Patents
Literature
973 results about "Ligament structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Peritoneal ligament: a fold of peritoneum or other membranes. Fetal remnant ligament: the remnants of a fetal tubular structure. Periodontal ligament: a group of fibers that attach the cementum of teeth to the surrounding alveolar bone.
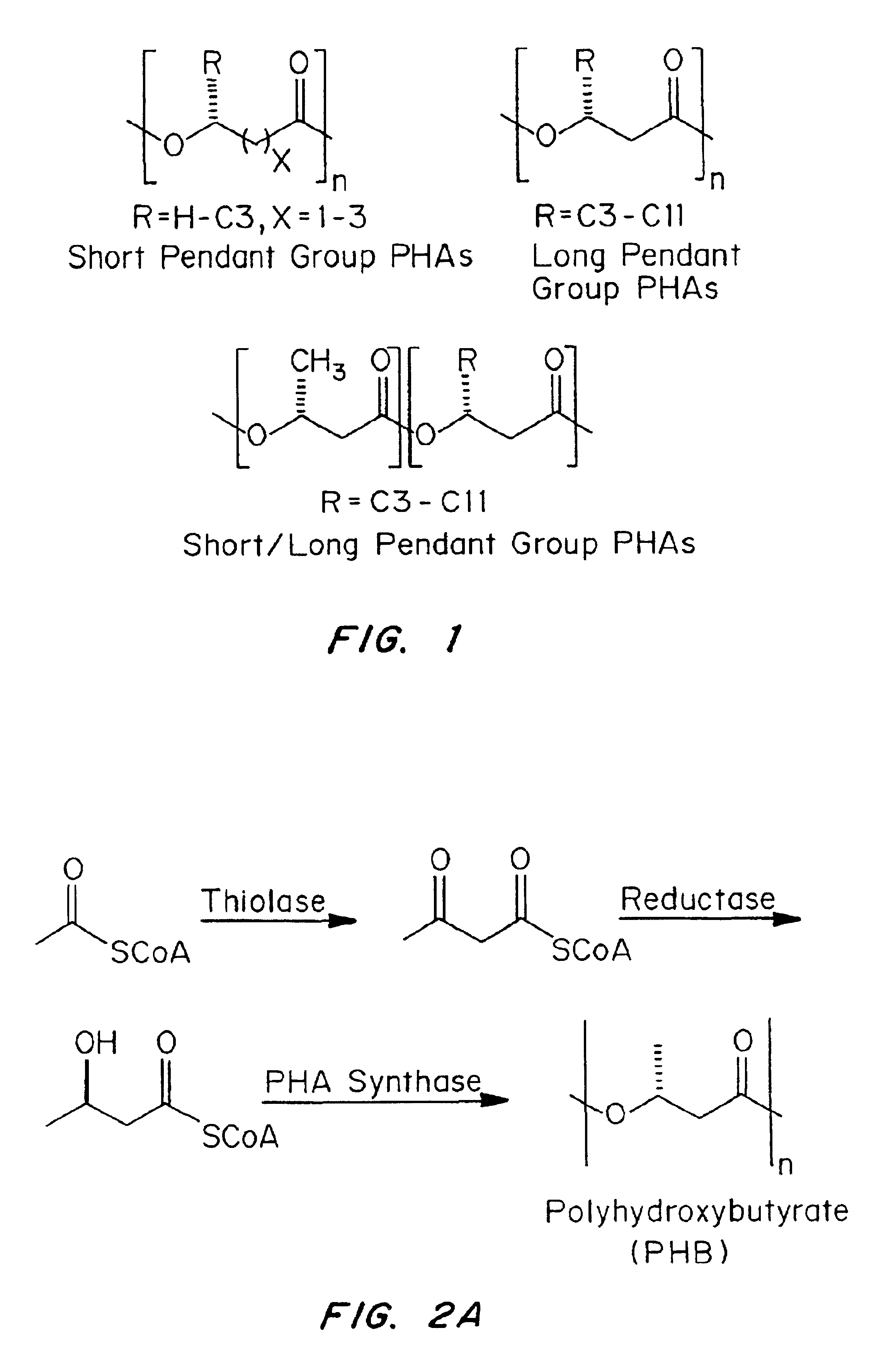
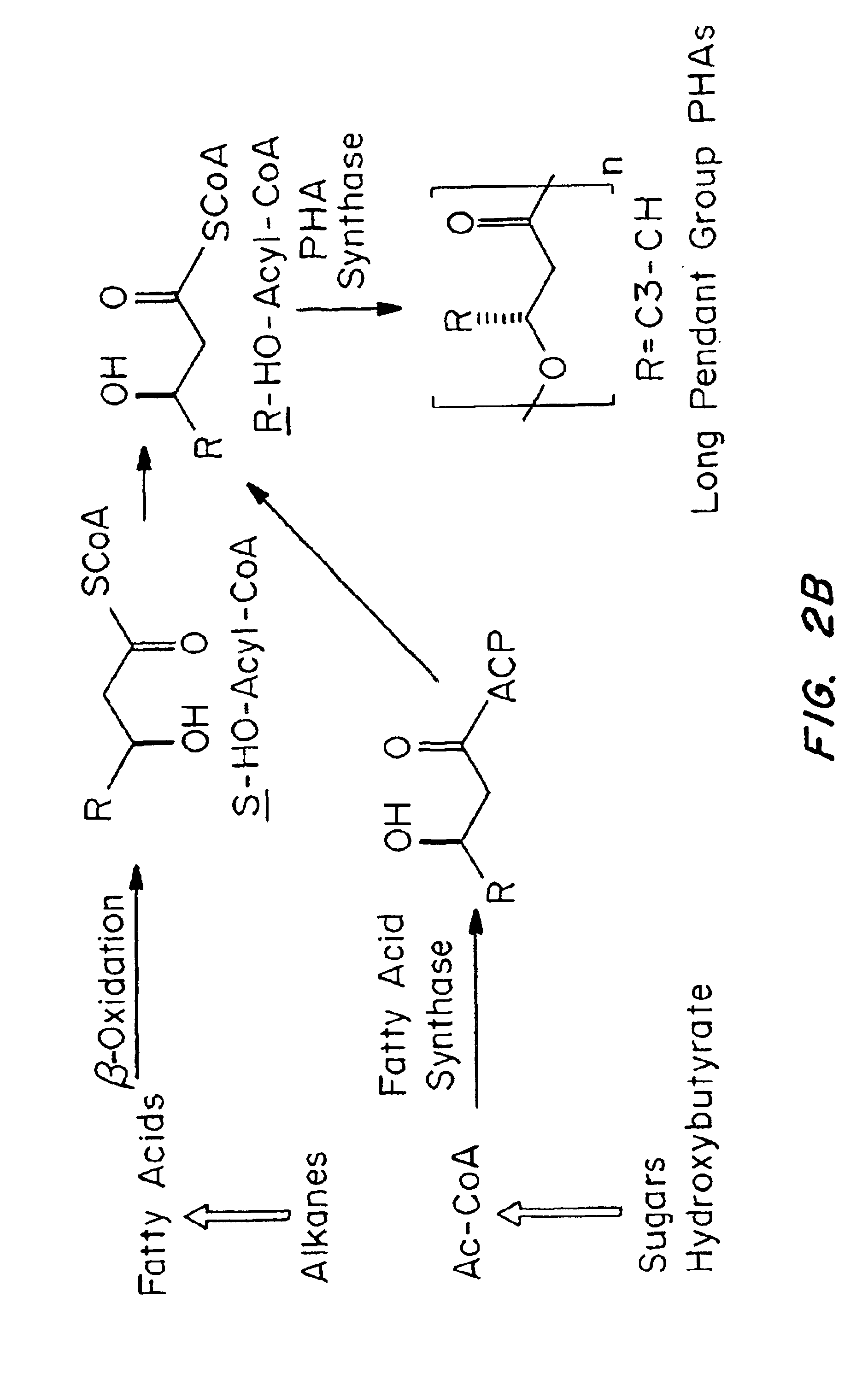
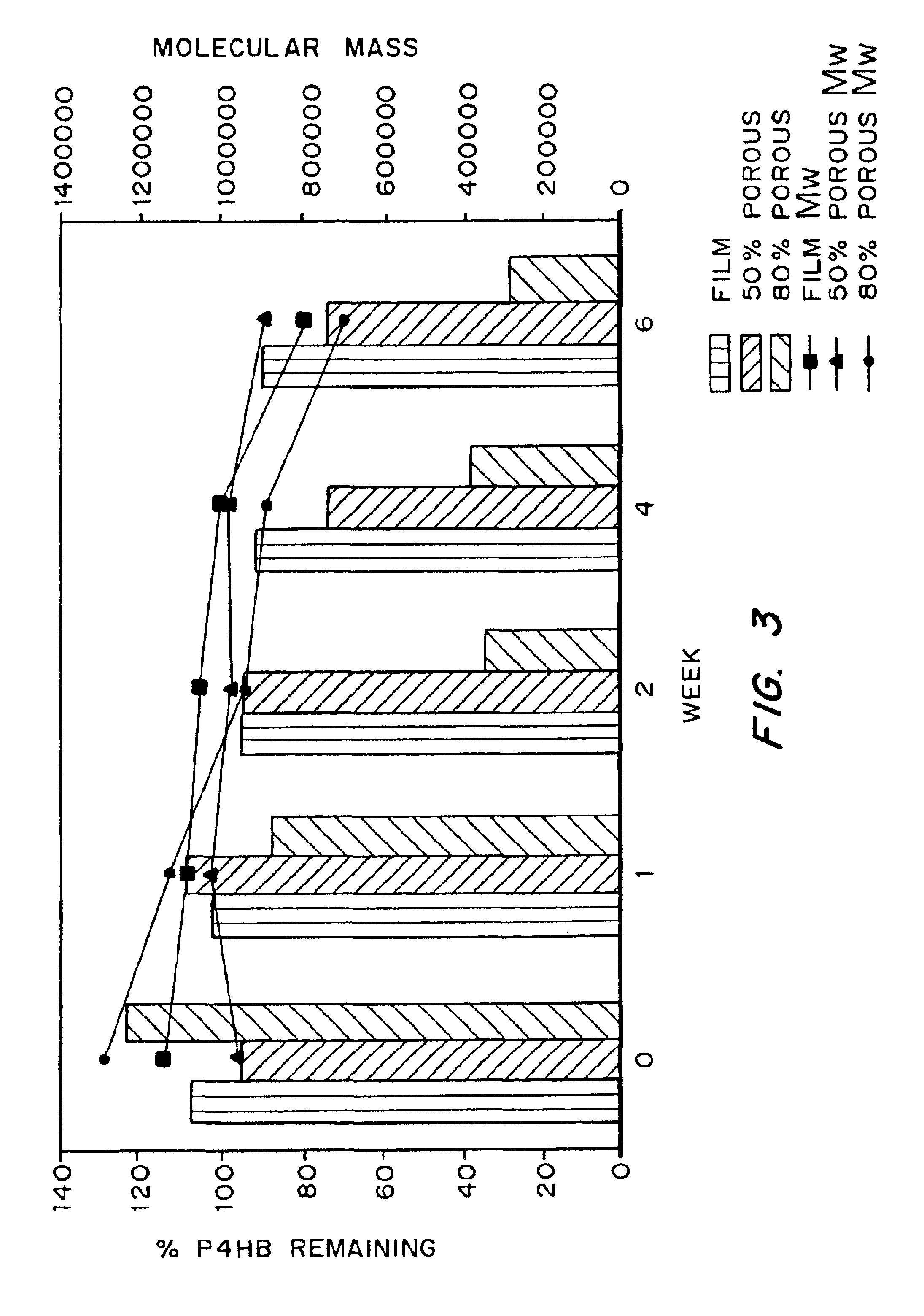
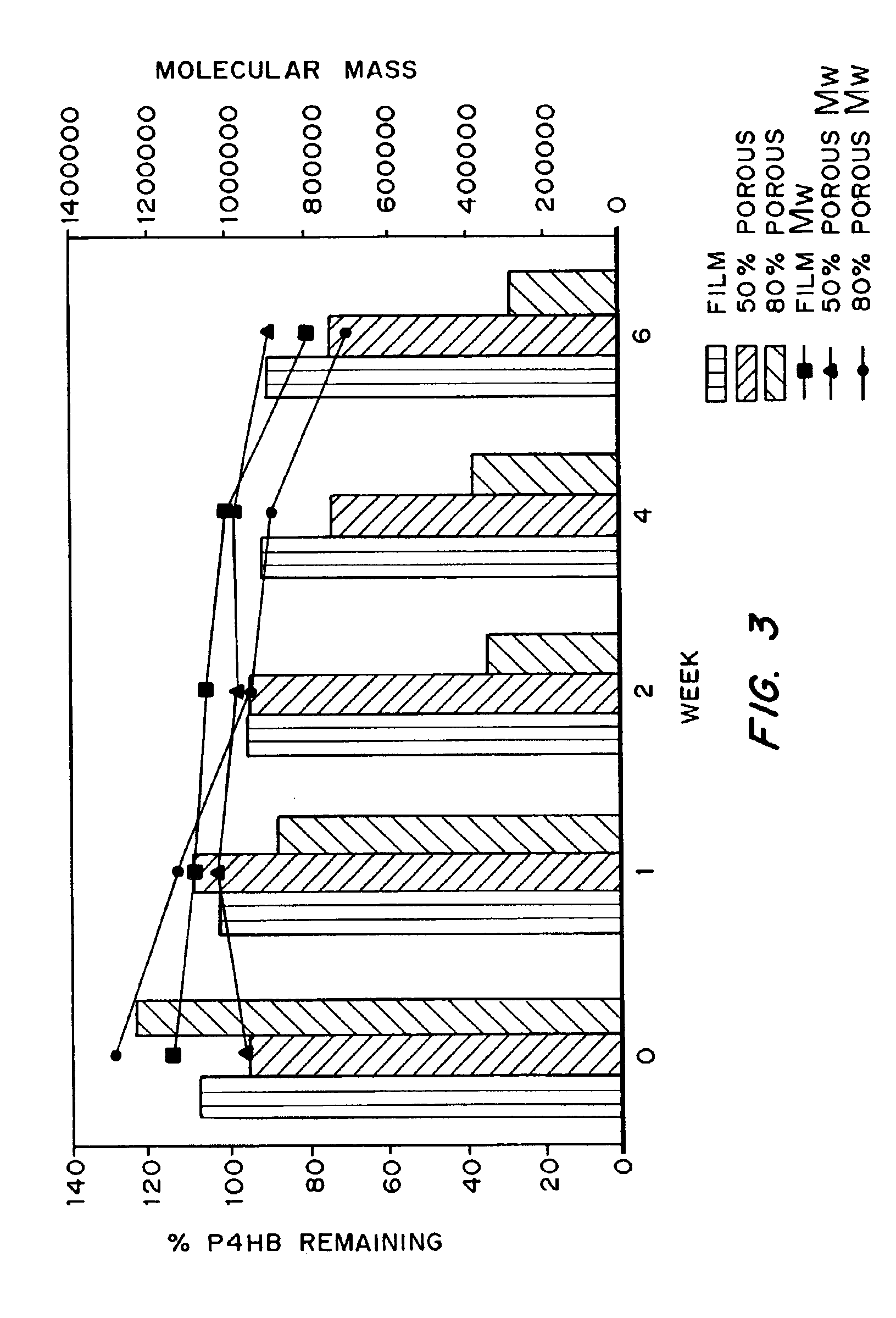
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
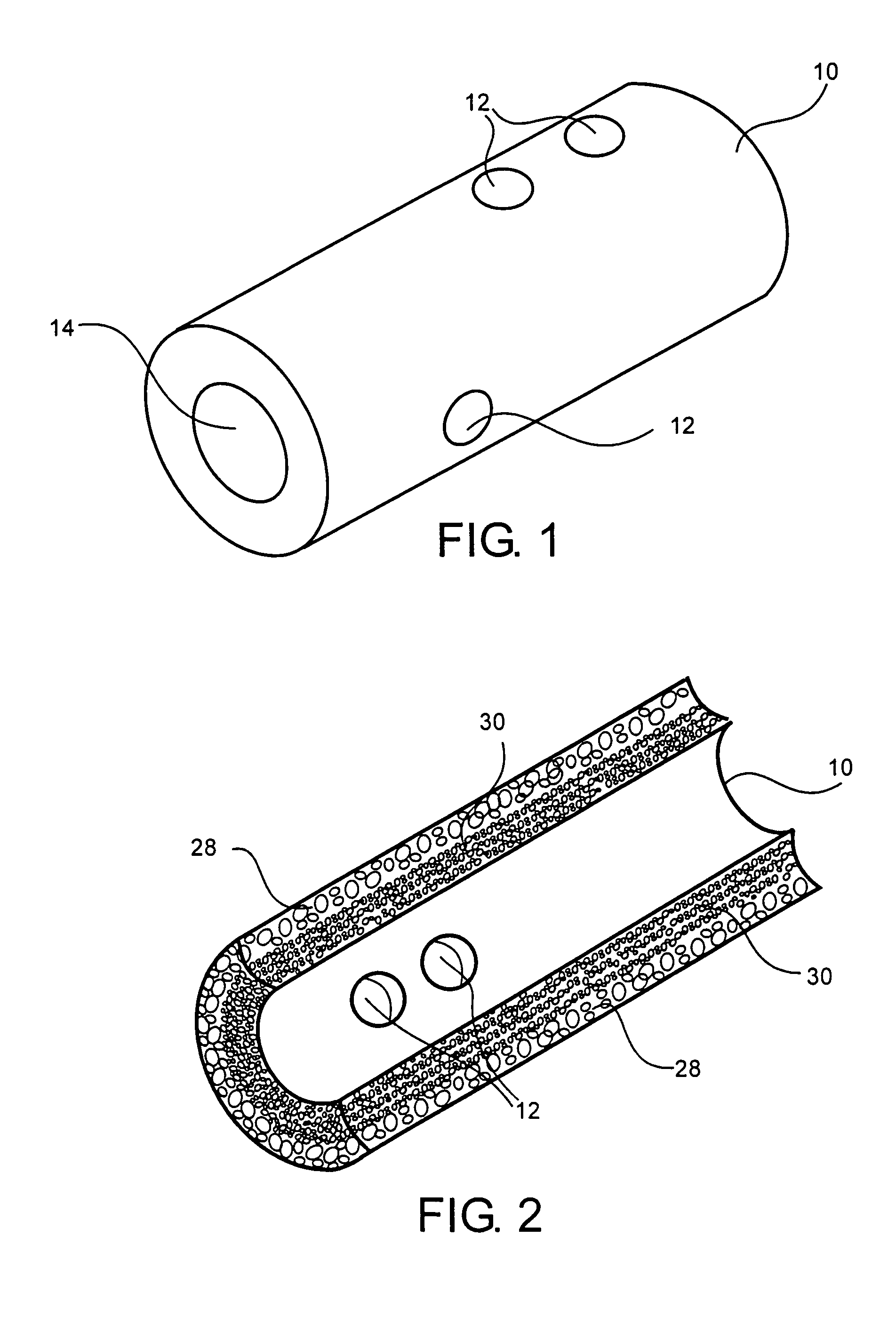
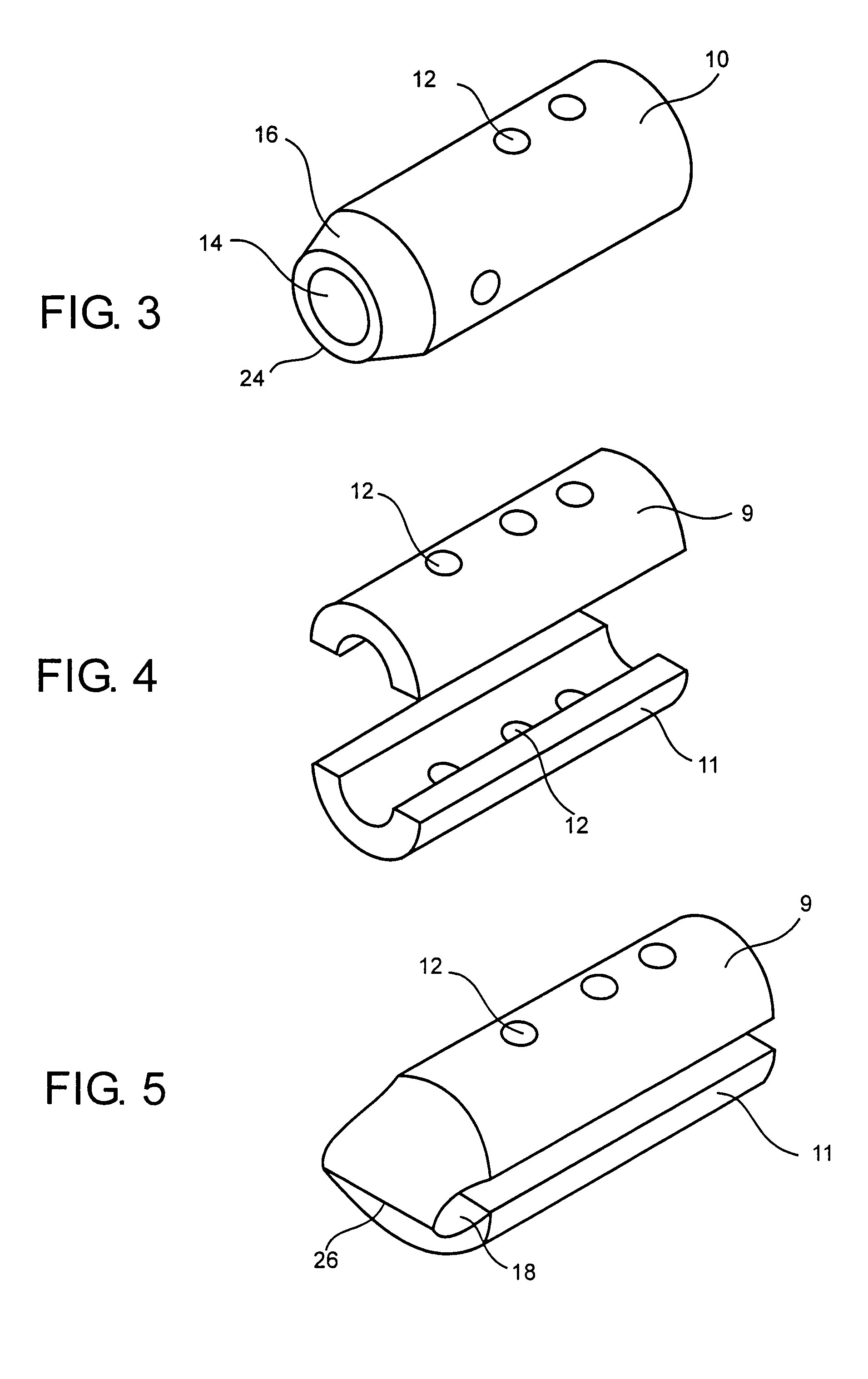
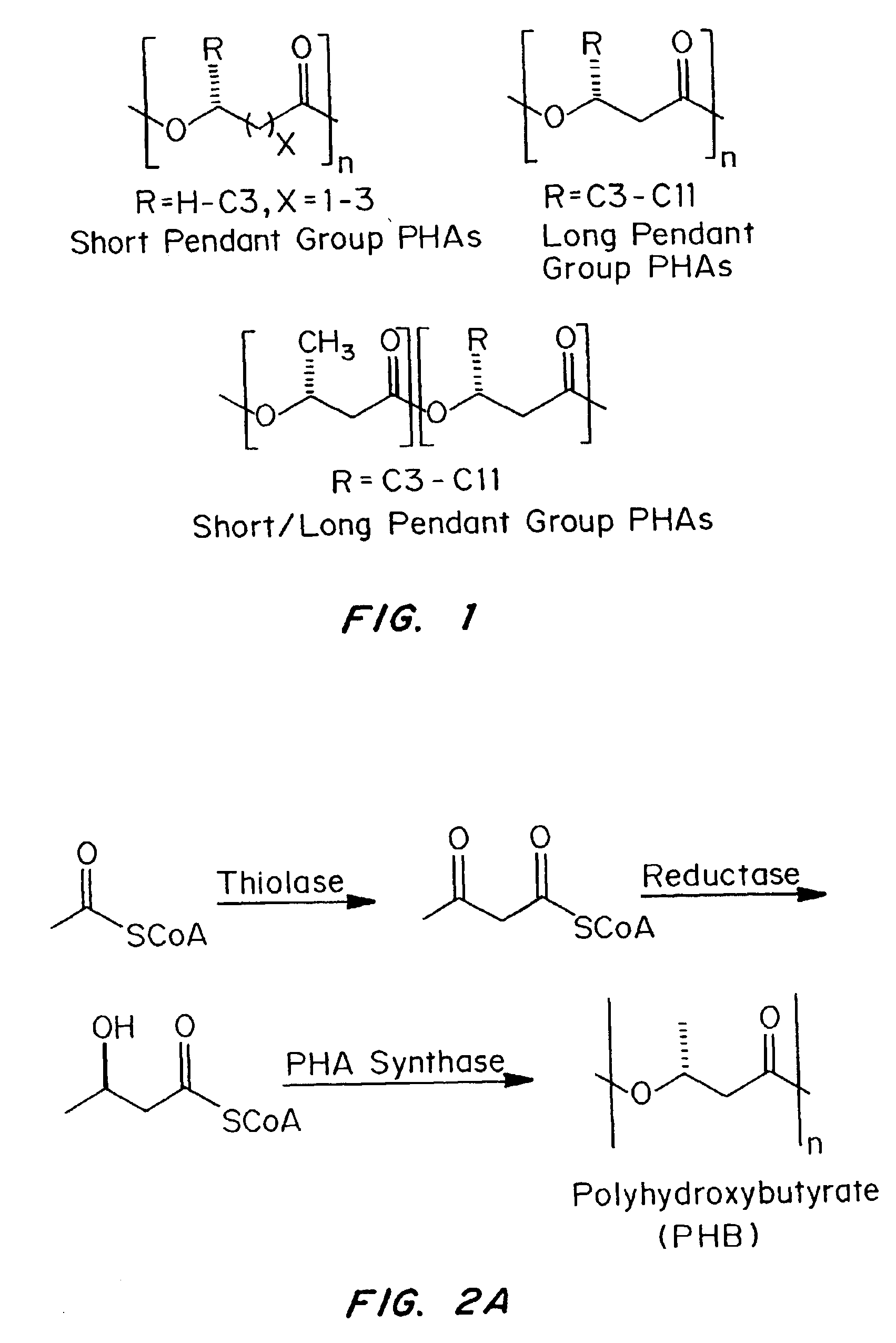
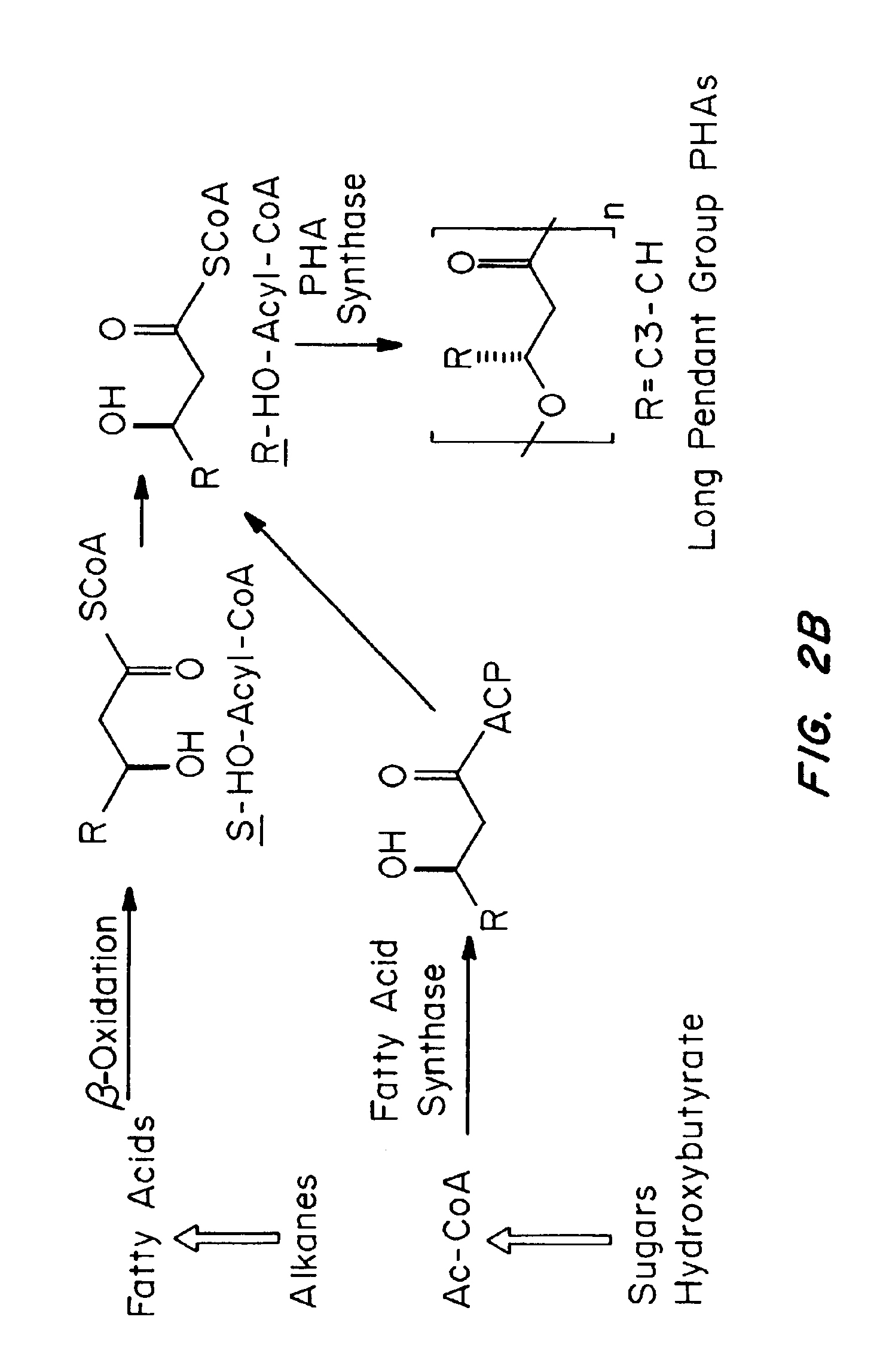
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
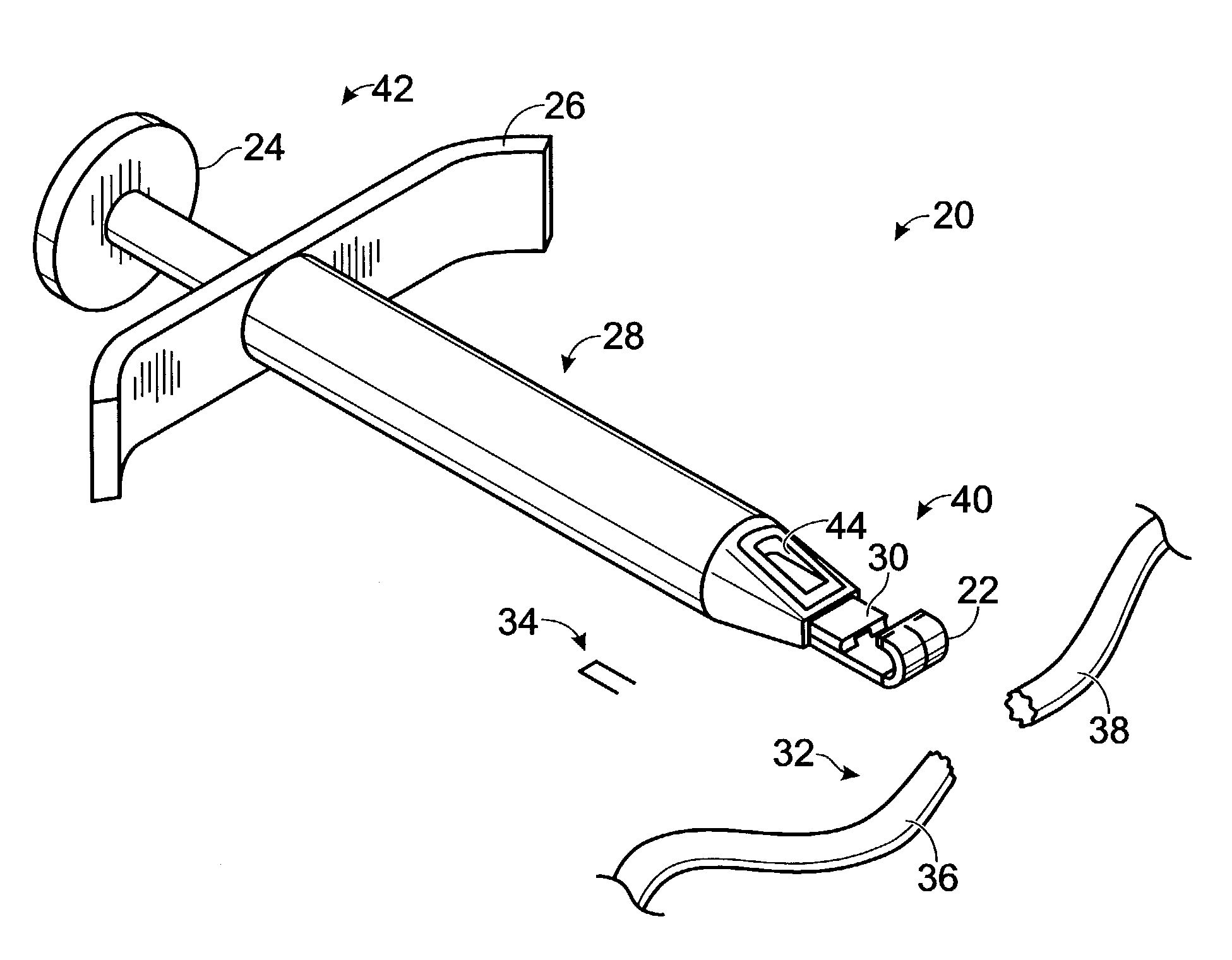
Connective tissue repair system
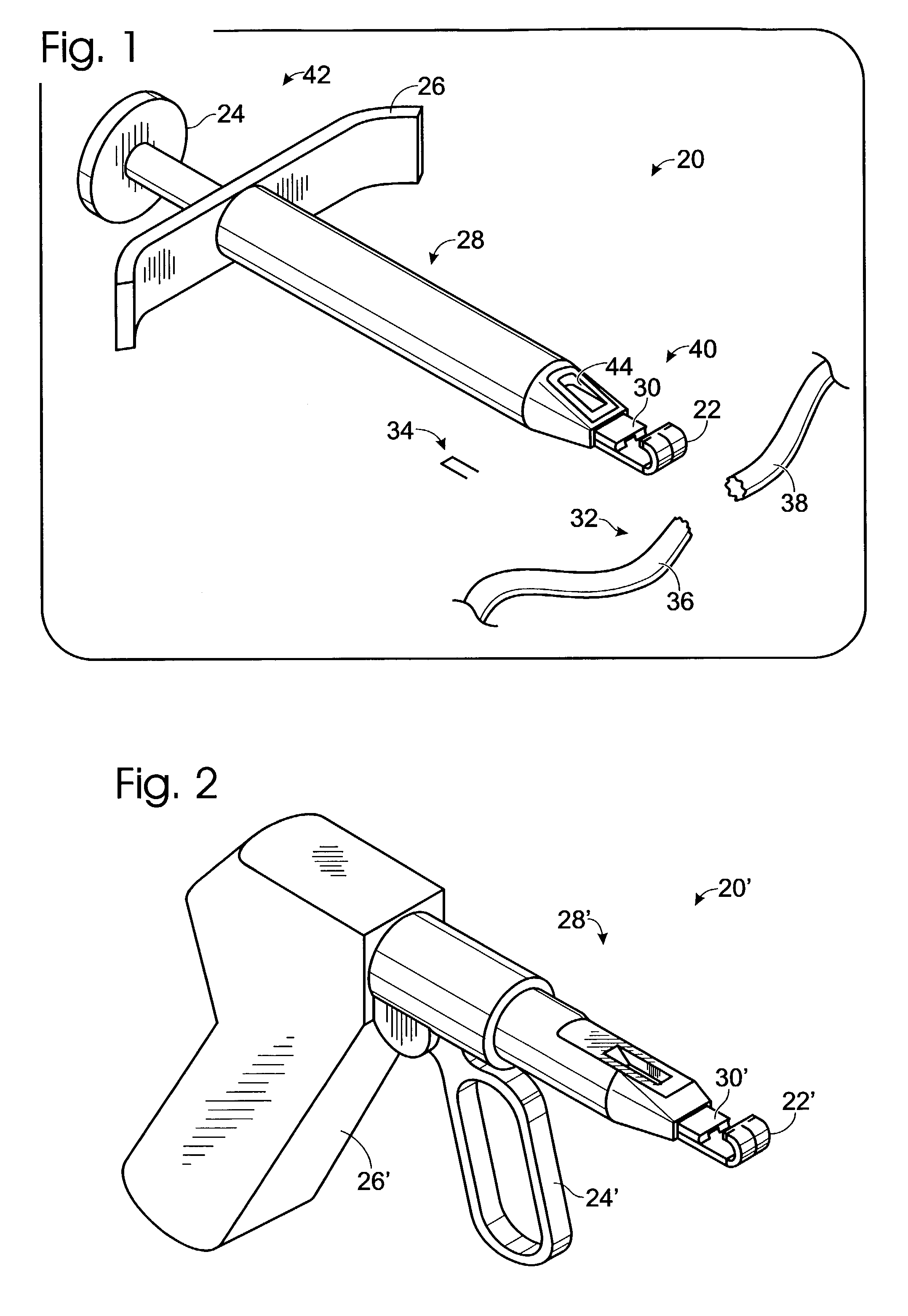
Systems, including apparatus and methods, for repairing injured connective tissue. These systems may include, among others, a surgical stapler and staples for repairing partially or completely severed tendons and / or ligaments.
Owner:ACUMED
Ligament fixing system
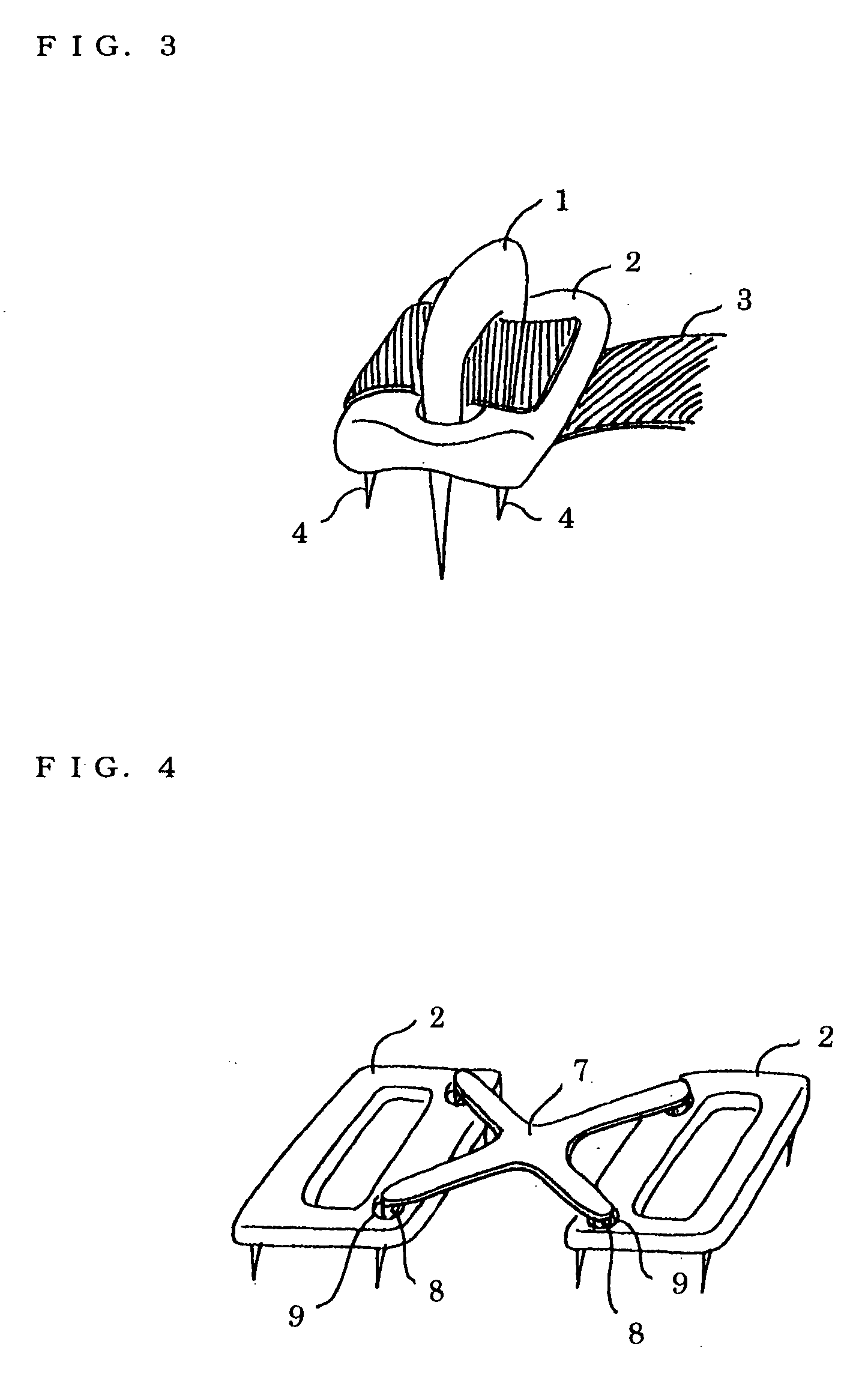
An inexpensive ligament fixing system capable of providing an efficient fixing force and accurately driving a staple with less invasion, comprising a flat-shaped plate having a plurality of drilled holes and curved bottom and upper surfaces and formed by casting and a cross bar used to allow a parallelism, to be checked, wherein the plate is fixed to a ligament and the folded-up ligament is further fixed with the staple, the tips of the leg parts of the staple are moved from the centerline to the inside, a cut-in is provided on the insides of the leg parts, the cross sections of the leg parts are formed in a polyhedron, the plate is pressed and driven by a driving device having a driving structure by a thrust bar is used.
Owner:KOSEKI TOMOAKI
Use of reinforced foam implants with enhanced integrity for soft tissue repair and regeneration
A biocompatible tissue repair stimulating implant or "scaffold" device is used to repair tissue injuries, particularly injuries to ligaments, tendons, and nerves. Such implants are especially useful in methods that involve surgical procedures to repair injuries to ligament, tendon, and nerve tissue in the hand and foot. The repair procedures may be conducted with implants that contain a biological component that assists in healing or tissue repair.
Owner:DEPUY MITEK INC
Collagen biofabric and methods of preparation and use therefor
InactiveUS20040048796A1Improved biophysical propertyImprove featuresSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgical GraftWound dressing
The present invention relates to collagenous membranes produced from amnion, herein referred to as a collagen biofabric. The collagen biofabric of the invention has the structural integrity of the native non-treated amniotic membrane, i.e., the native tertiary and quaternary structure. The present invention provides a method for preparing a collagen biofabric from a placental membrane, preferably a human placental membrane having a chorionic and amniotic membrane, by decellularizing the amniotic membrane. In a preferred embodiment, the amniotic membrane is completely decellularized. The collagen biofabric of the invention has numerous utilities in the medical and surgical field including for example, blood vessel repair, construction and replacement of a blood vessel, tendon and ligament replacement, wound-dressing, surgical grafts, ophthalmic uses, sutures, and others. The benefits of the biofabric are, in part, due to its physical properties such as biomechanical strength, flexibility, suturability, and low immunogenicity, particularly when derived from human placenta.
Owner:CELLULAR THERAPEUTICS DIV OF CELGENE +1
Comprehensive tissue attachment system
InactiveUS20050090827A1Precise level of tensionEasy constructionSuture equipmentsLigamentsAnatomical structuresLigament structure
Bone anchors, methods for deploying anchors, and systems for attaching ligaments and tendons to bone are disclosed. The bone anchors of the present invention are operative to remain firmly positioned within a target site of bone and provide means for selectively adjusting the degree of tension to one or more sutures secured thereto. The bone anchors are further operative to be utilized to connect tendons and ligaments directly to bone, as well as may be selectively utilized to adjustably position an implant or other anatomical structure held thereby. There is further disclosed methods for deploying a bone anchor utilizing a blind procedure that is expeditious, accurate and substantially less traumatic than prior art bone deployment techniques.
Owner:GEDEBOU TEWODROS
Three-dimensional culture of pancreatic parenchymal cells cultured living stromal tissue prepared in vitro
InactiveUS6022743AIncrease surface areaIncreased proliferationImmobilised enzymesSurgical needlesLigament structureIn vivo
A stromal cell-based three-dimensional cell culture system is prepared which can be used to culture a variety of different cells and tissues in vitro for prolonged periods of time. The stromal cells and connective tissue proteins naturally secreted by the stromal cells attach to and substantially envelope a framework composed of a biocompatible non-living material formed into a three-dimensional structure having interstitial spaces bridged by the stromal cells. The living stromal tissue so formed provides the support, growth factors, and regulatory factors necessary to sustain long-term active proliferation of cells in culture and / or cultures implanted in vivo. When grown in this three-dimensional system, the proliferating cells mature and segregate properly to form components of adult tissues analogous to counterparts in vivo, which can be utilized in the body as a corrective tissue. For example, and not by way of limitation, the three-dimensional cultures can be used to form tubular tissue structures, like those of the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts, as well as blood vessels; tissues for hernia repair and / or tendons and ligaments; etc.
Owner:REGENEMED
Soft tissue repair devices, systems, and methods
Owner:CONEXTIONS INC
Concave probe for arthroscopic surgery
InactiveUS6135999AElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingThermal energyArthroscopic procedure
Disclosed herein is a new arthroscopic probe with a concave distal tip which simultaneously constrains and cuts tissue. It is particularly adapted to cutting ligaments and tendons. Also disclosed is a thermal energy delivery apparatus which includes (a) a probe means with a distal end and a proximal end, wherein the distal end has a concave tip; (b) a first electrode means positioned at the distal end of the probe means, wherein the first electrode means is configured to deliver sufficient thermal energy to cut ligaments or tendons; and (c) a cabling means coupled to the proximal end of the probe means. In another embodiment of the invention a controller for controlling the delivery of energy and liquid to a surgical instrument with a temperature sensor is disclosed. The energy is supplied by an energy source and the liquid is supplied by a pump. The controller includes a temperature and a flow regulator. The temperature regulator is coupled to the energy source and coupled to the pump. The temperature regulator is responsive to a first temperature indication from the temperature sensor to determine that the first temperature indication exceeds a setpoint and to reduce an energy level from the energy source. The flow regulator is coupled to the pump and coupled to the temperature regulator. The flow regulator includes responsiveness to the first temperature indication to increase a flow of the liquid from the pump.
Owner:ORATEC INTERVENTIONS
System and method for repairing tendons and ligaments
InactiveUS20080188936A1Relieves at least part of the separation forcesPrevent sutures from tearing through the deviceSuture equipmentsLigamentsLigament structureTension member
An implant and method for the repair of a tendon or a ligament along at least one load direction. The implant includes at least one first anchor portion and at least one tension member oriented along a load direction. The first anchor portion preferably has a larger surface area of engagement with the tendon or ligament to spread loads across more tissue. The tension member is preferably secured to the first anchor portion with an overlapping attachment. Tension on the tension member is preferably adjustable by the surgeon.
Owner:TORNIER INC
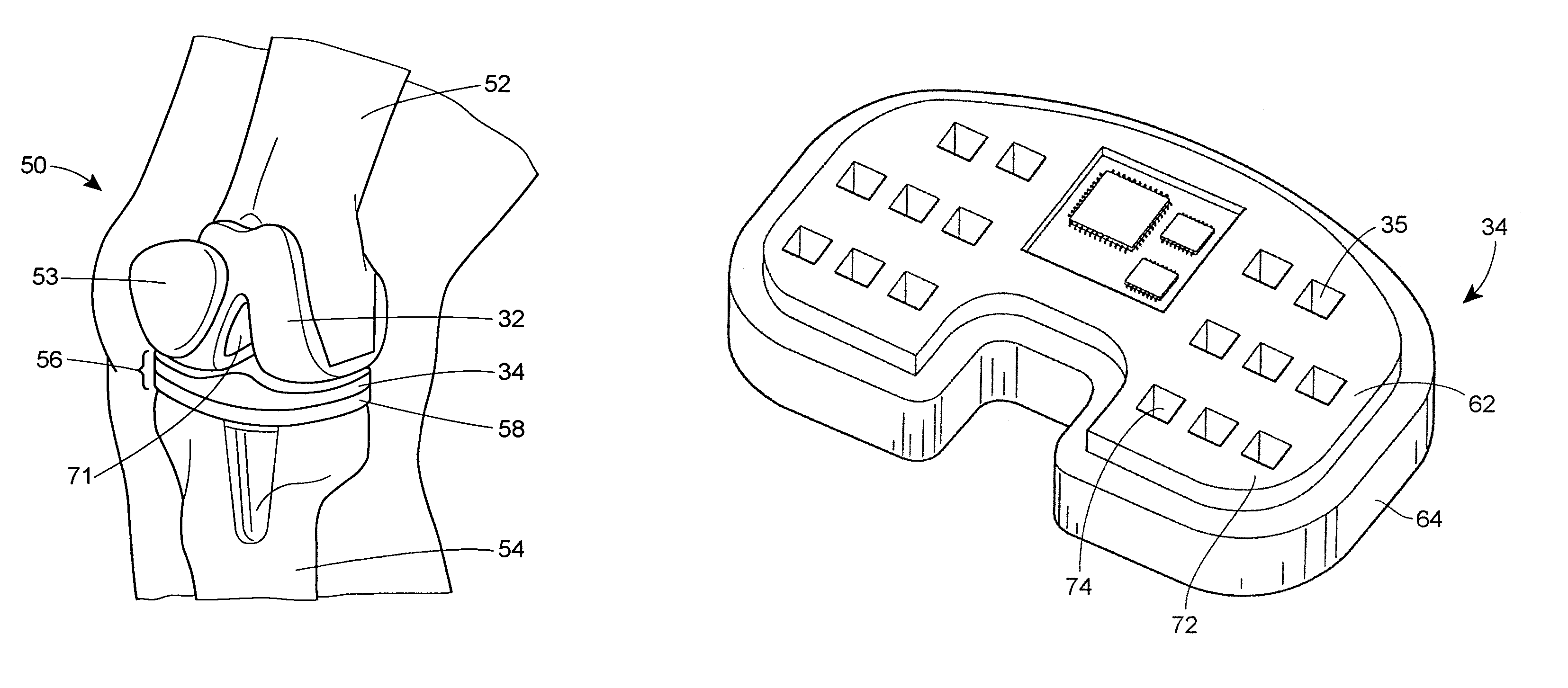
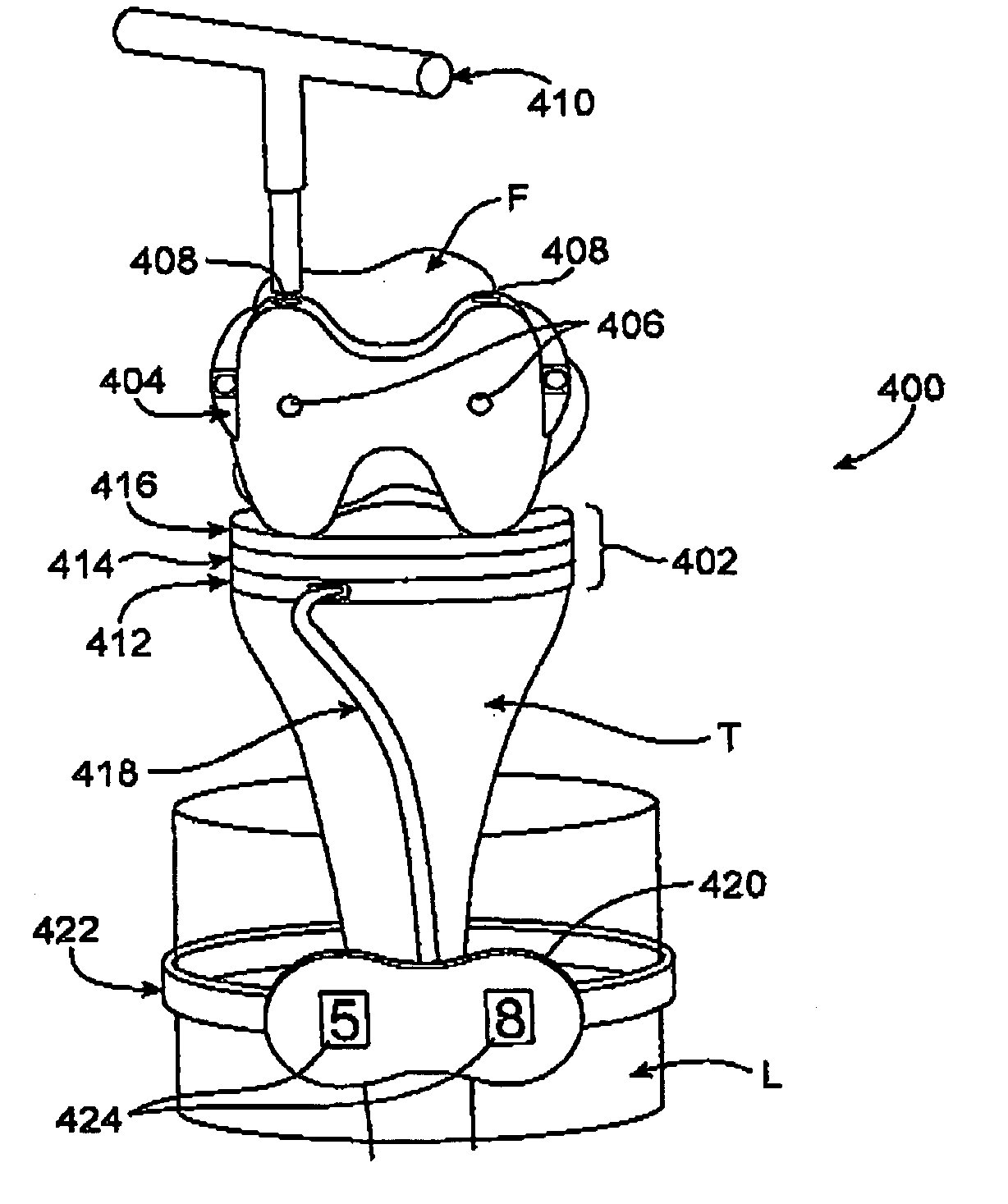
System and method for prosthetic fitting and balancing in joints
InactiveUS7575602B2Physical therapies and activitiesFinger jointsProsthesis fittingArtificial joints
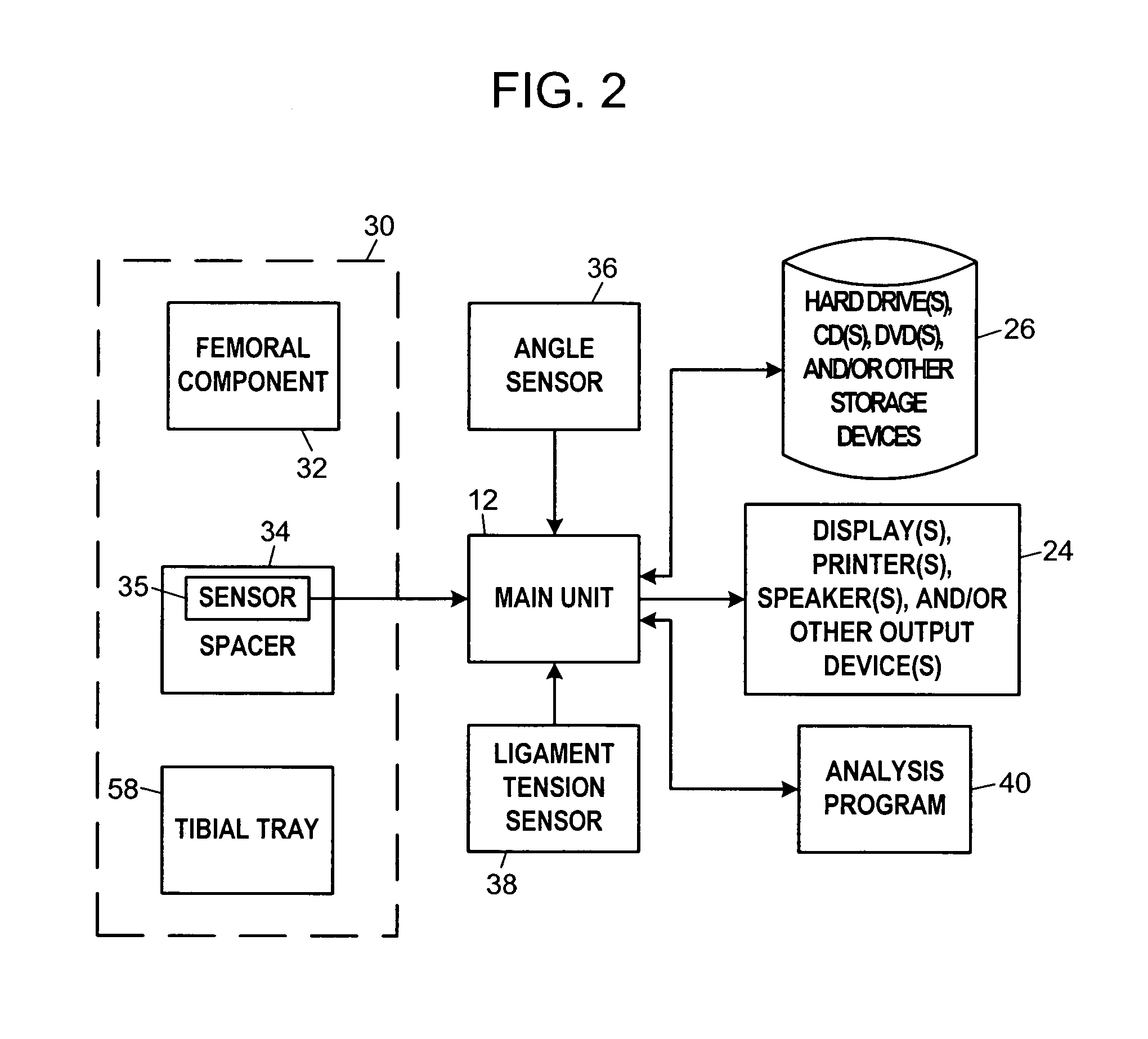
A system and method for prosthesis fitting in joints comprising an artificial condyle and a spacer which cooperates with the condyle to form an artificial joint. The spacer embedded with at least one sensor which is responsive to a force generated between the condyle and the spacer. The artificial joint is adapted to move between a flexed position and an extended position defining a range of motion. The sensor is responsive to the force and generates an output representative of that force. The output is transmitted, either wirelessly or other, to a processor which utilizes an analysis program to display a representation of the forces applied. A practitioner utilizing the displayed analysis may intraoperatively determine the adjustments and balancing required within the artificial joint. The system may also utilize a ligament tension sensor which generates data representative of tension on a ligament of the artificial joint, and a joint angle sensor responsive to the range of motion of the artificial joint. The processor may be adapted to store the outputted sensor data to provide the practitioner with statistically relevant historical data.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Bariatric sleeve
InactiveUS20060161265A1Increased axial stabilityLess movementSuture equipmentsStentsIntestinal structureGastrointestinal device
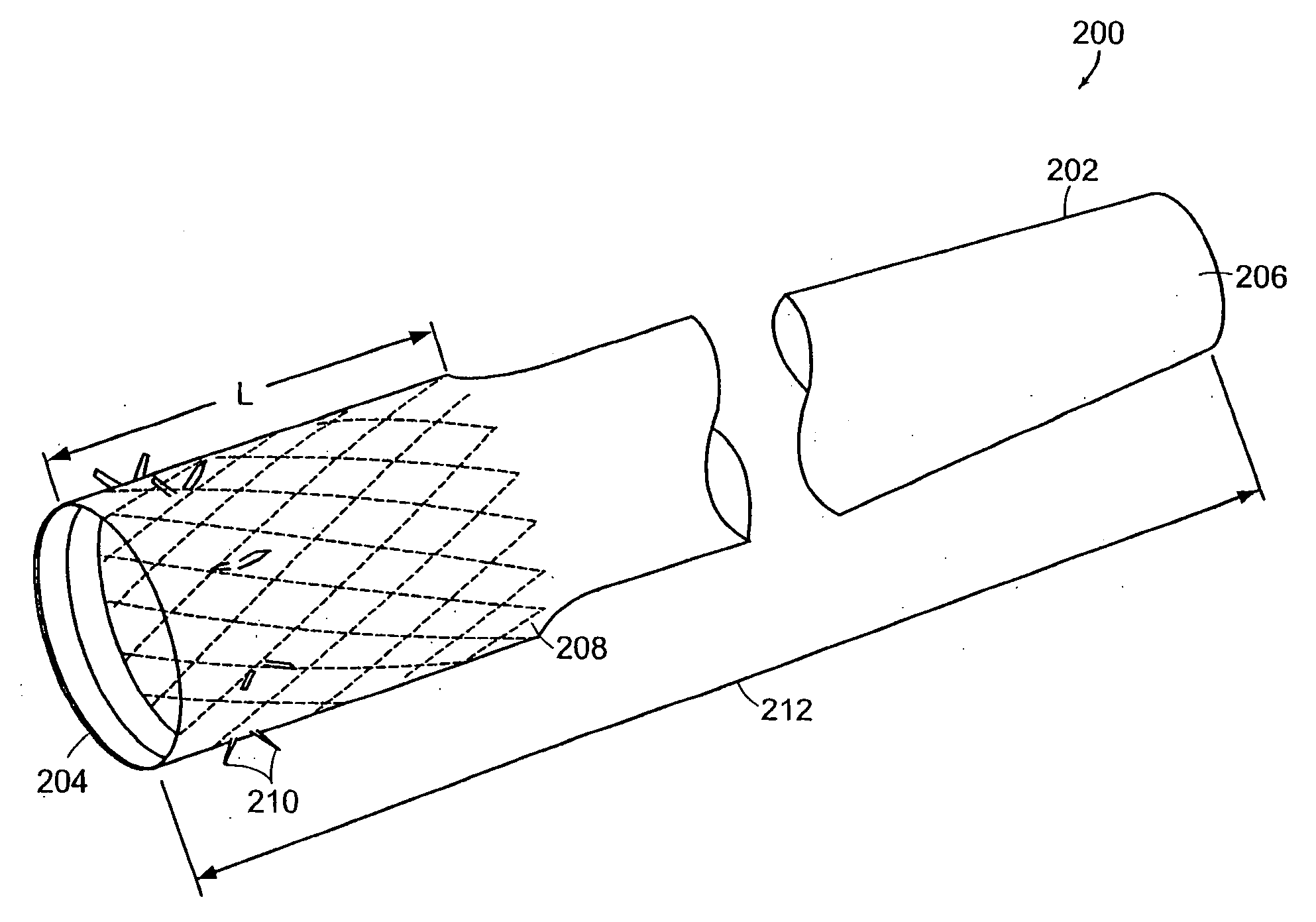
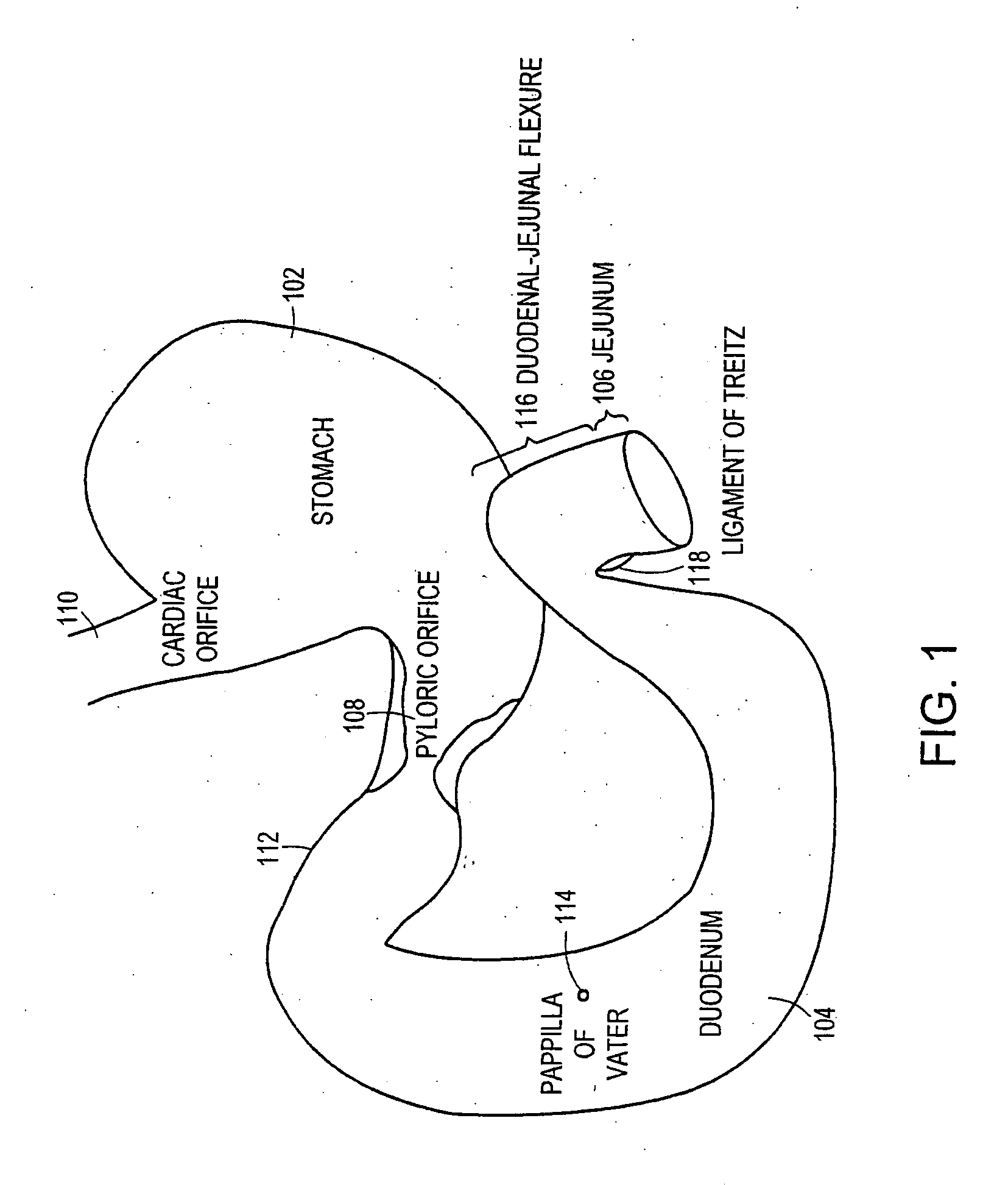
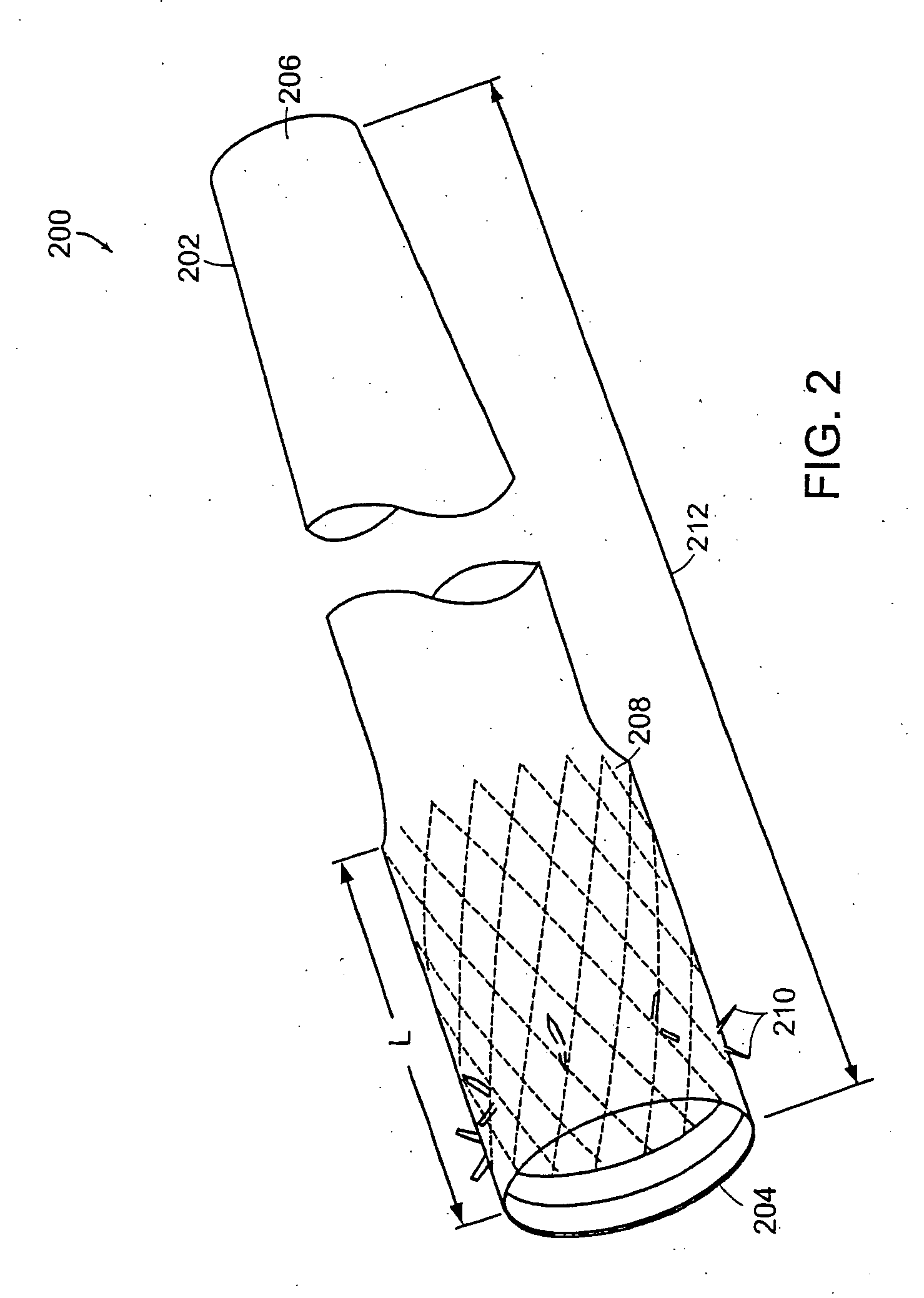
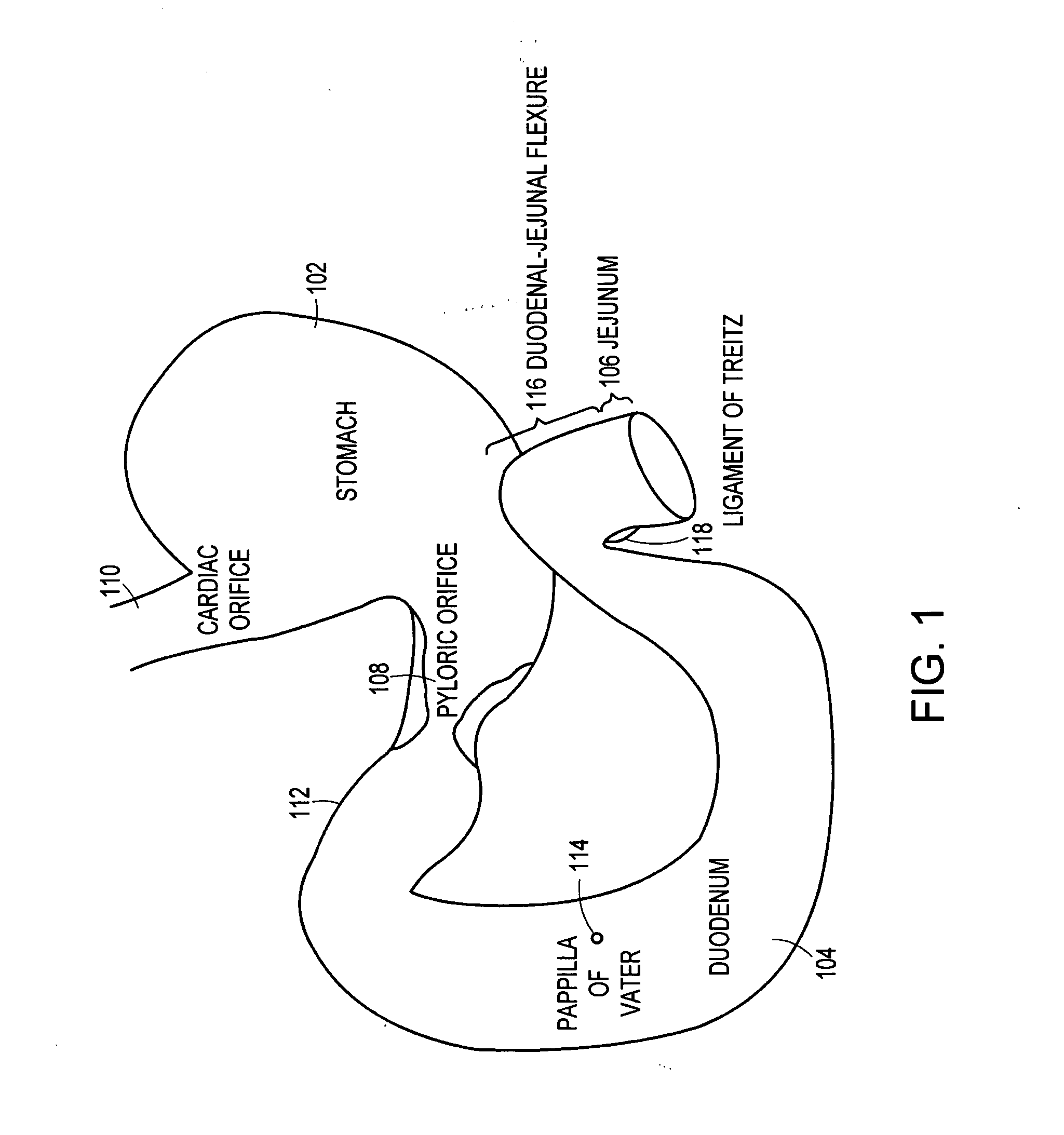
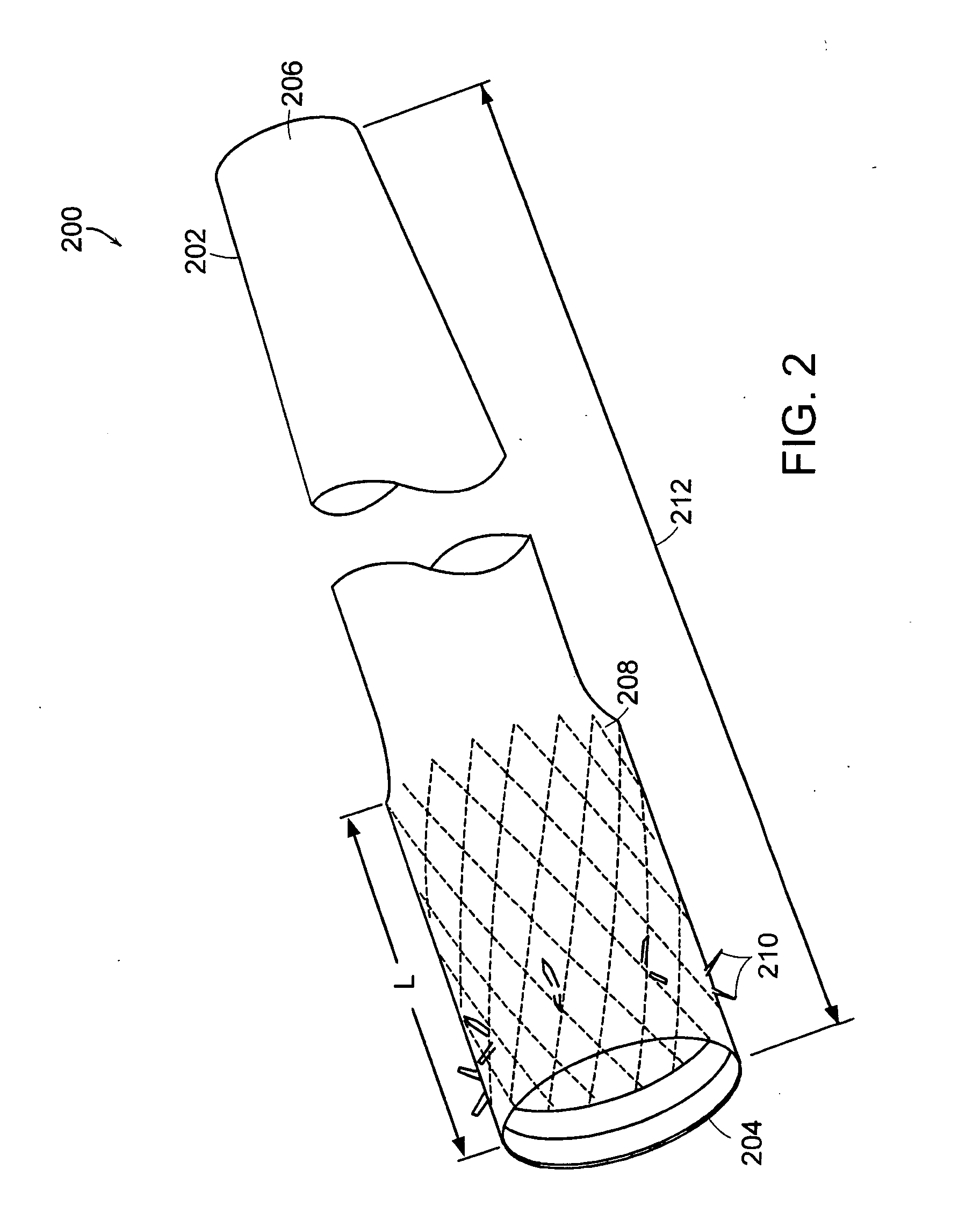
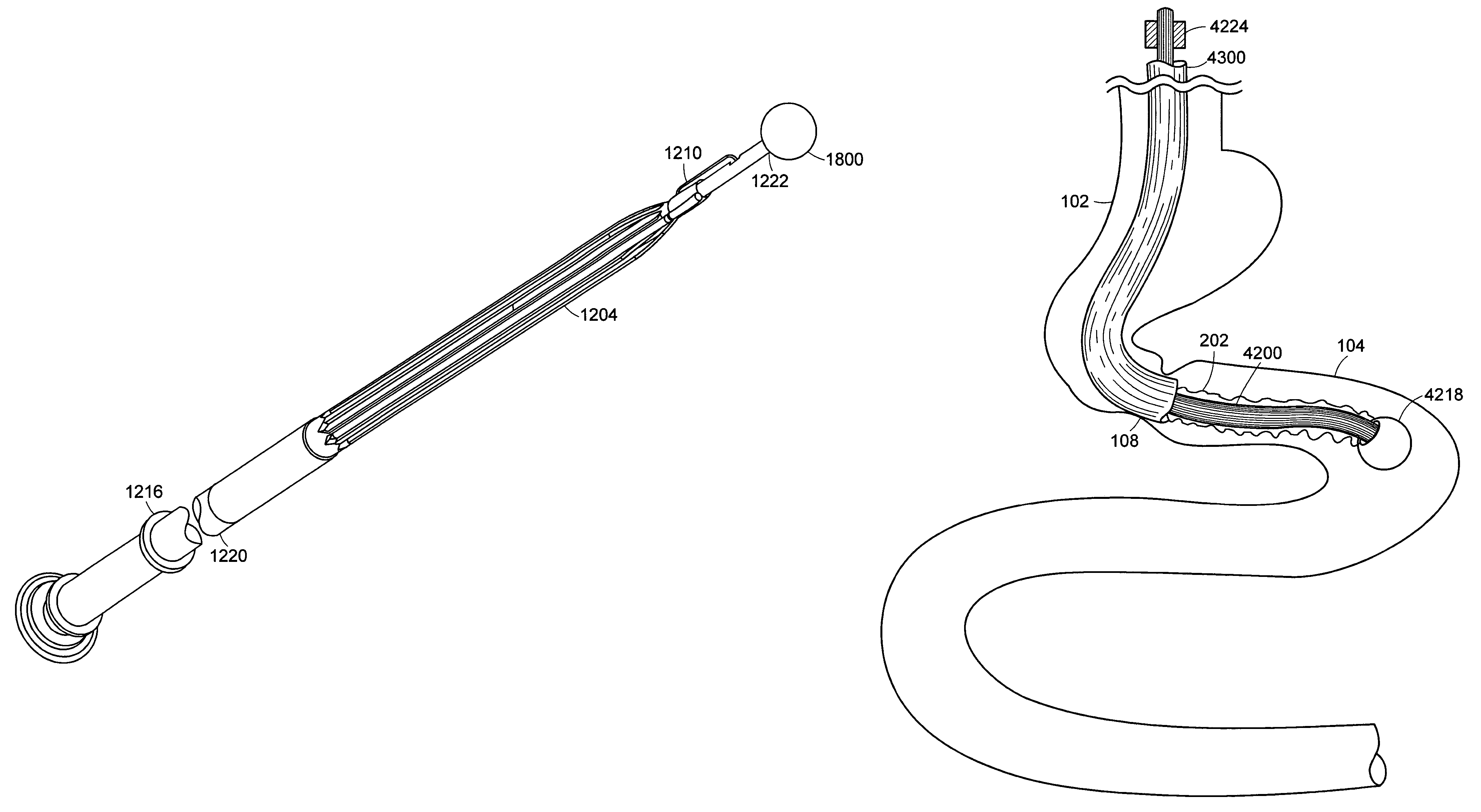
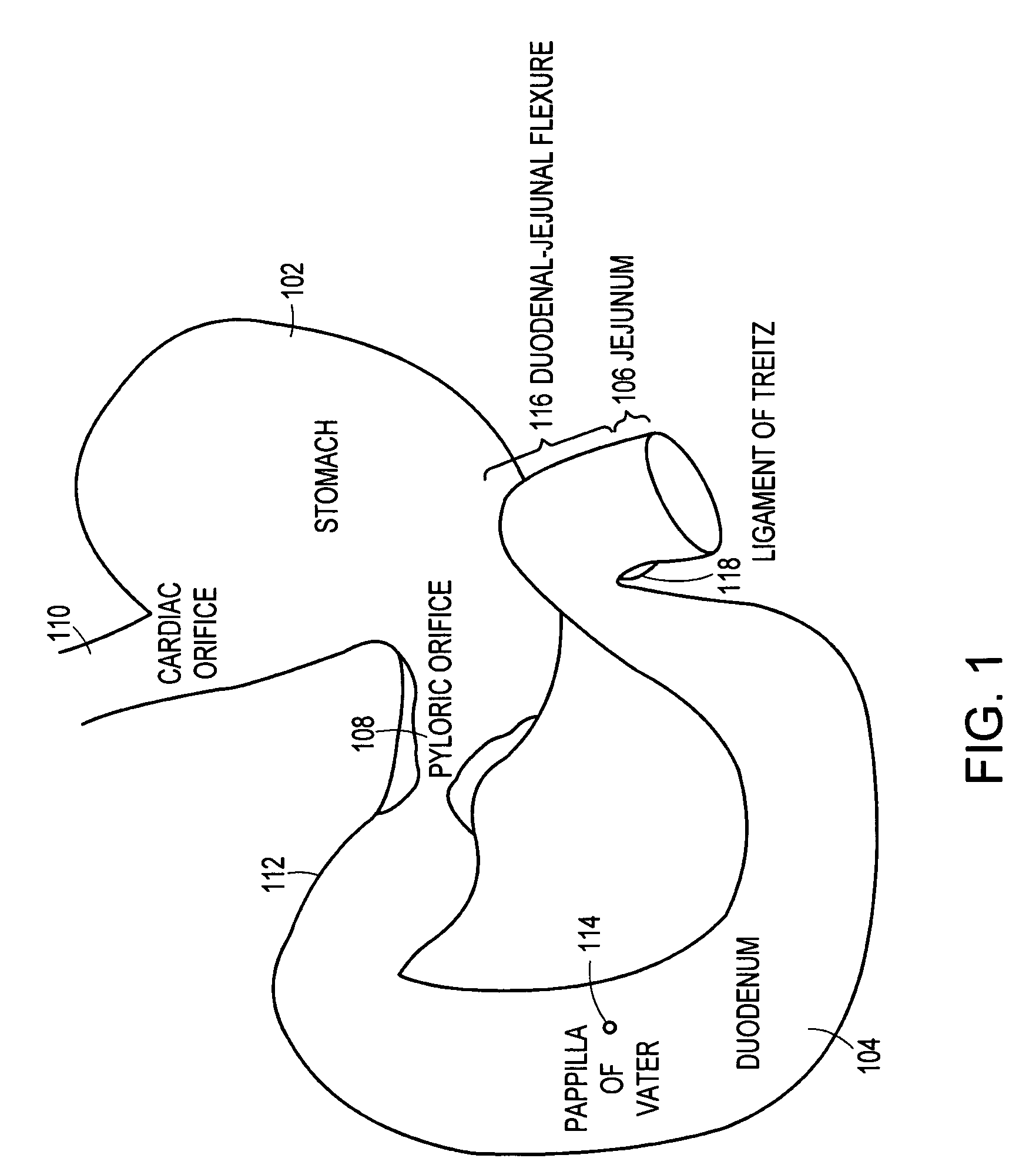
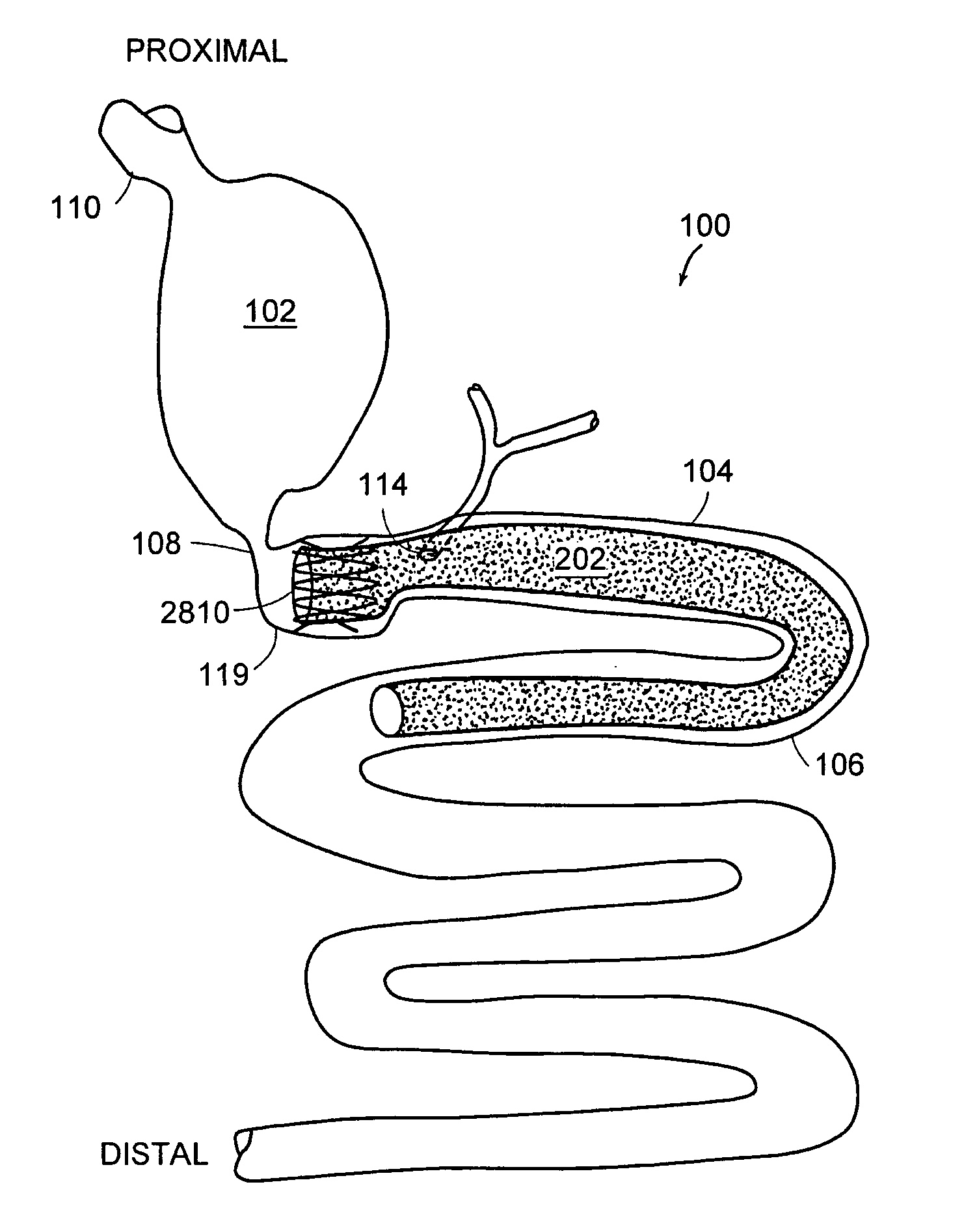
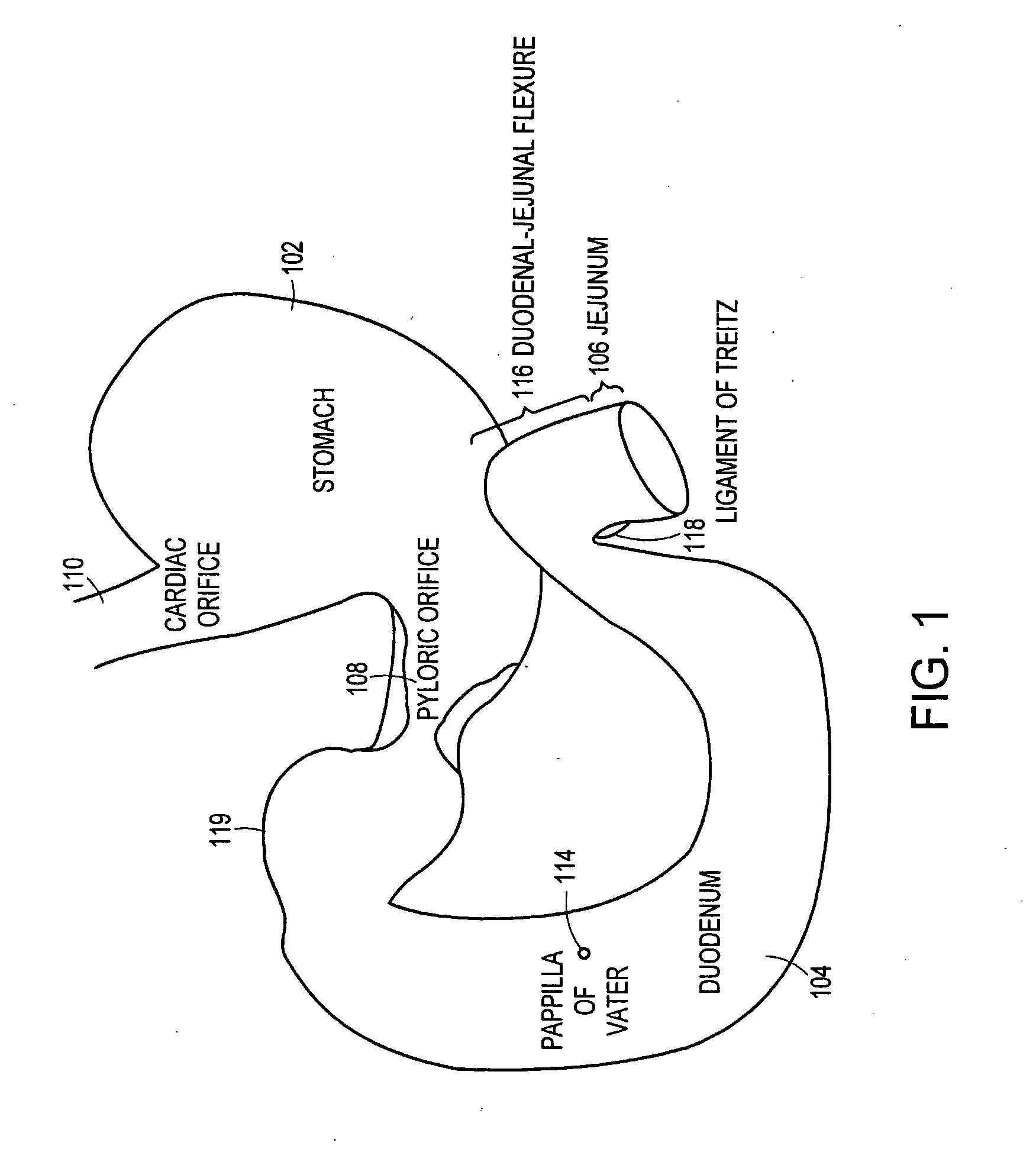
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the stomach and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for anchoring the device to the stomach and a flexible sleeve. When implanted within the intestine, the sleeve can limit the absorption of nutrients, delay the mixing of chyme with digestive enzymes, altering hormonal triggers, providing negative feedback, and combinations thereof. The anchor is collapsible for endoscopic delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Dynamic knee balancer with opposing adjustment mechanism
ActiveUS20050267485A1Accelerated programImproved surgical outcomeDiagnosticsJoint implantsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationRange of motion
A device for performing a surgical procedure on a knee comprises a femoral assembly comprising a stationary femoral member attachable to the distal femur, an adjustable femoral member movably coupled with the stationary member to adjust tension in at least one ligament of or adjacent the knee and an adjustment mechanism coupled to the assembly. The adjustable member includes at least one positioning feature that moves relative to the distal femur as the adjustable member is adjusted and identifies at least one position on the distal femur. The adjustable member is movably couplable with a tibial member engaged with a proximal tibia to allow the knee to be moved through a range of motion without removing the femoral and tibial members. The mechanism includes an actuator positioned proximate a medial or lateral portion of the adjustable member. The actuator is configured to adjust an opposite portion of the adjustable member.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Bone-tendon-bone implant
An implant for repairing soft tissue injuries is provided comprising at least one channel for receiving a soft tissue graft such as a tendon, ligament, or other soft tissue, to be implanted in a patient. The implant assembled with the graft is designed to fit into a bony defect, such as a graft tunnel, formed in bone of a patient. The implant can be biodegradable, and the implant-graft assembly has a pull-out strength sufficient to withstand everyday use during patient recovery.
Owner:OSTEOBIOLOGICS
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6867247B2Reduce probabilityHigh porositySuture equipmentsStentsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
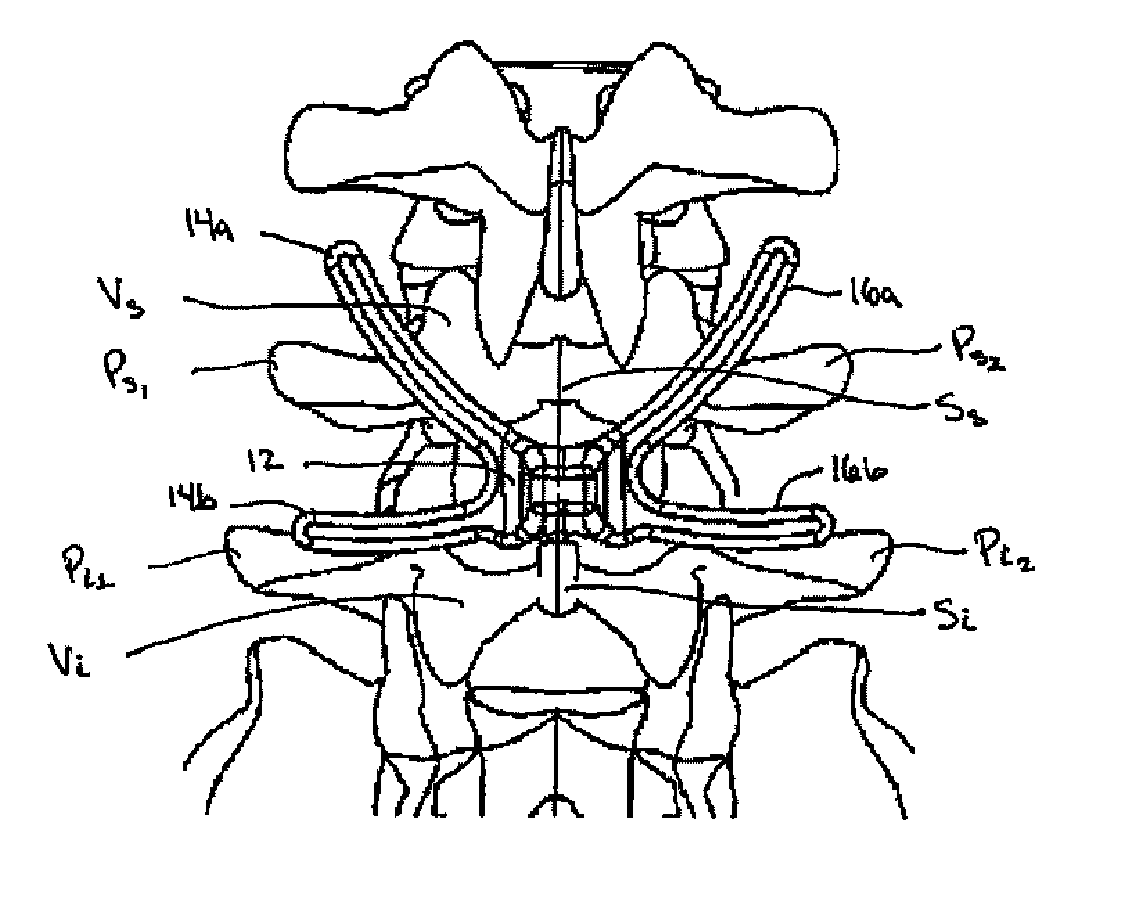
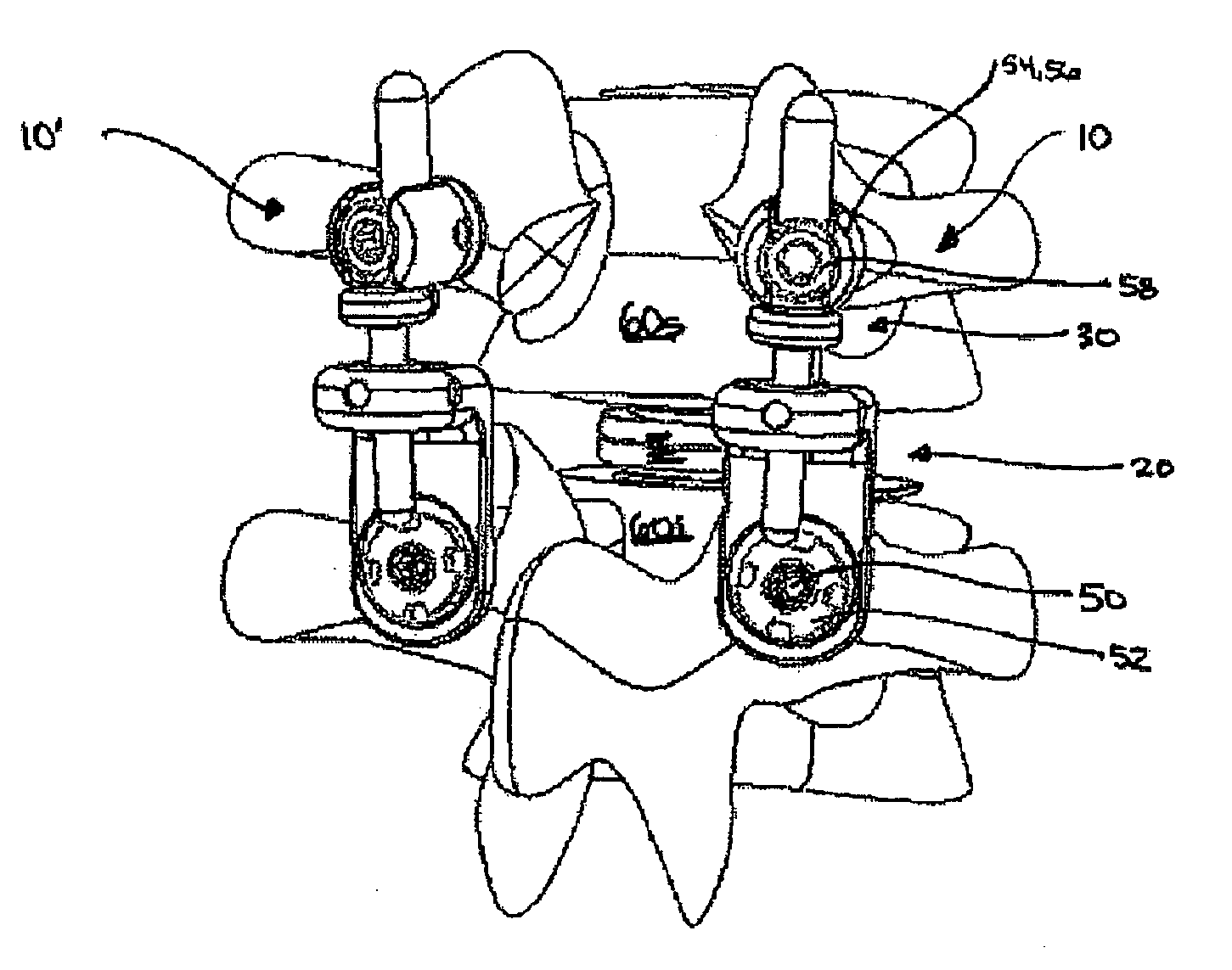
System for stabilizing the vertebral column including deployment instruments and variable expansion inserts therefore
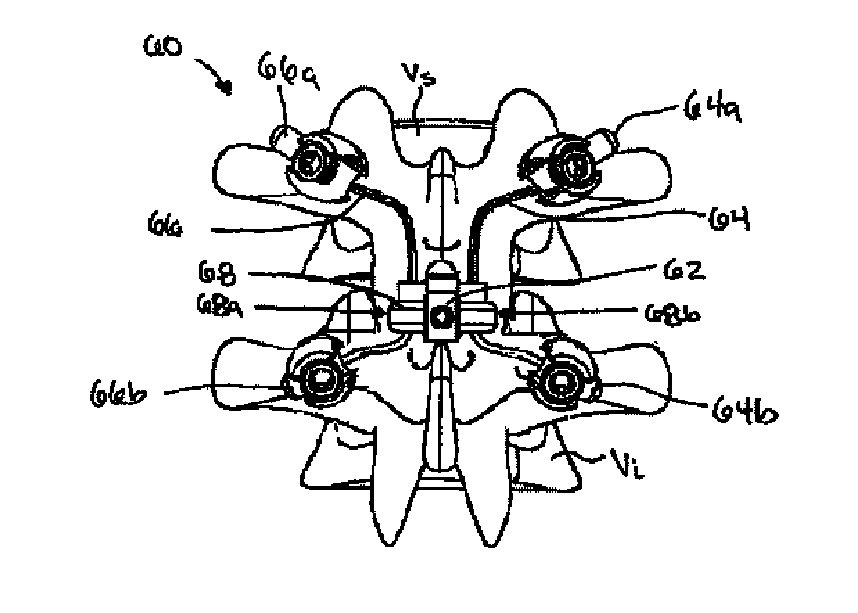
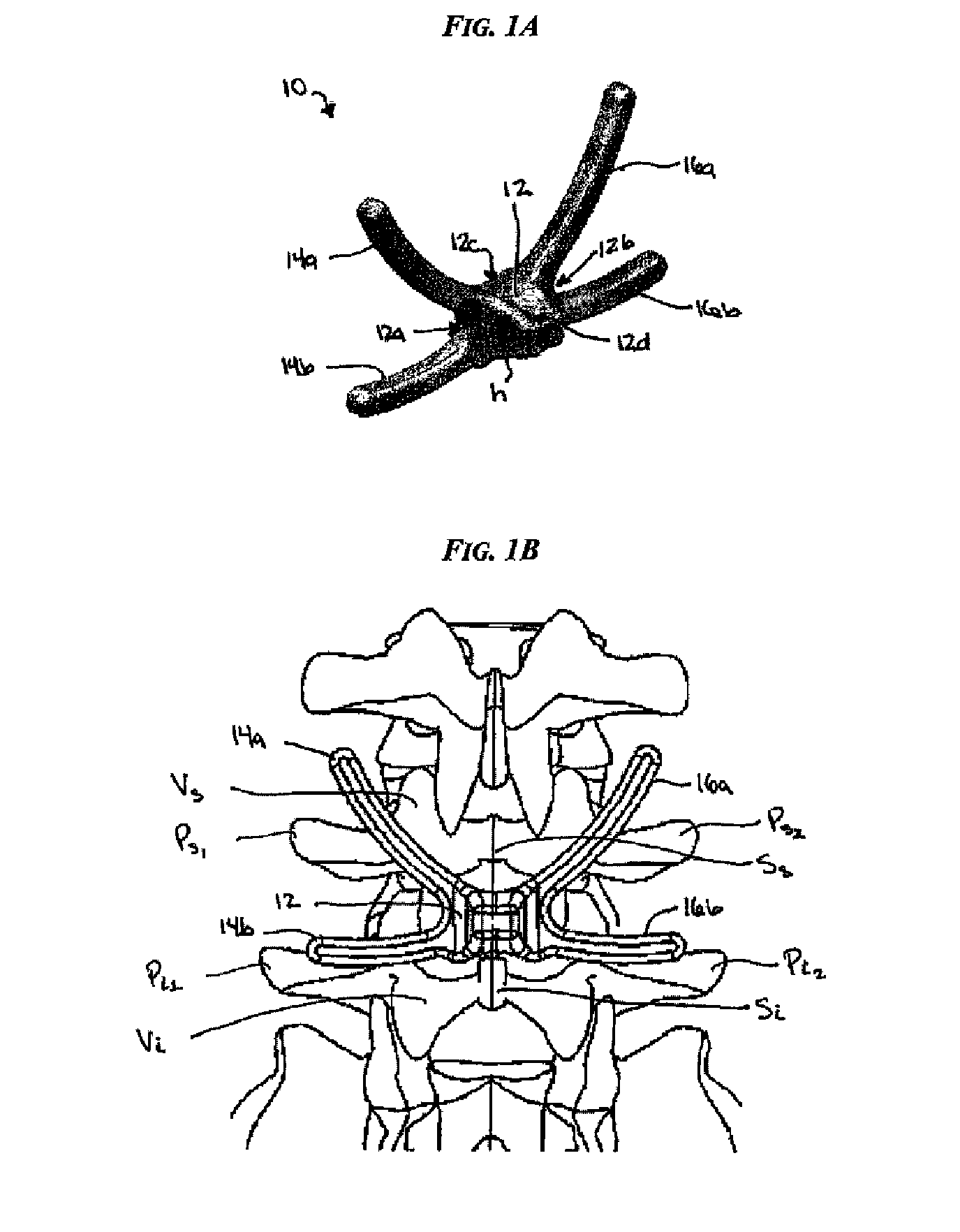
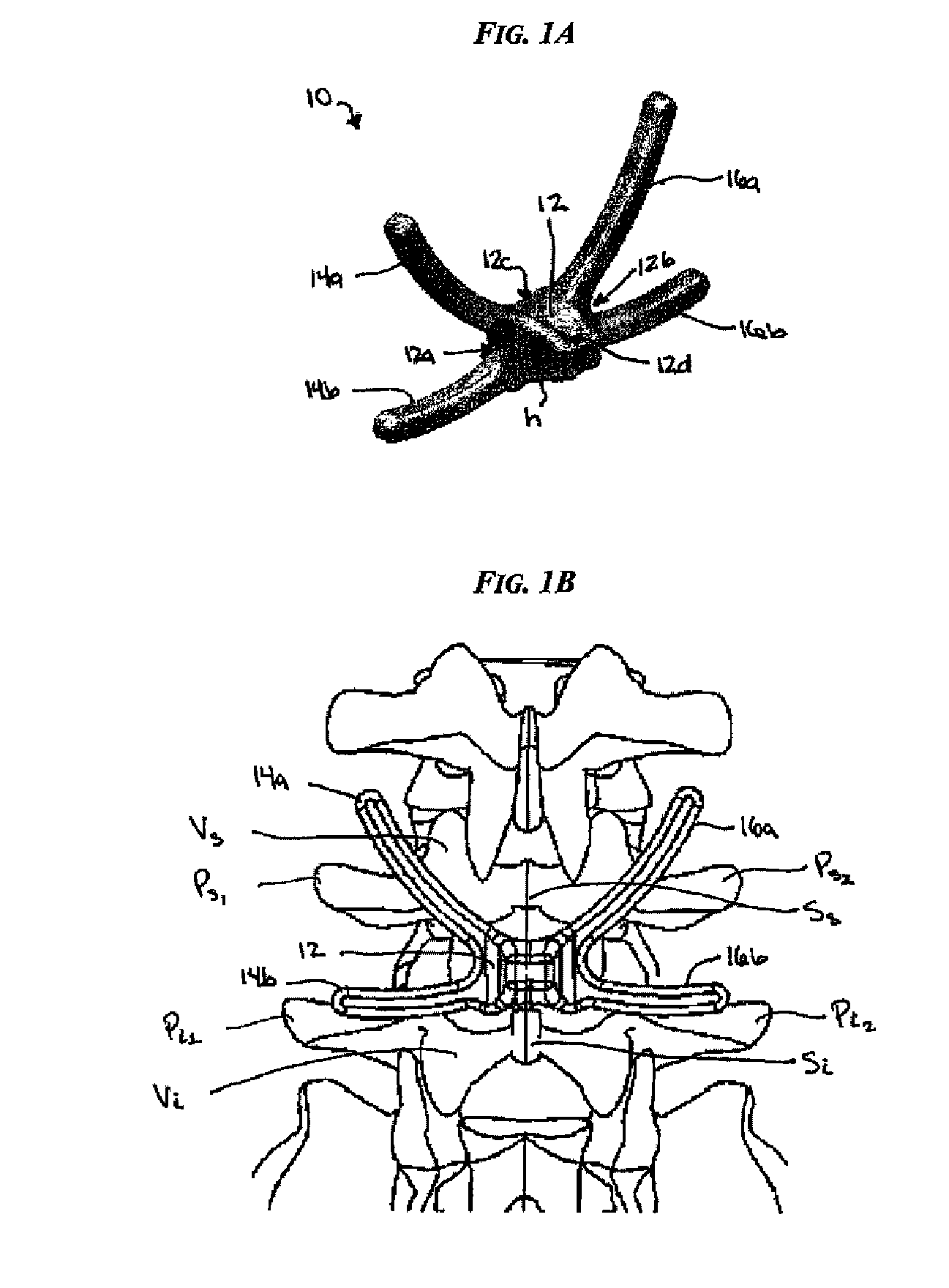
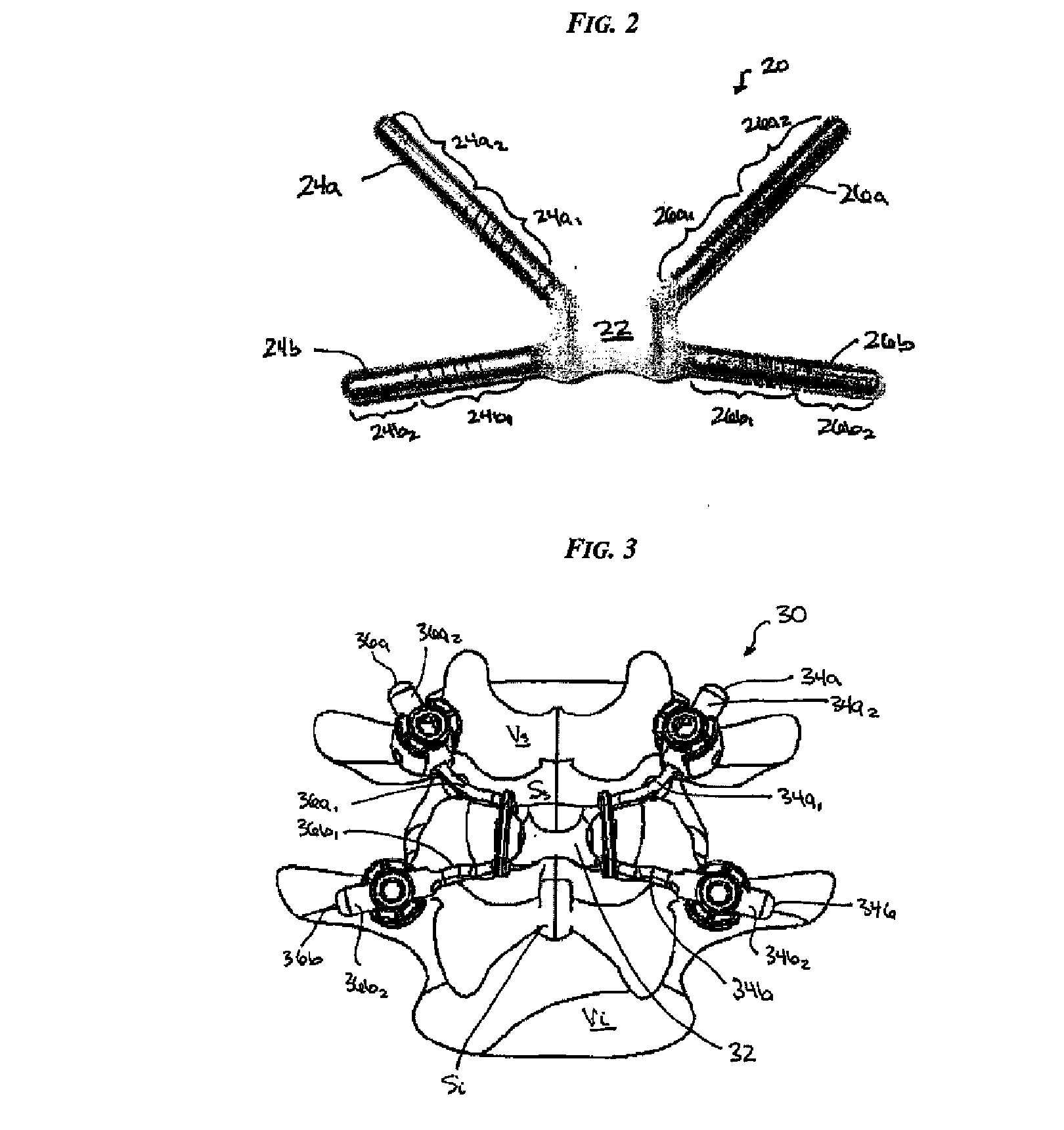
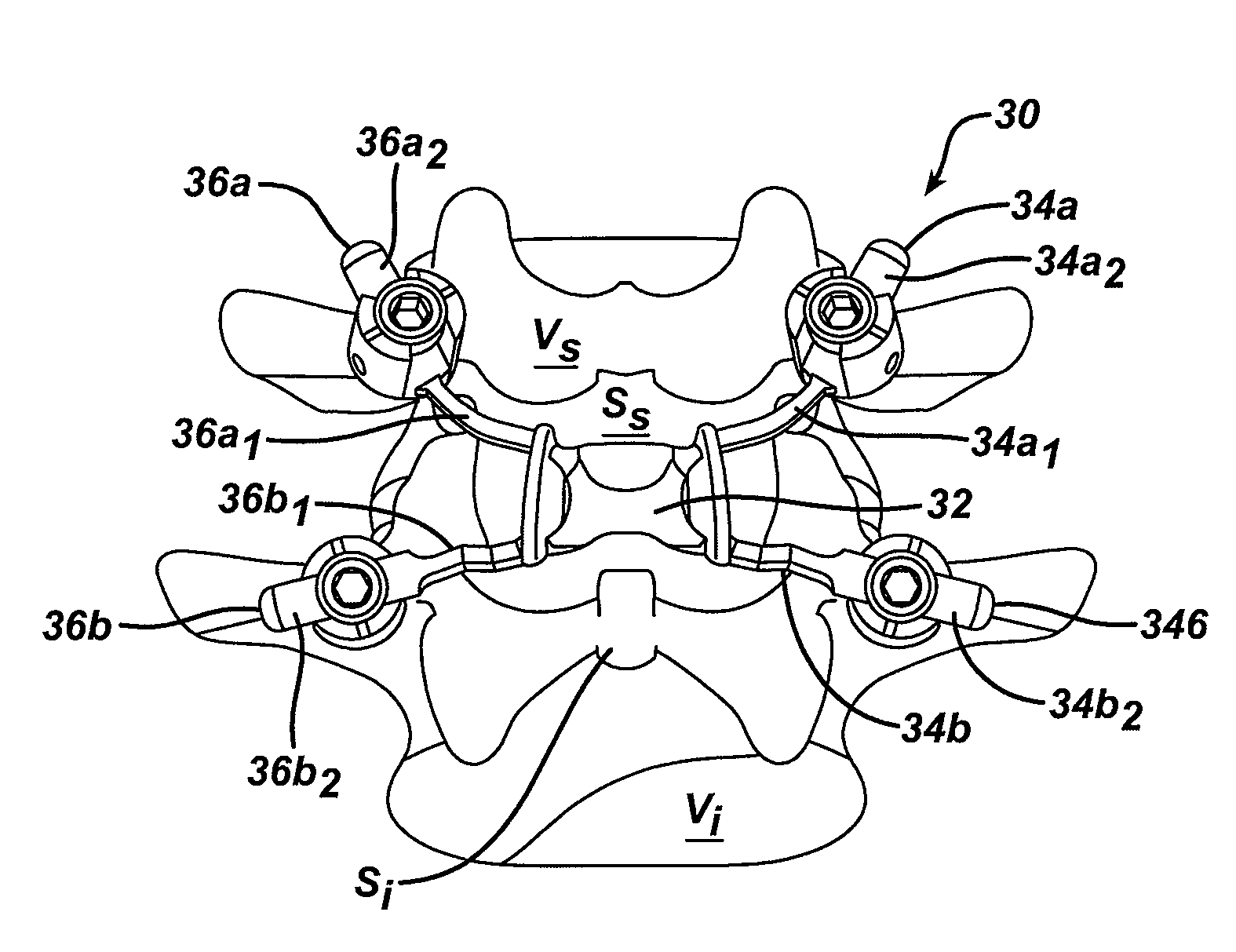
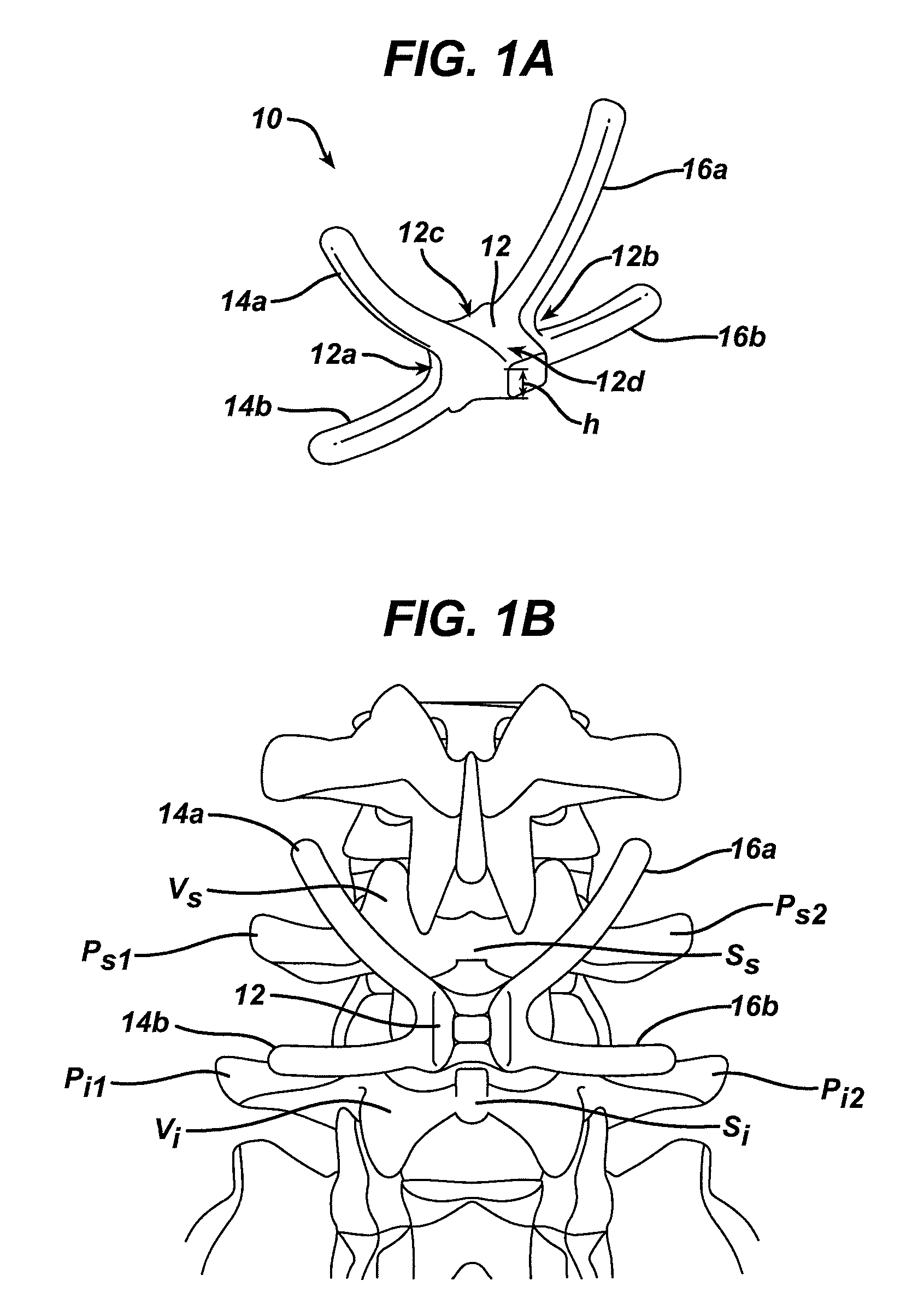
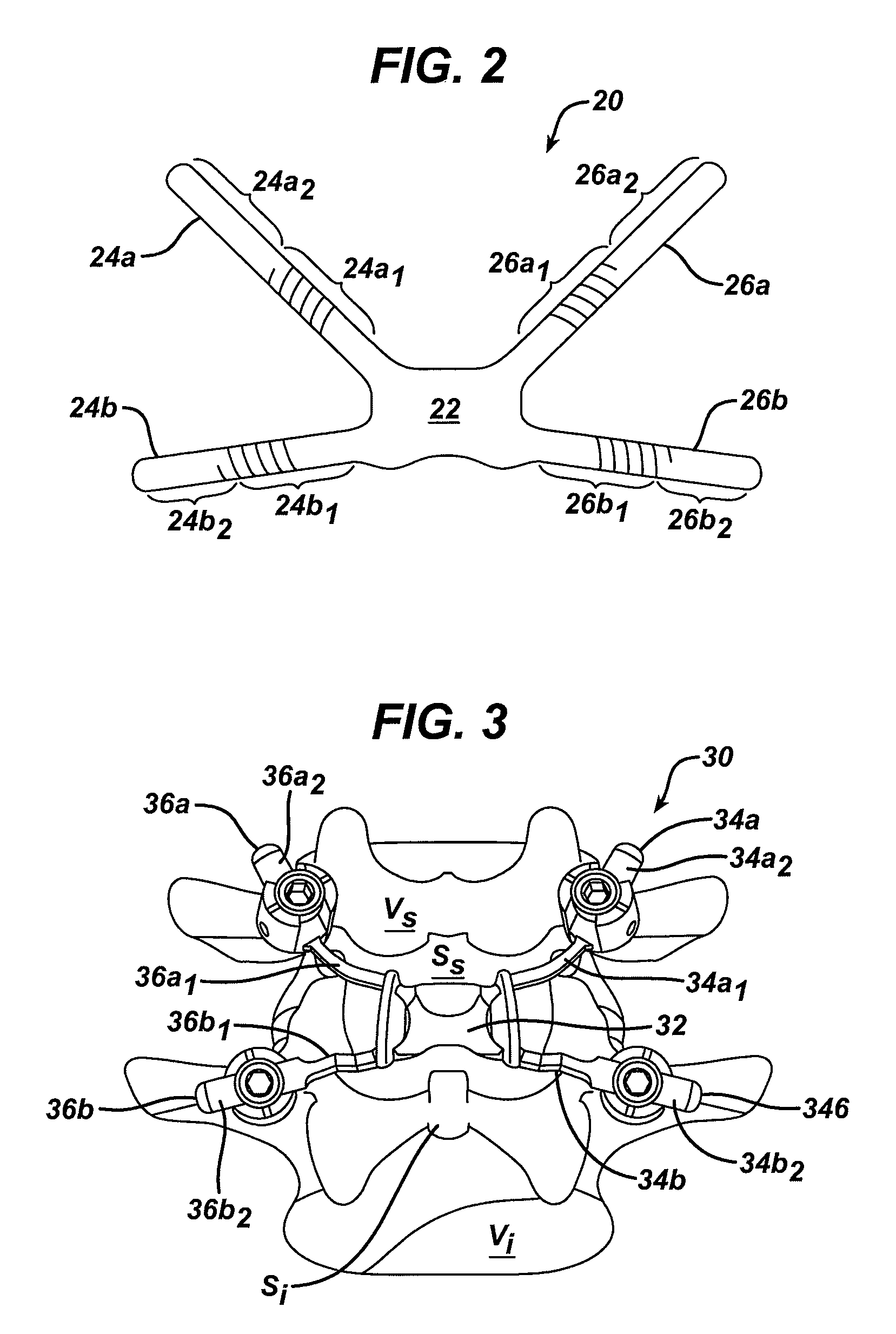
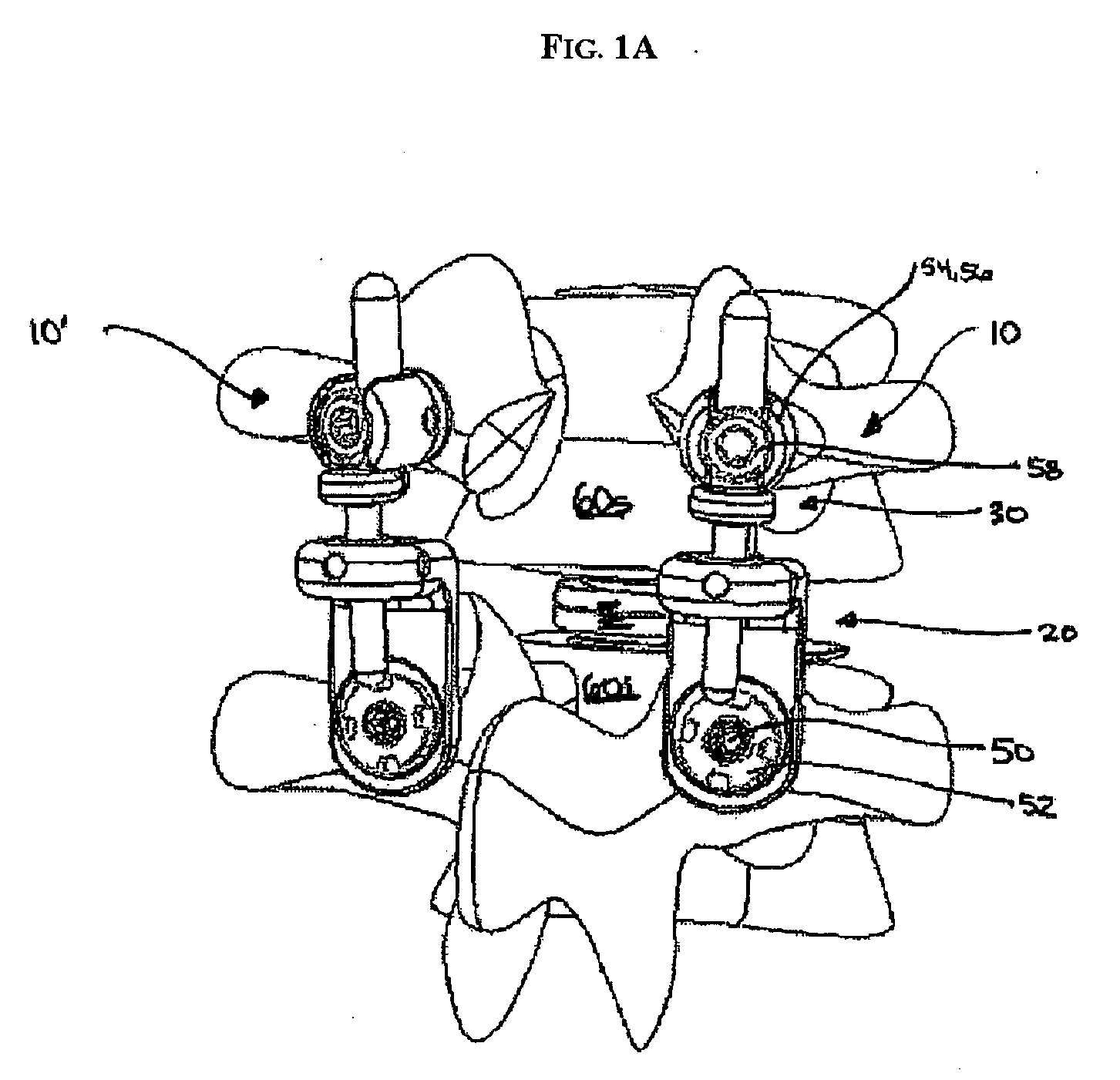
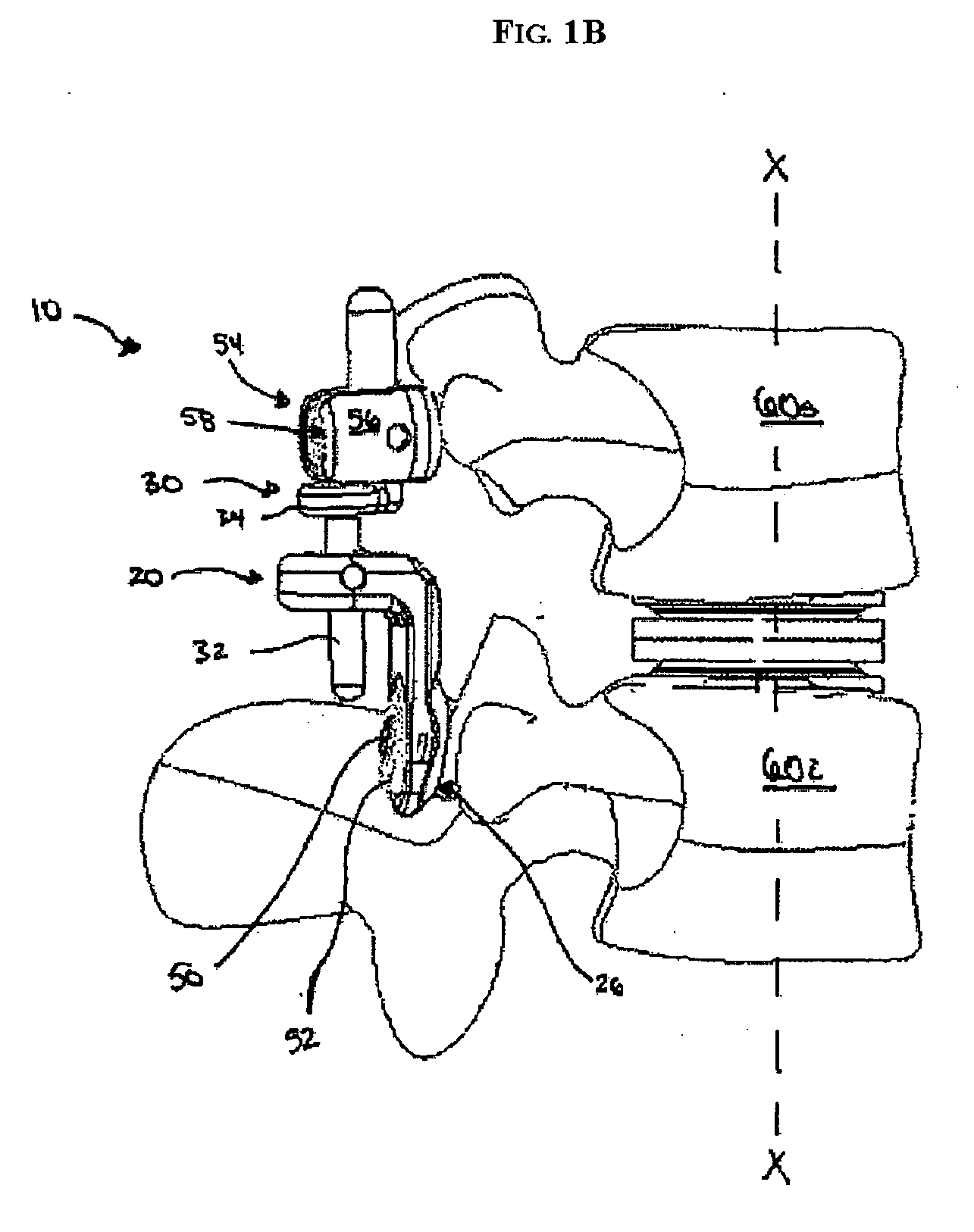
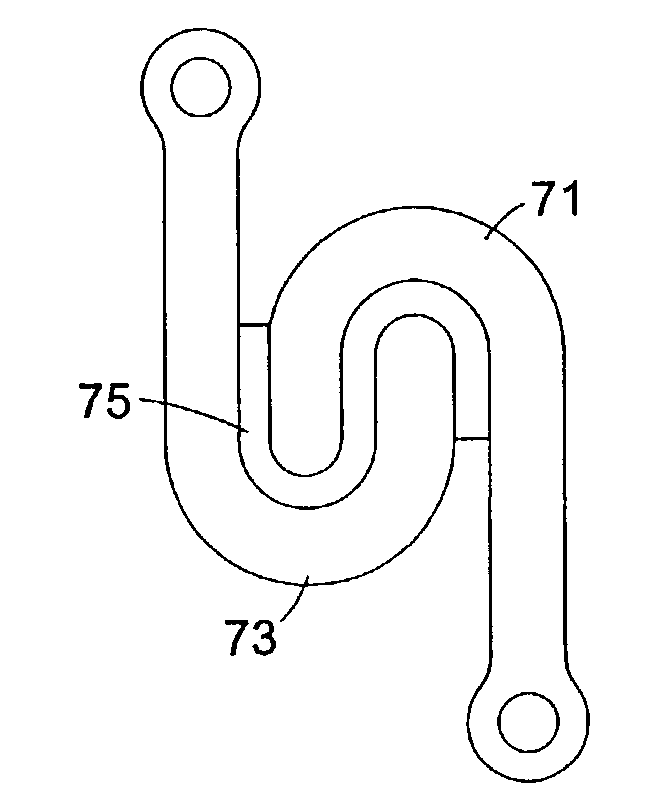
InactiveUS6905512B2Stabilize spineStabilizing the being's vertebral columnJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral spaceLigament structure
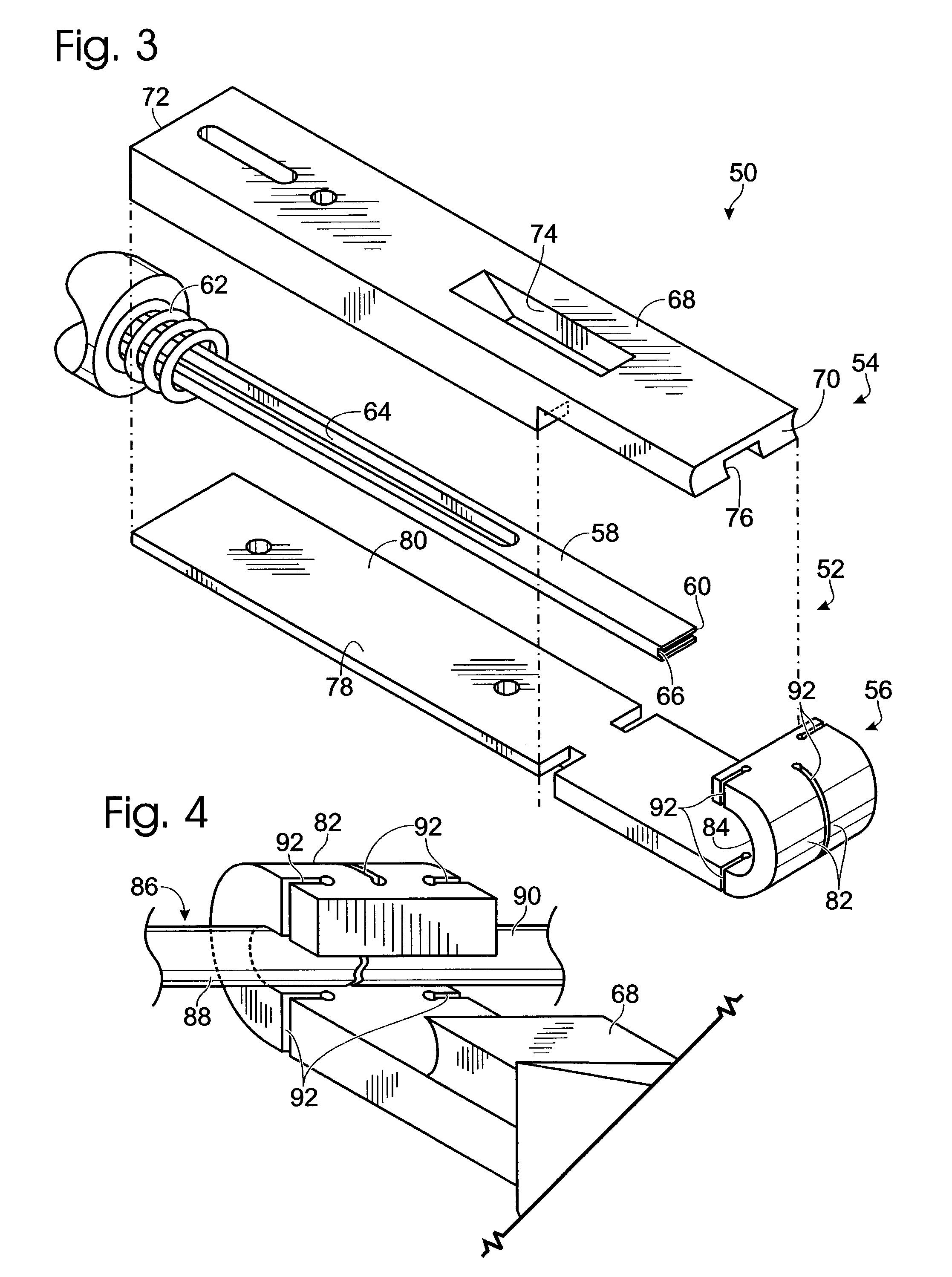
A system is provided for stabilizing adjacent vertebra without excision of bone or resection of ligaments comprising an expansion device and a deployment system which includes a hollow expandable insert and an expansion insert. The expandable insert includes a cylindrical body having a pair of slots having a threaded outer surface. The expandable insert is located with the slots oriented perpendicular to the vertebral column between the vertebrae. The thread cuts into the cortical bone contiguous to the intervertebral space but not substantially into the cancellous bone. The expandable insert is internally threaded. The expansion insert is externally threaded and arranged to be screwed into a bore in the expandable insert by the deployment system, whereupon the slots open to spread the vertebrae apart. The deployment system includes a tool having projecting fingers located within the slots to enable the expandable insert to be screwed into the intervertebral space.
Owner:PHOENIX BIOMEDICAL
Mobile spine stabilization device
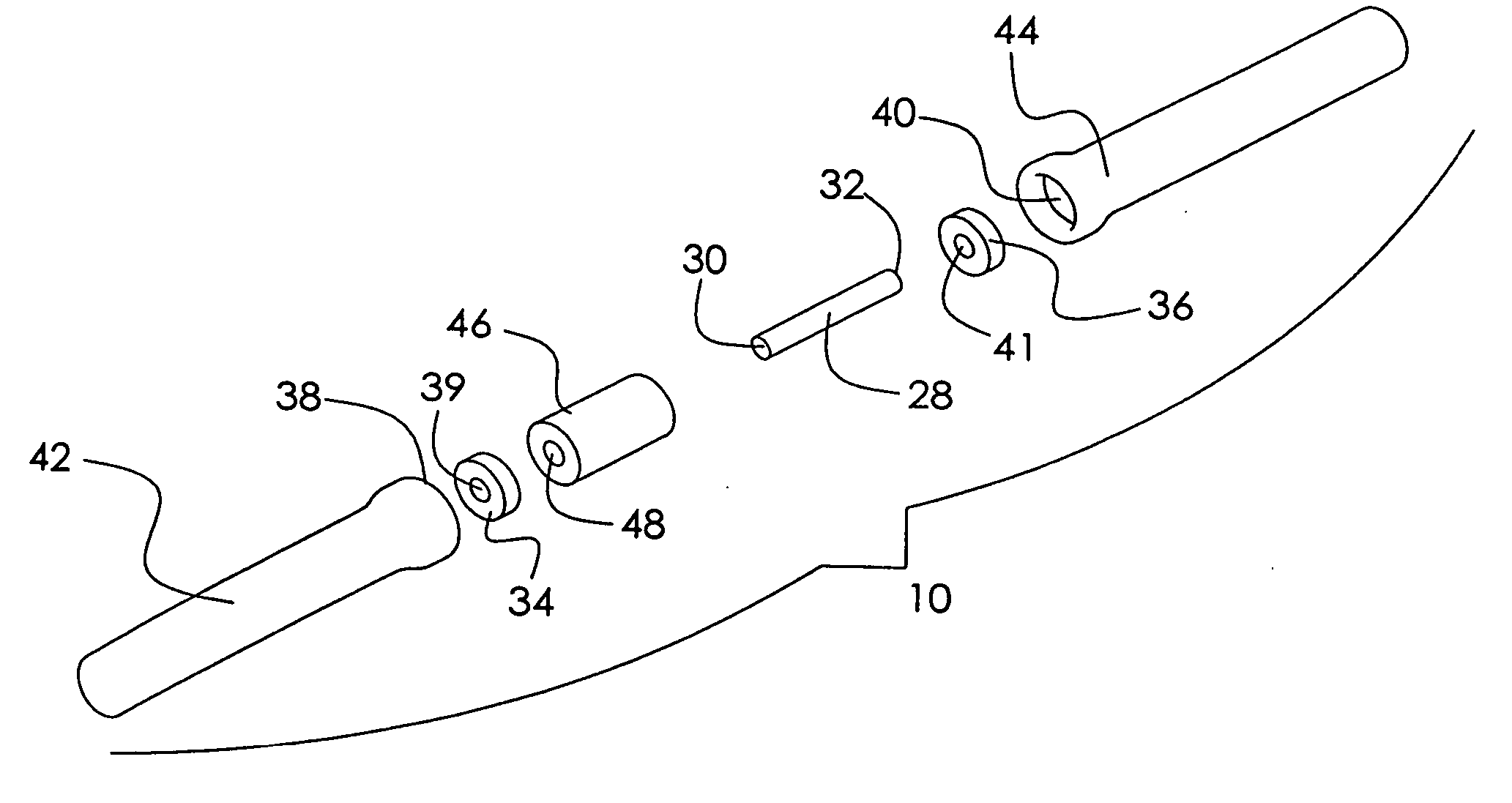
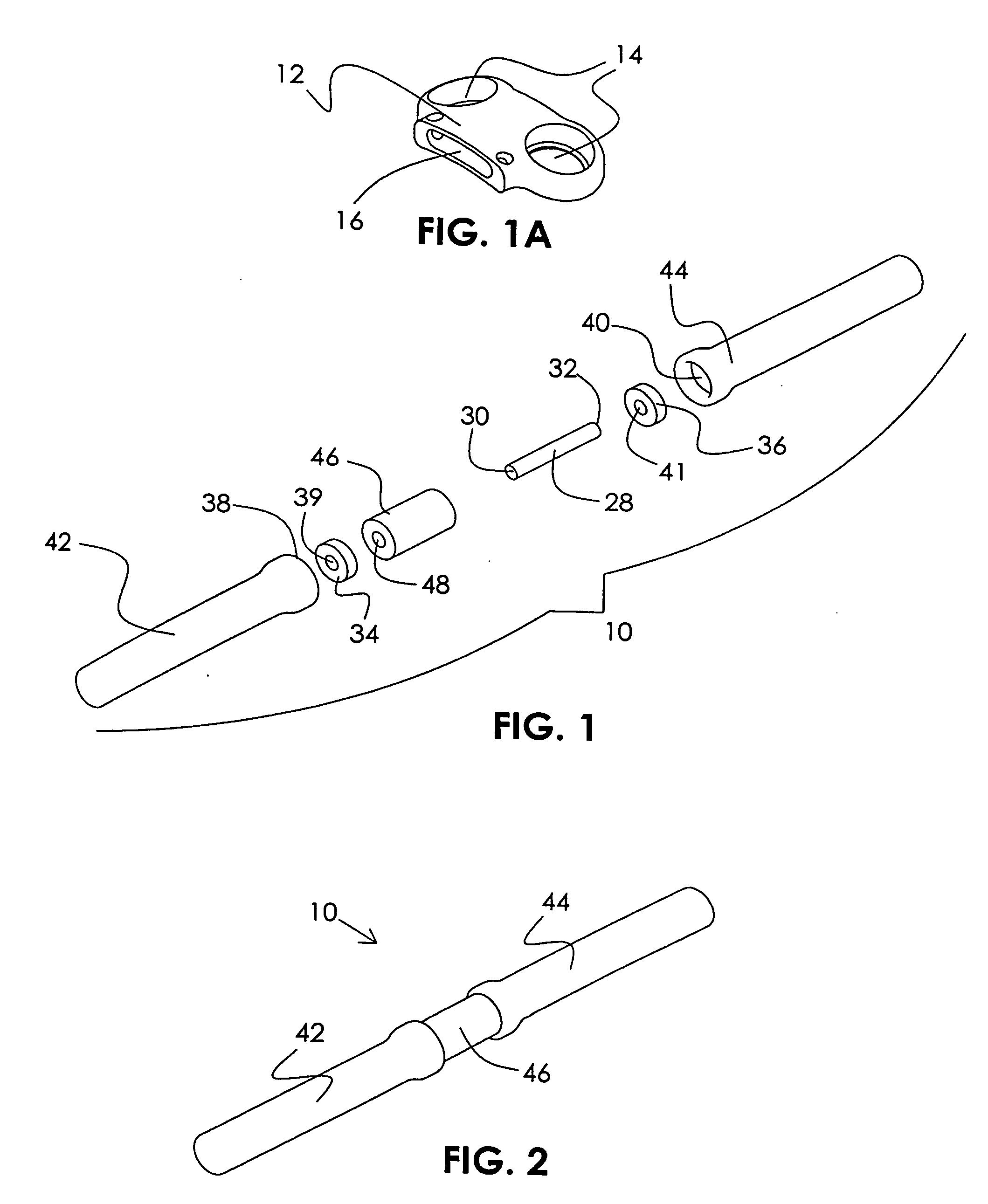
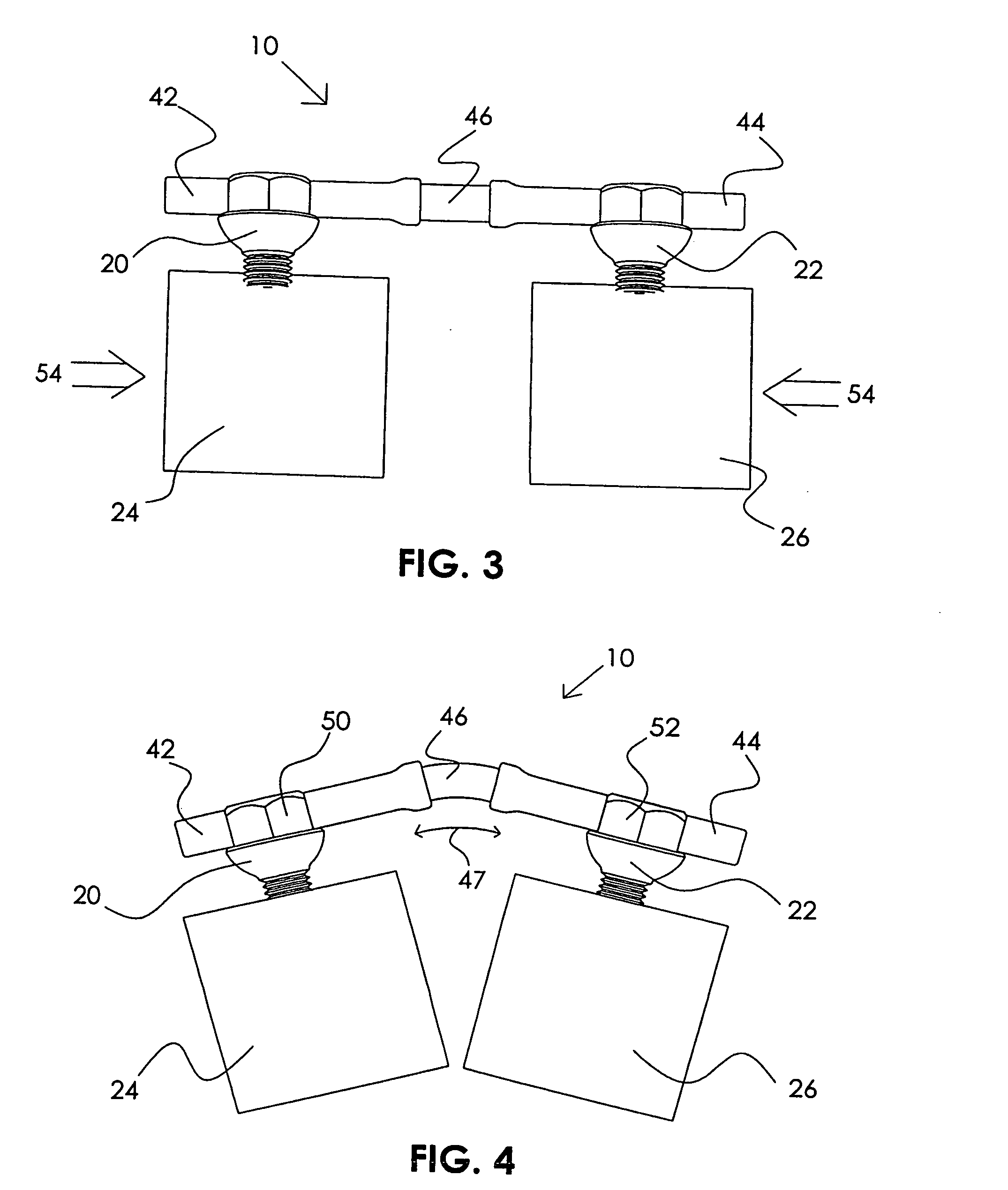
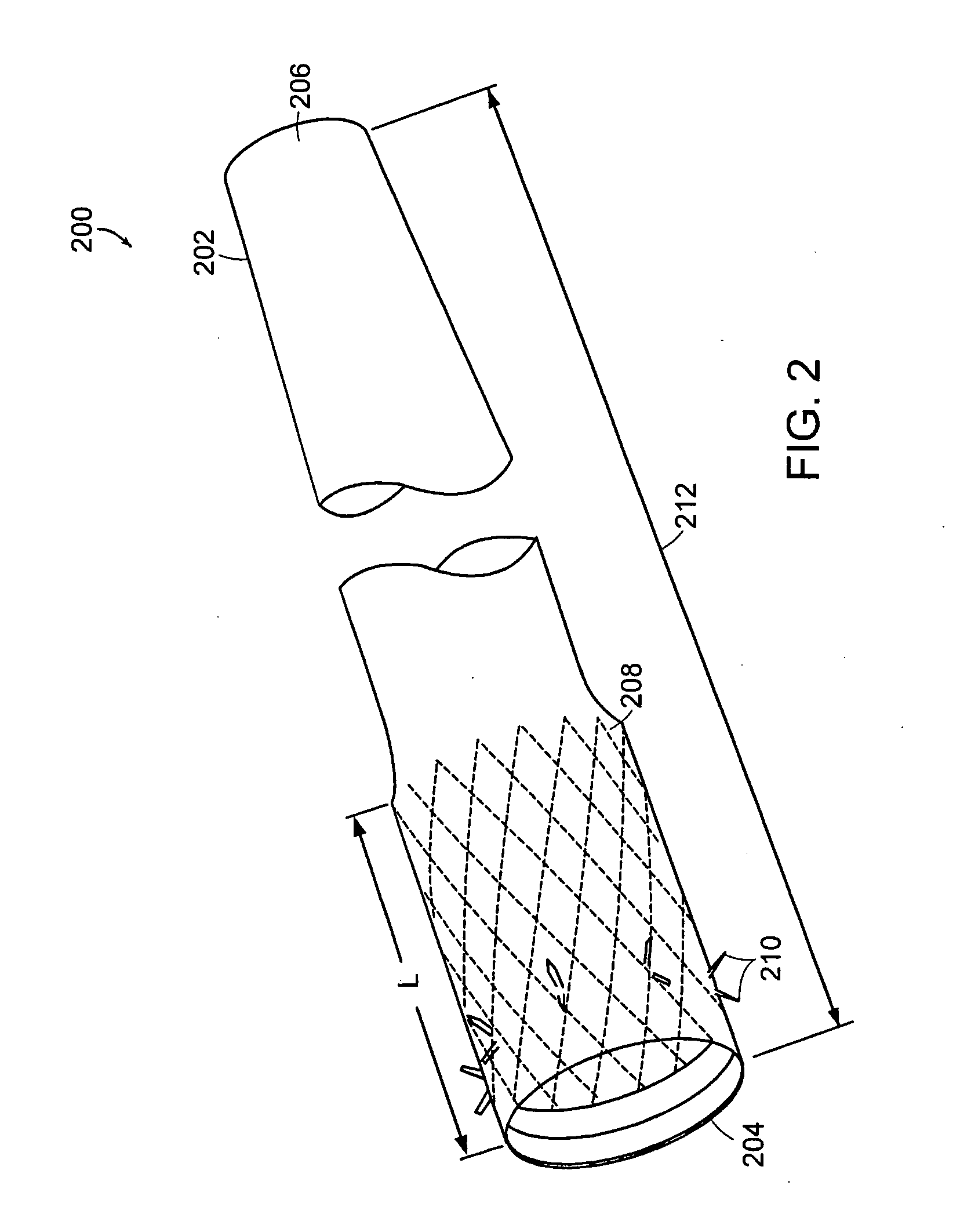
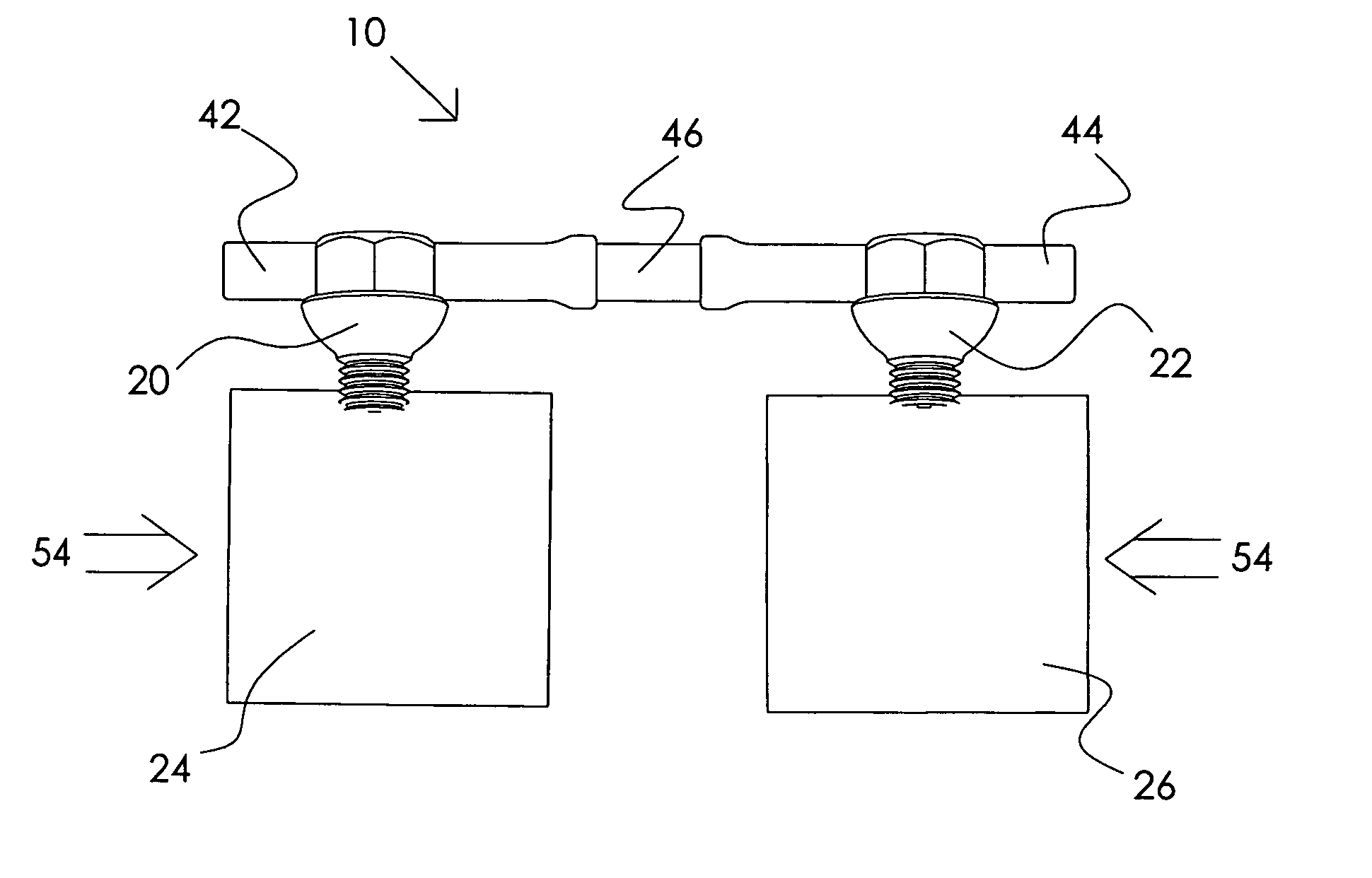
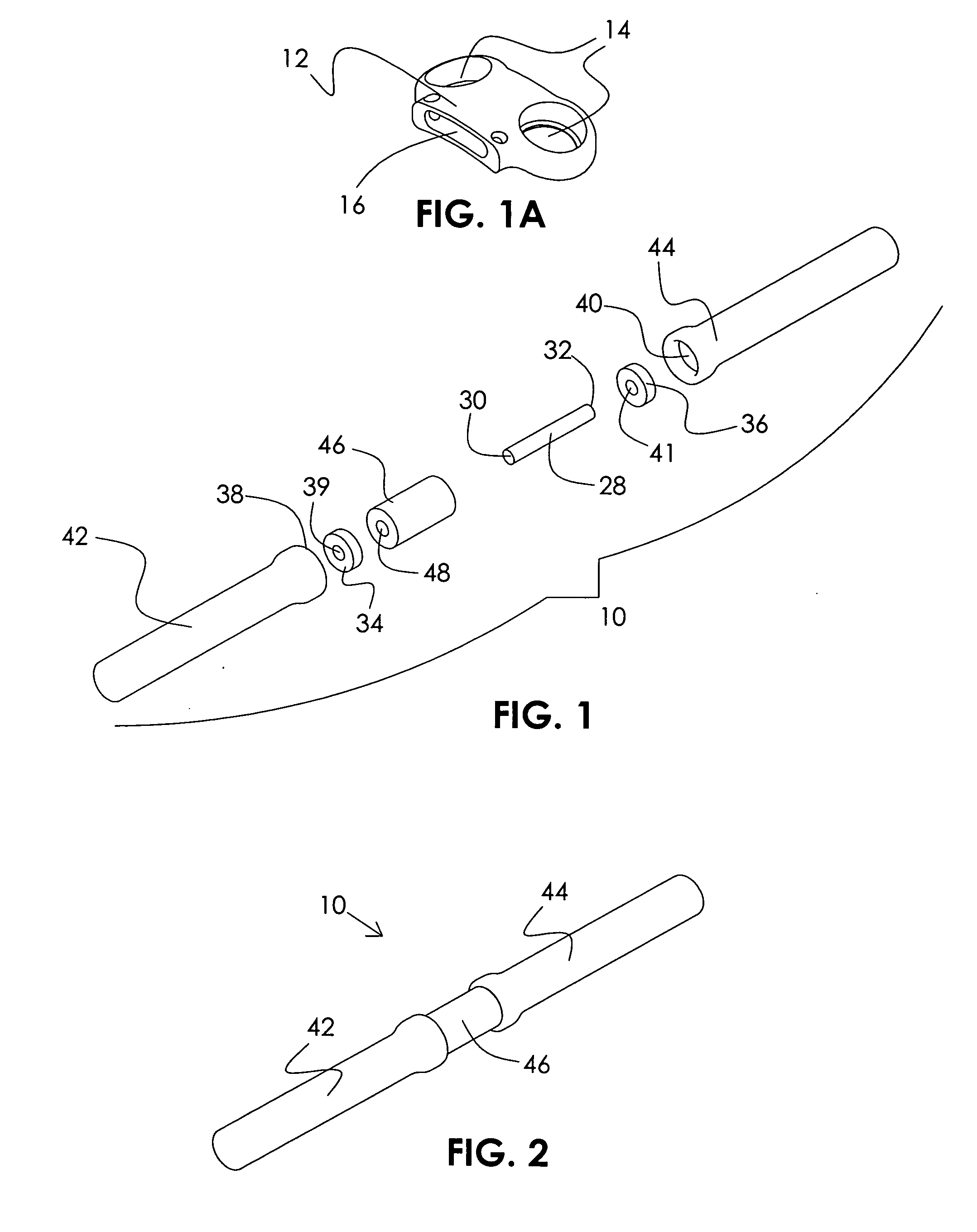
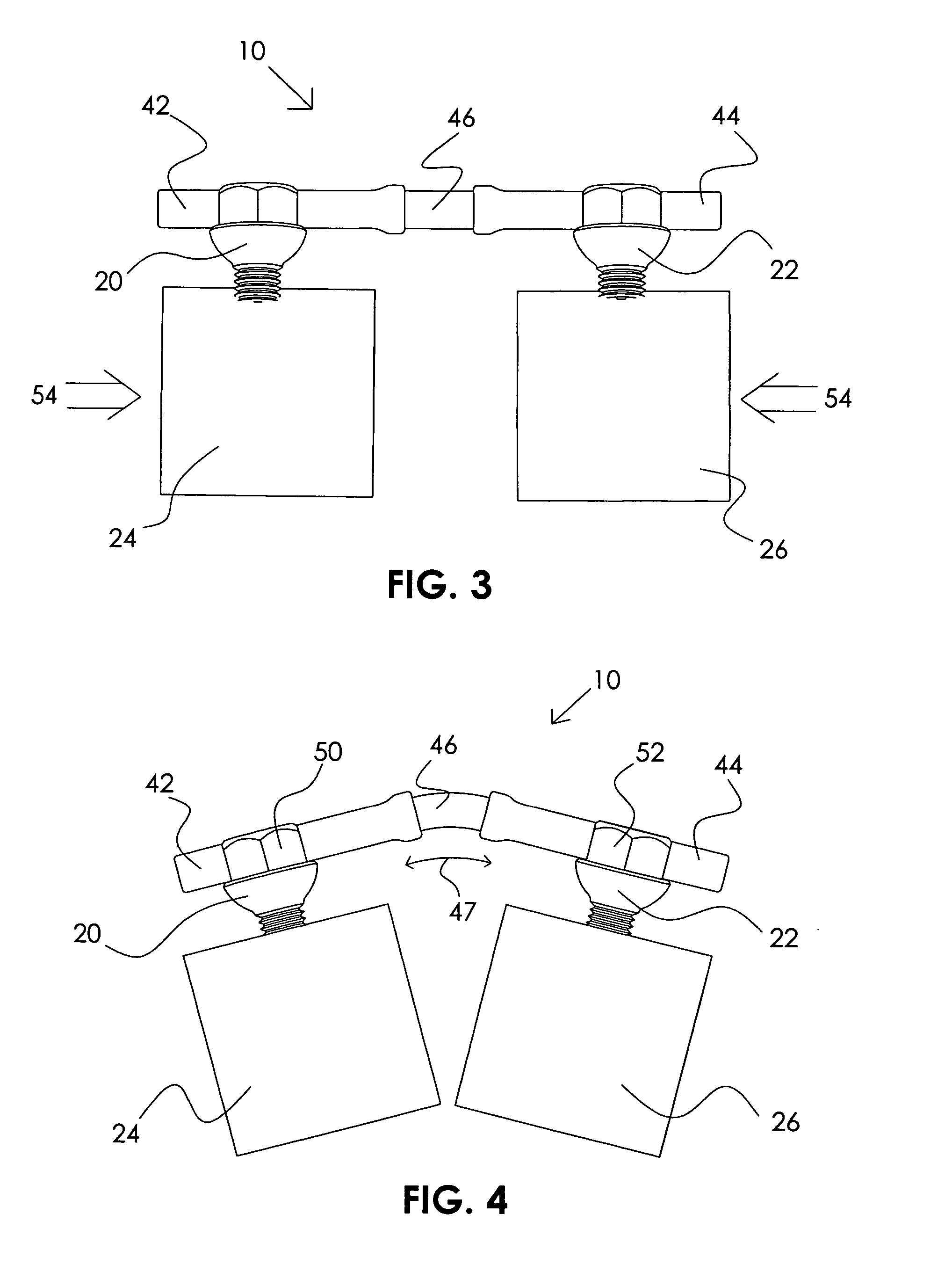
InactiveUS20060264937A1Limit range of motionConstraining bending forceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnMedicine
An orthopedic device is described for stabilizing the spinal column between first and second vertebral bodies. The device has first and second screws adapted for fixation to the first and second vertebral bodies, respectively. The device further includes an elongated ligament with a first end connected to the first screw and the second end operatively connected with the second screw. The ligament is made preferably of a nickel titanium alloy selected to have ductile inelastic properties at body temperature and is capable of continuous plastic deformation to allow relative constrained motion between the vertebral bodies. In a preferred embodiment the second pedicle screw includes a bearing for receiving the ligament in a slideably engageable relationship. The device further includes optional first and second dampening members surrounding the ligament for restraining the spinal column during flexion and extension. Other preferred devices and kits containing such devices are also described.
Owner:WHITE PATRICK
Anti-obesity devices
InactiveUS20050085923A1Controlled absorptionChange habitsSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceLigament structure
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the stomach and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for anchoring the device to the stomach and a flexible sleeve to limit absorption of nutrients in the duodenum. The anchor is collapsible for endoscopic delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Posterior dynamic stabilization cross connectors
Various methods and devices are provided for stabilizing the posterior elements of the spine, and more preferably methods and devices are provided for sharing the load with the intervertebral disc, the facet joints, the ligaments, and the muscles of the spinal column. In certain exemplary embodiments, methods and devices are provided for substantially controlling or providing resistance to movement, e.g., flexion, extension, lateral bending, and / or axial rotation, of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
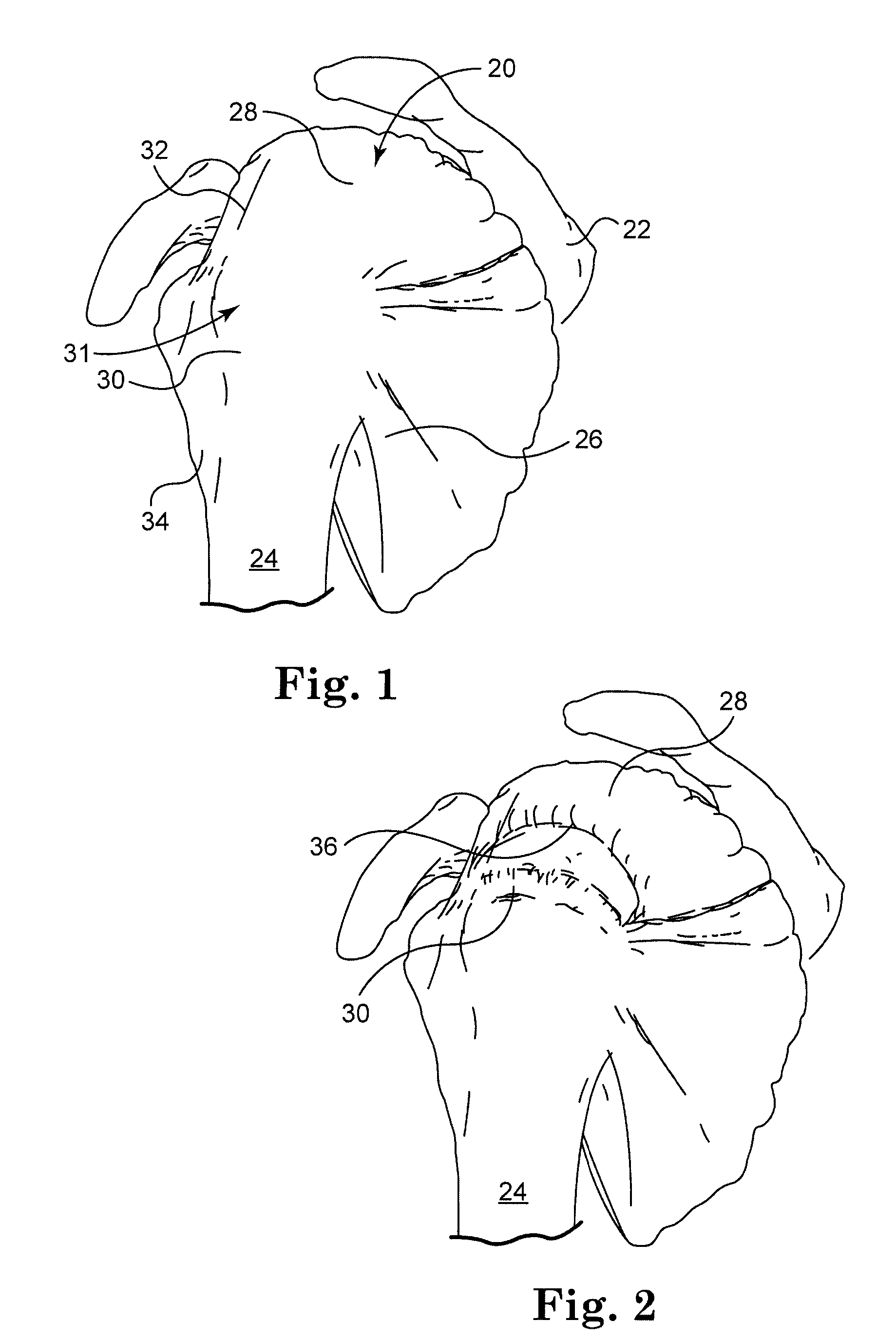
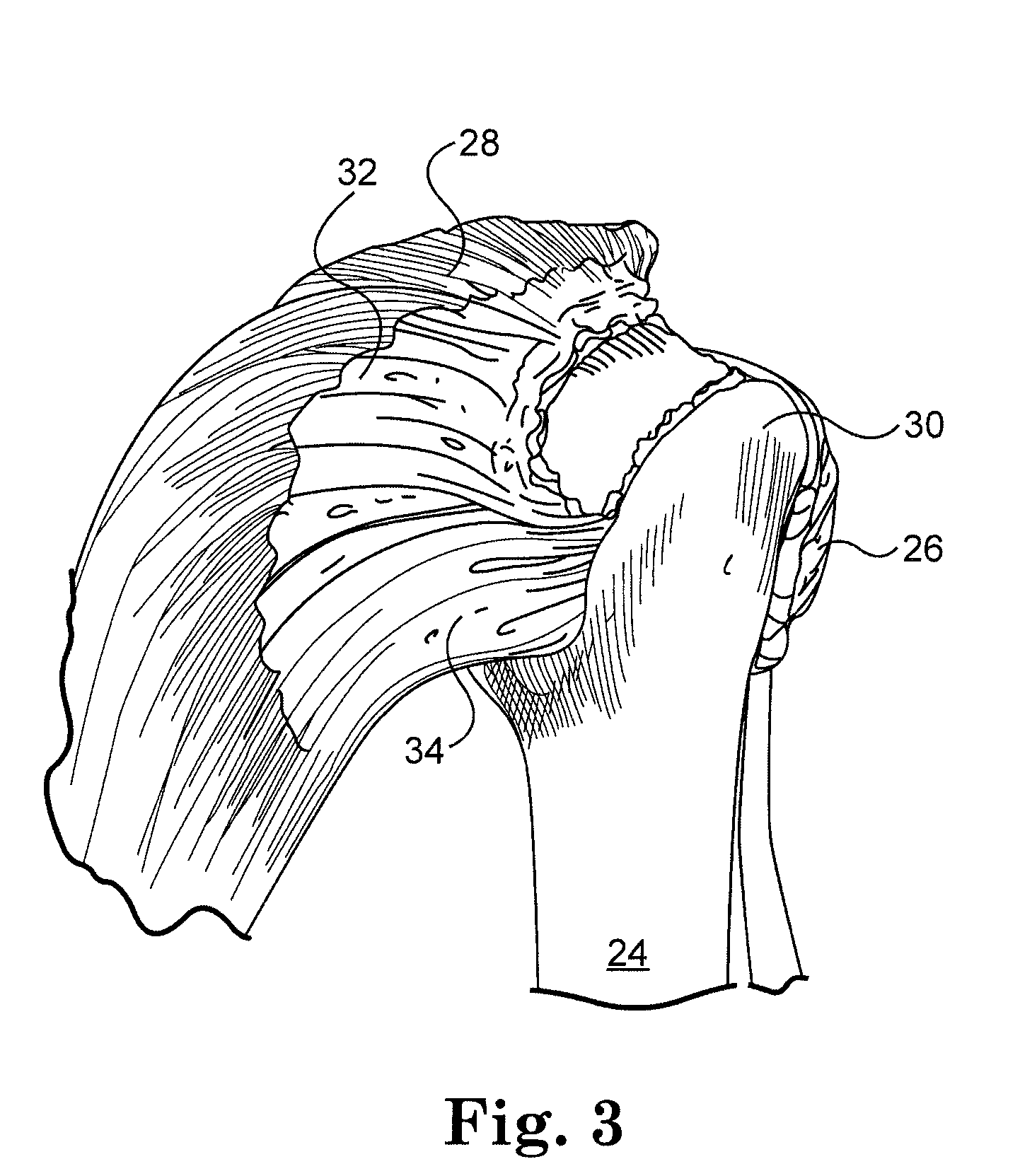
Knee prosthesis with graft ligaments
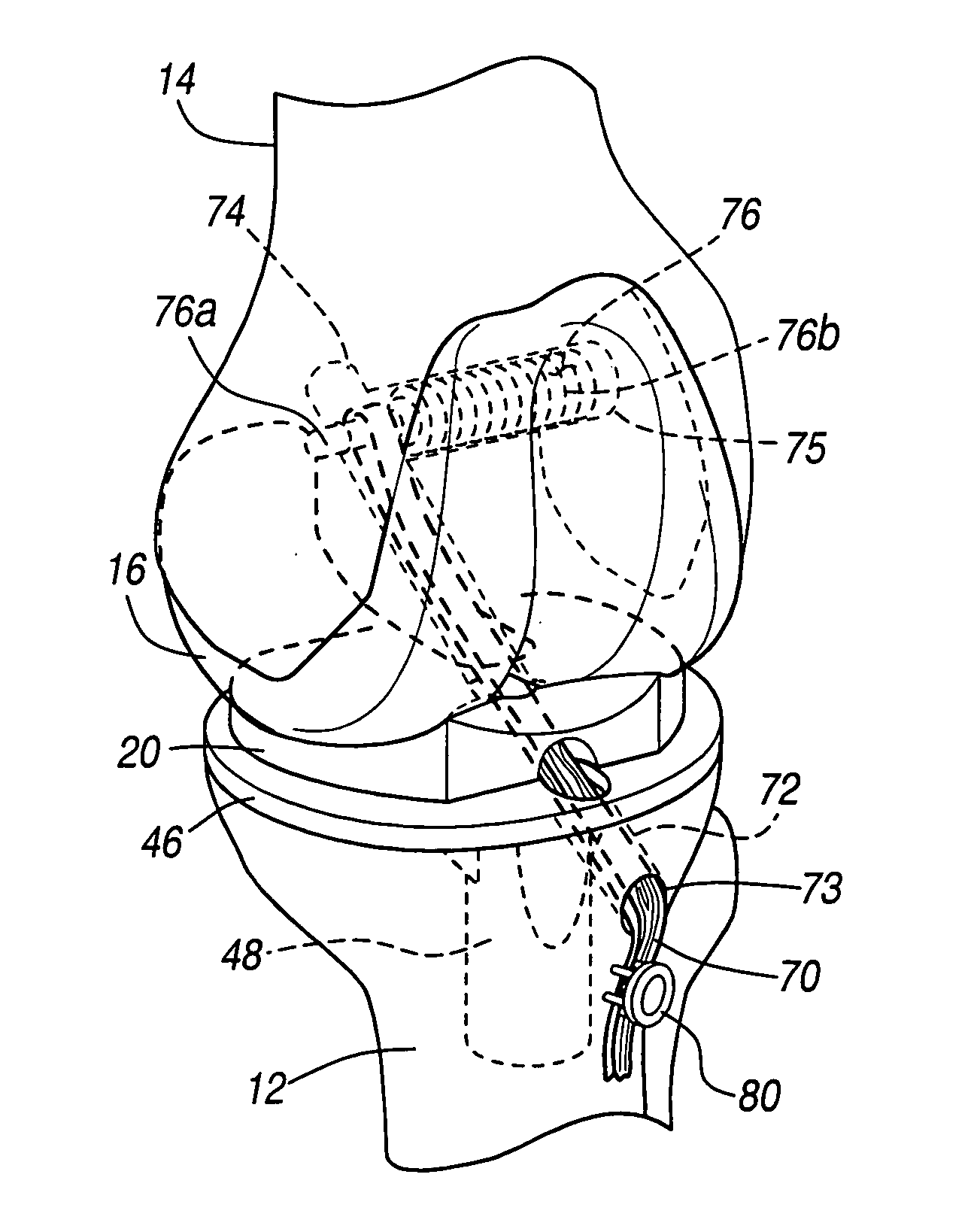
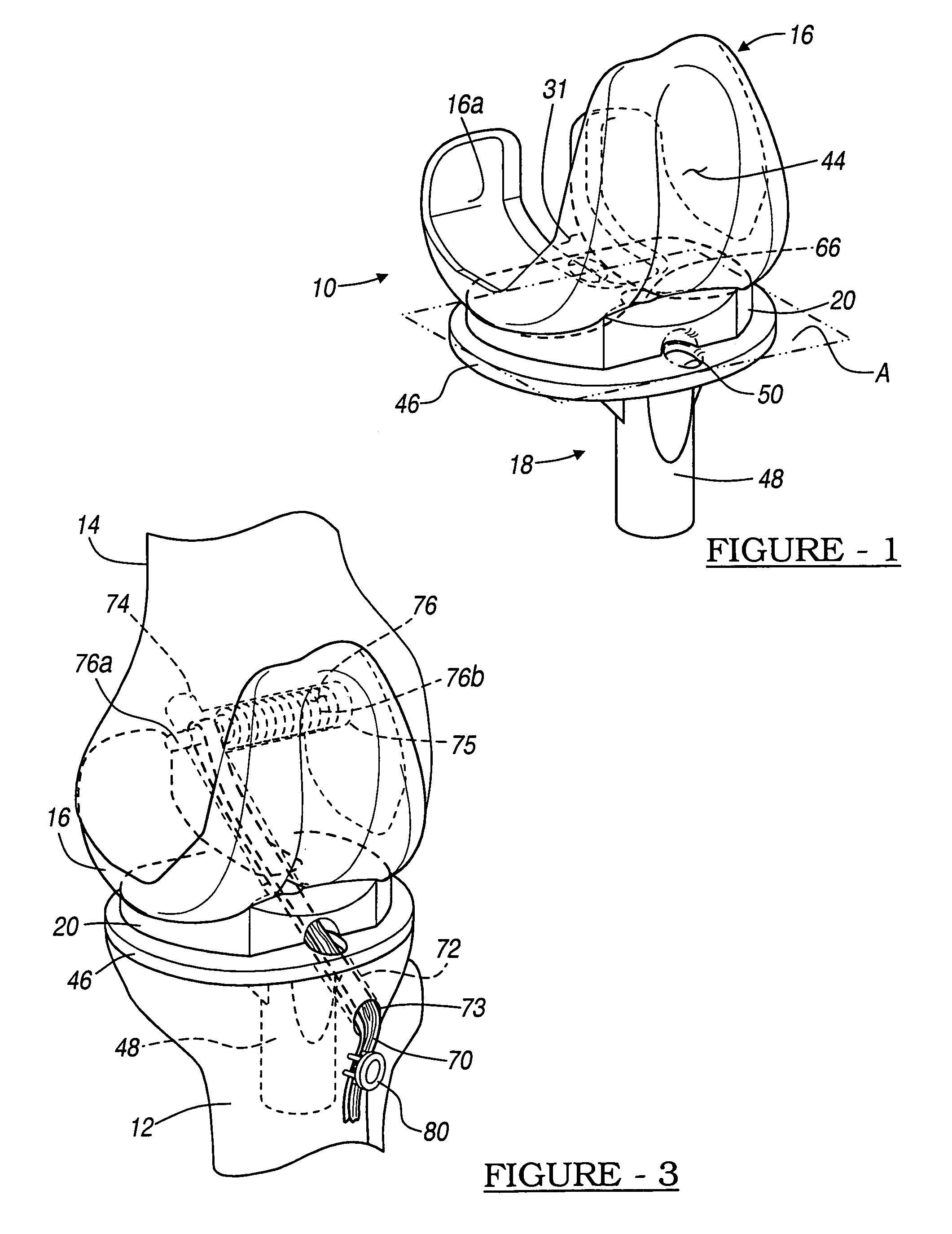
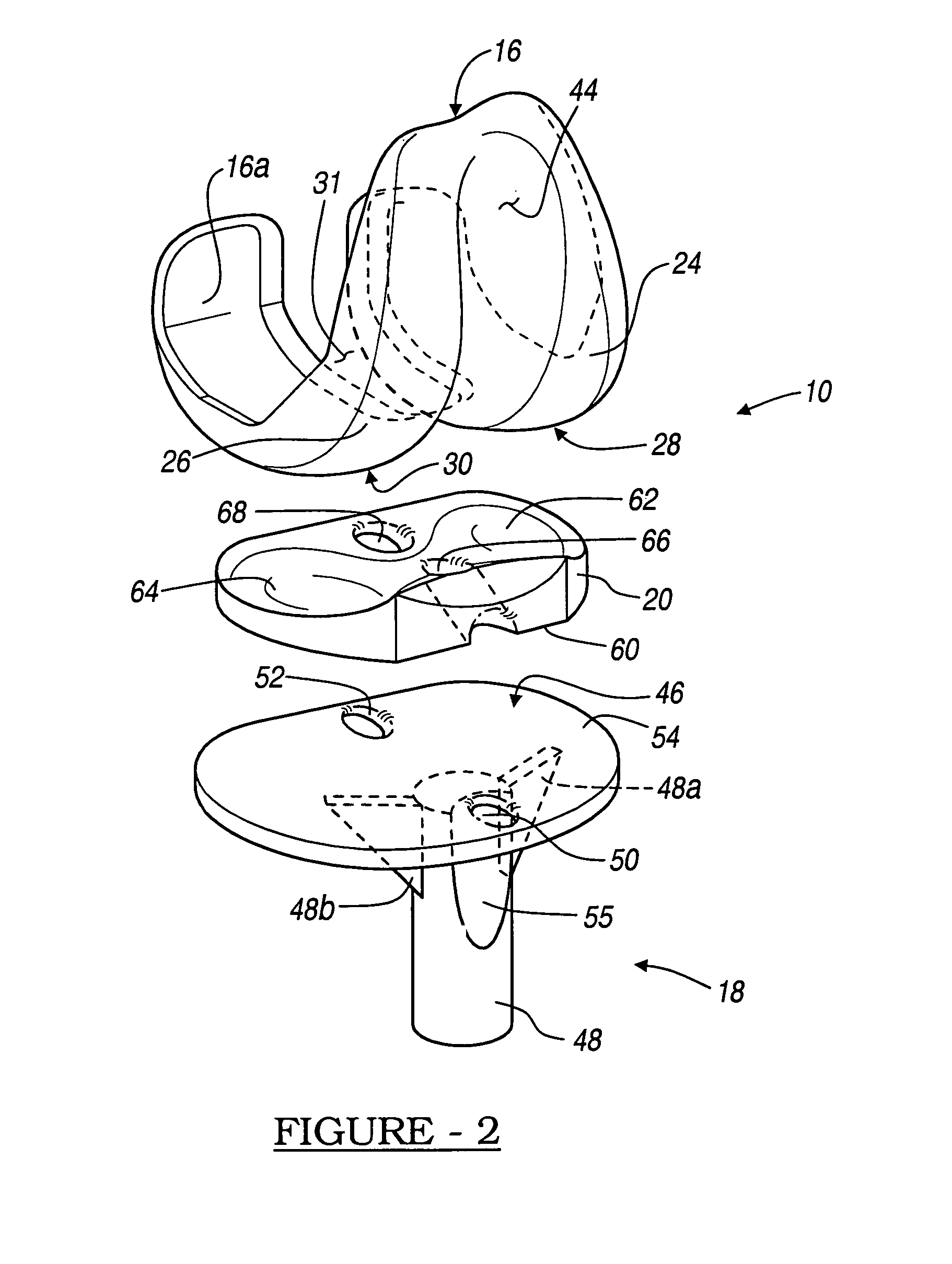
The invention relates to a knee joint prosthesis having a bearing and a biologic ligament for replacing the articulating knee portion of a femur and a tibia. The knee joint prosthesis includes a femoral component, a tibial component, a bearing member, and a biologic ligament. The femoral component includes a first femoral bearing surface and a second femoral bearing surface. The tibial component includes a tibial bearing surface. The bearing member includes a first bearing surface which is operable to articulate with the first femoral bearing surface, a second bearing surface which is operable to articulate with the second femoral bearing surface and a third bearing surface which is operable to articulate with the tibial bearing surface. The biologic ligament is coupled to both the tibia and the femur to prevent the knee joint from dislocating and guiding the femoral component along a desired path during extension and flexion.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
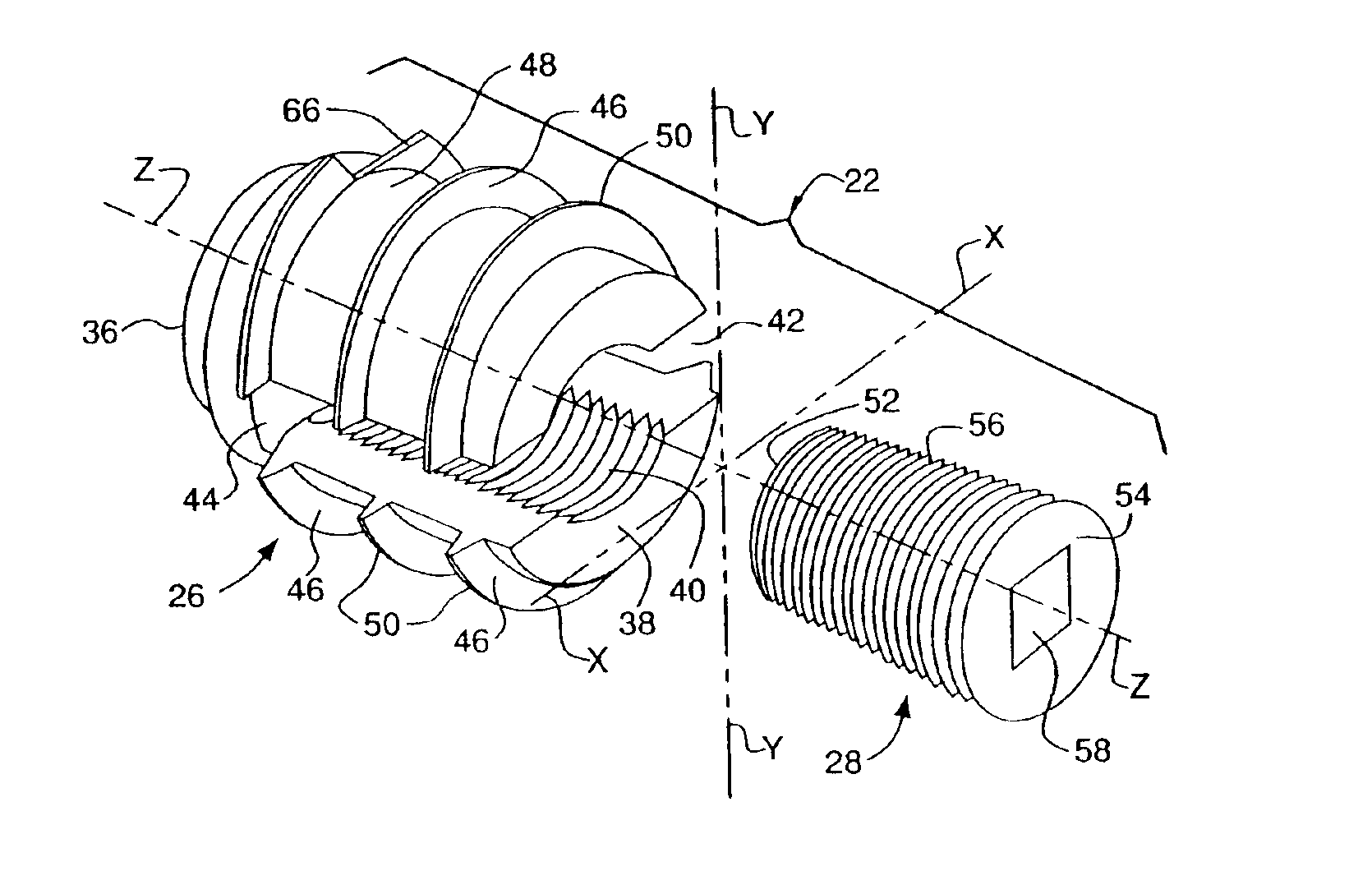
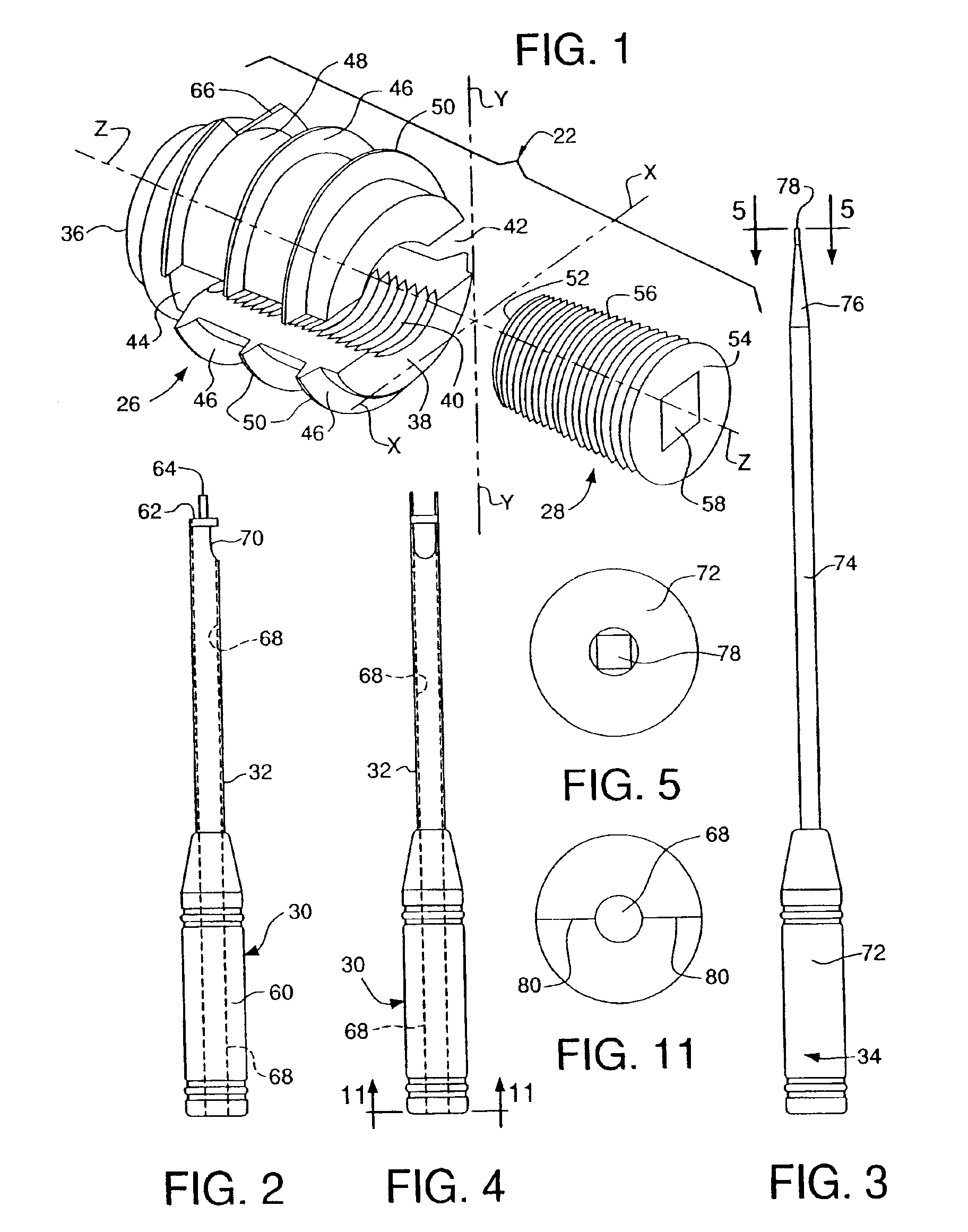
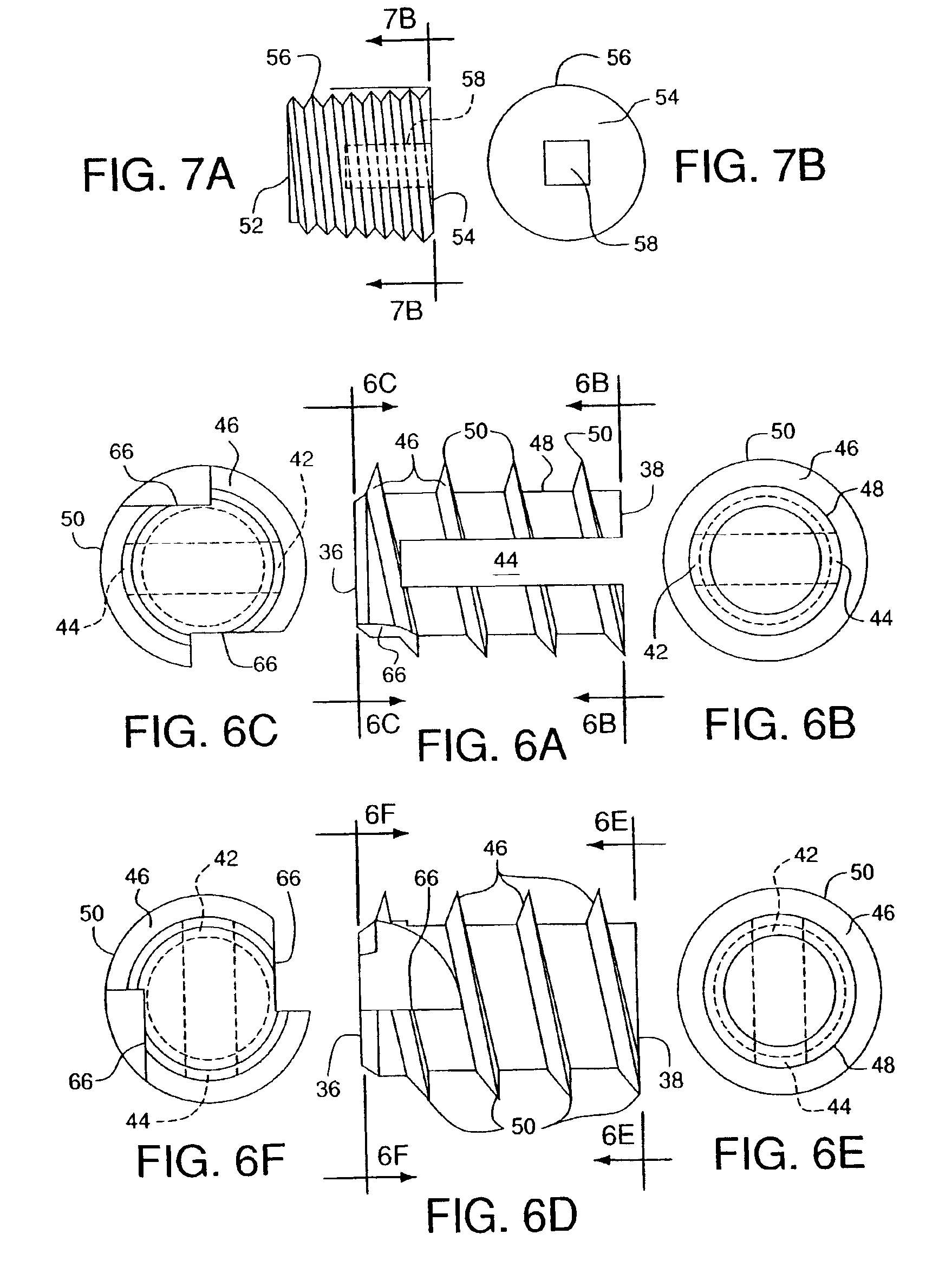
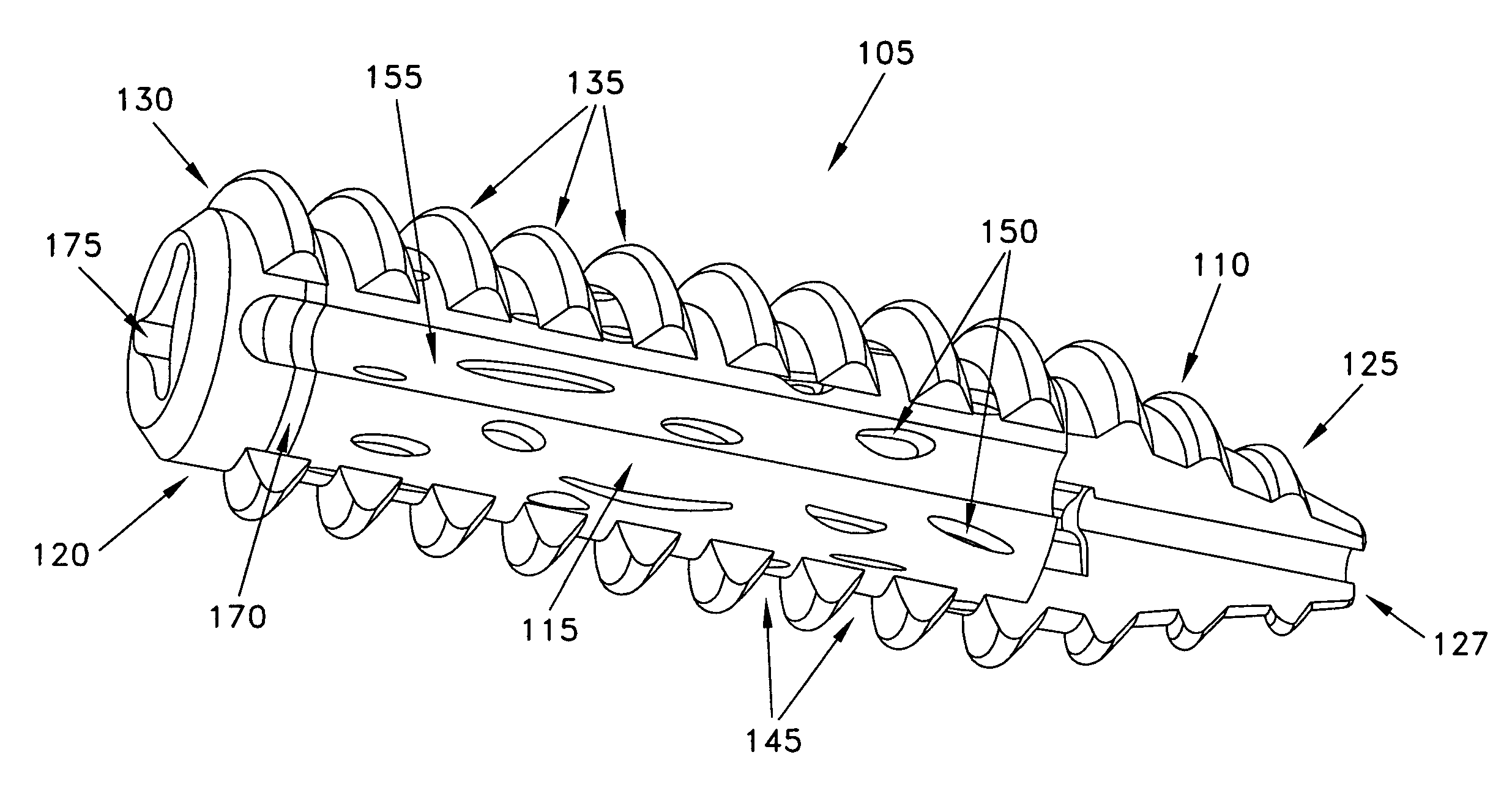
Composite interference screw for attaching a graft ligament to a bone, and other apparatus for making attachments to bone
InactiveUS20080154314A1Promoting superior bone-to-ligament ingrowthShort-term strengthSuture equipmentsBone implantInterference screwsHelical coil
An interference screw comprising:an open helical coil having a proximal end and a distal end aligned along a longitudinal axis and defining an internal volume, with the internal volume communicating with the region exterior to the open helical coil through the spacing between the turns of the open helical coil; andat least one runner disposed within the internal volume and connected to multiple turns of the open helical coil.
Owner:HEALICOIL
Posterior dynamic stabilization systems and methods
Various methods and devices are provided for stabilizing the posterior elements of the spine, and more preferably methods and devices are provided for sharing the load with the intervertebral disc, the facet joints, the ligaments, and the muscles of the spinal column. In certain exemplary embodiments, methods and devices are provided for substantially controlling or providing resistance to movement, e.g., flexion, extension, lateral bending, and / or axial rotation, of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Posterior dynamic stabilization x-device
ActiveUS7658752B2Internal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Various methods and devices are provided for stabilizing the posterior elements of the spine, and more preferably methods and devices are provided for sharing the load with the intervertebral disc, the facet joints, the ligaments, and the muscles of the spinal column. In certain exemplary embodiments, methods and devices are provided for substantially controlling or providing resistance to movement, e.g., flexion, extension, lateral bending, and / or axial rotation, of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
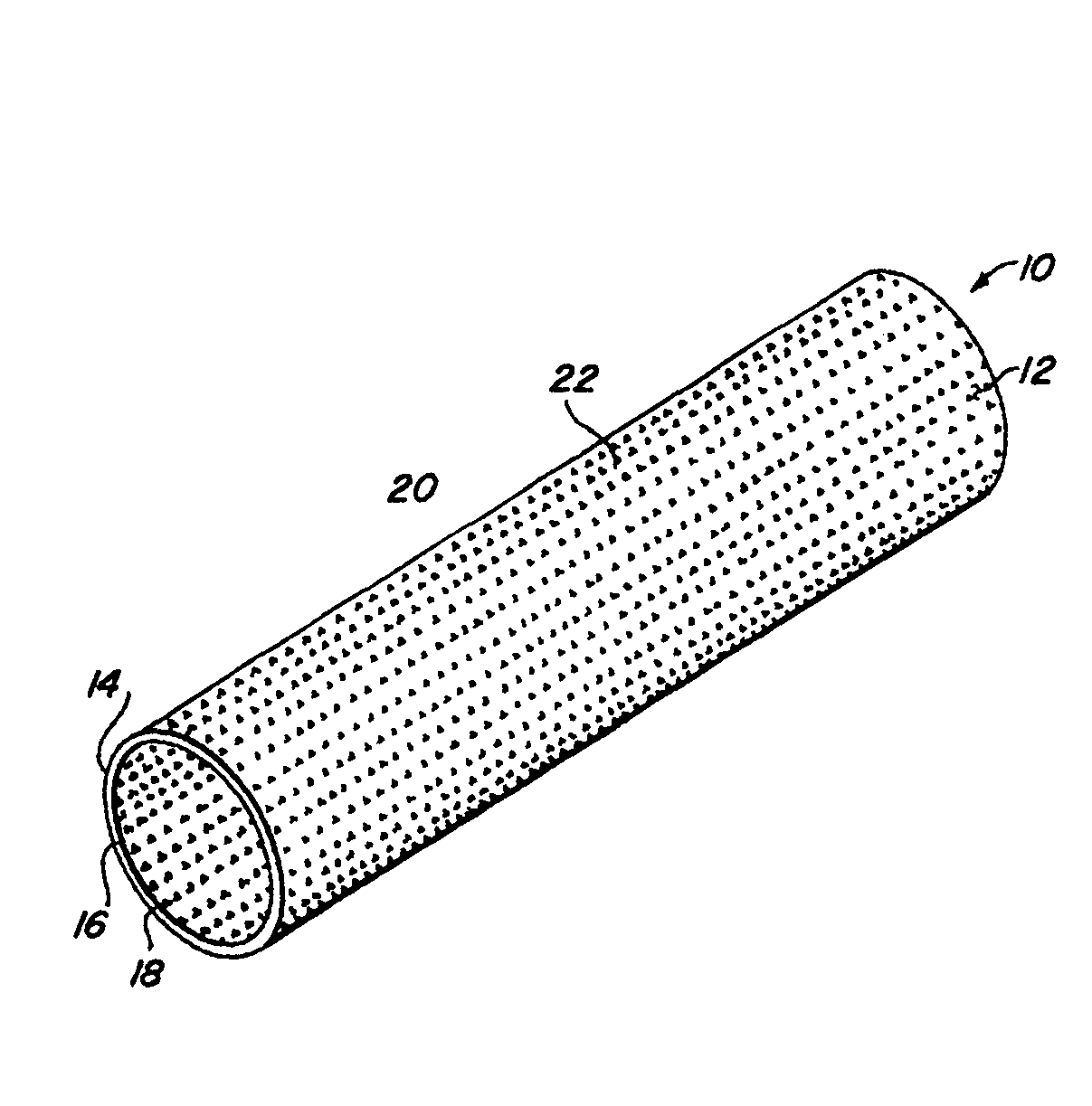
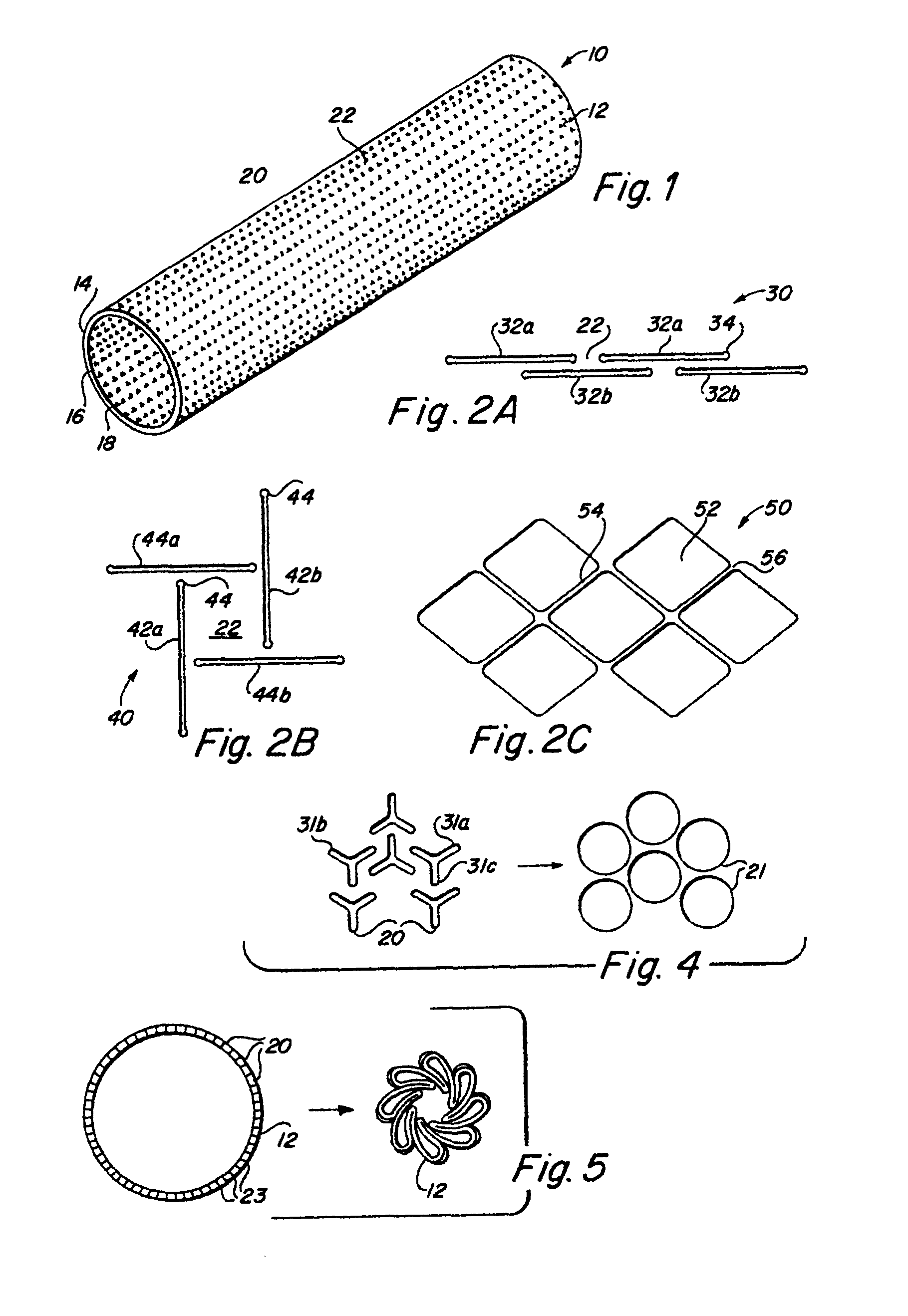
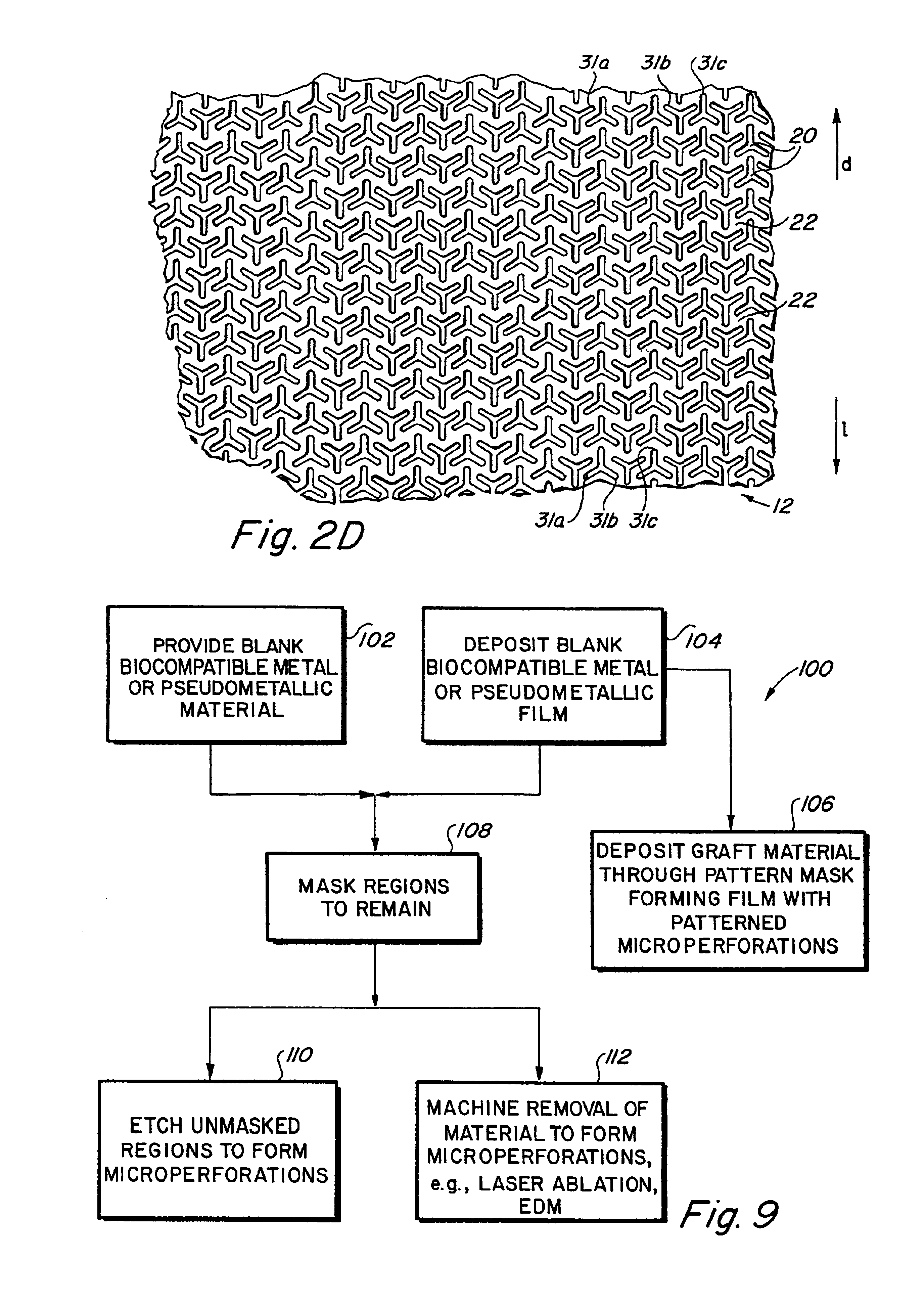
Complaint implantable medical devices and methods of making same
InactiveUS6936066B2Give flexibilityFacilitating transmural endothelializationStentsHeart valvesSurgical GraftMetallic materials
Implantable medical grafts fabricated of metallic or pseudometallic films of biocompatible materials having a plurality of microperforations passing through the film in a pattern that imparts fabric-like qualities to the graft or permits the geometric deformation of the graft. The implantable graft is preferably fabricated by vacuum deposition of metallic and / or pseudometallic materials into either single or multi-layered structures with the plurality of microperforations either being formed during deposition or after deposition by selective removal of sections of the deposited film. The implantable medical grafts are suitable for use as endoluminal or surgical grafts and may be used as vascular grafts, stent-grafts, skin grafts, shunts, bone grafts, surgical patches, non-vascular conduits, valvular leaflets, filters, occlusion membranes, artificial sphincters, tendons and ligaments.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Anti-obesity devices
InactiveUS7122058B2Limit absorptionModify their heating habitsSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceImplanted device
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
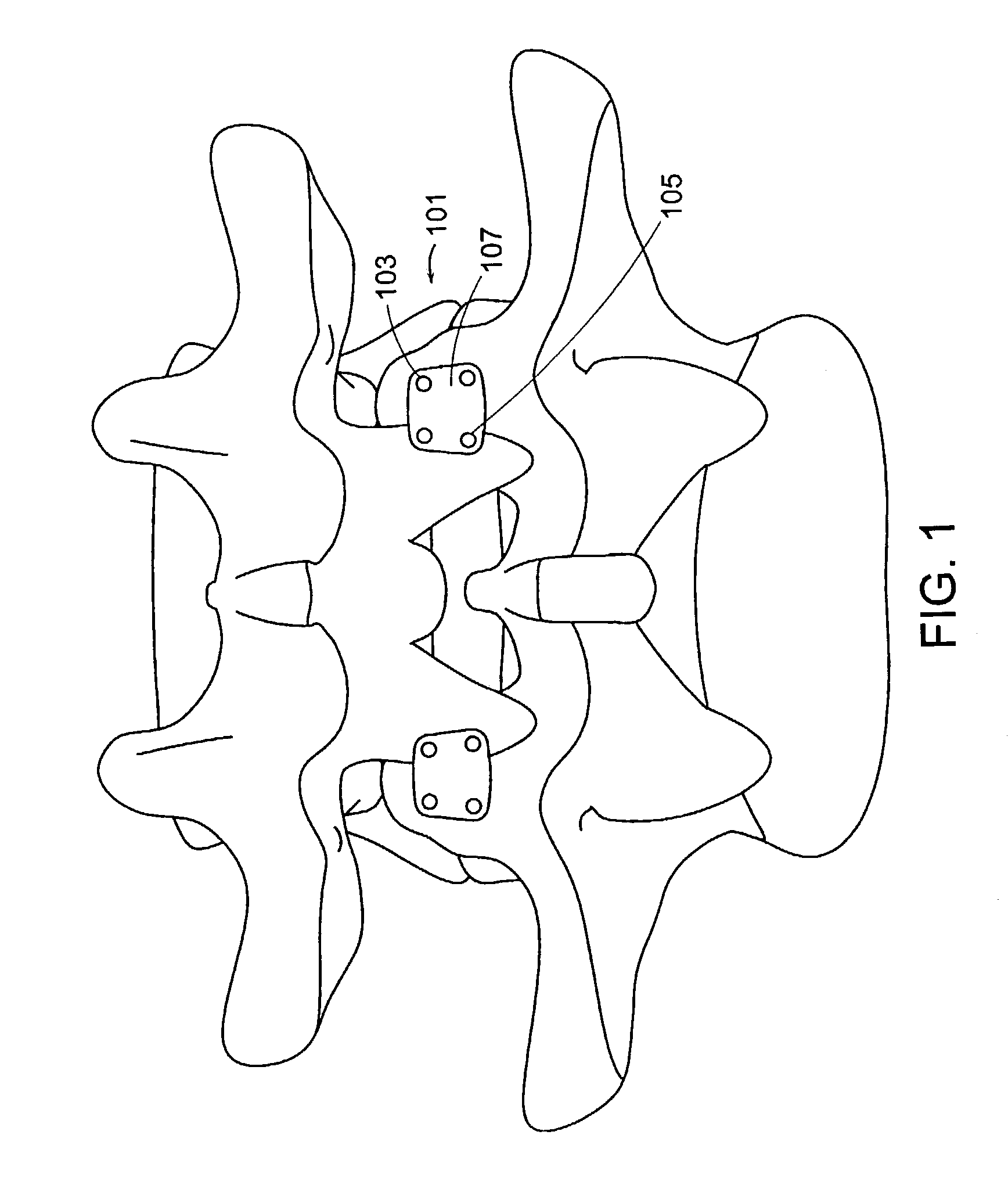
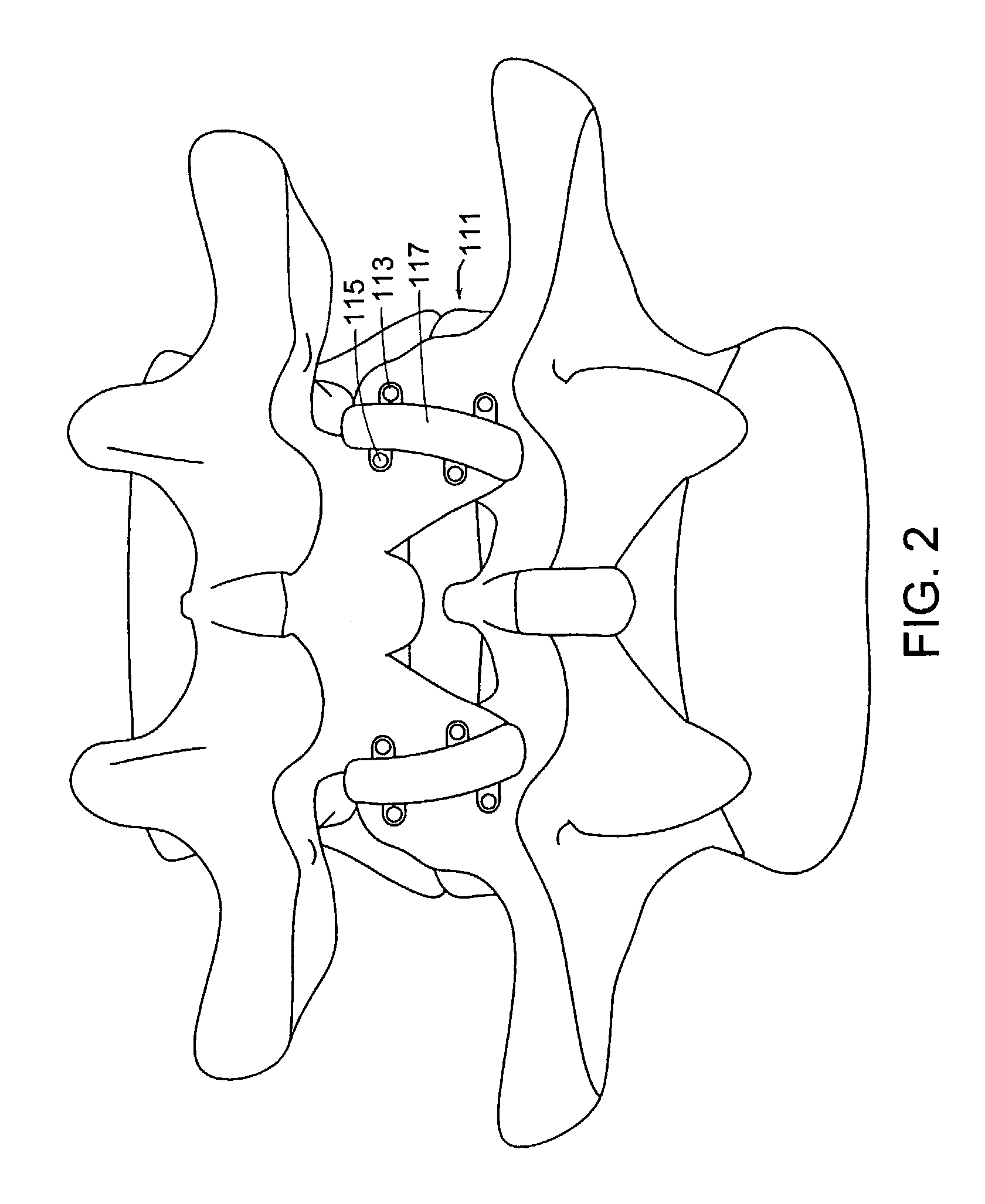
Artificial facet joint
InactiveUS20060149229A1Facilitate controlled movementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnLigament structure
Various methods and devices for replacing damaged, injured, diseased, or otherwise unhealthy posterior elements, such as the facet joints, the lamina, the posterior ligaments, and / or other features of a patient's spinal column, are provided. In one exemplary embodiment, the methods and devices are effective to mimic the natural function of the spine by allowing flexion, extension, and lateral bending of the spine, while substantially restricting posterior-anterior shear and rotation of the spine.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Intestinal sleeve
ActiveUS20050125075A1Controlled absorptionChange habitsSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceInsertion stent
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the duodenum and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for attaching the device to the duodenum and an unsupported flexible sleeve to limit absorption of nutrients in the duodenum. The anchor can include a stent and / or a wave anchor and is collapsible for catheter-based delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Orthopedic stabilization device
InactiveUS20060264935A1Limit range of motionRestore range of motionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnLigament structure
An orthopedic device is described for stabilizing the spinal column between first and second vertebral bodies. The device has first and second anchors adapted for fixation to the first and second vertebral bodies, respectively. The device further includes an elongated bridge with first and second ends operatively connected to the first and second anchors, respectively. The bridge contains an implantable ligament made preferably of a nickel titanium alloy selected to have inelastic properties at body temperature, wherein the bridge is capable of continuous plastic deformation to allow relative constrained motion between the vertebral bodies. In a preferred embodiment the device further includes a dampening member surrounding the ligament, which may be a wire, tube or band. In another preferred embodiment the device includes rigid rod members each correspondingly retained with either end of the ligament, and independently attached to the vertebral bodies with anchors. The rigid rod members are correspondingly connected to either end of the ligament. In yet another preferred embodiment, the device includes plate segments correspondingly retained with either end of the ligament, and independently attached to the vertebral bodies with a plurality of anchors. Other preferred devices and kits containing such devices are also described.
Owner:WHITE PATRICK
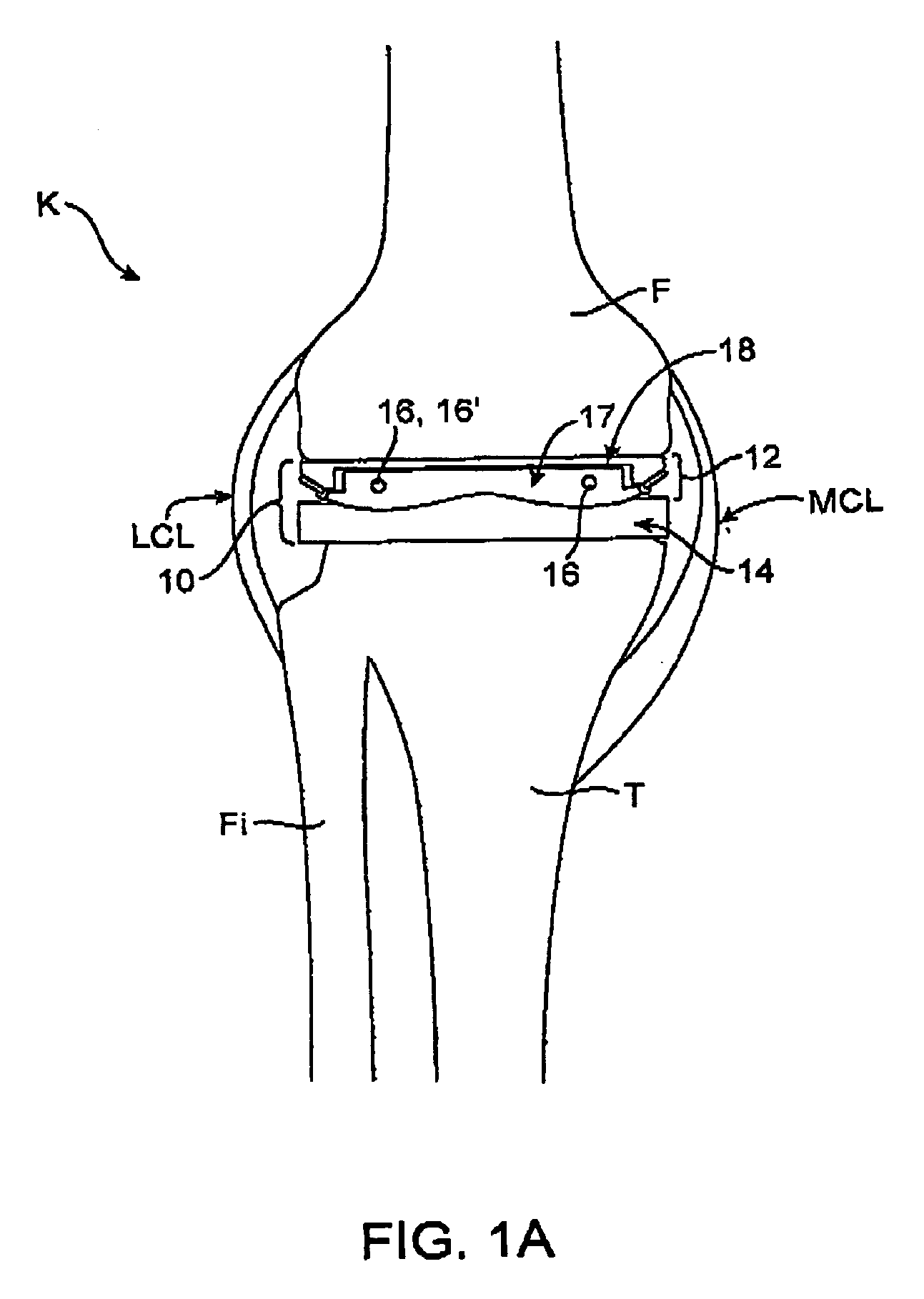
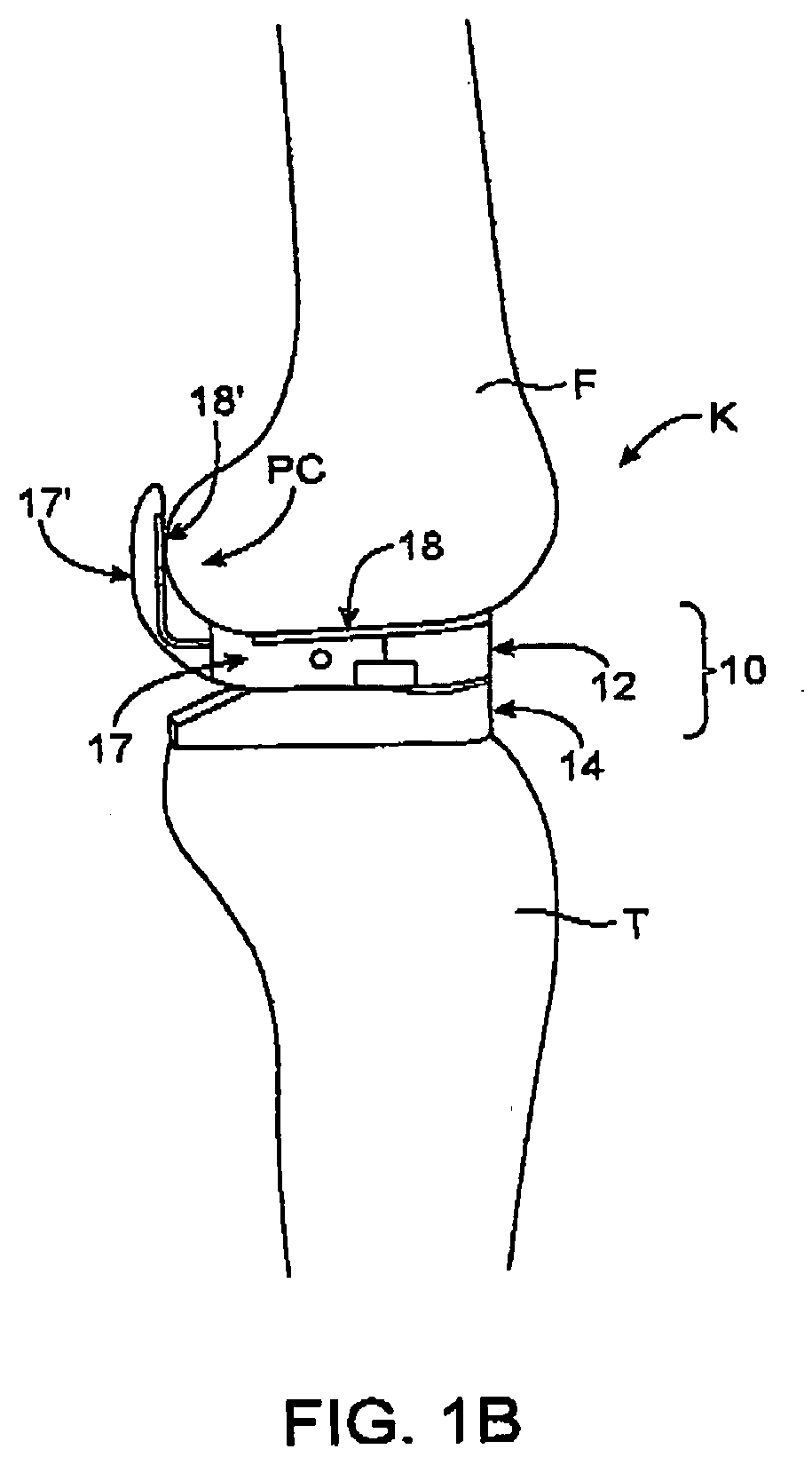
Prosthetic facet joint ligament
InactiveUS7101398B2Relief the painProcess stabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisProsthesisLigament structure
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com