Patents
Literature
247 results about "Intravascular catheter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
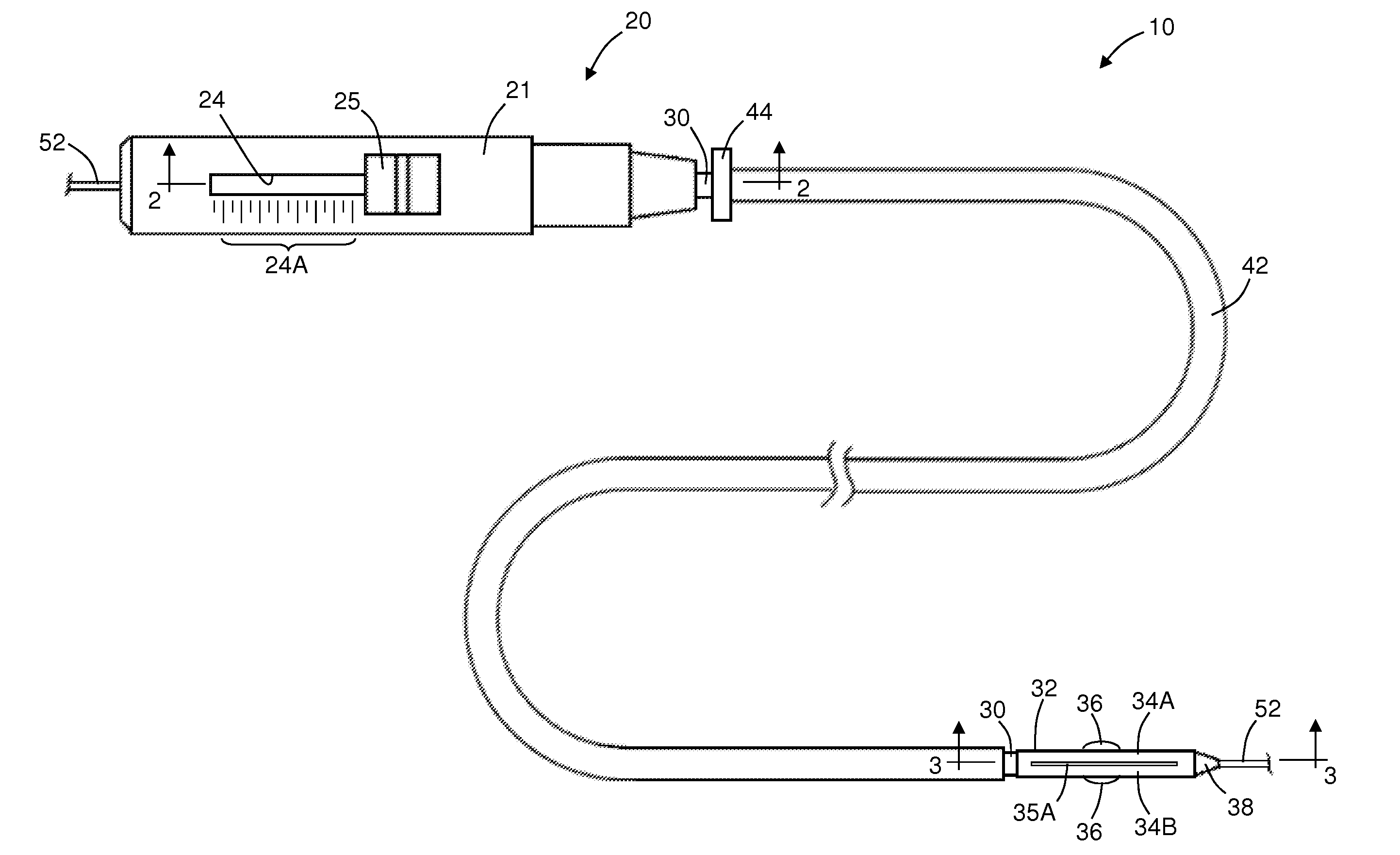
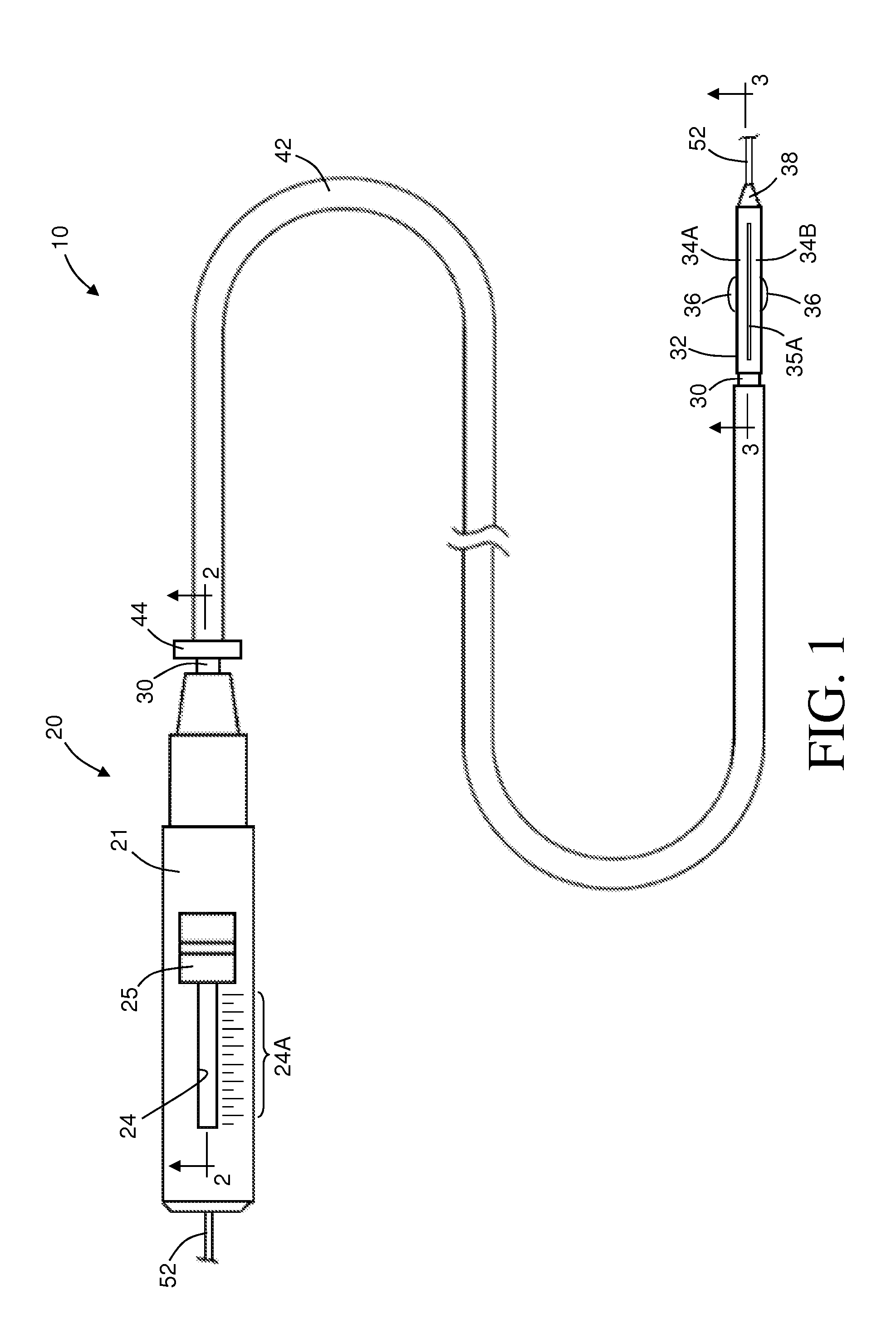
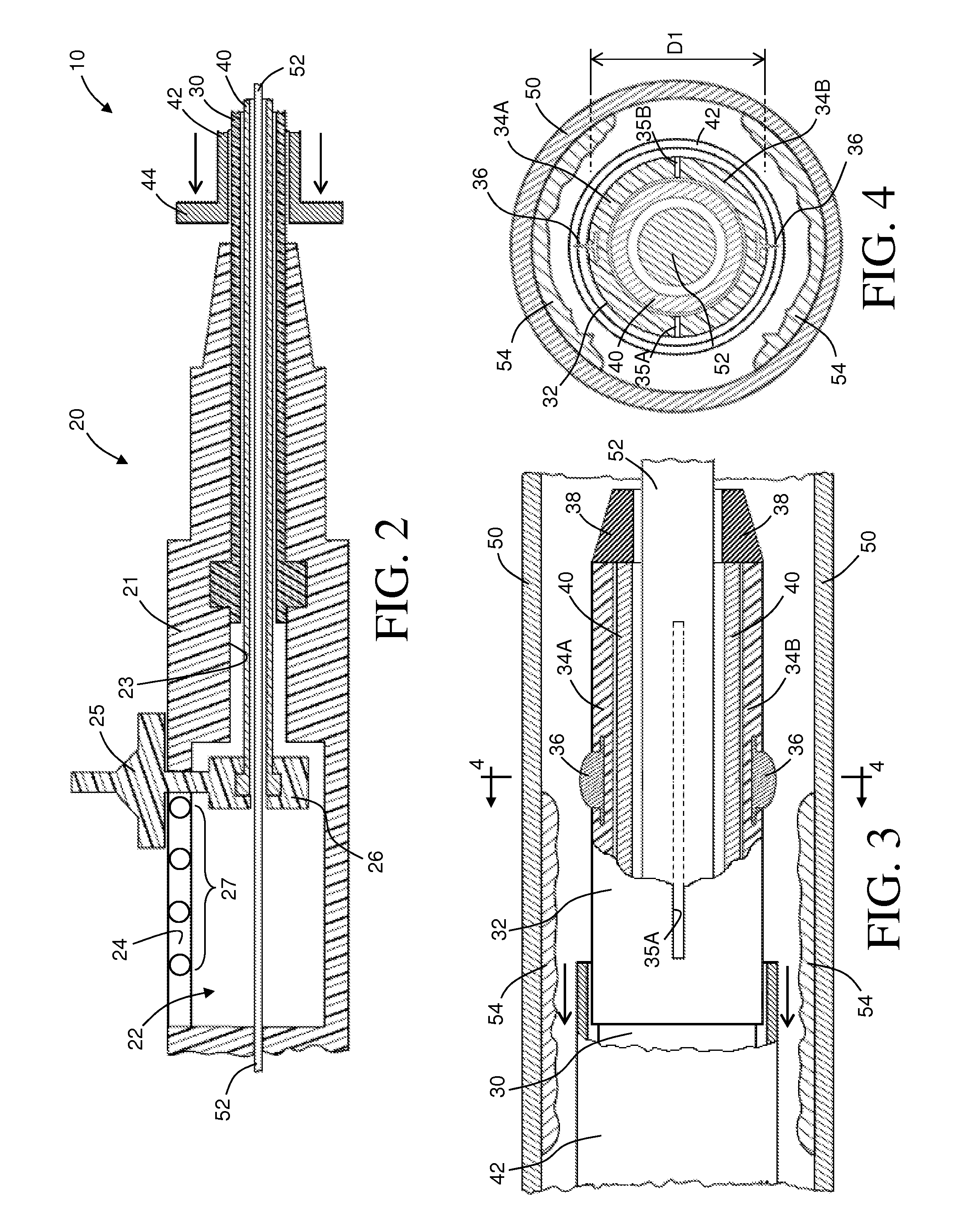
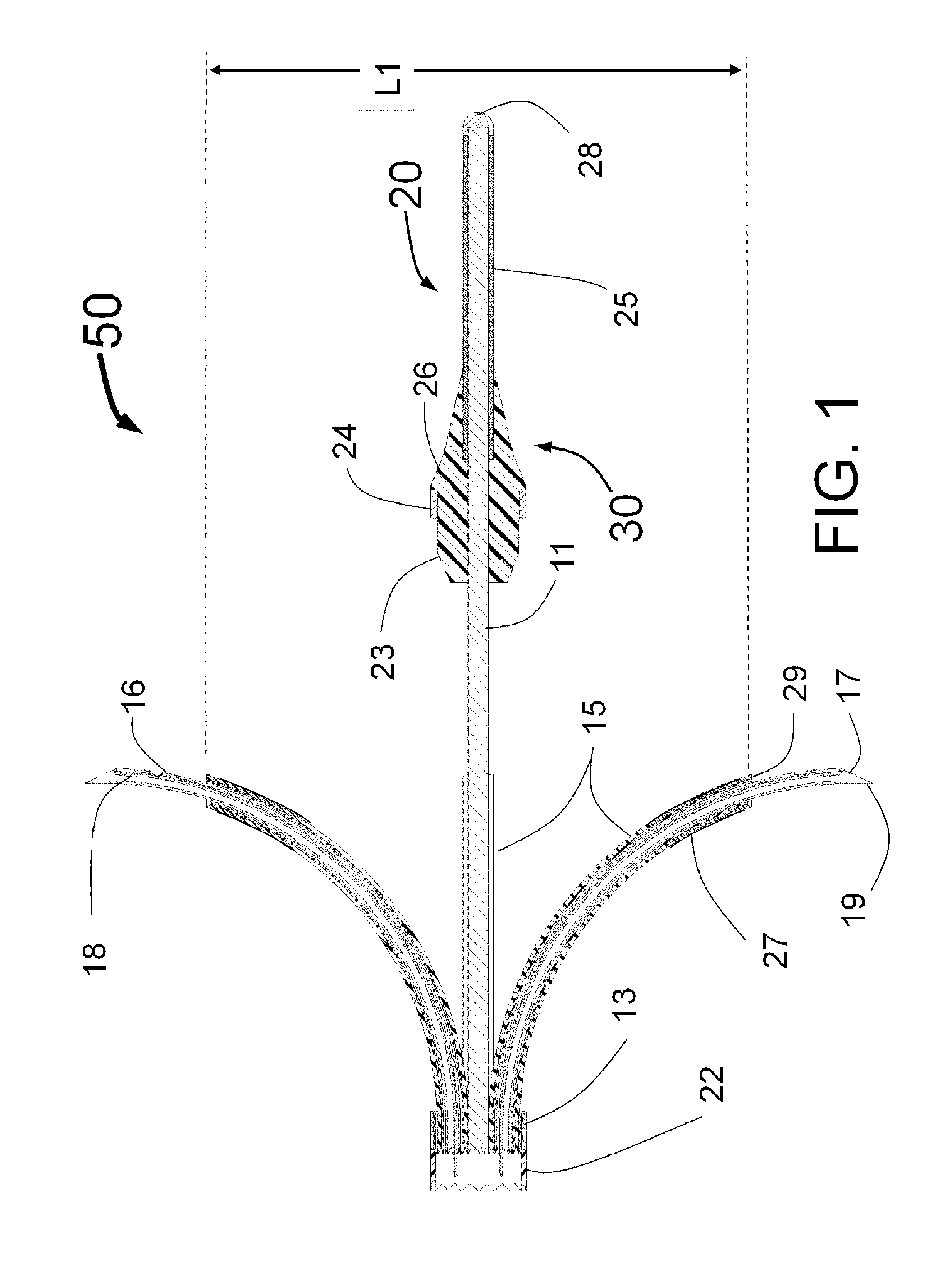
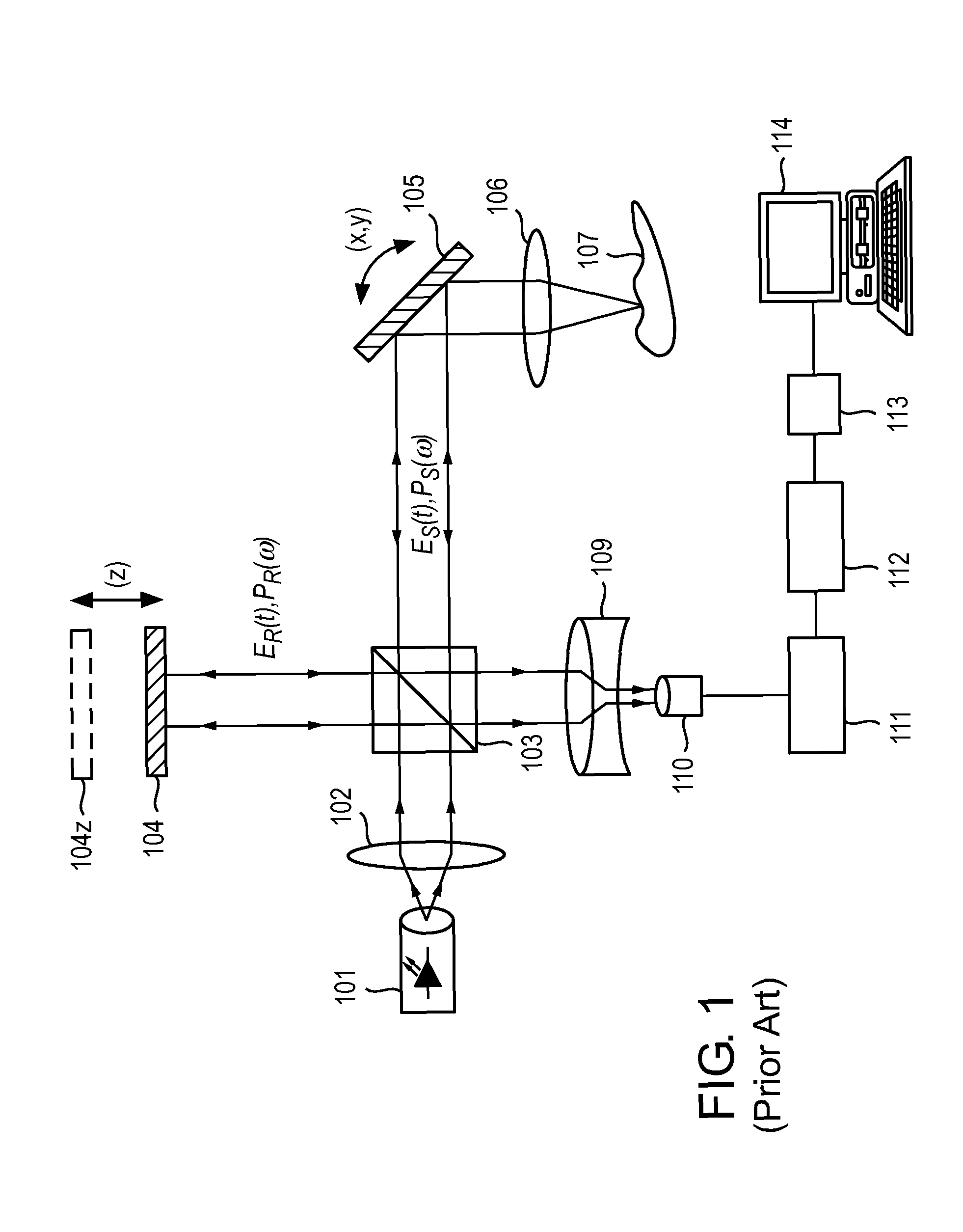
Summary Information: Intravascular catheter. Intravascular catheter: An intravascular catheter is a thin hollow plastic tube that is placed into a blood vessel to introduce or remove fluid, monitor blood pressure, and introduce surgical instruments.
Vascular treatment method and device
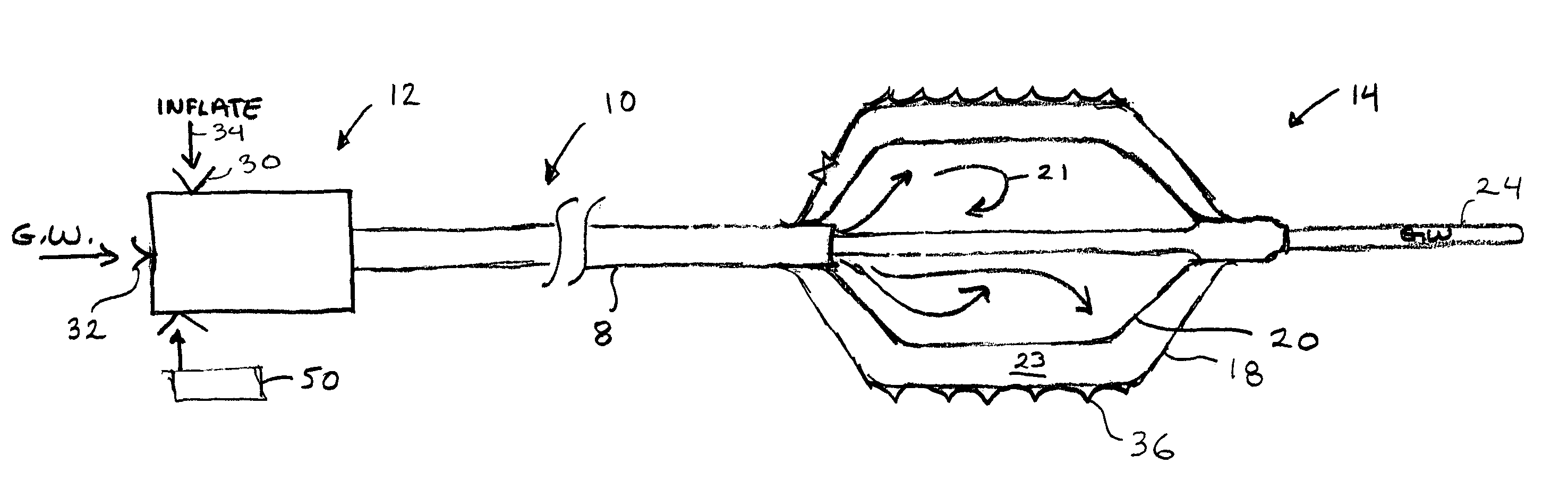
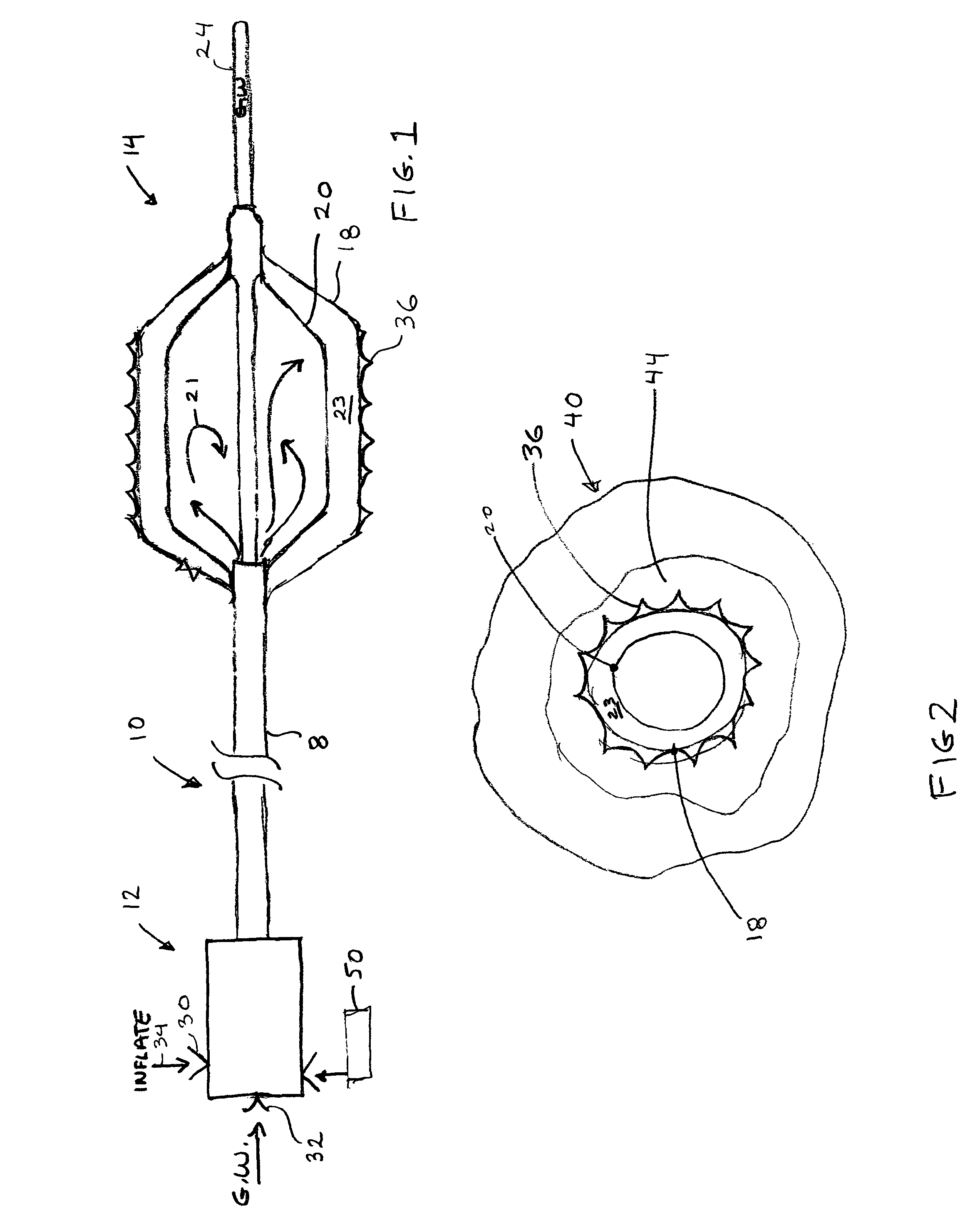
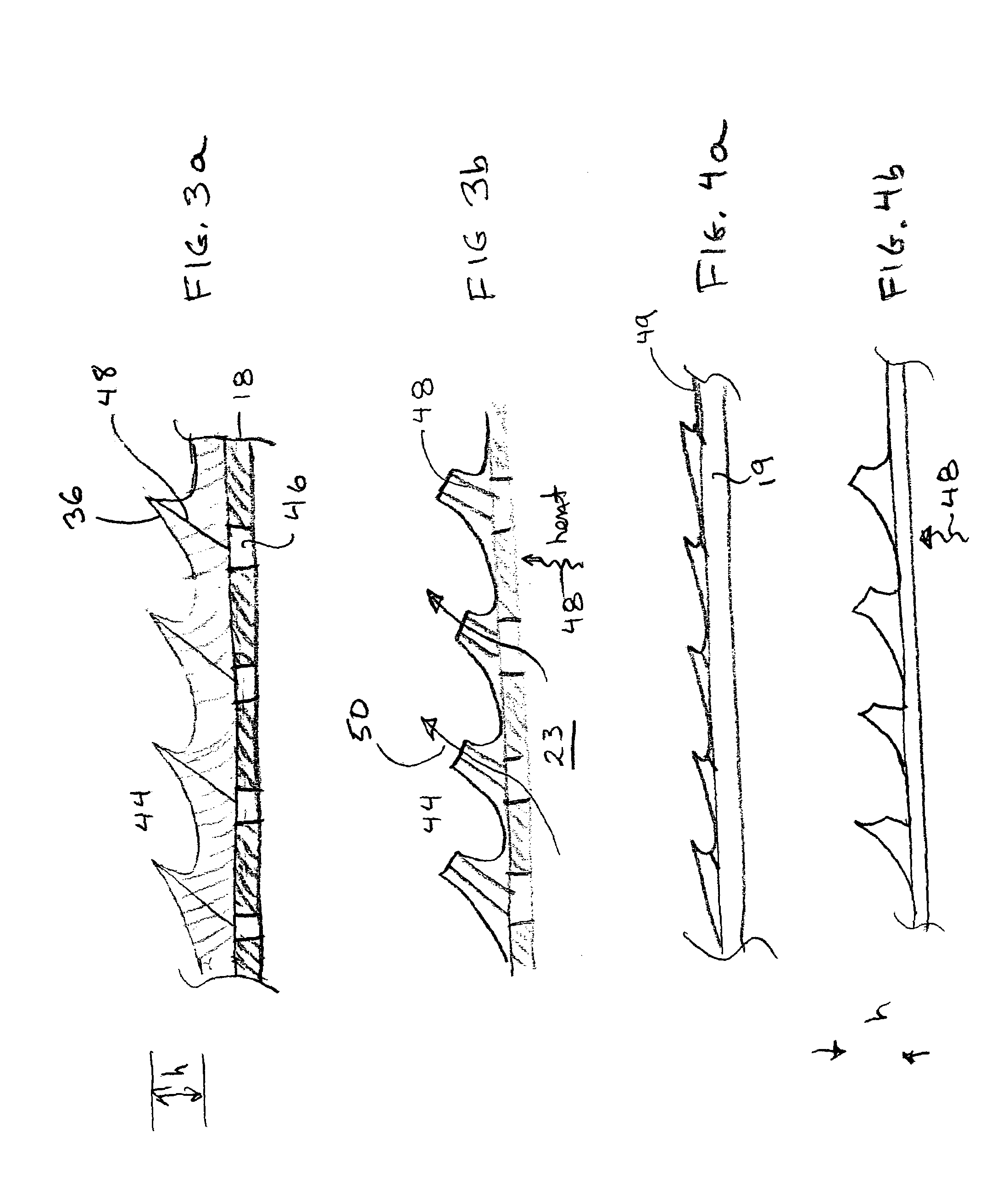
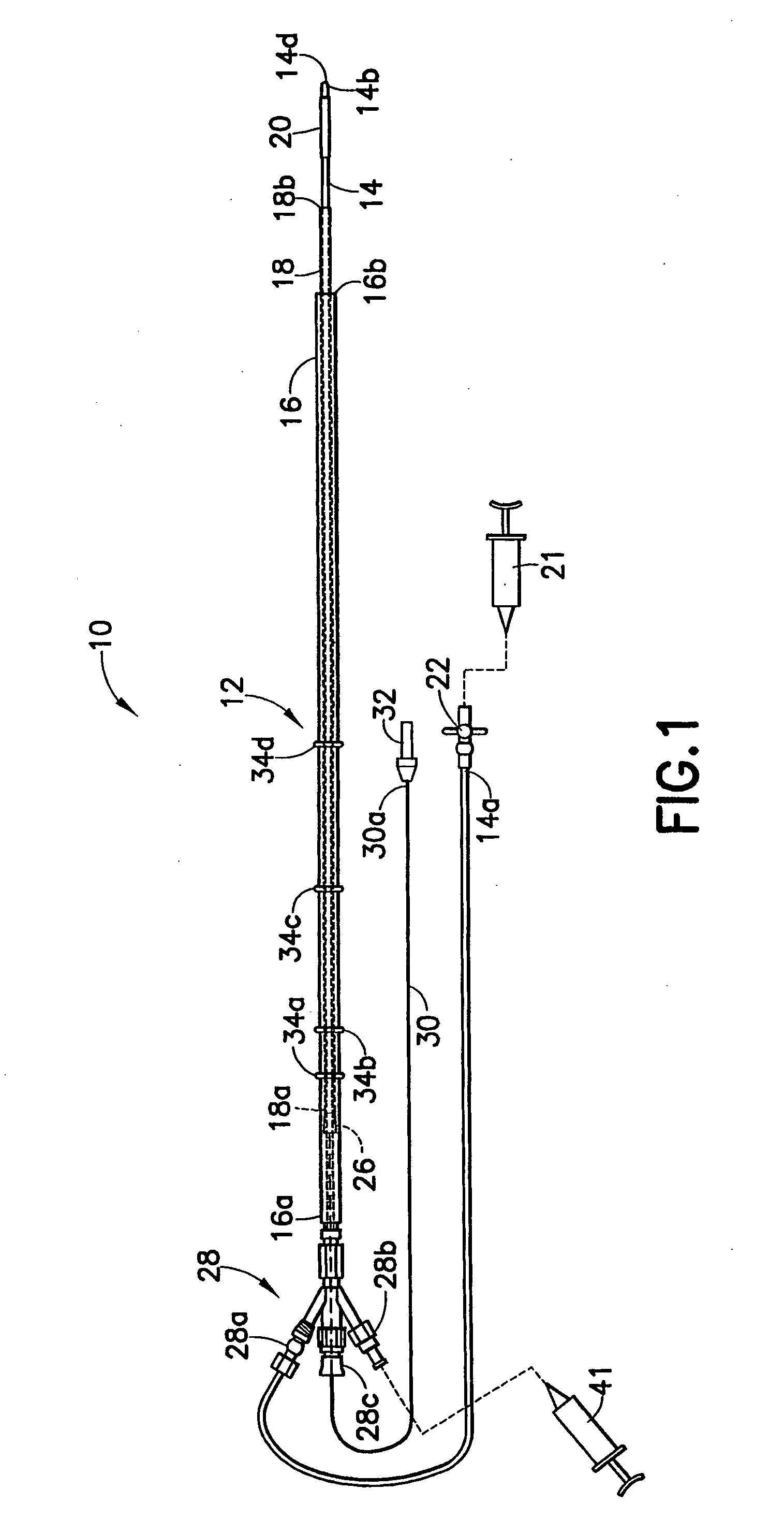
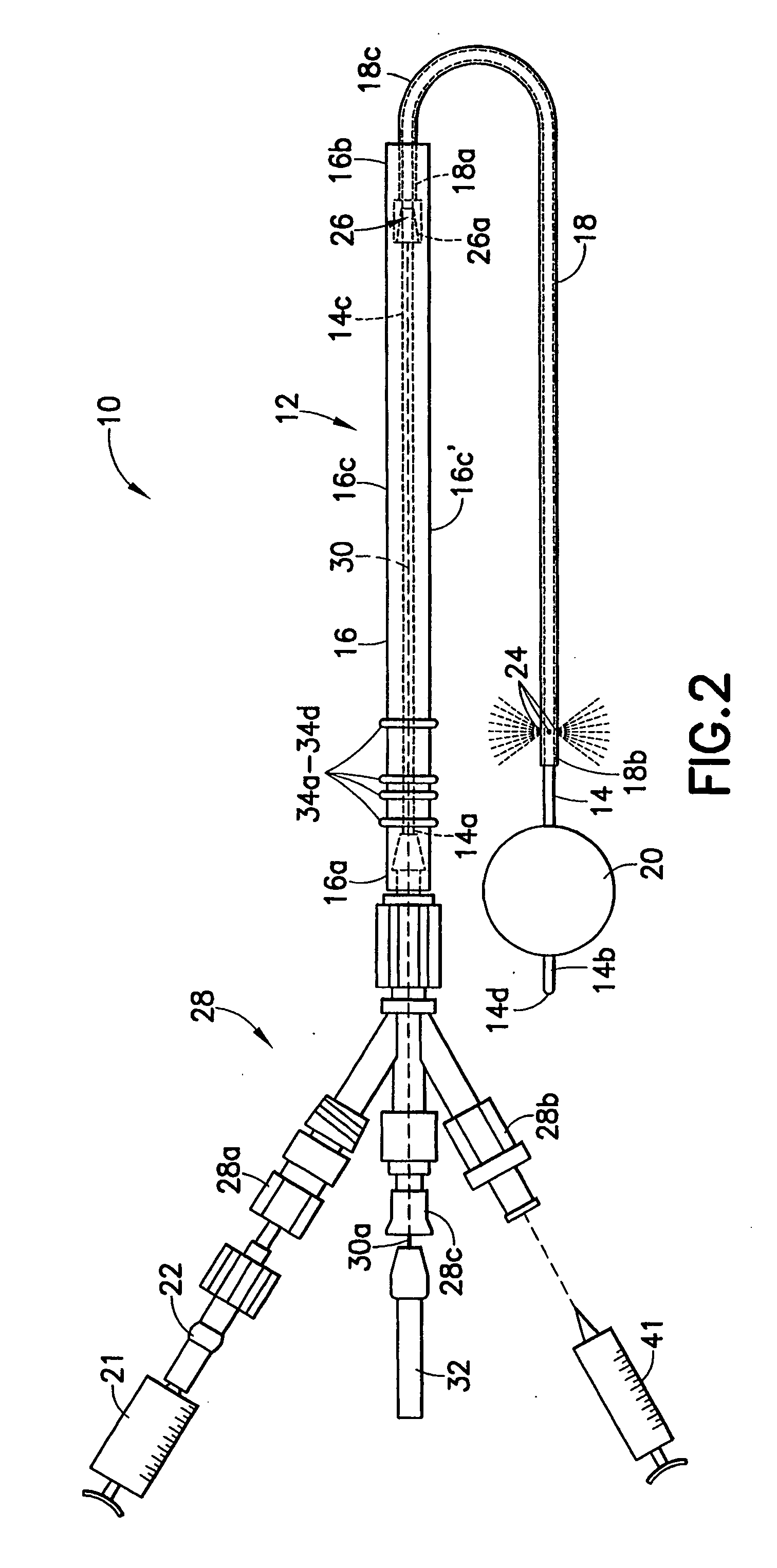
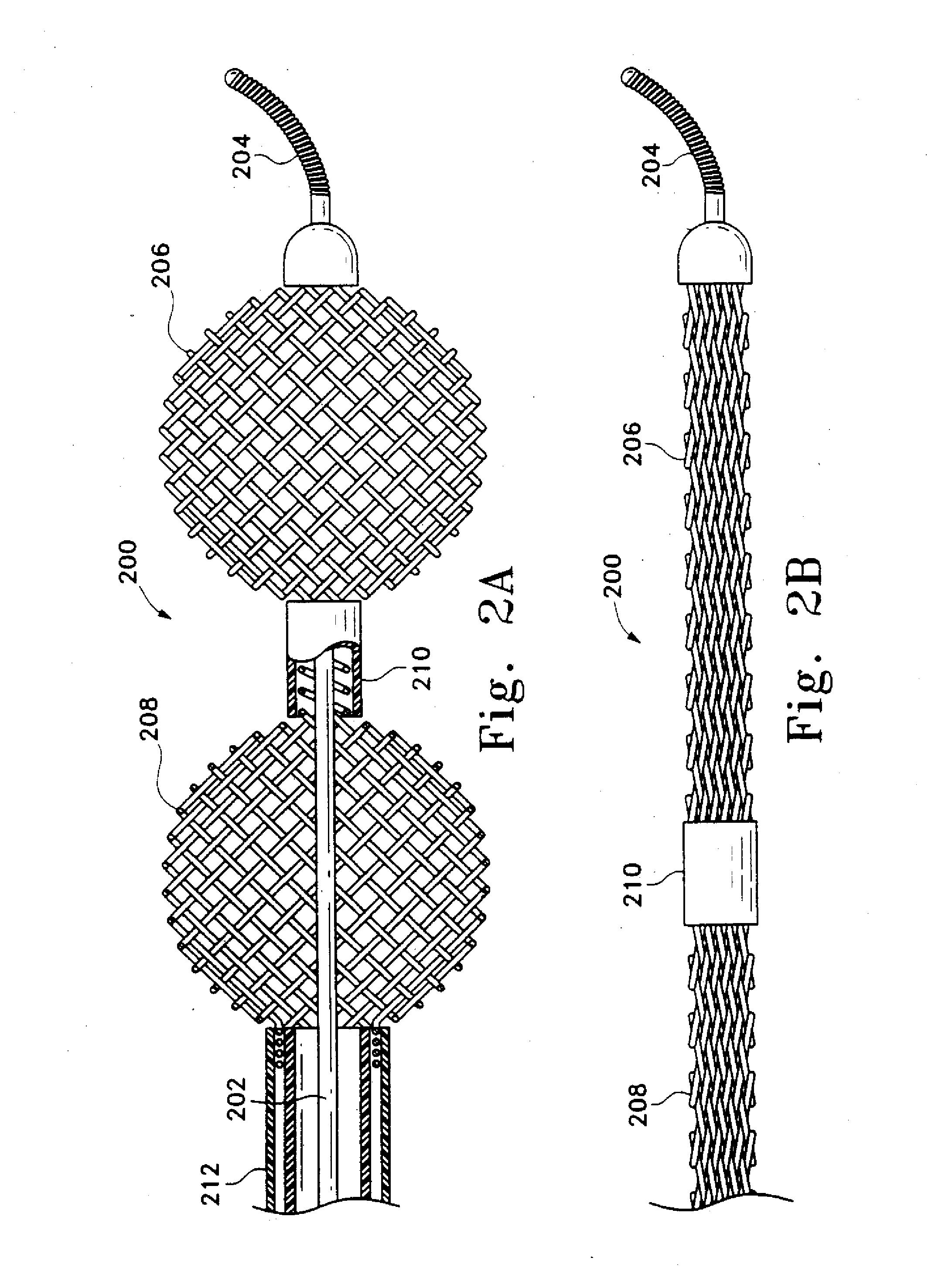
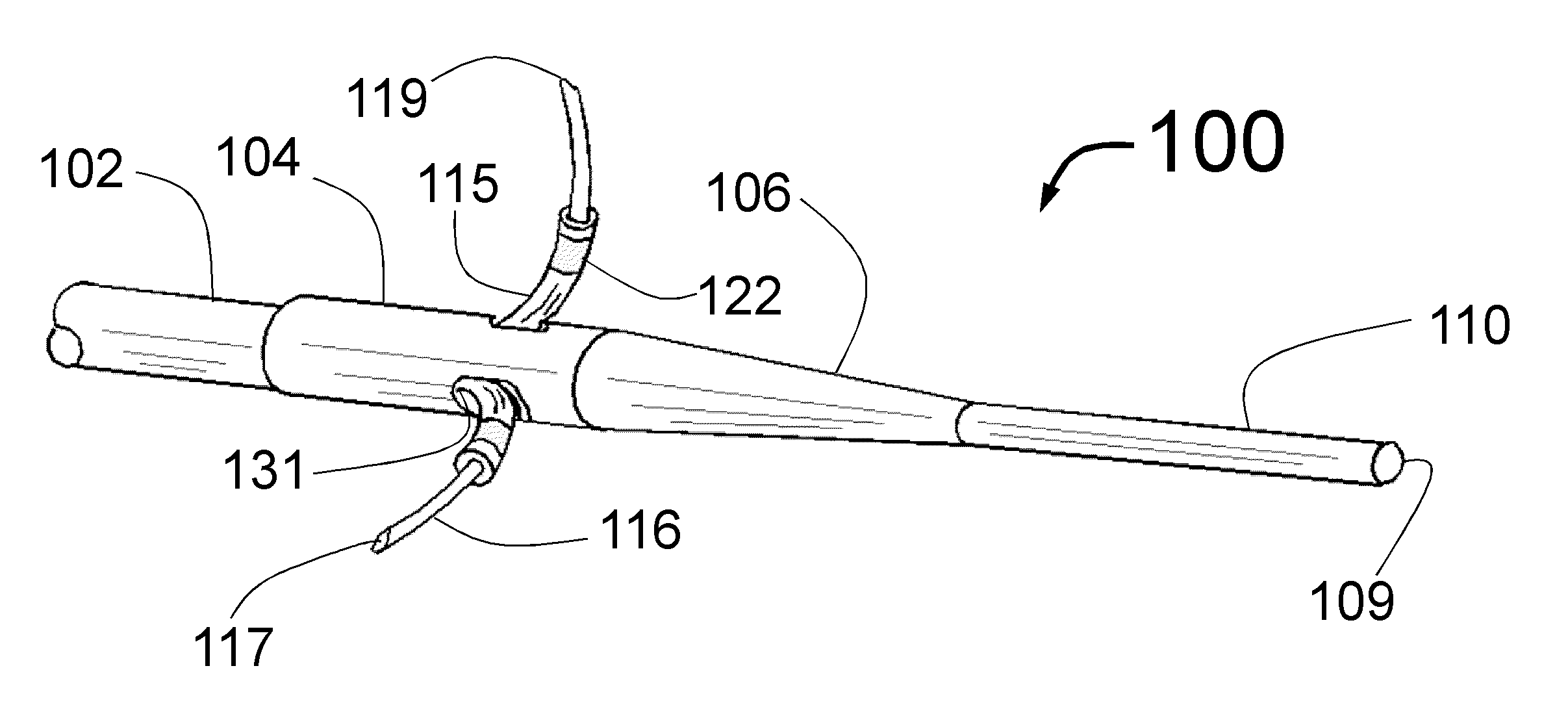
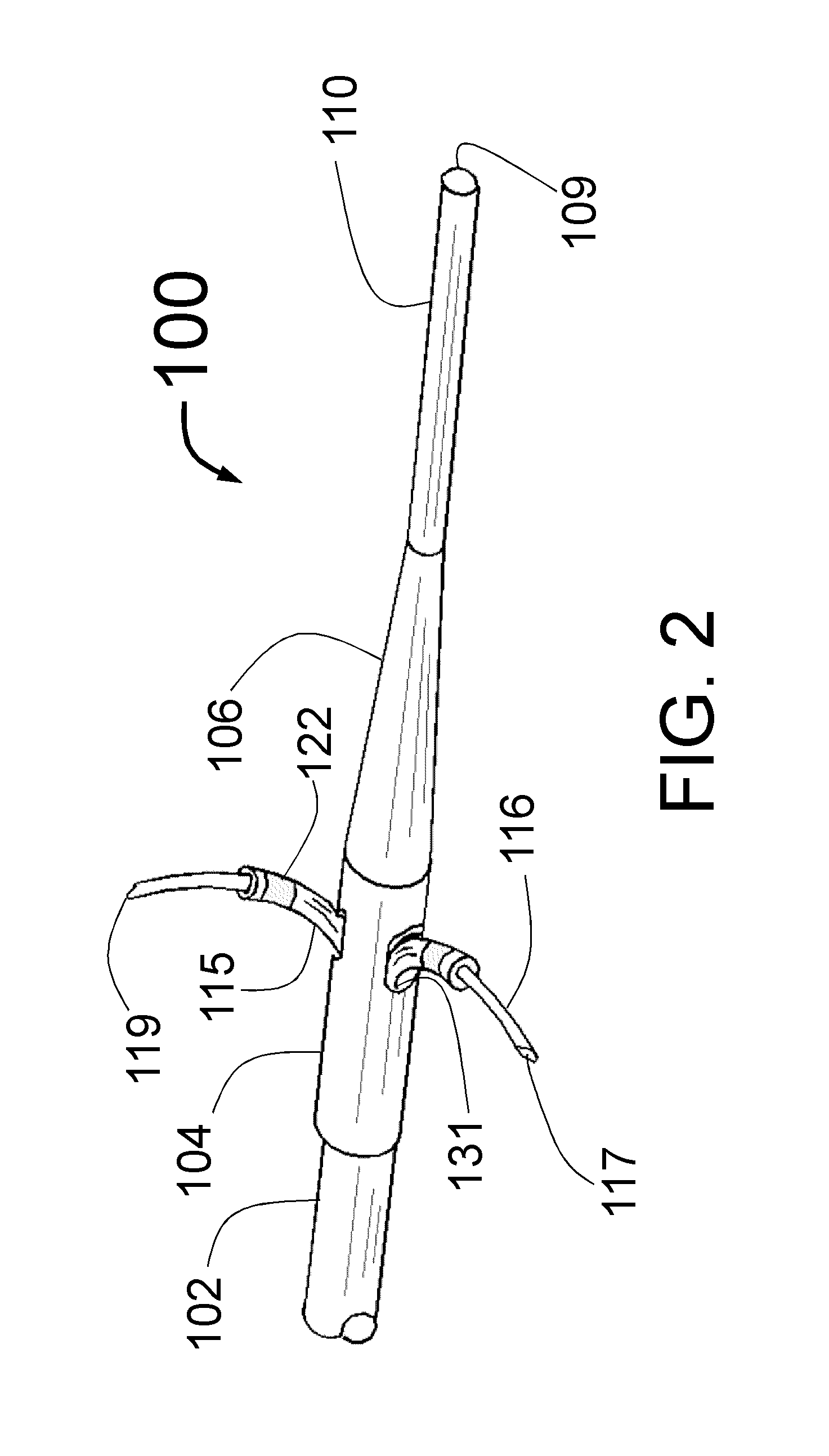
An intravascular catheter with micro spines that penetrate arterial wall to delivery drug or mechanical injury to the vessel wall inducing a “stent” like healing process in the vessel.
Owner:NFOCUS NEUROMEDICAL
Occludable intravascular catheter for drug delivery and method of using the same
Methods and apparatus for treating the interior of a blood vessel include a variety of catheter designs, methods and apparatus for occluding a blood vessel, methods and apparatus for locating an occlusion device, methods and apparatus for locating a treating device at the site of blood vessel tributaries, and methods and apparatus for dispensing treating agent.
Owner:VEIN RX
Methods and systems for the inhibition of vascular hyperplasia
InactiveUS6210393B1Limited extentQuick layeringUltrasound therapyStentsSmooth muscleVascular proliferation
Post-interventional neointimal hyperplasia in arteries is treated by the application of ultrasonic energy. Usually, an intravascular catheter having an interface surface is positioned at a target site in the artery which has previously been treated. The interface surface is vibrationally excited to apply energy to the arterial wall in a manner which inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation in the neointimal layer.
Owner:PHARMASONICS
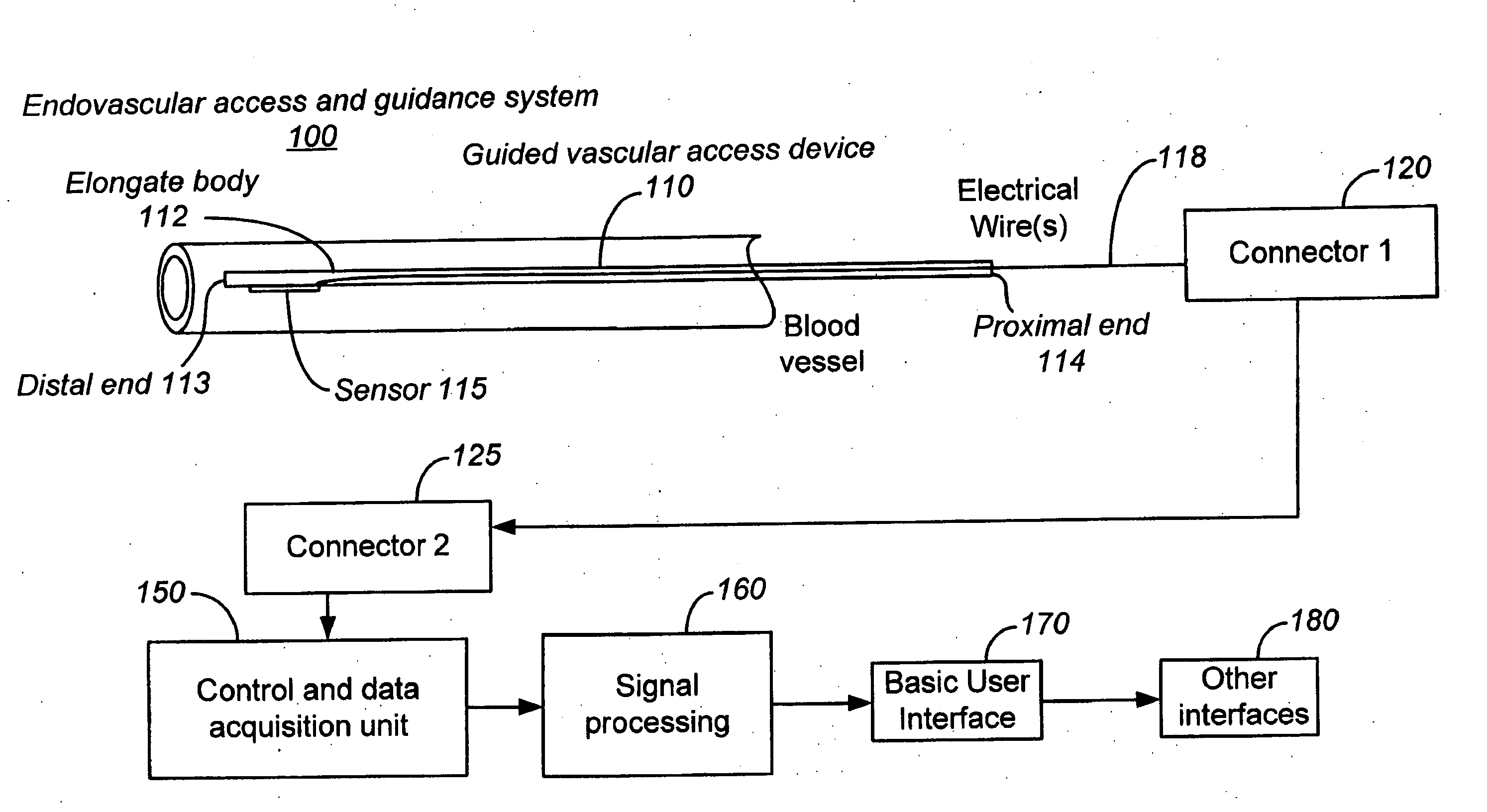
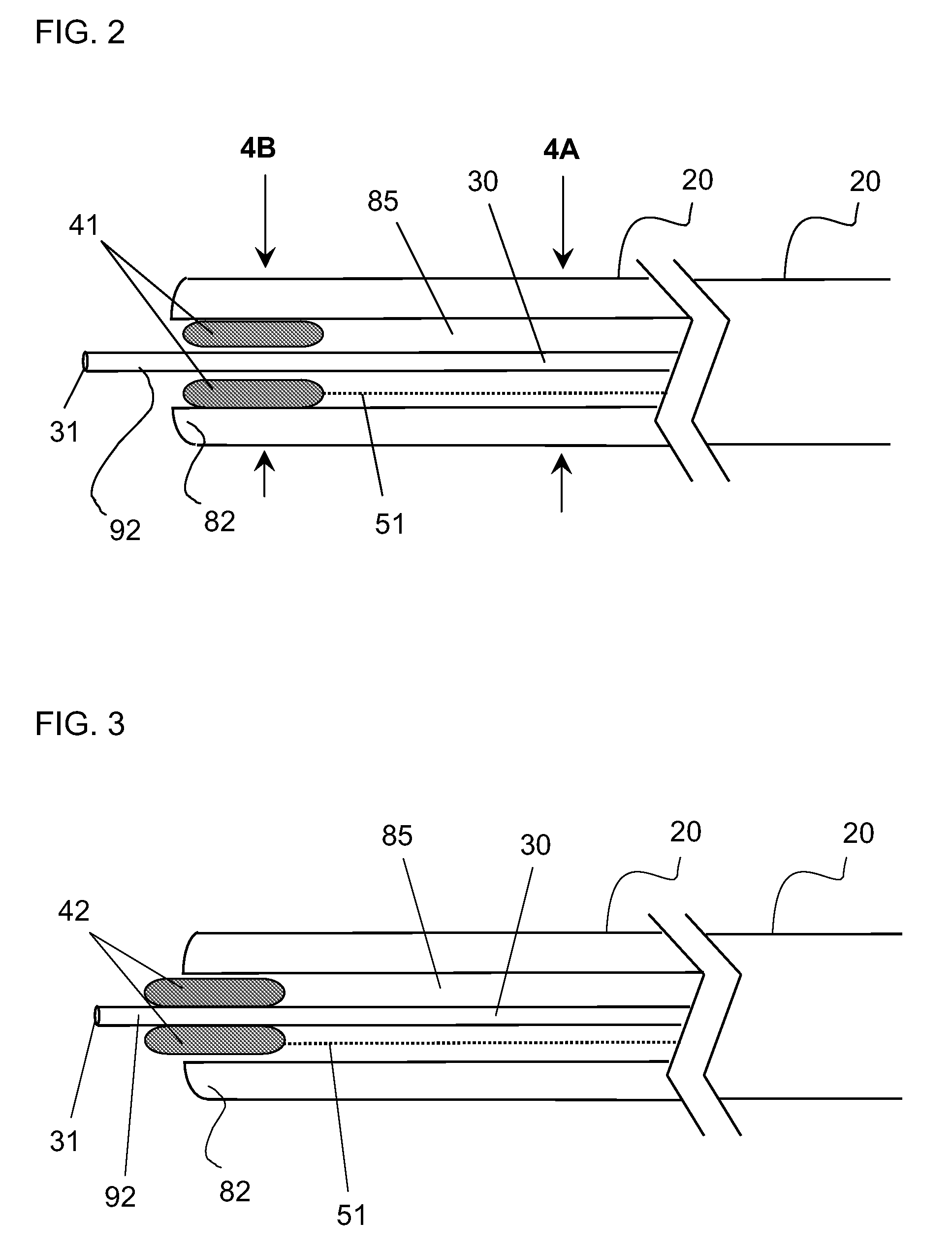
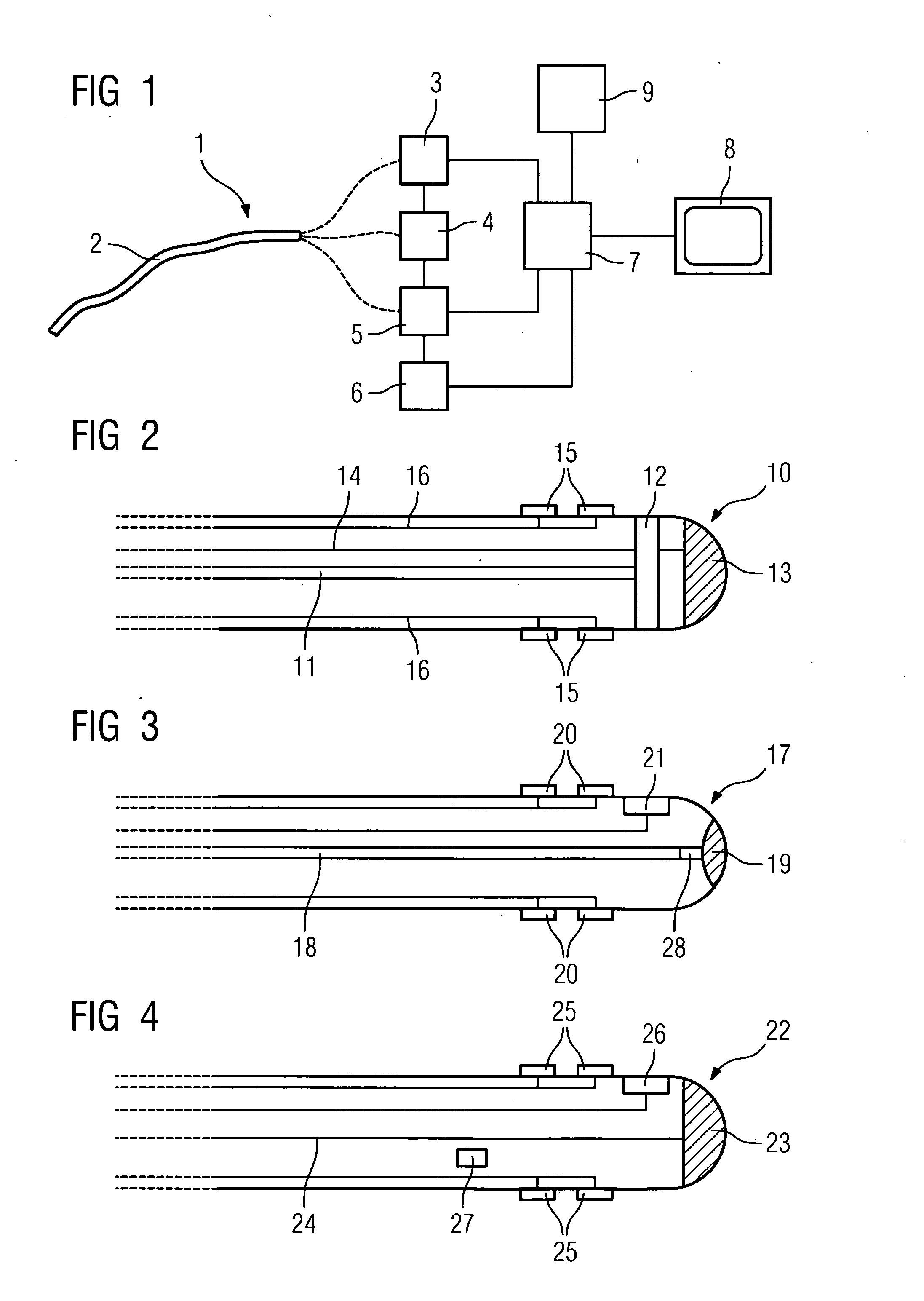
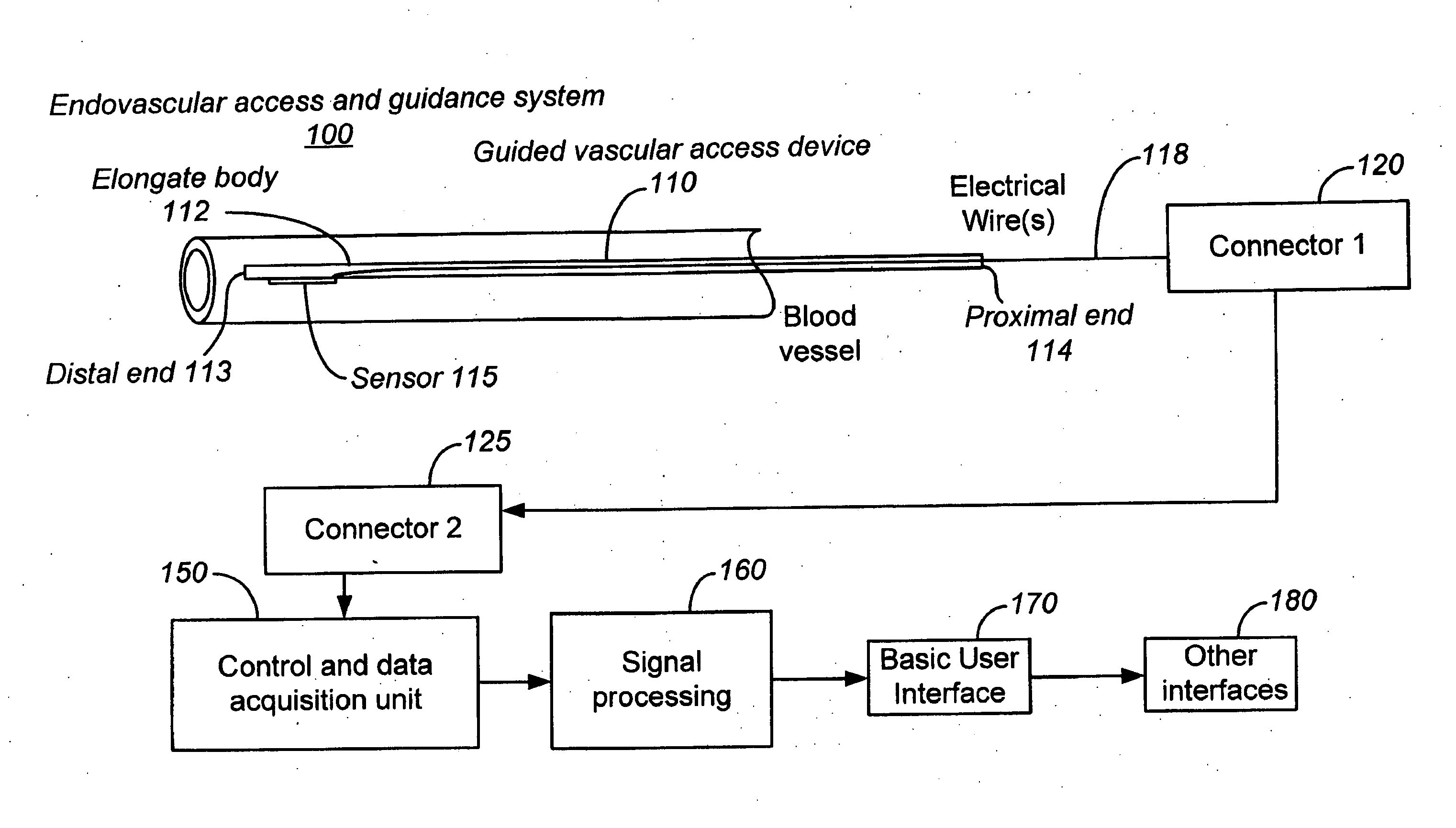
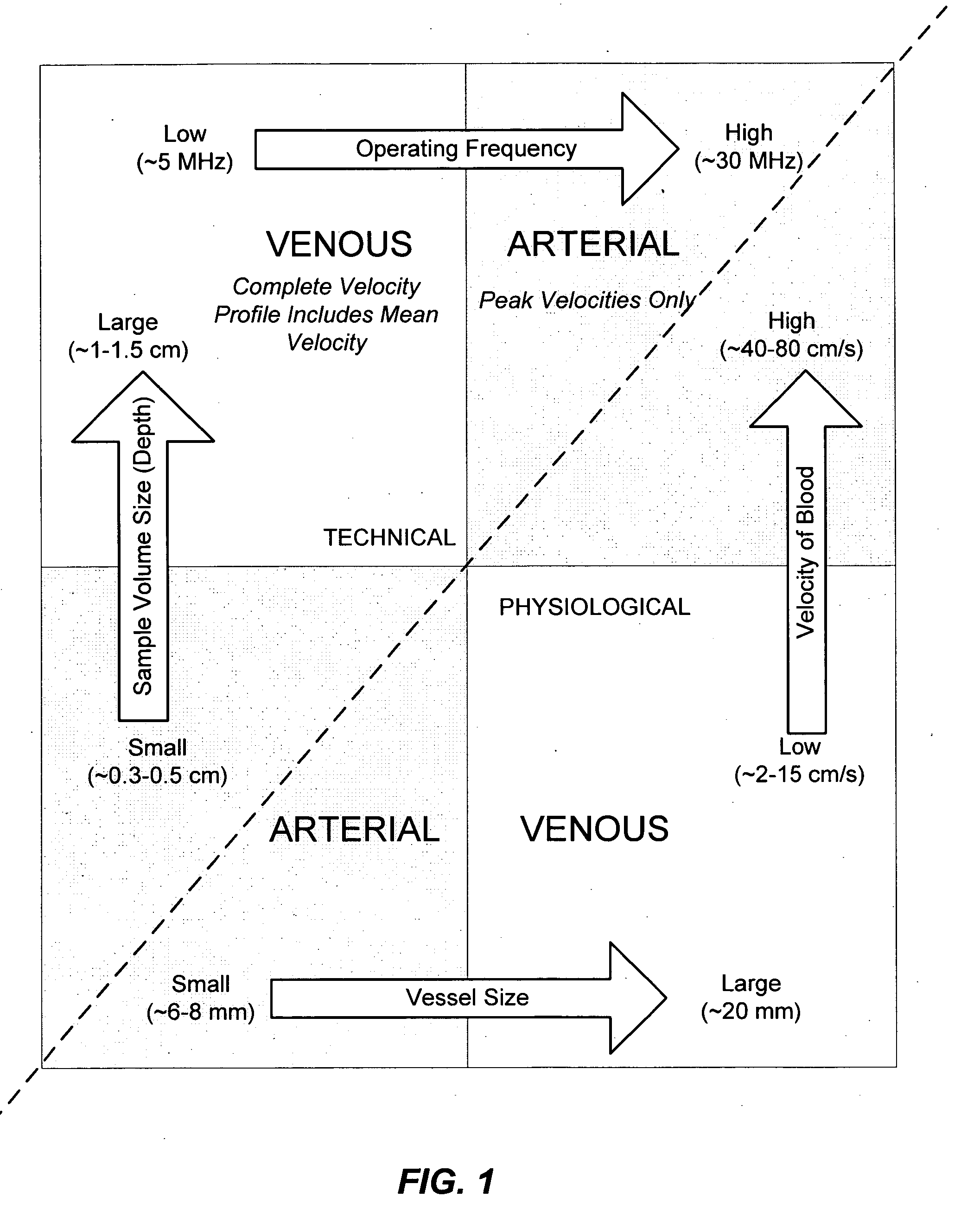
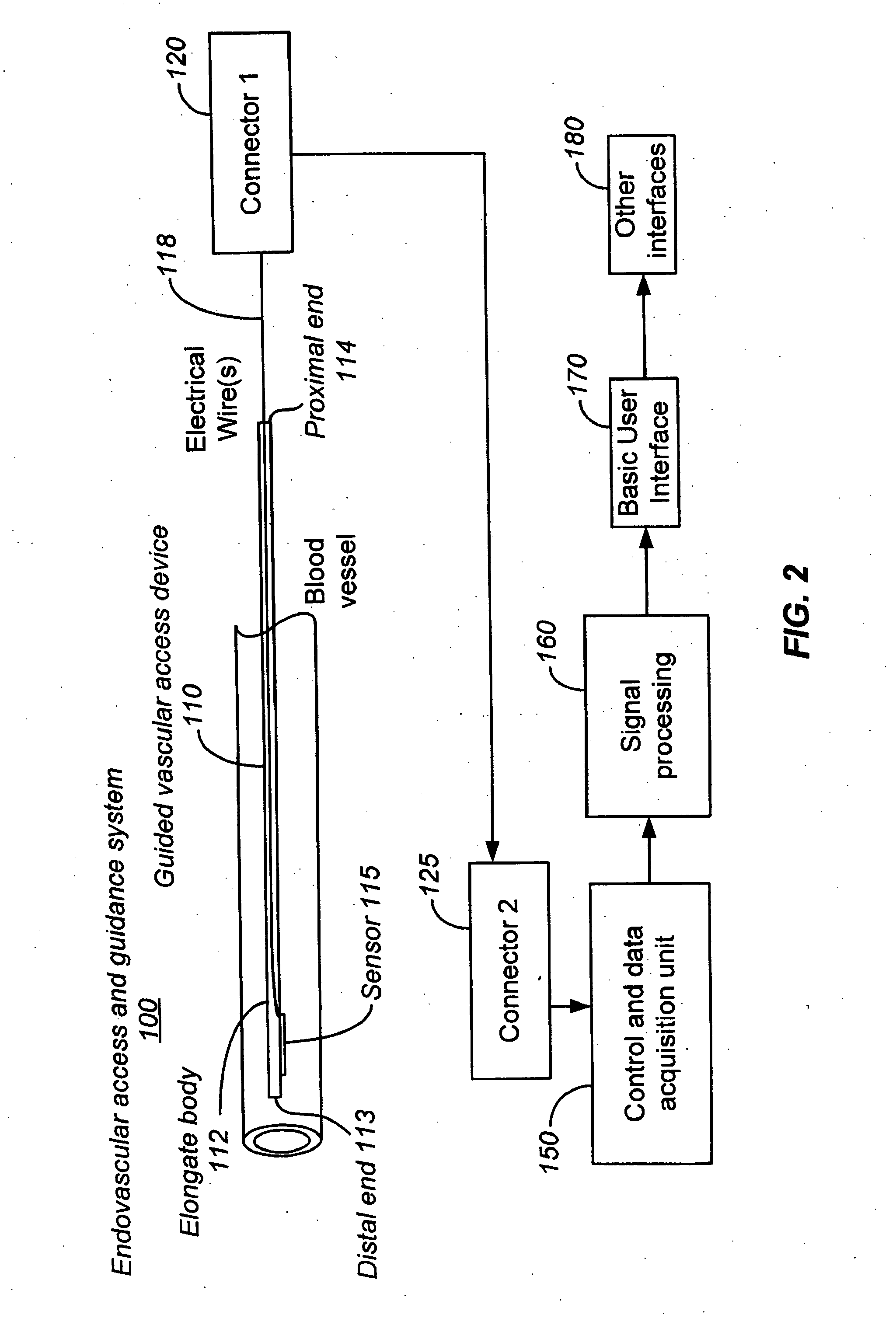
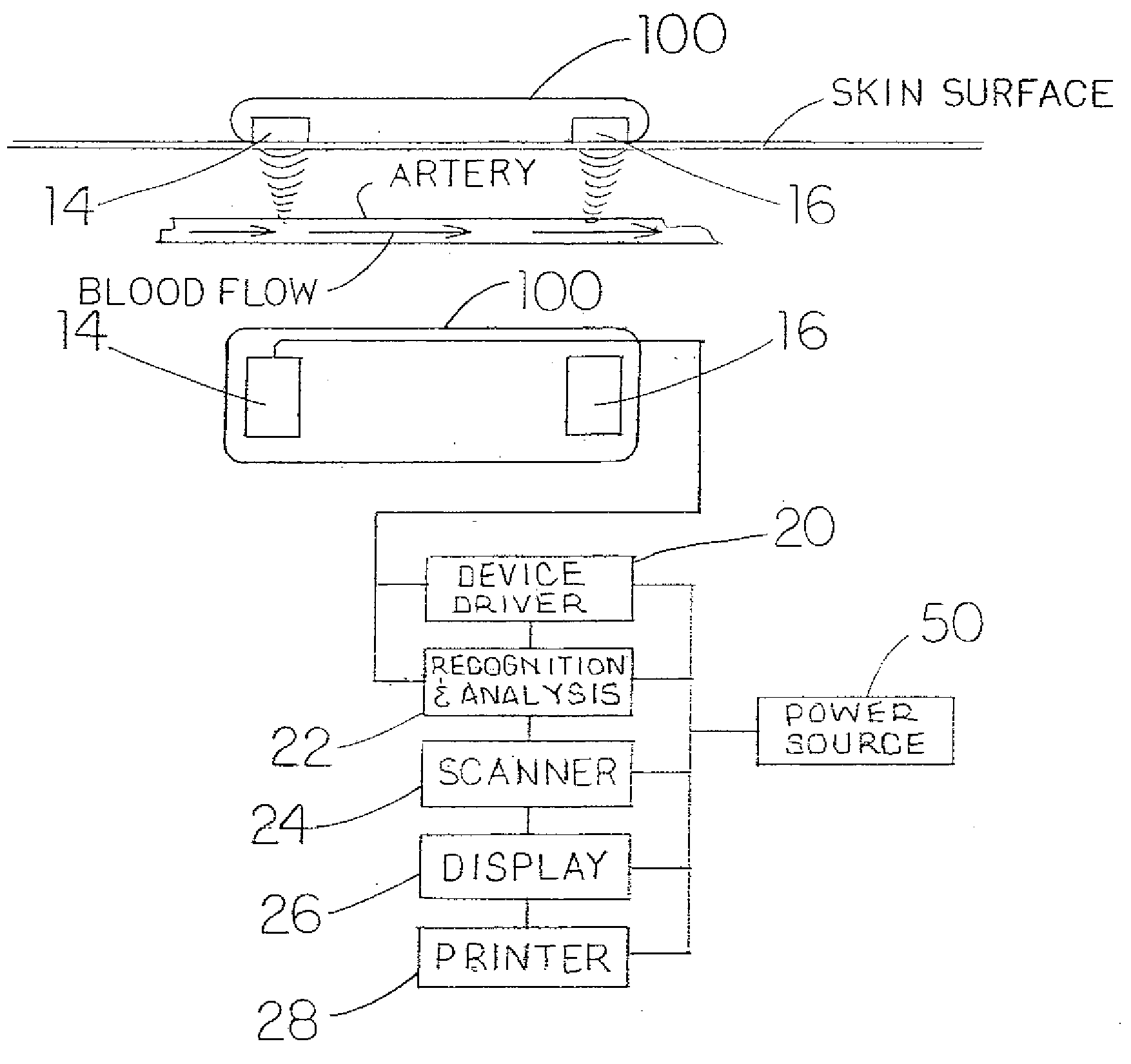
Ultrasound methods of positioning guided vascular access devices in the venous system
ActiveUS20070016068A1Diagnostic probe attachmentBlood flow measurement devicesGuidance systemVascular Access Devices
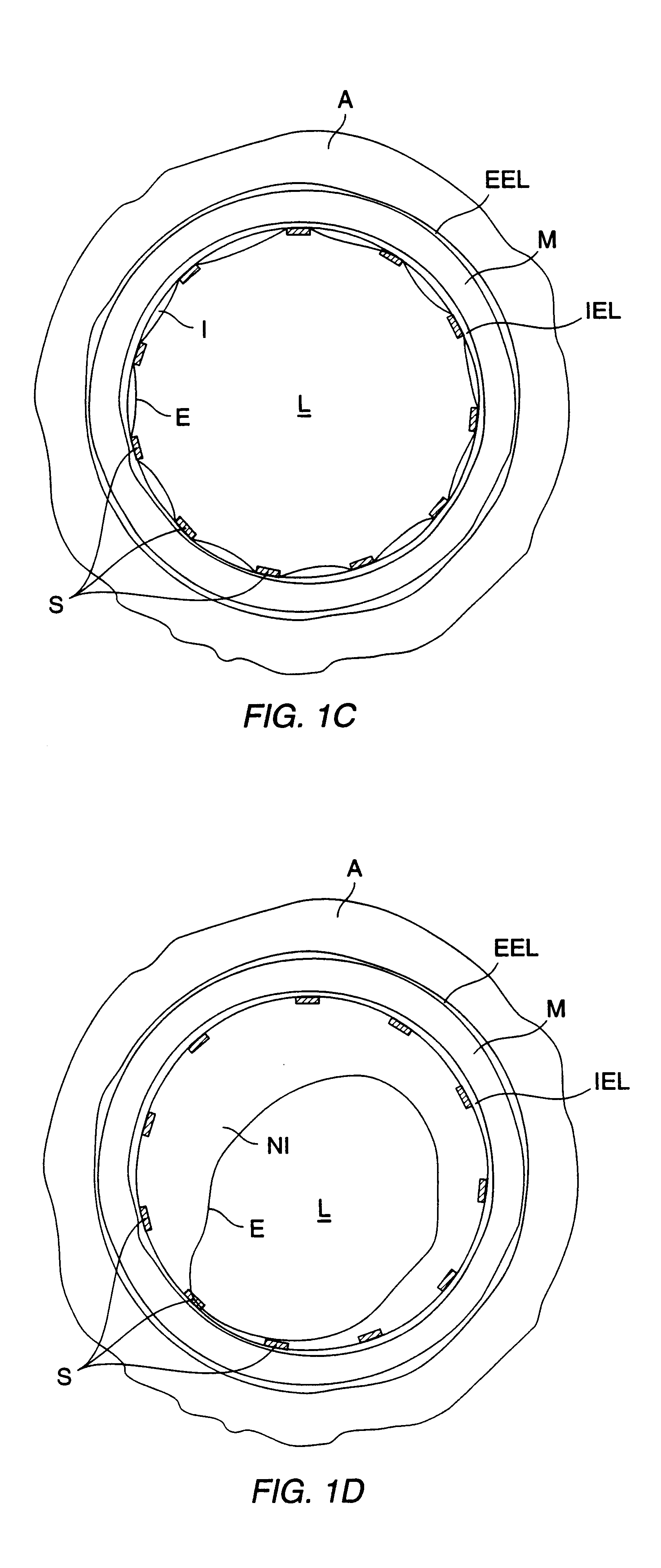
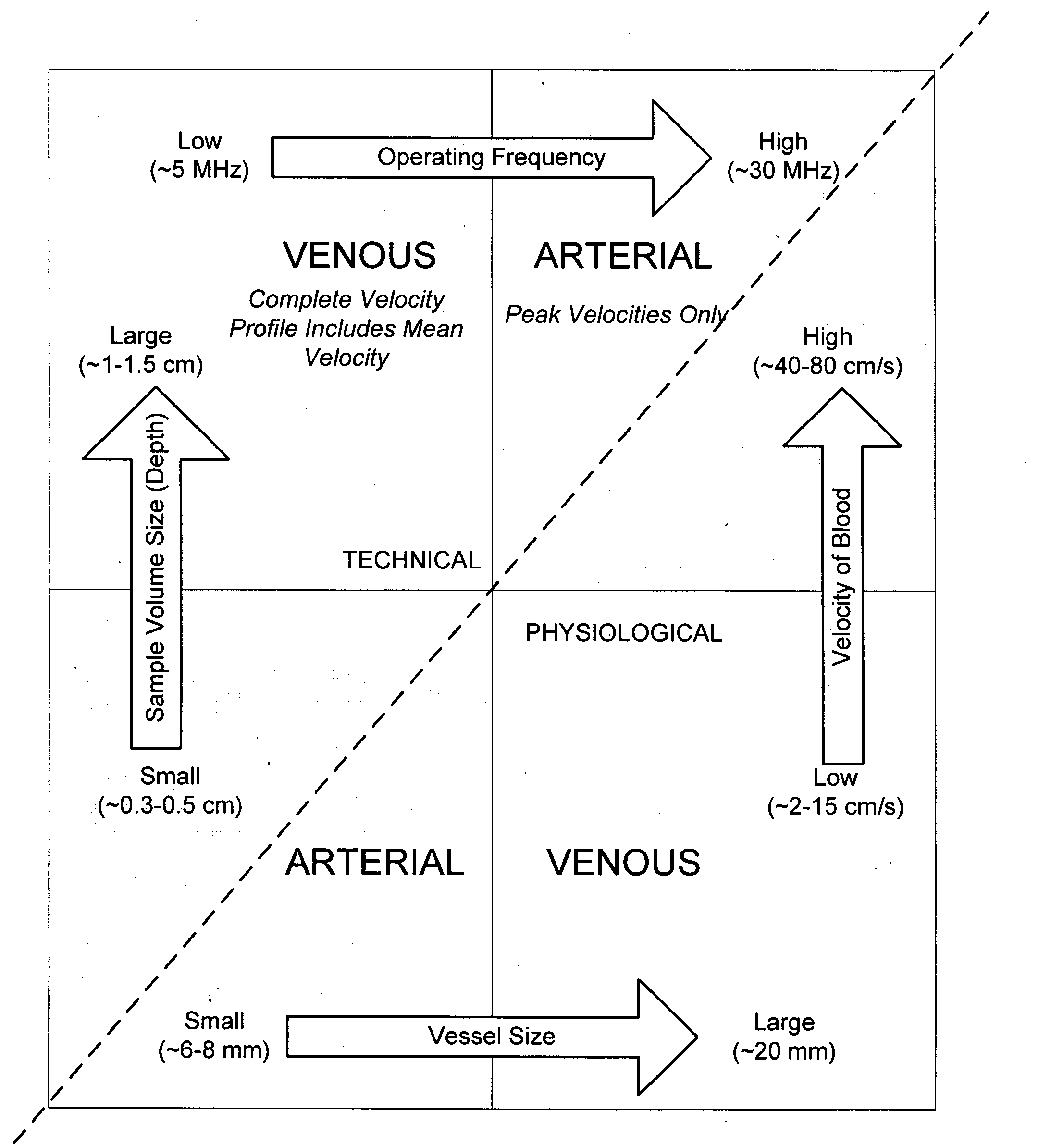
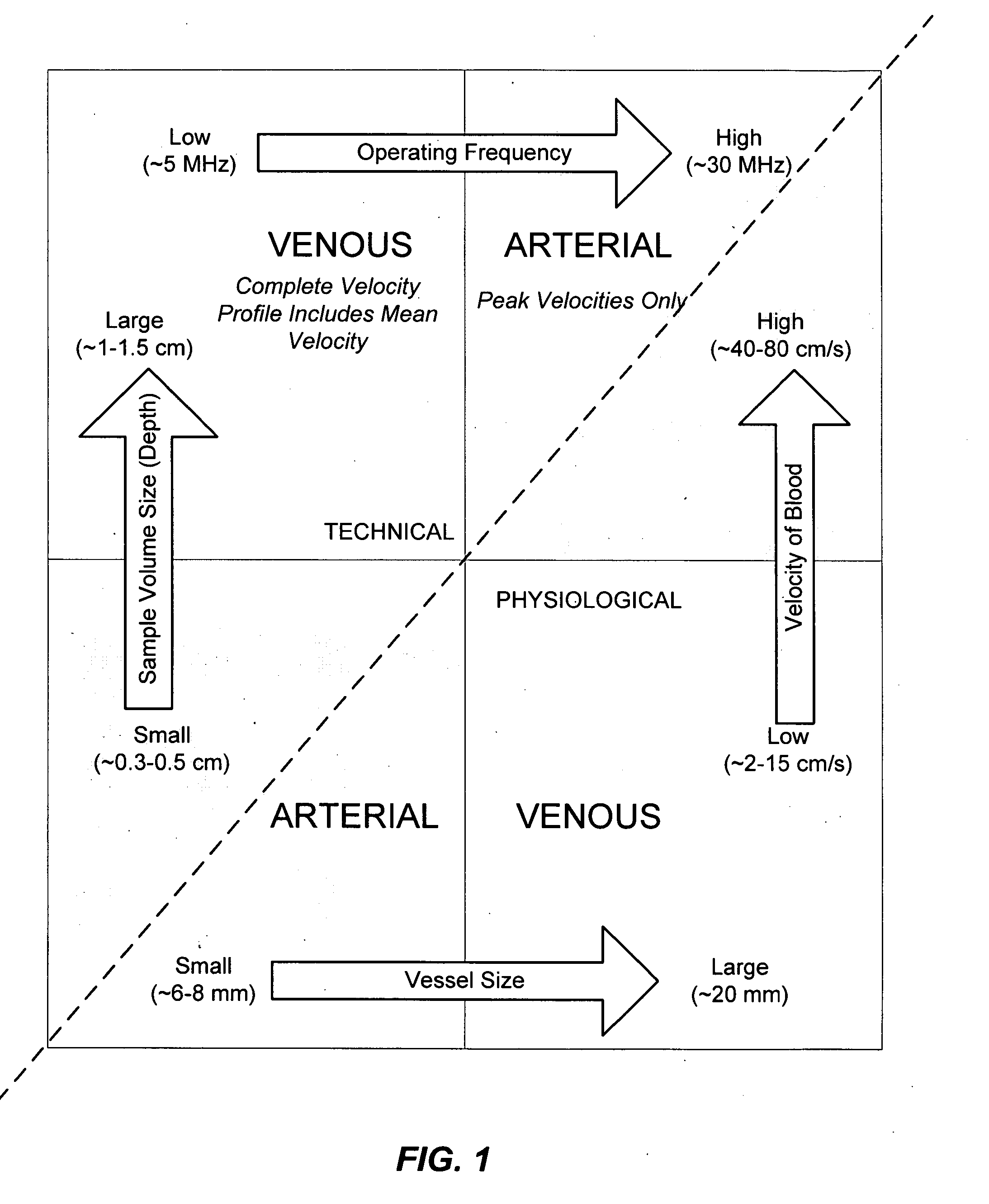
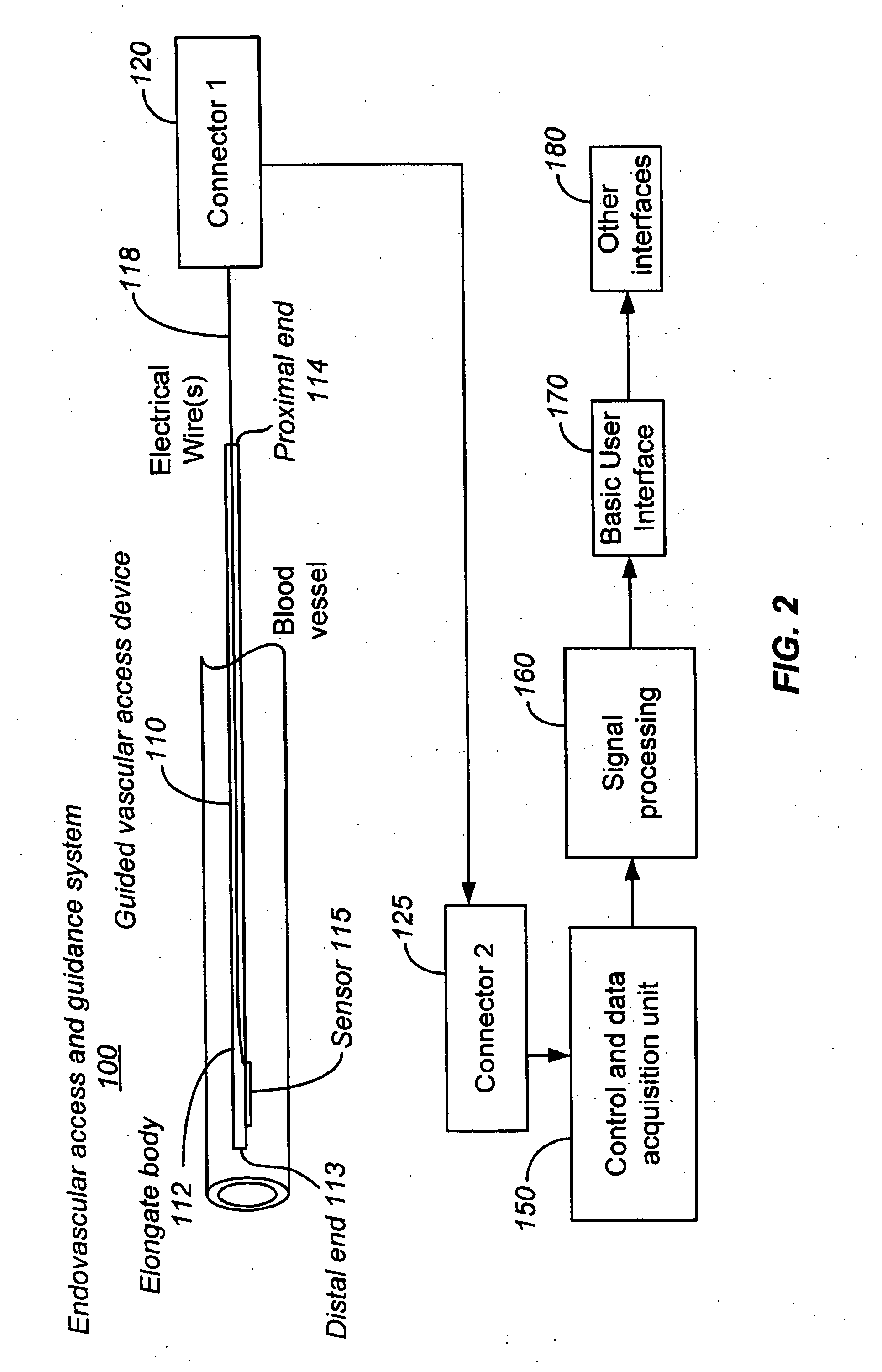
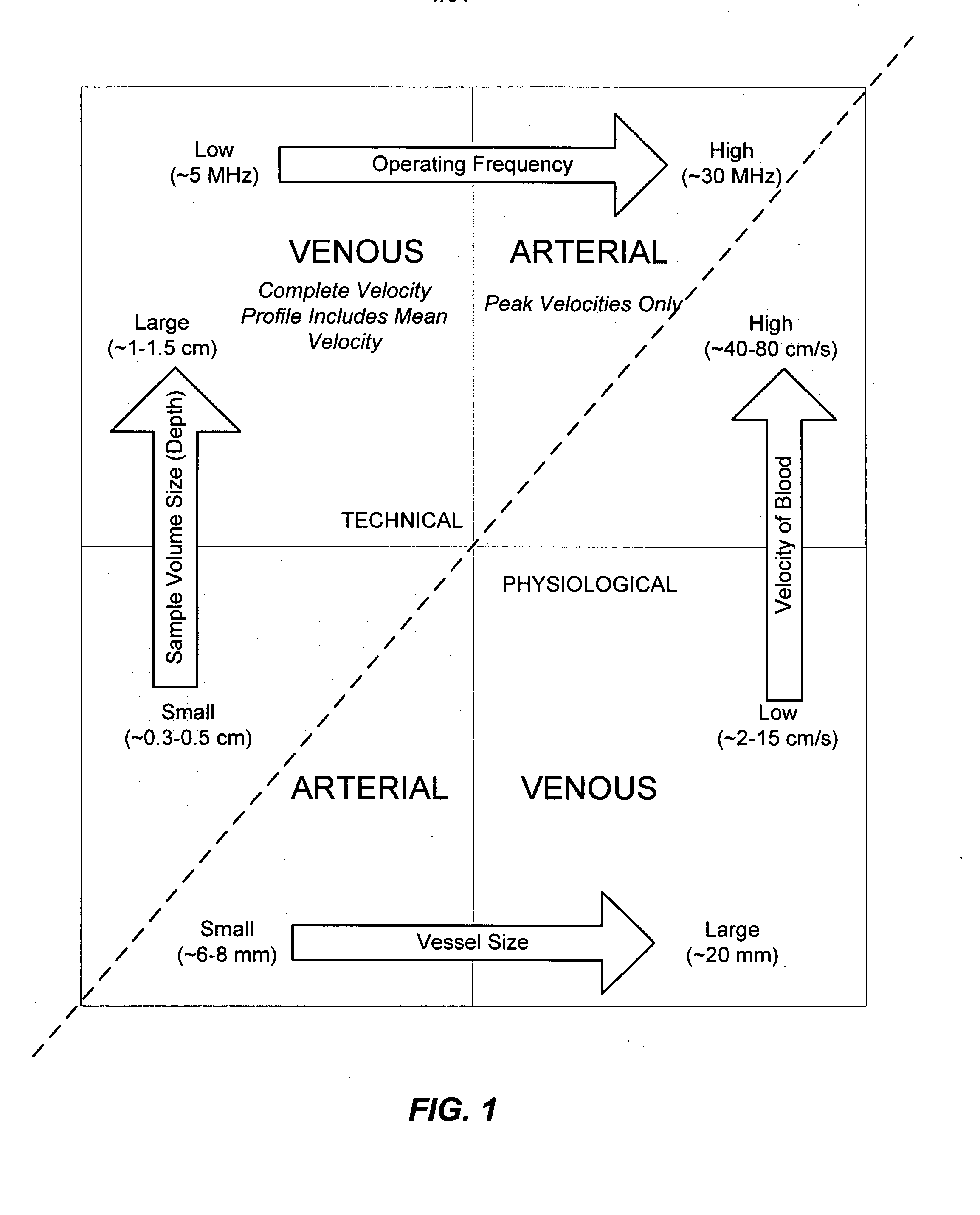
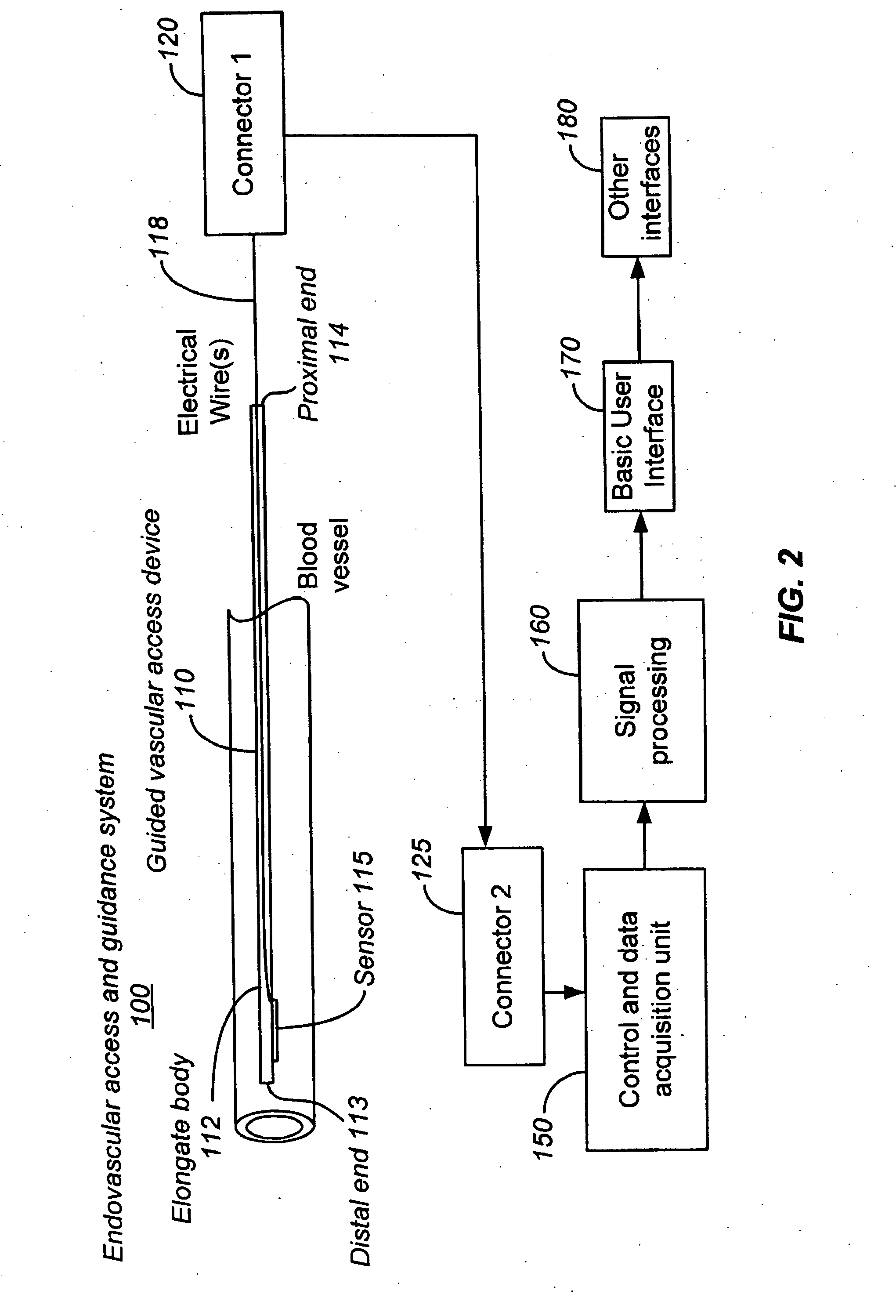
The invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices, such as catheters, stylets, guidewires and other flexible elongate bodies that are typically inserted percutaneously into the venous or arterial vasculature. Currently these goals are achieved using x-ray imaging and in some cases ultrasound imaging. This invention provides a method to substantially reduce the need for imaging related to placing an intravascular catheter or other device. Reduced imaging needs also reduce the amount of radiation that patients are subjected to, reduce the time required for the procedure, and decrease the cost of the procedure by reducing the time needed in the radiology department. An aspect of the invention includes, for example, an endovenous access and guidance system. The system comprises: an elongate flexible member adapted and configured to access the venous vasculature of a patient; a sensor disposed at a distal end of the elongate flexible member and configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient provided by the sensor and to provide position information regarding the position of the distal end of the elongate flexible member within the venous vasculature of the patient; and an output device adapted to output the position information from the processor.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
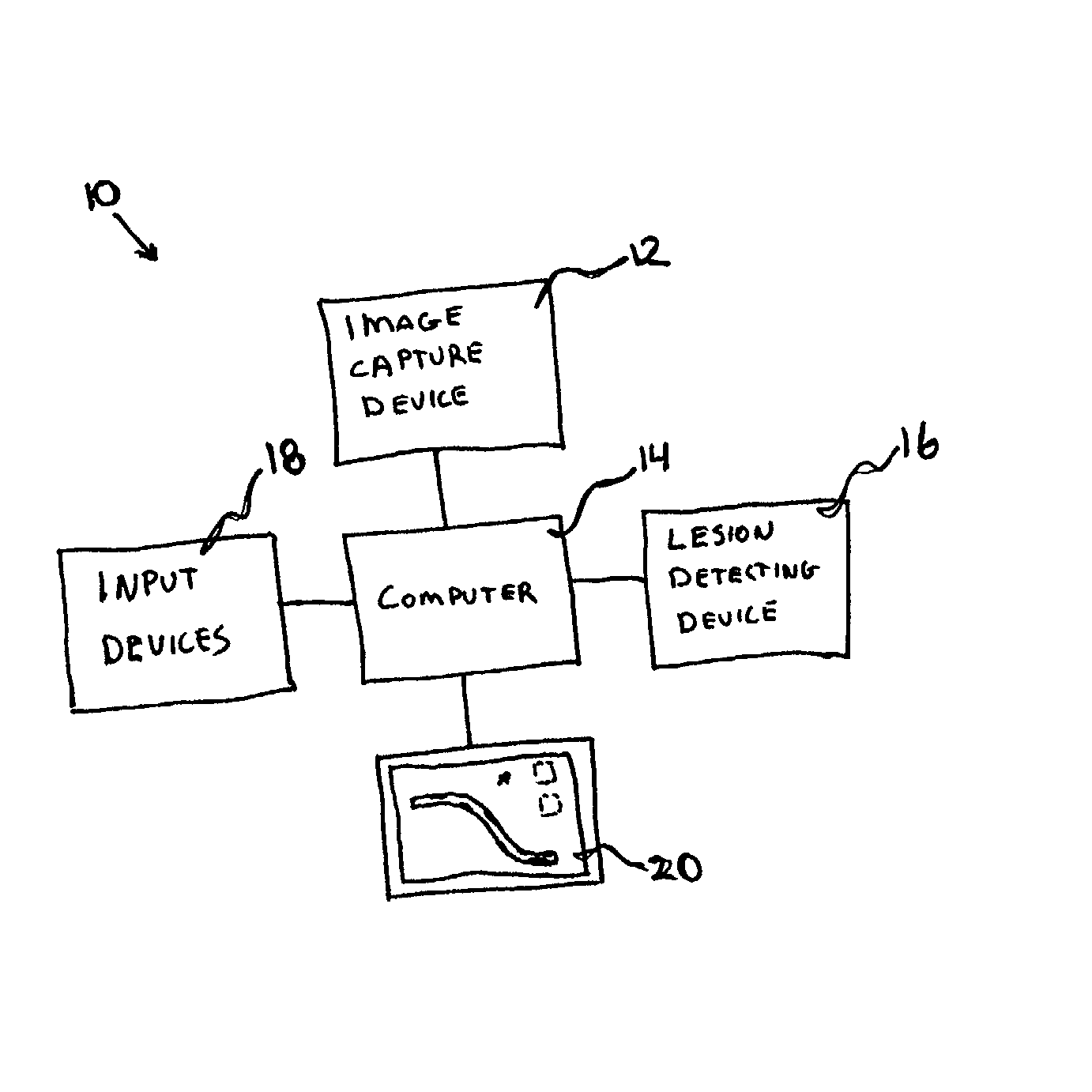
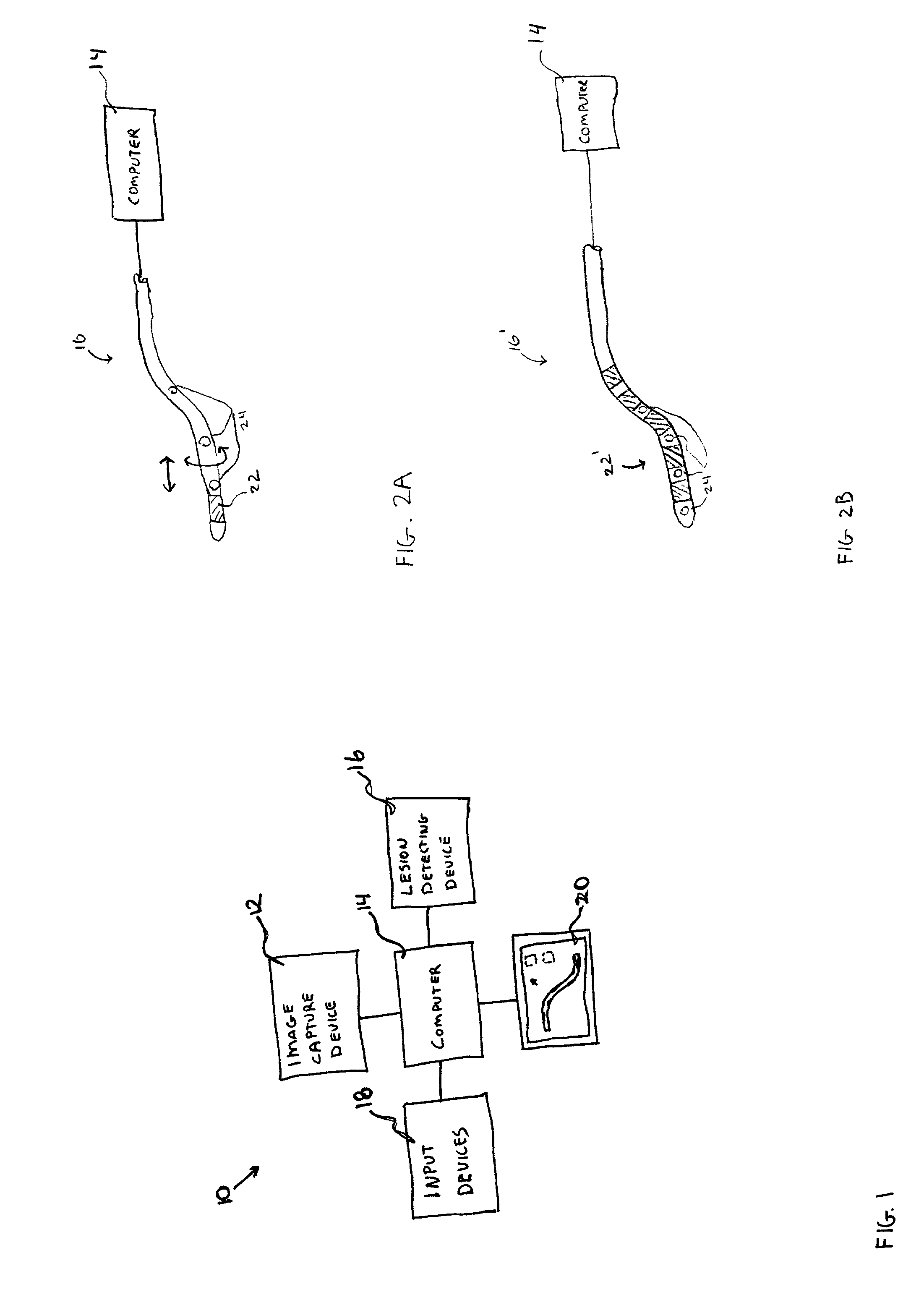
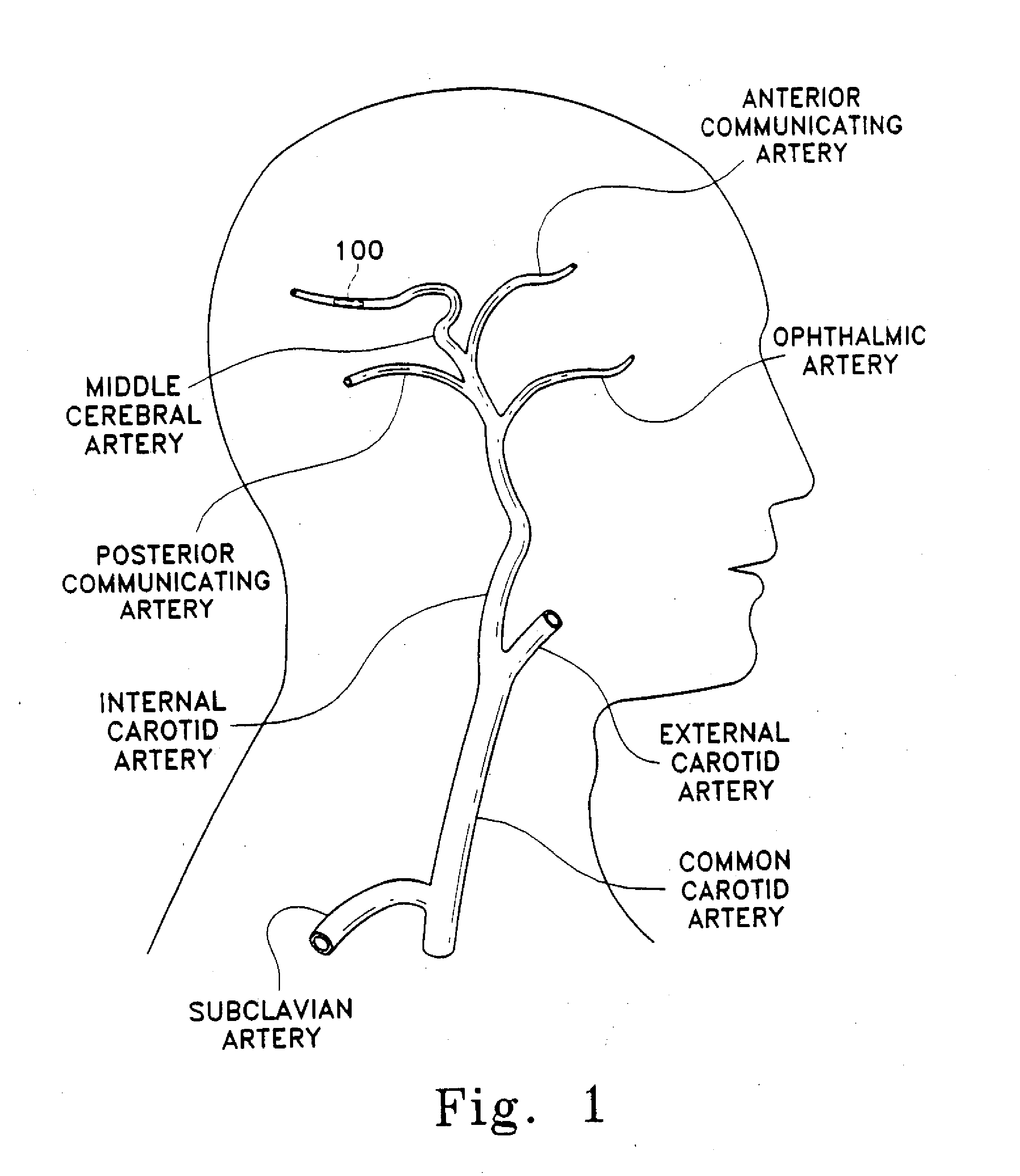
Localizing intravascular lesions on anatomic images
InactiveUS20020115931A1Sensitive highEffective characterizationSurgical navigation systemsMedical devicesIntravascular catheterBlood vessel
Methods and systems for localizing intravascular lesion in a body lumen. In exemplary embodiments, the methods comprise providing or acquiring an image of the body lumen and displaying information about the lesion with or on the image. In some configurations the information is obtained with an intravascular catheter.
Owner:IMETRX
Endovenous access and guidance system utilizing non-image based ultrasound
The invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices, such as catheters, stylets, guidewires and other flexible elongate bodies that are typically inserted percutaneously into the venous or arterial vasculature. Currently these goals are achieved using x-ray imaging and in some cases ultrasound imaging. This invention provides a method to substantially reduce the need for imaging related to placing an intravascular catheter or other device. Reduced imaging needs also reduce the amount of radiation that patients are subjected to, reduce the time required for the procedure, and decrease the cost of the procedure by reducing the time needed in the radiology department. An aspect of the invention includes, for example, an endovenous access and guidance system. The system comprises: an elongate flexible member adapted and configured to access the venous vasculature of a patient; a sensor disposed at a distal end of the elongate flexible member and configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient provided by the sensor and to provide position information regarding the position of the distal end of the elongate flexible member within the venous vasculature of the patient; and an output device adapted to output the position information from the processor.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Method and apparatus for detecting and treating vulnerable plaques
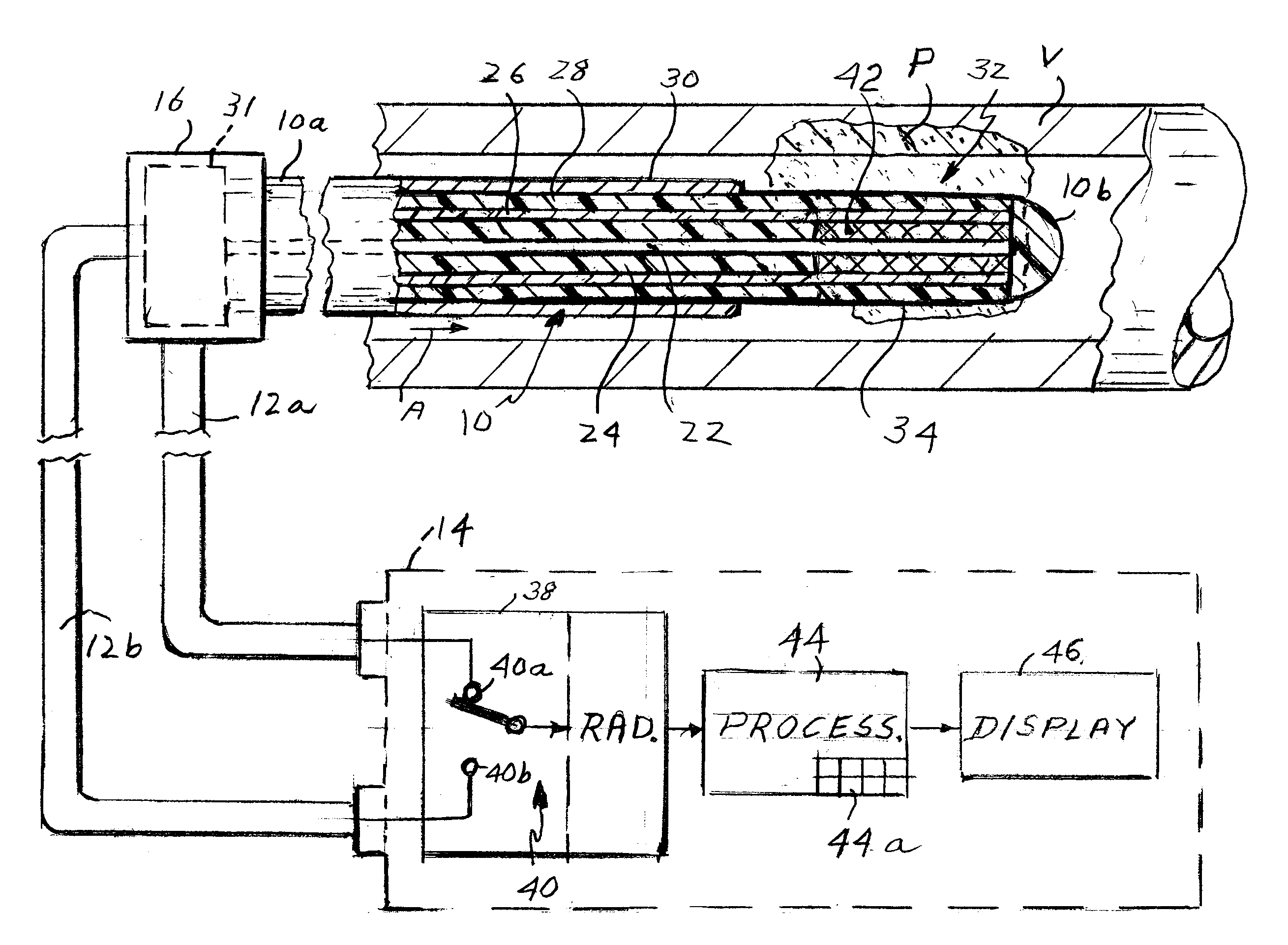
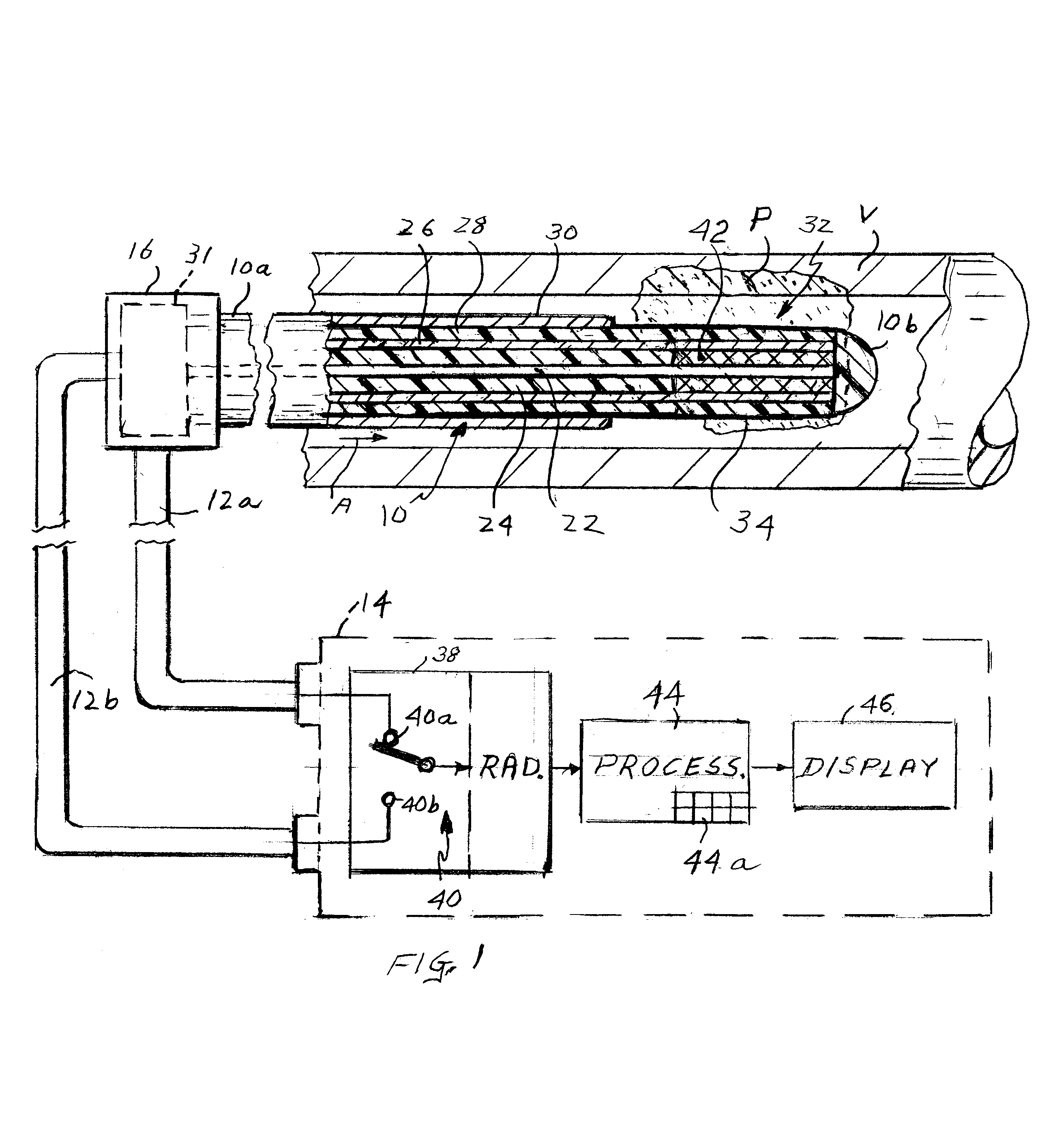
Apparatus for detecting vulnerable plaques embedded in the wall of a patient's blood vessel includes an intravascular catheter containing a microwave antenna, an extra-corporeal radiometer having a signal input, a reference input and an output, a cable for electrically connecting the antenna to the signal input, and a device for applying an indication of the patient's normal tissue temperature to the reference input so that when the catheter is moved along the vessel, the locations of the vulnerable plaques are reflected in a signal from the output as thermal anomalies due to the higher emissivity of the vulnerable plaques as compared to the normal tissue. A second embodiment of the apparatus has two coaxial antennas in the catheter serving two radiometers. One measures the temperature at locations in the vessel wall, the other measures the temperature at the surface. By subtracting the two signals, the locations of vulnerable plaque may be visualized. The apparatus employs a special diplexer for separating the signals from the two antennas and a method of detecting and possibly destroying the plaques is also disclosed.
Owner:CORAL SAND BEACH LLC
Method and apparatus of assessing transvascular denervation
InactiveUS20120296232A1Smooth connectionEnhanced signalSurgical instrument detailsCatheterDenervationIntravascular catheter
Embodiments of the invention provide catheter devices for assessing transvascular denervation. A method of assessing denervation comprises: introducing intravascularly a catheter to a vessel of a patient, the catheter including one or more recording elements; performing a baseline recording of responses by supplying nerve stimulation to the vessel and recording responses of the vessel to the nerve stimulation; denervating at least some tissue proximate the vessel after performing the baseline recording; performing a post-denervation recording of responses, after the denervating, by supplying nerve stimulation to the vessel and recording responses of the vessel to the nerve stimulation; and assessing denervation of the vessel based on a comparison of the responses of the baseline recording and the responses of the post-denervation recording.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
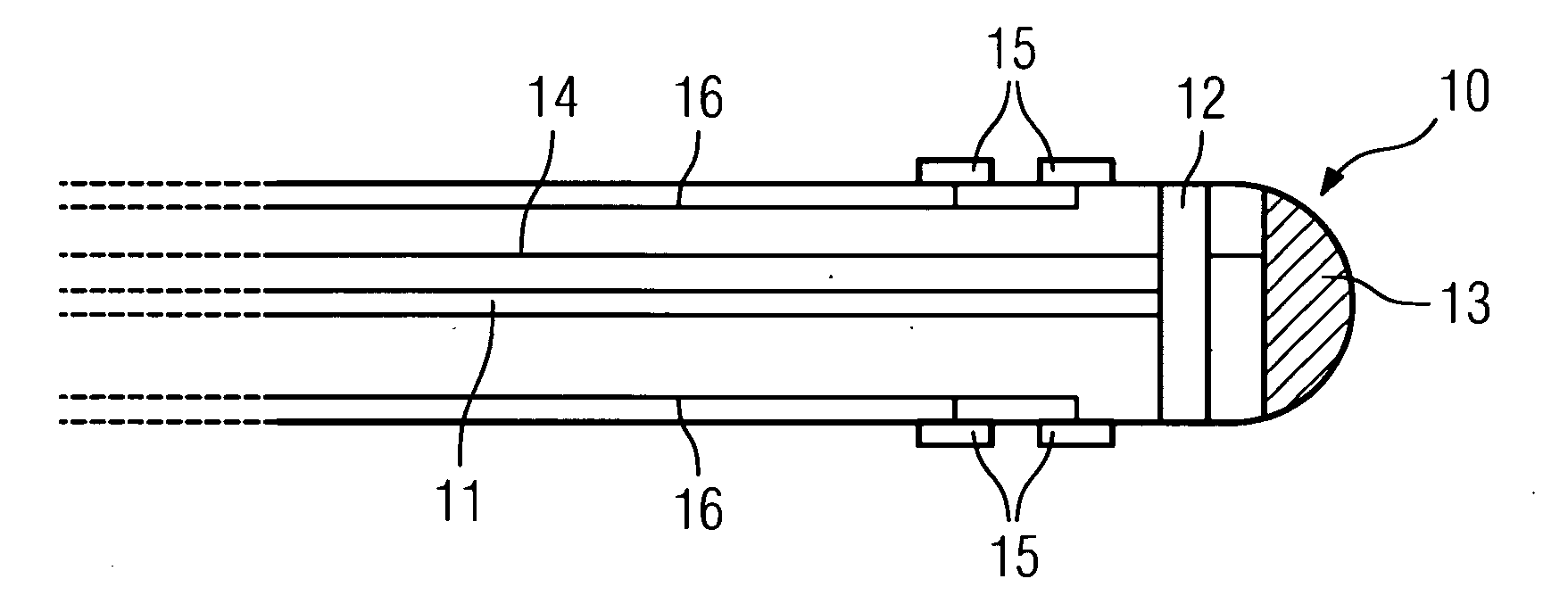
Ablation tip catheter device with integrated imaging, ECG and positioning devices
InactiveUS7479141B2Simple fashionWork process safetyElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyBlood Vessel TissueAnimal body
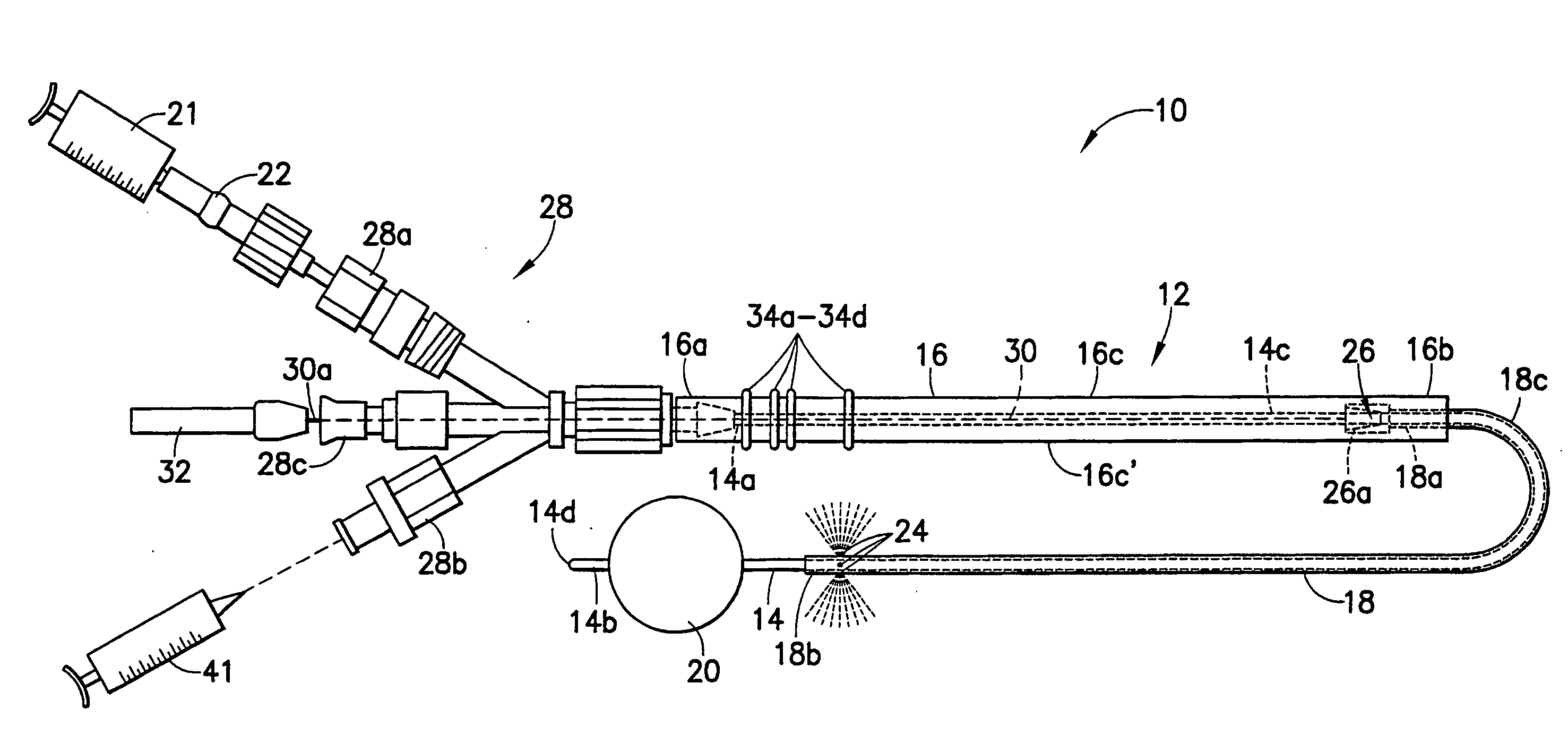
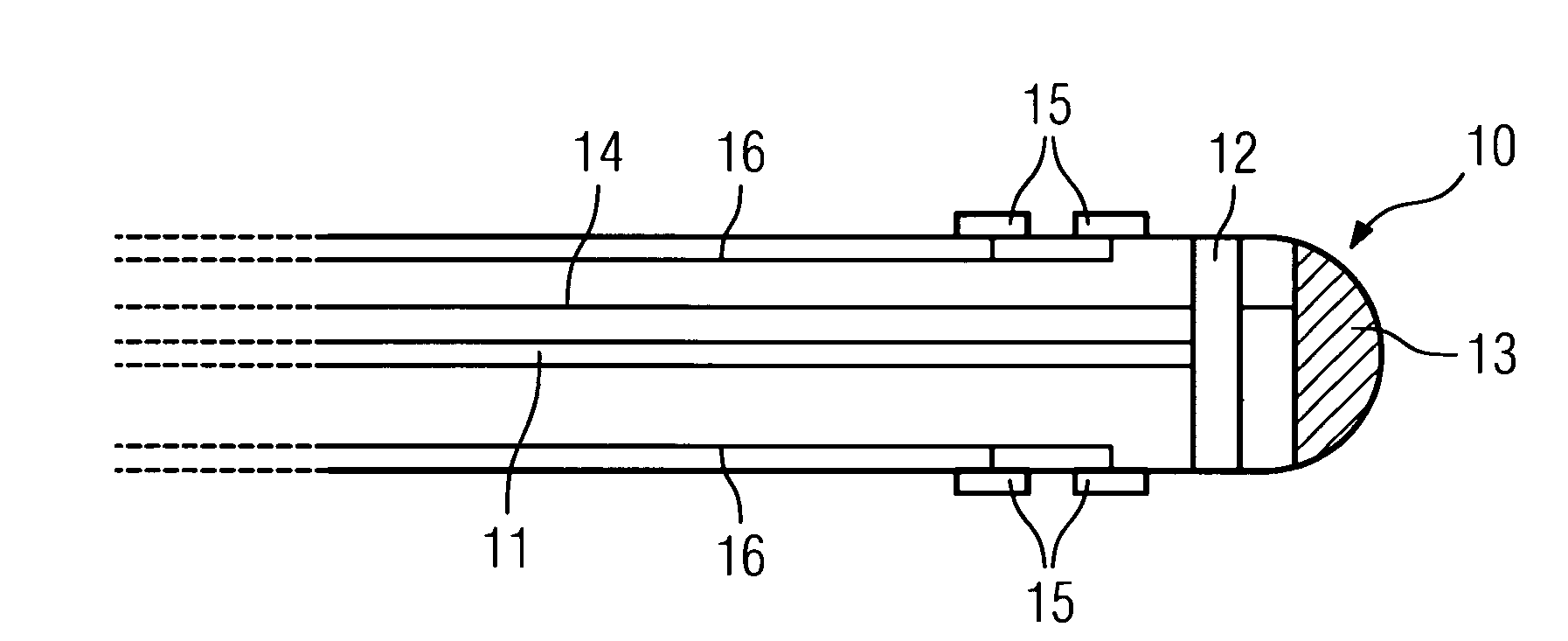
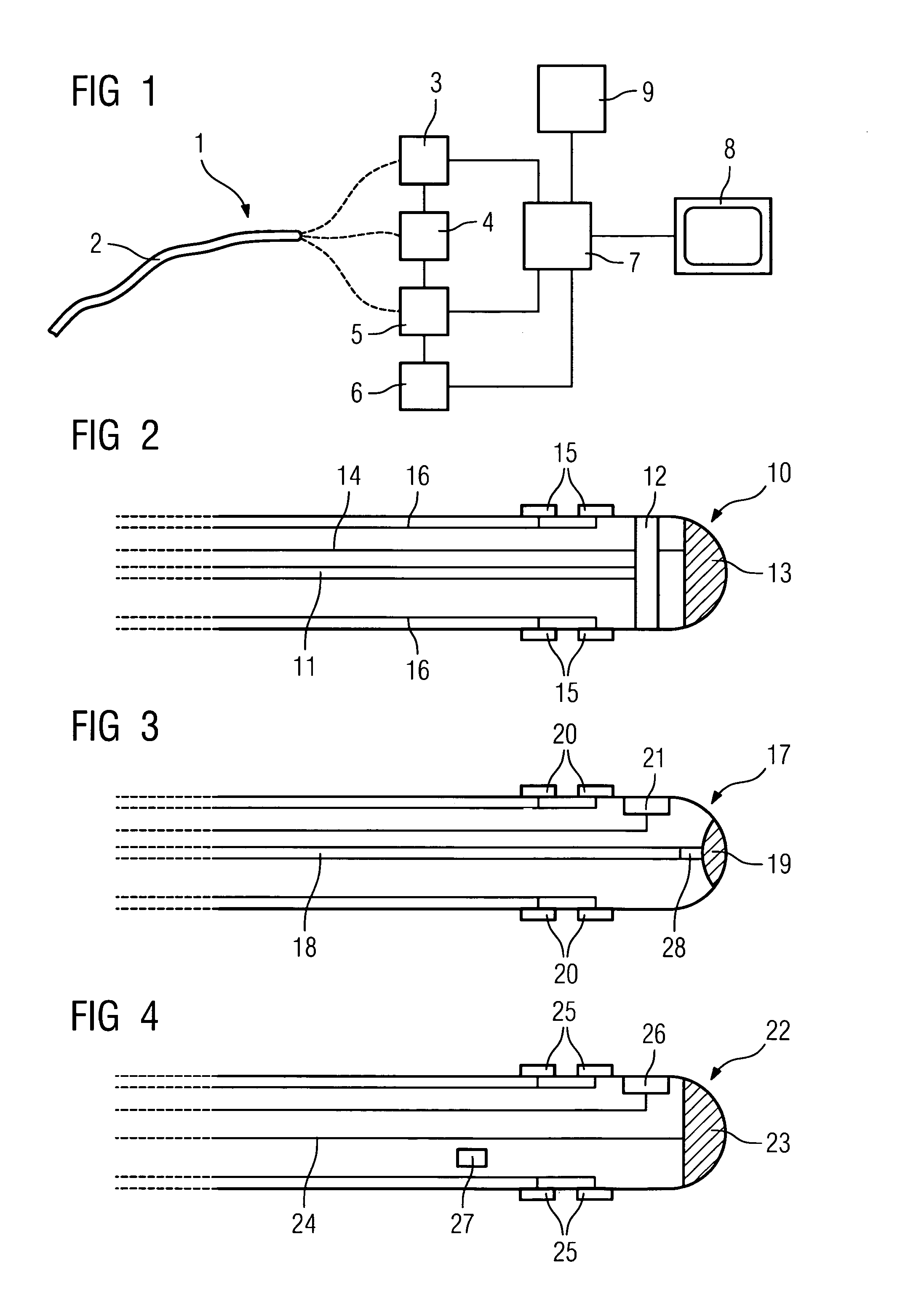
Catheter device comprising a catheter (2), particularly an intravascular catheter, for insertion into an organ or vessel of the human or animal body, with a device for ablation of the adjacent organ tissue or vessel tissue using high-frequency currents in the region of the tip of the catheter, a device (3, 11, 12, 18, 19, 23, 24) being integrated for capturing images of the organ or vessel in the region of the tip of the catheter (10, 17, 22).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Apparatus and Method for Guided Chronic Total Occlusion Penetration
InactiveUS20080294037A1For accurate placementAvoids and reduces complicationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryTotal occlusionIntravascular catheter
An apparatus and method for guided penetration of a chronic total occlusion in a blood vessel are disclosed. The invention is directed to an apparatus that facilitates accurate placement of a drilling tip within a body lumen using ultrasound-based detection to determine the position of the intravascular catheter relative to the vessel occlusion and vessel walls.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
Catheter device
InactiveUS20050148836A1Simple fashionWork process safetyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyBlood Vessel TissueAnimal body
Catheter device comprising a catheter (2), particularly an intravascular catheter, for insertion into an organ or vessel of the human or animal body, with a device for ablation of the adjacent organ tissue or vessel tissue using high-frequency currents in the region of the tip of the catheter, a device (3, 11, 12, 18, 19, 23, 24) being integrated for capturing images of the organ or vessel in the region of the tip of the catheter (10, 17, 22).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
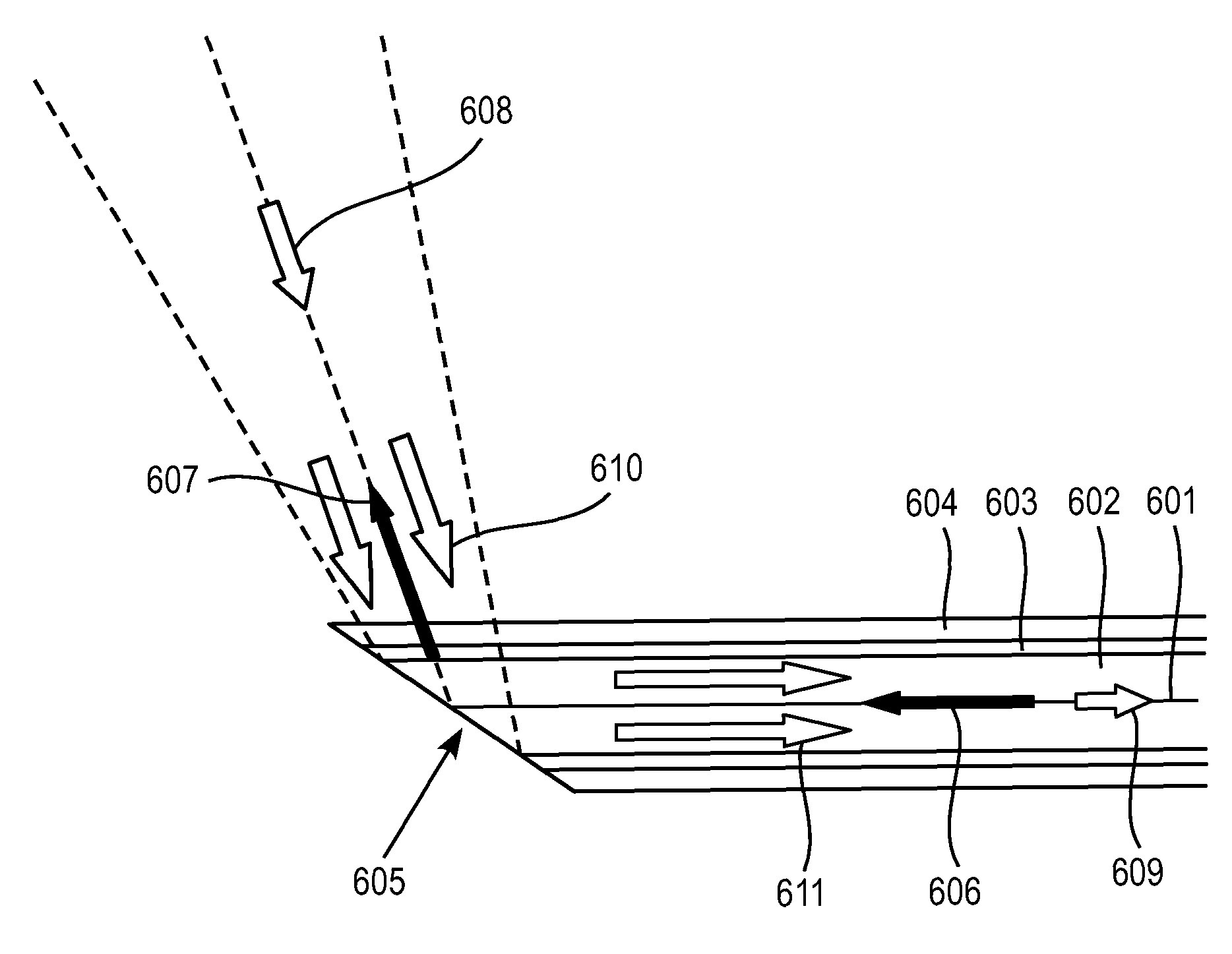
Endovascular access and guidance system utilizing divergent beam ultrasound
The invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices, such as catheters, stylets, guidewires and other flexible elongate bodies that are typically inserted percutaneously into the venous or arterial vasculature. Currently these goals are achieved using x-ray imaging and in some cases ultrasound imaging. This invention provides a method to substantially reduce the need for imaging related to placing an intravascular catheter or other device. Reduced imaging needs also reduce the amount of radiation that patients are subjected to, reduce the time required for the procedure, and decrease the cost of the procedure by reducing the time needed in the radiology department. An aspect of the invention includes, for example, an endovenous access and guidance system. The system comprises: an elongate flexible member adapted and configured to access the venous vasculature of a patient; a sensor disposed at a distal end of the elongate flexible member and configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the venous vasculature of the patient provided by the sensor and to provide position information regarding the position of the distal end of the elongate flexible member within the venous vasculature of the patient; and an output device adapted to output the position information from the processor.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Medical clot treatment device with distal filter
This is a surgical device usually delivered through an intravascular catheter. It may be used in several ways. It may, for instance, be used to open a clear passageway adjacent thrombus to allow both blood and medication to bypass the clot. It may be used to pierce and to remove thrombus. These thrombus are often found in tortuous vasculature. The device includes several sections. The device has a core element, typically a core wire. Placed around the distal end of the core element is a collapsible but preferably self expanding proximal cage assembly and a distal filter, preferably a self-expanding cage assembly or other filter component. The various portions of those components are preferably radio-opaque. The proximal end of the proximal cage is typically is affixed to an actuator in such a way as to allow expansion of the cage after deployment. The proximal cage assembly may be used for collecting emboli or for displacing them to allow blood flow to resume, either with or without concurrent clot-dissolving drug treatment. The distal sector, whether a self-expanding cage or fan, is placed distally of the thrombus to collect portions of the thrombus which may loosen during the treatment or removal procedure.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
Transcutaneous medical device dressings and method of use
InactiveUS7137968B1Coloring be generateAdvantage of easeCatheterInfusion needlesSkin contactAdhesive
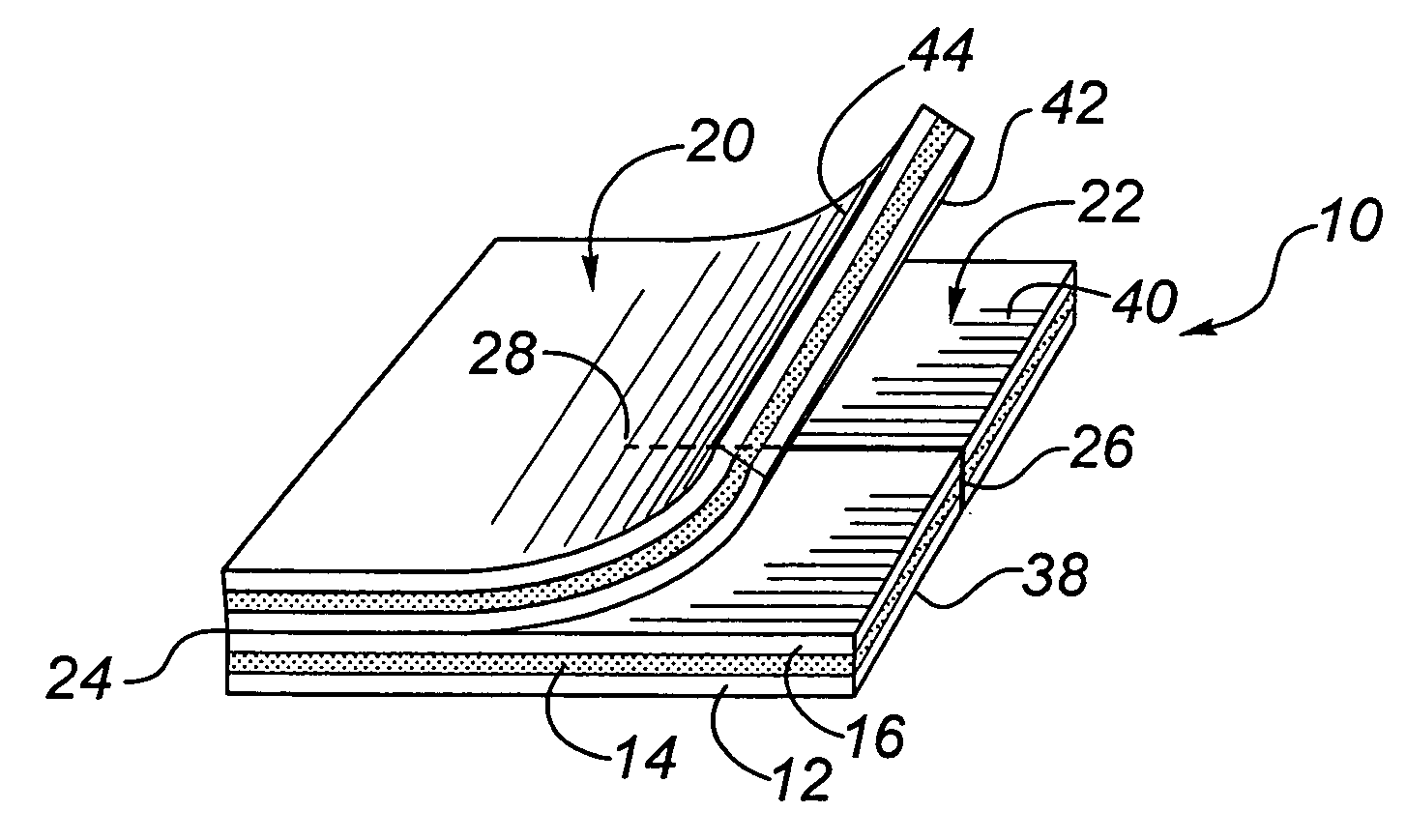
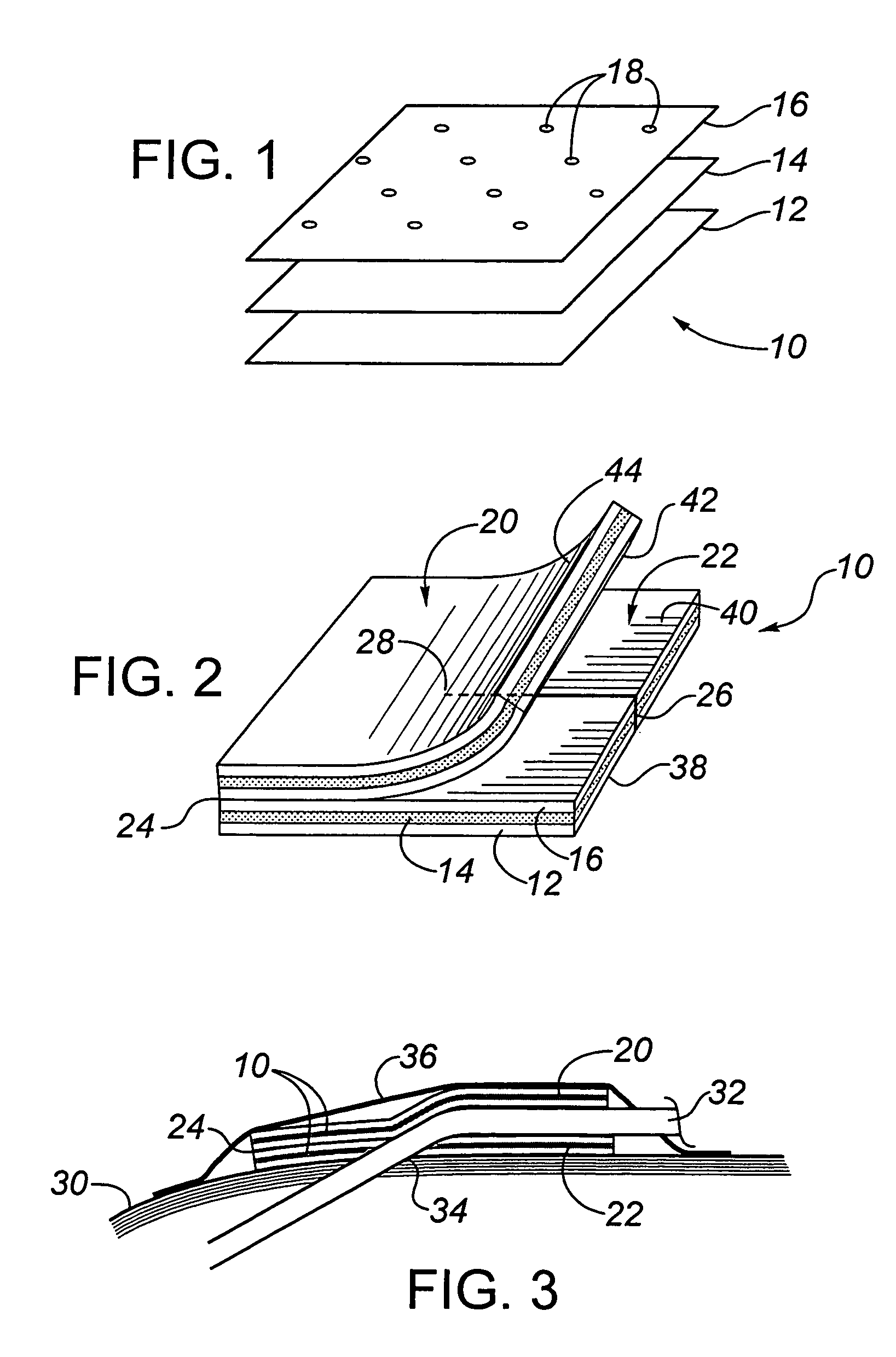
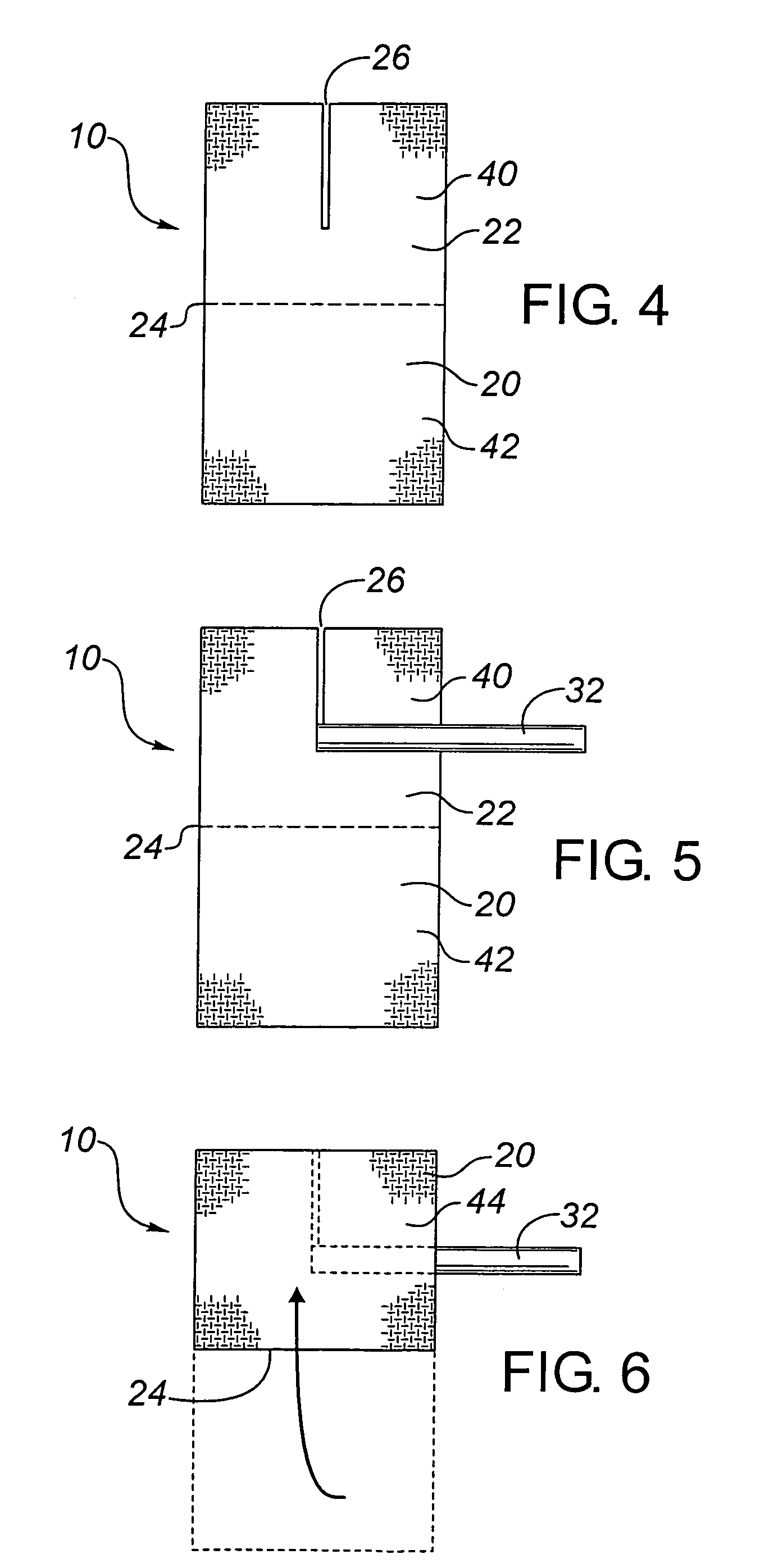
A transcutaneous device dressing and method for its use with a transcutaneous medical device, such as an intravascular catheter, which punctures the skin of a patient and which has a portion of the medical device protruding from the skin which can lead to infection. The dressing includes a top and a bottom dressing, both being formed from a flexible material and having upper and lower surfaces, with the lower surface being the skin facing surface in use. The bottom dressing has a slit formed therein extending from one edge inwardly to a termination point within the confines of the bottom dressing. An anti-microbial material is provided without the use of adhesives at the upper and lower surfaces of the bottom dressing, and at least at the lower surface of the top dressing. In use, the bottom dressing is placed next to the skin, the slit allowing the bottom dressing to surround the puncture site such that the lower surface of the bottom dressing is in contact with the skin while the upper surface of the bottom dressing is in contact with a portion of the medical device protruding from the skin. The top dressing is placed above the puncture site such that its lower surface is in contact with a portion of the medical device protruding from the skin. In this way, there is exposure of the portion of the medical device protruding from the skin to the anti-microbial activity of the anti-microbial material.
Owner:NUCRYST PHARMA
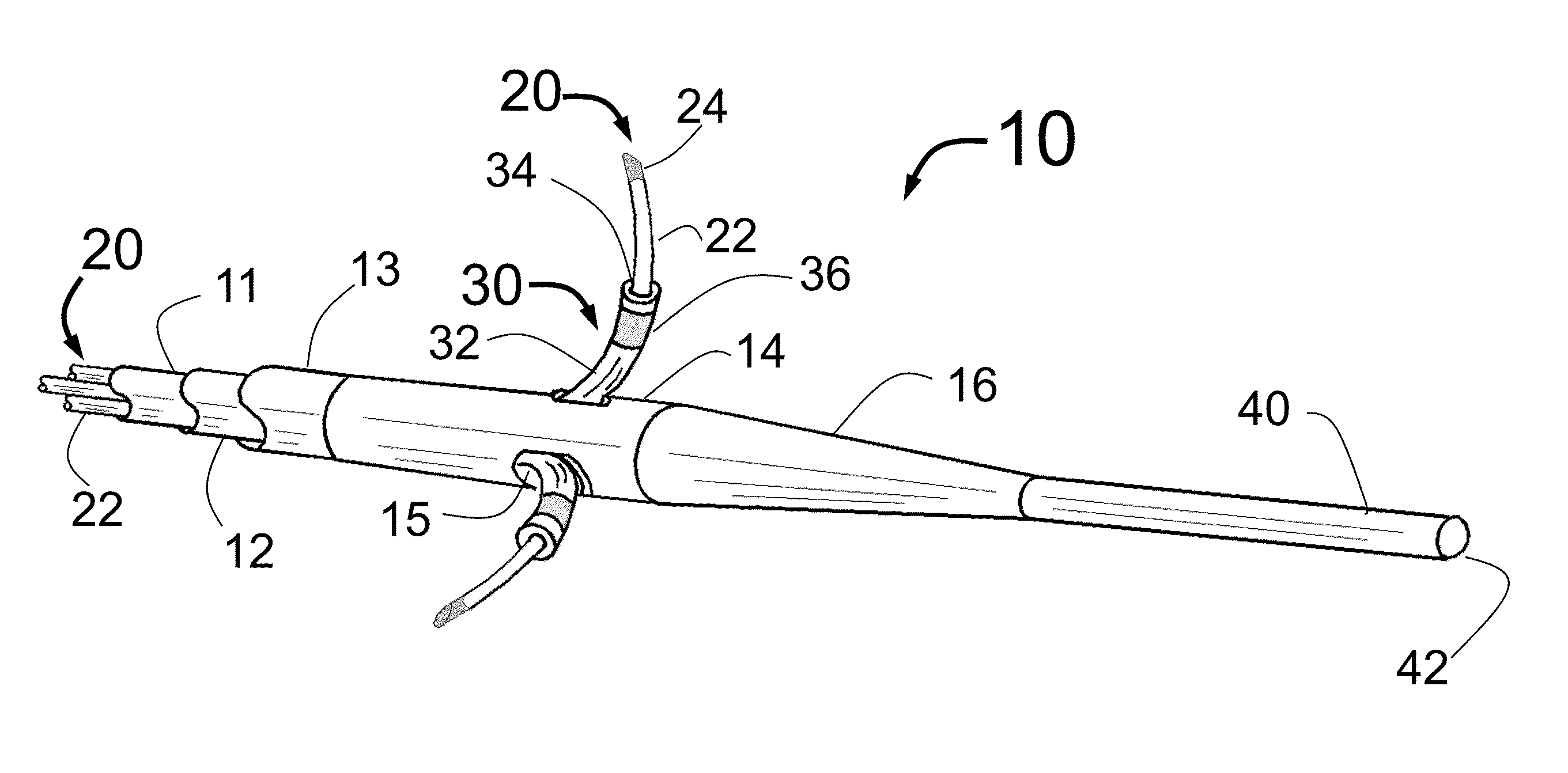
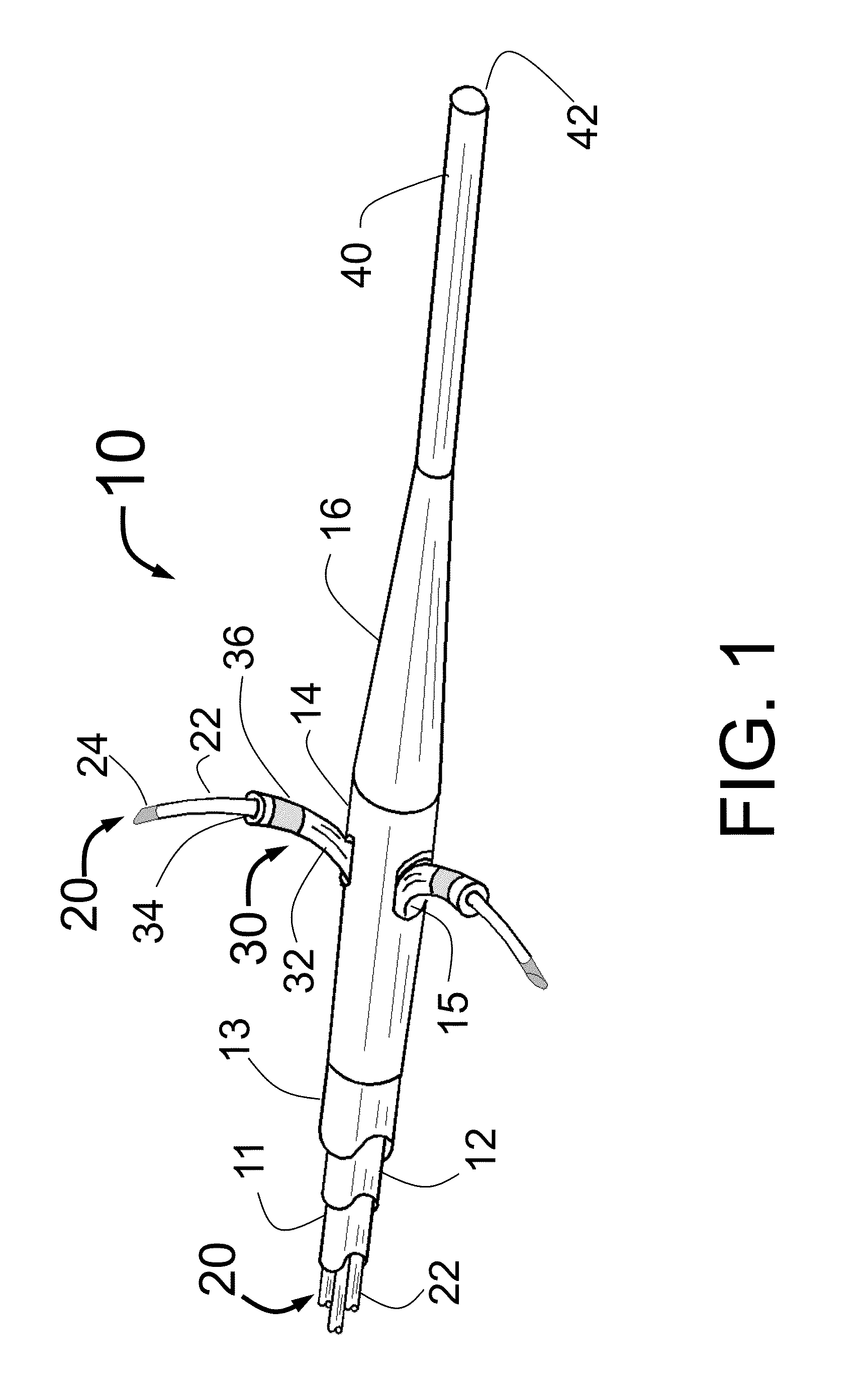
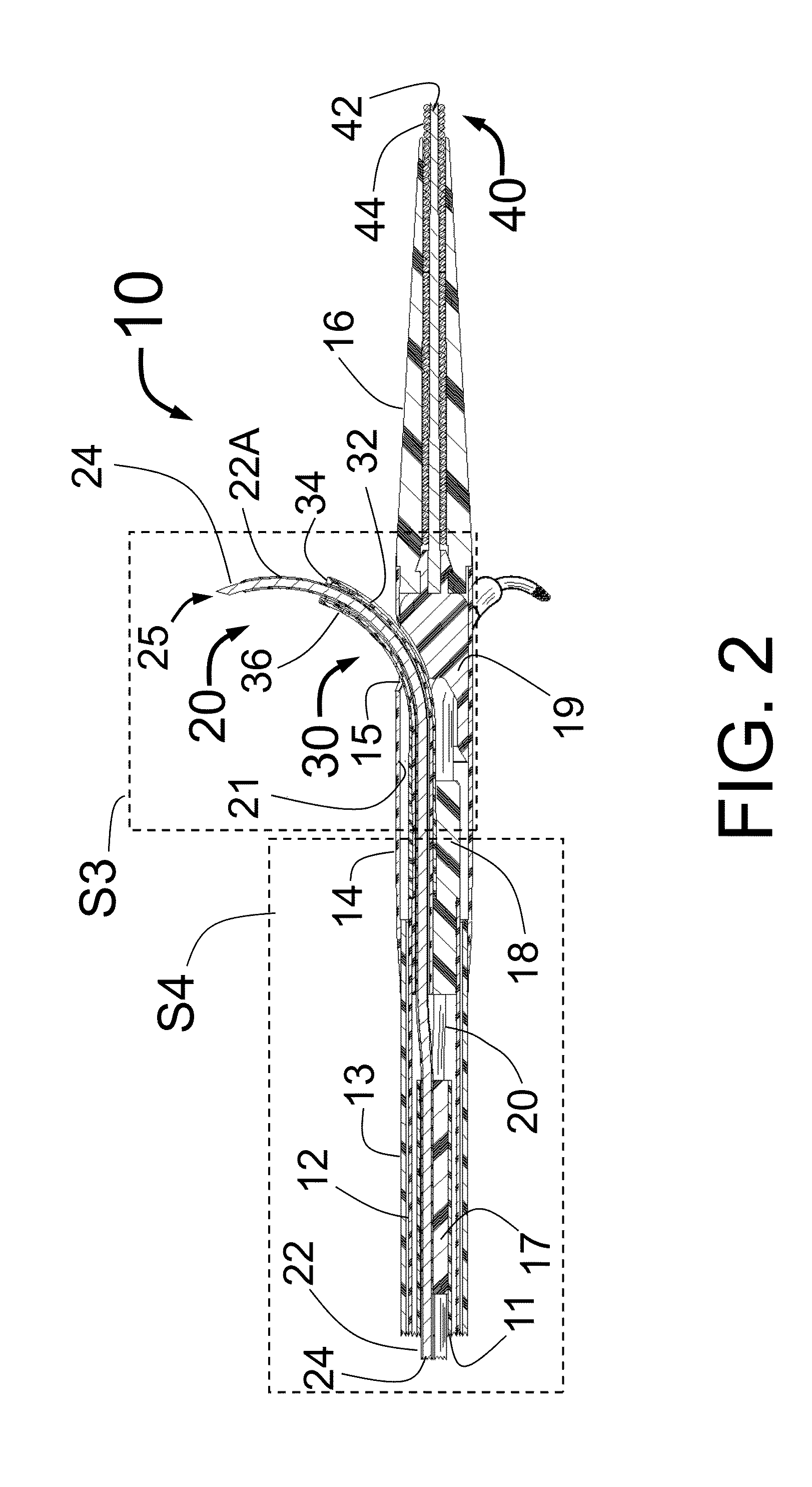
Intravascular Catheter Having An Expandable Incising Portion
An intravascular catheter device is provided for use during a surgical procedure. The catheter device includes a catheter tube having an expandable portion with a plurality of struts each defining an outer surface. The expandable portion is operable between a closed position, wherein the expandable portion has a first diameter, and an opened position, wherein the expandable portion has a second diameter that is larger than the first diameter. An incising element is provided on the outer surface of at least one of the struts. The incising element has a blade that extends outwardly in a radial direction from the outer surface of the strut for creating an incision in atherosclerotic material located within a blood vessel when the expandable portion is in the opened position.
Owner:VENTUREMED GRP INC
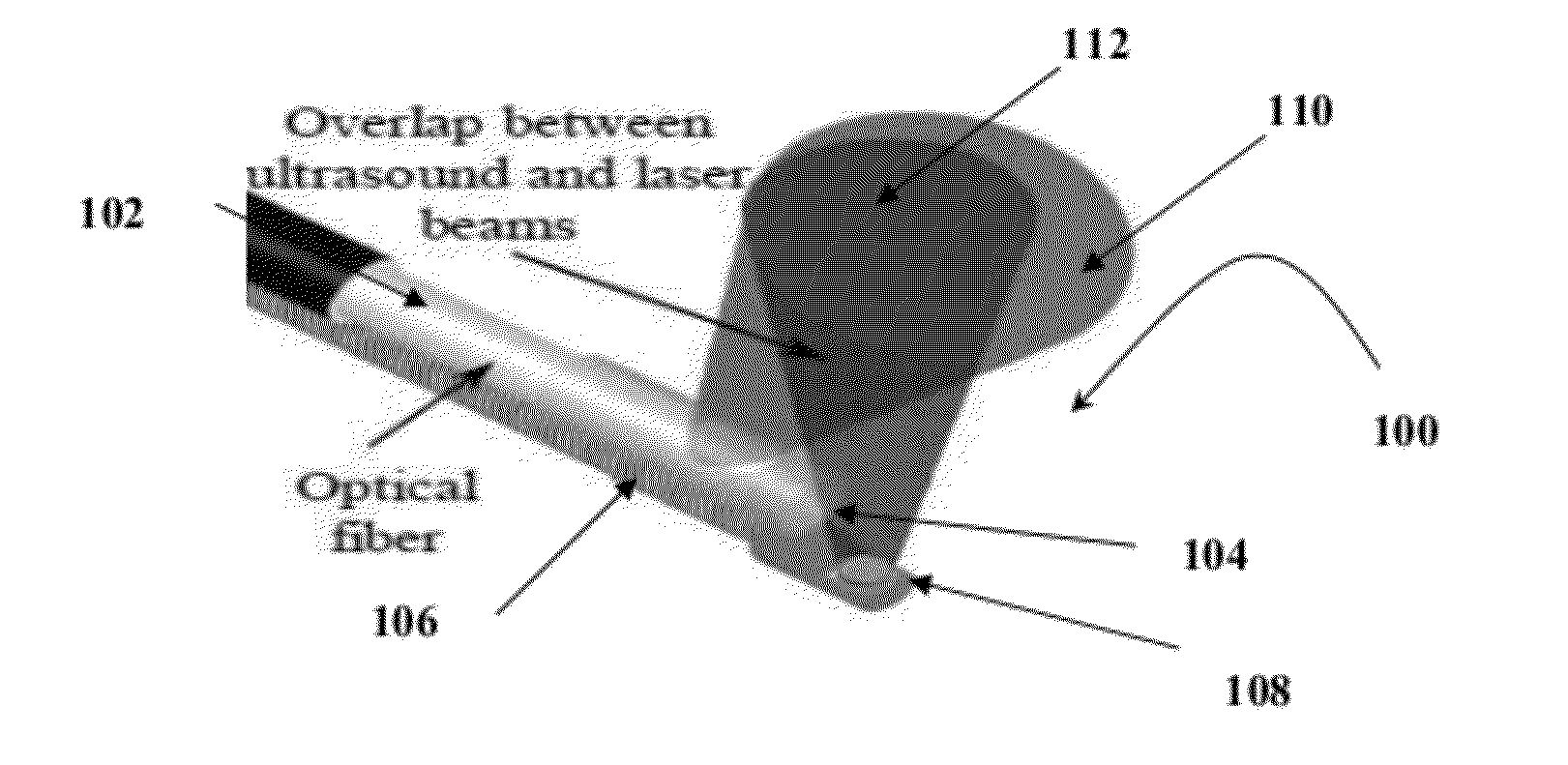
Catheter for intravascular ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging
InactiveUS20120271170A1Protect partsAvoid mechanical damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorElastography
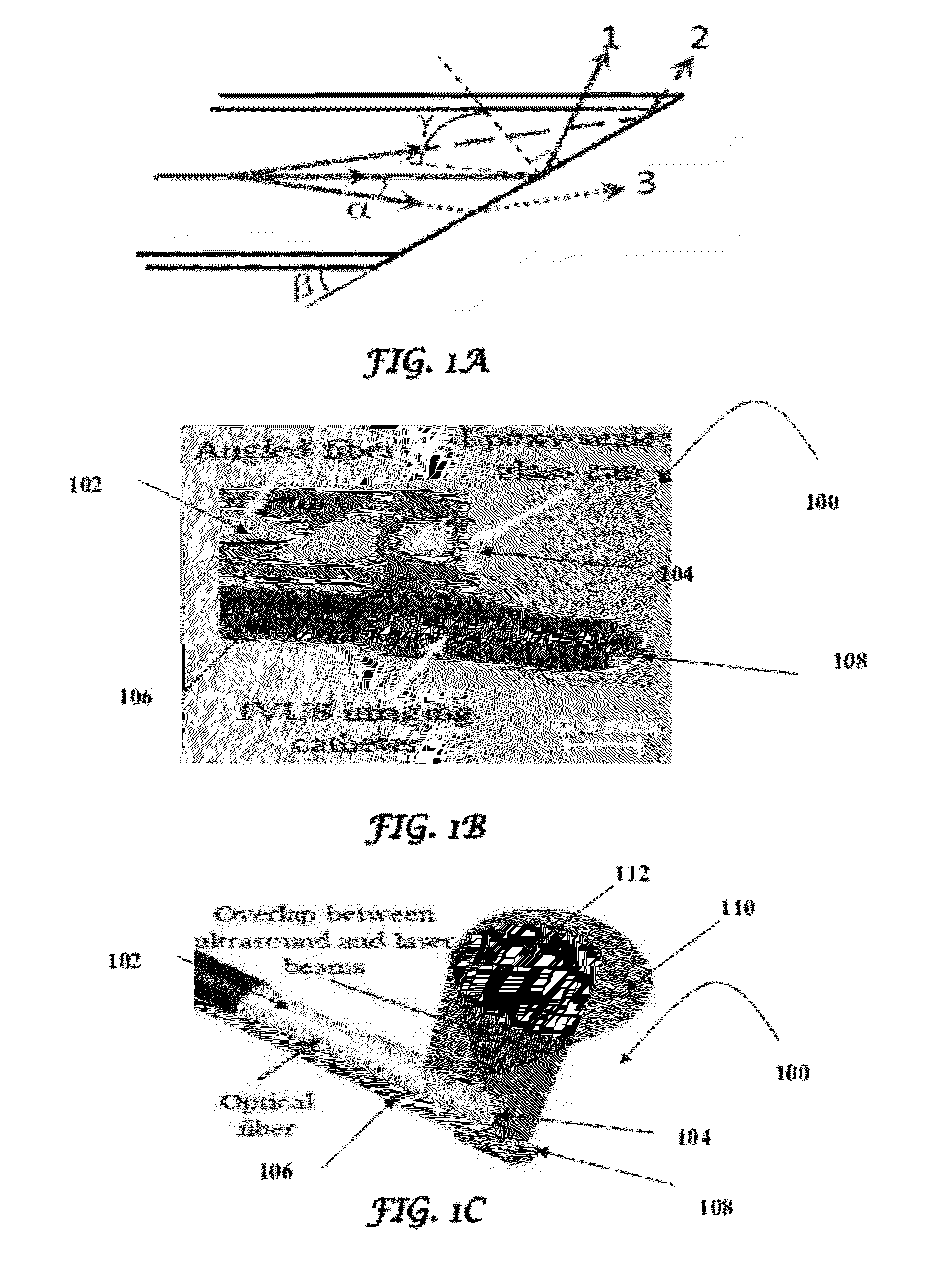
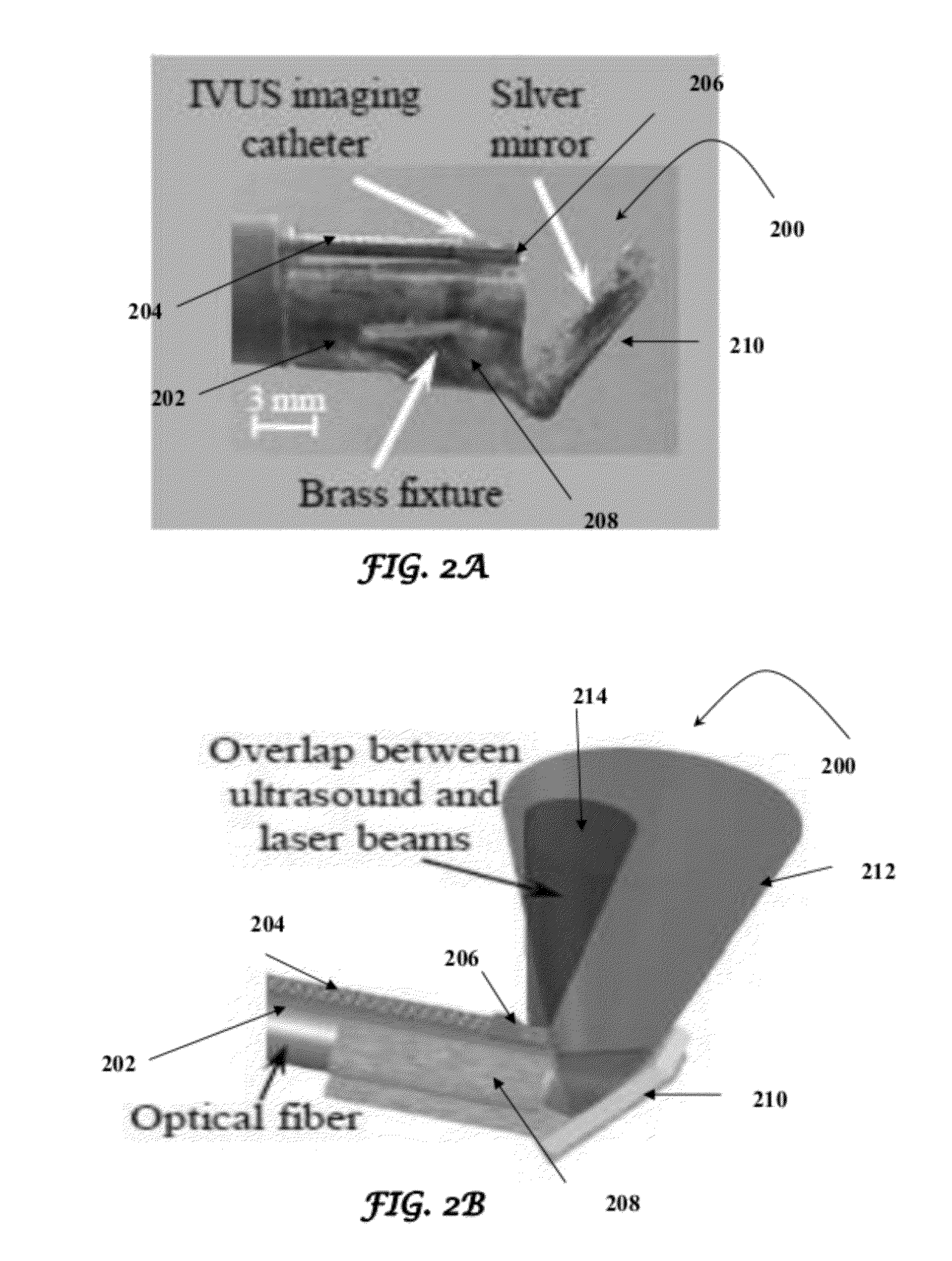
A design and a fabrication method for an intravascular imaging and therapeutic catheters for combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and for optical and / or acoustic therapy of hollow organs and diseased blood vessels and tissues are disclosed in the present invention. The invention comprises both a device—optical fiber-based intravascular catheter designs for combined IVUS / IVPA, and elasticity imaging and for acoustic and / or optical therapy—and a method of combined ultrasound, photoacoustic, and elasticity imaging and optical and / or acoustic therapy. The designs of the catheters are based on single-element catheter-based ultrasound transducers or on ultrasound array-based units coupled with optical fiber, fiber bundles or a combination thereof with specially designed light delivery systems. One approach uses the side fire fiber, similar to the one utilized for biomedical optical spectroscopy. The second catheter design uses the micro-optics in the manner of a probe for optical coherent tomography.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Peri-vascular tissue ablation catheter with support structures
ActiveUS8740849B1Add supportImprove uniformityHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiagnosticsVascular tissueGuide tube
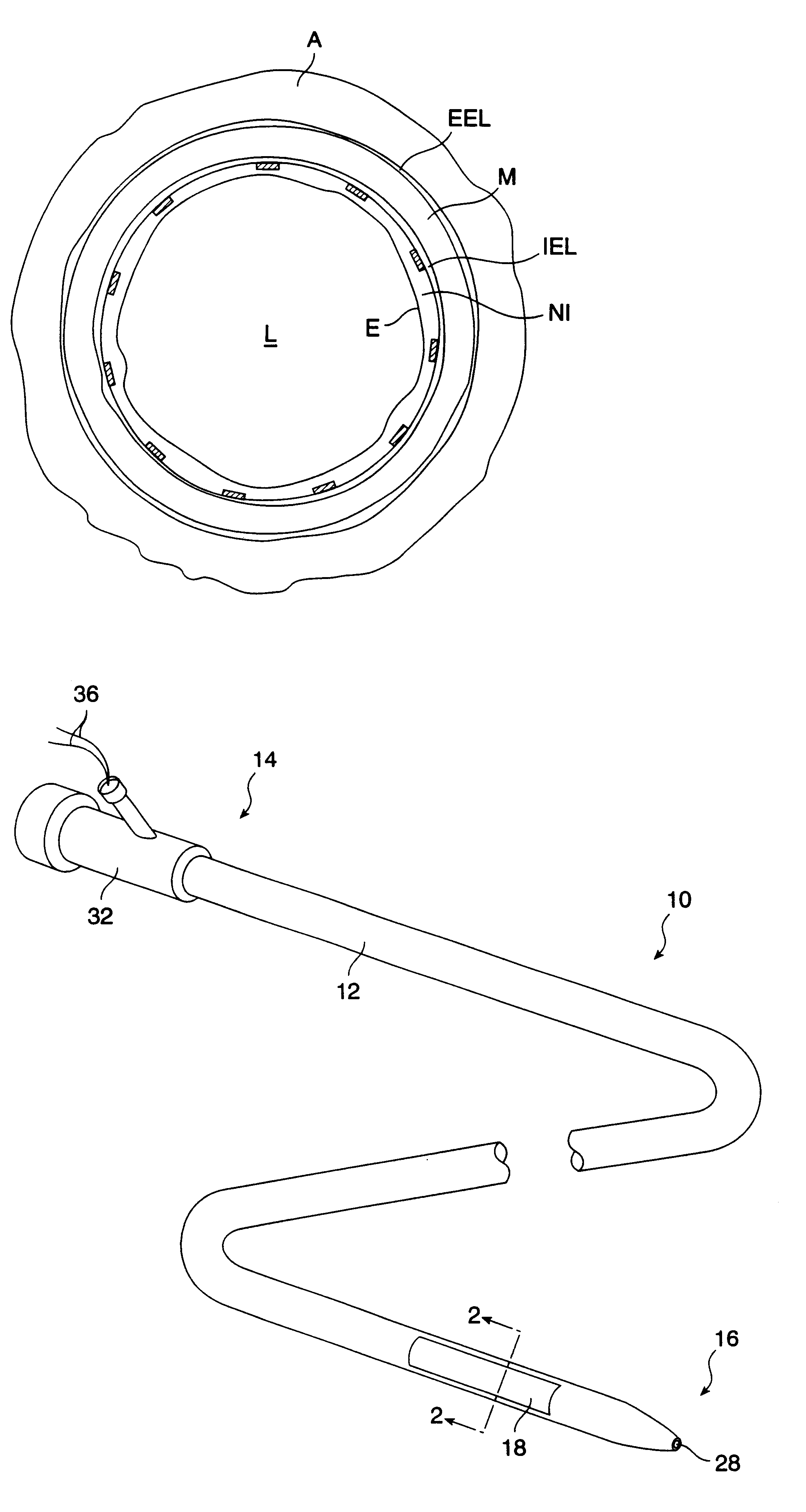
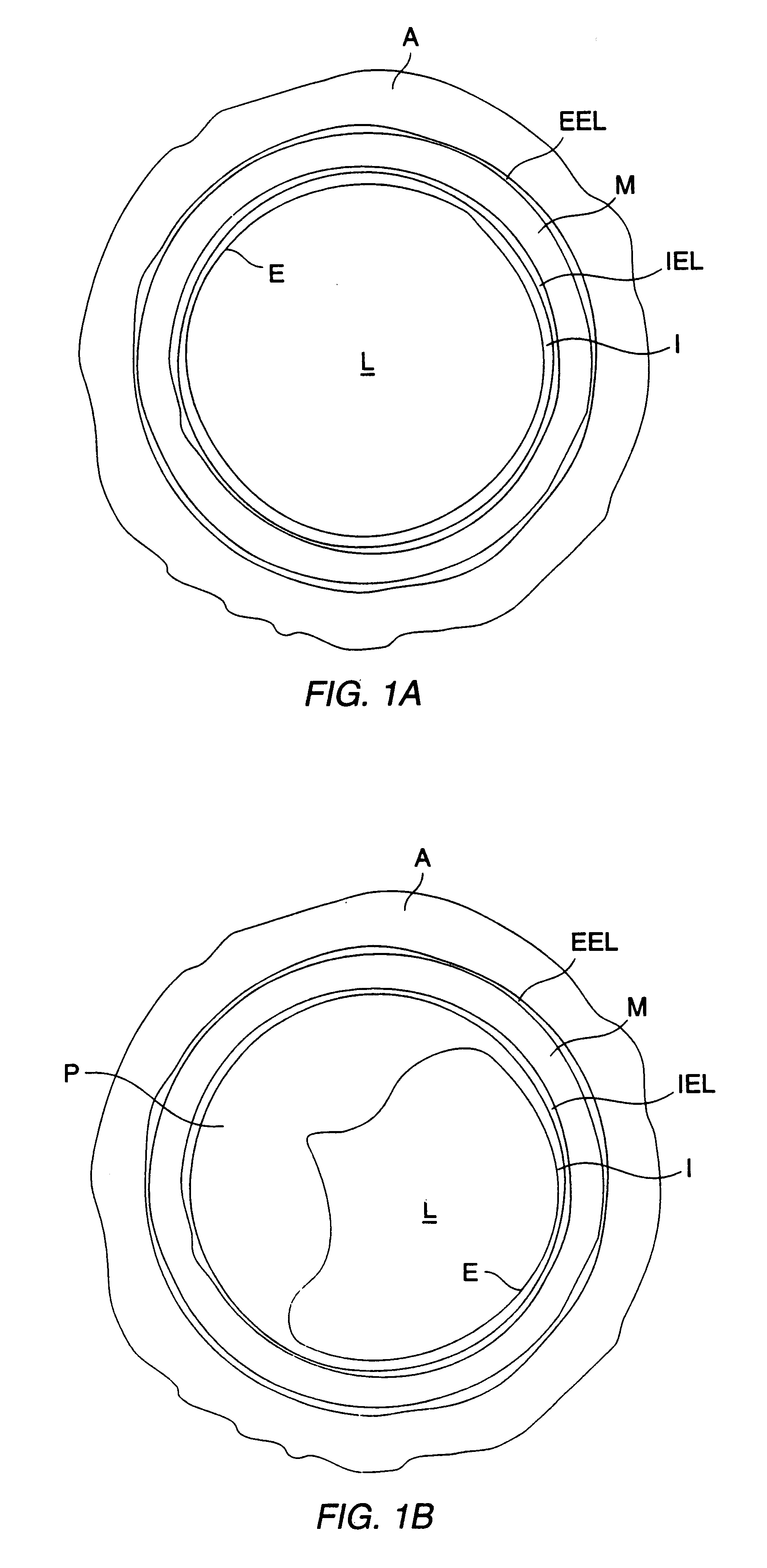
An intravascular catheter for peri-vascular and / or peri-urethral tissue ablation includes multiple needles advanced through supported guide tubes which expand with open ends around a central axis to engage the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the injection an ablative fluid for ablating tissue, and / or nerve fibers in the outer layer or deep to the outer layer of the vessel, or in prostatic tissue. The system also includes means to limit and / or adjust the depth of penetration of the ablative fluid into and beyond the tissue of the vessel wall. The preferred embodiment of the catheter includes structures which provide radial and lateral support to the guide tubes so that the guide tubes open uniformly and maintain their position against the interior surface of the vessel wall as the sharpened injection needles are advanced to penetrate into the vessel wall.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
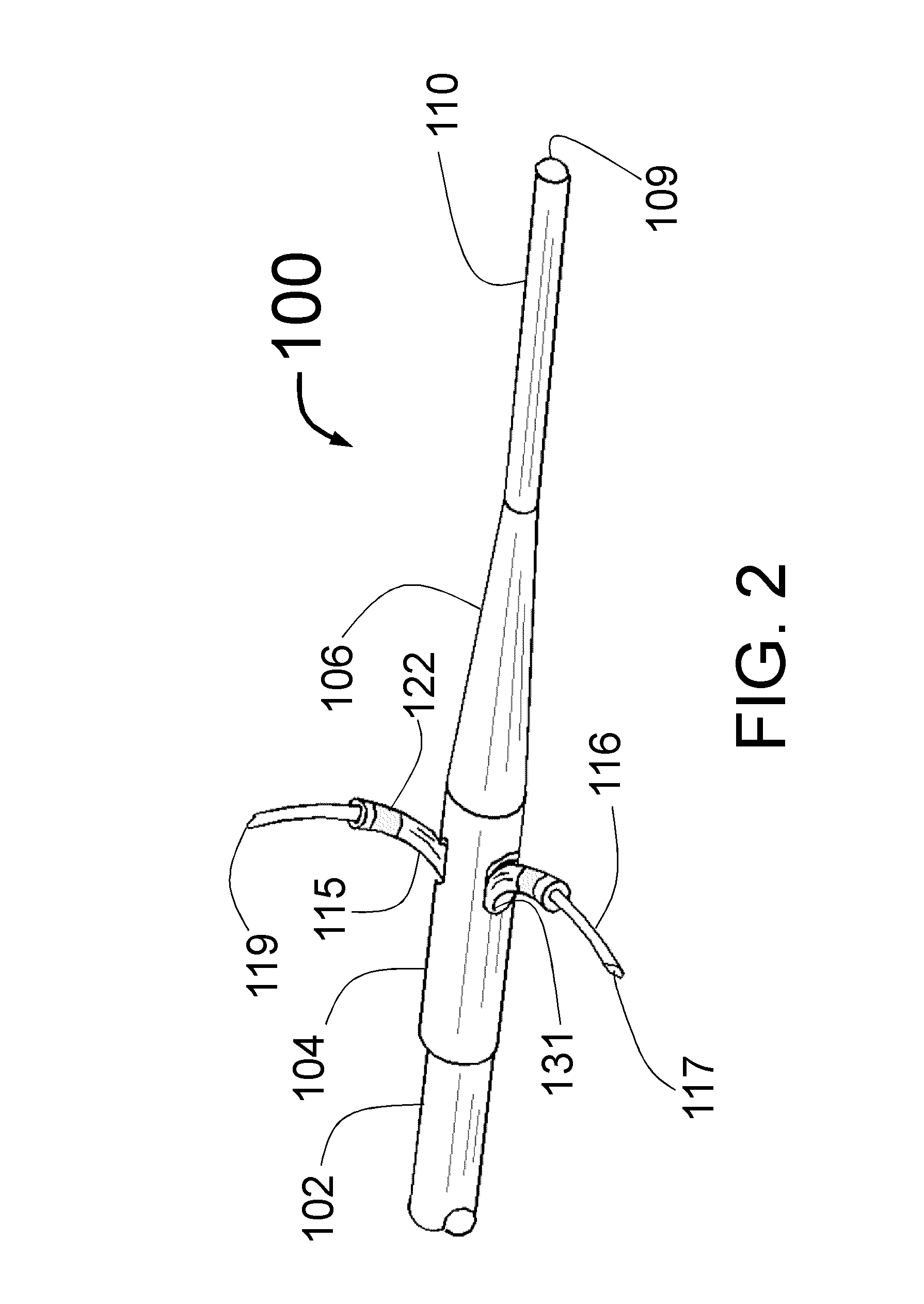
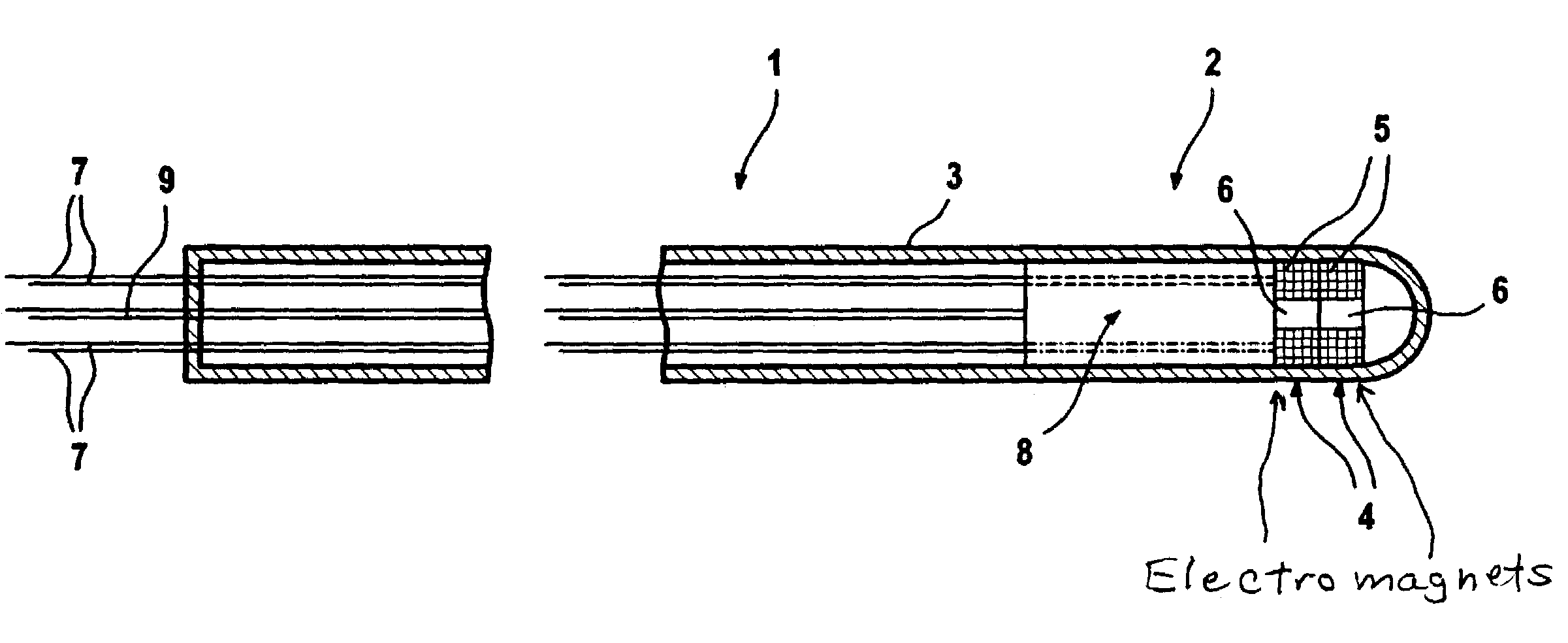
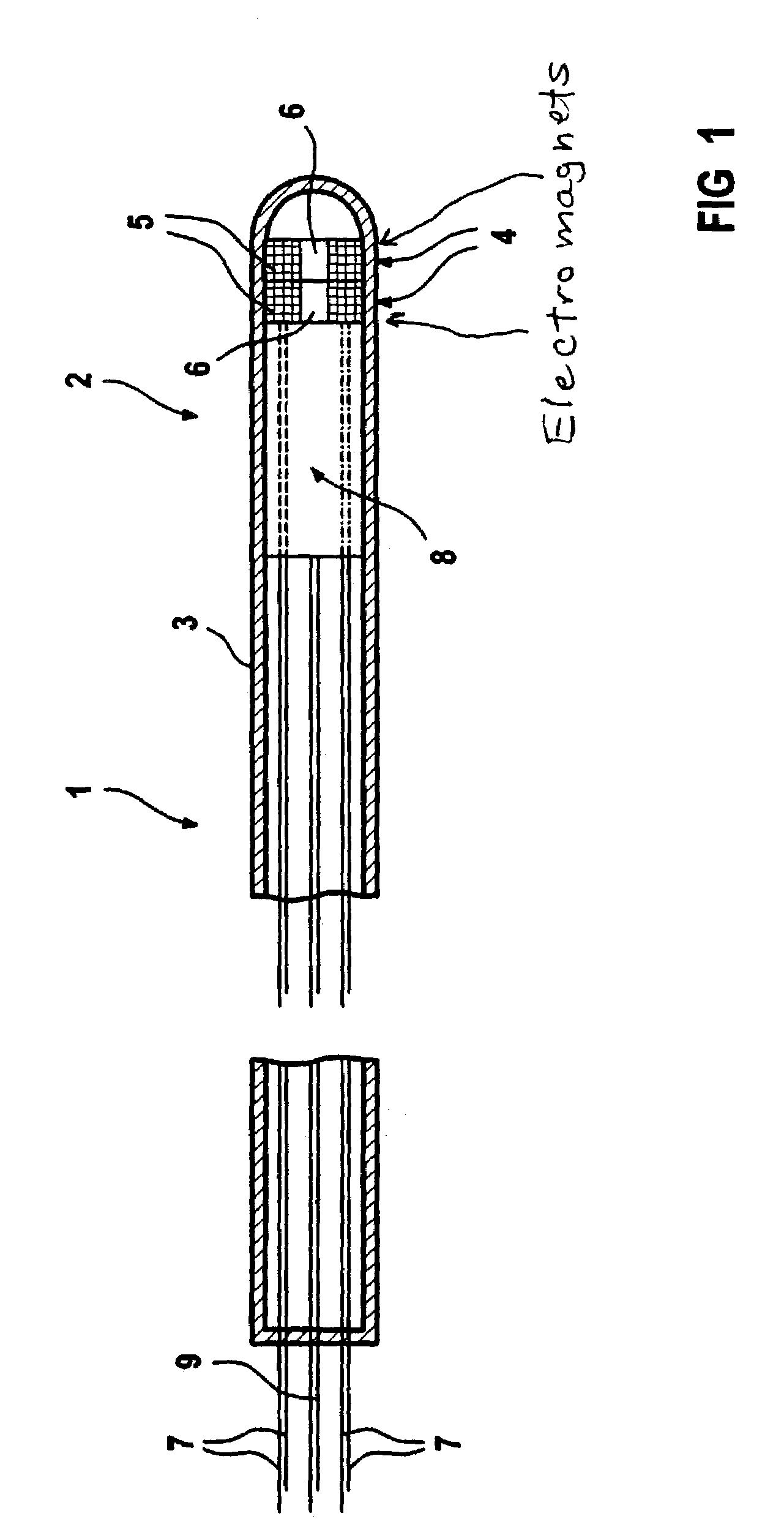
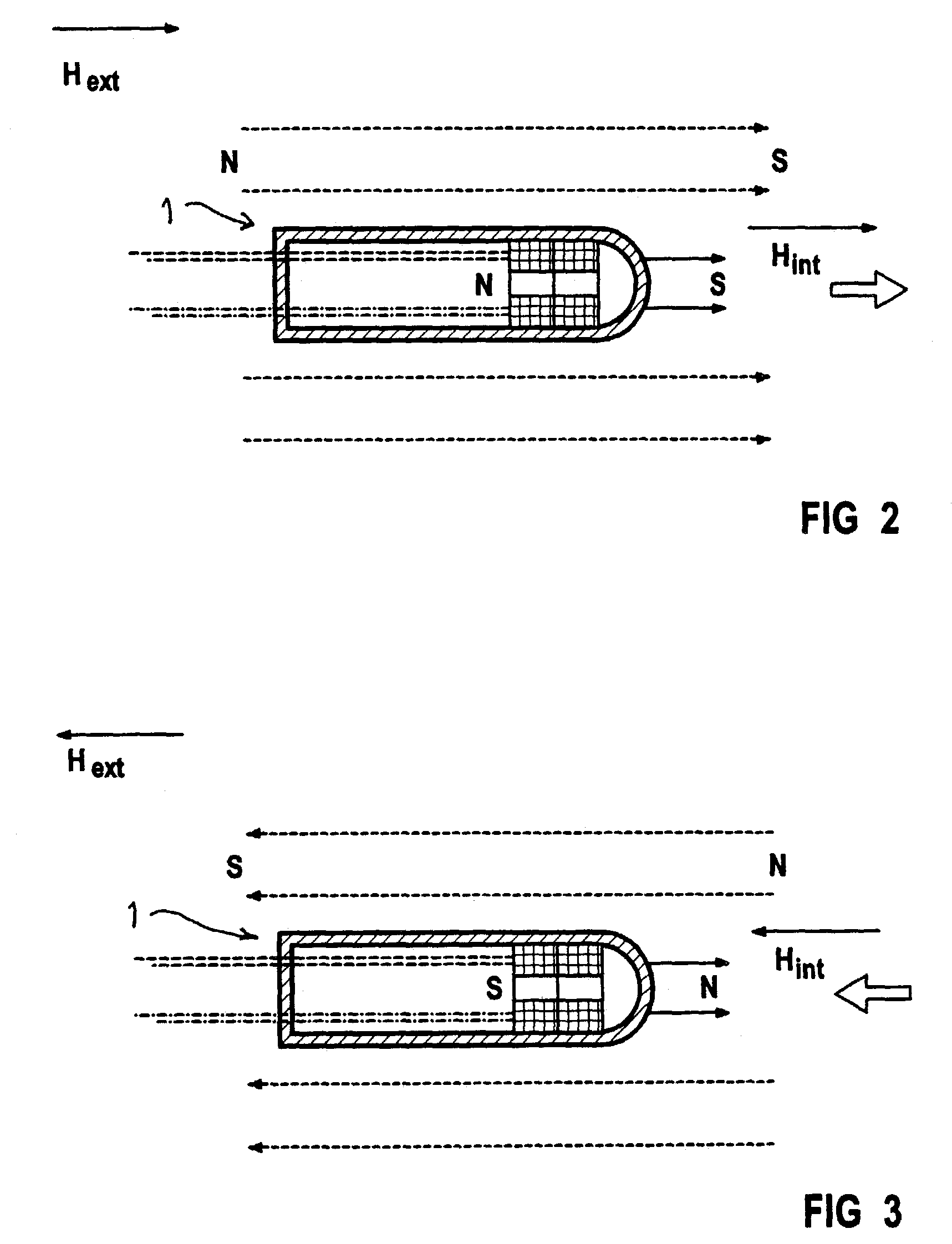
Catheter with variable magnetic field generator for catheter guidance in a subject
InactiveUS7686767B2Reduce decreaseSimpler navigation and movementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterIntravascular catheterBlood vessel
A catheter, particularly an intra-vascular catheter, has at least one magnetic field-generating element arranged in the catheter envelope in the region of the catheter tip, characterized in that the magnetic field of which is variable while the catheter is inserted into a patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Transvascular catheter for extravascular delivery
ActiveUS20140121641A1Reduce or eliminate patient discomfort and painReduces potential traumaBalloon catheterSurgical needlesHuman bodyPerfusion
An intravascular catheter for peri-vascular and / or peri-urethral tissue ablation includes multiple needles advanced through guide tubes which may be supported by an expandable balloon. The guide tubes expand with open ends around a central axis to engage the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the injection an ablative fluid for ablating tissue, and / or nerve fibers in the outer layer or deep to the outer layer of the vessel, or in prostatic tissue. The diameter of the inflated balloon is less than the inside diameter of the vessel, allowing perfusion across the inflated balloon and guide tubes.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
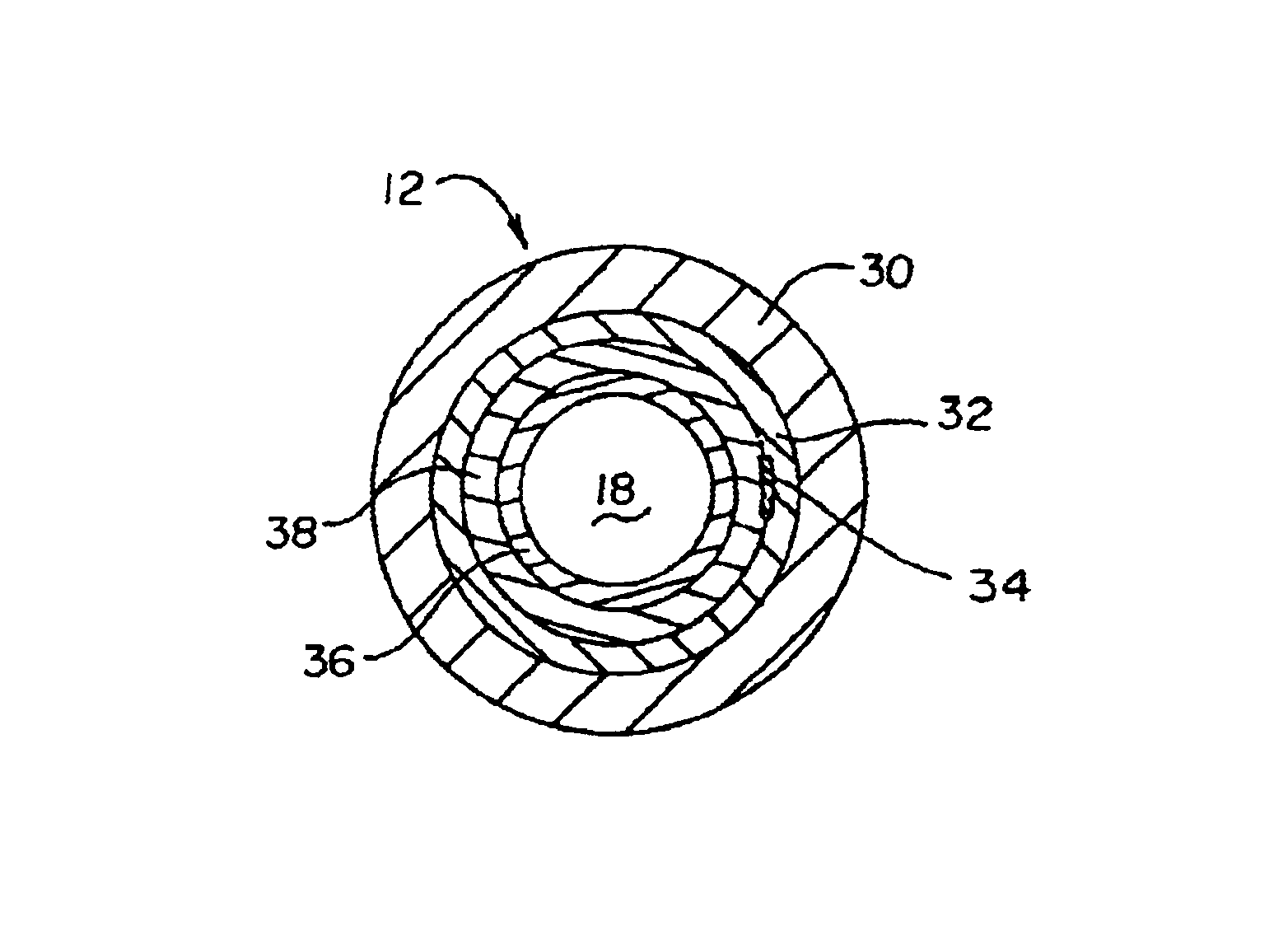
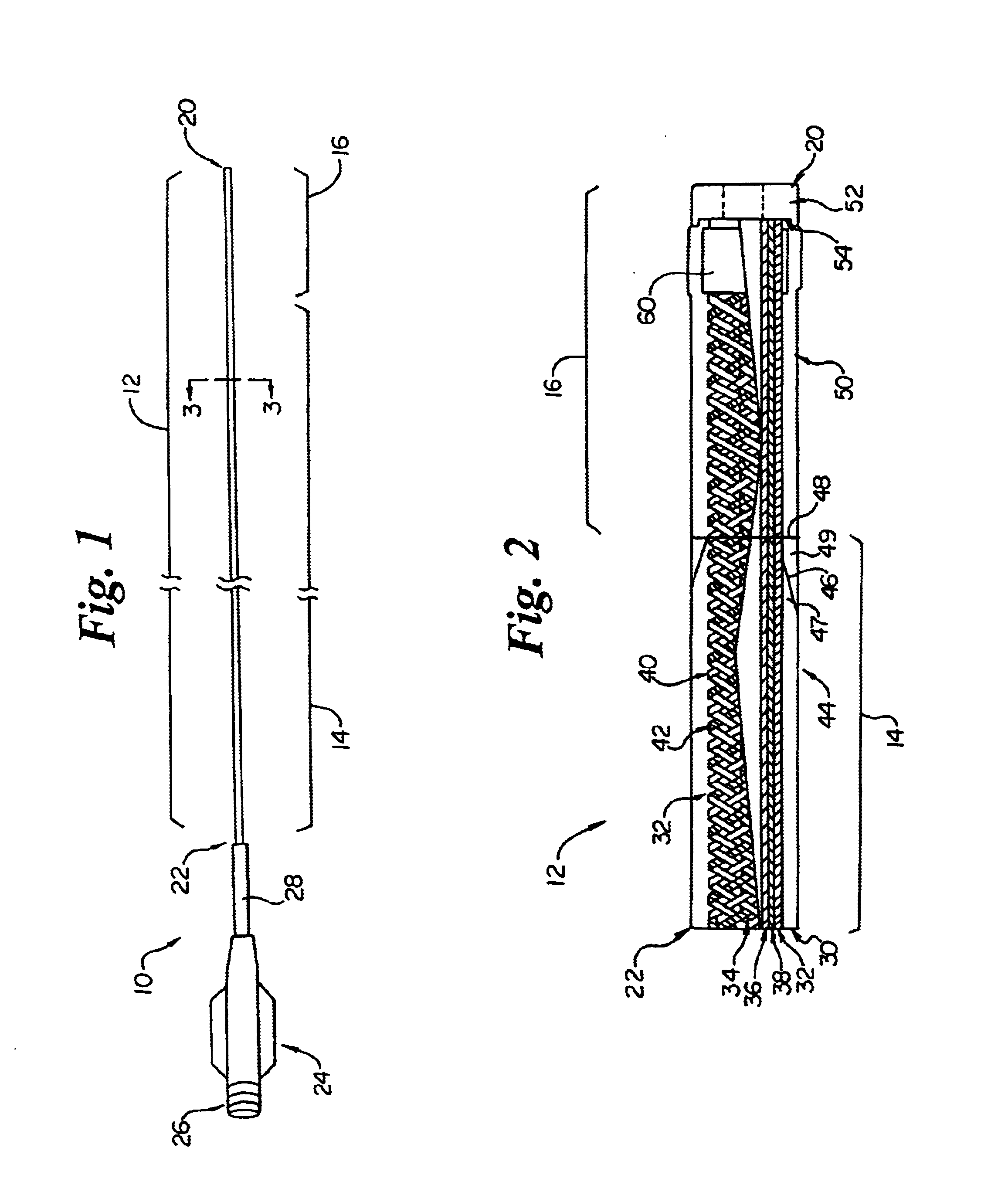
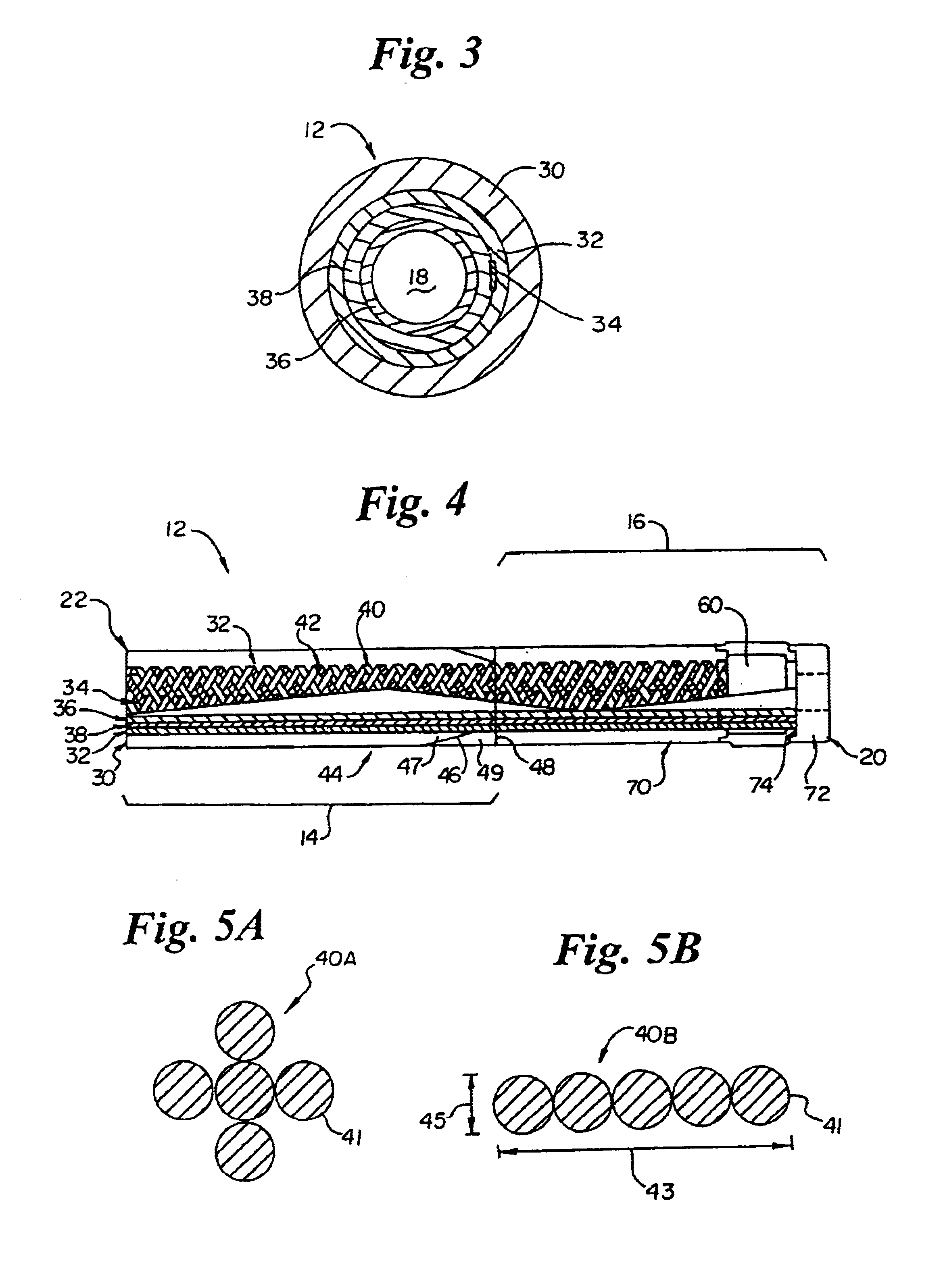
Intravascular catheter with composite reinforcement
InactiveUS6866660B2Increase flexibilityGood flexibilityCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringIntravascular catheterGuide tube
An intravascular catheter that exhibits the combined features of superior flexibility, softness, radiopacity and oval / kink resistance. The catheter includes an elongate shaft having a proximal region, a distal region and a lumen extending therethrough. The proximal region of the shaft includes an inner lubricious polymer layer, a reinforcement layer and an outer layer. The reinforcement layer comprises a braid having one or more metallic members and a plurality of polymer members wherein each polymer member comprises a plurality of monofilaments, preferably formed of LCP. The polymer members of the braid provide improved flexibility and softness in addition to high burst pressure. The metallic member(s) of the braid provide improved radiopacity and oval / kink resistance. The catheter may also include a longitudinal member extending along the reinforcement layer.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
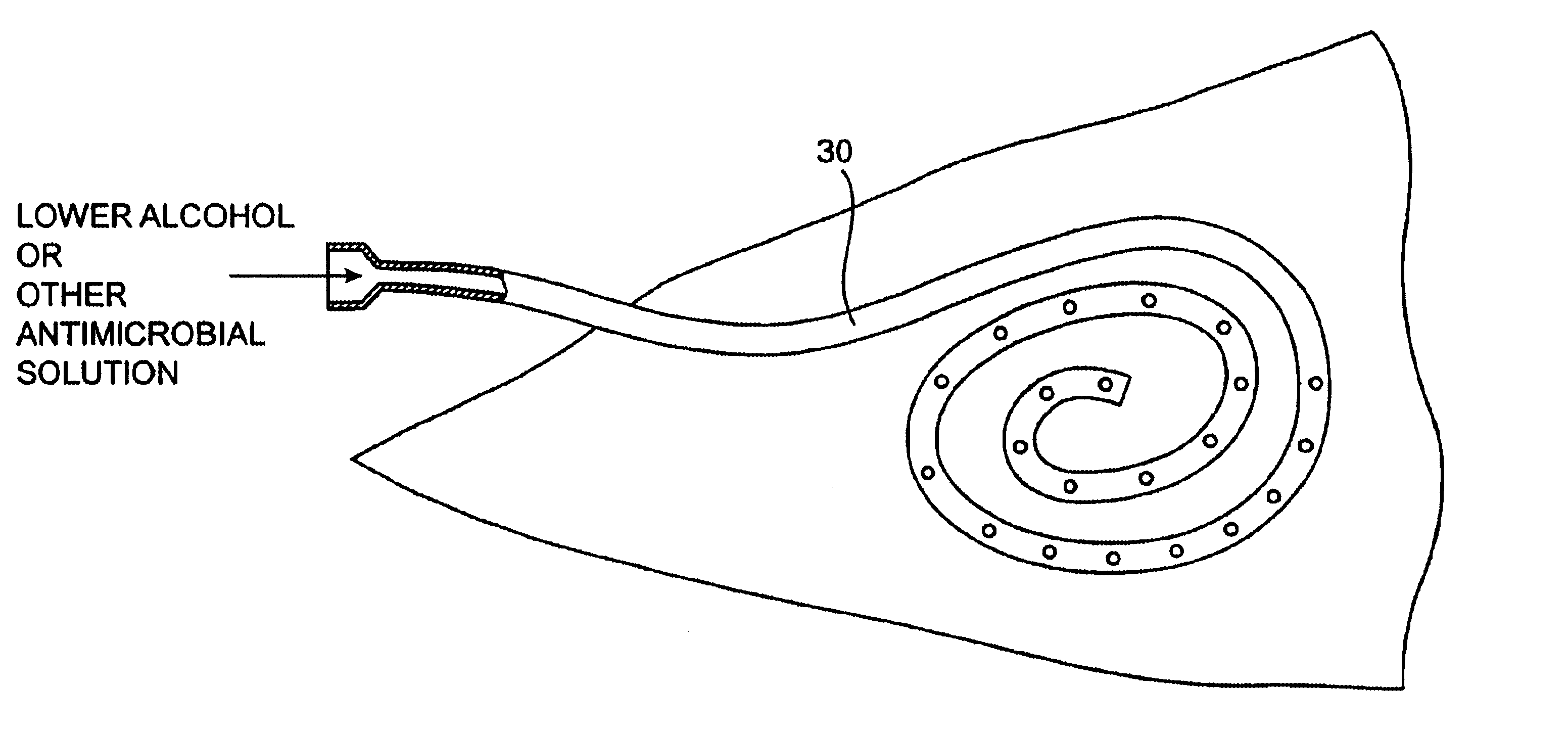
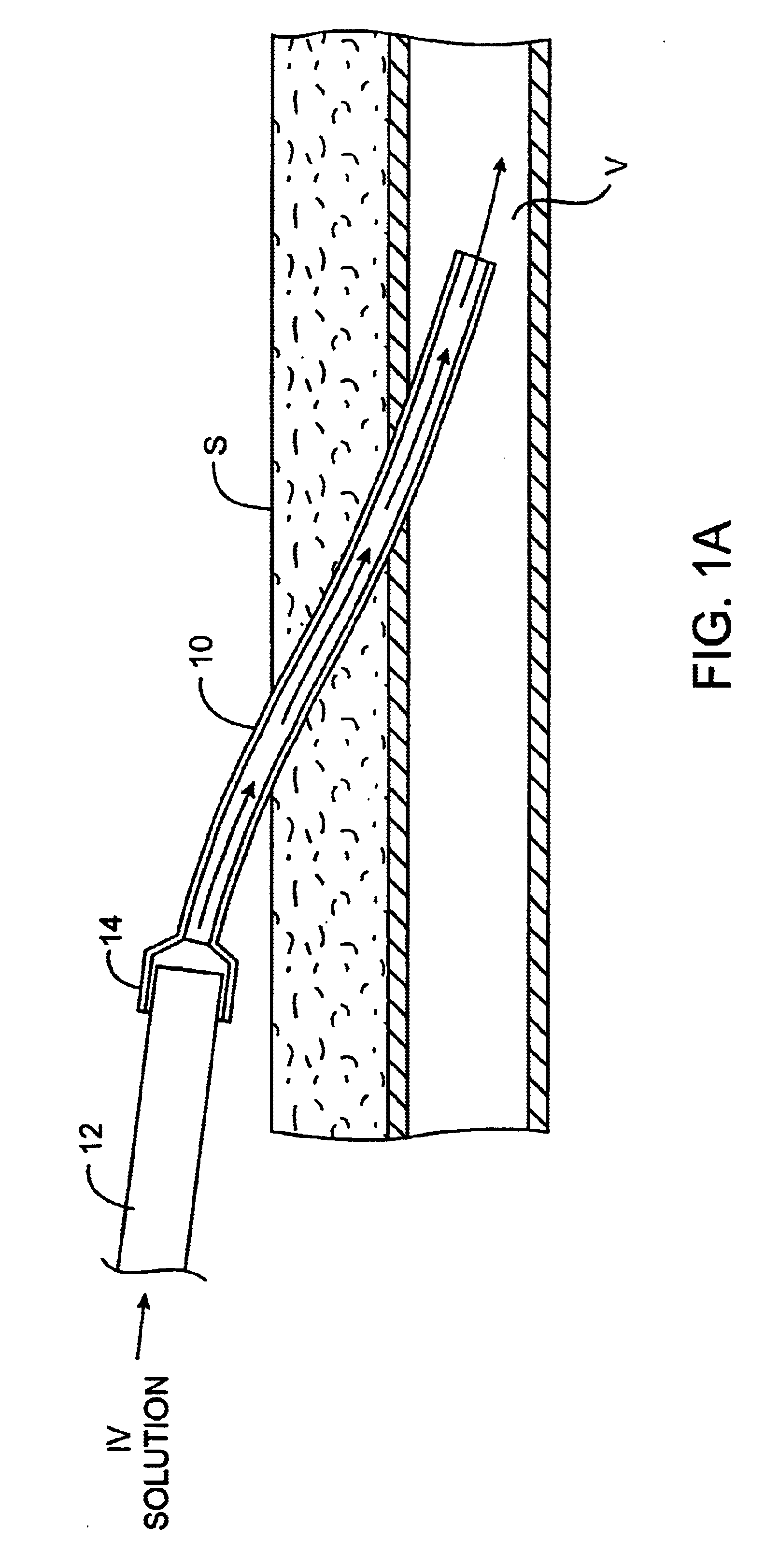
Methods and kits for locking and disinfecting implanted catheters
InactiveUS6685694B2Reduce riskInhibiting fouling and plugging of the lumenDialysis systemsMedical devicesTriclosanThrombus
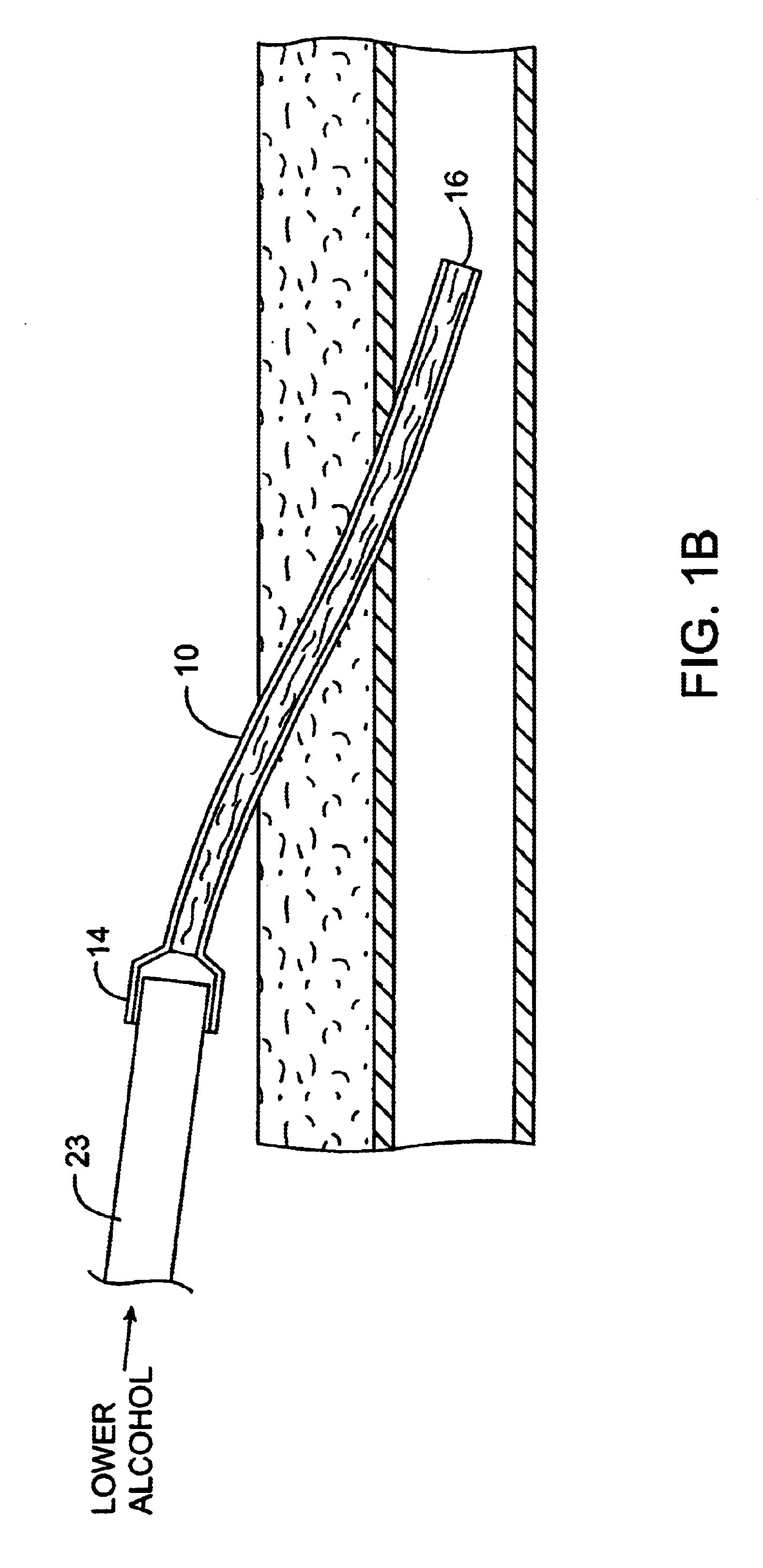
Implanted catheters are locked with a solution comprising a lower alcohol, typically ethanol, propanol, or butanol, in a range from 1% to 99% by volume, and an additive in a range from 1% to 99% by volume, the additive comprising an anti-microbial, typically taurolidine or triclosan, or an anti-coagulant, typically riboflavin, sodium citrate, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, or citric acid. The use of an alcohol and additive solution can effectively reduce fouling of the catheter, particularly clotting and thrombus in intravascular catheters, as well as eradicate existing infections and / or reduce the risk of potential infections. Existing infections and / or potential infections can be further reduced by employing a catheter body which permits an anti-microbial solution to penetrate into the catheter body and preferably through the catheter into tissue surrounding the implanted catheter.
Owner:EXCELSIOR MEDICAL
Method And Apparatus For The Detection Of Neural Tissue
InactiveUS20150208934A1SensorsNeuroelectric signal measurementIntravascular catheterBiomedical engineering
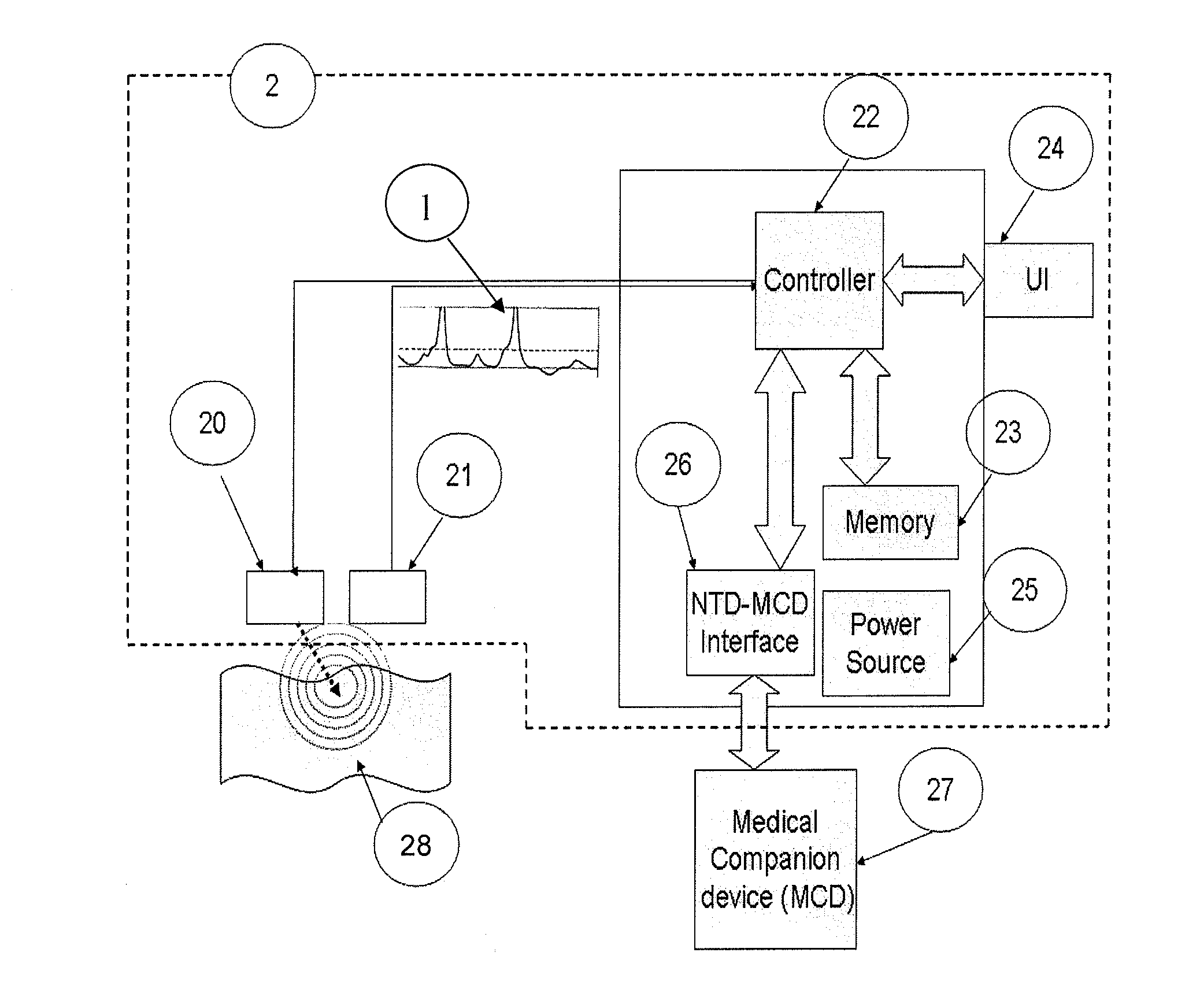
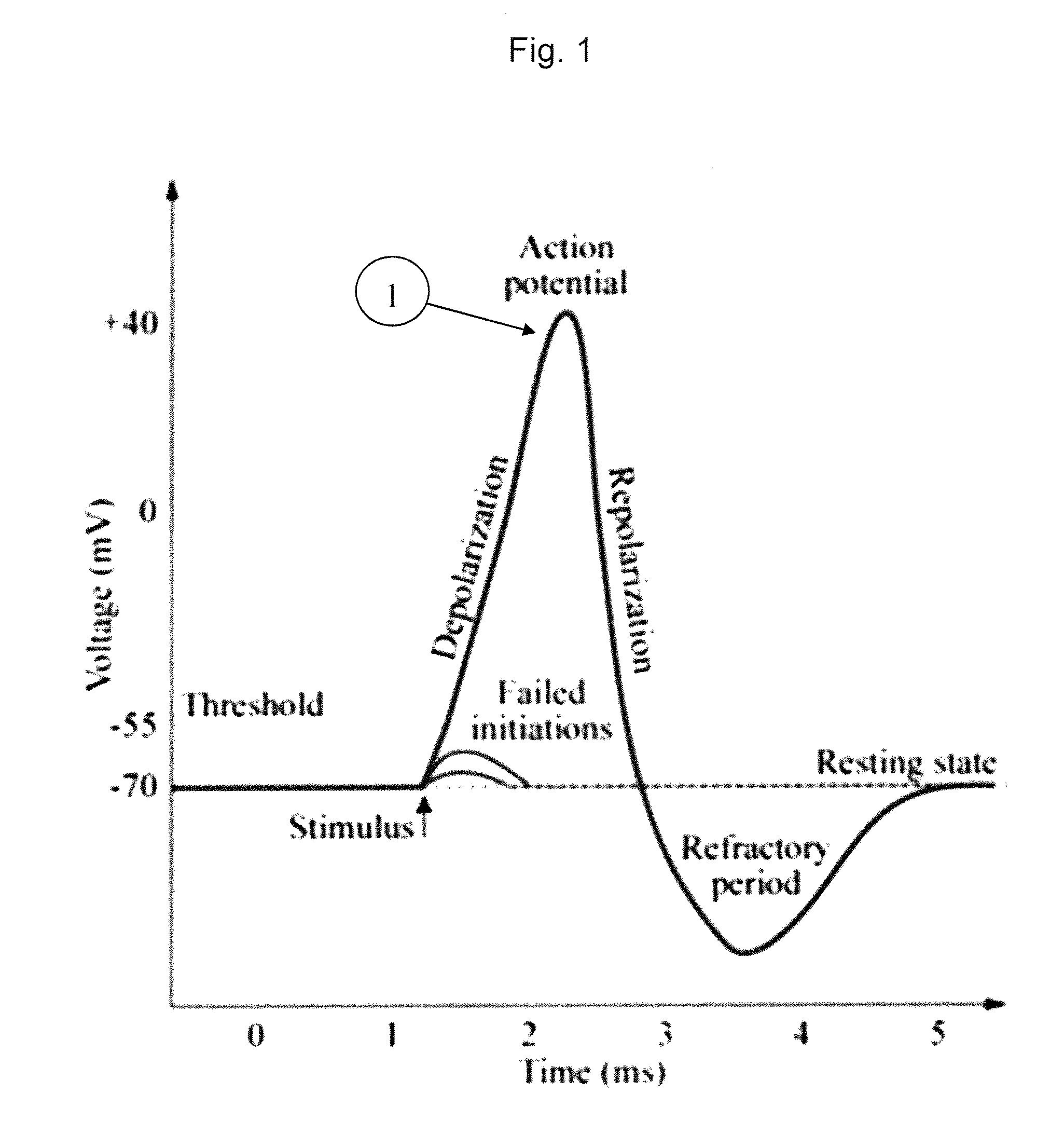
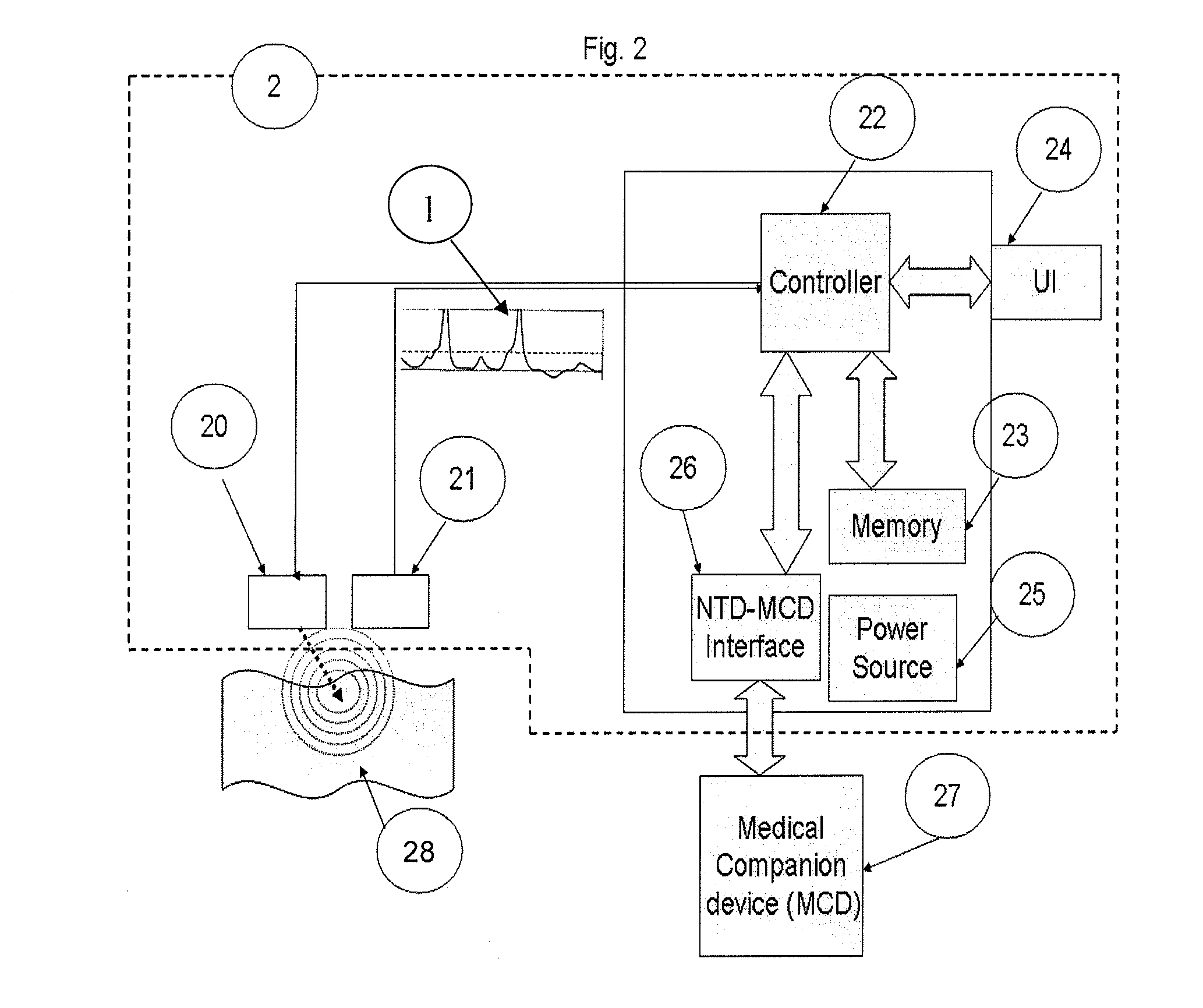
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for neural tissue detection carried out using the Neural Tissue Detector (NTD), which is the apparatus that embodies the hardware aspect of the invention. The NTD enables neural tissue detection by stimulating a small tissue area and by measuring possible occurrences of induced response from neural tissue, if neural tissue is present in said small stimulated tissue area. The information gathered by the measurement provides a real-time assessment of the nature of the tissue which is targeted by the NTD. The invention is applicable to all types of neural tissues, including motor, and / or sensory and / or other types of neural tissues. The invention offers particular advantages in robot based surgical procedures or intravascular catheter based procedures but can also be used for manual surgery, according to different specific embodiments.
Owner:SZTRUBEL GENEVIEVE +1
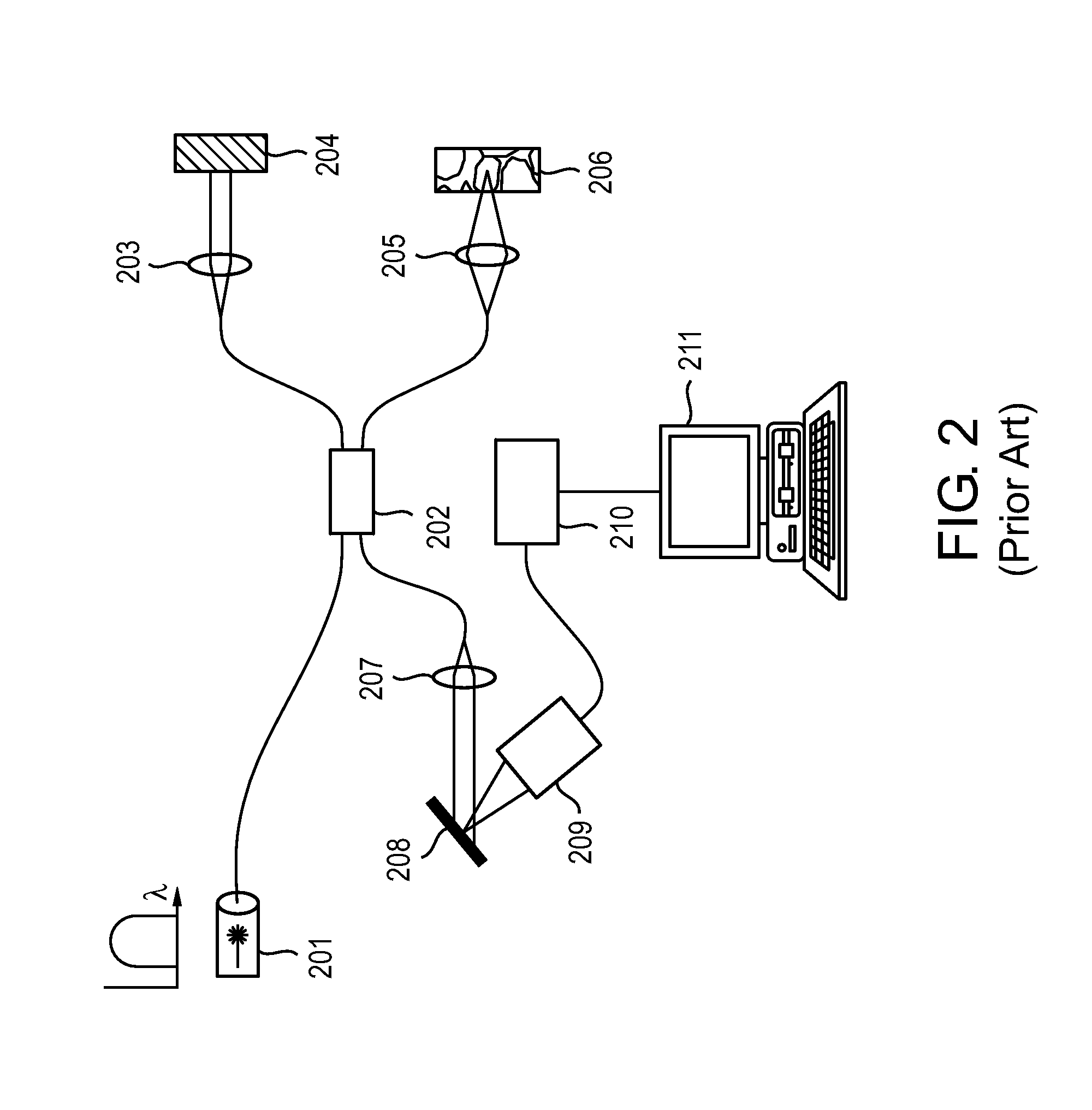
Optical catheter configurations combining raman spectroscopy with optical fiber-based low coherence reflectometry
The present invention provides apparatuses and methods for sample analysis, such as tissue analysis, that integrate high wavenumber (HW) Raman spectroscopy for chemical composition analysis and optical coherence tomography (OCT) to provide depth and morphological information. The invention also provides side-viewing optical probes that are based on a single double clad optical fiber for performing the combined HW Raman spectroscopy and OCT. Intravascular catheter embodiments and related vascular diagnostic methods are also provided.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
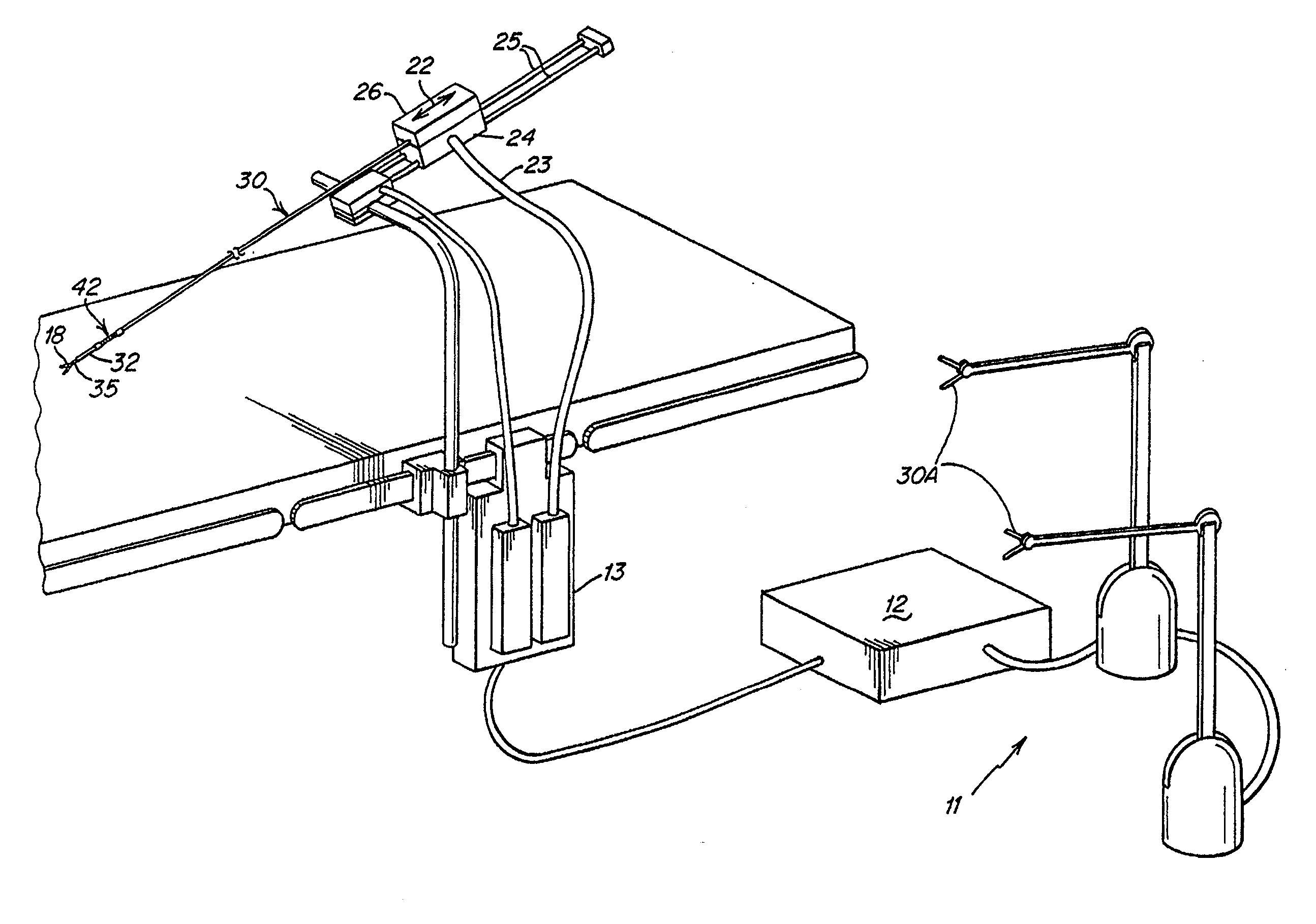
Flexible instrument
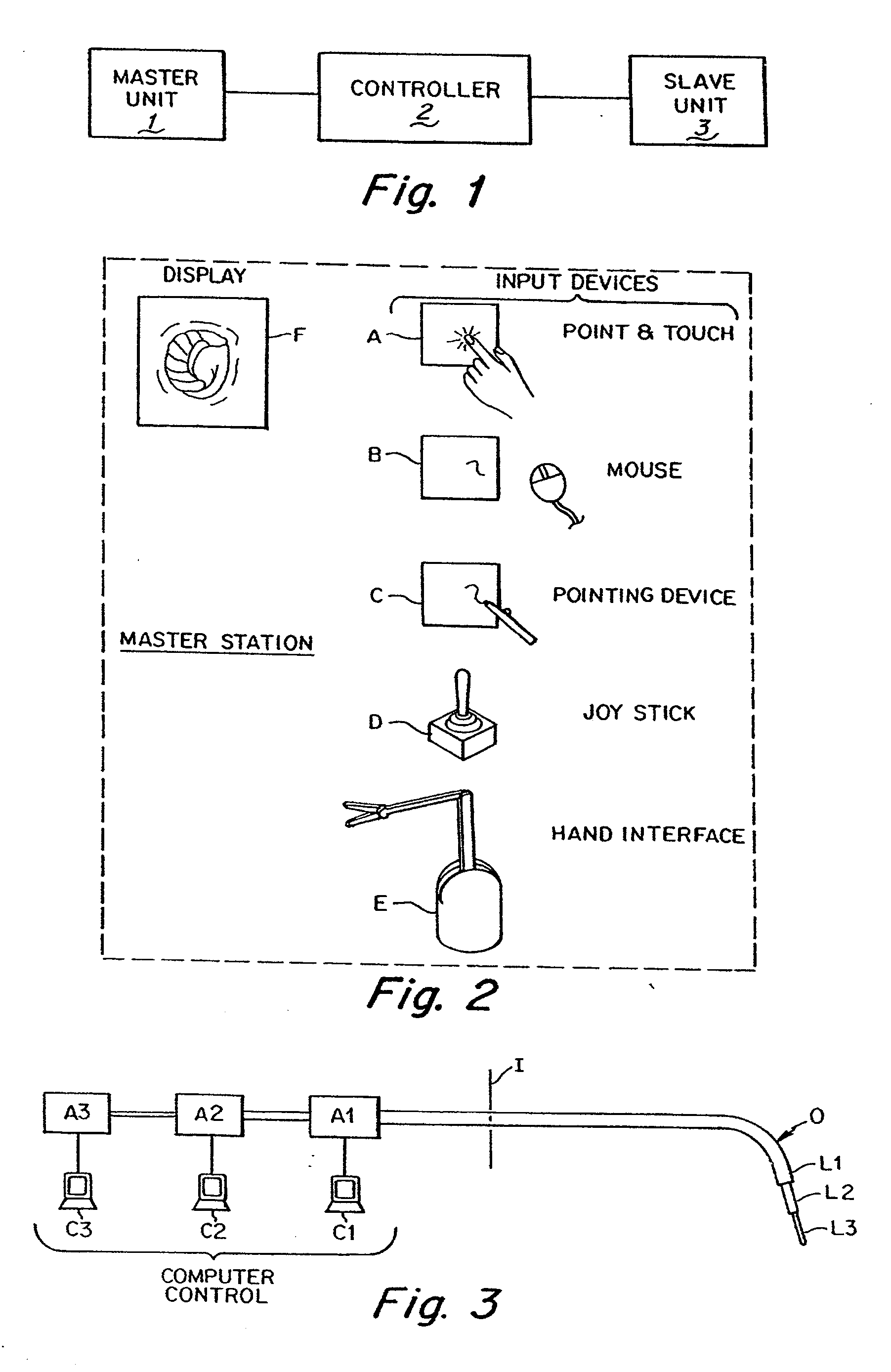
InactiveUS20070260115A1Suture equipmentsProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringDegrees of freedom
A medical instrument assembly and robotic medical system are provided. The medical instrument assembly comprises an intravascular catheter having an elongated flexible shaft, and a drivable mechanism to which the flexible catheter shaft is mounted. The drivable mechanism has an actuating element configured for effecting movement of the catheter within at least one degree-of-freedom. The medical instrument assembly further comprises a receiver to which the drivable mechanism is configured for being removably mated. The receiver is configured for operably coupling a drive unit to the actuating element. The robotic medical system comprises the medical instrument assembly, a user interface configured for generating at least one command, a drive unit coupled to the receiver, and an electric controller configured, in response to the command(s), for directing the drive unit to drive the actuating element via the receiver to effect movement of catheter to the degree(s)-of-freedom.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
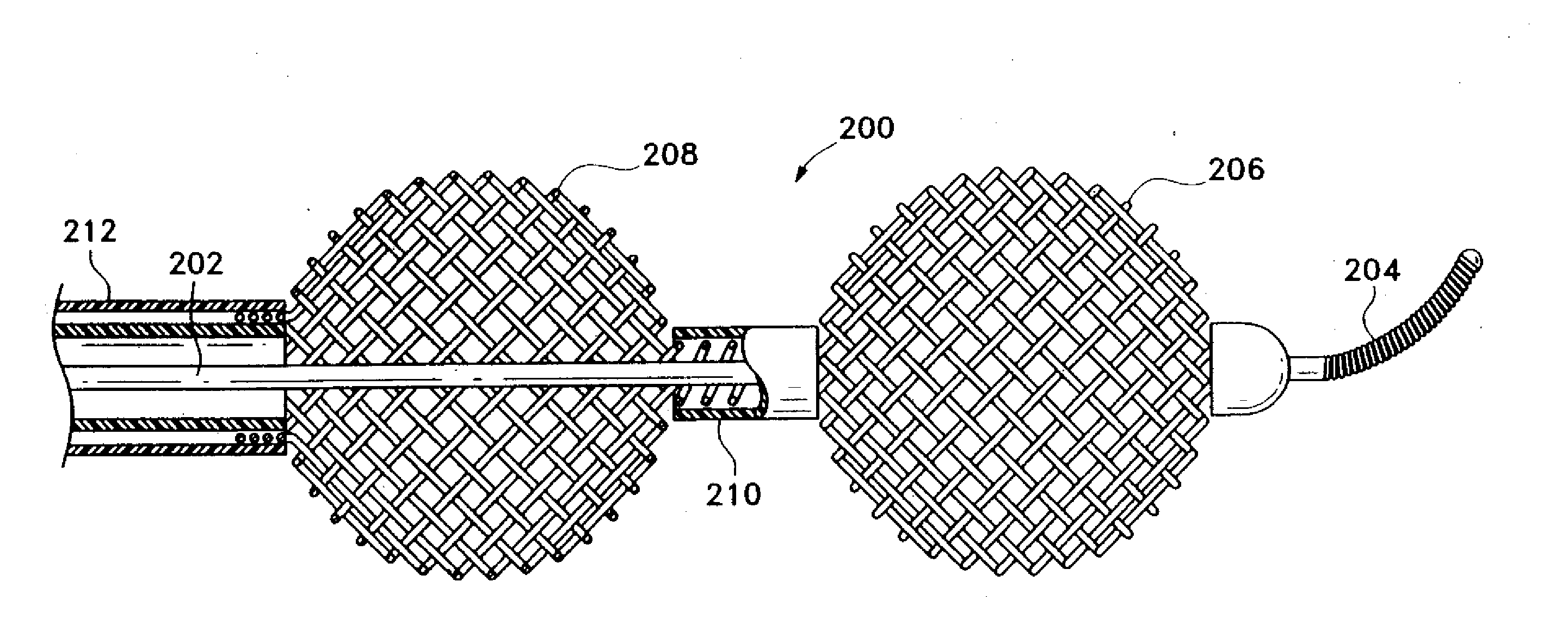
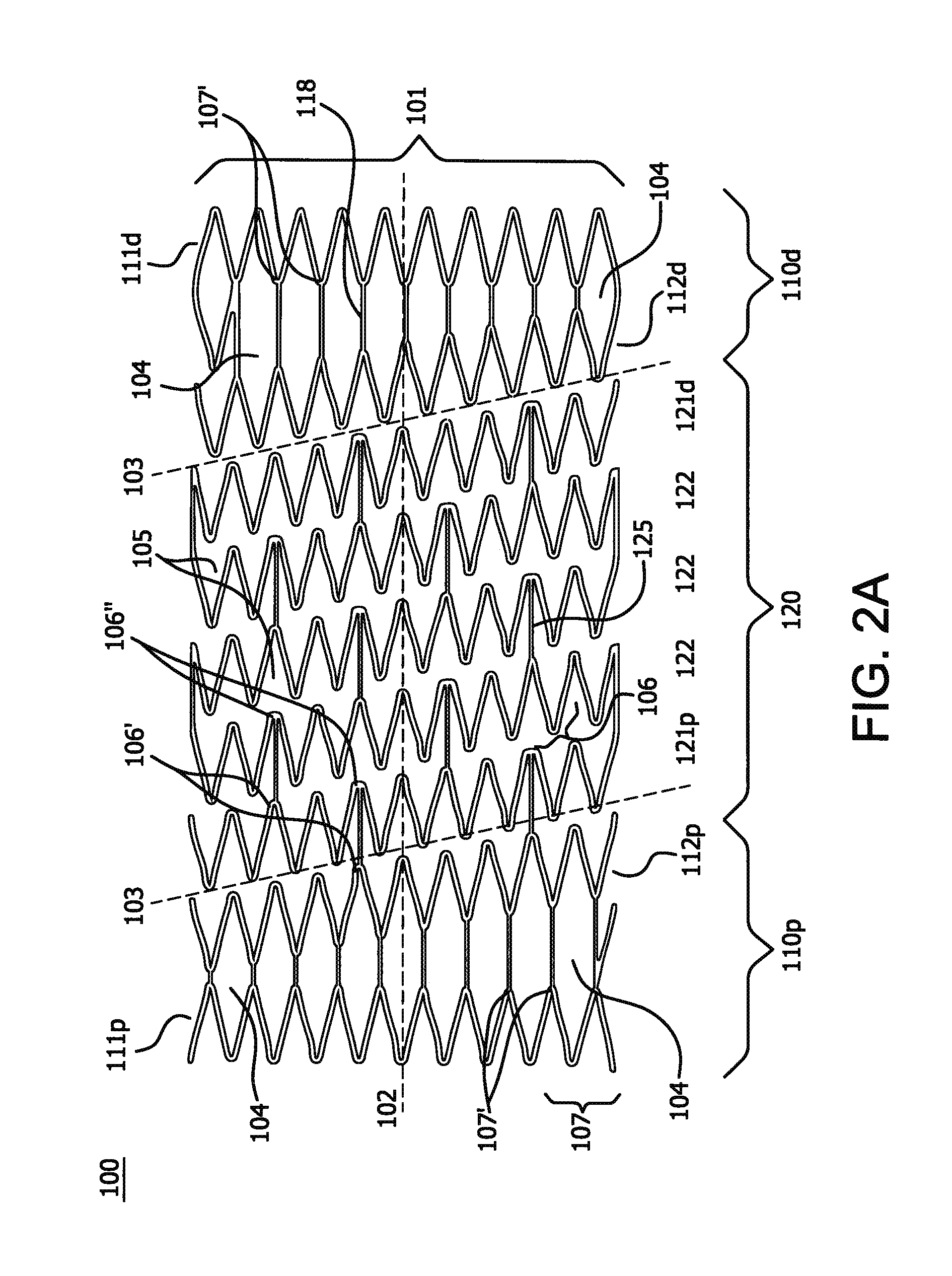
Stent
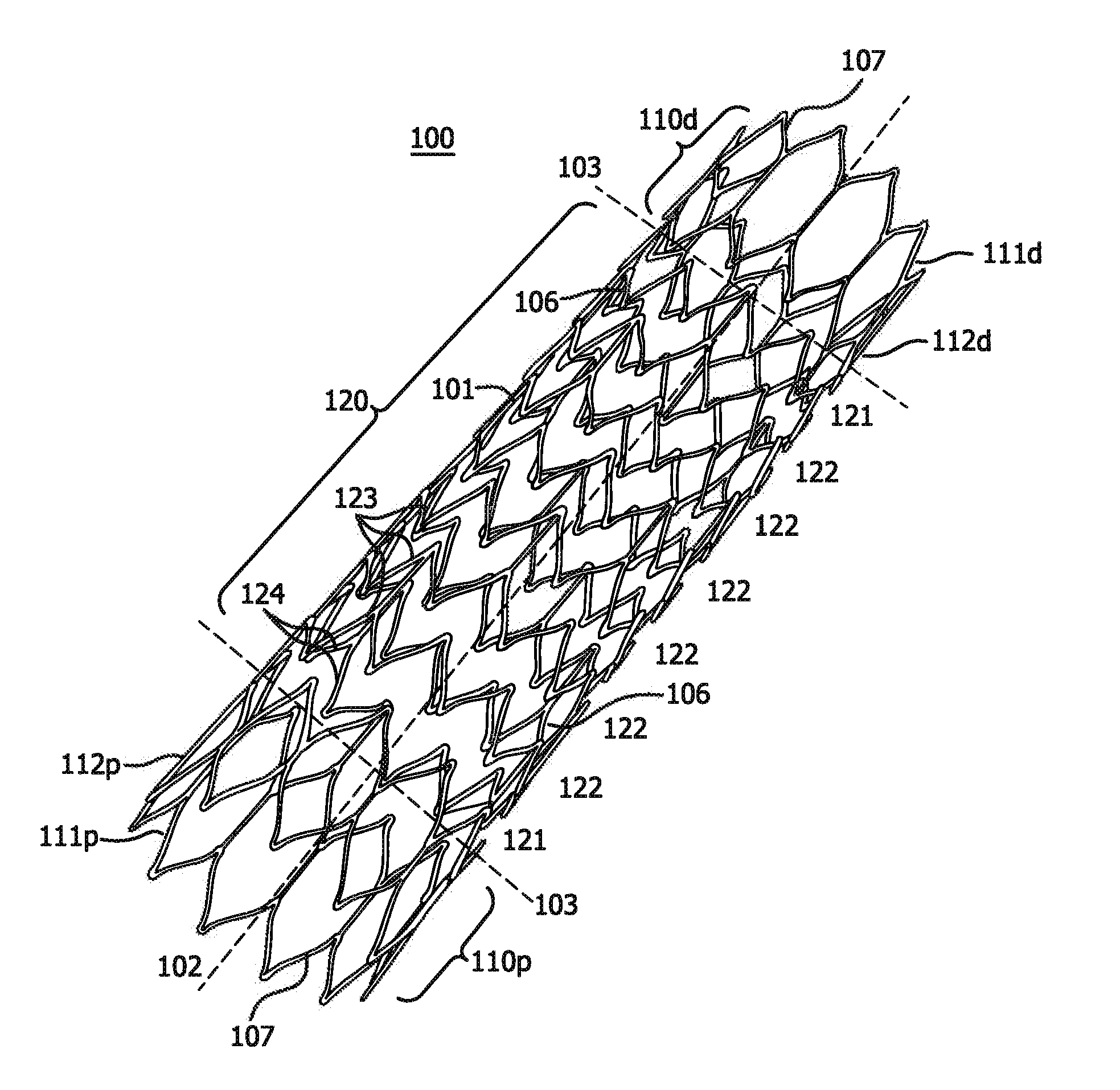
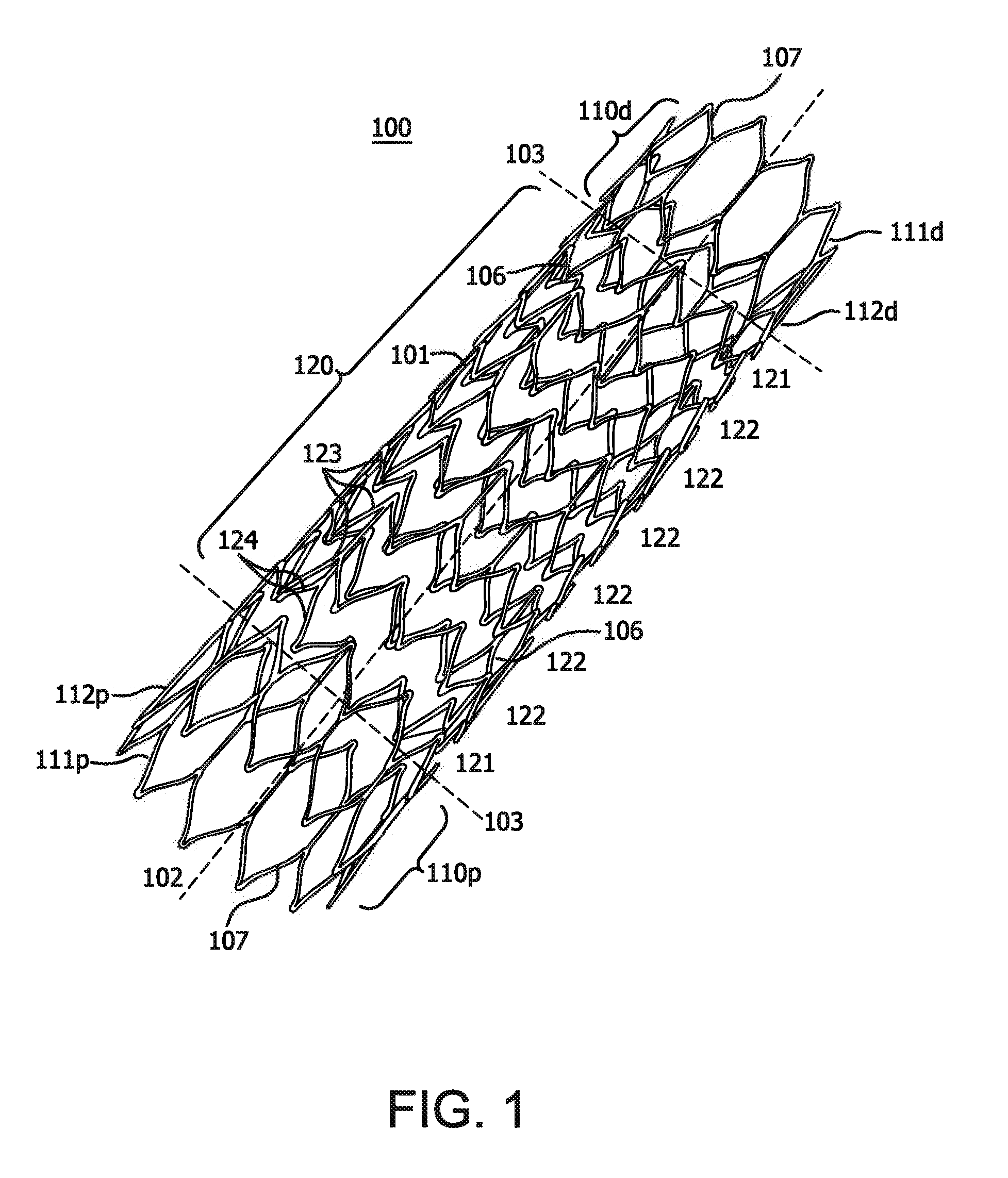
ActiveUS20120303112A1Low profileEnhance the imageStentsBlood vesselsSurgical operationIntravascular catheter
The invention relates to a medical device and a method of using it. The device is a stent which can be percutaneously deliverable with (or on) an endovascular catheter or via other surgical or other techniques and then expanded. The stent is configured to have a central portion defined by “open” cells and at least two end portions, defined by “closed” cells, spaced apart and directly connected to the distal and proximal ends of the central portion of the stent. The stent may also optionally have a covering or a lattice with openings.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Multiparameter whole blood monitor and method
InactiveUS20090270695A1Increase turnaround timeRemove uncertaintyBlood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsPulse pressureIntravascular catheter
Owner:NEW PARADIGM CONCEPTS
Blood pump systems and methods
ActiveUS20150209498A1Wide range of operationsReduce decreaseOther blood circulation devicesControl devicesWear resistantControl system
The present invention relates to a rotary blood pump with a double pivot contact bearing system with an operating range between about 50 mL / min and about 1500 mL / min. The rotary blood pump is part of a blood pump system that includes blood conduit(s), a control system with optional sensors, and a power source. Embodiments of the present invention may include elements such as wear resistant bearing materials, a rotor back plate for magnetic attraction of the rotor to reduce bearing pivot bearing forces and wear, a rotor size and shape and a bearing gap that combine to create a hydrodynamic bearing effect and reduce bearing pivot bearing forces and wear, improved intravascular conduits with increased resistance to thrombosis, conduit insertion site cuffs to resist infection, and conduit side ports amenable to the easy insertion of guidewire and catheter-based medical devices.
Owner:ARTIO MEDICAL INC
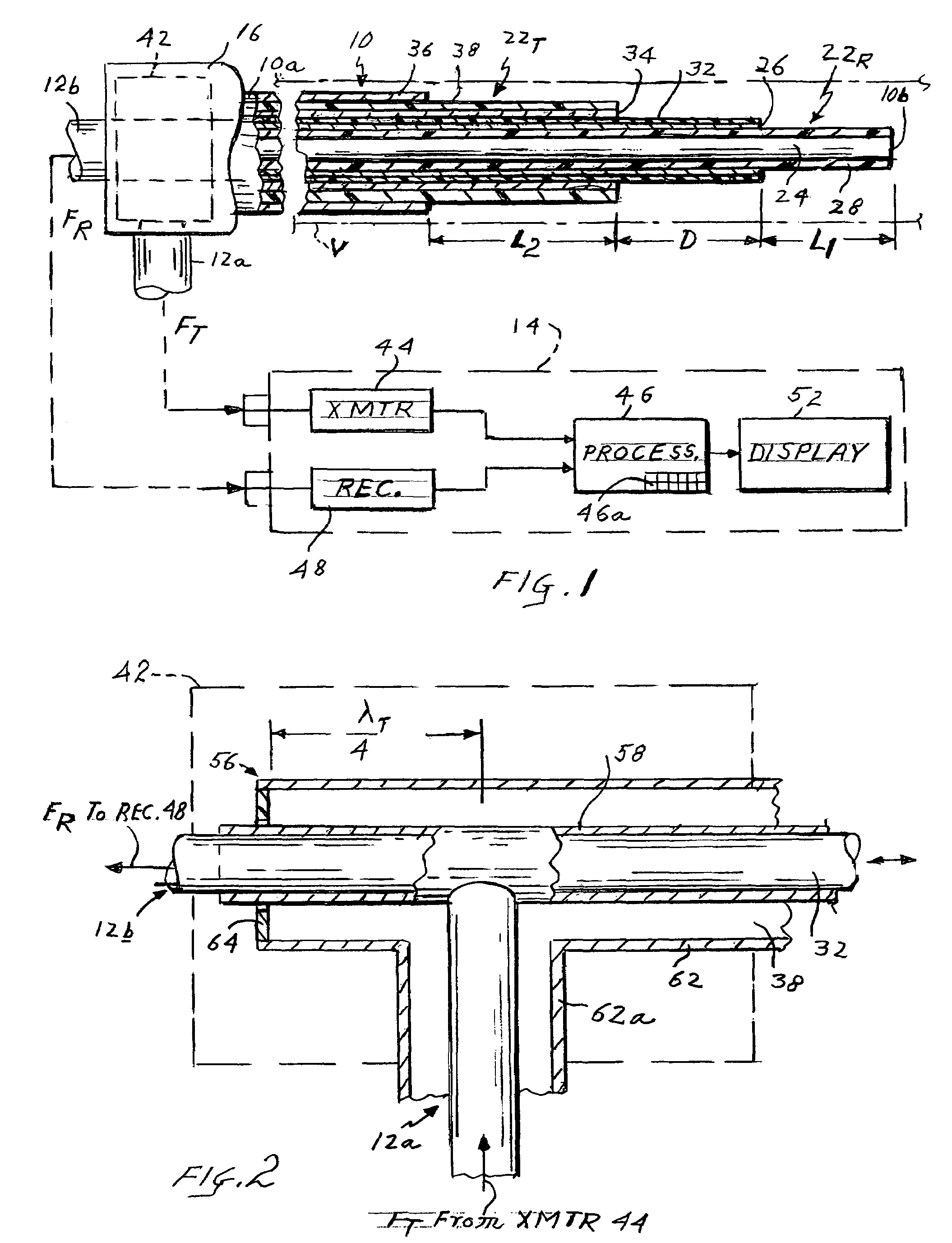
Apparatus for measuring intravascular blood flow
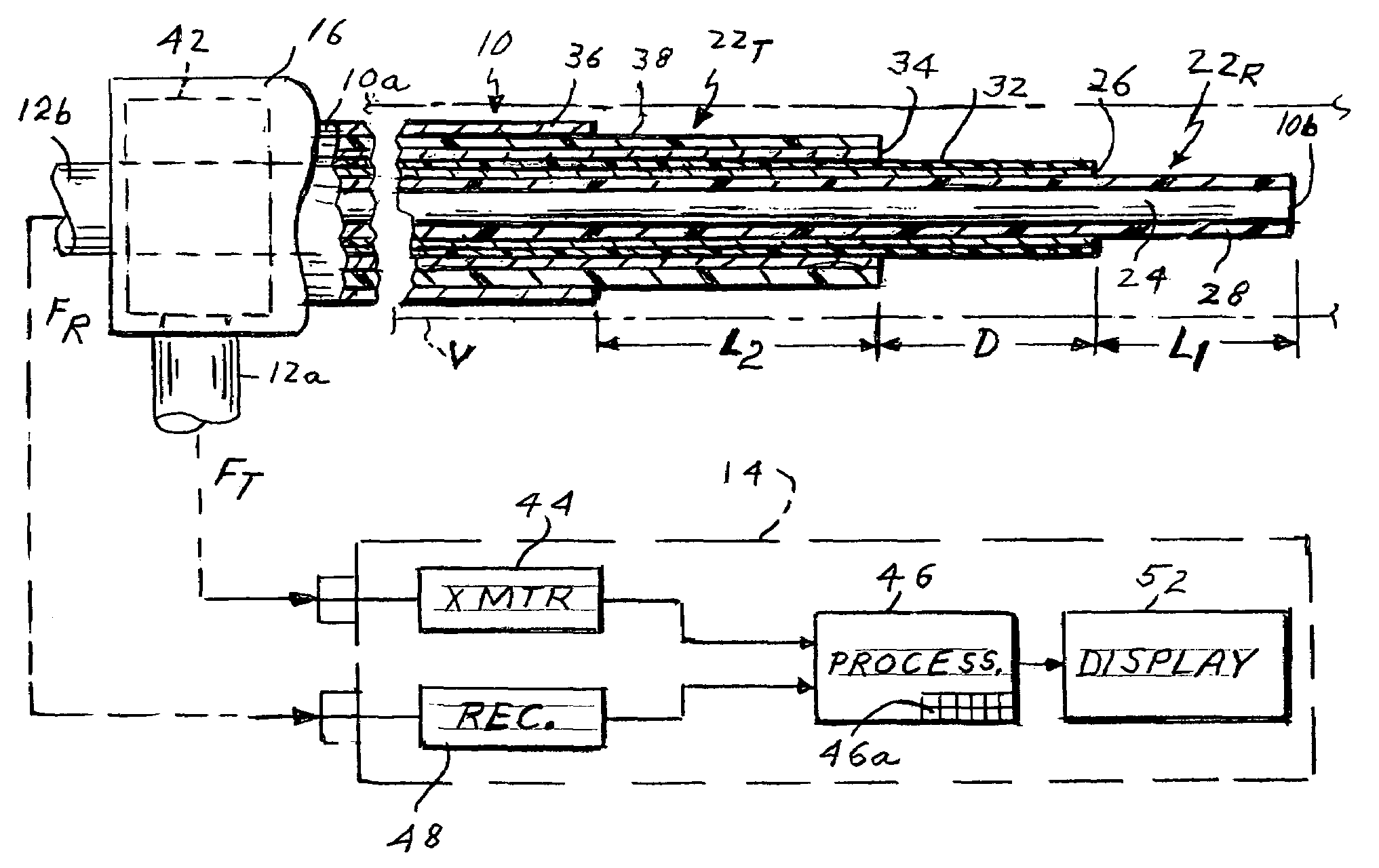
ActiveUS7263398B2Reduce usageQuickly and accurately measure blood flow rateCatheterSensorsCoaxial cableNormal blood volume
Microwave apparatus for measuring the blood flow rate in a patient's blood vessel includes an intravascular catheter having proximal and distal ends and containing an inner coaxial cable forming a first antenna and an outer cable coaxial with the inner cable and forming a second antenna, the first antenna extending axially beyond the second antenna a selected distance. The apparatus also includes a control unit including a microwave transmitter, a microwave receiver and a processor controlling the transmitter and receiver. A diplexer is connected between the first and second antenna and the control unit to couple signals from the transmitter to the second antenna but not to the receiver and to couple signals from the first antenna to the receiver but not to the transmitter. The transmitter transmits microwave pulses to the first antenna which heat blood around that antenna. When the heated blood volume flows to the second antenna this is detected at the receiver which produces a detect signal. The processor measures the time interval between each pulse a subsequent detect signal and divides that time interval into the axial distance between the two antennas to compute the flow rate.
Owner:CORAL SAND BEACH LLC
Apparatus for effective ablation and nerve sensing associated with denervation
An intravascular catheter for nerve activity ablation and / or sensing includes one or more needles advanced through supported guide tubes (needle guiding elements) which expand to contact the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the needles to be advanced though the vessel wall into the extra-luminal tissue including the media, adventitia and periadvential space. The catheter also includes structures which provide radial and lateral support to the guide tubes so that the guide tubes open uniformly and maintain their position against the interior surface of the vessel wall as the sharpened needles are advanced to penetrate into the vessel wall. Electrodes near the distal ends of the needles allow sensing of nerve activity before and after attempted renal denervation. In a combination embodiment ablative energy or fluid is delivered from the needles in or near the adventitia to ablate nerves outside of the media while sparing nerves within the media.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
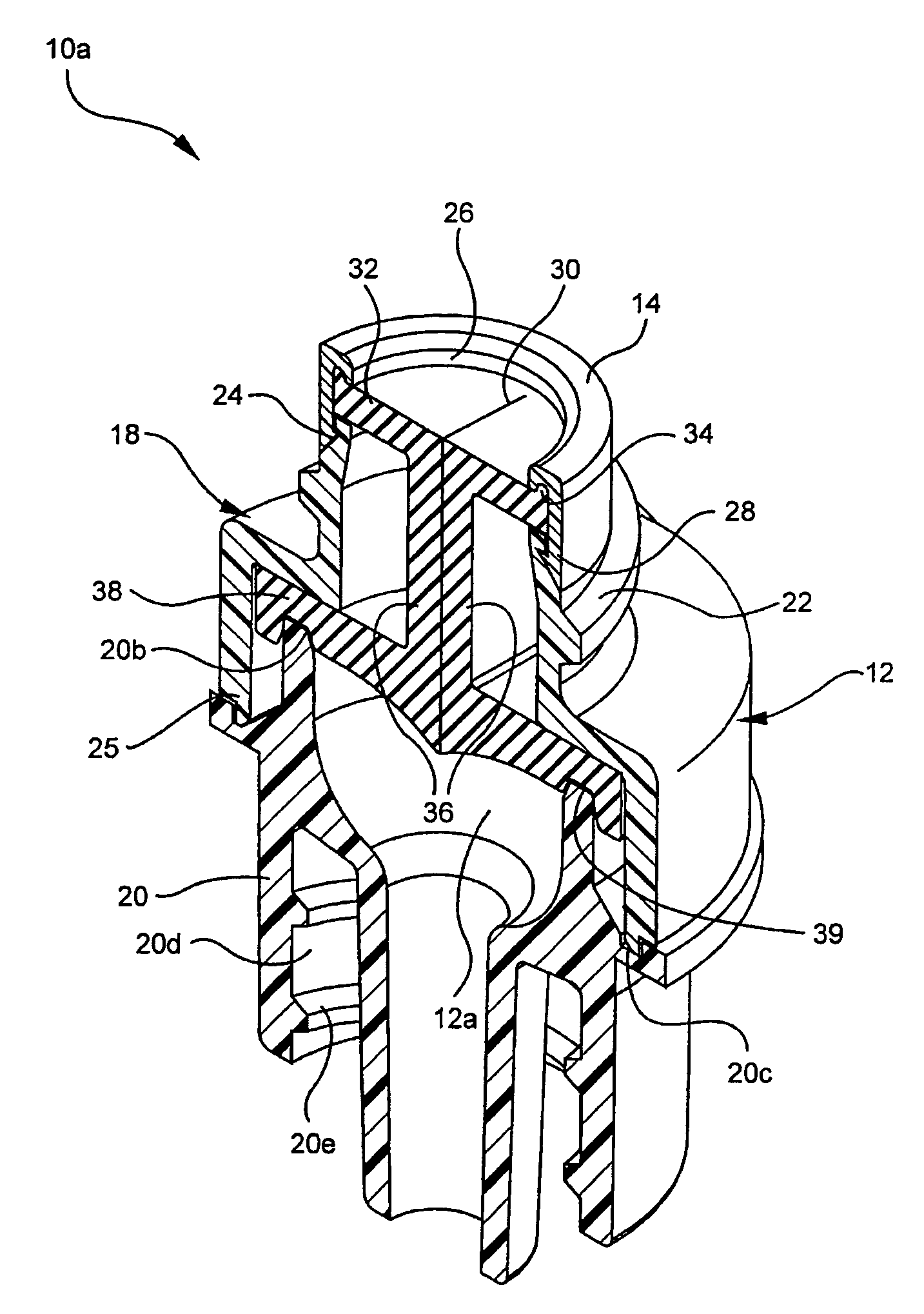
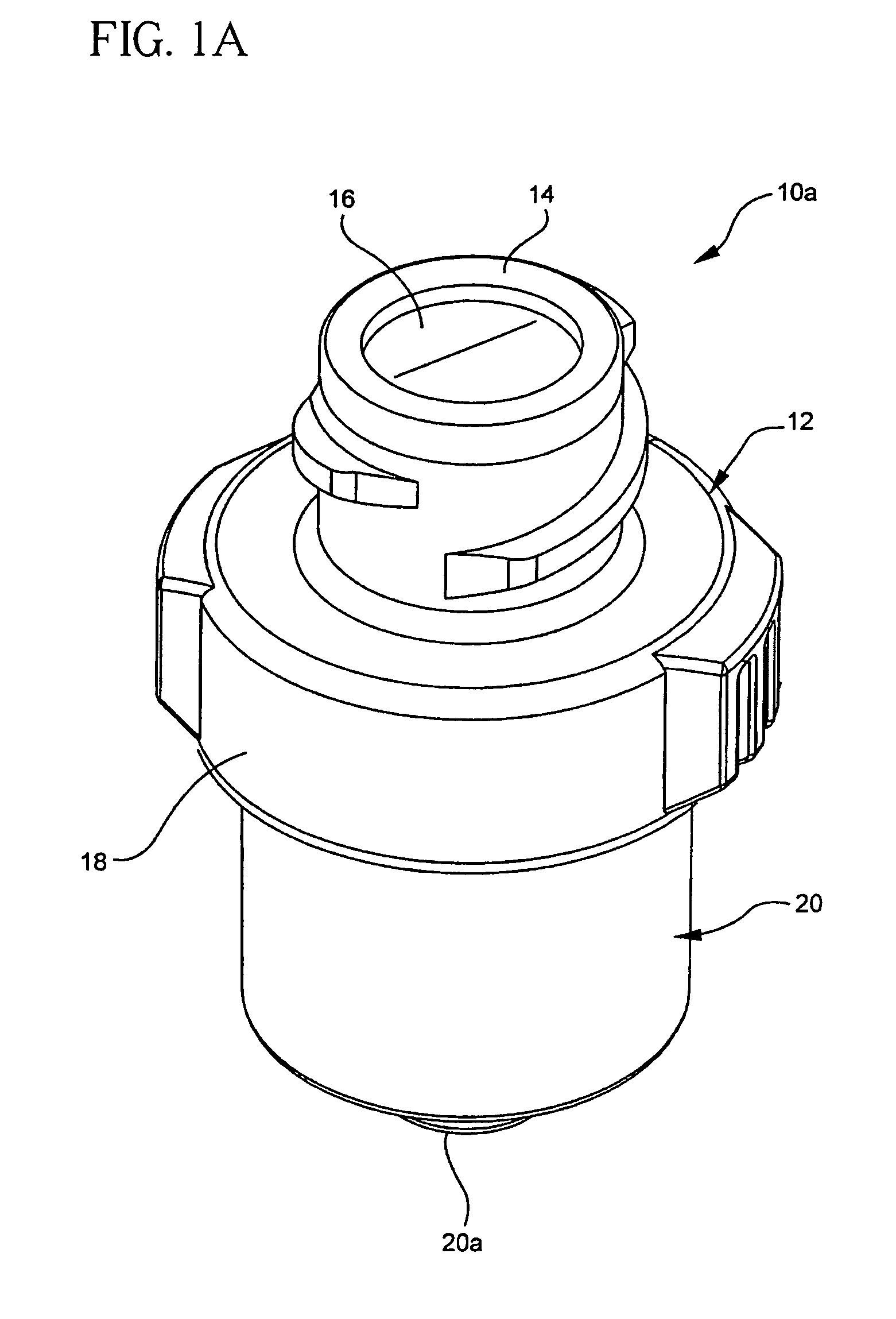
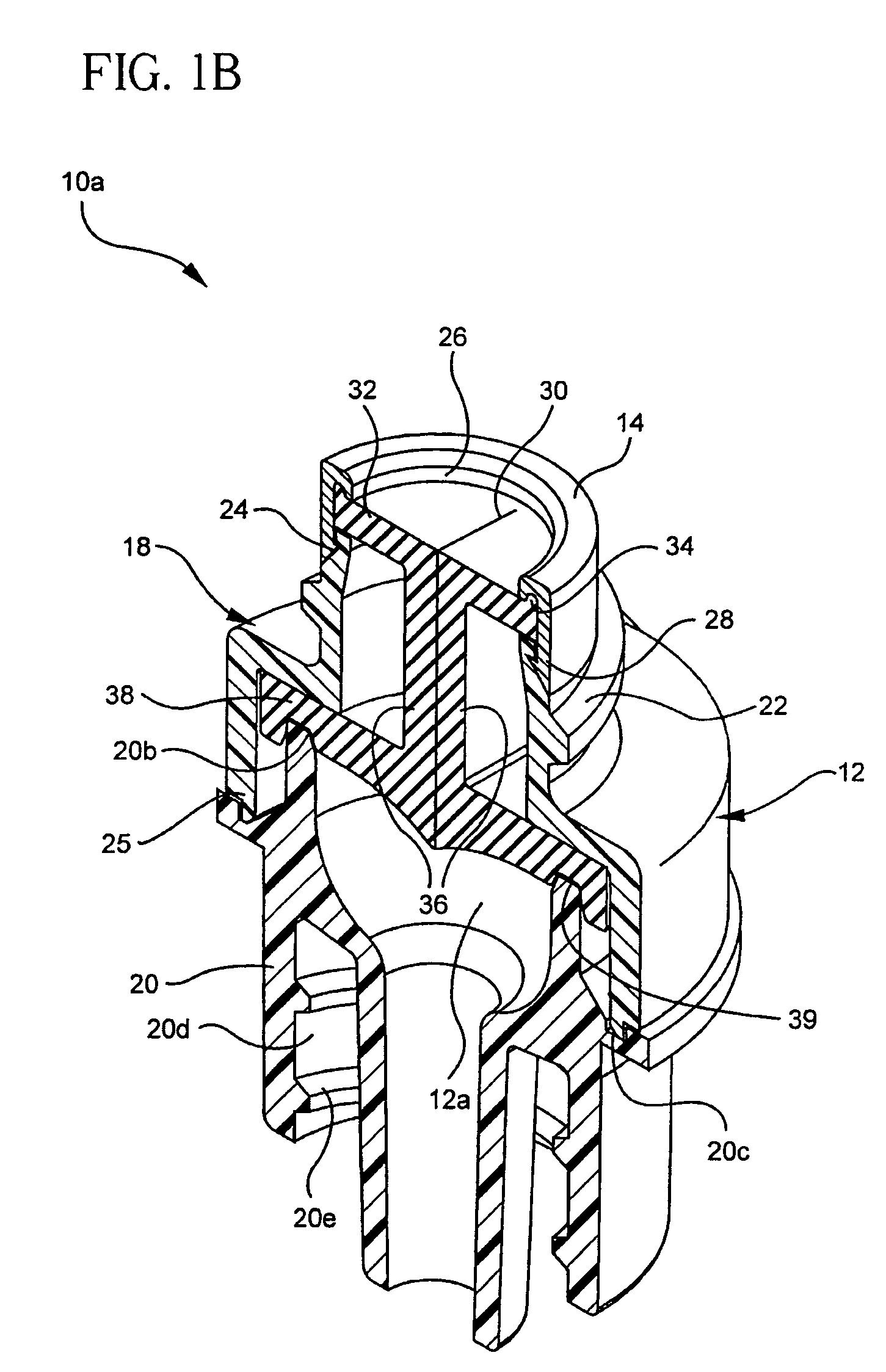
Medical access device
ActiveUS7717882B2Minimizes axial and rotational movementImprove performanceMedical devicesWood working apparatusMedical deviceIntravascular catheter
A medical access device provides needleless access to patient fluid lines such as intravascular catheters. A preformed crimp ring is attached around a septum and the top end of the housing of the medical access device. The crimp ring is configured to hold the septum in place. The septum provides access for a tubular portion of a medical device such as a male luer taper of a syringe. The crimp ring is then attached by mechanical attachment and / or chemical adhesion to the housing to minimize axial and rotational movement between the septum and the housing.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com