Patents
Literature
228 results about "Iliac artery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
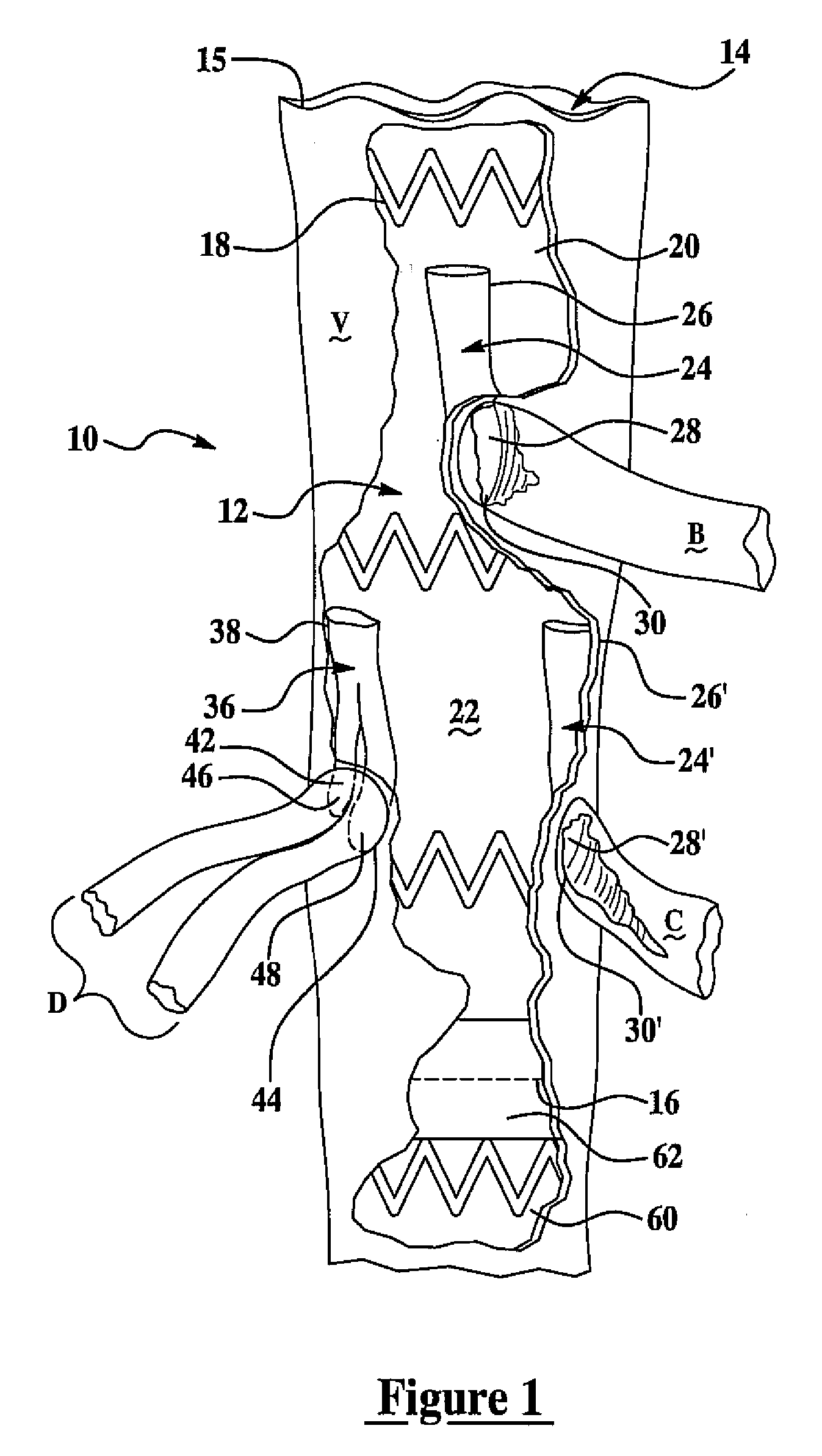
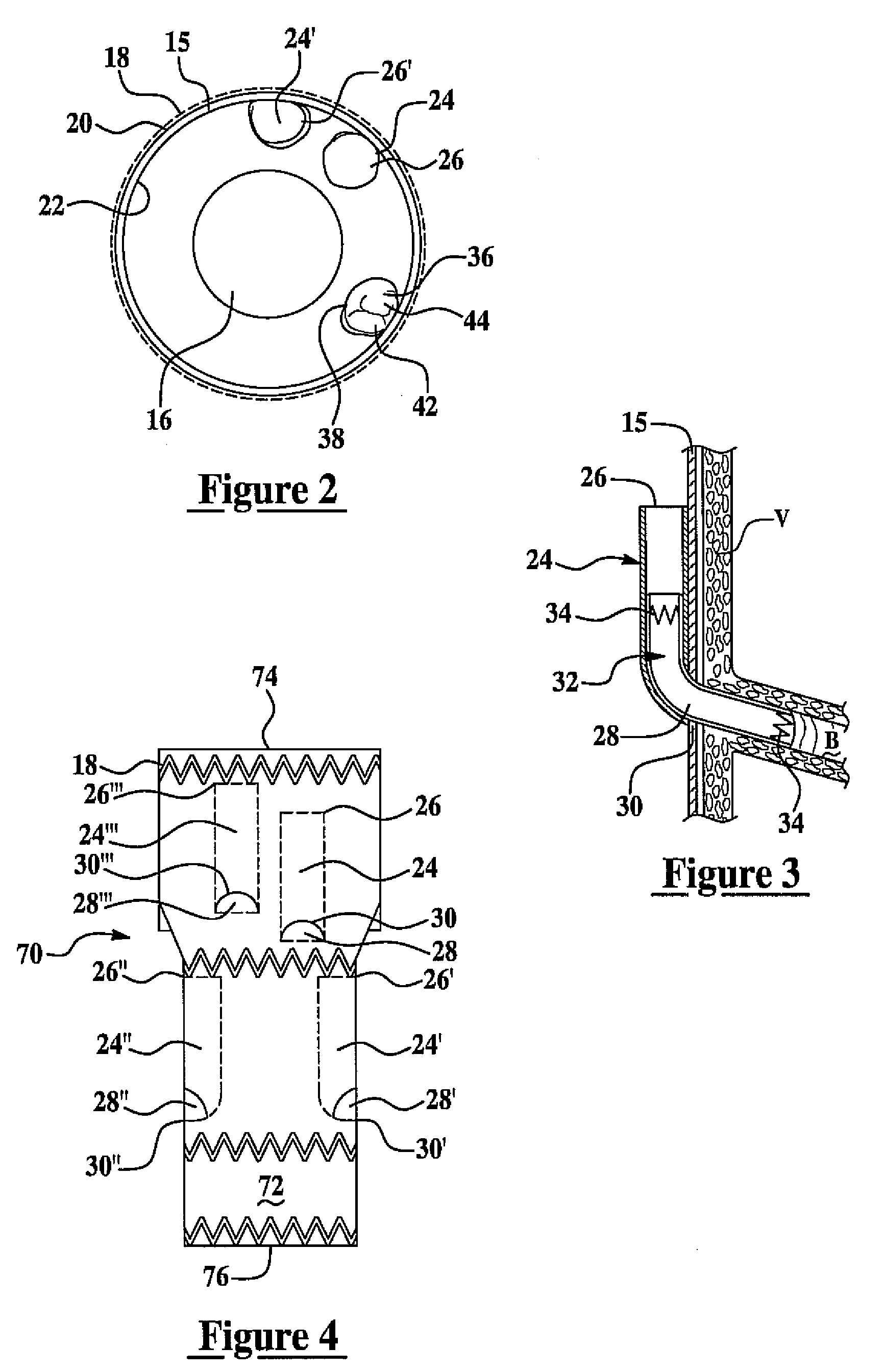
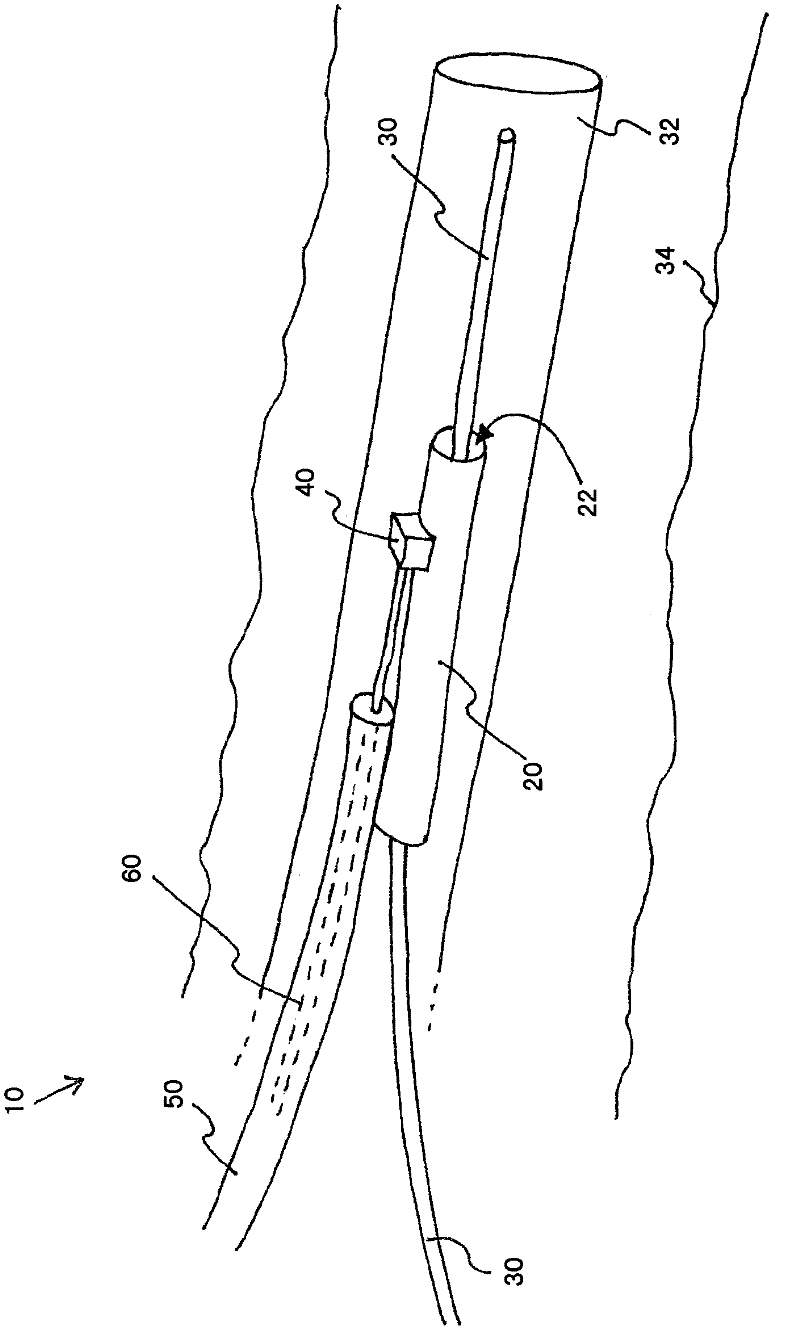
Intravascular thromboembolectomy device and method using the same
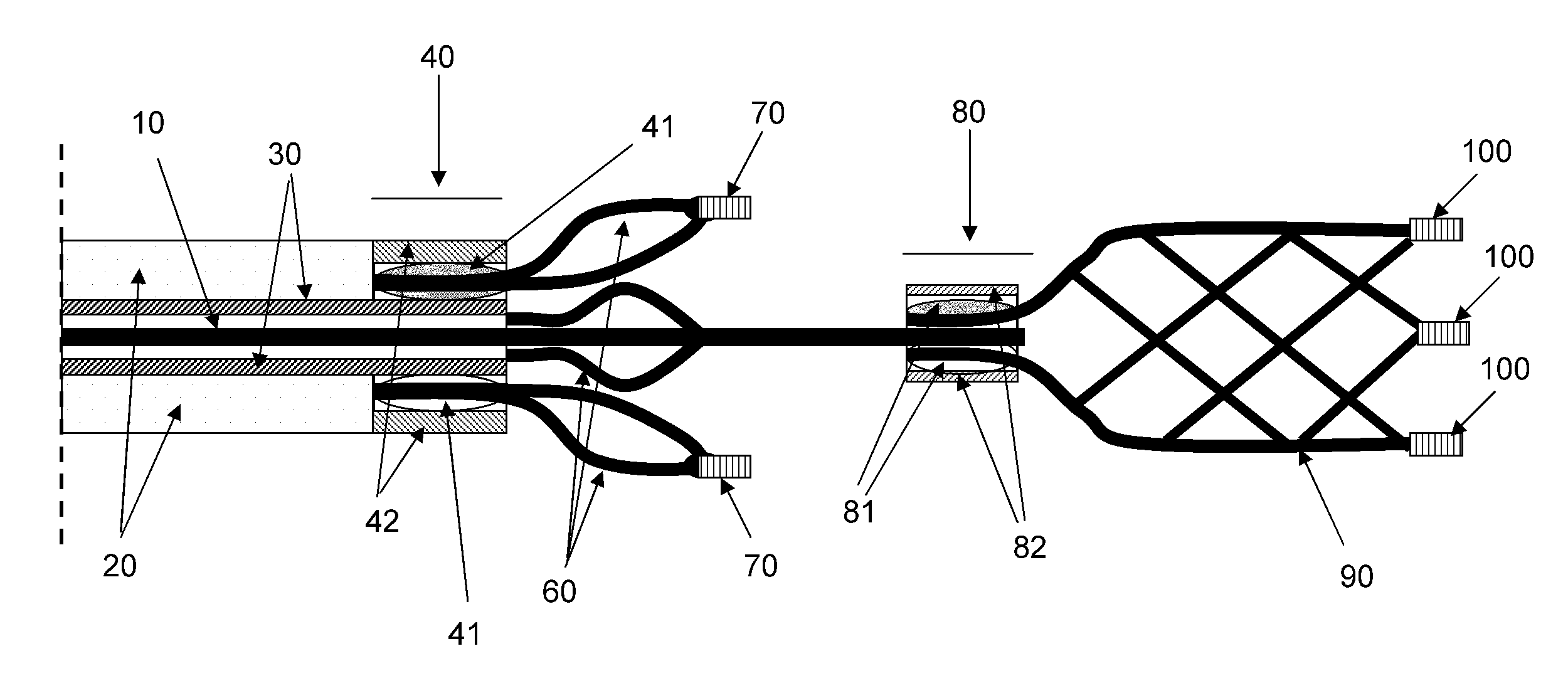
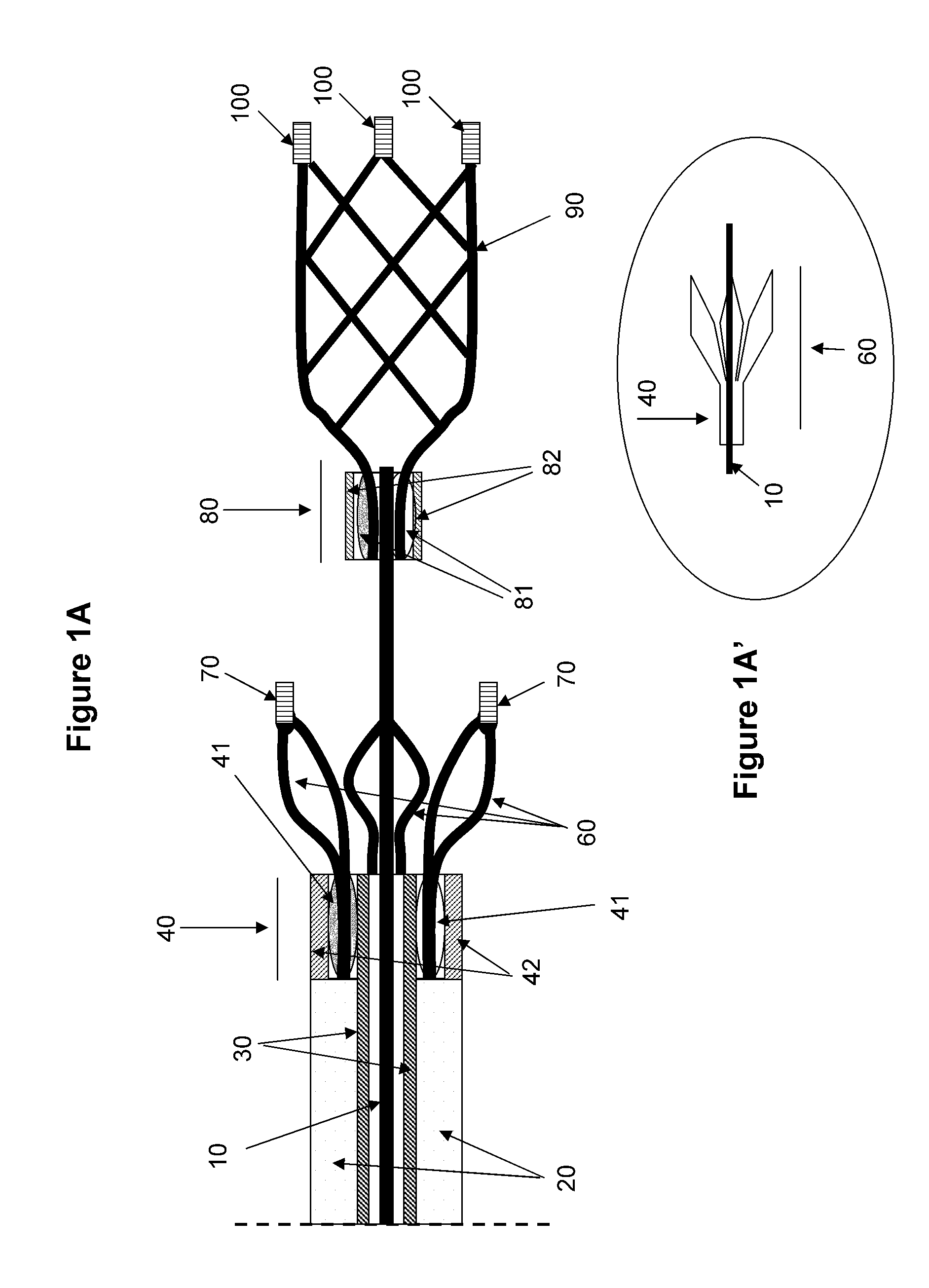
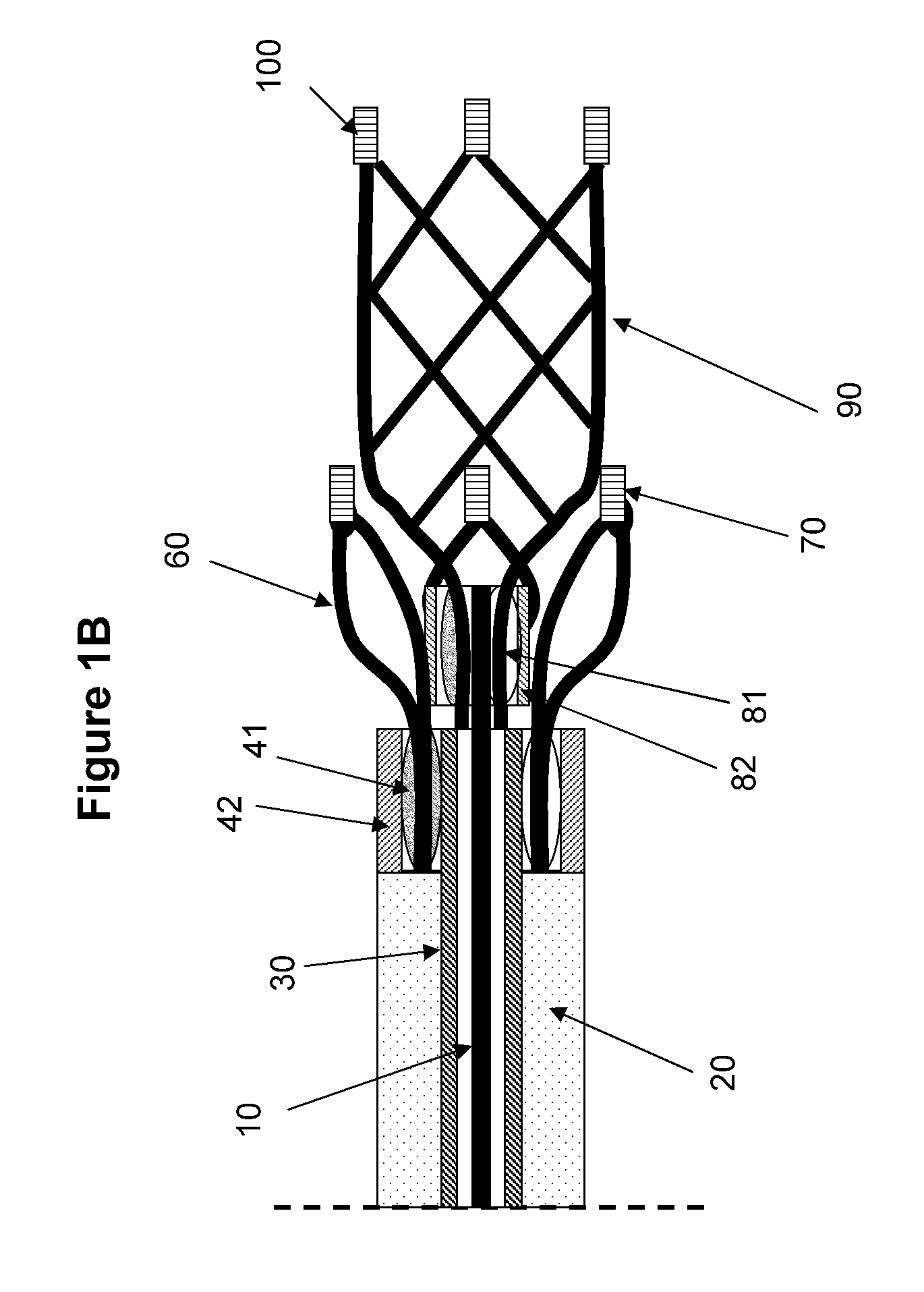
A device and a method for increasing or restoring a flow in a body lumen are provided. The device and the method may treat conditions related to a stroke, such as an ischemic stroke, by removing an occlusion from a blood vessel and / or reopen a blood vessel. The device may comprise a tubing compartment, a central wire, and an engaging compartment. The engaging compartment may comprise a distal engaging element and a proximal engaging element. A clot or occlusion present in the body lumen such as an artery may be engaged in and / or between the distal and proximal engaging elements. Further, the positions of one or both of the engaging elements and the distance therebetween can be adjusted to ensure the engagement of the clot or occlusion.
Owner:LIKEMARK MEDICAL
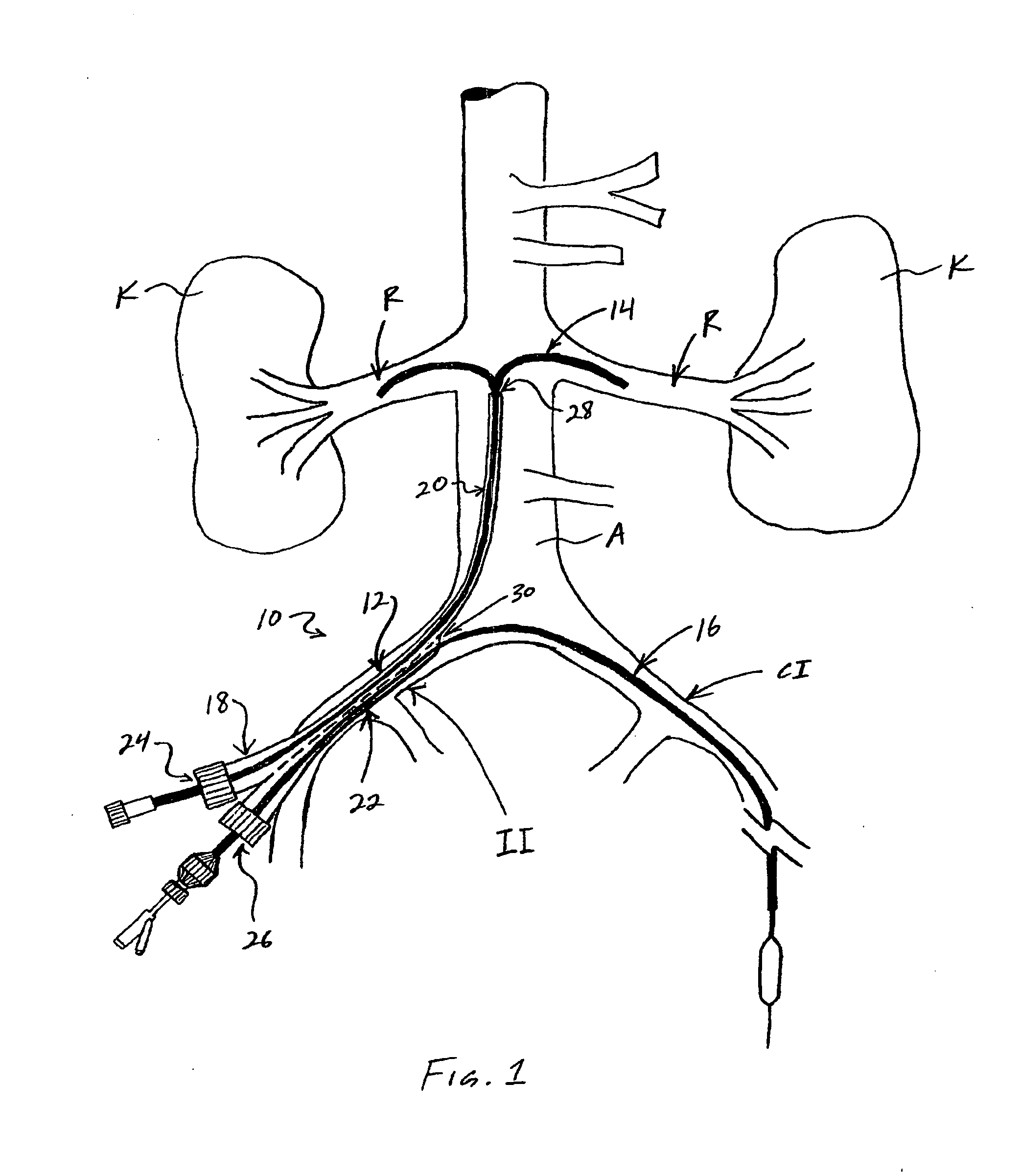
Sheath for use in peripheral interventions
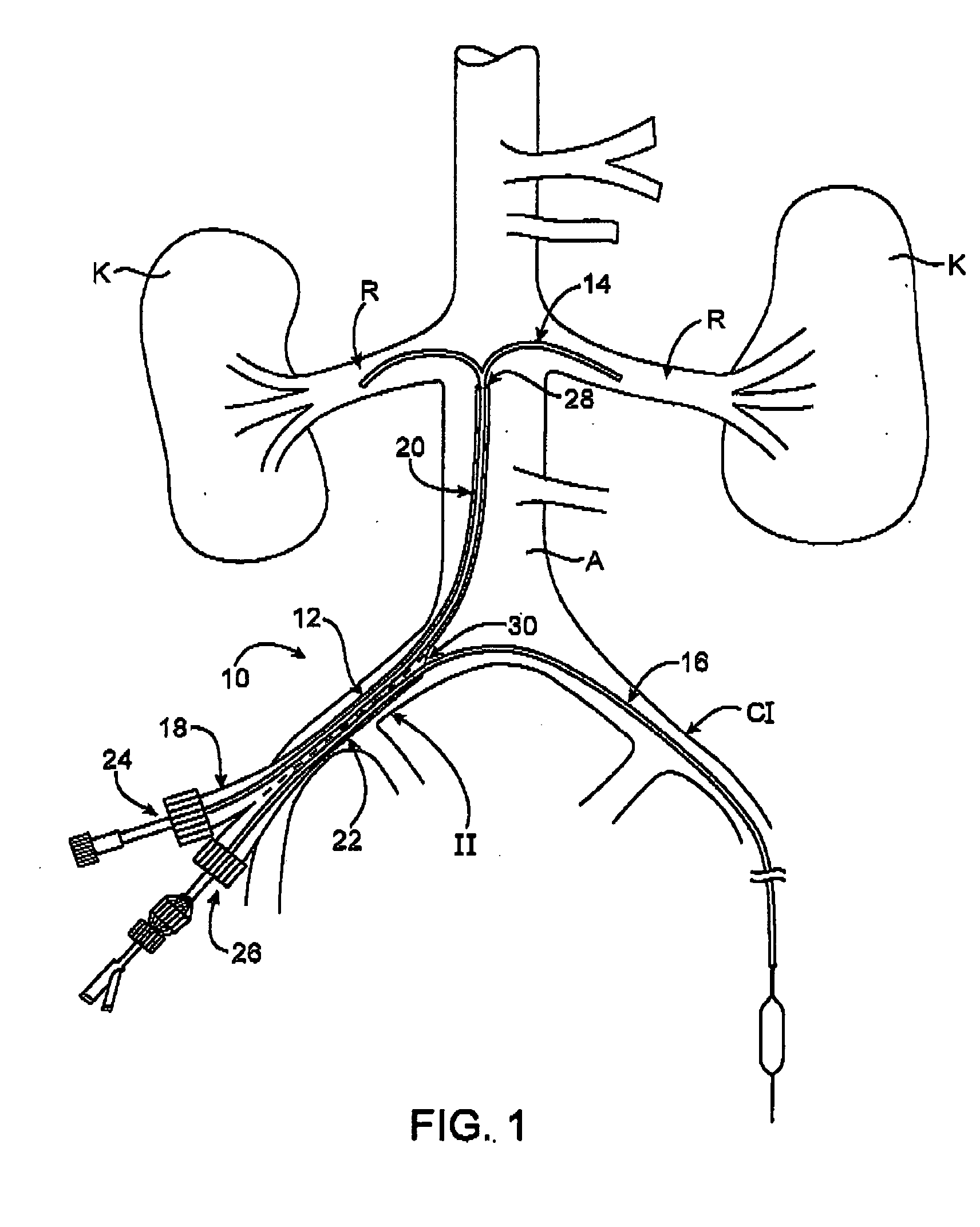
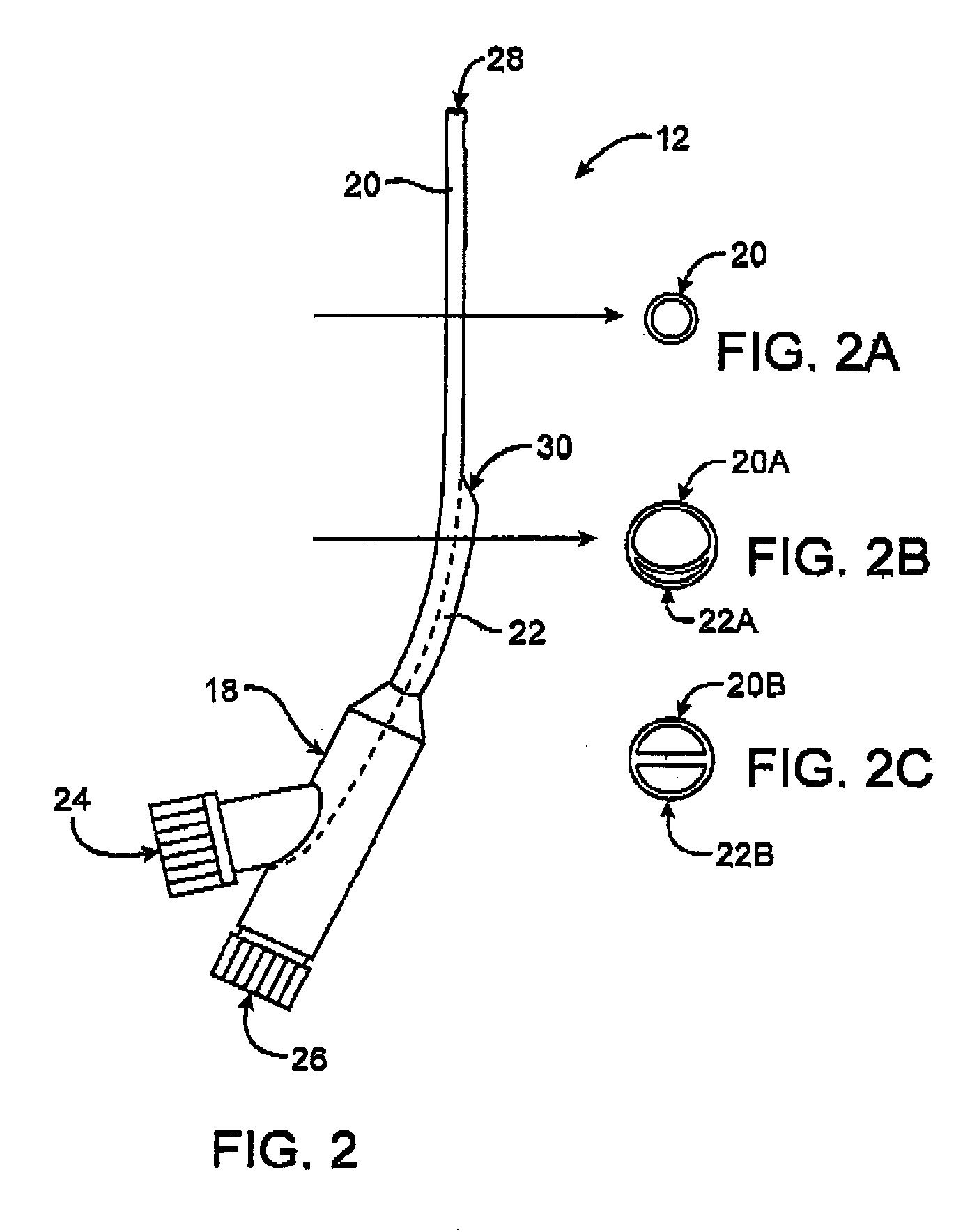
A dual lumen introducer sheath provides access to at least one renal artery and at least one peripheral blood vessel of a patient. The introducer sheath includes a proximal hub comprising first and second ports, a first lumen, and a second lumen. The first lumen extends from the first port to a first distal aperture and has sufficient length such that when the first port is positioned outside the patient the first distal aperture is positionable in the abdominal aorta at or near origins of the patient's renal arteries. The second lumen extends from the second port to a second distal aperture, has a shorter length than the length of the first lumen, and is configured to allow passage of a catheter device through the second lumen and into or through an iliac artery contralateral to an insertion point of the introducer sheath into the patient.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Devices and methods for treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms
InactiveUS20090287145A1Minimize the possibilityReduce the overall diameterStentsSurgeryIliac arteryArtery aneurysm
Methods and devices with two individual tubes for treating abdominal aortic aneurysm that bypass the aneurysm and are placed from the upper aorta to the iliac arteries. A separate upper cuff may also be provided, to secure the tubes above the aneurysm.
Owner:ALTURA MEDICAL
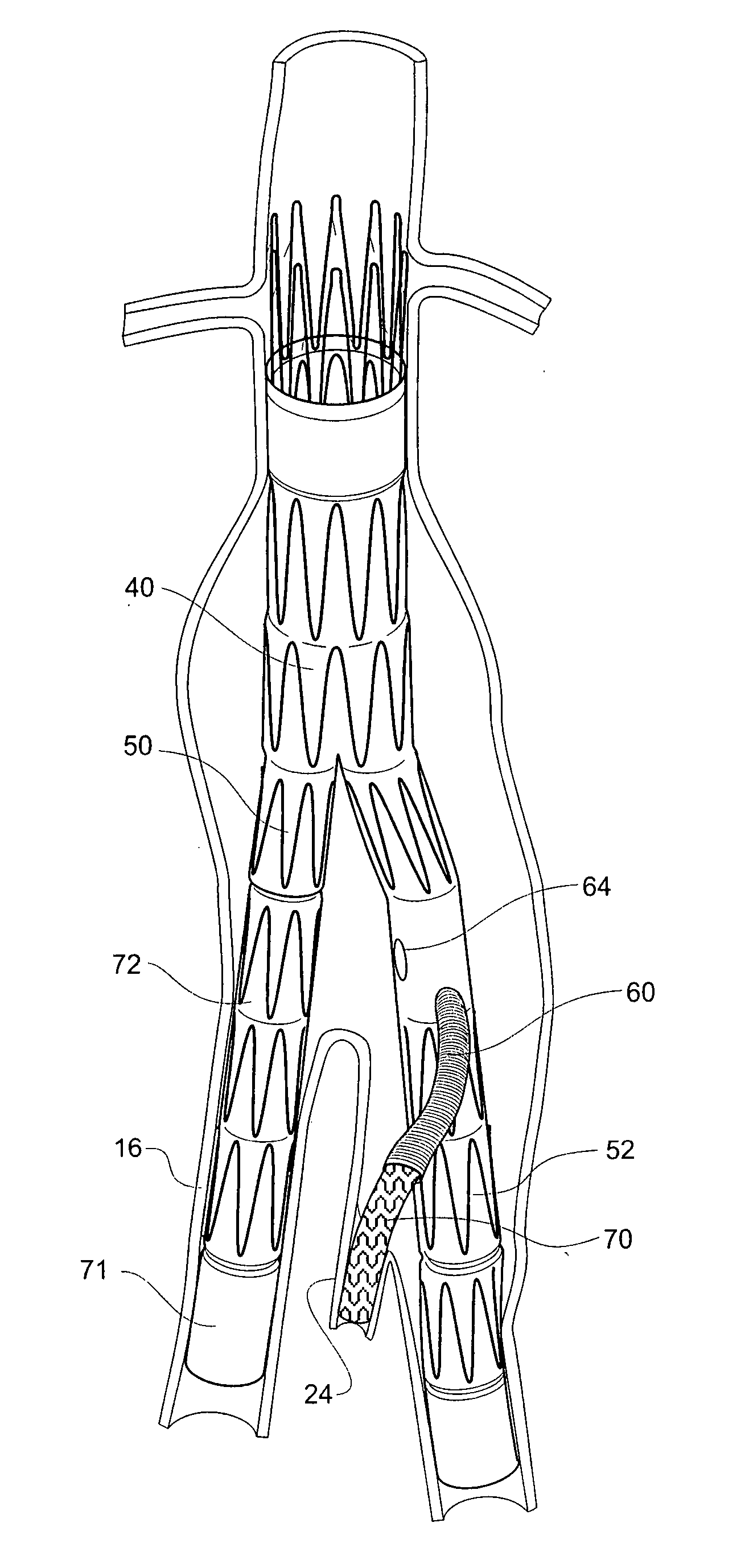
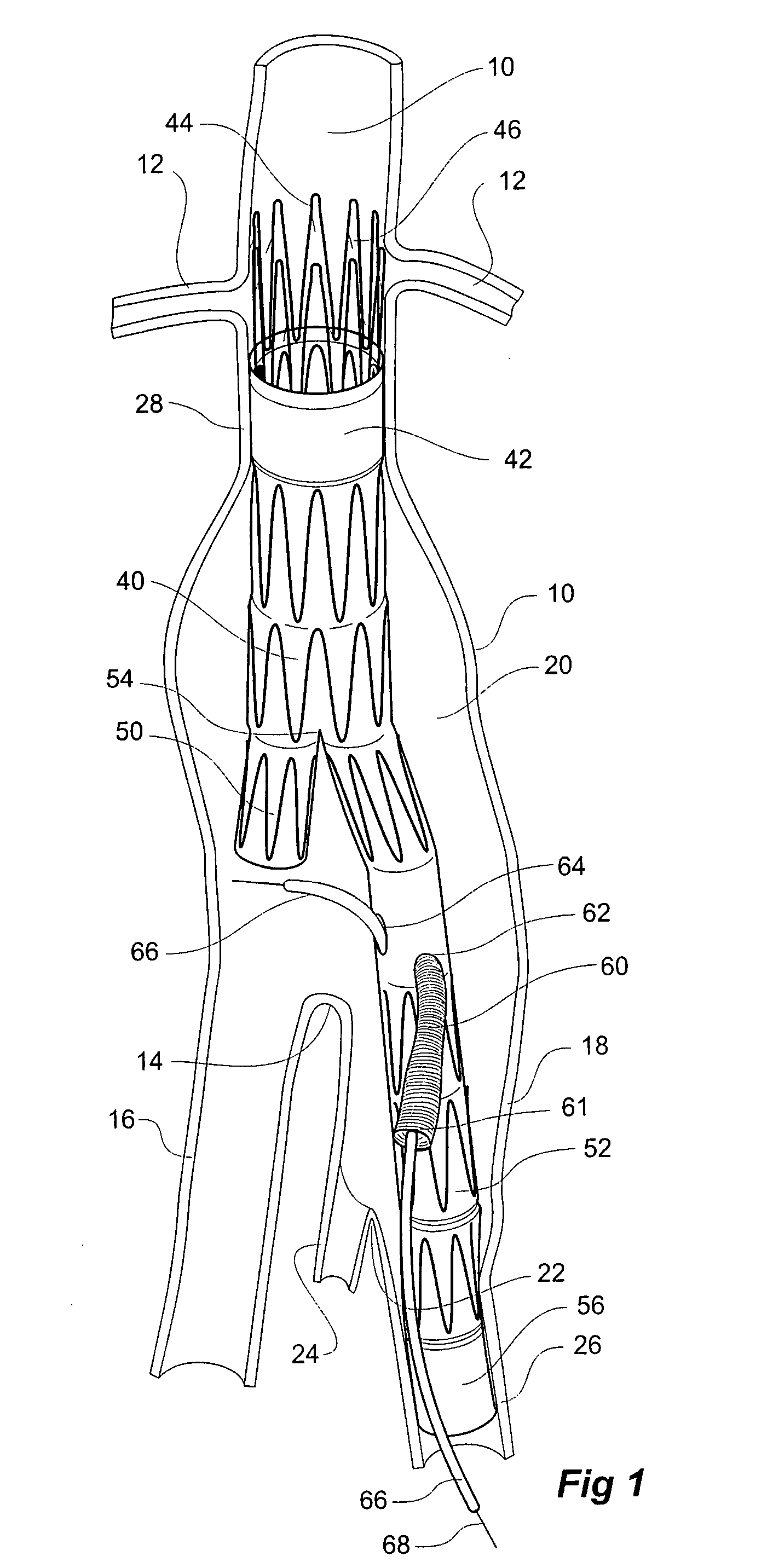
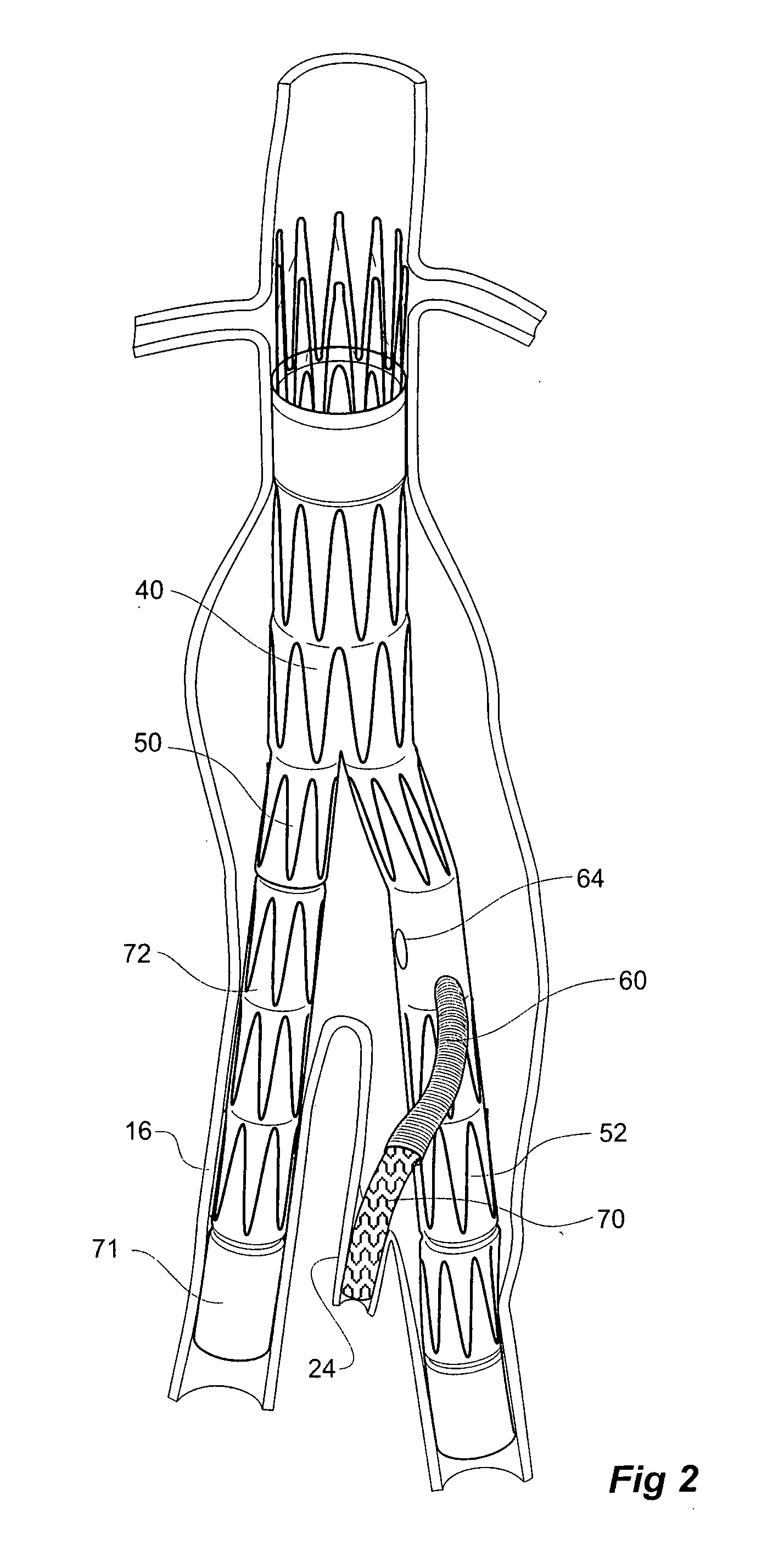
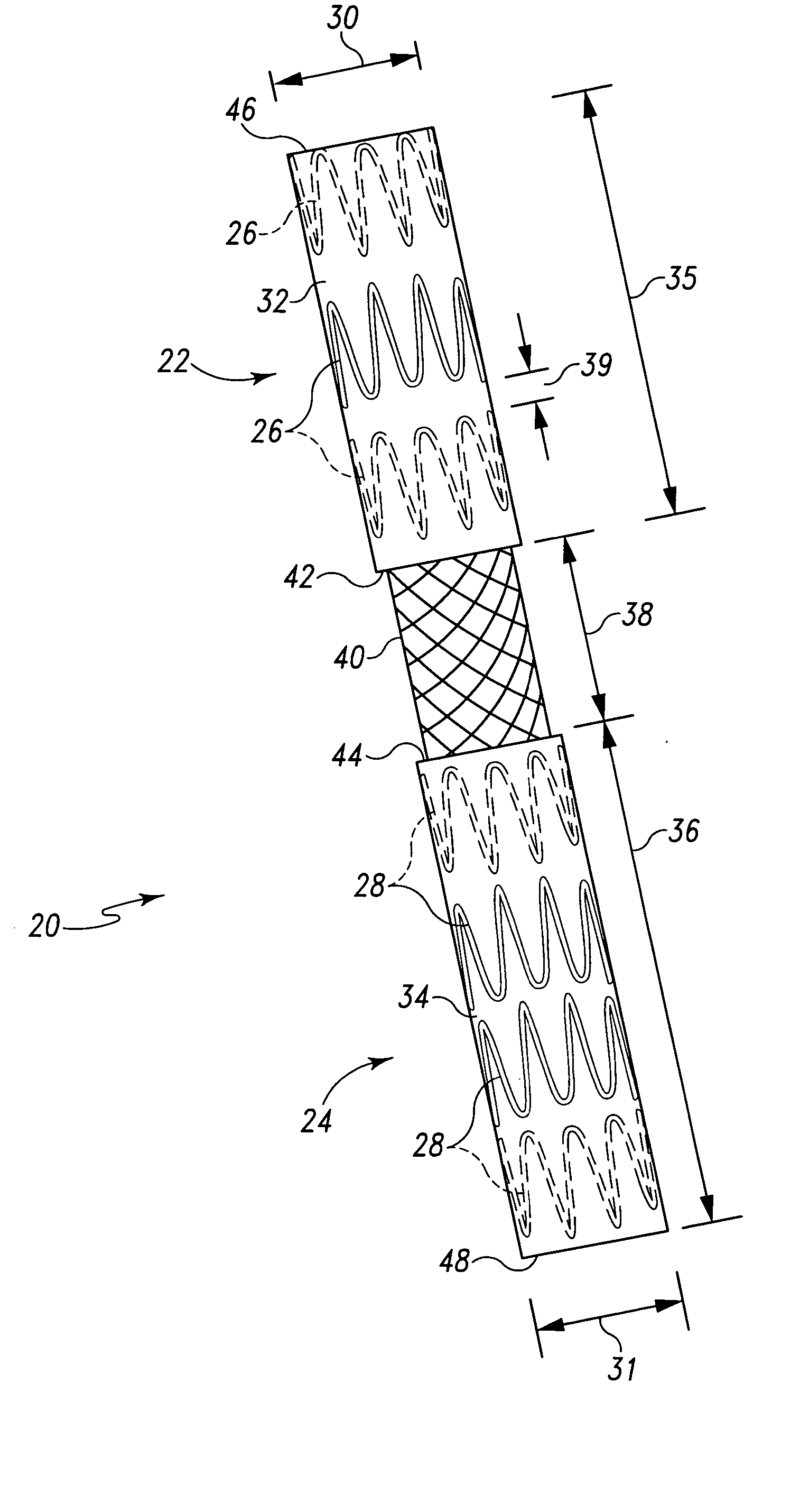
Twin bifurcated stent graft
A stent graft (40) has a tubular body with a first bifurcation (54) with first and second legs (50, 52) extending from the bifurcation. One of the legs (52) has a further bifurcation (62) to define a side arm. The stent graft can be deployed into the vasculature of a patient with the tubular body being in an aorta of the patient, a first leg extending down an iliac artery, a second leg being directed towards a contralateral iliac artery and the side arm directed to an internal artery of one of the iliac arteries. One of the legs can include a valved aperture to enable the placement of an indwelling catheter therethrough
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +1
Expandable cerebrovascular sheath and method of use
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, small cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The sheath is configured for use in the upper vascular system and has utility in the introduction and removal of therapeutic or diagnostic microcatheters. The access route is through the femoral arteries or the iliac arteries to the cerebrovasculature. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration during advancement to the cerebrovasculature. The distal end of the sheath is subsequently expanded using a radial dilatation device, which is removed prior to the introduction of microcatheters. The sheath can be inserted in a first, small cross-sectional configuration, be expanded diametrically to a second, larger cross-sectional configuration, and then be reduced to a diametrically smaller size for removal.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Interconnected leg extensions for an endoluminal prosthesis
An endoluminal prosthesis includes two stent grafts with a flexible bridge extending between and connected to the stent grafts. The prosthesis can be part of a prosthesis assembly for treatment of branched vascular systems and can function as an interconnected leg extension prosthesis in combination with a main bifurcated prosthesis. In treating abdominal aortic aneurysms, the prosthesis can be deployed within both iliac arteries.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Systems and methods for transcatheter aortic valve treatment
ActiveUS20110213459A1Shorter and straight access pathEasy to placeSuture equipmentsStentsTRANSCATHETER AORTIC VALVE IMPLANTCatheter
Devices and methods are configured to allow transcervical or subclavian access via the common carotid artery to the native aortic valve, and implantation of a prosthetic aortic valve into the heart. The devices and methods also provide means for embolic protection during such an endovascular aortic valve implantation procedure.
Owner:SILK ROAD MEDICAL
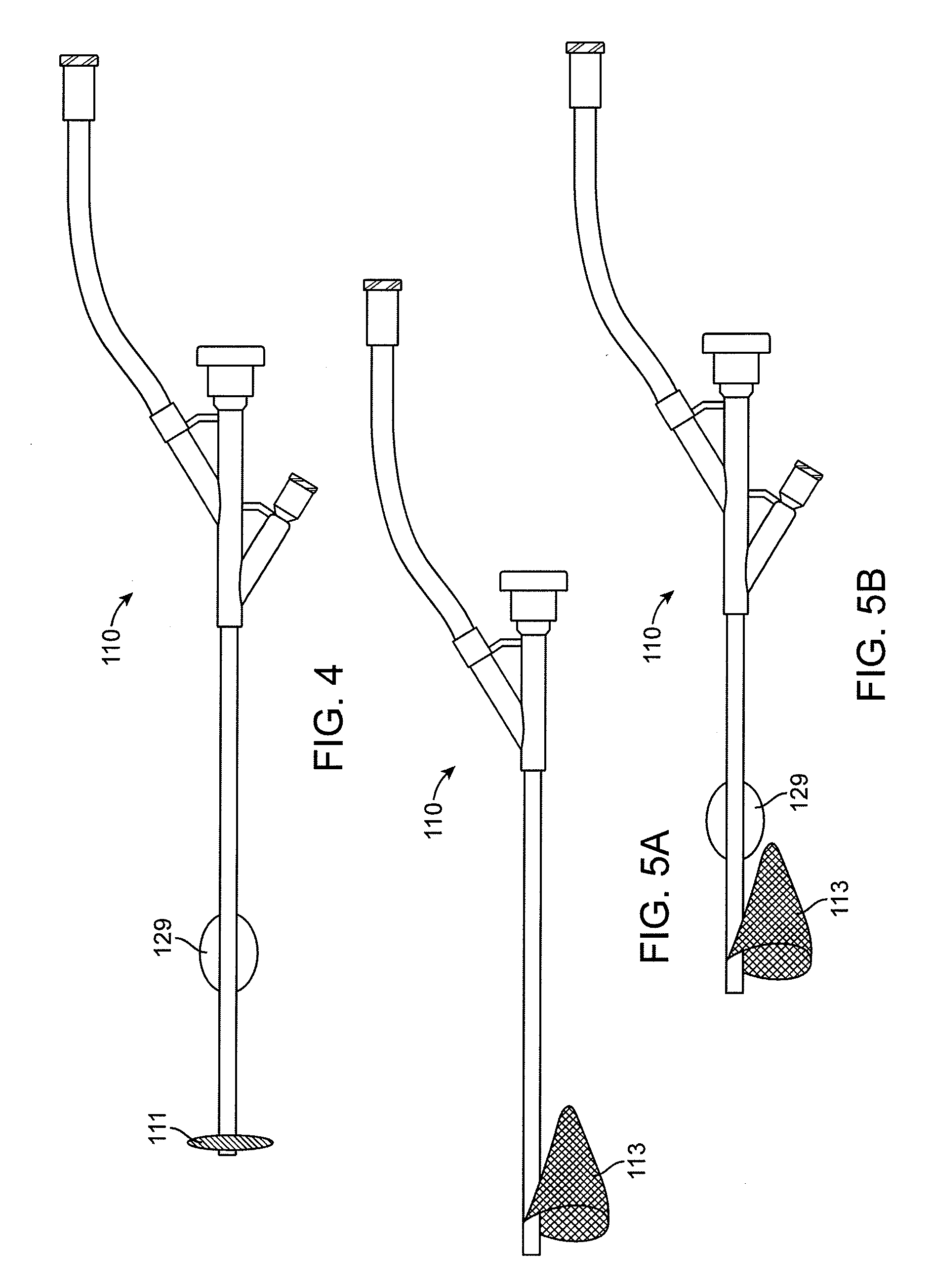
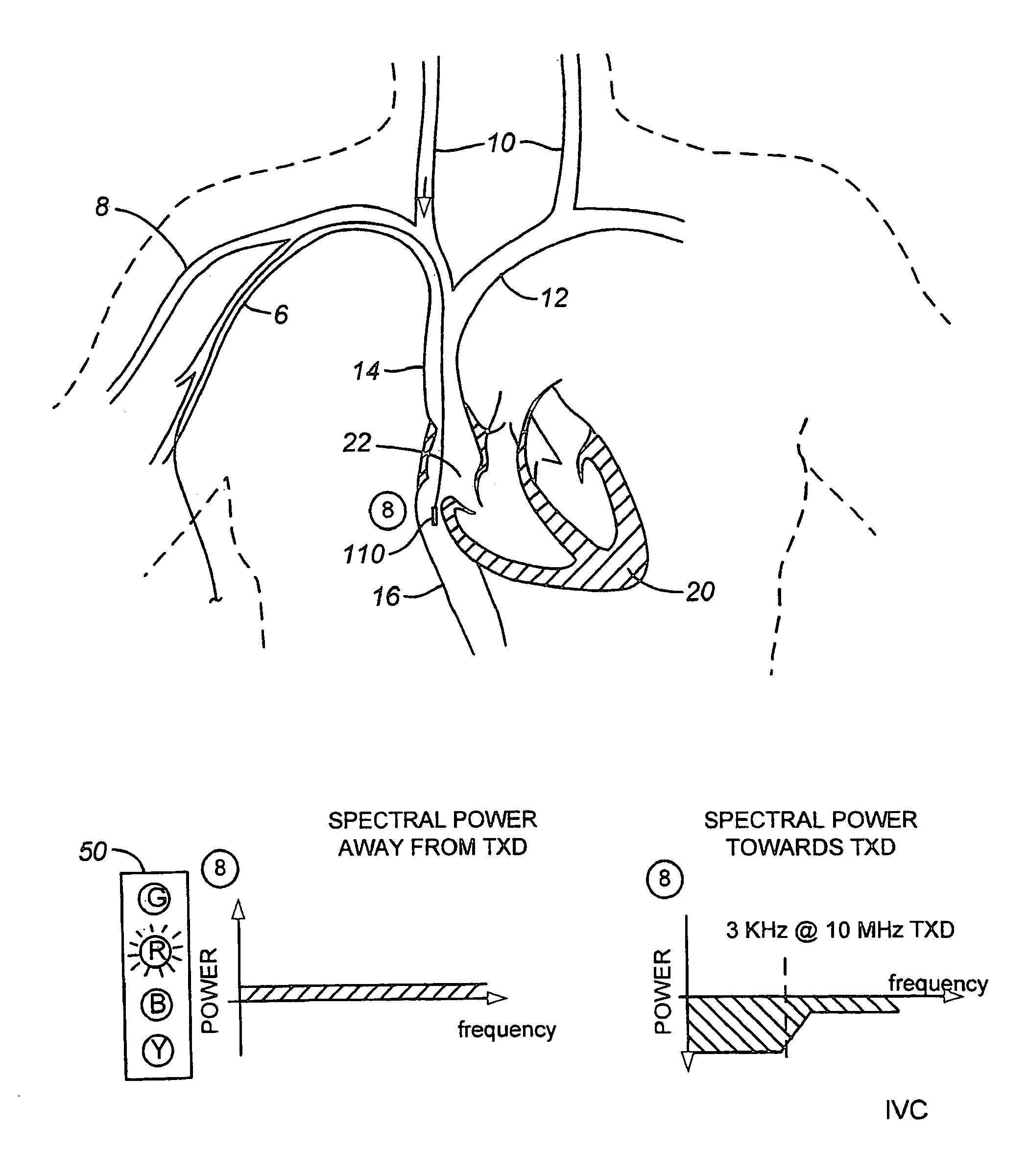
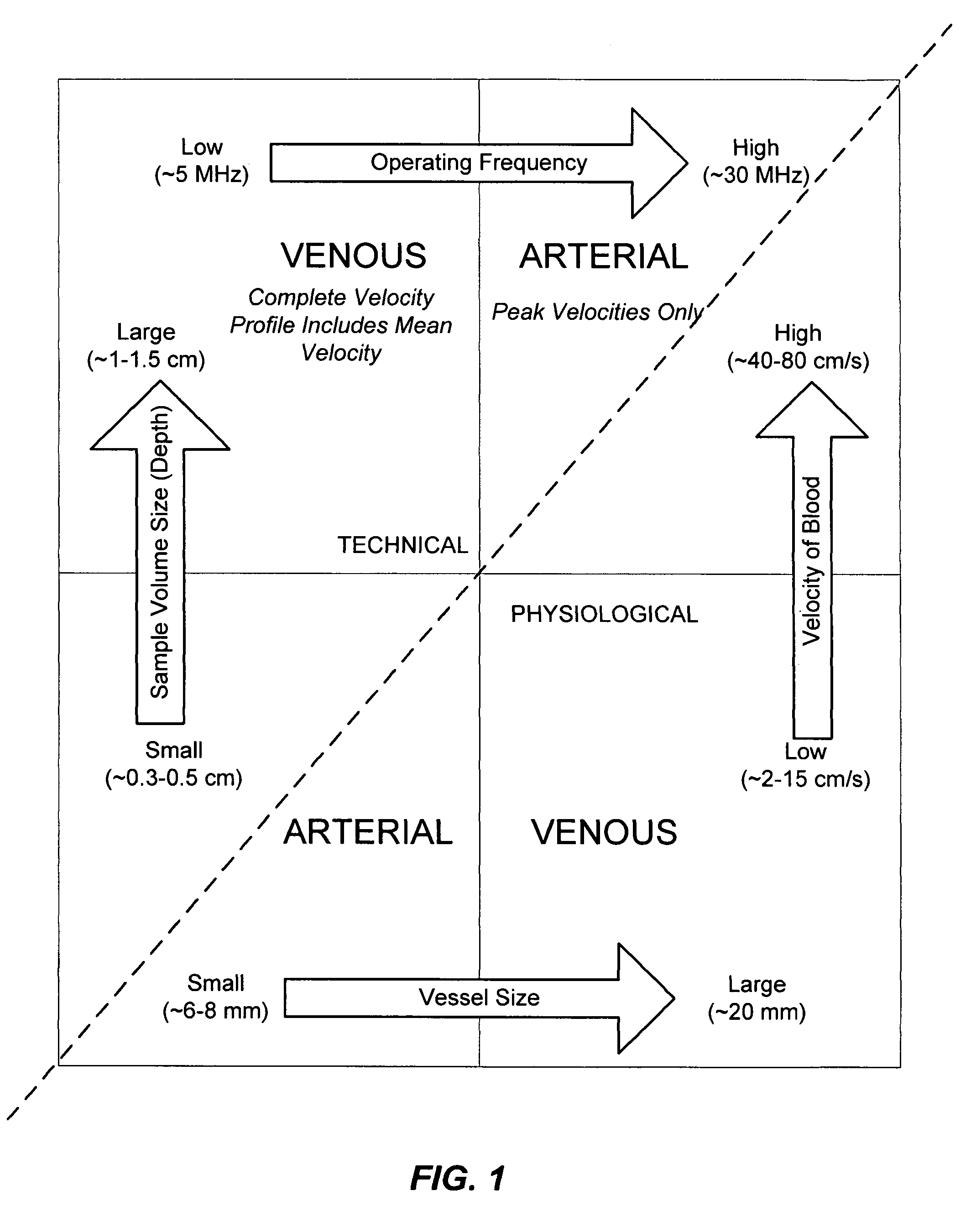
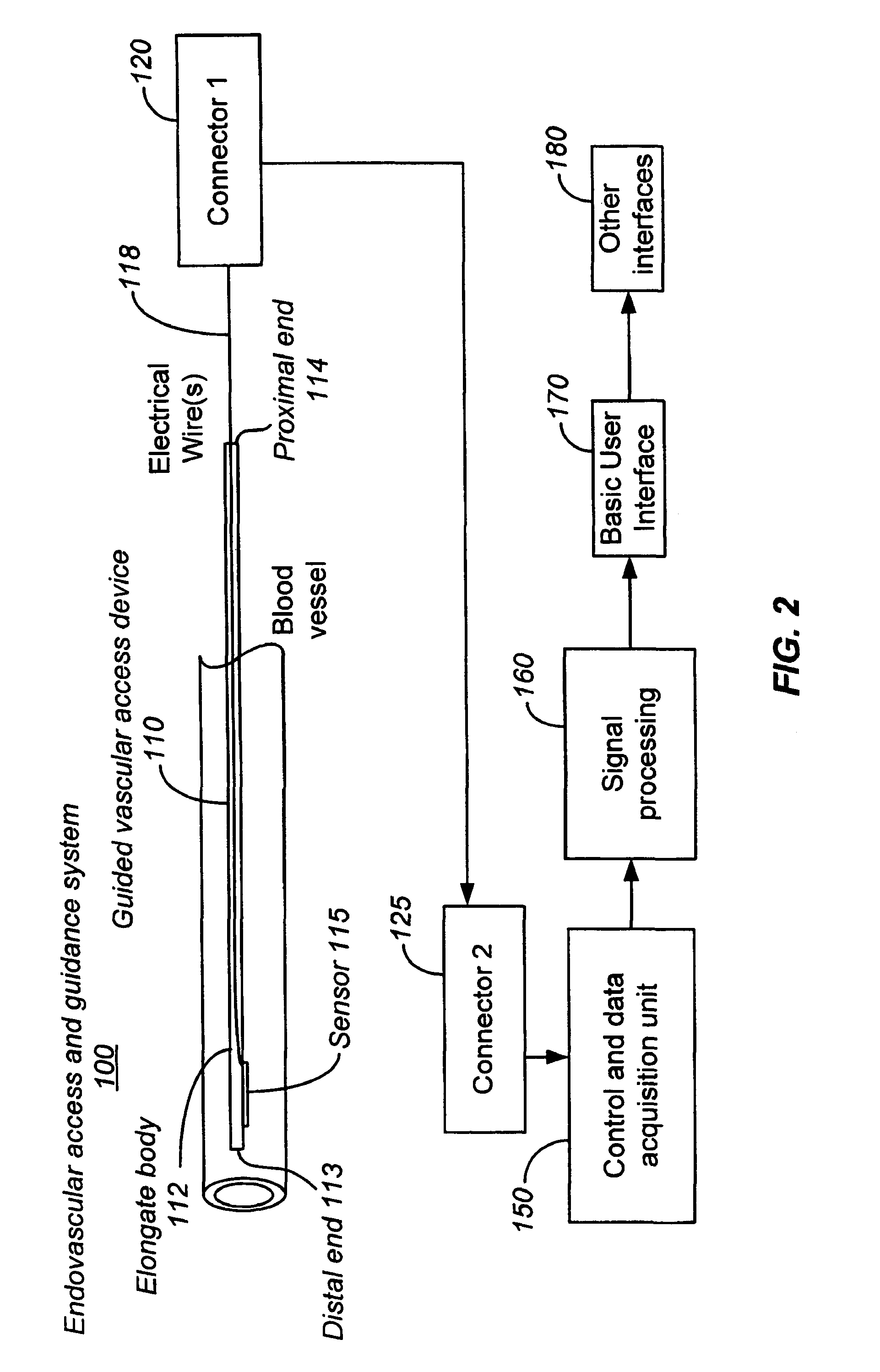
Ultrasound methods of positioning guided vascular access devices in the venous system
The invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices, such as catheters, stylets, guidewires and other flexible elongate bodies that are typically inserted percutaneously into the venous or arterial vasculature. An aspect of the invention includes, for example, an endovenous access and guidance system. The system comprises: an elongate flexible member adapted and configured to access the venous vasculature of a patient; a sensor disposed at a distal end of the elongate flexible member and configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient provided by the sensor and to provide position information regarding the position of the distal end of the elongate flexible member within the venous vasculature of the patient; and an output device adapted to output the position information from the processor.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Expandable intra-aortic balloon pump sheath
ActiveUS20080183136A1Inhibit bindingAvoid interferenceInfusion syringesCatheterAccess routeIntraaortic balloon pump
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, low cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The sheath is configured for use in the vascular system and has utility in the introduction and removal of balloon counterpulsation catheters. The access route is through the femoral arteries and the iliac arteries into the aorta, where an intra-aortic balloon pump catheter is positioned to provide cardiac support. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration during advancement to the arteries into the aorta. The distal end of the sheath is subsequently expanded using a radial dilatation device.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
In-Situ Forming Foams for Embolizing or Occluding a Cavity
The present invention provides systems and methods for occluding and / or embolizing a cavity within a patient by delivering a prepolymer material into or onto a cavity and forming an expanding foam within the cavity. The inventions methods are applicable to occluding a variety of cavities, including blood vessels, aneurysms, left arterial appendages, vascular malformations and the like.
Owner:ARSENAL MEDICAL
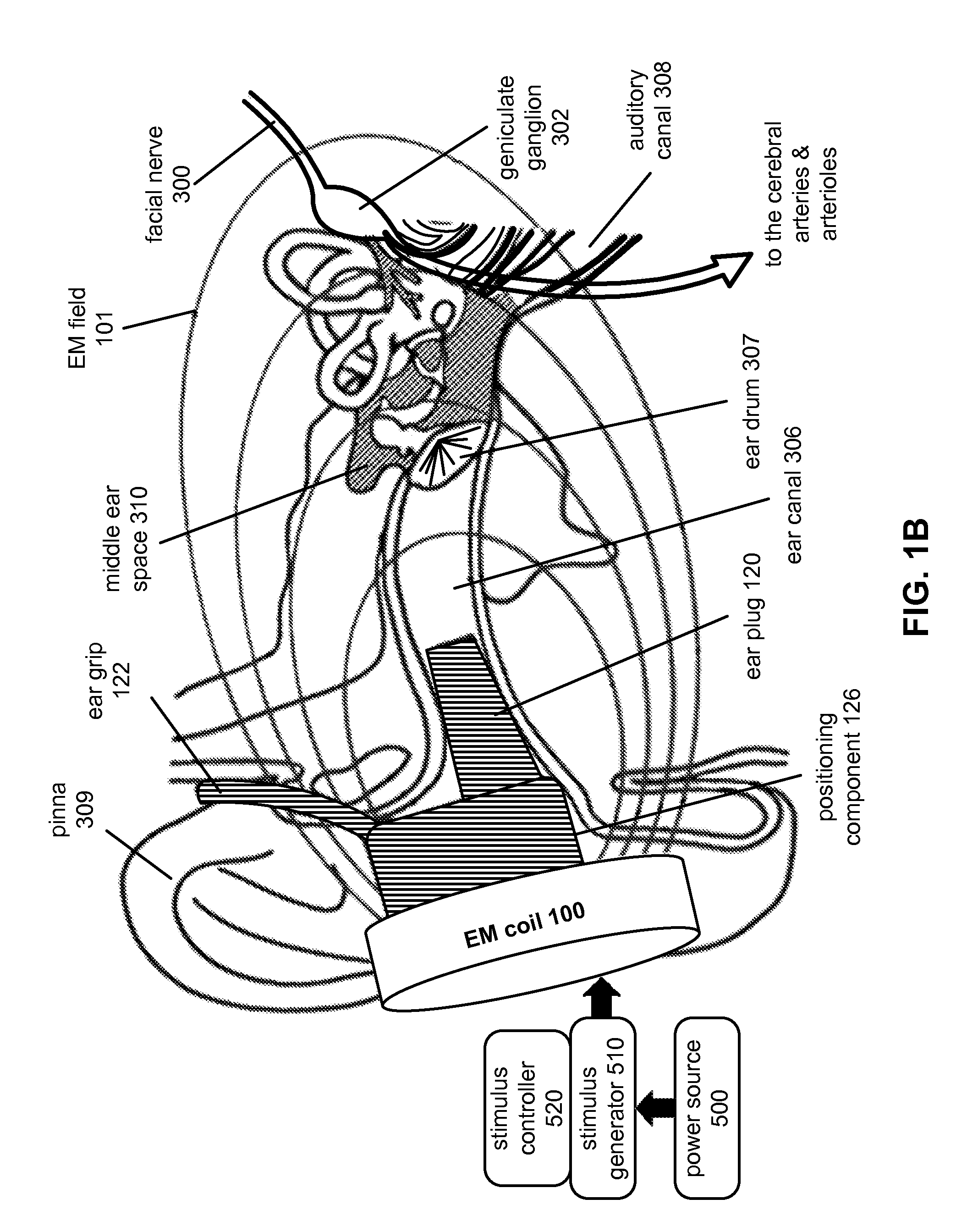
Modulating Function of Neural Structures Near the Ear
ActiveUS20130150653A1Increase blood flowIncrease cerebral blood flowUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyNervous systemModulation function
Stimulation of the facial nerve system (e.g., electrically, electromagnetically, etc.) in ischemic stroke patients will cause dilation of occluded arteries and dilation of surrounding arteries, allowing for blood flow to circumvent the obstruction and reach previously-deprived tissue. The device approaches the facial nerve and its branches in the vicinity of the ear. In use, the device can be inserted into the ear canal and / or placed in proximity to the ear in order to stimulate the facial nerve system non-invasively (e.g., using an electromagnetic field). The device can be used in the emergency treatment of acute stroke or chronically variations for long-term maintenance of blood flow to the brain and stroke prevention. Additional embodiments of the device may be adapted for use on different regions of the body.
Owner:NERVIVE
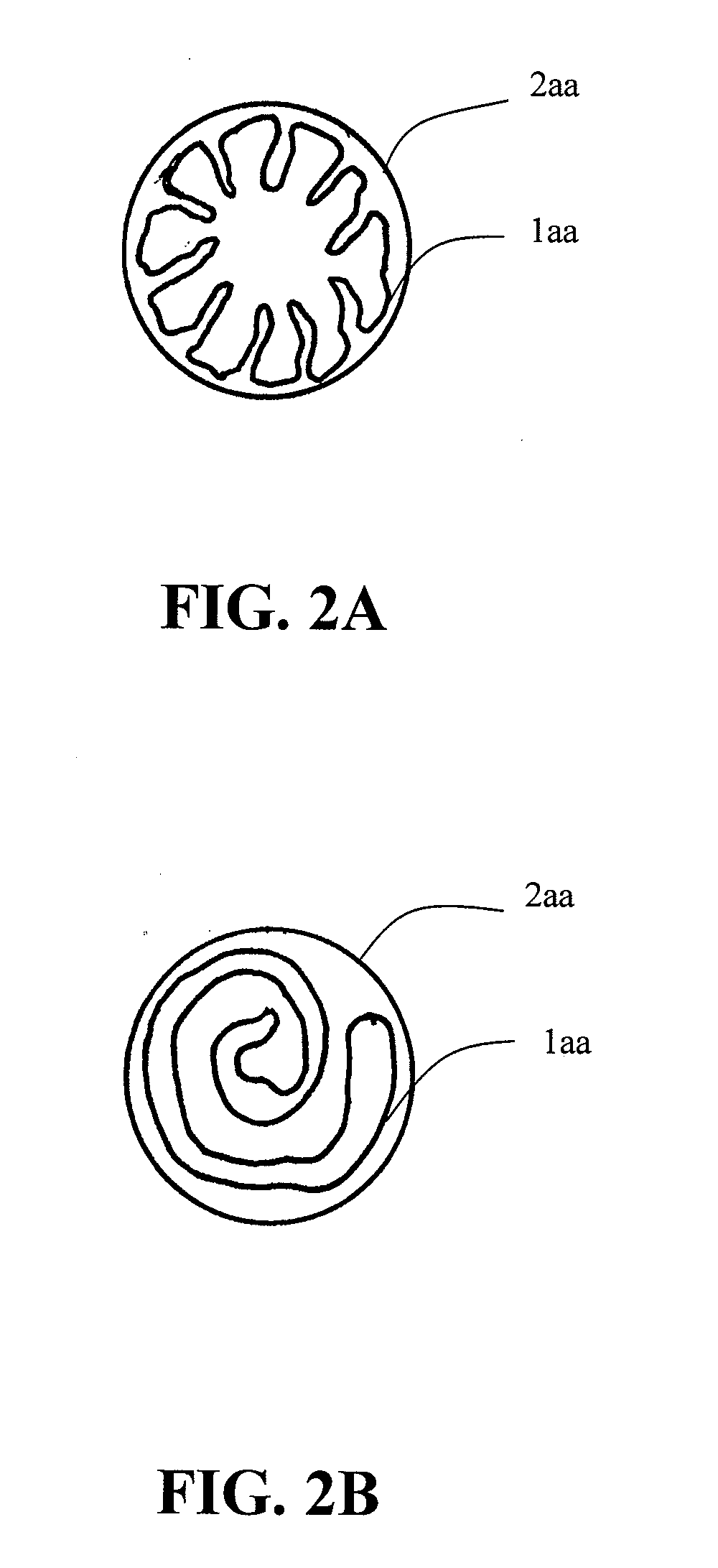
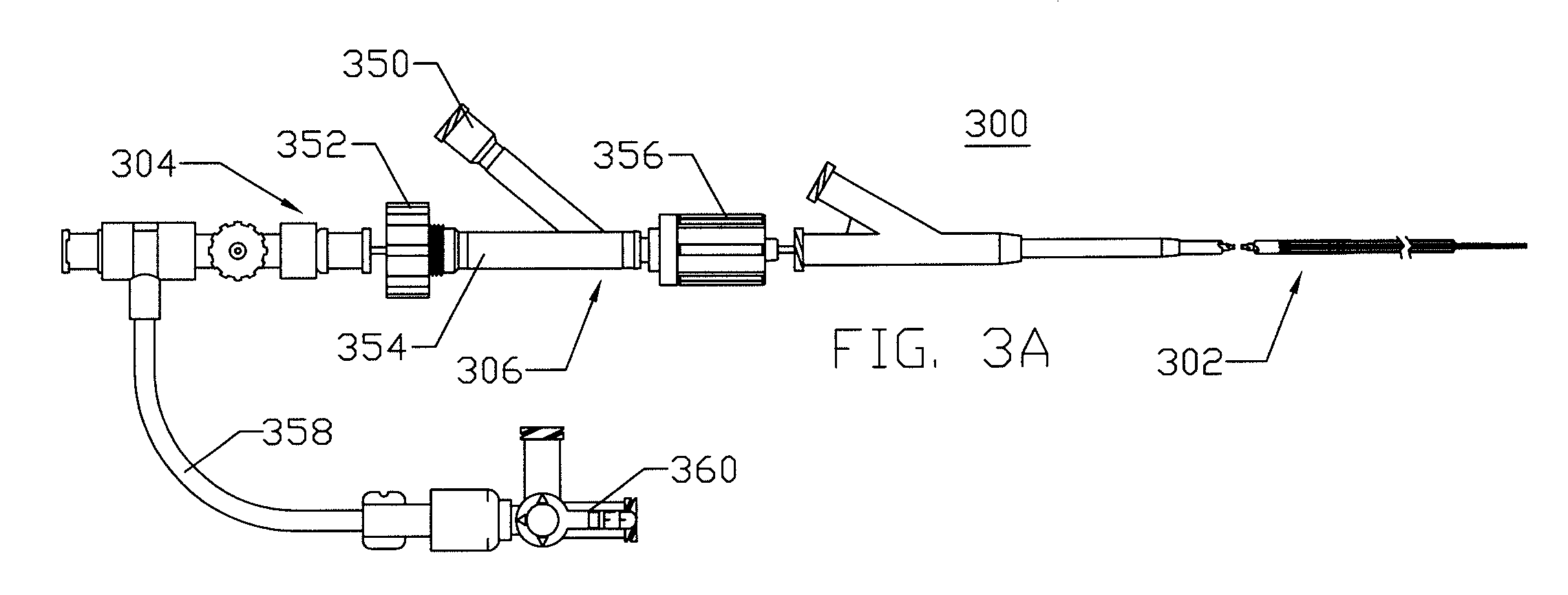
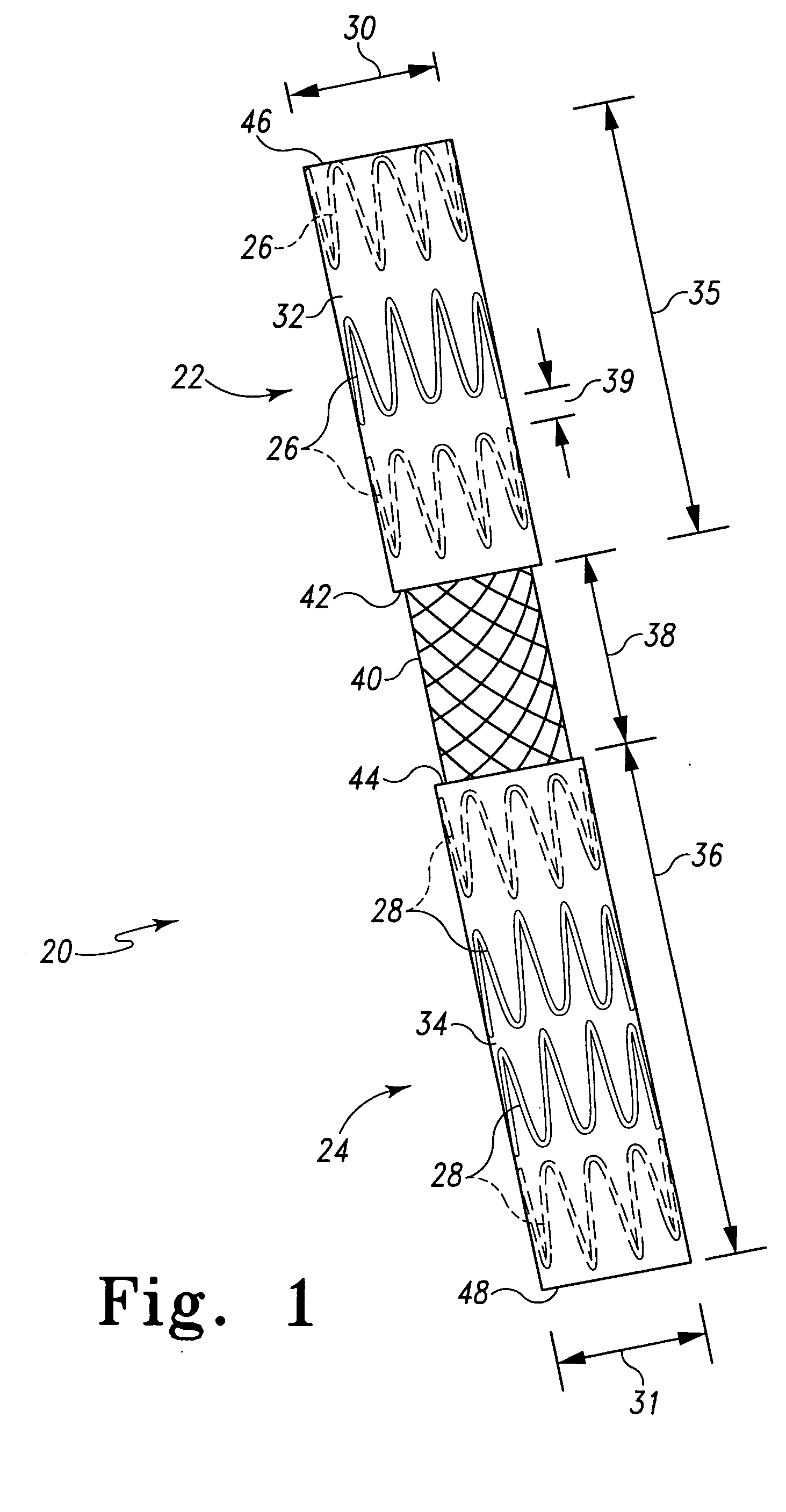
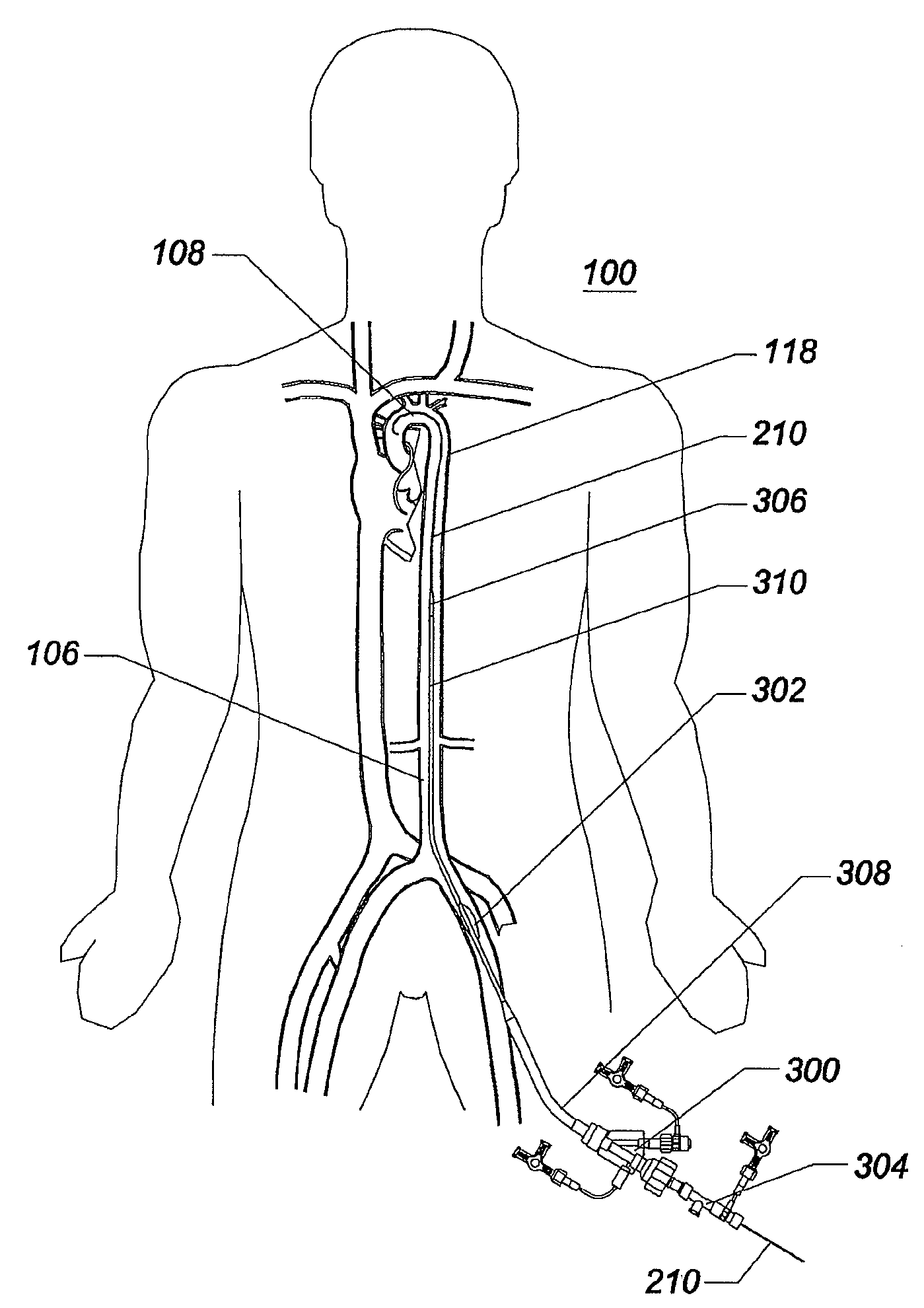
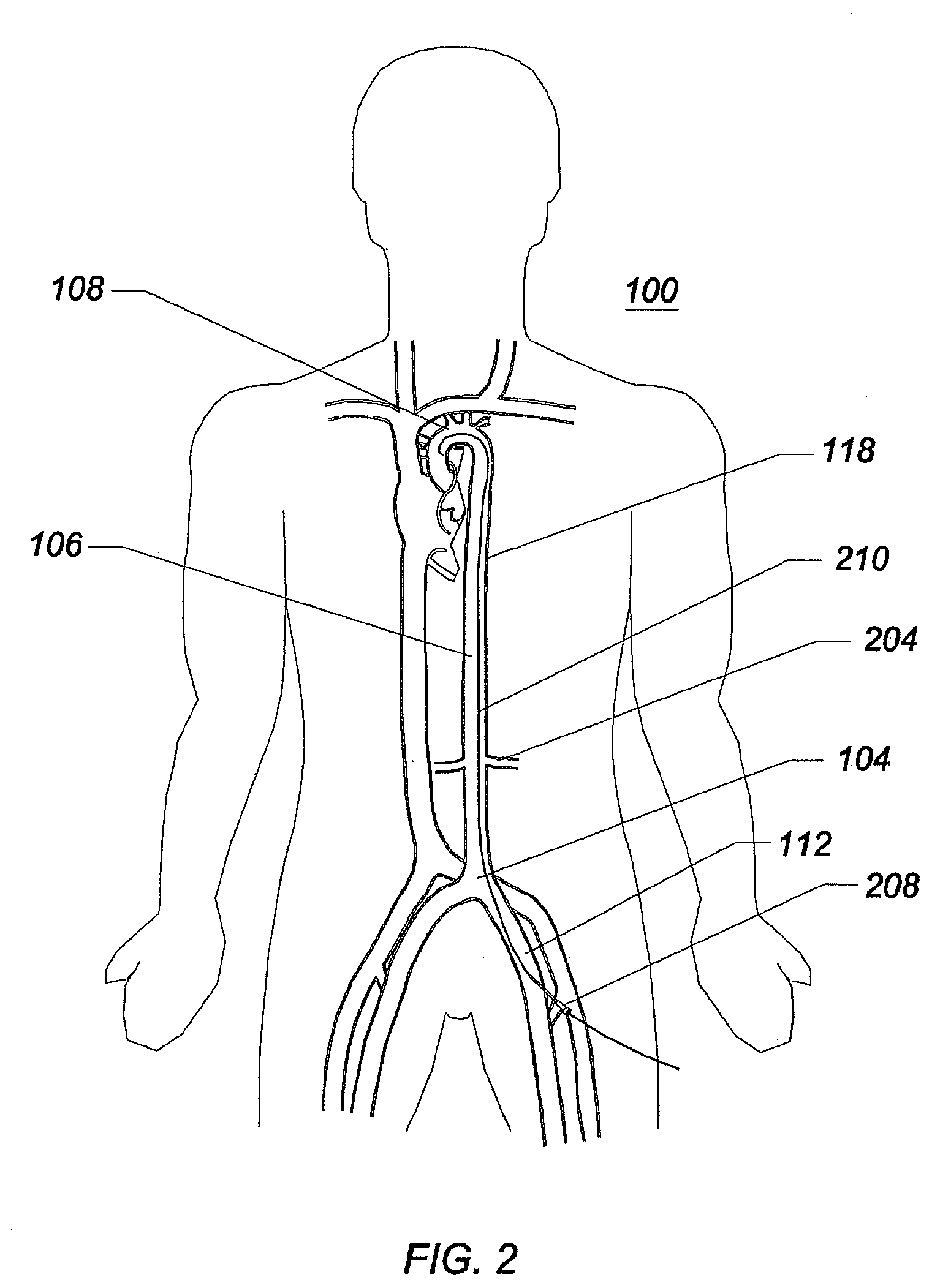
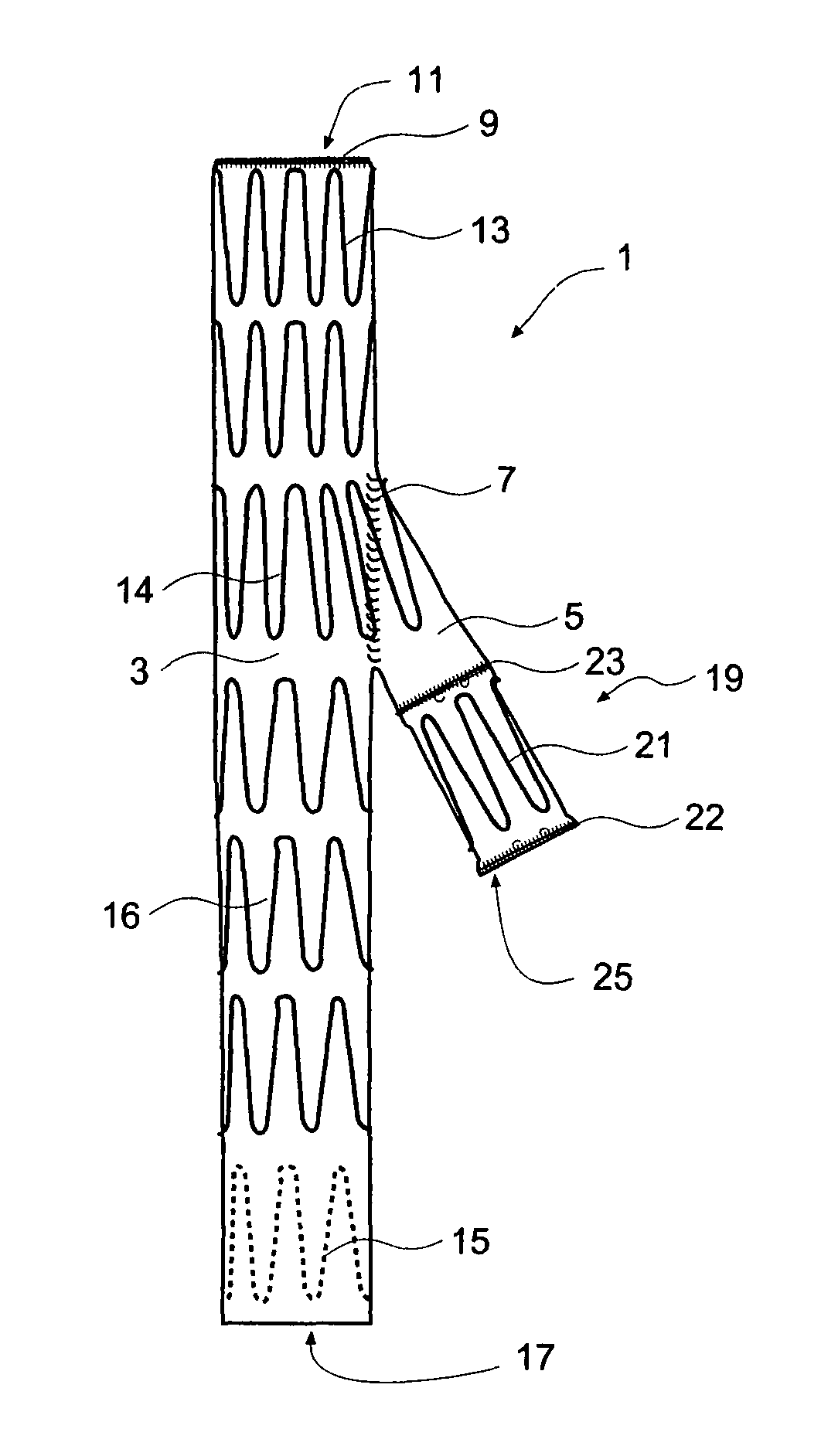
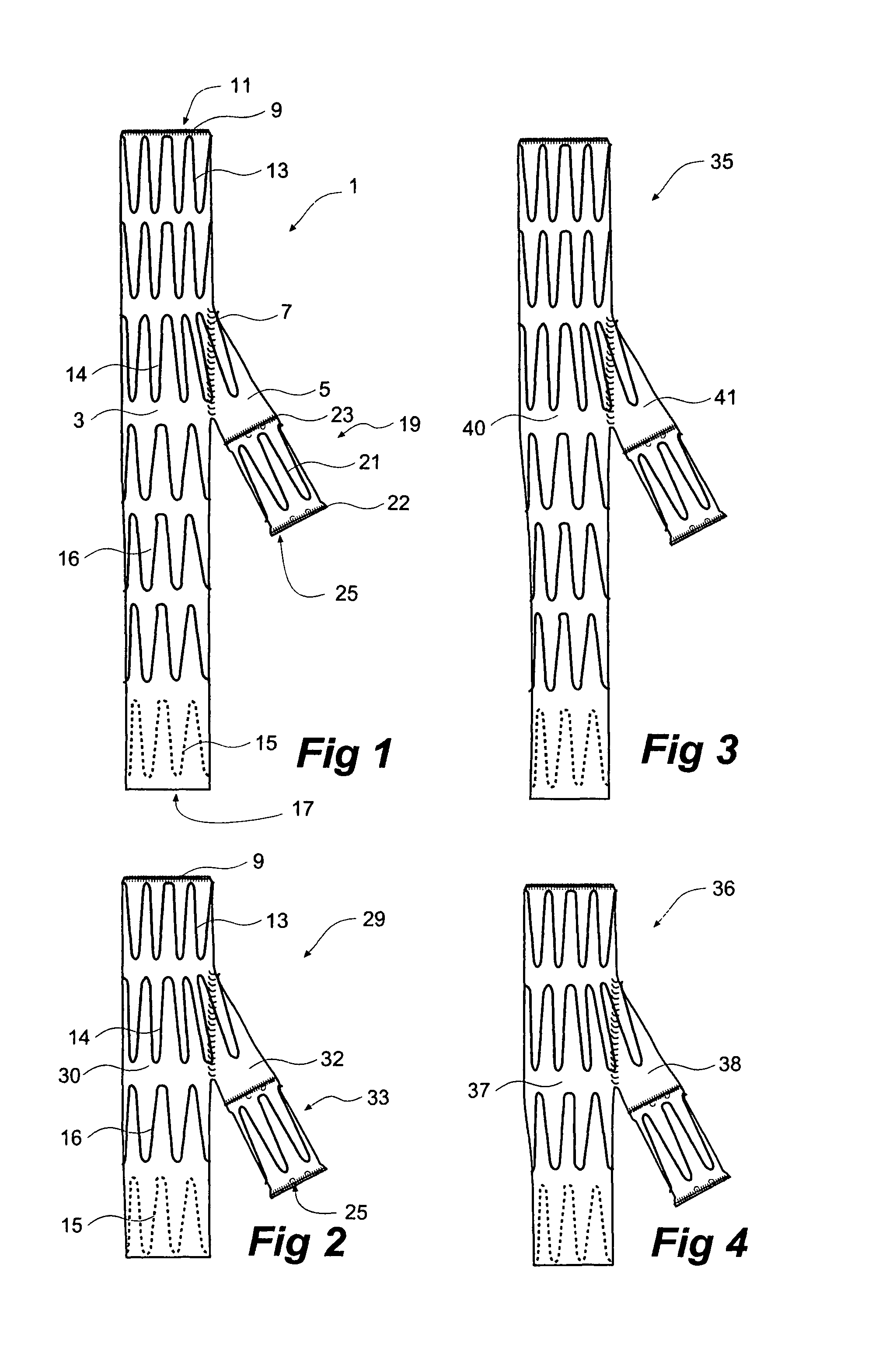
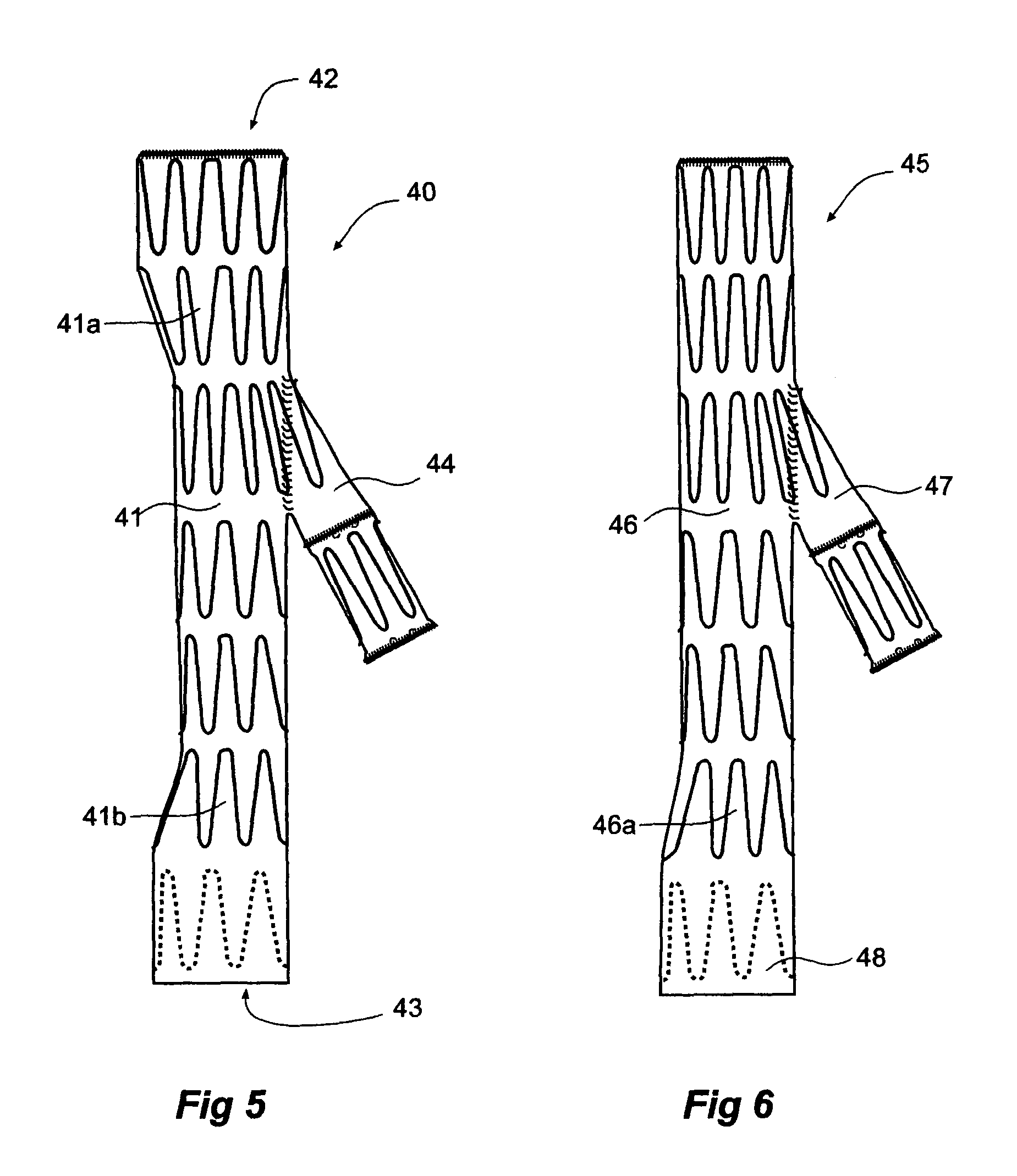
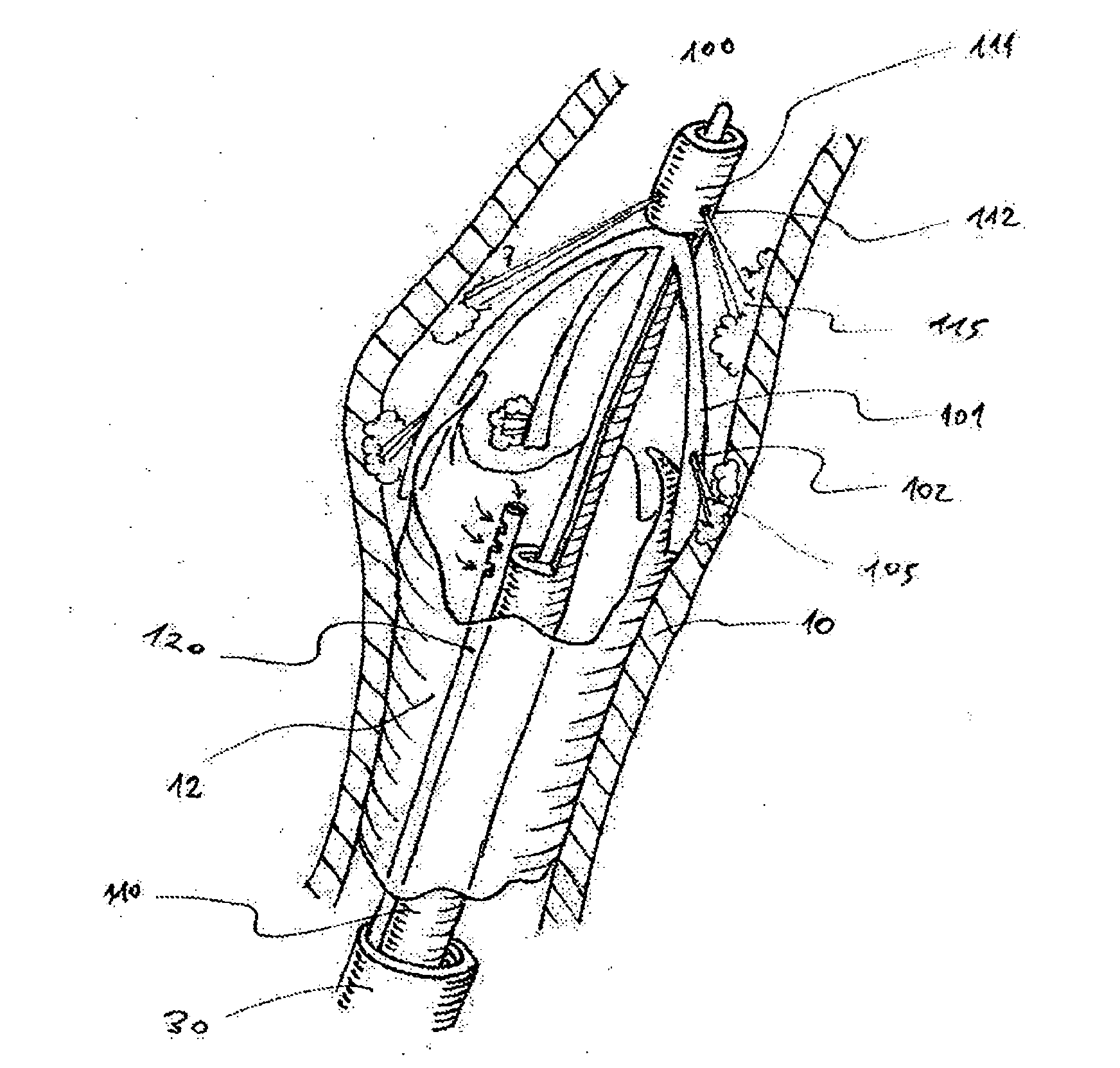
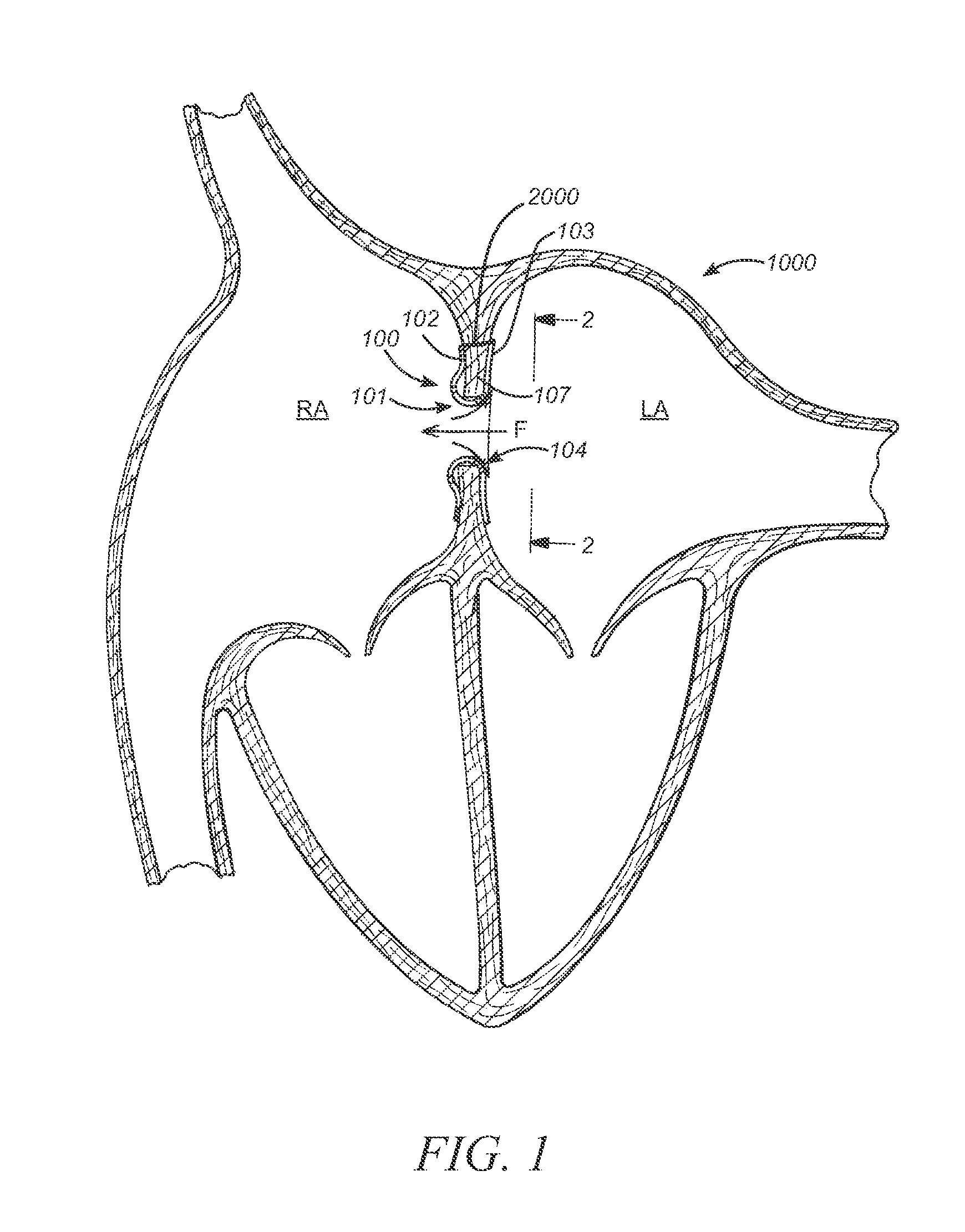
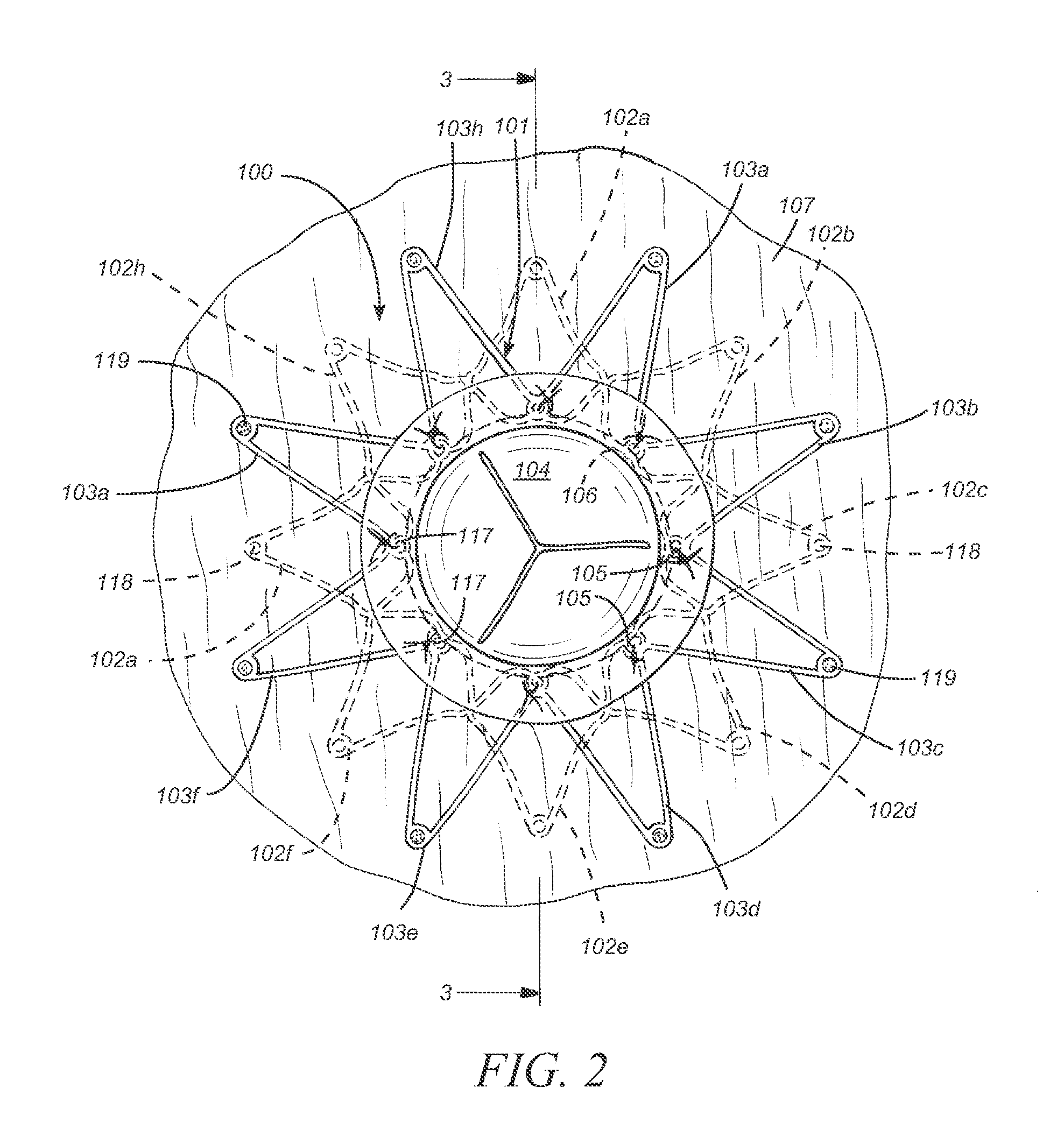
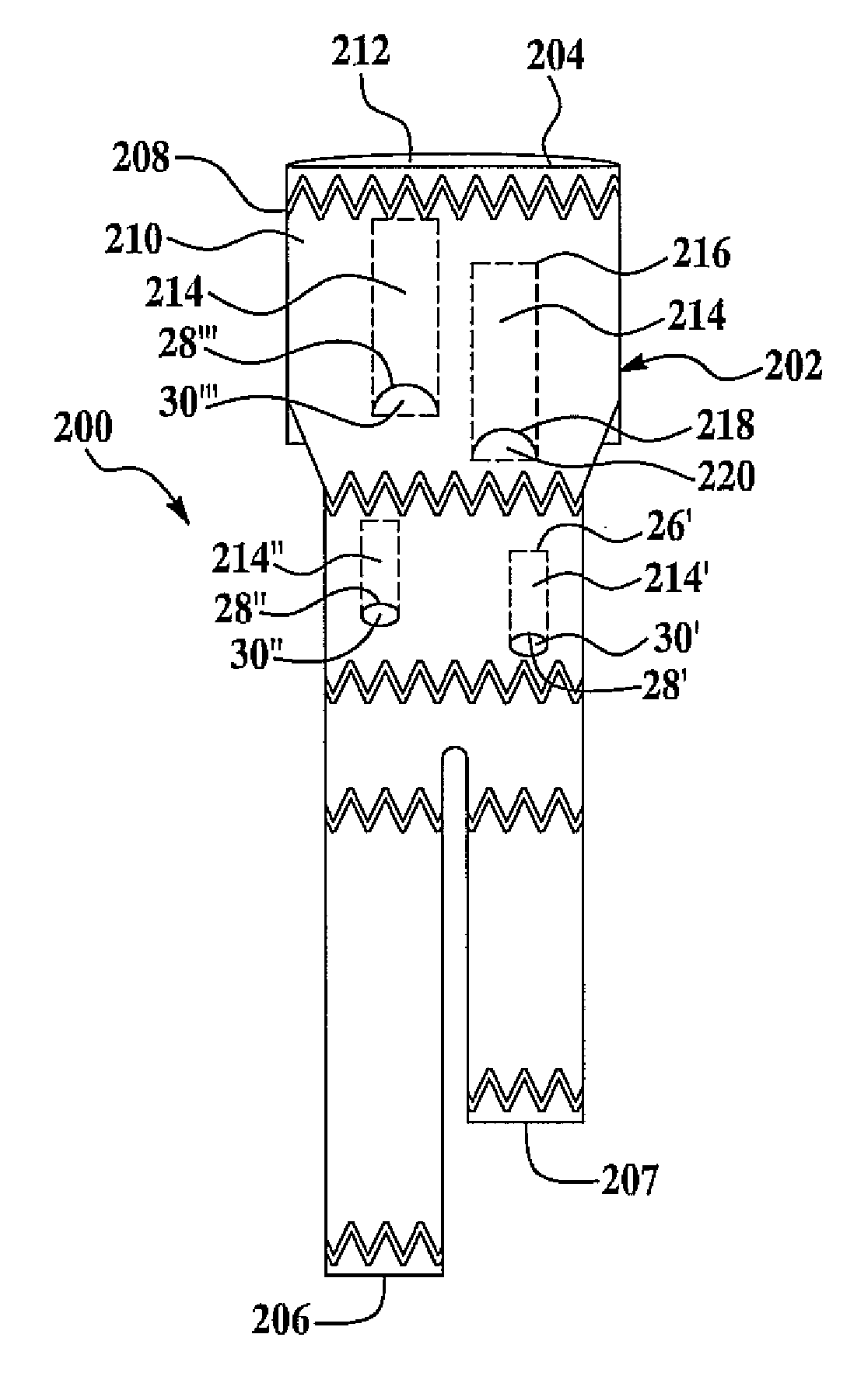
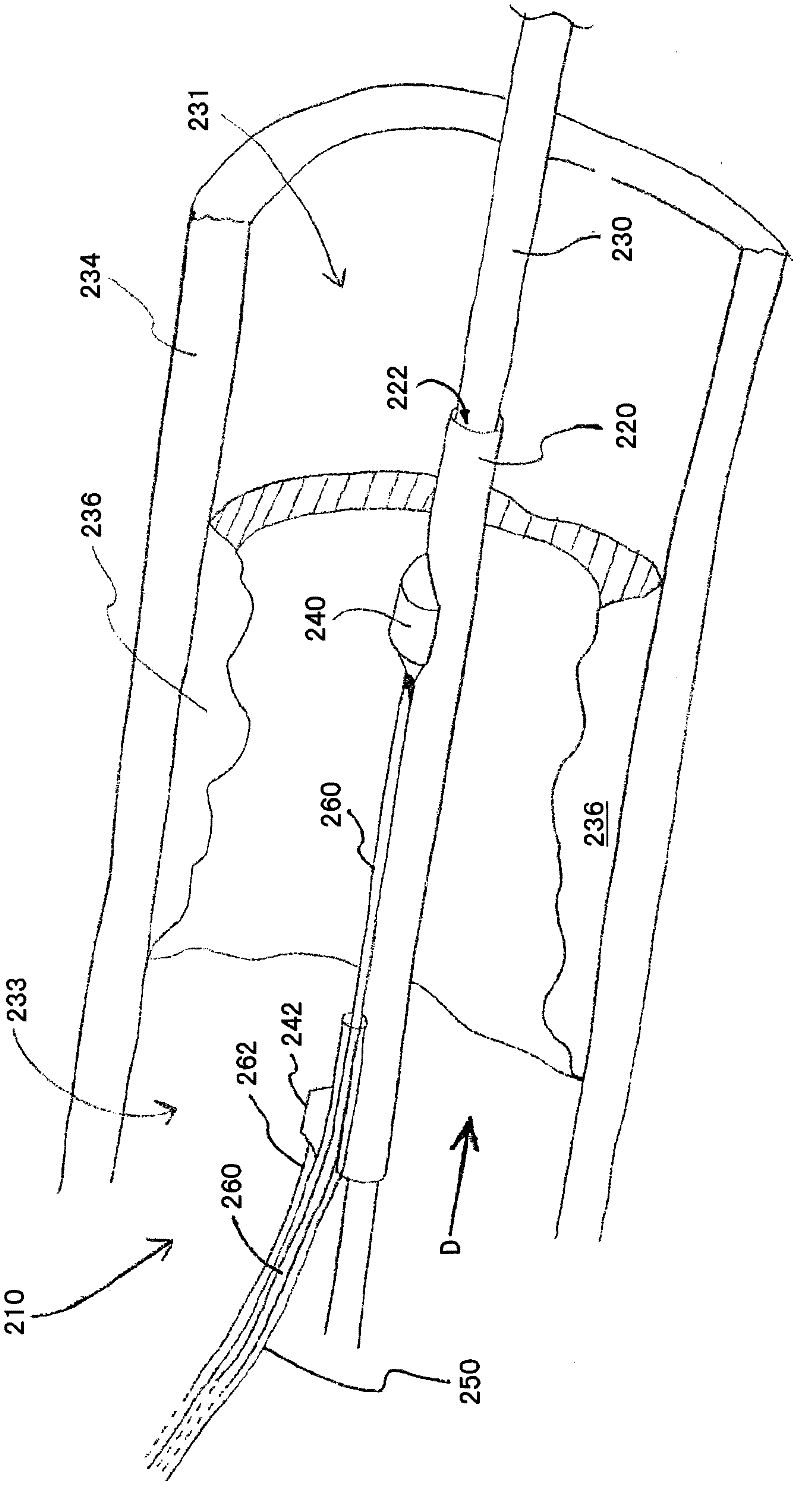
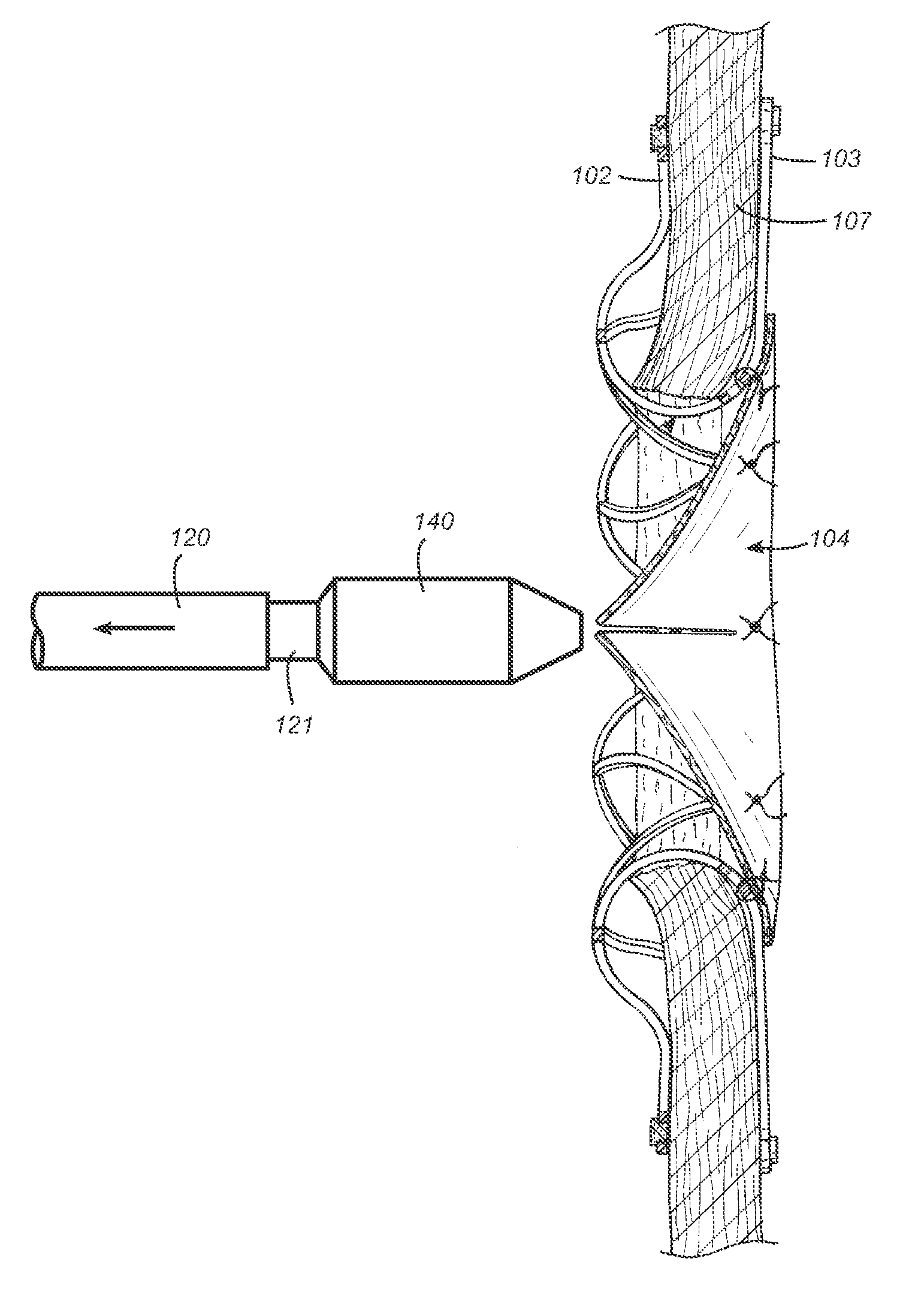
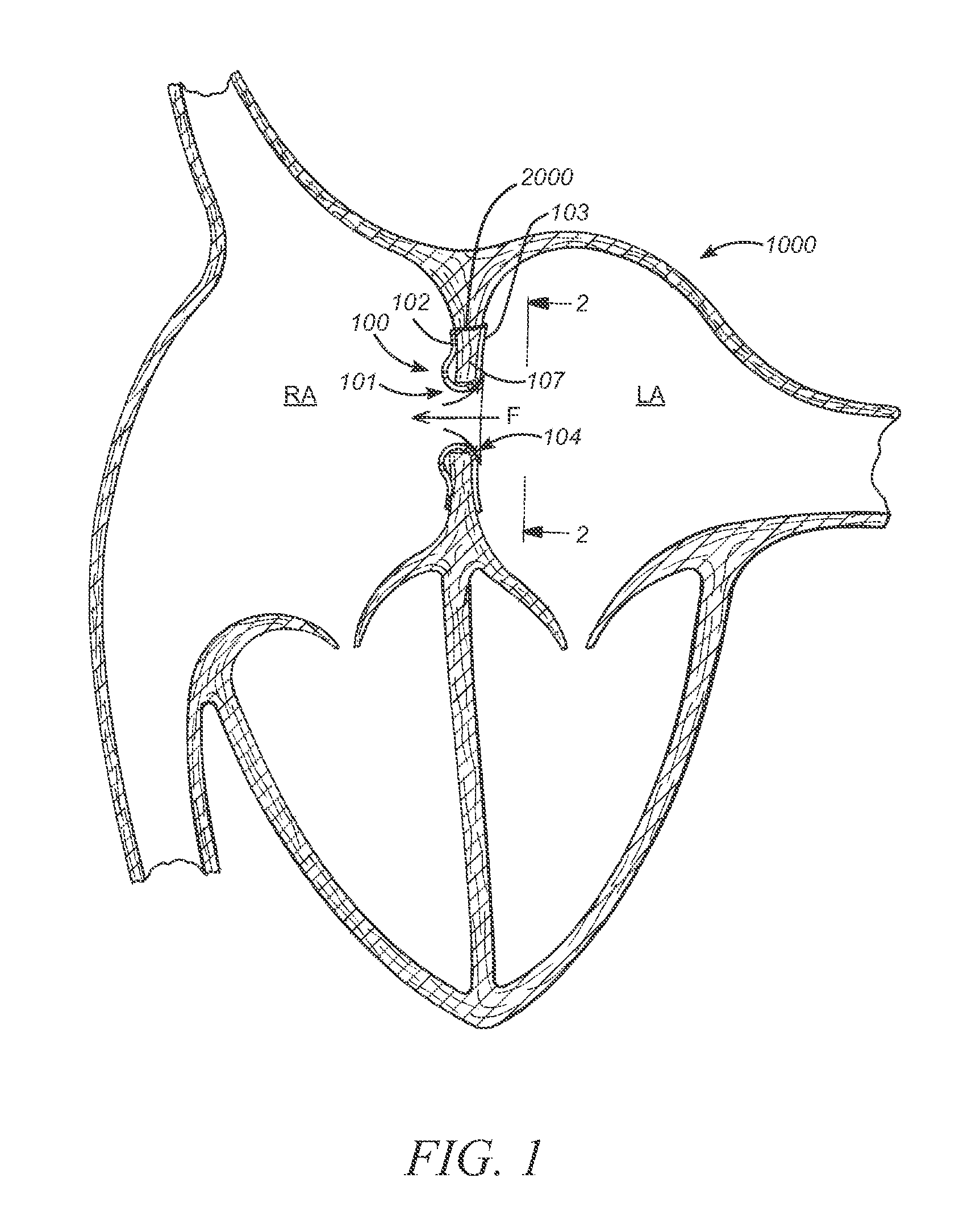
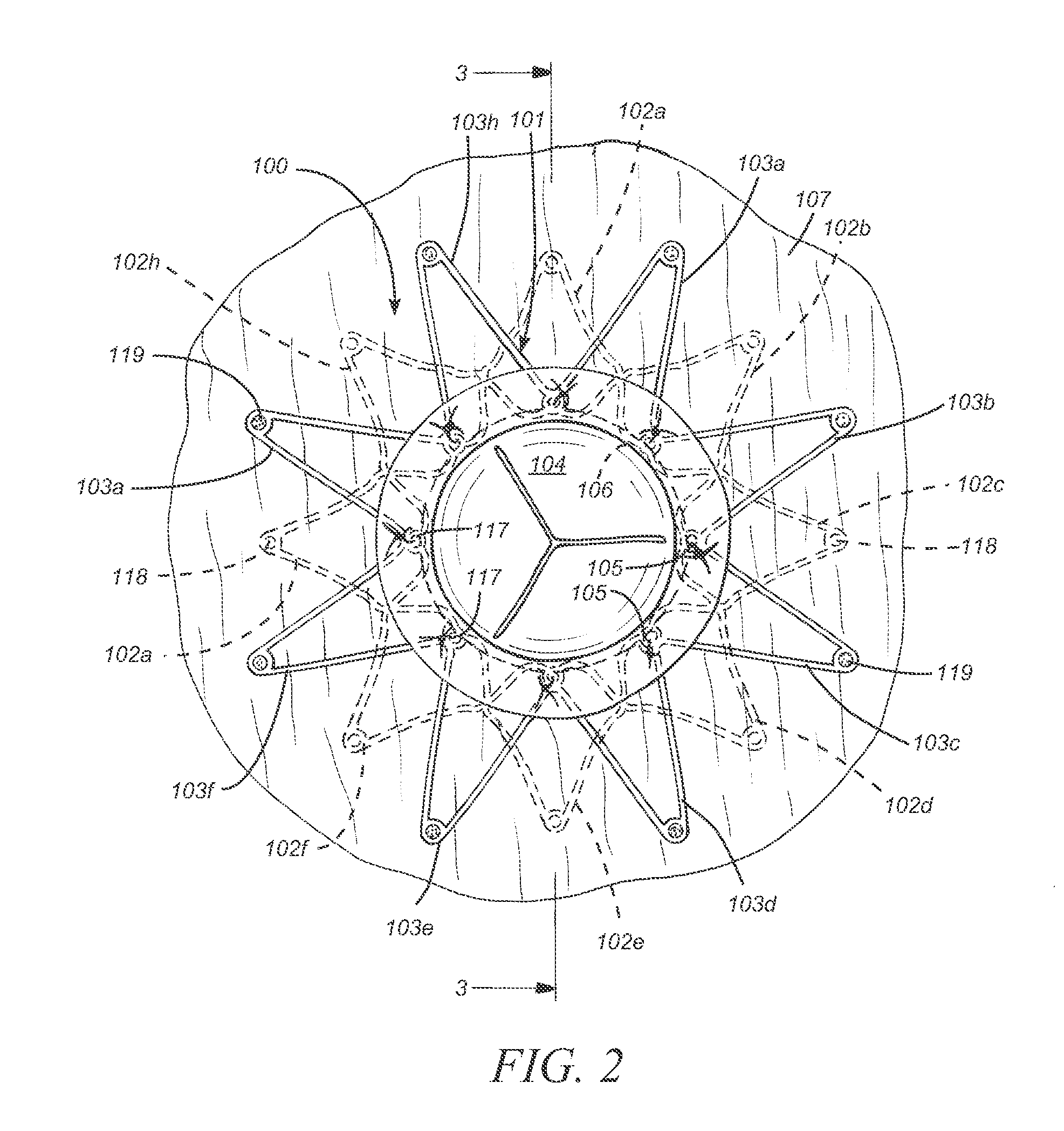
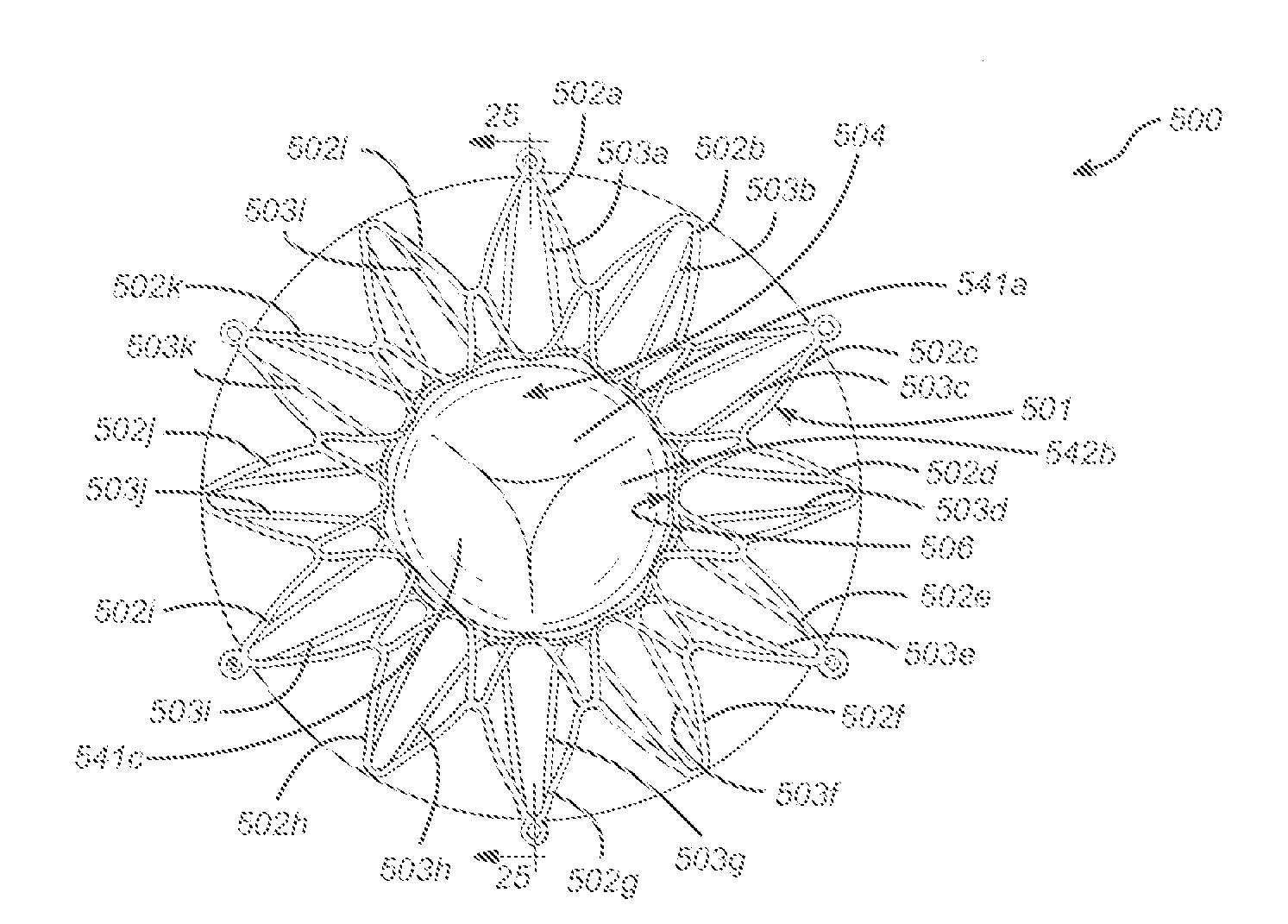
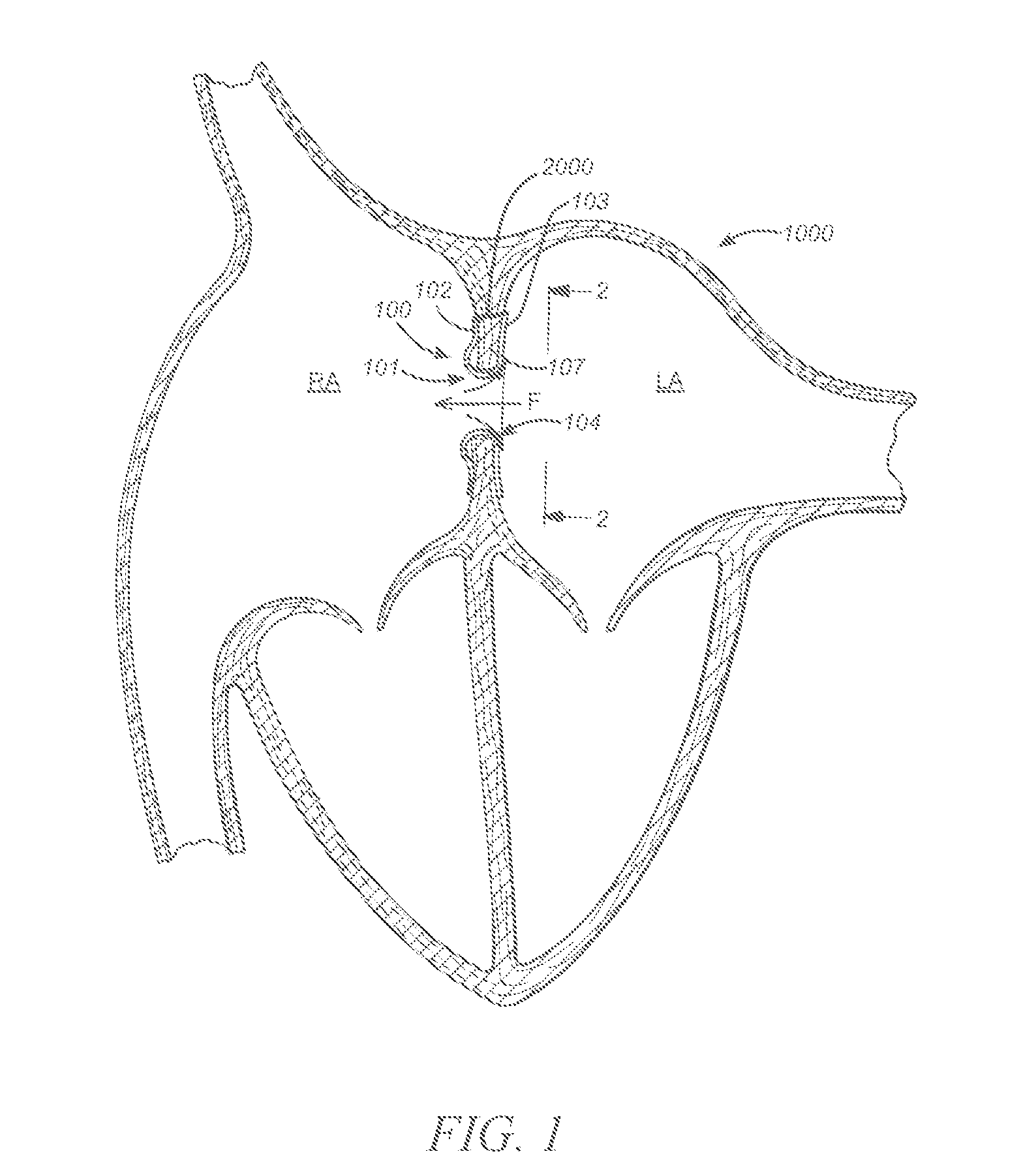
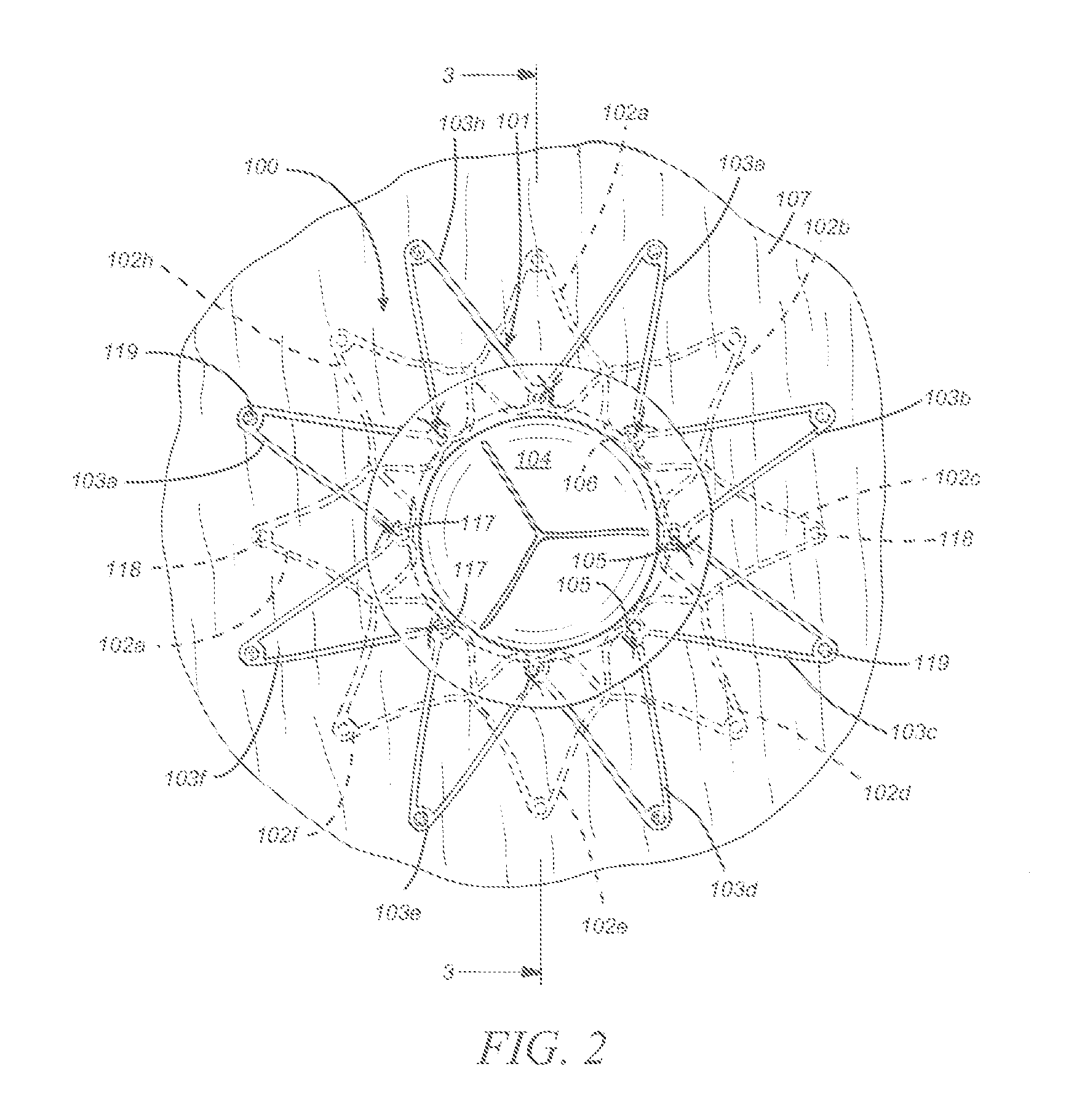
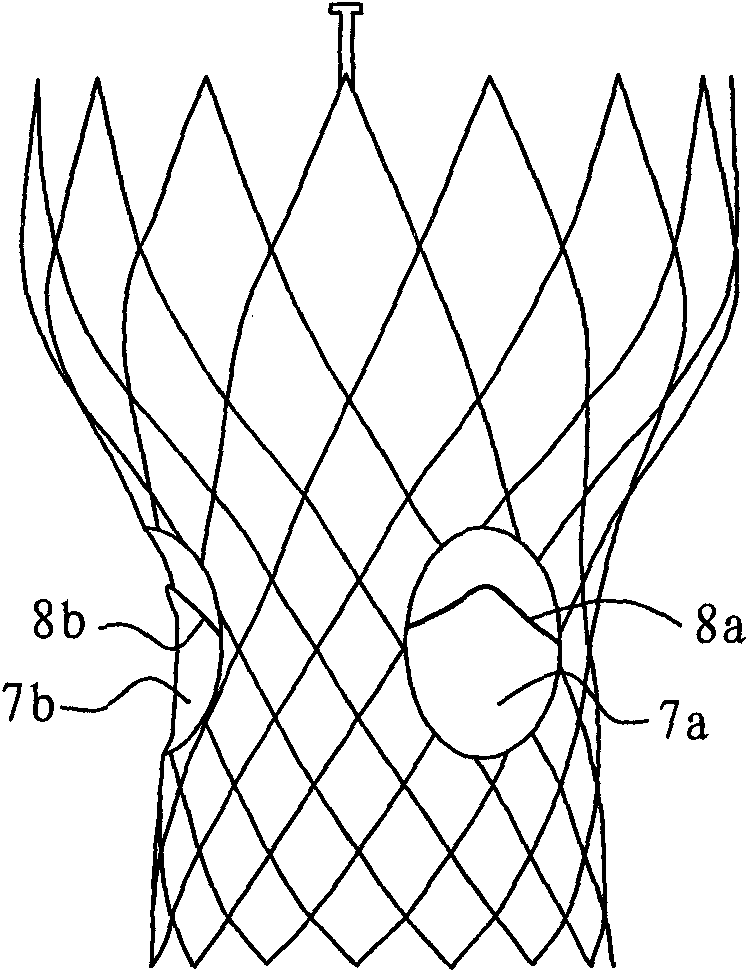
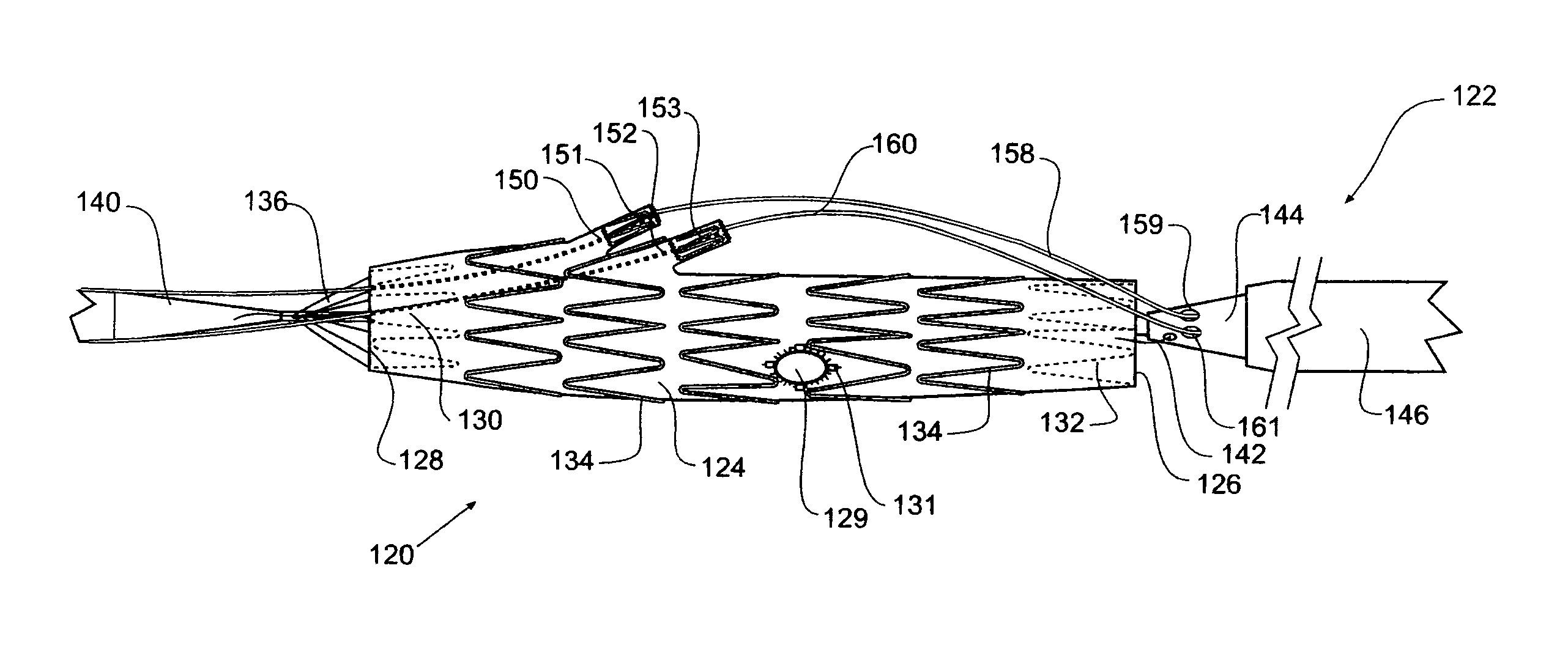
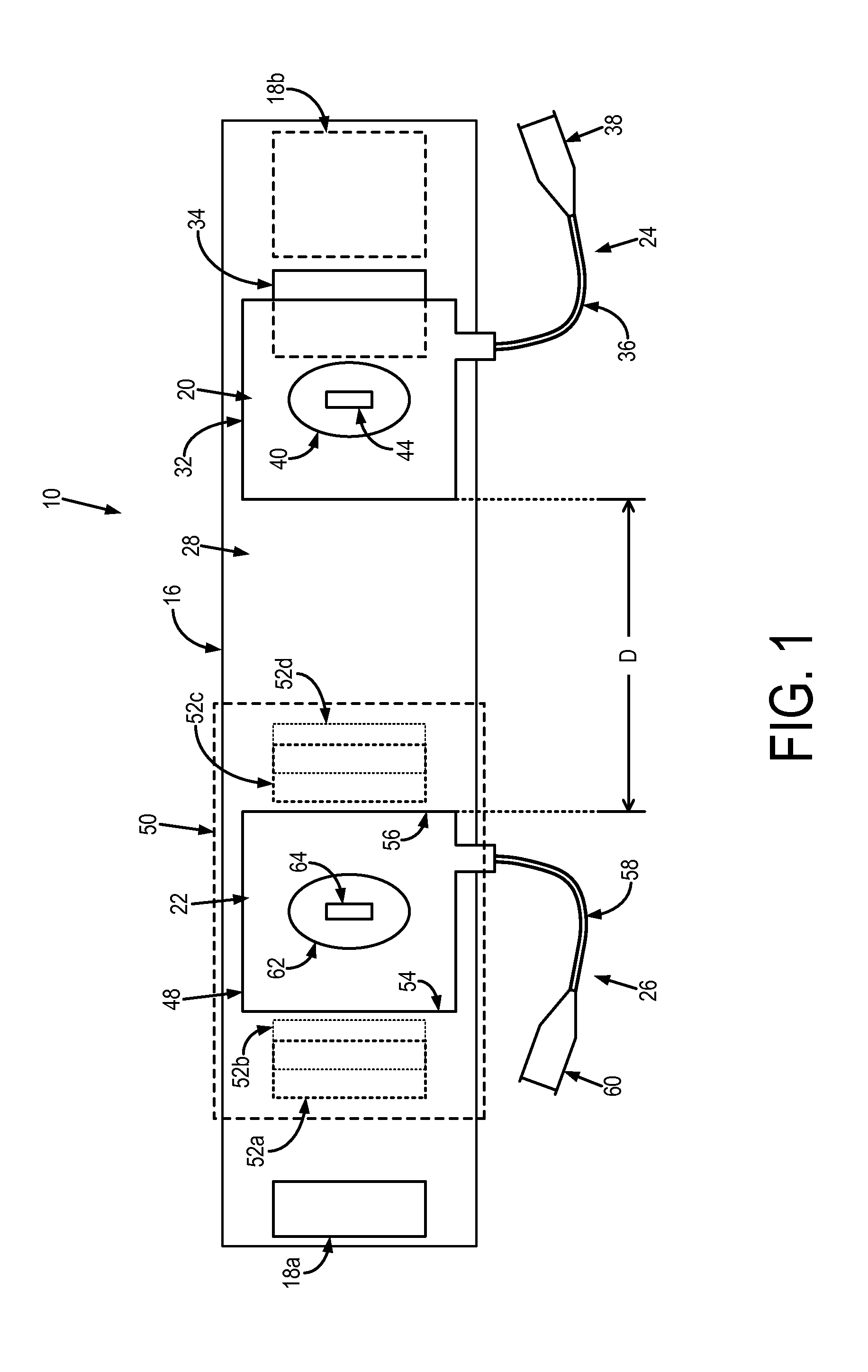
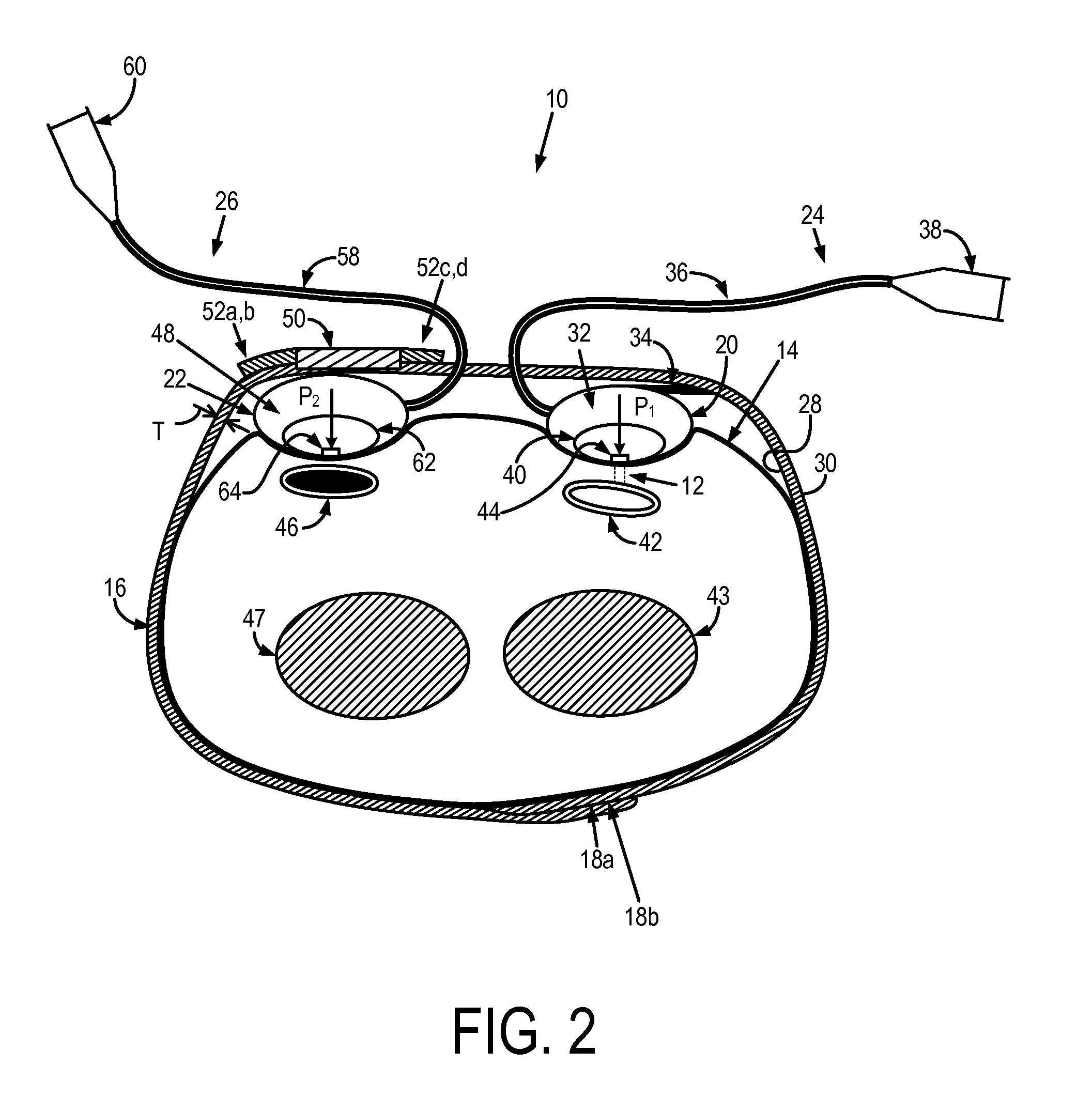
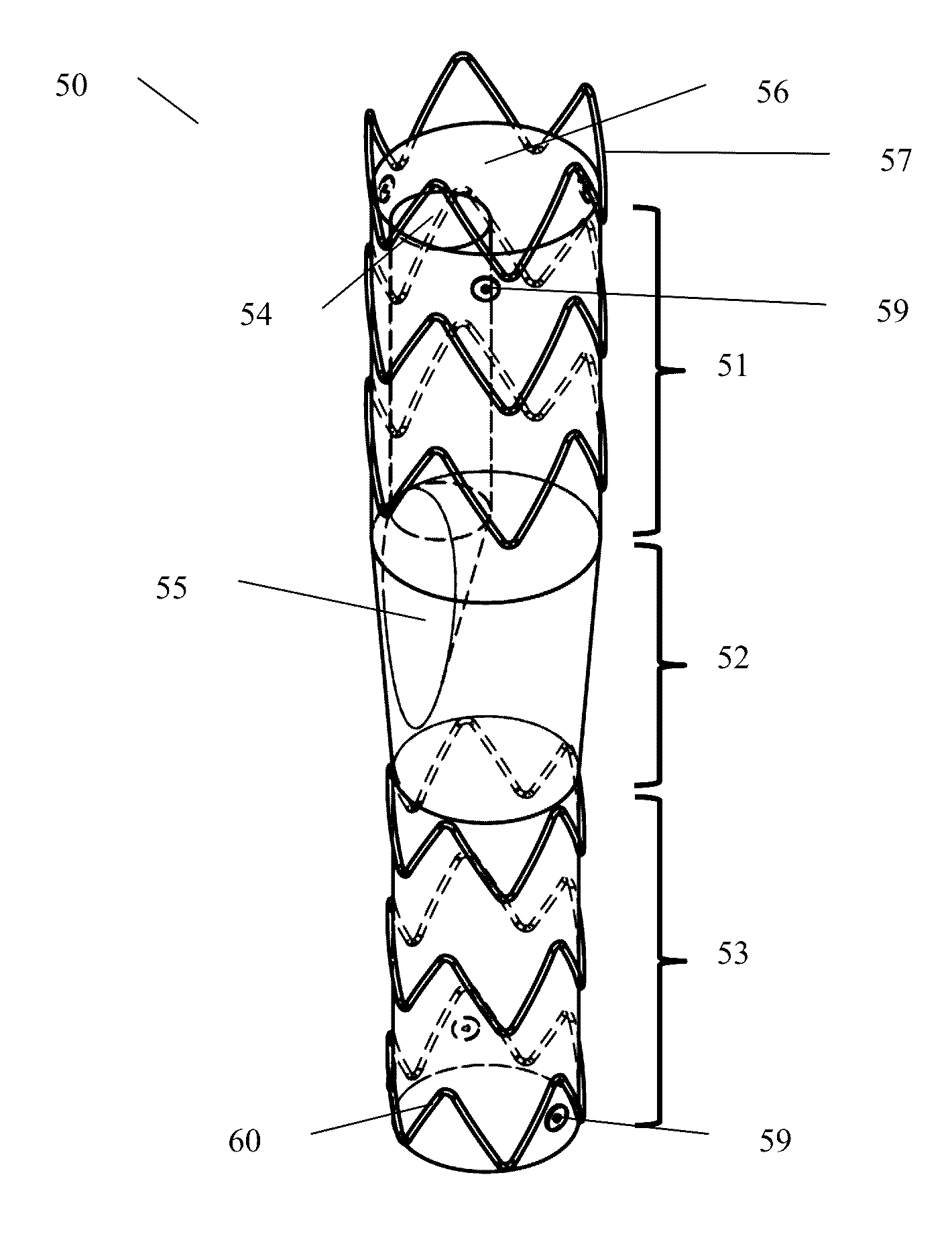
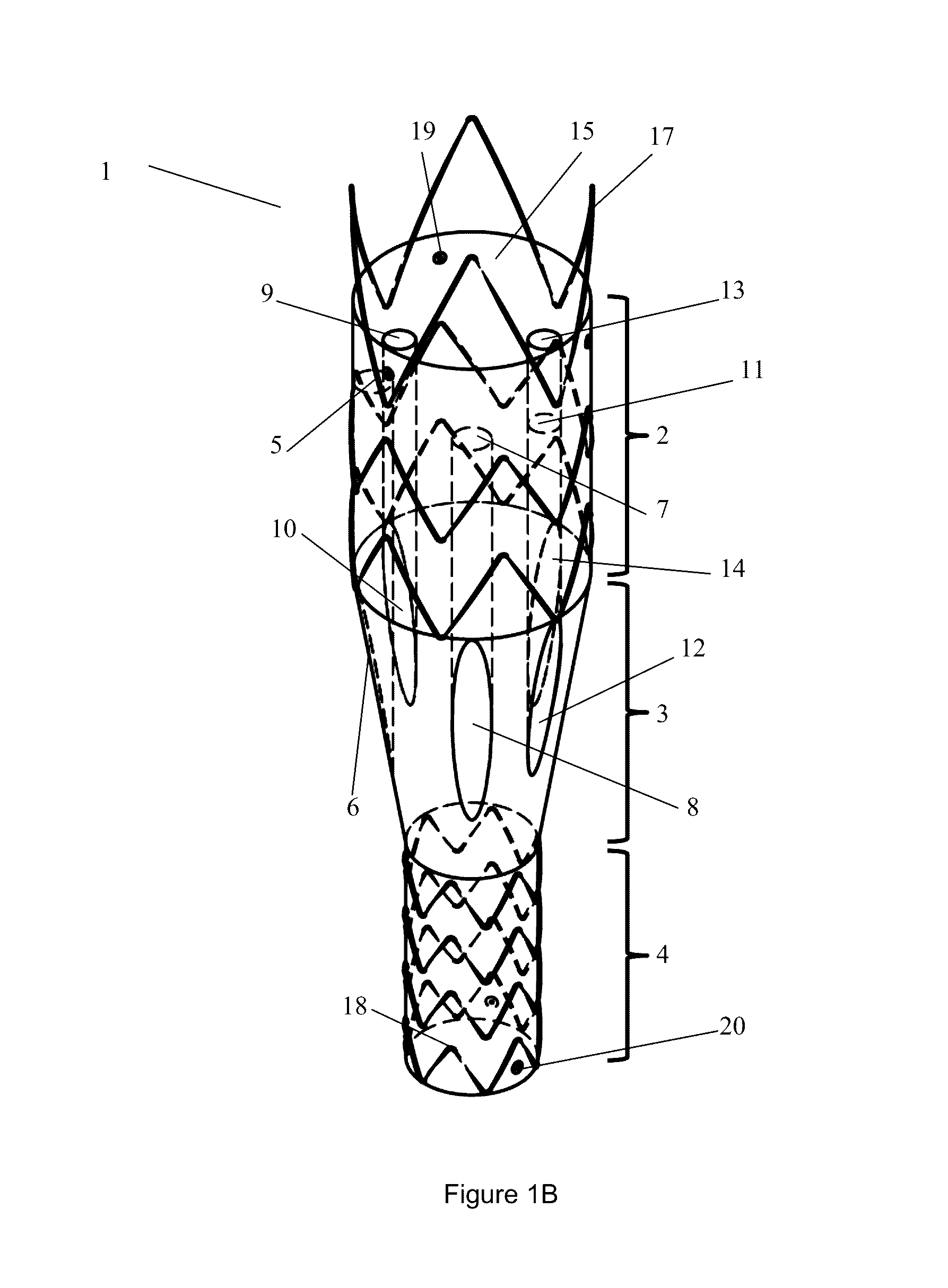
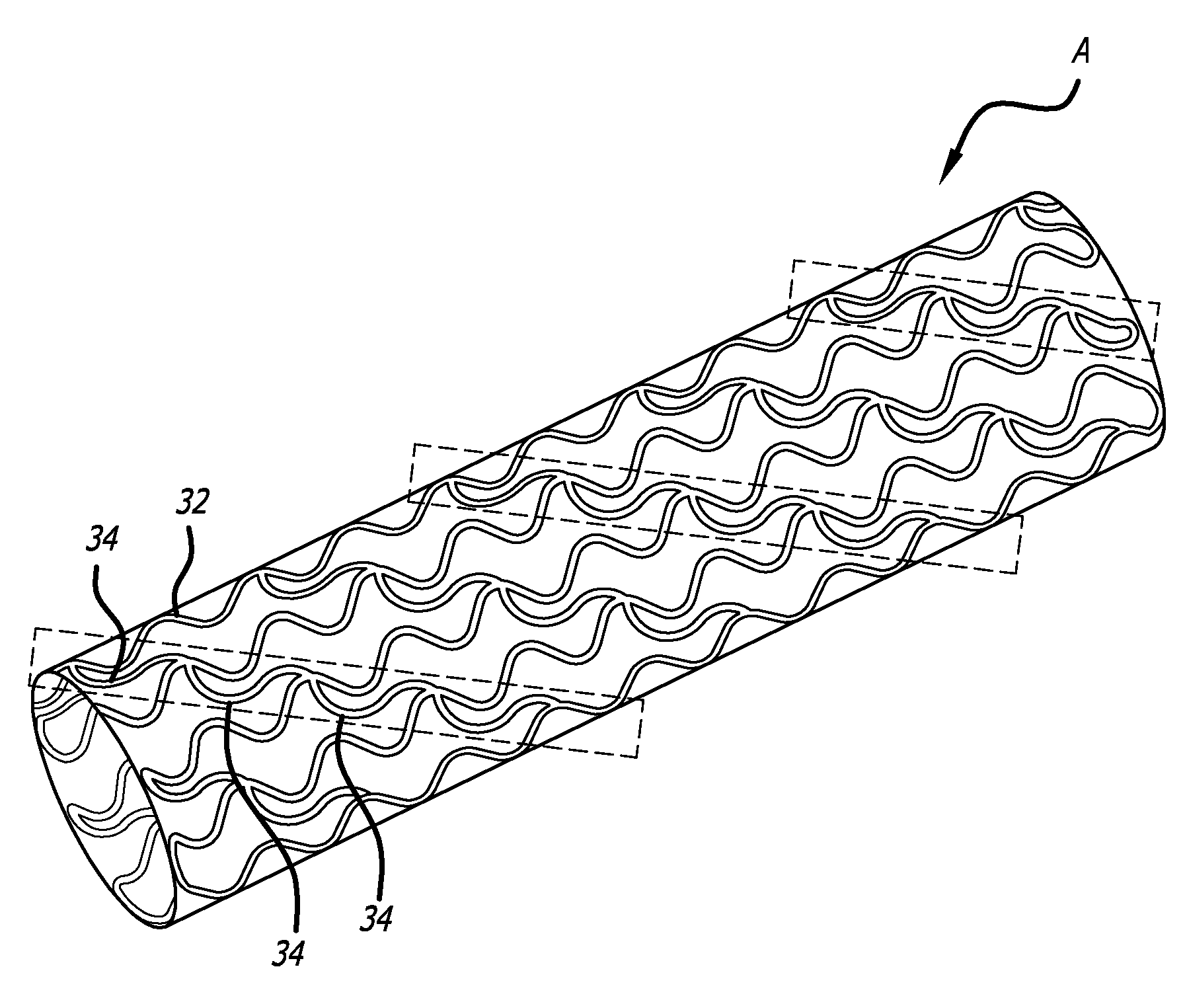
Iliac artery stent graft
A side branch stent graft (1) suitable for the iliac arteries has a main tubular body (3) of a biocompatible graft material and a tubular side branch (5). The tubular side branch is affixed into the main tubular body so that a side branch lumen is in fluid communication with a main lumen. There is at least one external zig-zag stent (13) on the main tubular body proximal of the tubular side branch, one central external stent (14) which also encompasses the side arm, at least one external zig-zag stent (16) on the main tubular body distal of the tubular side branch and one internal zig-zag stent (15) at the distal end of the main tubular body. A reinforcing ring (9) is around the proximal end of the main tubular body and stitched thereto.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Devices and methods for percutaneous endarterectomy
Devices and methods are provided for percutaneously treating atherosclerotic plaques within blood vessels. Atherosclerotic plaques cause significant morbidity and mortality by narrowing the arteries, which adversely affects blood flow, and by acting as a source for thrombi and emboli thus causing acute organ ischemia. Current treatments include open surgery with its inherent drawbacks, and stenting, which is less invasive but leaves the plaque material in the artery, which promotes restenosis. The present invention combines the advantages of both approaches. In general, the invention provides tools that enable percutaneously dissecting the plaque from the arterial wall and removing it from the body.
Owner:ANGIOWORKS MEDICAL
Control devices for deploying a prosthesis
InactiveUS20110295183A1Reduce pressureRelieve symptomsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesPatients symptomsLeft atrial pressure
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for implanting a prosthesis into a heart of a mammal, such as a person. The disclosure includes a prosthesis that acts as a pressure vent between the left and right atria of the heart. The disclosure also includes a mounting tool for mounting the prosthesis onto a loading tool, the loading tool useful for loading the prosthesis onto a device for delivering the prosthesis into the patient's heart. Control devices and methods for using these devices are also disclosed. The intracardiac pressure vents disclosed allow sufficient flow from the left atrium to the right atrium to relieve elevated left atrial pressure and resulting patient symptoms. The devices also limit the amount of flow from the right atrium to the left atrium to minimize the potential for thrombi or other embolic material from entering arterial circulation.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Arterial flashback confirmation chamber
ActiveUS8412300B2Overcome limitationsExtension of timeInfusion syringesMedical devicesVascular Access DevicesVascular closure device
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
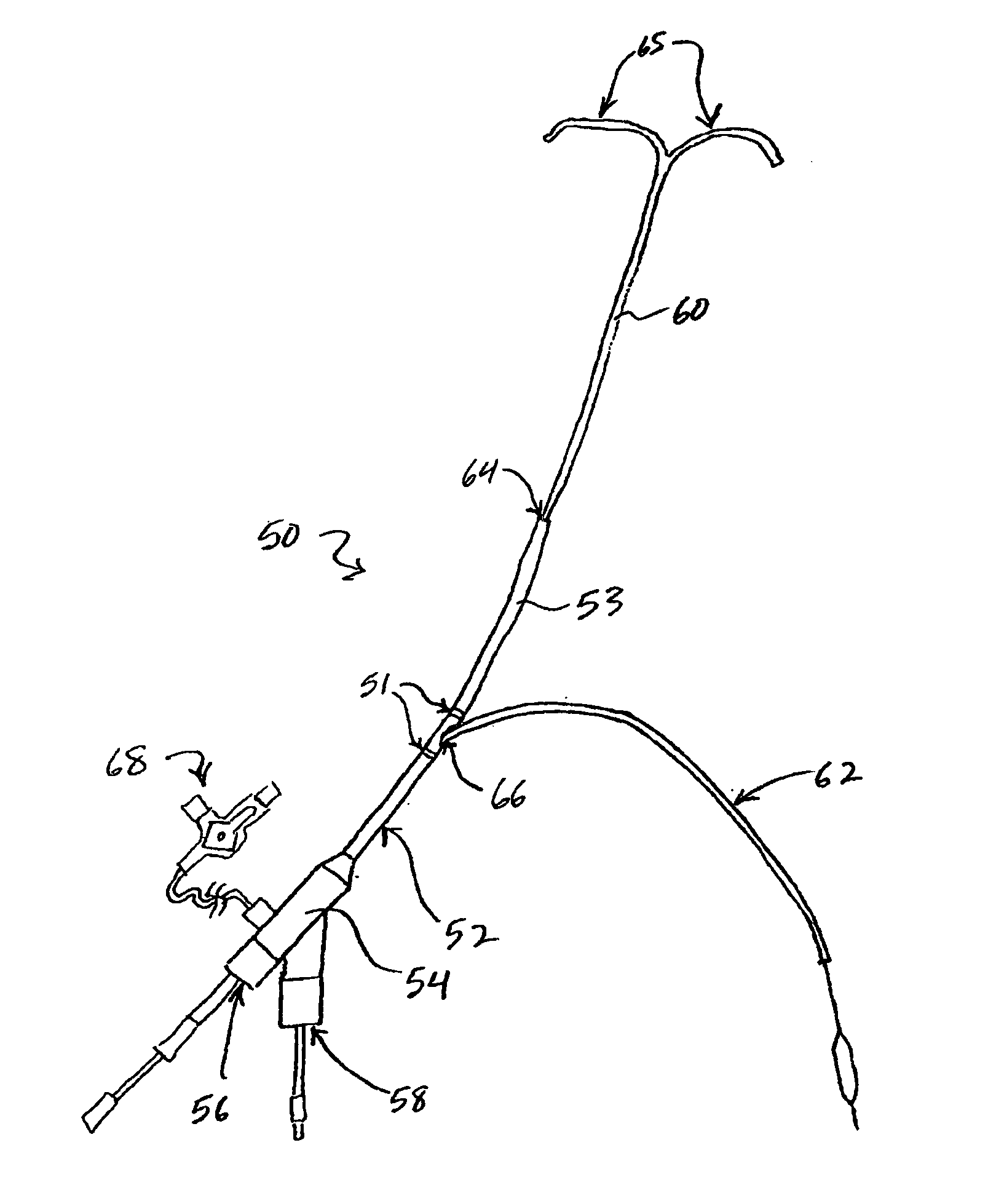
Methods and systems for establishing retrograde carotid arterial blood flow
ActiveUS20110166497A1Limit and prevent releasePromote blood circulationOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationVeinFlow diverter
Interventional procedures on the carotid arteries are performed through a transcervical access while retrograde blood flow is established from the internal carotid artery to a venous or external location. A system for use in accessing and treating a carotid artery includes an arterial access device, a shunt fluidly connected to the arterial access device, and a flow control assembly coupled to the shunt and adapted to regulate blood flow through the shunt between at least a first blood flow state and at least a second blood flow state. The flow control assembly includes one or more components that interact with the blood flow through the shunt.
Owner:SILK ROAD MEDICAL
Vascular endograft
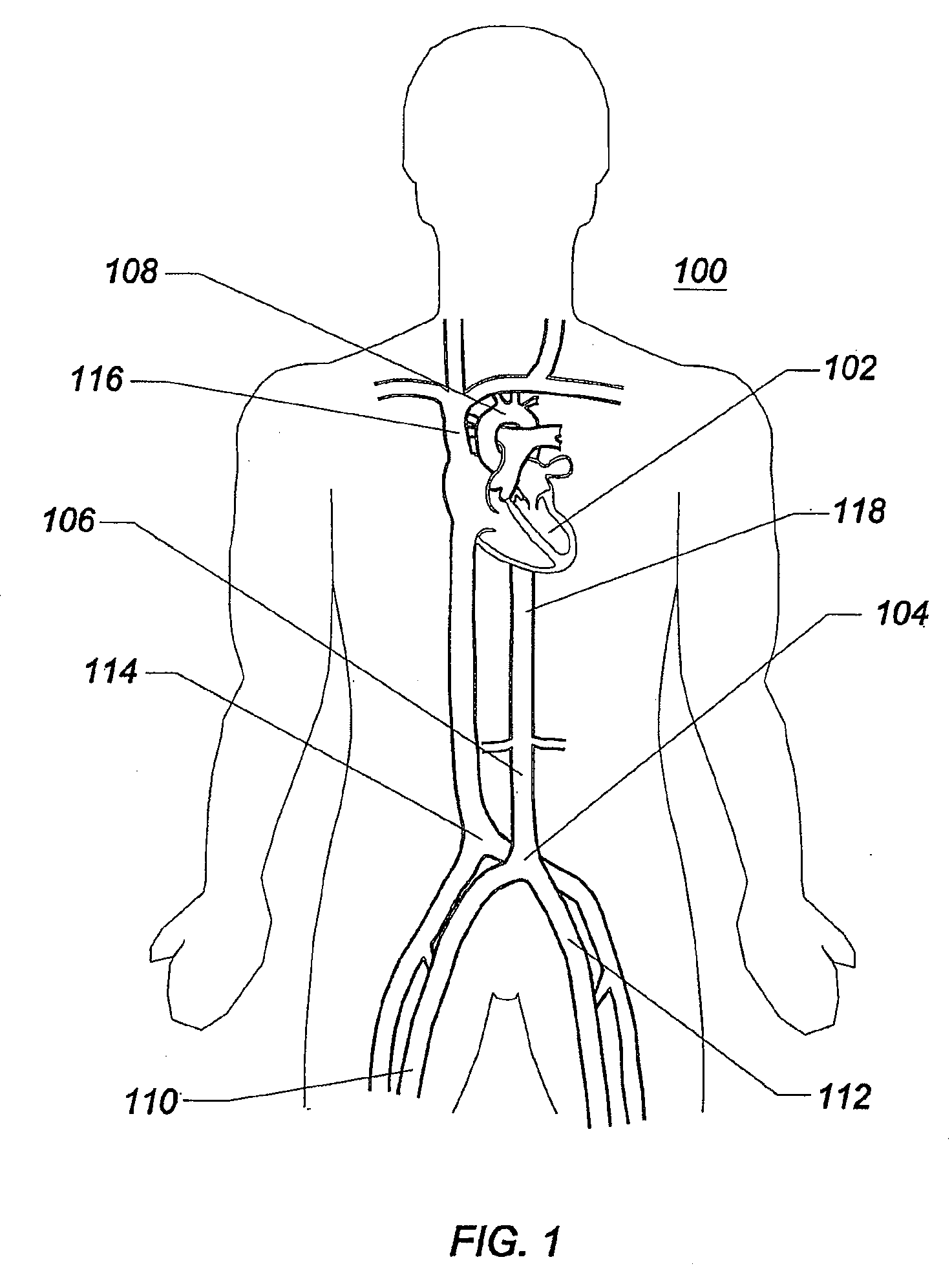
An endograft for a vessel having a vascular branch extending from the vessel is provided. The endograft includes a main body having a wall separating interior and exterior surfaces and adapted to be inserted within the vessel. The main body is characterized by a single proximal opening and two distal openings and at least one aperture extending through the wall. At least one stent is secured to the main body that upon expansion pressure fits the main body into the vessel. An open tunnel is secured to the interior surface of the main body around the main body aperture and secured somewhere along the tunnel length to provide fluid communication between the interior and exterior surfaces of the main body through the aperture and with the vascular branch in proximity to the main body aperture. The tunnel is readily formed independent of an expandable stent. Through the addition of further apertures and tunnels, an endograft is well suited for revascularizing the celiac, superior mesenteric artery and renal arteries for the treatment of a suprarenal aortic aneurysm. The insertion of a sleeve positioned partly within the tunnel and extending beyond the exterior surface of the main body into the vascular branch assures continued fluid flow to the vascular branch. The two distal openings are adapted to engage the iliac arteries.
Owner:KHOURY MEDICAL DEVICES
Physiological sensor delivery device and method
Owner:ACIST MEDICAL SYST
Sheath for use in peripheral interventions
A dual lumen introducer sheath provides access to at least one renal artery and at least one peripheral blood vessel of a patient. The introducer sheath includes a proximal hub comprising first and second ports, a first lumen, and a second lumen. The first lumen extends from the first port to a first distal aperture and has sufficient length such that when the first port is positioned outside the patient the first distal aperture is positionable in the abdominal aorta at or near origins of the patient's renal arteries. The second lumen extends from the second port to a second distal aperture, has a shorter length than the length of the first lumen, and is configured to allow passage of a catheter device through the second lumen and into or through an iliac artery contralateral to an insertion point of the introducer sheath into the patient.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Radial Artery Closure Device
InactiveUS20160213373A1Reduce radial pressureLess forceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUlnar arteryBlood pressure
A radial closure device has a compression element to place compression force against the radial access site. The invention further comprises an occlusion element that places an occlusion force against the ulnar artery to reduce blood pressure at the arteriotomy site and increase blood flow in the radial artery thereby reducing radial artery occlusion and reducing the time and compression force to achieve hemostasis. A radial restriction element can also be placed upstream of the access site to further reduce radial blood pressure at the arteriotomy site.
Owner:DRASLER WILLIAM JOSEPH +3
Mounting tool for loading a prosthesis
ActiveUS20110295366A1Reduce pressureRelieve symptomsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesPatients symptomsLeft atrial pressure
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for implanting a prosthesis into a heart of a mammal, such as a person. The disclosure includes a prosthesis that acts as a pressure vent between the left and right atria of the heart. The disclosure also includes a mounting tool for mounting the prosthesis onto a loading tool, the loading tool useful for loading the prosthesis onto a device for delivering the prosthesis into the patient's heart. Control devices and methods for using these devices are also disclosed. The intracardiac pressure vents disclosed allow sufficient flow from the left atrium to the right atrium to relieve elevated left atrial pressure and resulting patient symptoms. The devices also limit the amount of flow from the right atrium to the left atrium to minimize the potential for thrombi or other embolic material from entering arterial circulation.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Methods for loading a prosthesis
ActiveUS20110295182A1Reduce pressureRelieve symptomsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesPatients symptomsThrombus
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Artificial valve displacement device and stent
The invention discloses a stent of an artificial valve displacement device. The stent is in a mesh cylindrical structure formed by an aorta stent, a valve stent and an outflow channel stent which are sequentially connected. Three hollow-out areas are distributed on the side wall of the valve stent and respectively correspond to the top ends of three valves during opening. At least two fixed lugs are arranged on the top edge of the aorta stent. The heights of the top edges of the fixed lugs are different from each other. The shape of a hollow-out area is round, oval or diamond. The artificial valve displacement device can be used for displacing a pathological heart valve without a surgical operation, passes through blood vessels during displacement and is transplanted into the heart through femoral artery; and the heart and the aorta are incised without the operation. It is convenient to transplant, has long service life and favorable positioning effect, not only reduces the difficulty of the operation, but also realizes the recovery.
Owner:VENUS MEDTECH (HANGZHOU) INC
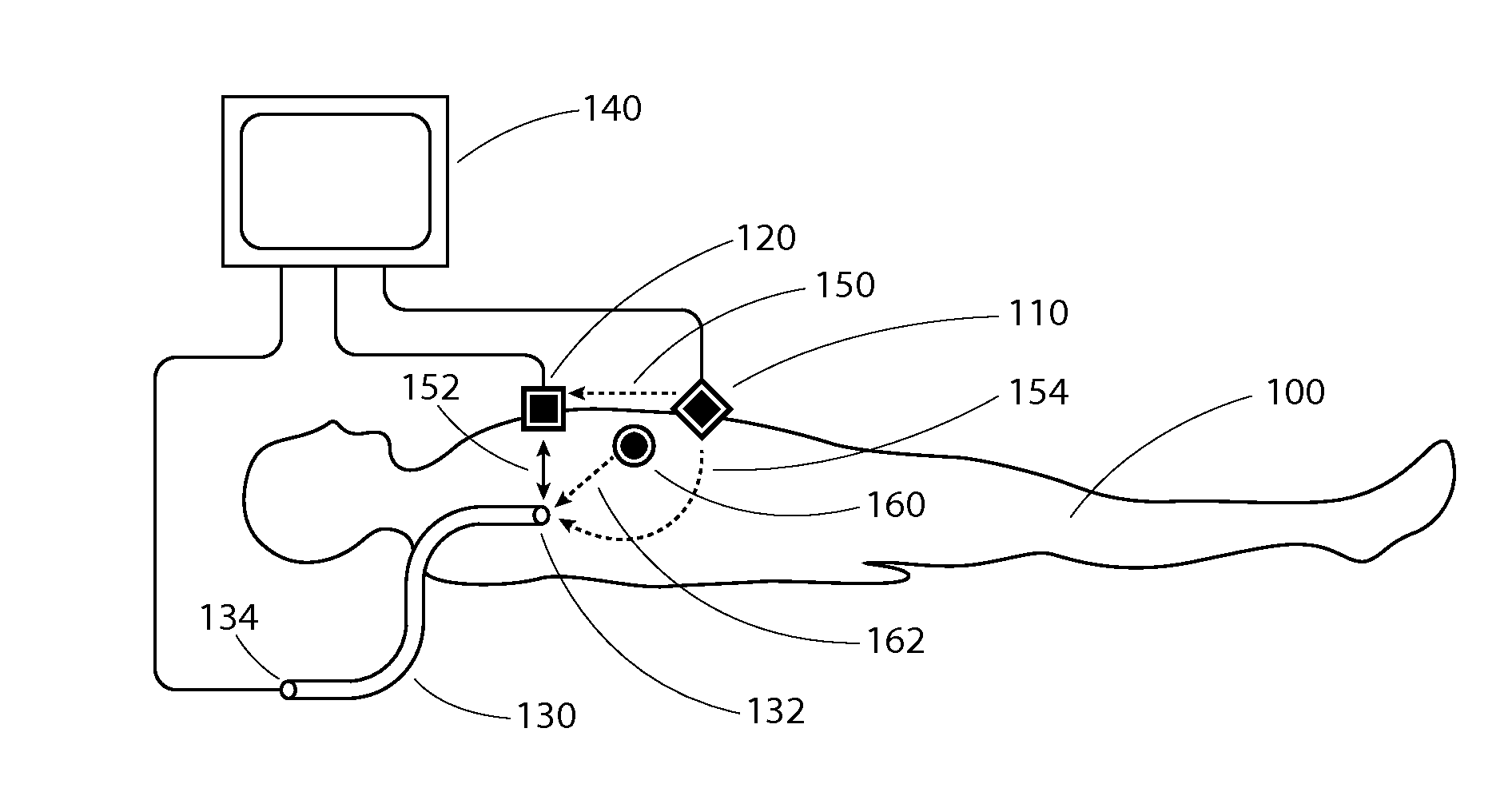
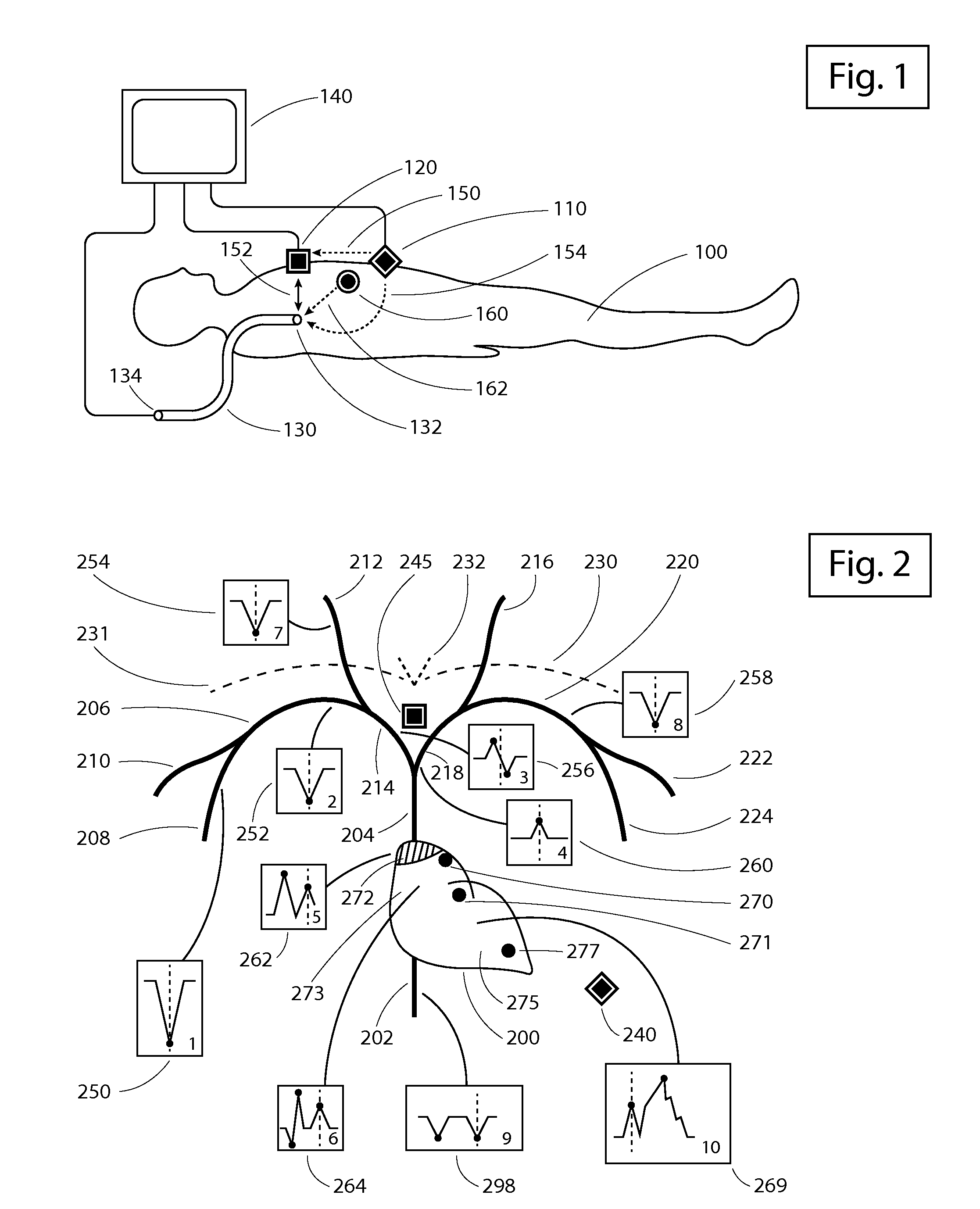
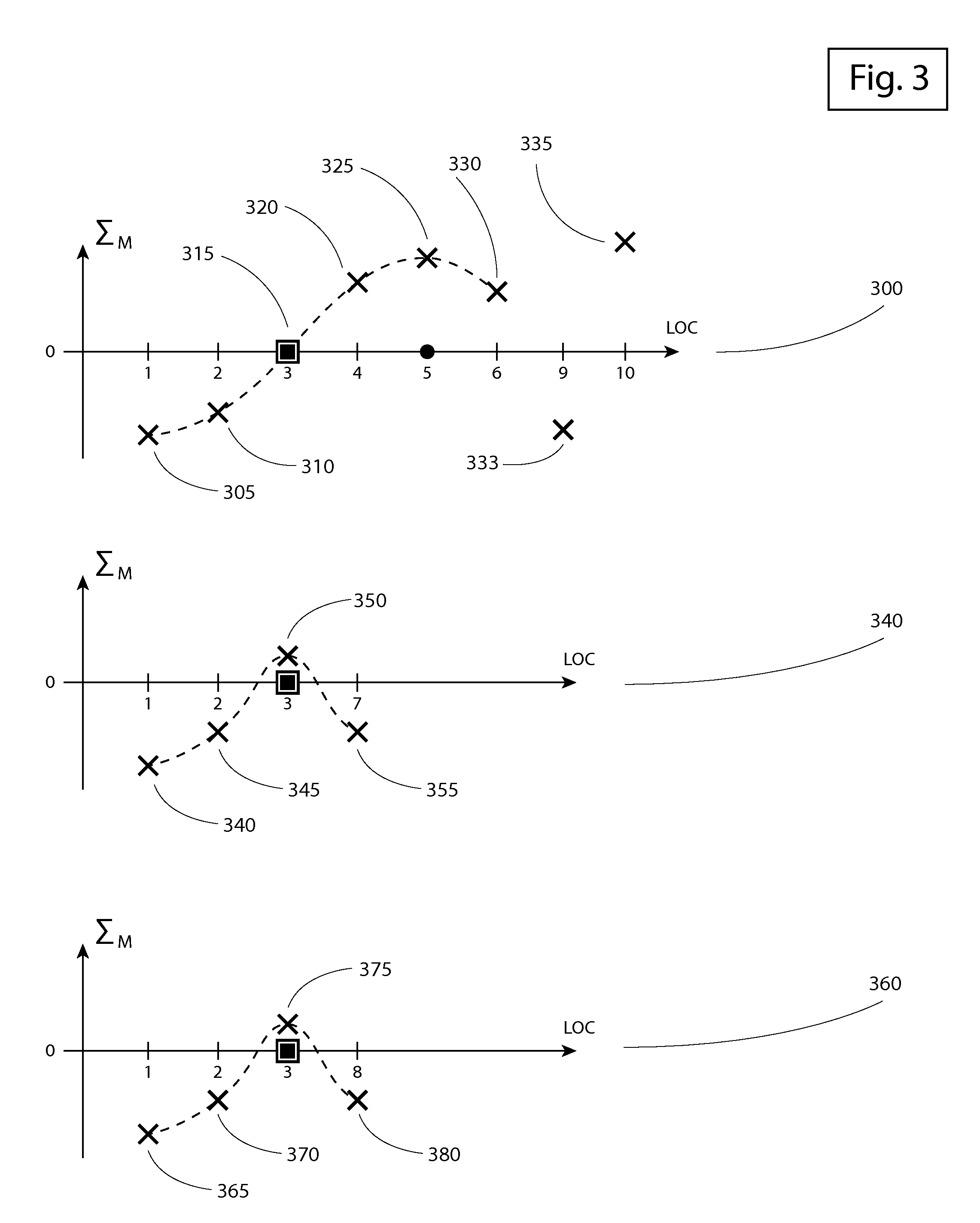
Apparatus and method for intravascular catheter navigation using the electrical conduction system of the heart and control electrodes
ActiveUS20150289781A1Easy to identifyElectrocardiographySurgical navigation systemsCardiac pacemaker electrodeData acquisition
A new apparatus, algorithm, and method (all called Invention) are introduced herein to support navigation and placement of an intravascular catheter using the electrical conduction system of the heart (ECSH) and control electrodes placed on the patient's skin. According to the present Invention, an intravascular catheter can be guided both in the arterial and venous systems and positioned at different desired locations in the vasculature in a number of different clinical situations. The catheter is connected to the apparatus using, for example, sterile extension cables, such that the apparatus can measure the electrical activity at the tip of the catheter. Another electrode of the apparatus is placed for reference on the patient's skin. In one embodiment of the present Invention, a control electrode is placed on the patient's chest over the manubrium of the sternum below the presternal notch. In this case, if a catheter is inserted in the venous system, for example in the basilic vein, the Invention will indicate if the tip of the catheter navigates from the insertion point in the basilic vein into the subclavian vein on the same side, into the subclavian vein counter laterally, into the jugular vein, into the superior vena cava, into the cavoatrial junction (CAJ), into the right atrium (RA), into the right ventricle (RV), or into the inferior vena cava (IVC). For the same location of a control electrode, if a catheter is inserted in the arterial system, the Invention will indicate when the tip of the catheter is navigating into the arch of the aorta, into the right coronary artery, into the left circumflex artery, or into the left ventricle (LV). In another embodiment of the present Invention, a control electrode can be placed on the sternum over the xiphoid process. In one embodiment of the present invention, a catheter can be inserted in the arterial systems by arterial radial, brachial or axillary access. In another embodiment of the present Invention, a catheter may be inserted into either the arterial or the venous systems by femoral or saphenous access. In one aspect of the present Invention, navigation maps are introduced for different locations in the vasculature which allow for easy identification of the location of the catheter tip. In another aspect of the present Invention, a novel algorithm is introduced to compute a navigation signal in real time using electrical signals from the tip of the catheter and from control electrodes. In another aspect of the present Invention, a novel algorithm is introduced to compute in real time navigation parameters from the navigation signal computes according to the present Invention. In another aspect of the present Invention, a method is introduced which makes use of the navigation signal to allow for placing an intravascular catheter at a desired location in the vasculature relative to the ECSH and to the control electrodes placed on the skin. In another aspect of the present Invention, the electrical signals obtained from control electrodes and from the tip of the catheter may be generated by the natural ECSH, e.g., the sino-atrial node (SAN), by artificial (implanted) pacemakers or by electrical generators external to the body. In yet another aspect of the Invention, an apparatus is introduced which supports data acquisition required by the computation of a navigation signal according to the present Invention.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
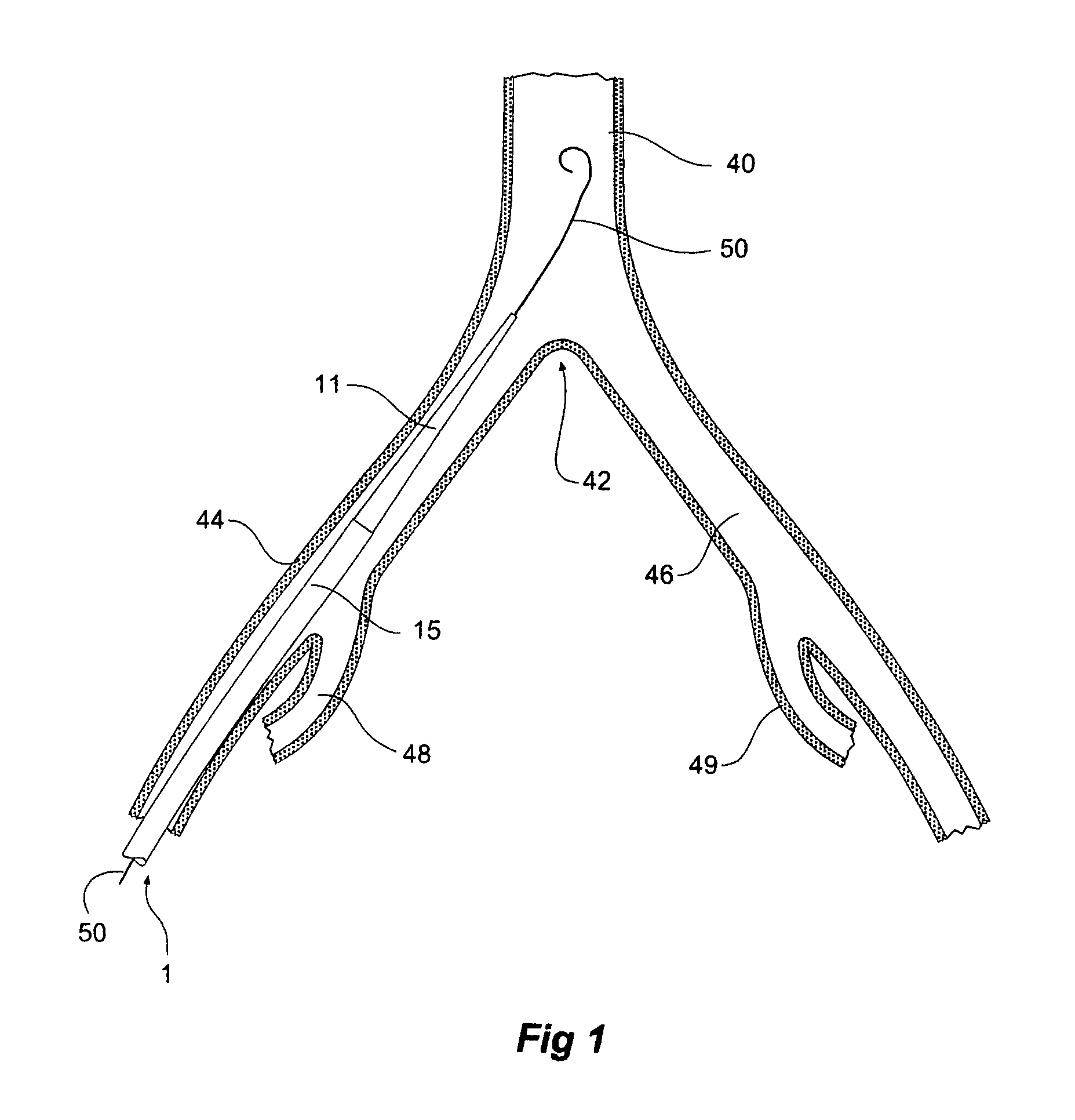
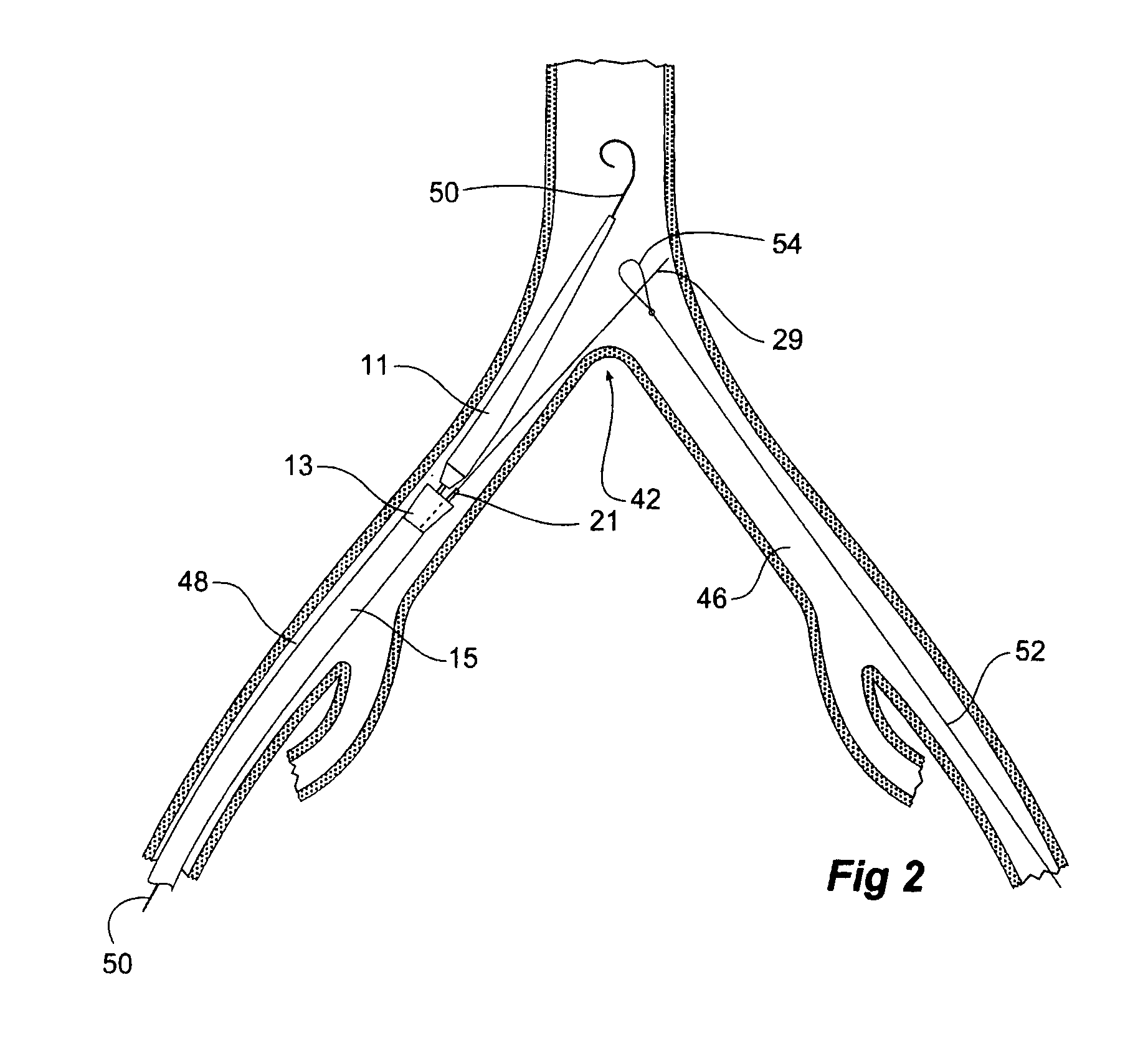
Introducer for a side branch device
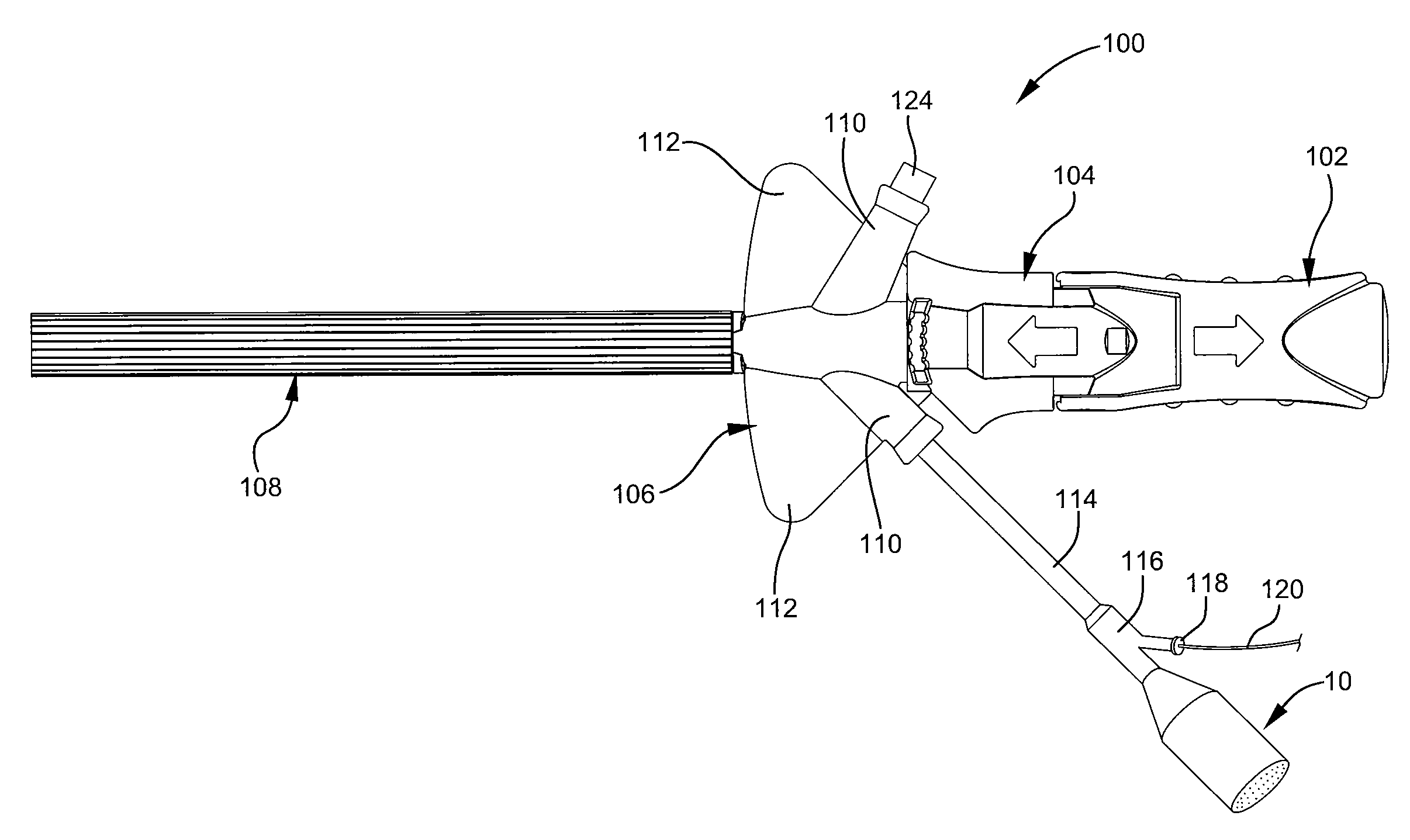
An introduction arrangement for a fenestrated or branched stent graft (13) intended for deployment into the lumen of a vessel having a blind vessel extending from it. The introducer (1) has a distal end intended to remain outside a patient in use and a proximal end with a nose cone dilator (11) and an arrangement to retain the branched stent graft distally of the nose cone dilator. A sheath (15) on the introducer extends over the branched stent graft to the nose cone dilator. An indwelling catheter (21) extends from the distal end of the introducer and enters the fenestration or side arm and through to the nose cone dilator, the indwelling catheter has a guide wire (29) extending through it. The guide wire can be extended beyond the nose cone dilator in use before the sheath is withdrawn from the branched stent graft so that it can be snared from the contra-lateral artery.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
System and method for achieving patent hemostasis in arteries
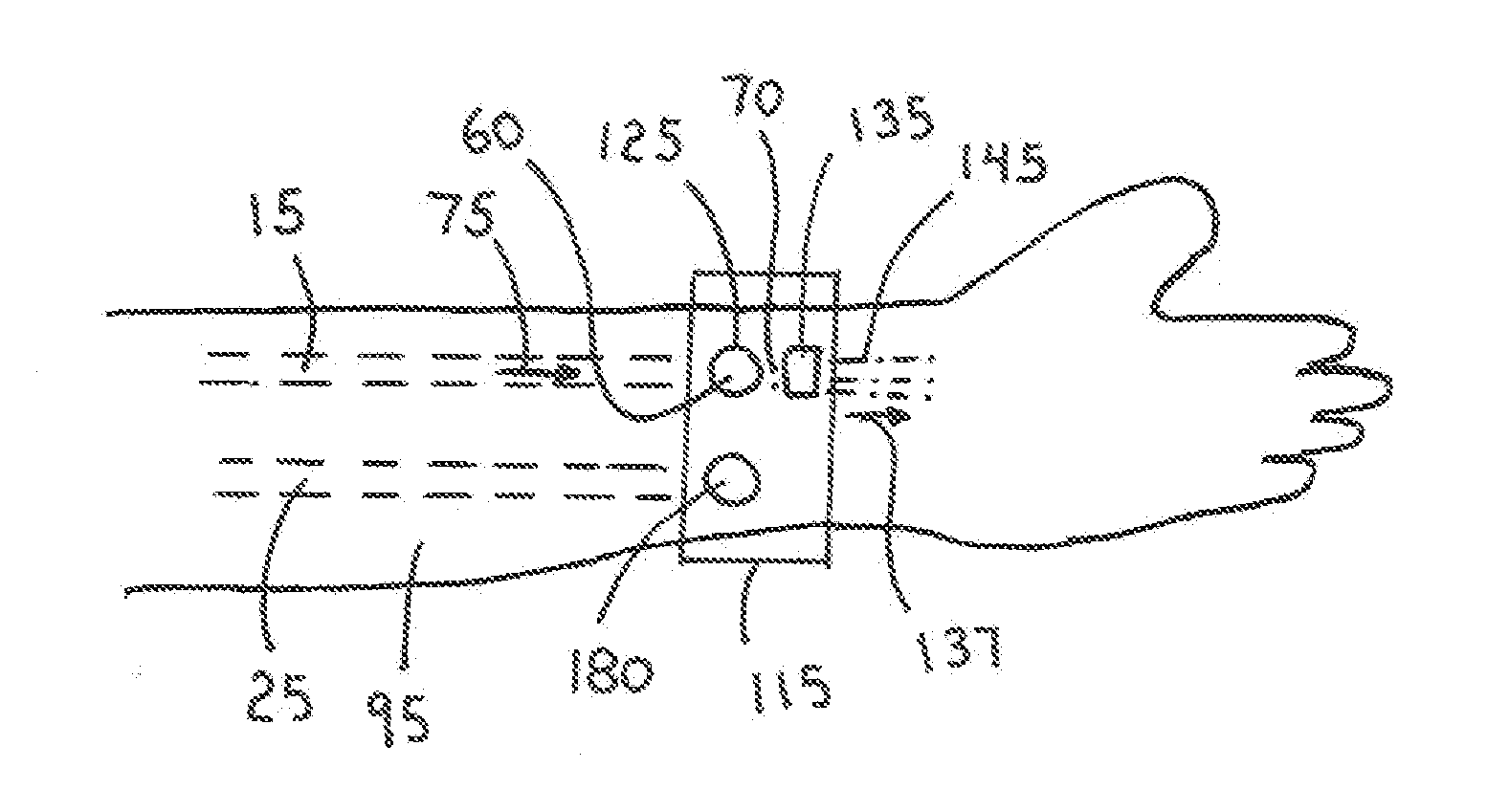
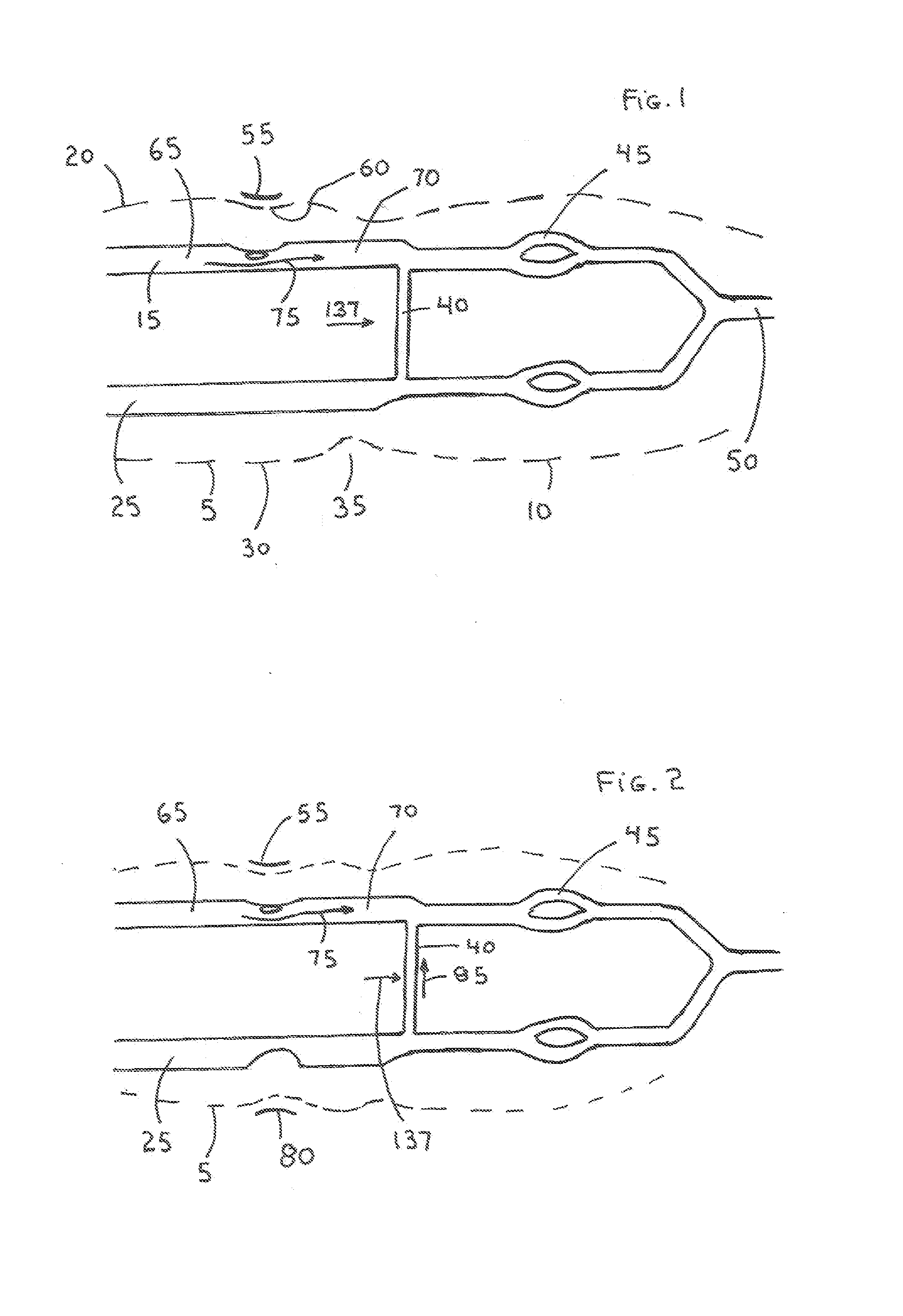
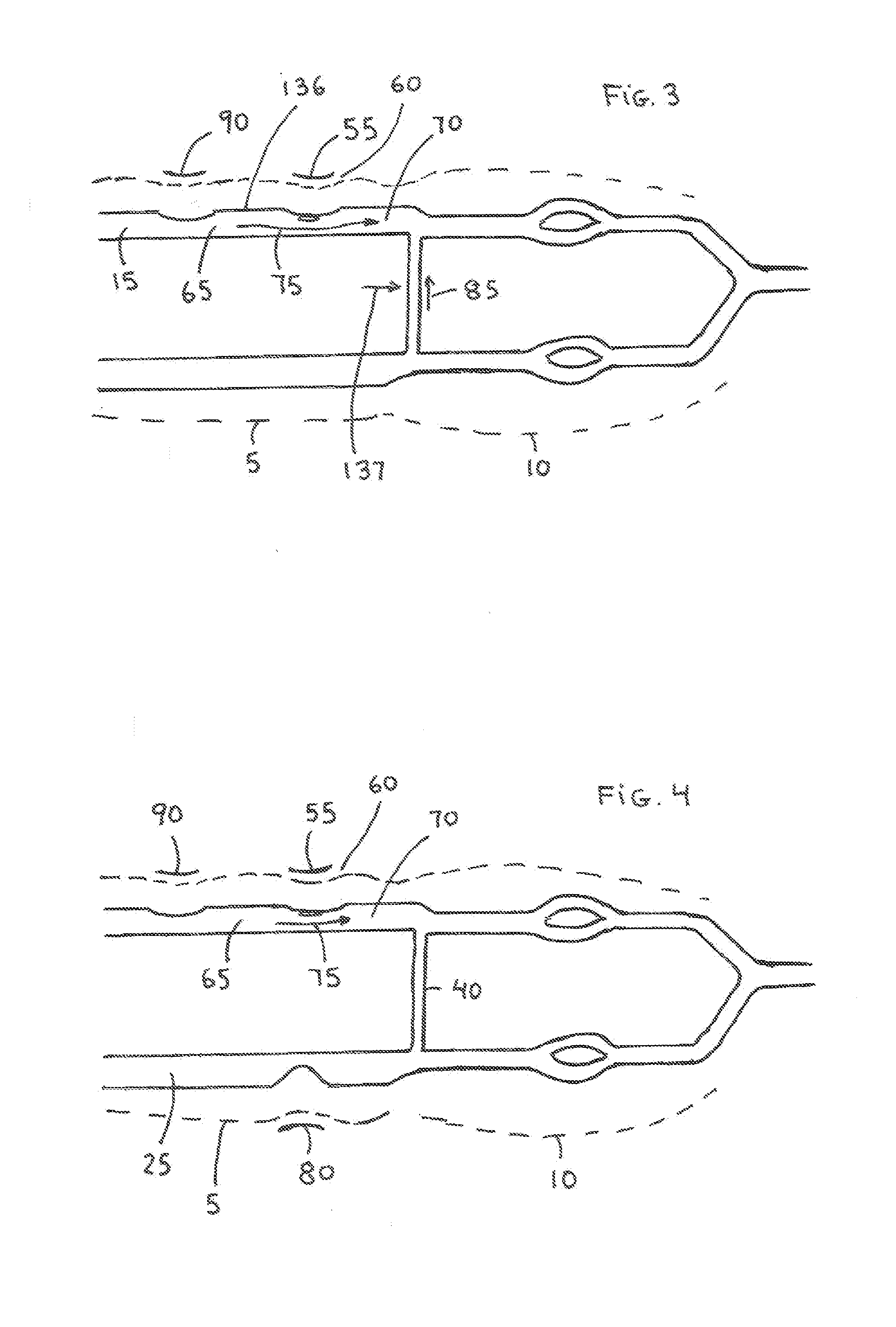
InactiveUS20160174952A1Overcomes drawbackSufficient pressureTourniquetsSurgical veterinaryIliac arteryWrist
A system for achieving patent hemostasis in arteries of a patient's wrist is disclosed. The system includes a flexible band for enclosure about the wrist at a puncture site. A first and second balloon are coupled to an inner surface of the flexible band. The second balloon is positioned relative to the first balloon such that a distance between the first balloon and the second balloon results in the first balloon being positioned proximal a first artery and the second balloon being positioned proximal a second artery when the flexible band is enclosed about the wrist. Upon inflation of the first balloon and the second balloon, patent hemostasis is achieved on the first artery and occlusive pressure is generated on the second artery.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
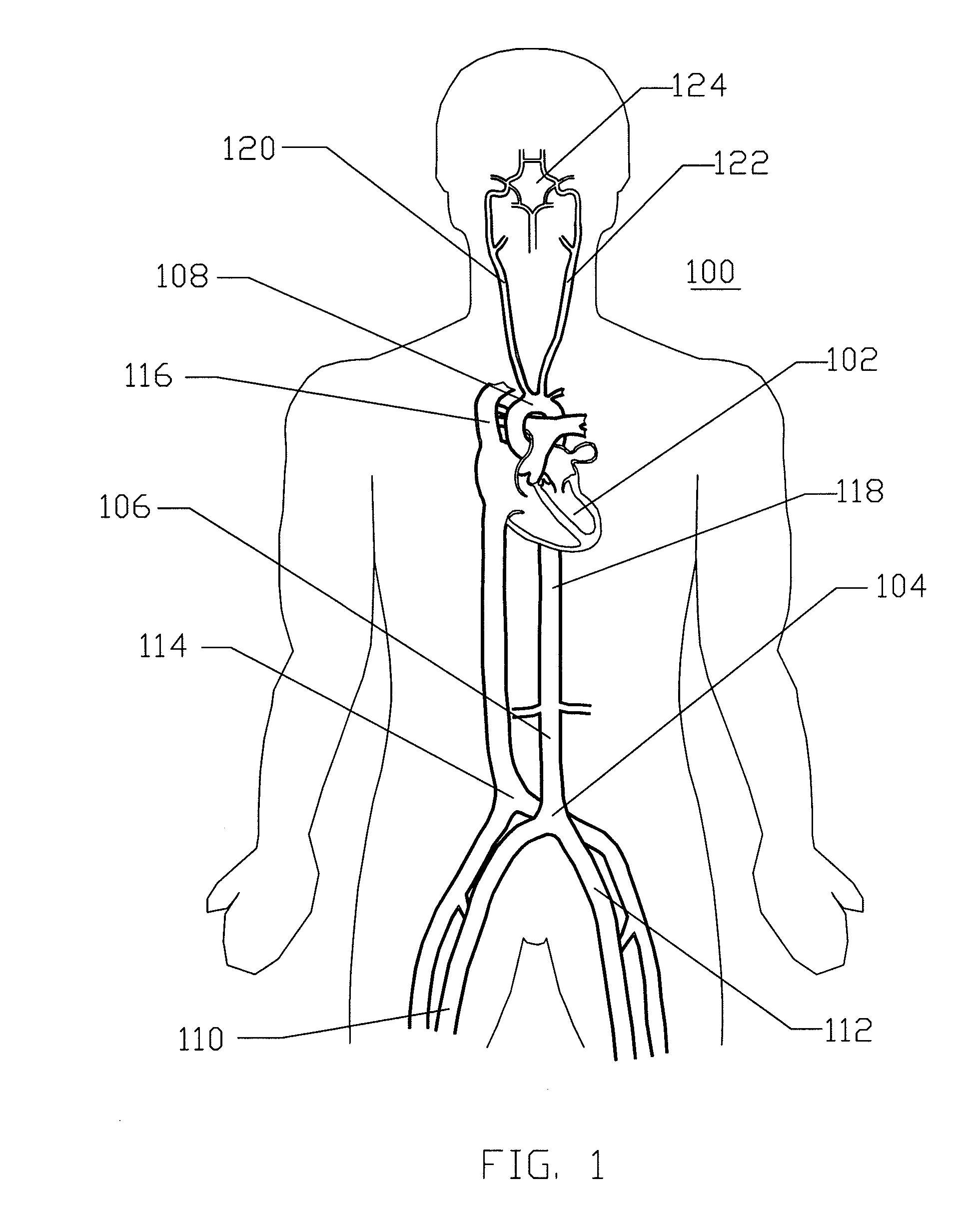
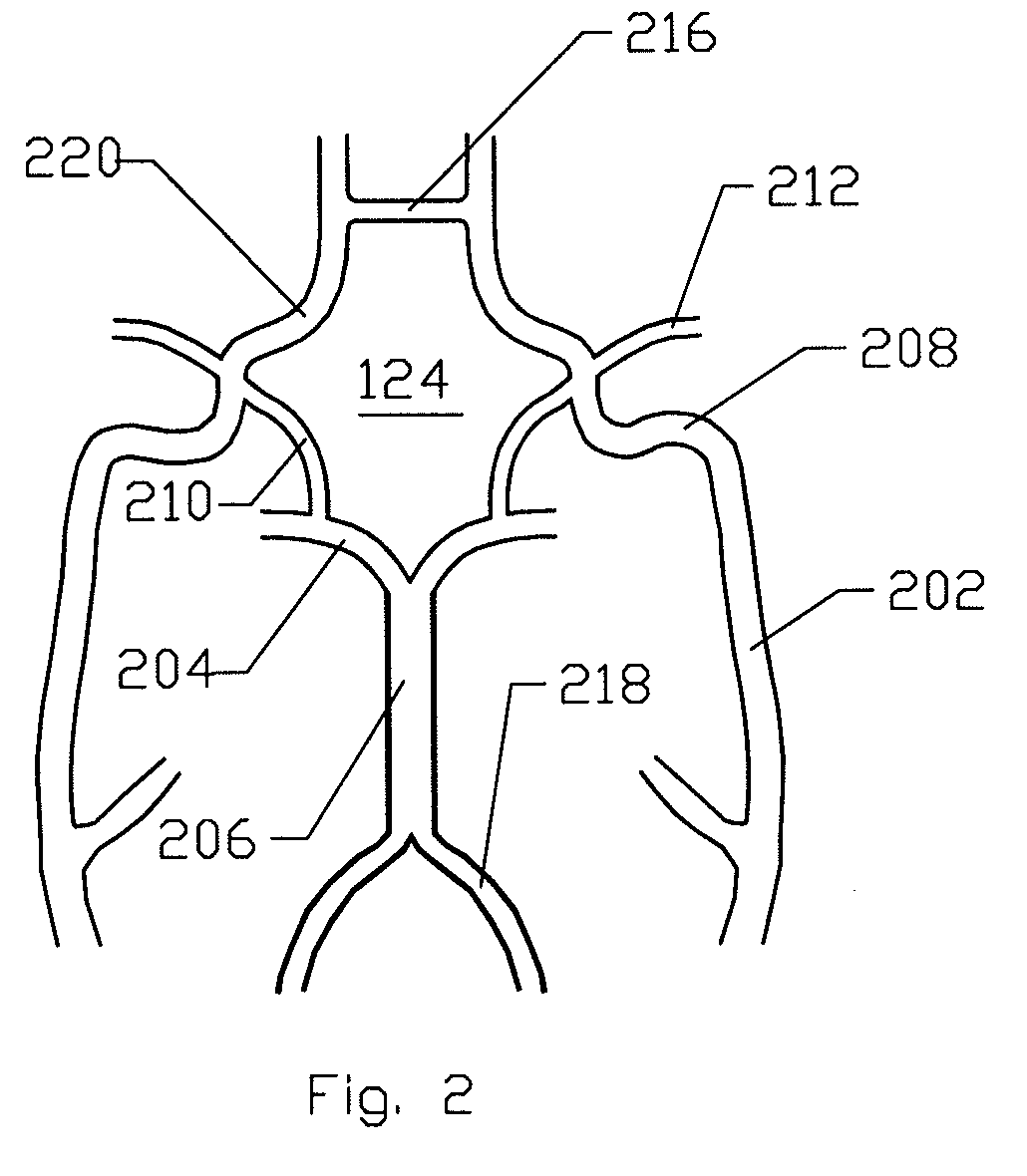
Endoprosthesis for endovascular treatment of thoracic-abdominal aortic aneurysms or dissections and endoprosthesis for endovascular treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms or dissections which compromise the iliac arteries
The present invention relates to an endoprosthesis for endovascular treatment of thoracic-abdominal aortic aneurysms or dissections, wherein the endoprosthesis has a proximal region, an intermediate region and a distal region, comprising five inner cylinders parallel to the longitudinal axis of the endoprosthesis, said inner cylinders, having elliptical apertures in the intermediate region. The present invention also relates to an endoprosthesis for endovascular treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms or dissections which compromise the iliac arteries, wherein the endoprosthesis has a proximal region, an intermediate region and a distal region, comprising an inner cylinder parallel to the longitudinal axis of the endoprosthesis, said inner cylinder having an elliptical aperture in the intermediate region.
Owner:BIOKYRA PESQUISA E DESENVOLVIMENTO
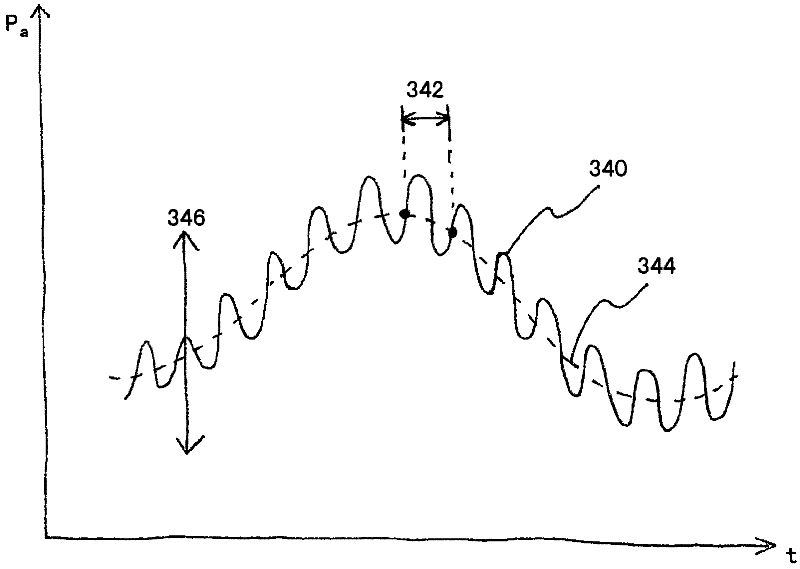
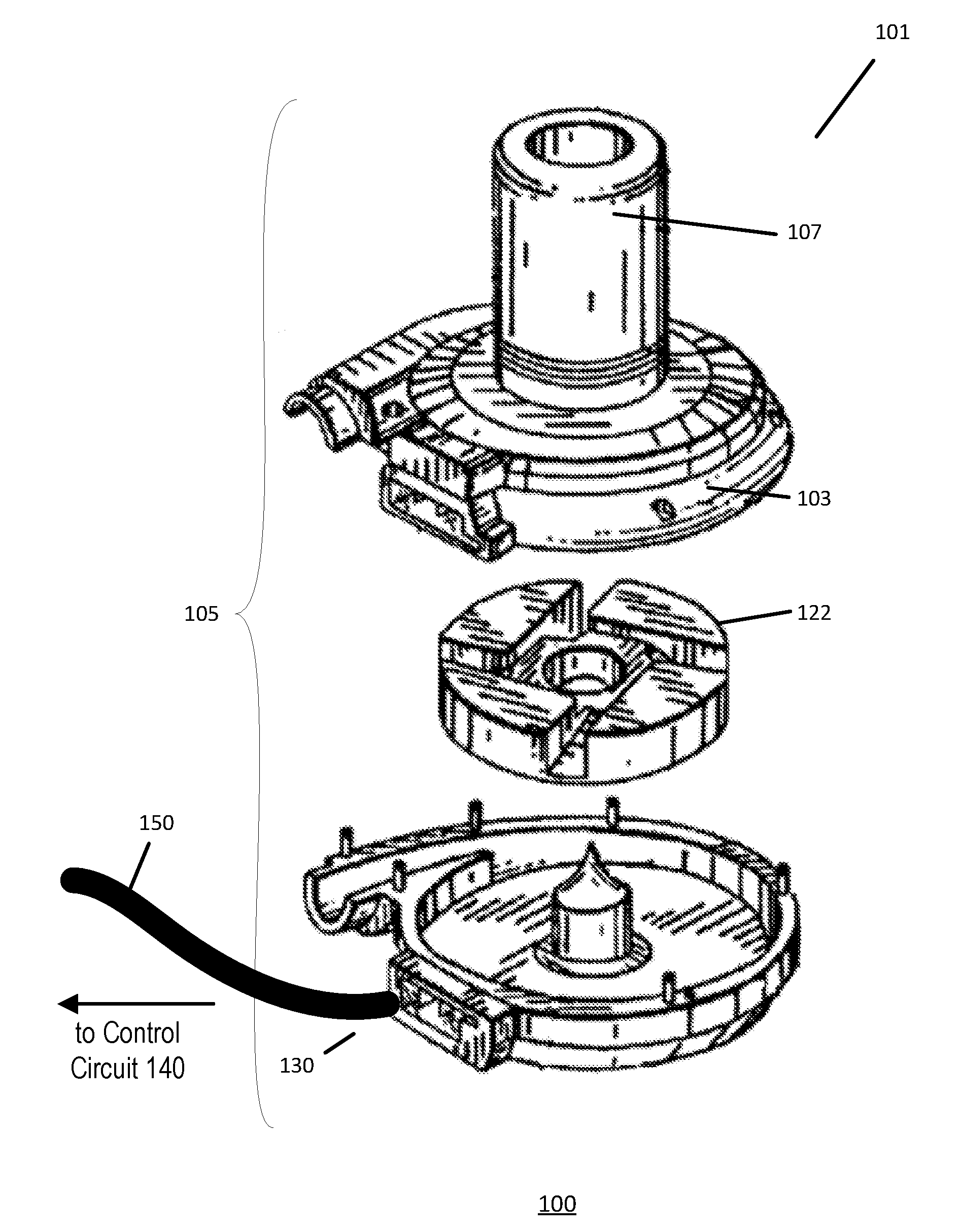
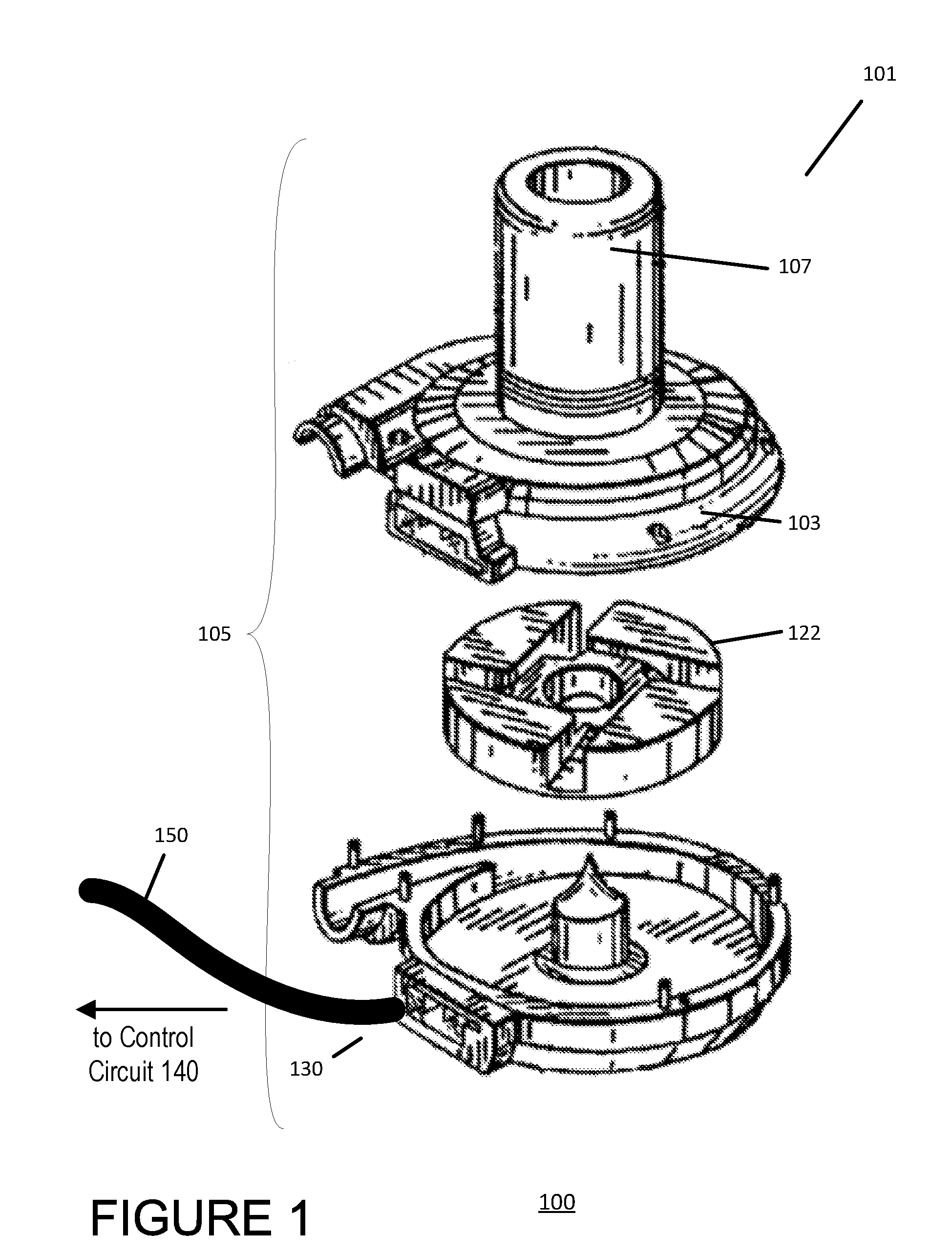
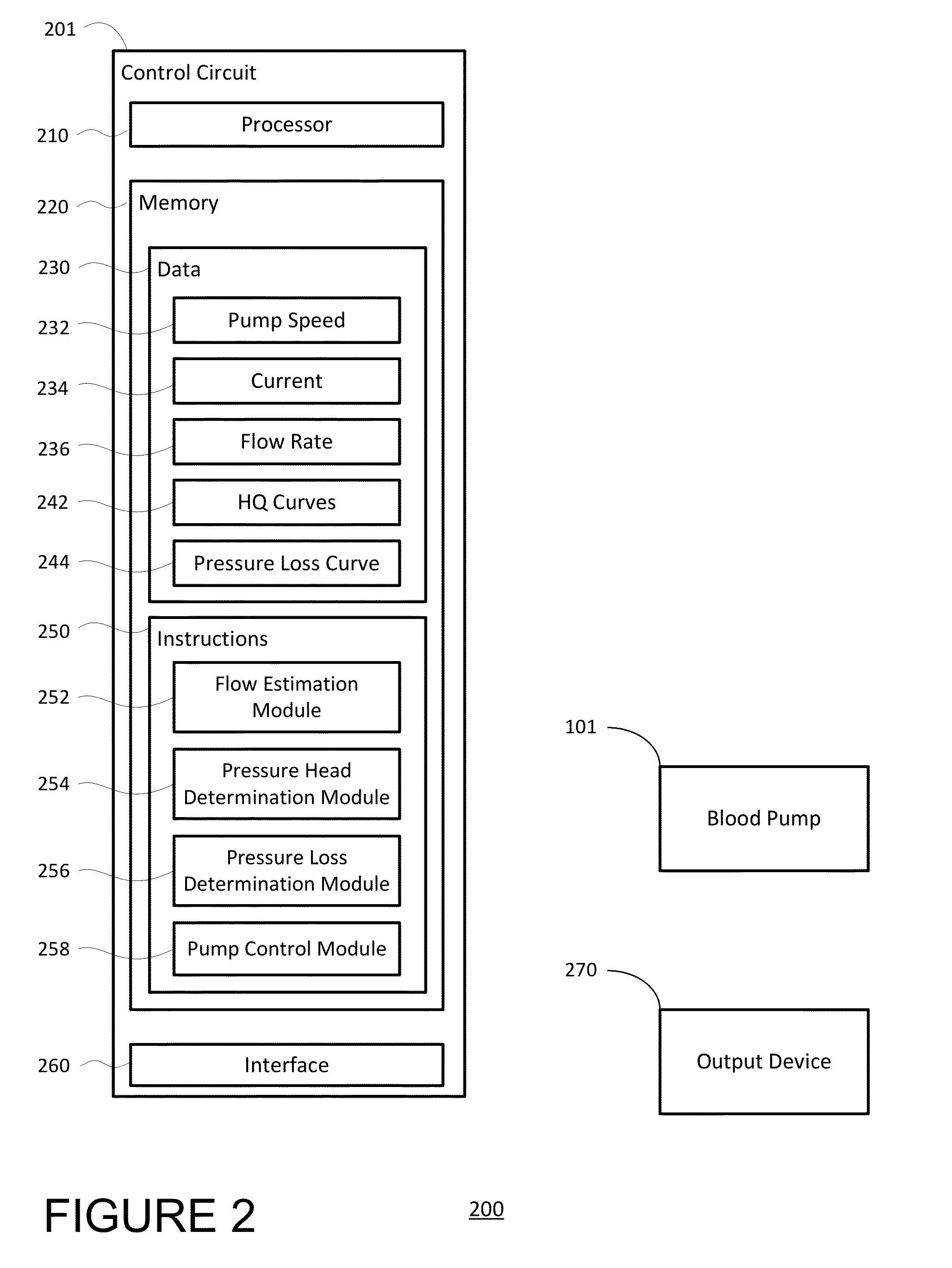
Mean arterial pressure estimation
The present disclosure provides for a method of monitoring the mean arterial pressure of a patient having a blood pump. The method may involve identifying a segment of time associated with diastole of the patient's cardiac cycle, determining a first parameter of the blood pump corresponding to the identified segment of time, and estimating the mean arterial pressure of the patient based at least in part on the first parameter.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
Endoprostheses for peripheral arteries and other body vessels
InactiveUS7867273B2High degreeIncrease resistanceStentsBlood vesselsCoronary arteriesInsertion stent
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Implantable human kidney replacement unit
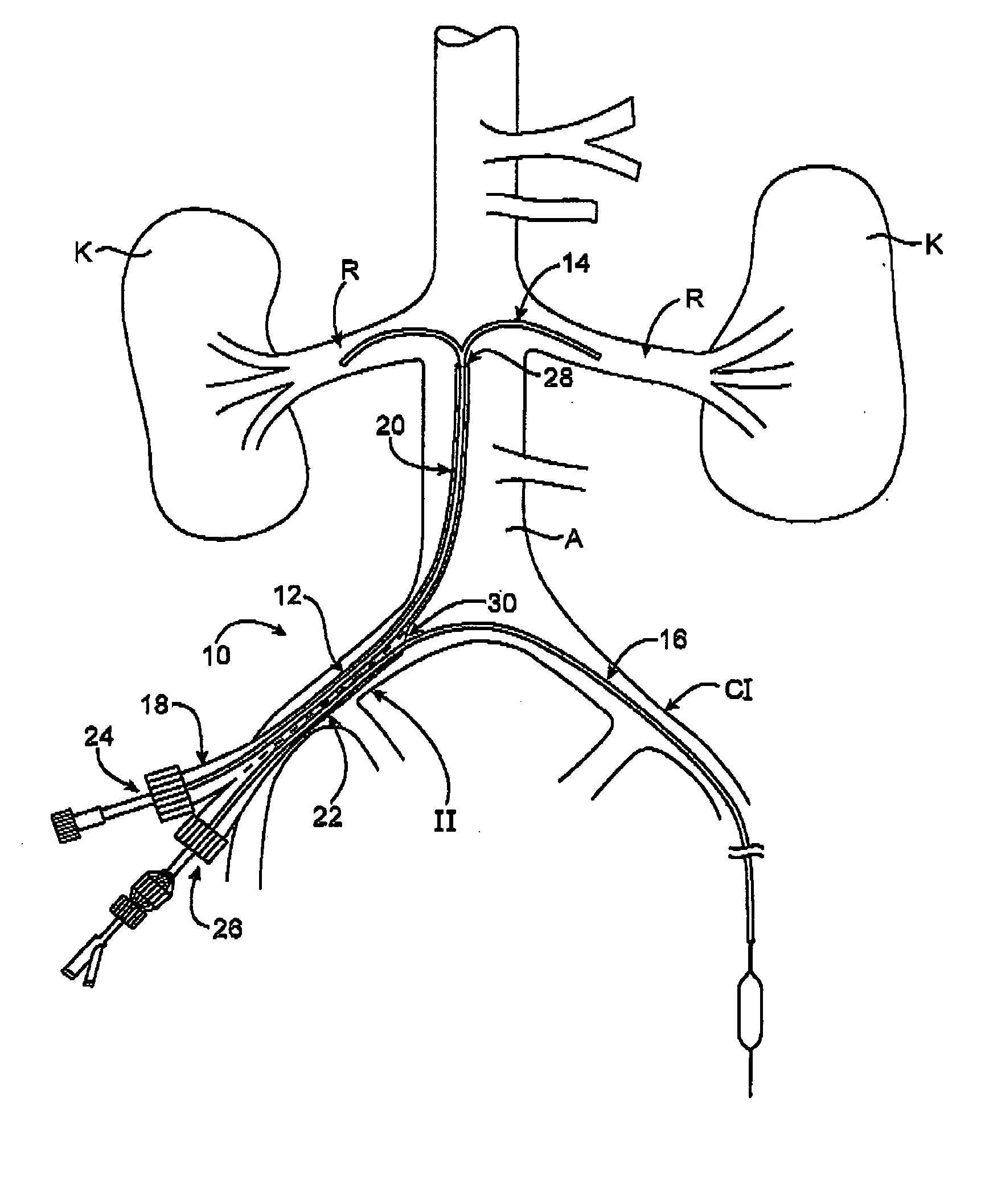
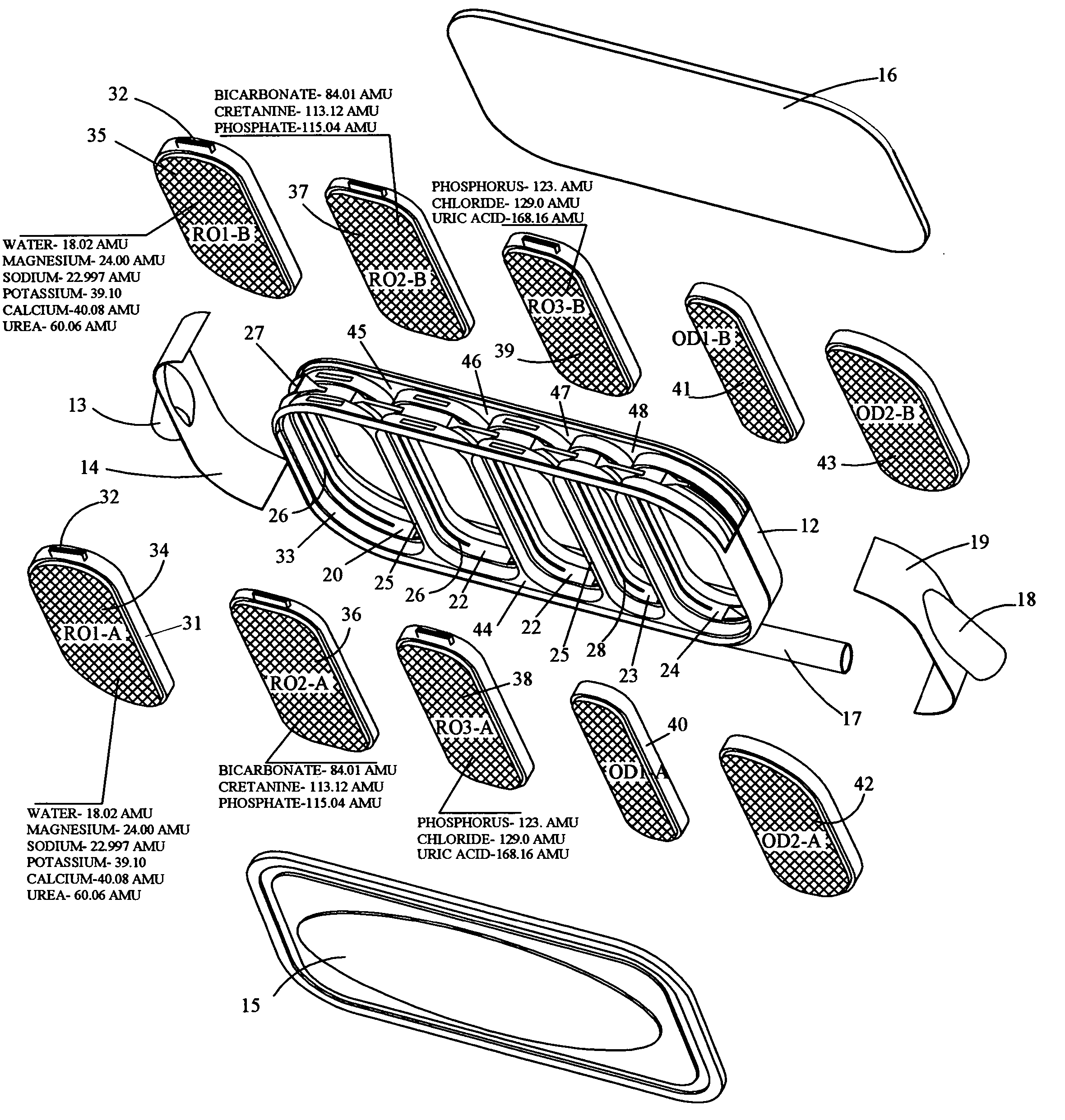
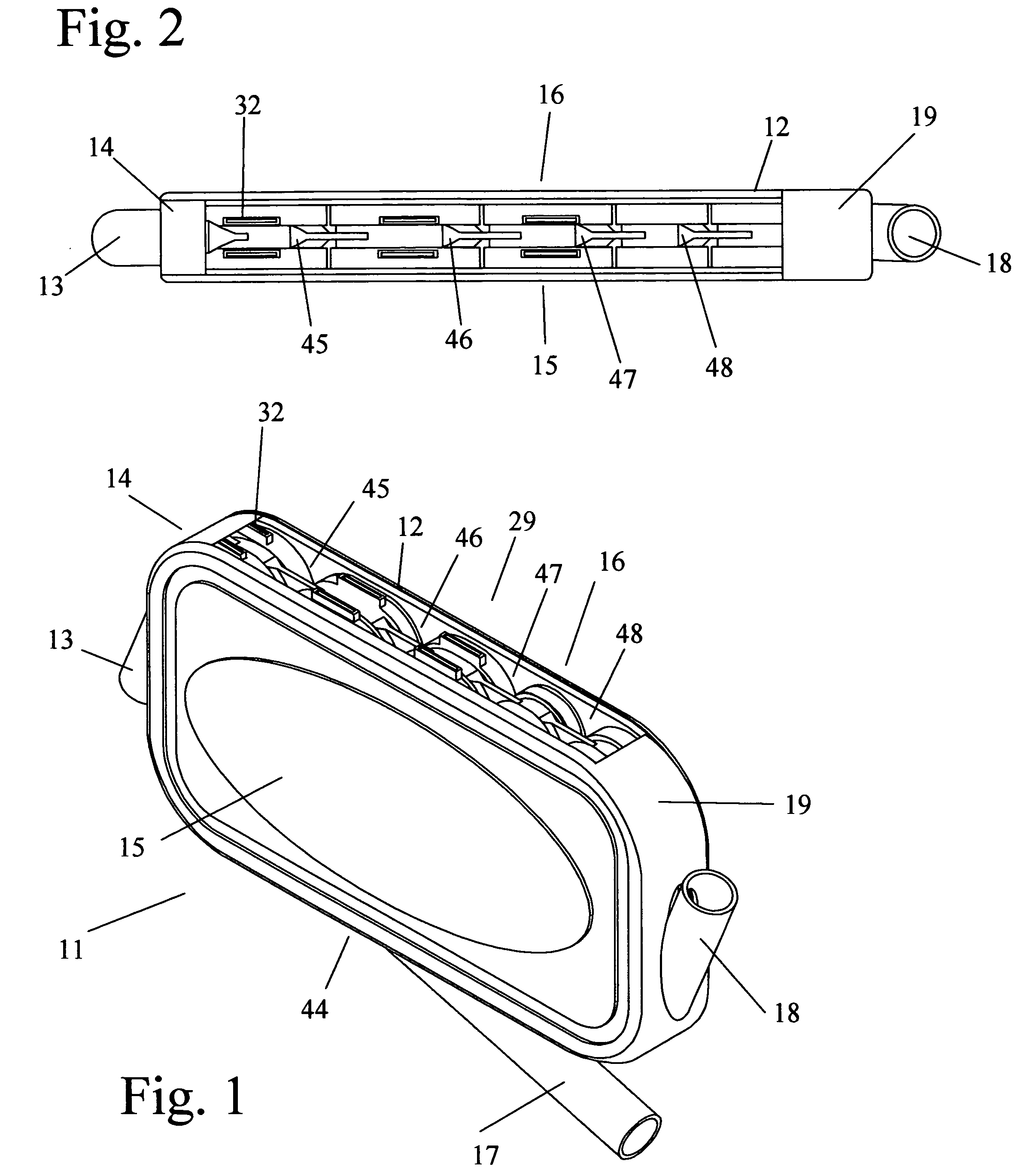
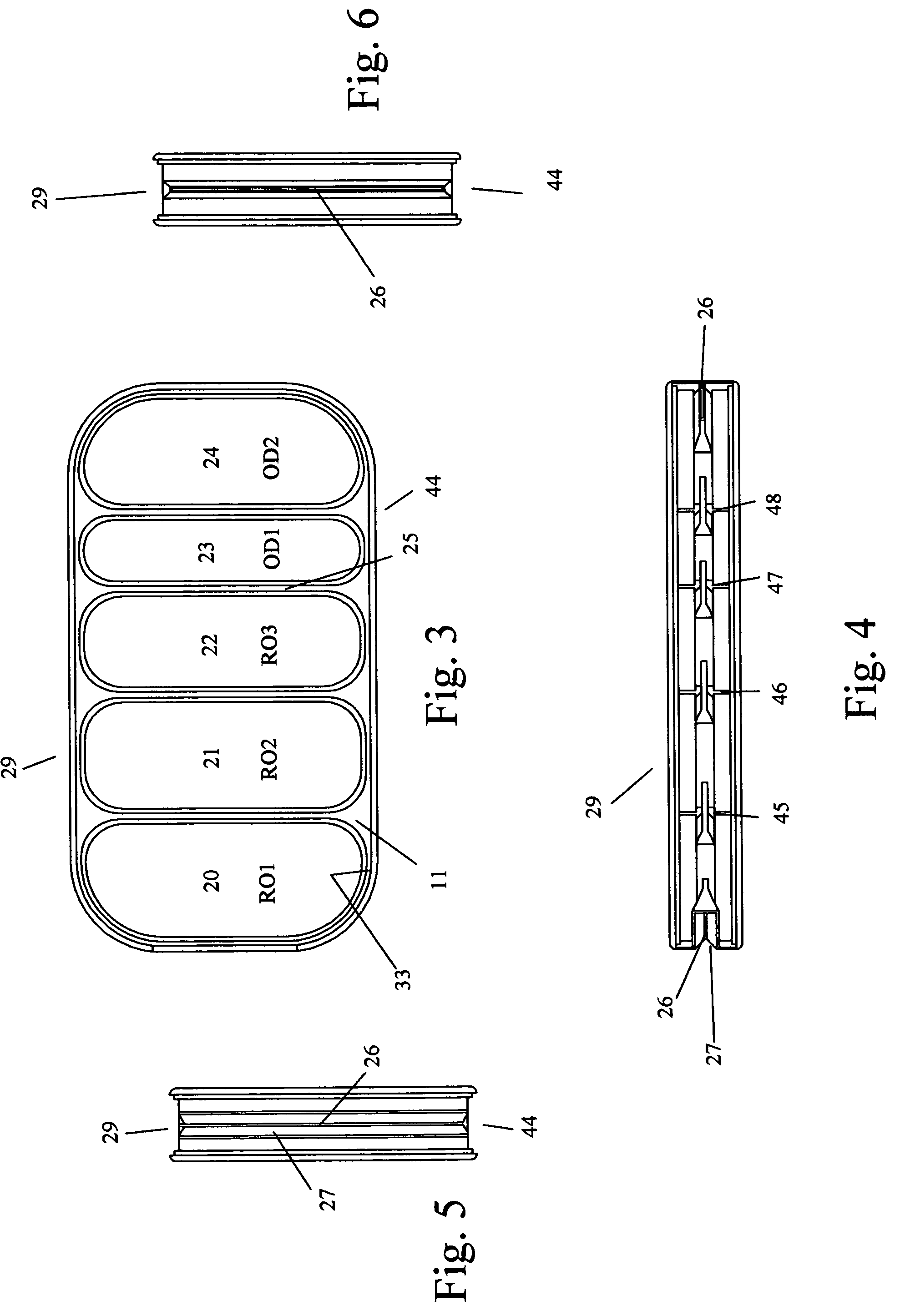
An implantable human kidney replacement unit. Fully functional self contained, providing patients with end stage renal disease the freedom of traveling and moving about normally. Replacing donor kidneys. Implanted in the flank with at least one inlet and outlet tube each, sutured to the iliac artery and vain, at least one urine tube to the ureter. The housing constructed of anti-coagulant bacteriostatic materials has a plurality of reverse-osmosis process chambers with semipemeable membranes through the unit, followed by osmosis-diffusion chambers and membranes. Blood from the artery enters the first of the chambers. Small molecules such as water, magnesium, sodium, potassium, calcium, urea etc. are extracted from the blood according to their weight in atomic mass units as blood wipes past the self-cleaning membrane cartridges in the chambers. Molecules are further separated and urea sent to the bladder with excess water and electrolytes. The remainder is channeled to at least one diffusion chamber and reabsorbed into the blood. The same process is repeated in the other chambers where selected larger molecules such as creatinine and phosphorus are excreted, and some diffused back into the blood.
Owner:LUDLOW ROLAND G
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com