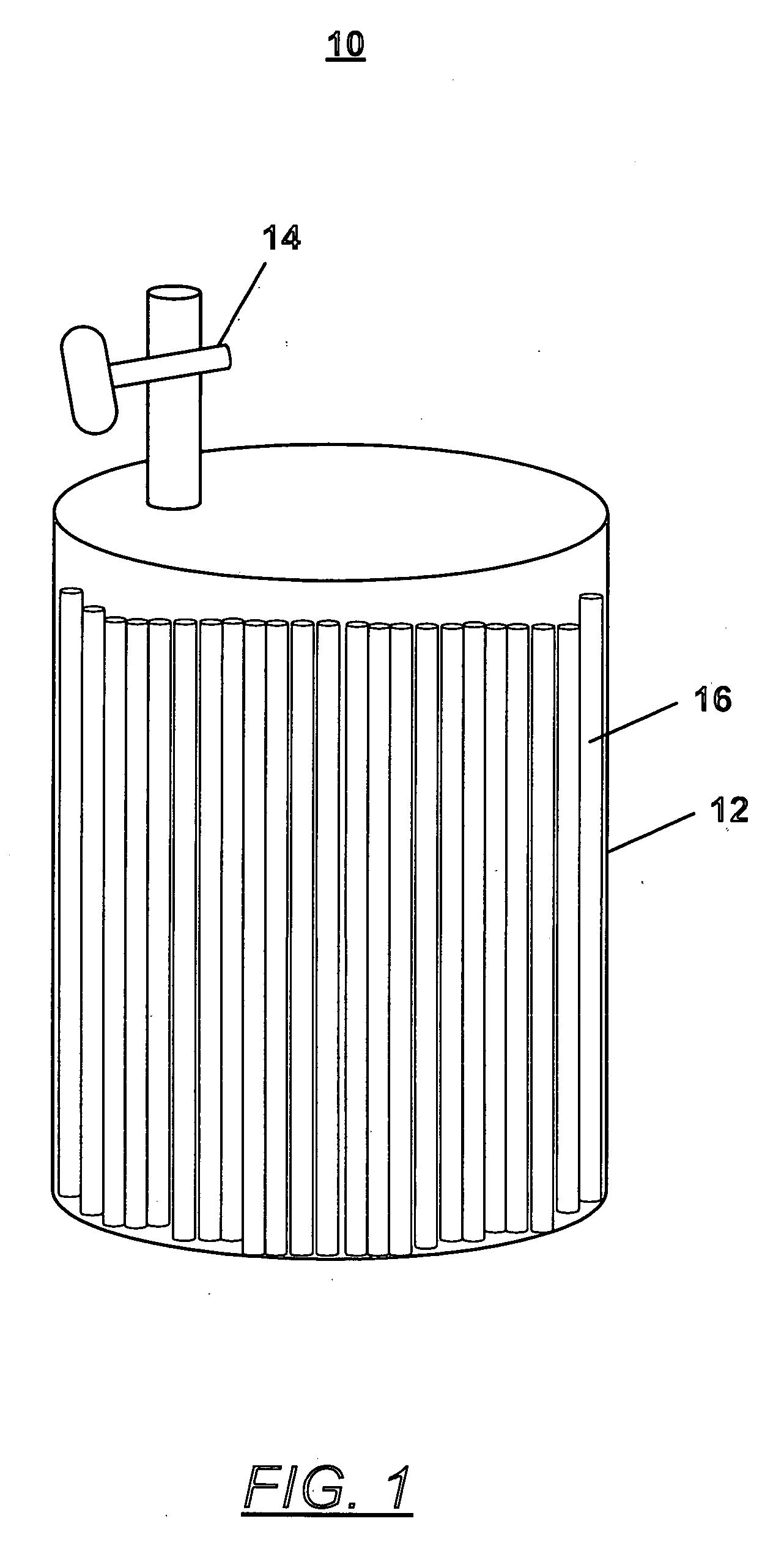
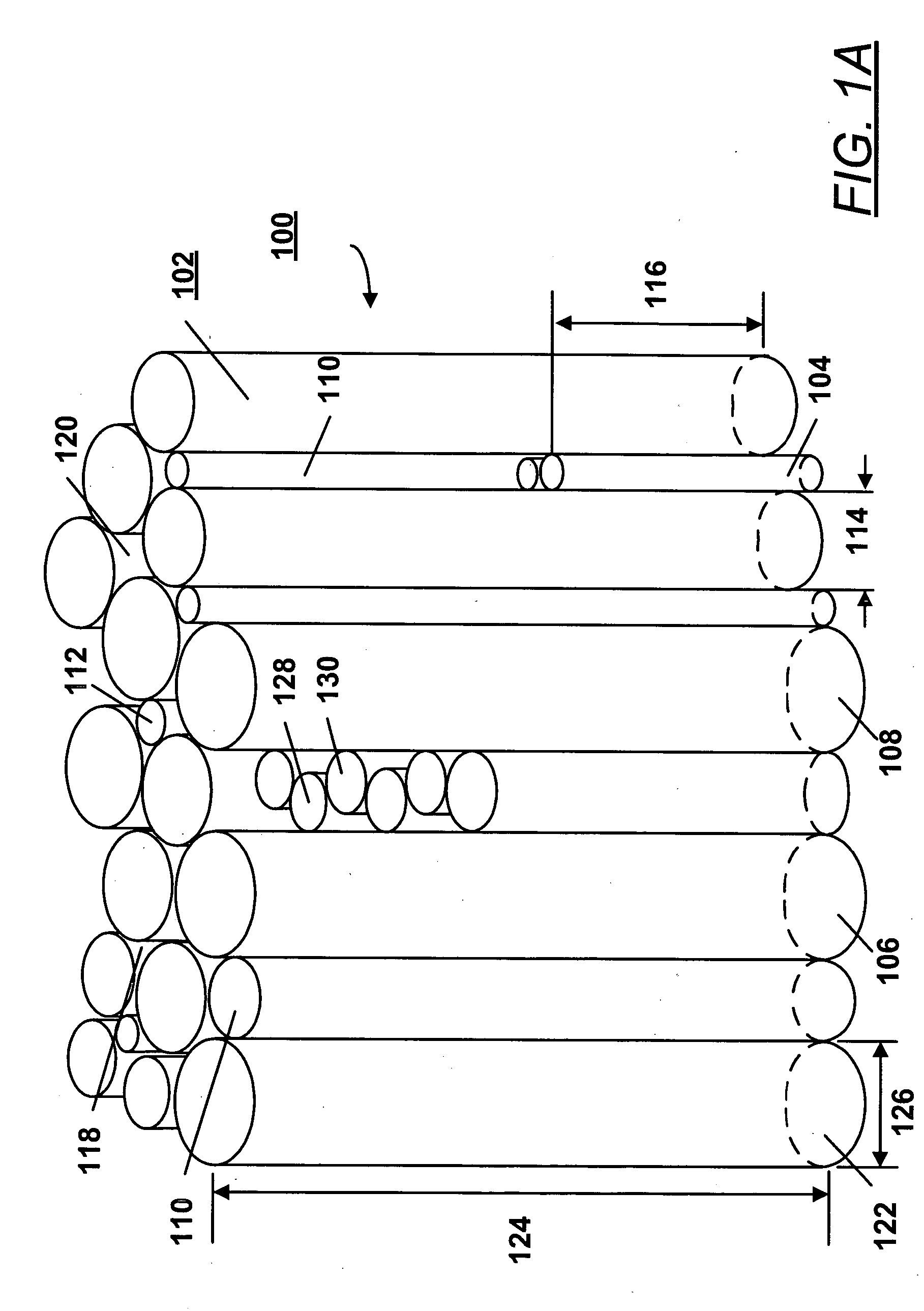
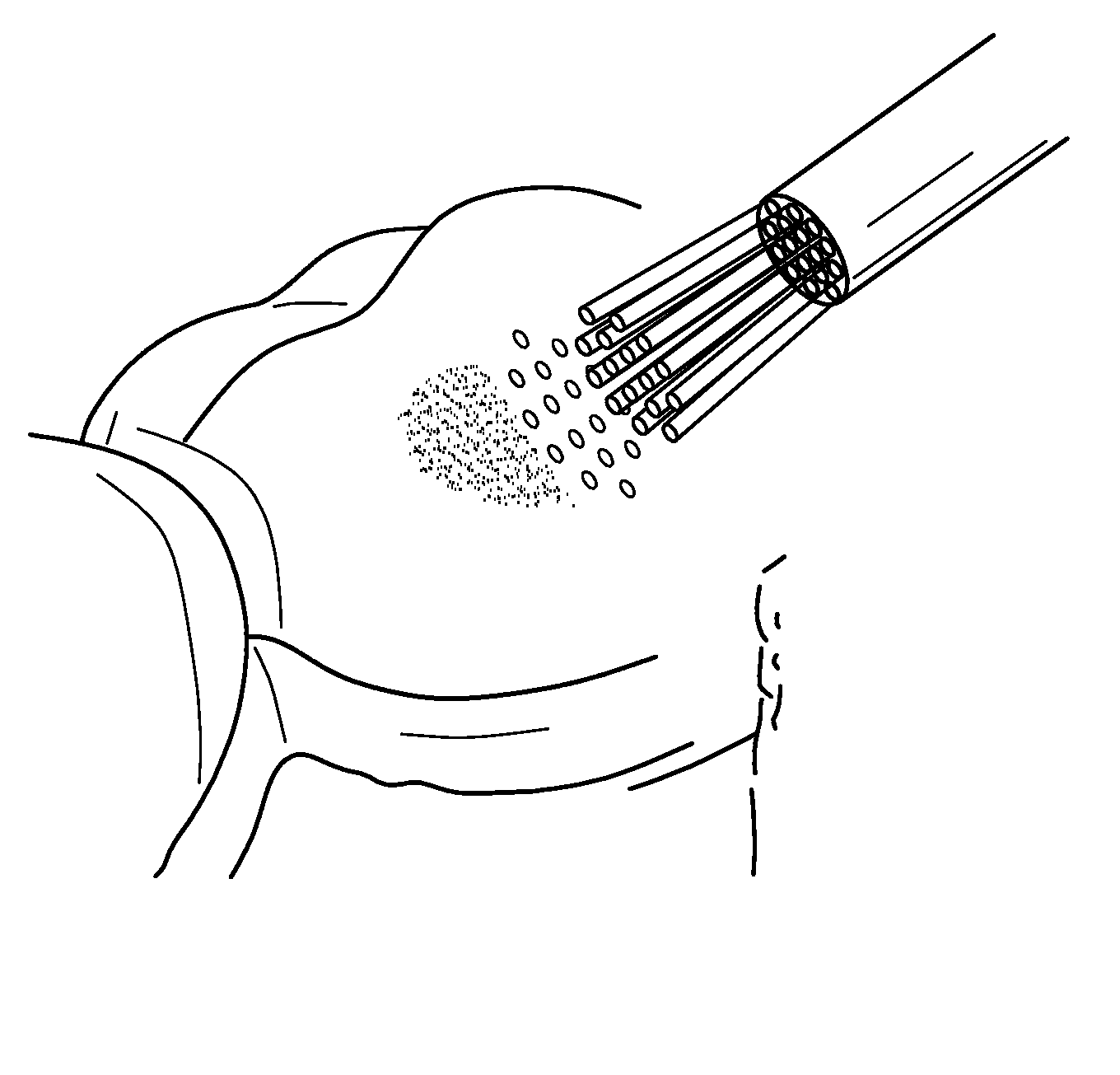
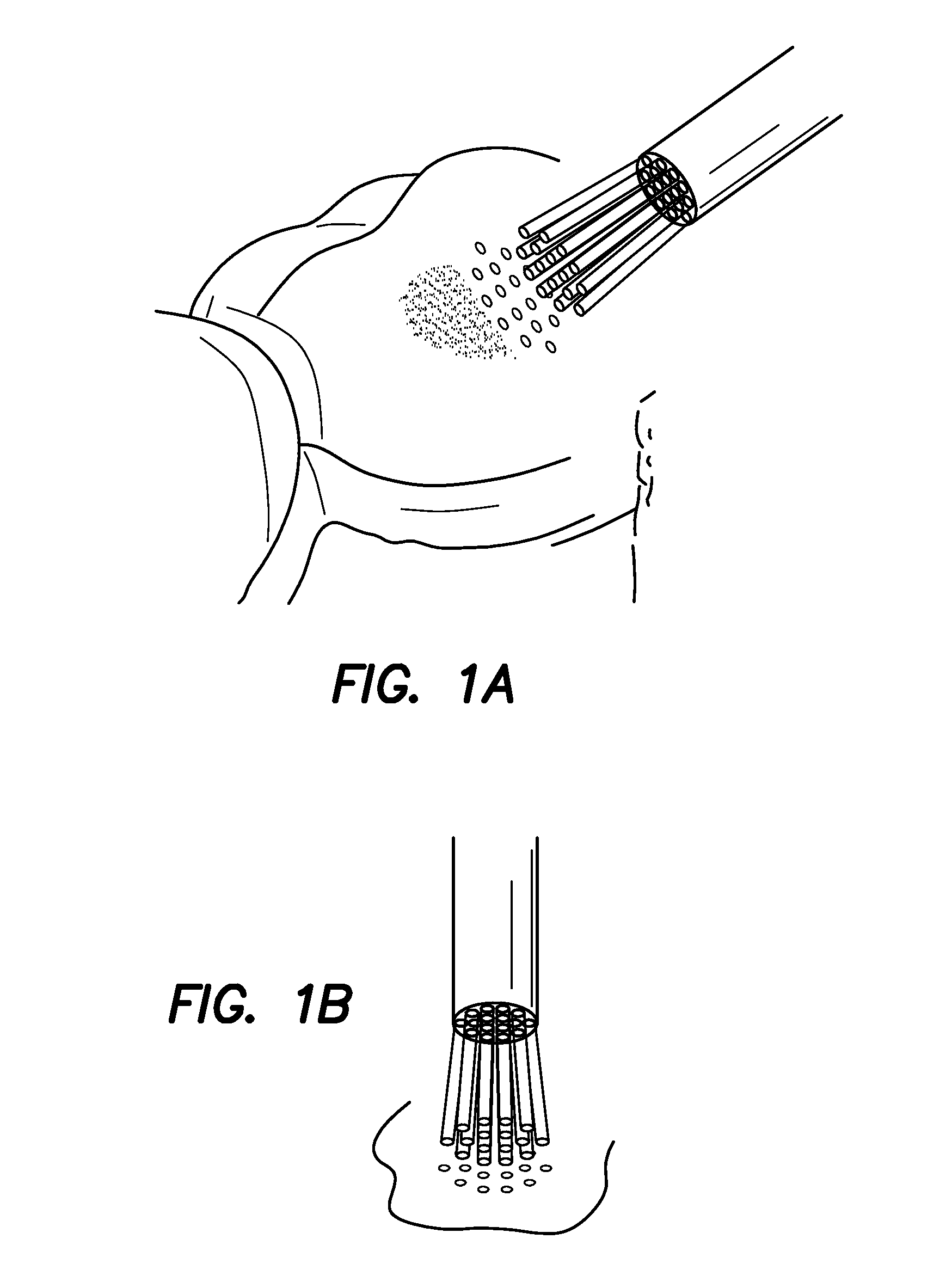
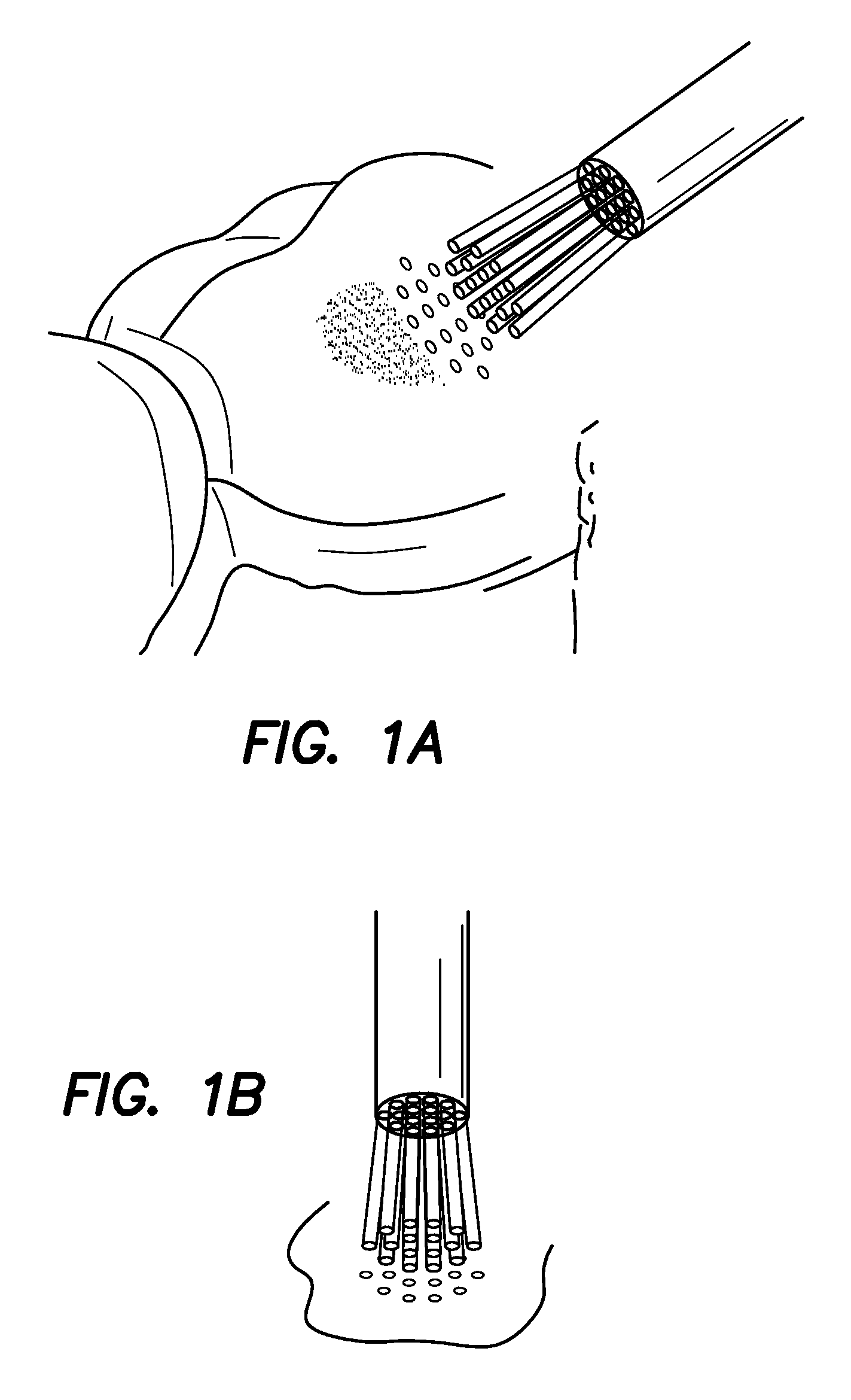
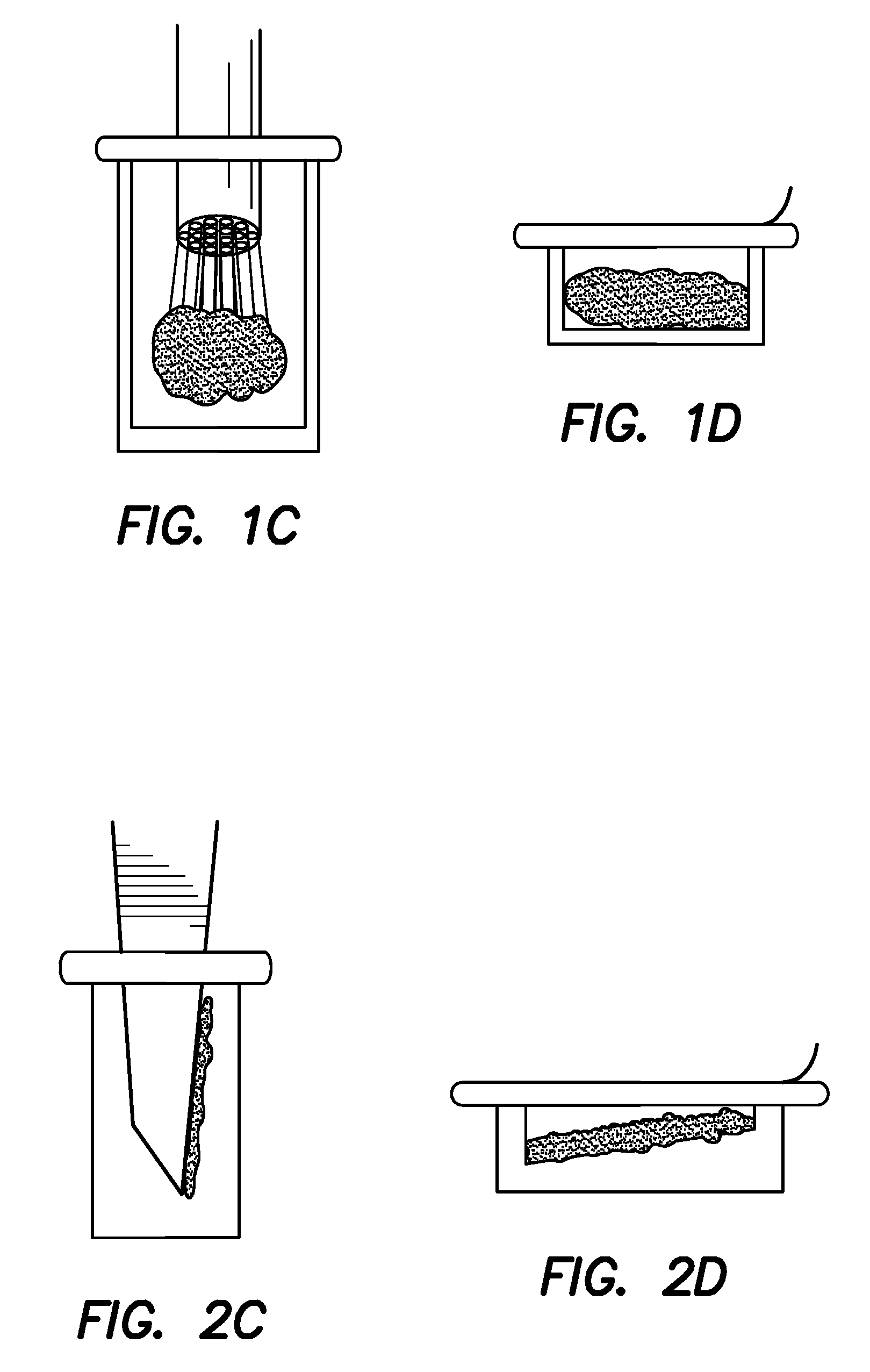
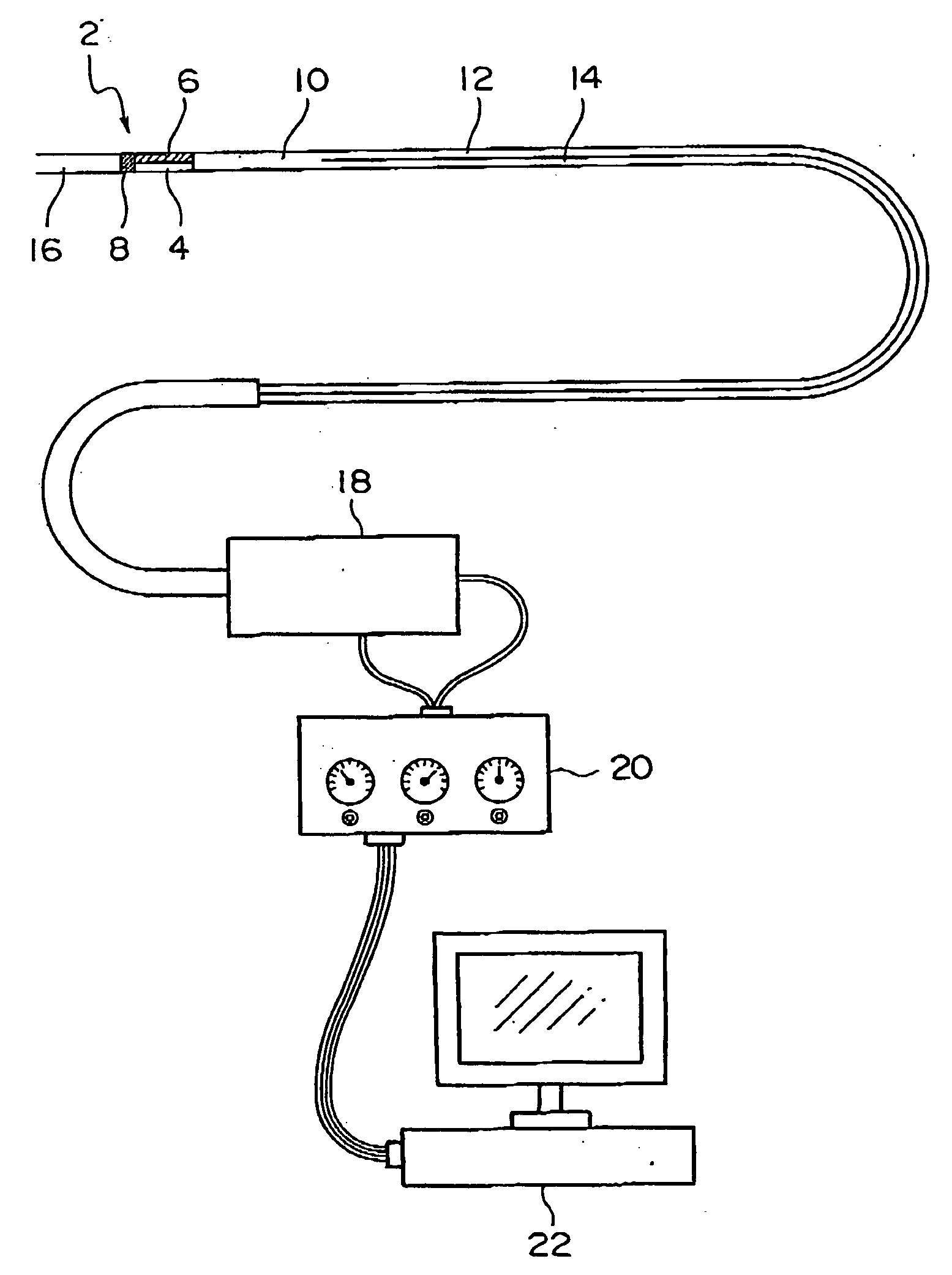
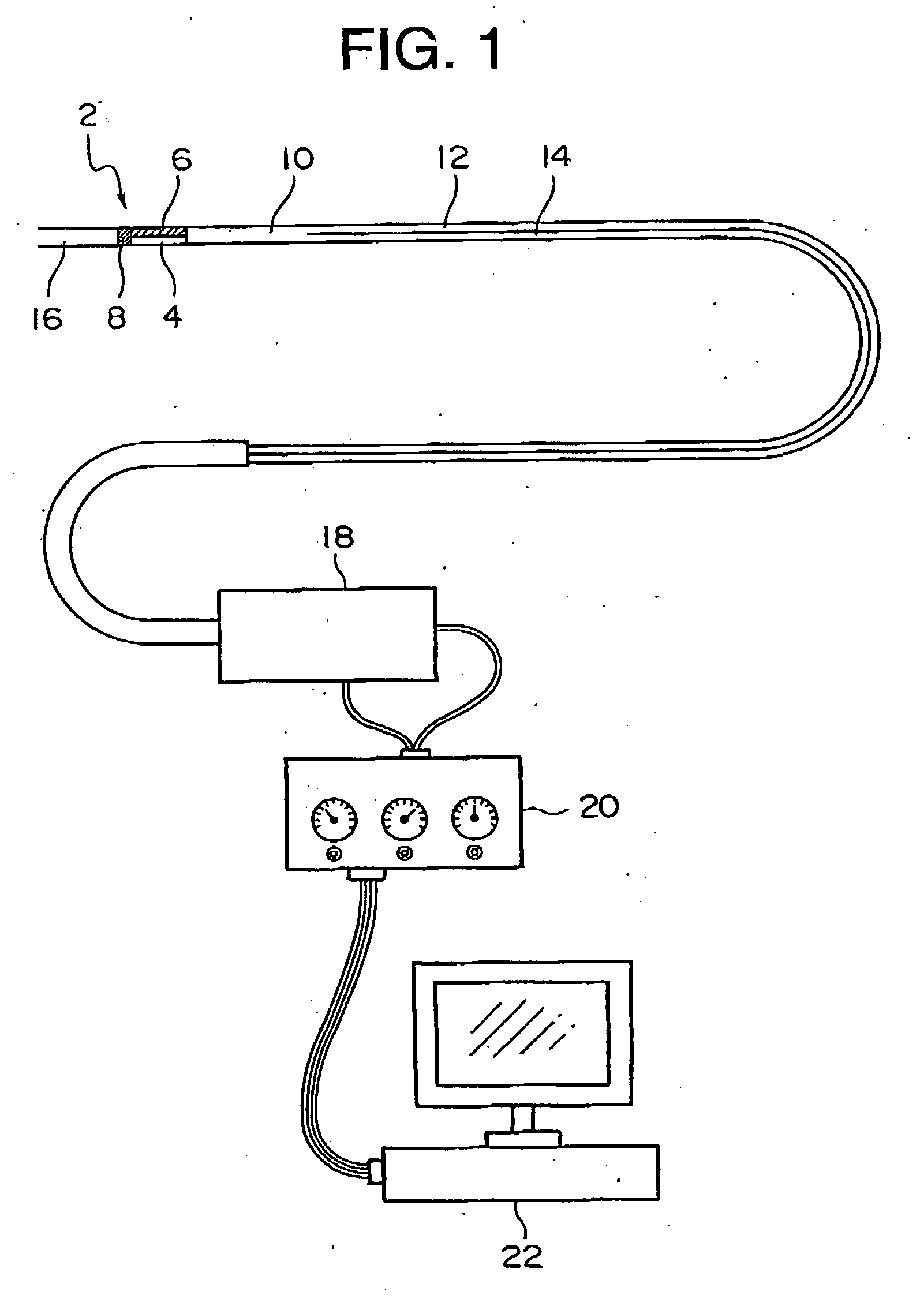
Patents
Literature
172 results about "Tubule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A tubule is: a small tube or fistular structure a minute tube lined with glandular epithelium any hollow cylindrical body structure a minute canal found in various structures or organs of the body a slender elongated anatomical channel
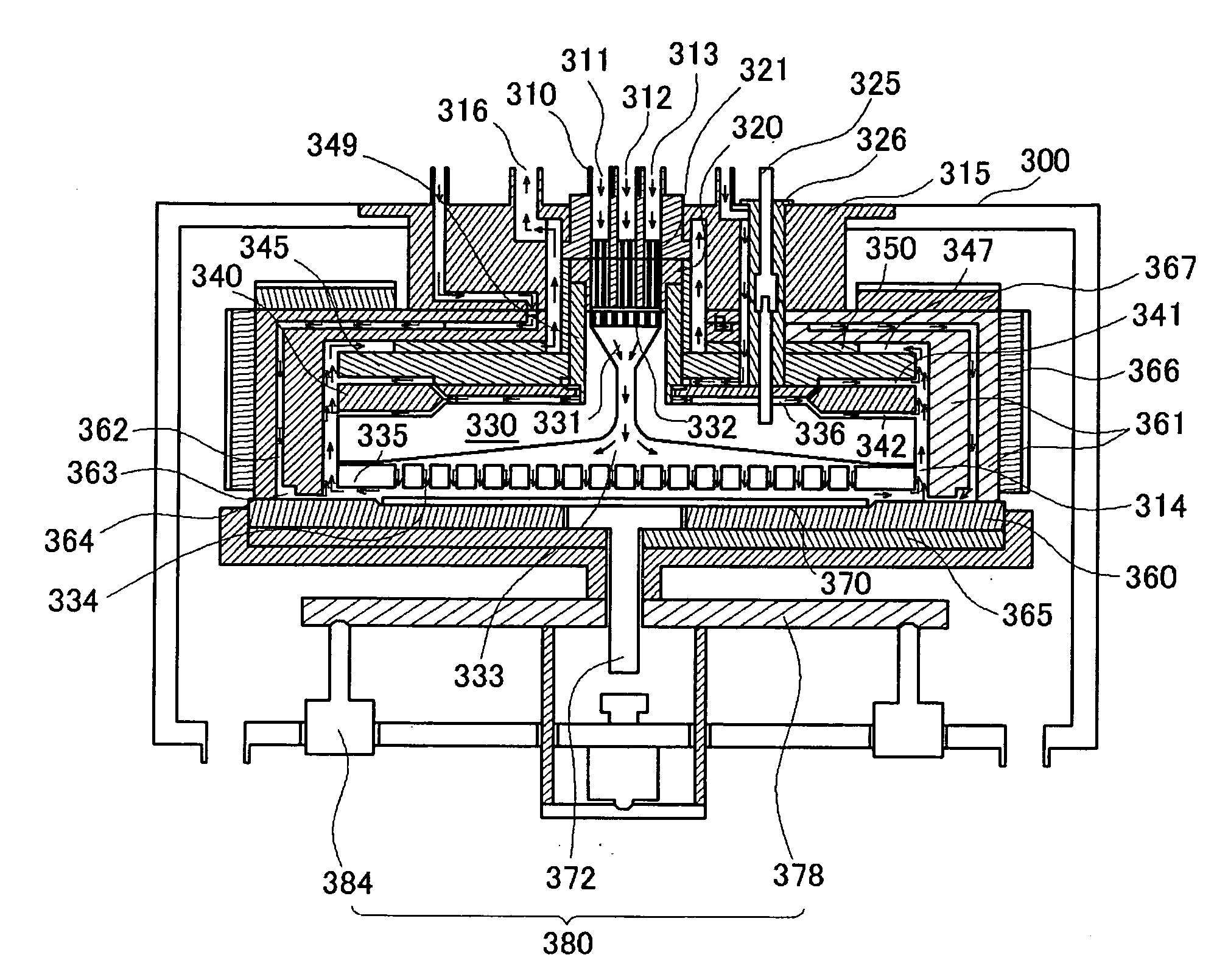
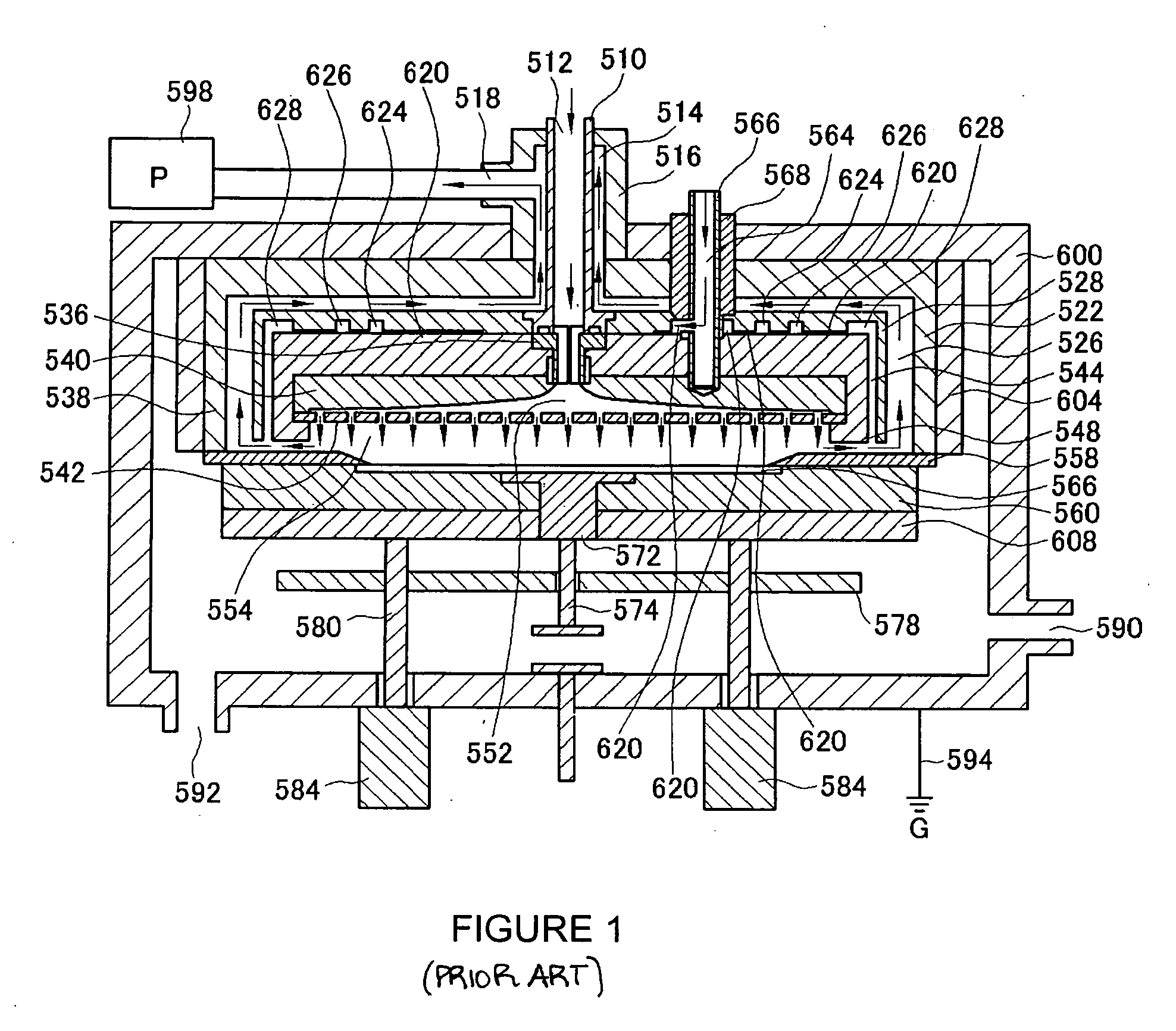
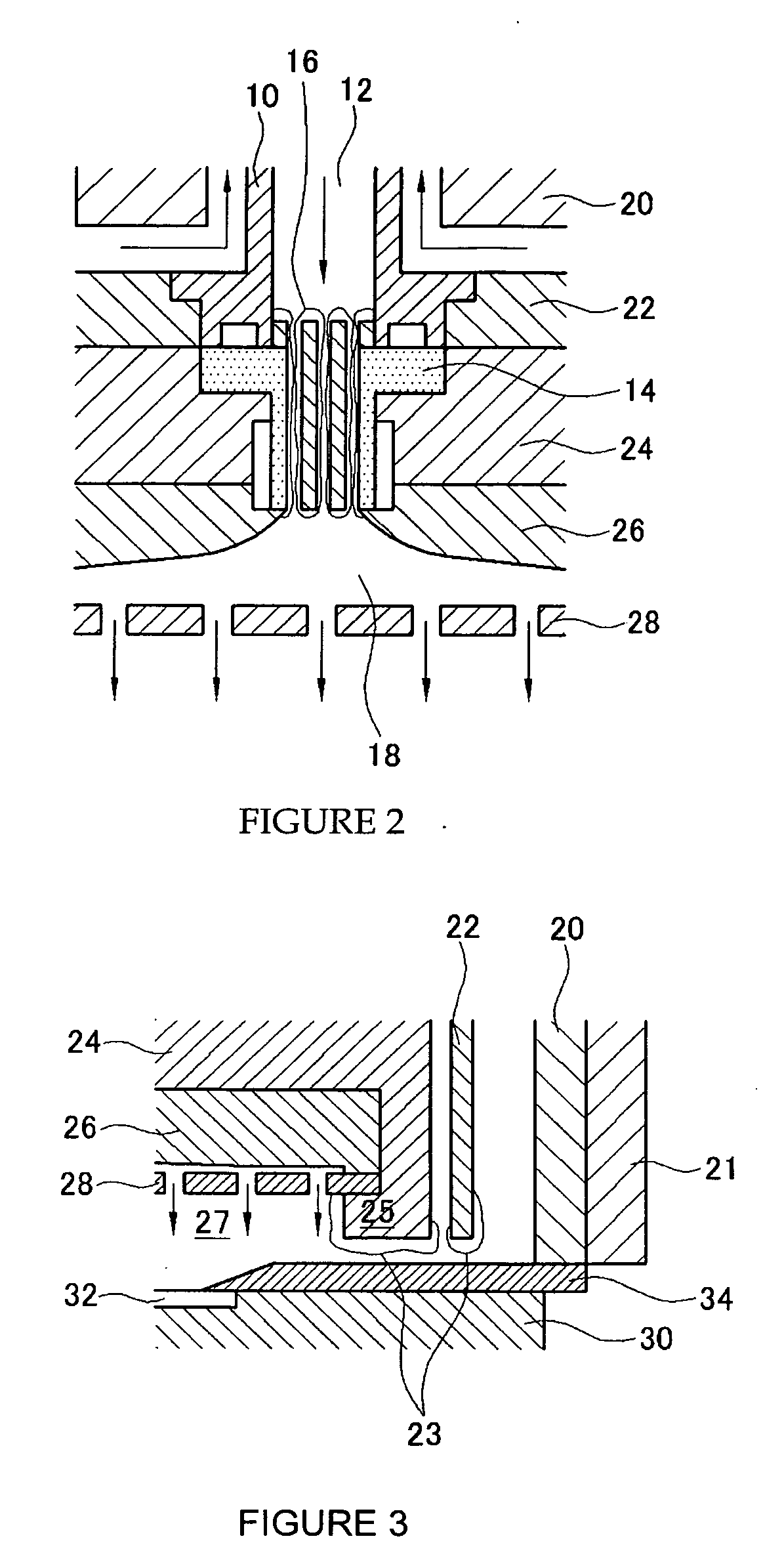
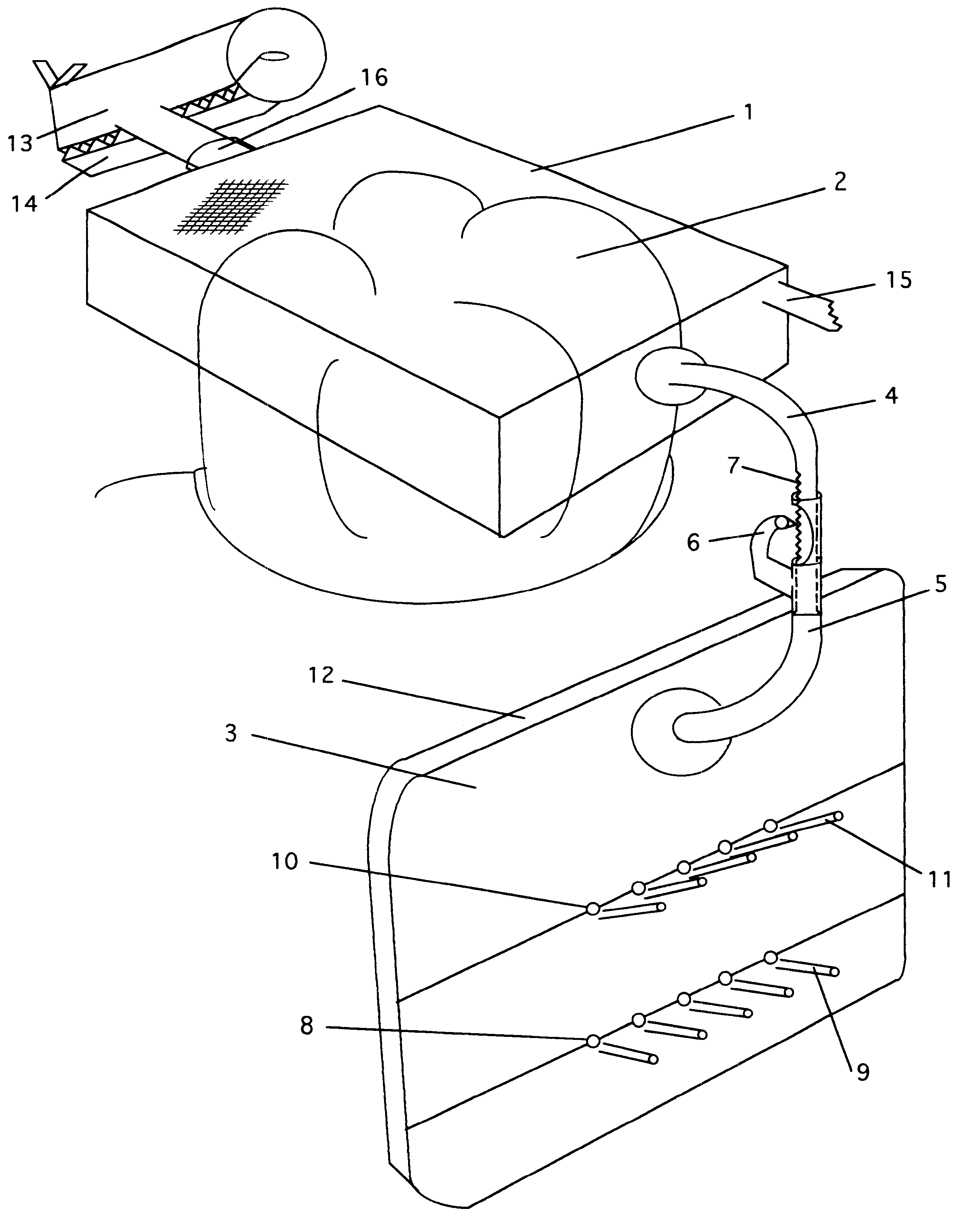
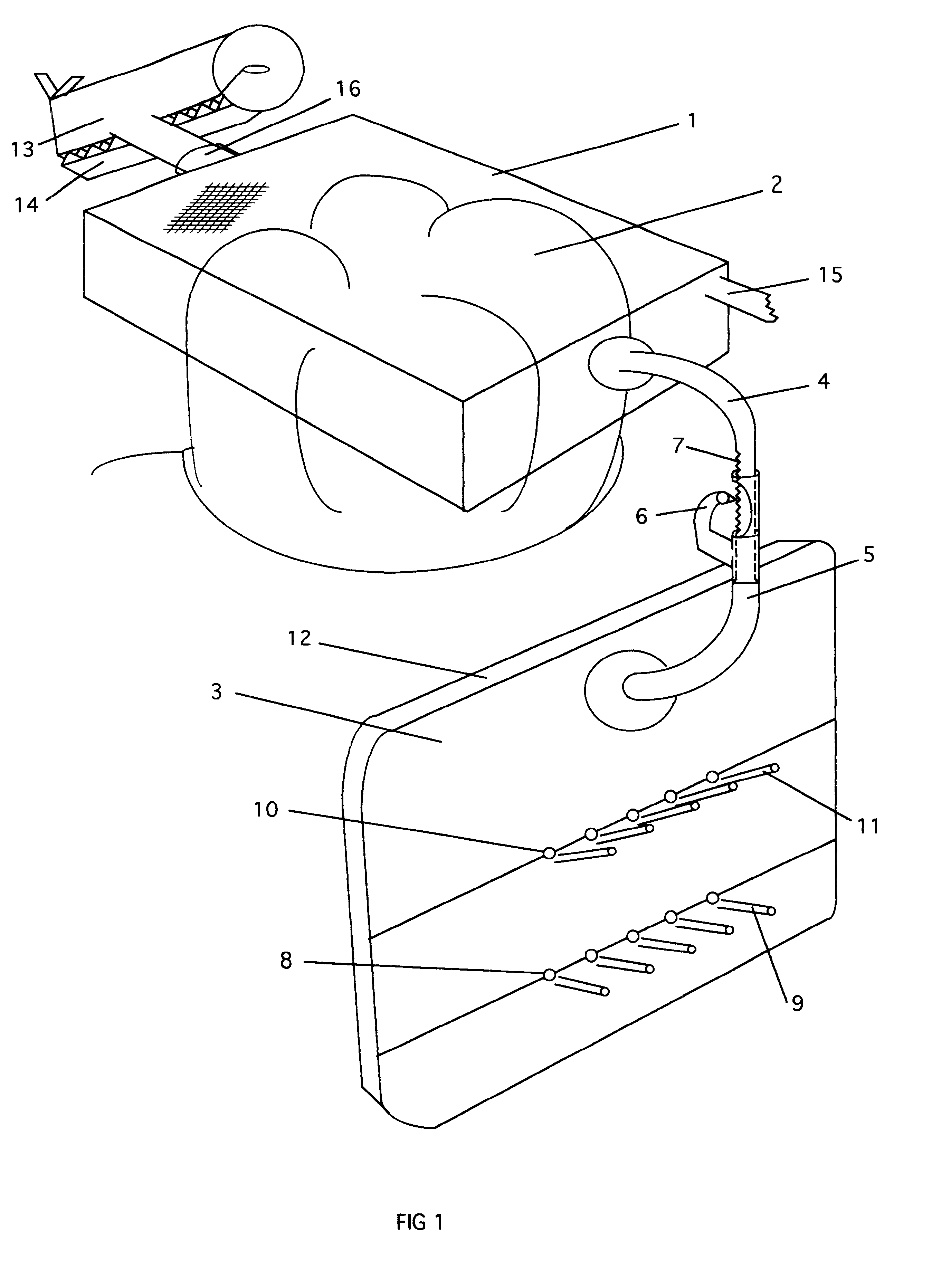
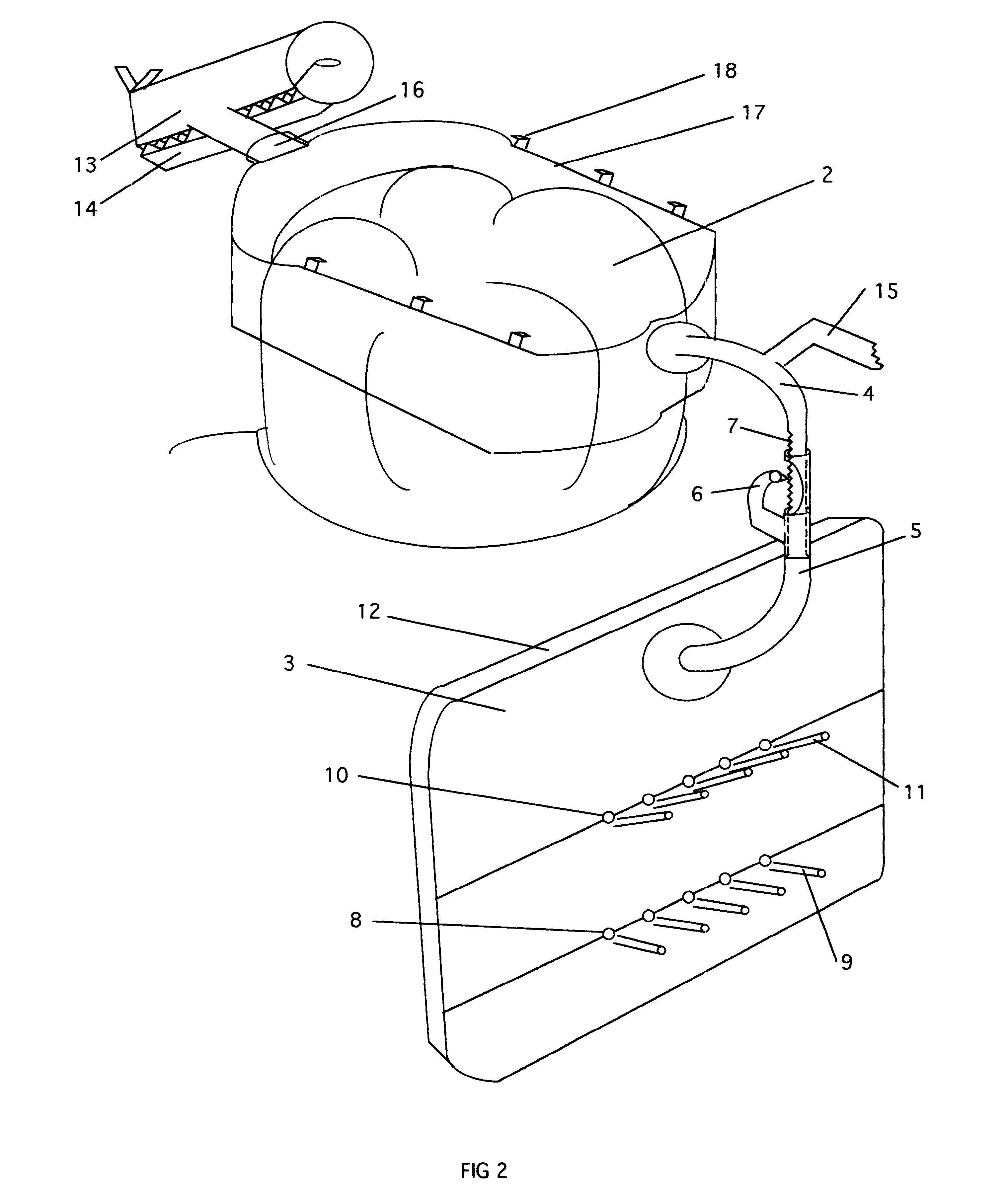
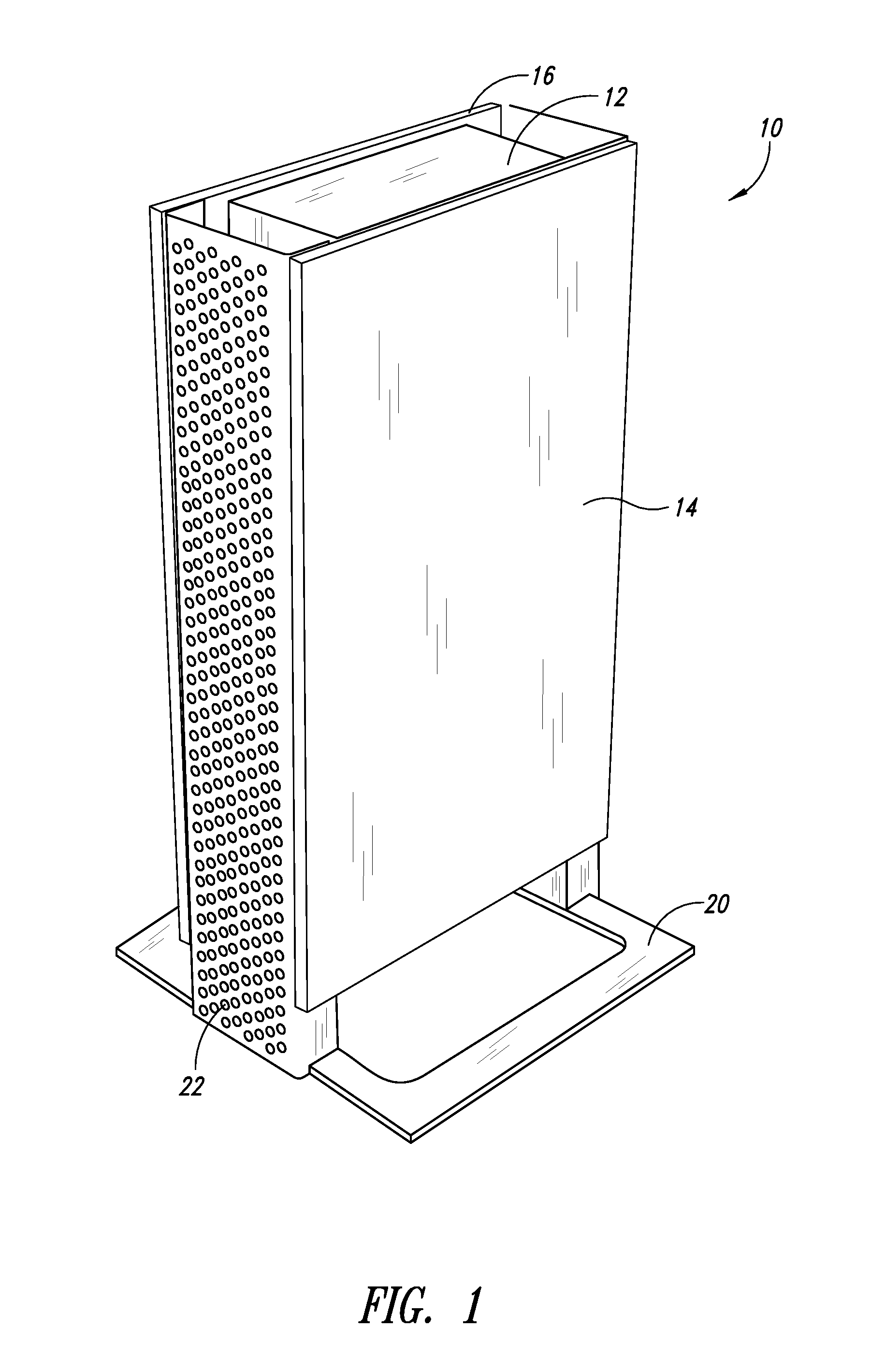
Atomic layer deposition apparatus
InactiveUS20060137608A1Uniform thicknessEasy to controlChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringAtomic layer deposition
An atomic layer deposition (ALD) apparatus is, suitable for thermal ALD and plasma-enhanced ALD of conductive and non-conductive films. The ALD apparatus can maintain electrical insulation of a gas dispersion structure, such as a showerhead assembly, which acts as an RF electrode to generate plasma inside a reaction chamber while depositing electrically conductive films in the reaction chamber. Fine tubules of micro-feeding tube assembly prevents plasma generation in them and reactive gases each have separate flow paths through the micro-feeding tube assembly. Process gases out of the micro-feeding tube assembly enter narrow grooves of a helical flow inducing plate and form helical flows which mix well each other. Symmetrically mounted pads on showerhead assembly and flow guiding plate maintain a symmetrical gap through which an inert gas flows continuously to keep reactive gases outside the gap and unwanted film deposition in the gap. Longer operating time before maintenance (cleaning) and thus higher productivity can be achieved.
Owner:ASM GENITECH KOREA
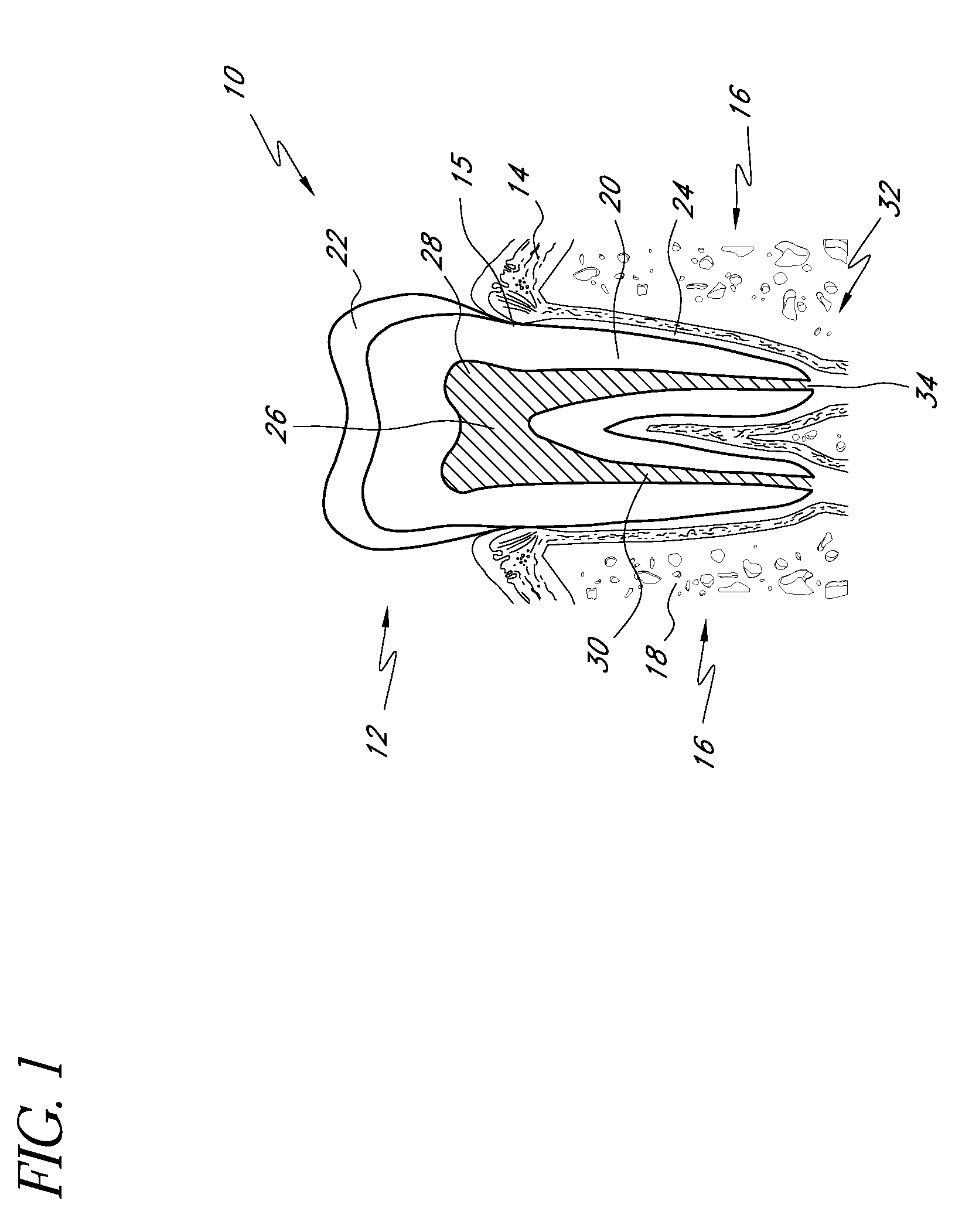
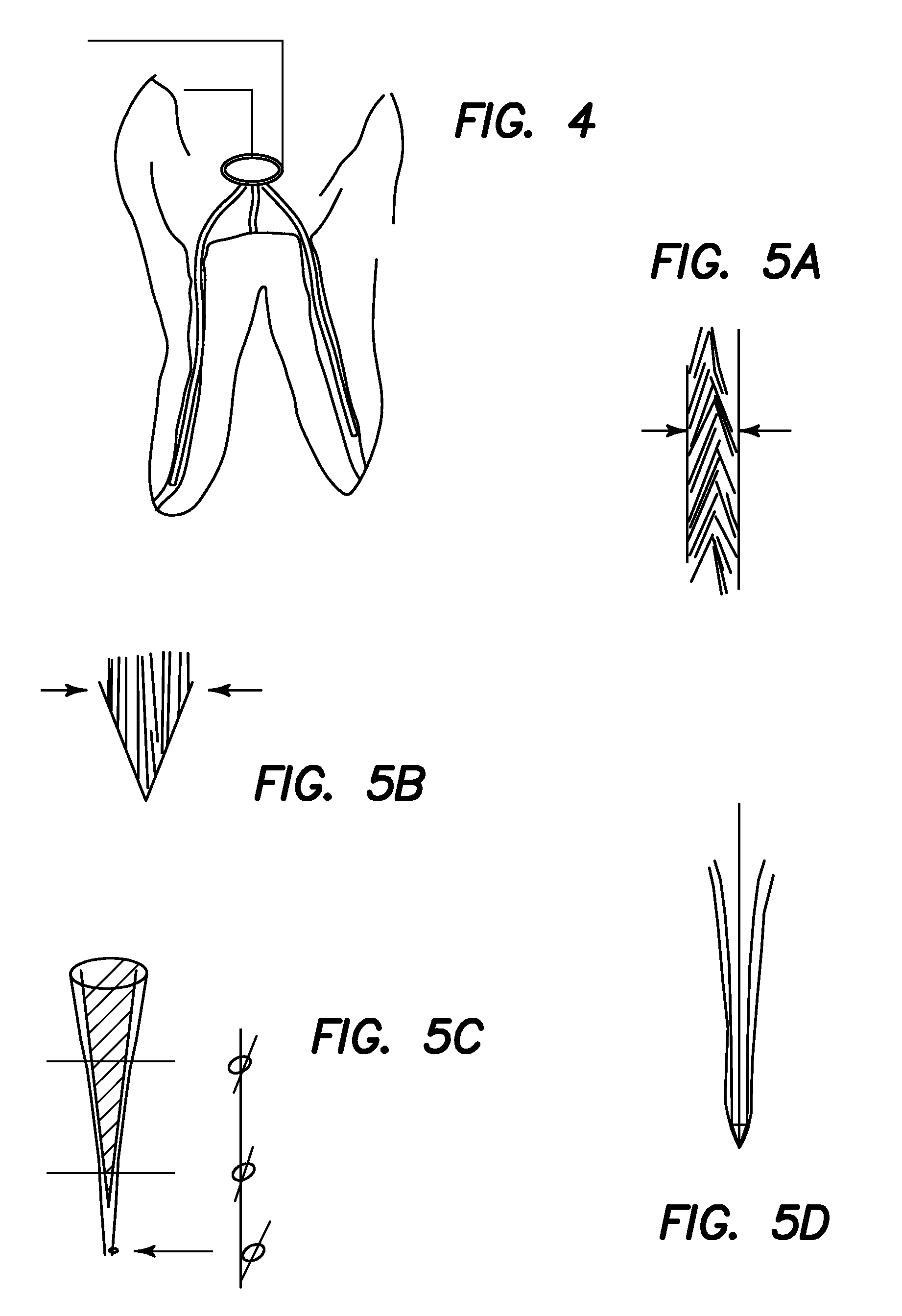
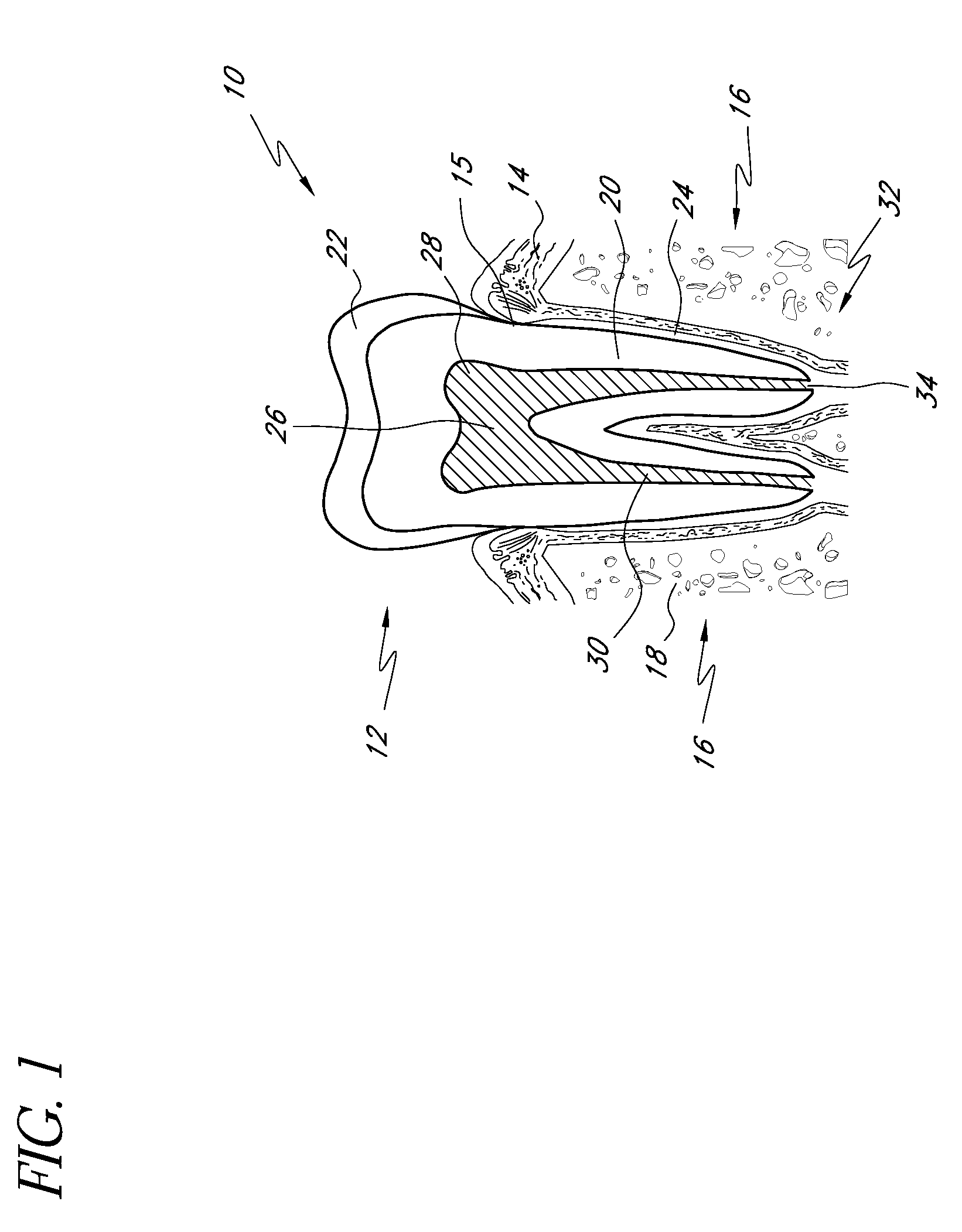
Apparatus and methods for treating root canals of teeth
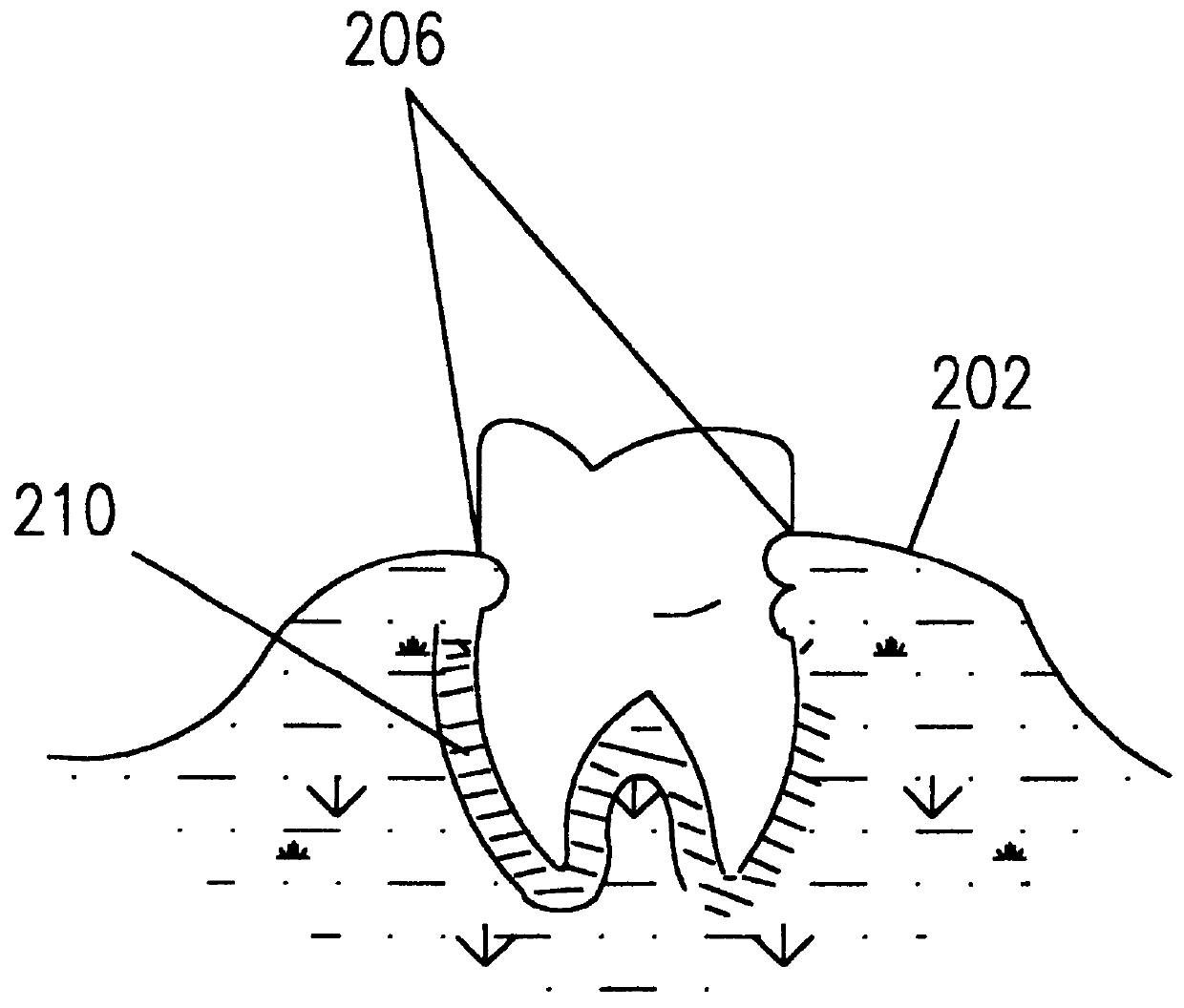
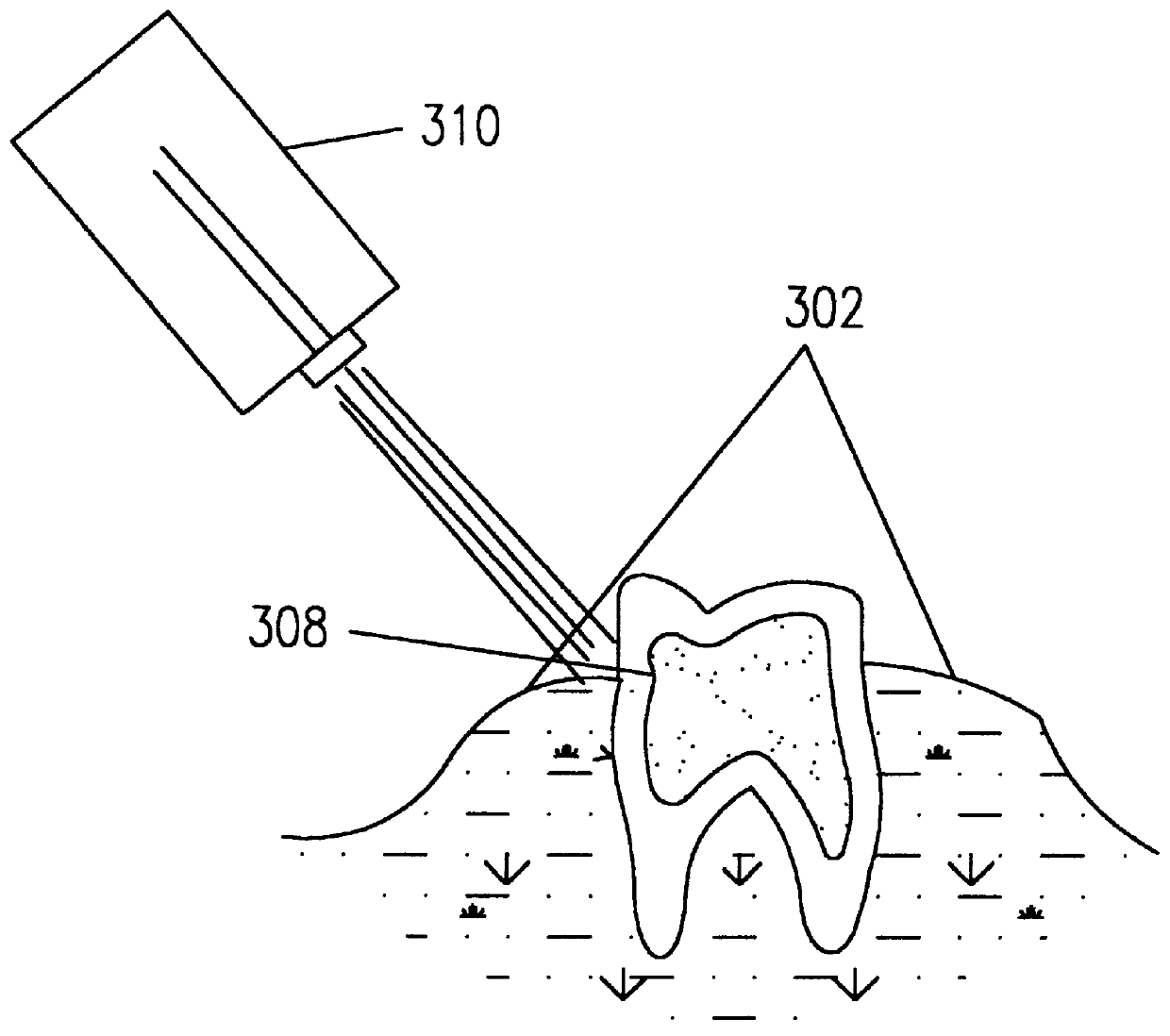
Apparatus and methods for endodontic treatment of teeth provide effective cleaning of organic material (such as pulp and diseased tissue) from the root canal system. In an embodiment, a compressor system generates high pressure liquid (e.g., water) that flows through an orifice to produce a high-velocity collimated jet of liquid. The high-velocity jet is directed toward a surface of a tooth, for example, an exposed dentinal surface, and impingement of the jet onto the surface generates an acoustic wave that propagates throughout the tooth. The acoustic wave effectively detaches organic material from dentinal surfaces and tubules. The detached organic material is flushed from the root canal system by the liquid jet and / or by additional irrigation.
Owner:SONENDO
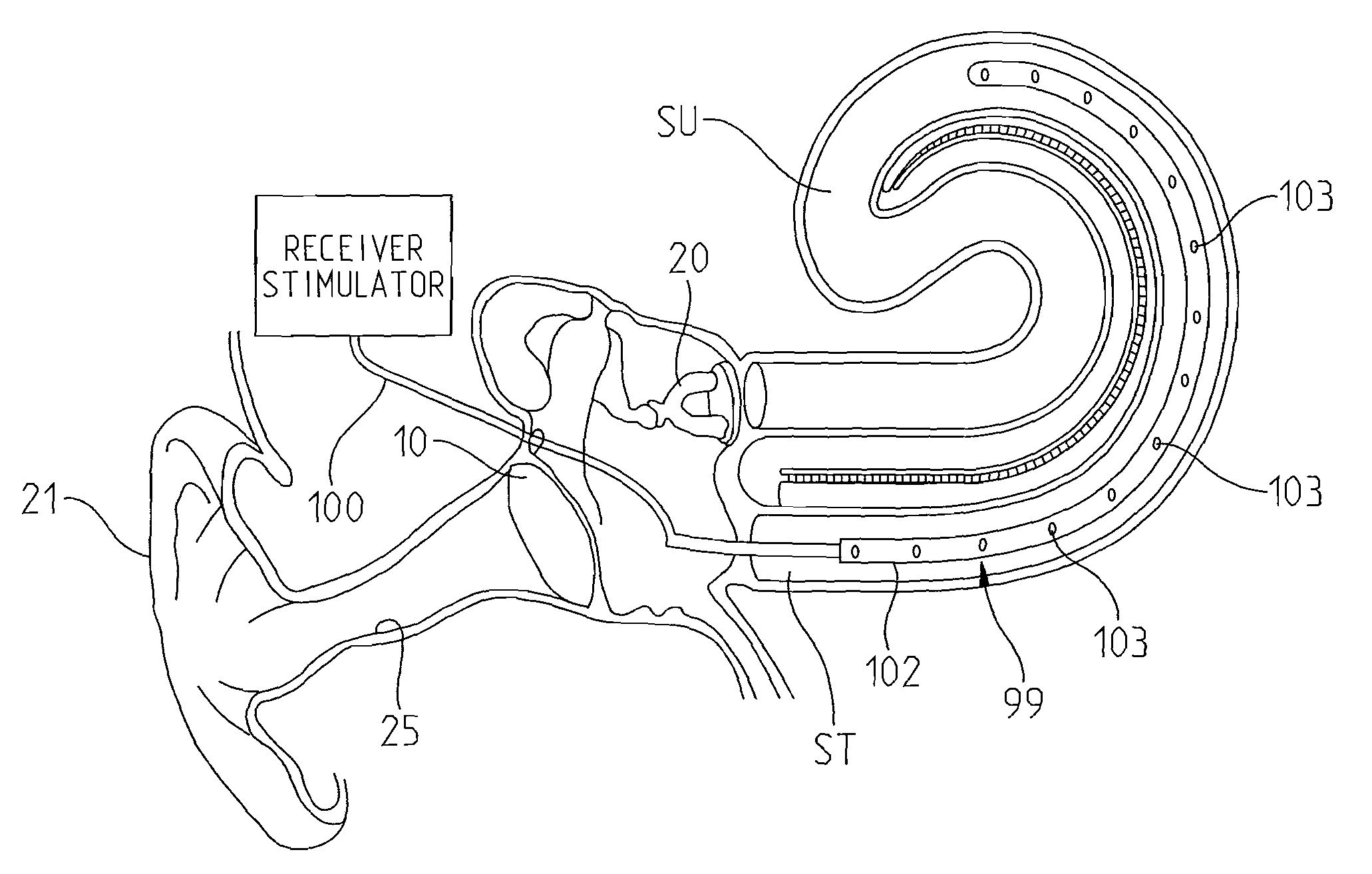
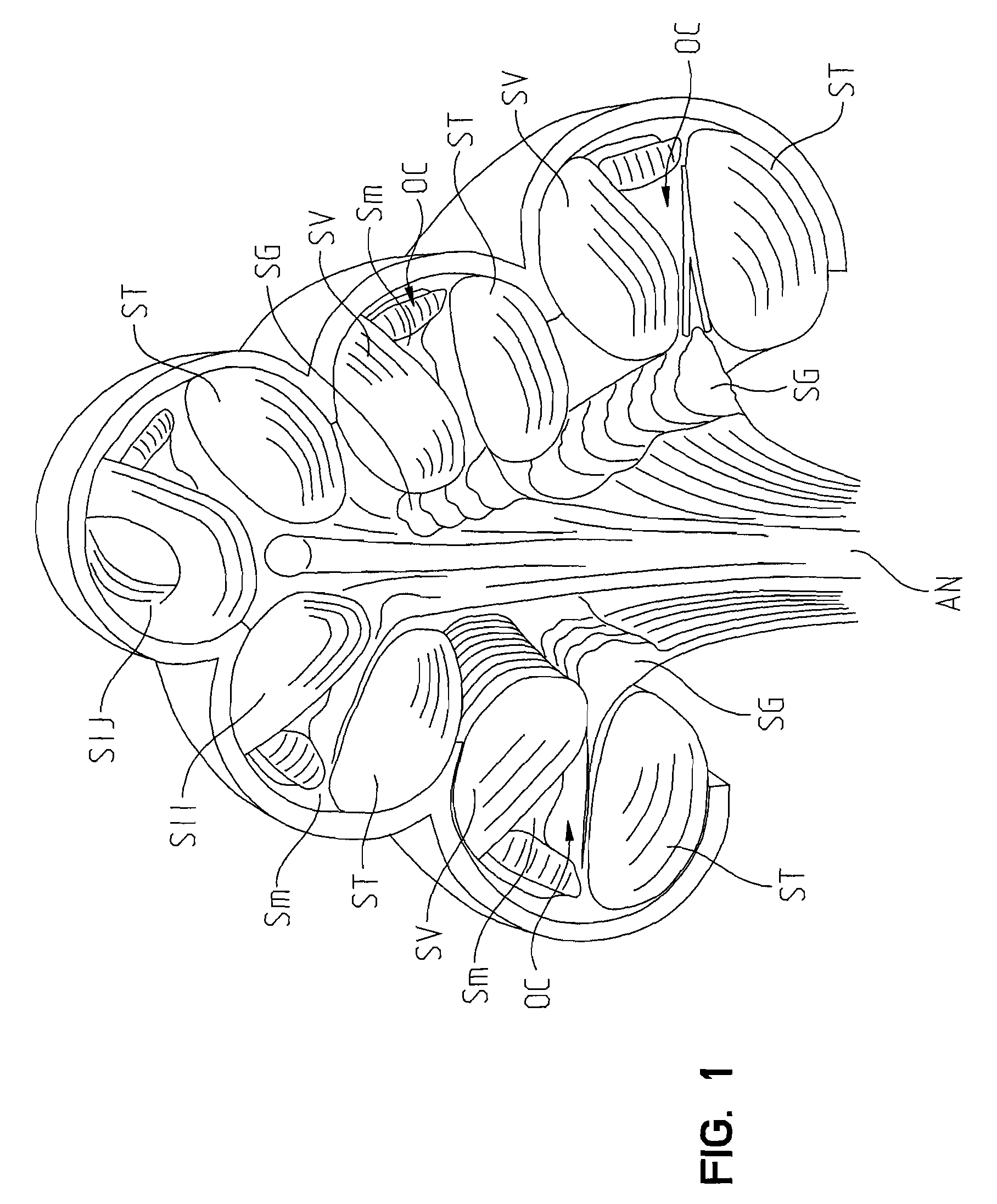
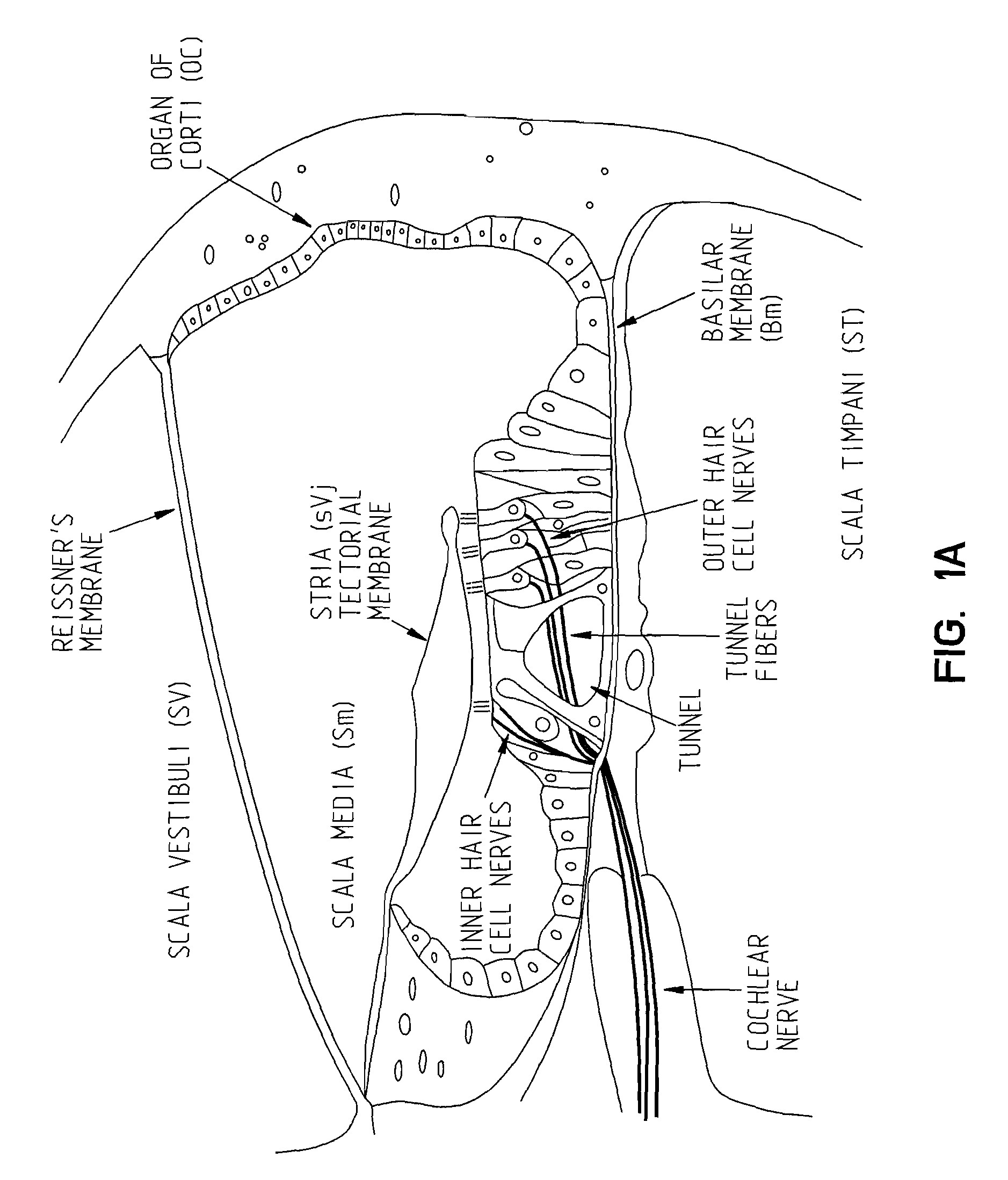
Intracochlear Nanotechnology and Perfusion Hearing Aid Device
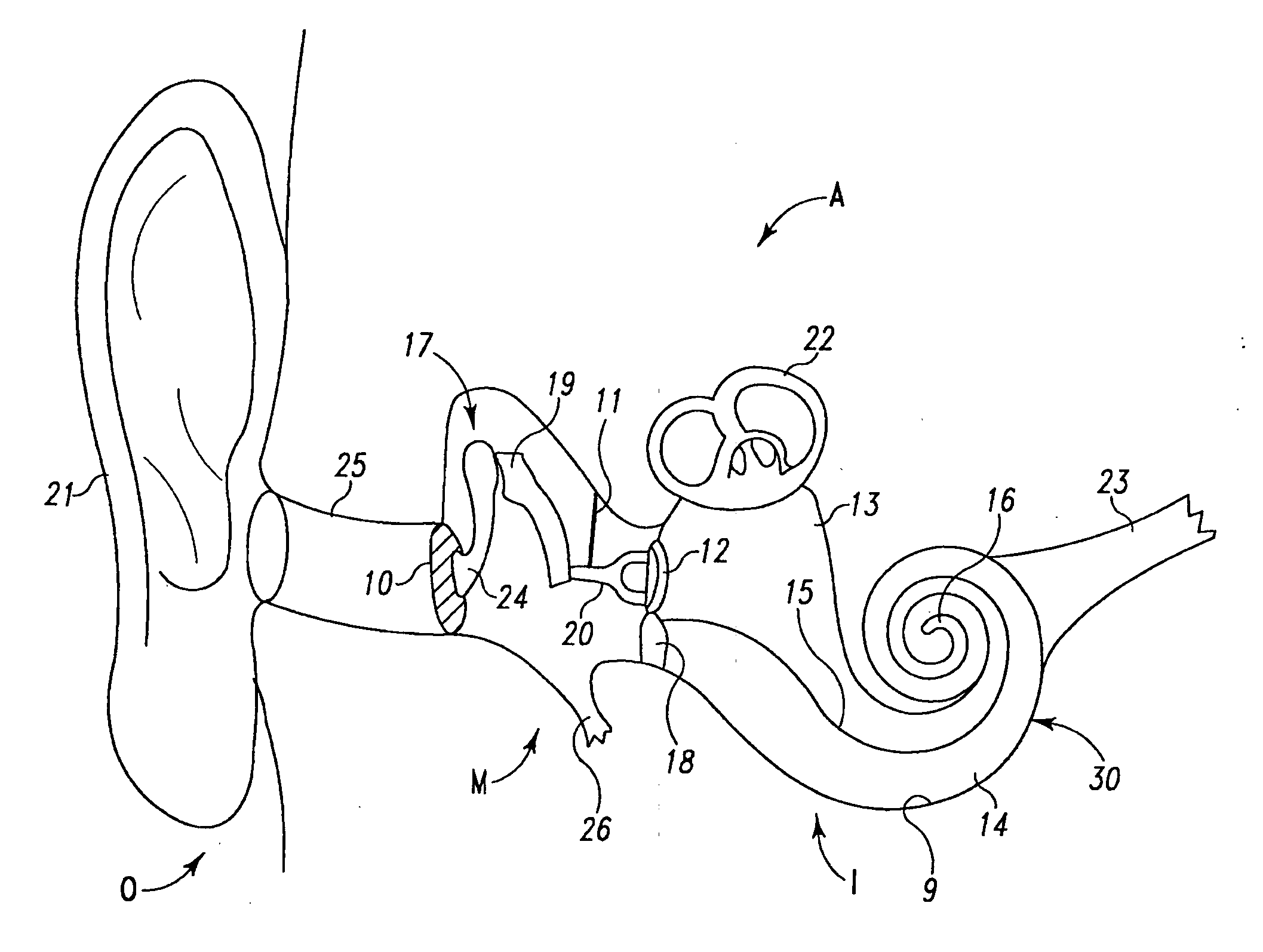
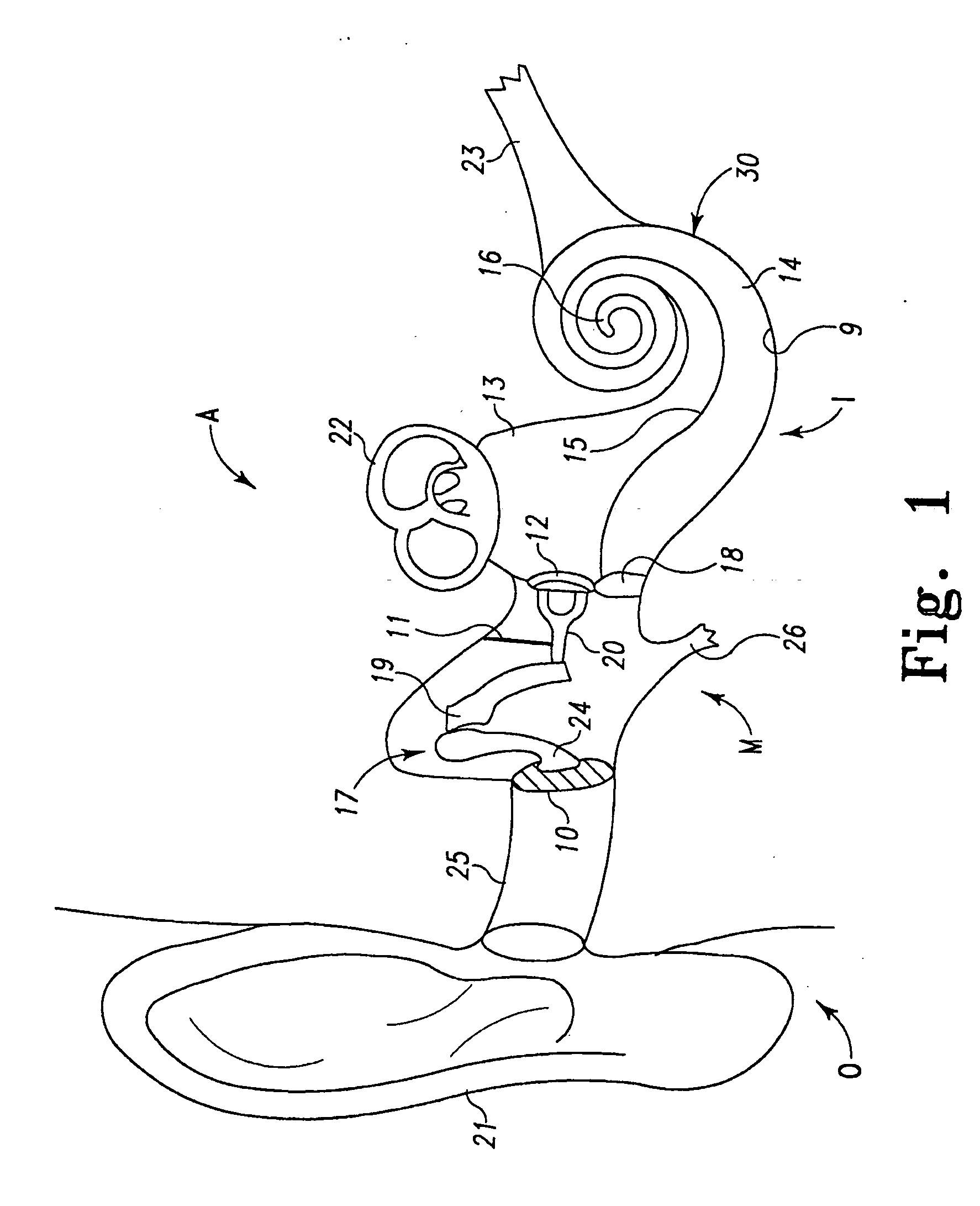
An intra-cochlear implant is provided for aiding in the hearing of a patient. The implant includes a body portion implantable within an interior of a cochlea of a patient. The body portion has a proximal end, a distal end and a primary axis. A plurality of signal carrying electrodes extends along the body portion. The electrodes have proximal ends and distal ends, with the proximal ends being capable of receiving a signal from a signal generator, and the distal ends being capable of delivering the received signal to an anatomical receptor within a cochlea. At least several of the plurality of electrodes have a nanoelectrode-sized portion. The implant also may include a fluid delivery system of tubules, reservoirs, and pumps for the delivery of chemicals and cells to activate regeneration of neural elements lost during the hearing loss process.
Owner:DOMESTIC ASSET LLP
Sample processing
ActiveUS7718421B2Easy to prepareContaminate processBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSurgeryBiomedical engineering
A sample processing tubule may include a first segment, a second segment, and a third segment. Each segment may be defined by the tubule, may be fluidly isolated, at least in part by a breakable seal, may be so expandable as to receive a volume of fluid expelled from another segment, and may be so compressible as to contain substantially no fluid when so compressed. Each segment may contain at least one reagent.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Dental cortical plate alignment platform
InactiveUS6592368B1Reduced risk of breakageReduce traumaImpression capsSurgical needlesOpaque markerCortical plate
This application relates to a dental apparatus for the initial and subsequent guidance of drills, hypodermic needles, or drug delivery devices into the cortical plate of human mandibular and maxillary bones. The invention comprises a thin platform with one or a plurality of angled or straight preformed perforations serving as entrance ports. Each port is optimally heralded by a radio-opaque marker to enable a view of the tooth root prior to drilling for a superior selection of a nerve deadening site and a whisker tubule visually displaying the drill's angle. The platform can be positioned on either the inner or outer side of the cortical plate, and is optimized for use with a dedicated indexing bite apparatus, a dedicated rubber dam style clamp, or by attachment to a RINN positioner or the like.
Owner:LVI GLOBAL
Device and method to treat oral disease in small animals
InactiveUS6086363ARemove complicationsEliminate chronic symptomTeeth fillingAnimal teeth treatmentOral diseasePretreatment method
A laser system and method are described that will improve dental treatments in small animals, particularly in situations where periodontal disease has progressed to the advanced stages of periodontitis and when dental pulp is exposed by fracture or disease. A laser system is employed to achieve enhanced precision by selectively ablating affected tissue without damaging the collateral tissue. The laser system is also capable of sealing the tubules and eradicating bacteria within the periodontium to significantly reduce the risk of infection. Additional pre-treatment methods may be employed to further enhance the laser therapy.
Owner:BIOLITEC PHARMA MARKETING
Thrombectomy and tissue removal method
InactiveUS6984239B1Reduce local pressureIncrease speedMedical devicesFluid jet surgical cuttersThrombusHigh pressure
A device for removing a thrombus or other tissue deposit from the cardiovascular system, natural or synthetic tubule or cavity found in the human body of a patient without the need to surgically access the location of the thrombus or other tissue deposit via a cut-down or other surgical procedure. A flexible metal or high pressure plastic tube conveys an extremely high pressure stream of sterile saline or other physiologic solution to at least one jet at the distal end of the catheter. At least one jet is directed at the opening of a large exhaust lumen or other target. The jet(s) is responsible for providing a localized negative pressure which entrains tissue into the jet from break-up of the debris. This jet(s) can also provide stagnation pressure in the exhaust lumen which drives the tissue or thrombotic debris out of the exhaust lumen. Operation of the device with tip pressure greater than 500 psi provides this device with the entrainment and exhaust characteristics which contribute to its effectiveness. The rate of exhaust of tissue debris is metered to ensure minimal local impact on the vasculature at the site of the thrombus deposit. A fluid metering means, such as a roller pump, controls the rate of exhaust such that it is in balance with the saline input or can be adjusted to be greater or less than the input. A positive displacement pump operating at steady or pulsatile flow provides the high pressure saline to the tip of the catheter.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
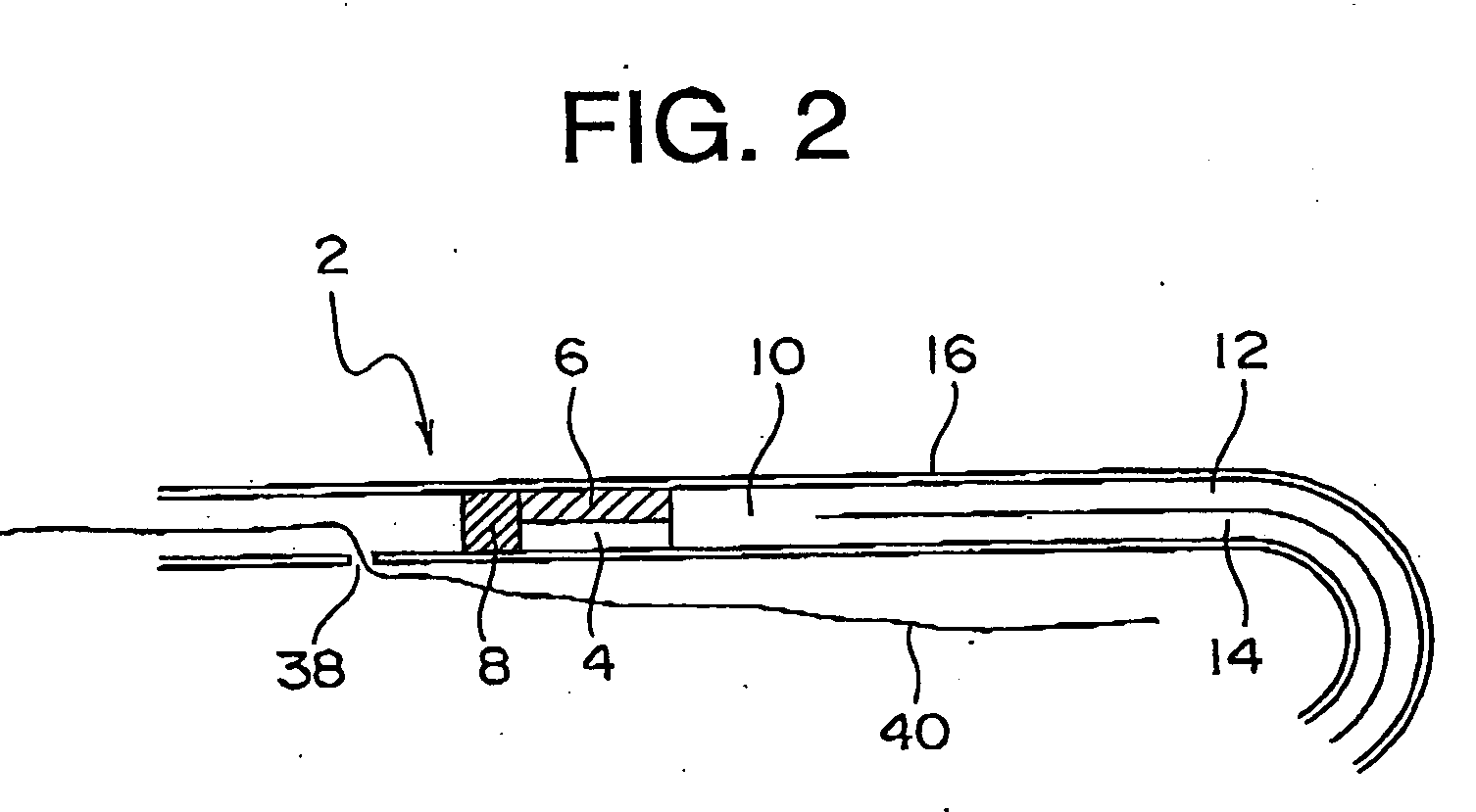
Oral Care Composition To Reduce Or Eliminate Dental Sensitivity
InactiveUS20080267891A1Reduce sensitivityReduce penetrationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsDentinal TubuleTubule
The invention includes an oral care composition that reduces and / or eliminates the perception of tooth sensitivity. The composition includes an adherent material and particles having an average particle size of about 8 microns or less. The particles are present in the composition in an amount of about 5% by weight. Also included within the scope of the invention are related methods, such as methods of occluding a dentin tubule.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
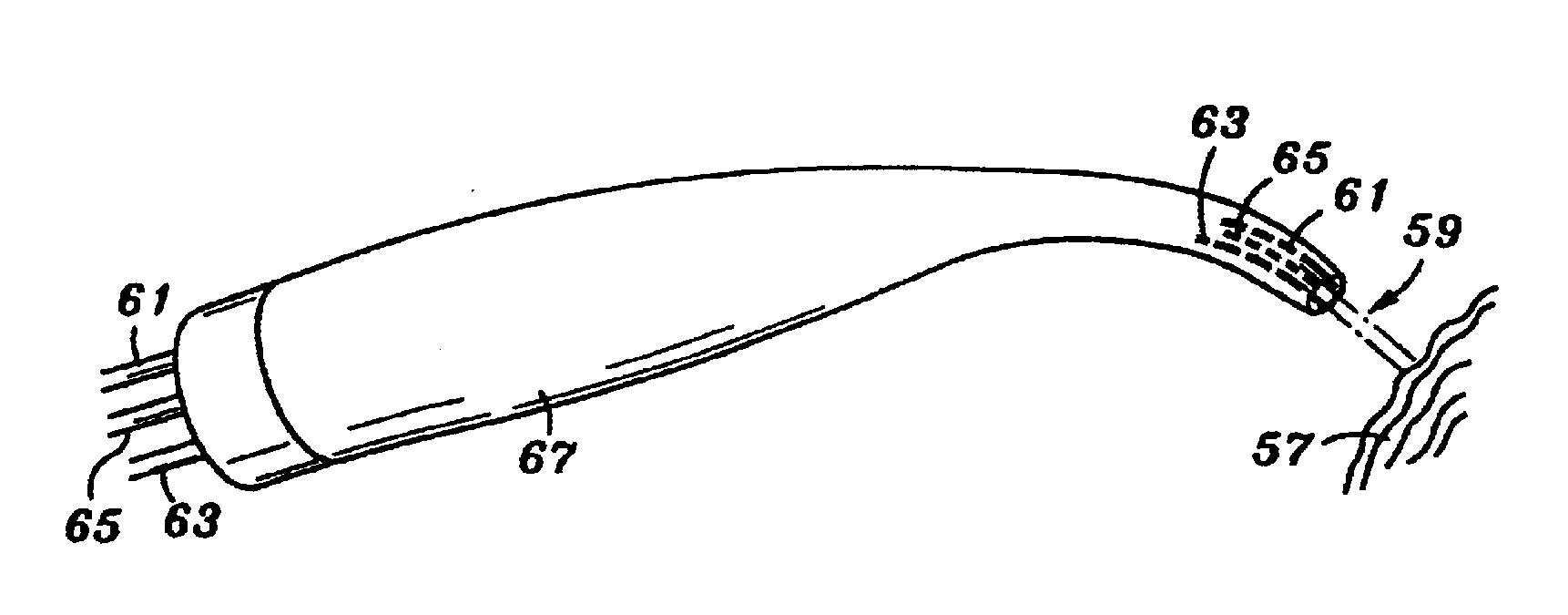
Fluid controllable laser endodontic cleaning and disinfecting system
ActiveUS20090042171A1Promote absorptionIncrease coverageWheelchairs/patient conveyanceDental toolsFiberActive agent
An endodontic probe is used to perform disinfection procedures on target tissues within root canal passages and tubules. The endodontic probe can include an electromagnetic radiation emitting fiber optic tip having a distal end and a radiation emitting region disposed proximally of the distal end. According to one aspect, the endodontic probe can include a porous structure that encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip excluding the radiation emitting region and that is loaded with biologically-active particles, cleaning particles, biologically-active agents, or cleaning agents for delivery from the porous structure onto the target tissues. Another aspect can include provision of the endodontic probe with an adjustable channel-depth indicator, which encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip besides the radiation emitting region and which is movable in proximal and distal directions along a surface of the fiber optic tip to facilitate the provision of depth-of-insertion information to users of the endodontic probe.
Owner:BIOLASE TECH INC
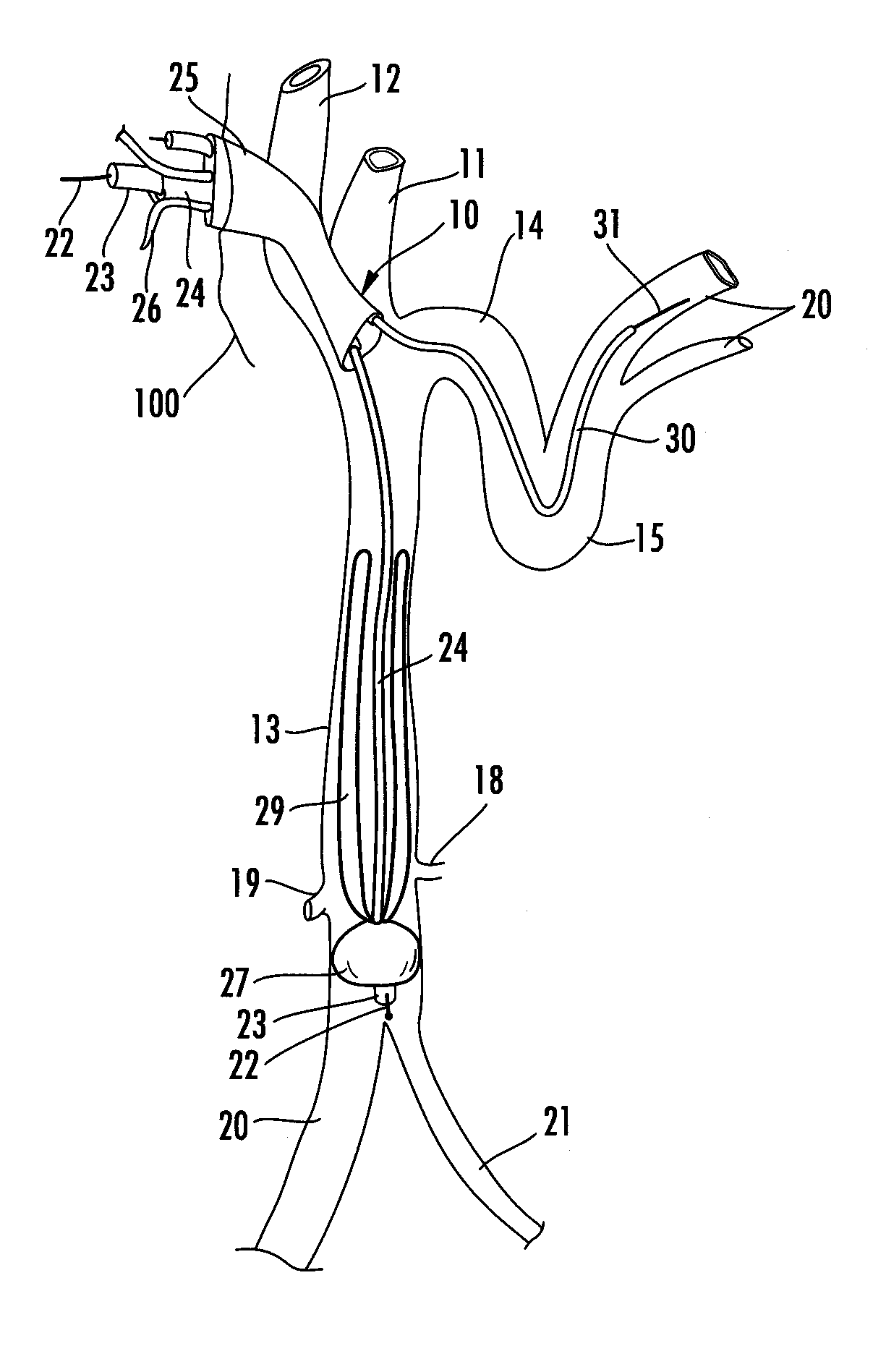
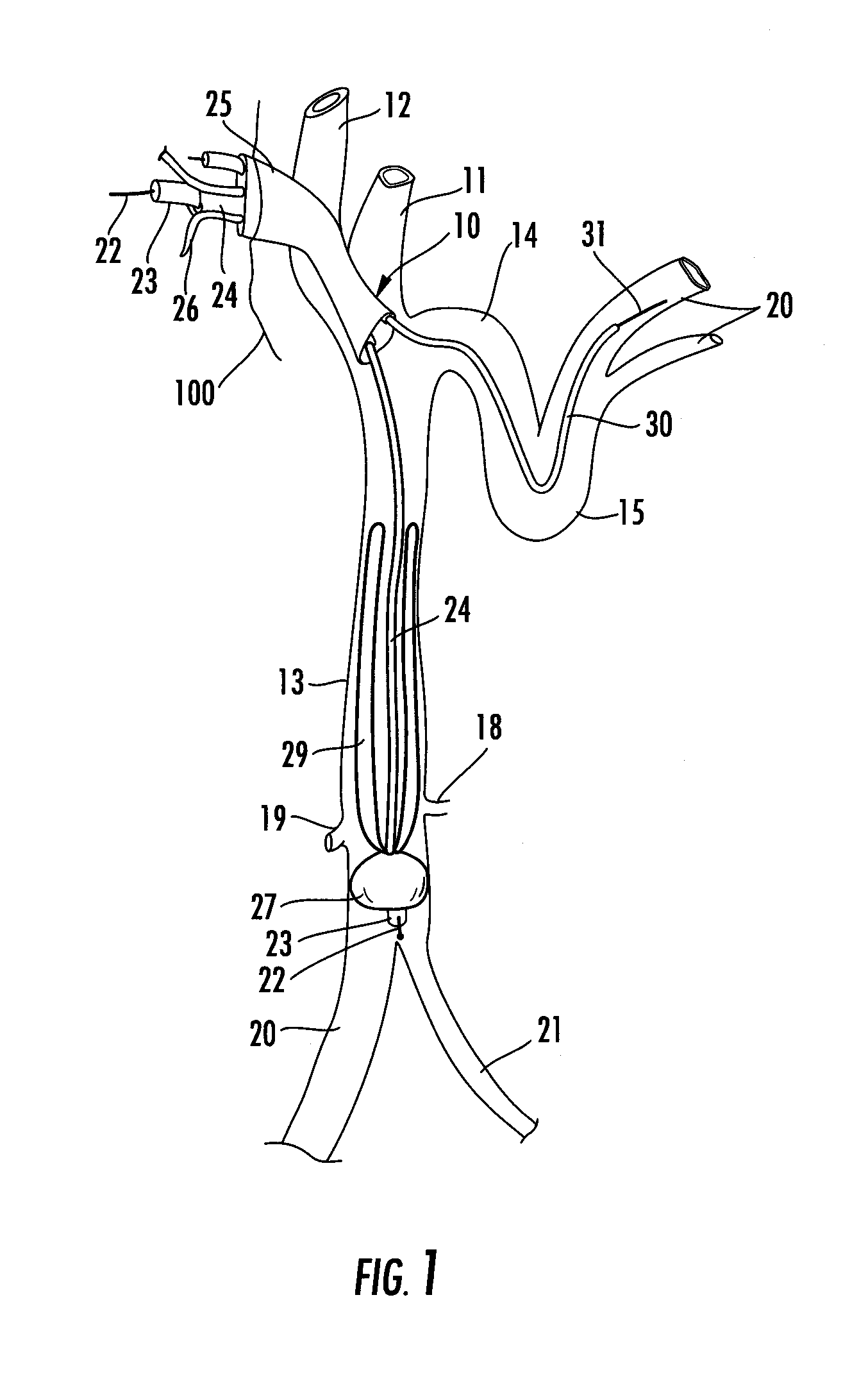
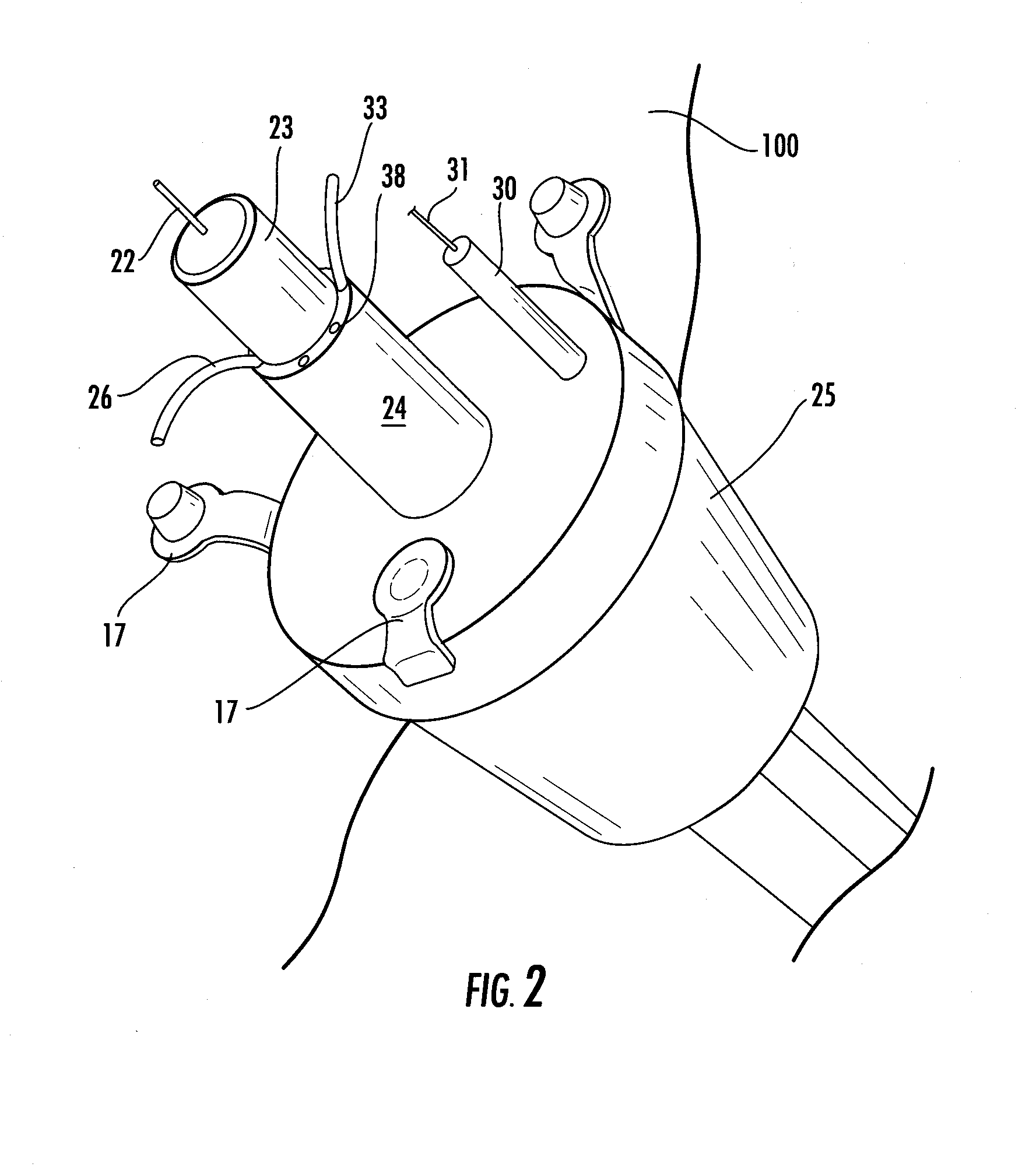
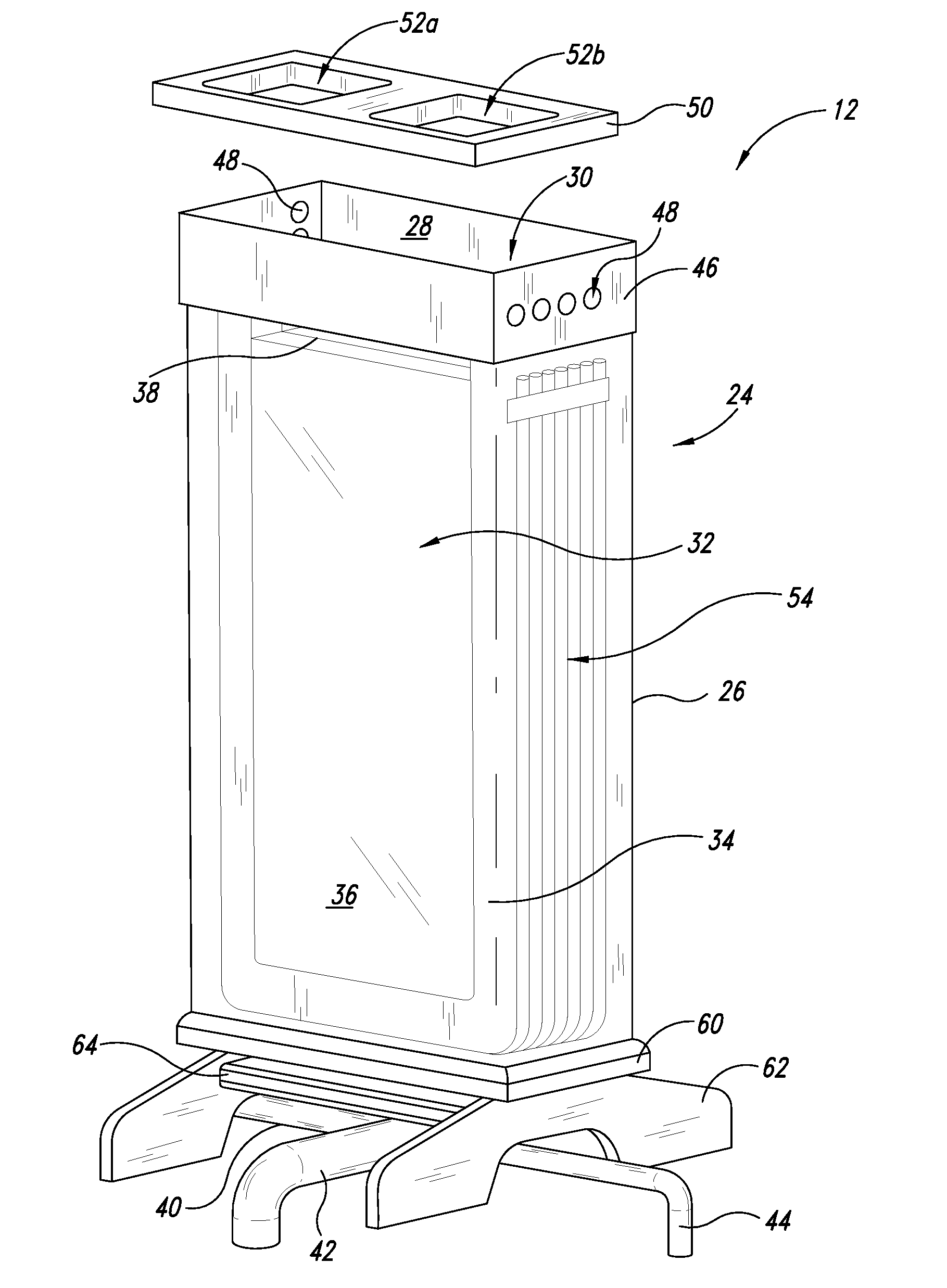
Catheter for treatment of severe pulmonary emboli
A catheter system for treating pulmonary emboli has an multi-channel access port for establishing and maintaining communication with the vascular system and provide guidance for endovascular catheterization. One catheter may traverse the port and extend through the heart to the pulmonary arteries to inject lysing agents, contrast media, medicaments and to remove blood clots. Another catheter may traverse the port and extend through the vena cava to other parts of the venous tree to supply the same agents and to remove blood clots there. A third catheter may telescope over the treatment catheter through the vena cava and occlude the affected vein. Gas pervious tubules on the third catheter provide oxygen enrichment of the venous blood.
Owner:LARY RES & DEV
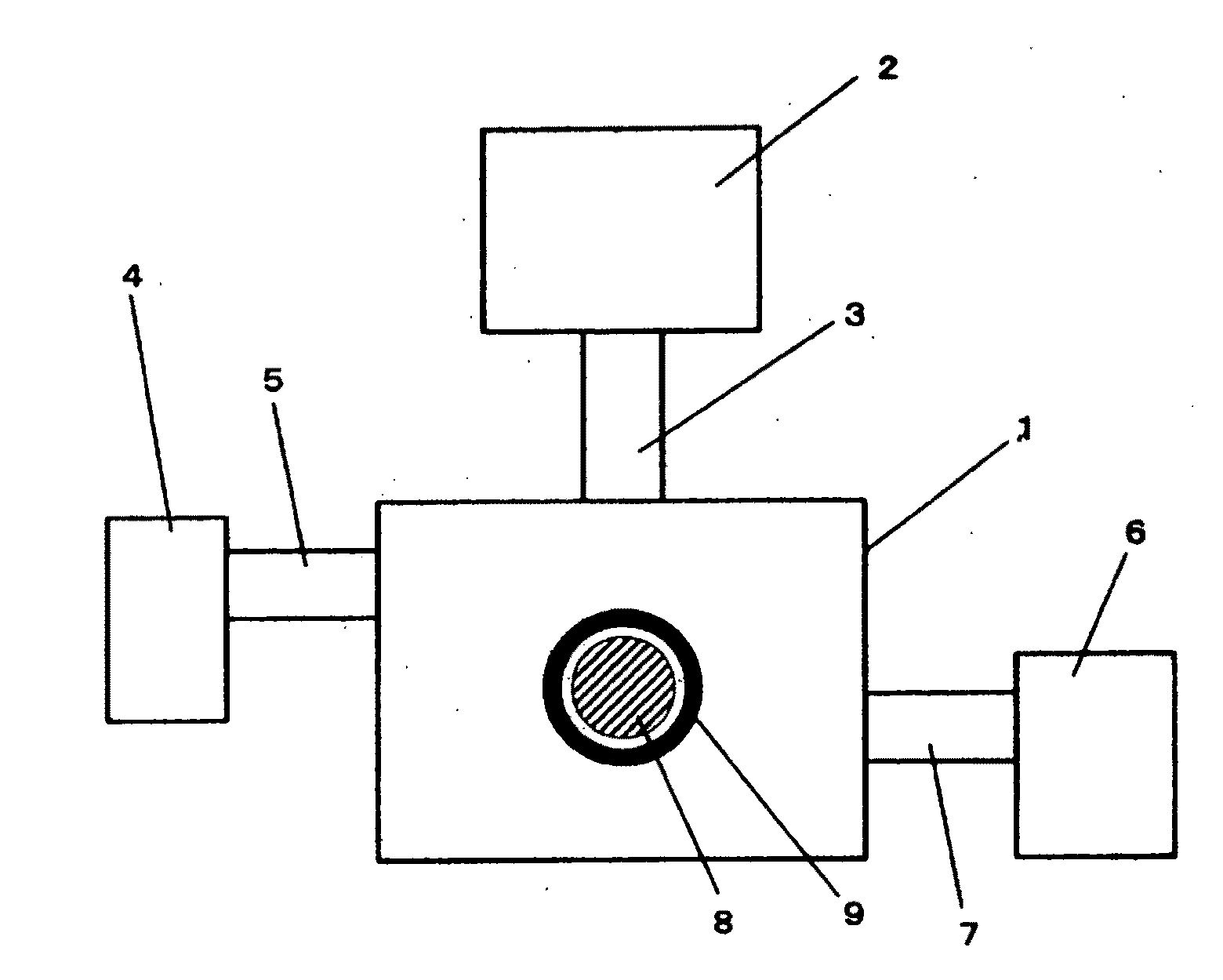
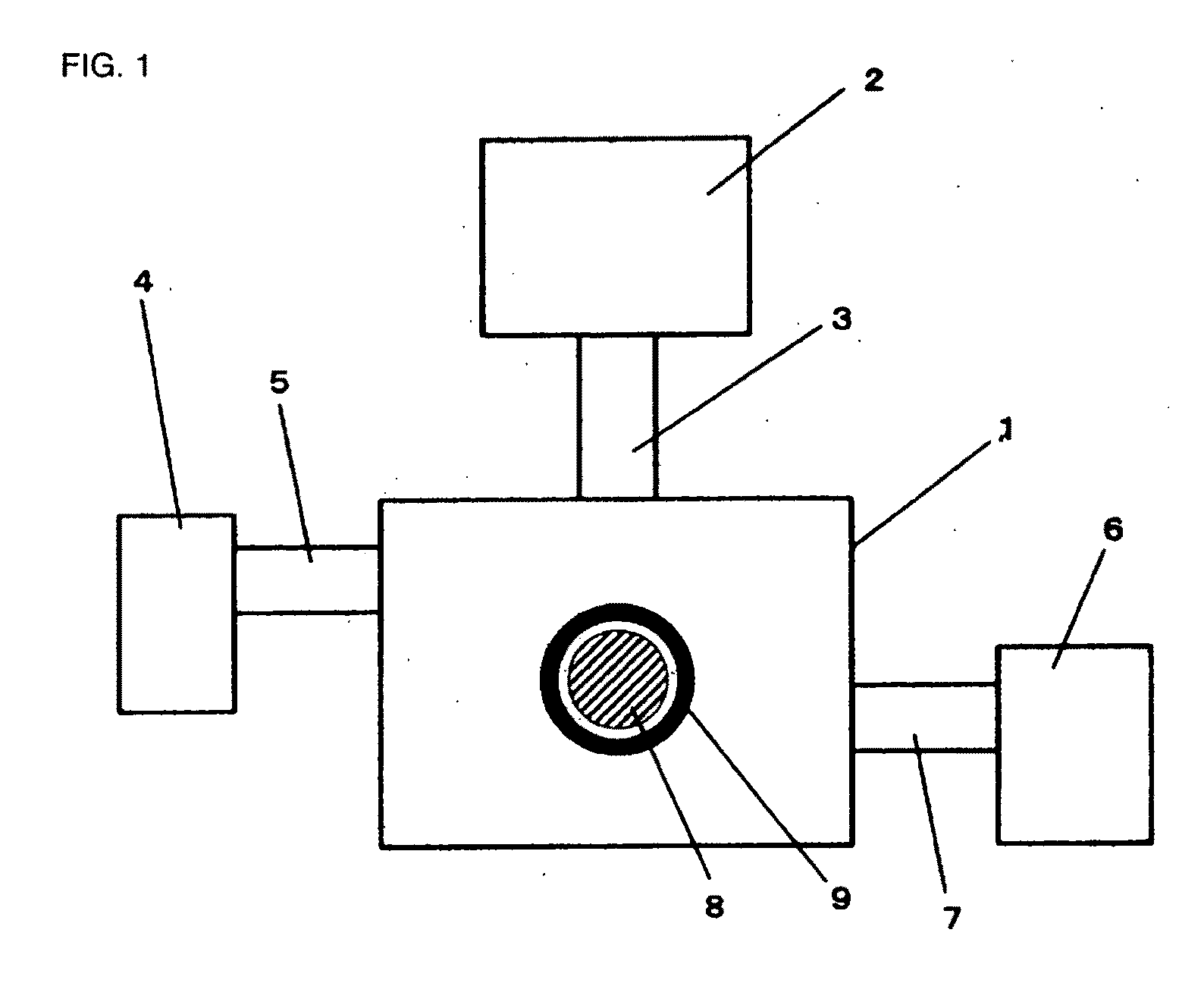
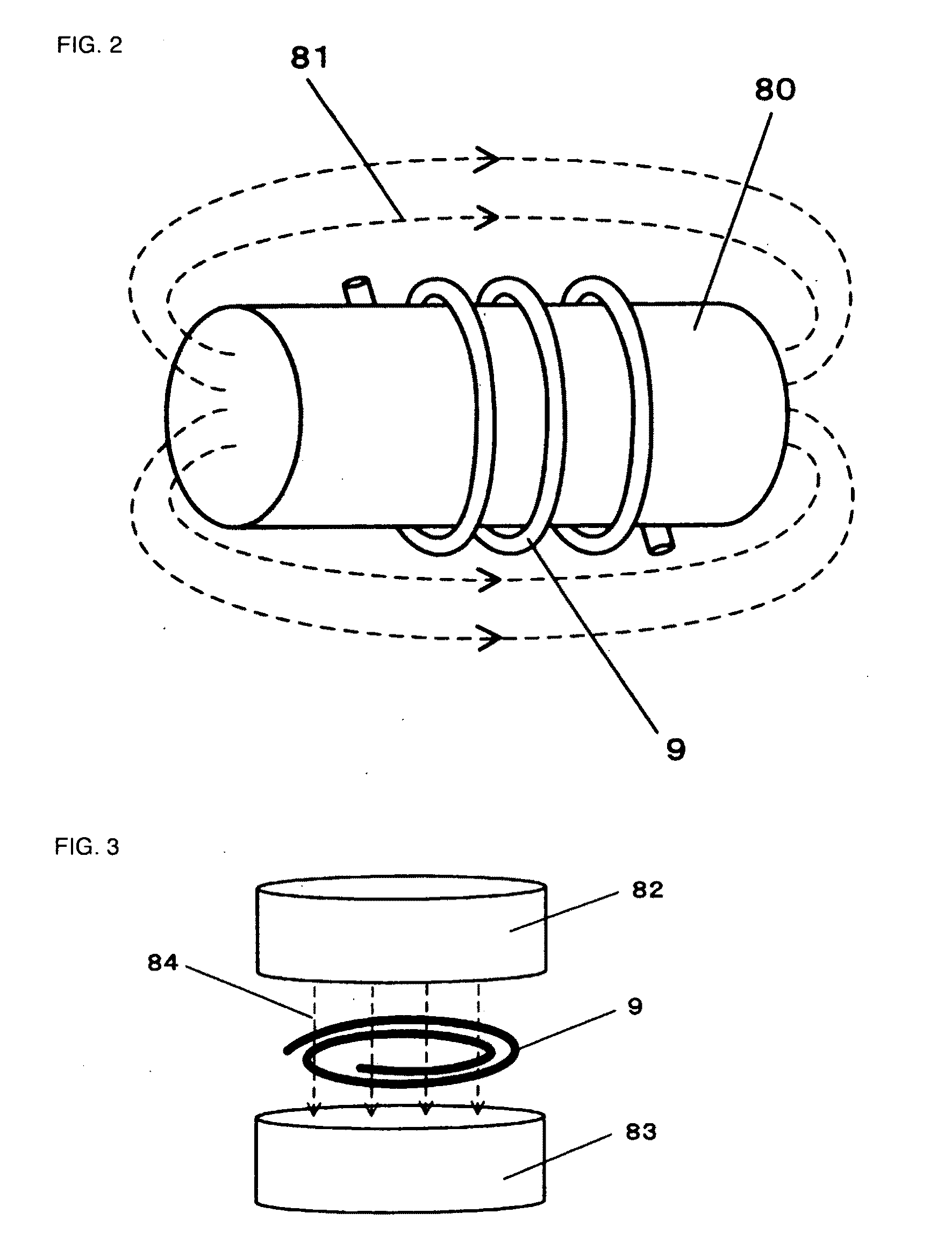
Plasma generating device and method
InactiveUS20110079582A1Highly clean stateHighly safe stateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInternal pressureMicrowave emission
An object of the invention is to provide a plasma generating device and method for generating plasma through electrodeless discharge within a long tubule and carrying out a plasma process on the inside of the long tubule. The plasma generating device has a container 1 for containing a long tubule 9, the internal pressure of which can be adjusted, a magnetic field applying means 8 for applying a magnetic field in at least part of the long tubule, and a microwave supplying means 2 for emitting microwaves into the container, and is characterized in that plasma is generated within the long tubule by emitting microwaves into the container in such a state that a magnetic field is applied in at least part of the long tubule.
Owner:YONESU AKIRA +1
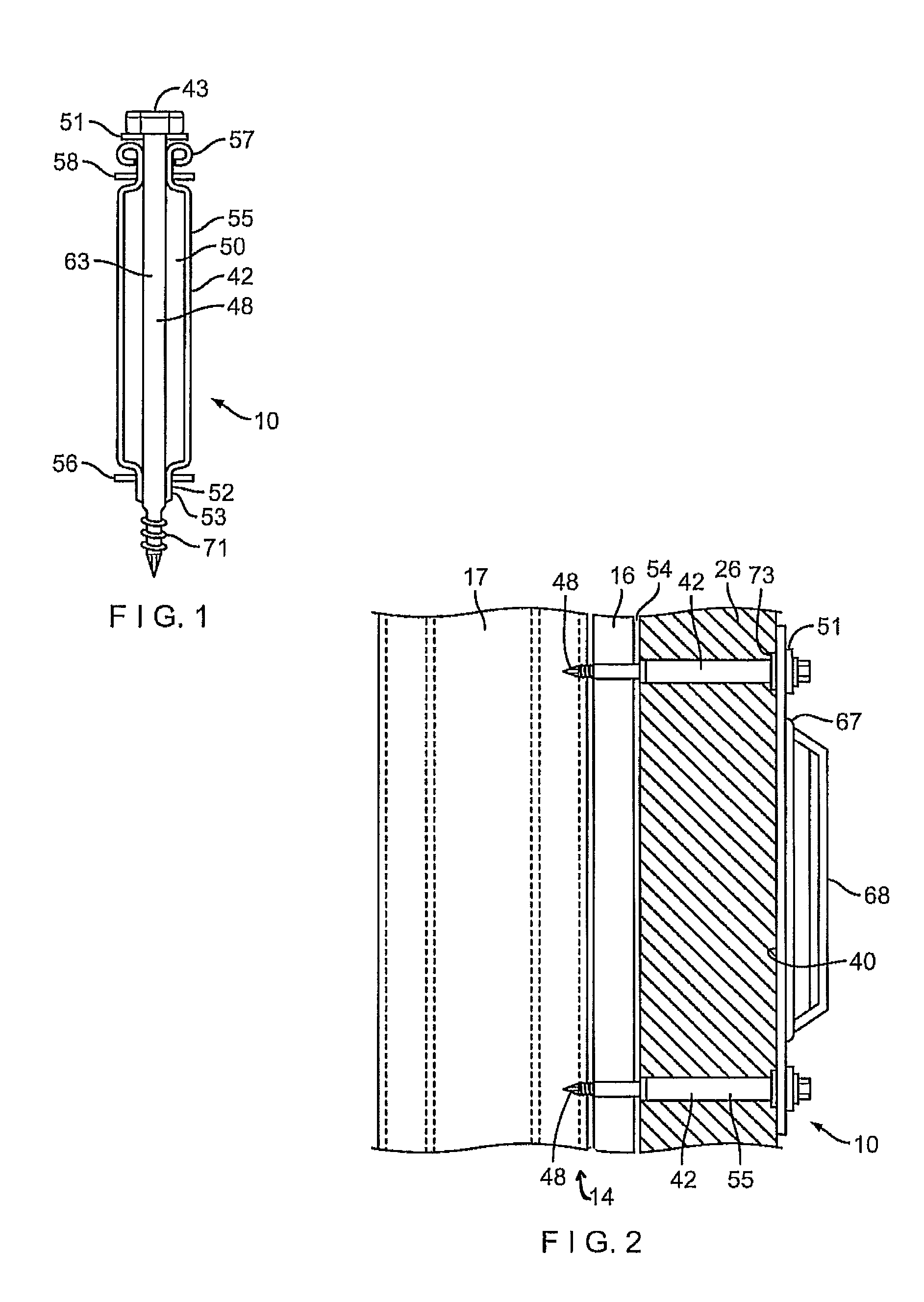
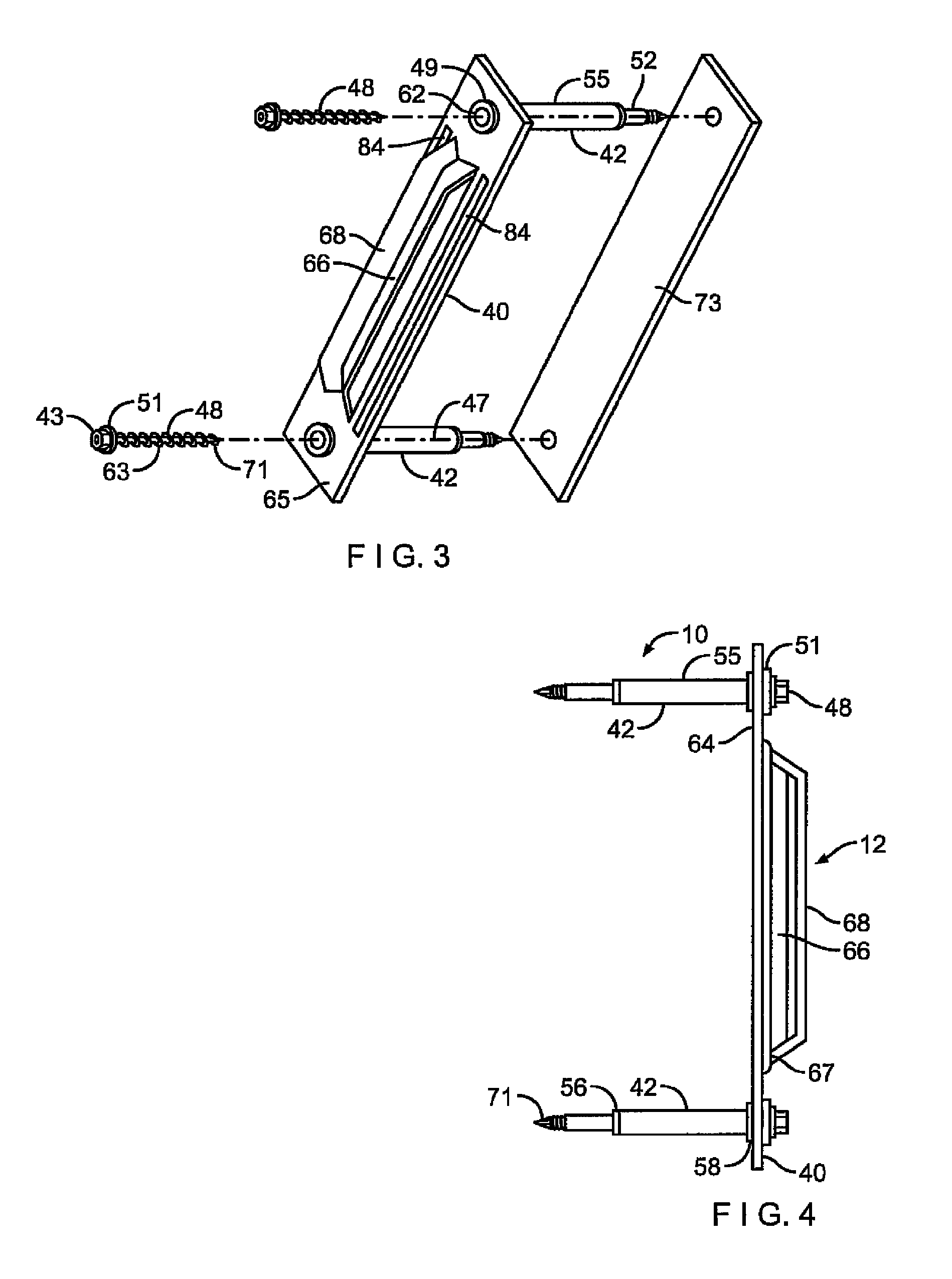
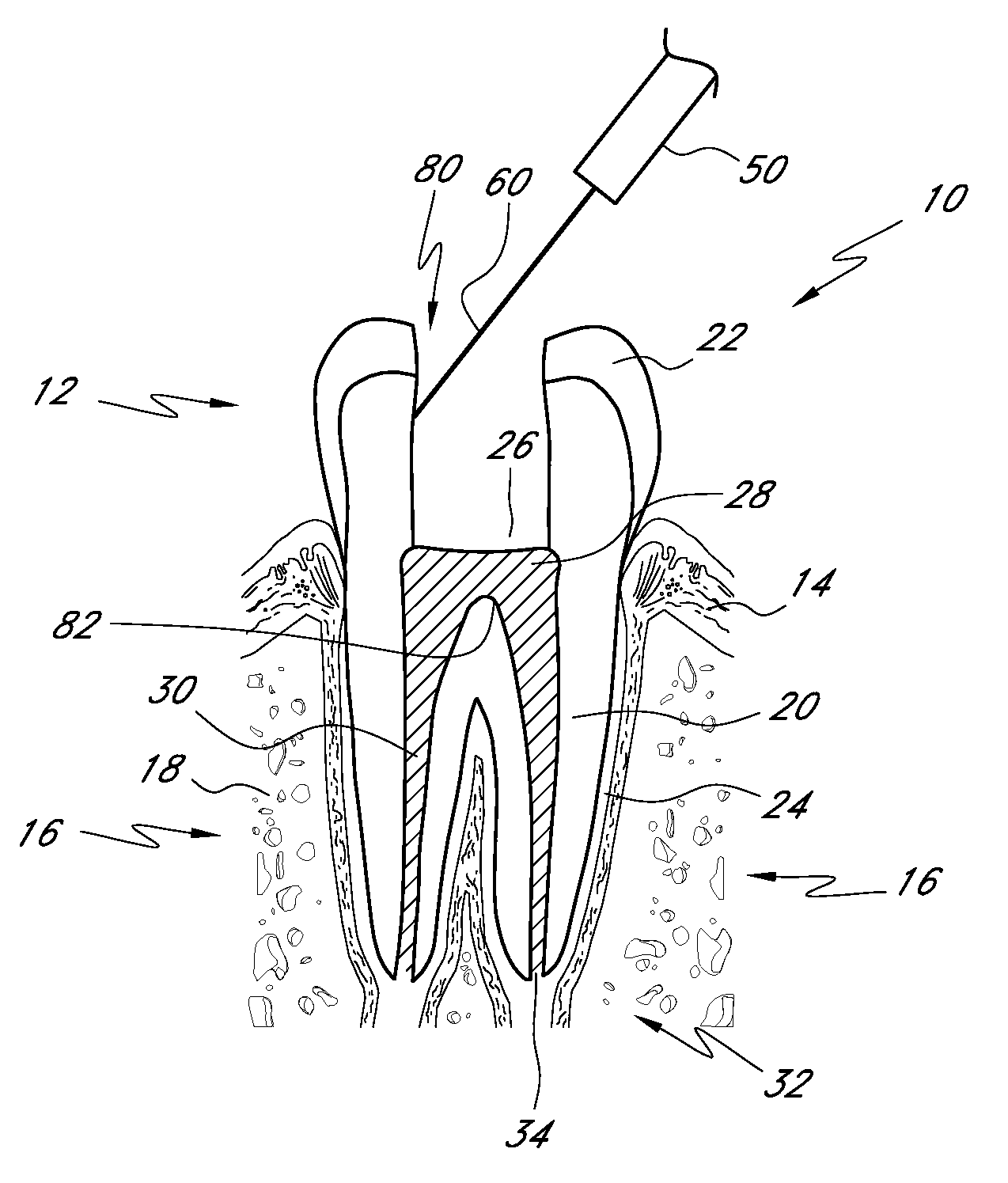
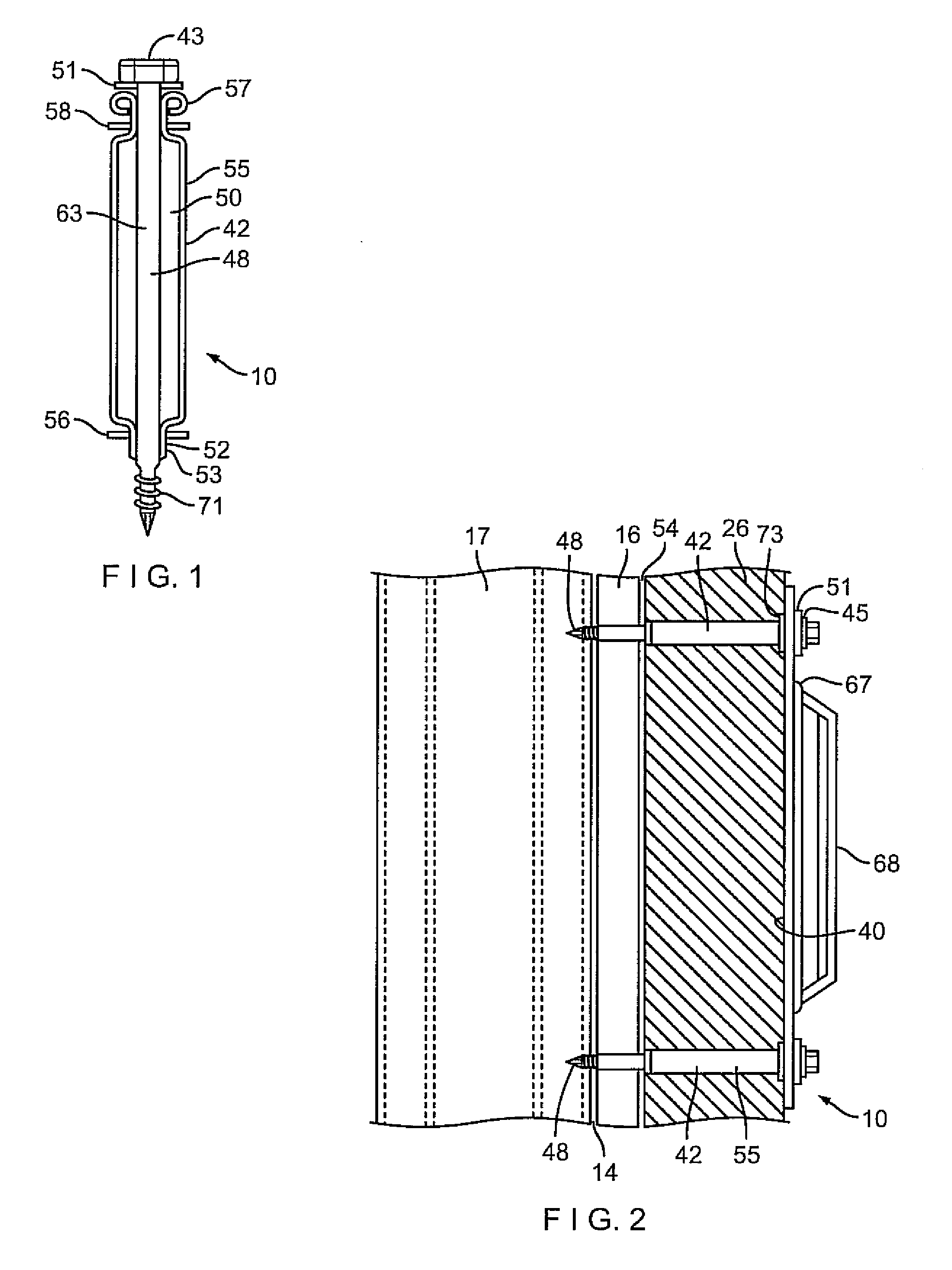
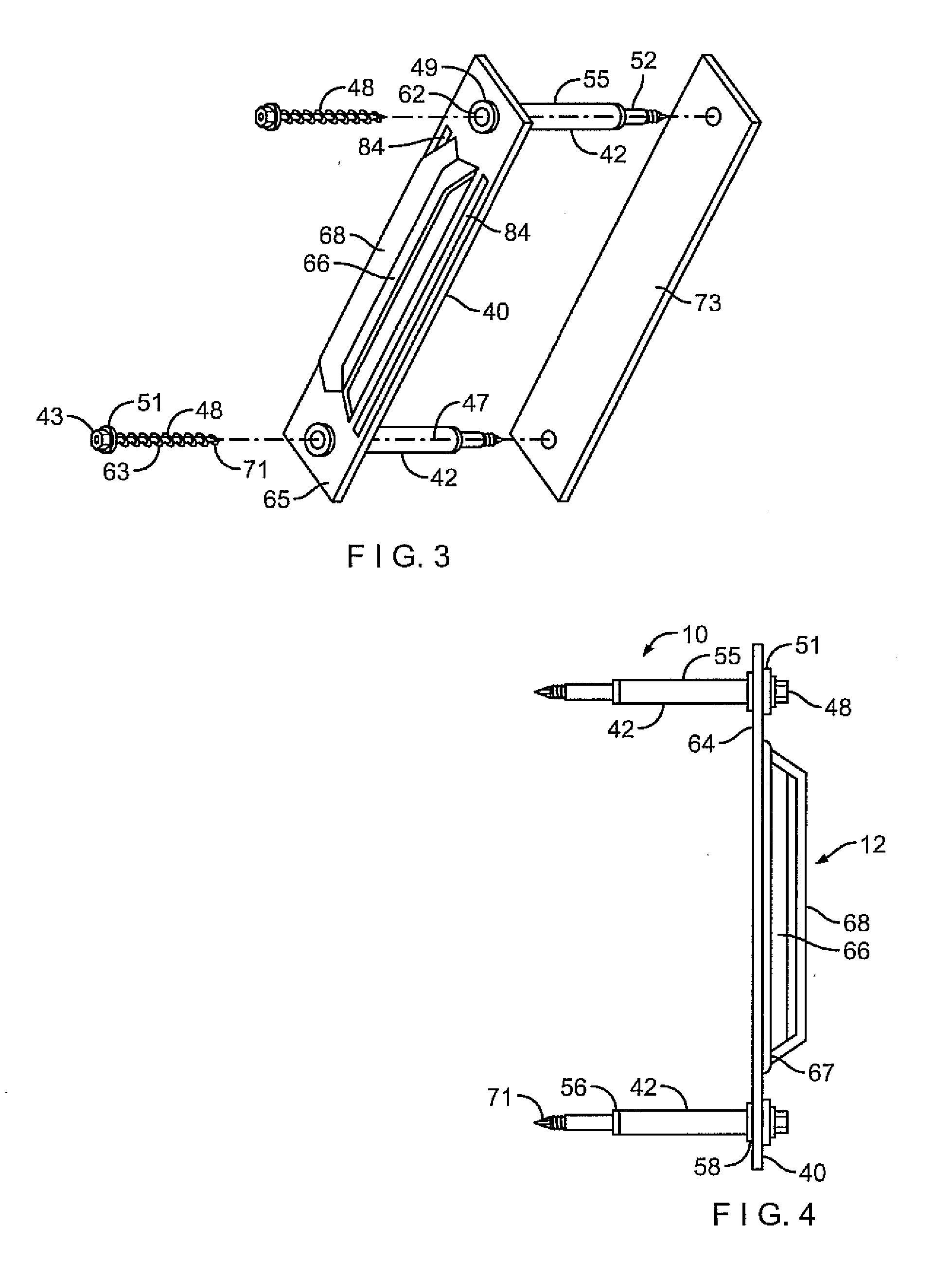
Thermally isolating tubule for wall anchor
ActiveUS8516763B2High levelPrevent disengagementCeilingsConstruction materialSurface mountingWater vapor
A tubule assembly for thermally isolating a surface-mounted wall anchor and an anchoring system employing the same are disclosed. The thermally-isolated tubule assembly is adaptable to varied anchor structures and for use with interlocking veneer ties and reinforcement wires to provide a high-strength surface mounted anchoring system for cavity walls. The stepped cylinders sheath the mounting hardware to limit insulation tearing and resultant loss of insulation integrity. The tubule assembly is thermally-isolated through the use of a series of strategically placed compressible nonconductive fittings and set within the perimeter of the anchor base. Seals are formed which preclude penetration of air, moisture, and water vapor into the wall structure.
Owner:HOHMANN & BARNARD INC
Apparatus and methods for treating root canals of teeth
Apparatus and methods for endodontic treatment of teeth provide effective cleaning of organic material (such as pulp and diseased tissue) from the root canal system. In an embodiment, a compressor system generates high pressure liquid (e.g., water) that flows through an orifice to produce a high-velocity collimated jet of liquid. The high-velocity jet is directed toward a surface of a tooth, for example, an exposed dentinal surface, and impingement of the jet onto the surface generates an acoustic wave that propagates throughout the tooth. The acoustic wave effectively detaches organic material from dentinal surfaces and tubules. The detached organic material is flushed from the root canal system by the liquid jet and / or by additional irrigation.
Owner:SONENDO
Extra-cochlear implanted hearing aid device
ActiveUS20070005117A1Promote growthEasily and efficiently transmitHead electrodesHearing aidTunica intima
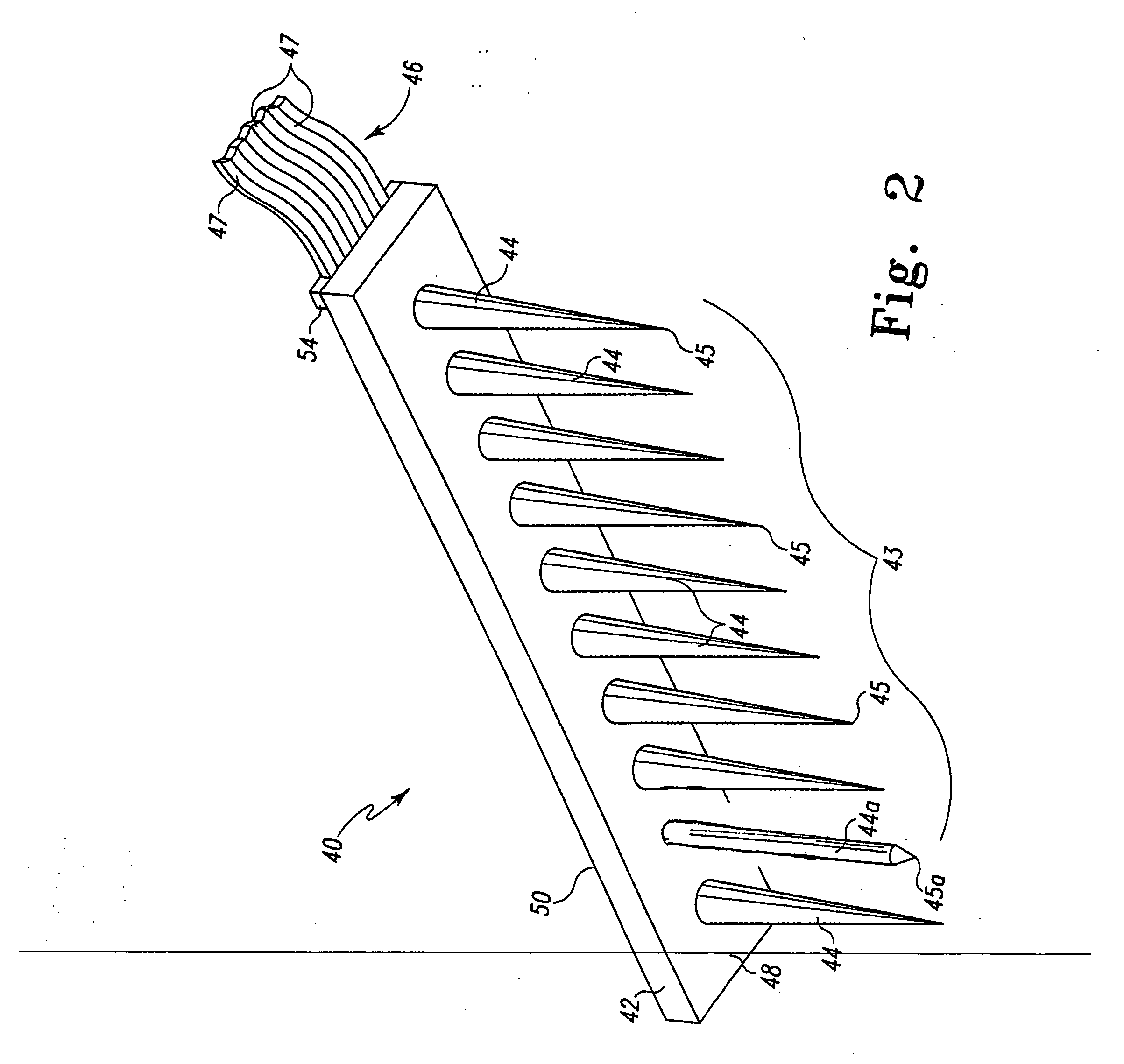
An extra-cochlear hearing aid implant is characterized by a pad having a plurality of electrode prongs that extend therefrom and which are adapted to provide an electrical stimulus to hearing cells within the cochlea. The electrode pad is adapted to be placed onto endosteum overlying the cochlea in an “extended soft surgery” technique. The prongs are configured to pierce the endosteum and extend into the cochlea. In one form, the extra-cochlear hearing aid implant also includes hollow tubules that extend from the pad and which are adapted to supply and withdraw neurotrophic proteins and other materials in a fluid into and from the cochlea, and also to provide electrical stimulus to the hearing cells.
Owner:DOMESTIC ASSET LLP
Fluid controllable laser endodontic cleaning and disinfecting system
ActiveUS8002544B2Promote absorptionIncrease coverageWheelchairs/patient conveyanceDental toolsFiberActive agent
An endodontic probe is used to perform disinfection procedures on target tissues within root canal passages and tubules. The endodontic probe can include an electromagnetic radiation emitting fiber optic tip having a distal end and a radiation emitting region disposed proximally of the distal end. According to one aspect, the endodontic probe can include a porous structure that encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip excluding the radiation emitting region and that is loaded with biologically-active particles, cleaning particles, biologically-active agents, or cleaning agents for delivery from the porous structure onto the target tissues. Another aspect can include provision of the endodontic probe with an adjustable channel-depth indicator, which encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip besides the radiation emitting region and which is movable in proximal and distal directions along a surface of the fiber optic tip to facilitate the provision of depth-of-insertion information to users of the endodontic probe.
Owner:BIOLASE INC
Thermally isolating tubule for wall anchor
ActiveUS20120308330A1Prevent disengagementPrevent water penetrationConstruction materialWashersSurface mountingWater vapor
A tubule assembly for thermally isolating a surface-mounted wall anchor and an anchoring system employing the same are disclosed. The thermally-isolated tubule assembly is adaptable to varied anchor structures and for use with interlocking veneer ties and reinforcement wires to provide a high-strength surface mounted anchoring system for cavity walls. The stepped cylinders sheath the mounting hardware to limit insulation tearing and resultant loss of insulation integrity. The tubule assembly is thermally-isolated through the use of a series of strategically placed compressible nonconductive fittings and set within the perimeter of the anchor base. Seals are formed which preclude penetration of air, moisture, and water vapor into the wall structure.
Owner:HOHMANN & BARNARD INC
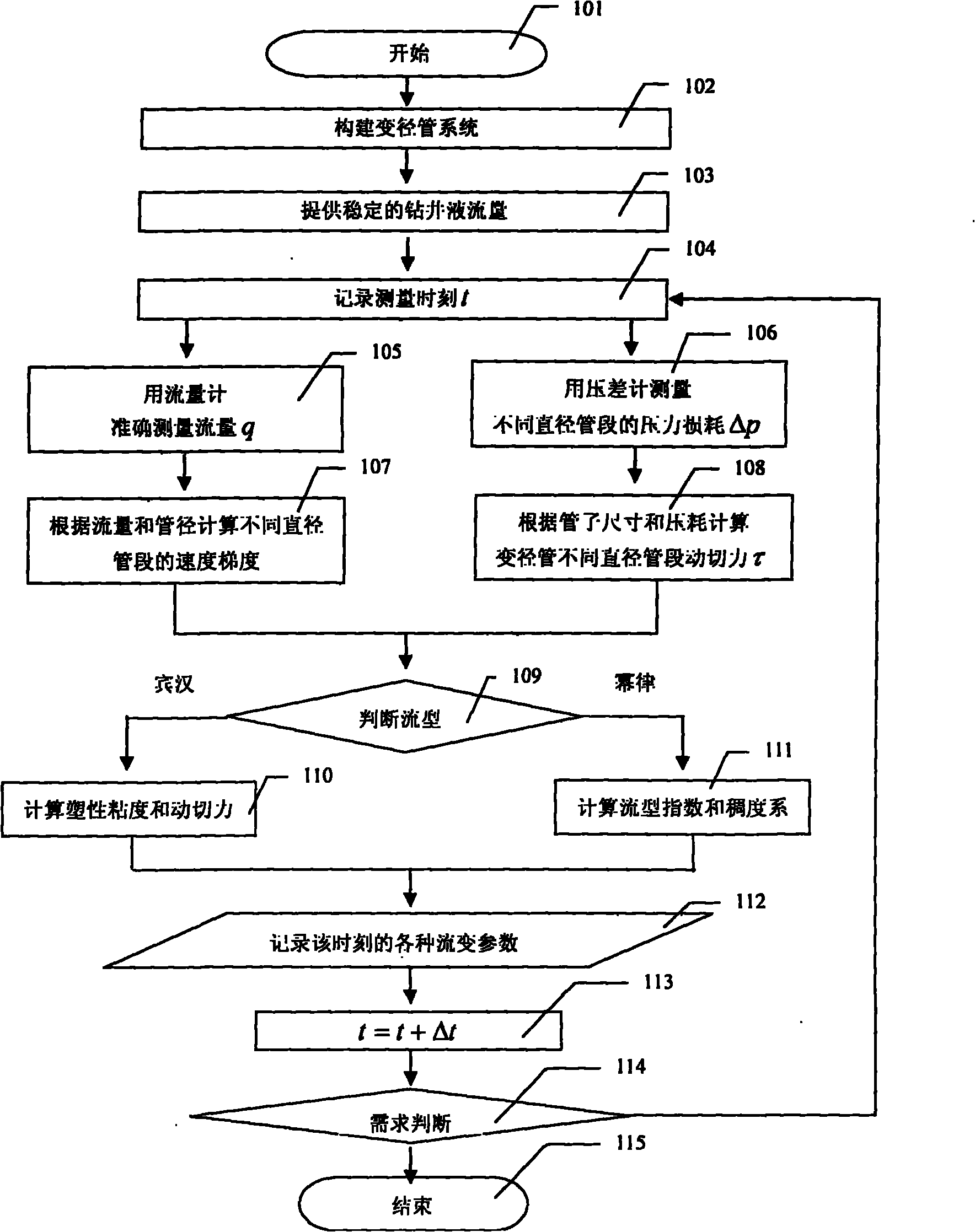
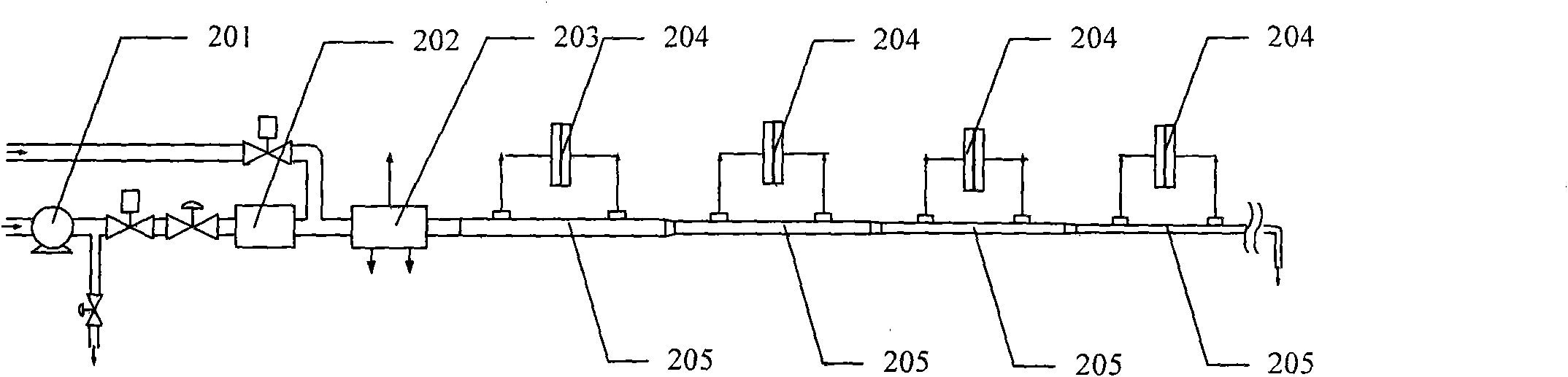
Variable-diameter-tube drilling fluid rheology measuring method
ActiveCN102374960ARealize online measurementImprove measurement efficiencyDirect flow property measurementCurrent velocityShear stress
The invention relates to a variable-diameter-tube drilling fluid rheology measuring method which is especially suitable for on-line detections of in situ drilling fluid rheology. The method comprises steps that: a variable-diameter-tube system is composed of 2 to 20 segments of tubules with different diameters, wherein the tubules are connected in series; a stable flow rate is provided for the variable-diameter-tube system by using a constant flow pump and a buffer; current velocities in different diameter segments of the variable-diameter-tube system are calculated according to the flow rate and the cross section areas of the tubules; velocity gradients in different diameter segments are calculated according to the current velocities and diameters of the different diameter segments of the variable-diameter-tube system; pressure losses in different diameter segments of the variable-diameter-tube system are detected by using a differential pressure gauge; shear stress values of the different diameter segments of the variable-diameter-tube system are calculated according to the pressure losses; and rheology parameters such as plastic viscosity, dynamic shearing force, flow pattern index, and consistency coefficient of the measured drilling fluid can be calculated according to the shear stress values under different velocity gradients. With the method provided by the invention, drilling fluid rheology and variation conditions thereof can be measured in real-time without changing the flow rate.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +3
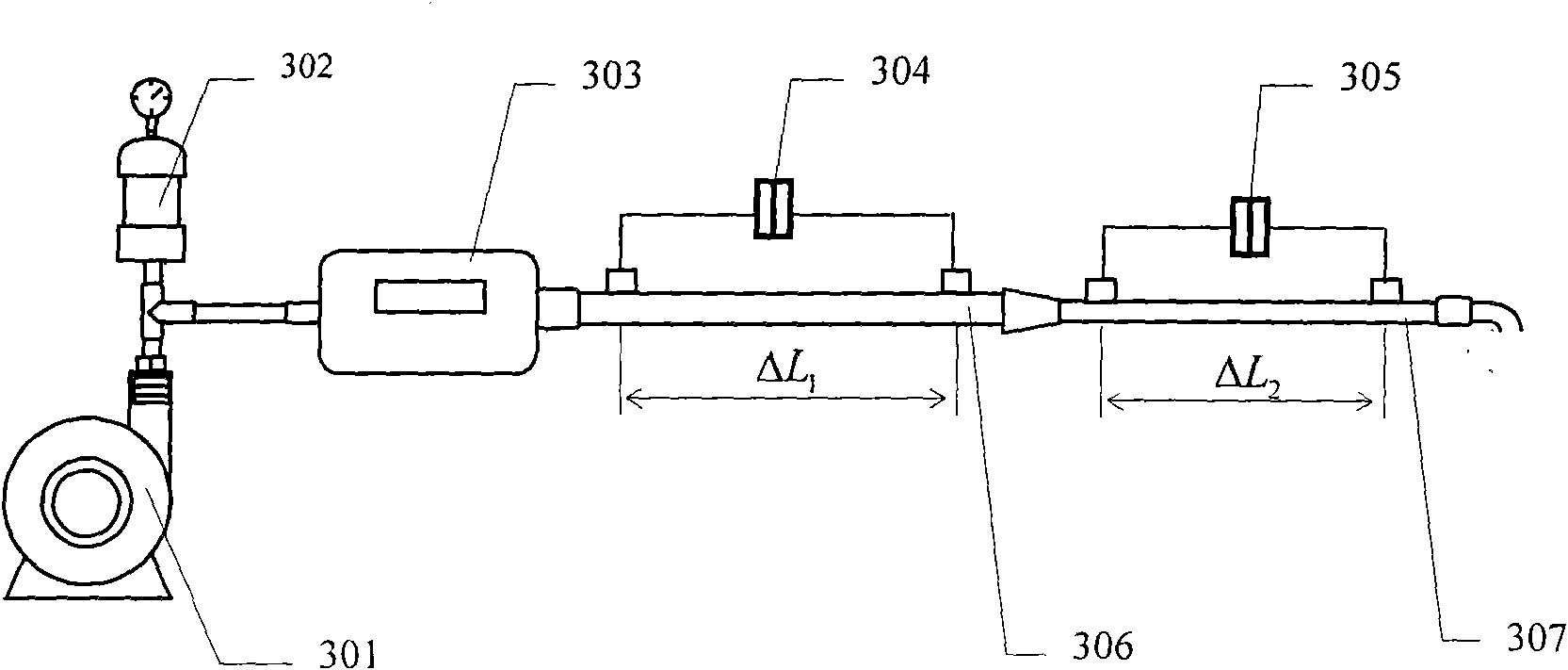
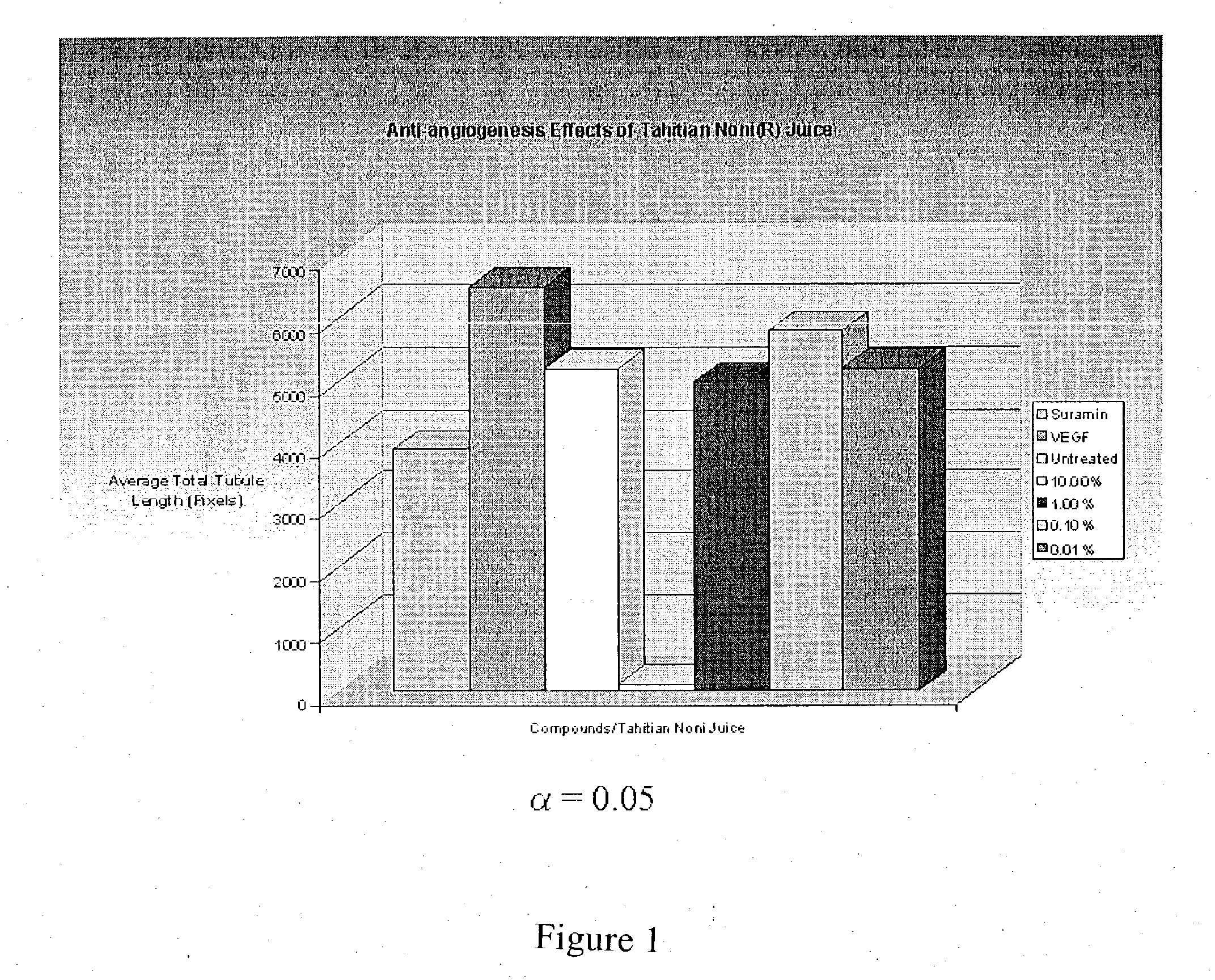
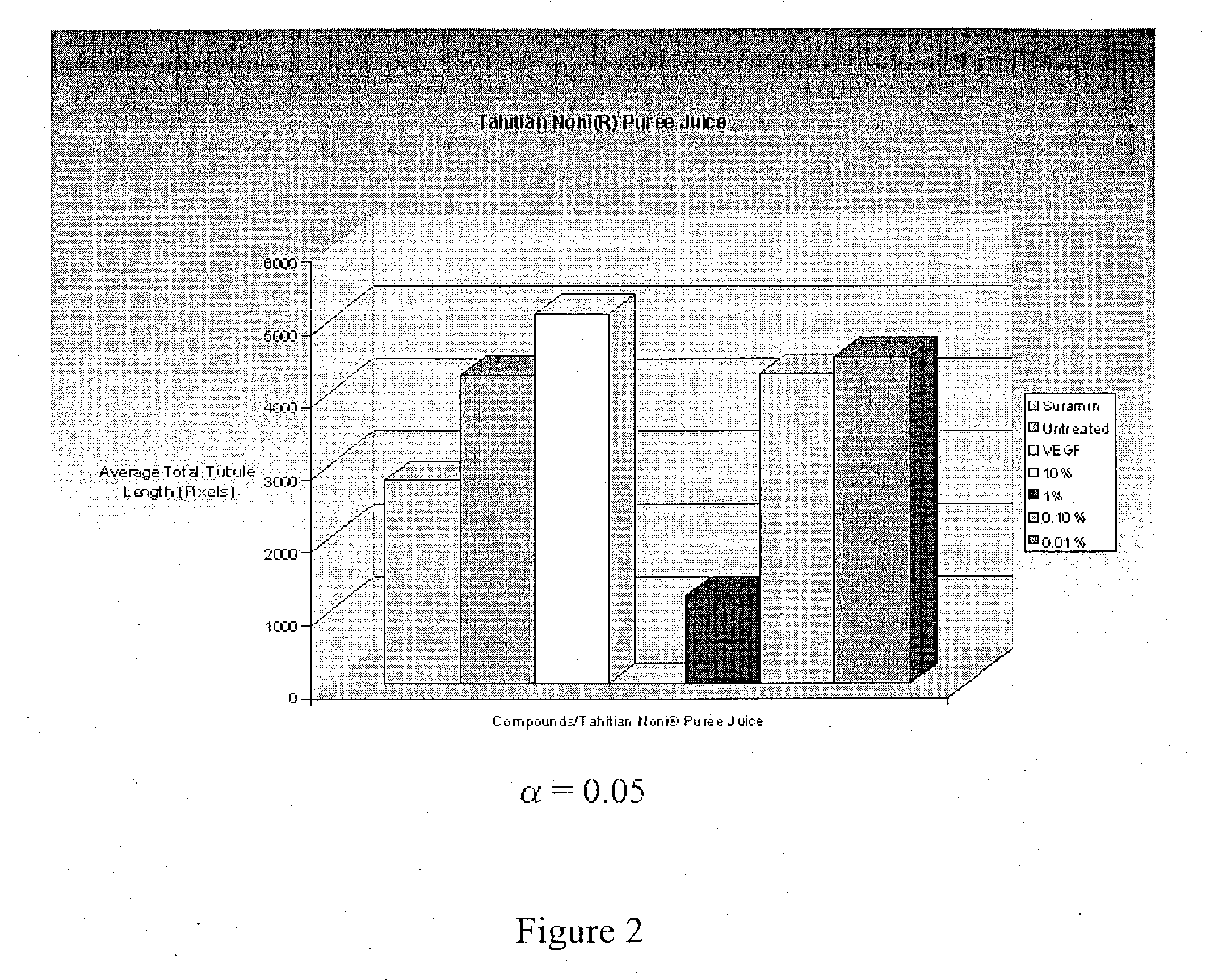
Anti-angiogenesis effects of morinda citrifolia
InactiveUS20040086583A1Inhibit angiogenesisPrevent further growthBiocideUnknown materialsAnti-Angiogenesis EffectFruit juice
The present invention features a method of inducing an anti-angiogenesis effect within a tumorous region in the body of a mammal, wherein the method comprises the steps of administering, to a patient, a formulation comprising processed Morinda Citrifolia, wherein the processed Morinda citrifolia blocks formation of new blood vessels within a tumorous region by inhibiting tubule elongation and endothelial cell migration. Blocking the growth factors of said endothelial cells within said tumorous region inhibits tubule elongation and endothelial cell migration. In a preferred embodiment, the processed Morinda citrifolia comprises fruit juice and puree juice in various concentrations.
Owner:TAHITIAN NONI INT INC
Electric propulsion testing platform gaseous-propellant supply device
InactiveCN101539482AConstant flow and constant pressureConstant pressureEngine testingEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention discloses an electric propulsion testing platform gaseous-propellant supply device which consists of a high pressure gas cylinder, a gas cylinder manual valve, a gas cylinder pressure gauge, a discompressor, a discompressor valve, a discompressor pressure gauge, a metallic hose, a filter in front of a flow controller, the flow controller, a premixing cavity, a pressure sensor, a penetration front manual valve, a penetration flanged joint, an electromagnetic valve, a filter in front of an engine, a tee joint and a stainless steel canaliculus tubule. The gaseous-propellant supply device can propel gas which has single component in certain flow rate and pressure intensity, provides mixed gas propelling agent with certain mixing ratio, and has the advantages of stable work and accurate control of the flow rate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Tunnelling probe
InactiveUS20090298004A1Accurate cutting operationPromote absorptionTeeth fillingSurgical instrument detailsFiberActive agent
An electromagnetically induced cutting mechanism provides accurate cutting operations on soft tissues. The electromagnetically induced cutter is adapted to interact with atomized fluid particles. A tissue remover comprises an aspiration cannula housing a fluid and energy guide for conducting electromagnetically induced cutting forces to the site within a patient's body for aspiration of soft tissue. An endodontic probe is used to perform disinfection procedures on target tissues within root canal passages and tubules. The endodontic probe can include an electromagnetic radiation emitting fiber optic tip having a distal end and a radiation emitting region disposed proximally of the distal end. According to one aspect, the endodontic probe can include a porous structure that encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip excluding the radiation emitting region and that is loaded with biologically-active particles, cleaning particles, biologically-active agents, or cleaning agents for delivery from the porous structure onto the target tissues. Another aspect can include provision of the endodontic probe with an adjustable channel-depth indicator, which encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip besides the radiation emitting region and which is movable in proximal and distal directions along a surface of the fiber optic tip to facilitate the provision of depth-of-insertion information to users of the endodontic probe.
Owner:BIOLASE TECH INC
Probes and biofluids for treating and removing deposits from tissue surfaces
ActiveUS20090075229A1Promote absorptionIncrease coverageTeeth fillingWheelchairs/patient conveyanceActive agentElectromagnetic radiation
An endodontic probe is used to perform disinfection procedures on target tissues within root canal passages and tubules. The endodontic probe can include an electromagnetic radiation emitting fiber optic tip having a distal end and a radiation emitting region disposed proximally of the distal end. According to one aspect, the endodontic probe can include a porous structure that encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip excluding the radiation emitting region and that is loaded with biologically-active particles, cleaning particles, biologically-active agents, or cleaning agents for delivery from the porous structure onto the target tissues. Another aspect can include provision of the endodontic probe with an adjustable channel-depth indicator, which encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip besides the radiation emitting region and which is movable in proximal and distal directions along a surface of the fiber optic tip to facilitate the provision of depth-of-insertion information to users of the endodontic probe.
Owner:BIOLASE TECH INC
Oral care composition to reduce or eliminate dental sensitivity
InactiveUS20080268001A1Reduce sensitivityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSilica particleDentinal Tubule
The invention includes an oral care composition that reduces and / or eliminates the perception of tooth sensitivity. The composition includes an adherent material and silica particles having an average particle size of about 8 microns or less. The silica particles are present in the composition in an amount of about 5% by weight. Also included within the scope of the invention are related methods, such as methods of occluding a dentin tubule.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Probes and biofluids for treating and removing deposits from tissue surfaces
ActiveUS8221117B2Promote absorptionIncrease coverageTeeth fillingWheelchairs/patient conveyanceFiberActive agent
An endodontic probe is used to perform disinfection procedures on target tissues within root canal passages and tubules. The endodontic probe can include an electromagnetic radiation emitting fiber optic tip having a distal end and a radiation emitting region disposed proximally of the distal end. According to one aspect, the endodontic probe can include a porous structure that encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip excluding the radiation emitting region and that is loaded with biologically-active particles, cleaning particles, biologically-active agents, or cleaning agents for delivery from the porous structure onto the target tissues. Another aspect can include provision of the endodontic probe with an adjustable channel-depth indicator, which encompasses a region of the fiber optic tip besides the radiation emitting region and which is movable in proximal and distal directions along a surface of the fiber optic tip to facilitate the provision of depth-of-insertion information to users of the endodontic probe.
Owner:BIOLASE INC
Antifreeze used for freezing and preserving boar semens as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101796945AImprove survival rateImprove integrityDead animal preservationArtificial inseminationZoology
The invention discloses an antifreeze used for freezing and preserving boar semens as well as preparation and application thereof. The antifreeze used for freezing and preserving the boar semens, which is provided by the invention, contains pigeon egg yolk and concretely comprises the following components in parts by volume: 82 to 90 of freezing base liquid and 10 to 18 of pigeon egg yolk. The antifreeze used for freezing and preserving the boar semens, which is provided by the invention, has simple preparation method, easy material acquirement, reliable effect and easy popularization, is suitable for insemination after long-time preservation and long-distance transportation after the artificial insemination of the frozen semens of the tubules of boars and the ultra-low temperature freezing of the semens of the boars, can obviously enhance the survival rate of the semens, the integrity of the acrosomes and the integrity of the plasmalemma after the boar semens are frozen and unfrozen, and keeps the insemination activity of the boar semens.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Radiation detector
InactiveUS20050012043A1Sensitivity is deterioratedSmall sizeHandling using diaphragms/collimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansRadioactive agentThree vessels
The present invention provides a radiation detector capable of detecting the radioactive substance accumulated in the tissue inside a body by inserting a detection unit into blood vessels. In the radiation detector of the present invention, comprising a detection unit (2) having a bar-type scintillator (4) which emits light by an incidence of radiation so as to transmit the light from the scintillator through an optical fiber, the detection unit is formed in a size capable of being inserted into the tubules while fine convexoconcaves are provided on the peripheral surface of the scintillator.
Owner:NIHON MEDI PHYSICS CO LTD +2
Oral Care Composition To Reduce Or Eliminate Dental Sensitivity
InactiveUS20090092562A1Reduce sensitivityReduce penetrationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsDentinal TubuleTubule
The invention includes an oral care composition that reduces and / or eliminates the perception of tooth sensitivity. The composition includes an adherent material and particles having an average particle size of about 8 microns or less. The particles are present in the composition in an amount of about 5% by weight. Also included within the scope of the invention are related methods, such as methods of occluding a dentin tubule.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Tubule-blocking silica materials for dentifrices
Precipitated silica materials are provided for utilization as abrasives or thickeners within dentifrice formulations that simultaneously effectuate tubule blocking within tooth dentin to reduce dentin sensitivity. Such precipitated silica materials have sufficiently small particle sizes and exhibit certain ionic charge levels by, for example, adjusting the zeta potential properties of the precipitated silica materials through treatment with certain metals to permit effective static attraction and eventual accumulation within dentin tubules when applied to teeth from a dentifrice formulation.
Owner:J M HUBER CORP
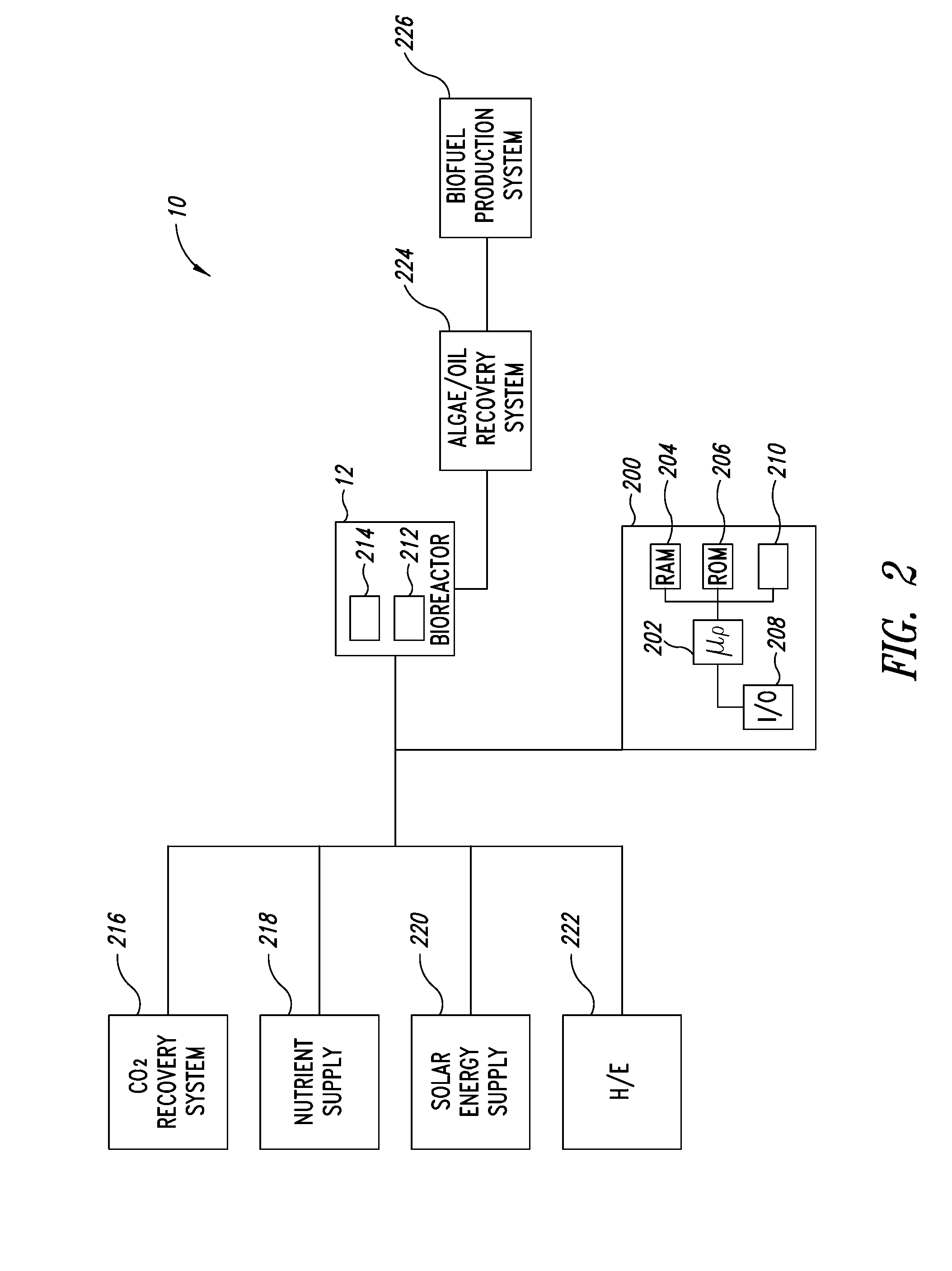
Systems, devices, and, methods for releasing biomass cell components
InactiveUS20100035321A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular componentCisterna
Systems, devices, and methods for releasing one or more cell components from a photosynthetic organism. A bioreactor system is operable for growing photosynthetic organisms. Some of the methods include contacting the photosynthetic organism with an energy-activatable sensitizer, and activating the energy-activatable sensitizer, thereby releasing a cellular component from at least one of, for example, a membrane structure, tubule, vesicle, cisterna, organelle, cell compartment, plastid, or mitochondrion, associated with the photosynthetic organisms.
Owner:BIONAVITAS
Tubule high-density type method for freezing pig jism and the products thereof
InactiveCN101062058AIncrease vitalityGood repeatabilityDead animal preservationMammal material medical ingredientsHigh densityFistula
The invention discloses a high density freezing maintain pig seminal fluid method with fistula and product in animal propagation technical domain, which comprises the following steps: collecting fresh seminal fluid; detecting; pre-treating the seminal fluid; defreezing; proceeding assessment procedure of defreeze seminal fluid; diluting with freezing diluting liquid; storing with high density super low temperature with 0. 25mL fistula; stabilizing the defreezing sperm above 0. 5 and average active at 0. 58; reaching the highest at 0. 68; proceeding pig external fertilization with the sperm; getting 54. 3% cleavage ratio and 48. 5% morula developing ratio; meeting one sperm dosage with sperm quantity of one 0. 25mL fistula. This invention possesses larger using latent force and market developing prospect.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com