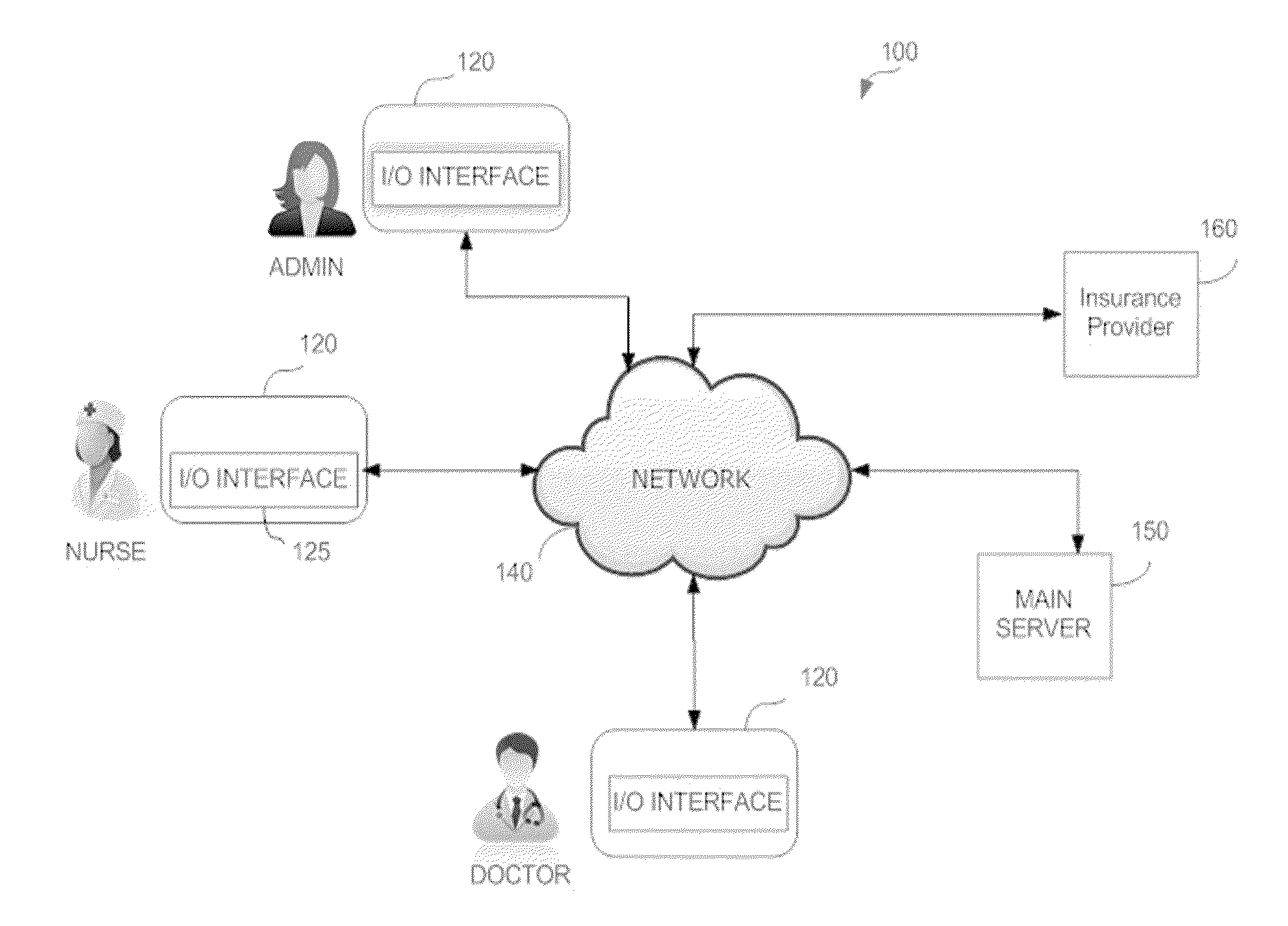
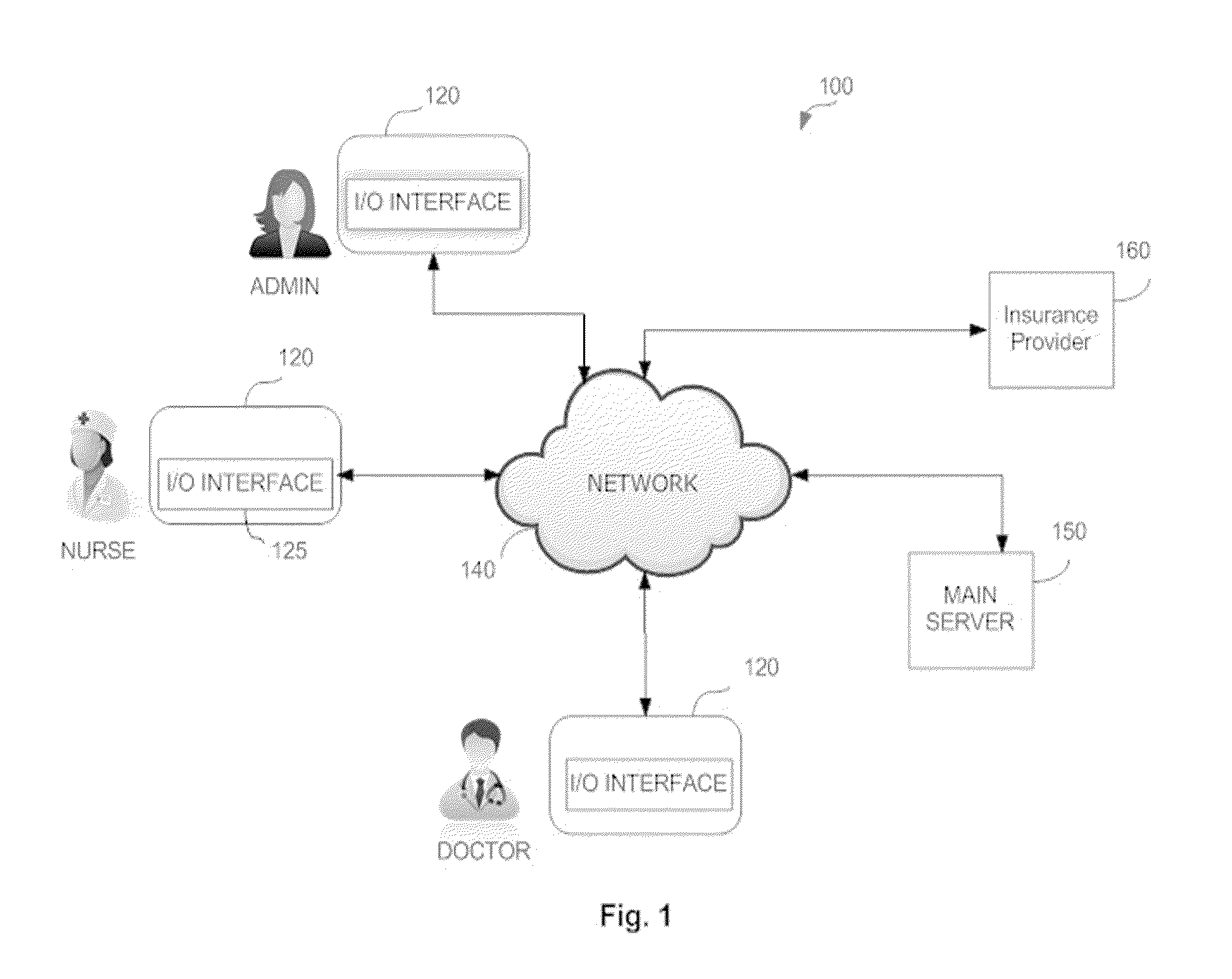
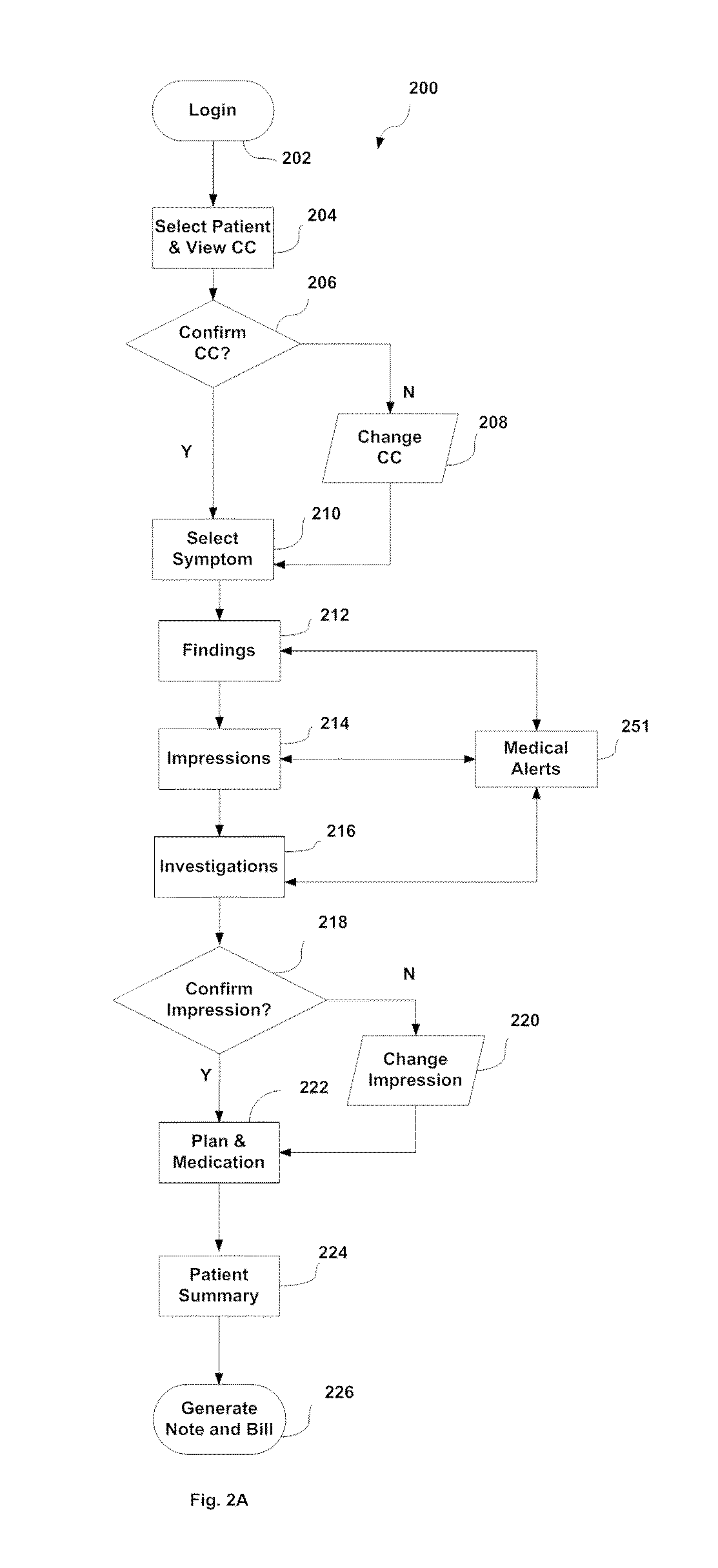
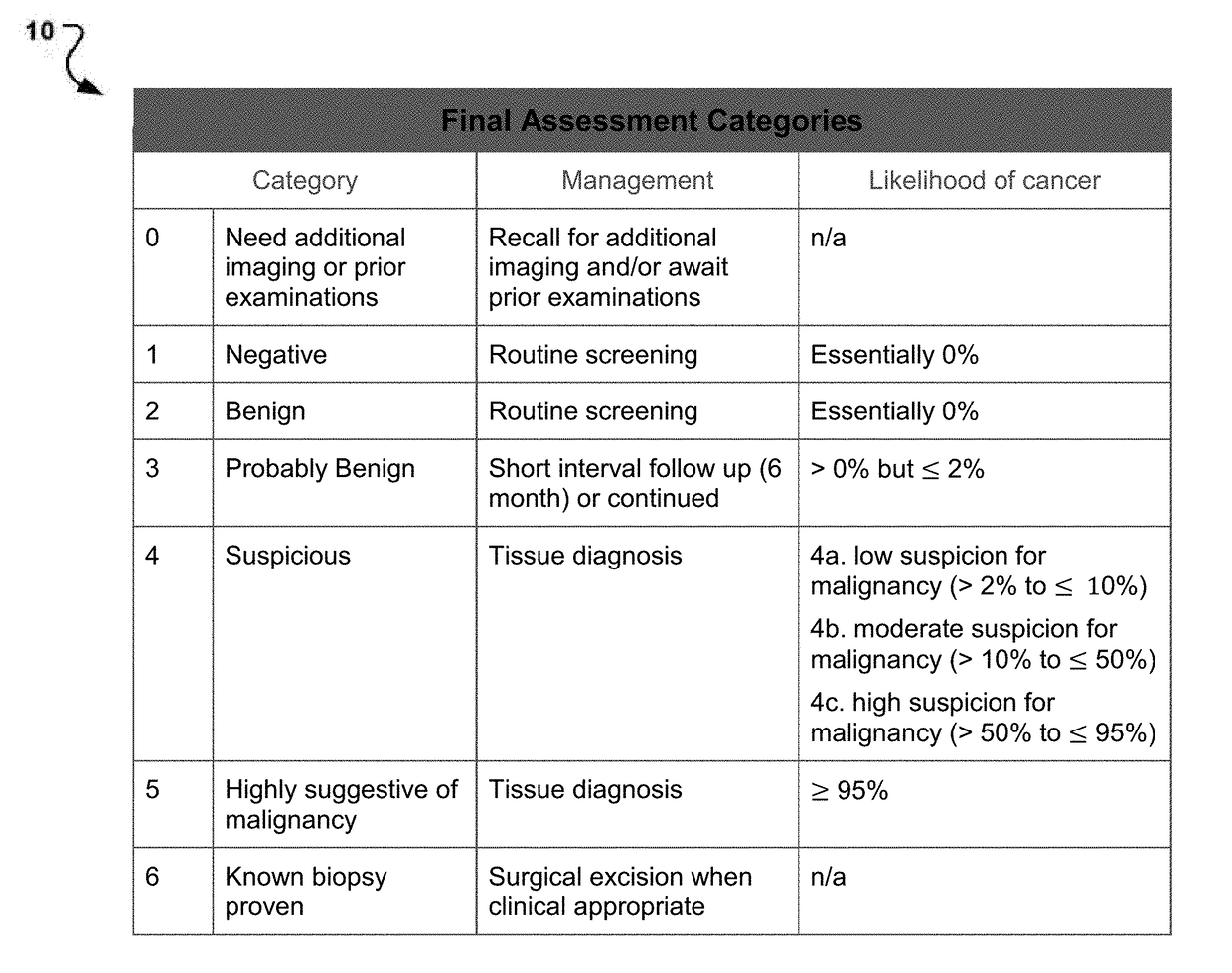
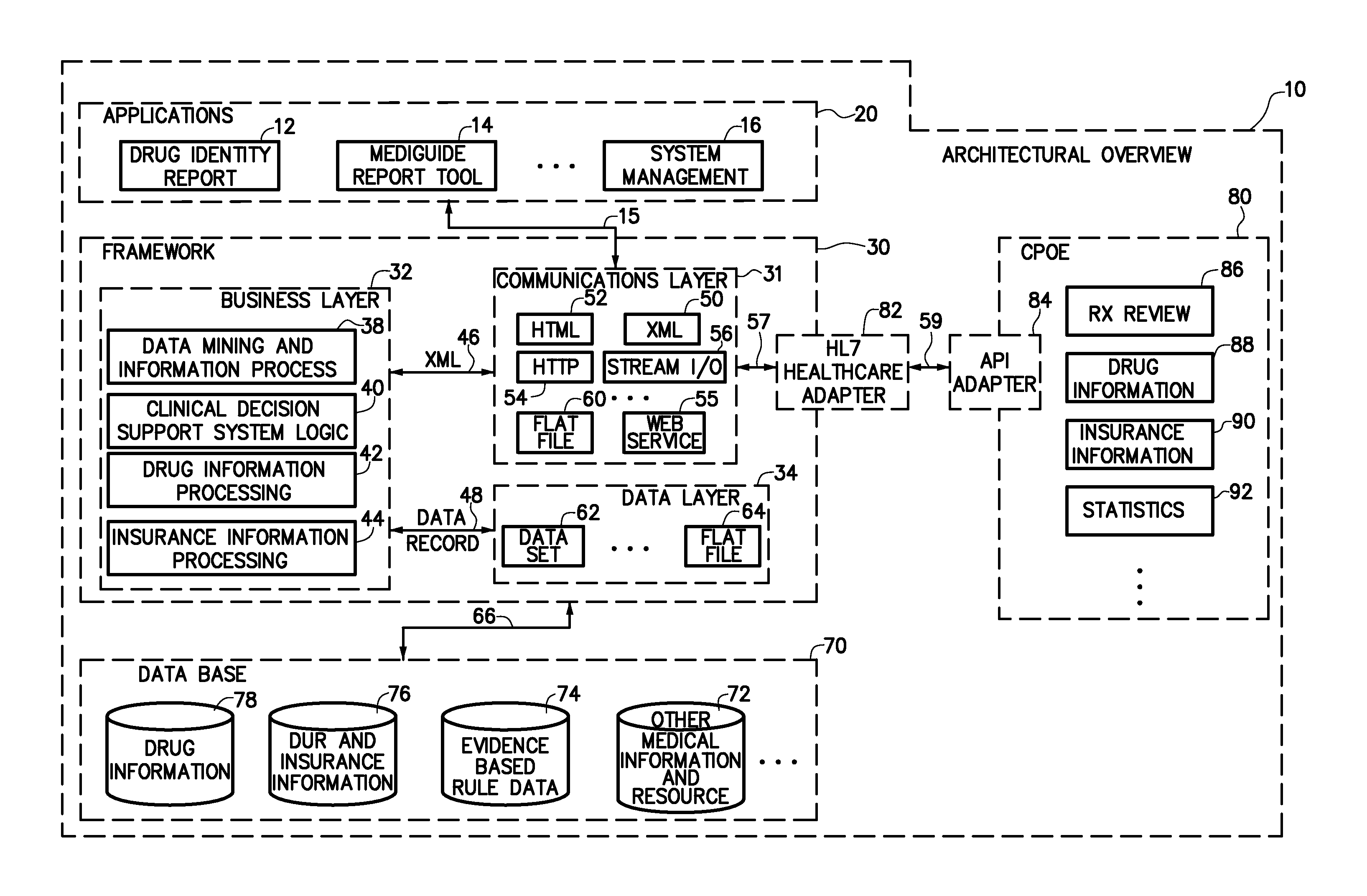
Patents
Literature
229 results about "Clinical decision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clinical decision making is a balance of known best practice (the evidence, the research), awareness of the current situation and environment, and knowledge of the patient. It is about 'joining the dots' to make an informed decision.
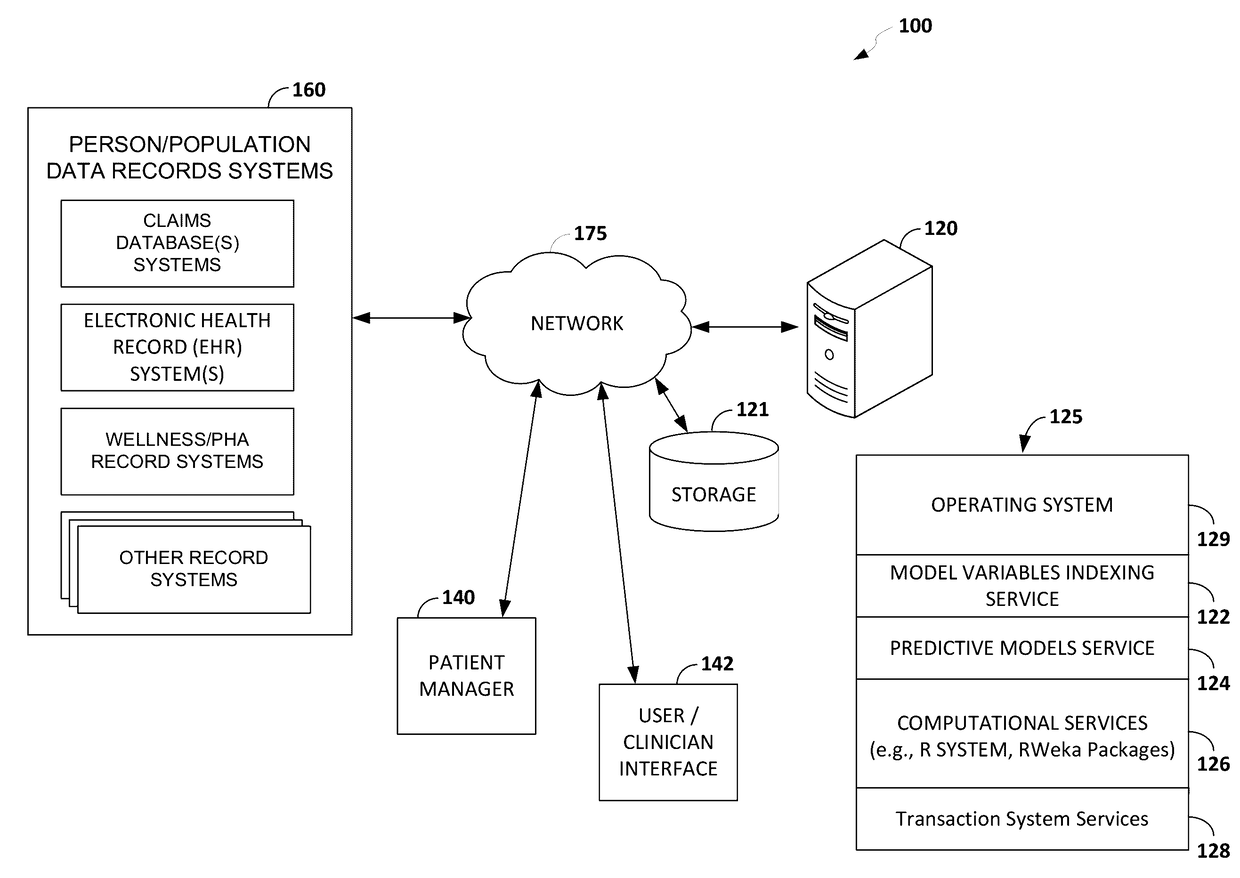
System and method for improving clinical decisions by aggregating, validating and analysing genetic and phenotypic data
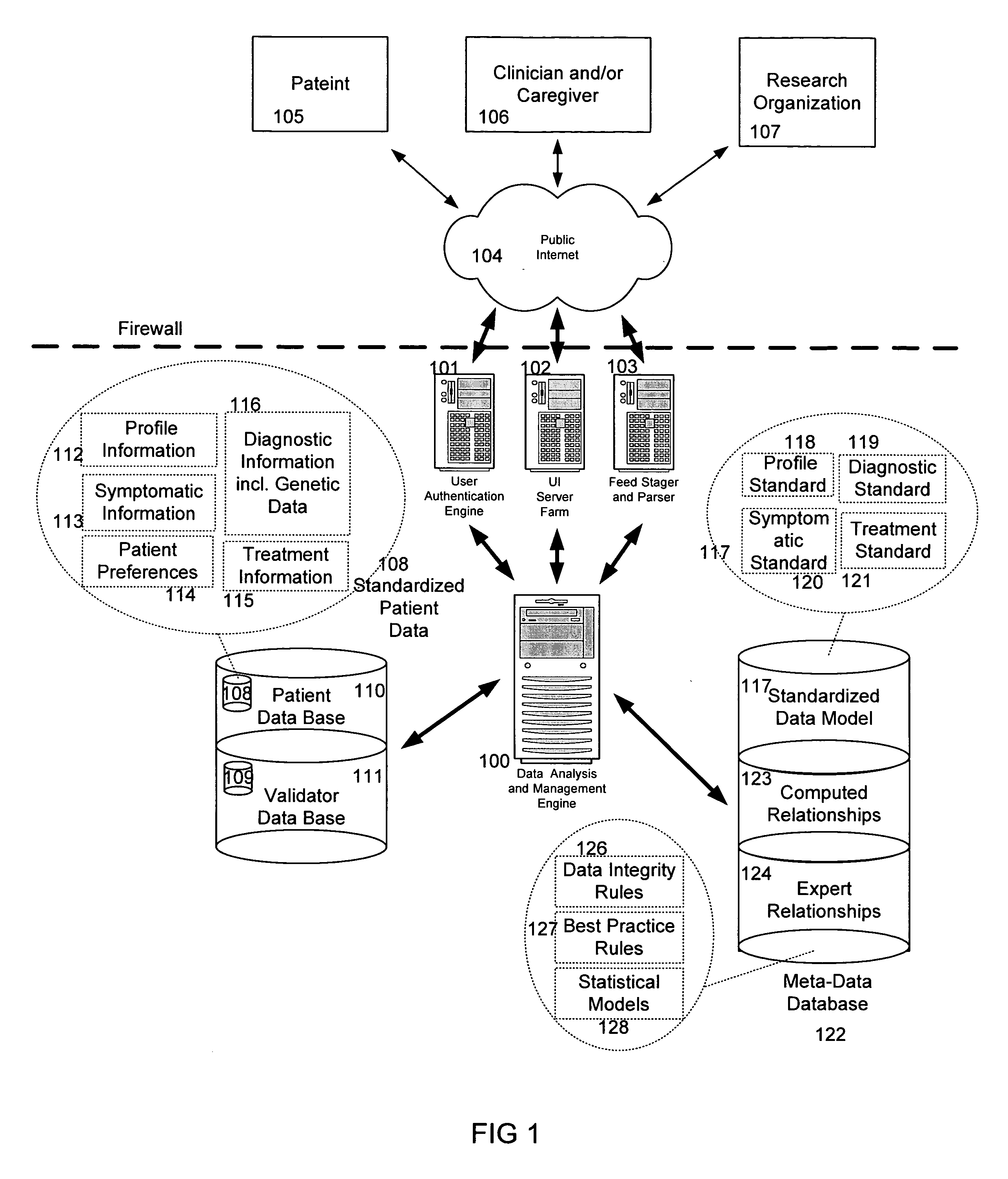
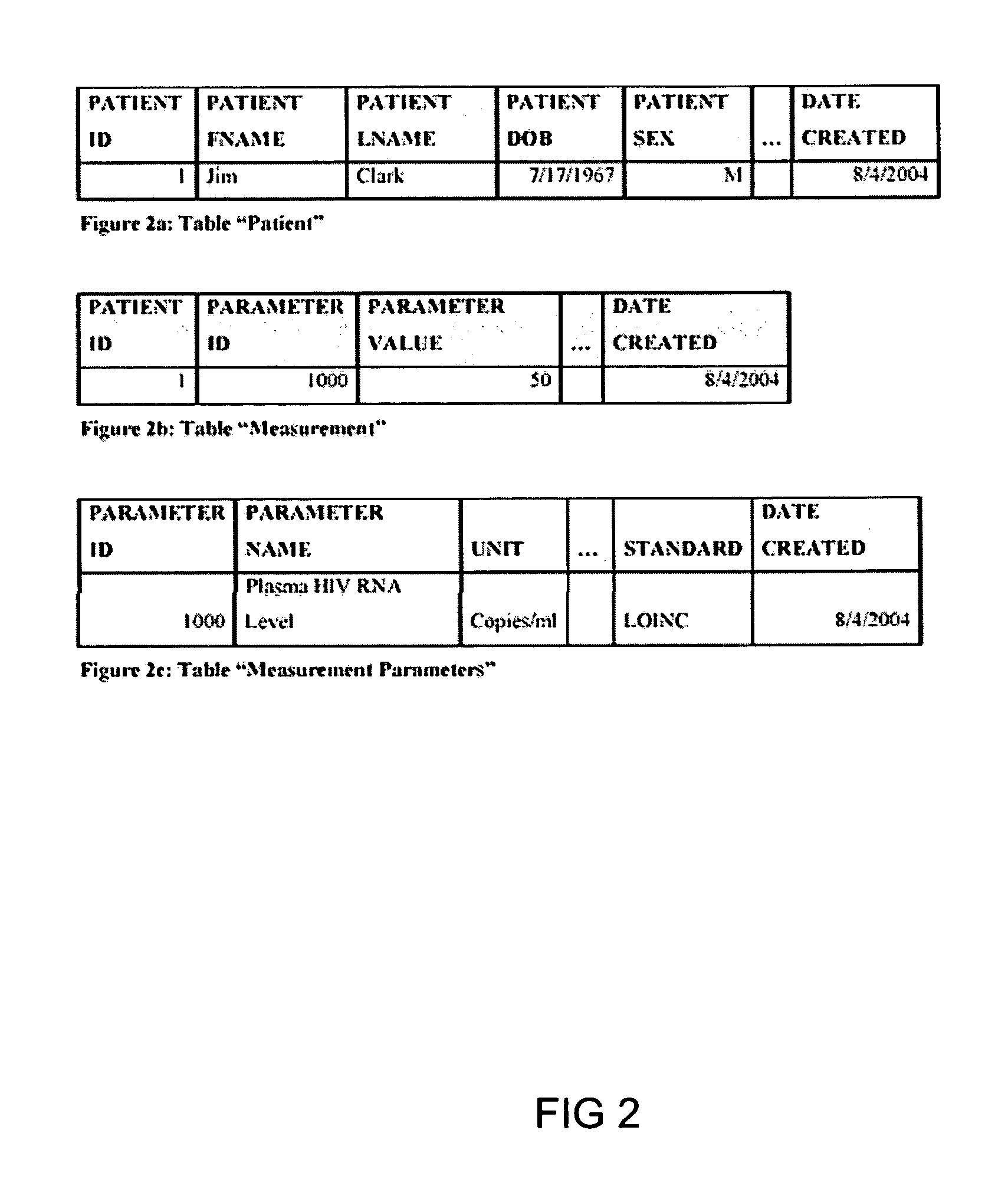
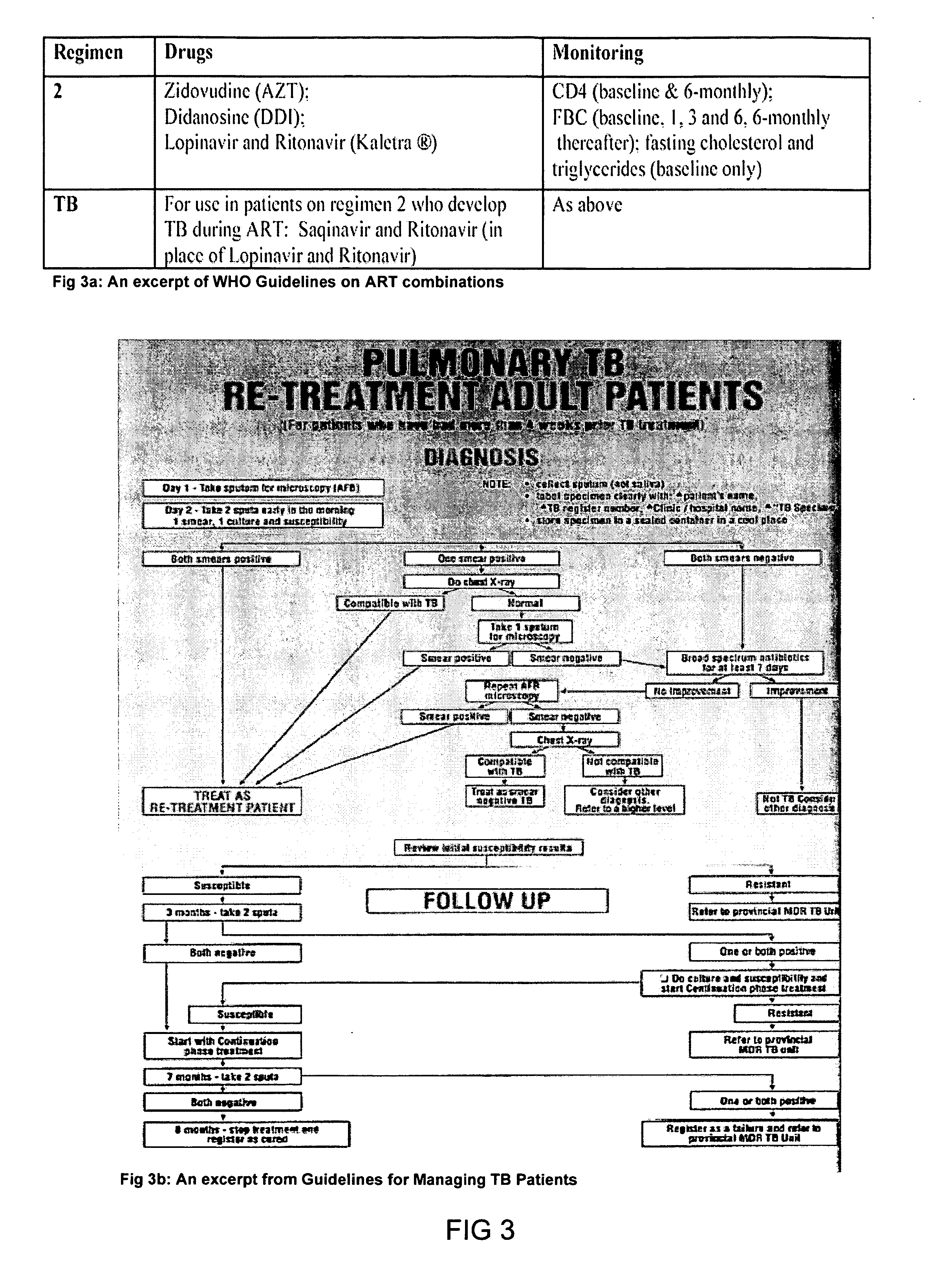
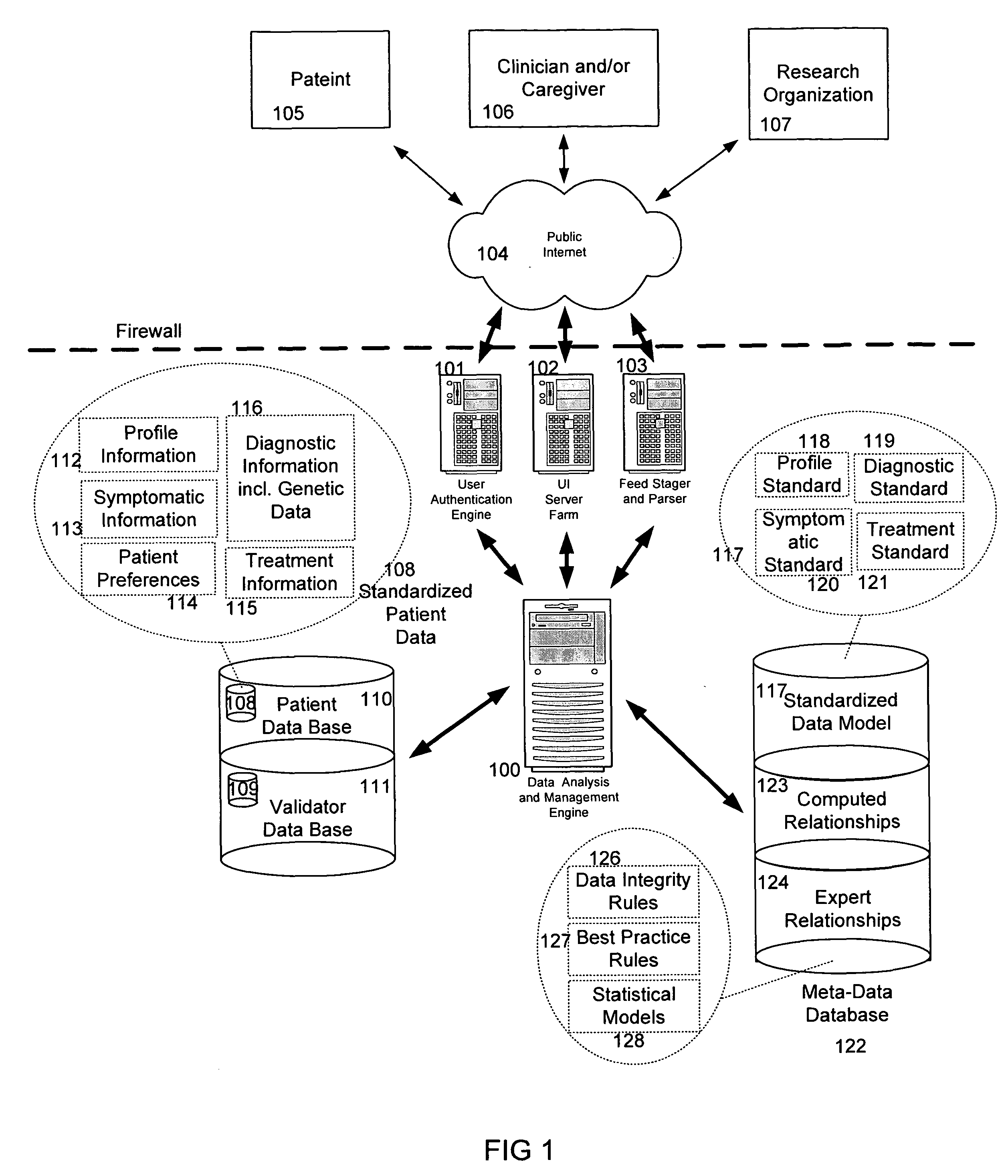
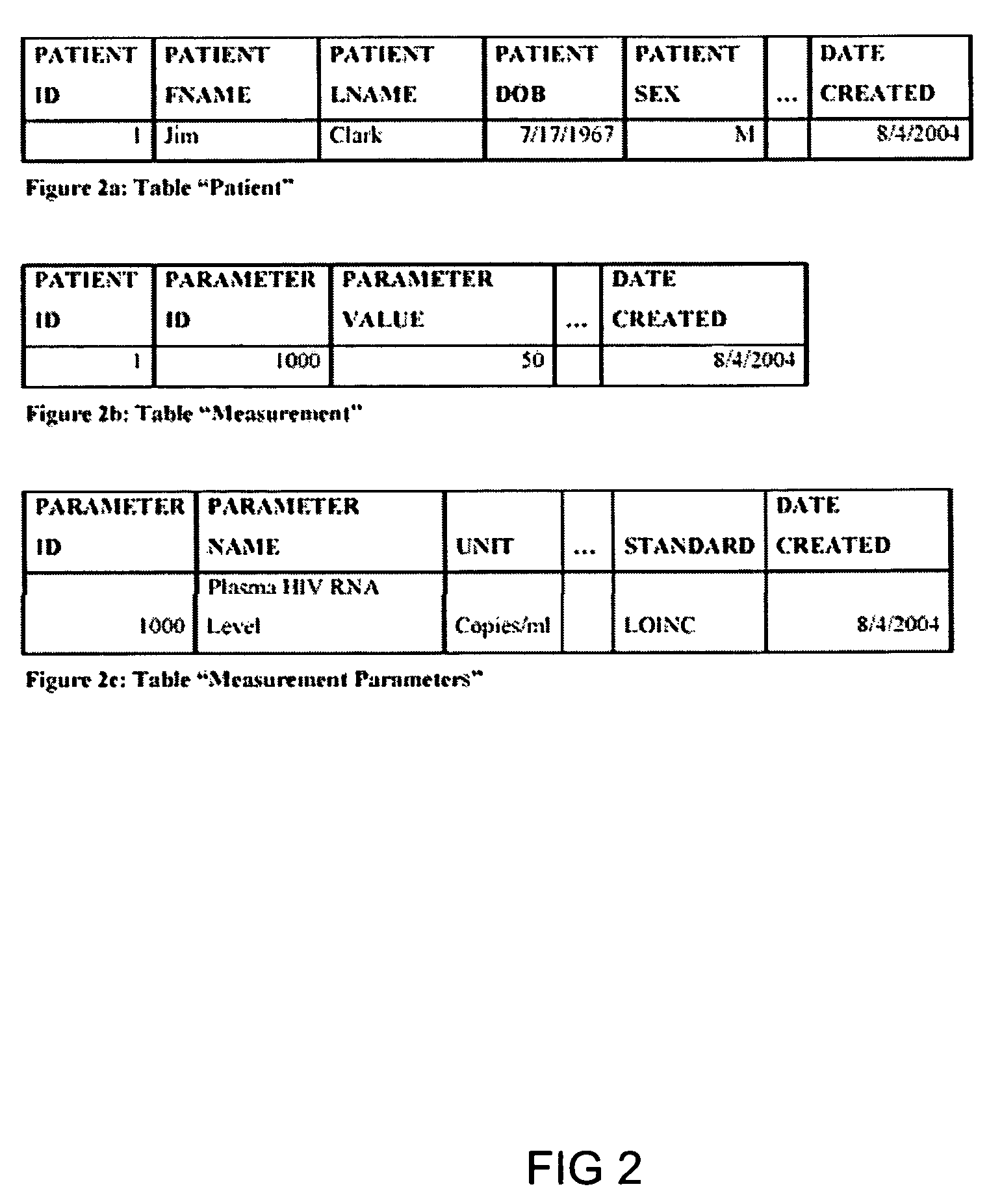
The information management system disclosed enables caregivers to make better decisions, faster, using aggregated genetic and phenotypic data. The system enables the integration, validation and analysis of genetic, phenotypic and clinical data from multiple subjects who may be at distributed facilities. A standardized data model stores a range of patient data in standardized data classes that encompass patient profile information, patient symptomatic information, patient treatment information, and patient diagnostic information including genetic information. Data from other systems is converted into the format of the standardized data classes using a data parser, or cartridge, specifically tailored to the source system. Relationships exist between standardized data classes that are based on expert rules and statistical models. The relationships are used both to validate new data, and to predict phenotypic outcomes based on available data. The prediction may relate to a clinical outcome in response to a proposed intervention by a caregiver. The statistical models may be inhaled into the system from electronic publications that define statistical models and methods for training those models, according to a standardized template. Methods are described for selecting, creating and training the statistical models to operate on genetic, phenotypic and clinical data, in particular for underdetermined data sets that are typical of genetic information. The disclosure also describes how security of the data is maintained by means of a robust security architecture, and robust user authentication such as biometric authentication, combined with application-level and data-level access privileges.
Owner:NATERA
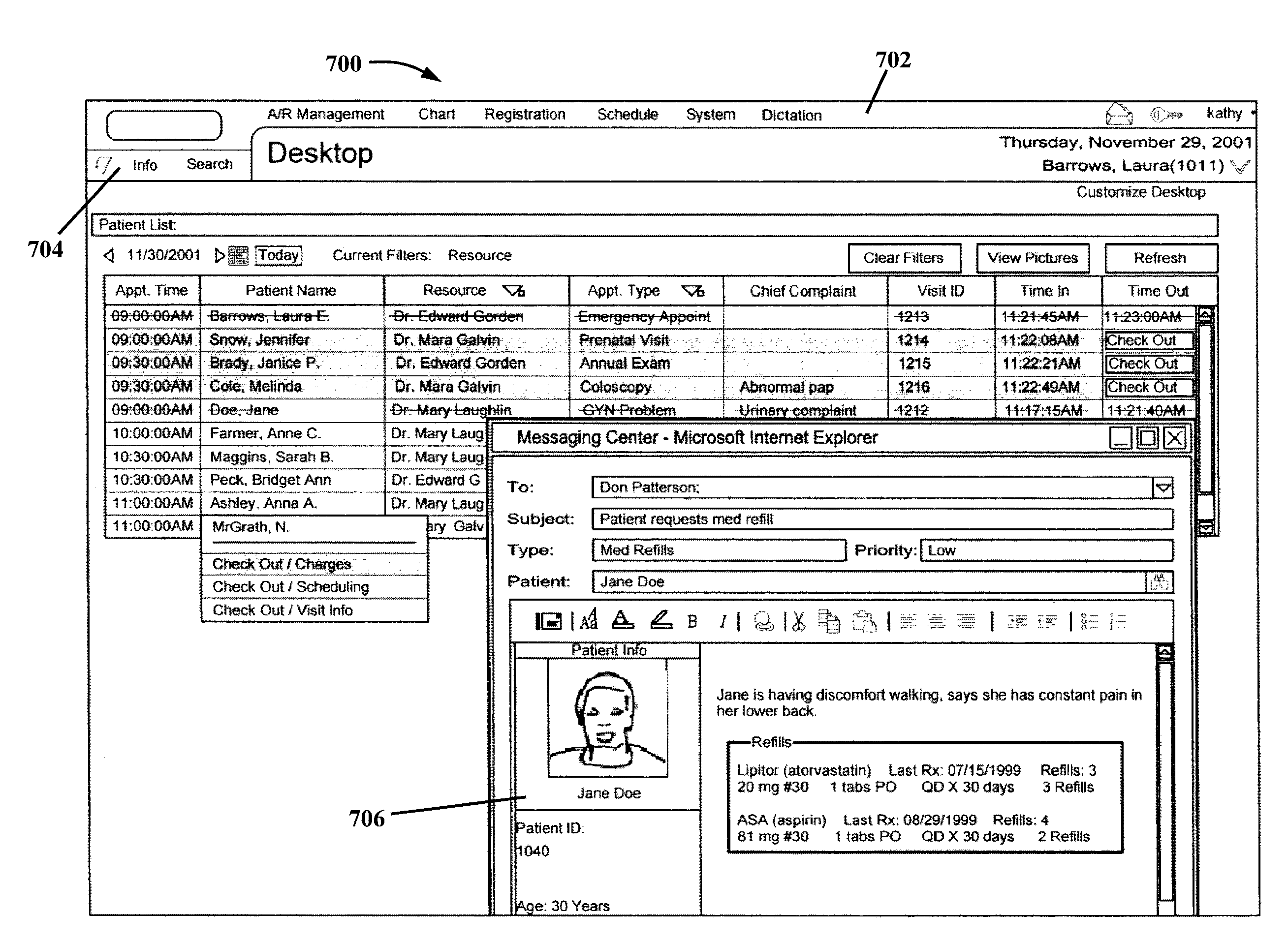
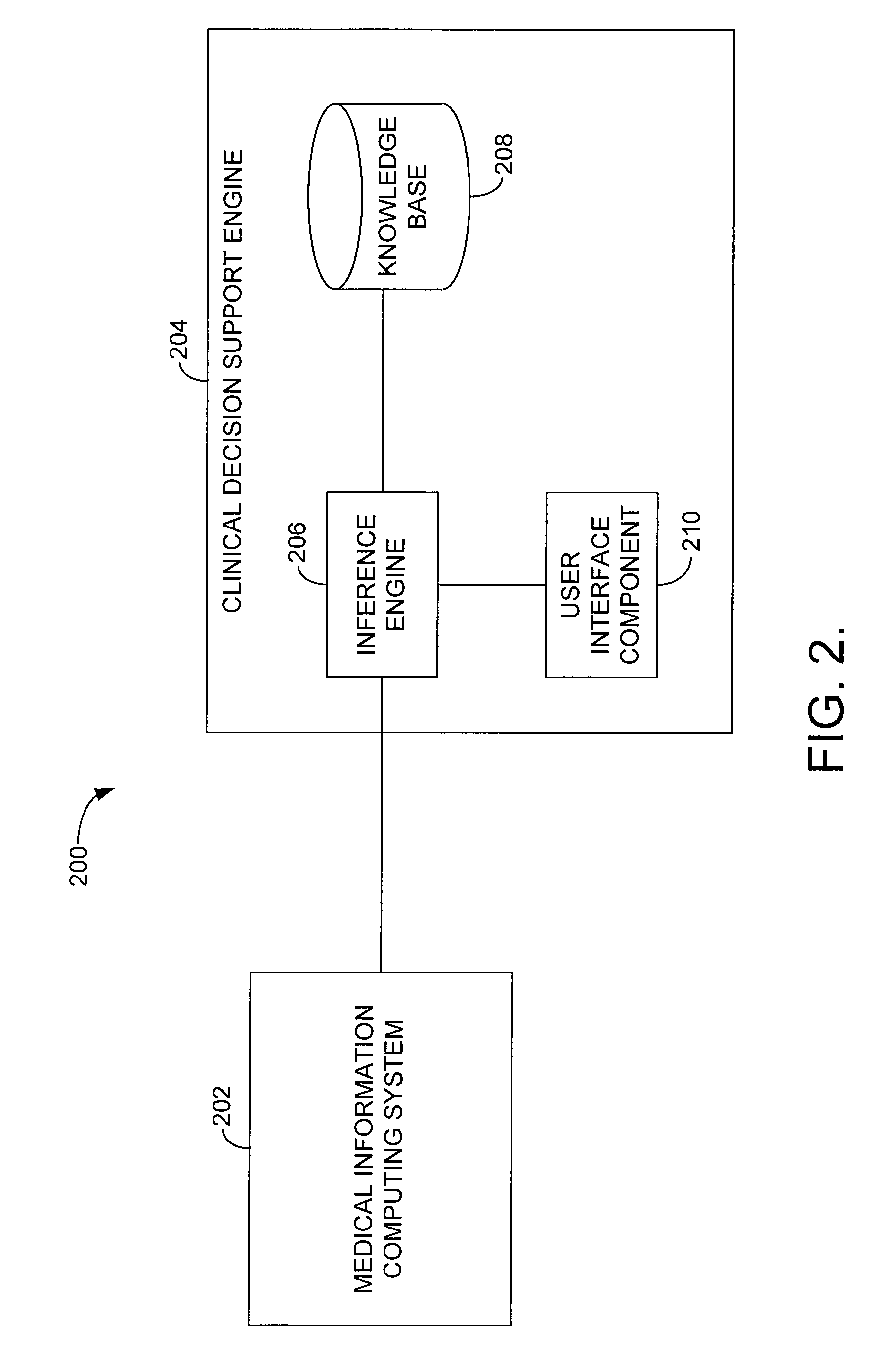
Integrated medical software system with clinical decision support
InactiveUS20110301982A1Readily apparentMedical data miningMedical automated diagnosisSoftware systemClinical decision support system
An integrated medical software system with embedded transcription functionality is disclosed. The system comprises a clinical module for capturing clinical data for a patient in a first electronic document and a communication component that communicates the clinical data to a rule-based clinical decision support (CDS) system and receives at least one of an alert, warning, reminder, and recommendation back from the CDS system based on the clinical data. The CDS system is configured to compare the clinical data against a knowledge base to identify the at least one of an alert, warning, reminder, and recommendation; the clinical data is serialized into a standardized database language and placed into a first electronic clinical document defined by a clinical document exchange standard before being communicated to the CDS system; and the at least one of an alert, warning, reminder, and recommendation is provided in a second electronic clinical document defined by the clinical document exchange standard when received back from the CDS system.
Owner:GREENWAY MEDICAL TECH
System and method for improving clinical decisions by aggregating, validating and analysing genetic and phenotypic data
The information management system disclosed enables caregivers to make better decisions by using aggregated data. The system enables the integration, validation and analysis of genetic, phenotypic and clinical data from multiple subjects. A standardized data model stores a range of patient data in standardized data classes comprising patient profile, genetic, symptomatic, treatment and diagnostic information. Data is converted into standardized data classes using a data parser specifically tailored to the source system. Relationships exist between standardized data classes, based on expert rules and statistical models, and are used to validate new data and predict phenotypic outcomes. The prediction may comprise a clinical outcome in response to a proposed intervention. The statistical models and methods for training those models may be input according to a standardized template. Methods are described for selecting, creating and training the statistical models to operate on genetic, phenotypic, clinical and undetermined data sets.
Owner:NATERA
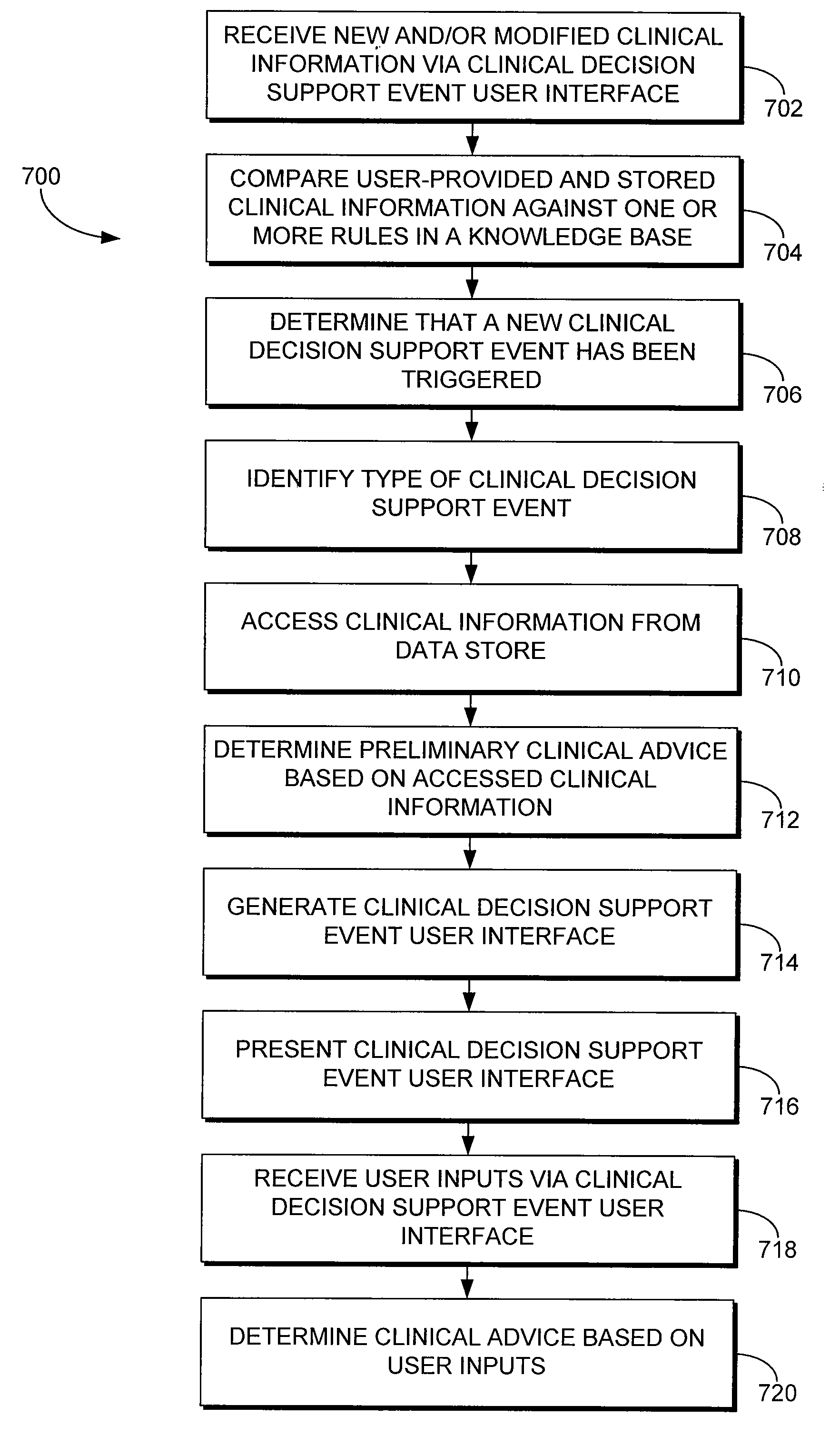
User interface for clinical decision support
User interfaces for proactive and interactive clinical decision support events are provided. When a clinical decision support event is initiated for a patient, relevant stored clinical information associated with the patient is accessed. A user interface is generated using the stored clinical information. A clinician may interact with the user interface by providing user-provided clinical information that may add to and / or modify the stored clinical information in the user interface. Clinical advice is provided via the user interface based on the stored clinical information and the user-provided clinical information.
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
Apparatus and method for monitoring blood glucose levels including convenient display of blood glucose value average and constituent values
A method of presenting glucose data to a person with diabetes from a blood glucose meter is provided in which an effective meal average (EMA) value is presented, followed by two or more of the individual values that make up the EMA, to provide improved feedback data for clinical decisions by patients who need to alter their dose of insulin. The EMA can also comprise a measure of the variability of its constituent values. The EMA encompasses those values that occur at specified times such as 1 hour before and 1 hour after a specified meal time. The EMA is calculated over a limited number of days previous to the calculation (e.g., 3 days) and has a minimum number of values that must be obtained within the time and date ranges. An algorithm allows for exclusion of any given reading from the average (e.g., post-prandial or control solution readings). Patients can use 1 to 8 EMA on any given date range (e.g., preferably 4, that is, breakfast, lunch, supper and bedtime snack).
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
System and Methods for Personalized Clinical Decision Support Tools
InactiveUS20140350954A1Data processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisPersonalizationDisease risk
The use of a medical software platform to collect, normalize, and aggregate clinical data. Supports clinical care and provides research and clinical tools for institutions, healthcare providers, researchers, and patients. The invention provides a graphical interface to customize searches in the database for specified subsets of conditions, treatments or outcomes. The invention also provides a system and method for searching through clinical databases for desired terms which may provide additional information to a physician regarding patient care. Furthermore, this invention facilitates personalized medicine-based practices as relationships between genetics, personal heath data from multiple sources, disease risk and drug response can be more easily visualized and utilized for patient care and research.
Owner:ONTOMICS
Clinical decision-making artificial intelligence object oriented system and method
ActiveUS20150019241A1Improve decision-makingImprove fundamental understandingData processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisNODALMedicine
The present invention involves a system and method of providing decision support for assisting medical treatment decision-making. A patient agent software module processes information about a particular patient. A doctor agent software module processes information about a health status of a particular patient, beliefs relating to patient treatments, and the actual effects of treatment decisions. By filtering information over time from the patient agent into the doctor agent, a plurality of decision-outcome nodes are created and formed into a patient-specific outcome tree with the plurality of decision-outcome nodes. An optimal treatment is determined by evaluating the plurality of decision-outcome nodes with a cost per unit change function to output the optimal treatment. When additional information is available from at least one of the patient agent and the doctor agent, the filtering, creating, and determining steps are repeated thus allowing for the system to “reason over time”, continuously updating and learning as new information is received.
Owner:TEAM COGNITIVE AI INC
Clinical support systems and methods
ActiveUS20150227710A1Improve visualizationReduce deliveryMedical simulationData processing applicationsSelected interventionsClinical support
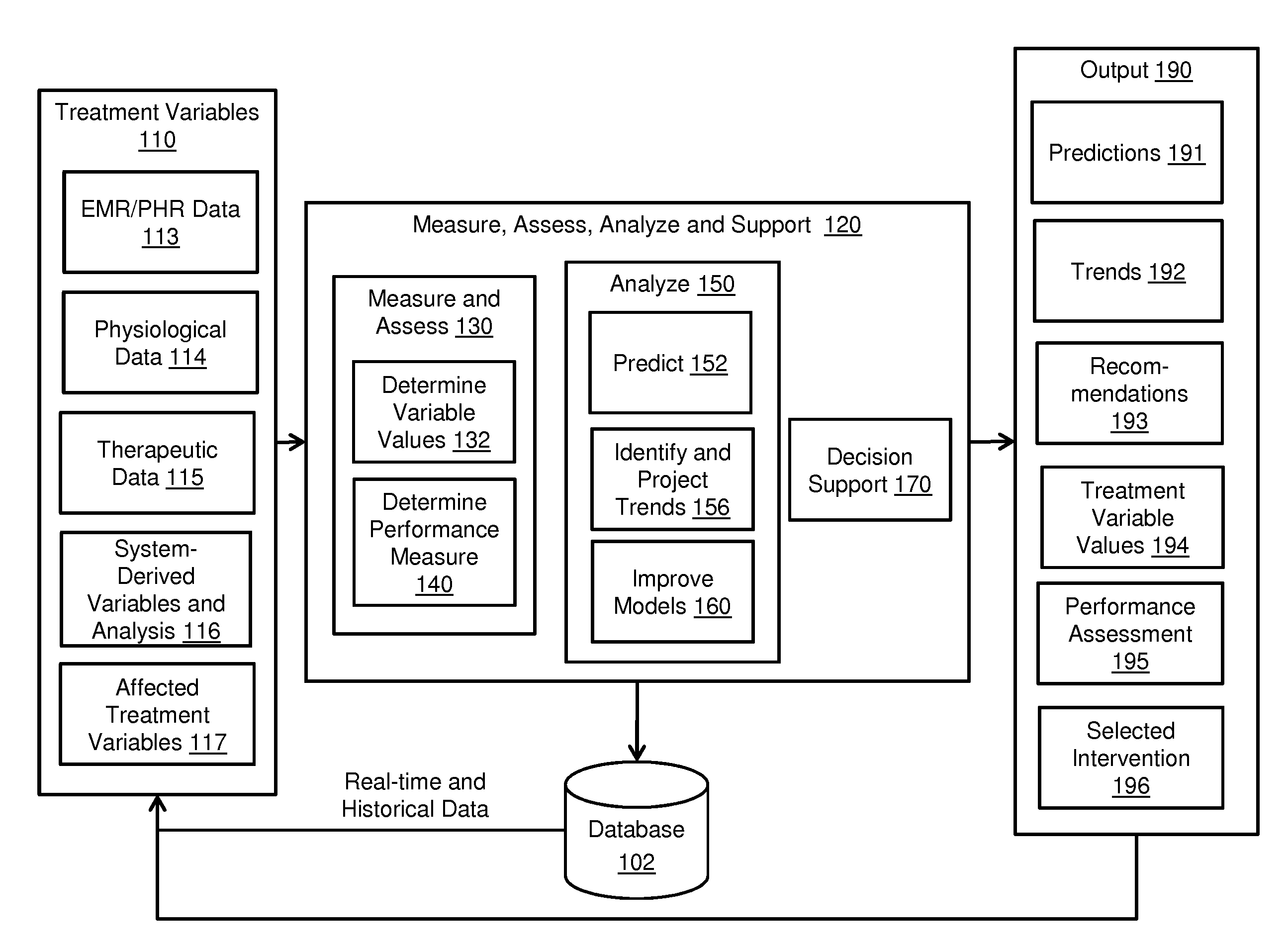
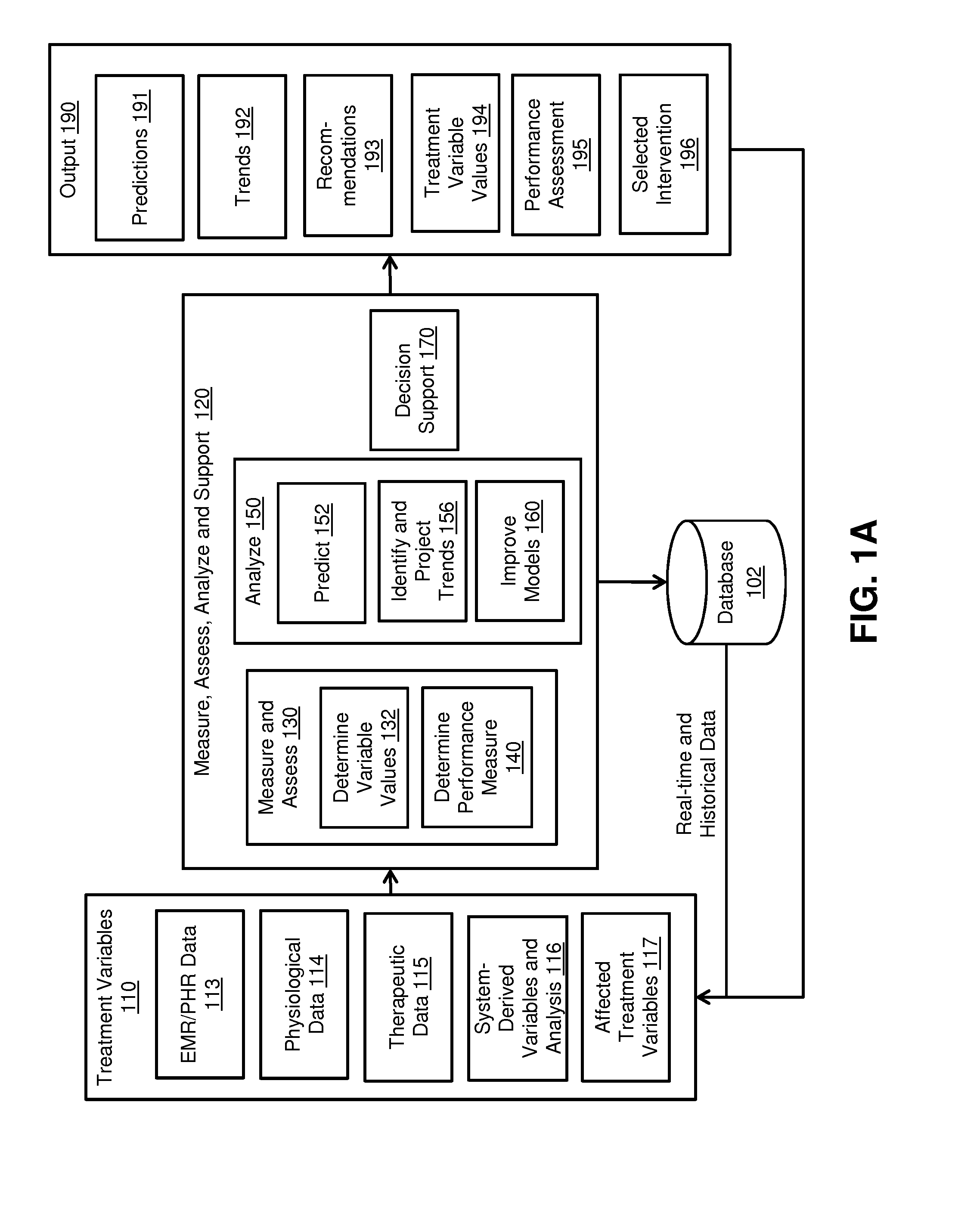
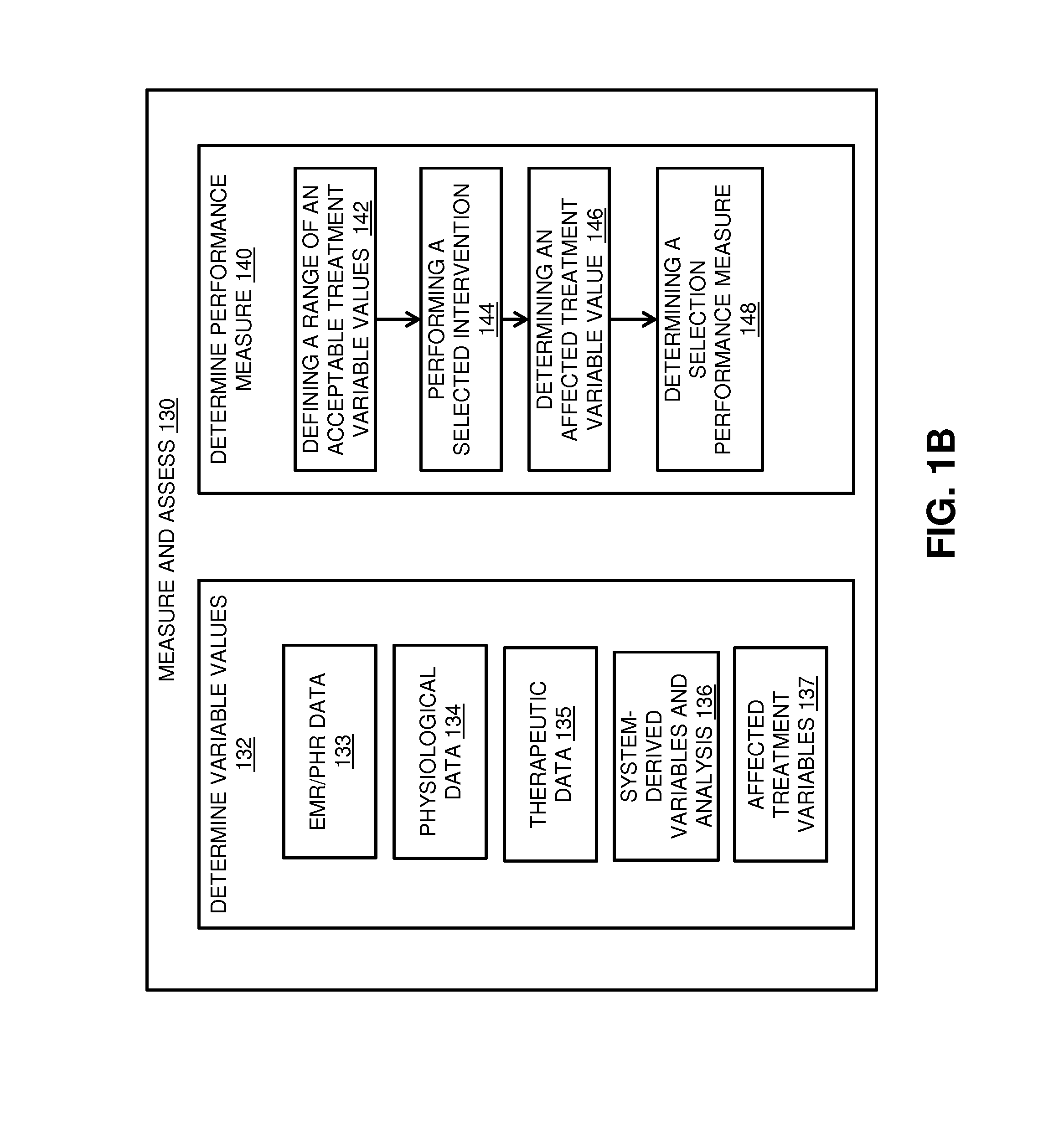
Embodiments of clinical support systems and methods are disclosed. In one embodiment, methods for clinical performance measurement are disclosed comprising defining a range of acceptable treatment variable values for a treatment variable of a subject, performing a selected intervention, determining an affected treatment variable value and determining a selection performance measure by comparing the affected treatment variable value to the acceptable treatment variable values. In one embodiment, methods for clinical decision training are disclosed comprising defining a treatment variable of a simulated subject, selecting an intervention on the treatment variable, modeling the selected intervention and presenting a visual representation of the selected intervention. In one embodiment, methods for clinical decision support are disclosed comprising defining a treatment variable of a subject, presenting a decision support variable as clinical decision support, performing a selected intervention and determining an affected treatment variable value.
Owner:ANALYTIC DIABETIC SYST
Machine learning clinical decision support system for risk categorization
ActiveUS20170140114A1Increased riskEfficient targetingEnsemble learningMedical automated diagnosisMedical recordRisk categorization
Improved risk categorization is provided for clinical decision support and forecasting future health care spend. A risk index is provided that improves on other risk stratification models by synthesizing electronic medical records and health questionnaires with an individual patient's claim histories. Machine learning algorithms catalogue patients into distinct group clusters, based on risk which may be associated with annual health care spending, thereby enabling administrators to forecast future health care spending on the individual and population level.
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
Method and system for facilitating clinical decisions
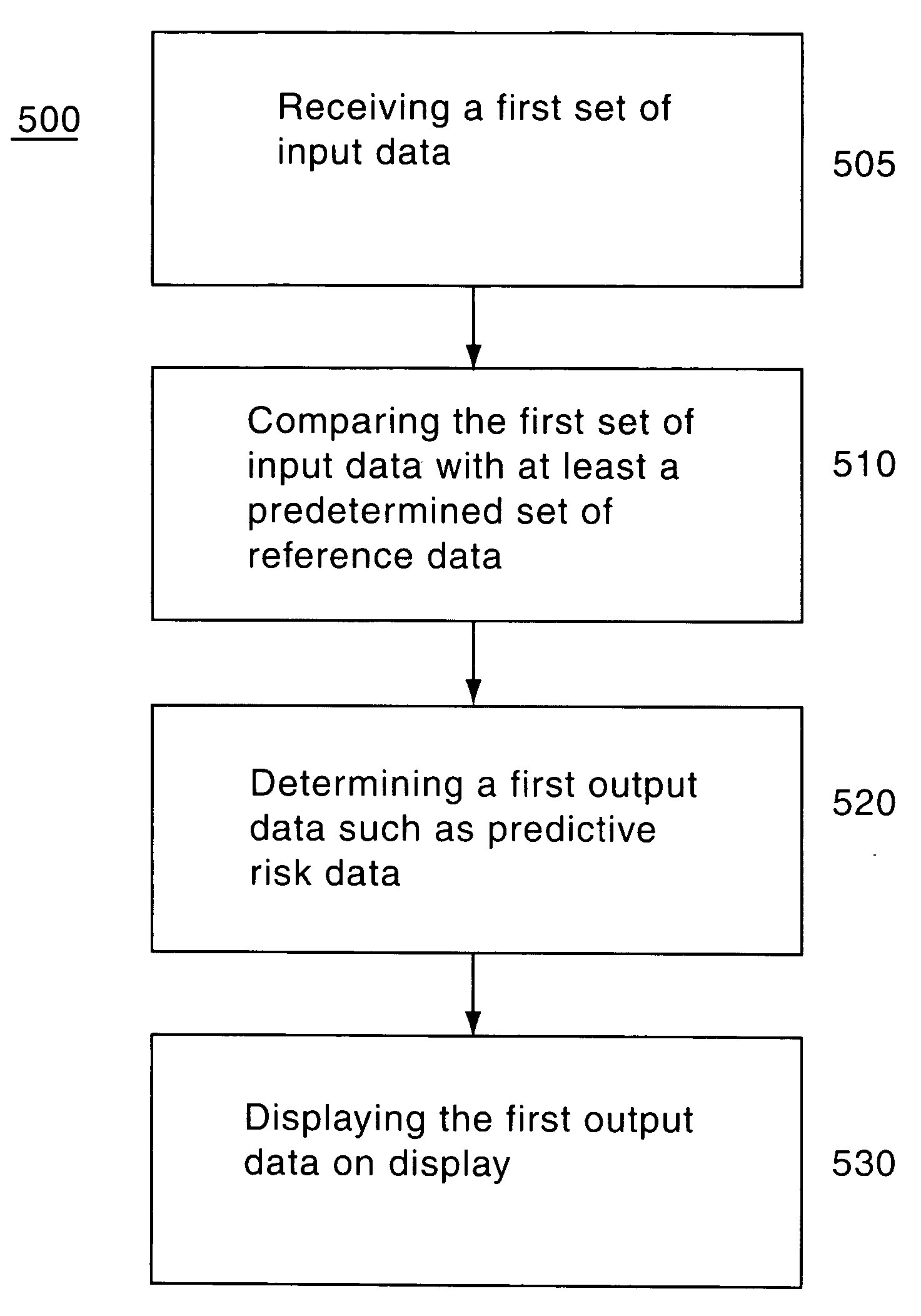
ActiveUS20060206359A1Facilitate health careFacilitate clinical decisionMedical data miningHealth-index calculationGraphicsMedical treatment
A method and system for providing information for facilitating health care and clinical decisions. The method includes receiving input data specifying patient information, comparing that data with one or more predetermined sets of reference data, and determining and displaying the output data. The output data can be displayed graphically, such as using bubbles of different color and size, to indicate risk factors and their contribution to potential health problems. After displaying the data, a second set of input data can be entered, and this data is compared to the first set of data and to one or more sets of reference data. A second set of output data is generatable and displayable alongside the first set of output data,
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
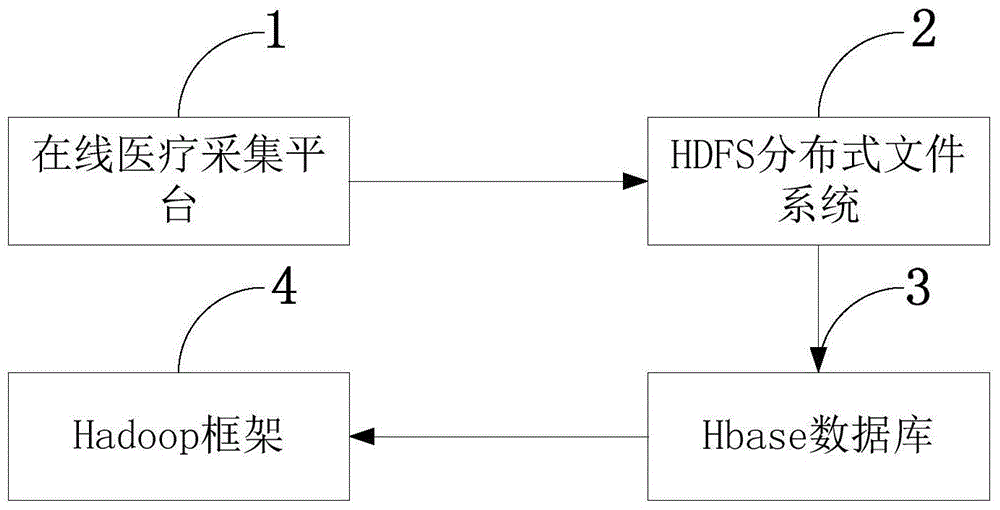
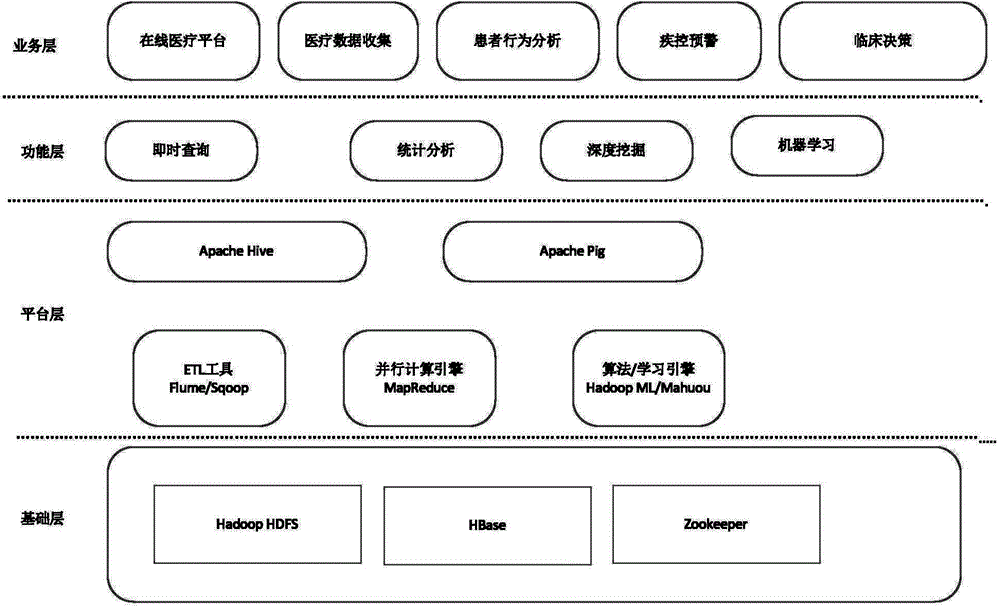
Medical big-data acquisition and analysis system and method
InactiveCN104699985AQuick analysisEarly warning outbreakSpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseBatch processing
The invention relates to a medical big-data acquisition and analysis system and method. The medical big-data acquisition and analysis method includes: installing a data acquisition unit at the place where medical data are acquired, and uploading the acquired data to an online medical acquisition platform; subjecting to the stored data to data processing; finding out a rule in the data; applying the data subjected to analysis to medical fields to carry out clinical decision and disease warning and analyze behaviors of patients. The medical big-data acquisition and analysis system comprises the online acquisition platform, an HDFS (hadoop distributed file system), an Hbase and a Hadoop frame, and is divided into four layers, namely a foundation layer, a platform layer, a function layer and a service layer. Staff health conditions can be acquired in real time, massive medical data are stored in a distributed manner, the massive data are analyzed rapidly by batch processing of big data, the clinical decision and disease warning are carried out, the behaviors of the patients are analyzed, multiple treatment schemes are put forward clinically, and early warnings are made for outbreaks of epidemic diseases.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Electronic health record system and method
InactiveUS20130110548A1Minimizes error in and delay in submission of claimLess time-consumingData processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisDocumentation procedureHealth history
Provided are a system and method for efficiently creating patient health records with help of expert clinical decision support. The system and method also ensures the doctor's documentation and diagnosis comply with the government healthcare quality measures.
Owner:KUTTY MOHAN
Methods and means of cad system personalization to reduce intraoperator and interoperator variation
ActiveUS20170200268A1Reduce difficultyIncrease the number ofImage enhancementImage analysisPersonalizationGuideline
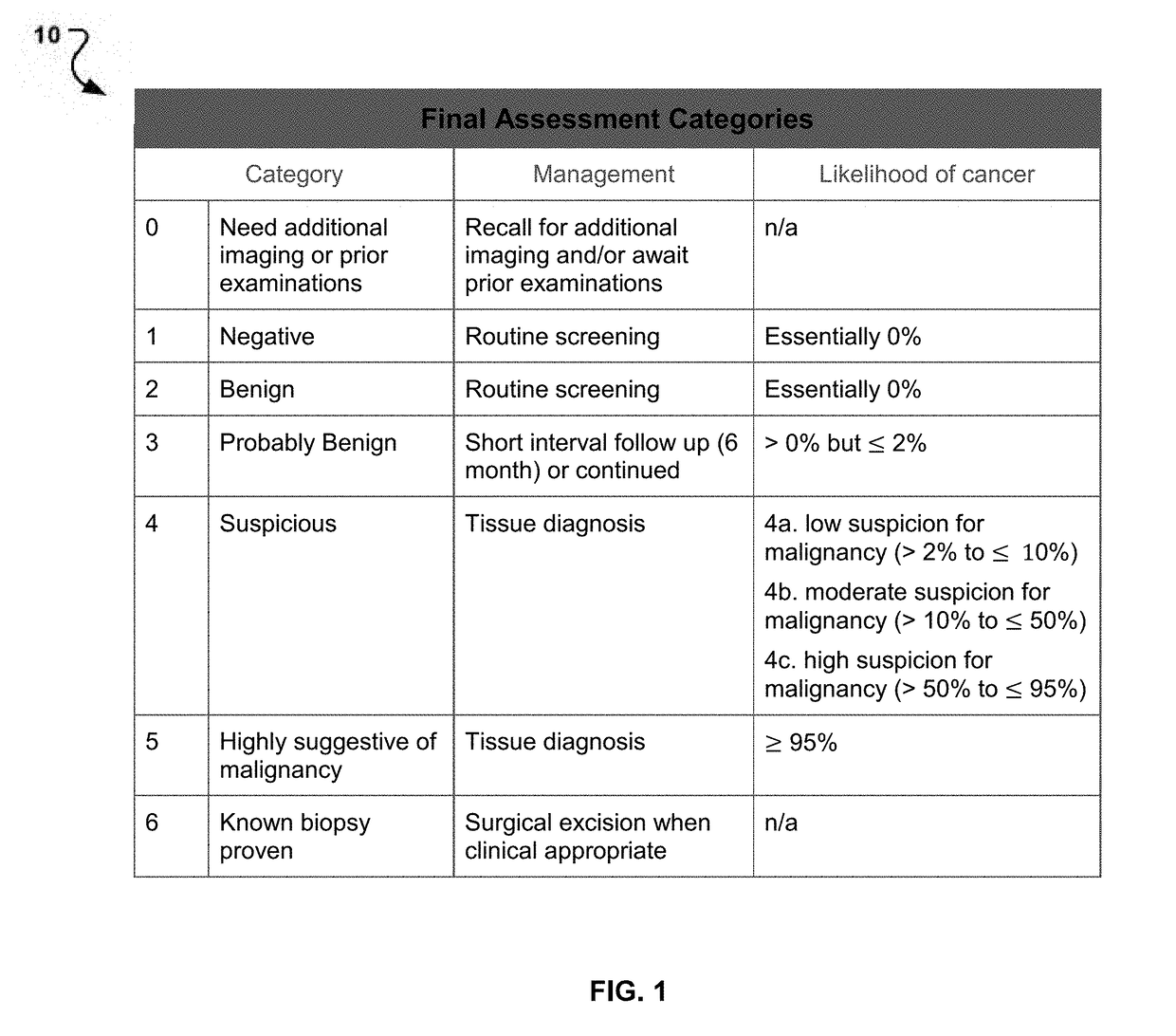
A system and method is disclosed to reduce variation of the clinical decision making process when an image reporting and data system (IRADS) for medical diagnosis is used. Image reporting and data systems provide guidelines for an operator to identify images as belonging to one of a number of categories and specific clinical actions are then recommended based upon such categories. Some clinical actions such as biopsies may be recommended by IRADS even when they are not necessary. The present inventive concept is configured to utilize a Computer-Assisted Diagnosis (CAD) system that is specifically programmed to minimize discrepancies between the recommended clinical actions of an individual or specific group of experts using the standard IRADS process and the optimum clinical actions based on correlation with biopsy proven data. The resulting CAD system reduces the number of unnecessary clinical actions such as biopsies based on the operator's error profile.
Owner:KOIOS MEDICAL INC
System and method for patient portal with clinical decision intelligence
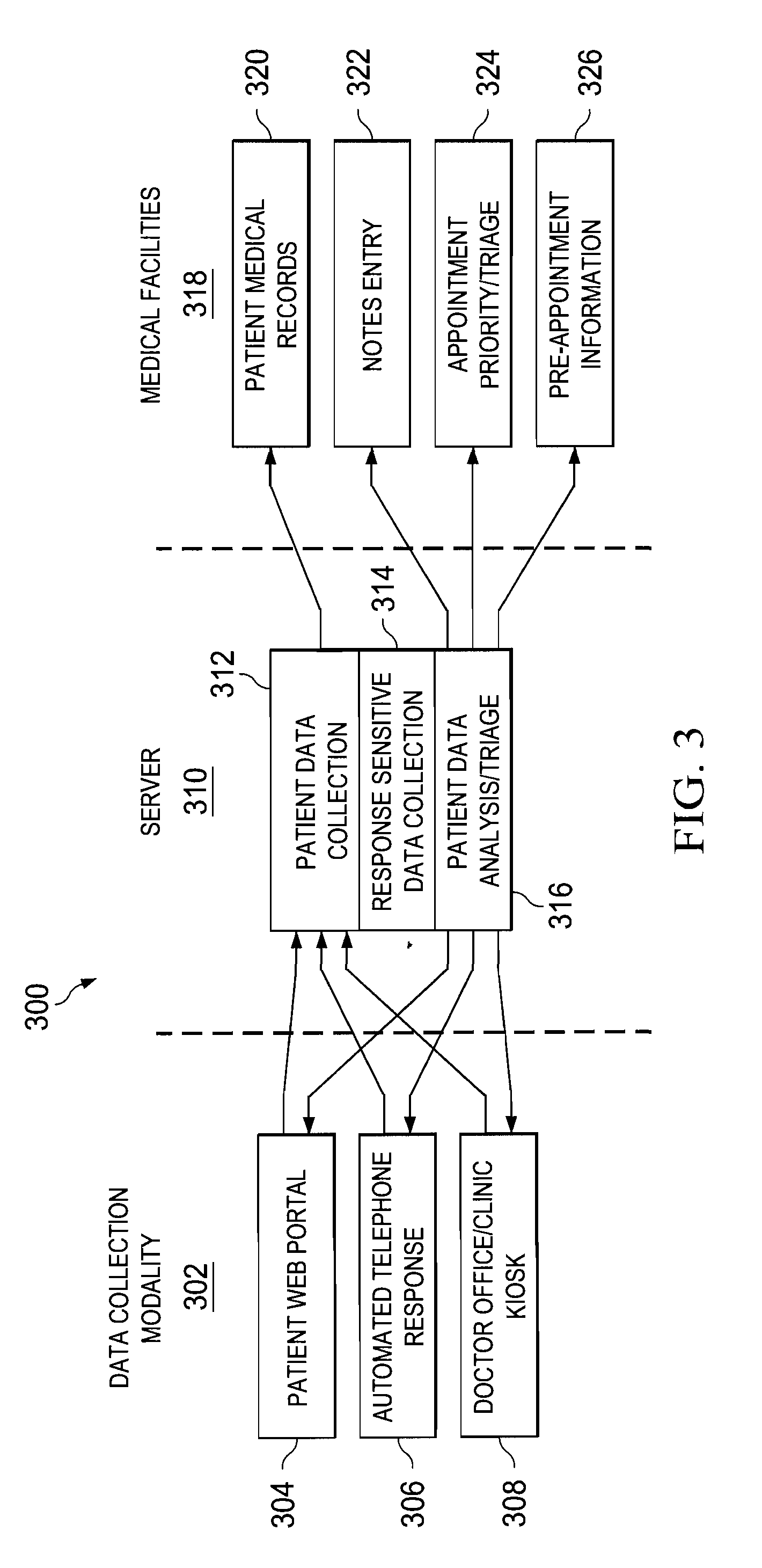
A computer-implemented method for transmitting a scheduled appointment to a patient. Input is received, wherein the input comprises at least one of current data provided by the patient, prior data provided by the patient prior to the current data, and known medical history of the patient. A possible condition of the patient is diagnosed based on the input. The appointment is scheduled for the patient based on the diagnosis. The scheduled appointment is transmitted to the patient.
Owner:IBM CORP
Healthcare information technology system for predicting development of cardiovascular conditions
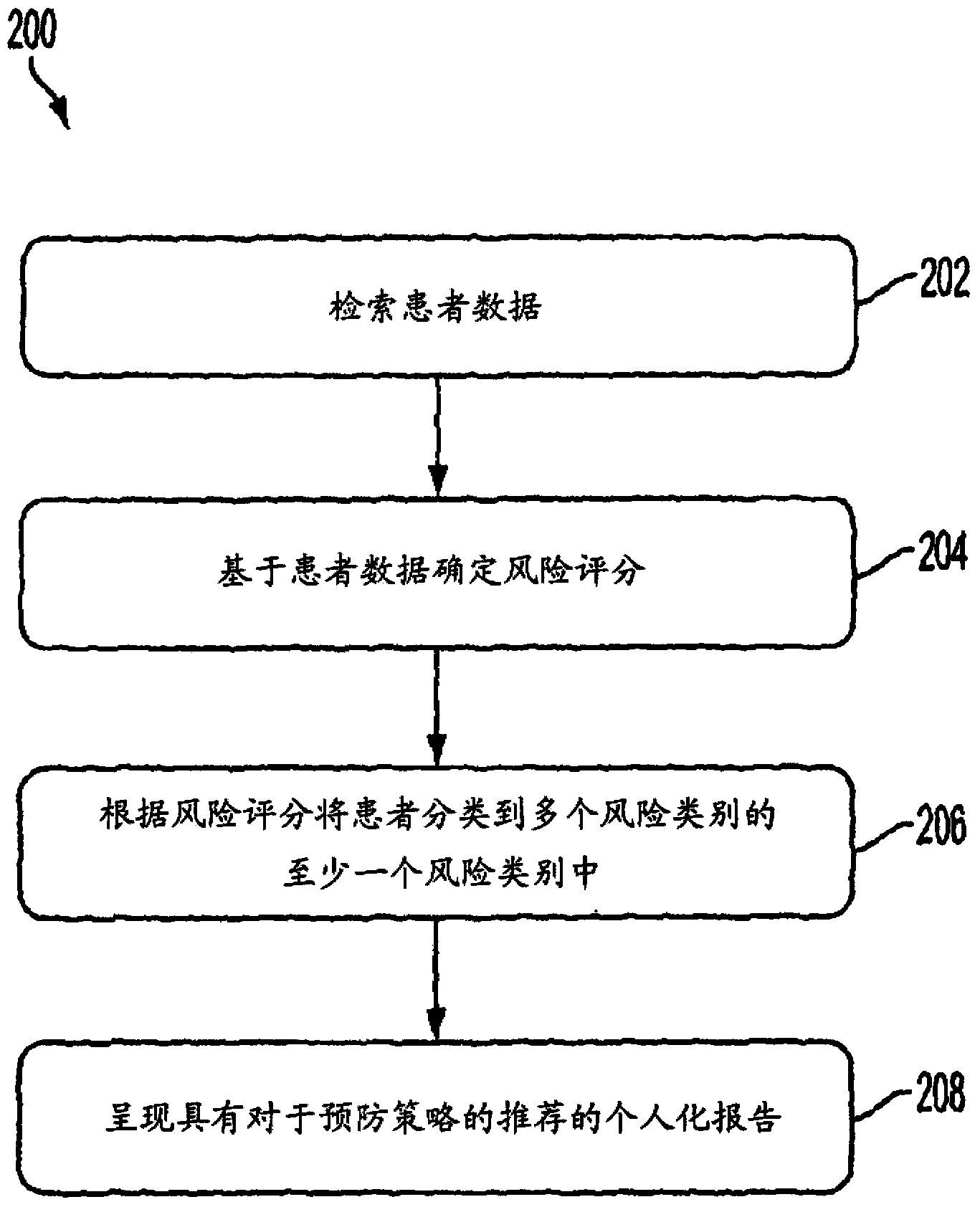
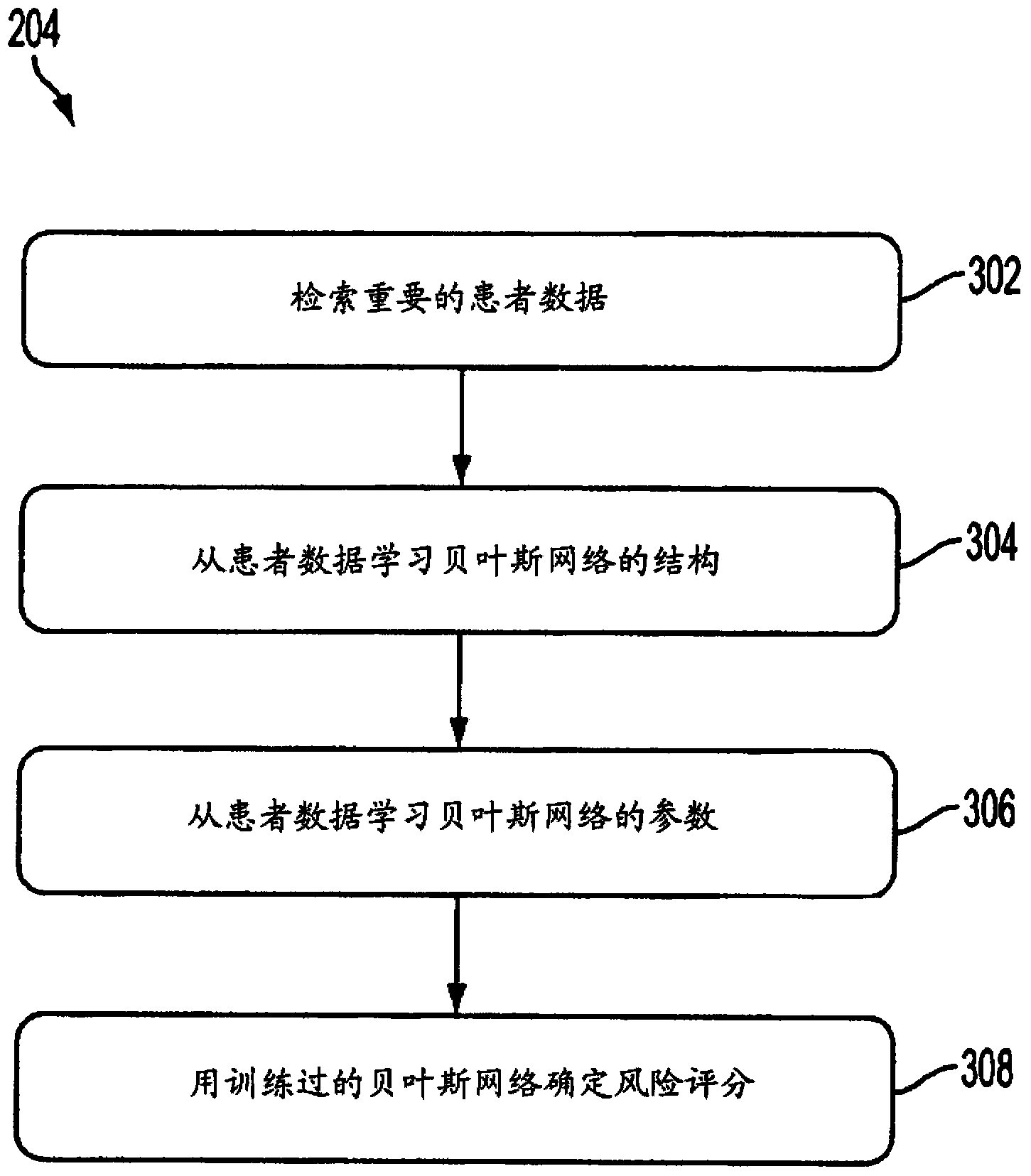
Described herein is a framework for predicting development of a cardiovascular condition of interest in a patient. The framework involves determining, based on prior domain knowledge relating to the cardiovascular condition of interest, a risk score as a function of patient data. The patient data may include both genetic data and non-genetic data. In one implementation, the risk score is used to categorize the patient into at least one of multiple risk categories, the multiple risk categories being associated with different strategies to prevent the onset of the cardiovascular condition. The results generated by the framework may be presented to a physician to facilitate interpretation, risk assessment and / or clinical decision support.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
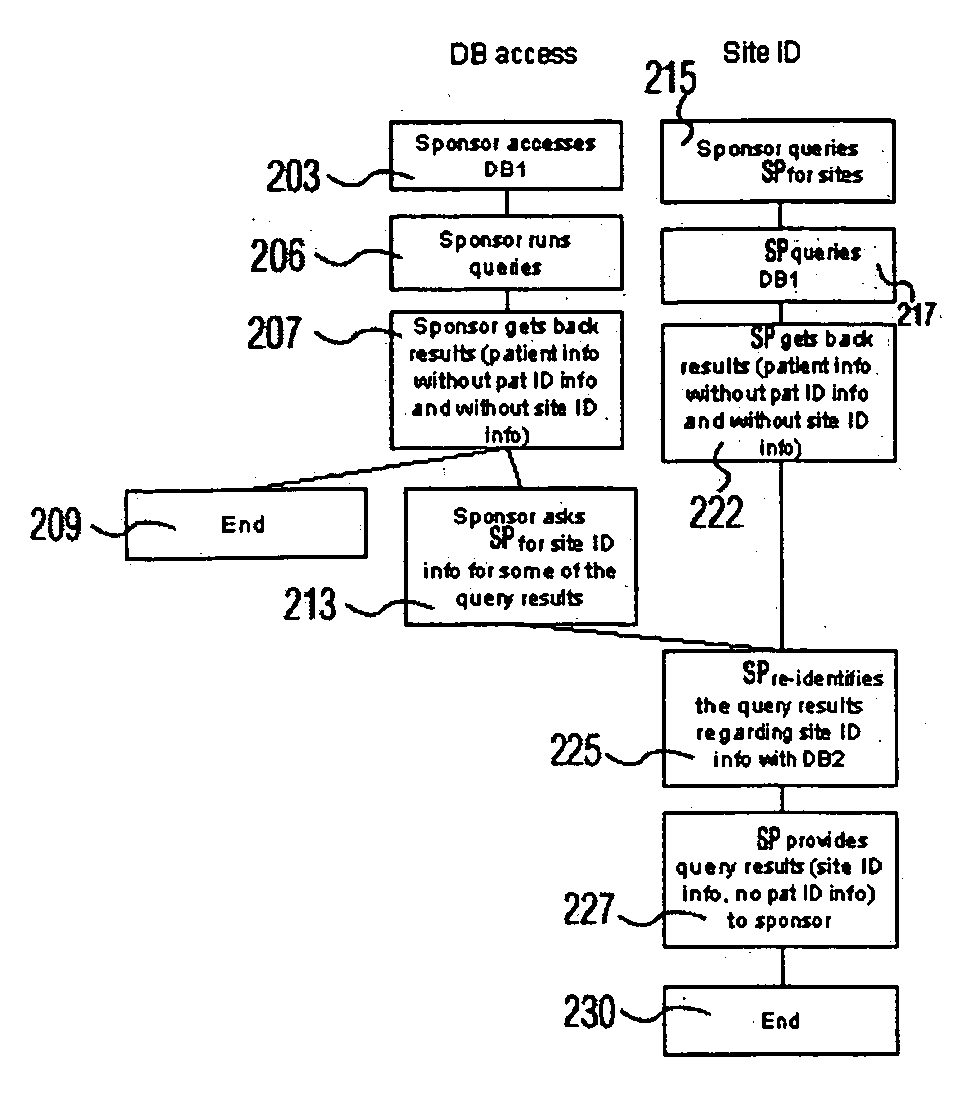
System for processing patient medical data for clinical trials and aggregate analysis
InactiveUS20050267782A1Easy to identifyMedical data miningData processing applicationsClinical trialData treatment
A system processes medical information of multiple patients to provide data for use in supporting clinical decision making. The system includes an interface for receiving, from a remote source, data representing patient non-specific medical information excluding patient specific information. The patient non-specific medical information comprises medical information of multiple individual patients treated at one or more healthcare organization sites. A data processor automatically, parses the received data, identifies, within the parsed received data, site specific information associated with a particular healthcare provider organization site and facilitates identification of the particular healthcare provider organization site. The data processor removes the identified site specific information from the data representing patient non-specific medical information to provide both patient and site non-specific, patient medical information representative data and stores both the patient and site non-specific, patient medical information representative data in a repository.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS HEALTH SERVICES CORPORAT
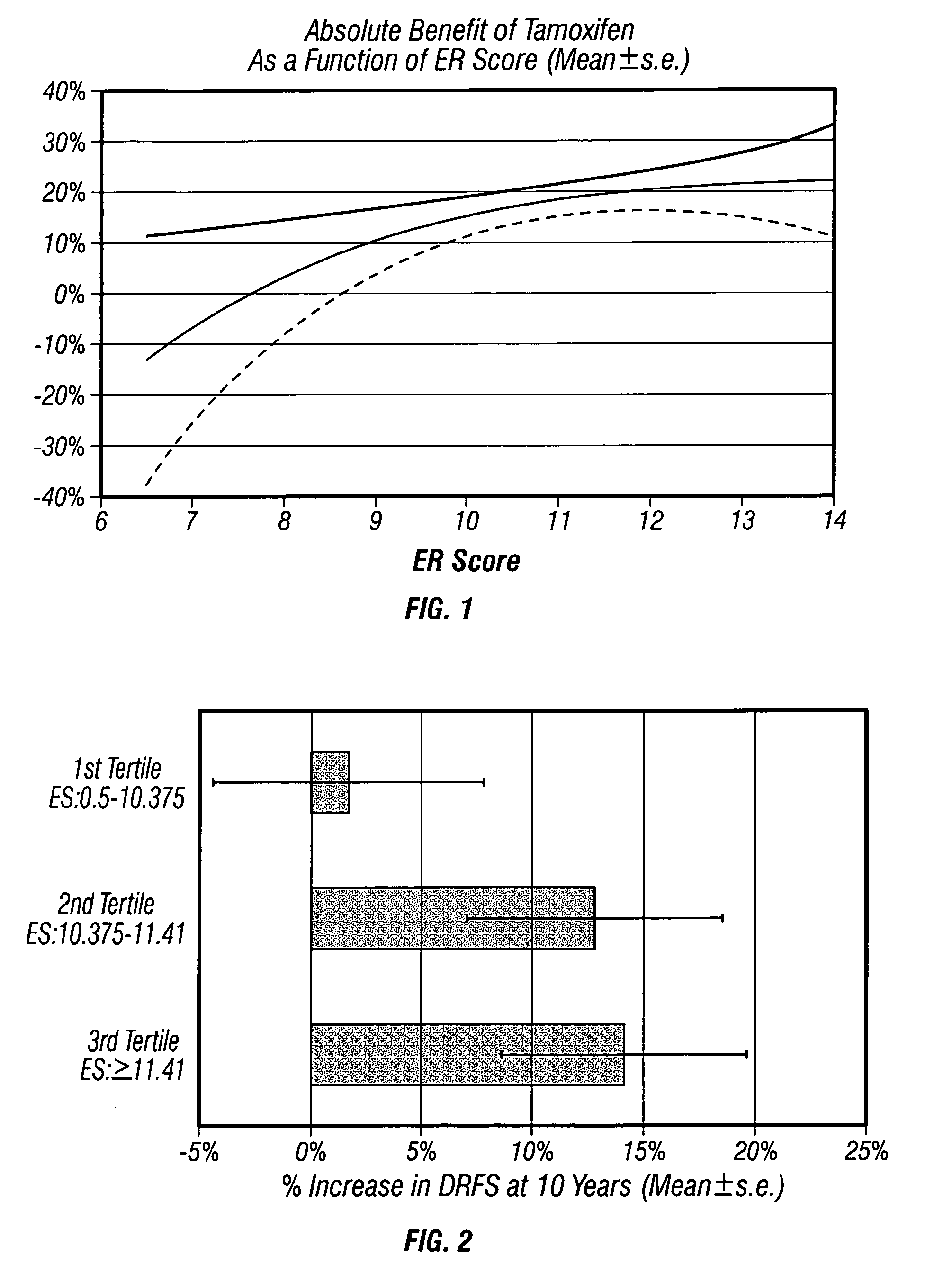
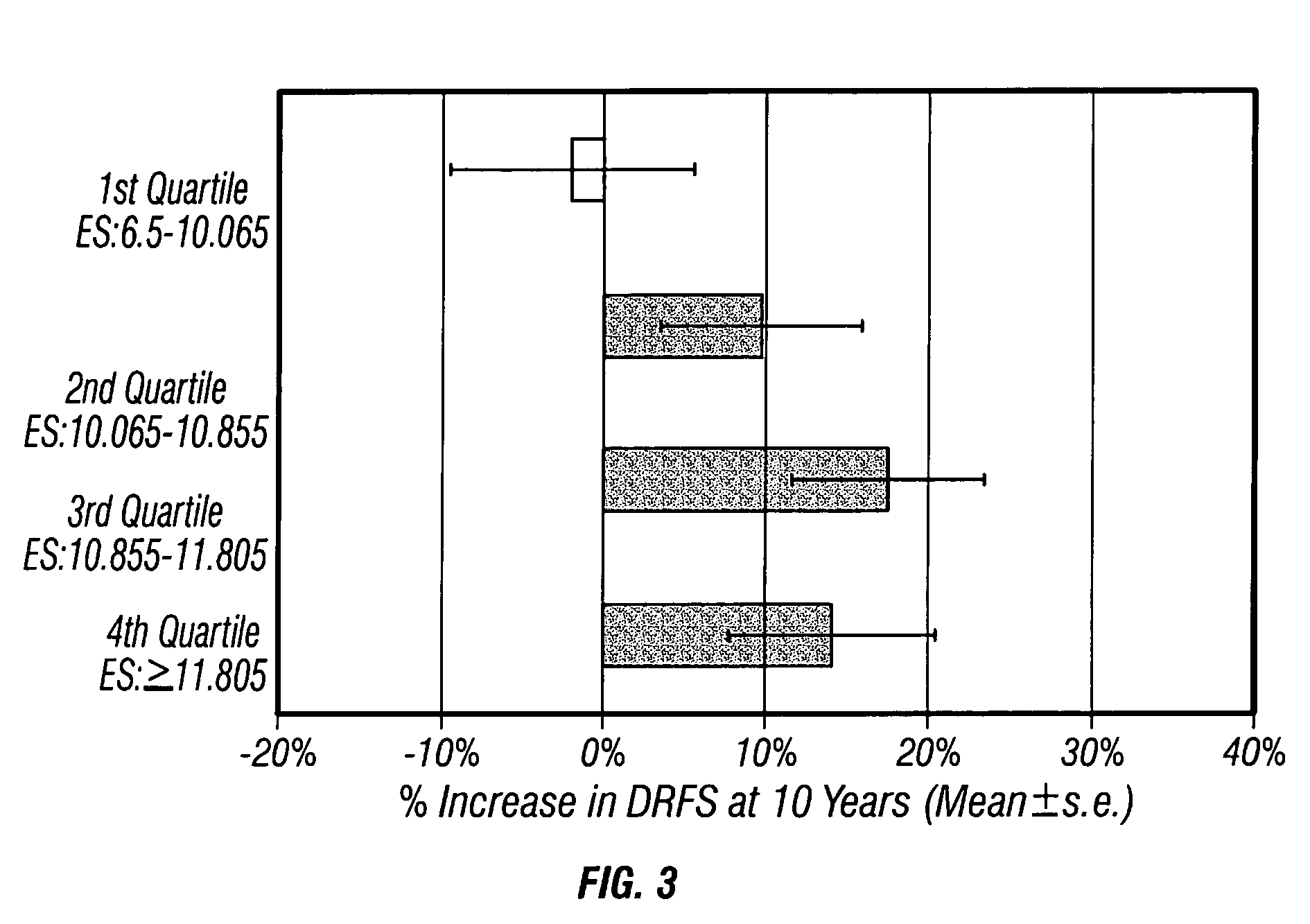
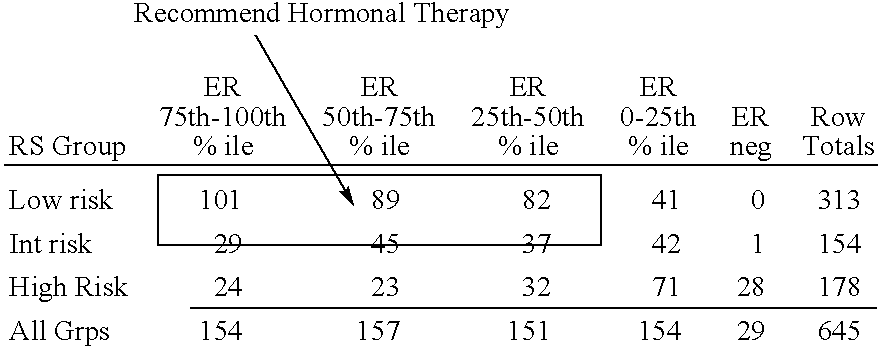
Molecular indicators of breast cancer prognosis and prediction of treatment response
ActiveUS7622251B2Reduce riskMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsAdjuvantLymph node negative
The present invention relates to quantitative molecular indicators that can guide clinical decisions in breast cancer, such as estrogen receptor (ESR1)-positive, lymph node-negative breast cancer. In particular, the invention concerns certain genes, the varied expression of which indicates the likelihood of recurrence of surgically resected breast cancer in patients who are not treated with a therapeutic agent in the adjuvant setting. In addition, the invention concerns the use of quantitative measurement of the expression of certain genes, including the ESR1 gene, that measure as a continuous variable, to determine (a) the likelihood of a beneficial response to the anti-estrogen therapeutic agent, such as tamoxifen; and (b) the potential magnitude of beneficial response to chemotherapy.
Owner:MICROSOFT CORP +2
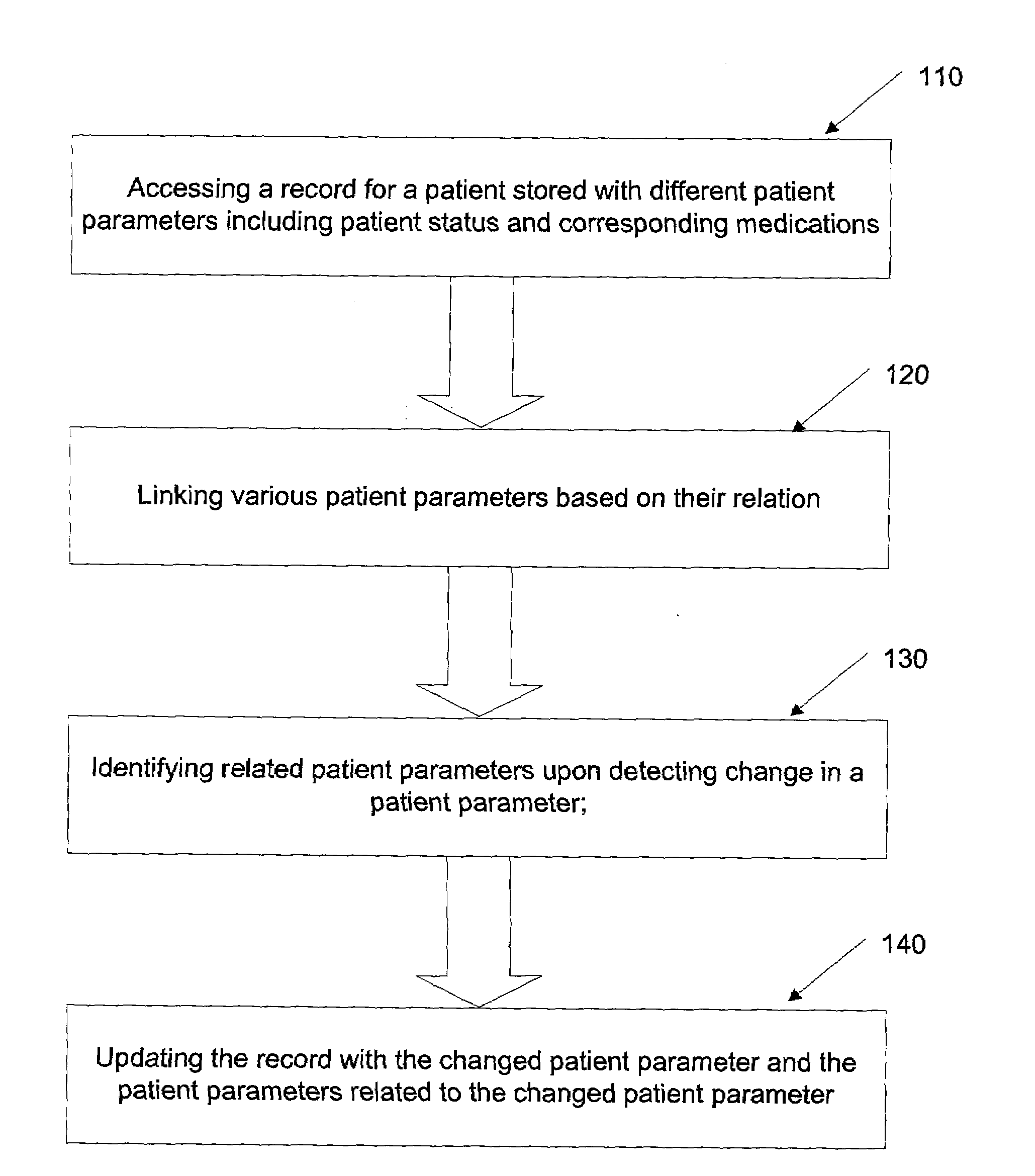
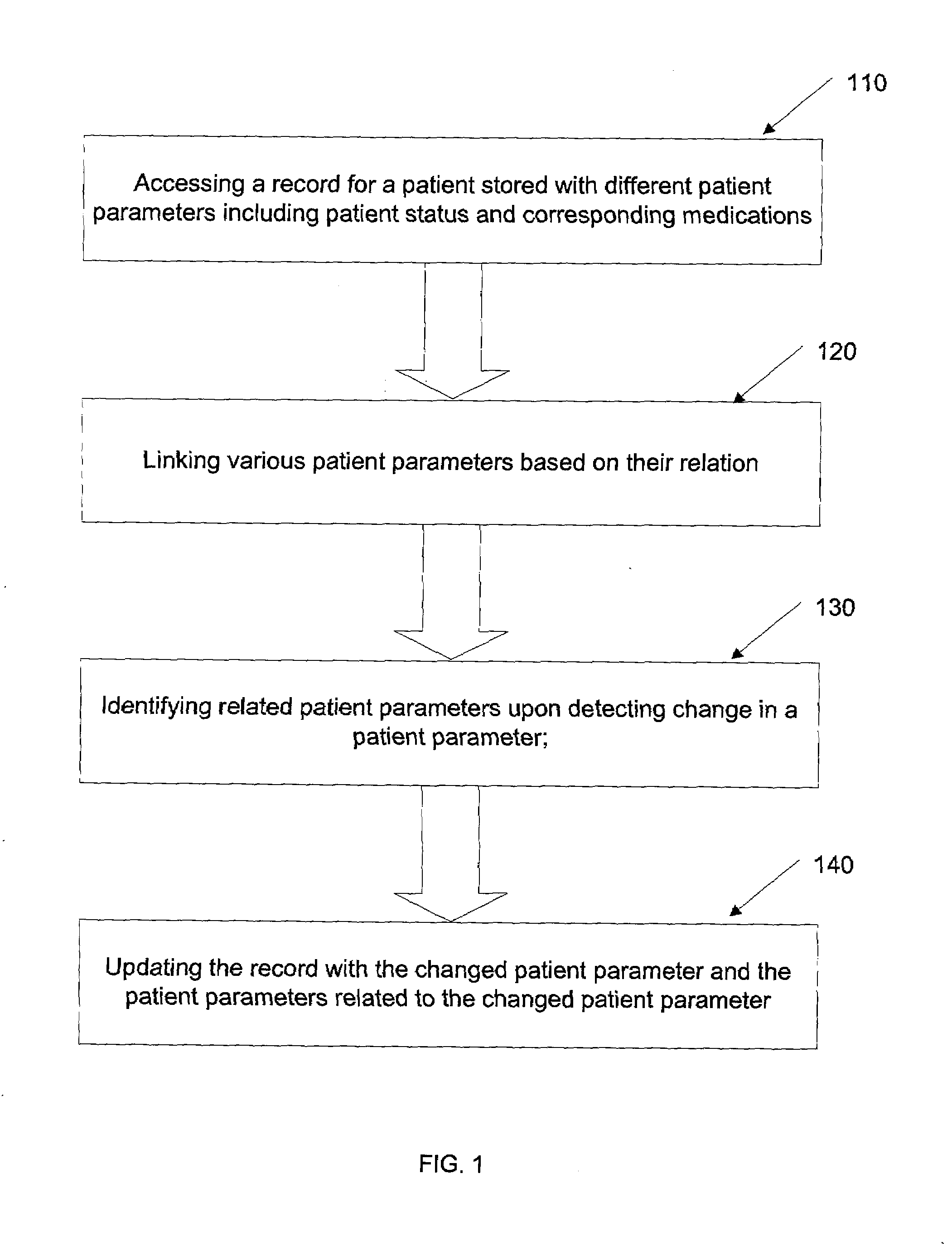
Method and system for providing clinical decision support
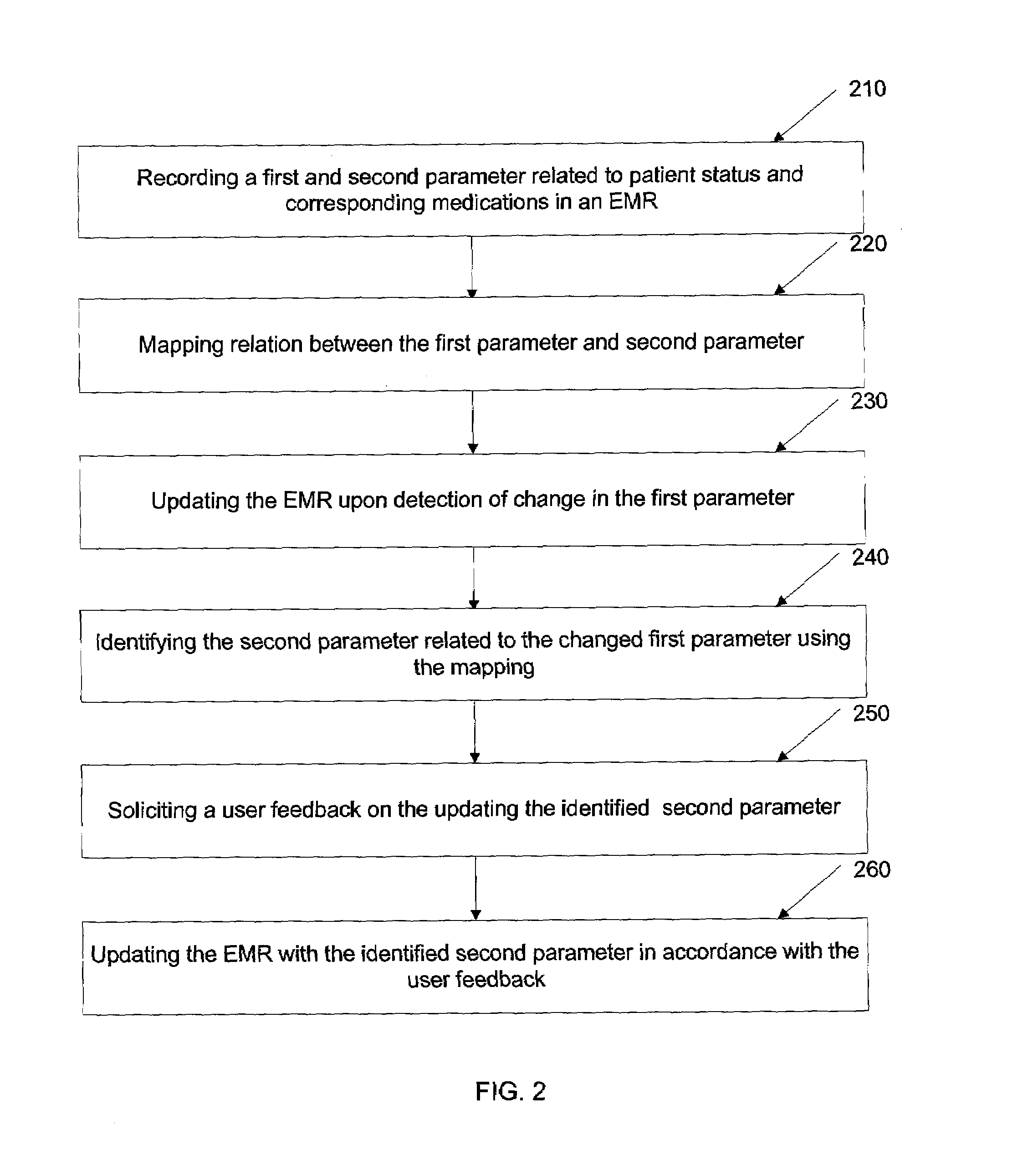
InactiveUS20090177493A1Simplify workImprove efficiencyMedical practises/guidelinesOffice automationMedical recordPatient status
A method and system for providing medical decision support is disclosed herein. The method comprises: accessing a record pertaining to a patient stored with different patient parameters, including patient status and linking various patient parameters based on their relation. A change in at least one patient parameter is detected and the corresponding related parameters are identified. The related patient parameter may be displayed to a clinician for assisting him in providing clinical decisions or for seeking his feedback on updating the related patient parameter in the record. The record is further updated with the detected change in patient parameter and corresponding changes in the related patient parameter. In an embodiment, the record is an electronic medical record.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods, systems, and devices for online triage
InactiveUS20140019162A1Shorten the timePromote resultsData processing applicationsMedical automated diagnosisPersonalizationNursing care quality
An automated triage system may include a patient database, a patient information system, a prioritized ranking system, and a nurse control panel system. The patient information system can include a user interface module, a clinical decision rules database, and a data processing engine. The patient information system may collect patient information data from a patient and generate a clinical determination based on the collected data. The prioritized ranking system may be configured to process to clinical determination to determine a prioritized ranking score for the patient. The nurse control panel system may be configured to process the prioritized ranking score and rank and display the patients in a patient queue, highlight clinically pertinent information, and generate a template response with personalized health information to save the nurse time and improve quality of care.
Owner:SKOWRONSKI JASON +3
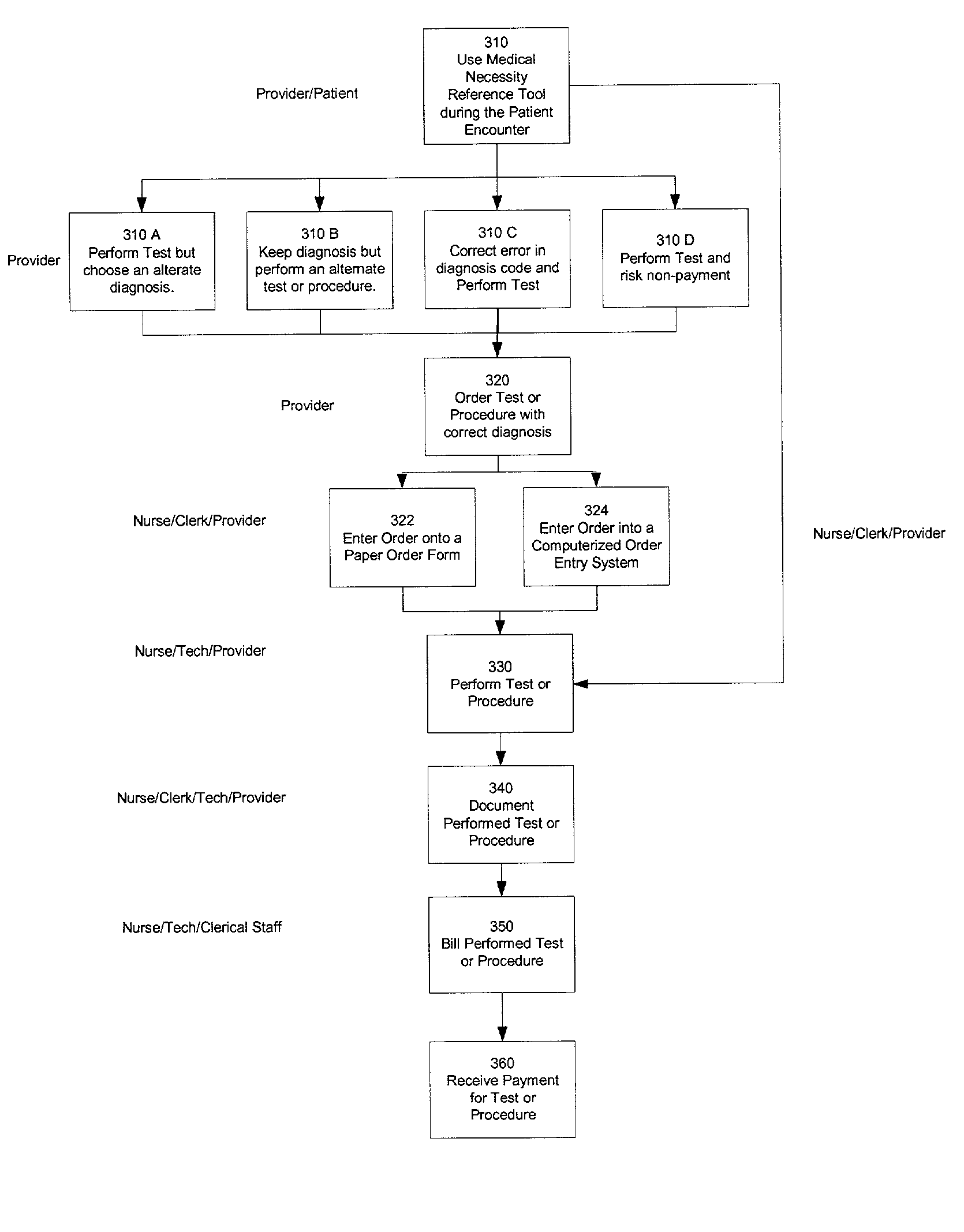
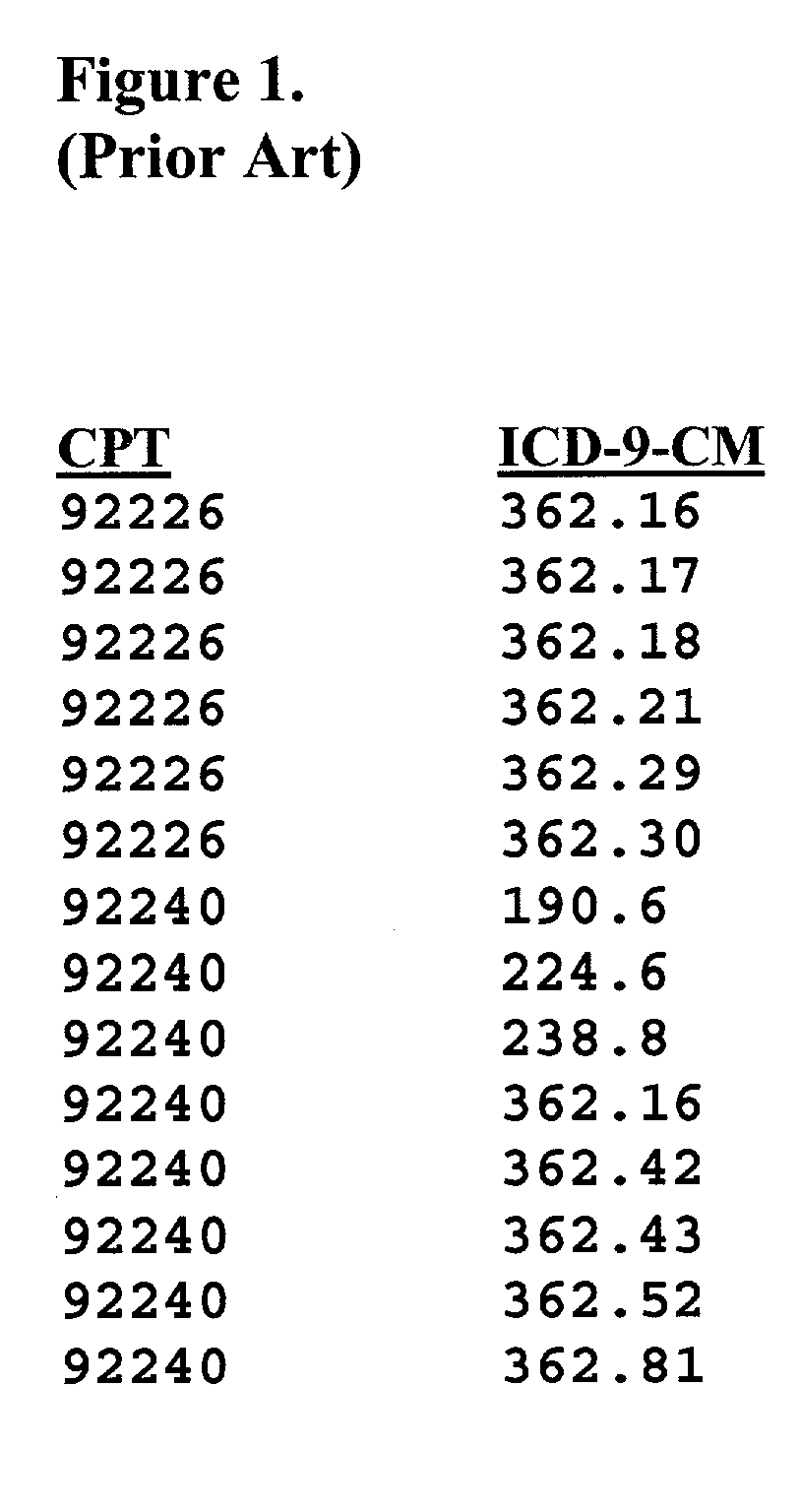
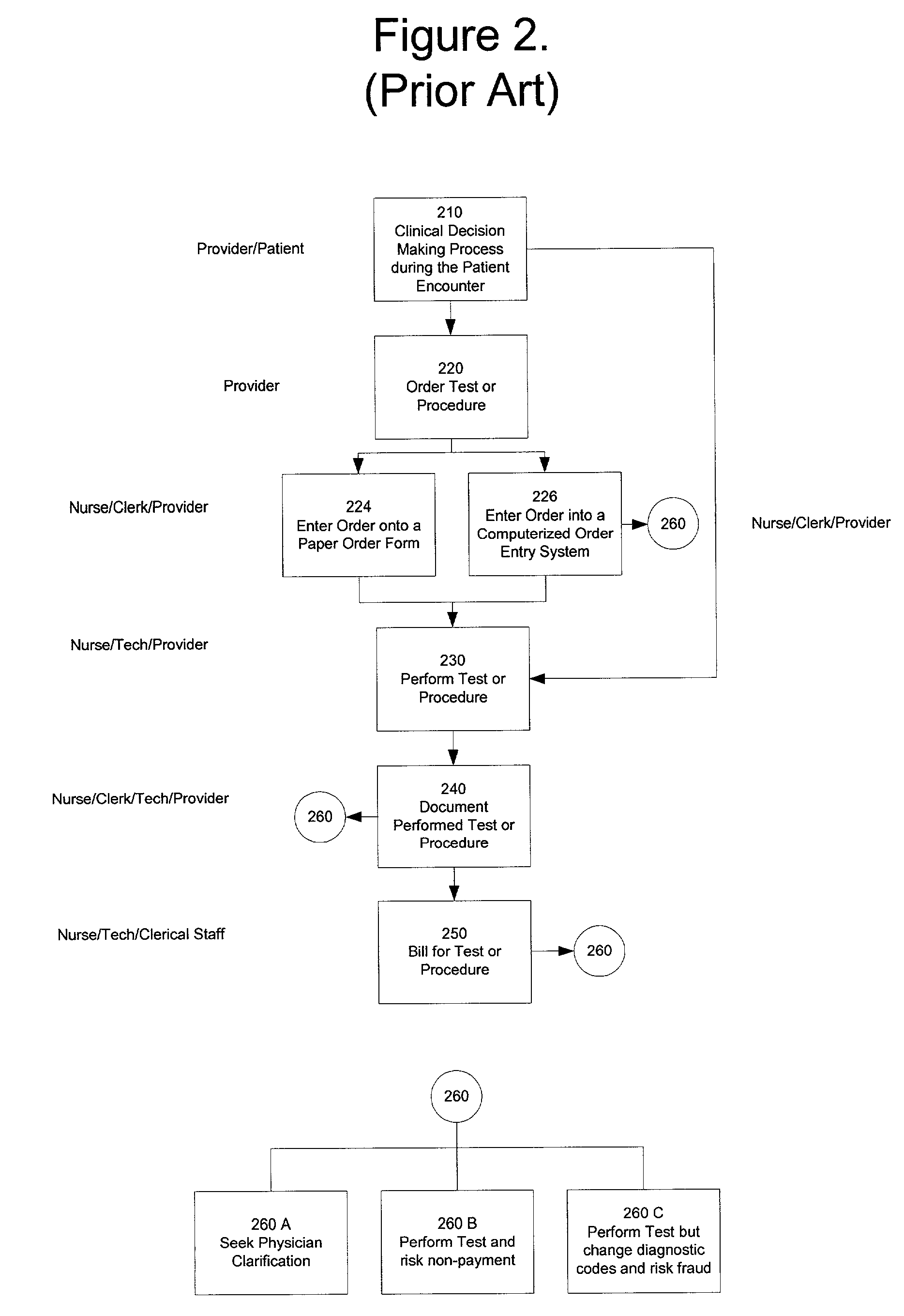
Method and apparatus for introducing medical necessity policy into the clinical decision making process at the point of care
A handheld device, such as a personal digital assistant ("PDA"), can be used at the point-of-care to find an appropriate pair of diagnosis code and procedure code for use in writing an order for further medical procedures for a particular patient. The choice of diagnosis code and procedure code can be checked for conformance with the requirements set forth in a particular set of medical necessity policy rules. In a preferred embodiment, the codes and rules are aggregated by medical specialty so that a specialist can work with solely those codes and rules that are relevant to that particular medical specialty. This abstract is provided as a tool for those searching for patents, and not as a limitation on the scope of the claims.
Owner:MED E MANAGER MDE
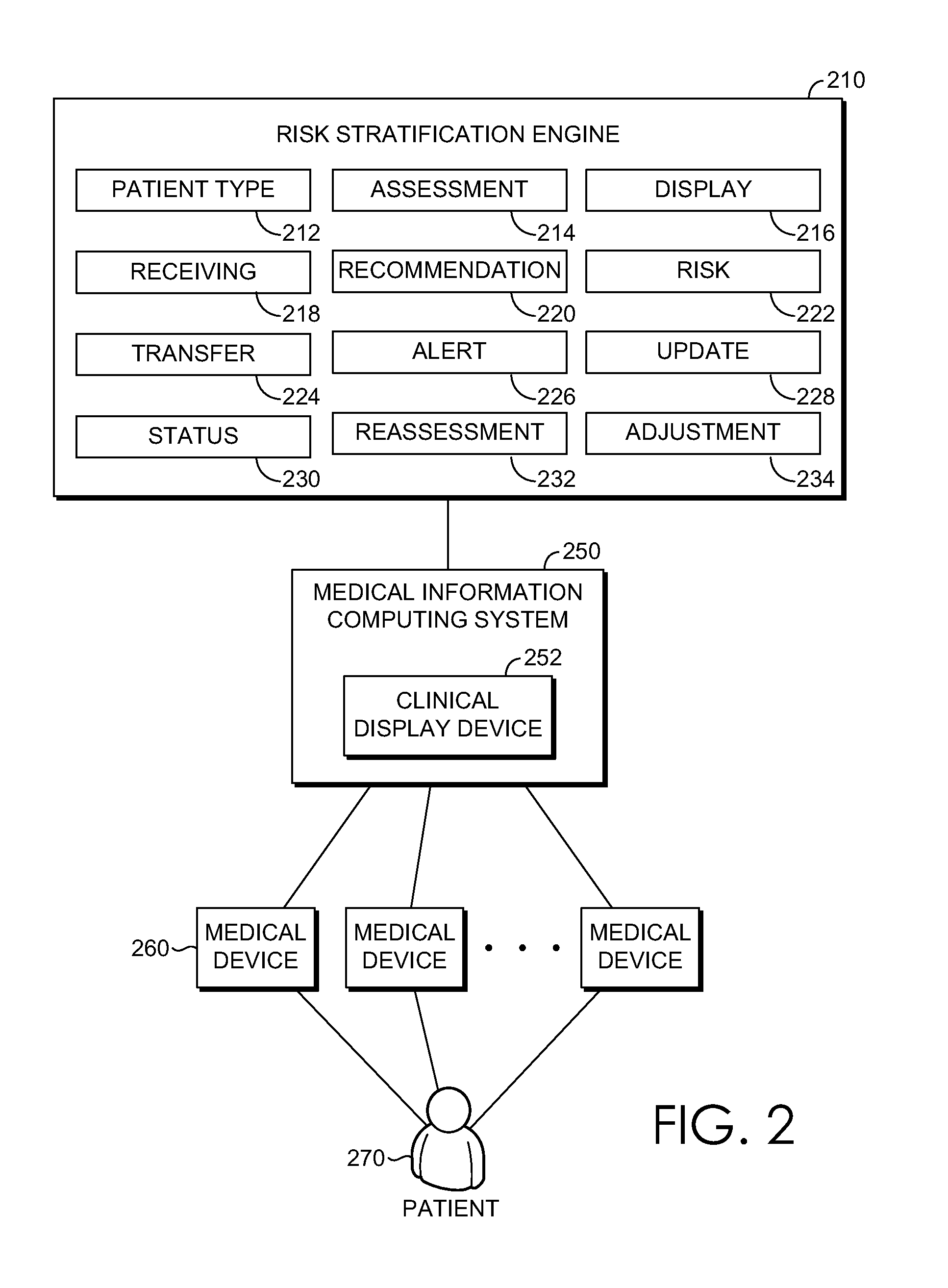
Advanced risk stratification for clinical decision support
Systems, methods, and user interfaces for providing dynamic risk stratification for clinical decision support are provided. Selections of patient types are received for patients. Assessments to utilize are determined in accordance with the patient types. The assessments are displayed to facilitate first clinicians assessing risk factors and contraindications for the patients. Information associated with the patients is received. Second clinicians may be alerted if risk factors for the patients are identified and the assessments have not been completed. Pharmacologic and / or mechanical prophylaxis is recommended and overall risk levels associated with the patients are indicated.
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
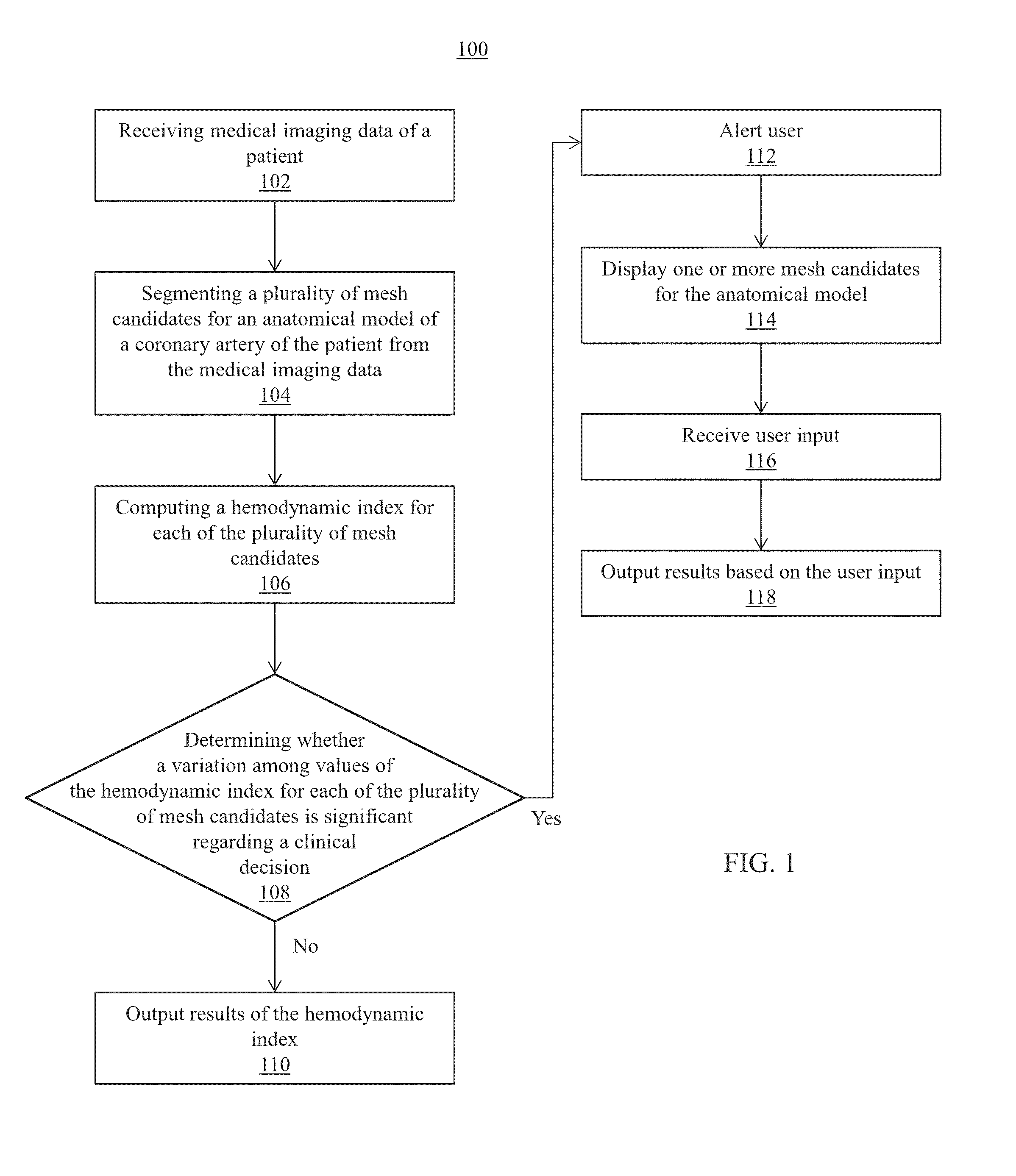
Method and System for Improved Hemodynamic Computation in Coronary Arteries
Systems and methods for non-invasive assessment of an arterial stenosis, comprising include segmenting a plurality of mesh candidates for an anatomical model of an artery including a stenosis region of a patient from medical imaging data. A hemodynamic index for the stenosis region is computed in each of the plurality of mesh candidates. It is determined whether a variation among values of the hemodynamic index for the stenosis region in each of the plurality of mesh candidates is significant with respect to a threshold associated with a clinical decision regarding the stenosis region.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Construction method and device for clinic decision auxiliary system and clinic decision auxiliary system
InactiveCN107887036AAlleviate inconvenient technical issuesMeet real needsMedical data miningMedical automated diagnosisMedical recordDisease
Owner:北京纽伦智能科技有限公司
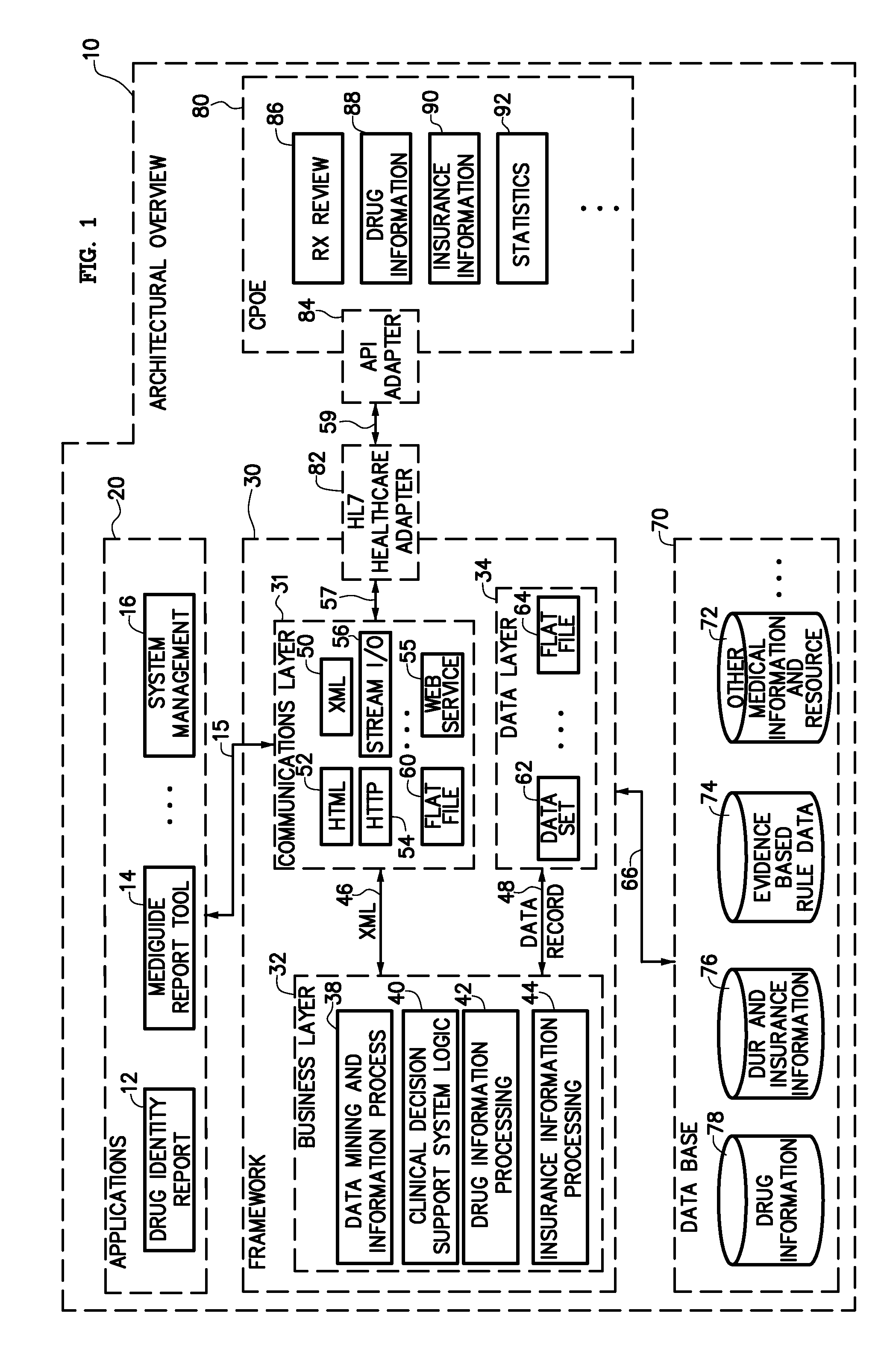
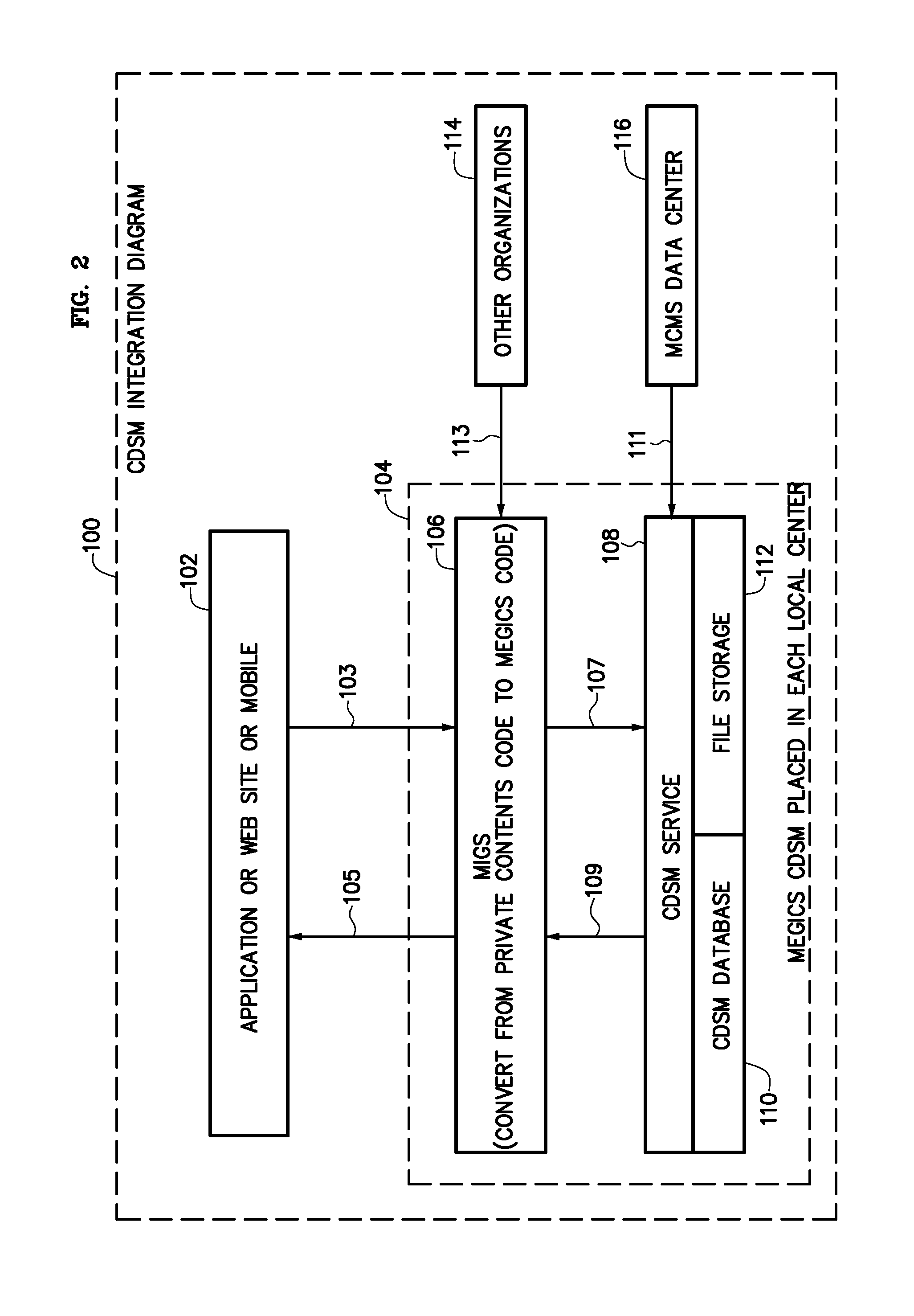
Support System for Improved Quality Healthcare
InactiveUS20120109689A1Quality improvementImprove efficiencyMedical communicationMedical data miningDecision takingUser satisfaction
The present invention, defined as MEGICS (Medical+Logics), has been developed in order to improve quality of care and enhance the efficiency of operation of healthcare facilities and providers. When front-line healthcare doctors and nurses make various clinical decisions, MEGICS management system can provide them with relevant clinical knowledge in a timely manner. MEGICS management system can, therefore, increase the level of user satisfaction and provide patients with better quality of healthcare services. The Inventor believes that the present invention, MEGICS, can penetrate a new market and be easily adopted by healthcare facilities, due to its flexible system structure, experience-based approach, and user-friendly features.
Owner:LEE JASON
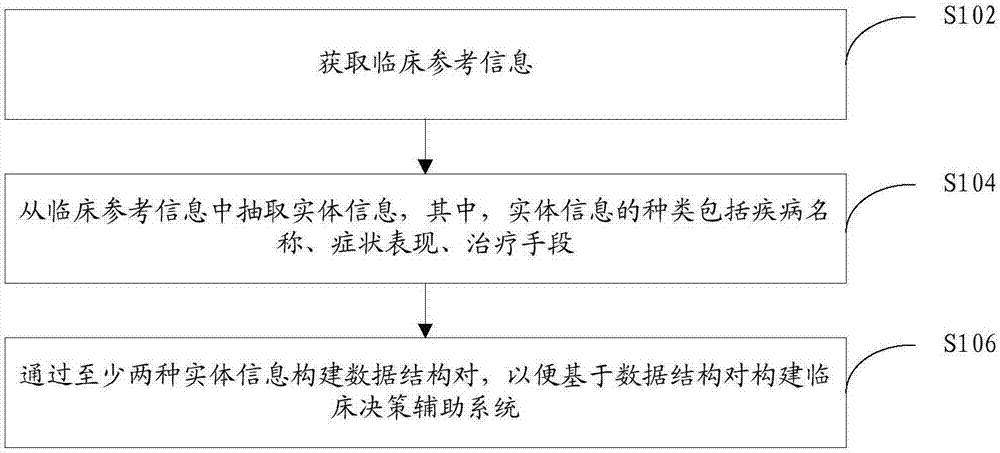
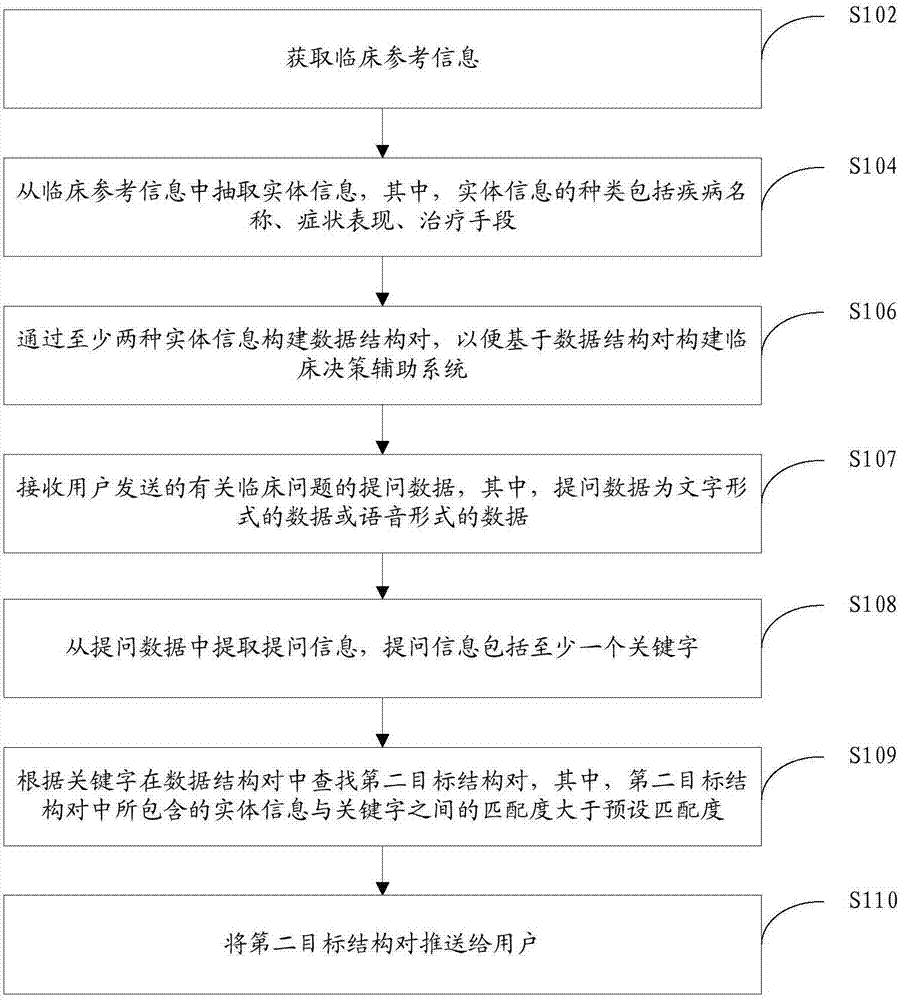
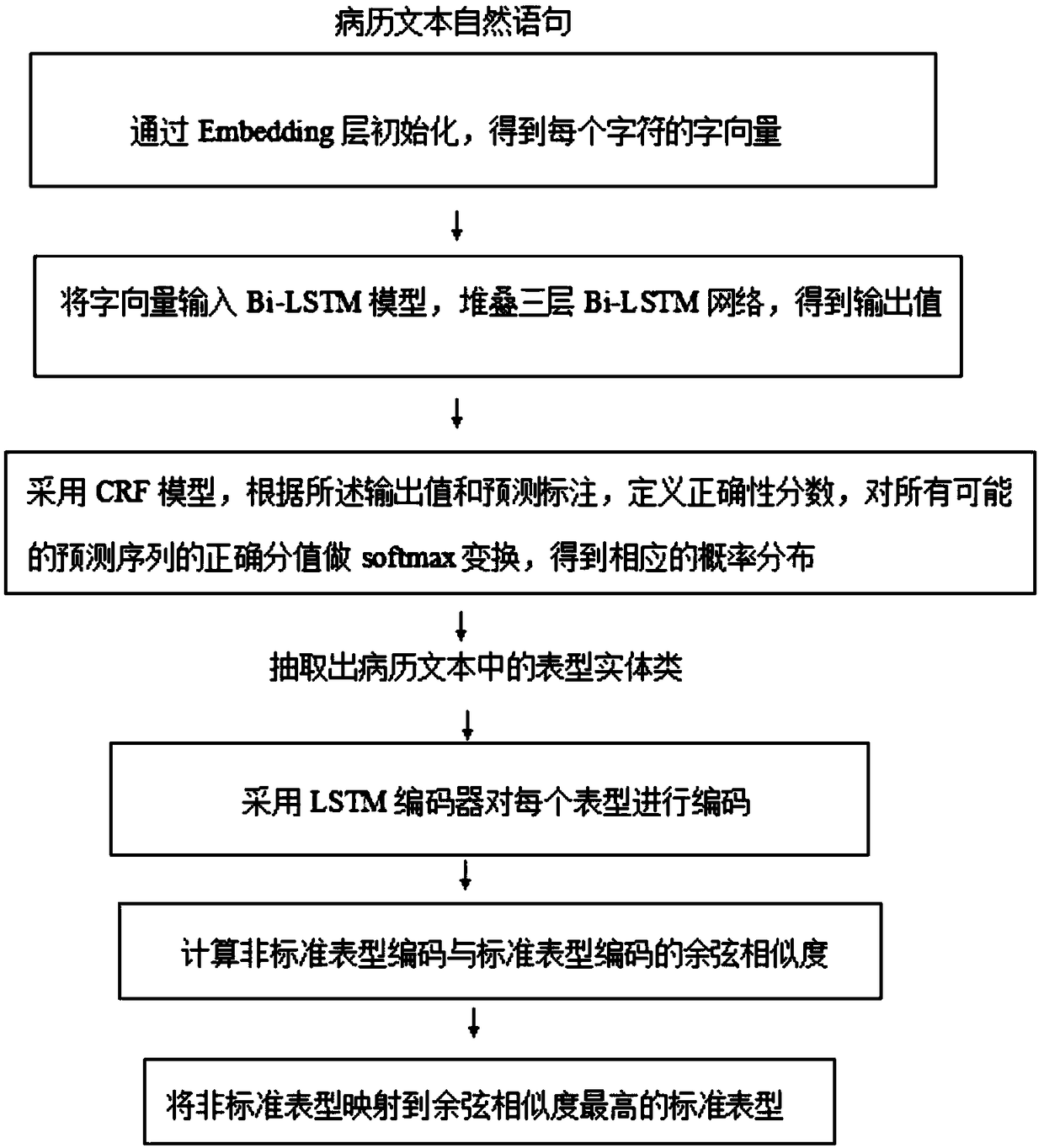
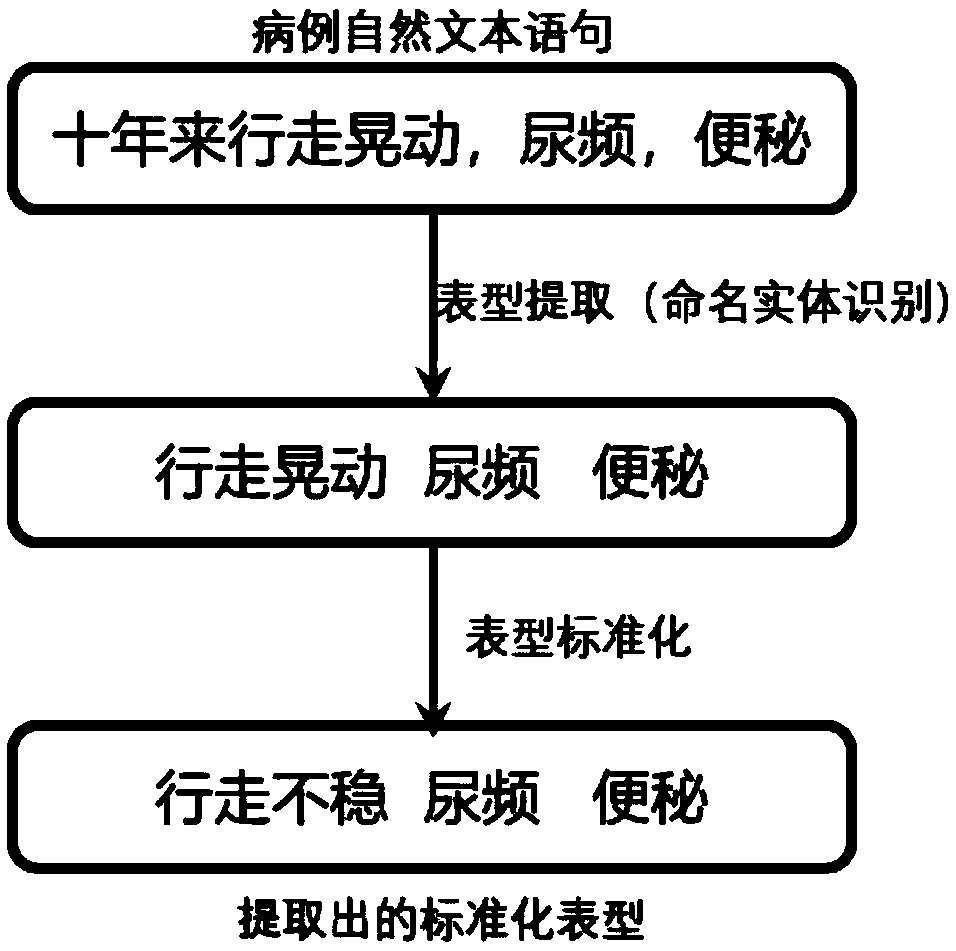
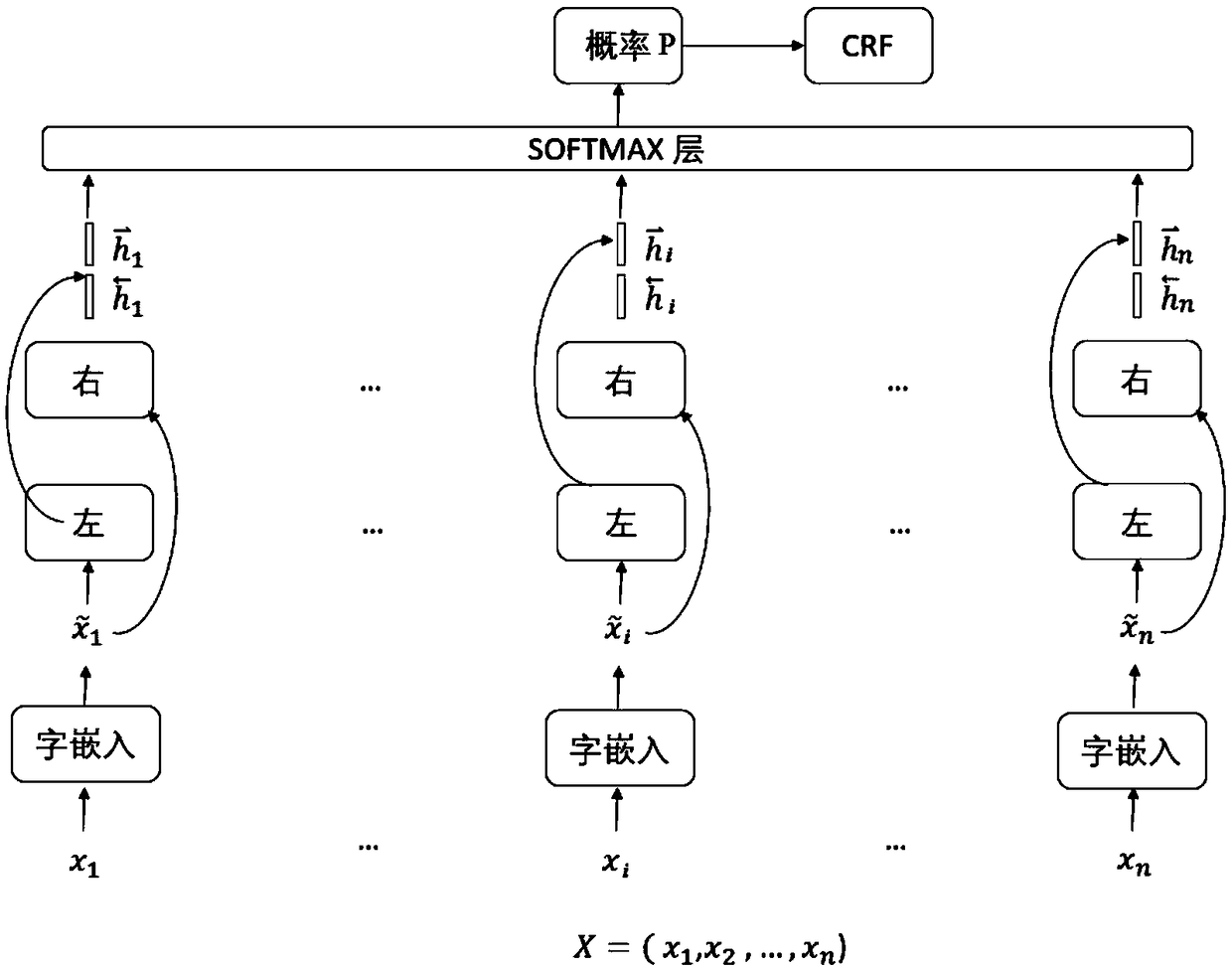
Electronic medical record phenotype extraction and phenotype name normalization method and system
ActiveCN109471895AImprove accuracyImprove recall accuracyDatabase management systemsPatient-specific dataMedical recordCosine similarity
The invention discloses an electronic medical record phenotype extraction and phenotype name normalization method. The method comprises the following steps: phenotypic extraction: taking natural statements of a medical record text as original data, and adopting Bi-; Named entity recognition is carried out on the LSTM model and the CRF model, and a phenotypic entity class is extracted; And phenotype standardization is carried out, an LSTM encoder is adopted to encode each phenotype, cosine similarity between non-standard phenotype codes and standard phenotype codes in the medical records is calculated, and the non-standard phenotype codes are mapped to the phenotype with the highest cosine similarity. The invention further discloses an electronic medical record phenotype extraction and phenotype name normalization system. According to the method, the named entity identification accuracy, the recall accuracy and the phenotypic mapping accuracy in the electronic medical record are improved; The labor consumption in the medical record structuring process is avoided, and the medical record structuring efficiency is improved; The method can more efficiently and accurately serve medical data mining, clinical decision support, clinical risk assessment and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method, Device and Computer Program Product for Monitoring a Subject
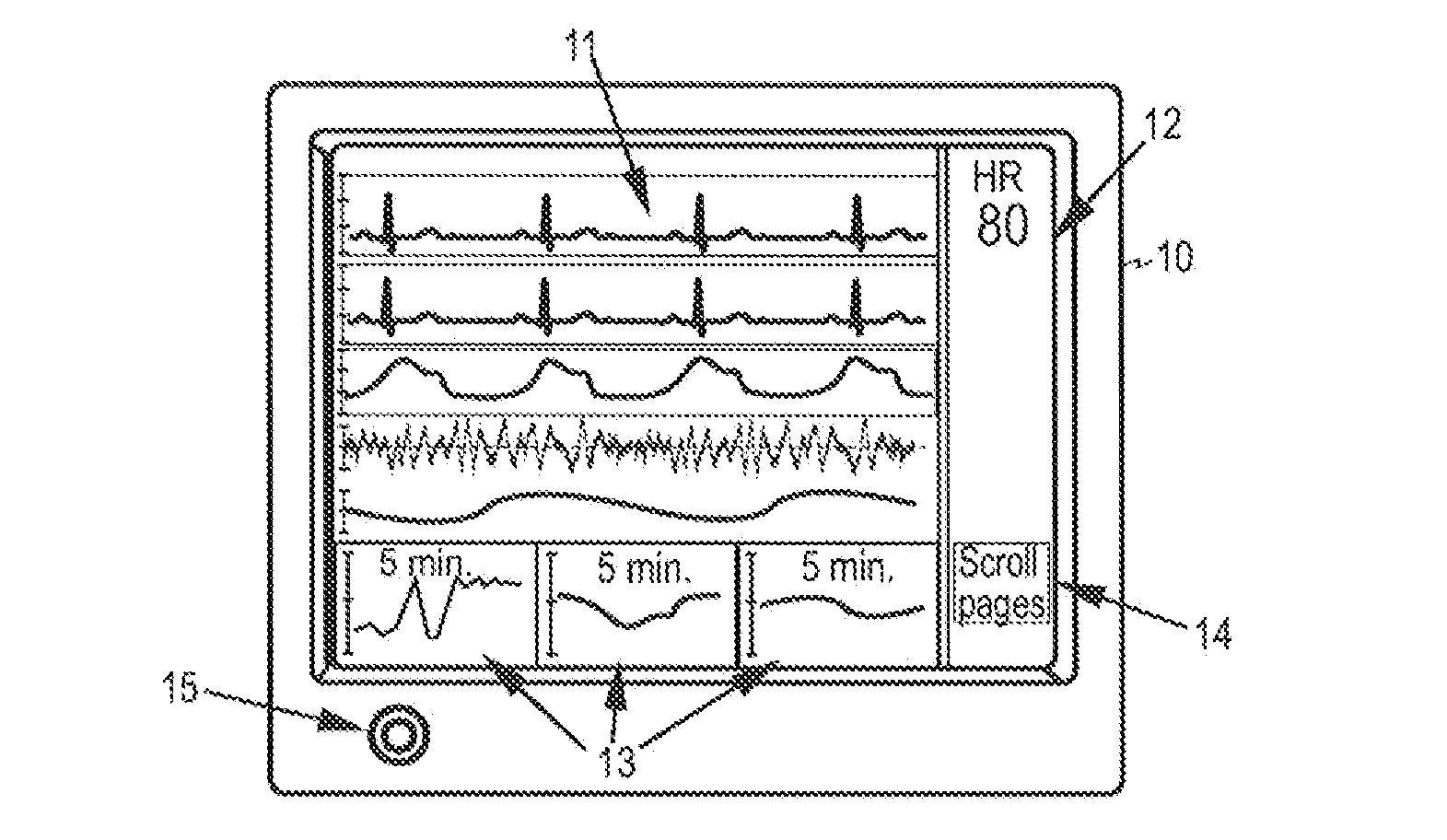
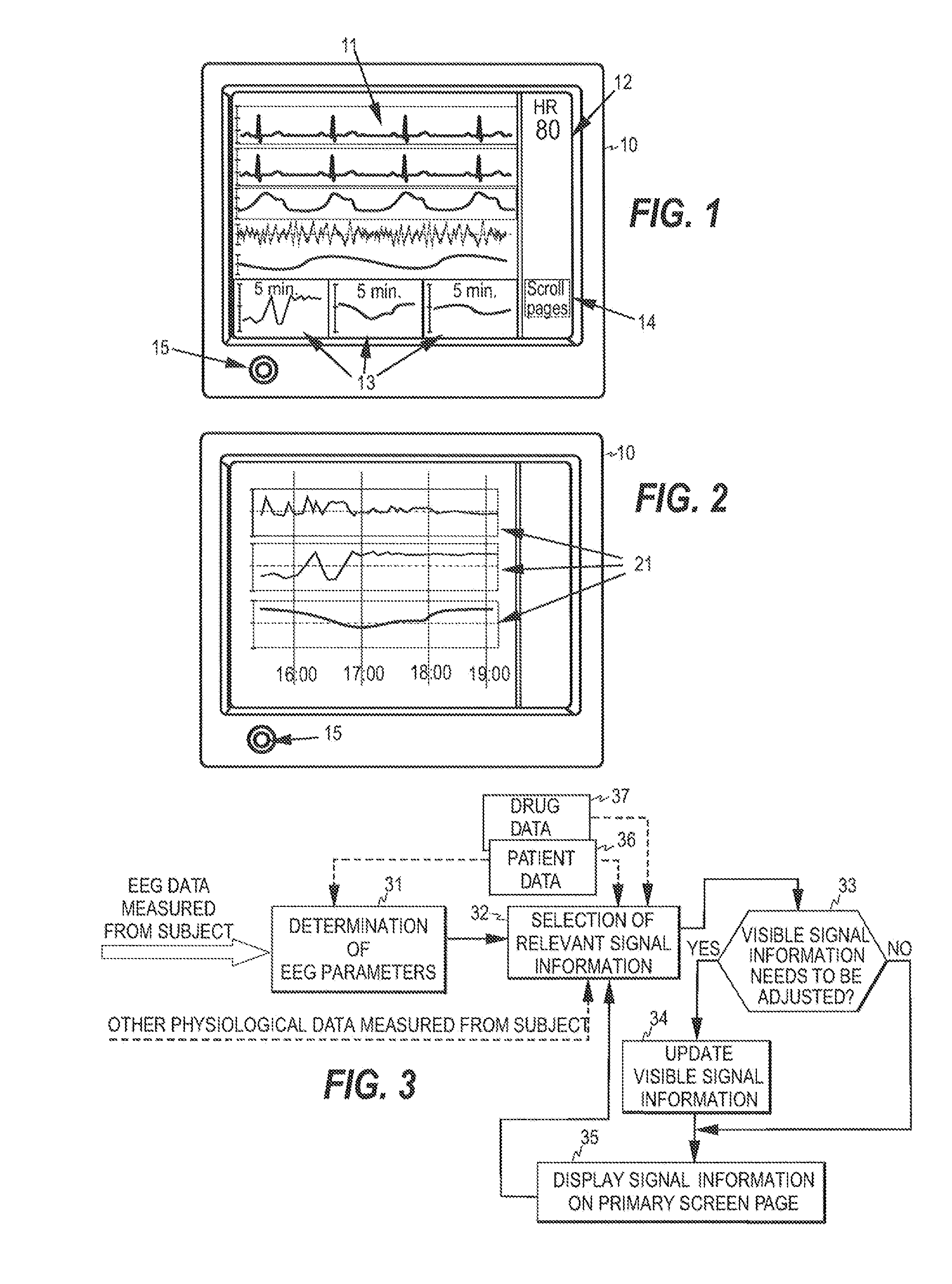
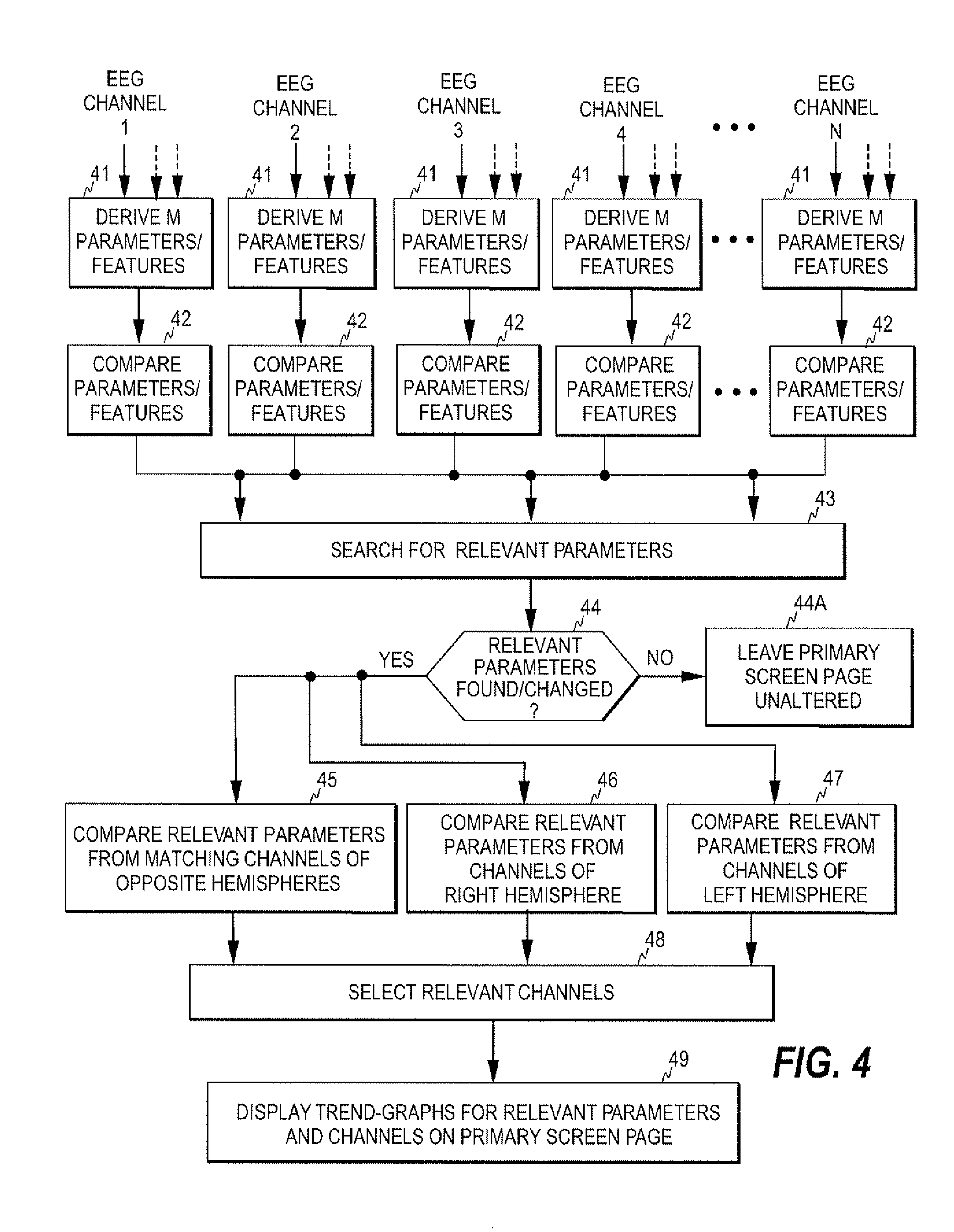
ActiveUS20100317931A1ElectroencephalographyDiagnostic signal processingPhysiologic StatesEngineering
A method, device, and computer program product for monitoring the physiological state of a subject is disclosed. A first plurality of physiological signals are acquired from the subject and a second plurality of signal parameters are determined based on the first plurality of physiological signals. Relevant signal information is selected from among the signal information produced and at least one screen page is displayed at a time, thereby to make at least part of the signal information visible to a user. The signal information visible to the user on the at least one screen page may then be revised based on the selection and without user interaction, thereby to accelerate clinical decision-making and to diminish the possibility of undetected changes in the state of the subject.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and System for Real Time, Cognitive Integration with Clinical Decision Support Systems featuring Interoperable Data Exchange on Cloud-Based and Blockchain Networks
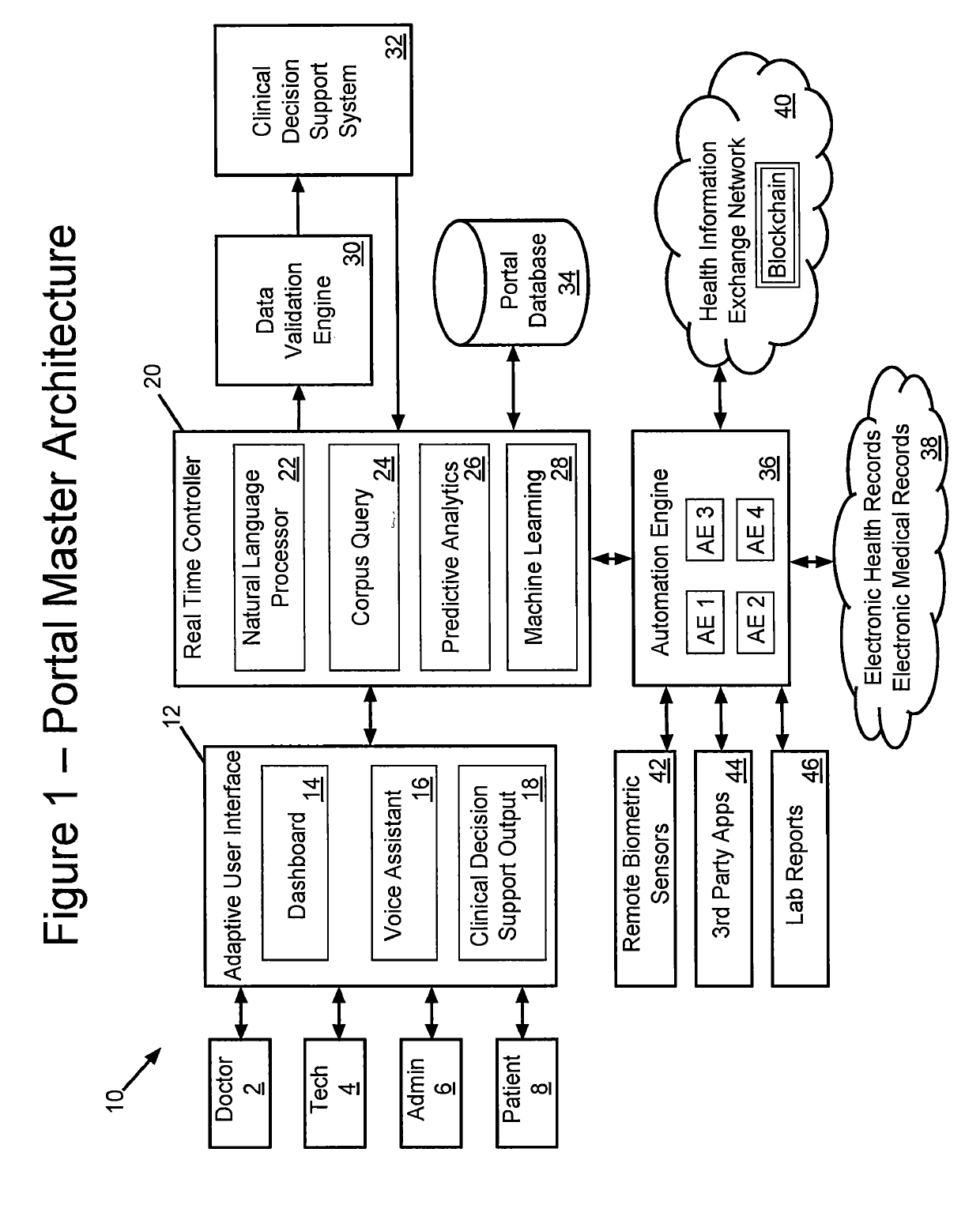
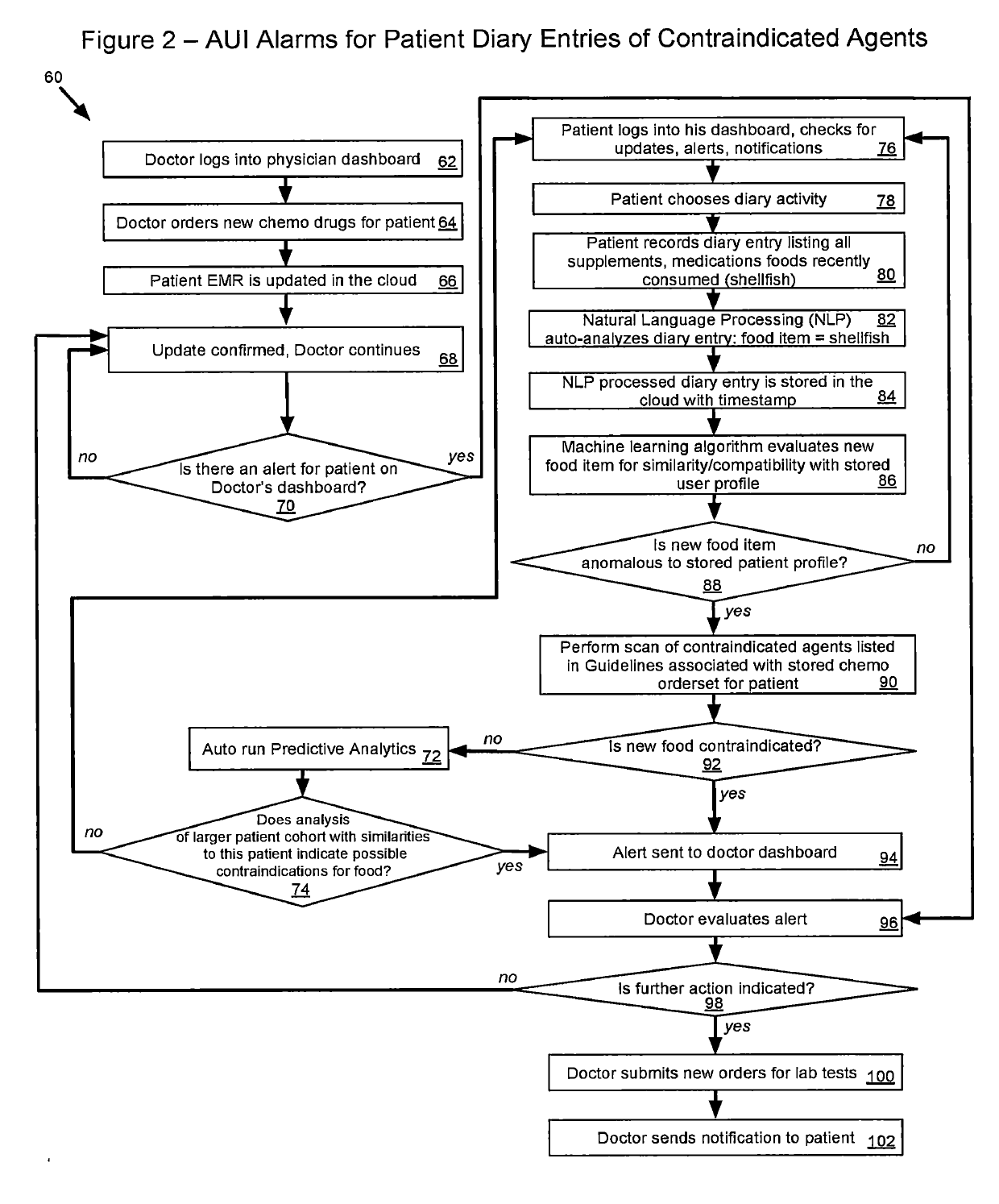
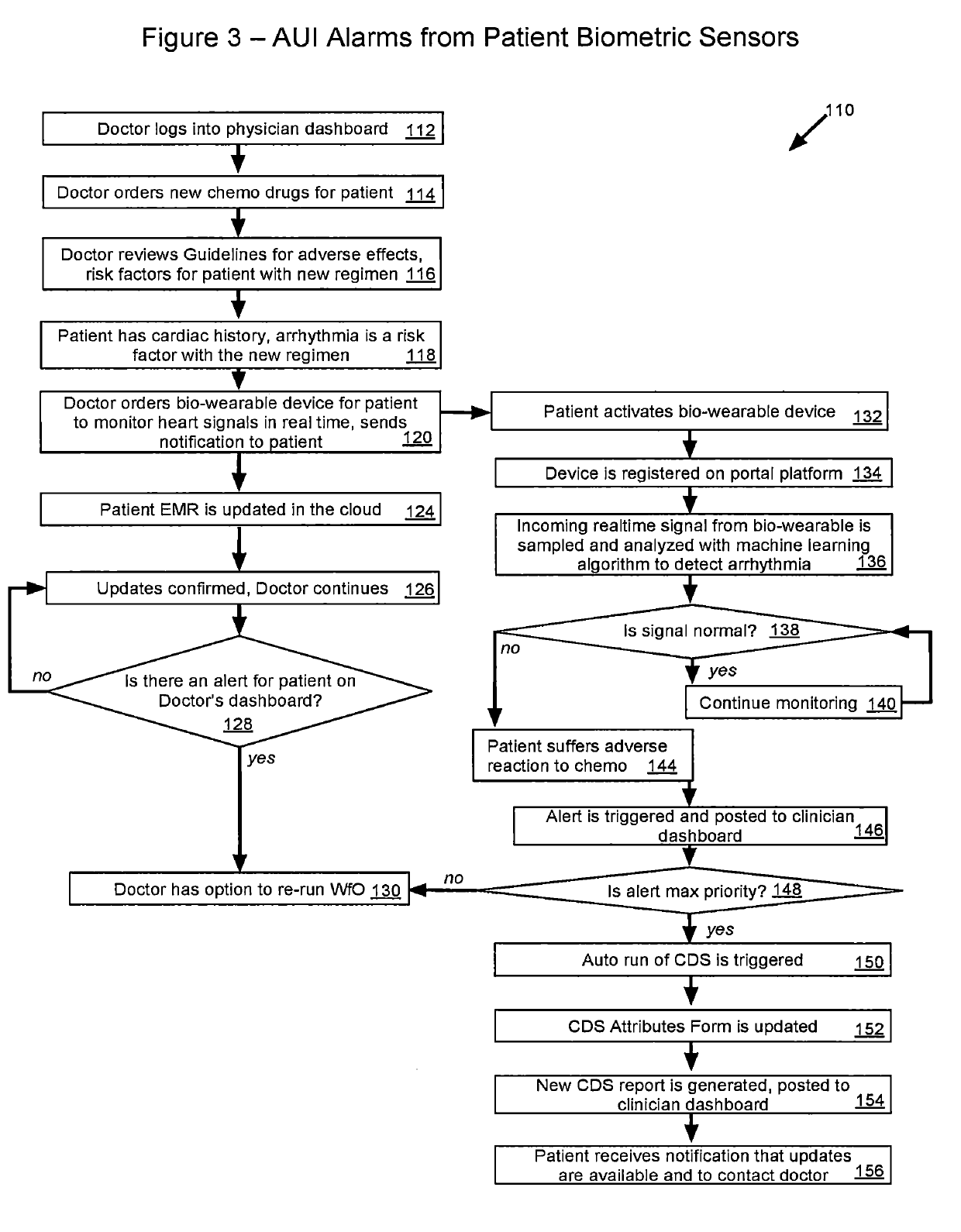
InactiveUS20190304582A1Improve automationImprove user engagementMedical data miningDigital data information retrievalDashboardMedical record
An informatics platform comprising method, system, and computer program is provided for interacting with clinical decision support systems such as the IBM Watson for Oncology, for the purpose of utilizing cognitive processing, machine learning and natural language processing to facilitate the manual to semi-automatic to automatic acquisition of a patient's electronic medical record data points, into a CDS system for populating the attributes questionnaire, for generating a patient diagnostic report of treatment recommendations. The platform supports deployment on several informatics architectures including client-server, cloud-based and blockchain.In a typical embodiment, the system is deployed as a Software-as-a-Service (SAAS) application; it implements a cloud-based, real-time architecture comprising: (a) an adaptive user interface providing responsive dashboards for real-time data presentation and user interaction, (b) a hub controller for real-time data flow transformation, (c) a data validation engine which incorporates cognitive natural language processing (NLP) to extract structured and unstructured patient record data from the EHR and employs methods that provide an optimally automated input to the CDS, (d) cloud storage of aggregated CDS data and other clinical datasets, and (e) plug-in support for additional cognitive capabilities such as predictive analytics and data mining.
Owner:PATIENT ONCOLOGY PORTAL INC
Method, Computer Program Product and System for Enabling Clinical Decision Support
ActiveUS20100332143A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce complexityMedical automated diagnosisDisease diagnosisWeb serviceBiomarker (petroleum)
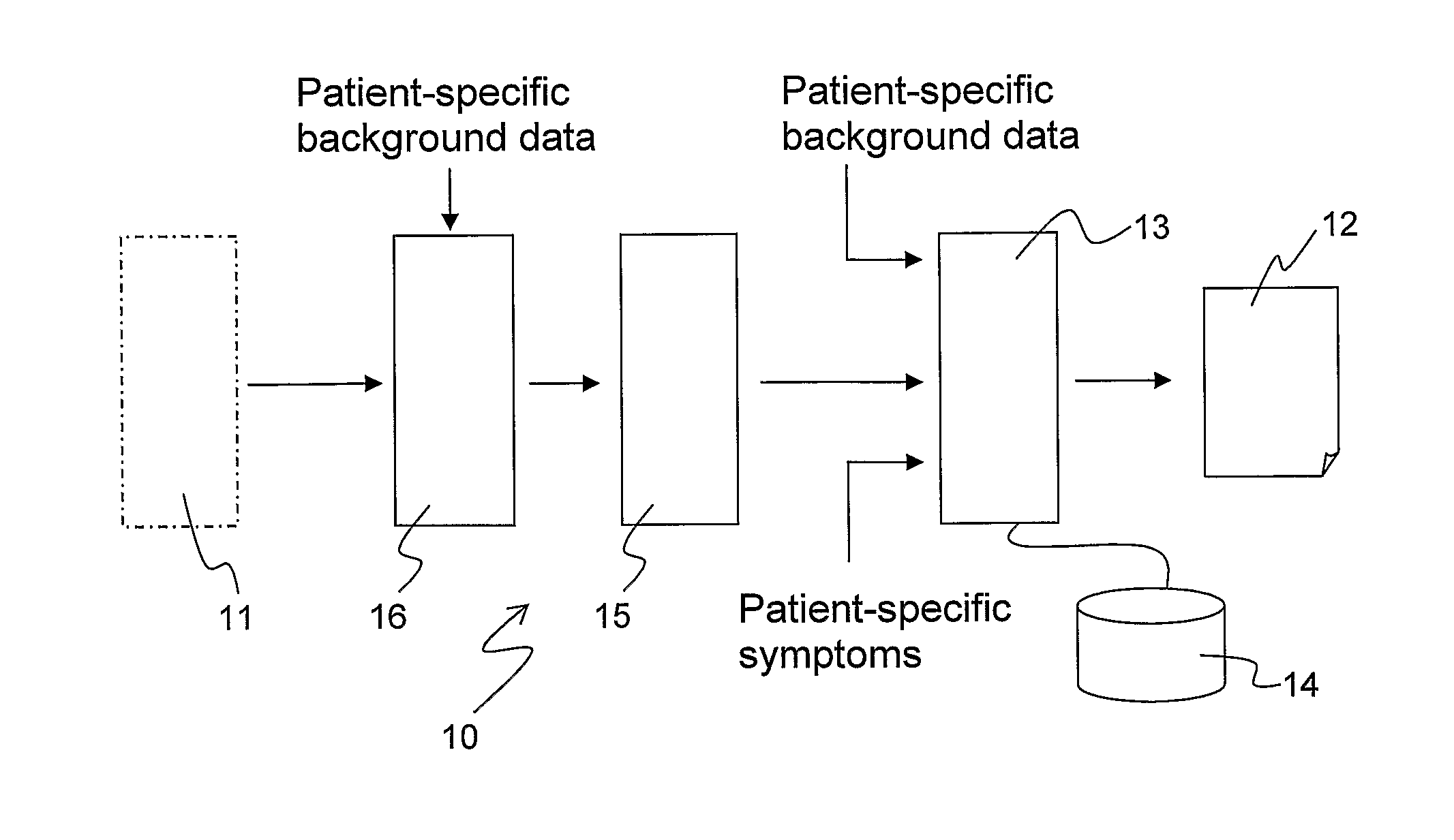
A method enables clinical decision support based on test results for a plurality of tested biomarkers. The method is executed by a data reduction module (15) and comprises the steps of receiving the test results from a testing facility (11); accessing a predefined structure in which available biomarkers are associated with hosts, at least one host being associated with a plurality of biomarkers; identifying a set of hosts by mapping the tested biomarkers to the structure; assigning a host value to each host in said set of hosts based on the test results of the tested biomarker(s) mapped to the host; and providing input data indicative of the set of hosts and the assigned host values for input to a computer-based decision engine (13) for generating the clinical decision support (12). The data reduction module (15) may be included in a system and implemented by computer-executable instructions running on a data processing device, such as a PC or a web server.
Owner:PHADIA AB
System and method for patient care
InactiveUS20090012812A1Easy to explainMoreMedical automated diagnosisPatient personal data managementClinical informationClinical staff
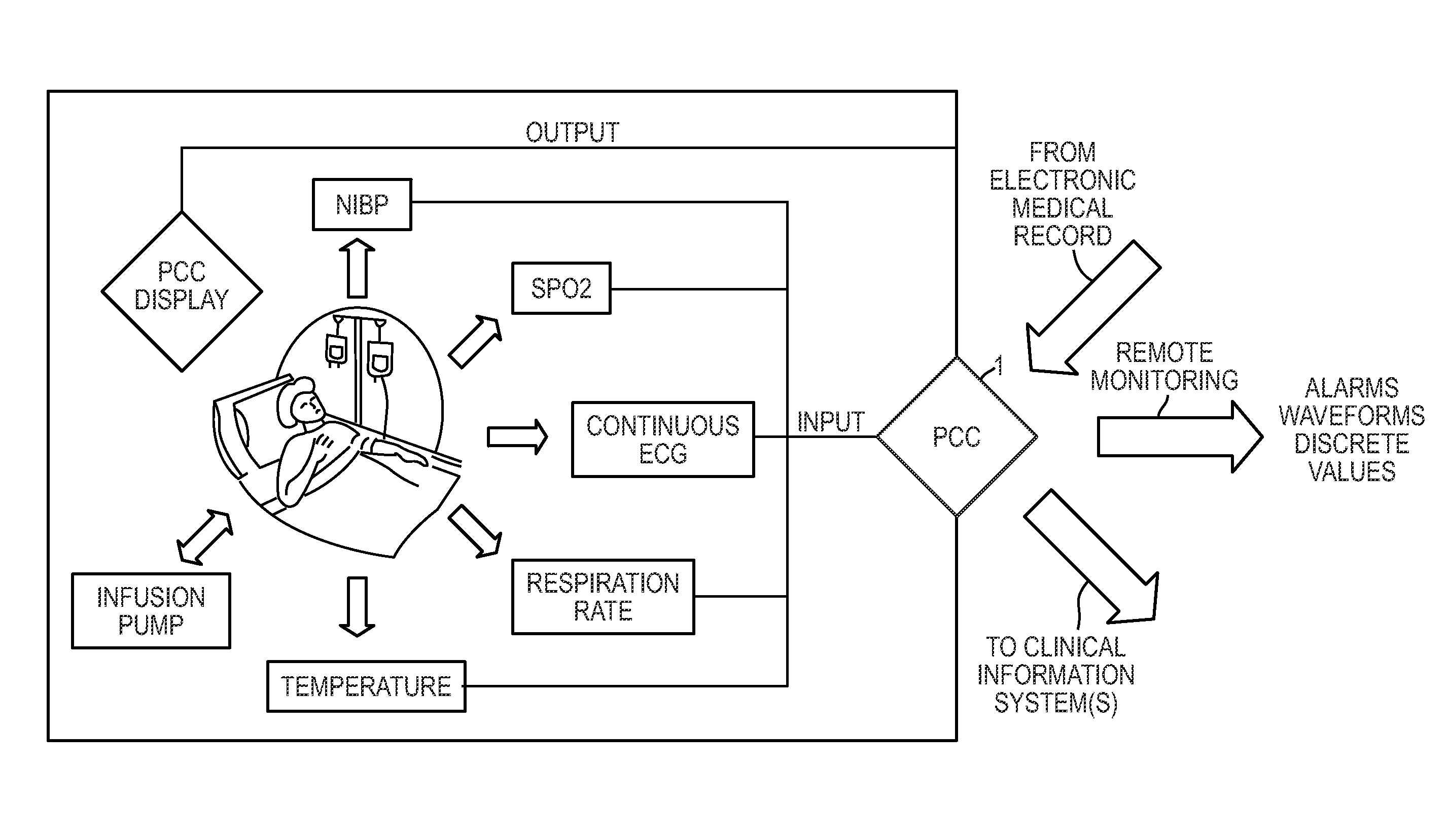
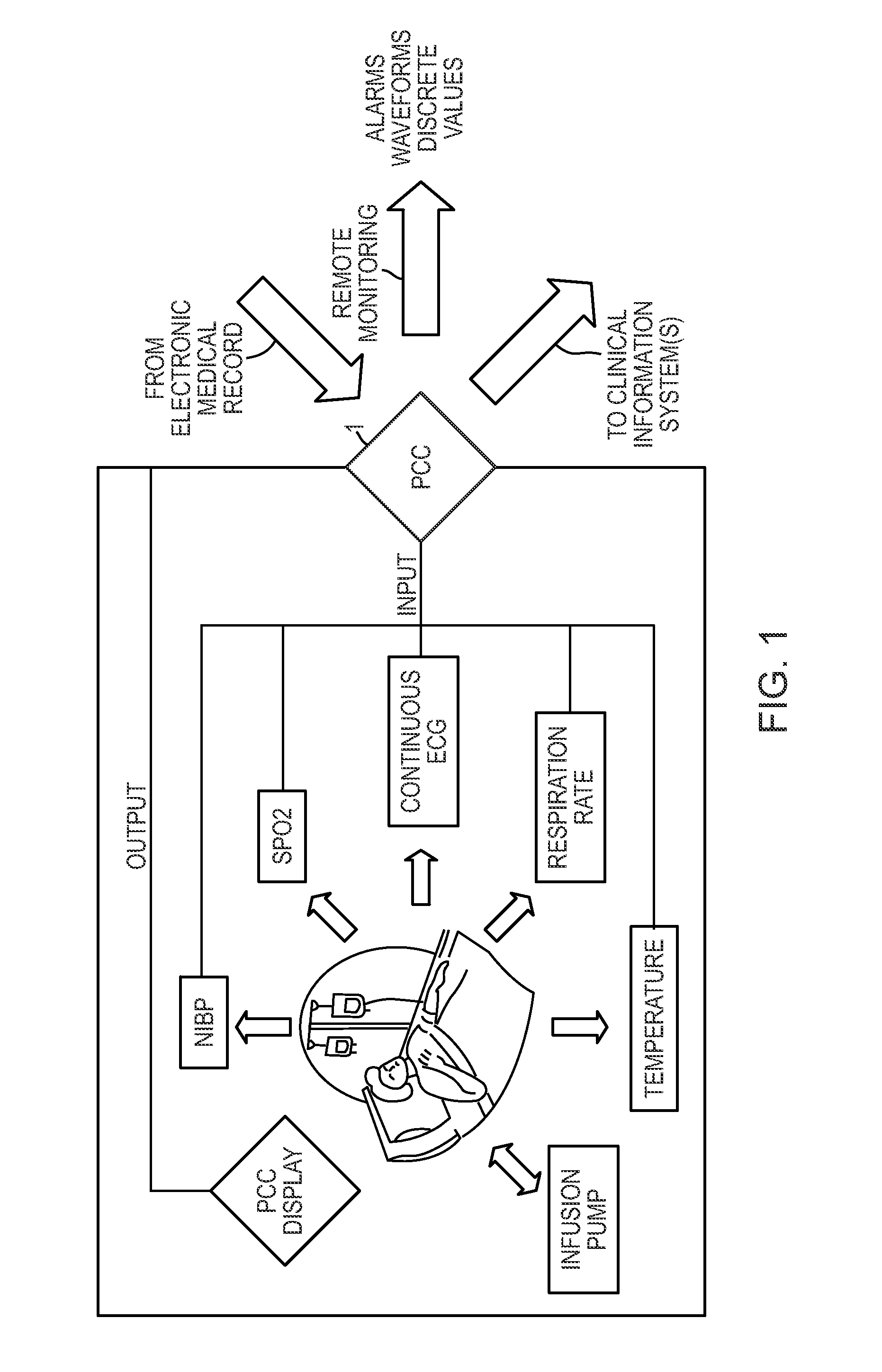
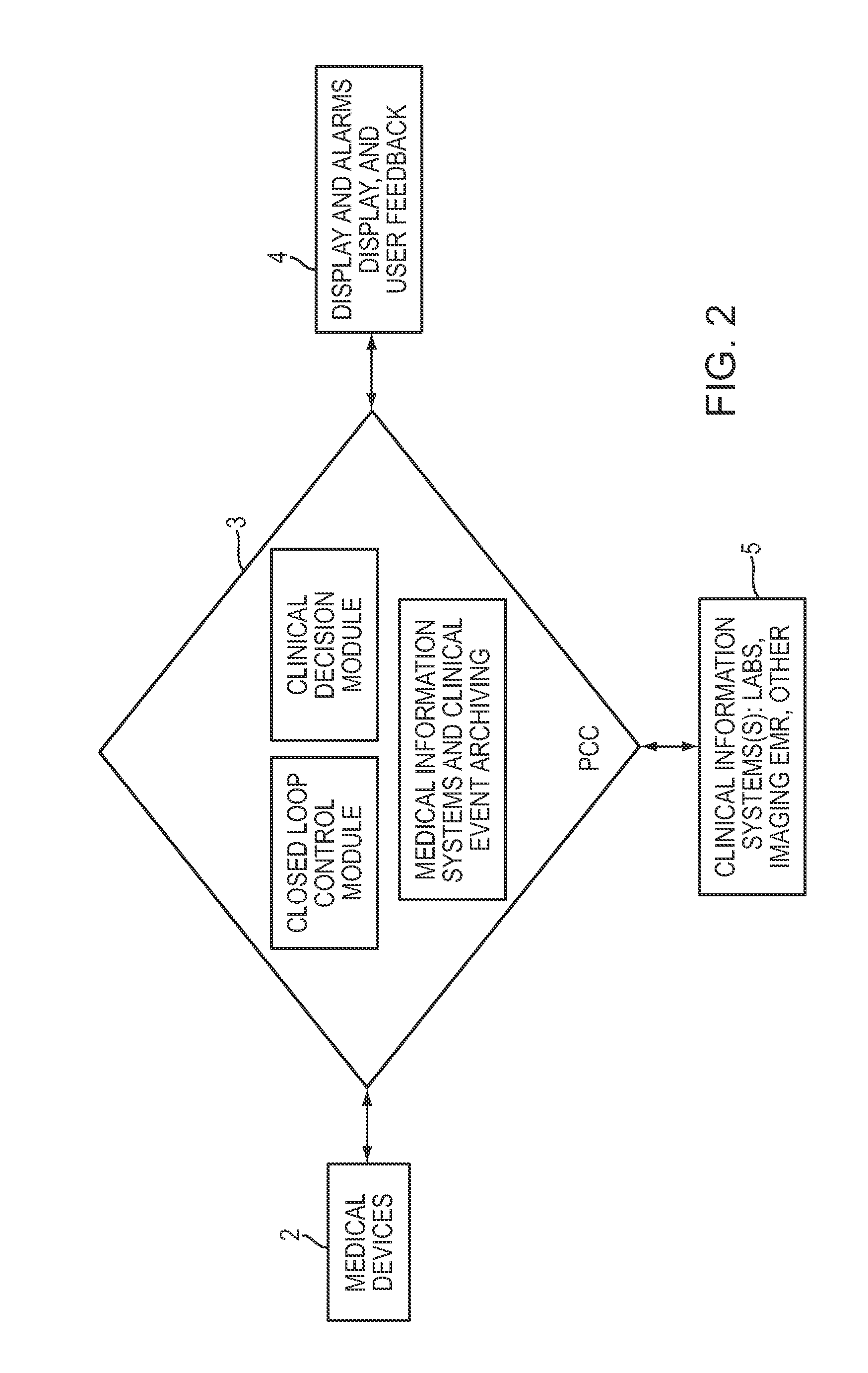
Embodiments of the present invention may integrate and analyze the output from various medical devices and clinical information systems in order to assist the clinical staff in making the more informed clinical decisions, output intelligent alarms, predict and prevent adverse events, and in some circumstances enable automated patient care.
Owner:RAUSCH TRACY +1
Sepsis early prediction method based on machine learning
PendingCN111261282AHigh predictive classification accuracyTimely treatmentCharacter and pattern recognitionMedical automated diagnosisMedical recordPatient need
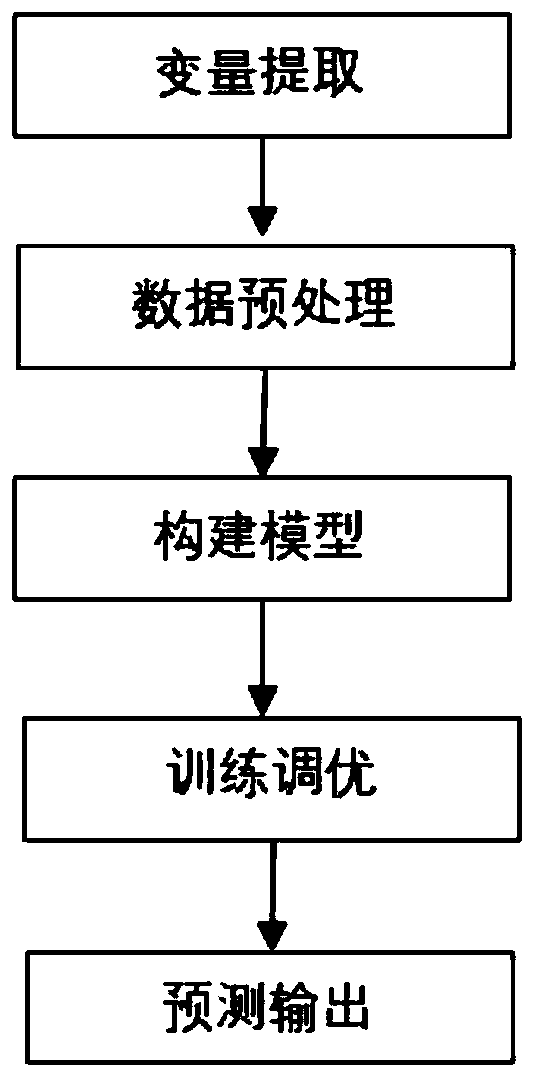
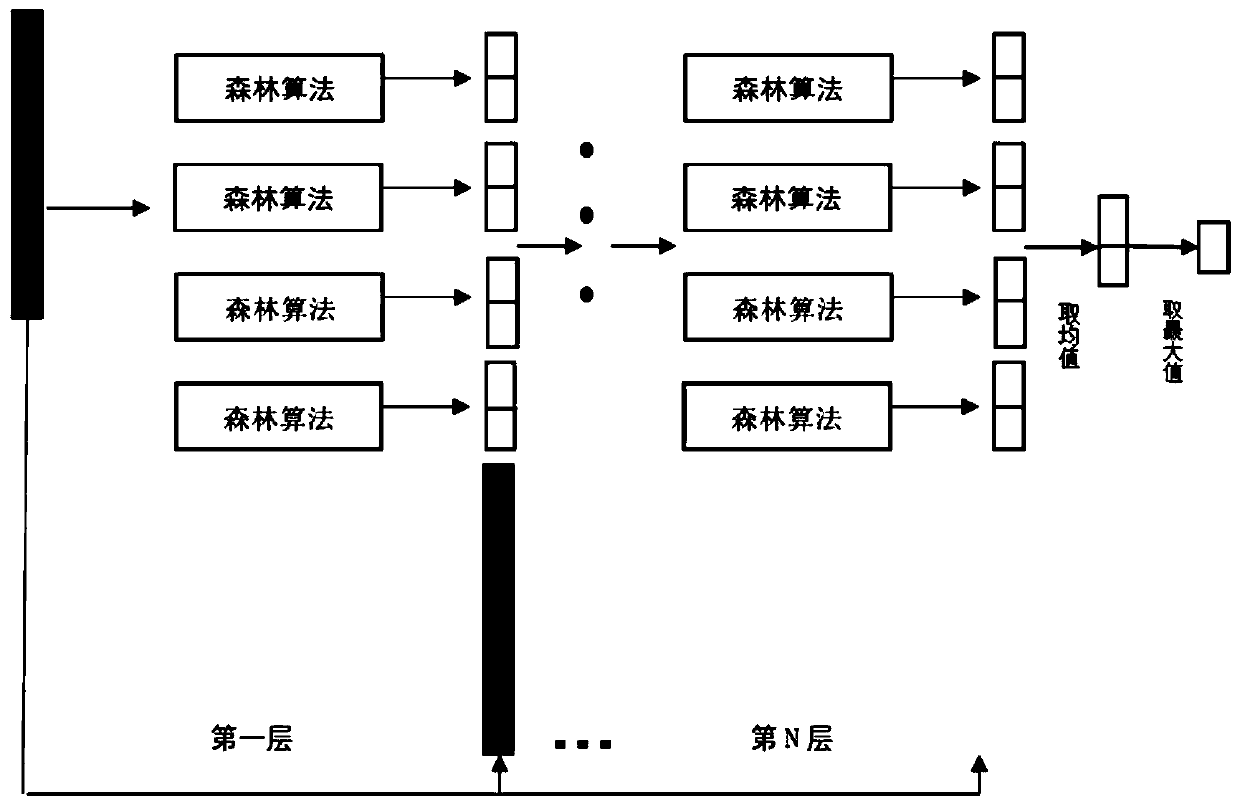
The invention discloses a sepsis early prediction method based on machine learning. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, extracting clinical data, including demographic statistics (suchas age and gender), vital sign variables (such as heart rate and systolic pressure) and laboratory measurement indexes (such as creatinine and platelet count), of a patient within 24 hours after a patient enters an ICU by utilizing an electronic medical record, preprocessing the data, inputting the preprocessed data into an improved deep forest algorithm model for training, and outputting the disease probability of the patient after training optimization. And meanwhile, the algorithm model can also sort characteristic variables and output an early warning factor which has great influence on early prediction of sepsis. Finally, corresponding variables of the patient needing to be predicted are input into the trained model, so that early prediction of sepsis can be carried out on the patient. According to the invention, early prediction is carried out on sepsis based on a machine learning method, doctors can be assisted in making clinical decisions, and the prediction accuracy is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com