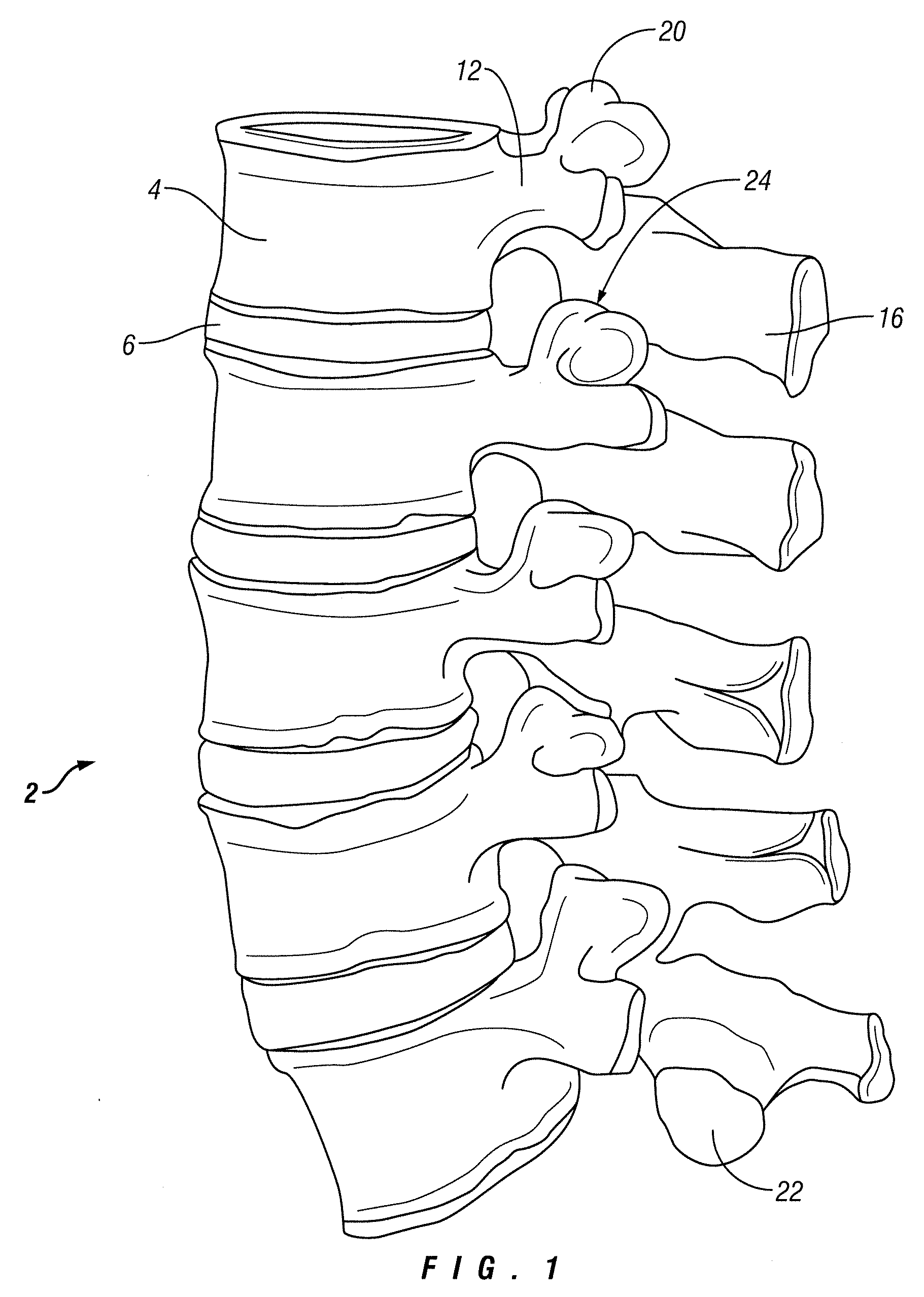Patents
Literature
791 results about "Lumbar vertebral column" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
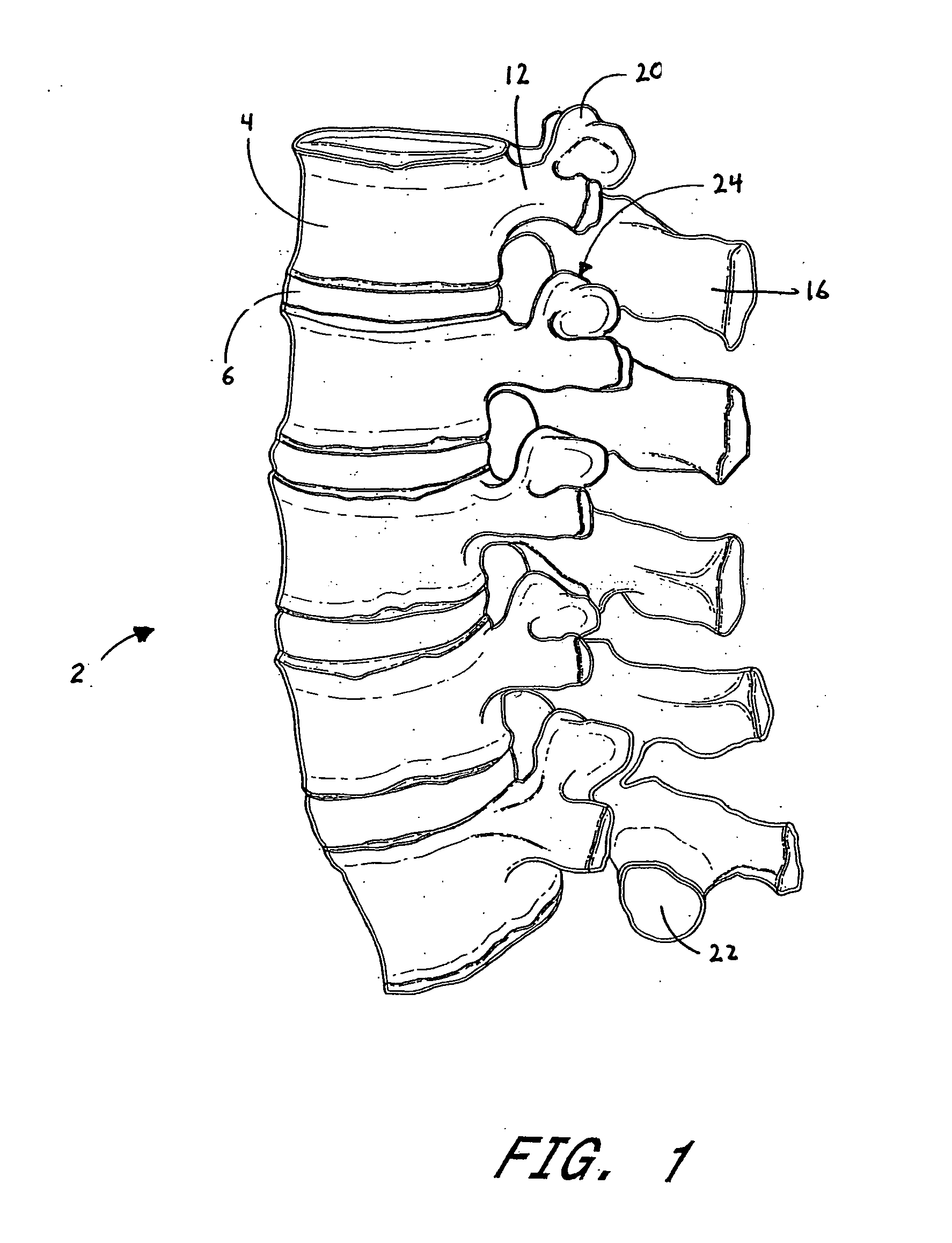
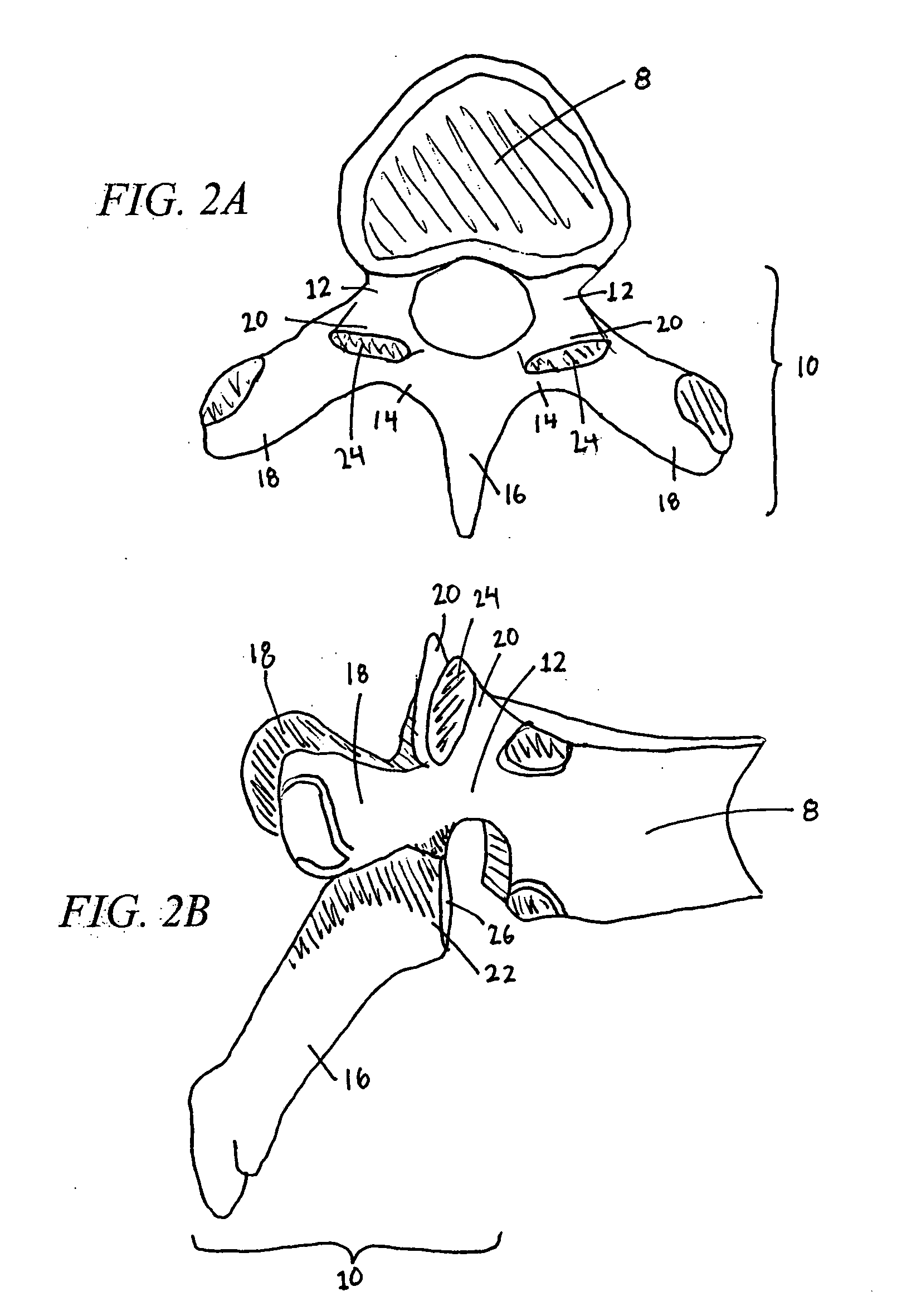
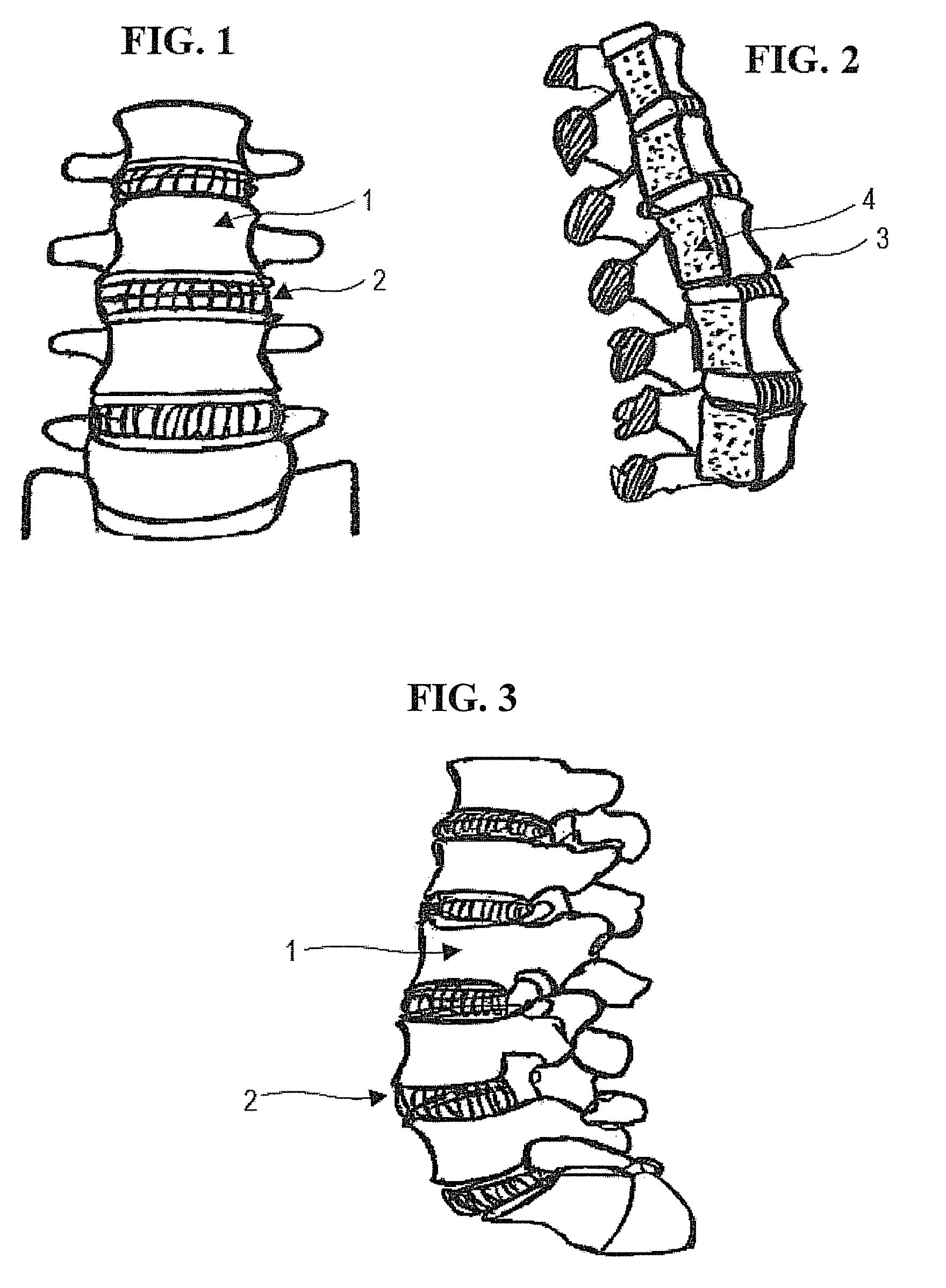
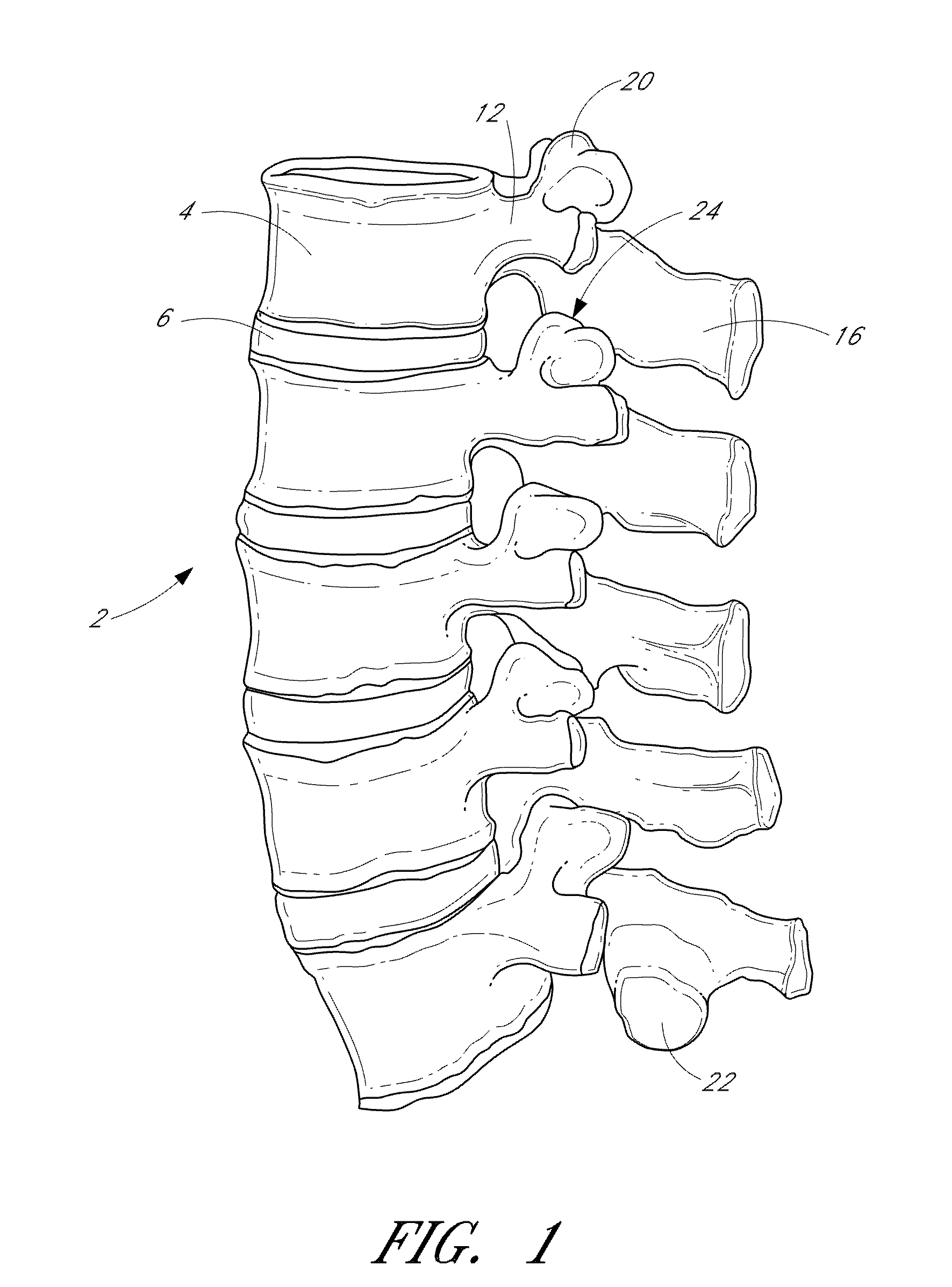
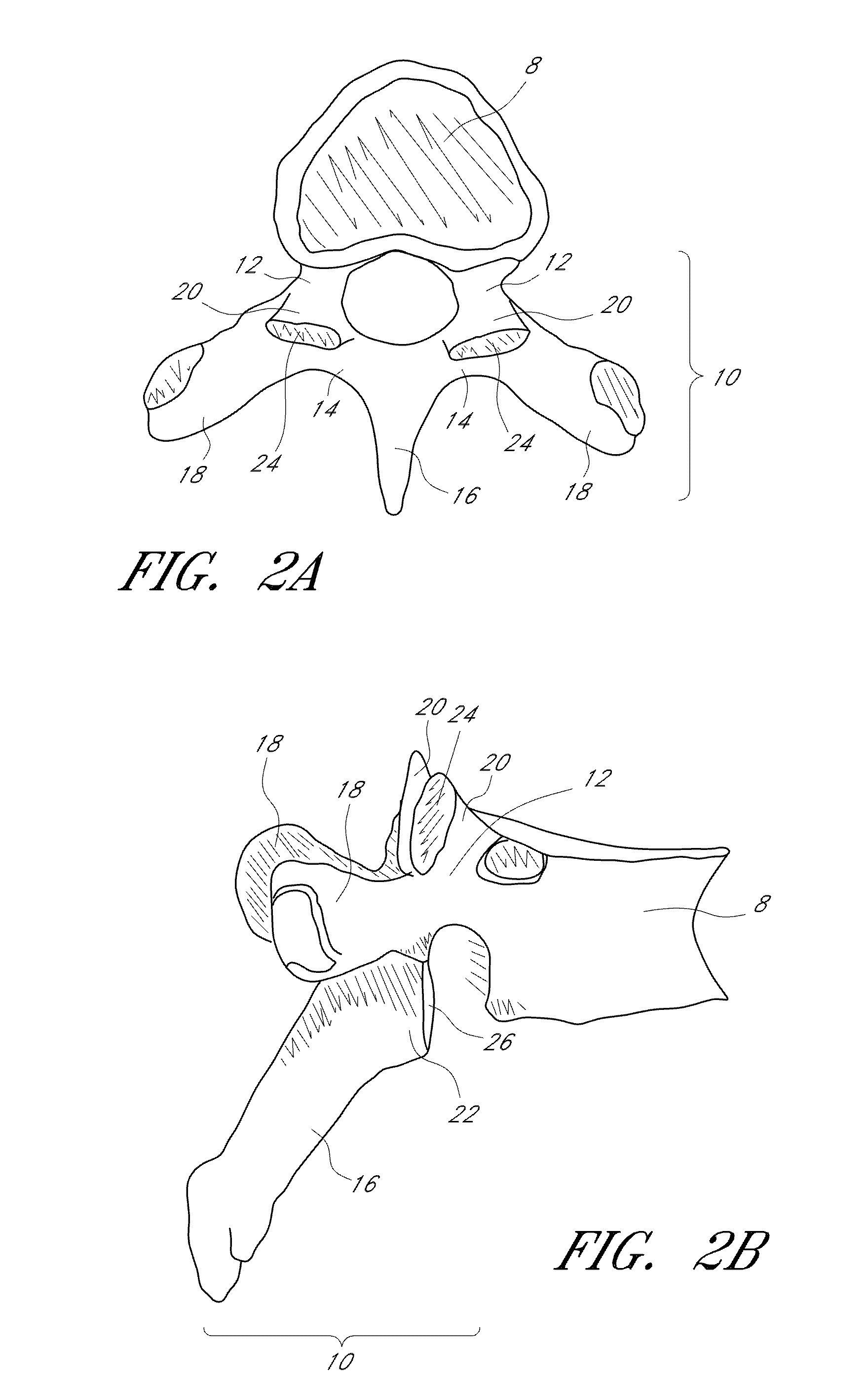
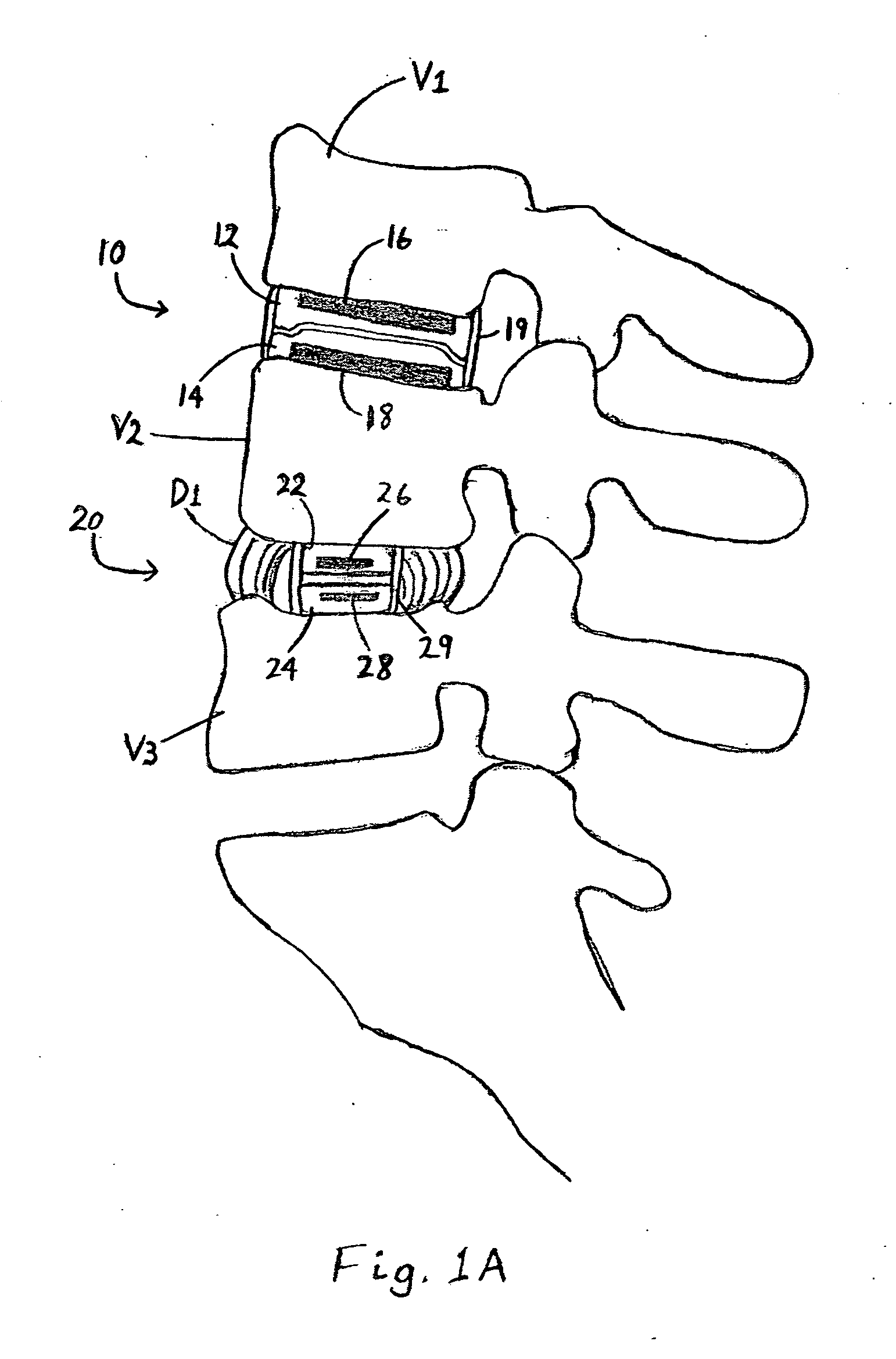
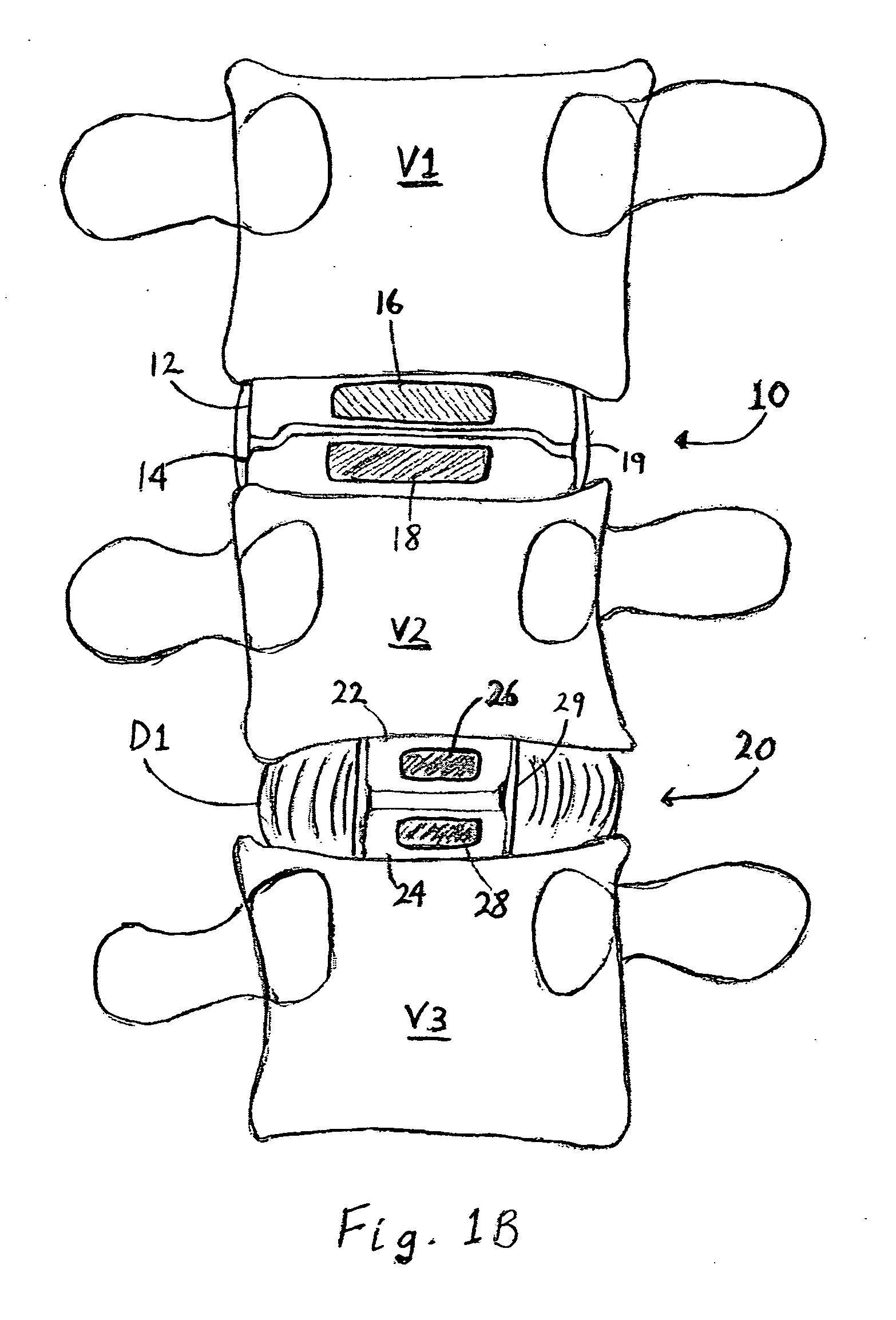
The vertebrae in the human vertebral column are divided into different regions, which correspond to the curves of the spinal column. The articulating vertebrae are named according to their region of the spine. Vertebrae in these regions are essentially alike, with minor variation.
Methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis
InactiveUS20060106381A1Effective treatmentPermit flexionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnDevice form
Surgical implants are configured for placement posteriorly to a spinal canal between vertebral bodies to distract the spine and enlarge the spinal canal. In the preferred embodiments the device permits spinal flexion while limiting spinal extension, thereby providing an effective treatment for treating spinal stenosis without the need for laminectomy. The invention may be used in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine. Numerous embodiments are disclosed, including elongated, length-adjustable components coupled to adjacent vertebral bodies using pedicle screws. The preferred embodiments, however, teach a device configured for placement between adjacent vertebral bodies and adapted to fuse to the lamina, facet, spinous process or other posterior elements of a single vertebra. Various mechanisms, including shape, porosity, tethers, and bone-growth promoting substances may be used to enhance fusion. The tether may be a wire, cable, suture, or other single or multi-filament member. Preferably, the device forms a pseudo-joint in conjunction with the non-fused vertebra. Alternatively, the device could be fused to the caudal vertebra or both the cranial and caudal vertebrae.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Posterior lumbar interbody fusion expandable cage with lordosis and method of deploying the same
A spinal fusion cage comprises an upper half-cage, a lower half-cage, and a plunger with a cam. The upper half-cage and lower half-cage have a first collapsed configuration which has a thin, flat, rectangular envelope and a second expanded configuration. The half-cages have at least one ramped surface on which the cam of the plunger rides. The cam bears against the ramped surface and spreading the two half-cages apart. A method of deploying a spinal fusion cage comprises the steps of disposing in a spinal space an upper half-cage and lower half-cage in a first collapsed configuration which has a thin, flat, rectangular envelope and a second expanded configuration. The method continues with the step of distally advancing a plunger between the upper half-cage and lower half-cage and spreading the two half-cages apart.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
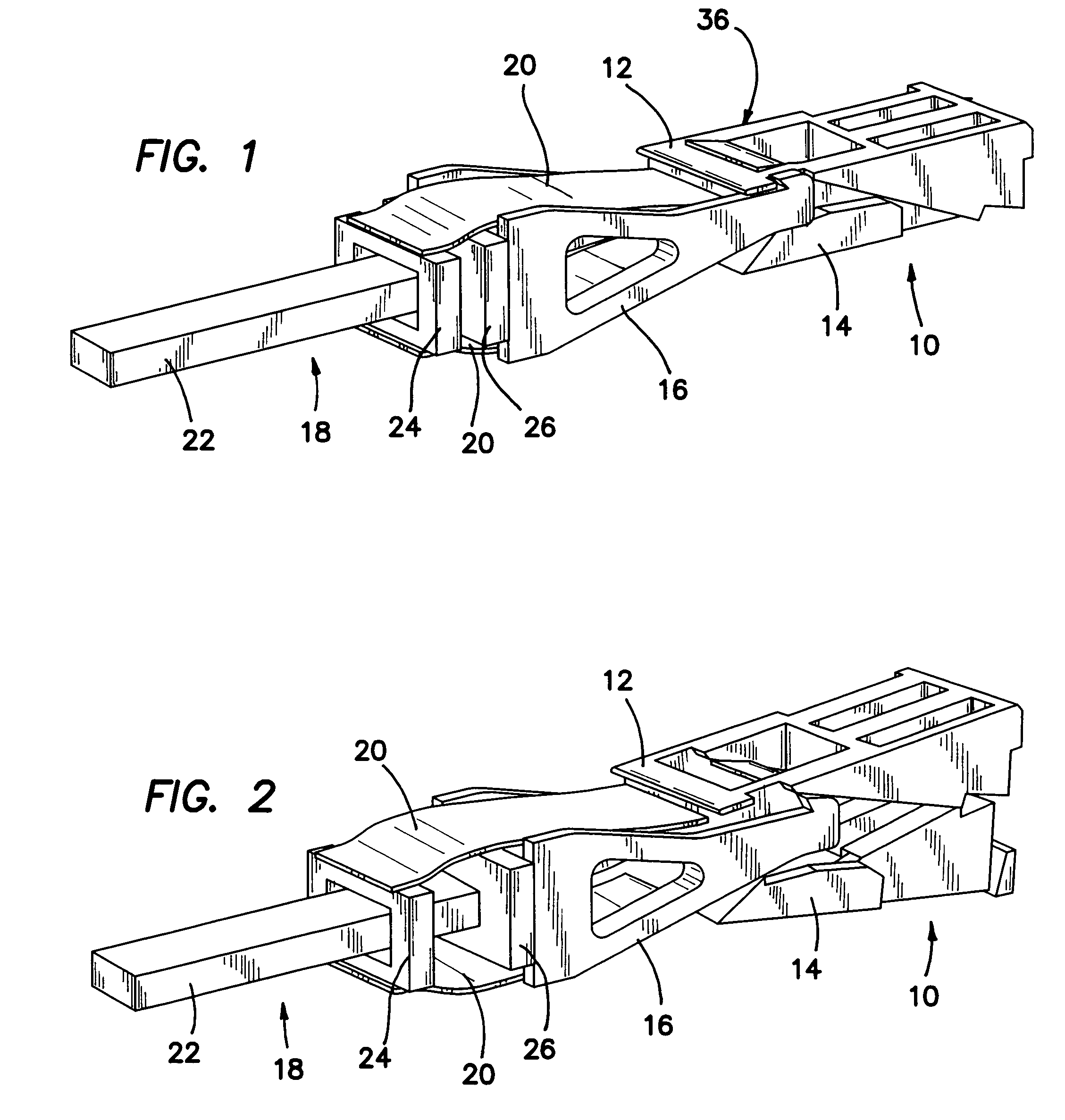
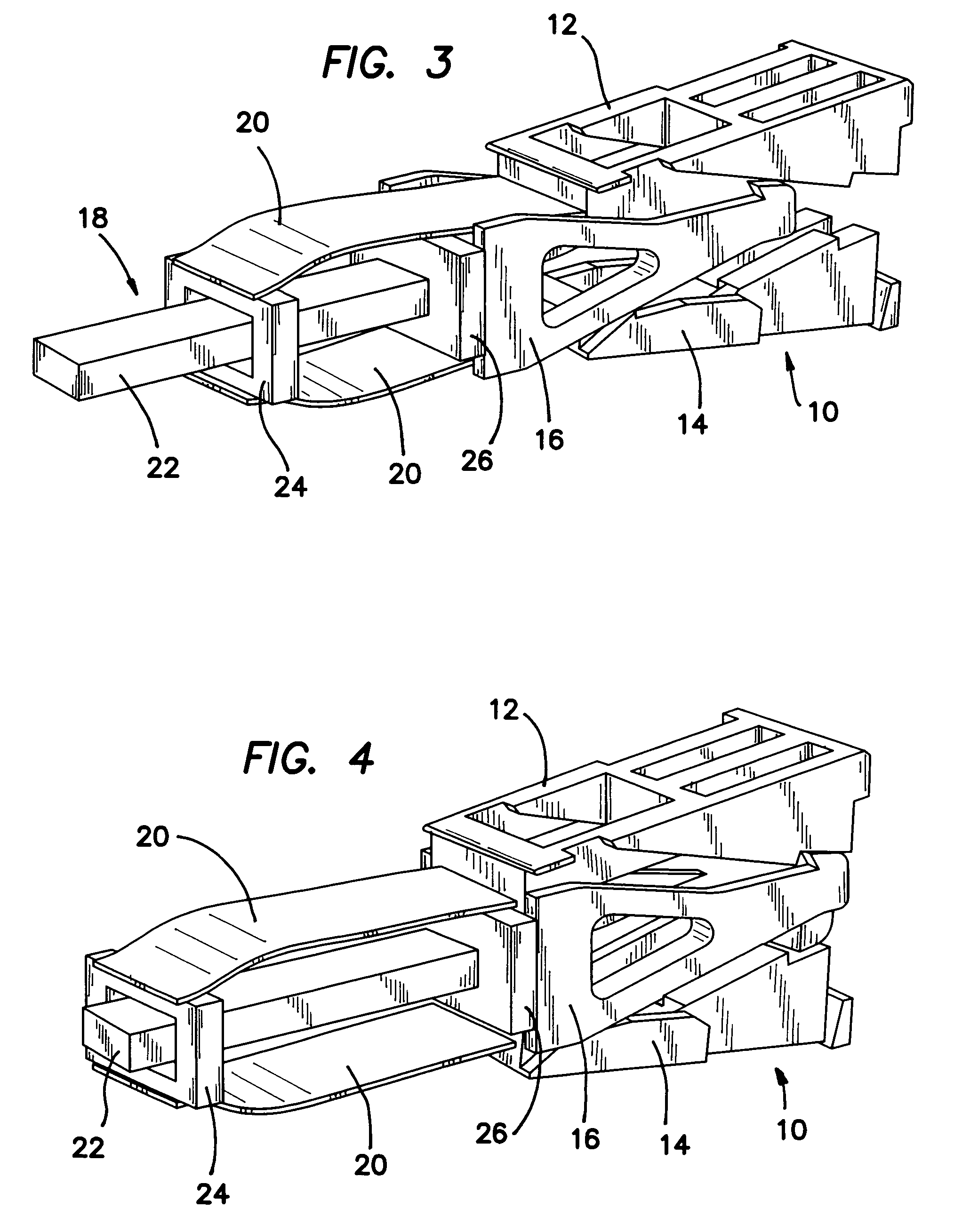
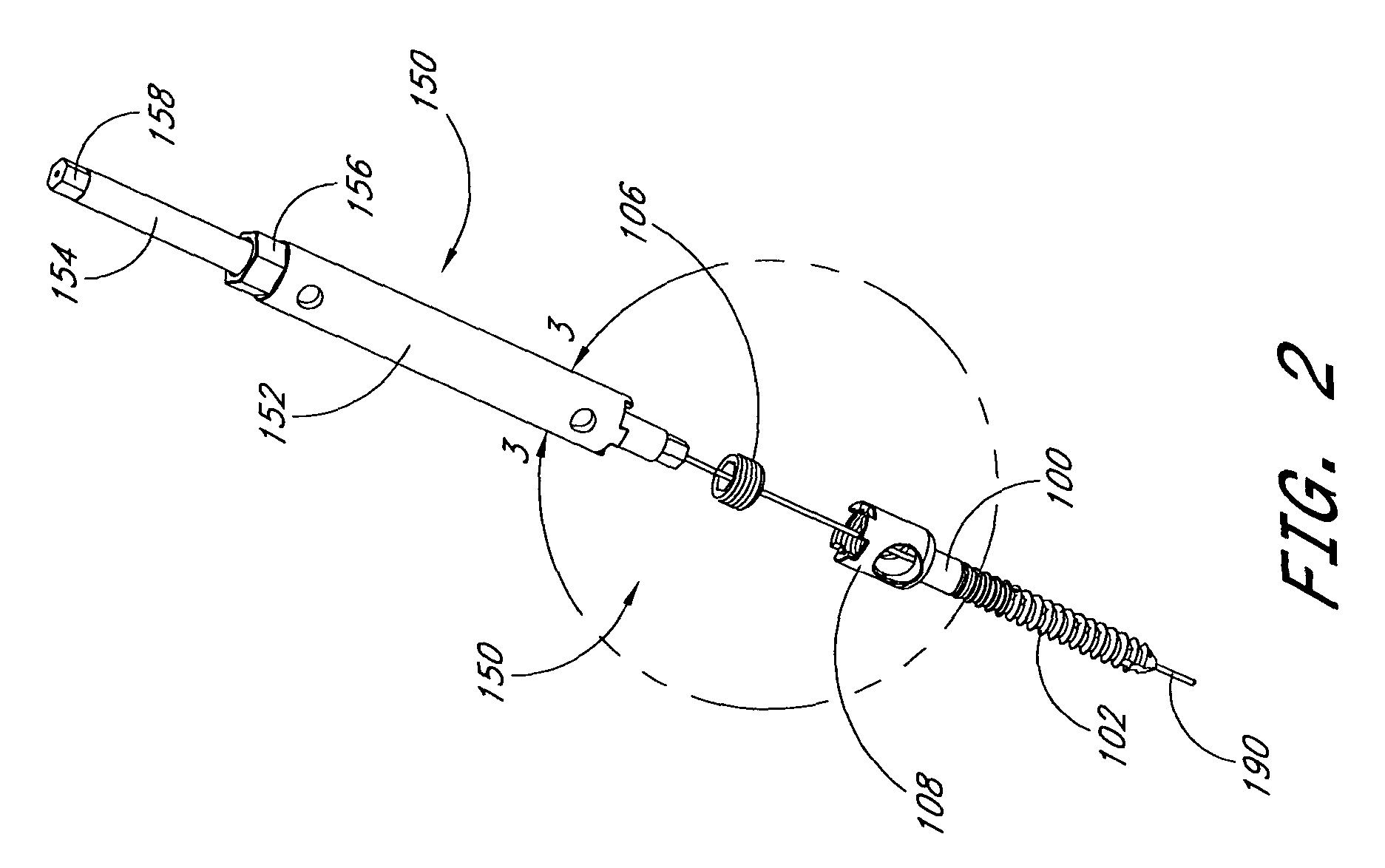
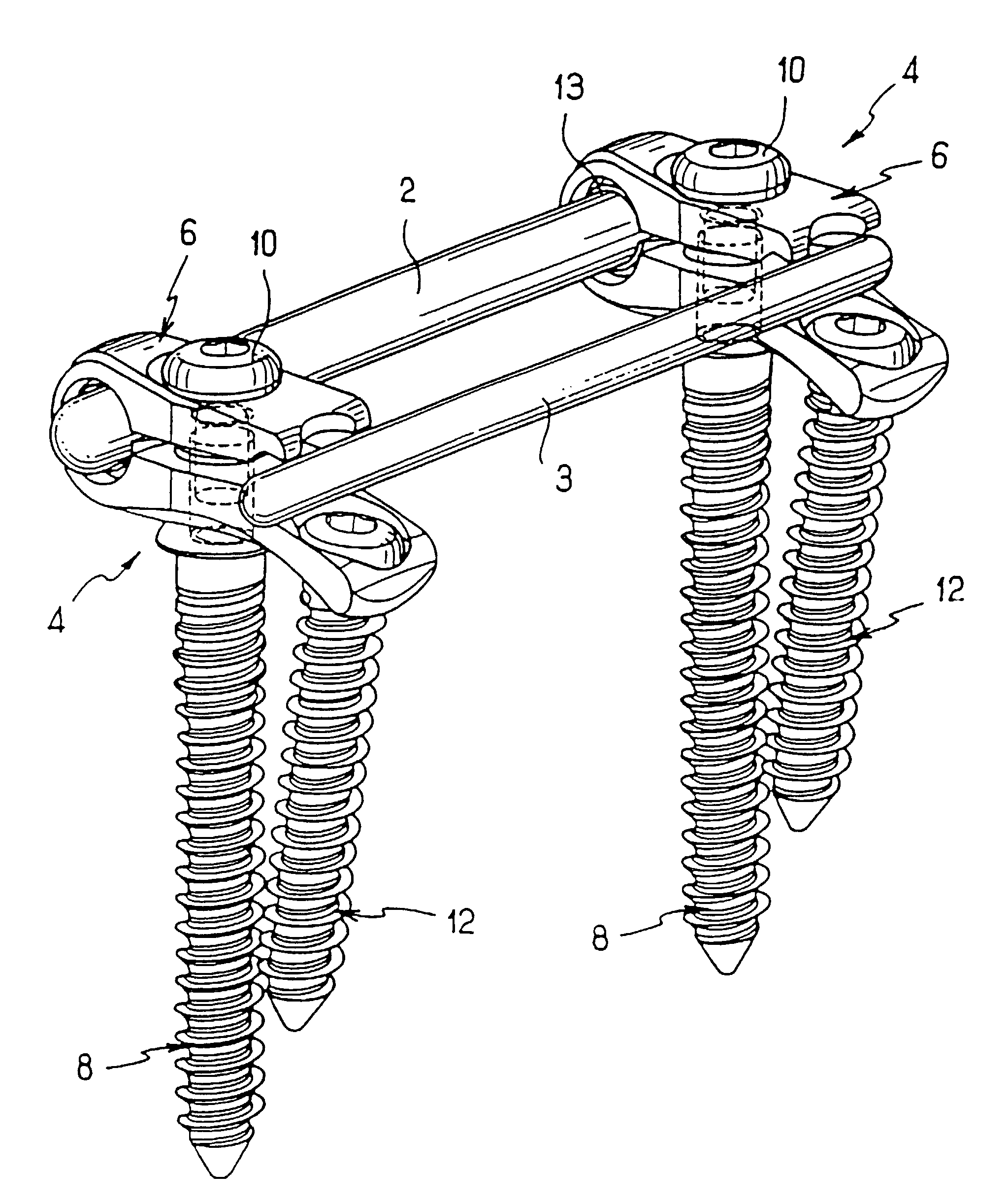
Articulating spinal fixation rod and system
The present invention relates generally to systems and methods for aligning and implanting orthopedic fixation or stabilization implants within the body. In one embodiment, the system includes at least two bone anchors, at least one of which is provided with a transverse portal and a locking member. In one aspect, the system also includes at least one linkage rod, for linking two or more bone anchors through their respective locking members. The linking rod may include at least one angularly adjustable joint, which may be fixed by actuating the locking member. The bone anchors and the linkage rod may be locked into place to form a spinal fusion or fixation prosthesis.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Biased angulation bone fixation assembly
InactiveUS6974460B2Reduce the overall diameterFacilitate pivotal movementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCouplingPlastic surgery
A bone fixation assembly including a coupling element having an inner surface defining a first bore coaxial with a first longitudinal axis, and a second bore coaxial with a second longitudinal axis, whereby the second longitudinal axis intersects the first longitudinal axis. The coupling element has a seat adjacent the lower end of the coupling element, the seat being defined by the inner surface of the coupling element. The assembly includes an anchoring element assembled with the coupling element, the anchoring element having a first end for insertion into bone and a head spaced from the first end, the head being in contact with the seat of the coupling element. The assembly provides sufficient angulation between adjacent anchoring elements securing a common orthopedic rod, and is particularly useful for assemblies mounted in spines having abnormal curvatures and in the cervicothoracic region of the spine.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Vertebral facet joint prosthesis and method of fixation
ActiveUS20050177240A1Reduce contactMaintain liquidityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFacet joint prosthesisArticular processes
Devices and methods for altering the spacing and motion at the facet joints of the vertebral column are provided. One embodiment of the invention comprises a prosthesis with surfaces configured to articulate with the facets of the facet joint. A retaining member for anchoring the prosthesis within the facet joint is optionally included. Methods for surgically and less invasively implanting the prosthesis and securing the prosthesis to the articular processes or surrounding soft tissue are also provided.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Methods for electrosurgical treatment of spinal tissue
InactiveUS20050004634A1Stiffening the interspinous tissue structureStabilizing the vertebral columnEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesThermal energySpinal ligaments
Systems, apparatus, and methods for treating spinal tissue and other body structures in open and endoscopic spine surgery to relieve symptoms, such as neck or back pain. In particular, the present invention provides methods for the controlled heating of various tissues in or around the vertebral column, including various interspinous tissues, such that spinal ligaments and cartilage surrounding the vertebrae and the facet joints are shrunk or tightened to stabilize the vertebral column of a patient. Thermal energy is applied to the target tissue in a subablation mode of an electrosurgical system to cause shrinkage of the tissue, thereby stiffening the interspinous tissue and stabilizing the vertebral column. In an exemplary embodiment, a high frequency RF voltage can be applied between one or more active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to heat a target interspinous tissue to within a temperature range at which irreversible shrinkage of the tissue occurs.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
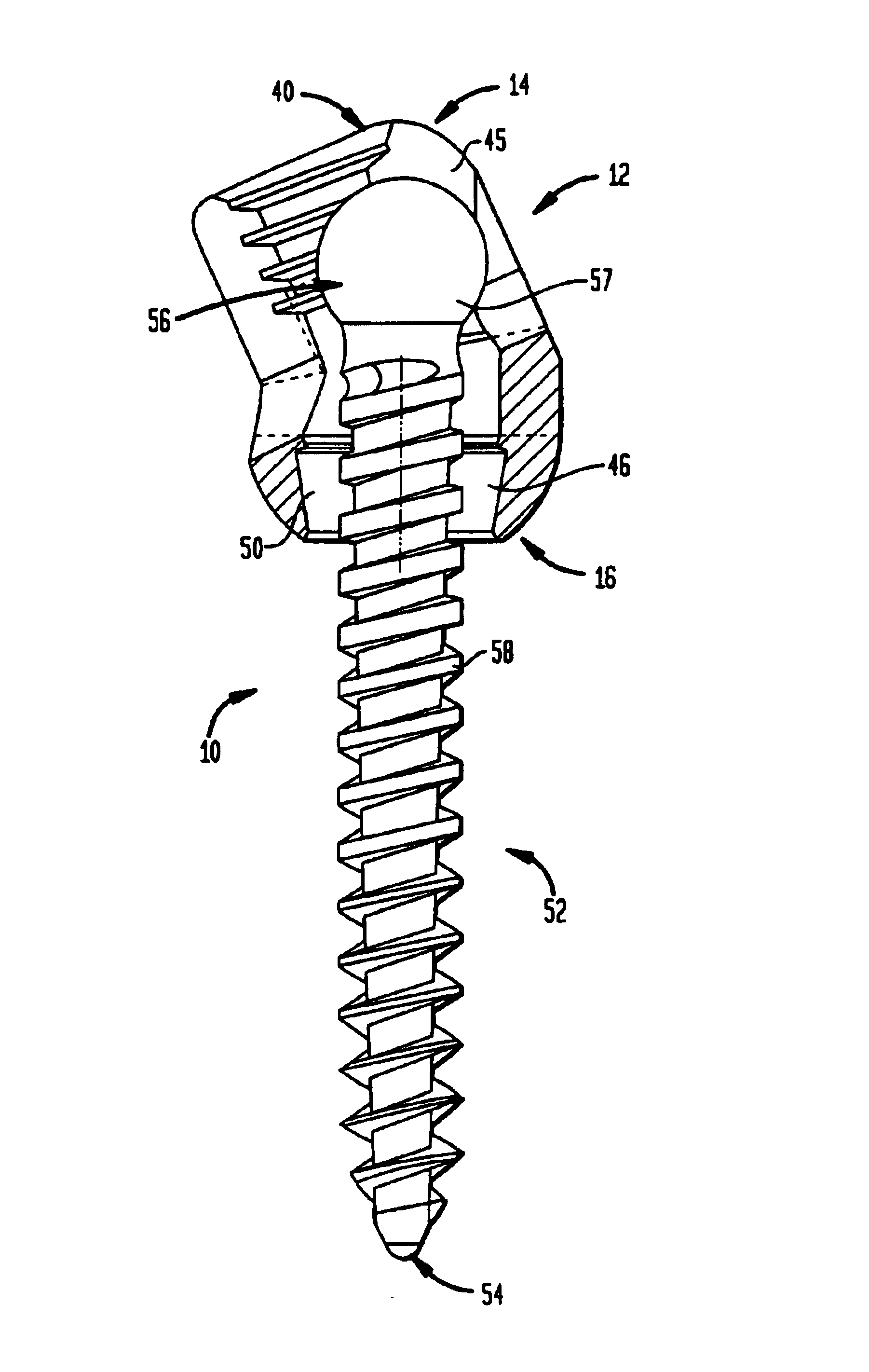
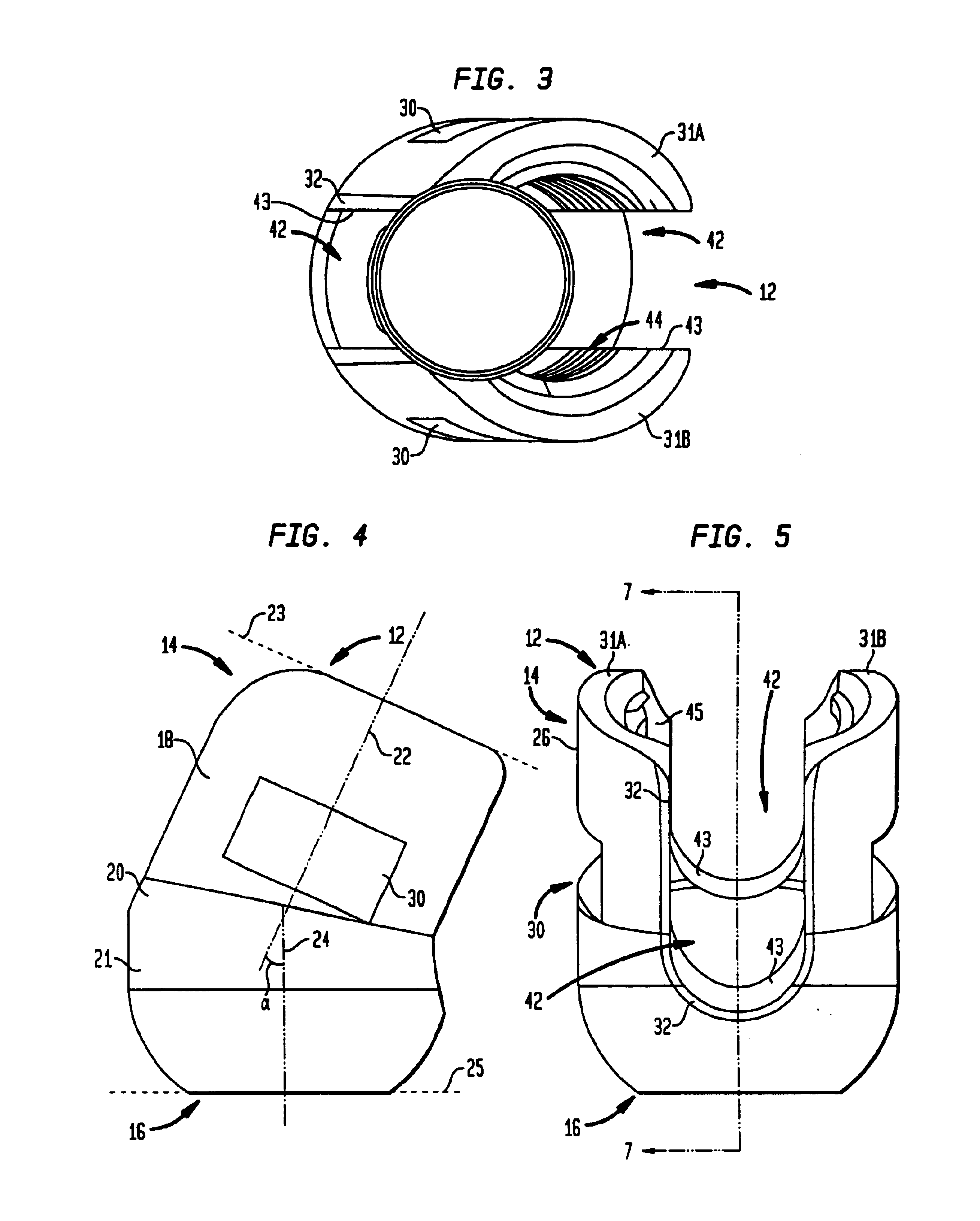
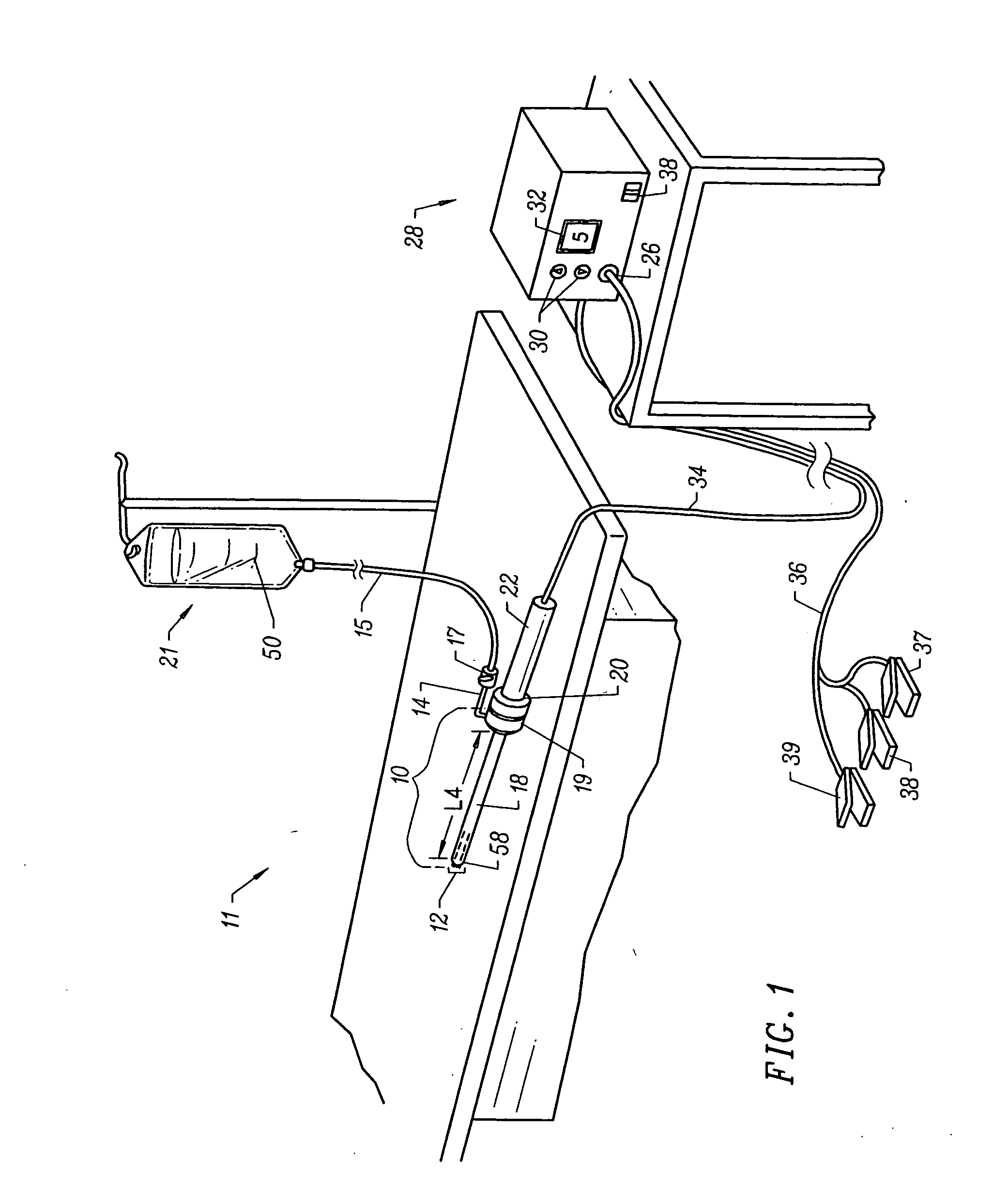
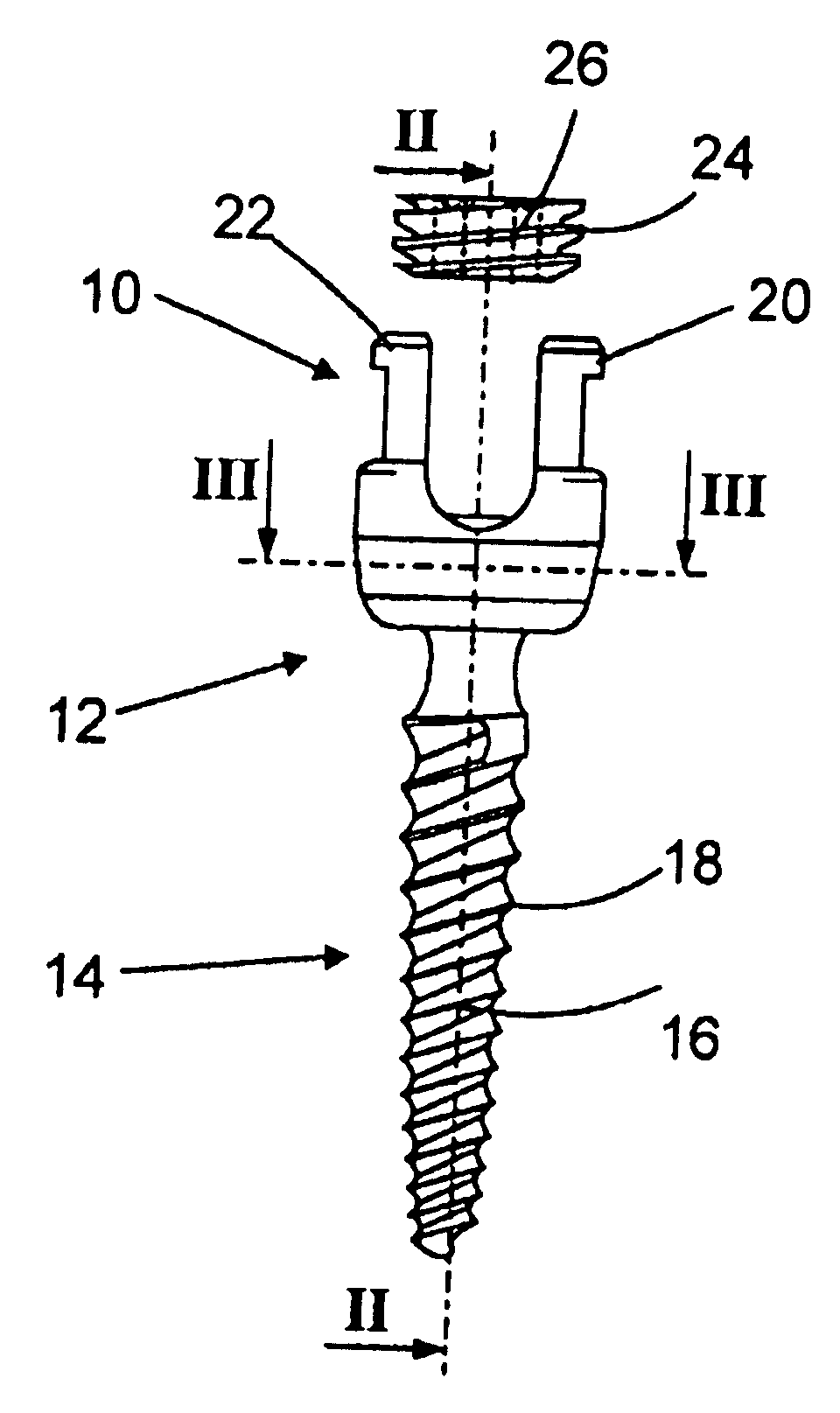
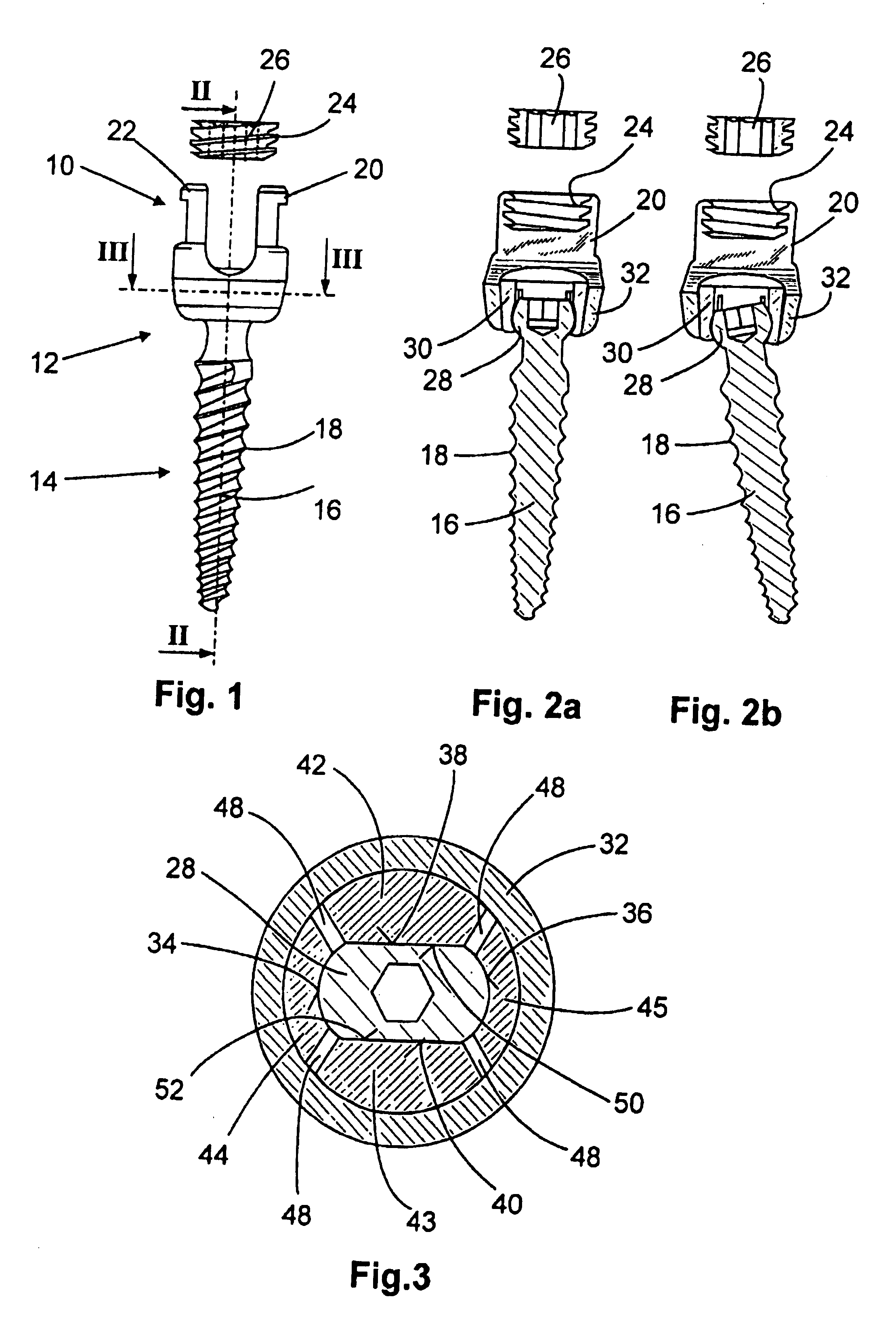
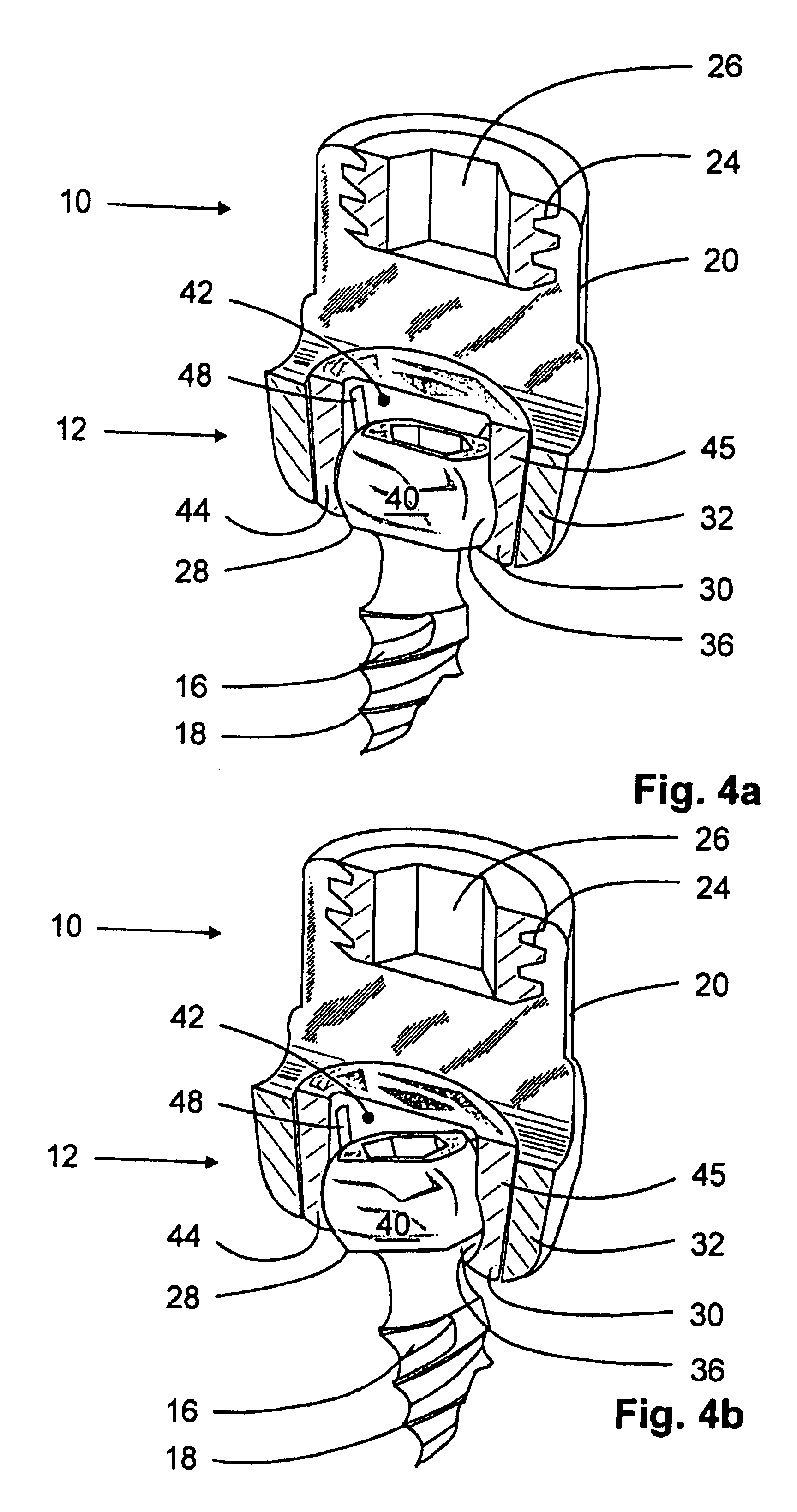
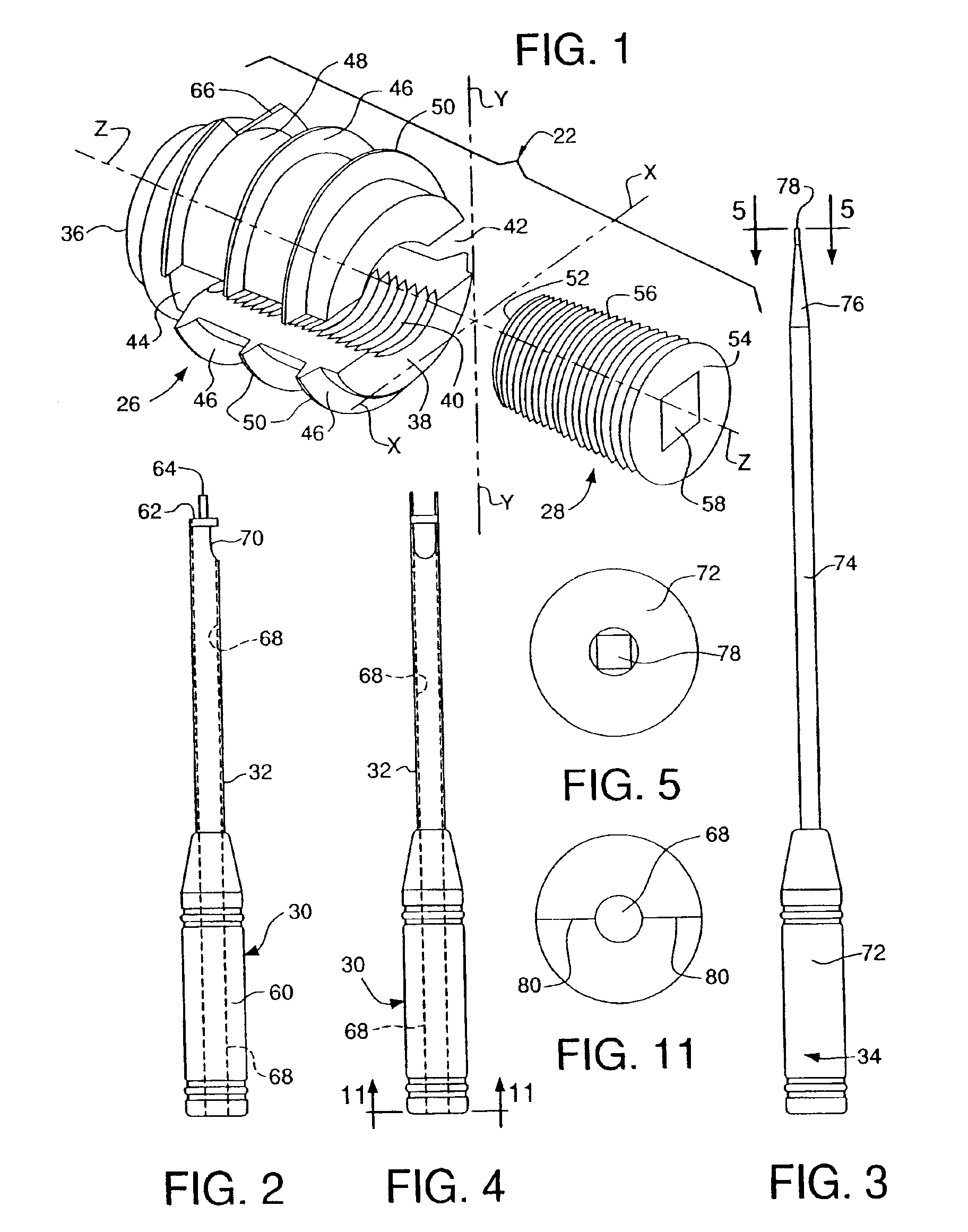
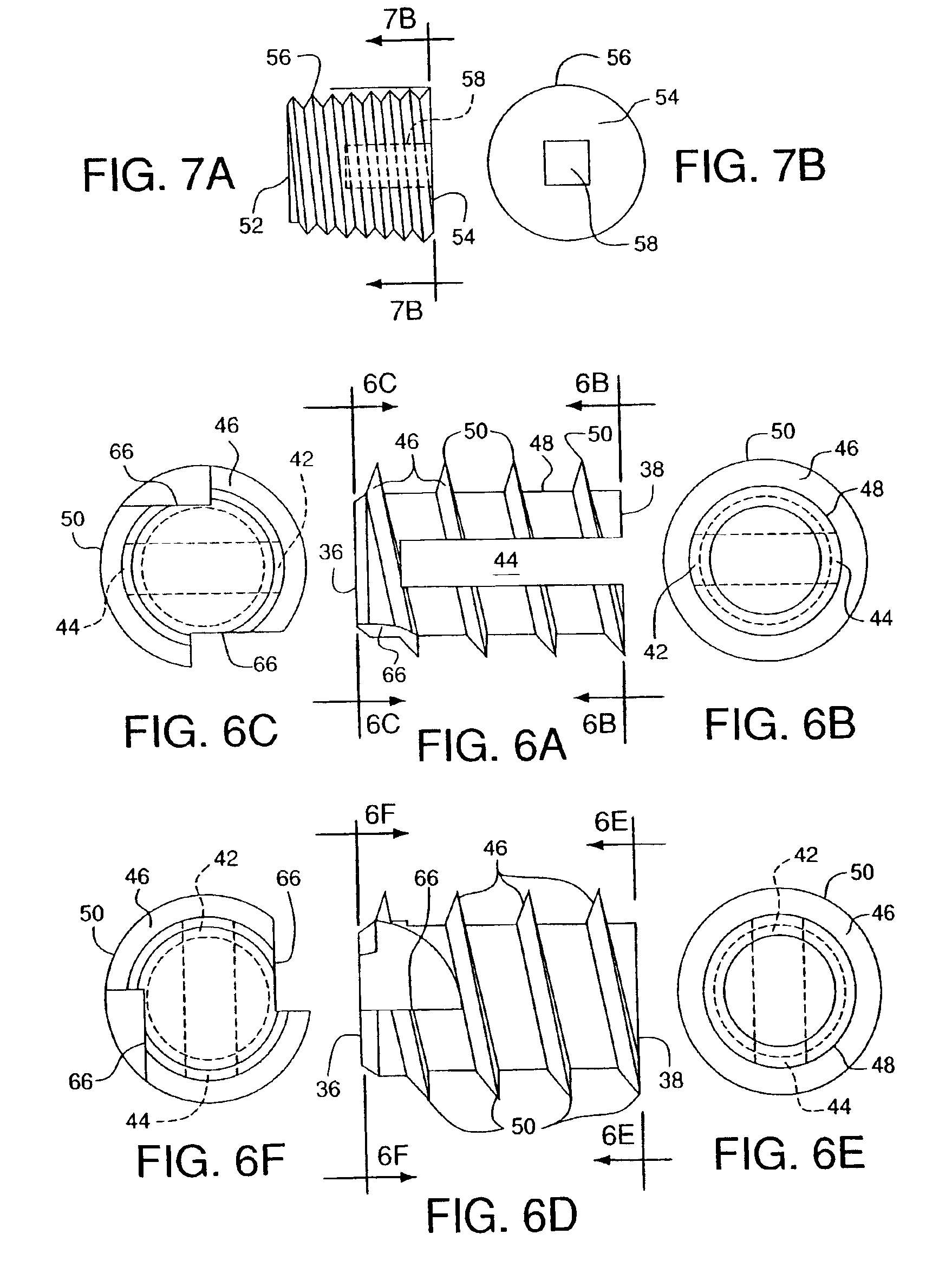
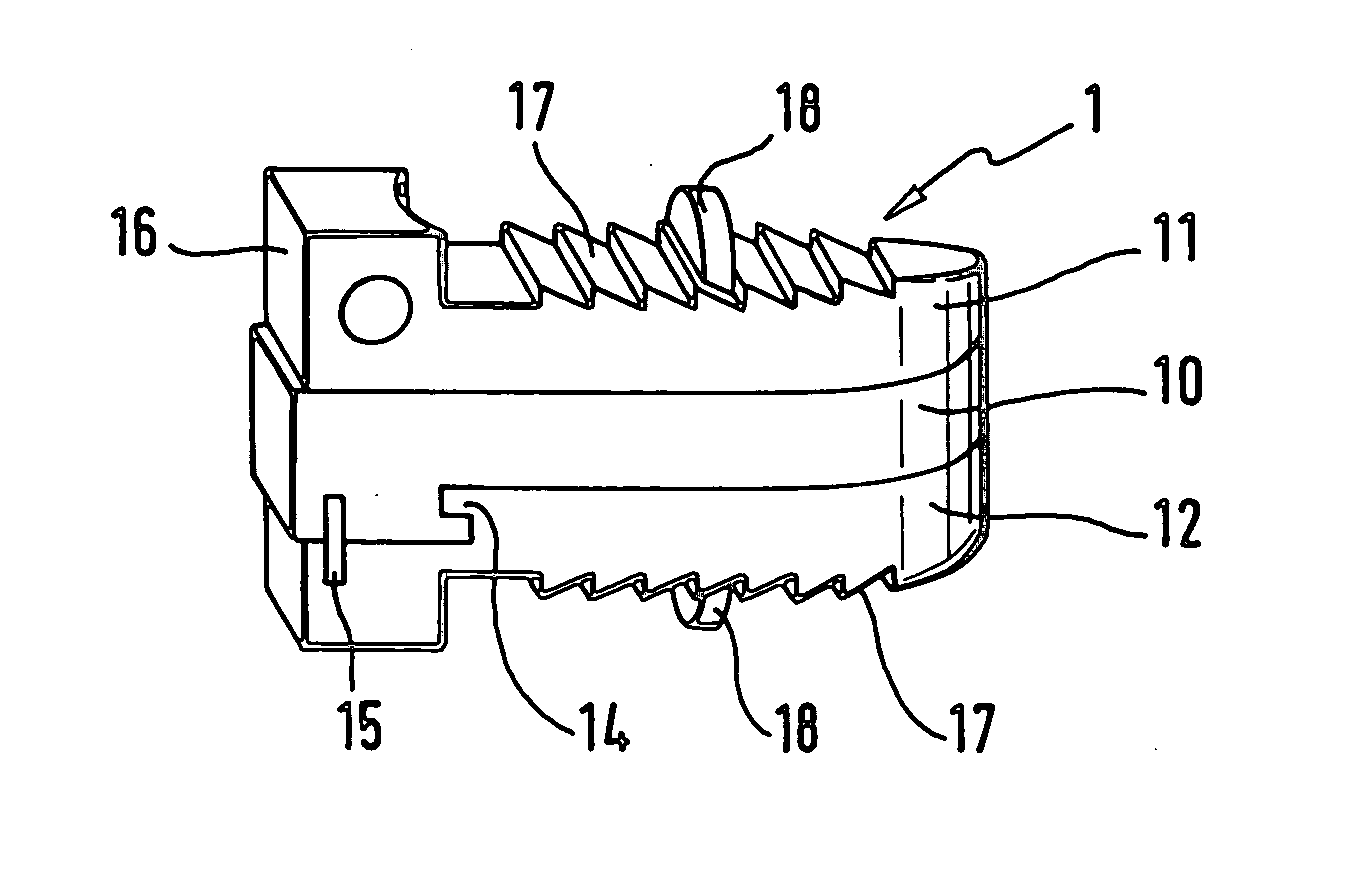
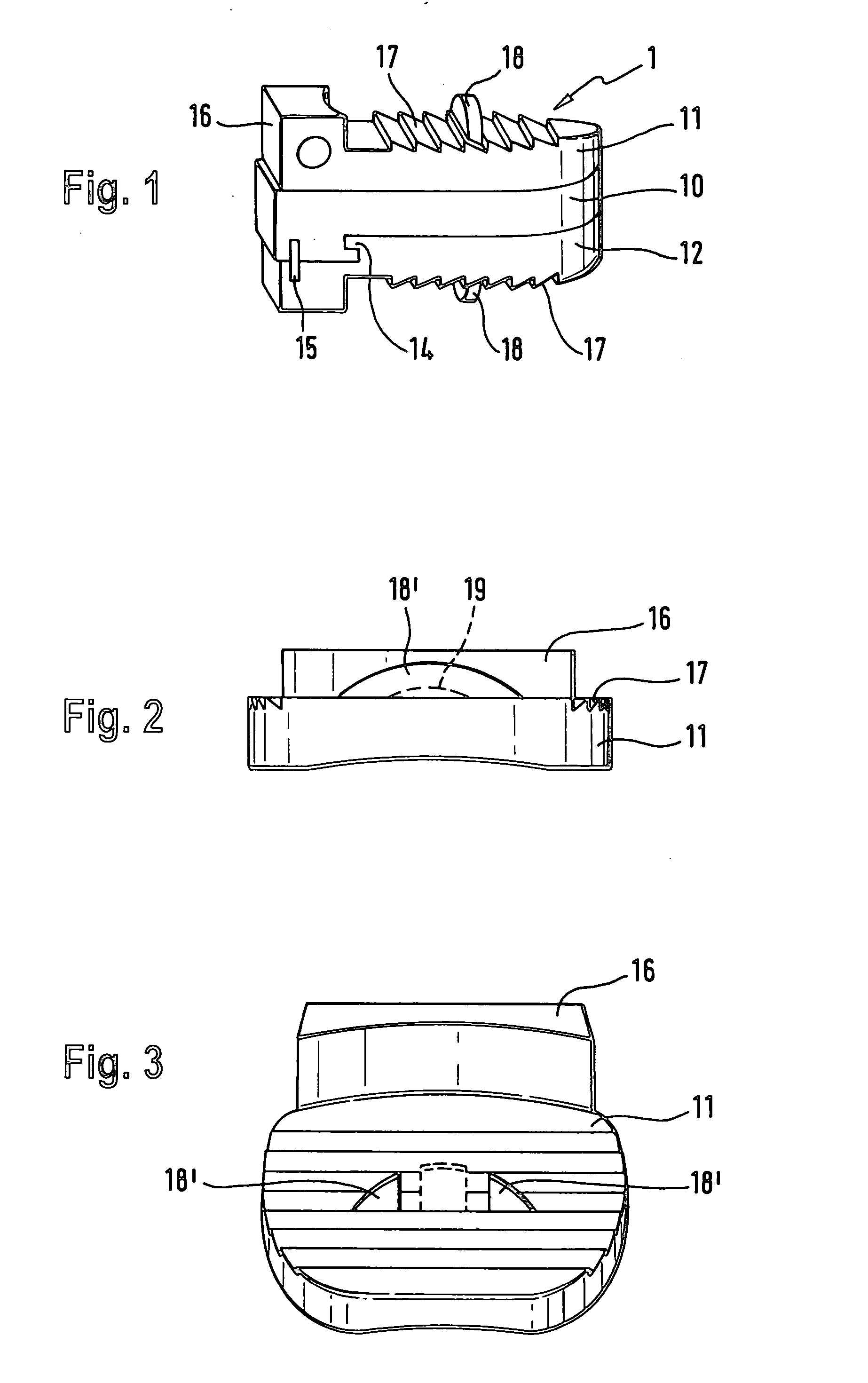
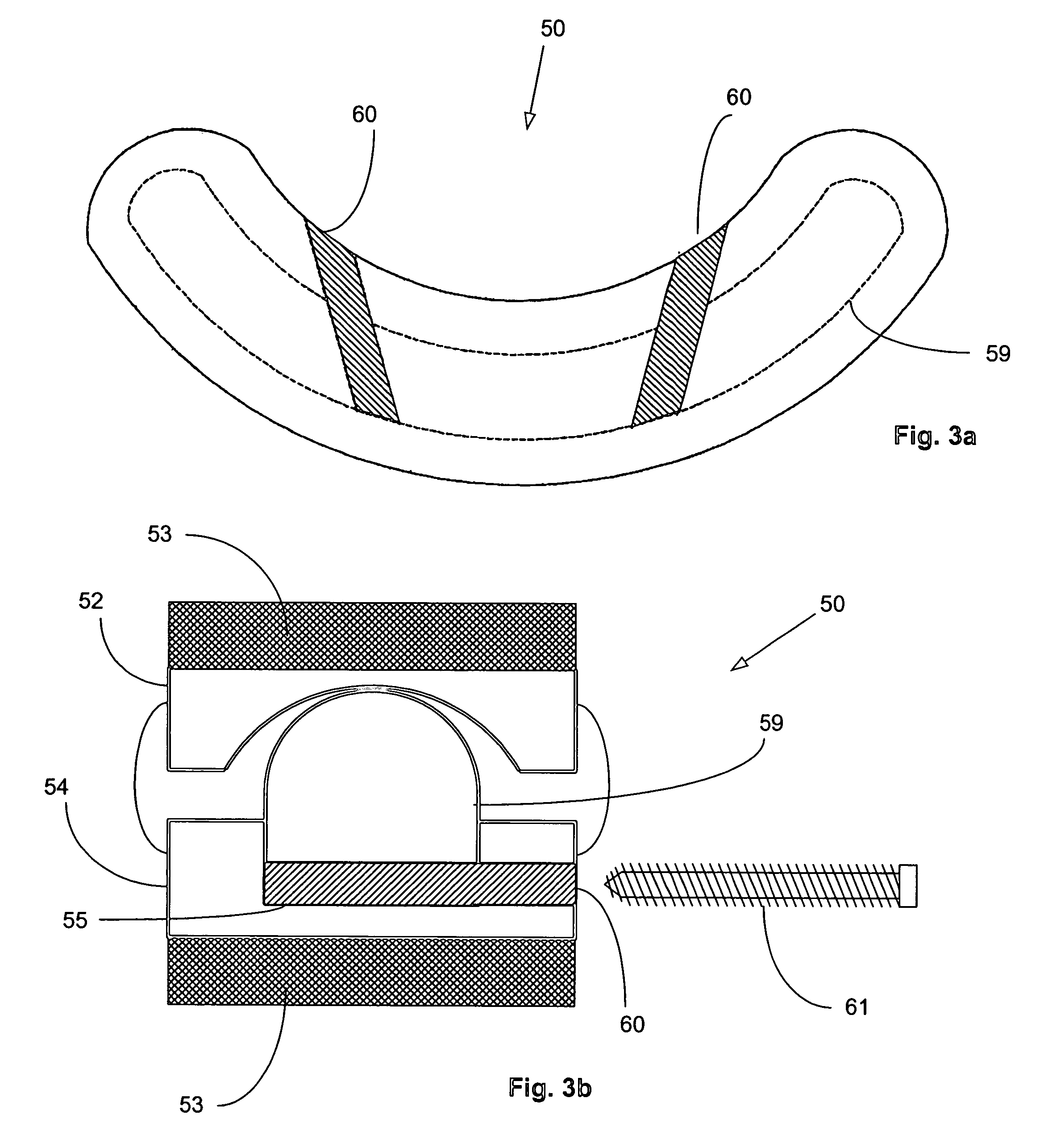
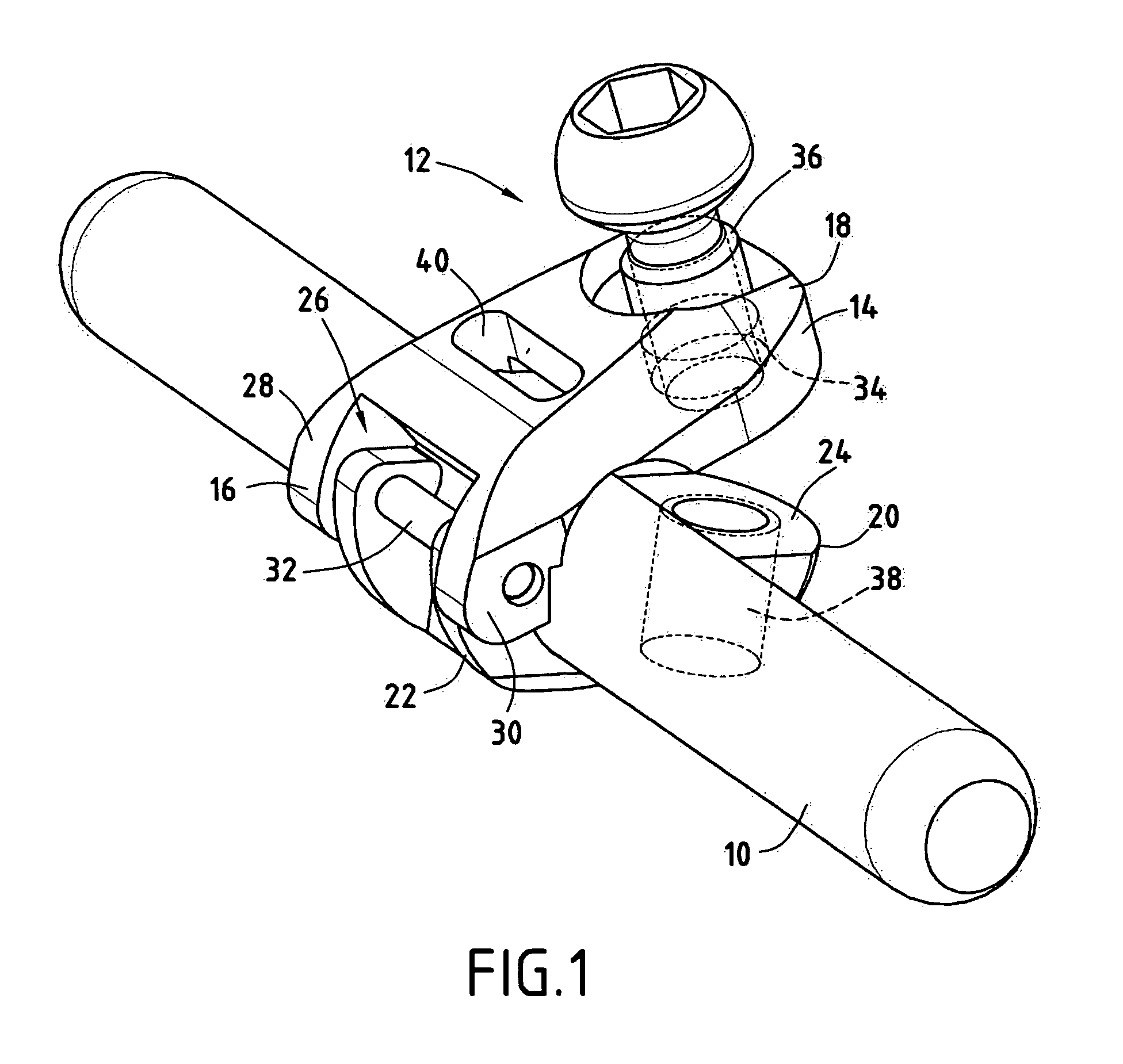
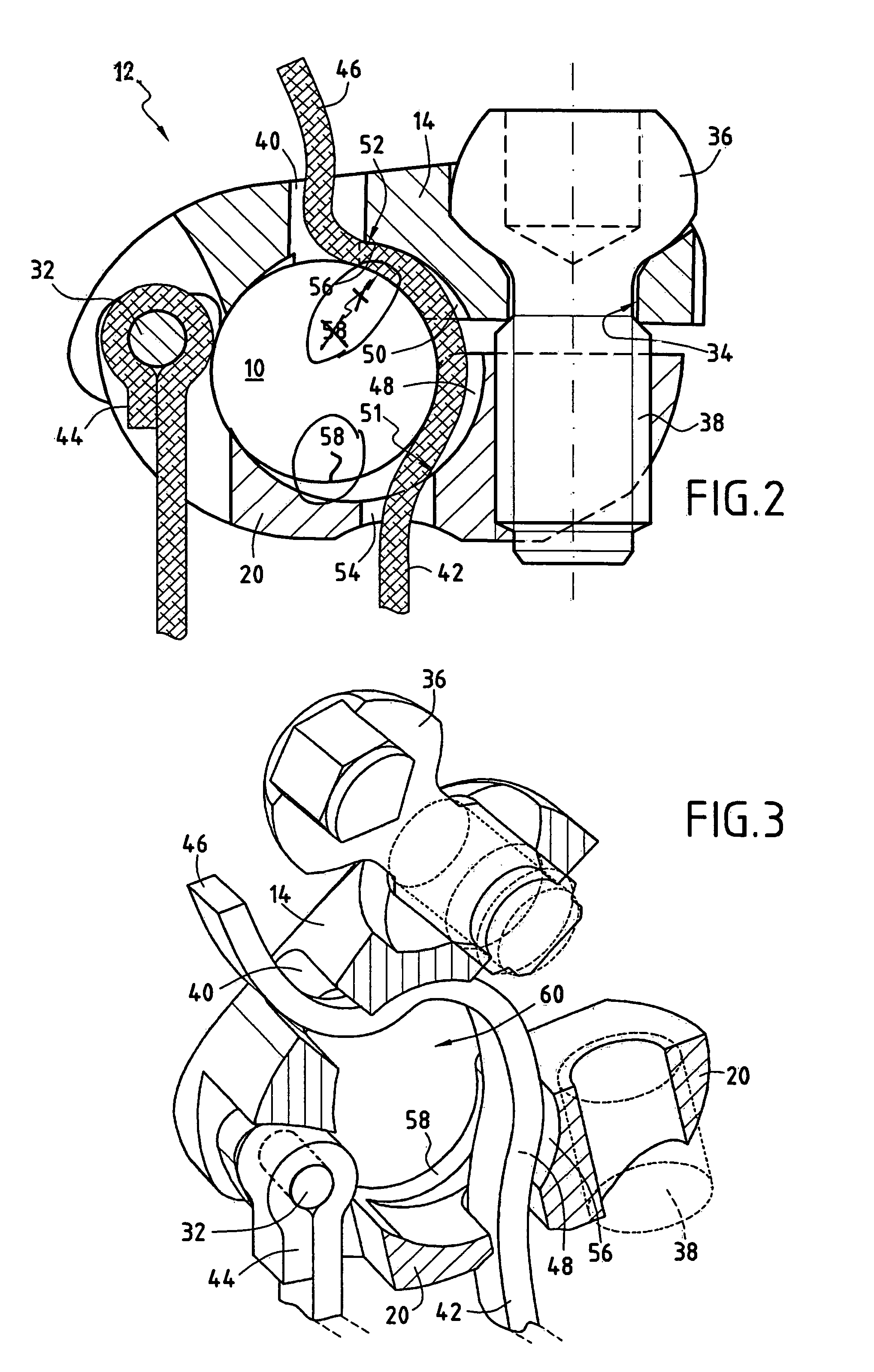
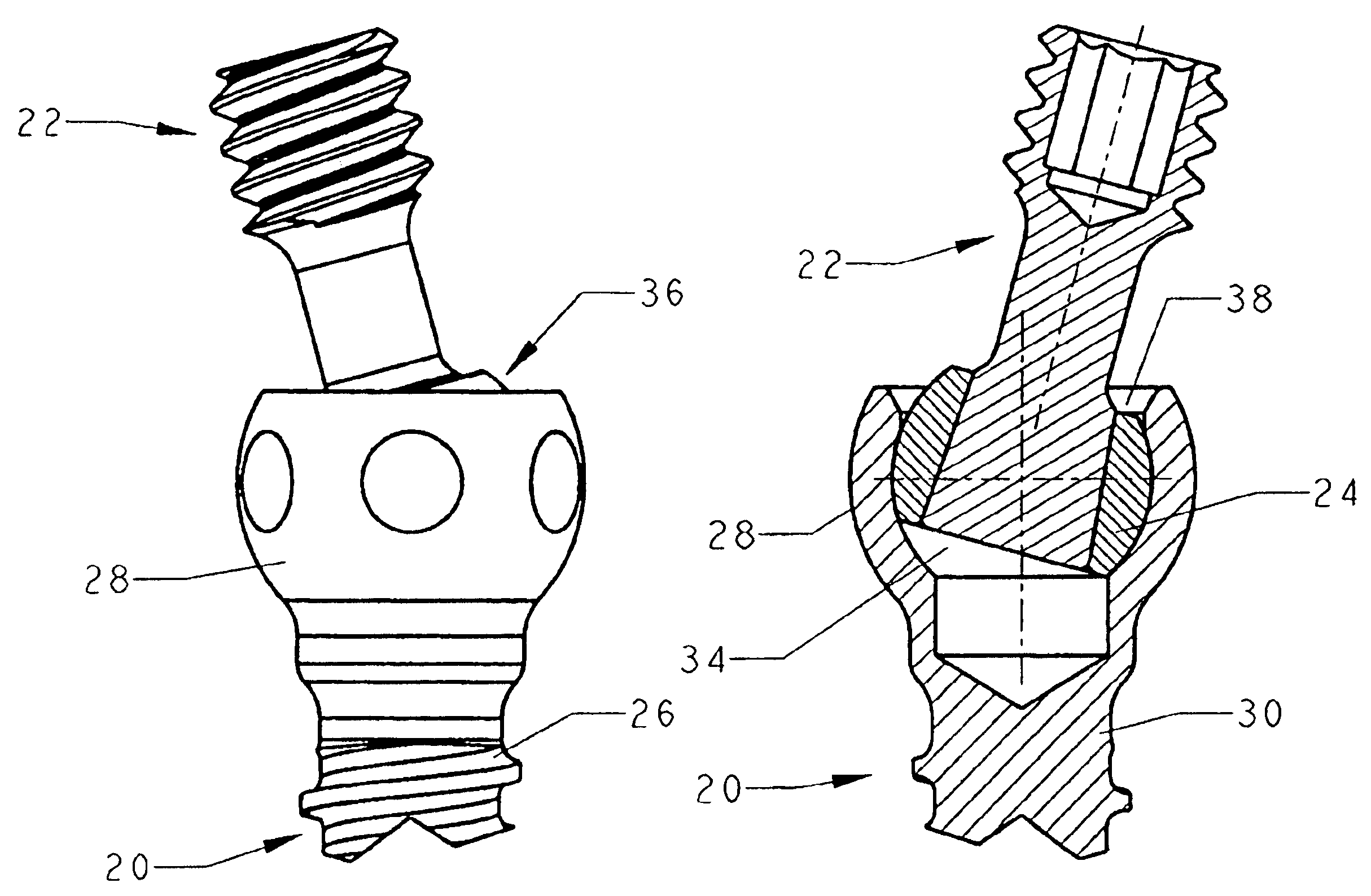
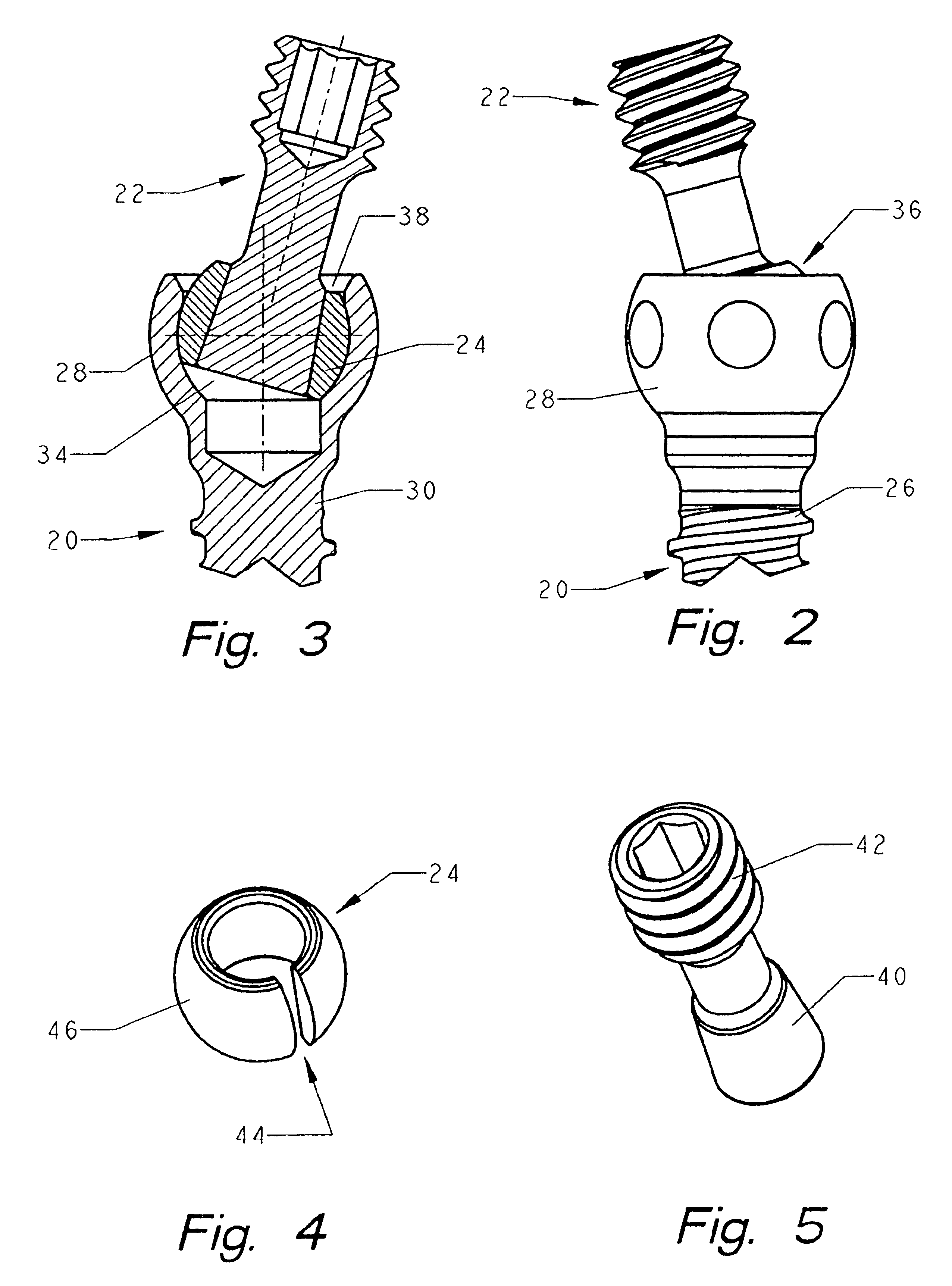
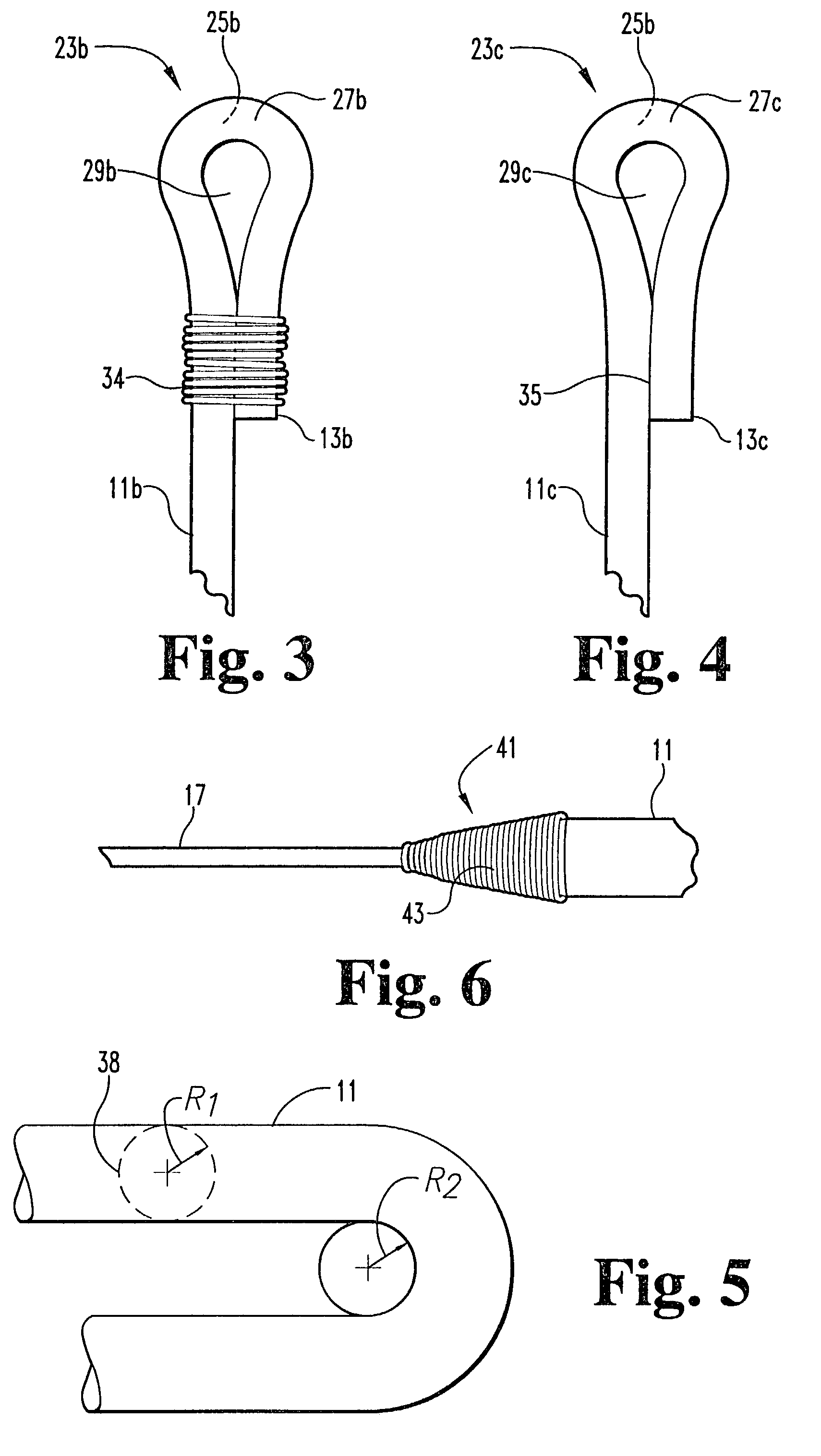
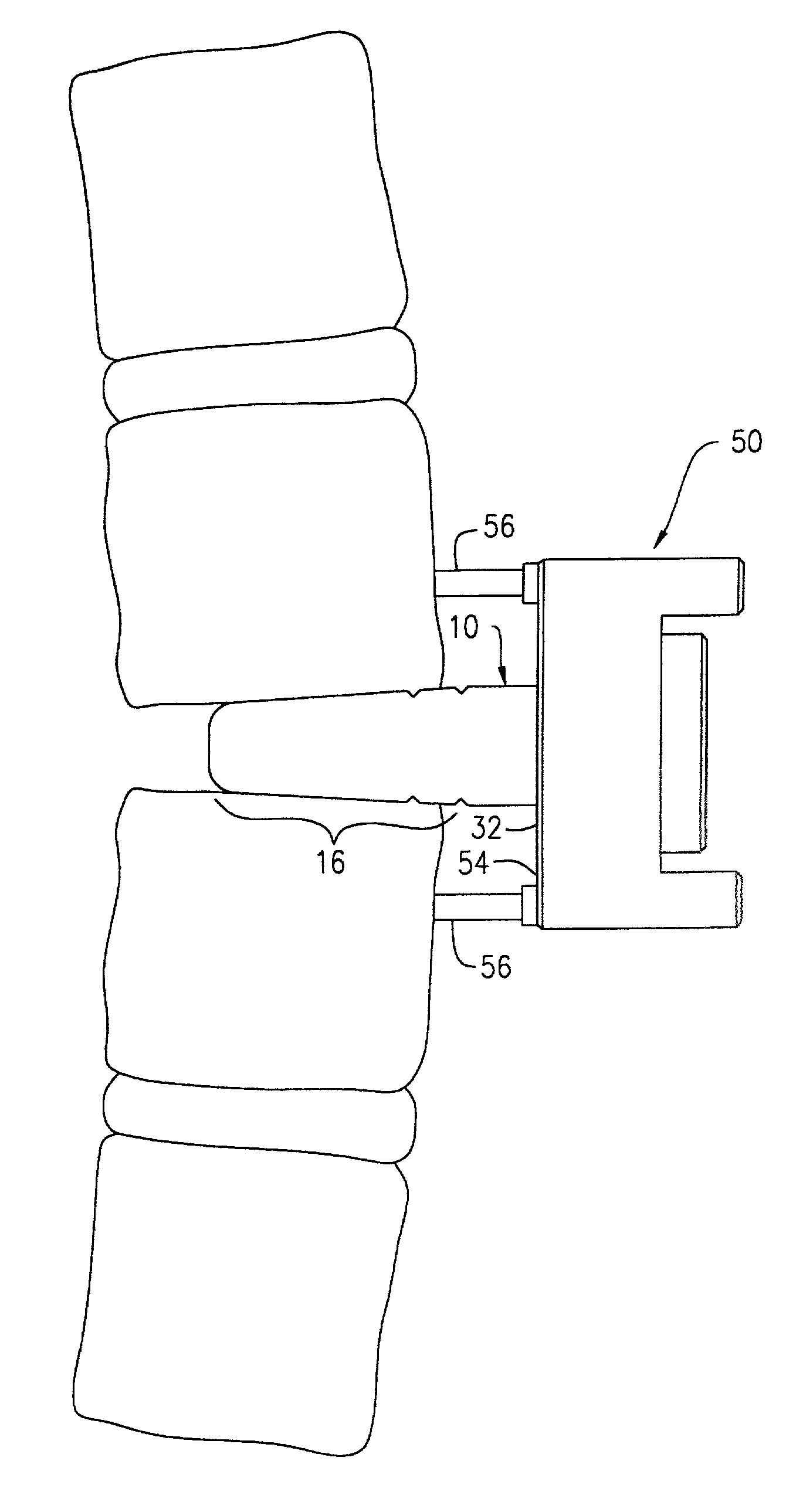
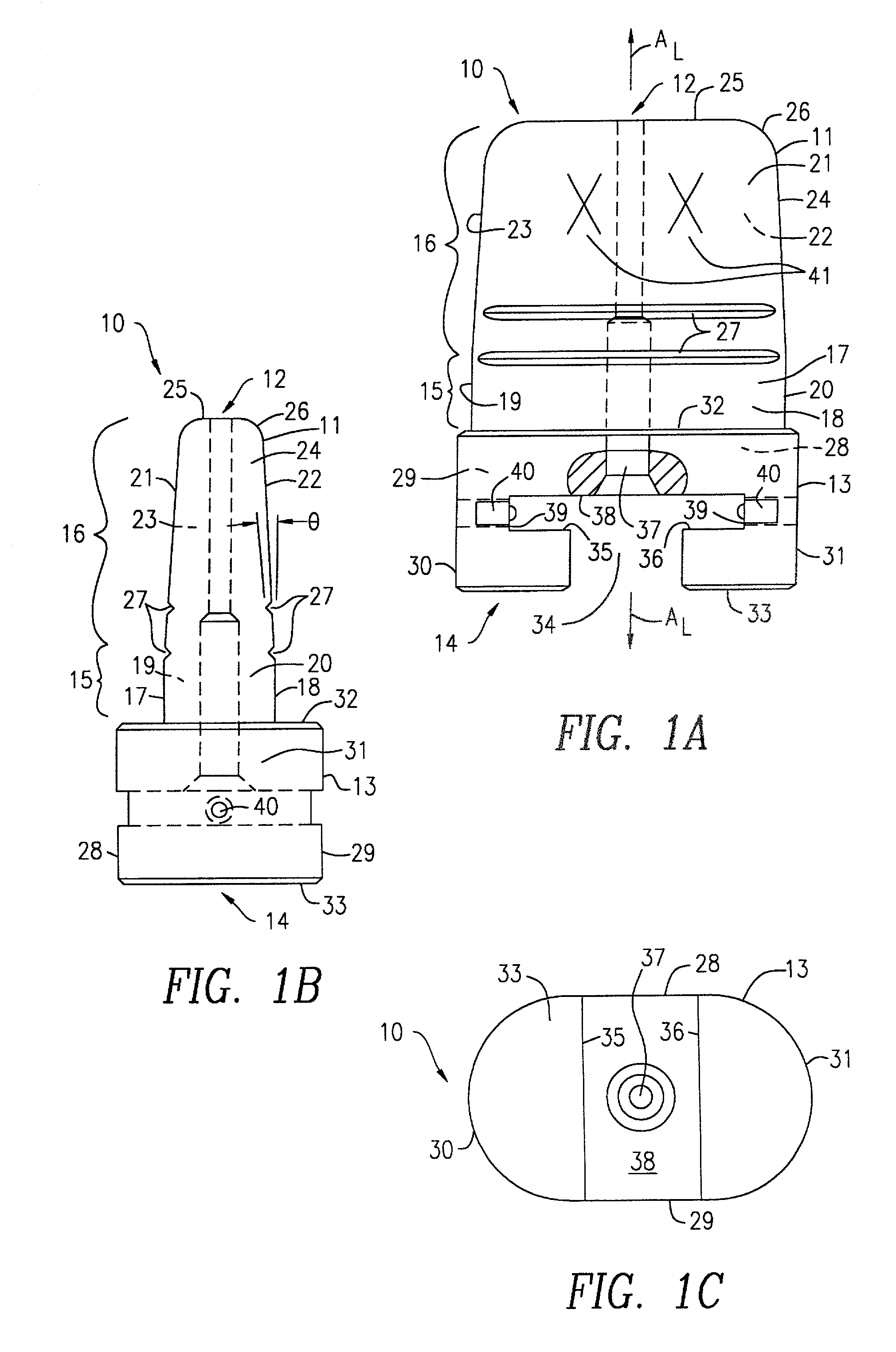
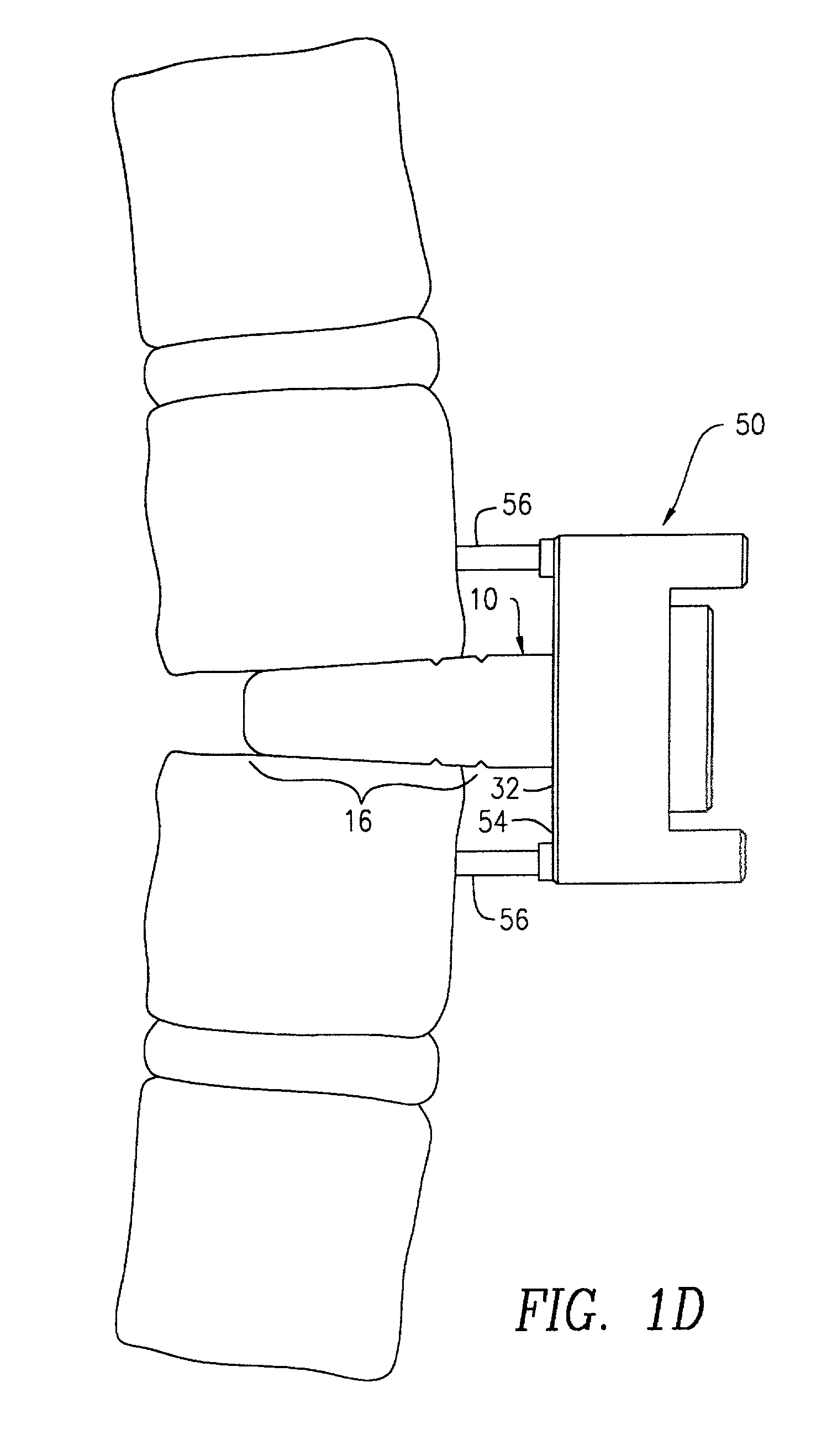
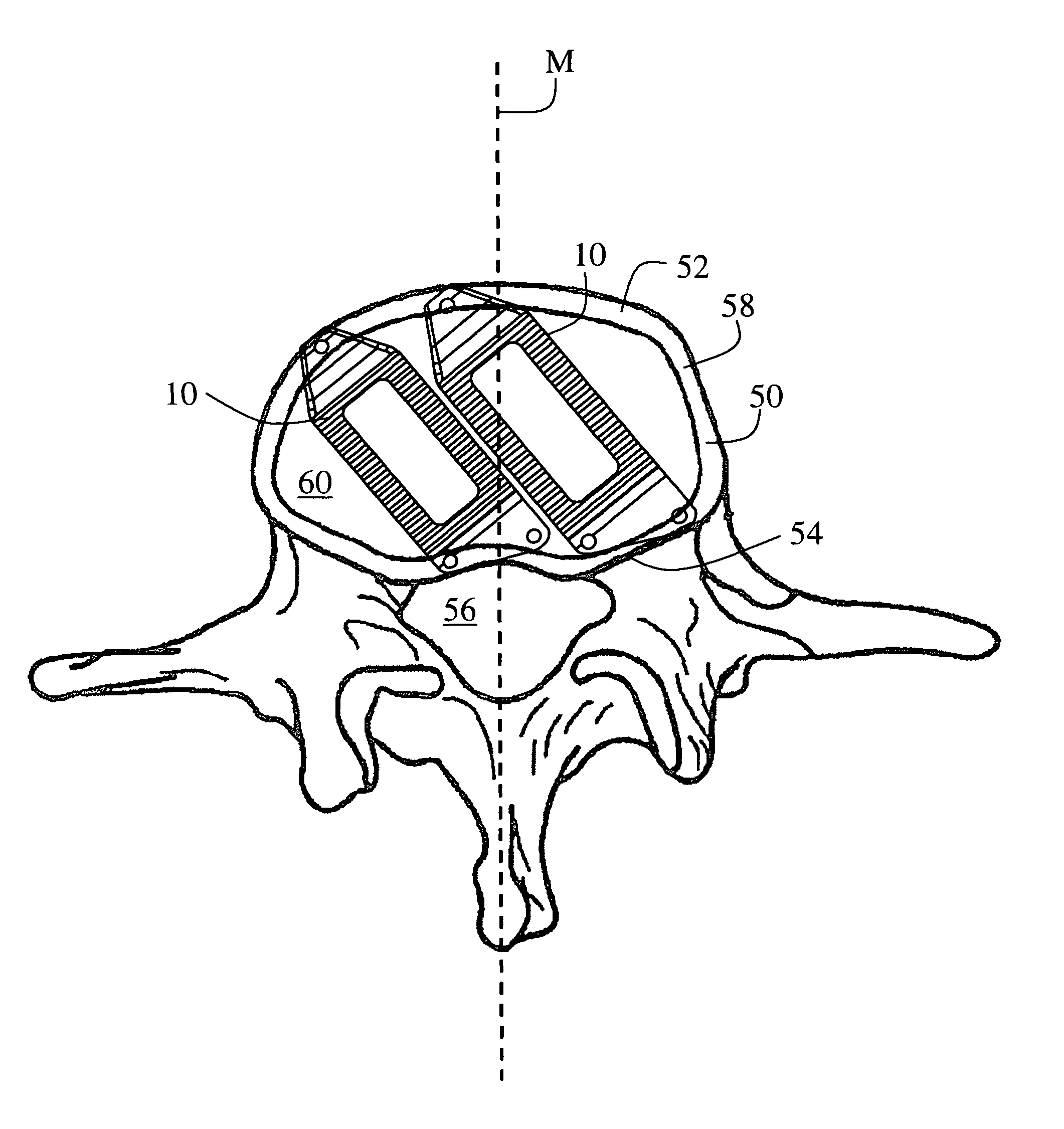
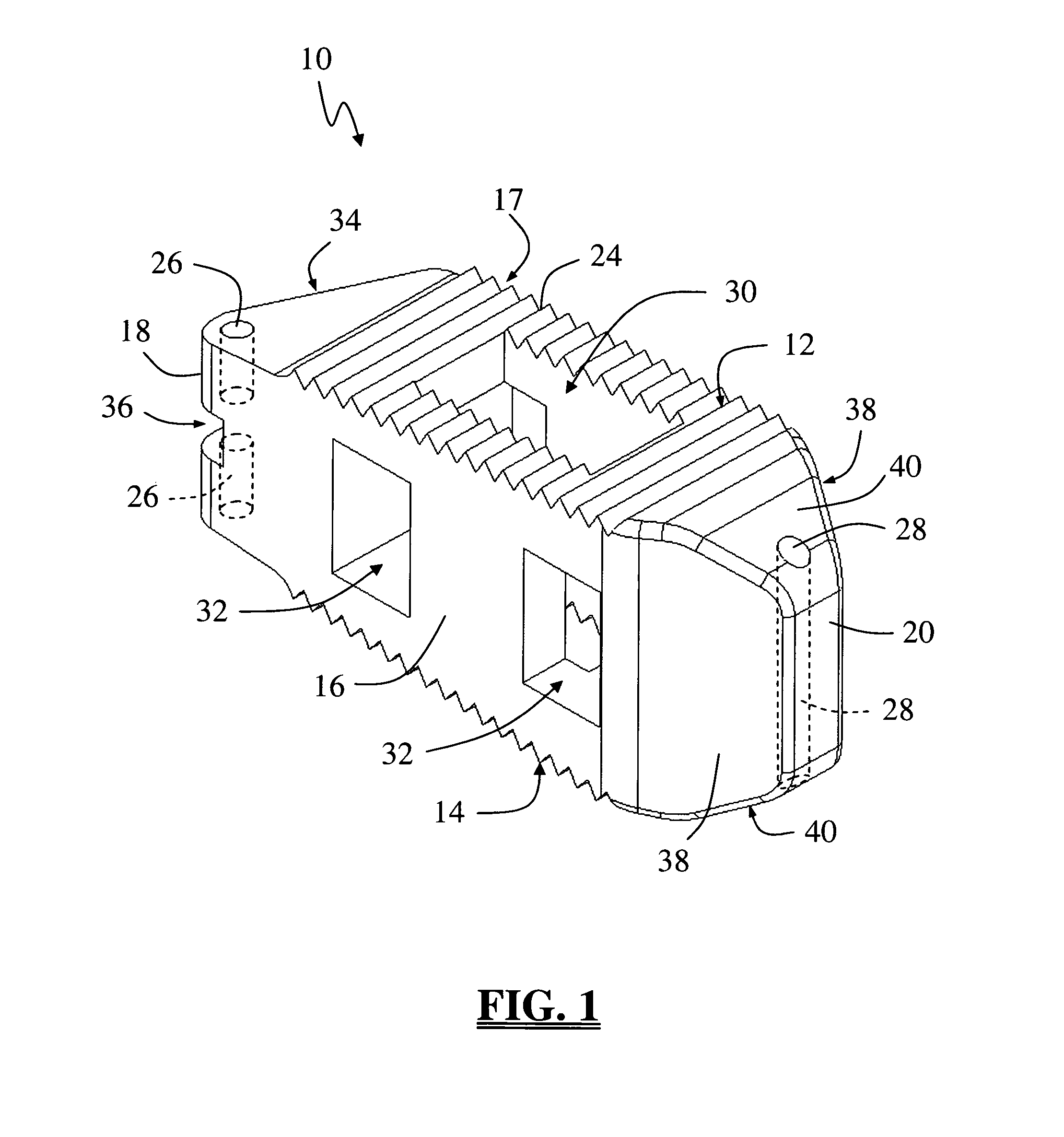
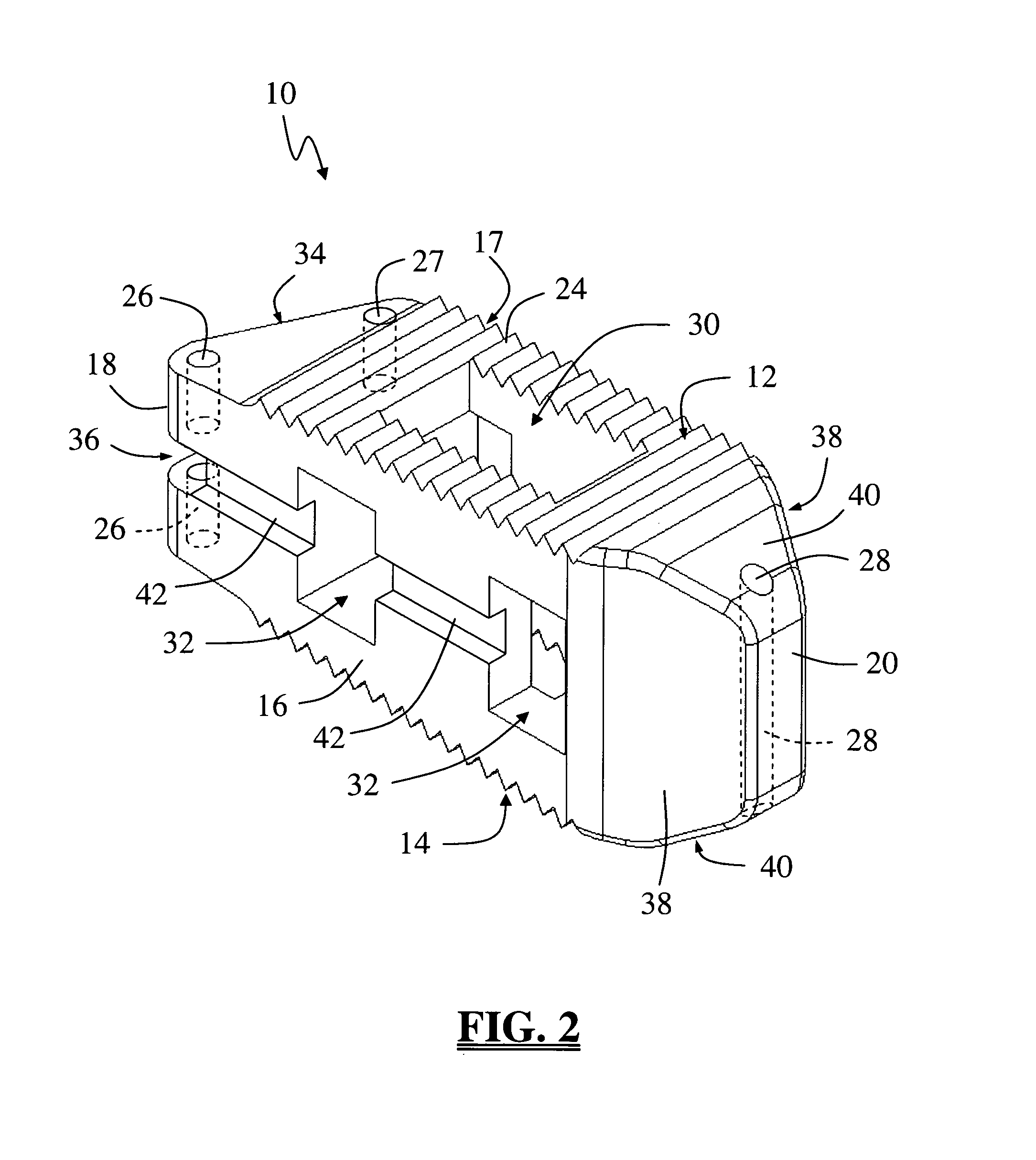
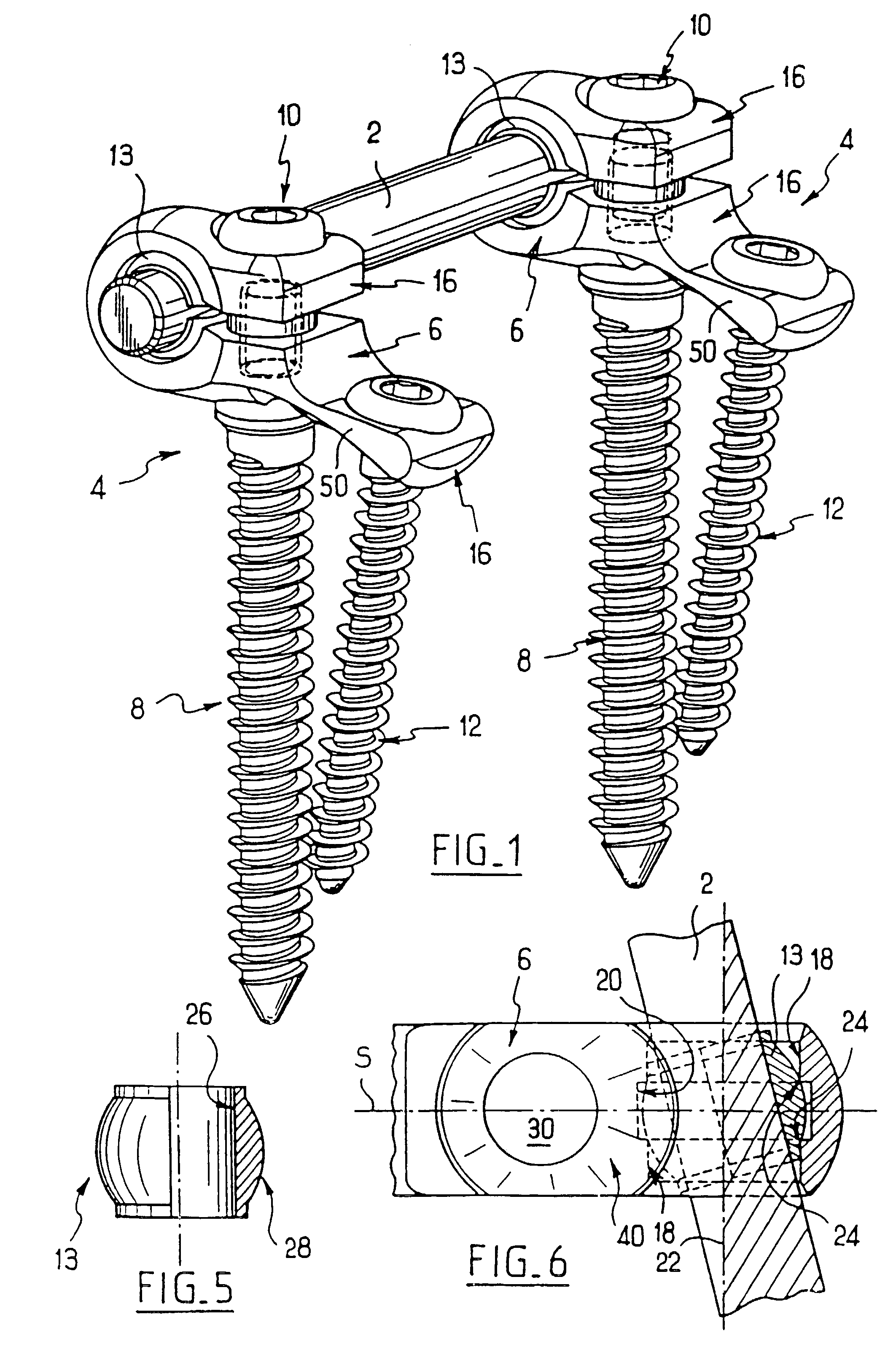
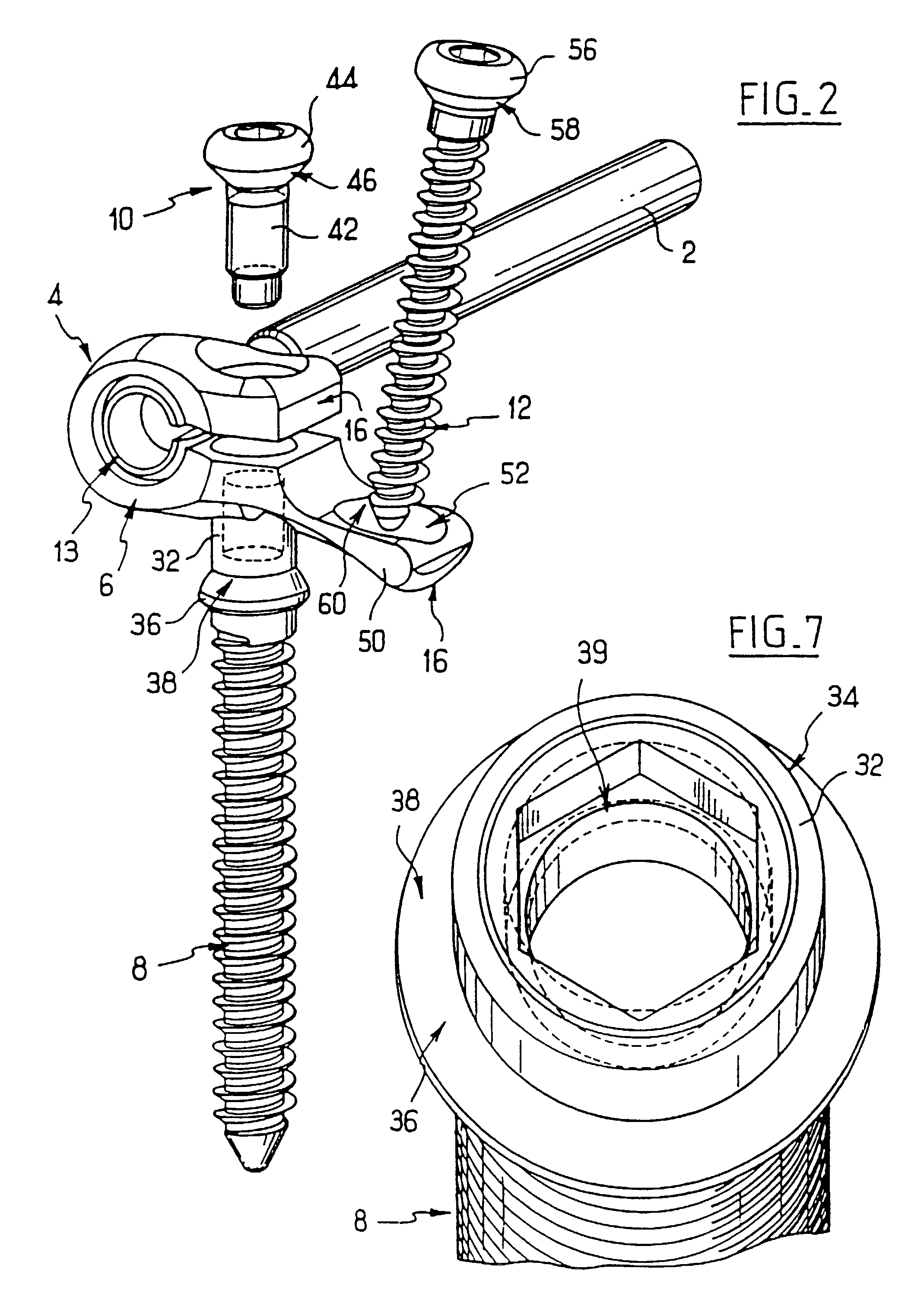
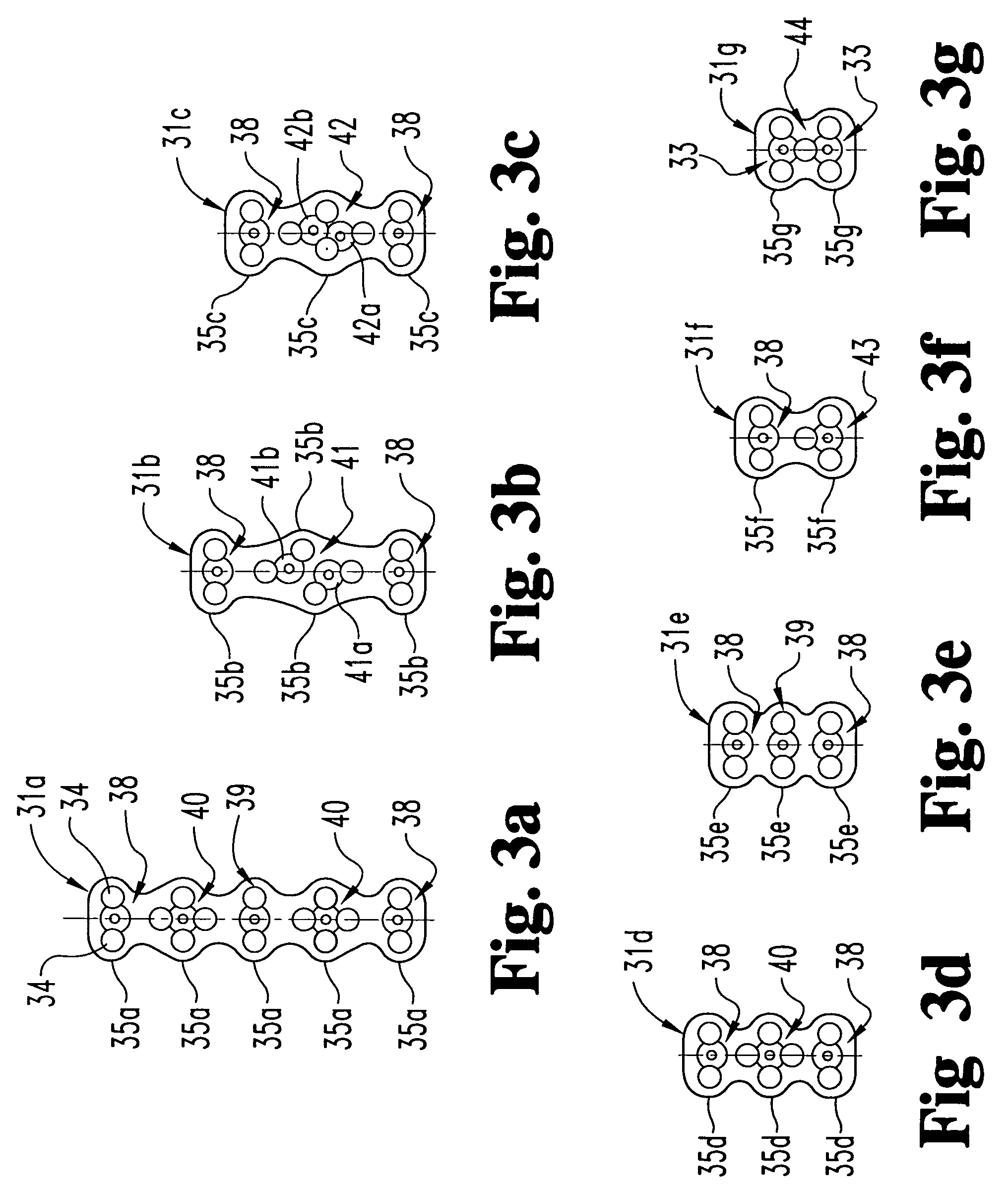
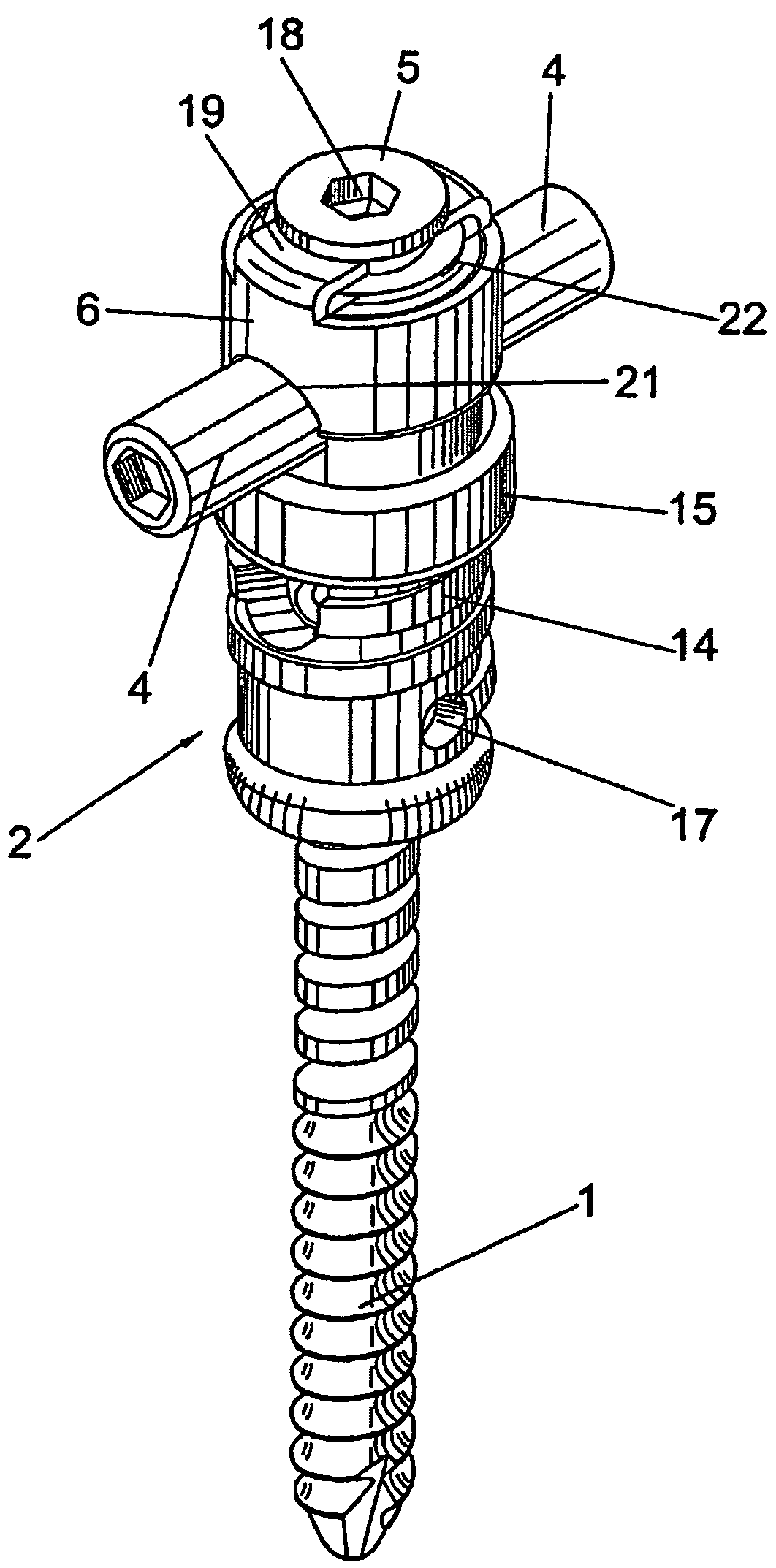
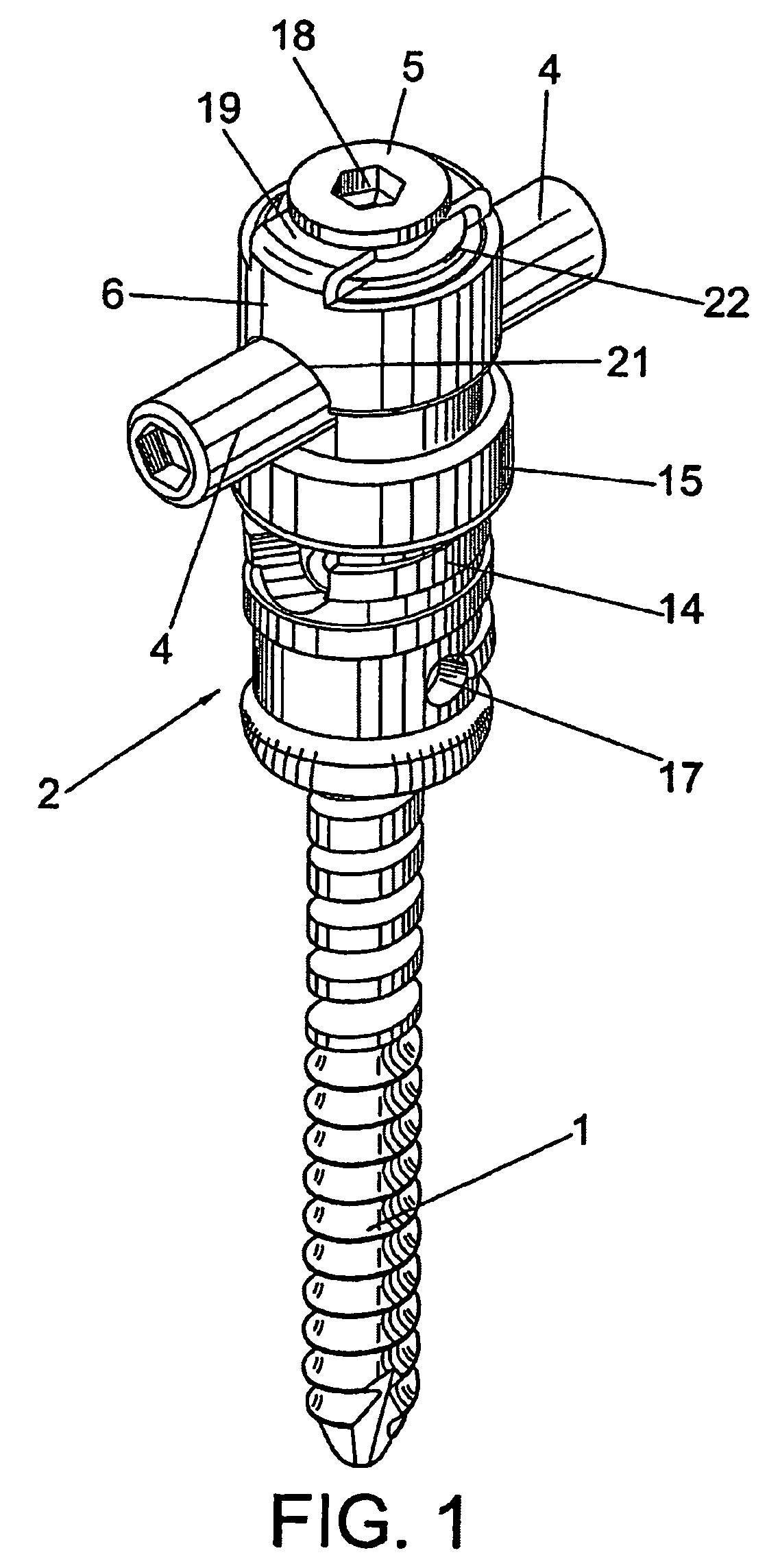
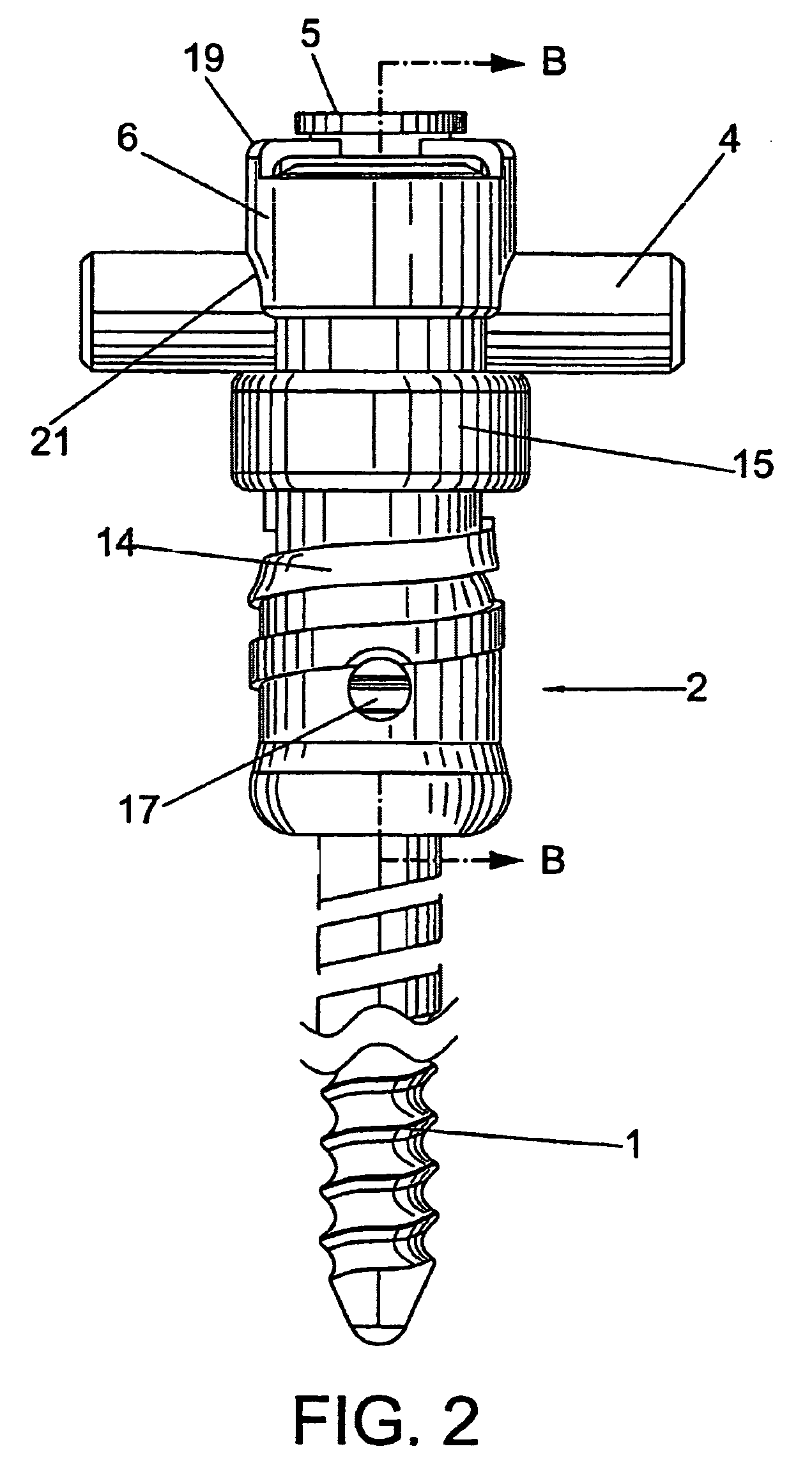
Anchoring element for securing a rod of a device for adjusting a human or animal vertrebal column on a vertreba
InactiveUS20060155277A1Lower clamping surfaceLower requirementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringLumbar vertebral column
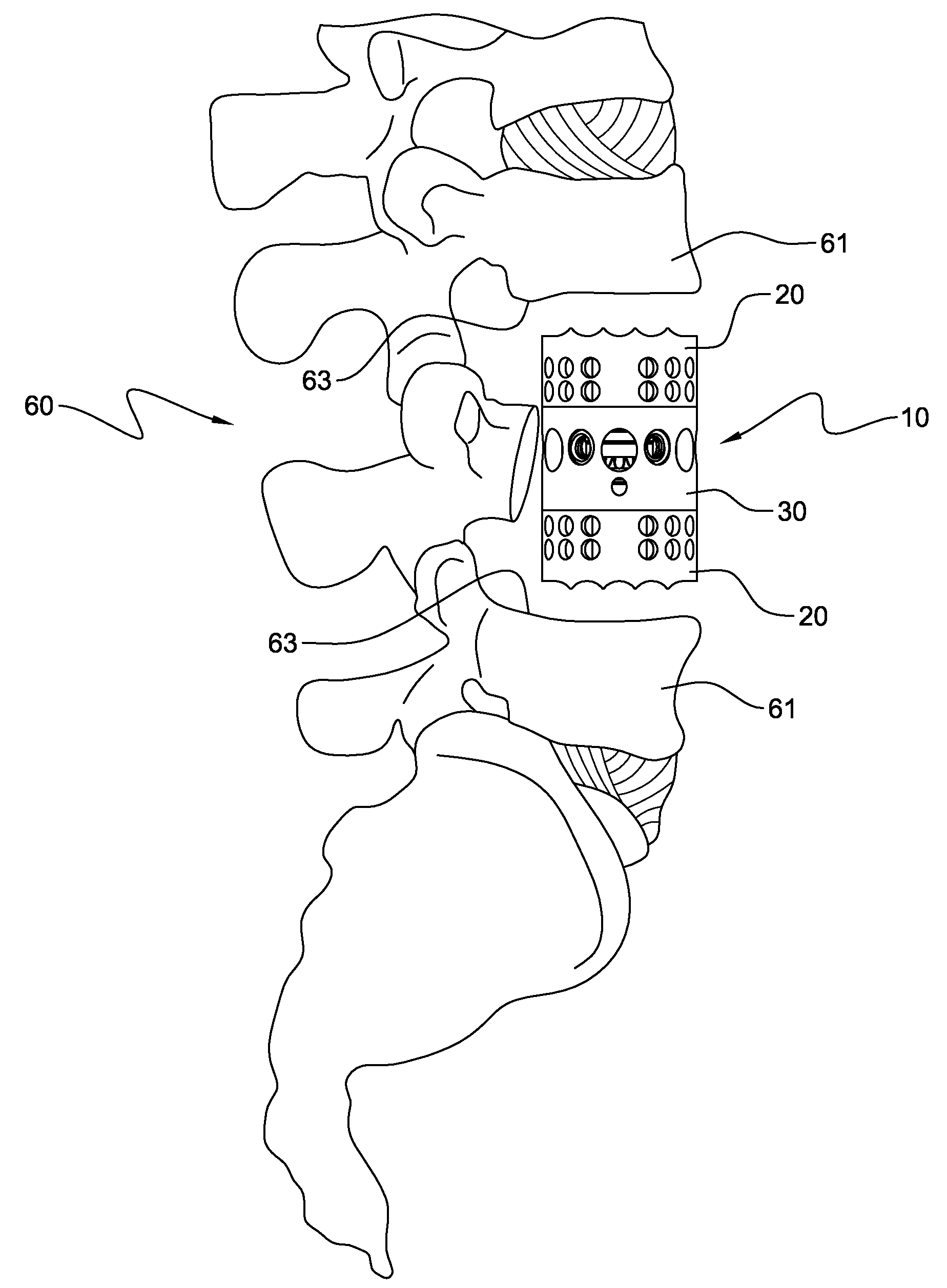
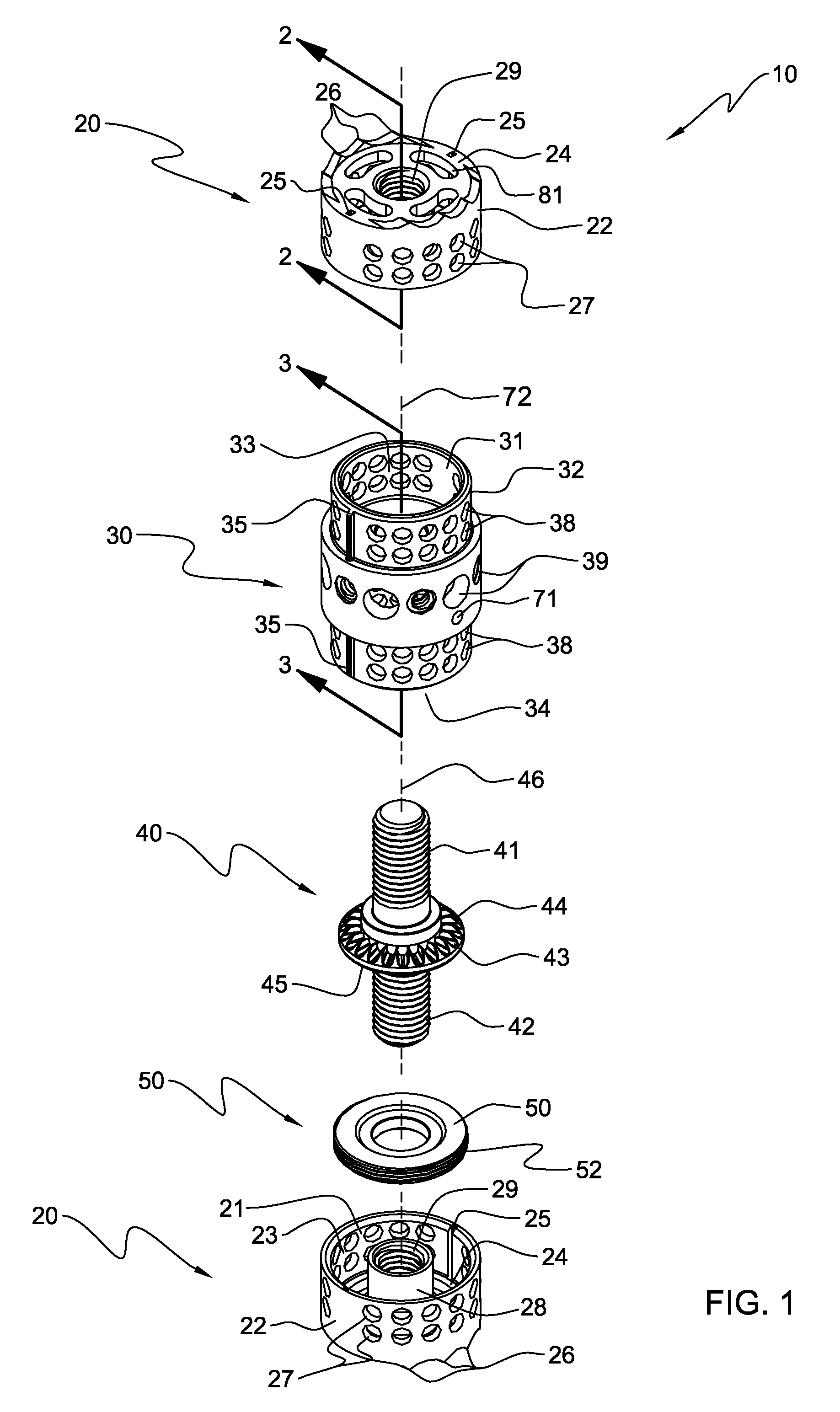
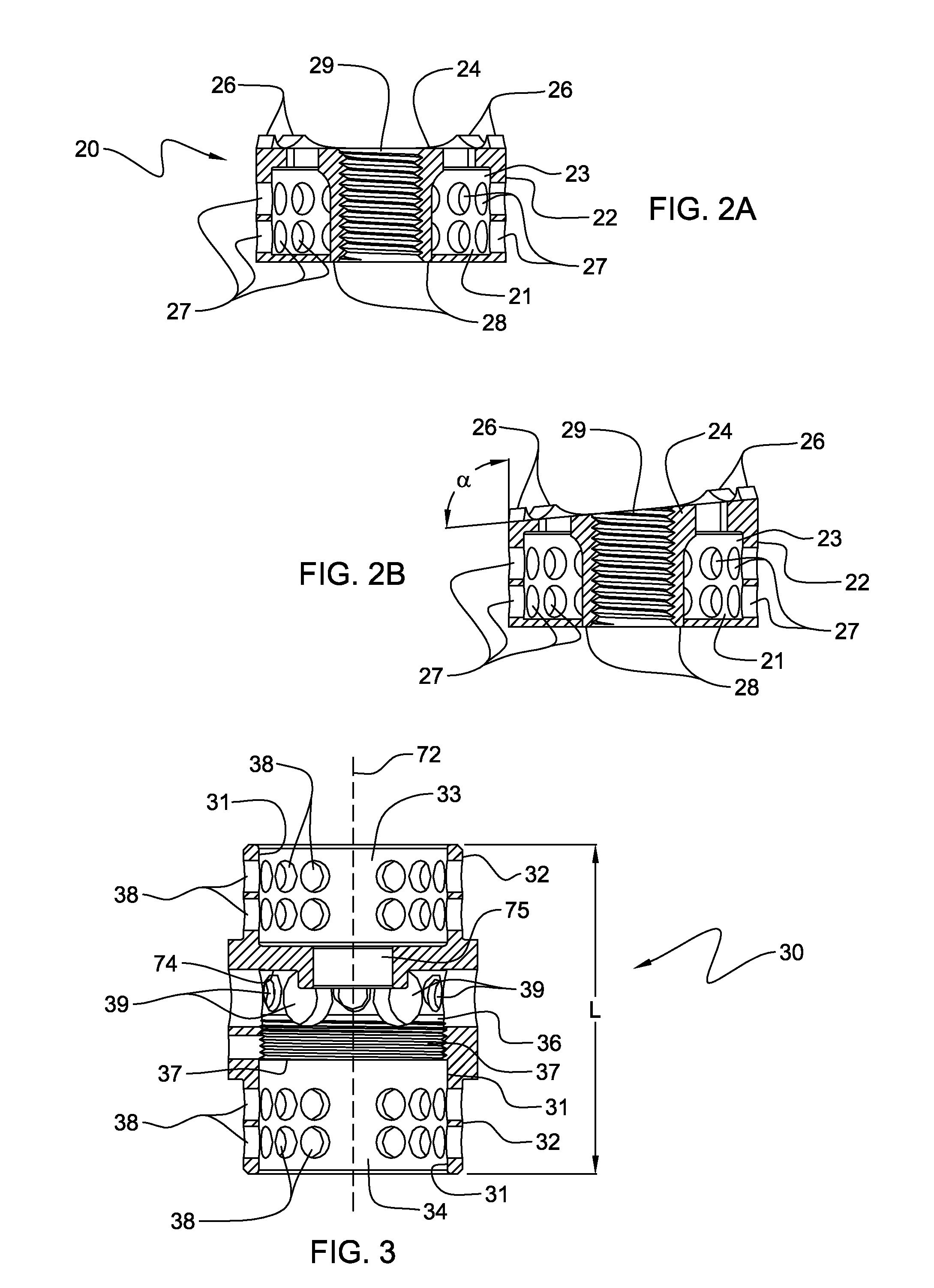
The invention relates to an anchoring element for securing a rod of a device for adjusting a human or animal vertebral column on a vertebra, comprising a retaining means (10) for receiving the rod, a safety element (26) placed on the retaining means and working against the rod, a securing element (14) which can be placed on the body of the vertebra, and a clamping device (12) which is arranged between the retaining means (10) and the securing element (14), comprising a ring-shaped mount (32), a partially conical-segment shaped bearing (28) and an intermediate element (30) which is embedded in the mount (32) and which engages the bearing, whereby the mounting (32) is moveable in a removed state in relation to the bearing (28), whereas the mount (32) is maintained in a clamped state on the bearing (28) by means of the intermediate element (30). The mount (32) is rigidly connected to the retaining means (10) and the bearing (28) is rigidly connected to the securing element (14). In order to enable said type of anchoring element, despite the fact that it is displaceably retained, to transmit relatively large amounts of force from the rod to the body of the vertebra without causing slipping, the bearing (28) comprises flat guiding surfaces (38, 40) which are formed laterally on two opposite sides (34, 36), and the intermediate element (30) is provided with corresponding counter surfaces (50, 52).
Owner:METZ STAVENHAGEN PETER
Method and apparatus for spine joint replacement
InactiveUS7090698B2Reduce frictionEliminate growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFacet joint prosthesisIntervertebral disc
A prosthesis for the replacement of the cartilaginous structures of a spine motion segment is described. The prosthesis comprises an intervertebral disc prosthesis in combination with a facet joint prosthesis.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC +1
Linearly expanding spine cage for enhanced spinal fusion
ActiveUS7819921B2Diameter minimizationEffectively distractBone implantSpinal implantsSpinal columnVertical axis
A linearly expanding spine cage has a minimized diameter in its unexpanded state that is equal to the diameter of an insertion groove cut into adjacent vertebral bodies. The cage conformably engages between the endplates of adjacent vertebrae to effectively distract the disc space, widen neuroforamina, stabilize the motion segments and eliminate pathologic spine motion. Angular deformities can be corrected, and natural curvatures maintained. The cage enhances spinal arthrodesis by creating a rigid spine segment. Expanding linearly (vertically, along the vertical axis of the adjacent spine) rather than uniformly, the cage height increases and holds the vertebrae with fixation forces greater than adjacent bone and soft tissue failure forces. Stability is thus achieved immediately, enabling patient function by eliminating painful motion. The cage width remains stable, so as to decrease impingement upon a second cage, or upon soft tissue structures in the immediate vicinity, including neural or vascular elements.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
System for stabilizing the vertebral column including deployment instruments and variable expansion inserts therefore
InactiveUS6905512B2Stabilize spineStabilizing the being's vertebral columnJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral spaceLigament structure
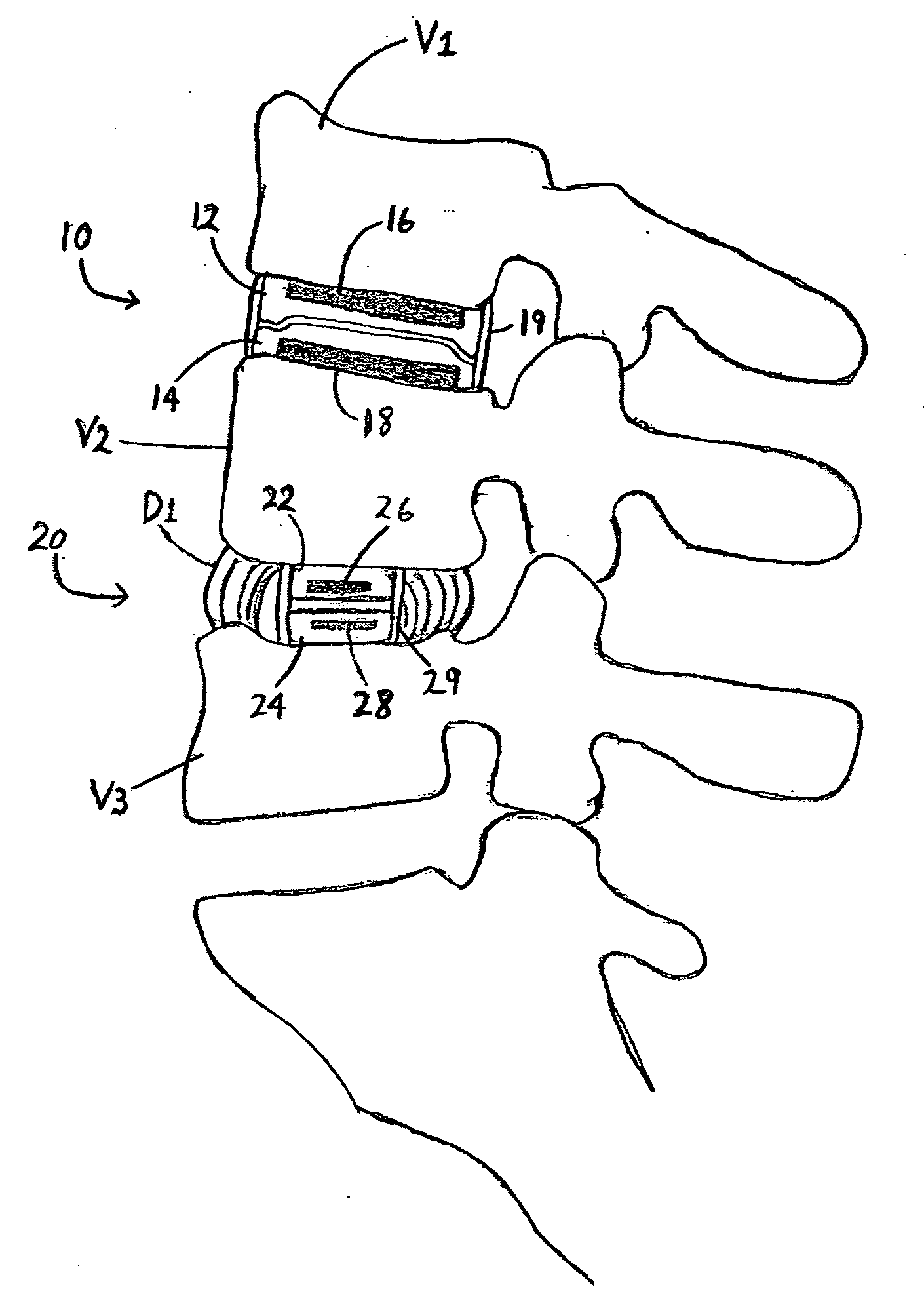
A system is provided for stabilizing adjacent vertebra without excision of bone or resection of ligaments comprising an expansion device and a deployment system which includes a hollow expandable insert and an expansion insert. The expandable insert includes a cylindrical body having a pair of slots having a threaded outer surface. The expandable insert is located with the slots oriented perpendicular to the vertebral column between the vertebrae. The thread cuts into the cortical bone contiguous to the intervertebral space but not substantially into the cancellous bone. The expandable insert is internally threaded. The expansion insert is externally threaded and arranged to be screwed into a bore in the expandable insert by the deployment system, whereupon the slots open to spread the vertebrae apart. The deployment system includes a tool having projecting fingers located within the slots to enable the expandable insert to be screwed into the intervertebral space.
Owner:PHOENIX BIOMEDICAL
Artificial functional spinal unit assemblies
InactiveUS20060195192A1Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical approachFunctional spinal unit
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
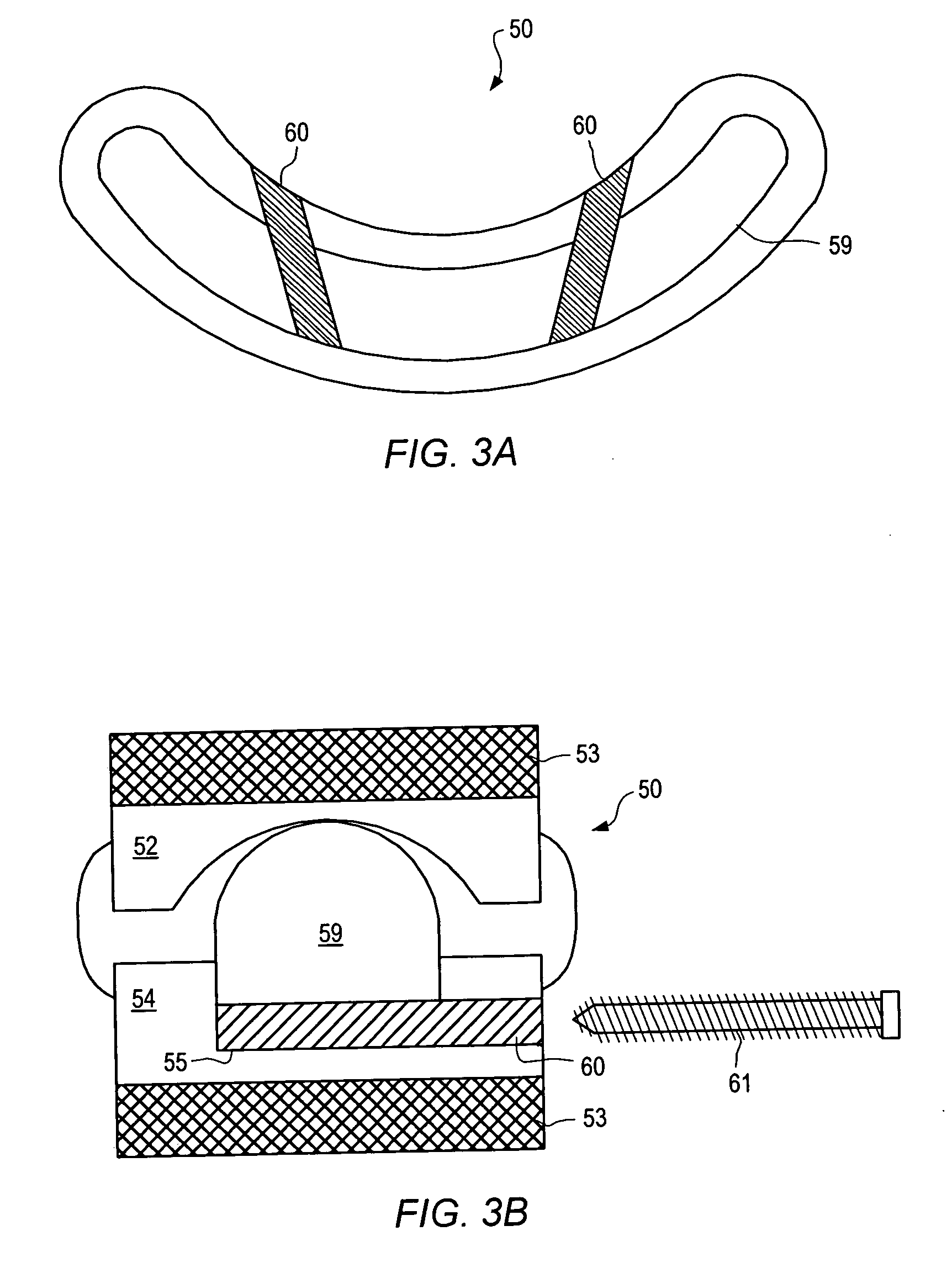
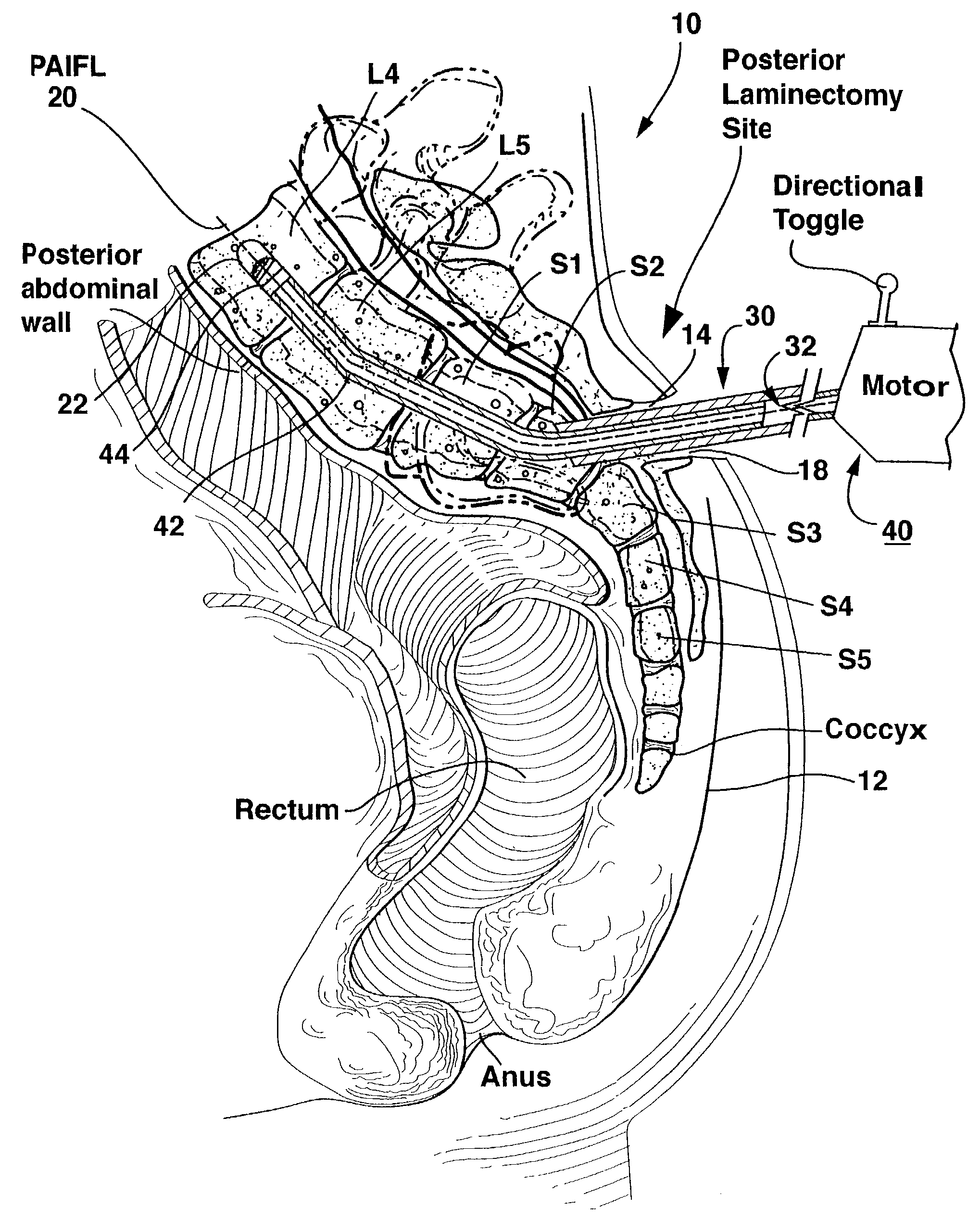
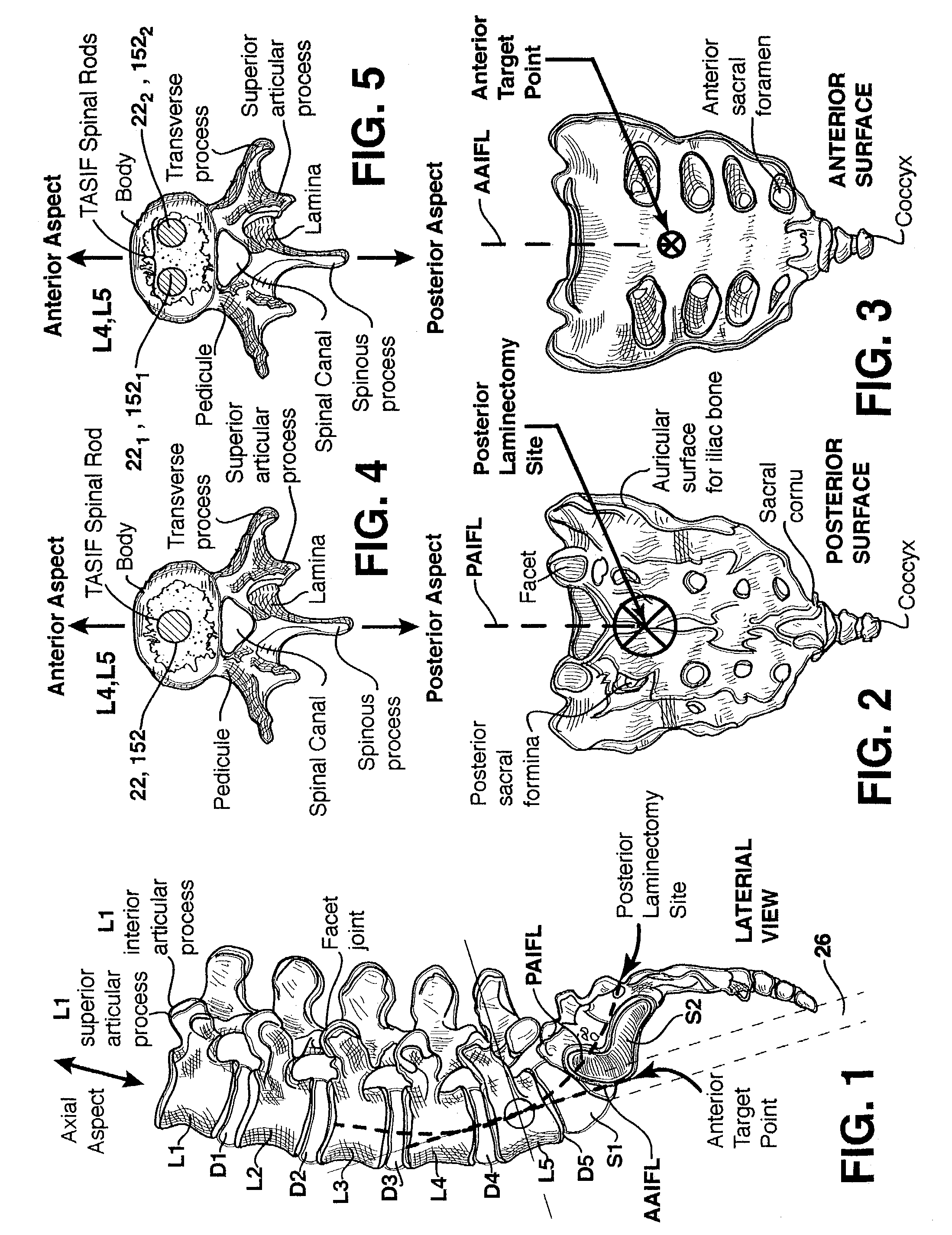
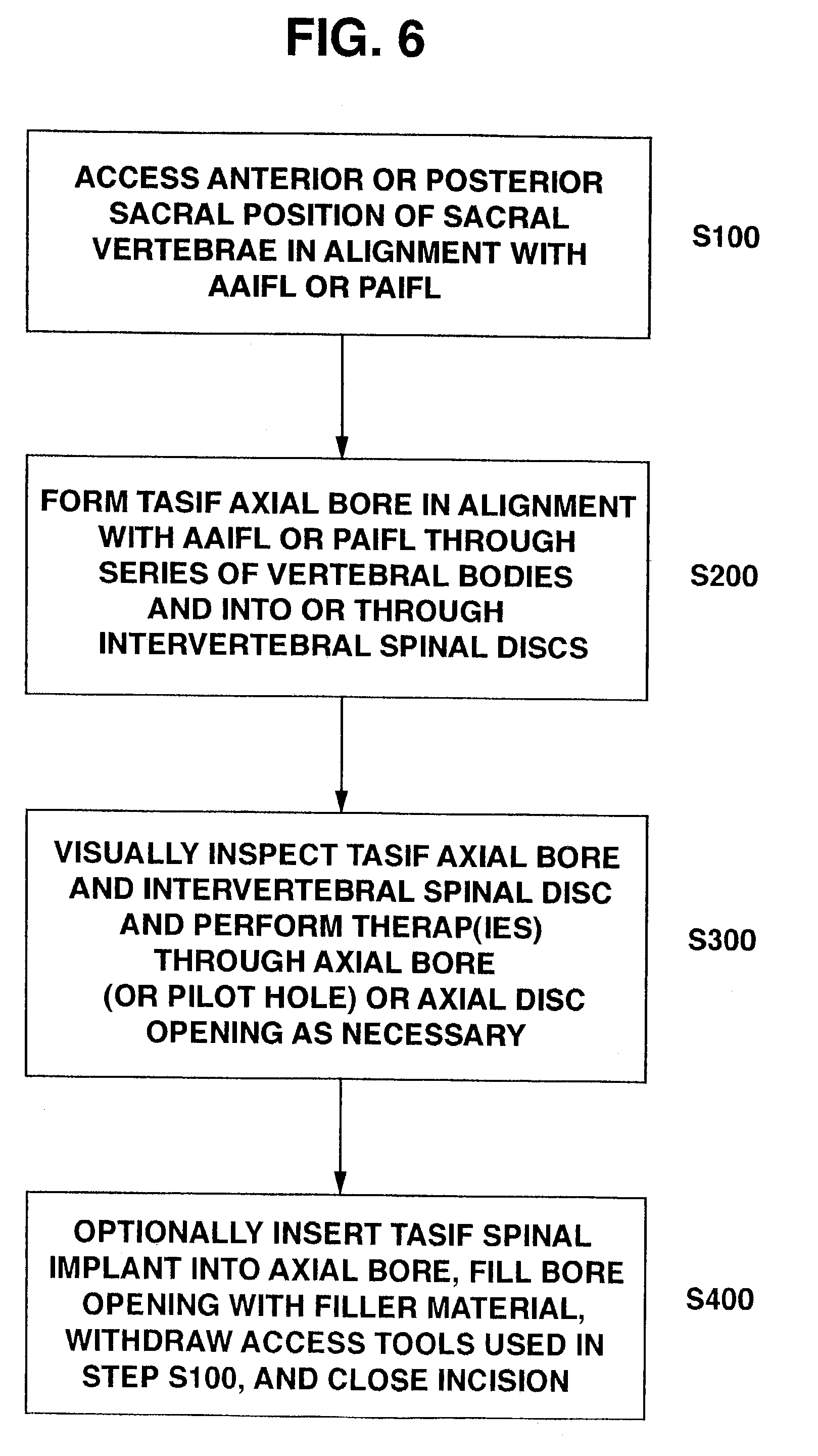
Method and apparatus for providing posterior or anterior trans-sacral access to spinal vertebrae
InactiveUS7087058B2Less discomfortMinimally invasiveInternal osteosythesisCannulasSpinal columnSacrum
Methods and apparatus for providing percutaneous access to vertebrae in alignment with a visualized, trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) line in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner are disclosed. A number of related TASIF methods and surgical tool sets are provided by the present invention that are employed to form a percutaneous pathway from an anterior or posterior skin incision to a respective anterior or posterior target point of a sacral surface. The percutaneous pathway is generally axially aligned with an anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line extending from the respective anterior or posterior target point through at least one sacral vertebral body and one or more lumbar vertebral bodies in the cephalad direction. The provision of the percutaneous pathway described herein allows for the formation of the anterior or posterior TASIF bore(s) and / or the introduction of spinal implants and instruments.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
Cervical Intervertebral Disc Prosthesis Comprising An Anti-Dislocation Device And Instruments
InactiveUS20080027550A1Easily advancedImprove connection reliabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsUnintended MovementSpinal column
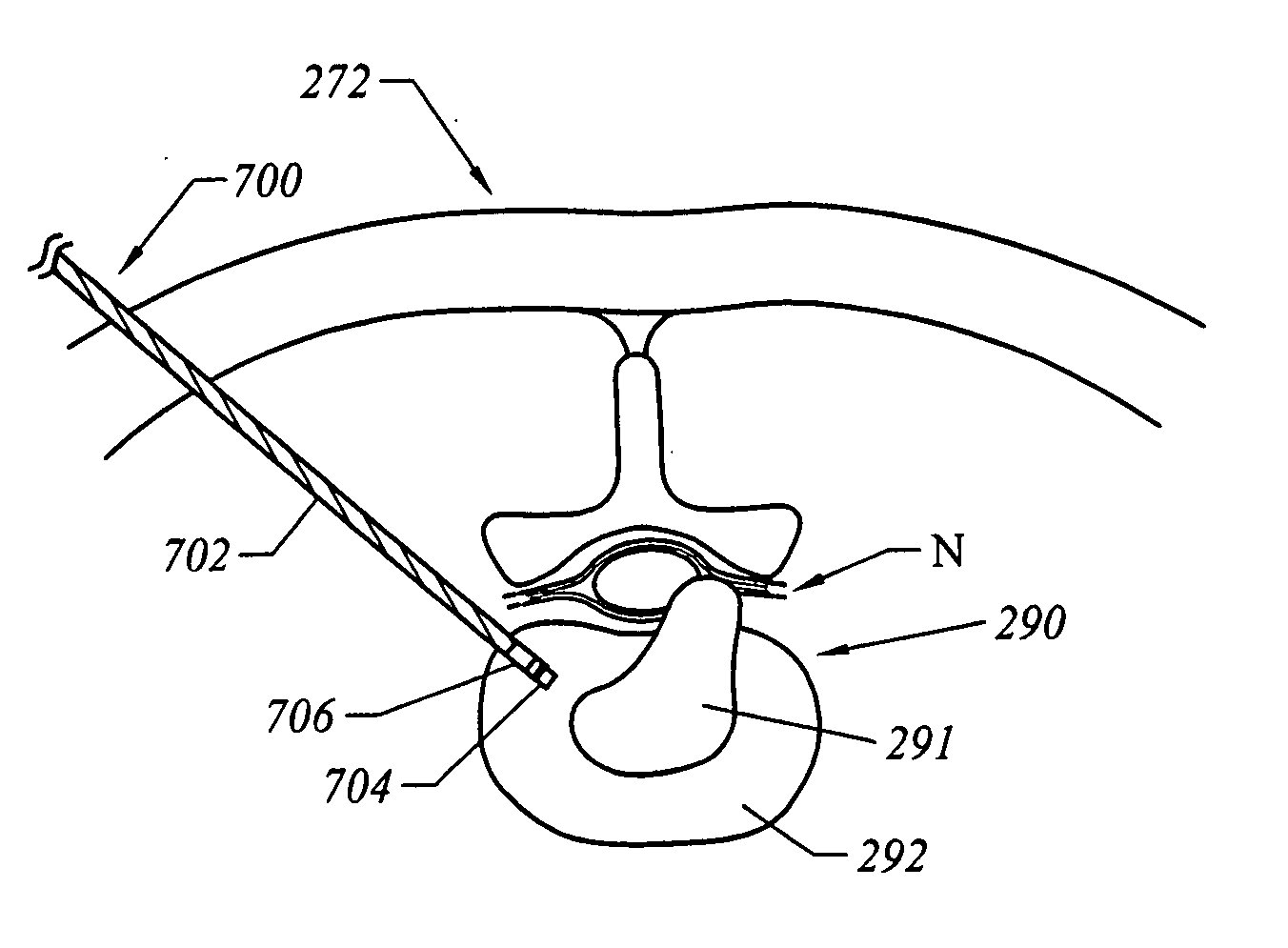
A cervical intervertebral prosthesis includes lower and upper anchoring plates with a prosthesis core arranged between them to create an articulated connection. The anchoring plates are designed to bear with their anchoring plate surfaces on adjacent vertebral bodies. At least one anchoring plate surface has a rib-like projection thereon which can be used to engage in the vertebral body with a form fit. In order to produce a corresponding recess in the vertebral body, an instrument having a handle, a stem, a head part and an excavating element that can be retracted into the head part may be used. This permits considerably improved securing of the cervical intervertebral prosthesis against unintended movement. The medullary canal running along the posterior margin of the vertebral column is in this way protected from damage.
Owner:CERVITECH INC
Bi-directional fixating transvertebral body screws and posterior cervical and lumbar interarticulating joint calibrated stapling devices for spinal fusion
ActiveUS7942903B2Traversing and exciting nerve rootsSame functionInternal osteosythesisBone implantCervical facet jointsLumbar vertebrae
Owner:MOSKOWITZ FAMILY LLC
Artificial spinal unit assemblies
ActiveUS7909869B2Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSurgical operation
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Apparatus for anterior intervertebral spinal fixation and fusion
Owner:INT SPINAL INNOVATIONS +2
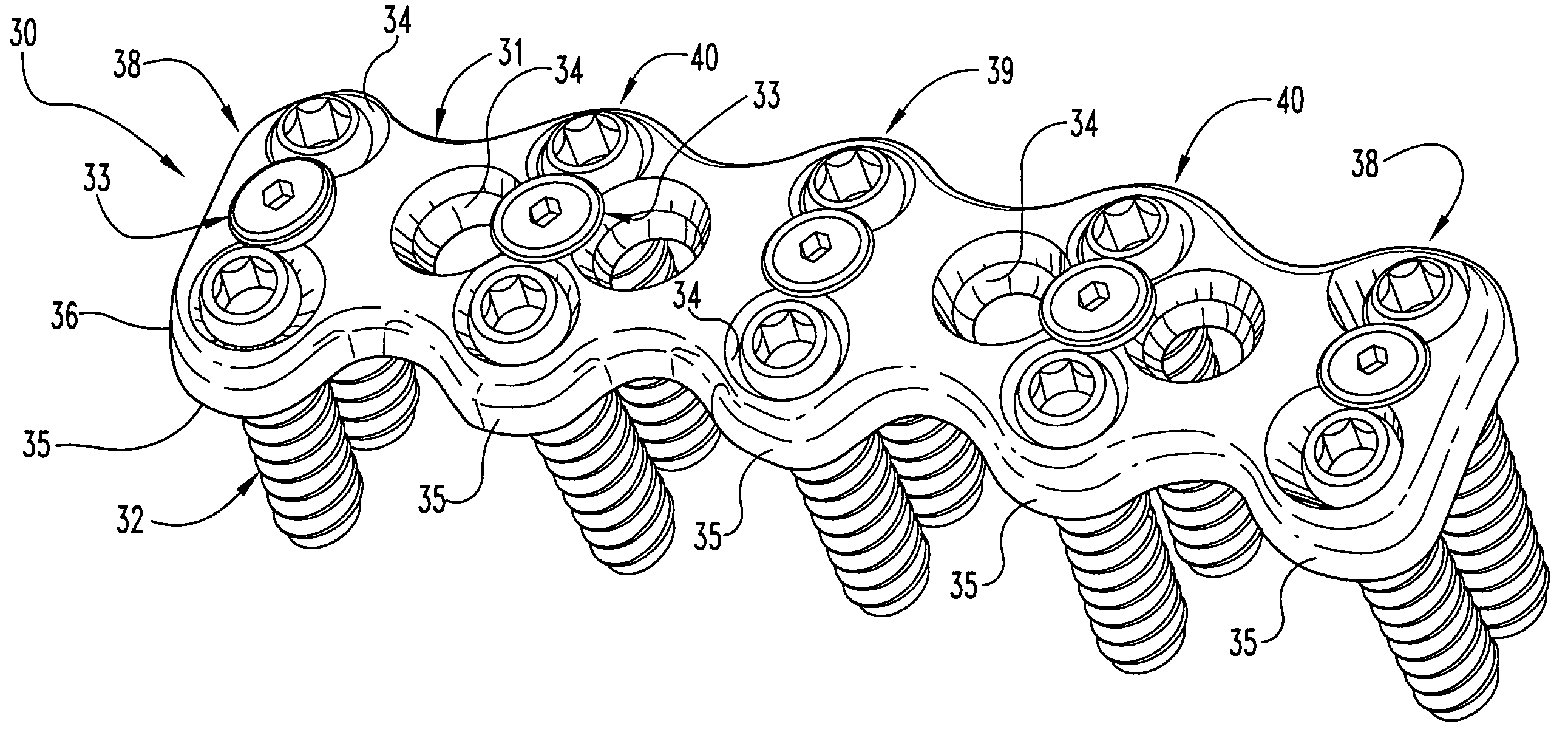
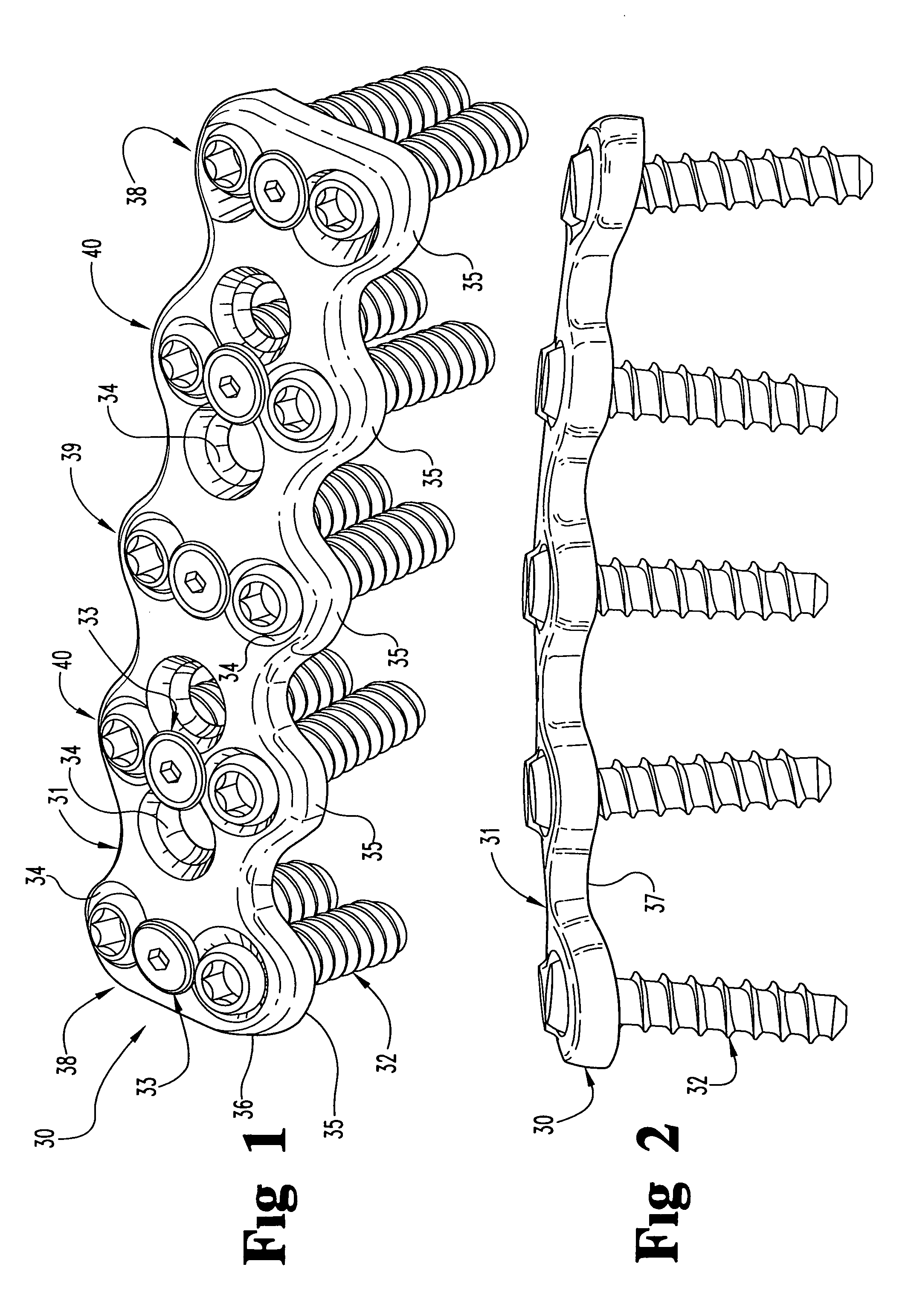
Flanged interbody fusion device with locking plate
InactiveUS20060235403A1Little strengthInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral spaceBiomedical engineering
Methods and devices are disclosed for treating the vertebral column. An integrated fixation plate and spacer having a retaining structure within the screw holes of the fixation plate to resist backout of screws attaching the fixation plate to the bone is provided. A movable joint may be provided between the fixation plate and spacer. In some embodiments, a screw hole insert is also provided to resist shear forces acting between the screw and fixation plate. In some embodiments, an integrated fixation plate and spacer system is provided, comprising two or more integrated fixation plate and spacer implants, wherein the fixation plates of each implant has a complementary configuration to allow attachment of the implants at adjacent intervertebral spaces. Alternative fixation systems are also contemplated.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Vertebral fixing system
InactiveUS7481828B2Avoid displacementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRelative displacementOrthodontic ligature
The present invention relates to a vertebral fixing system adapted to be mounted on a vertebra of the spine to connect it to a rod. The fixing system comprises: a connecting part adapted to face the rib and / or the transverse process and to be connected to the rod; an elongate flexible ligature adapted to connect together the connecting part and at least one rib and / or one transverse process; and an adjustable locking screw fastened to the connecting part and adapted to fix simultaneously in position the connecting part relative to the rod and at least one portion of the ligature relative to the connecting part, so as to prevent relative displacement of the rod and the vertebra in opposite directions.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE SAS
Implant and method for facet immobilization
ActiveUS20090264928A1Reduce relative motionRestores motionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisAdhesiveSacroiliac joint
Devices and methods are provided for immobilizing facet joints of the vertebral column. Embodiments of the invention provide an implant that is inserted in a facet joint from which cartilage has been removed, and which retains the approximate original spacing of the facets in the joint. A retaining arrangement, such as an adhesive, a threaded fastener, or a screw is then used to secure the implant in the joint.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
System and method for a spinal implant locking assembly
Provided are a system and method for a spinal implant locking assembly. In one example, the system includes a bone anchor, a polyaxial head coupled to a proximal end of the bone anchor, a spinal implant, and a locking assembly. The locking assembly may have a bearing post with a distal portion coupled to the polyaxial head and a proximal portion that extends through an opening in the spinal implant. The locking assembly may also have a bushing, a bearing element, and a threaded locking member. The threaded locking member may be configured to rotationally engage a threaded surface on at least one of the bearing post and the bushing.
Owner:THEKEN SPINE
Split ring bone screw for a spinal fixation system
InactiveUS6887242B2Corrected satisfactorilyLess-expensiveSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnSplit ring
An adjustable spinal fixation system is composed of a collection of anchoring assemblies attached, via a variety of connectors, to spine-stabilizing rods. The anchoring assemblies include a linking member attached in a ball-and-socket fashion to a bone-engaging member that is adapted to engage a spinal bone of a patient. The linking member joins one of the included connectors to an associated bone-engaging member. The connectors are selectively attached to one of the stabilizing rods. The anchoring assemblies each include a support collar and a split retention ring that cooperate to allow adjustment of the bone-engaging member and corresponding connector during surgery. When surgery is complete, a securing nut and locking bolt cooperate with the support collar and split retention ring to maintain the relative position of the entire fixation system, preventing unwanted movement between the system components.
Owner:MULLANE THOMAS
Flanged interbody fusion device
Methods and devices are disclosed for treating the vertebral column. An implant for treating the spine is provided comprising at least two articulations between the spacer and the bone facing surface of the fixation plate. Another implant for treating the spine is also provided, comprising two or more fixation plates attached to a spacer with two or more articulations, wherein the fixation plates are independently movable.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
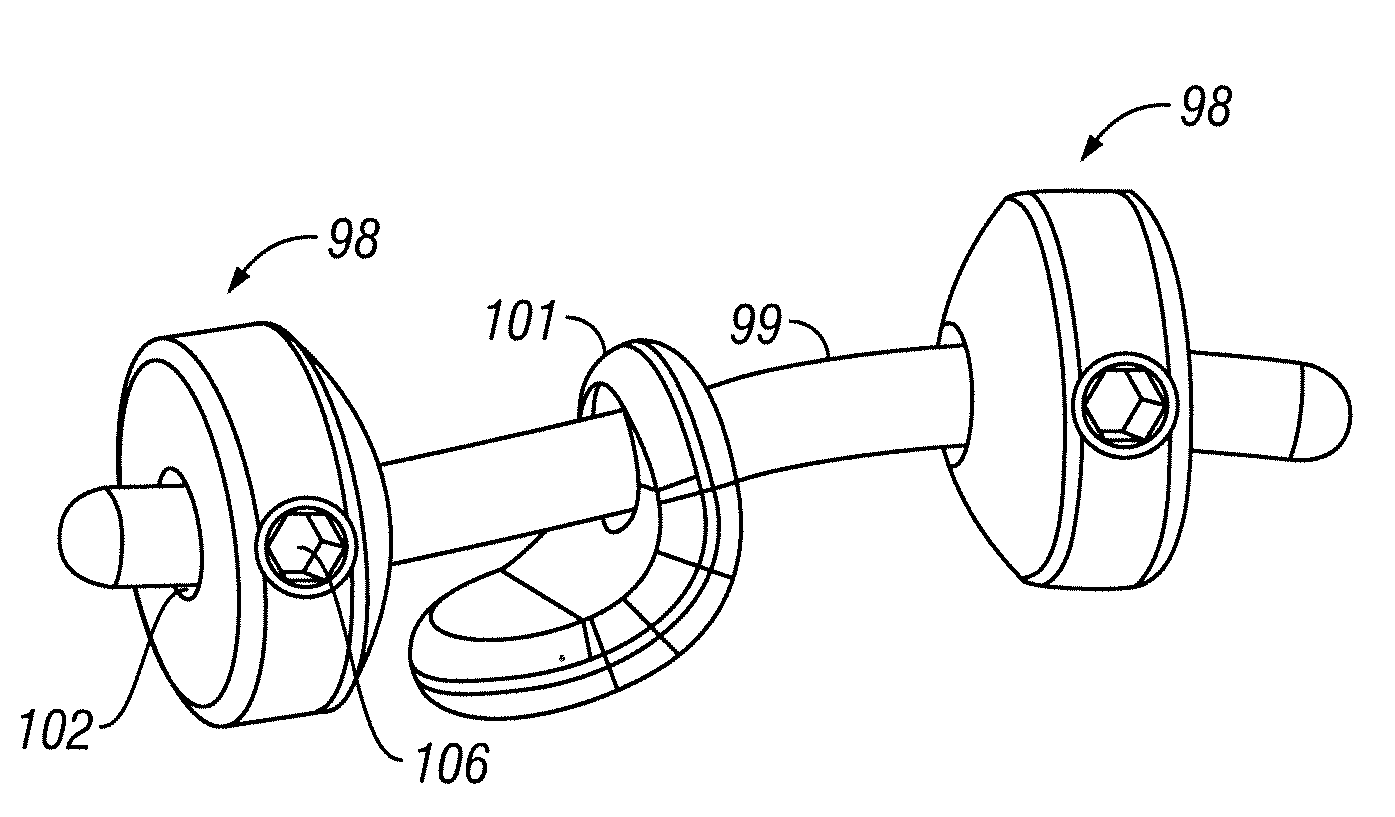
Adjustable spinal tether
An improved apparatus is provided to allow for an adjustable length tether for use in the spine and other parts of the body. The tether comprises an artificial strand with an eyelet formed in one end, the other end being looped through the eyelet. The other end is then secured with respect to the eyelet by a crimp, the excess length being cut off after the length of the tether has been given an appropriate tension. Alternatively, the eyelet end may be formed around a grommet. The crimp may be separate from the grommet or a part of the grommet. The mechanism by which the length is adjusted in some cases will take advantage of the shape memory properties of alloys such as nickel-titanium.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Instrument system for preparing a disc space between adjacent vertebral bodies to receive a repair device
InactiveUS7153304B2Restores natural lordosisInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSpinal columnLamina terminalis
An instrument system for preparing a disc space between adjacent vertebral bodies to receive a repair device includes a series of distractors for distracting the vertebral bodies in a manner that restores natural lordosis of the lumbar and cervical spine, a vertebrae immobilizing template to fix the positions of the bodies, a handle for employing the distractor and the template, and a reamer for cutting tissue from endplates of the vertebral bodies.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Spinal fusion implant and related methods
ActiveUS7867277B1Increase contactAvoids dural impingementBone implantJoint implantsIntervertebral discMedicine
A spinal fusion implant of non-bone construction to be introduced into any variety of spinal target sites. The spinal fusion implant of the present invention includes a top surface, a bottom surface, first and second lateral sides, a proximal (posterior) end and a distal (anterior) end. The spinal fusion implant of the present invention may be used to provide temporary or permanent fixation within an orthopedic target site. To do so, the spinal fusion implant may be introduced into a disc space while locked to a surgical insertion instrument and thereafter employed in the proper orientation and released. Once deposited in the disc space, the spinal fusion implant of the present invention effects spinal fusion over time as the natural healing process integrates and binds the implant.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Spinal osteosynthesis system for anterior fixation
InactiveUS7008423B2Easy to installImprove system stabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsIliac screwBiomedical engineering
The invention concerns a backbone osteosynthesis system comprising an elongated element, a vertebral screw, and a connecting element comprising two branches for clamping between them the linking element, at least one first branch being capable of being engaged onto the screw. The system comprises a second vertebral screw, the first branch having an extension capable of being engaged onto the second screw. The system may comprise a second elongated linking element.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Anterior cervical plating system
In one embodiment of the invention, an anterior fixation system includes a plate defining a plurality of screw holes, a number of screws and a number of locking assemblies for fixing the screws to the plate. The system includes two bone screws a fixed angle screw and a variable angle screw, that are configured to extend through the same screw openings in the fixation plate. The surgeon can select either the fixed or variable angled screws to be implanted with a single plate and can place either type of screw into any of the screw holes along the plate. The fixation plate according to the invention can include several screw holes in various patterns that provide the surgeon with great flexibility in the placement of bone screws depending upon the spinal anatomy and pathology. The invention further contemplates a locking assembly to lock one or more bone screws within a respective screw hole. In one embodiment, the locking assembly includes a washer that is held to the plate by a staked locking screw. The washer includes an outer surface that overlaps one or more screw holes. The washer is initially loosely held to the plate by the locking screw so that various tools and bone screws can be passed through the screw holes. In one embodiment of the washer, the washer includes cut-outs corresponding to the screw holes, along with a notch and key configuration for setting the locking washer in its locked configuration.
Owner:SDGI HLDG
Vertebral fixation device for the treatment of spondylolisthesis
The invention relates to a vertebral fixation device for the treatment of spinal conditions and more specifically spondylolisthesis. The inventive device comprises a screw (1) which is intended to be fixed to a bone and a tulip element (2) comprising vertical notches (3) in which a bar (4) moves vertically, the bar forming the connection between screws (1) belonging to other devices. The position of the aforementioned bar (4) is adjusted in relation to the bone using a support nut (15). Moreover, the bar (4) rests on the upper face of the support nut (15), such that the rotation of the nut (15) determines the vertical displacement of the bar (4) in relation to the bone, the bar remaining fixed in position by the closing screw (5). The invention further comprises a rosette element (8) having an inner housing which is used to house the head of the screw (1) in such a way that the head, and consequently the screw (1), remain connected to the tulip (2).
Owner:TRAIBER
Vertebral body replacement device and method for use to maintain a space between two vertebral bodies within a spine
ActiveUS20090112324A1Lengthened and shortenedIncrease spacingInternal osteosythesisBone implantEngineeringScrew thread
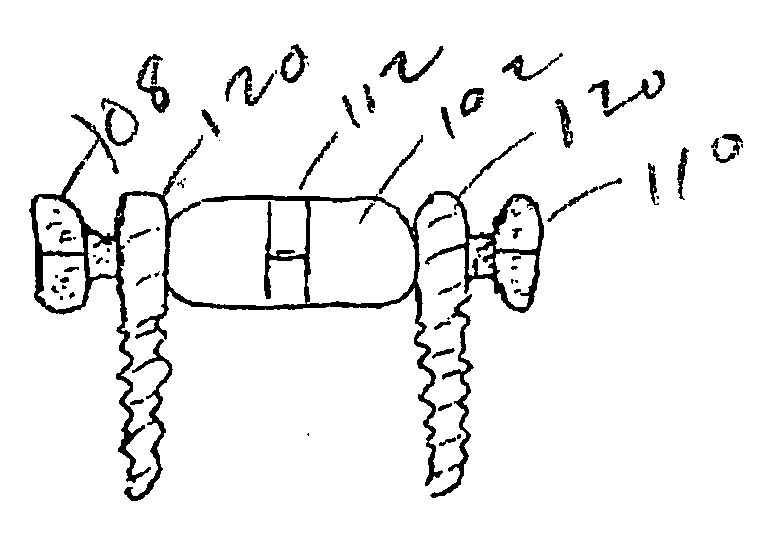
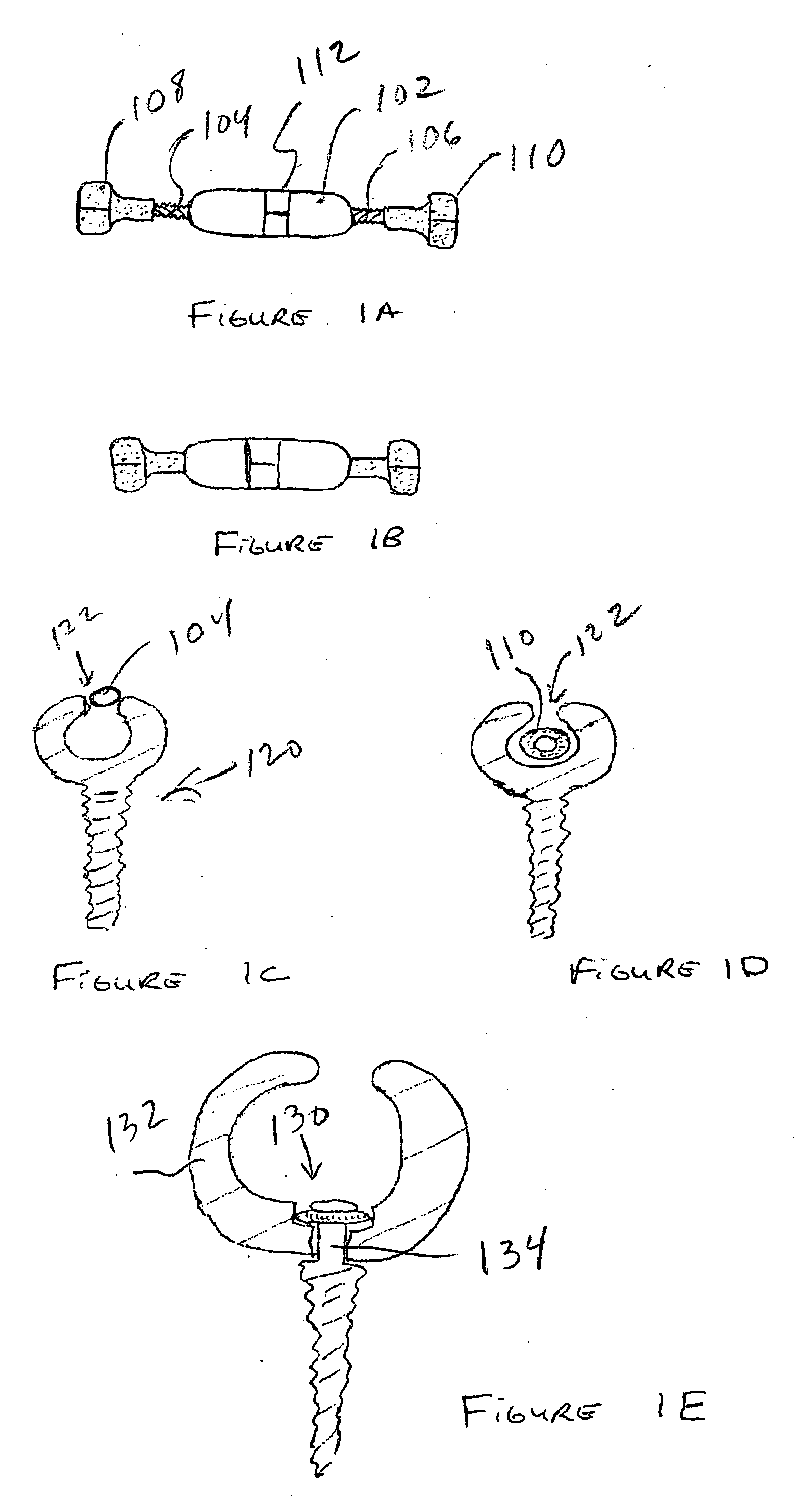
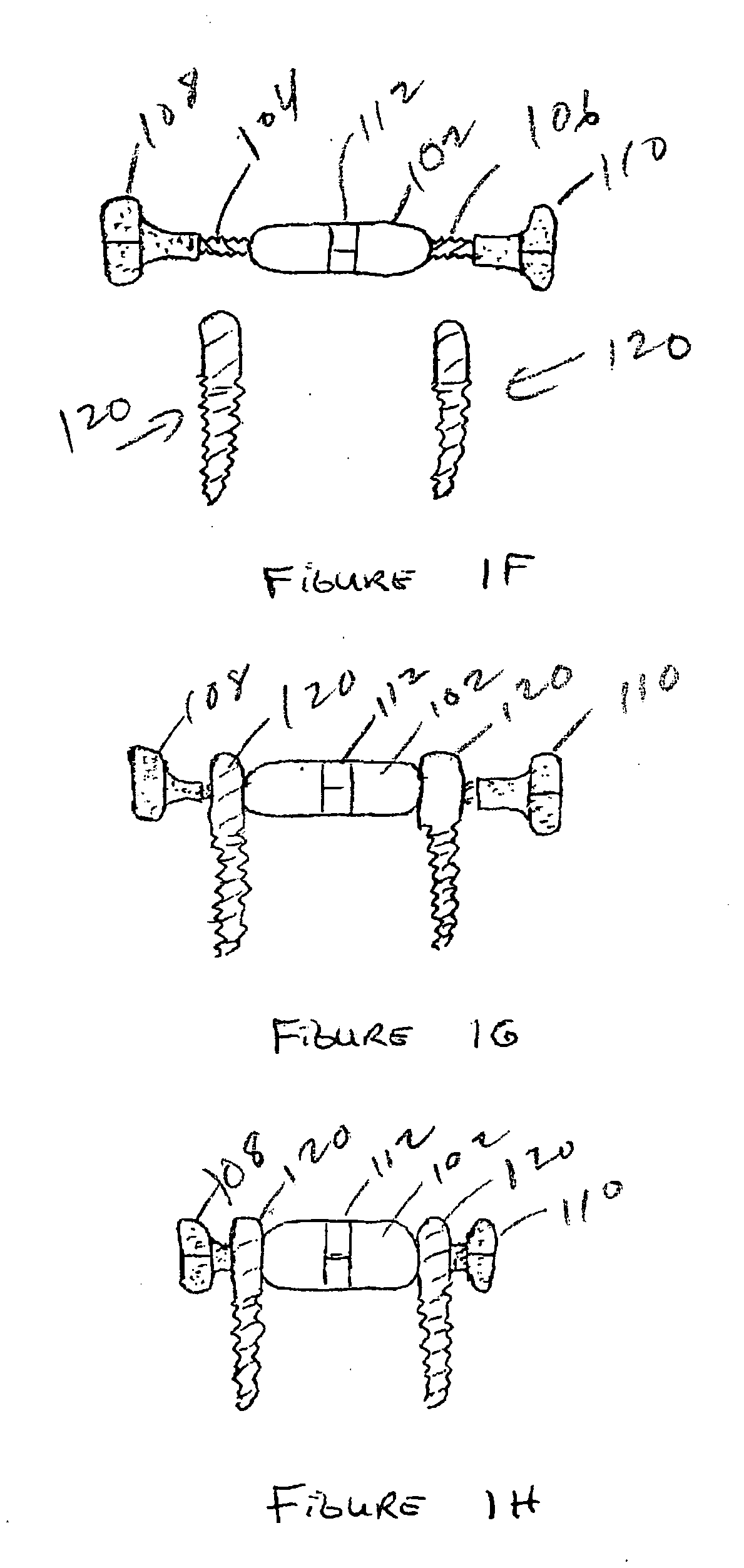
The vertebral body replacement device includes a body member and a central rod member that has two threaded portions and is configured to be operatively associated with the body member. The device also includes a first end member and a second end member with the end members being configured to threadingly engage the threaded portions of the central rod member. The body member and the two end members are further constructed to inhibit rotational movement of the two end members when the device is positioned within a space within a spine as the two end members will engage the adjacent respective vertebral bodies following rotational actuation of the central rod member causing the end members to move in an axial direction relative to the body member, thereby allowing the two end members to apply a force to the two vertebral bodies. A surgical method using the device is also disclosed.
Owner:AESCULAP IMPLANT SYST
Magnetic spinal implant device
InactiveUS20070179493A1Turn fasterRapidly offInternal osteosythesisBone implantMagnetic tension forceSpinal implant
A magnetic spinal implant device is disclosed. In one embodiment, the device includes: a first piece configured to be implanted into a patient and coupled to the patient's spine, wherein the first piece includes a recessed portion; a first magnet coupled to the first piece; a second piece configured to be implanted into the patient and juxtaposed with the first piece, wherein the second piece includes a base portion surrounding a raised portion, wherein the raised portion is configured to be at least partially received within the recessed portion of the first piece so as to facilitate alignment of the first and second pieces; and a second magnet coupled to the second piece, wherein the first magnet exerts a desired magnetic force on the second magnet.
Owner:KIM RICHARD C
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com