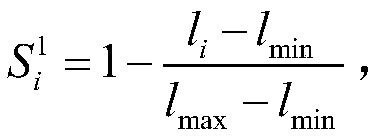Patents
Literature
65 results about "Great vessels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
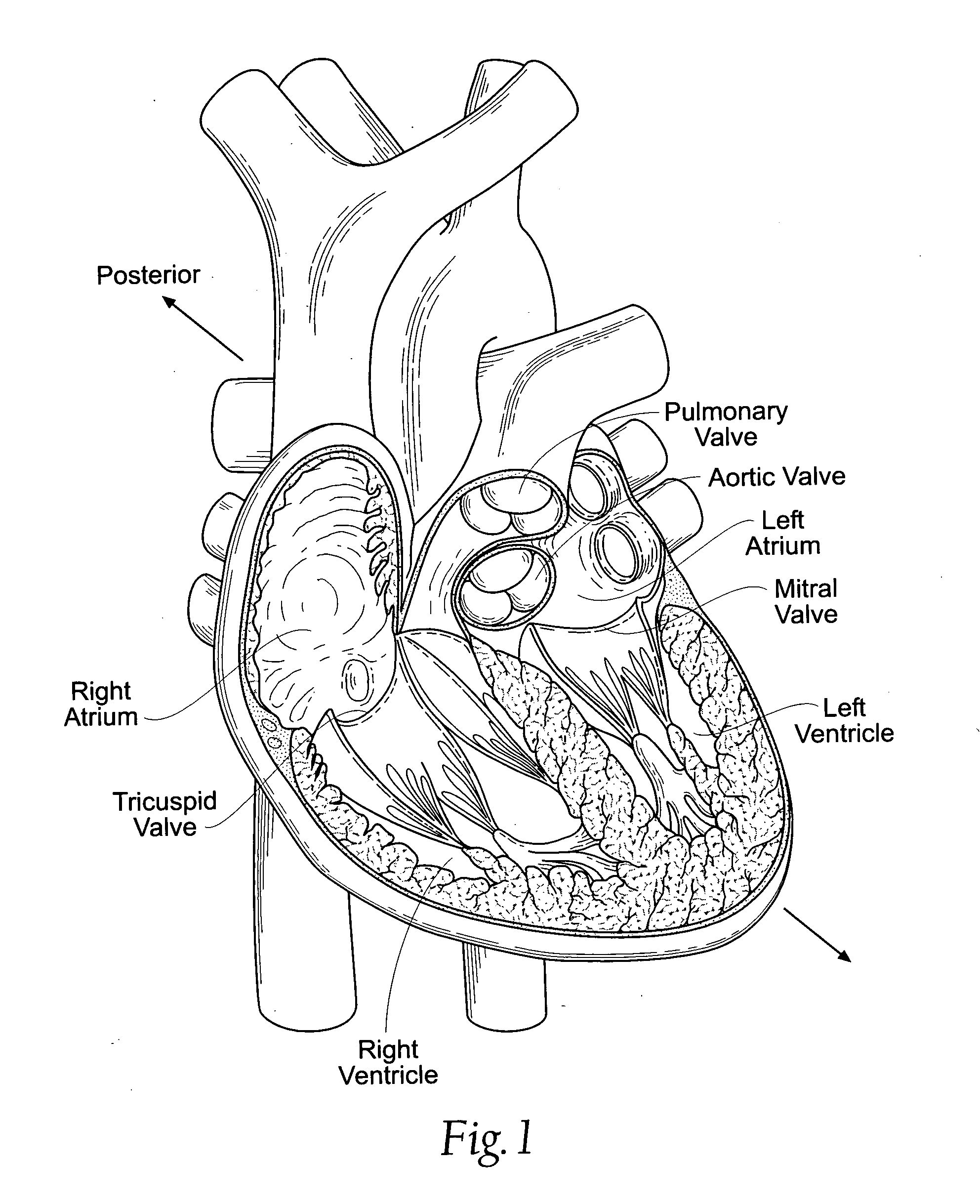
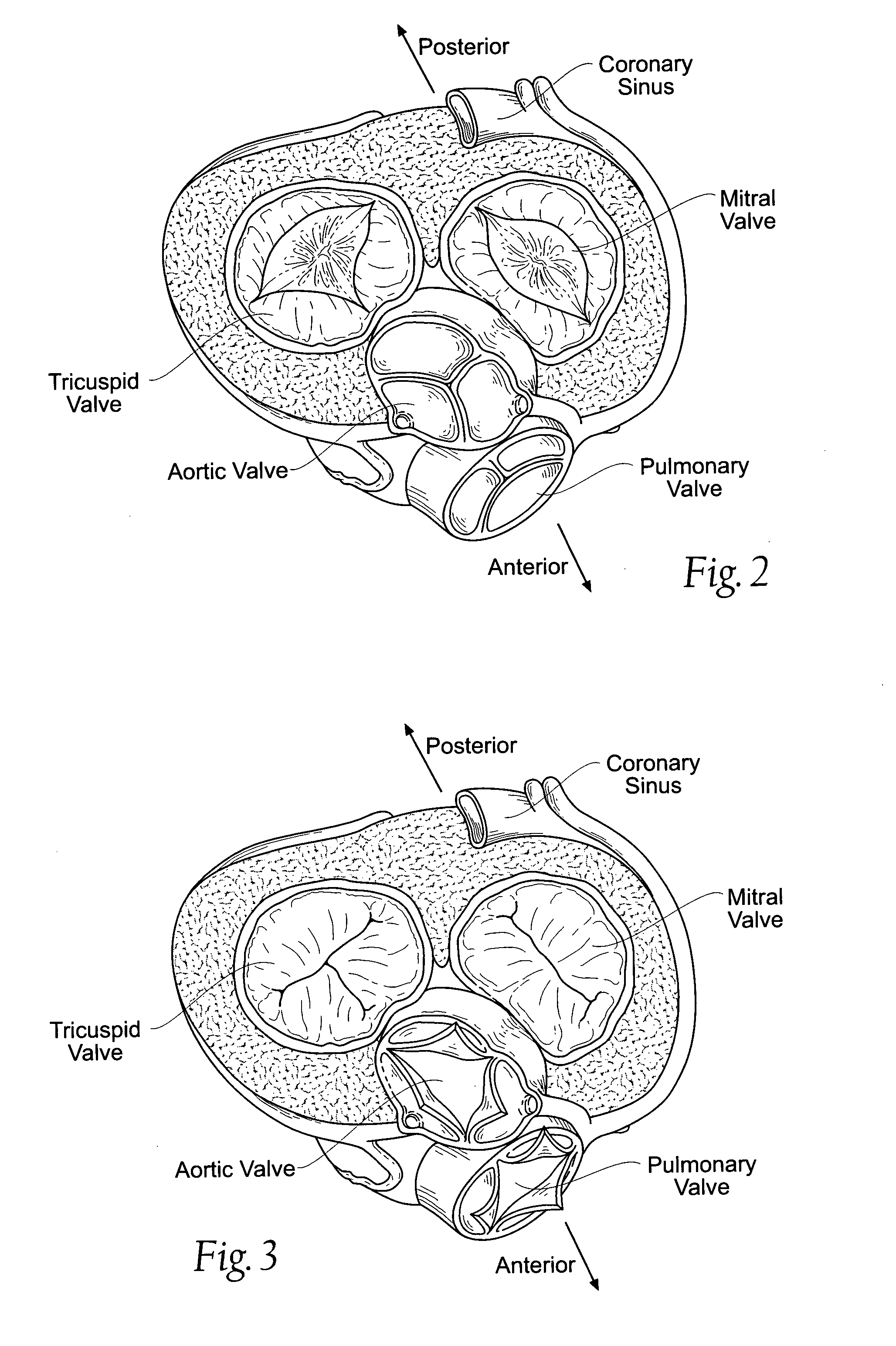
Great vessels are the large vessels that bring blood to and from the heart. Transposition of the great vessels is a group of congenital heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels.
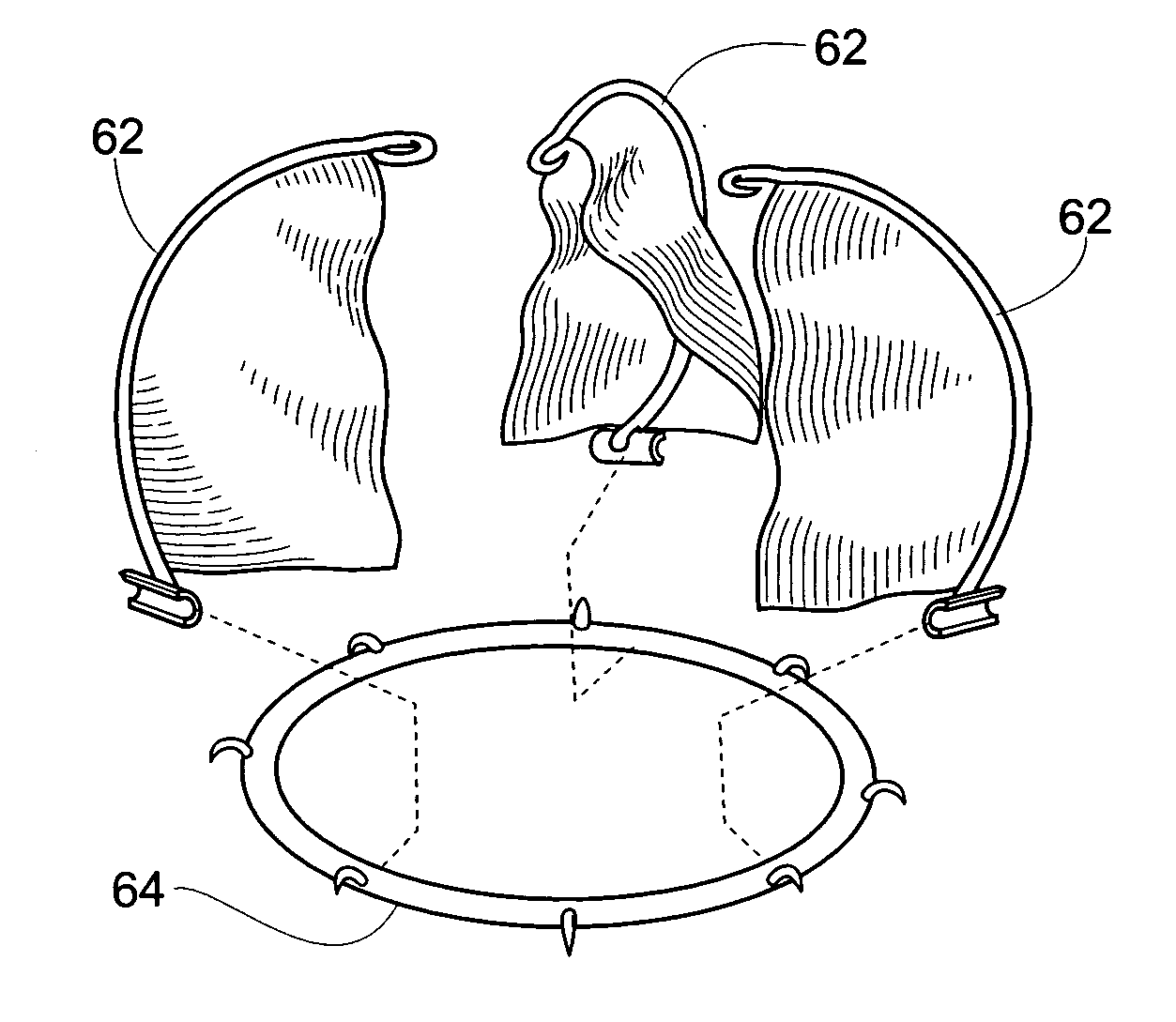
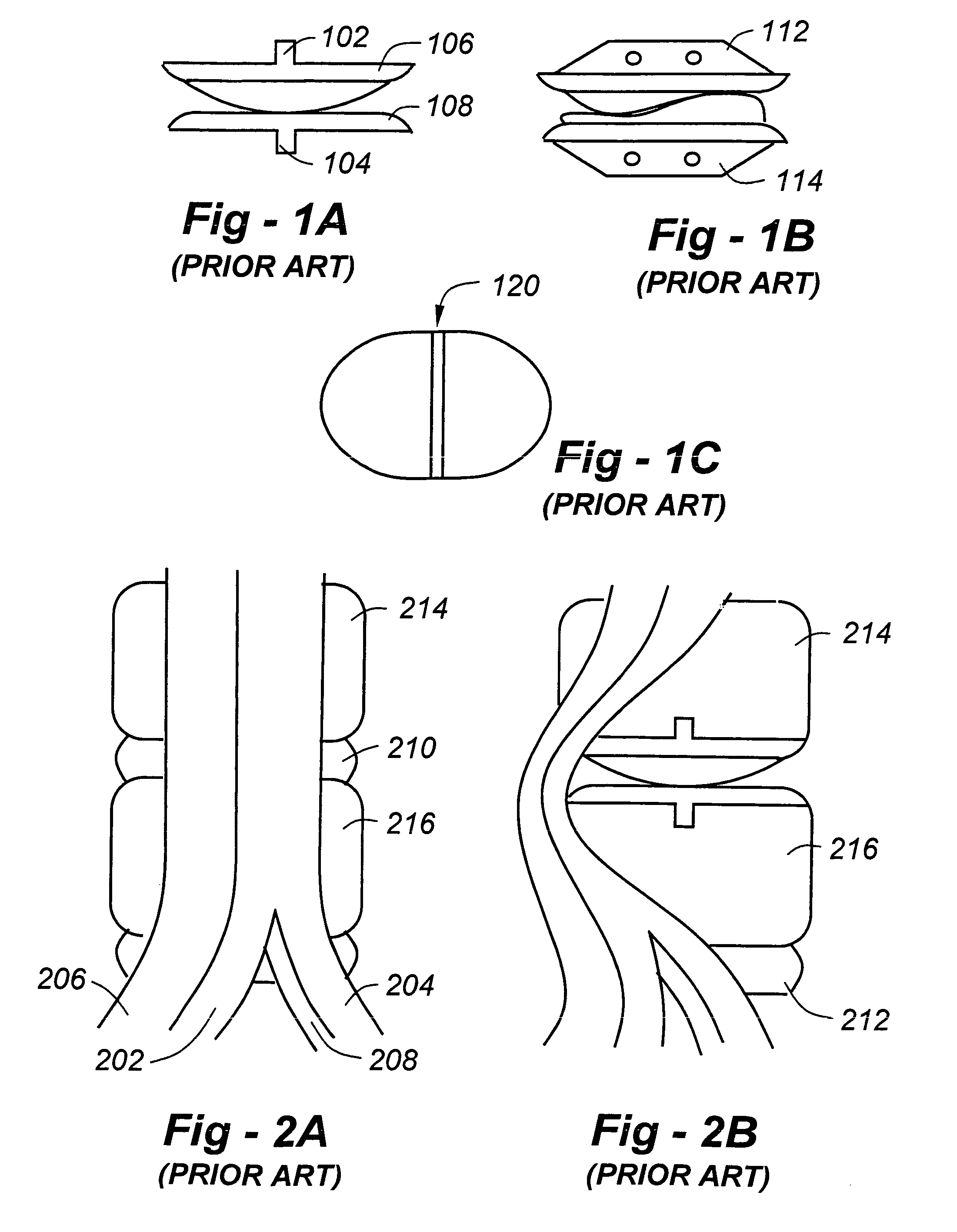
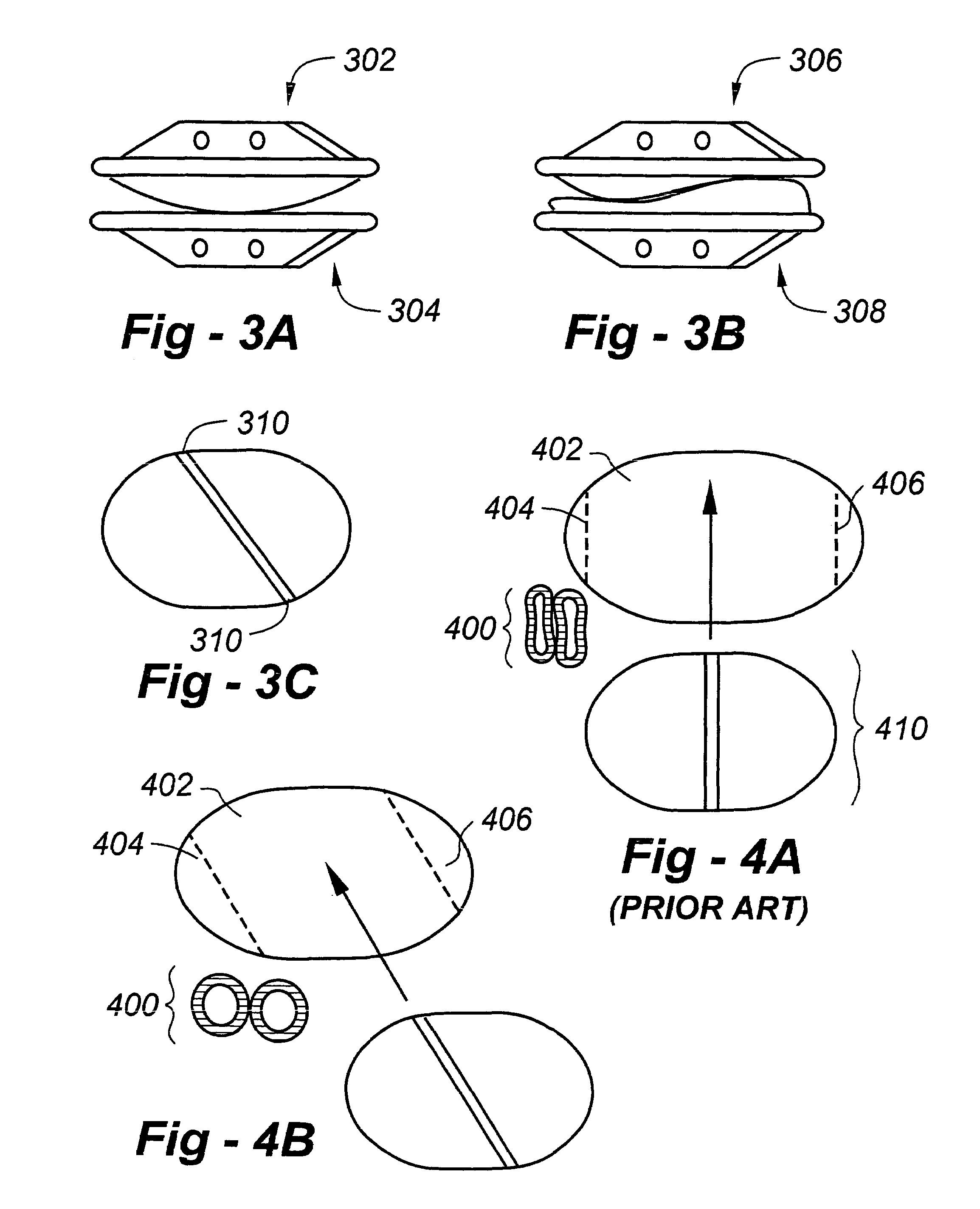
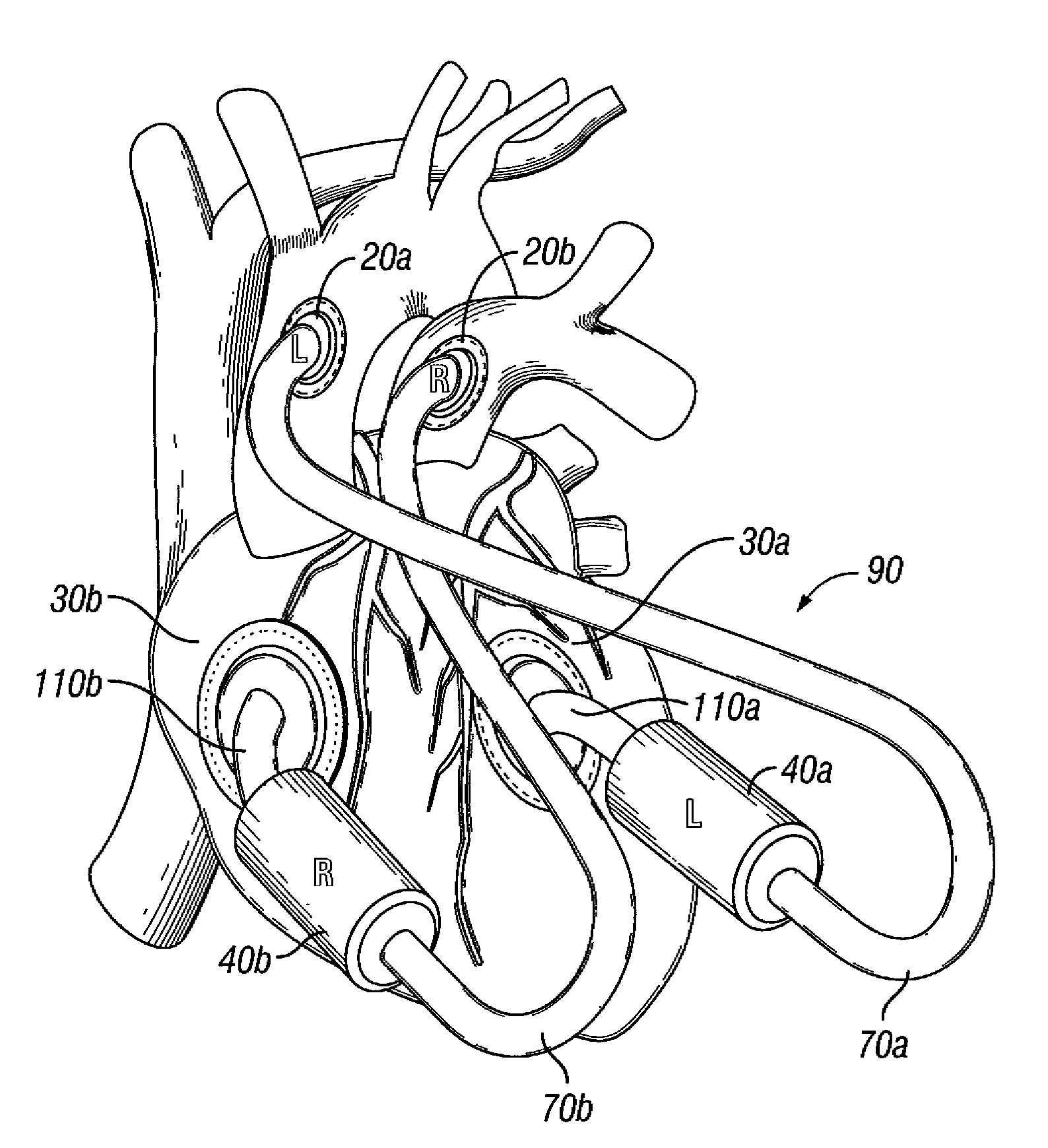
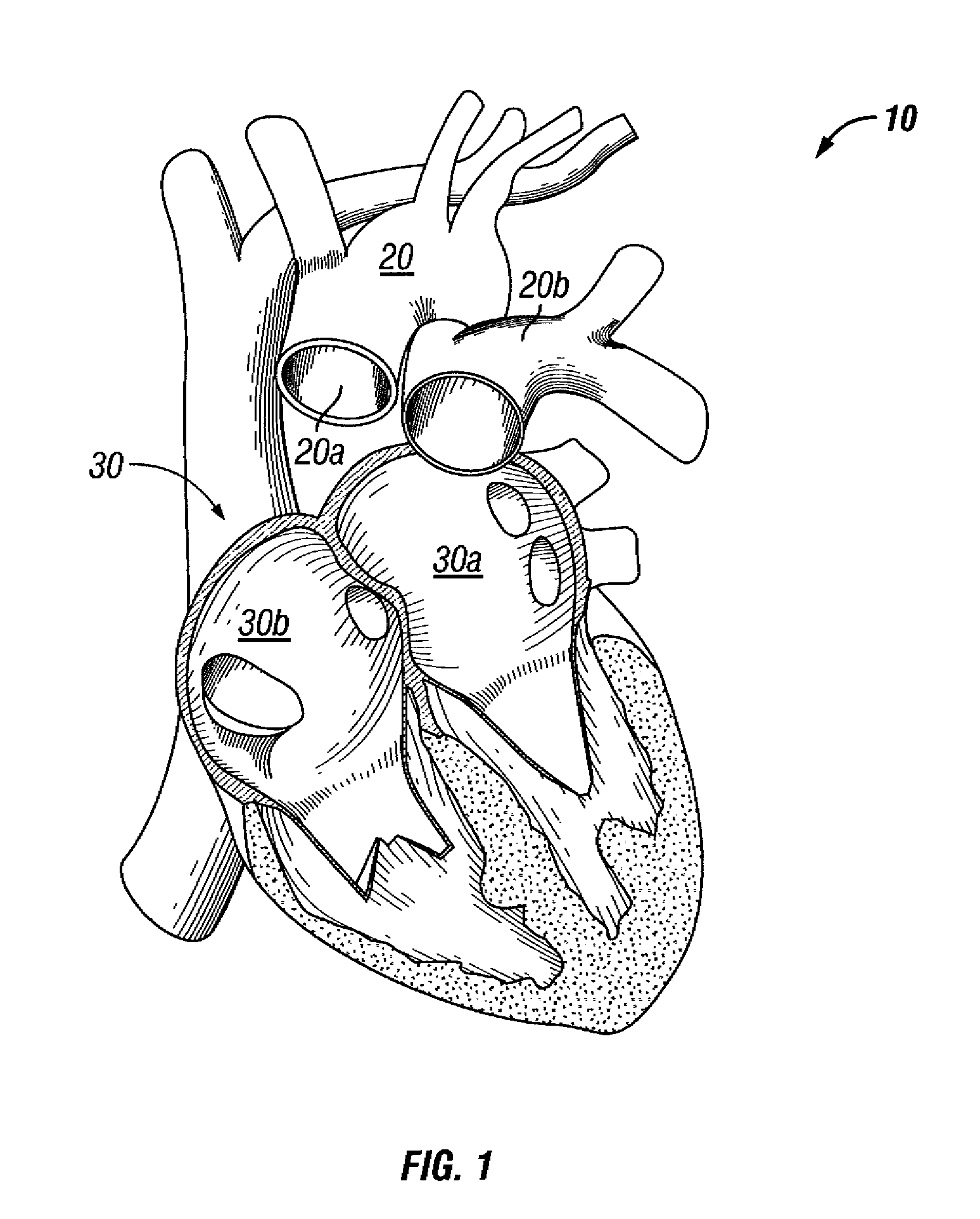
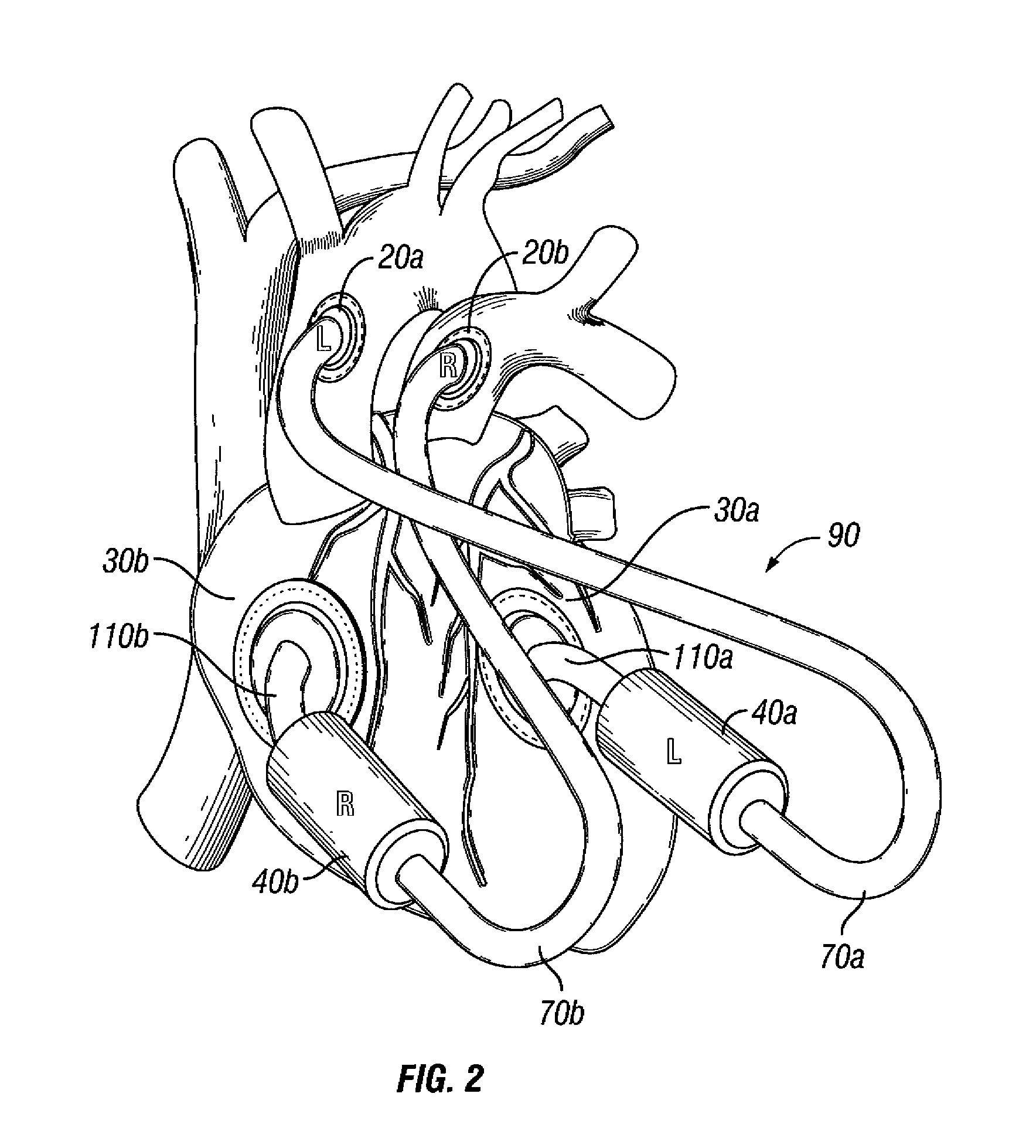
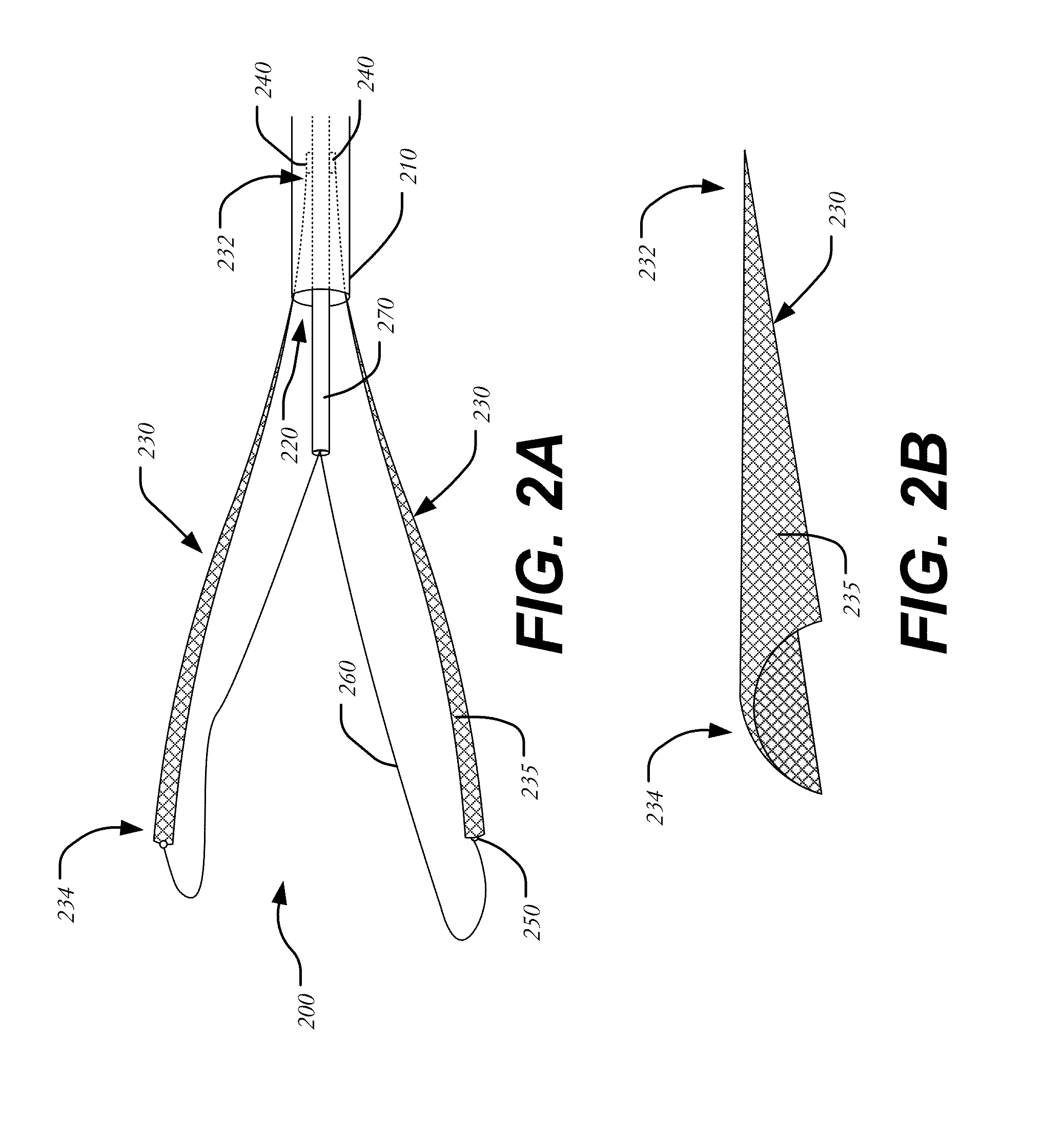
Suspended heart valve devices, systems, and methods for supplementing, repairing, or replacing a native heart valve
InactiveUS20050228495A1Good flexibility and compressibilityImprove foldabilityHeart valvesBlood vesselsHeart chamberBlood vessel
A valve prosthesis is sized and configured to rest within a blood path subject to antegrade and retrograde blood flow. A trestle element on the prosthesis extends across the blood path. A leaflet assembly is suspended from the trestle element and extends into the blood path in alignment with blood flow. At least one mobile leaflet member on the leaflet assembly is sized and configured to assume orientations that change according to blood flow direction. The mobile leaflet member has a first orientation that permits antegrade blood flow and a second orientation that resists retrograde blood flow. The valve prosthesis, when implanted in a heart chamber or great vessel, serves to supplement and / or repair and / or replace native one-way heart valve function.
Owner:AM DISCOVERY
Methods and apparatus for total disc replacements with oblique keels
Artificial disc replacement (ADR) systems with intradiscal components feature non anterior-posterior (A-P) or oblique-oriented keels such that the great vessels do not require as much retraction during insertion. The system may further include guides for aligning the ADR prior to insertion, and for cutting an oblique slot into a vertebral endplate to receive the keel. A screw adapted to penetrate a vertebral body may be used in conjunction with the keel. The screw and keel may converge, diverge or intersect. The screw may further include a mechanism providing a locking relationship with the keel. The system may further including a guide to direct drill bits and screws through holes in the keel. ADRs according to the invention may additionally, independently include a non-symmetrical endplate shaped so as to decrease the risk of injuring the great vessels. By virtue of the invention, a second ADR may be installed at a second level having a keel oriented differently from that of the ADR having an orientation other than anterior-to-posterior.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
Implantable device for telemetric measurement of blood pressure/temperature within the heart
ActiveUS20070118039A1Interference to data transmissionIncreased durabilityCatheterAngiographyCapacitive pressure sensorMinimally invasive procedures
A system and method for the intra corporal, telemetric measuring of blood pressure, particularly within the heart or a great vessel, includes a substantially rigid sensor chip mounted in a holder and an antenna. The holder is anchored within an appropriate location in the cardiovascular system, such as in the cardiac septum, via a catheter or other minimally-invasive procedure to position at least one capacitive pressure sensor on the chip in the blood flow to be sensed. Measured values are transmitted telemetrically from the chip to an extra corporal monitoring device.
Owner:ENDOTRONIX
Method for forming a blood flow in surgically reconstituted segments of the blood circulatory system and devices for carrying out said method
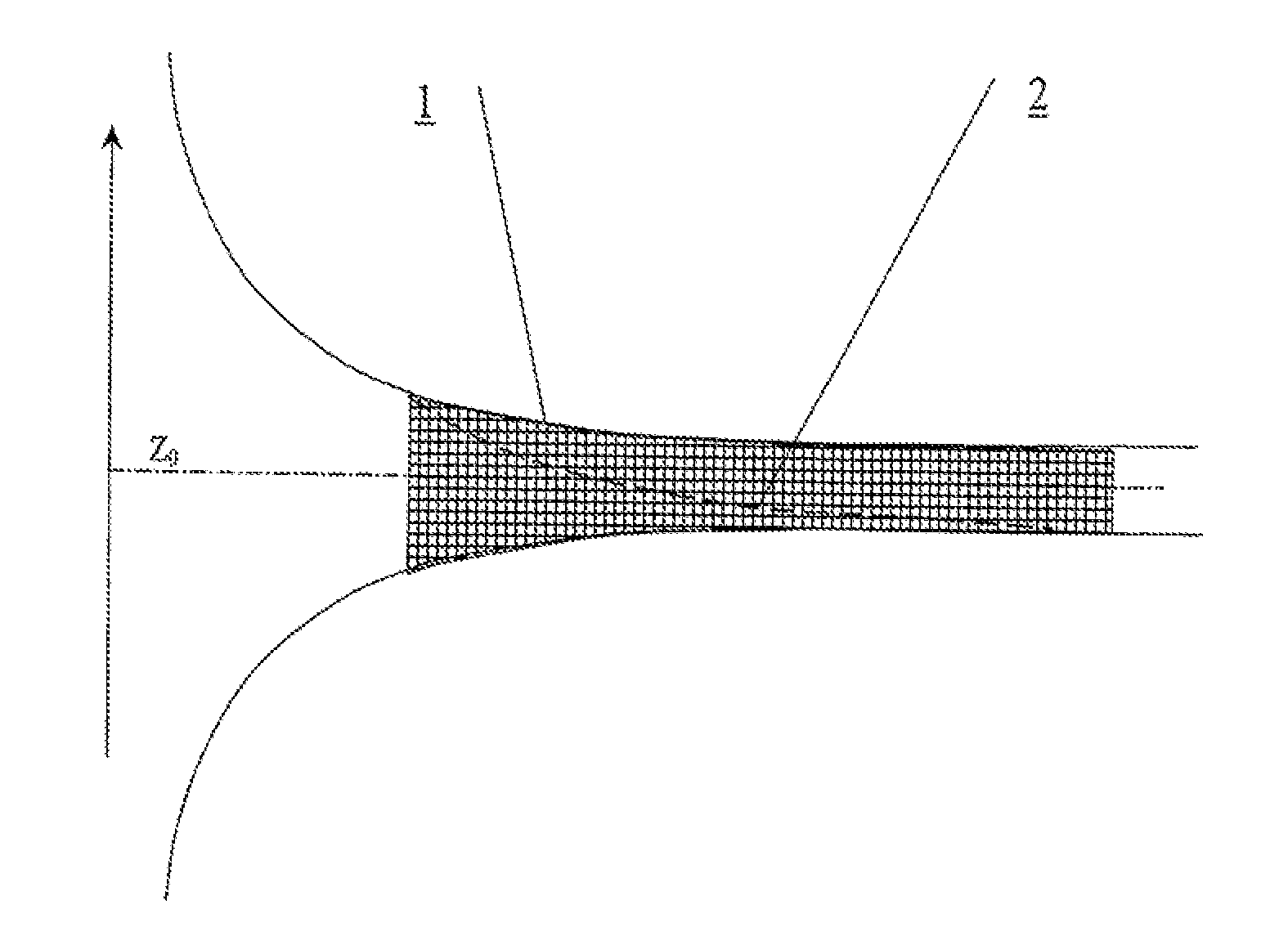
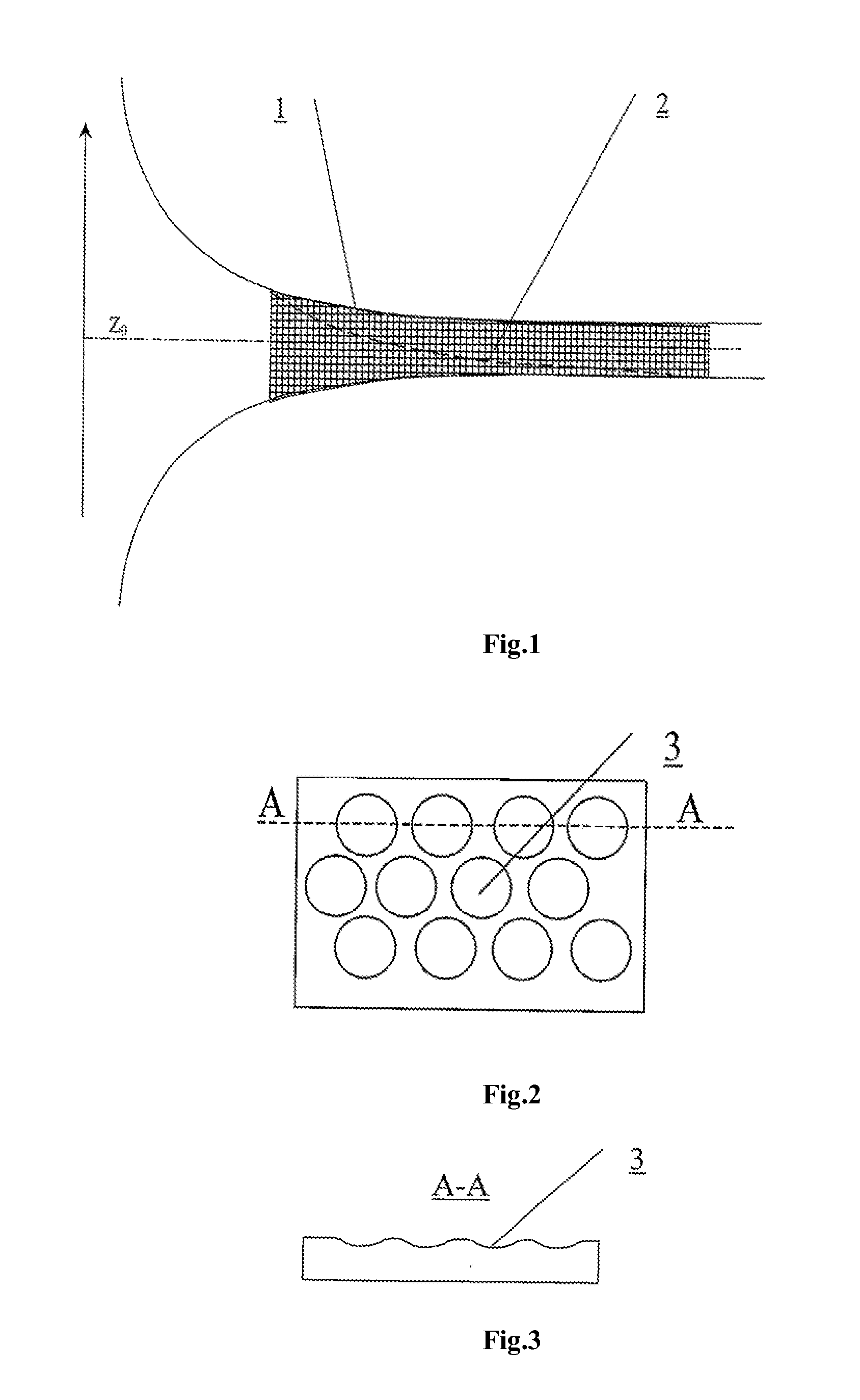
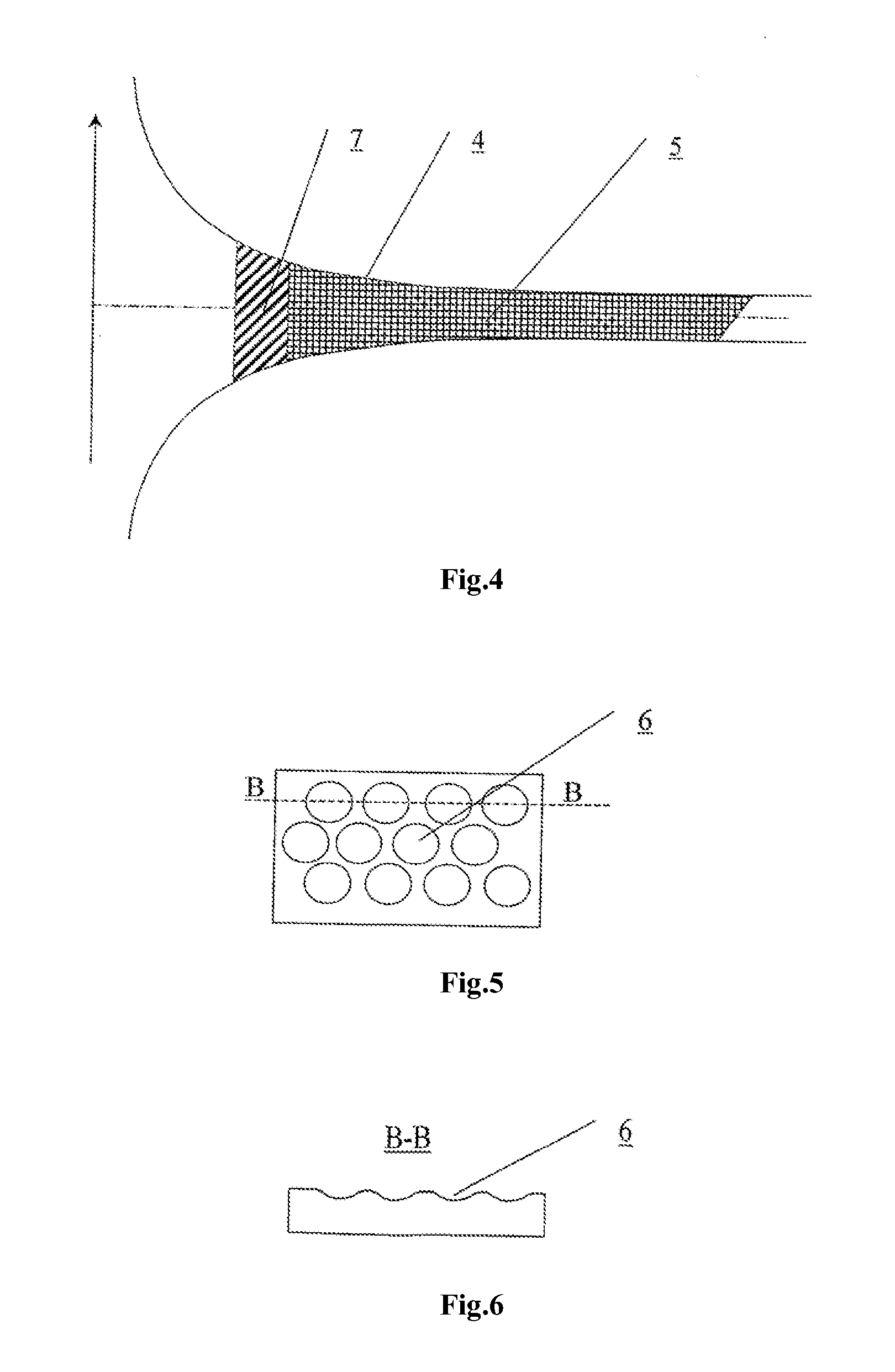
The invention relates to clinical cardiology and cardiovascular surgery. The method for forming a blood flow in research stands and in surgically reconstructed segments of the blood circulation system comprises diagnosing the individual condition of a patient's blood circulation system; measuring the blood flow velocity field in the heart chambers and great vessels; comparing the parameters measured against the physiological norm; determining parameters forming a swirled blood flow; and modeling an individual swirled blood current in the blood circulation system being diagnosed, the streamlined surfaces and guide elements of flow channels of the blood circulation system reconstructed being given shapes conforming to the flow lines of the restored normally swirled blood flow in accordance with formulas:Q(t)=[z+Z0(t)]2(1.1)ϕ=ϕ0+k(t)z(1.2)k(t)=Γ0(t) / 4πQ(t)C0(t)Vz=2C0(t)zVr=-C0(t)rVϕ=Γ0(t)2πr{1-exp[-C0(t)r22v]}(1.3)wherein: Vr, Vz, and Vφ are the radial, longitudinal, and tangential velocities of the swirled current; v is the kinematic viscosity of the medium; φ0 is the initial swirling angle in relation to the flow axis normal; φ, z and r are current values of the angular, longitudinal, and radial coordinates along the flow line; and Q(t), Z0(t), k(t), Γ0(t), and C0(t) are parameters of the swirled blood flow variable over time because of the non-stationary current and corresponding to the individual normal indicators for a physiologically swirled blood flow. The normal indicators are established by routine examination of a representative sample of patients having no changes in the cardiovascular system. A vessel prosthesis comprises a tube having an internal surface in contact with the blood flow provided with a pattern to swirl the blood flow in accordance with formulas (1.1 to 1.3) conforming to a specific localization of the segment being reconstructed. A cannula for para-corporeal perfusion devices comprises a flow channel having an internal surface that is provided with a longitudinal pattern to swirl the blood flow, the shape of the pattern being determined from formulas (1.1 to 1.3), relative to the specific localization of the point where the cannula is inserted into the vessel channel. A heart valve prosthesis comprises one or more shutoff elements arranged symmetrically in the center of a body of round and / or oval cross-section, the streamlined surfaces of the valve being provided with a pattern in accordance with formulas (1.1 to 1.3). A blood pump comprises a flow swirling unit, a flow channel, and valves at the inlet and outlet of the channel, the surface washed over by blood being provided with a relief variable over time in accordance with formulas (1.1 to 1.3). A swirling device comprises an end piece having a streamlined surface provided with guides in the form of ribs, grooves, or blades of a shape defined by formulas (1.1 to 1.3), the swirling angle of the guides relative to the flow axis being varied optionally an operator or by a special-purpose device for modeling different current conditions.
Owner:BOKERIYA LEO ANTONOVICH +2
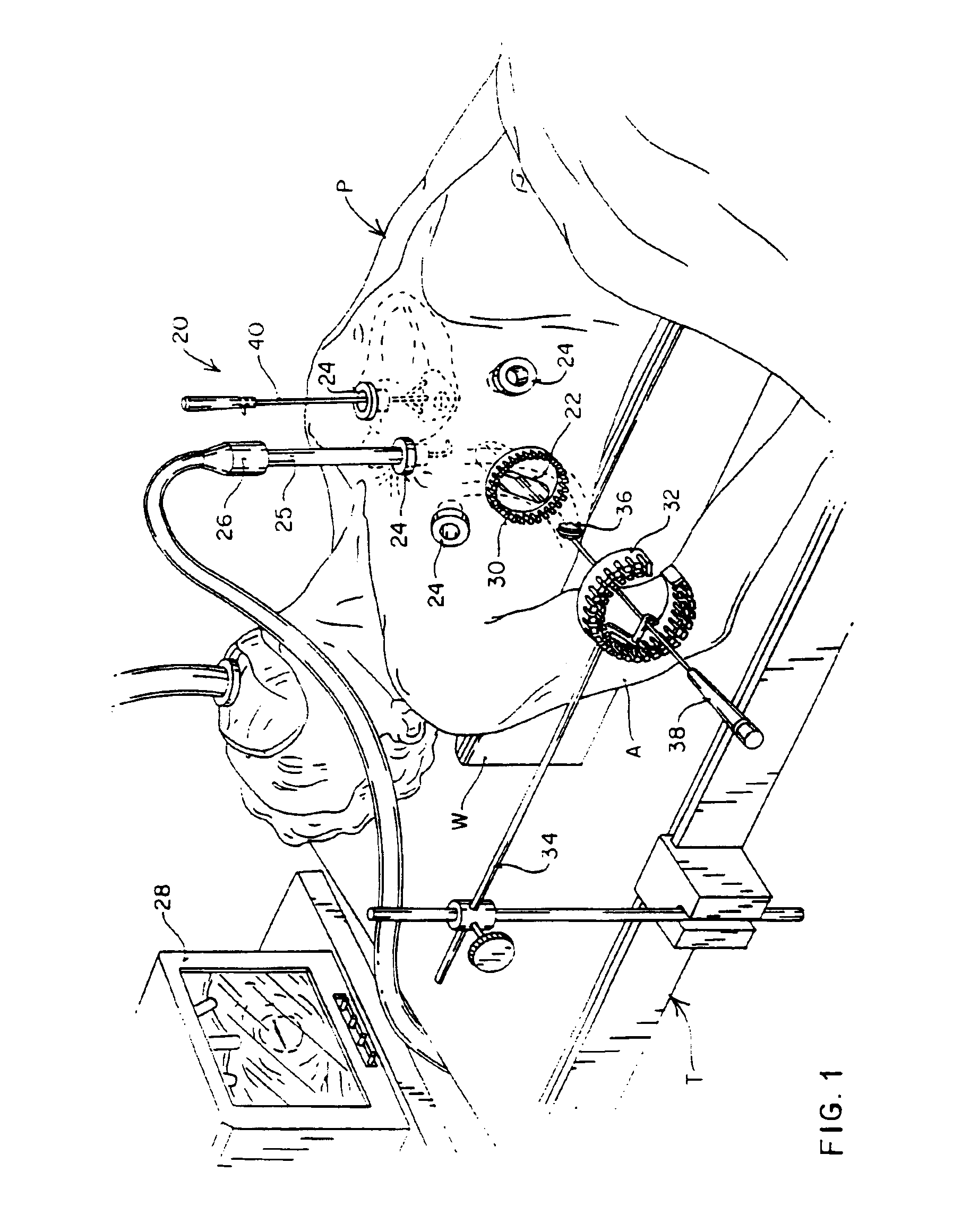
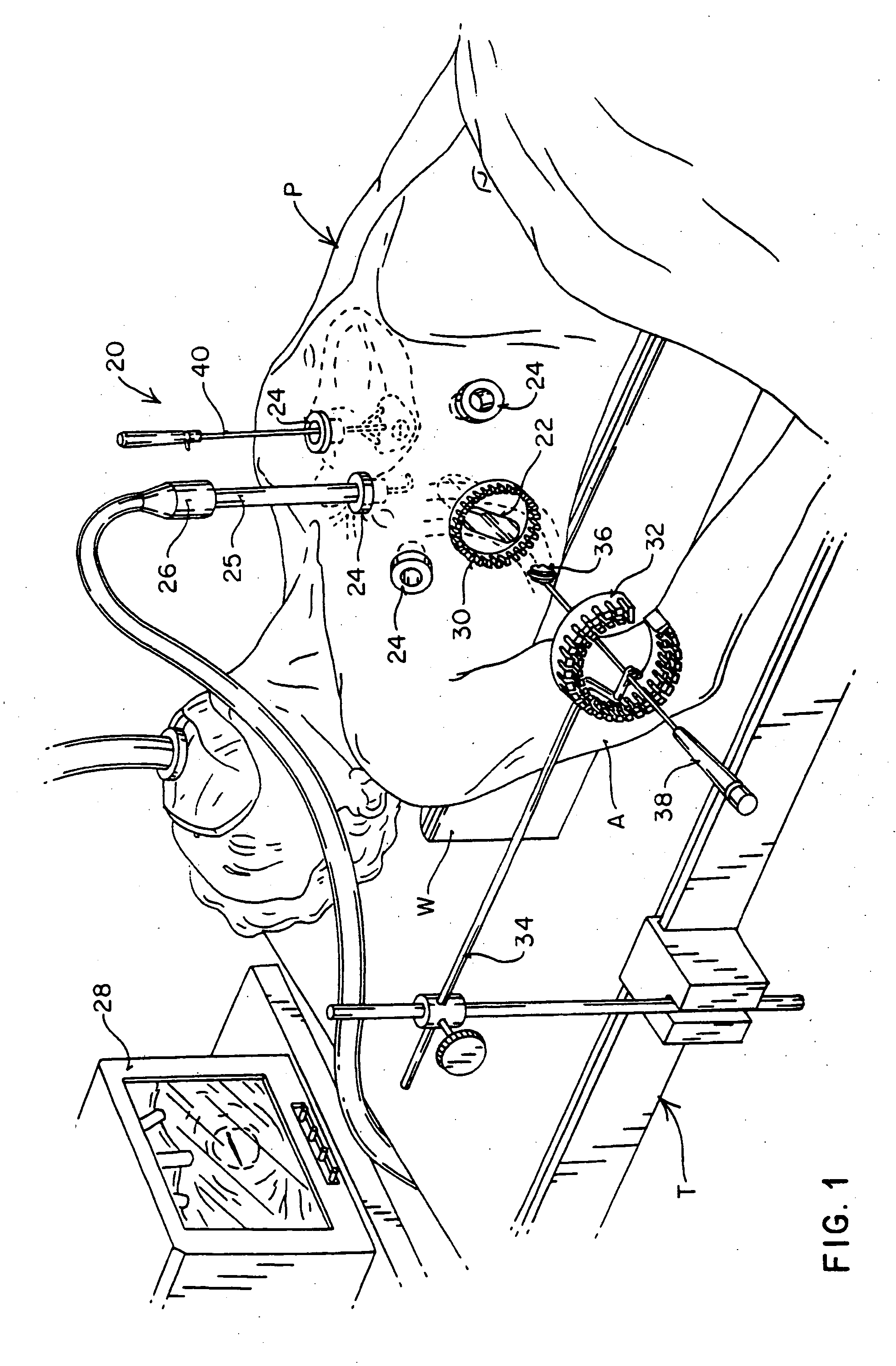
Minimally invasive cardiac surgery procedure
A minimally invasive approach for surgery on portions of the heart and great vessels. A parasternal incision is made extending across a predetermined number of costal cartilages, e.g., a right parasternal incision extending from the lower edge of the second costal cartilage to the superior edge of the fifth costal cartilage. One or more costal cartilages, e.g., the third and fourth, are then excised to provide access to the portion of the heart or great vessels of interest, for example between a point approximately three centimeters above supra annular ridge and the mid ventricular cavity, and a desired procedure completed. A minimally invasive procedure for repair or replacement of the aortic valve is disclosed that includes making a transverse incision of about 10 cm in length over the second or third intercostal space in the thorax of the patient, dividing the sternum transversely following the incision, retracting the transversely divided sternum, exposing the ascending aorta, and incising the ascending aorta to provide access to an area adjacent the aortic valve.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
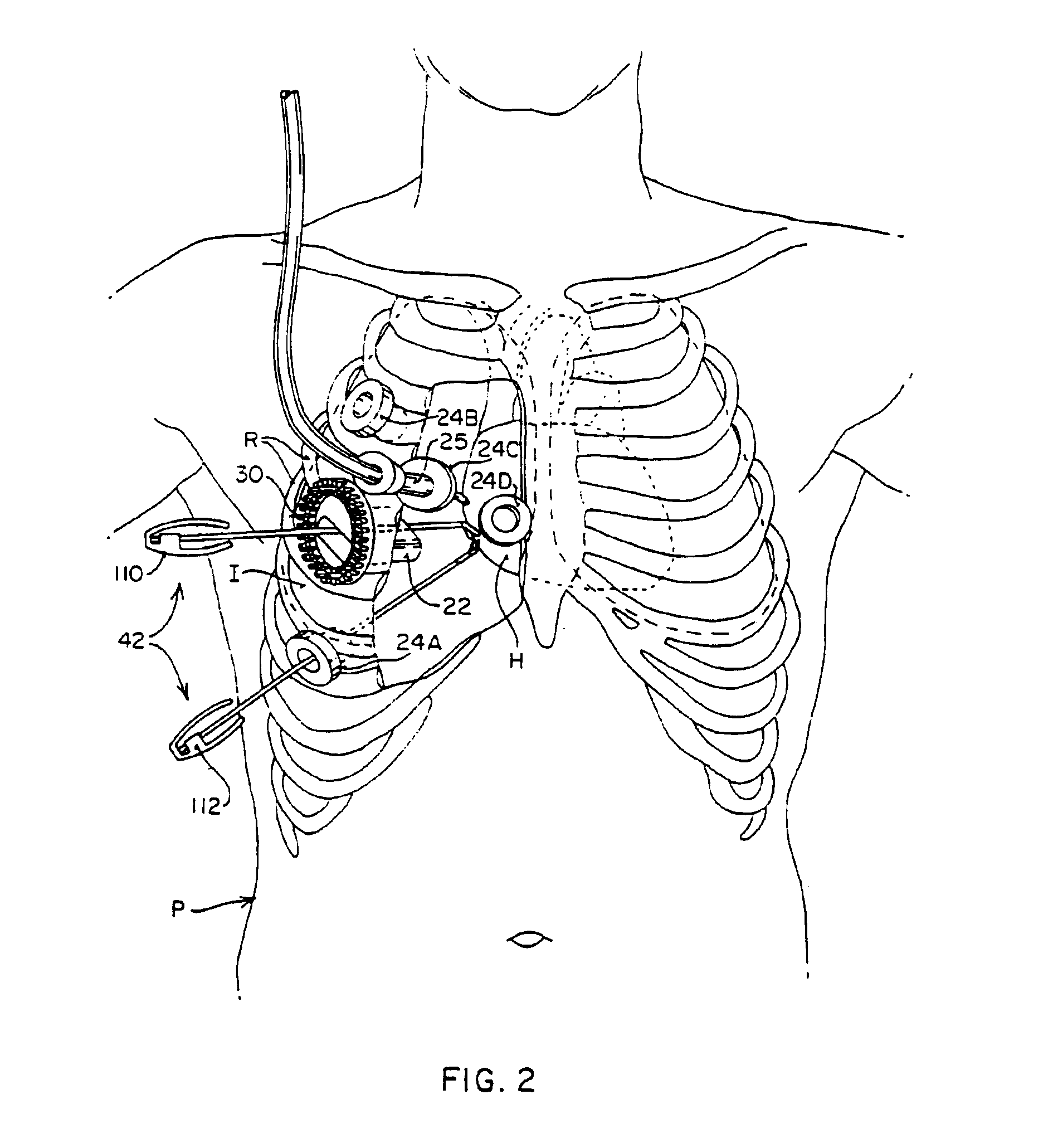
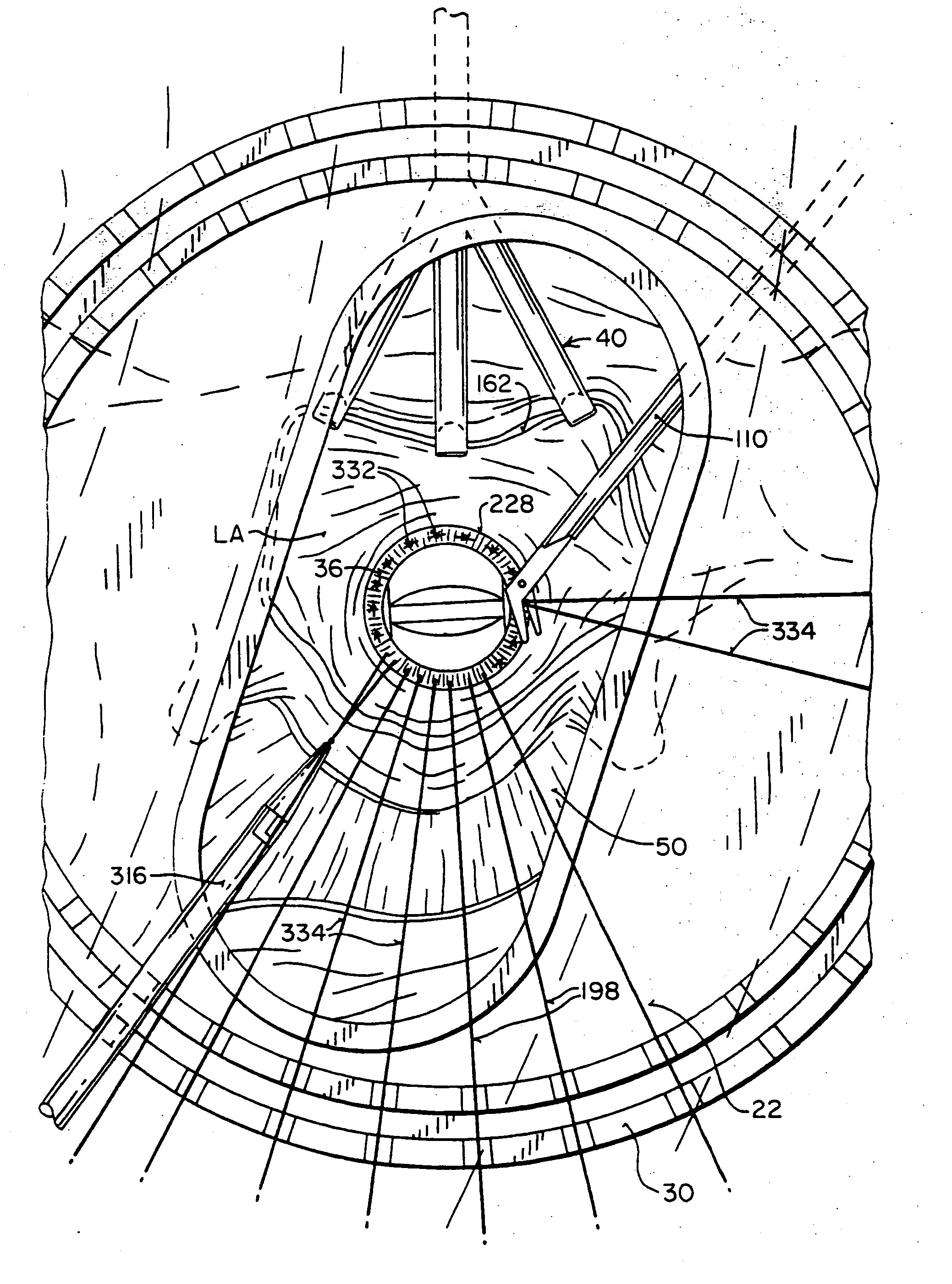
Devices and methods for intracardiac procedures
InactiveUS6899704B2Easy to replaceEasy to interveneSuture equipmentsCannulasAtrial cavityThoracic cavity
The invention provides devices and methods for performing less-invasive surgical procedures within an organ or vessel. In an exemplary embodiment, the invention provides a method of closed-chest surgical intervention within an internal cavity of a patient's heart or great vessel. According to the method, the patient's heart is arrested and cardiopulmonary bypass is established. A scope extending through a percutaneous intercostal penetration in the patient's chest is used to view an internal portion of the patient's chest. An internal penetration is formed in a wall of the heart or great vessel using cutting means introduced through a percutaneous penetration in an intercostal space in the patient's chest. An interventional tool is then introduced, usually through a cannula positioned in a percutaneous intercostal penetration. The interventional tool is inserted through the internal penetration in the heart or great vessel to perform a surgical procedure within the internal cavity under visualization by means of the scope. In a preferred embodiment, a cutting tool is introduced into the patient's left atrium from a right portion of the patient's chest to remove the patient's mitral valve. A replacement valve is then introduced through an intercostal space in the right portion of the chest and through the internal penetration in the heart, and the replacement valve is attached in the mitral valve position.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Devices and methods for intracardiac procedures
InactiveUS20060052802A1Easy to replaceLess-invasiveSuture equipmentsCannulasCardiac wallLess invasive
The invention provides devices and methods for performing less-invasive surgical procedures within an organ or vessel. In an exemplary embodiment, the invention provides a method of closed-chest surgical intervention within an internal cavity of a patient's heart or great vessel. According to the method, the patient's heart is arrested and cardiopulmonary bypass is established. A scope extending through a percutaneous intercostal penetration in the patient's chest is used to view an internal portion of the patient's chest. An internal penetration is formed in a wall of the heart or great vessel using cutting means introduced through a percutaneous penetration in an intercostal space in the patient's chest. An interventional tool is then introduced, usually through a cannula positioned in a percutaneous intercostal penetration. The interventional tool is inserted through the internal penetration in the heart or great vessel to perform a surgical procedure within the internal cavity under visualization by means of the scope. In a preferred embodiment, a cutting tool is introduced into the patient's left atrium from a right portion of the patient's chest to remove the patient's mitral valve. A replacement valve is then introduced through an intercostal space in the right portion of the chest and through the internal penetration in the heart, and the replacement valve is attached in the mitral valve position.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Methods and apparatus for artificial disc replacement (ADR) insertion and other surgical procedures
InactiveUS20060025778A1Safer and preciseAccurate placementDiagnosticsExcision instrumentsDistractionEngineering
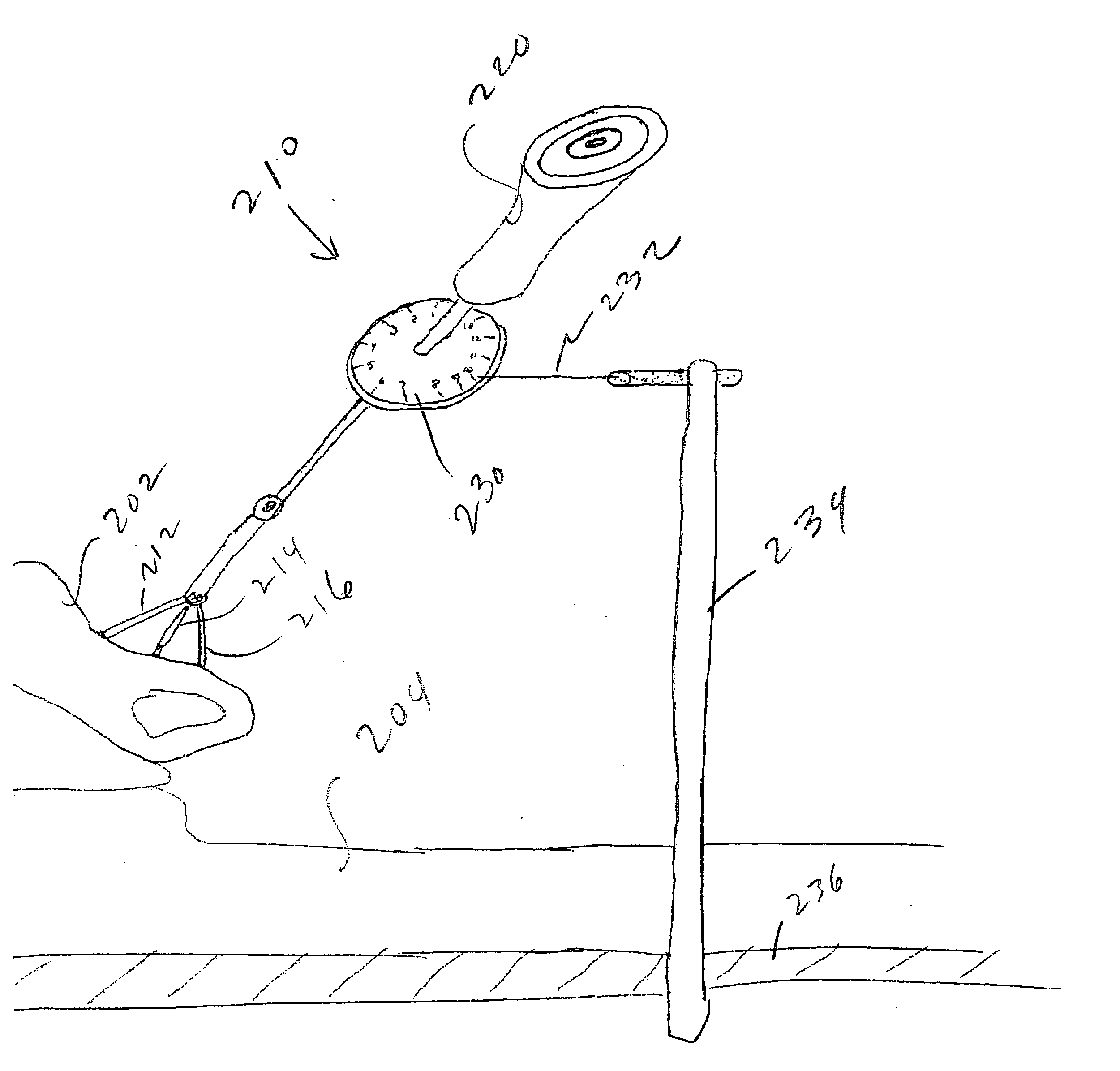
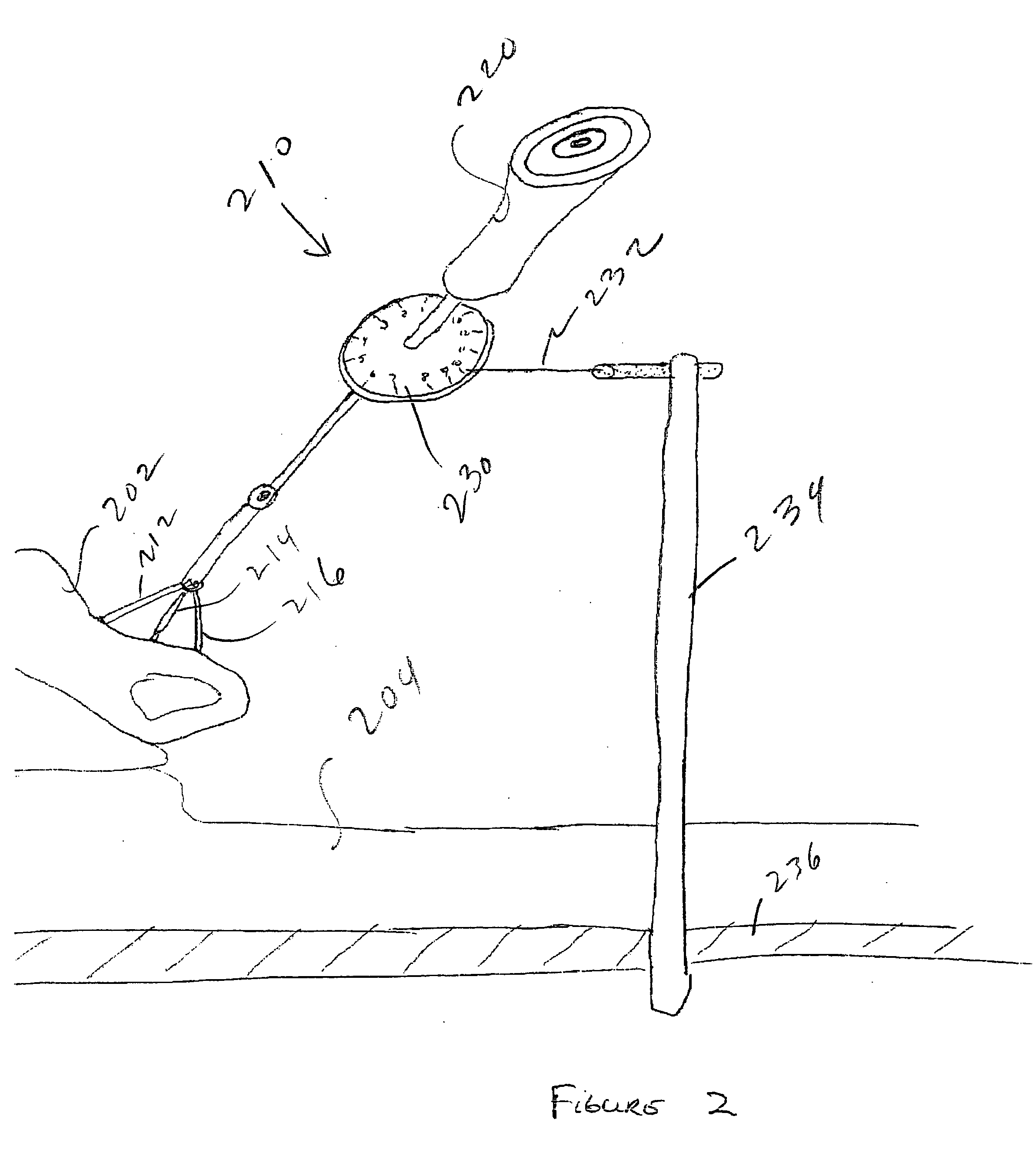
Improved methods and apparatus render ADR insertion safer and more precise. Certain surgical instruments according to the invention include a level enabling a user to align the instrument for proper placement of a surgical implant. A different surgical instrument includes two or more scopes mounted relative to the instrument permitting a user to simultaneously view more than one side of the instrument. A device for use with a surgical instrument having a long shaft includes a holder that surrounds at least a portion of the shaft allowing a user to control the instrument with both hands. A further surgical instrument comprises a set of retractors and one or more guards placed over the retractors for protecting the great vessels, nerves or other delicate structures during a surgical procedure. Surgical apparatus according to the invention comprises a platform mountable to an operating room table over a patient undergoing a surgical procedure, enabling a user to place their hands or attach an instrument while operating. Different surgical instruments include an indicator showing angular displacement or a wedge-shaped portion used for disc distraction. Also disclosed are blades designed for use with a power tool featuring a cutting edge configured such that rapid oscillation of the cutting tool reduces the pressure a user must apply the tool.
Owner:ANOVA
Protecting biological structures, including the great vessels, particularly during spinal surgery
InactiveUS20050126576A1Improve barrier propertiesAvoid formingRestraining devicesSurgeryIntracranial surgeryThoracic bone
Natural and / or synthetic materials to form a strong barrier between the skeletal system and the great vessels. In the preferred embodiments, a natural or synthetic material is used to prevent scar tissue from forming around the vessels and / or to act as barrier placed between the vessels and the skeletal system, including the spine. Devices according to the invention may also be used over the dura and nerves following laminectomy procedures, between the sternum and the pericardium or heart following cardiac procedures, in intra-abdominal procedures such as intestinal or vascular surgery, over the brain in intra-cranial surgery, over the ovaries or other organs or tissues in the female genitourinary system, over the prostate or other organ or tissues in the male genitourinary system, or in other surgeries on humans or animals.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
Method and apparatus for total disc replacements with oblique keels
Artificial disc replacement (ADR) systems with intradiscal components feature non anterior-posterior (A-P) or oblique-oriented keels such that the great vessels do not require as much retraction during insertion. The system may further include guides for aligning the ADR prior to insertion, and for cutting an oblique slot into a vertebral endplate to receive the keel. A screw adapted to penetrate a vertebral body may be used in conjunction with the keel. The screw and keel may converge, diverge or intersect. The screw may further include a mechanism providing a locking relationship with the keel. The system may further including a guide to direct drill bits and screws through holes in the keel. ADRs according to the invention may additionally, independently include a non-symmetrical endplate shaped so as to decrease the risk of injuring the great vessels. By virtue of the invention, a second ADR may be installed at a second level having a keel oriented differently from that of the ADR having an orientation other than anterior-to-posterior.
Owner:FERREE BRET
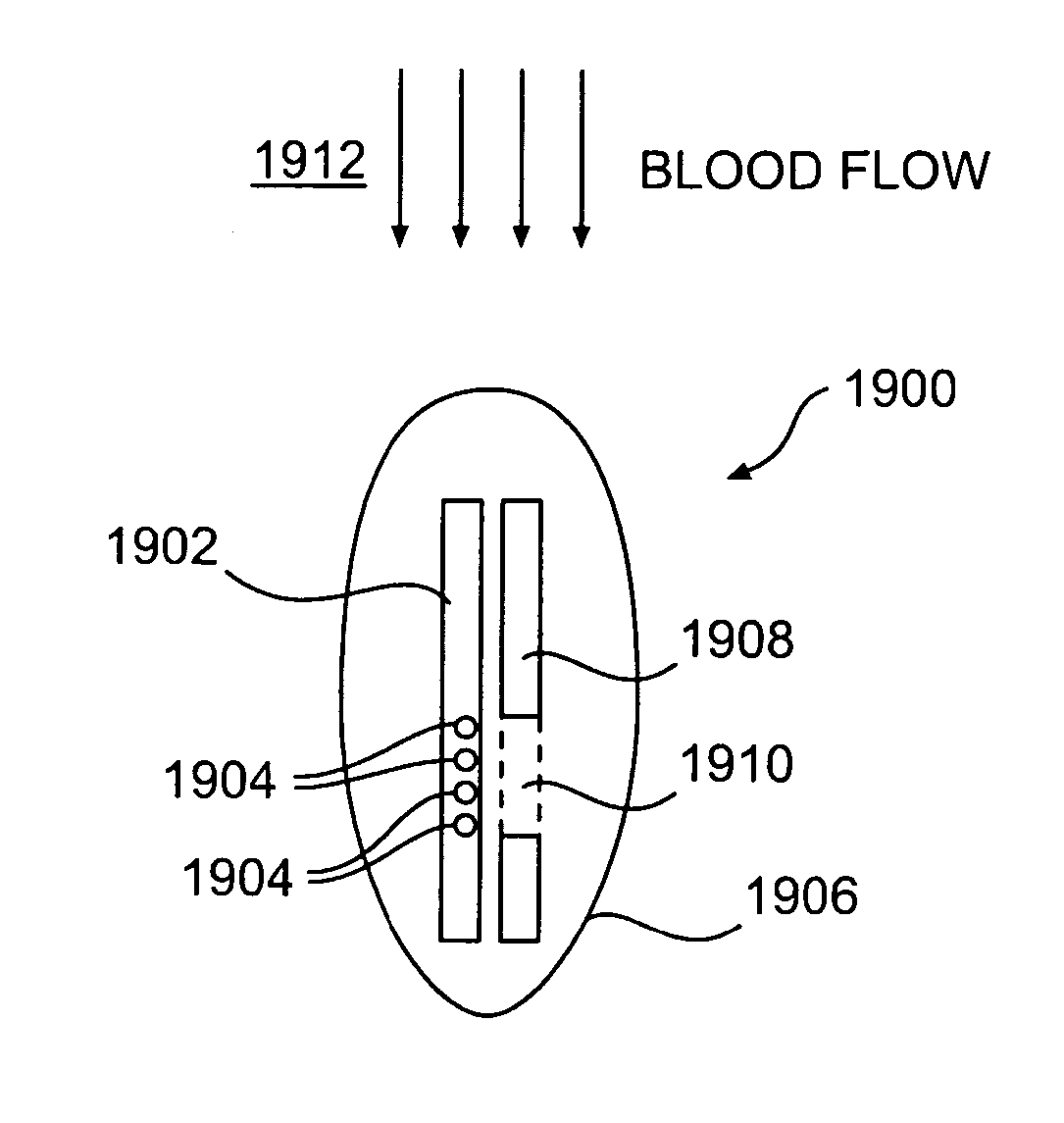
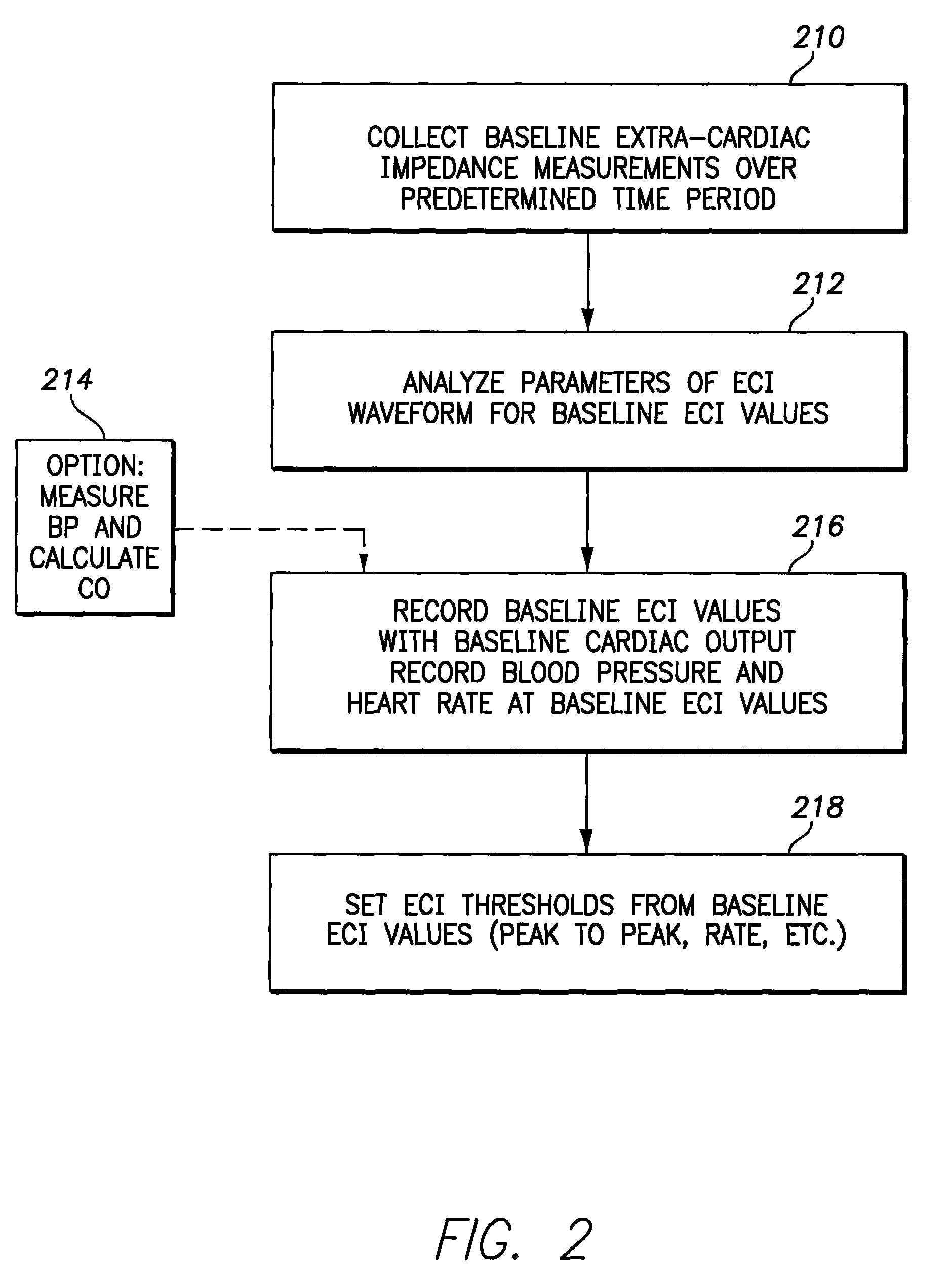
Extra-cardiac impedance based hemodynamic assessment method and system
A medical device is provided that comprises a lead assembly configured to be at least partially located proximate to the heart. The lead assembly includes an extra-cardiac (EC) electrode to be positioned proximate to at least one of a superior vena cava (SVC) and a left ventricle (LV) of a heart. The lead assembly includes a subcutaneous remote-cardiac (RC) electrode configured to be located remote from the heart such that at least a portion of the greater vessels are interposed between the RC electrode and the EC electrode to establish an extra-cardiac impedance (ECI) vector. The processor module measures extra-cardiac impedance along the ECI vector to obtain ECI measurements. The processor module assesses a hemodynamic performance based on the ECI measurements.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
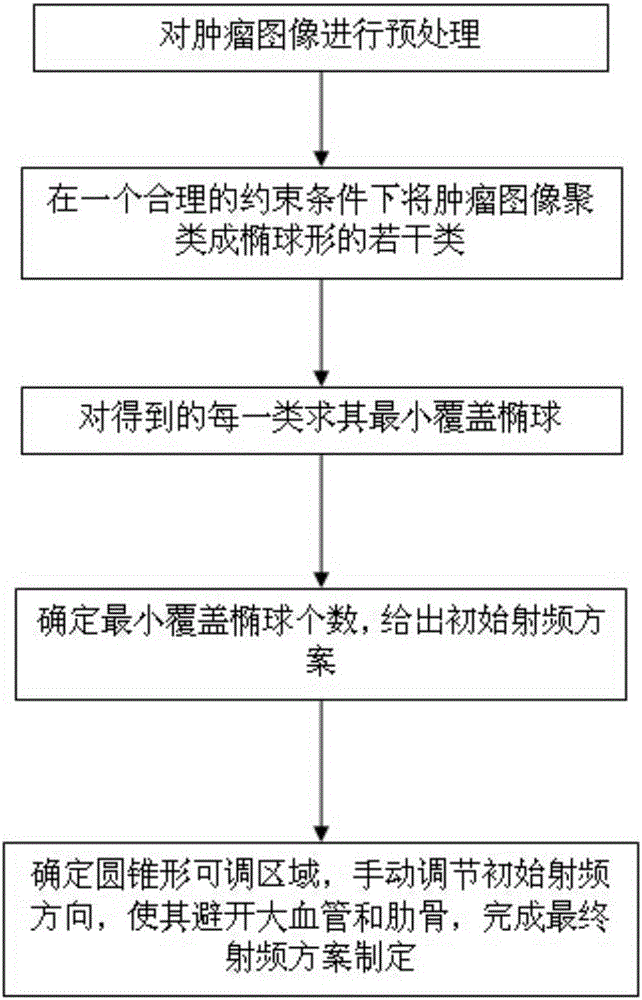
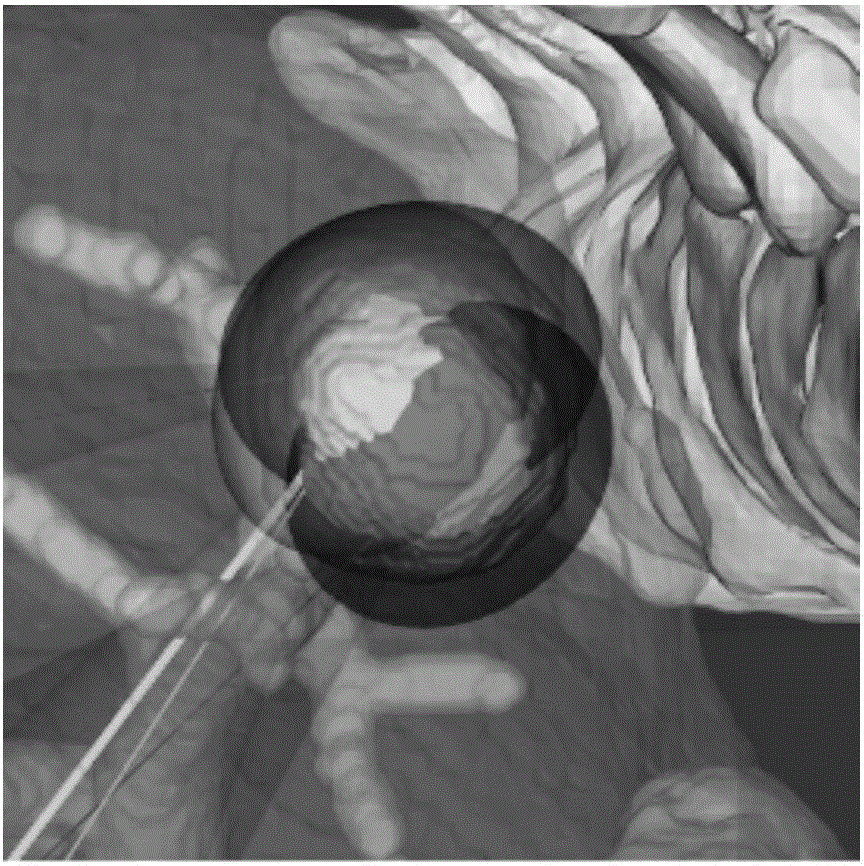
Method for precisely simulating radiofrequency ablation technology by utilizing ellipsoid to cover tumor
ActiveCN105997245AReduce harmAccurate and effective implementationImage enhancementImage analysisAbnormal tissue growthRf ablation
The invention relates to a liver tumor radiofrequency ablation technology, and aims at providing a method for precisely simulating radiofrequency ablation technology by utilizing ellipsoid to cover tumor. The method for precisely simulating radiofrequency ablation technology by utilizing ellipsoid to cover tumor comprises the following steps: preprocessing tumor images; clustering the tumor images into a plurality of ellipsoidal subclasses under reasonable constraint conditions; calculating the minimal coverage ellipsoids of each obtained class; giving an initial radiofrequency scheme by utilizing the number of the minimal ellipsoids automatically determined; determining an adjustable conical area, and manually adjusting the initial radiofrequency direction so as to completely keep away from great vessels and ribs, thus completing the establishment of the final radiofrequency scheme. According to the method, the purpose of designing the radiofrequency treatment scheme before operation can be realized, three-dimensional navigation can be conducted during operation, the adopted optimized algorithm can help a doctor more precisely and efficiently do operation, the harm of the operation to normal tissues can be reduced as far as possible, and the peripheral organs can be avoided, so that the radiofrequency ablation operation is safer and more effective.
Owner:中关村科技租赁股份有限公司
Total artificial heart system for auto-regulating flow and pressure
InactiveUS8226712B1Reduce resistanceMinimizing pressure gradientControl devicesBlood pumpsWhole bodyContinuous flow
The present invention is TAH system for auto-regulating blood flow and maintaining the asymmetric pressure balance in the mammalian cardiovascular system by decreasing the resistance in blood flow and minimizing the pressure gradients to exploit the in-flow pressure sensitivities of continuous flow pumps. The system further includes laminar flow generating manifolds connected to the atrium at one end and attached to pumps linked to the great vessels at the other, such that the in-let flow sensitivities of the pumps are maximized to auto-regulate blood flow, providing adequate pulmonary and systemic arterial flow to support normal metabolism and end-organ function and maintain the appropriate asymmetric physiologic pressure balance between the systemic and pulmonary systems of the mammalian cardiovascular system.
Owner:ALPHA DEV
Implantable pressure monitor
ActiveUS7682313B2Reduce and eliminate data transmission interferenceMinimize turbulenceCatheterAngiographyCapacitive pressure sensorMinimally invasive procedures
A system and method for the intra corporal, telemetric measuring of blood pressure, particularly within the heart or a great vessel, includes a substantially rigid sensor chip mounted in a holder and an antenna. The holder is anchored within an appropriate location in the cardiovascular system, such as in the cardiac septum, via a catheter or other minimally-invasive procedure to position at least one capacitive pressure sensor on the chip in the blood flow to be sensed. Measured values are transmitted telemetrically from the chip to an extra corporal monitoring device.
Owner:ENDOTRONIX
Wearable multi-field radiation whole-body hyperthermia device
ActiveCN101856290AIncrease body temperatureIncreased heating radiation doseTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingMulti fieldWhole body
The invention relates to medical healthcare equipment, in particular to a wearable multi-field radiation whole-body hyperthermia device. Heat is introduced into a radiating target (i.e., a great vessel) by means of probe beams, and the energy of ultrasound, infrared, laser, microwave, radio frequency and electromagnetic probes at each frequency range is introduced into a vascular circulation system through the radiation probe network composed of probe beams distributed on an attachment in the form of optimum biological heat absorption, and then heat is transferred throughout the body through a hemoperfusion method, so that the vivo tissue is rapidly heated through conduction of biological heat in the tissue. The device has the characteristics of high thermal utilization ratio, high blood flow rate and high specific heat, and thermal convection is rapidly conducted between the radiant heat and the tissue to realize whole-body hyperthermia, therefore, the device not only can realize the purposes of uniformity of the machine body and rapid temperature rise, but also avoid the phenomenon of local overheating, simultaneously, has the accessibility of a wearable device and is a high-efficiency hyperthermia equipment without ache.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
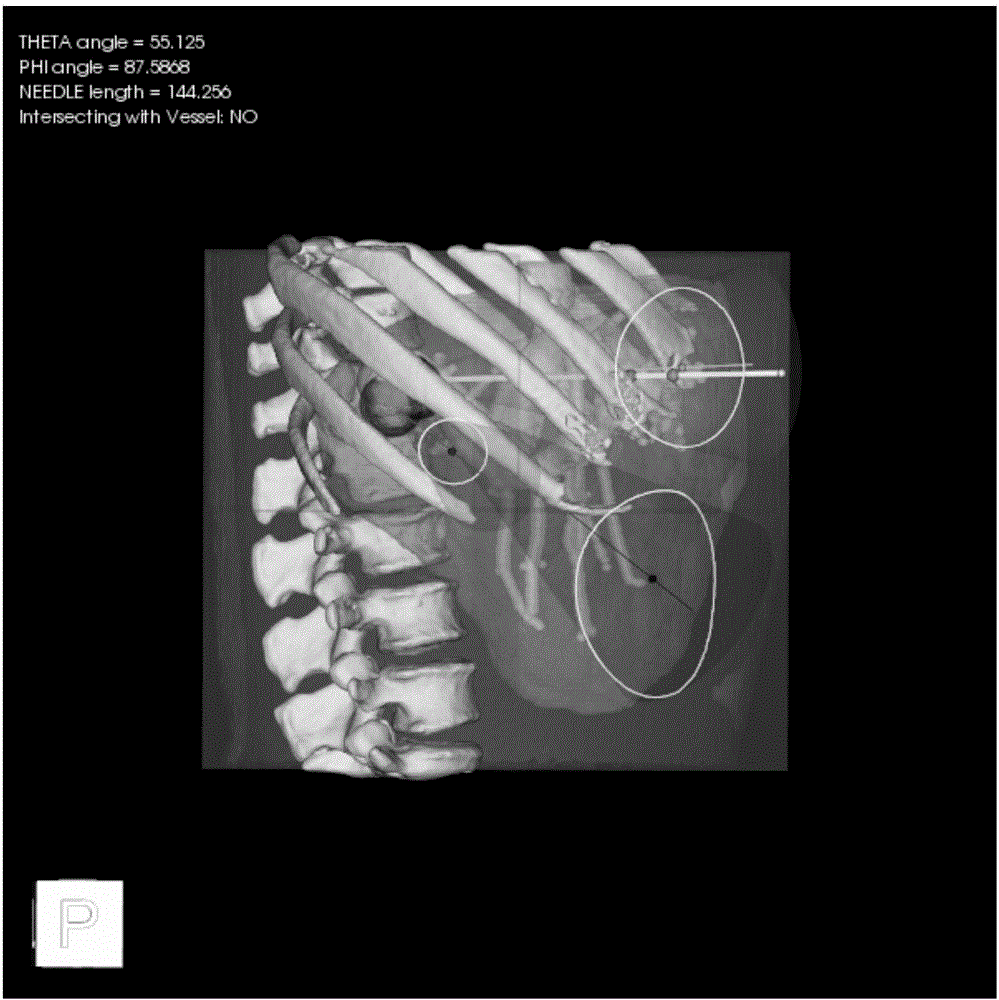
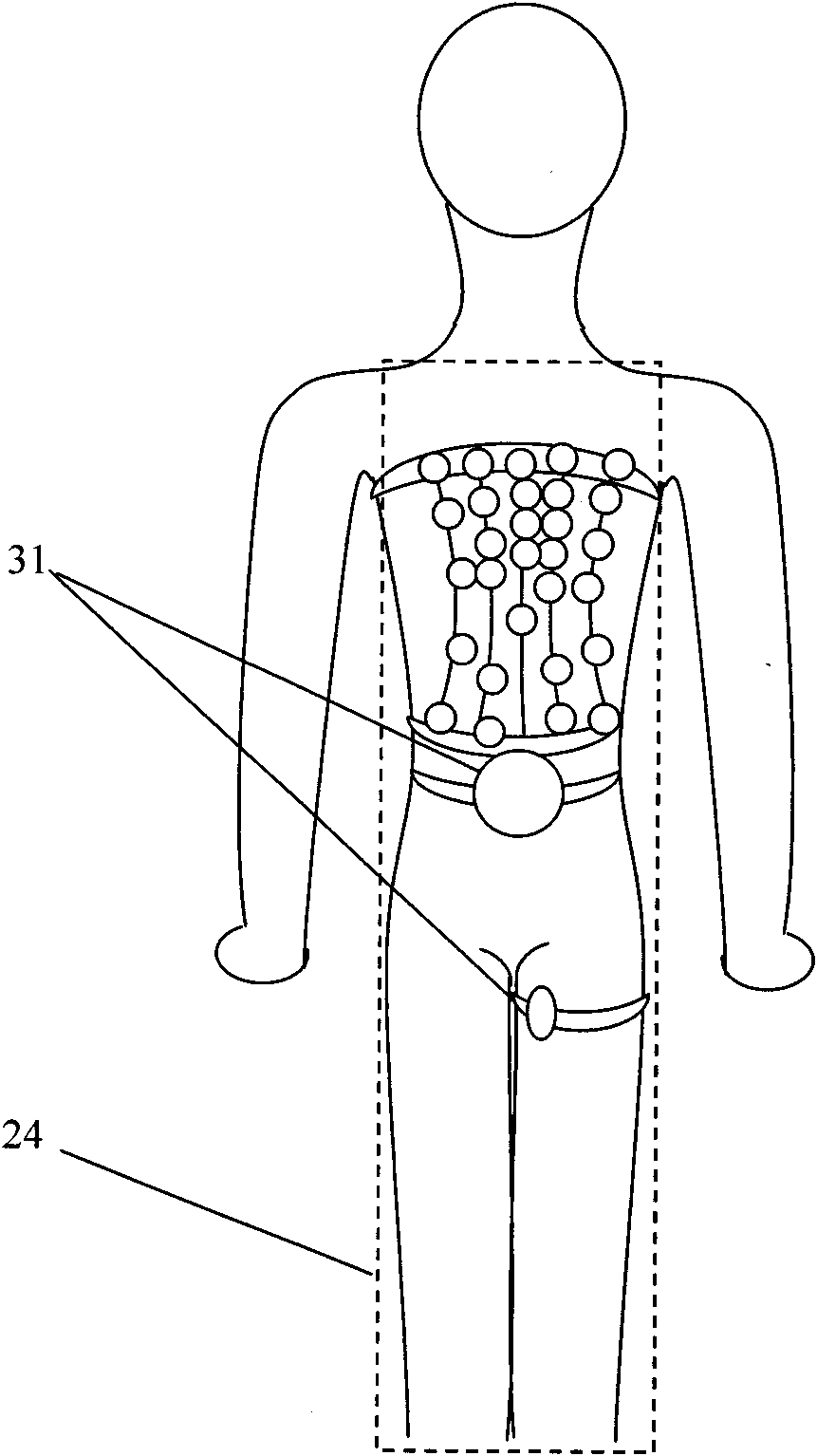
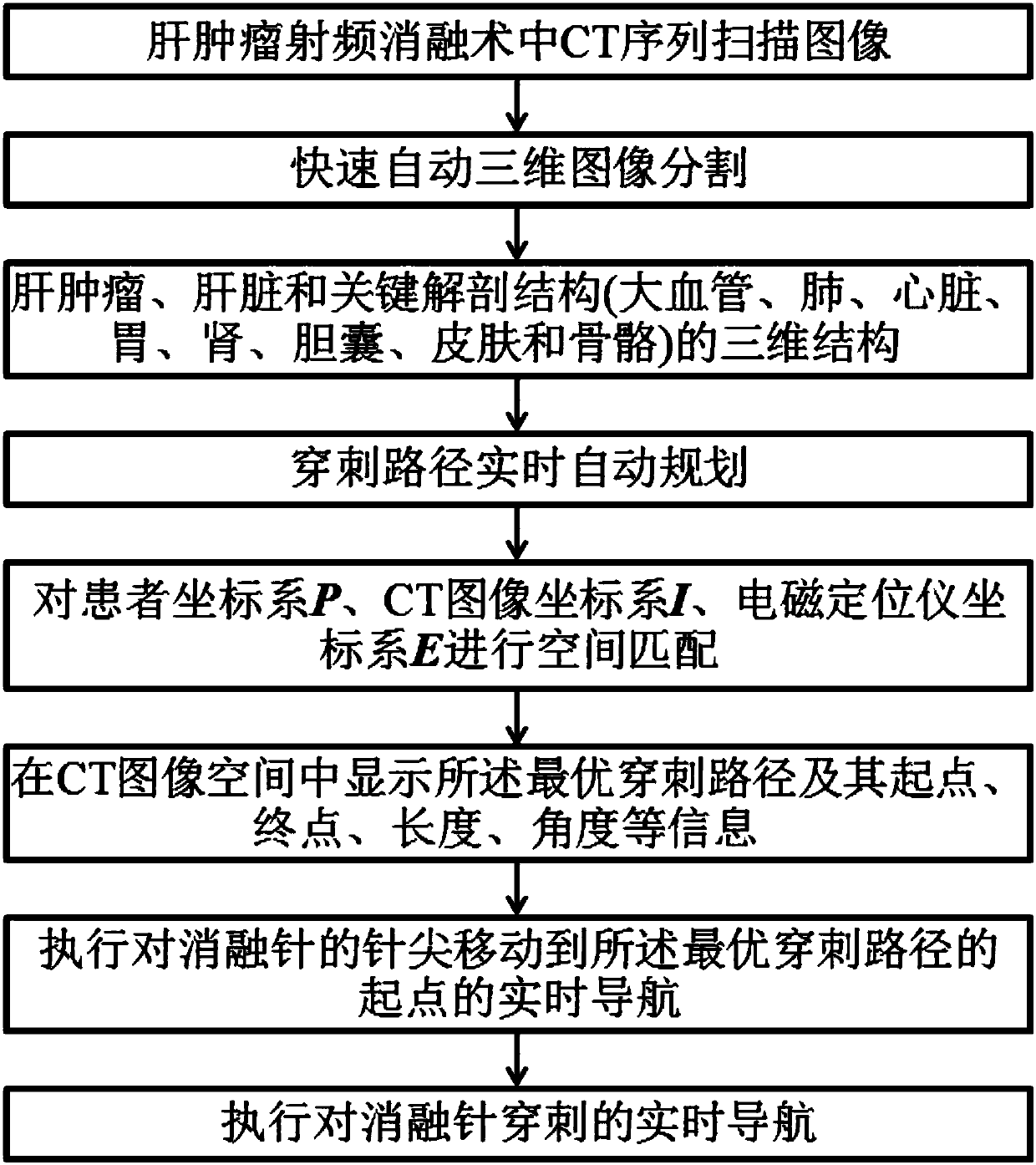
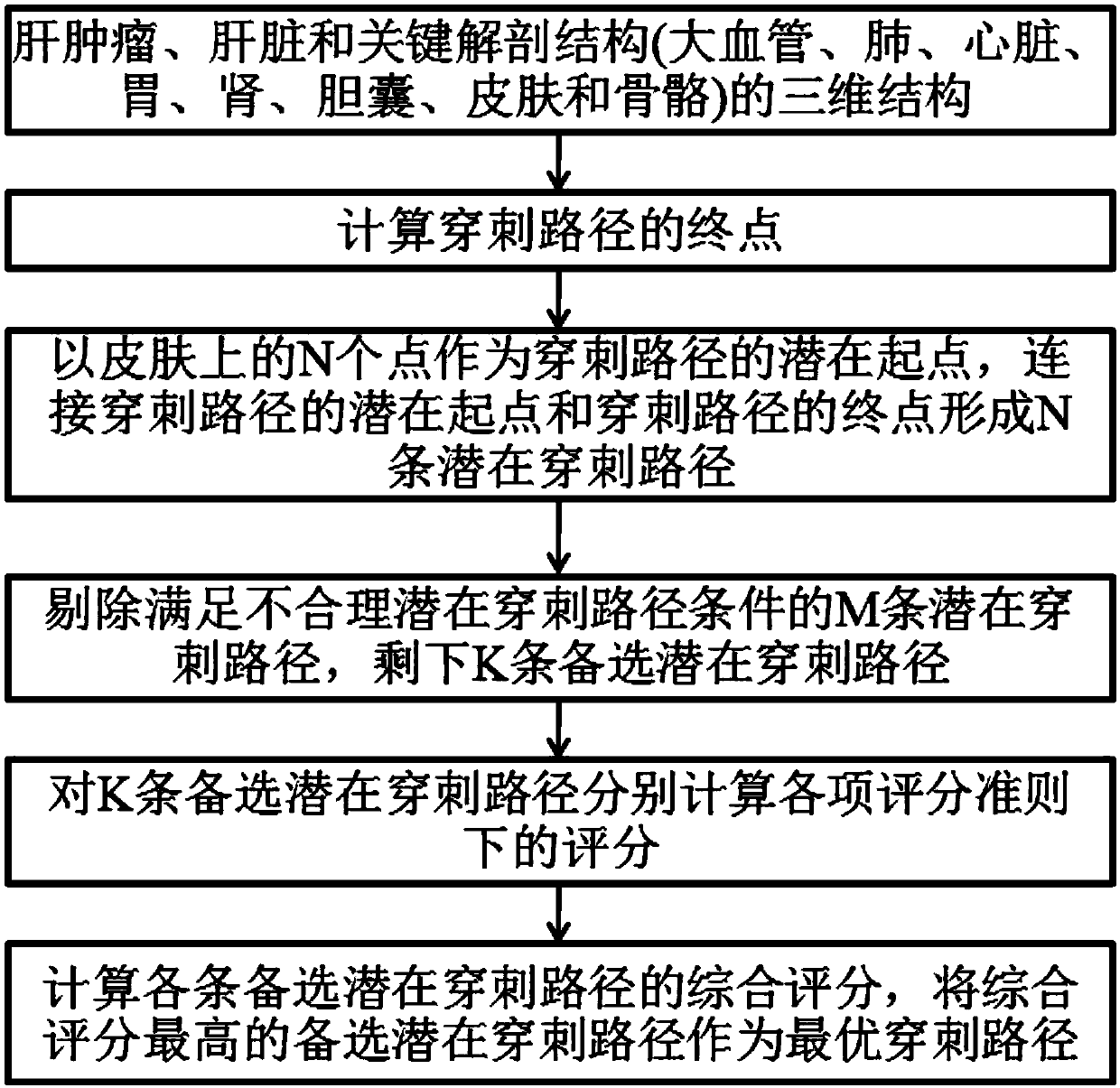
Puncture navigation method for CT guided liver tumor radiofrequency ablation
InactiveCN108618844ARealize automatic planningSurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingRadiofrequency ablationReal time navigation
The invention discloses a puncture navigation method for CT guided liver tumor radiofrequency ablation. The method comprises the steps that markers which can be identified by CT are placed on the bodysurface of a patient suffered from liver tumor, and three-dimensional structures of the liver tumor, liver and key dissection structures (great vessels, lung, heart, stomach, kidney, gallbladder, skin and skeleton) are automatically and rapidly extracted from CT sequence scanning images in the CT guided liver tumor radiofrequency ablation; real-time automatic planning of puncture routes is conducted to obtain the optimal puncture route; spatial matching is conducted on a patient coordinate system P, a CT image coordinate system I and an electromagnetic positioning instrument coordinate systemE; information of the starting point, ending point, length, angle and the like of the optimal puncture route is displayed in CT image space; the moving of needle tip of an ablation needle is executedto reach the starting point of the optimal puncture route to conduct real-time navigation; after the needle tip of the ablation needle is moved to the starting point of the optimal puncture route, real-time navigation of the puncturing of the ablation needle is executed.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Closable loop access guide catheter
InactiveUS8029461B2Significant changeStable supportMedical devicesCatheterBrachial arteryDistal portion
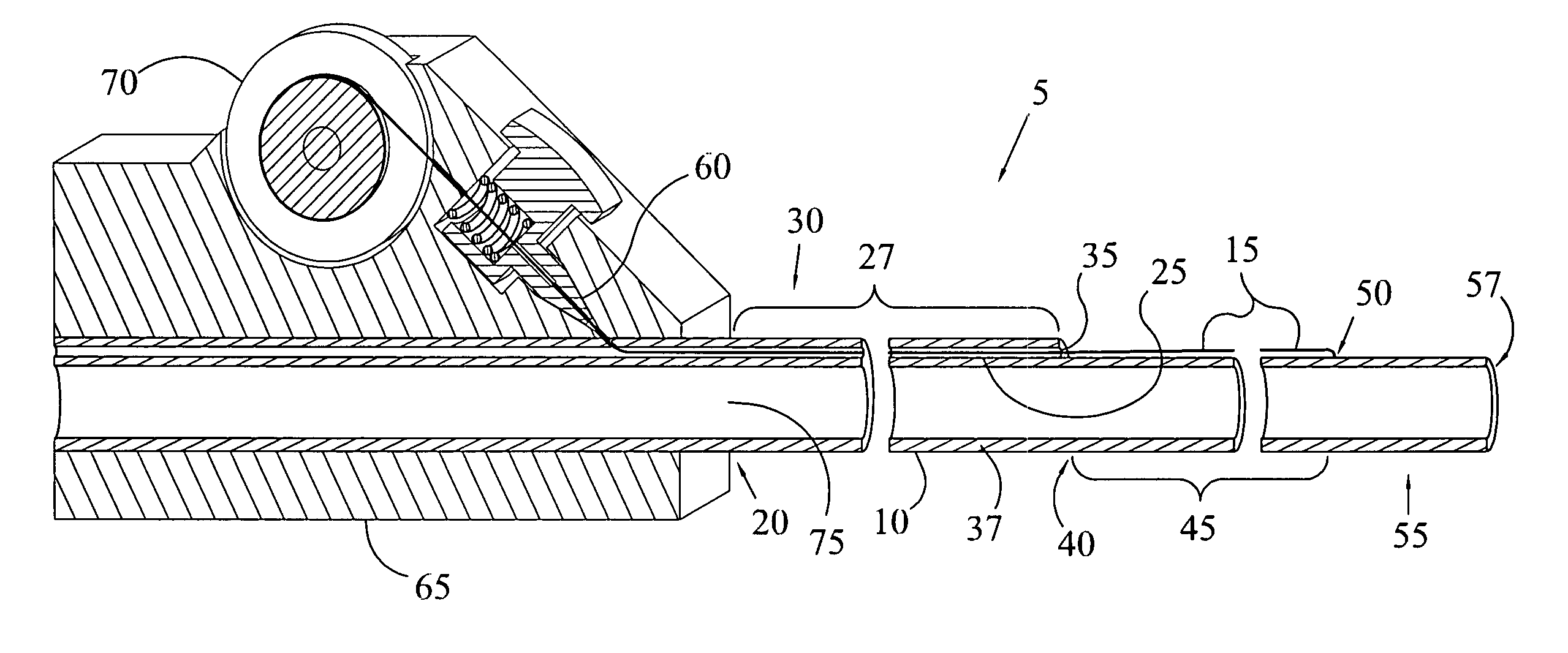
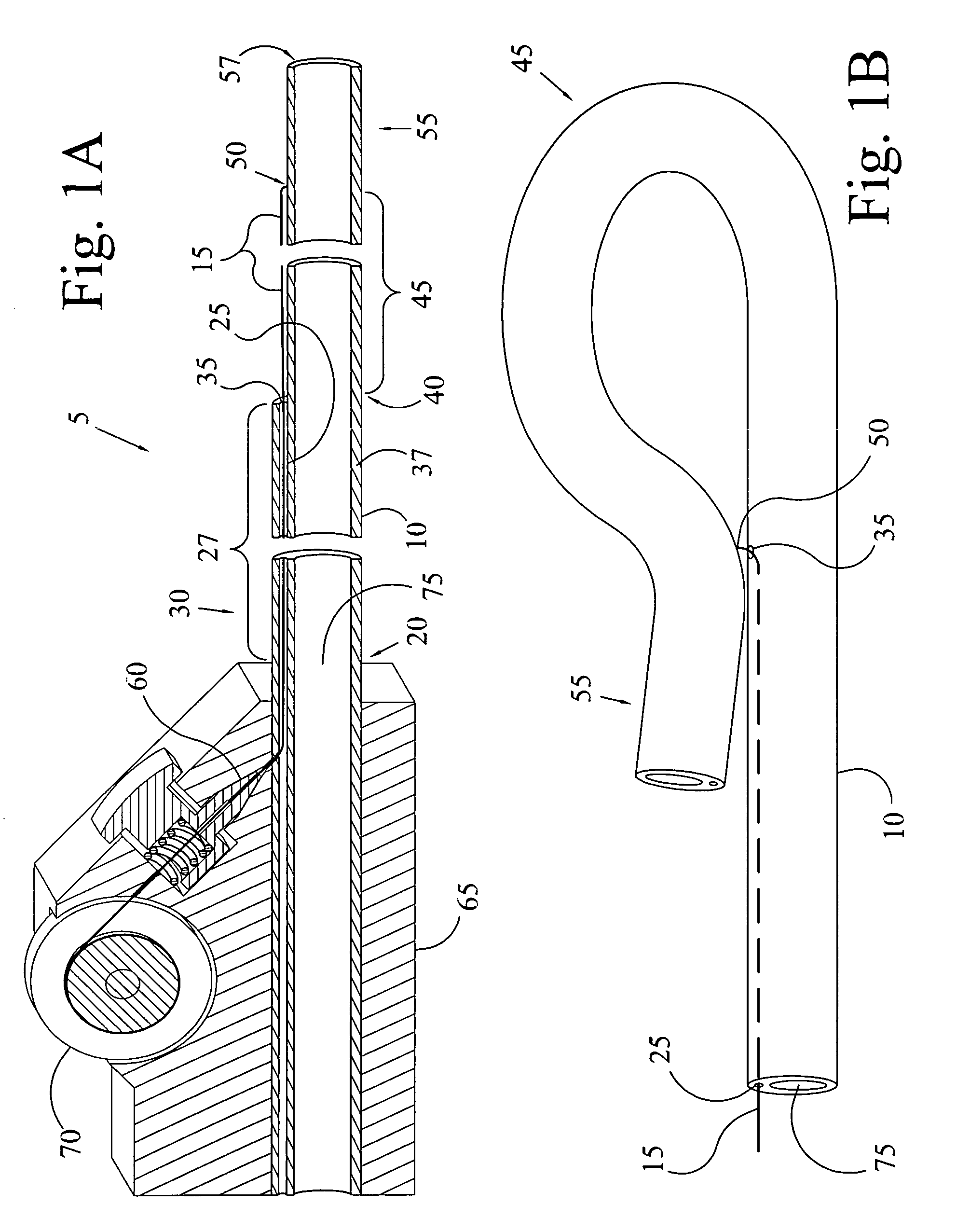
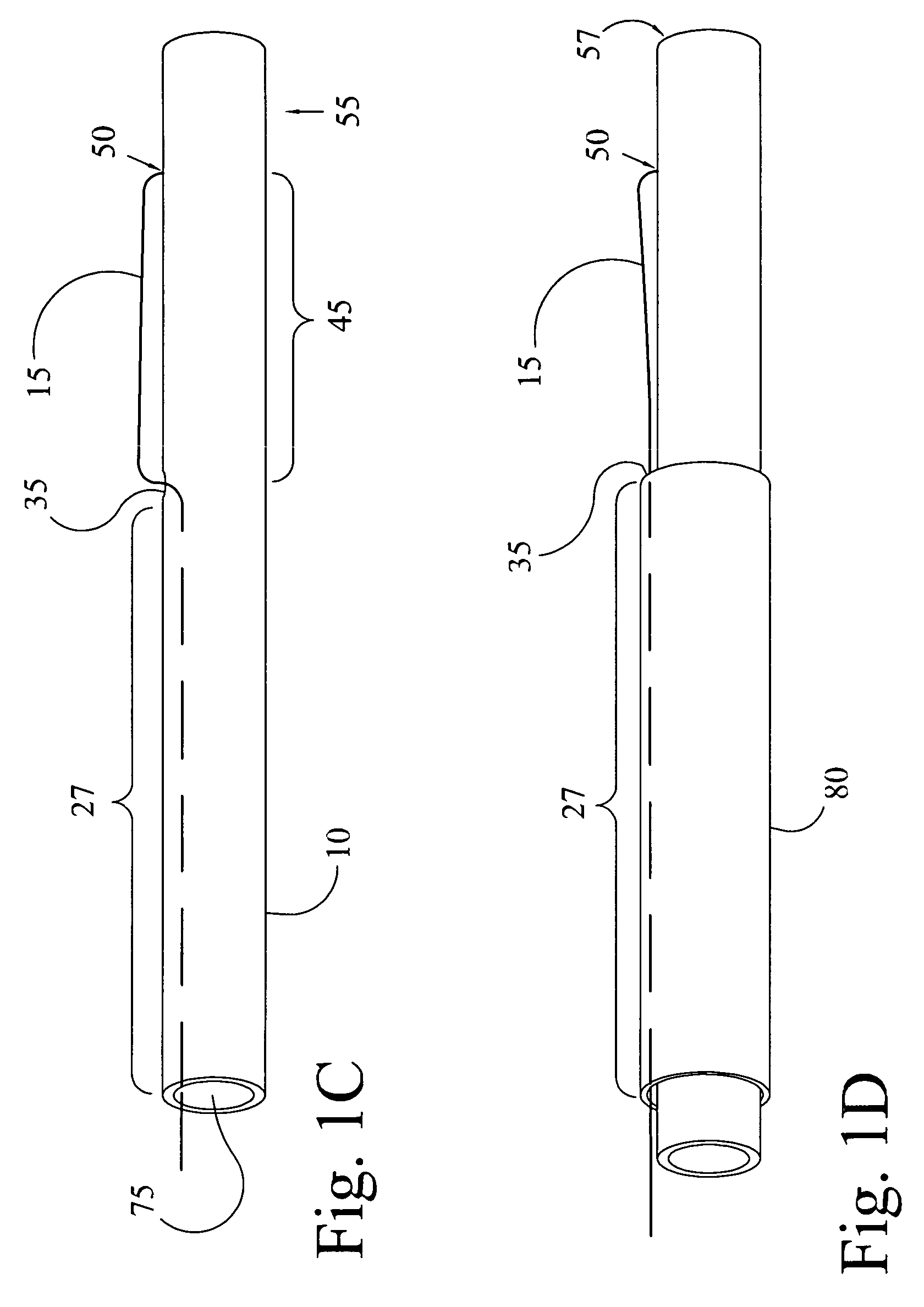
The Access guide catheter provides passage for therapeutic and diagnostic devices through vessels or conduits that return substantially in a direction from which they originated. One application is for delivery of therapeutic catheters to the carotid or cerebral arteries via access from the radial or brachial artery. The guide catheter enters the aorta from one of the great vessels, forms a closed loop in the aorta, and is directed back into a great vessel in an opposed direction. The distal portion of the guide catheter is advanced into the great vessel for support. Further support is attained by providing tension to the proximal shaft of the guide catheter. Flexibility of the guide catheter allows diagnostic angiograms to be performed prior to delivery of a therapeutic catheter or device.
Owner:THIELEN JOSEPH MICHAEL +1
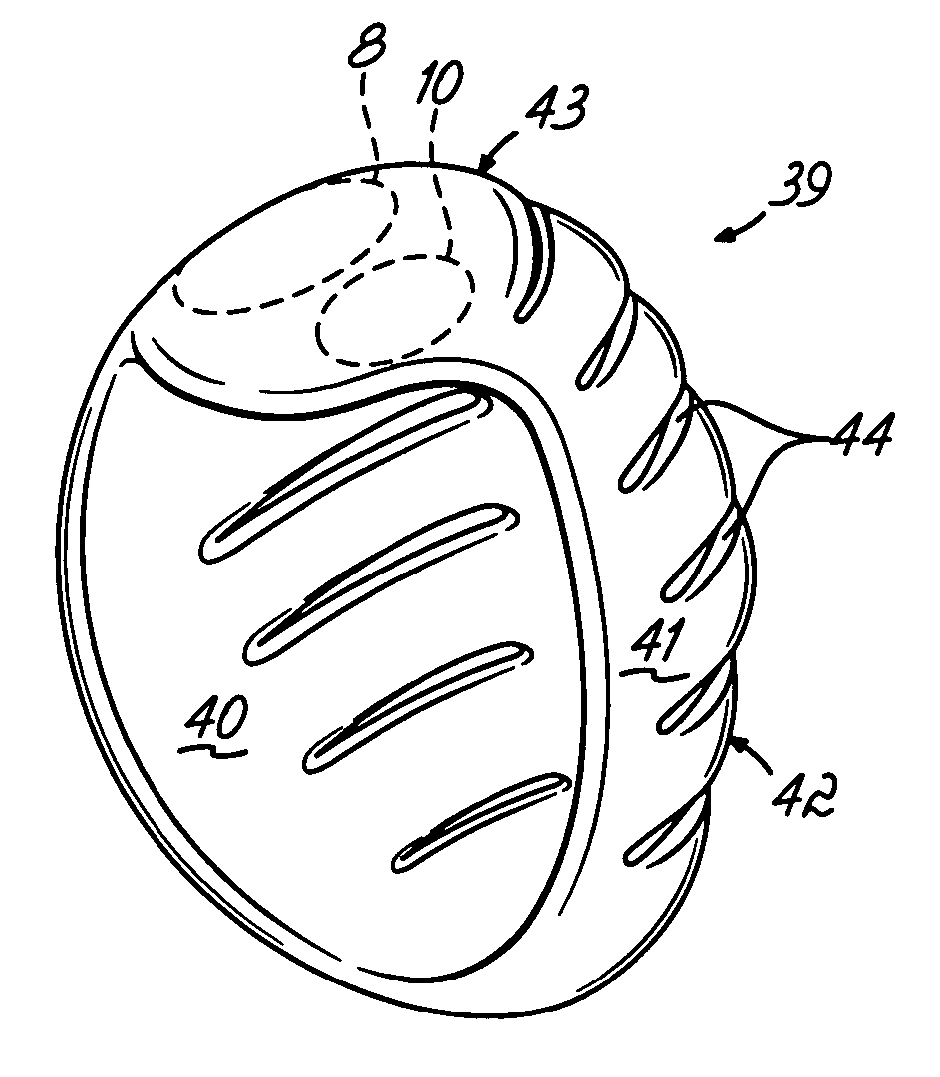
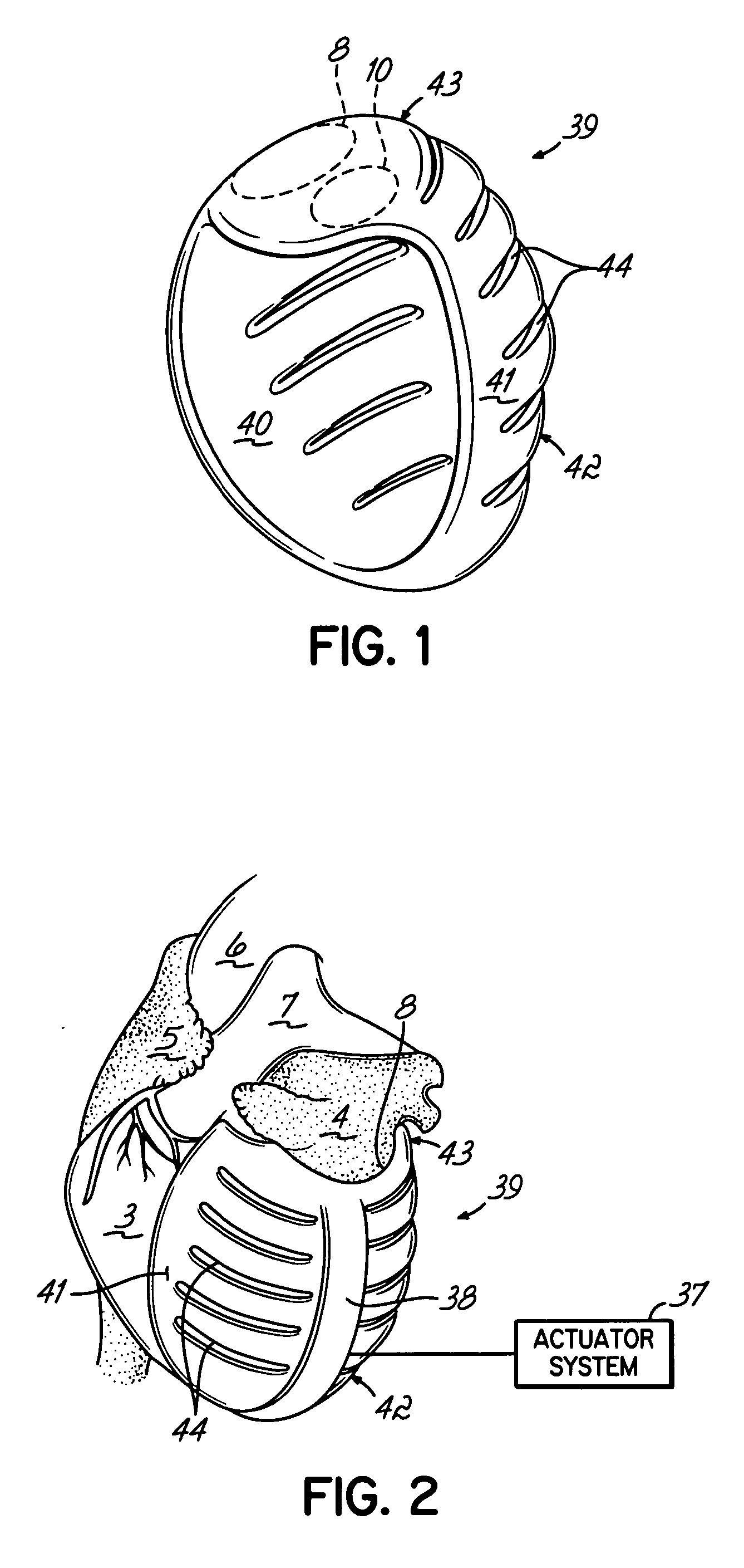
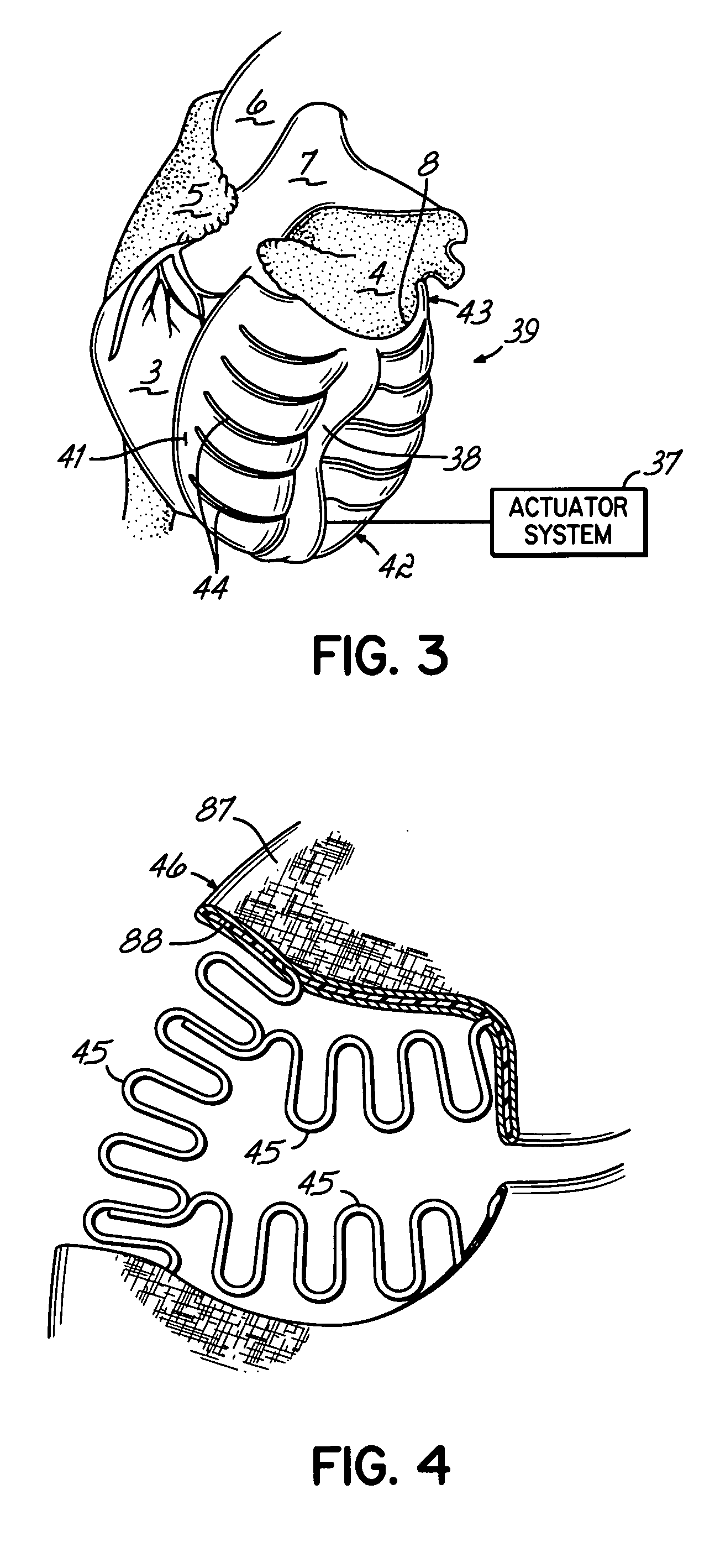
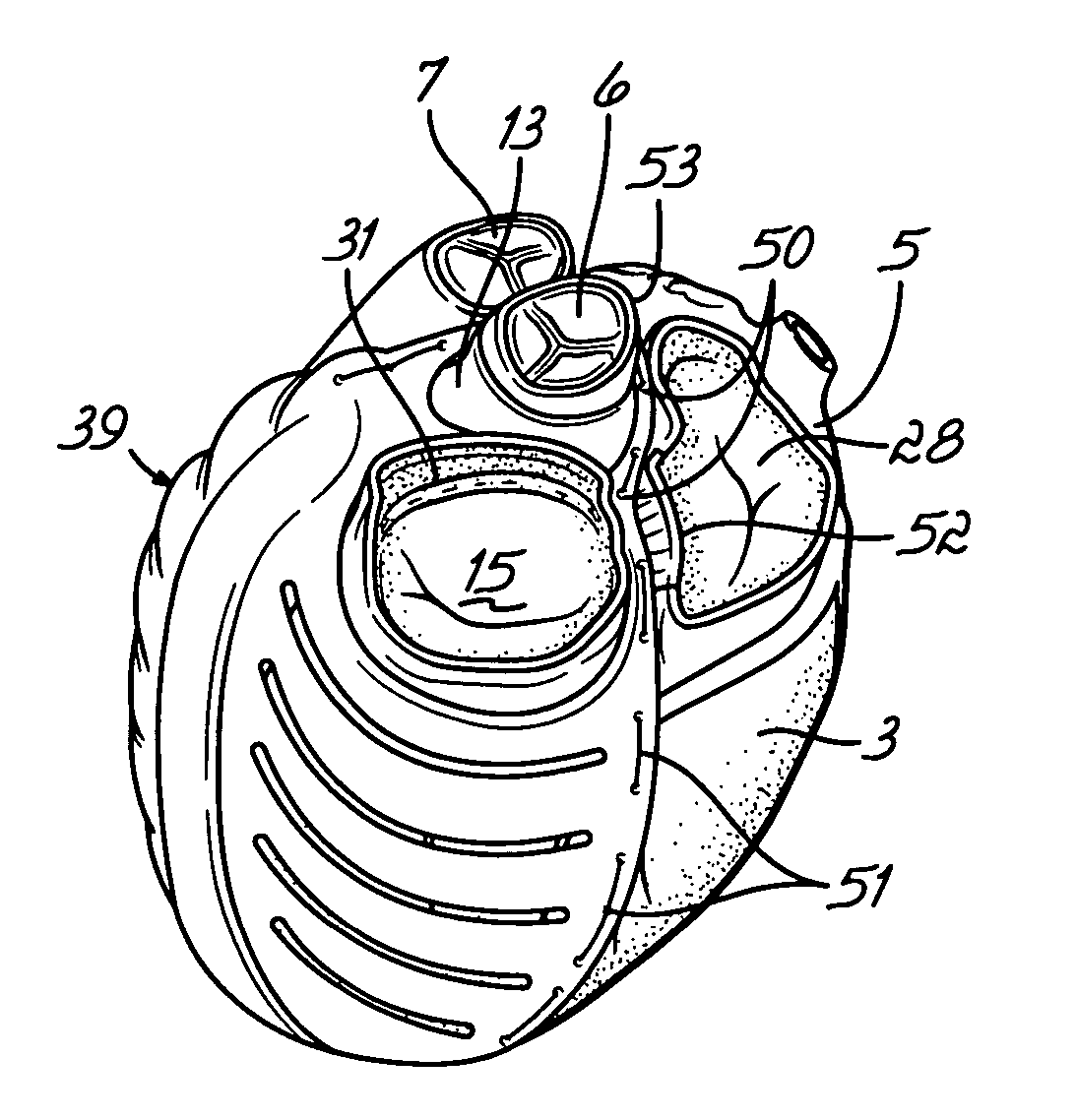
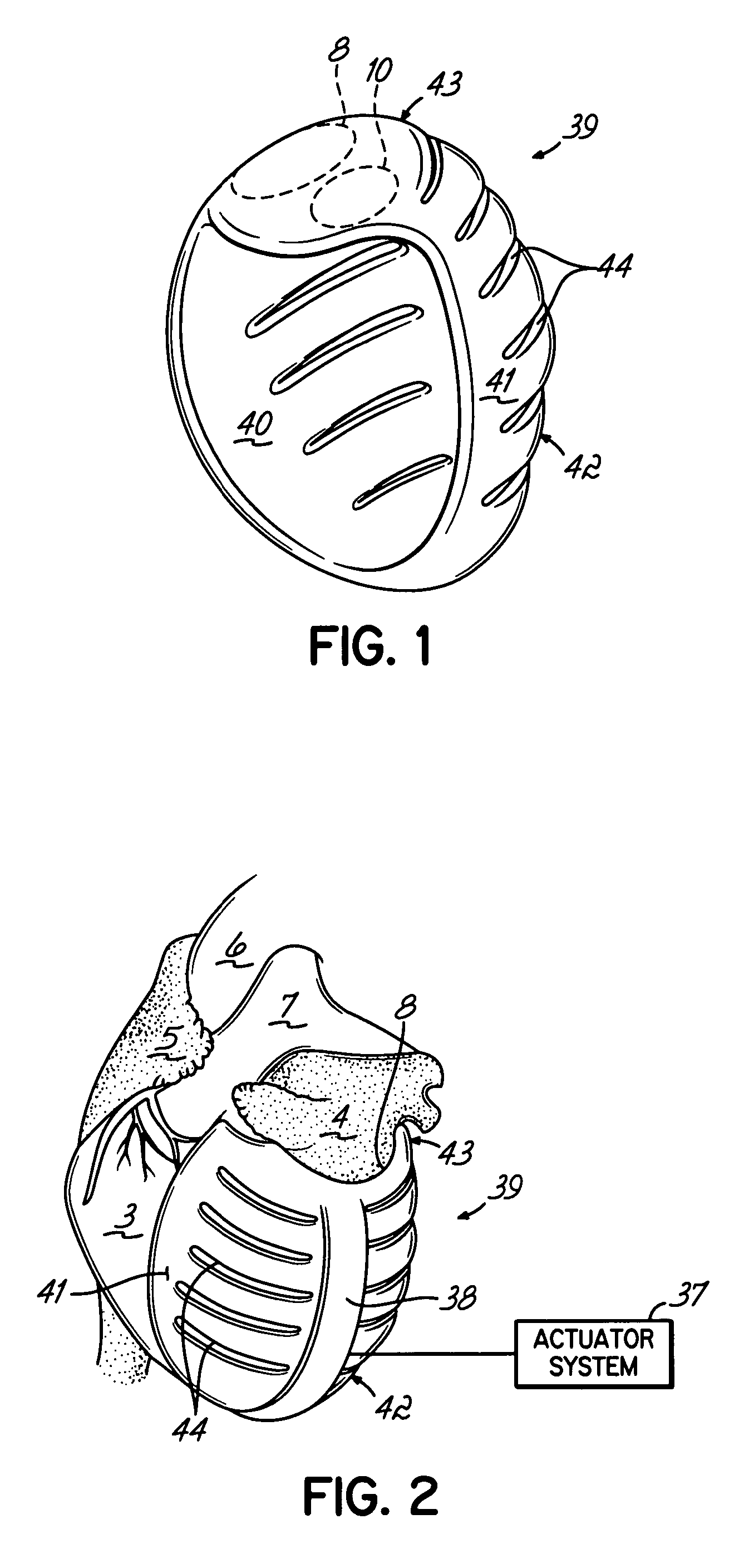
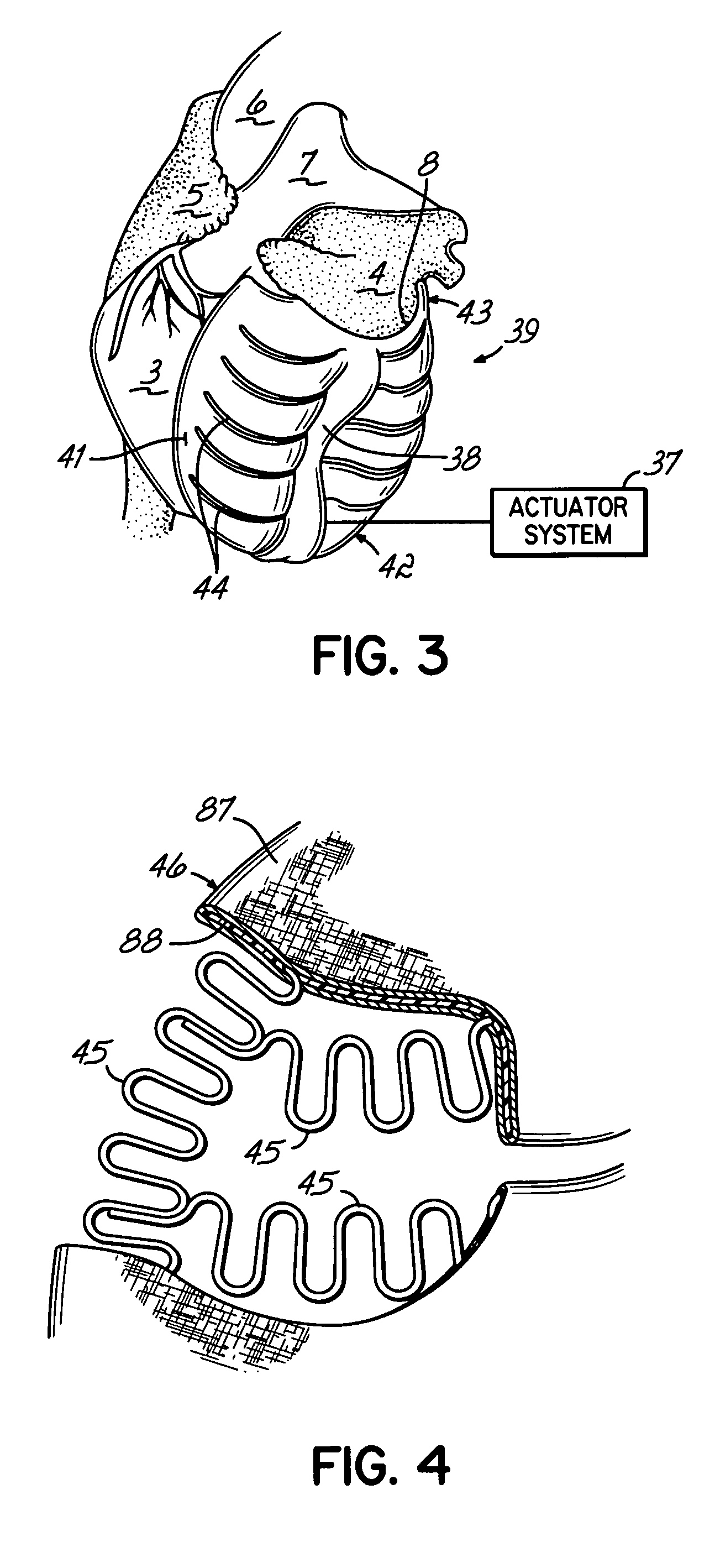
Deforming jacket for a heart actuation device
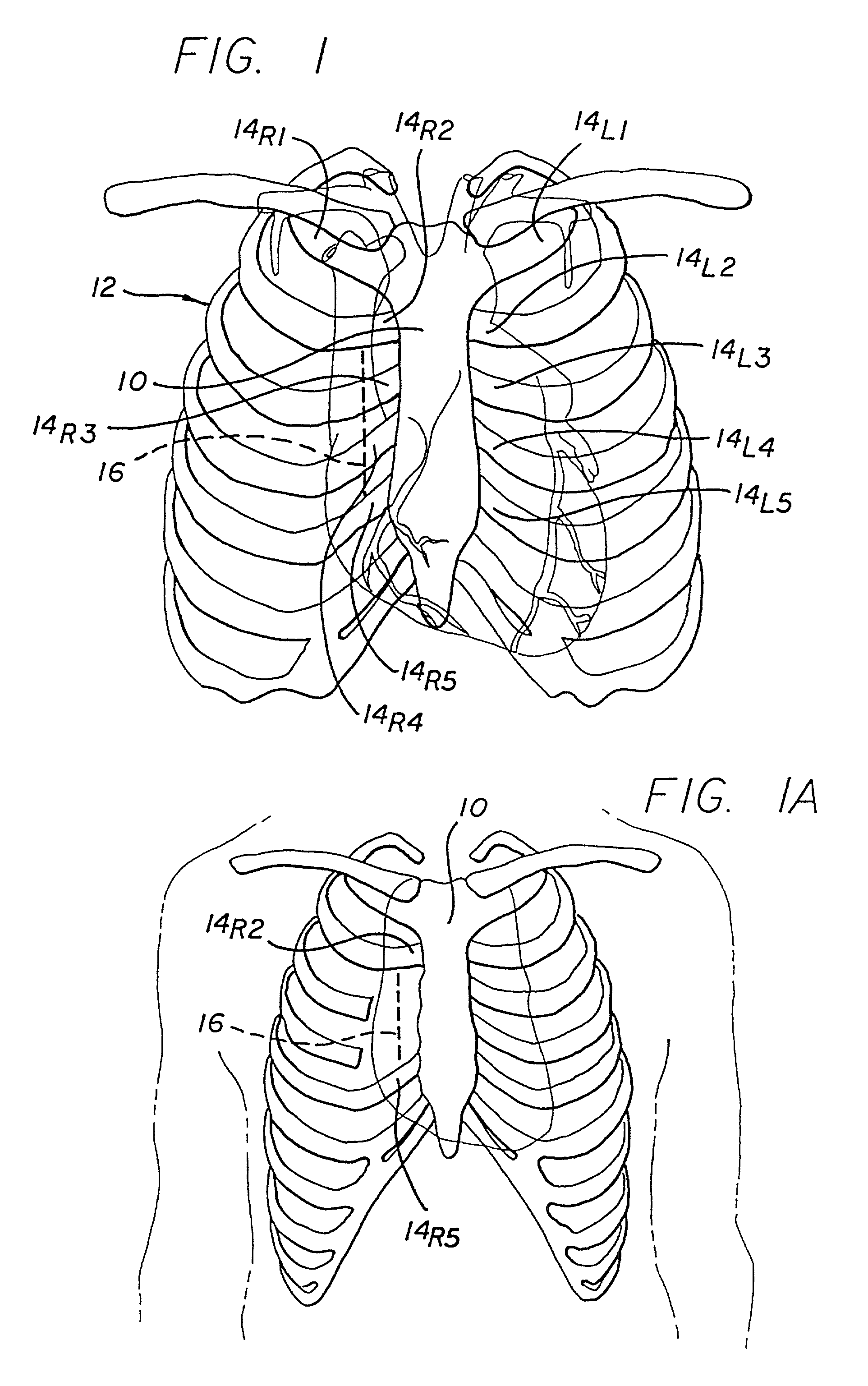
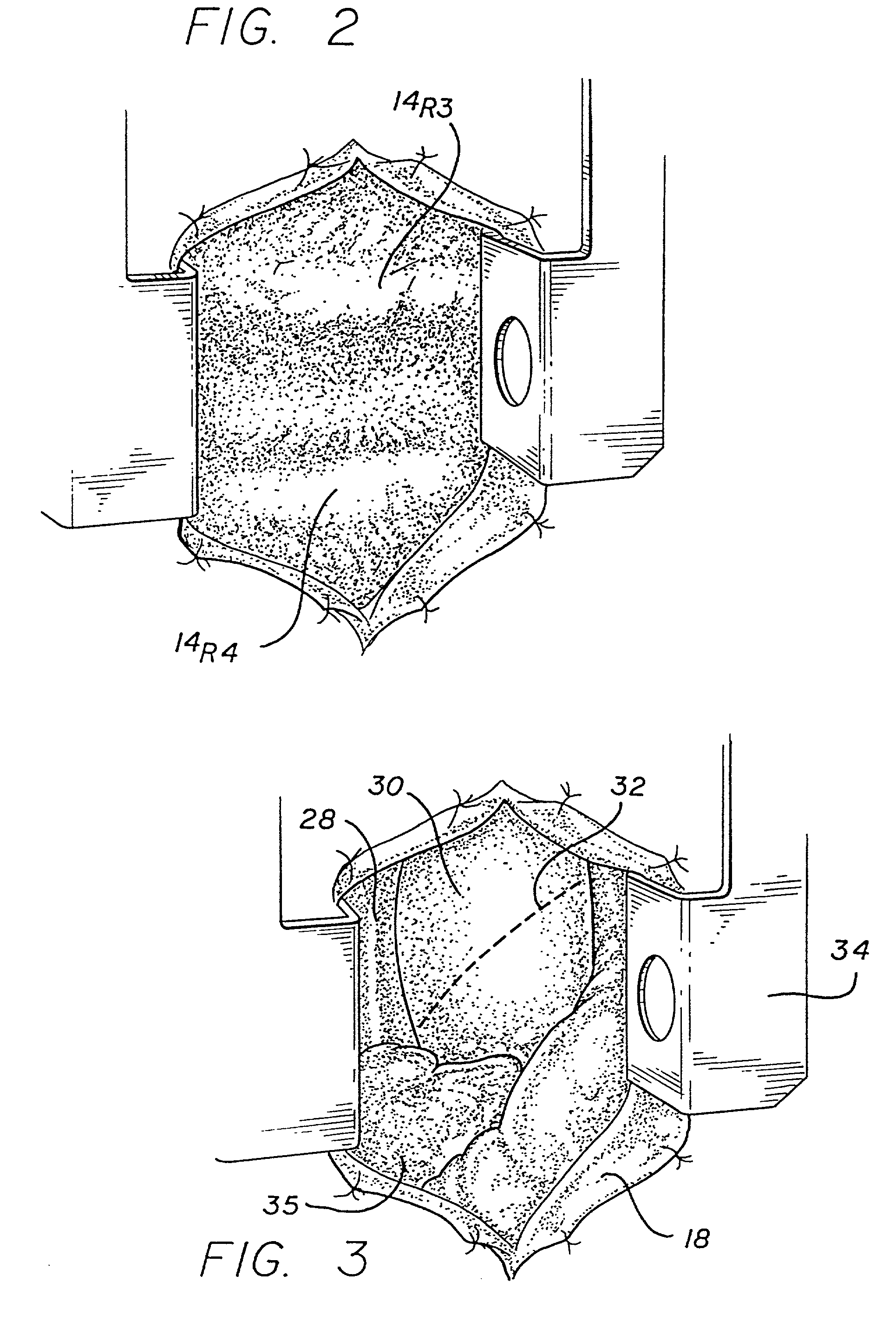
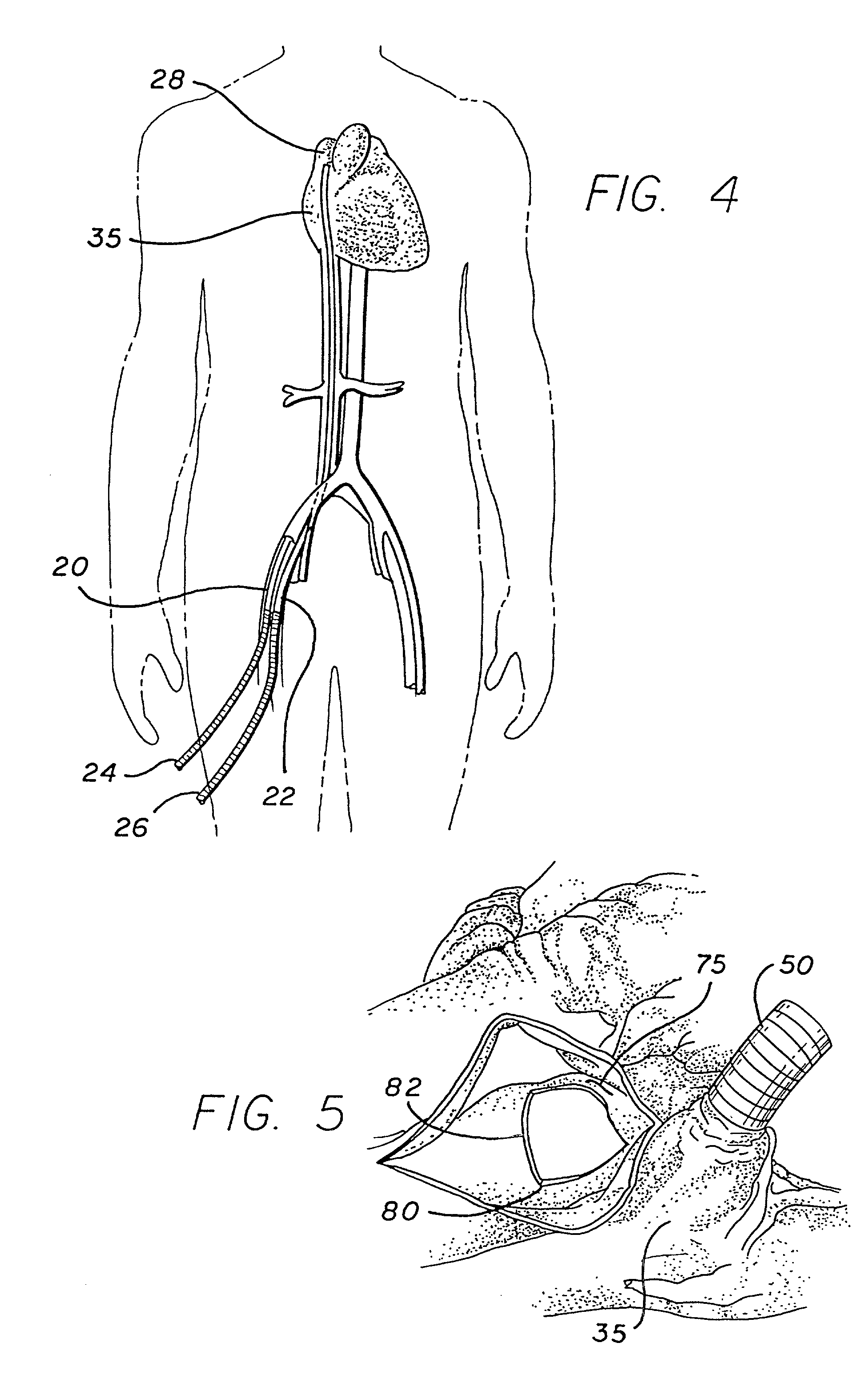
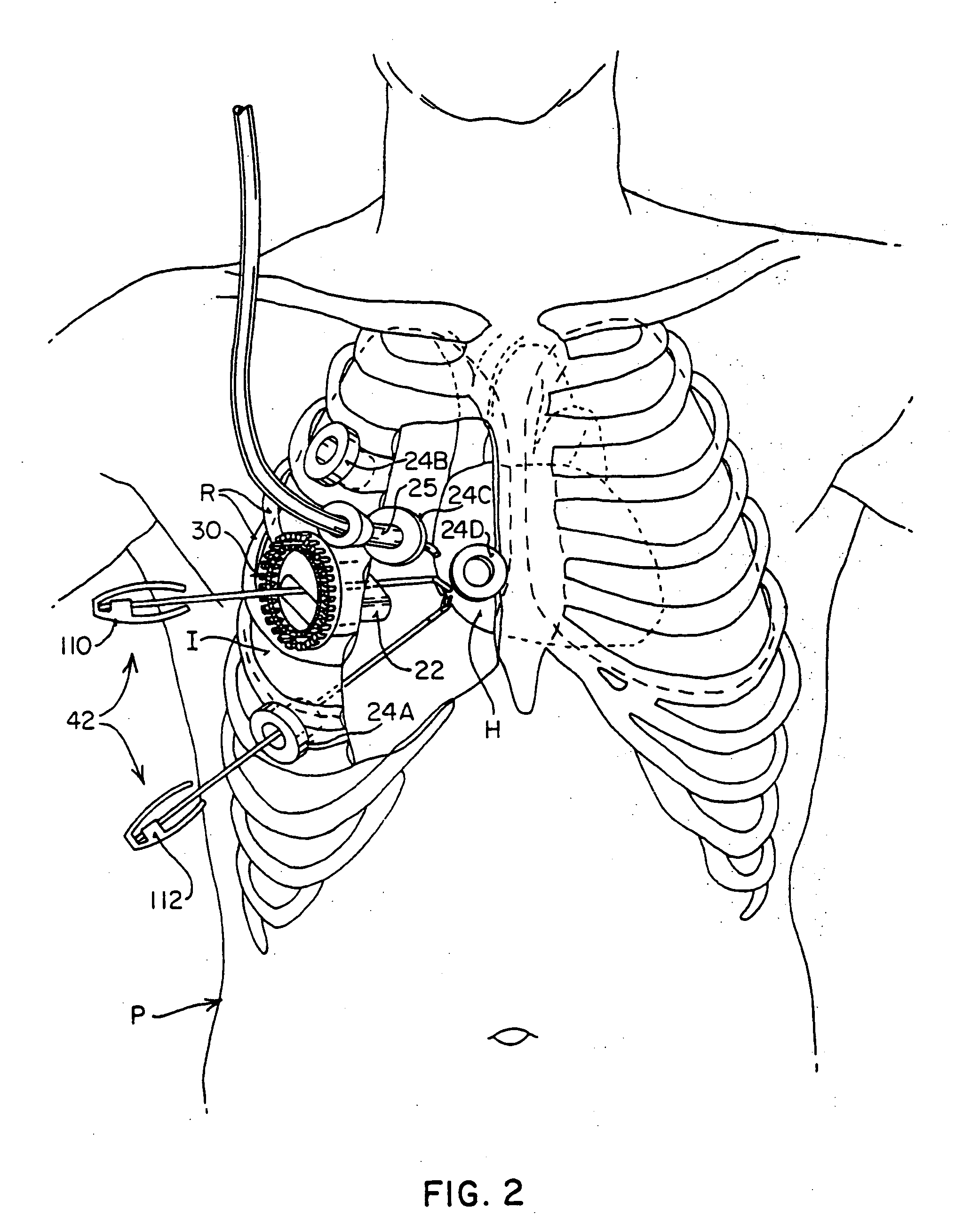
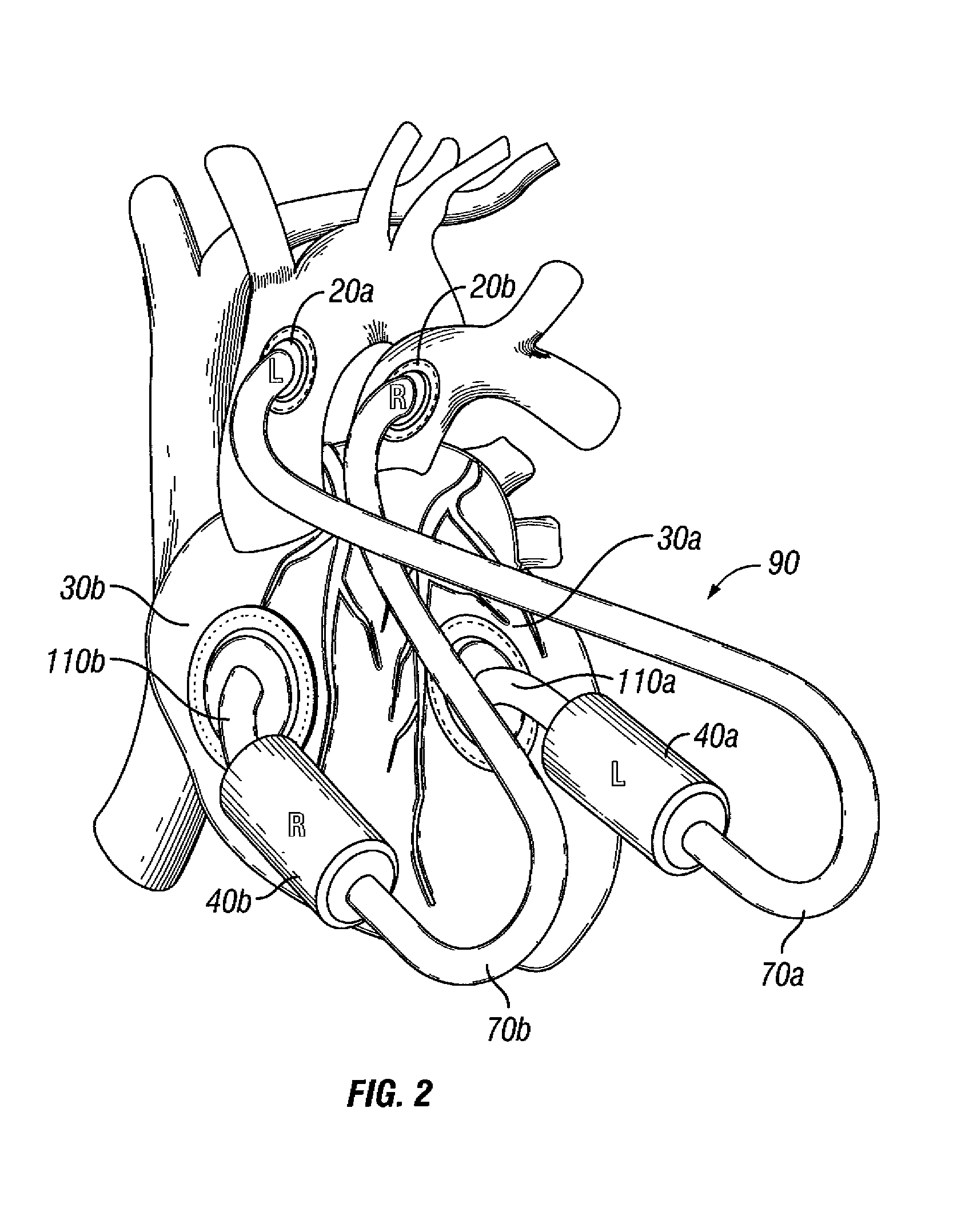
The invention consists of a cushioned active cyclically deforming cushion or jacket (39) that surrounds the outer or epicardial surface of at least one chamber (2, 3, 4, 5) of the natural heart, including its base, configured so that internal components may be suspended from the jacket (39) by heart wall-penetrating cords to complete a restraining harness over the entire 3-dimensional boundary of the chamber or chambers. The cushion or jacket (39) provides protective and stabilizing openings (8, 9, 10) for atria and their inflow valves as well as for great vessels and their outflow valves. It is equipped with one or more actuator mechanisms (37, 38) that cyclically change shape at one or more sites, thus altering heart wall shape and chamber volume.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Methods of preventing adhesions following laminectomies and other surgical procedures
InactiveUS20050074453A1Good treatment effectImprove effectivenessPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsPhage antibodiesSpinal nerve
Adhesions and scar formation following a surgical procedure are controlled by providing a human recombinant phage antibody, and introducing the antibody onto or into an area of the body following the procedure to inhibit adhesions, or scar formation. According to one embodiment, the antibody is used to prevent the formation of scar tissue following spinal surgery. This may be carried out by placing the antibody over the dura lining the spinal nerves and spinal cord. Alternatively, the antibody may be used to inhibit adhesions following abdominal surgery, or placed around the great vessels following an anterior approach to the spine or other regions. Importantly, the antibody may be used to inhibit adhesion formation adjacent to areas where growth factors are used to stimulate healing. The invention may further include the step of protecting the growth factors and / or the area of the body where stimulated healing is desired from the antibodies to the growth factors. As a further option, other medications or therapeutic substances may be added to the antibody(ies) to enhance healing or effectiveness.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
Deforming jacket for a heart actuation device
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
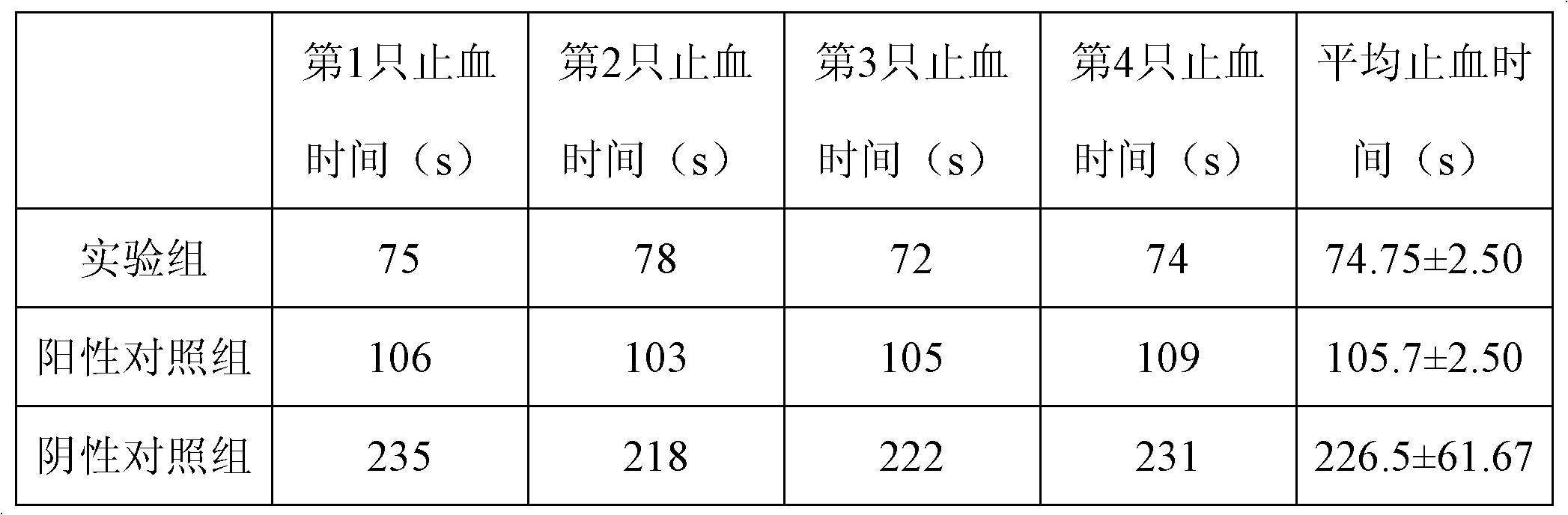
Starch stypticum and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102178691AImprove migration abilityRapid hemostasisOrganic active ingredientsSurgical drugsChemistryGreat vessels
The invention discloses a starch stypticum and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of medical preparations. The preparation method comprises the following steps: refining waxy maize starch to 4,000 to 10,000 meshes; centrifugally filtering after crosslinking, acidolysis and enzymolysis are completed; cleaning with distilled water; blasting and drying at constant temperature until the weight is constant; crushing, and screening through a 200-mesh screen; radiating by Co60 to disinfect to prepare the starch stypticum. The water absorption rate of the starch stypticum prepared by adopting the method is 2 to 3 times that of the conventional styptic materials, the starch stypticum can quickly stop bleeding in actual application, has quick styptic function in great vessel hemorrhage, even massive bleeding wound surface, and can be widely applied to surgeries of cardiothoracic and vascular surgery department, hepatobiliary surgery department, orthopedics department, general surgery department, obstetrics and gynecology department, urology surgery department and ear-nose-throat department and the like.
Owner:北京爱特康医疗科技有限公司
Locating method for magnetic resonance
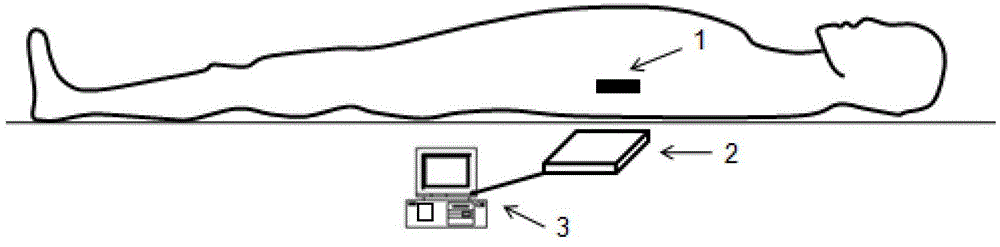
ActiveCN103431863AAchieve acquisitionSave Scanning EfficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsProton magnetic resonanceResonance
The invention relates to a positioning method for magnetic resonance. The method comprises the following steps: a, displaying a schematic diagram with a human body model and a scanning coil on visible human-machine interactive equipment which is arranged in a magnetic resonance equipment scanning room; b, starting a positioning beam after a patient lies on a bed in a magnetic resonance cavity, and positioning the positioning beam according to the position of the scanning coil; c, selecting the part to be scanned of the patient on the human-machine interactive equipment; d, moving the bed until the selected scanning part displayed on the human-machine interactive equipment is positioned under the positioning beam. The positioning method can be used for effectively positioning coils for performing combined scanning on the belly or great vessels and the like, so that coordinate information of unfixed important coil units can be acquired, and an operator can carry out positioning operation without repeatedly entering the scanning room. Therefore, the scanning efficiency is greatly improved, and the cost on scanning time of coil positioning in a pre-scanning mode can be eliminated.
Owner:ALLTECH MEDICAL SYST
Total artificial heart system for auto-regulating flow and pressure
InactiveUS8870951B1Reduce resistanceMinimizing pressure gradientControl devicesBlood pumpsWhole bodyContinuous flow
The present invention is TAH system for auto-regulating blood flow and maintaining the asymmetric pressure balance in the mammalian cardiovascular system by decreasing the resistance in blood flow and minimizing the pressure gradients to exploit the in-flow pressure sensitivities of continuous flow pumps. The system further includes laminar flow generating manifolds connected to the atrium at one end and attached to pumps linked to the great vessels at the other, such that the in-let flow sensitivities of the pumps are maximized to auto-regulate blood flow, providing adequate pulmonary and systemic arterial flow to support normal metabolism and end-organ function and maintain the appropriate asymmetric physiologic pressure balance between the systemic and pulmonary systems of the mammalian cardiovascular system.
Owner:ALPHA DEV
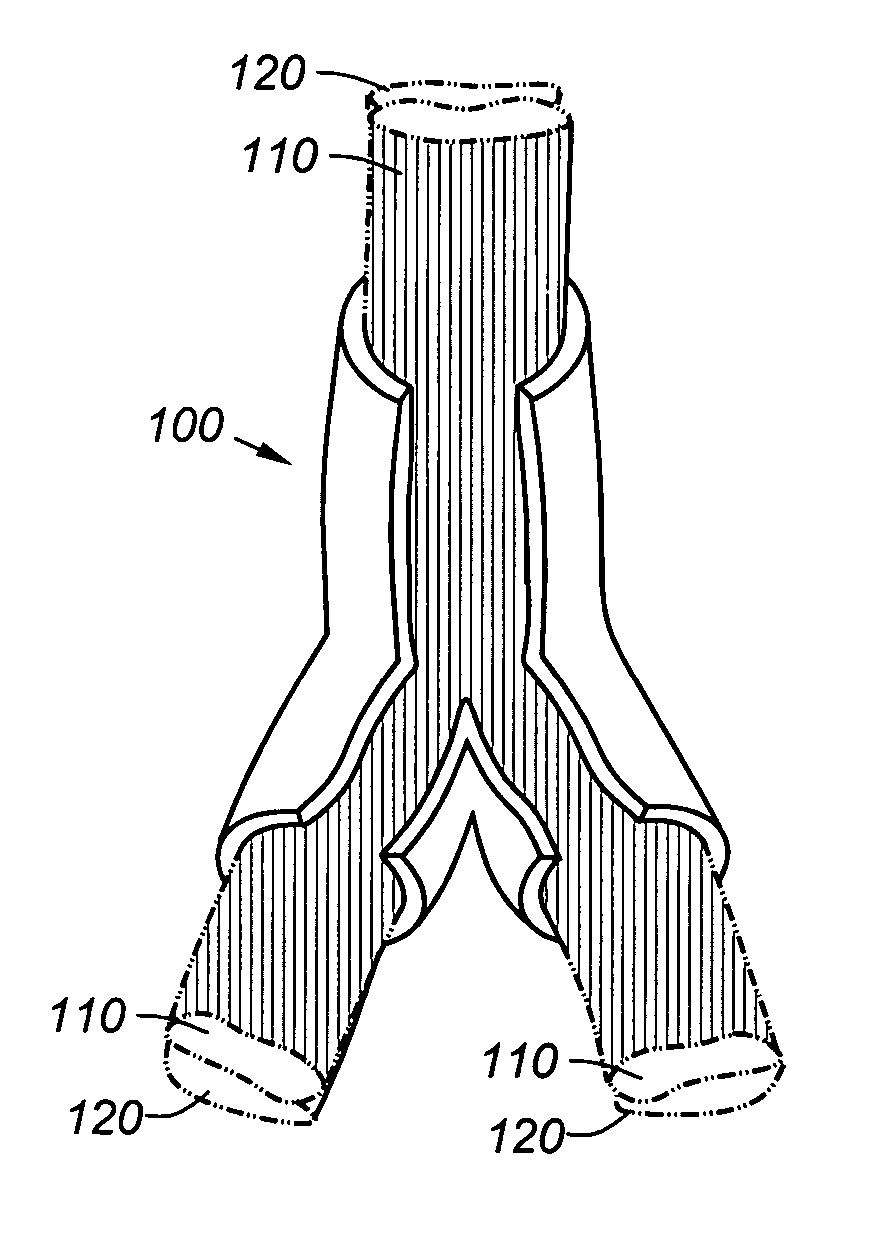
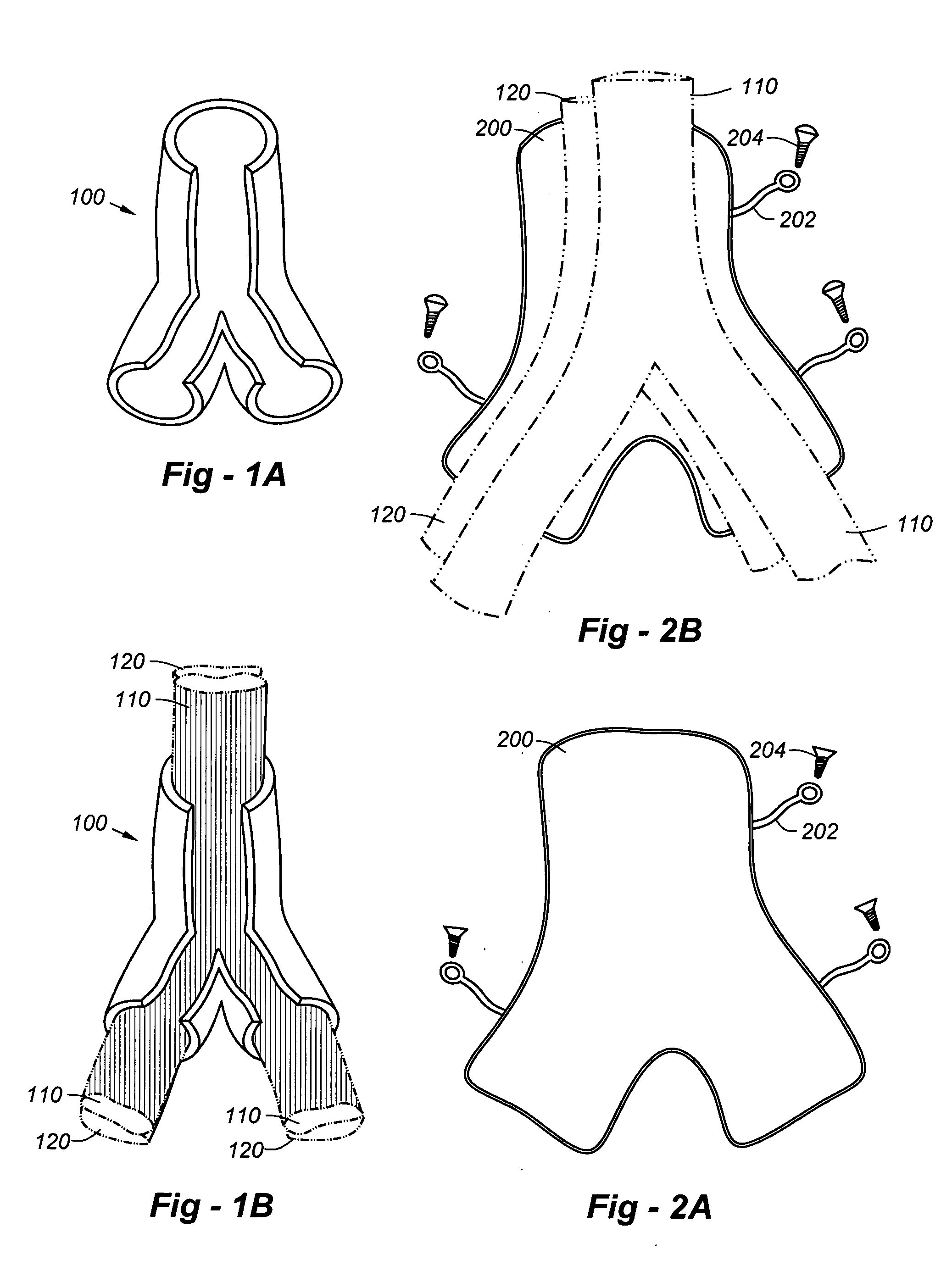
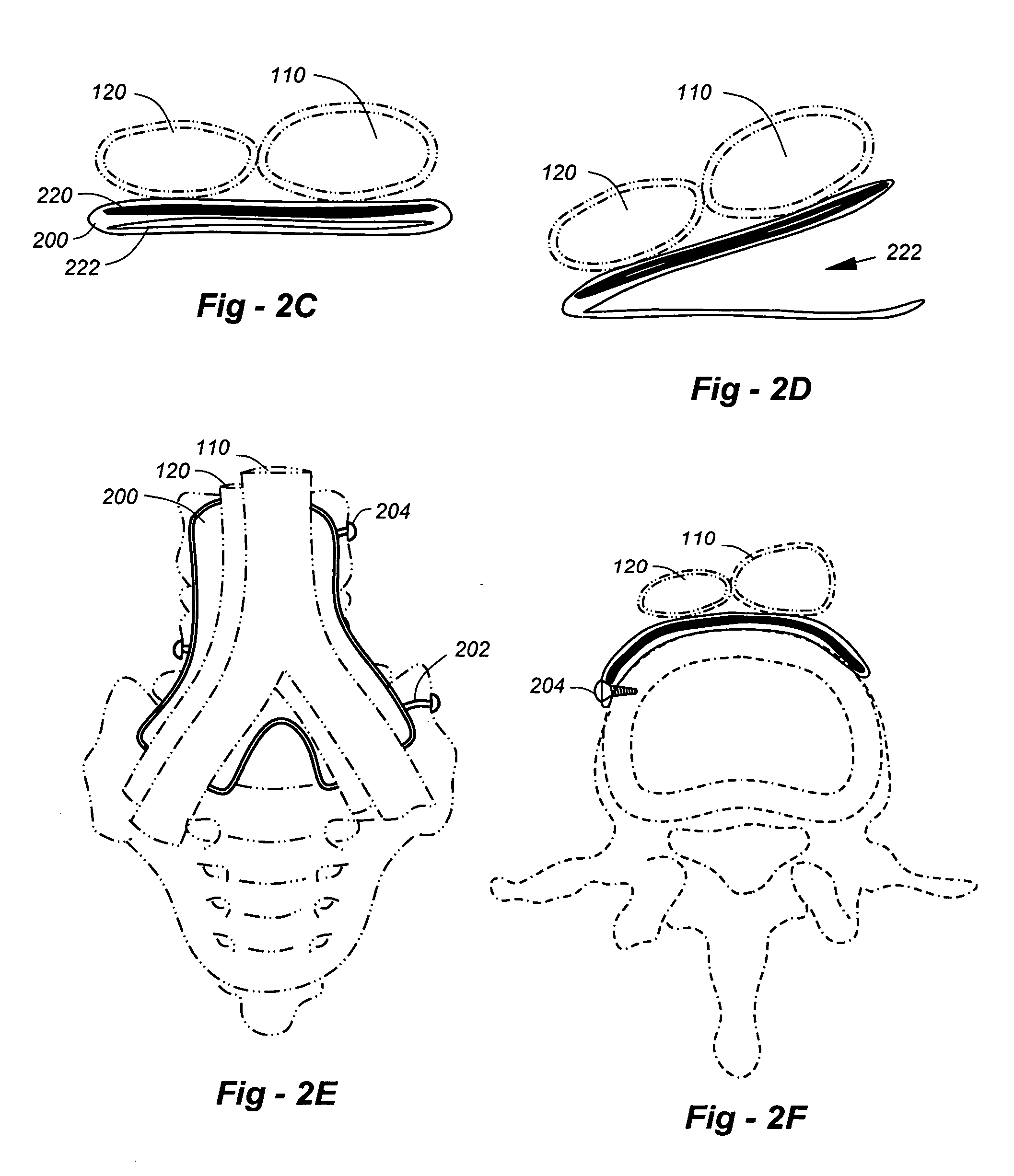
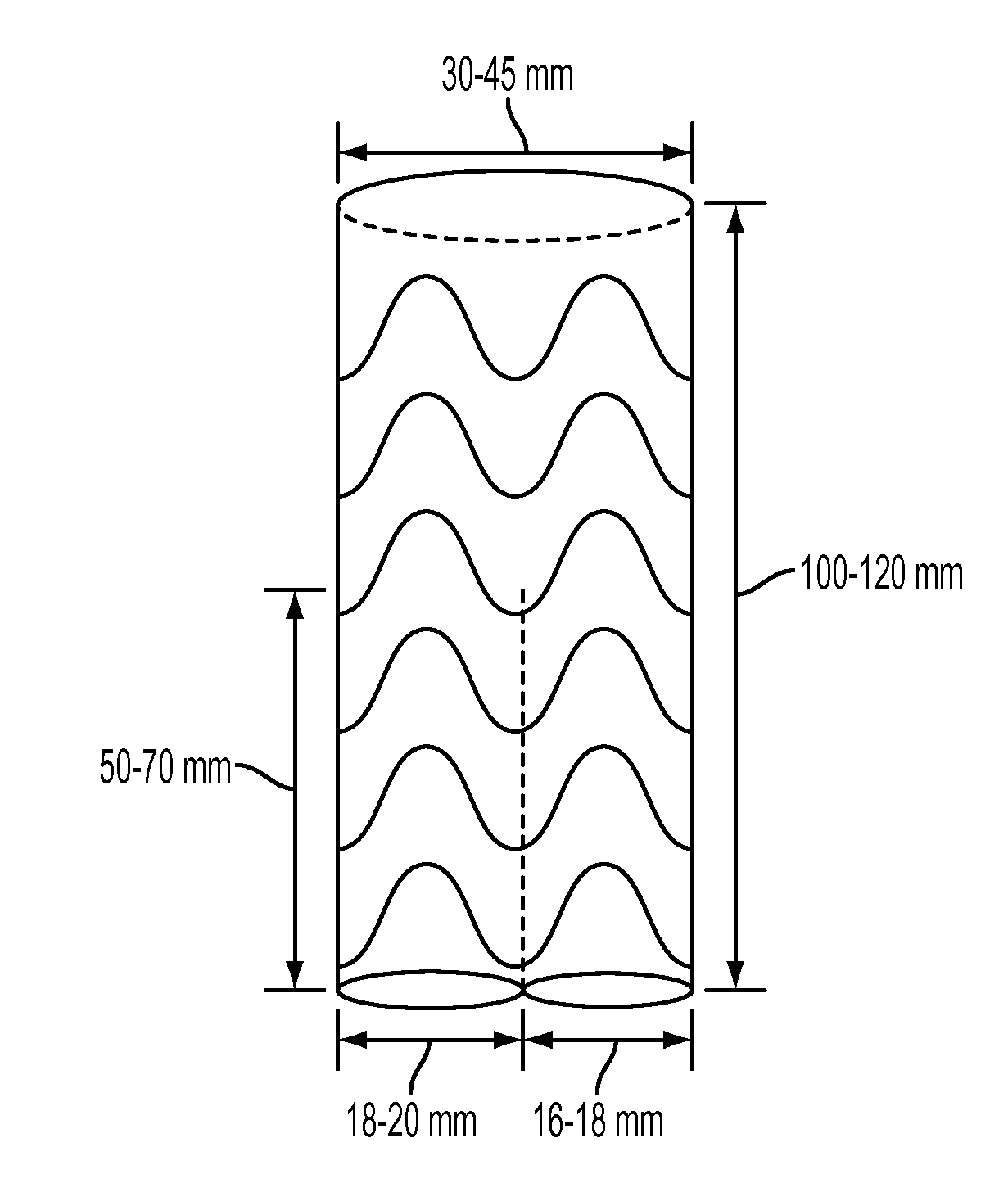
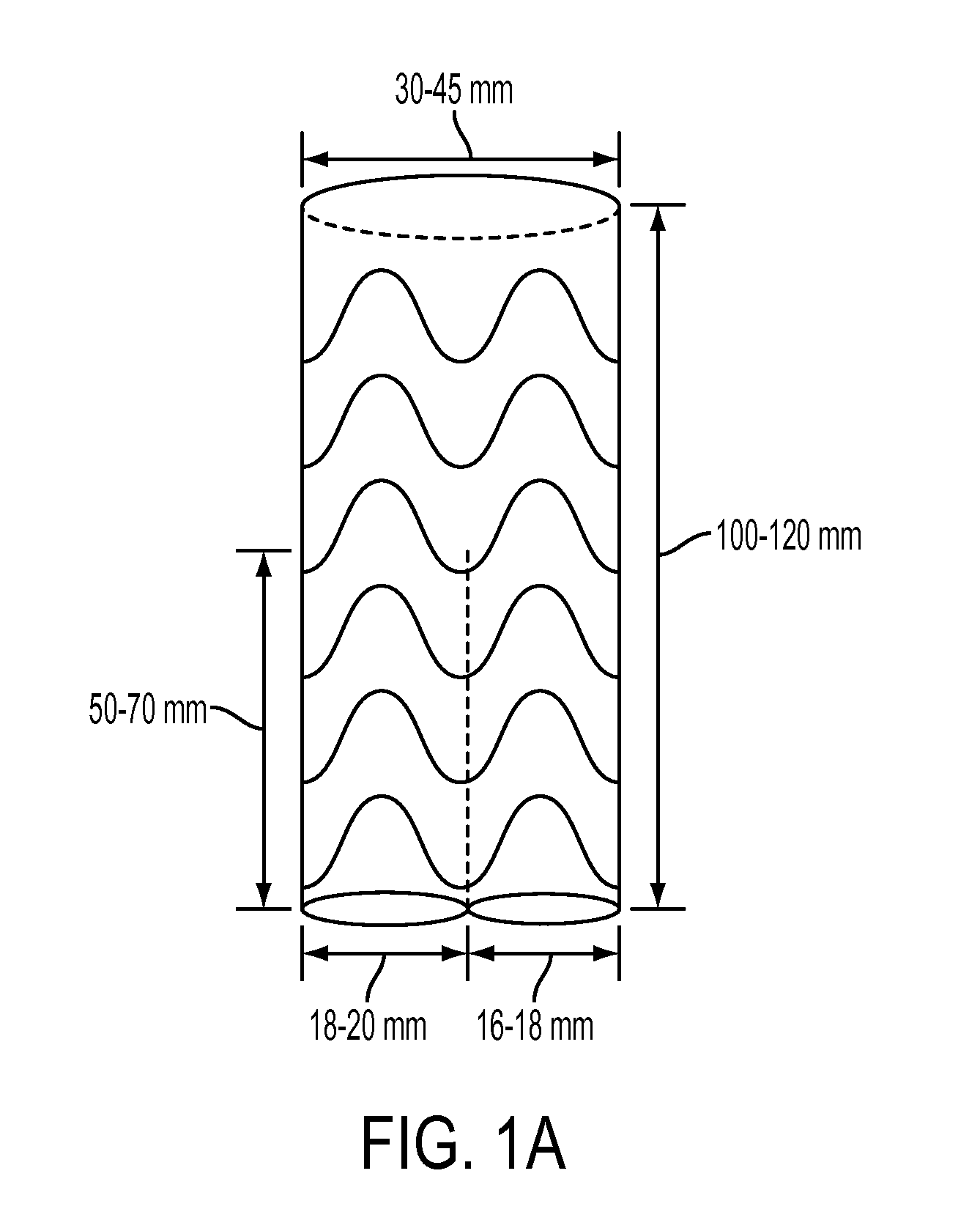
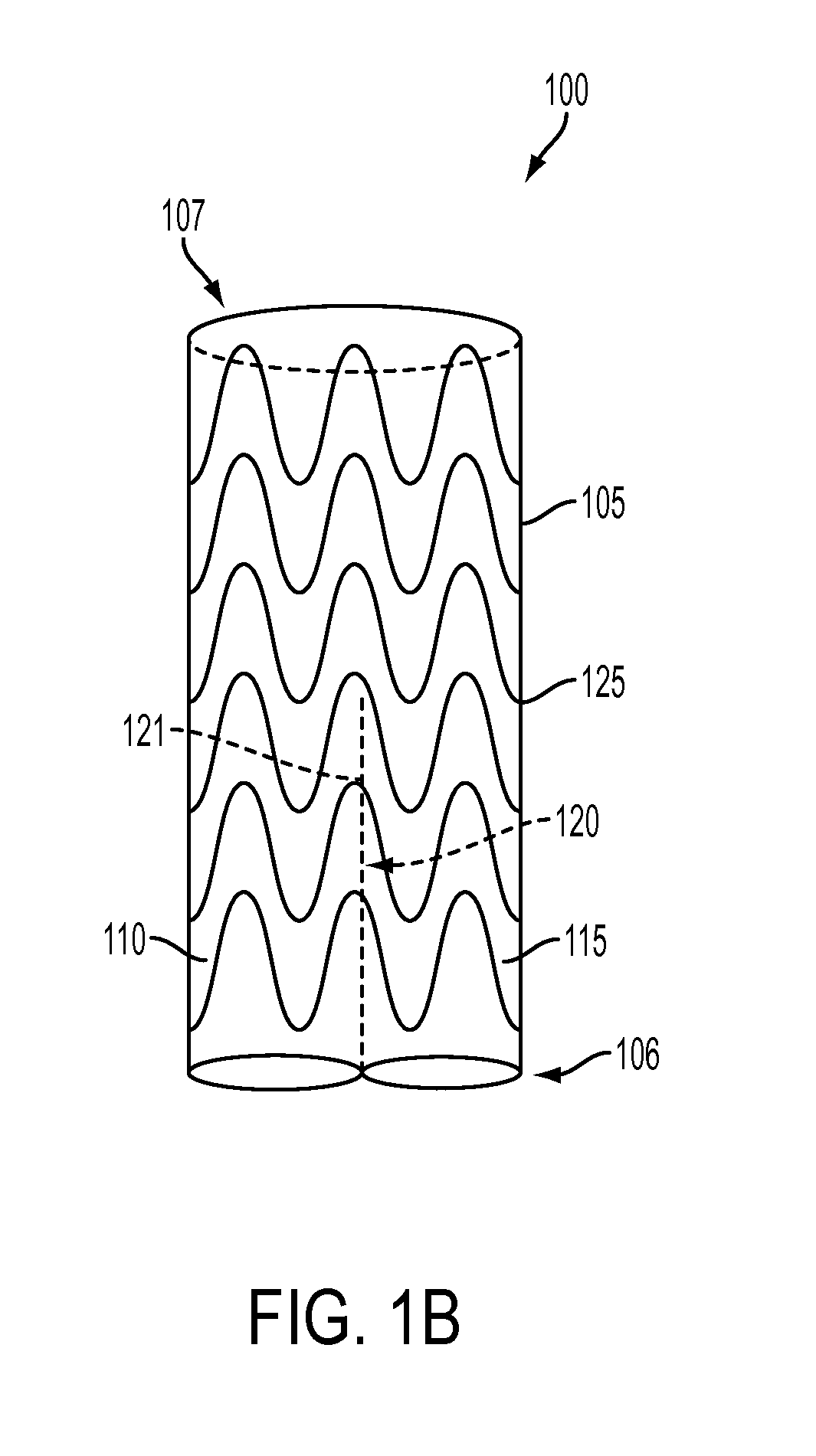
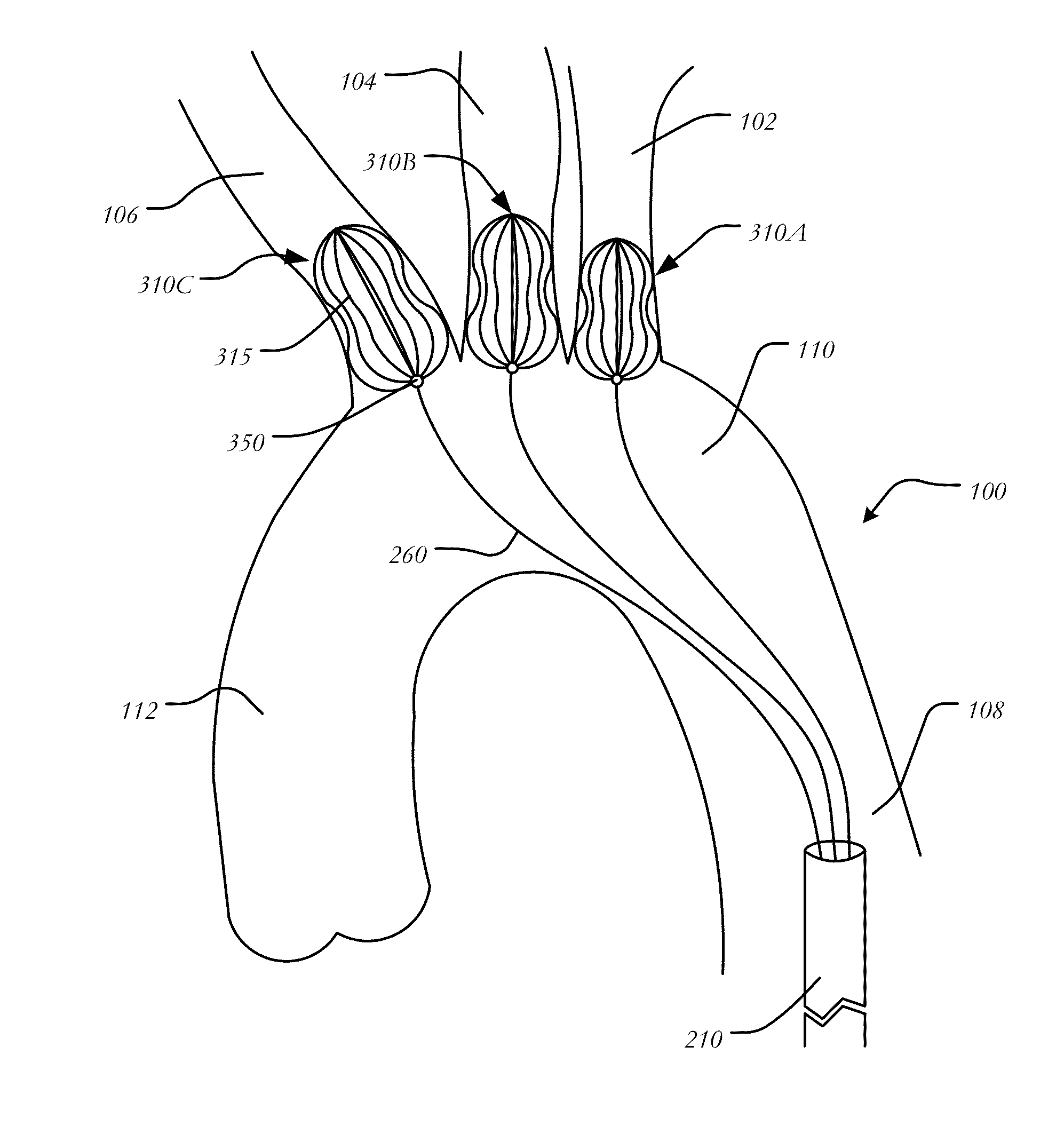
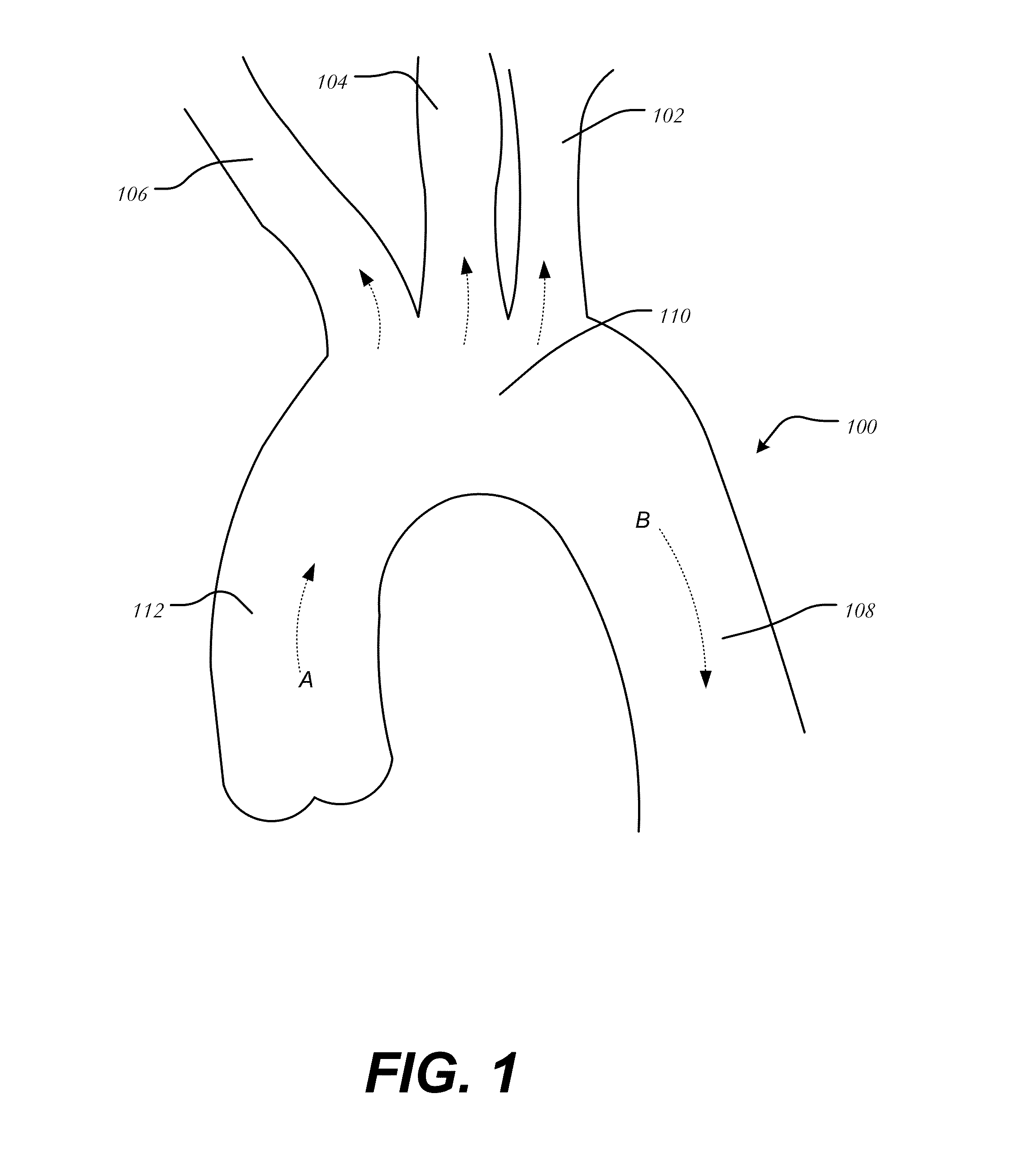
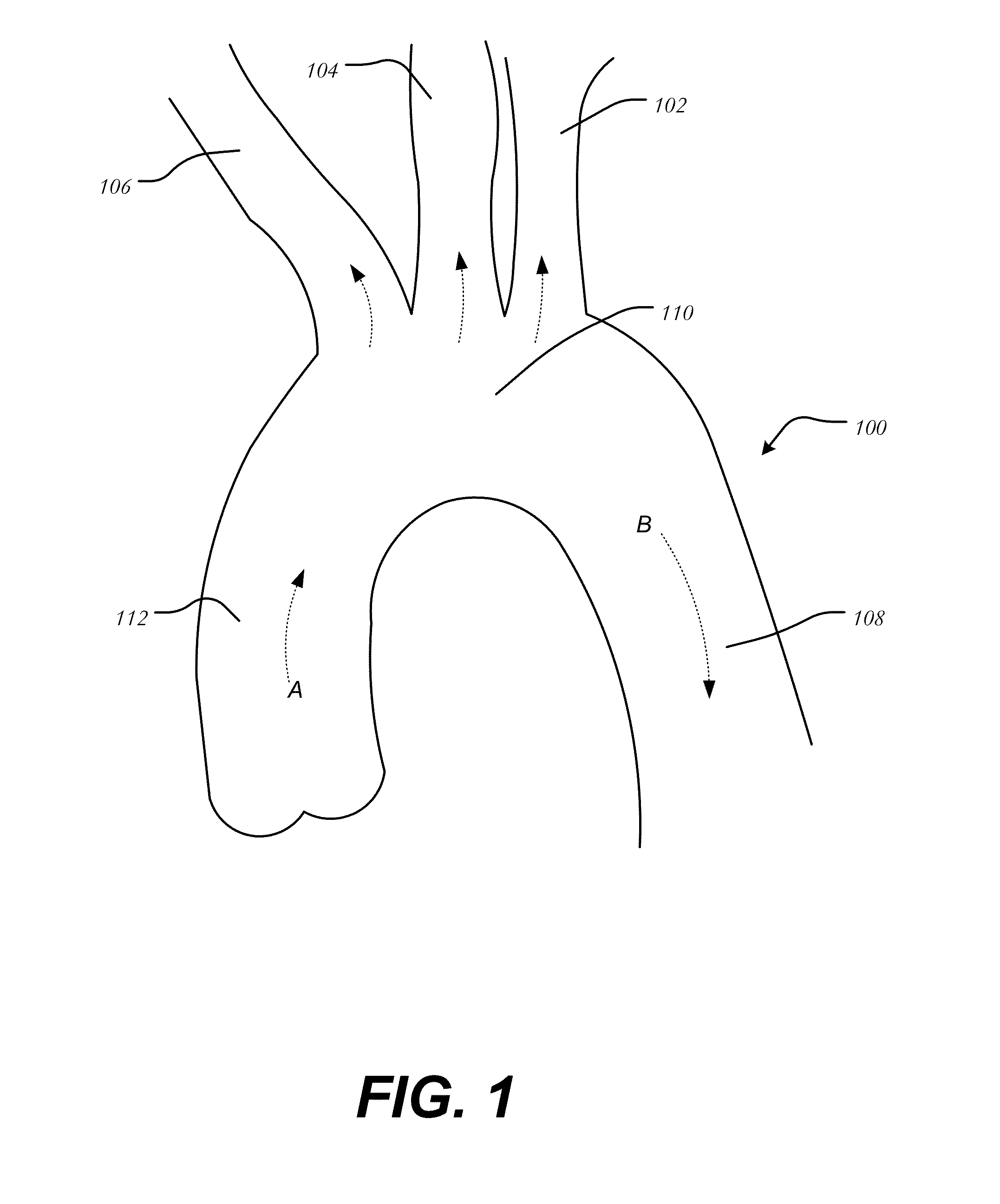
Debranching Great Vessel Stent Graft and Methods for Use
ActiveUS20130274853A1Maintain blood flowIncrease surgical optionStentsBlood vesselsStent graftingBlood vessel
A debranching Great vessel stent graft and methods for its use, where the stent graft comprises, a main body stent graft with a first bifurcation defining a first leg and a second leg, the main body stent graft has distal and proximal ends, the main body stent graft has a diameter at the proximal end in the range from about 18 mm to about 28 mm, the first leg and the second leg each have a diameter in the range from about 12 mm to about 18 mm, the distance from the proximal end of the main body to the distal end of the first leg is in the range from about 30 mm to about 50 mm, and the distance from the proximal end of the main body to the distal end of the second leg is in a range from about 50 mm to about 70 mm.
Owner:SANFORD HEALTH
Process and device for sterile blood sampling of live pigs
InactiveCN101755884AAvoid pollutionReduce pollutionBlood collection/stirring apparatusBlood collectionCatheter
The invention relates to a process and a device for sterile blood sampling of live pigs. The process comprises: fixing a live pig in a sterilized hermetic blood sampling system; puncturing the heart the live pig and the great vessel connected with the heart through a puncture needle to perform sterile blood sampling; and connecting the puncture needle with a blood collection container through a duct to collect blood, wherein the blood sampling speed is 0.5 to 5 L / 1 to 10 minutes, and the blood sampling amount is 0.5 to 5 L / 100 kg / pig. Compared with the prior art, the process has the advantages of simplicity, easy implementation, effective prevention of microbial contamination to pig blood, low cost and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI P & P BIOTECH
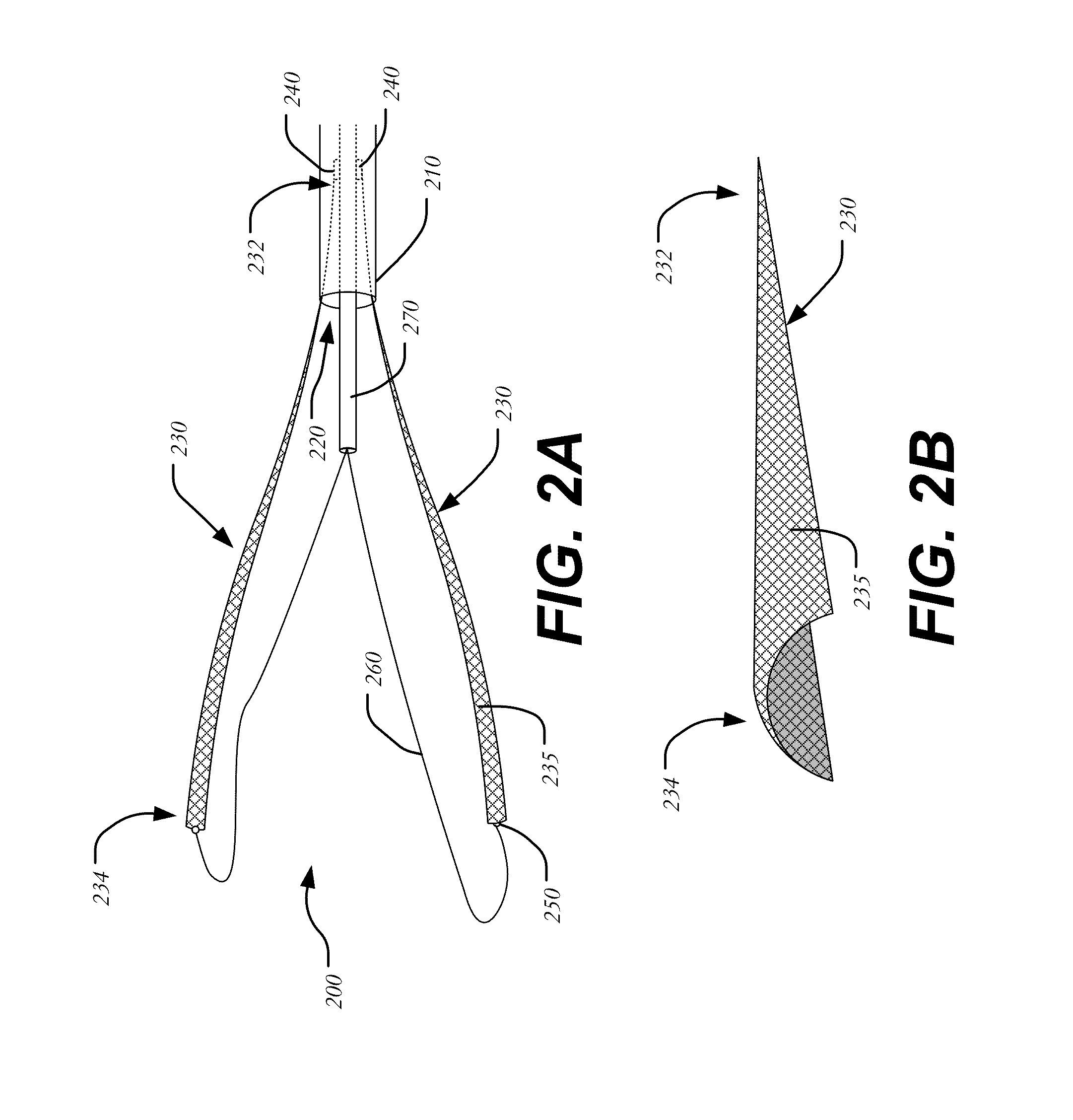
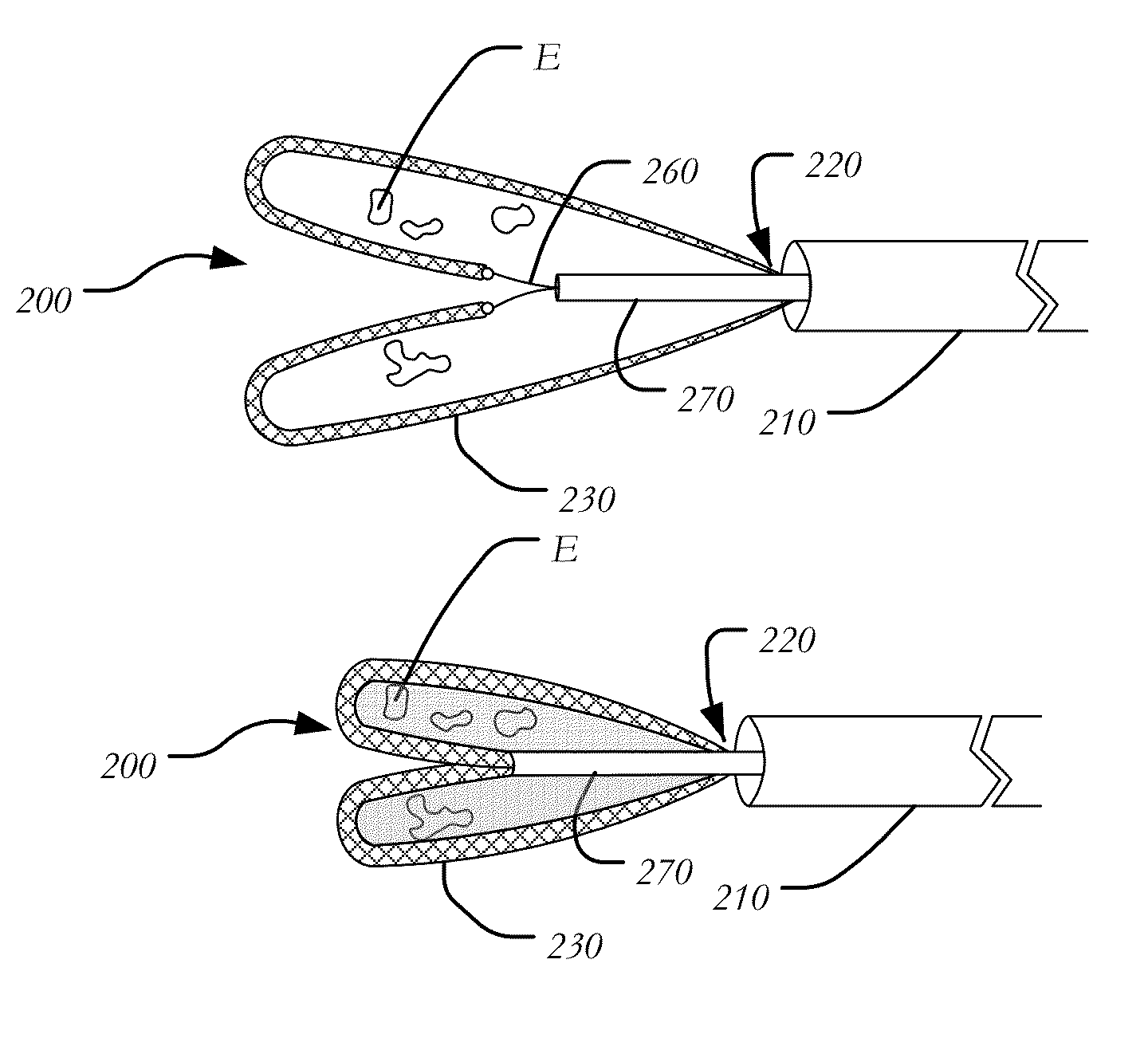
Aortic great vessel protection
A vessel protector system includes an outer sheath, an inner tube disposed within the outer sheath and moveable in a longitudinal direction relative to the outer sheath and at least one protector coupled to the inner tube, each of the at least one protector having a body formed from a filtering material and extending between a leading end and trailing end coupled to the inner tube, the body having a collapsed configuration and an expanded configuration. A snare is coupled to the leading end of the body at one end, and having a second end passing through the interior of the outer sheath, whereby the exertion of a pulling force on the second end of the snare contracts the at least one protector.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Aortic great vessel protection
A vessel protector system includes an outer sheath, an inner tube disposed within the outer sheath and moveable in a longitudinal direction relative to the outer sheath and at least one protector coupled to the inner tube, each of the at least one protector having a body formed from a filtering material and extending between a leading end and trailing end coupled to the inner tube, the body having a collapsed configuration and an expanded configuration. A snare is coupled to the leading end of the body at one end, and having a second end passing through the interior of the outer sheath, whereby the exertion of a pulling force on the second end of the snare contracts the at least one protector.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
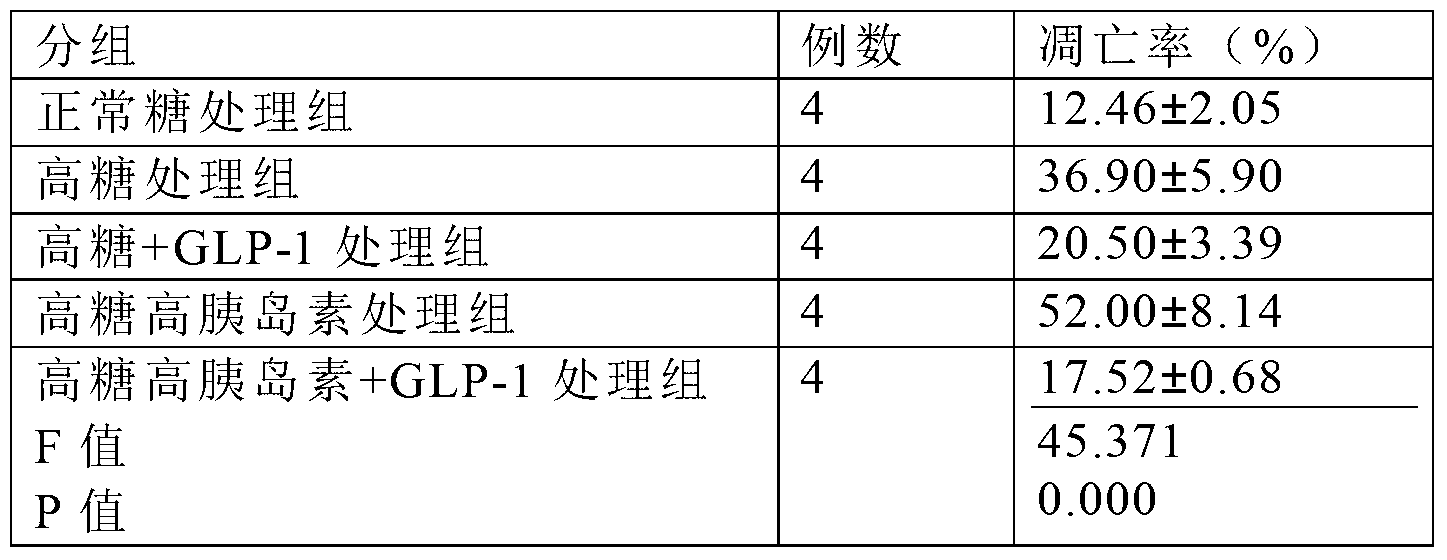
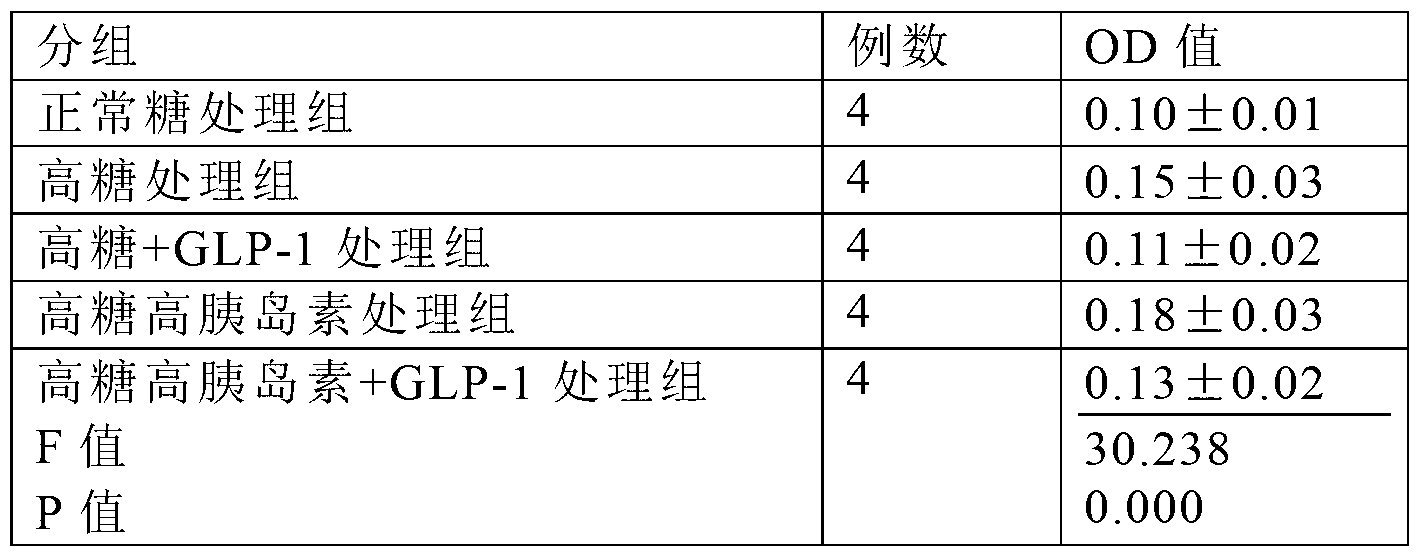
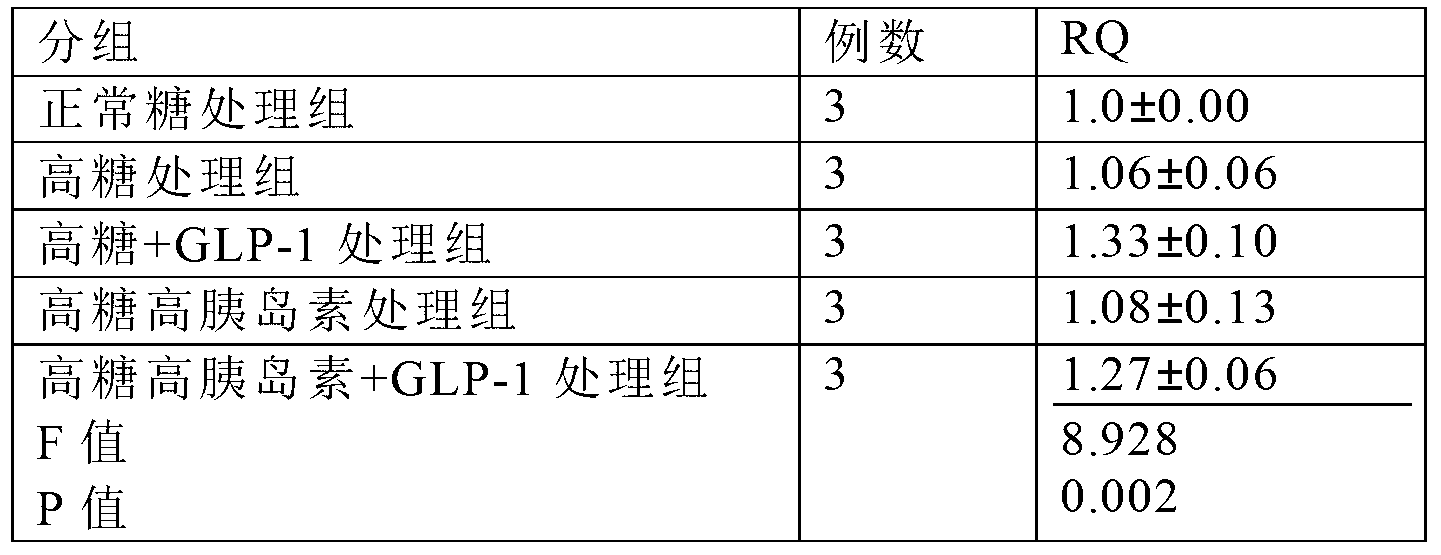
Use of GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) for preparing medicines for preventing and treating macrovascular complications of type 2 diabetes
InactiveCN103285379ANot easy to degradePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderScavengerGlucagon-like peptide-1
The invention provides use of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) for preparing medicines for preventing and treating macrovascular complications of type 2 diabetes. The experiments show that GLP-1 has the anti-apoptosis effect by inhibiting the JNK (Jun N-terminal Kinase) signal paths of aortic endothelial cells of mice, increasing expression of Bc1-2 and inhibiting the activity of caspase-3. The effect is probably completed by promoting ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) in scavenger-cells to exert anti-oxidative damage effect. GLP-1 in vitro and in vivo can remarkably improve degree of injury of great vessels of mice with type 2 diabetes. Therefore, GLP-1 can be used for preparing medicines for preventing and treating macrovascular complications of type 2 diabetes. The invention further provides a pharmaceutical composition for preparing medicines for preventing and treating macrovascular complications of type 2 diabetes.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Electromagnetic controllable occlusion system for celiac great vessels
ActiveCN103142283ASimple and fast operationOperate quickly and safelySurgeryWhole bodyControllability
An electromagnetic controllability occlusion system for celiac great vessels comprises an internal magnetic vessel occlusion device, an external electromagnet element and central control equipment, wherein the internal magnetic vessel occlusion device corresponds to an external electromagnet element which is connected with the central control equipment; the internal magnetic vessel occlusion device is placed on the surface of an infrahepatic vena cava and used for pressing and occluding vessels; the external electromagnet element is integrated into an operating bed mattress and used for locating the internal magnetic vessel occlusion device and gradually increasing the current of the external electromagnet element; and occlusion of postcava or aorta abdominalis is realized through attraction between the external electromagnet element and the internal magnetic vessel occlusion device. The electromagnetic controllability occlusion system can be operated simply, conveniently, quickly and safely, avoids defects of longer operation time, vessel injury and the like, which are caused by vessel separation in an open appendectomy or laparoscopic surgery , and simultaneously solves the problem of instable systemic hemodynamics probably caused by a traditional vessel occlusion method.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Covered stent used in chest great vessel cavity
InactiveCN104352288ANo local abnormal stressLocal abnormal stress preventionStentsBlood vesselsAorta aorticStraight tube
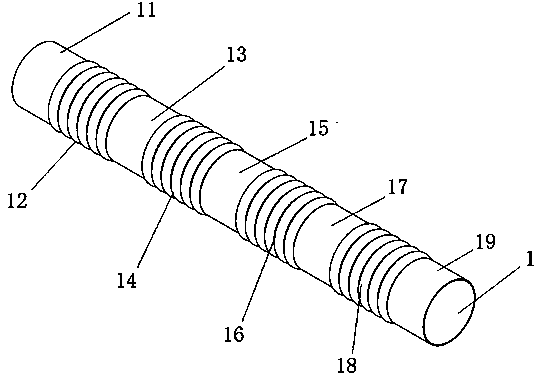
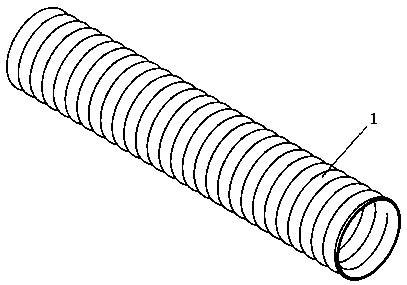
The invention relates to a covered stent used in a chest great vessel cavity. Compared with the prior art, the defects that a covered stent is incapable of overcoming straightening force and is poor in practicability are overcome. The covered stent comprises artificial blood vessels (1) and support frames (2), wherein each artificial blood vessel (1) comprises a plurality of straight pipes and a plurality of pleated pipes; the straight pipes are connected at intervals through the pleated pipes; the support frames (2) are wrapped on each straight pipe respectively; the straight pipes are arranged at the two ends of each artificial blood vessel (1) respectively. The covered stent has certain longitudinal stretching deformation capacity, can fit the physiological bending of an aorta, and eliminates the straightening force after a traditional stent is bent, so that the blood vessel wall of the aorta is uniformly stressed.
Owner:章庆春 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com