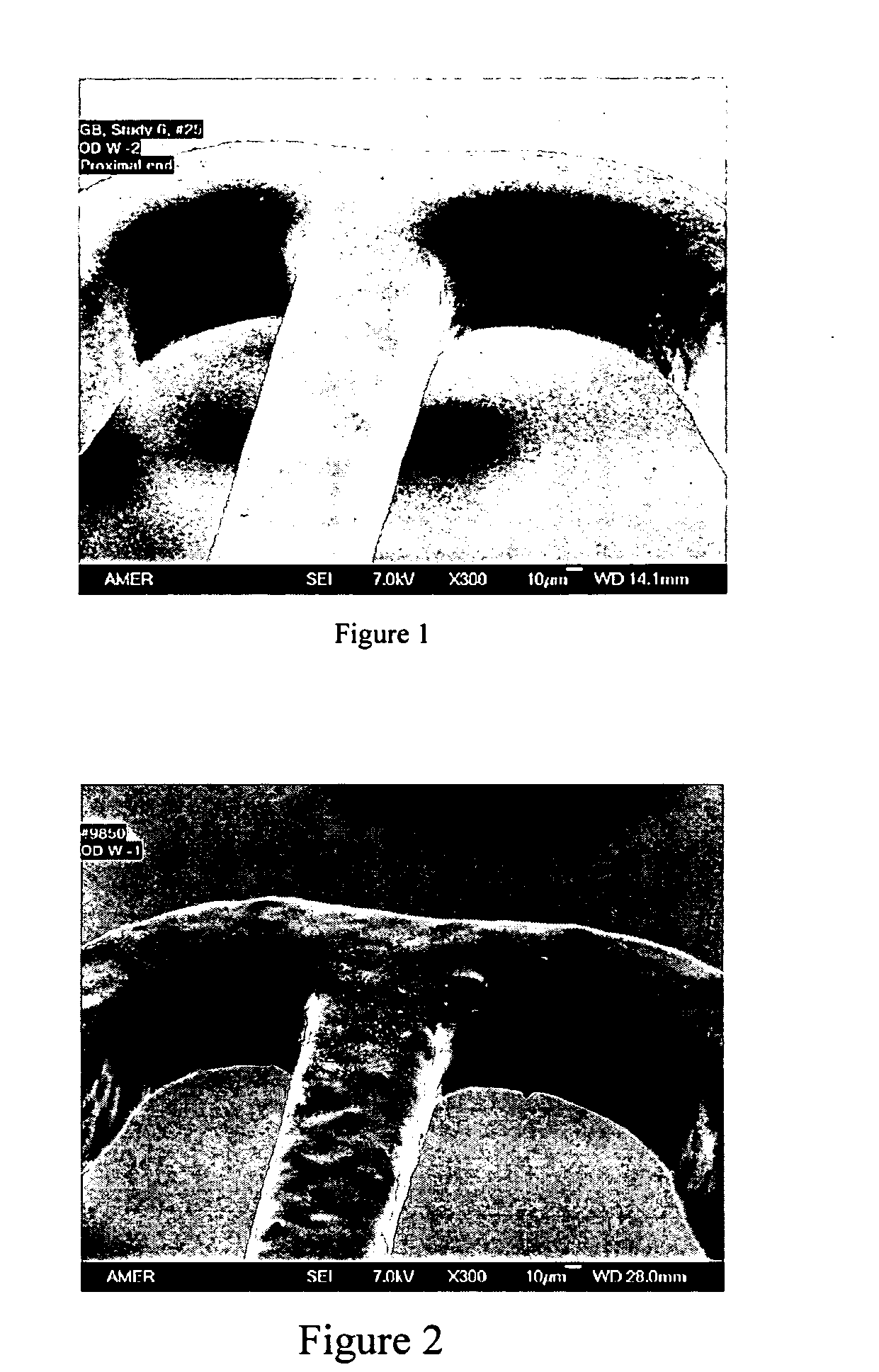
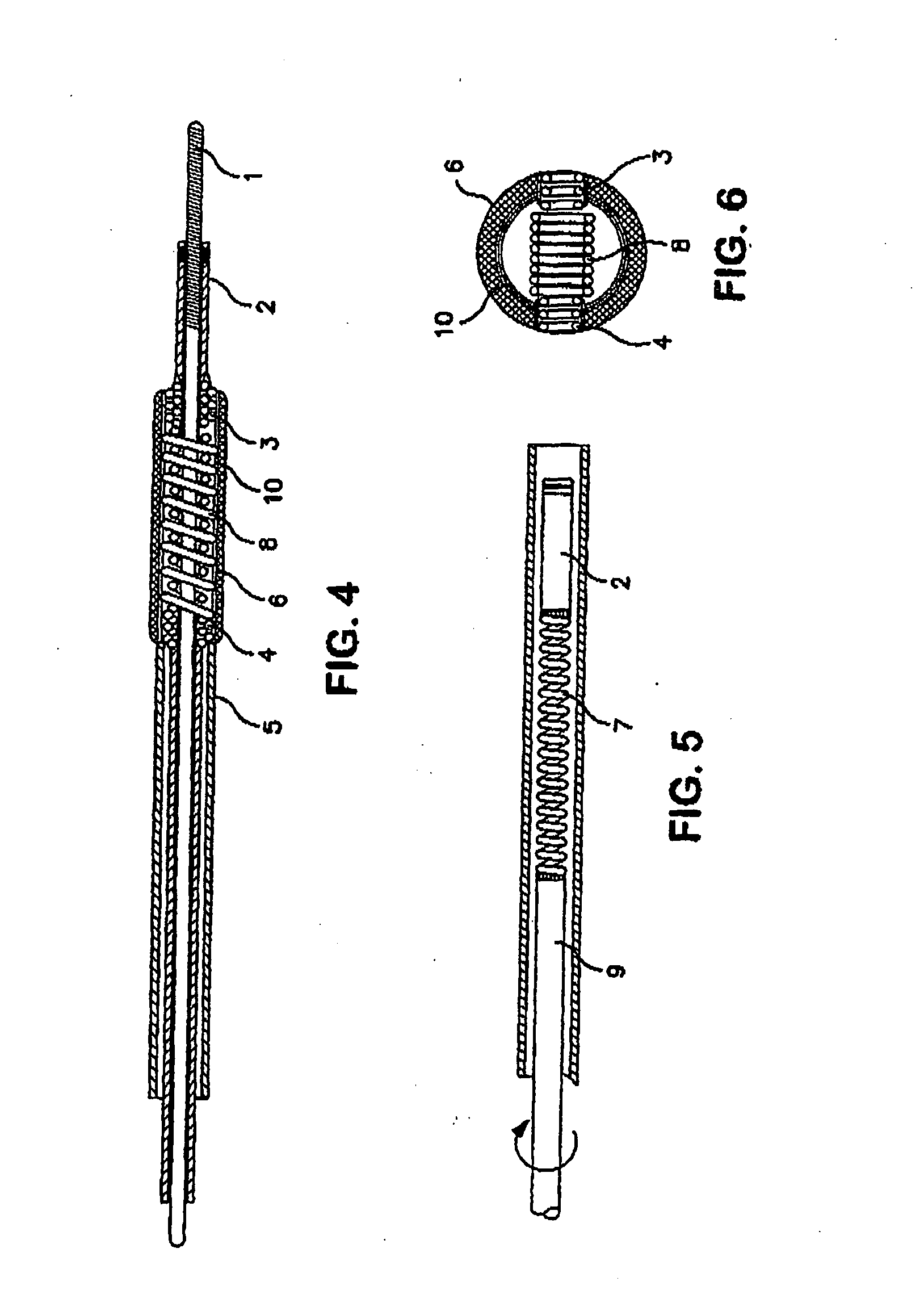
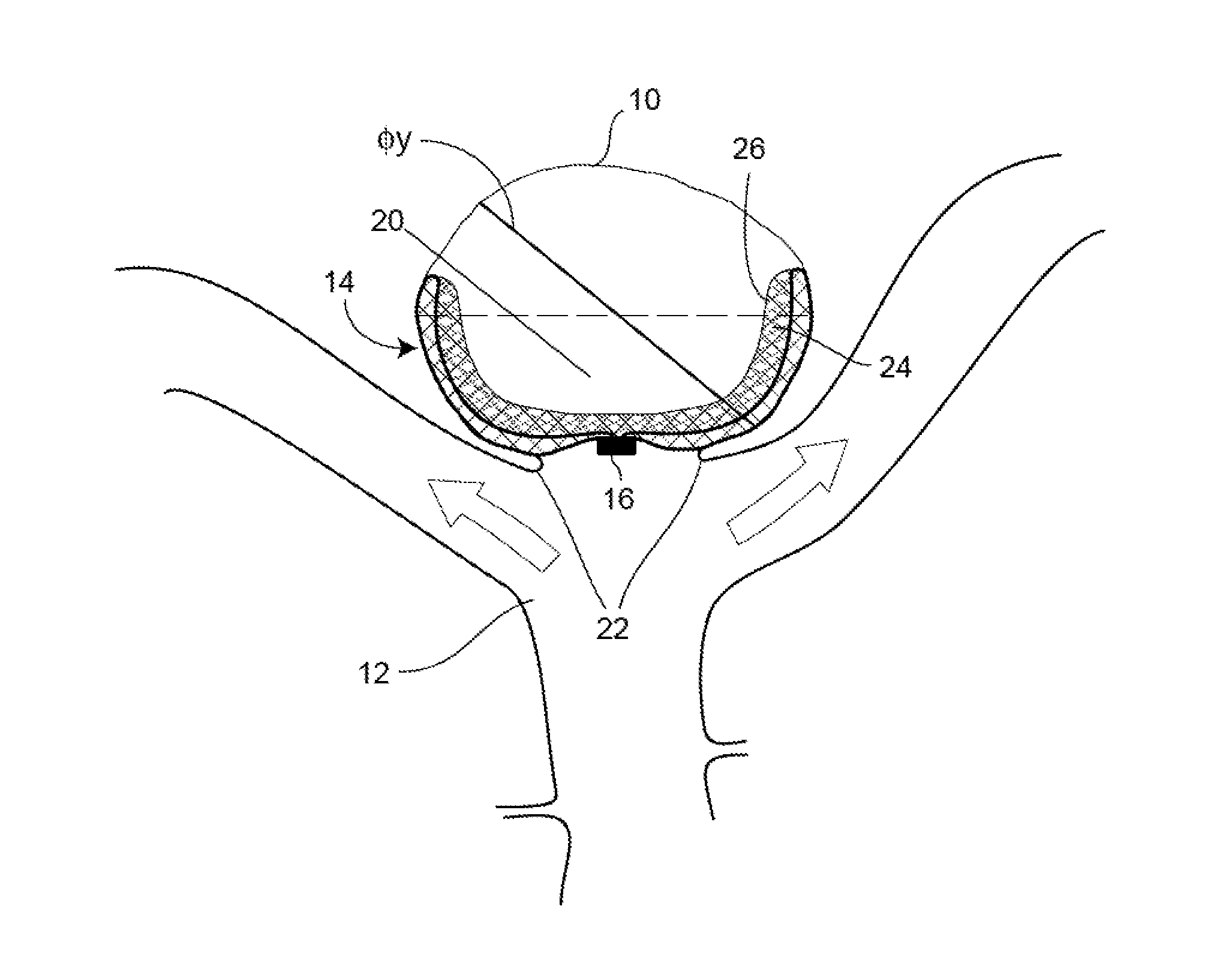
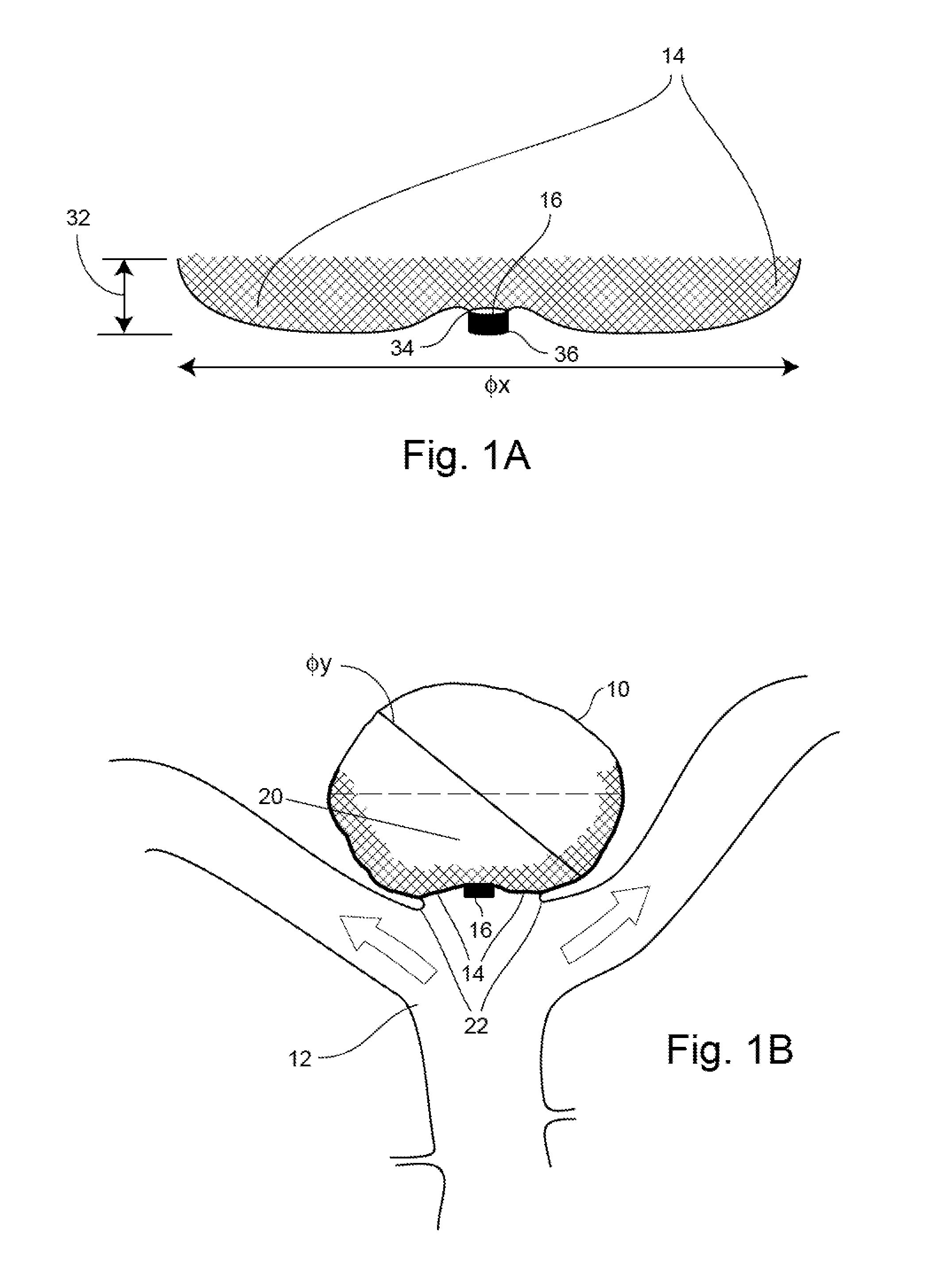
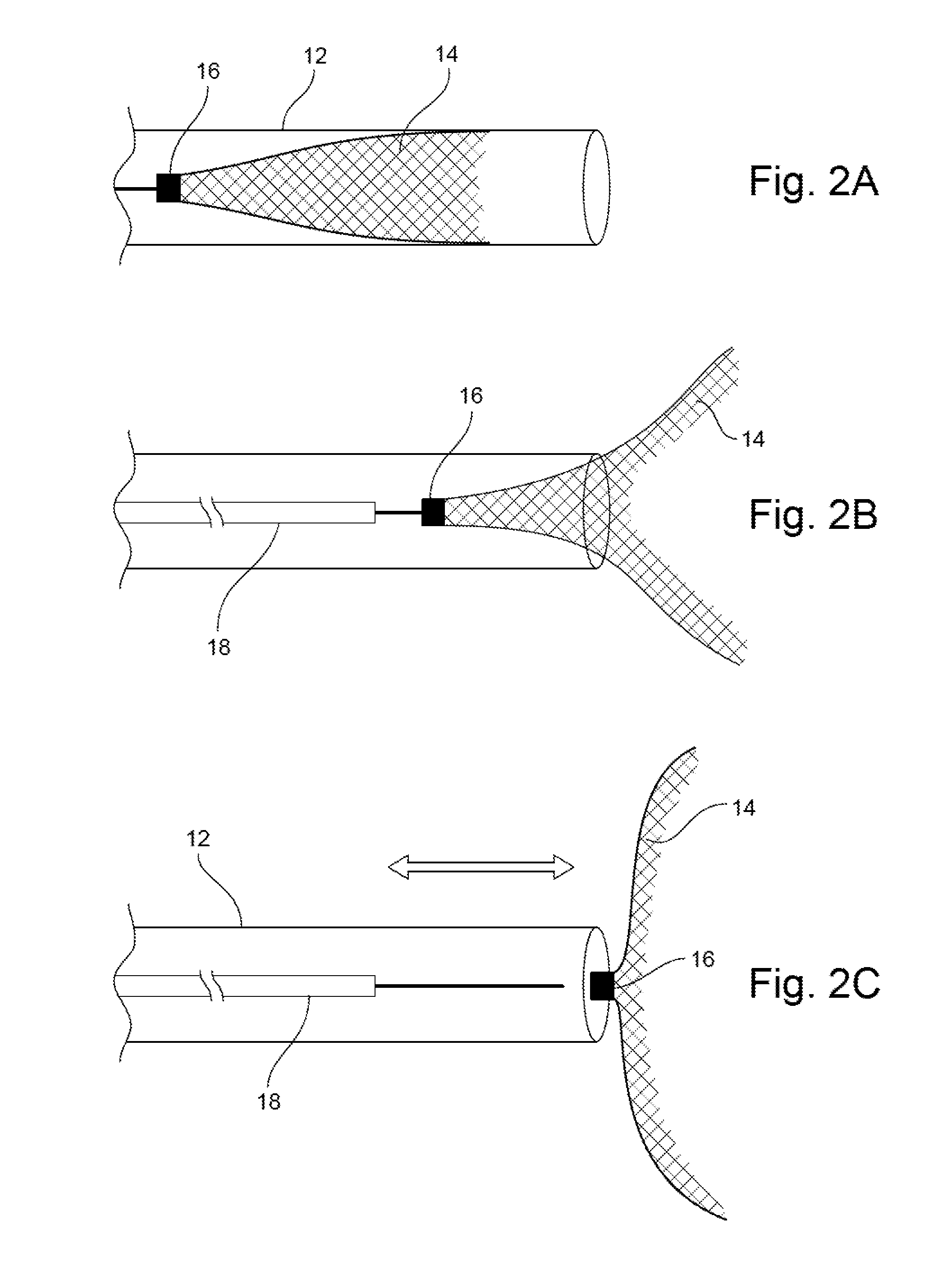
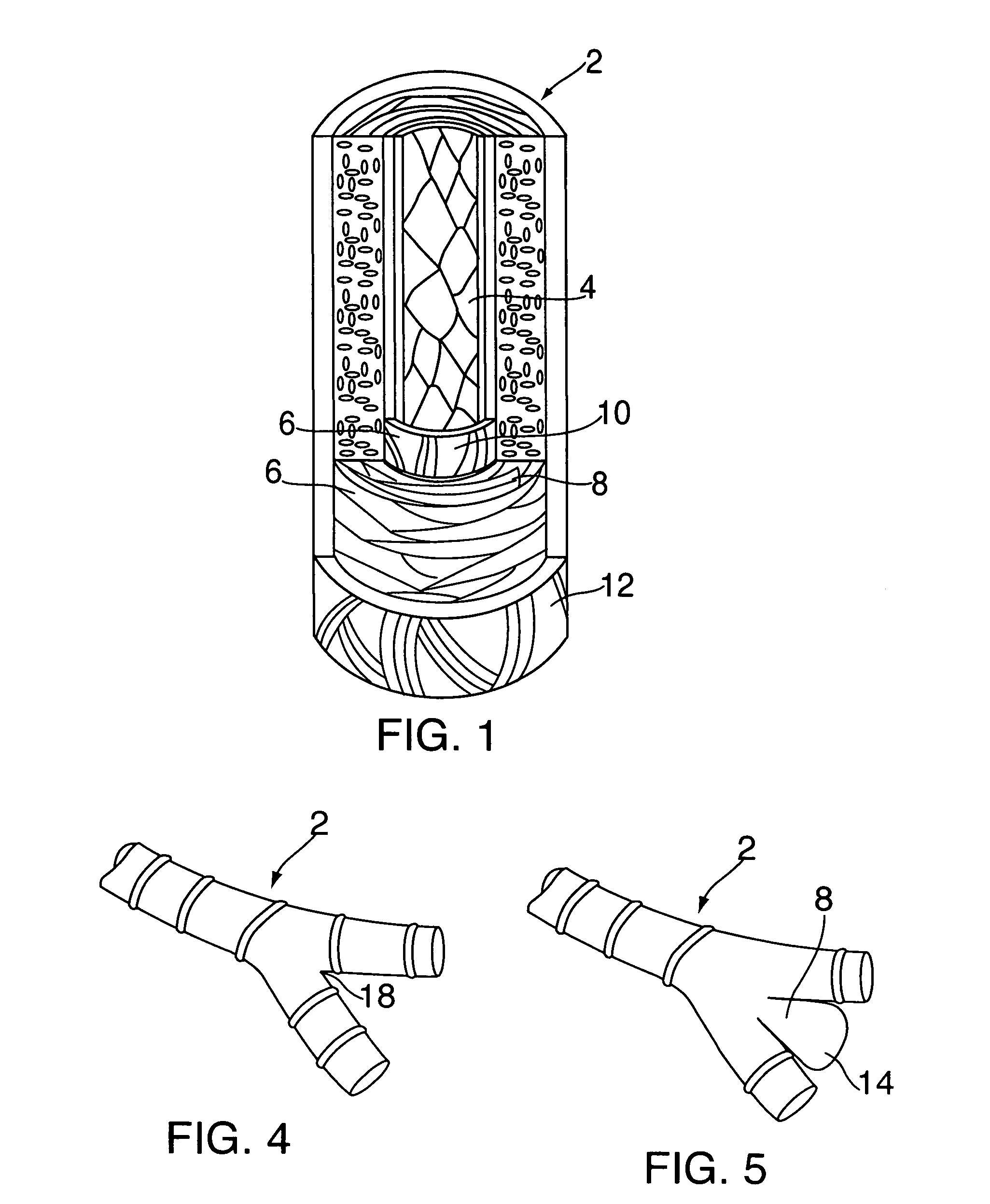
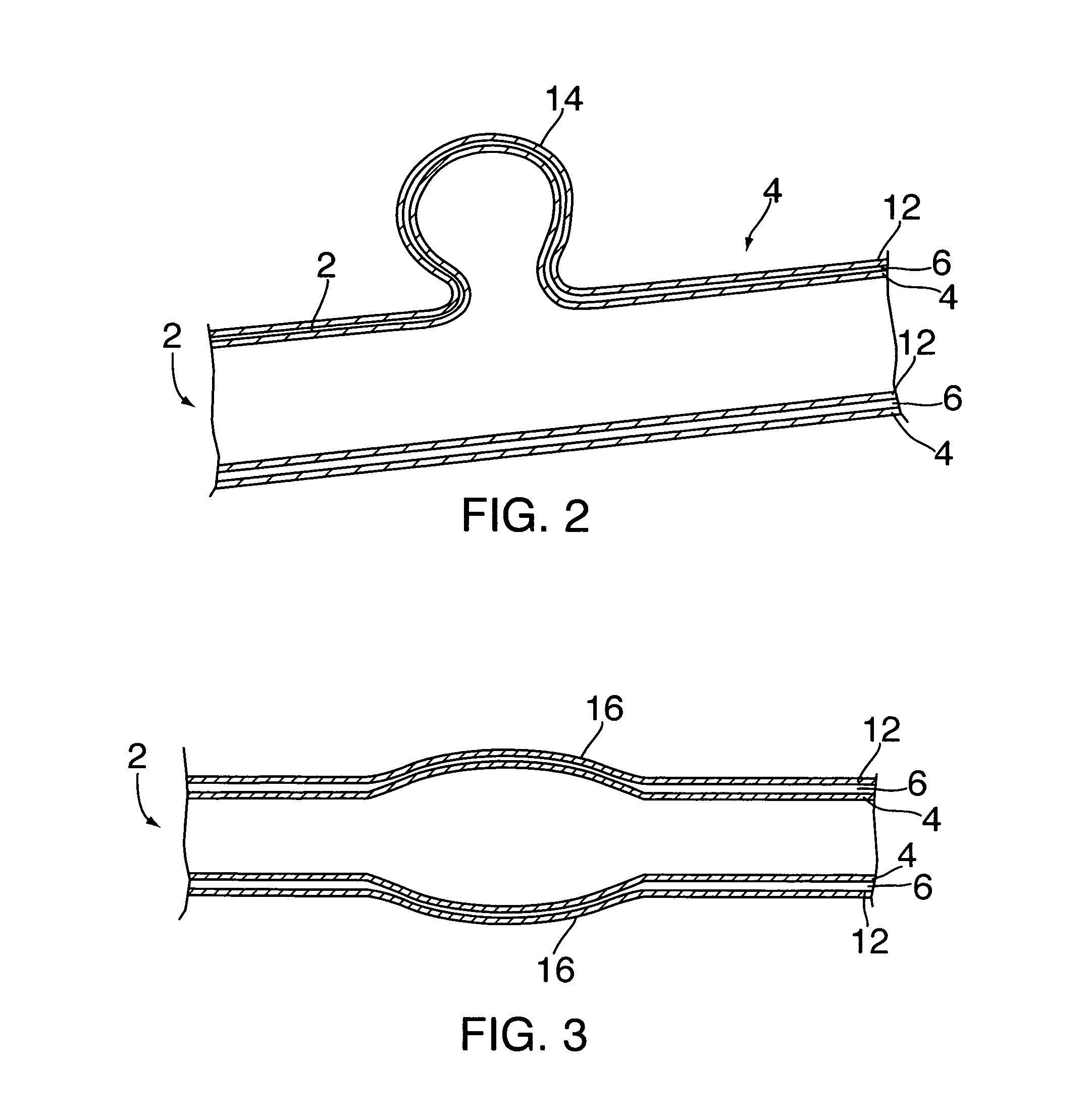
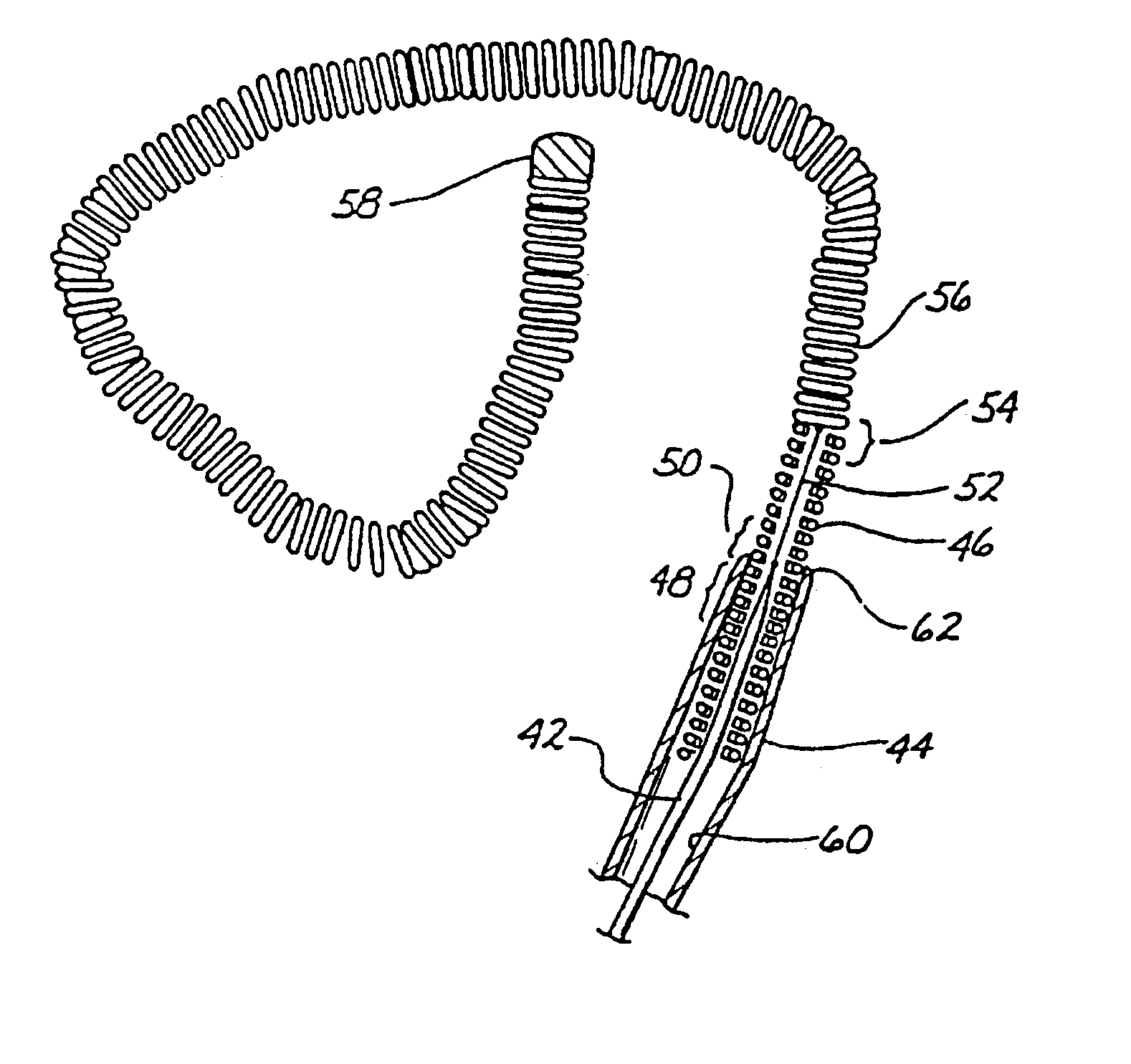
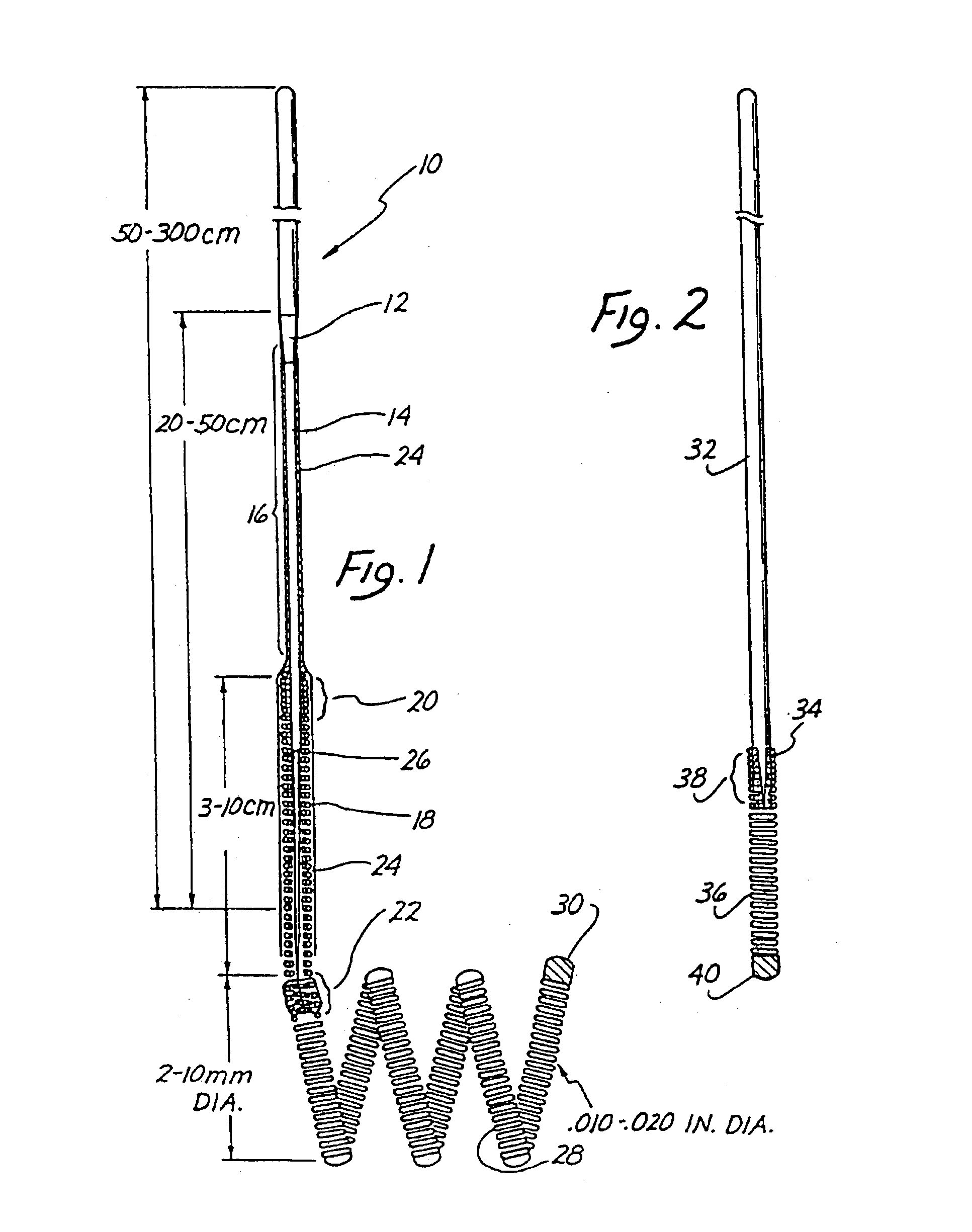
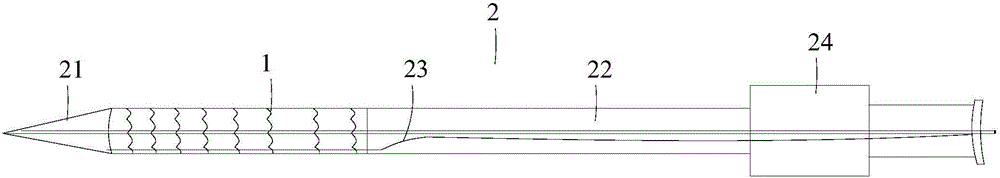
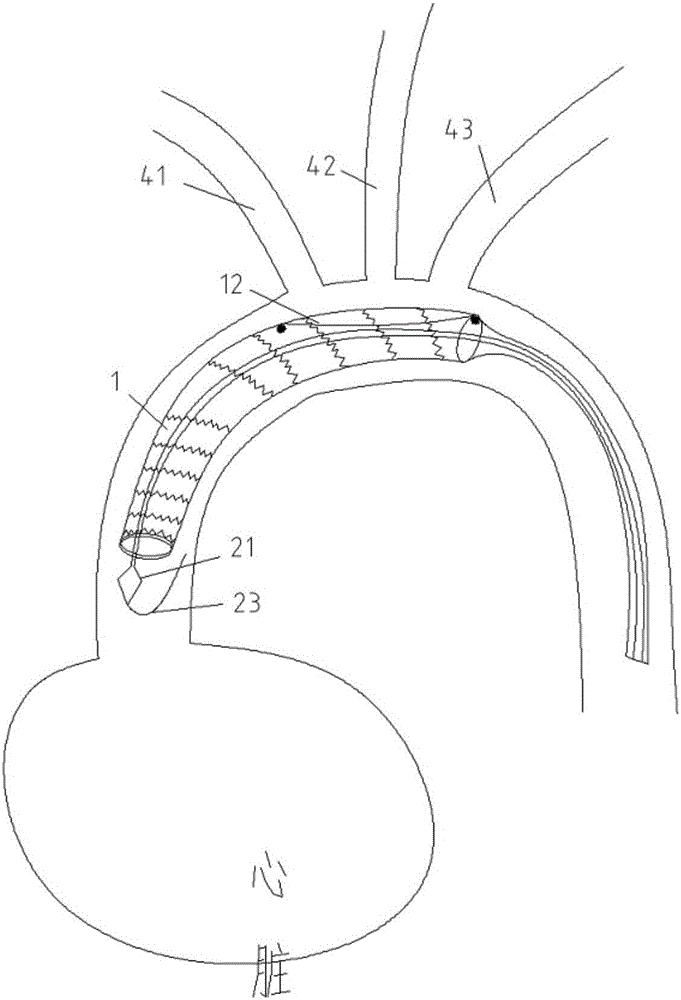
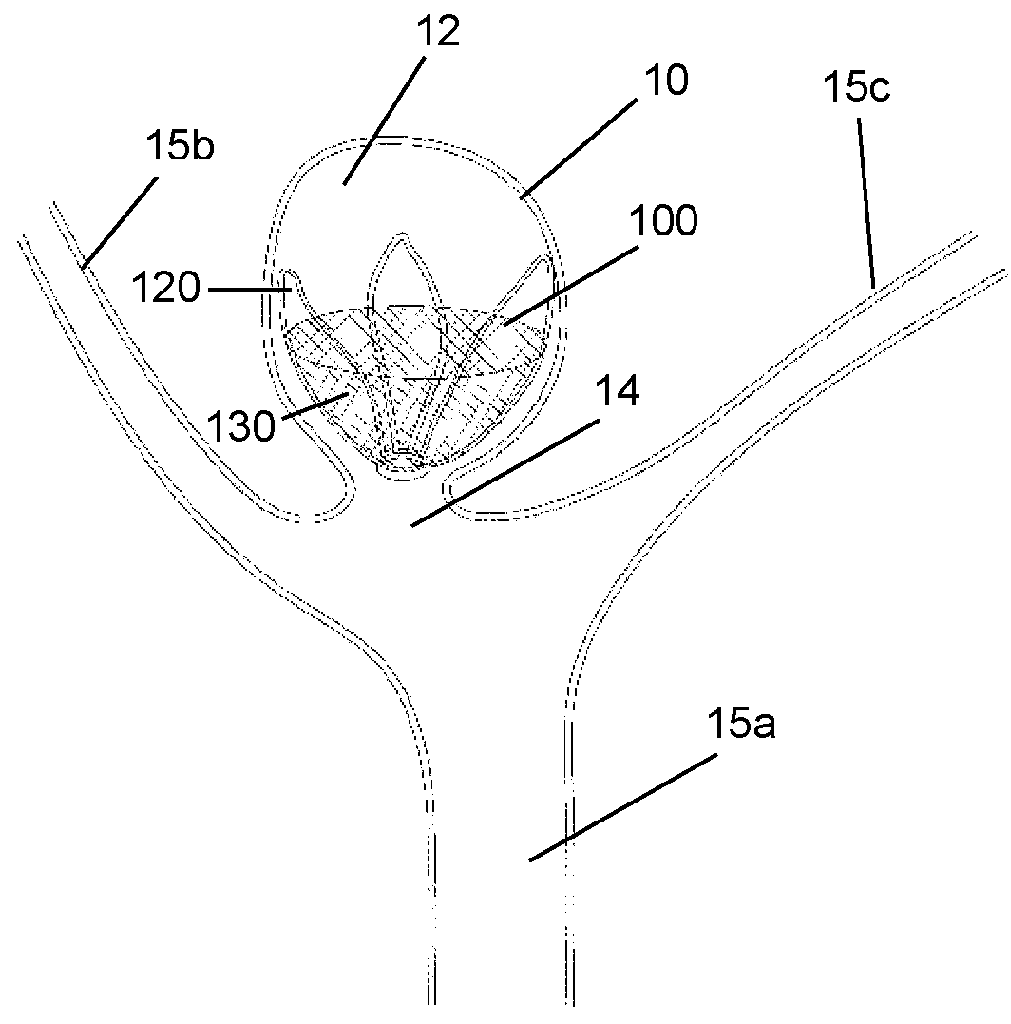
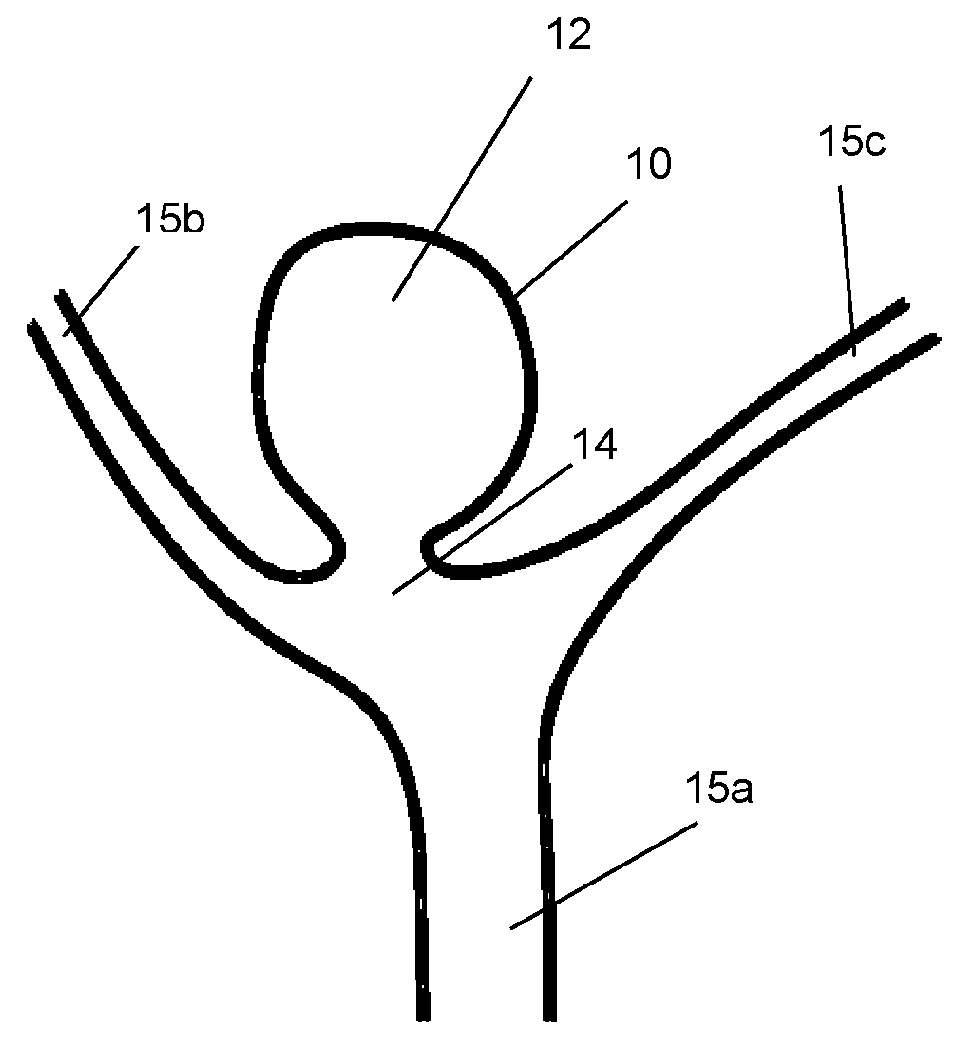
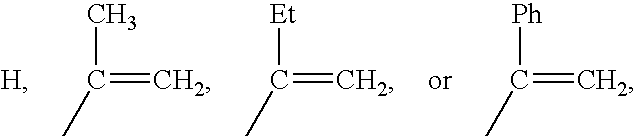Patents
Literature
192 results about "Artery aneurysm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
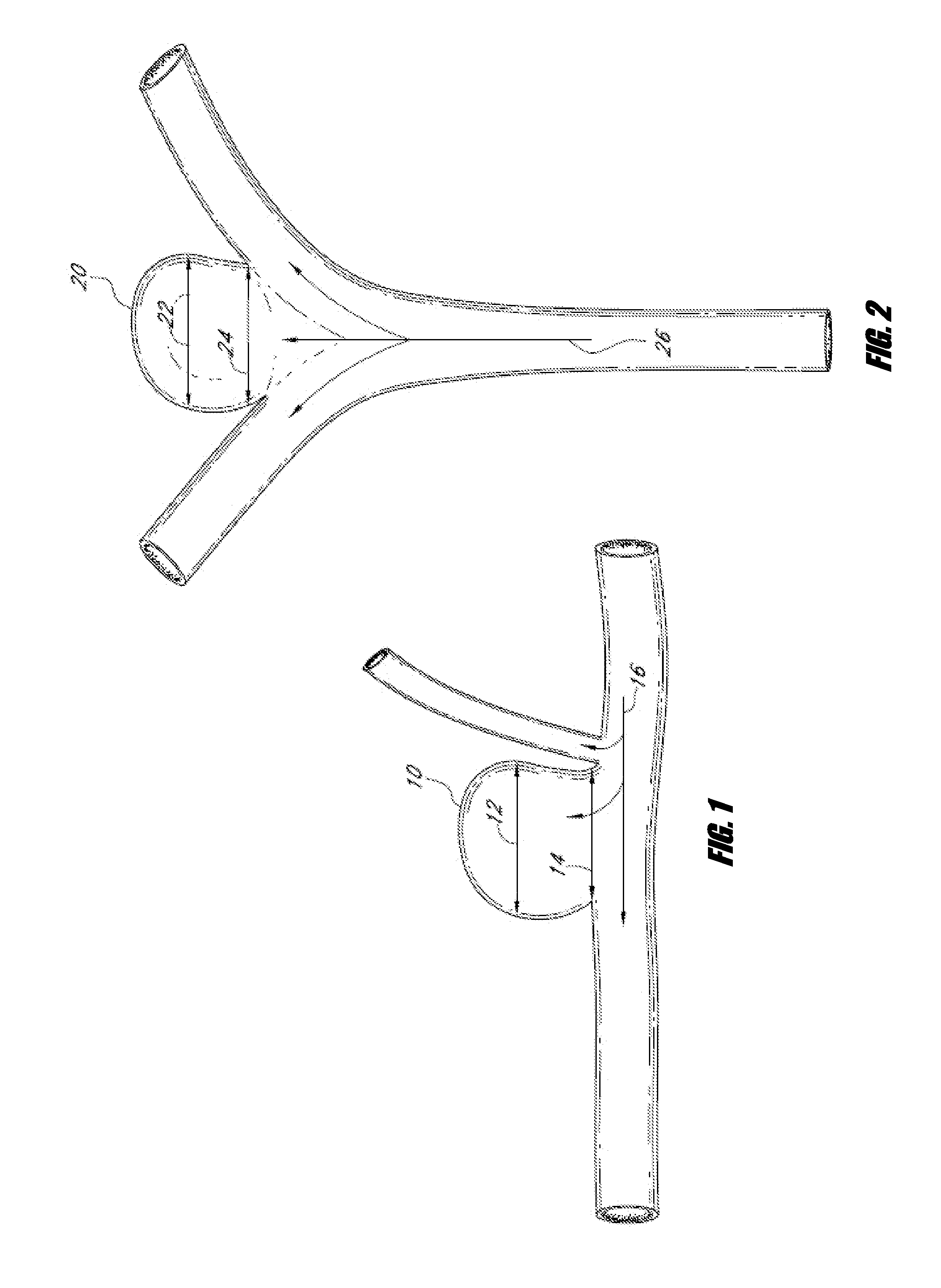
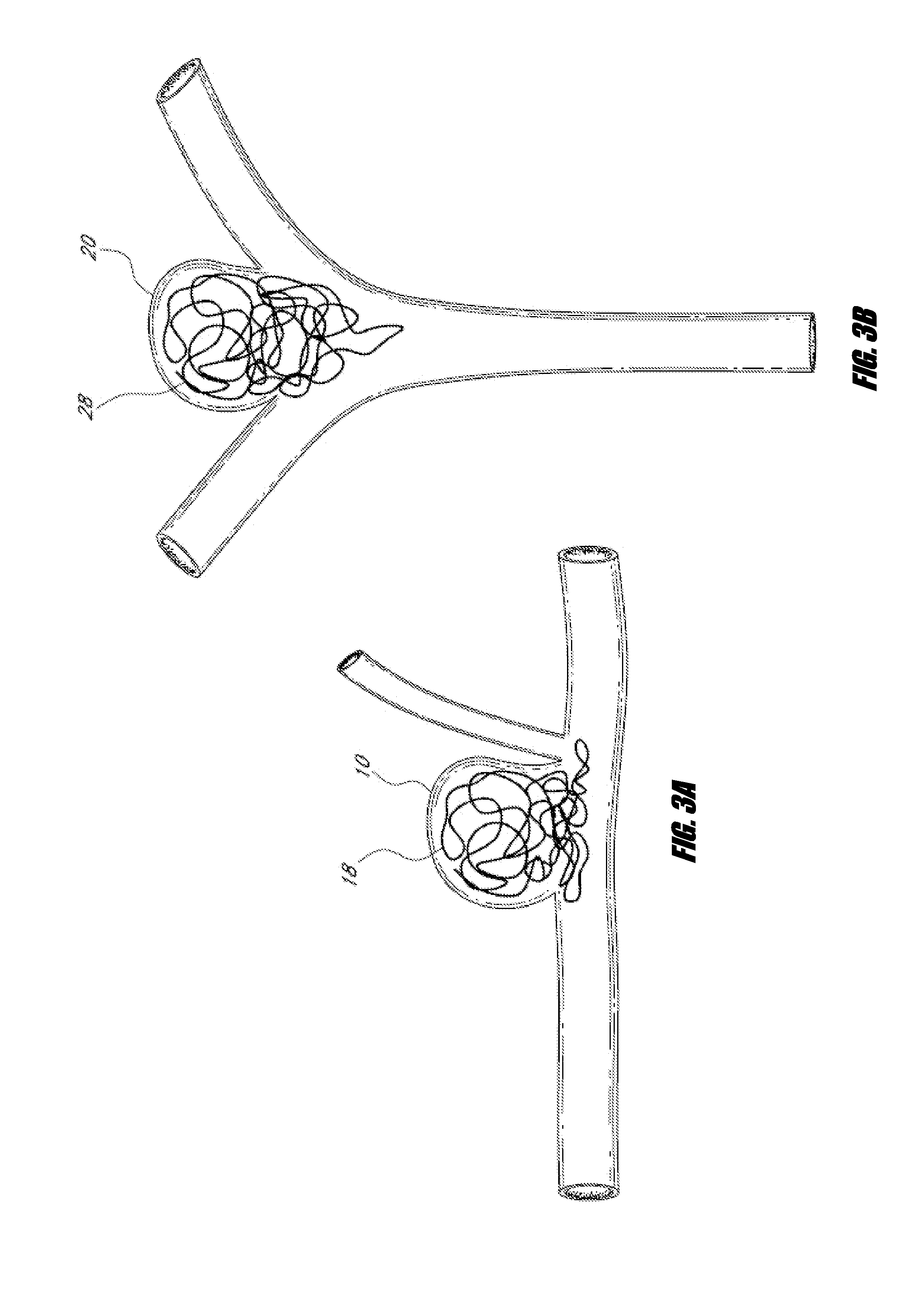
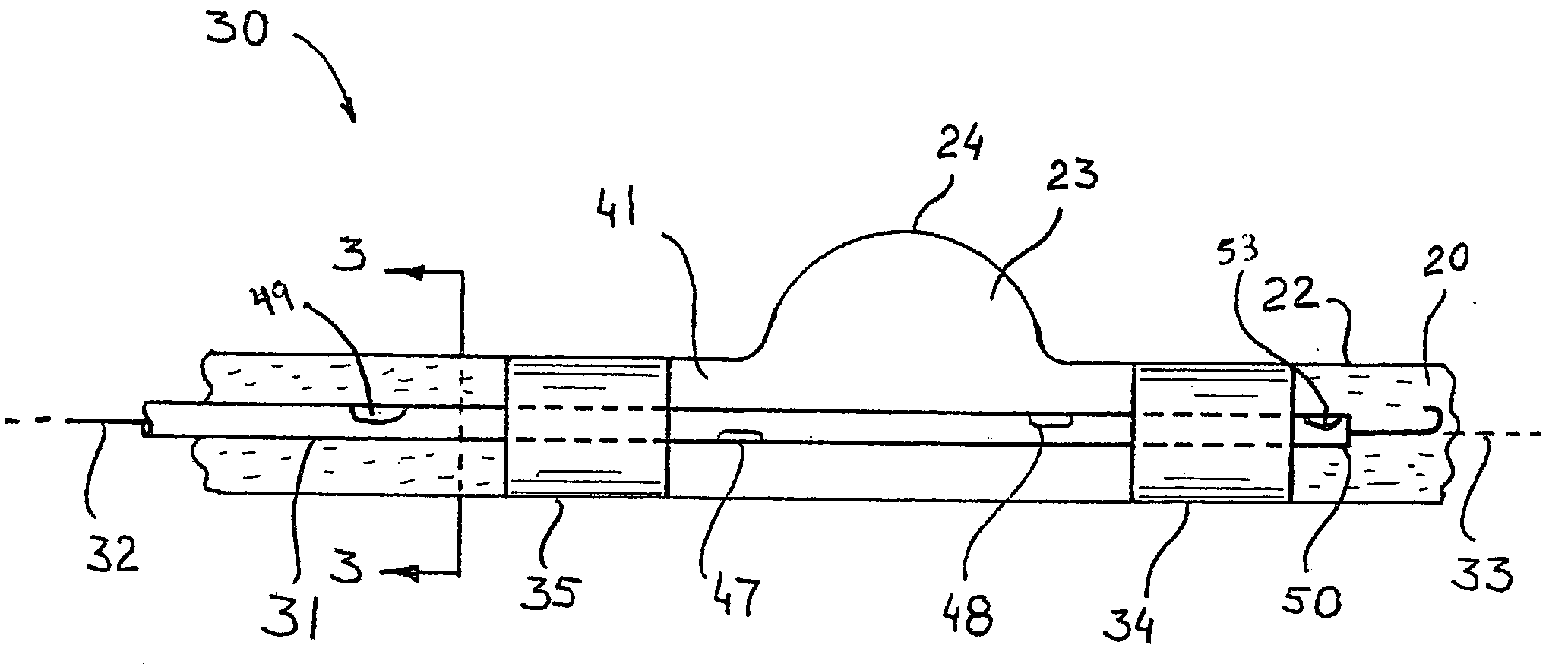
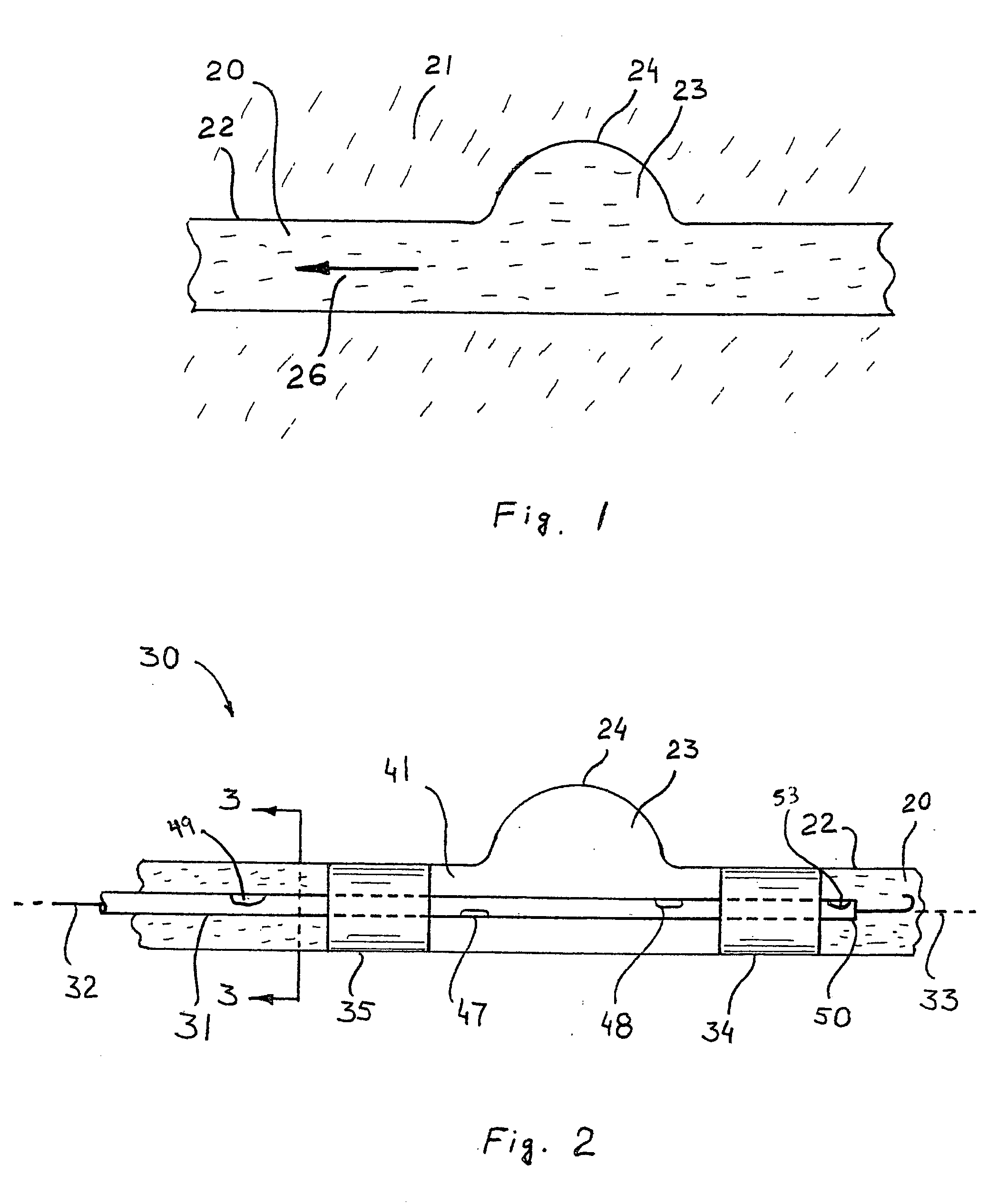
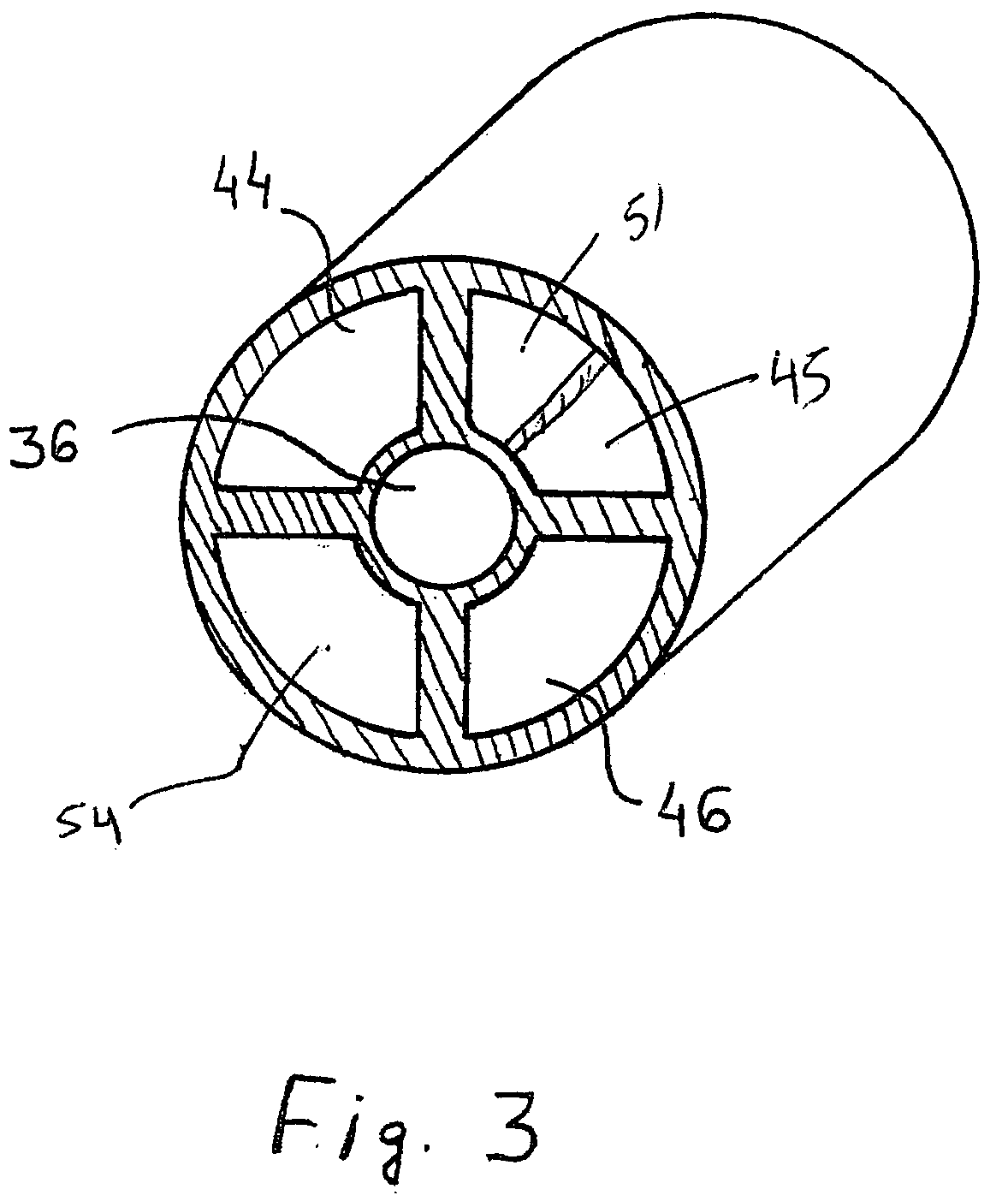
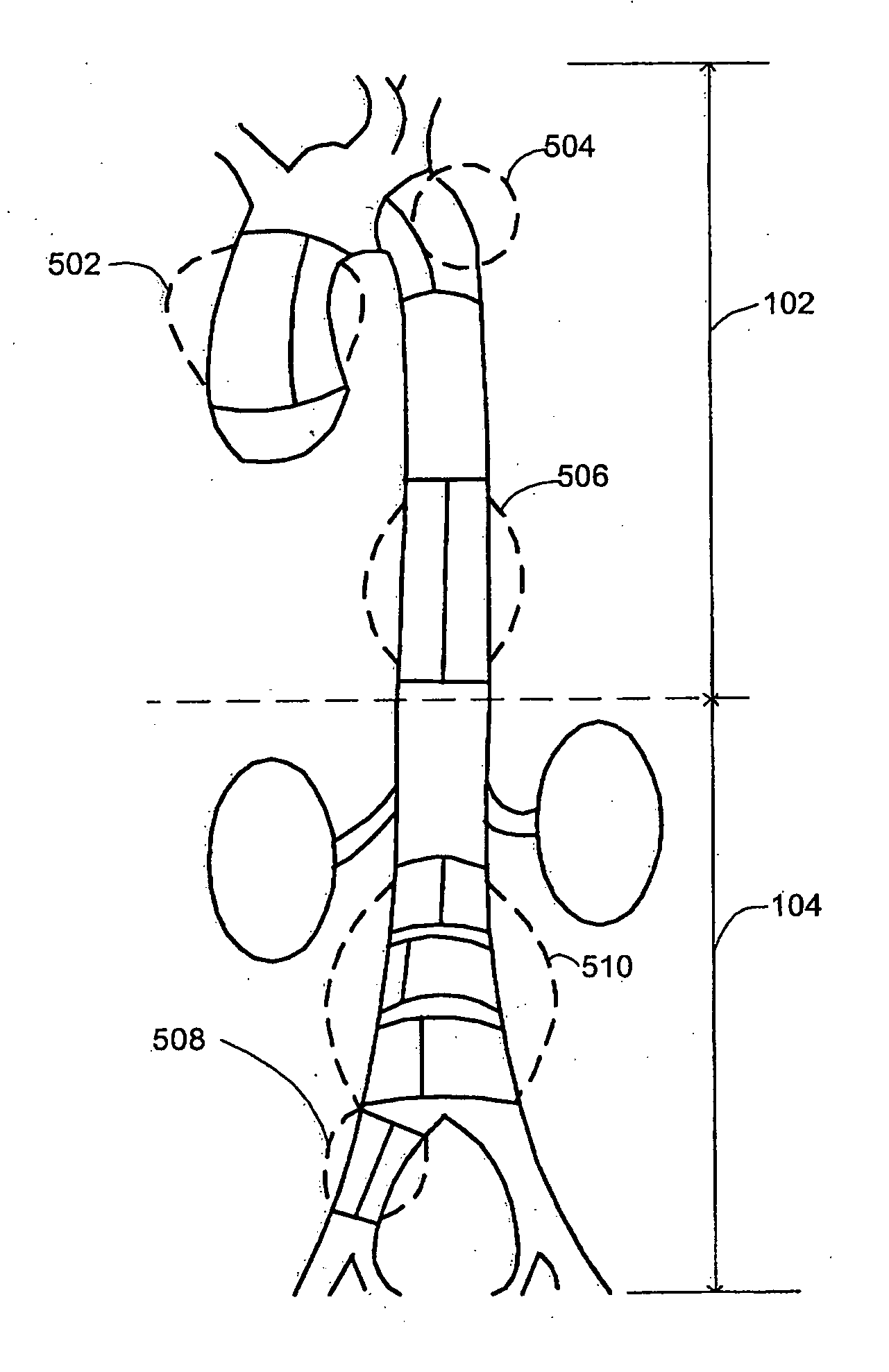
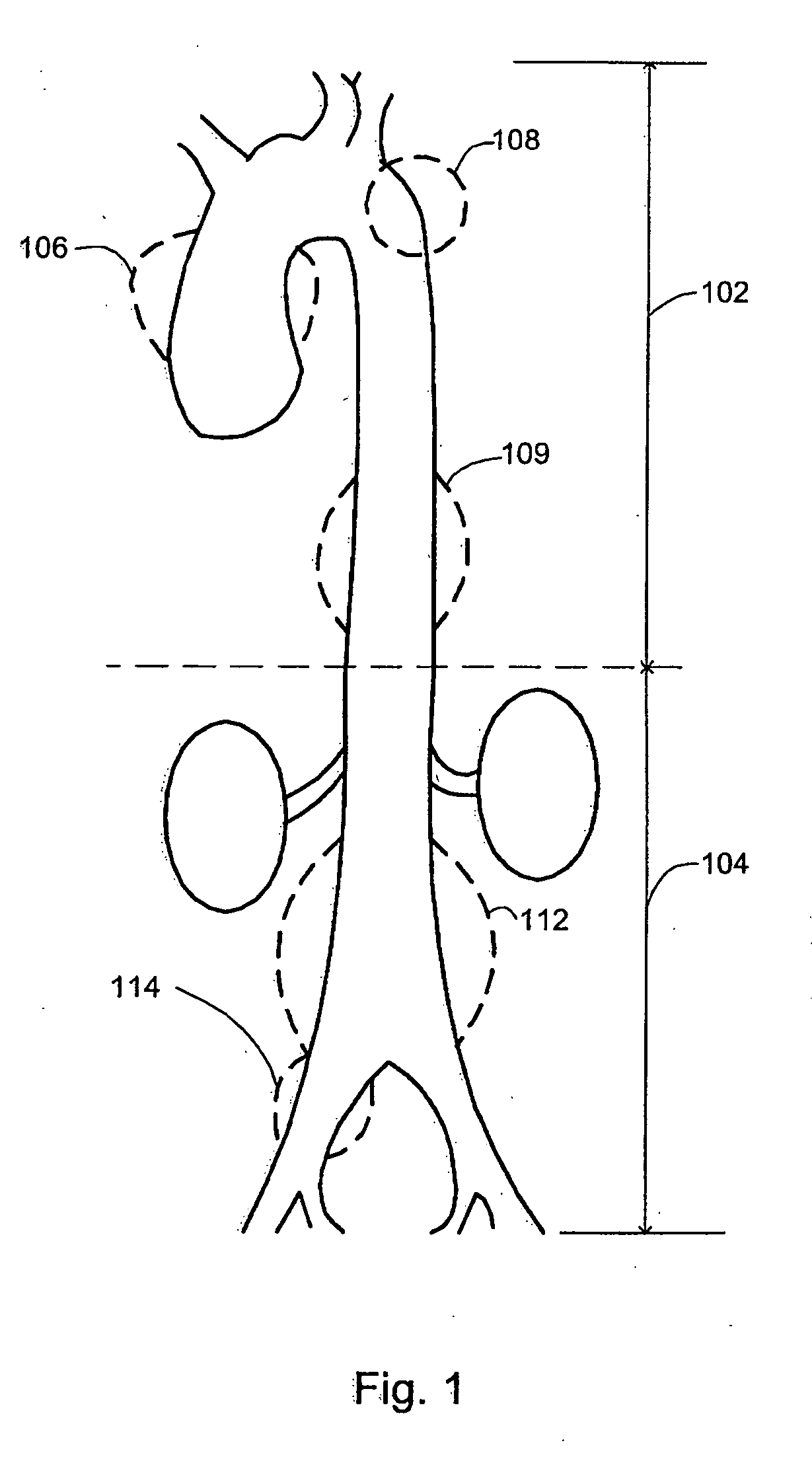
An aneurysm is a balloon-like bulge in an artery. Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood from your heart to your organs. Aortic aneurysms are aneurysms that occur in the aorta, the main artery carrying oxygen-rich blood to your body.
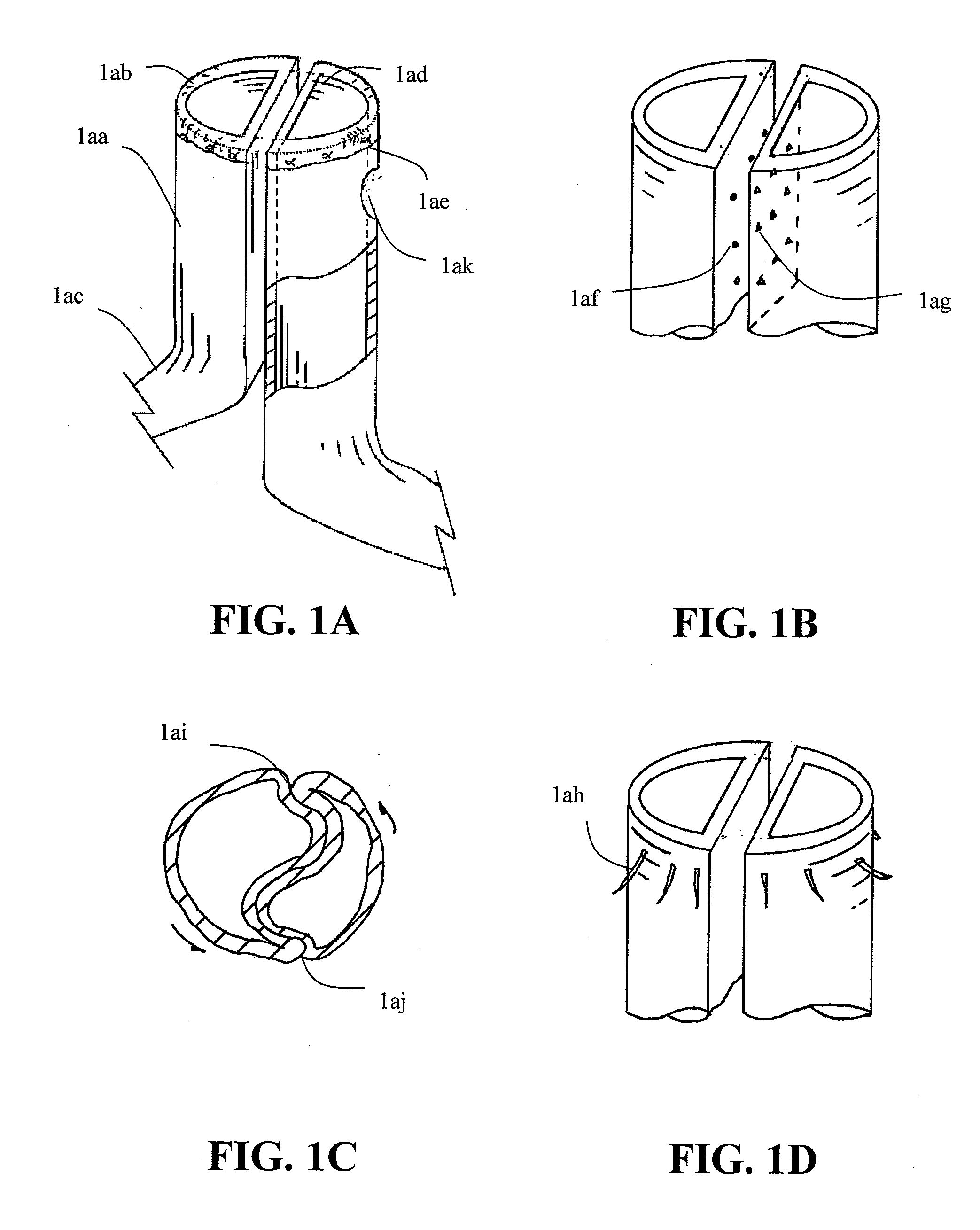
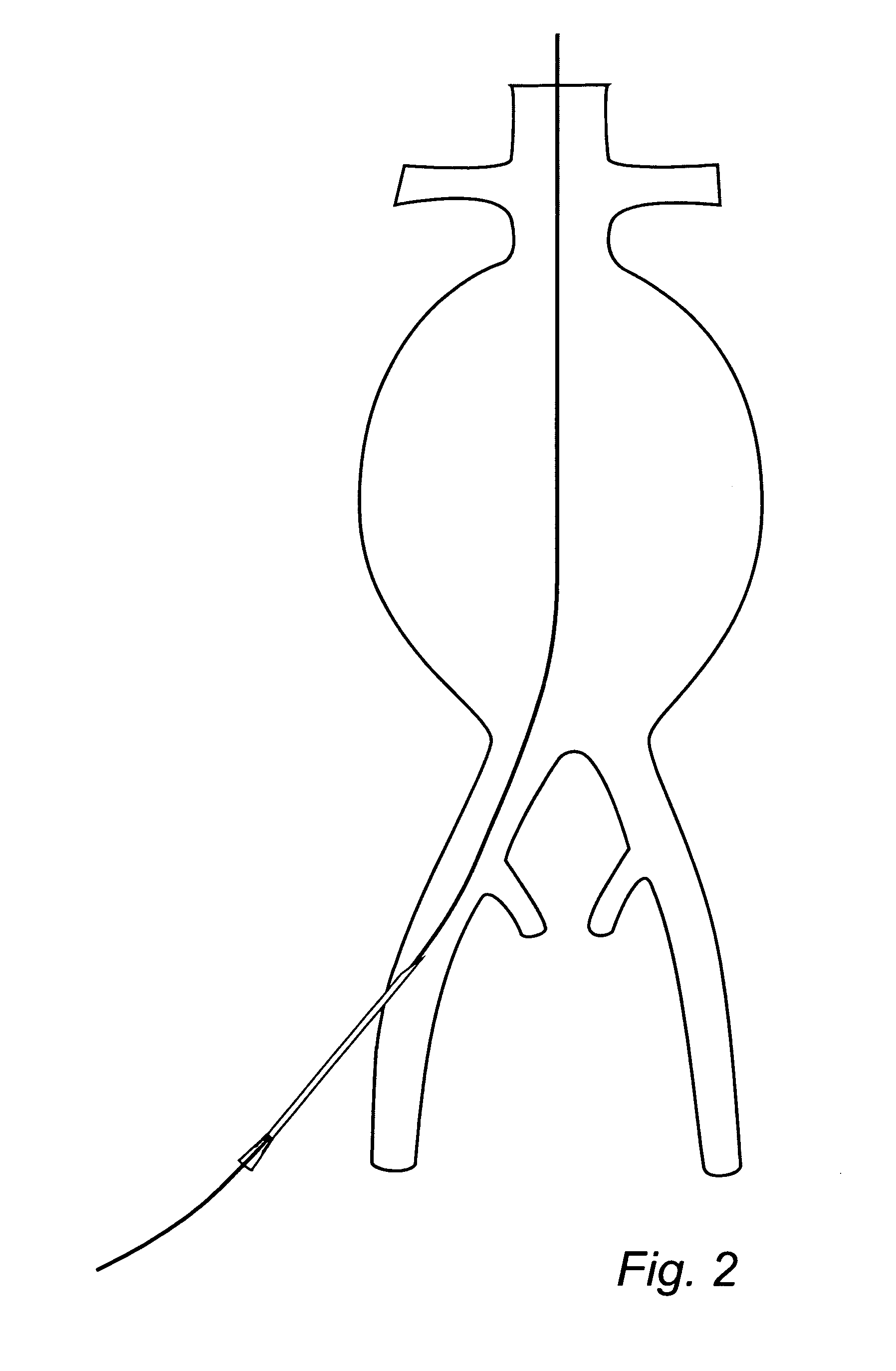
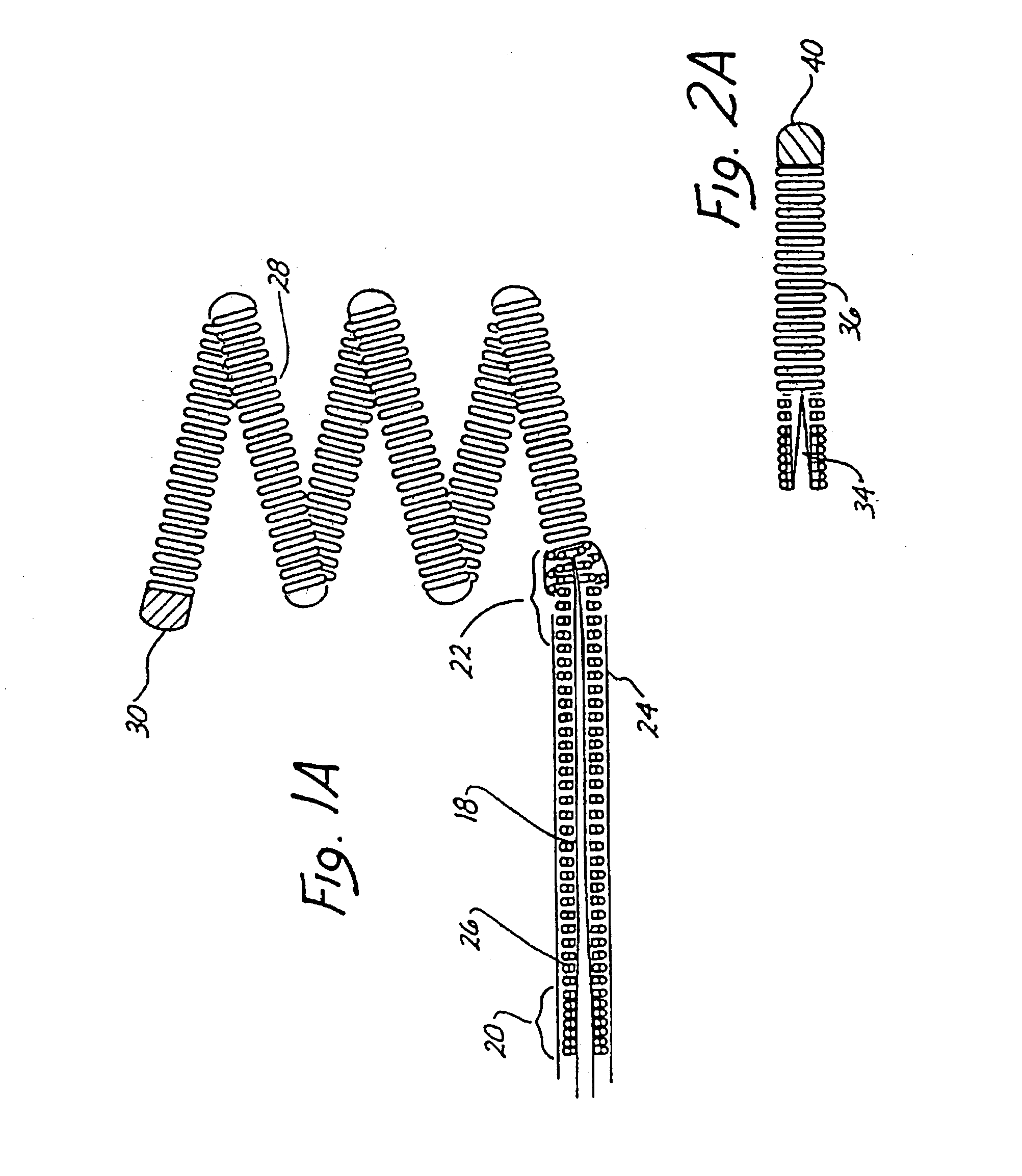
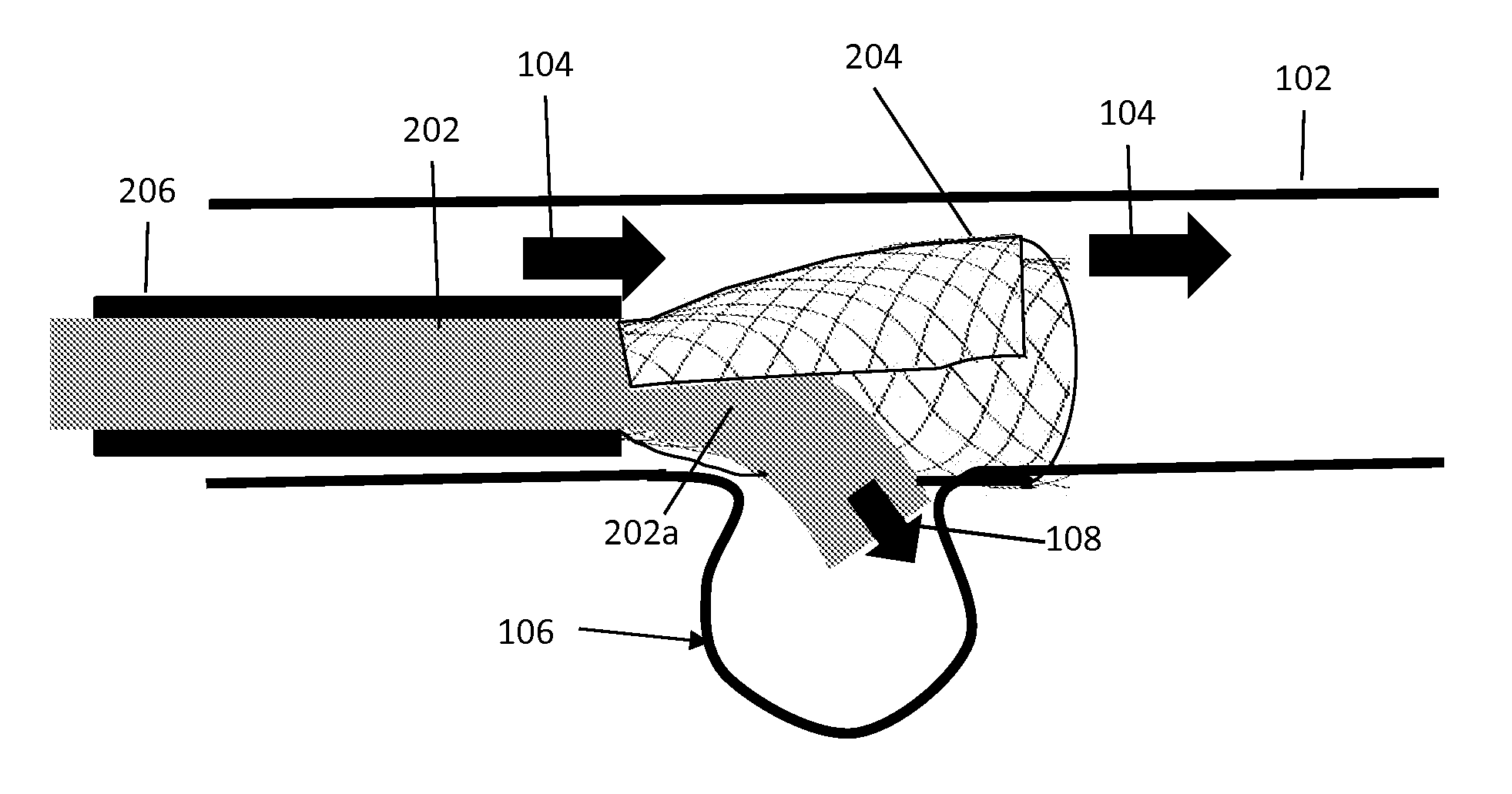
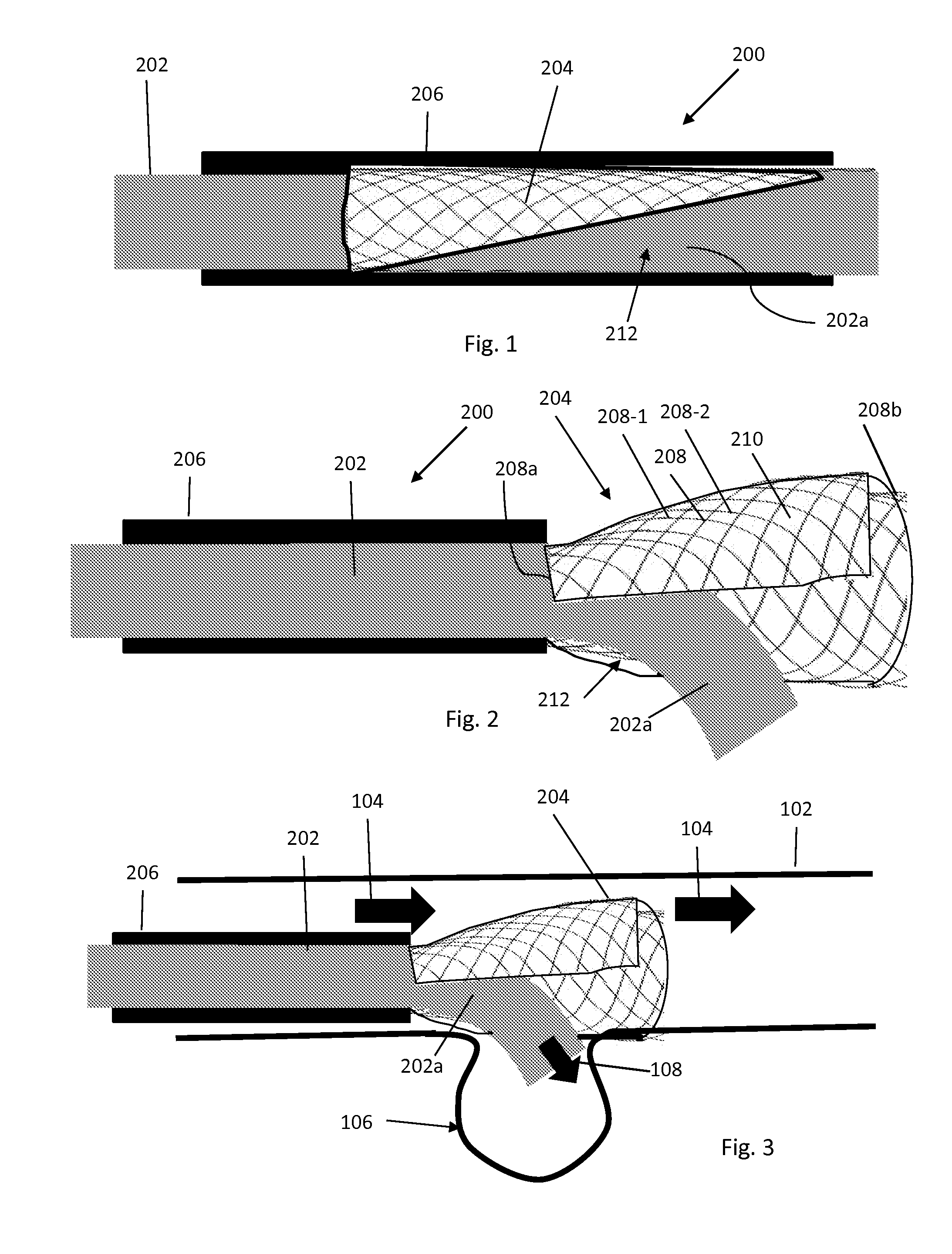
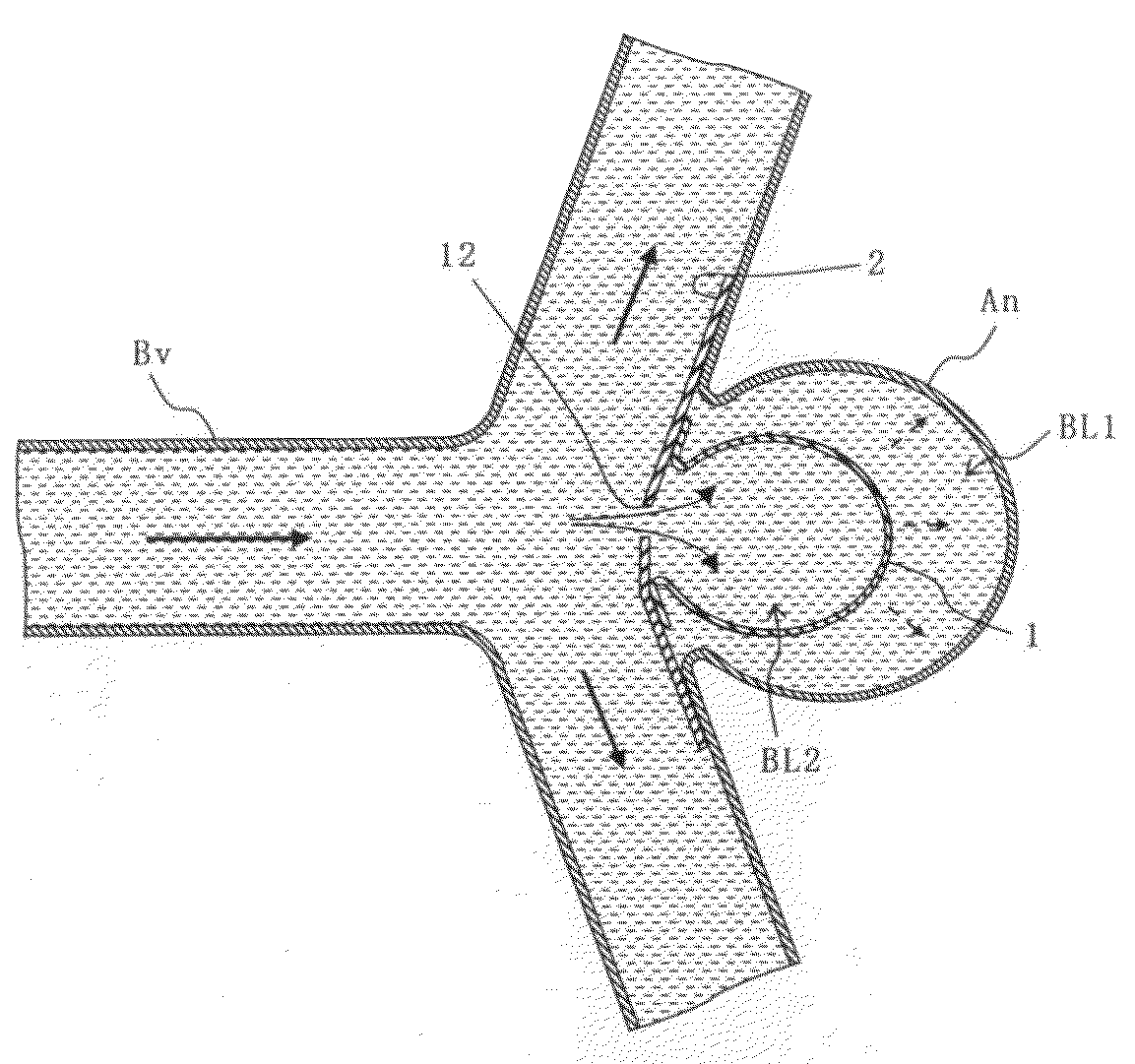
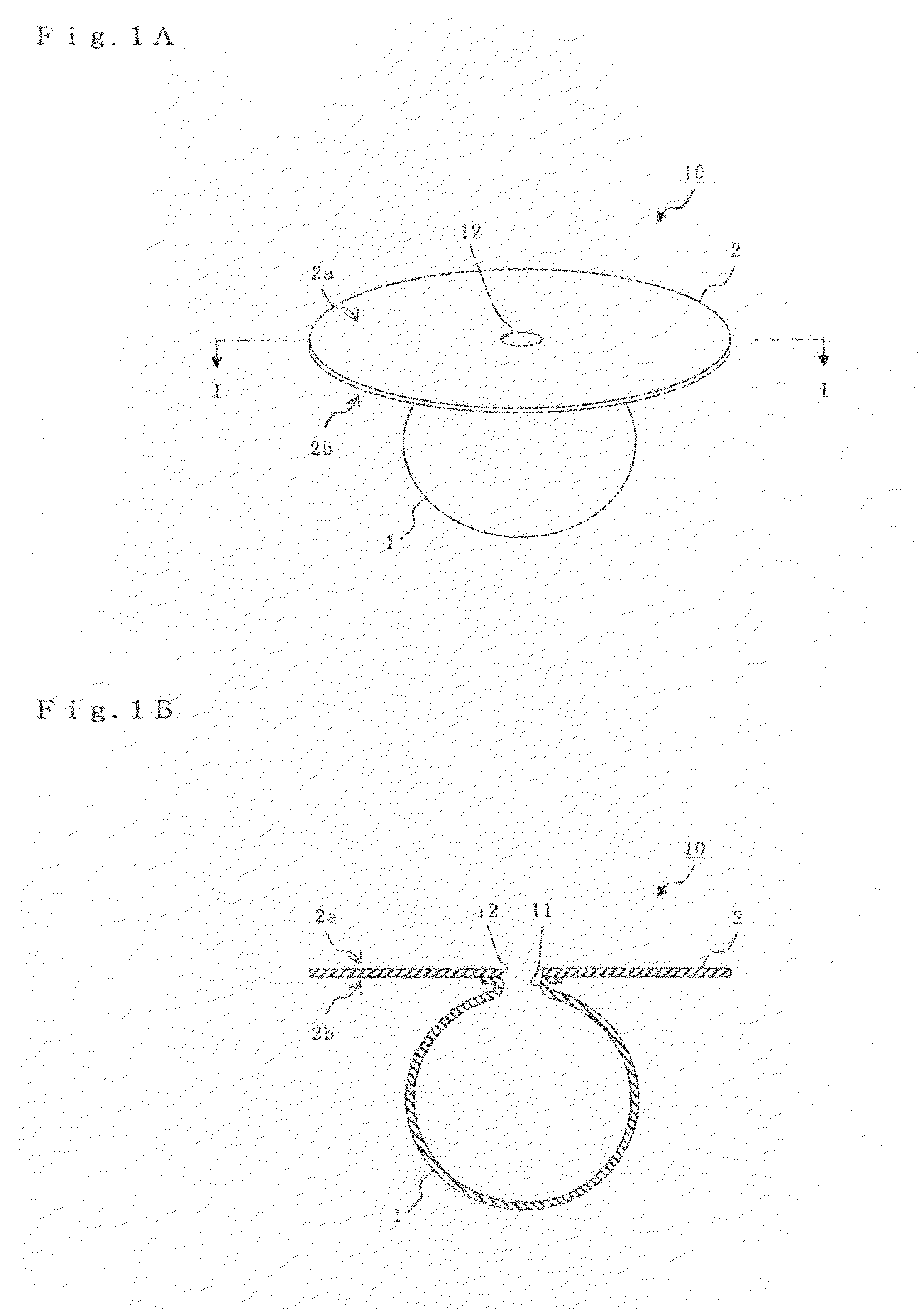
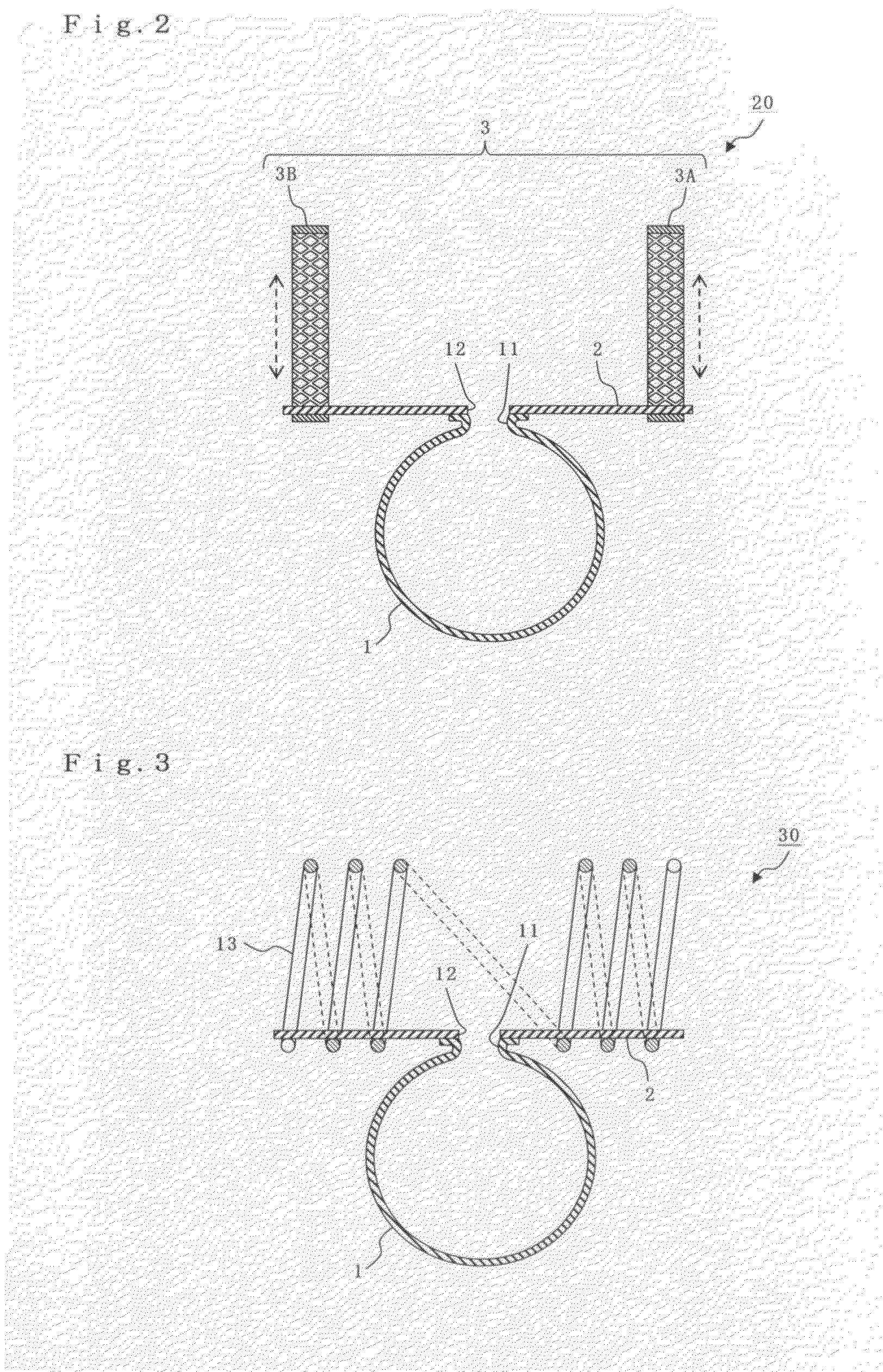
Means and method for the treatment of cerebral aneurysms
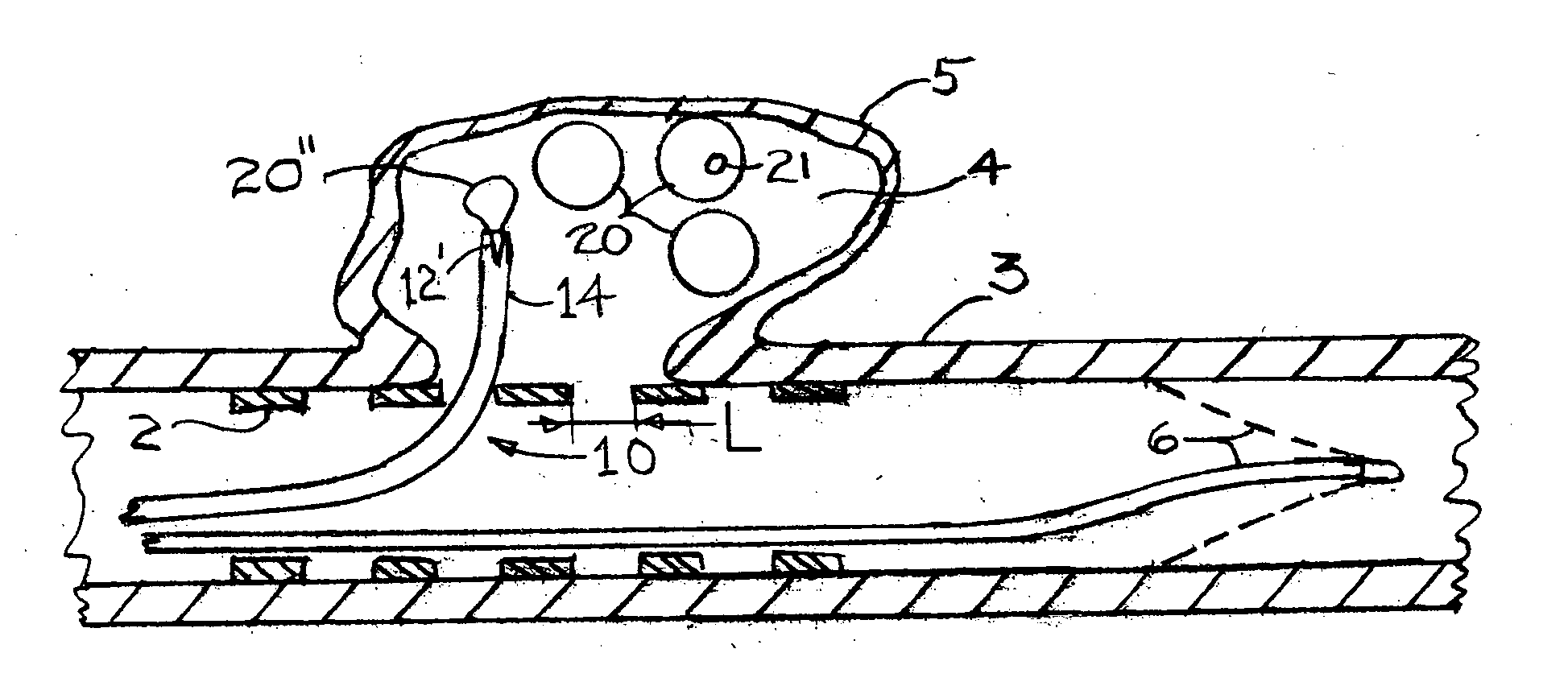
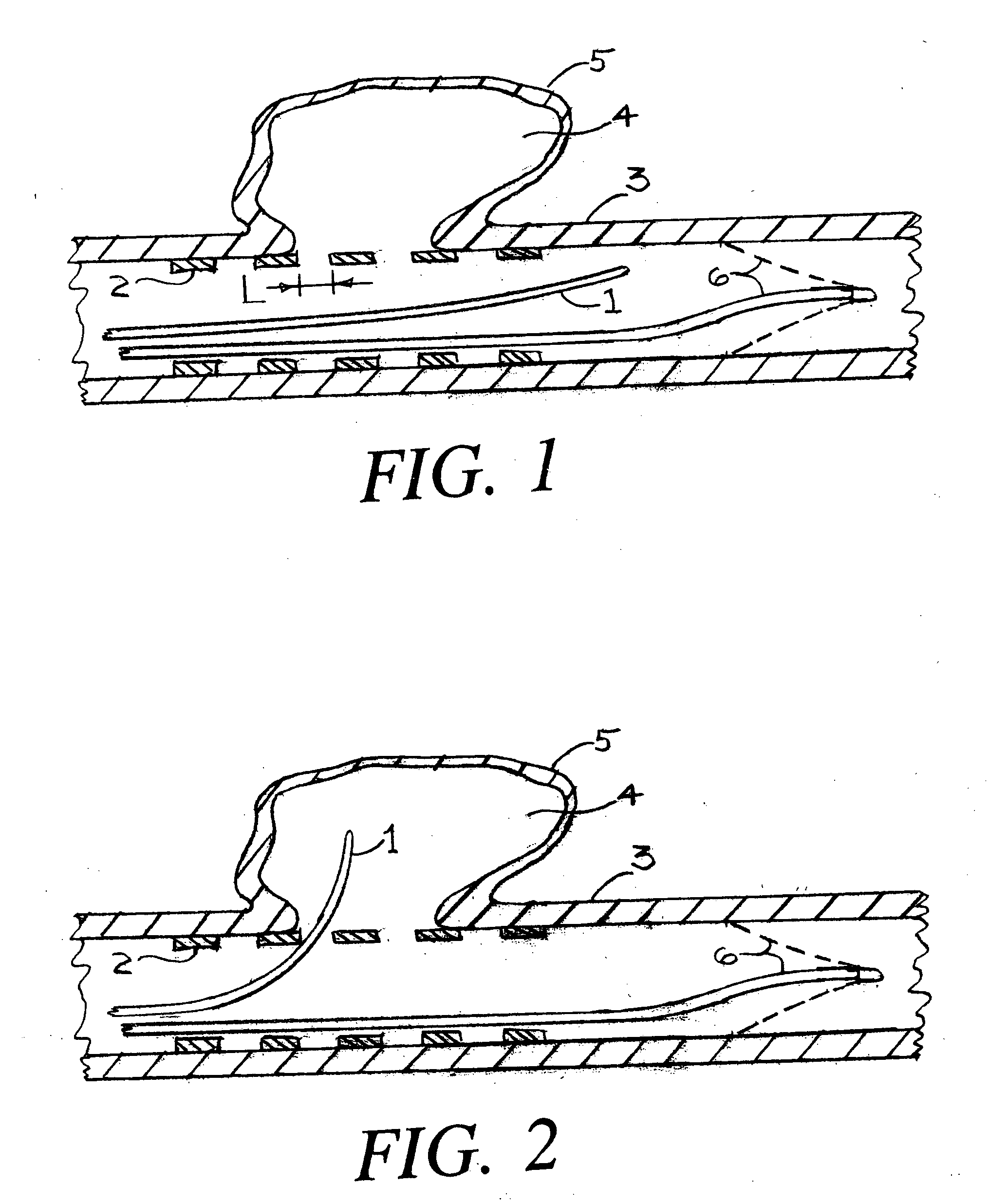
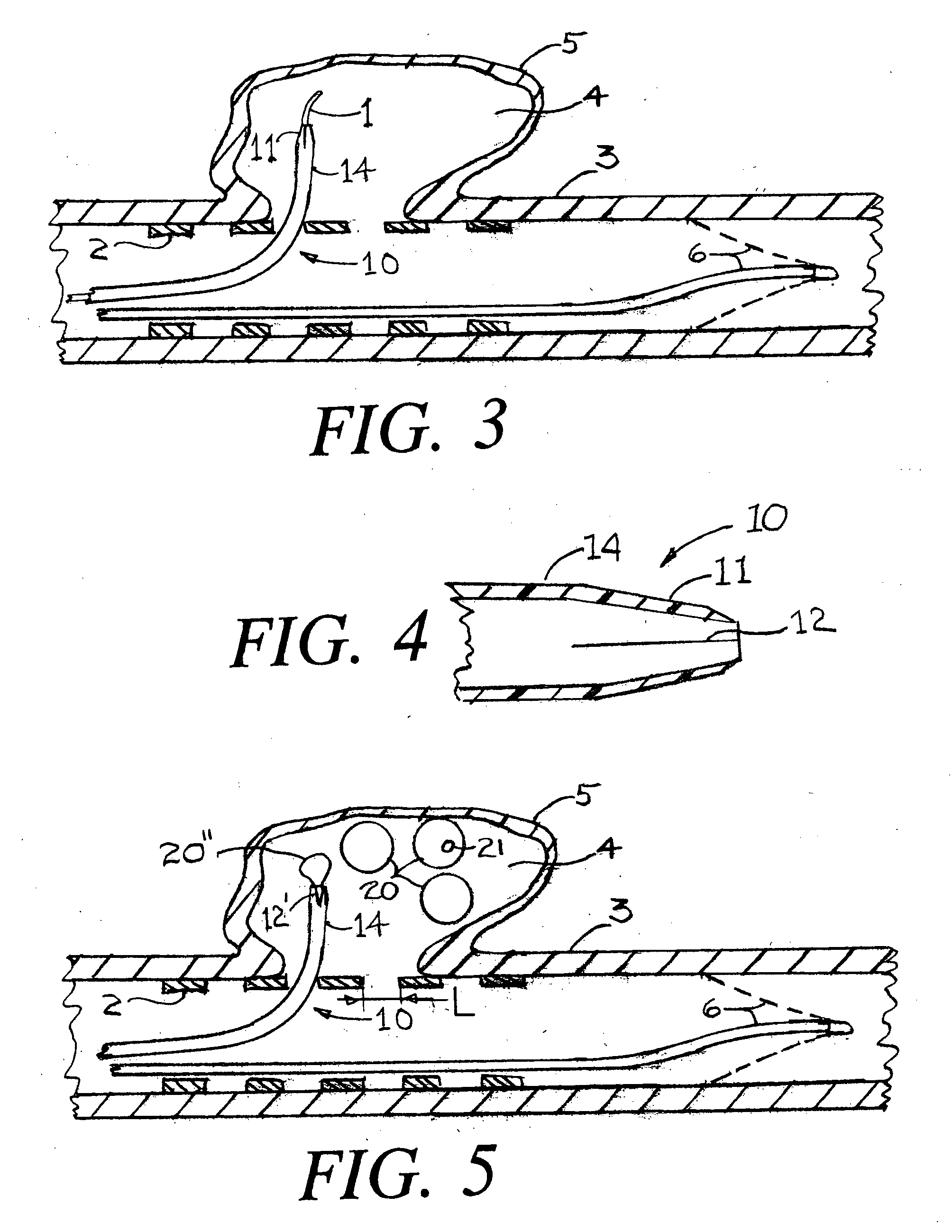
Disclosed is a system for the treatment of cerebral aneurysms using a stent and a aneurysm pocket fill structure delivery system. One embodiment of the present invention uses a highly radiopaque, drug eluting stent that is deployed with its sidewall over the ostium of the aneurysm pocket. A fill structure delivery catheter is then advanced through the patient's vascular system until the catheter's distal end is situated within the aneurysm pocket. Compressed aneurysm pocket filling structures are then pushed through the fill structure delivery catheter. As the aneurysm pocket filling structures emerge from an opening in the catheter's distal end, they promptly expand so that their minimum dimension is sufficiently large so that they cannot pass through the spaces between the struts of the stent that cover the ostium of the aneurysm pocket.
Owner:FISCHELL ROBERT E +1
Methacrylate copolymers for medical devices
A polymer of hydrophobic monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains the polymer and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer or polymer blend and optionally a biobeneficial material and / or a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Vascular occlusion devices and methods
A device for in situ treatment of vascular or cerebral aneurysms comprises an occlusion device having a flexible, longitudinally extending elastomeric matrix member that assumes a non-linear shape to conformally fill a targeted site. The occlusion device comprises a flexible, longitudinally extending elastomeric matrix member, wherein the device assumes a non-linear shape capable of fully, substantially, or partially conformally filling a targeted vascular site. In one embodiment the vascular occlusion device comprises a first longitudinally extending structural element having a longitudinally extending lumen and an outer surface; a second longitudinally extending structural element extending through the lumen; and an elastomeric matrix member surrounding the outer surface, wherein the second structural member does not engage or attach to the first structural element or the elastomeric matrix.
Owner:BIOMERIX CORP
Devices and methods for treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms
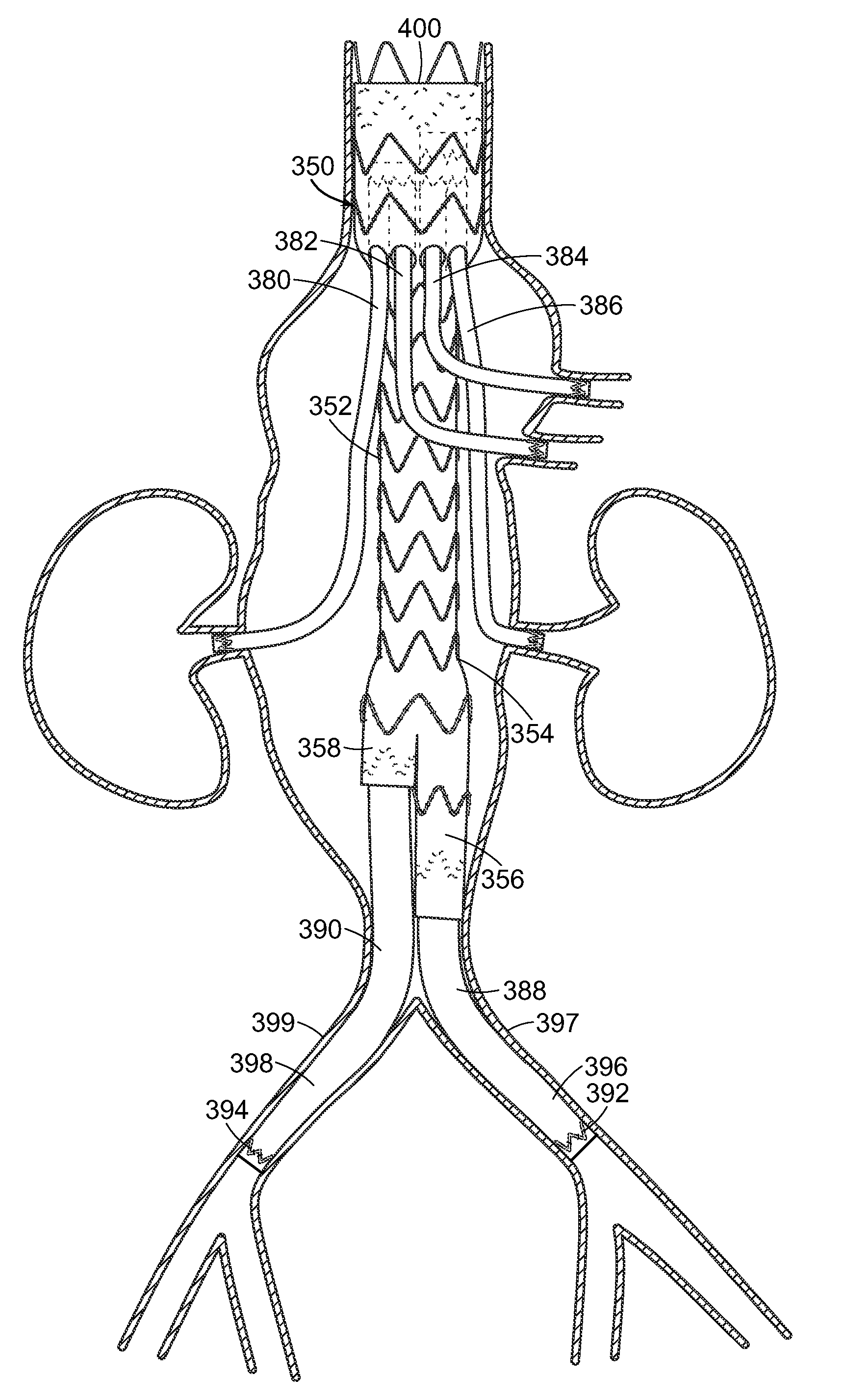
InactiveUS20090287145A1Minimize the possibilityReduce the overall diameterStentsSurgeryIliac arteryArtery aneurysm
Methods and devices with two individual tubes for treating abdominal aortic aneurysm that bypass the aneurysm and are placed from the upper aorta to the iliac arteries. A separate upper cuff may also be provided, to secure the tubes above the aneurysm.
Owner:ALTURA MEDICAL
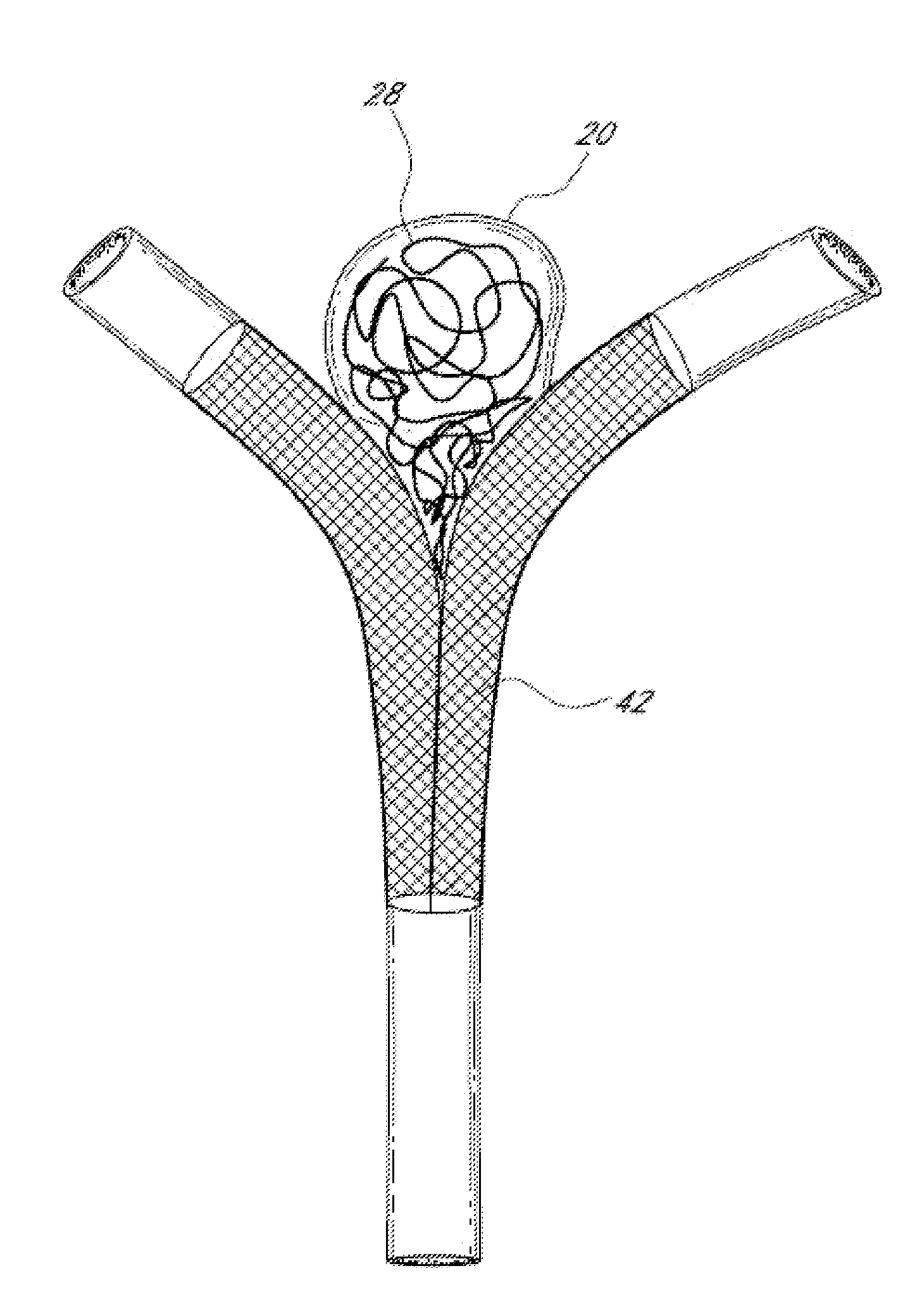
Device and method for treating ruptured aneurysms
InactiveUS20100324649A1Reduce the overall diameterNarrow diameterStentsBlood vesselsEndoscopic surgeryEndoscopic Procedure
A stent device for treating an aneurysm is disclosed. The stent device comprises an expandable balloon with a channel extending through said balloon from one side to another, and a supporting stent connected to said balloon. In an operative disposition, when the expandable balloon is expanded, the supporting stent is arranged at least partly within said channel of said expandable balloon. Further, the supporting stent has walls which are permeable to blood. The stent device may be introduced and removed by endoscopic procedures, with a relatively simple procedure. Thus, the stent device is highly useable for fast and temporary treatment of ruptured aneurysms.
Owner:GRAFTCRAFT I GOTEBORG
Vascular remodeling device
ActiveUS20120143237A1Good flexibilityGood wall appositionStentsDilatorsIliac AneurysmEmbolization material
Described herein are vascular remodeling devices that include a proximal section, an intermediate section, and a distal section. During deployment, the proximal section can expand from a compressed delivery state to an expanded state and anchors the device in an afferent vessel of a bifurcation. The distal section expands from the compressed delivery state to an expanded state that may be substantially planar, approximately semi-spherical, umbrella shaped, or reverse umbrella shaped. The distal section is positioned in a bifurcation junction across the neck of an aneurysm or within an aneurysm. The intermediate section allows perfusion to efferent vessels. Before or after the device is in position, embolic material may be used to treat the aneurysm. The distal section can act as a scaffolding to prevent herniation of the embolic material. The device can be used for clot retrieval with integral distal embolic protection.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Intravascular deliverable stent for reinforcement of abdominal aortic aneurysm
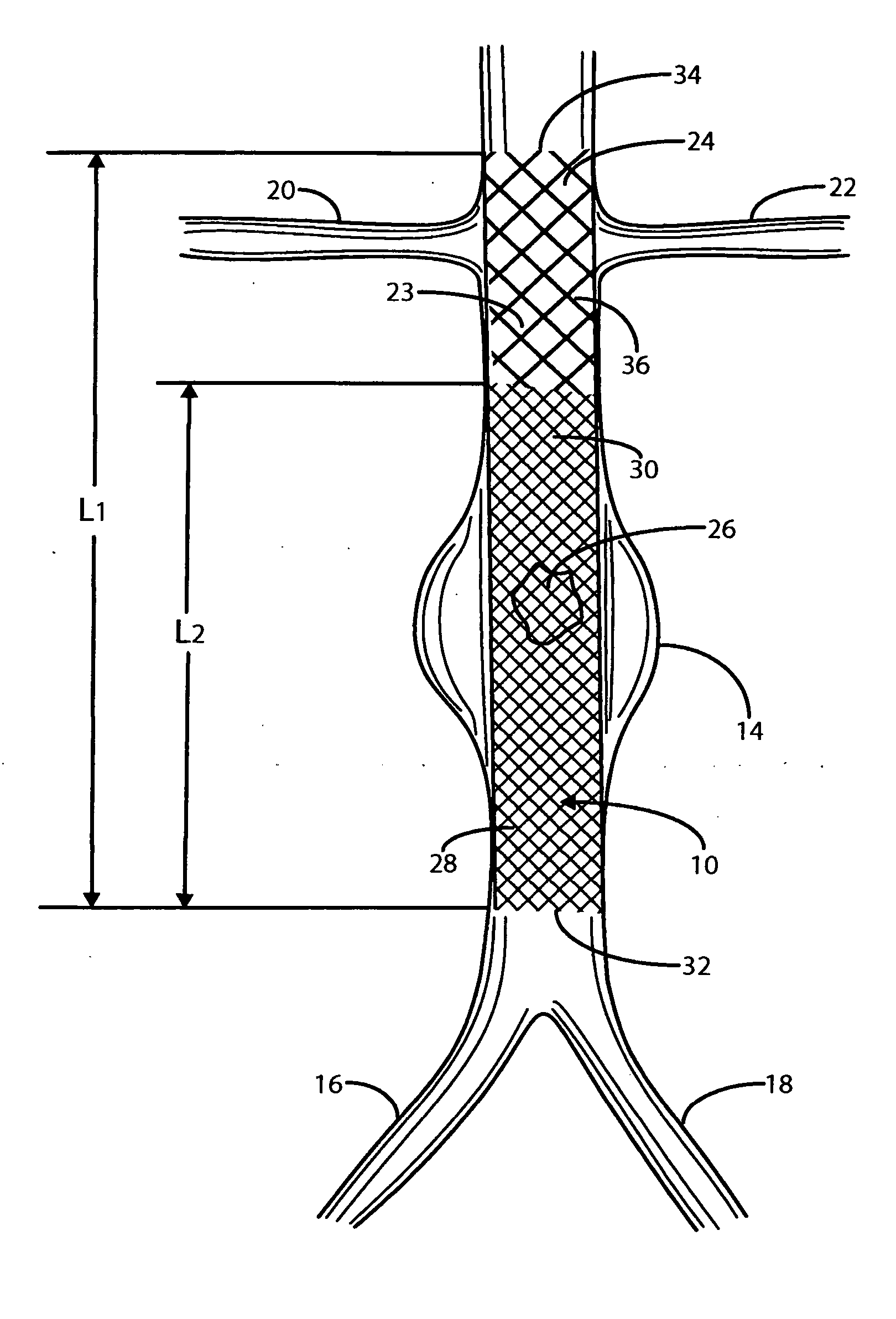
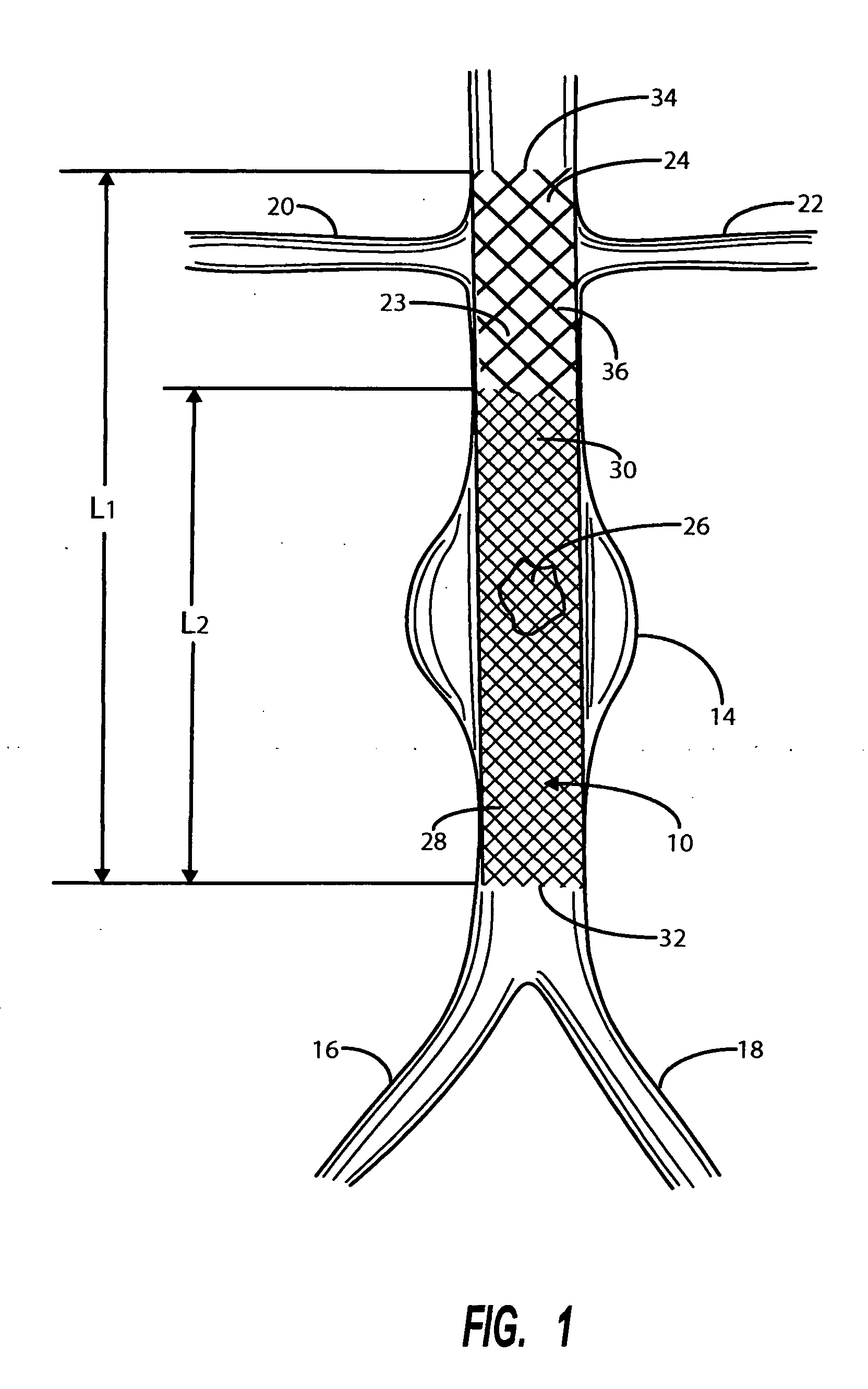
A stent / graft especially designed to be used in a minimally invasive surgical procedure for treating an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) comprises an innermost tubular structure of a length (L1) formed by braiding a relatively few strands of shape memory alloy wire. The pick and pitch of the braid are such as to provide relative large fenestrations in the tubular wall. A portion of the innermost tubular structure of a length L2<L1 is surrounded by a further braided tubular structure having relatively many strands that occlude the fenestrations of the innermost tubular structure. The composite structure can be stretched to reduce the outer diameter of the stent / graft, allowing it to be drawn into a lumen of a delivery catheter. The catheter can then be advanced through the vascular system to the site of the AAA and then ejected, allowing it to self-expand with the portion L2 bridging the aneurysm. The portion L1>L2 does not block blood flow to the renal arteries while the portion L2 prevents the aneurysm to grown and burst.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
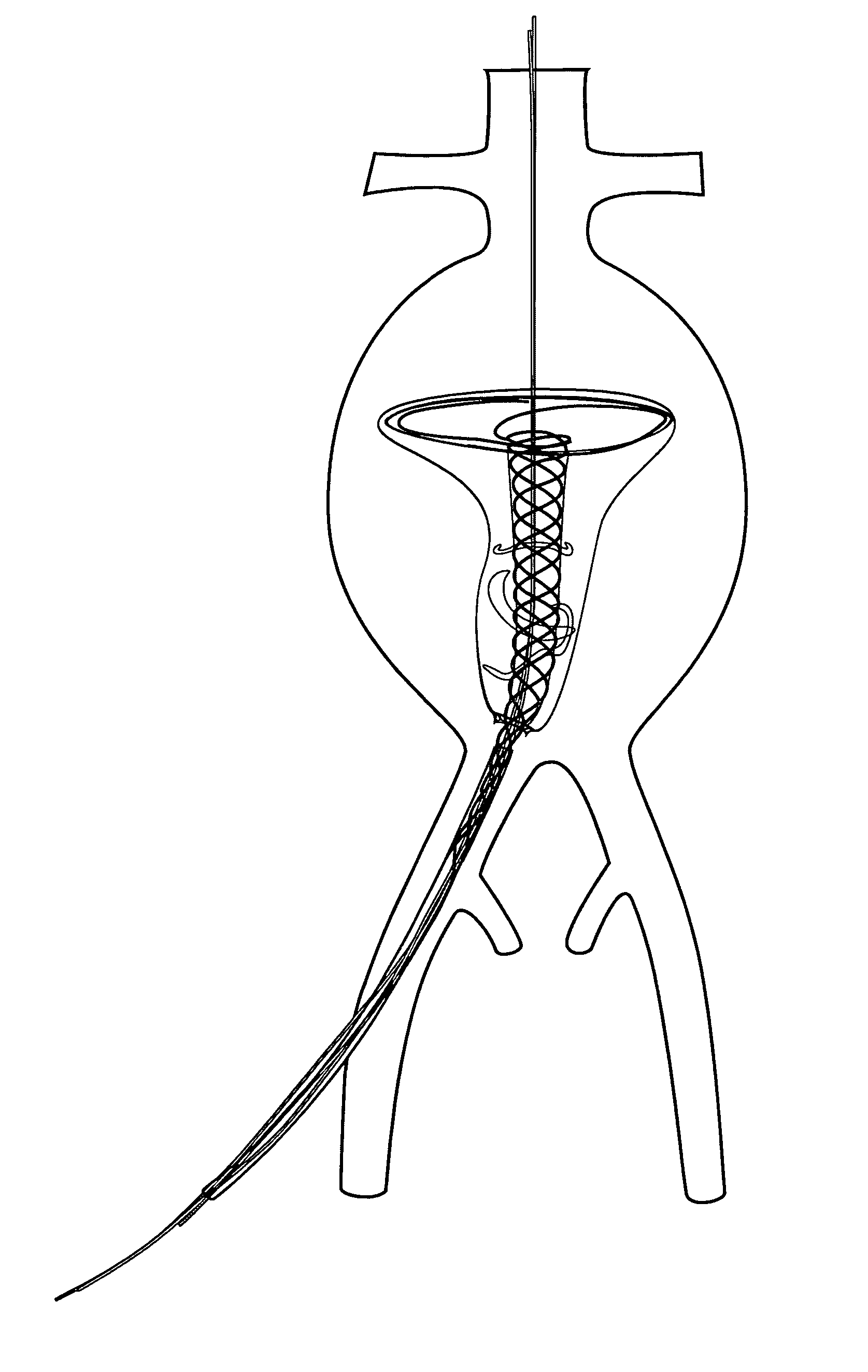
Self-Expandable Endovascular Device For Aneurysm Occlusion
The self-expandable endovascular apparatus for aneurysm occlusion of the invention comprises a deformable shape memory frame with at least a partial segment covering comprised of a matrix implant material. The device can be folded and / or stretched to adopt a narrow profile for loading into a coaxial delivery device and expands in place as it adopts its original shape on release from the device into an aneurysm. A method of treating an aneurysm, comprises the steps of: (a) providing the self-expandable endovascular apparatus inserted into a lumen of a delivery device comprising a proximal end and a distal end, the distal end having a distal tip; (b) advancing the distal tip of the delivery device into an opening in an aneurysm having an interior sac; (c) advancing the apparatus through the lumen into the opening; and (d) withdrawing the delivery device, whereby the apparatus expands into the sac and covers the opening.
Owner:BIOMERIX CORP
Occlusion Device
ActiveUS20150313605A1Minimization requirementsReduce riskDilatorsDiagnostic markersMedicineBlood vessel
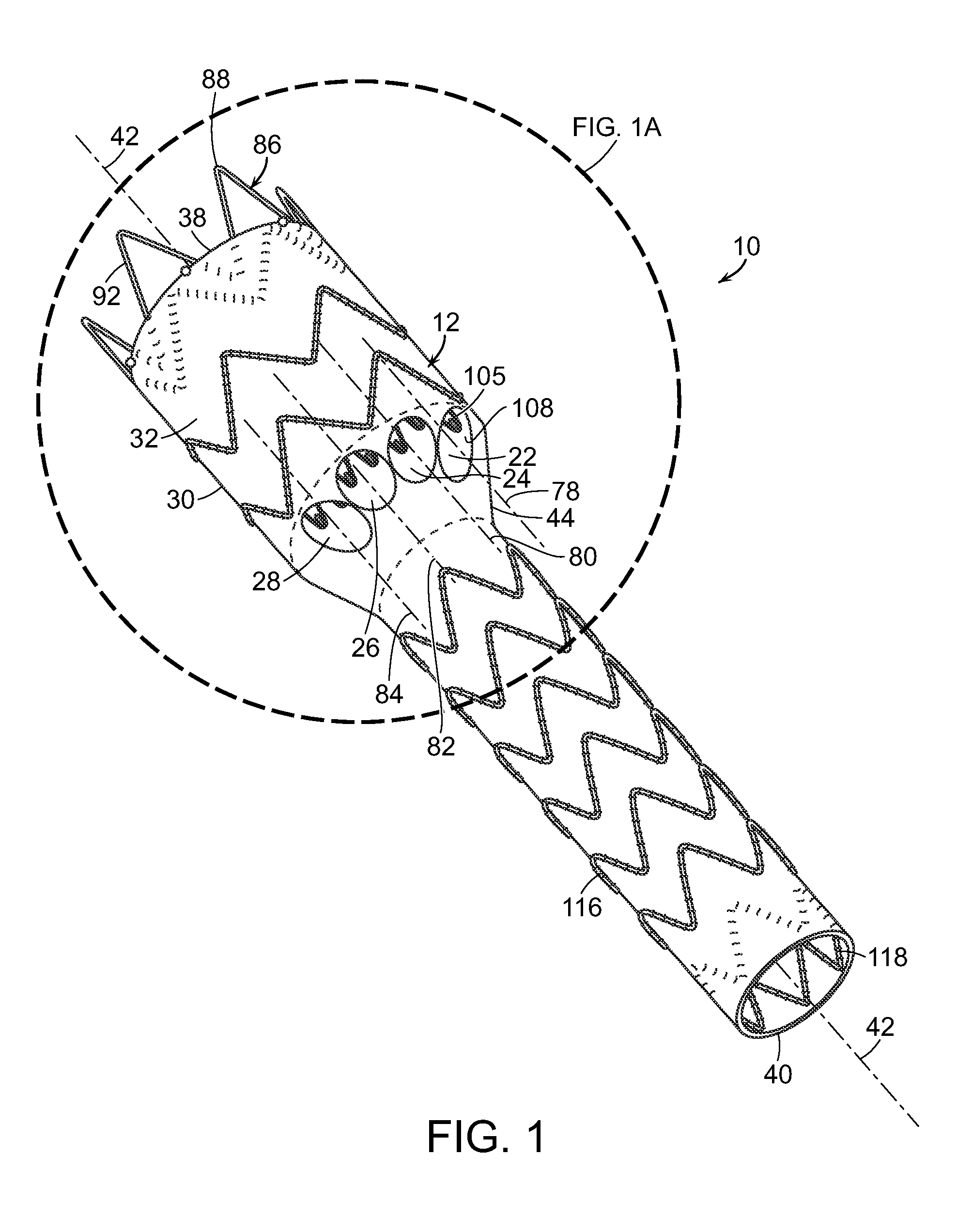
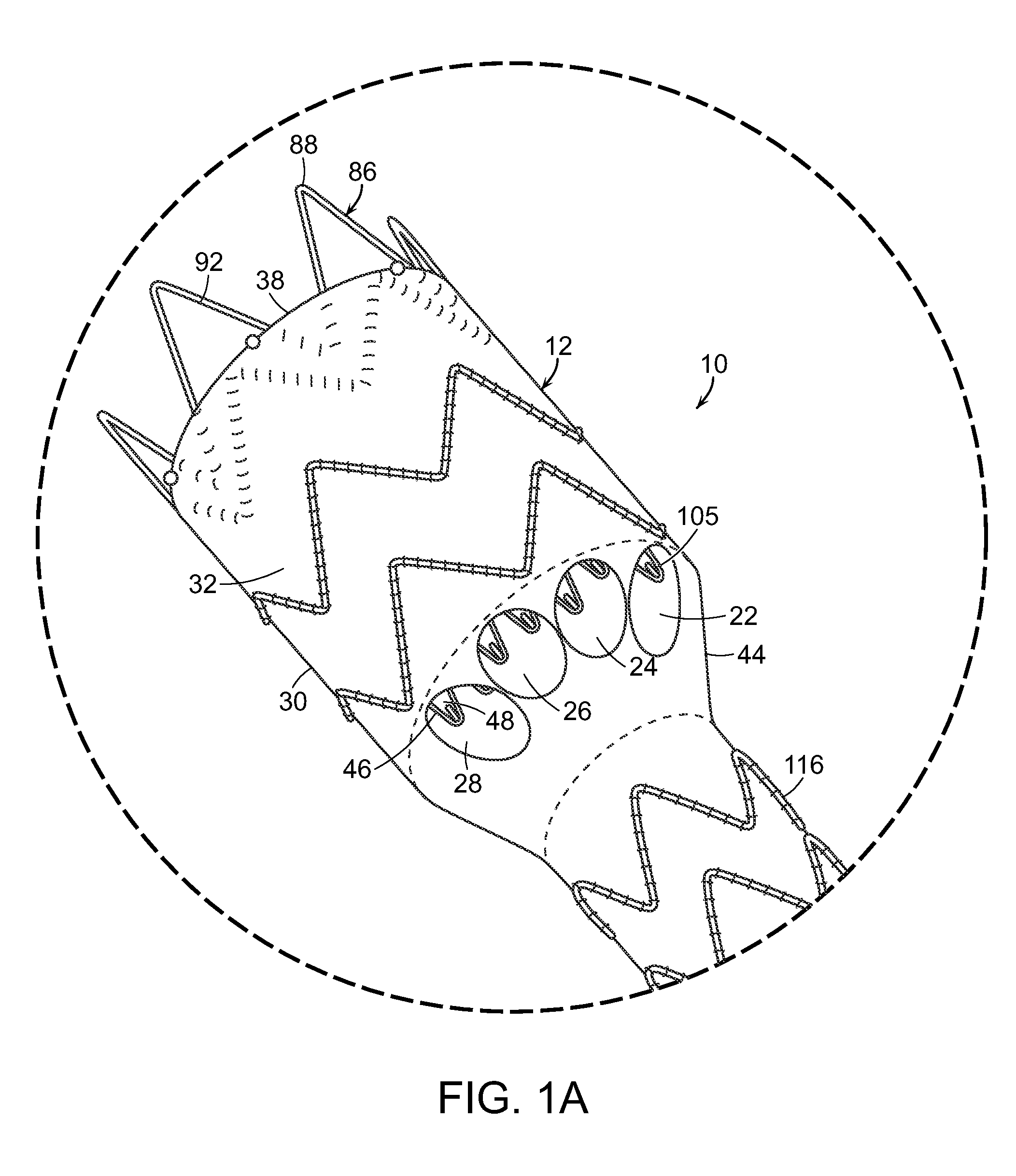
Provided herein is an occlusion device for intrasaccular implantation and / or vascular occlusion comprising: (a) a substantially solid marker having a proximal end, and a distal end; and (b) a low profile resilient mesh body attached to the distal end of the marker, the body having a delivery shape and a deployed shape capable of conforming to aneurysm walls; wherein the body has a diameter greater than a diameter of an aneurysm to be treated. Also provided herein is a kit comprising the occlusion device disclosed herein and a means for delivery thereof. Methods of manufacture and use of the occlusion device disclosed herein are also disclosed.
Owner:CERUS ENDOVASCULAR
Vascular repair devices and methods of use
A vascular repair device assembly includes a main prostheses, first internal prostheses, an optional second internal prostheses, and at least two sub-prostheses. Methods for delivering vascular repair devices include delivering a vascular repair device through a blood vessel to the aneurysm site, aligning a proximal open end of a main prosthesis cranially to the site of the aneurysm patient and directing a distal end of at least one additional one vascular repair device through a proximal end of at least a first internal lumen, and aligning the proximal end of the additional vascular repair device into a distal end of the at least one sub-prosthesis.
Owner:BOLTON MEDICAL INC
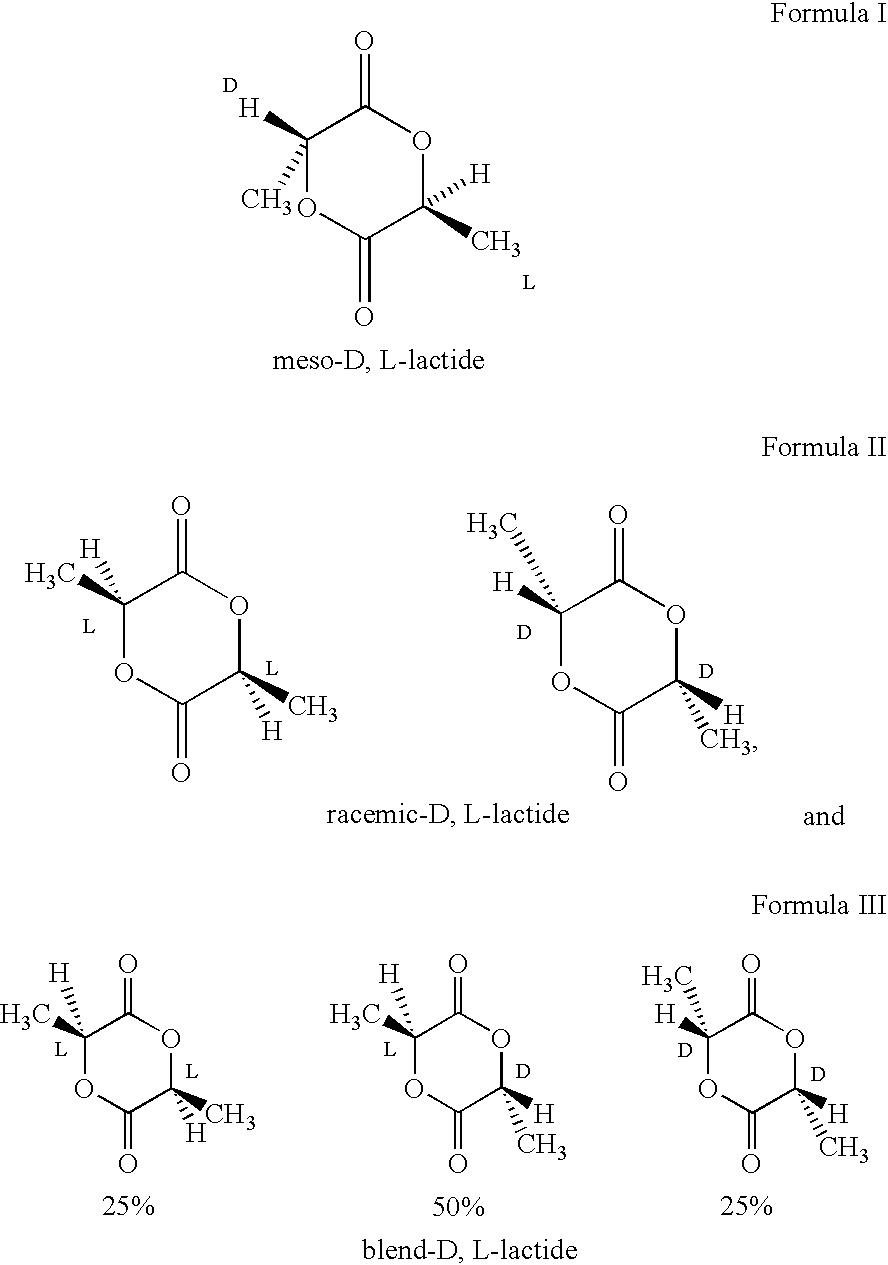
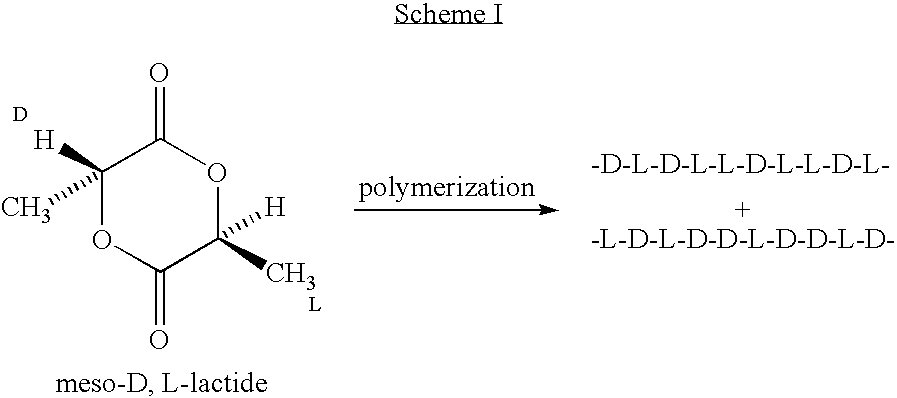
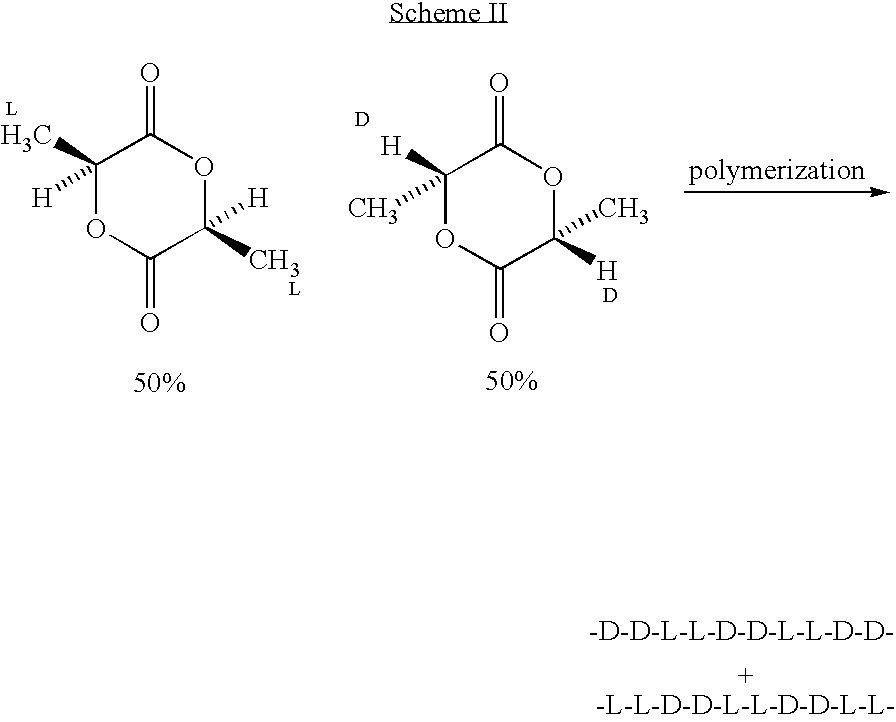
Amorphous poly(D,L-lactide) coating
Implantable devices formed of or coated with a material that includes an amorphous poly(D,L-lactide) formed of a starting material such as meso-D,L-lactide are provided. The implantable device can be used for the treatment, mitigation, prevention, or inhibition of a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Methods and devices for extravascular intervention
The present invention relates to methods for treating an aneurysm or other vascular condition in a patient by implanting an extravascular intervention device at least partially around a blood vessel, or portion thereof, having the vascular condition. The present invention also provides extravascular devices for use in treating patients with aneurysms and other vascular conditions. The extravascular intervention devices provide extravascular support to vascular walls of an aneurysm, thereby reducing the stress on the aneurysm walls and reducing the risk of rupture. The extravascular intervention devices may further be used as means for administering therapeutic agents to vascular targets extravascularly.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Extra-Vascular Wrapping for Treating Aneurysmatic Aorta in Conjunction with Endovascular Stent-Graft and Methods Thereof
InactiveUS20100292774A1Inhibiting scar tissue formationPreventing scar tissue formationStentsOcculdersEndovascular treatmentVascular ring
A system for treating an aneurysmatic abdominal aorta, comprising (a) an extra-vascular wrapping (EVW) comprising (i) at least one medical textile member adapted to at least partially encircle a segment of aorta in proximity to the renal arteries, and (ii) a structural member, wherein EVW is adapted for laparoscopic delivery, and (b) an endovascular stent-graft (ESG) comprising (i) a compressible structural member, and (ii) a substantially fluid impervious fluid flow guide (FFG) attached thereto. Also described is an extra-vascular ring (EVR) adapted to encircle the neck of an aortic aneurysm. Further described are methods for treating an abdominal aortic aneurysm, comprising laparoscopically delivering the extra-vascular wrapping (EVW) and endovascularly placing an endovascular stent-graft (ESG). Also described are methods to treat a type I endoleak.
Owner:ENDOSPAN
Methods for vascular reconstruction of diseased arteries
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Aneurysm treatment devices and methods
An aneurysm treatment device for in situ treatment of aneurysms comprises a collapsible member having a first shape wherein the first shape is an expanded geometric configuration, and a second shape, wherein the second shape is a collapsed configuration that is loadable into a catheter. The aneurysm treatment device is capable or returning to the first shape in the sac of an aneurysm upon deployment, where it occludes the aneurysm. In another embodiment an occlusion device comprises a flexible, longitudinally extending elastomeric matrix member that assumes a non-linear shape to conformally fill a targeted vascular site.
Owner:BIOMERIX CORP
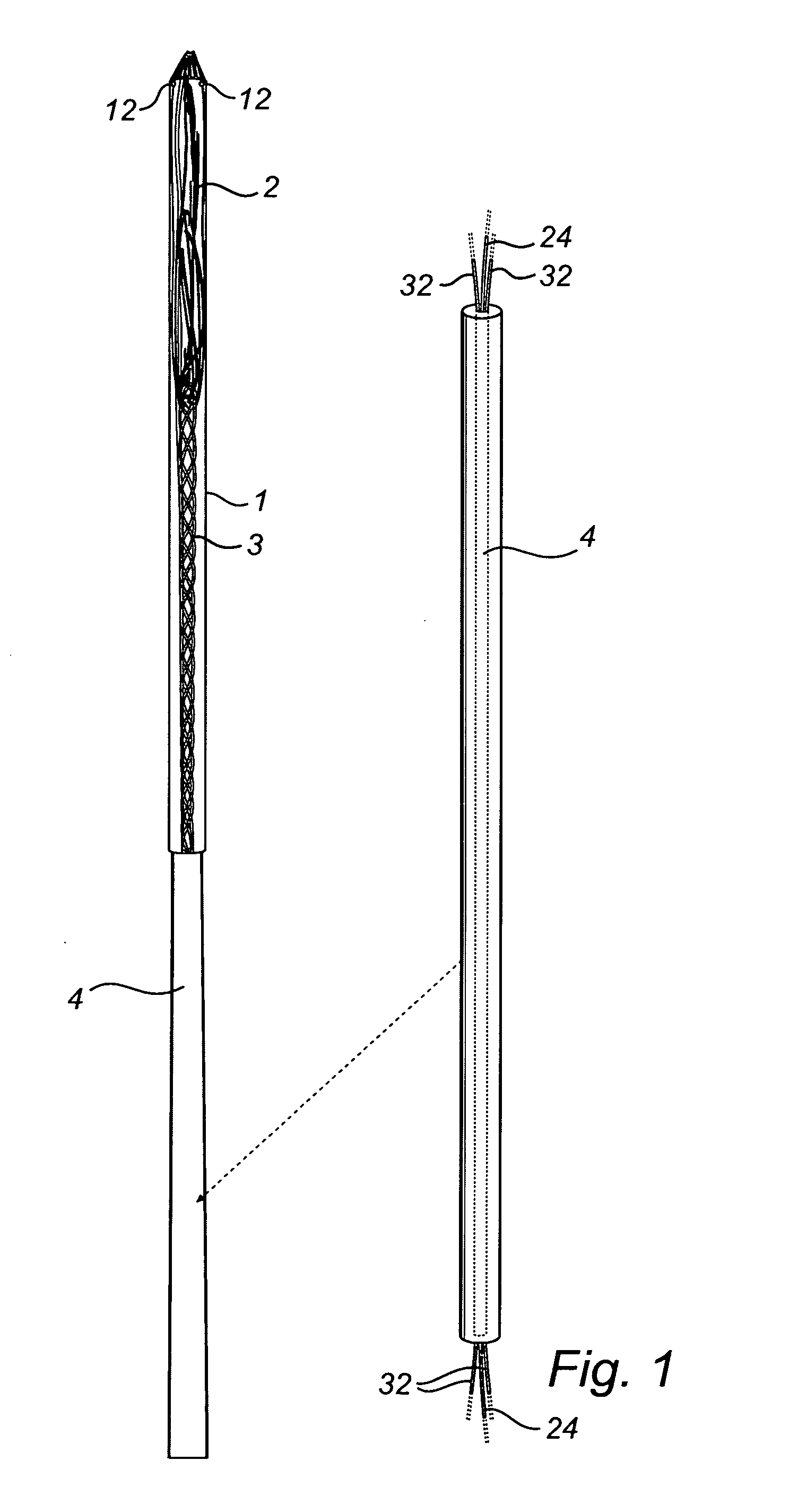
Endovascular electrolytically detachable wire and tip for the formation of thrombus in arteries, veins, aneurysms, vascular malformations and arteriovenous fistulas
An artery, vein, aneurysms vascular malformation or arterial fistula is occluded through endovascular occlusion by the endovascular insertion of a platinum wire and / or tip into the vascular cavity. The vascular cavity is packed with the tip to obstruct blood flow or access of blood in the cavity such that the blood clots in the cavity and an occlusion if formed. The tip may be elongate and flexible so that it packs the cavity by being folded upon itself a multiple number of times, or may pack the cavity by virtue of a filamentary or fuzzy structure of the tip. The tip is then separated from the wire mechanically or by electrolytic separation of the tip from the wire. The wire and the microcatheter are thereafter removed leaving the tip embedded in the thrombus formed within the vascular cavity. Movement of wire in the microcatheter is more easily tracked by providing a radioopaque proximal marker on the microcatheter and a corresponding indicator marker on the wire. Electrothrombosis is facilitate by placing the ground electrode on the distal end of the microcatheter and flowing current between the microcatheter electrode and the tip.REEAXMINATION RESULTS The questions raised in reexamination request 90 / 007,231, filed Oct. 4, 2004 have been considered and the results thereof are reflected in this reissue patent which constitutes the reexamination certificate required by 35 U.S.C. 307 as provided in 37 CFR 1.570(e), for ex parte reexaminations, or the reexamination certificate required by 35 U.S.C. 316 as provided in 37 CFR 1.99(e) for inter partes reexaminations.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
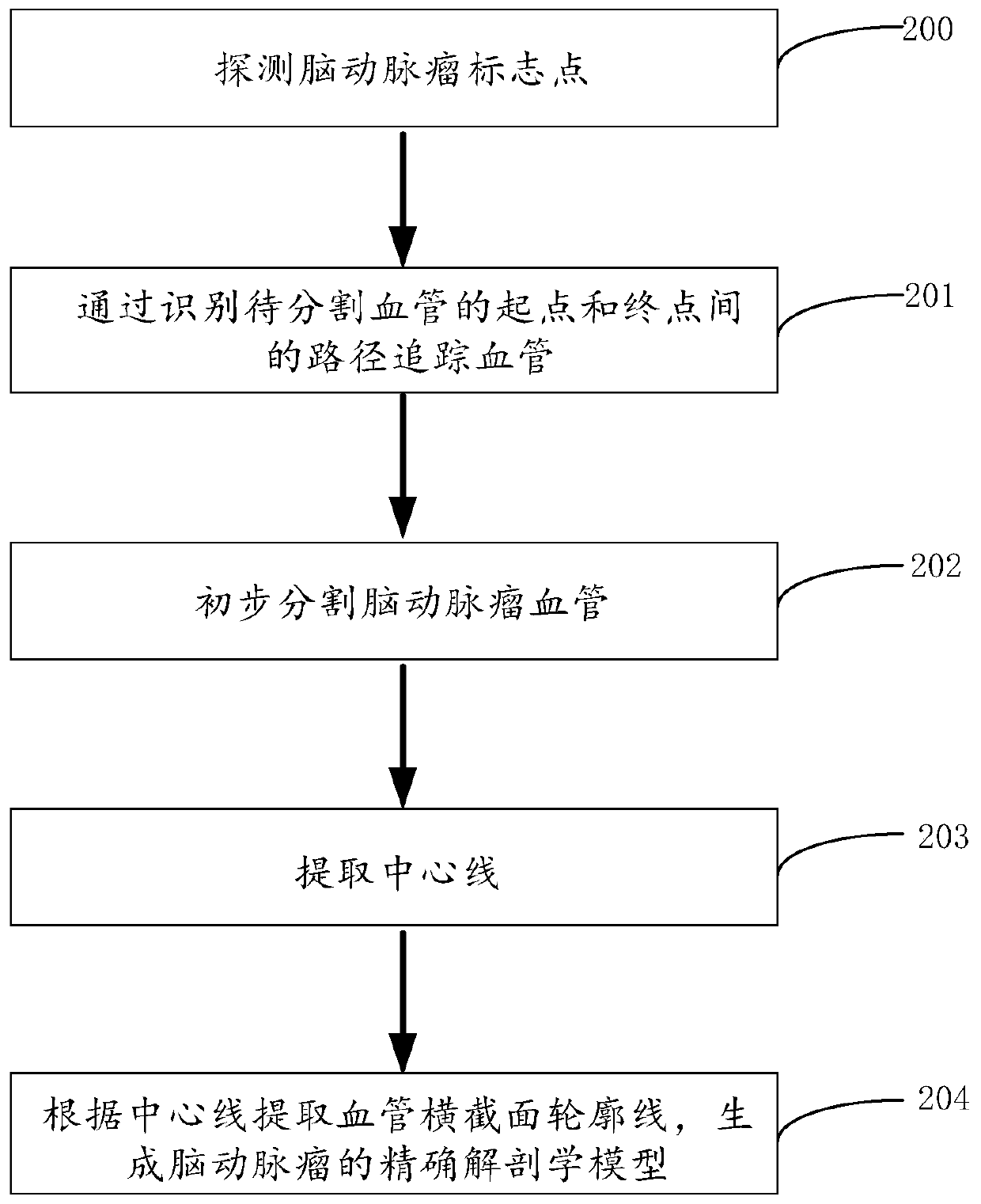
Method for aiding stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms by virtual parent artery reconstruction
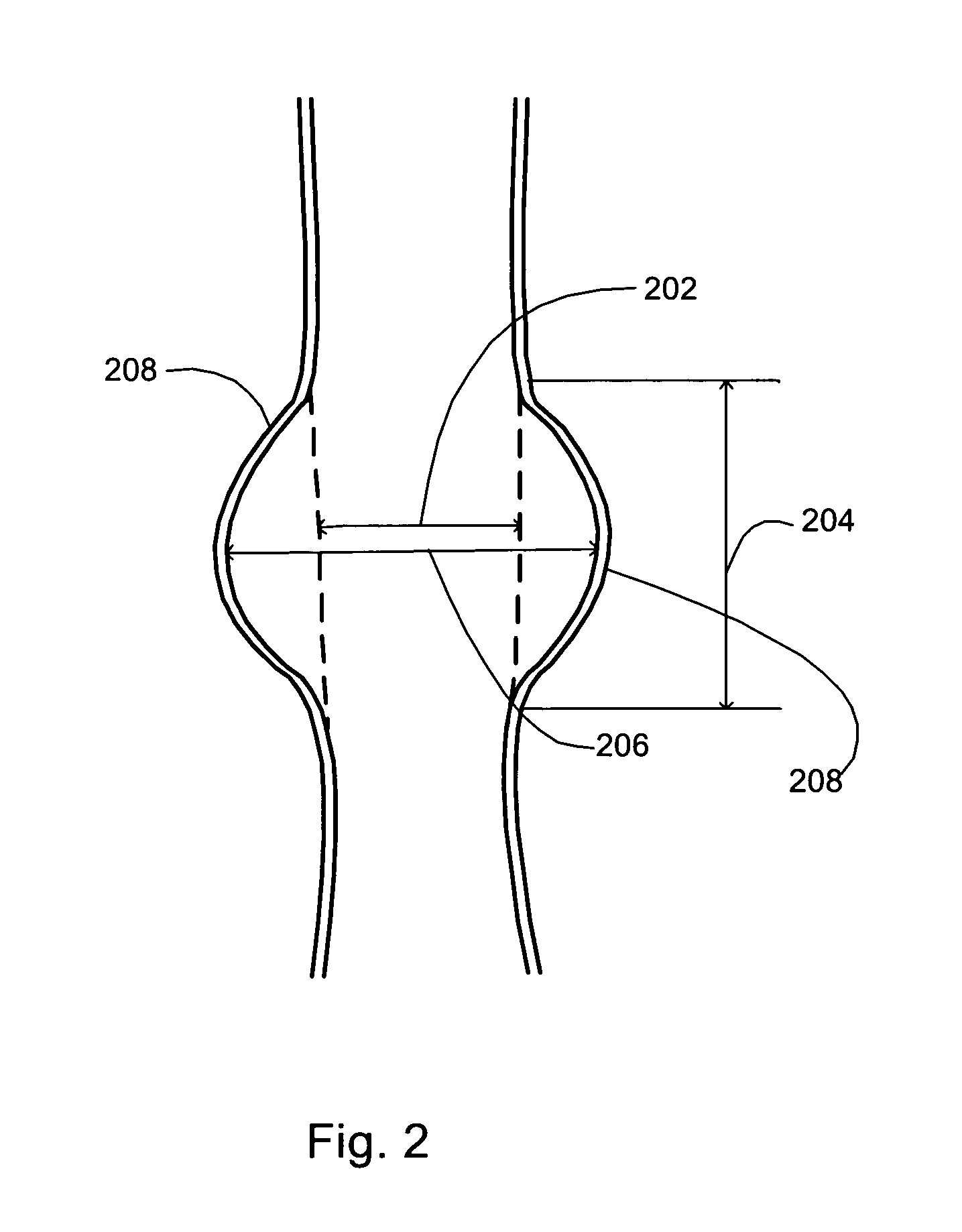
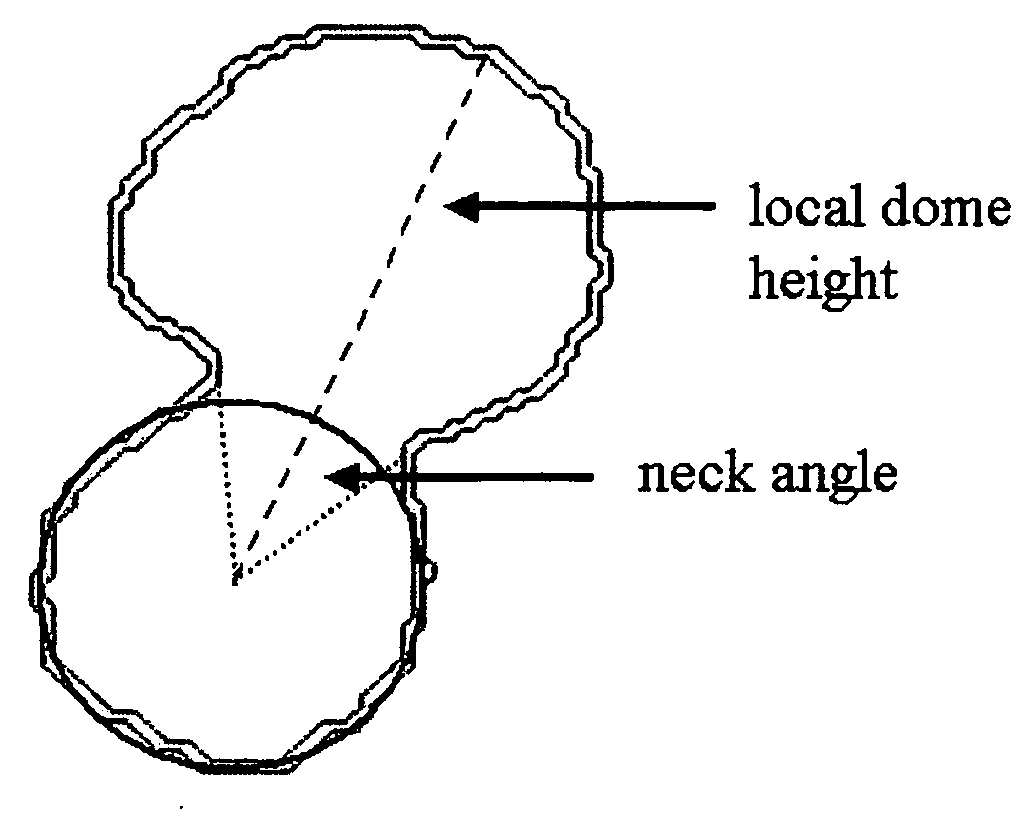
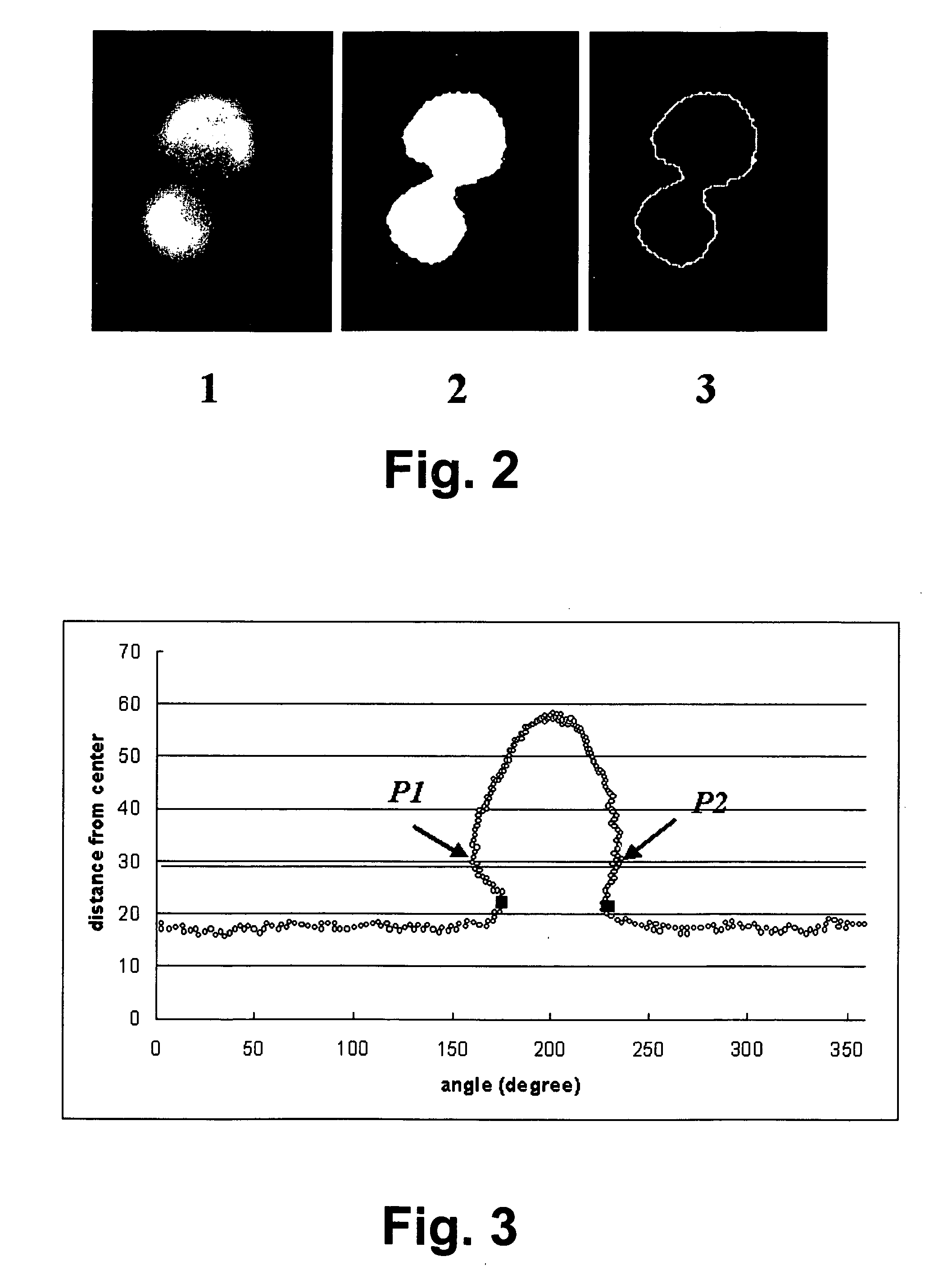
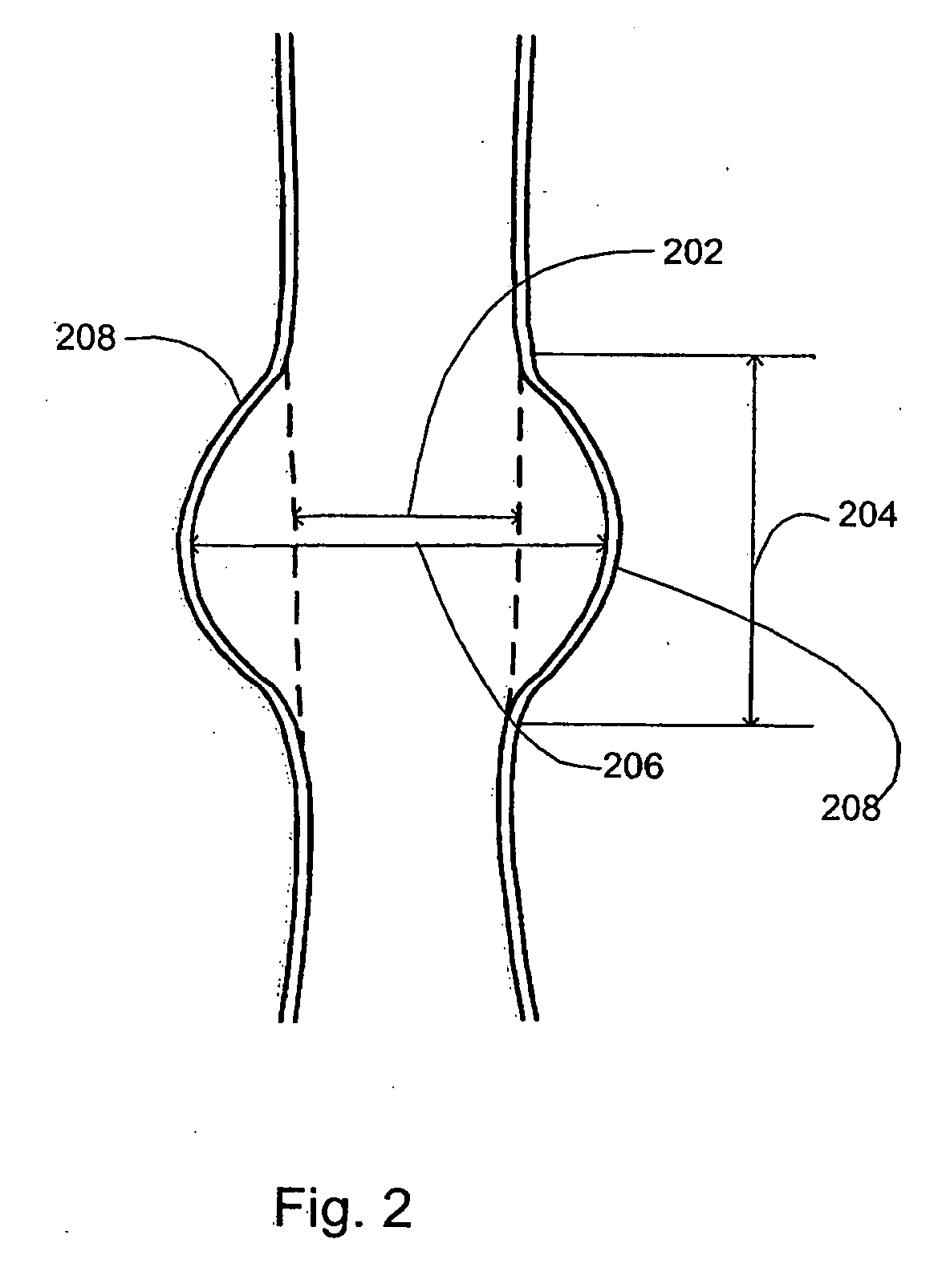
A method of creating a surface model of an intracranial aneurysm in an artery having a lumen, the aneurysm having a neck and a dome and the virtual reconstruction of the parent artery across the lateral extension of the aneurysm neck. The method includes the steps of: determining a center and radius of the artery over the lateral extension of the aneurysm; determining the boundary points that mark the boundary between the aneurysm neck and the artery; determining the angle of the aneurysm neck with respect to the artery, for various cross sections of the neck; determining the length of the neck; determining the height of the dome; estimating the area of the neck; and creating the surface model of the intracranial aneurysm in the artery, using the results from the previous steps.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Method and apparatus for treating aneurysms
Owner:LESCHINSKY BORIS
Methods and devices for extravascular intervention
InactiveUS20060106406A1Avoid the needTourniquetsWound clampsBlood vesselAnterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm
The present invention relates to methods for treating an aneurysm or other vascular condition in a patient by implanting an extravascular intervention device to partially encircle a blood vessel, or portion thereof, having the vascular condition. The present invention also provides extravascular devices for use in treating patients with aneurysms and other vascular conditions. The extravascular intervention devices provide extravascular support to vascular walls of an aneurysm, thereby reducing the stress on the aneurysm walls and reducing the risk of rupture. The extravascular intervention devices may further be used as means for administering therapeutic agents to vascular targets extravascularly.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
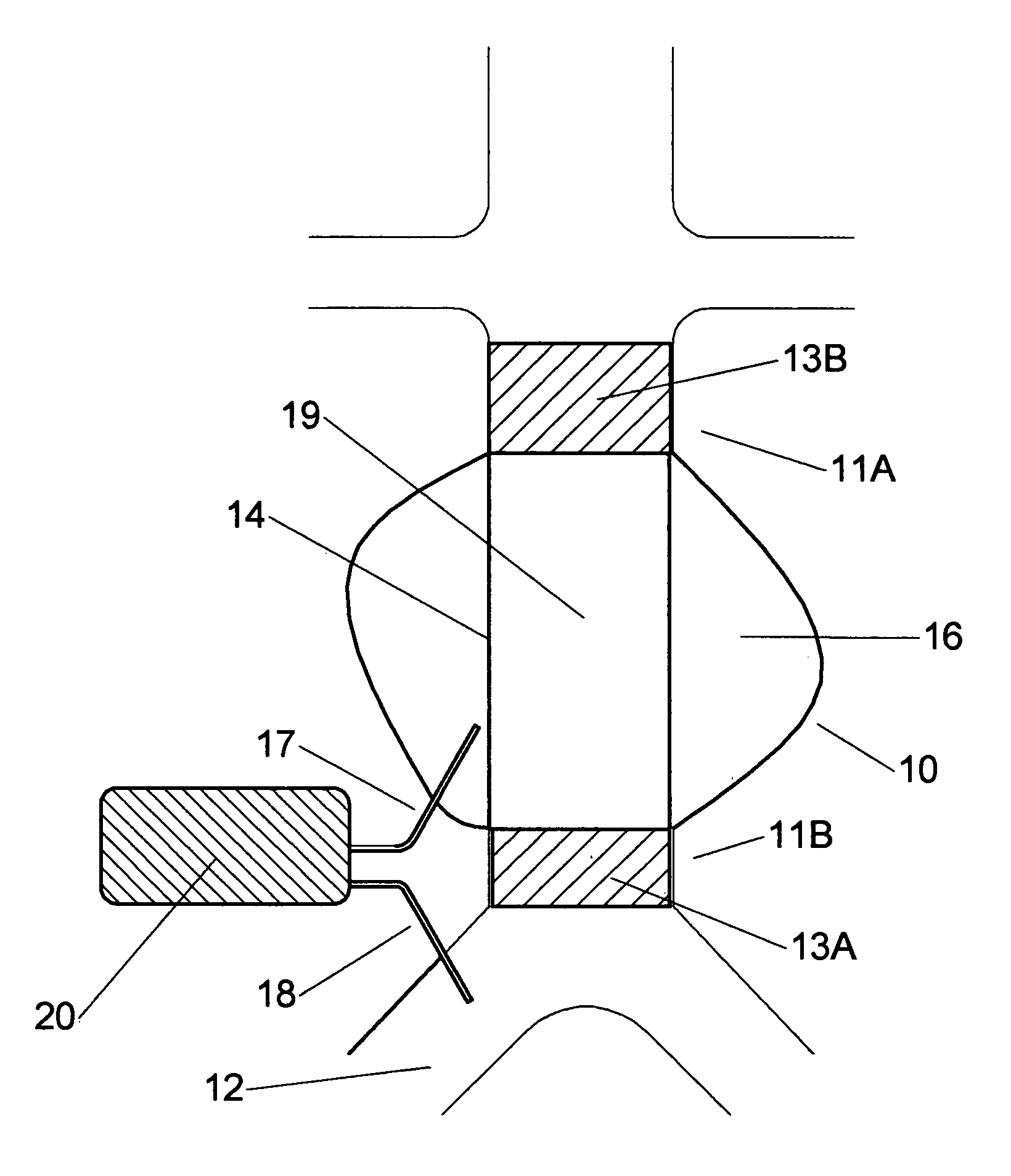
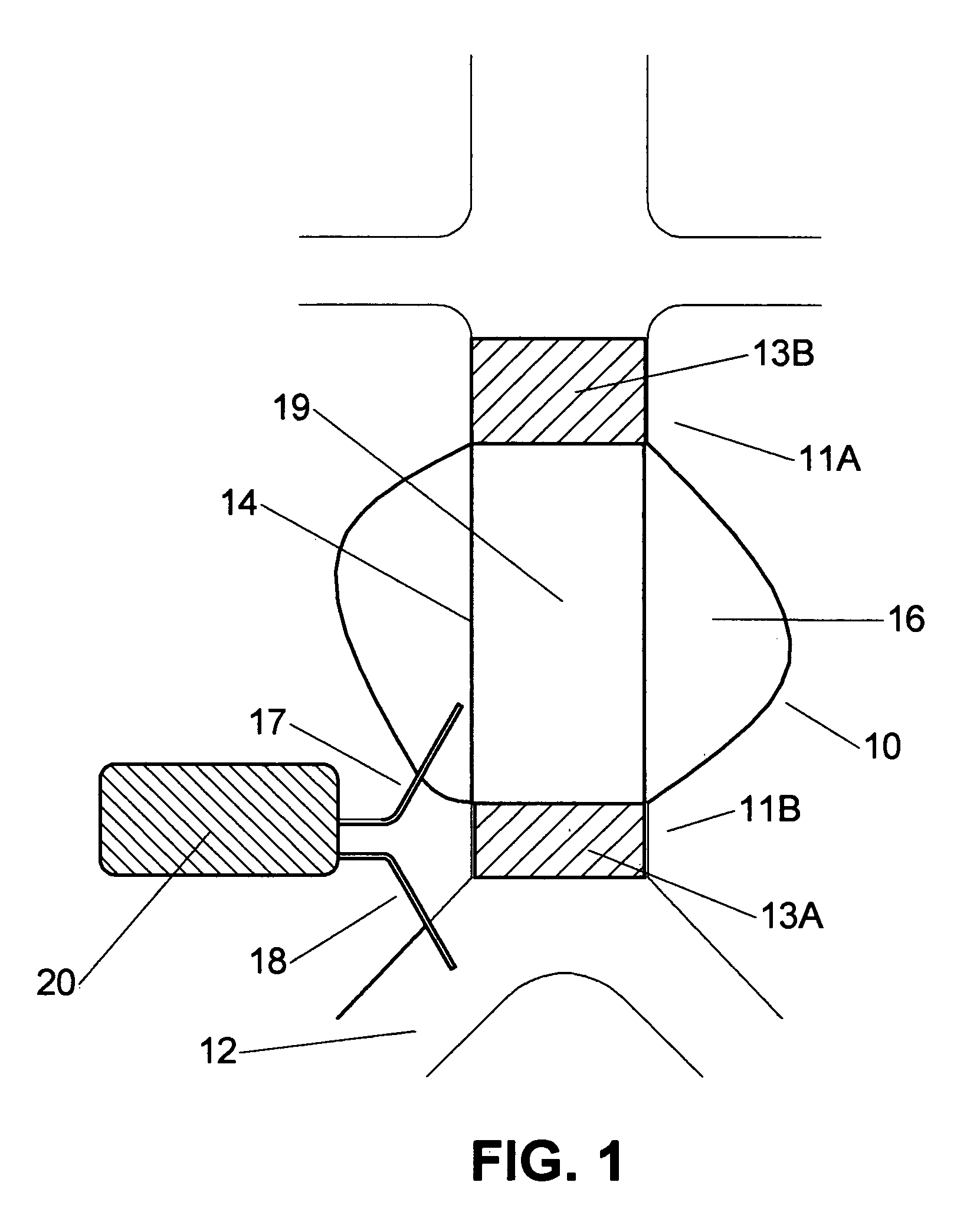
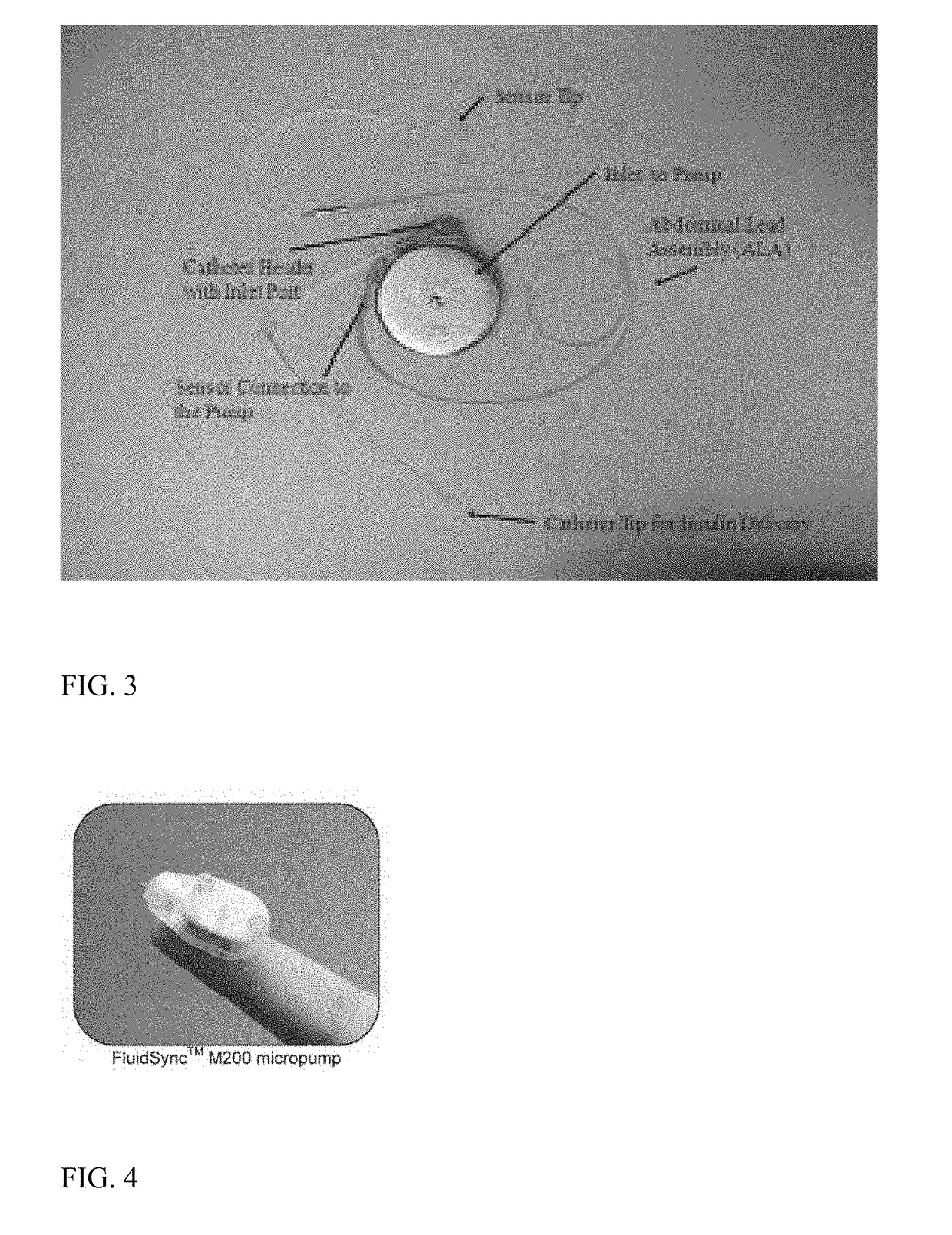
Implantable device for monitoring aneurysm sac parameters
A device for measuring physiological parameters within an aneurysm sac that has been excluded from blood flow by an endoprosthesis. The device is comprised of at least two sensors, one placed in the aneurysm sac and another in a systemic artery. A differential between the readings of the two sensors can then be calculated, making the device easily calibrated in vivo and insensitive to changes in atmospheric pressure.
Owner:FITZ MATTHEW J
Stent/stent graft for reinforcement of vascular abnormalities and associated method
InactiveUS8747453B2Reduce morbidityIncrease the diameterStentsBlood vesselsStent graftingBlood vessel
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Poly(ester amide) block copolymers
Provided herein is a copolymer that includes a soft block (A) that contains poly(ester amide) (PEA) and a hard block (B). The copolymer can be any of AB, ABA or BAB type block copolymers. By varying the relative amount of the PEA block and the hard block, one can obtain a copolymer with a Tg for mechanical integrity in drug-delivery stent applications. The copolymer can be used alone or optionally in combination with a biobeneficial material and / or a biocompatible polymer to form an implantable device or a coating on an implantable device. When the copolymer is used in combination with a biobeneficial material, the copolymer and the biobeneficial material can be co-deposited or applied in sequence during the coating process. A coating formed of the copolymer may also include a bioactive agent. The implantable device can be implanted in a patient to treat, prevent, or ameliorate a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, and / or tumor obstruction.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Covered stent for aortic dissection surgery, delivery device and use method thereof
InactiveCN105832447AAvoid punctureFacilitates a tight fitStentsBlood vesselsAortic dissectionLeft subclavian artery
The invention discloses a covered stent for an aortic dissection surgery, a delivery device and a use method thereof. The stent comprises a main body, wherein the main body decreases progressively from the heart near end with a large diameter to a far end with a small diameter, and the superior border of the middle piece of the main body is a rotary island; a tectorial membrane is arranged except the rotary island, and the two ends of the main body and the rotary island are provided with positioning marks. The delivery device comprises a delivery sheathing canal, a suture and a traction guide wire, wherein the suture is sewn on the outer side surface of the covered stent, and the two side edges of the covered stent at the near end of the left subclavian artery are sewn up by the suture; the stent is closed up to be in a semi-contraction state by the traction guide wire through the suture, and the covered stent is closed up and wrapped in the delivery sheathing canal; the delivery sheathing canal is provided with a steeple, and the far end of the traction guide wire penetrates through the handle of the delivery sheathing canal and is fixed. The covered stent for the aortic dissection surgery is used for a dissecting aneurysm surgery of the lesser curvature side of aortic arch and an interventional minimally invasive surgery of an aortic dissection near the brachiocephalic trunk, so that the trauma of a thoracotomy is avoided, and the athe lumen crevasse occlusion is directly implemented.
Owner:杨威
Aneurysm closure device
The invention relates to devices, a systems, and associated methods for use, delivery, and manufacture for changing the blood flow into an aneurysm designed to induce aneurysm thrombosis and / or the exclusion from blood flow and pressure of the aneurysm in order to prevent further growth and eventual rupture. In some embodiments, the various aspects of the invention are directed to treating a cerebral aneurysm.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Detection and tracking of interventional tools
InactiveUS20100226537A1Improve visibilityEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescence3d rotational angiography
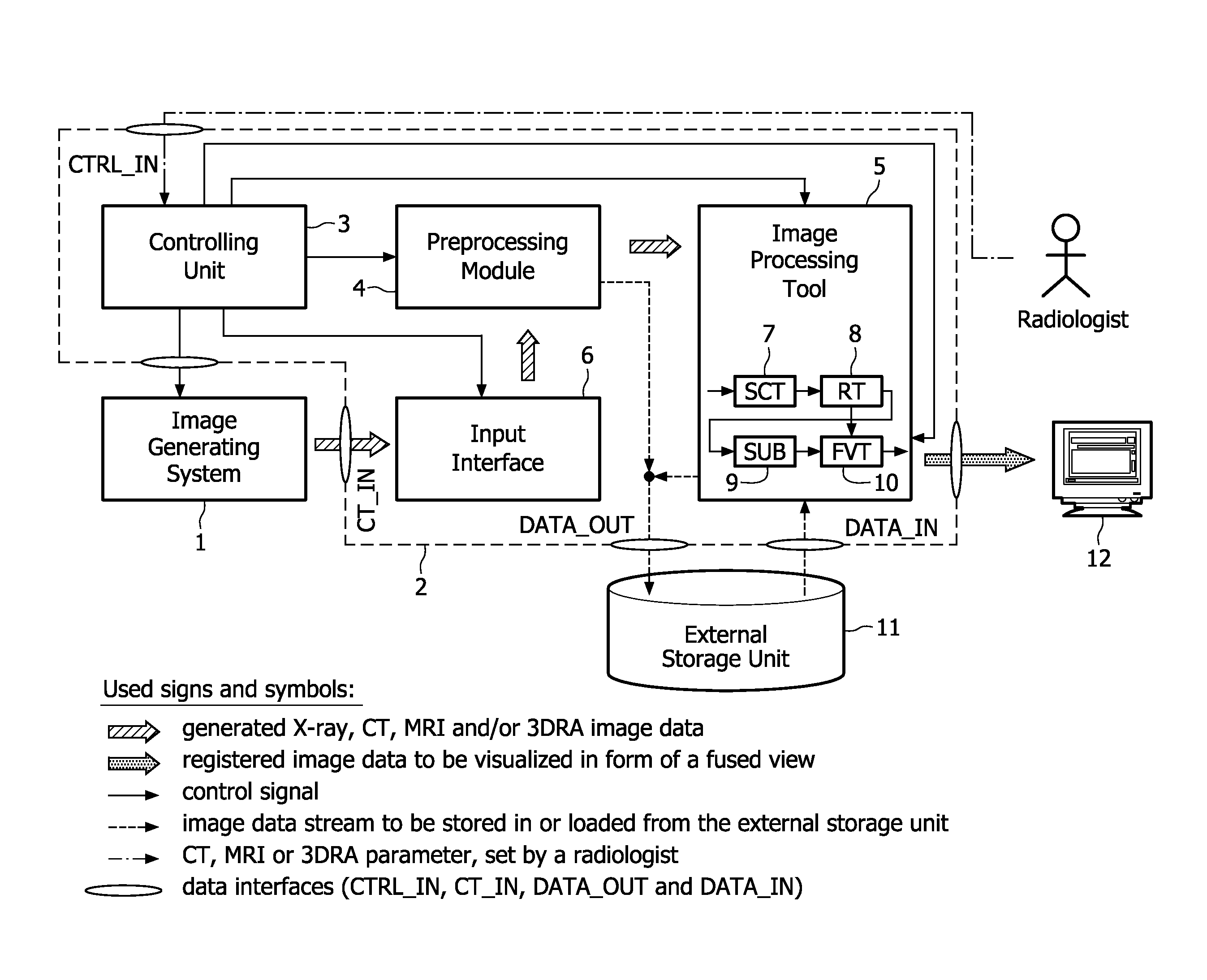
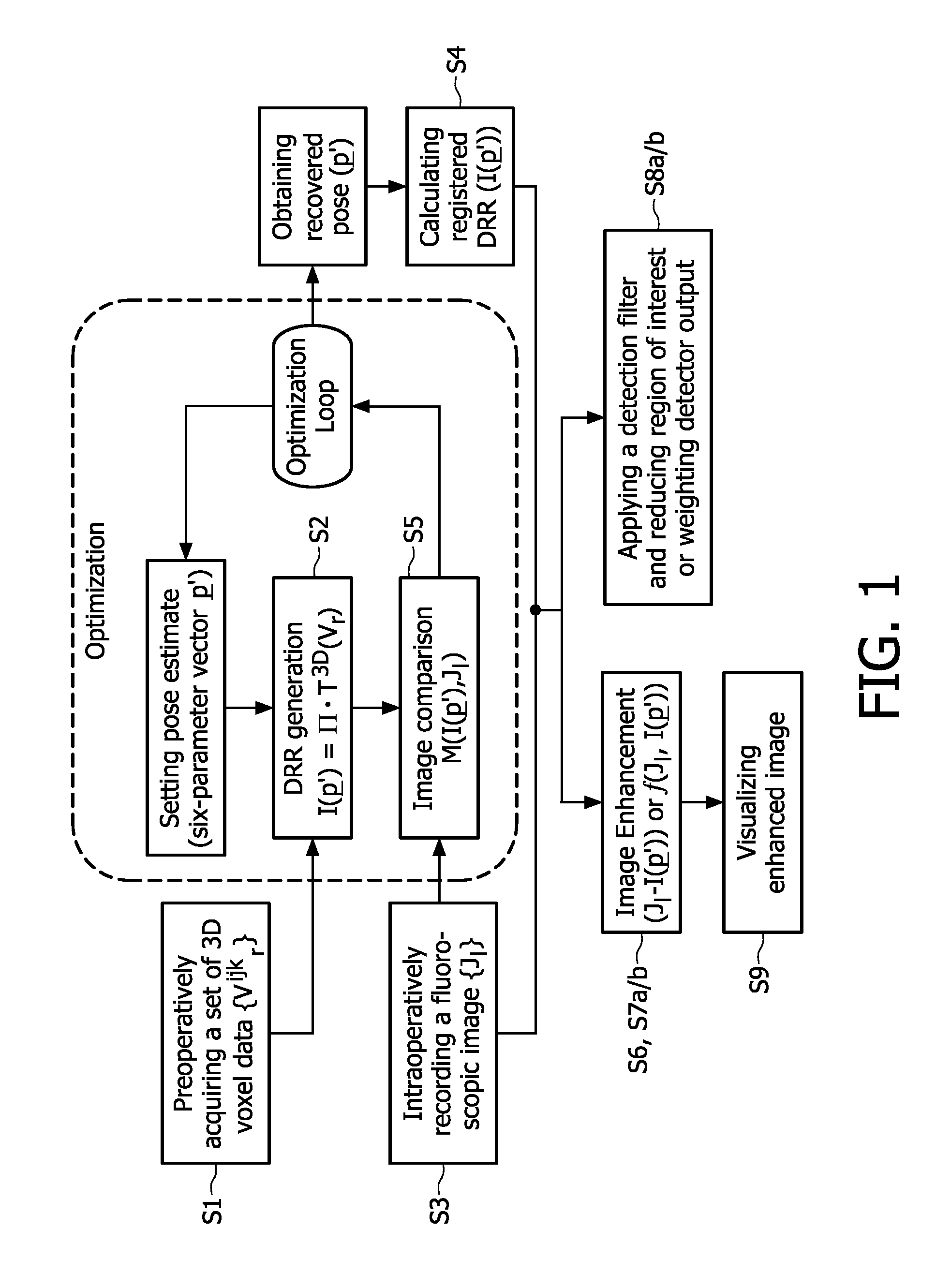
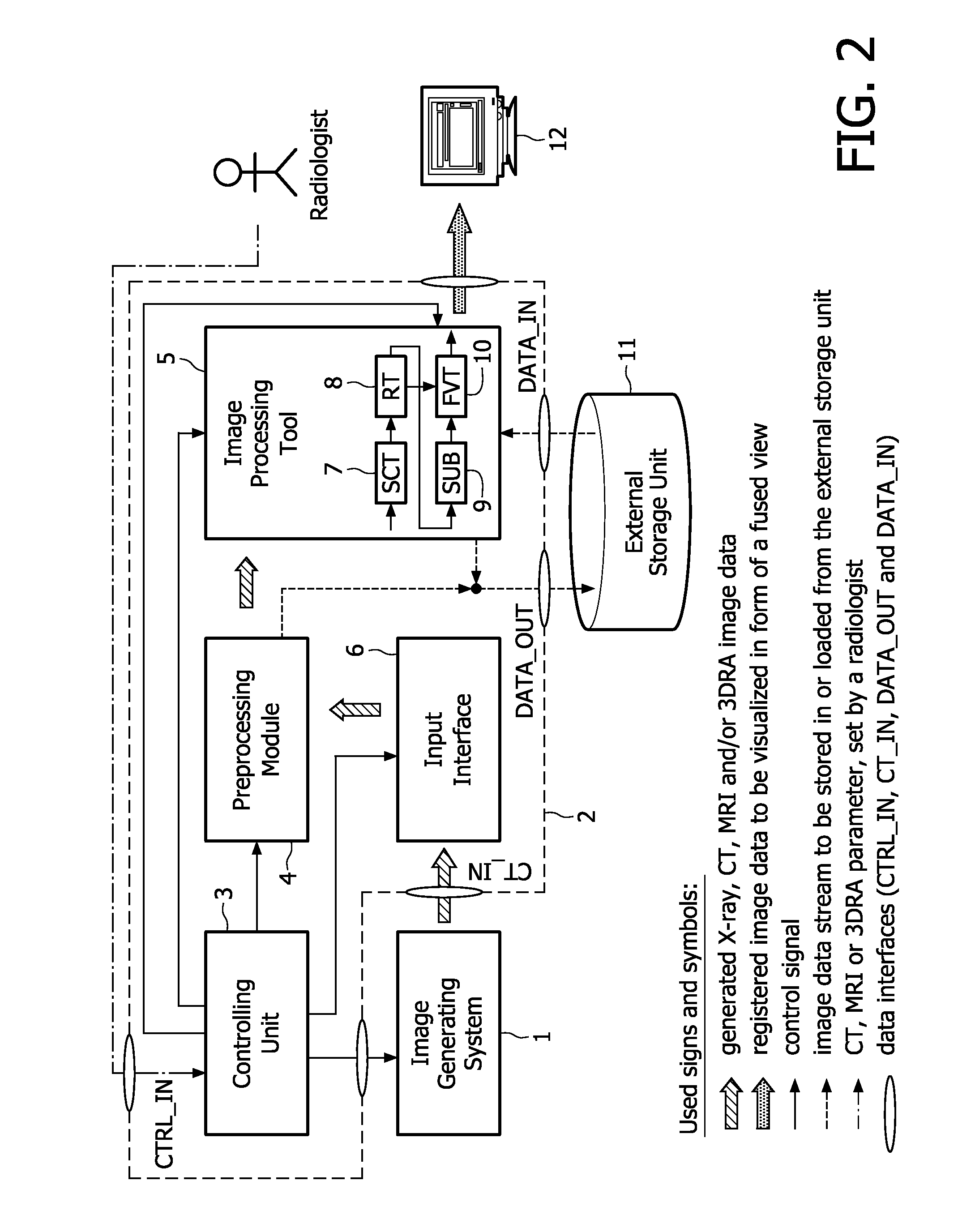
The present invention relates to minimally invasive X-ray guided interventions, in particular to an image processing and rendering system and a method for improving visibility and supporting automatic detection and tracking of interventional tools that are used in electrophysiological procedures. According to the invention, this is accomplished by calculating differences between 2D projected image data of a preoperatively acquired 3D voxel volume showing a specific anatomical region of interest or a pathological abnormality (e.g. an intracranial arterial stenosis, an aneurysm of a cerebral, pulmonary or coronary artery branch, a gastric carcinoma or sarcoma, etc.) in a tissue of a patient's body and intraoperatively recorded 2D fluoroscopic images showing the aforementioned objects in the interior of said patient's body, wherein said 3D voxel volume has been generated in the scope of a computed tomography, magnet resonance imaging or 3D rotational angiography based image acquisition procedure and said 2D fluoroscopic images have been co-registered with the 2D projected image data. After registration of the projected 3D data with each of said X-ray images, comparison of the 2D projected image data with the 2D fluoroscopic images—based on the resulting difference images—allows removing common patterns and thus enhancing the visibility of interventional instruments which are inserted into a pathological tissue region, a blood vessel segment or any other region of interest in the interior of the patient's body. Automatic image processing methods to detect and track those instruments are also made easier and more robust by this invention. Once the 2D-3D registration is completed for a given view, all the changes in the system geometry of an X-ray system used for generating said fluoroscopic images can be applied to a registration matrix. Hence, use of said method as claimed is not limited to the same X-ray view during the whole procedure.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Compositions and methods for producing vascular occlusion using a solid-phase platelet binding agent
InactiveUS6960352B2Decreased blood flowInhibition of activationPowder deliverySurgical adhesivesThrombusSolid tumor
The present invention relates generally to methods and compositions for targeting and delivering solid-phase platelet-dependent vascular occlusion agents. In particular, particles or coils or stents coated with platelet binding agents are directed to target vasculature, such as the vasculature of solid tumor masses or AV-malformations or aneurysms or endoleaks; the solid-phase agent then binds and activates platelets, which in turn bind and activate other platelets. This process results in the rapid formation of a platelet-mediated thrombus about the solid-phase agent causing vessel occlusion.
Owner:VIREXX MEDICAL CORP
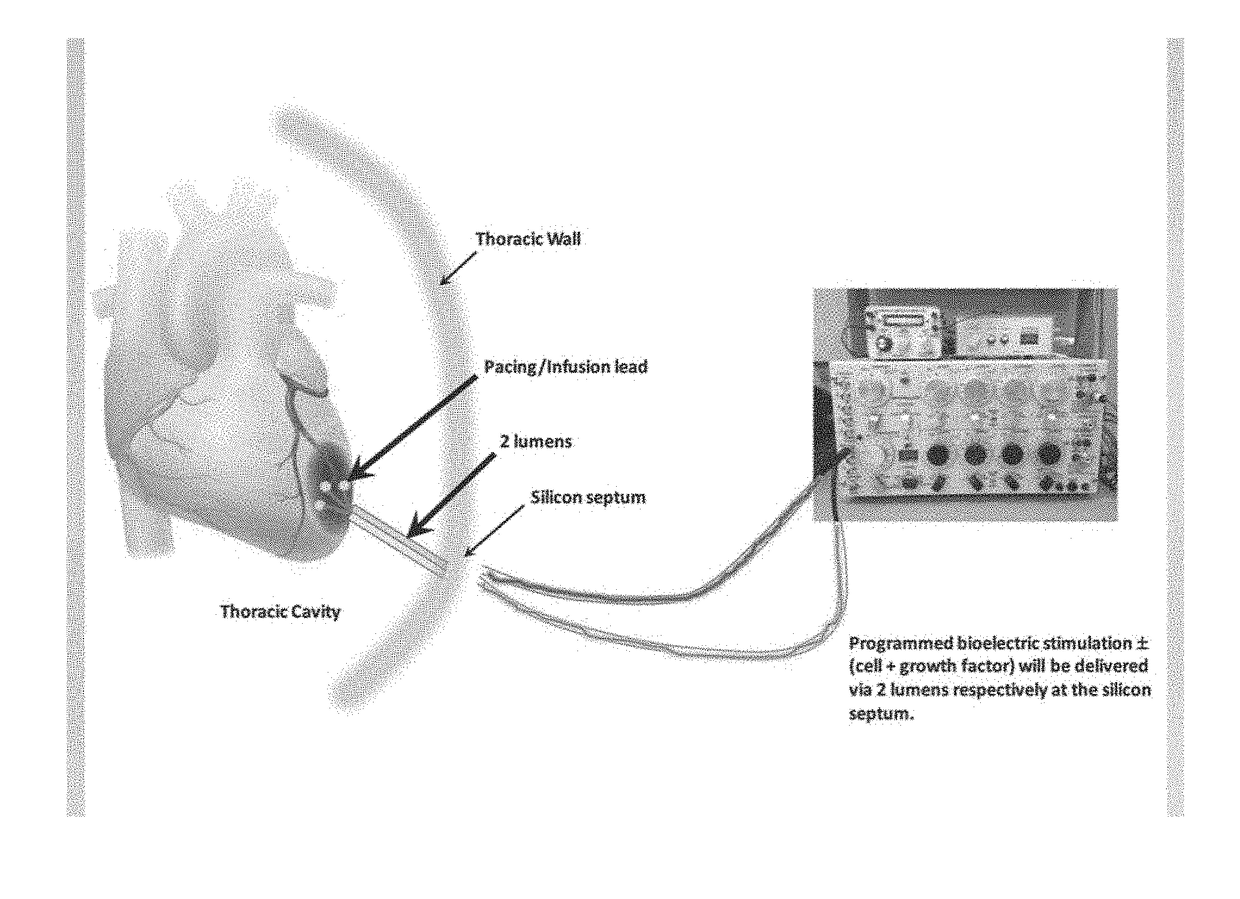
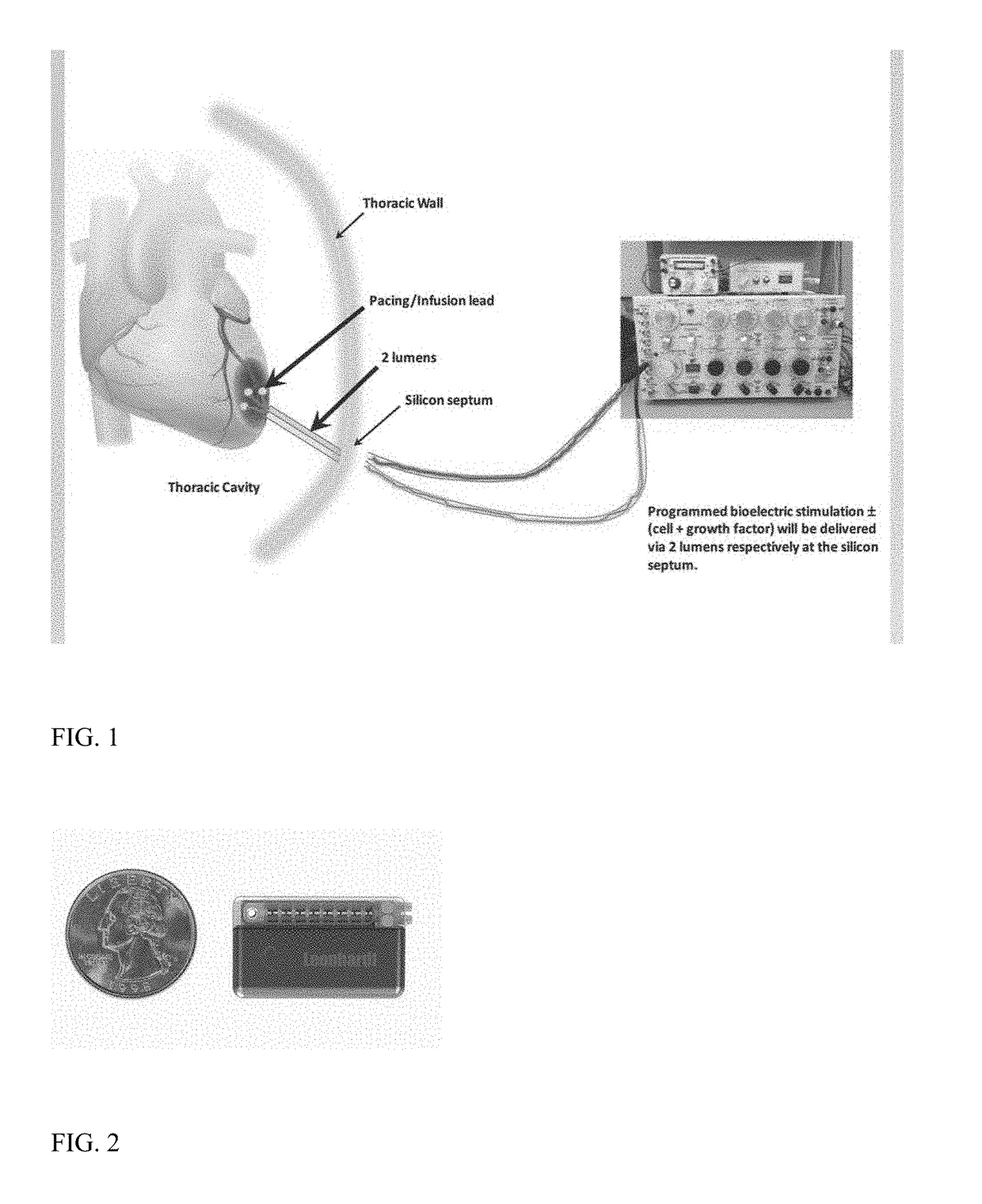
Bioelectric stimulator
ActiveUS20180064935A1Quality improvementExpansion quantityElectrotherapyMedical devicesDiseaseControl release
Described is a low voltage, pulsed electrical stimulation device for controlling expression of, for example, follistatin, a muscle formation promotion protein, by tissues. Epicardial stimulation is especially useful for heart treatment. Follistatin controlled release is also useful for treating other ailments, such as erectile dysfunction, aortic aneurysm, and failing heart valves.
Owner:LEONHARDT VENTURES LLC
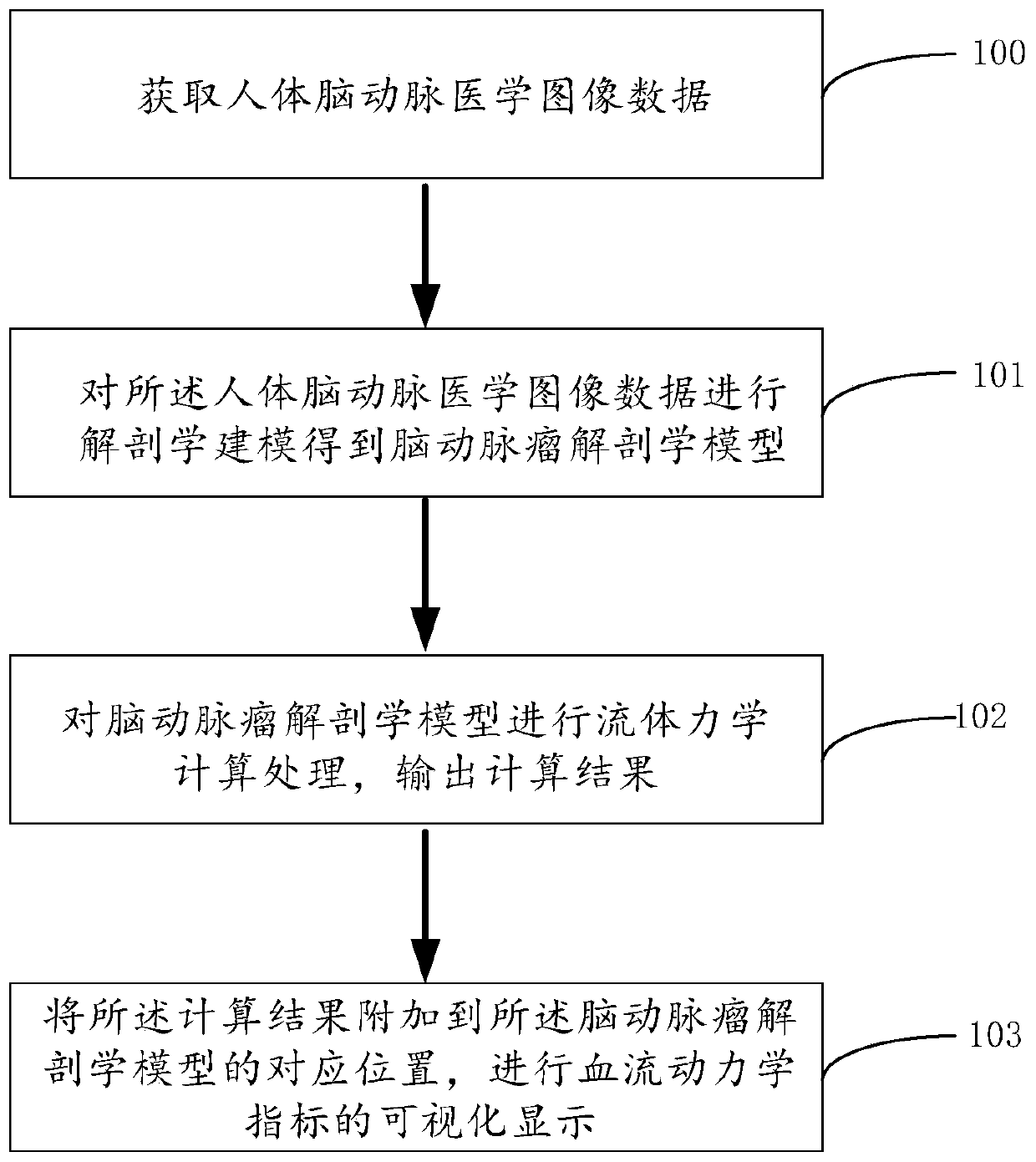
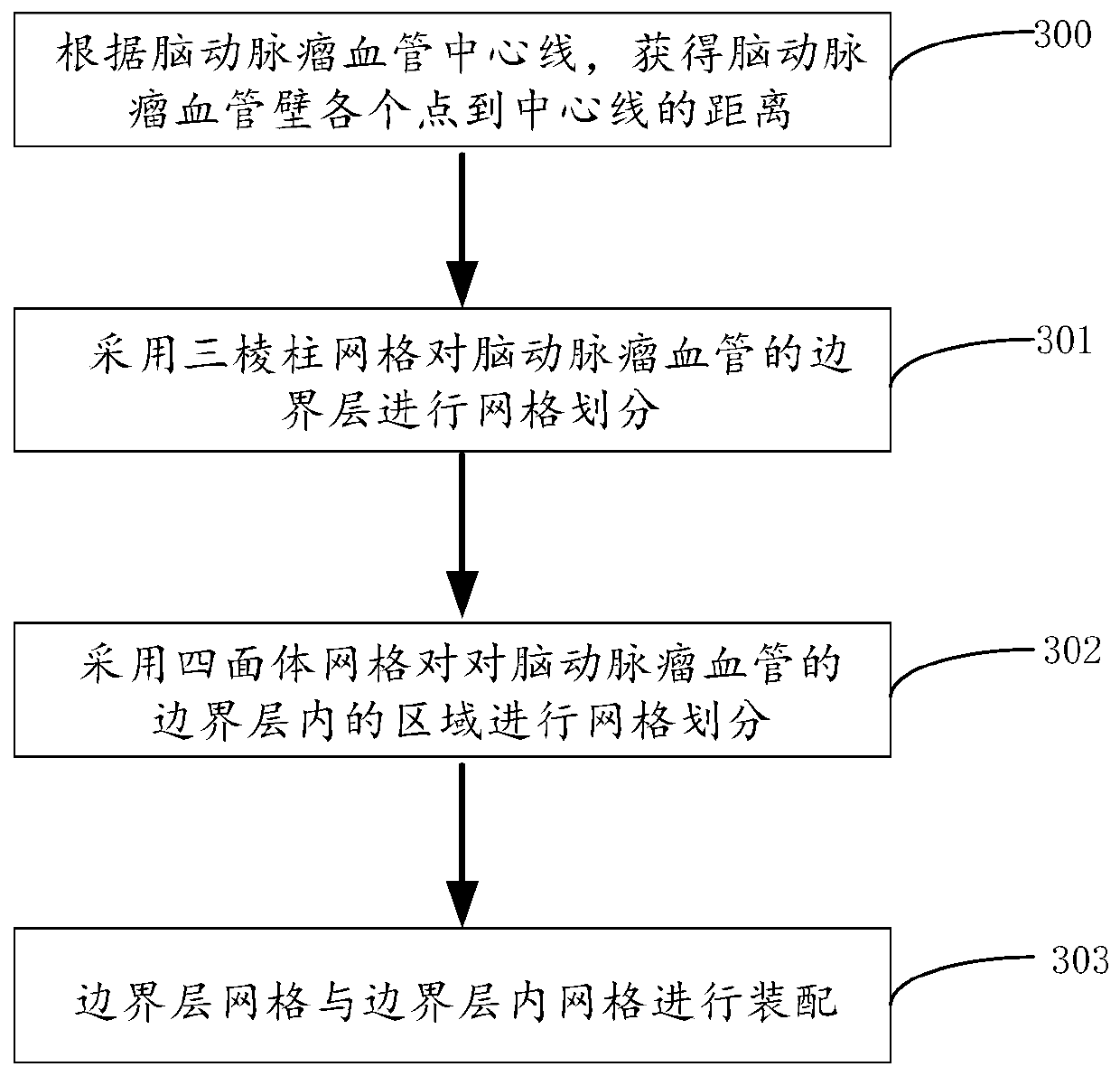
Cerebral aneurysm hemodynamic index evaluation method, system and device and medium
PendingCN110866914AEvaluation non-invasiveEvaluation scienceImage enhancementDiagnostic signal processingHuman bodyBlood flow
The invention discloses a cerebral aneurysm hemodynamic index evaluation method, system and device and a medium. The evaluation method comprises the following steps: acquiring human body cerebral artery image data; carrying out anatomical modeling on the human body cerebral artery medical image data to obtain a cerebral aneurysm anatomical model; fluid mechanics calculation processing is conductedon the cerebral aneurysm anatomical model, and outputting a calculation result; and adding the calculation result to a corresponding position of the cerebral aneurysm anatomical model, and carrying out visual display of hemodynamic indexes. According to the method, the system, the equipment and the medium, the hemodynamic indexes of the cerebral aneurysm can be obtained according to the medical image data of the human cerebral artery. Therefore, the relationship between the hemodynamic characteristics and the occurrence, development and rupture of the aneurysm can be analyzed based on the obtained hemodynamic indexes, and a theoretical basis is provided for risk factor assessment and interventional therapy of the cerebral aneurysm.
Owner:BEIJING GUANSHENGYUN MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Flow Directional Infusion Device
A flow directional infusion device includes a filter valve located at the distal end of a catheter. The filter valve constrains delivery of an embolic agent through the catheter to the locus of the aneurysm. In order to provide such delivery, the valve includes a longitudinal opening, radial opening or is otherwise partially permeable in a direction of the aneurysm so that the embolic agent or a delivery element for such agent is limited toward the aneurysm. In addition, the filter valve permits and directs blood flow within the blood vessel about the aneurysm during the treatment without obstructing the vessel and without allowing retrograde flow of the embolic agent in the vessel upstream of the aneurysm.
Owner:TRISALUS LIFE SCI INC
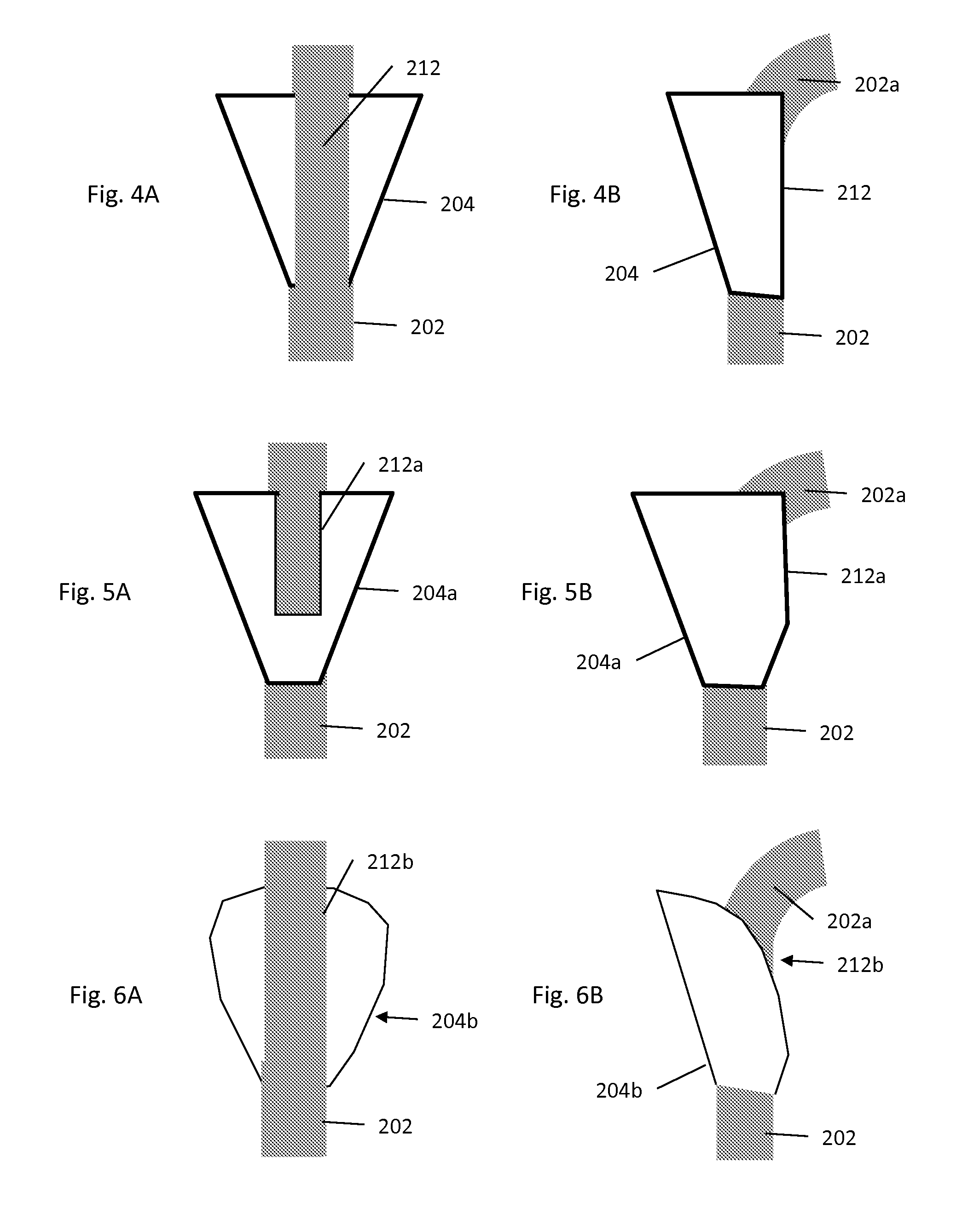
Aneurysm embolization device and operation method thereof
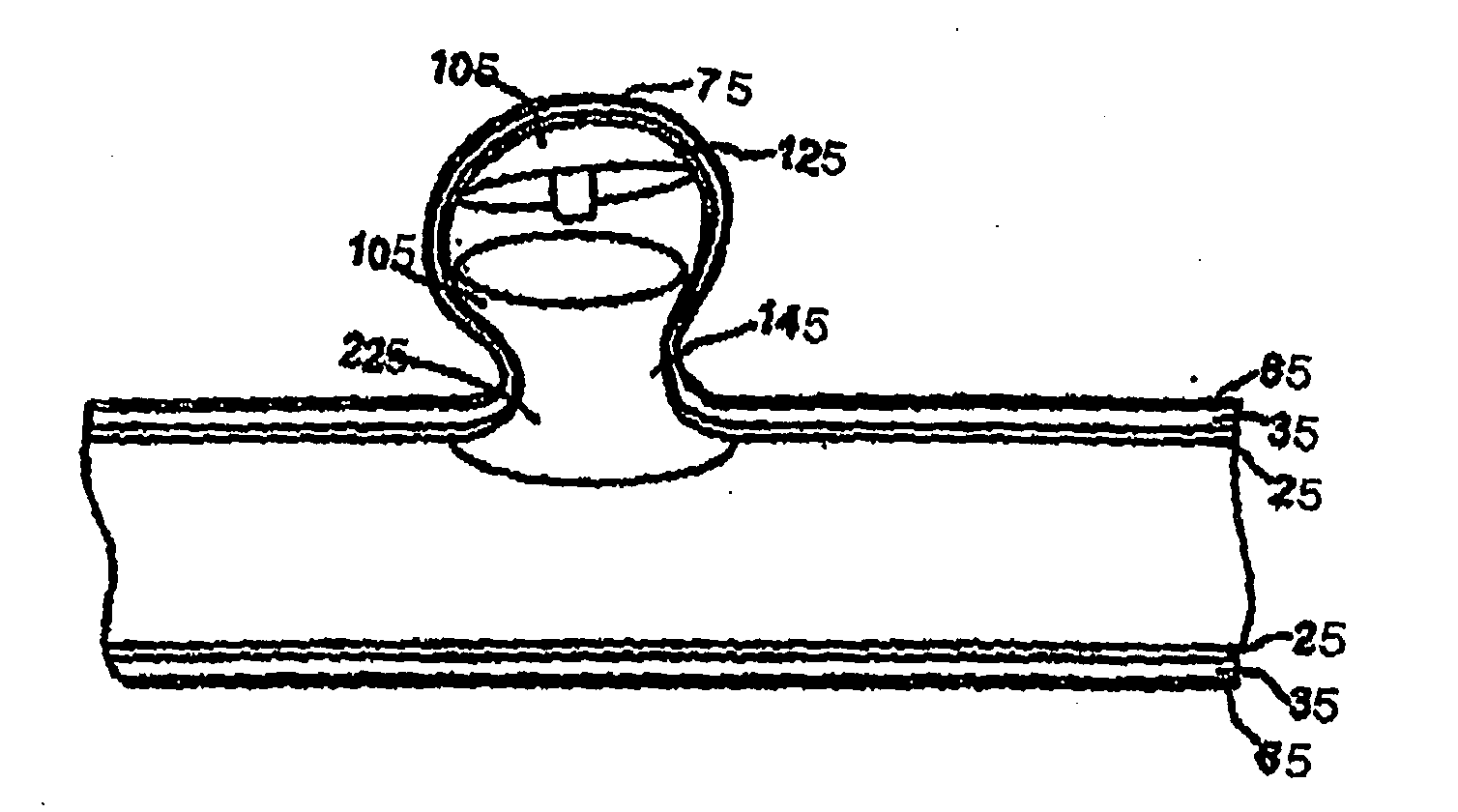
InactiveUS20100160949A1Occluding an aneurysm readily and reliablyStentsBalloon catheterIliac AneurysmAneurysm embolization
An aneurysm embolization device includes at least: a sac-shaped balloon dome part which is inserted into the aneurysm, then expanded and left therein; and a balloon plane part which is provided at an opening of the balloon dome part and covers a mouth part of the aneurysm. The balloon plane part has a hole communicating with the inside of the balloon dome part. The aneurysm embolization device thus constituted is housed into a lumen of a protective outer sheath member formed of a flexible elongated-body having the lumen therein. A tip part of the protective outer sheath member is placed at a desired position, and the aneurysm embolization device is ejected from the tip part of the protective outer sheath member. The aneurysm embolization device thus ejected includes the balloon dome part placed at a desired position and the balloon plane part deploying to cover the desired position.
Owner:TAKUMA NORIKATA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com