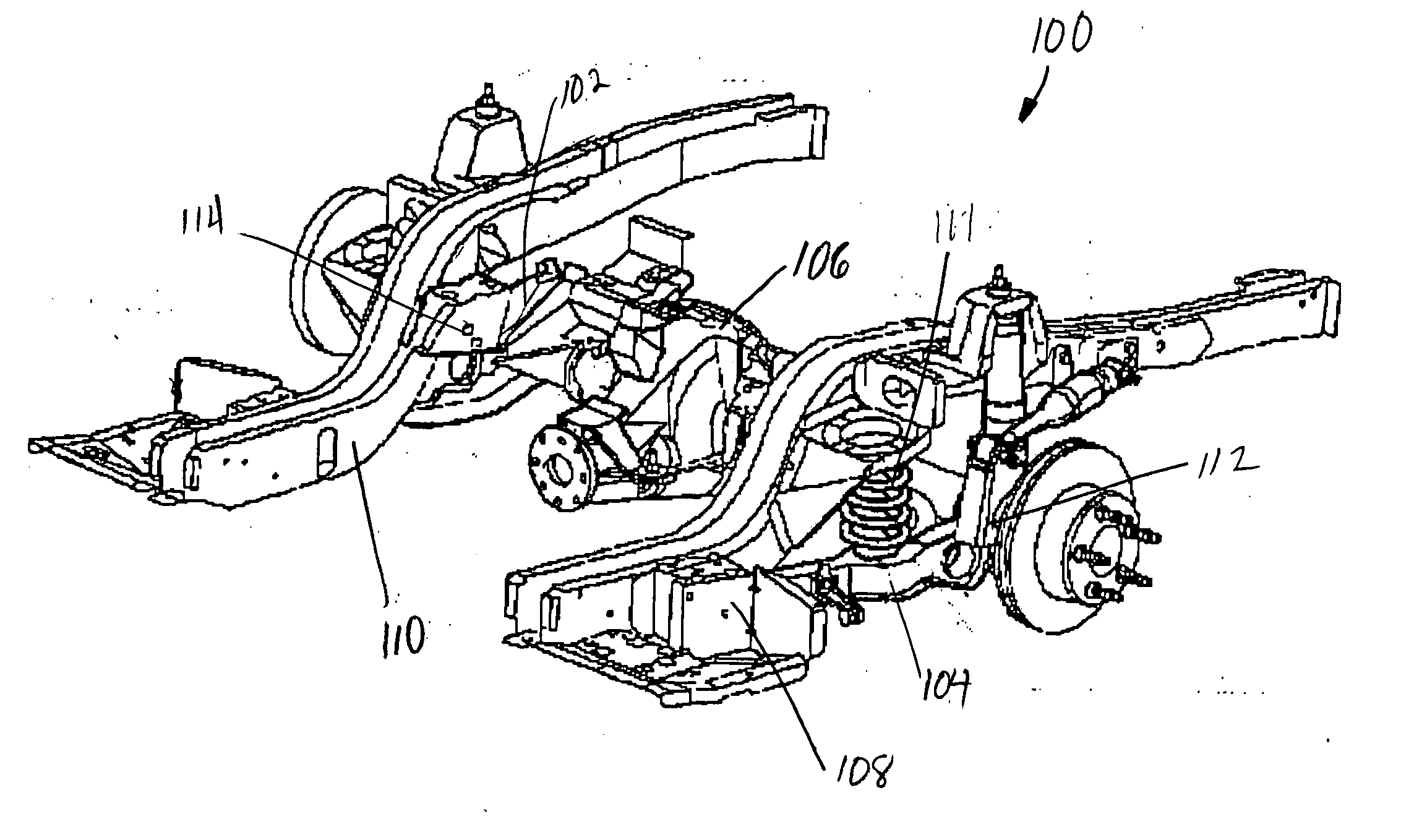
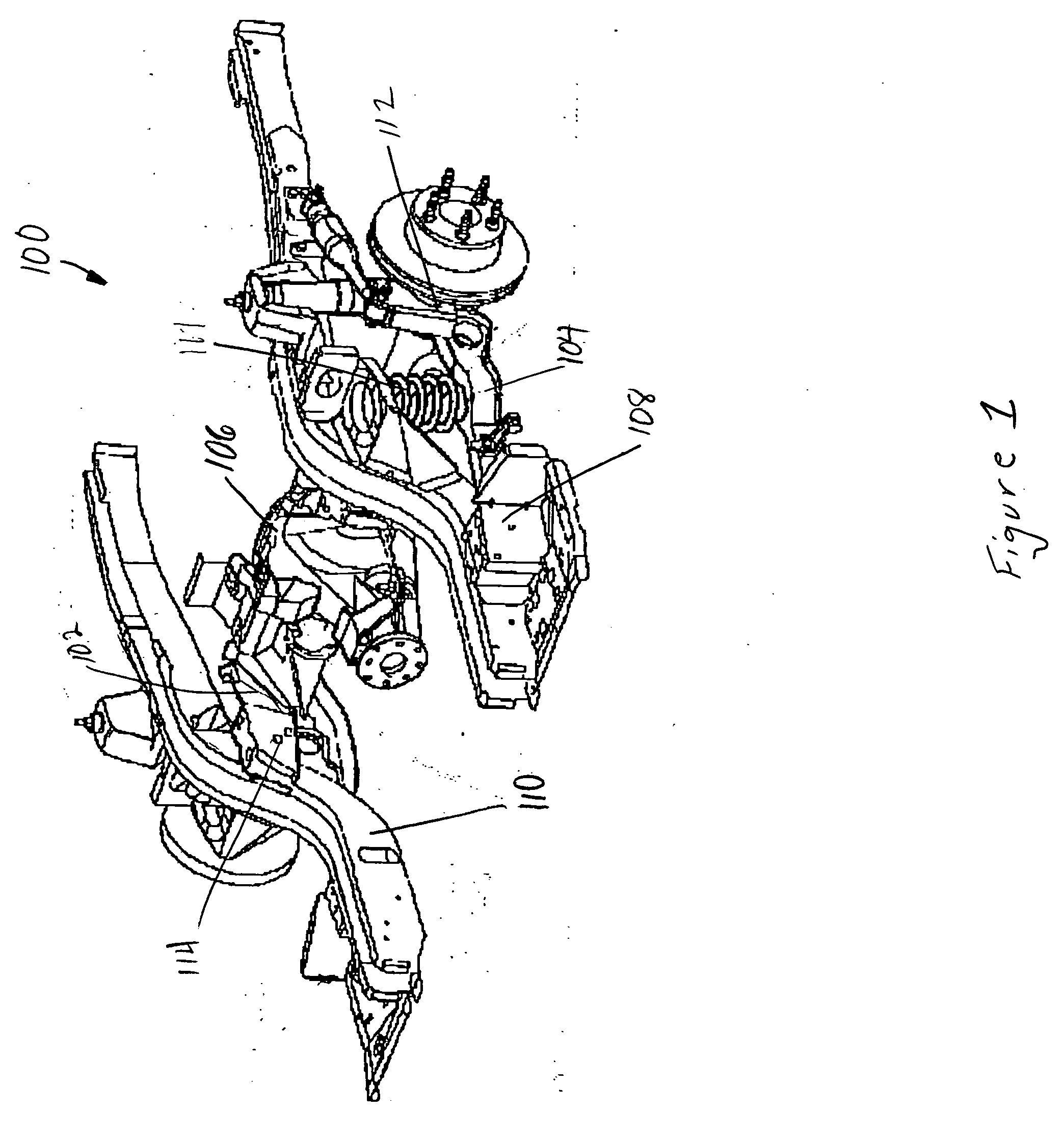
Lower control arm kit for vehicle with four link rear suspension
InactiveUS20060071441A1Reduce unsprung weightEasy to bendInterconnection systemsResilient suspensionsSpherical bearingControl arm
The present invention provides a suspension tuning device and kit for vehicles with four link rear suspensions. More specifically, the suspension tuning device generally comprises a pair of billet aluminum lower control arms each having a spring platform rotatably secured to a weight jacking bolt and a removable / replaceable sway bar attachment plate. Each end of the control arms include a transverse thru-bore adapted to accept a three part urethane bushing or a spherical bearing. The lower control arms are constructed to mount within a standard four link rear suspension, such as that supplied on a FORD MUSTANG, to permit quick suspension alterations throughout a predetermined range.
Owner:STEEDA AUTOSPORTS
Bearing plate for use in fracture fixation having a spherical bearing hole with yielding expandability
InactiveUS20060241612A1Ease resistance of plateLinear productionJoint implantsBone platesSpherical bearingEngineering
A bearing plate for use in bone fixation for fractures, fusion osteotomies and the like, and the plate is provided with one or more spherical holes in which expandable spherical bearings can be rotatably supported. Each of the holes is formed at its periphery in such a way as to provide yielding expansibility of the hole so that upon expansion of the bearing, the hole expands with it to provide elastic resistance to the expanding bearing.
Owner:MEDOFF ROBERT J +2
Laparoscopic trainer and method of training
Owner:WANG SHYH JEN +1
Force feedback functioning manual input device and onboard instrument control system having it
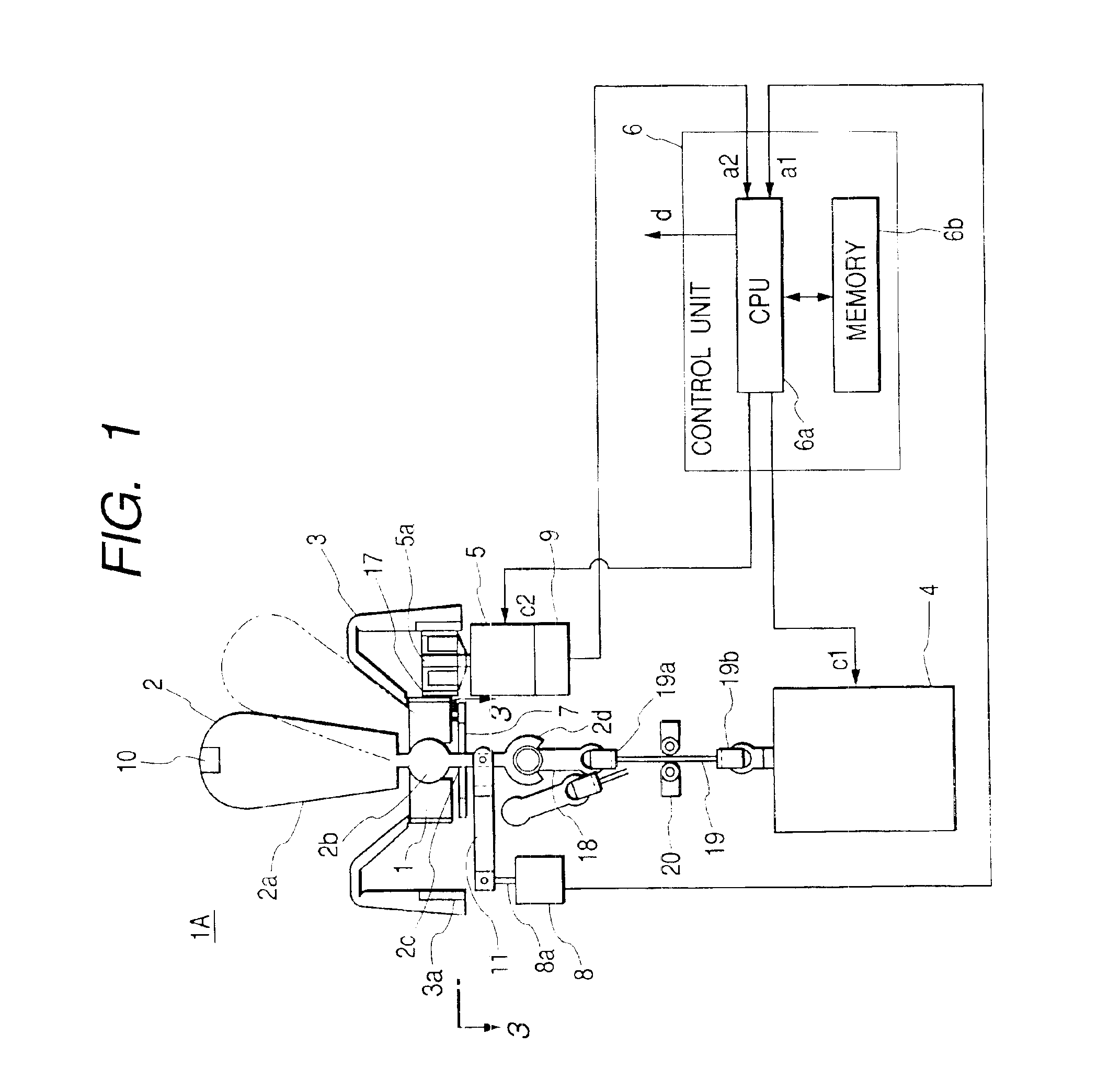
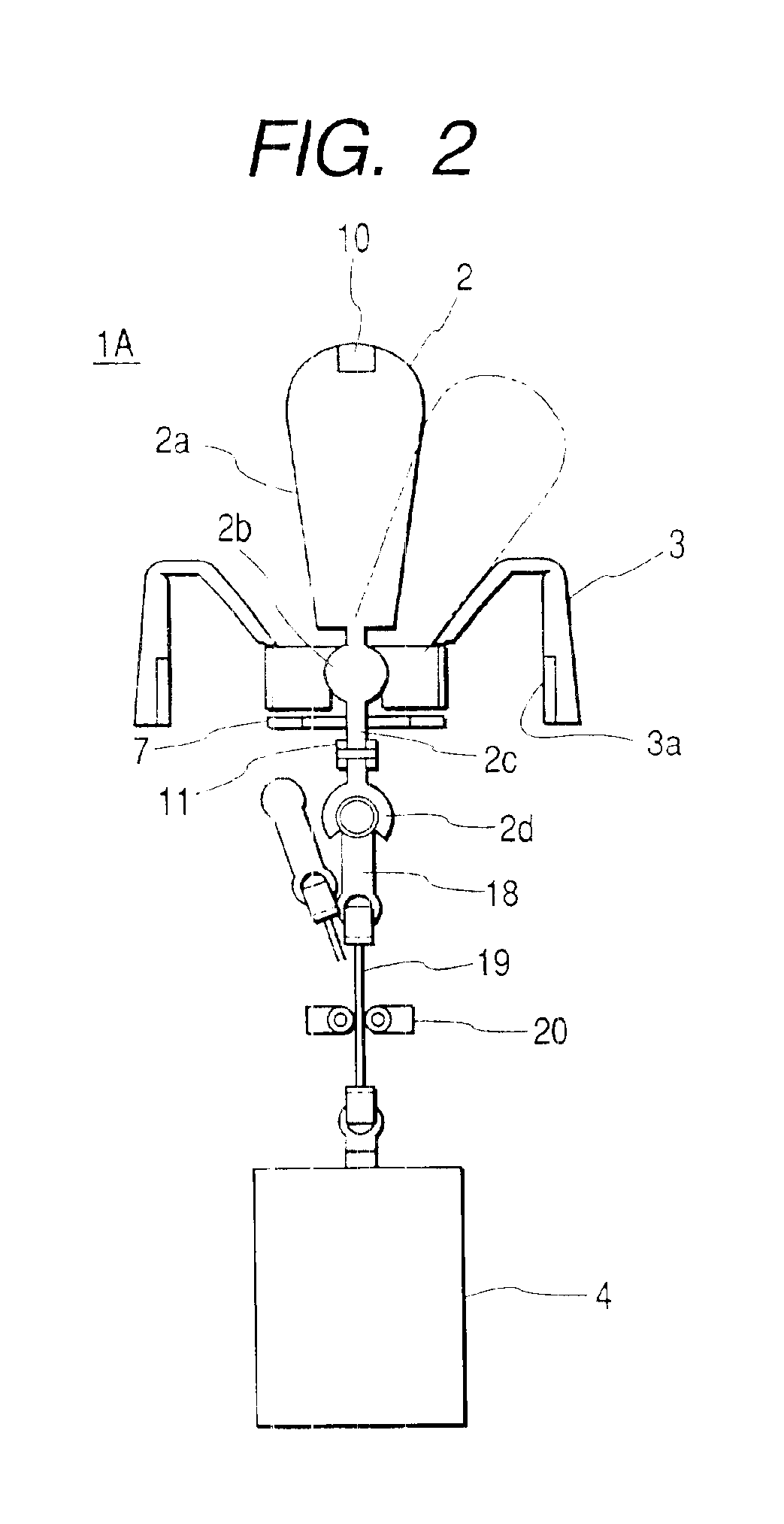
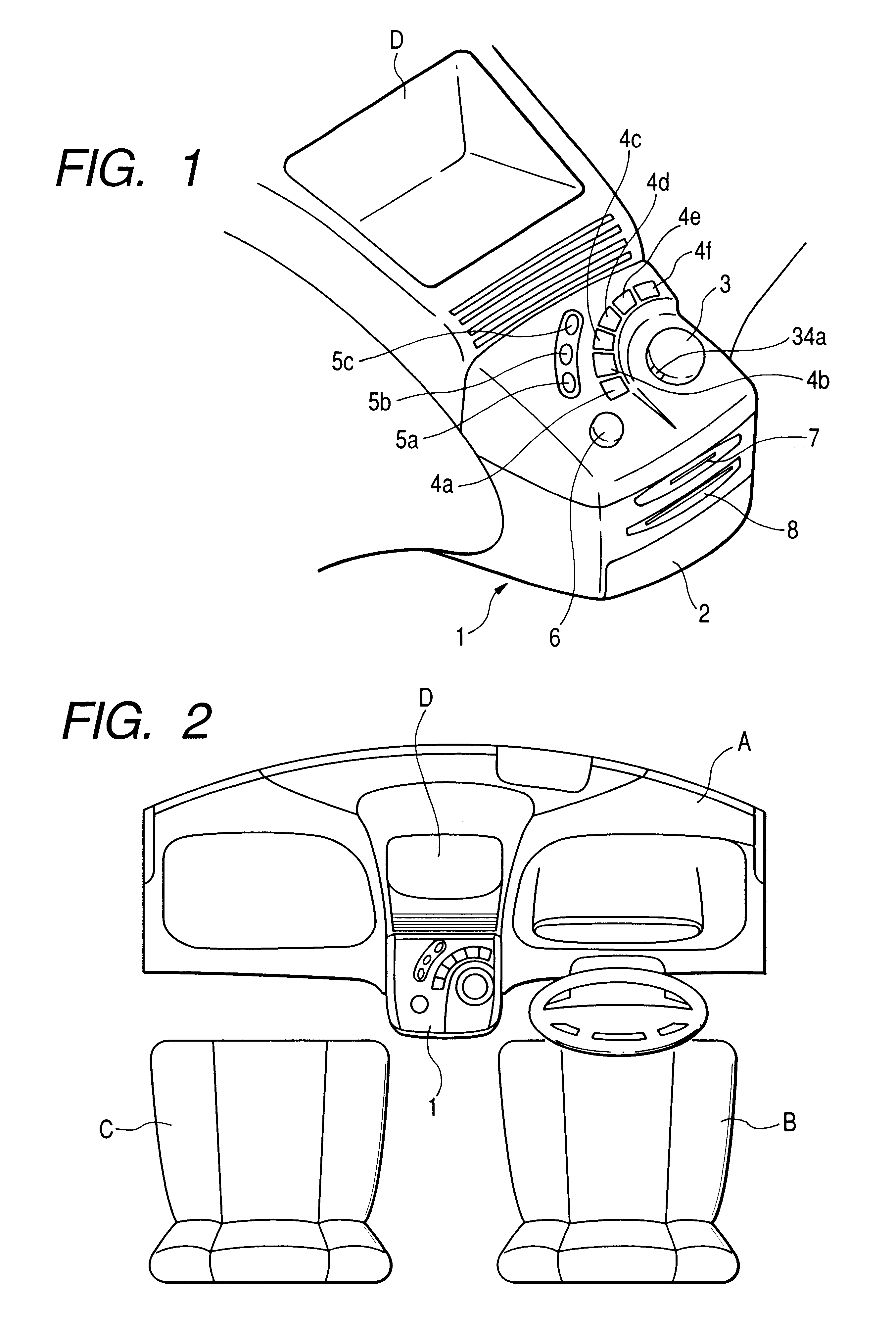
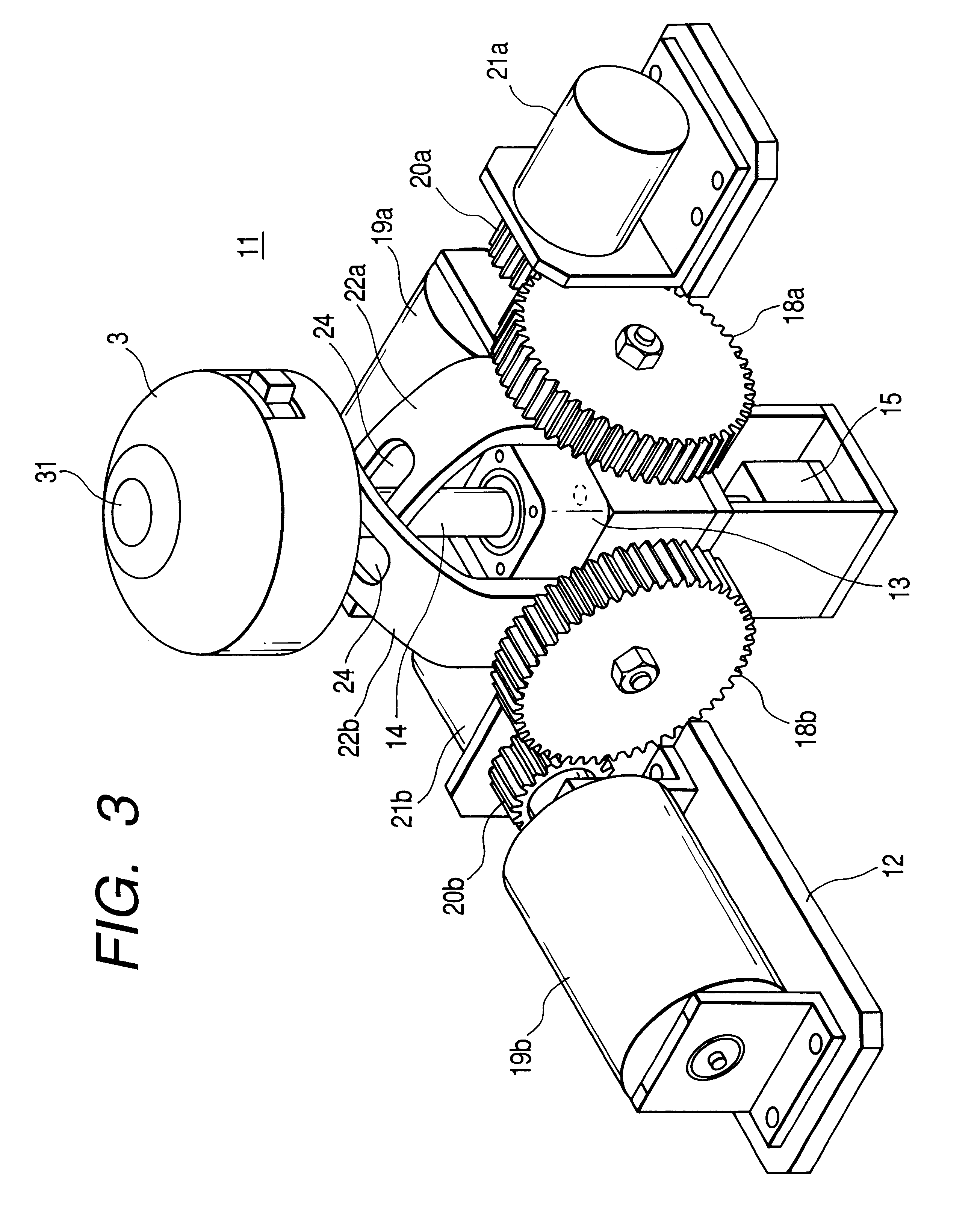
InactiveUS6859198B2Easy to operateMinimize the numberManual control with multiple controlled membersCathode-ray tube indicatorsSpherical bearingJoystick
A manual in put device is provided with a spherical bearing, a joystick type knob held swingably on the spherical bearing, a rotary knob disposed coaxially with the joystick type knob, a first actuator for loading an external force on the joystick type knob, a second actuator for loading an external force on the rotary knob, a control unit for controlling these first and second actuators, a guide member for defining an operation direction of the joystick type knob, first detection means for detecting an operation state of the joystick type knob, and second detection means for detecting an operation state of the rotary knob. In an onboard instrument control device, the built-in manual input device is contained in a box and the joystick type knob and the rotary knob and push button switches used for instrument selection are disposed on an upper surface of the box.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
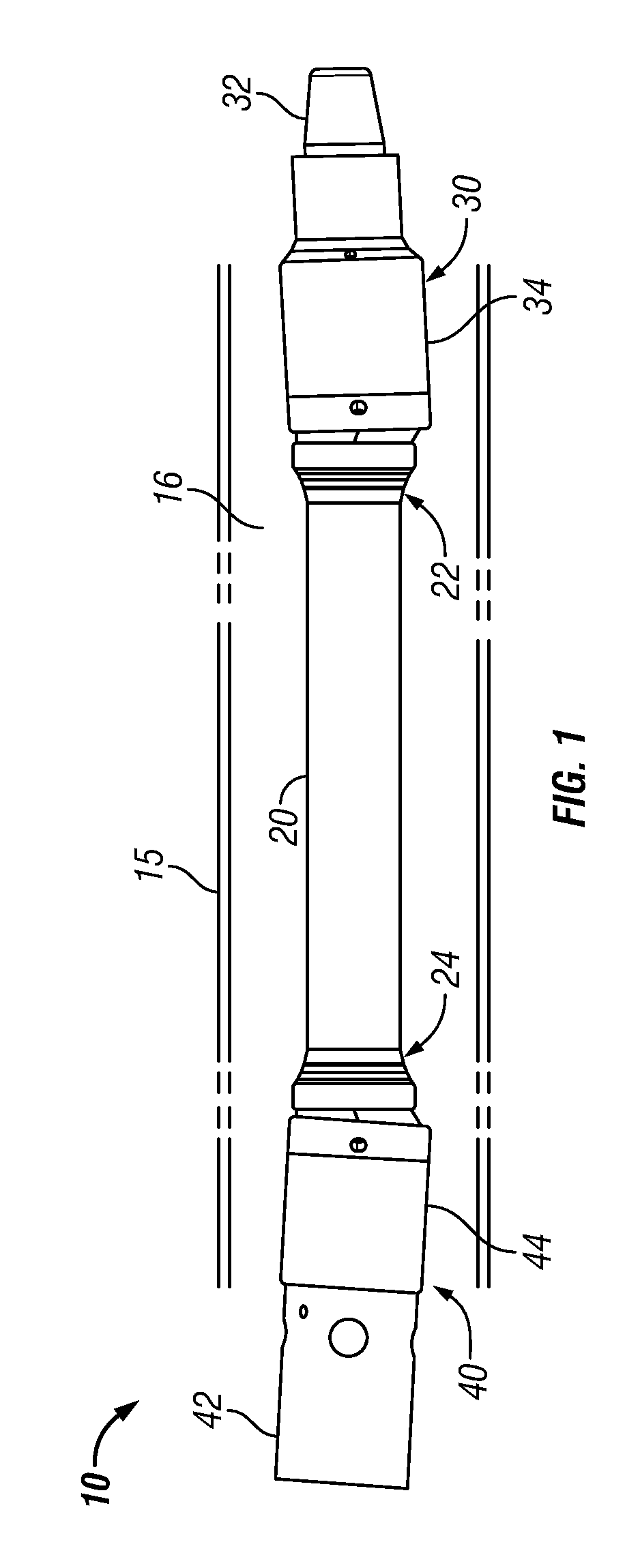
Drive shaft assembly for a downhole motor
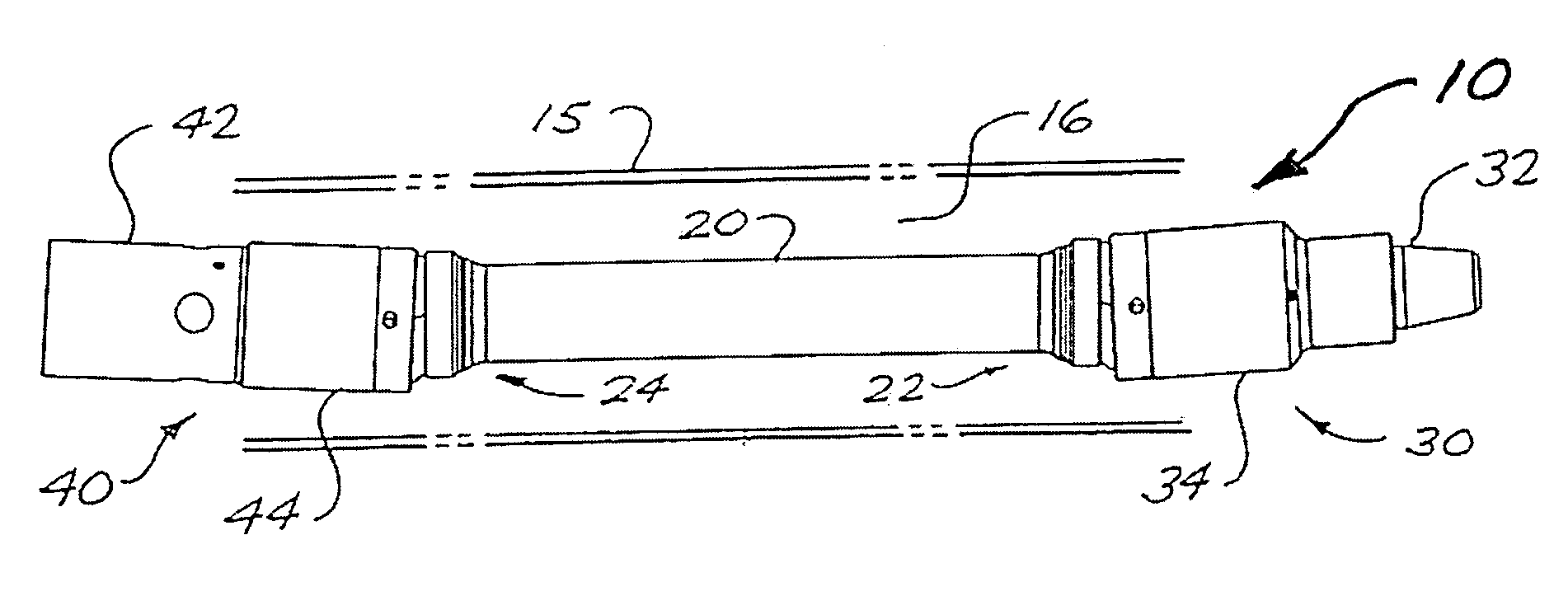
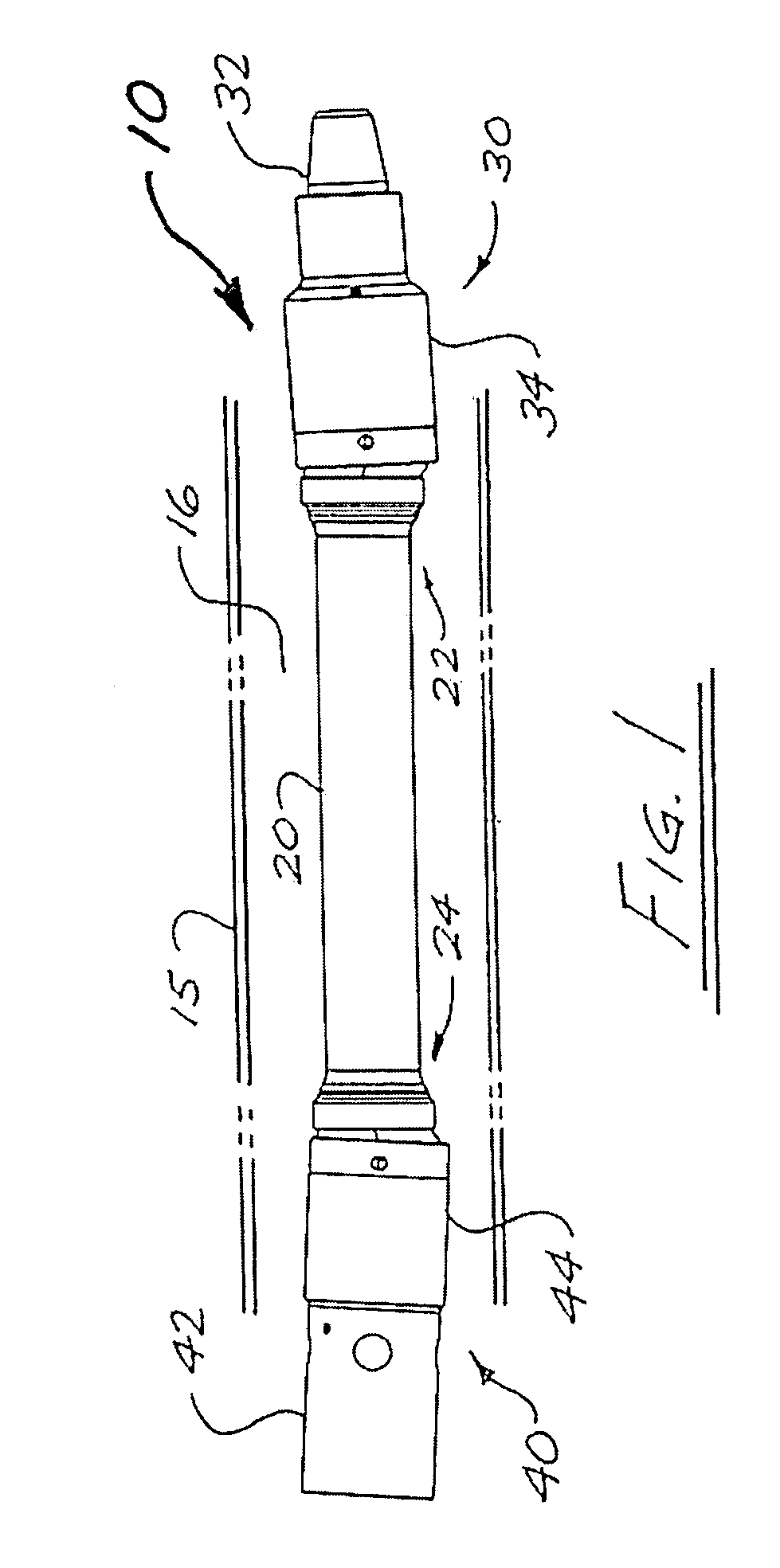
ActiveUS20090275415A1Improve pronunciationIncrease capacityYielding couplingDrilling rodsRotational axisSpherical bearing
A drive shaft assembly for a downhole motor includes a drive shaft formed with convexly spherical bearing surfaces on each end, and end housings with concavely spherical bearing surfaces for mating contact with the spherical bearing surfaces of the drive shaft, thereby facilitating omni-directional articulation between the drive shaft and the end housings while transferring axial thrust loads between the drive shaft and end housings across the interface of the mating spherical bearing surfaces. Torque is transferred between the drive shaft and end housings through two or alternatively four swivelling drive keys mounted to each end of the drive shaft and engageable with complementary drive key slots in the end housings. Full and constant torque-transferring contact is thus provided between the swivelling drive keys and the end housings irrespective of any angular offset between the drive shaft and the end housings, resulting from omni-directional articulation of the drive shaft relative to the end housing. The omni-directional center of rotation at each end of the drive shaft coincides with the geometric centerpoint of the corresponding convexly spherical bearing surface, which corresponds to the intersection of the drive shaft's rotational axis, the end housing's rotational axis, and the drive key swivel axis.
Owner:DRECO ENERGY SERVICES ULC
Large dump truck suspension
InactiveUS6086076APrevent rotationEliminate torsional loadsInterconnection systemsResilient suspensionsSpherical bearingEngineering
PCT No. PCT / AU96 / 00180 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 11, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 11, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 29, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 30223 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 3, 1996A suspension system for a large dump truck. The dump truck having a main frame with laterally spaced frame members each associated with a rear wheel mounting hub with a wheel on each of its sides. Each hub is attached to a respective frame member by an attachment member pivotally attached to the respective frame member by a pivotal mounting and a suspension spring pivotally attached to the hub by a spherical bearing and to the respective frame member at a pivot mounting. The connections of the hub allow for limited pivotal movement of the hub about transverse and longitudinal axes relative to the frame members. A dump body is pivotally attached to the frame members at the pivot mounting or to the rear and above a suspension pivotal connection at a body pivotal connection.
Owner:BHP AUSTRALIA COAL PTY LTD
High endurance high capacity ball transfer unit
Owner:ROLLER BEARING OF AMERICA
Rotatable camera to move carema len in panning or tilting by single motor
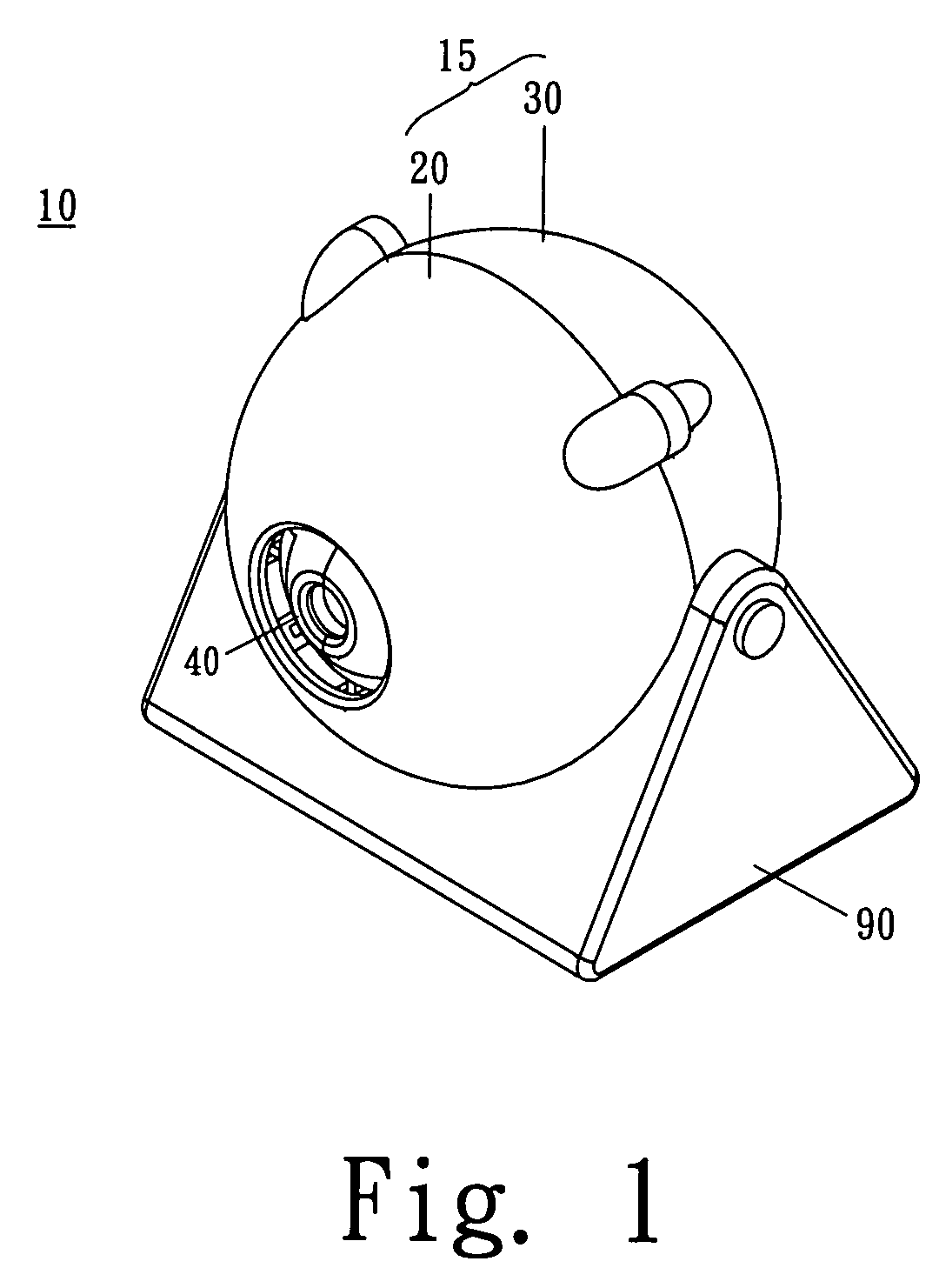
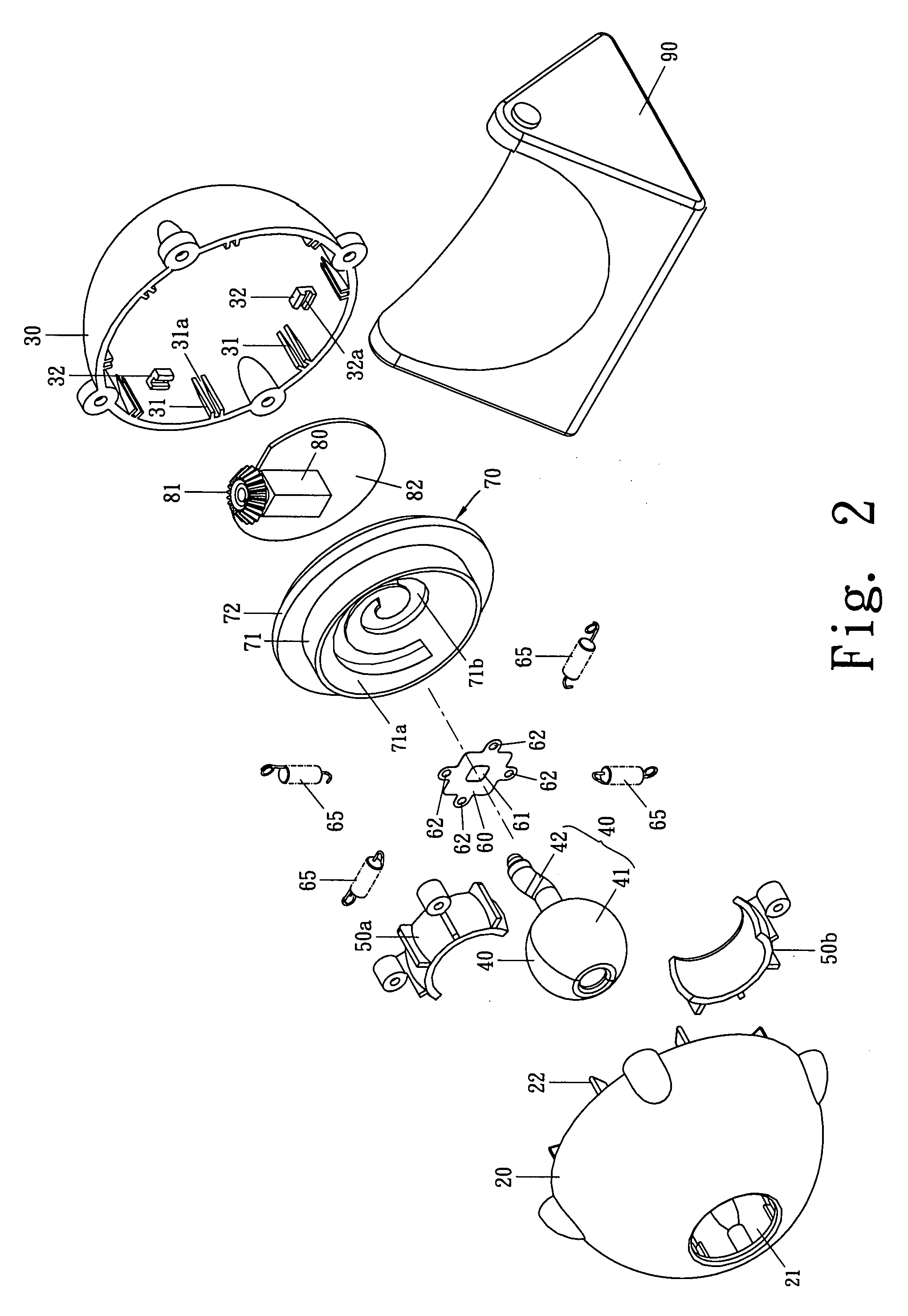
InactiveUS20080079848A1Smooth movementMove quicklyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensSpherical bearing
A rotatable camera has a motor, a lens unit comprising a photographing head and a driving rod coupled to the photographing head, a spherical bearing support for pivotally mounting the photographing head, and a rotatable disc driven in rotation motion by the motor to drive the driving rod of the lens unit move along a spiral shaped locus, and, when the motor is driven, the photographing head is at the same time driven by the driving rod to rotate and change its angular position, so that the rotatable camera employs only a single motor to drive the photographing head of the lens unit to rapidly move to the direction to be monitored, particularly, due to no time delay any corners shall be monitored by the rotatable camera.
Owner:COMPAL ELECTRONICS INC
Drive shaft assembly for a downhole motor
ActiveUS8033917B2Improve pronunciationIncrease capacityYielding couplingDrilling rodsRotational axisSpherical bearing
Owner:NOV CANADA ULC
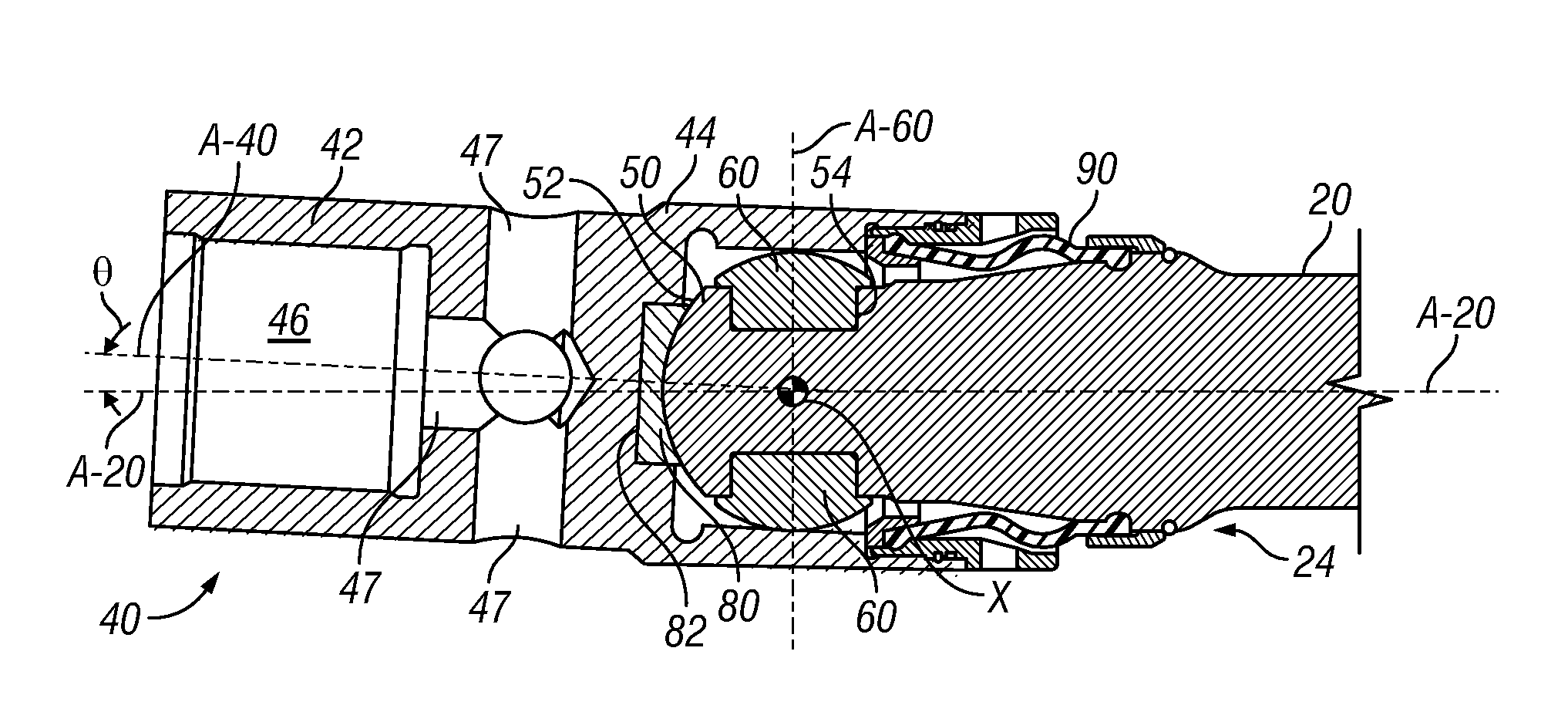
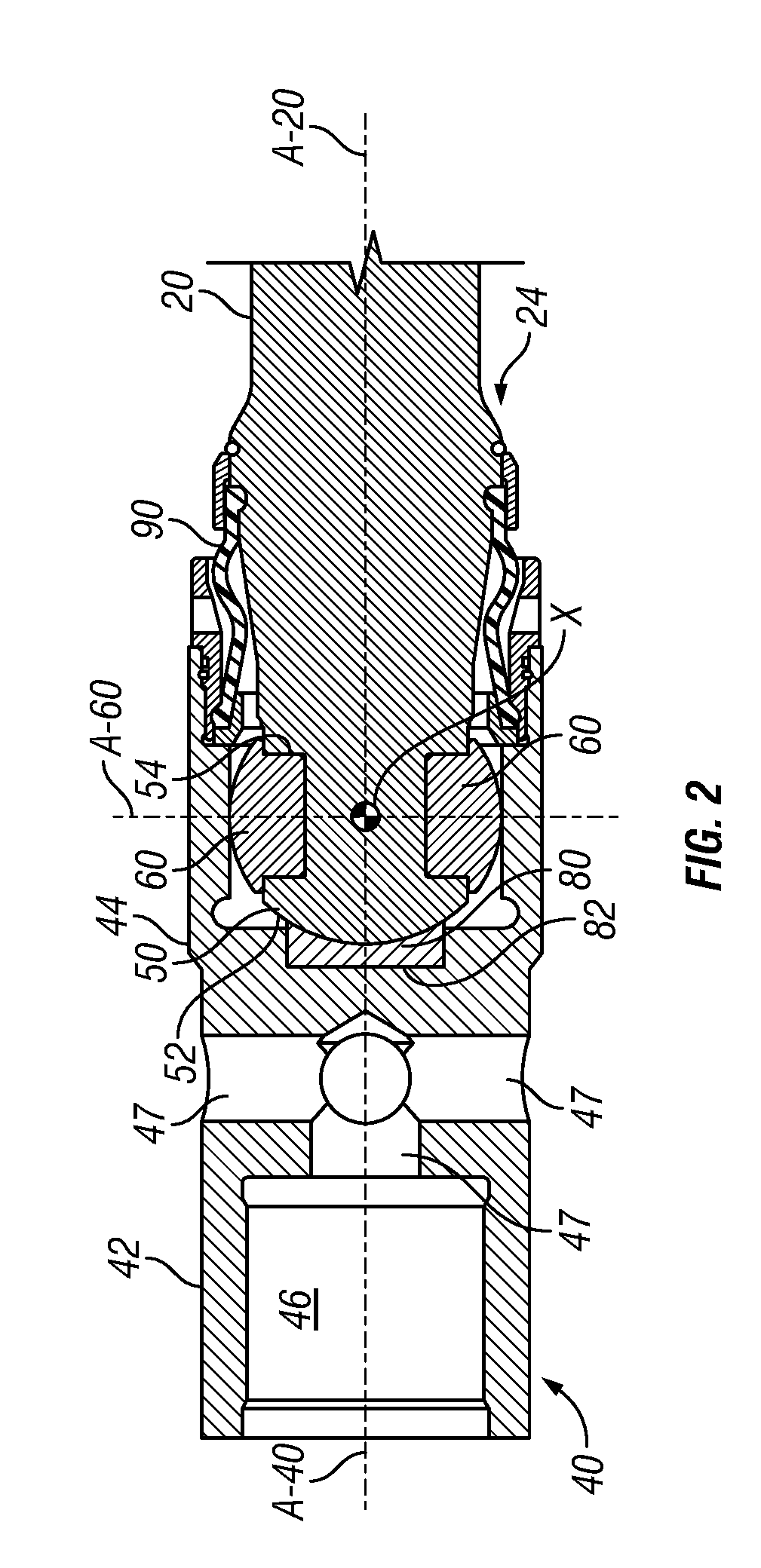
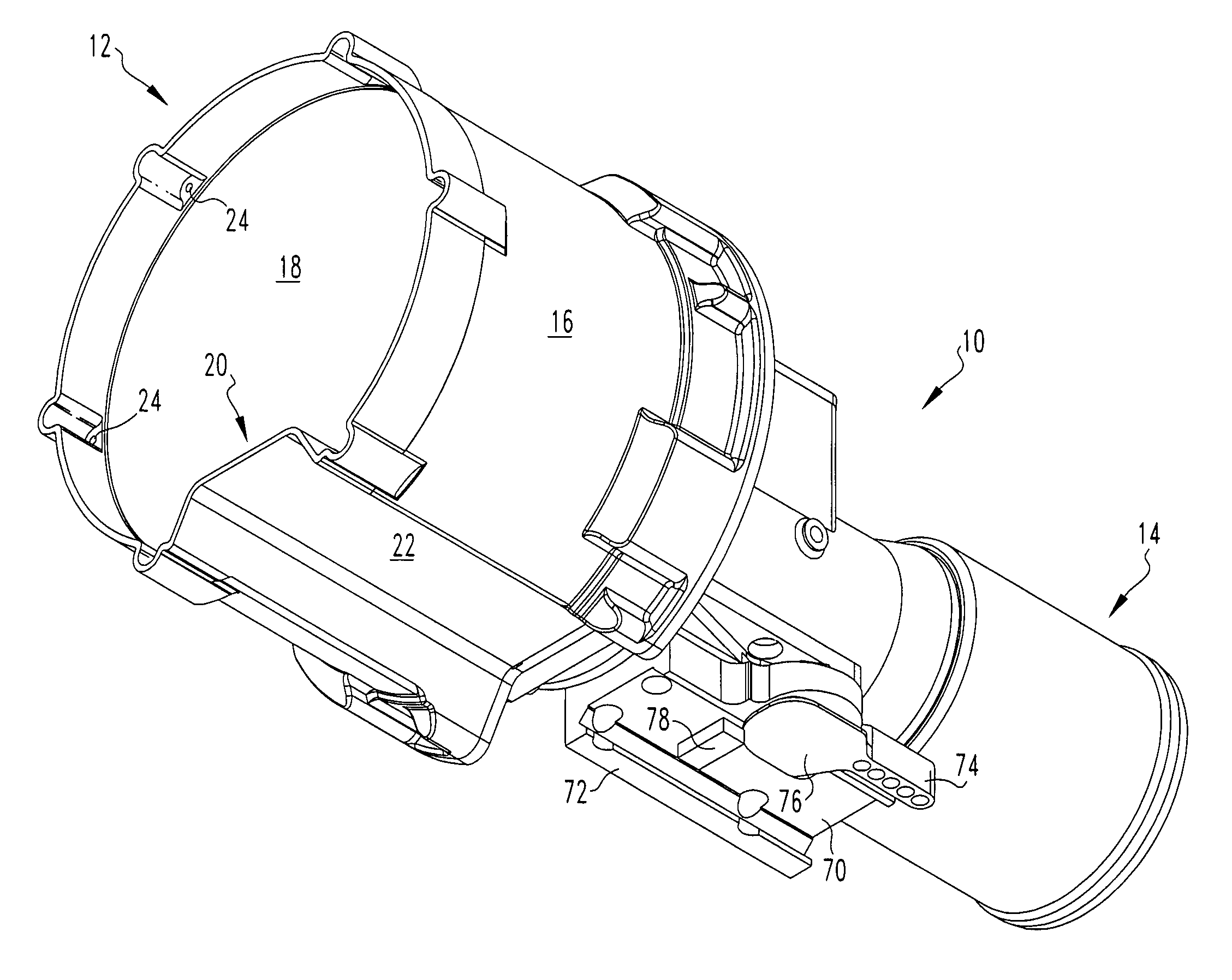
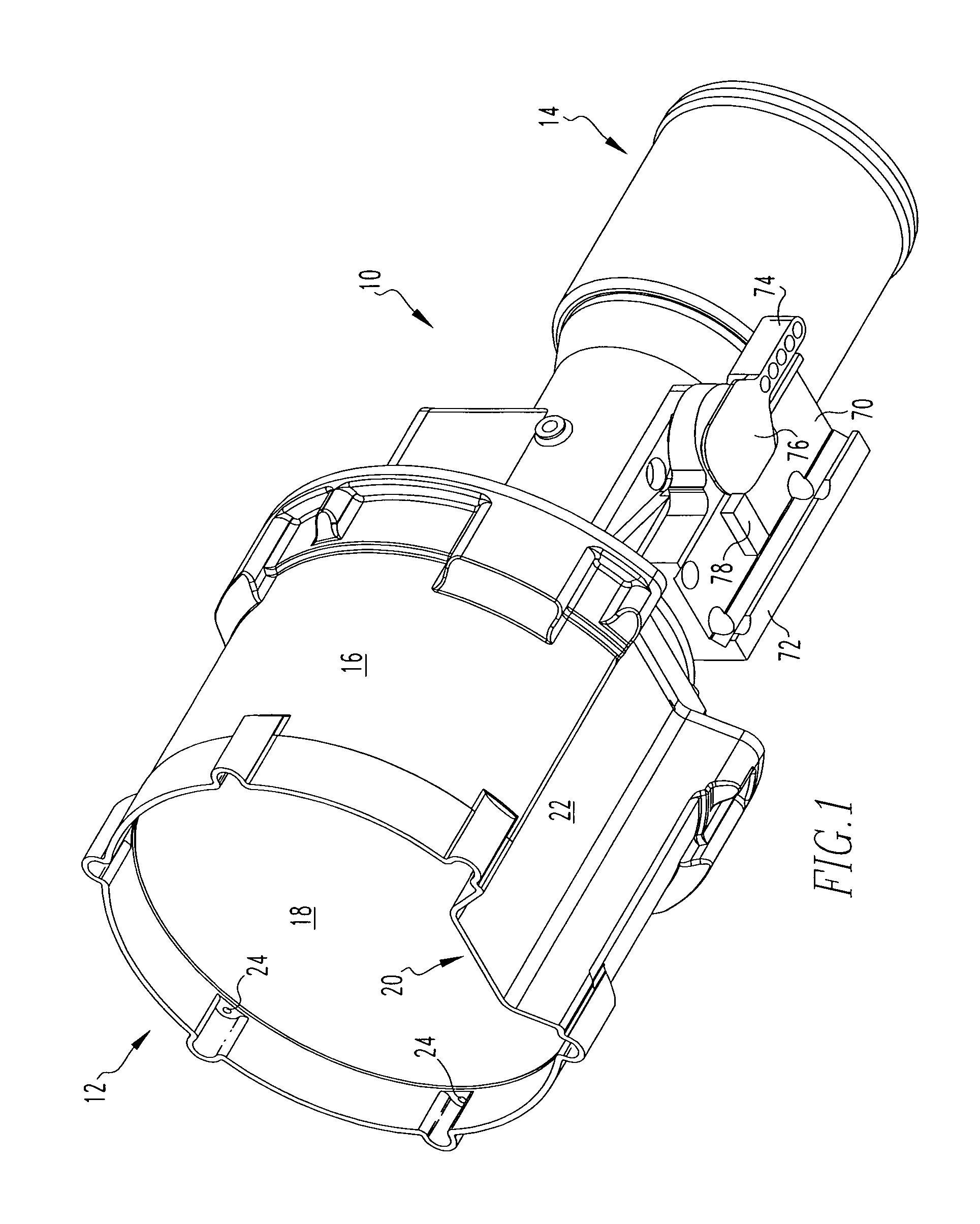
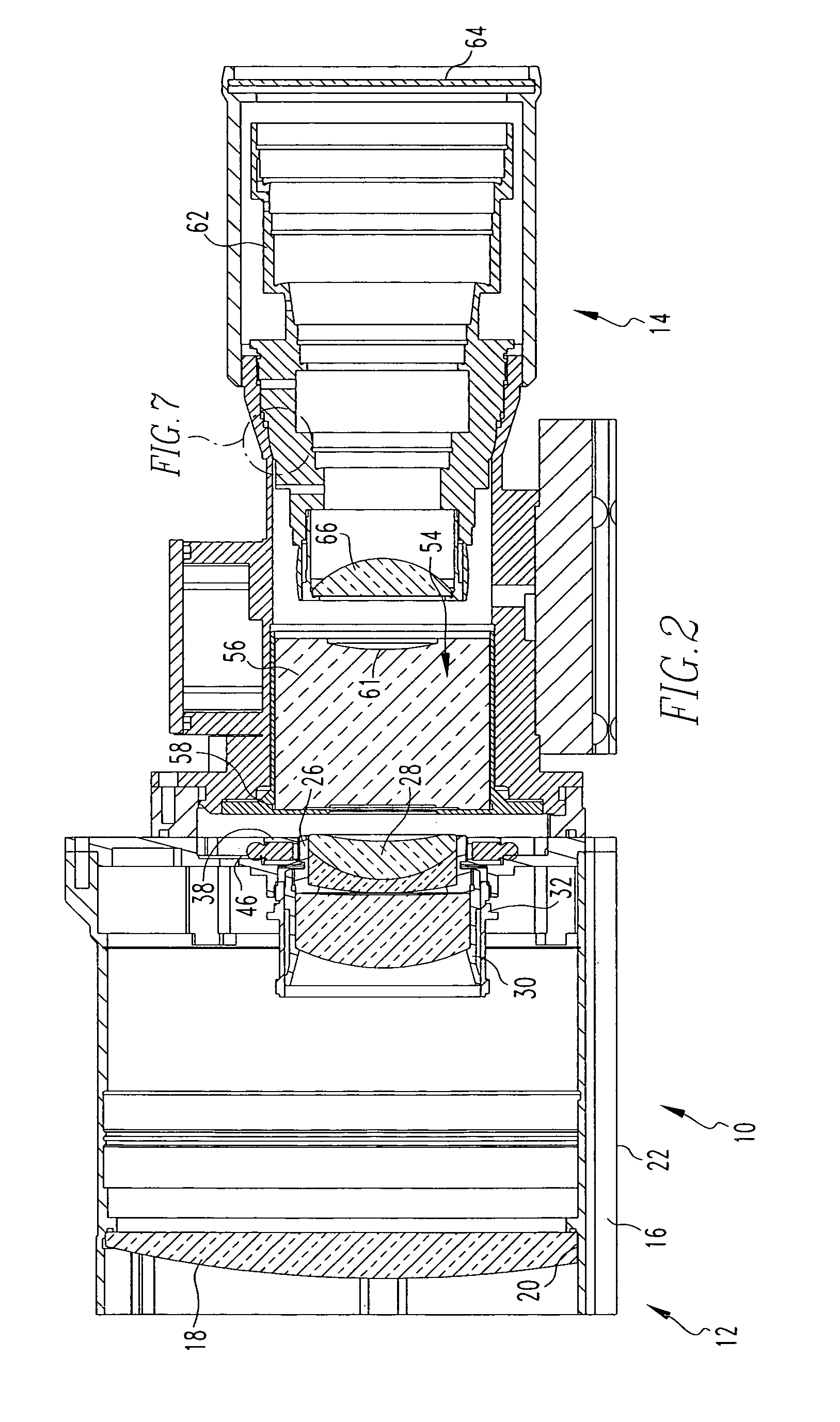
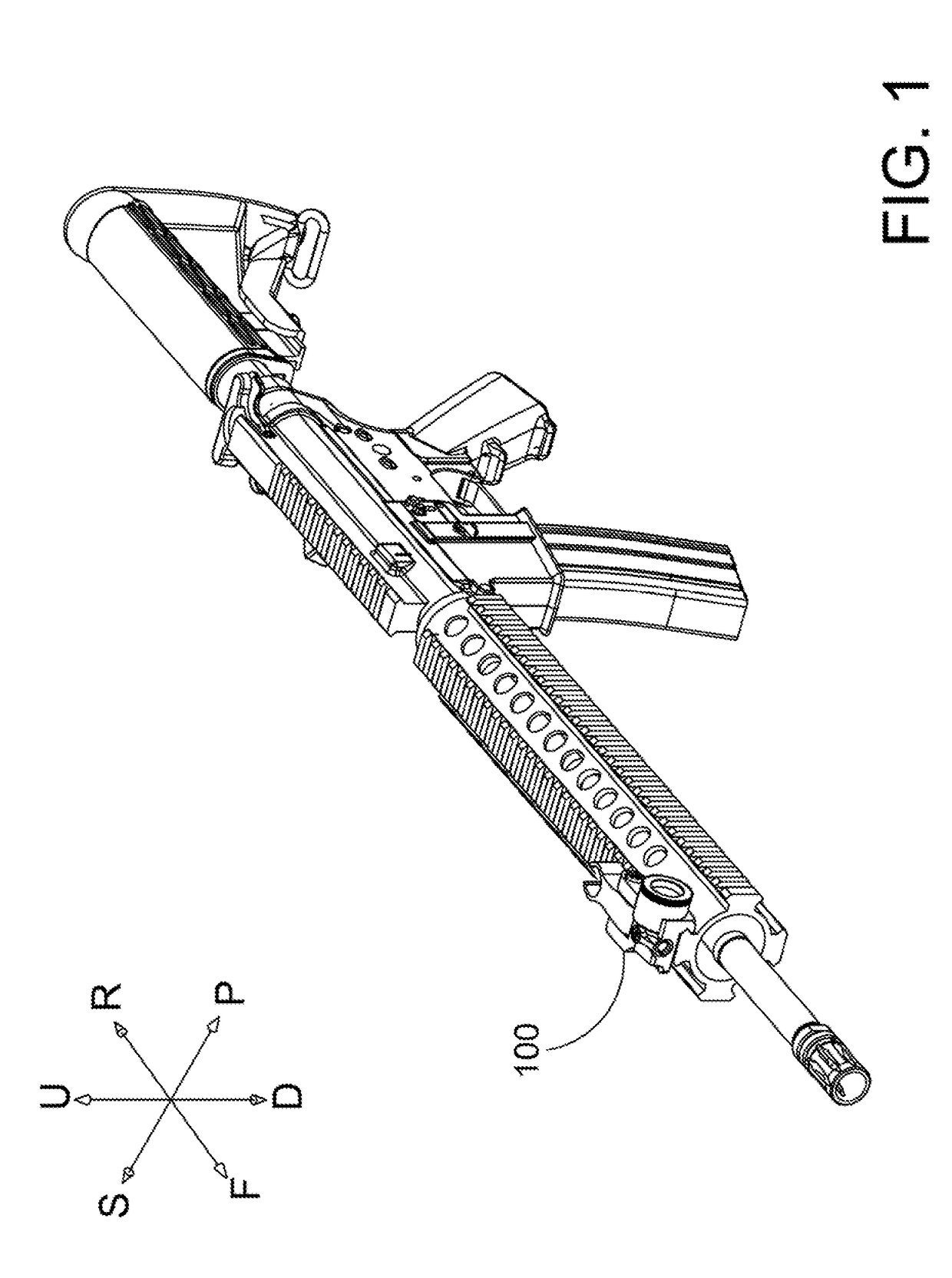
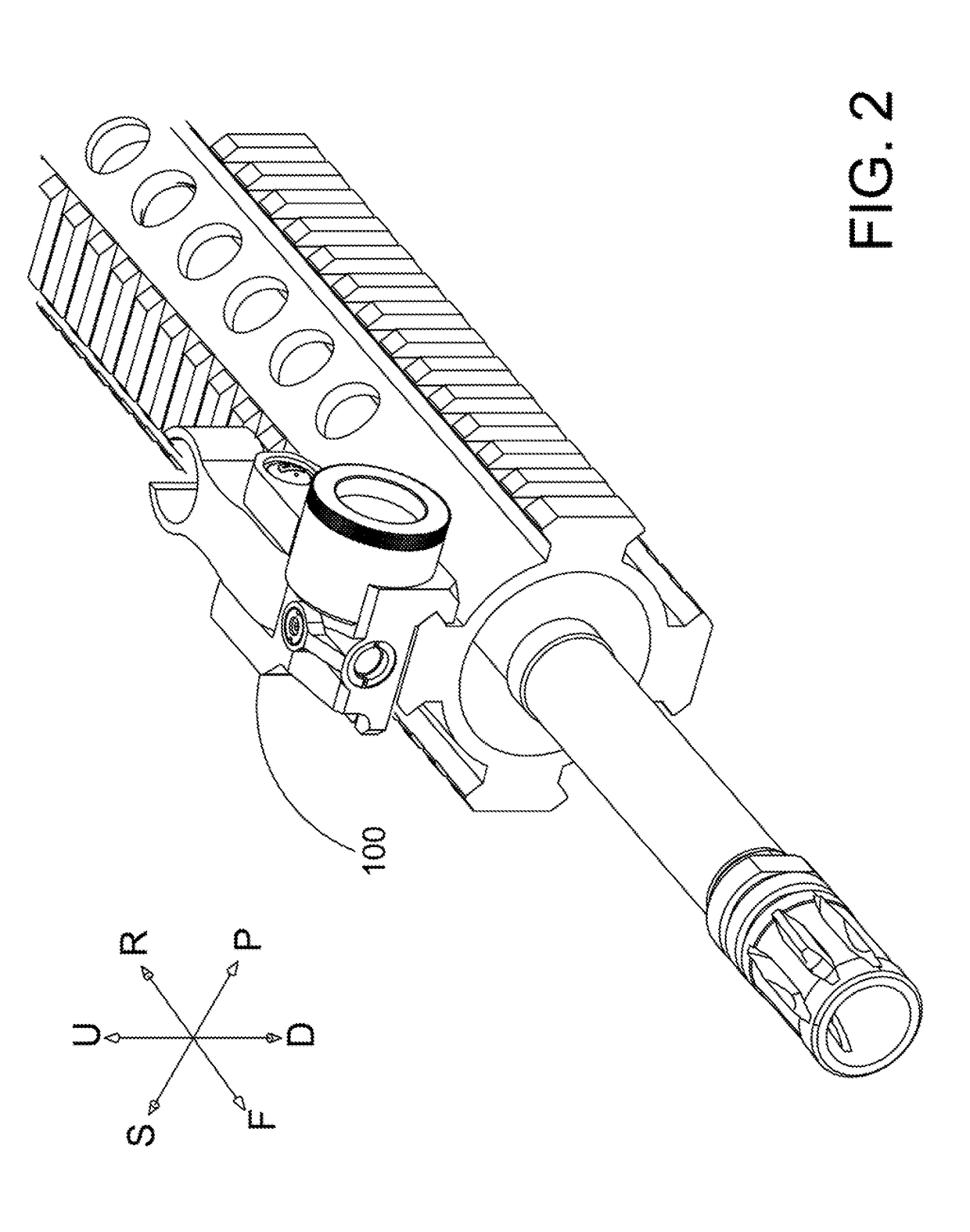
Night sight for use with a telescopic sight
A night sight includes a notched bottom portion, permitting the use of a large objective lens for maximized light gathering capability while also permitting the night sight to be mounted with its center line relatively close to the center line of the barrel of the weapon with which it is used. This configuration permits the night sight to be mounted so that its center line is the same as the center line of a daytime telescopic sight used in conjunction with the night sight. The night sight includes a focusing assembly having decreased sensitivity to tilt or decenter, and a collimator mounted within a spherical bearing so that the collimator may be precisely aligned during assembly of the night sight. The night sight thereby ensures that an image viewed through the night sight appears to originate from the same angle as that with which the image entered the objective lens, and further resists a need to compensate for parallax during aiming.
Owner:FLIR SURVEILLANCE
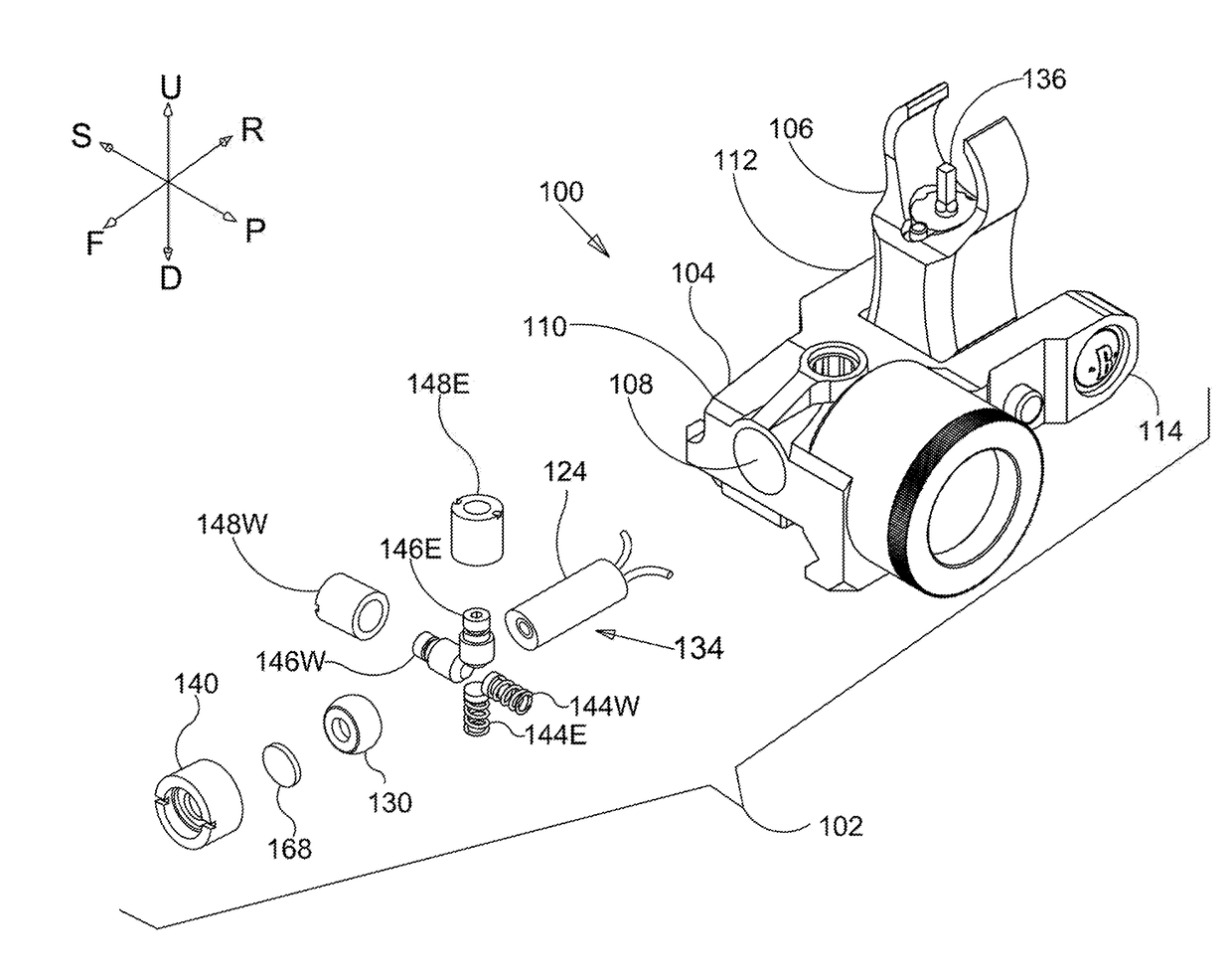
Lever handle type haptic input apparatus equipped with electromagnetic brake
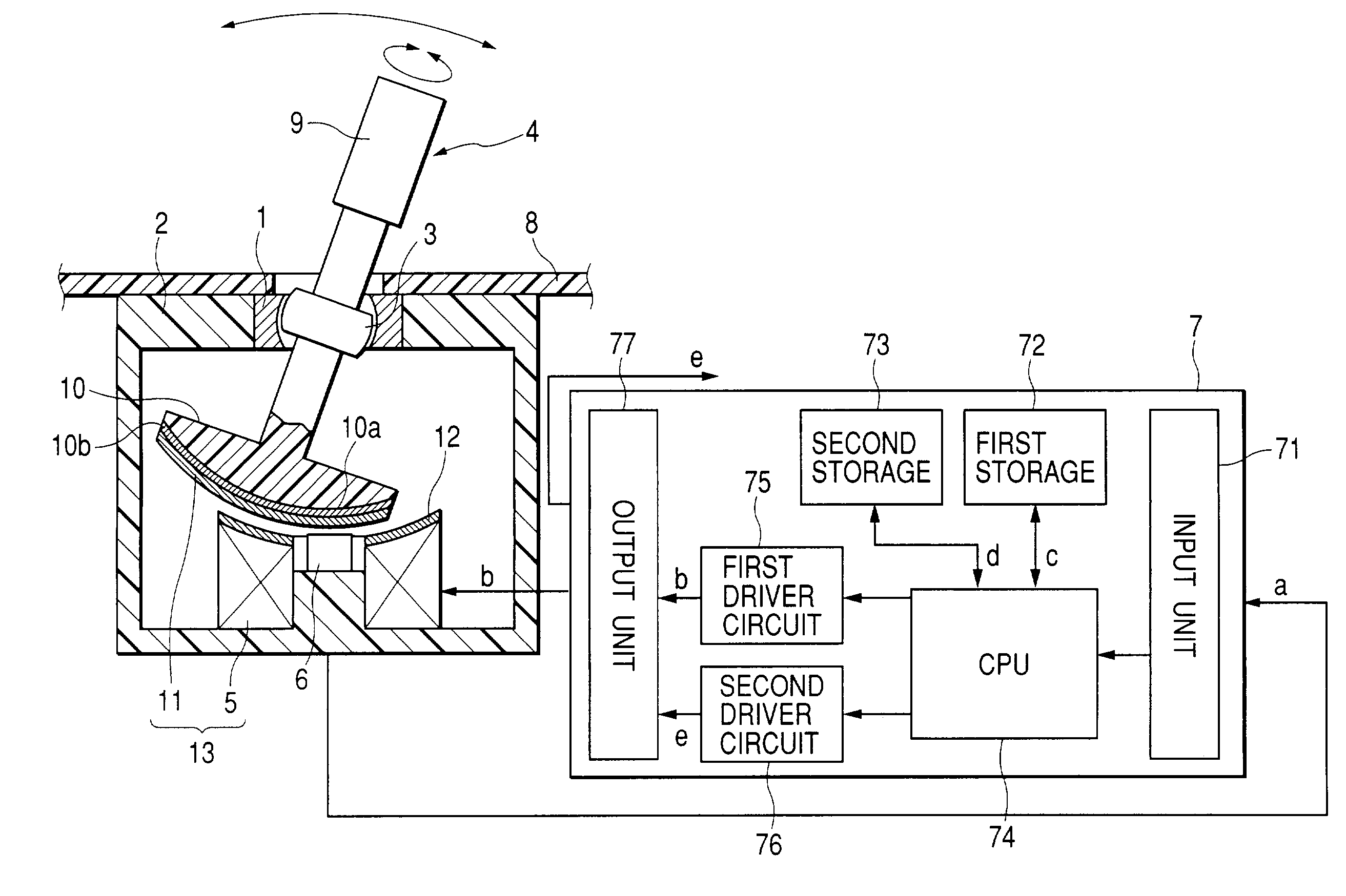
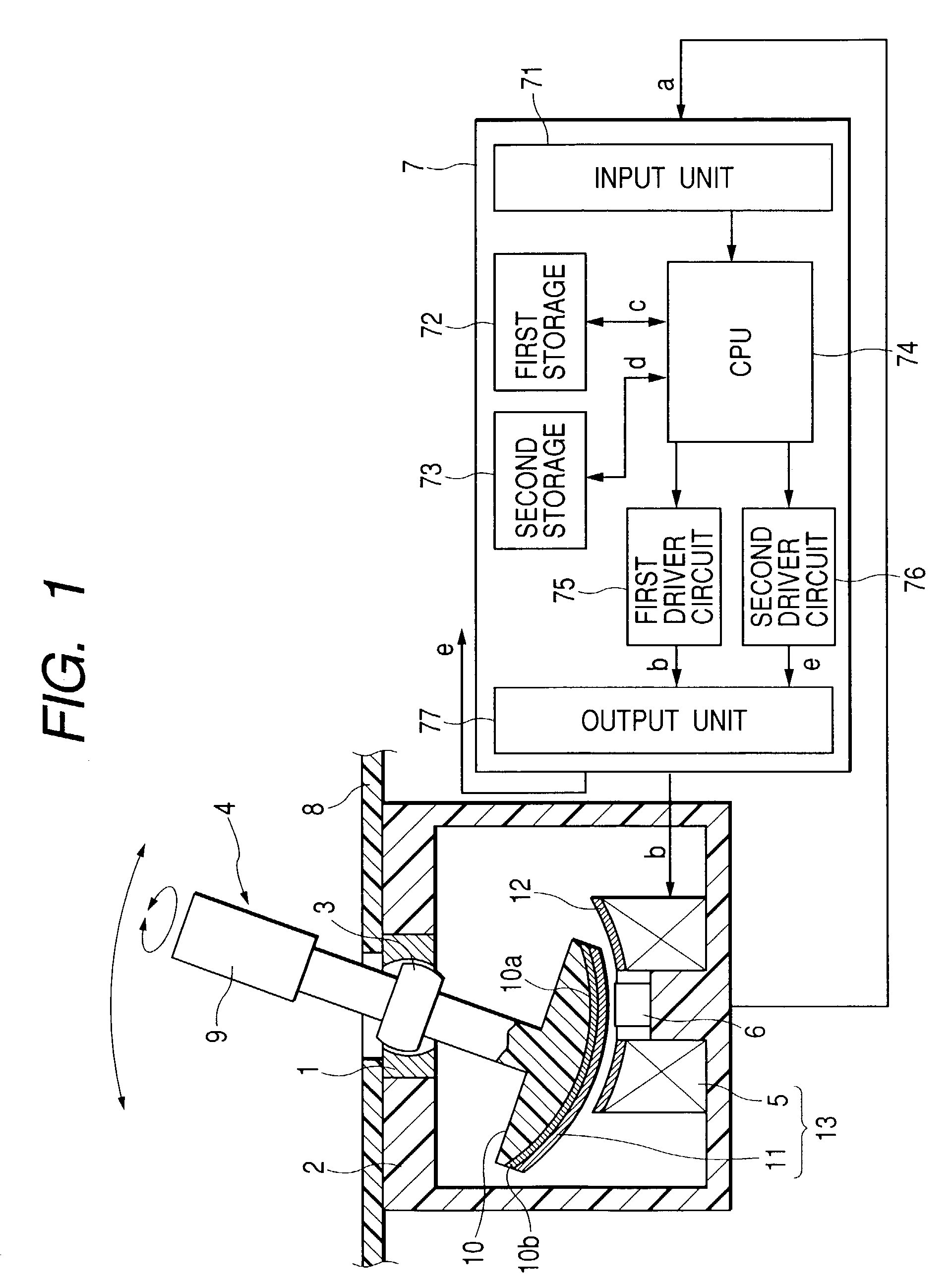
InactiveUS7176892B2Simple structureEliminate such defectivenessInput/output for user-computer interactionManual control with multiple controlled membersDriver circuitSpherical bearing
A haptic input apparatus includes: a supporting member having a spherical bearing; a lever handle having a spherical portion to be supported by the spherical bearing; an electromagnetic coil arranged opposite to a lower end surface of the lever handle; detection means for detecting an operating state of the lever handle; and control means for taking in an output signal a from the detection means to output a driving signal b of the electromagnetic coil based on the output signal a. The control means reads outs a control signal c from the electromagnetic coil corresponding to an output signal a to be inputted from the detection means from a first storage to output to a first driver circuit. The first driver circuit D / A converts the control signal c outputted from the CPU for amplifying, and outputs a driving signal b from the electromagnetic coil.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
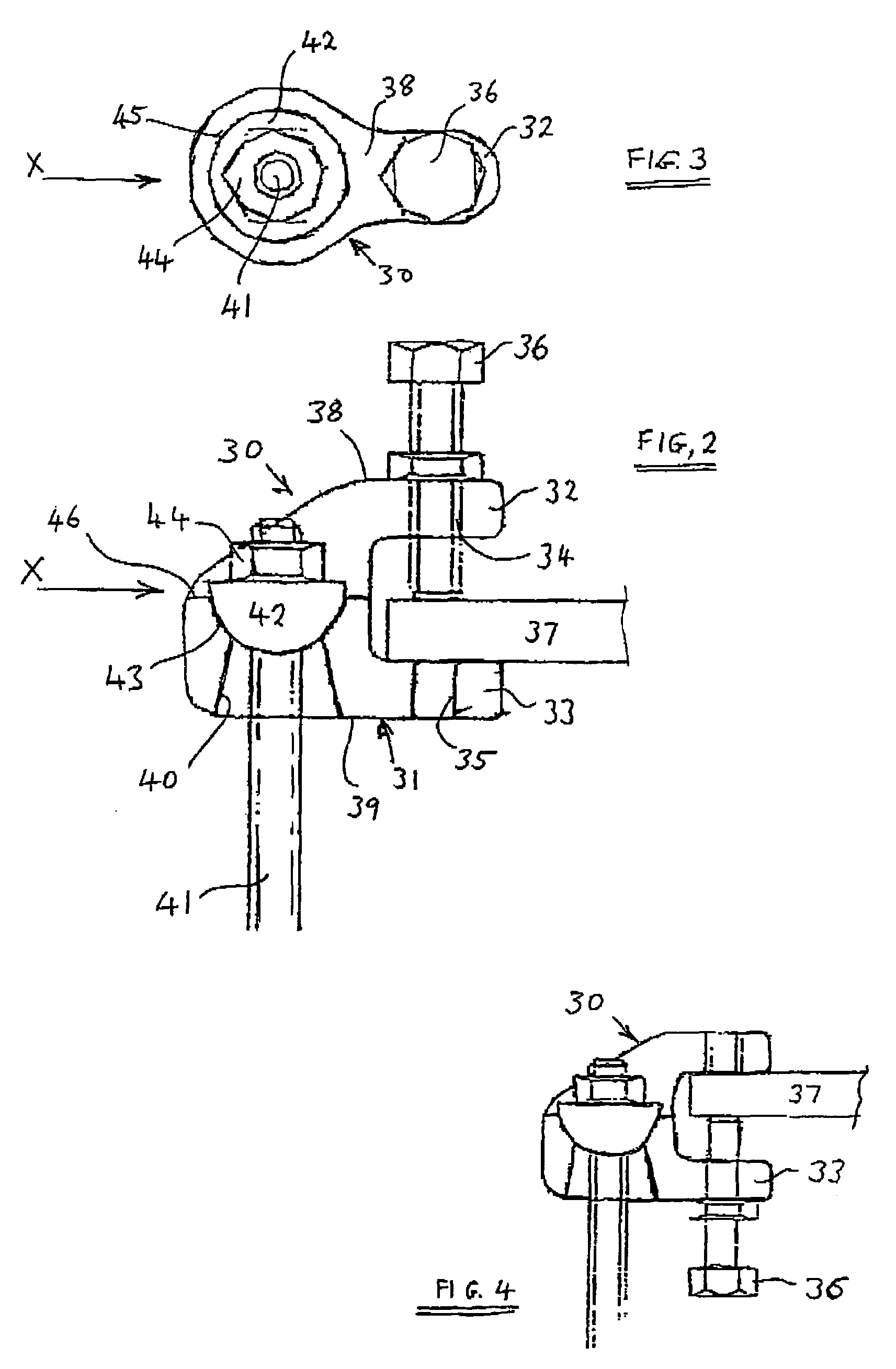
Pivotable suspension element
A pivotable suspension element includes a support member having a part-spherical bearing surface clamp element and a body portion, the body portion having an integral formation of a slot to receive a part of a component to which the pivotable suspension element may be secured; a locator formation for the clamp element whereby, in use, the clamp element may be operated to clamp a flange in the slot; a part-spherical seat, and a through-passage extending through the body from the part-spherical seat, wherein the curvature of the part-spherical seat of the body portion corresponds substantially with that of the bearing surface of the support member and wherein the cross-sectional size of the through-passage increases in a direction away from the part-spherical seat.
Owner:ACCESS TECH
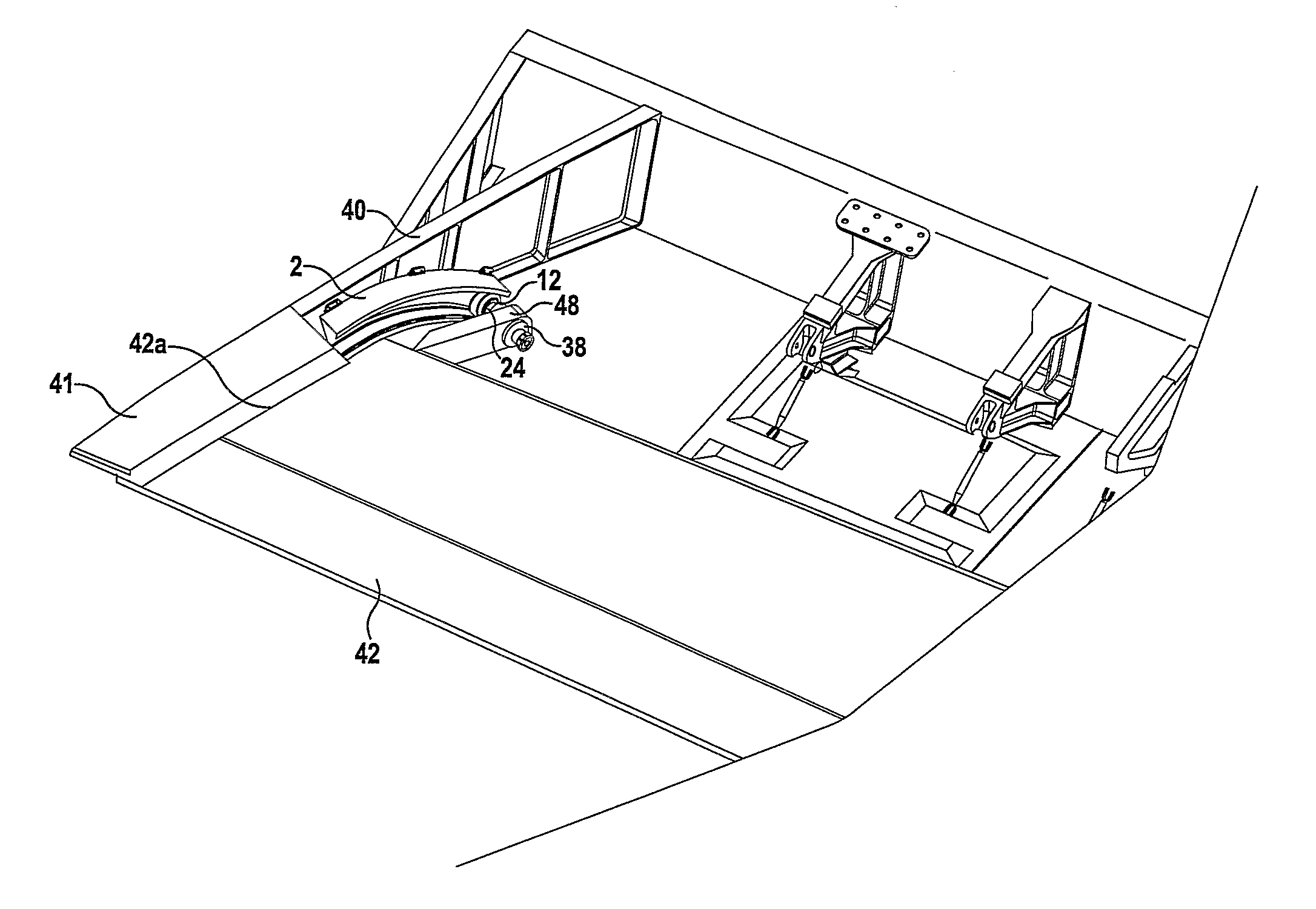
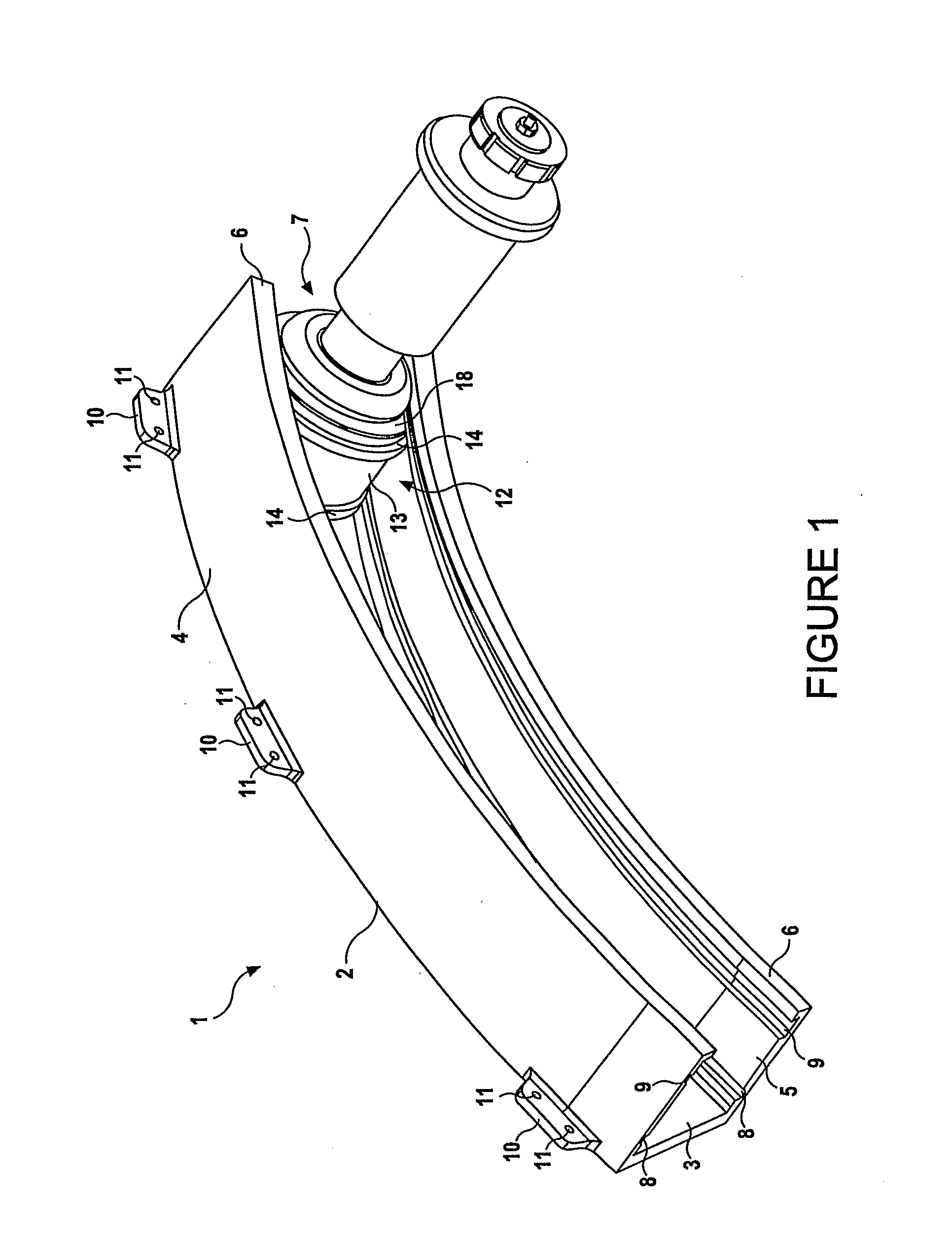
Support assembly
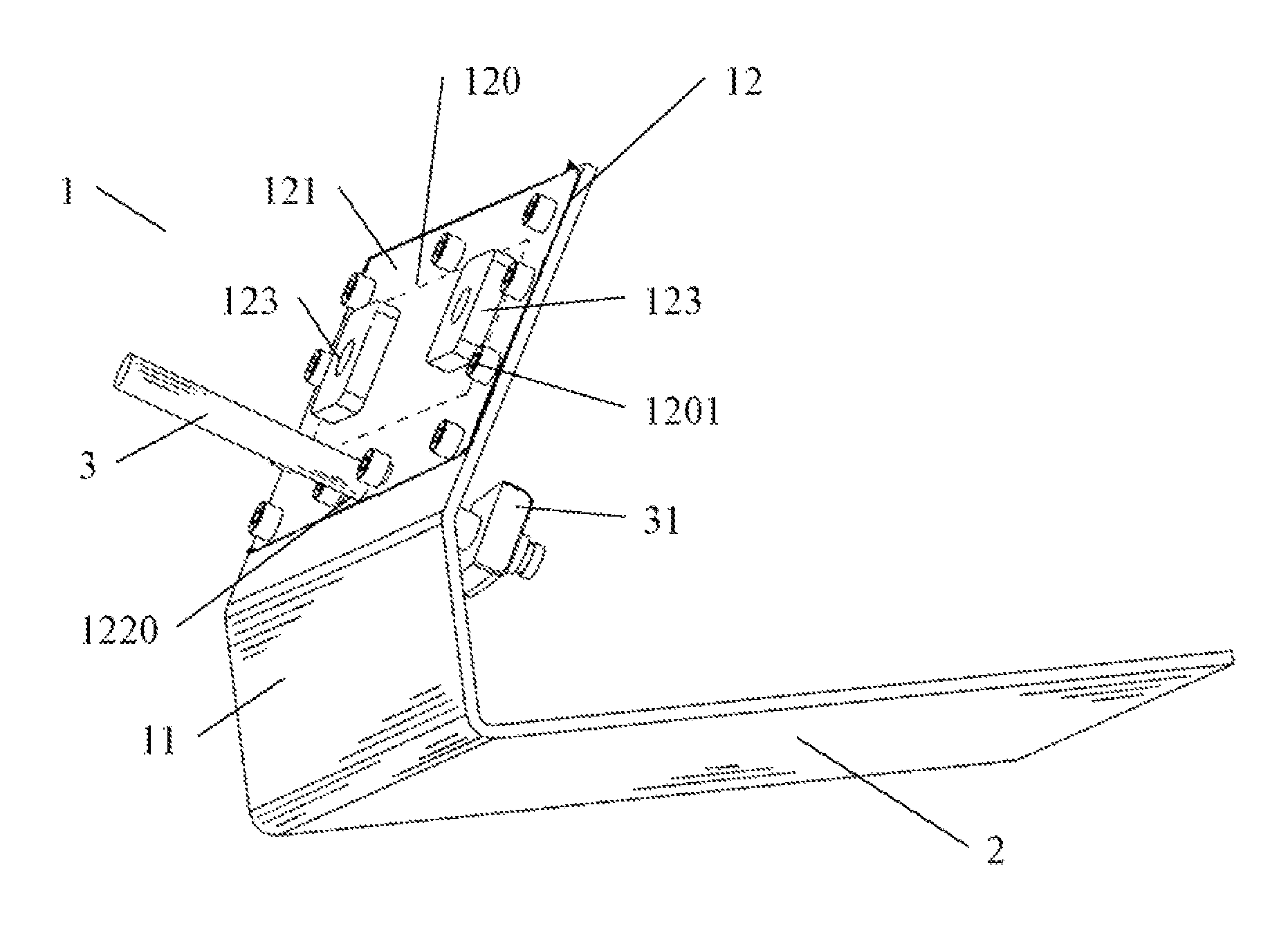
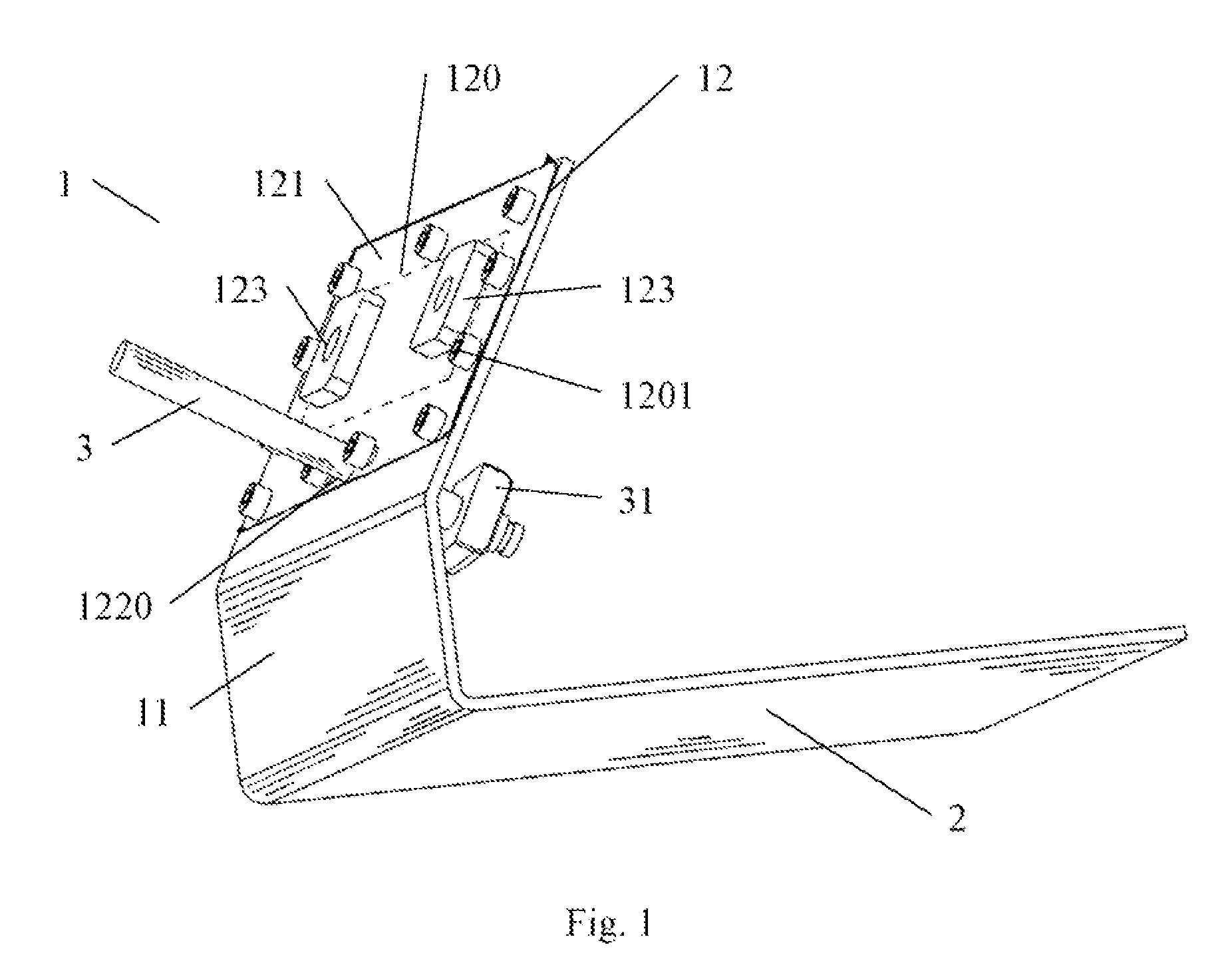
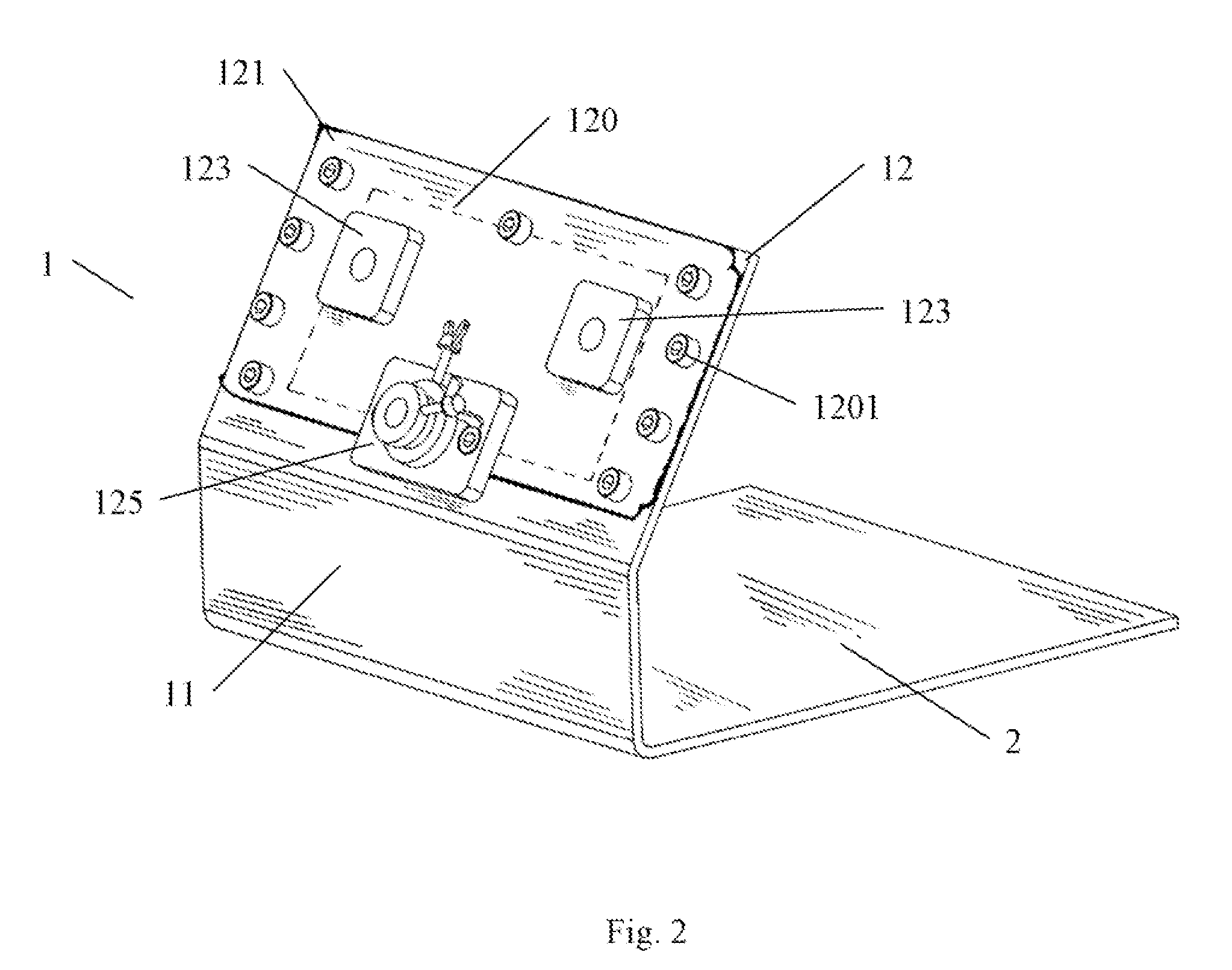
A support assembly (1) for guiding a flap (42) on an aircraft wing (41) during deployment of the flap is disclosed. The assembly comprises a guide track (2) defining a two-dimensional path, a cylindrical bearing follower (12) having a longitudinal axis constrained so as to follow said path during flap deployment, a shaft (23) extending from the bearing follower and, a spherical bearing coupling an end of the shaft to the bearing follower such that the bearing follower is rotatable relative to the shaft about the longitudinal axis of the bearing follower as it travels along the track. The spherical bearing also enabling rotation of the shaft about its longitudinal axis relative to the bearing follower and rotation of the shaft about a centre point of the spherical bearing such that the flap is fret to move in multiple directions.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Roadheader gearbox
InactiveUS20130324354A1Precise positioningToothed gearingsGearing detailsSpherical bearingGear system
A gearbox includes a shaft input spherical bearing and a shaft output spherical bearing enabling the ring gear to float within the housing and not engage the housing. The shaft output spherical bearing permits angular displacement of the output shaft with respect to the longitudinal axis of said output shaft. A spline connection enables the ring gear to pivot with respect to the cover. Loads transmitted to the housing of the gearbox are not transferred to the gear systems and the gear systems self-align within the housing.
Owner:FAIRFIELD MFG CO INC
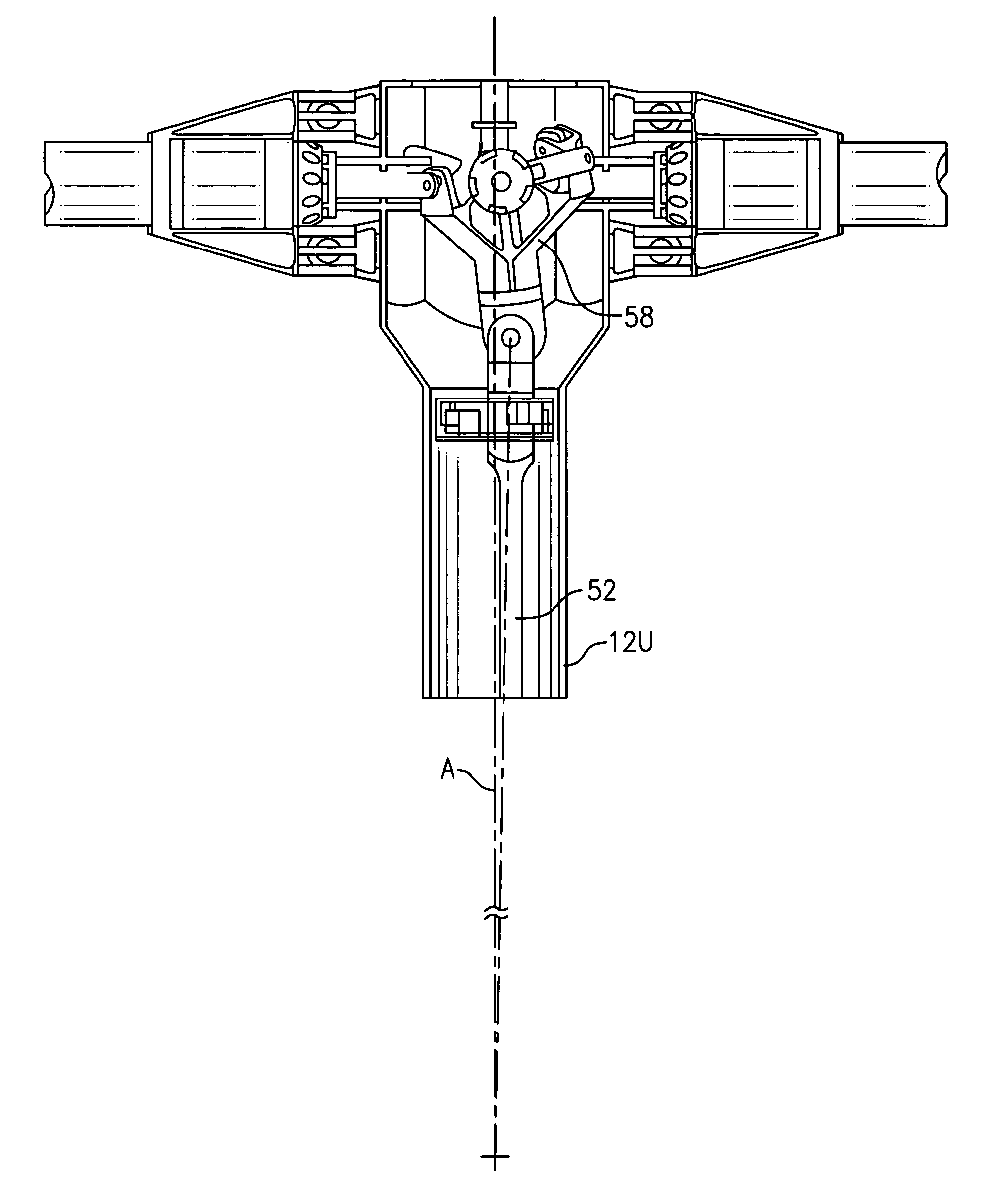
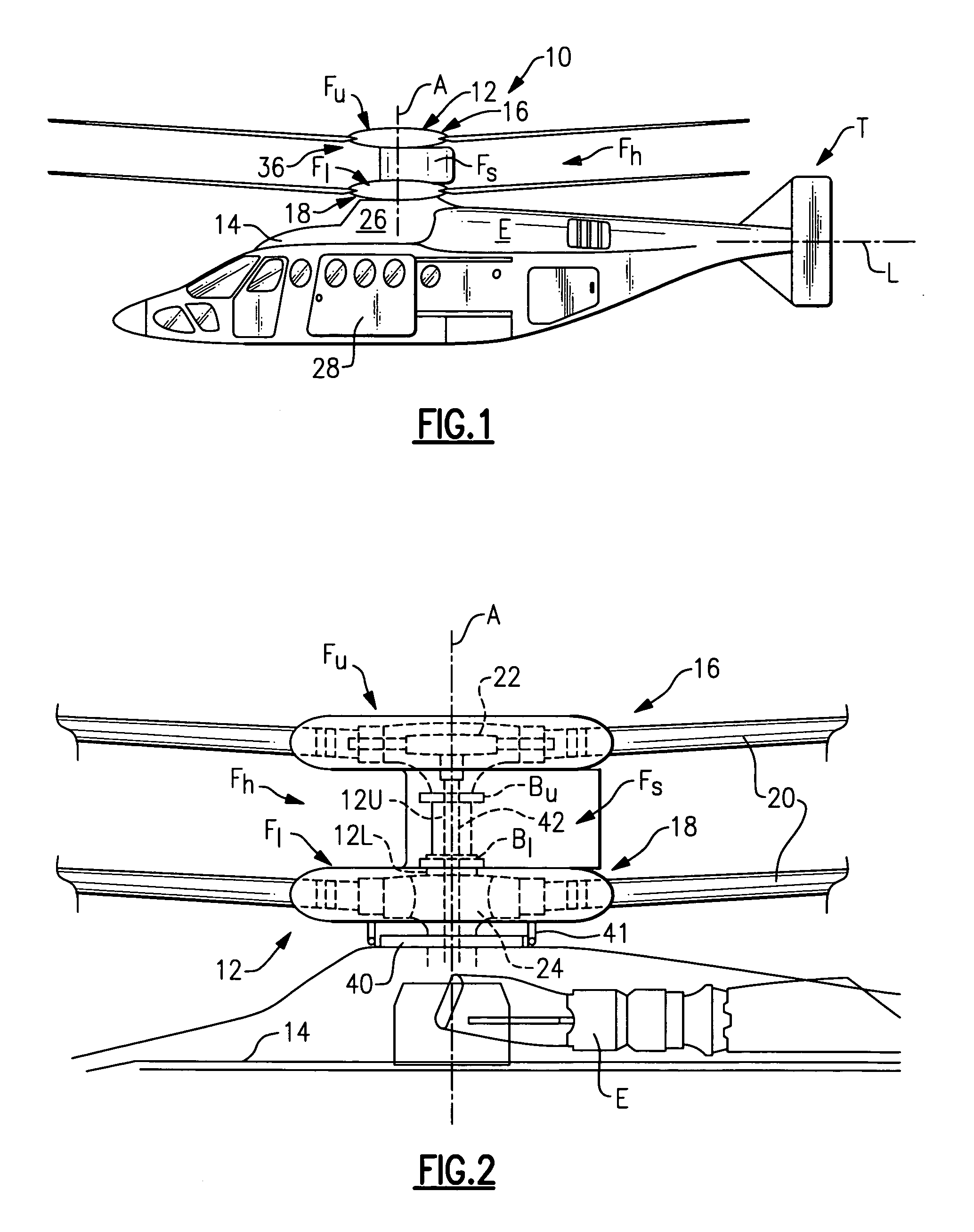
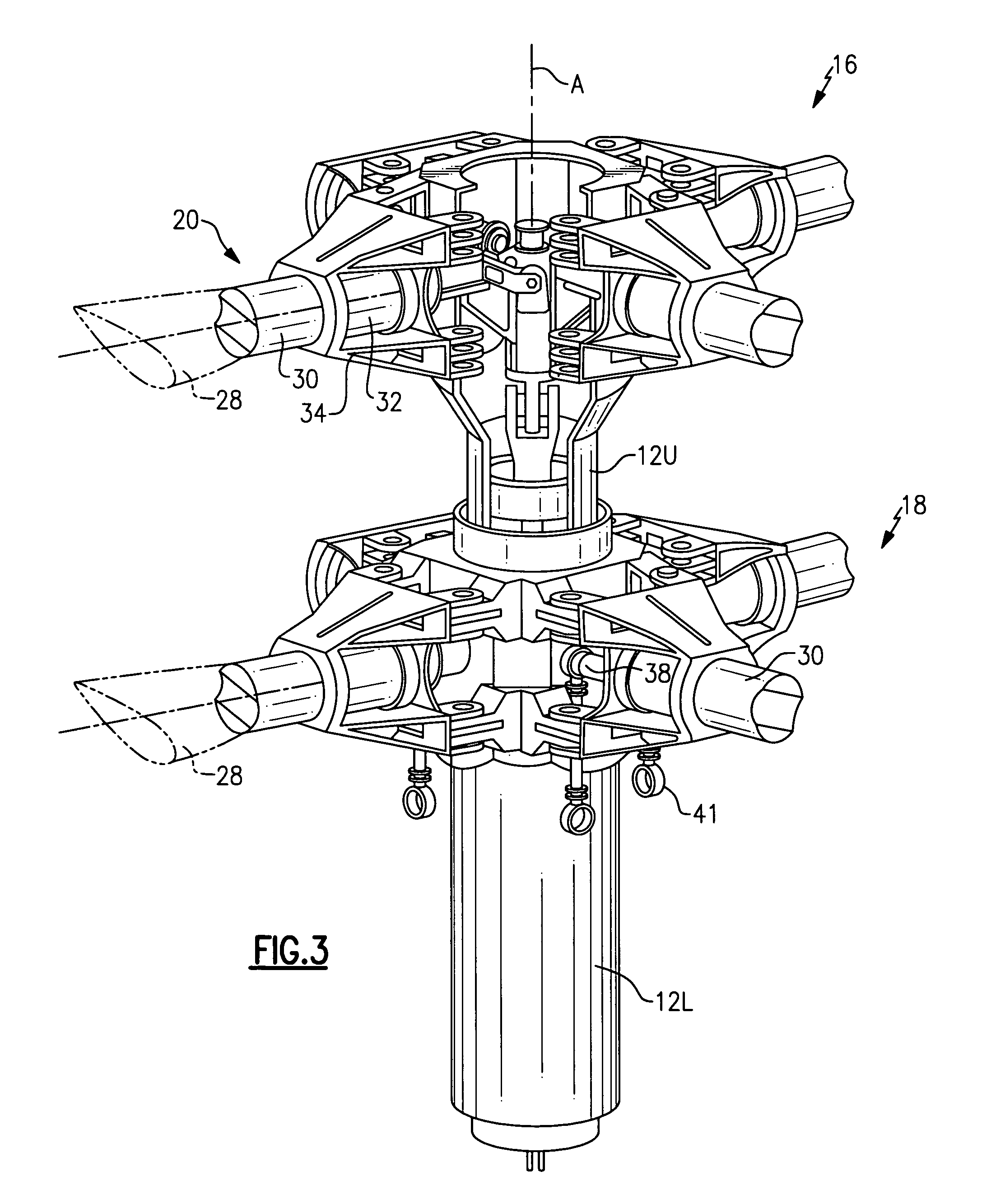
Upper rotor control system for a counter-rotating rotor system
An upper rotor control system is contained within an upper rotor shaft and upper hub assembly of a contra-rotating rigid rotor system. A collective servo assembly includes a hydraulic actuator that provides collective pitch to all blades through axial extension / retraction of the control rod relative the upper rotor shaft for collective pitch control of the rotor blades. The collective servo assembly includes a spherical bearing for attachment of the control rod to aircraft structure. An X-Y positioner assembly includes a bearing arrangement which allows the shaft to rotate, while the X-Y positioner assembly remains non-rotational therein. The X-Y positioner assembly includes a multitude of hydraulic actuators, orthogonally positioned, to tilt the control rod about the spherical bearing off the axis of rotation of the upper rotor shaft for cyclic pitch control of the rotor blades.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
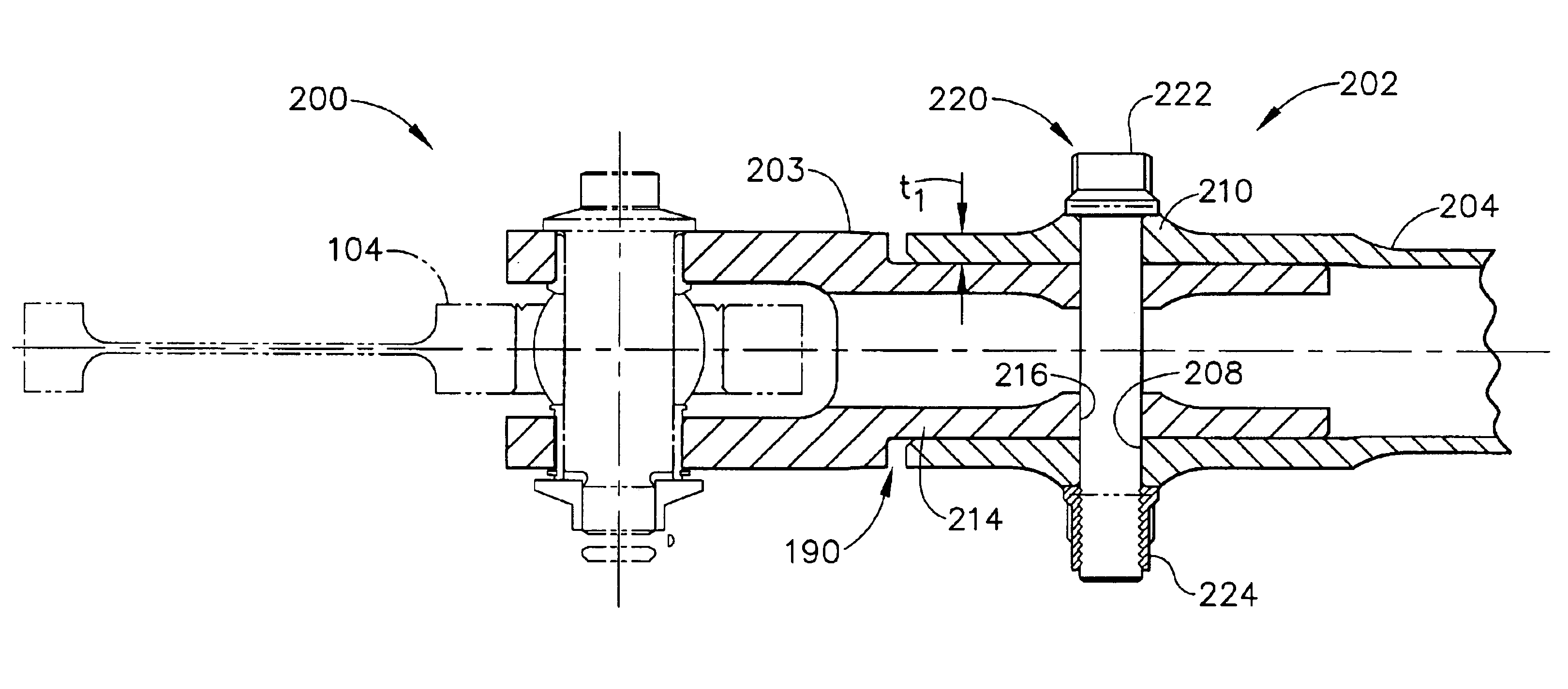
Methods and apparatus for mounting a gas turbine engine
A method enables a thrust link including a clevis to be coupled to a mounting lug including a spherical bearing. The method comprises positioning the spherical bearing within the thrust link clevis, and coupling the thrust link to the mounting lug by inserting a fastener through the clevis such that the fastener extends from one side of the clevis through the spherical bearing to the other side of the clevis, and such that fuse element included with at least one of the fastener and the clevis is positioned within a structural load path defined between the clevis and the thrust link, wherein the fuse element is configured to fail when subjected to a predetermined load.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rope-driven redundancy mechanical arm
InactiveCN101028712AEliminates prone to slippage problemsEliminate slippageJointsArmsSpherical bearingDrive wheel
A redundant manipulator driven by strings is composed of a base, a one-freedom elbow joint consisting of fixing platform, drive wheel, joint rod, drive axle and manipulating strings, and the three-freedom wrist and shoulder joints consisting of fixed platform, movable platform, joint rod, spherical bearing, and manipulating strings. Said manipulating string and / or drive wheel have stop mechanism, preventing skid.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
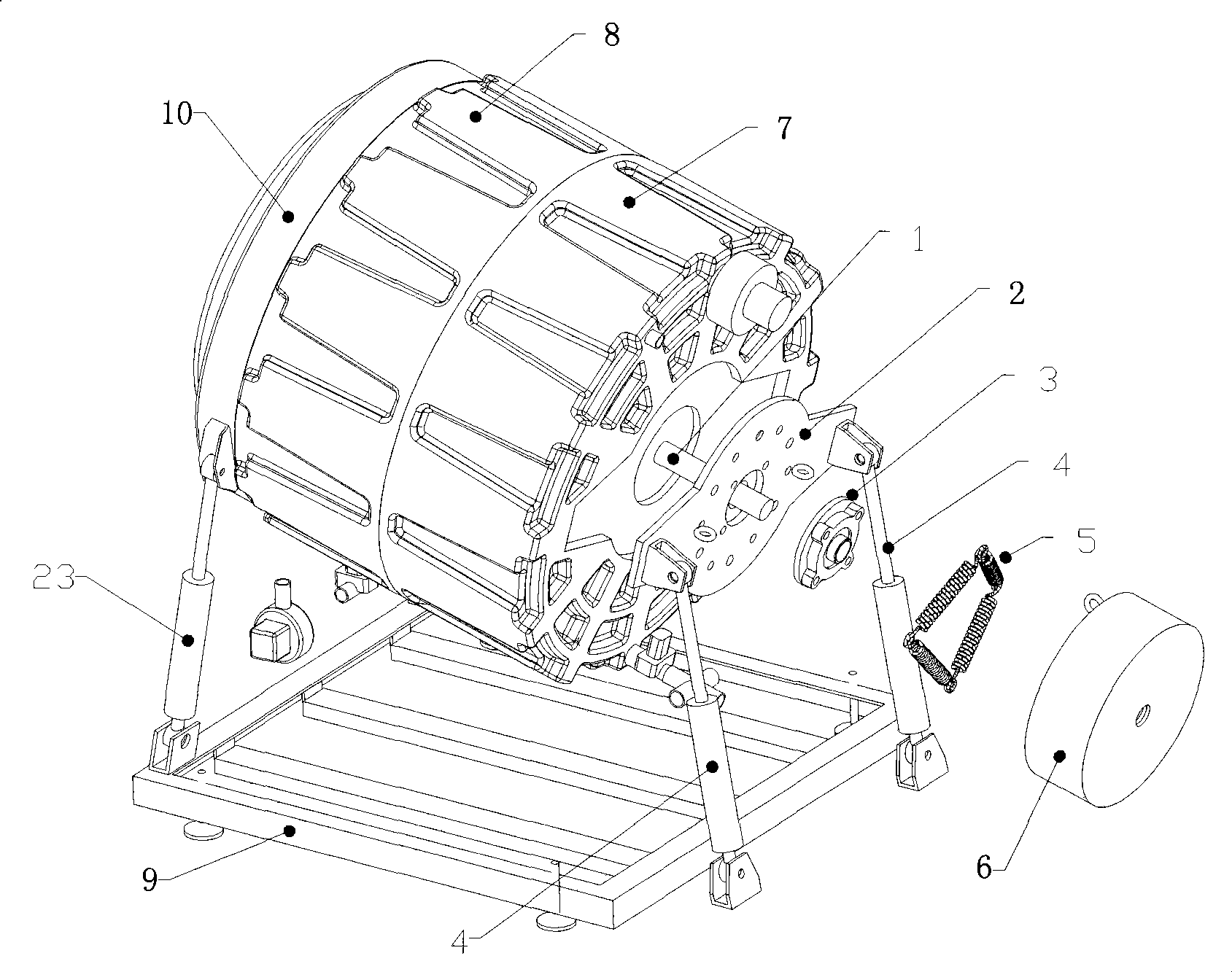
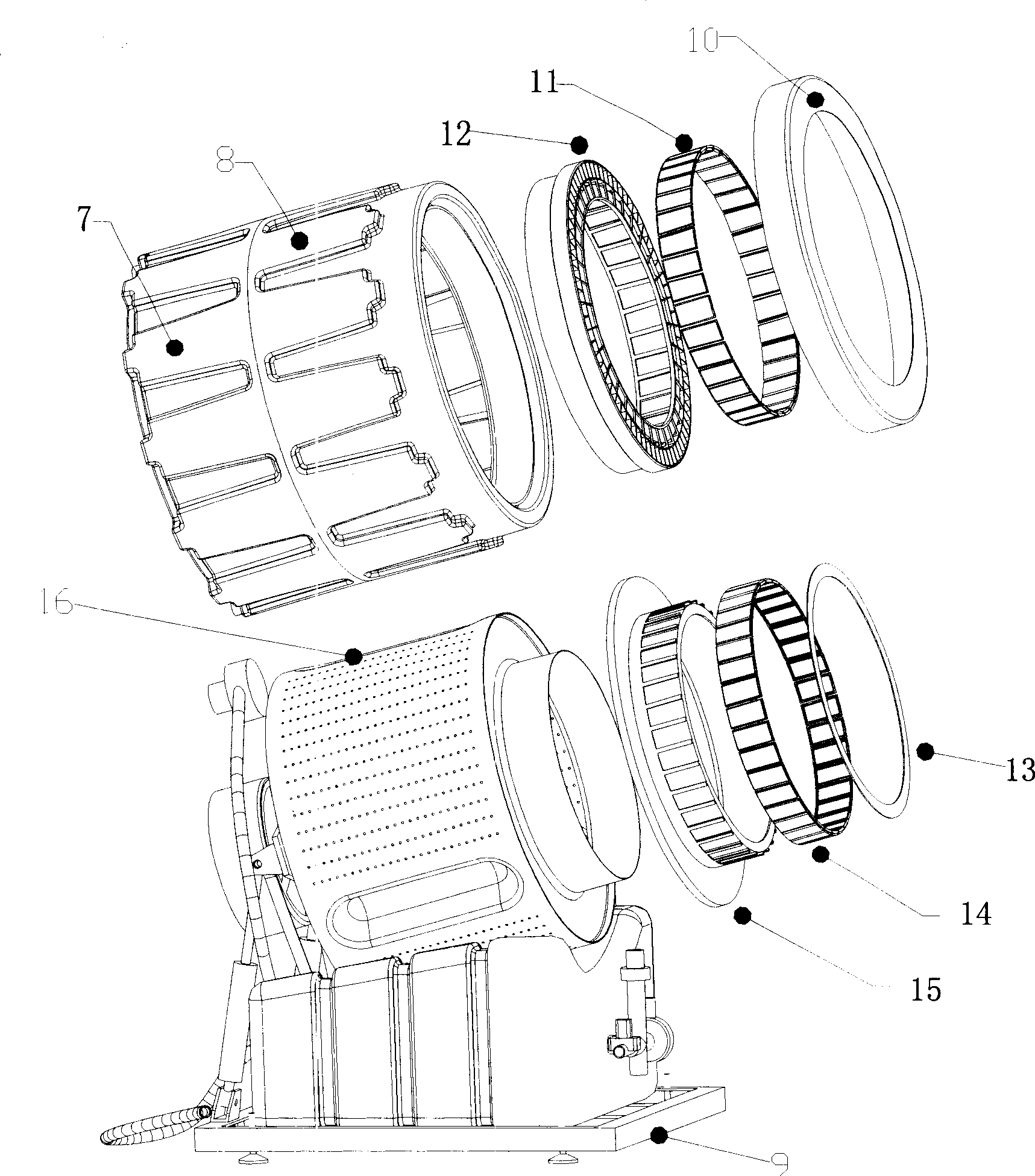
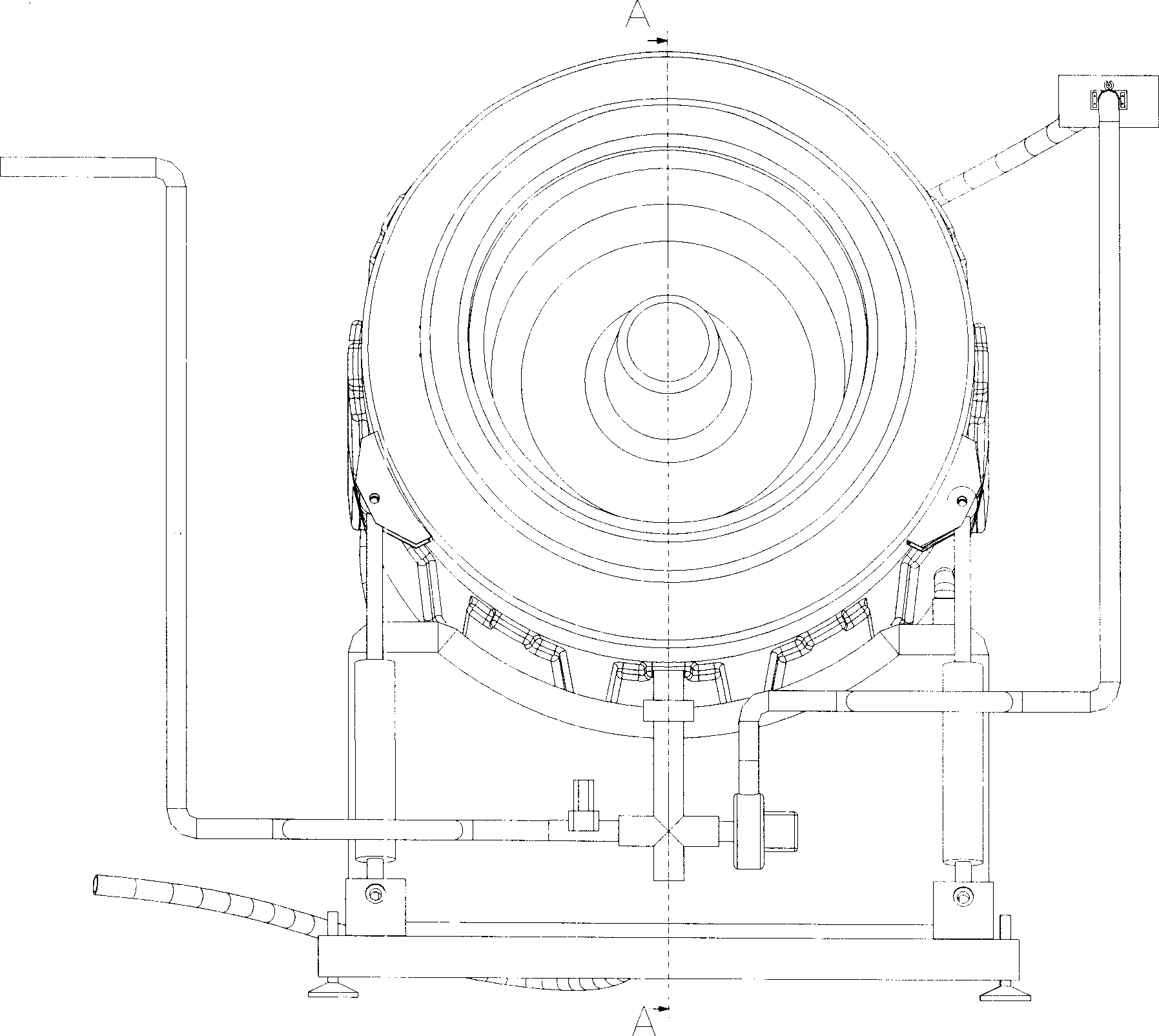
Magnetic suspension drum-type washing machine
InactiveCN101381946AImprove stabilityImprove reliabilityOther washing machinesTextiles and paperSpherical bearingElectric machinery
The invention provides a magnetic-suspension roller washing machine. A roller of the washing machine adopts two-end support, wherein one end of the roller is supported by spherical bearing with a seat, and the other end of the roller is supported through magnetic suspension. Meanwhile, a stator part of a driving motor of the roller is flexibly limited by use of a spring, thereby realizing that the motor can drive the roller and can produce certain swing with the roller at the same time. As the roller adopts the two-end support, operation steadiness is increased, and the flexible limit of the driving motor further reduces the transfer of swing energy, thereby increasing the stability and reliability of the washing machine, increasing laundry amount and reducing the operation noise of the washing machine.
Owner:唐红元
Multi-function gunsight
A multi-function gunsight for aiming a firearm comprises a body and a sight arm pivotally coupled to the body for rotation between a stowed orientation and a deployed orientation. The body defining a laser cavity, a starboard cavity, and a port cavity. A laser housing is disposed inside the laser cavity defined by the body. The laser housing supports a semiconductor chip that emits laser light and a collimating lens that collimates the laser light emitted by the semiconductor chip. A forward end of the laser housing is coupled to a spherical bearing. The spherical bearing constrains movement of the laser housing in three translation degrees of freedom corresponding to translation along x, y, and z axes of an x-y-z coordinate system. The spherical bearing allows rotation of the laser housing about at least the x and y axes of the x-y-z coordinate system.
Owner:BUSHNELL
Bearing plate for use in fracture fixation having a spherical bearing hole with yielding expandability
InactiveUS7749257B2Linear productionLow elastic modulusBone platesExternal osteosynthesisSpherical bearingEngineering
A bearing plate for use in bone fixation for fractures, fusion osteotomies and the like, and the plate is provided with one or more spherical holes in which expandable spherical bearings can be rotatably supported. Each of the holes is formed at its periphery in such a way as to provide yielding expansibility of the hole so that upon expansion of the bearing, the hole expands with it to provide elastic resistance to the expanding bearing.
Owner:MEDOFF ROBERT J +2
Drive shaft assembly for a downhole motor
A drive shaft assembly for a downhole motor includes a drive shaft formed with convexly spherical bearing surfaces on each end, and end housings with concavely spherical bearing surfaces for mating contact with the spherical bearing surfaces of the drive shaft, thereby facilitating omni-directional articulation between the drive shaft and the end housings while transferring axial thrust loads between the drive shaft and end housings across the interface of the mating spherical bearing surfaces. Torque is transferred between the drive shaft and end housings through two or alternatively four swivelling drive keys mounted to each end of the drive shaft and engageable with complementary drive key slots in the end housings. Full and constant torque-transferring contact is thus provided between the swivelling drive keys and the end housings irrespective of any angular offset between the drive shaft and the end housings, resulting from omni-directional articulation of the drive shaft relative to the end housing. The omni- directional center of rotation at each end of the drive shaft coincides with the geometric centerpoint of the corresponding convexly spherical bearing surface, which corresponds to the intersection of the drive shaft's rotational axis, the end housing's rotational axis, and the drive key swivel axis.
Owner:DRECO ENERGY SERVICES ULC
Method for preparing steel-based copper-alloy thermometal spherical bearing seat blank
The invention discloses a method for preparing a steel-based copper-alloy thermometal spherical bearing seat blank which is produced on a vertical centrifugal casting machine comprising an electric induction heating device and a cooling device. The preparation method sequentially comprises the steps that a steel shell of a bearing seat is preprocessed, and the preprocessed steel shell is placed on a rotary table of the vertical centrifugal casting machine; technological quantity of copper-alloy particles are added in the steel shell, and the rotary table is started; the heating device is started for heating to enable the copper-alloy particles to be molten; the steel shell is cooled to enable the molten copper-alloy to be solidified and metallurgically-bonded on the surface of the inner sphere of the steel shell to obtain the steel-based copper-alloy thermometal spherical bearing seat blank. The method has the advantages that the technological procedure is short, device investment is little, manufacturing cost is low, labor intensity is low, and the on-site environment is good.
Owner:CRRC QISHUYAN INSTITUTE CO LTD
Clamping mechanism for device for testing high-temperature direct tensile strength of ultrahigh-temperature ceramics
InactiveCN104330314AEven by forceExact tensile strengthMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSpherical bearingEngineering
The invention discloses a clamping mechanism for a device for testing the high-temperature direct tensile strength of ultrahigh-temperature ceramics. The clamping mechanism is structurally characterized in that an upper wedge clamp (3) is connected with an upper pull rod (1) of a tester, a circular supporting beam (2) is transversely clamped in a wedge groove of the upper wedge clamp (3), a flexible cable (4) for fixing a test piece (5) by being wound around the upper end of the test piece (5) is wound and fixed together with the circular supporting beam (2), a lower wedge clamp (15) for clamping the lower end of the test piece (5) is connected with a bulb rod (8), a bulb of the bulb rod (8) is mounted in a ball bowl composed of an upper spherical bearing (12) and a lower spherical bearing (10), and the upper spherical bearing (12) and the lower spherical bearing (10) are connected with each other by use of a bolt (11). The clamping mechanism for the device for testing the high-temperature direct tensile strength of the ultrahigh-temperature ceramics has the beneficial effects that the center line of the test piece is located in the same straight line with the straight line of pull under the action of the pull, the test piece is prevented from being bent and distorted, the stress on the test piece in the center line is even, a test result is kept accurate and reliable, and the repeatability is good.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
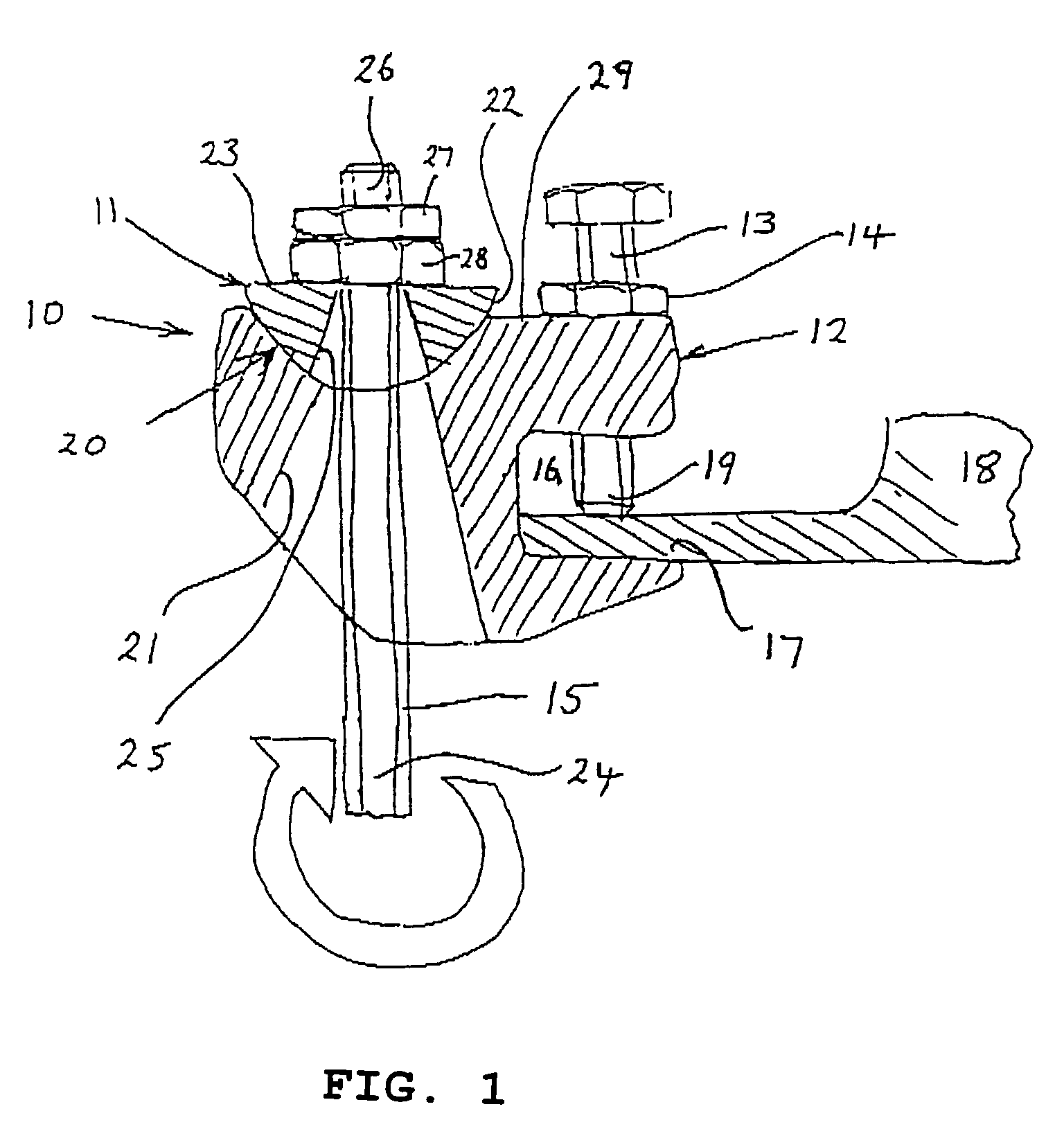
Prosthetic femoral joint
A prosthetic hip joint replacement system has a femoral component with a tapered trunion thereon. A modular head with a part-spherical outer surface terminating in a planar surface, engages the trunion. An acetabular cup member is provided for receiving the part-spherical head of a femoral implant, the cup member has a cavity having a part-spherical inner surface for receiving the modular head. The part-spherical inner surface of the cup defines a polar axis and an equator centered about a pole of the cavity. The cavity has a part-circular opening spaced from the pole a greater distance than the equator. Thus the inner part-spherical bearing surface extends beyond the 180° which the equator extends. The configuration of the part-spherical inner bearing surface causes a movement of translation of the head during rotation so that there is a crescent shaped retention area on each opposed side thereof. The opening has a non-circular or planar portion alignable with the planar head surface during insertion of the head in the cavity and a plane parallel to the non-circular portion through the center of the portion of the opening being offset from a parallel plane containing the polar axis of the cavity.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Bridge rotation device and bridge rotation construction method
The invention relates to a bridge rotation device and a bridge rotation construction method. The rotation device comprises a spherical bearing, a bracket and a track, wherein the spherical bearing is arranged at the bottom of one end of a bridge; the bracket is fixed on one end of the bridge provided with the spherical bearing; the track is in the shape of a circular arc and takes the spherical bearing as the circle center; and a flexible cable or a rigid member is arranged between the top end of the bracket and the bridge. In addition, the rotation device is provided with a lift winch, the flexible cable on the lift winch is connected at the top end of the bracket, and the flexible cable passes through a main sliding location element which is arranged on the track and slides along the track or the winch to be directly installed on a main sliding platform on the track. Besides, the rotation device comprises a rotation driving device for driving the bridge to rotate additionally. The rotation device can ensure that the bridge can not swing in the rotation process, so as to enable the bridge to stably rotate, thereby saving the cost and being used repeatedly.
Owner:徐国彬
Electrically blockable swiveling lever control
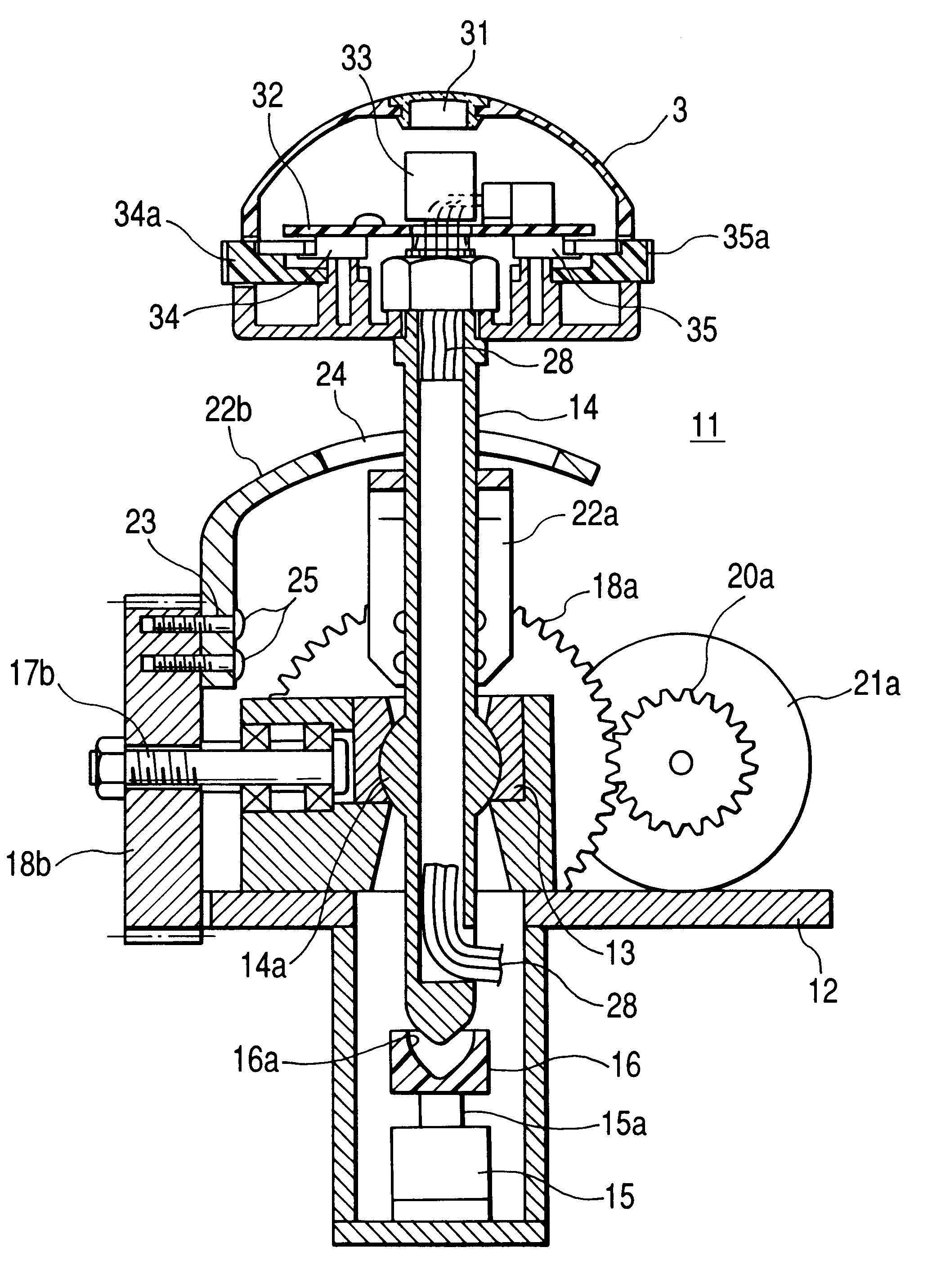
The description relates to a closure for mounting in an opening in a thin wall, such as a sheet metal cabinet door, which comprises a housing and which has, at one end, a bearing support for an actuation lever and, at its other end, a lock device for the actuation lever and a fastening device such as a clamping clip therebetween. The housing has a partially spherical bearing surface with a cylindrical bore hole proceeding from it, wherein a partial ball with a first bearing for a closure drive shaft extending through the cylindrical bore hole and with a second bearing for the actuation lever is arranged in the cylindrical bore hole, and the two bearings enable a rotation of the partial ball in relation to the housing and a swiveling of the actuation lever in relation to the partial ball around an axis vertical to the closure drive shaft and to the extension of the lever.
Owner:DIRAK DIETER RAMSAUER KONSTRUKTIONSELEMENTE GMBH & CO KG
Semiconductor wafer, polishing apparatus and method
InactiveUS7137874B1Improve flatnessReduces wafer edge roll-offPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesSpherical bearingEngineering
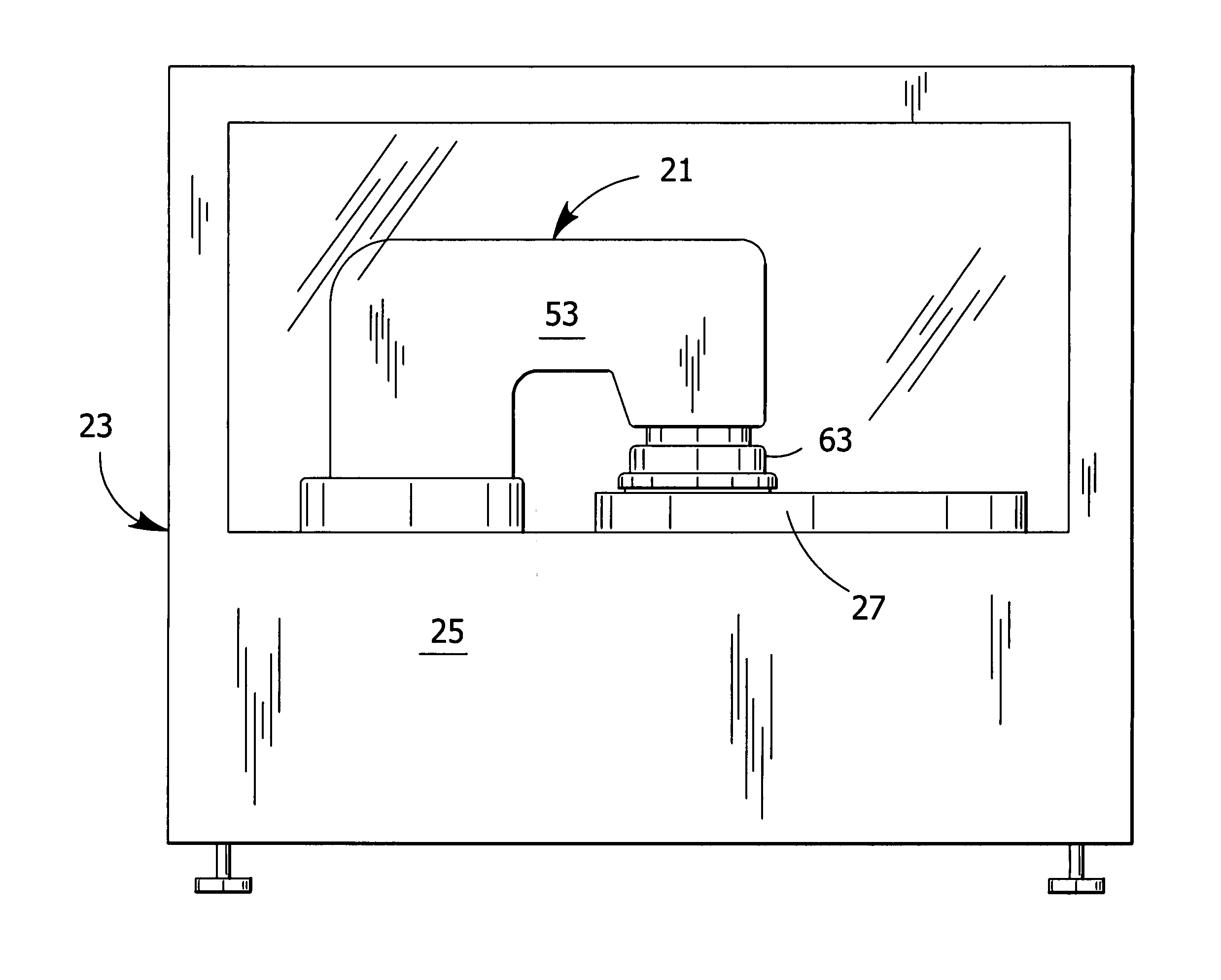
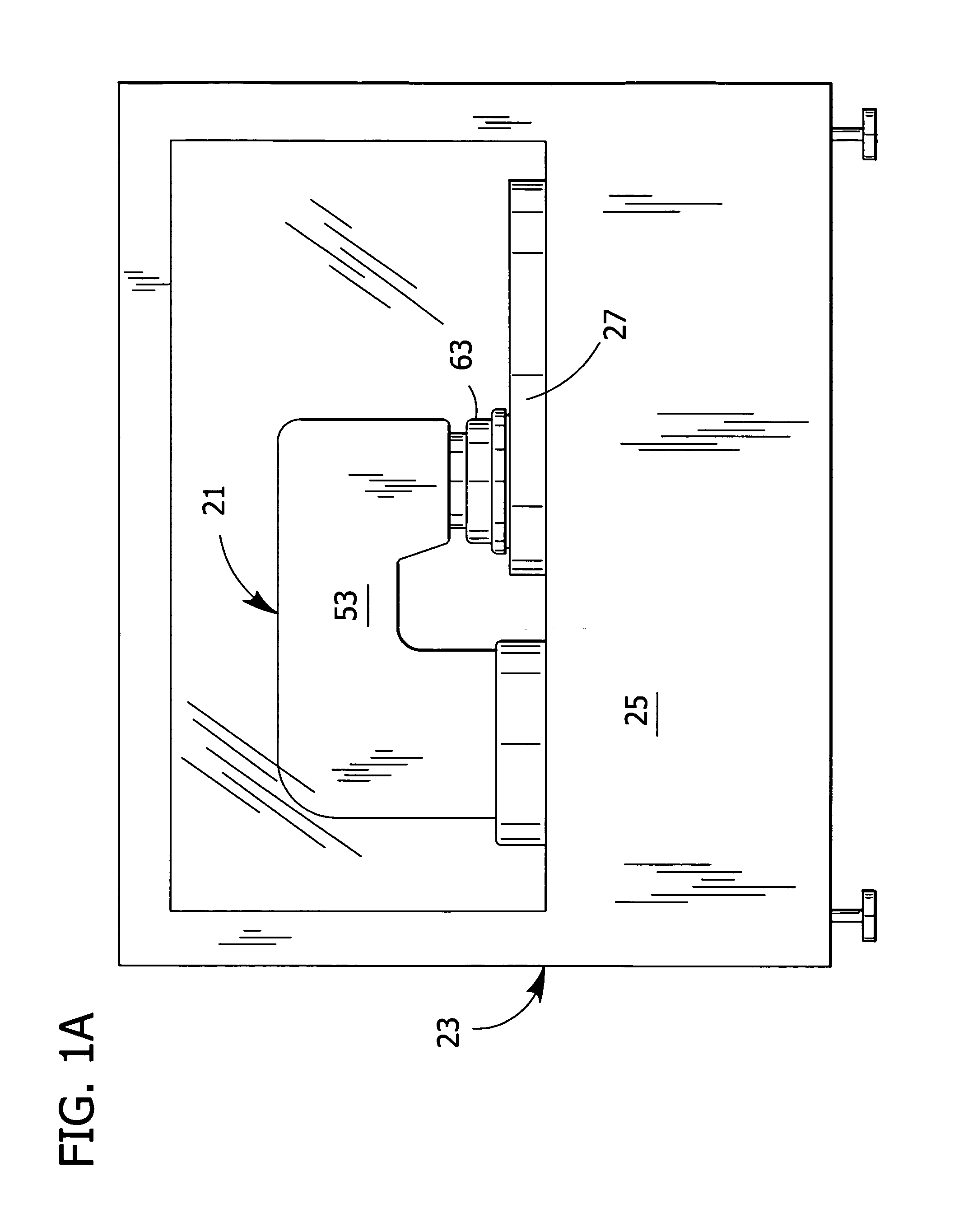
A wafer polishing apparatus for polishing a semiconductor wafer. The polisher comprises a base (23), a turntable (27), a polishing pad (29) and a drive mechanism (45) for driven rotation of a polishing head (63). The polishing head is adapted to hold at least one wafer (35) for engaging a front surface of the wafer with a work surface of the polishing pad. A spherical bearing assembly (75) mounts the polishing head (63) on the drive mechanism for pivoting of the polishing head about a gimbal point (p) lying no higher than the work surface when the polishing head holds the wafer in engagement with the polishing pad. This pivoting allowing the plane of the front surface of the wafer to continuously align itself to equalize polishing pressure over the front surface of the wafer, while rotation of the polishing head is driven by the driving mechanism. This maintains the front surface and work surface in a continuously parallel relationship for more uniform polishing of a semiconductor wafer, particularly near the lateral edge of the wafer. A cassette of wafers and method of polishing are also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
Vehicular input device including single manual operating unit for operating various electronic devices mounted on vehicle
InactiveUS6366442B1Engagement/disengagement of coupling partsManual control with multiple controlled membersSpherical bearingDrive shaft
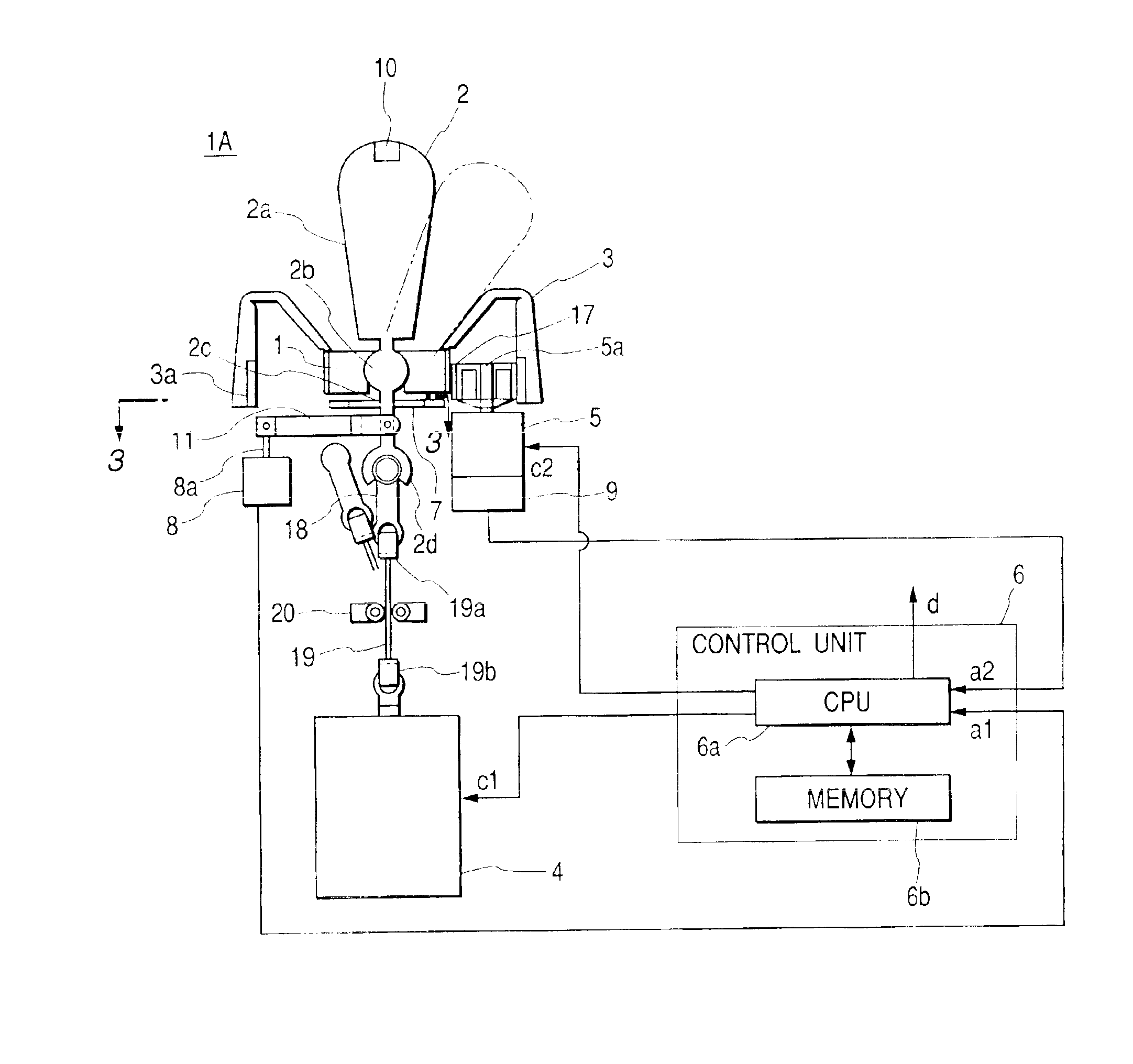
A vehicular input device is disclosed which can afford a high stability of movable portions and an excellent power saving characteristic without impairing the operability of a manual operating unit. A mechanical portion of the vehicular input device is provided with a spherical bearing, a pivot shaft supported pivotably by the spherical bearing, a solenoid disposed below the spherical bearing, and a clamp member for clamping the pivot shaft, the clamp member being secured to an upper end portion of a drive shaft of the solenoid. A lower end portion of the pivot shaft is formed in a conical shape which becomes smaller in diameter gradually downwards. In an upper surface of the clamp member which is opposed to the lower end portion of the pivot shaft there is formed a generally conical depression into which the lower end portion of the pivot shaft can be inserted. An ON-OFF operation of the solenoid is controlled by a photointerrupter which is disposed within or near a manual operating unit and which detects a human finger trying to operate the manual operating unit.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com