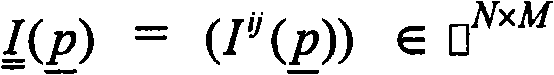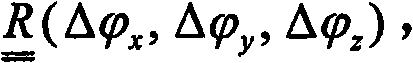Patents
Literature
50 results about "Arterial stenosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
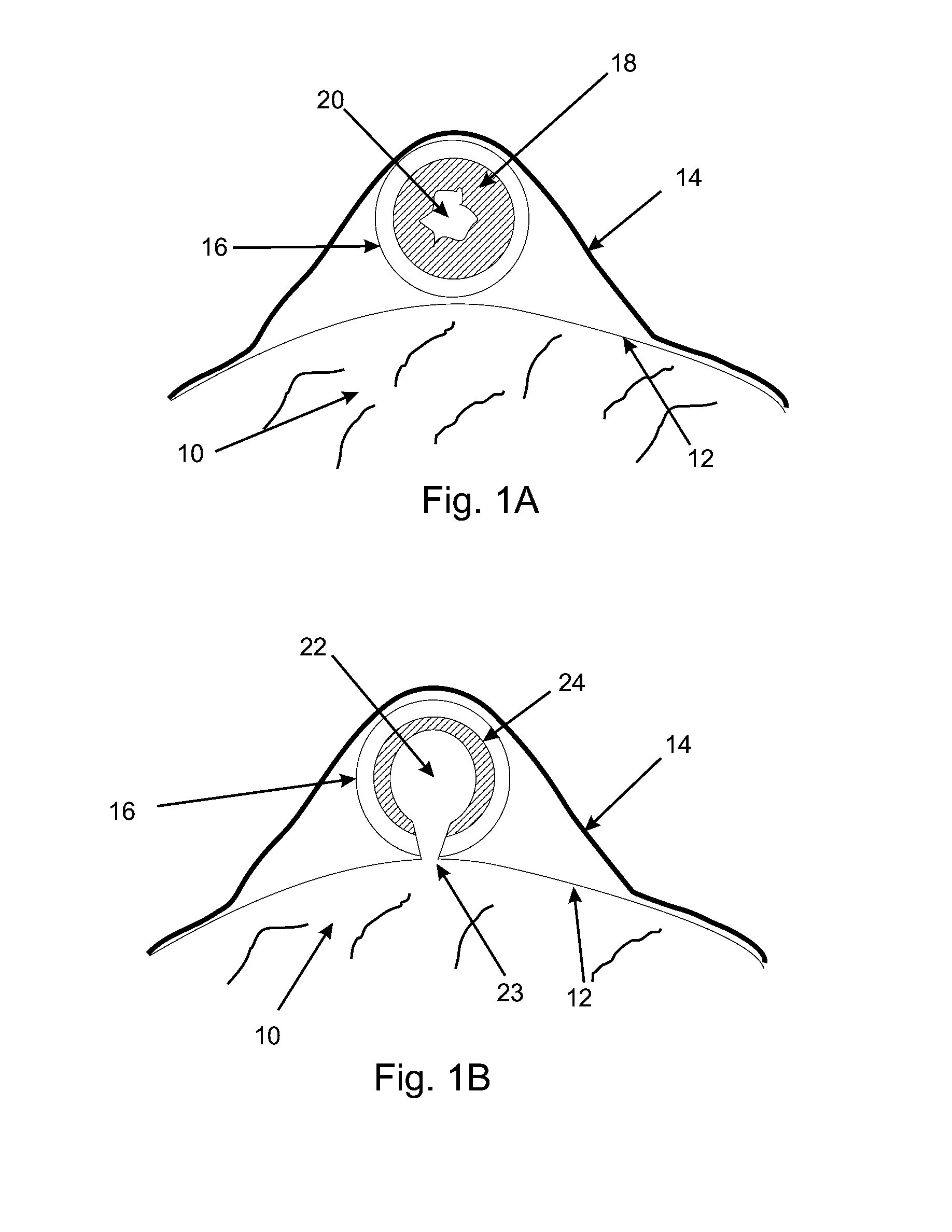
Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is a condition in which the arteries that supply blood to the kidneys narrow. The renal arteries are responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood to your kidneys, which in turn helps the kidneys rid your body of waste and excess fluid.
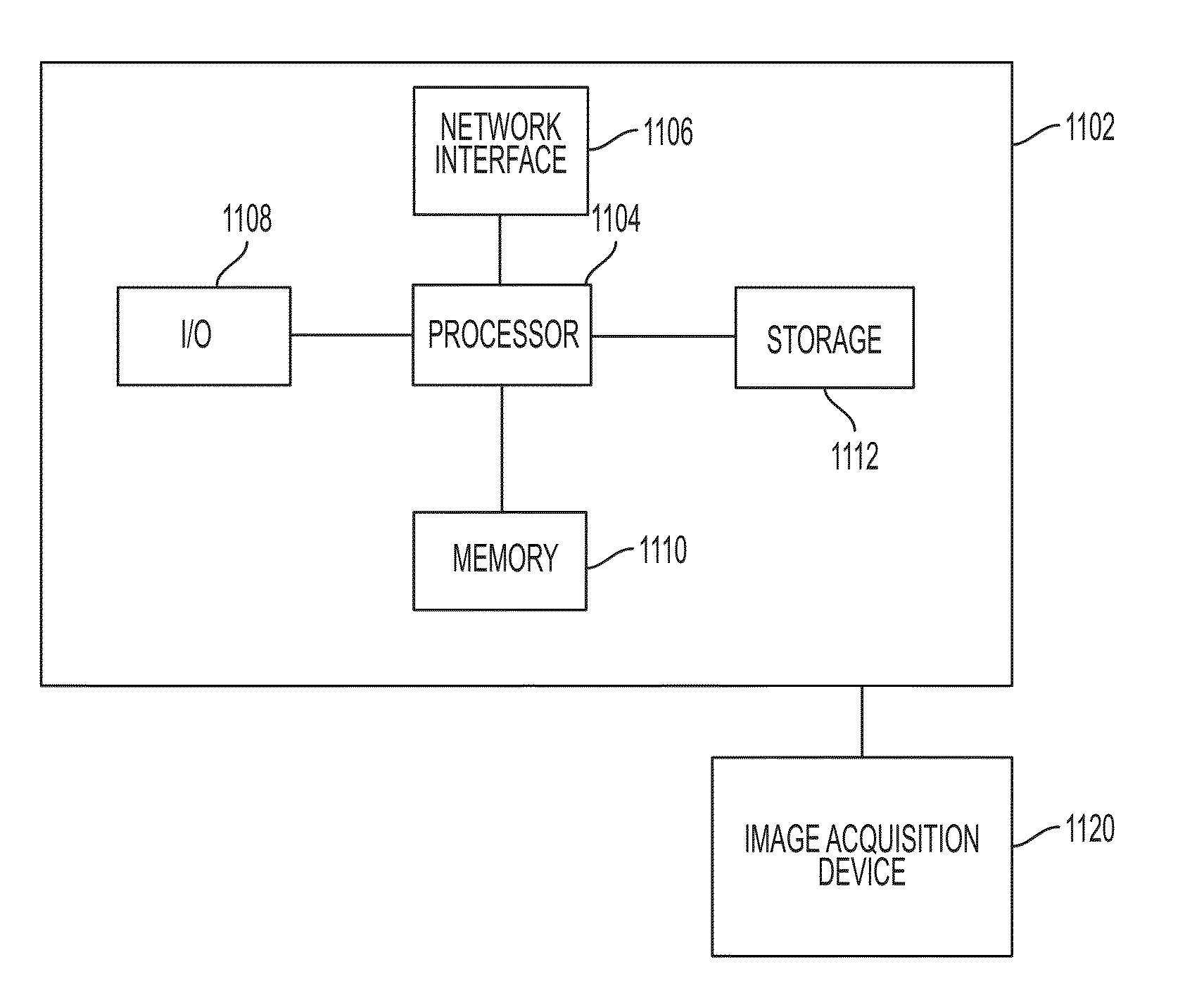
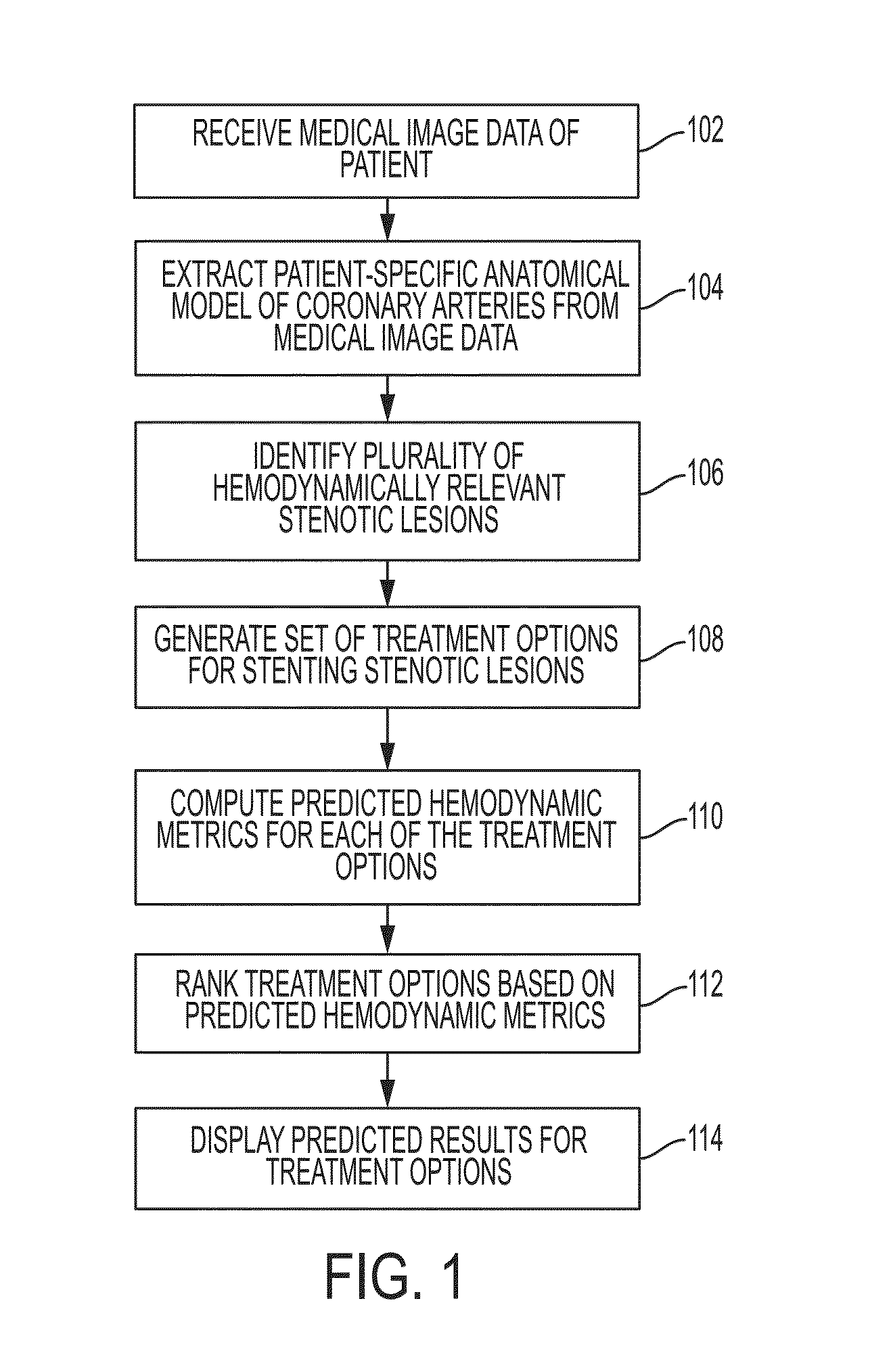
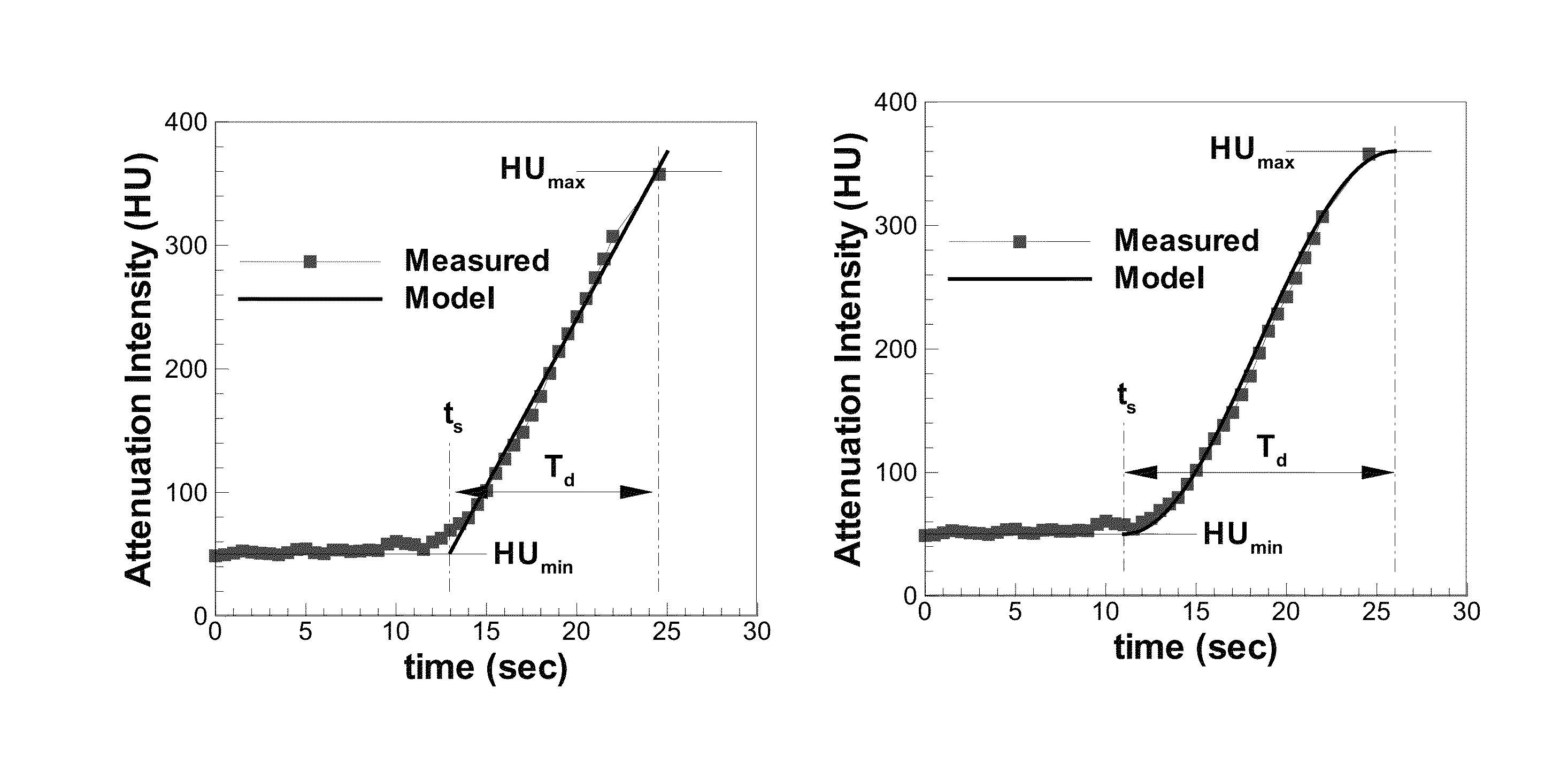
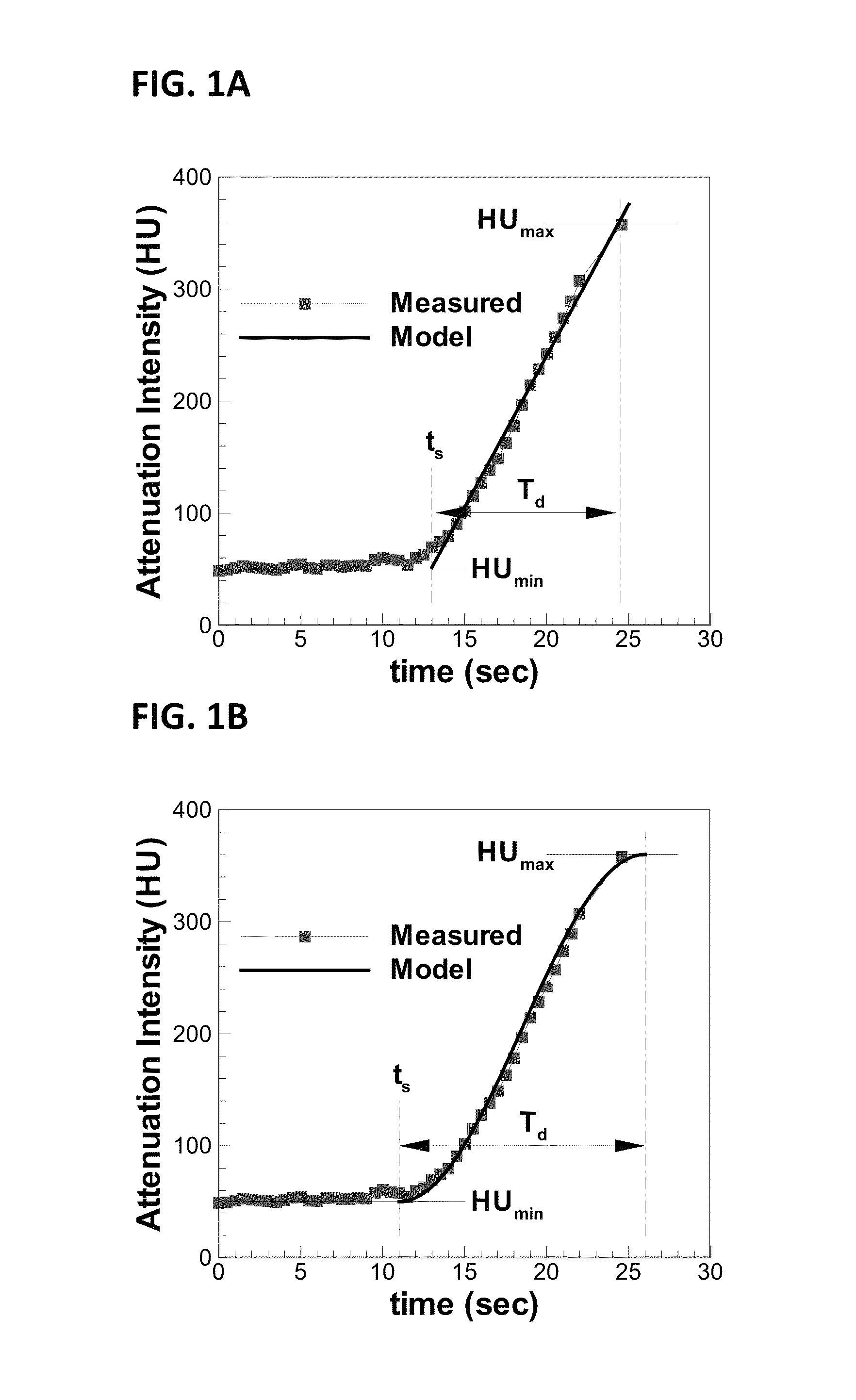
Method and System for Automated Therapy Planning for Arterial Stenosis
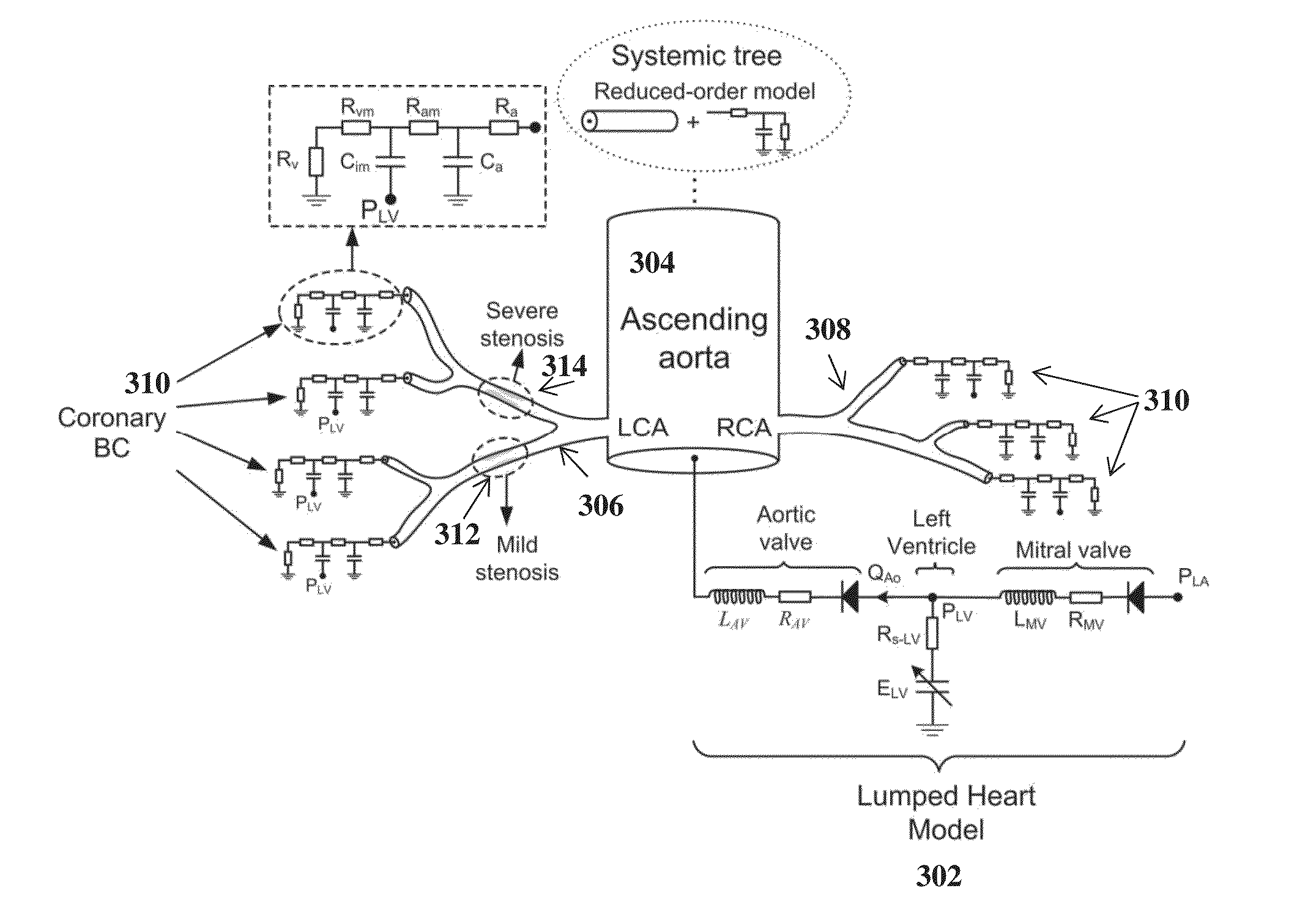
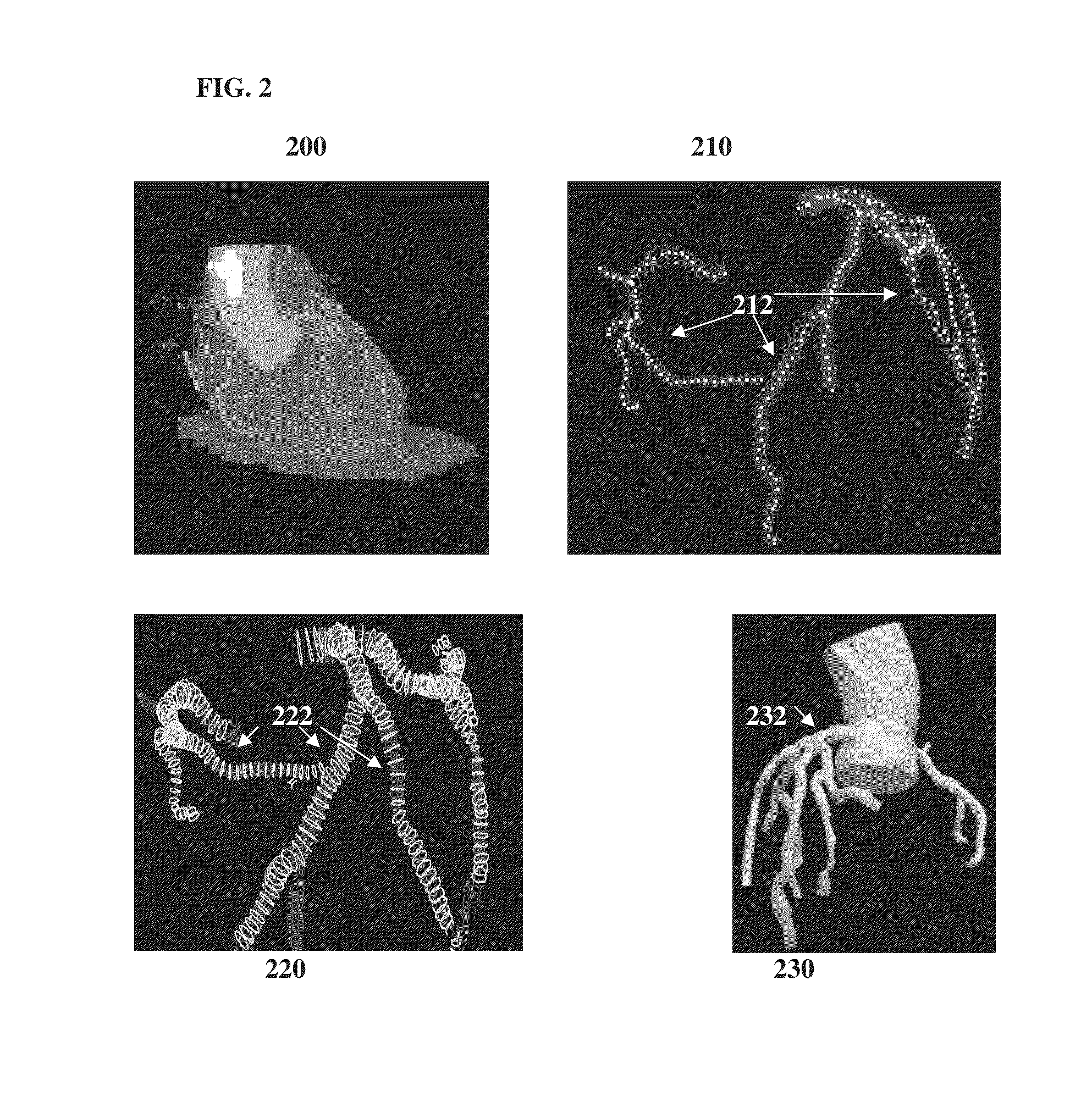
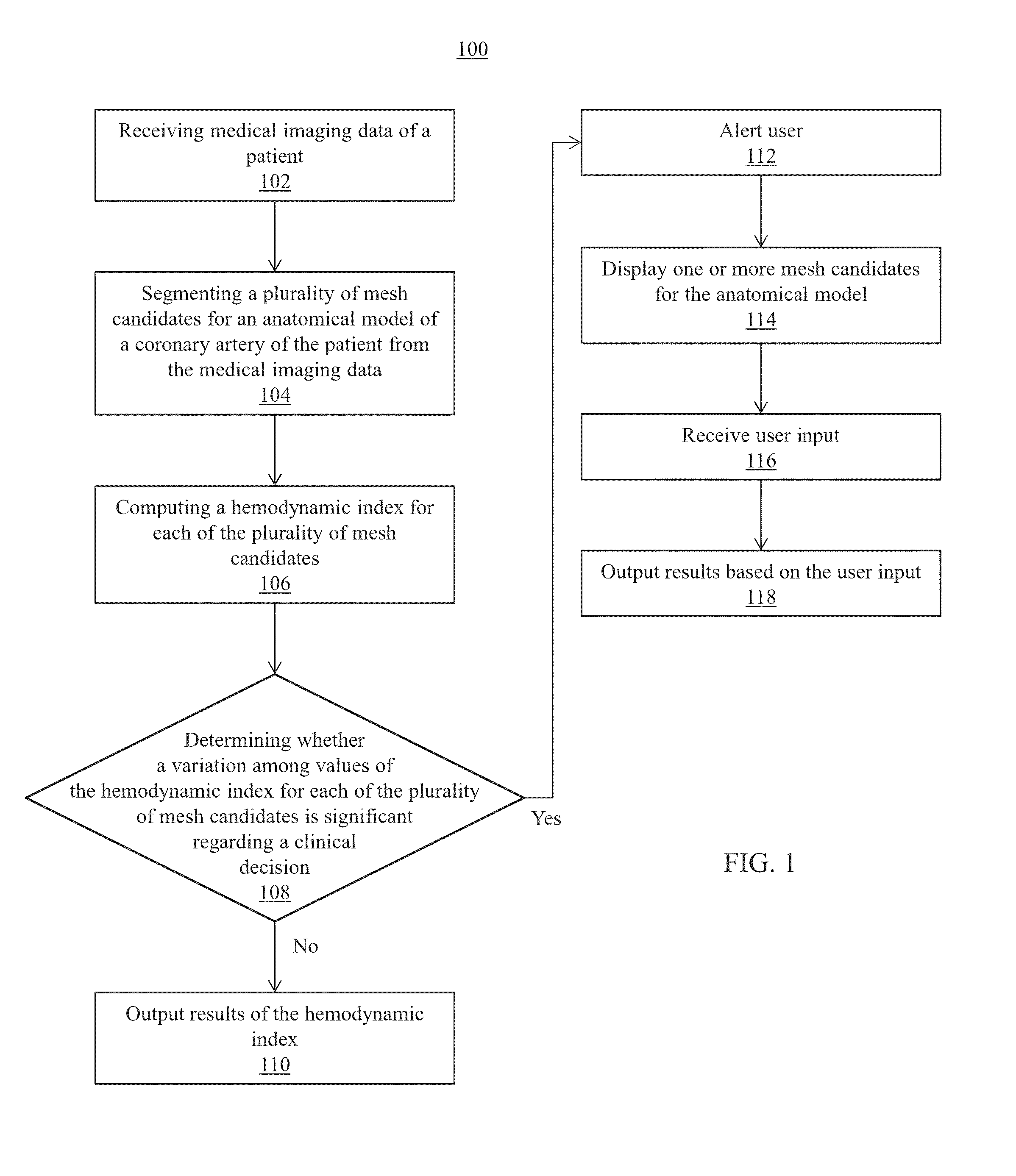
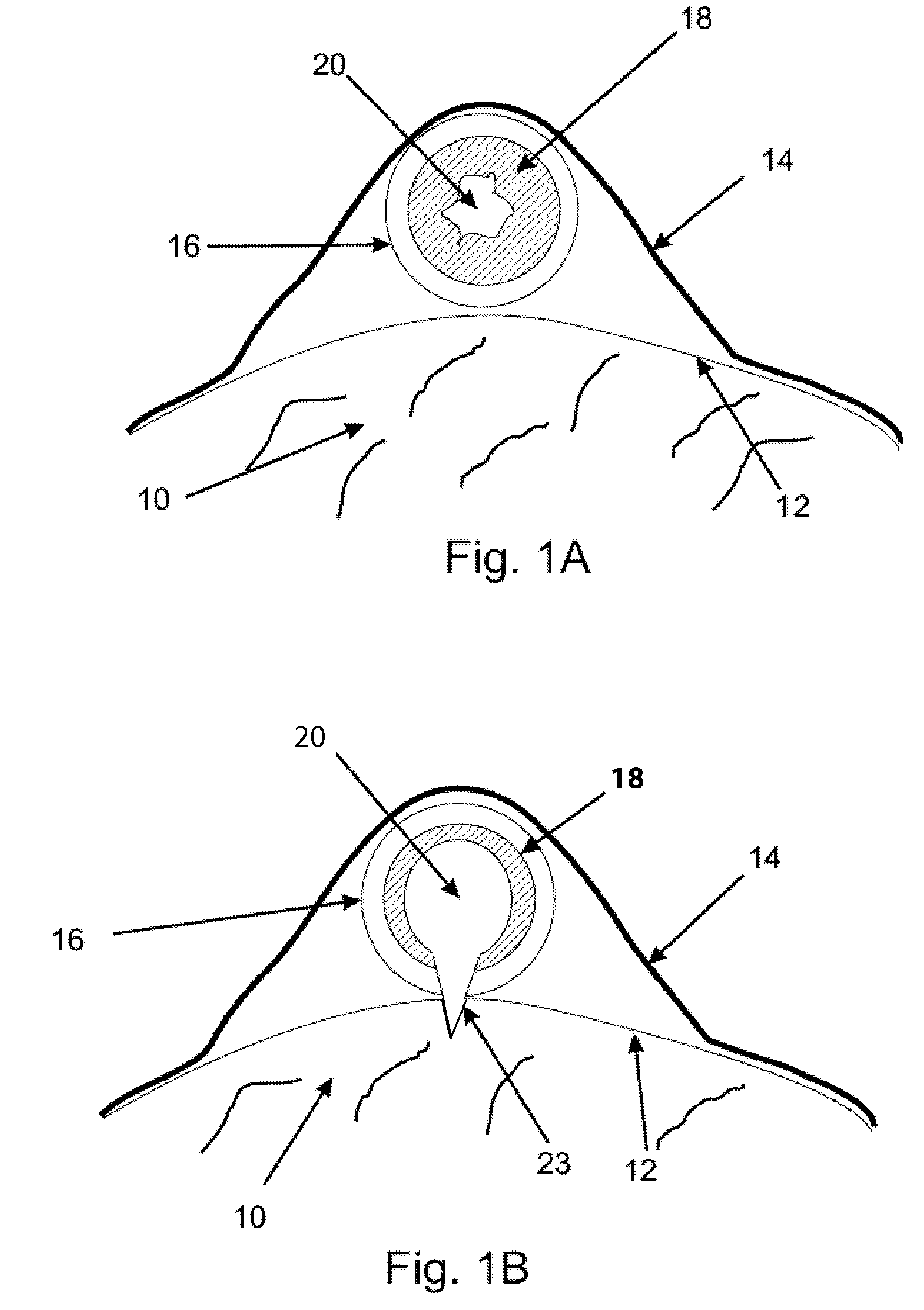
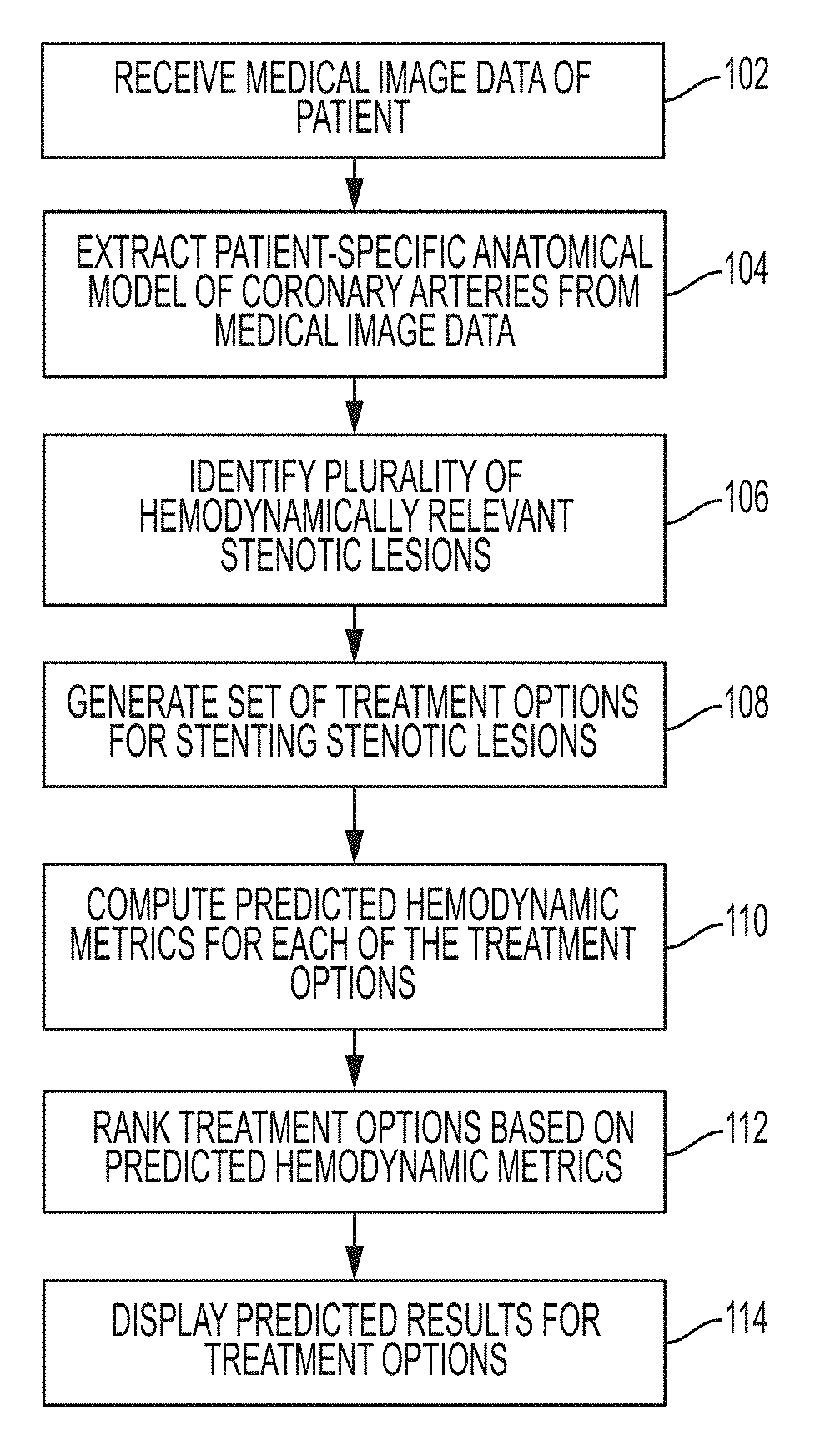
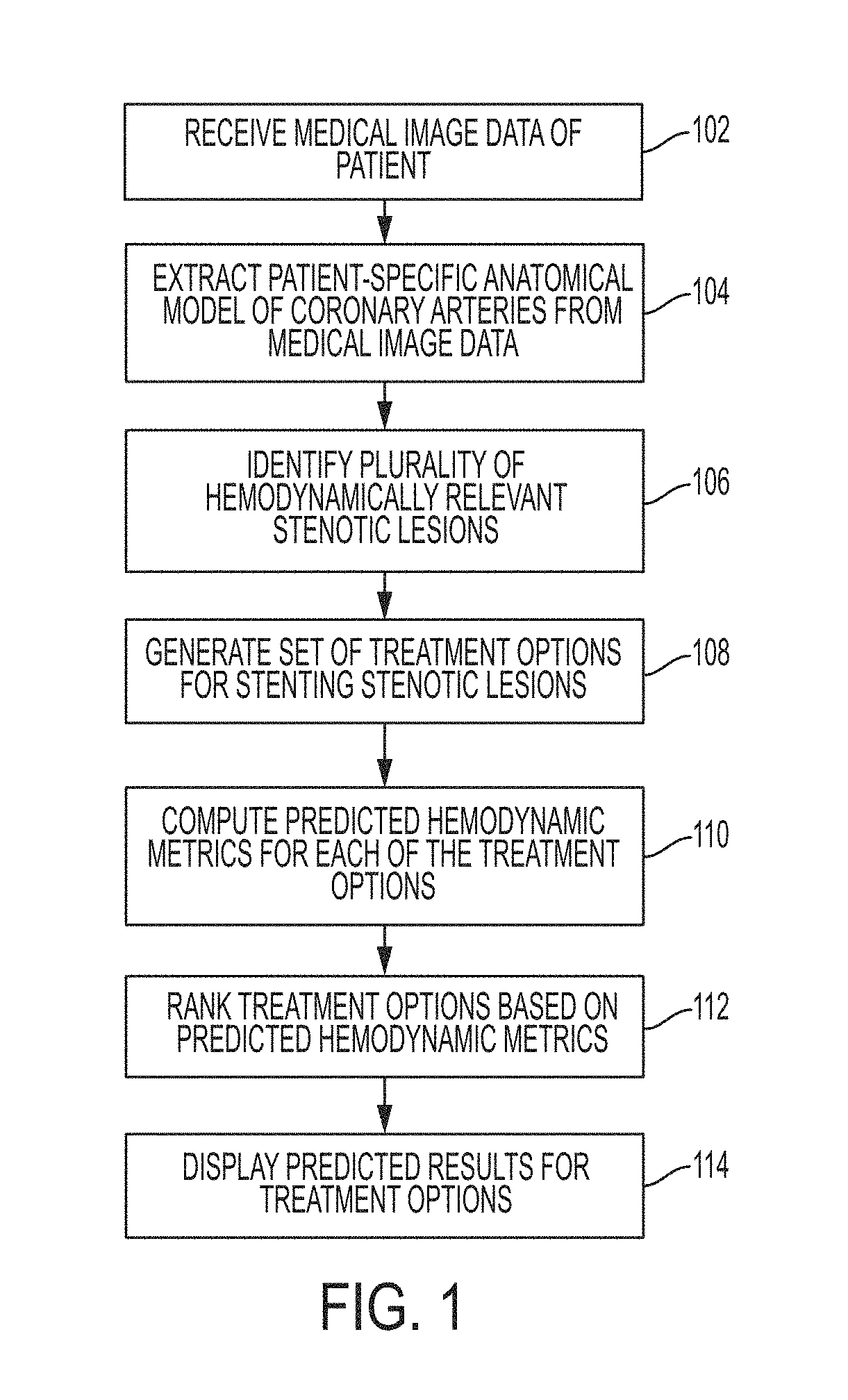
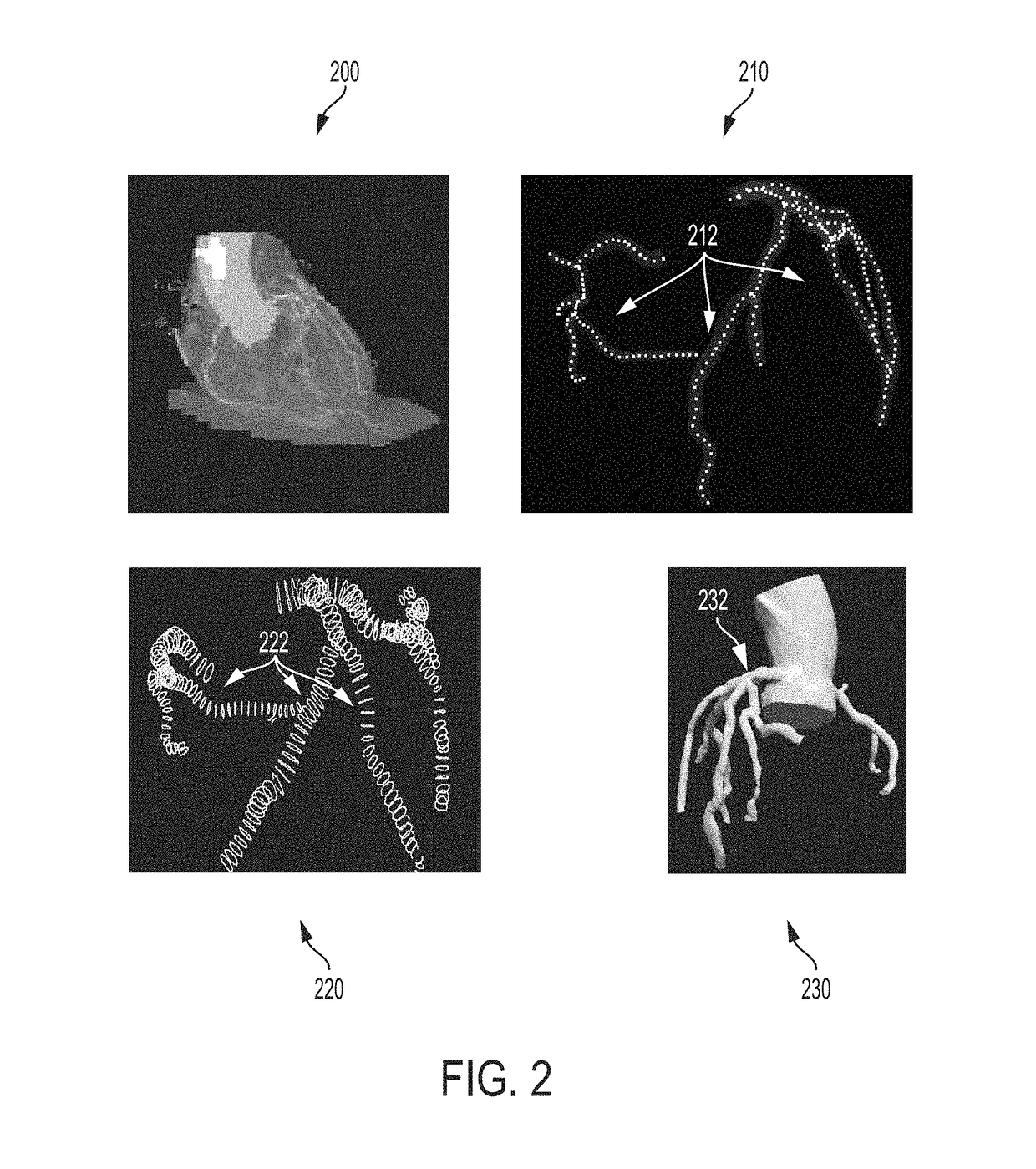
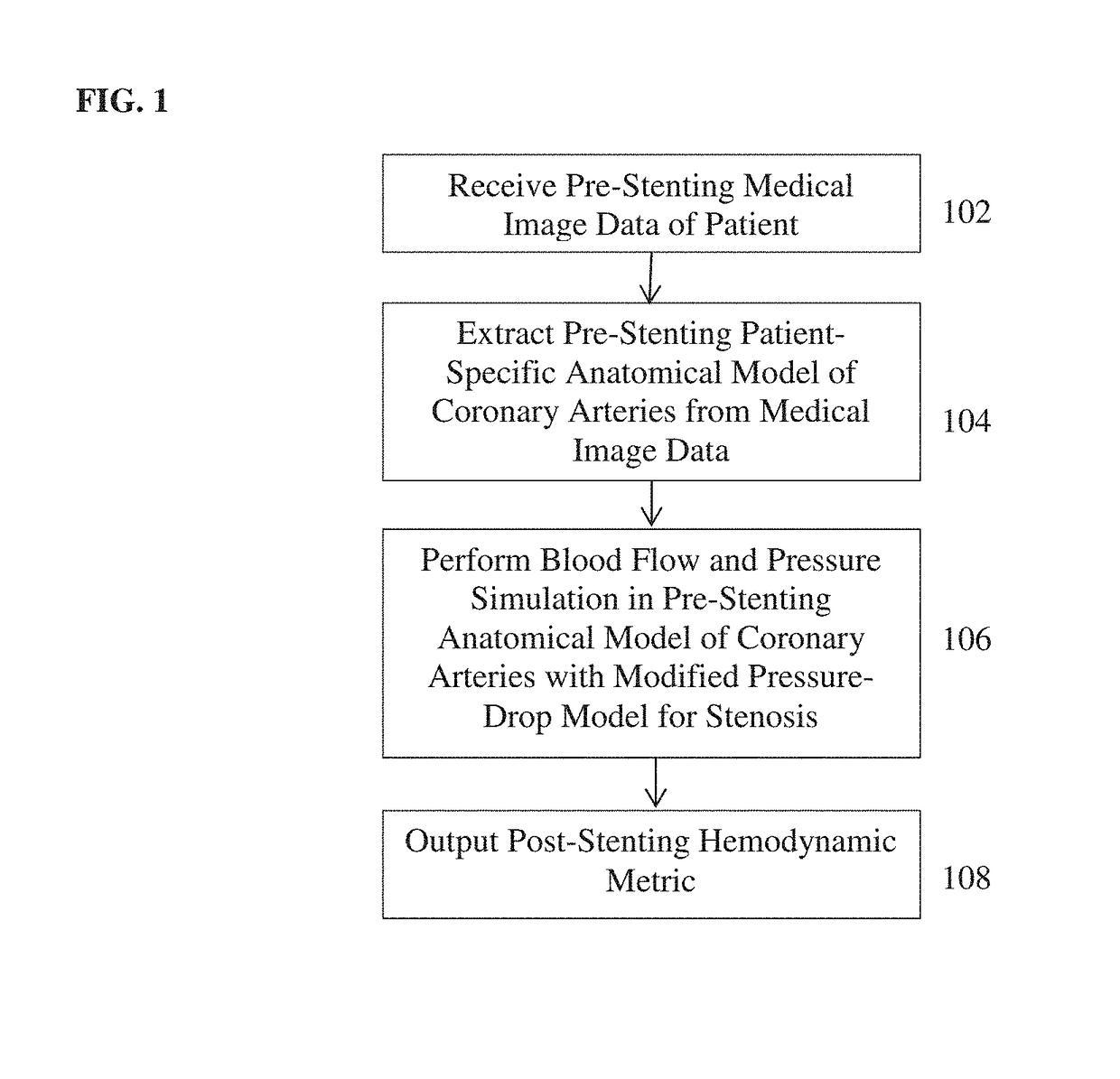
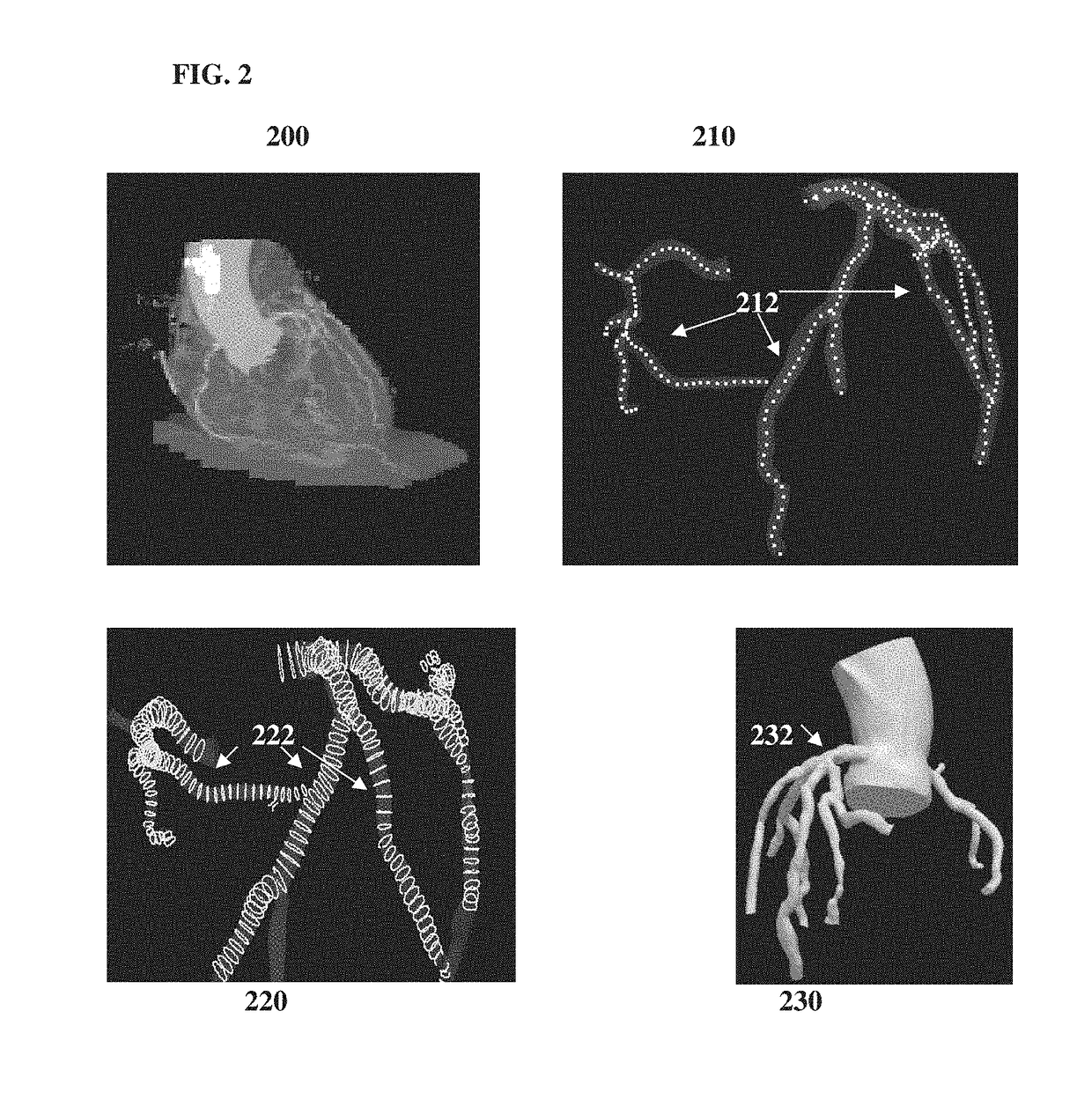
A method and system for automated decision support for treatment planning of arterial stenoses is disclosed. A set of stenotic lesions is identified in a patient's coronary arteries from medical image data of the patient. A plurality of treatment options are generated for the set of stenotic lesions, wherein each of the plurality of treatment options corresponds to a stenting configuration in which one or more of the stenotic lesions are stented. For each of the plurality of treatment options, predicted hemodynamic metrics for the set of stenotic lesions resulting from the stenting configuration corresponding to that treatment option are calculated.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Medicinal balloon catheter and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a medicinal balloon catheter and a preparation method thereof. The balloon outside surface of the medicinal balloon catheter is grinded and processed through ultraviolet laser to form the concave-convex non-planar structure on the balloon outside surface. The gaps within the non-planar structure form a drug storage layer. The wavelength of the ultraviolet laser is within the range of 10-400nm. The wall thickness of the medicinal balloon catheter is 15-25 microns. The thickness of the non-planar structure is 8-12 microns. Owning to the concave-convex non-planar structure of the balloon outside surface of the medicinal balloon catheter in the invention, the medicinal adsorption storage capacity is fundamentally improved, namely firstly, the amount of the adsorbed medicine is greatly increased, secondly when medicine adsorbed on balloon passes through blood vessels to reach the site of lesion, the medicine adsorbed on the outer wall of the balloon can be maintained as much as possible and cannot be washed off by blood in the blood vessels and cause loss, and can be effectively transferred to the site of lesion by the balloon so as to have effectively therapeutic action. The medicinal balloon catheter of the invention can be used in not only coronary heart disease, but also various diseases caused by other narrow vessels such as lower extremity arterial stenos is or occlusion caused by diabetes.
Owner:成都维德医疗器械有限责任公司
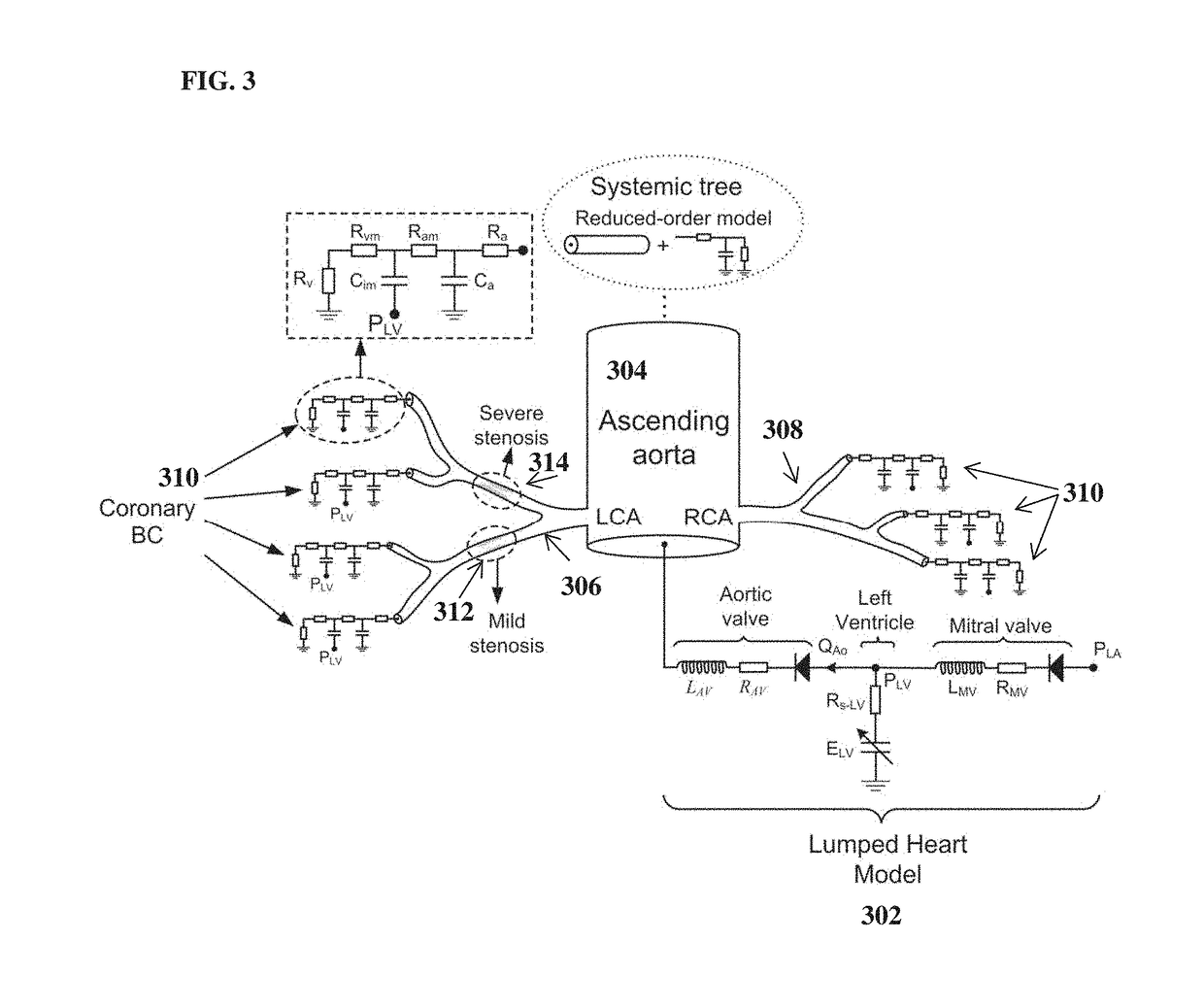
Method and System for Prediction of Post-Stenting Hemodynamic Metrics for Treatment Planning of Arterial Stenosis
A method and system for prediction of post-stenting hemodynamic metrics for treatment planning of arterial stenosis is disclosed. A pre-stenting patient-specific anatomical model of the coronary arteries is extracted from medical image data of a patient Blood flow is simulated in the pre-stenting patient-specific anatomical model of the coronary arteries with a modified pressure-drop model that simulates an effect of stenting on a target stenosis region used to compute a pressure drop over the target stenosis region. Parameter values for the modified pressure-drop model are set without modifying the pre-stenting patient-specific anatomical model of the coronary arteries. A predicted post-stenting hemodynamic metric for the target stenosis region, such as fractional flow reserve (FFR), is calculated based on the pressure-drop over the target stenosis region computed using the modified pressure-drop model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Treatment of Coronary Stenosis
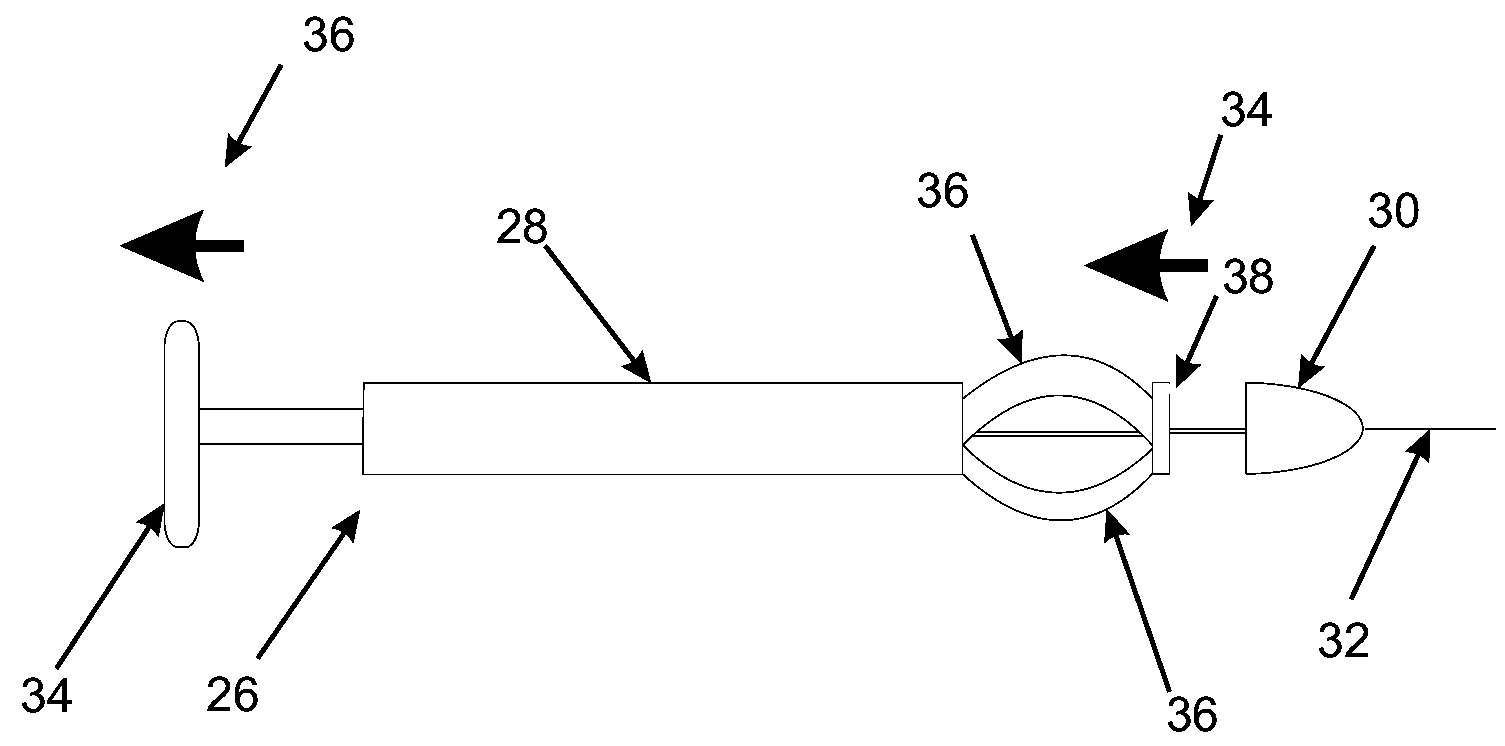
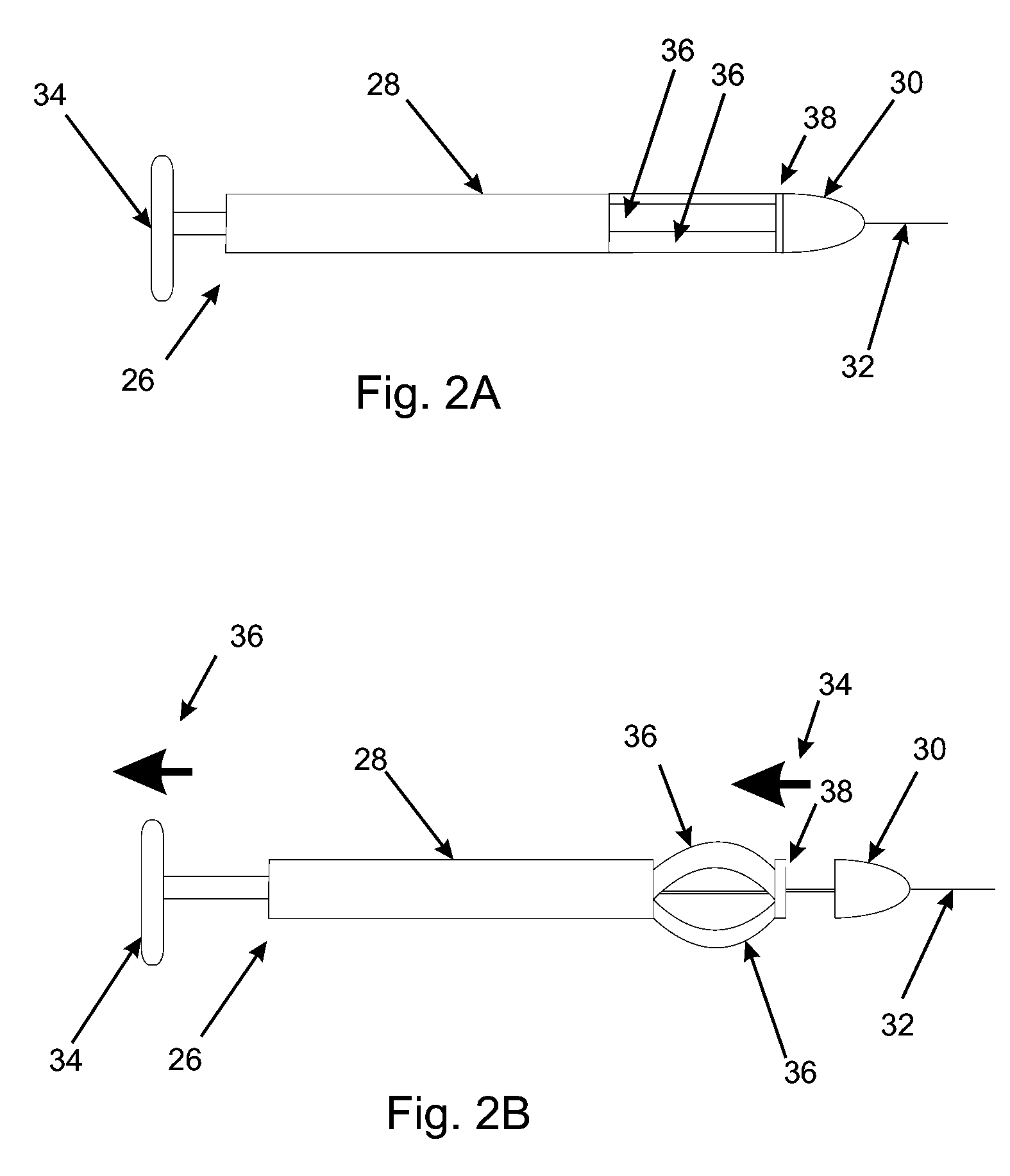
The invention describes includes a device and method for dilating a coronary arterial stenosis and for creating a transection in the myocardium. The transection creates a new artery composed partially of the old artery and partially of the normal healing tissue and myocardium. Several dilating means are described, as well as several cutting means and alignment means by which the cutting means may be located and properly oriented. In operation, the dilating means, cutting means and alignment means are advanced in the distal end of a catheter, which may be guided into position by a guidewire.
Owner:LARY RES & DEV
Detection and tracking of interventional tools
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and system for quantification of arterial stenosis
InactiveUS20050119573A1Accurately determineBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency spectrumArterial stenosis
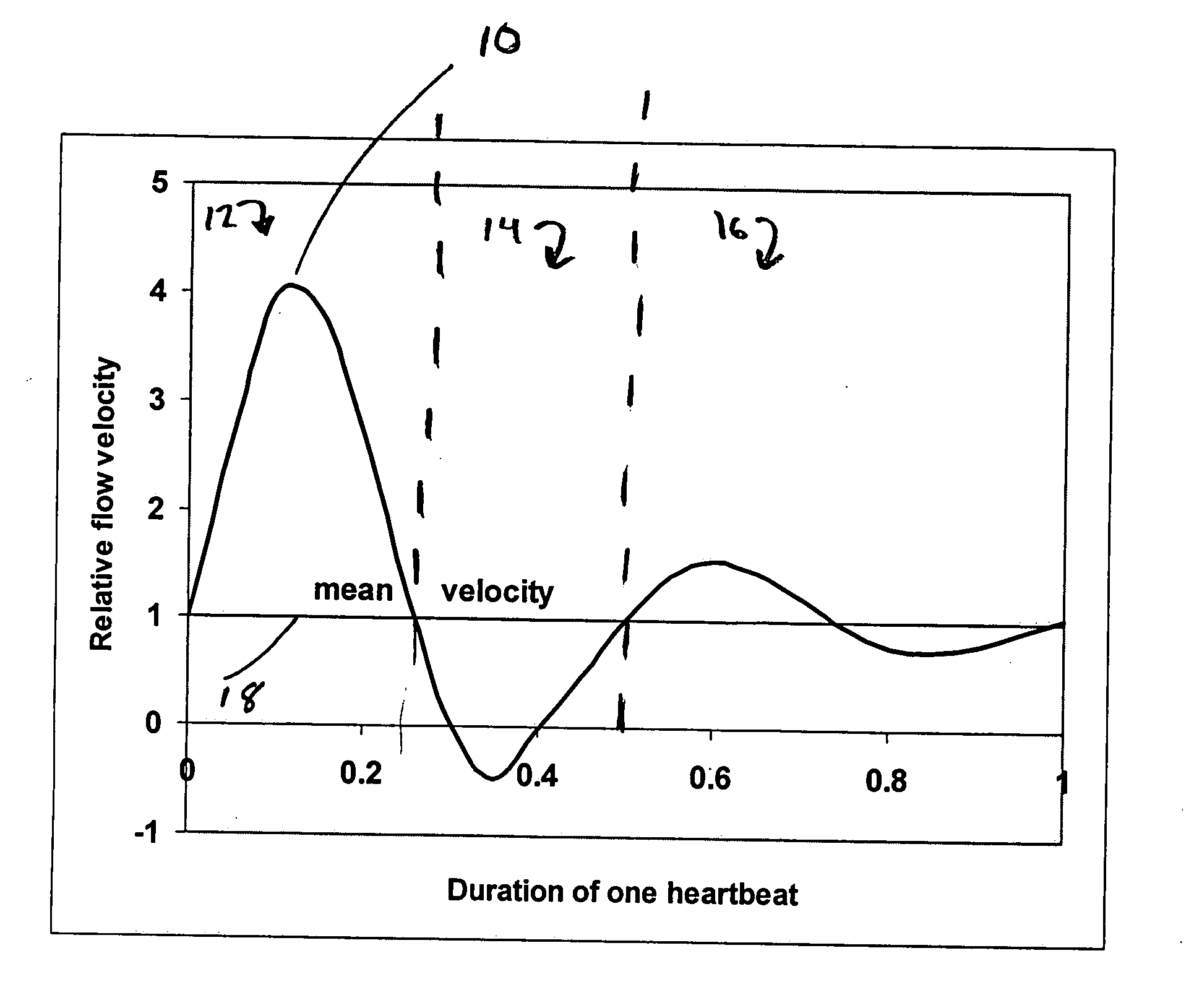
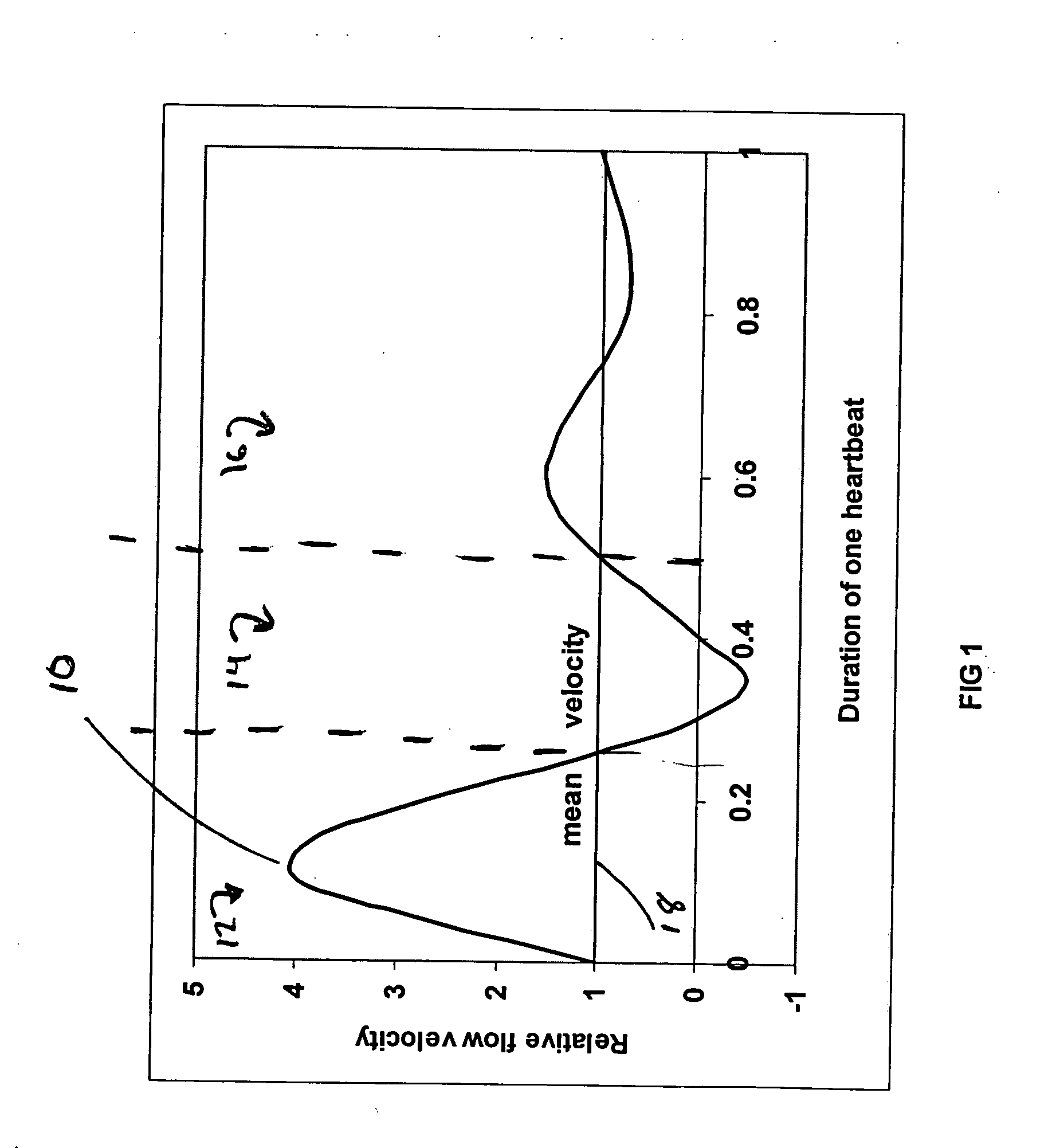
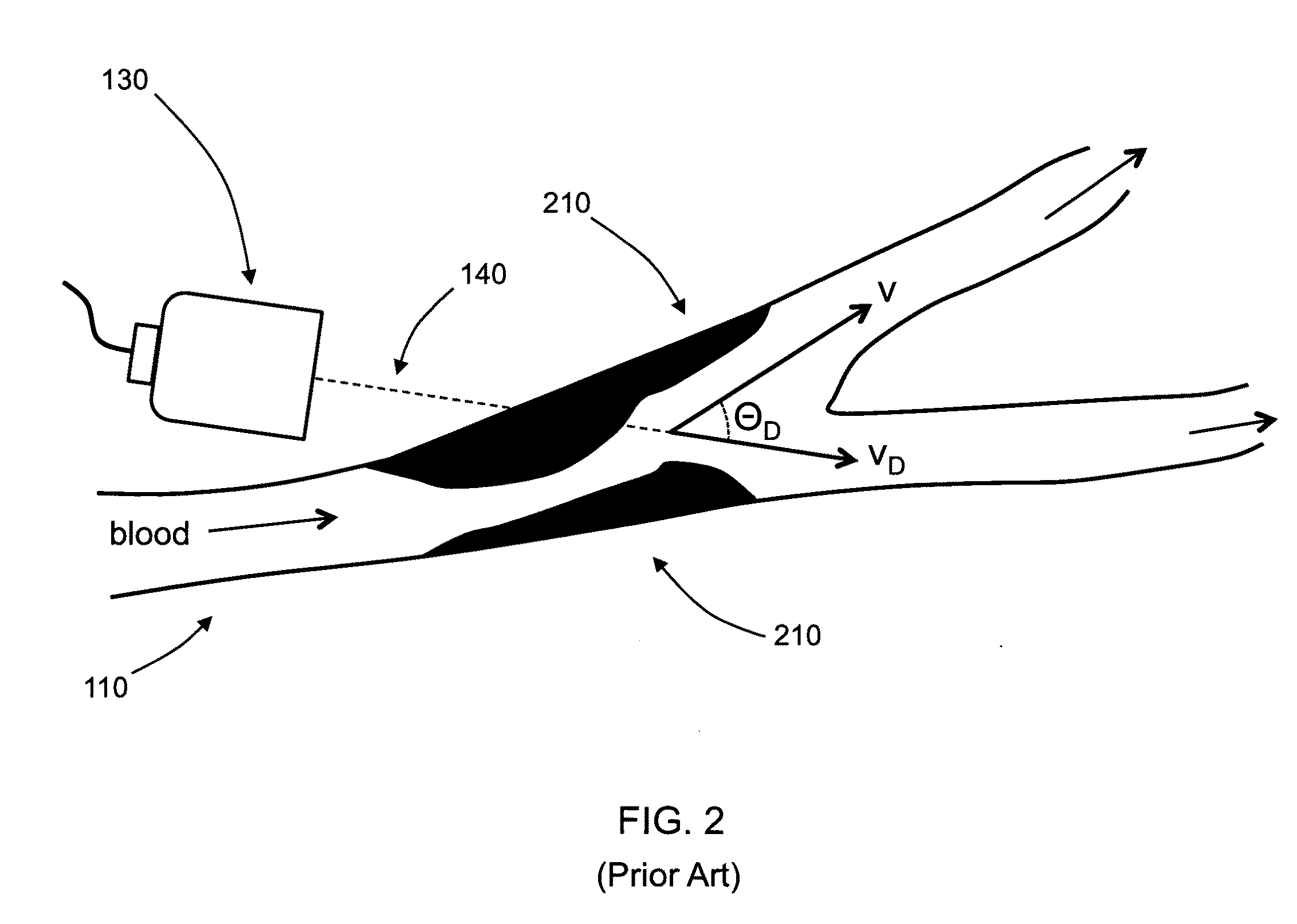
A method is proposed that identifies and quantifies stenoses in arteries based on an analysis of Doppler frequency shifts from several heartbeats. It is non-invasive and individual insensitive. Pulsatile flow through a blood vessel with wall roughness and / or variable lumen area generates flow disturbances, which lead to variations in the shape of the Doppler shift frequency spectrum. One or several frequency bands that are affected by these flow disturbances are selected from the overall Doppler shift frequency spectrum. Next, one or several parameters, which characterize the selected frequency bands and vary with the degree of stenosis, are used in a linear function to calculate the percentage of lumen area reduction. This method applies in the clinically important range of lumen area reduction of 10-70% with a standard error of 5% or less. For lumen area reductions greater than about 70%, the standard error is larger. A system for practical implementation is also proposed.
Owner:VAS SCAN
Method and System for Improved Hemodynamic Computation in Coronary Arteries
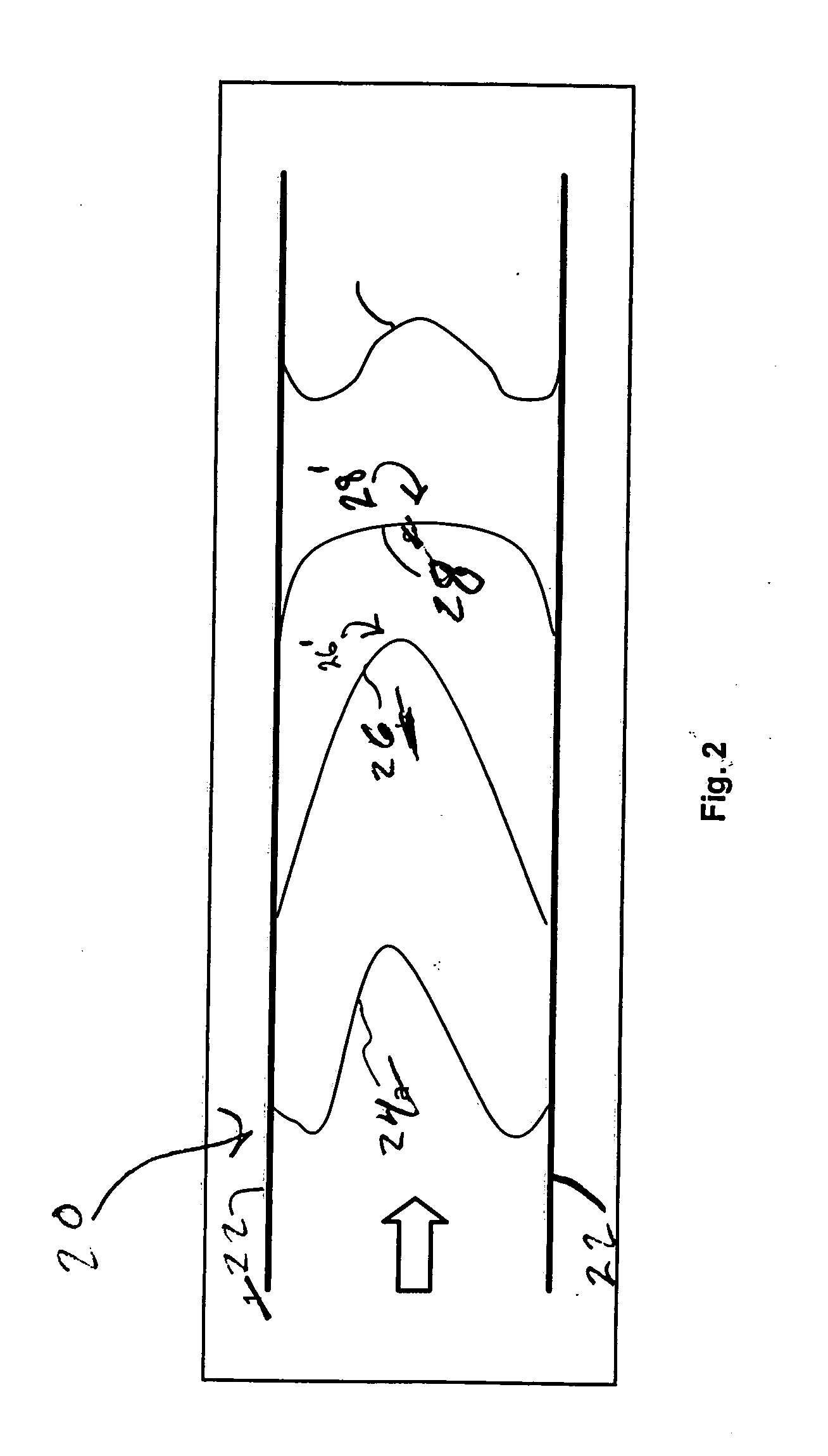
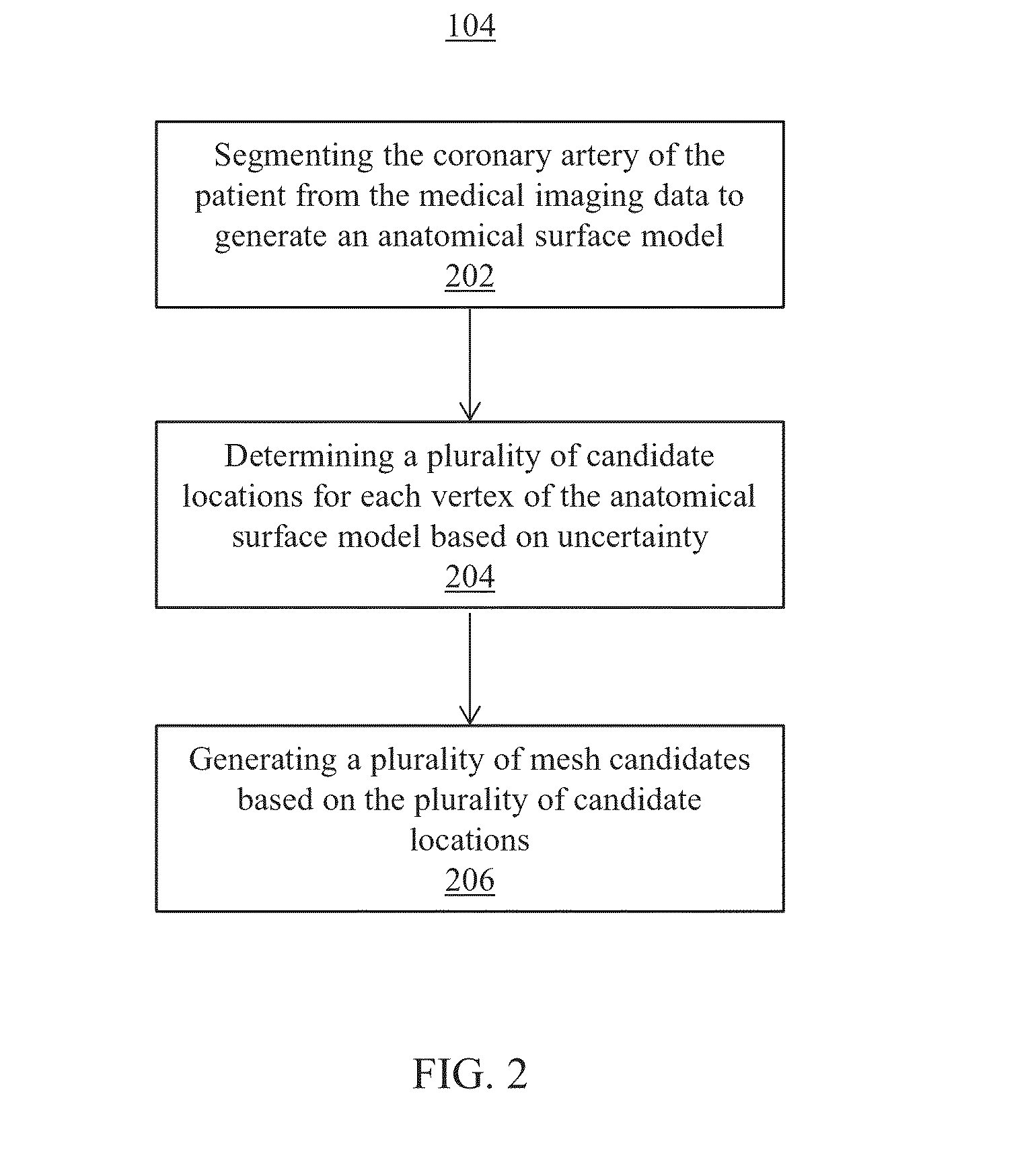
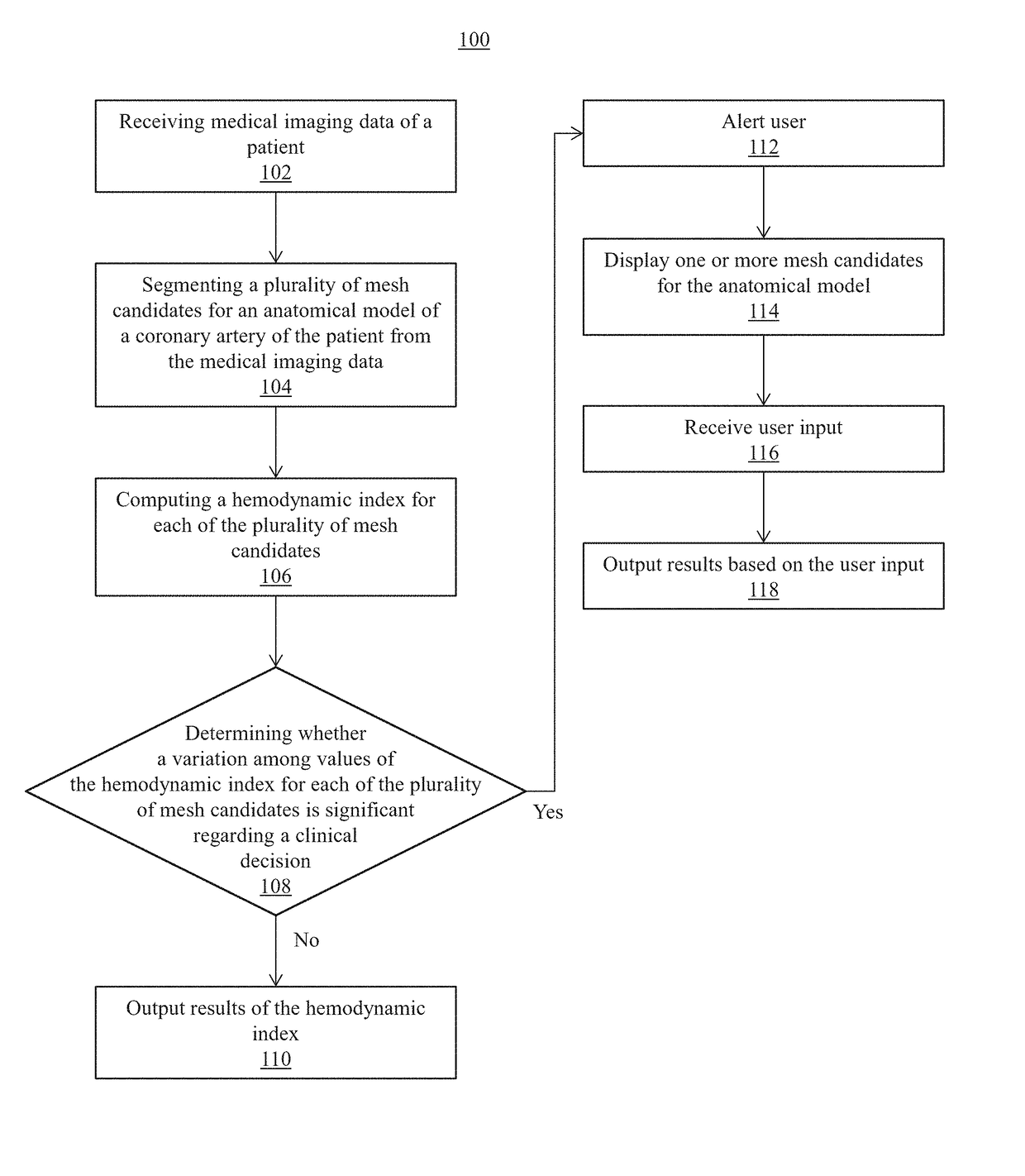
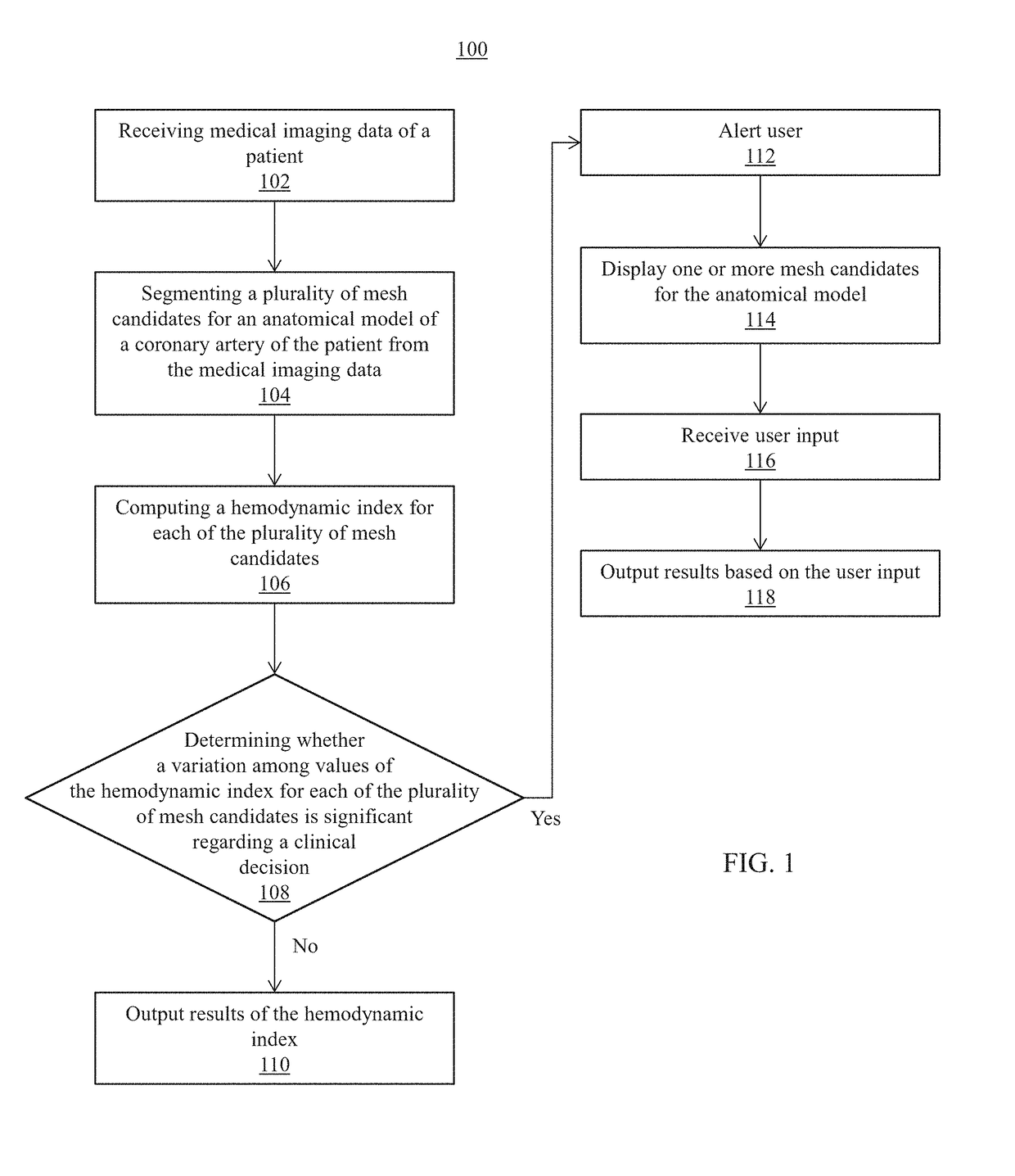
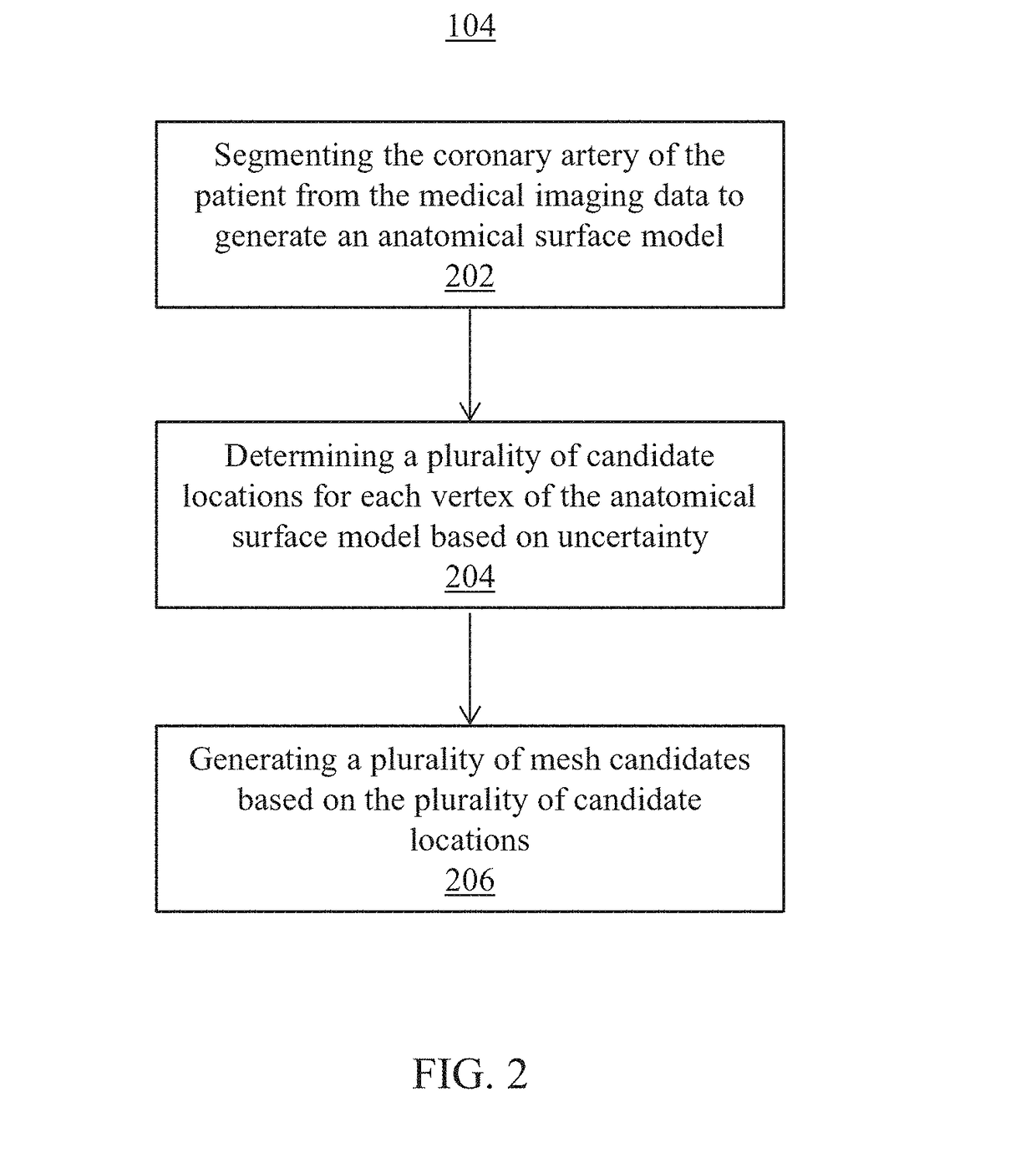
Systems and methods for non-invasive assessment of an arterial stenosis, comprising include segmenting a plurality of mesh candidates for an anatomical model of an artery including a stenosis region of a patient from medical imaging data. A hemodynamic index for the stenosis region is computed in each of the plurality of mesh candidates. It is determined whether a variation among values of the hemodynamic index for the stenosis region in each of the plurality of mesh candidates is significant with respect to a threshold associated with a clinical decision regarding the stenosis region.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for Estimating Flow Rates and Pressure Gradients in Arterial Networks from Patient Specific Computed Tomography Angiogram-Based Contrast Distribution Data
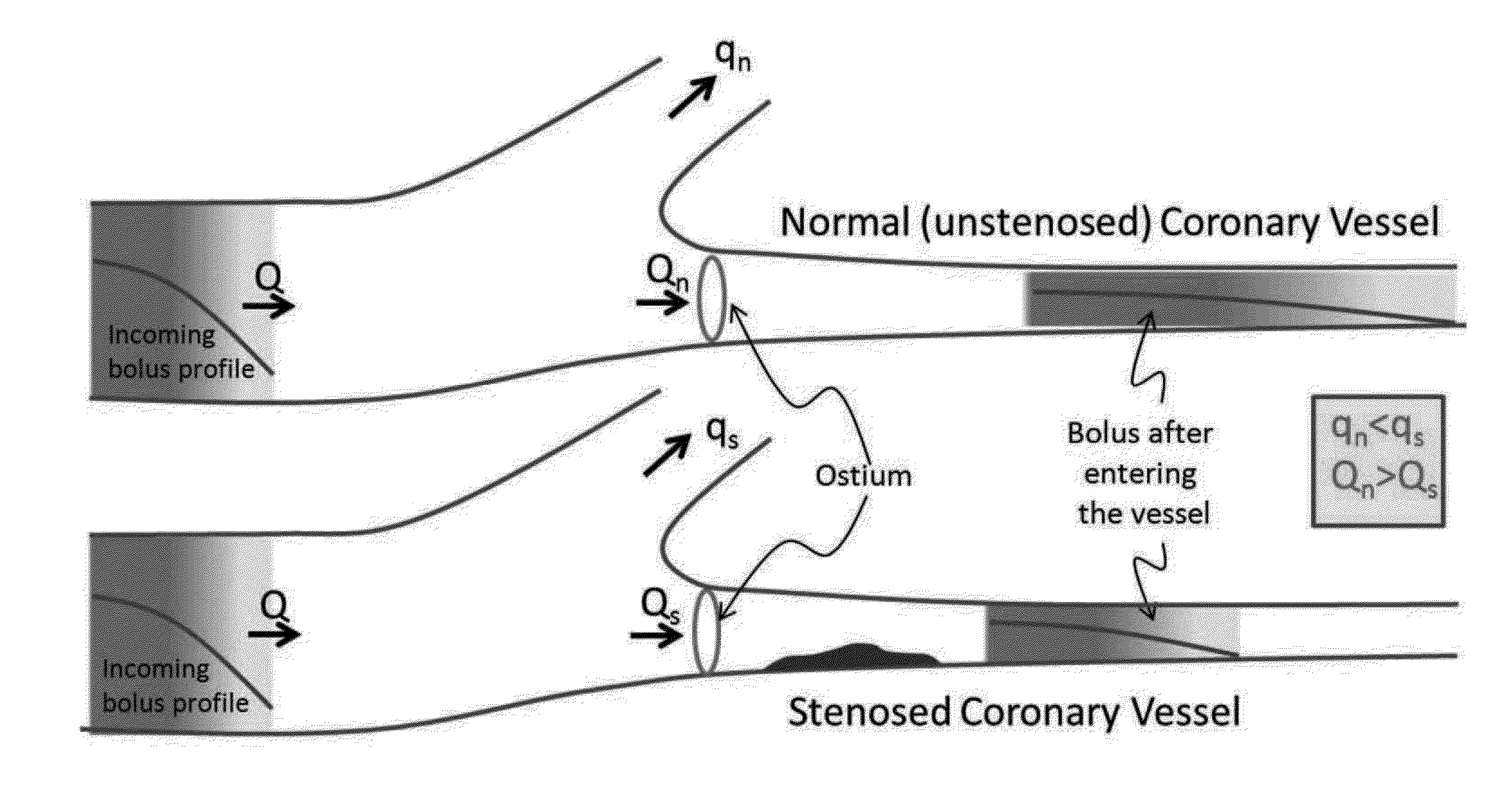
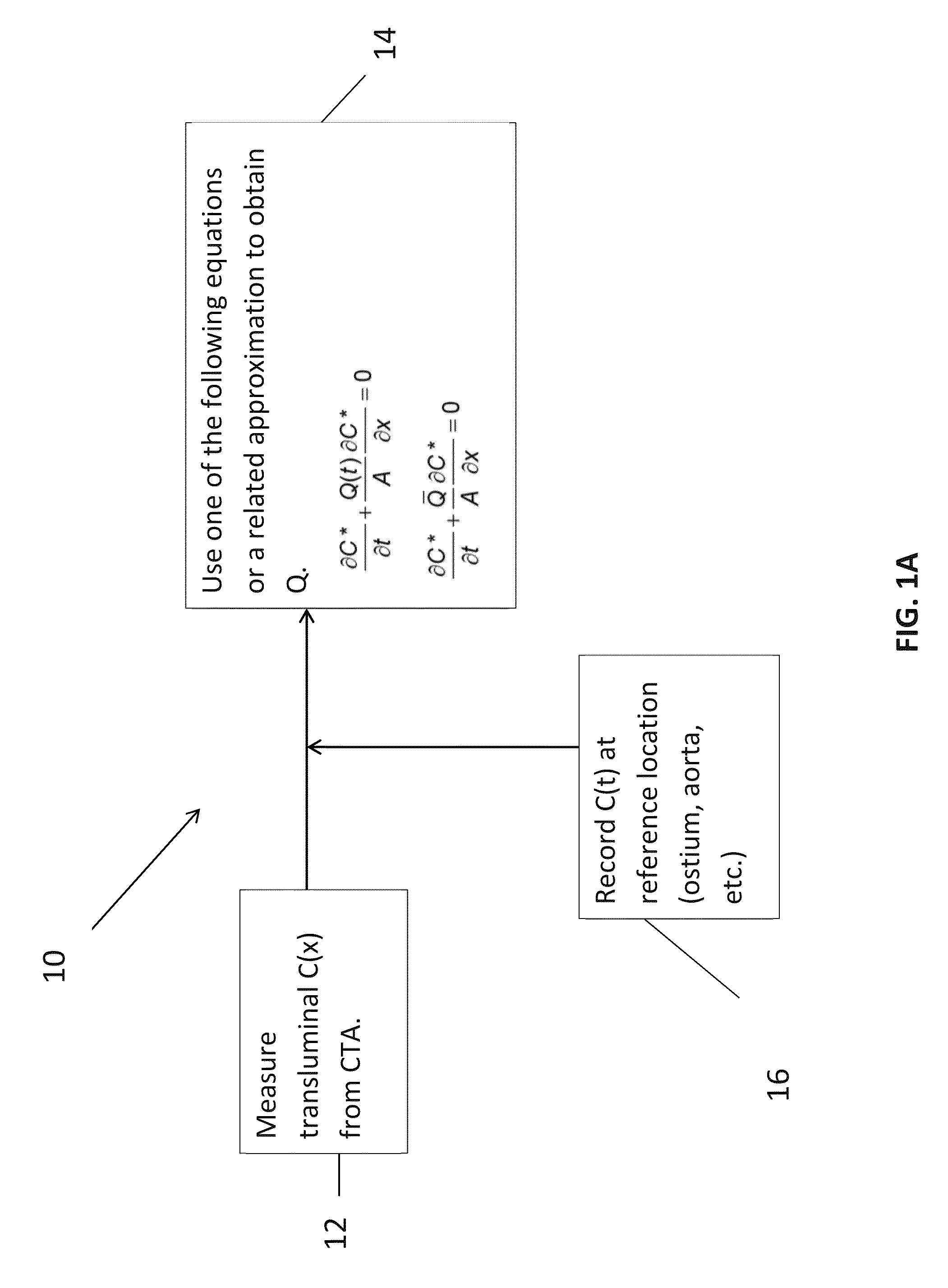
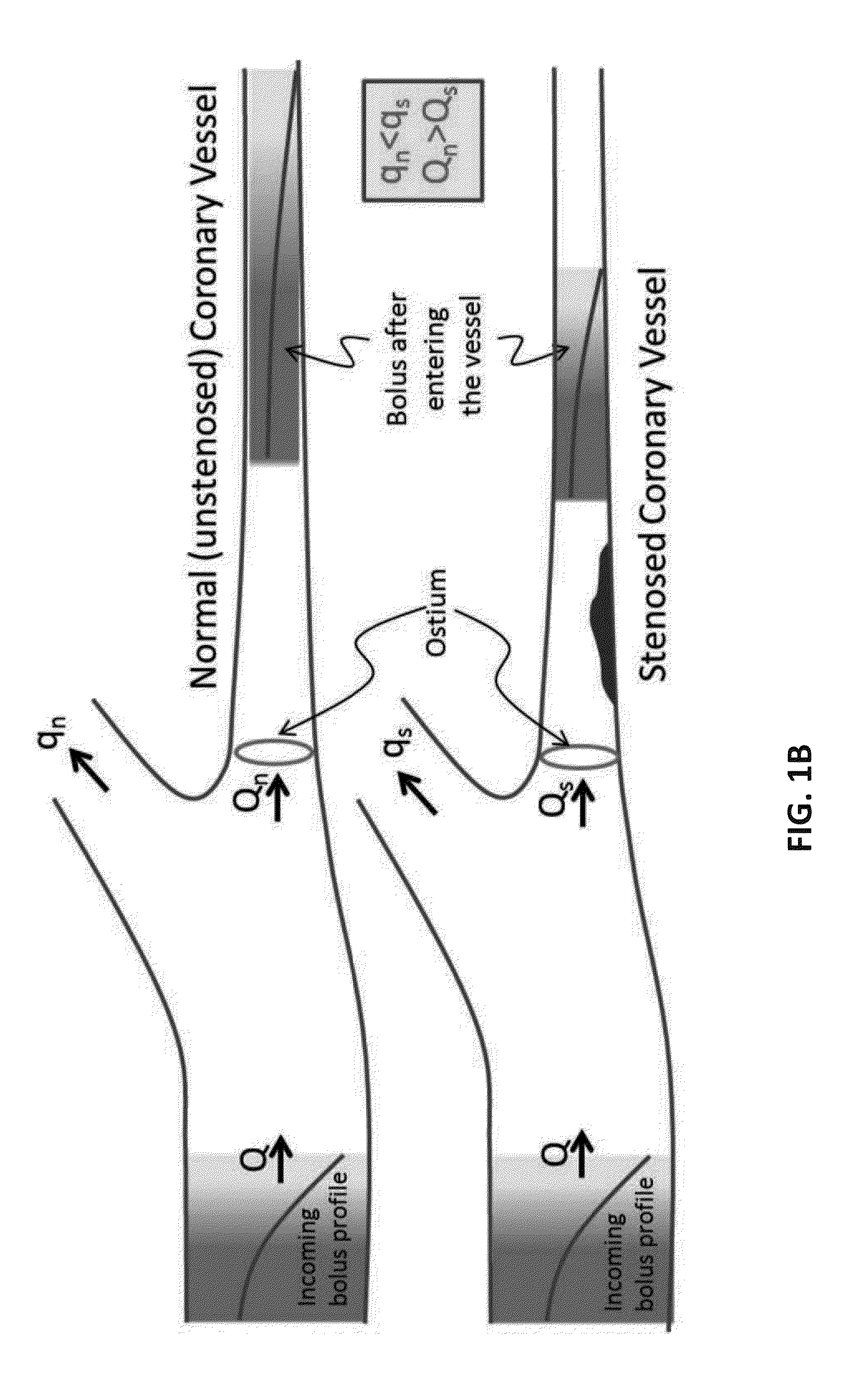
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a method for non-invasively determining the functional severity of arterial stenosis in a selected portion of an arterial network. The method includes gathering patient-specific data related to concentration of a contrast agent within an arterial network using a coronary computed tomography angiography scan (CCTA). The data can be gathered under rest or stress conditions. Estimation of a loss coefficient (K) can be used to eliminate the need for data gathered under stress. The data is used to calculate a transluminal attenuation gradient (TAG). The data may be corrected for imaging artifacts at any stage of the analysis. TAFE is used to determine an estimate of flow velocity. Once velocity is determined, pressure gradient, coronary flow reserve, and / or fractional flow reserve can be determined through a variety of methods. These estimates can be used to estimate functional severity of stenosis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Detection and tracking of interventional tools
InactiveUS20100226537A1Improve visibilityEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescence3d rotational angiography
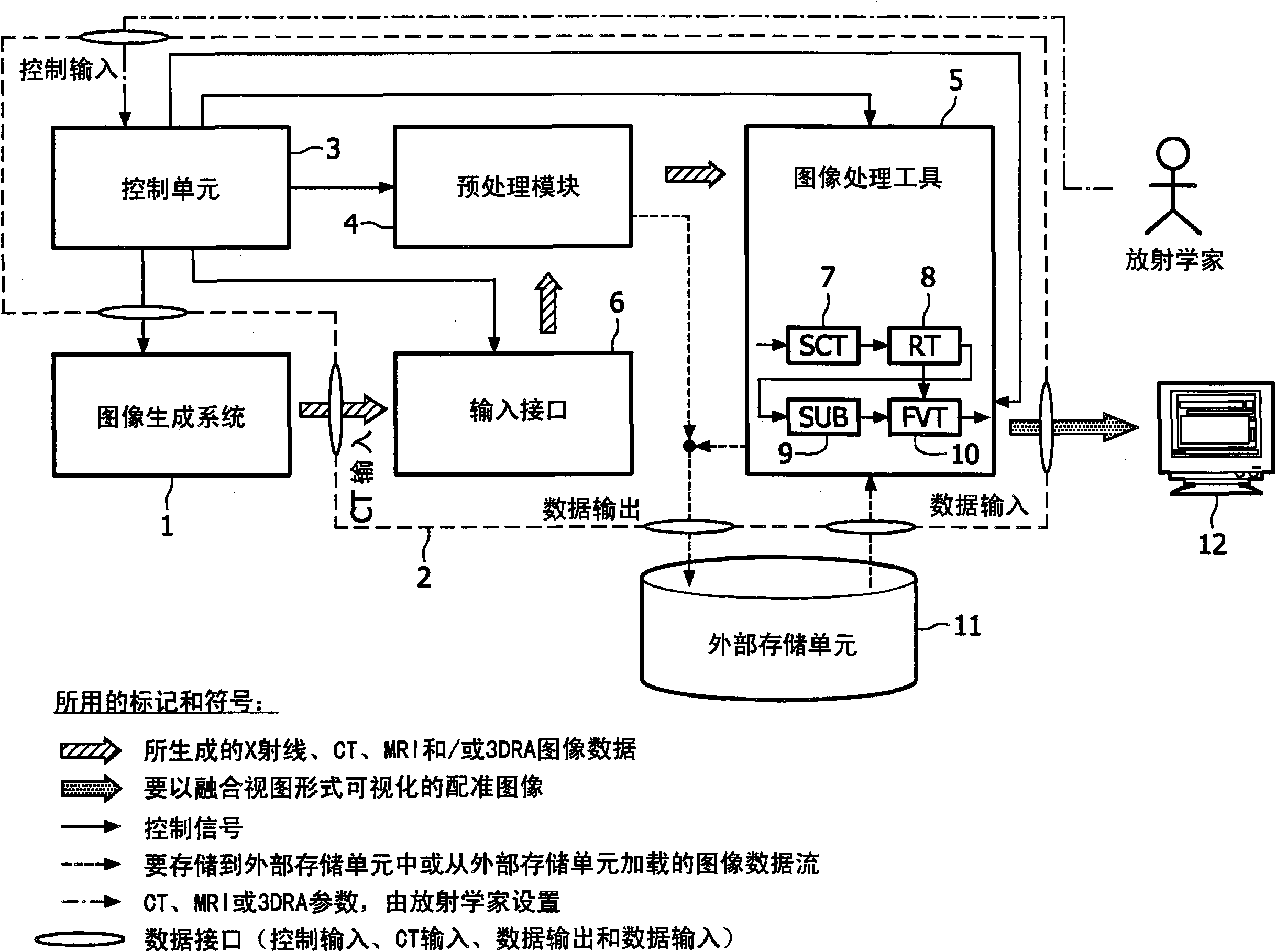
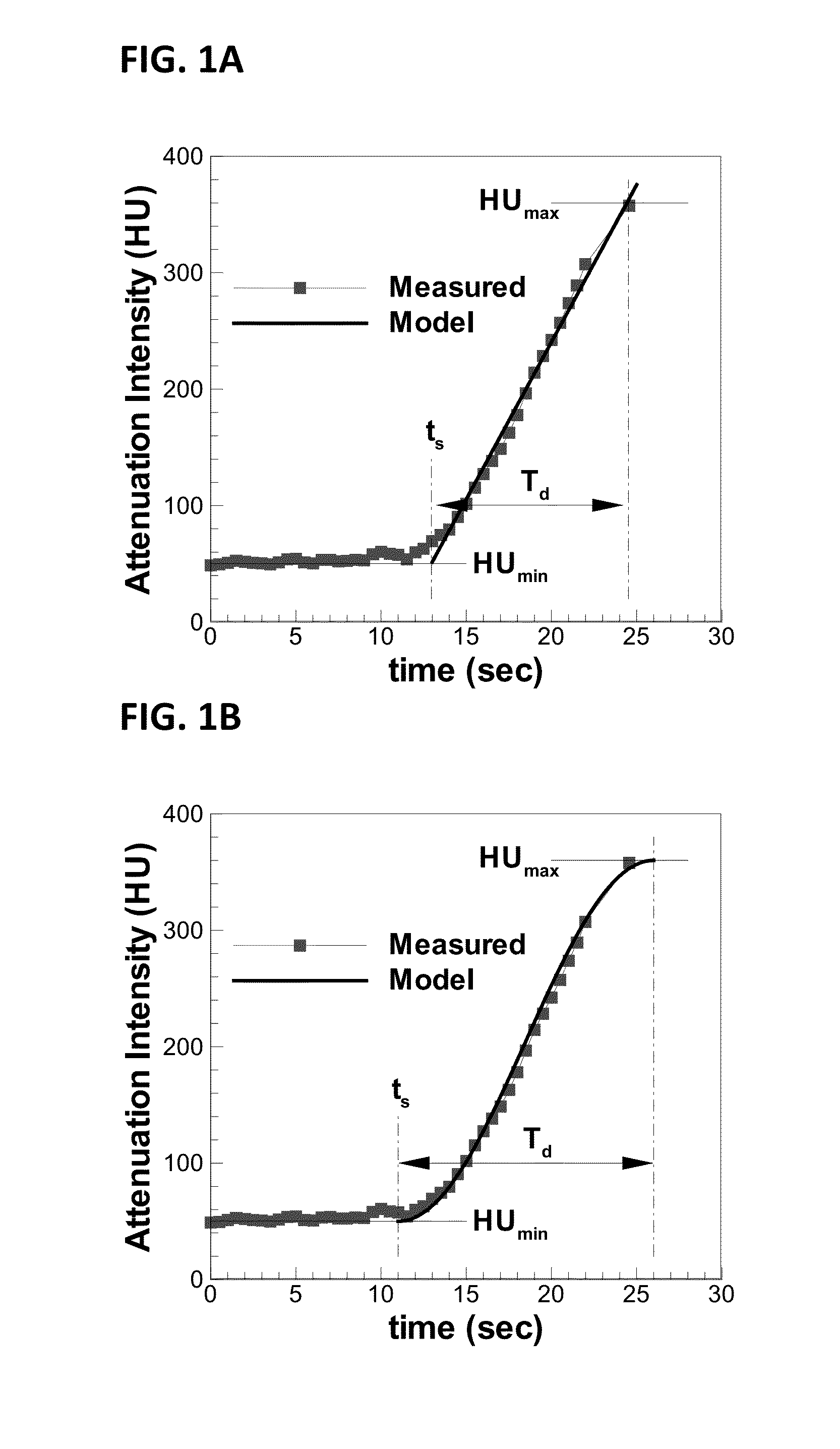
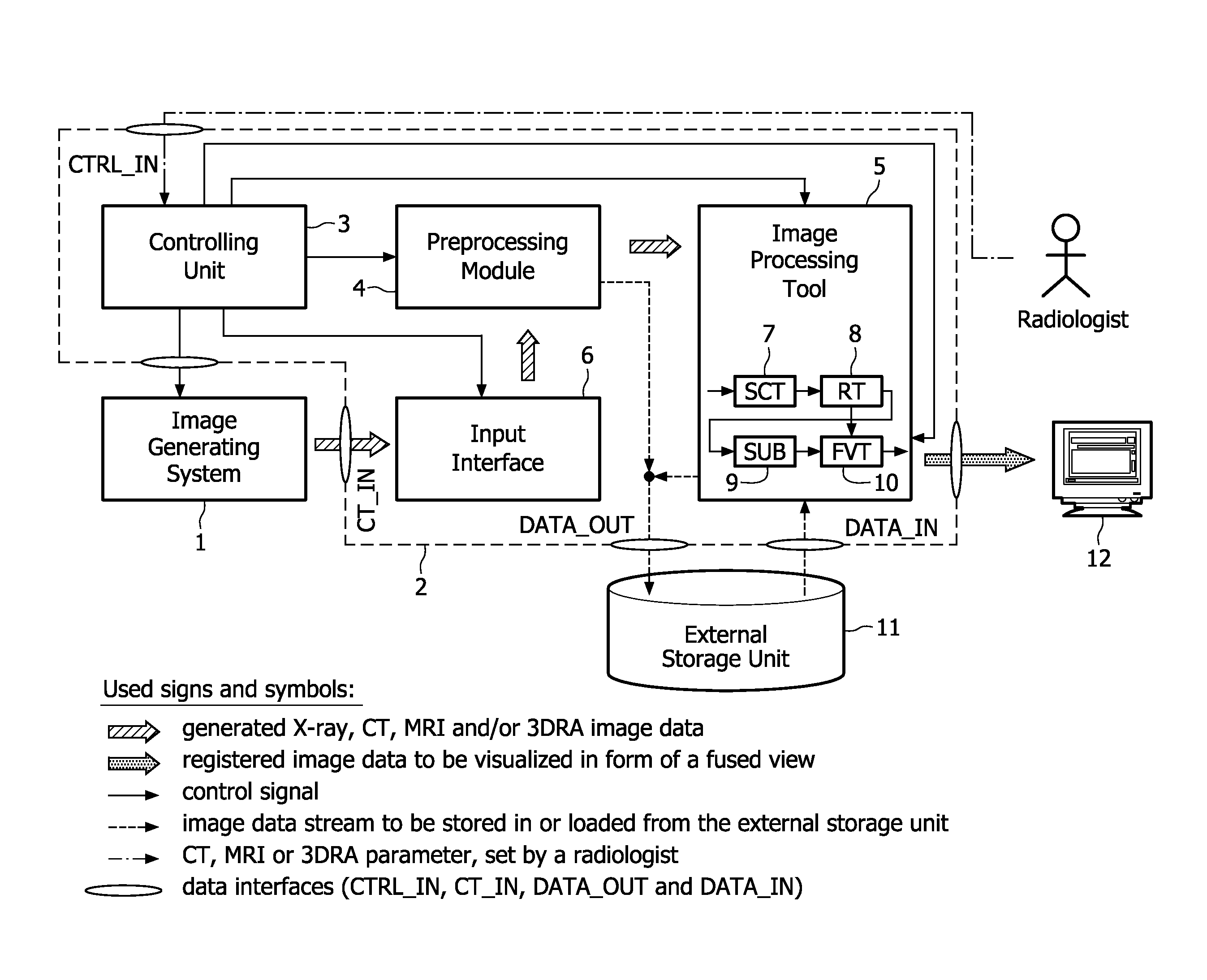
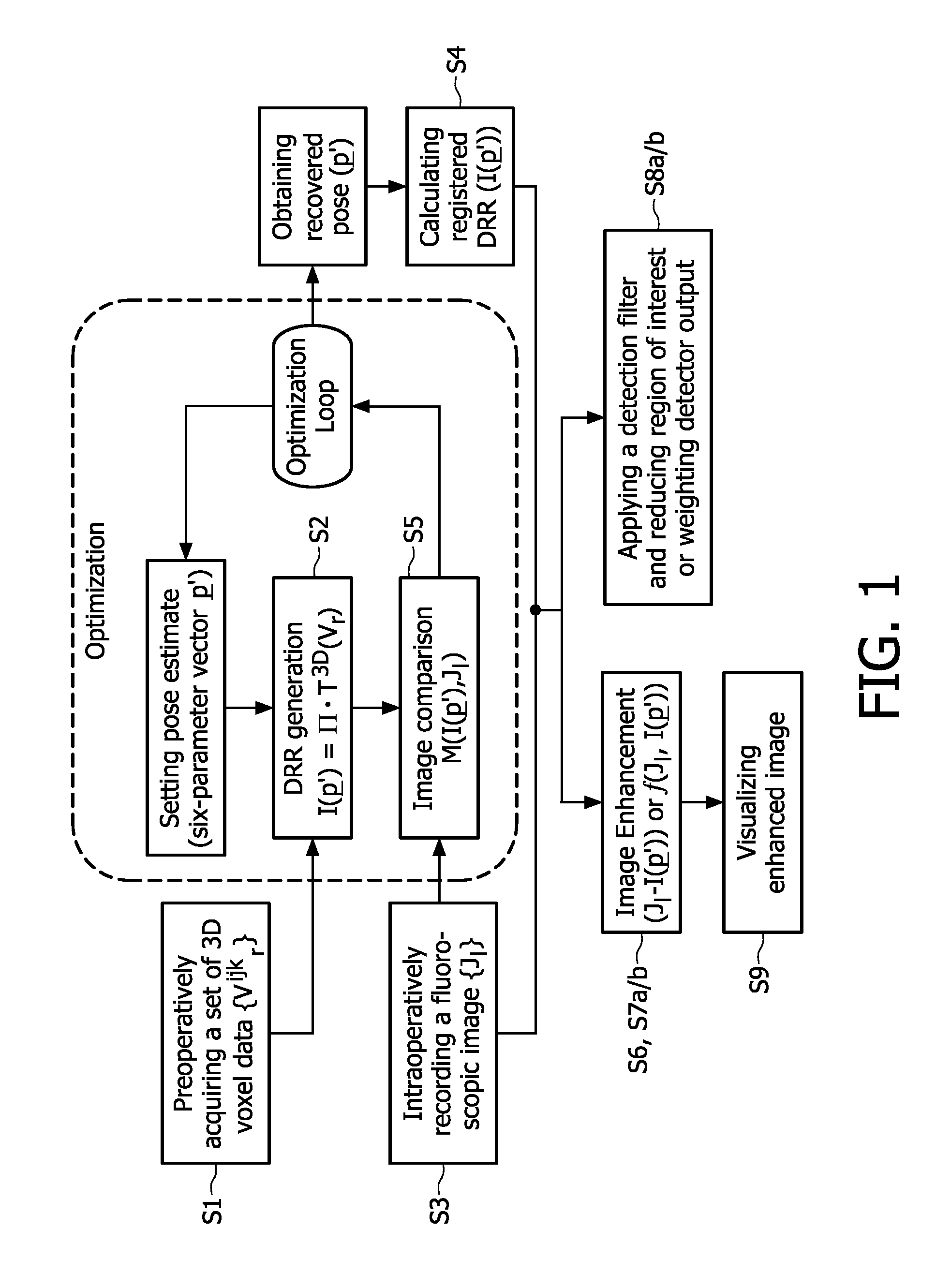
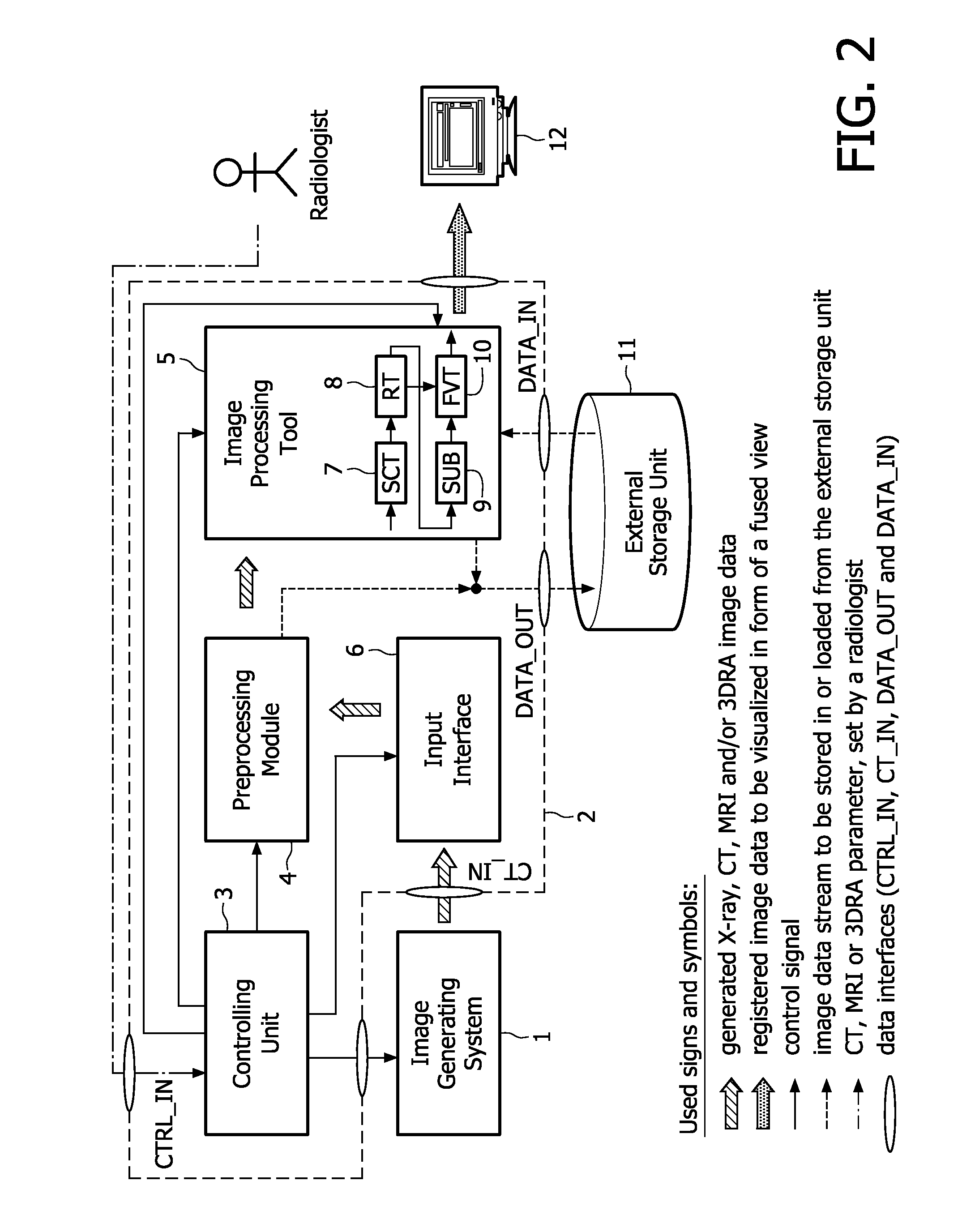
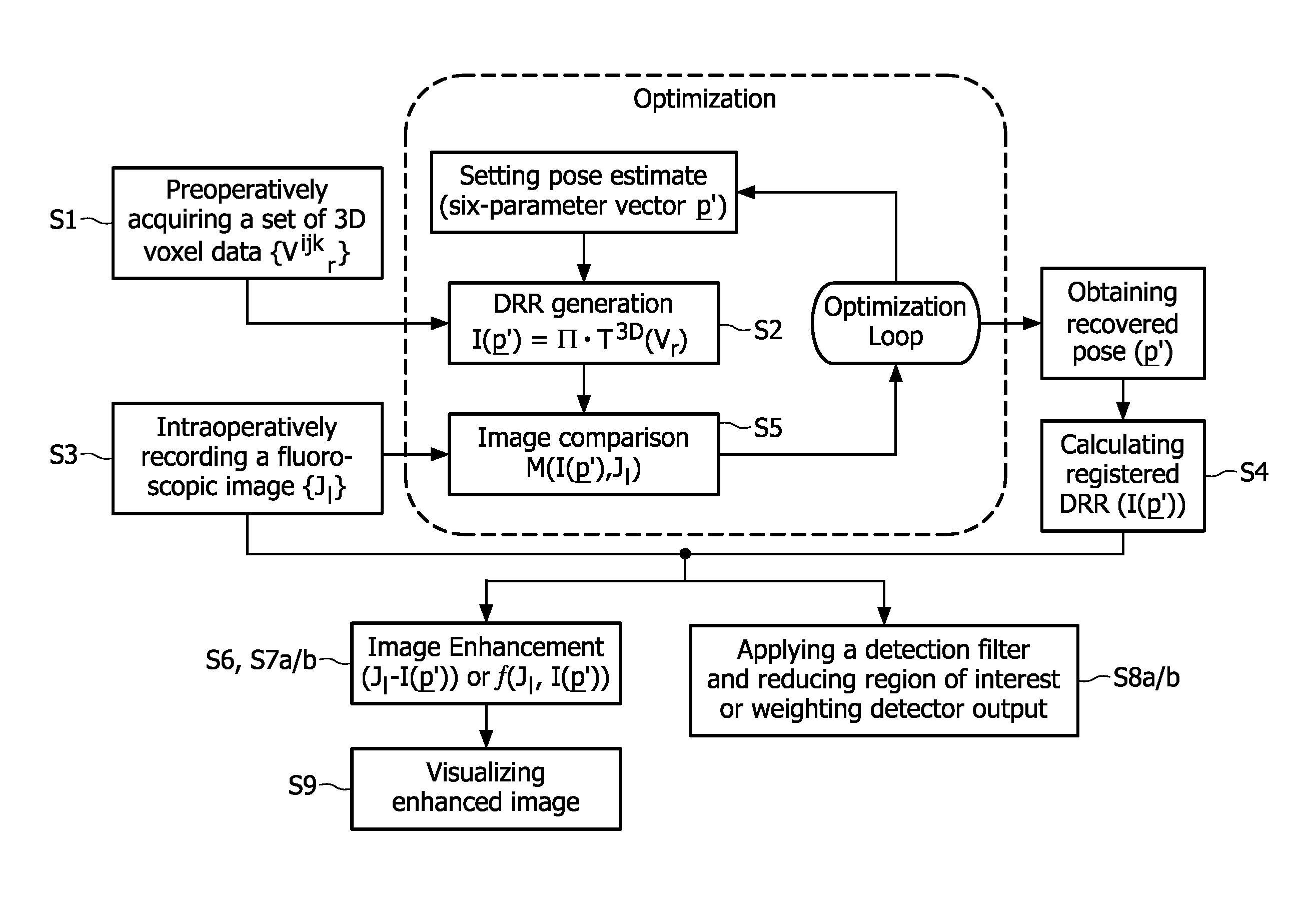
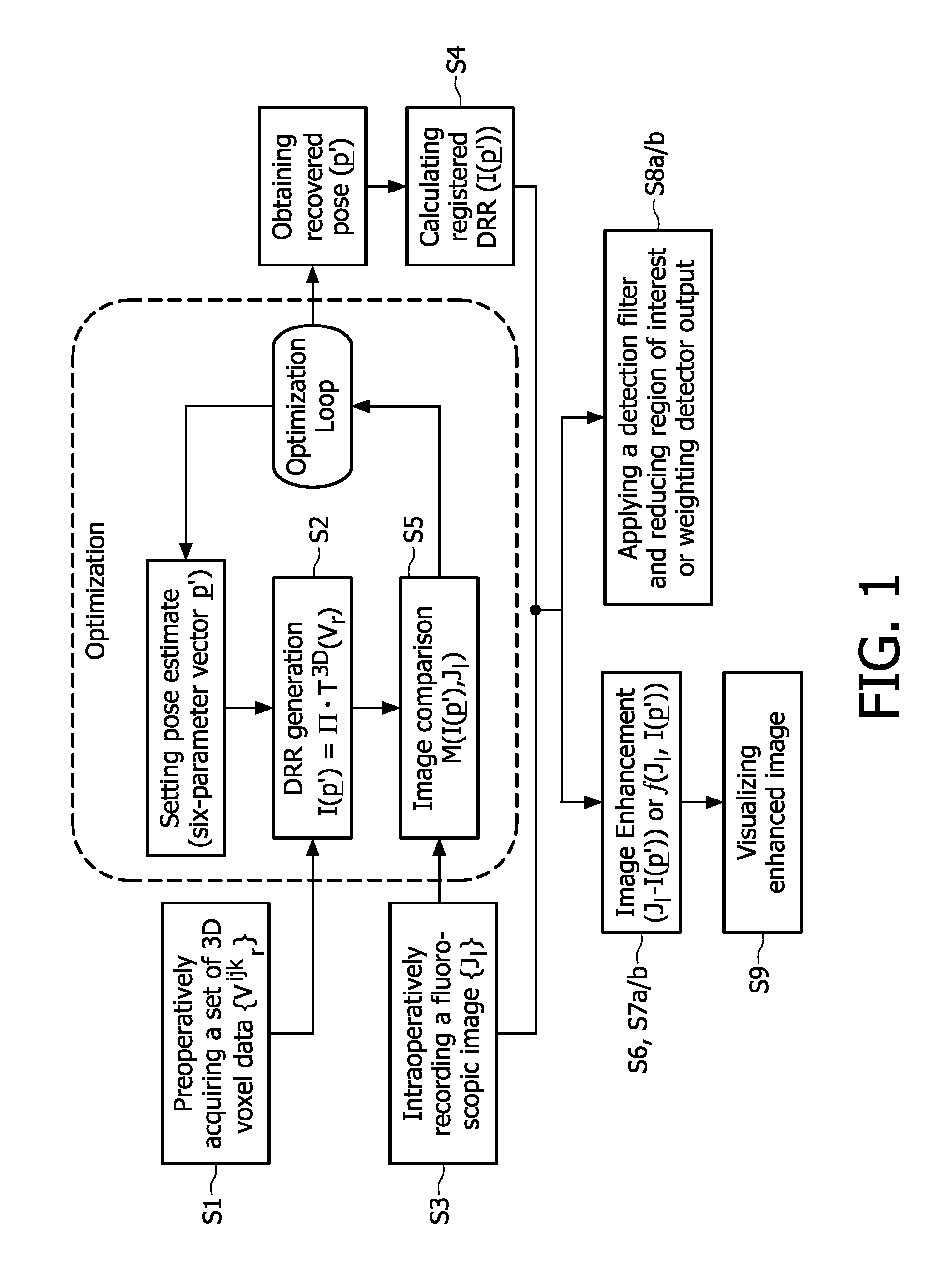
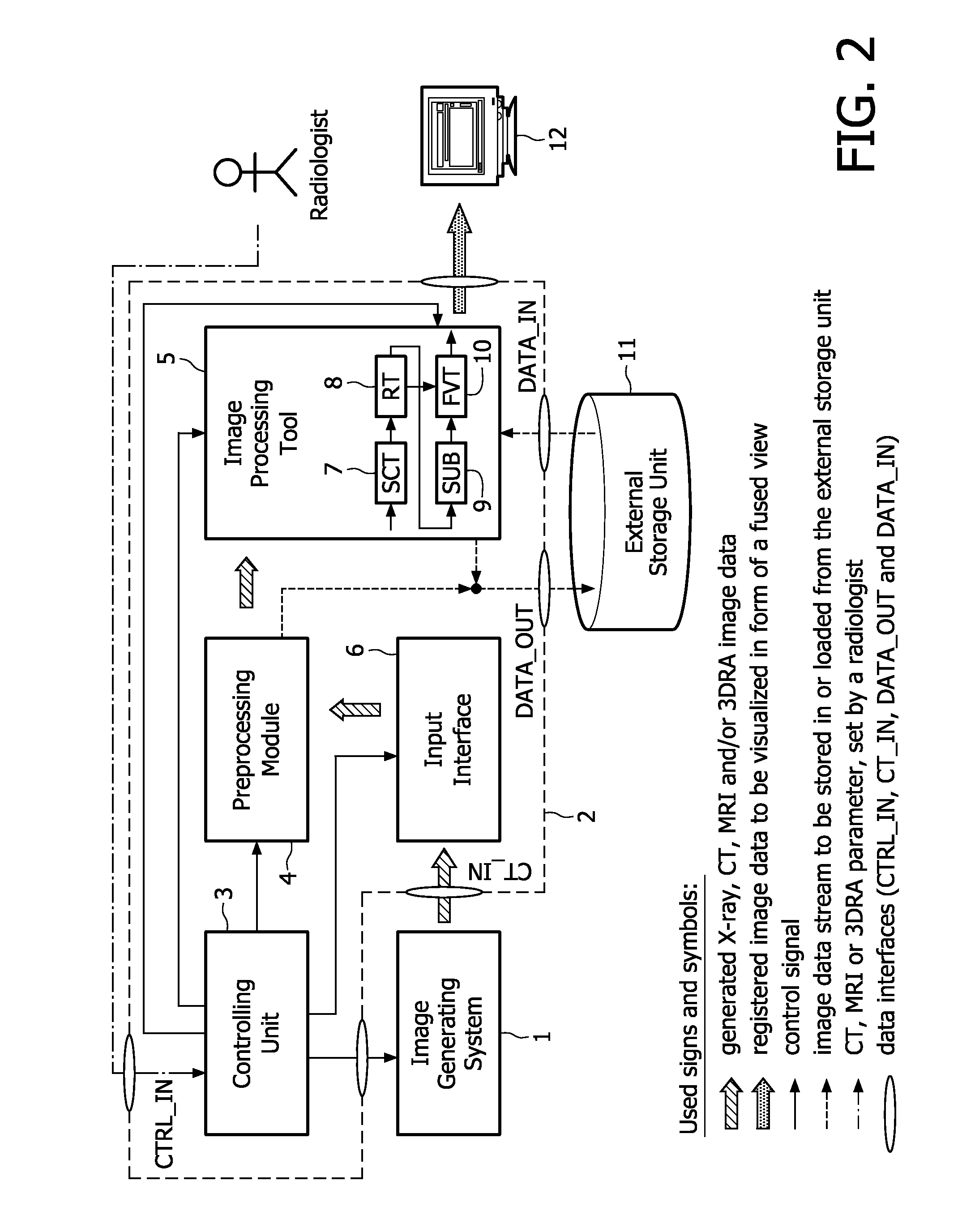
The present invention relates to minimally invasive X-ray guided interventions, in particular to an image processing and rendering system and a method for improving visibility and supporting automatic detection and tracking of interventional tools that are used in electrophysiological procedures. According to the invention, this is accomplished by calculating differences between 2D projected image data of a preoperatively acquired 3D voxel volume showing a specific anatomical region of interest or a pathological abnormality (e.g. an intracranial arterial stenosis, an aneurysm of a cerebral, pulmonary or coronary artery branch, a gastric carcinoma or sarcoma, etc.) in a tissue of a patient's body and intraoperatively recorded 2D fluoroscopic images showing the aforementioned objects in the interior of said patient's body, wherein said 3D voxel volume has been generated in the scope of a computed tomography, magnet resonance imaging or 3D rotational angiography based image acquisition procedure and said 2D fluoroscopic images have been co-registered with the 2D projected image data. After registration of the projected 3D data with each of said X-ray images, comparison of the 2D projected image data with the 2D fluoroscopic images—based on the resulting difference images—allows removing common patterns and thus enhancing the visibility of interventional instruments which are inserted into a pathological tissue region, a blood vessel segment or any other region of interest in the interior of the patient's body. Automatic image processing methods to detect and track those instruments are also made easier and more robust by this invention. Once the 2D-3D registration is completed for a given view, all the changes in the system geometry of an X-ray system used for generating said fluoroscopic images can be applied to a registration matrix. Hence, use of said method as claimed is not limited to the same X-ray view during the whole procedure.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Thermal sensing device for thermal mapping of a body conduit
InactiveUS20050240117A1Facilitate communicationIncrease pressureCompression machinesCatheterAngioplasty balloon catheterPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention relates to apparatus, systems, and methods utilizing cryogenic cooling in an angioplasty balloon catheter for treatment of arterial stenosis and prevention of restenosis. More particularly, the present invention relates to an angioplasty balloon catheter utilizing expansion of compressed gas to effect Joule-Thomson cooling of an angioplasty balloon, and optionally further incorporating external temperature sensors utilizable to identify a locus for treatment of arterial stenosis. The present invention further relates to angioplasty treatment systems incorporating such a catheter, and to cryogenic angioplasty methods for treating arterial stenosis and discouraging restenosis.
Owner:GALIL MEDICAL
Method and system for improved hemodynamic computation in coronary arteries
Systems and methods for non-invasive assessment of an arterial stenosis, comprising include segmenting a plurality of mesh candidates for an anatomical model of an artery including a stenosis region of a patient from medical imaging data. A hemodynamic index for the stenosis region is computed in each of the plurality of mesh candidates. It is determined whether a variation among values of the hemodynamic index for the stenosis region in each of the plurality of mesh candidates is significant with respect to a threshold associated with a clinical decision regarding the stenosis region.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Automated detection of asymptomatic carotid stenosis
InactiveUS20090292208A1Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsCarotid imtMeasurement plane
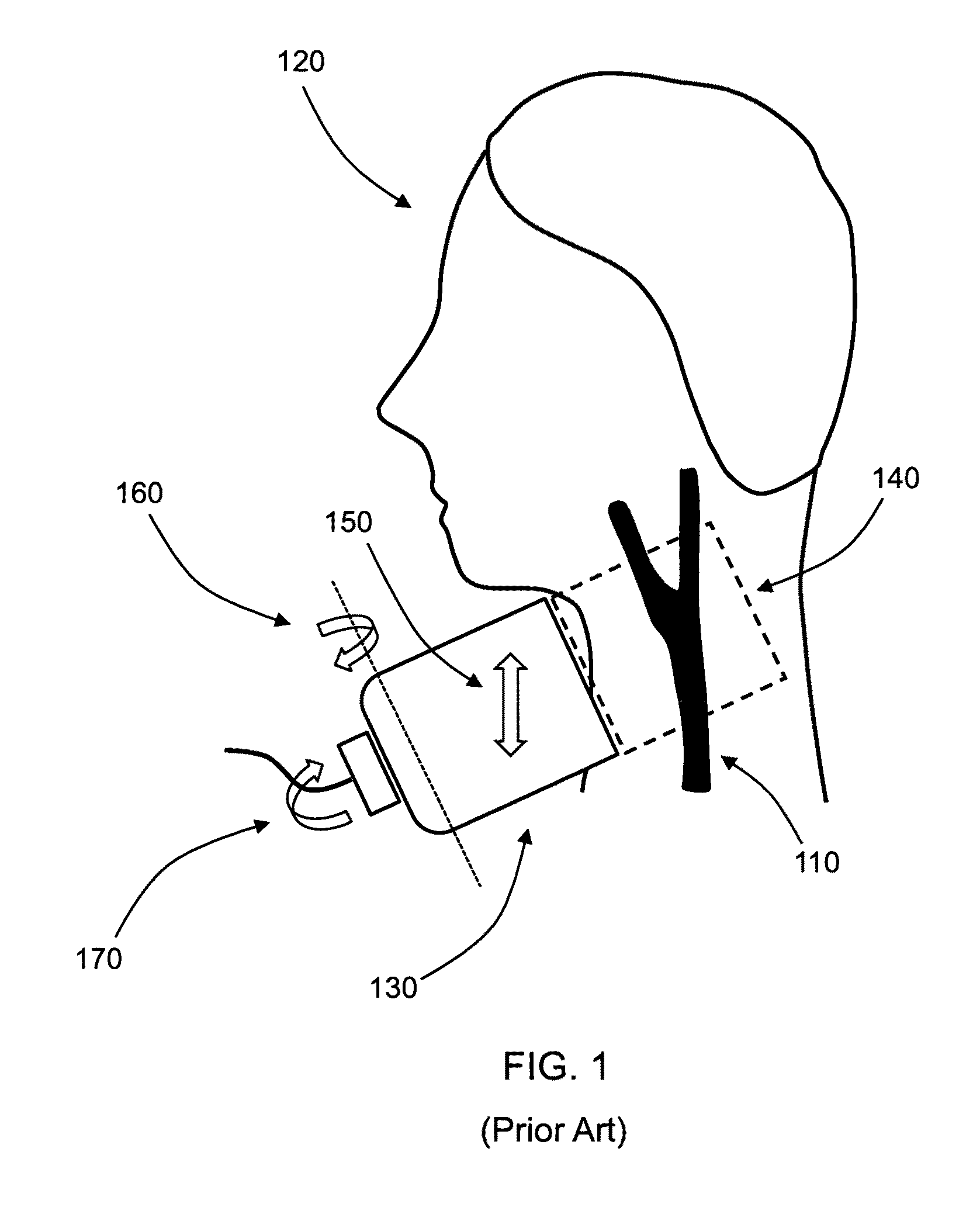
Peak blood velocity measurement for automated stenosis detection is provided. Ultrasound measurements of the peak blood velocity are corrected by a calculation of the Doppler angle, which exists from misalignment of the ultrasound transducer axis and the true blood velocity. The direction of the blood velocity and the Doppler angle are found by imaging a set of planar cross-sections of a blood vessel, such as the carotid artery, to obtain velocity maps of the blood flowing in the blood vessel. Peak blood velocity can be correlated with an amount of stenosis therefore accurate peak blood velocity measurements are necessary for medical diagnosis. Automated stenosis detection allows for implementation in many medical settings. A capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducer array is also provided to measure the planar cross-sectional images.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Recyclable and adjustable interventional stent for constricting blood vessels
The invention discloses a recyclable and adjustable interventional stent for constricting blood vessels, wherein the stent main body is divided into three parts; the stent is waist drum shape; the upper and lower parts of the stent are respectively provided with an expanding part, which has supporting and locating effects; and a part with changeable opening diameter is arranged in the middle of the stent. The expanding part at the upper end of the stent has no tectorial membrane or has tectorial membrane; the middle opening diameter changeable part and the upper half part of the expanding part at the lower end of the stent are covered with pericardium in anti-calcification treatment; and metallic line rings are threaded at the lowermost edge of the stent. A transportation composite conduit is composed of two parts of an epitheca and an inner core. The inner core is a hollow tube. An outer side wall at the tube sharping part has a wire-hanging groove for hanging metallic lines at inferior margin of the stent. The stent is used for replacing normal pulmonary banding so as to improve curative effect and reduce related complication rate and death rate. Adhesion is not formed around the cardio great vessels and pulmonary stenosis is not formed, so the difficulty of the radical operation is not increased. The stent is suitable for other situations for reducing artery blood flow and pressure.
Owner:张石江 +1
Congenital heart disease surgical saccule dilating catheter special for children
InactiveCN102357278APrecise positioningThe scale is not easy to controlStentsBalloon catheterBalloon dilatation catheterSaccule
The invention discloses a congenital heart disease surgical saccule dilating catheter special for children. The heart disease surgical saccule dilating catheter special for children comprises a wire guide port, a water injection port, a fixed sleeve, an outer catheter, an inner catheter, a saccule and a guide wire; the rear end of the saccule is fixed on the outer wall of the front end of the outer catheter; the front end of the saccule is fixed on the outer wall of the front end of the inner catheter; a cavity which is formed by the inner catheter and the outer catheter is communicated with the water injection port; the guide wire is inserted into the inner catheter; the saccule is a small saccule which has a shape of a waist drum and of which the middle part is thick and two heads are thin; the total length of the saccule is 15 to 20mm; the diameter of each of two ends of the saccule is 15 to 20mm; the diameter of each of two heads of the saccule is 8 to 20mm; and the diameter of the middle part of the saccule is 2 / 3 to 4 / 5 the diameter of each of the two heads. The diameter of the middle part of the saccule is smaller than that of each of two heads, so the saccule can be accurately positioned on the narrow part of an artery and does not slip; the outer catheter is provided with scale marks to ensure accurate positioning; the chance that a patient suffering from pulmonary stenosis is damaged when the saccule is dilated can be obviously reduced, and safety of straight open thoracotomy is higher. The blank of the saccule dilating catheter special for the children at present is filled.
Owner:NANJING CHILDRENS HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Method for estimating flow rates and pressure gradients in arterial networks from patient specific computed tomography angiogram-based contrast distribution data
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a method for non-invasively determining the functional severity of arterial stenosis in a selected portion of an arterial network. The method includes gathering patient-specific data related to concentration of a contrast agent within an arterial network using a coronary computed tomography angiography scan (CCTA). The data can be gathered under rest or stress conditions. Estimation of a loss coefficient (K) can be used to eliminate the need for data gathered under stress. The data is used to calculate a transluminal attenuation gradient (TAG). The data may be corrected for imaging artifacts at any stage of the analysis. TAFE is used to determine an estimate of flow velocity. Once velocity is determined, pressure gradient, coronary flow reserve, and / or fractional flow reserve can be determined through a variety of methods. These estimates can be used to estimate functional severity of stenosis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Treatment of coronary stenosis
The invention describes includes a device and method for dilating a coronary arterial stenosis and for creating a transection in the myocardium. The transection creates a new artery composed partially of the old artery and partially of the normal healing tissue and myocardium. Several dilating means are described, as well as several cutting means and alignment means by which the cutting means may be located and properly oriented. In operation, the dilating means, cutting means and alignment means are advanced in the distal end of a catheter, which may be guided into position by a guidewire.
Owner:LARY RES & DEV
Method and system for automated therapy planning for arterial stenosis
A method and system for automated decision support for treatment planning of arterial stenoses is disclosed. A set of stenotic lesions is identified in a patient's coronary arteries from medical image data of the patient. A plurality of treatment options are generated for the set of stenotic lesions, wherein each of the plurality of treatment options corresponds to a stenting configuration in which one or more of the stenotic lesions are stented. For each of the plurality of treatment options, predicted hemodynamic metrics for the set of stenotic lesions resulting from the stenting configuration corresponding to that treatment option are calculated.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Stabilized L-Arginine platelet aggregation inhibitory compositions and processes for making same
Linking Magnesium ions to Nitric Oxide precursor L-Arginine, chemically 2-amino-5-guanidino valeric acid, with a platelet aggregation inhibitor compound such as, but not limited to acetylsalicylic acid or clopidogrel bisulfate, unexpectedly results in a pharmaceutically stabilized compositions with extended shelf life to be taken orally to provide gradual release vasodilatory and anti-platelet aggregation pharmacological activity with reduced potential for producing gastrointestinal lesions. L-Arginine releases ADNO (Arginine derived Nitric Oxide) in the coronary artery epithelium as EDRF (endothelium dependent relaxing factor) to dilate the arteries to promote blood flow to the myocardium, and the platelet aggregation inhibitor such acetylsalicylic acid or clopidogrel and others of this class of drugs inhibits or antagonizes the aggregation adhesion of platelets in the blood stream. Aggregated or clumped blood platelets contribute to arterial stenosis due to formation of atherosclerotic plaques that occlude coronary and other circulatory arteries. In addition to coronary arteries, atherosclerotic plaques can occlude and stenose carotid arteries and femoral arteries due to aggregated or clumped blood platelets, and the subject of this patent discovery will also be of cardiovascular health benefit respectively in preventing carotid cerebrovascular accidents and femoral artery leg circulation disease.
Owner:KAPLAN LEONARD L
Method for Estimating Flow Rates, Pressure Gradients, Coronary Flow Reserve, and Fractional Flow Reserve from Patient Specific Computed Tomography Angiogram-Based Contrast Distribution Data
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a method for non-invasively determining the functional severity of coronary artery stenosis. The method includes gathering patient-specific data related to concentration of a contrast agent within a coronary artery of a patient using a coronary computed tomography angiography scan (CCTA). The patient-specific data is used to calculate a patient-specific transluminal attenuation gradient for the coronary artery of the patient. The patient specific transluminal attenuation gradient is used to determine an estimate of a coronary flow velocity, pressure gradient, loss coefficient, coronary flow reserve, and / or fractional flow reserve for the patient. Coronary flow velocity, pressure gradient, loss coefficient, coronary flow reserve, and fractional flow reserve can then be used to estimate the functional severity of coronary artery stenosis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
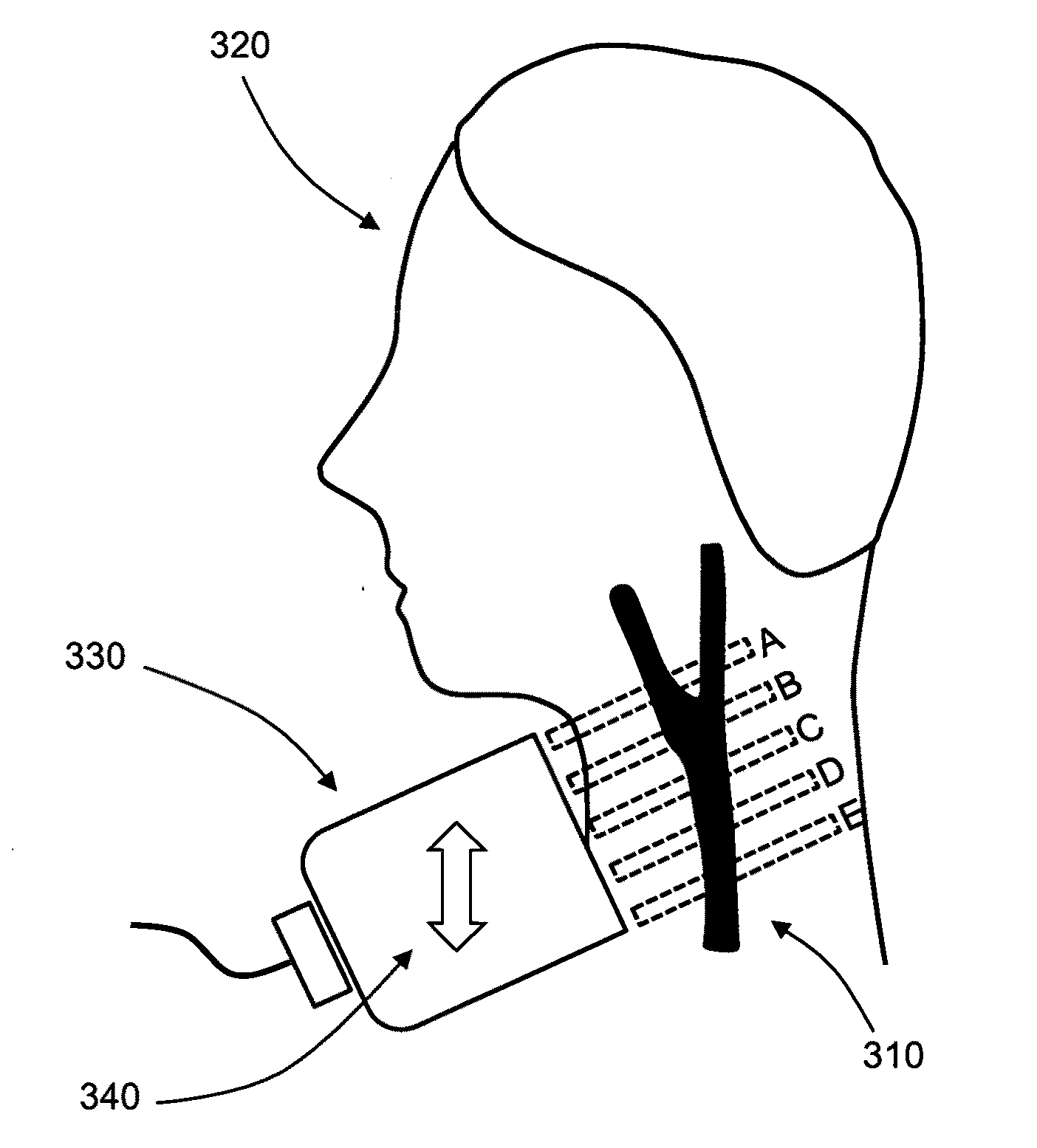
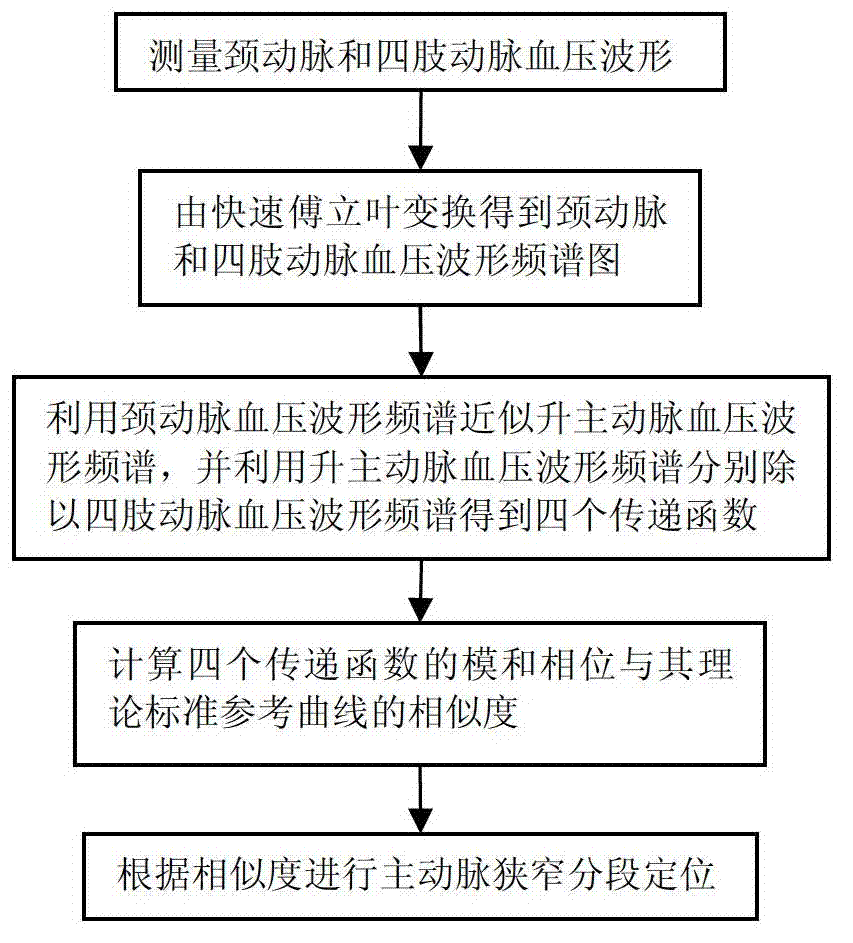
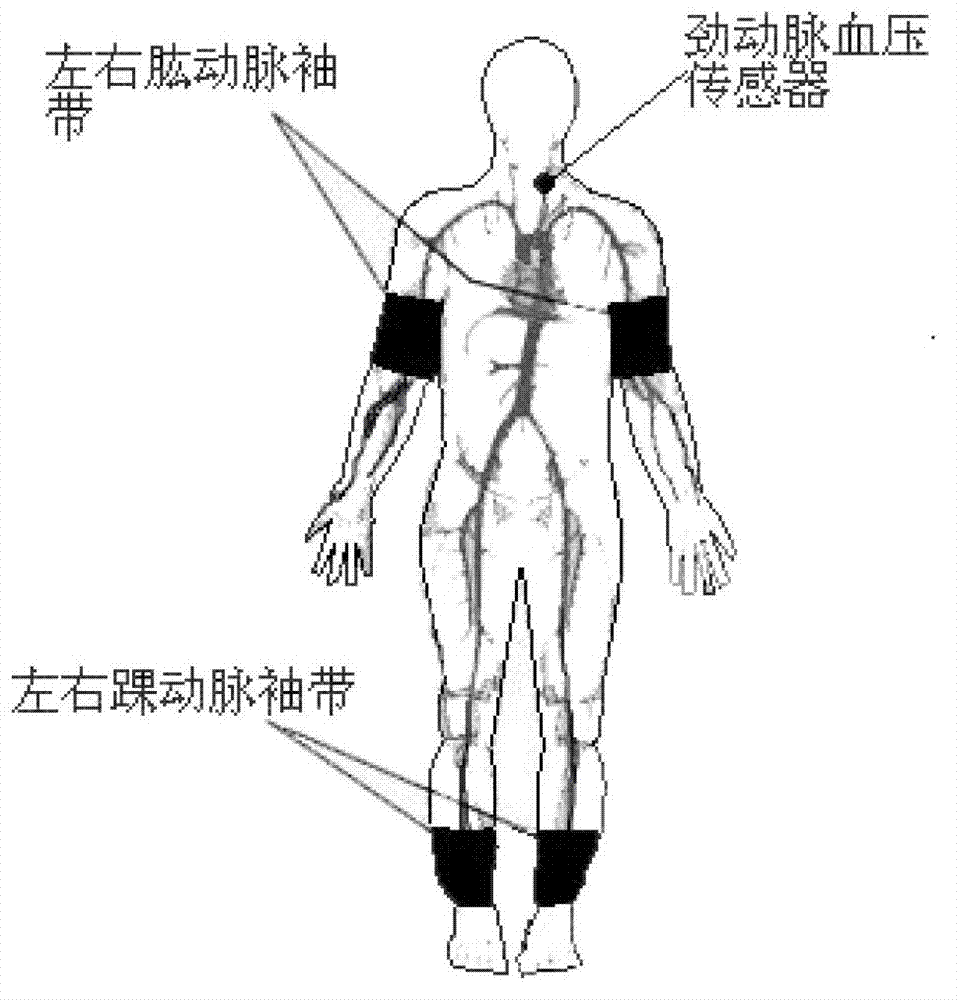
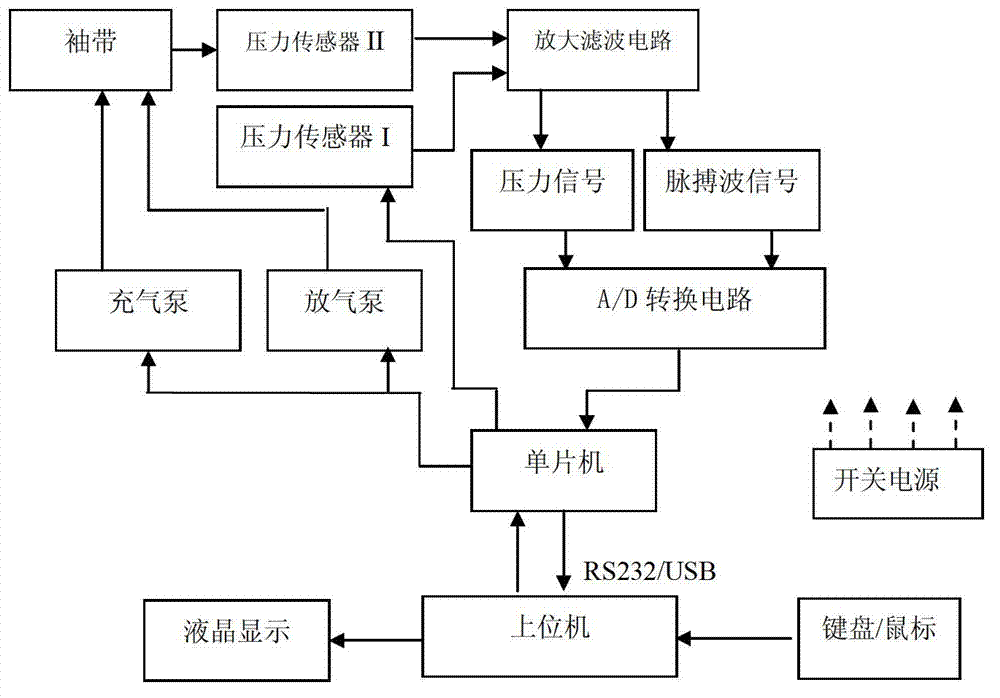
Non-invasive detection method and system for aortic stenosis section by section positioning by transfer function
The invention discloses a non-invasive detection method and a system for aortic stenosis section by section positioning by a transfer function. According to the system, firstly a single chip microcomputer is utilized to control a pressure sensor to measure a carotid artery blood pressure signal, a four-limb cuff oscillometric method is utilized to measure blood pressure signals of four limbs, then blood pressure signals of five ways are sent to an upper computer, the signals are subjected to a fast fourier transform in the upper computer to obtain frequency spectrums of blood pressure wave forms of a carotid artery and an artery of four limbs, the carotid artery blood pressure wave form frequency spectrum is similar to an ascending aorta blood pressure frequency spectrum, and four-limb blood pressure wave form frequency spectrums are sequentially divided by the ascending aorta blood pressure frequency spectrum to obtain four transfer functions. Finally, whether the artery has a stenosis or not and the area and degree of the stenosis are judged according to similarity of modes and phase angles of four actually measured transfer functions and a theoretical standard reference curve. Besides, the non-invasive detection system for aortic stenosis section by section positioning is further disclosed. By means of the non-invasive detection method and the system for the aortic stenosis section by section positioning by the transfer function, pulse waves of the carotid artery and the artery of four limbs are merely required to be measured to achieve the non-invasive detection of the aortic stenosis, and defect that four limbs and a thoracic aorta stenosis can not be positioned by existing detecting technologies and systems is overcome.
Owner:四川宇峰科技发展有限公司
Detection and tracking of interventional tools
InactiveUS8831303B2Improve visibilityEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisVoxel volumeFluorescence
The present invention relates to minimally invasive X-ray guided interventions, in particular to an image processing and rendering system and a method for improving visibility and supporting automatic detection and tracking of interventional tools that are used in electrophysiological procedures. According to the invention, this is accomplished by calculating differences between 2D projected image data of a preoperatively acquired 3D voxel volume showing a specific anatomical region of interest or a pathological abnormality (e.g. an intracranial arterial stenosis, an aneurysm of a cerebral, pulmonary or coronary artery branch, a gastric carcinoma or sarcoma, etc.) in a tissue of a patient's body and intraoperatively recorded 2D fluoroscopic images showing the aforementioned objects in the interior of said patient's body, wherein said 3D voxel volume has been generated in the scope of a computed tomography, magnet resonance imaging or 3D rotational angiography based image acquisition procedure and said 2D fluoroscopic images have been co-registered with the 2D projected image data. After registration of the projected 3D data with each of said X-ray images, comparison of the 2D projected image data with the 2D fluoroscopic images—based on the resulting difference images—allows removing common patterns and thus enhancing the visibility of interventional instruments which are inserted into a pathological tissue region, a blood vessel segment or any other region of interest in the interior of the patient's body. Automatic image processing methods to detect and track those instruments are also made easier and more robust by this invention. Once the 2D-3D registration is completed for a given view, all the changes in the system geometry of an X-ray system used for generating said fluoroscopic images can be applied to a registration matrix. Hence, use of said method as claimed is not limited to the same X-ray view during the whole procedure.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
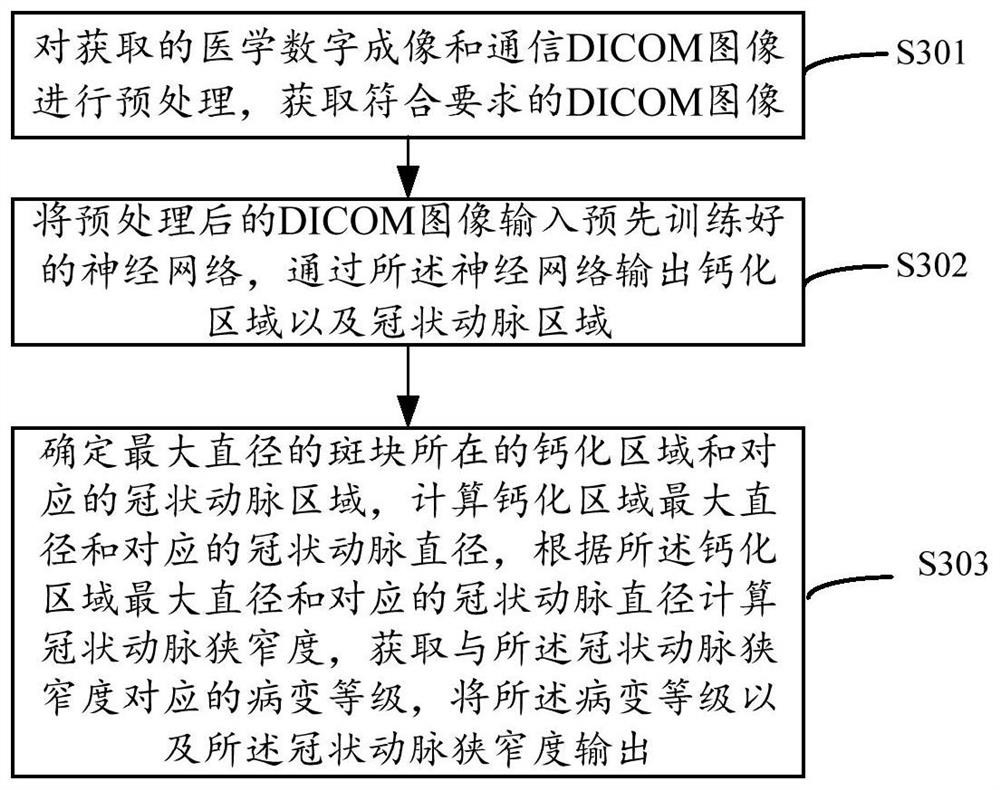
Coronary artery stenosis estimation method, system and device
PendingCN111833343AEfficient use ofEasy to captureImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesDICOM
The invention discloses a coronary artery stenosis estimation method, system and device. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the preprocessing of an obtained medical digital imaging and communication DICOM image, and obtaining a DICOM image meeting the requirements; inputting the preprocessed DICOM image into a pre-trained neural network, and outputting a calcified area and a coronary artery area through the neural network; determining a calcified area where the plaque with the maximum diameter is located and a corresponding coronary artery area; calculating the maximum diameter of the calcified area and the corresponding coronary artery diameter, calculating the coronary artery stenosis degree according to the maximum diameter of the calcified area and the corresponding coronaryartery diameter, obtaining the lesion level corresponding to the coronary artery stenosis degree, and outputting the lesion level and the coronary artery stenosis degree.
Owner:北京小白世纪网络科技有限公司
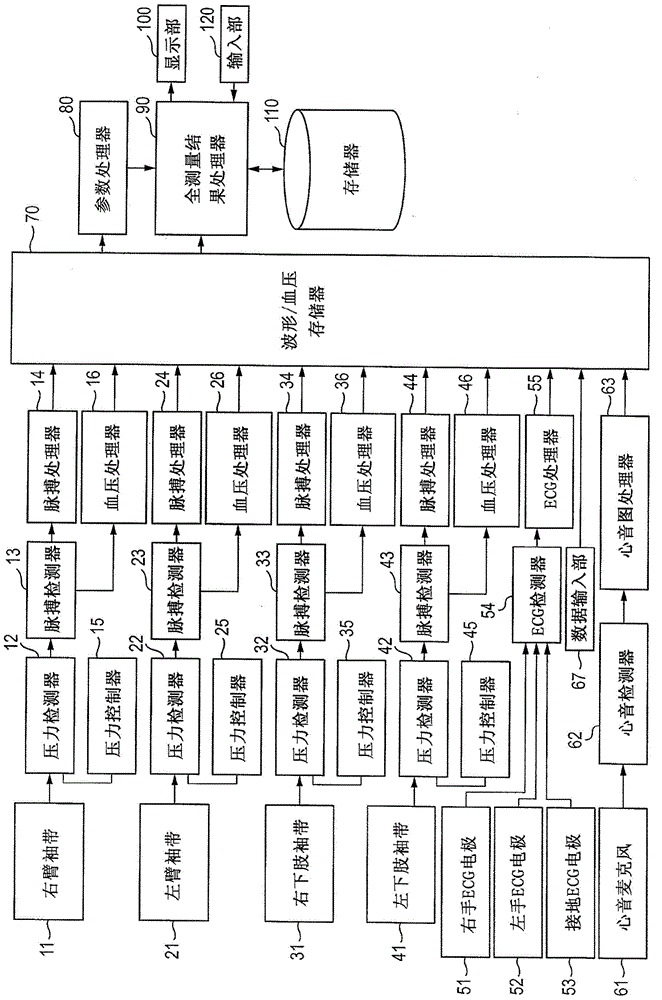
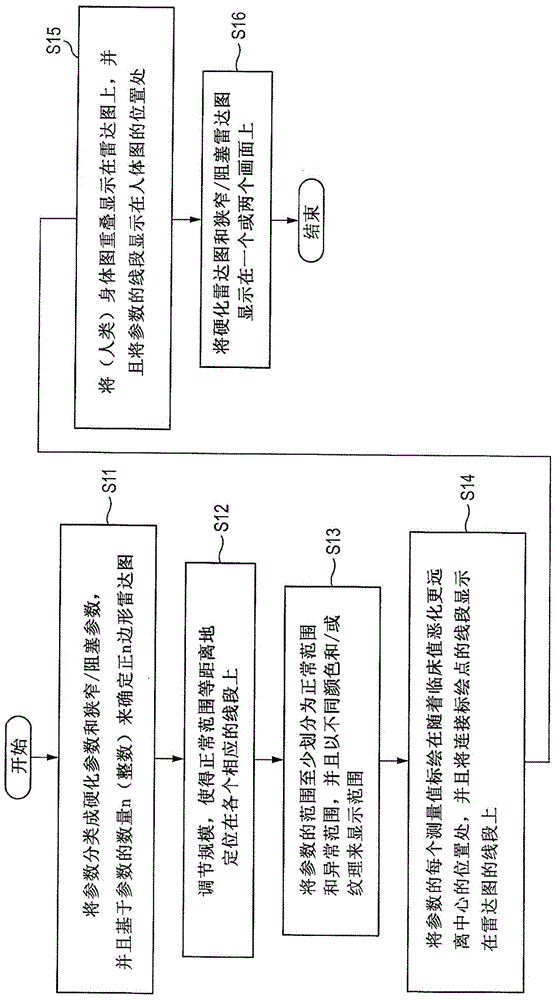
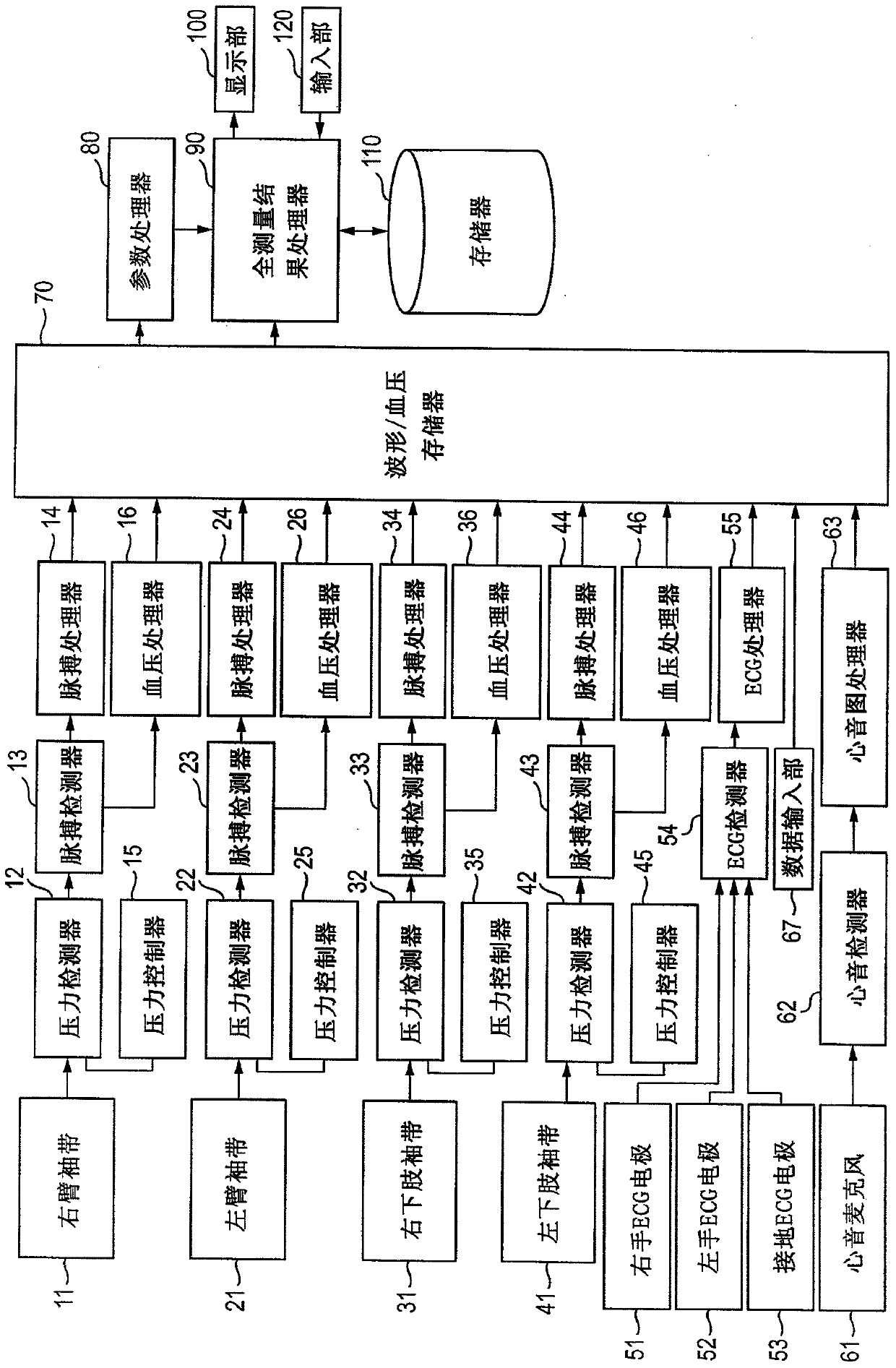
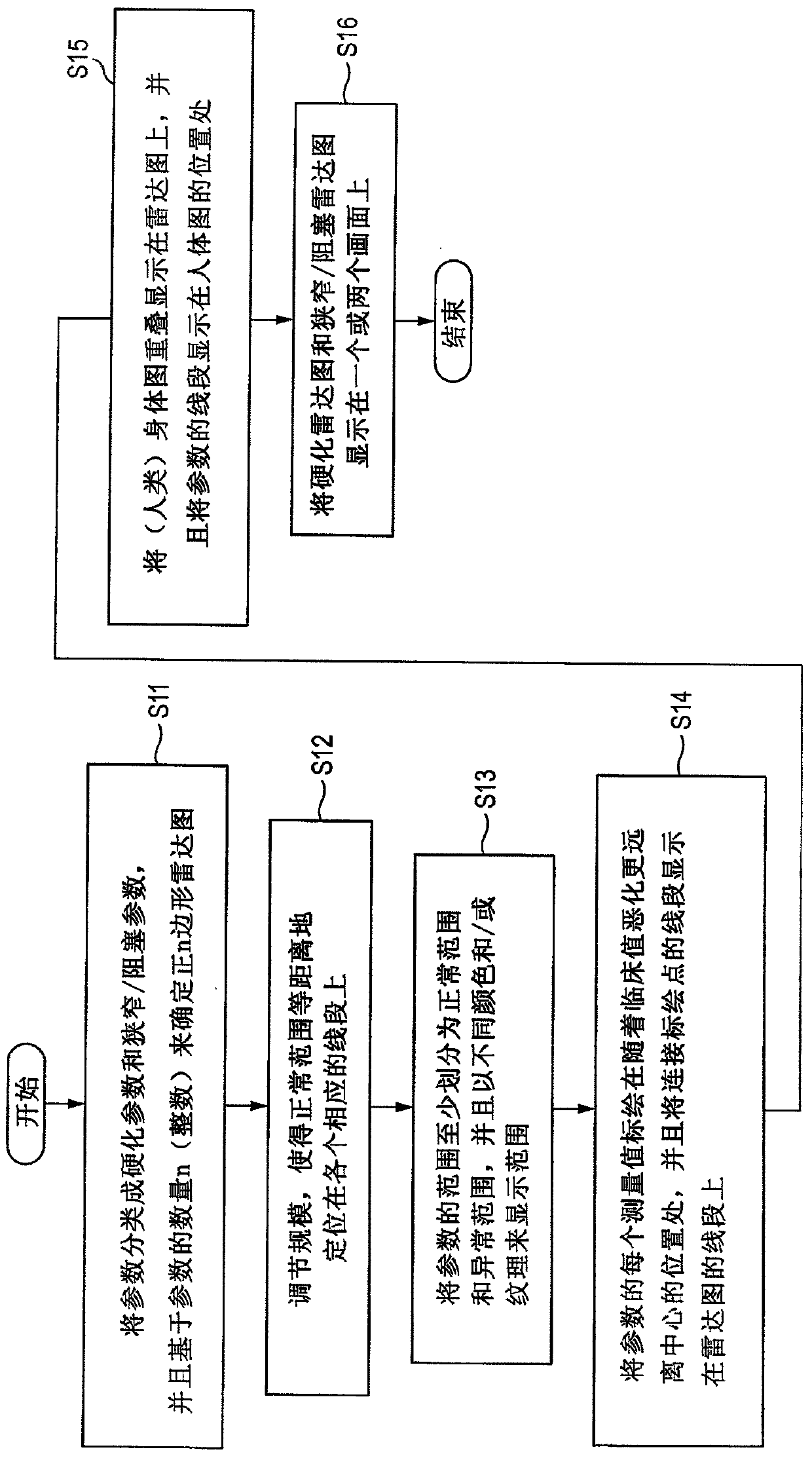
Biological information displaying apparatus and biological information displaying method
ActiveCN104545802ADisplay measured valueAccurate diagnosisImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringClinical valueMedicine
A biological information displaying apparatus includes: a calculator which is configured to calculate measurement values of parameters based on a plurality of biological signals obtained by an acquiring unit, the parameters including: sclerosis parameters relating to arterial sclerosis; and stenosis and / or occlusion parameters relating to arterial stenosis and / or occlusion; a display which is configured to display information; and a display controller which is configured to produce different radar charts of the sclerosis parameters and the stenosis and / or occlusion parameters, and which is configured to display the measurement values of the parameters on the display, on respective one of line segments that radially extend from a center in each of the radar charts, while plotting each of the measurement values of corresponding parameters at a position that is remoter from the center as a clinical value is worse.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
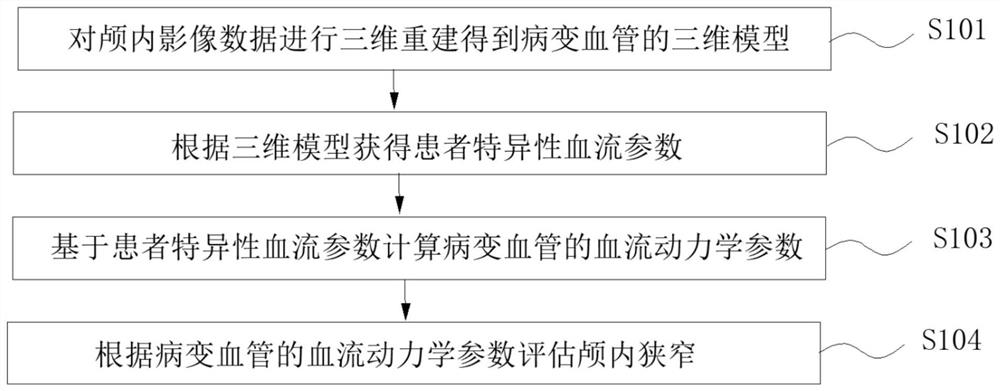
Functional evaluation method and system for intracranial vascular stenosis, electronic equipment and medium
PendingCN114287954AThe results are objective and reliableStrong diagnostic basisBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionBlood flowEngineering
The invention provides a functional evaluation method and system for intracranial vascular stenosis, electronic equipment and a medium, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the three-dimensional reconstruction of intracranial image data, and obtaining a three-dimensional model of a lesion blood vessel; acquiring specific blood flow parameters of the patient according to the three-dimensional model; calculating hemodynamic parameters of lesion blood vessels based on the patient-specific blood flow parameters; and according to the hemodynamic parameters of the lesion blood vessel, evaluating intracranial vascular stenosis. According to the functional evaluation method for intracranial vascular stenosis, the problem that the intracranial stenosis is inaccurately judged only through the intracranial liability artery stenosis degree in the prior art is solved.
Owner:HANGZHOU ARTERYFLOW TECH CO LTD
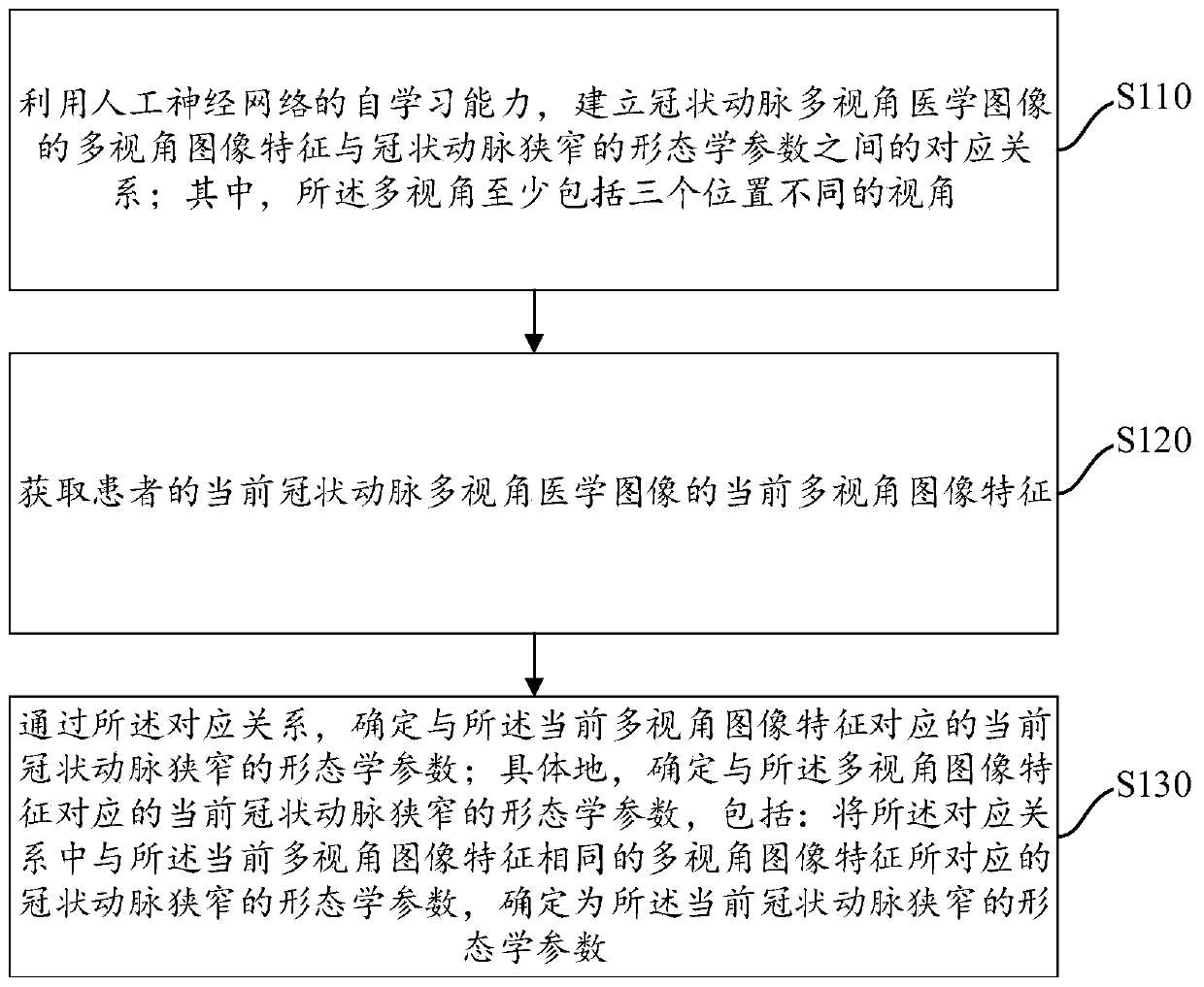
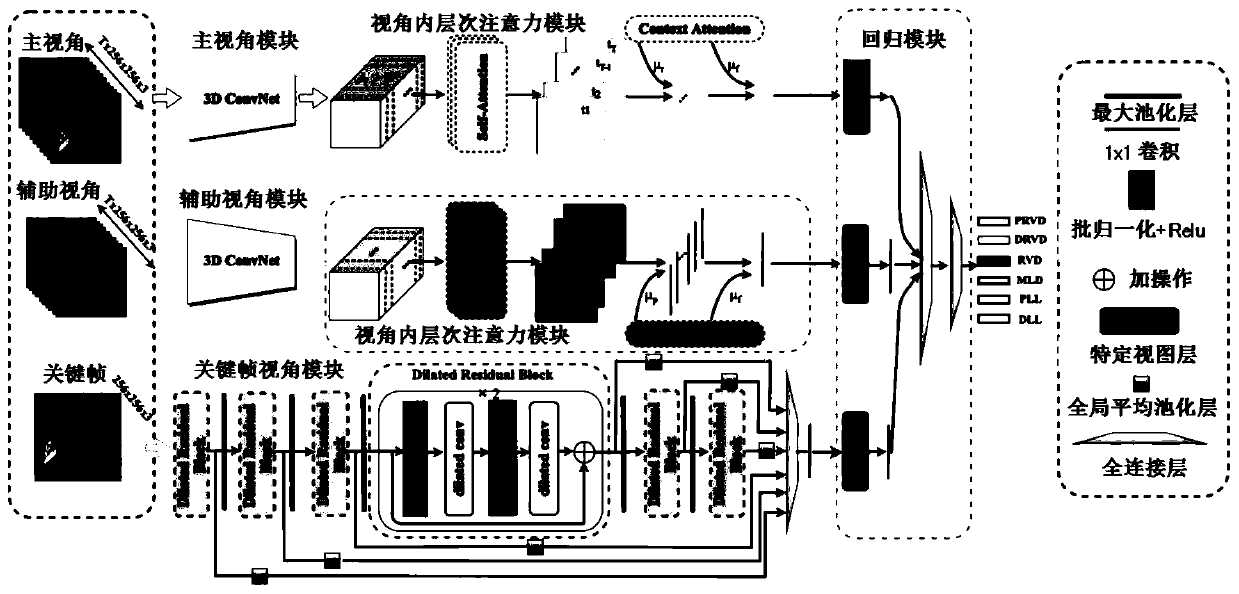
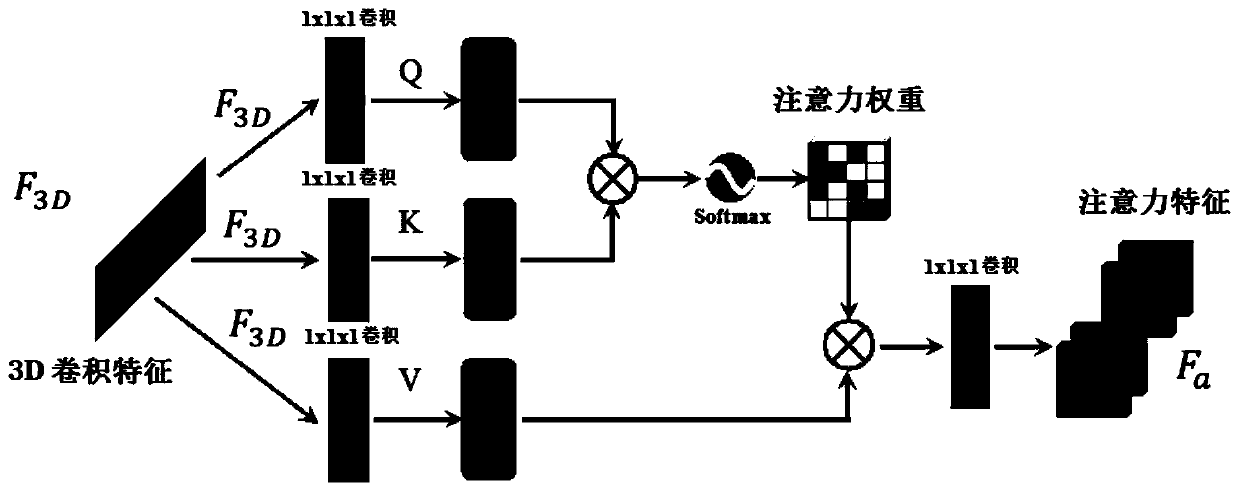
Coronary artery stenosis quantification method and device
ActiveCN111340794AMitigating the effects of stenosis quantificationImage enhancementImage analysisCoronary arteriesArterial stenosis
The invention provides a coronary artery stenosis quantification method and device, and the method comprises the steps: building the corresponding relation between the multi-view image features of a coronary artery multi-view medical image and the morphological parameters of coronary artery stenosis through the self-learning capability of an artificial neural network; obtaining current multi-viewimage features of the current coronary artery multi-view medical image of the patient; determining morphological parameters of the current coronary artery stenosis corresponding to the current multi-view image features through the corresponding relationship; specifically, determining the morphological parameters of the current coronary artery stenosis corresponding to the multi-view image features, which includes that the morphological parameters of the coronary artery stenosis corresponding to the multi-view image features identical to the current multi-view image features in the corresponding relation are determined as the morphological parameters of the current coronary artery stenosis. The morphological parameters of coronary artery stenosis are predicted based on multiple perspectives, and the influence of stenosis overlapping with other blood vessels on stenosis quantification is relieved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Methods and compositions for the rapid and enduring relief of inadequate myocardial function
InactiveUS7109206B2Relieve symptomsReducing a coronary artery stenosisBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsLipid formationNiacin
Disclosed are methods and compositions for reducing coronary artery stenosis, restoring blood flow to infarcted myocardium, improving myocardial perfusion, reducing heart attacks or other adverse cardiovascular events, or treating symptoms of inadequate myocardial function in a mammal involving administering to the mammal (a) a compound that includes eicosapentaeneoic acid or docosahexaeneoic acid and (b) a cholesterol-lowering therapeutic, combined with dietary restrictions (resulting in aggressive loading of marine lipids), whereby a serum LDL concentration of less than 75 mg / dl (and preferably less than 55 mg / dl) is achieved. One particular method involves administering to the mammal a combination that includes (a) a compound that includes an eicosapentaeneoic or docosahexaeneoic acid (for example, a marine lipid) and (b) a cholesterol synthesis or transfer inhibitor, and which may also optionally include aspirin and / or niacin. The methods and compositions of the invention may also further include a bile acid sequestrant and / or buspirone. Also disclosed are methods for treating heart disease that involve administration of buspirone.
Owner:HEART CARE PARTNERS
Pulse-beat invigorating and heart protecting oral Chinese medicine decoction
PendingCN110694031ASymptoms improvedImprove blood supplyAnthropod material medical ingredientsAcupunctureCoronary heart diseaseCardiac functioning
The invention relates to a pulse-beat invigorating and heart protecting oral Chinese medicine decoction, in particular to an oral traditional Chinese medicine decoction for treating coronary heart disease, coronary artery stenosis and infarction by pure traditional Chinese medicine. The invention solves the problems of complex treatment procedure, high pain of patients, trauma and high operation risk. Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae, Lignum Santali Albi, Rhizoma Chuanxiong, Pheretima, Eupolyphaga Seu Steleophaga, Hirudo, Rhizoma Sparganii, Rhizoma Curcumae, Radix Pseudostellariae, Fructus Crataegi, Spina Gleditsiae, Stigma Croci, Radix Paeoniae Rubra, Semen Persicae and Radix Astragali are adopted in the invention. The pulse-beat invigorating and heart protecting oral Chinese medicine decoction has effects of promoting blood circulation and dispelling blood stasis, dredging collaterals, clarifying and inducing resuscitation, regulating flow of QI and resolving depression, warmly invigorating QI of the kidney, reinforcing the kidney to supplement essence, promoting blood circulation to remove blood stasis, and resolving thrombus, and is used for coronary heart disease, stricture of artery and blockage. By the pulse-beat invigorating and heart protecting oral Chinese medicine decoction, the symptoms of patients can be improved rapidly, thrombi and fatty plaques on the wall of blood vessels are dissolved, blood viscosity is reduced, coronary artery stenosis is relieved or eliminated, thrombi are dissolved, blockage is eliminated, myocardial blood supply and nutrition supply are improved, and cardiac functions are improved. The effective rate reaches 95% or above.
Owner:邓想民
Method and system for prediction of post-stenting hemodynamic metrics for treatment planning of arterial stenosis
A method and system for prediction of post-stenting hemodynamic metrics for treatment planning of arterial stenosis is disclosed. A pre-stenting patient-specific anatomical model of the coronary arteries is extracted from medical image data of a patient Blood flow is simulated in the pre-stenting patient-specific anatomical model of the coronary arteries with a modified pressure-drop model that simulates an effect of stenting on a target stenosis region used to compute a pressure drop over the target stenosis region. Parameter values for the modified pressure-drop model are set without modifying the pre-stenting patient-specific anatomical model of the coronary arteries. A predicted post-stenting hemodynamic metric for the target stenosis region, such as fractional flow reserve (FFR), is calculated based on the pressure-drop over the target stenosis region computed using the modified pressure-drop model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Expansion injection system for preventing and treating arterial stenosis
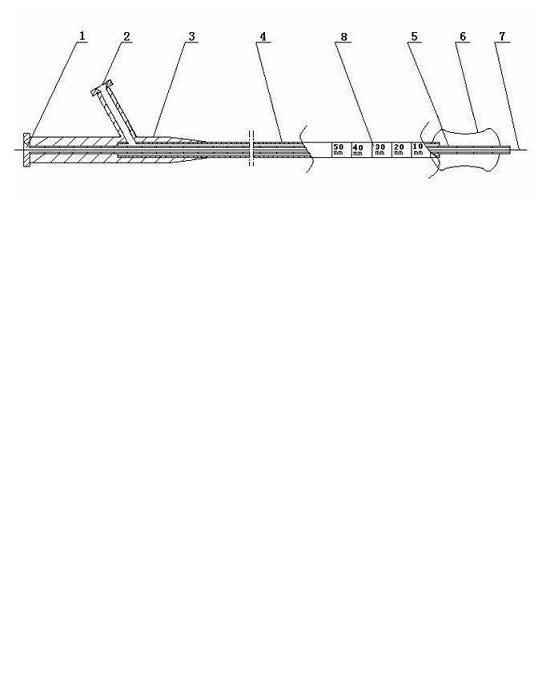
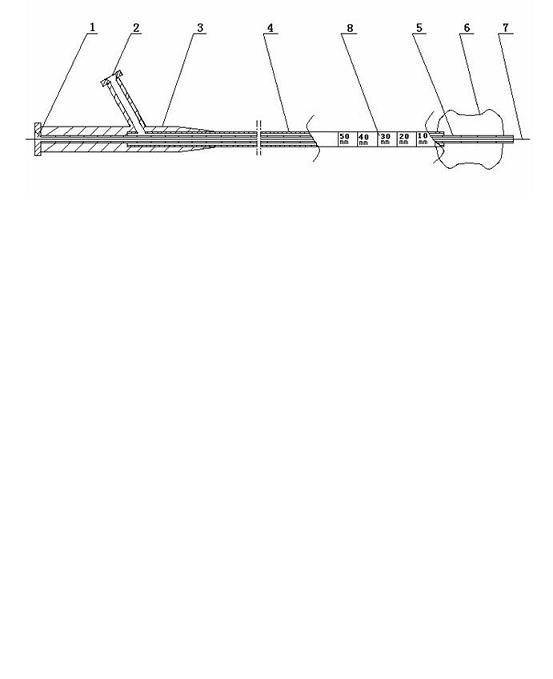
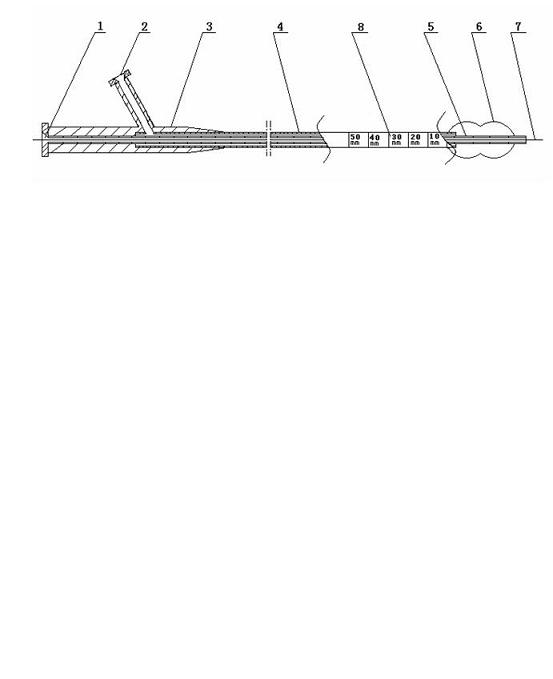
PendingCN112155685AGuaranteed stabilityEnsure consistencyBalloon catheterSurgical needlesInjection portCatheter
The invention relates to an expansion injection system for preventing and treating arterial stenosis, which comprises a catheter, wherein a guide wire channel and a water injection channel extending in the long axis direction of the catheter are arranged inside the catheter; a first balloon which is wrapped at one end of the catheter, wherein the inner cavity of the first balloon is communicated with the water injection channel, and after the first balloon is filled with water, both ends of the first balloon are tapered structures; a catheter joint which is connected to the other end of the catheter, wherein a water injection port and a medicine injection port are formed in the catheter joint, the water injection channel is communicated with the water injection channel, and a medicine injection port is connected with the puncture guide tube base; a guide wire port which is provided on the catheter joint or the catheter, and is communicated with the guide wire channel; a puncture guidetube which is arranged in the catheter, wherein one end of the puncture guide tube passes through the catheter and is attached to the taped surface of the end close to the first balloon in the long axis direction of the catheter, and the other end of the puncture guide tube extends through the inside of the catheter to connect with the puncture guide tube base; and a puncture needle, wherein the needle tail of the puncture needle is connected with a needle, and passes through the puncture guide tube base. The invention has advantages of guaranteeing the stability of a puncture angle and preventing the balloon from damage effectively.
Owner:湖州艾路通医疗科技有限公司
Biological information display device and biological information display method
A biological information display device comprising: a calculator configured to calculate measured values of parameters based on a plurality of biological signals obtained through an acquisition unit, the parameters including hardening parameters related to arteriosclerosis and arterial stenosis and / or occlusion-related stenosis and / or occlusion parameters; a display configured to display information; and a display controller configured to generate different radar maps of stiffening parameters and stenosis and / or occlusion parameters, and the The display control unit is configured to display the measured value of the parameter on the display part at a position from the center of each radar chart as the clinical value deteriorates further from the center. on each line segment extending radially.
Owner:NIHON KOHDEN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com