Patents
Literature
182 results about "Arterial Intima" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
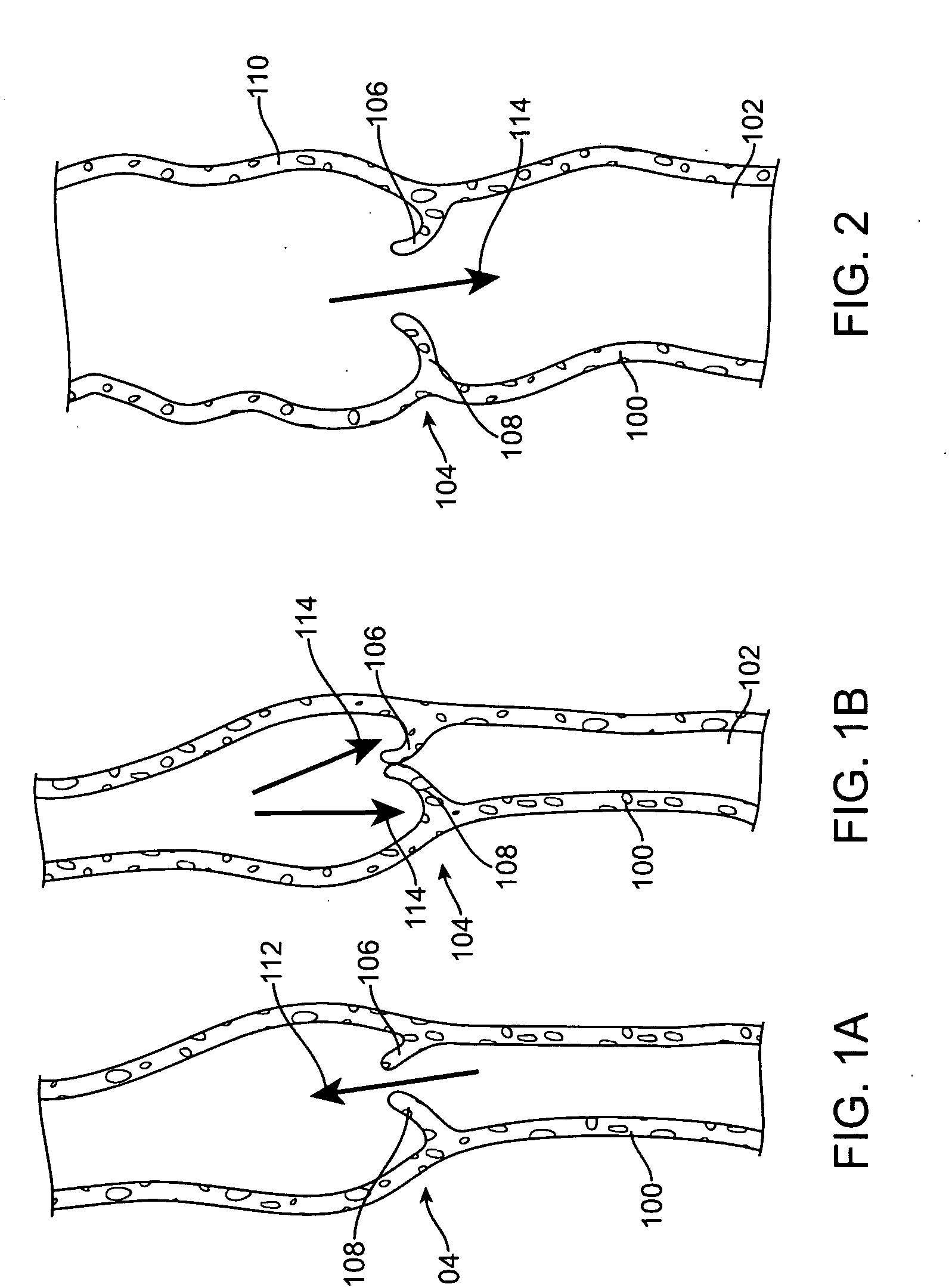
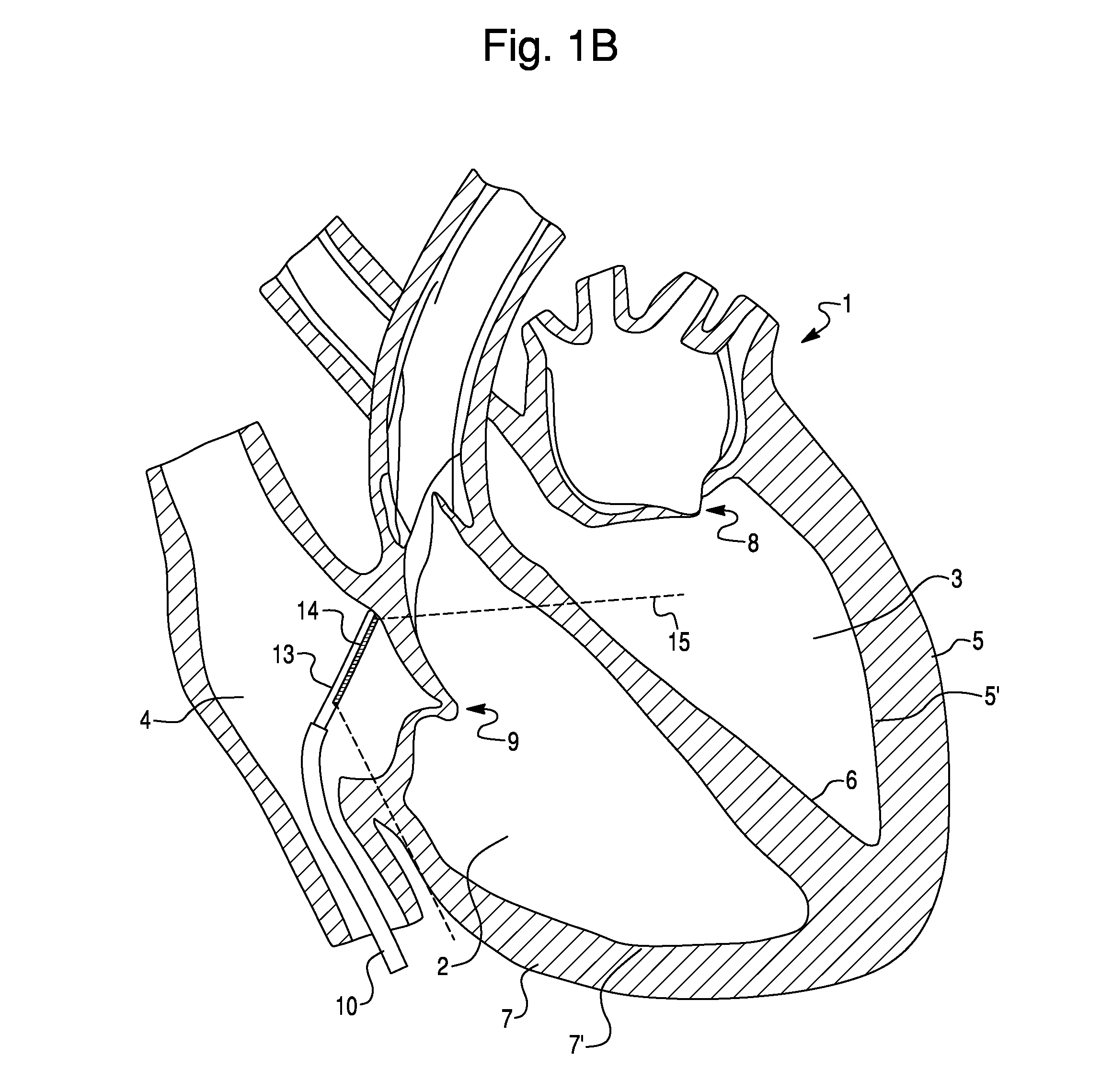
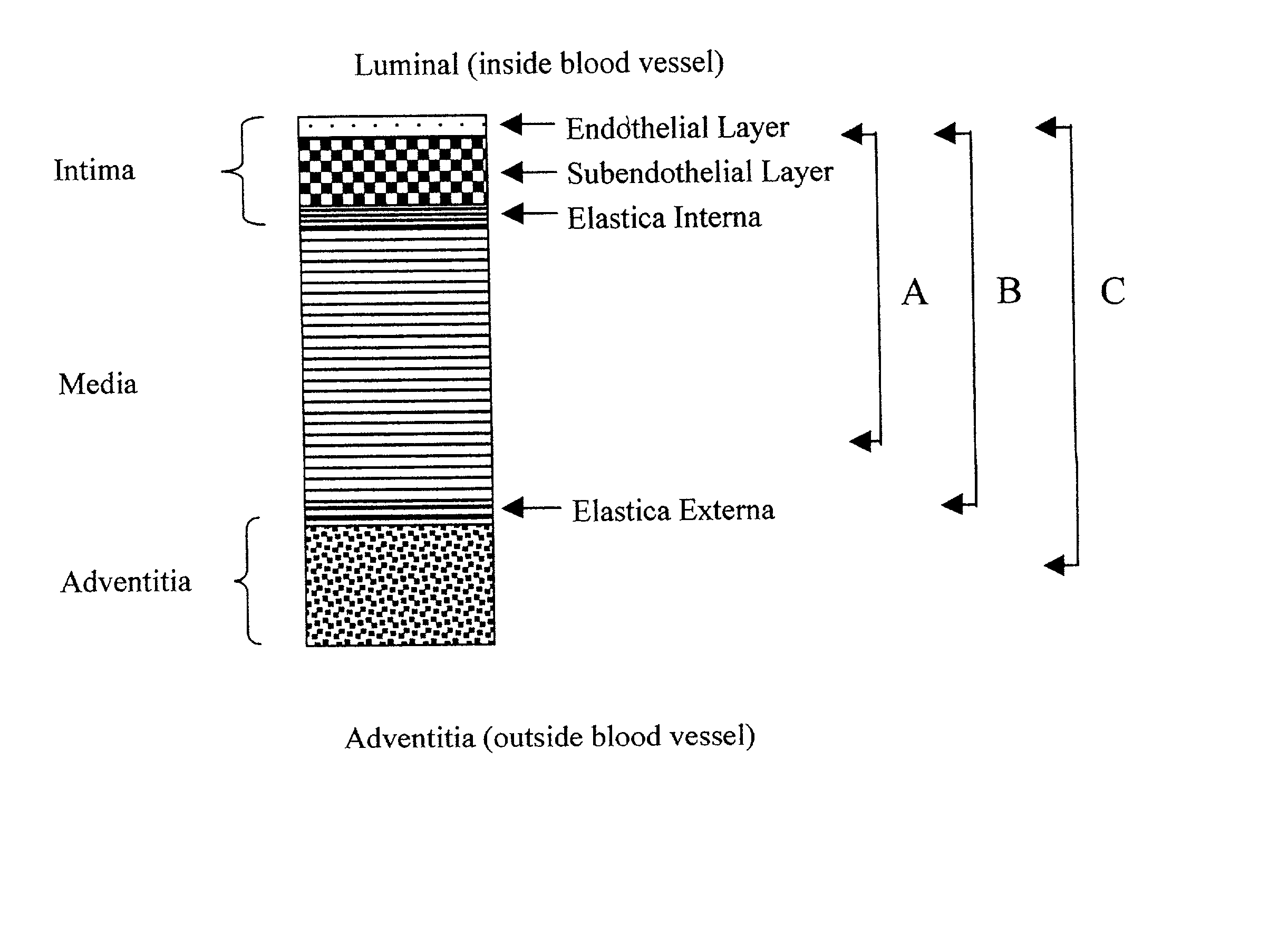
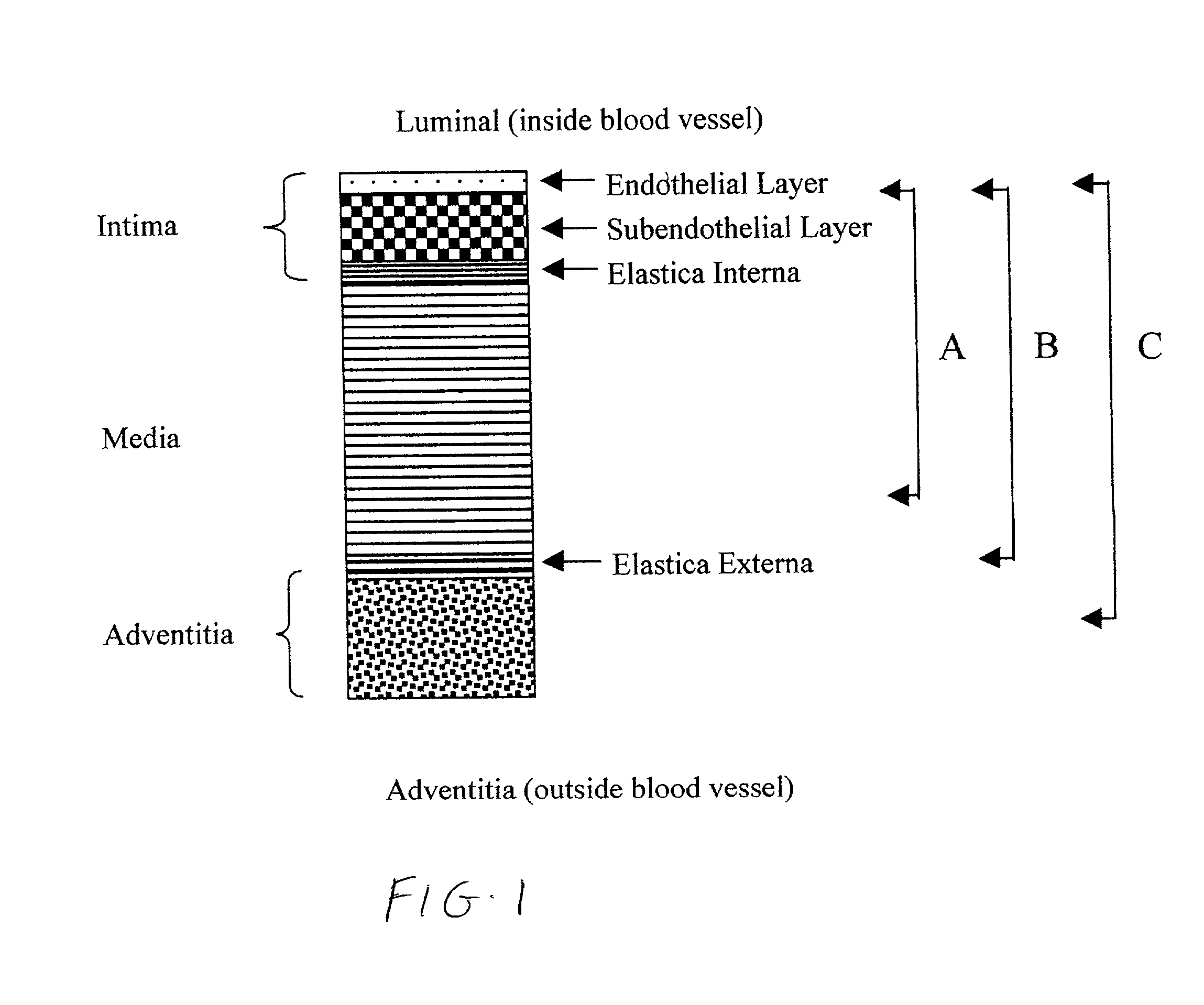
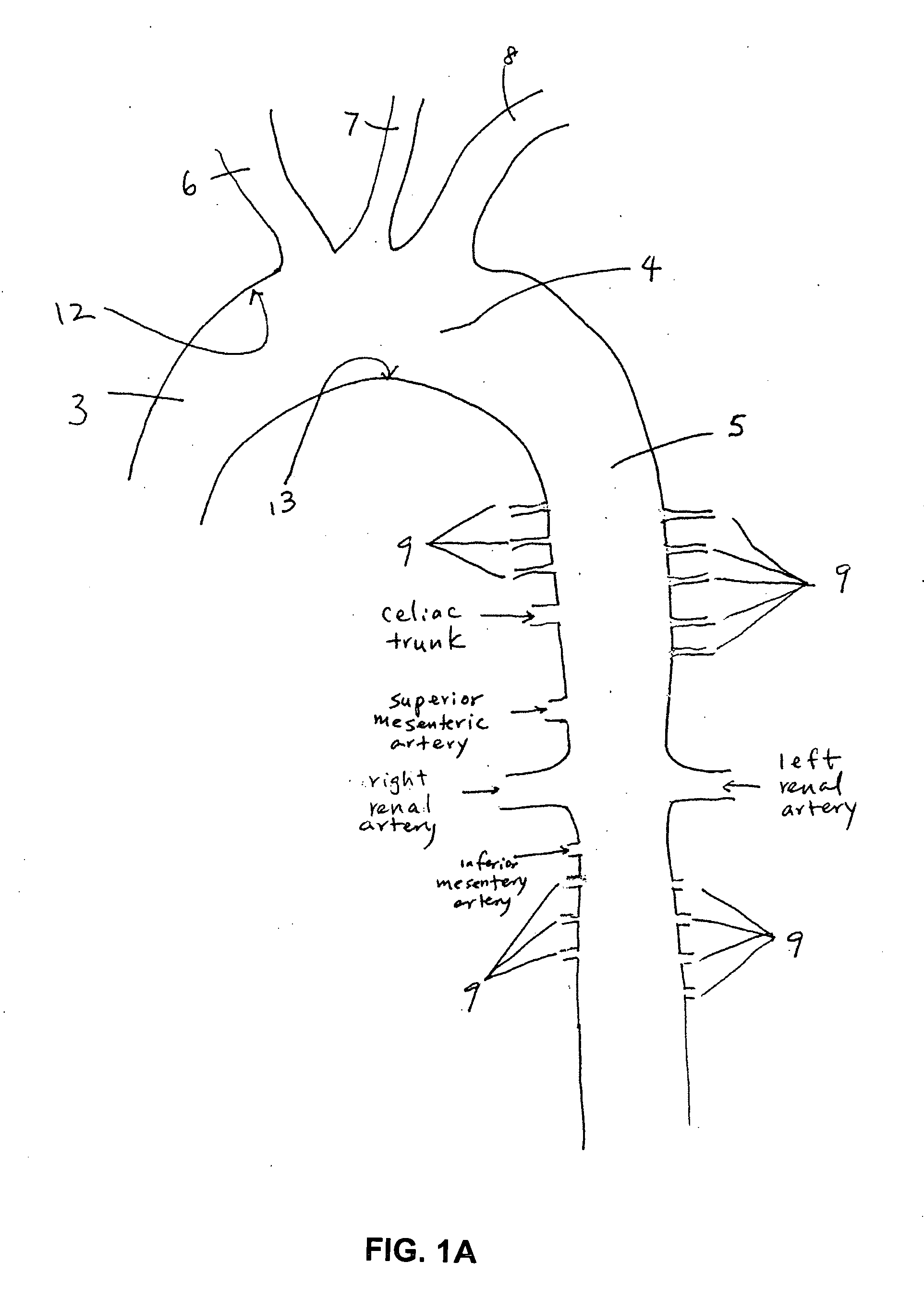
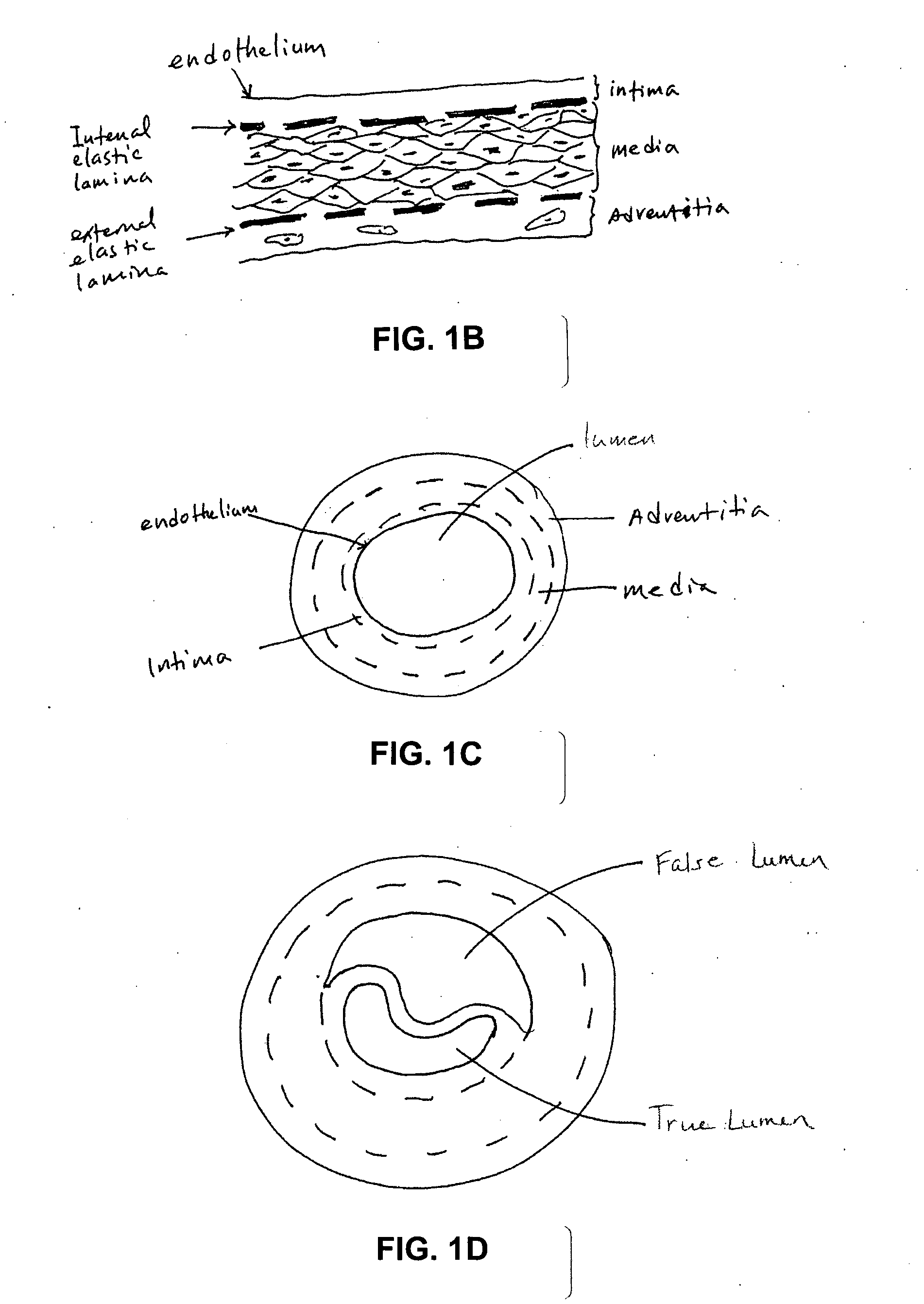
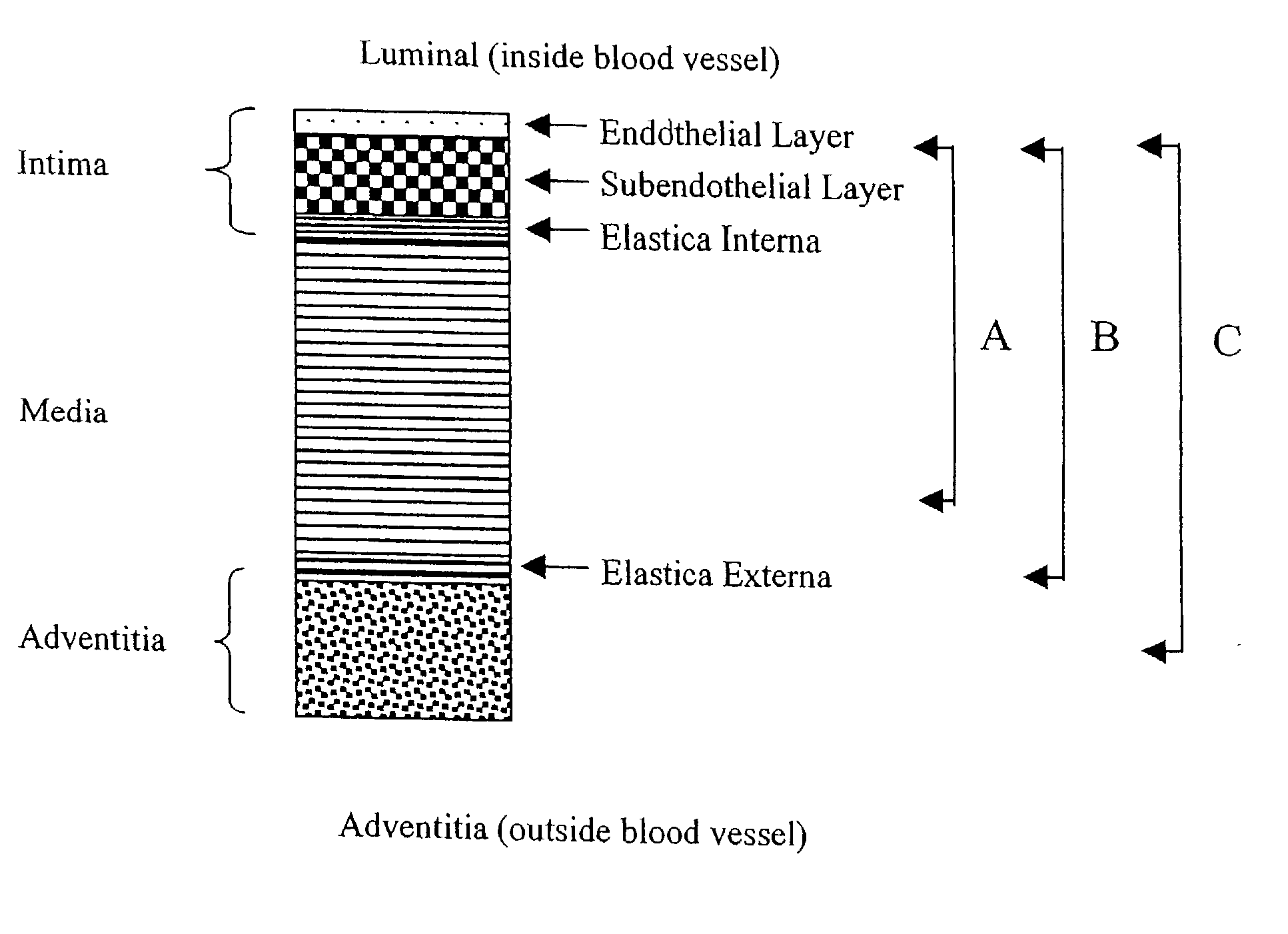
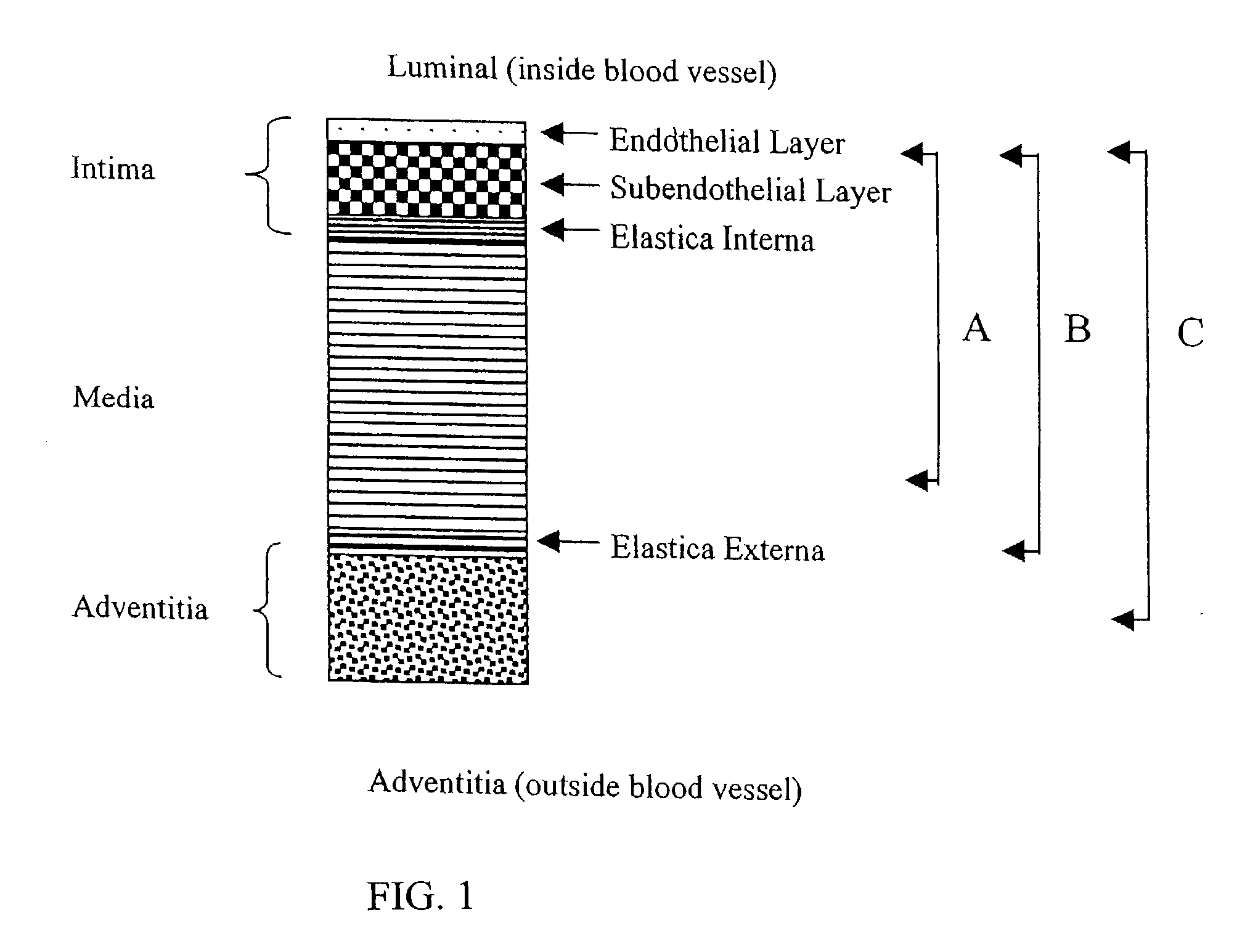
The tunica intima (New Latin inner coat), or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelial cells and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow.
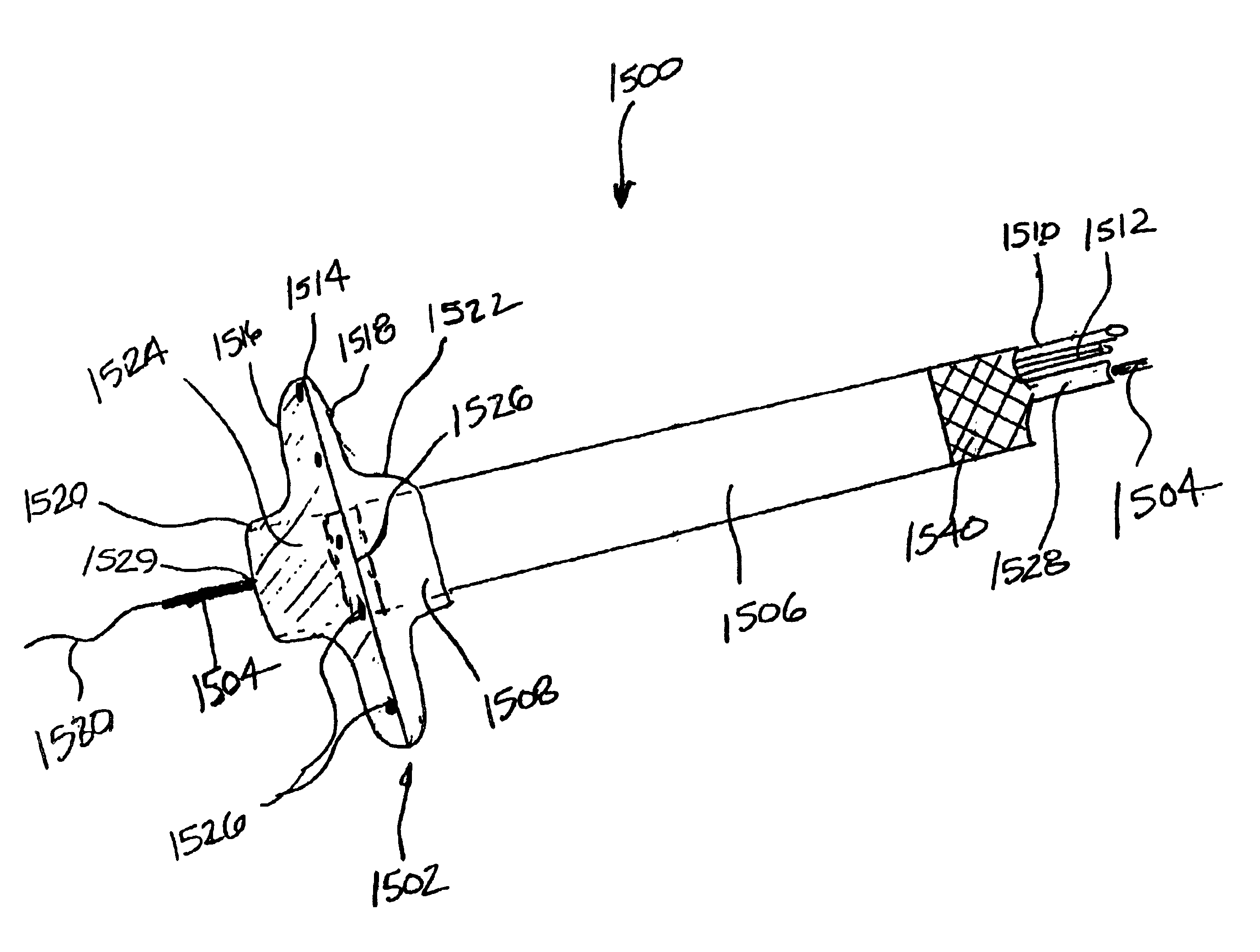
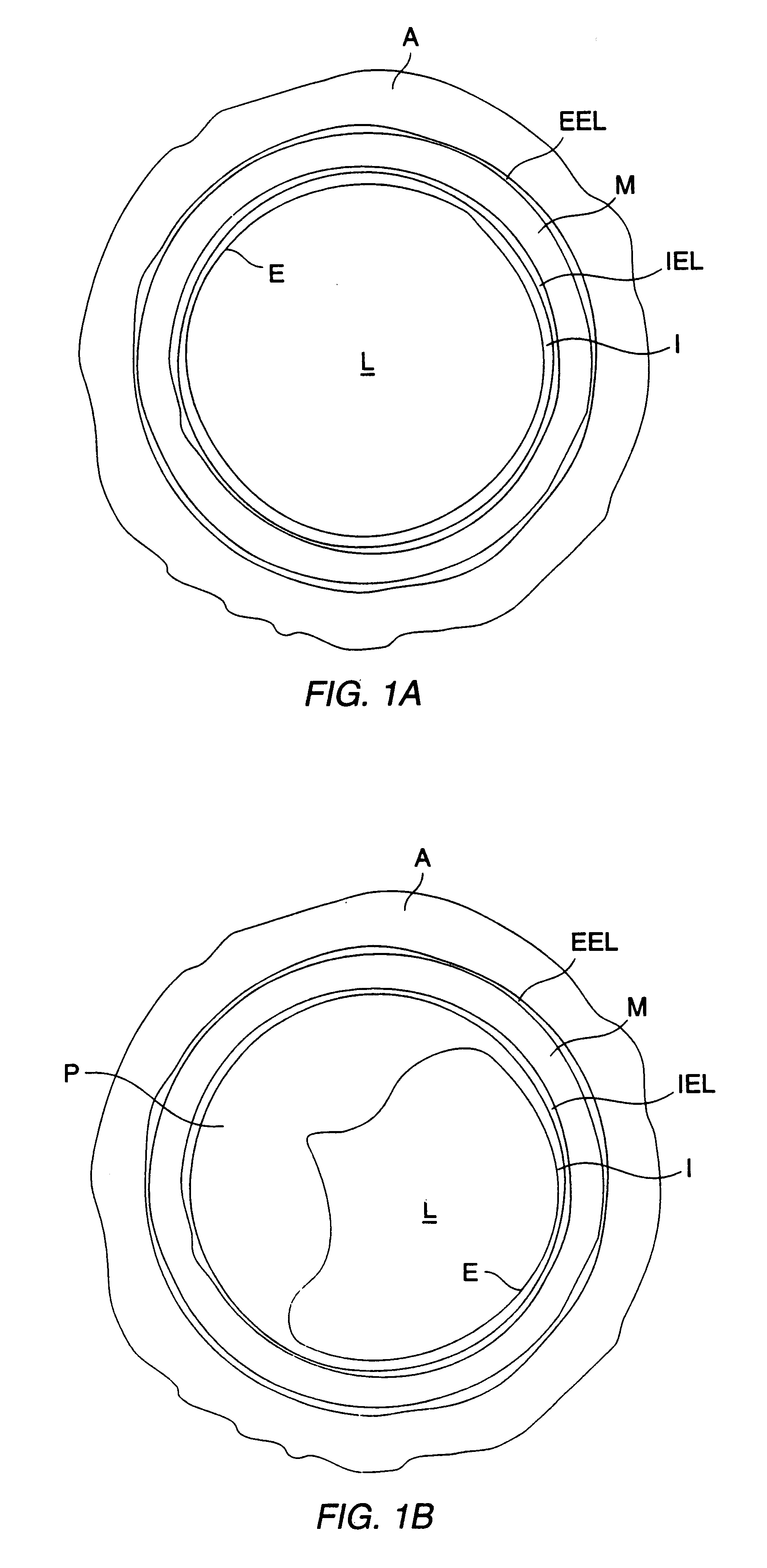
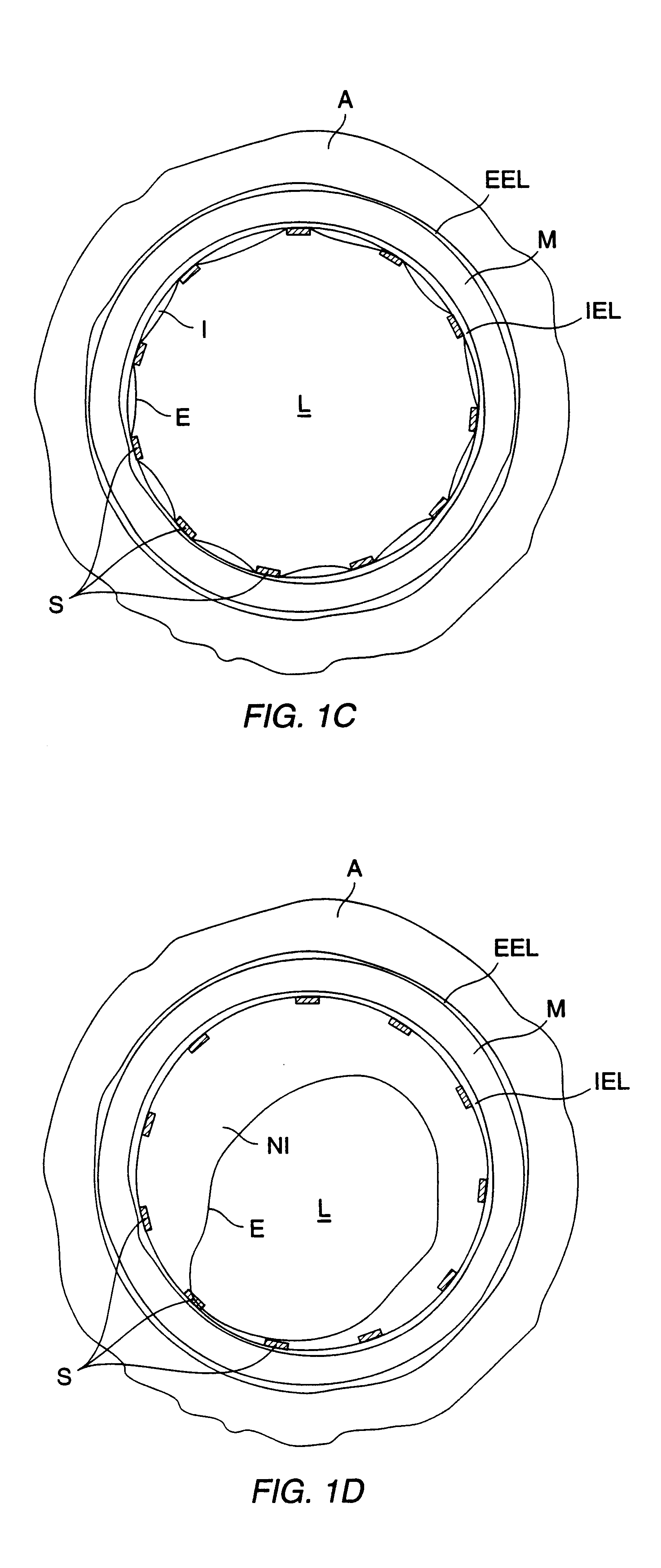
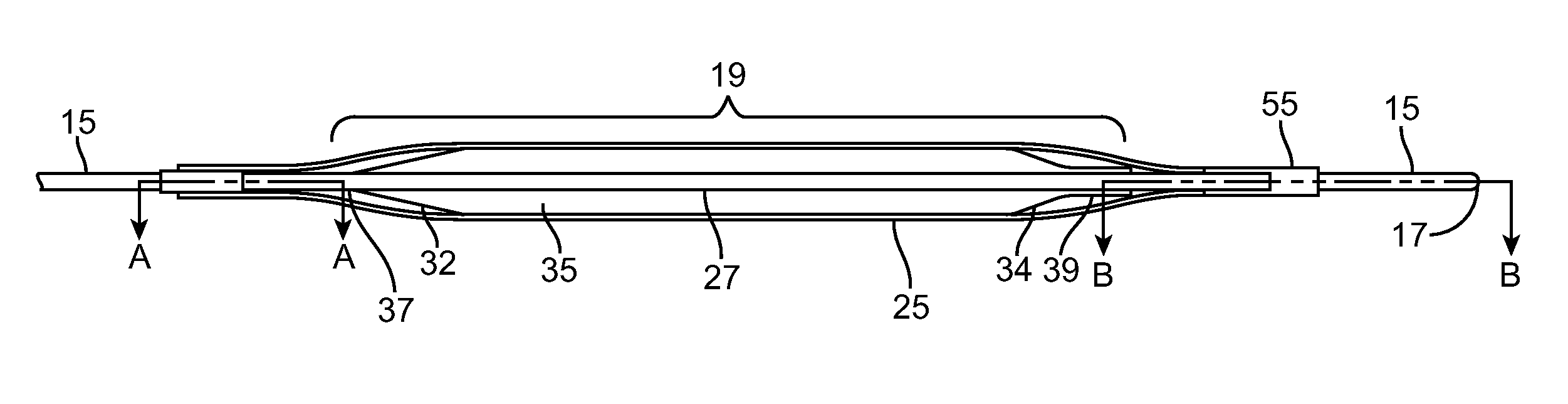
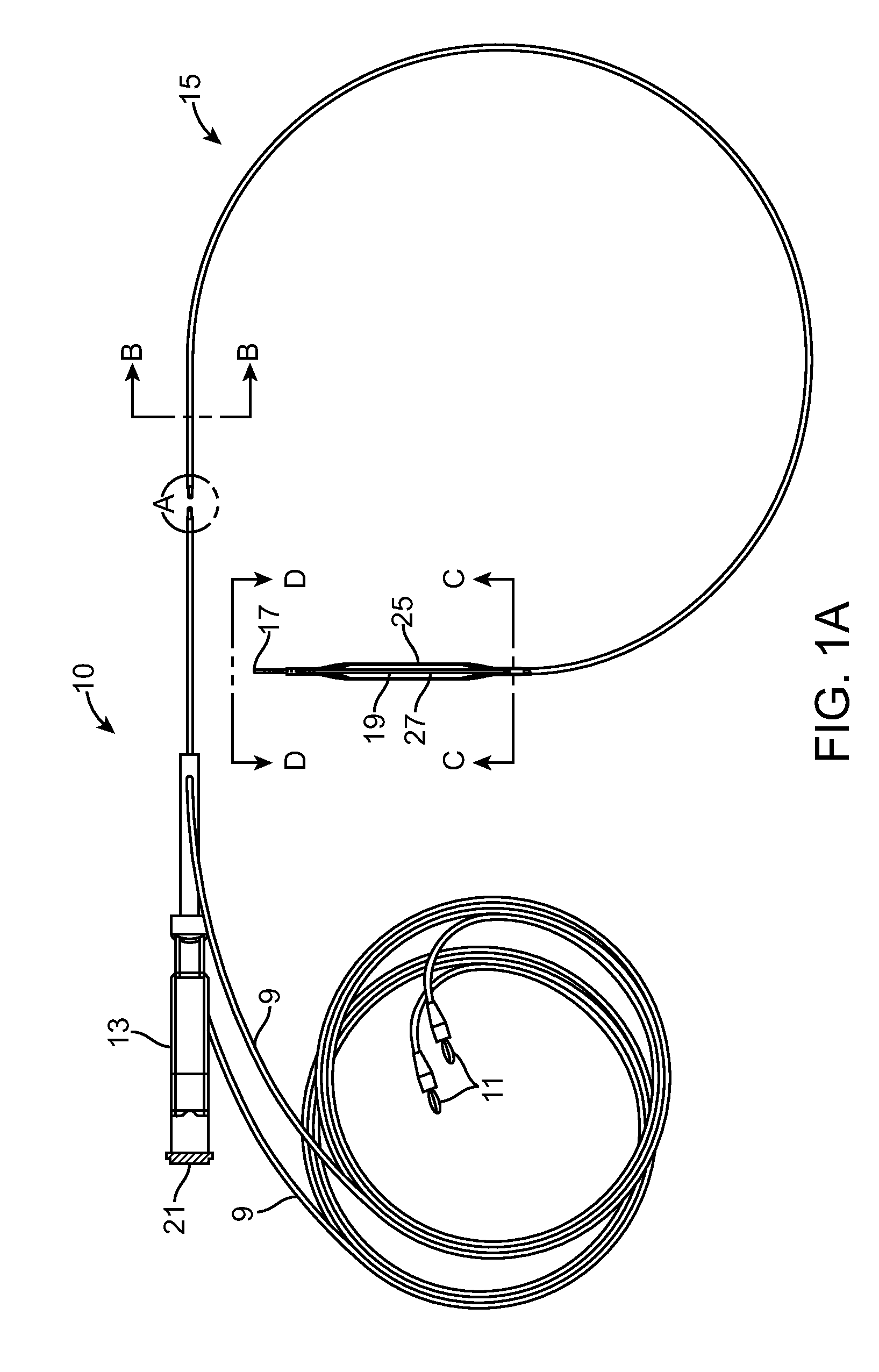
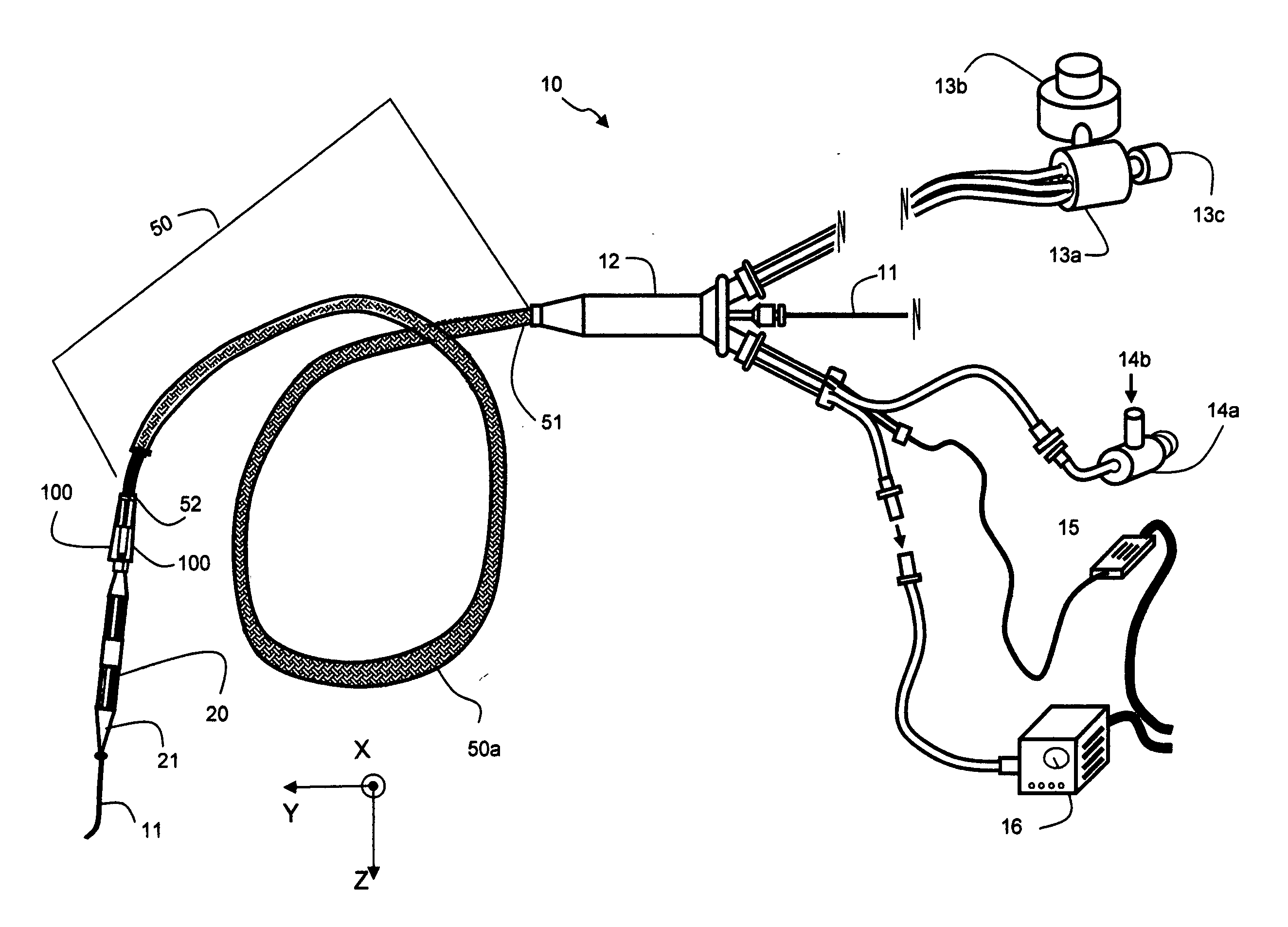
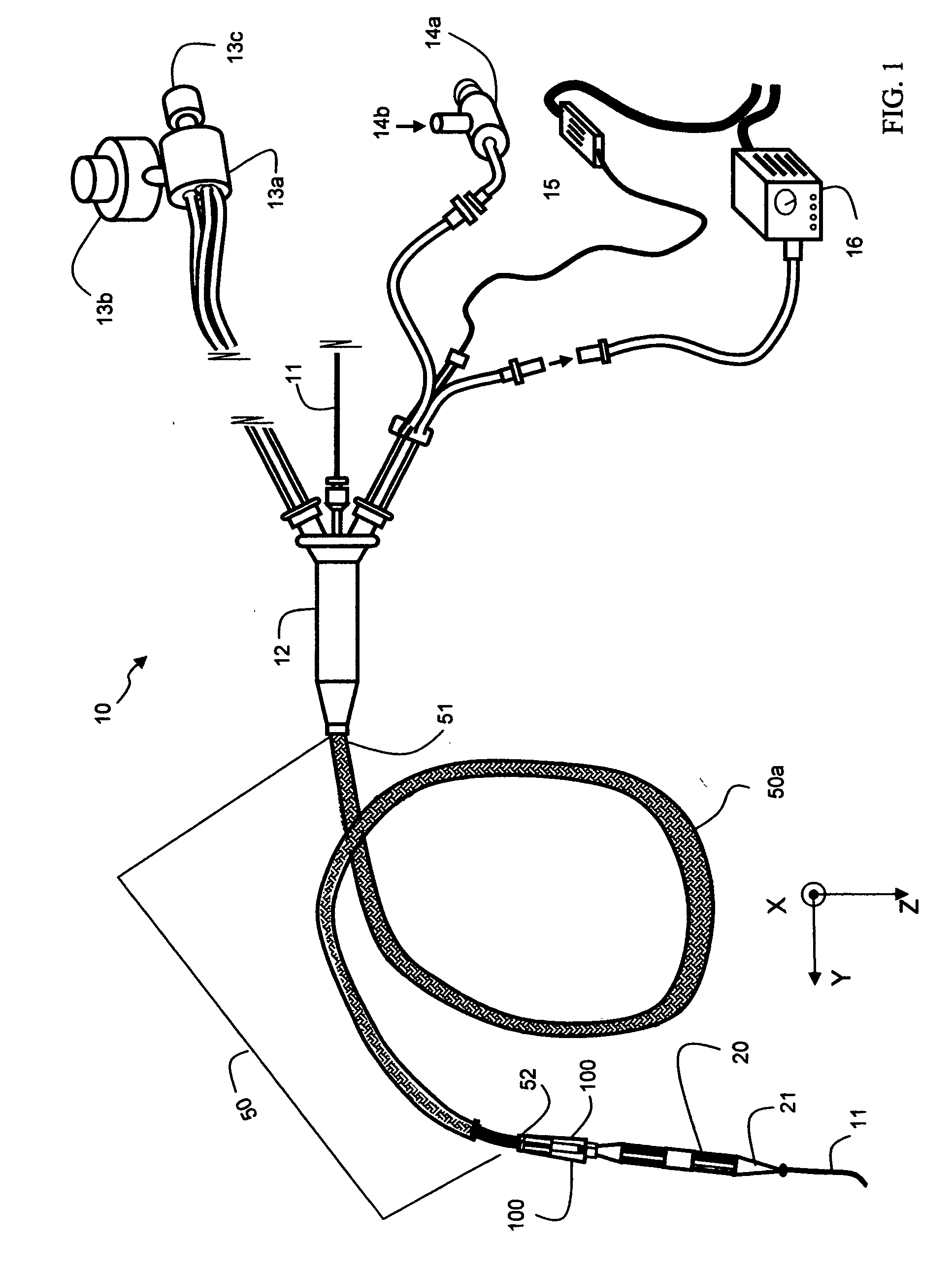
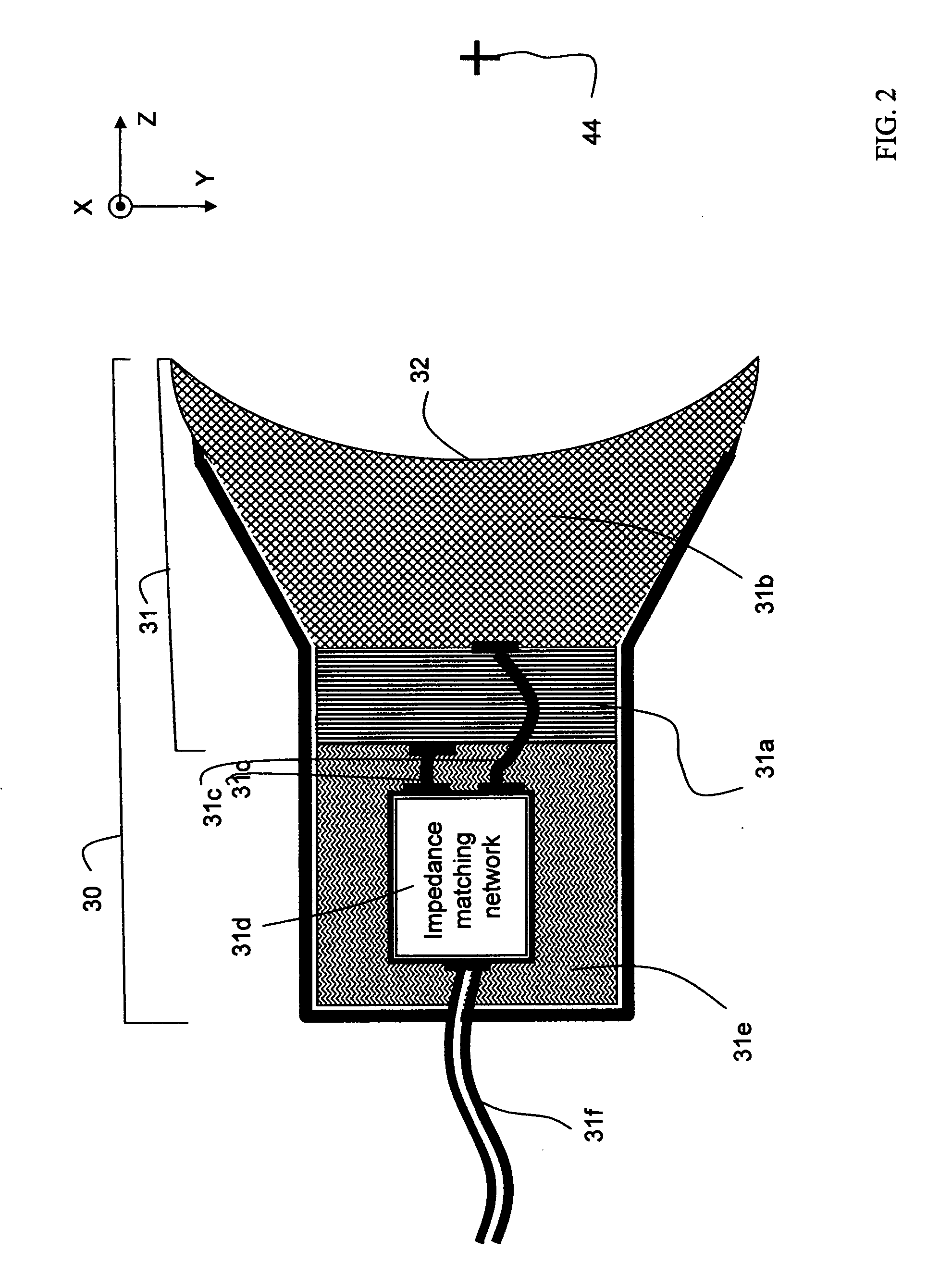
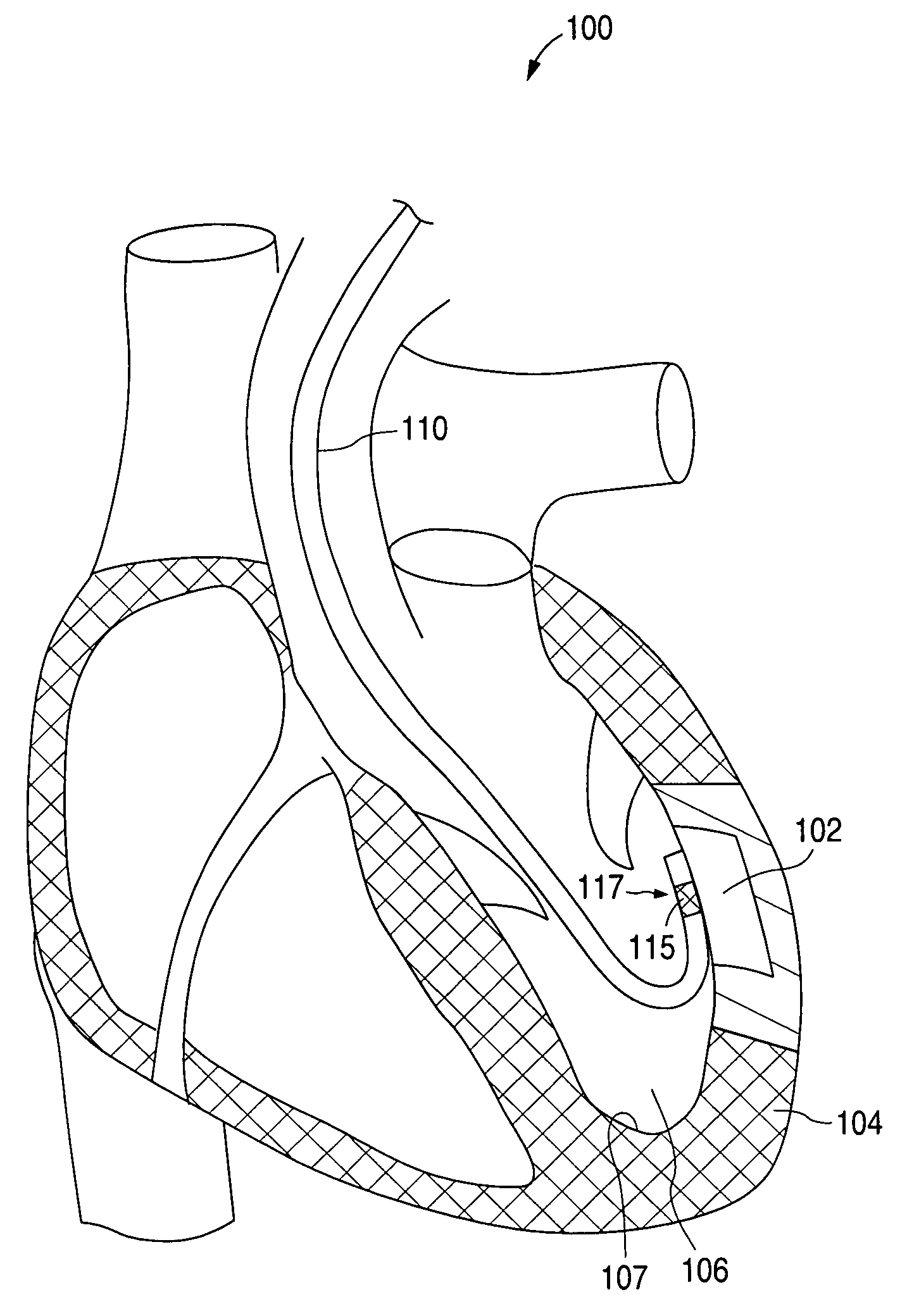
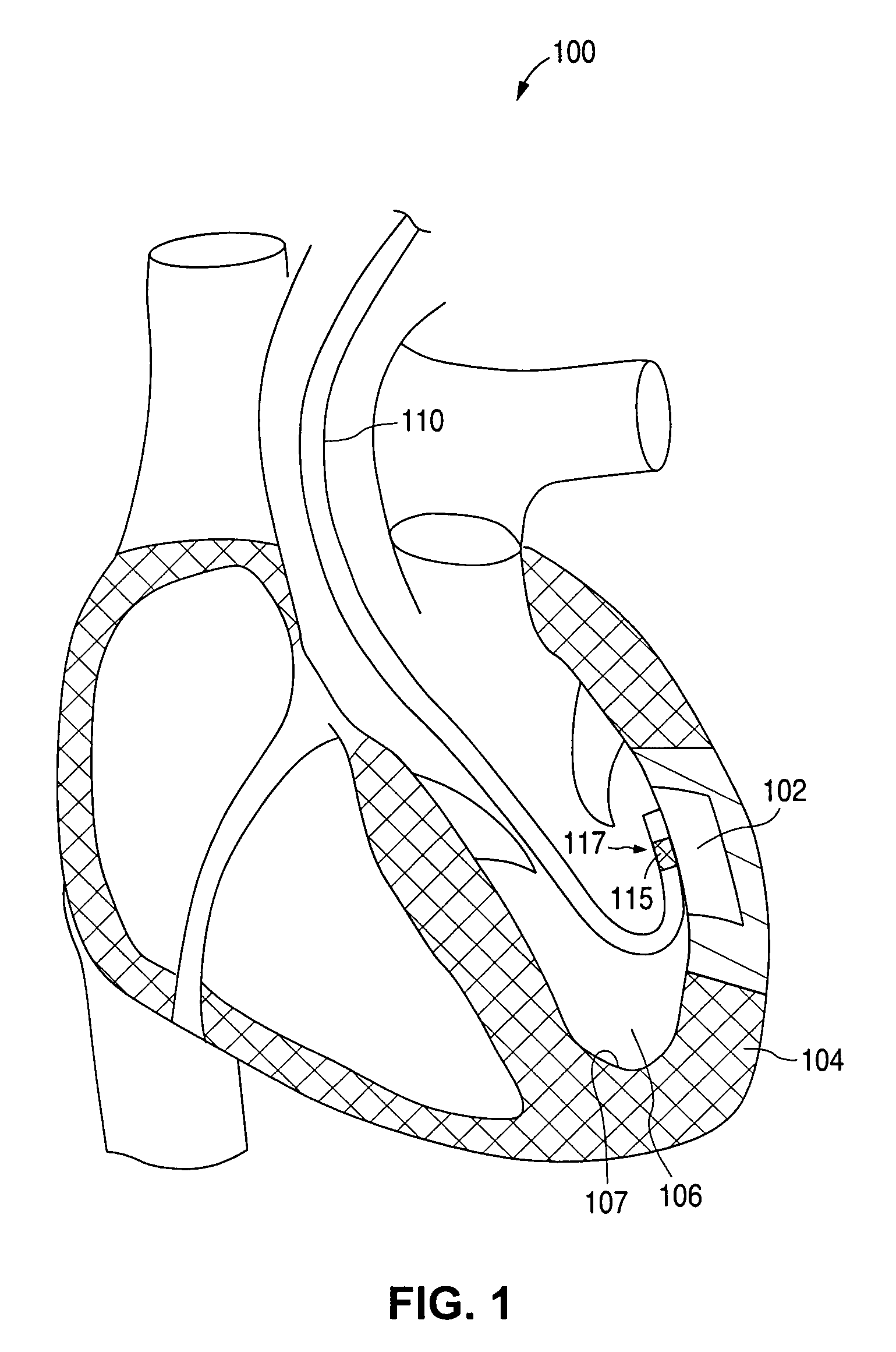
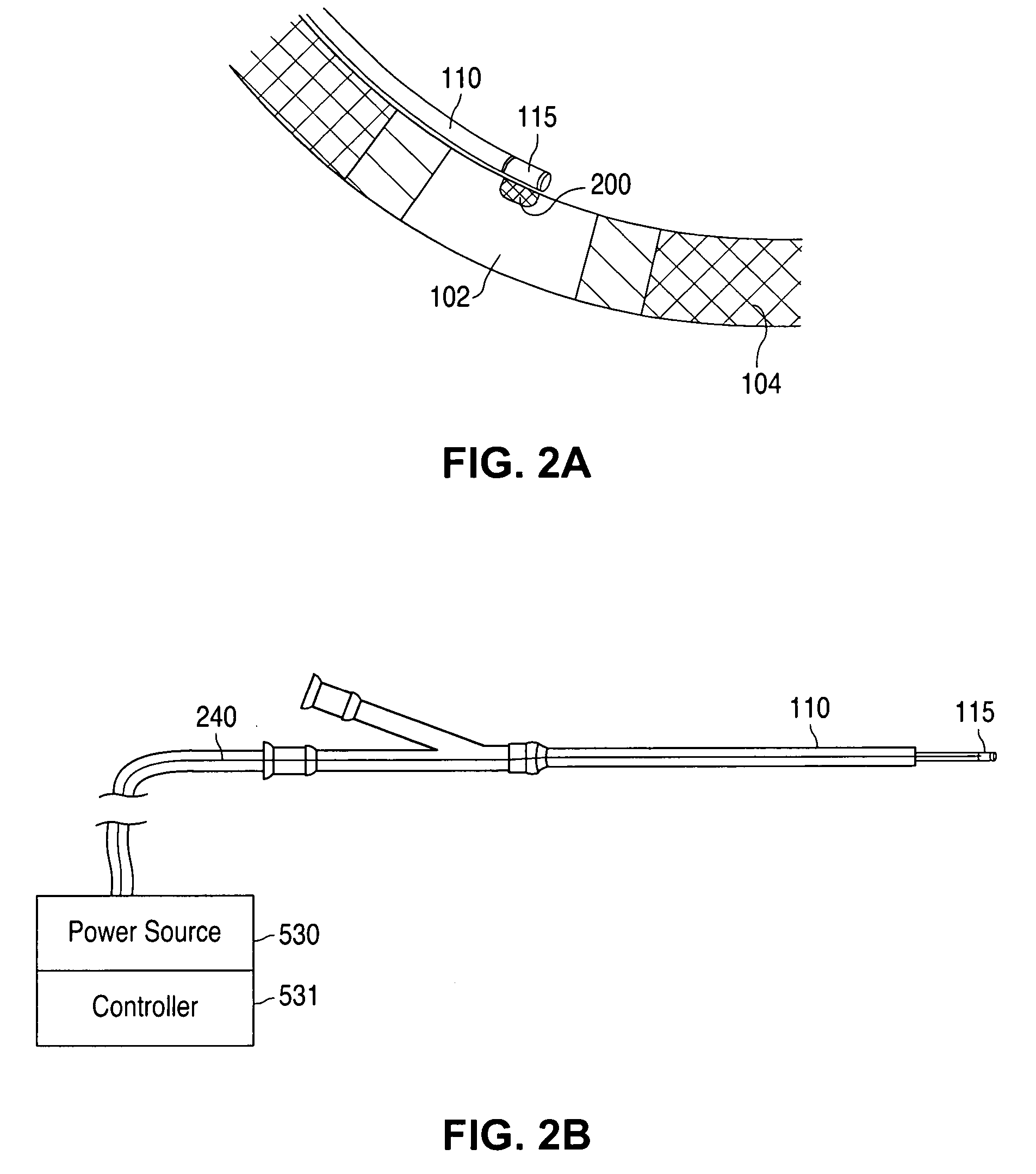
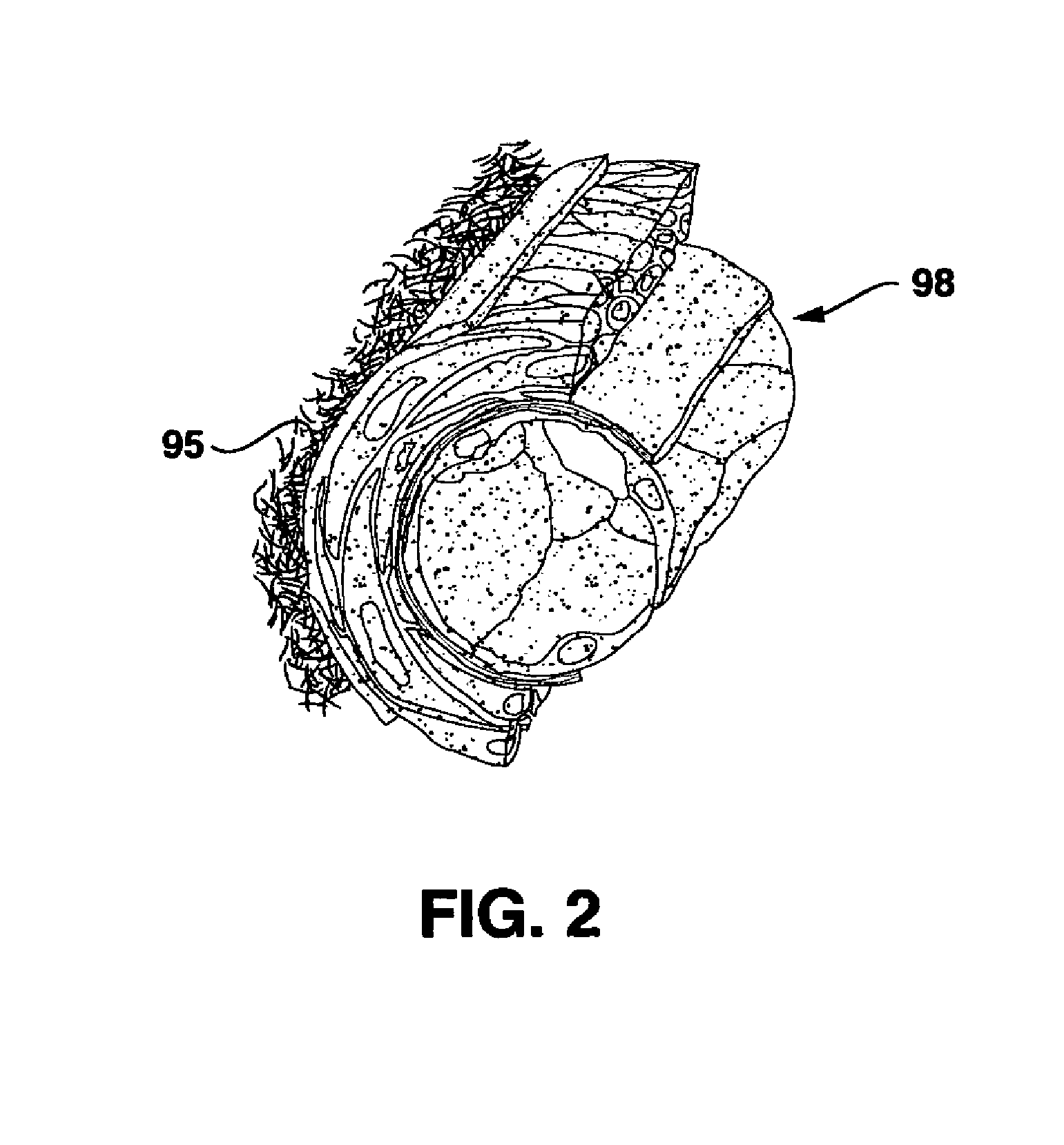
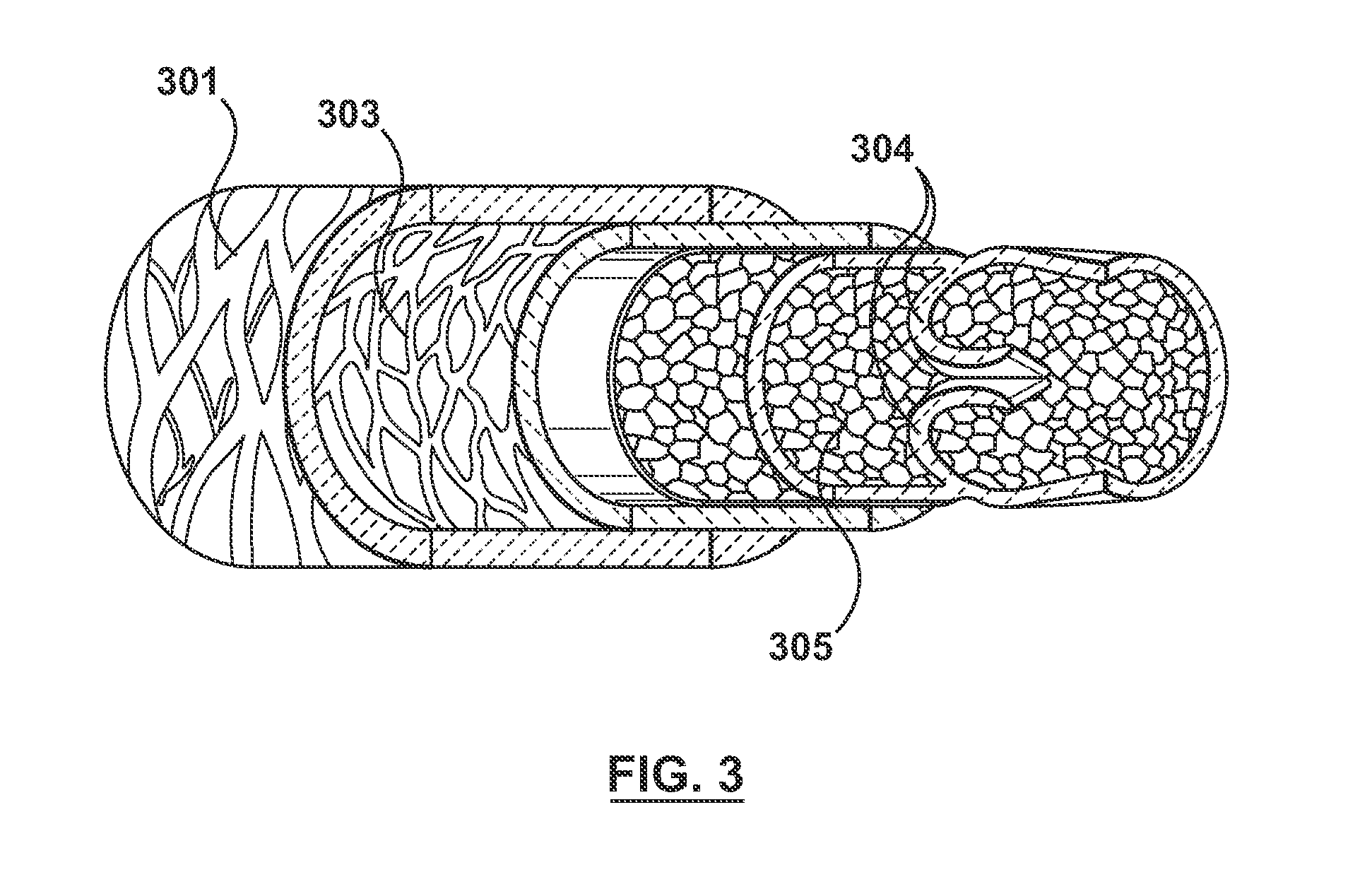
Devices and methods for creating lesions in endocardial and surrounding tissue to isolate focal arrhythmia substrates
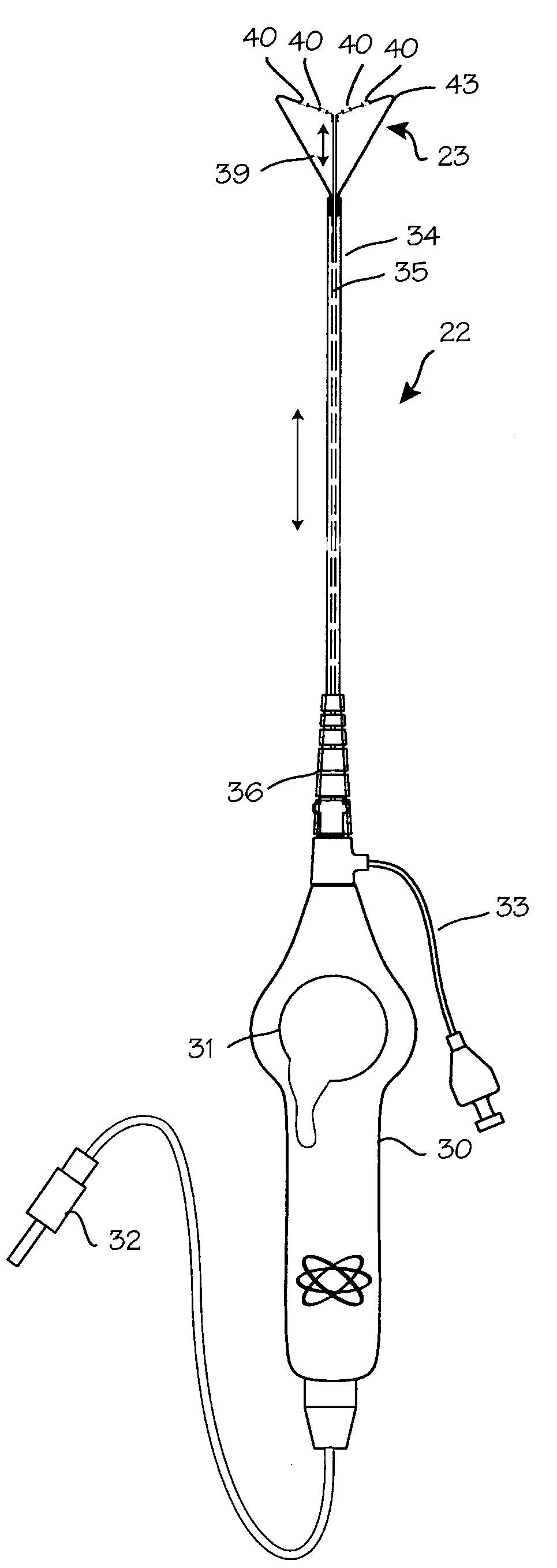
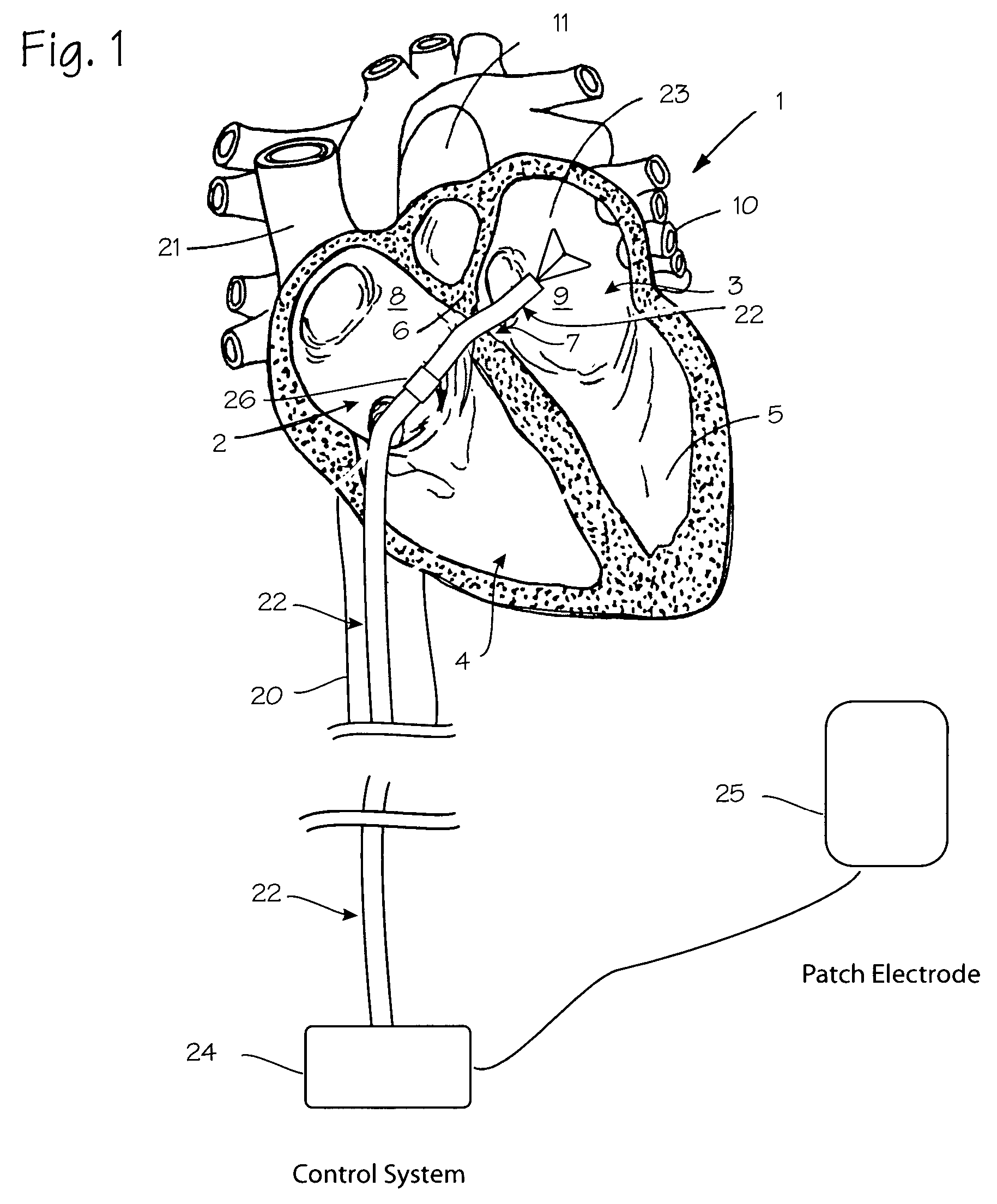
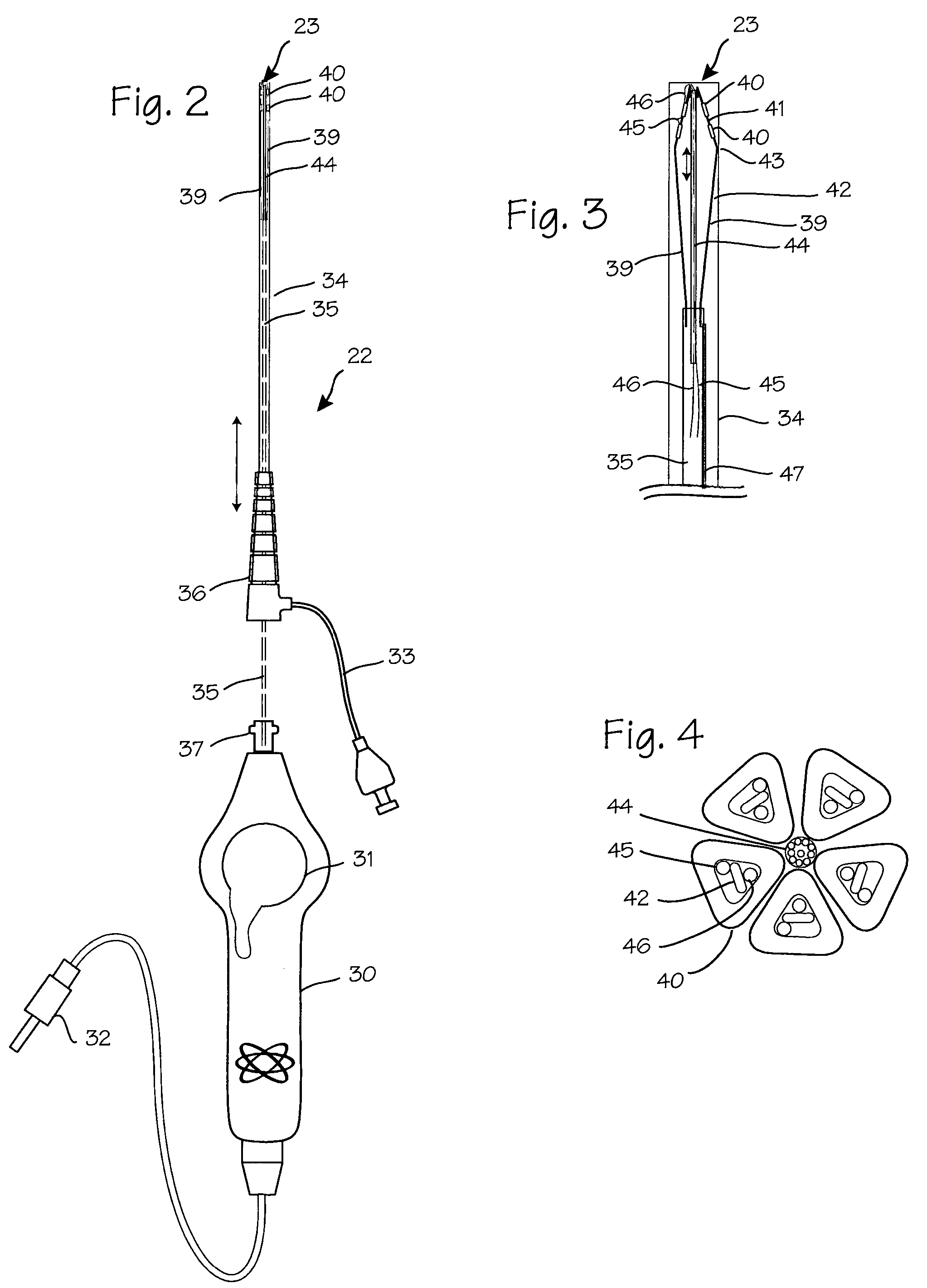
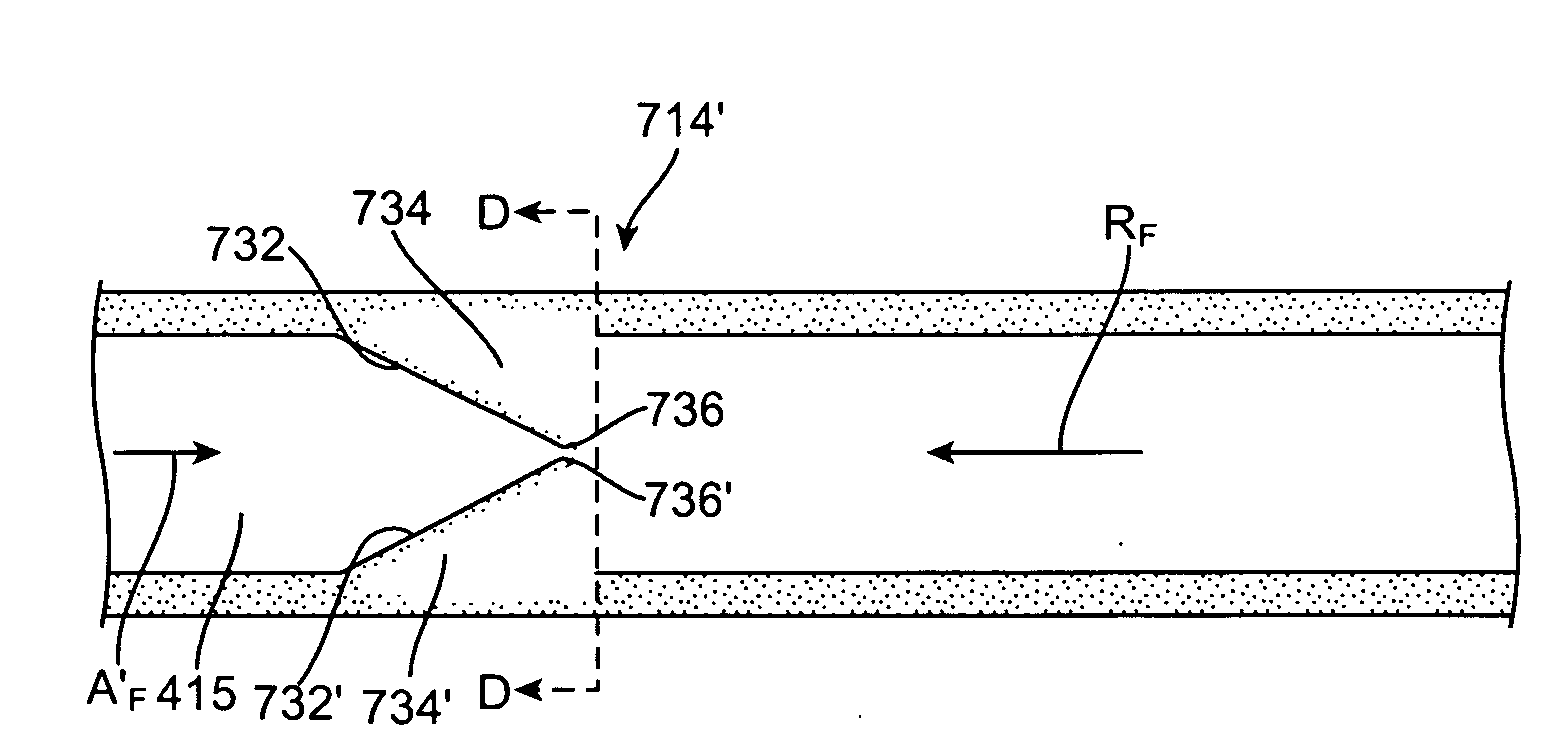
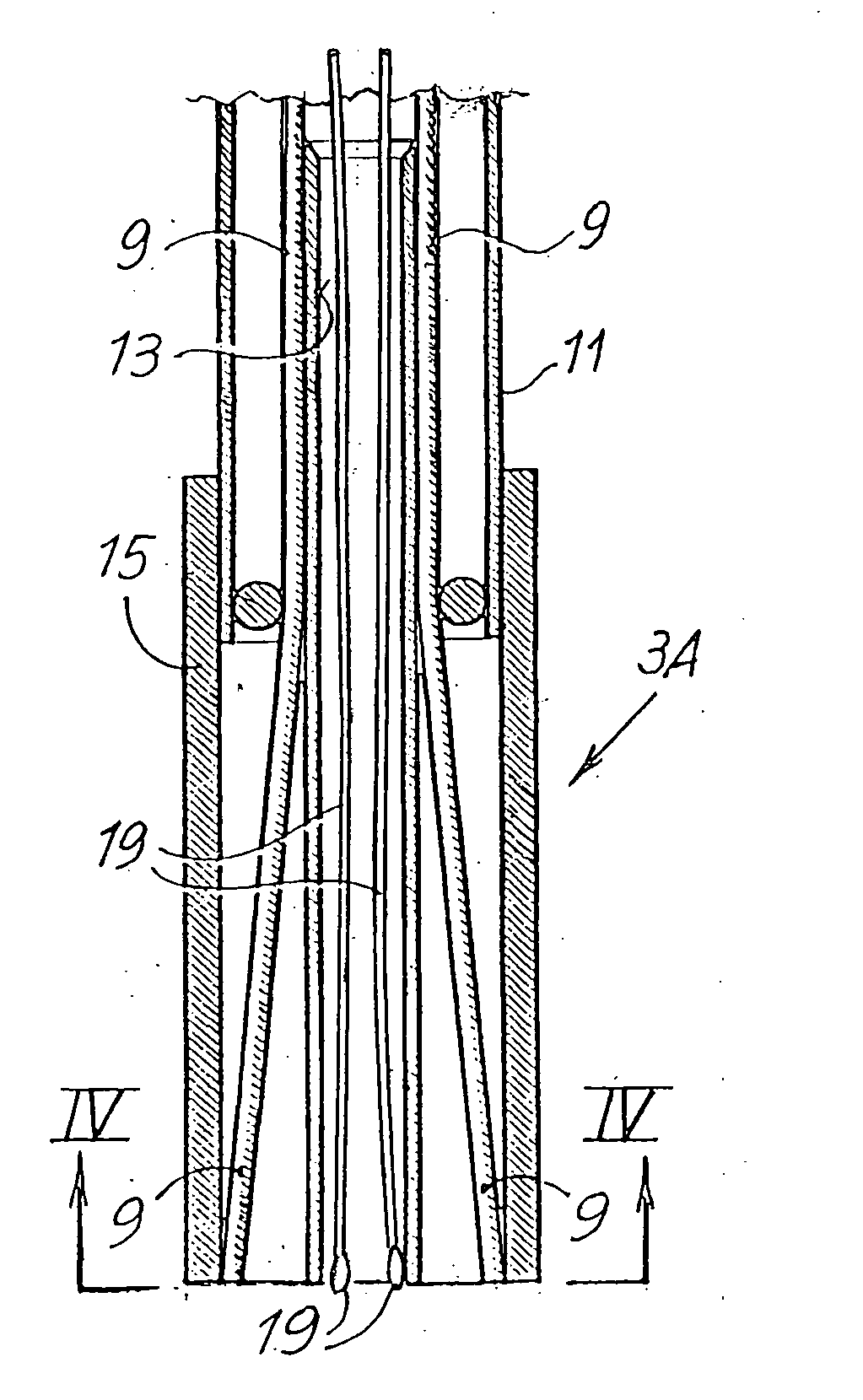
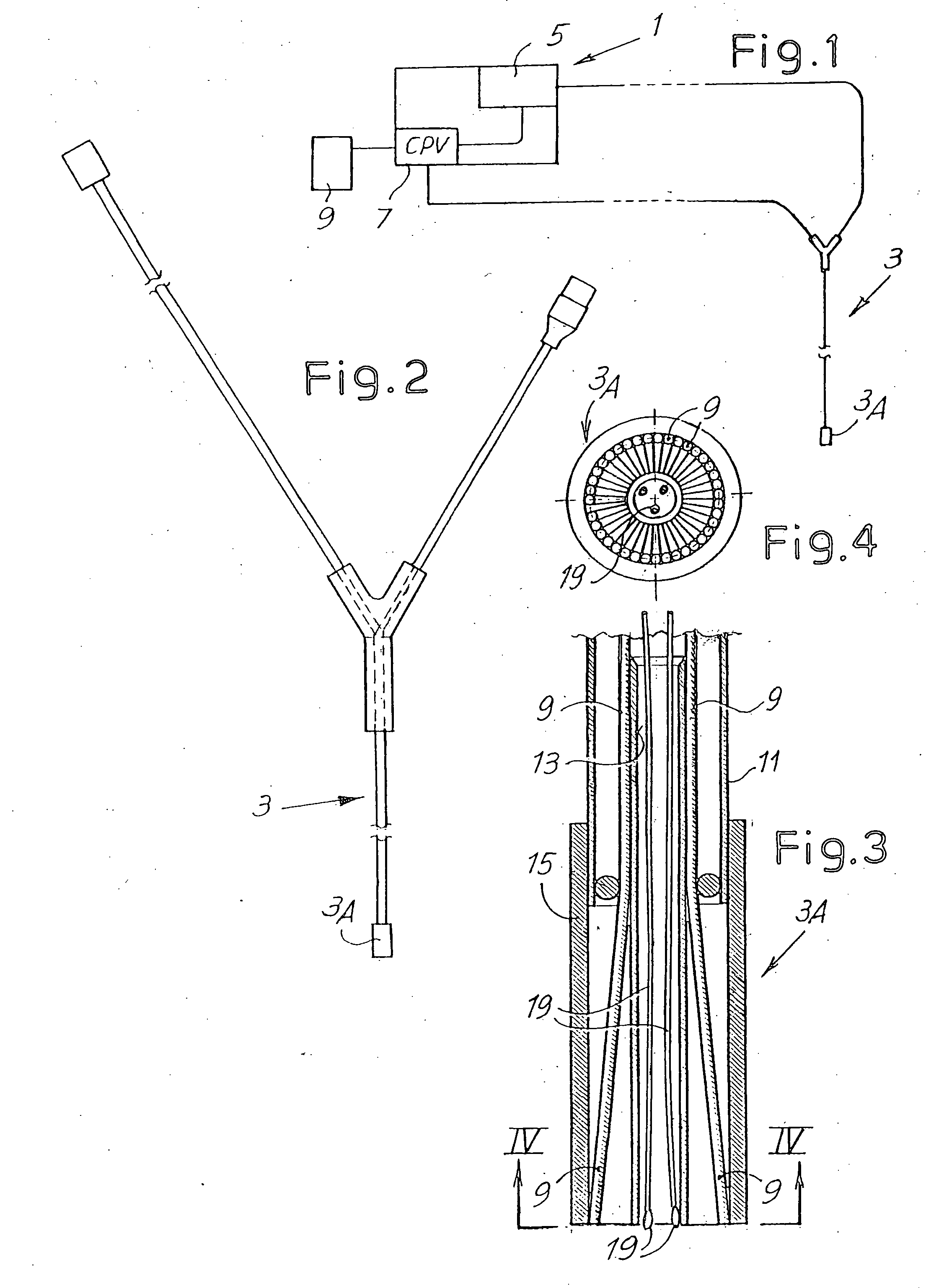
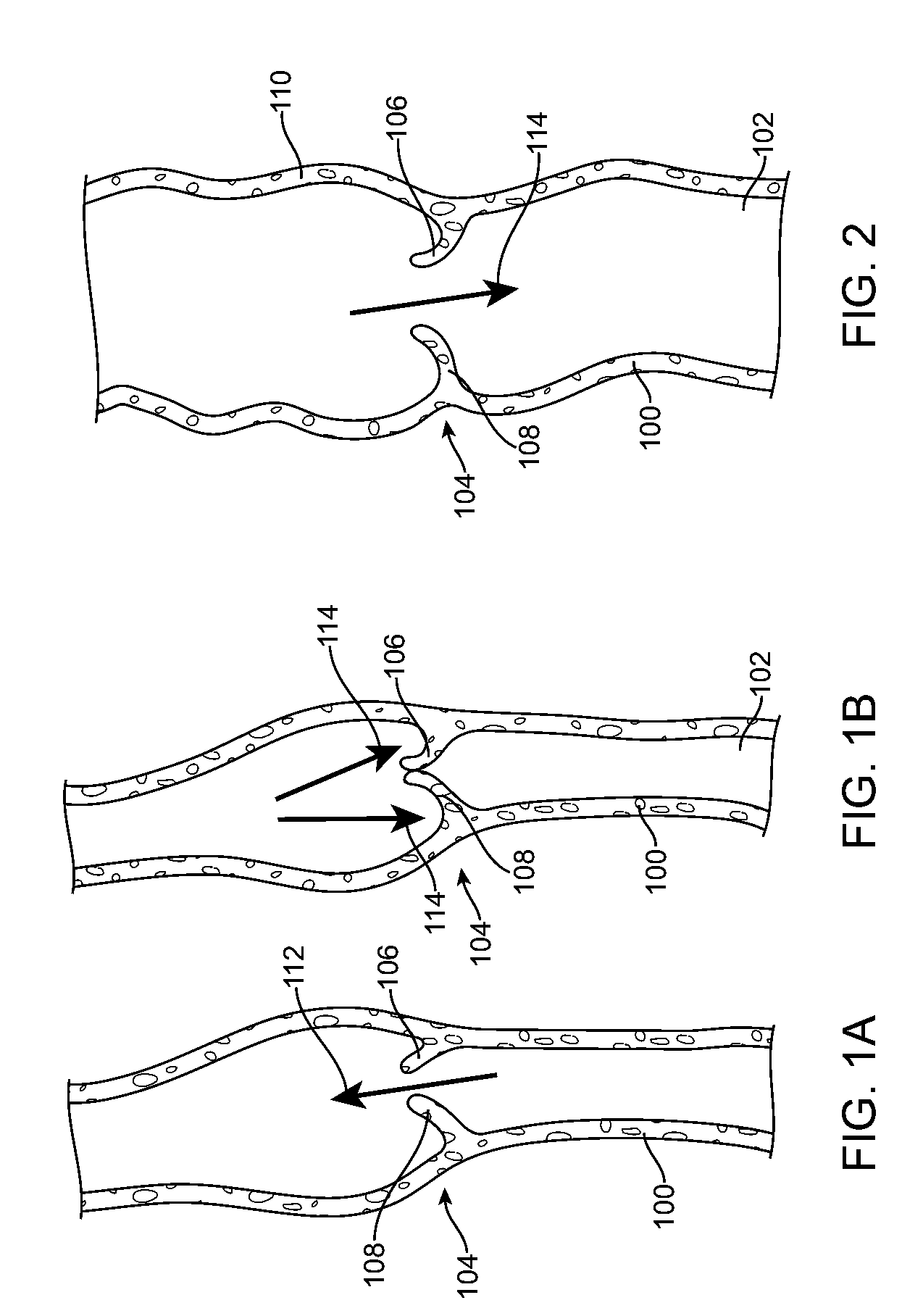
Devices and methods are provided for creating lesions in endocardial tissues surrounding a vessel opening to thereby isolate focal arrhythmia substrates, including an invasive catheter assembly comprising an elongate body having a longitudinal axis and first and second lumens, a first catheter having a distally mounted expandable anchor body disposed in the first lumen, and a second catheter having a distally mounted electrode disposed in the second lumen, the elongate body having a first distal opening accessing the first lumen through which the first catheter may be extended axially relative to the longitudinal axis of the elongate body and a second distal opening accessing the second lumen through which the second catheter may be extended at an angle relative to the longitudinal axis of the elongate body. The disclosed invention also includes an elongate catheter having an expandable electrode body mounted on one end, wherein the electrode body is configured to form an enlarged circumferential region when expanded, the enlarged circumferential region defining a distal facing surface of the electrode body, the distal facing surface including an area configured to emit radio frequency (RF) energy.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods and systems for the inhibition of vascular hyperplasia
InactiveUS6210393B1Limited extentQuick layeringUltrasound therapyStentsSmooth muscleVascular proliferation
Post-interventional neointimal hyperplasia in arteries is treated by the application of ultrasonic energy. Usually, an intravascular catheter having an interface surface is positioned at a target site in the artery which has previously been treated. The interface surface is vibrationally excited to apply energy to the arterial wall in a manner which inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation in the neointimal layer.
Owner:PHARMASONICS
Irreversible electroporation device and method for attenuating neointimal
InactiveUS20090248012A1Promote resultsPrevent excessive cell lysingElectrotherapyInfusion devicesPercent Diameter StenosisTunica intima
Restenosis or neointimal formation may occur following angioplasty or other trauma to an artery such as by-pass surgery. This presents a major clinical problem which narrows the artery. The invention provides a device and a method whereby vascular cells in the area of the artery subjected to the trauma are subjected to irreversible electroporation which is a non-thermal, non-pharmaceutical method of applying electrical pulses to the cells so that substantially all of the cells in the area are ablated while leaving the structure of the vessel in place and substantially unharmed due to the non-thermal nature of the procedure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
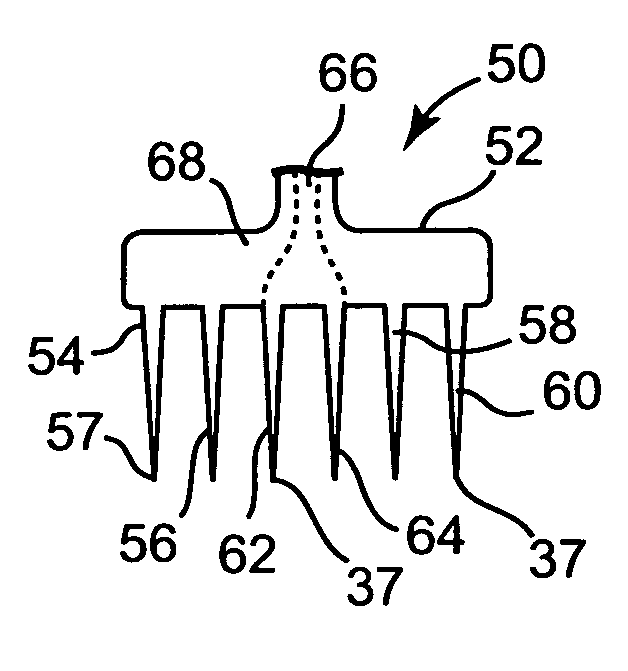
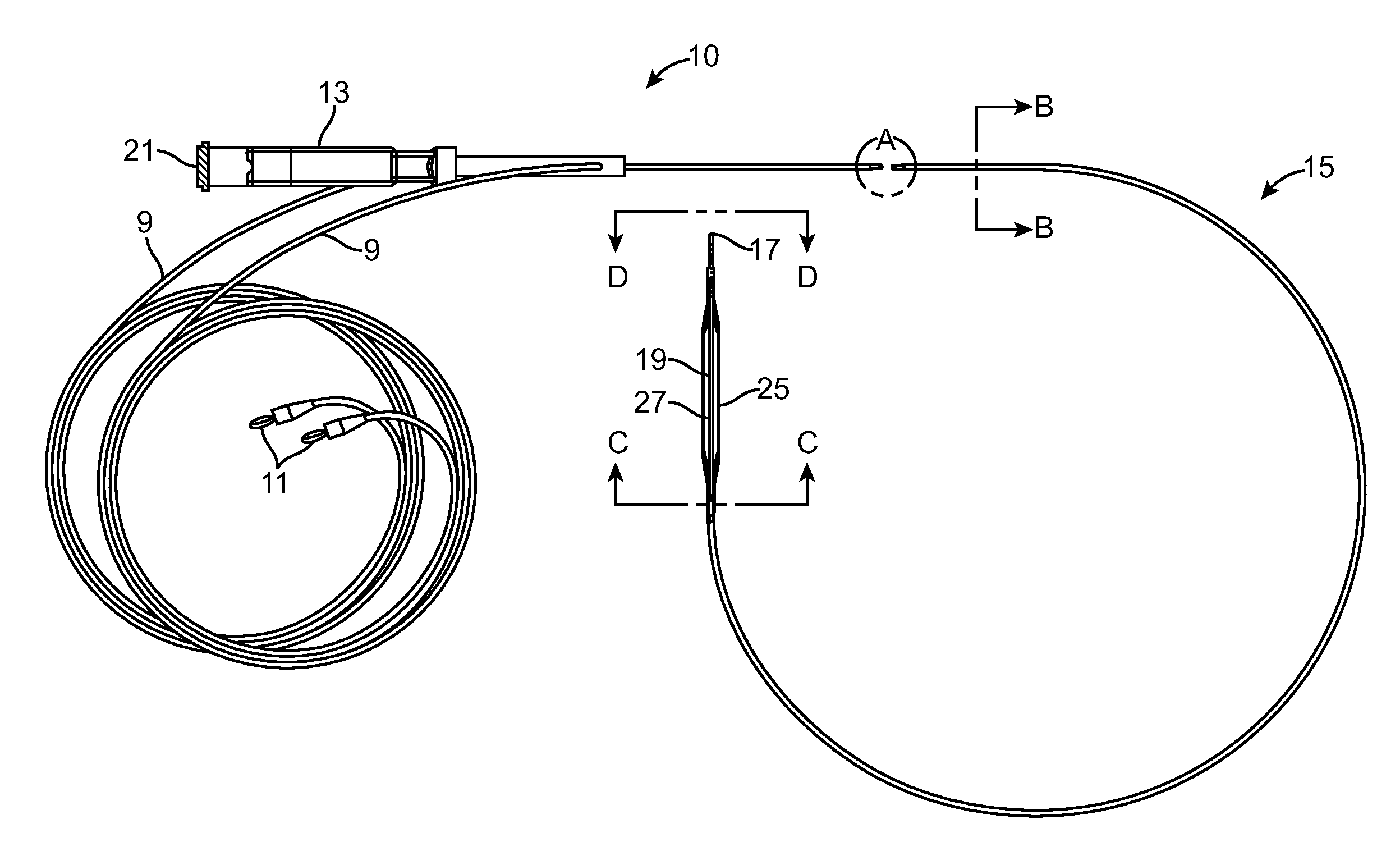
Atrial ablation catheter and method of use
InactiveUS7429261B2Easy to deployEasy to retractElectrotherapySurgical instrument detailsTunica intimaElectrode array
An atrial ablation catheter and methods for its use. The endocardial catheter includes an electrode array particularly adapted to locate and ablate foci of arrhythmia which are required for sustained atrial fibrillation is provided. The array is easily deployed and retracted from the catheter, and presents a distally oriented electrode array that can be pressed against the wall of the atrium.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
Compliant blood vessel graft
ActiveUS20070293932A1Smoothening of irregularitiesReduce the differenceStentsSurgeryVenous SegmentVenous graft
Stents and methods of using stents are provided. Stents of the invention provide external support structure for a blood vessel segment disposed within, wherein the stents are capable of resilient radial expansion in a manner mimicking the compliance properties of an artery. The stent may be formed of a knitted or braided mesh formed so as to provide the needed compliance properties. A venous graft with the stent and a vein segment disposed within is provided, wherein graft is capable of mimicking the compliance properties of an artery. Methods of selecting stents for downsizing and methods of using the stents of the invention in downsizing and smoothening are provided. Methods of replacing a section of an artery with a venous graft including a stent of the invention are provided. Methods of reducing intimal hyperplasia in implanted vein segment in a venous graft using stents of the invention are provided.
Owner:VASCULAR GRAFT SOLUTIONS
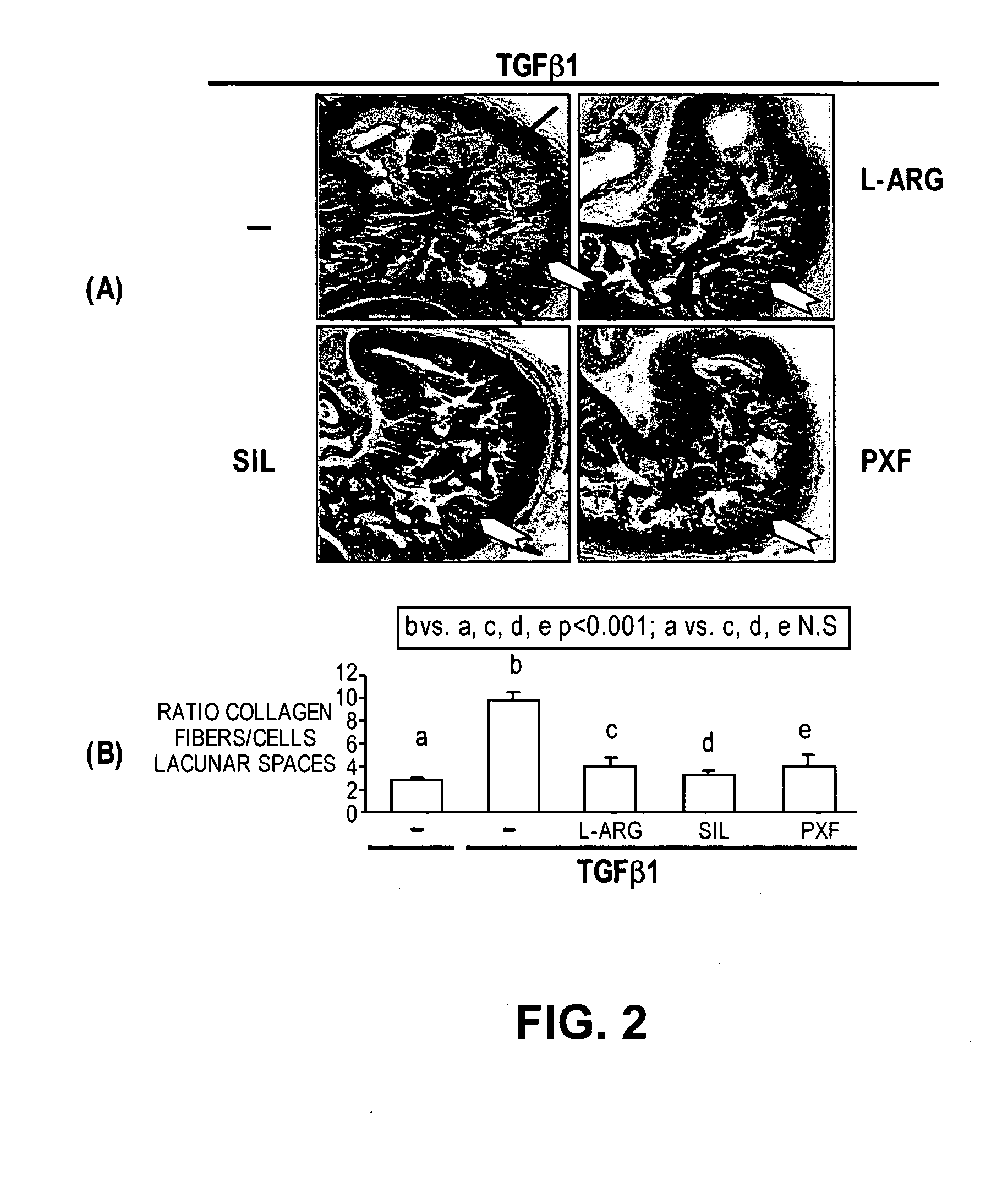
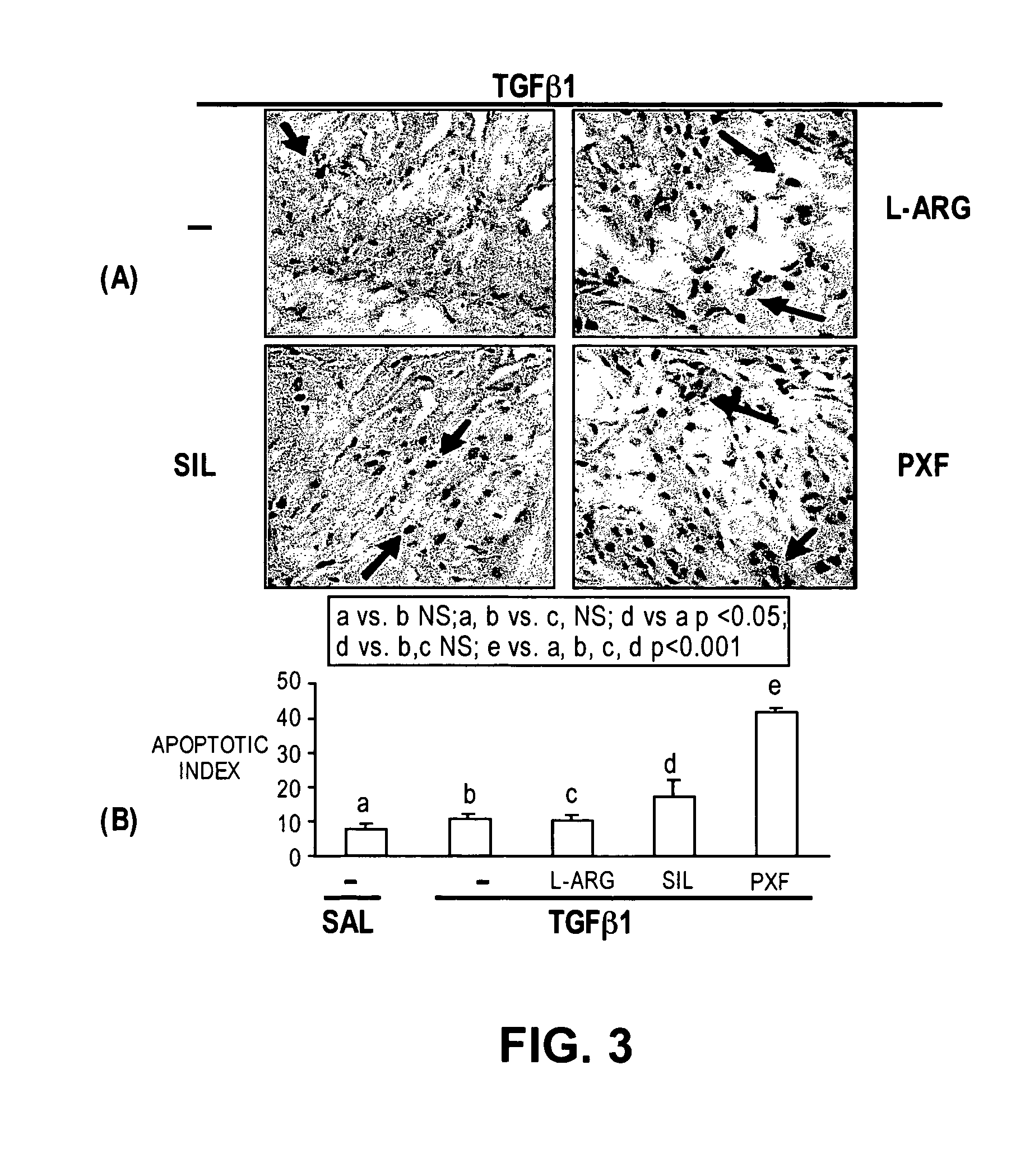
Methods of use of inhibitors of phosphodiesterases and modulators of nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species, and metalloproteinases in the treatment of peyronie's disease, arteriosclerosis and other fibrotic diseases
ActiveUS20050085486A1Increasing NO levelReduce expressionBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismFemale Sexual Arousal DisorderCyclase
The present methods and compositions are of use for treatment of conditions involving fibrosis, such as Peyronie's disease plaque, penile corporal fibrosis, penile veno-occlusive dysfunction, Dupuytren's disease nodules, vaginal fibrosis, clitoral fibrosis, female sexual arousal disorder, abnormal wound healing, keloid formation, general fibrosis of the kidney, bladder, prostate, skin, liver, lung, heart, intestines or any other localized or generalized fibrotic condition, vascular fibrosis, arterial intima hyperplasia, atherosclerosis, arteriosclerosis, restenosis, cardiac hypertrophy, hypertension or any condition characterized by excessive fibroblast or smooth muscle cell proliferation or deposition of collagen and extracellular matrix in the blood vessels and / or heart. In certain embodiments, the compositions may comprise a PDE-4 inhibitor, a PDE-5 inhibitor, a compound that elevates cGMP and / or PKG, a stimulator of guanylyl cyclase and / or PKG, a combination of a compound that elevates cGMP, PKG or NO with an antioxidant that decreases ROS, or a compound that increases MMP activity.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
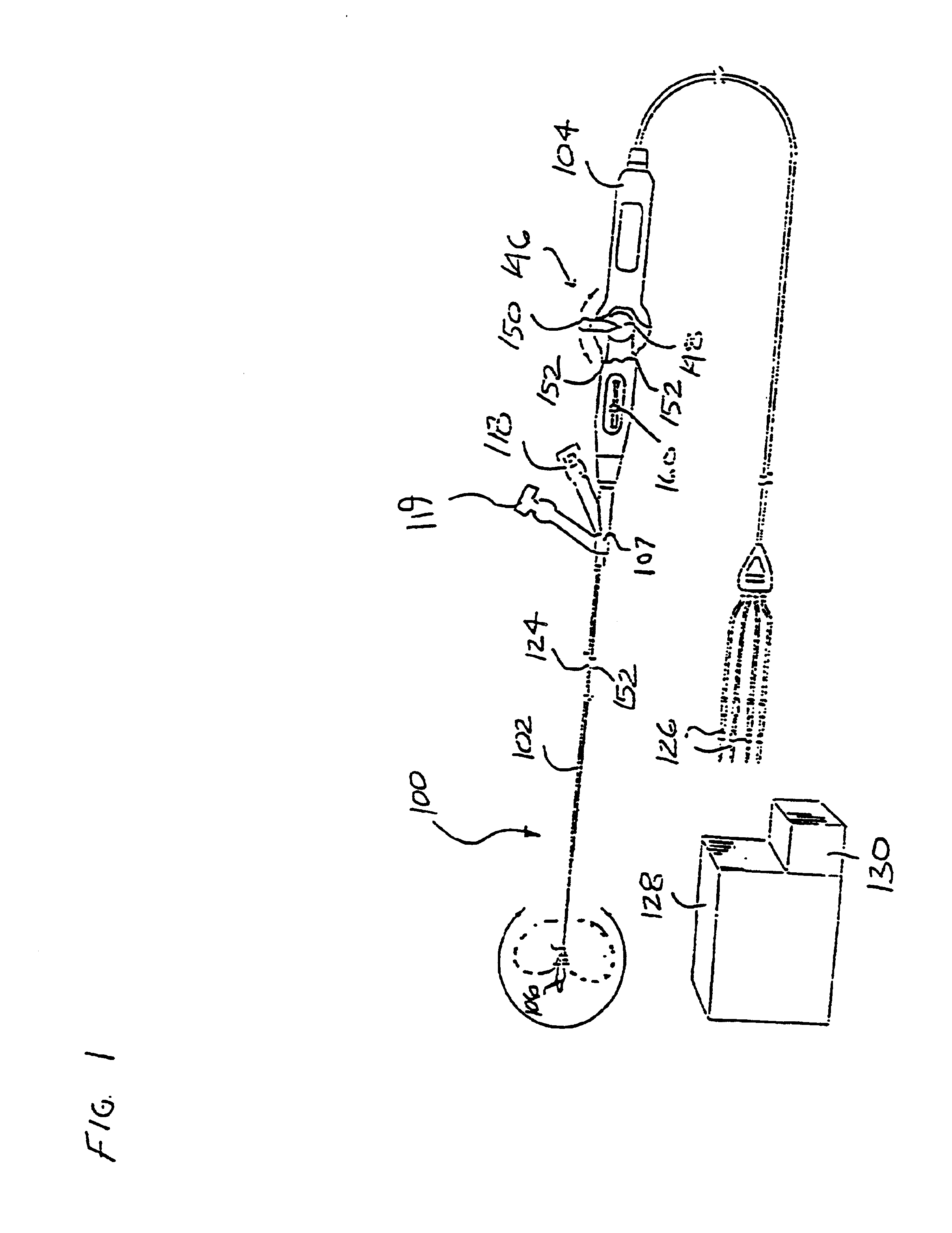
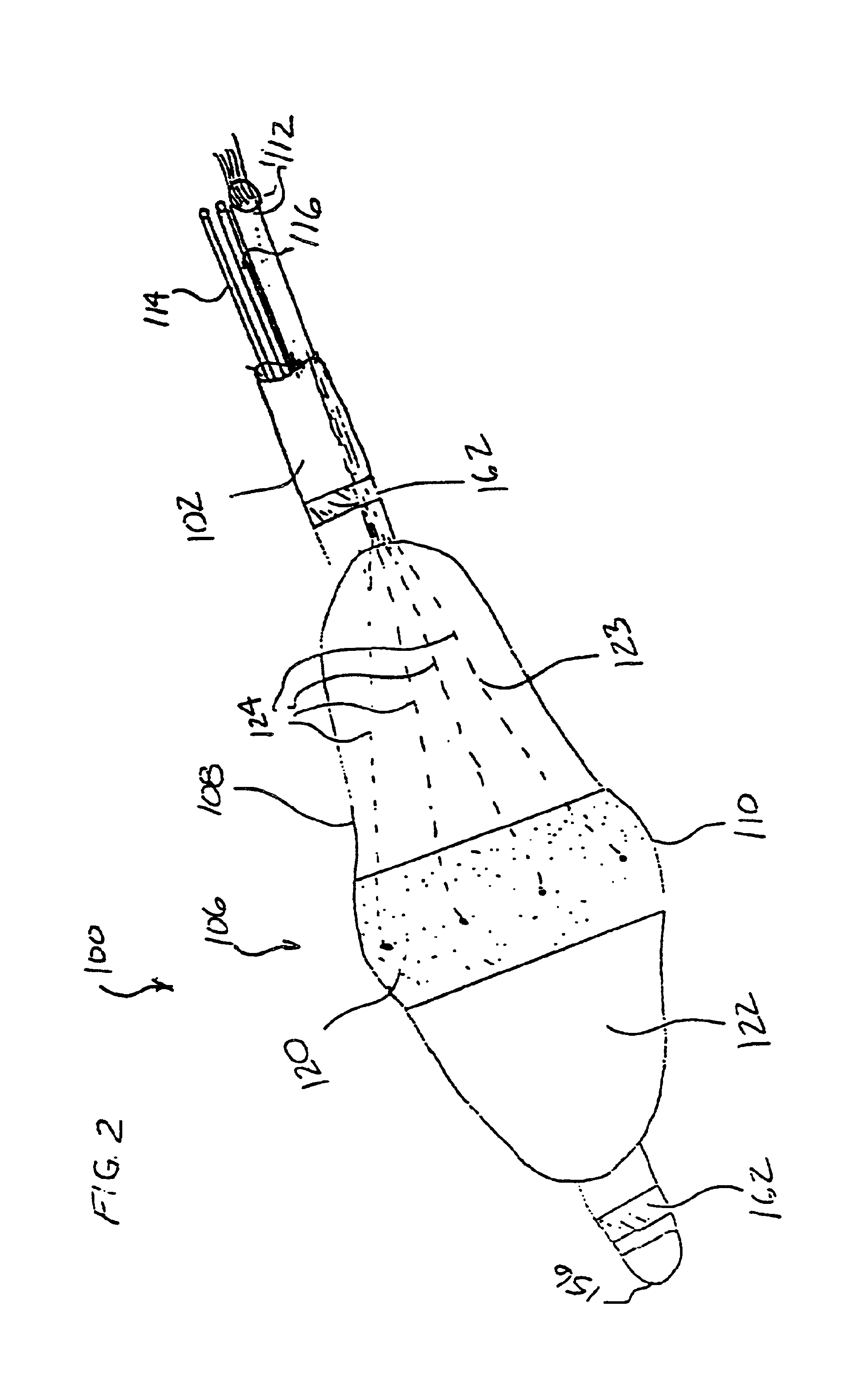
Kink resistant introducer with mapping capabilities
InactiveUS7229450B1Introducer stifferLess maneuverableElectrocardiographySurgeryElectrical conductorCardiac muscle
An introducer system for use with a pacemaker lead includes a plastic sheath compatible for insertion within a body, a first end configured for insertion into the body with a second end extending out of the body. A central lumen of the sheath is configured to permit introduction of the lead and includes a flexible, kink-resistant section smooth on its outer surface with a helical pleat defining a helical groove enabling a conductor extending from the mapping probe to the pacing system analyzer to be received in the helical groove of the sheath. A mapping probe at the first end of the sheath is connectable to a pacing system analyzer for seeking a location on the myocardial surface of the heart or an endocardial location at which optimal pacing parameters can be achieved prior to implantation of the lead.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
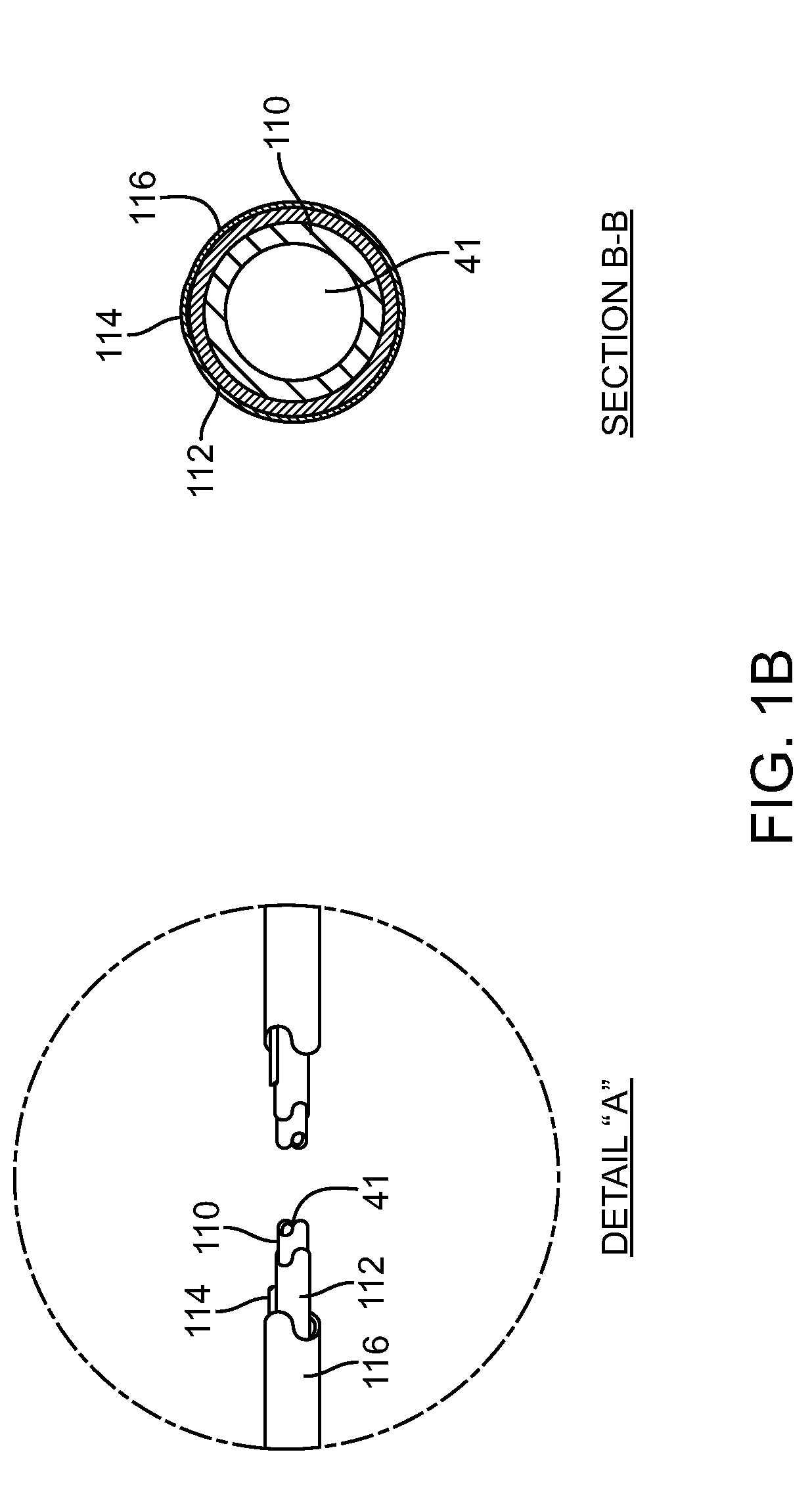
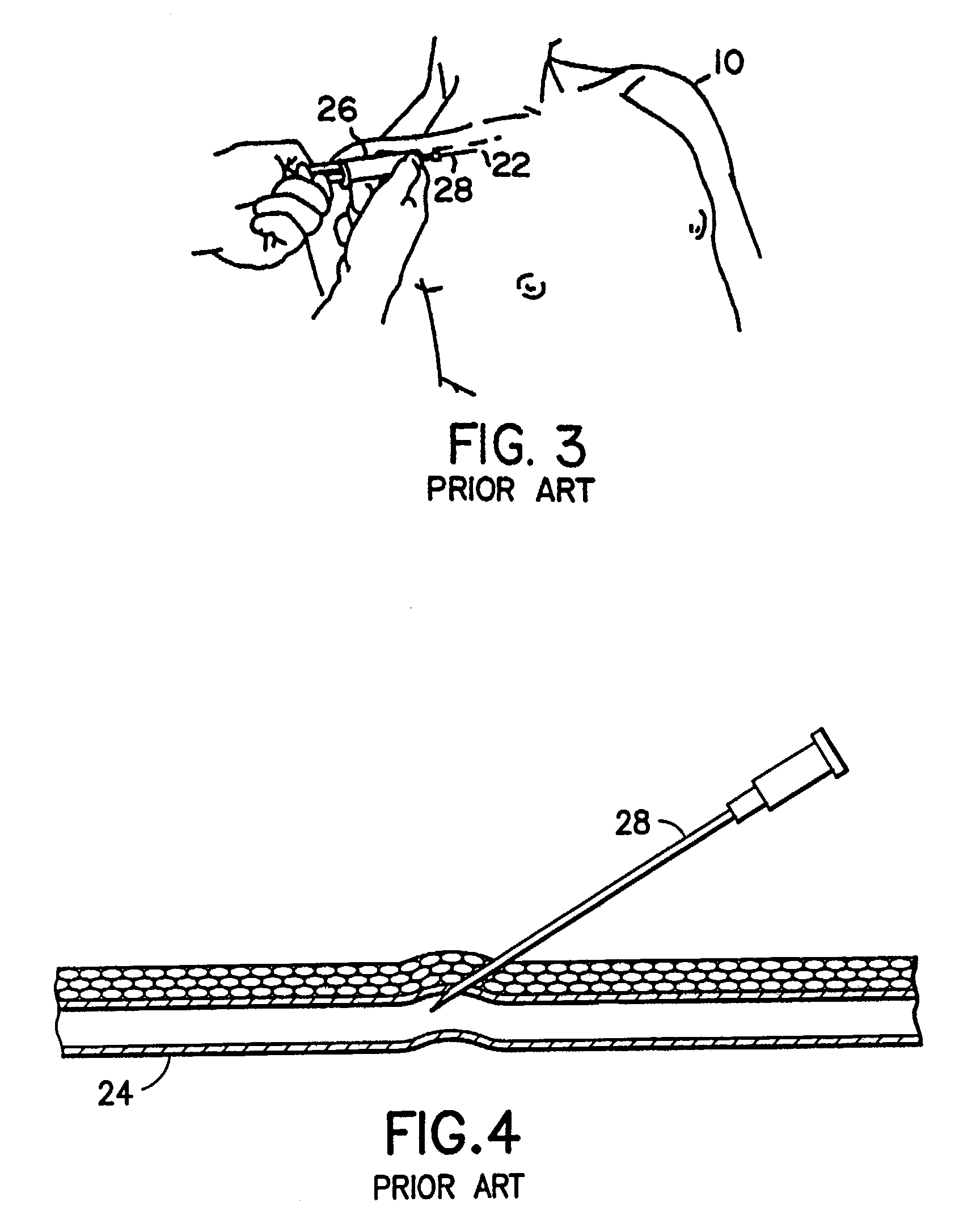
Method and apparatus for performing anastomosis with eversion of tissue edges and joining of exposed intima of the everted tissue
A ring for use in anastomosis. Preferably, the ring is integrally formed from metal, and includes a ring portion and tines and docking members that extend from the ring portion. The ring portion and tines are malleable, and preferably also the docking members are malleable. The ring portion and tines are malleable in the sense that once deformed from a first shape into a second shape, they will not relax back into the first shape from the second. To install the ring in a vessel with the ring portion extending around an incision or other orifice, the tines pierce the tissue around the orifice and are curled against an anvil. The action of curling the tines inverts the tissue near the orifice edges to expose the inside surface of the vessel or organ. Other aspects of the invention are a method and apparatus for installing an anastomosis ring in an incision or other orifice in a vessel or other organ, a method and apparatus for precisely aligning two anastomosis rings (each installed in an incision or other orifice of a different organ) and fastening the aligned rings together. The clips can be crimped onto the aligned rings, or they can be spring clips which are sprung onto the aligned rings to clamp the rings together by spring force. Also within the scope of the invention are crimping and spring clips for use in listening together two aligned anastomosis rings. In other embodiments, the invention is a method for performing an anastomosis by installing an anastomosis ring in an orifice in an organ, installing another anastomosis ring in an orifice in another organ, precisely aligning the two installed anastomosis rings, and fastening the aligned rings together.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Intravascular ultrasound catheter device and method for ablating atheroma
InactiveUS20060241524A1Prolong time-integrated emulsificationEnhance reabsorptionChiropractic devicesMedical devicesCavitationUltrasound angiography
An intravascular catheter device having a catheter and an ultrasound ablation manifold is proposed for generating cavitations and acoustic jet streams in the blood to ablate atheroma. The ablation manifold has a power transducer and a coupled leaky acoustic cavity. The leaky acoustic cavity contains a first portion of ultrasonic power emission for intra-cavity ablation while allowing a second portion of ultrasonic power emission to leak outside for an extra-cavity ablation. The power transducer and the leaky acoustic cavity are configured to form a confocal resonant cavity. An intervening bird cage is coupled to the resonant cavity for stronger resonance while maintaining ultrasound leakage. A protective shield is mounted around the waist of bird cage to strengthen resonance and to prevent damaging the intima from an otherwise normal incidence of high intensity ultrasound. A microbubble releasing device and micro pump are also included to further increase the ablation efficacy.
Owner:YU QI
Method for treating ischemia
InactiveUS7001336B2Cell damage causedMinimizes injuryUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCurve shapeCardiac muscle
A method and apparatus for improving blood flow to an ischemic region (e.g., myocardial ischemia) a patient is provided. An ultrasonic transducer is positioned proximate to the ischemic region. Ultrasonic energy is applied at a frequency at or above 1 MHz to create one or more thermal lesions in the ischemic region of the myocardium. The thermal lesions can have a gradient of sizes. The ultrasound transducer can have a curved shape so that ultrasound energy emitted by the transducer converges to a site within the myocardium, to create a thermal lesion without injuring the epicardium or endocardium.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Compliant blood vessel graft
ActiveUS7998188B2Smoothening of irregularitiesReduce the differenceStentsSurgeryVenous SegmentVenous graft
Stents and methods of using stents are provided. Stents of the invention provide external support structure for a blood vessel segment disposed within, wherein the stents are capable of resilient radial expansion in a manner mimicking the compliance properties of an artery. The stent may be formed of a knitted or braided mesh formed so as to provide the needed compliance properties. A venous graft with the stent and a vein segment disposed within is provided, wherein graft is capable of mimicking the compliance properties of an artery. Methods of selecting stents for downsizing and methods of using the stents of the invention in downsizing and smoothening are provided. Methods of replacing a section of an artery with a venous graft including a stent of the invention are provided. Methods of reducing intimal hyperplasia in implanted vein segment in a venous graft using stents of the invention are provided.
Owner:VASCULAR GRAFT SOLUTIONS
Device and method for ablation of cardiac tissue
InactiveUS7294143B2Improving impedanceEasy to doSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingRf ablationPresent method
Methods for delivering precise amounts of fluid into cardiac tissue for the purpose of facilitating ablation of the tissue along a desired lesion line. One method injects fluid through a hollow needle. The injected fluid can be a highly conductive fluid injected in conjunction with radiofrequency ablation to create an ablative virtual electrode. The injected conductive fluid can provide deeper and narrower conduction paths and resulting lesions. Radiofrequency ablation can be performed at the same time as the fluid injection, using the injection device as an electrode, or subsequent to the fluid injection, using a separate device. In some methods, the injected fluid is a protective fluid, injected to protect tissue adjacent to the desired lesion line. Fluid delivery can be endocardial, epicardial, and epicardial on a beating heart. The present methods find one use in performing maze procedures to treat atrial fibrillation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus for Percutaneously Creating Native Tissue Venous Valves
Percutaneous apparatus for forming a bicuspid venous valve from autologous tissue are disclosed. A multilumen catheter is disclosed that includes a delivery shaft positioned on either side of the balloon. When the balloon is inflated within the vein at a treatment location where a bicuspid valve is to be created, the delivery shafts are pressed into the wall of the vein by the inflated balloon so that exit ports in the delivery shafts are at diametrically opposed locations. The delivery shafts may than be used to deliver puncture elements through the exit ports and into the vessel wall to gain access to a subintimal layer of the vein wall. In this manner, the inventive multilumen catheter aids in making properly positioned flaps of venous tissue for creating a bicuspid venous valve from autologous tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Irreversible electroporation device and method for attenuating neointimal formation
InactiveUS20140163551A1Avoid heat damageObtaining target areaElectrotherapyInfusion devicesPercent Diameter StenosisIrreversible electroporation
Restenosis or neointimal formation may occur following angioplasty or other trauma to an artery such as by-pass surgery. This presents a major clinical problem which narrows the artery. The invention provides a device and a method whereby vascular cells in the area of the artery subjected to the trauma are subjected to irreversible electroporation which is a non-thermal, non-pharmaceutical method of applying electrical pulses to the cells so that substantially all of the cells in the area are ablated while leaving the structure of the vessel in place and substantially unharmed due to the non-thermal nature of the procedure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
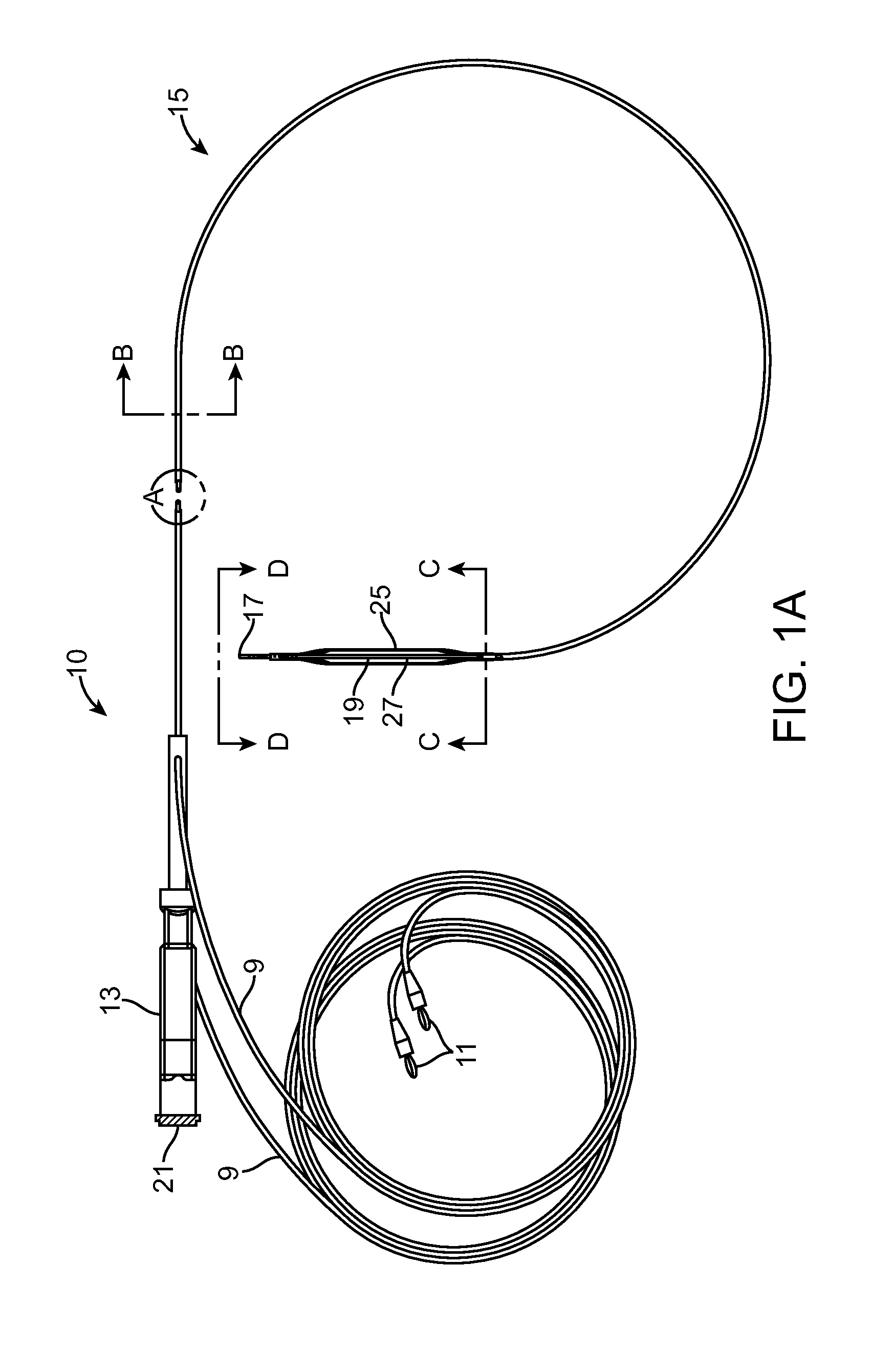
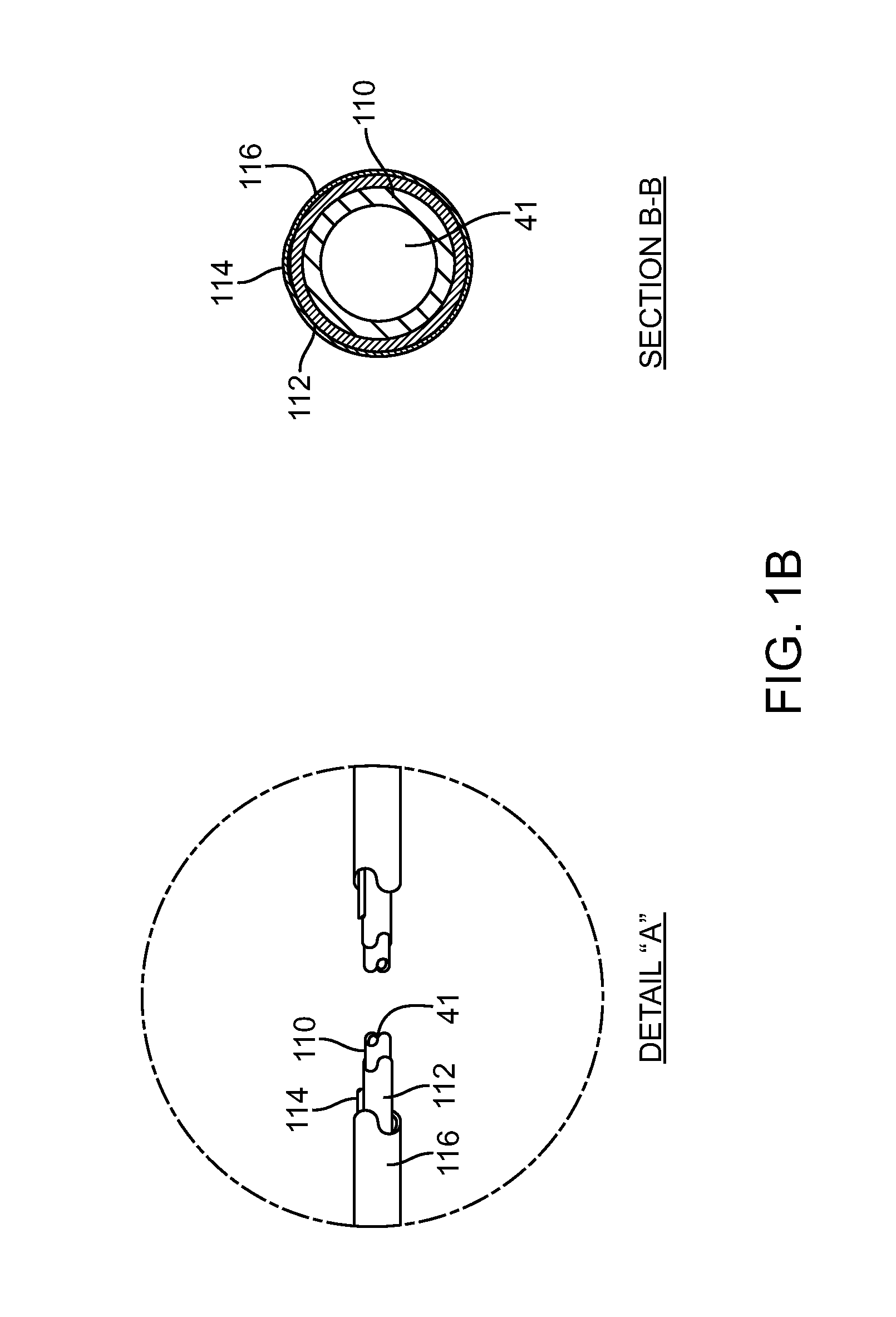
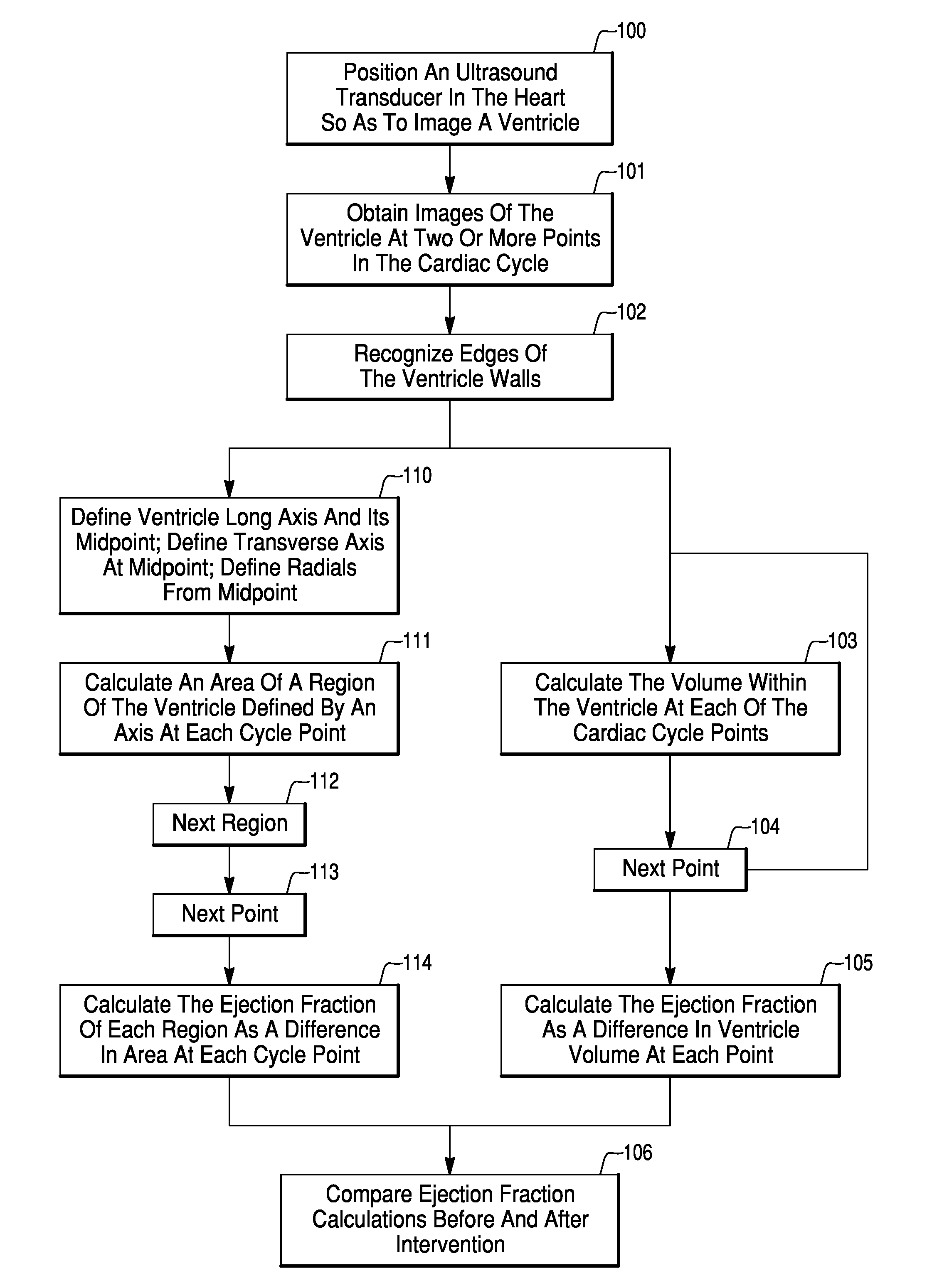
Method for Evaluating Regional Ventricular Function and Incoordinate Ventricular Contraction
InactiveUS20080009733A1Minimize impactEfficient communicationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterUltrasonic sensorCardiac feature
A method for assessing cardiac function using an ultrasound imaging catheter system includes positioning an ultrasound catheter so the ultrasound transducer can image a ventricle, obtaining images of the ventricle at two or more times within the cardiac cycle, recognizing an edge of the endocardium, measuring dimensions of the ventricle, calculating a volume or area of the ventricle at the two or more points in the cardiac cycle, and calculating the ejection fraction based upon the difference in volume or area at the two or more times in the cardiac cycle. The method can be used to determine a location for an intervention, such as placement of a pacemaker pacing lead, and may be performed before and after an intervention to assess the impact of the treatment on cardiac function.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Ultrasonograph and ultrasonography
InactiveUS20070219447A1Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsTunica mediaRadiology
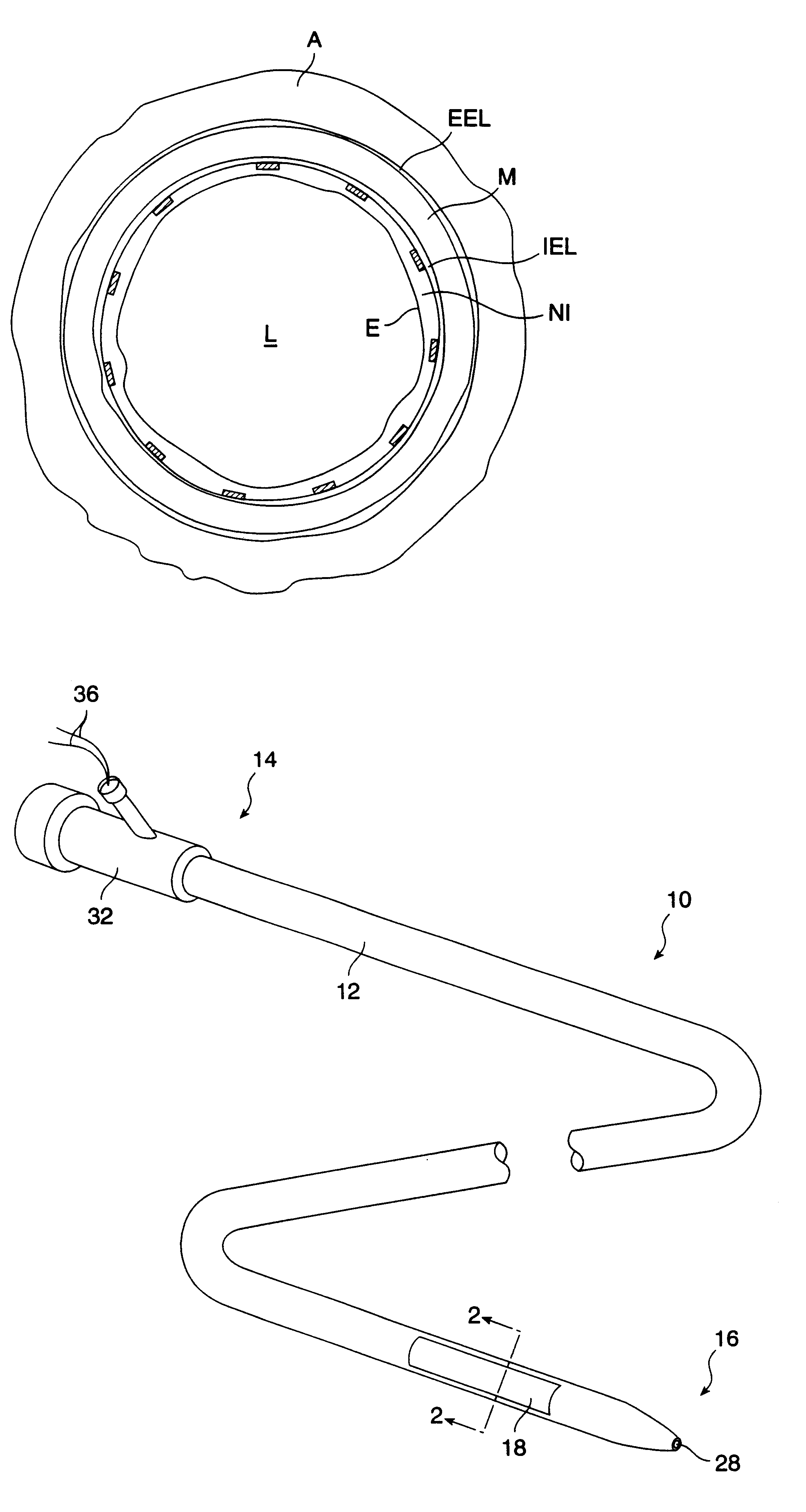
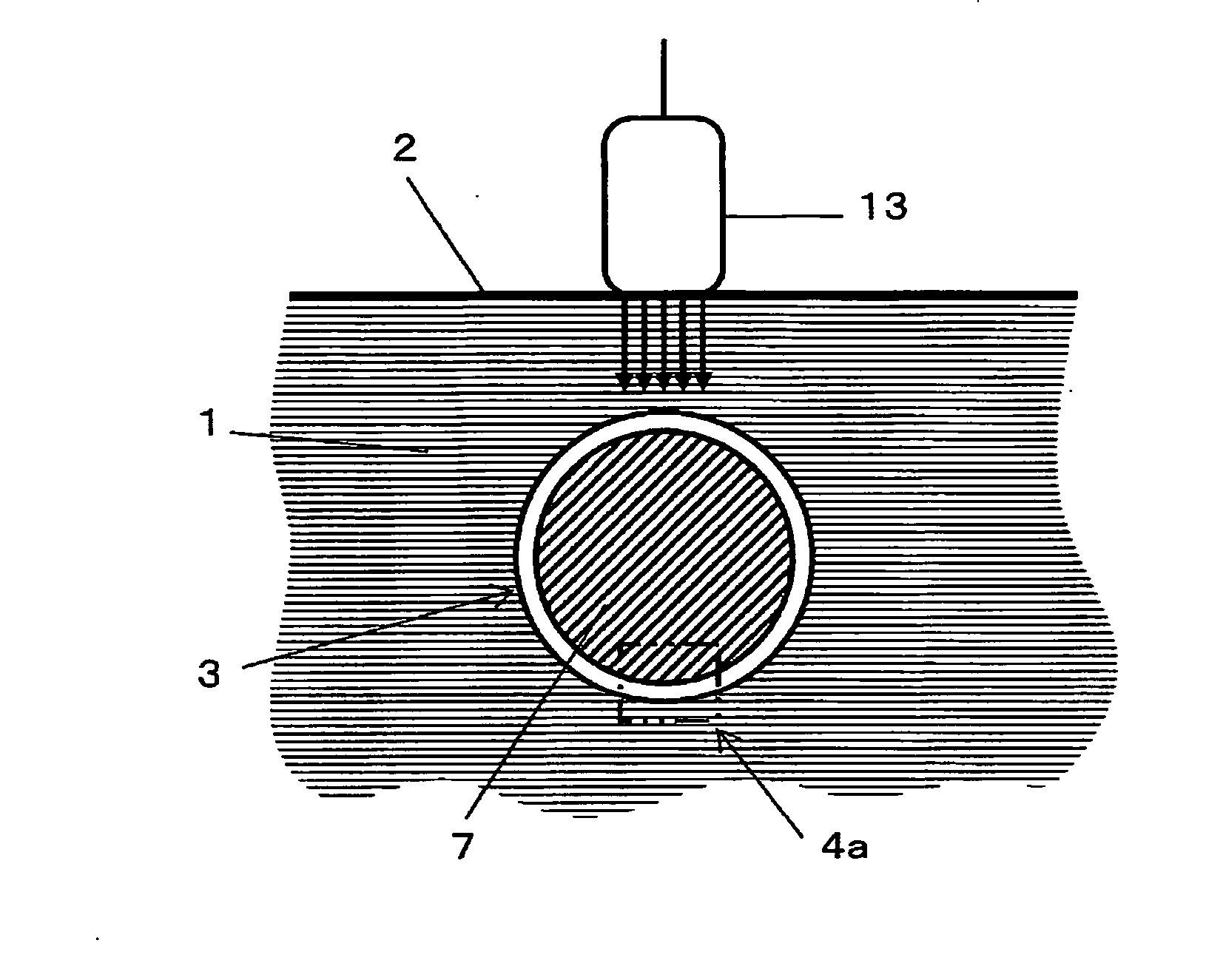
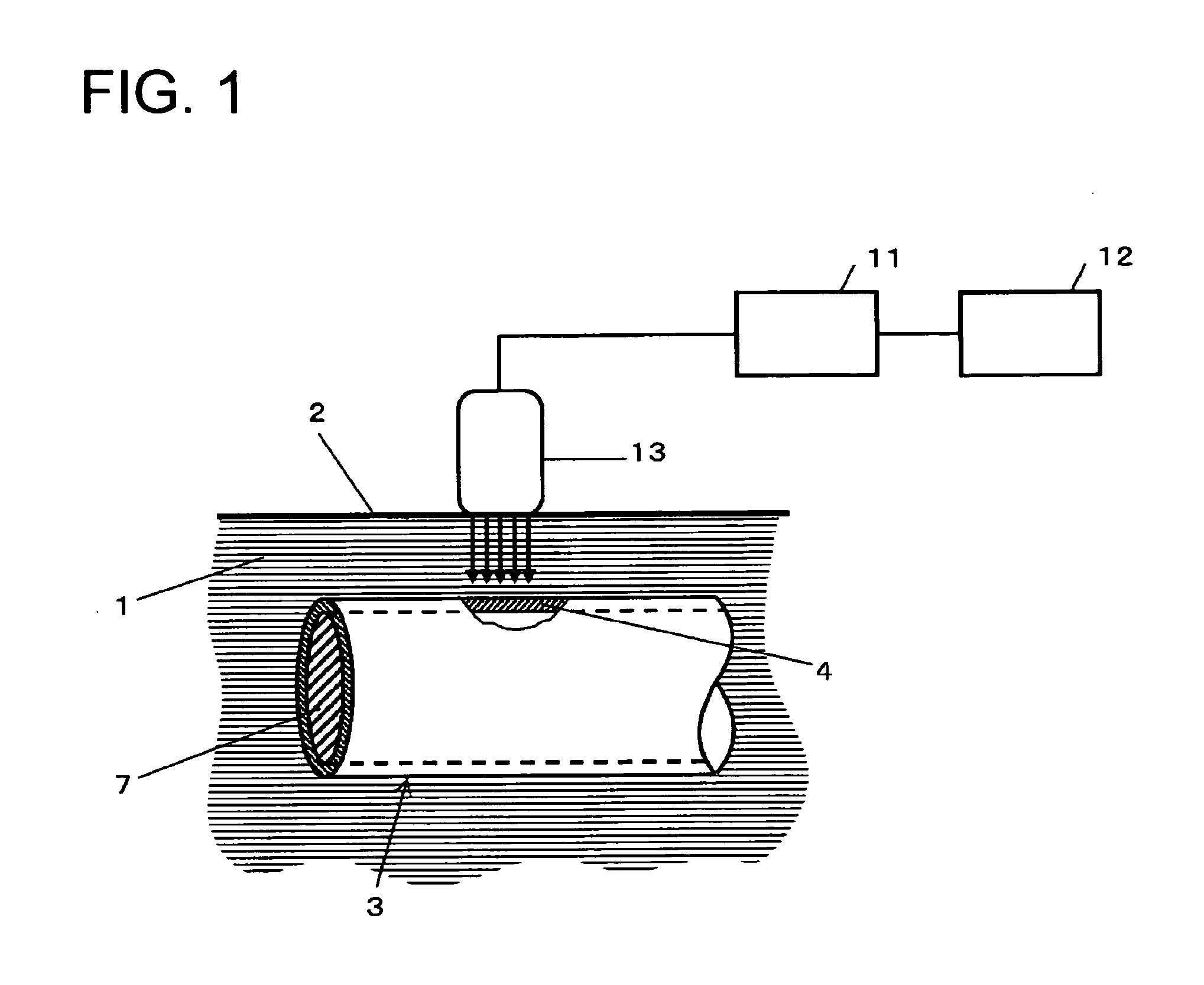
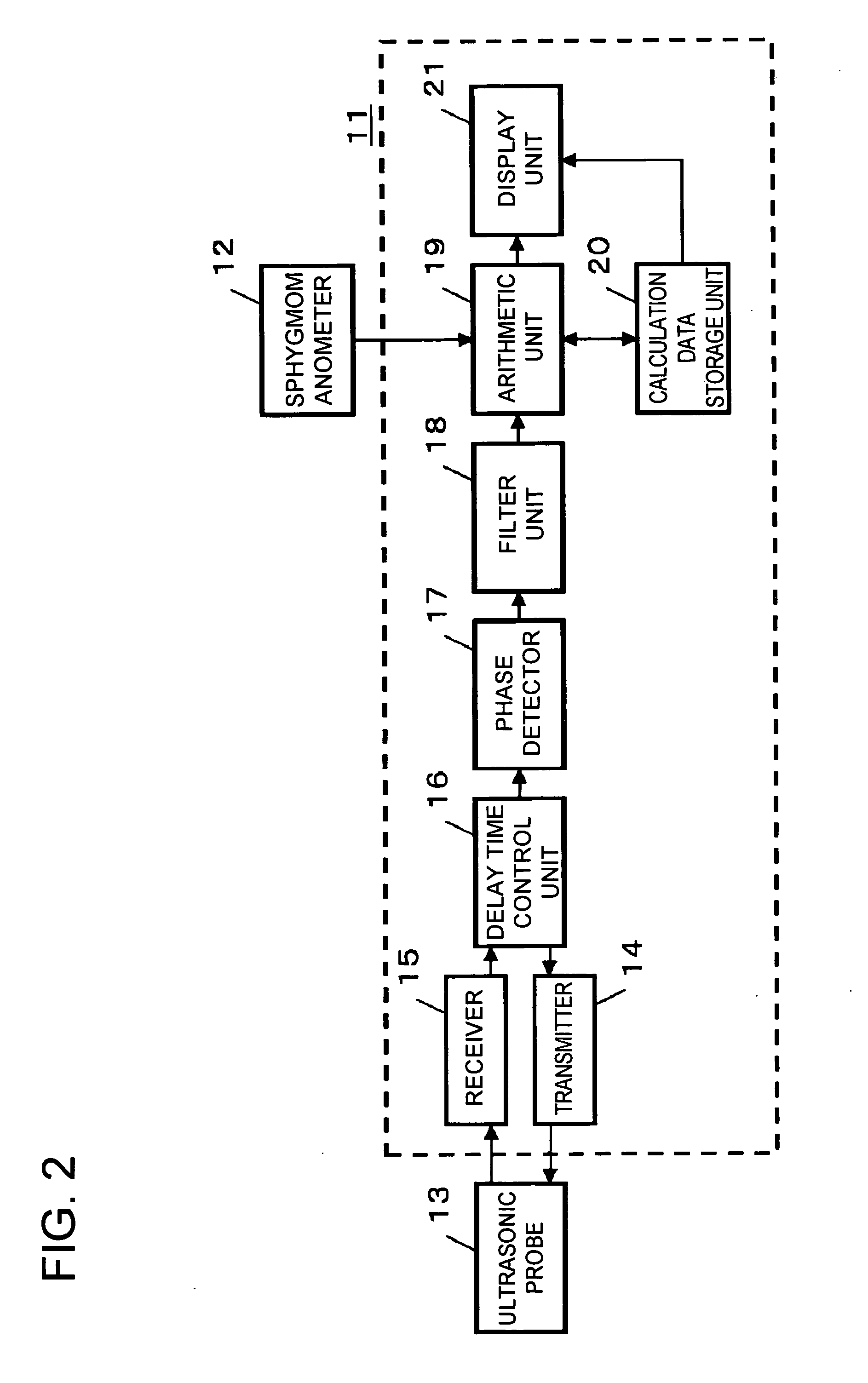
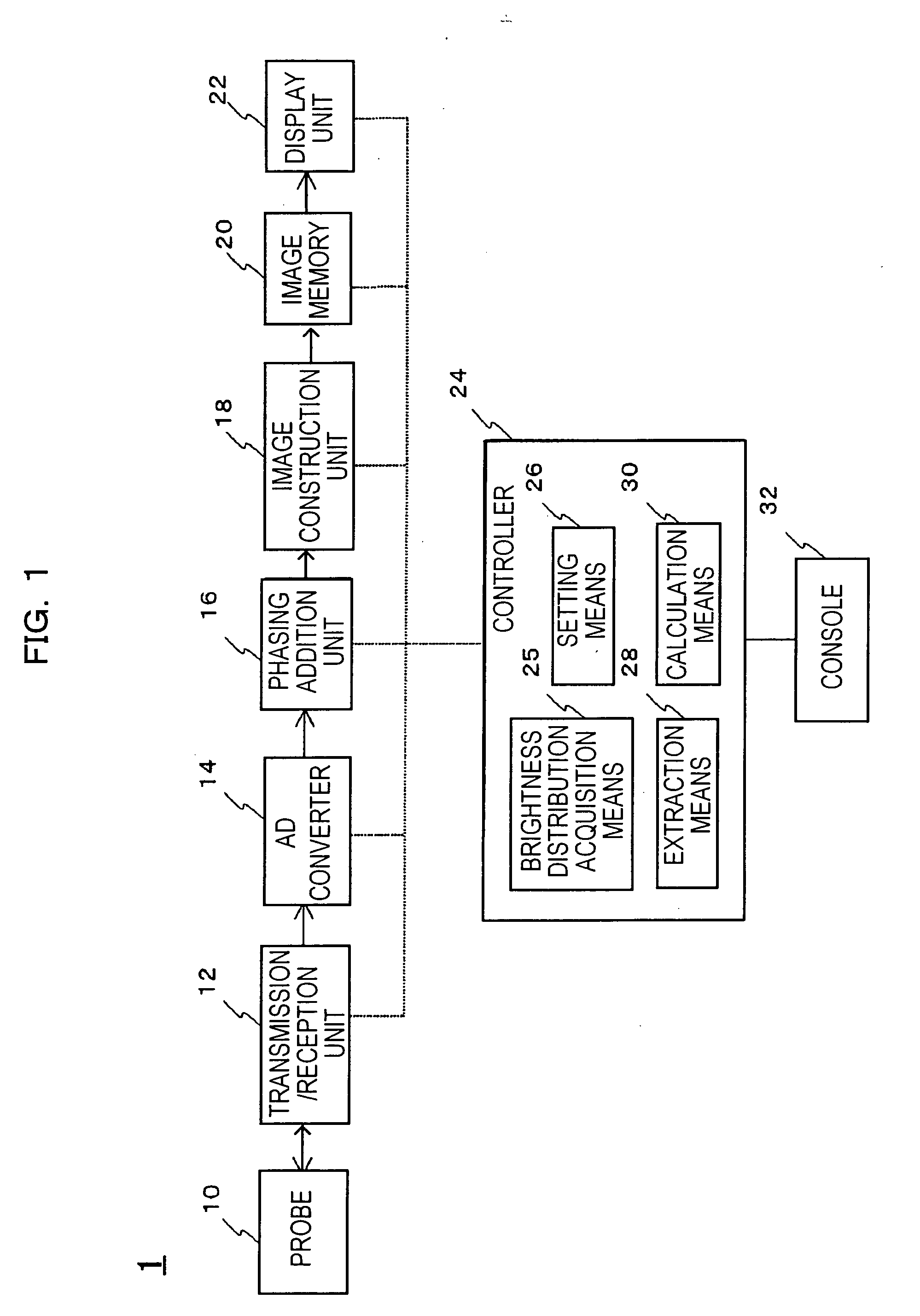
A new technique is disclosed for providing an ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus and an ultrasonic diagnostic method, by which it is possible to diagnose vascular endothelial function with high sensitivity through measurement of changes of elastic modulus of vascular wall in the region of tunica intima and tunica media with high precision by using ultrasonic waves in the diagnosis of vascular endothelial reaction after the stopping of avascularization. According to this technique, the apparatus comprises an arithmetic unit 19 for obtaining elastic modulus of a vascular wall 4, and the apparatus is provided with at least one of a calculation data storage unit 20 for storing changes over time of elastic modulus of vascular wall when artery is avascularized and the avascularization is then stopped, or a display unit 21 for displaying changes over time of elastic modulus of the vascular wall.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Automatic dividing method of ultrasound carotid artery plaque
ActiveCN102800088AGuaranteed reasonablenessOvercome limitationsImage analysisOrgan movement/changes detectionCurve fittingTherapeutic effect
The invention belongs to the field of intersection of a computer technology and medical images, and in particular relates to a dividing method of plaque in the cross section direction of carotid artery blood vessel in an ultrasound image. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: selecting the current frame image; dividing to obtain profiles of internal and external membranes of the blood vessel; extracting the plaque and dividing the interested area; detecting an initial plaque external boundary: carrying out curve fitting on each column of pixel point gray value between the internal and external membrane profiles on a polar coordinate image obtained through conversion in the interested area, and detecting the pixel point with the minimum gray value and nearest to the external membrane profile as the initial plaque external boundary point; carrying out level set evolution to obtain the final plaque external boundary; and using the area between the final external boundary and the internal membrane profile as the plaque area. By adopting the dividing method of ultrasound carotid artery plaque, plaque can be accurately divided, the workload of doctors can be greatly reduced, and the plaque size and area calculated on the basis of the division result can help doctors analyze the lesion degree and treatment effect.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Device, a catheter, and a method for the curative treatment of varicose veins
InactiveUS20060189967A1Increase supplyReduce intrusionCatheterSurgical instrument detailsTunica mediaFiber
Described herein are a device and a method for the treatment of varicose veins via laser radiation, and in particular using a holmium laser. The radiation of a laser source (5) is injected in a fiber (3) that can be inserted in the vessel to be treated. The laser source emits a radiation such as to cause a hyalinizing sclerosis with structural modifications both to the fibers of the collagen (shrinkage) and to the extracellular matrix of the median coat of the vein by the photothermal effect, substantially without thermal stress of the morphological component of the tunica media and of the tunica intima.
Owner:EL EN SPA
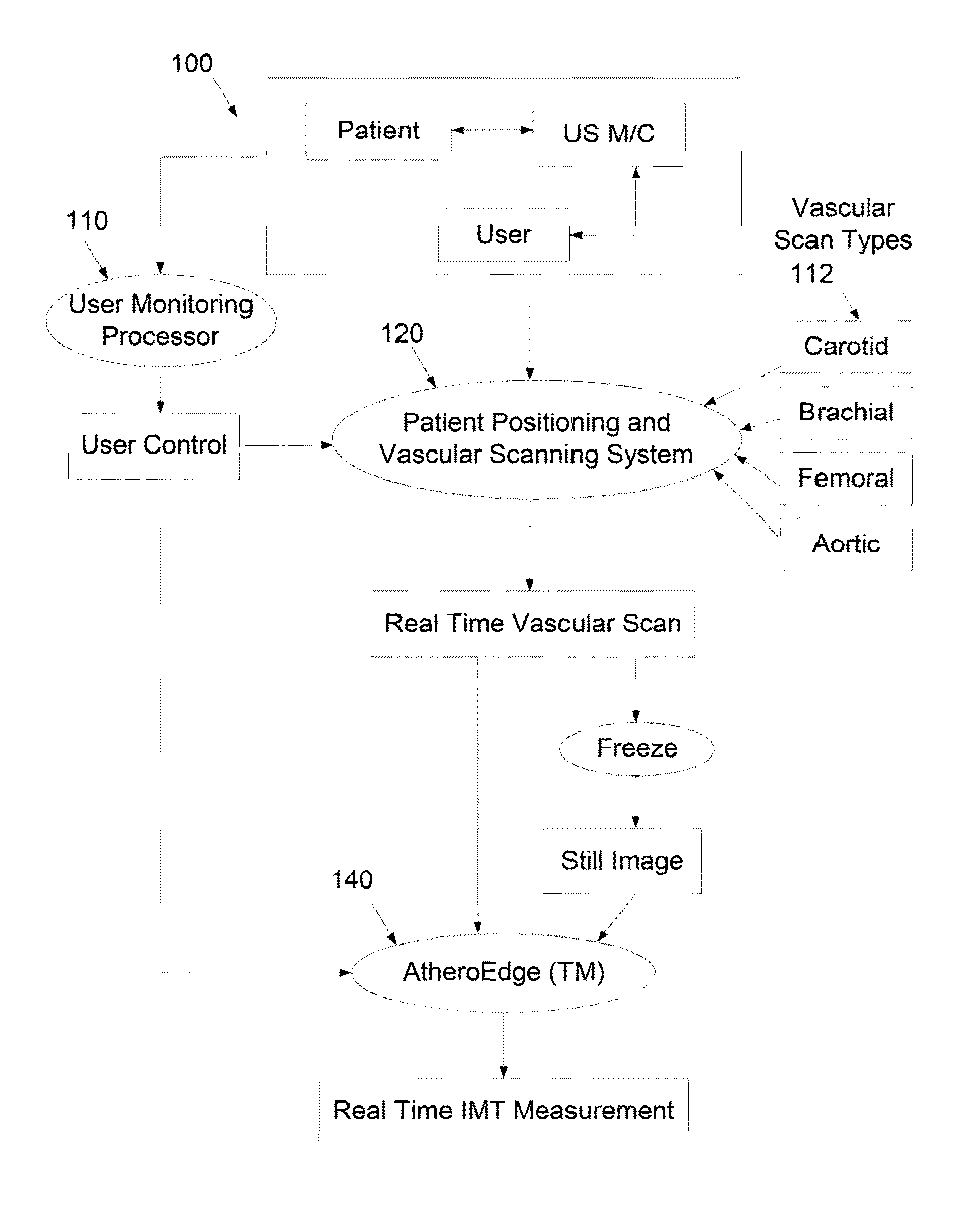
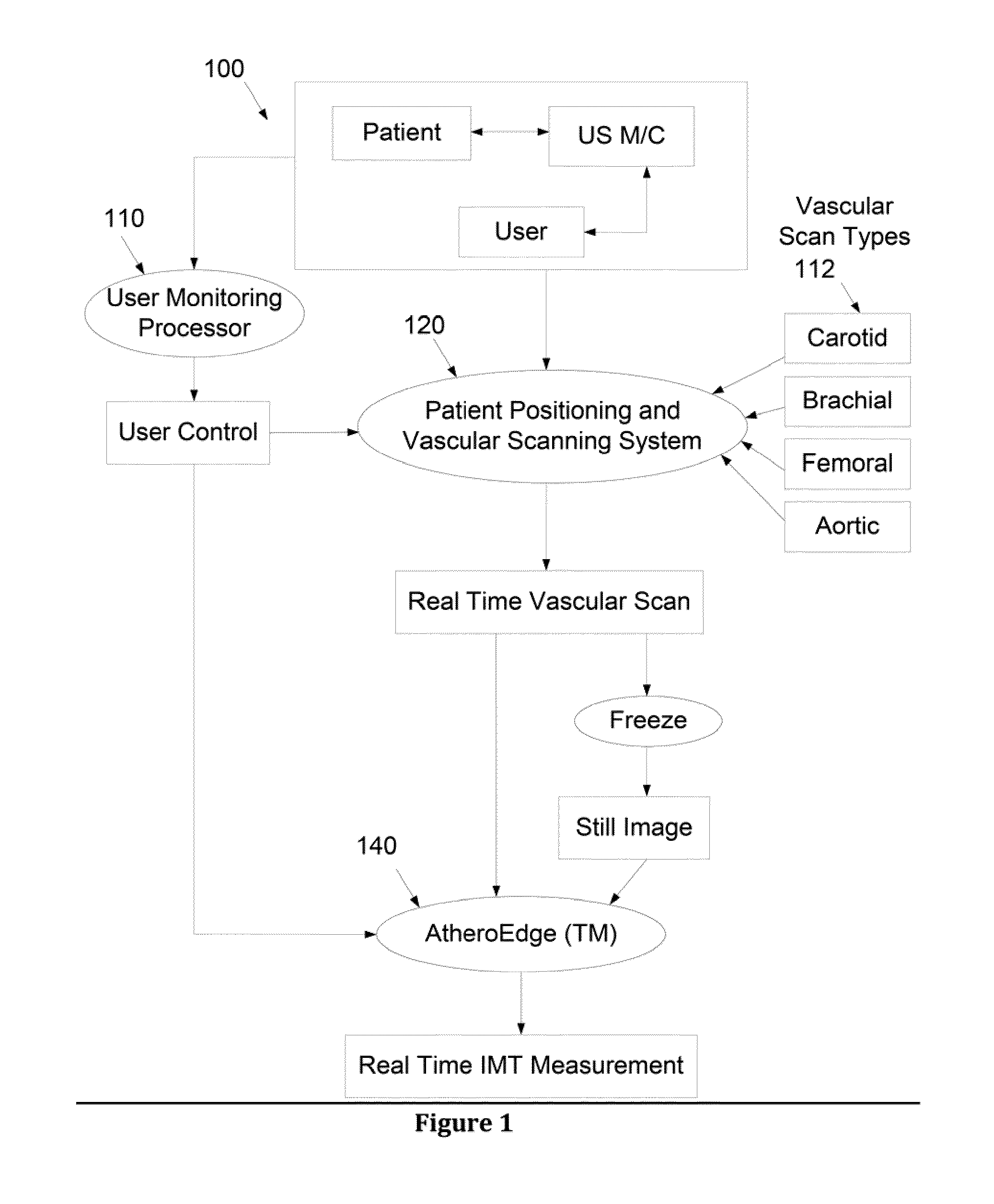
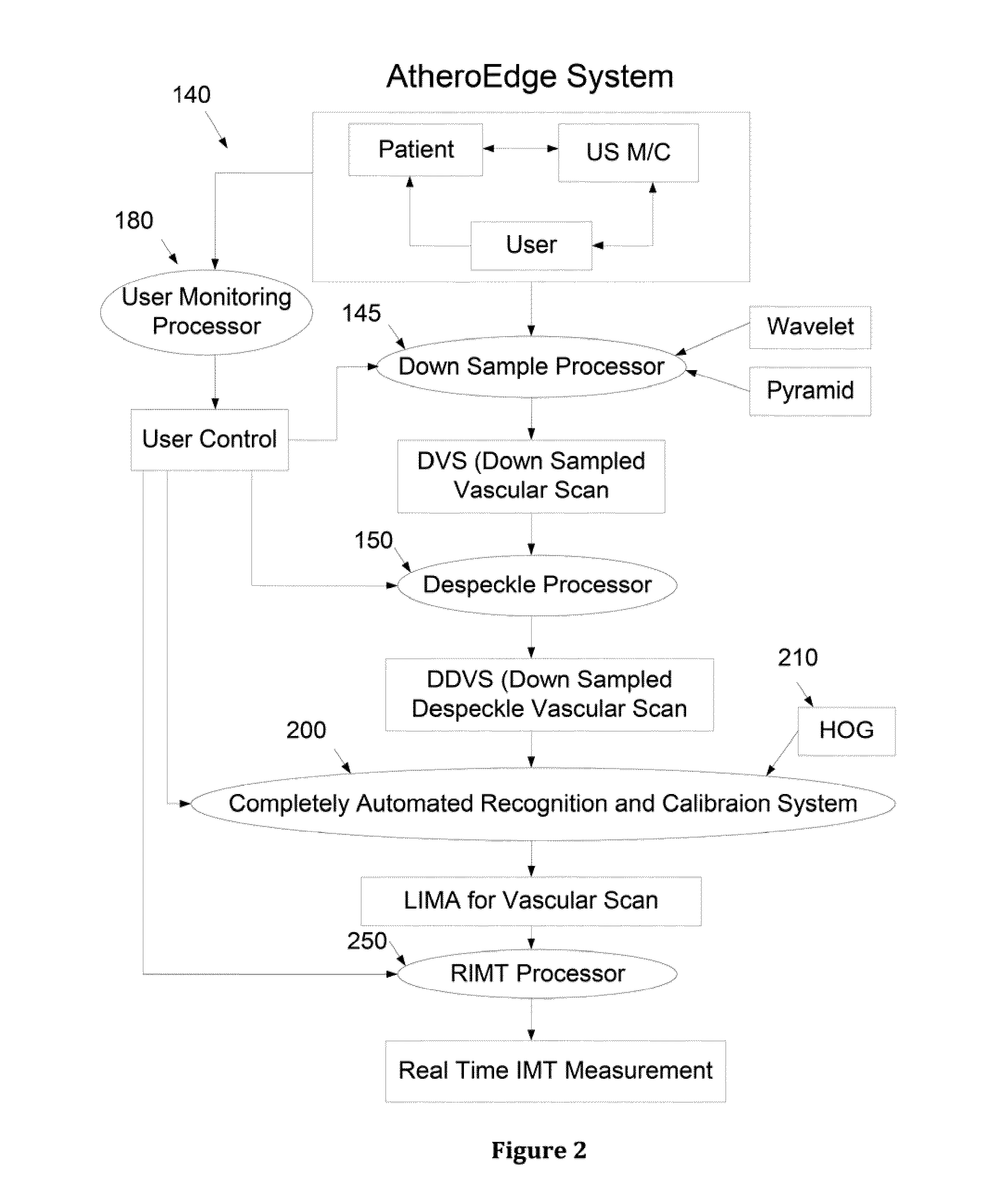
Ultrasound carotid media wall classification and imt measurement in curved vessels using recursive refinement and validation
InactiveUS20110257527A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementBlood vesselImaging data
A computer-implemented system and method for intima-media thickness (IMT) measurements using a validation embedded segmentation method. Various embodiments include receiving biomedical imaging data and patient demographic data corresponding to a current scan of a patient; checking the biomedical imaging data in real-time to determine if an artery of the patient has a calcium deposit in a proximal wall of the artery; acquiring arterial data of the patient as a combination of longitudinal B-mode and transverse B-mode data; using a data processor to automatically recognize the artery by embedding anatomic information; using the data processor to calibrate a region of interest around the automatically recognized artery; automatically computing the weak or missing edges of intima-media and media-adventitia walls using labeling and connectivity; and determining the intima-media thickness (IMT) of an arterial wall of the automatically recognized artery.
Owner:SURI JASJIT S
Percutaneous Methods for Creating Native Tissue Venous Valves
Percutaneous methods of forming a venous valve from autologous tissue are disclosed. The methods include percutaneously creating one or two subintimal dissections for forming one or two flaps of intimal tissue. In one method, a puncture element is delivered by a catheter based delivery system to a treatment site where a new venous valve is to be created. The puncture element is deployed to gain access to a subintimal layer of the vein wall. A dilation balloon is than positioned and inflated within the subintimal layer to create a flap and corresponding pocket / sinus in the vein, which than acts as a one-way monocuspid valve in the manner of a native venous valve. In a similar manner, methods of forming new bicuspid venous valves by subintimal dissections are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Vascular tissue composition
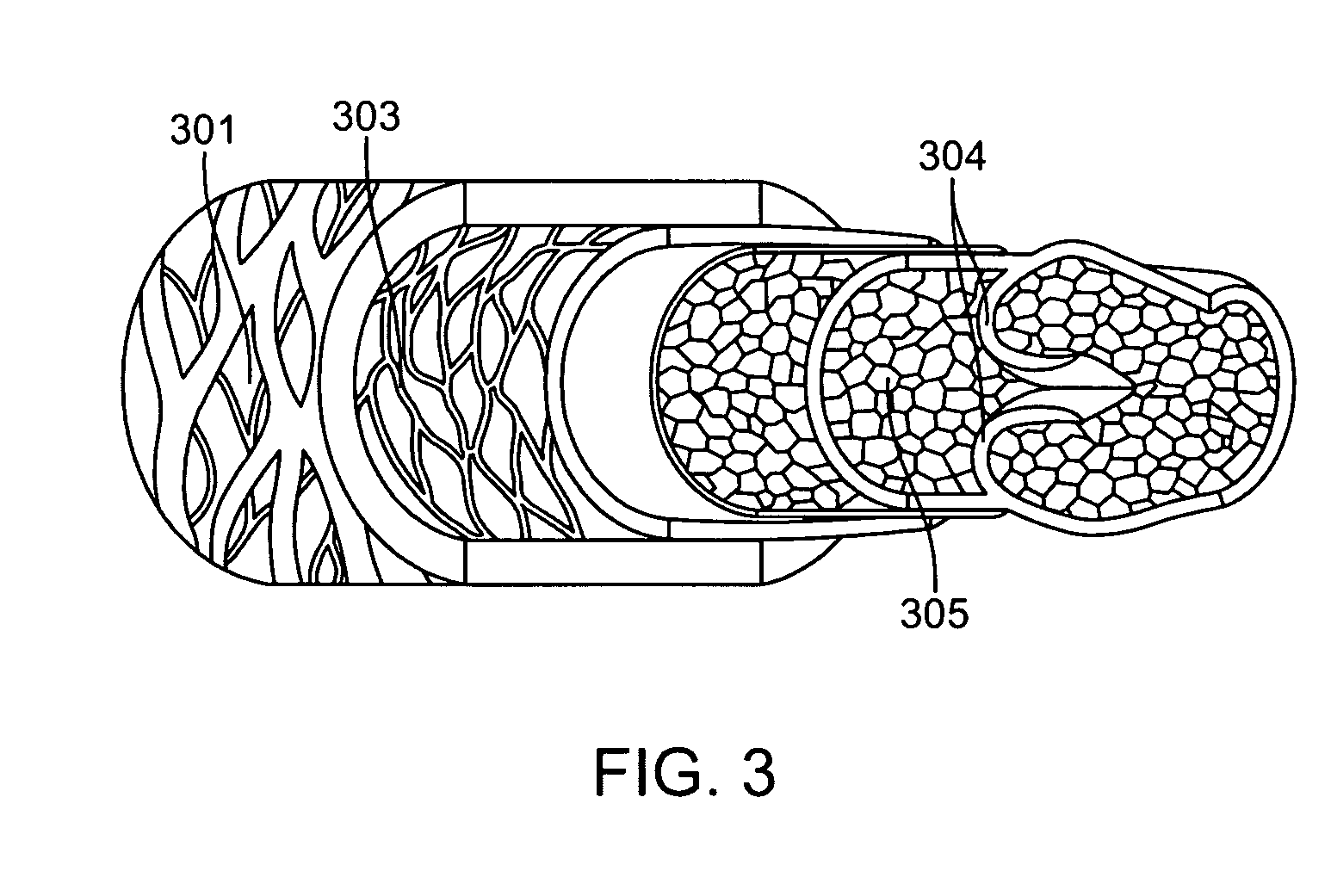
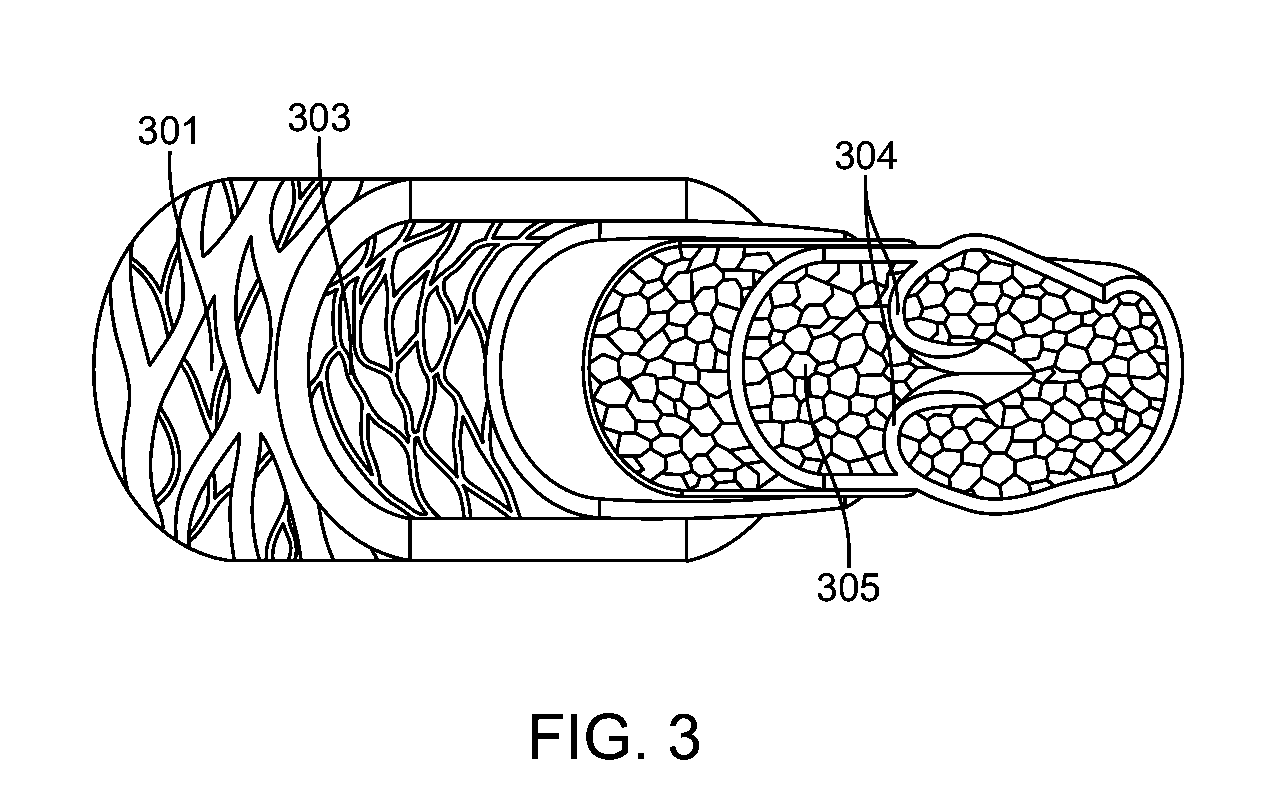
A tissue composition includes the subendothelial layer, the elastica interna, and at least a portion of the tunica media of a blood vessel harvested from a mammal, with the endothelial cells removed from the blood vessel. The tissue composition can also include a portion of the tunica adventitia of a blood vessel harvested from a mammal. The tissue composition can be formed into a graft, a patch, a connective tissue for surgical repair, an orthopedic graft, and a substrate for cell growth, among other applications. The tissue composition can also be fluidized, or made into powdered form.
Owner:YANG JUN
Implant for aortic dissection and methods of use
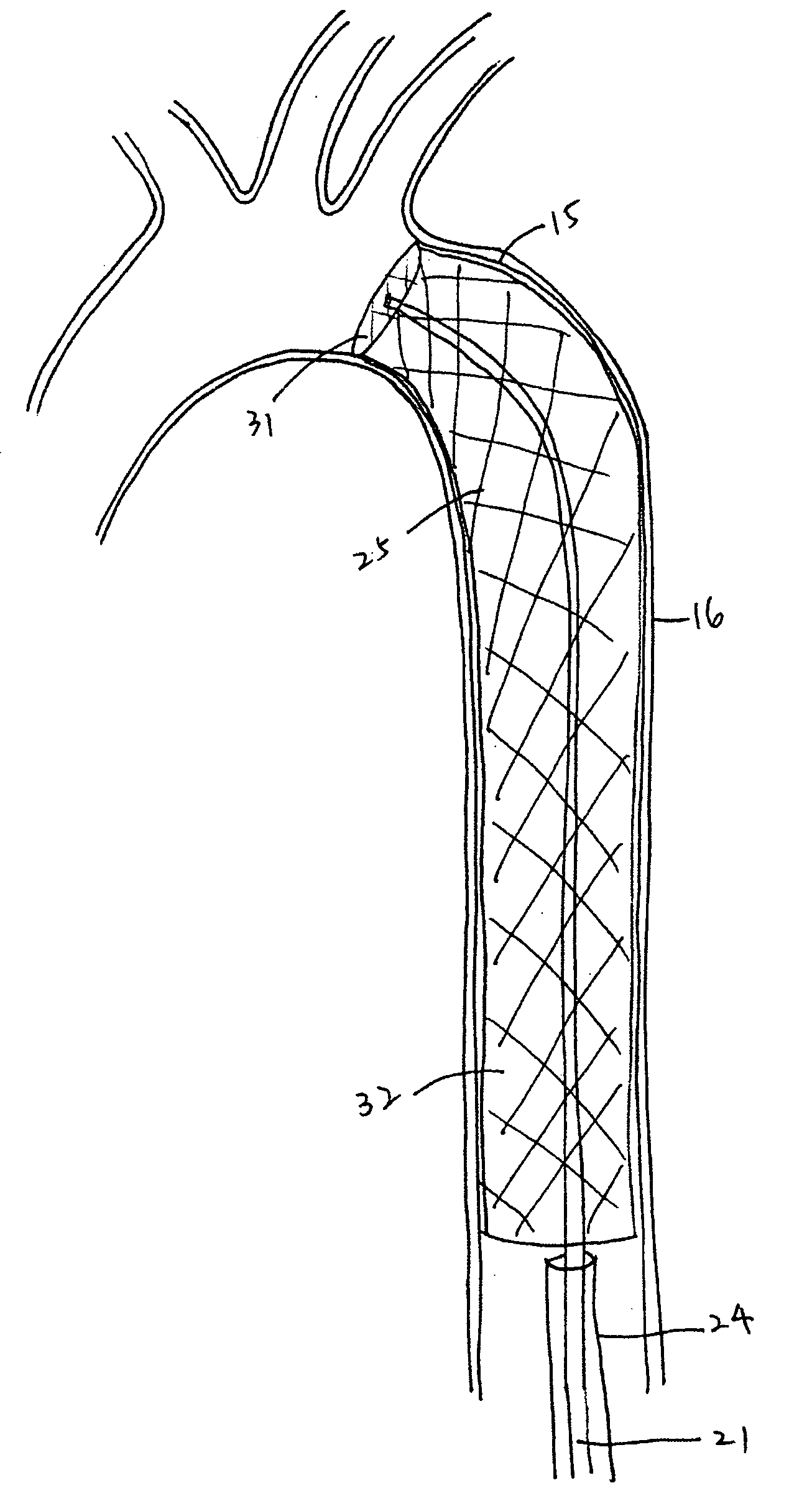
Methods and devices for treating an aortic dissection having an entry point downstream of the takeoff of the left subclavian artery. The devices include a catheter that carries an endoluminal implant at a distal region of the catheter. The implant is a self-expanding tubular mesh or strutted stent. A capture sheath holds the stent in a compressed state for percutaneous delivery. The catheter is advanced to position the stent adjacent the entry point of the dissection. The stent is released by withdrawing the capture sheath. The stent expands to engage the intimal lining and press the intima into contact with the outer layers of the aorta and thereby promote healing of the dissection.
Owner:SAGE MEDICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for preventing dialysis graft intimal hyperplasia
ActiveUS7553326B2Reducing and preventing symptomPrevent proliferationSurgical instrument detailsCatheterAnticarcinogenIntimal proliferation
To prevent intimal hyperplasia within a dialysis graft, a flexible tube comprising the dialysis graft is coated interiorly before placement with an anticarcinogen or mitosis-inhibiting agent for preventing cell division. The graft can also be irradiated with light energy by directing light into the lumen of the tube that has been grafted in place, thereby preventing or reducing dialysis graft intimal hyperplasia and reducing inflammation. The light source can be a light emitting diode (LED) or a chemical light source, i.e., a chemiluminescent substance for producing cool light energy within the graft to prevent or reduce the symptoms of GIH. When phototherapy is used, the body is exposed to light radiation at the site of the graft in sufficient amount to prevent undesired cell proliferation within the vessels, the graft, or surrounding tissue where the invention is used without detectable damage to body tissue.
Owner:SWEET RICHARD M
Percutaneous methods and apparatus for creating native tissue venous valves
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
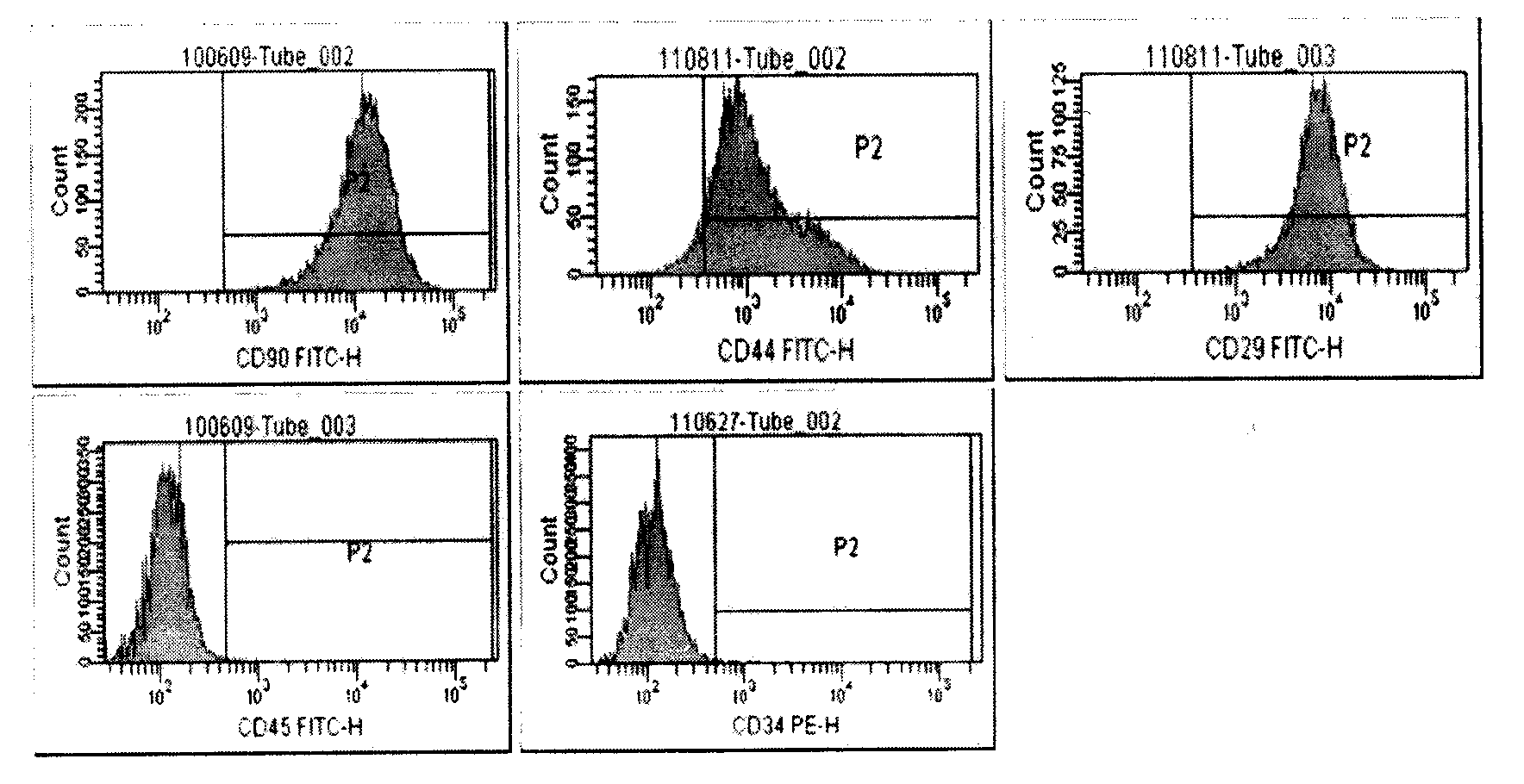
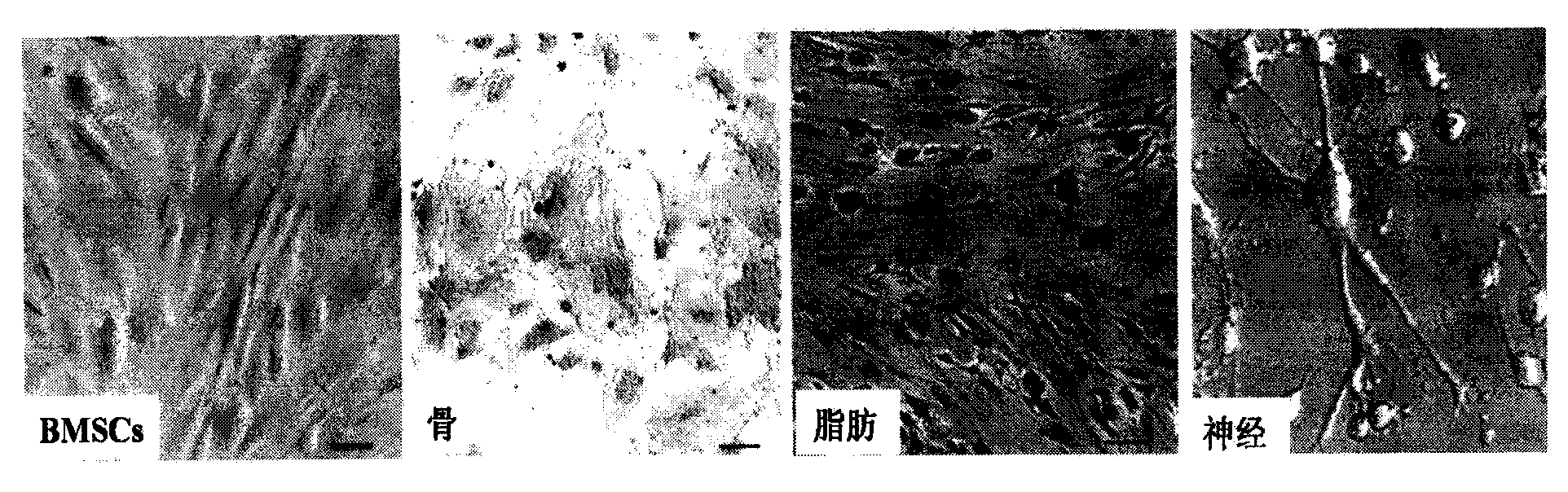
Preparation method and application of collagen scaffold composite bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs)
ActiveCN103705984AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationSurgeryIntrauterine deviceBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of collagen scaffold composite bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing single cell suspension after trypsinizing the BMSCs, uniformly dropwise adding the single cell suspension to a collagen scaffold, putting the collagen scaffold into an incubator to be cultured, and adding an L-DMEM complete medium to continue culture, thus obtaining the collagen scaffold composite BMSCs. The preparation method has the advantages that the following defects are overcome: endometria are seriously injured as intrauterine adhesion is mechanically separated by adopting hysteroscopic surgery, intrauterine devices or anti-adhesion materials are put after the surgery and estrogens are given after the surgery to promote intima growth; the problem of intima scars can not be solved; functional intima repair can not be achieved; adhesion is very easy to happen again. As active ingredients for treating serious endometrium injury, the BMSCs are convenient to obtain, secrete growth factors to improve the local microenvironment and immunoregulation, have good biocompatibility, degradability and safety, promote scarred endometrium repair and increase the intima thickness and local blood vessel density.
Owner:YANTAI ZHENGHAI BIO TECH
Vascular tissue composition
A tissue composition includes the subendothelial layer, the elastica interna, and at least a portion of the tunica media of a blood vessel harvested from a mammal, with the endothelial cells removed from the blood vessel. The tissue composition can also include a portion of the tunica adventitia of a blood vessel harvested from a mammal. The tissue composition can be formed into a graft, a patch, a connective tissue for surgical repair, an orthopedic graft, and a substrate for cell growth, among other applications. The tissue composition can also be fluidized, or made into powdered form.
Owner:YANG JUN
Method for inhibiting new tissue growth in blood vessels in a patient subjected to blood vessel injury
InactiveUS20080171701A1Preventing exaggerated restenosisPrevent exaggerated restenosisOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood vessel spasmPercent Diameter Stenosis
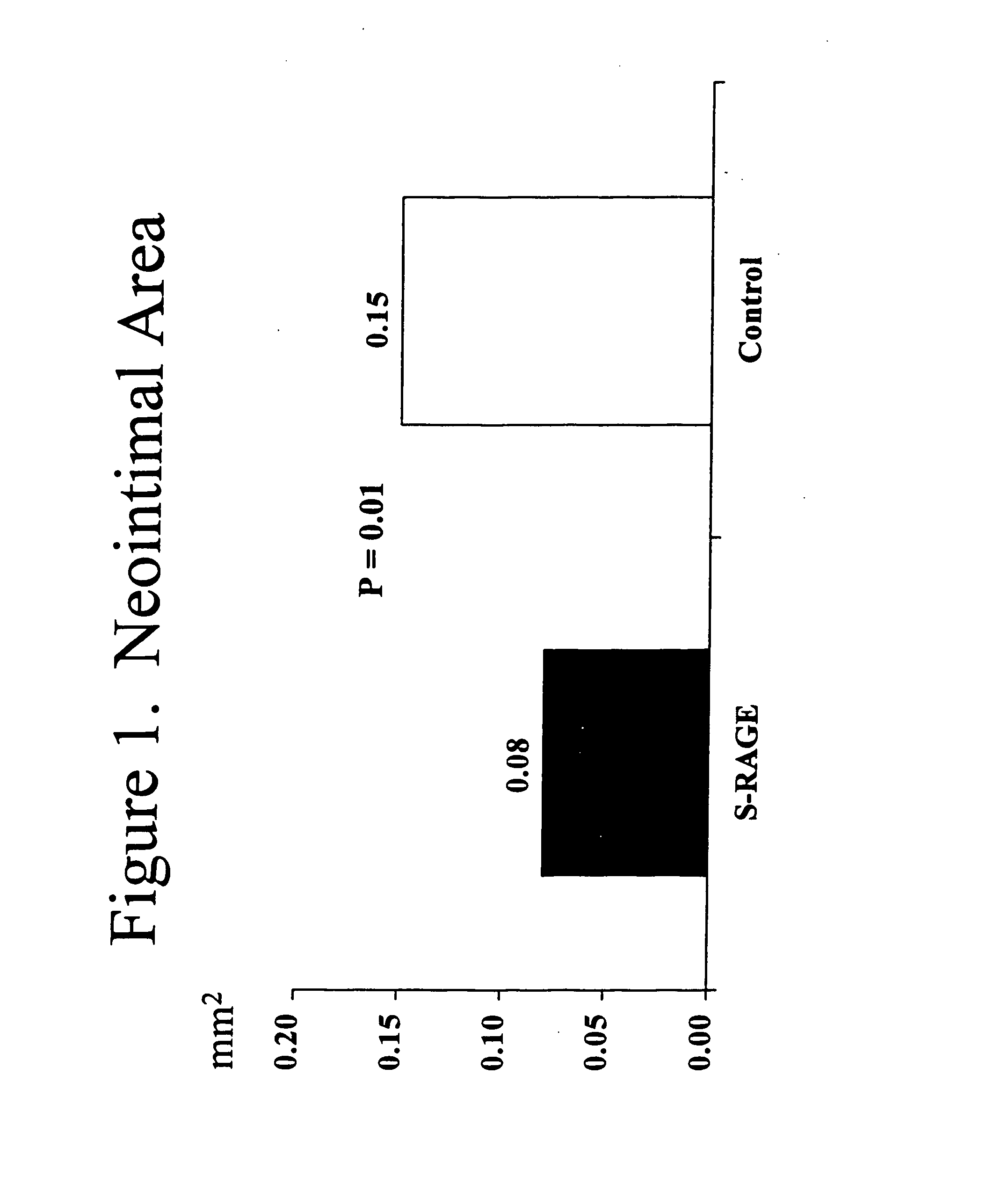
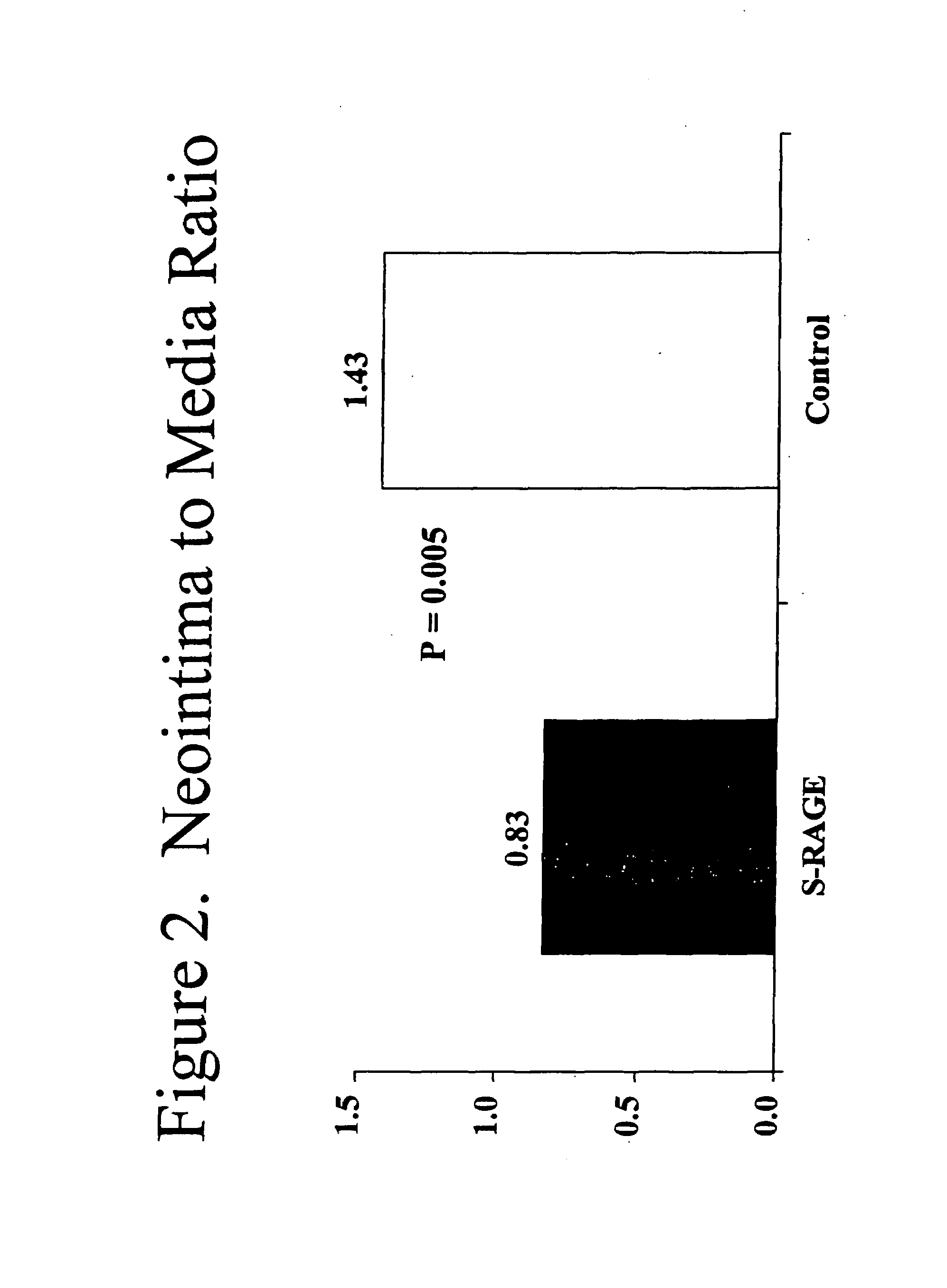
This invention provides for a method for inhibiting new tissue growth in blood vessels in a subject, wherein the subject experienced blood vessel injury, which comprises administering to the subject a pharmaceutically effective amount of an inhibitor of receptor for advanced glycation endproduct (RAGE) so as to inhibit new tissue growth in the subject's blood vessels. The invention also provides for method for inhibiting neointimal formation in blood vessels in a subject, wherein the subject experienced blood vessel injury, which comprises administering to the subject a pharmaceutically effective amount of an inhibitor of receptor for advanced glycation endproduct (RAGE) so as to inhibit neointimal formation in the subject's blood vessels. The invention also provides a method for preventing exaggerated restenosis in a diabetic subject which comprises administering to the subject a pharmaceutically effective amount of an inhibitor of receptor for advanced glycation endproduct (RAGE) so as to prevent exaggerated restenosis in the subject.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Medicinal coating layer supporting frame for preventing/treating renarrowing after inbellow arteria coronaria shaping operation
A medicine coated scaffold for preventing and treating the renarrowing of arteria coronaria after plastic operation features that the tatin kind of medicines which can suppress the growth of new tunia intime and the reproduction of smooth muscle cells is contained in the coated layer of scaffold and can be slowly released to prevent said renarrowing of arteria coronaria. Its advantages are high effect and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT MEDICAL (GROUP) CO LTD
Medical imaging diagnostic method
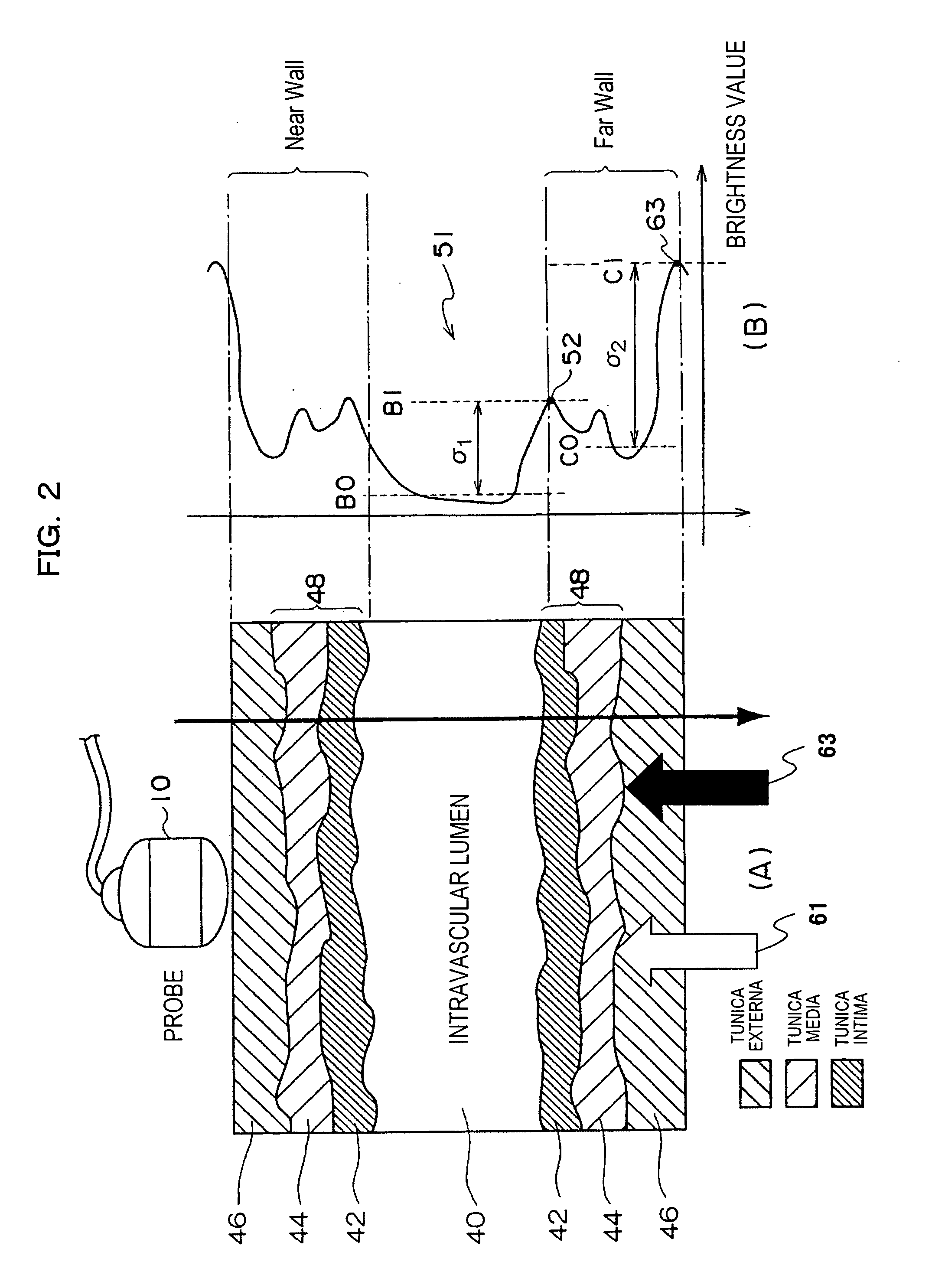
InactiveUS20070149877A1Improve accuracyEasy extractionOrgan movement/changes detectionCatheterTunica mediaTunica intima
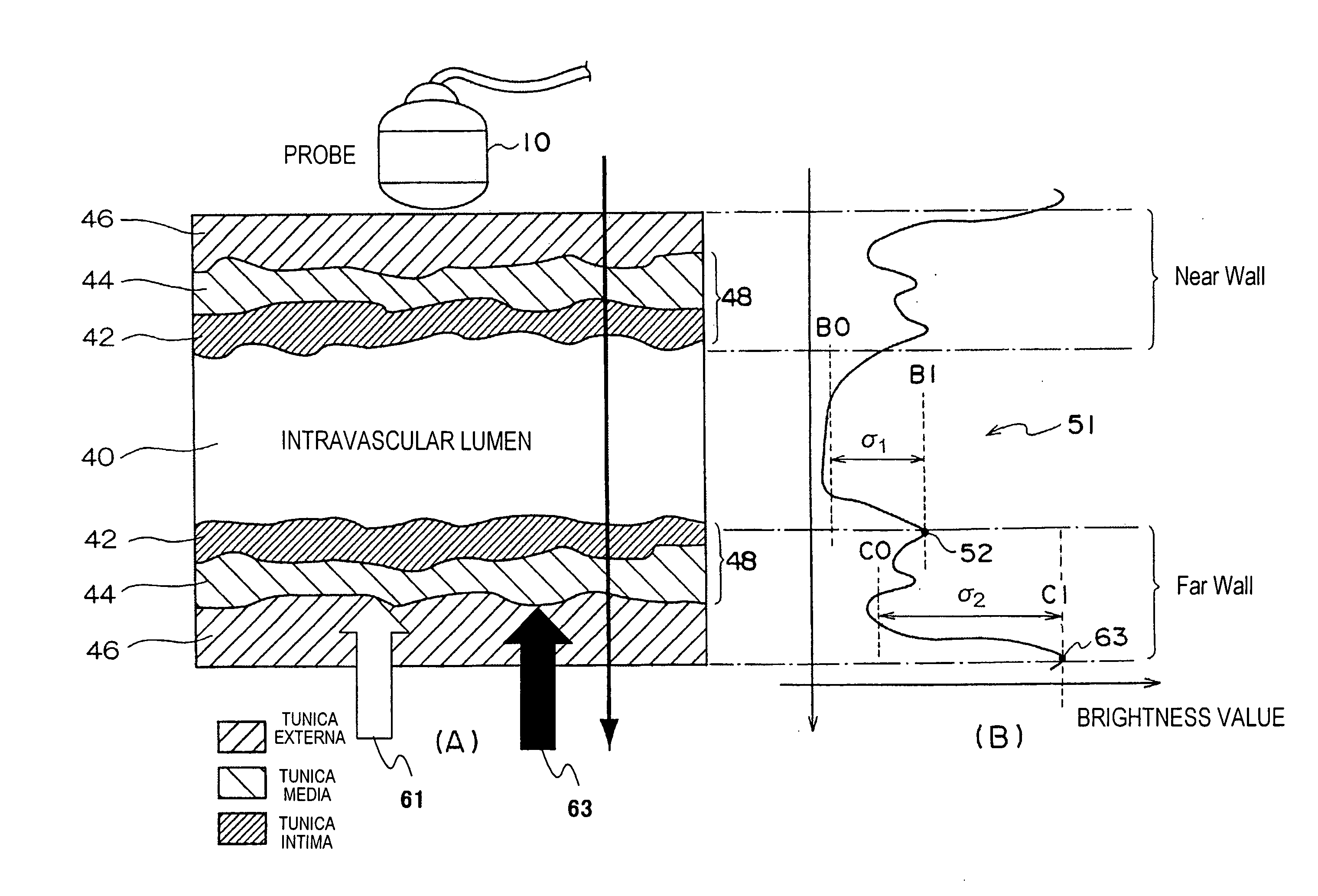
A medical imaging diagnosis apparatus for measuring the composite thickness of the tunica intima (42) and the tunica media (44) of a blood vessel of a subject by acquiring image data on the blood vessel. In order to improve the accuracy of the IMT measurement of the composite thickness, the medical imaging diagnosis apparatus has extracting means for extracting the tunica intima (42) and the tunica exterma (46) of the blood vessel on the basis of the brightness information of the image data to measure the composite thickness of the tunica intima and the tunica exterma of the vessel in reference to the two extracted regions.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Medicine coating rack
InactiveCN1552474AReduce formationPrevent restenosisOrganic active ingredientsSurgeryApoptosisThrombus
A scaffold with coated medicine layer is composed of scaffold body and medicine layer containing taxol or its derivative, anti-thrombocyte medicine and anti-inflammatory medicine. Its advantages are high effect to durably prevent the new growth of tunica intima, renarrowing and delayed thrombus, and no affection to normal endothelium process.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT MEDICAL (GROUP) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com