Patents
Literature
100 results about "Aorta aortic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
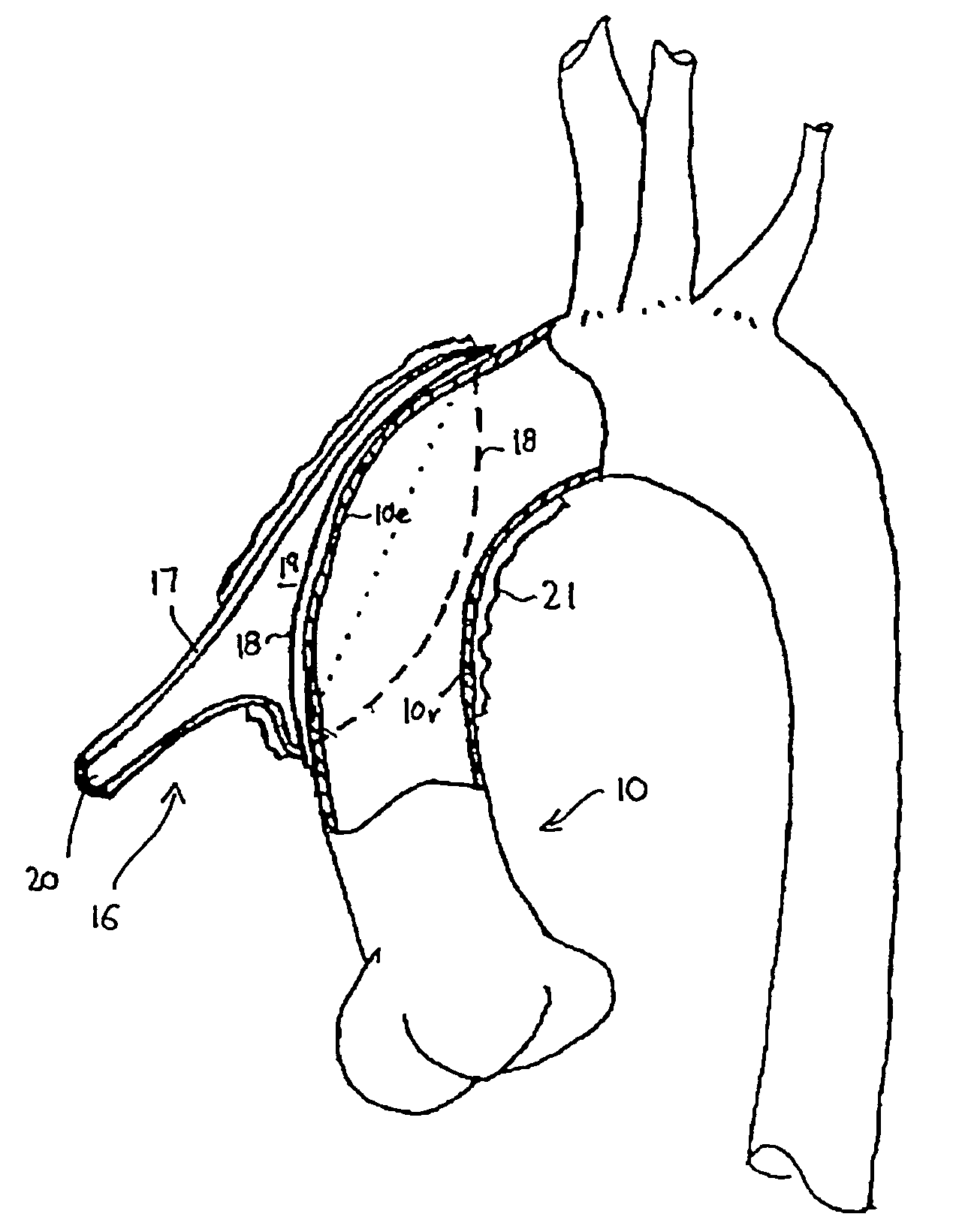
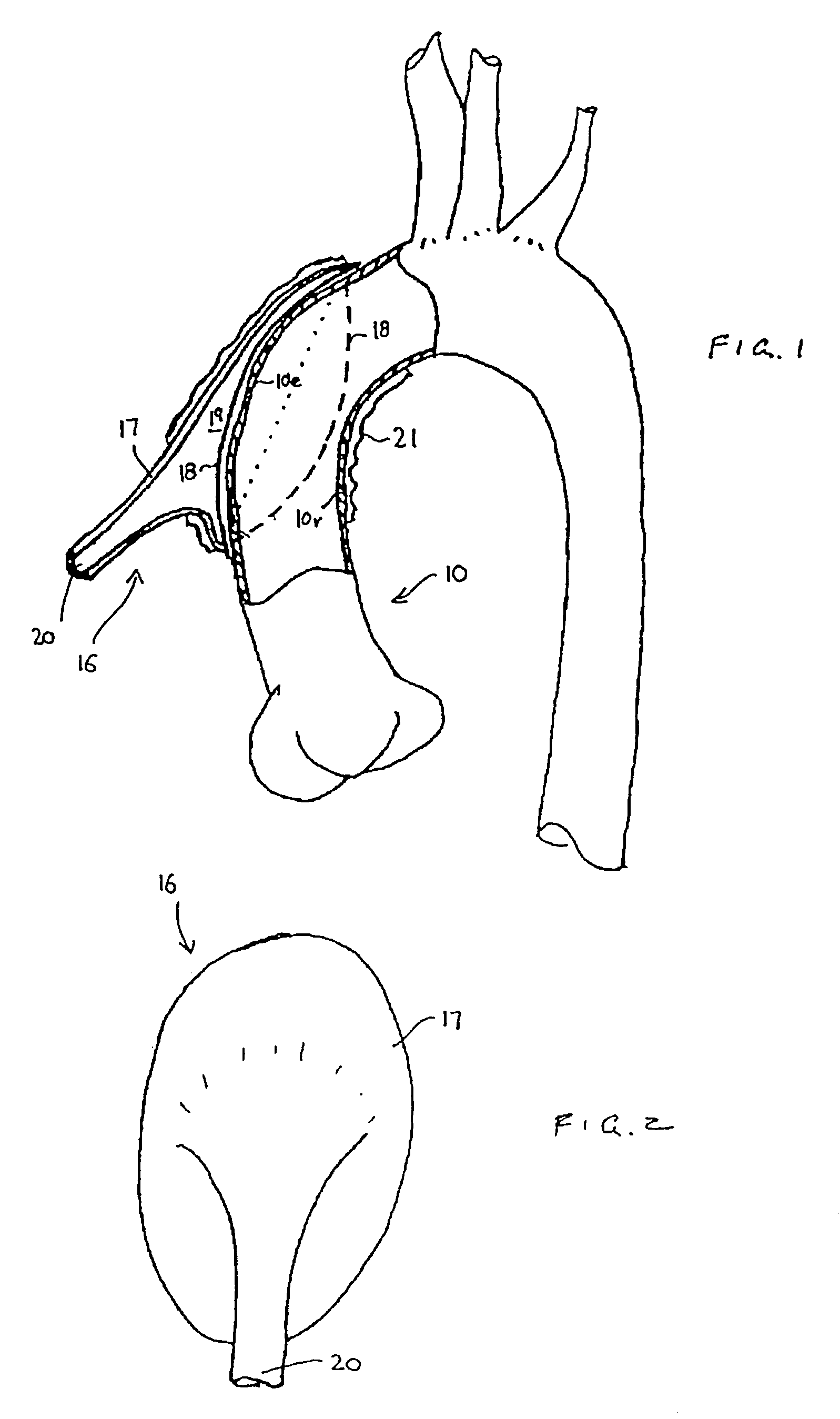
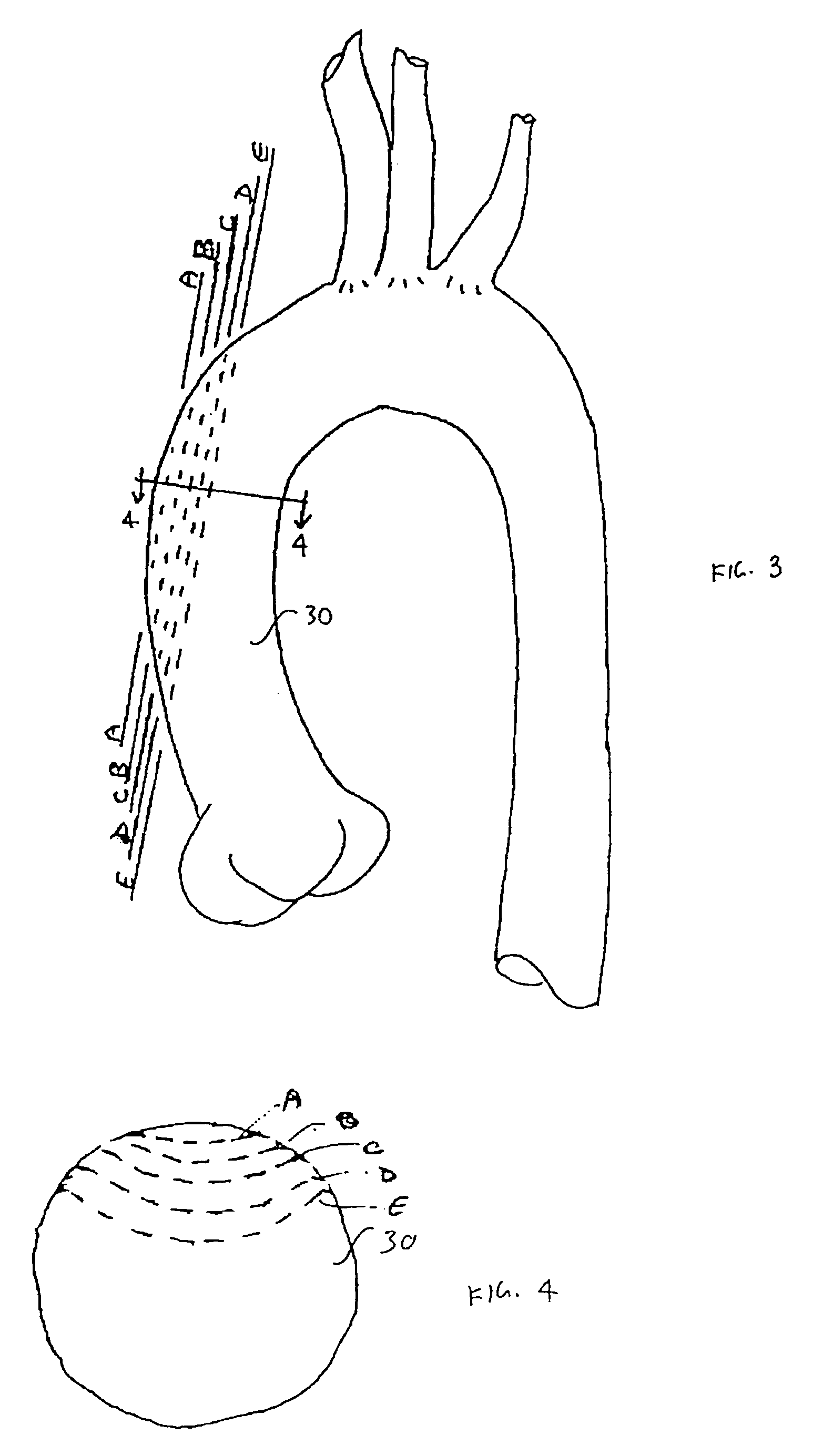
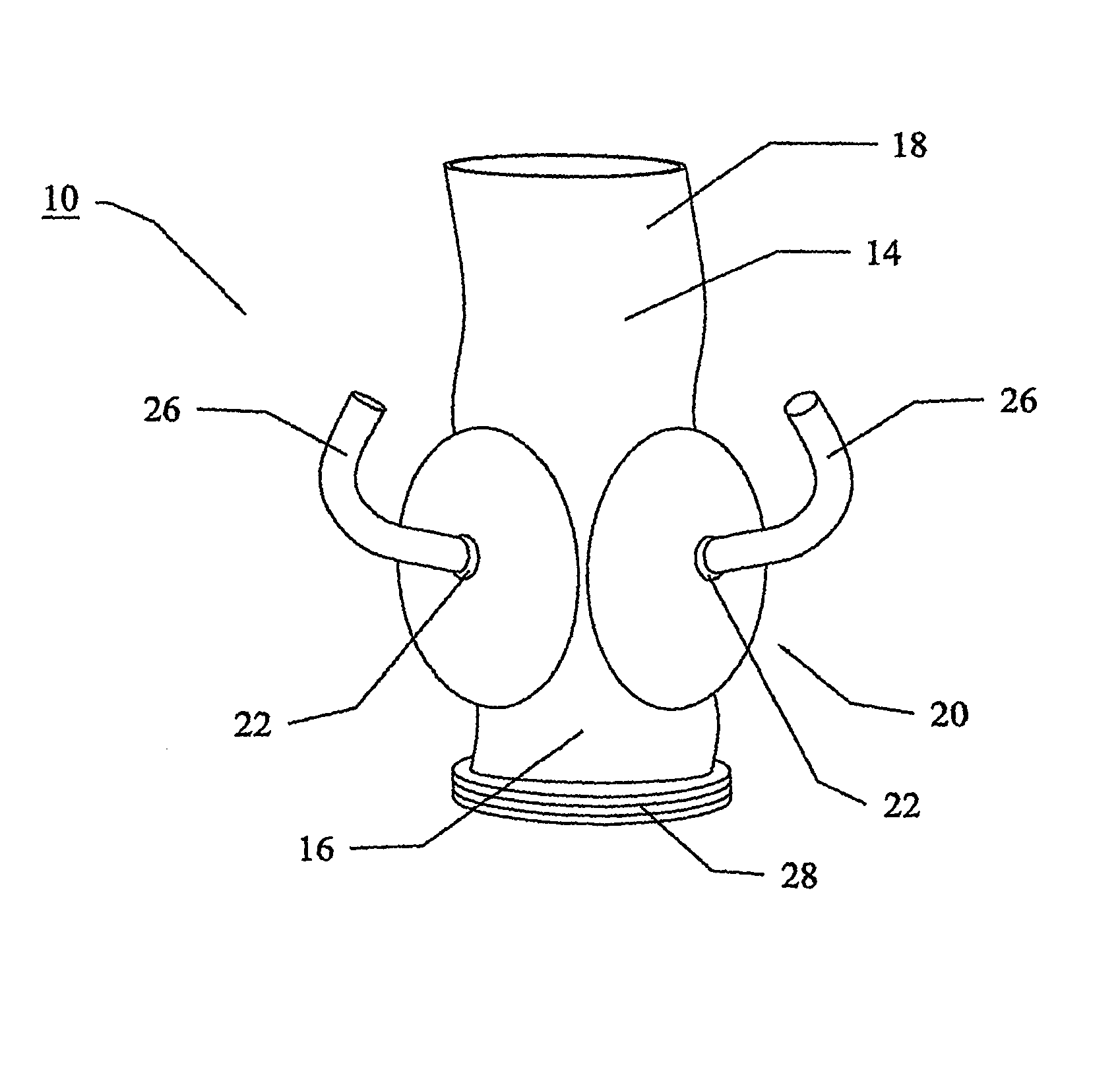
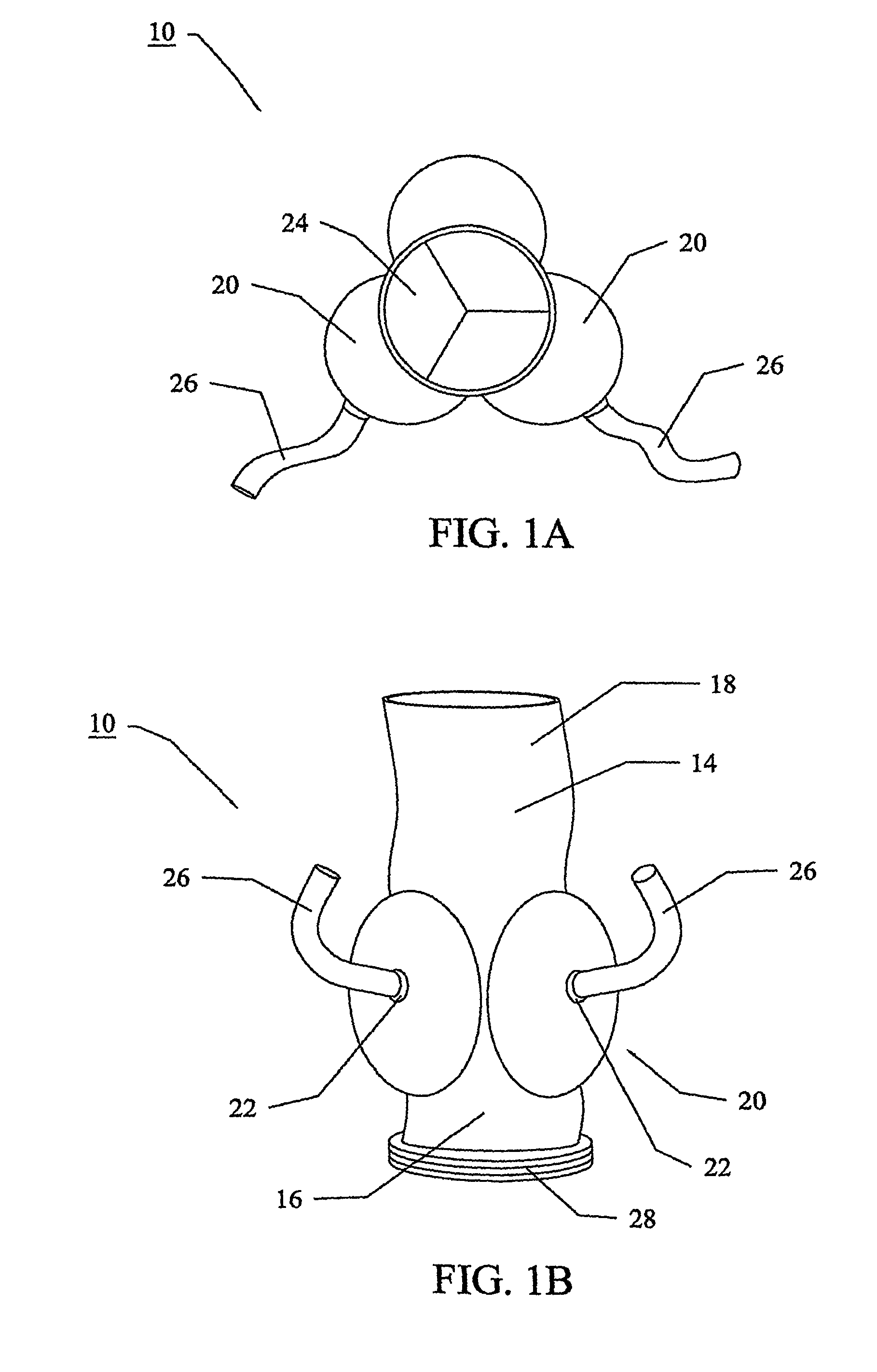
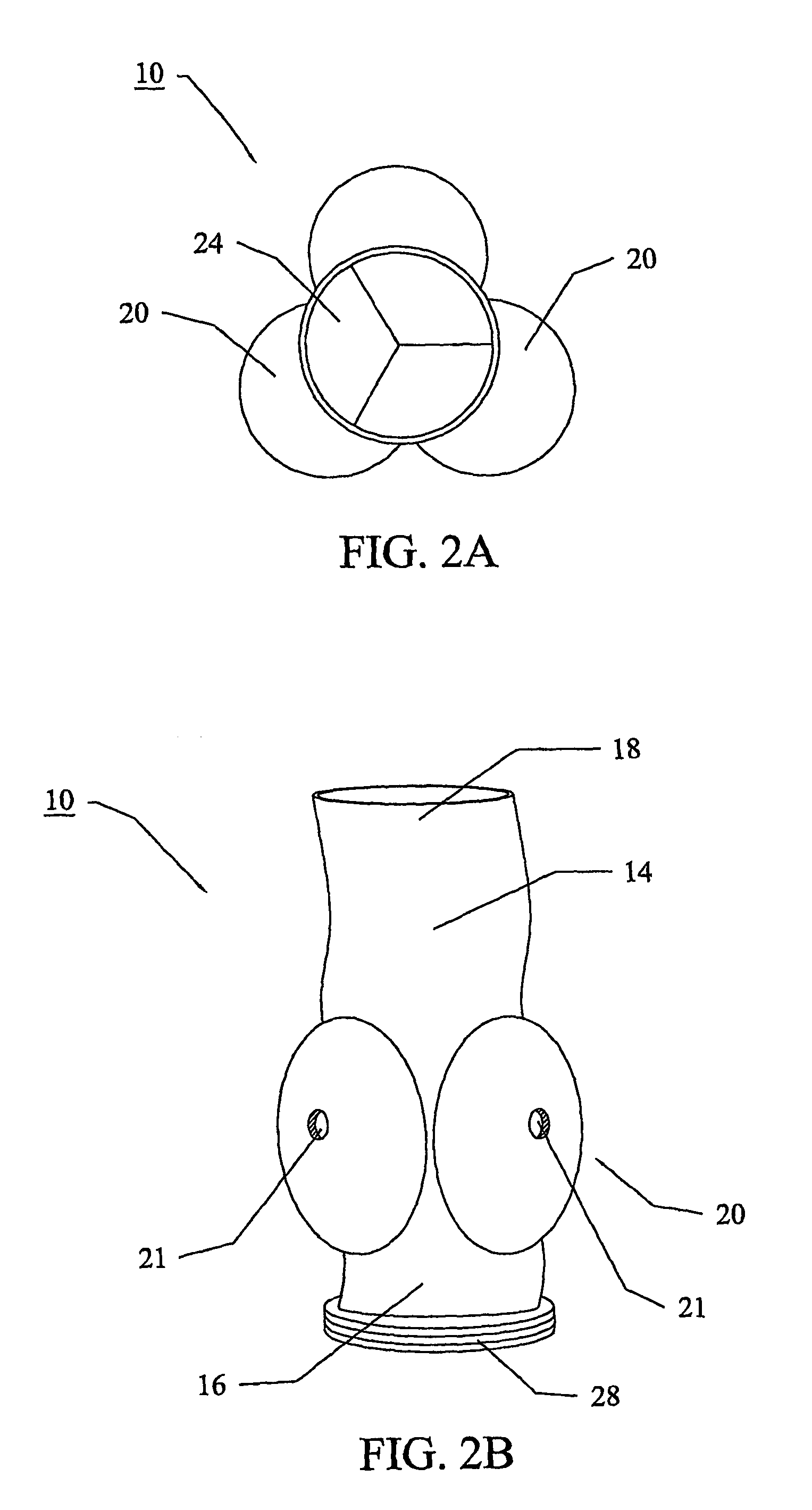
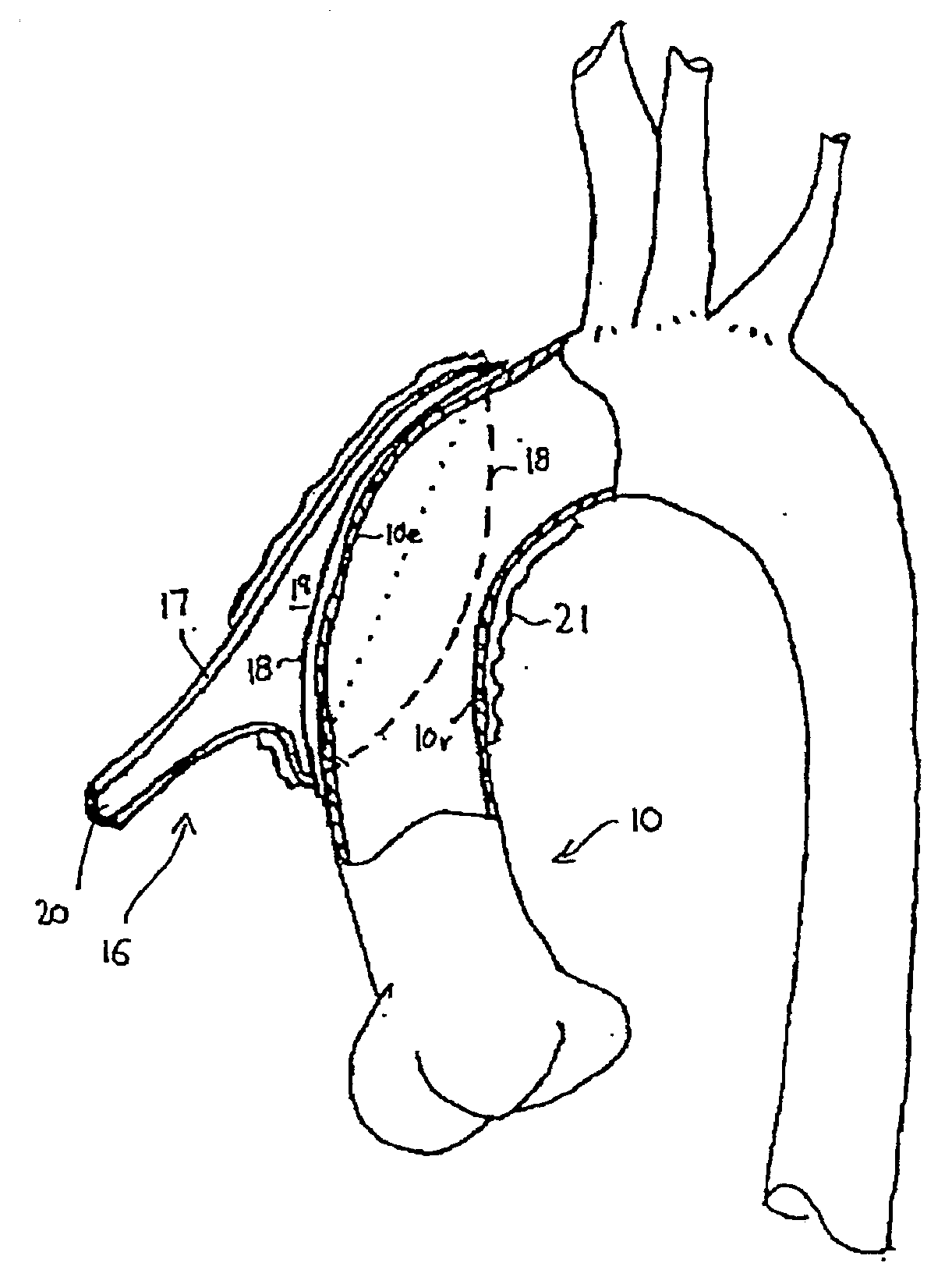
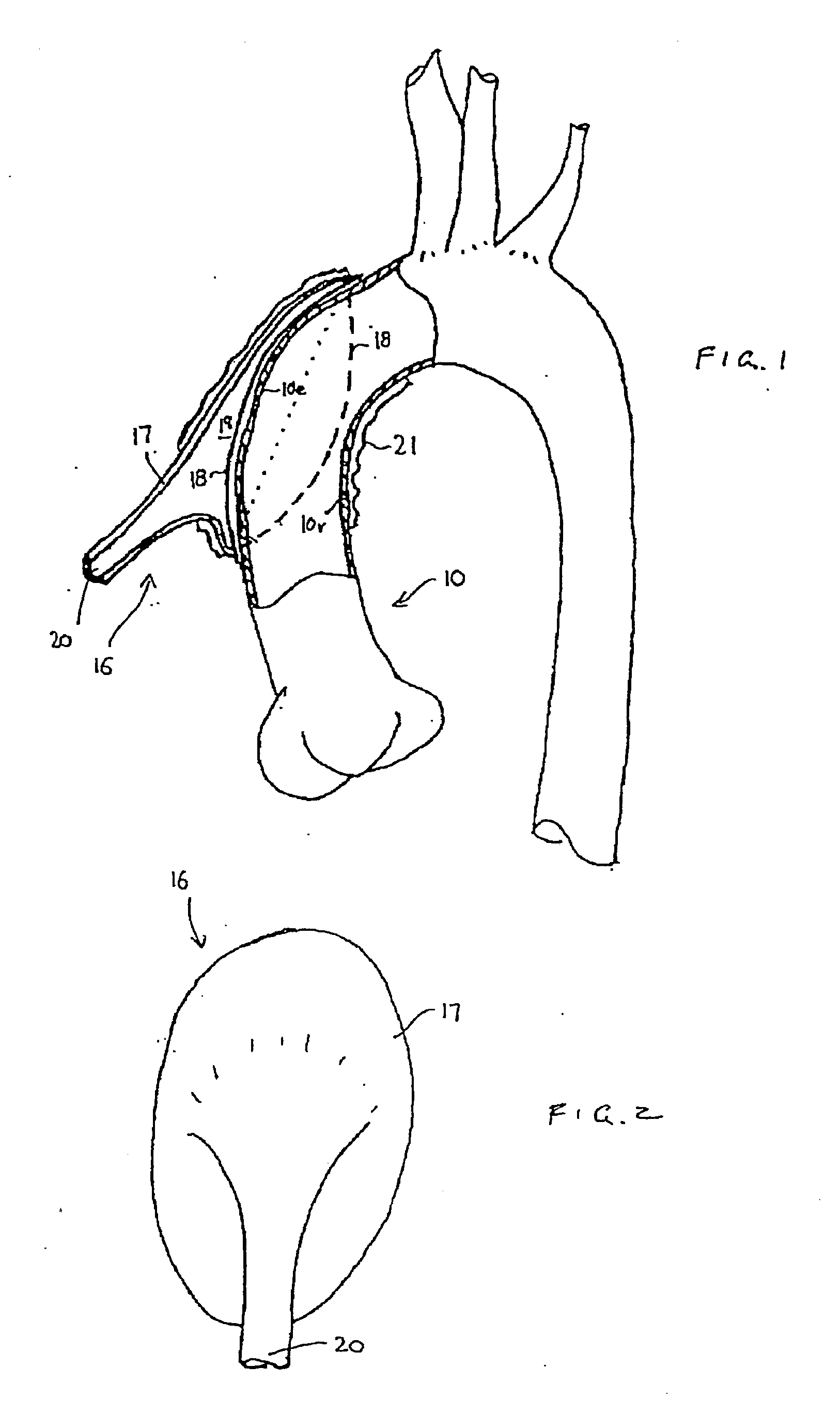
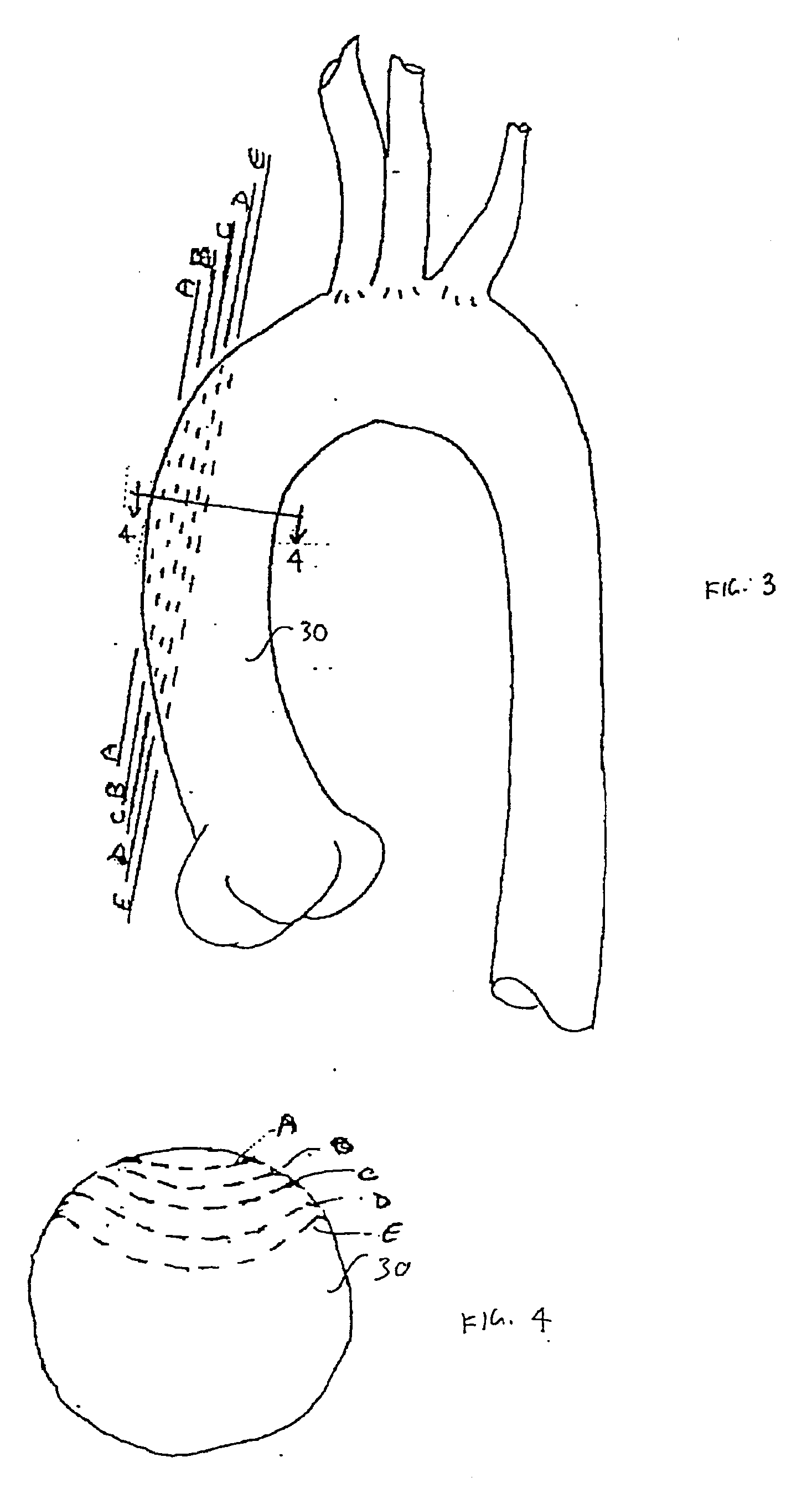
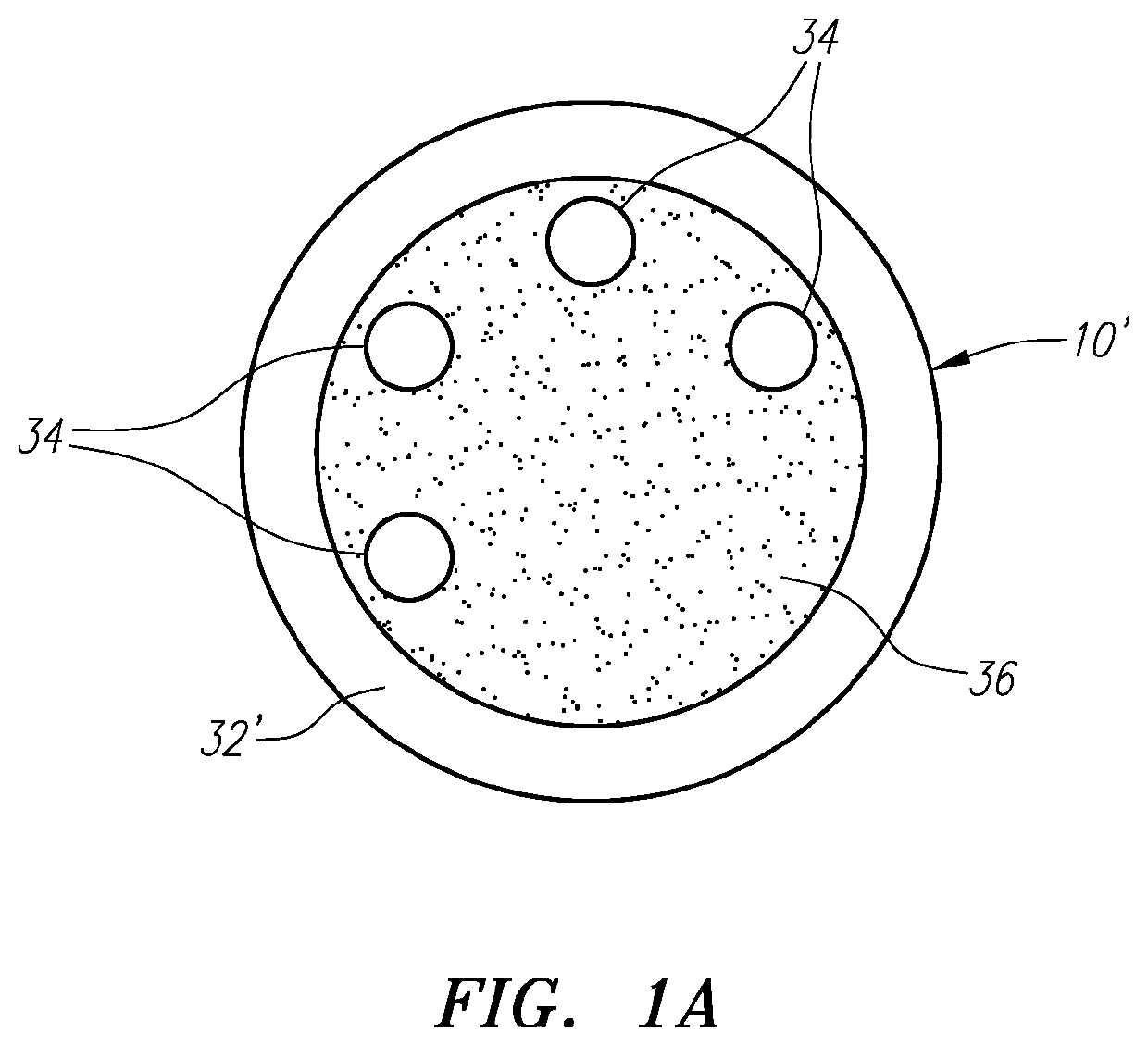
Heart assist device utilising aortic deformation
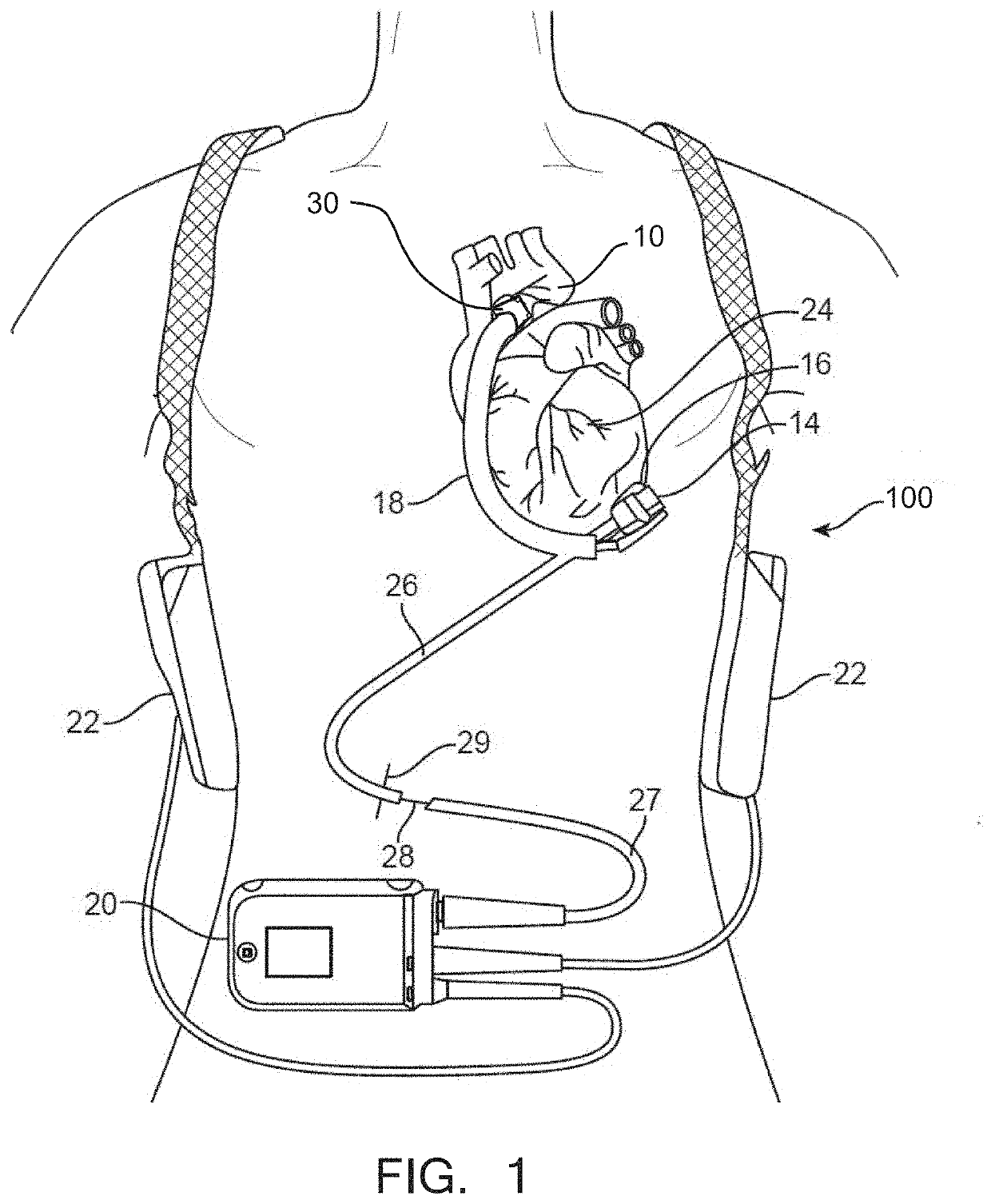
The present invention relates to providing counter-pulsation heart assist by deforming the aorta. In a preferred embodiment, the deformation pressure is applied by cyclically, preferably in synchrony with the diastolic period of the heart. The deformation pressure may be applied to the outer wall of the aorta or to a patch covering a resected opening in the wall of the aorta.
Owner:NUWELLIS INC
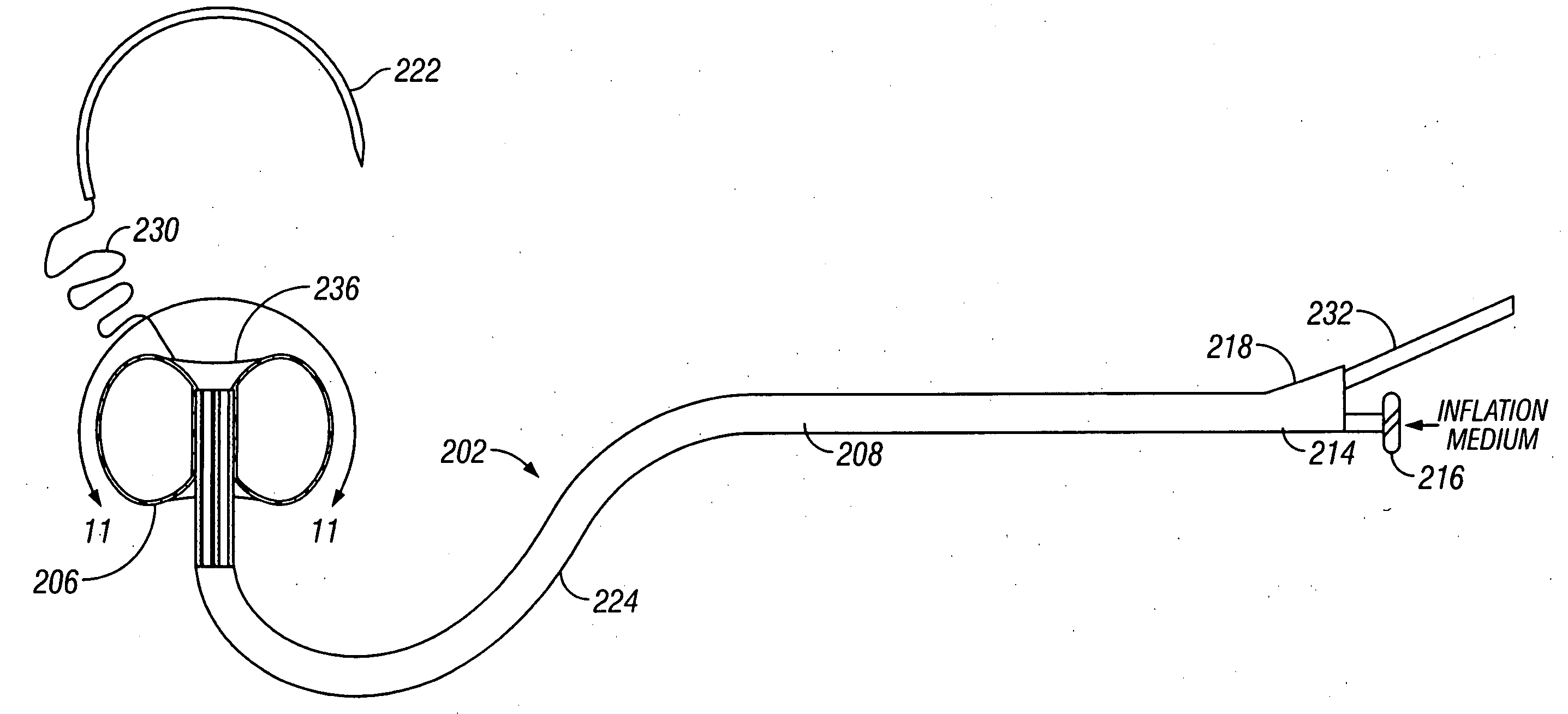
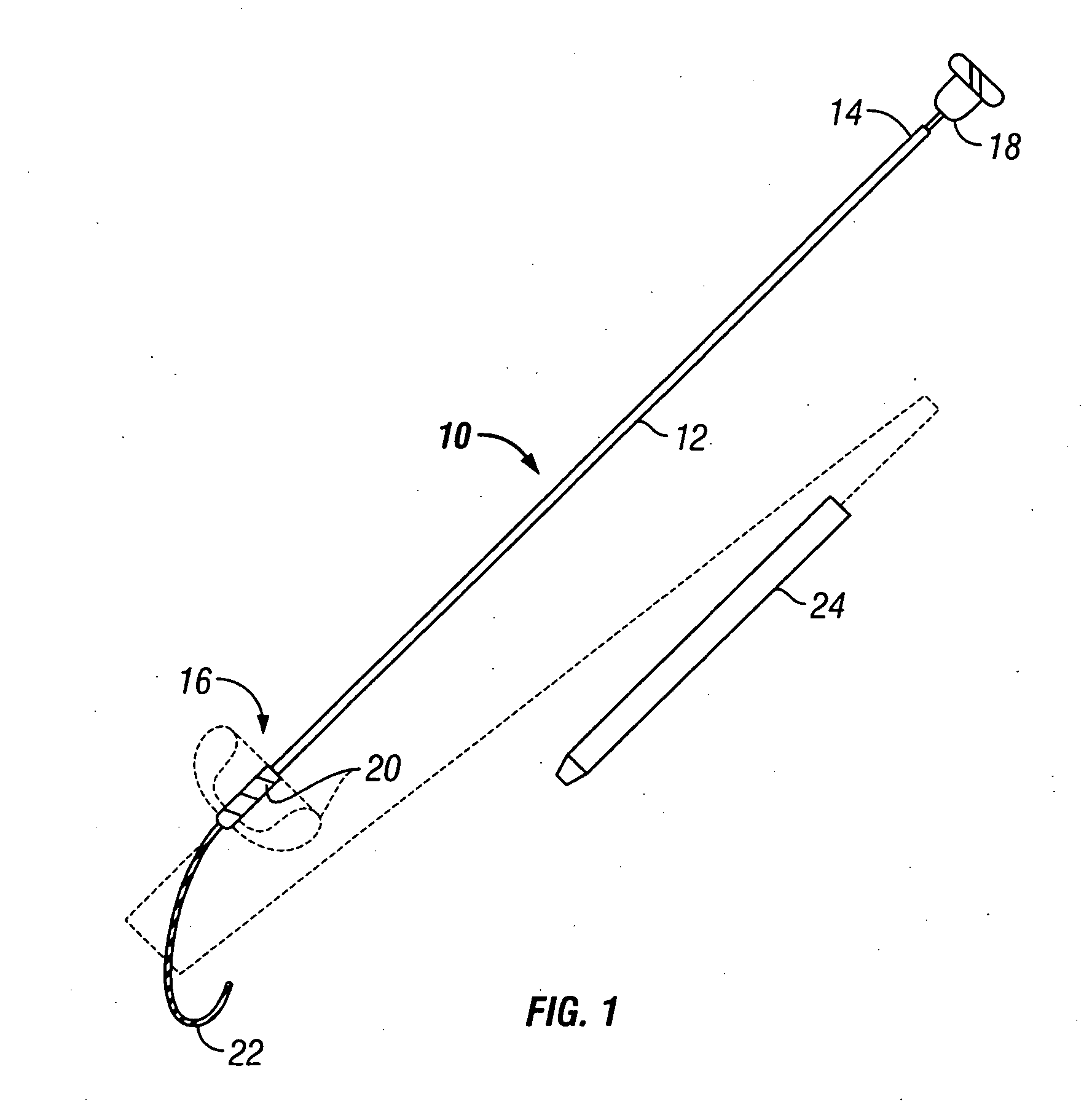
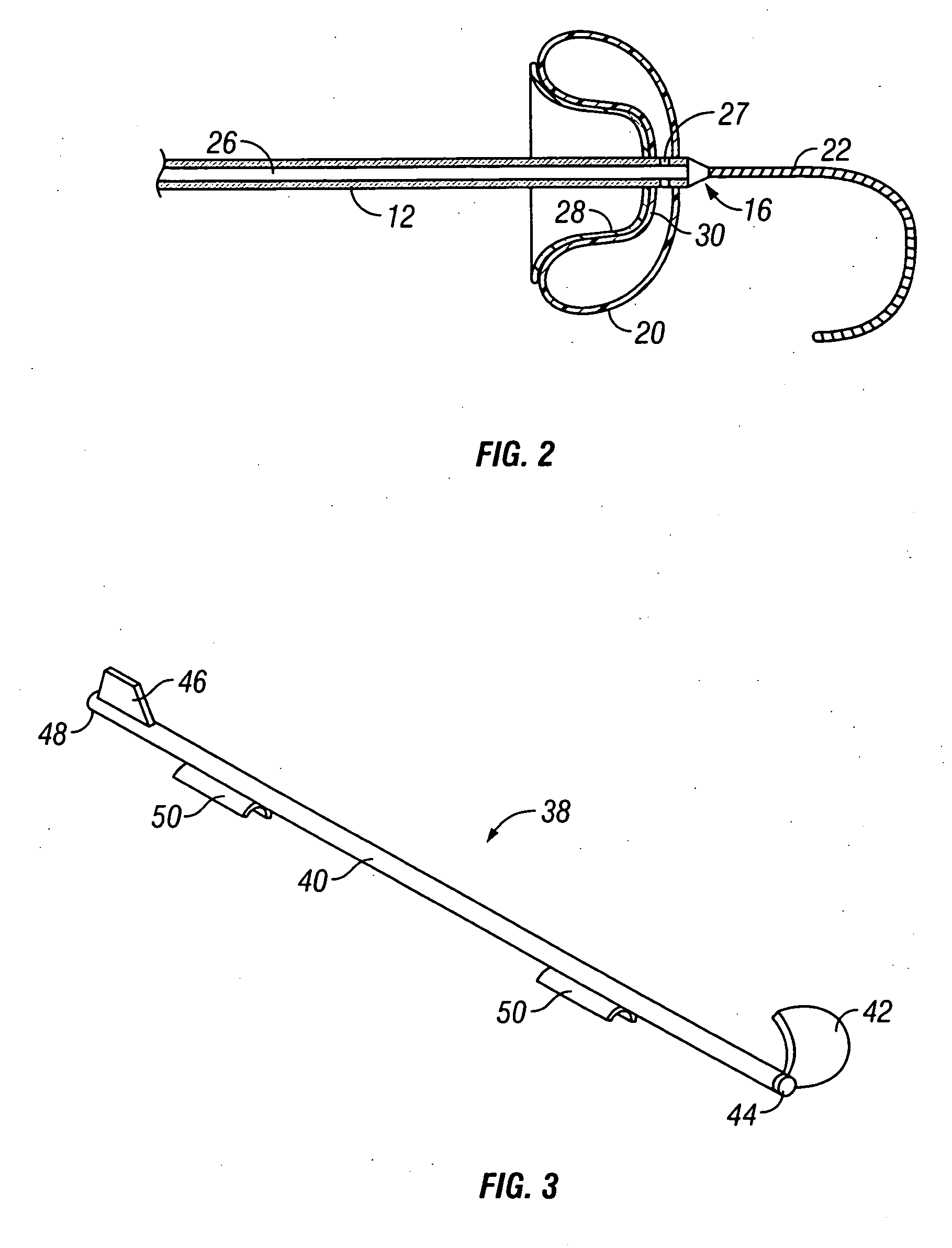
Methods and apparatus for forming anastomotic sites
InactiveUS20040215233A1Conveniently formedAvoid interferenceSuture equipmentsSurgical veterinaryEnd to side anastomosisThree vessels
Apparatus and methods are provided for forming a working space on the interior wall of a blood vessel, such as the aorta. The working space is isolated from blood flow and permits creation of an anastomotic hole and subsequent suturing of the hole to form an end-to-side anastomosis, even while the heart is beating. The apparatus comprises tools including inflatable barriers, such as cup-shaped balloons, which engage the inner wall of the blood vessel with minimum trauma and maximum sealing. In a first embodiment, the inflatable barrier is introduced through a penetration at the site of the anastomotic attachment. In a second embodiment, the inflatable barrier is introduced through a second penetration axially spaced-apart from the site of the anastomotic attachment.
Owner:MAGENTA MEDICAL CORP
Vascular prosthesis
The subject invention concerns vascular prosthetic devices and methods for ascending aorta and / or valve replacement in humans and animals. In one embodiment, a device of the invention includes a vessel-like structure having a first end adapted for surgical attachment to a left ventricle, a second end adapted for surgical attachment to an aorta, and, interposed between the first and second ends, a sinus portion configured in the shape of the sinuses of Valsalva in a human aortic valve.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
System and method for 2-d/3-d registration between 3-d volume and 2-d angiography
InactiveUS20120163686A1Highly accurate and robust -D/3-D alignmentConvenient registrationImage enhancementImage analysisIn planeCoronary arteries
A method for registering a 2-D DSA image to a 3-D image volume includes calculating a coarse similarity measure between a 2-D DRR of an aorta and a cardiac DSA image, and a 2-D DRR of a coronary artery and the cardiac DSA image, for a plurality of poses over a range of 2-D translations. Several DRR-pose combinations with largest similarity measures are selected as refinement candidates. The similarity measure is calculated between the refinement candidate DRRs and the DSA, for a plurality of poses over a range of 3-D translations and in-plane rotations. One or more DRR-pose combinations with largest similarity measures are selected as final candidates. The similarity measure between the final candidate DRRs the DSA are calculated for a plurality of poses over a range of 3D translations and 3D rotations, and a DRR-pose combination with a largest similarity measure is selected as a final registration result.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Heart Assist Device Utilising Aortic Deformation
The present invention relates to providing counter-pulsation heart assist by deforming the aorta. In a preferred embodiment, the deformation pressure is applied by cyclically, preferably in synchrony with the diastolic period of the heart. The deformation pressure may be applied to the outer wall of the aorta or to a patch covering a resected opening in the wall of the aorta.
Owner:NUWELLIS INC
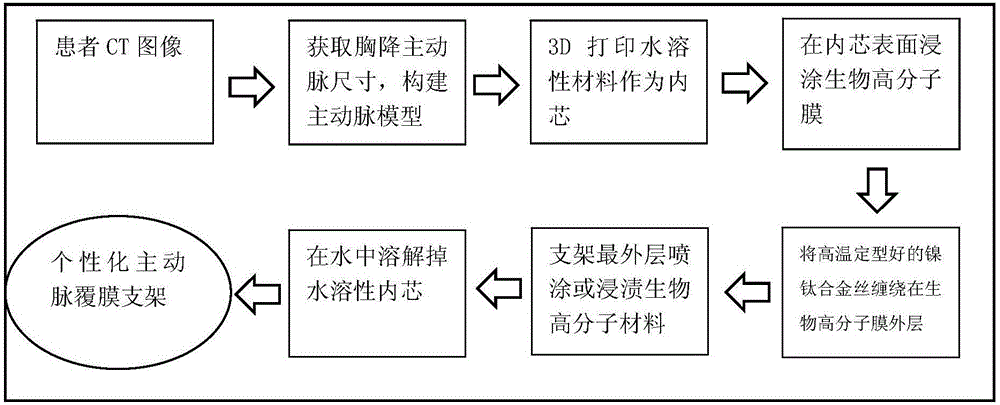
Method for forming aortic stent graft
InactiveCN106491241AEfficient preparationMade preciselyStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusAorta partDip-coating
The invention discloses a method for forming an aortic stent graft. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an image of aorta, and extracting a three-dimensional (3D) model of the aorta according to the image; extracting diameter characteristics of the aorta in the axial direction of the aorta of the 3D model; reconstructing an aortic vascular model according to the extracted diameter characteristics; 3D-printing a water-soluble vascular inner core according to the aortic vascular model; dip-coating a polymer film on a surface of the water-soluble vascular inner core; spirally weaving a metal mesh outside the treated water-soluble vascular inner core as a metal stent; bonding the polymer film and the metal stent, and then removing the water-soluble vascular inner core to obtain the aortic stent graft. The method provided by the invention can efficiently and accurately manufacture a vascular stent graft according to the actual size of a thoracic descending aorta of a patient based on a 3D printing technology, can effectively solve a detect that an existing equal-diameter vascular stent does not match a true vascular size of the patient, provides an effective medical means for treatment of acute vascular aneurysm, and has important clinical value.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
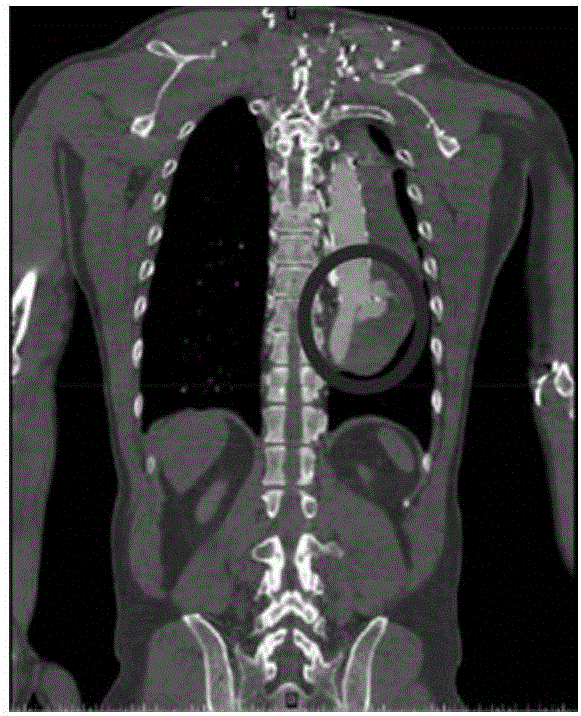
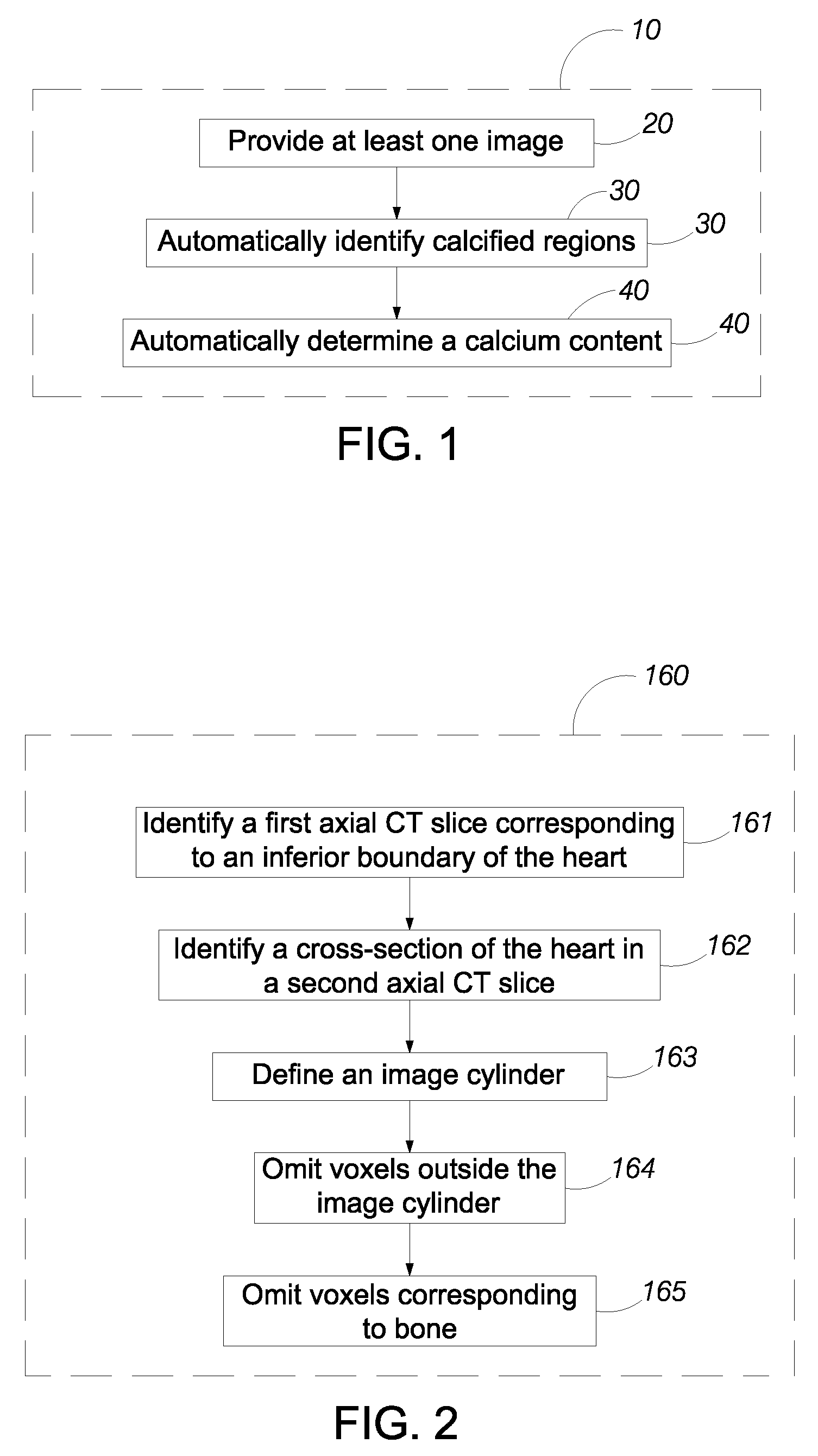
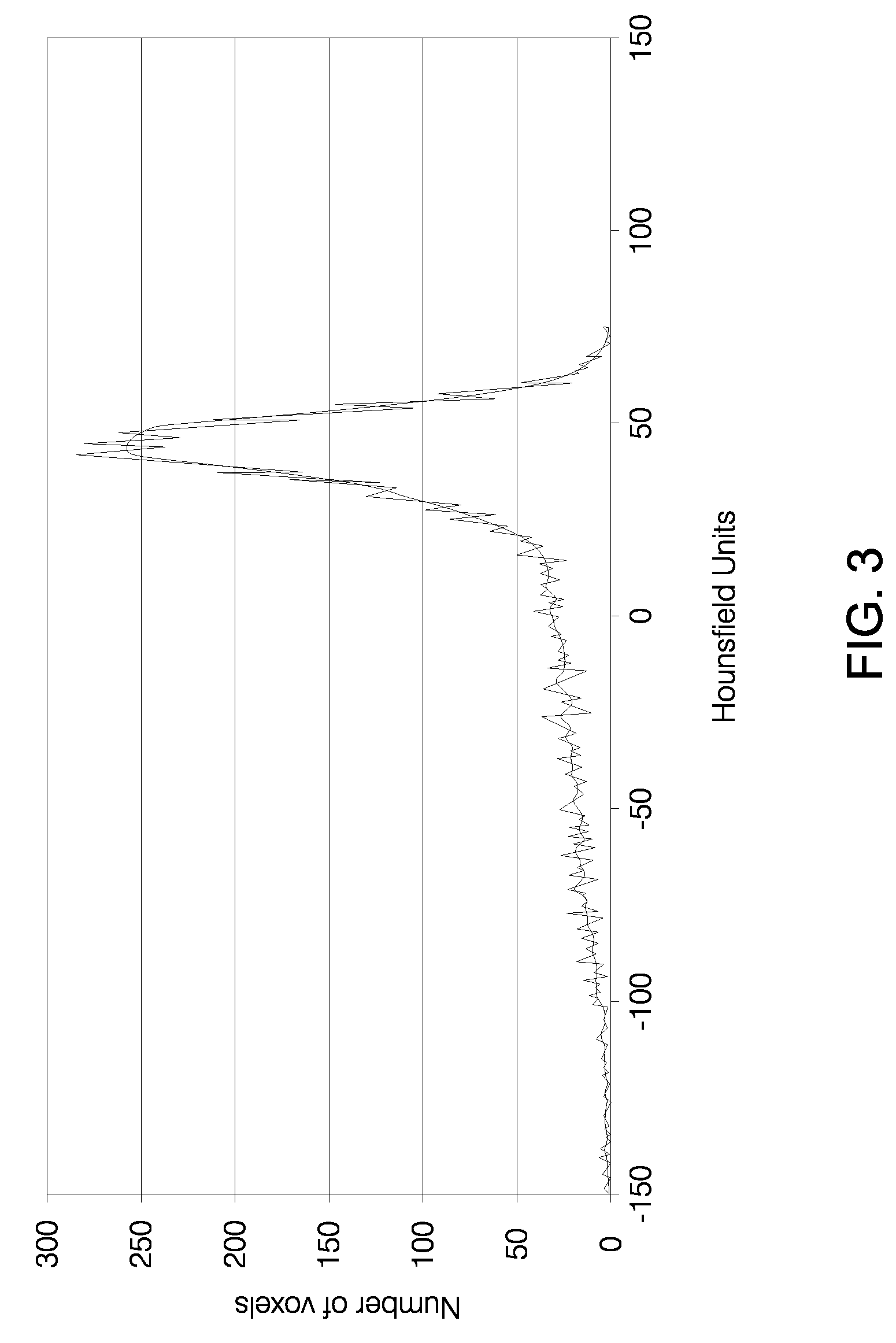
Automated Calcium Scoring of the Aorta
InactiveUS20080279435A1High precisionReduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelFollow up examination
A method automatically scores calcium in the aorta and other arteries of the body using calcium plaque definitions that include subject specific in vivo blood / muscle density measurements, subject specific voxel statistical parameters and 2D and 3D voxel connectivity criteria to automatically identify the plaques. The images are optionally calibrated with external phantoms or internal reference tissue. Aortic calcium is identified automatically without manual marking. Potential false plaques from bone are automatically excluded. A 3D coordinate system provides the specific coordinates of the detected plaques, which are displayed in a plaque map for follow-up exams or ease in plaque review.
Owner:ARNOLD BEN A
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation pressure wires and uses thereof
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Model building method for dissection of aorta, model and surgery simulation detection method
ActiveCN109700527AIncrease success rateComputer-aided planning/modelling3D modellingIliac arteryDissection
The invention provides a model building method for dissection of aorta, a model and a surgery simulation detection method. The model building method includes acquiring CTA video data of the aorta of apatient; building a three-dimensional model for the dissection of aorta according to the acquired CTA video data; performing 3D printing according to the three-dimensional model to prepare a model for dissection of aorta by utilizing a transparent material having elasticity same as that of blood vessels of the patient; arranging a pressure sensor on the inner side of the wall of the aorta in themodel for dissection of aorta, and arranging a flow sensor at an aorta branch outlet of the model for dissection of aorta. Accordingly, a physician can perform surgery simulation before actual surgeries.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
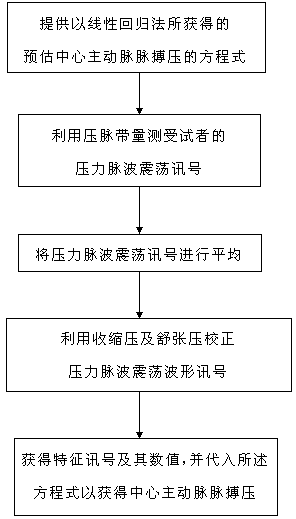
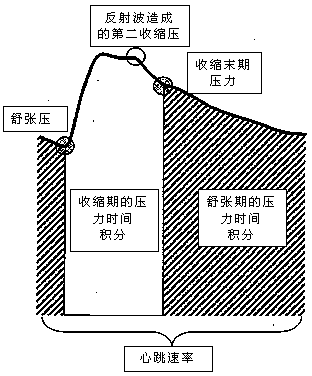
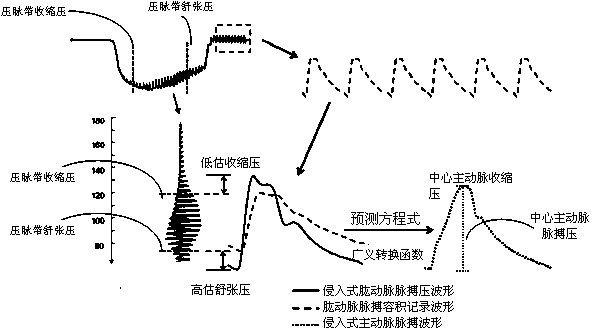
Method and device for estimating pulse pressure of central aorta by using pressure pulse wave vibration signals of tourniquet
The invention discloses a method for estimating pulse pressure of a central aorta by using pressure pulse wave vibration signals of a tourniquet. The method comprises the steps of (I) providing an equation for estimating the pulse pressure of the central aorta; (II) measuring the pressure pulse wave vibration signals in the tourniquet, wherein the pressure pulse wave vibration signals comprise brachial artery systolic pressure, brachial artery diastolic pressure and the pressure pulse wave vibration signal waveforms in the tourniquet; (III) averaging the pressure pulse wave vibration signal waveforms and carrying out correction by using the systolic pressure and the diastolic pressure; (IV) analyzing the corrected pressure pulse wave vibration signal waveforms to obtain a plurality of characteristic signal values, wherein the characteristic signal values are independent estimating variables of the equation of the step (I); (V) substituting the numerical value of the estimating variables into the equation for estimating the pulse pressure of the central aorta to obtain the pulse pressure of the central aorta. The invention further provides a device for estimating the pulse pressure of the central aorta by using the pressure pulse wave vibration signals of the tourniquet by using the method.
Owner:FARMAR LICENSING
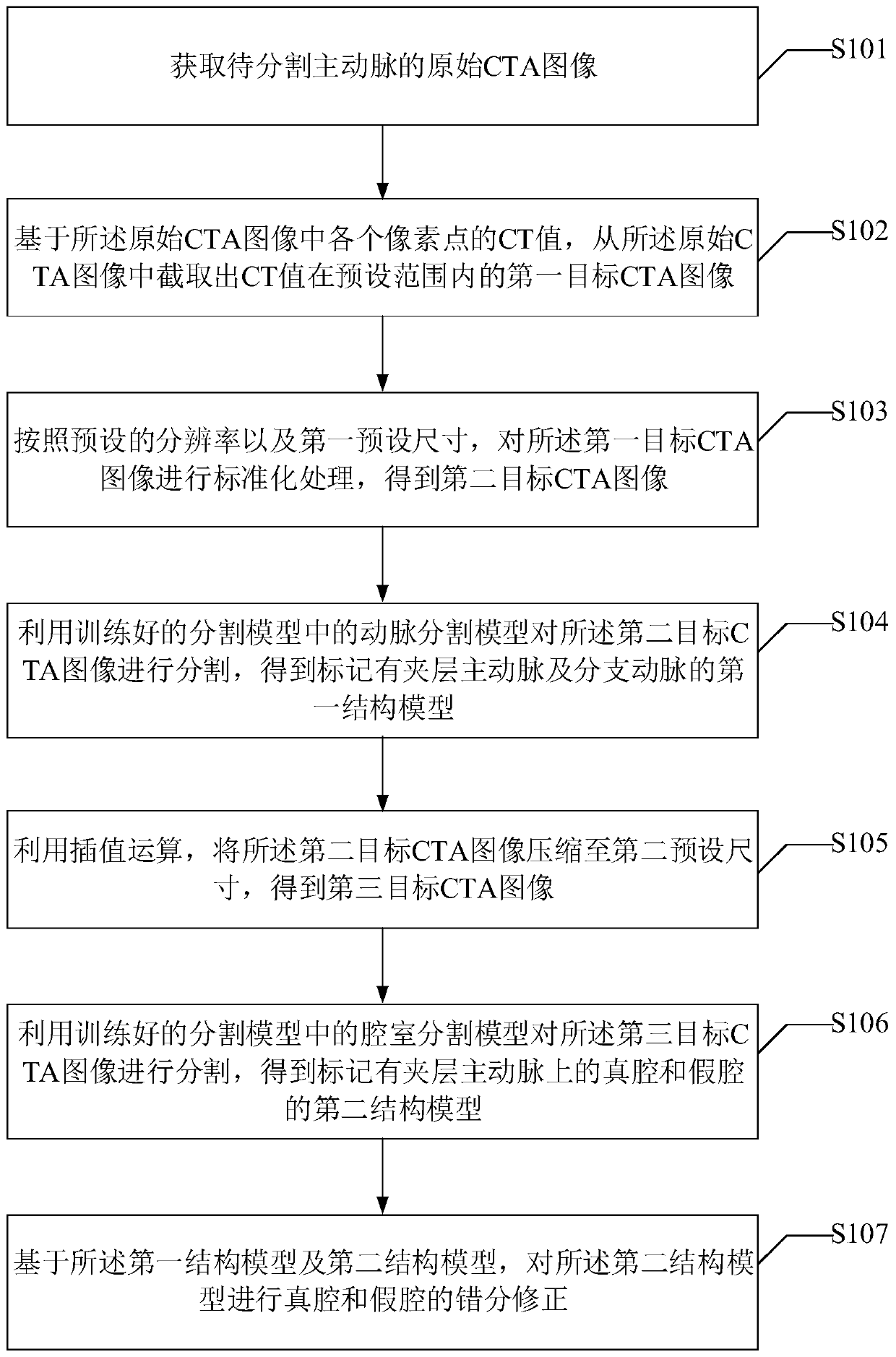
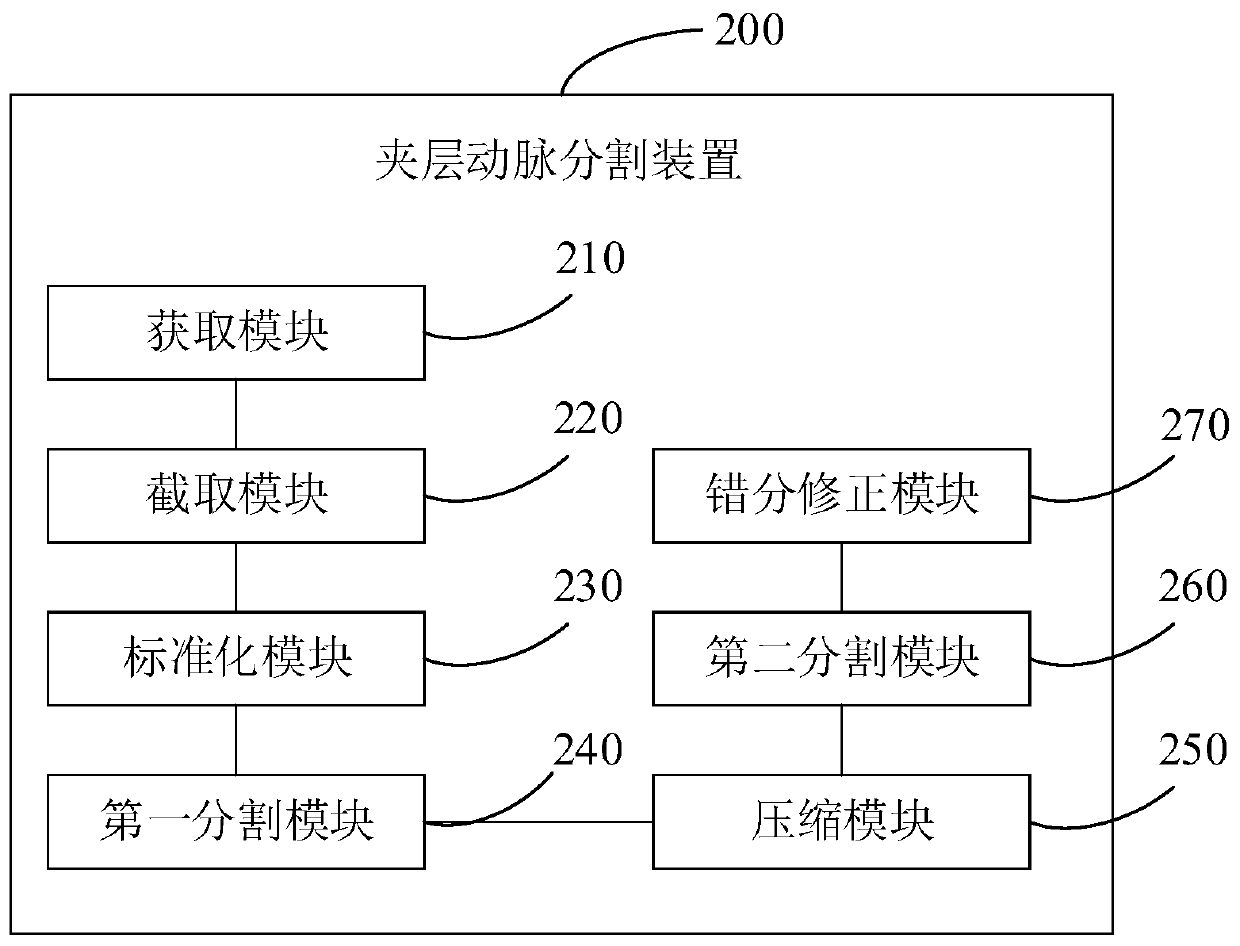
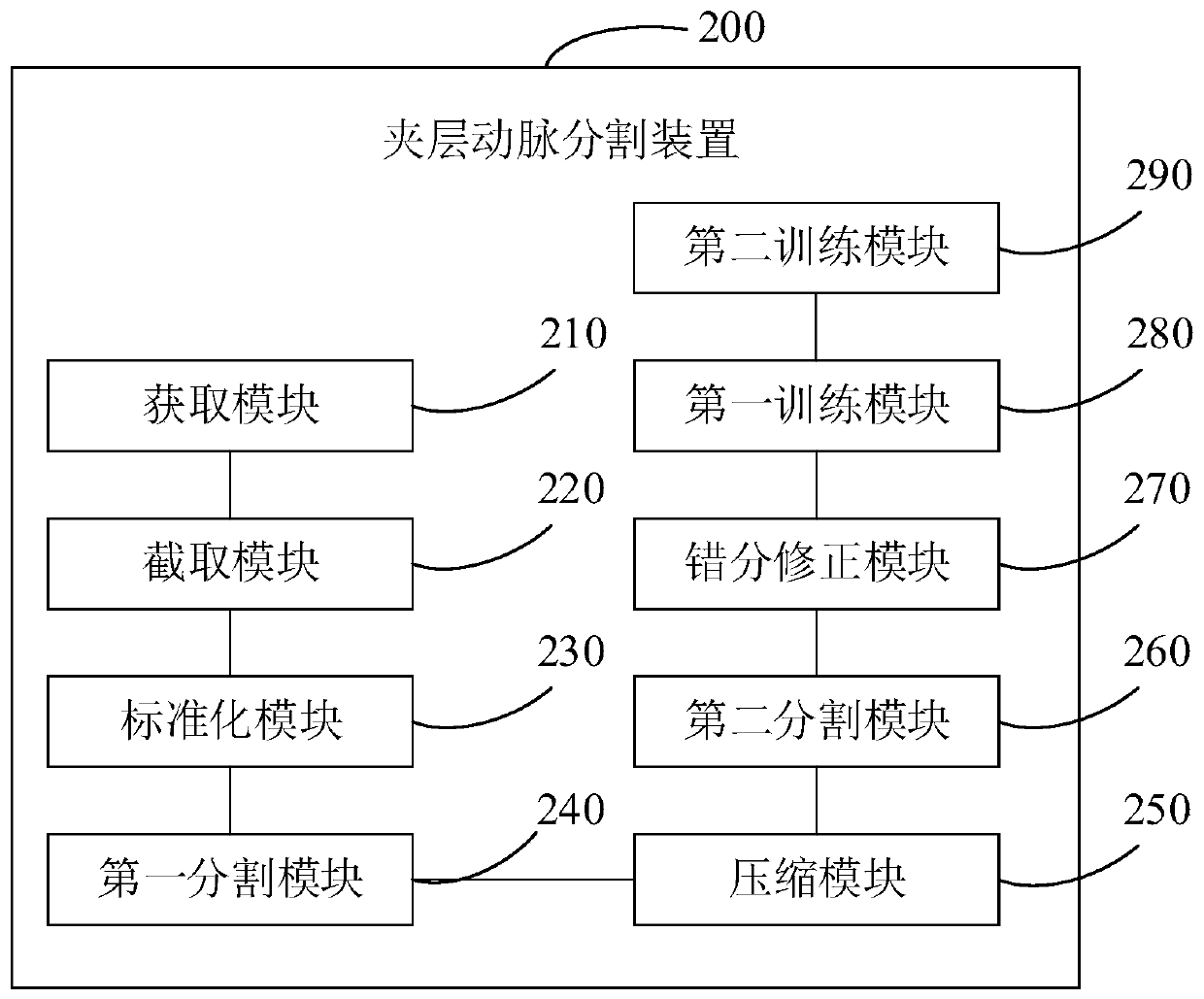
Dissection artery segmentation method and device
ActiveCN110796670AImprove segmentation efficiencyReduce image dataImage enhancementImage analysisAorta aorticRadiology
The invention provides a dissection artery segmentation method and device. The dissection artery segmentation method comprises the steps of obtaining an original CTA image of a to-be-segmented aorta;preprocessing the original CTA image to obtain a second target CTA image; segmenting the second target CTA image by using an artery segmentation model and a cavity segmentation model in the trained segmentation model to obtain a first structure model marked with an interlayer aorta and a branch artery and a second structure model marked with a true cavity and a false cavity on the interlayer aorta; and based on the first structure model and the second structure model, carrying out true cavity and false cavity misclassification correction on the second structure model. According to the dissection artery segmentation method, the original CTA image is subjected to standardization processing, and the standardized CTA image is segmented by using the artery segmentation model and the cavity segmentation model, so that the image data needing to be processed is greatly reduced, and the interlayer artery segmentation efficiency is effectively improved, and the segmentation precision is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
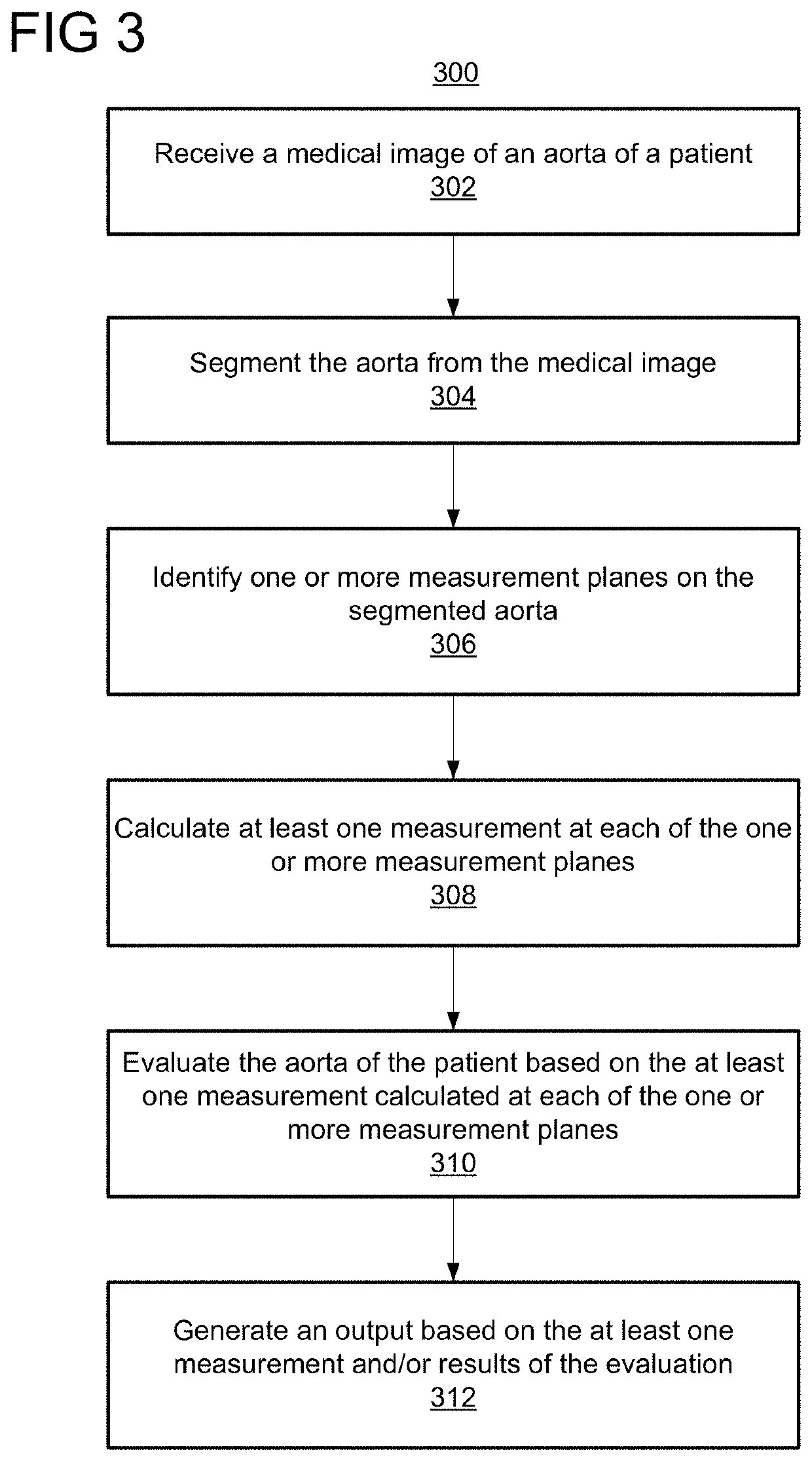
Automatic Detection and Quantification of the Aorta from Medical Images
Systems and methods are provided for evaluating an aorta of a patient. A medical image of an aorta of a patient is received. The aorta is segmented from the medical image. One or more measurement planes are identified on the segmented aorta. At least one measurement is calculated at each of the one or more measurement planes. The aorta of the patient is evaluated based on the at least one measurement calculated at each of the one or more measurement planes.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Implantable systems and methods for use therewith for monitoring and modifying arterial blood pressure without requiring an intravascular pressure transducer
InactiveUS8478403B2Increase pressureIncrease ratingsElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMedicineTransducer
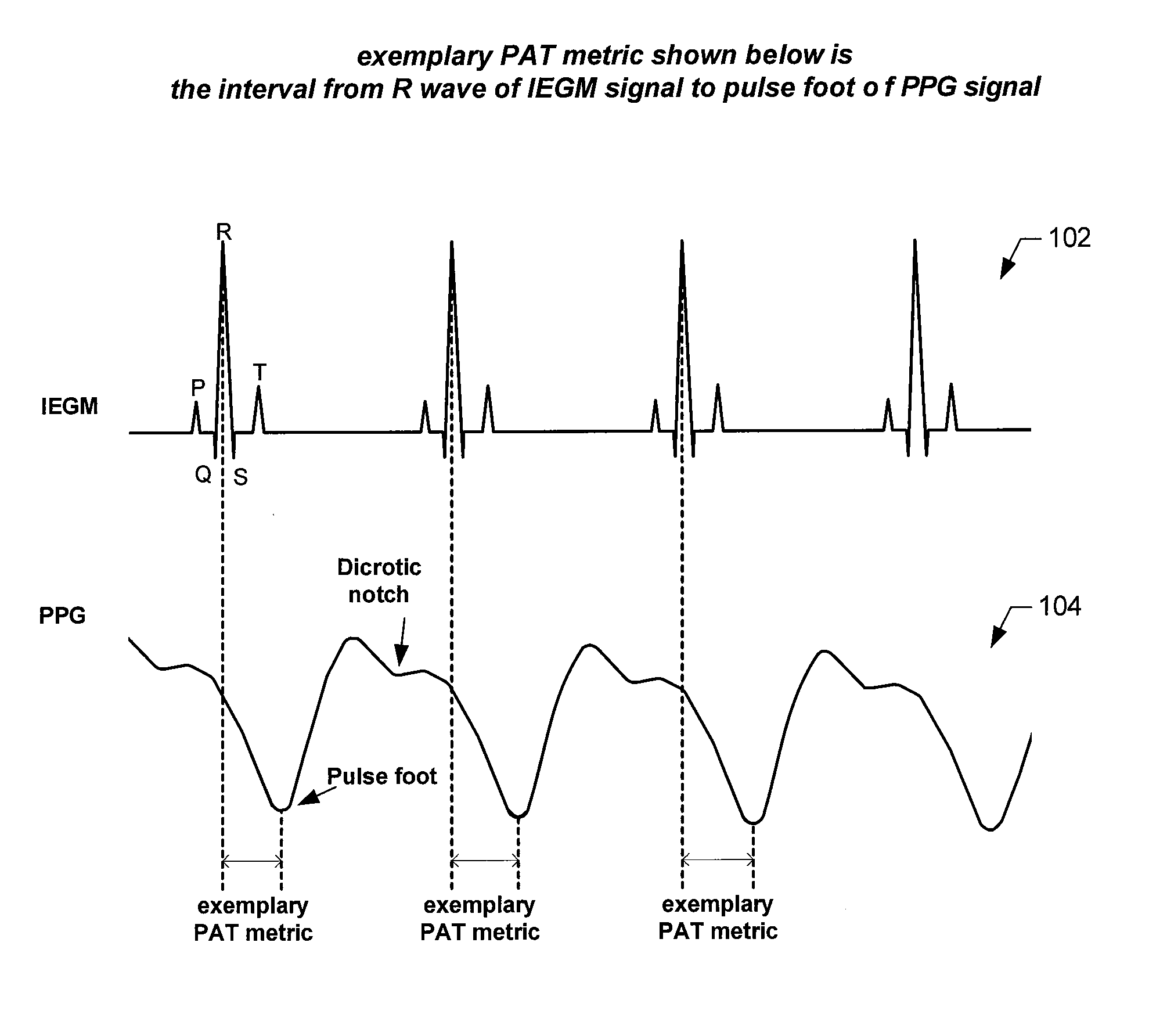
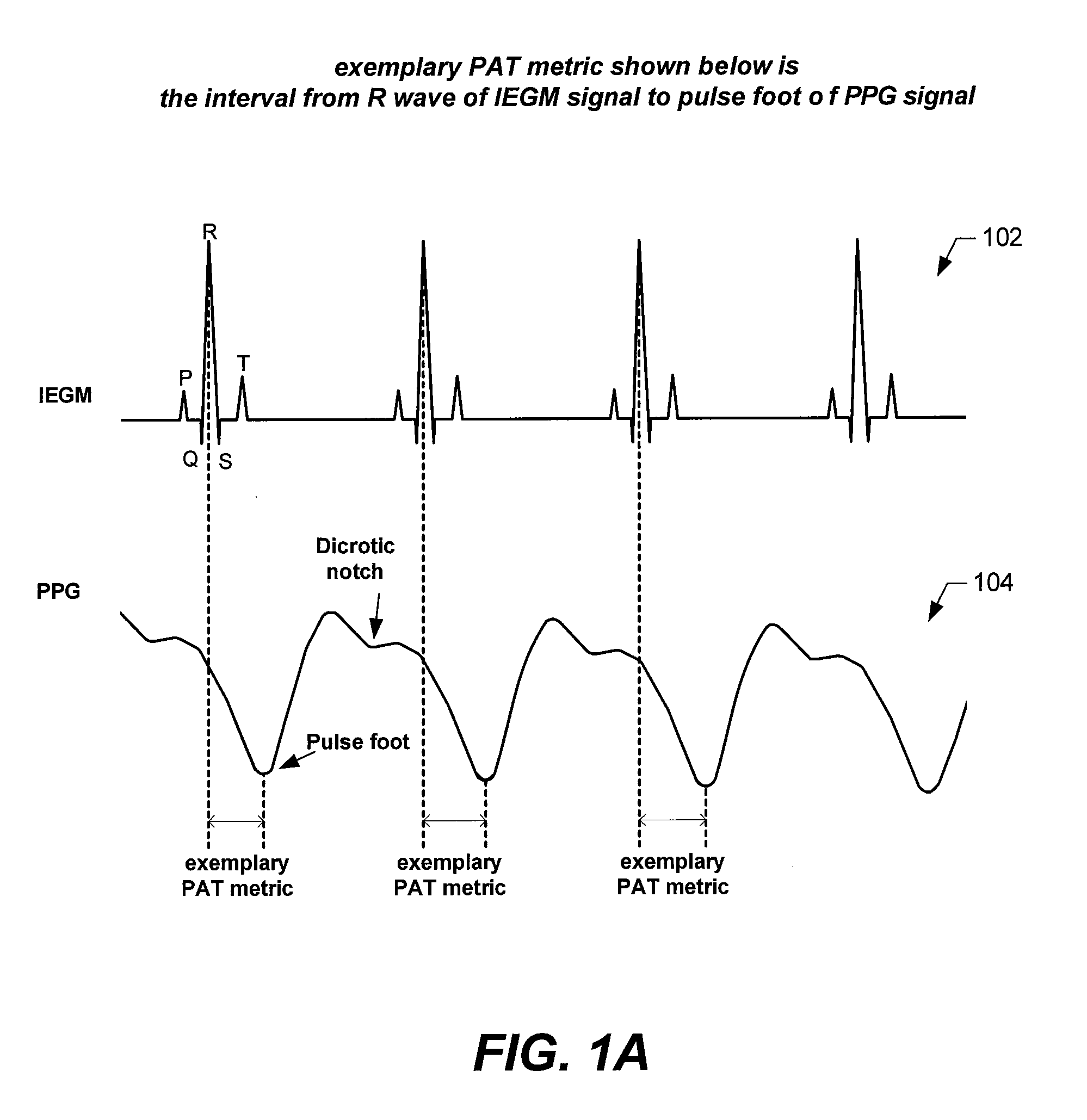
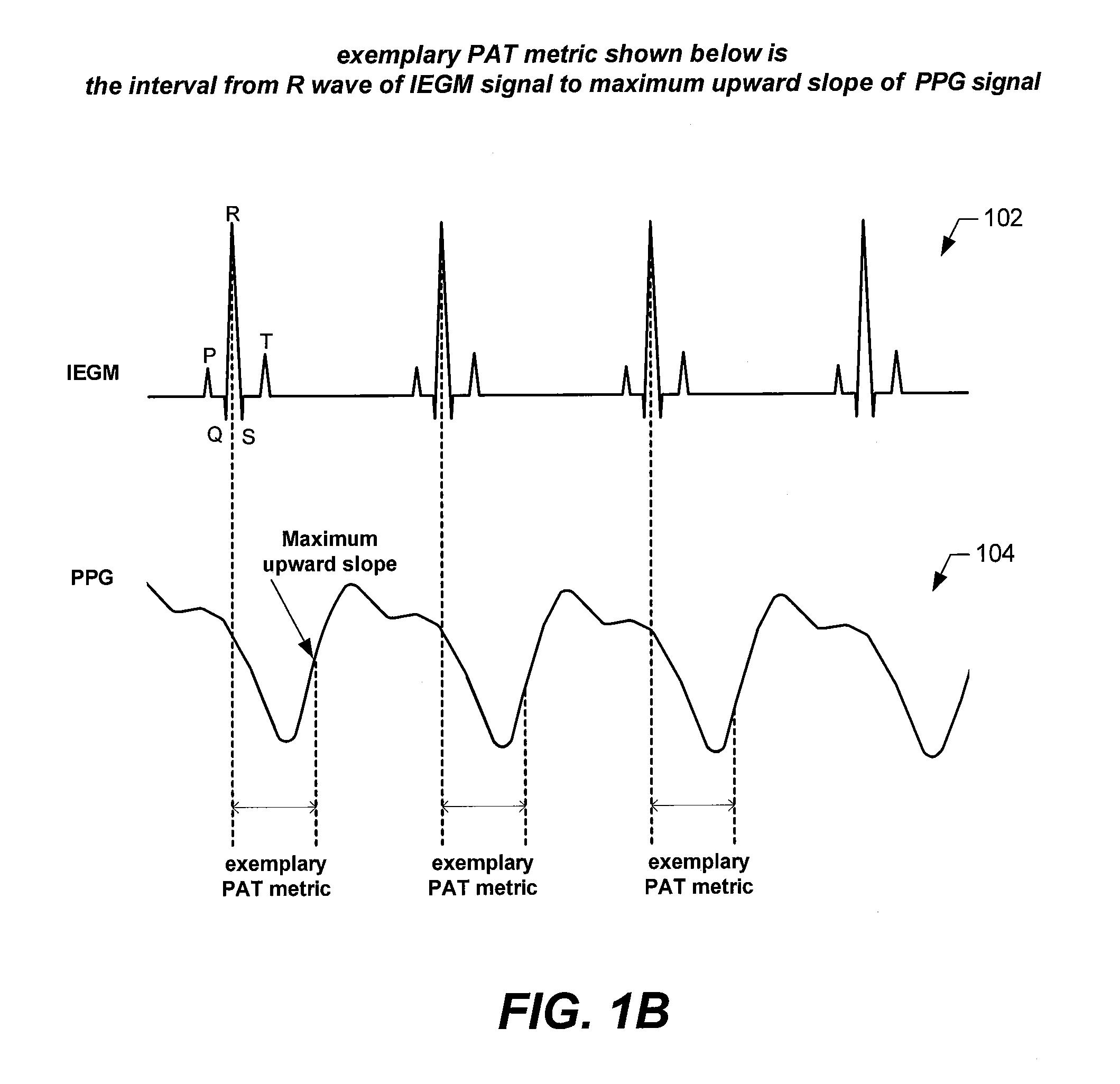
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to implantable systems, and methods for use therewith, that monitor and modify a patient's arterial blood pressure without requiring an intravascular pressure transducer. In accordance with an embodiment, for each of a plurality of periods of time, there is a determination one or more metrics indicative of pulse arrival time (PAT), each of which are indicative of how long it takes for the left ventricle to generate a pressure pulsation that travels from the patient's aorta to a location remote from the patient's aorta. Based on the one or more metrics indicative of PAT, the patient's arterial blood pressure is estimated. Changes in the arterial blood pressure are monitored over time. Additionally, the patient's arterial blood pressure can be modified by initiating and / or adjusting pacing and / or other therapy based on the estimates of the patient's arterial blood pressure and / or monitored changes therein.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
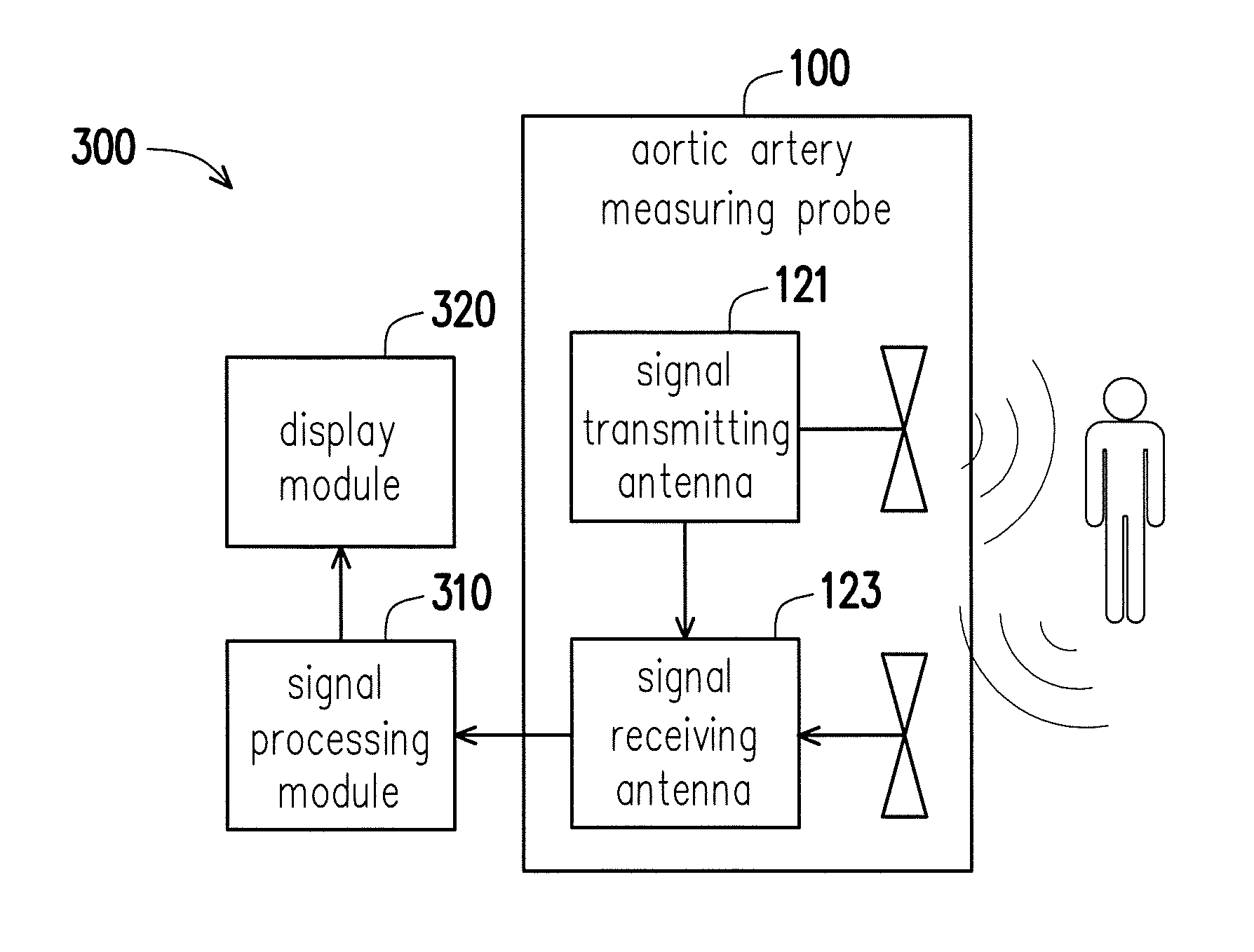
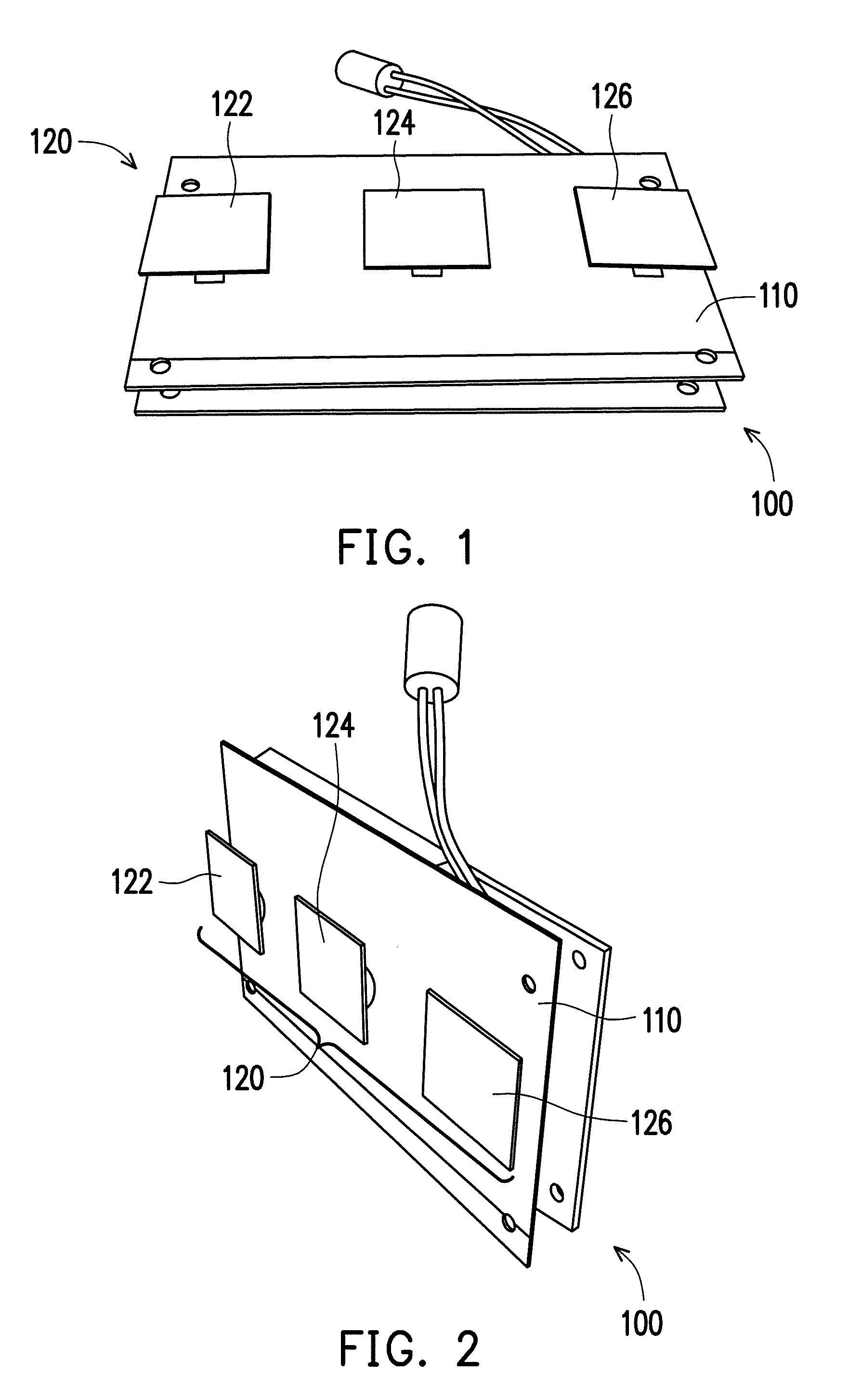
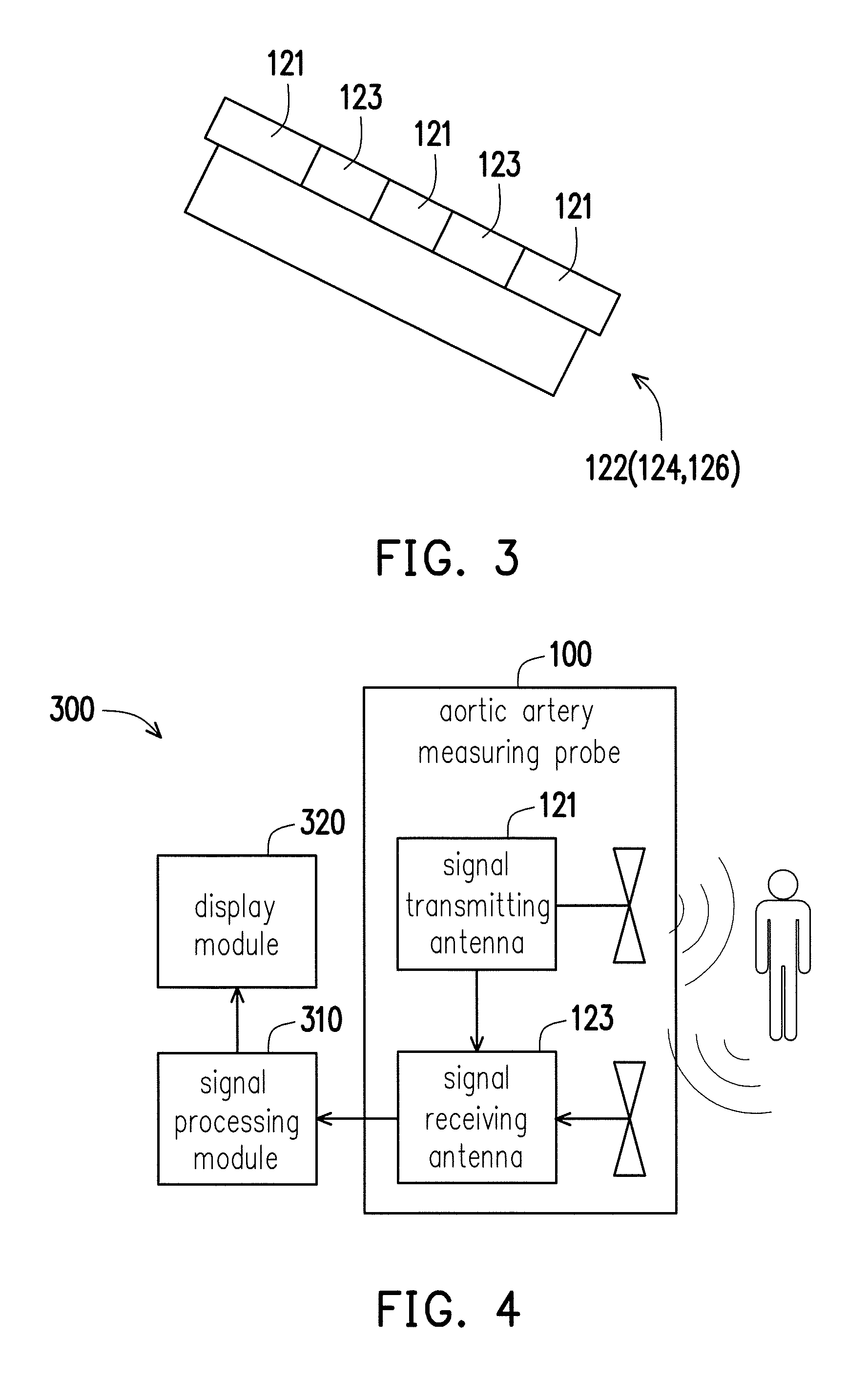
Aortic artery measuring probe, device and method of measuring diameter of aortic artery
ActiveCN103892799ASimple structureEasy to manufactureDiagnostics using lightSensorsUltra-widebandAorta aortic
An aortic artery measuring probe, device and a method of measuring the diameter of the aortic artery are provided. The aortic artery measuring device includes the aortic artery measuring probe and a signal processing module electrically connected to the aortic artery measuring probe. The aortic artery measuring probe includes a flexible substrate and a sensor array disposed thereon, wherein the sensor array includes M×N ultra-wideband sensors. The ultra-wideband sensors is positioned on a subject and the flexible substrate is deformed to a profile conforming to the profile of the subject. The ultra-wideband sensors transmit a radio wave into the subject and then the radio wave is reflected by a tissue interface of the artery wall of the aortic artery to form a reflected signal. The ultra-wideband sensors receive the reflected signal and the signal processing module analyzes the reflected signal to define the diameter of the aortic artery.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method and device for detecting coronary artery stenosis functional ischemia based on FFR
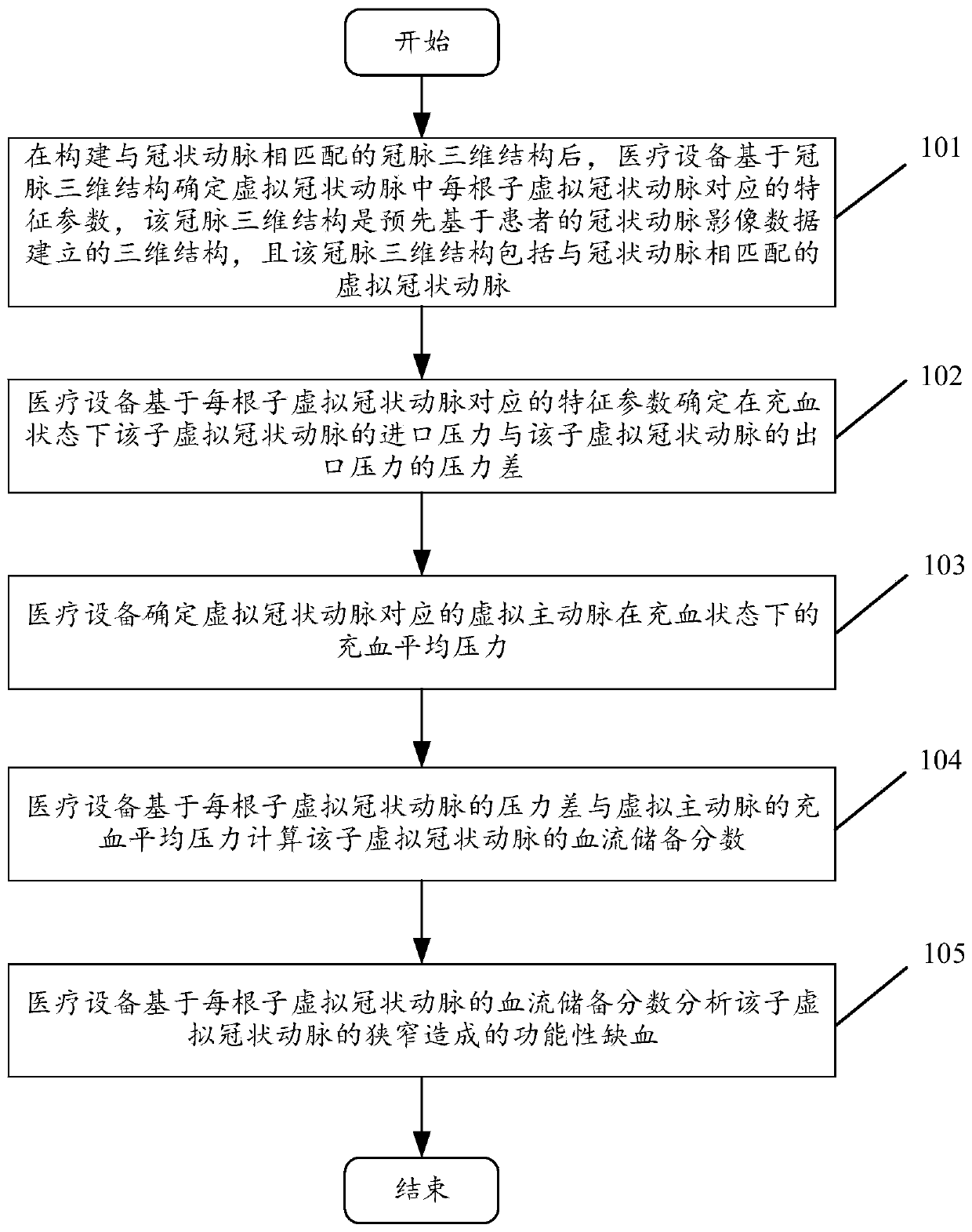
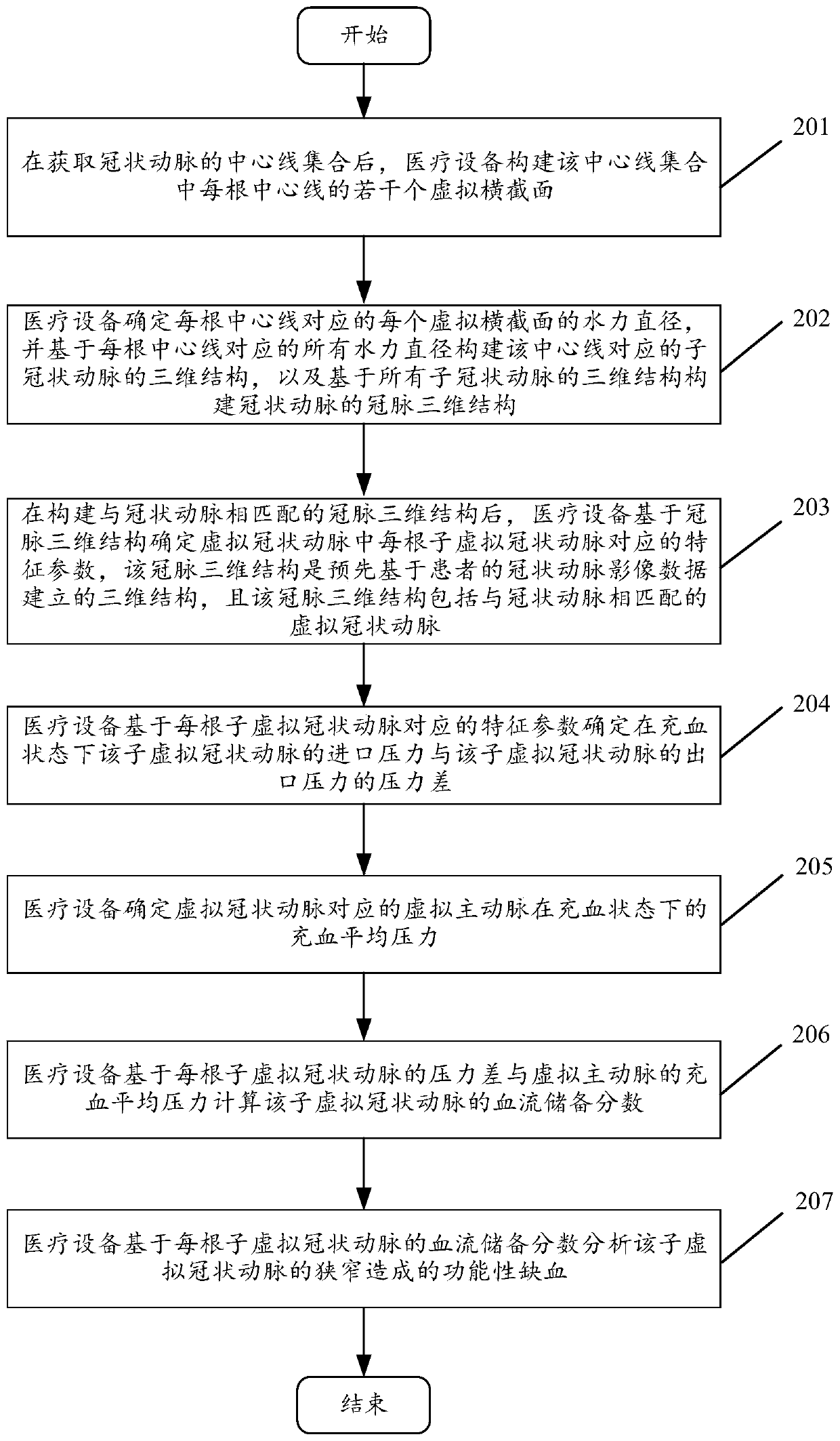
ActiveCN110916640AImprove determination accuracyDecrease the determination timeMedical simulationMedical data miningAorta aorticCoronary arteries
The invention discloses a method and device for detecting coronary artery stenosis functional ischemia based on FFR. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a three-dimensional structure of coronary artery, and determining the characteristic parameter corresponding to each sub-virtual coronary artery in a virtual coronary artery; determining a pressure difference between the inlet pressure of the sub-virtual coronary artery and the outlet pressure of the sub-virtual coronary artery under a congestion state based on the characteristic parameter, and determining the congestion average pressure of a virtual aorta corresponding to the virtual coronary artery under the congestion state; and calculating the fractional flow reserve of the sub-virtual coronary artery based on the pressure difference of each sub-virtual coronary artery and the congestion average pressure of the virtual aorta, and analyzing functional ischemia caused by the sub-virtual coronary artery stenosis based on the fractional flow reserve of each sub-virtual coronary artery. Visibly, implementation of the method can improve the determination accuracy of the fractional flow reserve (FFR) and reduce thedetermination duration so as to improve the detection accuracy and reduce the detection duration for functional ischemia caused by coronary artery stenosis.
Owner:唯智医疗科技佛山有限公司
Aortic artery measuring probe, device and method of measuring diameter of aortic artery
InactiveUS20140180057A1Avoid less flexibilityCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringSensor arrayUltra-wideband
An aortic artery measuring probe, device and a method of measuring the diameter of the aortic artery are provided. The aortic artery measuring device includes the aortic artery measuring probe and a signal processing module electrically connected to the aortic artery measuring probe. The aortic artery measuring probe includes a flexible substrate and a sensor array disposed thereon, wherein the sensor array includes M×N ultra-wideband sensors. The ultra-wideband sensors is positioned on a subject and the flexible substrate is deformed to a profile conforming to the profile of the subject. The ultra-wideband sensors transmit a radio wave into the subject and then the radio wave is reflected by a tissue interface of the artery wall of the aortic artery to form a reflected signal. The ultra-wideband sensors receive the reflected signal and the signal processing module analyzes the reflected signal to define the diameter of the aortic artery.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
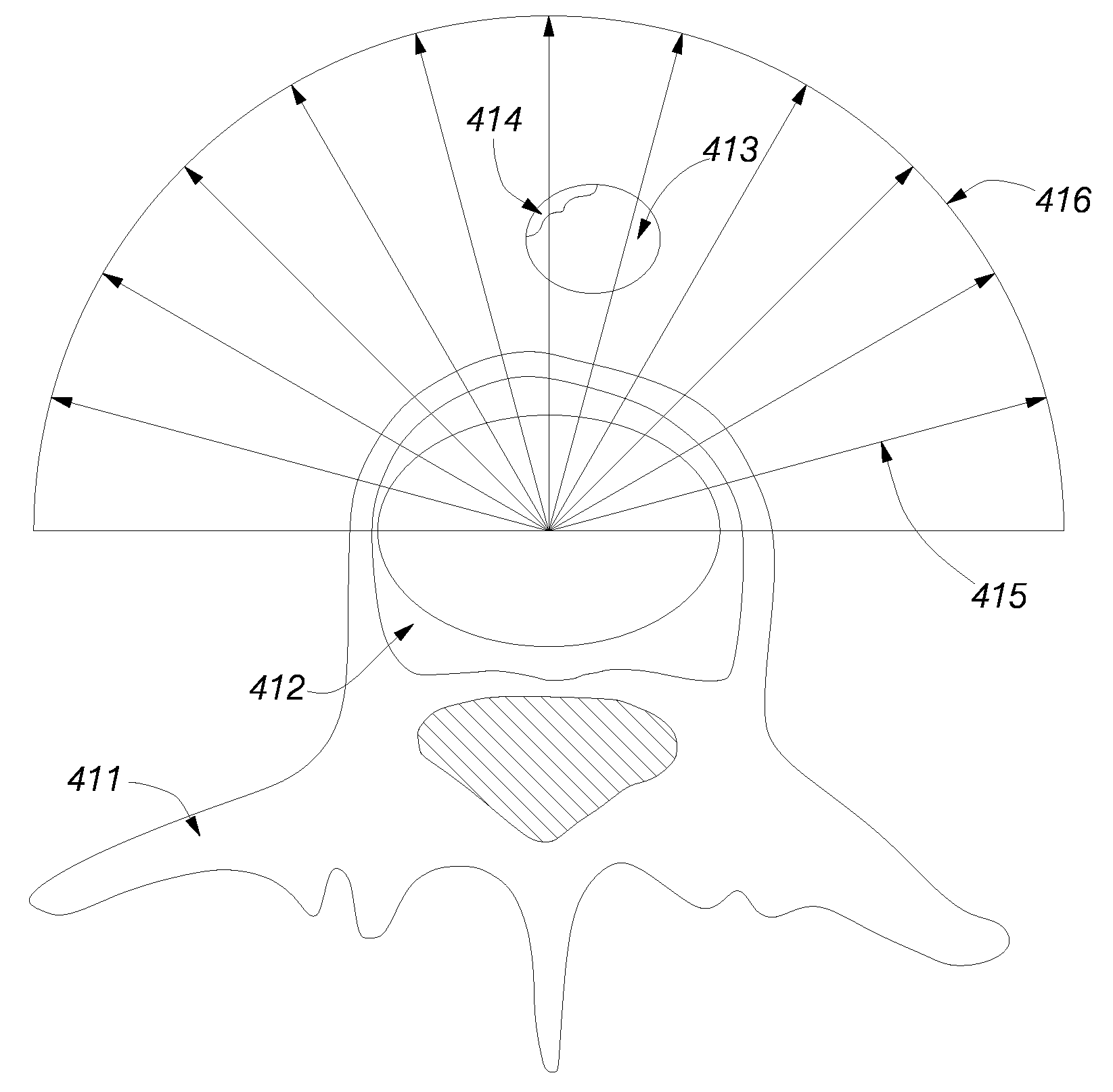
Method of deriving a quantitative measure of a degree of calcification of an aorta
A method of deriving a quantitative measure of a degree of calcification of a blood vessel such as an aorta by processing an image such as an X-ray image of at least a part of the blood vessel containing said calcification comprises:taking a starting set of digital data representative of an image of at least part of a blood vessel containing a calcification set against a background;estimating the boundary of the calcification;using inpainting to replace digital data in said starting set representing the calcification with data extrapolating the boundary of the background to extend over the area of calcification, and so generating an inpainted set of digital data; andcomputing the difference between the starting set of digital data and the inpainted set of digital data to obtain a quantitative measure of the degree of calcification of the blood vessel.
Owner:BIOCLINICA
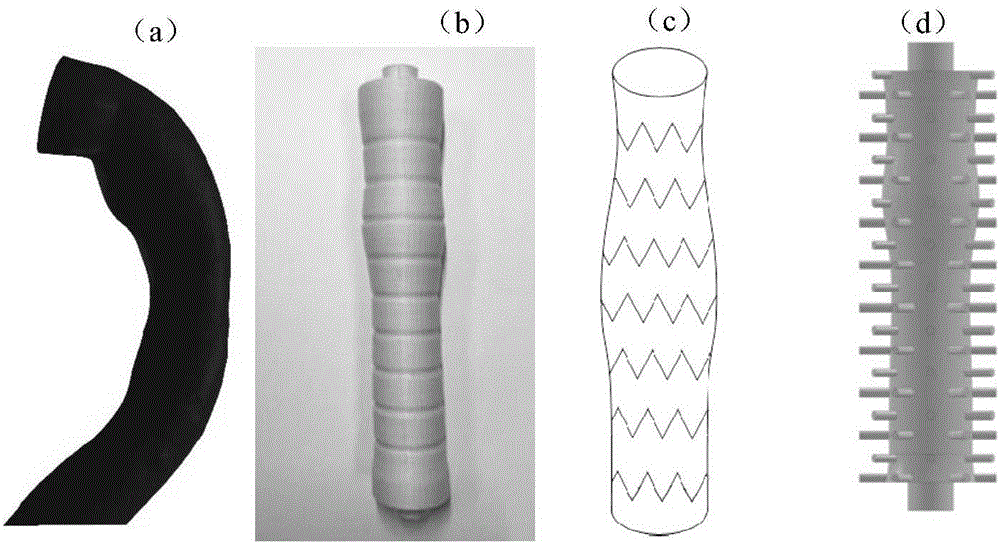
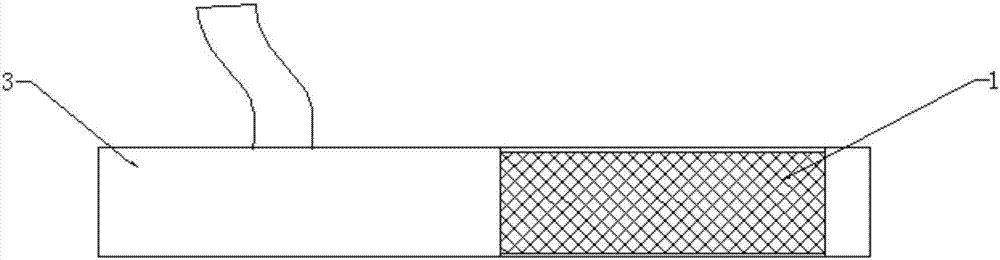
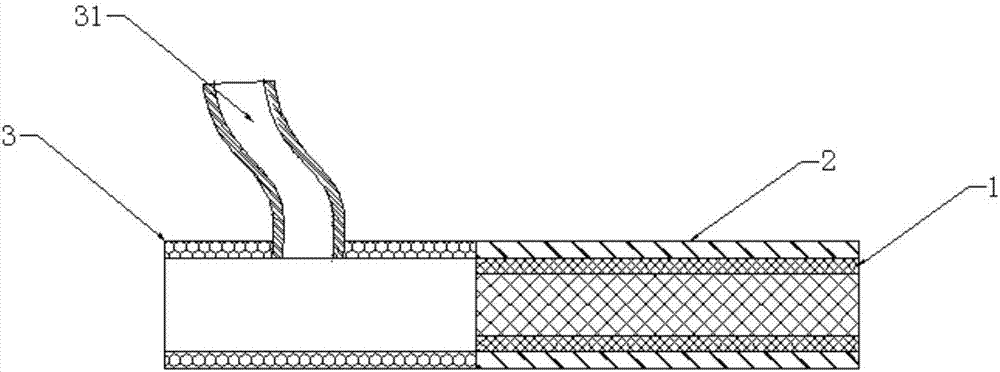
Covered stent used in chest great vessel cavity
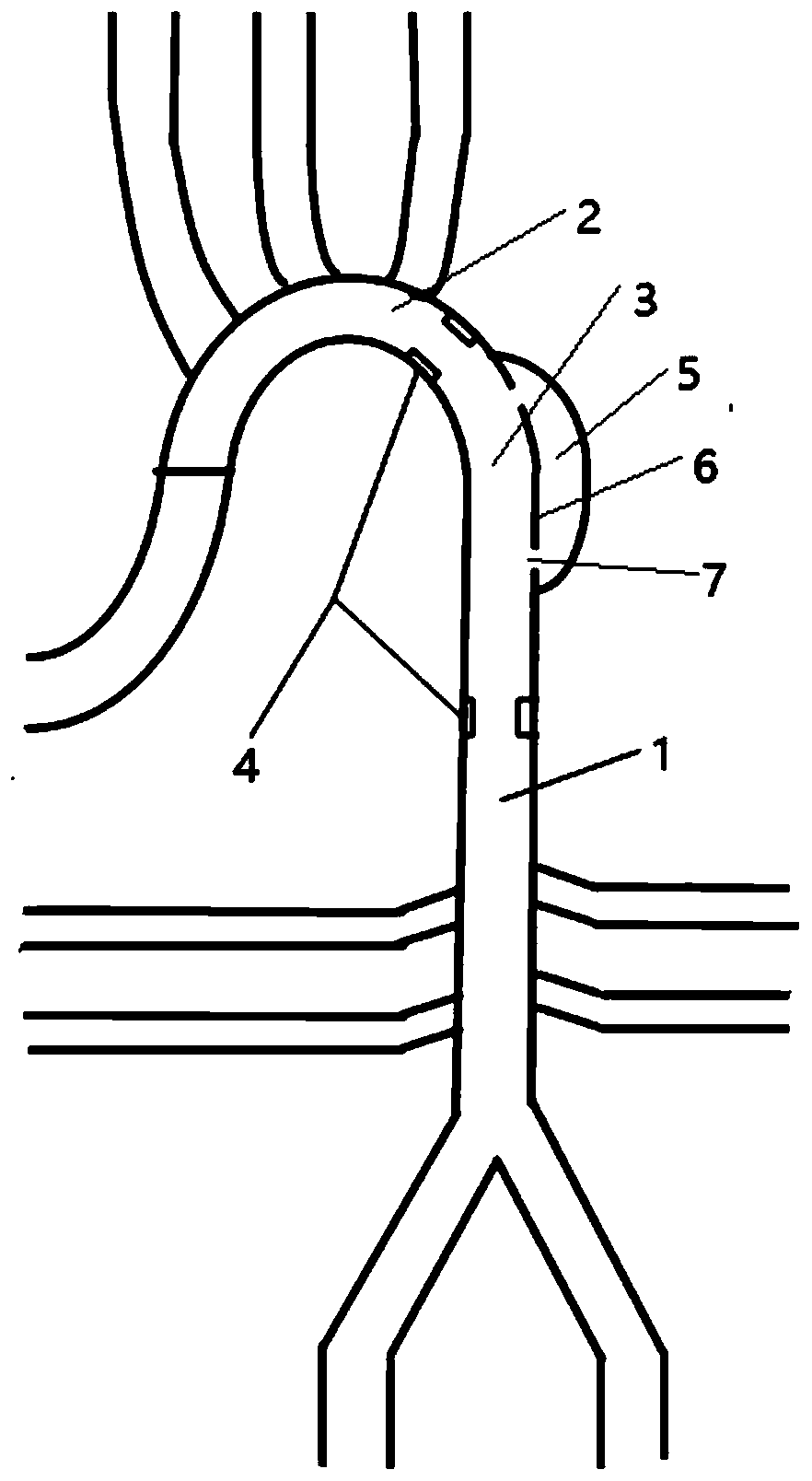
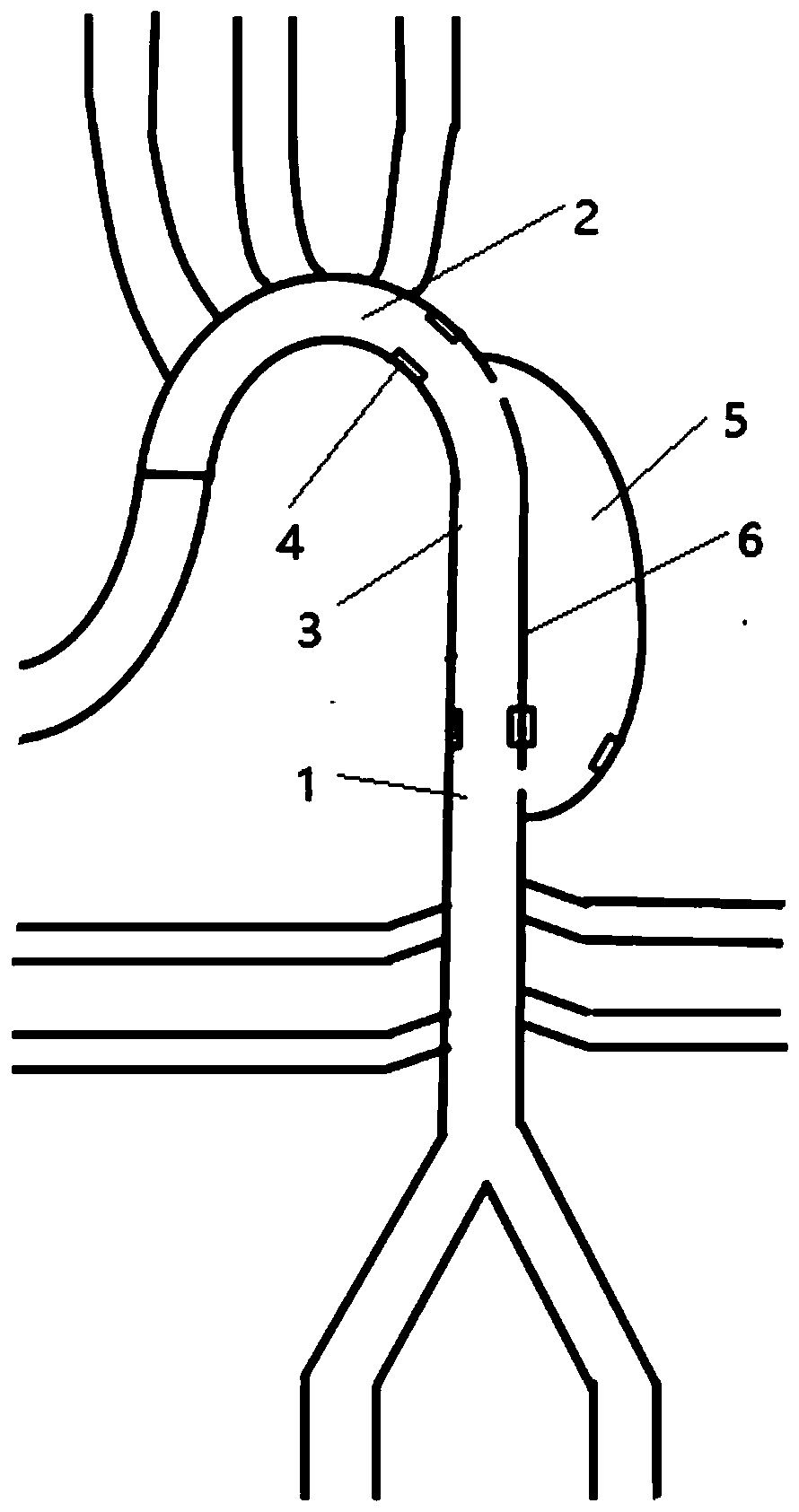
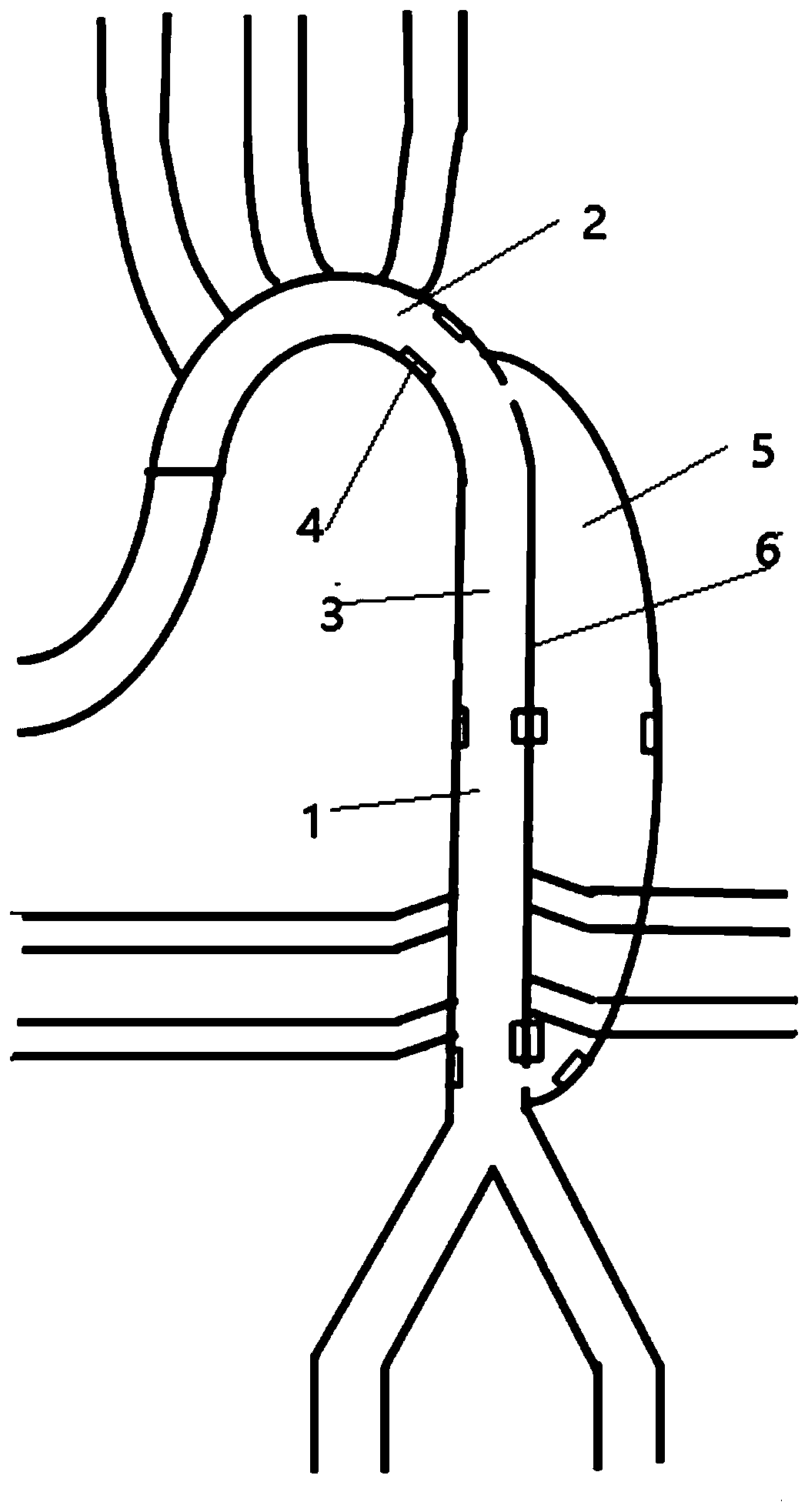
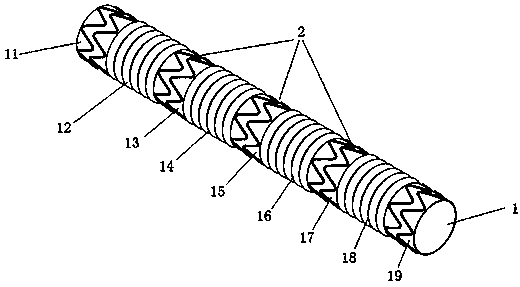
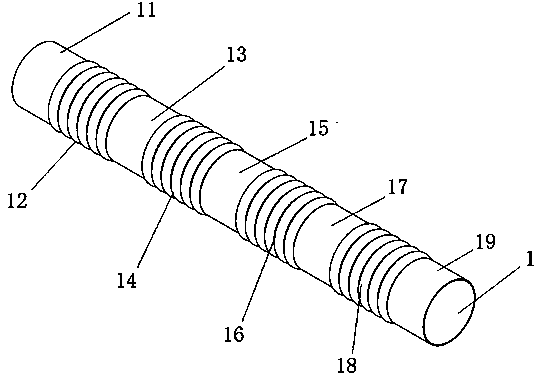
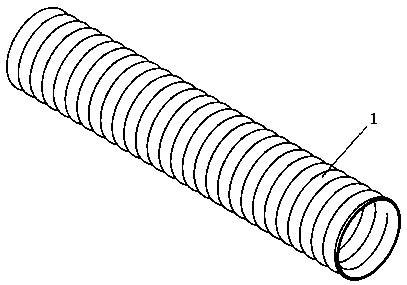
InactiveCN104352288ANo local abnormal stressLocal abnormal stress preventionStentsBlood vesselsAorta aorticStraight tube
The invention relates to a covered stent used in a chest great vessel cavity. Compared with the prior art, the defects that a covered stent is incapable of overcoming straightening force and is poor in practicability are overcome. The covered stent comprises artificial blood vessels (1) and support frames (2), wherein each artificial blood vessel (1) comprises a plurality of straight pipes and a plurality of pleated pipes; the straight pipes are connected at intervals through the pleated pipes; the support frames (2) are wrapped on each straight pipe respectively; the straight pipes are arranged at the two ends of each artificial blood vessel (1) respectively. The covered stent has certain longitudinal stretching deformation capacity, can fit the physiological bending of an aorta, and eliminates the straightening force after a traditional stent is bent, so that the blood vessel wall of the aorta is uniformly stressed.
Owner:章庆春 +1
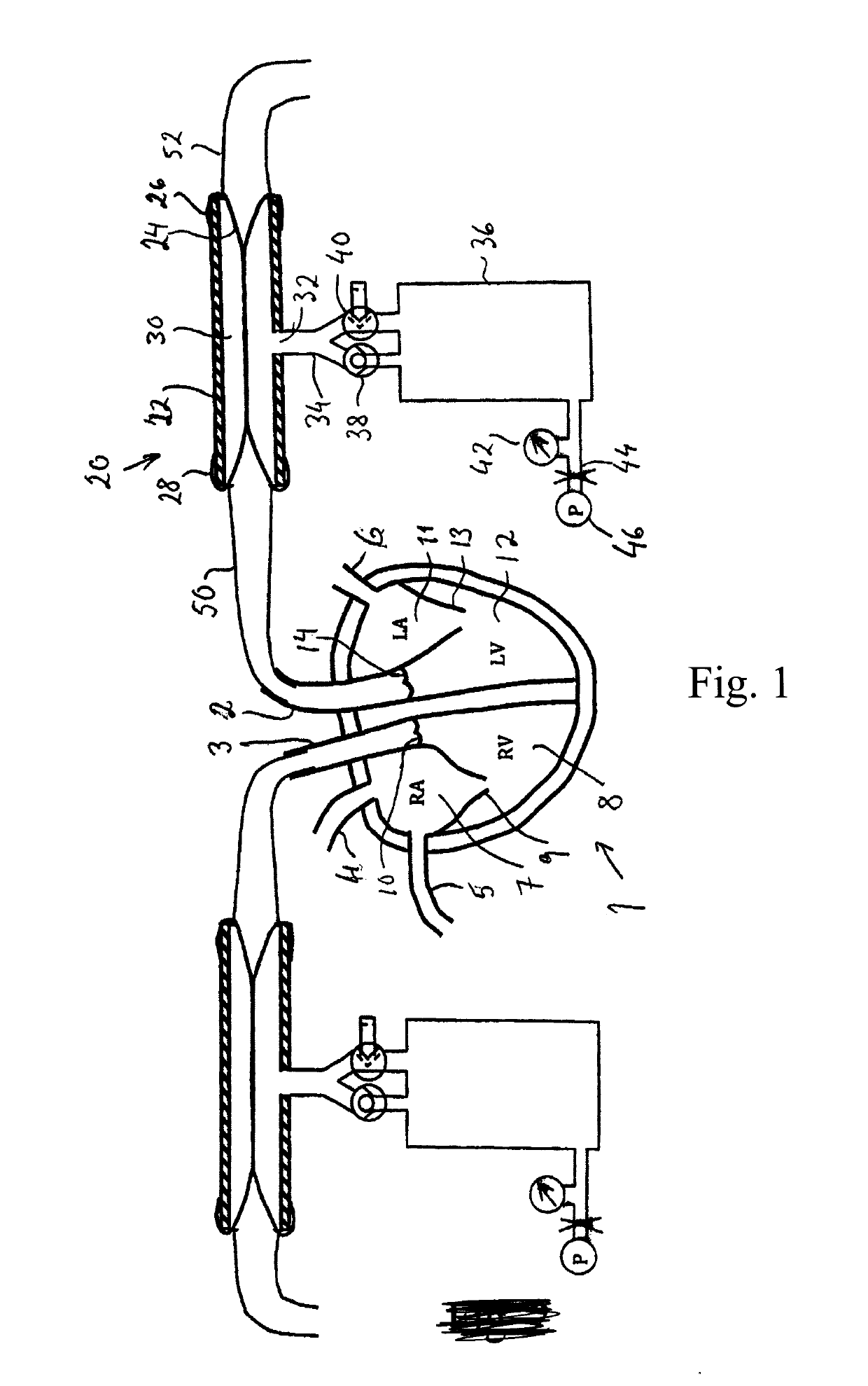
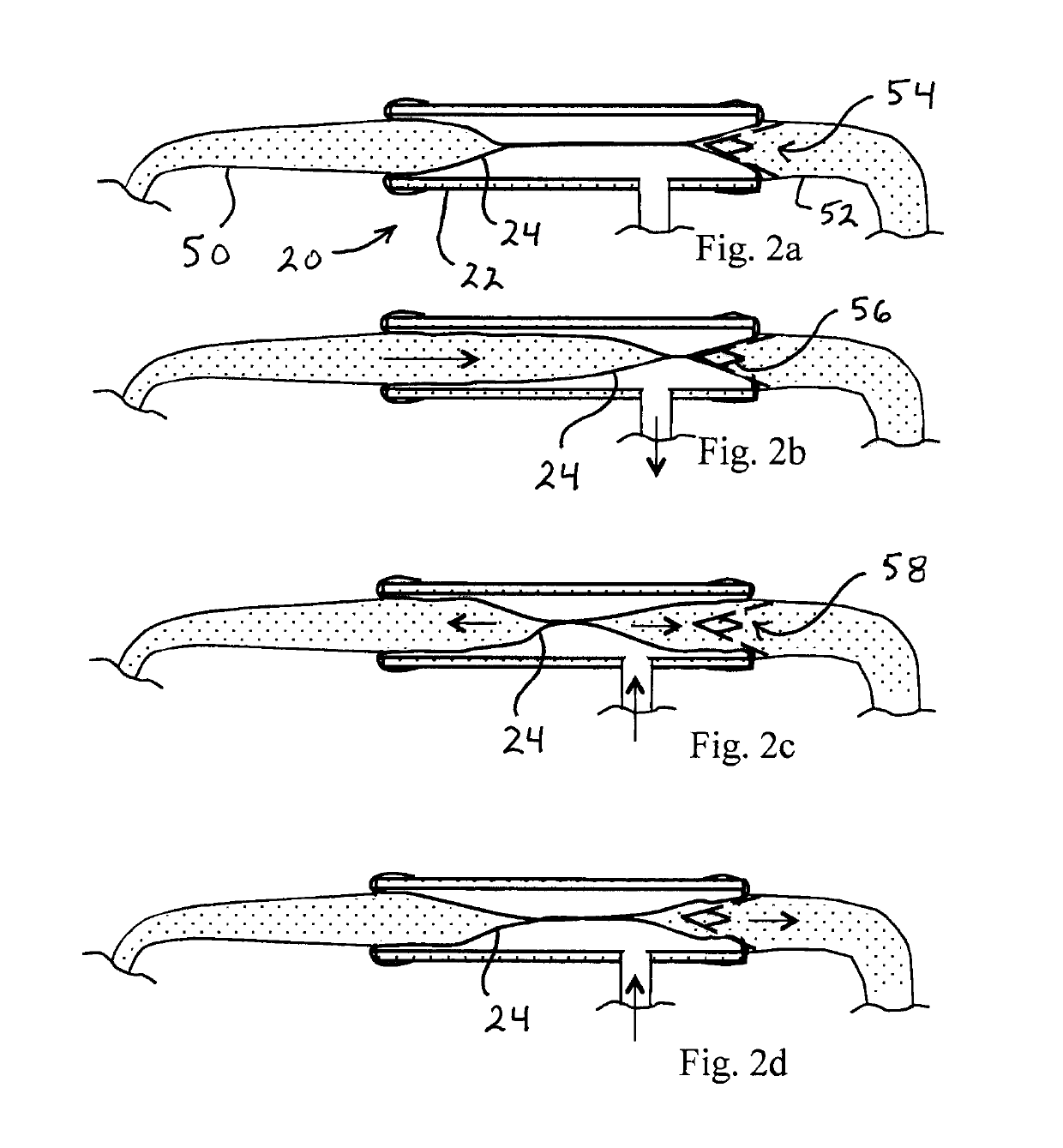
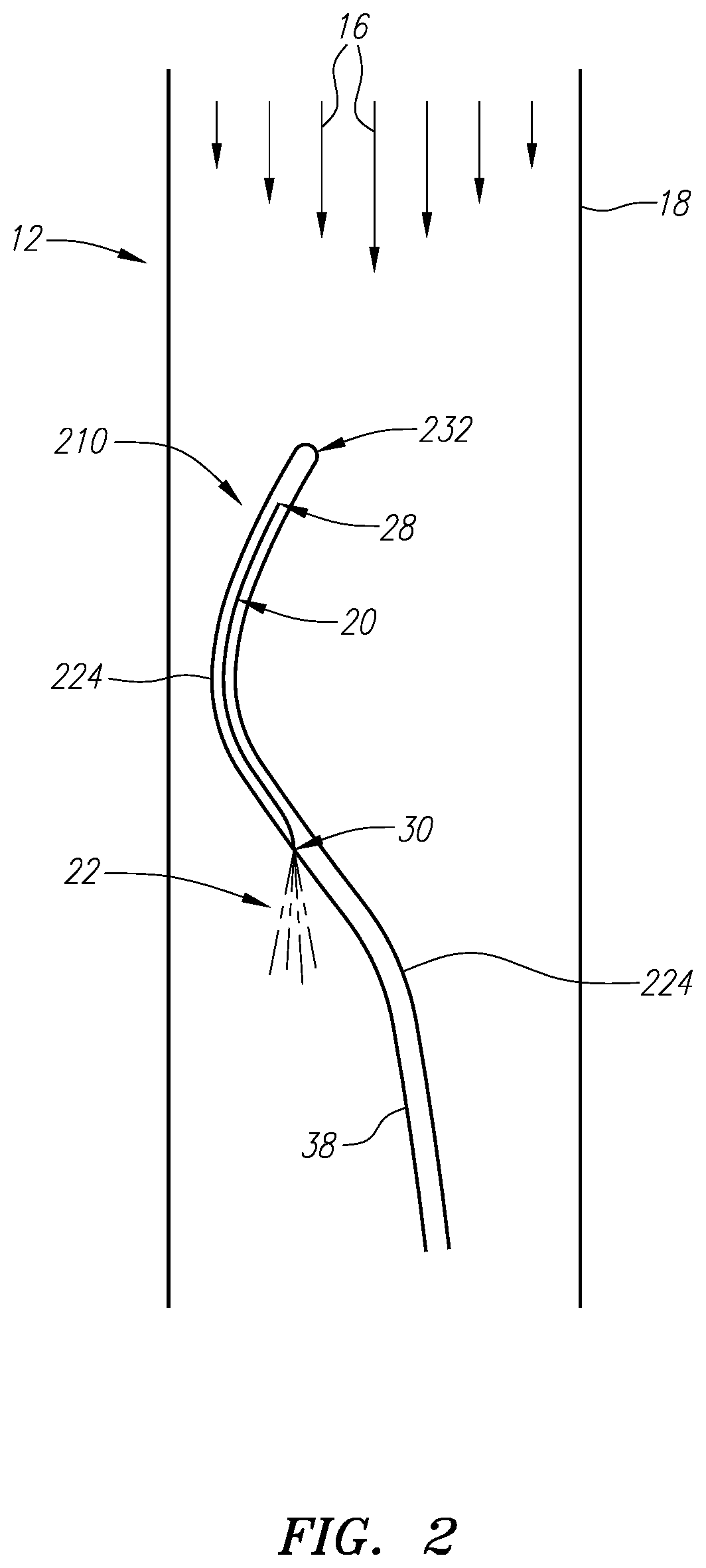
Afterload device for a beating heart during examination thereof
ActiveUS10405756B2Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate onePharmaceutical containersMedical devicesSystoleAfterload
An examination device for a heart. An afterload device connected to the aorta provides a counter-pressure by an annular space delimited between a rigid cylinder and an elastic tube inserted in the rigid cylinder. The annular space comprises a compressible medium, such as air, nitrogen gas or carbon dioxide and is connected to a reservoir providing a predetermined pressure corresponding to a diastolic pressure. The reservoir is connected to the annular space via a restriction and a back-flow valve. During diastole, the annular space is inflated by the reservoir and provides a diastolic counter pressure for providing coronary flow. During systole, the ejected fluid from the heart ventricle displaces the medium inside the annular space through the restriction to the reservoir, thereby removing energy from the fluid. The compressible medium forms a compliance. Also, there is a preload device comprising a vertical collapsible tube for preload of the atrium.
Owner:XVIVO PERFUSION
Methods and Devices for Creation of Communication Between Aorta and Left Atrium
Methods and devices are disclosed for the formation of a communication between the aorta and left atrium. The method includes introducing a puncturing device, positioning the device at a location along the aorta, and advancing the puncturing device to create a pathway. The method may include: a. via an inferior artery, advancing a perforating tip of the puncturing device towards the aorta; b. positioning the perforating tip adjacent a wall of the aorta, proximate the left atrium; and c. advancing the perforating tip to perforate through the wall of the aorta and then through a wall of the left atrium, to create a pathway between the aorta and the left atrium, wherein the creation of the pathway can be confirmed with at least one of fluoroscopy, electro-anatomical mapping, pressure measurement, contrast injection, and echocardiograph.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Catheter for infusion of cardiovascular fluid
ActiveUS20200016310A1Increase oxygenationFinish quicklyMulti-lumen catheterDialysis systemsAorta aorticBlood flow
Owner:OAKWOOD HEALTHCARE
Aortic dissection stent graft
PendingCN107115160ATraumaShorten stop cycle timeStentsBlood vesselsAorta aorticCirculatory arrest time
The invention provides an aortic dissection stent graft which comprises a metal stent, wherein a tectorial membrane is attached on the external part of the stent, the aortic dissection stent graft further comprises an artificial blood vessel, a branching vessel is arranged on the wall of the artificial blood vessel, one end of the artificial blood vessel is connected with the tectorial membrane attached on the surface of one end of the stent, and is used for perfusing blood during surgery. The tectorial membrane is attached on the external part of the stent to form a tubular shape. One end of the tubular tectorial membrane is connected with the artificial blood vessel which is further connected with the branching vessel. During surgery, the roots of aortic are cut off, and the stent is implanted at cleavage of an endarterium through a catheter. In addition, blood is perfused into the branching vessel, so that the perfused blood is used for being supplied to tissues of a lower body. By adopting the aortic dissection stent graft, the circulatory arrest time is shortened, the incision of femoral artery is not needed, and the surgery wound can be reduced, the surgery time can be shortened, and the complications caused by the blood retrograde perfusion of the femoral artery can also be avoided.
Owner:吴龙 +1
Method for determining patient-specific blood vessel information
ActiveUS10658085B2Simple conditionsReduce the amount of calculationMedical simulationCatheterAorta aorticCoronary arteries
The present invention relates to a method for determining patient-specific blood vessel information. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for determining patient-specific cardiovascular information by applying a simplified coronary circulation model thereto. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a method for determining a blood flow rate for branches of a blood vessel having originated from an artery of each patient. According to the present invention, the method for determining cardiovascular information by using a computer system comprises the steps of: receiving image data including a plurality of coronary arteries having originated from the aorta; processing the image data so as to generate a three-dimensional shape model of the plurality of coronary arteries; simulating a blood flow for the generated three-dimensional shape model of the plurality of coronary arteries; and determining a fractional flow reserve (FFR) of the respective coronary arteries with the blood flow simulation result. In the blood flow simulation step for the three-dimensional shape model of the plurality of coronary arteries, a computational fluid dynamics model is applied to the three-dimensional shape model of the coronary arteries, and a centralized parameter model to be combined with the computational fluid dynamics model uses a simplified coronary circulation model including coronary arteries, capillaries of the coronary arteries, and coronary veins.
Owner:KNU IND COOPERATION FOUND
Coronary artery segmentation method and device
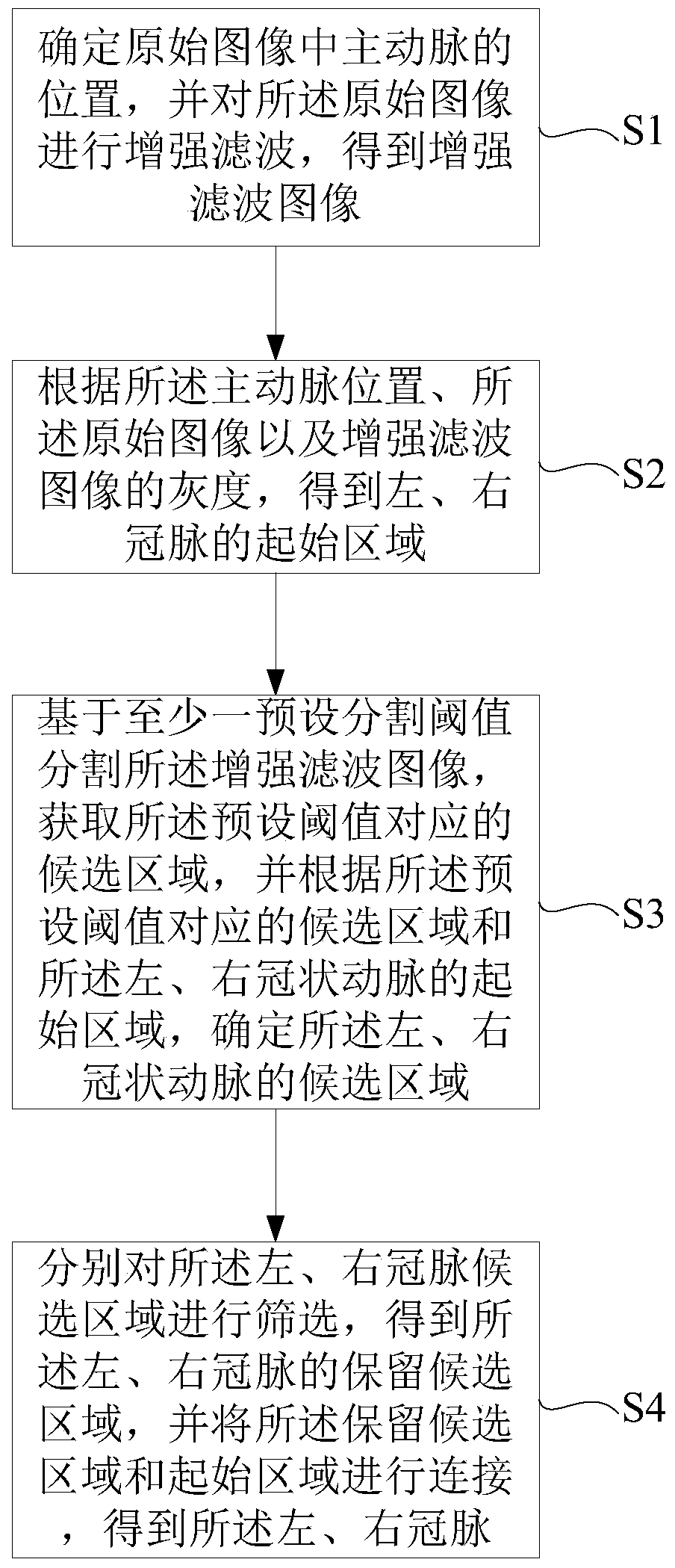
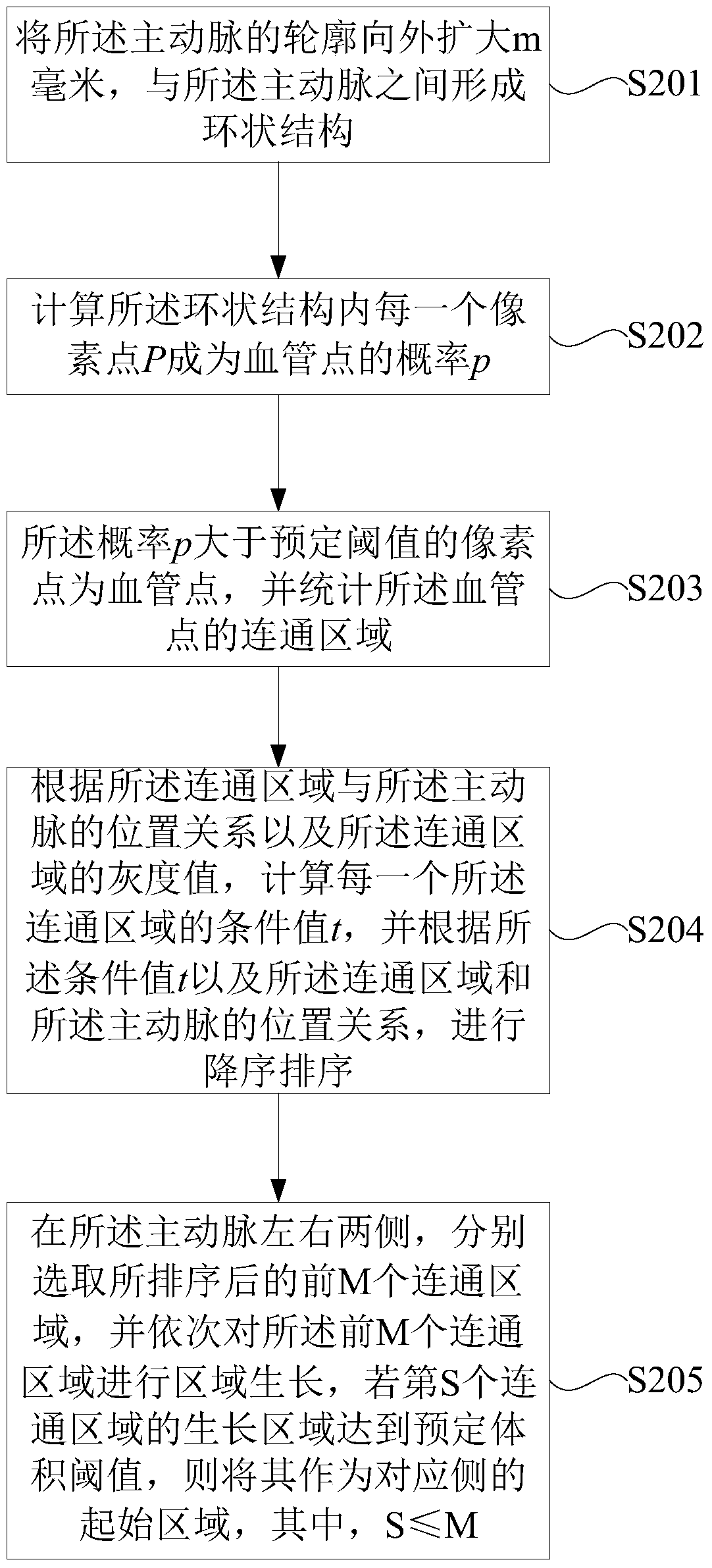
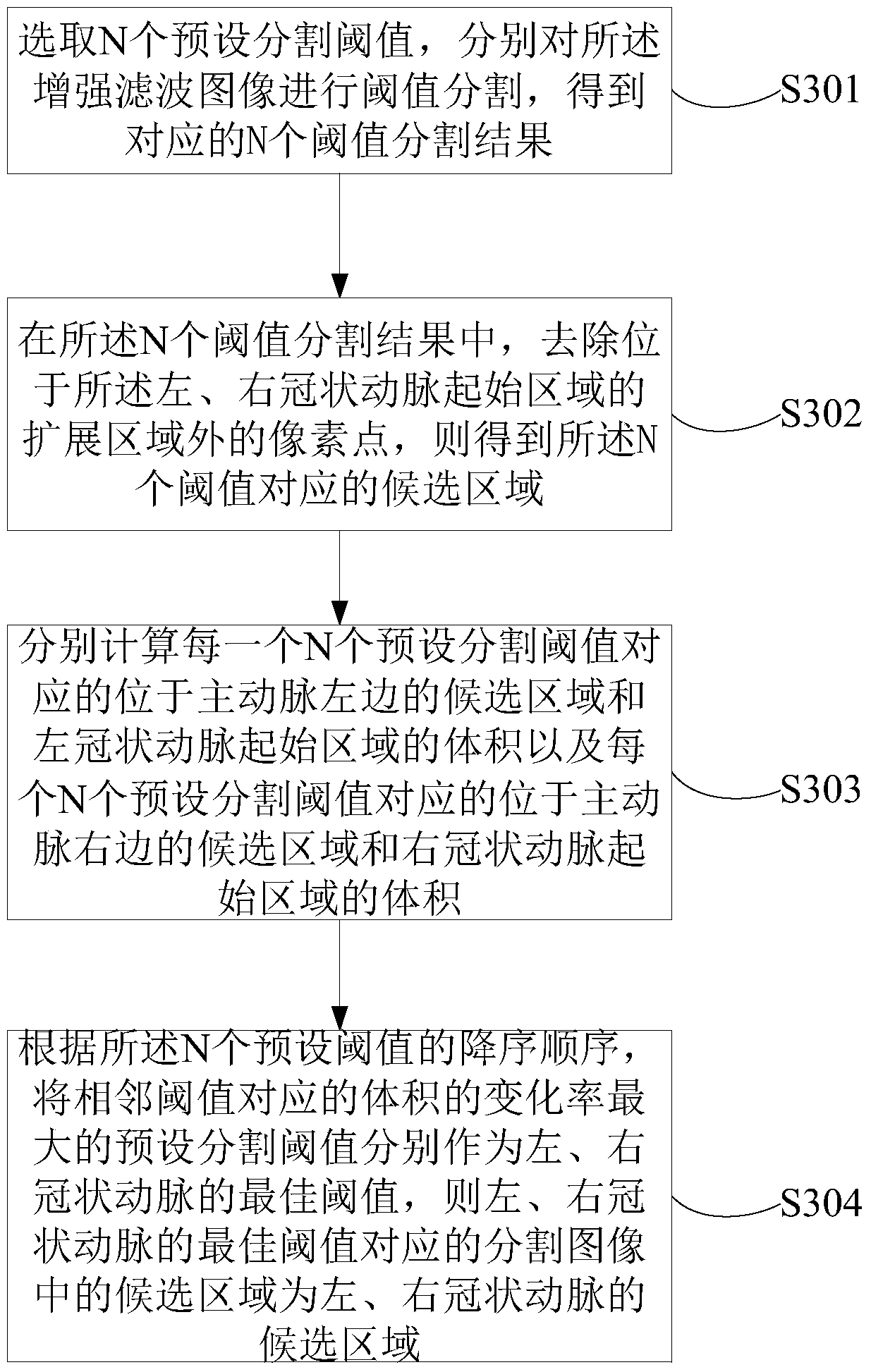
ActiveCN104978725BImprove robustnessAccurate candidate areaImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesAorta aortic
The invention provides a method and a device for dividing a coronary artery. The method comprises the following steps: (1) determining the position of an aorta in an original image, and performing reinforced filtering on the original image, thereby obtaining a reinforced filtered image; (2) obtaining the starting areas of a left coronary artery and a right coronary artery according to the position of the aorta, the original image and the gray scale of the reinforced filtered image; (3) dividing the reinforced filtered image based on at least one preset dividing threshold, obtaining a candidate area which corresponds with the preset threshold, and determining the candidate areas of the left coronary artery and the right coronary artery according to the candidate area and the starting areas of the left coronary artery and the right coronary artery; and (4) according to the position relationship between the aorta and the candidate areas of the left coronary artery and the right coronary artery, respectively screening the candidate areas of the left coronary artery and the right coronary artery, connecting the screened candidate areas with the starting areas, and obtaining the left coronary artery and the right coronary artery. The method and the device provided by the technical solution of the invention can wholly, accurately and automatically extract the left coronary artery and the right coronary artery, thereby facilitating qualitative and quantitative analysis and treatment for diseases of angiocardiopathy by a doctor.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
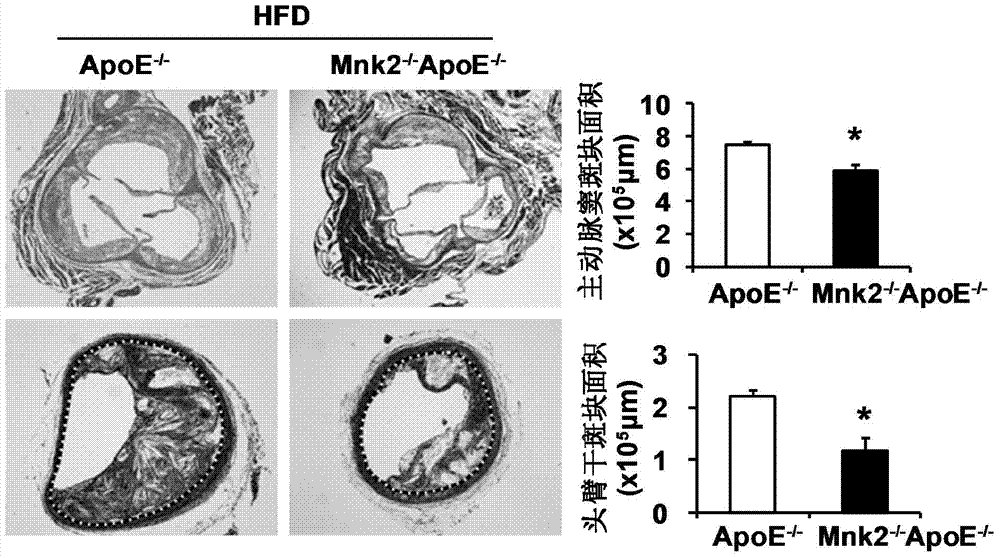
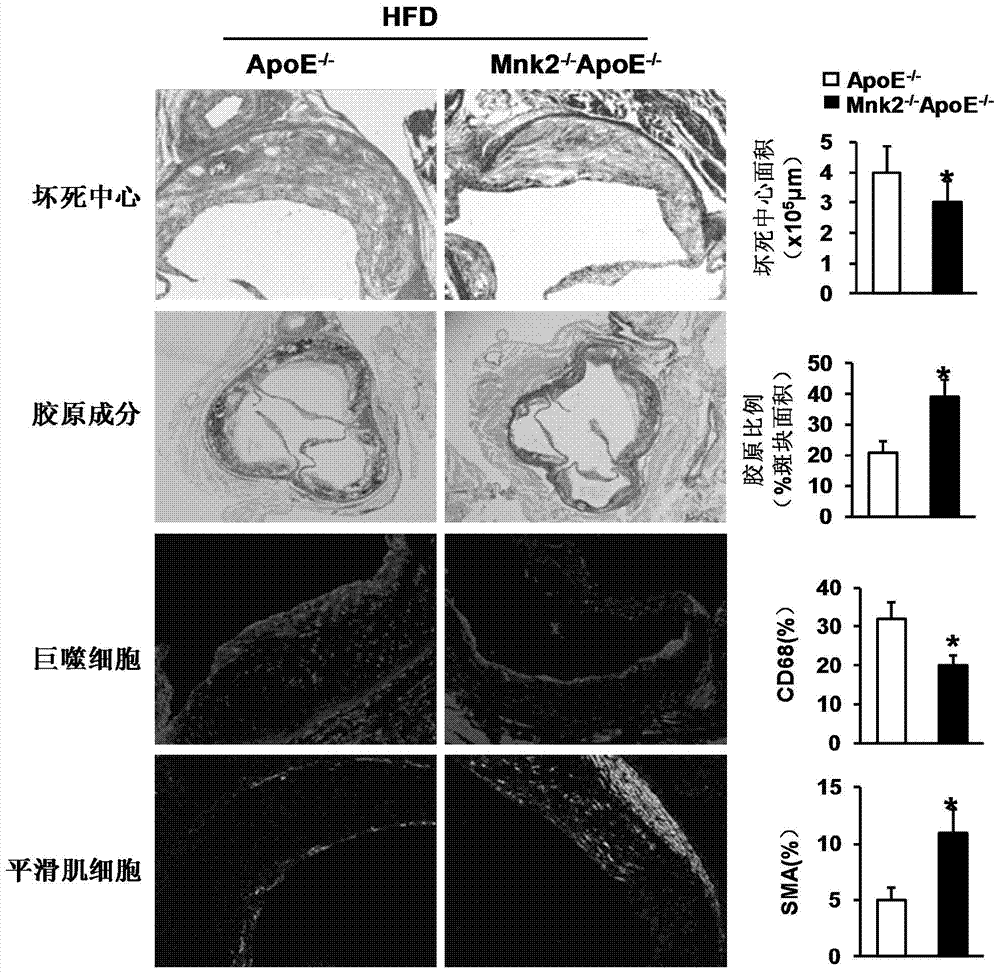
Function and application of MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) signal-integrating kinase 2 in treatment of atherosclerosis
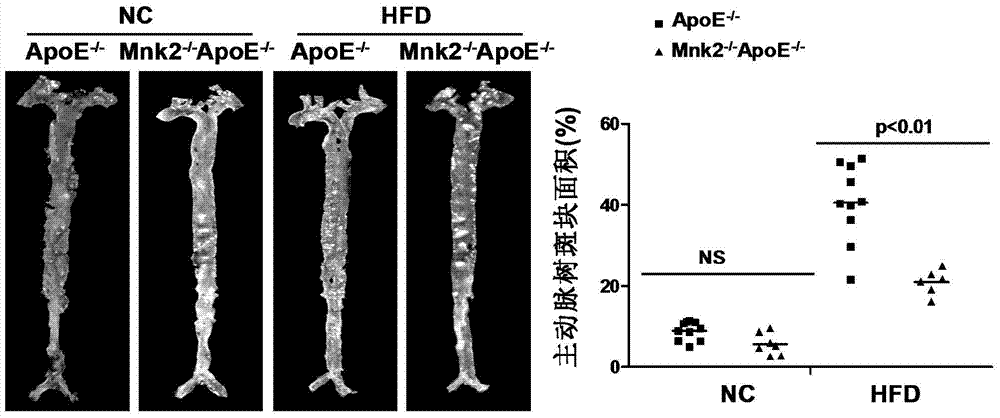
ActiveCN104232732APromotes atherosclerosisAlleviate and/or treat atherosclerosisGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMitogen-activated proteinAtheroma
The invention discloses a function and application of an MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) signal-integrating kinase 2 (Mnk2) in treatment of the atherosclerosis and belongs to the field of a function and application of a gene. According to the invention, an ApoE<- / -> mouse and an Mnk2<- / ->ApoE<- / -> mouse are used as experimental objects and an atherosclerosis module is obtained by high fat diet induction; the result shows that compared with the ApoE<- / -> mouse, the gene defect of the Mnk2 obviously reduces the plaque area of an aorta, reinforces stability of an aortic sinus plaque and obviously reduces the inflammatory response. The invention shows that the function of the Mnk2 in the atherosclerosis mainly represents promotion for forming of the aortic plaque and particularly promotion for the atherosclerosis. Aiming at the function of the Mnk2, the Mnk2 can be used as a drug target for screening a medicament for preventing, relieving and / or treating the atherosclerosis and an inhibitor of the Mnk2 can be used for preparing the medicament for preventing, relieving and / or treating the atherosclerosis.
Owner:武汉惠康基因科技有限公司
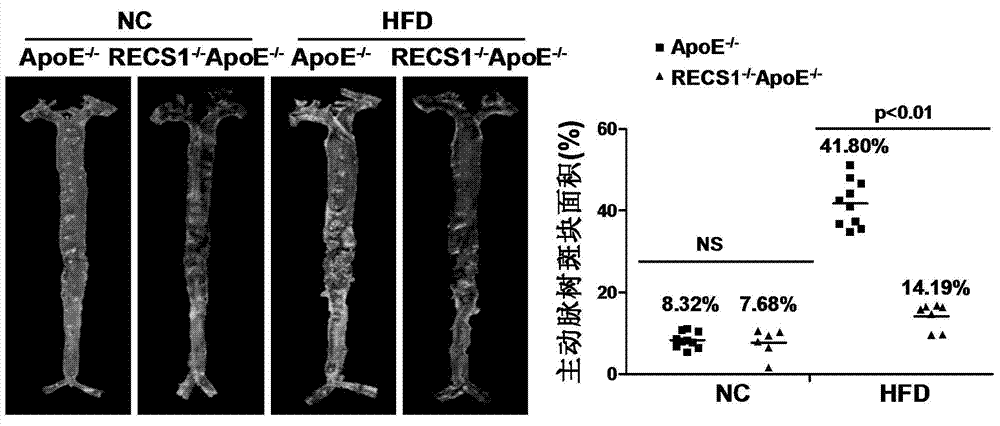
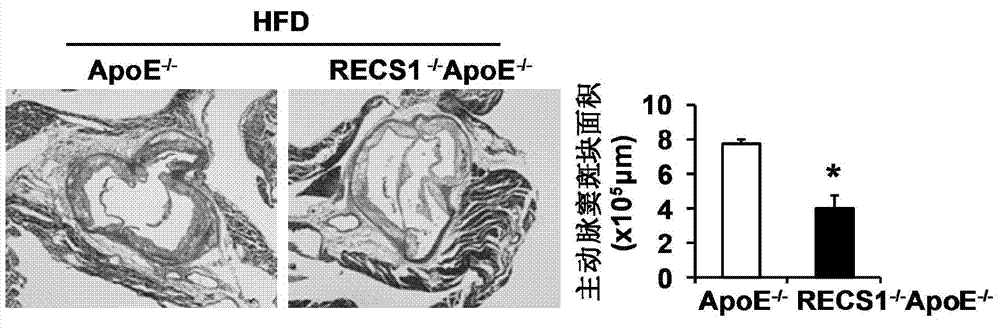
Function and application of blood shear stress responding protein 1 in treatment of atherosclerosis
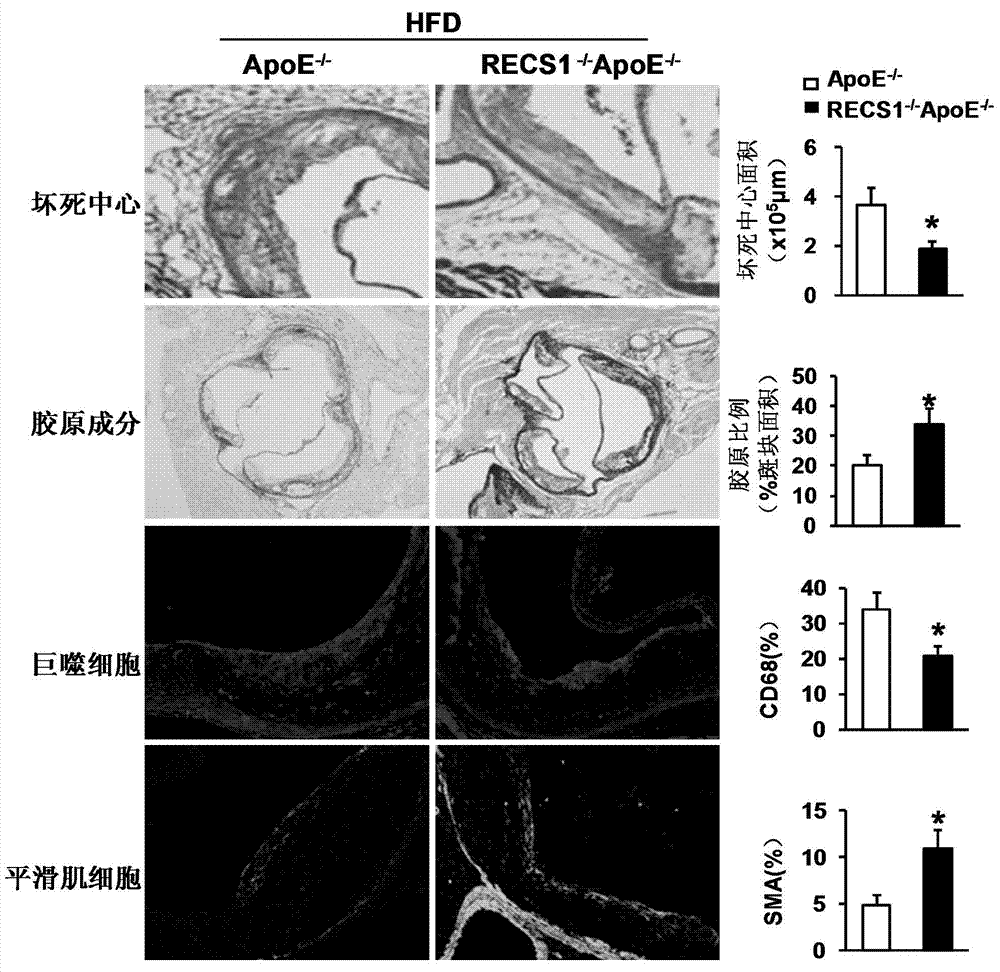
ActiveCN104324389APromotes atherosclerosisAlleviate and/or treat atherosclerosisGenetic material ingredientsAntibody ingredientsGene defectShear stress
The invention discloses a function and an application of a blood shear stress responding protein 1 (RECS1) in treatment of atherosclerosis and belongs to the field of functions and applications of genes. In the invention, an ApoE - / - mouse and an RECS1 - / - ApoE - / - mouse are employed as experimental subjects and an atherosclerosis model is obtained through high-fat diet induction. A result proves that compared with the ApoE - / - mouse, a RECS1 gene defect can significantly reduce a plague area in aorta, enhance stability of aortic sinus plagues and significantly alleviate inflammatory response, which indicate that the RECS1 in the atherosclerosis mainly has effects of promoting formation of a plague in the aorta, especially promoting the atherosclerosis. On the basis of the functions of the RECS1, the RECS1, as a drug target, can be used for screening a drug for preventing, alleviating and / or treating the atherosclerosis. An inhibitor of the RECS1 can be used for preparing a drug for preventing, alleviating and / or treating the atherosclerosis.
Owner:武汉惠康基因科技有限公司
Aortic connectors and methods of use
Connectors interfacing a mechanical circulatory system with a patient's natural vasculature are provided herein. Such connectors include aortic connectors that facilitate fluid coupling of an outflow graft tube from an implanted blood pump with a patient's aorta. Aortic connectors can include a substantially planar portion configured for sealed attachment with a wall of the aorta and a tubular connector portion extending from an inlet opening to an outlet opening. The substantially planar portion can include a flexible membrane for attachment to an outer surface of the aorta and / or a flange for engagement with an inner surface of the aorta. The tubular connector can extend from the substantially planar portion at a pre-determined angle and include one or more attachment features to facilitate rapid fluidly sealed attachment to the outflow graft tube.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Branch type aorta artificial stent conveying device
PendingCN112807142AReduce the difficulty of operationReduce surgical riskStentsBlood vesselsSurgical operationAorta aortic
The invention relates to a branch type aorta artificial stent conveying device. The branch type aorta artificial stent conveying device comprises a conveyor, an artificial stent arranged in the conveyor and a catcher used for cooperating with the conveyor. The catcher is guided into branch arterial blood vessel, the conveyor is guided into the focus position of the aorta, then a soft sheath is fixed, an outer tube is gradually withdrawn to expose branch guide wires, then the catcher is used for catching the branch guide wires, and therefore, branch arterial stents are guided into the branch arterial blood vessel through the branch guide wires. In the surgical operation process, due to the fact that the branch guide wires are not reserved on the aorta in advance, the phenomena of crossing and winding of the guide wires cannot occur, the surgical operation difficulty is reduced, the surgical operation is simpler, the surgical time is shortened, and the surgical risk is reduced.
Owner:周小彪
Graft implant method
A method for implanting an end portion of a graft within the body of a patient during a bypass grafting procedure is disclosed. The body has a circulatory system which includes a femoral artery and an aorta. The method includes the steps of (i) making an incision in the body of the patient so as to expose the femoral artery and an inguinal ligament, (ii) advancing an endoscope between the femoral artery and the inguinal ligament until a distal end of the endoscope is positioned at a wording site within the body, (iii) advancing the end portion of the graft between the femoral artery and the inguinal ligament to the working site, wherein said end portion advancing step includes the step of advancing the end portion of the graft through the endoscope, and (iv) forming an anastomosis between the end portion of the graft and the aorta at the working site.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Heart valve stent and heart valve prosthesis
PendingCN111053629APrevent weekly leakagePrevent conduction blockHeart valvesAorta aorticAtrioventricular heart block
The invention discloses a heart valve stent and a heart valve prosthesis. The heart valve stent comprises a stent main body, which comprises mutually connected grid structure units, wherein the stentmain body is divided into an inflow channel, a transition section and an outflow channel in the axial direction, the inflow channel, the transition section and the outflow channel are connected in sequence, the stent further comprises a limiting structure connected with the stent main body, and the limiting structure is distributed on the outflow channel or the transition section in the circumferential direction, and is provided with a first projection part for limiting the stent from moving from the inflow channel to the outflow channel. According to the invention, the limiting structure is arranged on the outflow channel of the stent, so that the stent can be prevented from moving towards the outflow channel under the scouring of blood flow; the inflow channel of the stent is arranged toadapt to the shape of the native tissue, and the outer skirt edge is arranged in the circumferential direction of the outer side of the inflow channel at the position attached to the native tissue, so that perivalvular leakage can be effectively prevented while the valve is prevented from moving towards the inflow channel; and the size of the inflow channel of the stent can be small so as to effectively prevent atrioventricular block, and the size of the outflow channel can be small so as to reduce the compression on the aorta.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT CARDIOFLOW MEDTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com