Patents
Literature
1425 results about "Axial rotation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
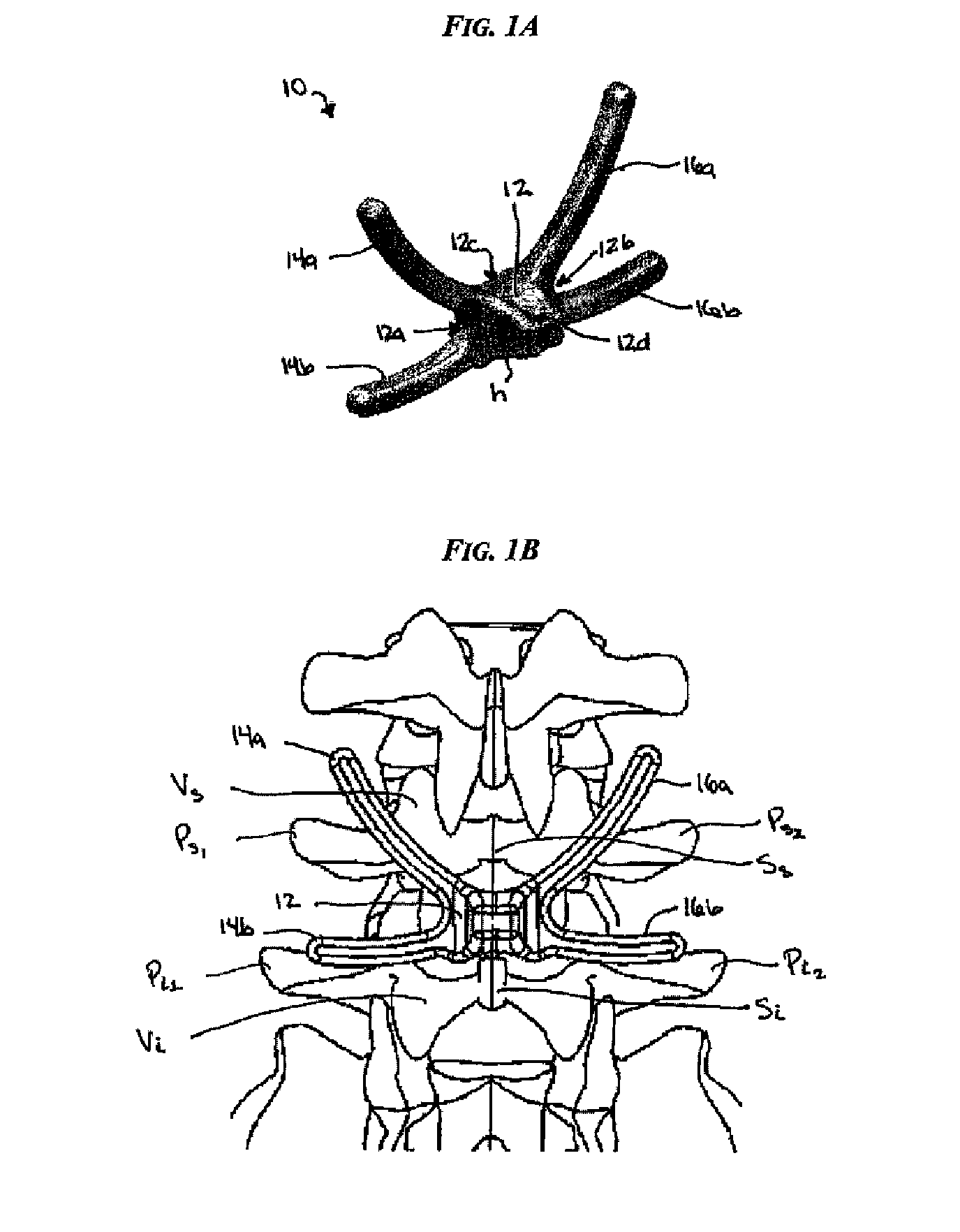
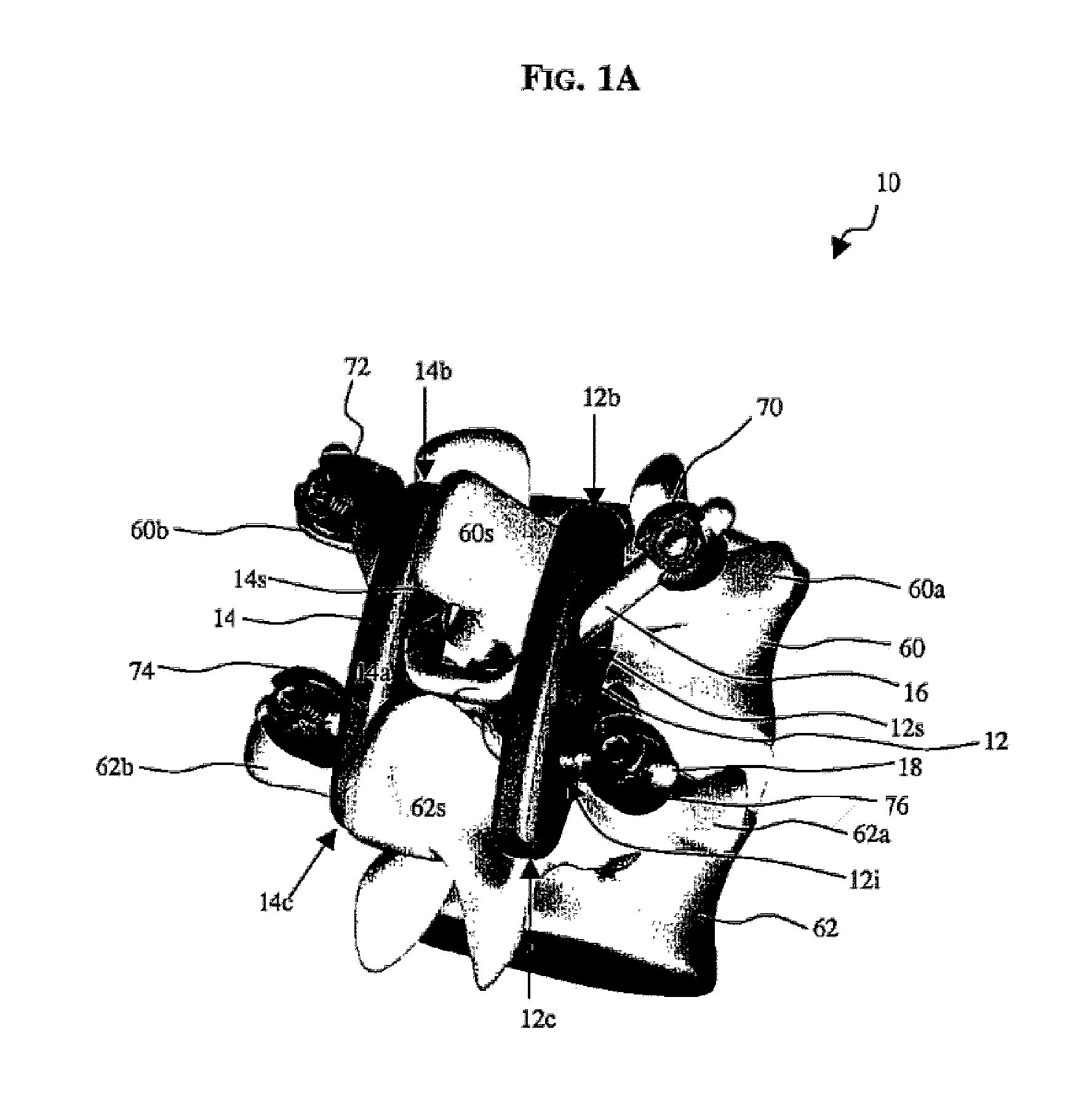
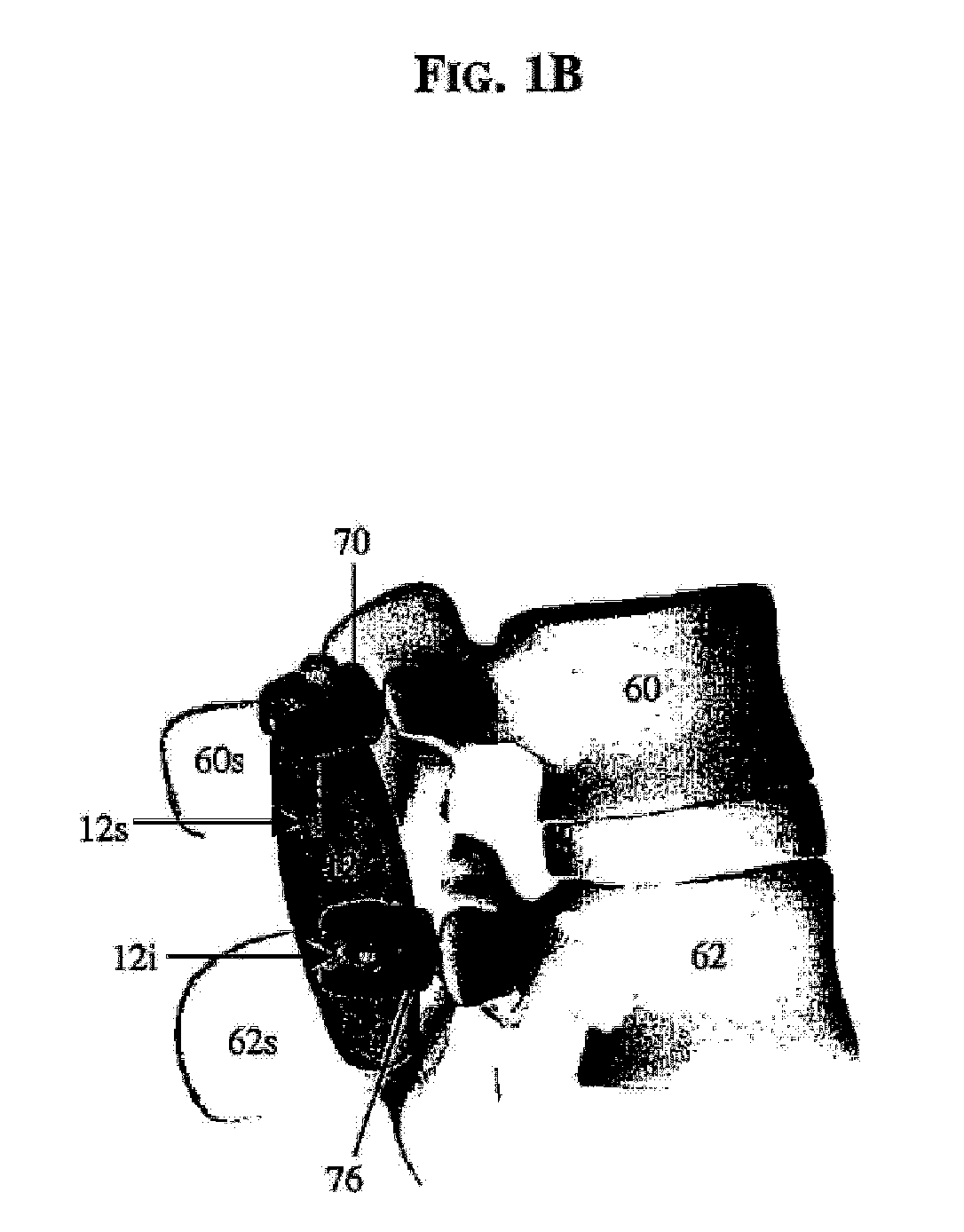
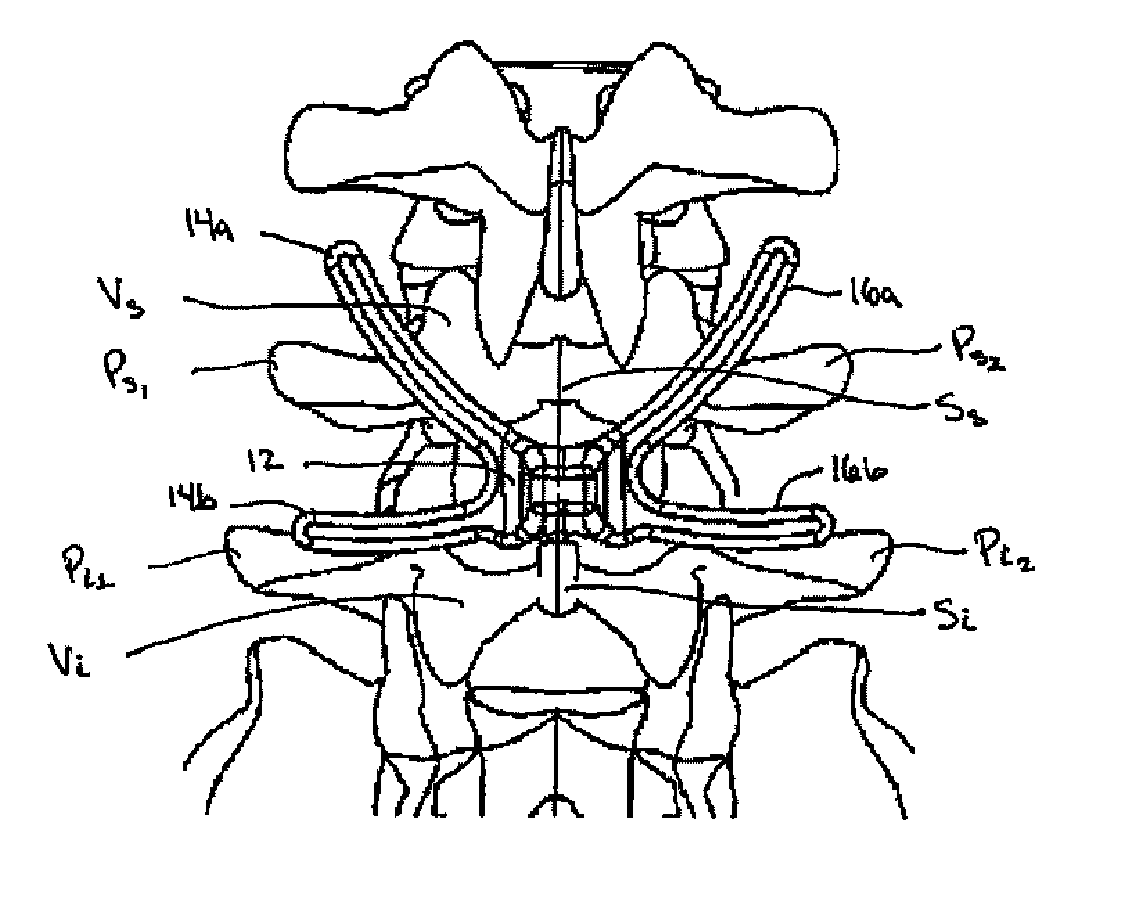
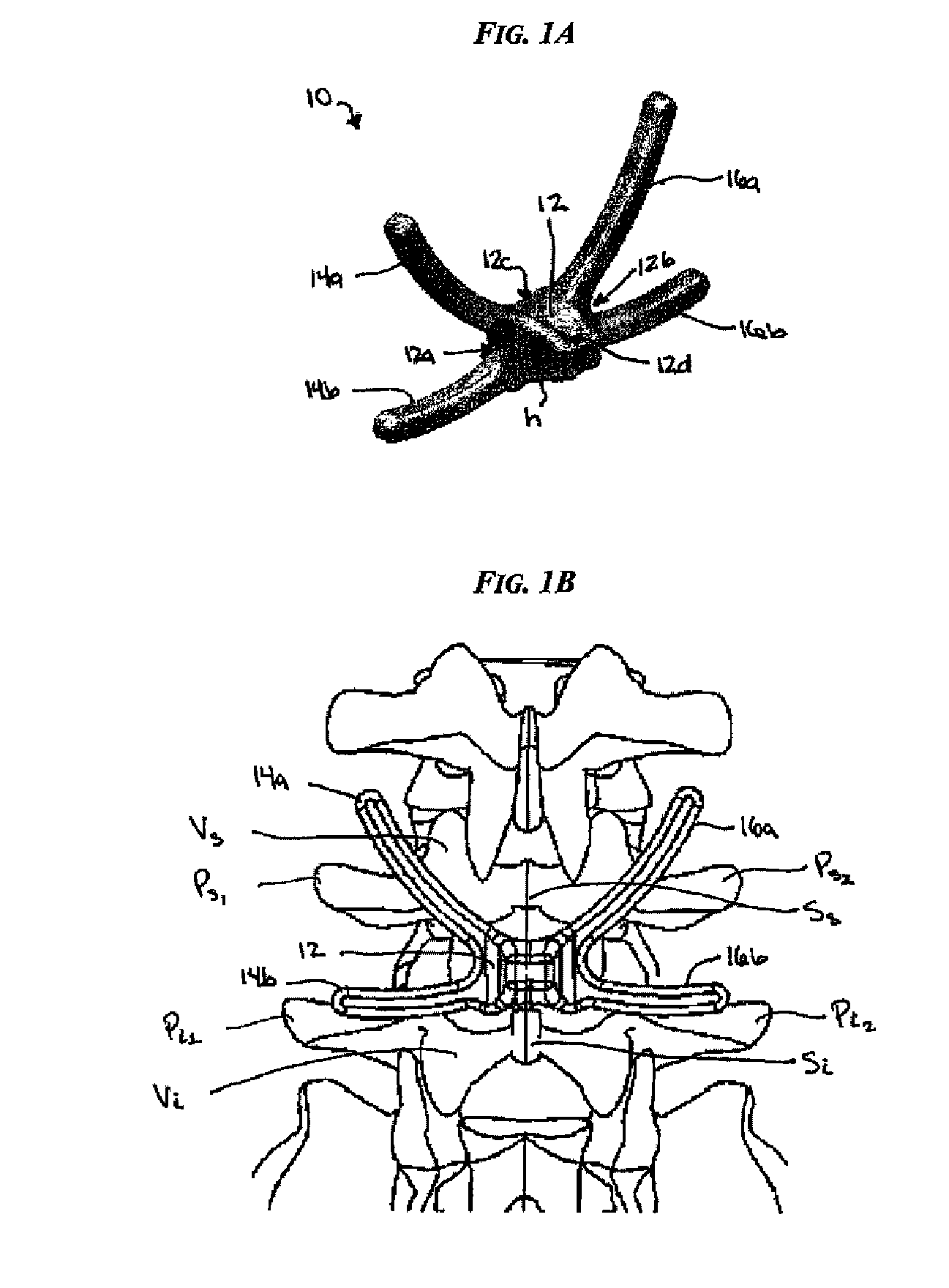
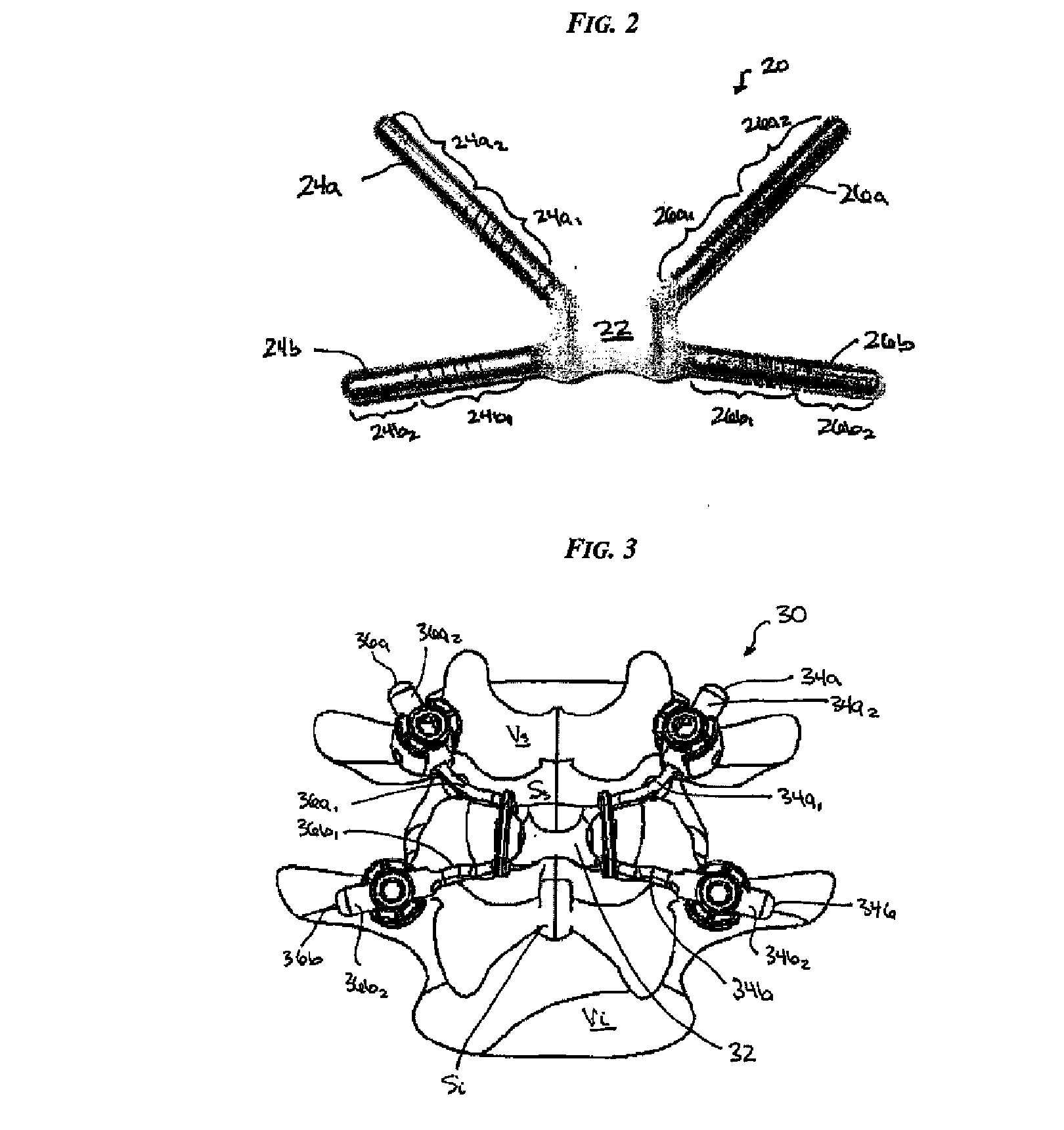
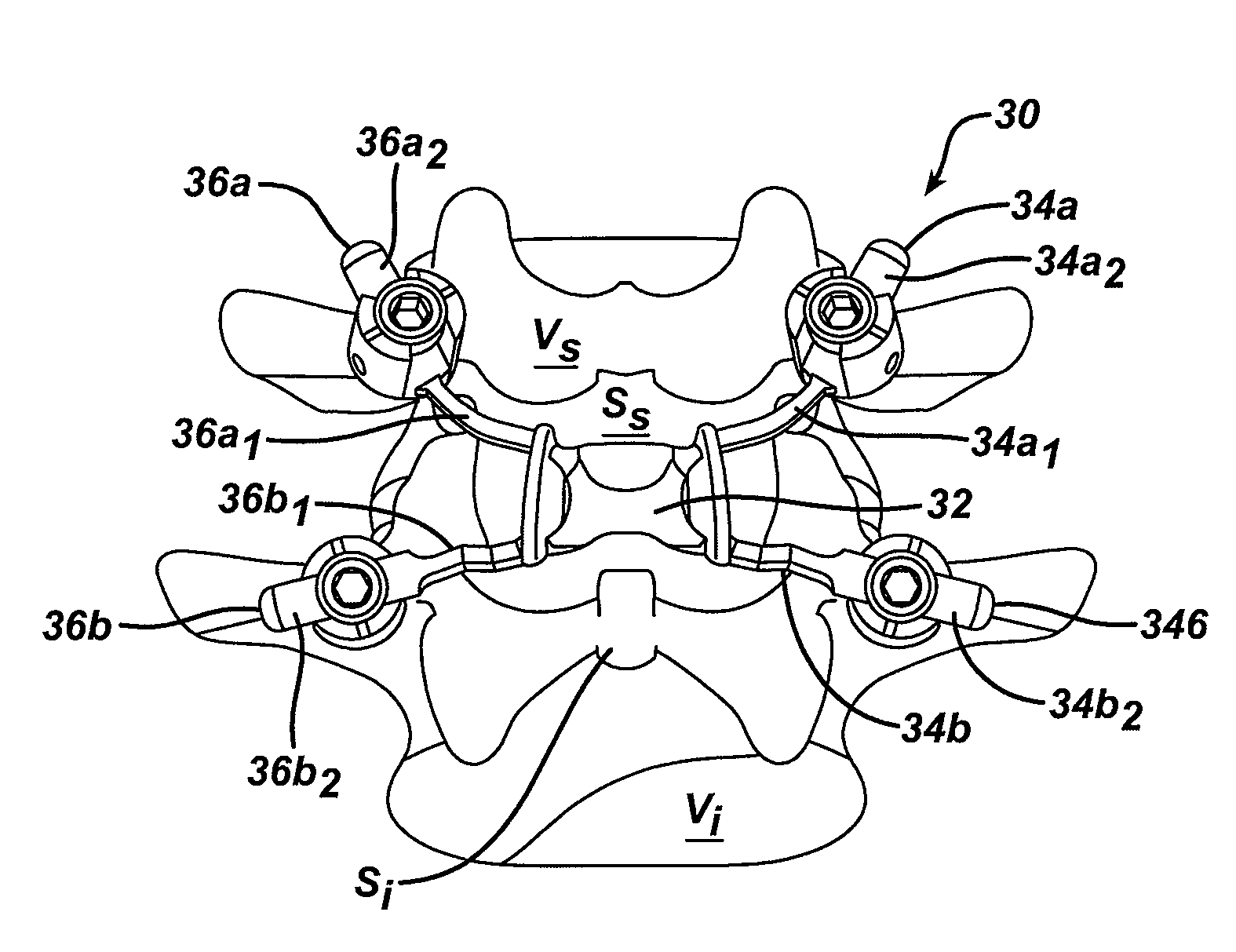
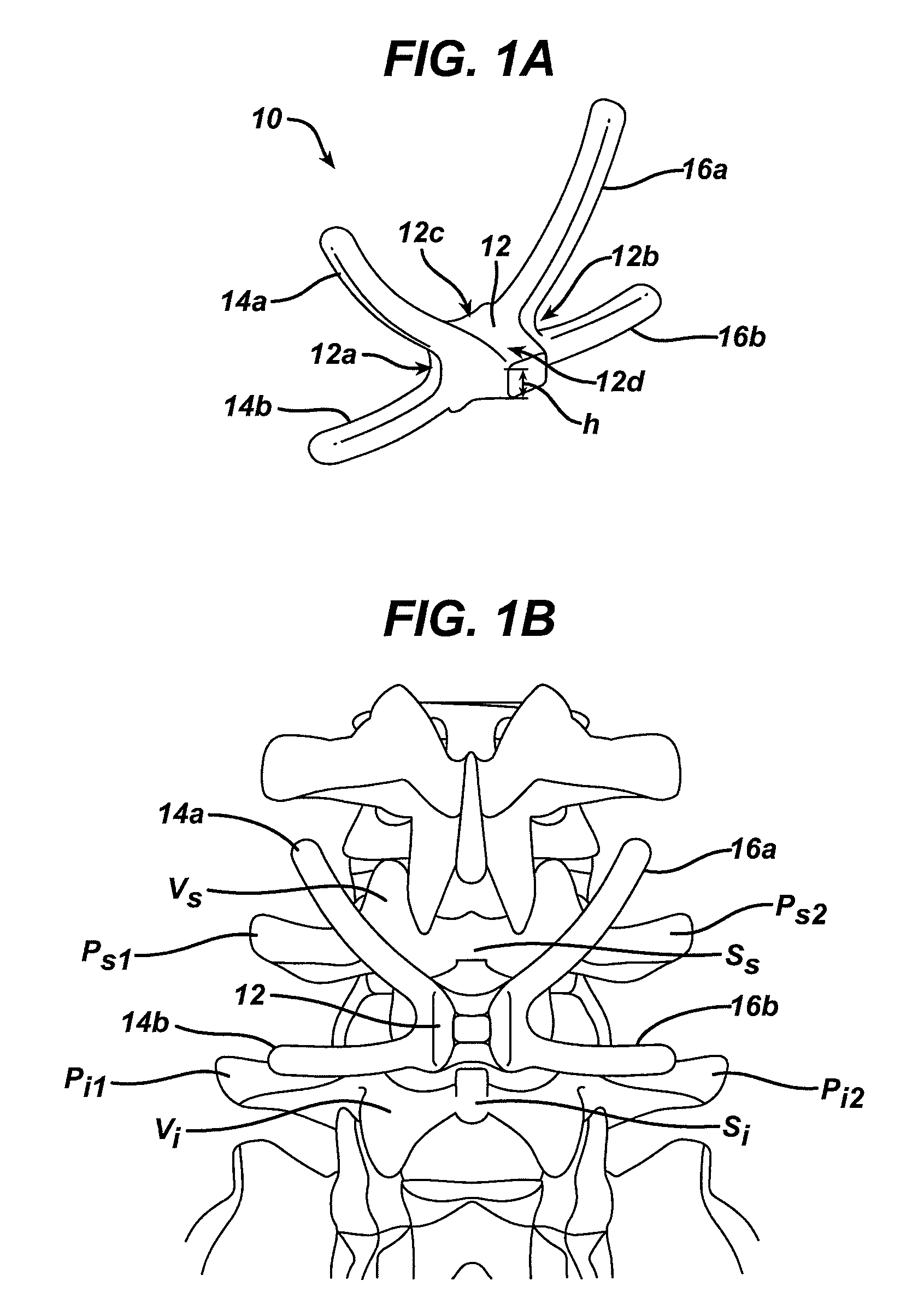
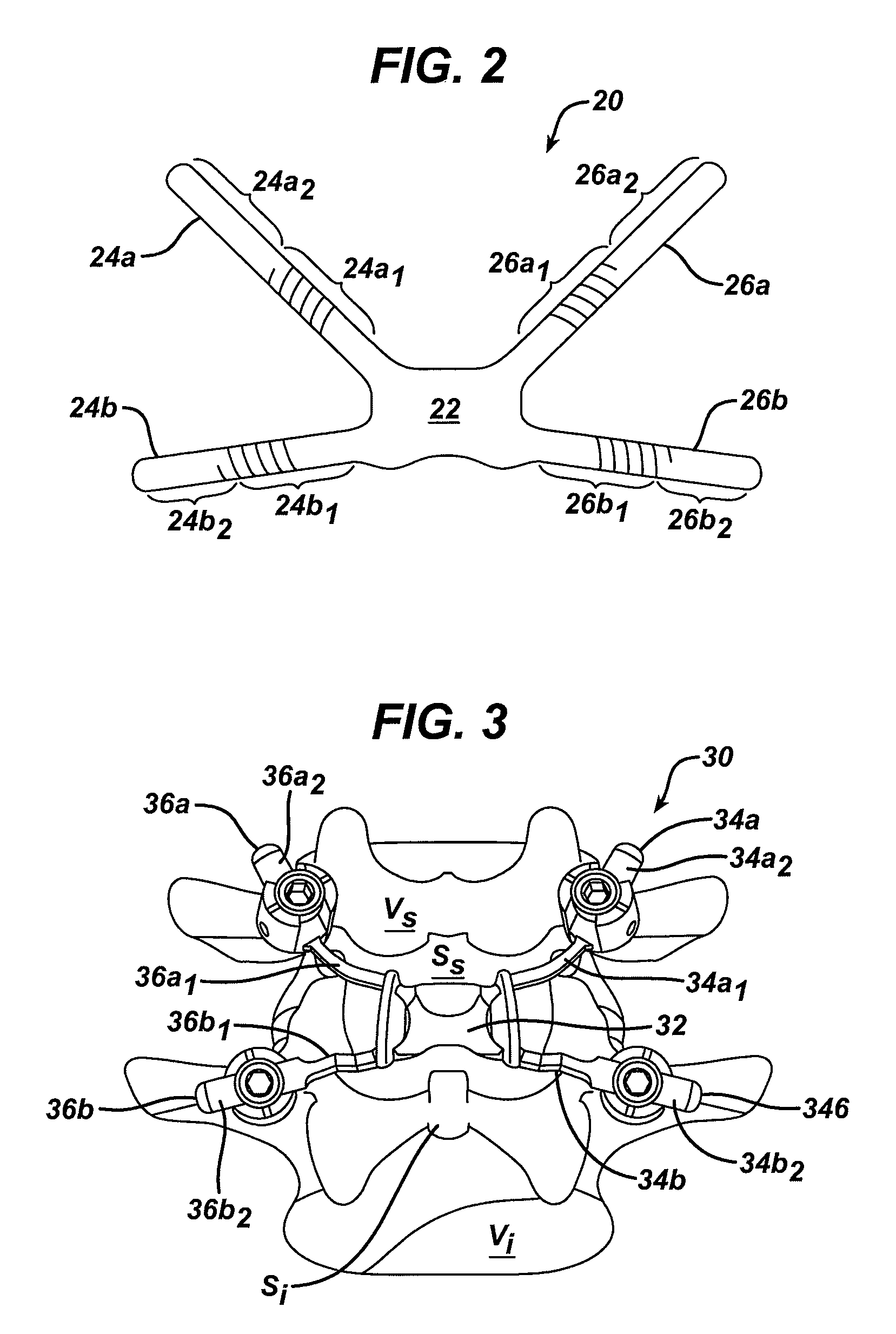
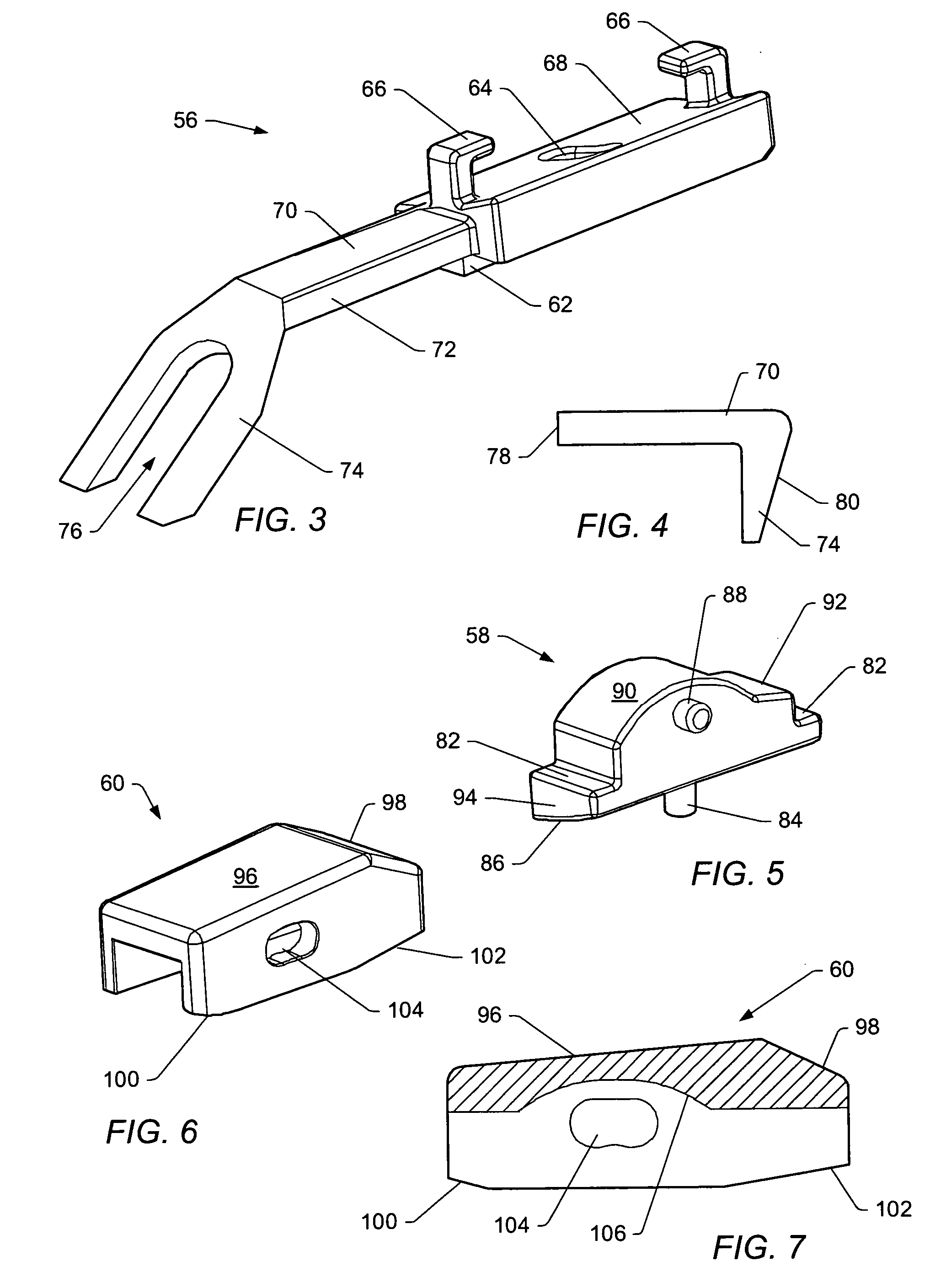
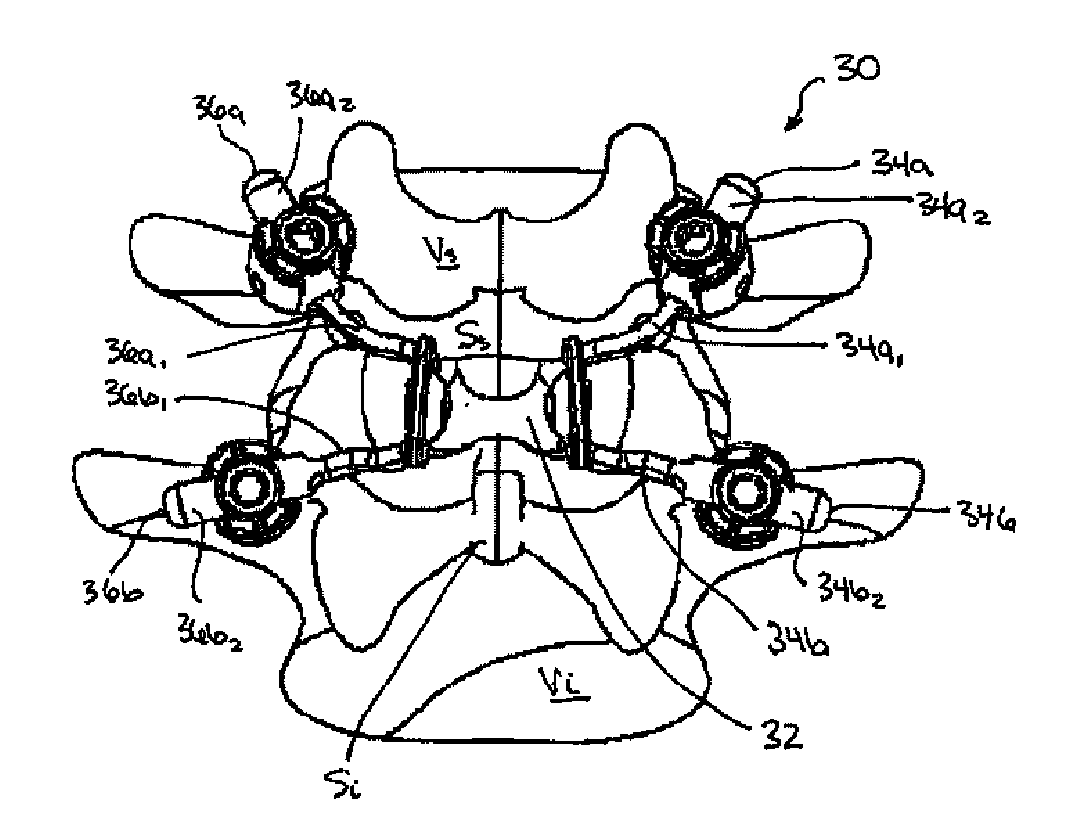
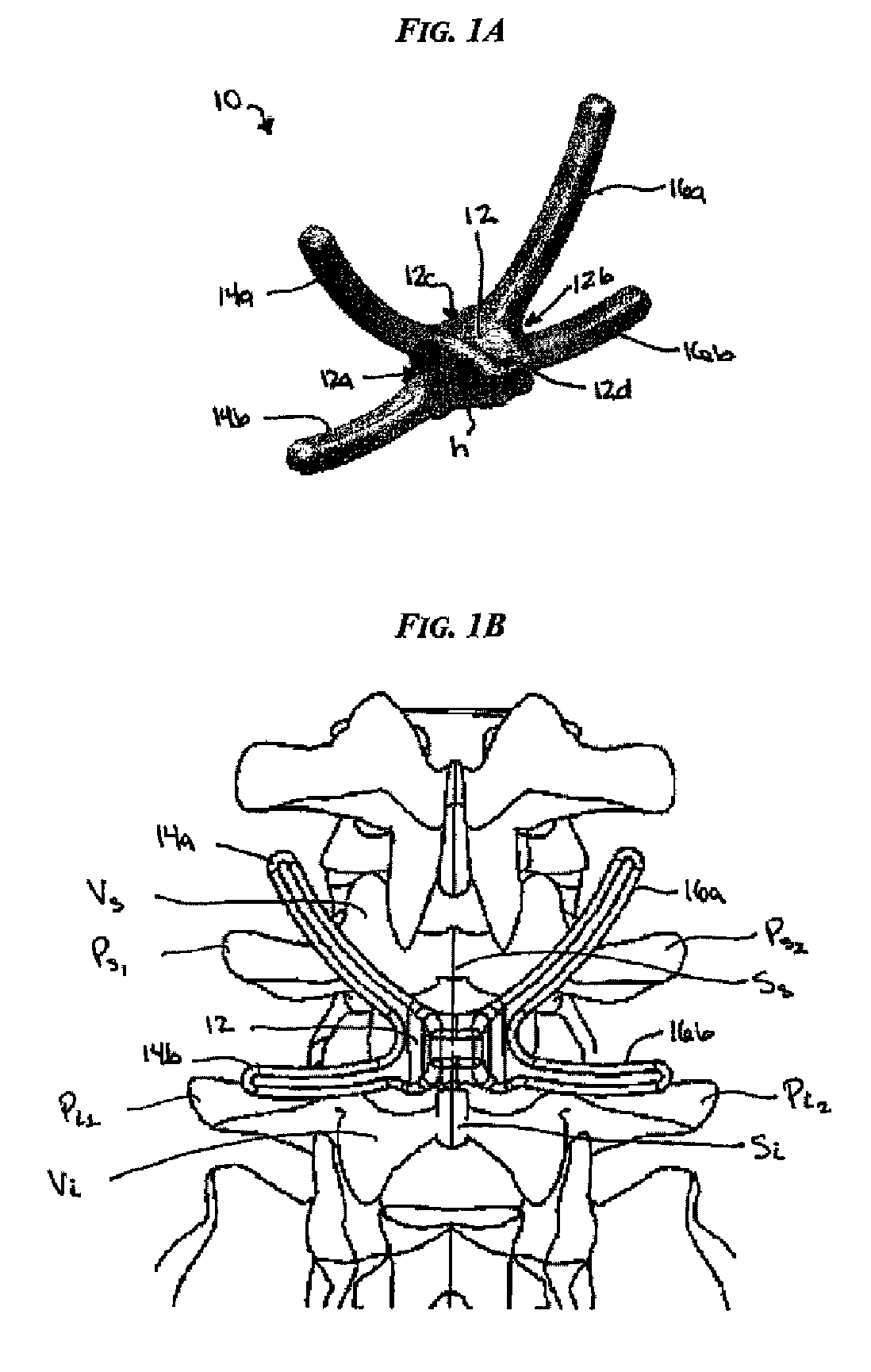
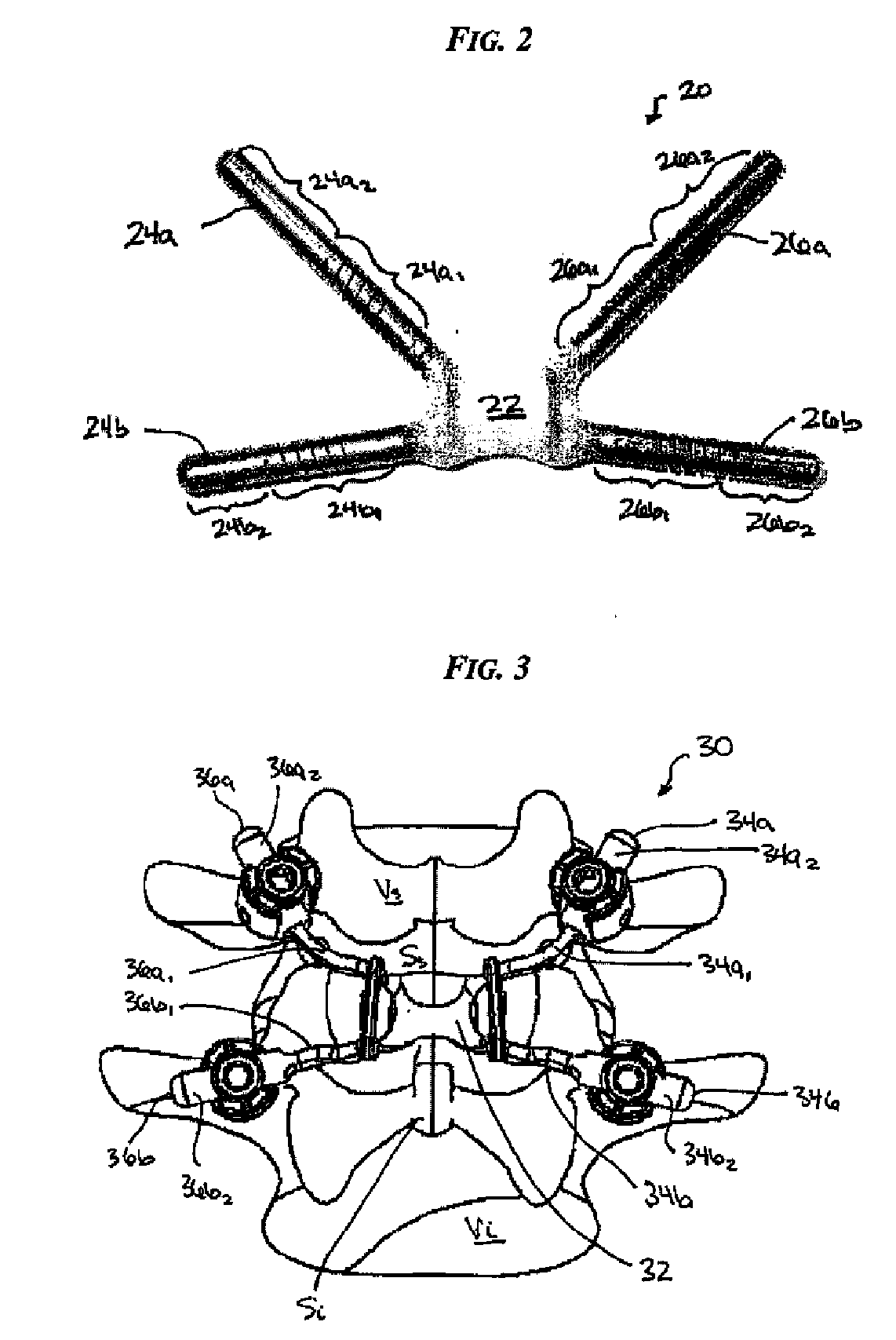
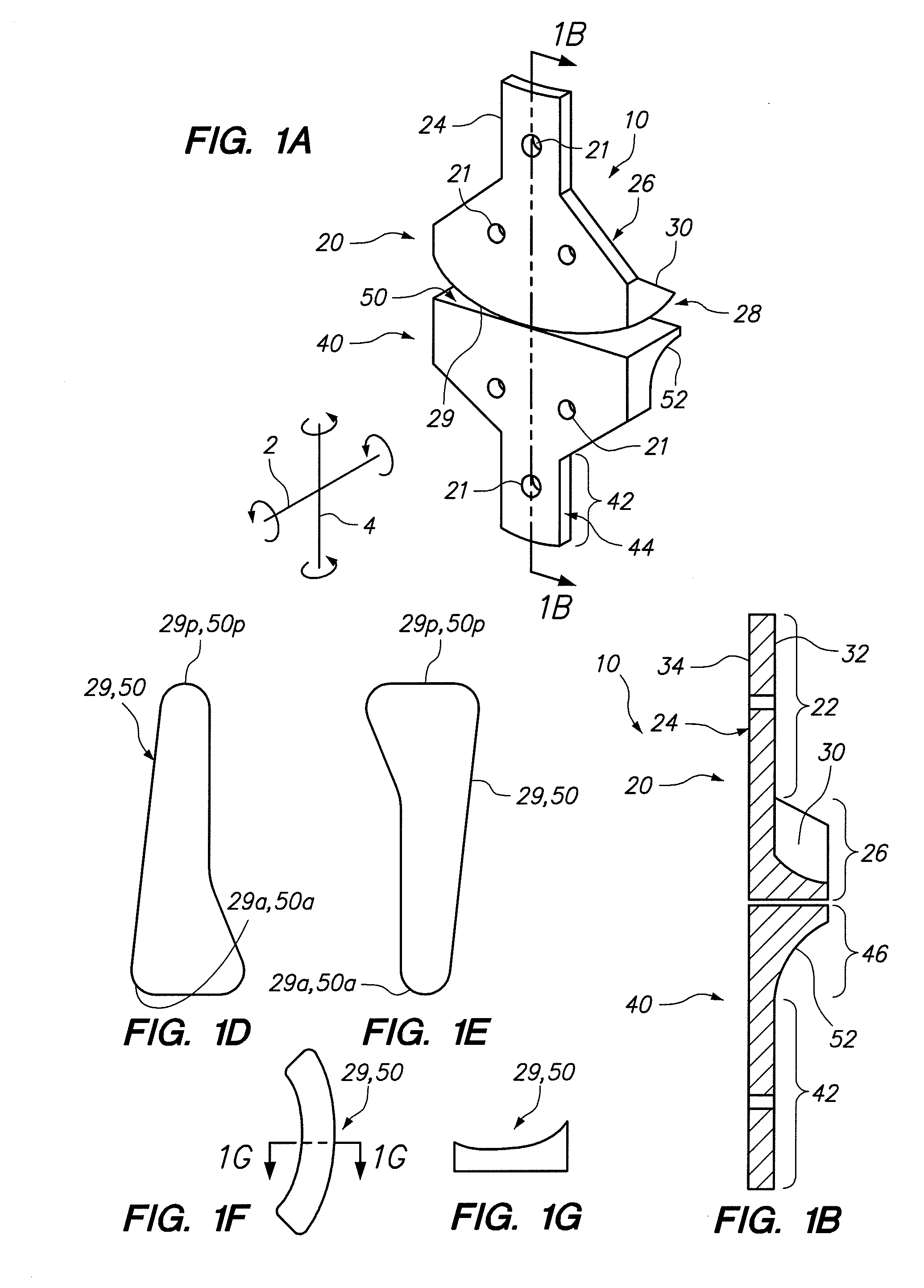
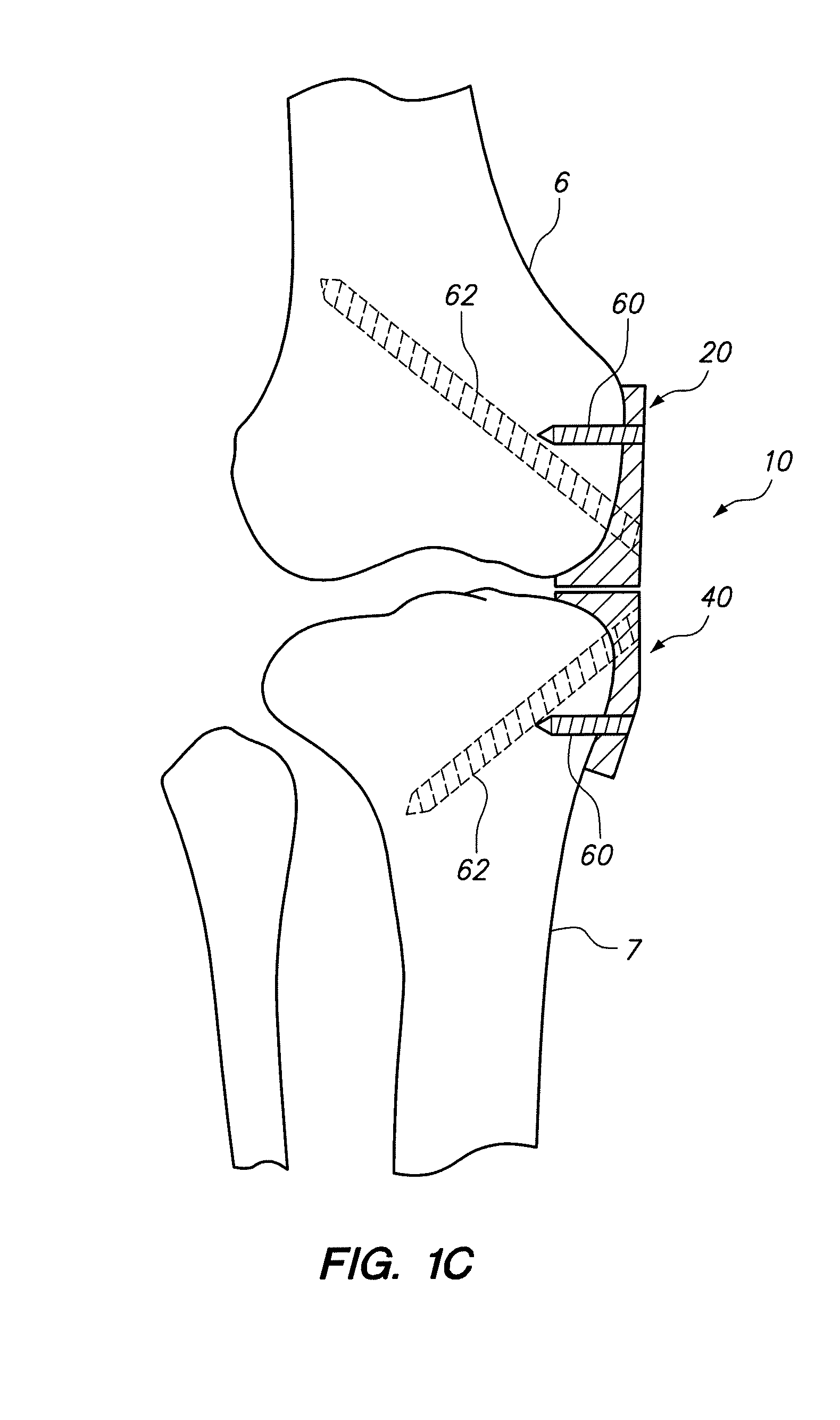
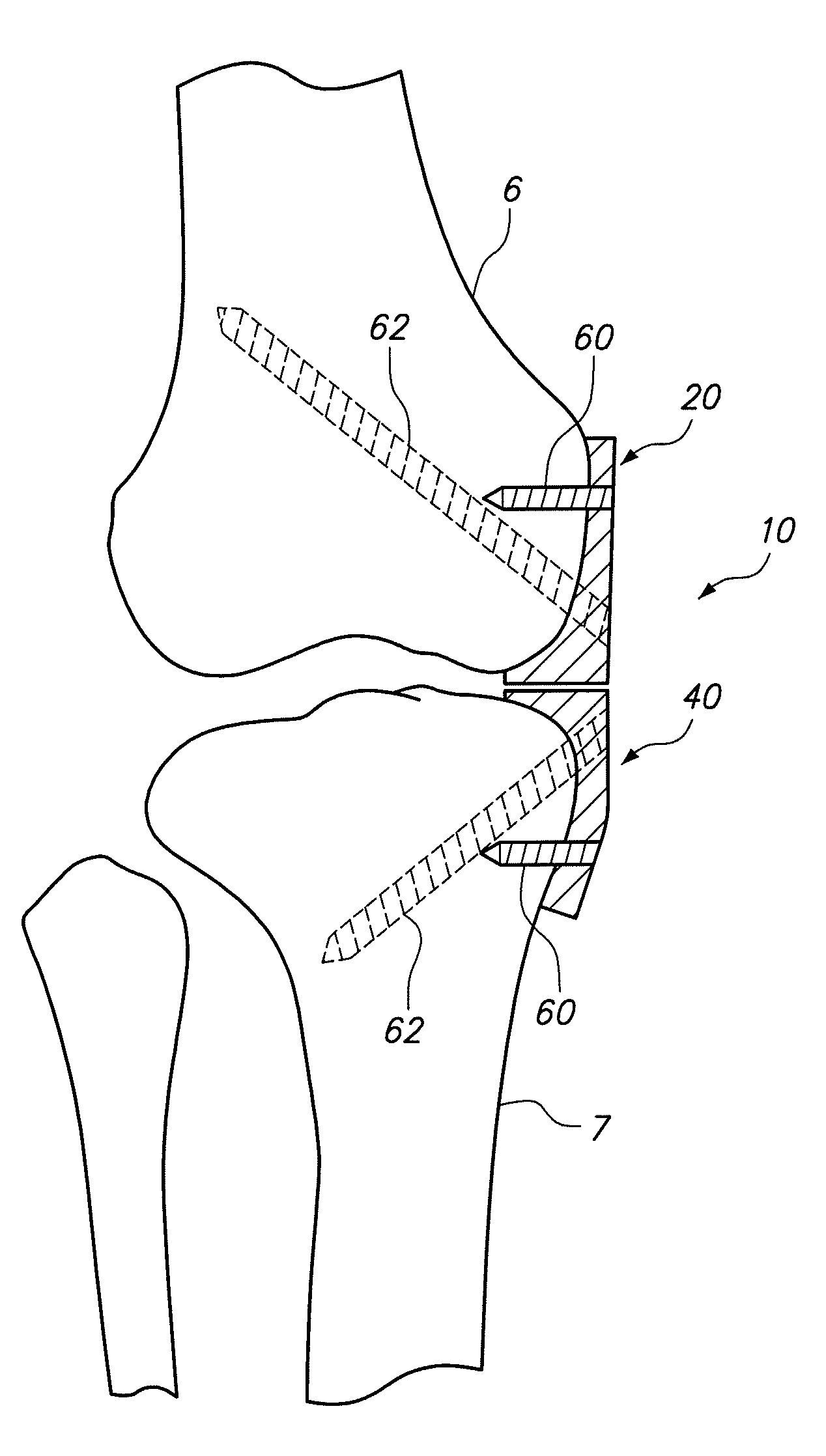
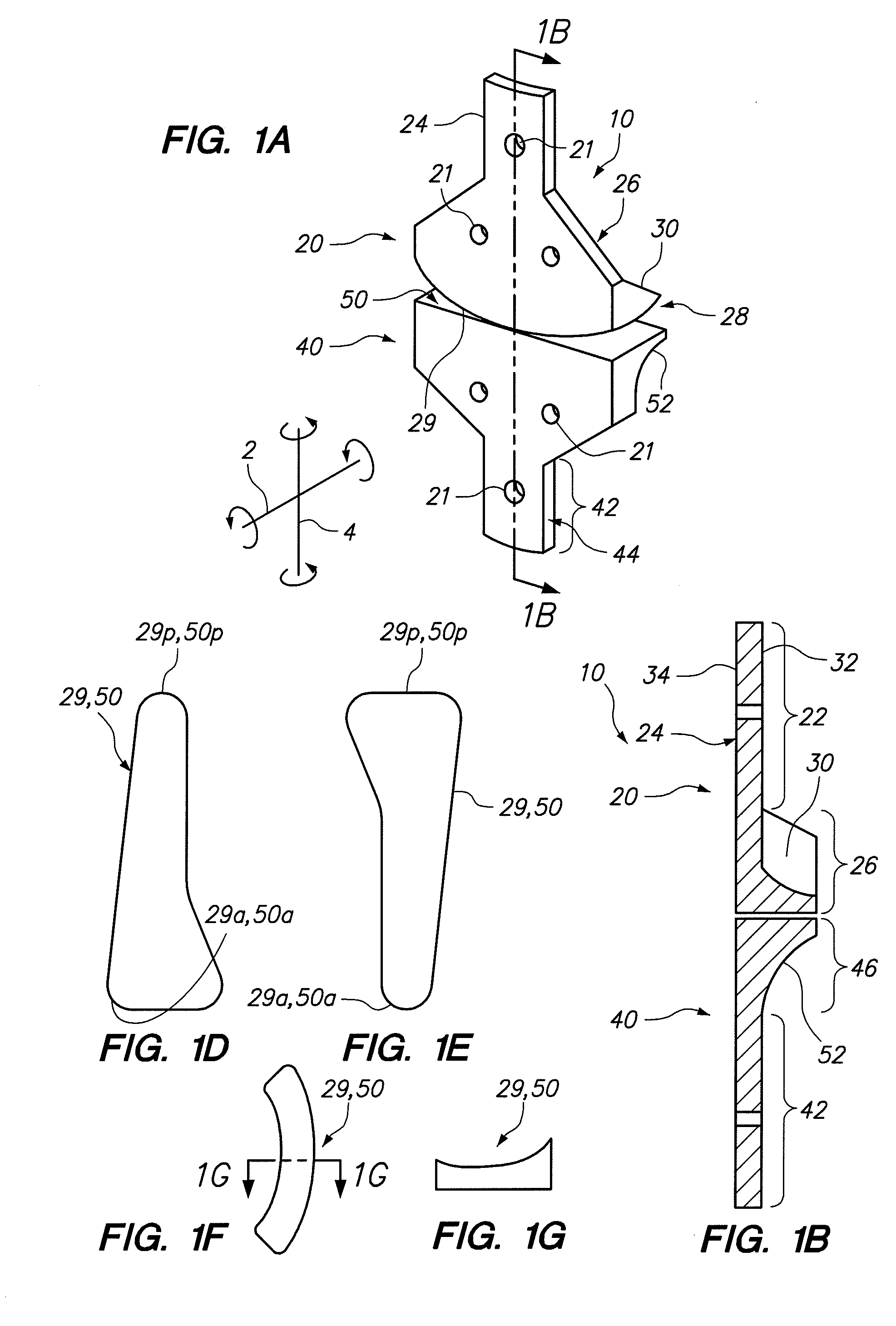
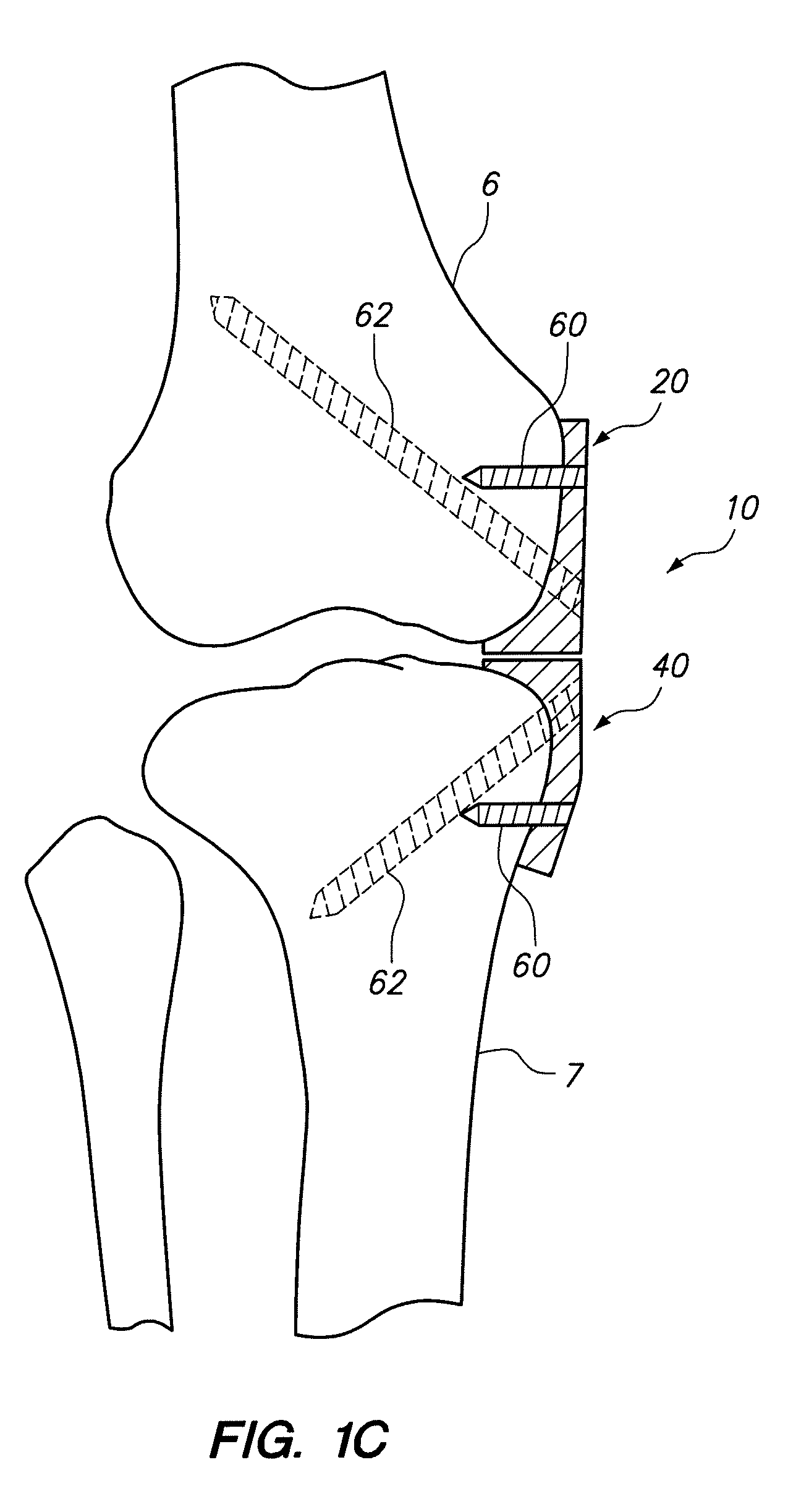
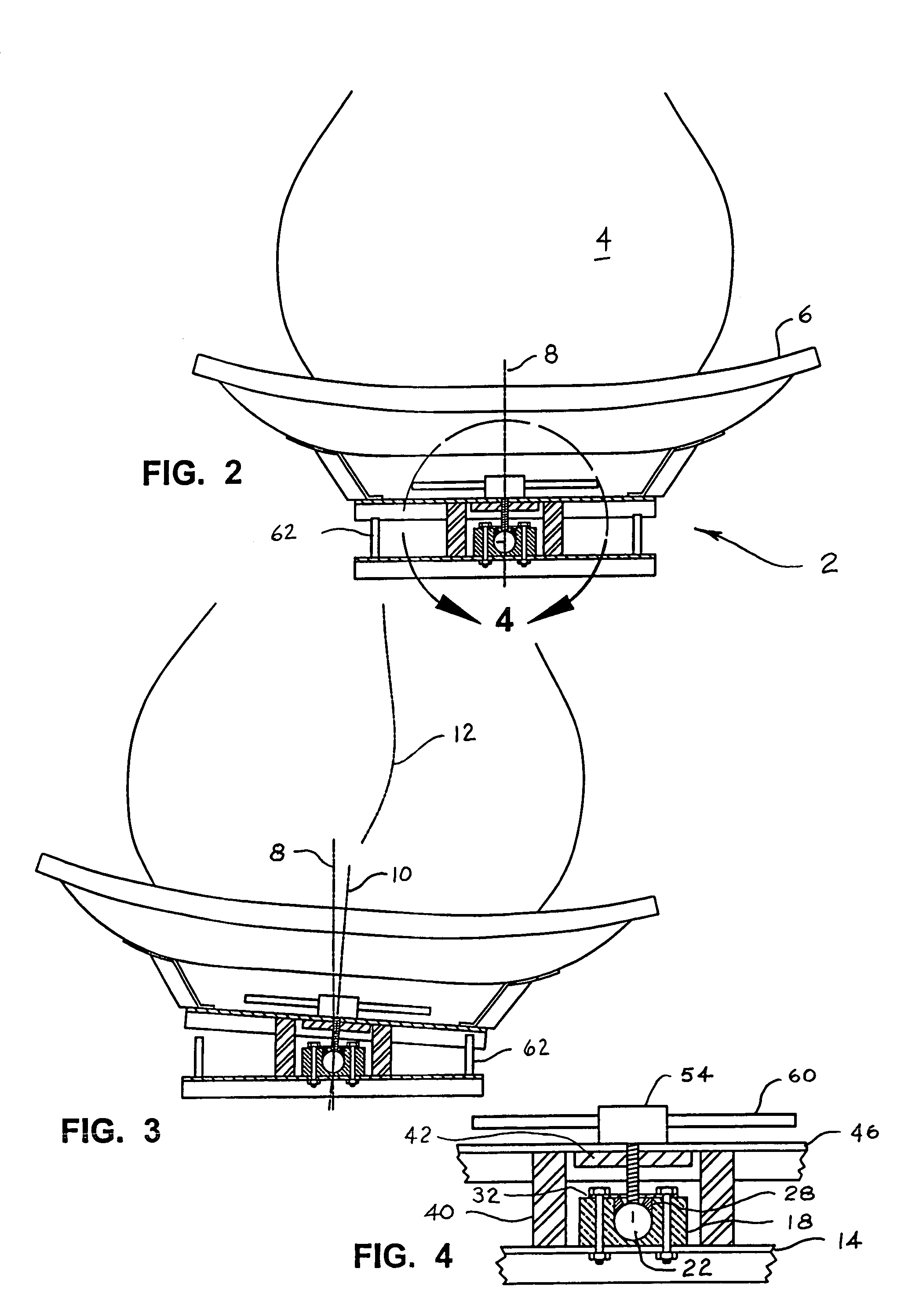
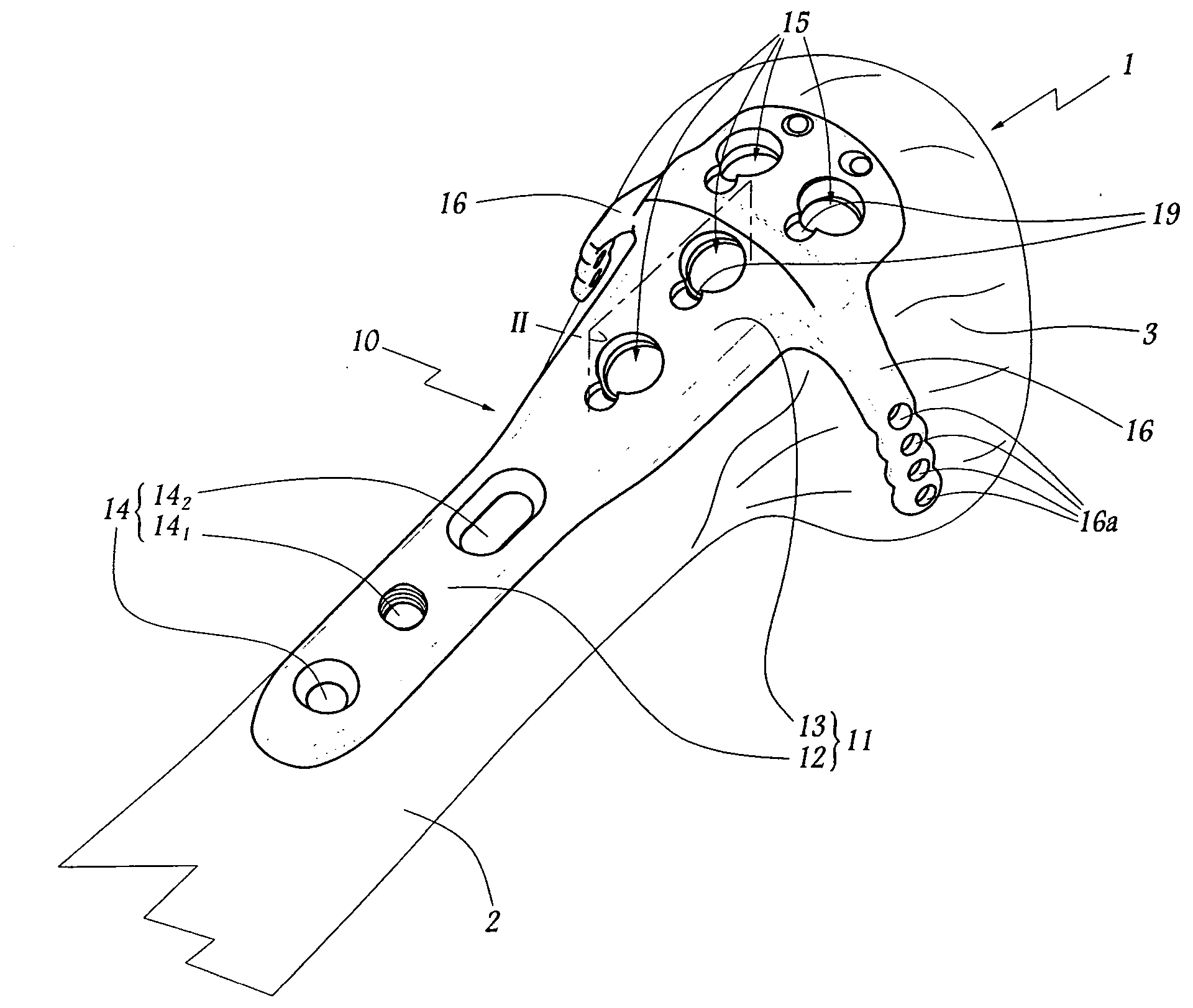
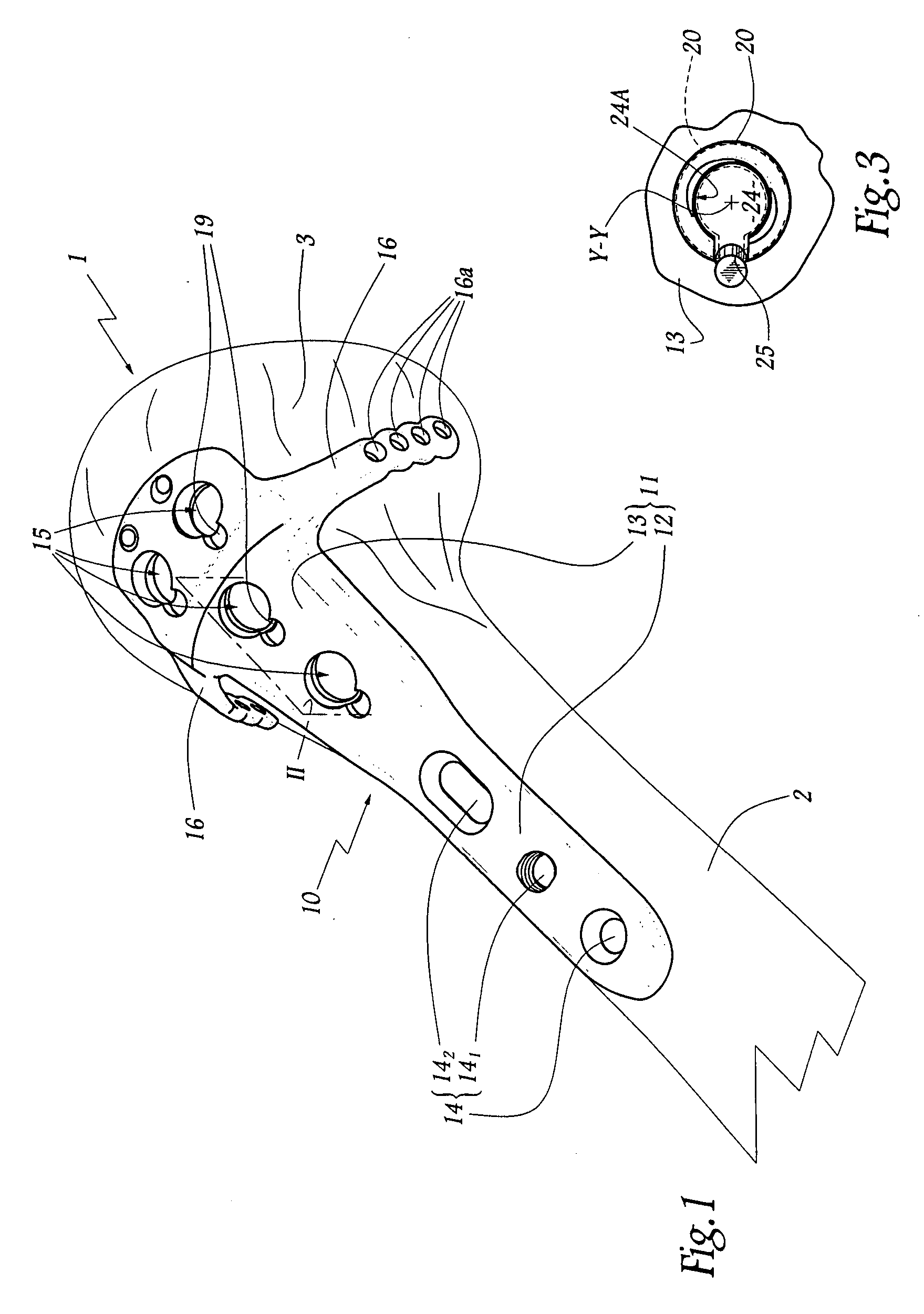
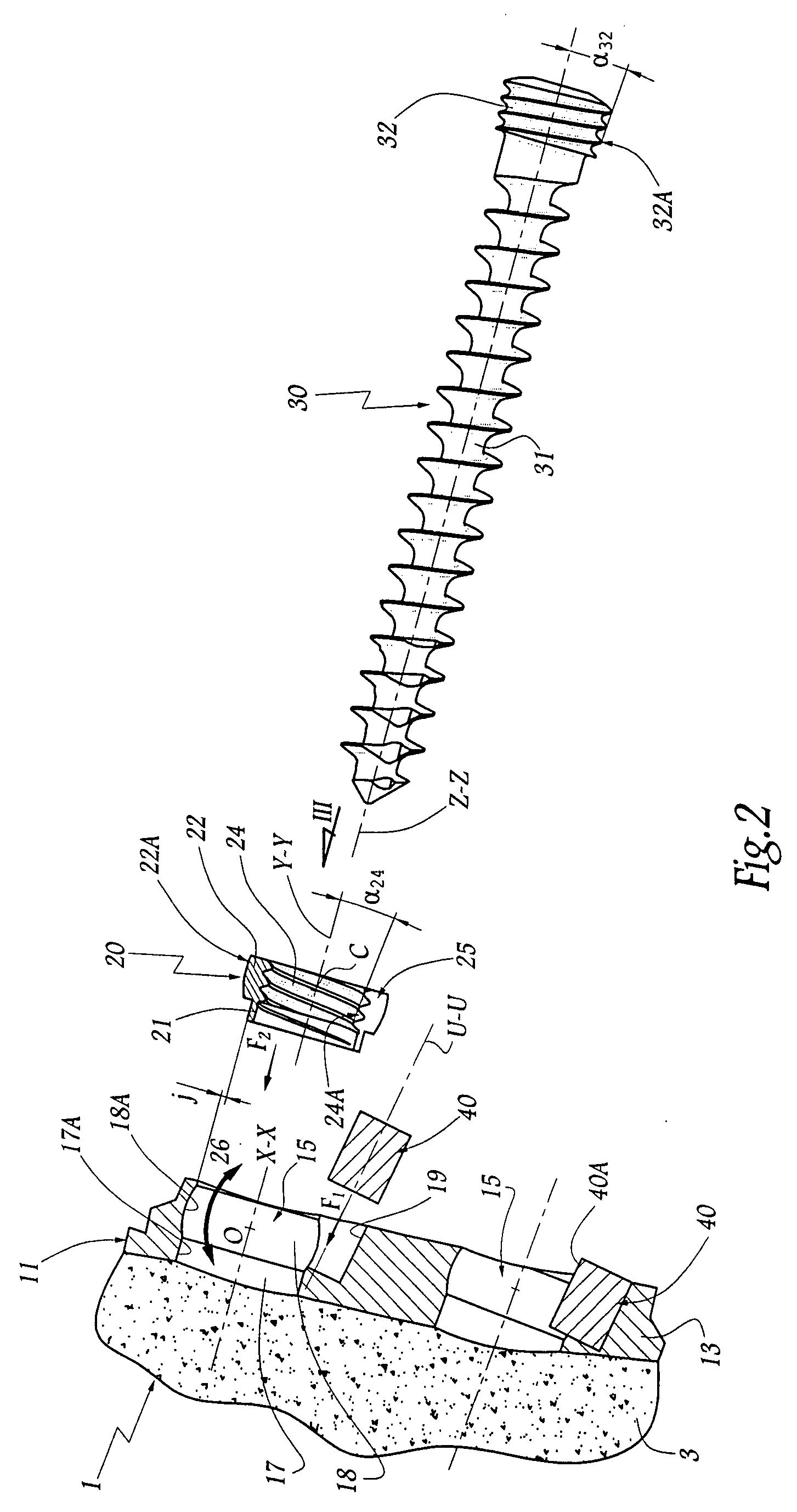
Posterior dynamic stabilization cross connectors
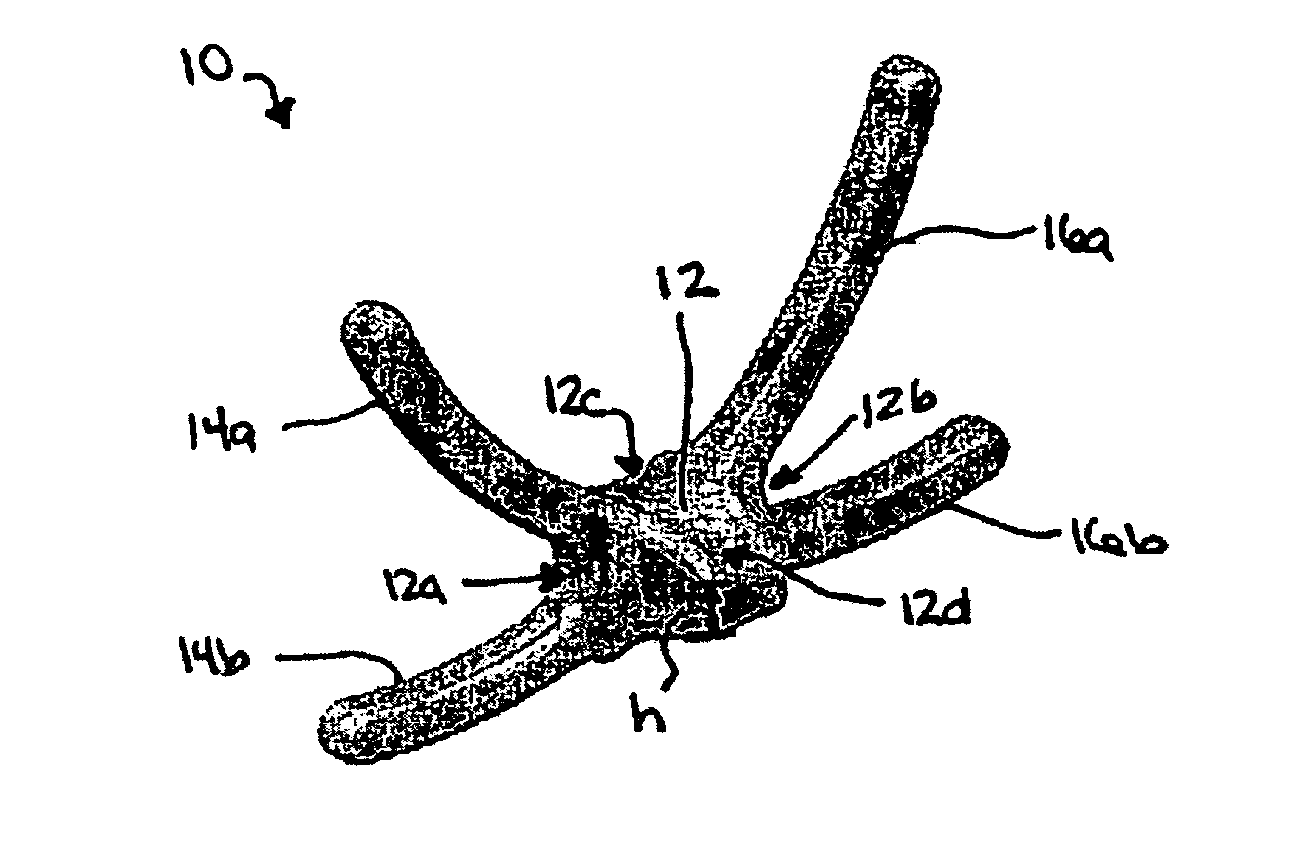
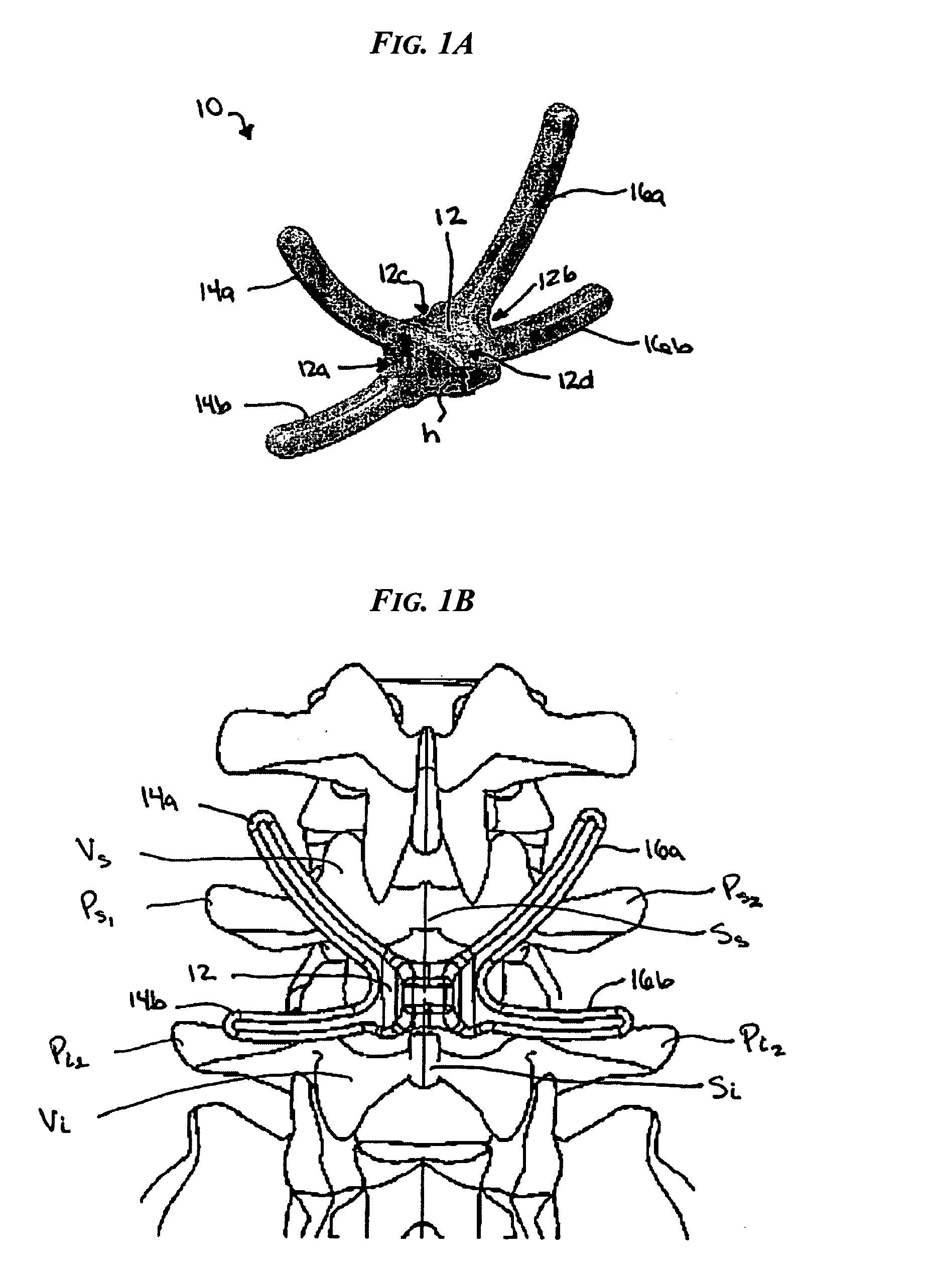
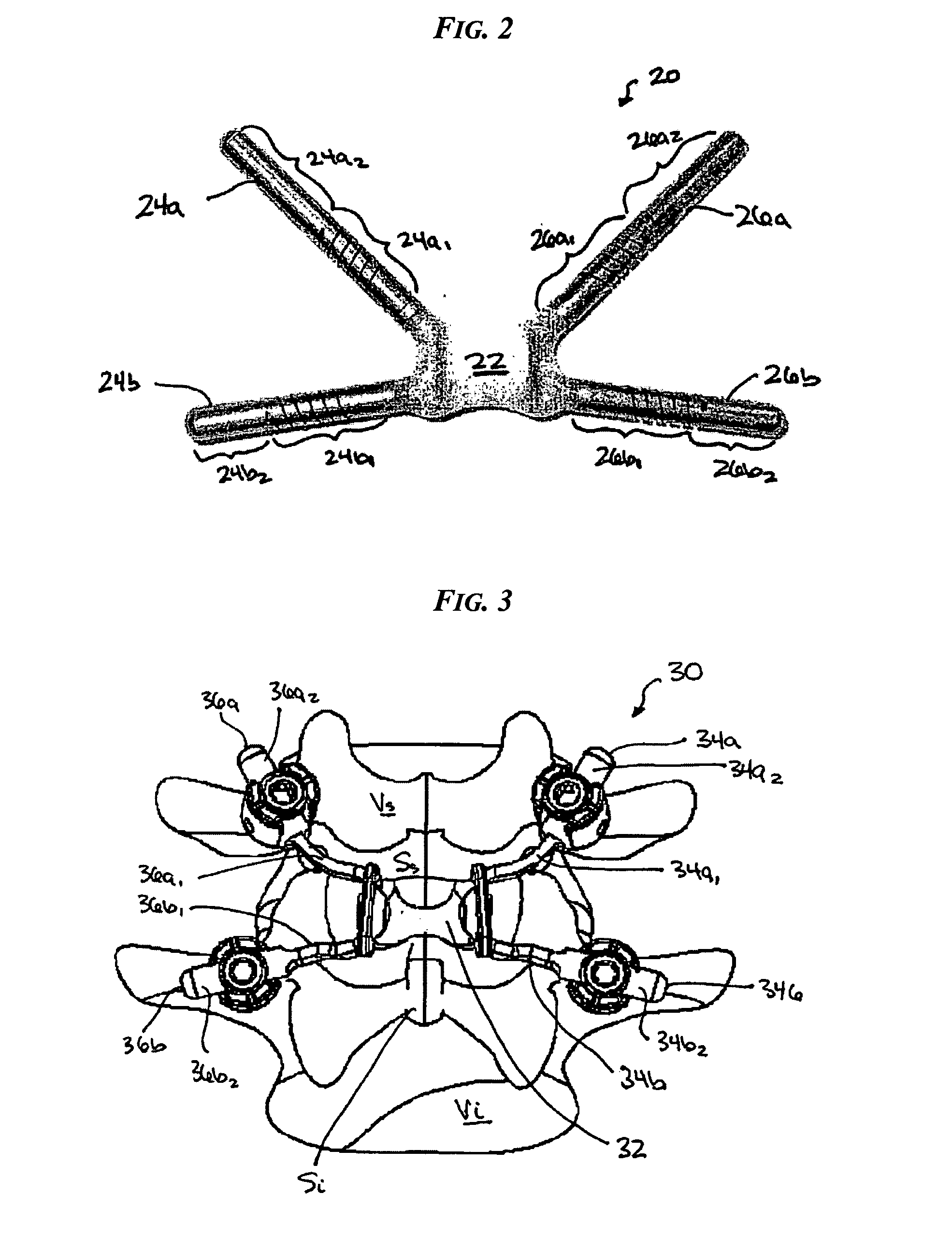
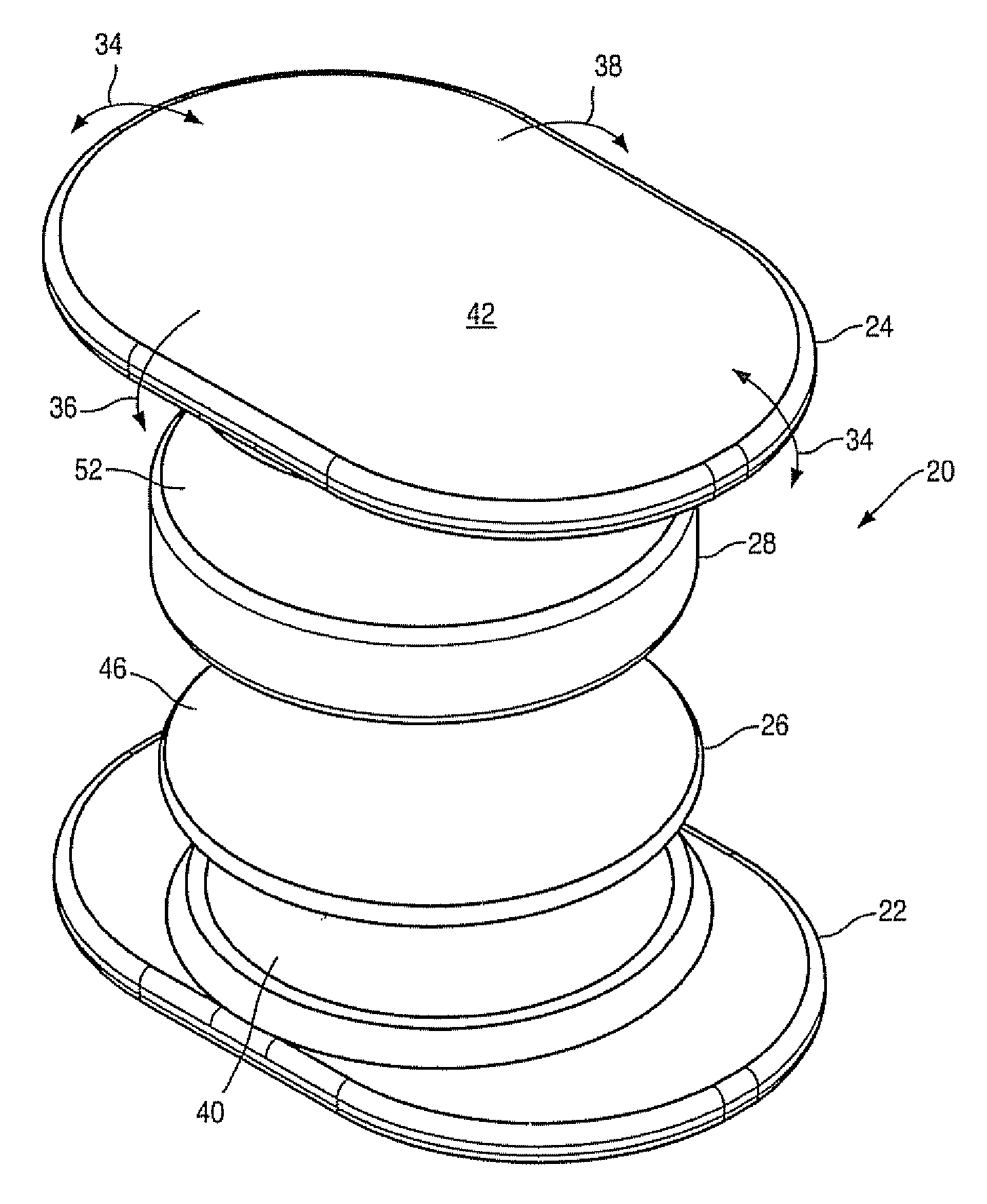
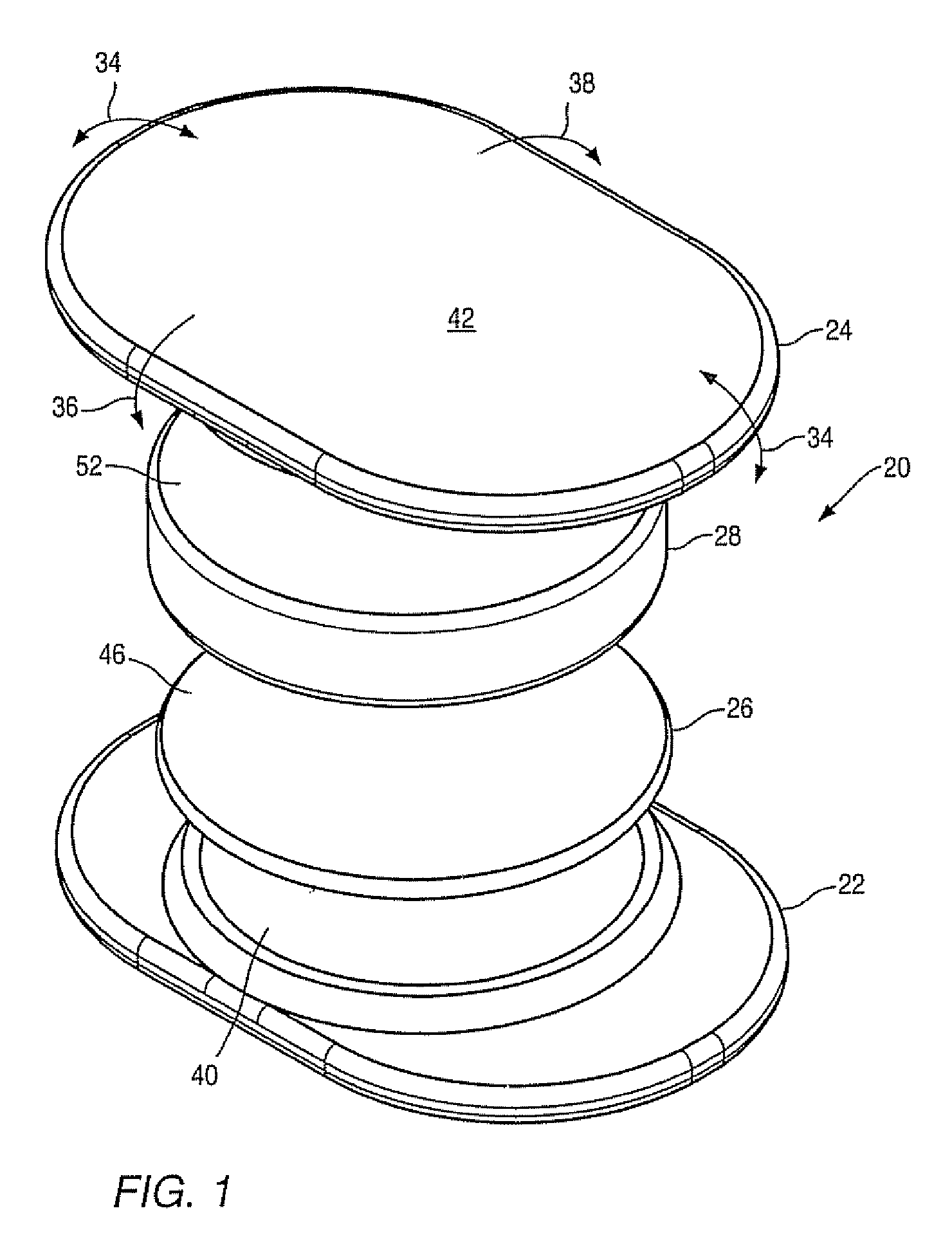
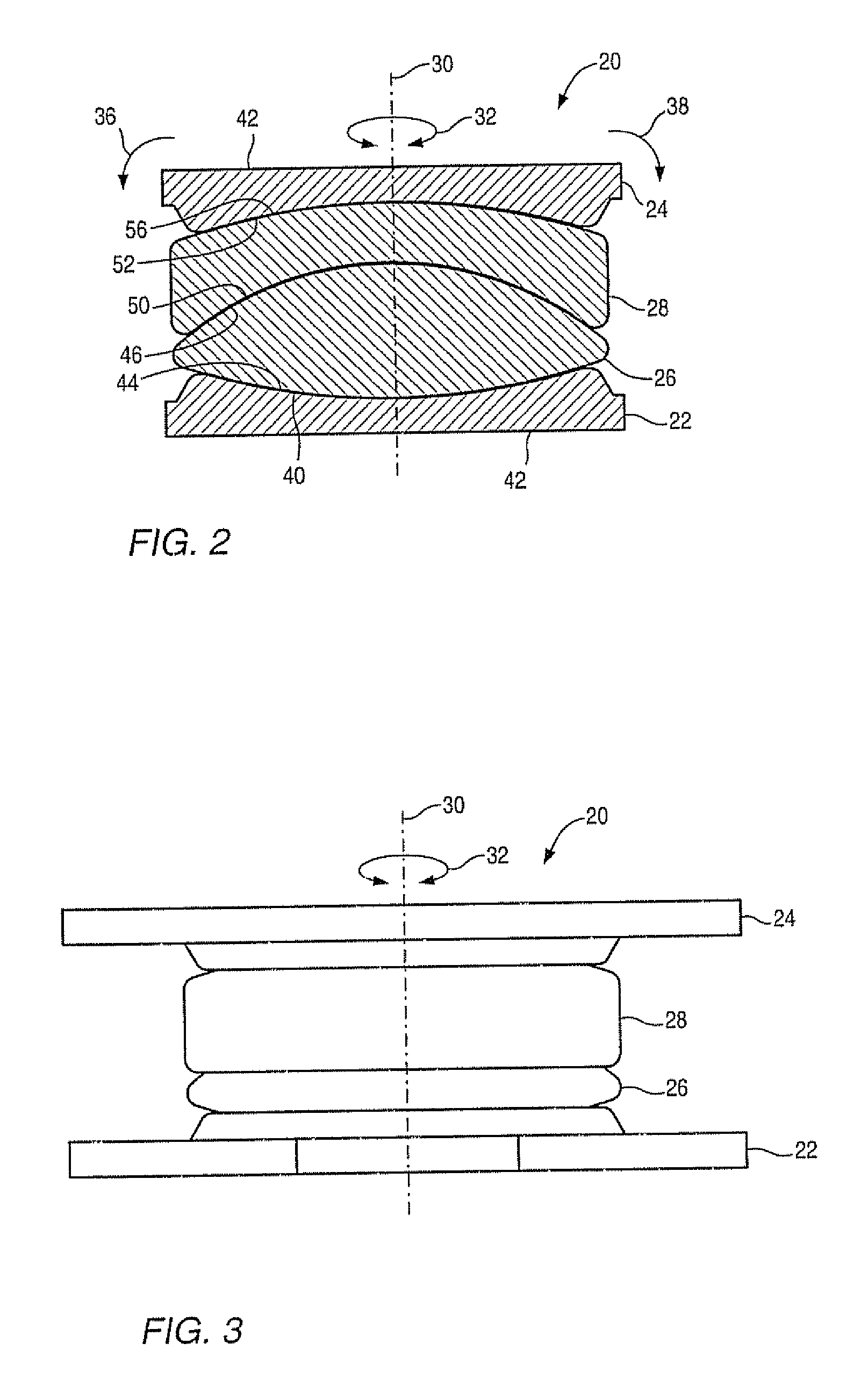
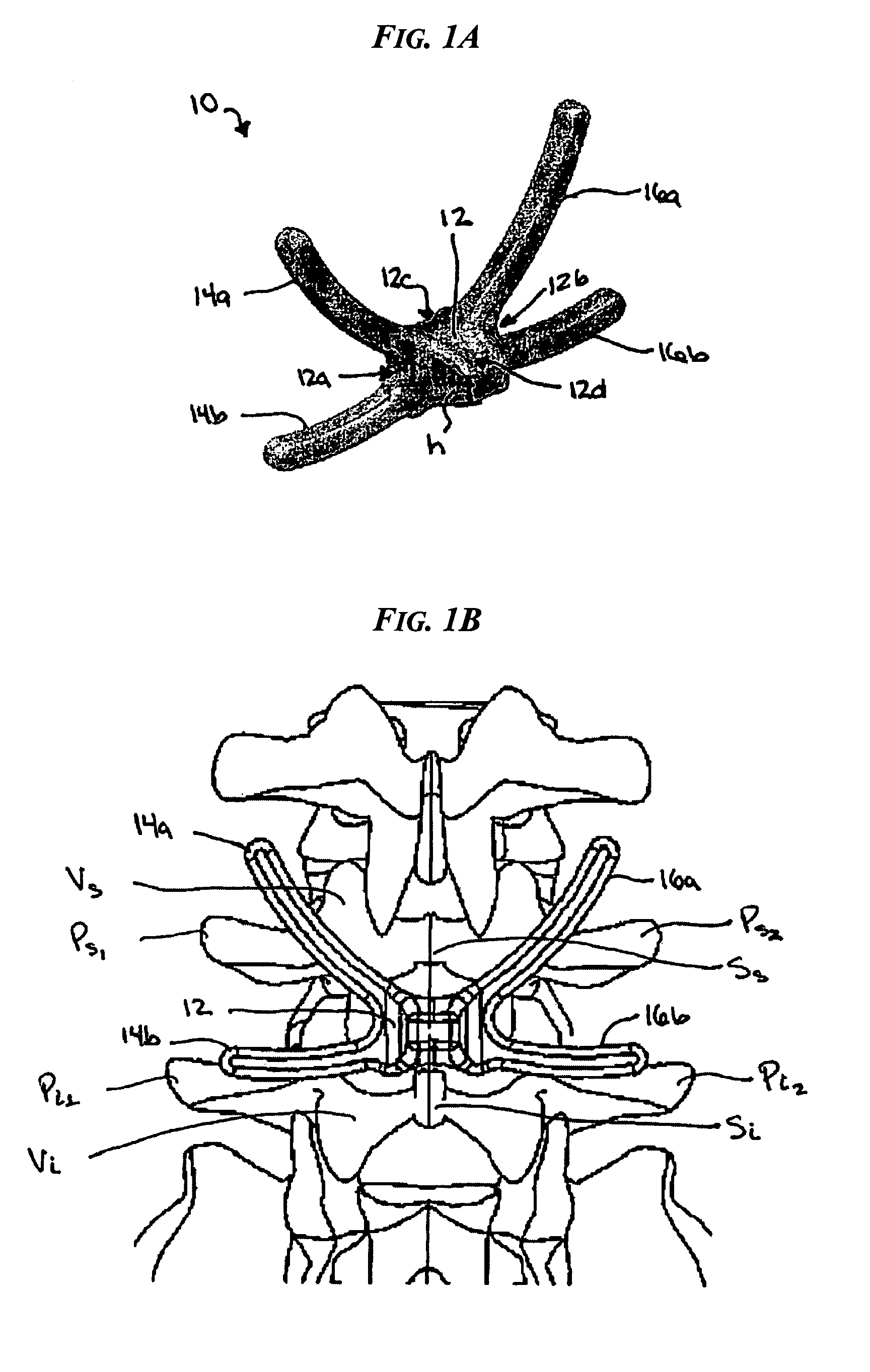
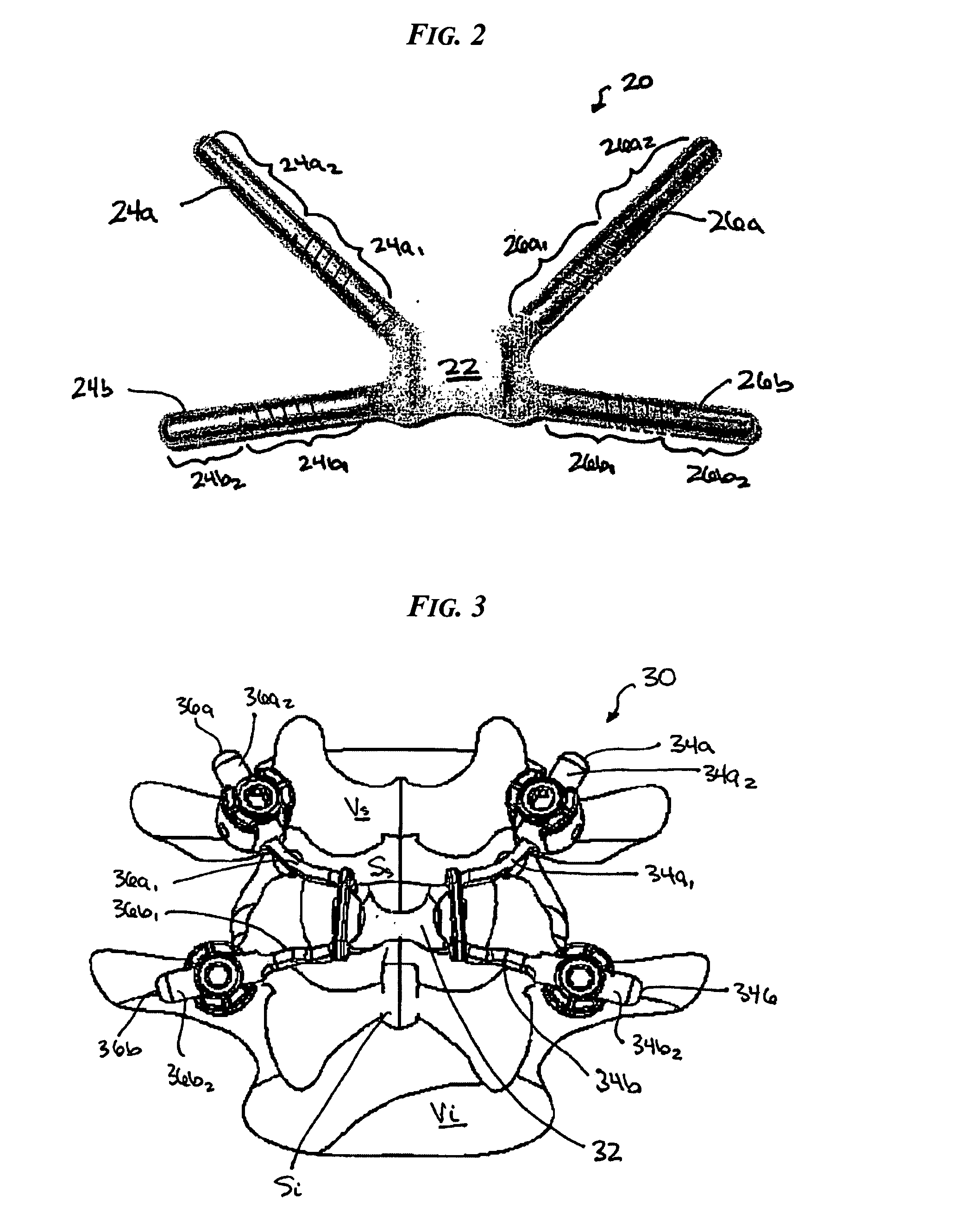
Various methods and devices are provided for stabilizing the posterior elements of the spine, and more preferably methods and devices are provided for sharing the load with the intervertebral disc, the facet joints, the ligaments, and the muscles of the spinal column. In certain exemplary embodiments, methods and devices are provided for substantially controlling or providing resistance to movement, e.g., flexion, extension, lateral bending, and / or axial rotation, of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
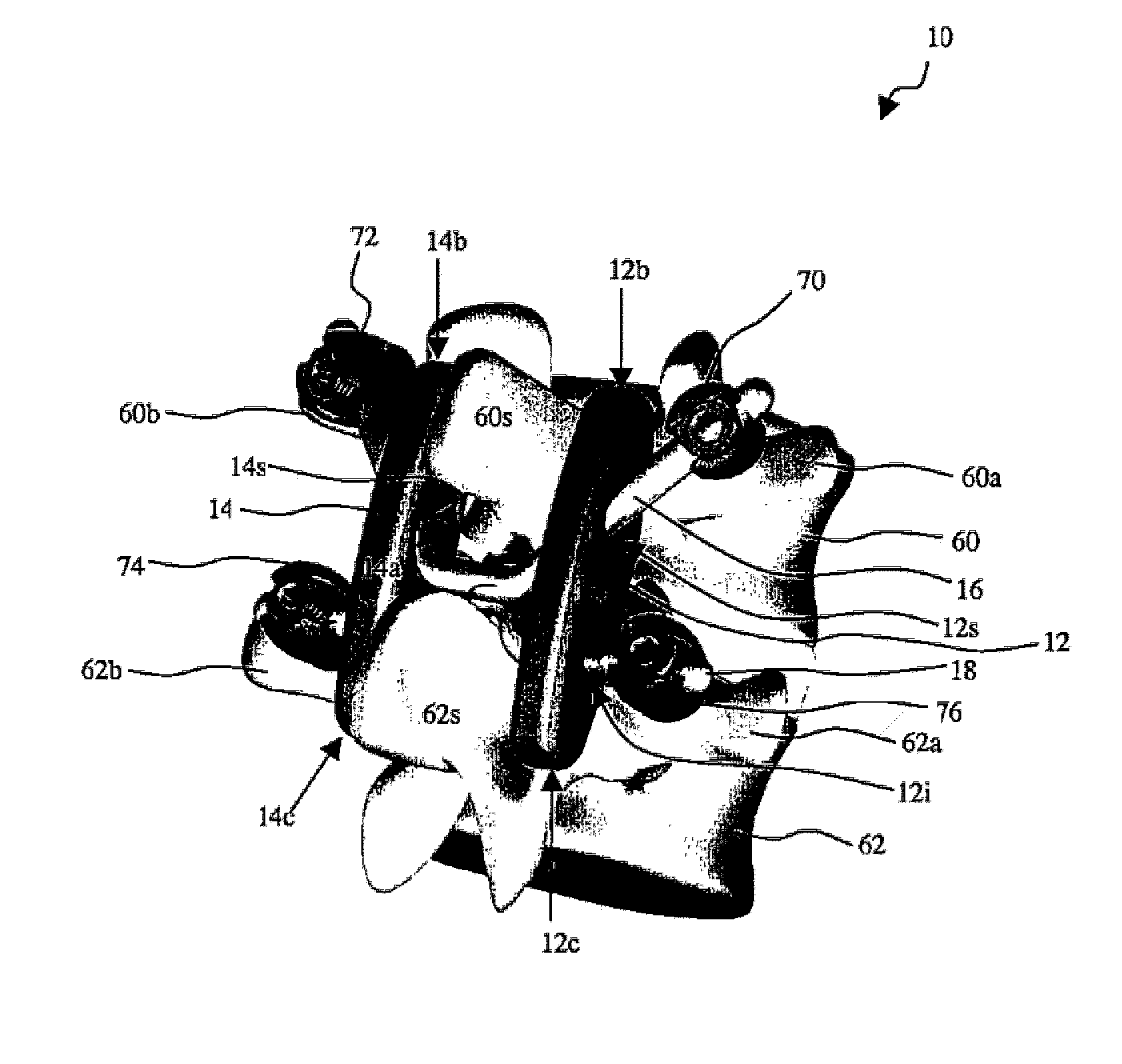
Posterior dynamic stabilizer devices
InactiveUS20060084991A1Restrict movementRepair and replacementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringPosterior stabilization
A posterior stabilization device is provided for controlling movement between adjacent vertebrae. In one exemplary embodiment, the stabilization device can include one or more joints that rely on rotational or sliding movement to allow flexion of adjacent vertebrae, and that control extension, lateral bending, axial rotation, and anterior-posterior shear, preferably by providing one or more flexible connectors and / or a flexible central spacer for connecting to the adjacent superior and inferior vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Posterior dynamic stabilization systems and methods
Various methods and devices are provided for stabilizing the posterior elements of the spine, and more preferably methods and devices are provided for sharing the load with the intervertebral disc, the facet joints, the ligaments, and the muscles of the spinal column. In certain exemplary embodiments, methods and devices are provided for substantially controlling or providing resistance to movement, e.g., flexion, extension, lateral bending, and / or axial rotation, of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
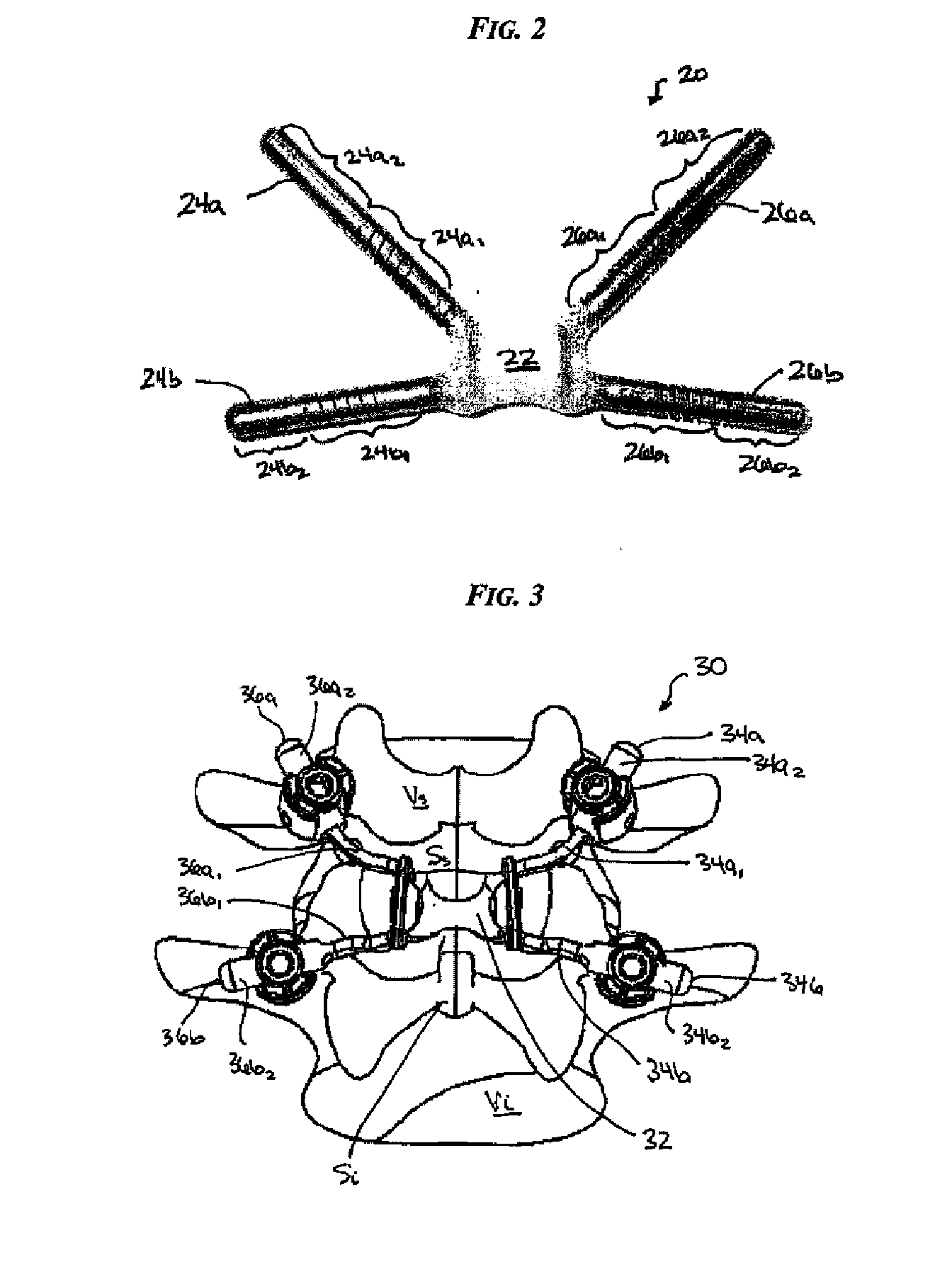
Posterior dynamic stabilization x-device
ActiveUS7658752B2Internal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Various methods and devices are provided for stabilizing the posterior elements of the spine, and more preferably methods and devices are provided for sharing the load with the intervertebral disc, the facet joints, the ligaments, and the muscles of the spinal column. In certain exemplary embodiments, methods and devices are provided for substantially controlling or providing resistance to movement, e.g., flexion, extension, lateral bending, and / or axial rotation, of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Posterior dynamic stabilization x-device
Various methods and devices are provided for stabilizing the posterior elements of the spine, and more preferably methods and devices are provided for sharing the load with the intervertebral disc, the facet joints, the ligaments, and the muscles of the spinal column. In certain exemplary embodiments, methods and devices are provided for substantially controlling or providing resistance to movement, e.g., flexion, extension, lateral bending, and / or axial rotation, of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Cervical disc replacement
InactiveUS6908484B2Immediate and short-term relief from painInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsArticular surfacesSpinal column
An articulating joint implant for use in the cervical spine includes a pair of opposing upper and lower elements having nested articulation surfaces providing a center of rotation of the implant above the adjacent vertebral body endplate surfaces in one mode of motion lateral bending and a center of rotation of the implant below those surfaces in flexion / extension, and that further permit axial rotation of the opposing elements relative to one another about the longitudinal axis of the spinal column through a range of angles without causing them to move in opposing directions along the longitudinal axis within that range. In preferred embodiments, the articulation surfaces further cause such opposite movement of the opposing elements beyond that range.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Dynamic posterior stabilization systems and methods of use
InactiveUS20060247635A1Internal osteosythesisJoint implantsFunctional spinal unitPosterior stabilization
A dynamic posterior stabilization system is provided to stabilize a human spine. In some embodiments, the dynamic posterior stabilization system includes a first bone fastener, a second bone fastener, and an elongated member coupled to the first bone fastener and the second bone fastener. The longitudinal position of the elongated member relative to the first bone fastener may be fixed. The longitudinal position of the second bone fastener relative to the elongated member may vary so that the dynamic posterior stabilization system can accommodate flexion / extension and / or lateral bending. The dynamic posterior stabilization system may also be able to accommodate axial rotation. Bias members may be coupled to the elongated member. The bias members may allow the dynamic posterior stabilization system to mimic the resistance behavior of a normal functional spinal unit.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Multi-level posterior dynamic stabilization systems and methods
Various methods and devices are provided for stabilizing the posterior elements of the spine, and more preferably methods and devices are provided for sharing the load with the intervertebral disc, the facet joints, the ligaments, and the muscles of the spinal column. In certain exemplary embodiments, methods and devices are provided for substantially controlling or providing resistance to movement, e.g., flexion, extension, lateral bending, and / or axial rotation, of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Facet-preserving artificial disc replacements
InactiveUS20060020342A1Reduce loadPrevent rotationSpinal implantsFastenersSpinal CurvaturesSacroiliac joint
Artificial disc replacement (ADR) components cooperate to limit axial rotation and / or lateral bending to a greater degree when the spine is extended than when the spine is a neutral to flexed position, thereby decreasing loads placed upon the facet joints. In the preferred embodiment, truncated articulating surfaces with non-articulating side surfaces allow increasing amounts of axial rotation and lateral bending as the total disc replacement (TDR) moves from full extension to full flexion. Limiting axial rotation and lateral bending of the TDR protects the facet joints and the Annulus Fibrosus, since the facet joints carry more load when the spine is extended than when the spine is flexed. Thus the invention serves to protect the facet joints while allowing normal or near-normal spinal motion.
Owner:FERREE BRET A +2
Anchoring barb for attachment to a medical prosthesis
ActiveUS20050240259A1Limited extentLimit longitudinal movementStentsBlood vesselsThin layerSpot welding
Disclosed is an anchoring element for an implantable prosthesis that includes a barb, wherein the anchoring element, which includes a basal portion, comprises a thin layer of material, such as a cannula or sheet of metal, that extends or wraps at least partially around the strut of the prosthesis to which it is attached. The barb is configured to extend outward from the basal portion to penetrate adjacent tissue. The anchoring element is either permanently affixed to the strut, such as by laser or spot welding, crimping, or some other method of bonding, or allowed to slide longitudinally over the strut between two points or stops in order to relieve any excessive loads placed upon the barb that could cause fracture. The anchoring element and strut may be configured to limit axial rotation of the barb, while still allowing longitudinal movement. In another embodiment, the slidable anchoring element may be manipulated following initial deployment to reorient the barb toward the implantation site.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Guide wire with magnetically adjustable bent tip and method for using the same
InactiveUS20070032746A1Increase the curvatureExpand accessGuide wiresSurgeryDistal portionSmall branch
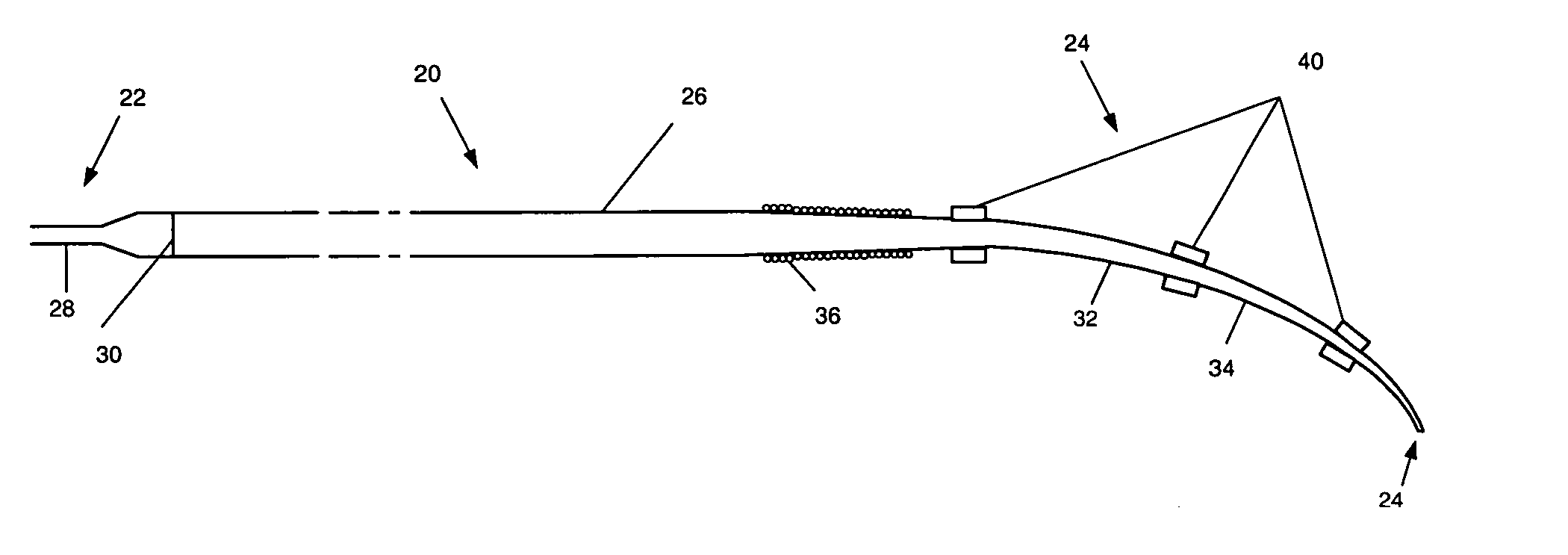
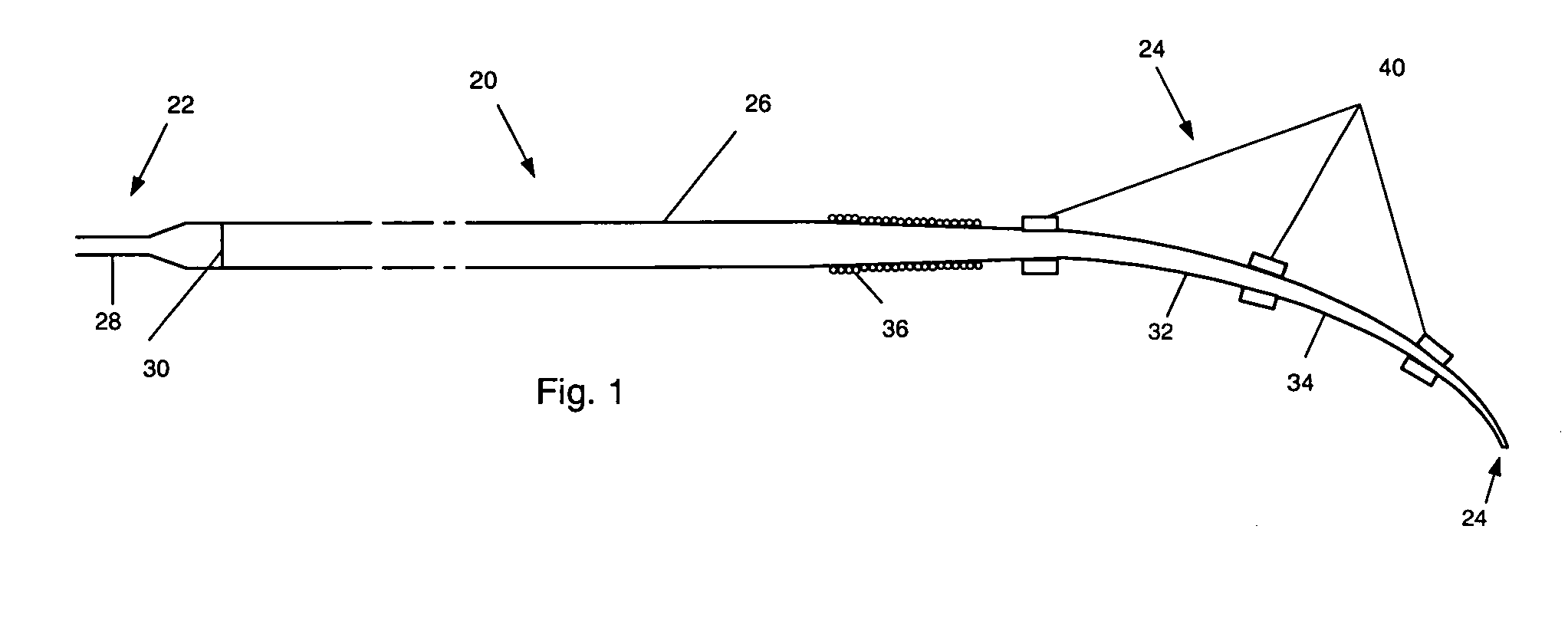
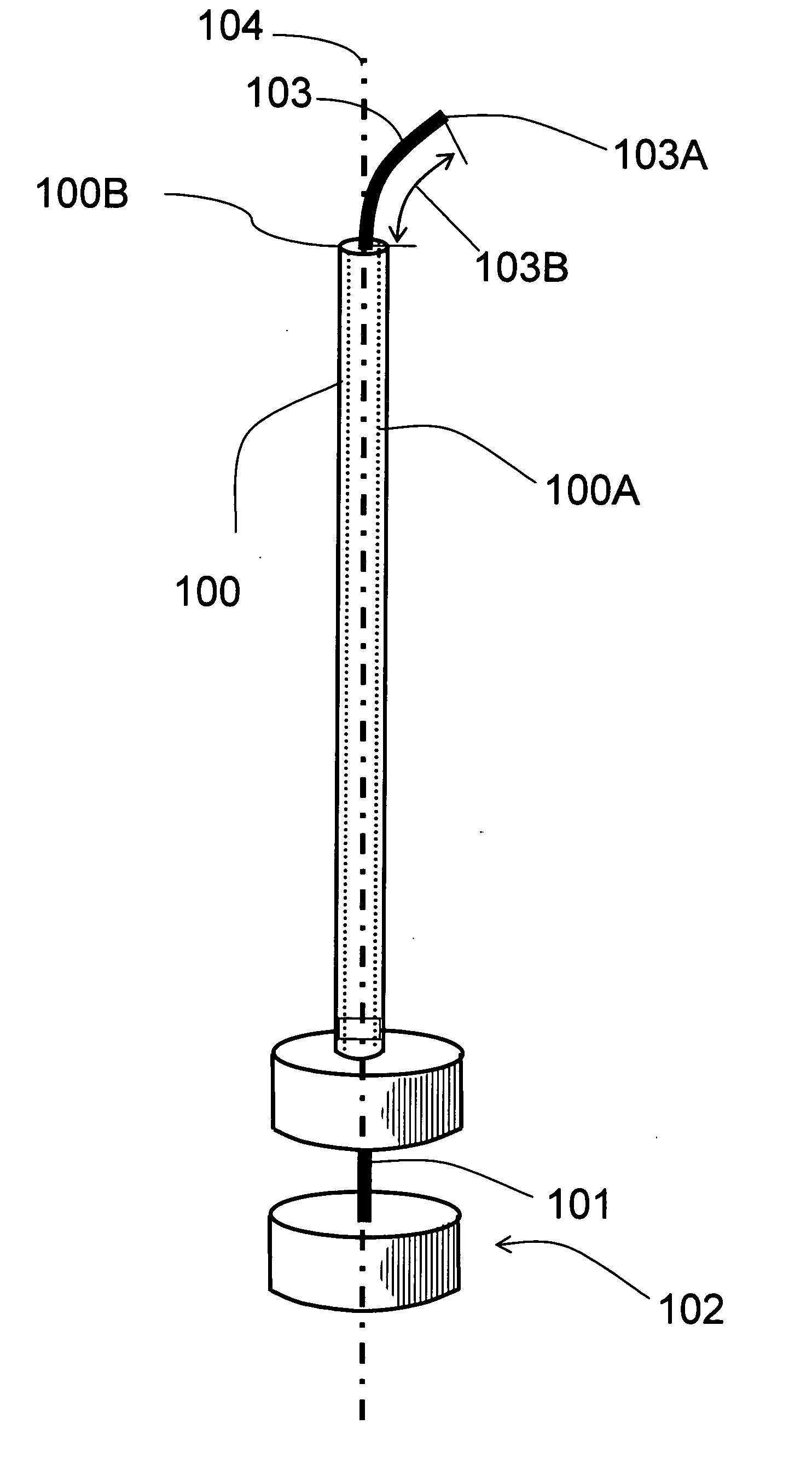
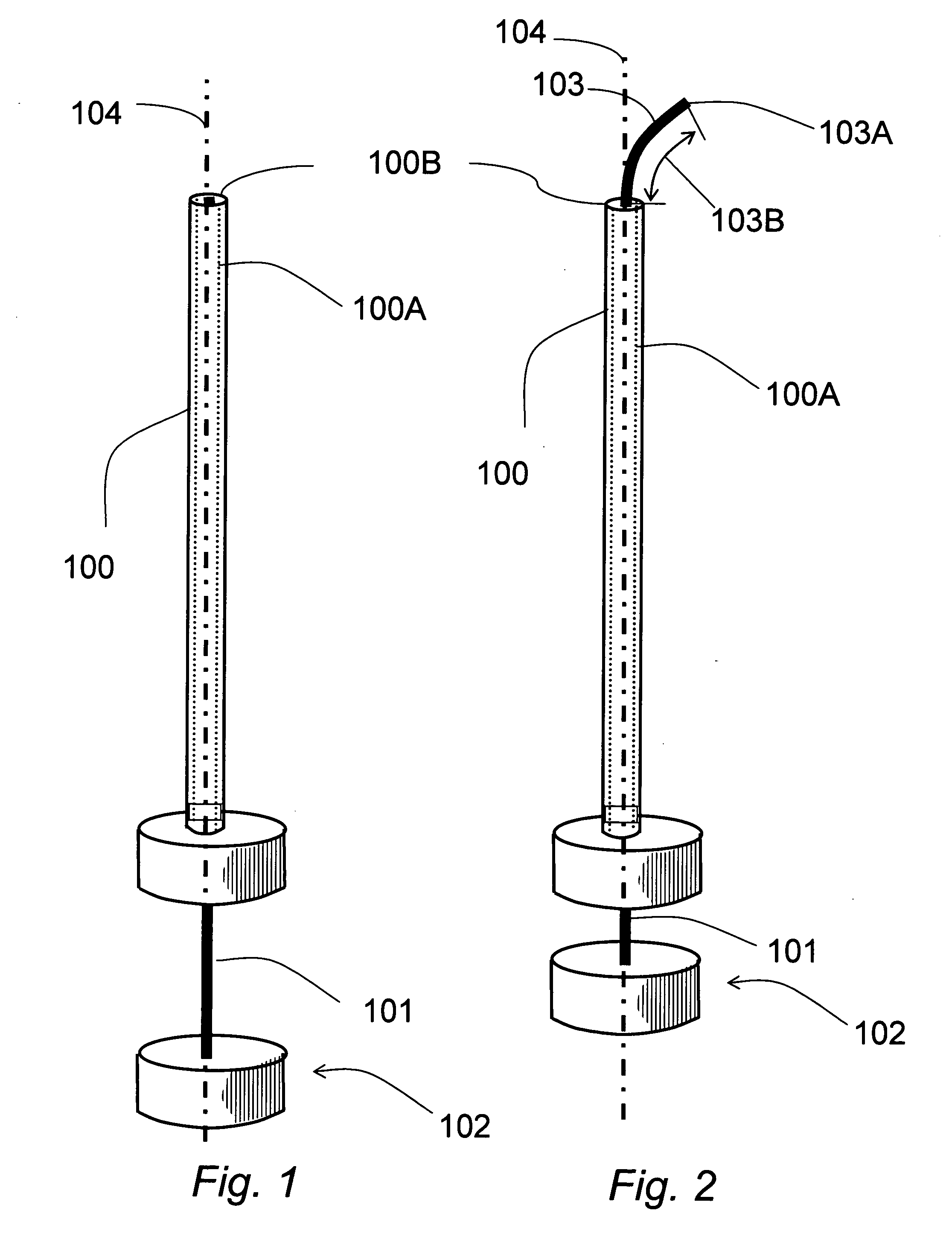
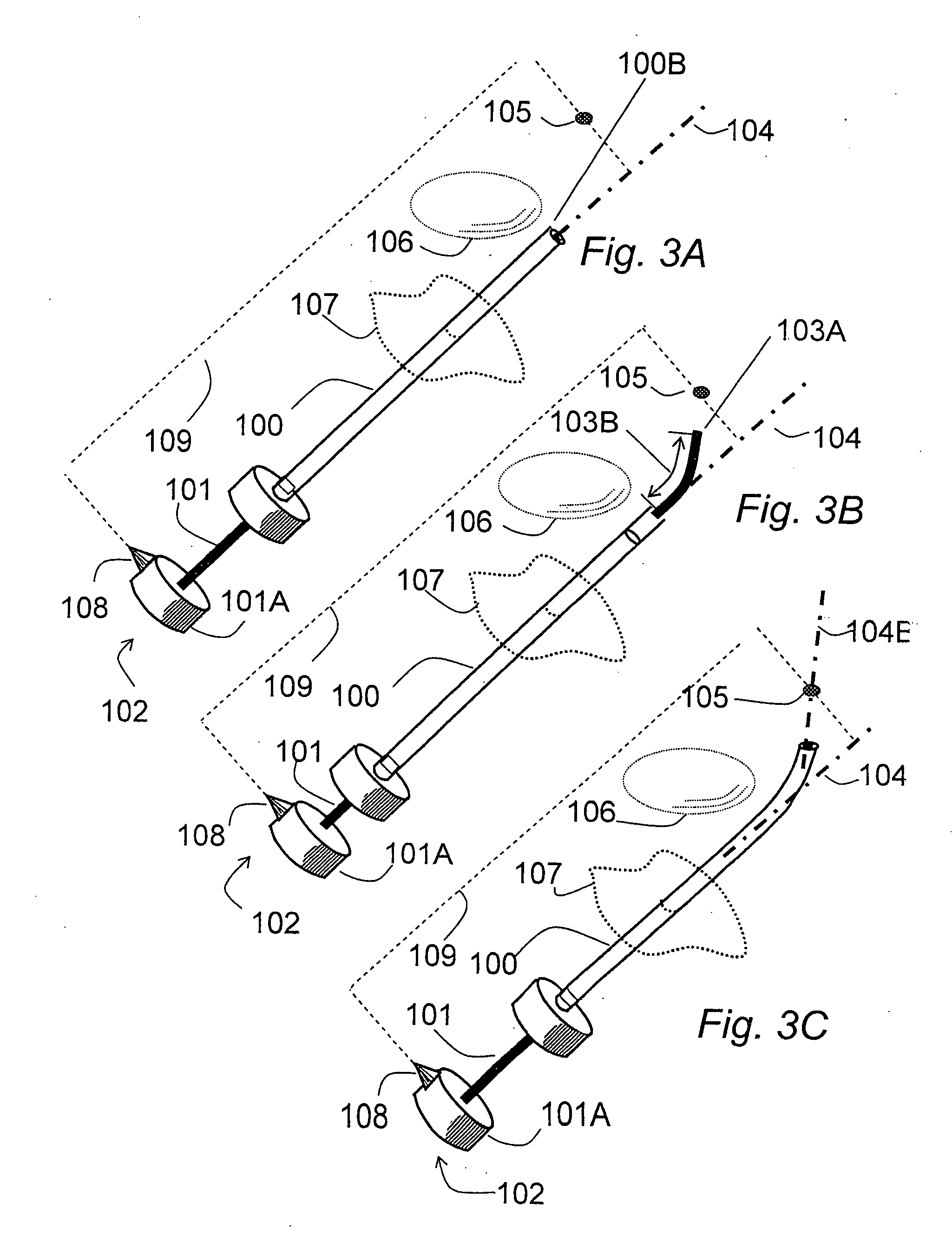
The guide wire invention relates to improvements in magnetically navigable medical guide wires for enabling, in addition to magnetic navigation, conventional navigation without the use of a magnetic field. The distal portion of the guide wire may be navigated by either manually applying an axial rotation to the guide wire or by applying a magnetic field to modify the curvature of the distal portion to access small branch vessels in a subject body. The distal portion of the guide wire can also be straightened or aligned with the longitudinal axis of the guide wire by applying a magnetic field that straightens the bent section in the direction of the longitudinal axis, which enables the guide wire to push through a lesion.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
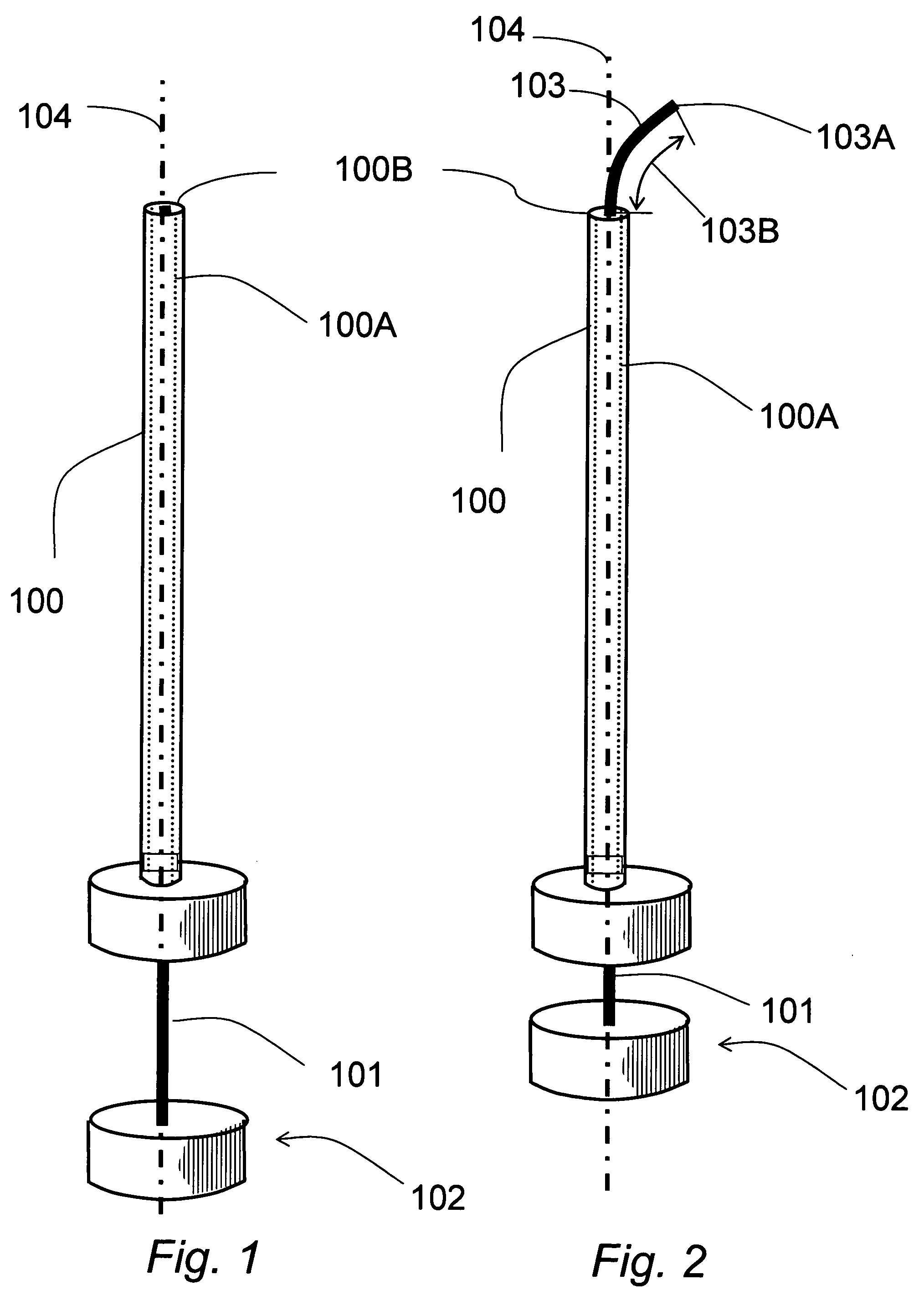
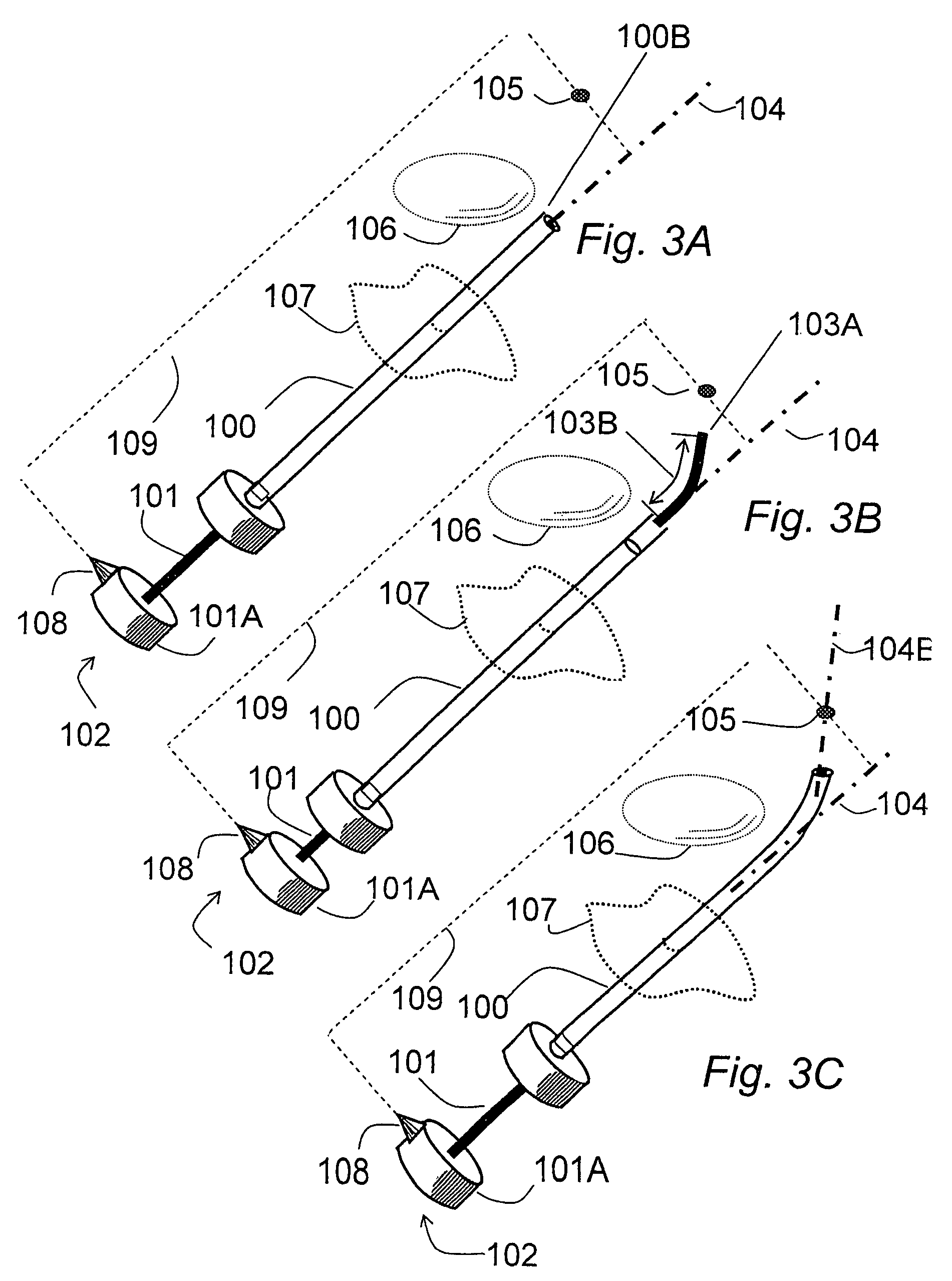
Steerable needle
InactiveUS20040133168A1Improved level of guidanceEasy to detectElectrotherapyInfusion syringesNeedle guidanceCannula tip
The invention relates to a needle guidance system provided by a needle with a steerable tip. The needle has a cannula and a stylet. The stylet adjacent to its tip has a naturally curved portion The stylet is movable in two degrees of freedom with respect to the cannula-axial translation and axial rotation with respect to the cannula axis. When extended, the stylet curves off-axis and provides cannula tip steering. Driving and / or steering systems may be provided to the orientation and relatively move the stylet.
Owner:SALCUDEAN SEPTIMIU E +3
Spinal disc implant
InactiveUS20080015698A1Reduced component wearEasy to keepInternal osteosythesisBone implantBiomedical engineeringAxial rotation
A disc implant is provided which maintains intervertebral spacing and stability of the spine. In an embodiment, a disc implant may include four or more components. Components of the disc implant may include engaging plates and two or more members positioned between the engaging plates. In certain embodiments, a disc implant may include a retainer positioned between one of the engaging plates and one of the members. Complementary portions of the implant components may allow for lateral movement, anteroposterior movement, and / or axial rotation of the engaging members relative to each other during use. In some embodiments, at least one of the members may include a stop to inhibit movement of adjacent vertebrae outside of normal physiological ranges.
Owner:MARINO JAMES F +2
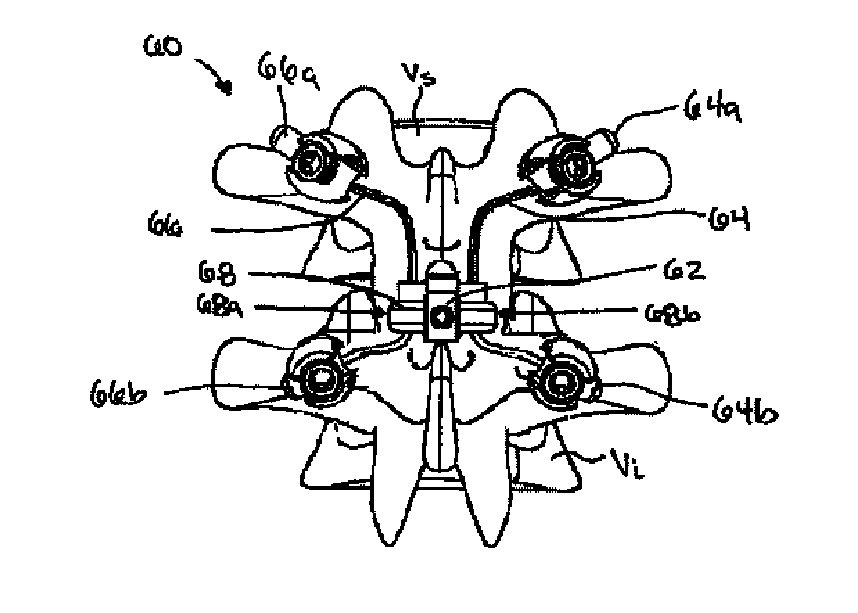
Posterior dynamic stabilization y-device
Various methods and devices are provided for stabilizing the posterior elements of the spine, and more preferably methods and devices are provided for sharing the load with the intervertebral disc, the facet joints, the ligaments, and the muscles of the spinal column. In certain exemplary embodiments, methods and devices are provided for substantially controlling or providing resistance to movement, e.g., flexion, extension, lateral bending, and / or axial rotation, of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
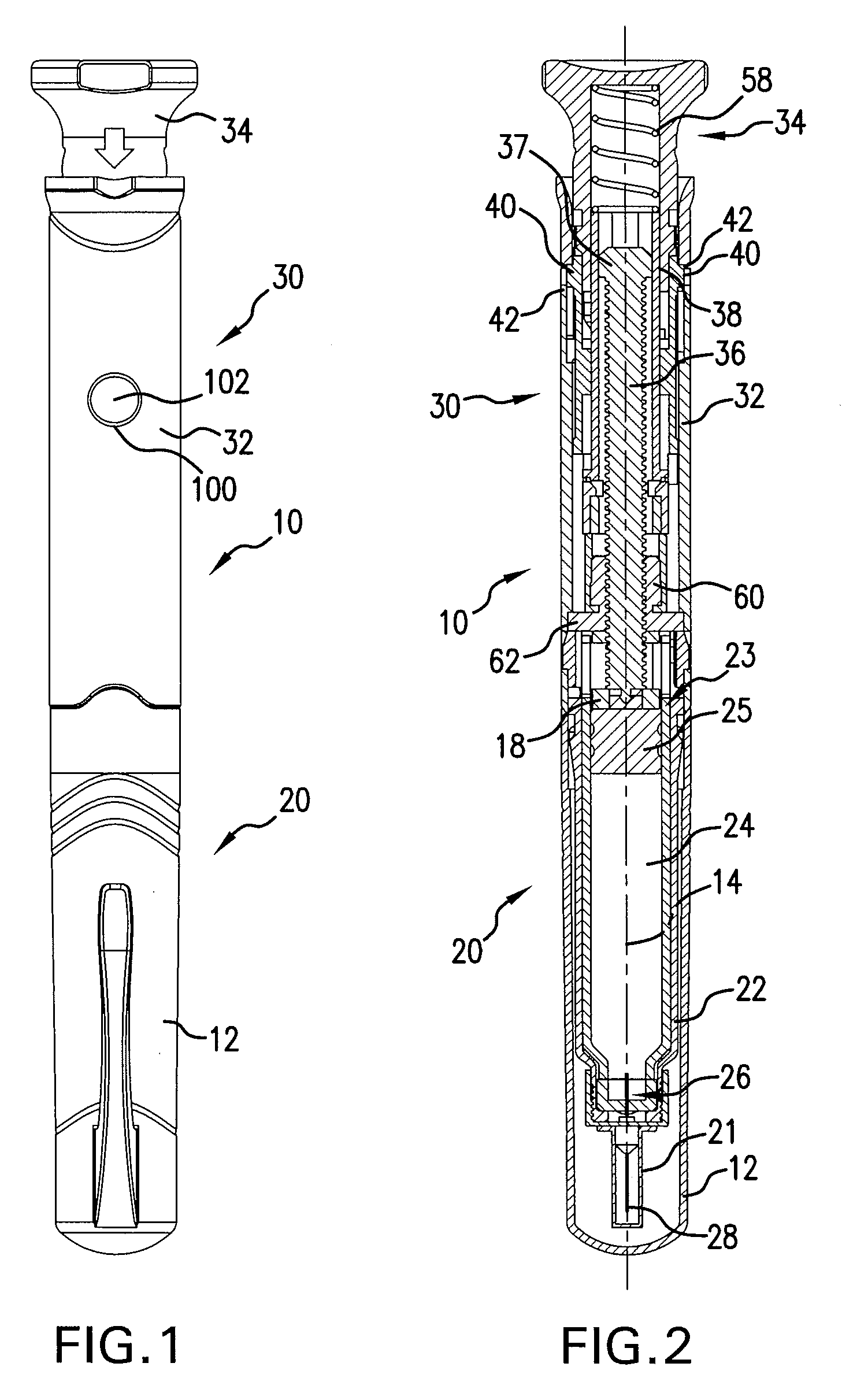
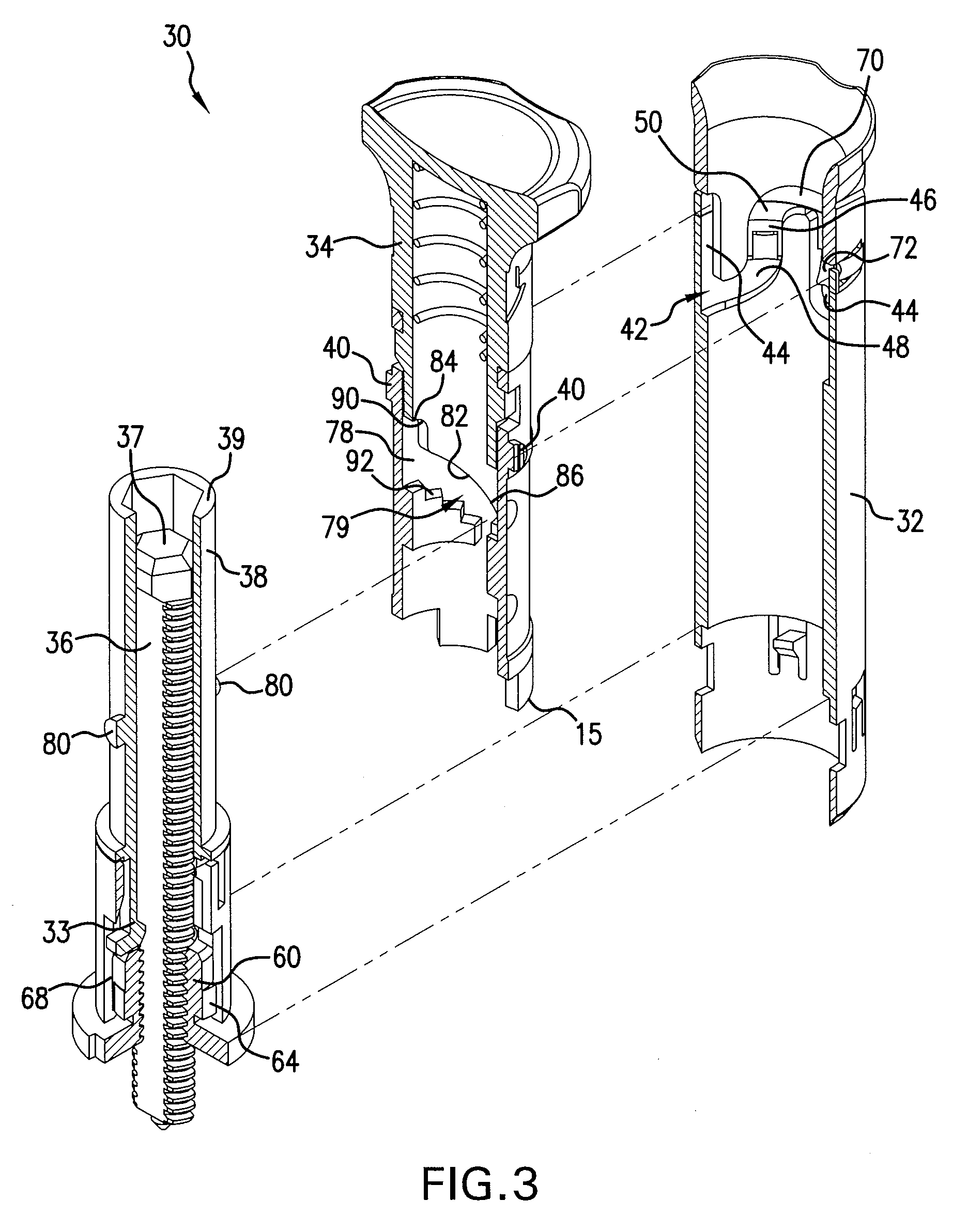
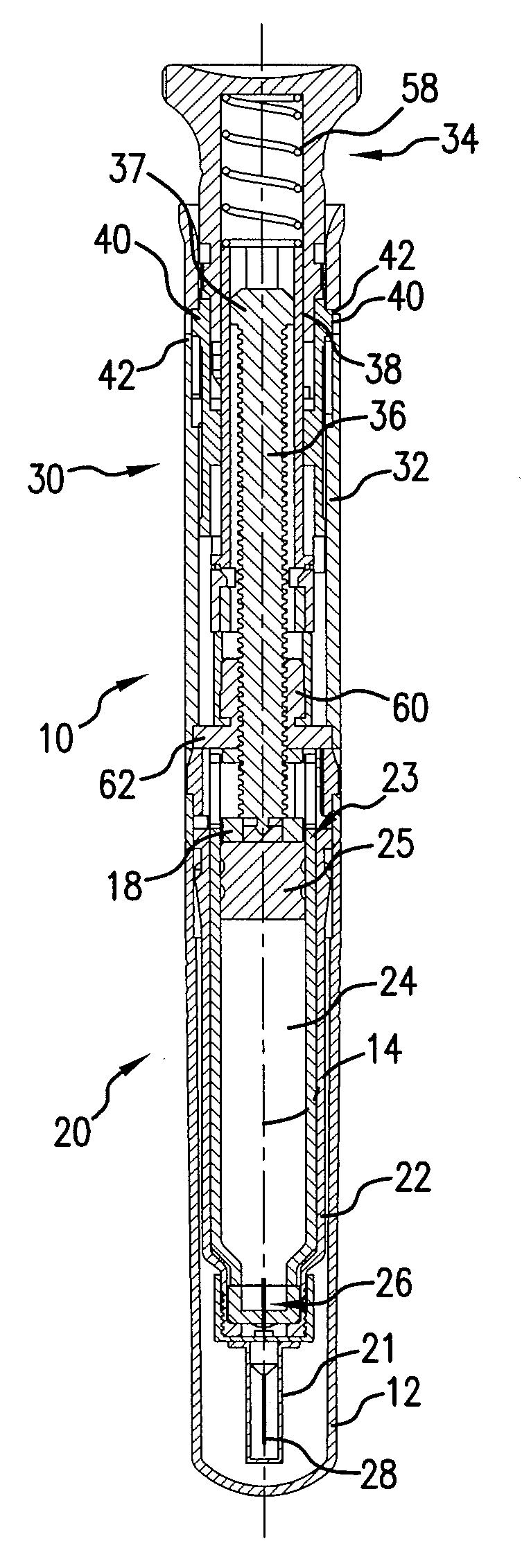
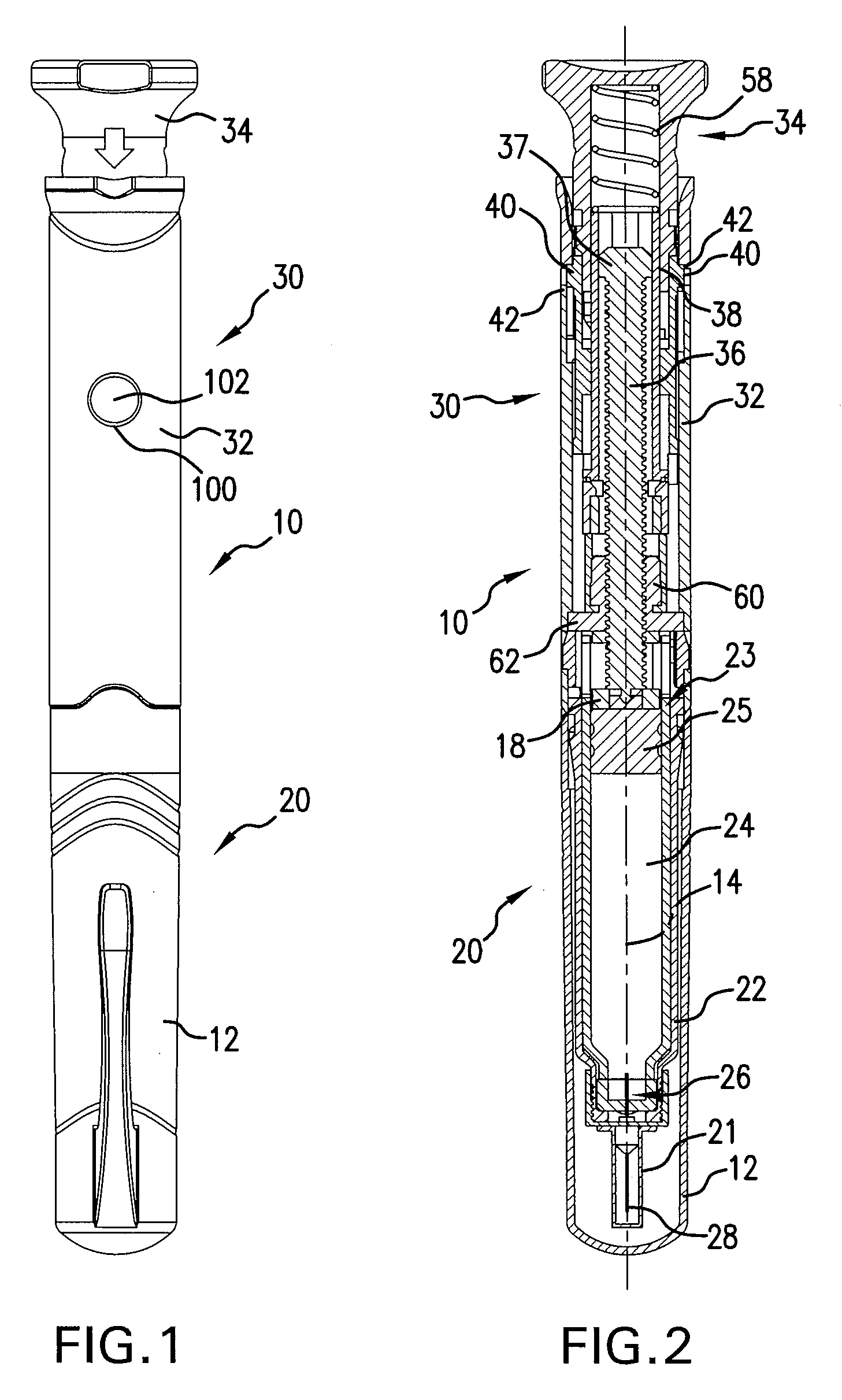
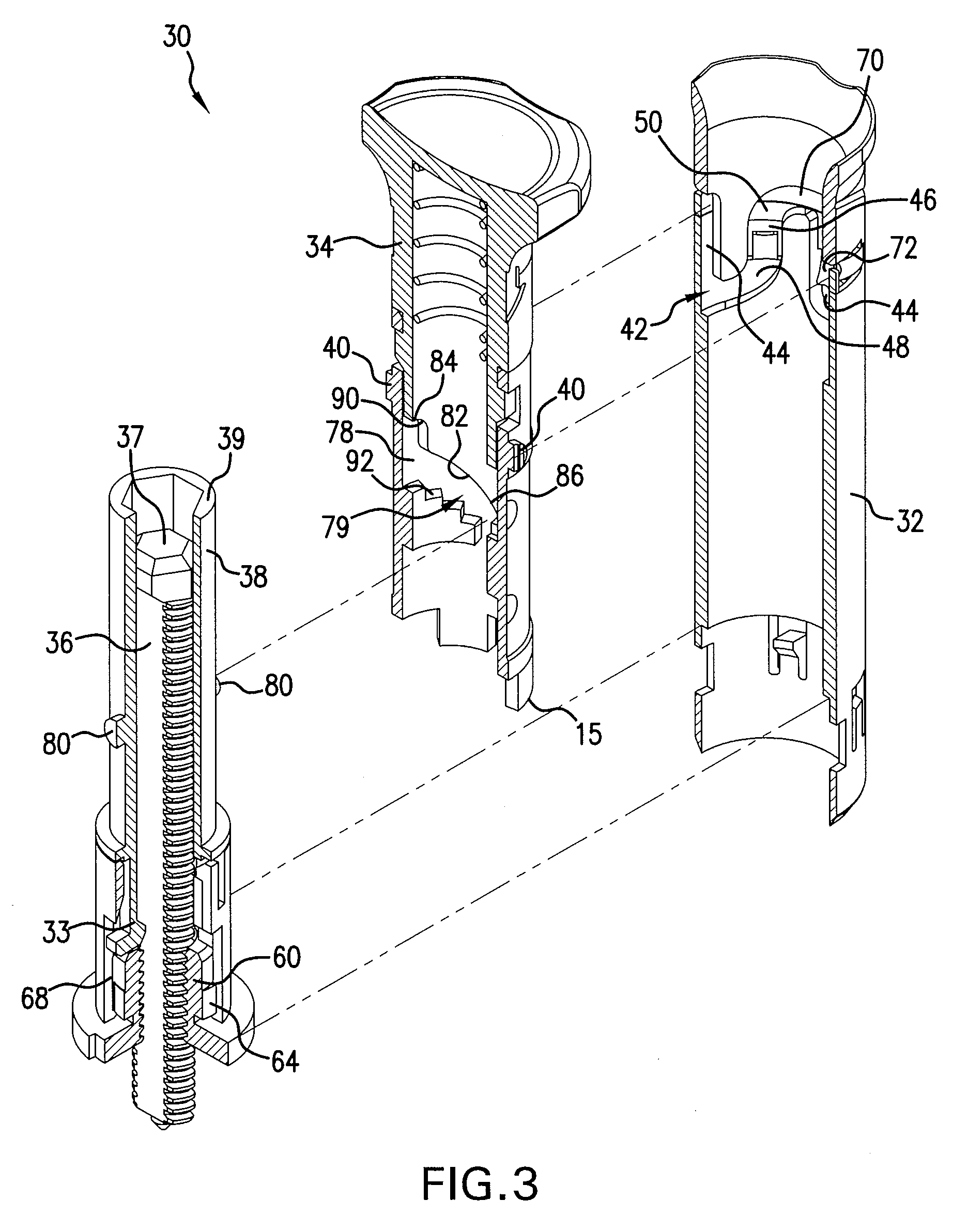
Injection device with cammed ram assembly
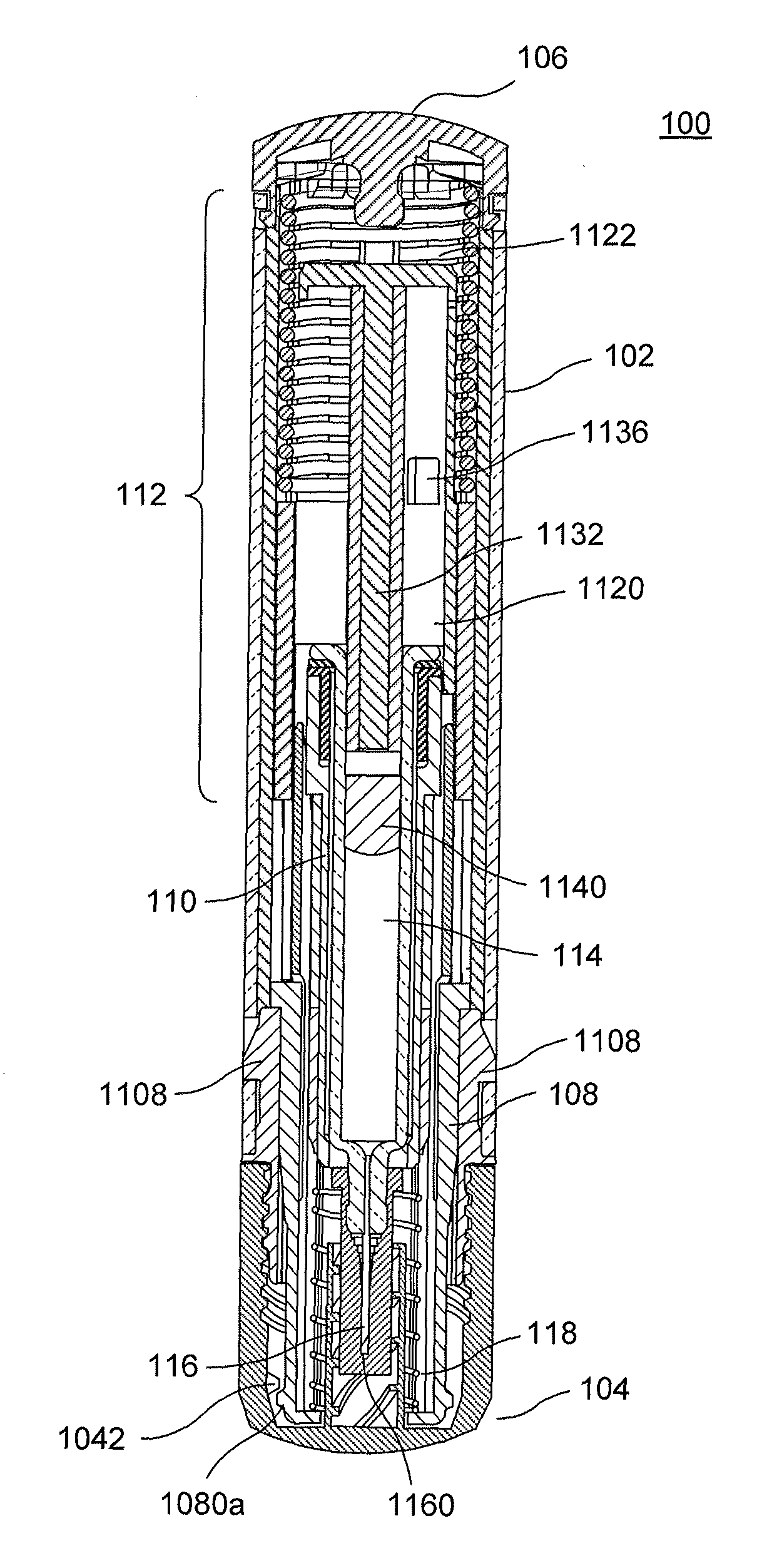
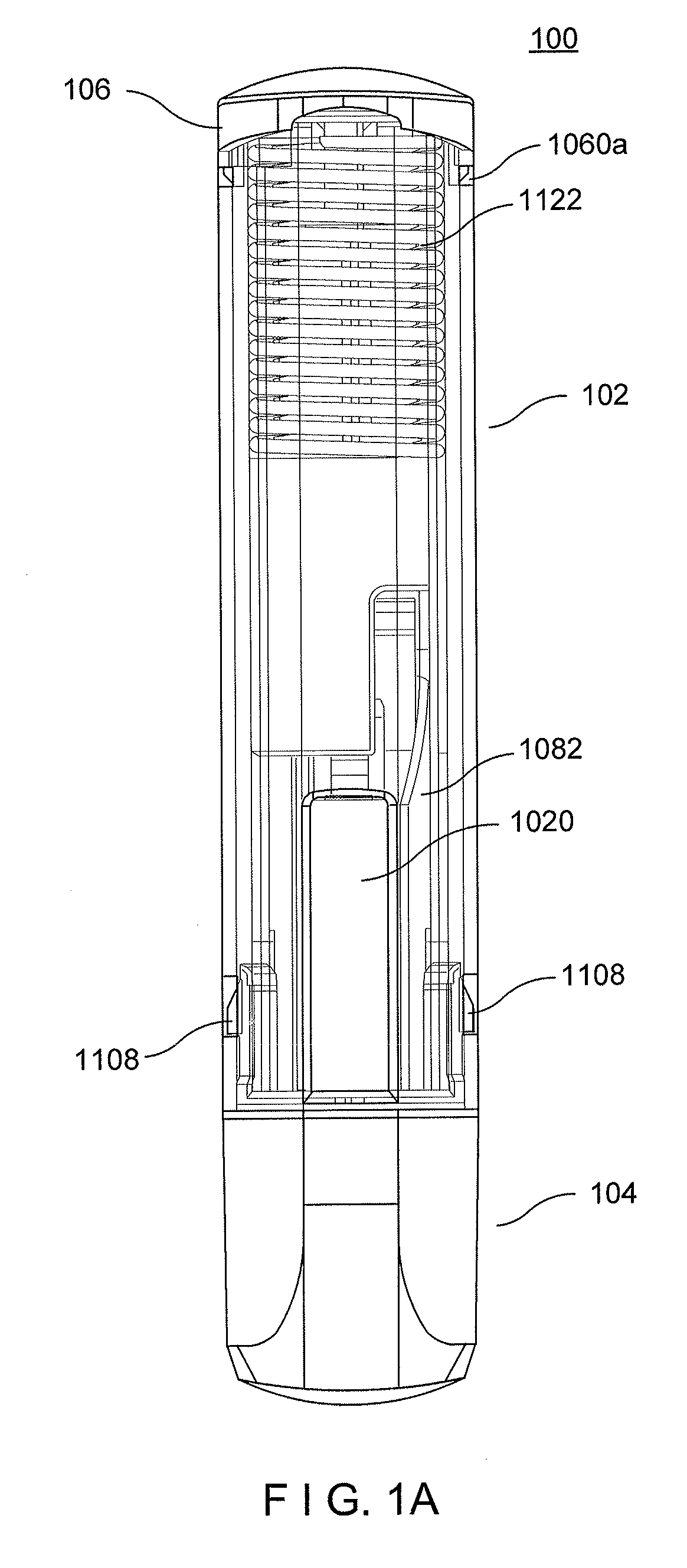
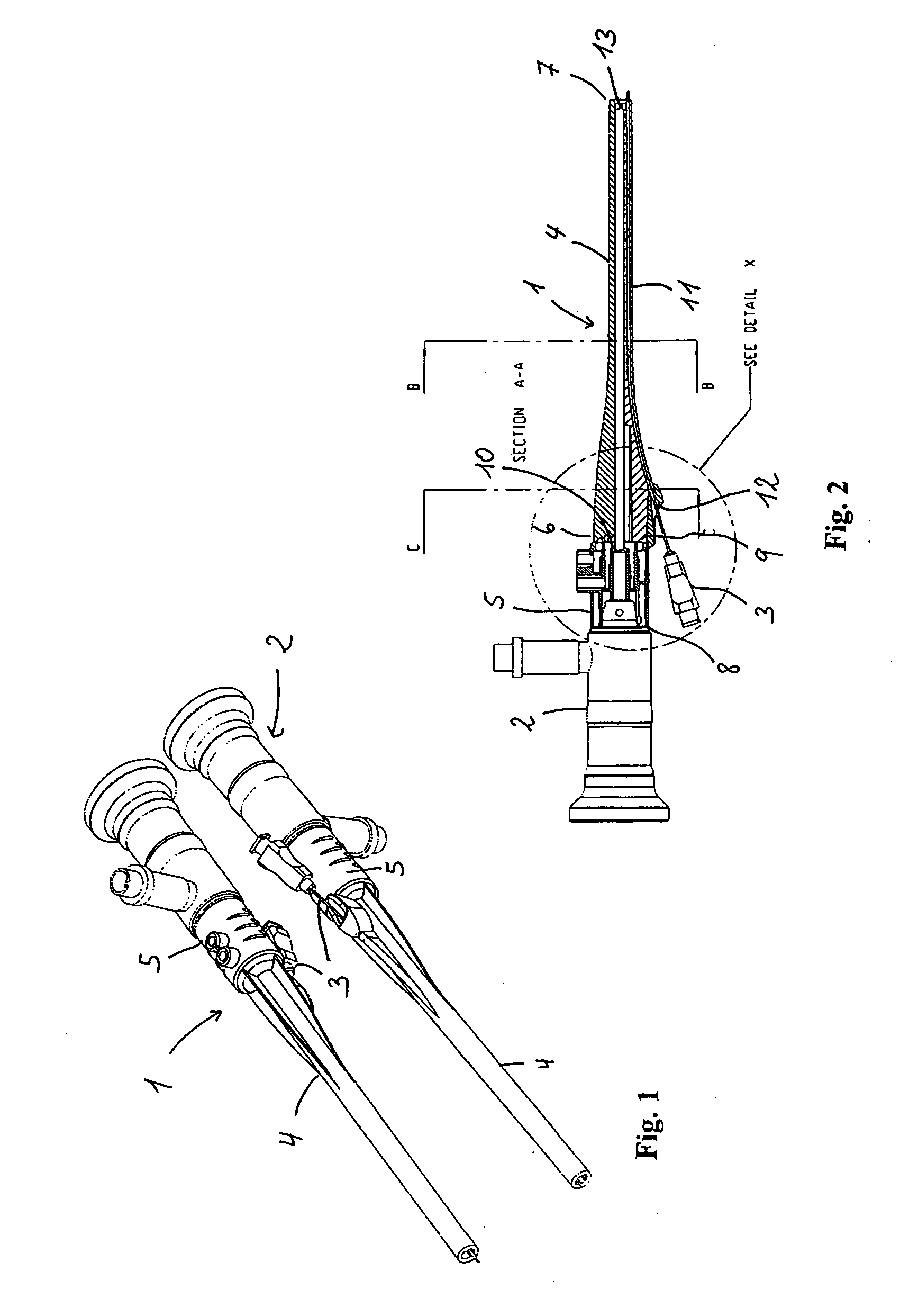
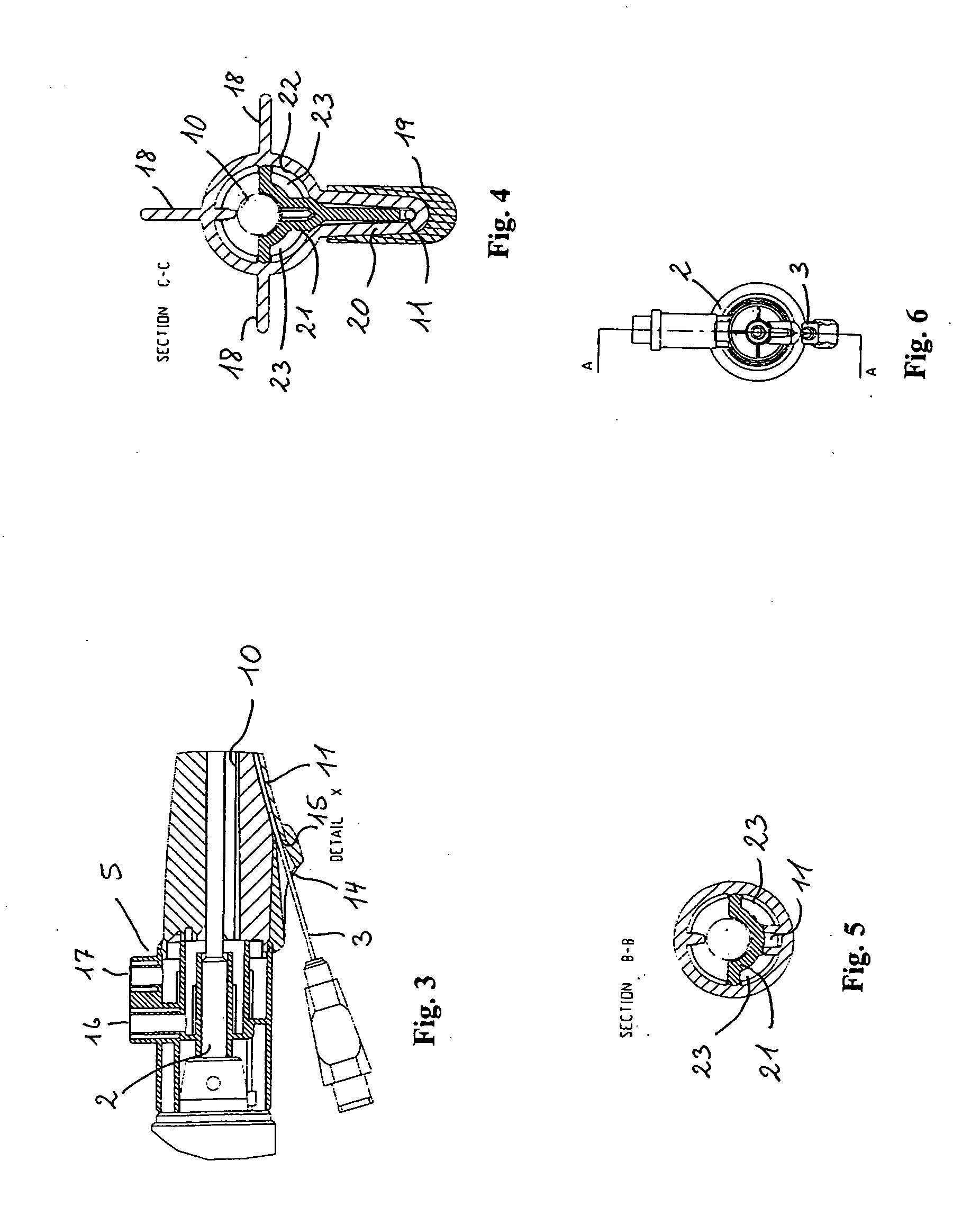
An exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure can provide an injector including a trigger mechanism, an energy source, and a user-operable firing-initiation member. The trigger member can include a trigger member having a retainer portion, and a ram assembly having a ram configured to pressurize a medicament container for expelling a medicament therefrom and a trigger engagement member configured to engage the retainer portion of the trigger member in a pre-firing condition. The energy source can be associated with the ram for powering the ram to expel the medicament, and the user-operable firing-initiation member can be operable for causing an axial rotation between the trigger engagement member and the retainer portion from the pre-firing condition to a firing condition in which the trigger engagement member is released from the retainer portion to allow the energy source to fire the ram.
Owner:ANTARES PHARMA
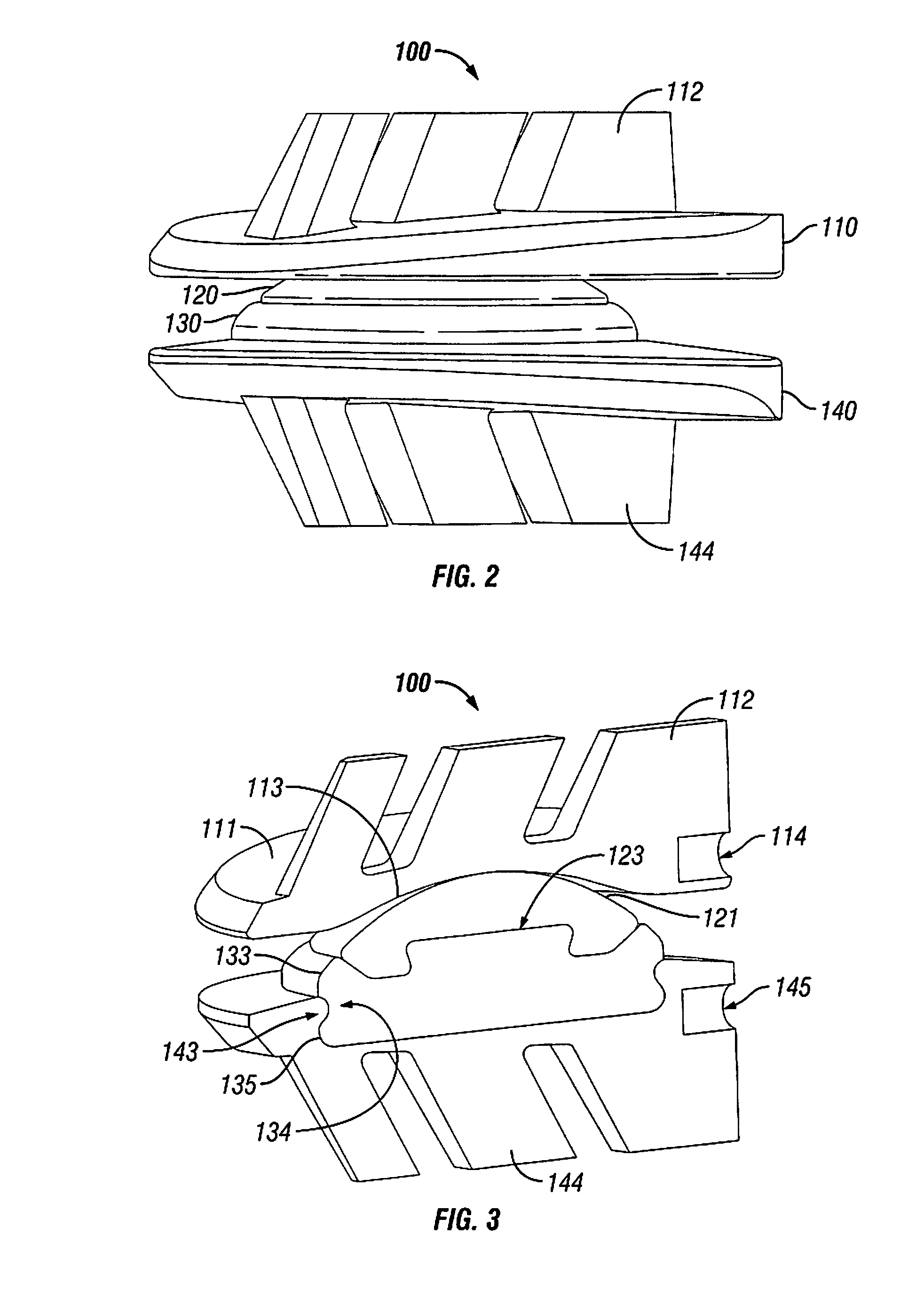
Tri-joint implant methods
Methods and devices are provided for replacing damaged, injured, diseased, or otherwise unhealthy elements of the spinal three-joint complex, such as the facet joints and discs. In one exemplary embodiment, a joint replacement system includes a facet replacement component that is adapted to replace and / or augment the facet joints, and a disc replacement component that is adapted to replace a spinal disc. The facet replacement component and the disc replacement component can couple to one another to allow and / or control flexion, extension, and / or lateral bending of the spine, preferably while substantially restricting posterior-anterior shear and axial rotation of the spine.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
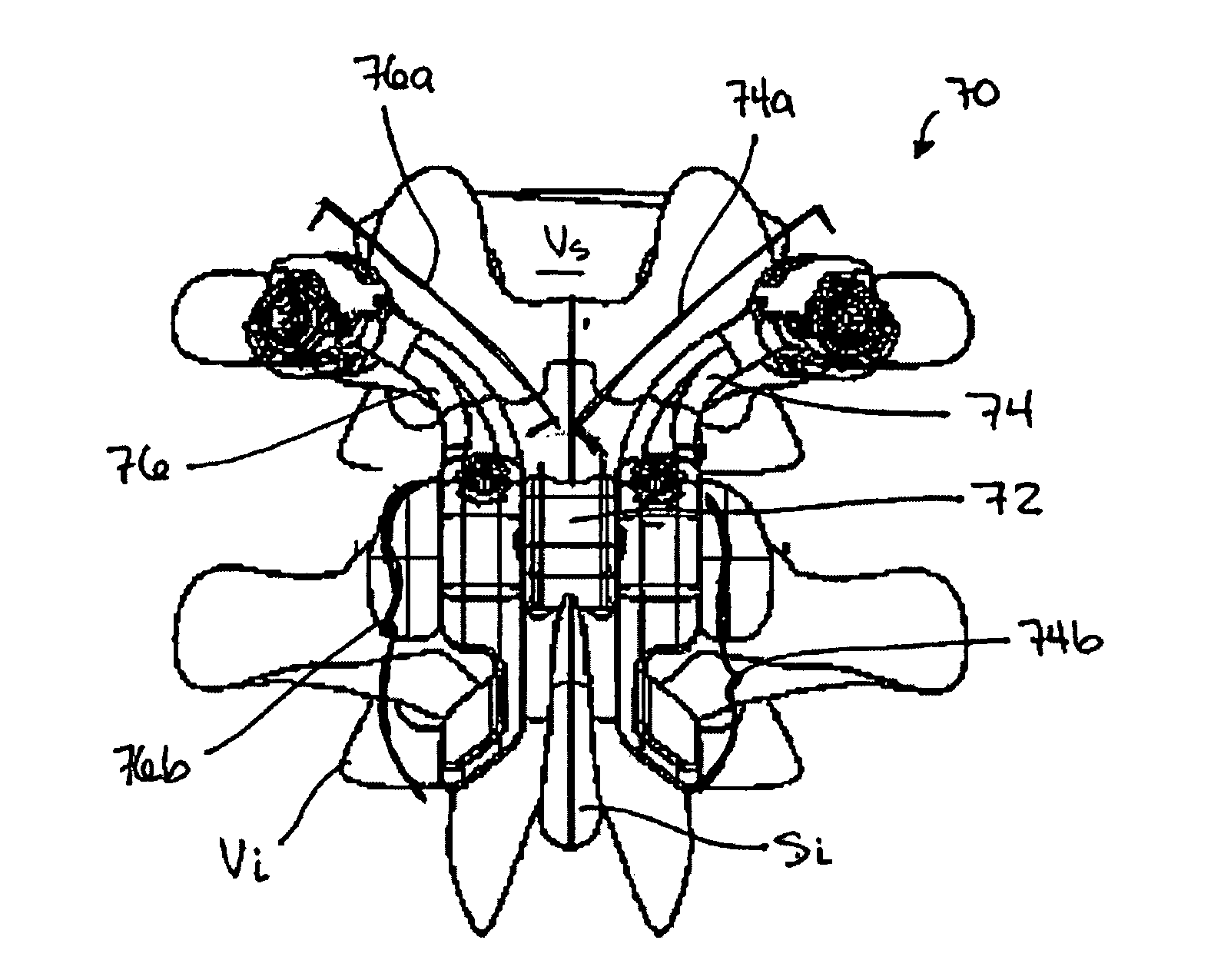
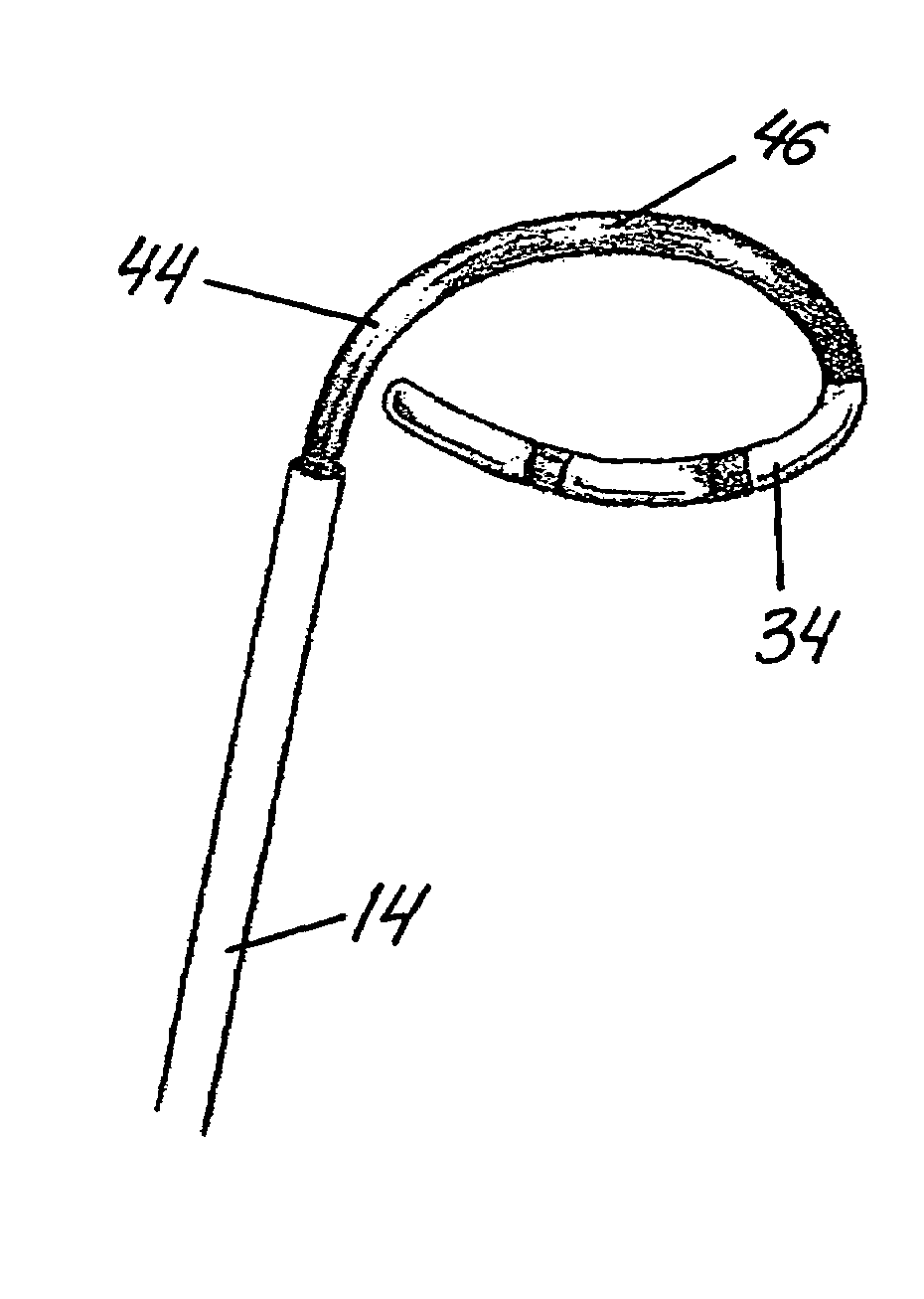
Catheter apparatus for treatment of heart arrhythmia
A catheter apparatus is provided for use in the treatment of heart arrhythmia having a catheter shaft, a mapping and ablation catheter disposed within the shaft, and a control mechanism coupled to both the shaft and catheter. The catheter shaft includes a main body and a coaxial tip section joined to the main body. The tip section can be rotated about a central axis and curved away from the central axis in a controlled manner. The mapping and ablation catheter can be extended outward from the catheter shaft where it is able to take the form of a pre-stressed curve. The control mechanism controls axial rotation of the tip section, the degree of deflection of the tip section and longitudinal movement of the mapping and ablation catheter with respect to the catheter shaft. Preferably, the mapping and ablation catheter forms a pre-stressed loop when it is fully extended from the catheter shaft.In another aspect of this invention, it provides a method for treatment of a heart arrhythmia having the steps of (1) obtaining cardiac image data from a medical imaging system, (2) creating a 3D model from this cardiac image data, (3) registering the 3D model to an interventional system, (4) positioning a catheter apparatus within a chamber of the heart, (5) displaying the catheter apparatus over the registered 3D model on the interventional system, (6) navigating the catheter apparatus within the heart guided by the registered 3D model, and (7) having the catheter apparatus ablate heart tissue at select locations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable brace for providing joint support
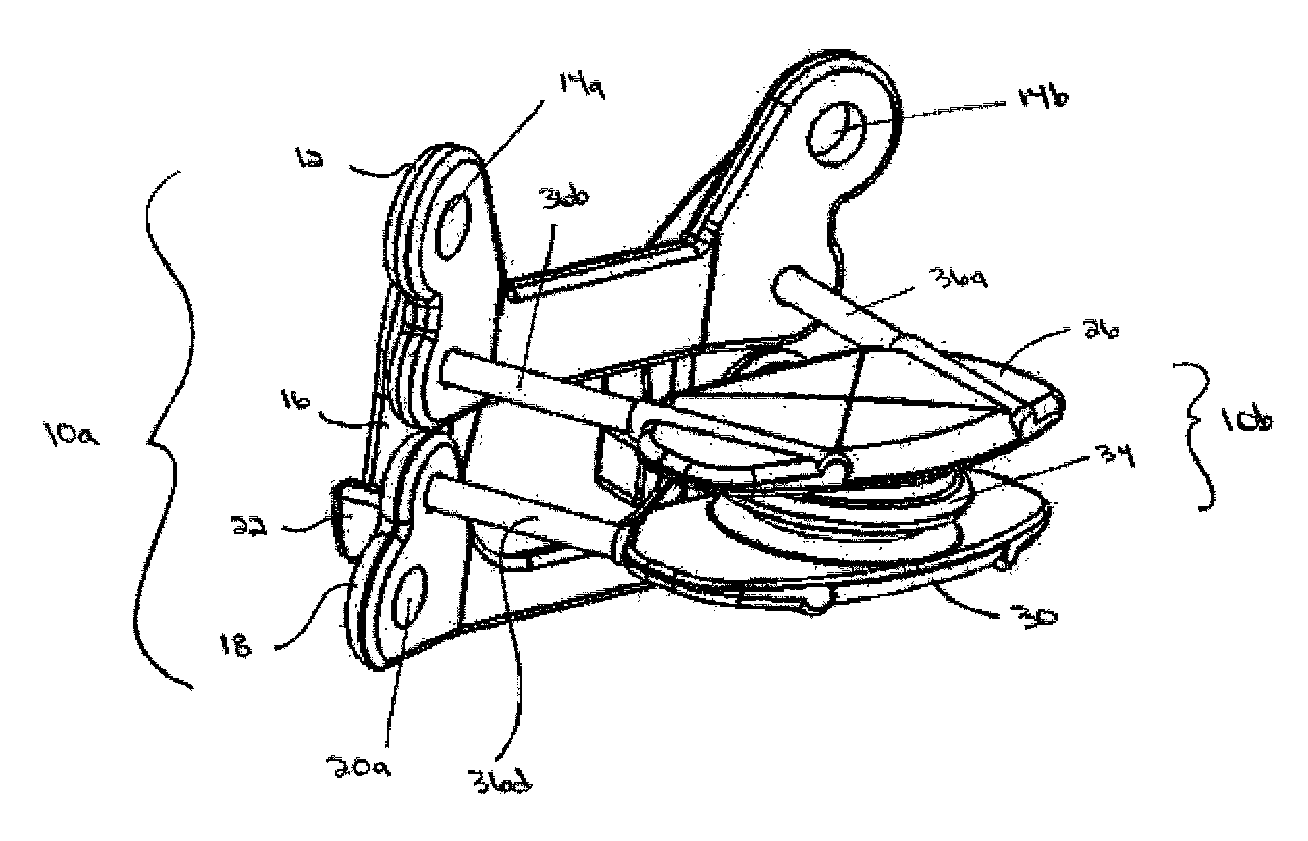
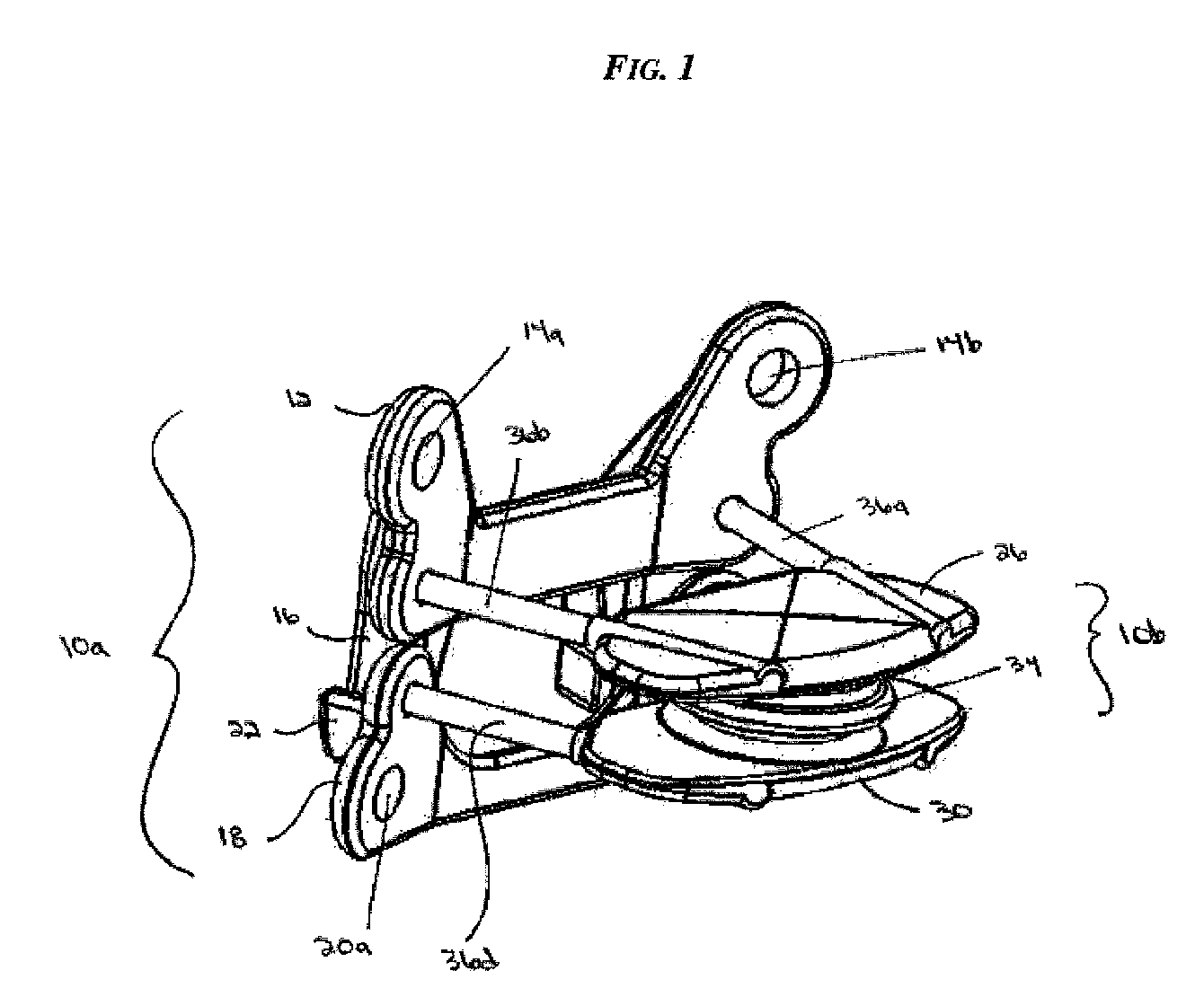
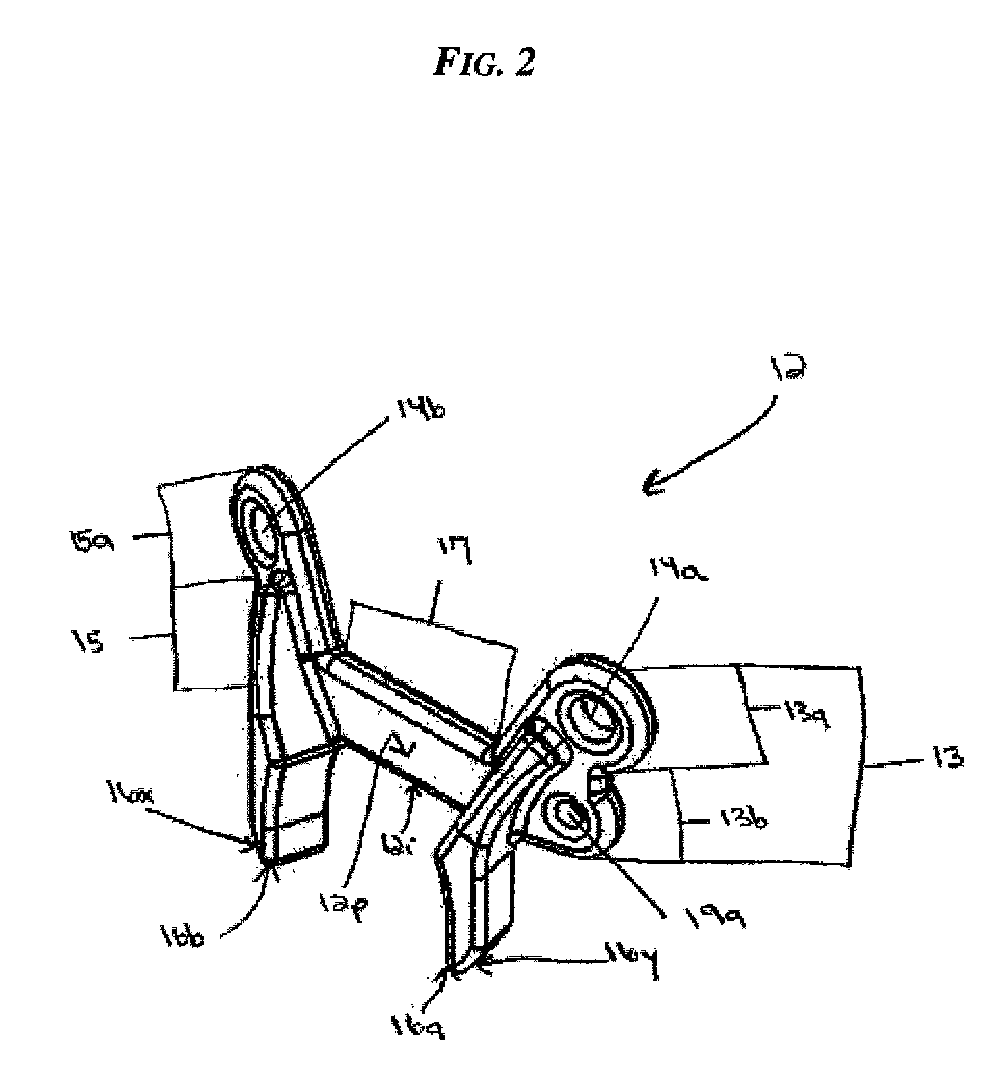
Internal braces and methods of implanting same. A brace can be implanted on one side of a joint, or a pair of braces can be implanted, one on each opposite side of a joint. Each brace supports the joint over at least a portion of its range of motion. Distraction may be provided, or load sharing can be accomplished without distraction. Relative axial rotation of the bones connected by the brace may be permitted. One or more compliant members may be provided in the brace.
Owner:MOXIMED INC
Implantable brace for providing joint support
Internal braces and methods of implanting same. A brace can be implanted on one side of a joint, or a pair of braces can be implanted, one on each opposite side of a joint. Each brace supports the joint over at least a portion of its range of motion. Distraction may be provided, or load sharing can be accomplished without distraction. Relative axial rotation of the bones connected by the brace may be permitted. One or more compliant members may be provided in the brace.
Owner:MOXIMED INC
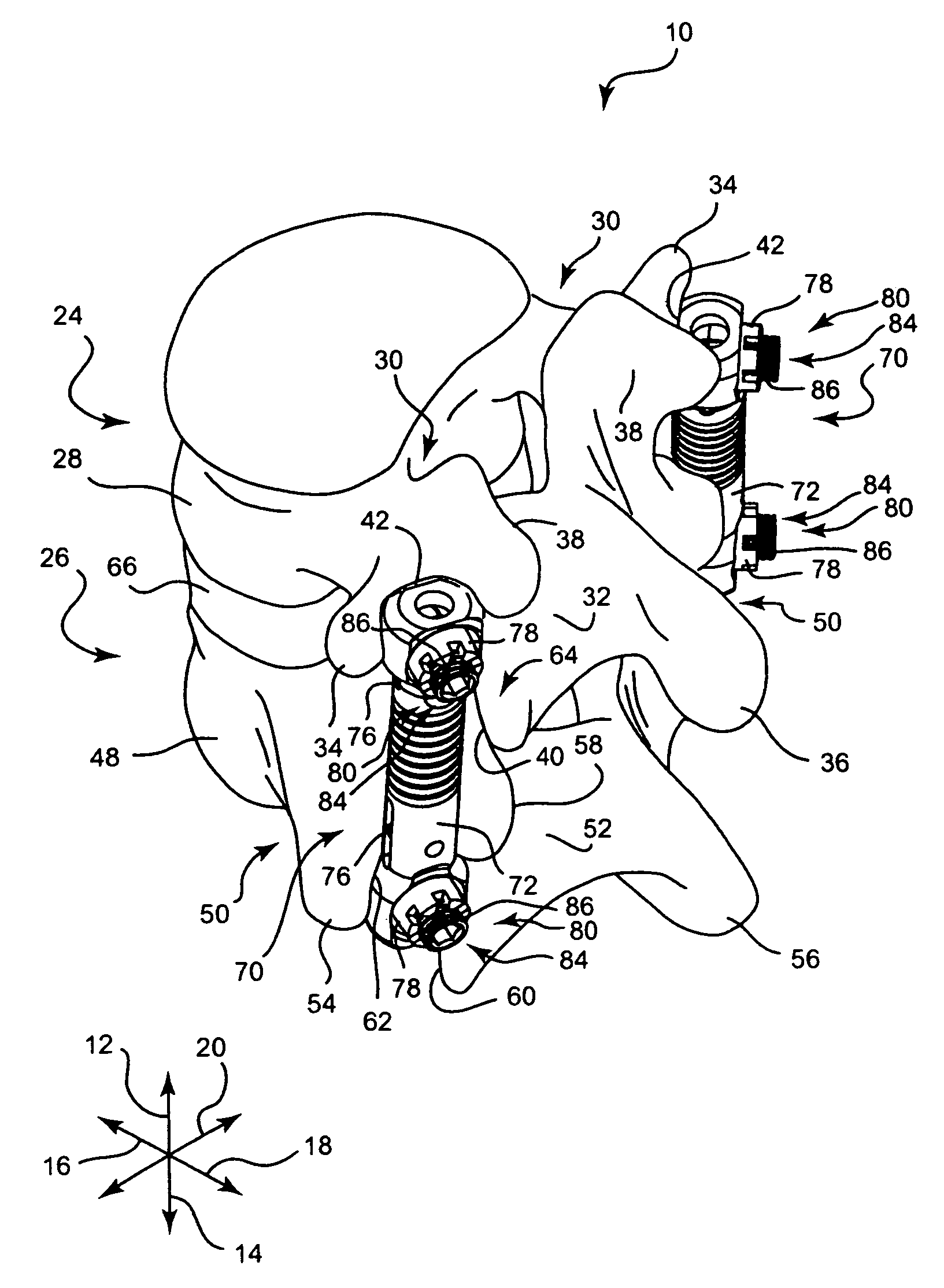
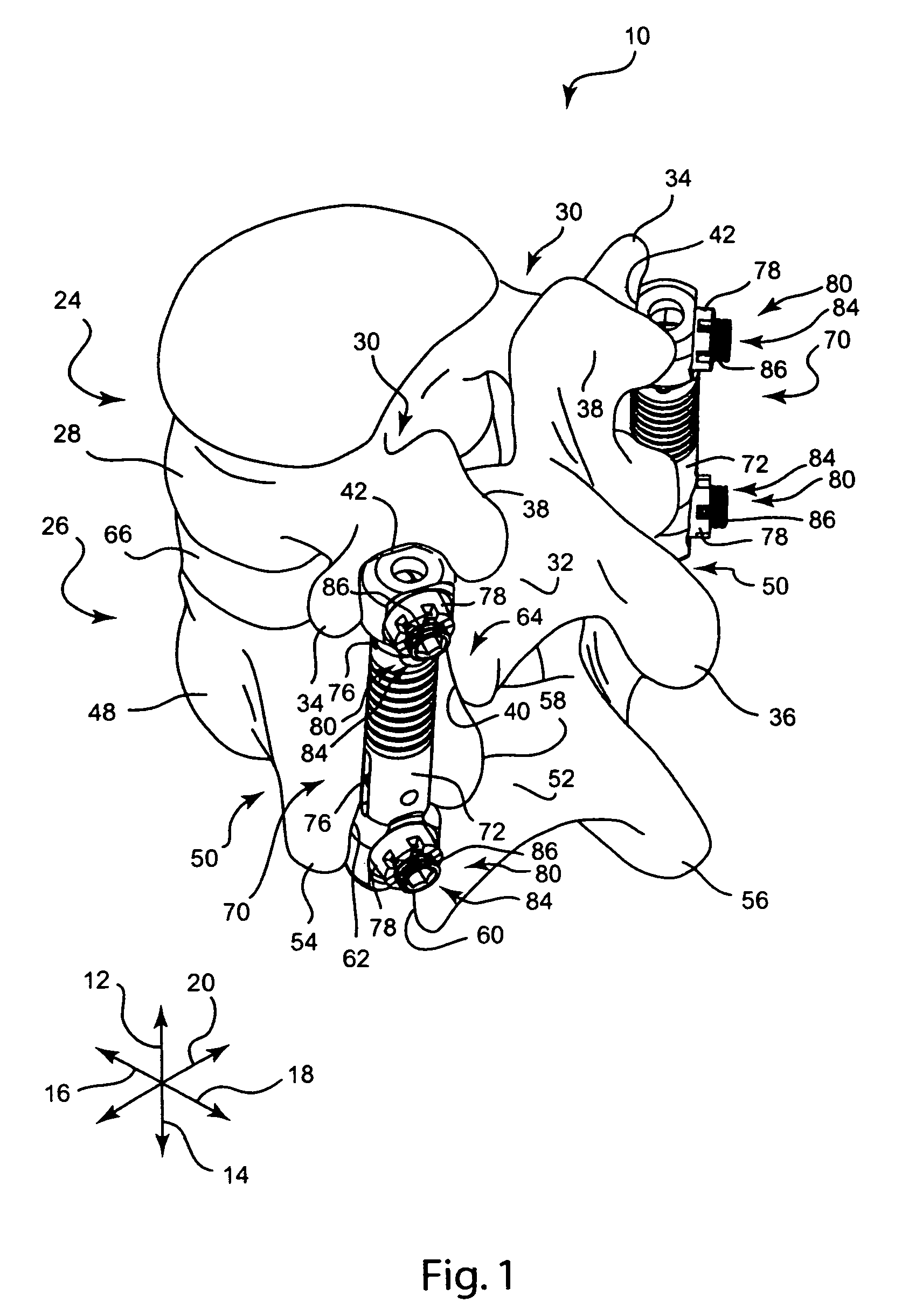
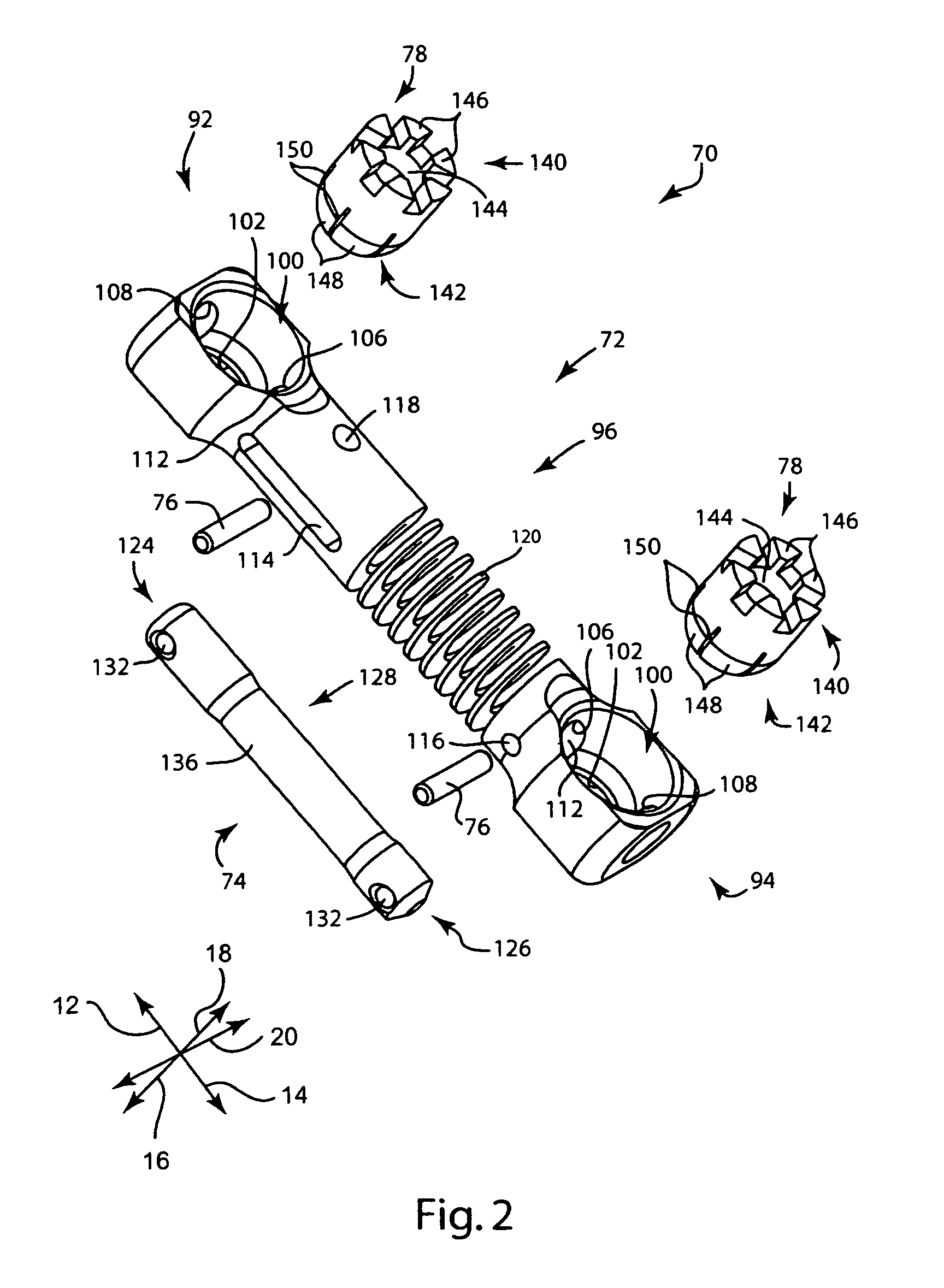
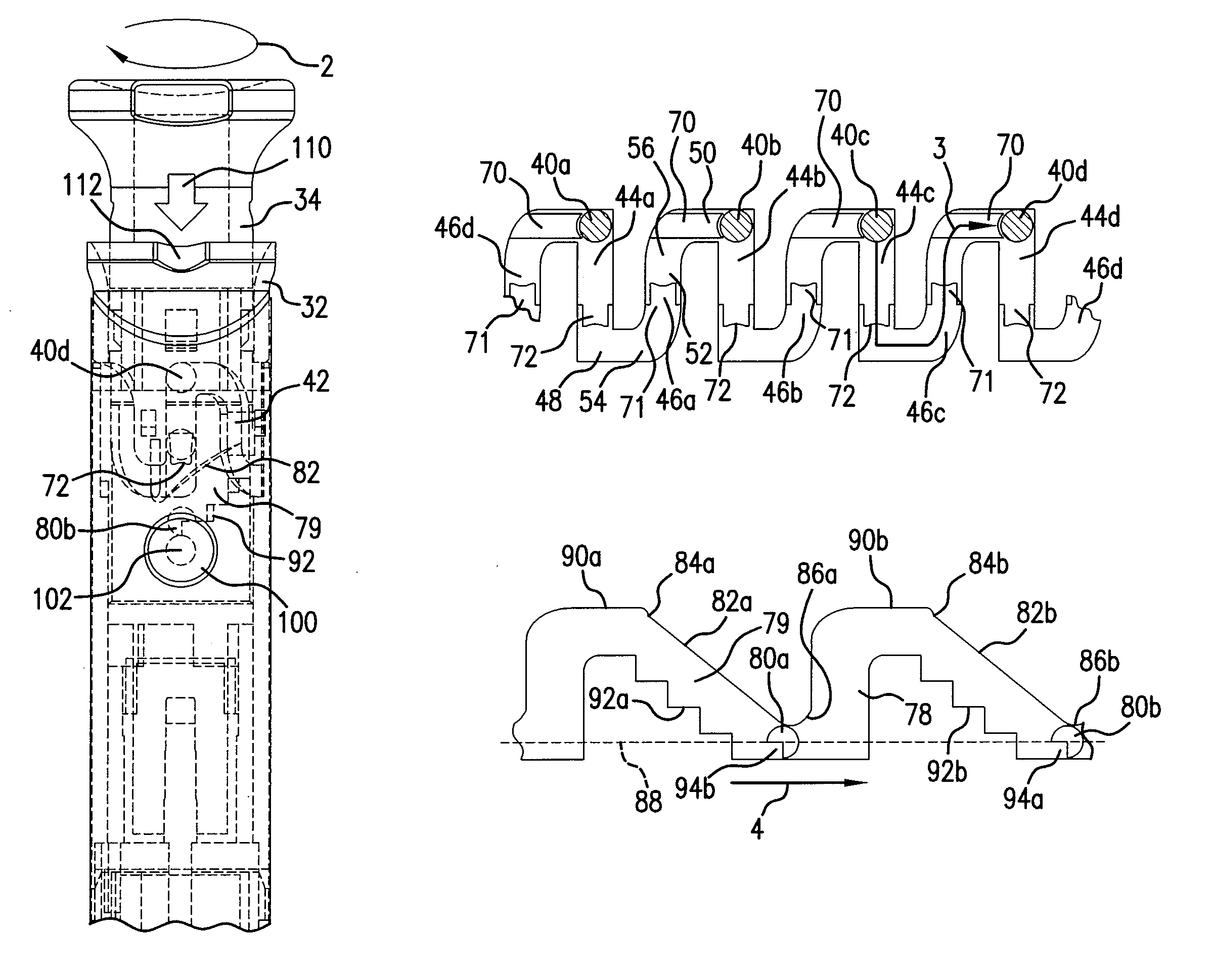
Apparatus and method for dynamic vertebral stabilization
InactiveUS7625393B2Avoid relative motionInsufficient stiffnessInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSet screwIntervertebral disc
A posterior vertebral stabilizer has a resilient member such as a linear spring, which operates in tension and compression. The resilient member may be kept straight by a stabilization rod extending through the spring, or by a telescoping assembly that encases the resilient member. The ends of the stabilizer are attachable to pedicles of adjacent vertebrae so that the stabilizer adds stiffness to control flexion and extension of the vertebrae. Two such stabilizers may be used, and may be connected together by a crosslink designed to limit relative rotation of the stabilizers. Thus, the stabilizers may restrict axial rotation and lateral bending between the vertebrae, while permitting stiffened flexion and extension. Such stabilizers help provide the stiffness of a healthy intervertebral disc. In the event that fusion of the joint becomes necessary, a set screw or other component may be used to further restrict flexion and extension.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Medical electrical lead connector arrangement including anti-rotation means
InactiveUS6854994B2Line/current collector detailsTransvascular endocardial electrodesEngineeringLead Conductor
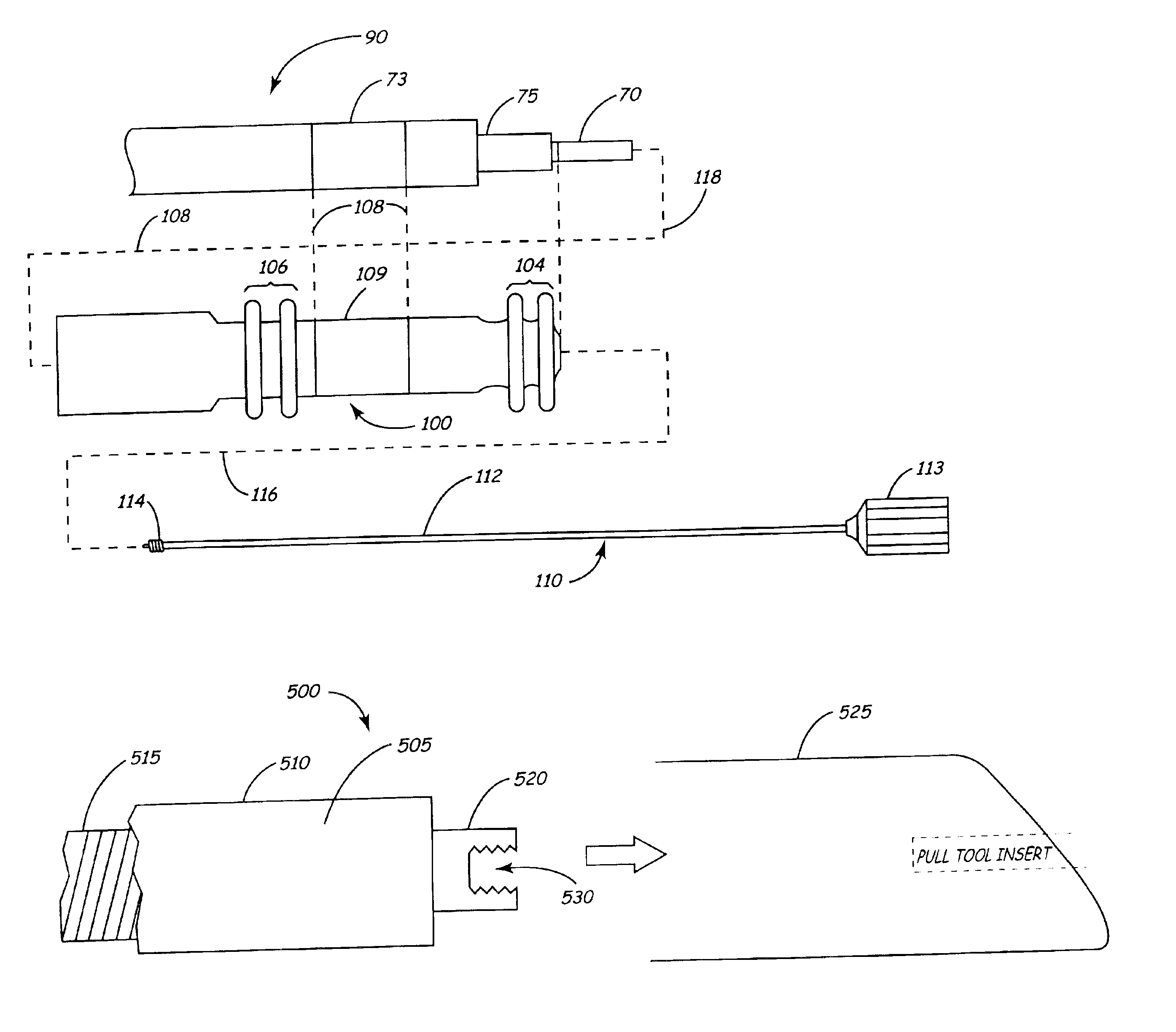
A lead connector arrangement includes a non-cylindrically shaped connector pin coupled to a lead conductor and a connector sleeve assembly for receiving the non-cylindrically shaped connector pin. The connector sleeve assembly includes an insert with an axial bore formed therein that complements the shape of the non-cylindrical connector pin. According to one embodiment, the non-cylindrical connector pin may be provided in the form of a triangular, square, rectangular, or hexagonal shape. The axial bore has a complimentary shape to receive the connector pin. When the connector pin is threaded through the connector sleeve assembly using a pull-wire device, the pull-wire device may be unscrewed from the connector pin without causing axial rotation of the lead conductor when the connector pin is fully inserted within the axial bore.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Lumbar flexing seating apparatus
InactiveUS7100983B1Degree of tilt is limitedImprove posturePortable framesOperating chairsButtocksEngineering
A buttocks seat is supported by a post tiltably affixed at a lower end to an upper face of a base. The post is also axially rotatable relative to the base, and threadably engaged with an underside of the seat for supporting the seat on the post, the seat squarely facing upright when the post is vertical. A hand wheel is affixed to the post for rotating the post relative to the seat and the base for selectively raising or lowering the seat relative to the base. A resilient bias urges the post to be vertical unless a seated user flexes his or her lumbar with sufficient force to overcome the bias. Preferably the post is tiltable over a conical range and the bias comprises a resiliently compressible, cylindrical ring coaxial with the post, and extending between and abutting the base and the underside of the seat.
Owner:GANT RICHARD A
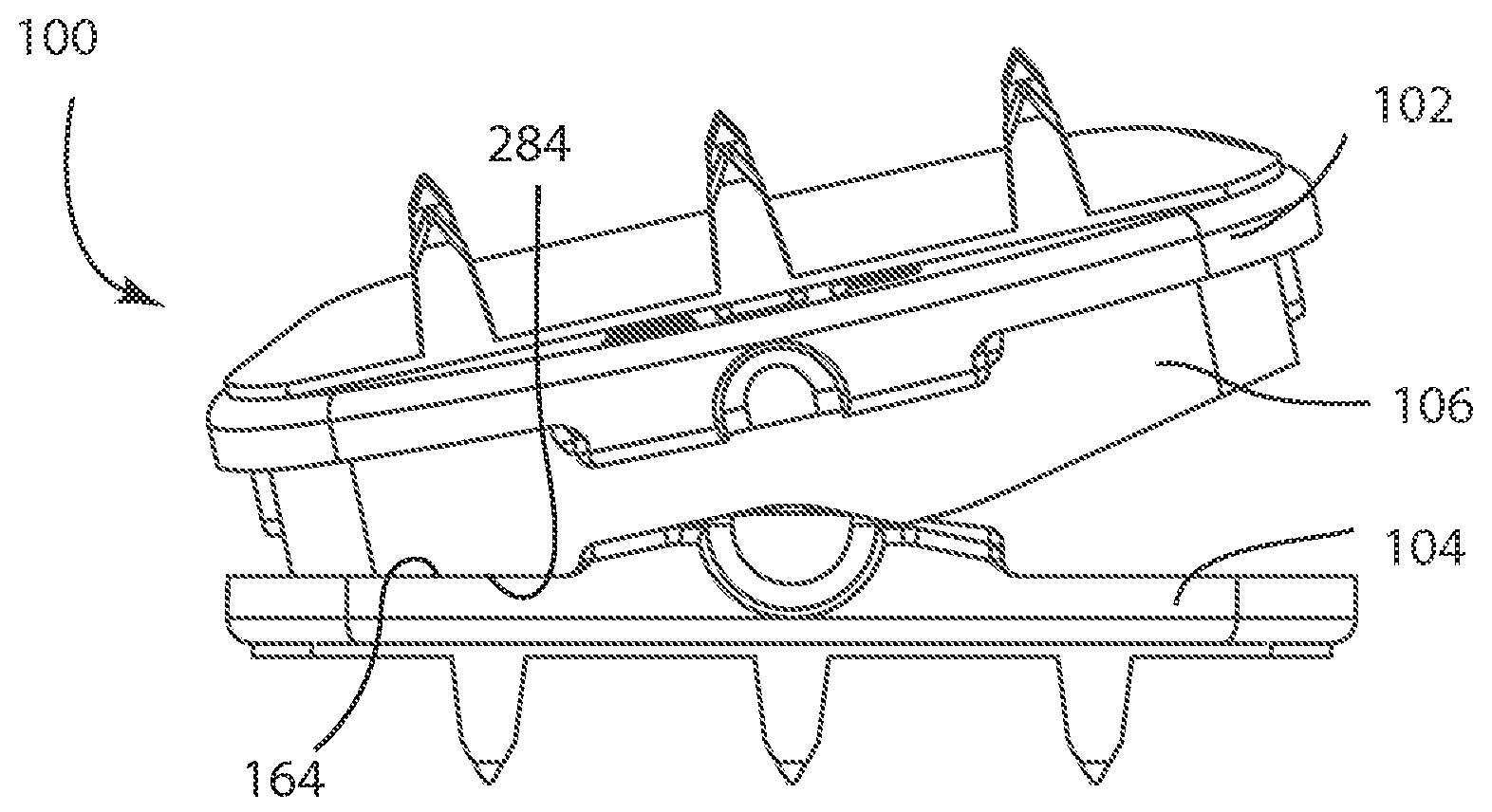
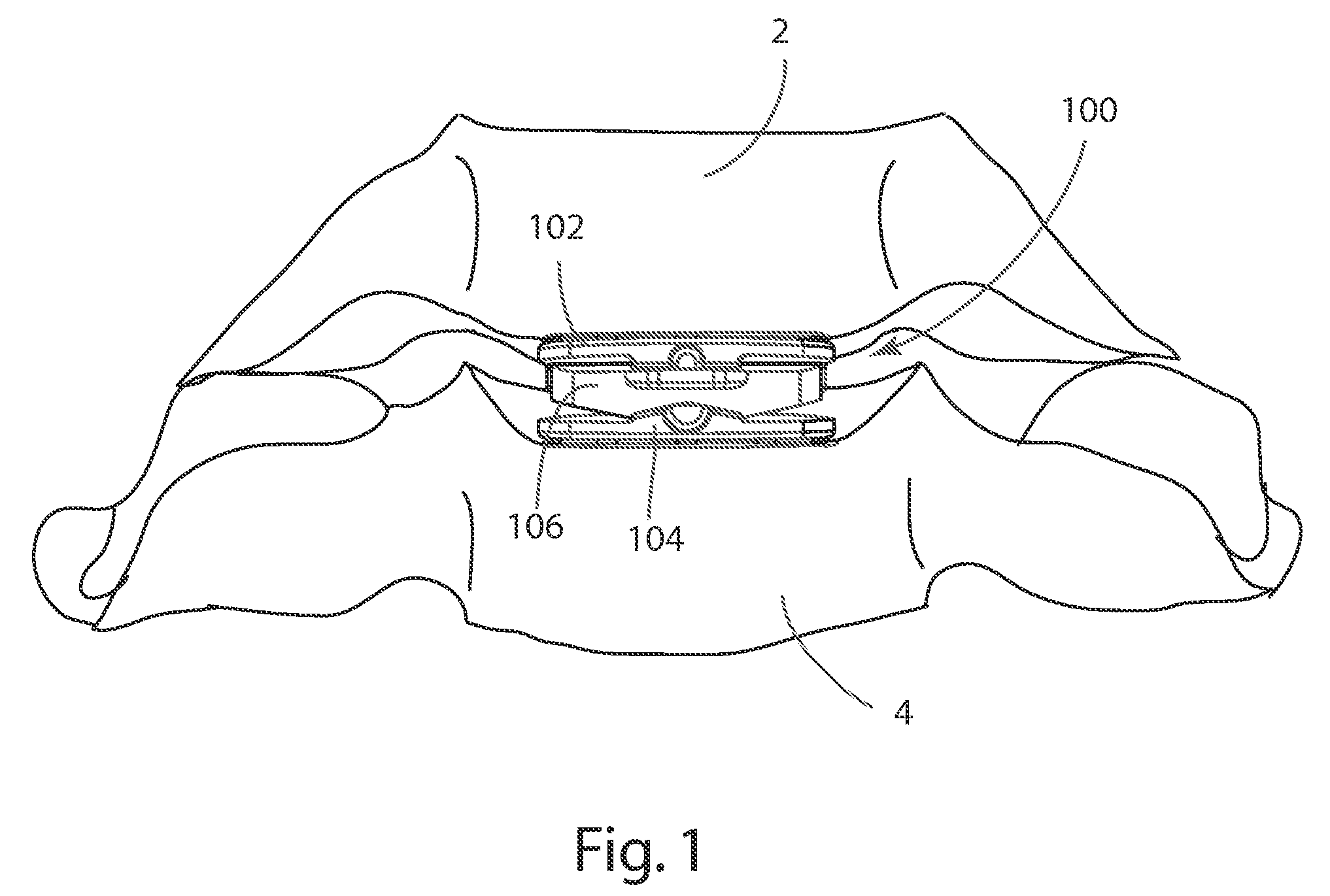
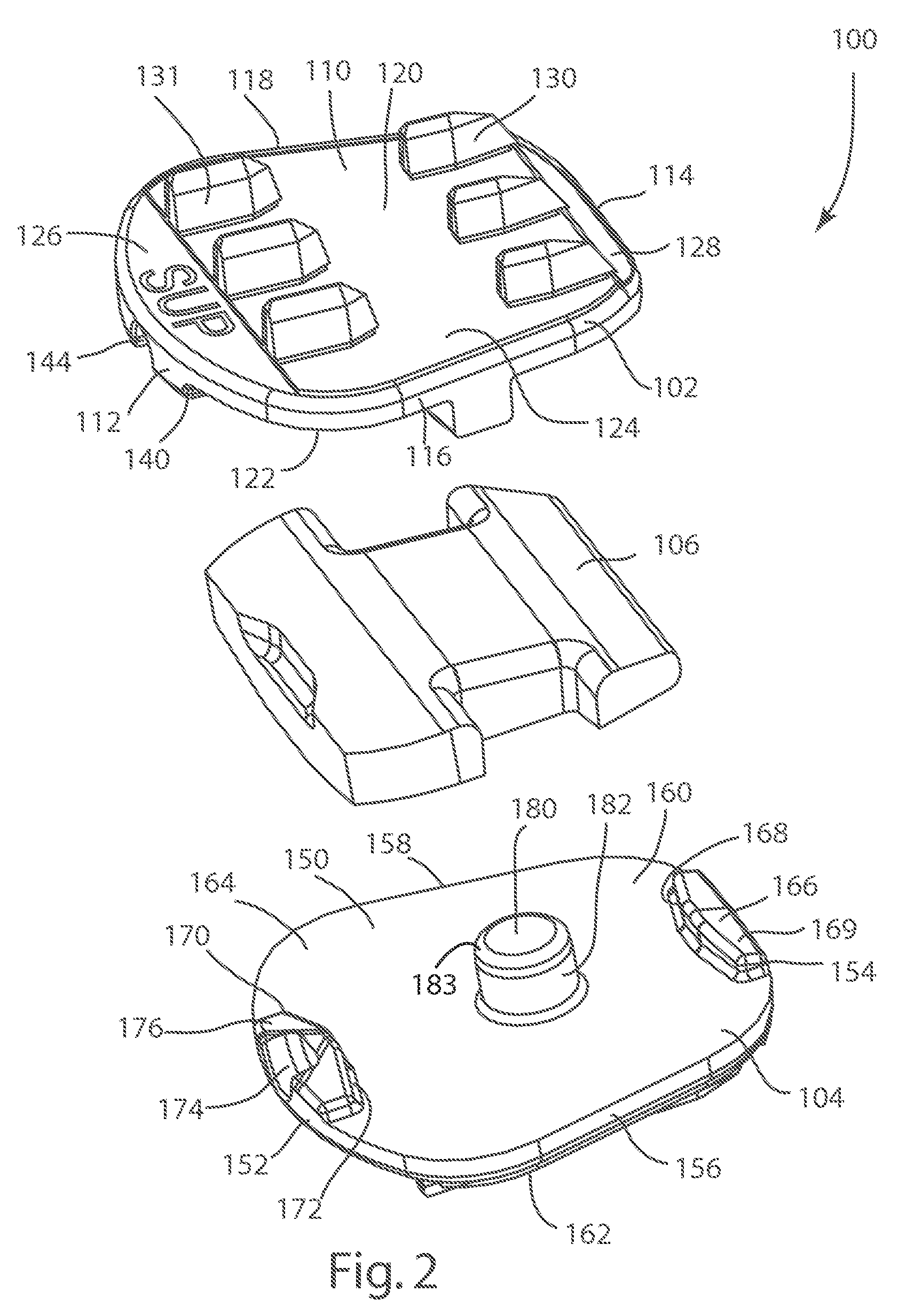
Systems and Methods for Vertebral Disc Replacement
ActiveUS20090076615A1Increase flexibilityEase of insertionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisArticular surfacesArticular surface
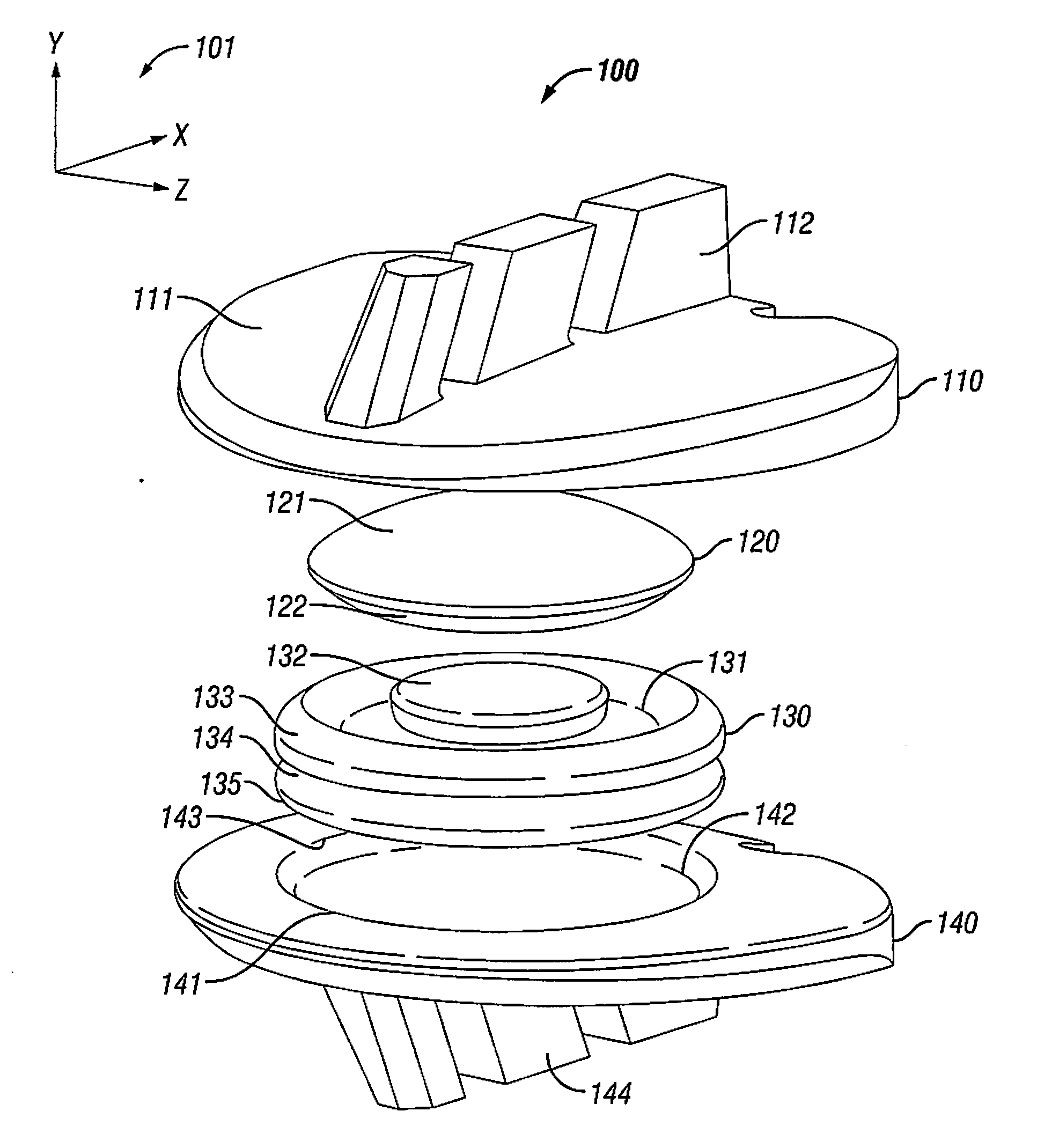
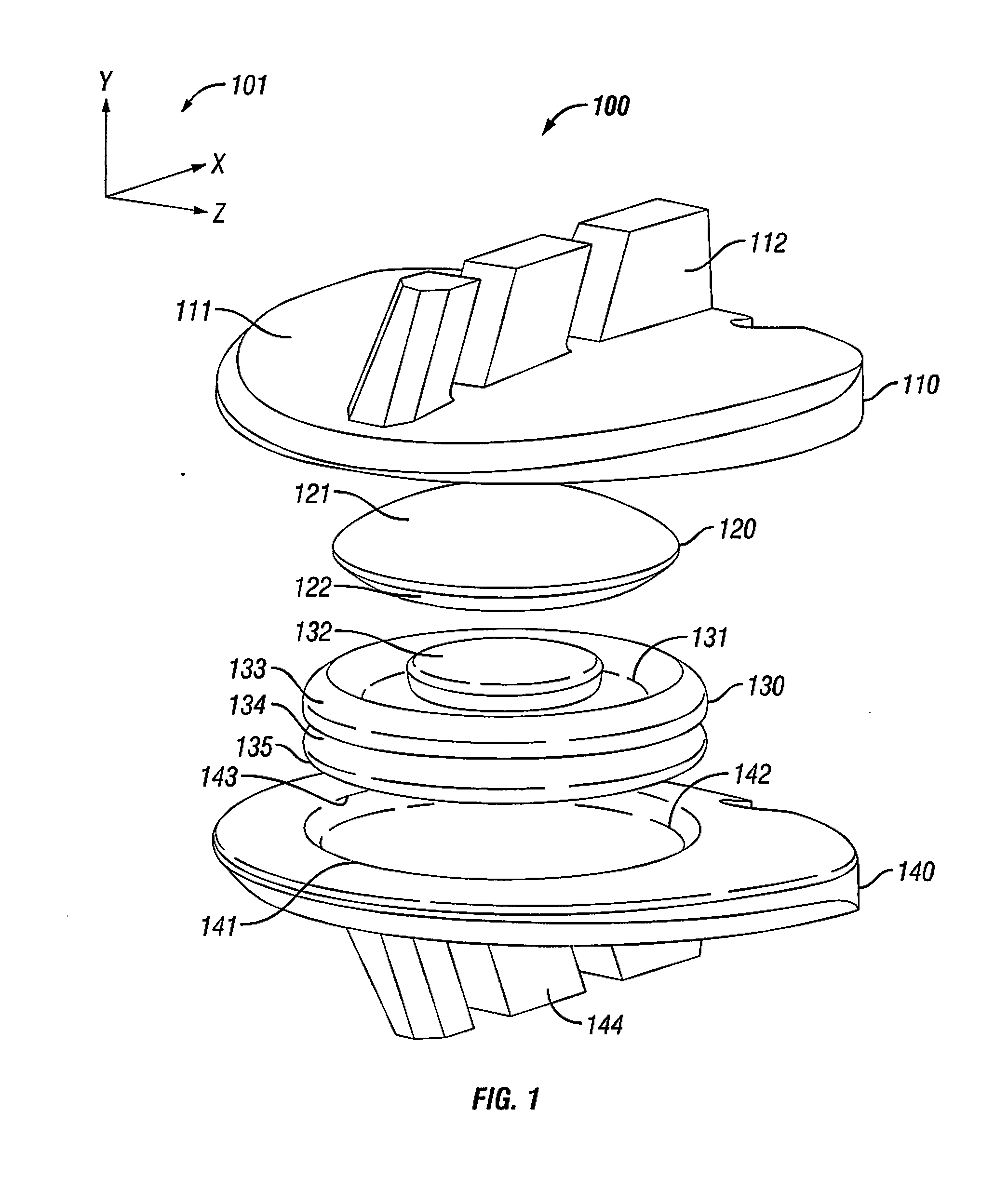
The present invention provides artificial disc prostheses, methods and instrumentation for implantation and revision thereof. Each prosthesis may comprise superior and inferior end plates and a nucleus positioned between articular surfaces of the end plates. The end plates may have planar bone engagement surfaces with a plurality of self-cutting teeth. The articular surfaces of the end plates may be planar or include a flattened portion. The nucleus includes superior and inferior articular surfaces which may comprise flattened portions such that when the articular surfaces of the nucleus and the end plates are placed in cooperation in a preferred orientation, the flattened and / or planar portions are aligned. Each prosthesis may provide flexion / extension, anterior / posterior translation, lateral bending, and / or axial rotation degrees of freedom. One embodiment comprises a prosthesis with a first joint providing flexion / extension and anterior / posterior translation, and a second joint providing lateral bending and axial rotation.
Owner:SYNERGY SPINE SOLUTIONS INC
Locking bone plate with bushing anti-rotation feature
InactiveUS20080119895A1Easy to produceInexpensive and effectiveSuture equipmentsLigamentsDistal portionEngineering
A locking plate intended to be implanted at a bone site and a method for producing and implanting this device. At least one expandable bushing is engaged with a through-hole in the plate. The bushing includes an exterior surface with at least one recess and a passageway including a threaded interior surface. The expandable bushing is initially in a first configuration that permits poly-axial rotation of the bushing within the through-hole. An elongated anchoring member is provided with a distal portion and a proximal portion including a head portion with threads complementary to the threads on the interior surface of the expandable bushing. The proximal portion expands the bushing to form a friction lock between the bushing and the plate in a selected polyaxial position in a second configuration. At least one discrete blocking member is fixedly engaged with the body portion of the plate and extends into the through-hole to engage with the recess on the expandable bushing. The blocking member inhibiting rotation of the expandable bushing relative to the through-hole.
Owner:TORNIER SA SAINT ISMIER
Endoscopic attachment device
ActiveUS20050049459A1Excellent templateExcellent matrixCannulasSurgical needlesEndoscopeBiomedical engineering
A sheath device (1) suitable for endoscopic instruments (2) and comprising an elongated tubular member (4) having a proximal end (6), a distal open end (7), and at least one fluid channel (23). A flushing unit (5) is connected to the proximal end (6) of the tubular member (4) and comprises a proximal open end (8) suitable for receiving a first endoscopic instrument (2), a fluid inlet (16) in contact with said fluid channel (23), and a fluid outlet (17). The tubular member and the flushing unit together define a first interior guiding passage (10) for sheathing at least a part of said first endoscopic instrument (2). The connection between the tubular member (4) and the flushing unit (5) allows for axial rotation of the tubular member (4) in relation to the flushing unit (5).
Owner:AXONICS WOMENS HEALTH LTD
Artificial Discs
A four-component artificial intervertebral disc may provide six degrees of movement: flexion, extension, lateral bending, axial rotation, axial deflection, and anterior / posterior translation. The disc may include a superior endplate, a superior core, an inferior core, and an inferior endplate. The superior endplate may include a concave mating surface, and the inferior endplate may include a spherical mating surface. The superior endplate may roll across the superior core to provide flexion, extension, and lateral bending. The superior endplate may twist or rotate atop the superior core to provide axial rotation, and the superior endplate may slide over the superior core to provide anterior / posterior translation. The superior core may be connected to the inferior core, and the inferior core may be connected to the inferior endplate. The inferior core may be made from a flexible material that may enable the artificial disc to expand or compress vertically.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
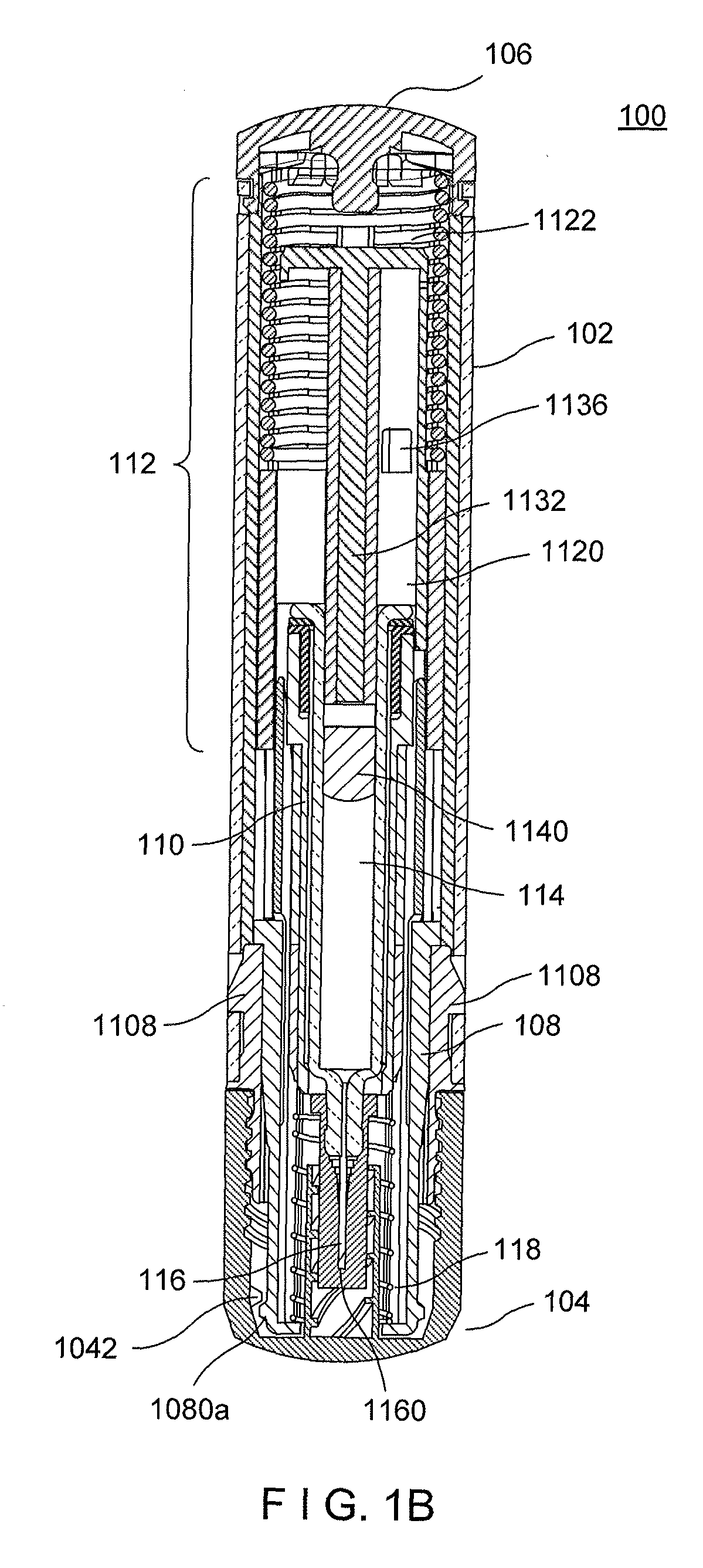
Multiple dosage injector
A medicament dispensing mechanism is disclosed that is configured to eject successive doses of the medicament from a medicament chamber. An embodiment of the dispensing mechanism includes a housing and a plunger rod configured for ejecting the doses of medicament from the chamber. The dispensing mechanism further includes an actuation mechanism that comprises a trigger associated with the housing and having a ready and a fired position with respect thereto. The trigger is configured for manipulation by a user for successive movement in a generally axial dosing motion from the ready position to the fired position in which the trigger is associated with the plunger rod to cause the plunger rod to eject one of the doses of a predetermined volume and a resetting motion from the fired position to the ready position that comprises axial rotation, wherein the trigger is uncoupled from the plunger rod during the resetting motion.
Owner:ANTARES PHARMA INC
Multiple dosage injector
A medicament dispensing mechanism is disclosed that is configured to eject successive doses of the medicament from a medicament chamber. An embodiment of the dispensing mechanism includes a housing and a plunger rod configured for ejecting the doses of medicament from the chamber. The dispensing mechanism further includes an actuation mechanism that comprises a trigger associated with the housing and having a ready and a fired position with respect thereto. The trigger is configured for manipulation by a user for successive movement in a generally axial dosing motion from the ready position to the fired position in which the trigger is associated with the plunger rod to cause the plunger rod to eject one of the doses of a predetermined volume and a resetting motion from the fired position to the ready position that comprises axial rotation, wherein the trigger is uncoupled from the plunger rod during the resetting motion.
Owner:ANTARES PHARMA INC
Steerable needle
InactiveUS7662128B2Improved level of guidanceElectrotherapyInfusion syringesNeedle guidanceCannula tip
The invention relates to a needle guidance system provided by a needle with a steerable tip. The needle has a cannula and a stylet. The stylet adjacent to its tip has a naturally curved portion. The stylet is movable in two degrees of freedom with respect to the cannula—axial translation and axial rotation with respect to the cannula axis. When extended, the stylet curves off-axis and provides cannula tip steering. Driving and / or steering systems may be provided to the orientation and relatively move the stylet.
Owner:SALCUDEAN SEPTIMIU E +3
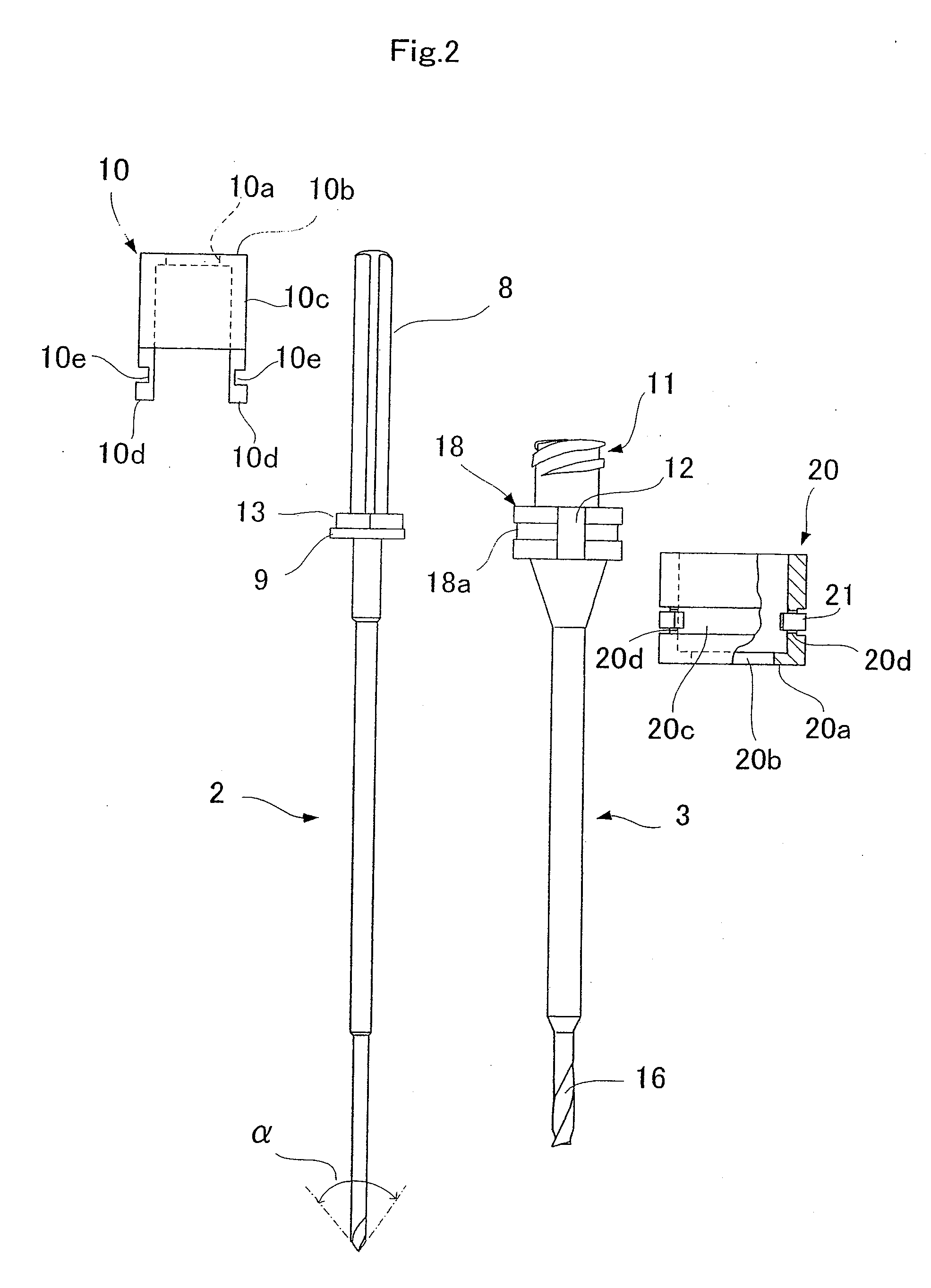
Bone marrow harvesting drill
InactiveUS20080177200A1Reduce cutting resistanceFast harvestSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsLocking mechanismBone chip
The bone marrow harvesting drill of the invention includes an inner needle having a cutting edge at the tip thereof; a tubular mantle that receives the inner needle thereinto so that the inner needle and the tubular mantle are detachably attached; and a lock mechanism that prevents the axial rotation of the tubular mantle and the inner needle relative to each other; the inner needle having a groove formed at the tip thereof projecting from the tubular mantle for discharging bone scraps produced by the cutting edge at the tip of the inner needle; and the tubular mantle having a cutting edge formed at the tip edge thereof and a helical groove extending from the tip edge to at least part of the peripheral surface of the tubular mantle so as to be flush with the groove of the inner needle.
Owner:JIMRO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com