Patents
Literature
280 results about "Anterior posterior" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
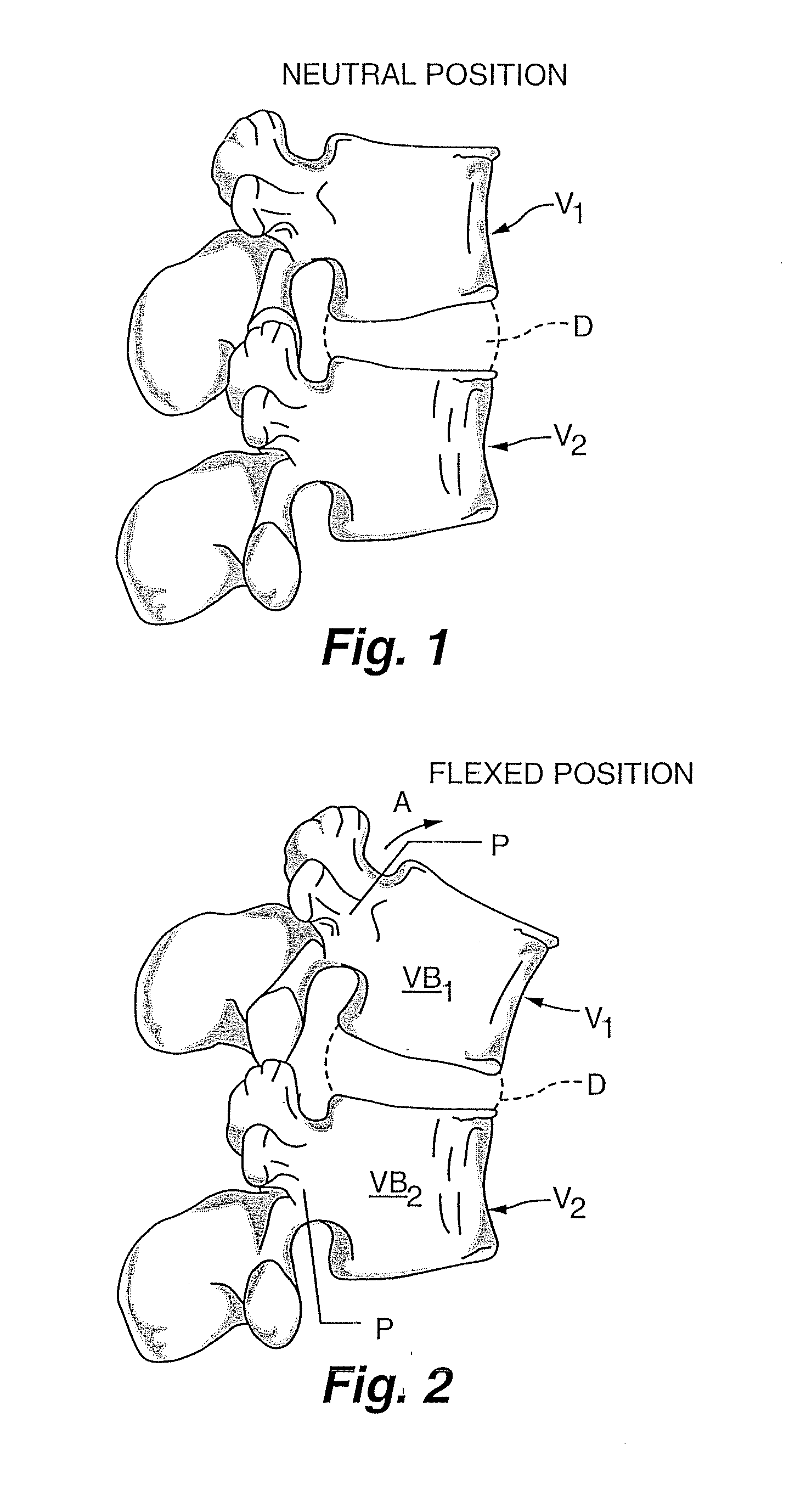
Posterior refers to something that is at the back or on the bottom, while anterior refers to something being in the front or on the top. Generally speaking, posterior and anterior refer to polar opposites.
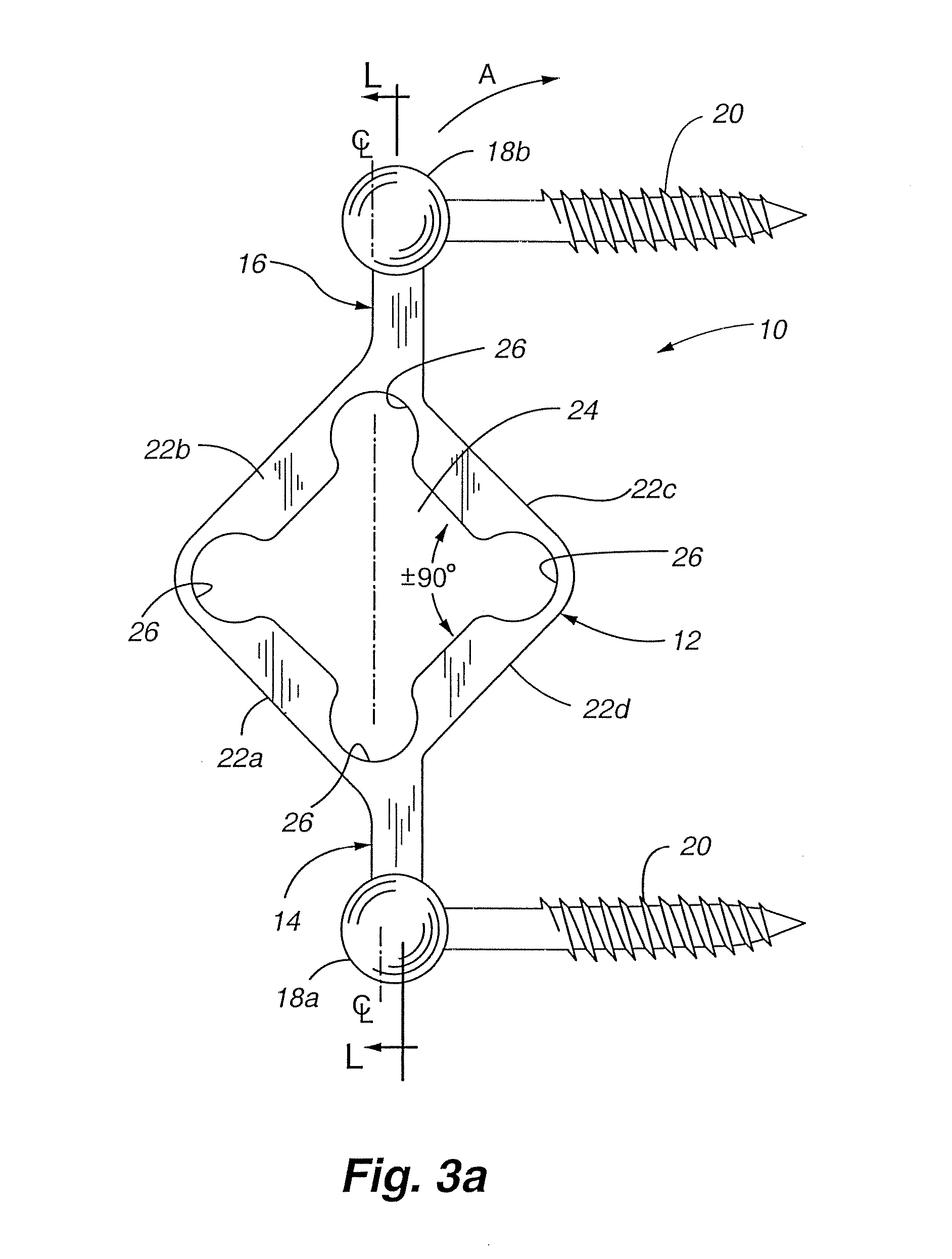
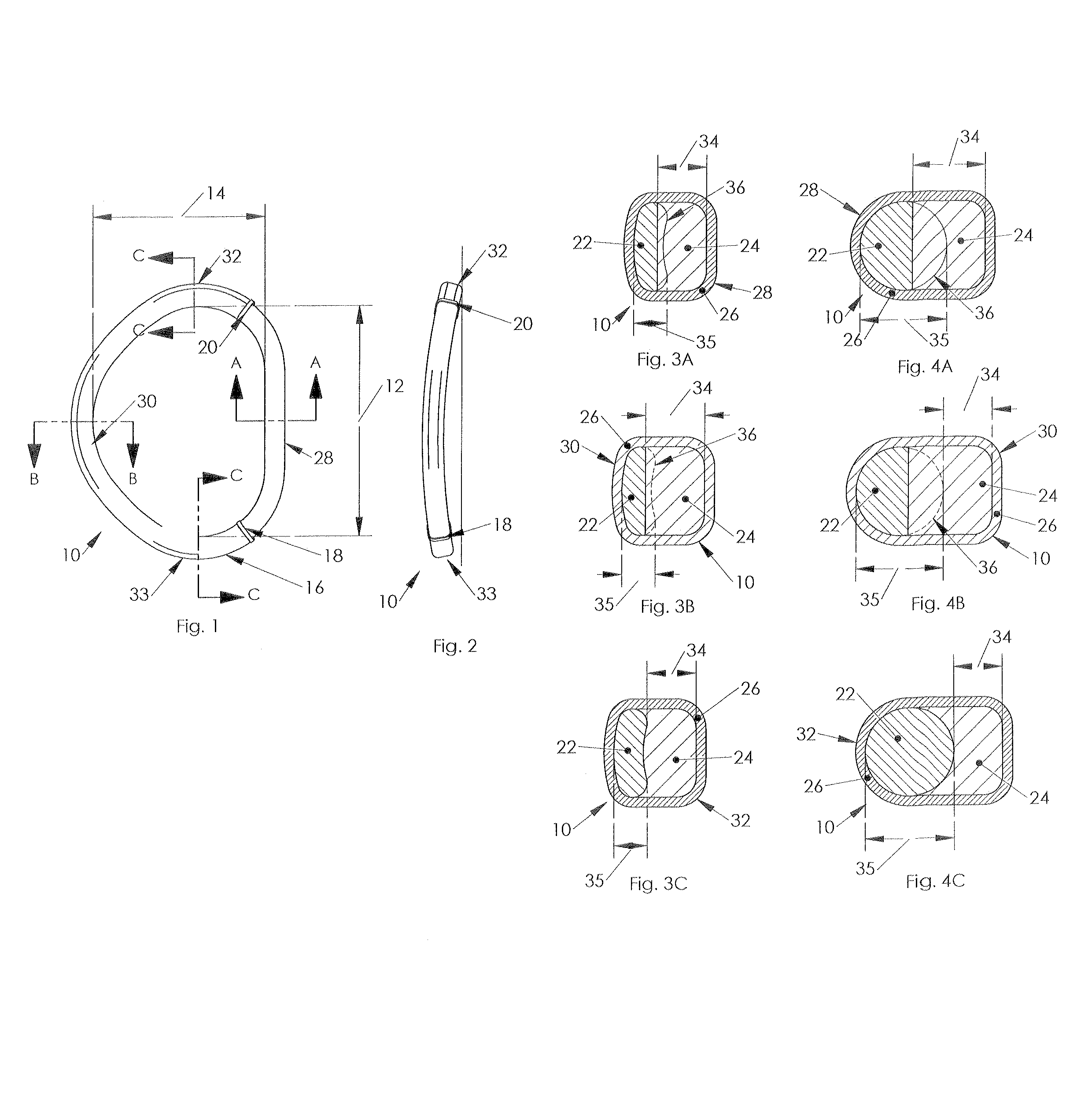
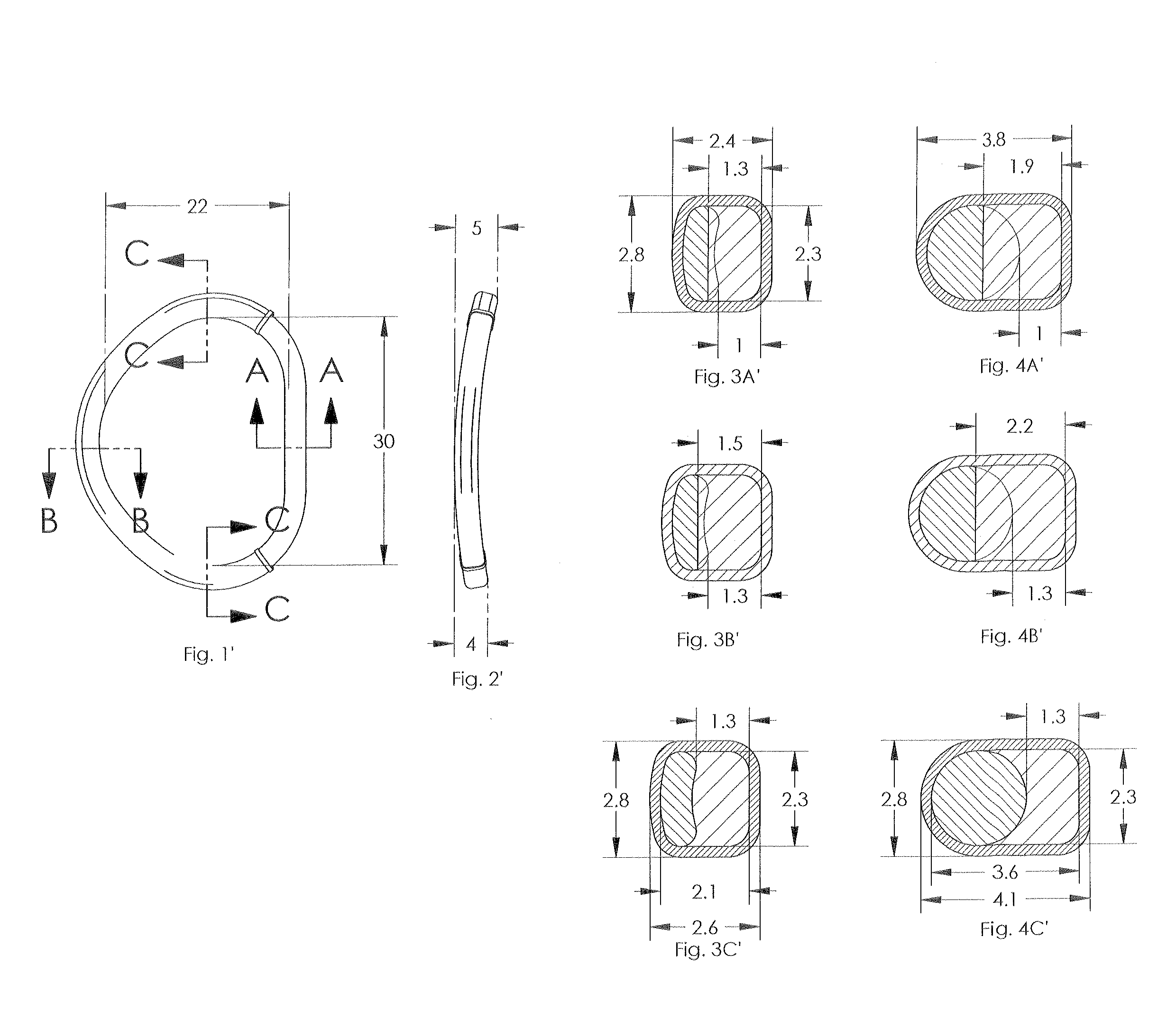
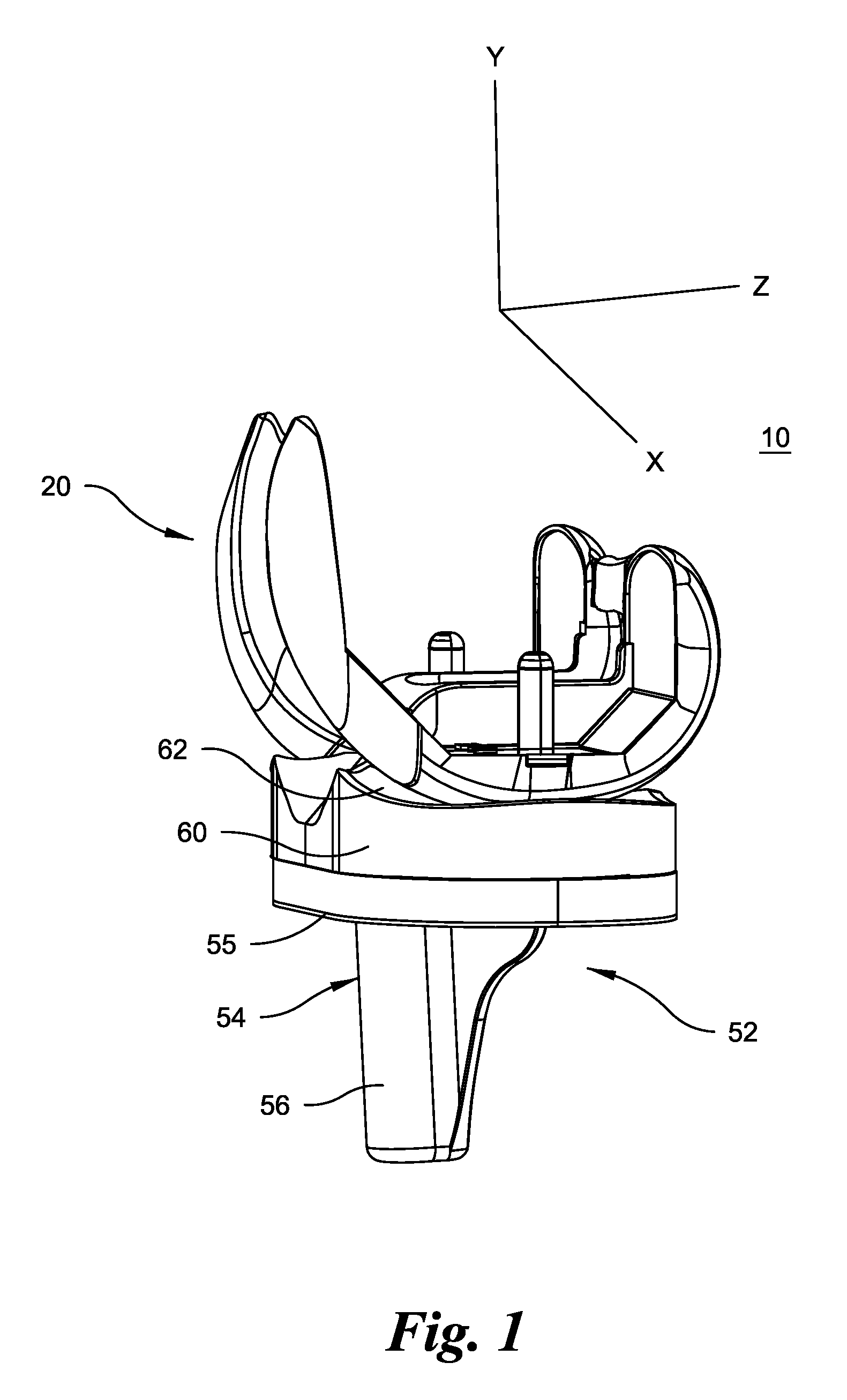
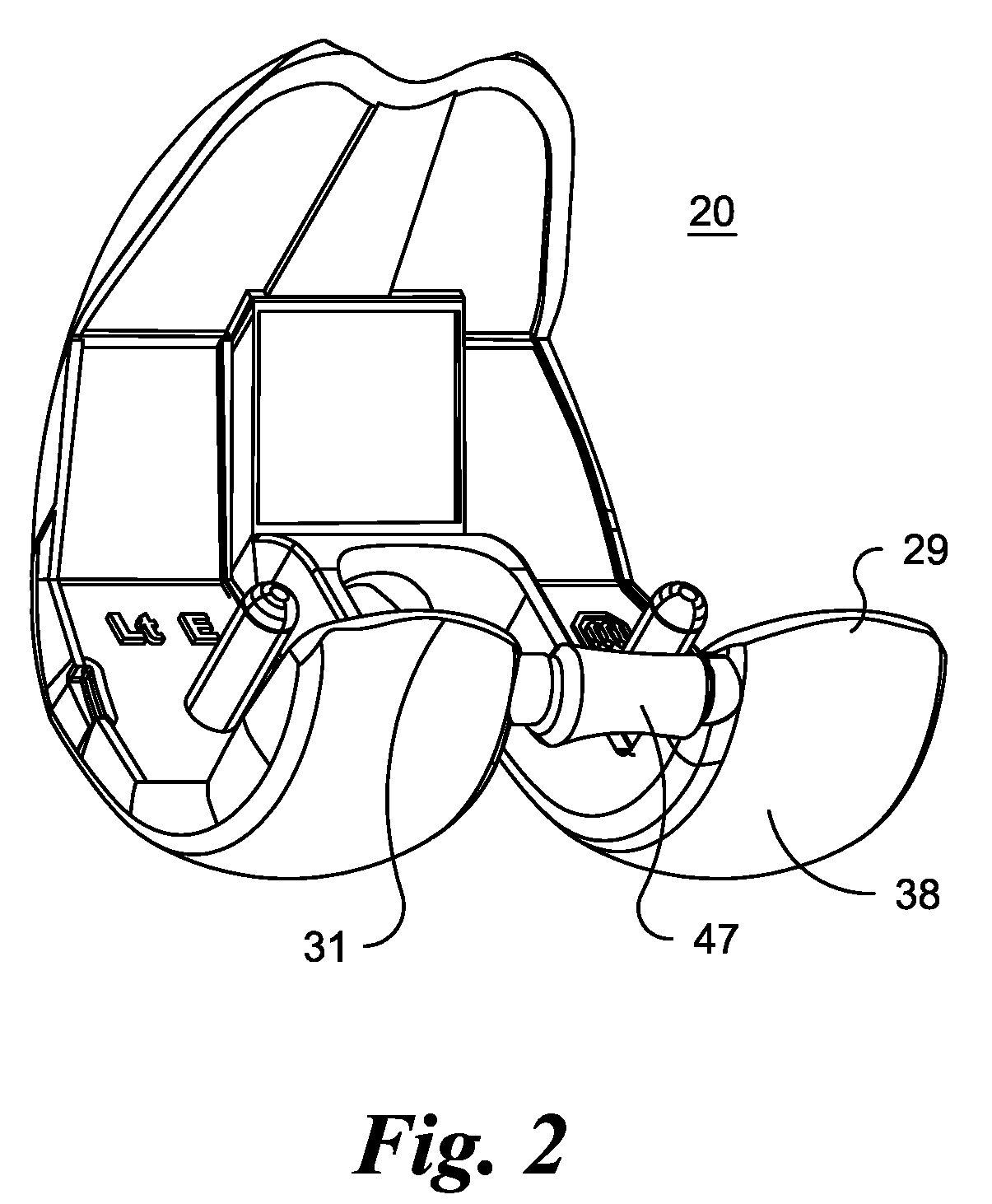
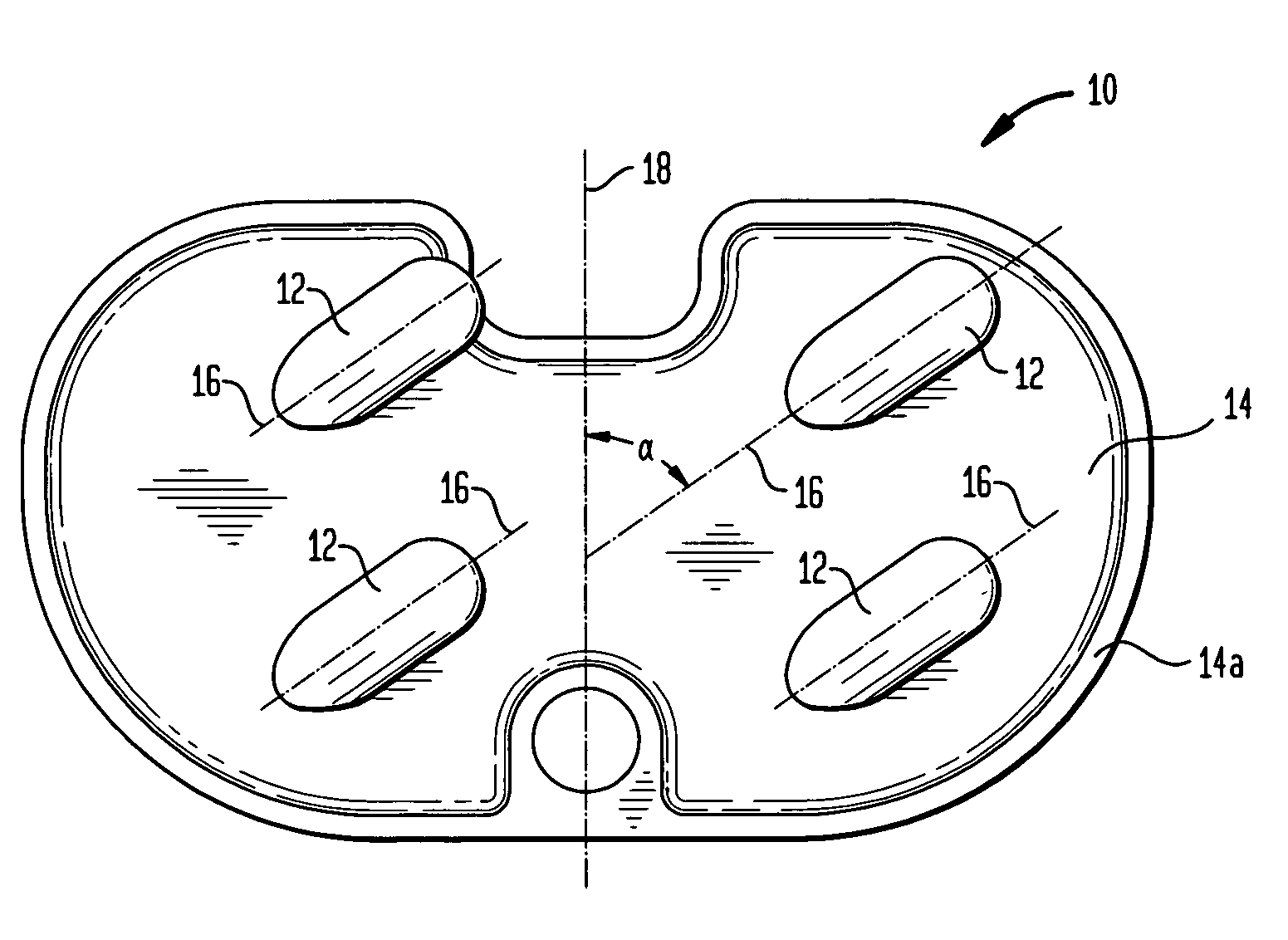
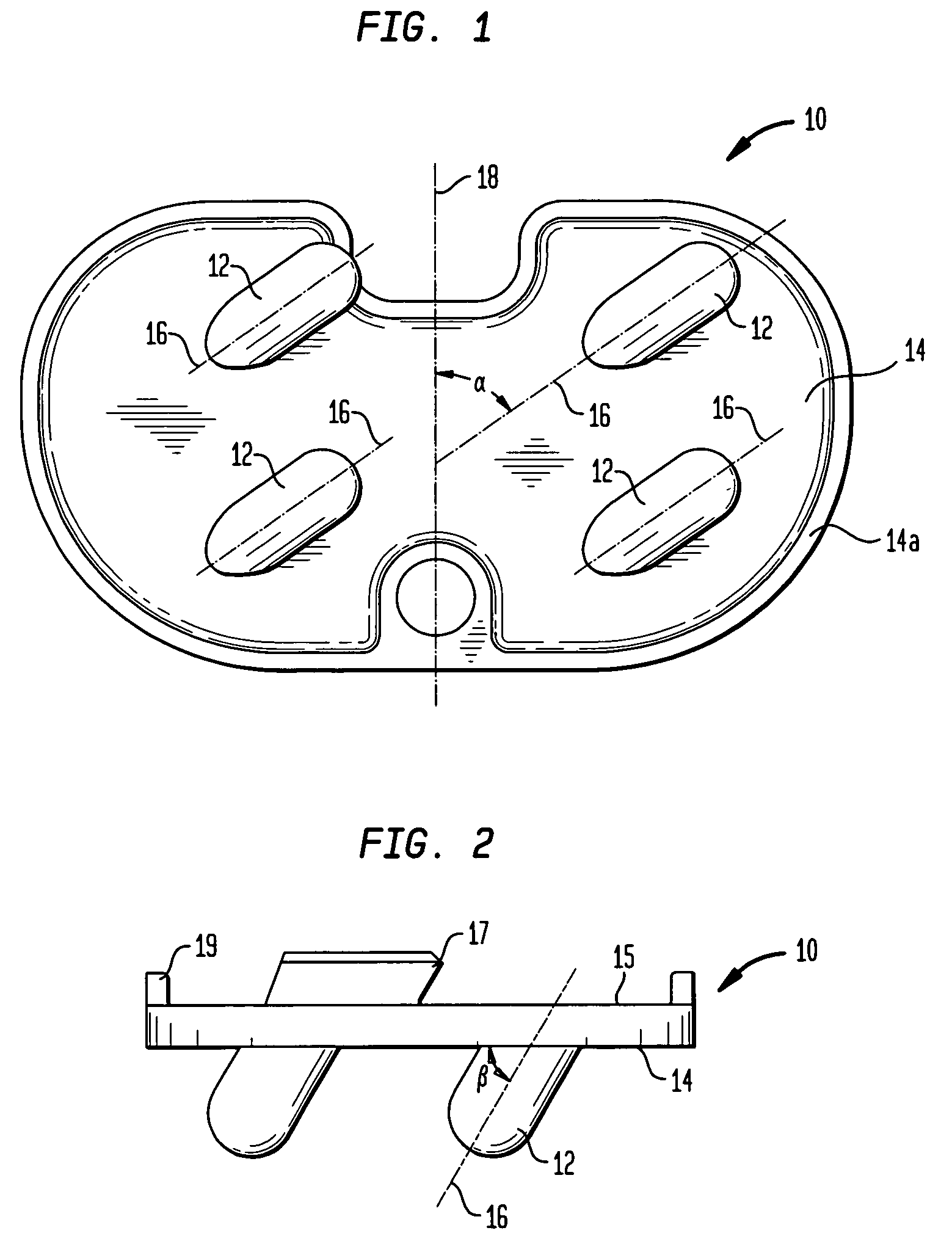
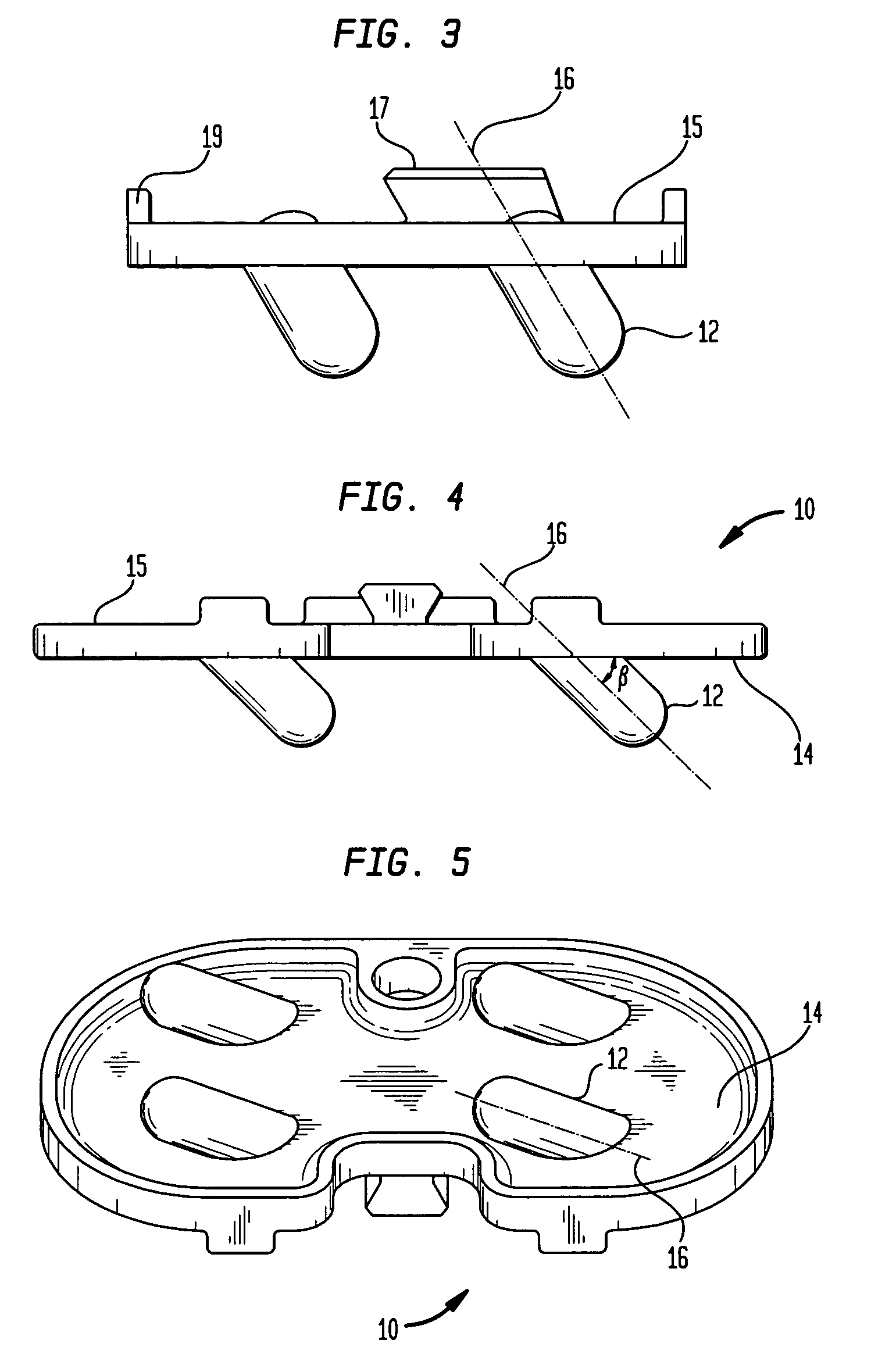
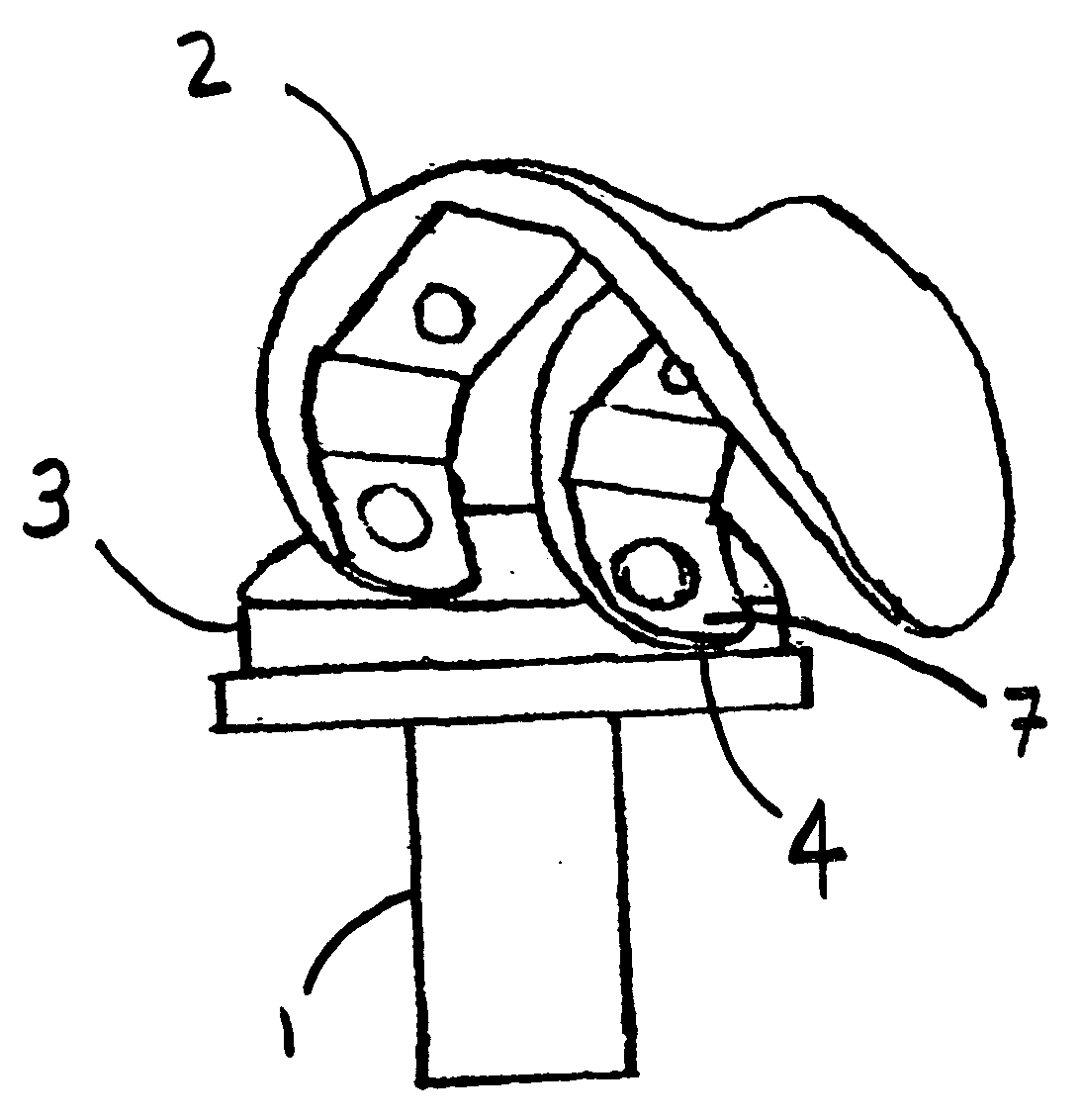
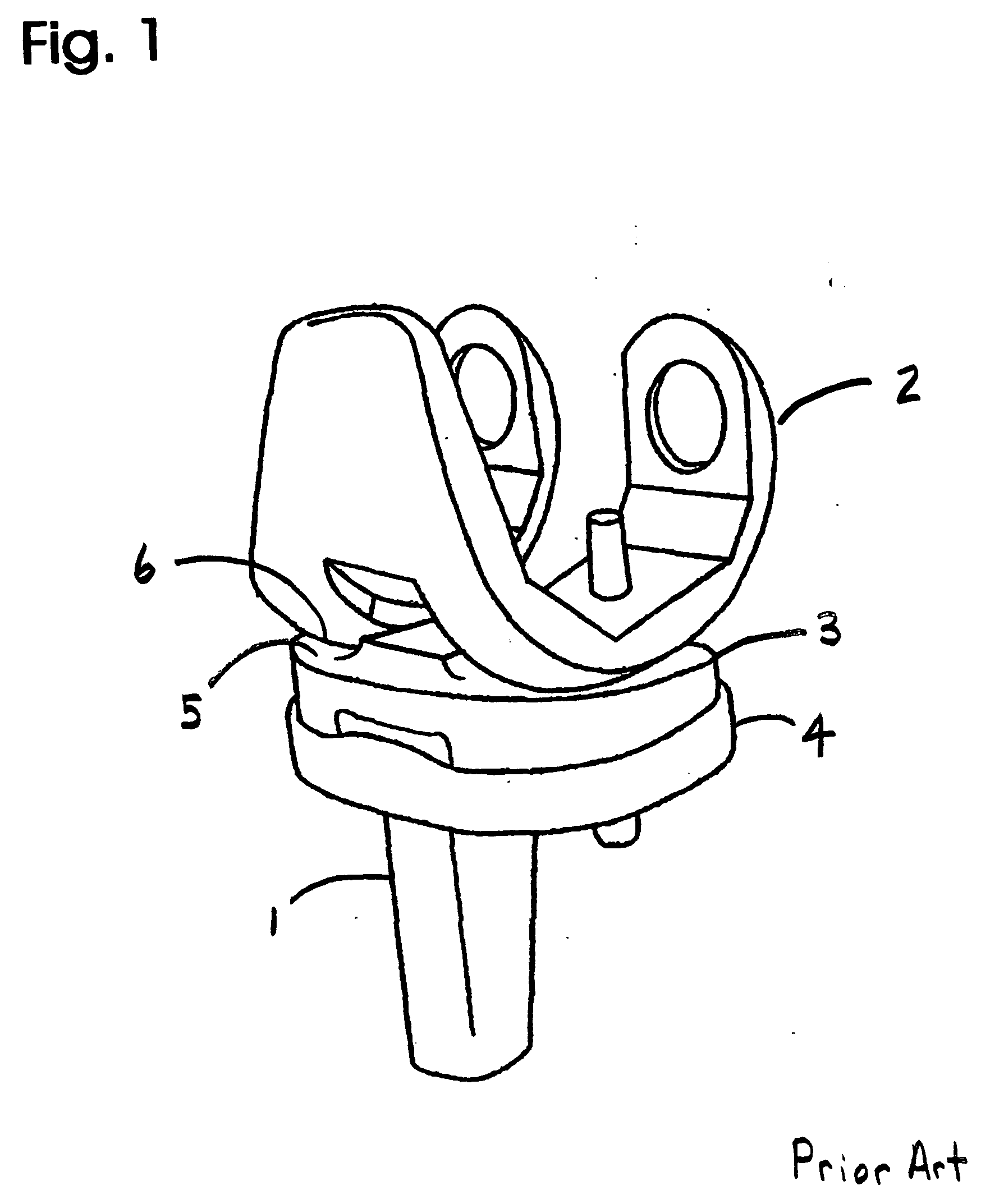
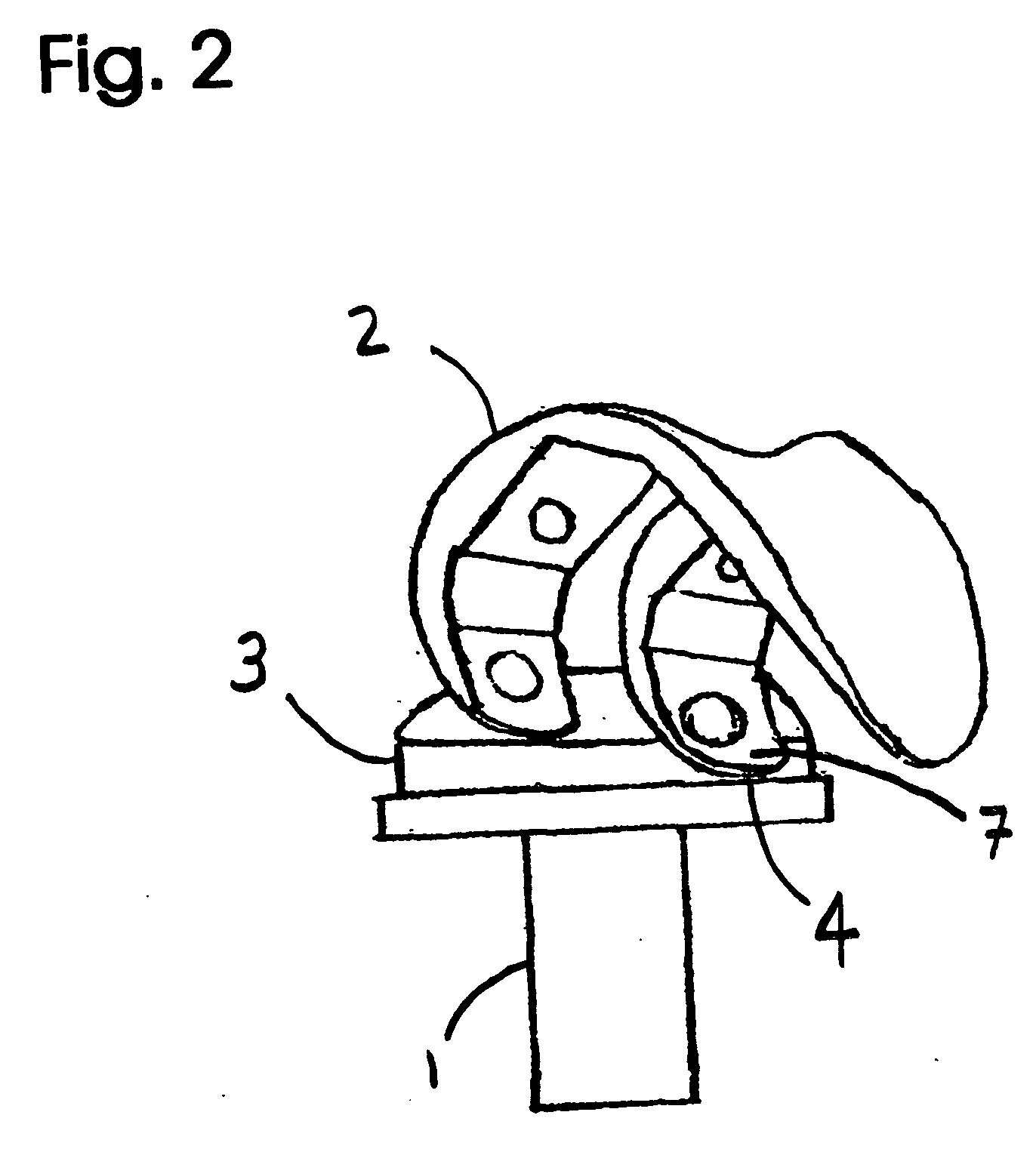
Total disc implant
InactiveUS6994727B2Impressive mechanicalImpressive tribologicalInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsHuman patientIntervertebral disk
A total disc implant (TDI) is provided for total replacement of a spinal disc or discs in a human patient or other mammal, wherein the TDI is designed to maintain a substantially full range of natural motion (ROM) following implantation. The TDI generally comprises, in one preferred form, upper and lower end plates for affixation to adjacent vertebral bodies, with an intervening insert disposed therebetween. The end plates each include elongated part-cylindrical surfaces oriented generally perpendicular to each other, with one of said surfaces extending in an anterior-posterior direction and the other extending in a medial-lateral direction. The intervening insert defines concave upper and lower part-cylindrical seats oriented for respectively engaging these part-cylindrical surfaces, wherein these part-cylindrical seats are defined by offset radii to include a somewhat flattened central base region merging smoothly with upwardly curving radiused sides.
Owner:AMEDICA A DELAWARE
Methods of minimally invasive unicompartmental knee replacement
InactiveUS7141053B2Easy to preparePrecise preparationJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaKnee Joint
A method of minimally invasive unicompartmental knee replacement includes accessing a knee through a minimal incision, forming a planar surface along a tibial plateau of the knee, forming a planar posterior surface along a posterior aspect of the corresponding femoral condyle, resurfacing a distal aspect of the femoral condyle to form a resurfaced area having a curved portion, implanting a prosthetic tibial component on the planar surface along the tibial plateau and implanting a prosthetic femoral component on the prepared surface of the femoral condyle formed by the planar posterior surface and the resurfaced area. The curved portion of the resurfaced area has an anterior-posterior curvature corresponding to a fixation surface of the prosthetic femoral component. Prior to implantation, the femur and tibia are prepared to receive fixation structure of the femoral and tibial components.
Owner:MICROPORT ORTHOPEDICS HLDG INC
Posterior dynamic stabilizer devices
InactiveUS20060084991A1Restrict movementRepair and replacementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringPosterior stabilization
A posterior stabilization device is provided for controlling movement between adjacent vertebrae. In one exemplary embodiment, the stabilization device can include one or more joints that rely on rotational or sliding movement to allow flexion of adjacent vertebrae, and that control extension, lateral bending, axial rotation, and anterior-posterior shear, preferably by providing one or more flexible connectors and / or a flexible central spacer for connecting to the adjacent superior and inferior vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Intervertebral prosthesis
An intervertebral prosthesis, in particular for the cervical spine, includes a first cover plate to be connected to a first vertebral body, a second cover plate to be connected to the second vertebral body, and a prosthesis core which forms an articulation with the second cover plate. The prosthesis core is held by a seat of the first cover plate which is designed as a guide device. The core can be pushed into the guide device from the ventral side in the anterior-posterior (AP) direction relative to the first cover plate. A limit-stop plate is provided on the ventral edge of the first cover plate. This limit-stop plate is displaceable in a slide guide between a locking position and a nonlocking position.
Owner:CERVITECH INC
Percutaneous annuloplasty system with anterior-posterior adjustment
ActiveUS20130226289A1Improve leaflet coaptationReduce refluxAnnuloplasty ringsTubular organ implantsCouplingCatheter
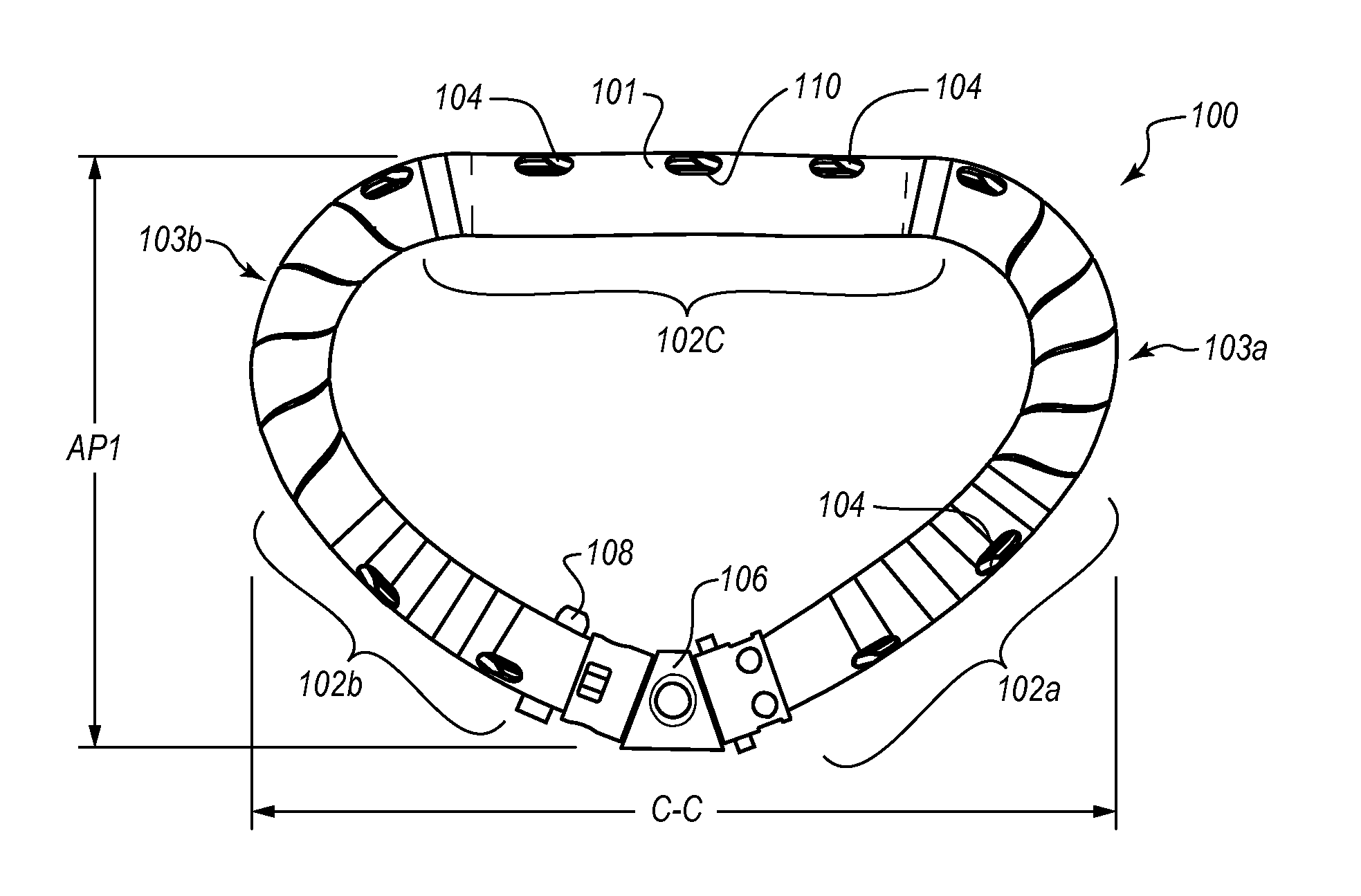
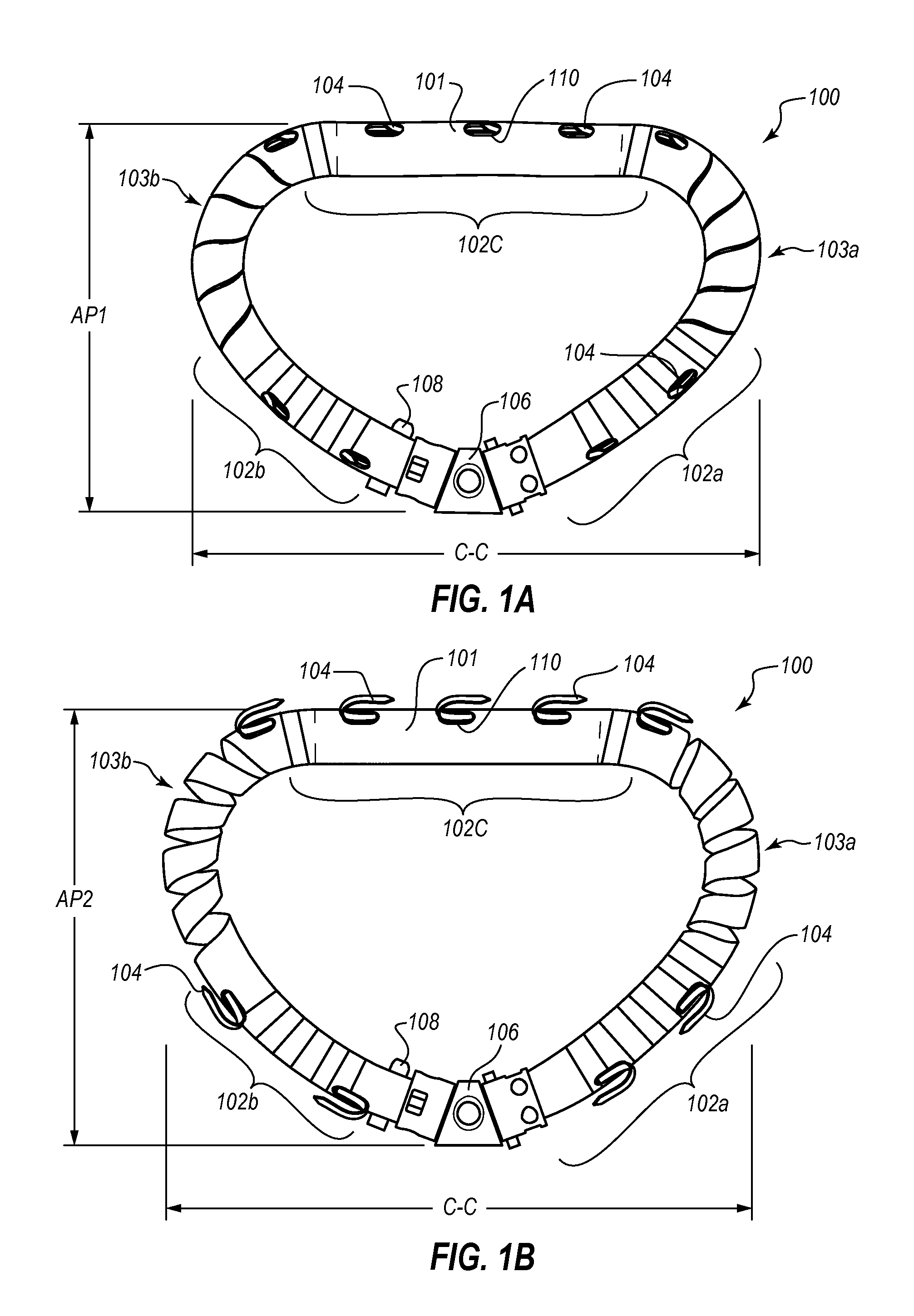
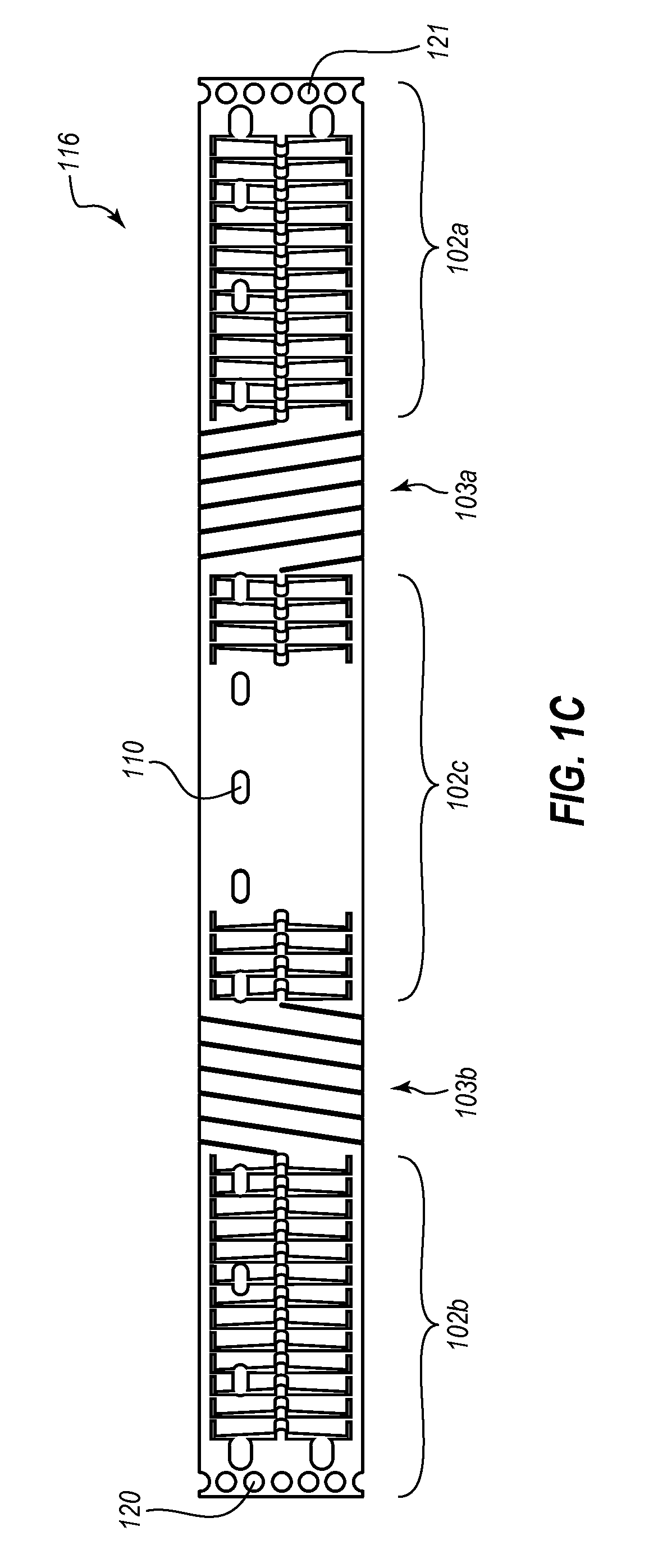
Apparatus, systems, and methods are provided for repairing heart valves through percutaneous transcatheter delivery and fixation of annuloplasty rings to heart valves. An annuloplasty ring includes an outer hollow body member including a plurality of regions. Adjacent regions cooperate with one another to change the body member from an elongate insertion geometry to an annular operable geometry. Adjacent regions are coupled by a biasing element or a stepped connector to allow expansion to an expanded state and contraction to a contracted state in the annular operable geometry. The annuloplasty ring also includes an internal anchor member located at least partially within the body member and having a plurality of anchors configured to attach the annuloplasty ring to tissue of a heart valve annulus. An angled ring closure lock allows coupling of the ends of an annuloplasty ring at an apex of a D-shape annular operable geometry.
Owner:VALCARE INC
Method and apparatus for percutaneous reduction of anterior-posterior diameter of mitral valve
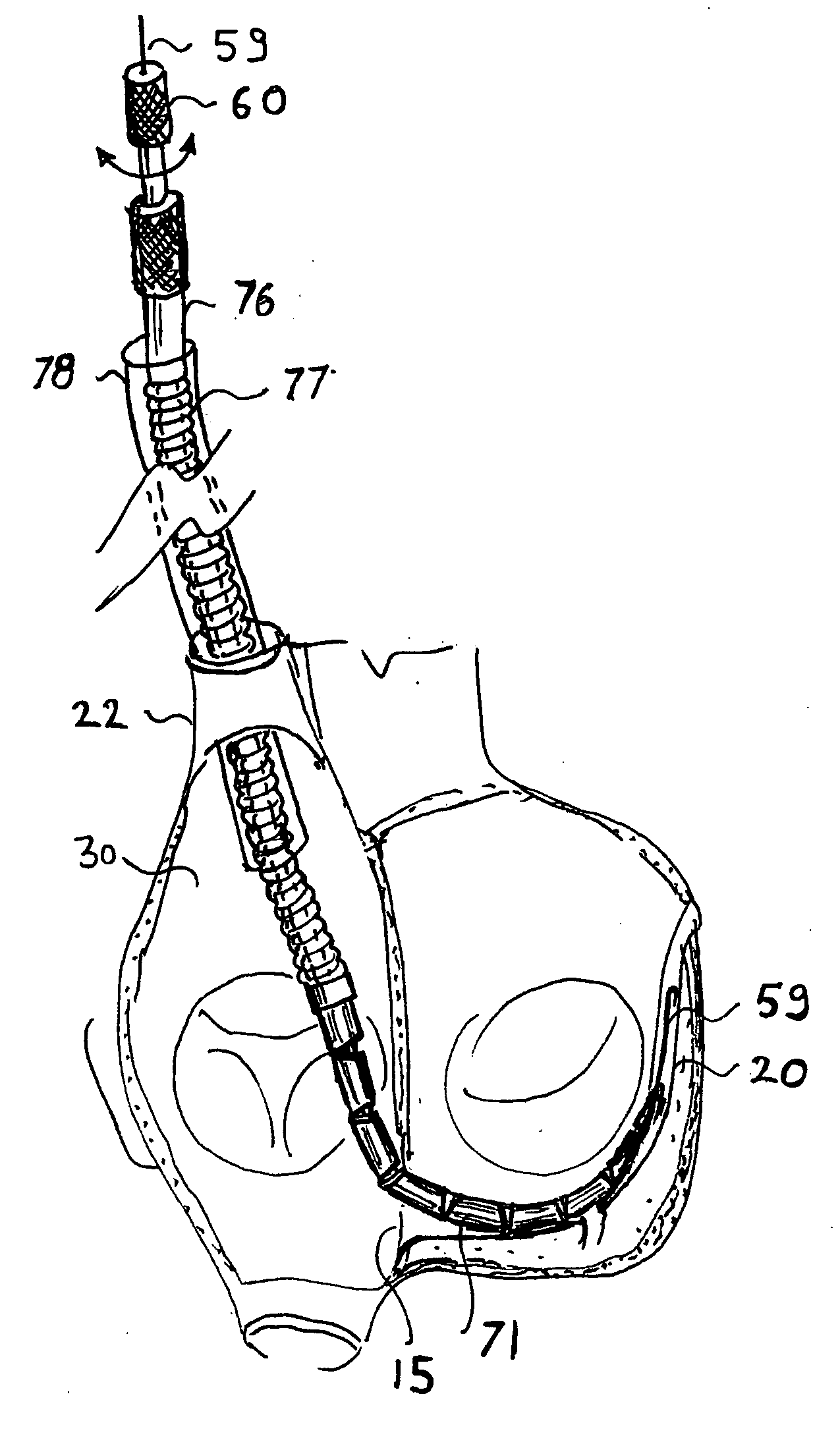
A method and apparatus for treating mitral regurgitation by approximating the septal and lateral (clinically referred to as anterior and posterior) annulus of the mitral valve. The distal end of the device is inserted into the coronary sinus of the heart and the proximal end of the device rests within the right atrium along the tendon of Todaro and extends to at least the membranous septum of the tricuspid valve. Because the coronary sinus approximates the lateral (posterior) annulus of the mitral valve and the tendon of Todaro approximates the septal (anterior) annulus of the mitral valve, the device encircles approximately one half of the mitral valve annulus. The apparatus is then adapted to deform the underlying structures i.e. the septal annulus and lateral annulus of the mitral valve in order to move the posterior leaflet anteriorly and the anterior leaflet posteriorly and thereby improve leaflet coaptation and eliminate mitral regurgitation.
Owner:KARDIUM
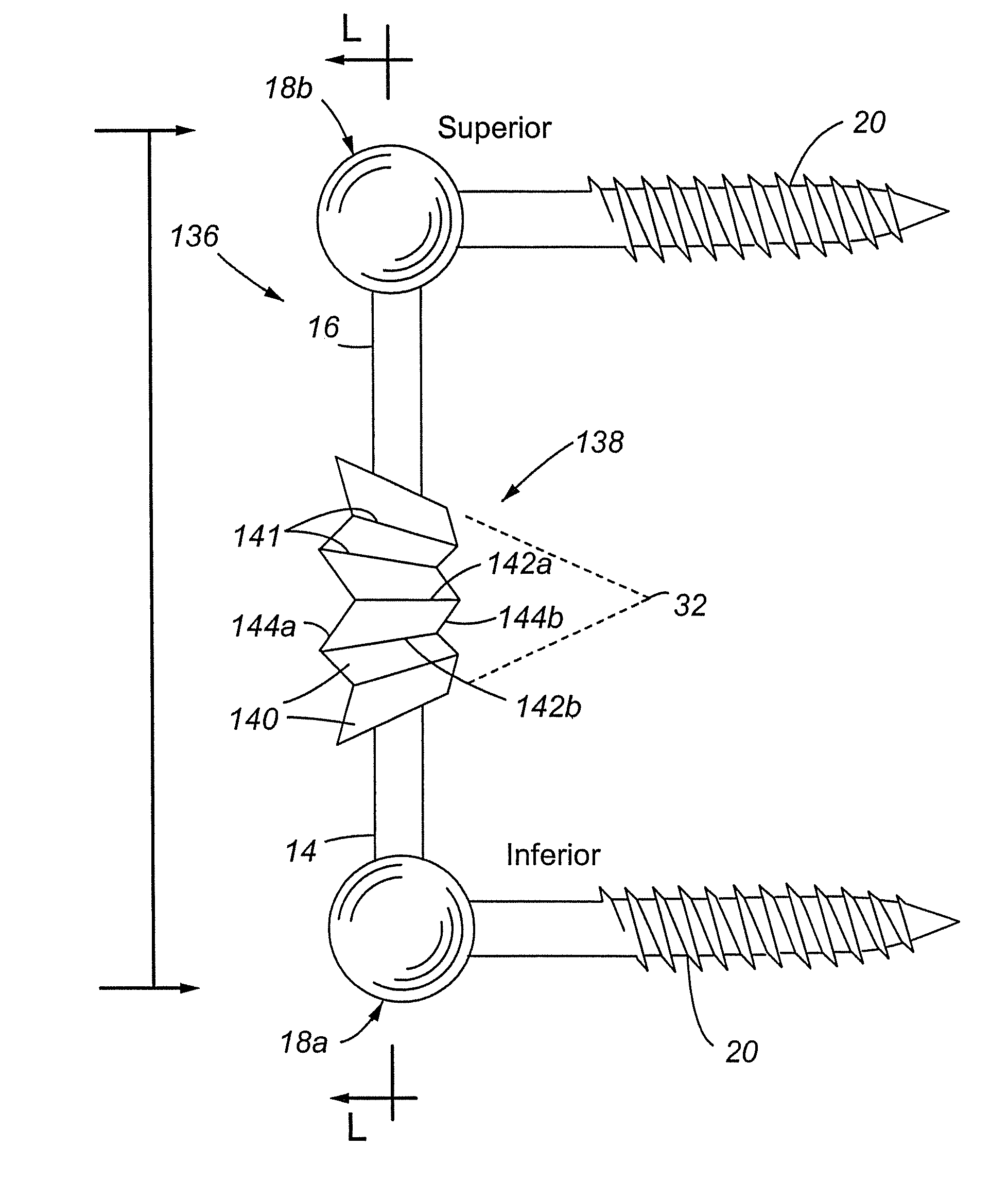
Dynamic fixation device and method of use
InactiveUS20070016193A1Avoid developmentPain minimizationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDynamic fixationPedicle screw
A dynamic fixation device is provided that allows the vertebrae to which it is attached to move in flexion within the normal physiological limits of motion, while also providing structural support that limits the amount of translation motion beyond normal physiological limits. The present invention includes a flexible portion and two ends that are adapted for connection to pedicle screws. In at least one embodiment of the present invention, the normal axis of rotation of the vertebrae is substantially duplicated by the dynamic fixation device. The flexible portion of the dynamic fixation device can include a flexible anterior-posterior segment, an anterior-posterior segment bounded by one or more zones with cuts in the rod portions, a flexible accordion-like segment, and / or a hinge portion.
Owner:RITLAND STEPHEN
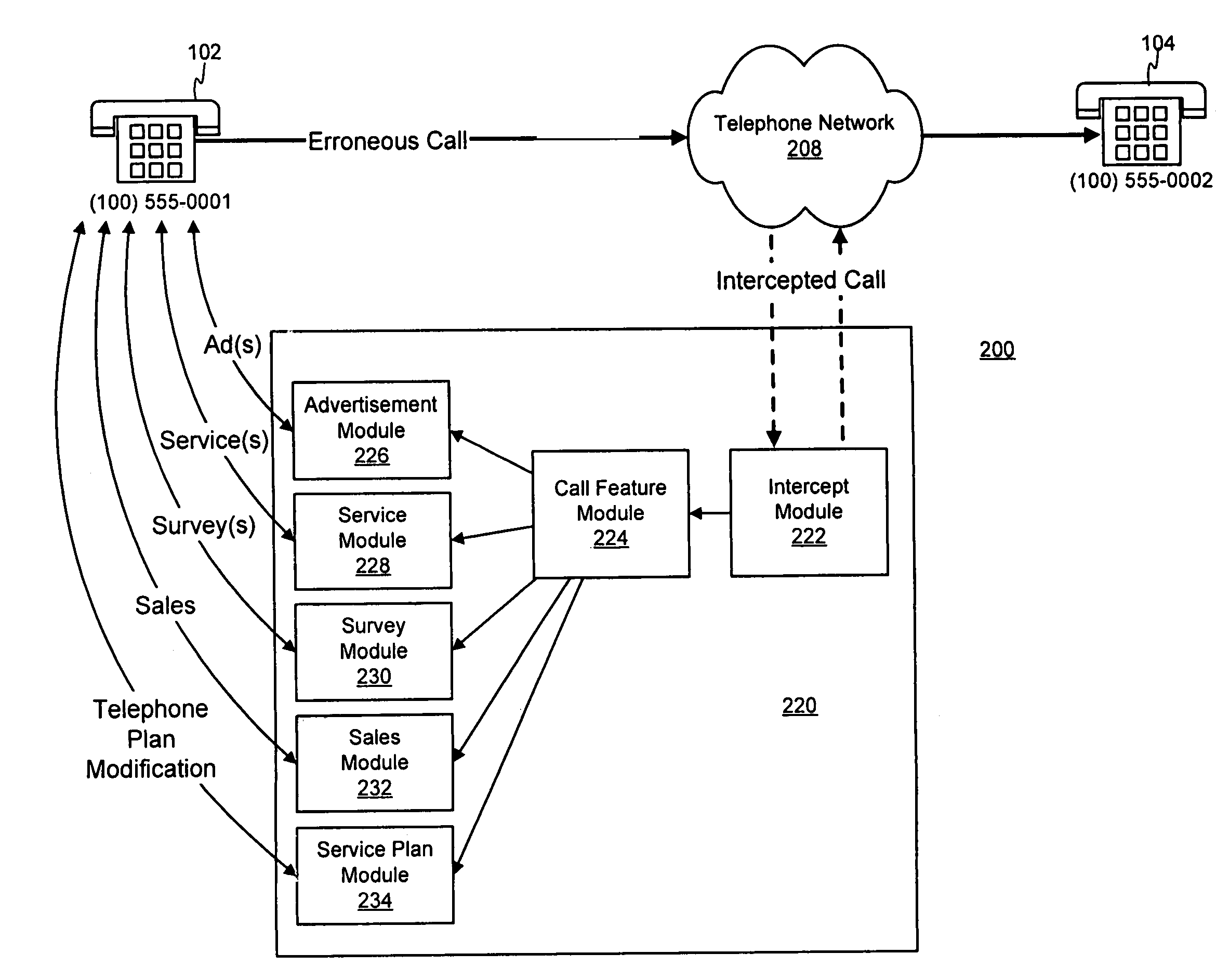
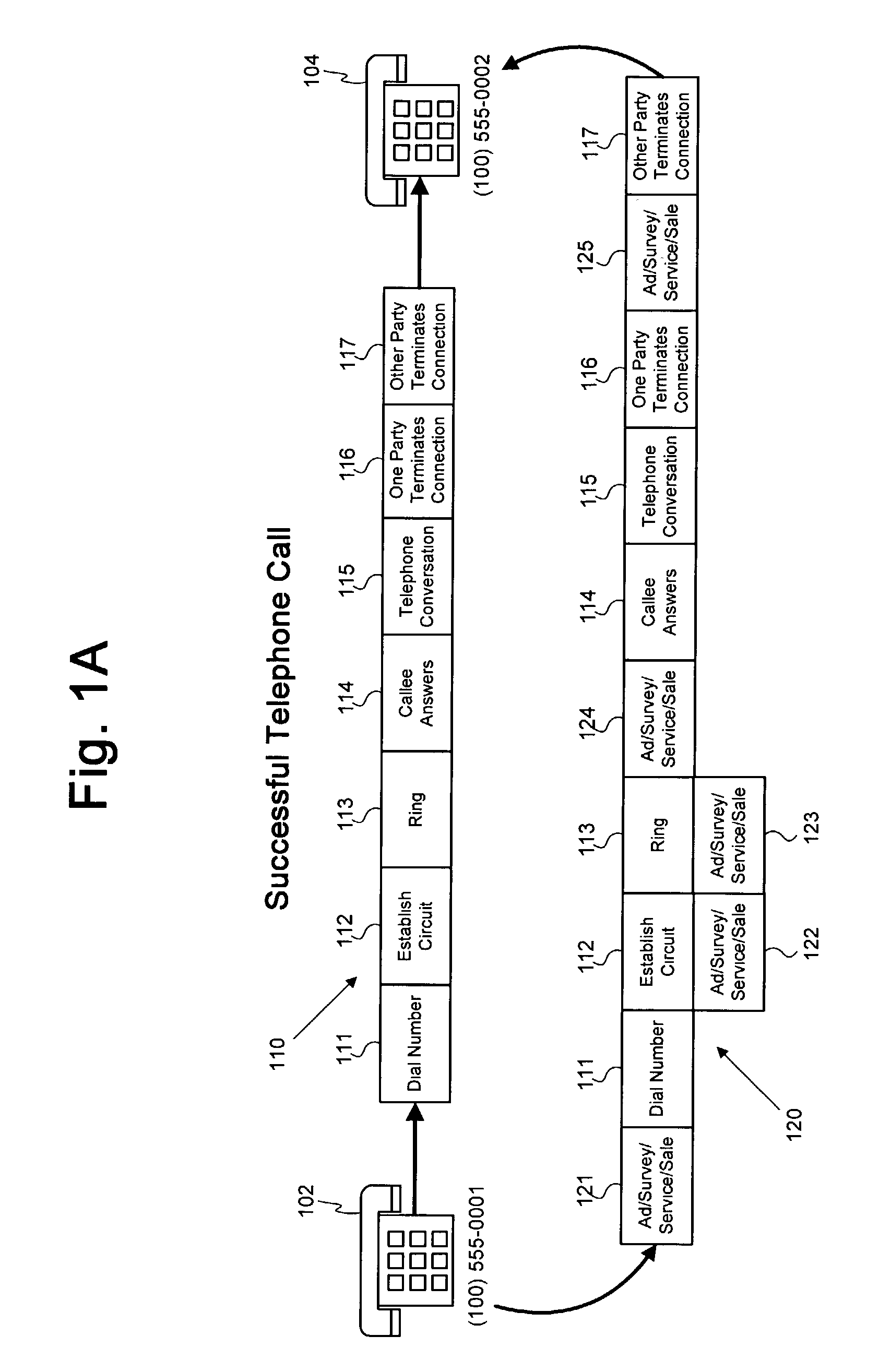
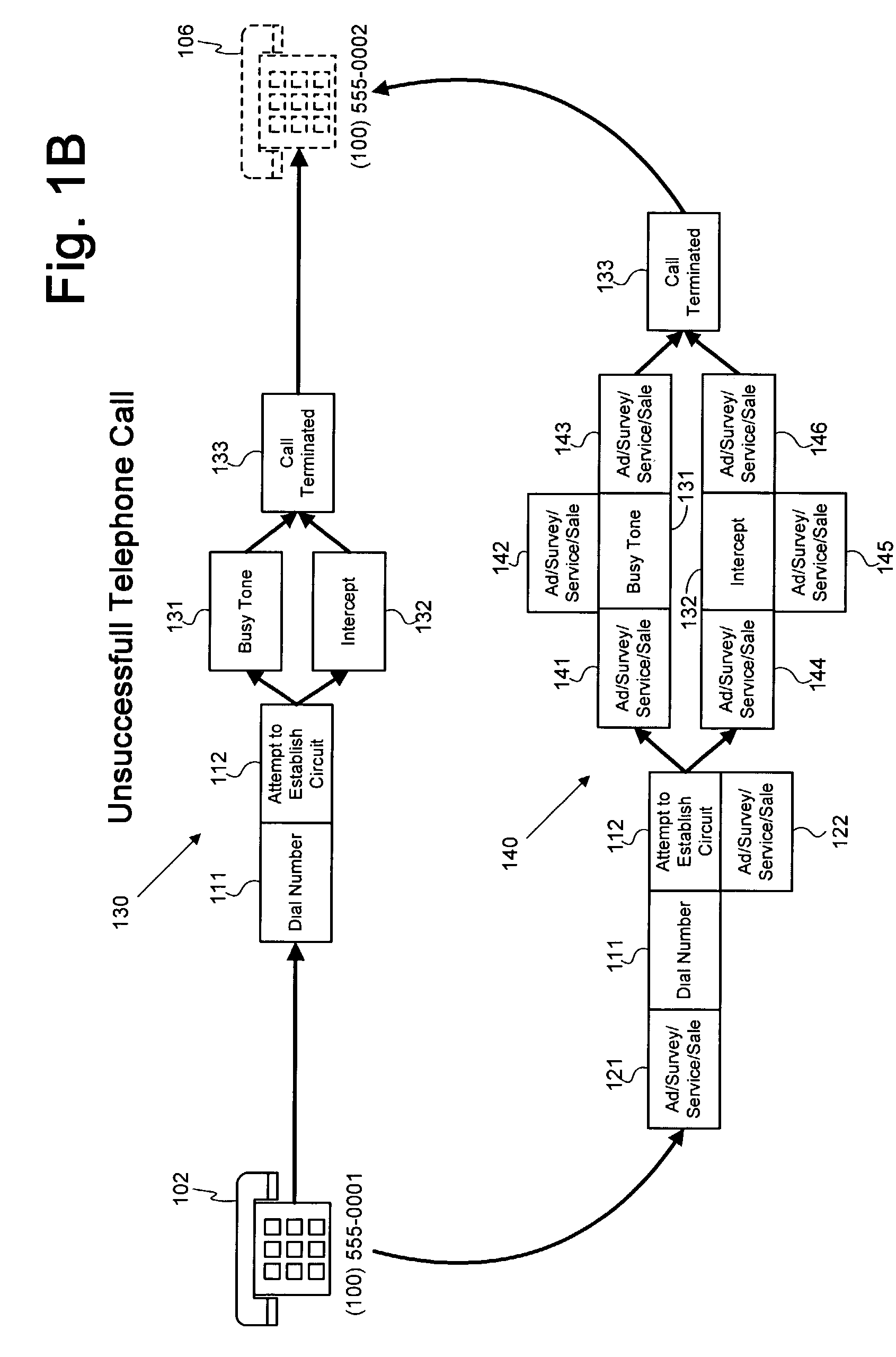
Method and system for providing advertising to telephone callers
A system and method for providing one or more advertisements, services, surveys, offers for goods / services, and / or offers to modify a telephone service plan (“intercept actions” collectively) to one or more parties to a telephone call are provided. One or more advertisements may be provided during one or more points along an unsuccessful or successful telephone call. One or more services may be provided gratuitously or in exchange for the presentation of one or more advertisements to recipient of the service. Additionally, a telephone service plan associated with the caller or callee may be analyzed and the caller / callee may be presented with the option to activate one or more service features that, at the time of the attempted call, are not activated in the telephone service plan. A survey may be provided to the caller / callee and the responses recorded. The caller / callee may also receive an offer for goods or services. These intercept actions may be provided during any of a plurality of points along a telephone call, such as prior to dialing; before, after or during a busy signal or ring tones; after one party disconnects but prior to the remaining party or parties disconnecting; and the like.
Owner:BOOKSTAFF BLAKE
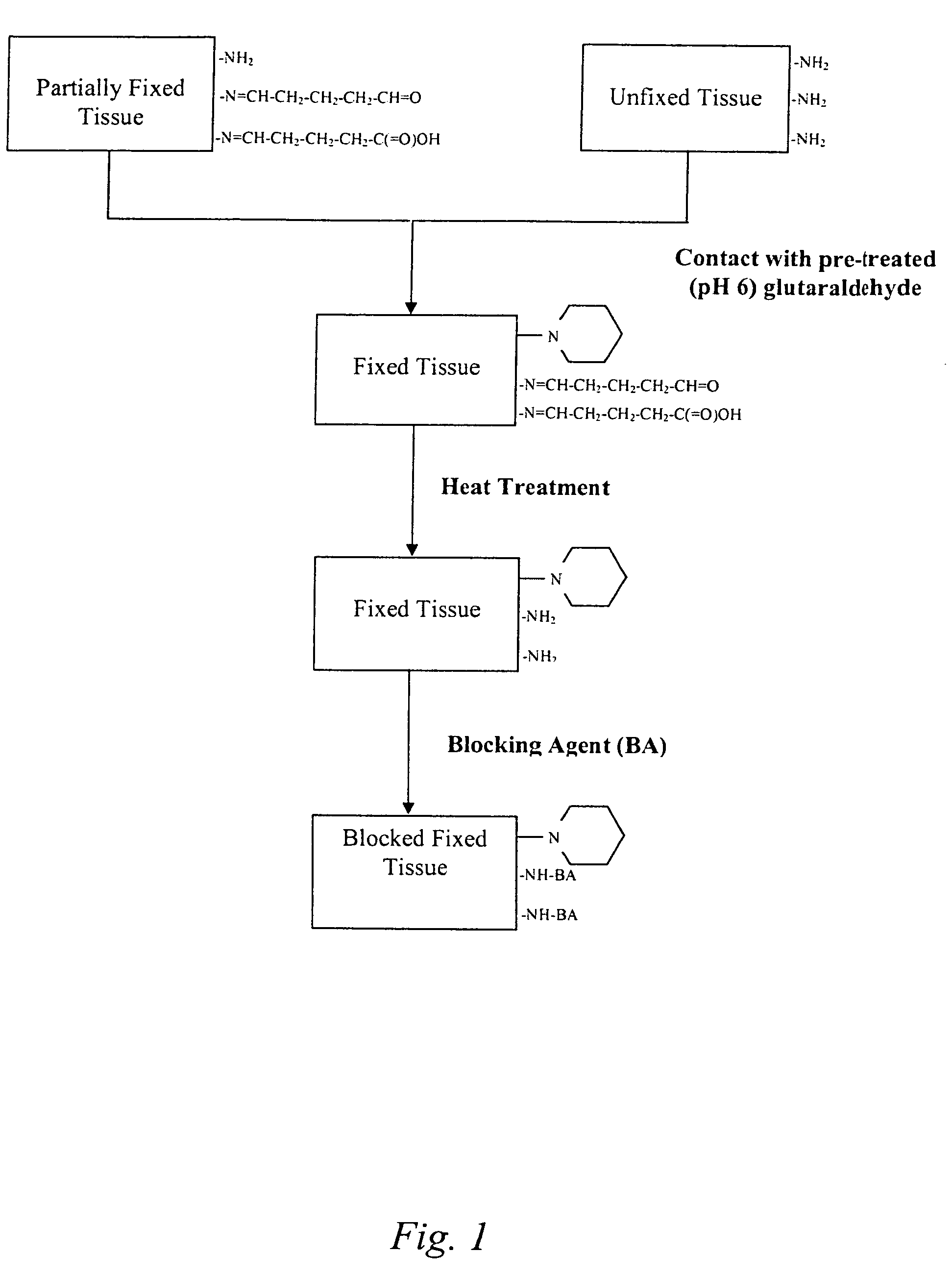
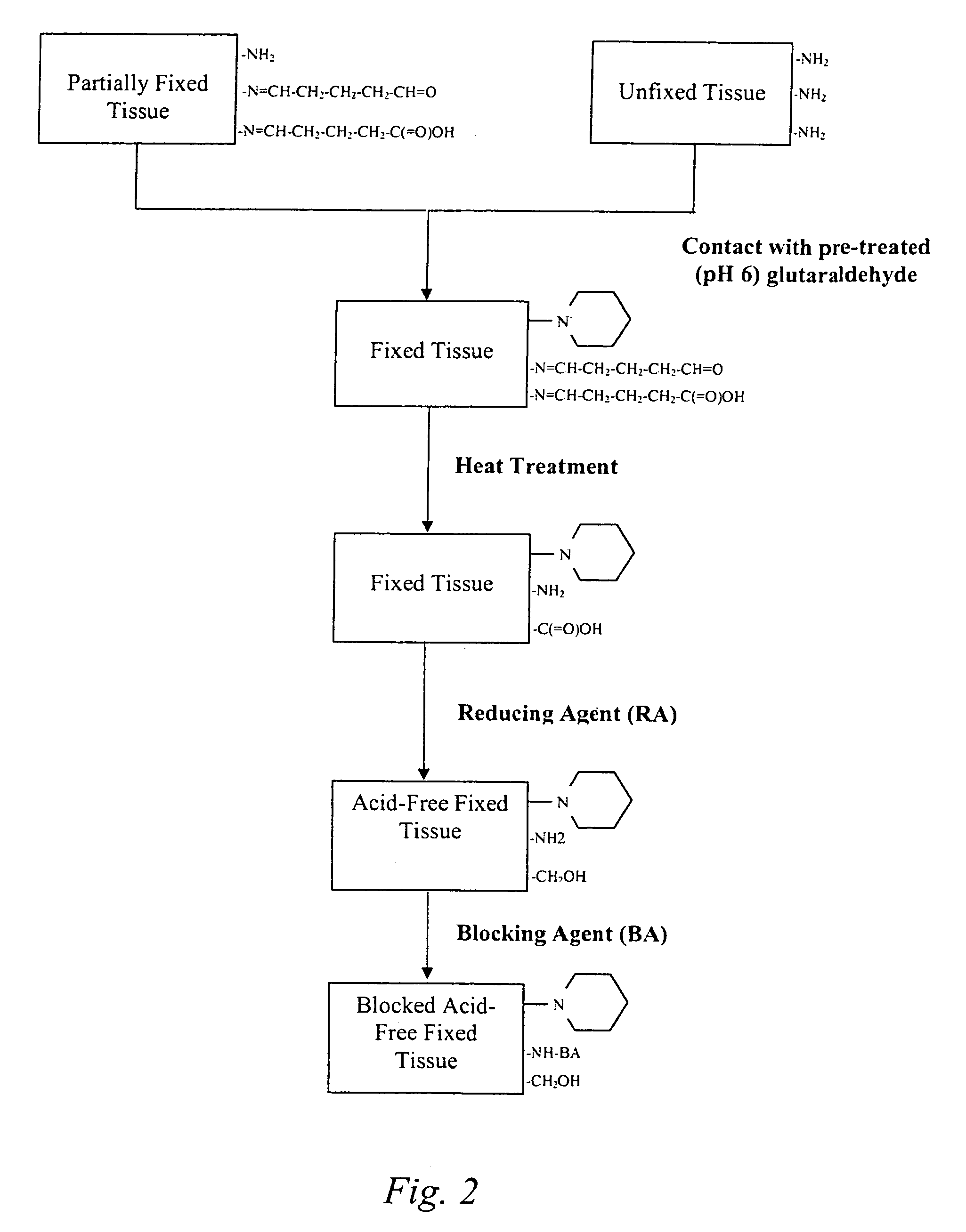
Treatment of bioprosthetic tissues to mitigate post implantation calcification
The present invention provides methods for treating tissue to inhibit post-implant calcification of a biological tissue. In one method of this invention, a tissue is immersed in or otherwise contacted with a pretreated glutaraldehyde solution, i.e., a heat-treated or pH-adjusted glutaraldehyde solution. The tissue may be partially fixed with glutaraldehyde prior to, after, or concurrently with the step of contacting the tissue with the pretreated gluteraldehyde. Contact with the pretreated gluteraldehyde produces free amine groups on the tissue, which are subsequently blocked by contacting the crosslinked tissue with a blocking agent. In another embodiment, a tissue is contacted with either a non-pretreated glutaraldehyde or a pH-adjusted glutaraldehyde solution for a period of time sufficient to crosslink the tissue. The crosslinked tissue is then treated with a reducing agent that reduces aldehyde and carboxylic acid groups on the fixed tissue.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method and apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy
Apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy, the apparatus comprising:cutting apparatus for forming an osteotomy cut in the tibia, the cutting apparatus comprising:targeting apparatus for identifying a cutting plane through the tibia and a boundary line for terminating a cut made along the cutting plane, wherein the boundary line is located within the tibia, parallel to the anterior-posterior slope of the tibia and parallel to the sagittal plane of the patient.A method for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy, the method comprising:positioning targeting apparatus for identifying a cutting plane through the tibia and a boundary line for terminating a cut made along the cutting plane, wherein the boundary line is located within the tibia, parallel to the anterior-posterior slope of the tibia and parallel to the sagittal plane of the patient;cutting the bone along the cutting plane, with the cut terminating at the boundary line;moving the bone on either side of the cut apart so as to form the wedge-like opening in the bone; andstabilizing the bone.
Owner:ARTHREX
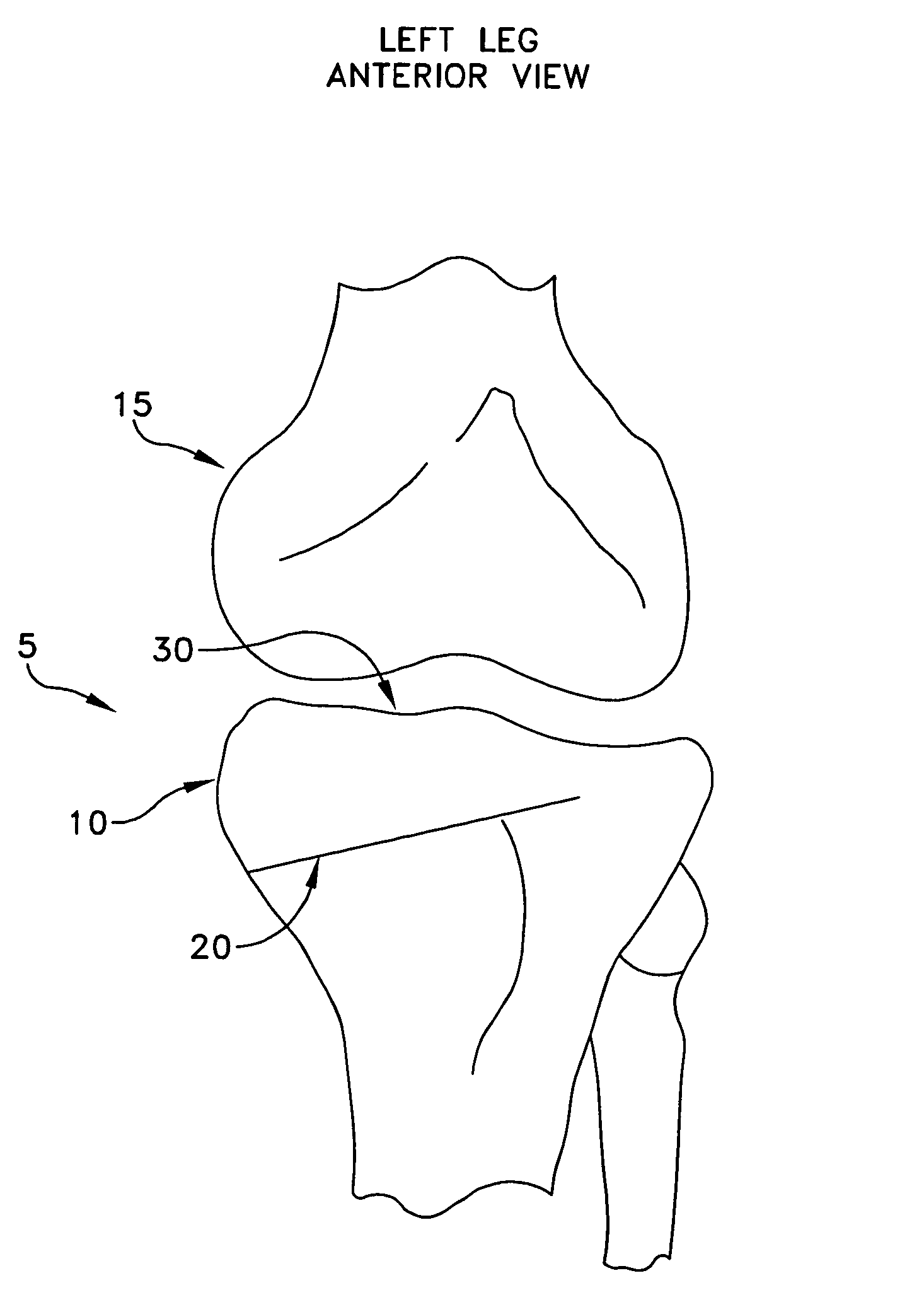
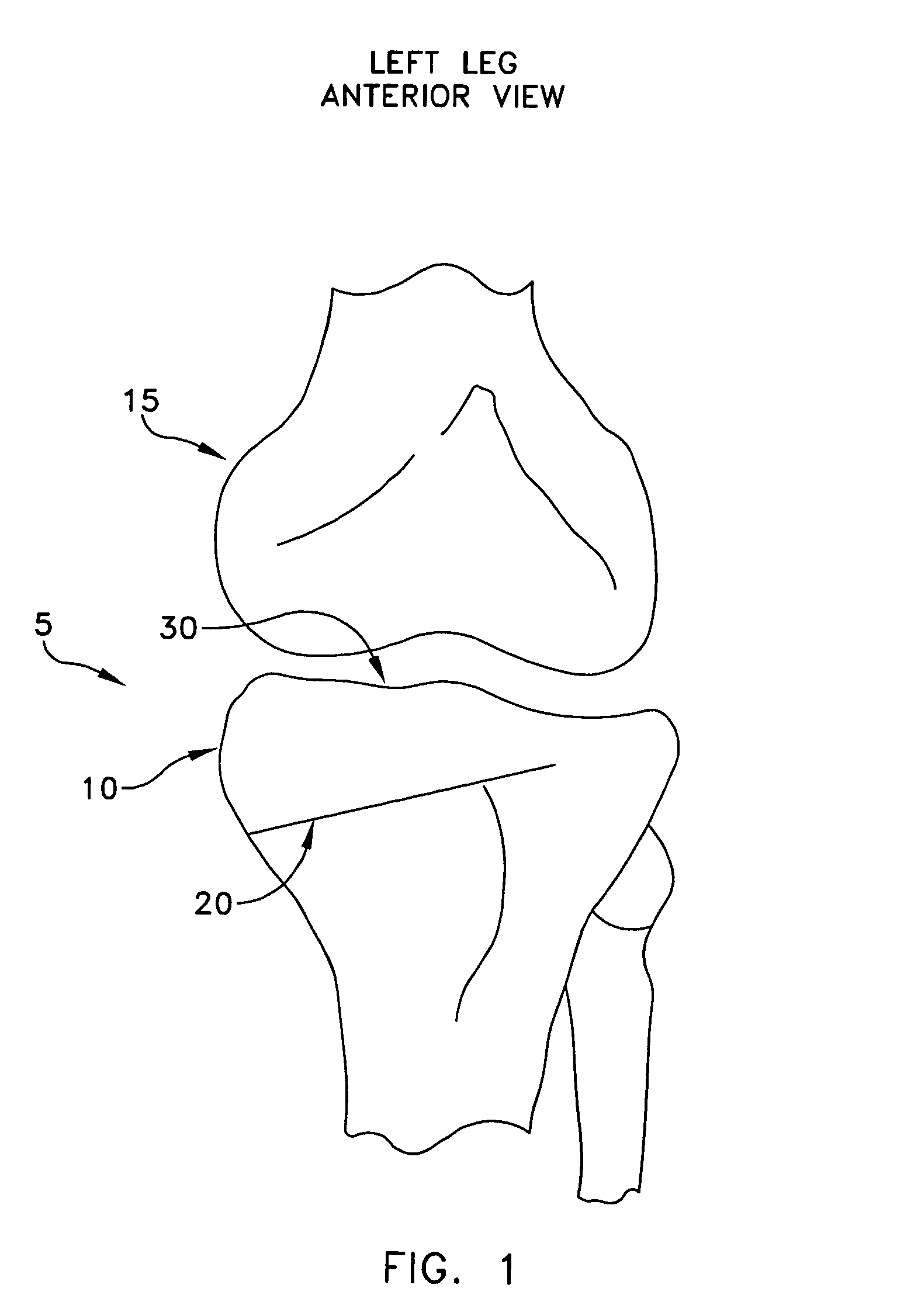
Spinal midline indicator
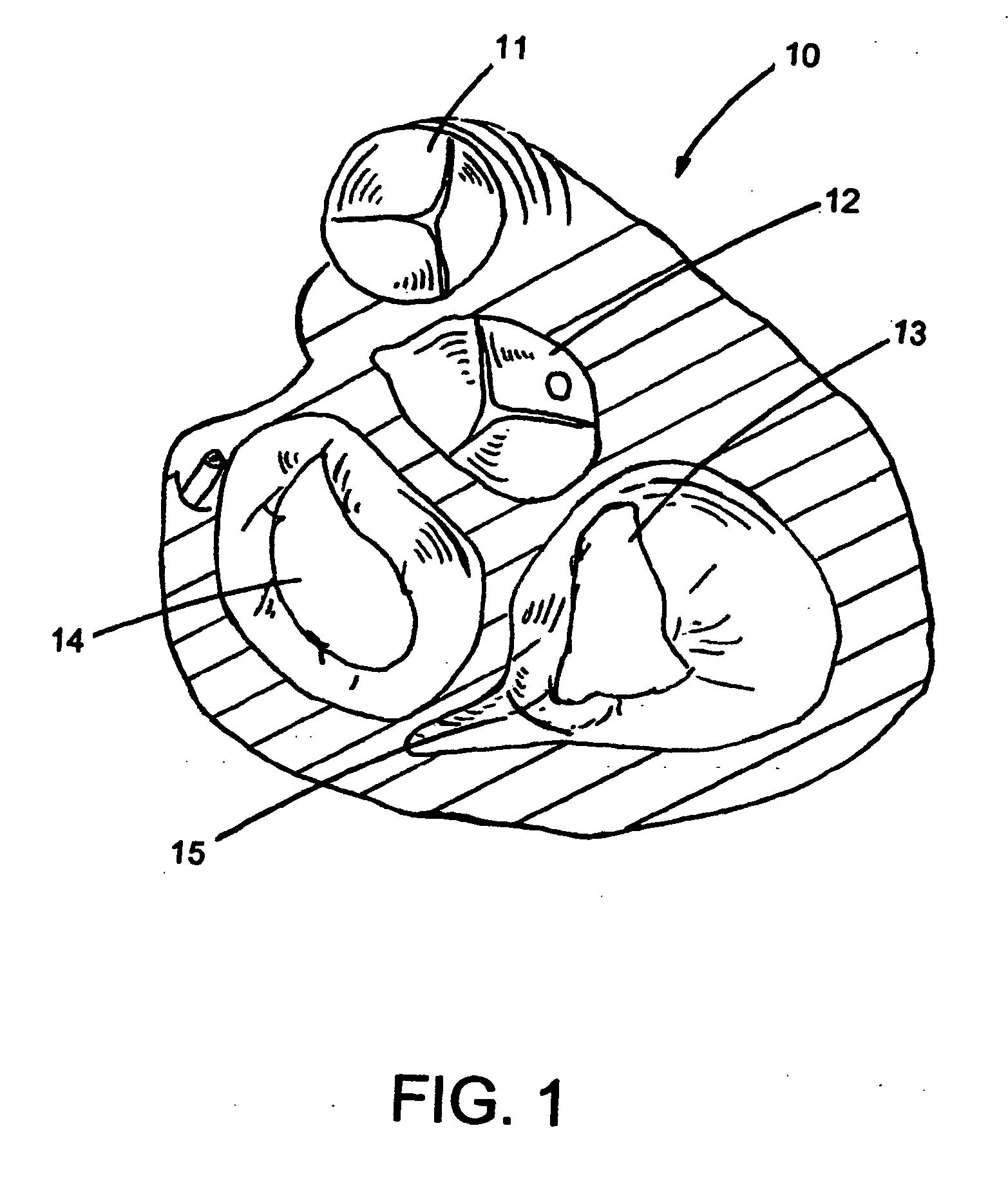
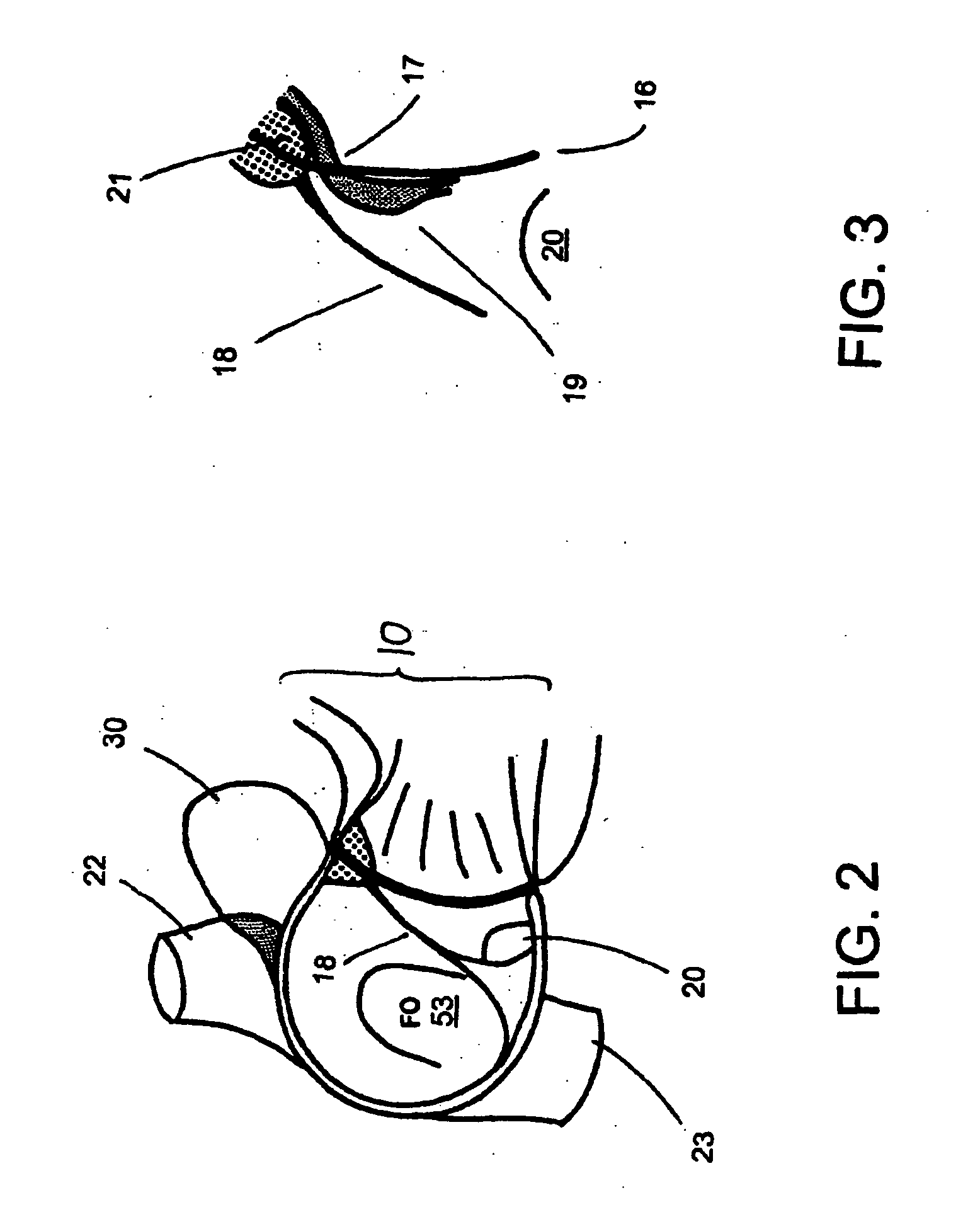
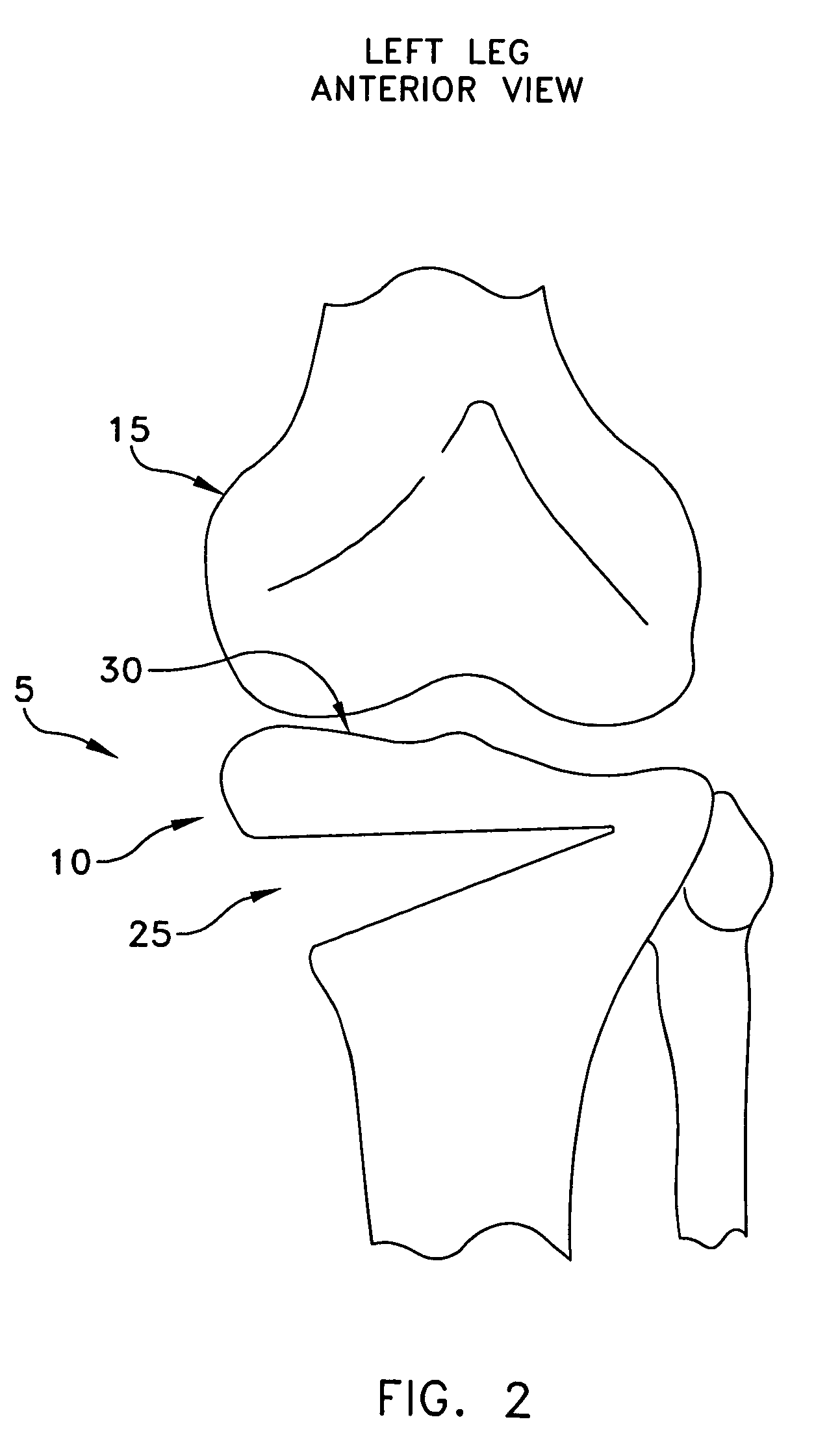
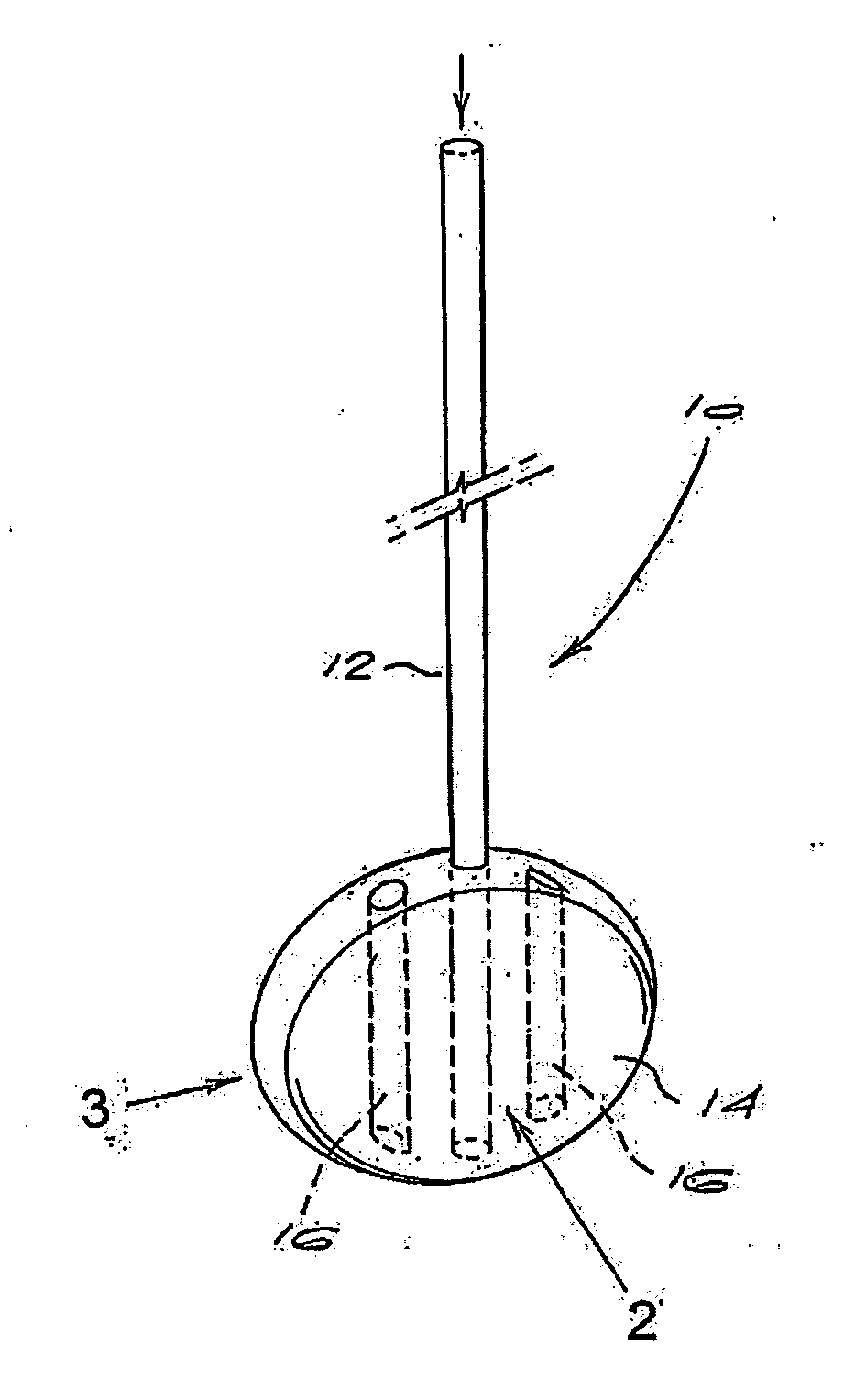
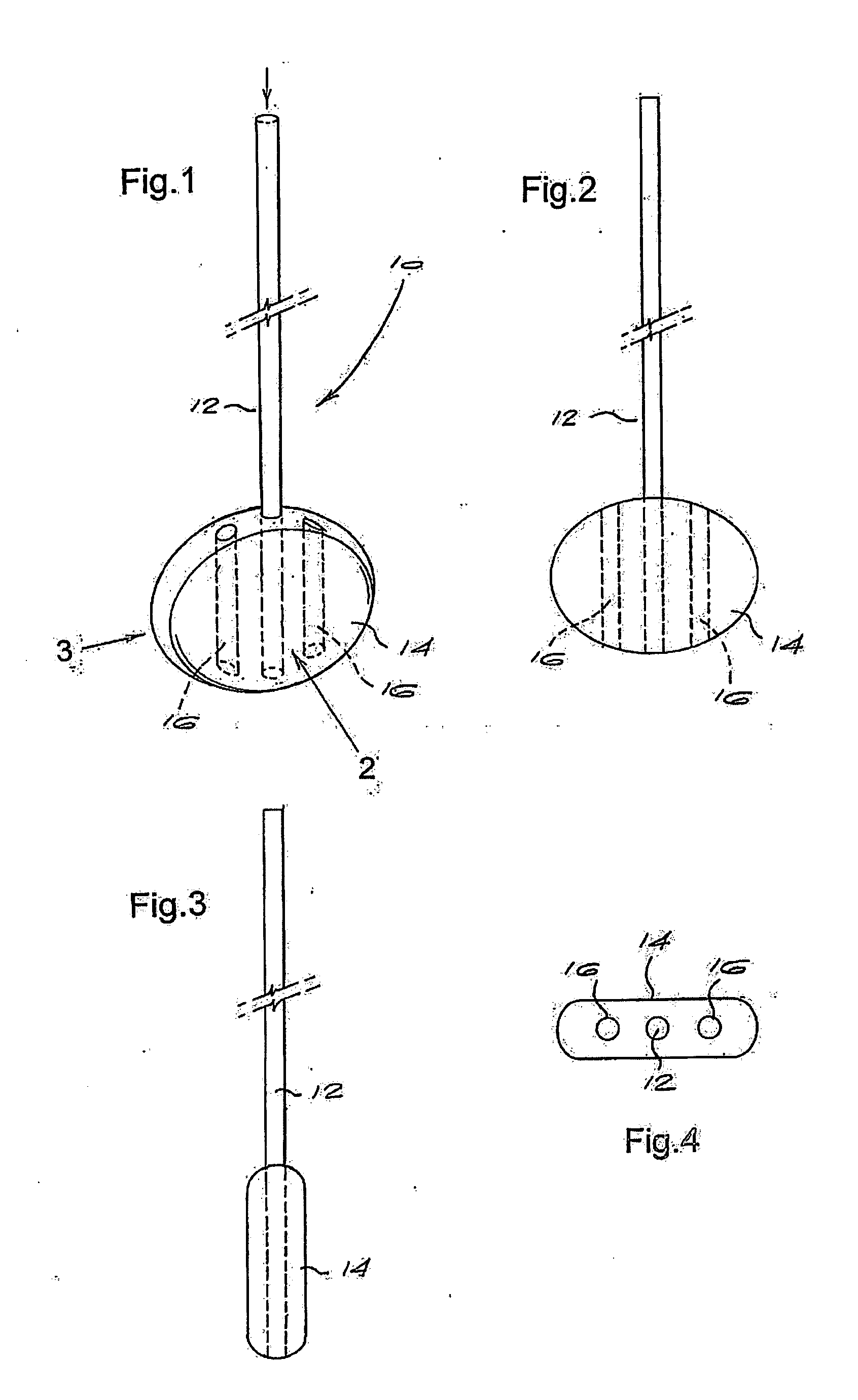
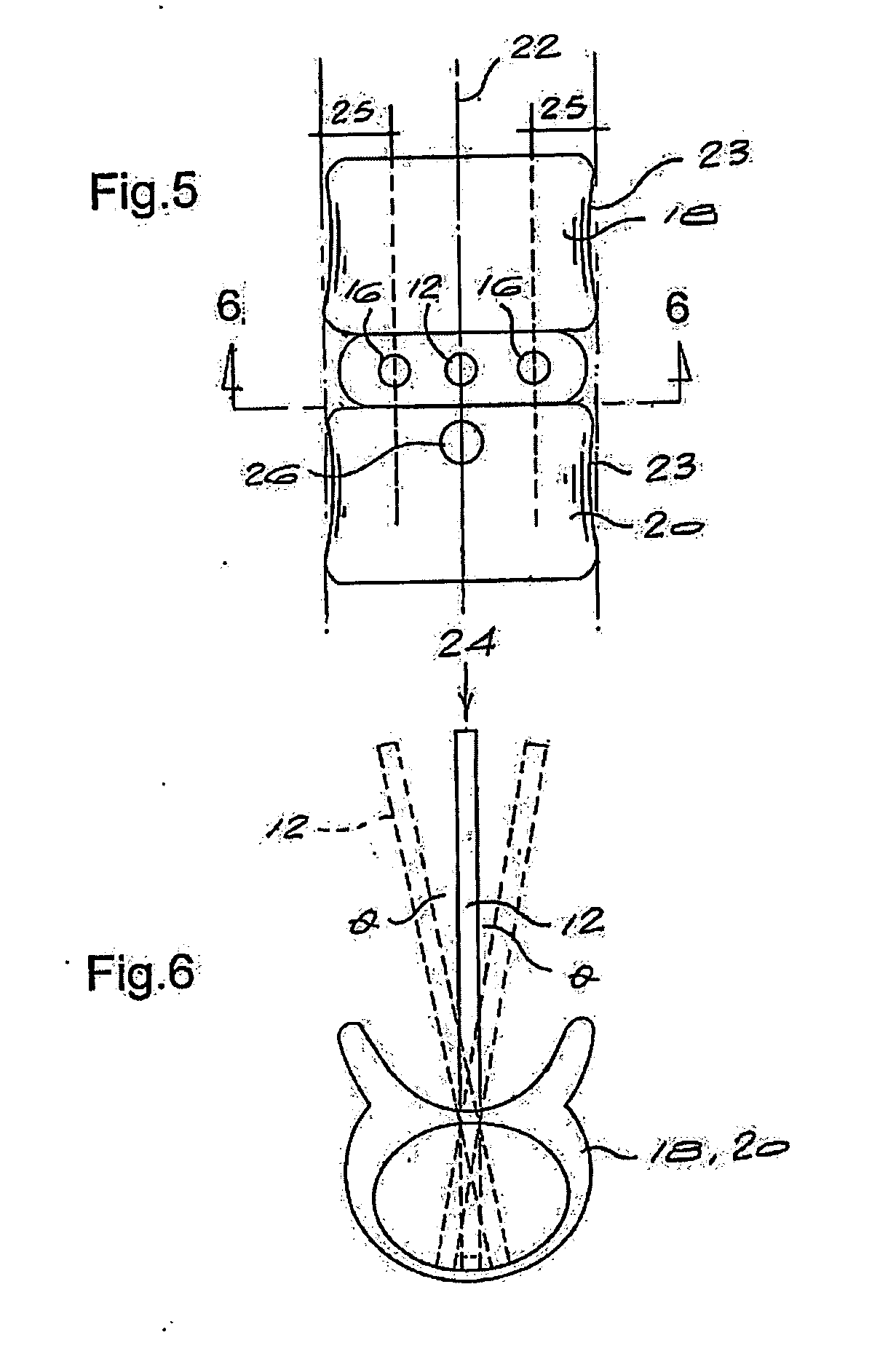
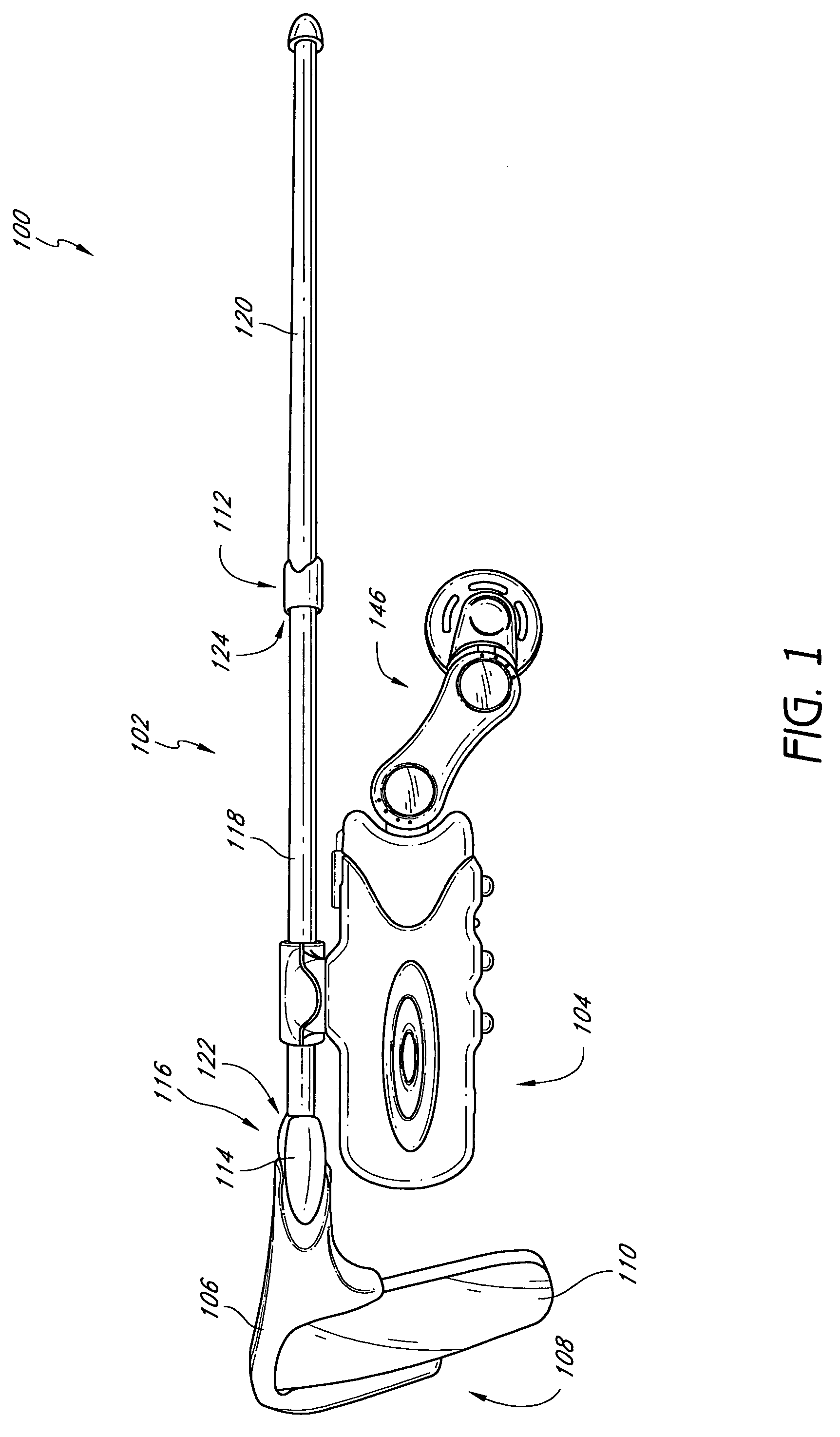
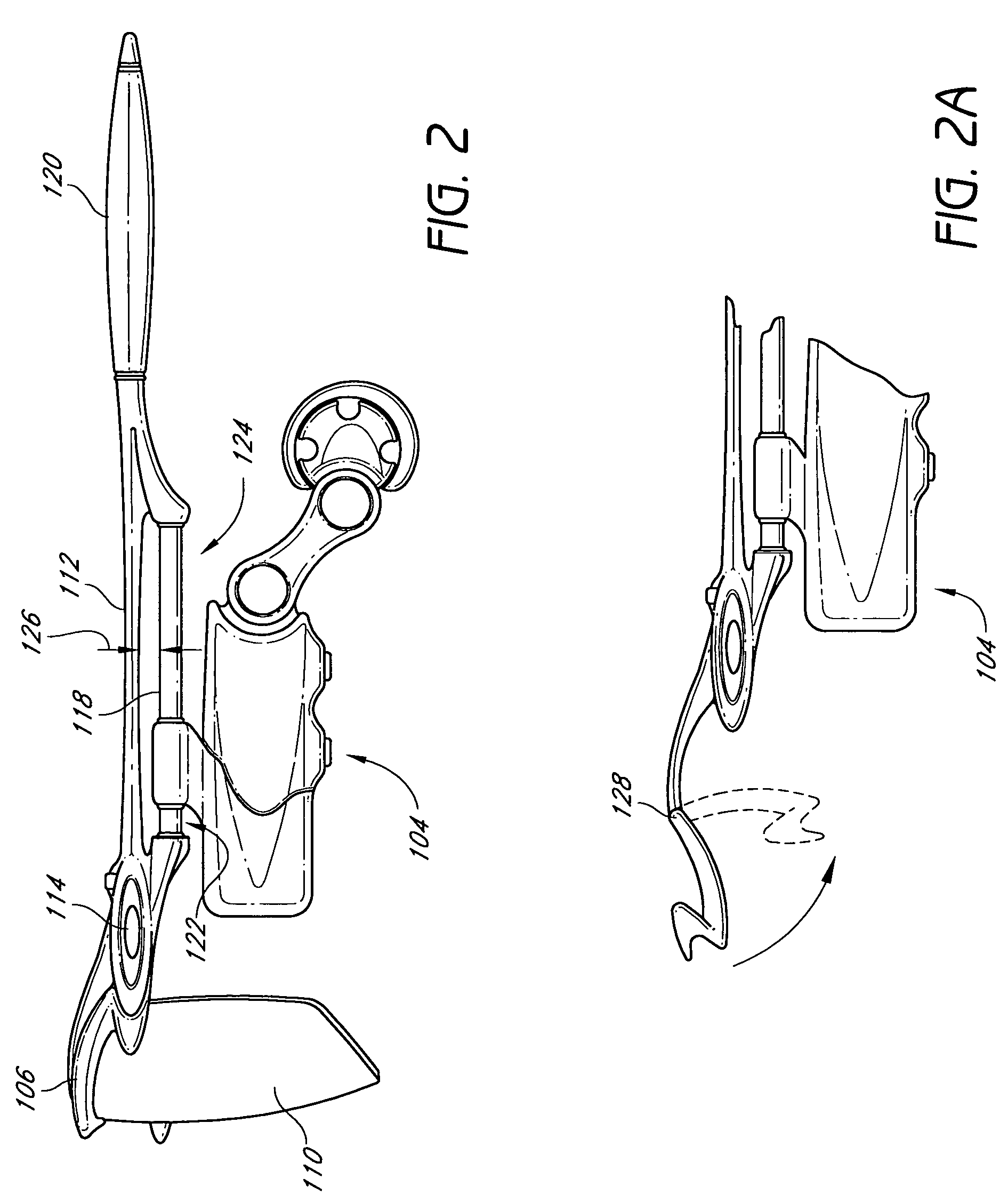
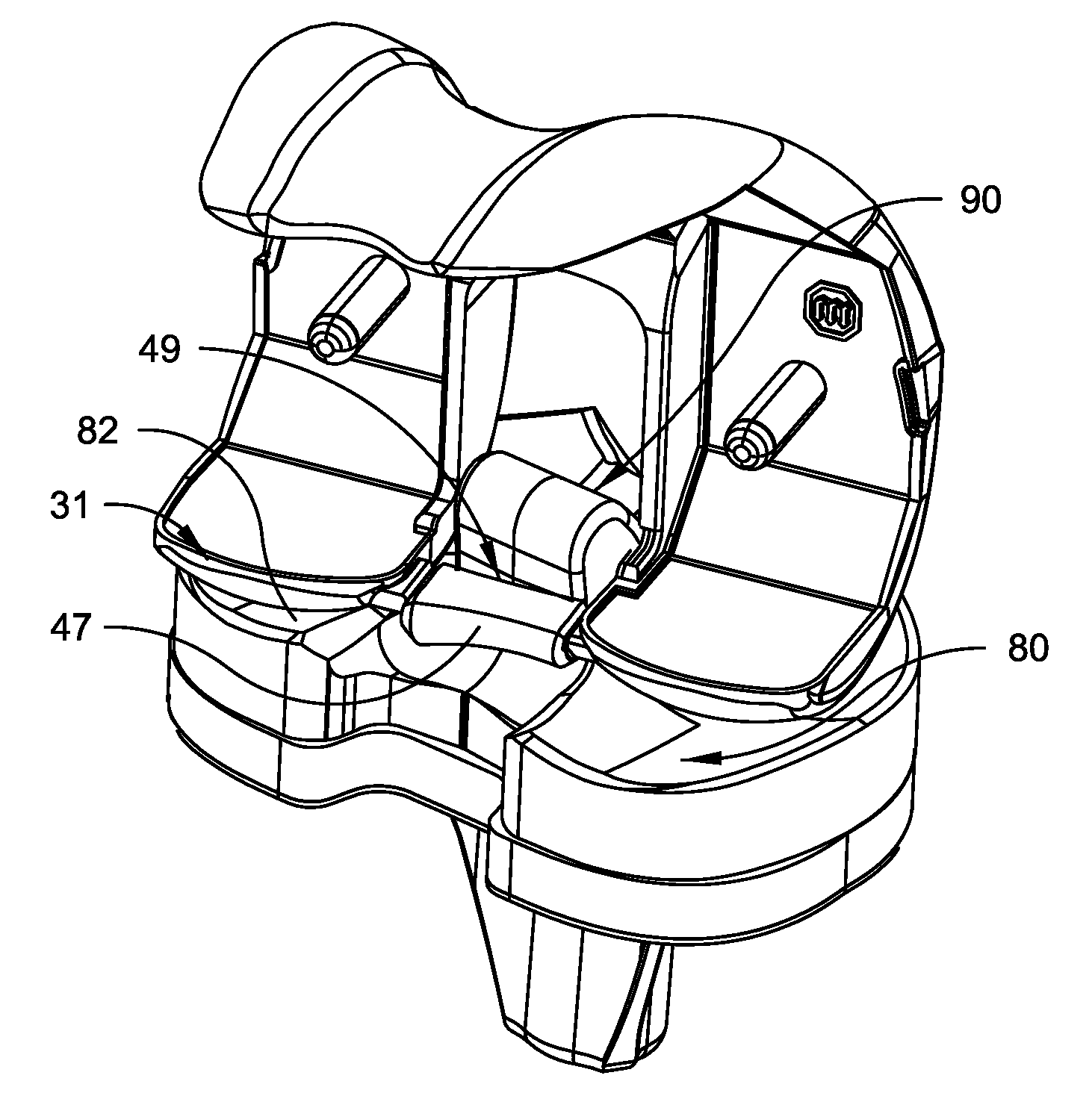
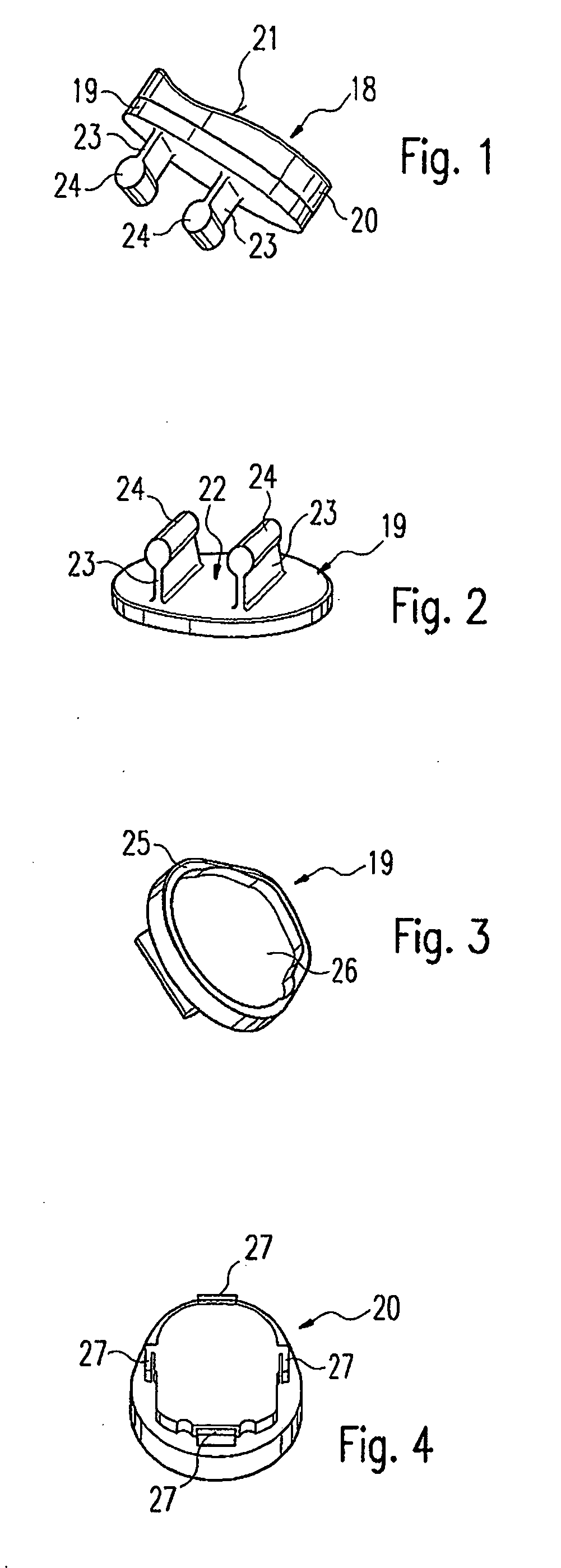
InactiveUS20060029186A1Easy to installDiagnostic markersJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringAnterior posterior
A spinal midline indicator (10) has a body (14) of radiolucent material for insertion between adjacent vertebrae (18, 20) and a radiographic marker (12) located centrally with the body to indicate the position of the spinal midline (22) in anterior-posterior images when the body is centrally located between the vertebrae. The radiographic marker is typically an elongate metal handle. The body may carry secondary radiographic markers (16) on opposite sides of and equidistant from the handle so that the handle indicates the position of the spinal midline when the body is placed centrally between the vertebrae.
Owner:SIMPLIFY MEDICAL PTY LTD
Devices, systems, and methods for performing atherectomy including delivery of a bioactive material
Devices, systems, and methods are employed to perform an atherectomy in an identified region to restore patency to arterial lesions. A bioactive material is introduced into the identified region before, after or during performing the atherectomy. The bioactive material can be introduced, e.g., on a balloon coated with the bioactive material, which is expanded in contact with the identified region to deliver the bioactive material. The bioactive material can be, e.g., at least one of a restenosis-inhibiting agent, a thrombus-inhibiting agent, and an anti-inflammatory agent.
Owner:ATHEROMED
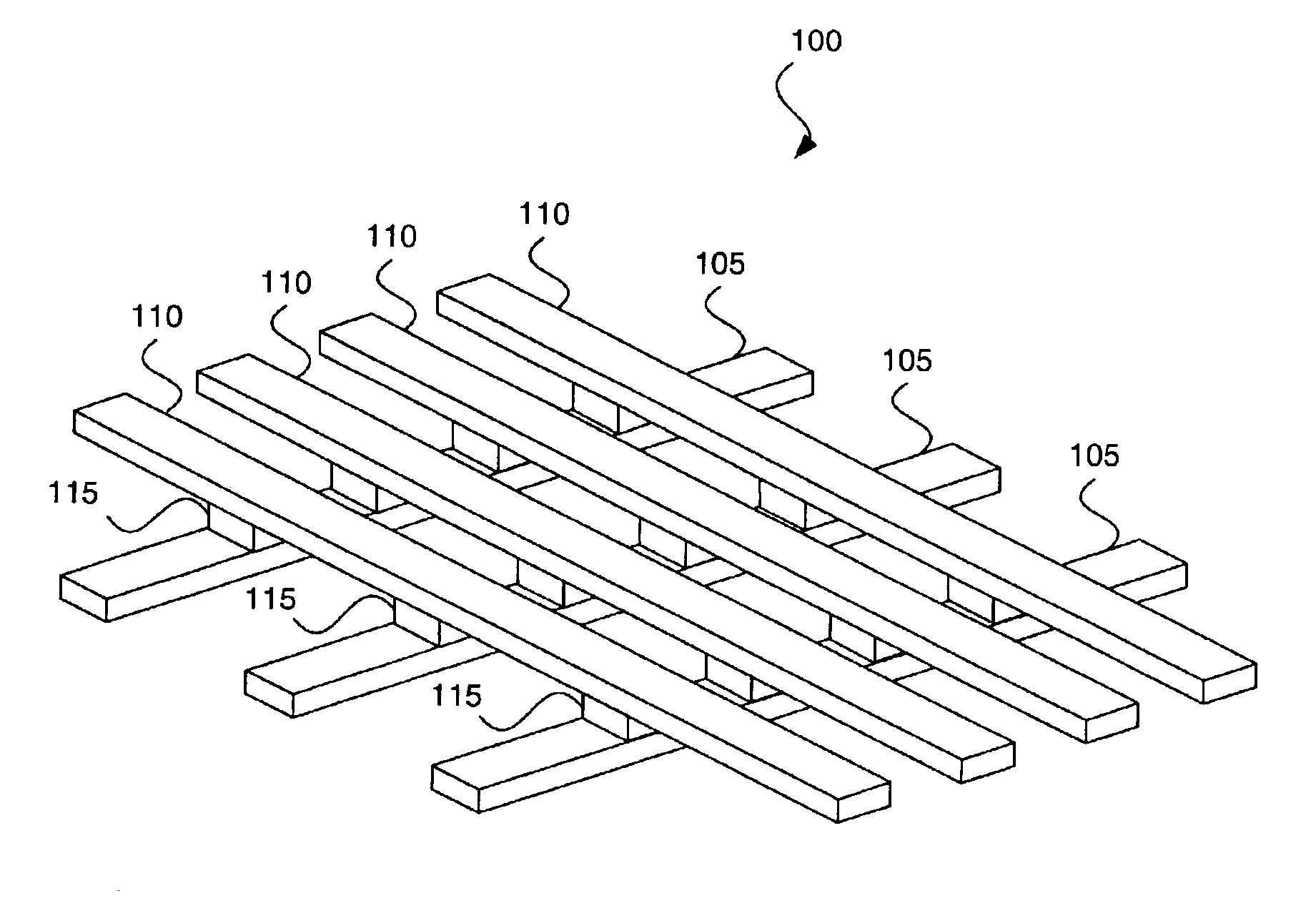
Modular femoral component for a total knee joint replacement for minimally invasive implantation
A femoral component (100) for a total knee joint replacement has a modular structure including a number of segments (102, 112), each of the segments (102, 112) having a femoral fixation surface (104, 114) for attachment to the distal end of a femur and at least one assembly surface (108) for joining with an adjacent segment (102, 112) of the modular femoral component (100). The assembly surfaces (108) are generally planar and arranged to be oriented generally in a plane extending in a proximal-distal direction and in an anterior-posterior direction when the femoral fixation surface (104, 114) is positioned on the distal end of the femur. Although the assembly surfaces (108) are generally planar, they may be shaped or provided with complementary structures (120) to assure self-alignment when the segments (102, 112) are assembled.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Modular orthopaedic implant system with multi-use stems
A knee implant system includes a femoral adapter. The femoral adapter has a threaded bore so that a stem extension can be threaded onto the proximal end of the adapter. The same stem extension can be threaded onto the distal end of the tibial tray so that the number of stem extensions required in the system is reduced. The femoral adapter has a tapered exterior surface so that a metaphyseal sleeve can be frictionally connected to the femoral adapter. The metaphyseal sleeve has a threaded bore so that the same type of stem extension can be threaded onto the metaphyseal sleeve. The system can include a group of adapters to give the surgeon the option of selecting the appropriate valgus angle and anterior-posterior position of the stem extension.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Method and system for computer assisted surgery for bicompartmental knee replacement
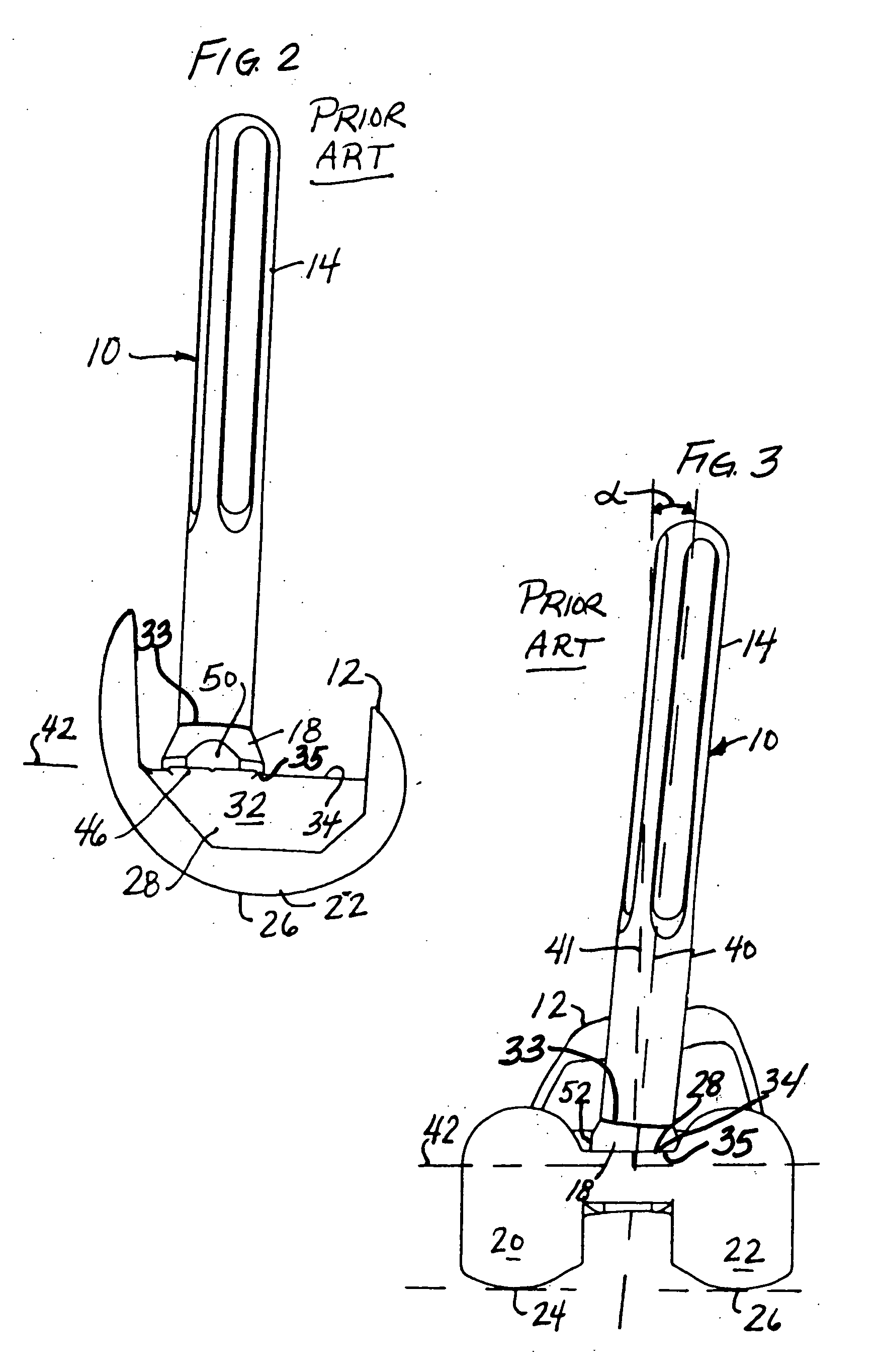
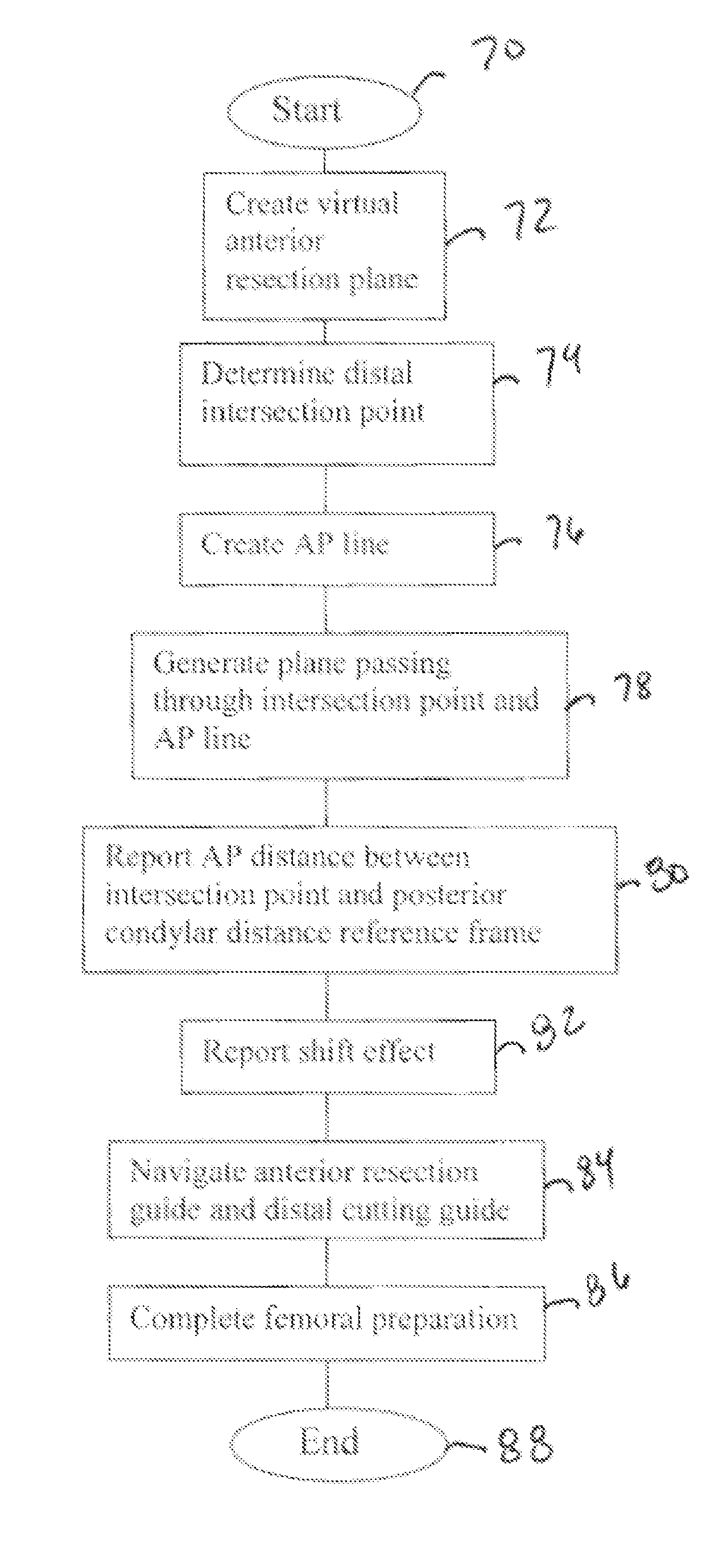
A method of resecting distal and anterior portions of a distal portion of a femur for a bicompartmental prosthesis is provided. The method includes generating a geometric representation of the distal portion of the femur. A virtual anterior resection plane is calculated at a predetermined depth and is oriented at a predetermined angle relative to the femur. The method identifies a distal-most point of a lateral portion of the virtual anterior resection plane and an AP line. A varus / valgus angle and an anterior-posterior distance are calculated. Anterior and distal resection guides are navigated according to the parameters calculated from the method.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS RECON
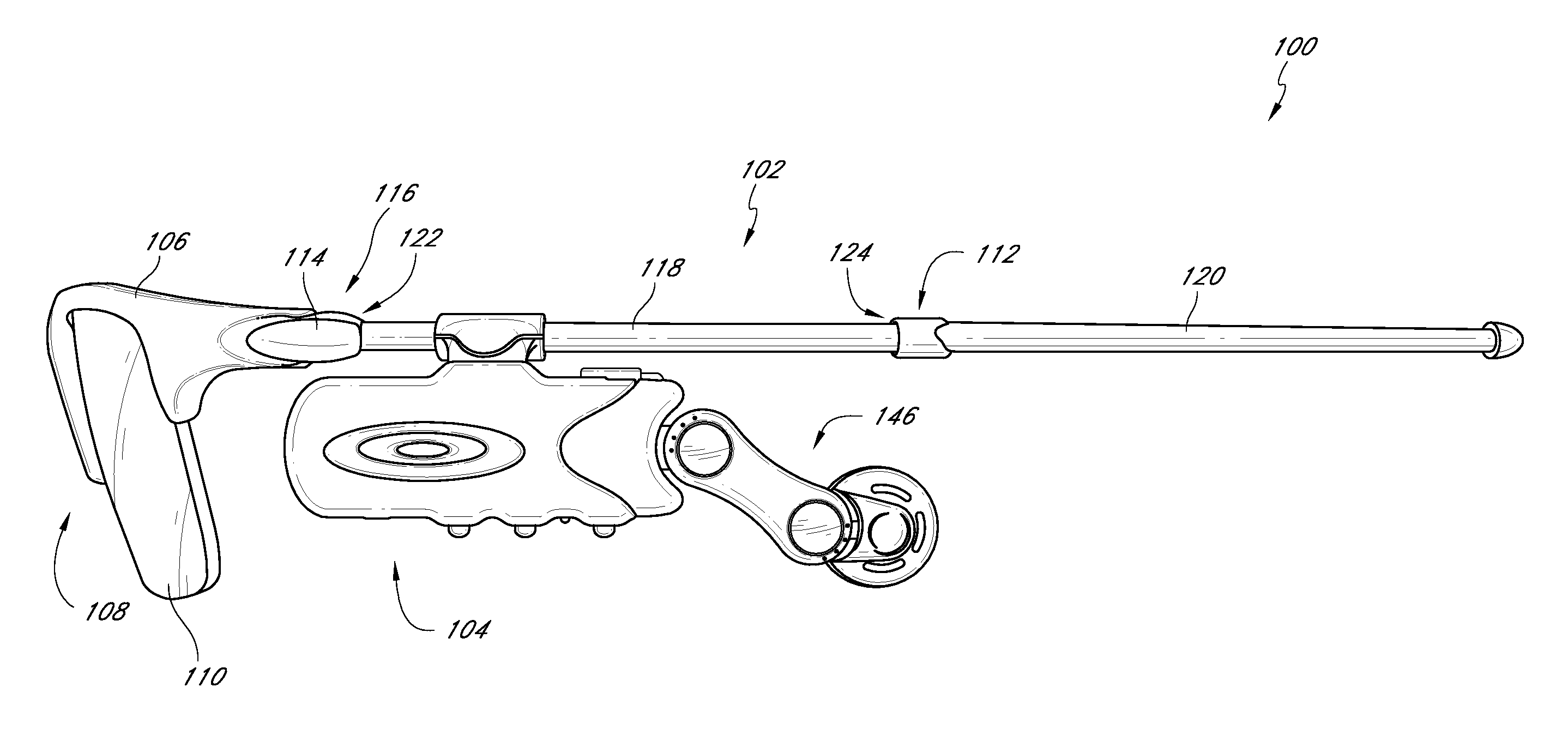
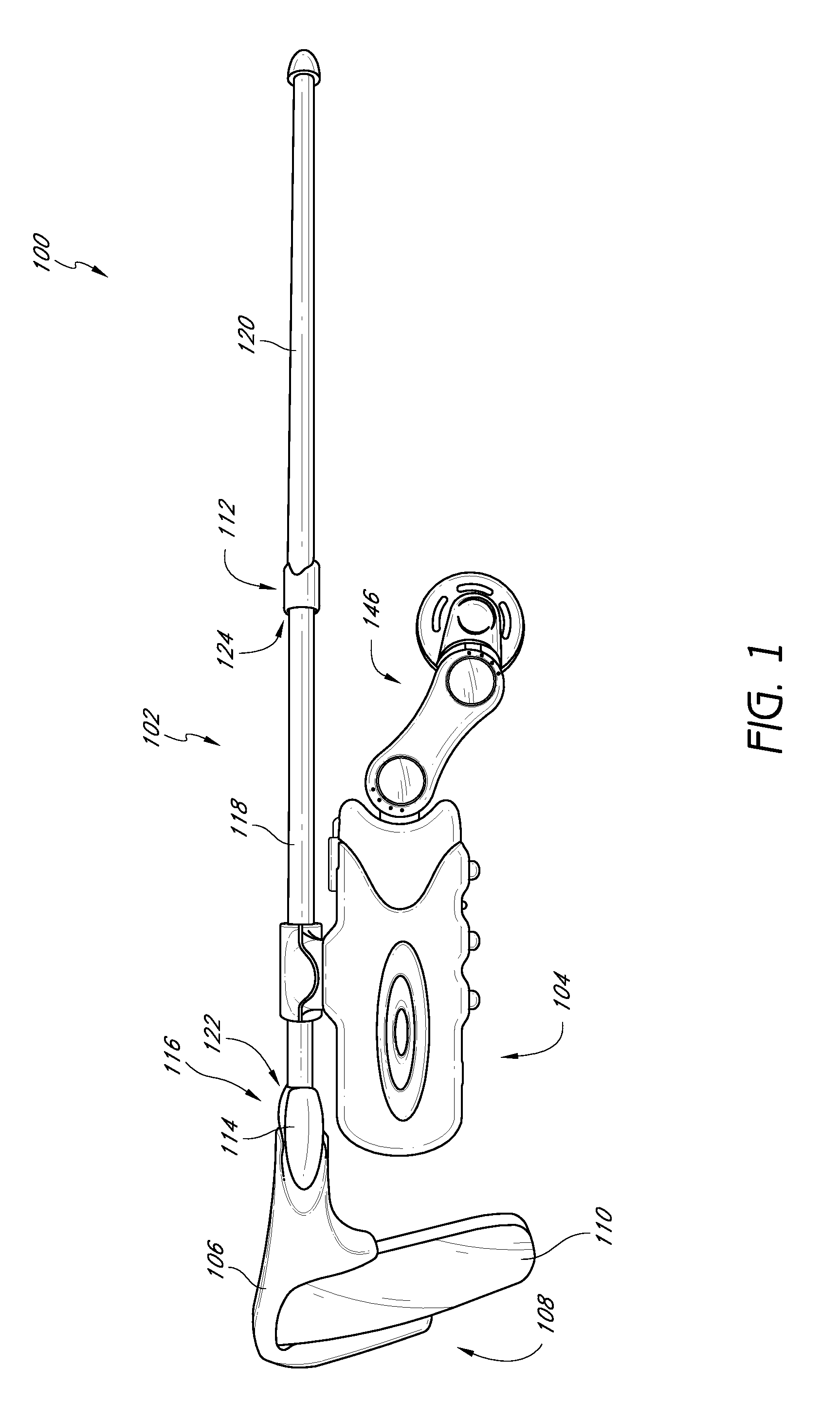
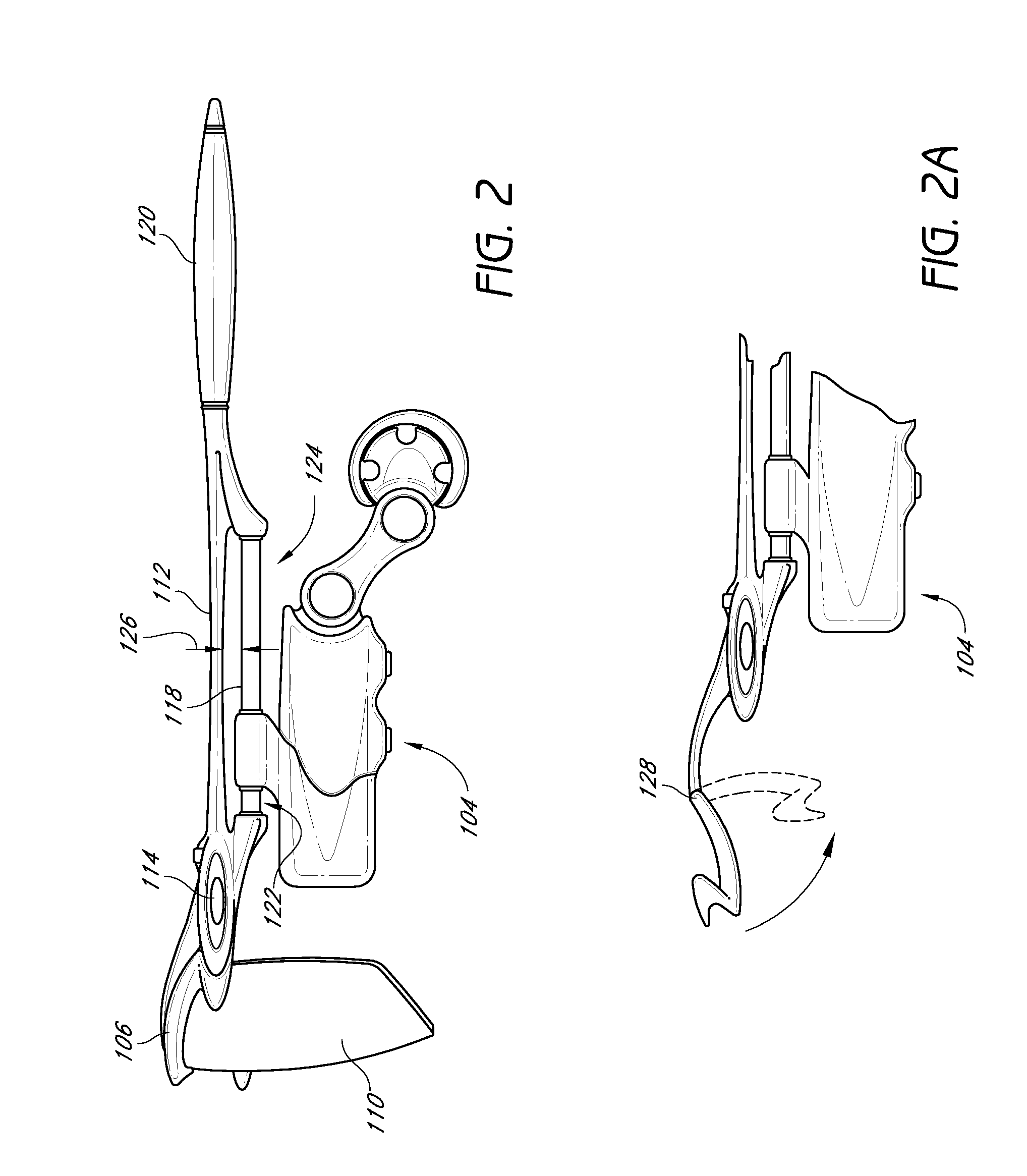
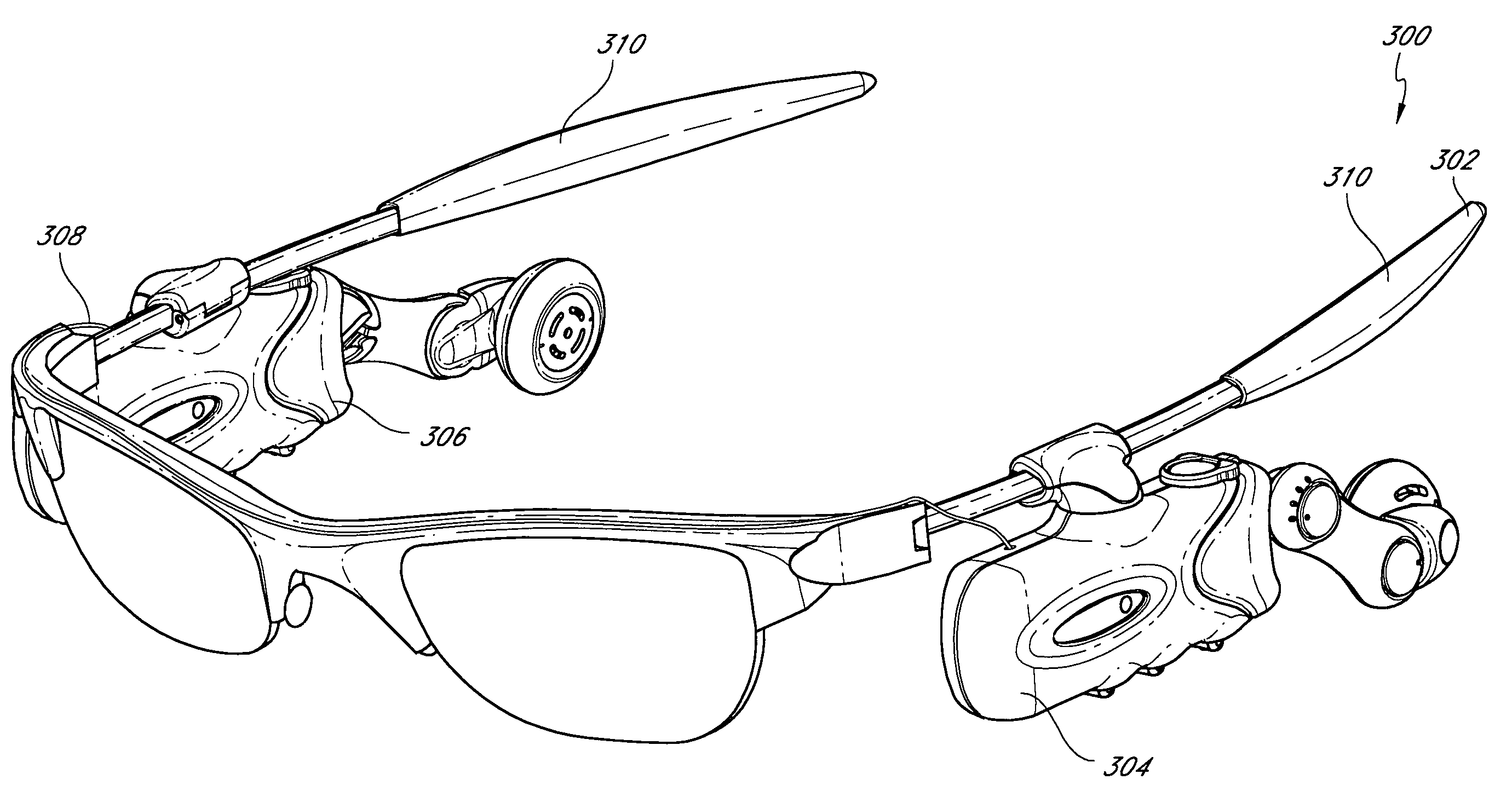
Eyewear with detachable adjustable electronics module
A detachable adjustable electronics module may be removably or permanently connected to eyewear. The module may include electronics for processing audio and / or video input and / or output signals. The module may be provided with an adjustable arm, for adjustably carrying a speaker. The module and / or the speaker may be adjusted relative to the wearer in any of the anterior-posterior direction, the inferior-superior direction and laterally. Rotation adjustments may also be accomplished. Eyewear may be provided with only a single module, on a single side, or with two modules, one on each side, such as to provide stereo audio or dual mono sound.
Owner:OAKLEY INC
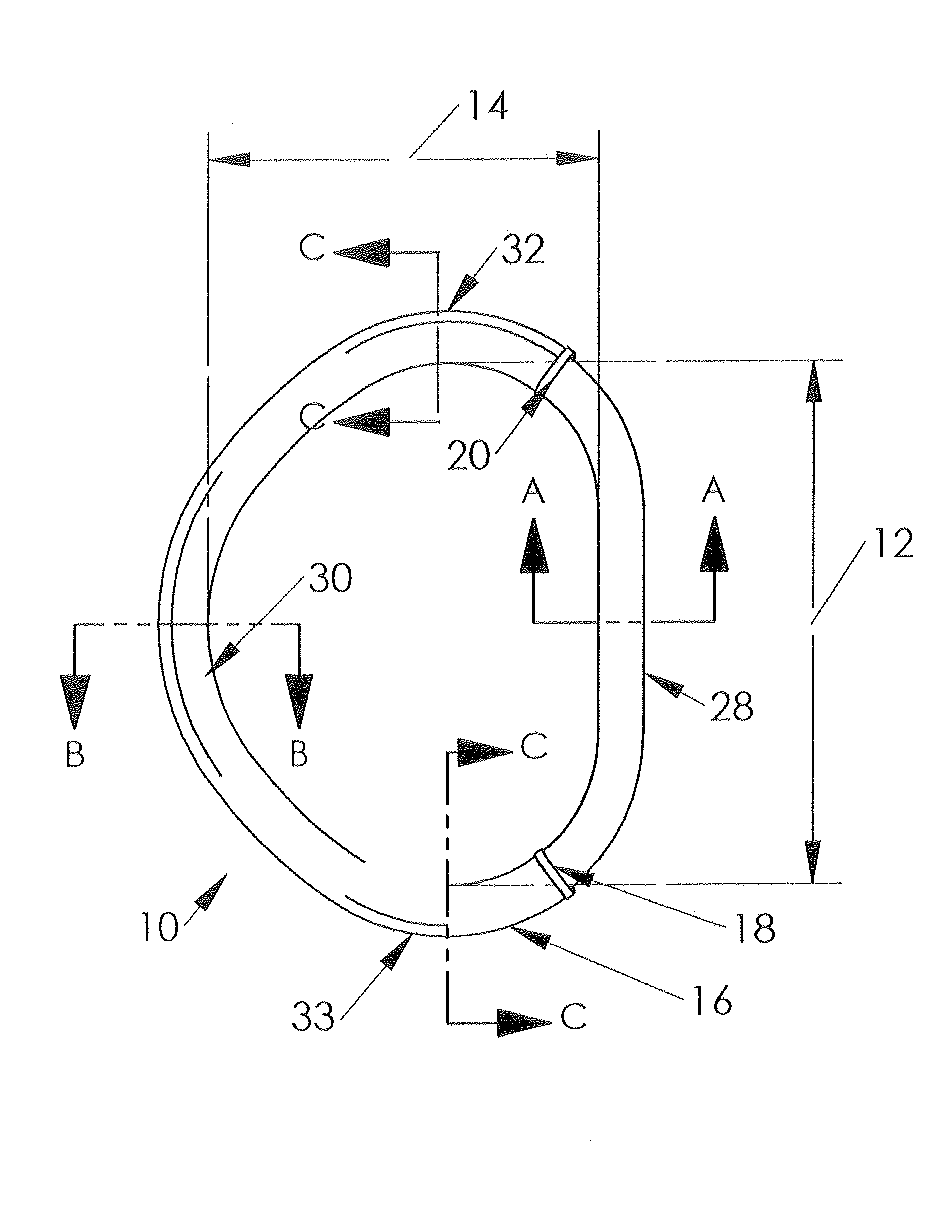
Mitral and tricuspid annuloplasty rings
ActiveUS20080086203A1Minimize the possibilityStay in shapeBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsMitral annuloplasty ringPosterior region
A mitral annuloplasty ring with an inner core and an outer band located therearound is disclosed. The ring has an anterior region, a posterior region opposite the anterior region, and two side regions therebetween. A cross-sectional width dimension of the outer band is greater in the posterior region of the ring than in the anterior region. A cross-sectional width dimension of a semi-flexible core is thinner in the anterior and posterior regions than in the side regions so that the mitral ring is more rigid in the anterior-posterior direction. A tricuspid annuloplasty ring of the invention has an inner core and an outer band located therearound. The inner core has an anterior region separated across a gap from a septal region, and a posterior region. A cross-sectional width dimension of the outer band is greater in the septal region than either the anterior or posterior regions.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
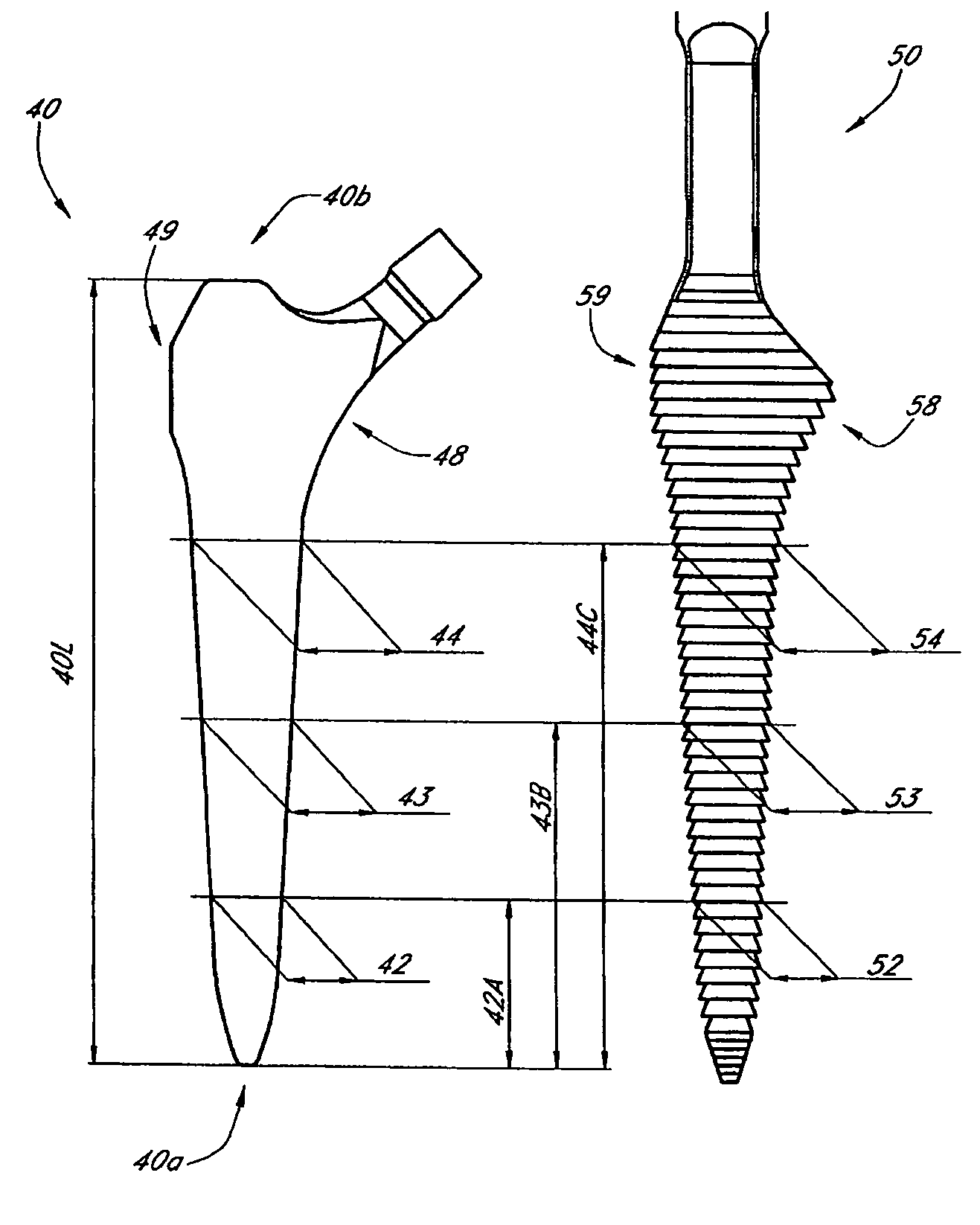
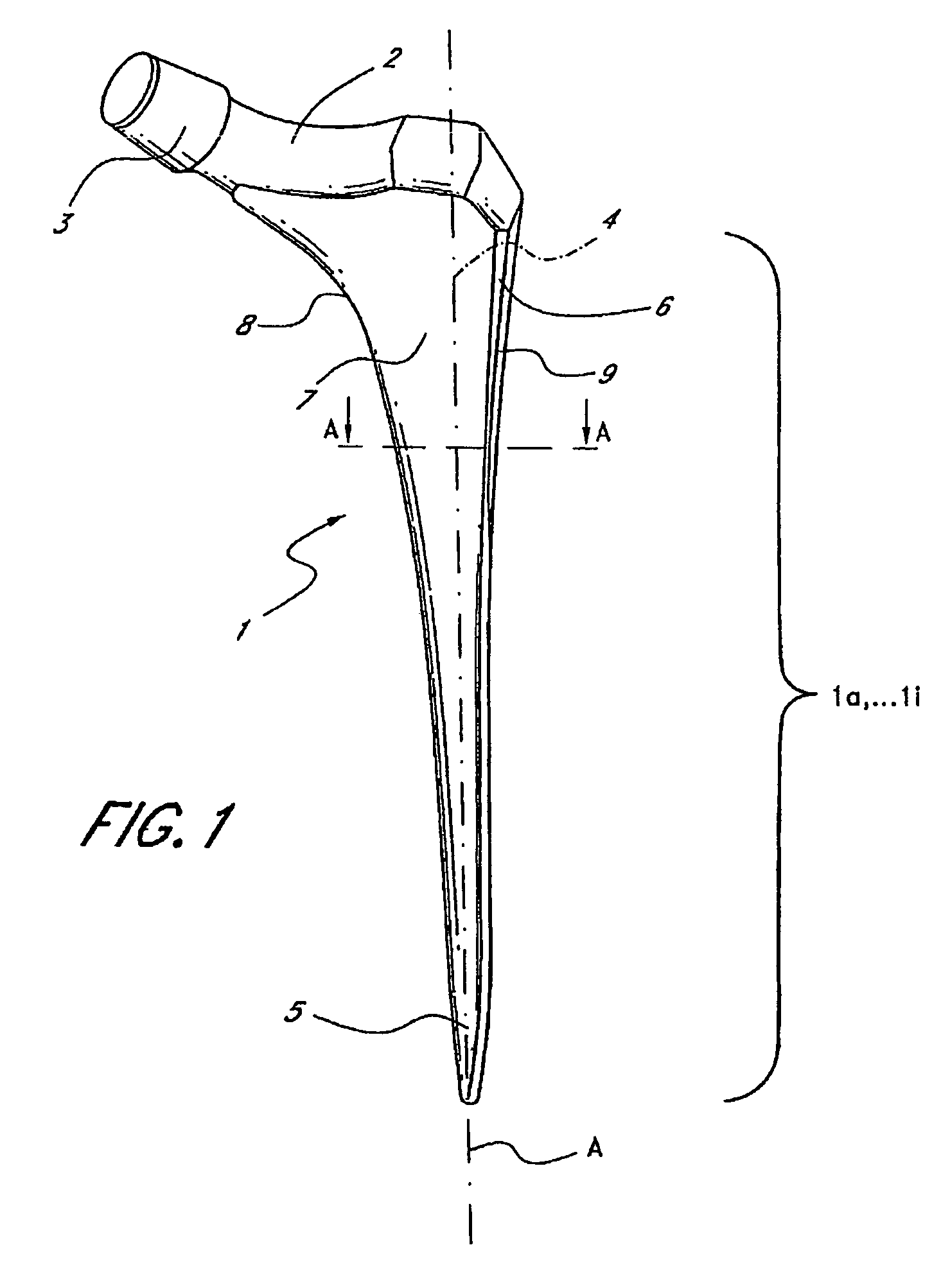
Leaflike shaft of a hip-joint prosthesis for anchoring in the femur
InactiveUS7494510B2Advantageous for revascularizationFacilitate revascularizationSurgeryJoint implantsRaspFemoral shaft
The present invention relates in certain embodiments to components of a hip-joint prosthesis. More particularly, embodiments of the invention relate to a leaf-like femoral shaft for use as part of a hip-joint prosthesis, and instruments (e.g., a rasp) and methods for implanting the shaft. The shaft includes an anchoring section extending between a proximal region and a distal end of the shaft. The shaft has a cross-sectional contour that defines a lateral side, a medial side, an anterior side and a posterior side. A corresponding rasp is preferably provided for each femoral shaft. The rasp is inserted into the femur to form a cavity having generally the same configuration as the rasp. The shaft is configured to be over-dimensioned in at least one of the anterior-posterior direction and medial-lateral direction relative to the rasped femur cavity. In one embodiment, the distance between diagonally opposite corner junctions of the shaft is substantially equal to the distance between corresponding diagonally opposite corner junctions of the femur cavity, so as to inhibit excess stress on the corticalis.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Holder Devices for Annuloplasty Devices Having a Plurality of Anterior-Posterior Ratios
ActiveUS20090192606A1Change ratioReduce time and costBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsBiomedical engineeringAnterior posterior
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
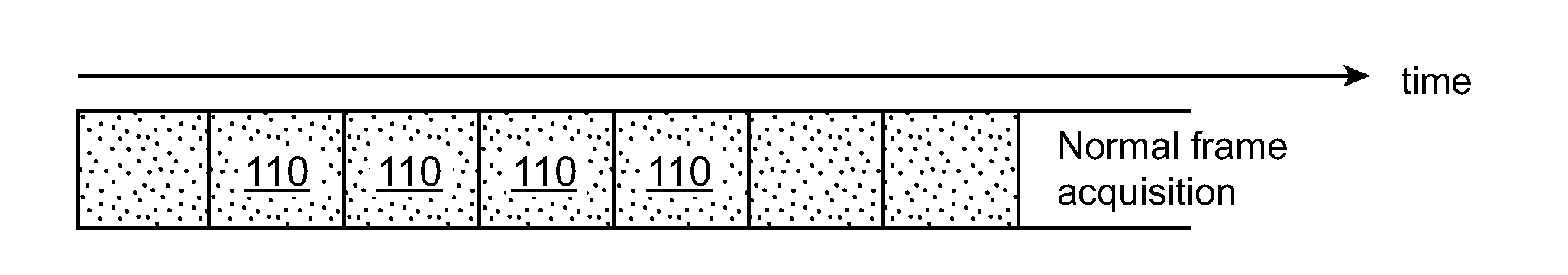
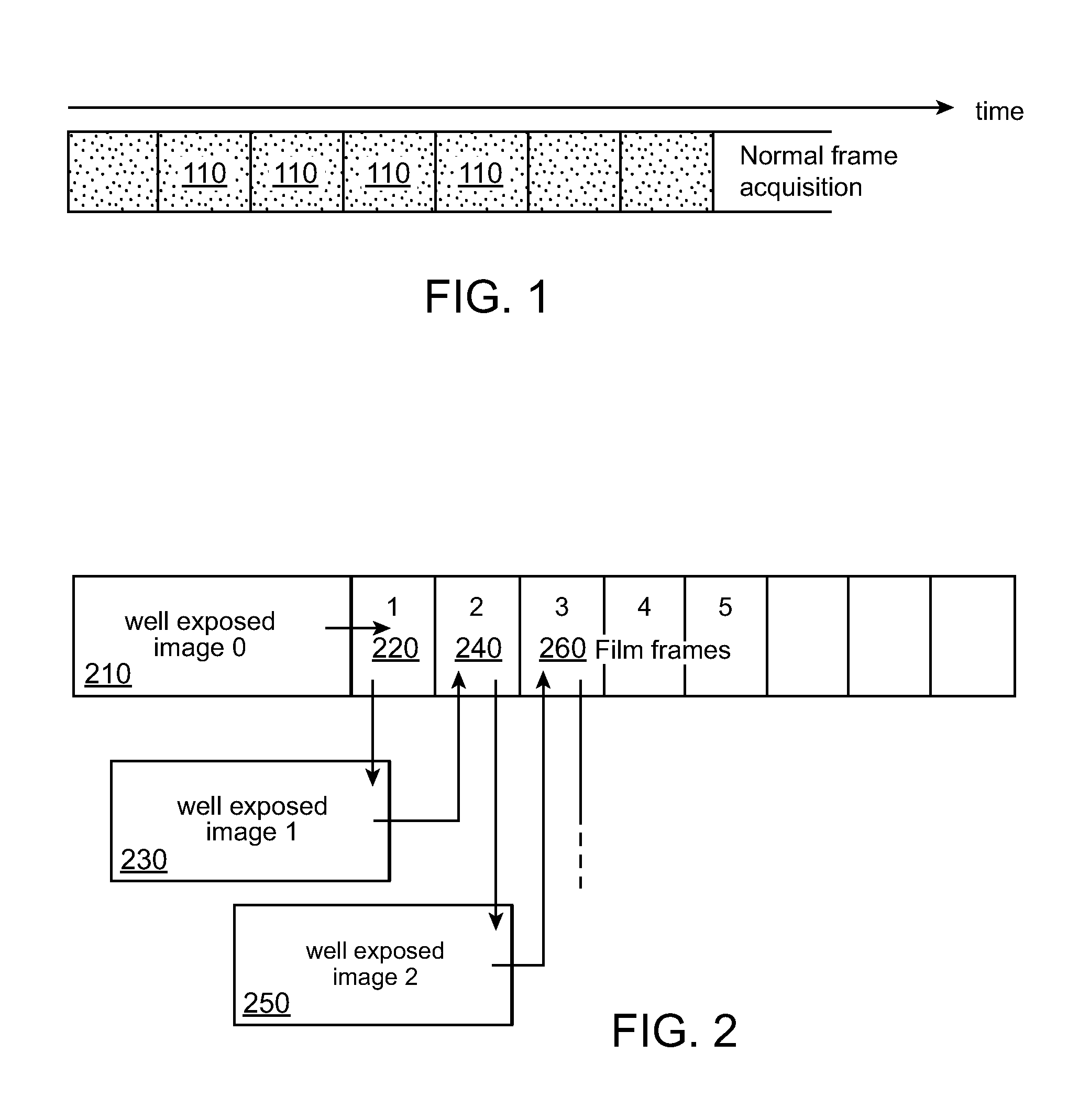
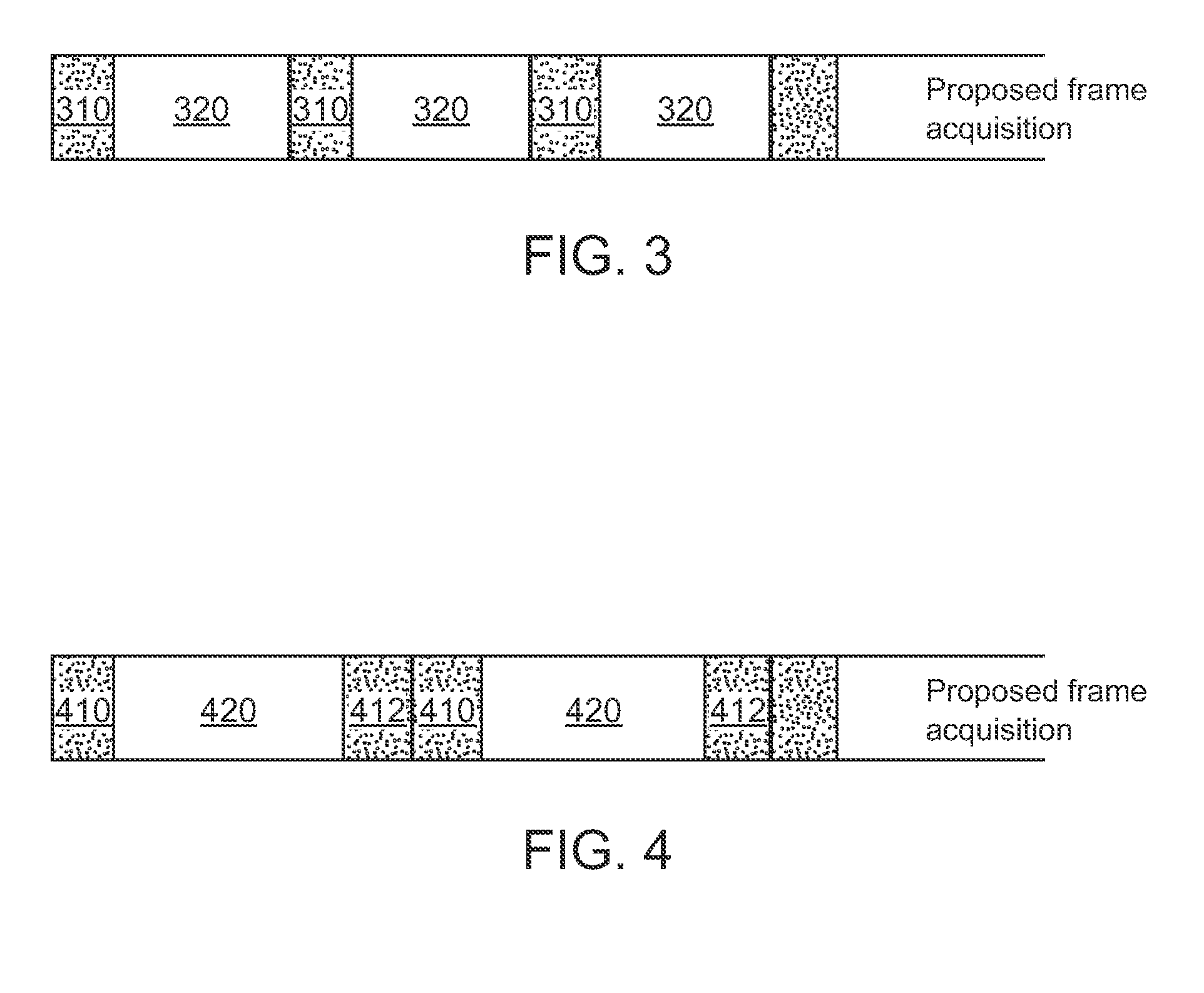
Low-light video frame enhancement
ActiveUS20090303343A1Enhance oneEnhance more parameterImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage extractionMultiple frame
A method of combining image data from multiple frames to enhance one or more parameters of video image quality includes acquiring a first image at a first exposure duration, as well as acquiring a second image at a second exposure duration shorter than the first exposure duration and at a time just before, just after or overlapping in time with acquiring the first image, such that the first and second images include approximately a same first scene. In this way, the second image is relatively sharp and under-exposed, while the first image is relatively well-exposed and less sharp than the second image. Brightness and / or color information are extracted from the first image and applied to the second image to generate an enhanced version of the second image.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Eyeglasses with detachable adjustable electronics module
A detachable adjustable electronics module may be removably or permanently connected to eyewear. The module may include electronics for processing audio and / or video signals. The module may be provided with an adjustable arm, for adjustably carrying a speaker. The module and / or the speaker may be adjusted relative to the wearer in any of the anterior-posterior direction, the inferior-superior direction and laterally. Rotation adjustments may also be accomplished. Eyewear may be provided with only a single module, on a single side, or with two modules, one on each side, such as to provide stereo audio or dual mono sound.
Owner:OAKLEY INC
Methods and apparatus for total disc replacements with oblique keels
Artificial disc replacement (ADR) systems with intradiscal components feature non anterior-posterior (A-P) or oblique-oriented keels such that the great vessels do not require as much retraction during insertion. The system may further include guides for aligning the ADR prior to insertion, and for cutting an oblique slot into a vertebral endplate to receive the keel. A screw adapted to penetrate a vertebral body may be used in conjunction with the keel. The screw and keel may converge, diverge or intersect. The screw may further include a mechanism providing a locking relationship with the keel. The system may further including a guide to direct drill bits and screws through holes in the keel. ADRs according to the invention may additionally, independently include a non-symmetrical endplate shaped so as to decrease the risk of injuring the great vessels. By virtue of the invention, a second ADR may be installed at a second level having a keel oriented differently from that of the ADR having an orientation other than anterior-to-posterior.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
Method and apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy
Apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy, the apparatus comprising:cutting apparatus for forming an osteotomy cut in the tibia, the cutting apparatus comprising:targeting apparatus for identifying a cutting plane through the tibia and a boundary line for terminating a cut made along the cutting plane, wherein the boundary line is located within the tibia, parallel to the anterior-posterior slope of the tibia and parallel to the sagittal plane of the patient.A method for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy, the method comprising:positioning targeting apparatus for identifying a cutting plane through the tibia and a boundary line for terminating a cut made along the cutting plane, wherein the boundary line is located within the tibia, parallel to the anterior-posterior slope of the tibia and parallel to the sagittal plane of the patient;cutting the bone along the cutting plane, with the cut terminating at the boundary line;moving the bone on either-side of the cut apart so as to form the wedge-like opening in the bone; andstabilizing the bone.
Owner:ARTHREX
Total Knee Replacement Prosthesis
A knee replacement prosthesis comprising a femoral component and a tibial component that enable anterior-posterior translation of the femur relative to the tibia and enable the tibia to rotate about its longitudinal axis during flexion of the knee. The femoral component connects to the distal end of a resected femur and includes medial and lateral condyles having distal, articulating surfaces, and a patellar flange having a patellar articulating surface. The tibial component connects to the proximal end of a resected tibia and includes a proximal bearing surface with medial and lateral concavities that articulate with the medial and lateral condyles. The articulating surfaces of the condyles and concavities are defined by sections of toroids.
Owner:MAXX ORTHOPEDICS INC
Glenoid prosthesis and method of implanting same
A glenoid prosthesis includes a bearing, the lateral side of which defines a concave bearing surface, and a carrier shell, the medial side of which comprises anchoring elements, wherein the medial side is generally flat. The prosthesis may be implanted in an anterior-posterior (A-P) by forming bores in the scapula in the A-P direction, wherein the anchoring elements extend into the bores. The scapula may be proceed to have a generally flat surface to correspond with the flat surface at the medial side of the prosthesis.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Orthopedic implant with angled pegs
An orthopedic implant, such as a tibial tray, includes a body having a bone contacting surface with at least one and preferably two pegs extending from the bone contacting surface. Each of the pegs has a longitudinal axis angled with respect to the bone contacting surface and also angled in at least one direction consisting of a medial-lateral direction, an anterior-posterior direction and an inferior-superior direction. In the case of the tibial tray, the pegs form a non-perpendicular angle with the bone contacting surface of the baseplate and are angled in both a posterior direction and a medial or lateral direction.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Total Knee Replacement Prosthesis With High Order NURBS Surfaces
A knee replacement prosthesis comprising a femoral component and a tibial component that enable anterior-posterior translation of the femur relative to the tibia and enable the tibia to rotate about its longitudinal axis during flexion of the knee. The femoral component connects to the distal end of a resected femur and includes medial and lateral condyles having distal, articulating surfaces, and a patellar flange having a patellar articulating surface. The tibial component connects to the proximal end of a resected tibia and includes a proximal bearing surface with medial and lateral concavities that articulate with the medial and lateral condyles. The condylar articulating surfaces and the said concavities are substantially defined by non-uniform, rational B-spline surfaces (NURBS).
Owner:MAXX ORTHOPEDICS INC
Physiological total knee implant
The present invention generally comprises a fixed bearing prosthesis and a mobile bearing prosthesis. The fixed bearing prosthesis comprises a tibial component, a femoral component and a meniscal component and addressees the loss of congruency during deep knee flexion and the possible direct, repetitive contact of the tibial and femoral components. The tibial component of the fixed bearing prosthesis includes a tibial platform having an anterior and posterior edge. The meniscal component of the fixed bearing prosthesis includes a posterior ridge overlapping the posterior edge of the tibial platform that prevents metal-to-metal contact during deep knee flexion. The mobile bearing prosthesis comprises generally a tibial component, a femoral component and a meniscal component addresses the lack of conformity to natural biomechanical movement. The tibial component comprises a tibial platform having a curved rail system designed to mimic the asymmetrical rotation of femoral rollback while simultaneously providing sufficient anterior-posterior translation.
Owner:TARABICHI SAMIH
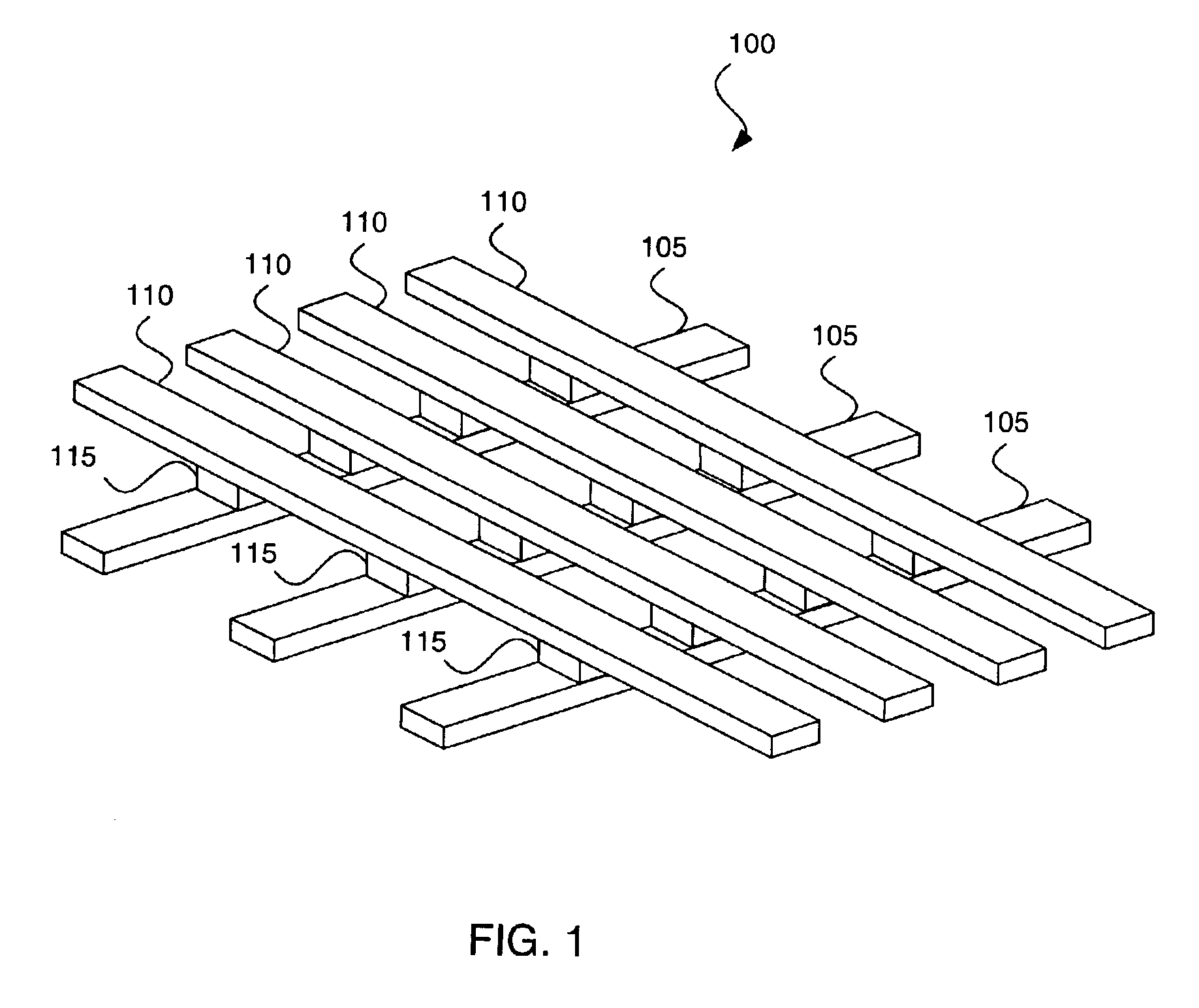
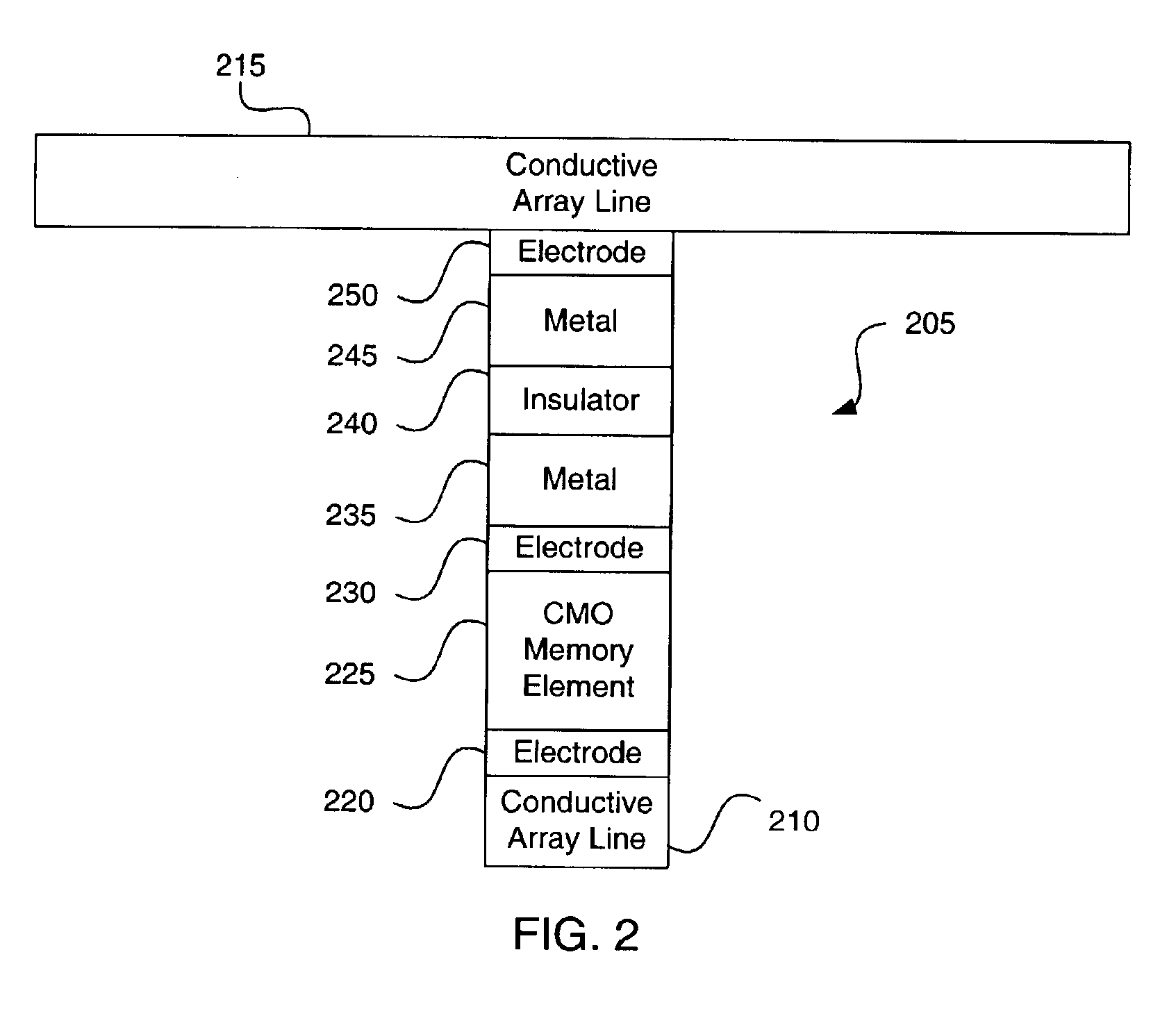
Providing a reference voltage to a cross point memory array
Providing a reference voltage to a cross point memory array. The invention is a cross point memory array and some peripheral circuitry that, when activated, provides a reference voltage to a cross point array in order to prevent unselected conductive array lines from floating to an undesired voltage. The peripheral circuitry can be activated before, after or during selection of a specific memory plug. If the peripheral circuitry is activated during selection, only the unselected conductive array lines should be brought to the reference voltage. Otherwise, all the conductive array lines can be brought to the reference voltage.
Owner:UNITY SEMICON
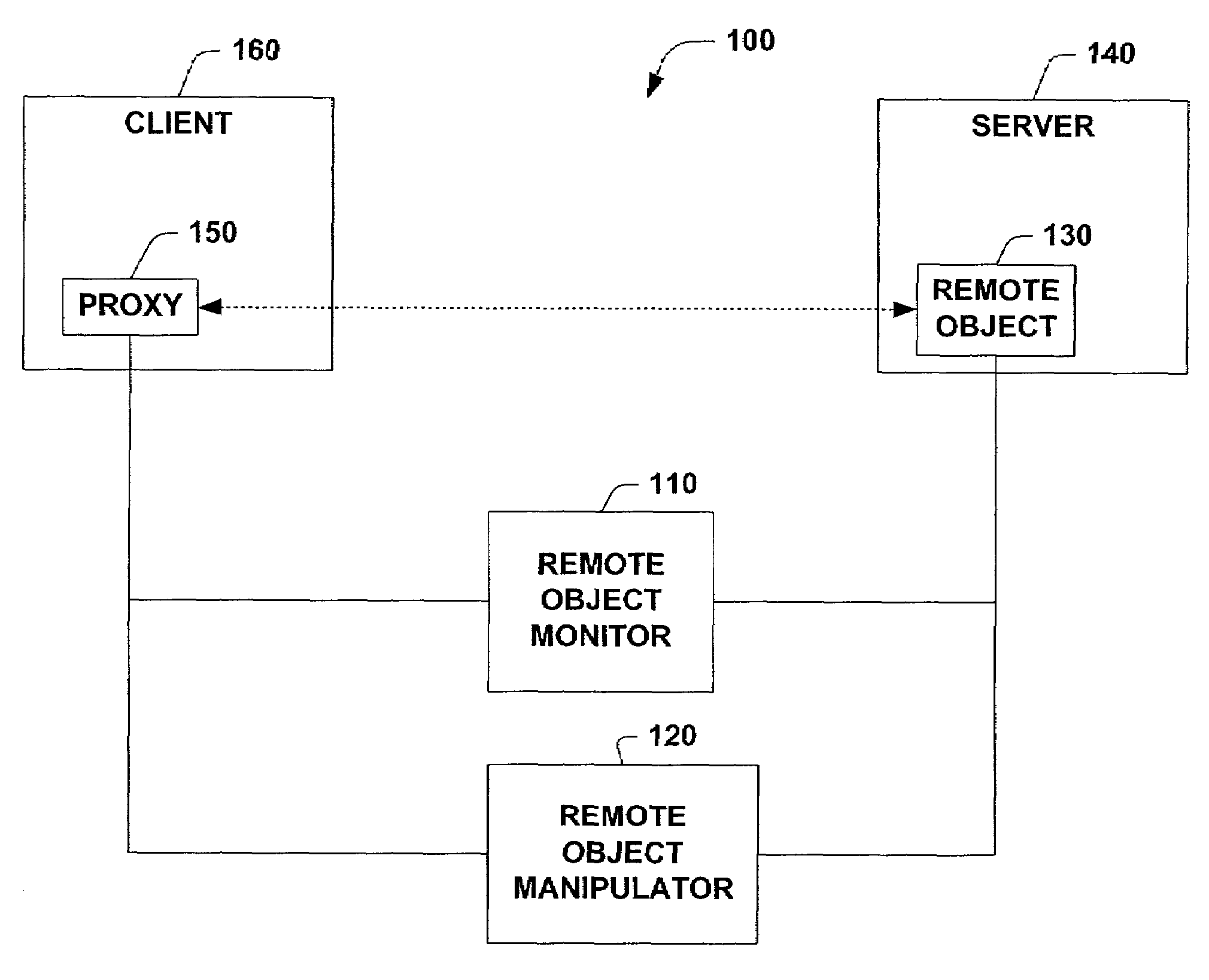
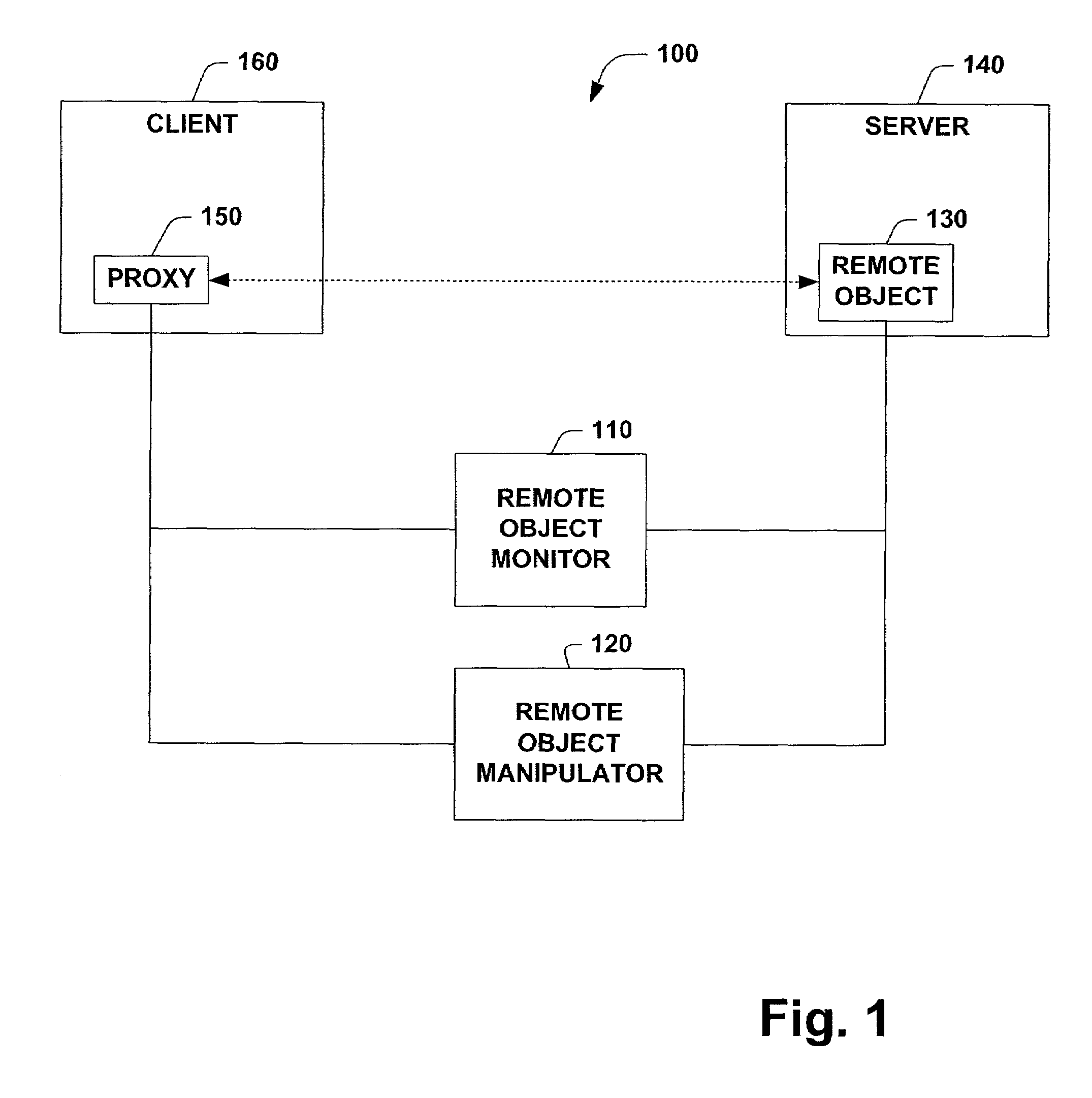
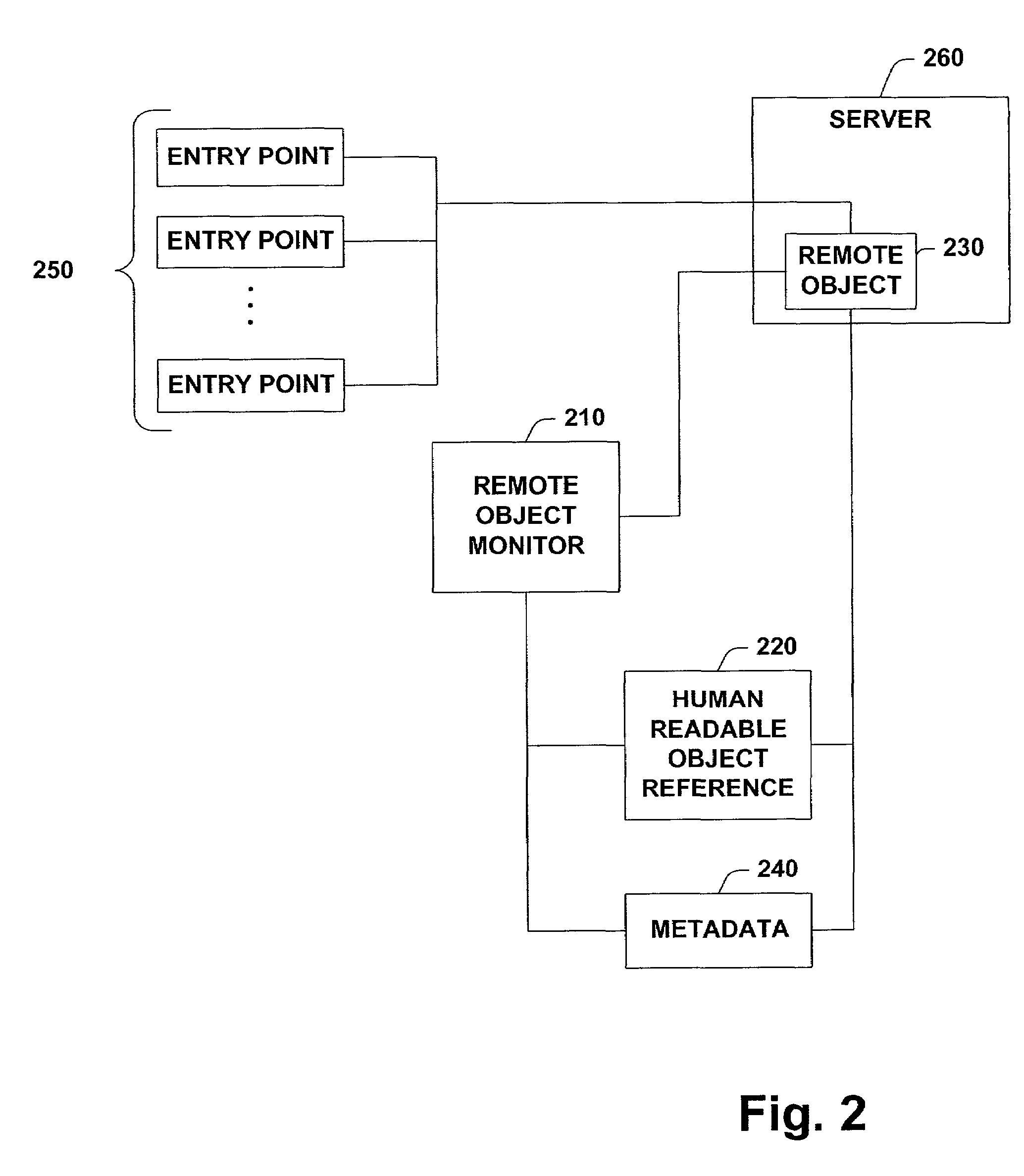
Remoting features
InactiveUS7155728B1To offer comfortEasy to produceProgram controlEntry pointUniform resource identifier
A system and method that provides remoting services in a distributed object system is provided. The system includes a remote object monitor and a remote object manipulator. The remote object monitor can provide a human readable reference to a remote object, where the human readable reference is a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) and can include protocol information, protocol data, an application name and an object URI (Uniform Resource Identifier). The remote object monitor can also provide metadata concerning a remote object, where the metadata can include information concerning interfaces implemented by a remote object, the type of a remote object, the class hierarchy of a remote object, methods implemented by a remote object, properties implemented by a remote object and attributes implemented by a remote object. The remote object monitor can also provide entry points and code interception for custom attribute based activation processing that can be performed before, after and / or substantially in parallel with non-attribute code associated with a remote object. The remote object monitor can also monitor and / or control the lifetime of a remote object, using, for example, a lease manager. The remote object manipulator can also update metadata concerning a remote object and can control the lifetime of a remote object via a lease manager, for example.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com