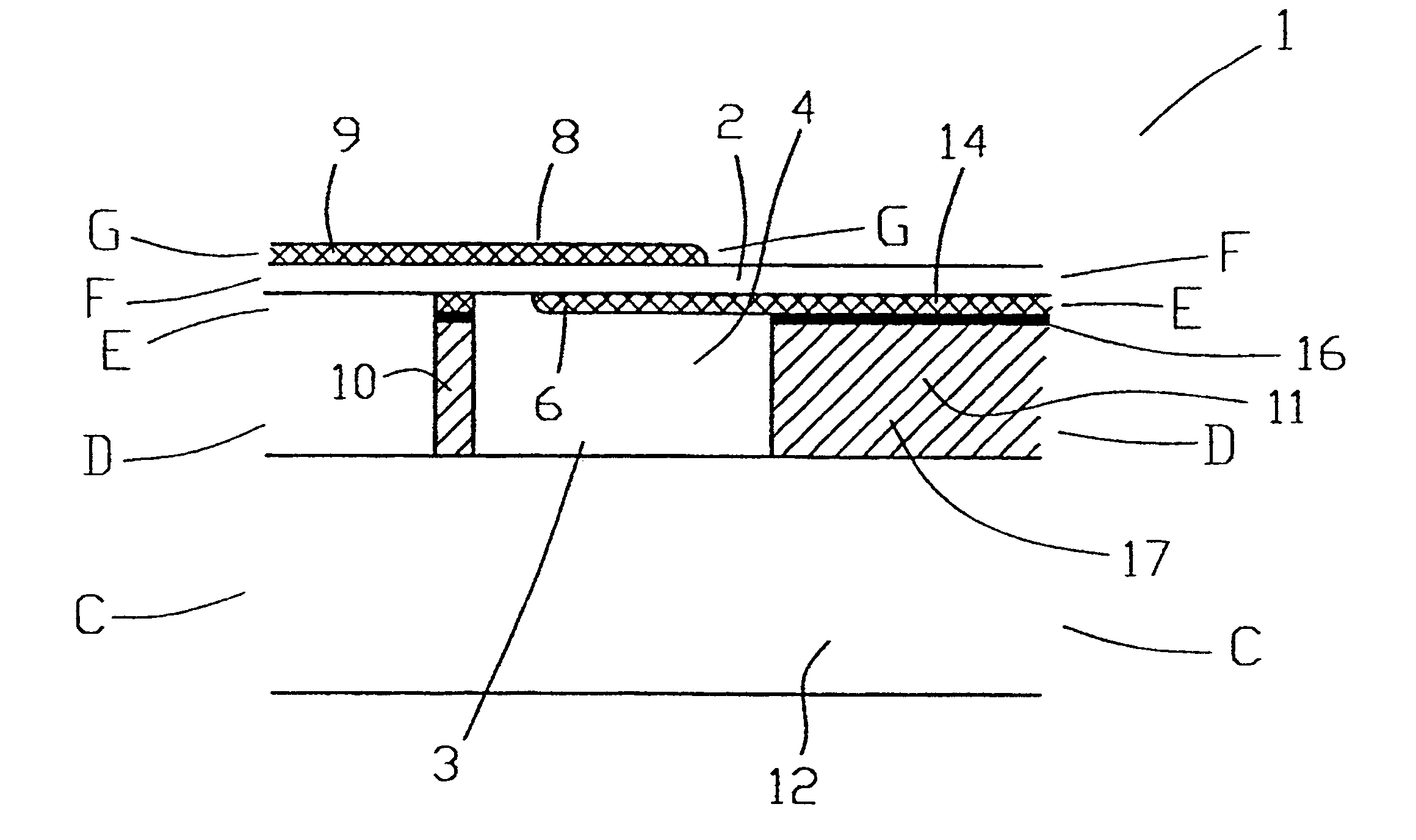
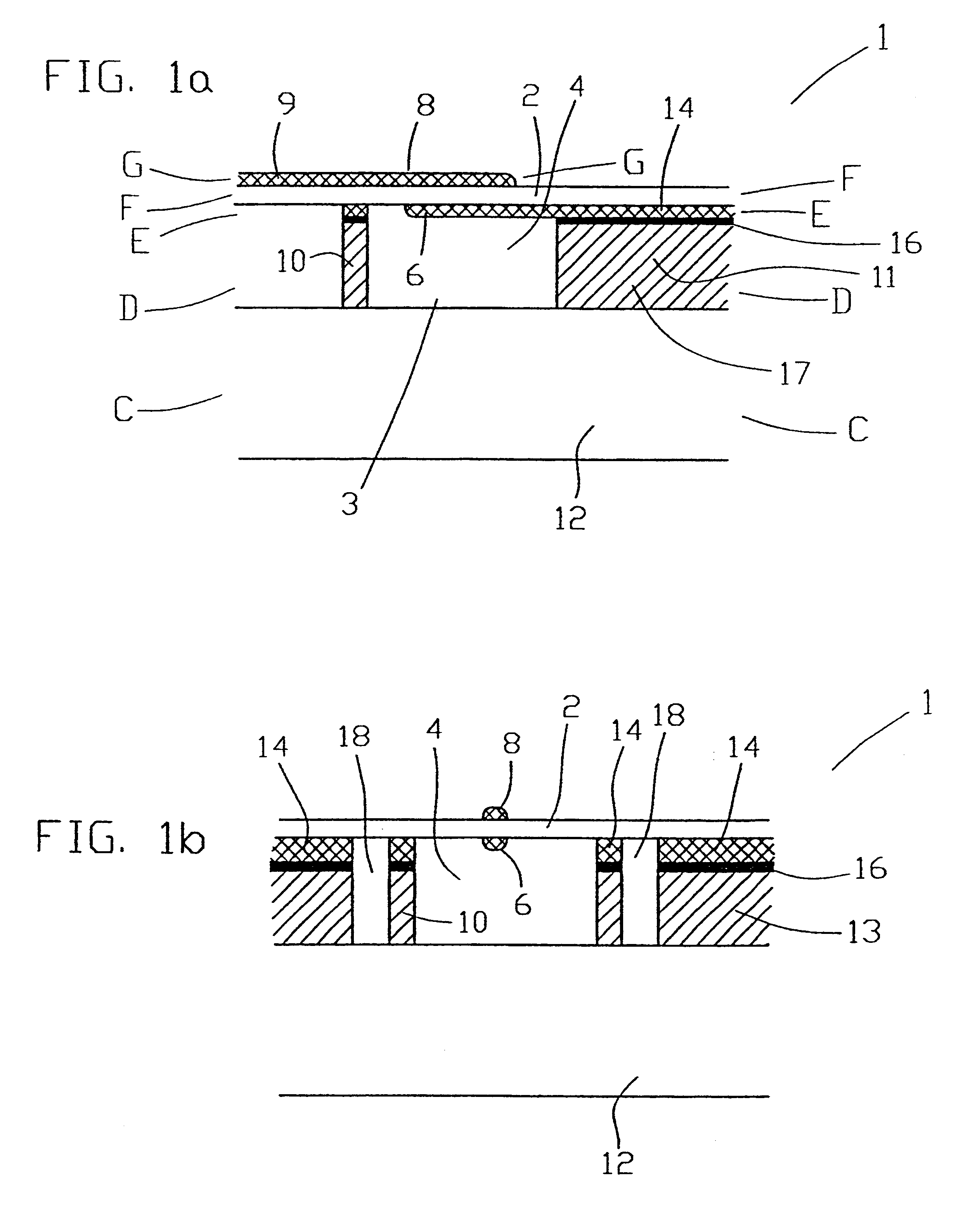
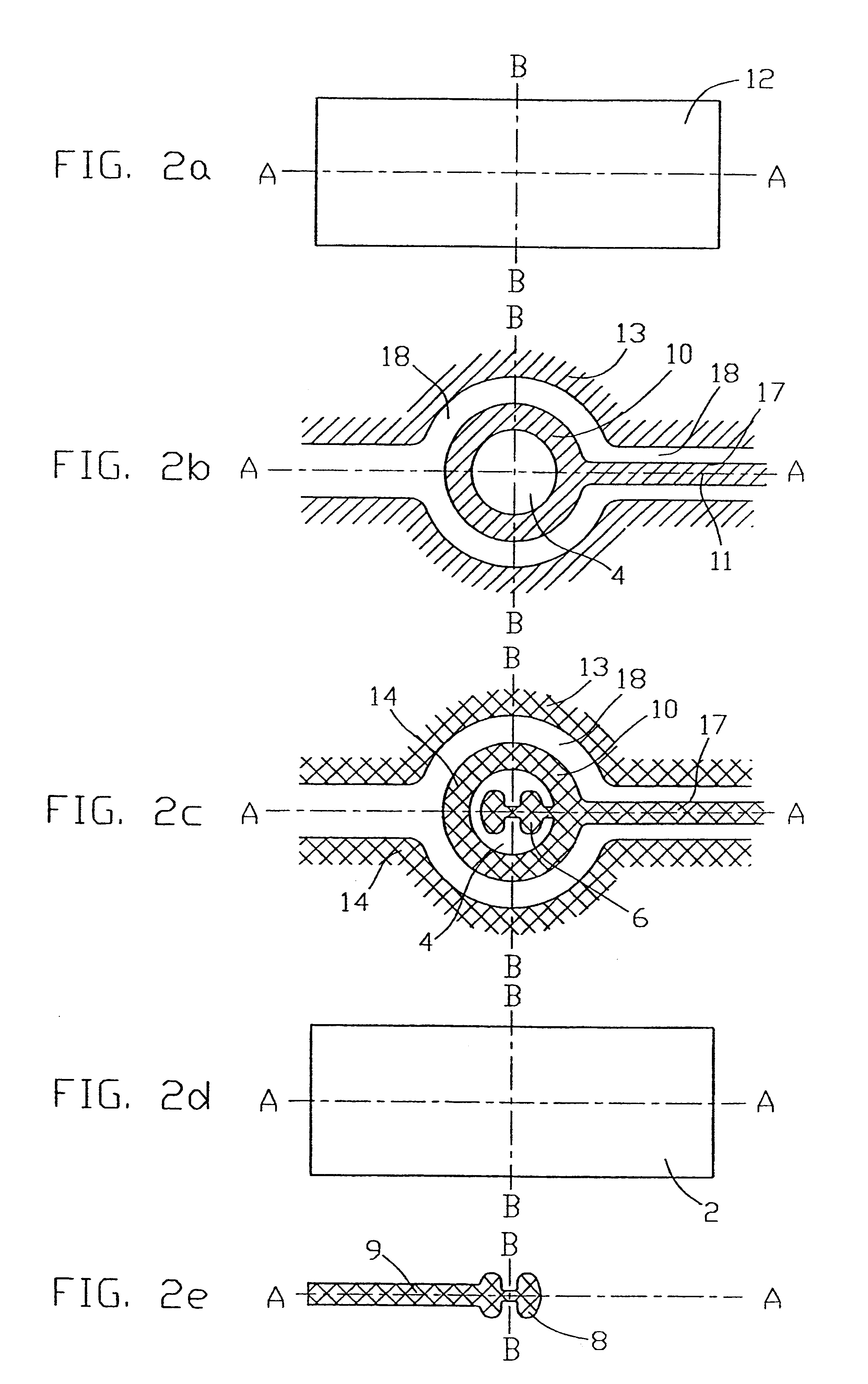
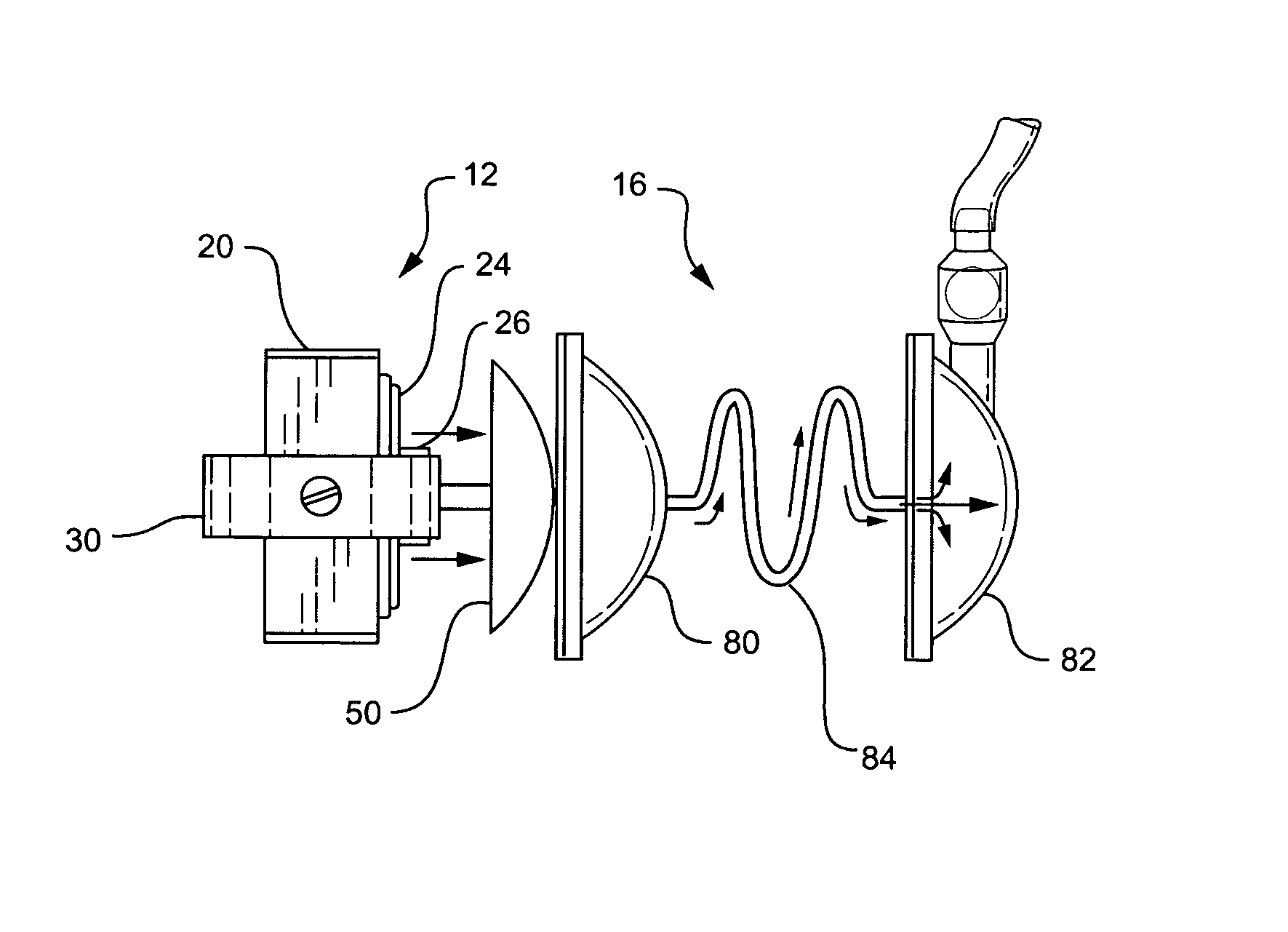
Patents
Literature
228 results about "Pulsatile flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
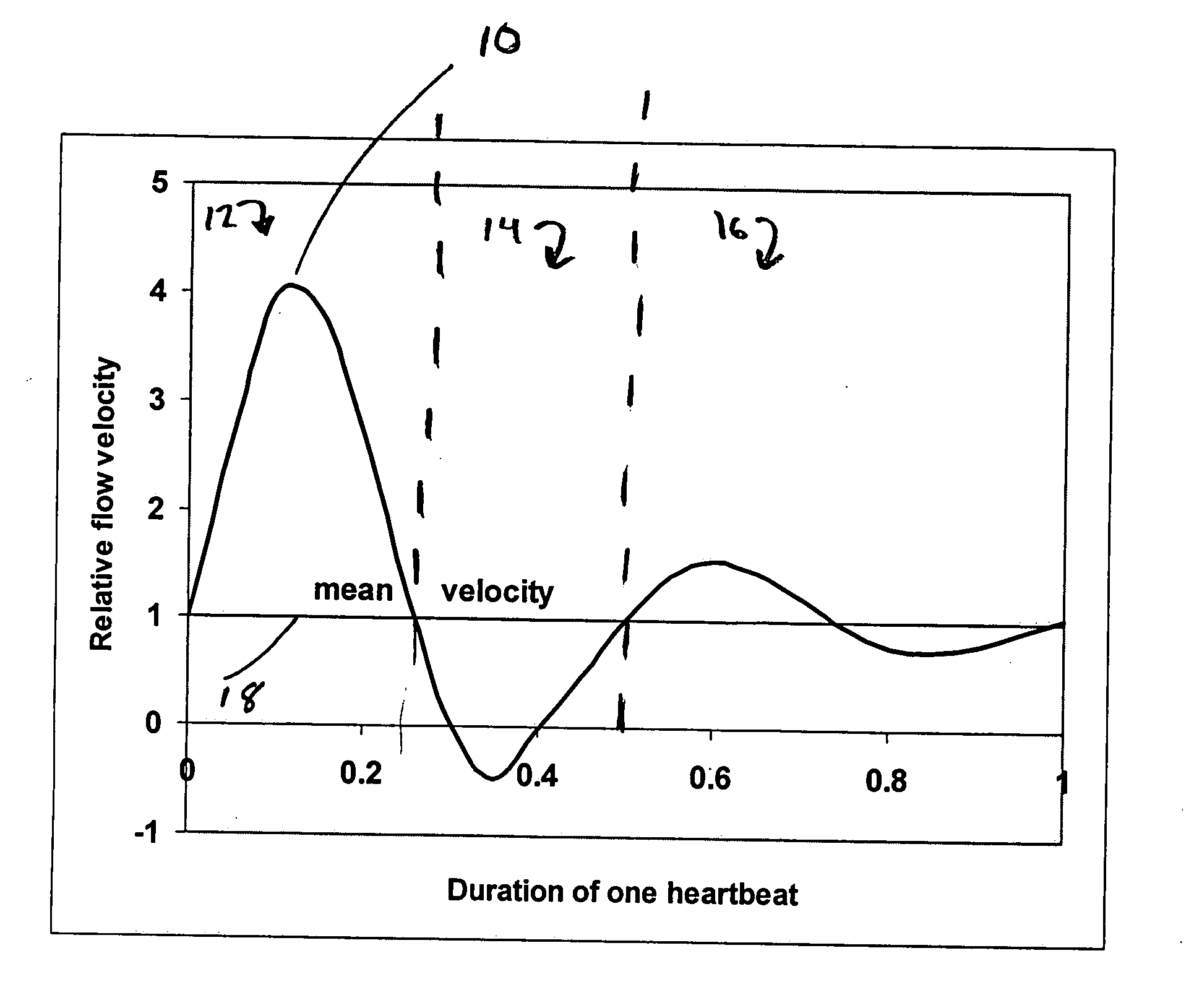
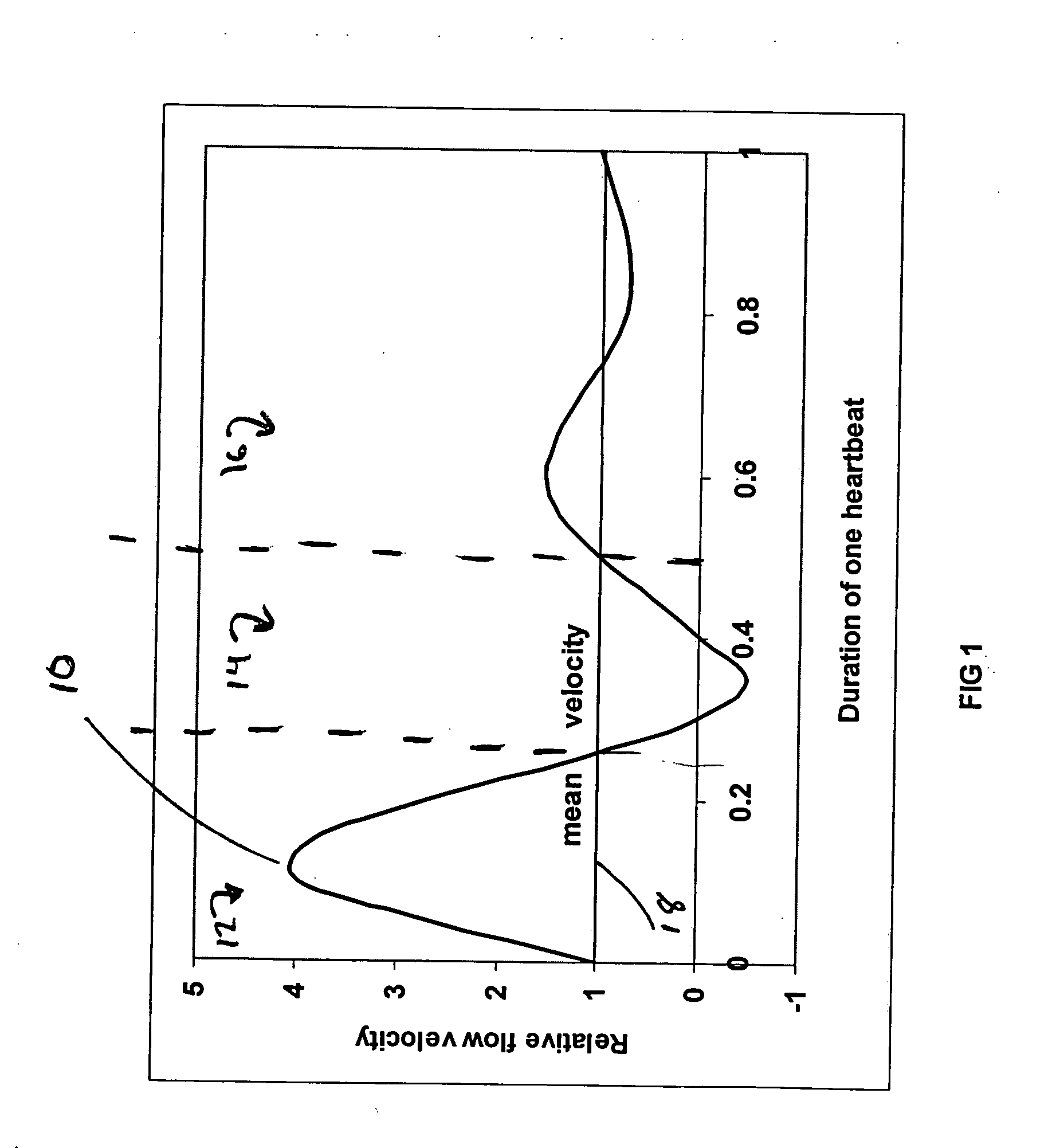
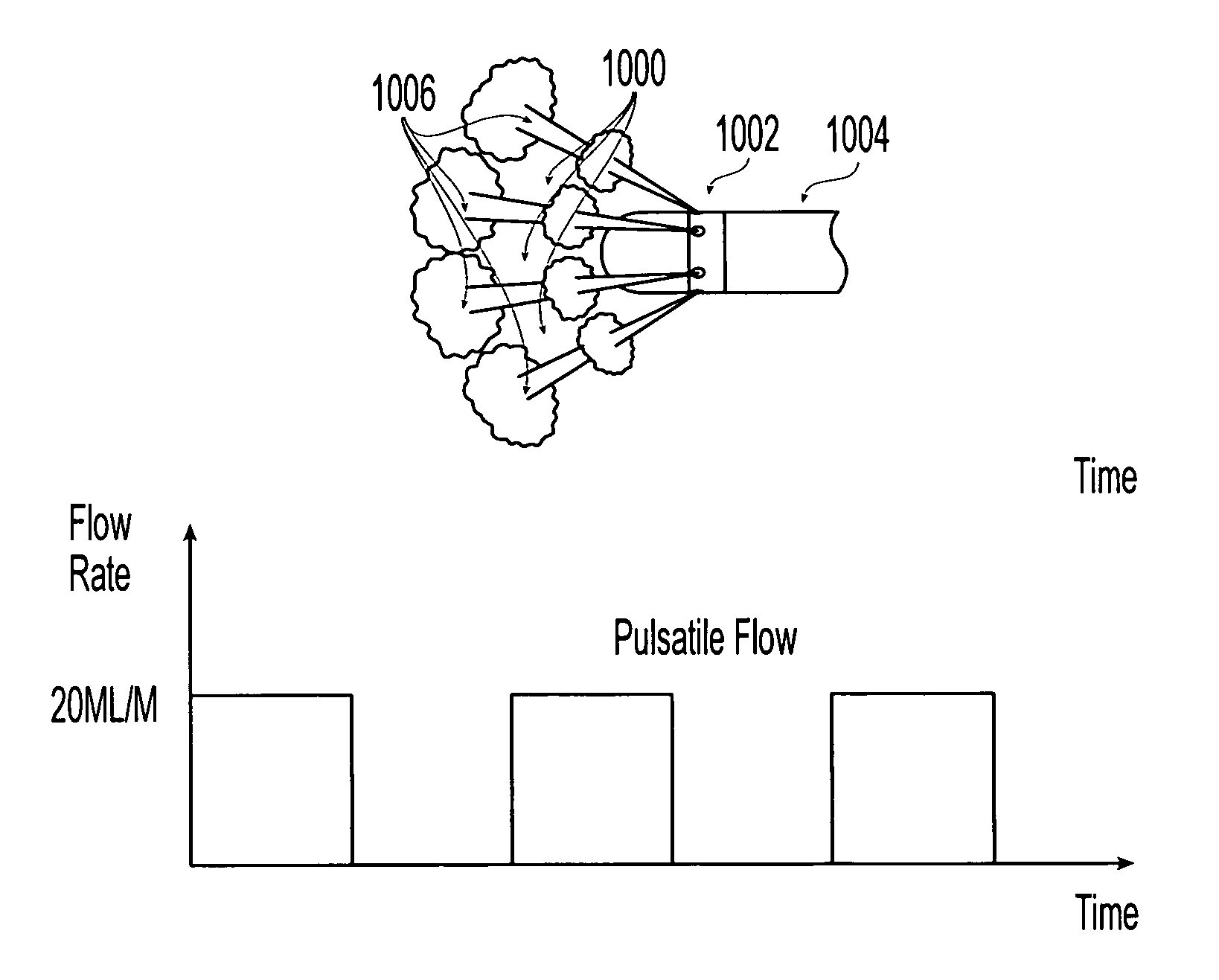
In fluid dynamics, a flow with periodic variations is known as pulsatile flow, or as Womersley flow. The flow profiles was first derived by John R. Womersley (1907–1958) in his work with blood flow in arteries. The cardiovascular system of chordate animals is a very good example where pulsatile flow is found, but pulsatile flow is also observed in engines and hydraulic systems, as a result of rotating mechanisms pumping the fluid.
System and method for monitoring pressure, flow and constriction parameters of plumbing and blood vessels
InactiveUS6237398B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringPulsatile flow
The present invention provides a system and method of quantifying flow, detecting a location of an obstruction and quantifying a degree of the obstruction in a pipe characterized in pulsatile flow. The method includes the steps of (a) attaching at least two spaced pressure sensors onto inner walls of the pipe; (b) using the at least two spaced pressure sensors for recording pressure records associated with each of the at least two pressure sensors within the pipe; and (c) using the pressure records for quantifying the pulsatile flow in the pipe, for detecting the location of the obstruction in the pipe and for quantifying the degree of the obstruction in the pipe.
Owner:TELESENSE
Fluid pump
ActiveUS7238165B2ElectrocardiographyOther blood circulation devicesEngineeringCardiopulmonary bypass time
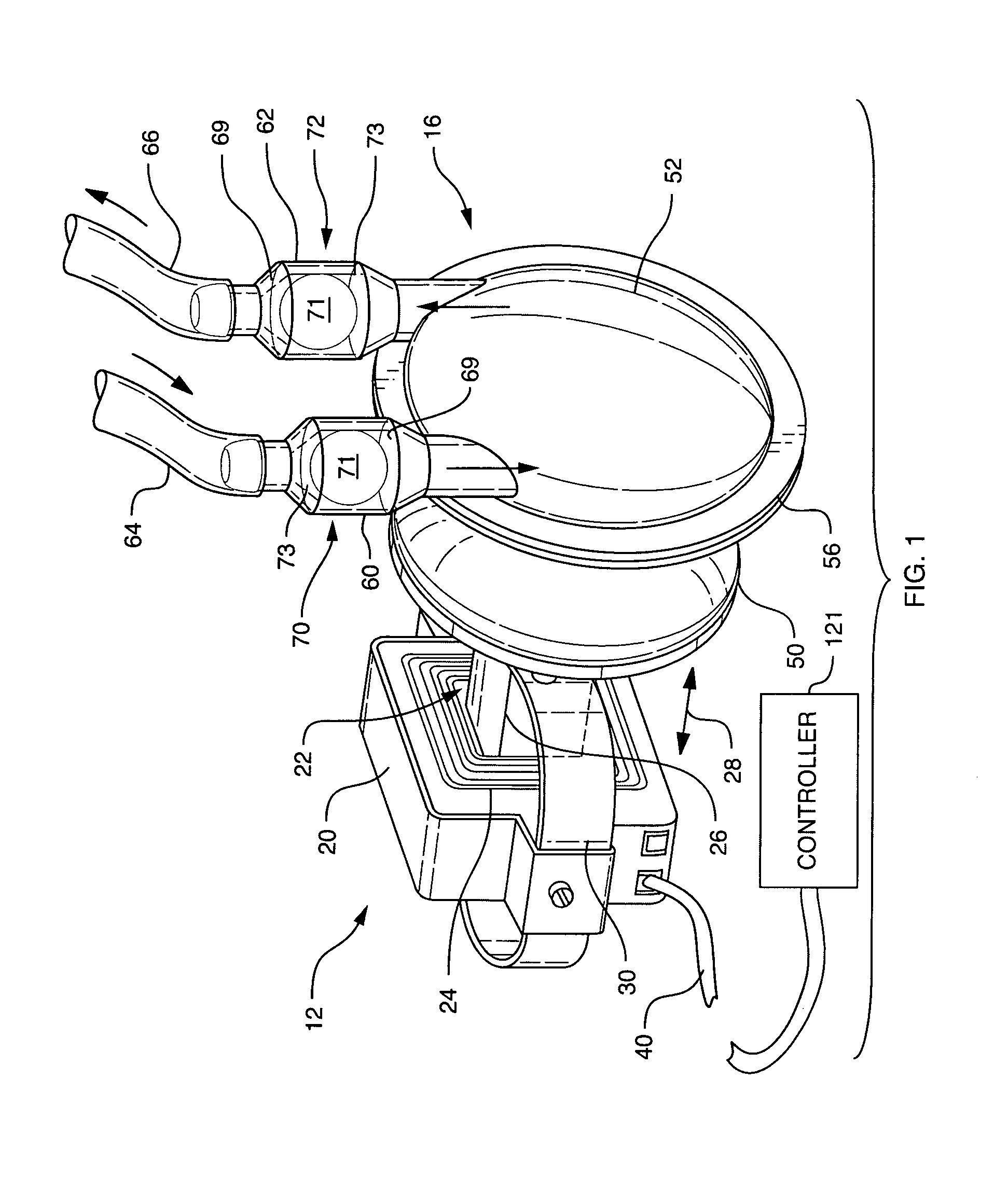
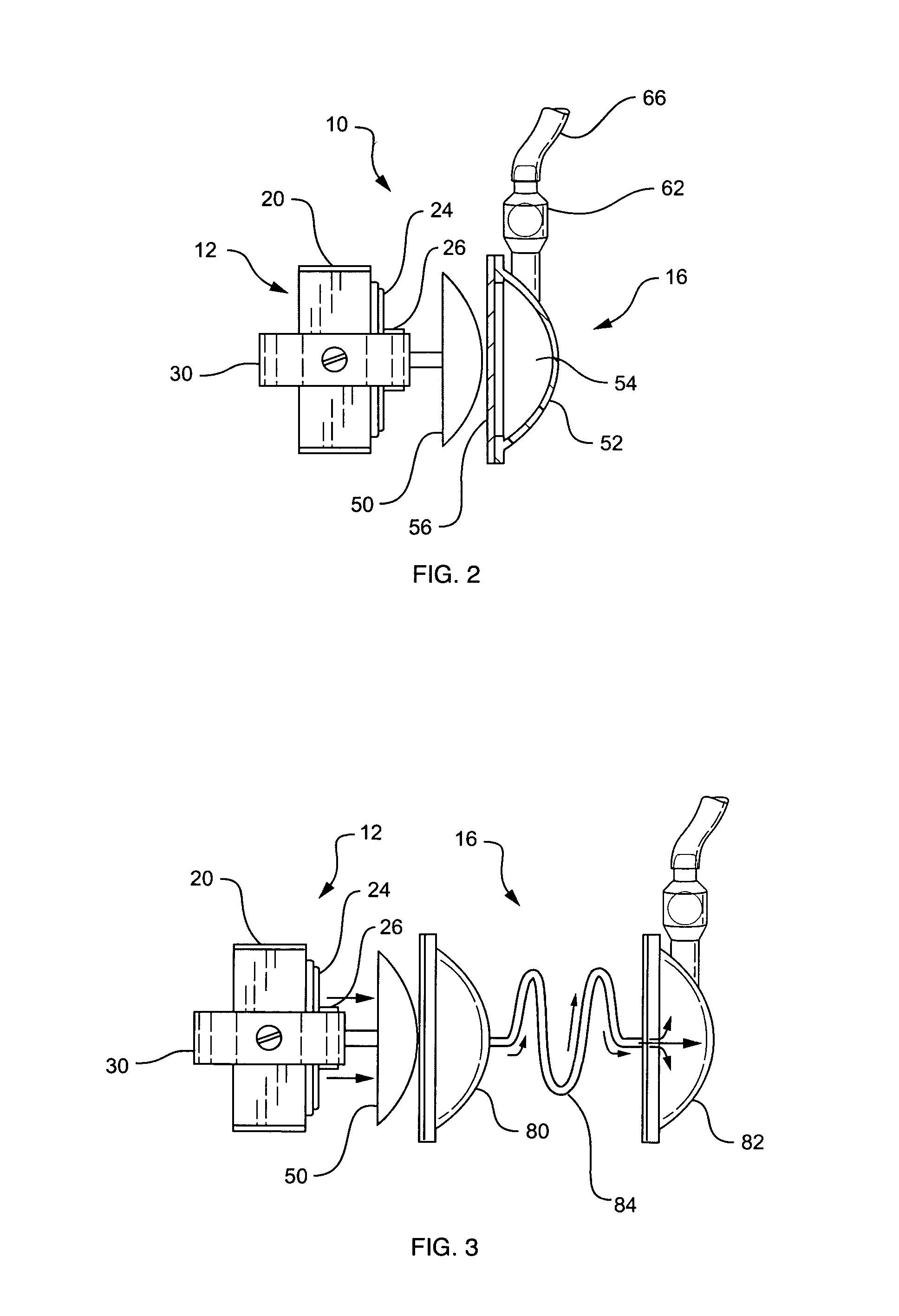
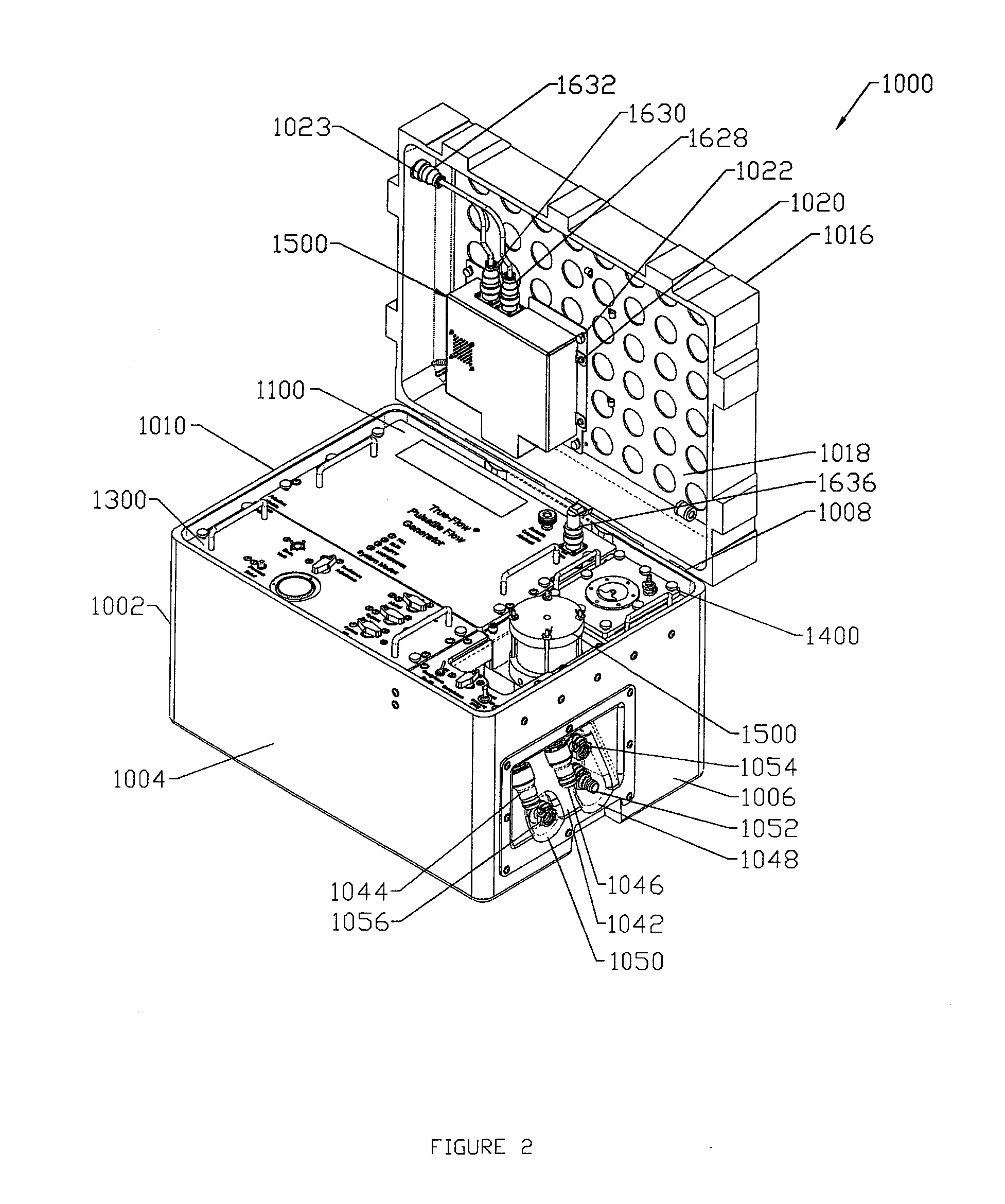
A pumping system 10 provides a physiological pulsatile flow and includes controller 121, a pump drive head 50 coupled to a motor 12 and a fluid housing 52 having at least one port 60. The port 60 includes a ball valve retainer region 69, a valve seat 73, and an occluder ball 71 disposed in the ball valve retainer region 69. During operation, the motor 12 forces the fluid in and out the fluid housing 52 and causes the occluder ball 71 to move from a first position whereby the fluid cannot pass through the port 60, to a second position whereby the fluid moves annular to and generally around the occluder ball 71. This movement creates a slight flow reversal that “breaks up” any blood clots that may form. The pumping system may be used as part of a cardiopulmonary bypass system, a ventricular assist device (VAD) and / or a heart pump.
Owner:DESIGN MENTOR
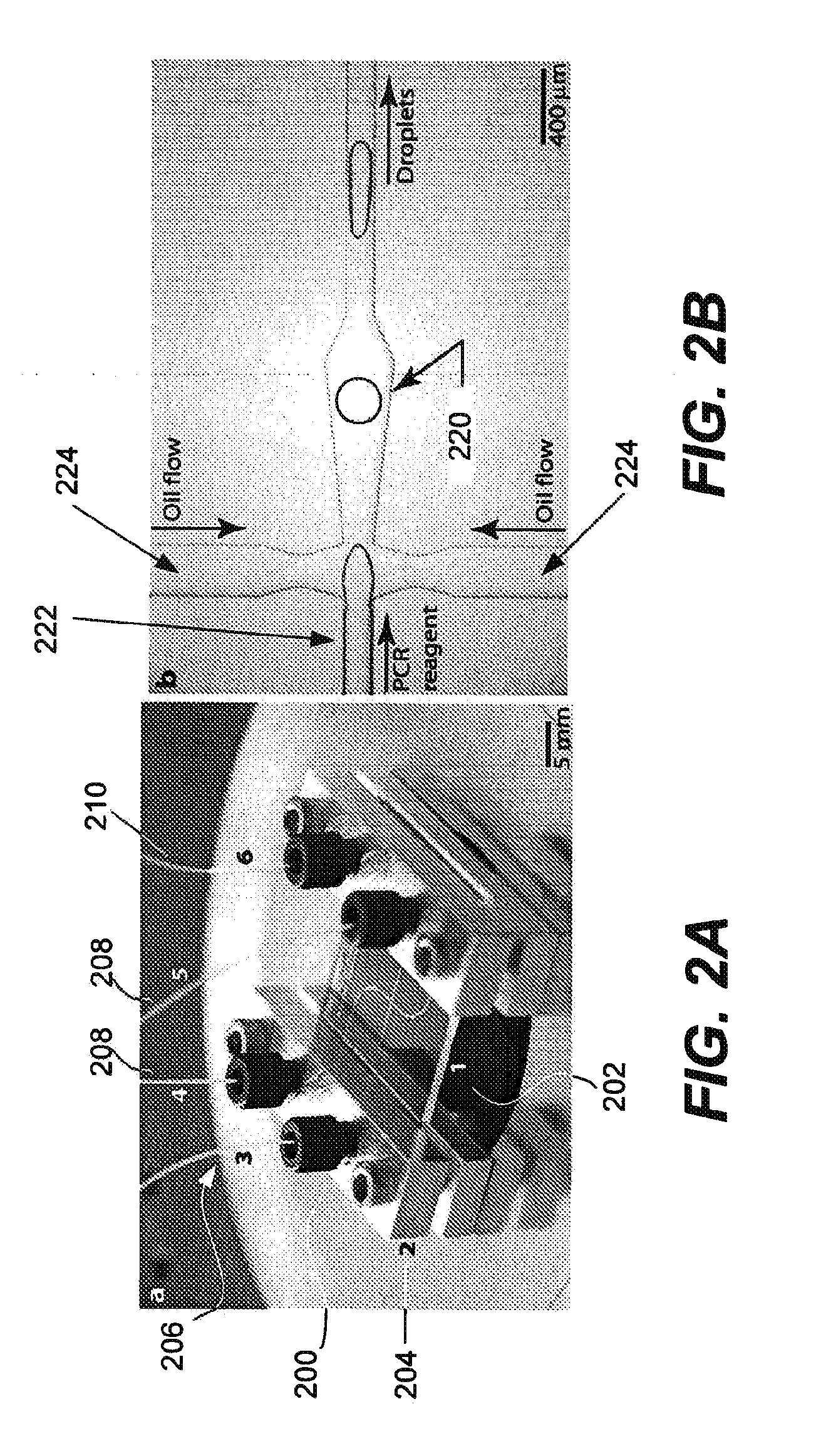
Microfabricated droplet generator for single molecule/cell genetic analysis in engineered monodispersed emulsions
ActiveUS20100285975A1Efficient routingEfficient single-molecule amplificationTransportation and packagingLibrary screeningEmulsionMicroparticle
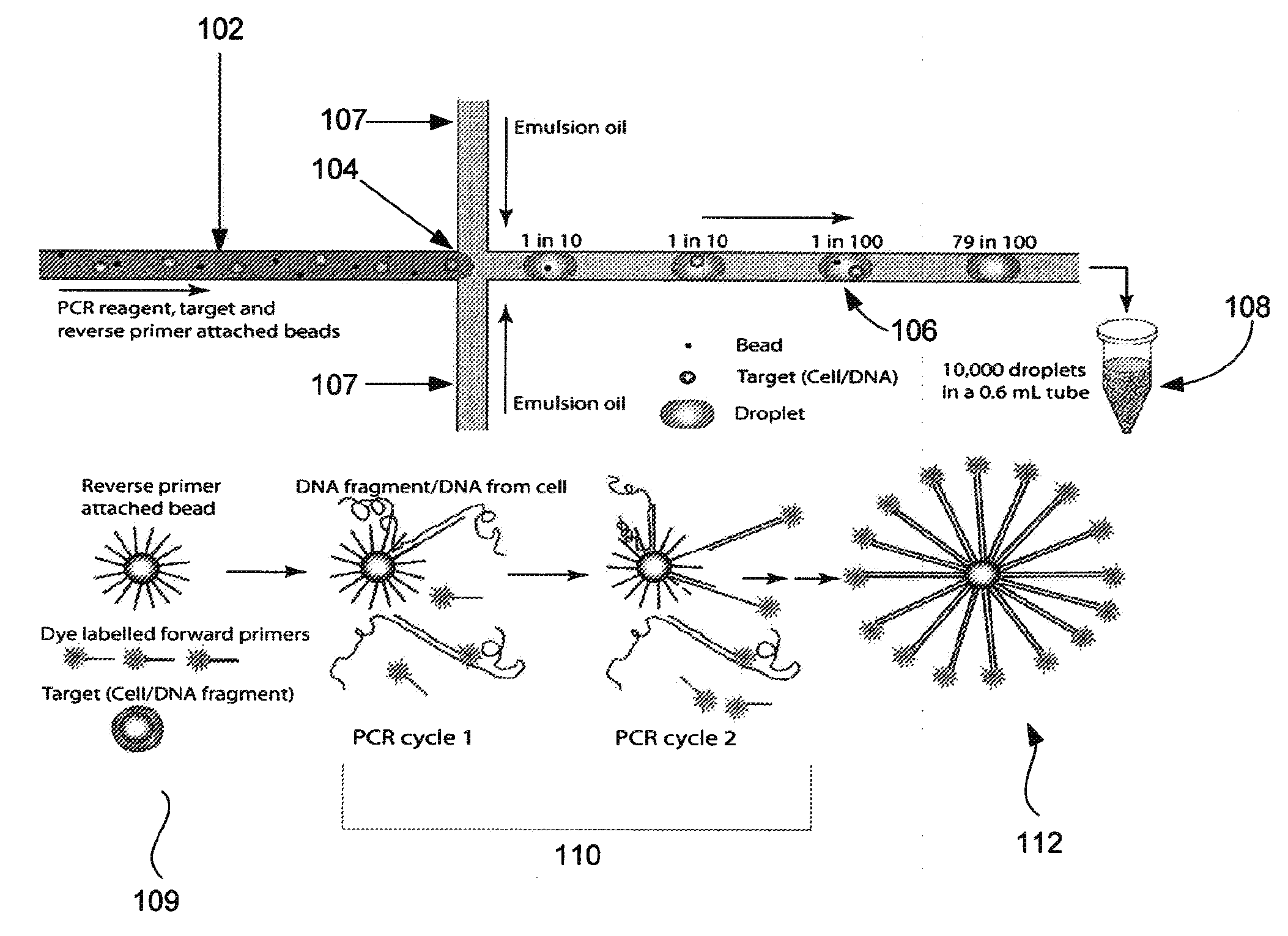
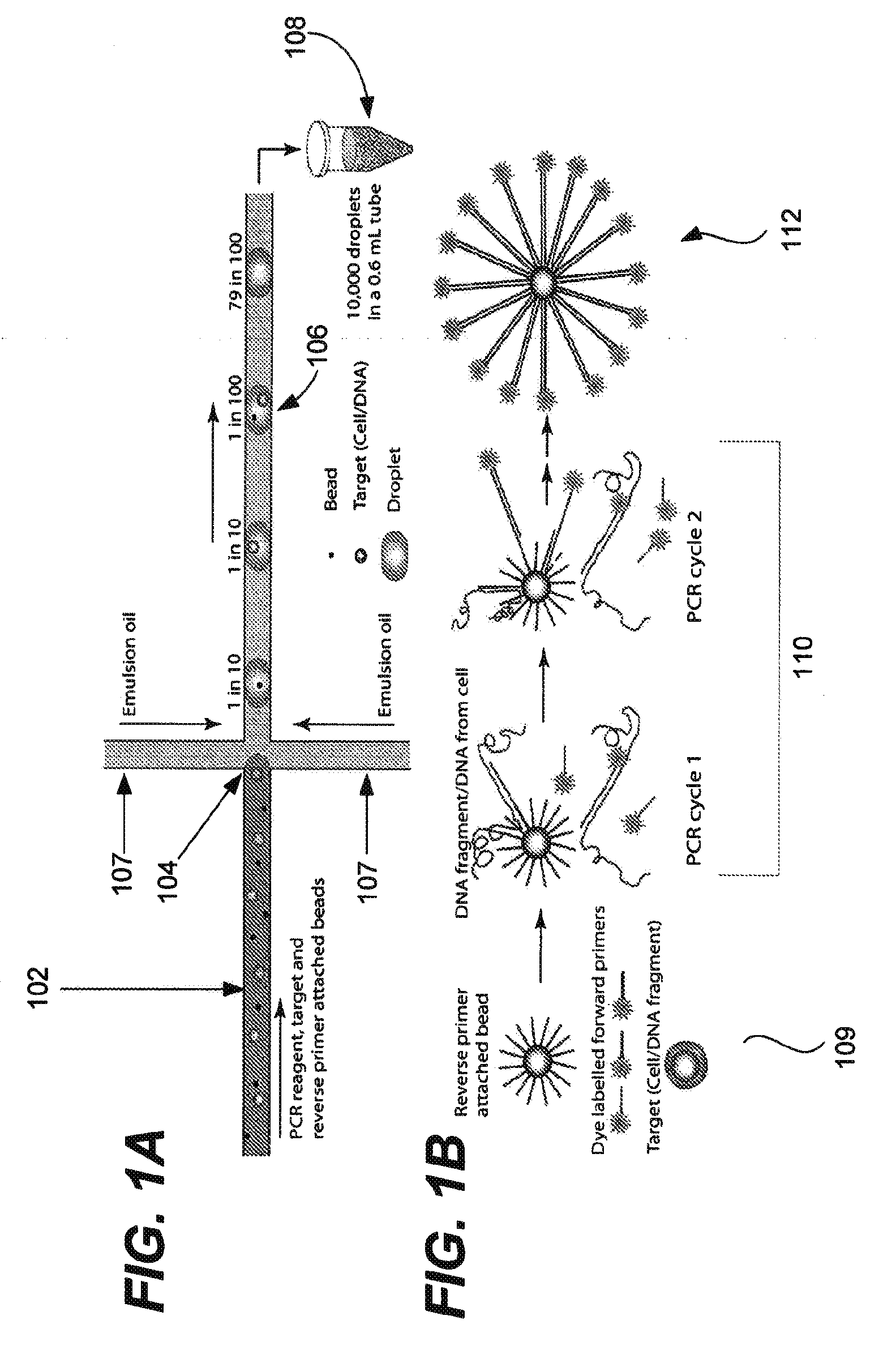
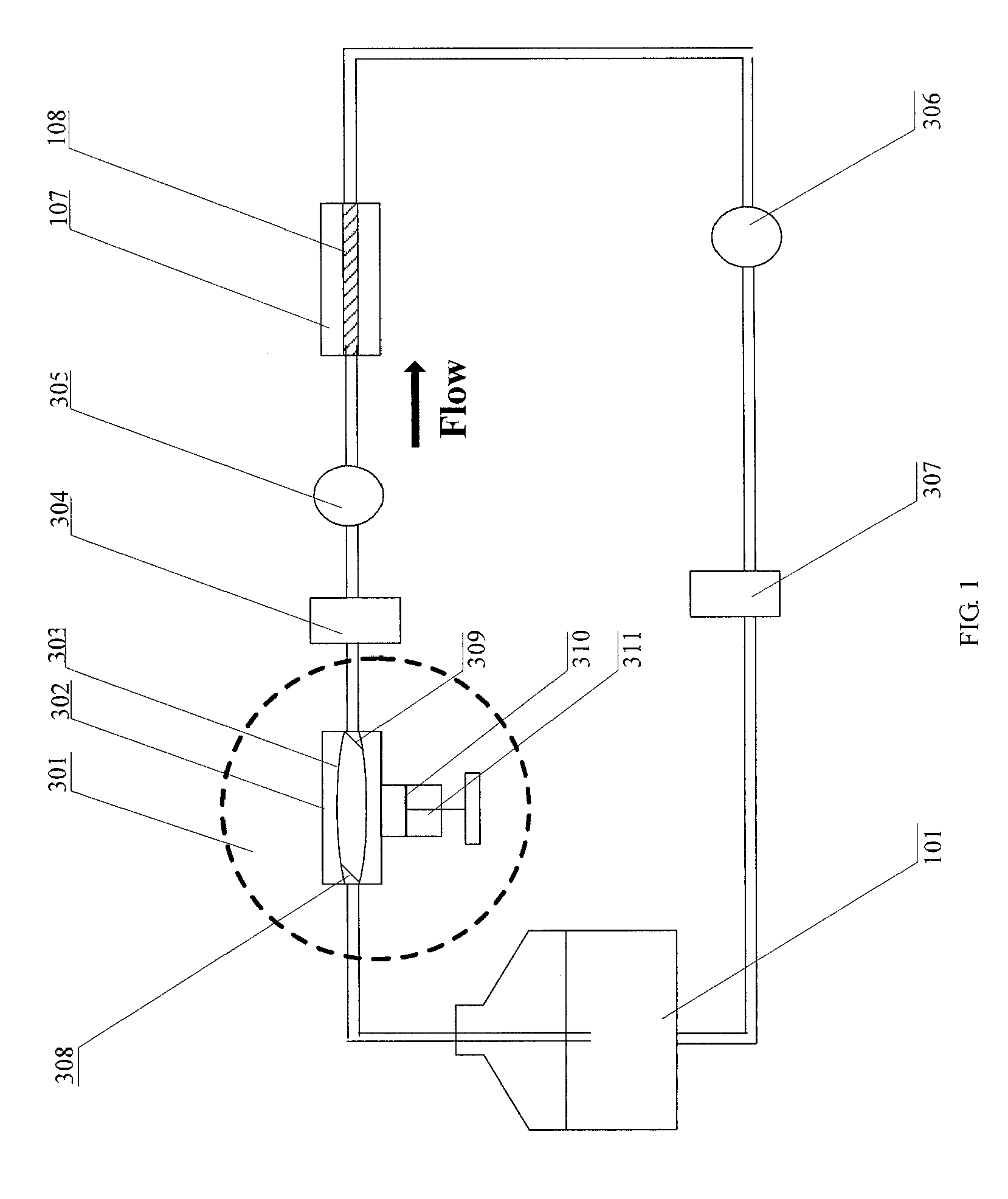
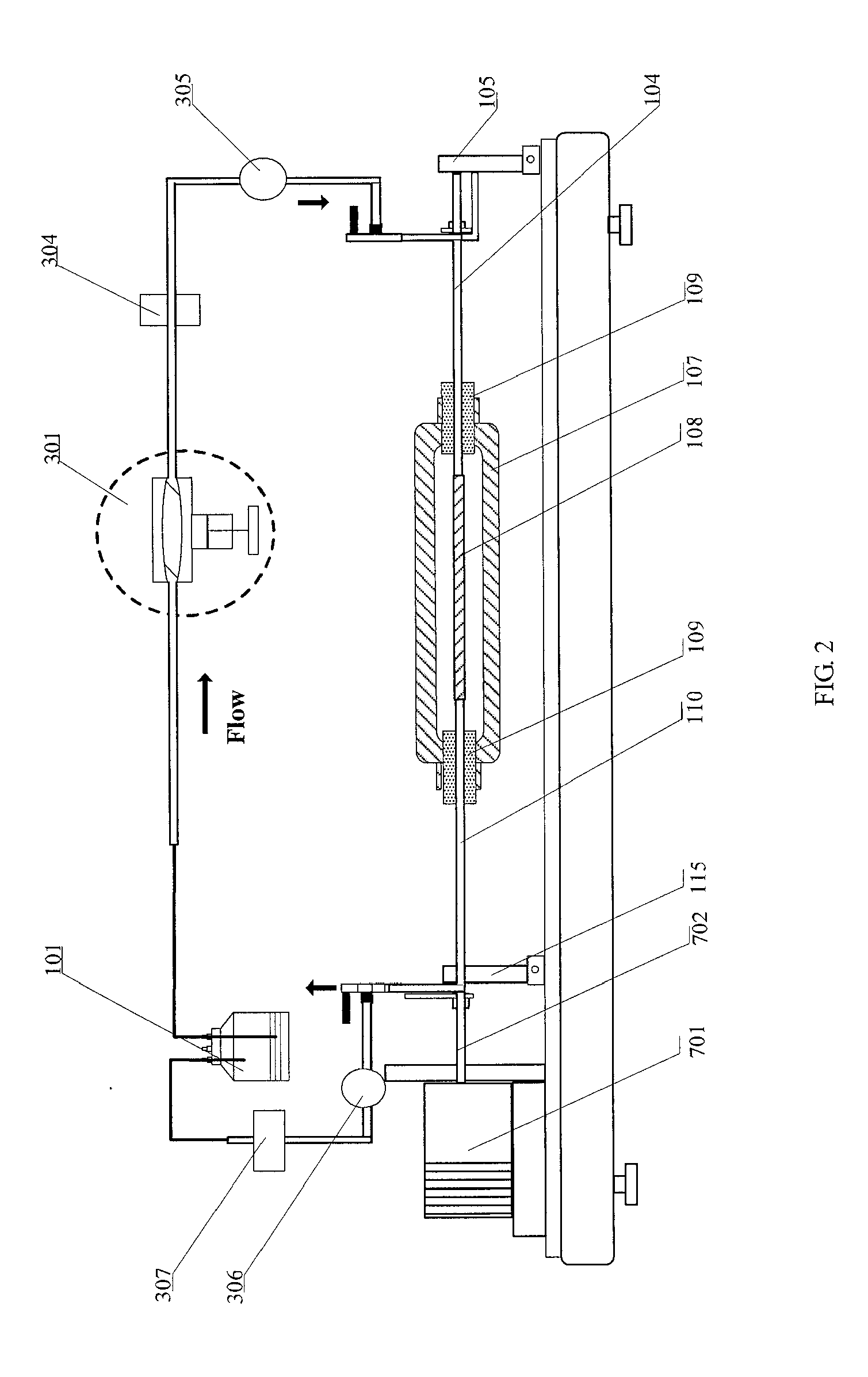
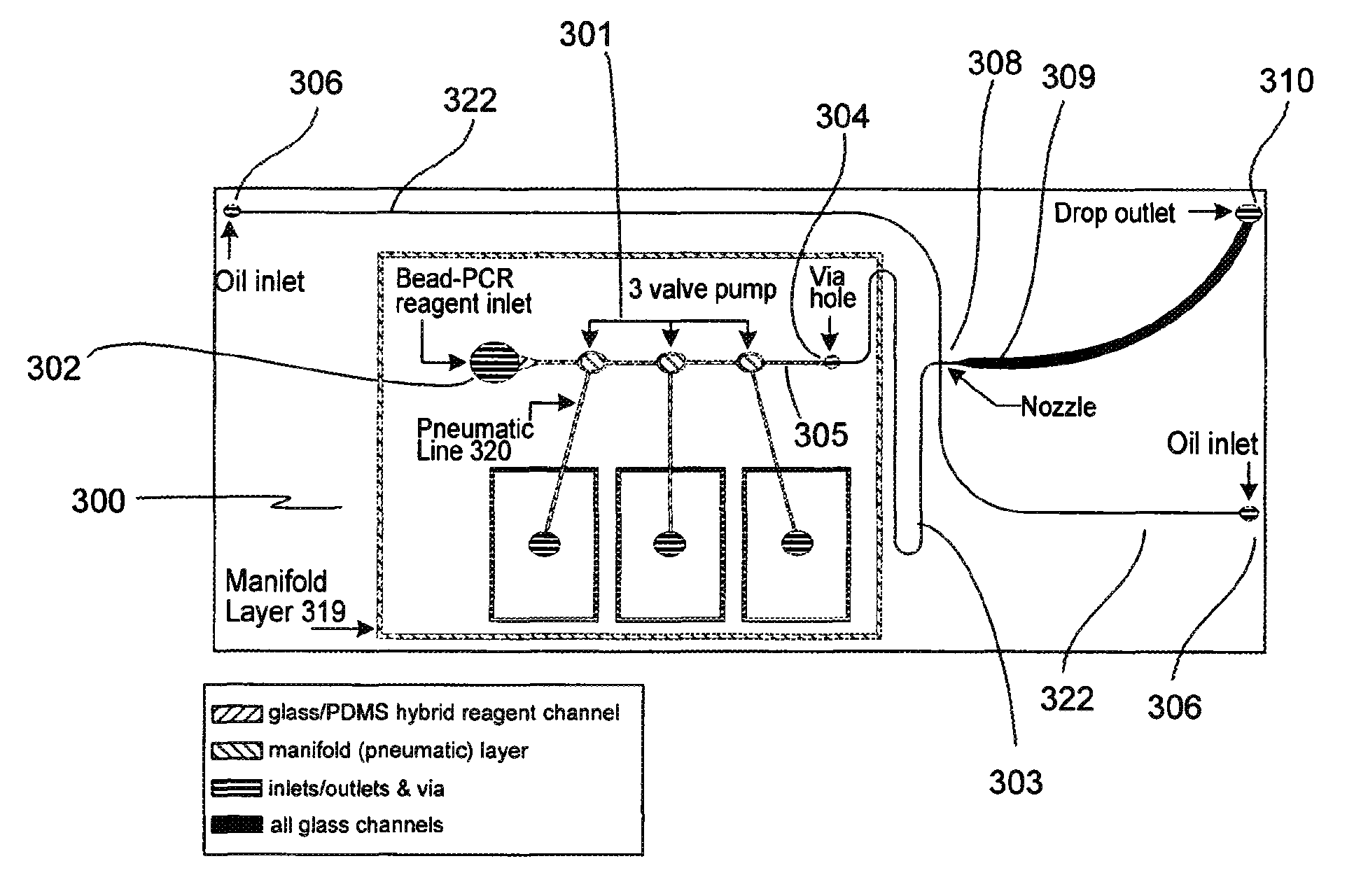
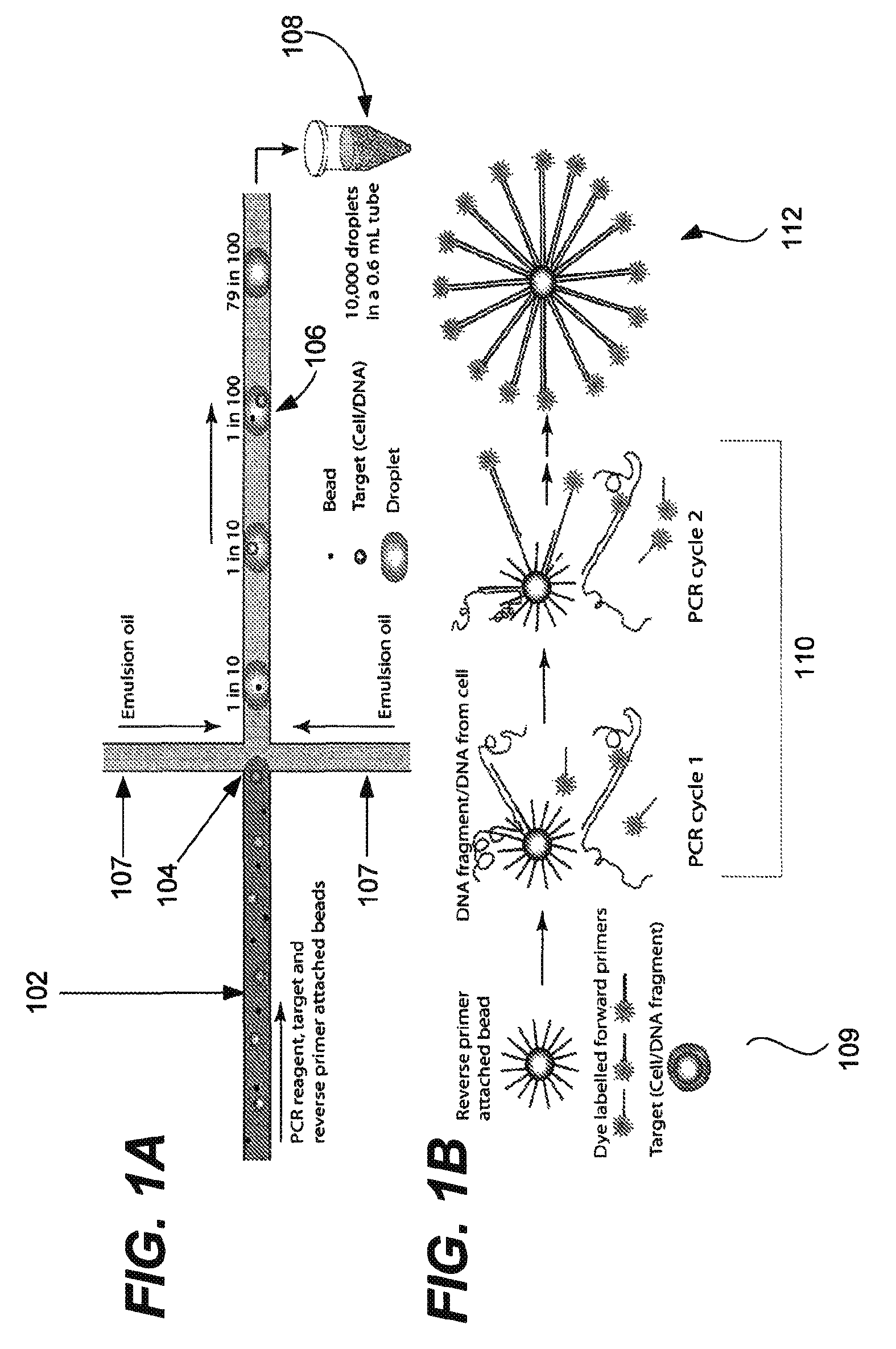
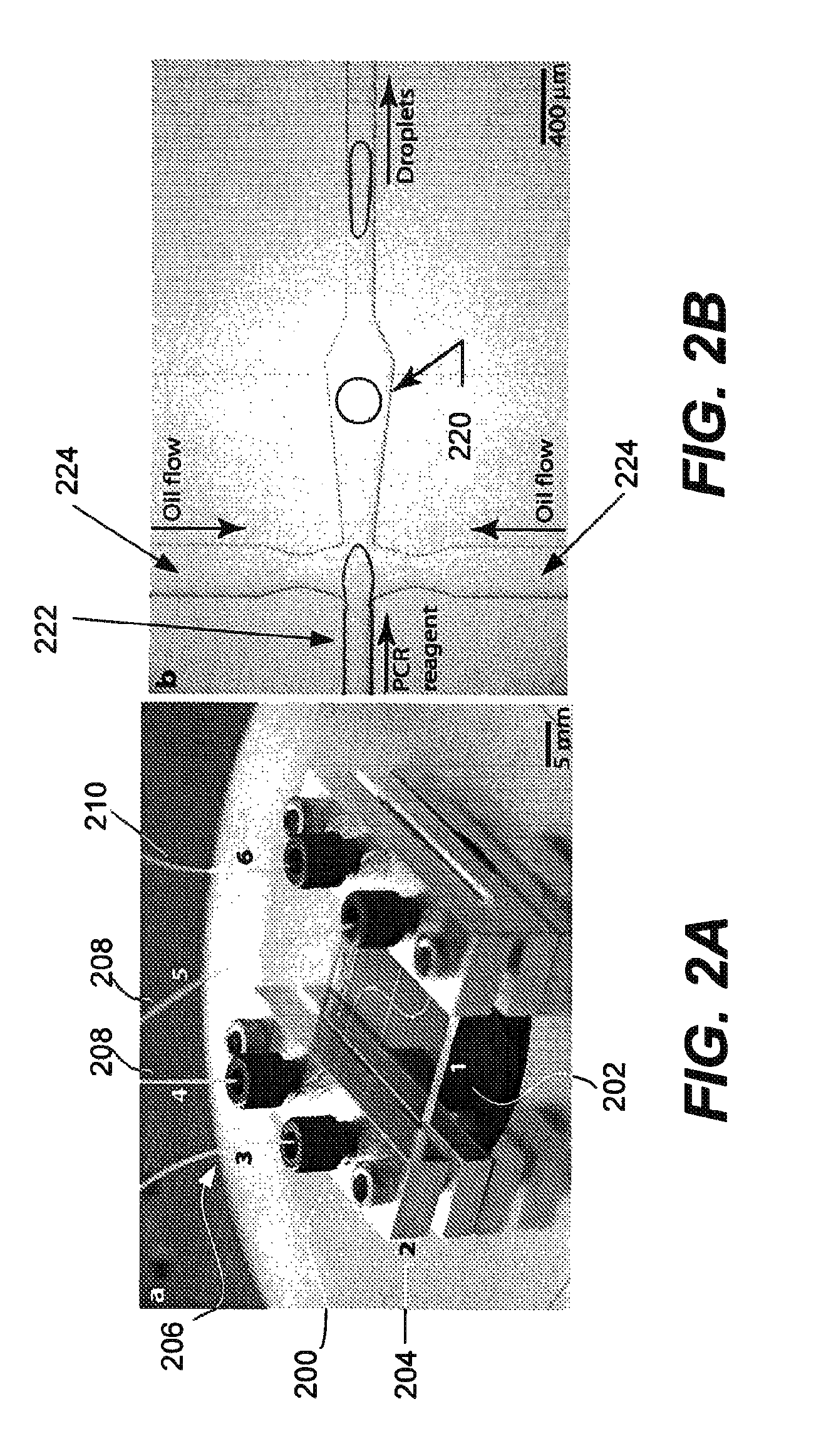
Provided are microfluidic designs and methods for rapid generation of monodisperse nanoliter volume droplets of reagent / target (e.g., molecule or cell) mix in emulsion oil. The designs and methods enable high-throughput encapsulation of a single target (e.g., DNA / RNA molecules or cells) in controlled size droplets of reagent mix. According to various embodiments, a microfabricated, 3-valve pump is used to precisely meter the volume of reagent / target mix in each droplet and also to effectively route microparticles such as beads and cells into the device, which are encapsulated within droplets at the intersection of the reagent channel and an oil channel. The pulsatile flow profile of the microfabricated pumps provides active control over droplet generation, thereby enabling droplet formation with oils that are compatible with biological reactions but are otherwise difficult to form emulsions with.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
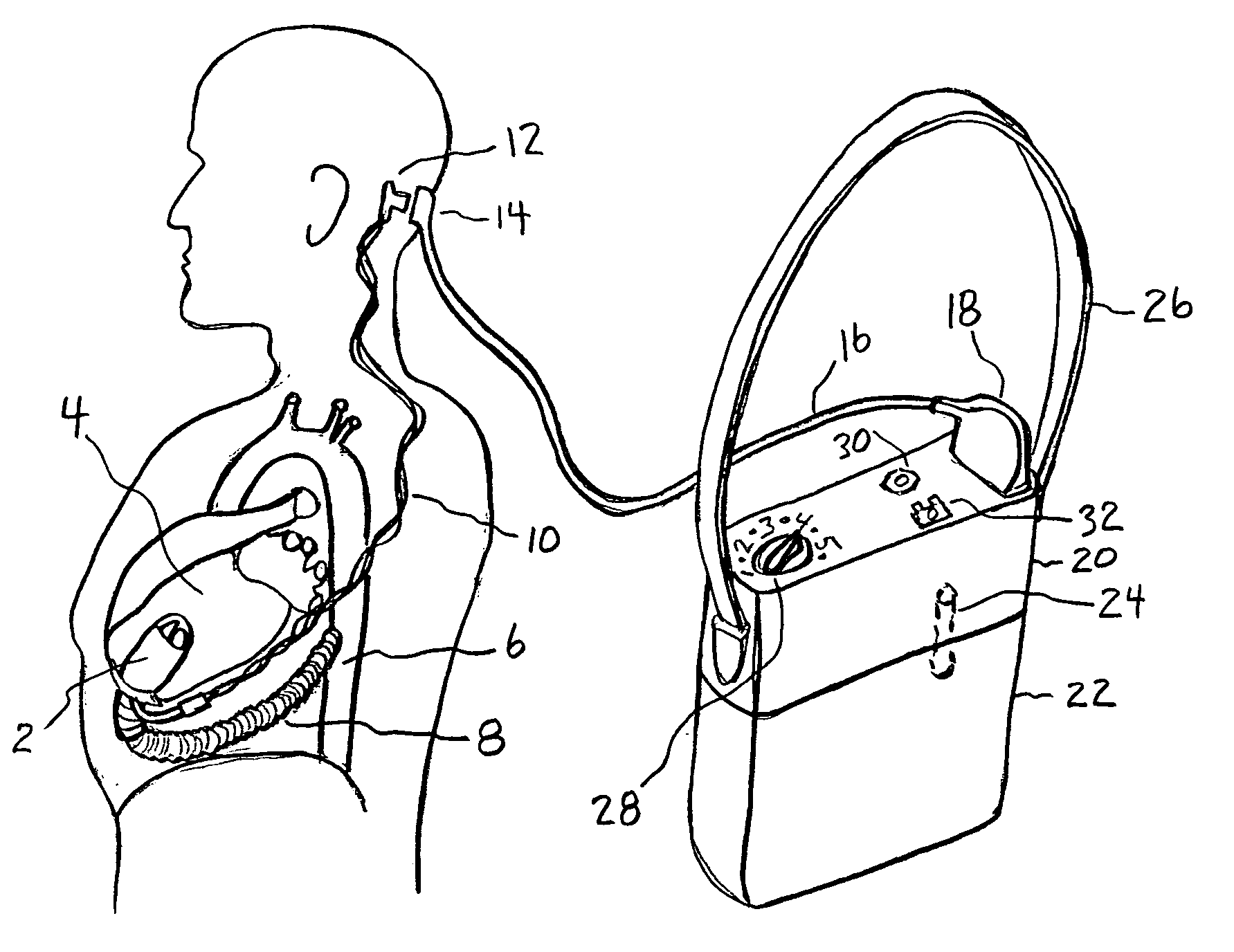
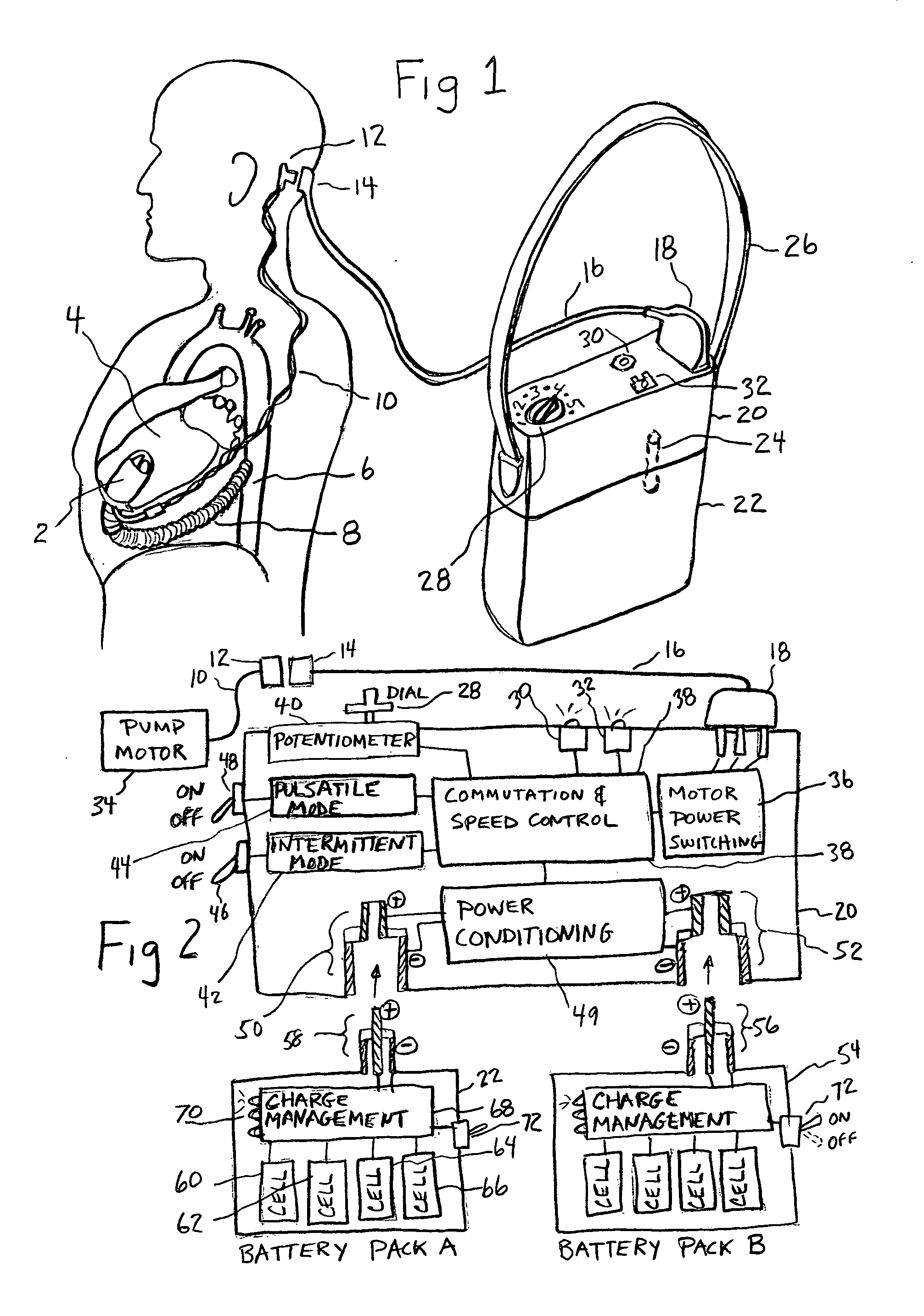
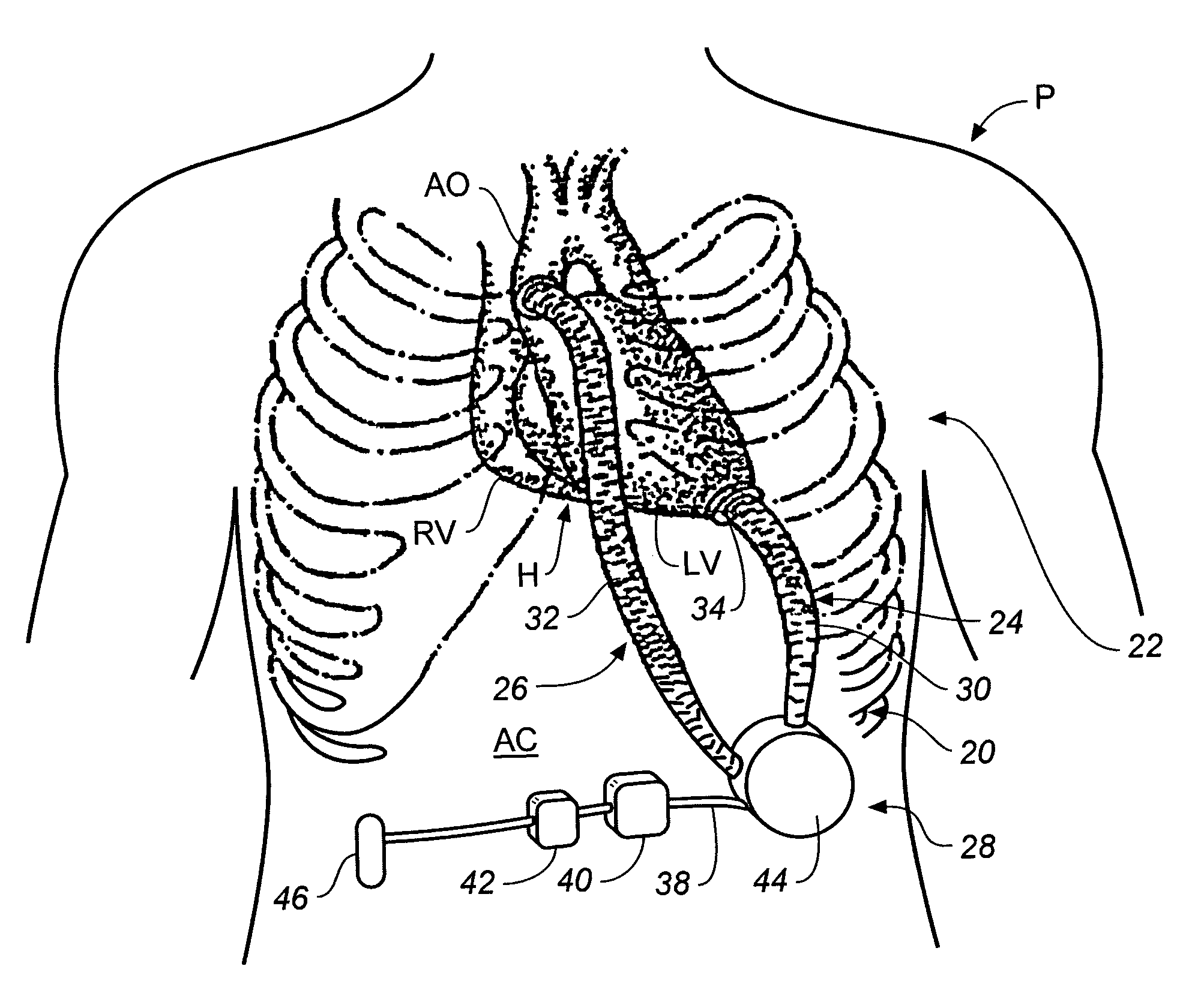
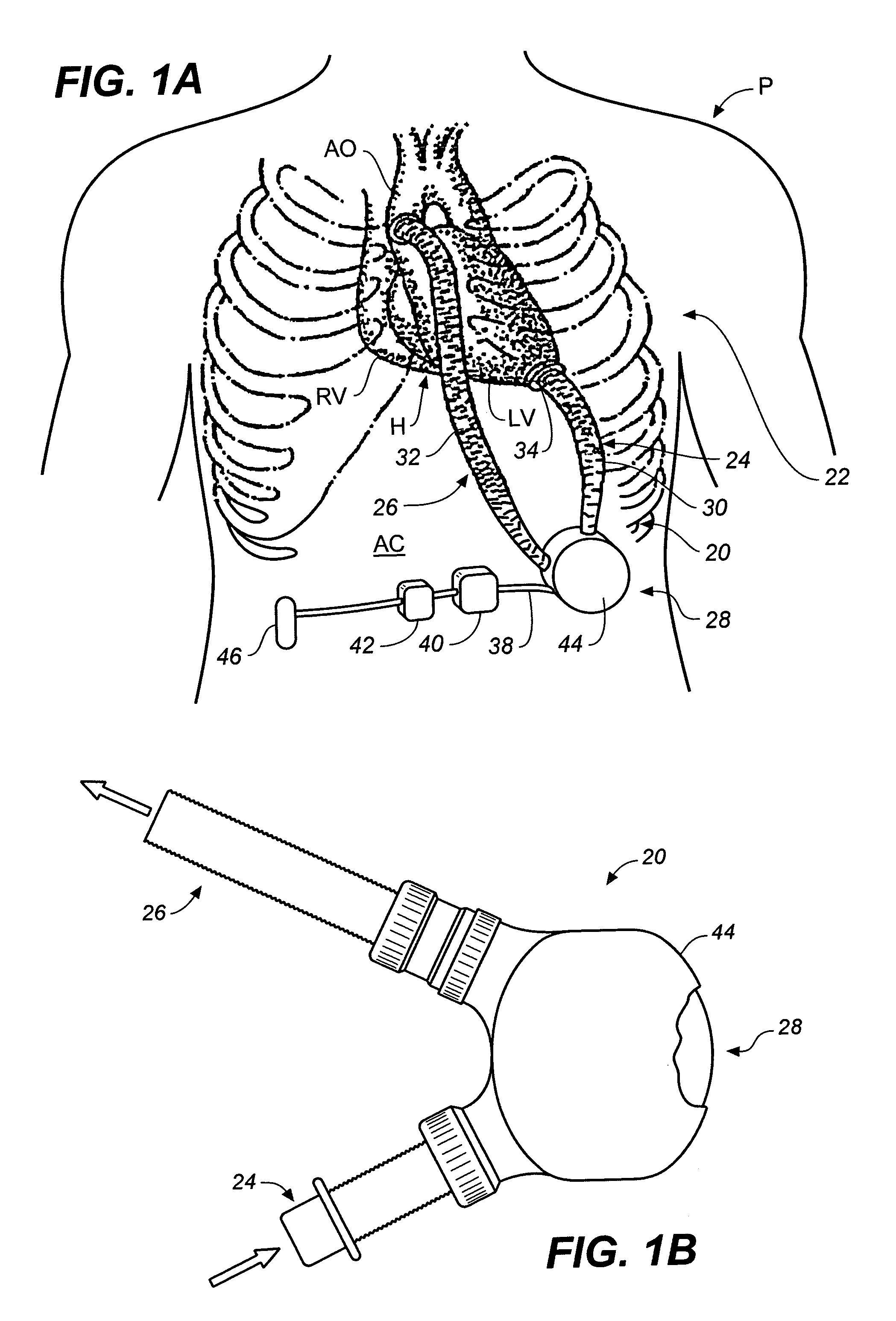
Artificial heart power and control system
InactiveUS20050071001A1Secure attachmentReduce trafficPrimary cell maintainance/servicingControl devicesControl theoryElectric cables
The present invention provides a human engineered power and control system for artificial hearts or assist devices configured for ease of use, ruggedness, and high reliability. Battery powered systems of the prior art have required multiple cables and connectors that are subject to failure due to damage or wear. In the present invention, direct connection of the batteries to the control system eliminates multiple cables and connectors used with previous designs. A novel method of connecting batteries to the control system and exchanging batteries without interruption of power is provided in a compact user friendly configuration. The control system may provide periodic reductions in assist device flow to permit the natural ventricle to eject blood through the natural outflow valve, open the valve leaflets to prevent them from adhering together, and achieve sufficient washout to prevent thrombosis. Using either software based control or software independent electronic circuitry, the flow pumped by the artificial heart is reduced for a long enough period of time to permit at least a few beats of the natural heart to generate sufficient pressure to open the outflow valve. In a control system embodiment in which the patient manually adjusts the pump speed to incremental settings for rest and exercise conditions, a pulsatile flow mode is disclosed which provides approximately the same flow at a given incremental setting as the pump produces when running in a constant speed mode at the same setting. As the patient learns which speed setting is best for daily activities, the patient may use the same setting with either a pulsatile or constant pump speed mode.
Owner:EDER JEFFREY
Pressure gauge, blood pressure gauge, method of determining pressure values, method of calibrating a pressure gauge, and computer program
InactiveUS20120065525A1Efficiently determinedTesting/calibration apparatusEvaluation of blood vesselsTime informationBlood pressure
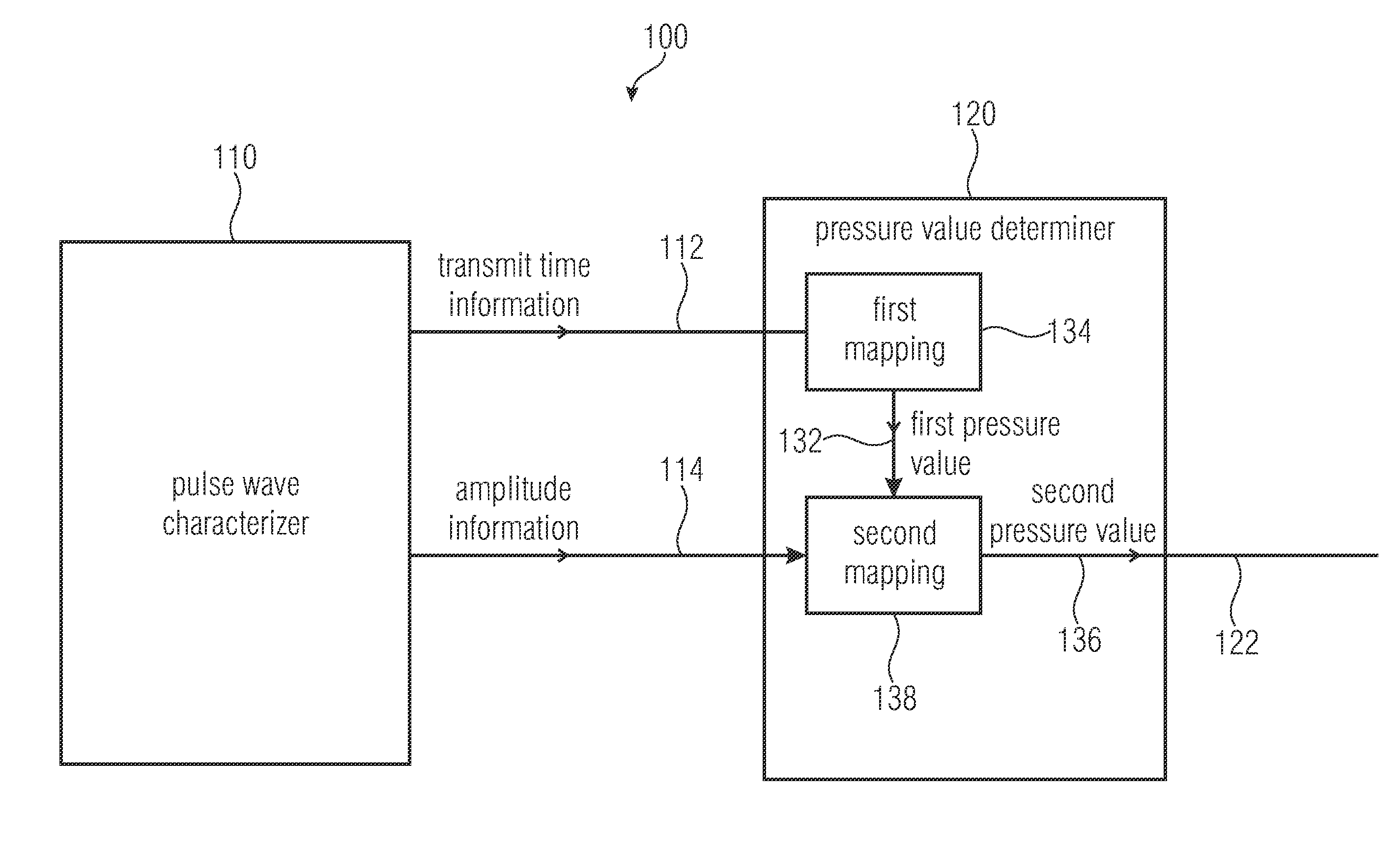
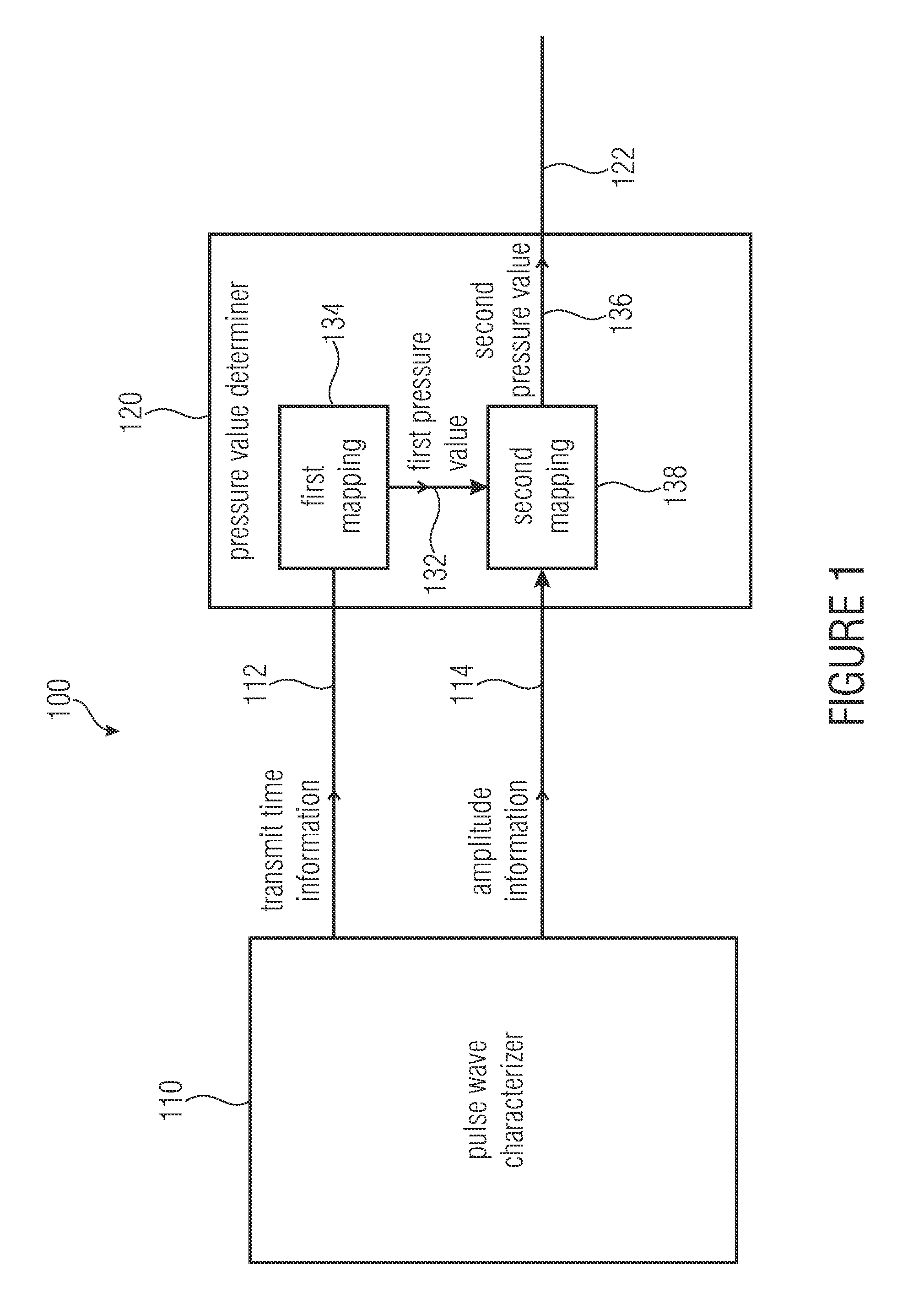
A pressure gauge for determining at least one pressure value describing a pressure of a fluid flowing in a pulsating manner in a phase of the pulsating flow, includes a pulse wave characterizer. The pulse wave characterizer is configured to obtain transmit time information of a pulse wave, and amplitude information of the pulse wave. The pressure gauge additionally includes a pressure value determiner configured to obtain a first pressure value describing a pressure of the fluid in a first phase, on the basis of the transmit time information and while using a mapping. The pressure value determiner is further configured to obtain a second pressure value describing a pressure of the fluid in a second phase, on the basis of the first pressure value and the amplitude information while using a mapping.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
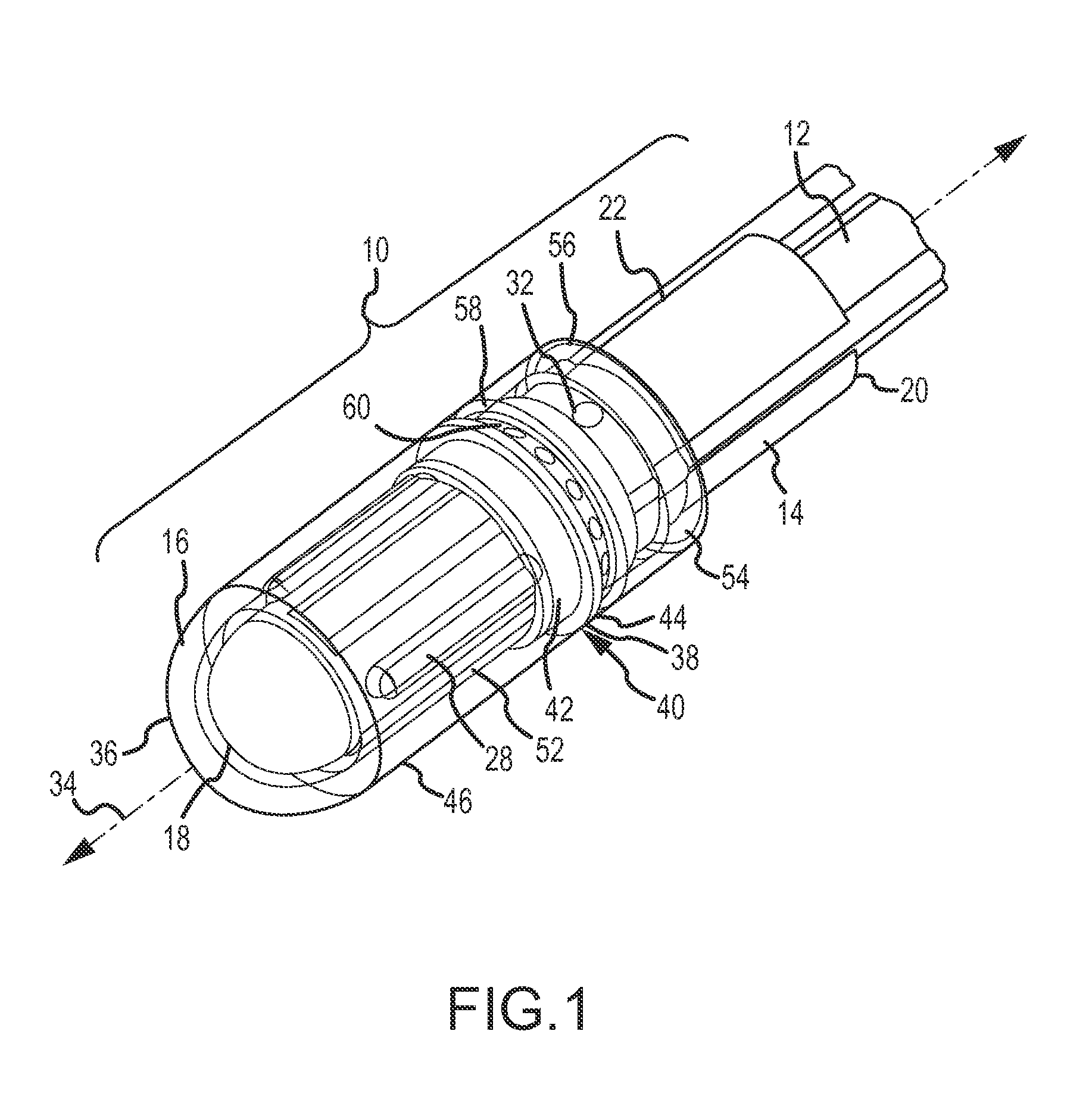
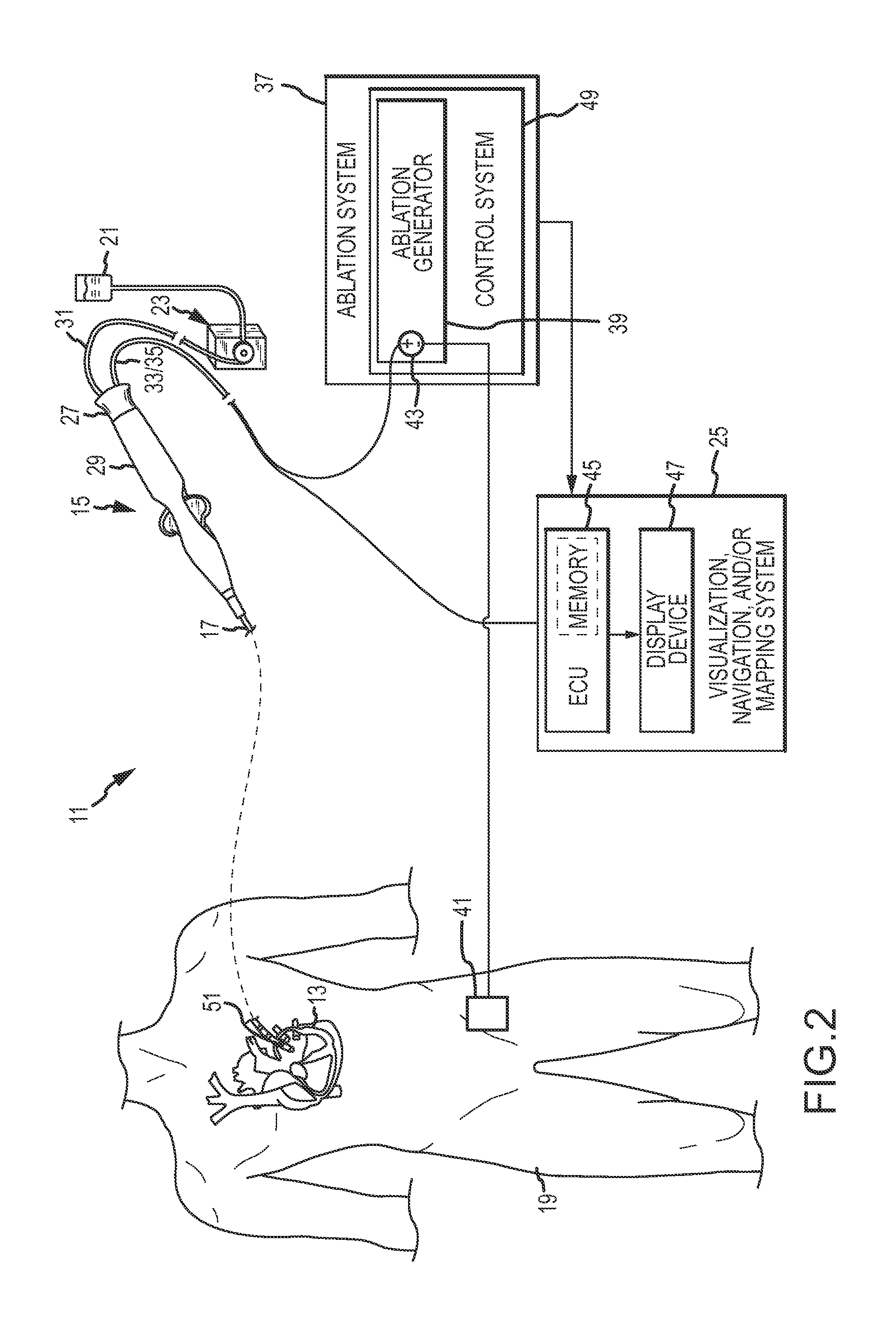
Ablation electrode assemblies and methods for using same
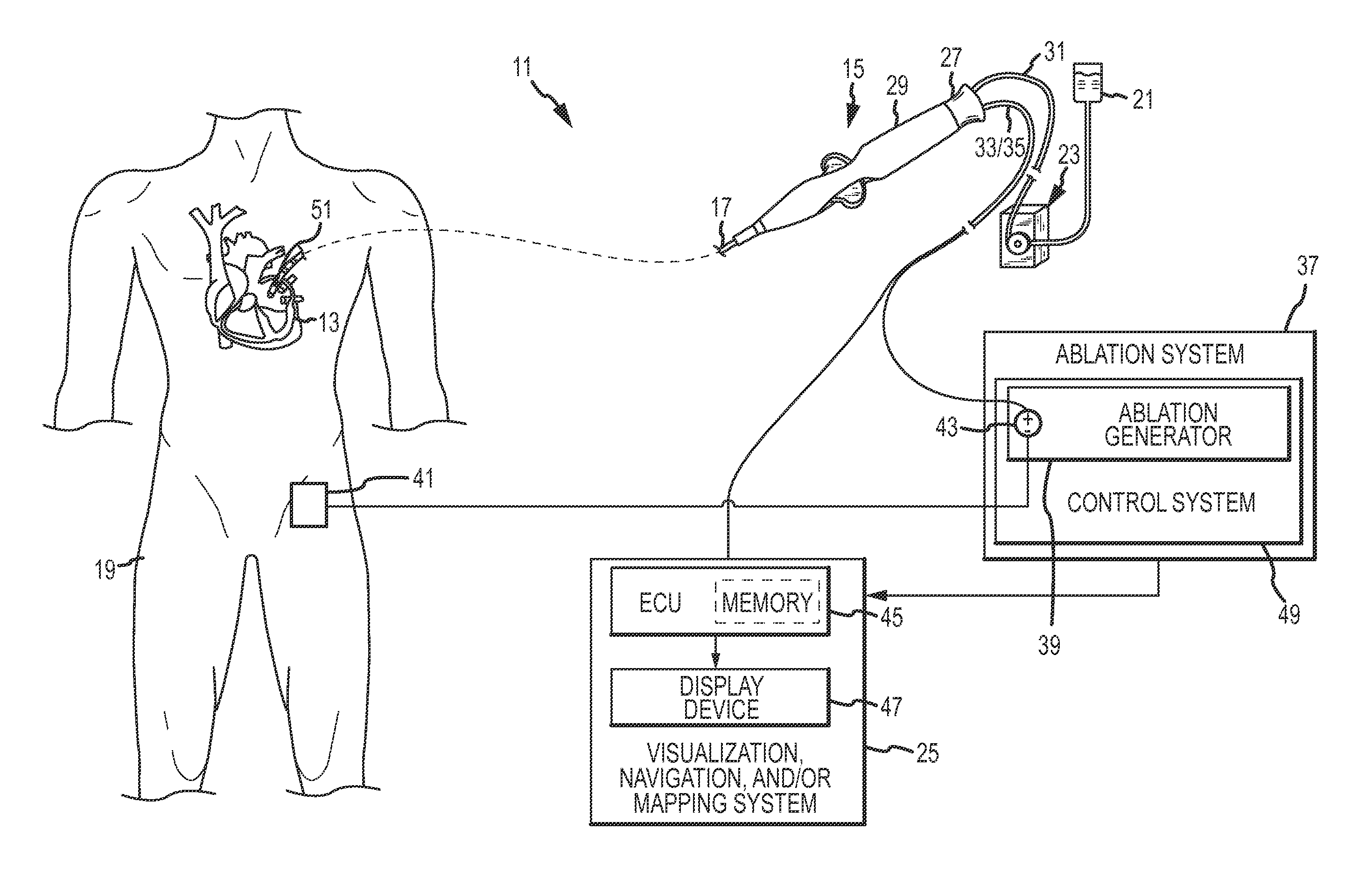
ActiveUS20120165809A1Mitigate effect of orientationImprove abilitiesSurgical instruments for heatingTemperature sensorsCardiac AblationPulsatile flow
Ablation electrode assemblies include an inner core member and an outer shell surrounding the inner core member. The inner core member and the outer shell define a space or separation region therebetween. The inner core member is constructed from a thermally insulative material having a reduced thermal conductivity. In an embodiment, the space is a sealed or evacuated region. In other embodiments, irrigation fluid flows within the space. The ablation electrode assembly further includes at least one thermal sensor in some embodiments. Methods for providing irrigation fluid during cardiac ablation of targeted tissue are disclosed that include calculating the energy delivered to irrigation fluid as it flows within the ablation electrode assembly through temperature measurement of the irrigation fluid. Pulsatile flow of irrigation fluid can be utilized in some embodiments of the disclosure.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Thrombectomy and tissue removal method
InactiveUS6926726B2Increase speedReduce local pressureCannulasSurgical instrument detailsThrombusHigh pressure
A method for removing thrombus or other material from a natural or synthetic body vessel or cavity without the need for direct surgical access. The method includes providing a device supplying high pressure fluid to at least one distal orifice, causing high pressure fluid to emanate from the orifice creating at least one fluid jet, and using the fluid jet to break up material in the vessel. The method further includes directing at least one fluid jet at the opening of an exhaust lumen or target incorporated into the device and using the jet to provide a localized negative pressure which entrains material into the jet for break-up. The method optionally includes using the jet to provide stagnation pressure which drives material along the exhaust lumen. The method optionally includes metering the exhaust to match the fluid input or to be greater or less than the input. A positive displacement pump operating at steady or pulsatile flow provides the high pressure saline to the distal end of the catheter.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
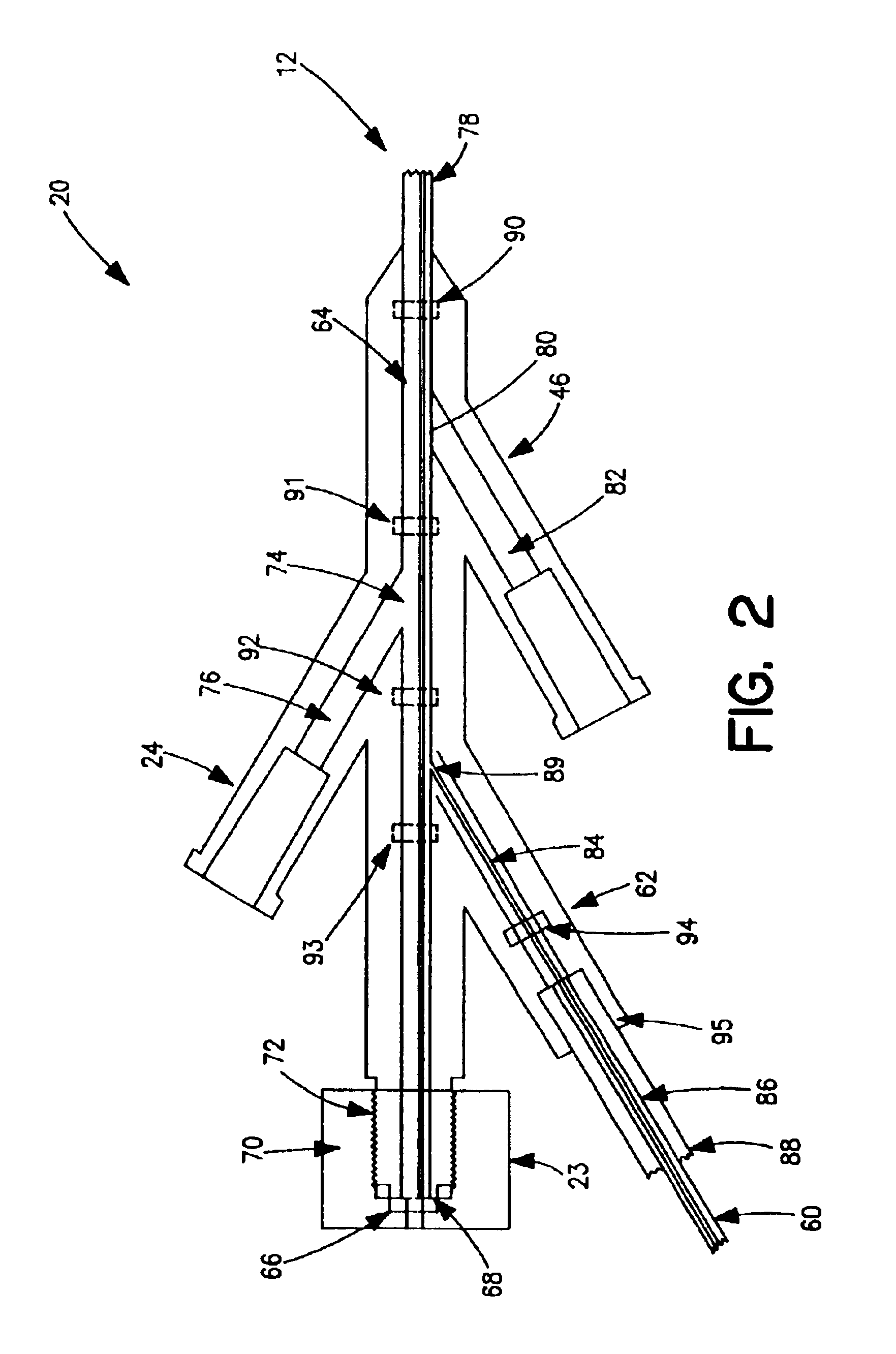
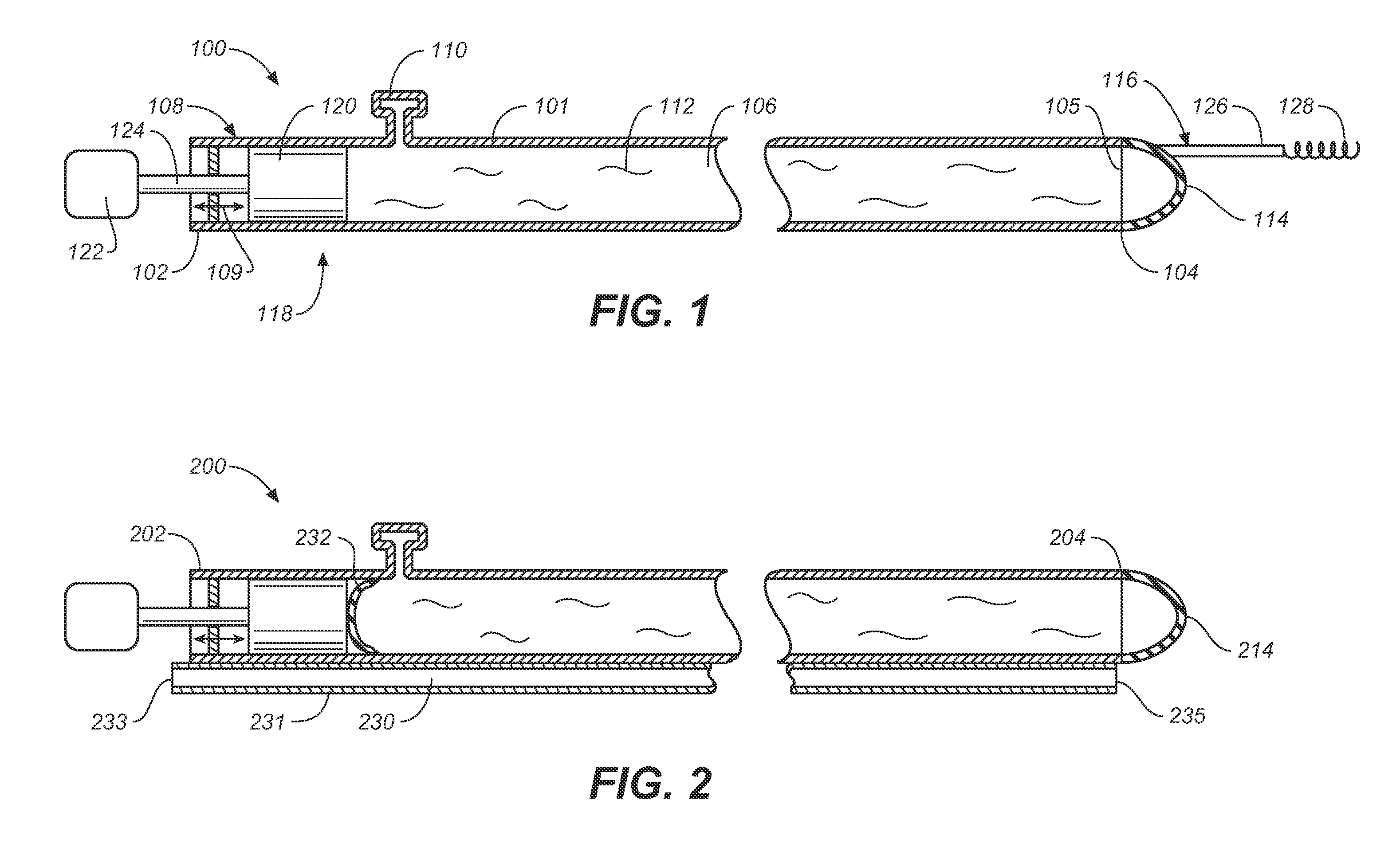
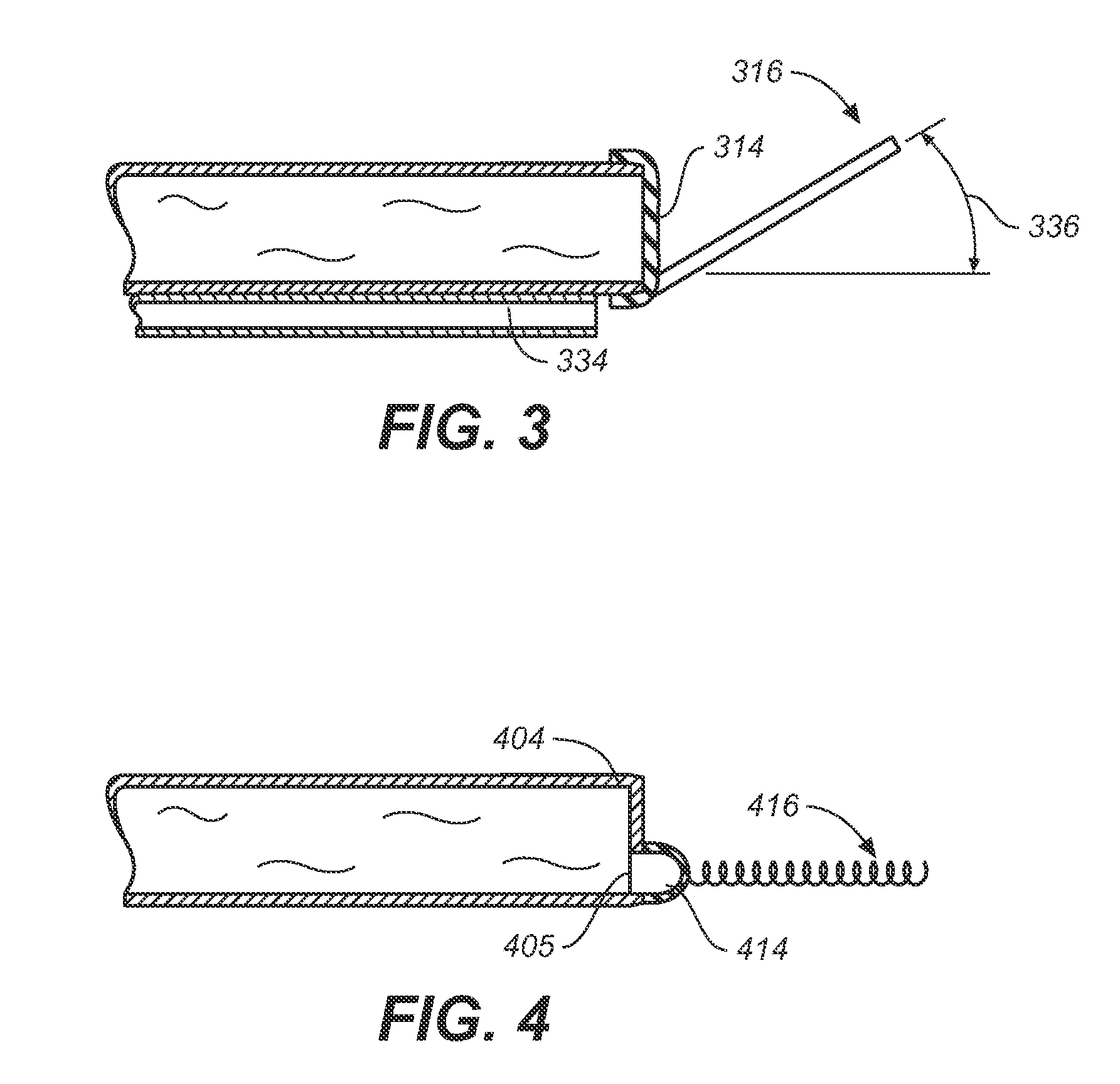
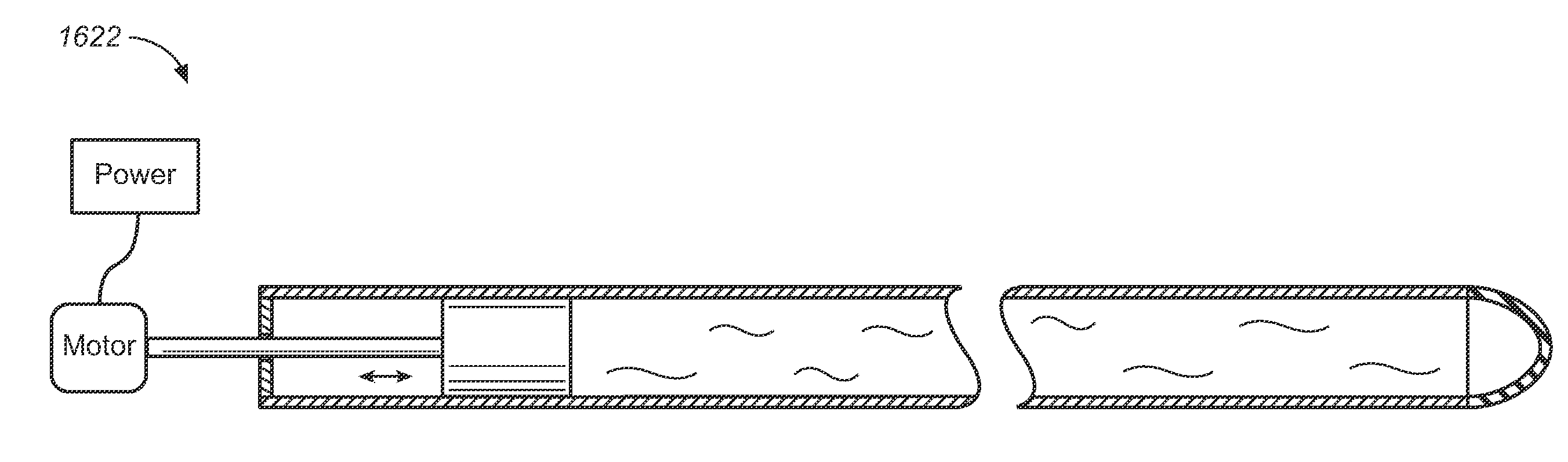
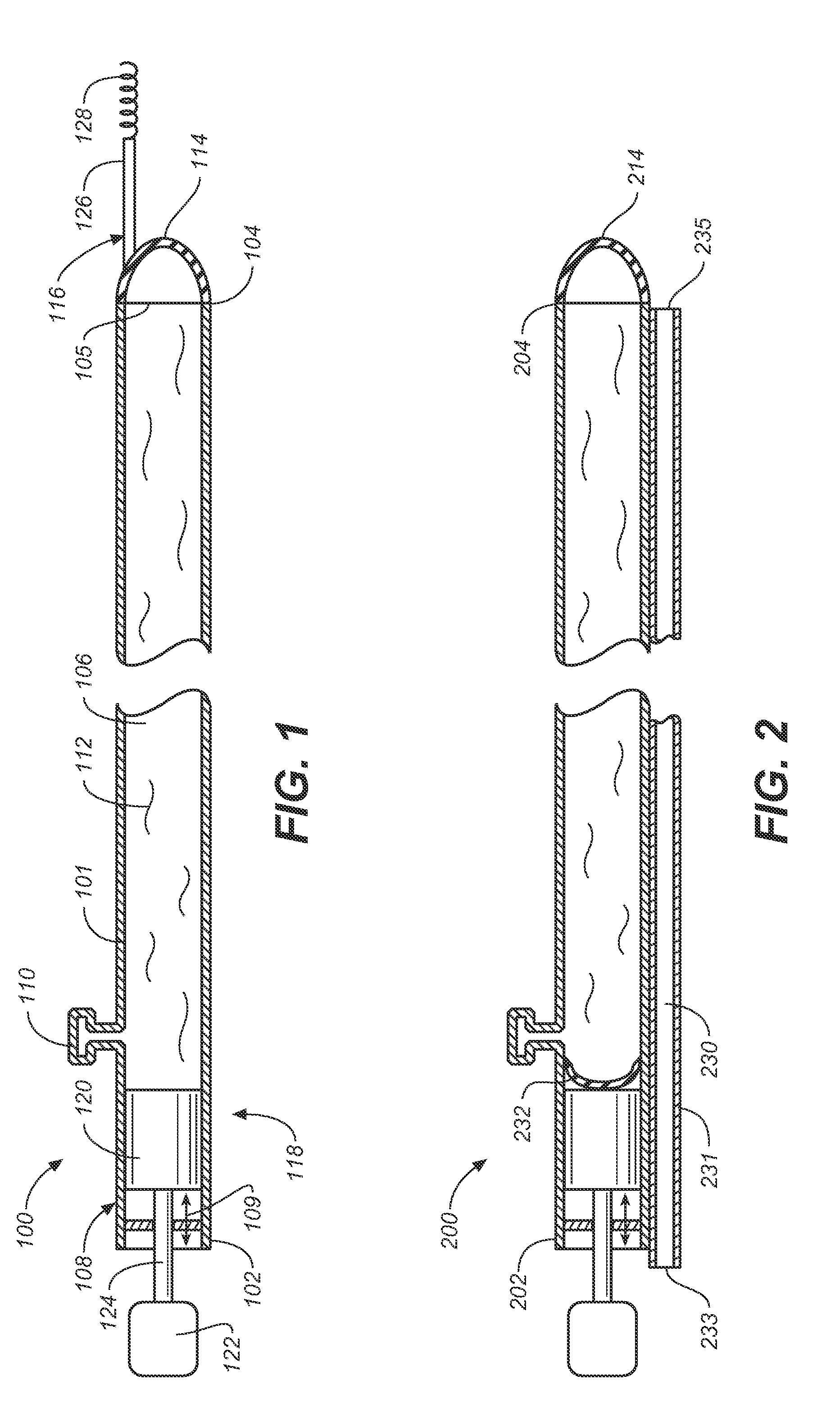
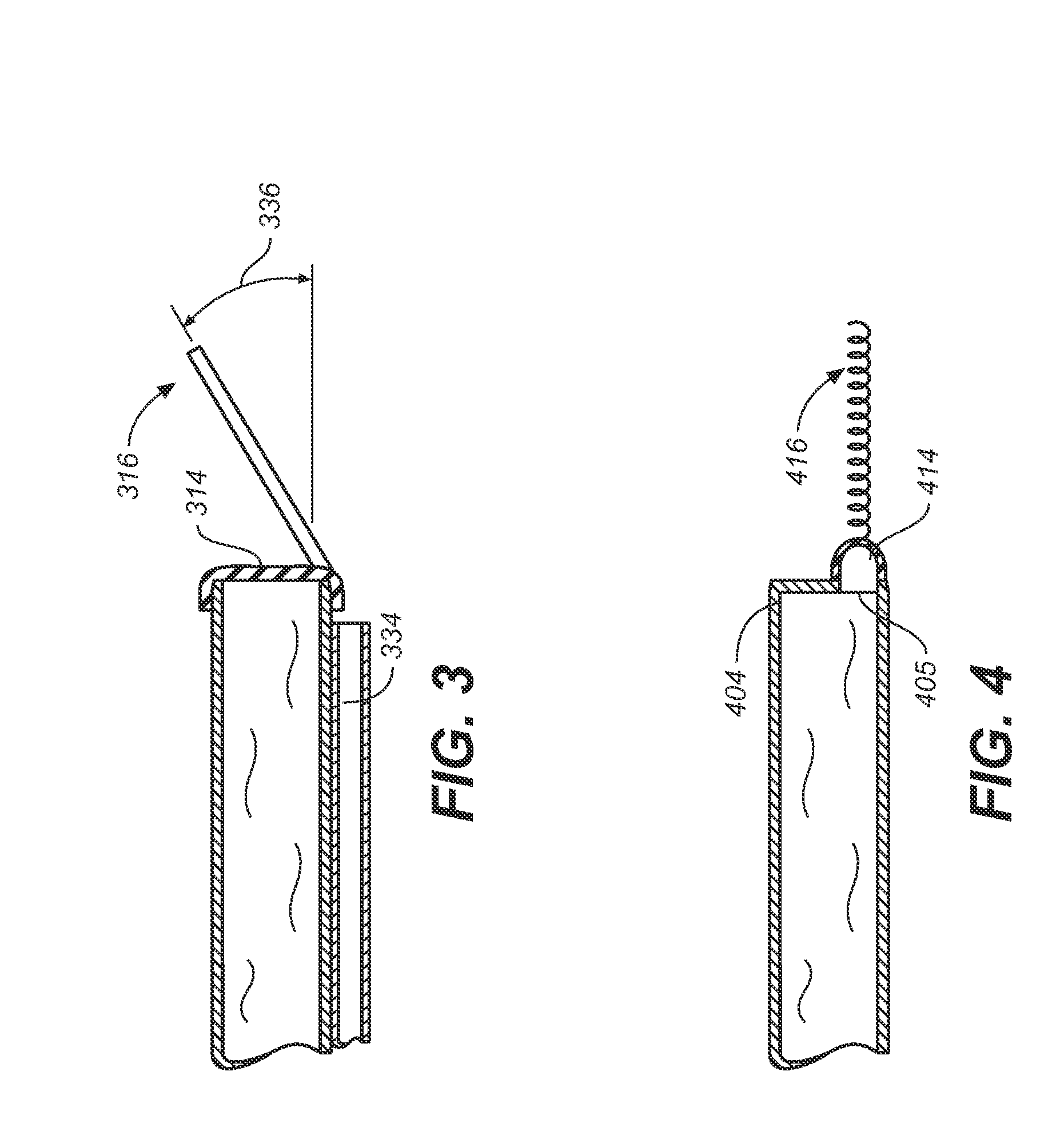
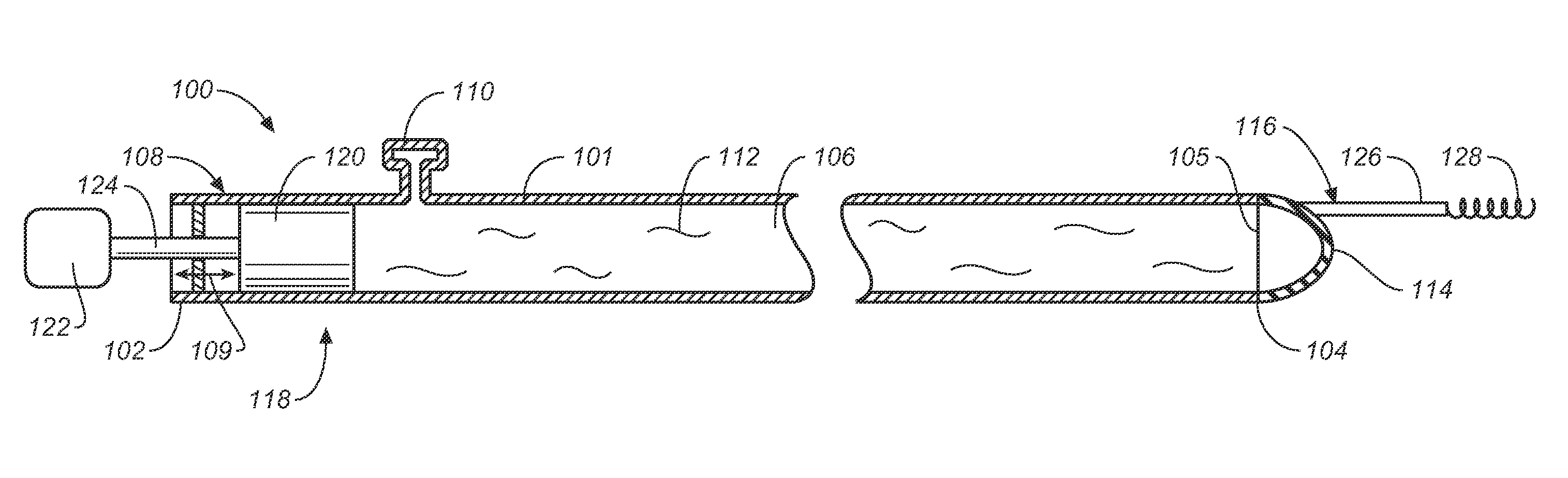
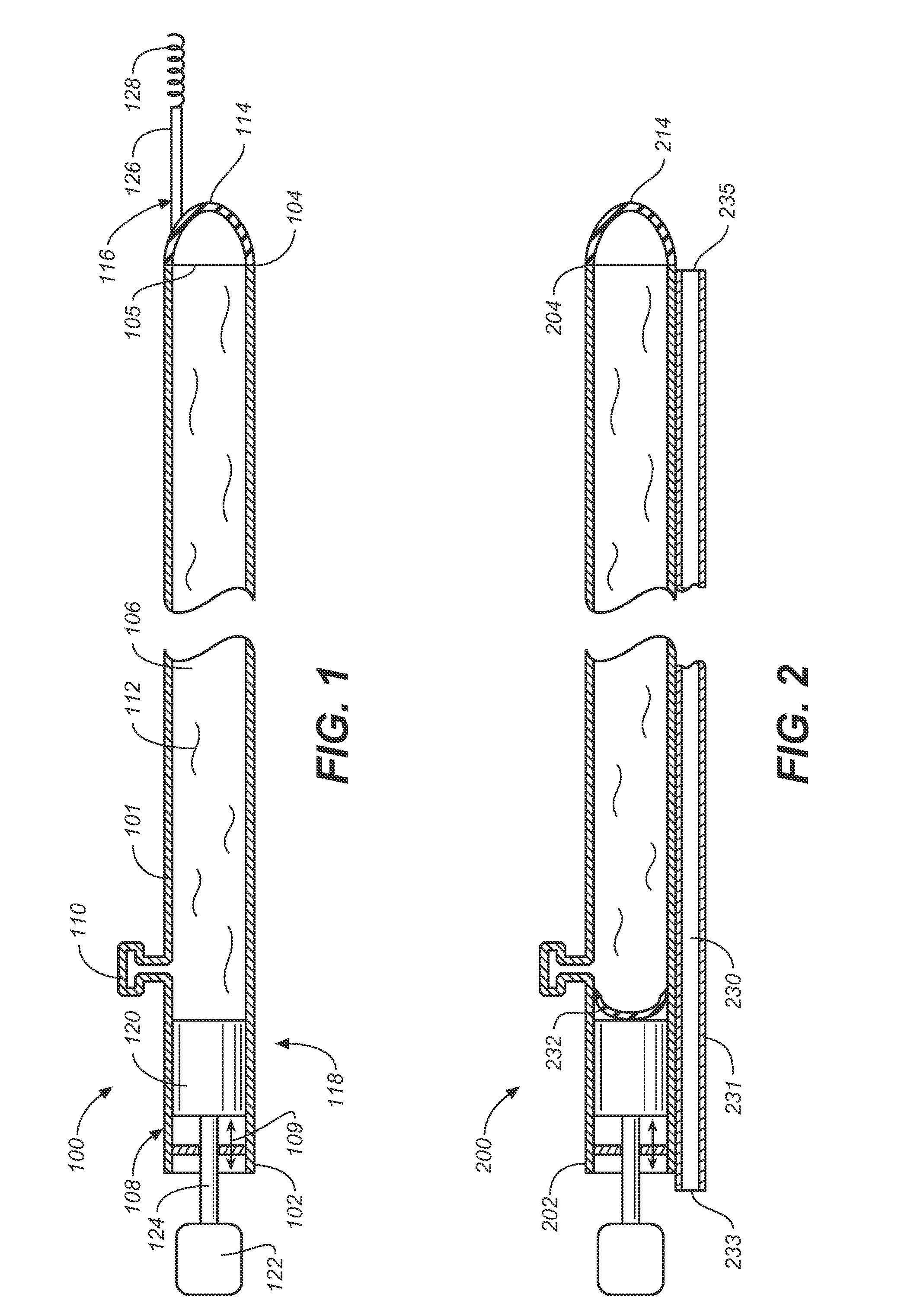
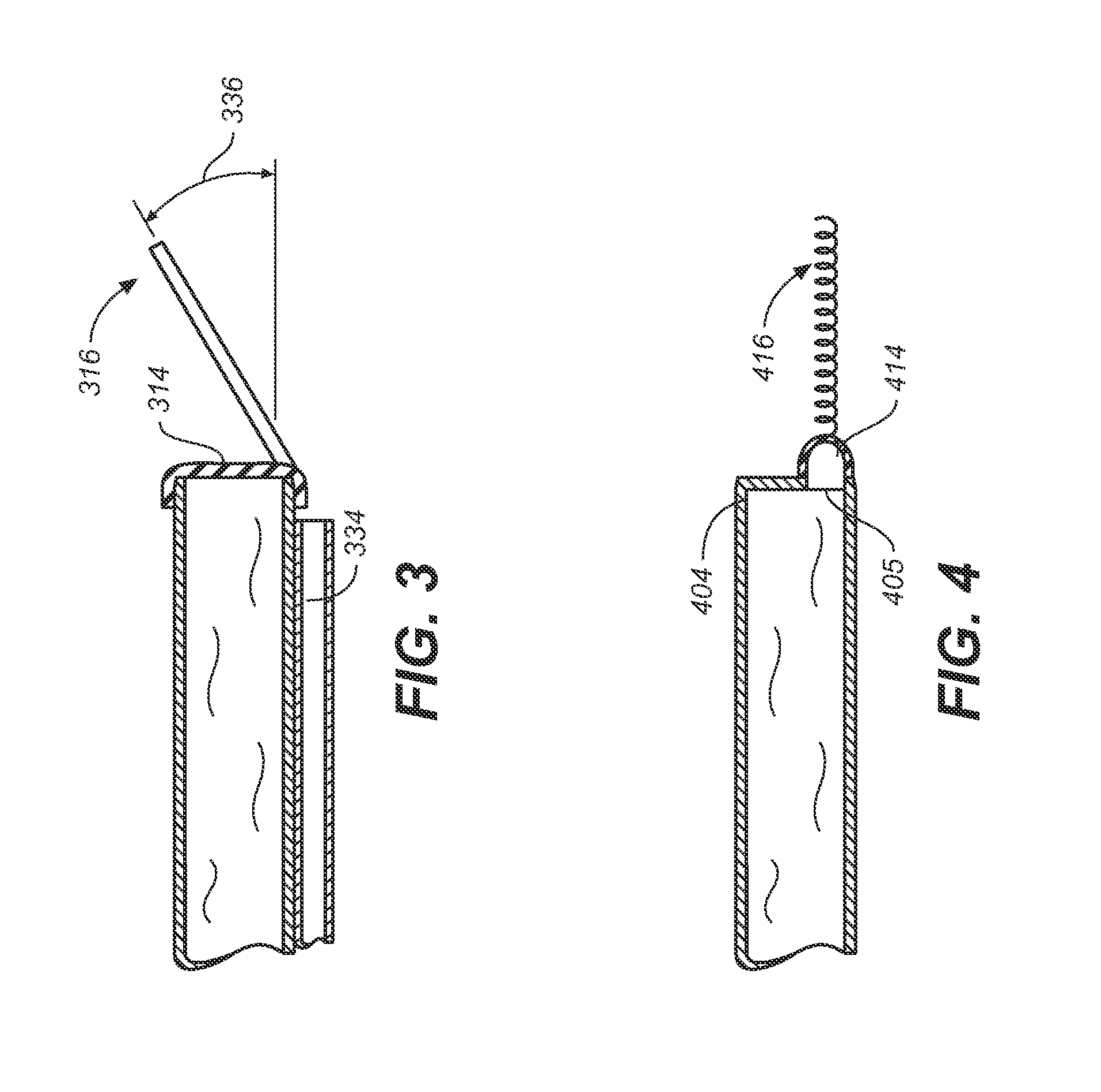
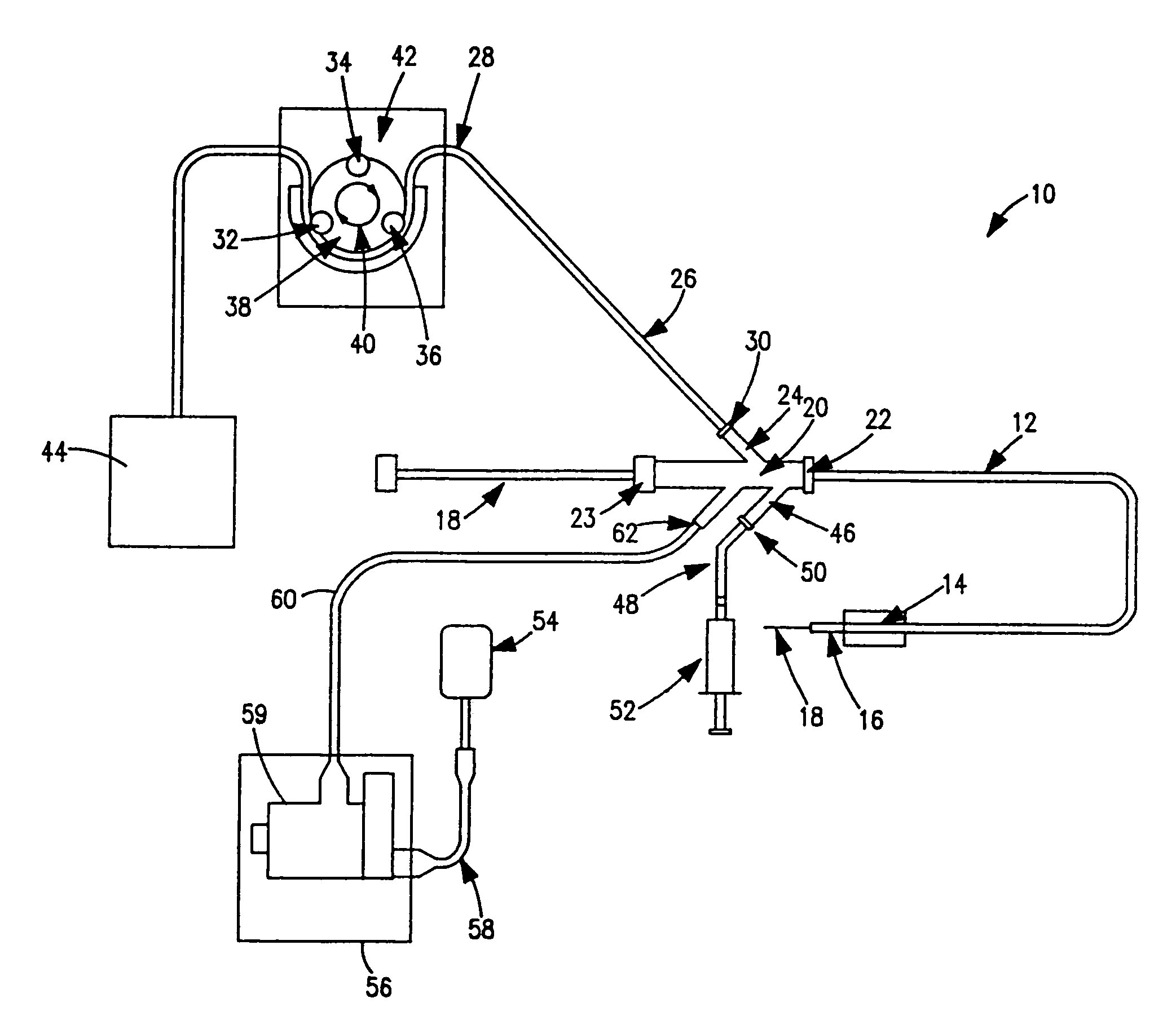
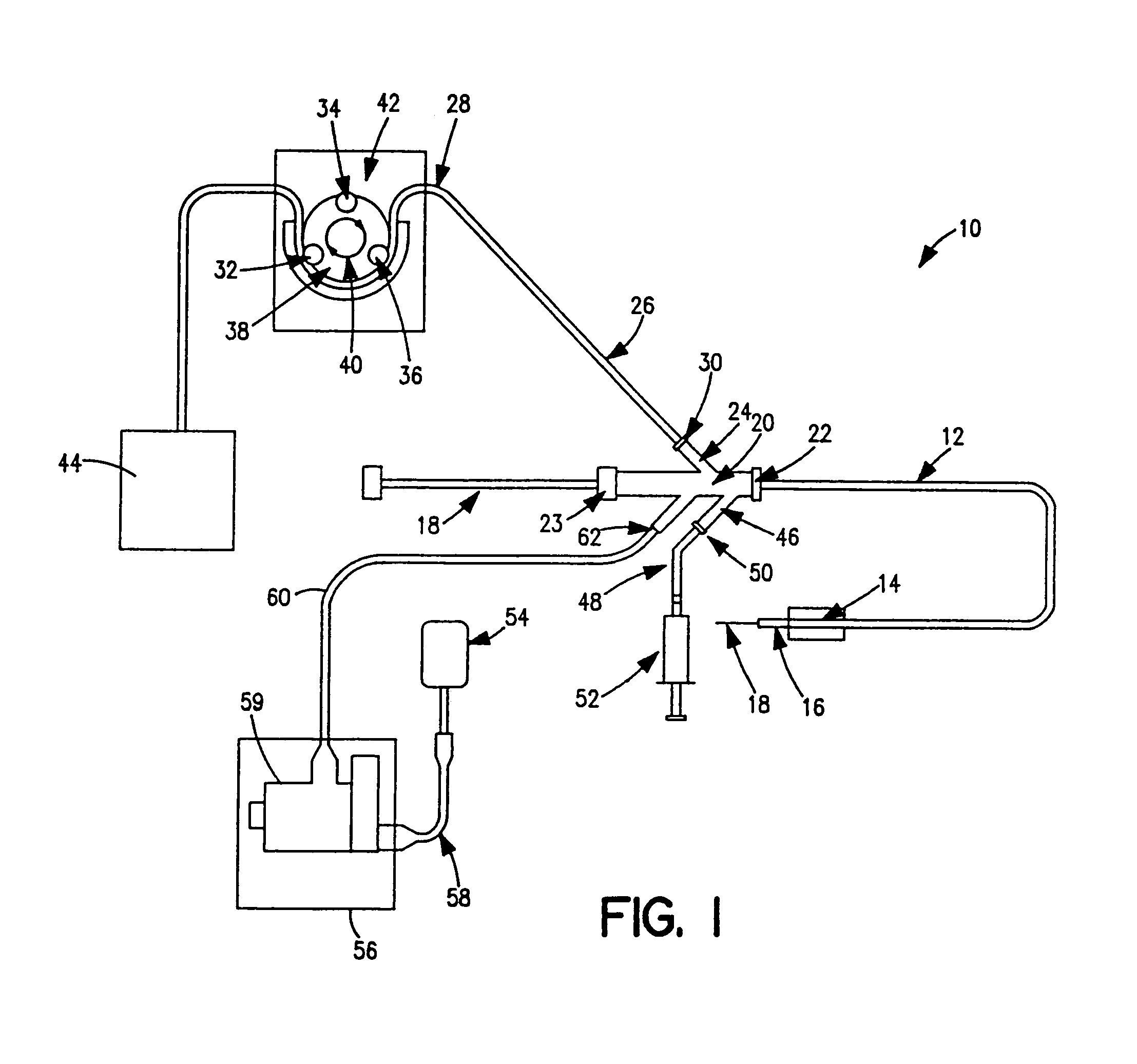
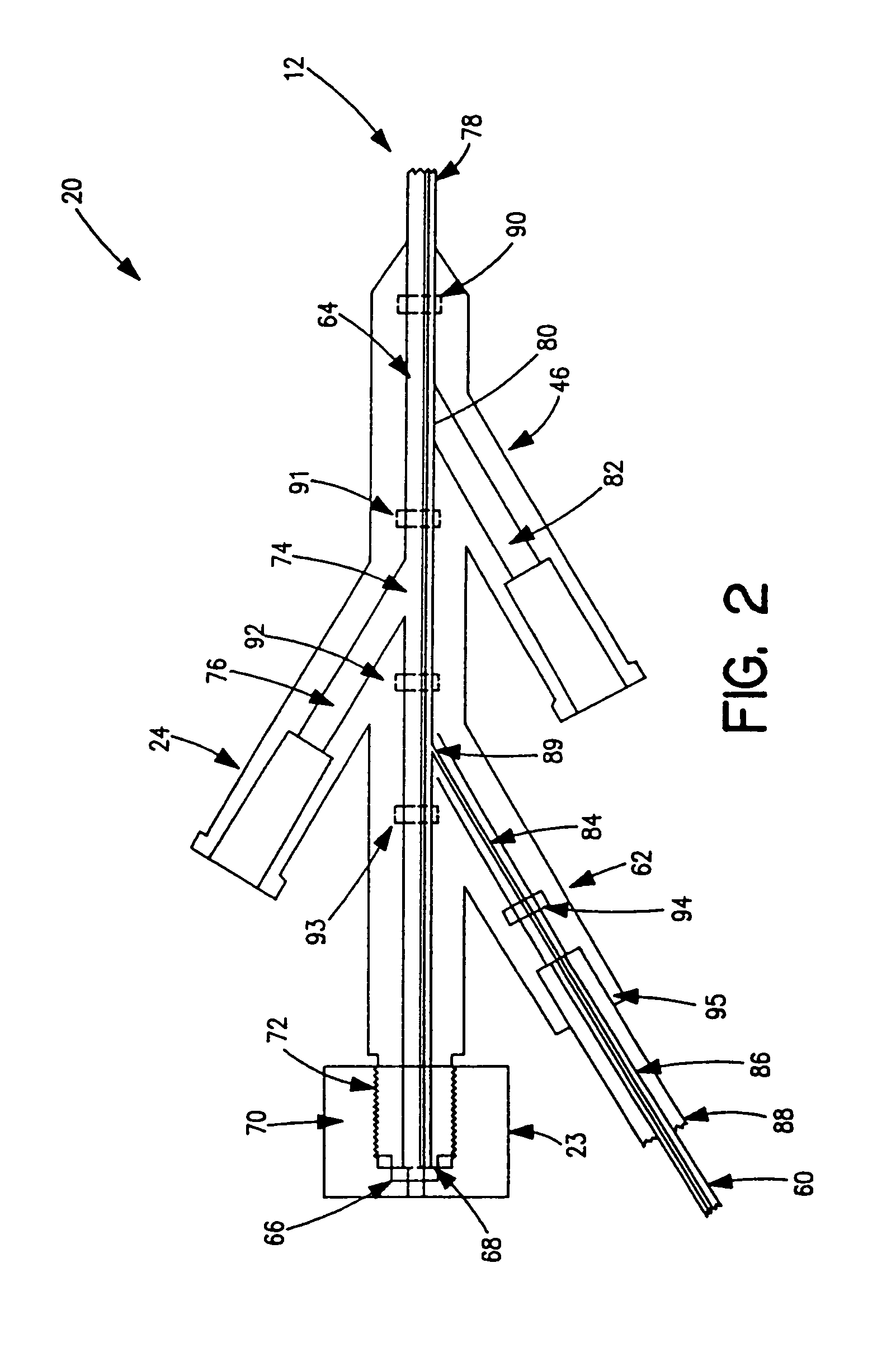
Miniature, pulsatile implantable ventricular assist devices and methods of controlling ventricular assist devices
ActiveUS6969345B2Small sizeSmall and efficient and atraumatic and fully implantableControl devicesBlood pumpsSystoleEngineering
A pumping system for assisting either or both ventricles of the heart. In one embodiment, separate devices are provided for each ventricle. In another embodiment, one device provides both right and left pumping. The pumping system is small, efficient, atraumatic, and fully implantable. In addition, the pumping system can provide pulsatile flow during systole. The ventricular assist device includes an actuator plate between a pair of serially connected pumping chambers that operate in a two-stroke mode, specifically a power stroke and a transfer stroke. The ventricular assist device also includes an electromagnetic drive system that provides adjustment to the pump pressure according to the current through an electromagnet. For the pumping system, springs provide a “spring force” on the actuator plate that is towards the high-pressure pump chamber. The bias force allows the springs to store and deliver energy from the electromagnetic drive system to provide better utilization of the pump components, and to reduce the pump size and consumption of electricity.
Owner:WORLD HEART
Method for controlling the position of a permanent magnetically supported rotating component
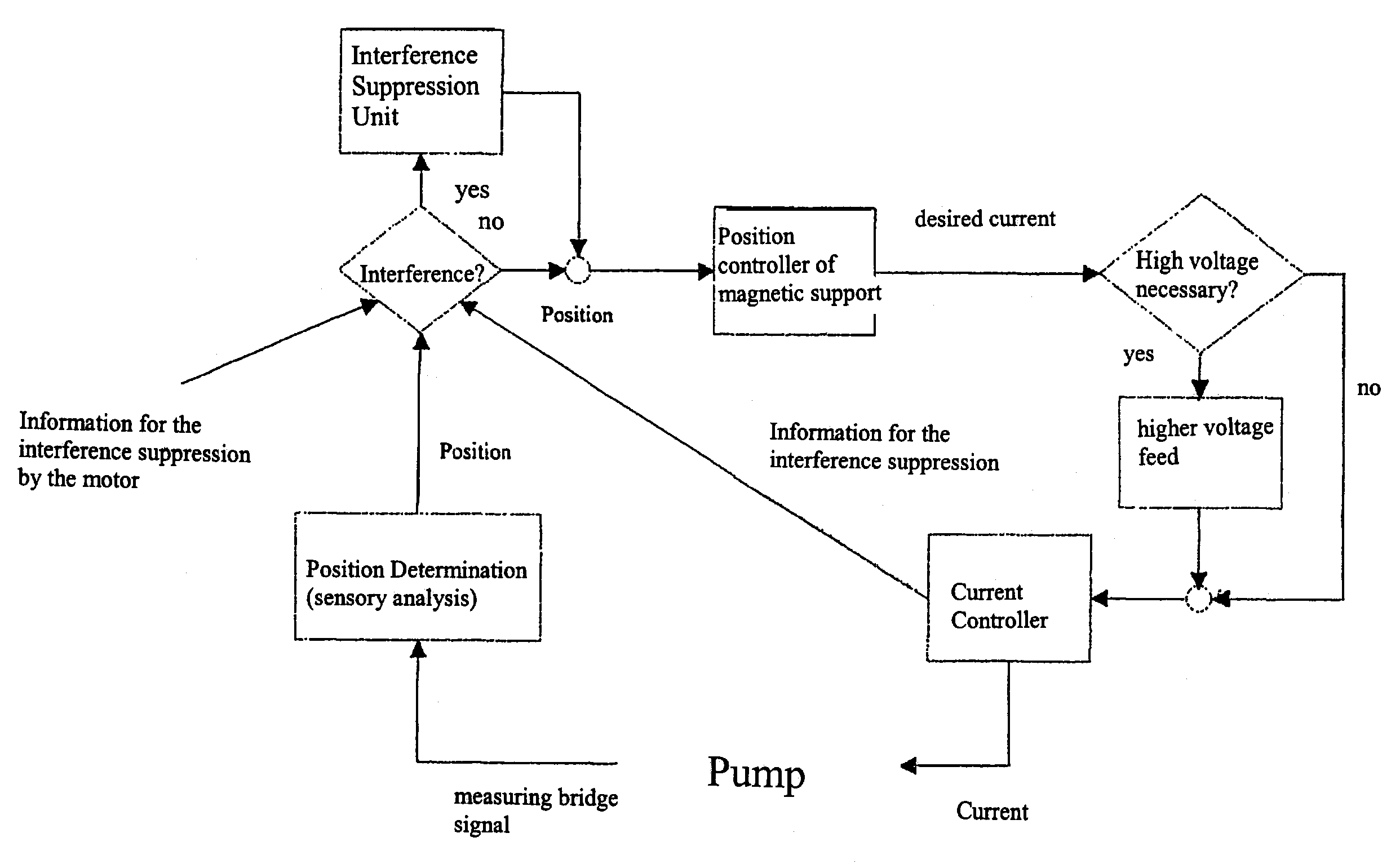
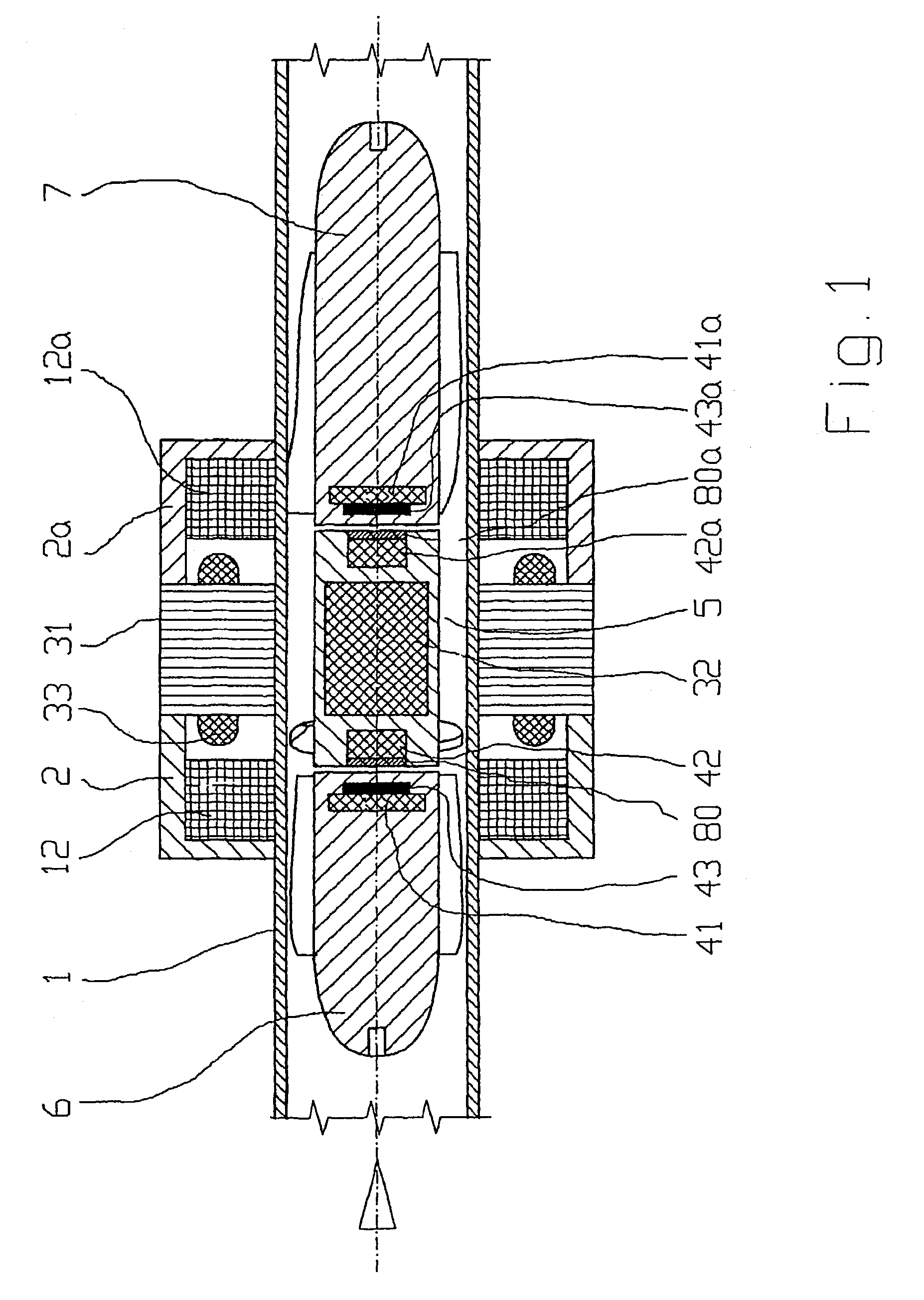
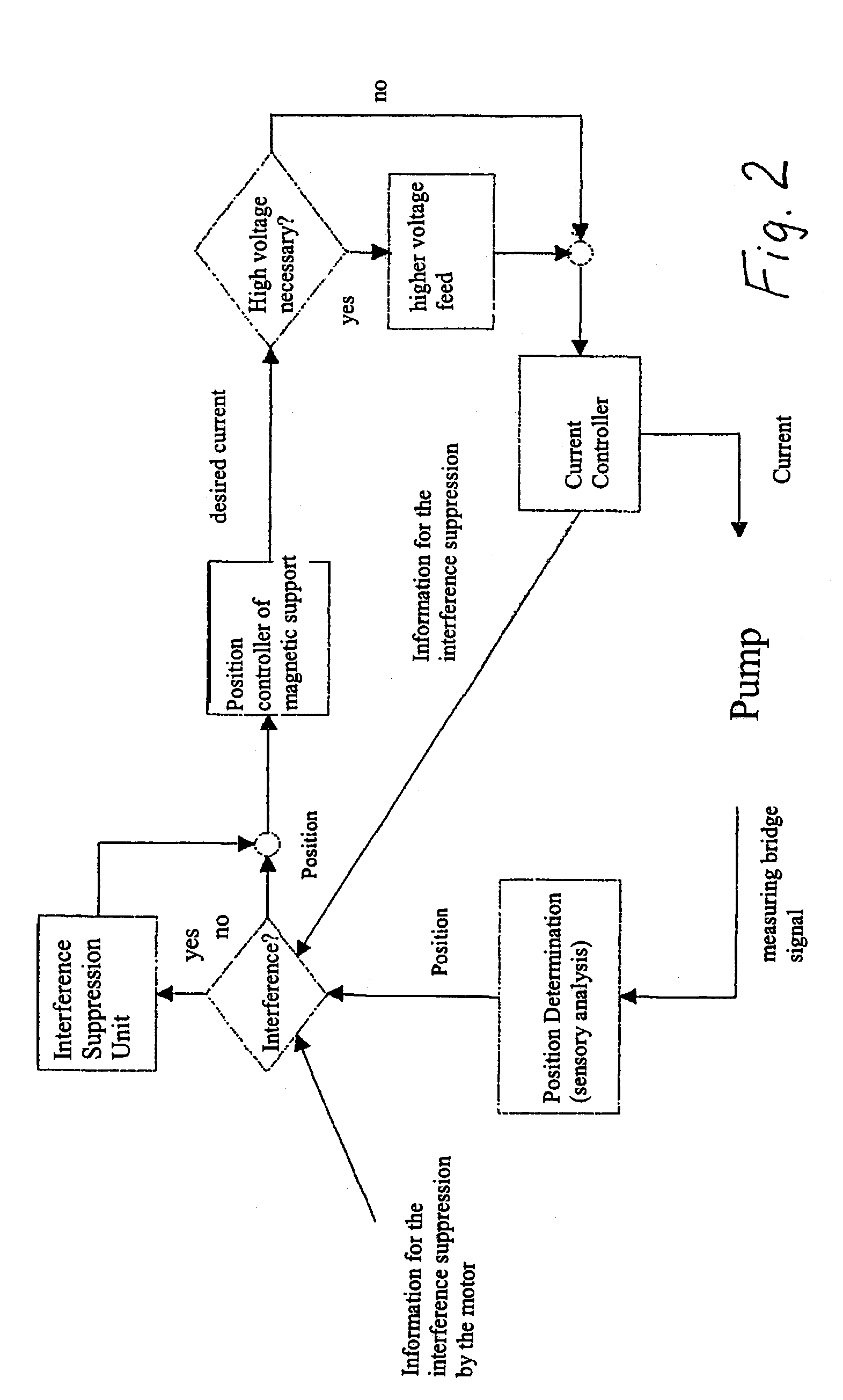
InactiveUS7229474B2Reduce dissipationProduced heat energyPump componentsHeart stimulatorsPulsatile flowHigh voltage
Since disruptive forces can be continuously exerted upon a rotor during a pulsatile flow through a pump with a magnetically mounted rotor (permanent magnets and addition control current coils), it is necessary to adjust position i.e. modify axial rotor position very quickly. The control current should only result in small amounts of losses. According to the invention, the current is pulse-width modulated by the control current coils by means of a set value predetermined by a controller which is arranged downstream from a position sensing system. If the set value is high, it is switched to a higher voltage level and the real value of the position sensing system is stored for a defined period of time, respectively beginning with the switching flank of the control current, and the position sensing system is disconnected during said period of time.
Owner:BERLIN HEART GMBH
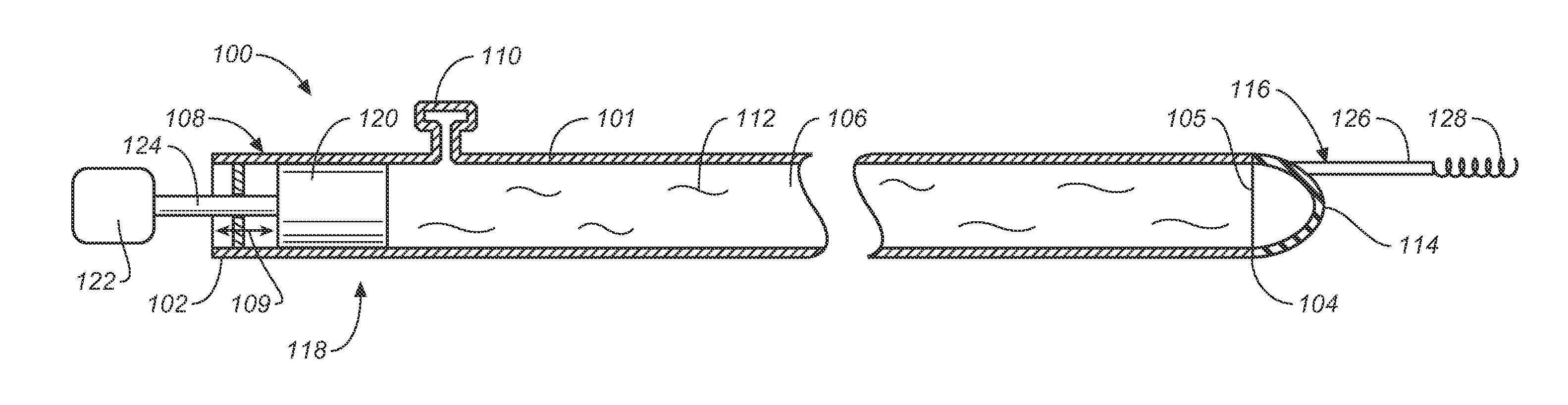
Hydrodynamic Thrombectomy Catheter
A catheter apparatus for removing an obstruction within a body lumen includes an elongate tubular shaft defining a lumen and a flexible membrane that fluidly seals the distal end of the tubular shaft. At least one cutting element or tool is attached to and distally extends from the flexible membrane. An actuating mechanism is operatively connected to a proximal end of the tubular shaft. The actuating mechanism displaces a fluid disposed within the lumen of the tubular shaft in such a manner that the fluid oscillates the flexible membrane and the cutting element attached thereto. Accordingly, the catheter apparatus uses pulsatile fluid flow through the tubular shaft to transmit energy from the driving mechanical at the proximal end of the catheter apparatus to the flexible membrane at the distal end of the catheter apparatus. The transmitted energy causes the cutting element to oscillate and break up a target blood clot.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Hydrodynamic Thrombectomy Catheter
A catheter apparatus for removing an obstruction within a body lumen includes an elongate tubular shaft defining a lumen and a flexible membrane that fluidly seals the distal end of the tubular shaft. At least one cutter member is attached to and distally extends from the flexible membrane. An actuating mechanism is operatively connected to a proximal end of the tubular shaft. The actuating mechanism displaces a fluid disposed within the lumen of the tubular shaft in such a manner that the fluid oscillates the flexible membrane and the cutter member attached thereto. Accordingly, the catheter apparatus uses pulsatile fluid flow through the tubular shaft to transmit energy from the driving mechanical at the proximal end of the catheter apparatus to the flexible membrane at the distal end of the catheter apparatus. The transmitted energy causes the cutting member to oscillate and break up a target blood clot.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Hydrodynamic Thrombectomy Catheter
A catheter apparatus for removing an obstruction within a body lumen includes an elongate tubular shaft defining a lumen and a flexible membrane that fluidly seals the distal end of the tubular shaft. At least one cutting element or tool is attached to and distally extends from the flexible membrane. An actuating mechanism is operatively connected to a proximal end of the tubular shaft. The actuating mechanism displaces a fluid disposed within the lumen of the tubular shaft in such a manner that the fluid oscillates the flexible membrane and the cutting element attached thereto. Accordingly, the catheter apparatus uses pulsatile fluid flow through the tubular shaft to transmit energy from the driving mechanical at the proximal end of the catheter apparatus to the flexible membrane at the distal end of the catheter apparatus. The transmitted energy causes the cutting element to oscillate and break up a target blood clot.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Thrombectomy and tissue removal method
InactiveUS6984239B1Reduce local pressureIncrease speedMedical devicesFluid jet surgical cuttersThrombusHigh pressure
A device for removing a thrombus or other tissue deposit from the cardiovascular system, natural or synthetic tubule or cavity found in the human body of a patient without the need to surgically access the location of the thrombus or other tissue deposit via a cut-down or other surgical procedure. A flexible metal or high pressure plastic tube conveys an extremely high pressure stream of sterile saline or other physiologic solution to at least one jet at the distal end of the catheter. At least one jet is directed at the opening of a large exhaust lumen or other target. The jet(s) is responsible for providing a localized negative pressure which entrains tissue into the jet from break-up of the debris. This jet(s) can also provide stagnation pressure in the exhaust lumen which drives the tissue or thrombotic debris out of the exhaust lumen. Operation of the device with tip pressure greater than 500 psi provides this device with the entrainment and exhaust characteristics which contribute to its effectiveness. The rate of exhaust of tissue debris is metered to ensure minimal local impact on the vasculature at the site of the thrombus deposit. A fluid metering means, such as a roller pump, controls the rate of exhaust such that it is in balance with the saline input or can be adjusted to be greater or less than the input. A positive displacement pump operating at steady or pulsatile flow provides the high pressure saline to the tip of the catheter.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
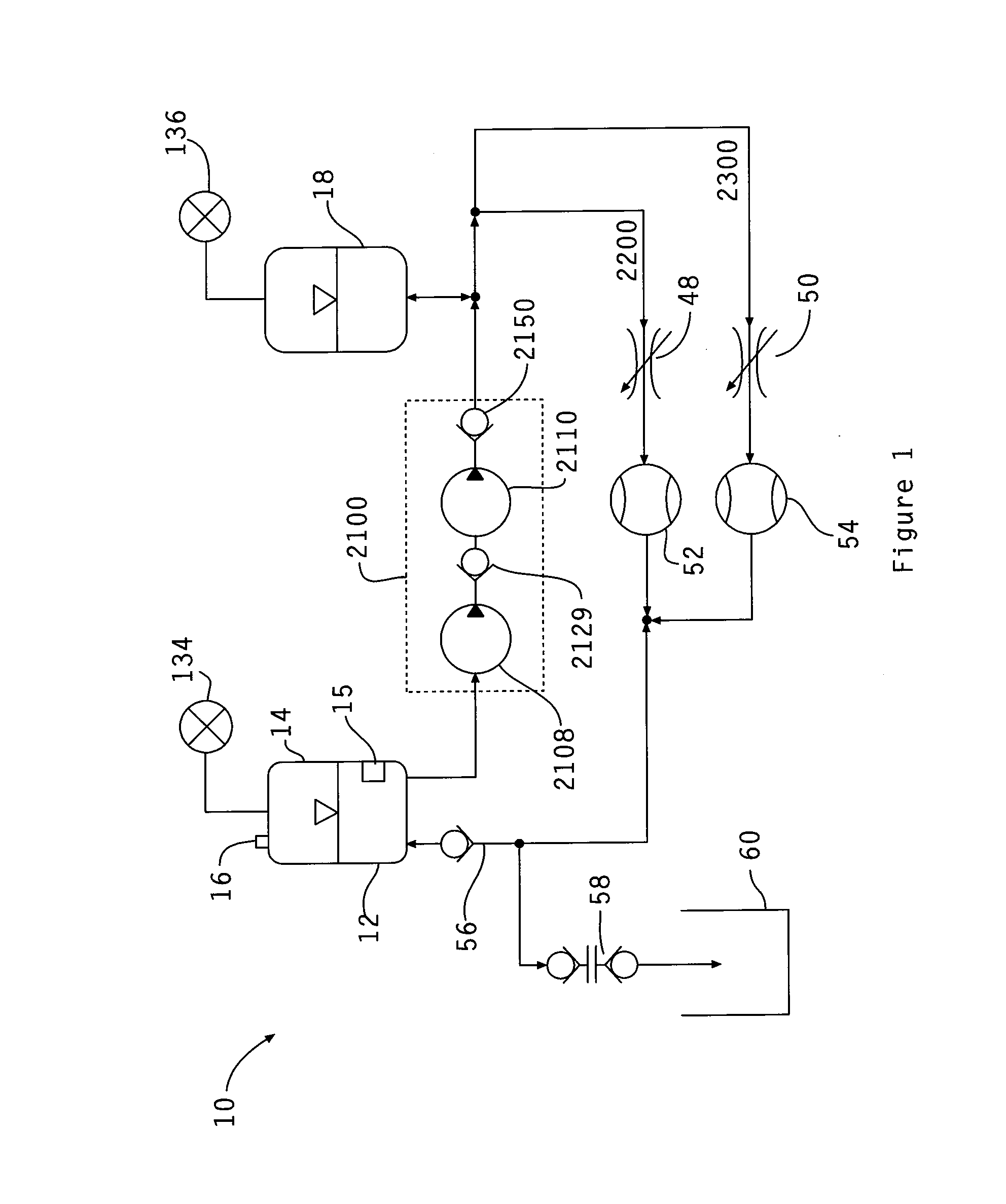
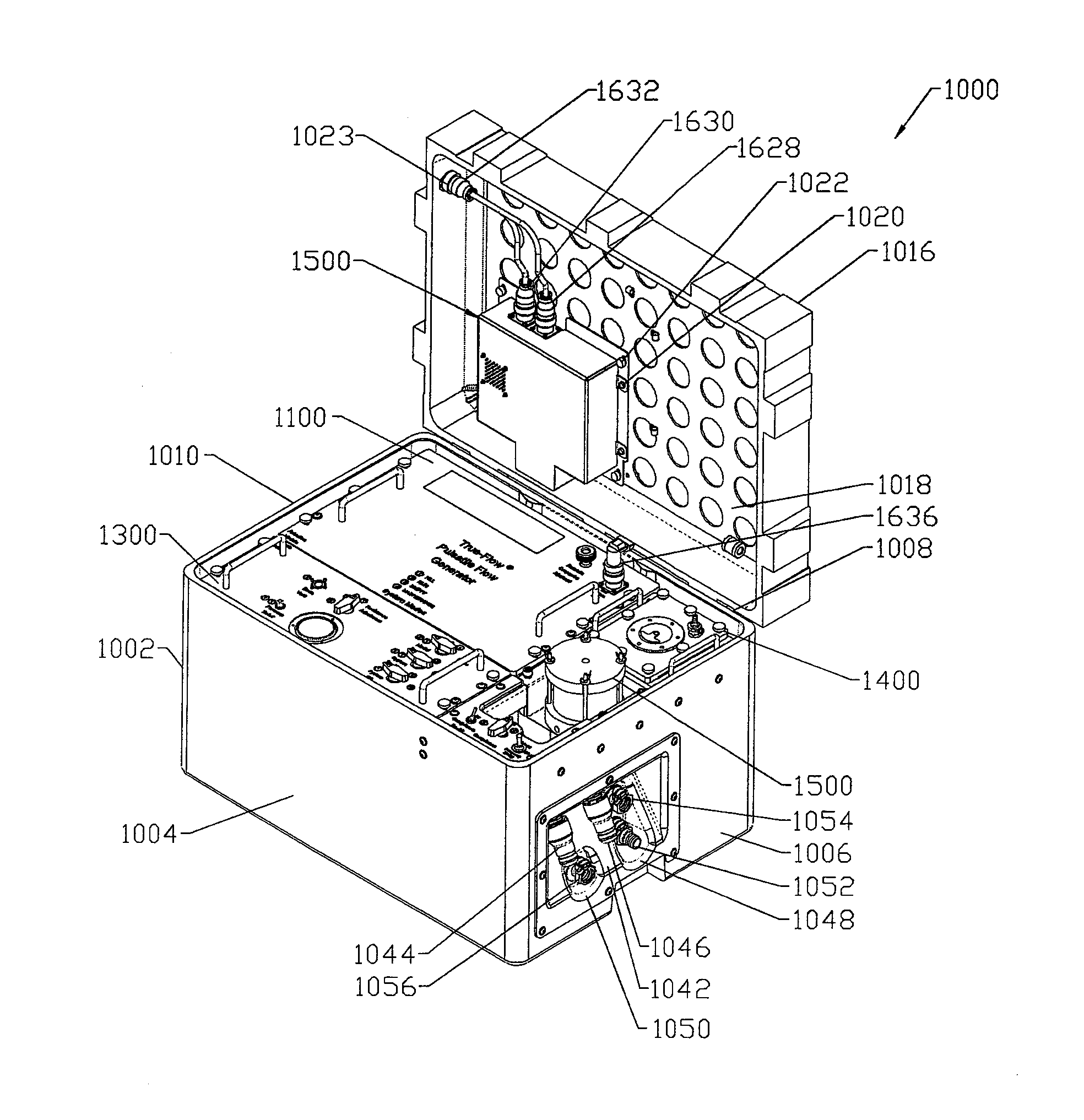
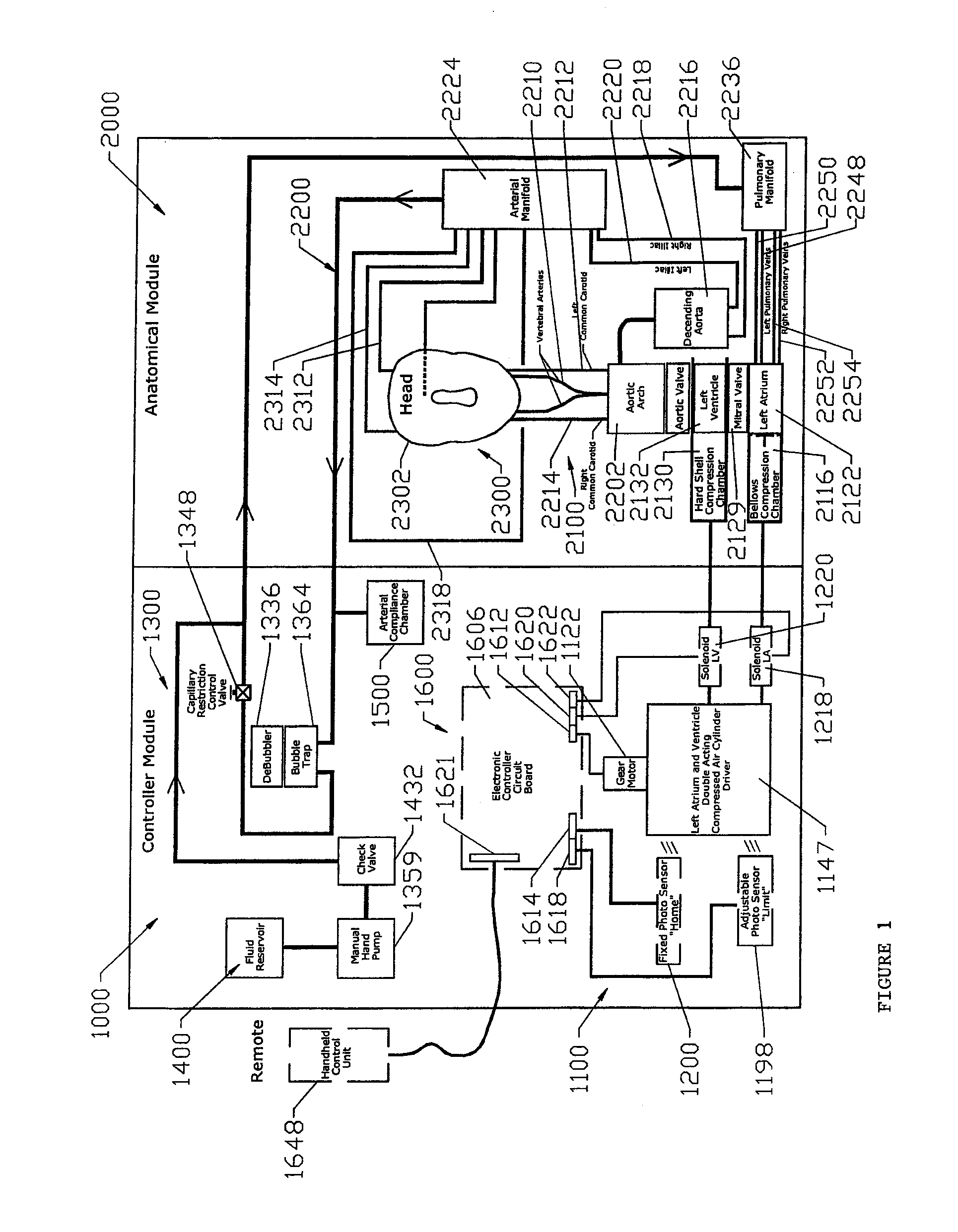
Cardiac simulation device
ActiveUS20160027345A1Accurate gradientAccurate volume fractionEducational modelsDiseaseAutomatic control
The present invention describes a device and system for simulating normal and disease state cardiovascular functioning, including an anatomically accurate left cardiac simulator for training and medical device testing. The system and device uses pneumatically pressurized chambers to generate ventricle and atrium contractions. In conjunction with the interaction of synthetic valves which simulate mitral and aortic valves, the system is designed to generate pumping action that produces accurate volume fractions and pressure gradients of pulsatile flow, duplicating that of a human heart. Through the use of a control unit and sensors, one or more parameters such as flow rates, fluidic pressure, and heart rate may be automatically controlled, using feedback loop mechanisms to adjust parameters of the hydraulic system simulate a wide variety of cardiovascular conditions including normal heart function, severely diseased or injured heart conditions, and compressed vasculature, such as hardening of the arteries.
Owner:MENTICE
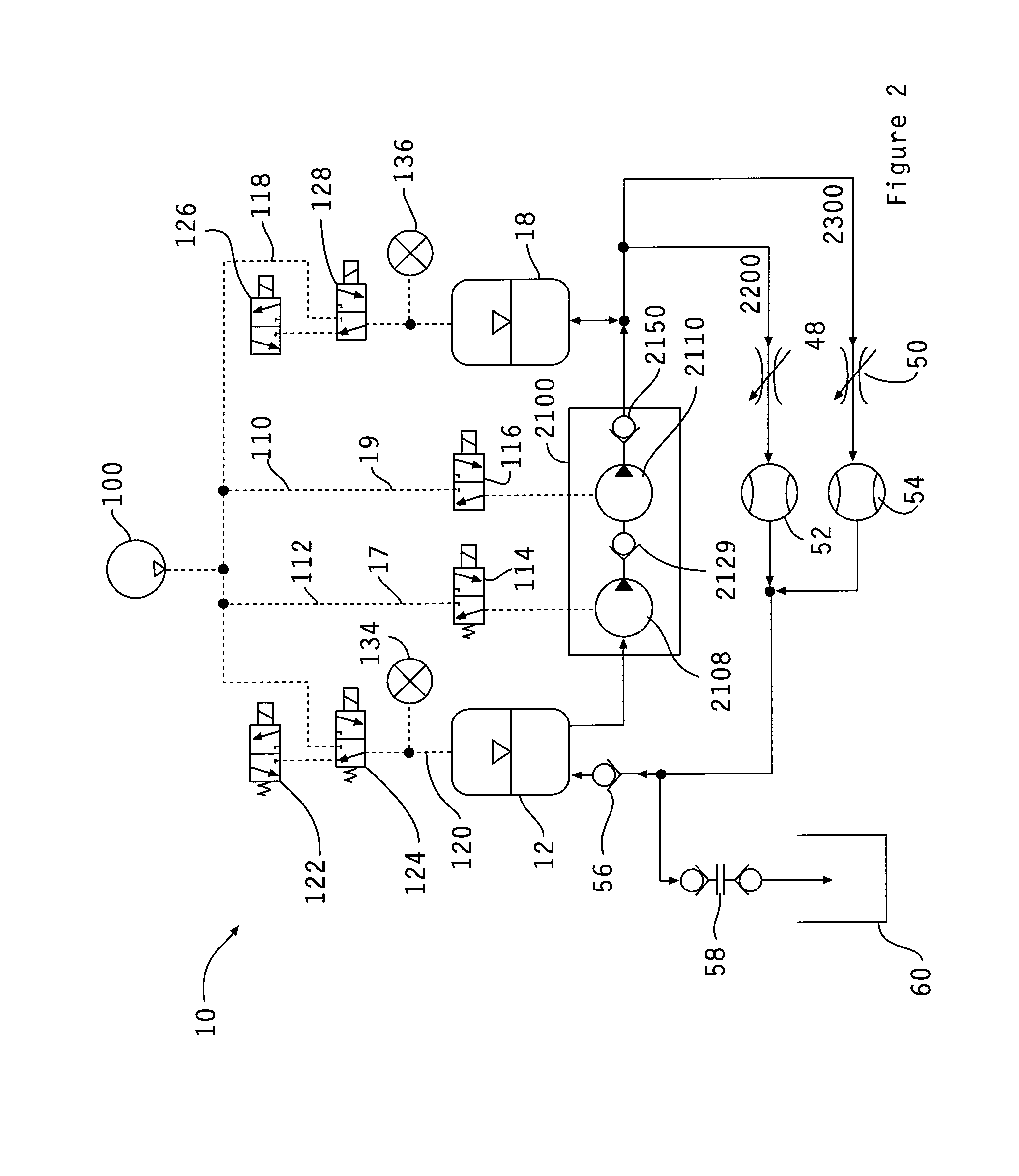
Cardiac Simulation Device
ActiveUS20130196301A1Reduced collateral damageEliminate riskEducational modelsDiseaseElectronic controller
The present invention describes a device and system for simulating normal and disease state cardiac functioning, including an anatomically accurate left cardiac simulator for training and medical device testing. The system and device uses pneumatically pressurized chambers to generate ventricle and atrium contractions. In conjunction with the interaction of synthetic mitral and aortic valves, the system is designed to generate pumping action that produces accurate volume fractions and pressure gradients of pulsatile flow, duplicating that of a human heart. Through the use of a remote handheld electronic controller and manual adjustments from a main control panel, the air pressure level, fluidic pressure, and heart rate is controlled to induce contractions that simulate a wide variety of heart conditions ranging from normal heart function to severely diseased or injured heart conditions.
Owner:MENTICE
Method and apparatus for treating renal disease with hemodialysis utilizing pulsatile pump
InactiveUS20110098624A1Improve transportation efficiencyDead region can be reducedSemi-permeable membranesControl devicesDiseaseNephrosis
A method of removing toxins from blood from a patient in need of such toxin removal includes: providing a countercurrent dialysis filter (20) having a blood compartment and a dialysate compartment separated from the blood compartment by a semi-permeable membrane; conveying blood from the patient through the blood compartment of a countercurrent filter (20) an back to the patient; and drawing dialysate from a reservoir (32) through the dialysate compartment of the countercurrent filter (20). At least one of the blood or dialysate experiences pulsatile flow. The steps are carried out such that blood toxins are drawn from the blood compartment through the semi-permeable membrane into the dialysate compartment.
Owner:EAST CAROLINA UNIVERISTY
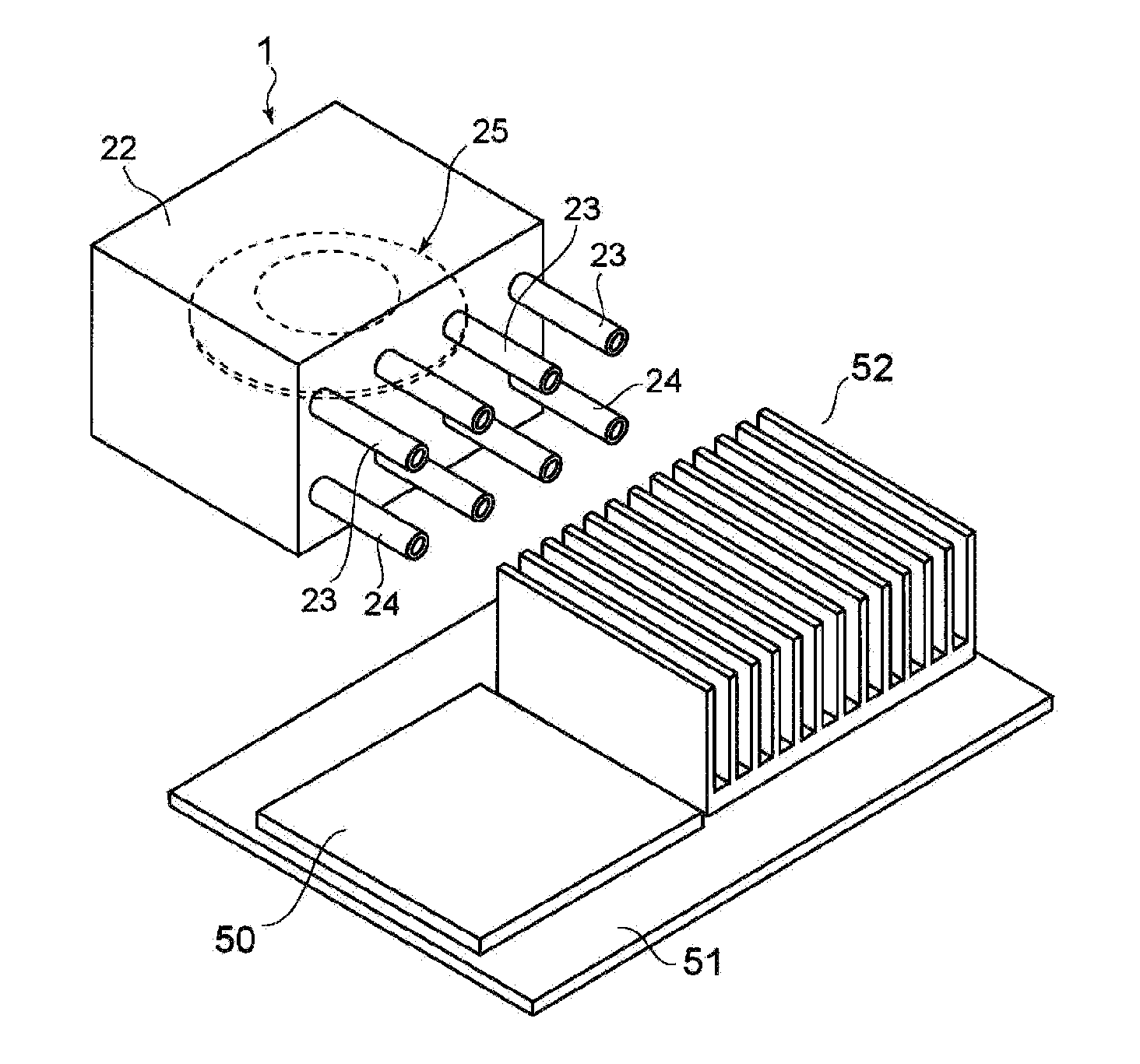
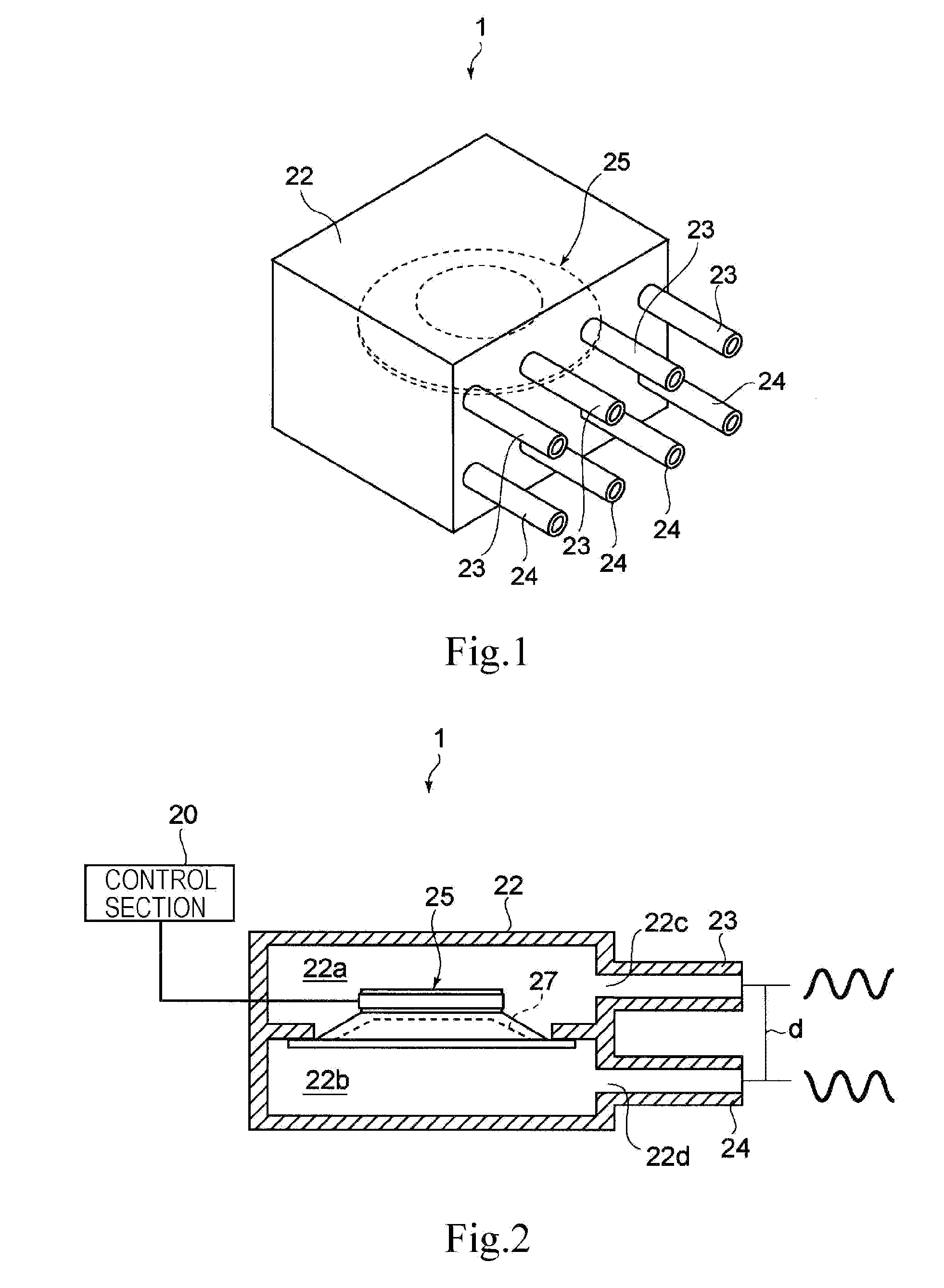
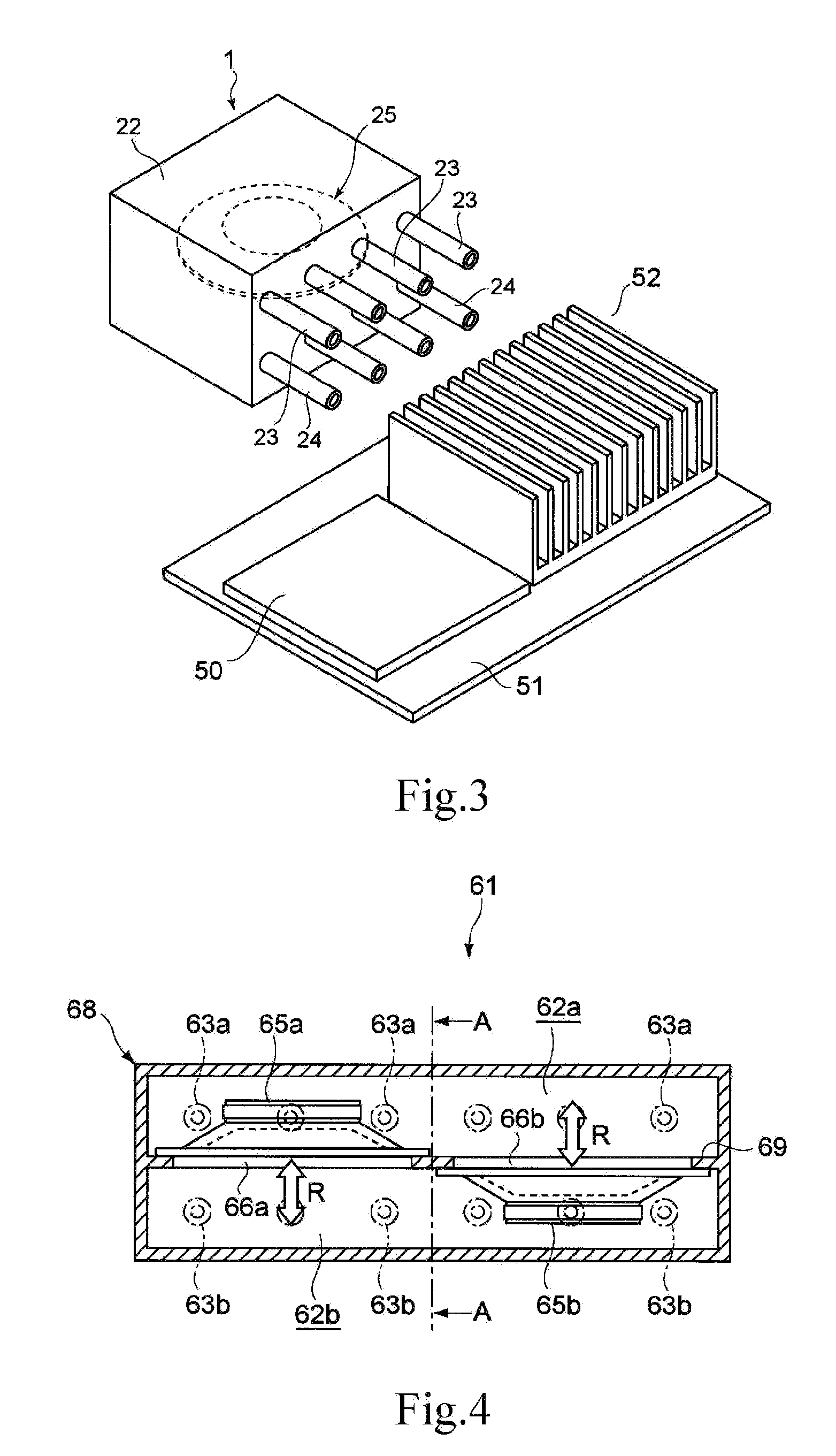
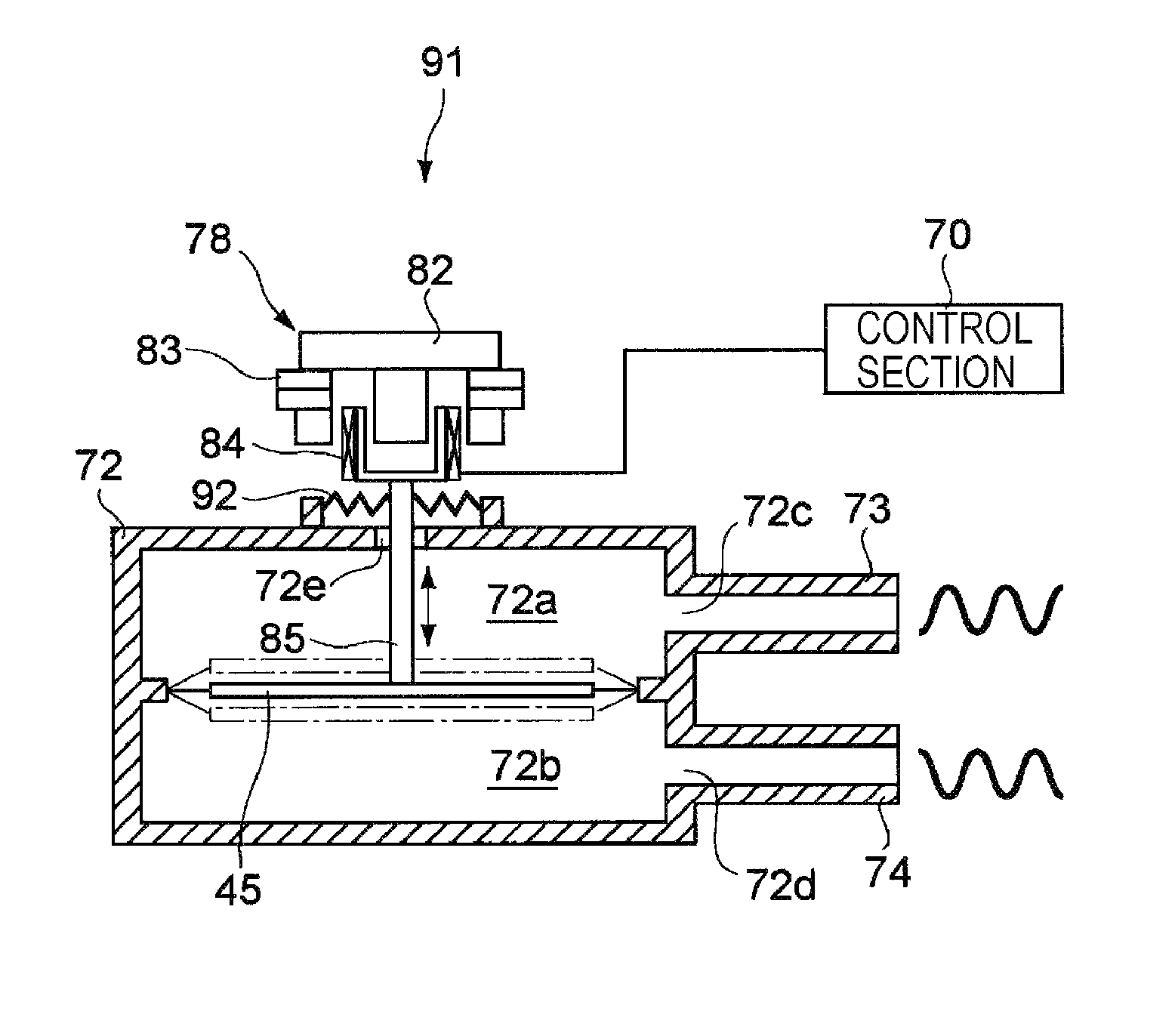
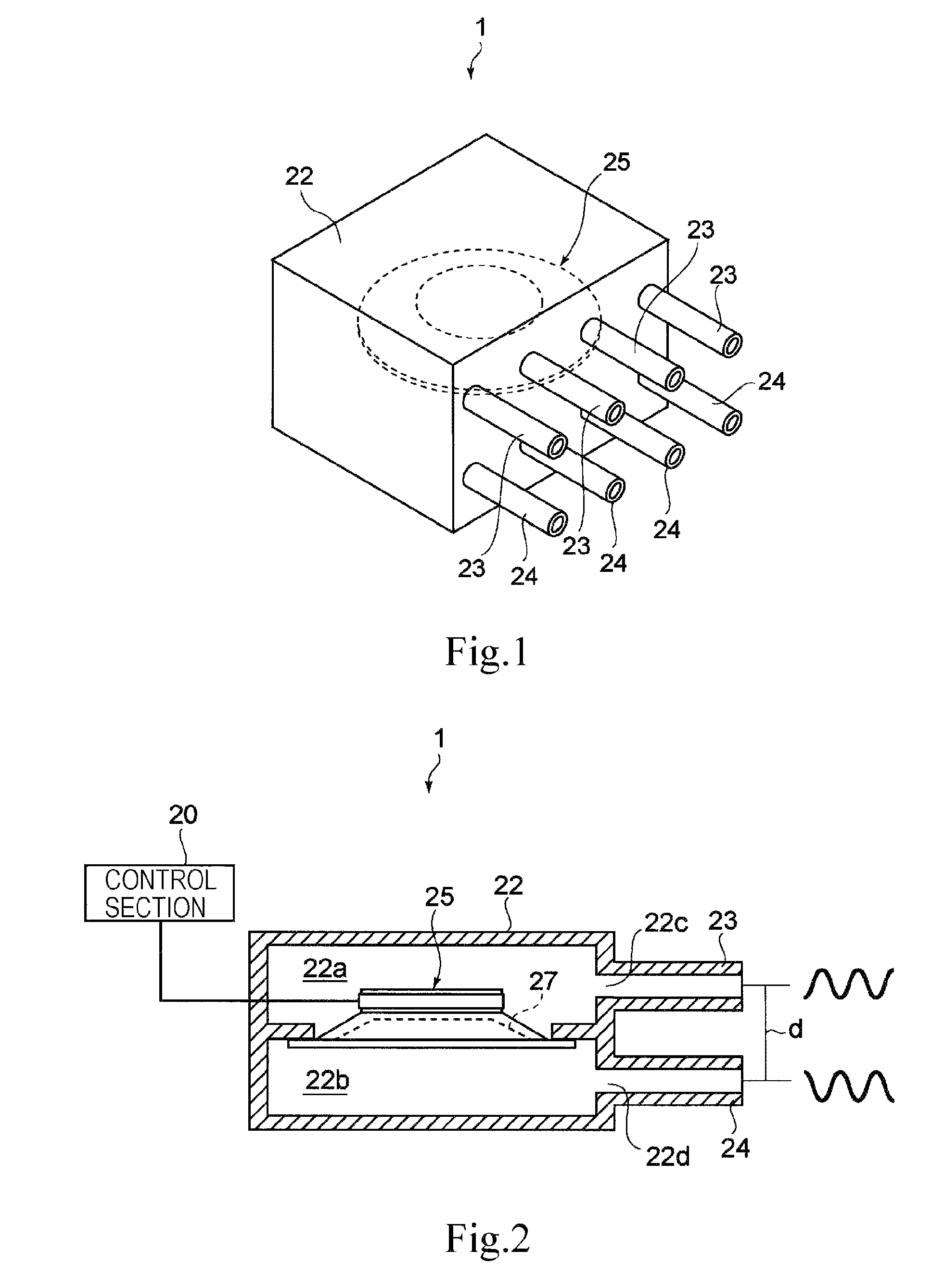
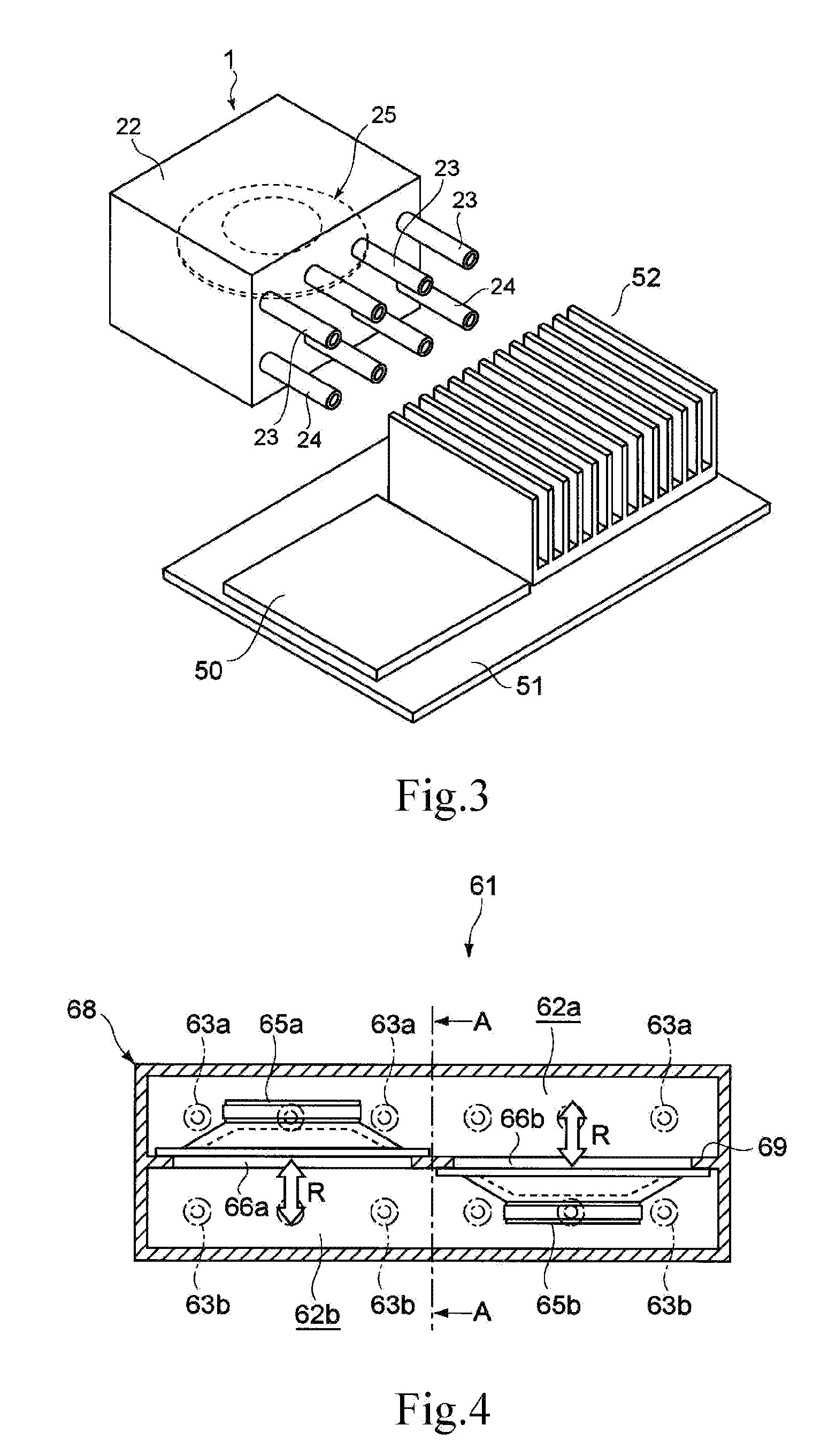
Gas ejector, electronic device, and gas-ejecting method
InactiveUS20090219686A1Avoid noiseEfficiently dissipatedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFlexible member pumpsNoise generationProduct gas
A gas ejector capable of effectively dissipating heat generated from a heater while inhibiting noise generation as little as possible, an electronic device equipped with the gas ejector, and a gas-ejecting method are offered. A gas ejector (1) according to the present invention includes a vibrator (25) and ejects gas in a form of a pulsating flow such that vibration of the vibrator allows sound waves respectively generated upon ejection of the gas ejected from nozzles (23) and (24) to deaden out each other. Also, a control section (20) optimizes the frequency of the vibrator (25), hence, by increasing the gas ejection quantity as much as possible while inhibiting noise generation, heat of a heater is effectively dissipated.
Owner:SONY CORP
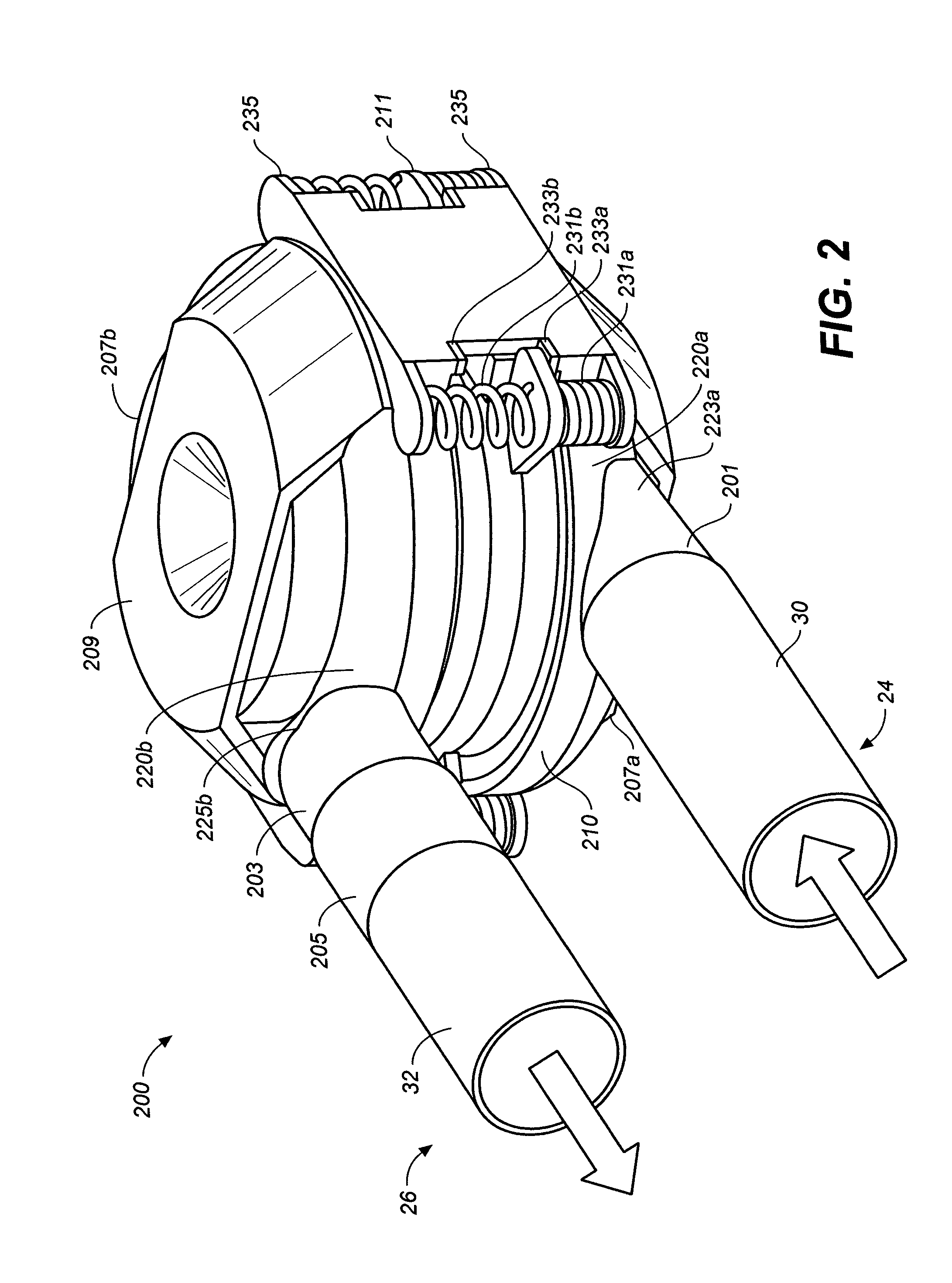
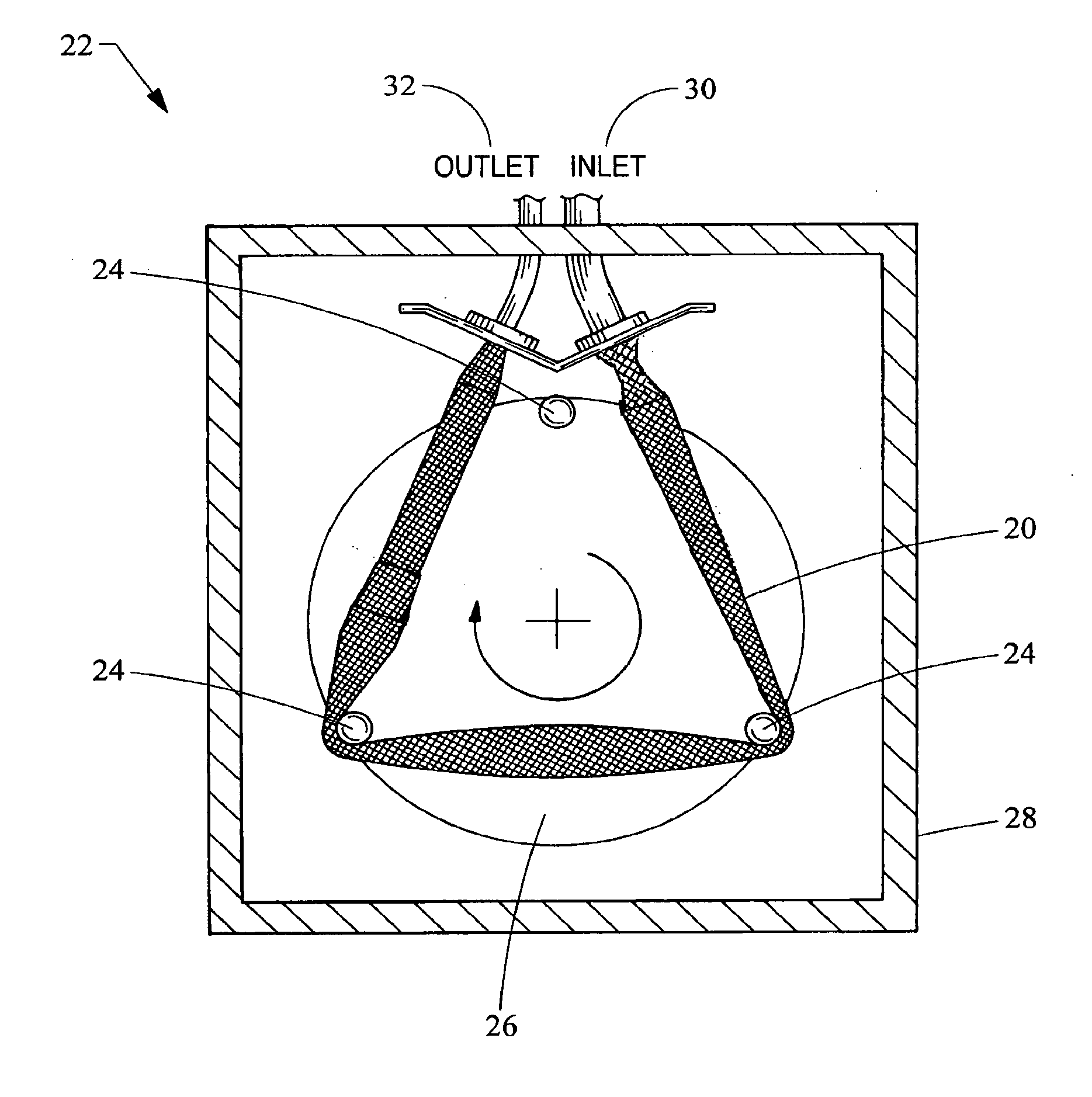
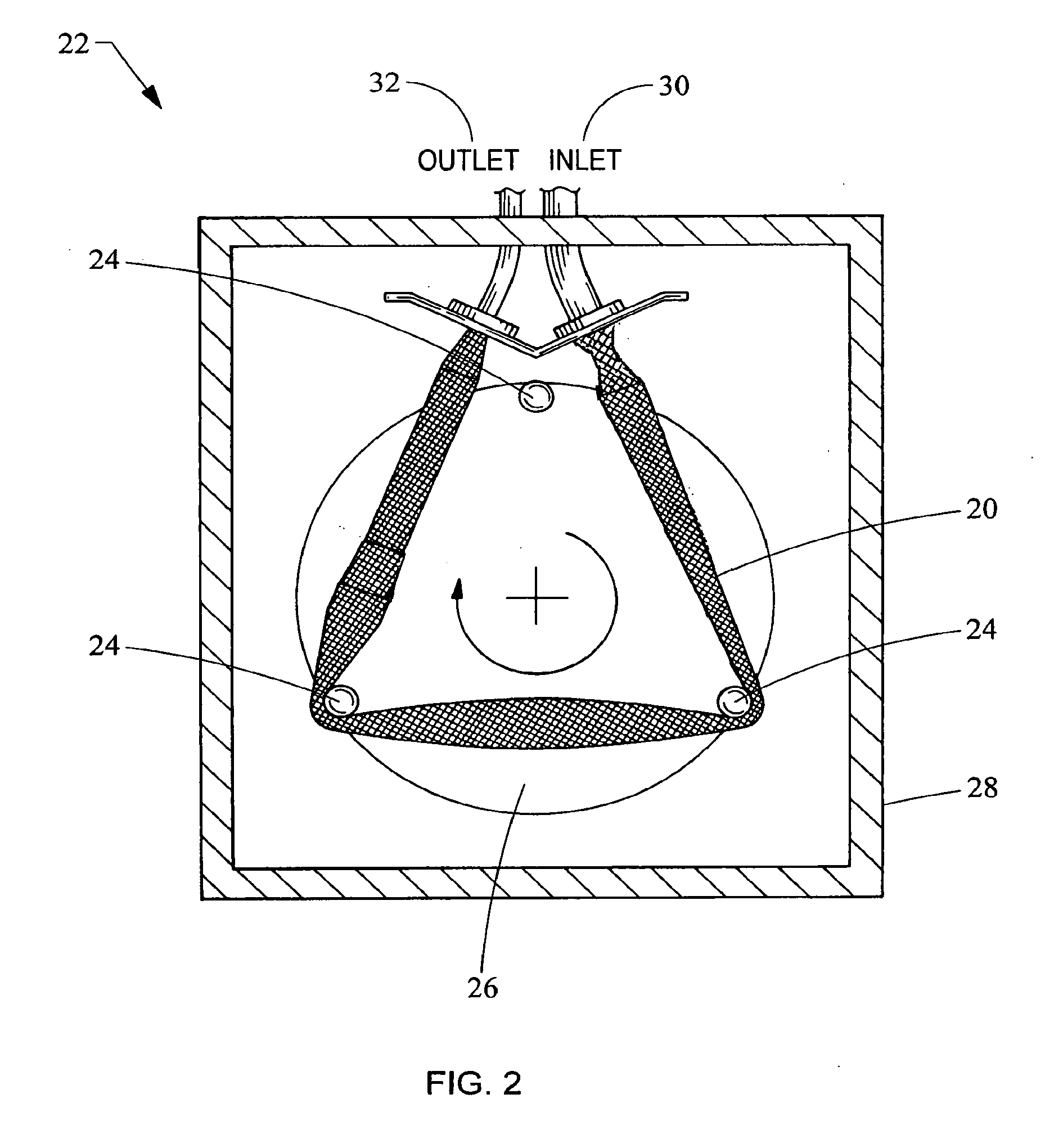
Pulsatile rotary ventricular pump
A roller pump conduit defining a pump chamber is provided. The roller pump conduit includes a roller contact portion having a fill region and a delivery region. The fill region has a first taper configured to determine volume delivery per revolution of a roller head. The delivery region has a pressure region having a second taper and a discharge region having a third taper. The third taper has a lesser degree of taper than the second taper. The delivery region is configured to produce a pulsatile flow out of the conduit.Furthermore, a roller pump having a roller pump conduit is provided. The roller pump conduit of the roller pump has a fill region and a delivery region, the fill region having a first taper, and the delivery region having a second and third taper, wherein the third taper has lesser degree of taper than the second taper.
Owner:MICHIGAN CRITICAL CARE CONSULTANTS
Method and system for quantification of arterial stenosis
InactiveUS20050119573A1Accurately determineBlood flow measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency spectrumArterial stenosis
A method is proposed that identifies and quantifies stenoses in arteries based on an analysis of Doppler frequency shifts from several heartbeats. It is non-invasive and individual insensitive. Pulsatile flow through a blood vessel with wall roughness and / or variable lumen area generates flow disturbances, which lead to variations in the shape of the Doppler shift frequency spectrum. One or several frequency bands that are affected by these flow disturbances are selected from the overall Doppler shift frequency spectrum. Next, one or several parameters, which characterize the selected frequency bands and vary with the degree of stenosis, are used in a linear function to calculate the percentage of lumen area reduction. This method applies in the clinically important range of lumen area reduction of 10-70% with a standard error of 5% or less. For lumen area reductions greater than about 70%, the standard error is larger. A system for practical implementation is also proposed.
Owner:VAS SCAN
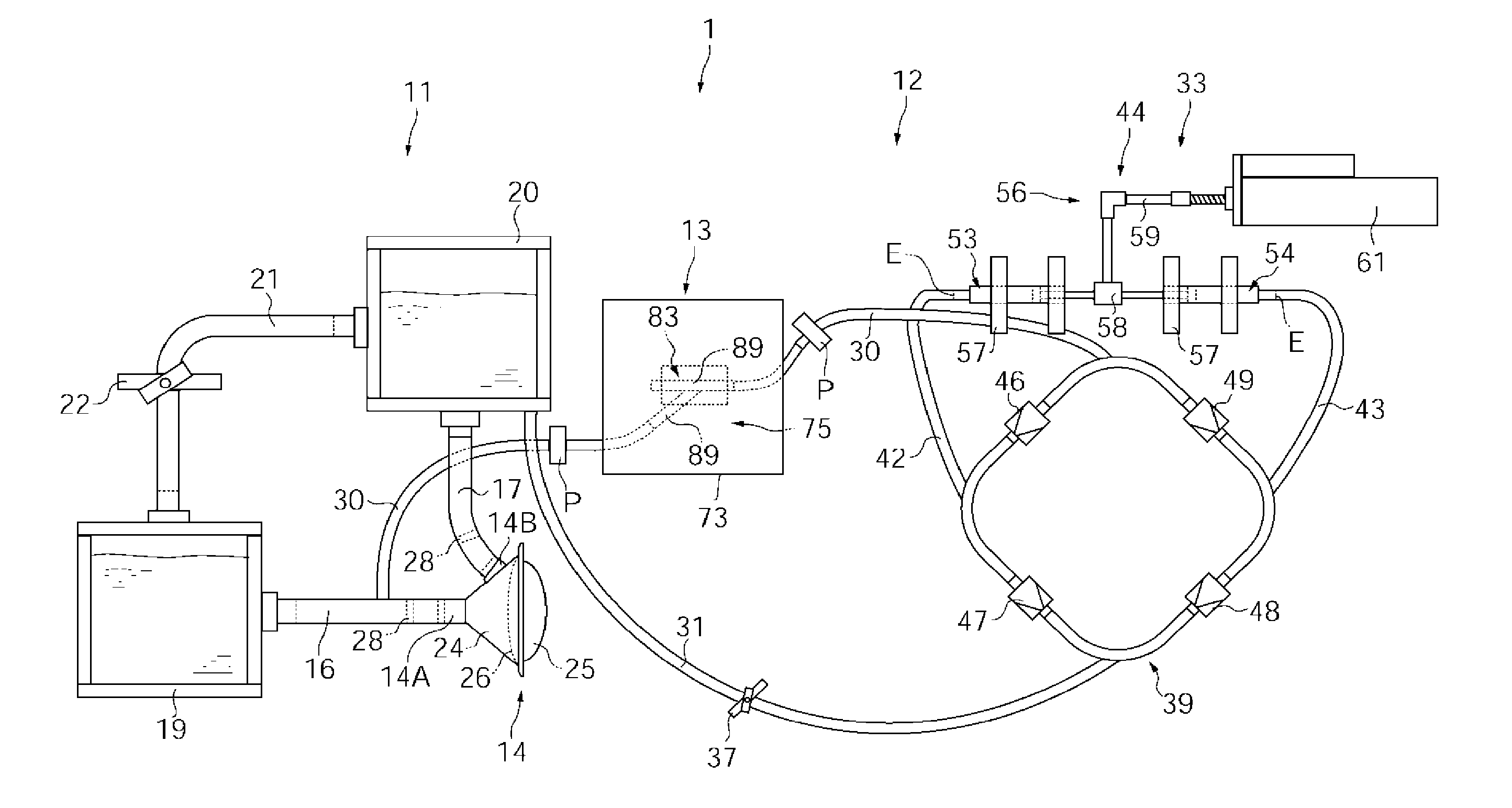
Fluid delivery apparatus with flow rate sensing means
InactiveUS20140060015A1Value can be obtainedControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsInternal combustion piston enginesCommon railEvaporation
A fluid delivery apparatus with a flow sensing means for delivering a first fluid into a second fluid. In a fluid delivery apparatus using a common rail method, which produces a pulsated flow, the flow sensing means generates sensing signals indicative of the flow rate and the temperature of the second fluid, the delivery rate of the first fluid, and the evaporating rate of the first fluid, while in a fluid delivery apparatus using a pump metering method, the flow sensing means is able to provide a sensing signal indicative of the delivery rate of the first fluid. The sensing signals can be used in a feedback control for controlling delivery rate, in limiting delivery rate according to the evaporation capability of the first fluid, and in a diagnostic system detecting failures and abnormalities in the fluid delivery apparatus.
Owner:YAN MI +1
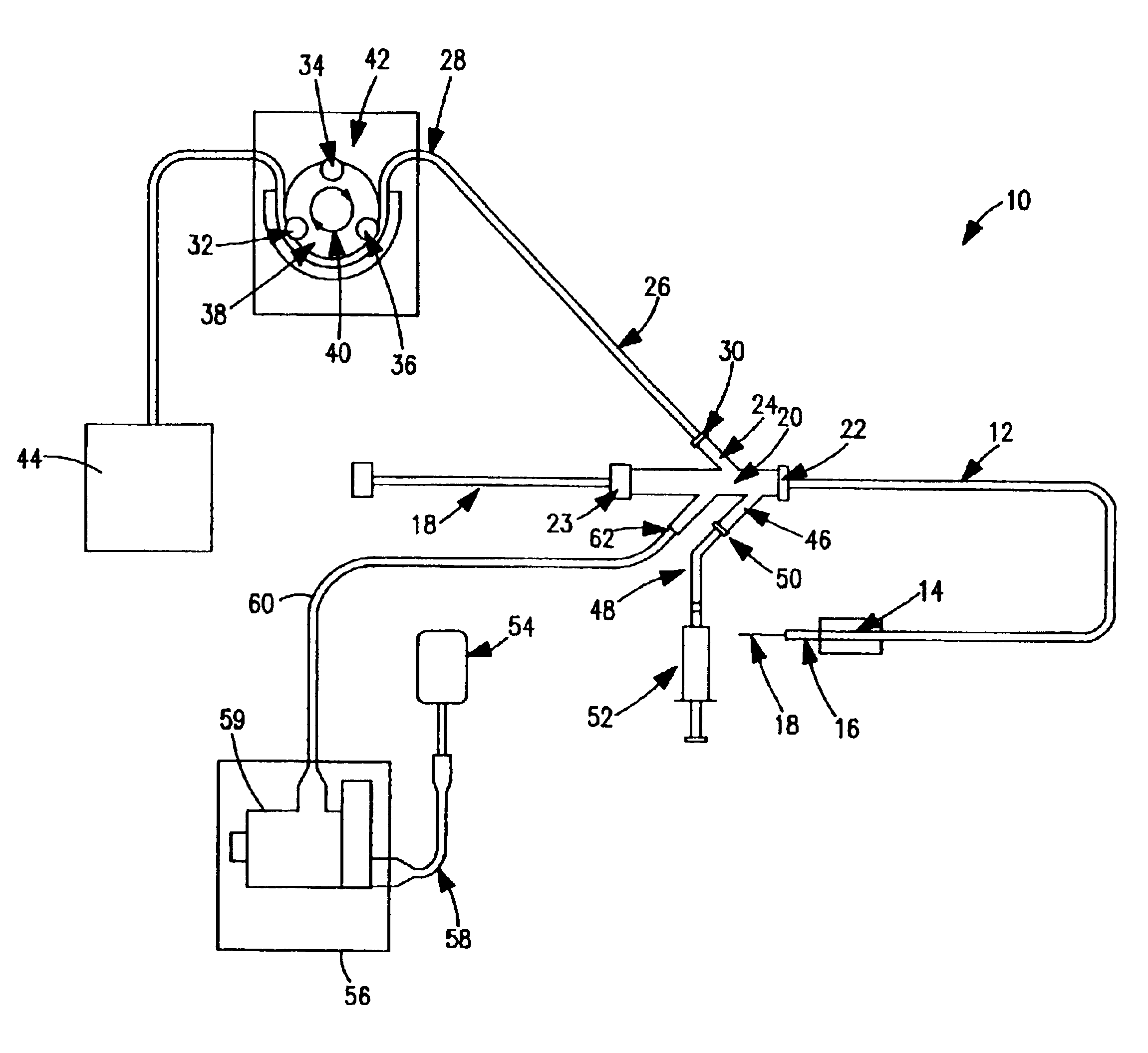
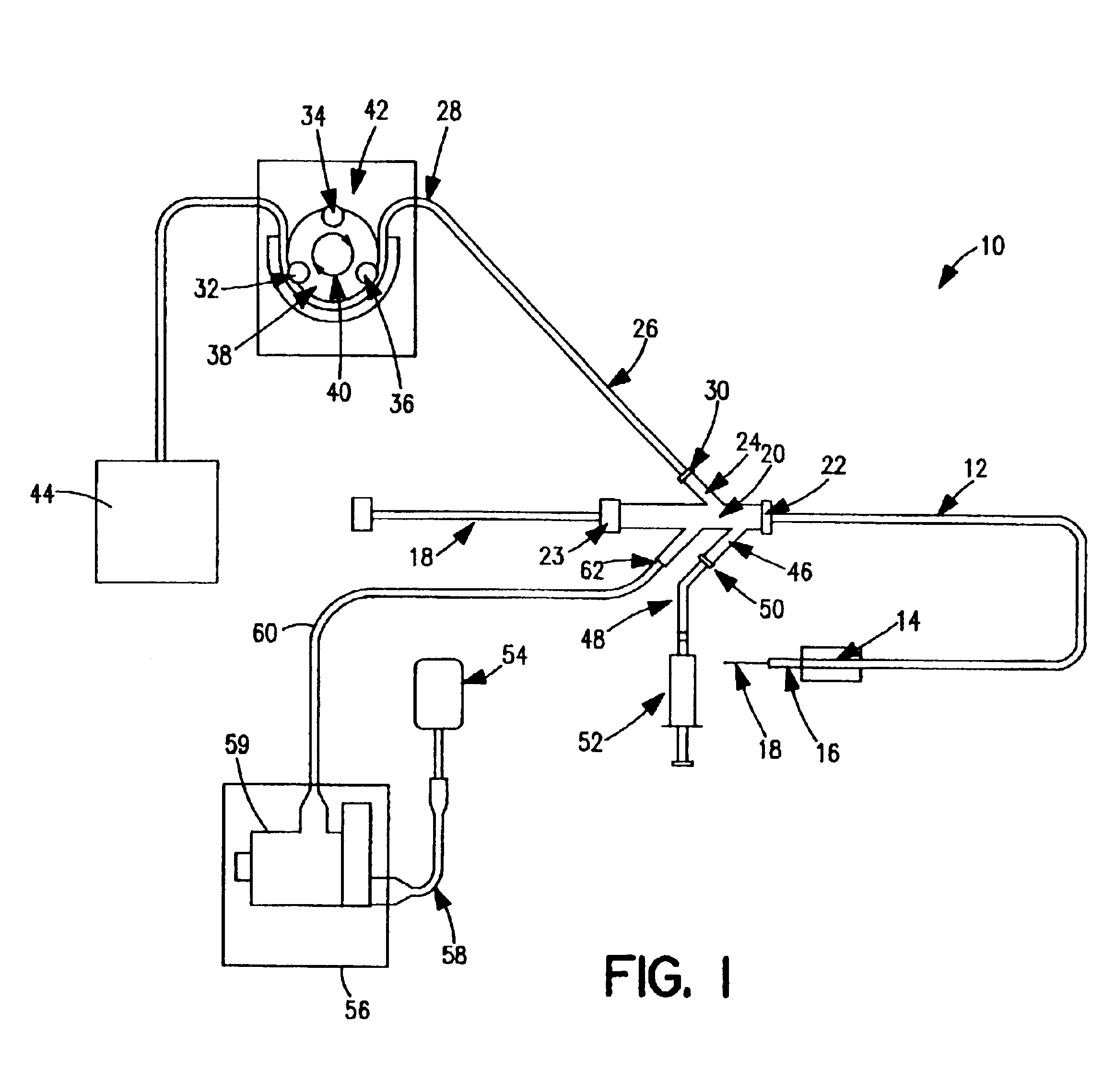
Irrigated ablation catheter system with pulsatile flow to prevent thrombus
ActiveUS8690870B2Prevent thrombusSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesCooling effectThrombus
The invention relates to an ablation catheter which controls the temperature and reduces the coagulation of biological fluids on an electrode of a catheter, prevents the impedance rise of tissue in contact with the electrode, and maximizes the potential energy transfer to the tissue, thereby allowing an increase in the lesion size produced by the ablation. The electrode includes passages positioned to allow saline flow out of an inner cavity of the electrode. This fluid flow is pulsatile to increase turbulence, reducing areas of stagnant flow, and produces a desired cooling effect.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Gas ejector, electronic device, and gas-ejecting method
InactiveUS8081454B2Increase the number ofLower resonant frequencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsWorking fluid for enginesNoise generationSpray nozzle
A gas ejector capable of effectively dissipating heat generated from a heater while inhibiting noise generation as little as possible, an electronic device equipped with the gas ejector, and a gas-ejecting method are offered. A gas ejector (1) according to the present invention includes a vibrator (25) and ejects gas in a form of a pulsating flow such that vibration of the vibrator allows sound waves respectively generated upon ejection of the gas ejected from nozzles (23) and (24) to deaden out each other. Also, a control section (20) optimizes the frequency of the vibrator (25), hence, by increasing the gas ejection quantity as much as possible while inhibiting noise generation, heat of a heater is effectively dissipated.
Owner:SONY CORP
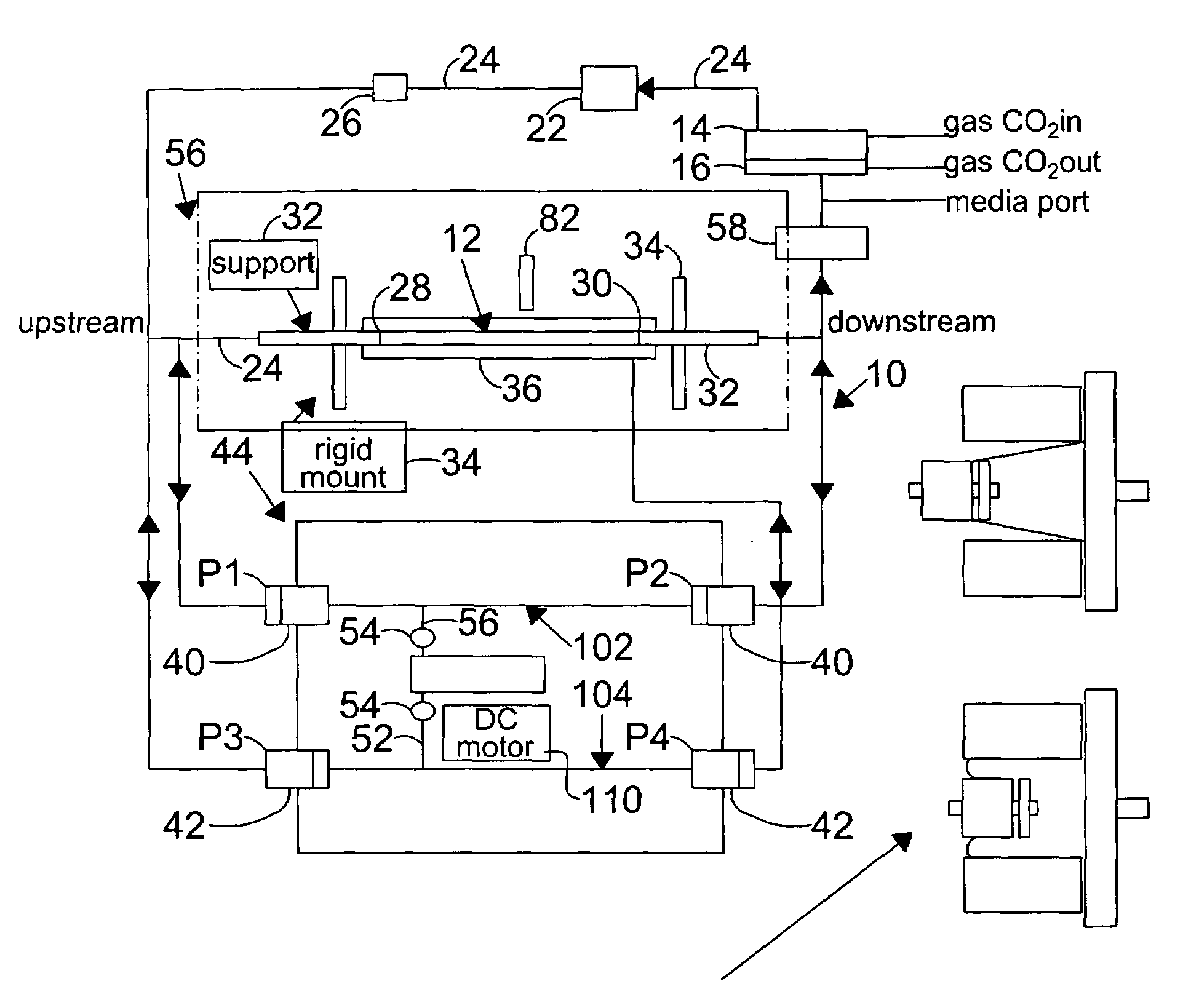
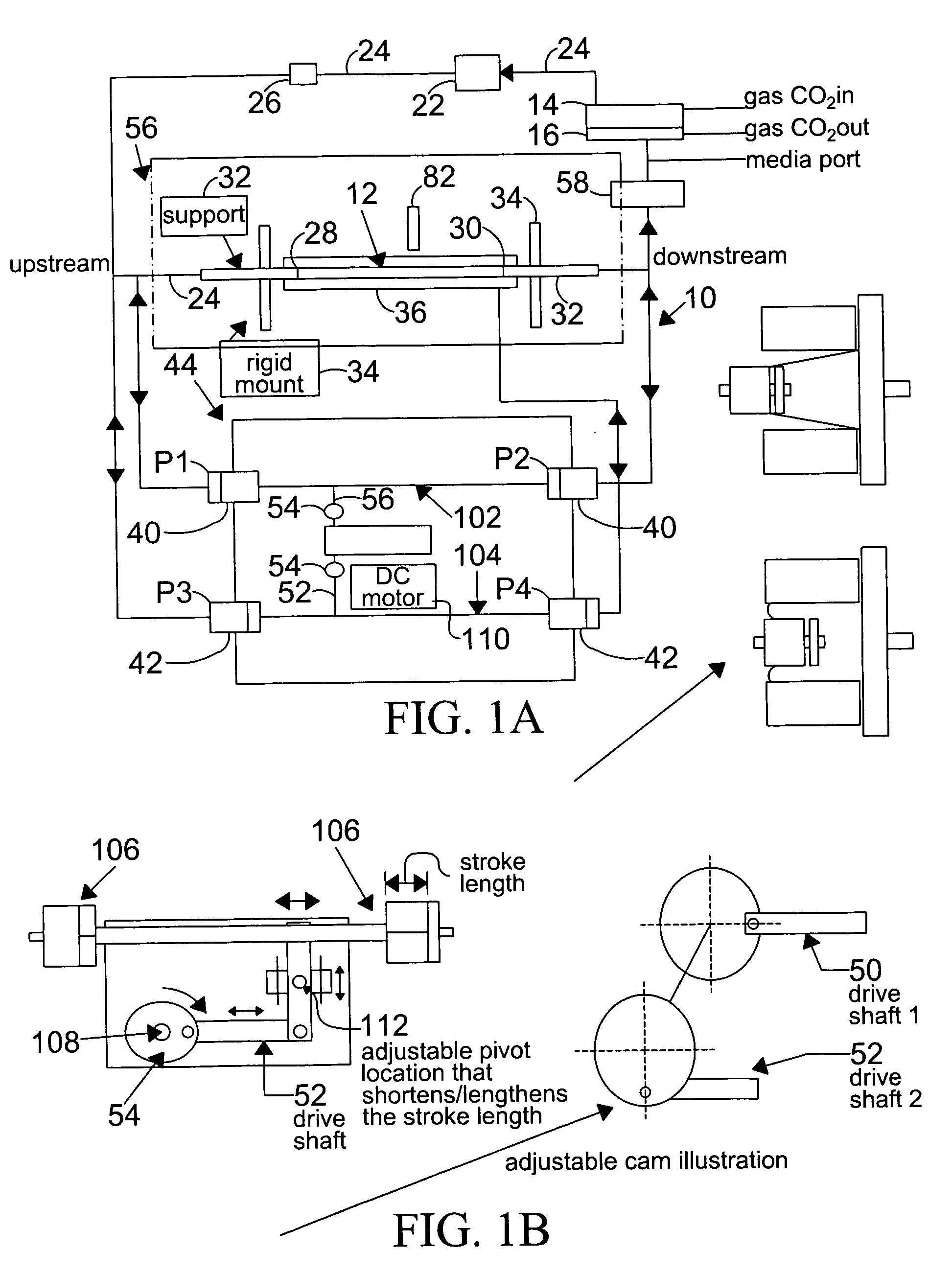
System and method to simulate hemodynamics
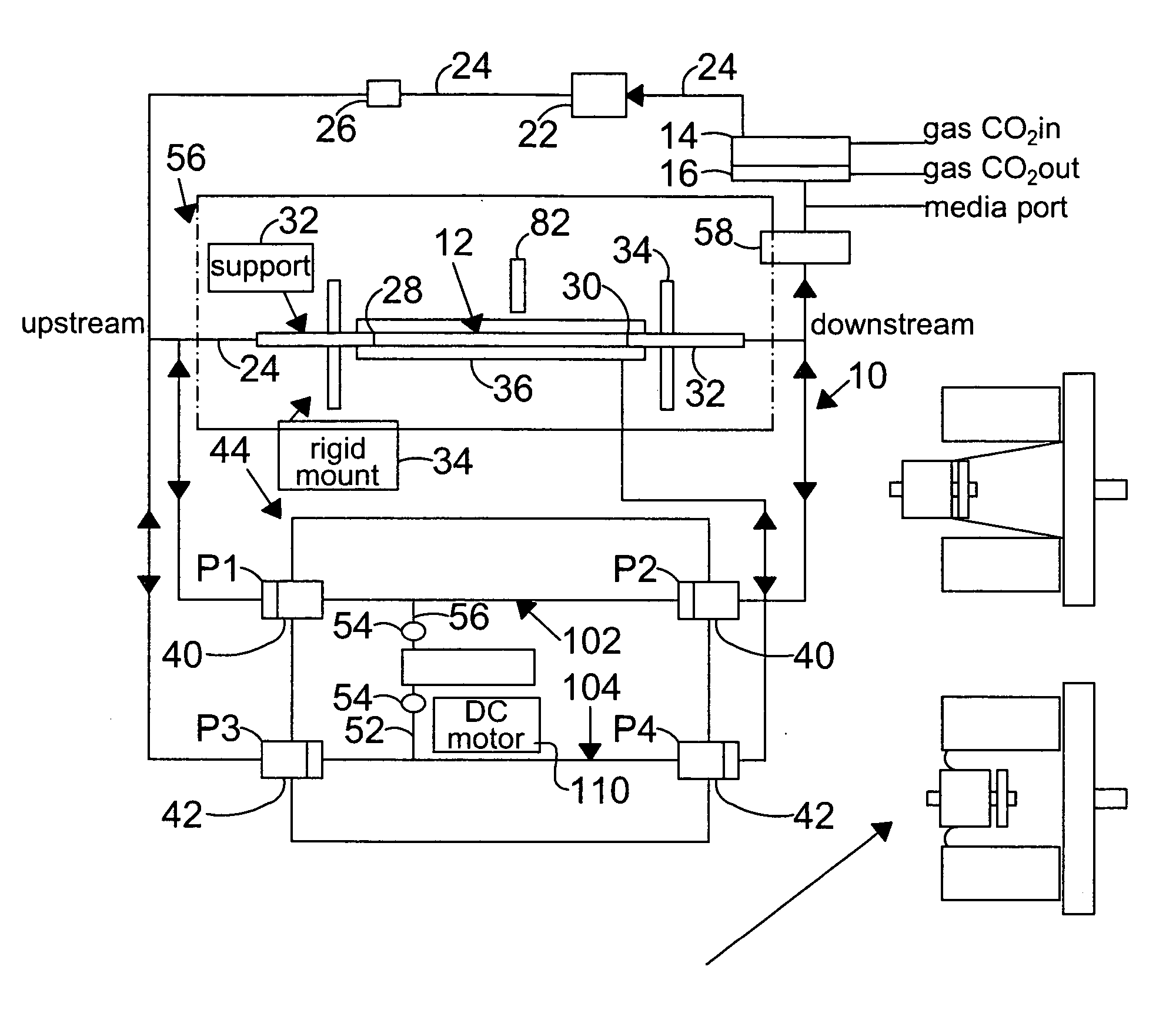
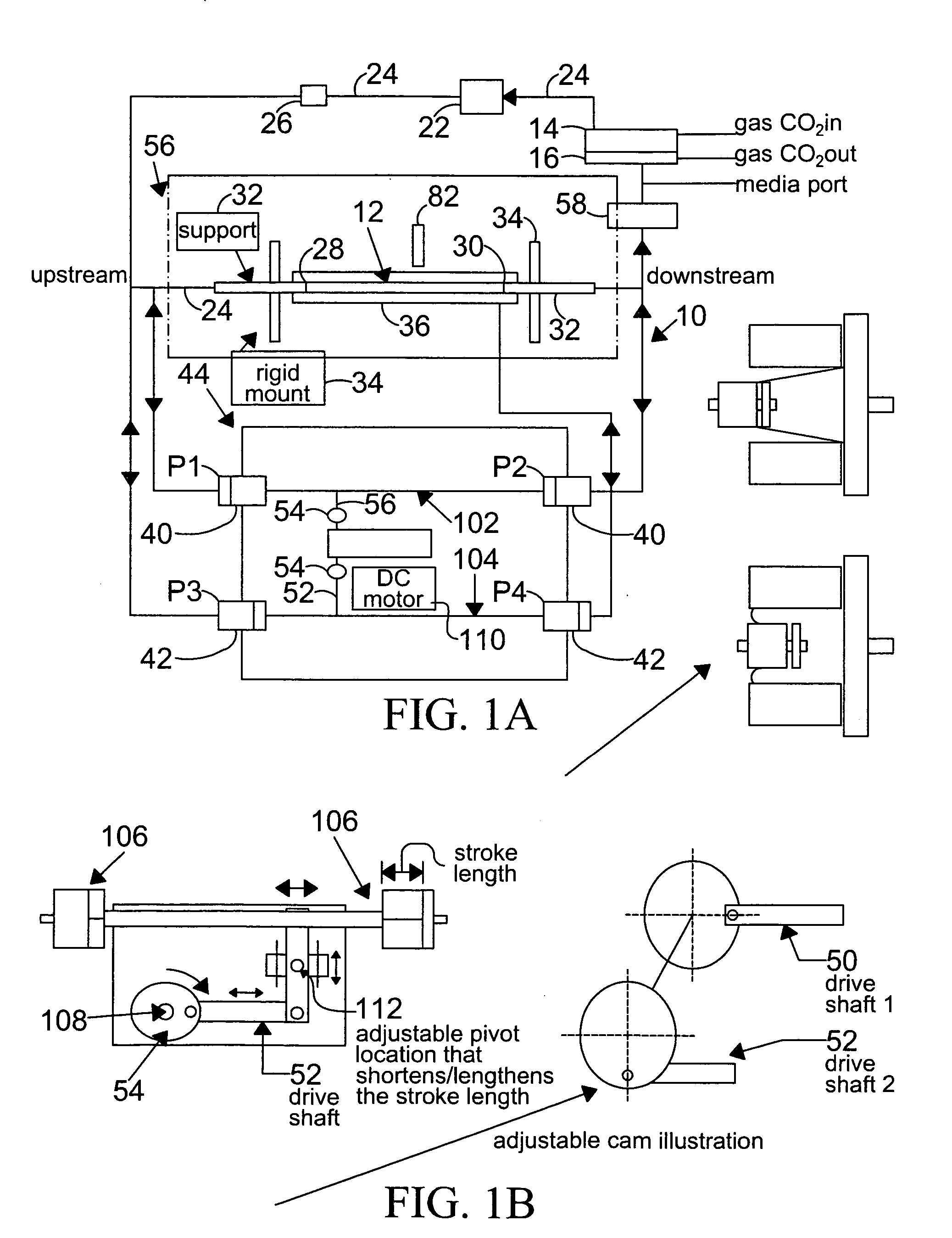
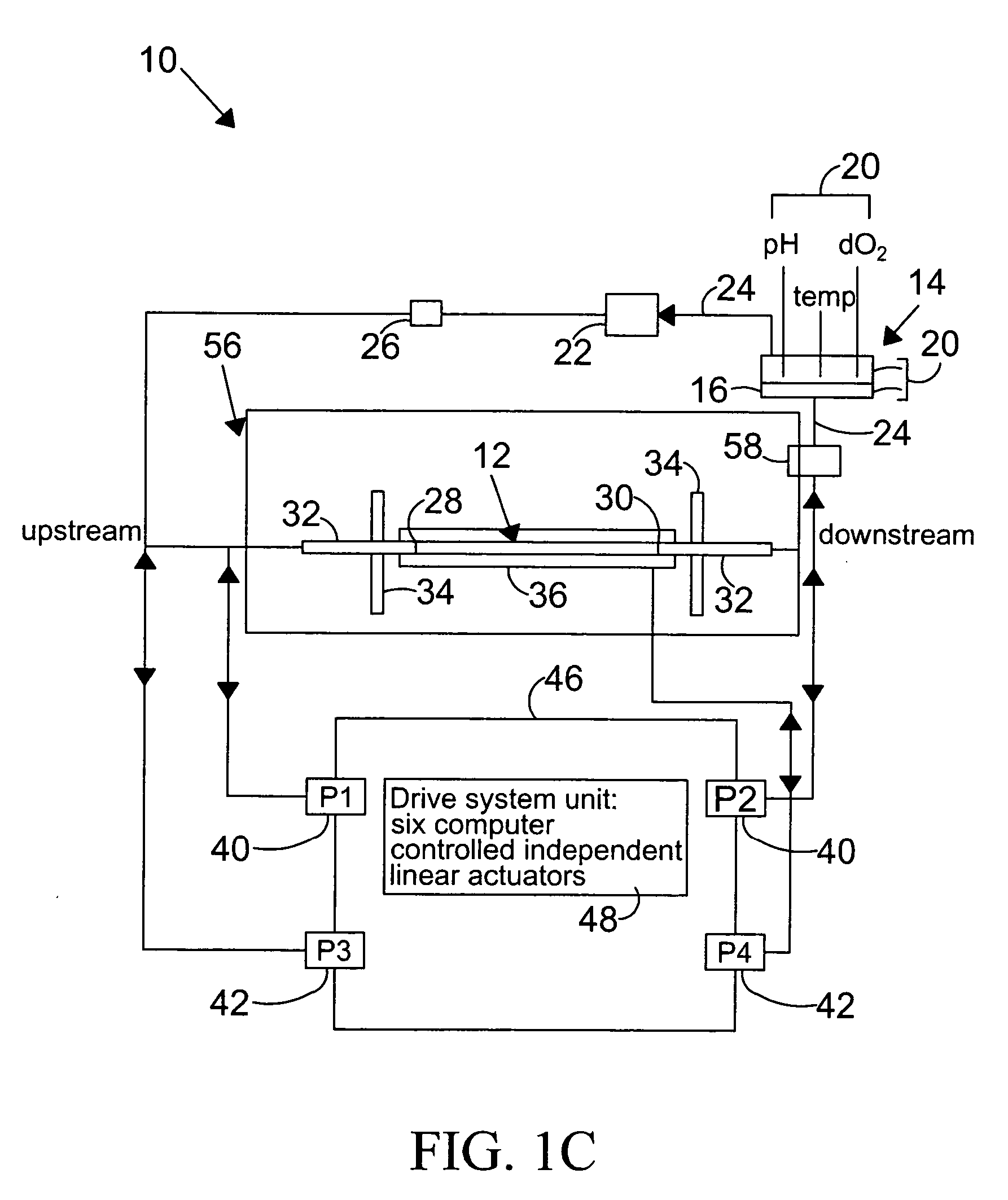
InactiveUS7063942B2Independent controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWall shearDrive shaft
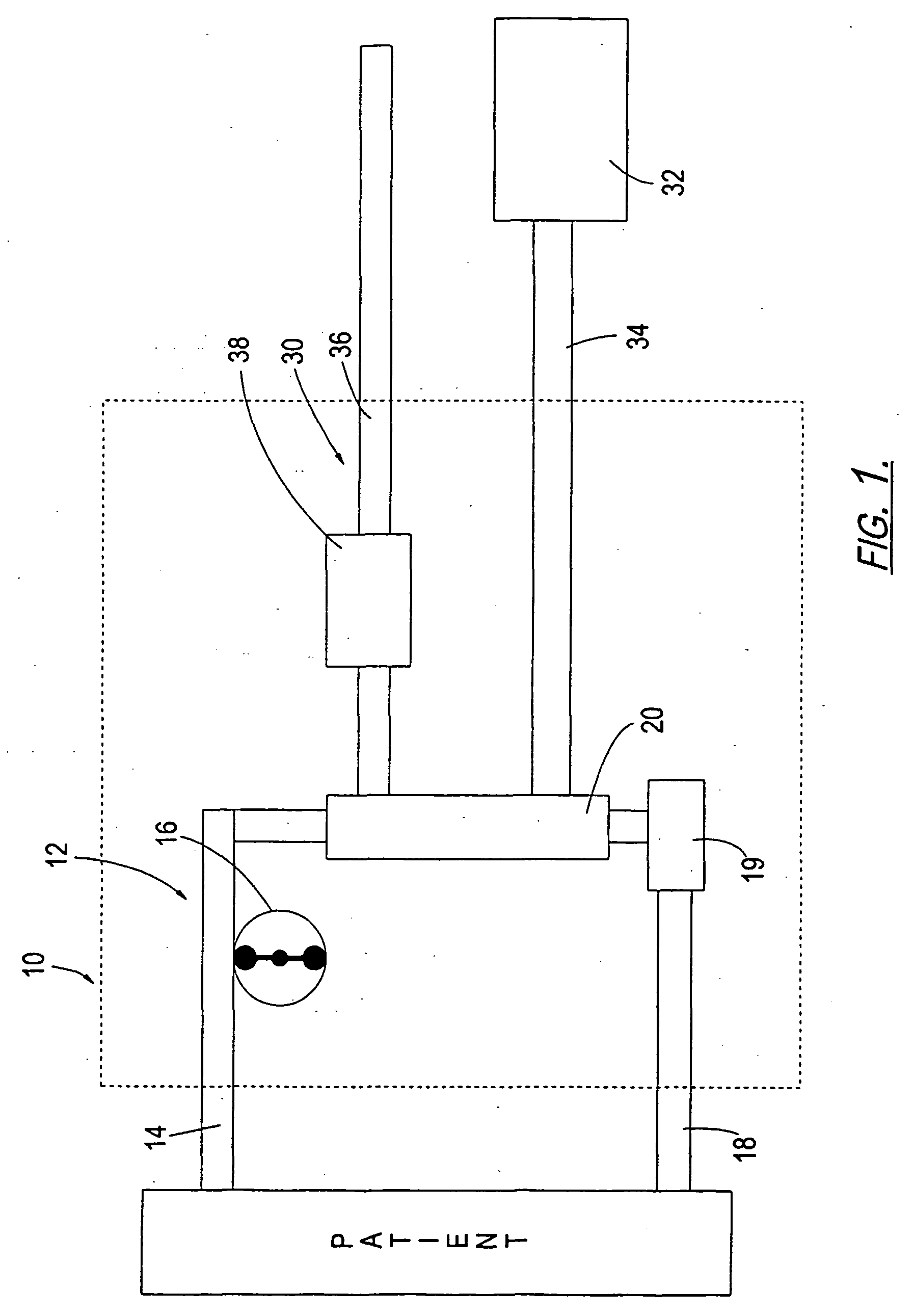
A system for hemodynamic simulation comprises a vessel having properties of a blood vessel, a reservoir containing a quantity of fluid, tubing connecting the vessel and reservoir, and at least one pump for circulating the fluid within the system. Fluid can be tissue culture medium or blood analog fluid, and the vessel may include mammalian cells attached to its inside. A drive system, comprising two reciprocating drive shafts that are coupled by a cam, enables the uncoupling of pulsatile flow and pulsatile pressure to provide independent control over wall shear stress and circumferential strain. The shaft drives two pumps that are 180 degrees out-of-phase and are connected upstream and downstream of the vessel, and effect this uncoupling.
Owner:VICTOR KRSTEC +1
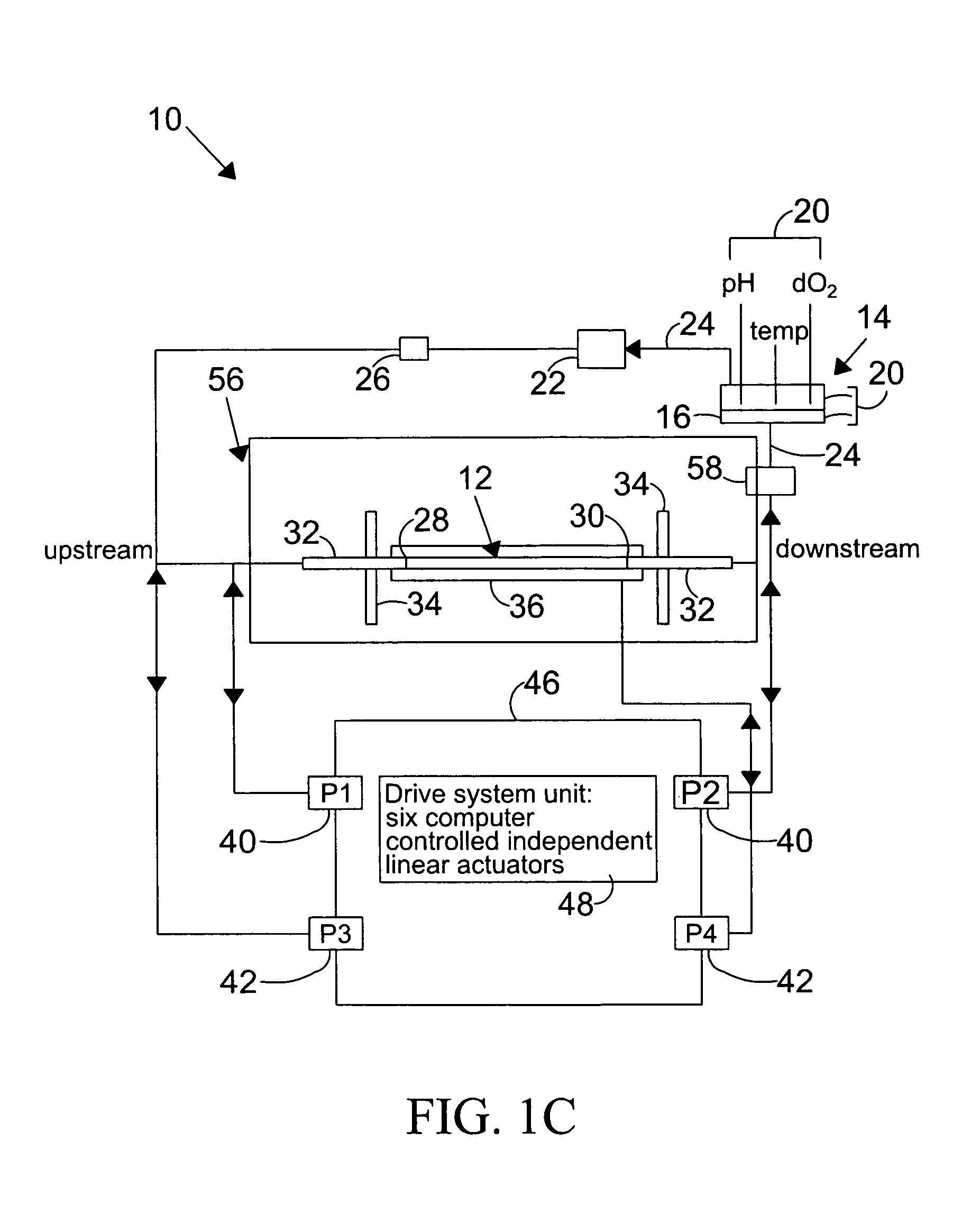
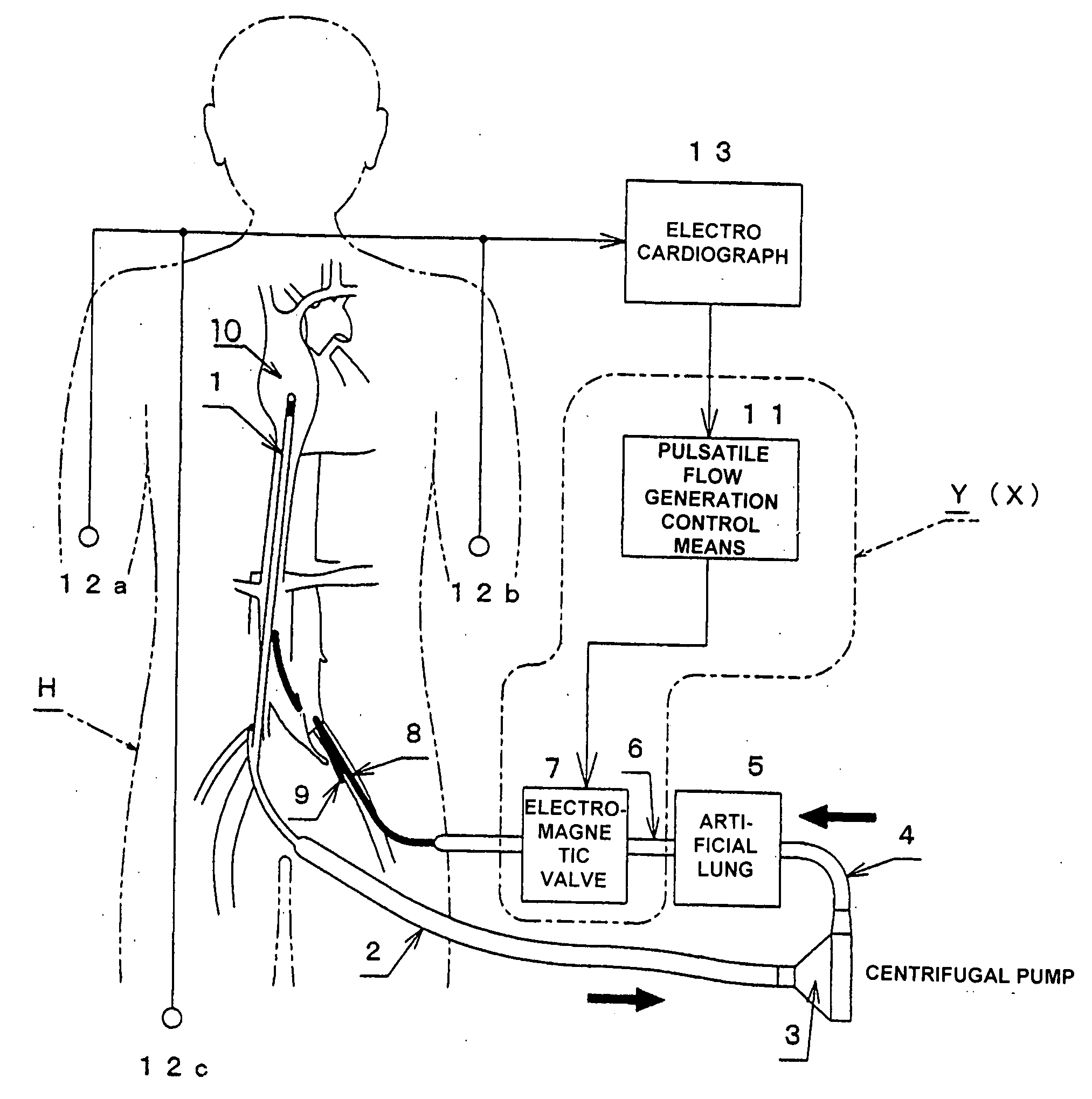
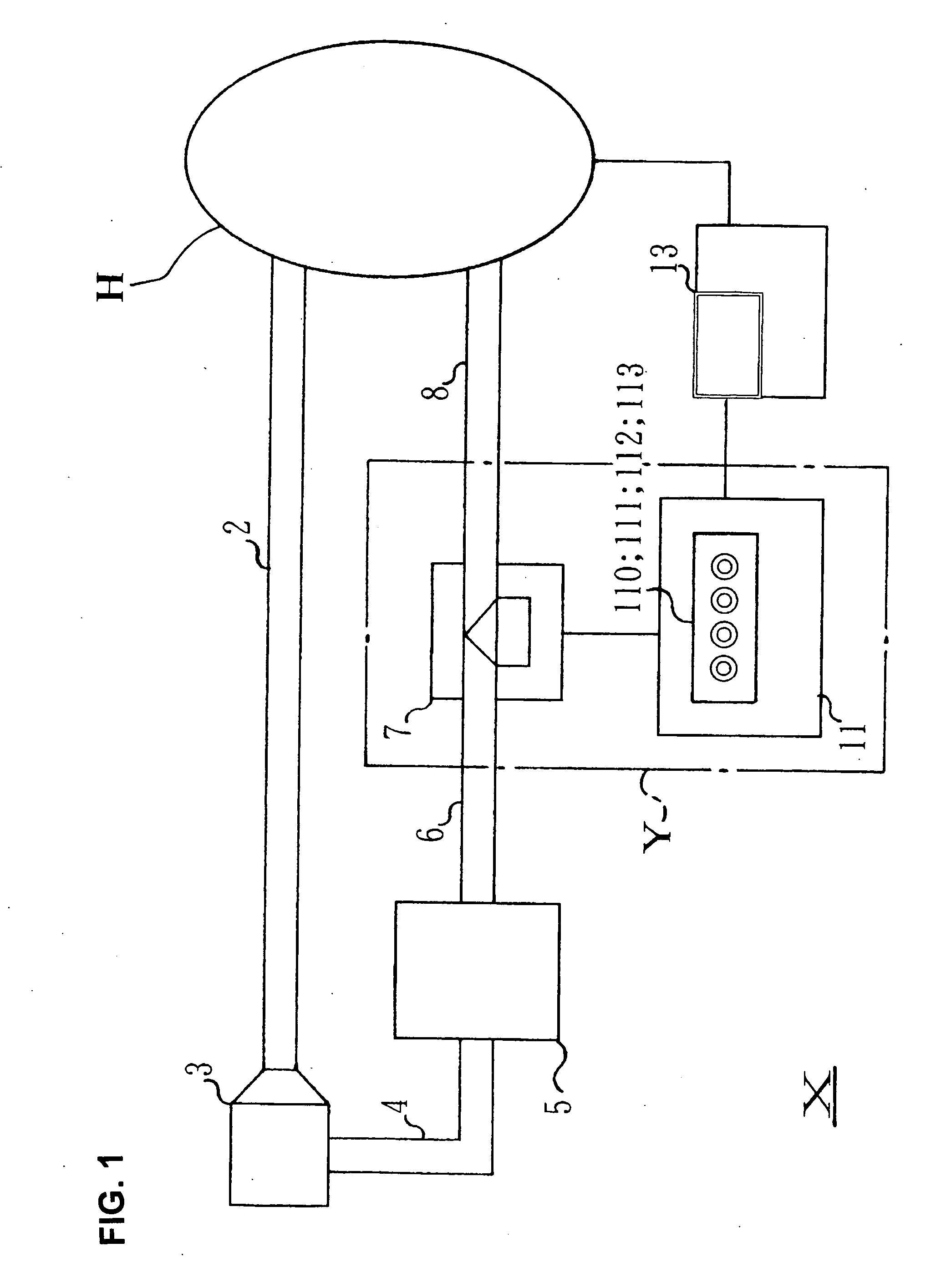
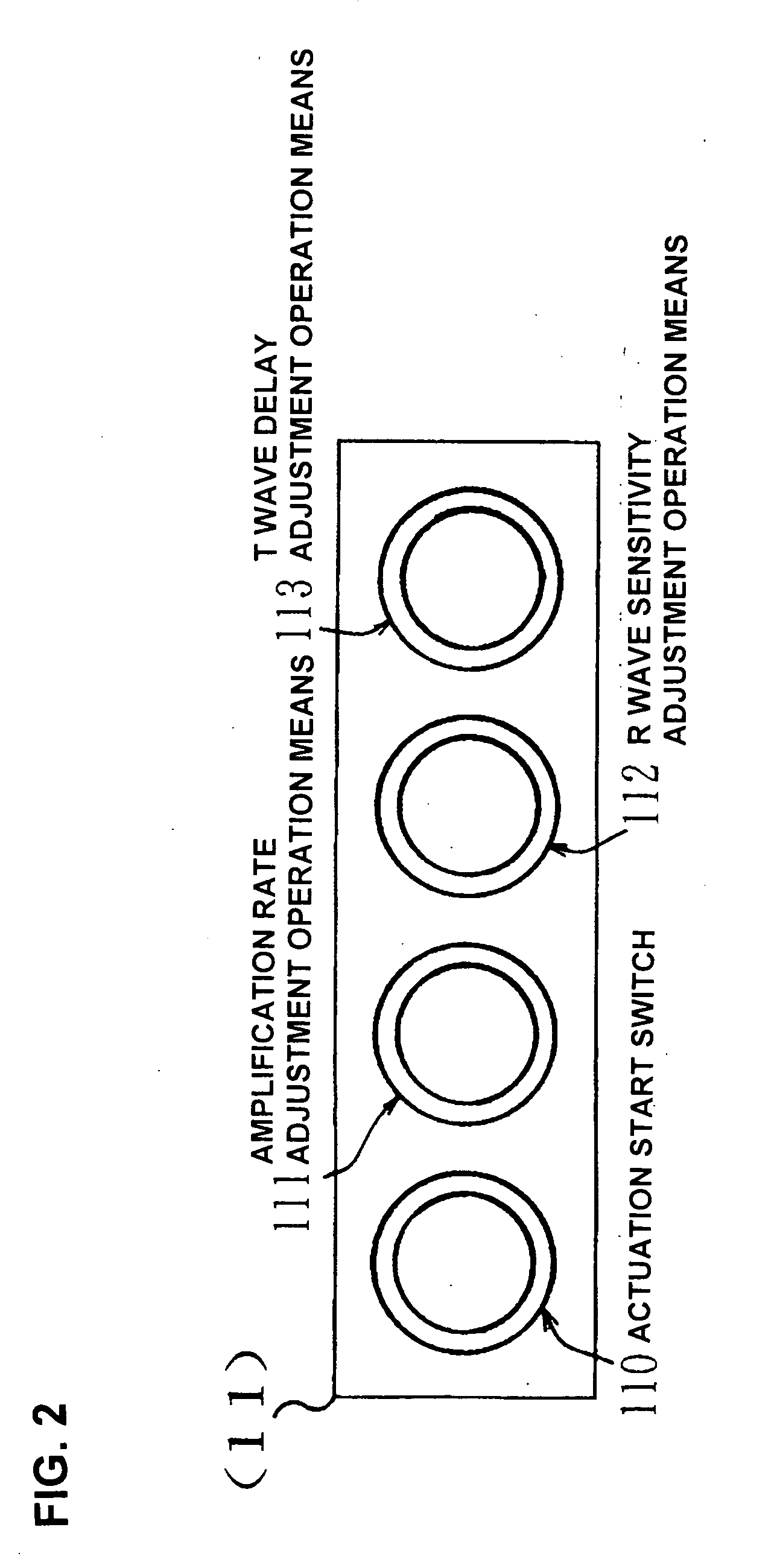
Pulsation-type auxiliary circulation system, pulsatile flow generation control device, and pulsatile flow generation control method
InactiveUS20080249456A1Enhancing auxiliary circulation effectCoronary artery blood flow is increasedElectrocardiographyOther blood circulation devicesSystoleTreatment effect
Pulsatile flow in synchronization with the systole and diastole of a patient's own pulse is generated during auxiliary circulation therapy administered to a patient under cardiac dysfunction. As a result, the diastole augmentation function is maintained, blood flow to the coronary artery is increased, and the therapeutic effect of intending to restore cardiac function without applying after-loading to the heart is improved.Pulsatile flow generation control device Y incorporated in a pulsation-type auxiliary circulation system (X) as an apparatus system having an electromagnetic valve 7 in blood supply lines (4, 6, 8) on the delivery side of artificial lung 5 and a control means 11 for performing control-output relating to the opening and closing operation of the electromagnetic valve 7. The control means 11 has at least a delay circuit and is such that the electromagnetic valve 7 is actuated to close and is maintained closed for a predetermined time interval based on delay detection and is actuated to open based on delay cancellation so that blood flow is periodically interrupted.
Owner:JOSHO GAKUEN EDUCATIONAL FOUND
System and method to simulate hemodynamics
InactiveUS20060210959A1Independent controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWall shearDrive shaft
A system for hemodynamic simulation comprises a vessel having properties of a blood vessel, a reservoir containing a quantity of fluid, tubing connecting the vessel and reservoir, and at least one pump for circulating the fluid within the system. Fluid can be tissue culture medium or blood analog fluid, and the vessel may include mammalian cells attached to its inside. A drive system, comprising two reciprocating drive shafts that are coupled by a cam, enables the uncoupling of pulsatile flow and pulsatile pressure to provide independent control over wall shear stress and circumferential strain. The shaft drives two pumps that are 180 degrees out-of-phase and are connected upstream and downstream of the vessel, and effect this uncoupling.
Owner:DANCU MICHAEL B
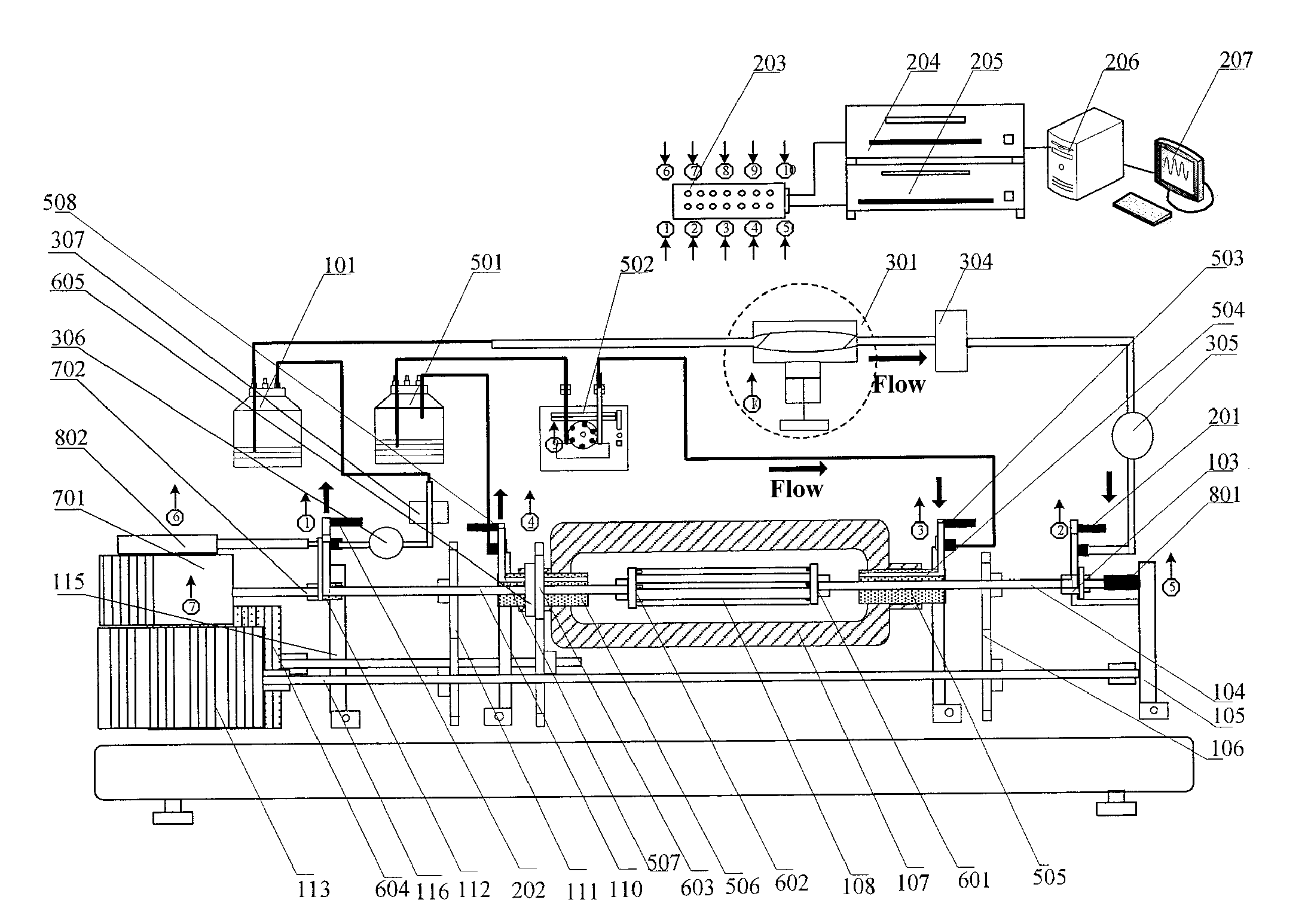
Perfusion type vascular tissue bioreactor with rotary and stretching functions
InactiveUS20090181448A1Improve mass transfer effectRotation speed and directionDead animal preservationStress based microorganism growth stimulationVascular tissueBlood Vessel Tissue
The present invention in one aspect provides a bioreactor for vascular construct that comprises a pulse-generating device with simple structure and reliable and stable pulse-generating operation. In another aspect, the present invention provides bioreactor for vascular construct that implements rotation of vascular construct and culture chamber, axial stretching of vascular construct, and duplicating pulsatile flow.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Microfabricated droplet generator for single molecule/cell genetic analysis in engineered monodispersed emulsions
ActiveUS8454906B2Efficient routingQuick buildTransportation and packagingLibrary screeningEmulsionMicroparticle
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for collecting and using placenta cord blood stem cells
ActiveUS20090123437A1Raise countBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsPeristaltic pumpCord blood stem cell
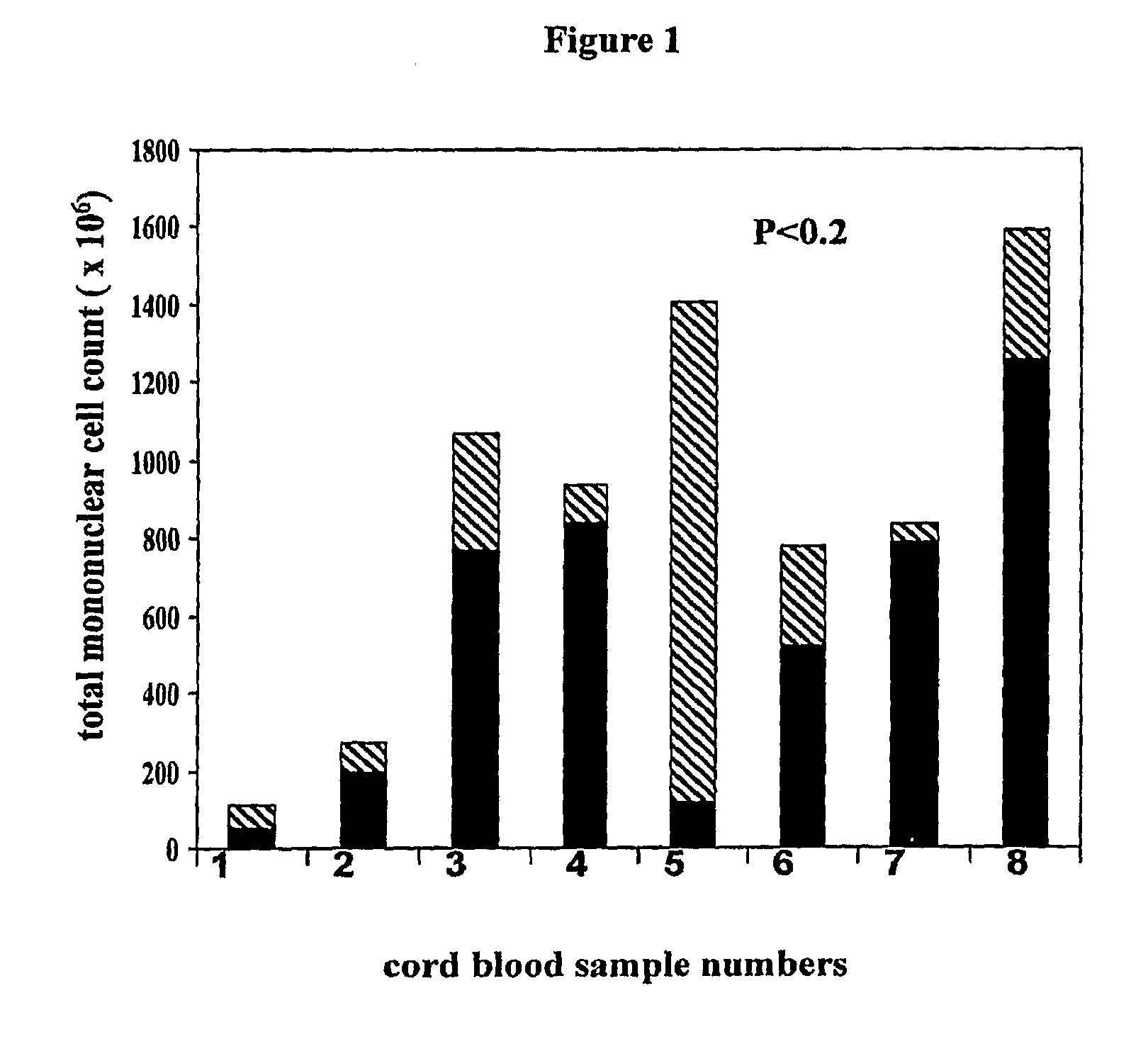
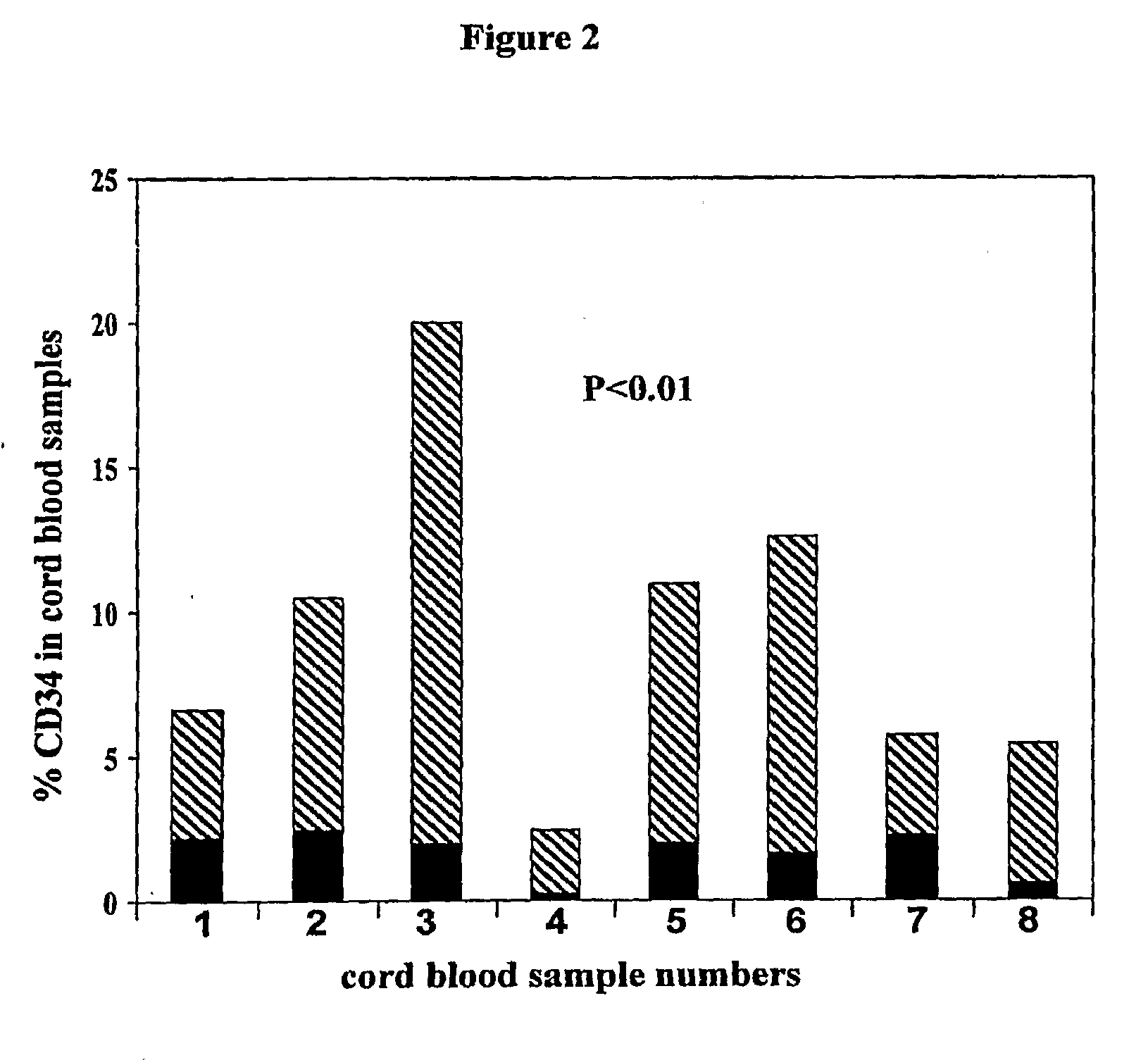
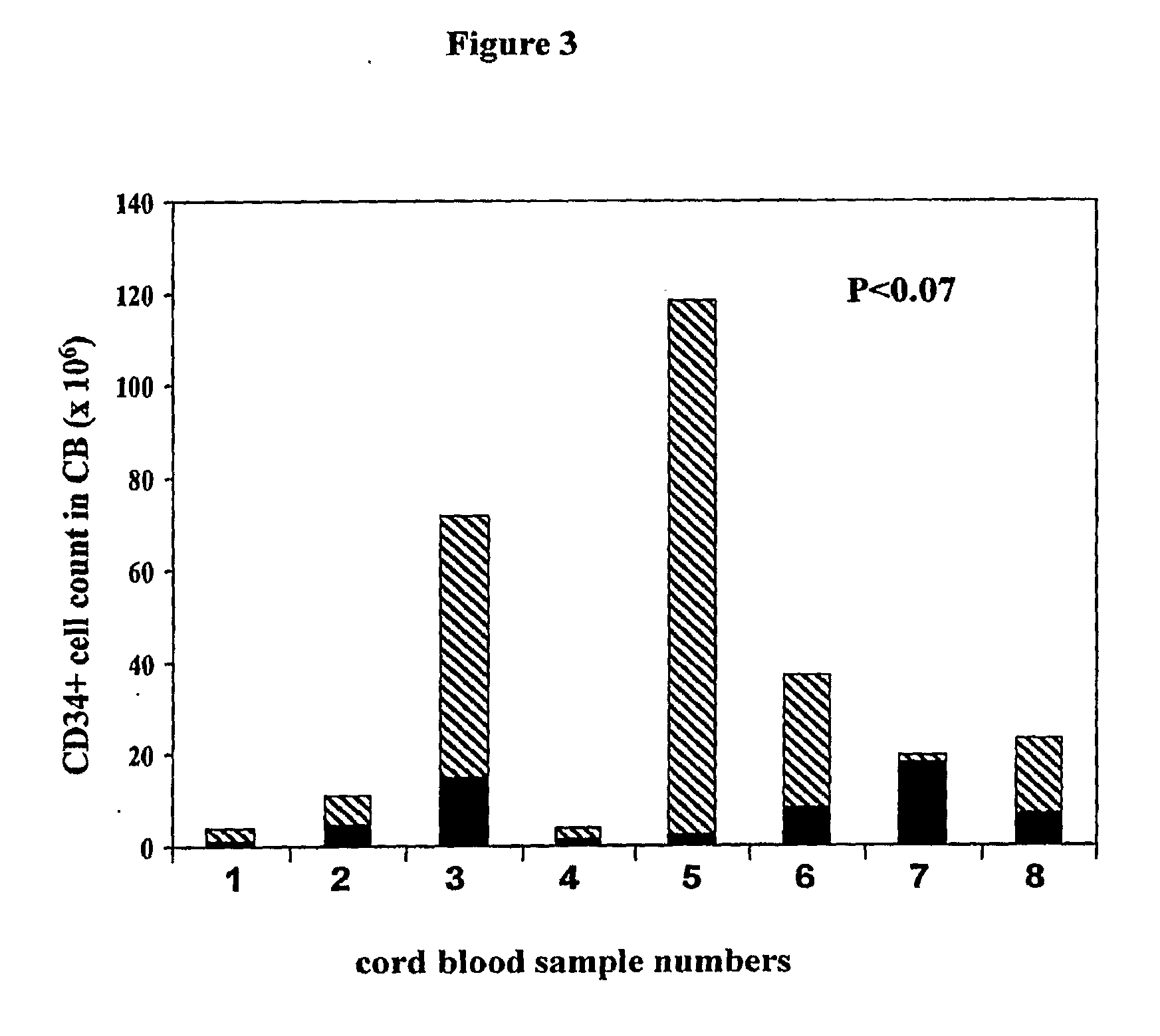
An innovative method of collecting cord blood stem cells from an isolated mammalian non-exsanguinated or partially exsanguinated placenta by placental perfusion is described and also an easy method for safe long duration cold storage of the placenta. Placental perfusion can include perfusing the isolated placenta with a pulsatile flow of perfusion solution, for example, using a pulsatile or peristaltic pump or device. The stem cells can then be isolated from the perfusate. Significantly increased amounts of CD133+ stem cells can be collected from the perfusate. The perfusion solution can include an anticoagulant. The isolated mammalian placenta need not be treated with an anticoagulant prior to perfusing. The isolated placenta can be free from an anticoagulant prior to perfusing.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
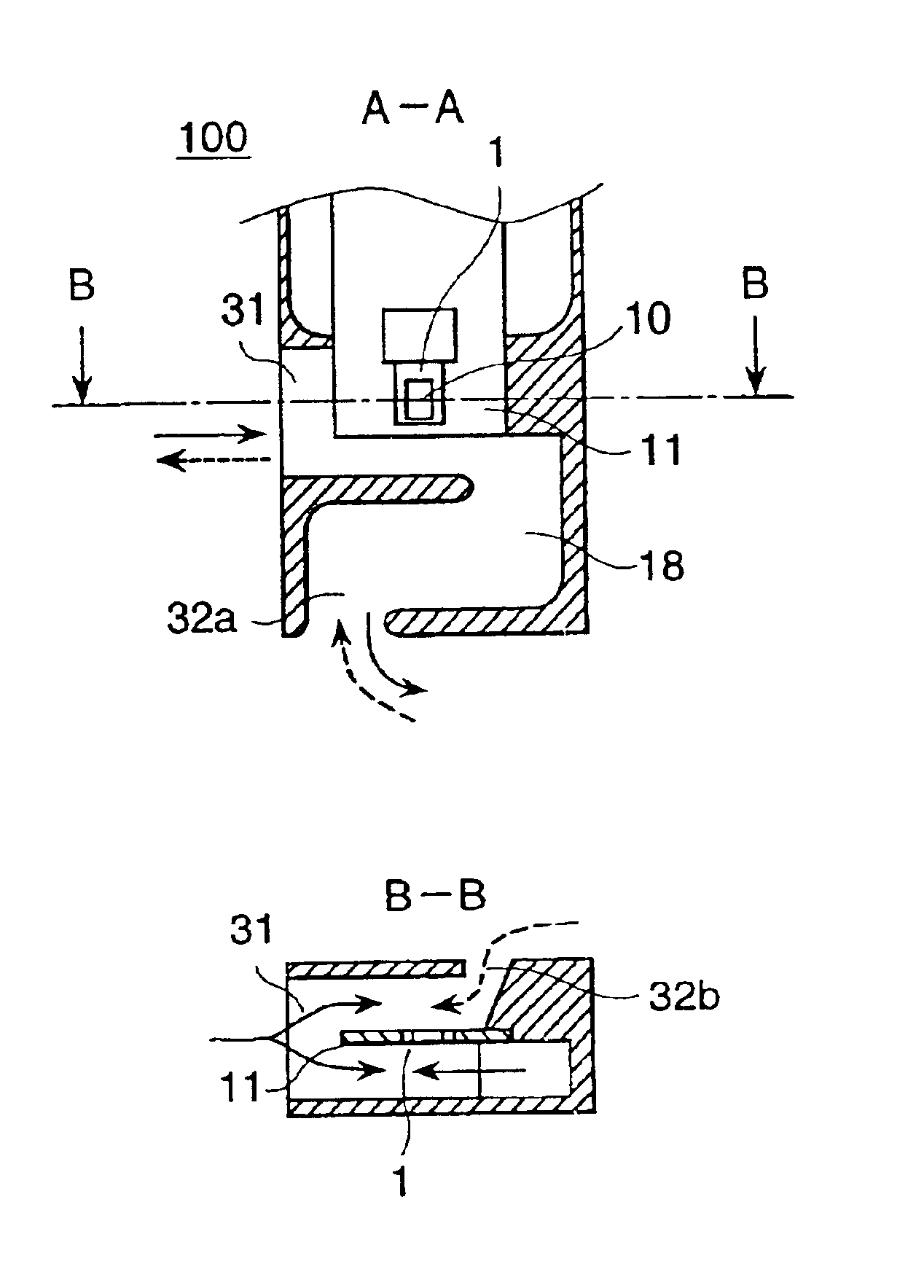
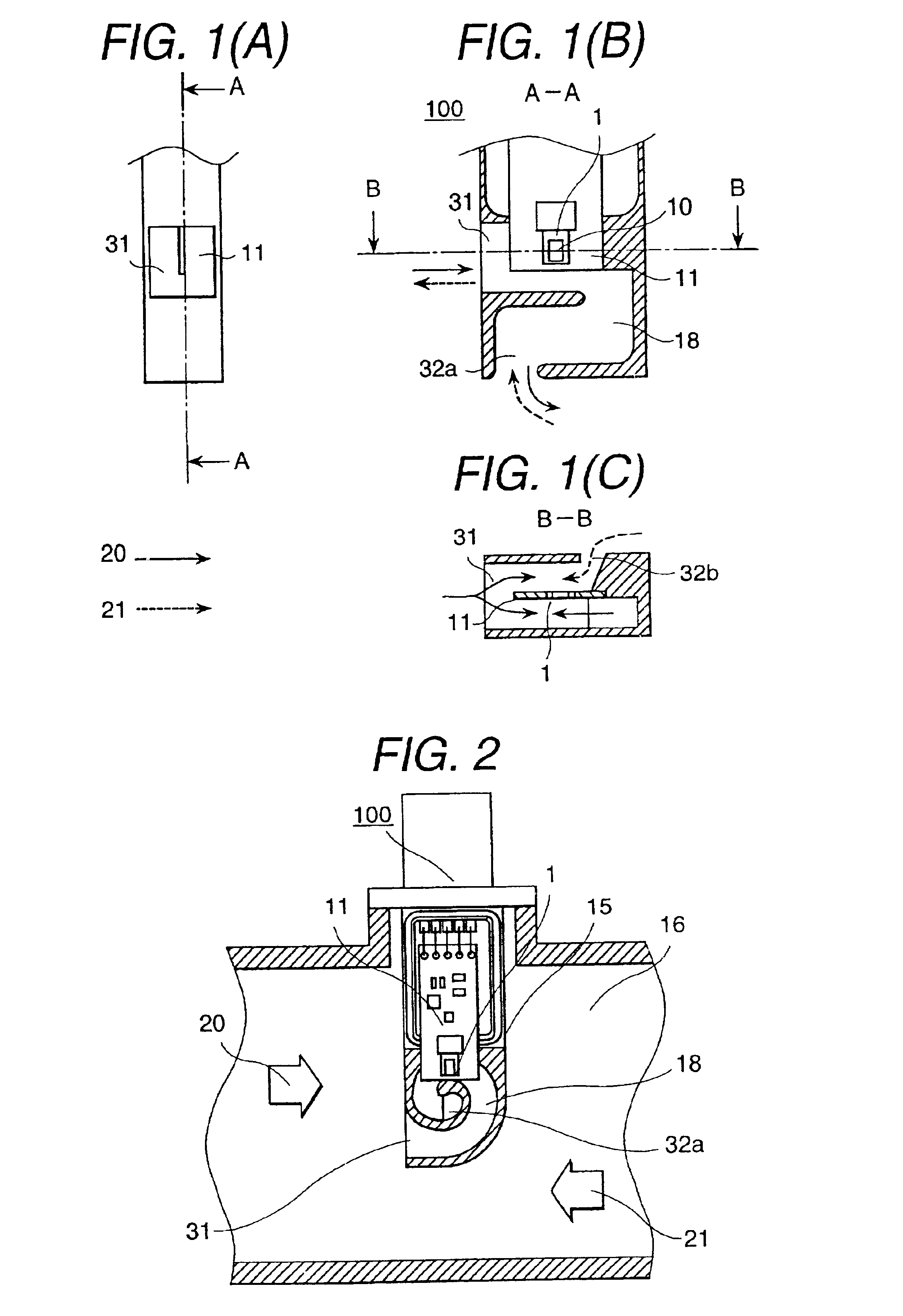
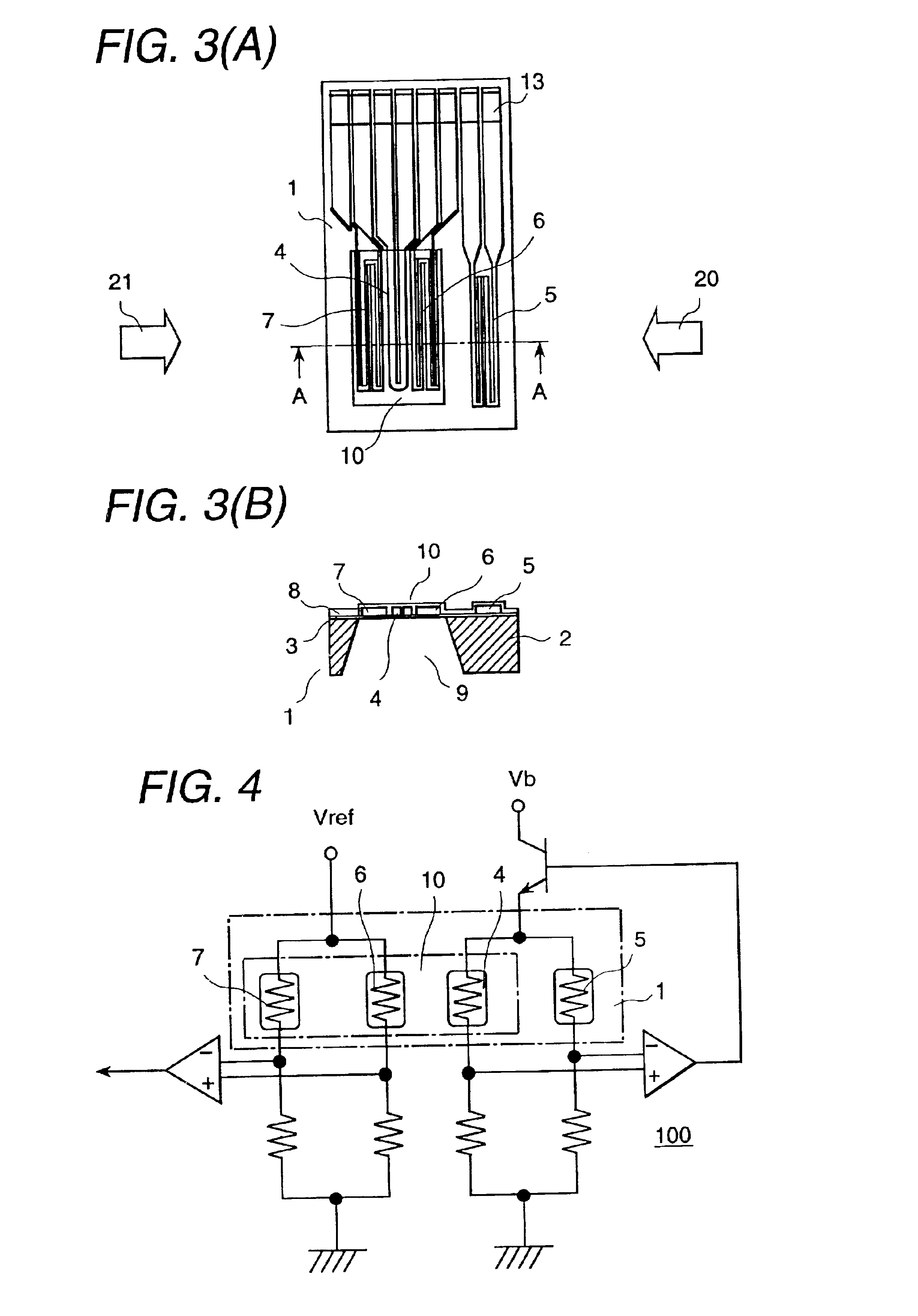
Thermal-type flow meter with bypass passage
InactiveUS6851311B2Electrical controlVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
System for evaluating cardiac surgery training
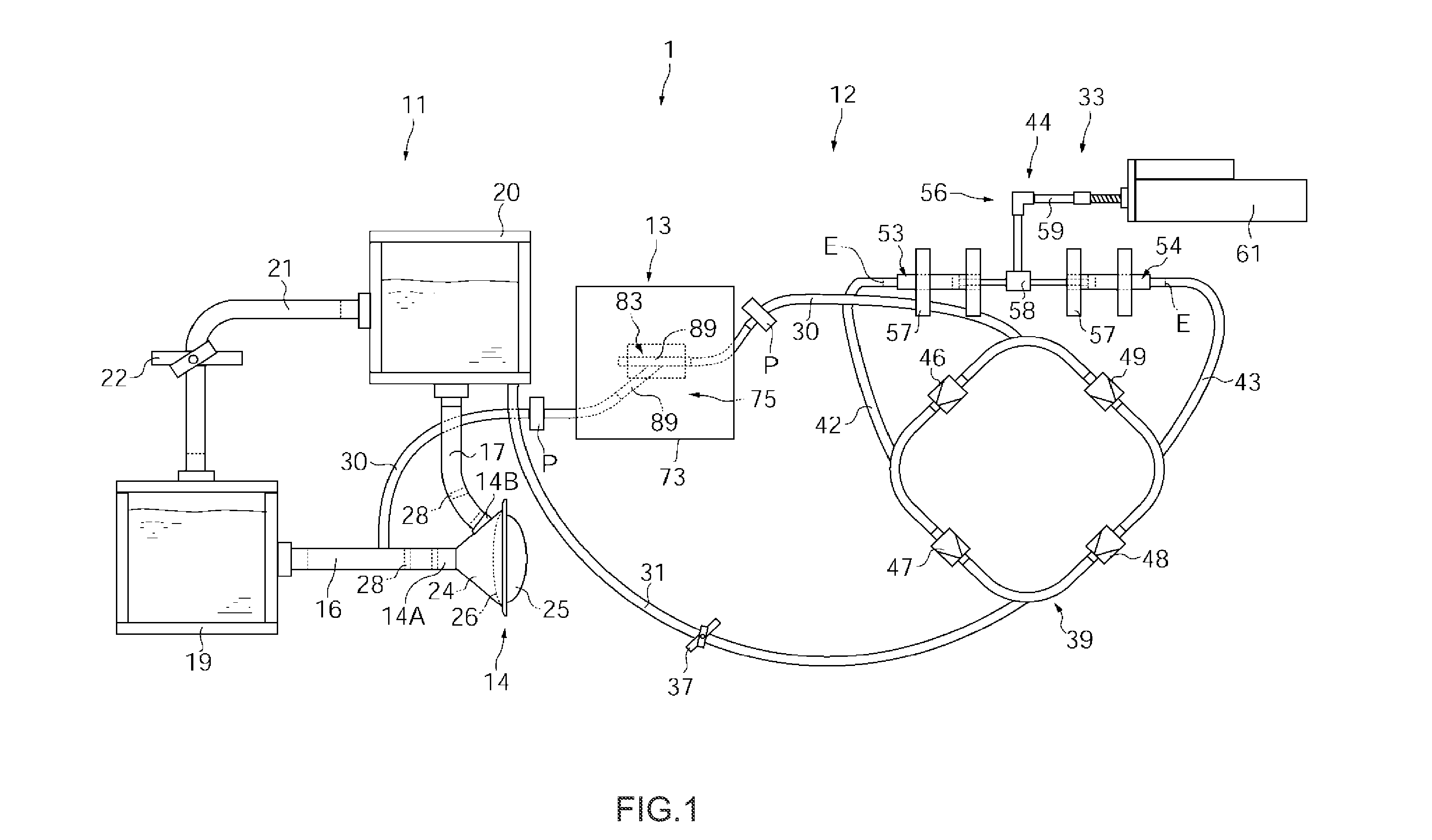
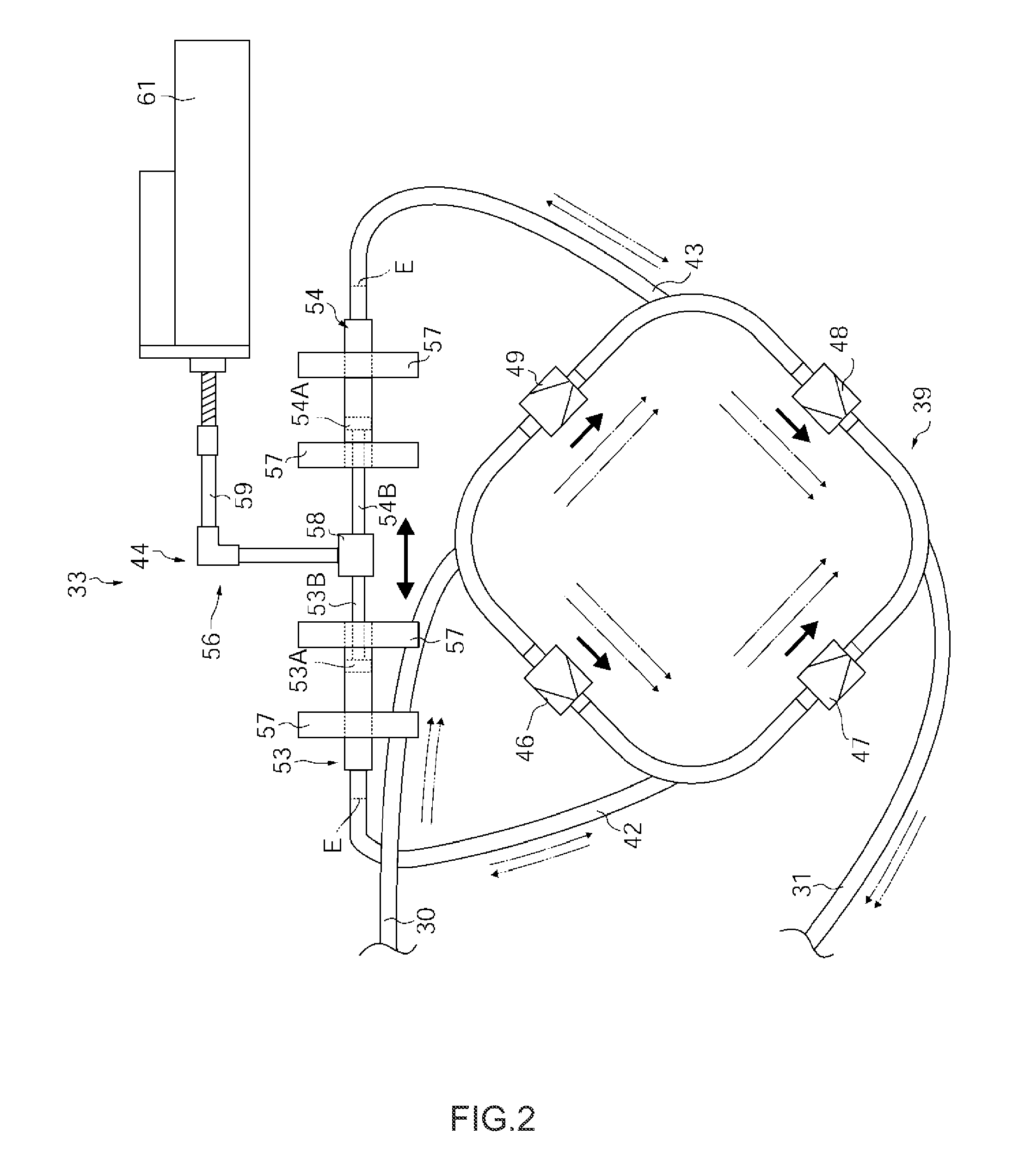
InactiveUS20110217684A1Accurate assessmentDevice miniaturizationSurgeryEducational modelsCoronary arteriesSurgery training
A system for evaluating training 1 comprises a pulsating flow generating unit 11 for imparting a pulsating flow to a designated fluid, a coronary artery flow generating unit 12 that branches off from that pulsating flow generating unit 11 and by which a flow condition of that pulsating flow can be converted to generate a coronary artery flow, and a surgery training unit 13 provided between the pulsating flow generating unit 11 and the coronary artery flow generating unit 12 and that operates to enable coronary artery bypass surgery training under pulsation. This system for evaluating training 1 has a circuit configured to enable the coronary artery flow fluid generated by the coronary artery flow generating unit 12 to pass through a simulated blood vessel that has been subjected to a designated treatment in training using the surgery training unit 13.
Owner:PARK YOUNG KWANG +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com