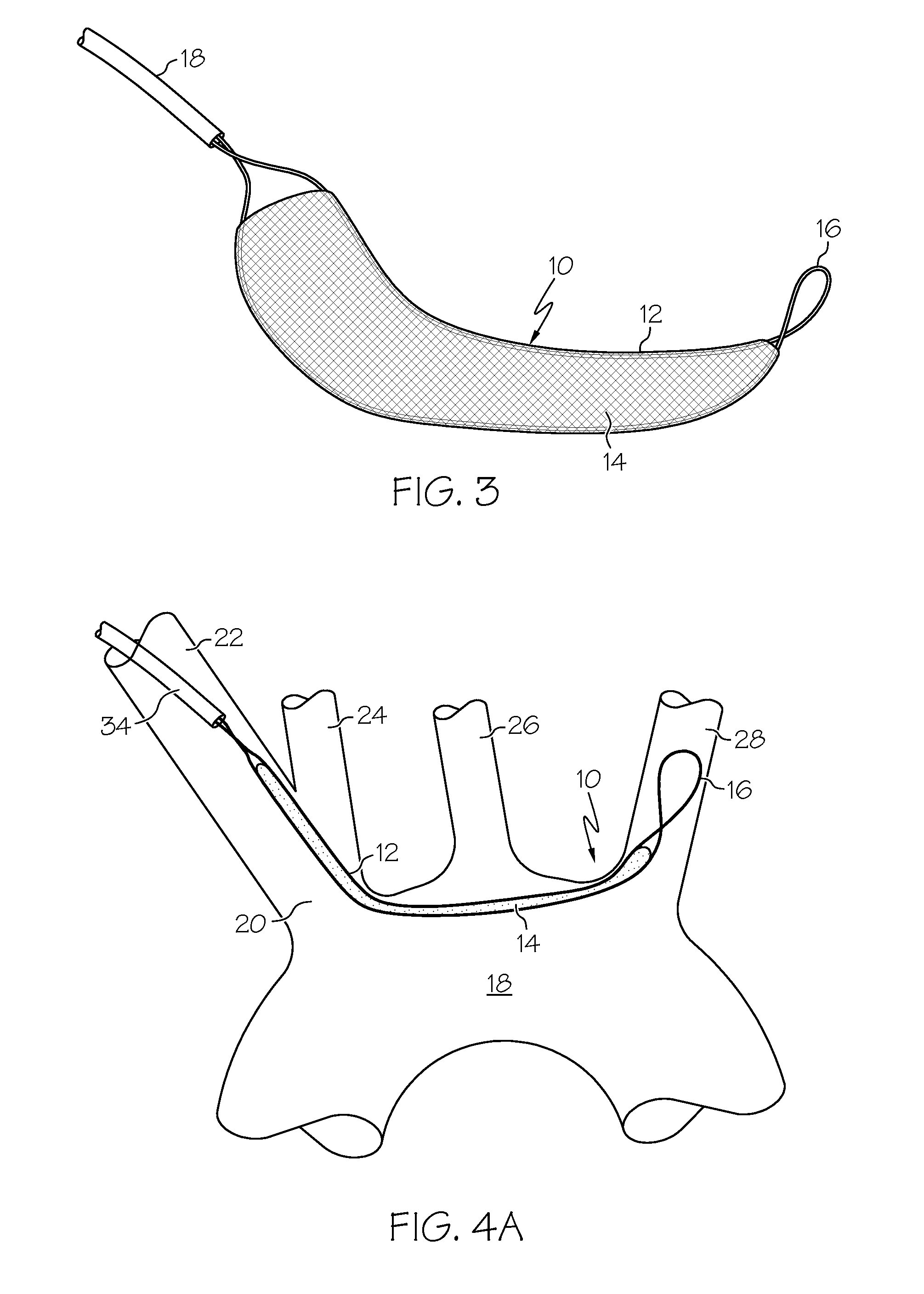
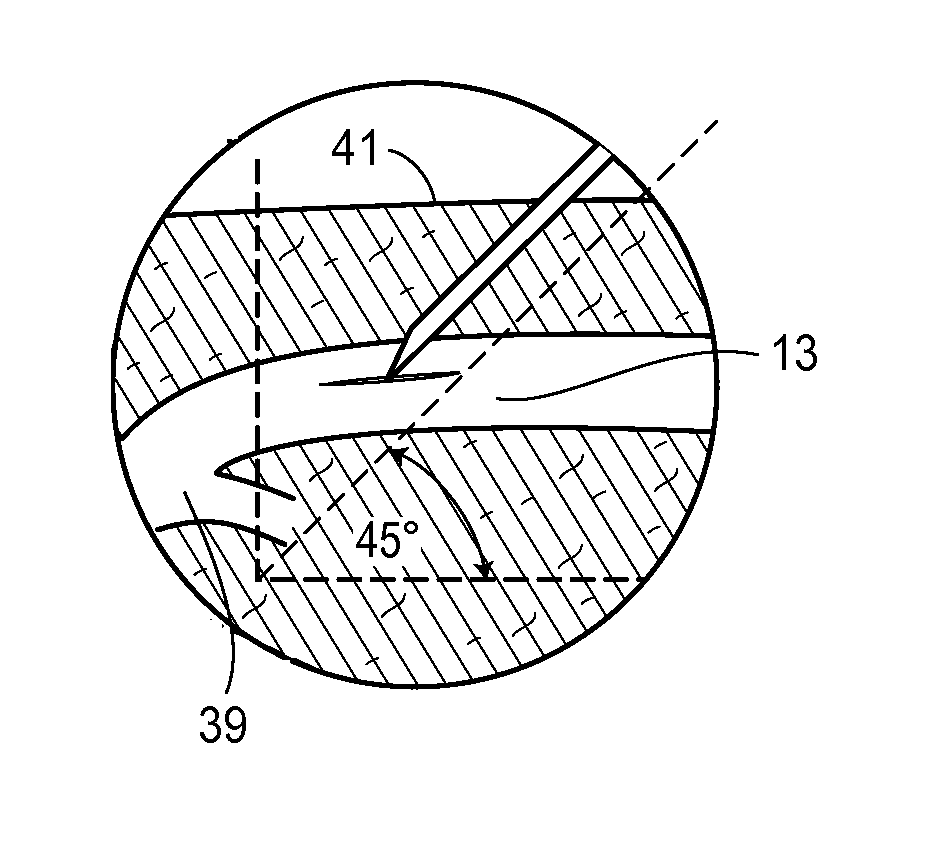
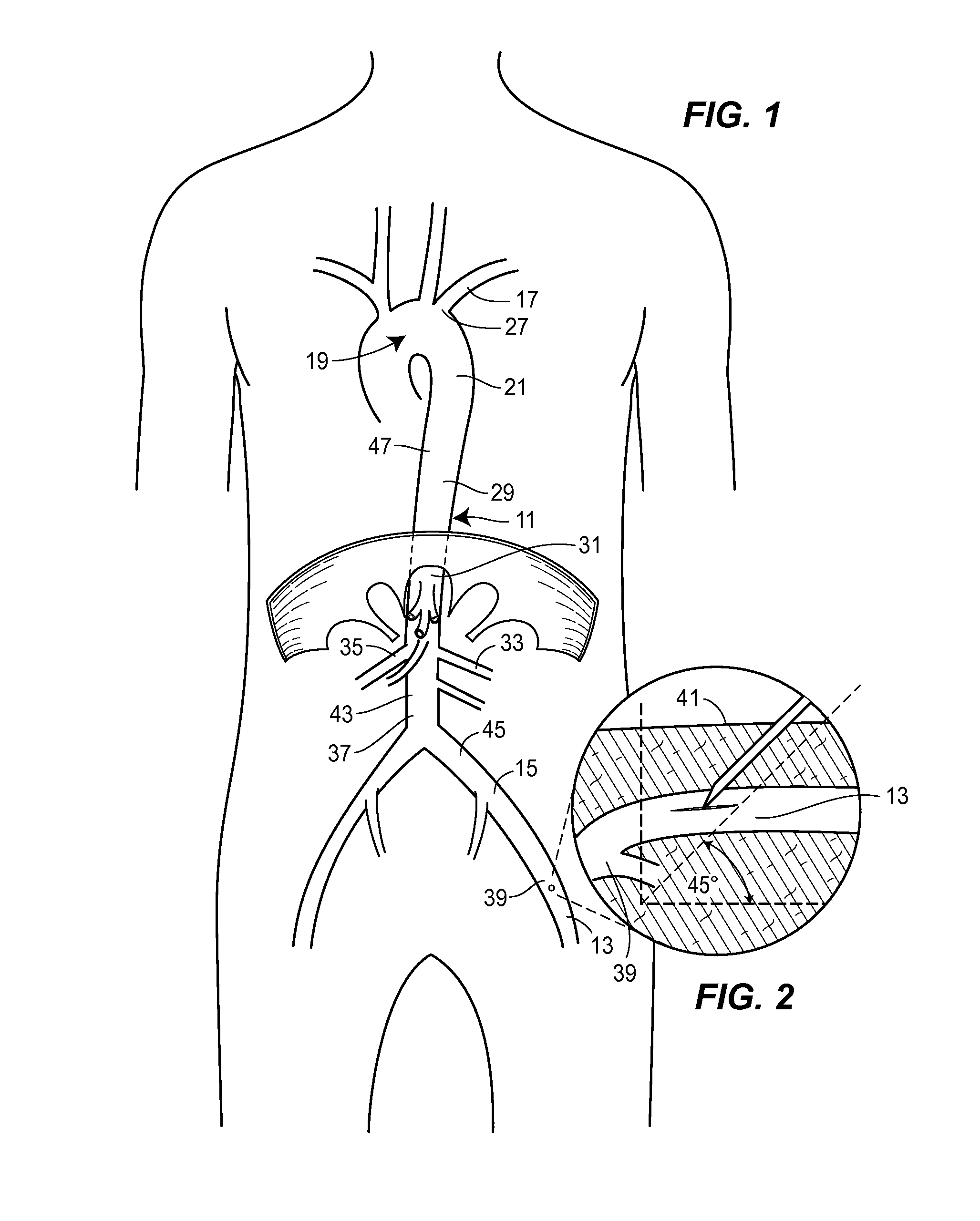
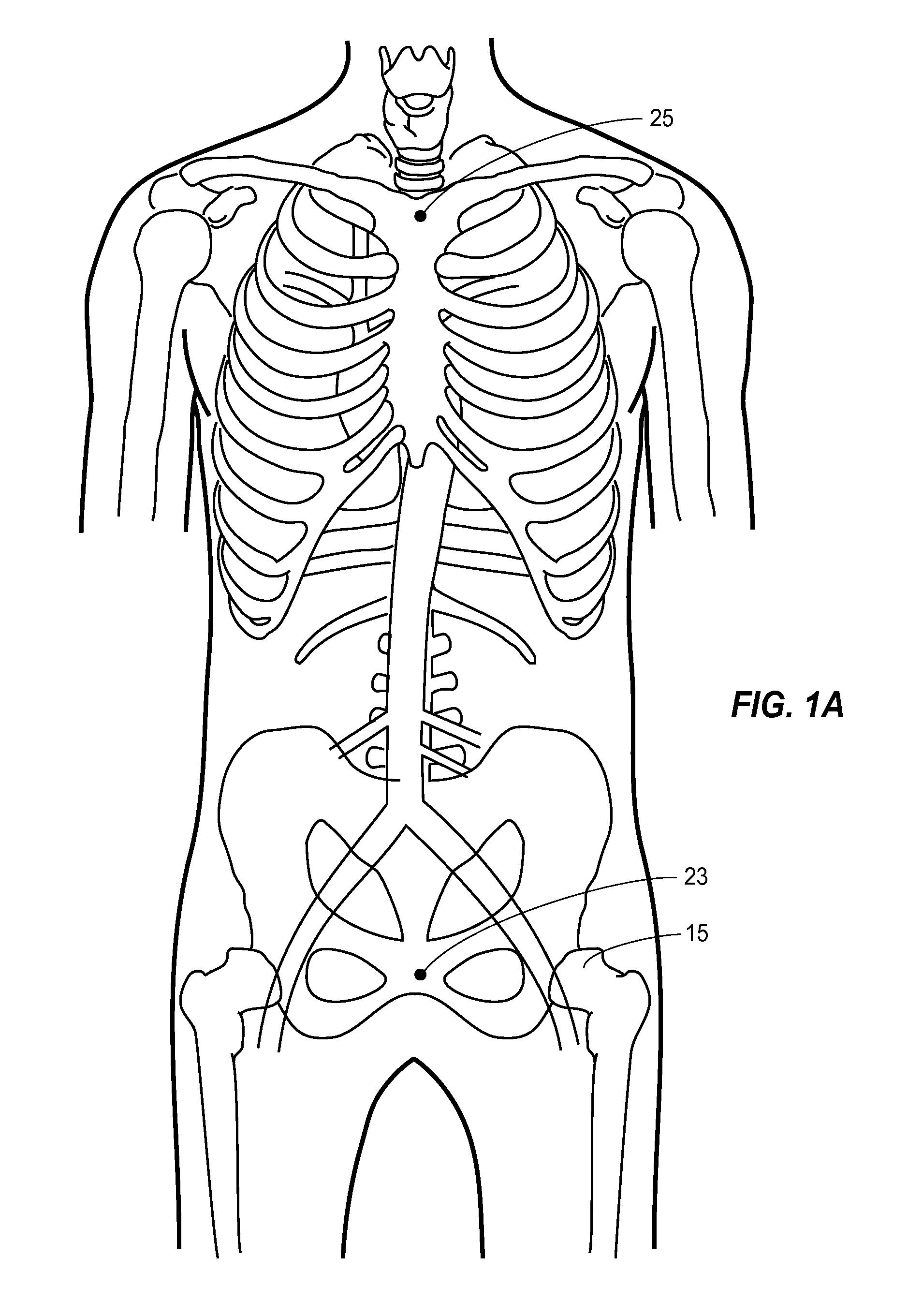
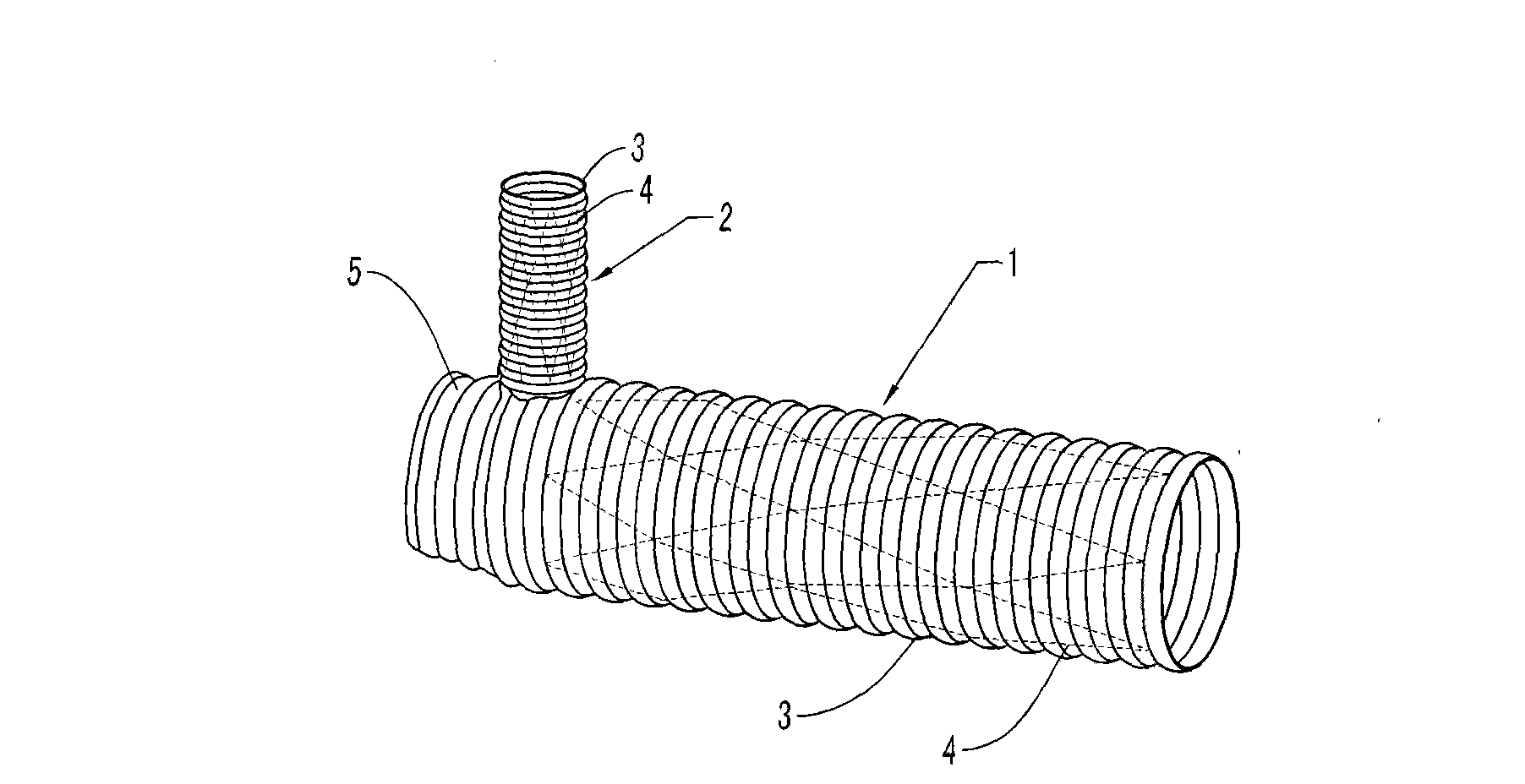
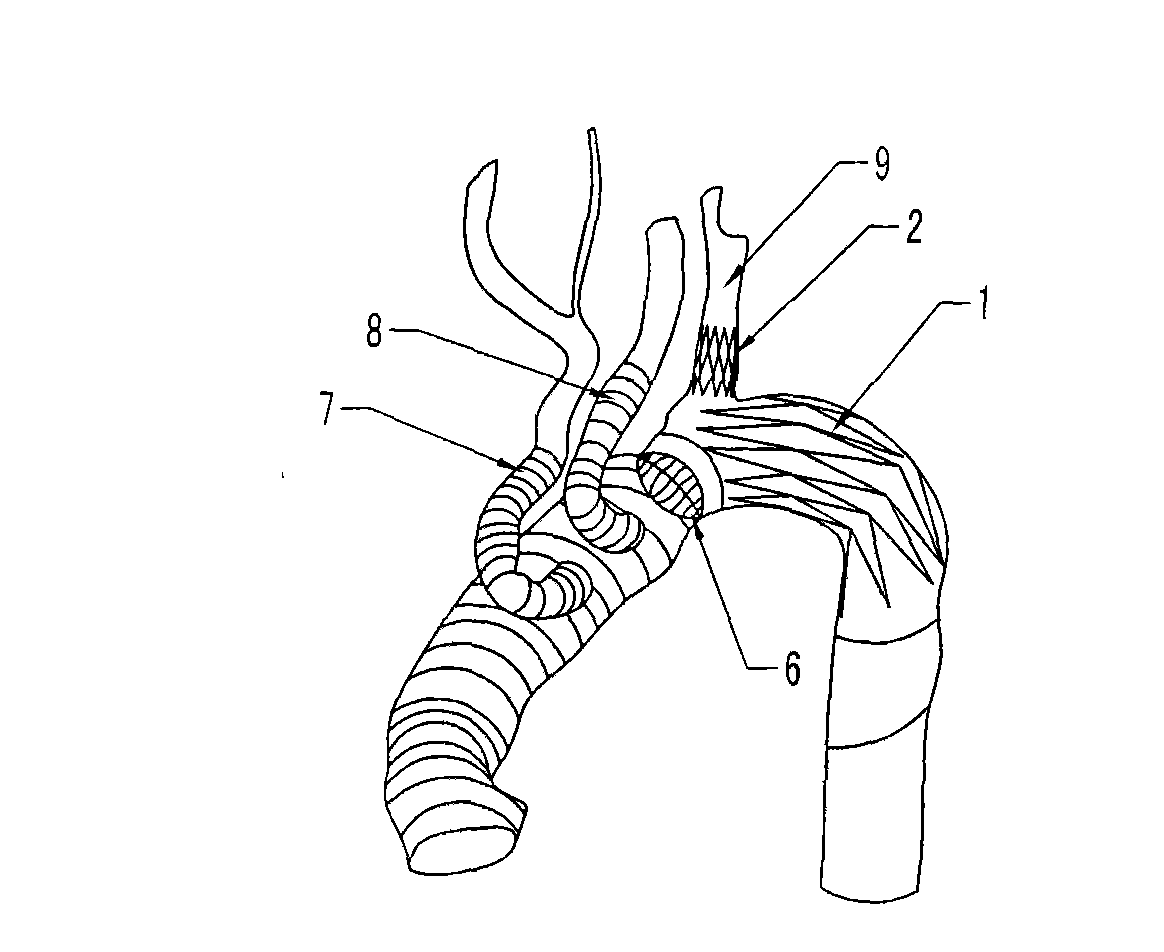
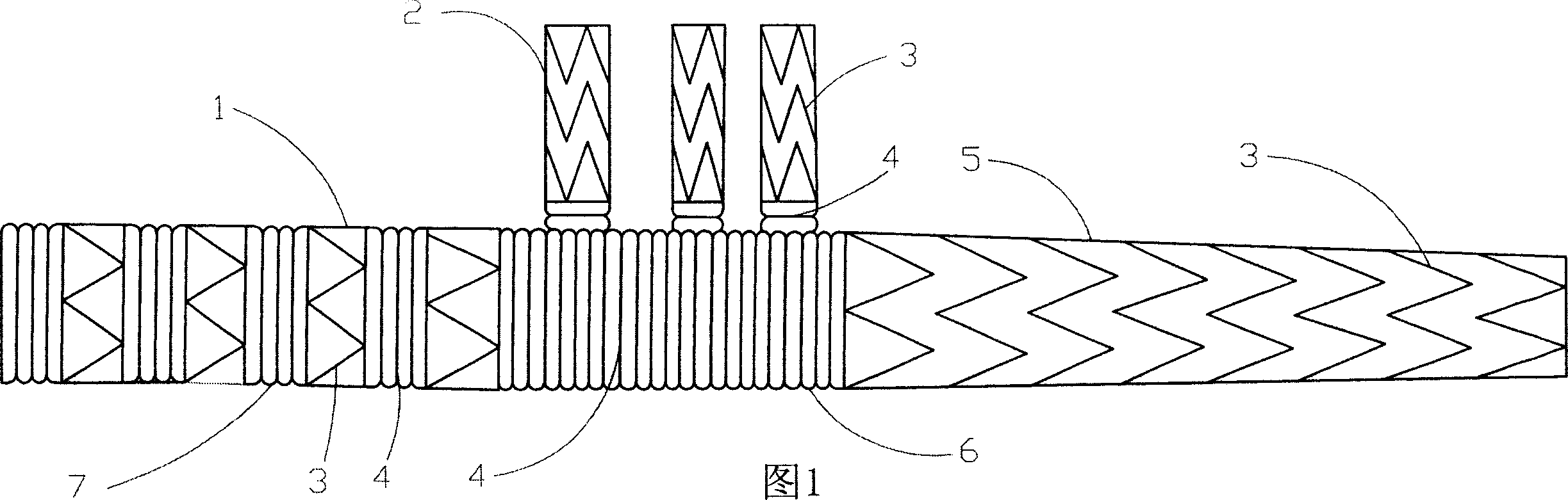
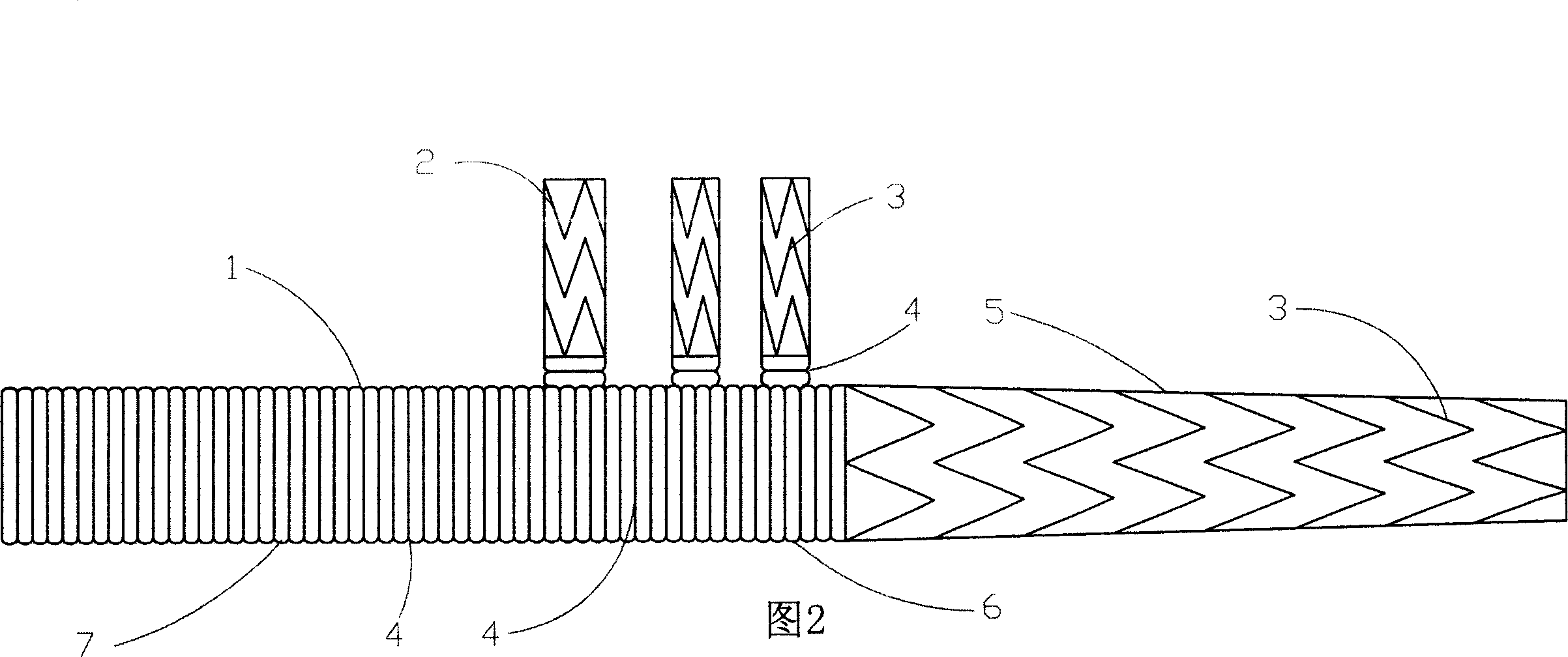
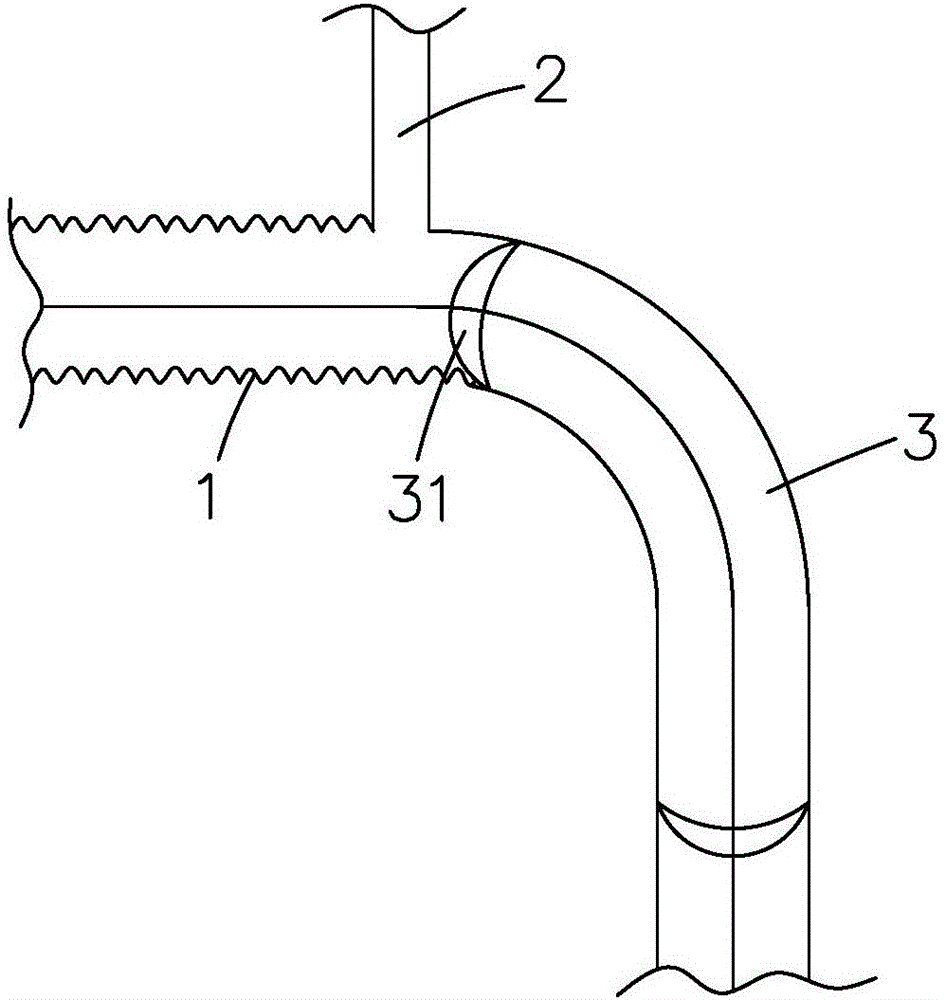
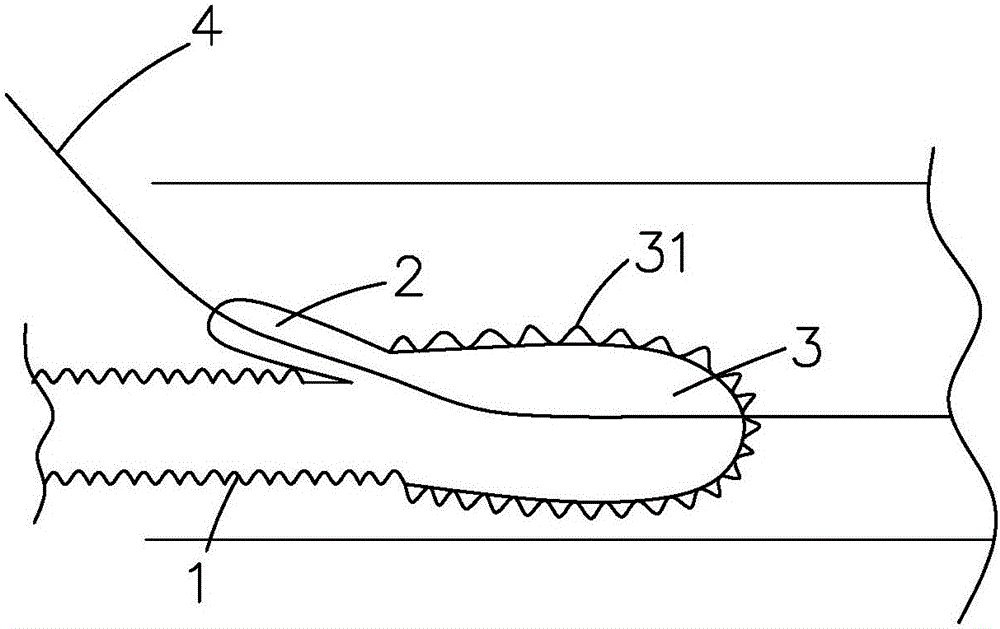
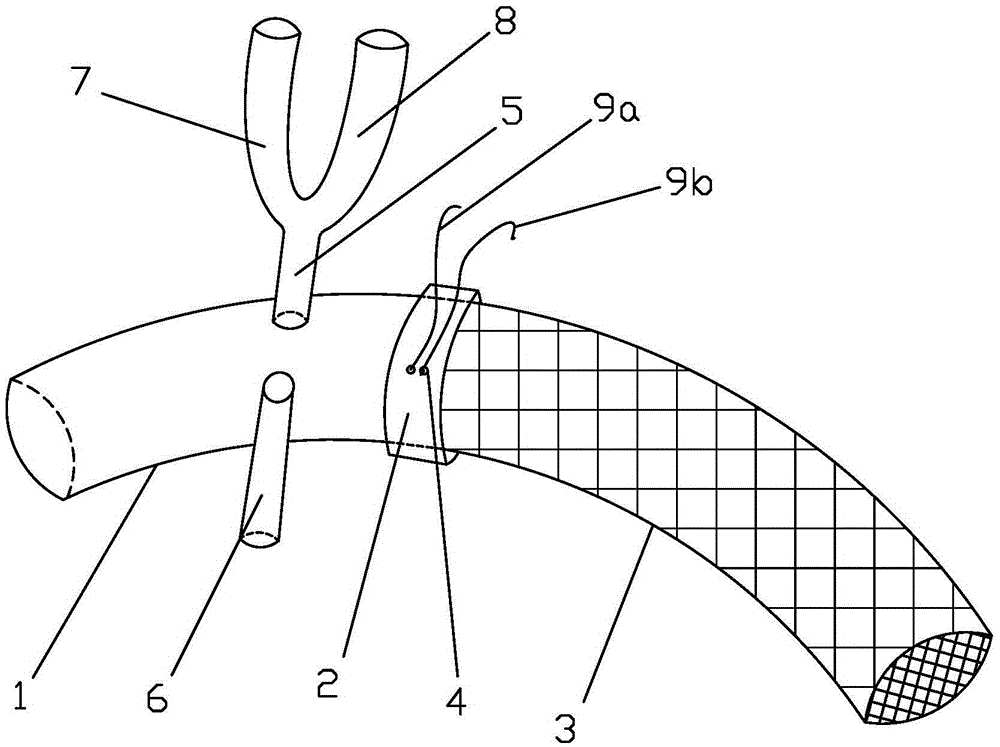
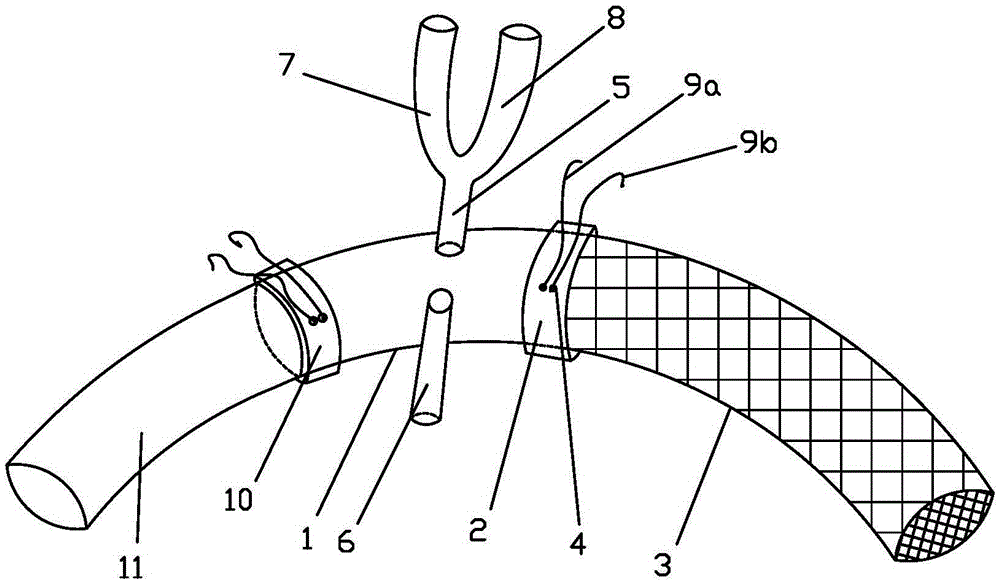
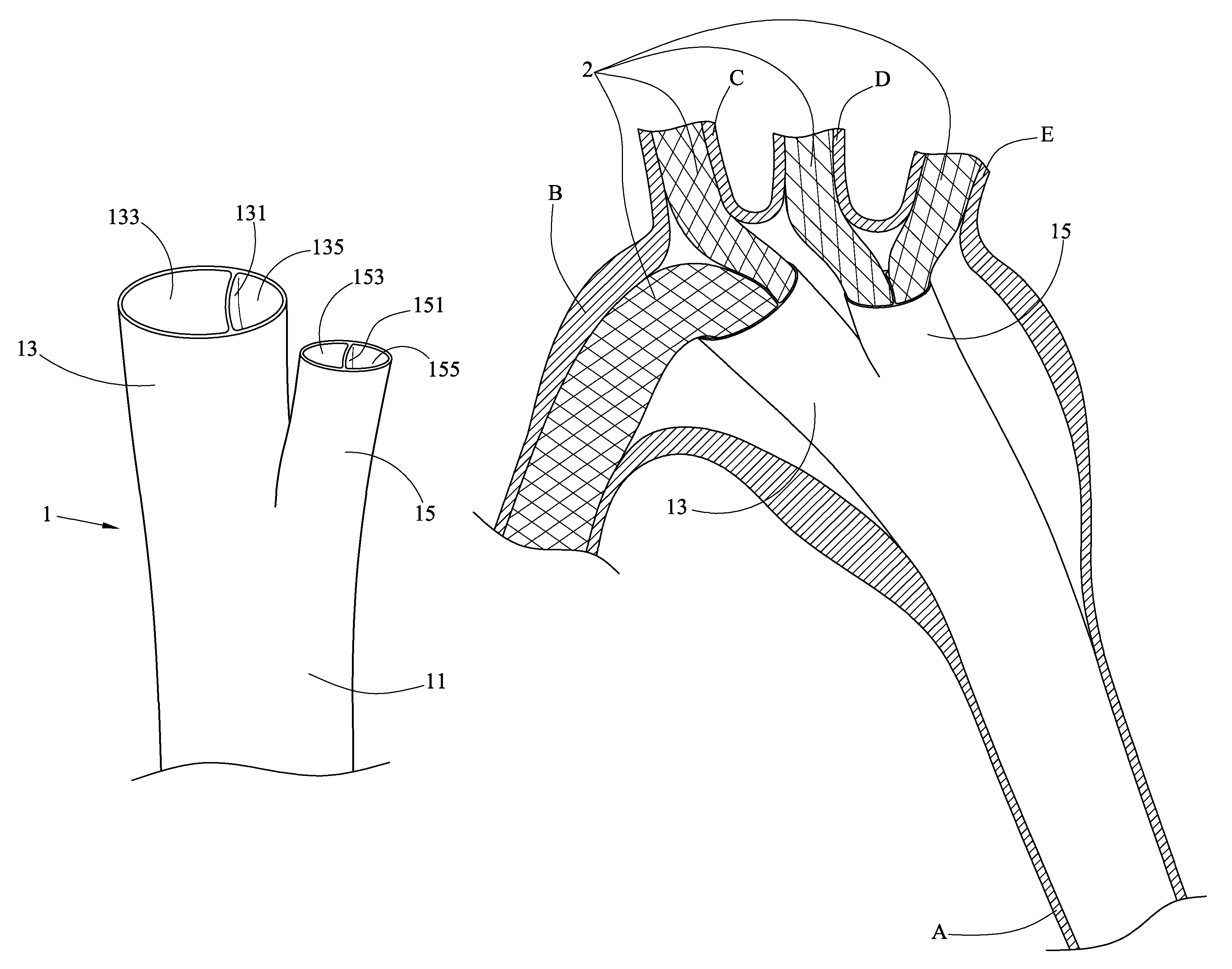
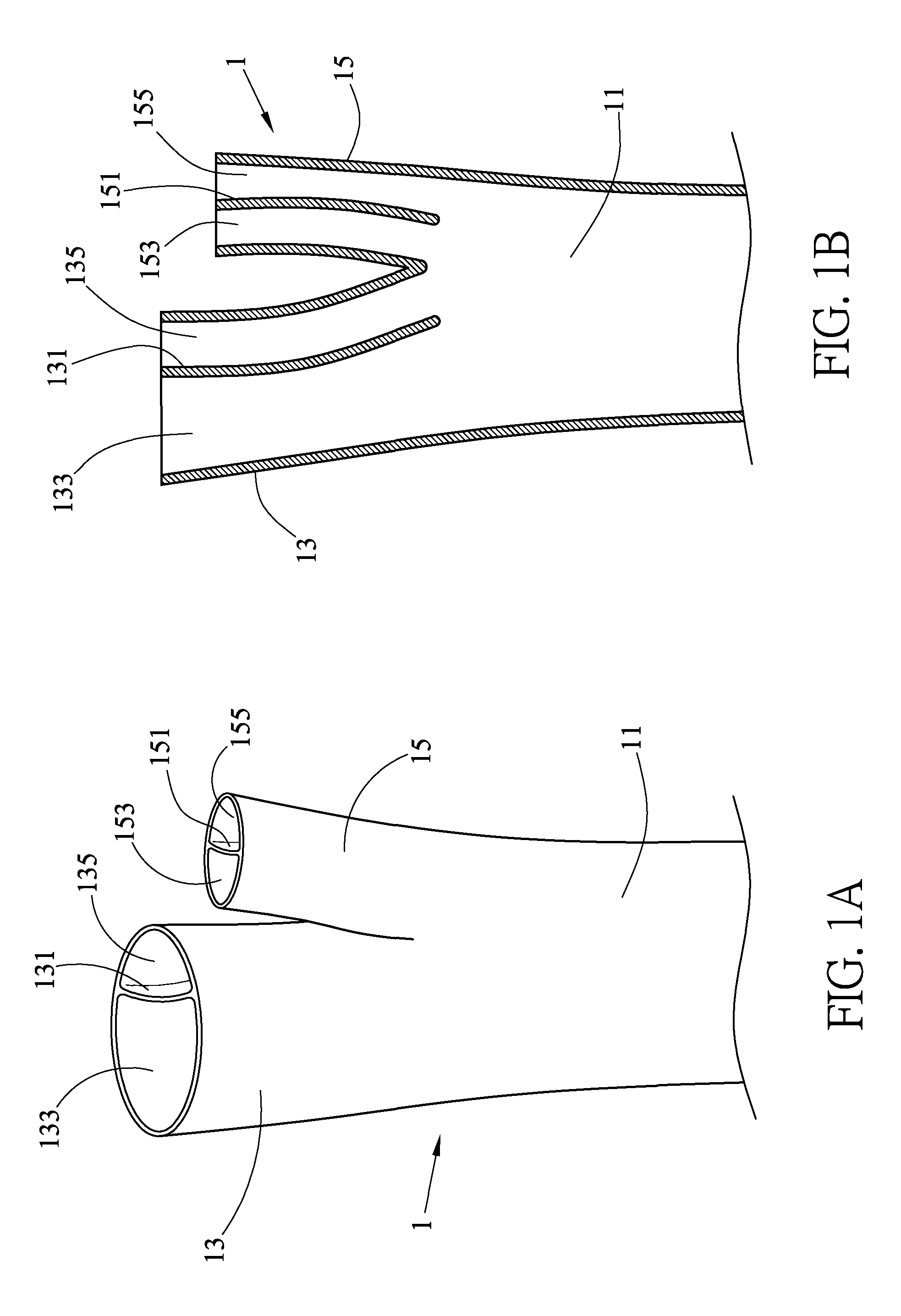
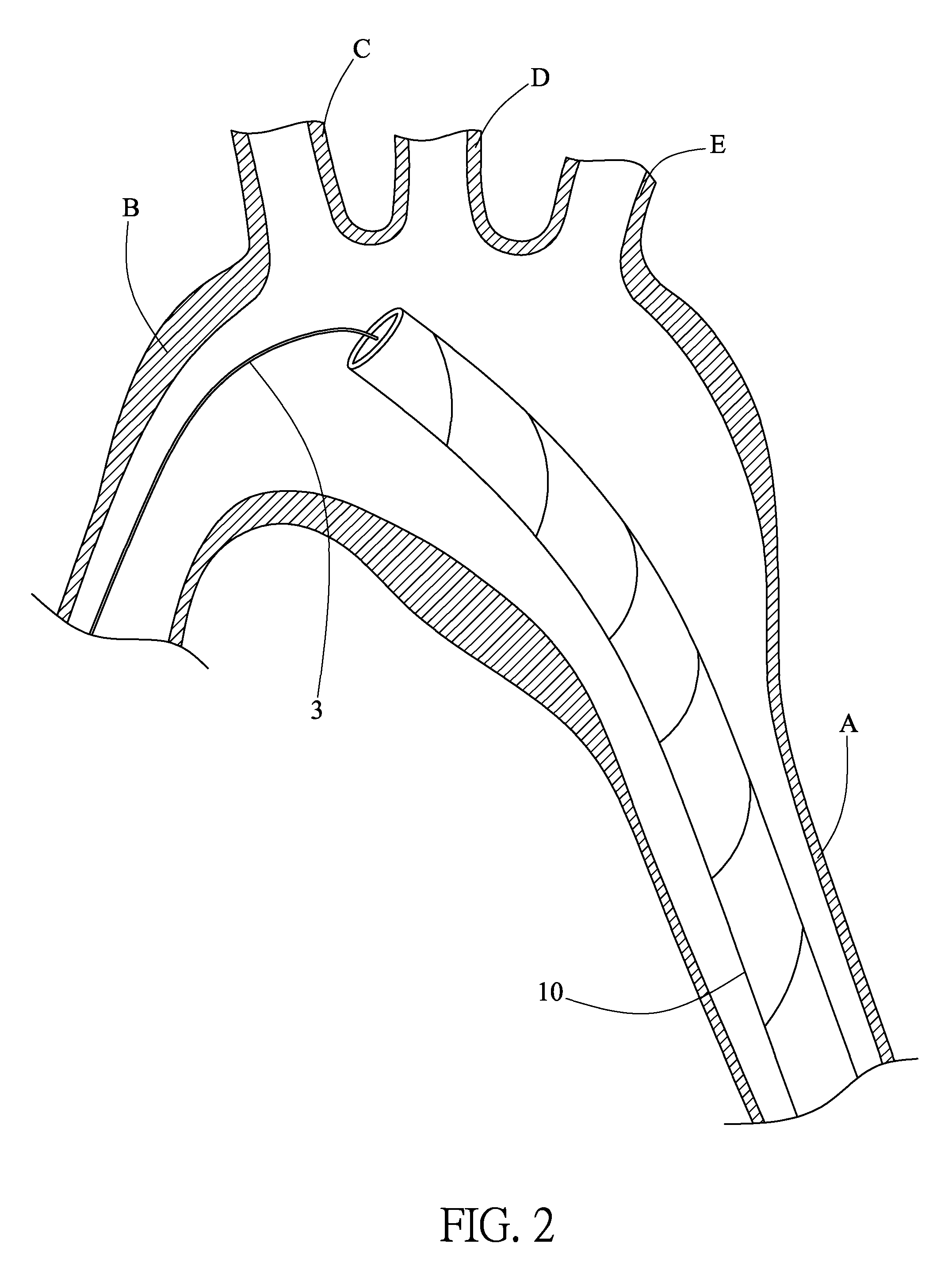
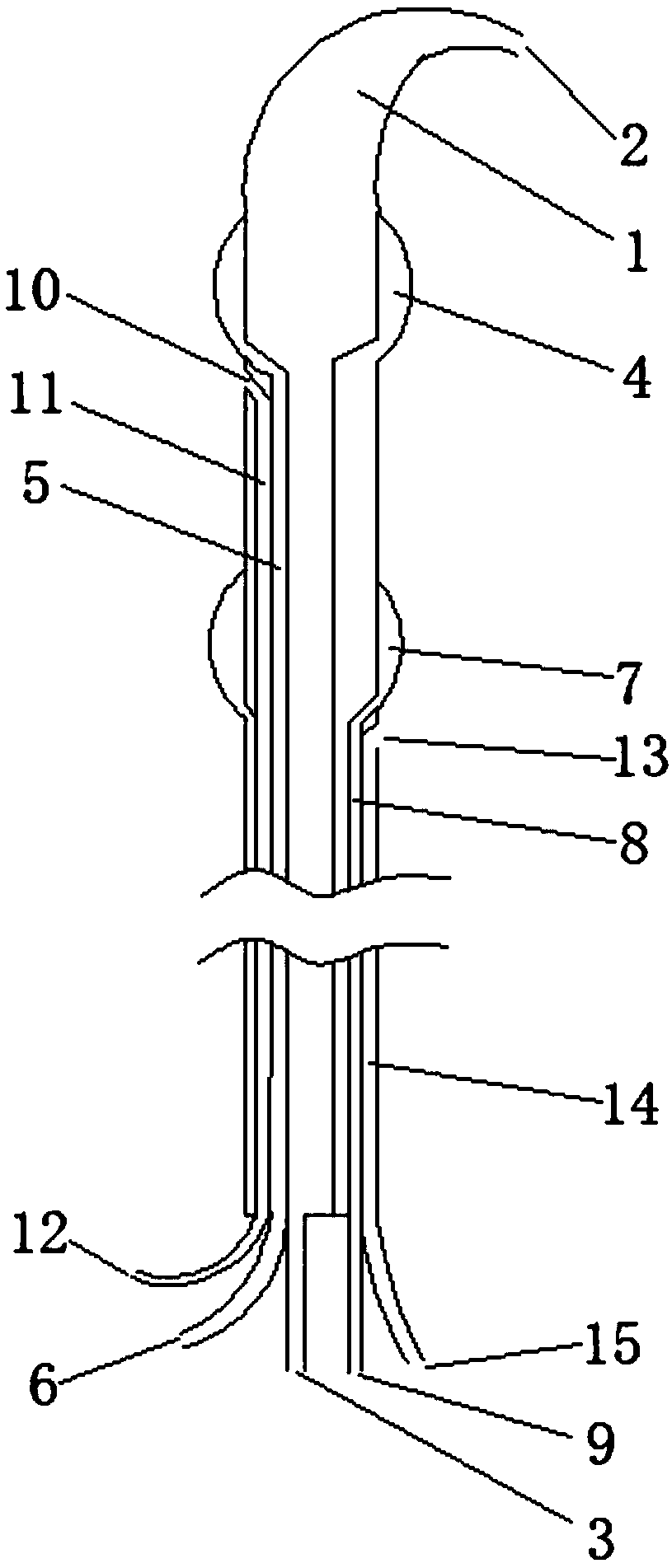
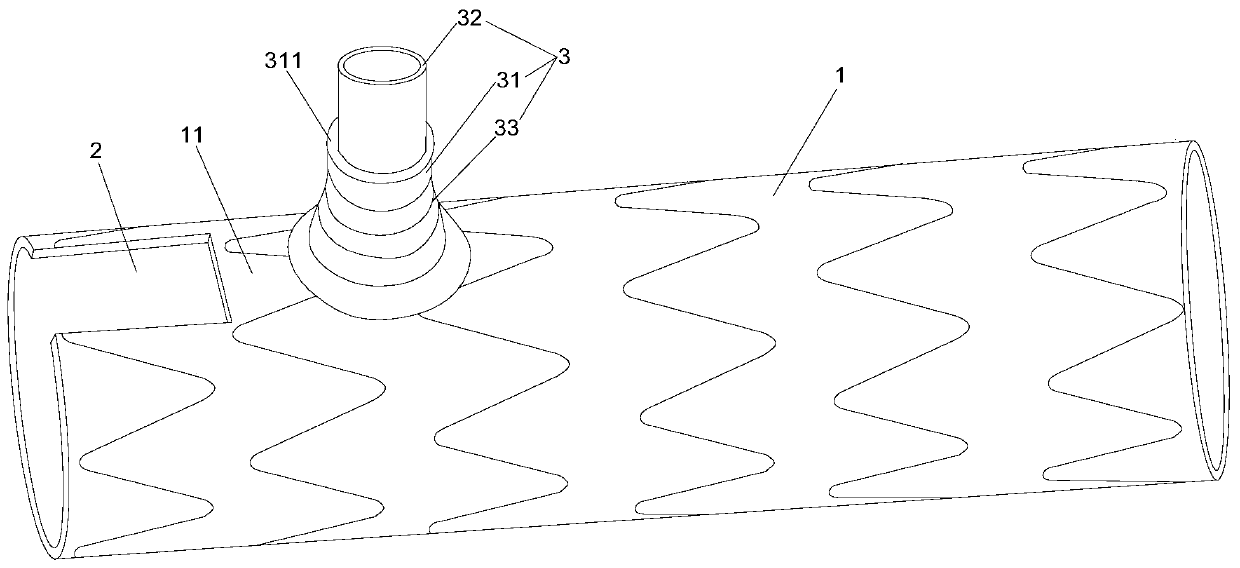
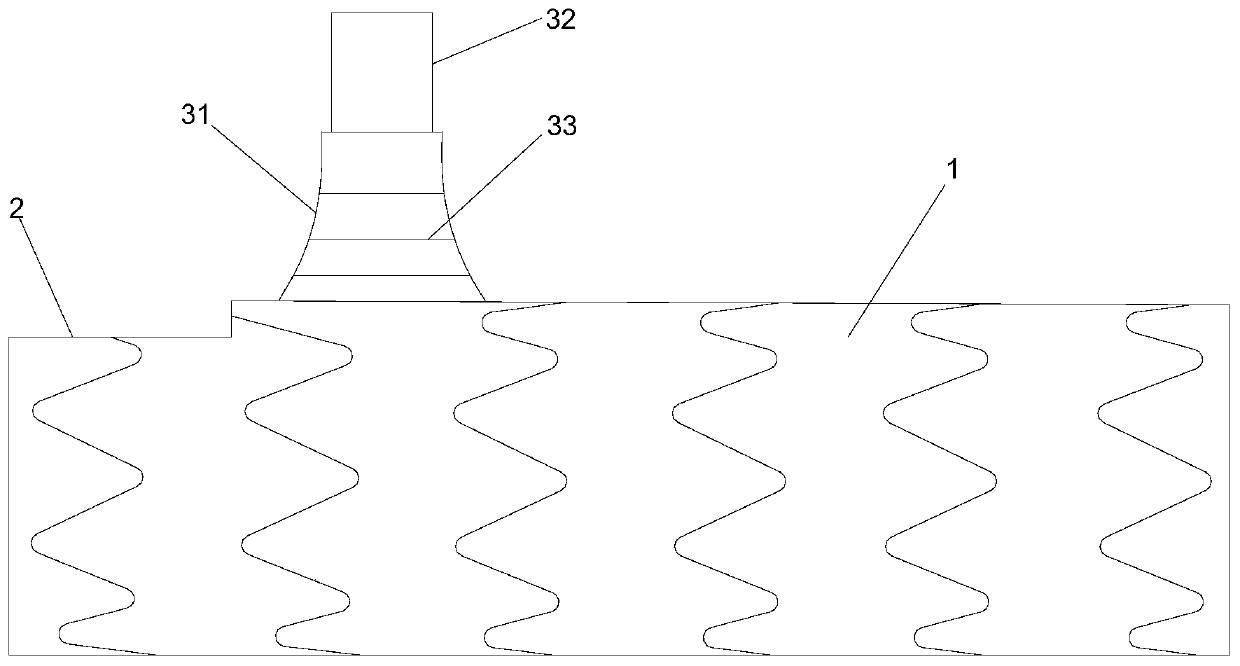
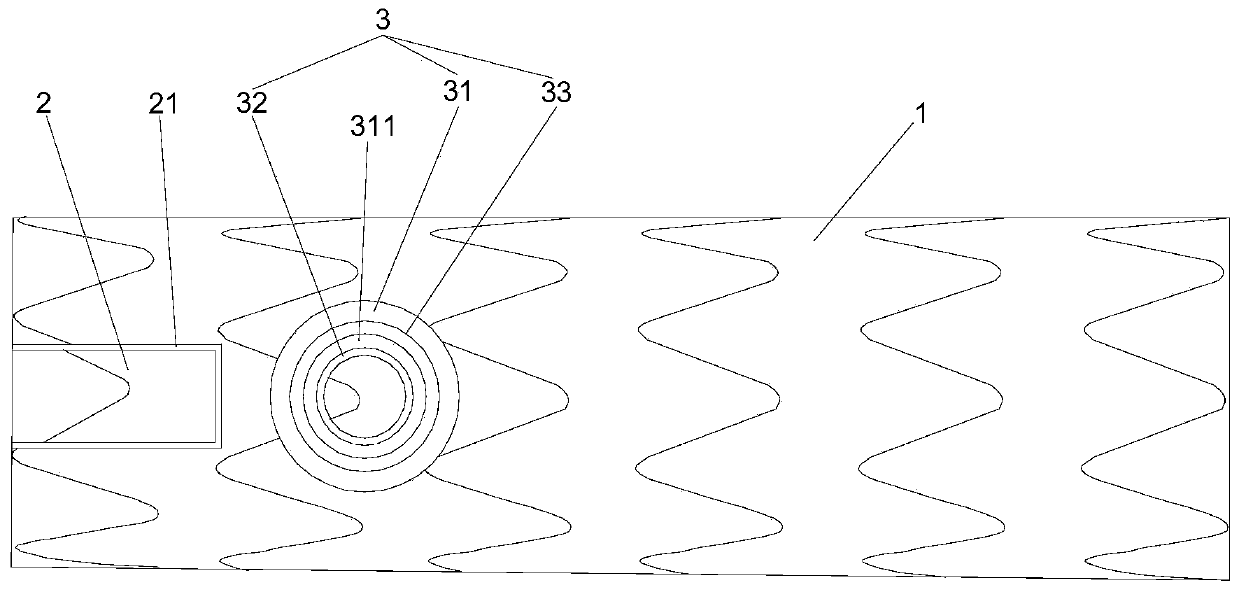
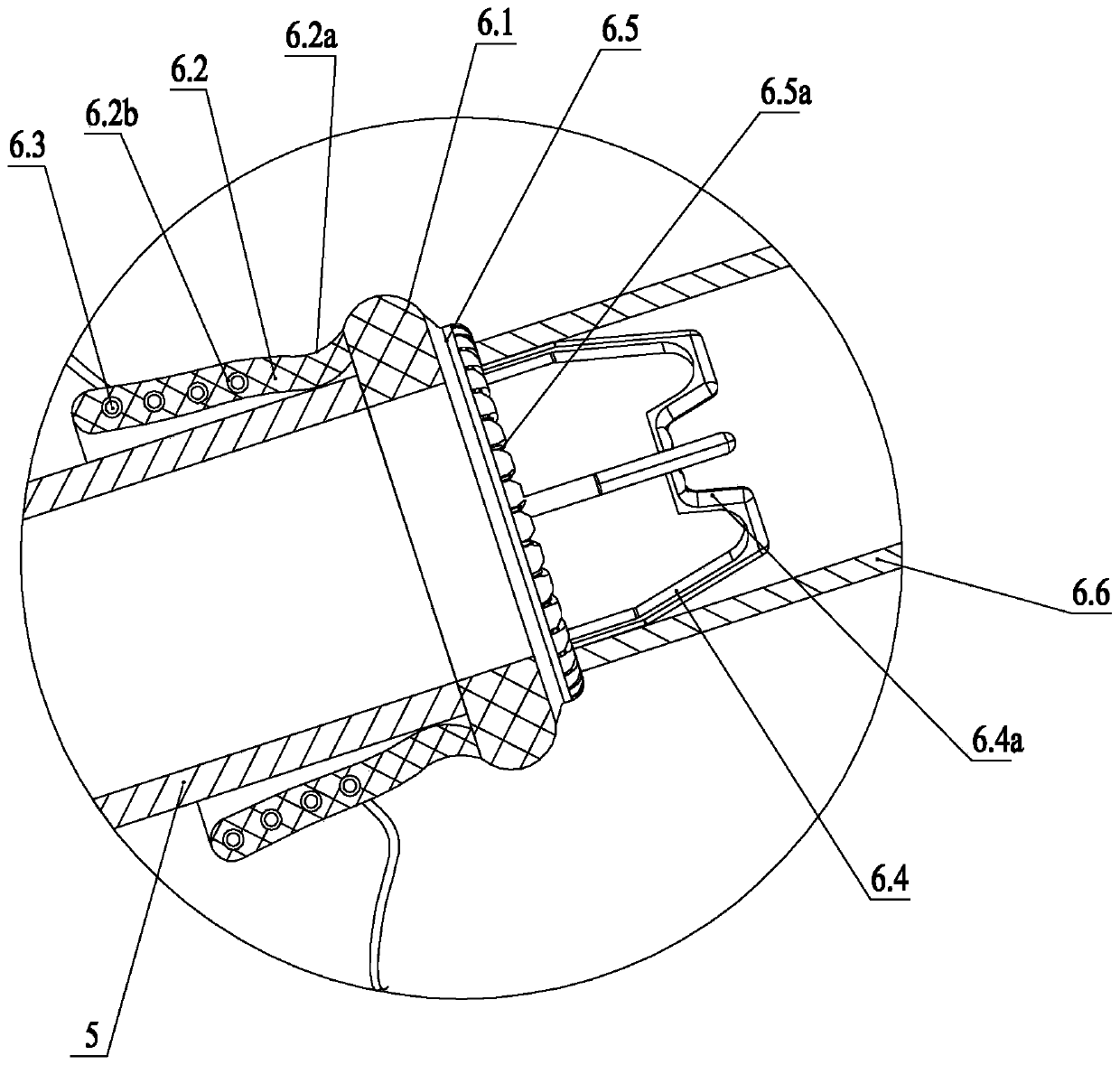
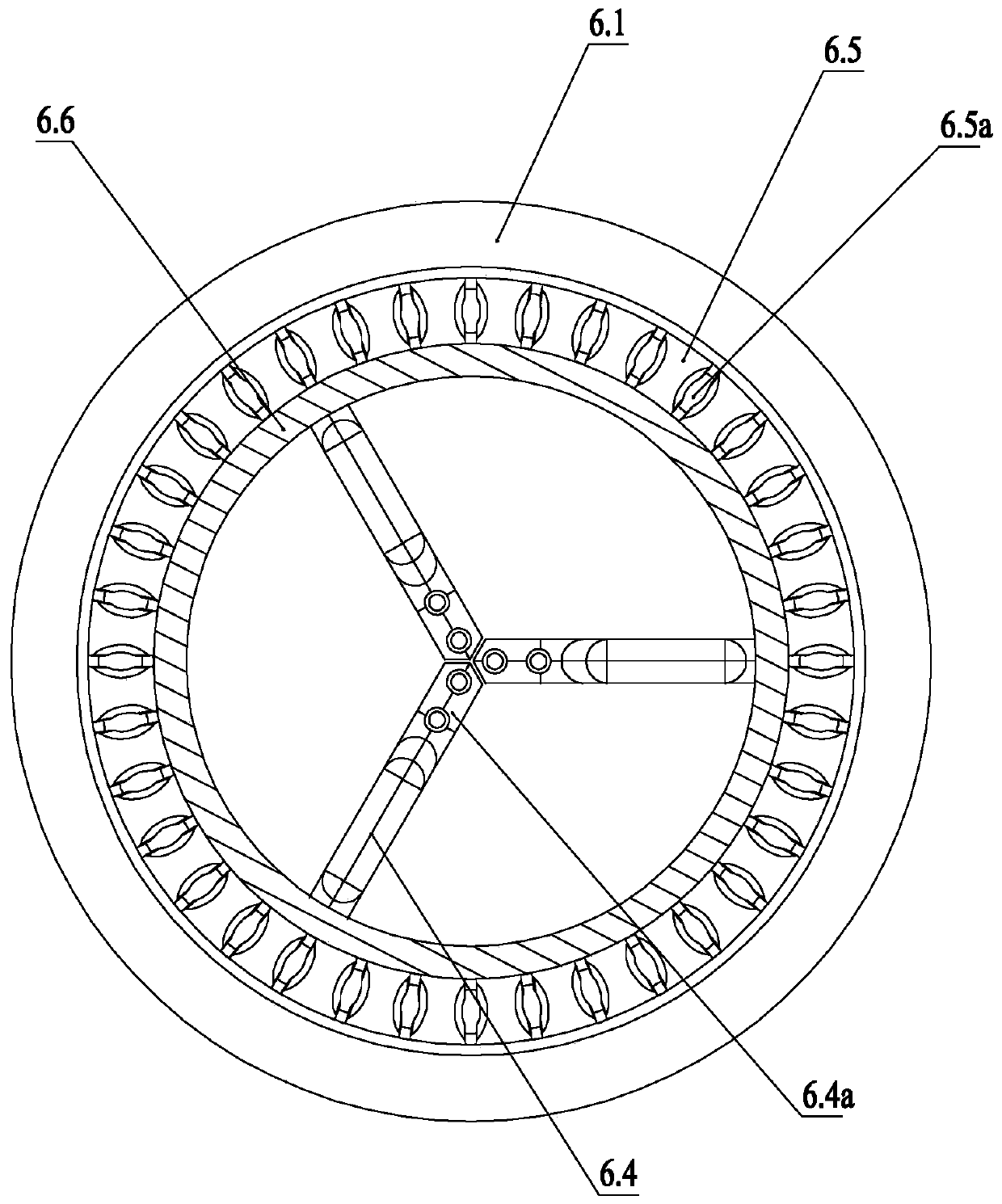
Patents
Literature
57 results about "Left subclavian artery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
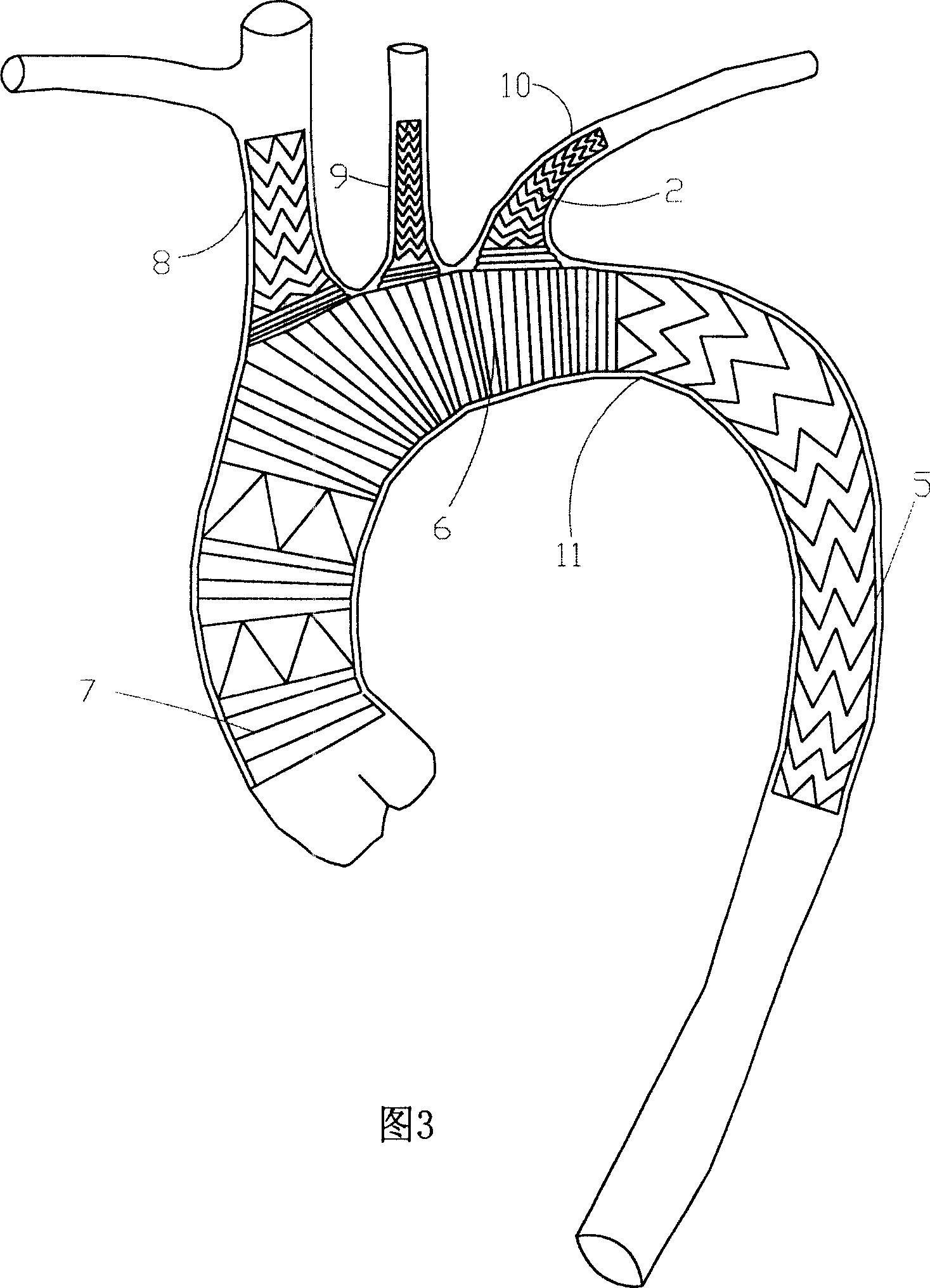
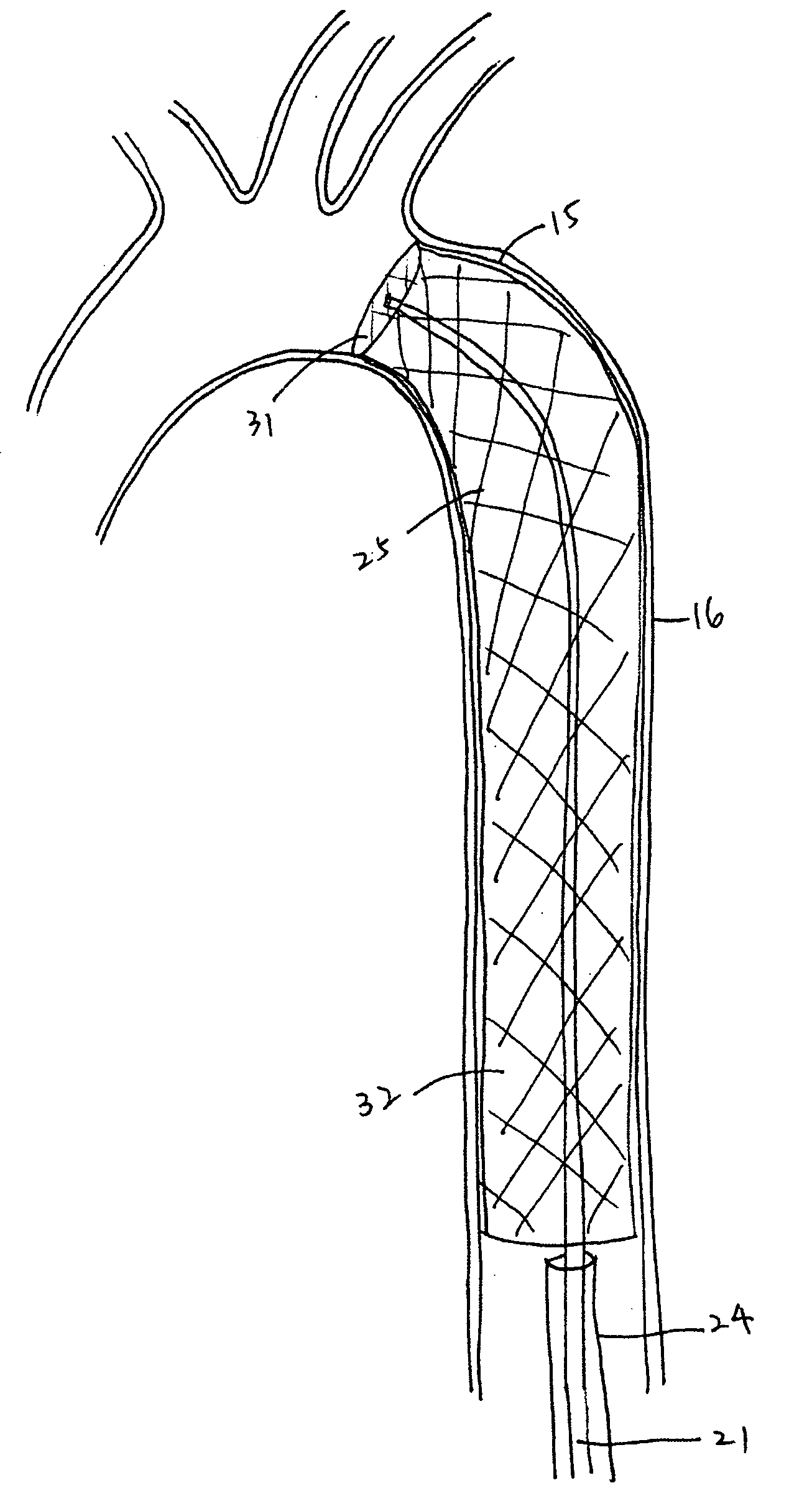
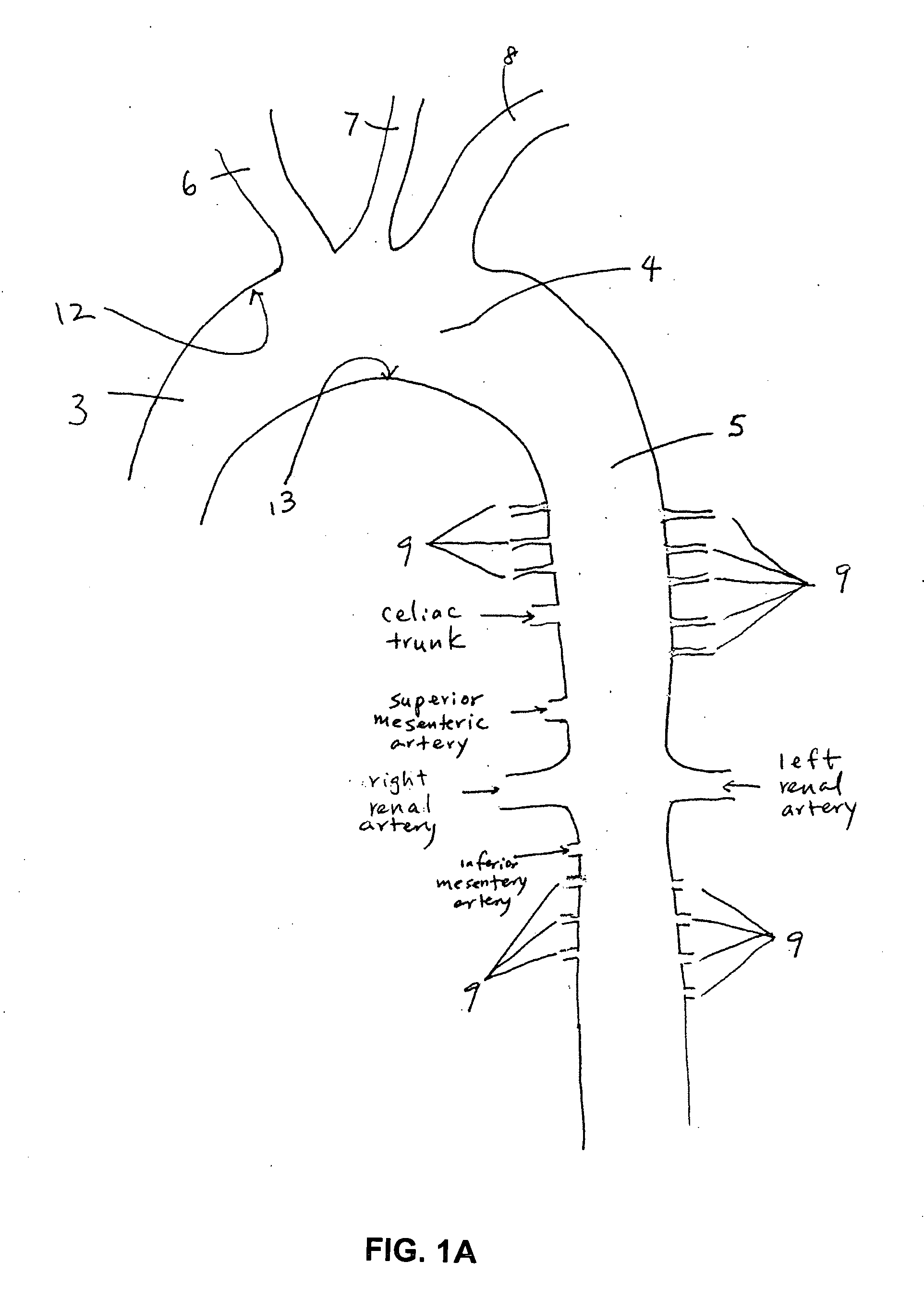
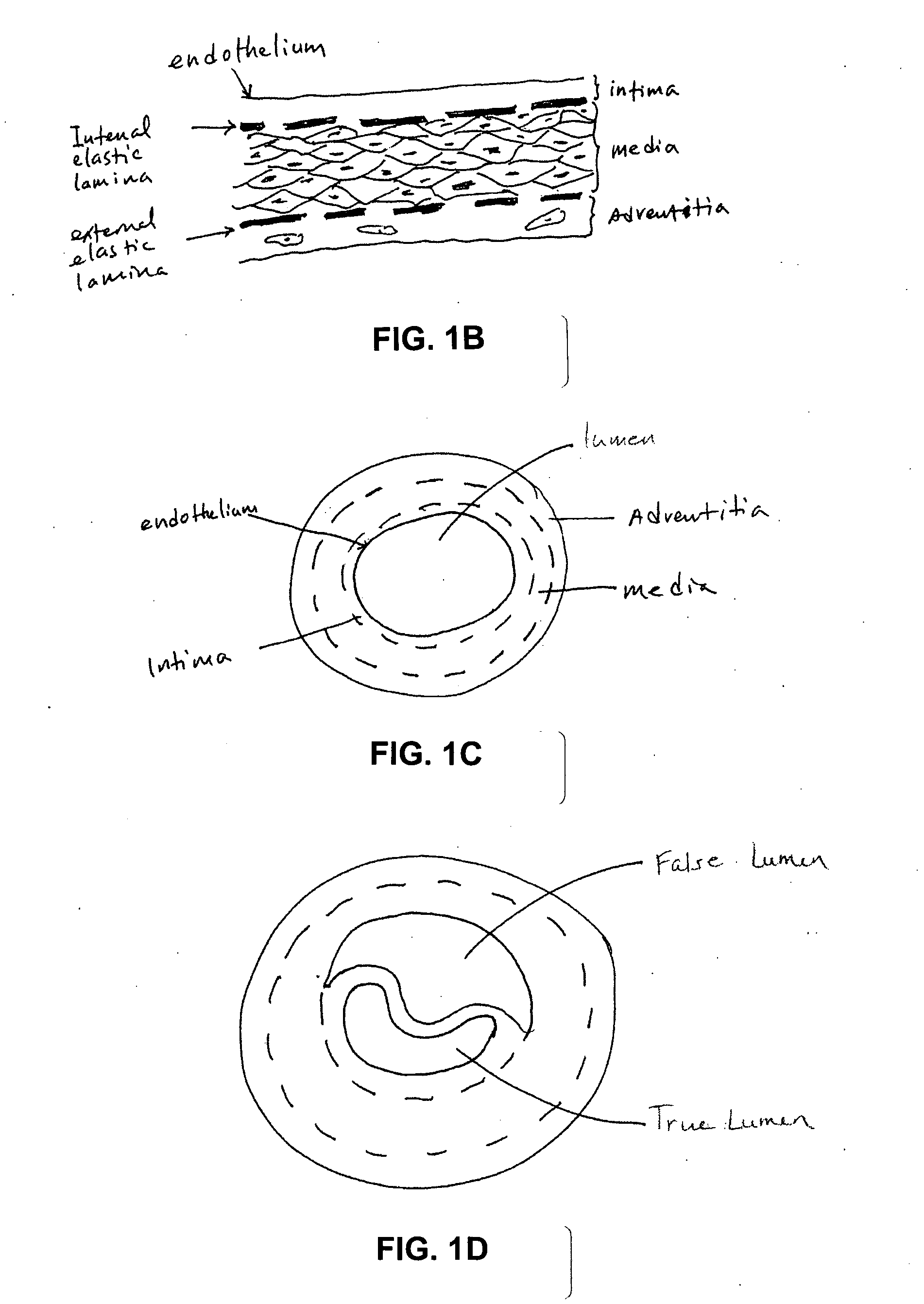
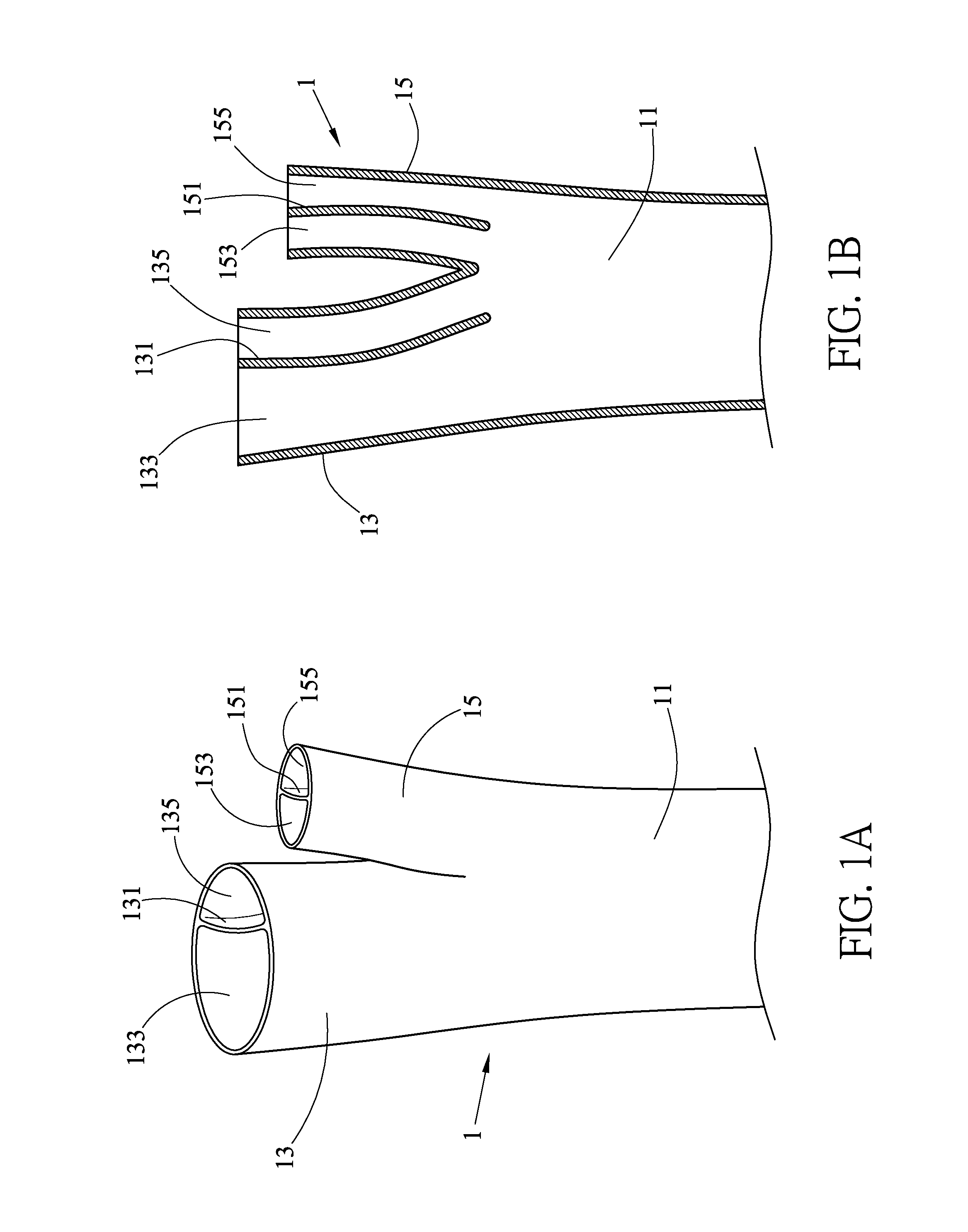
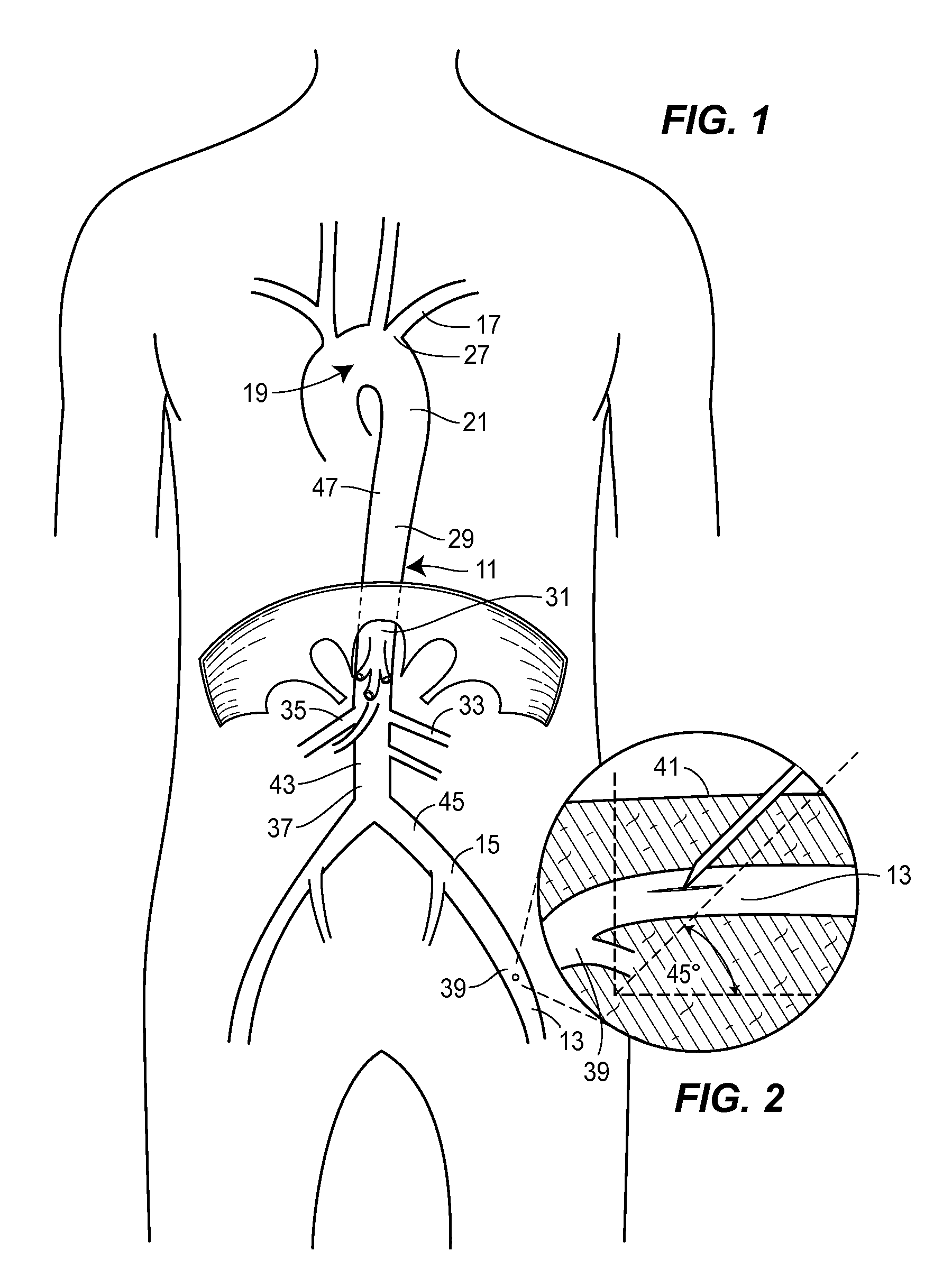
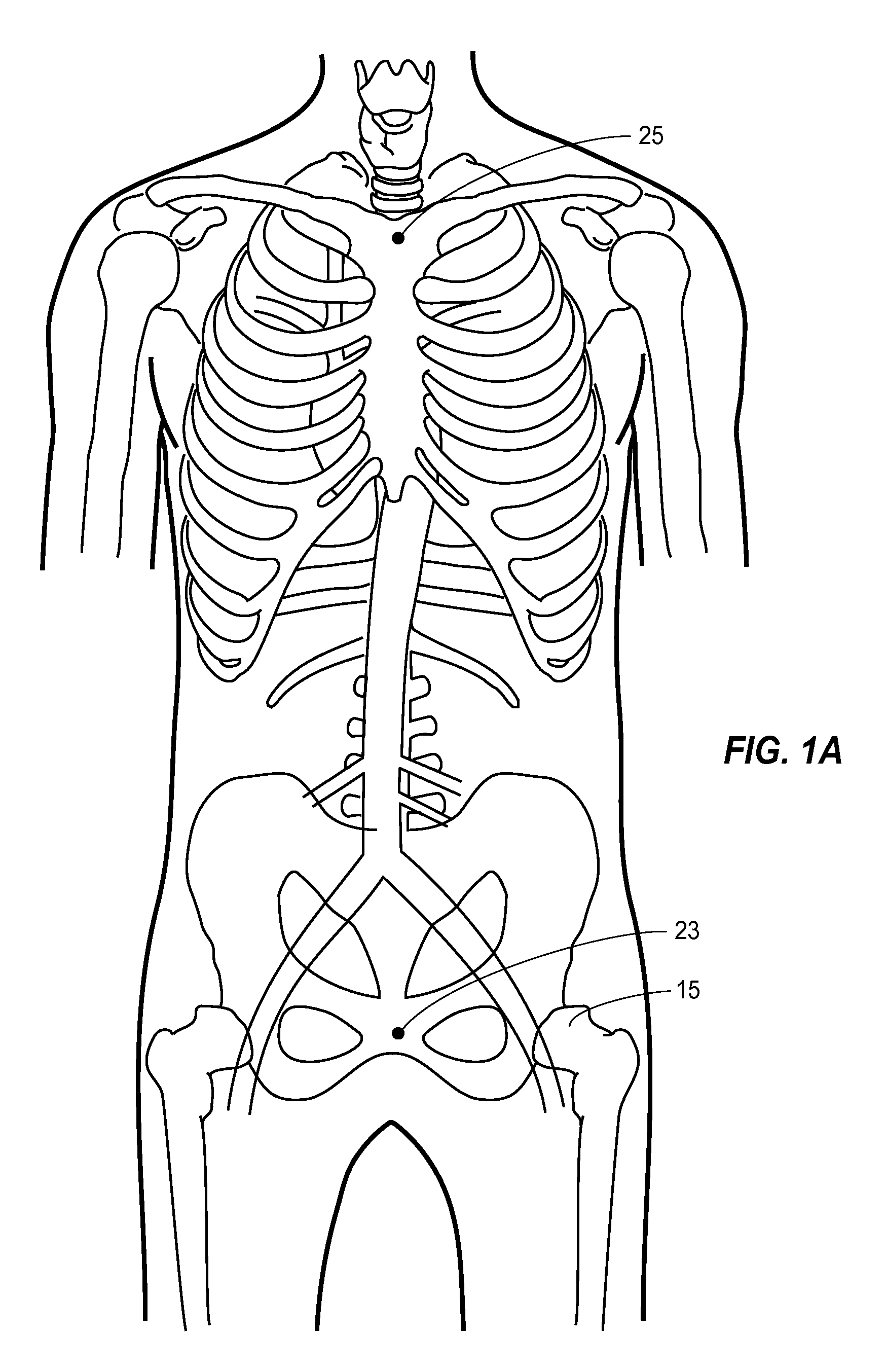
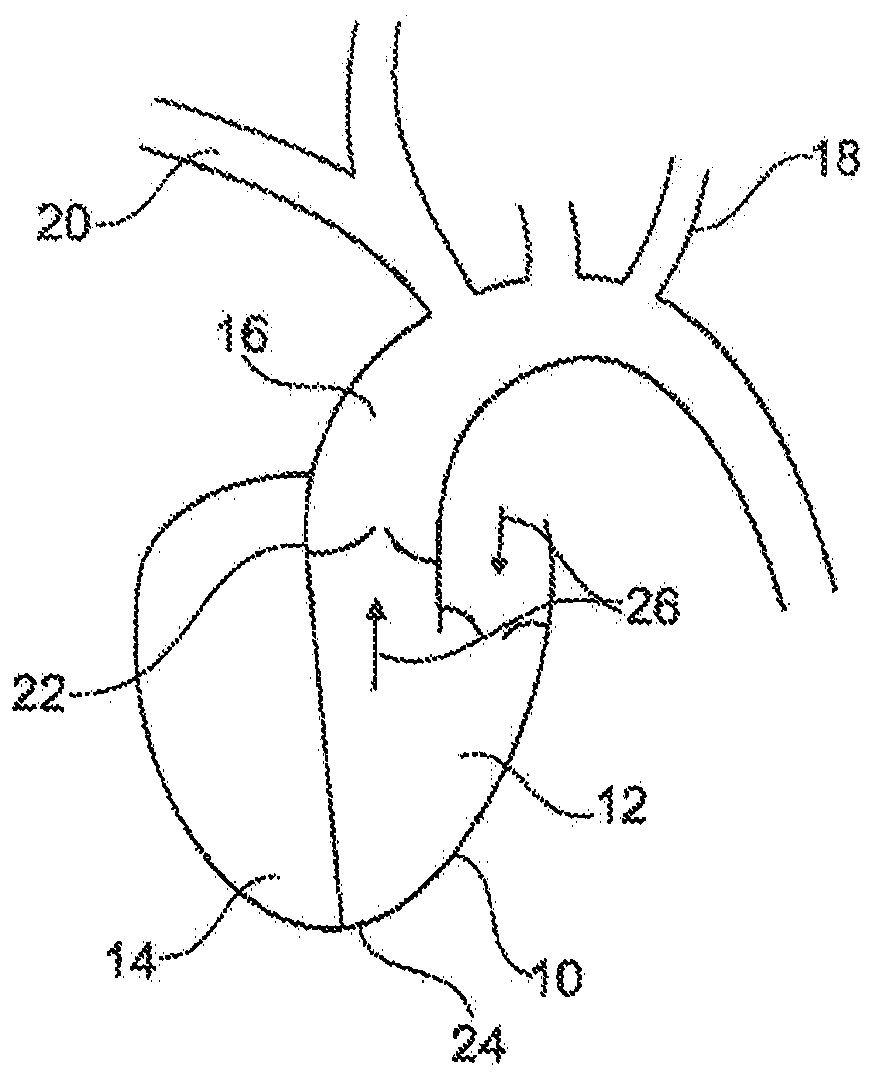
Anatomical terminology. In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax.
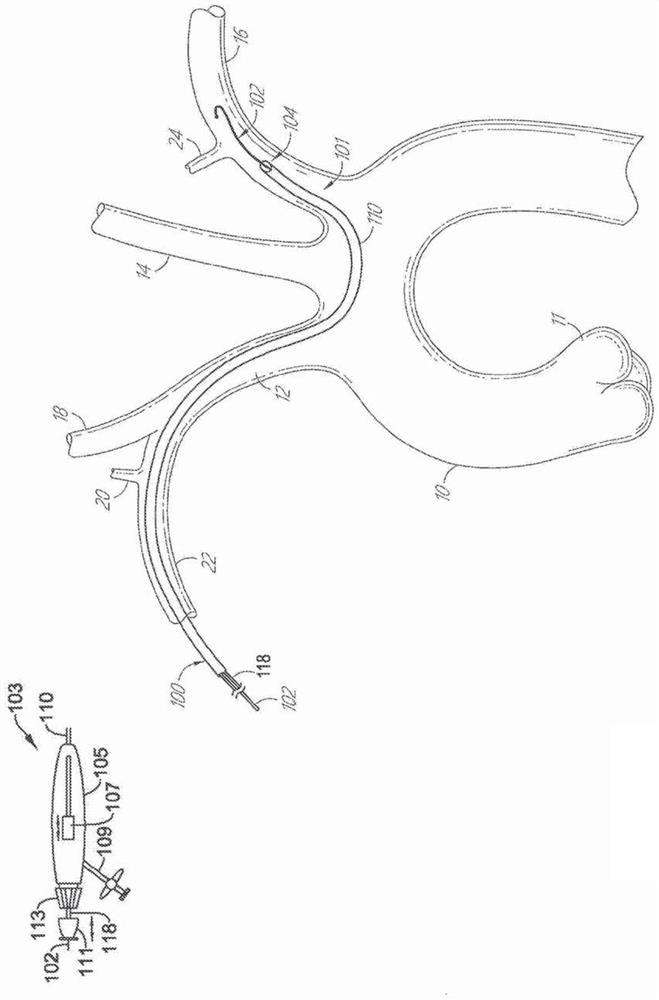
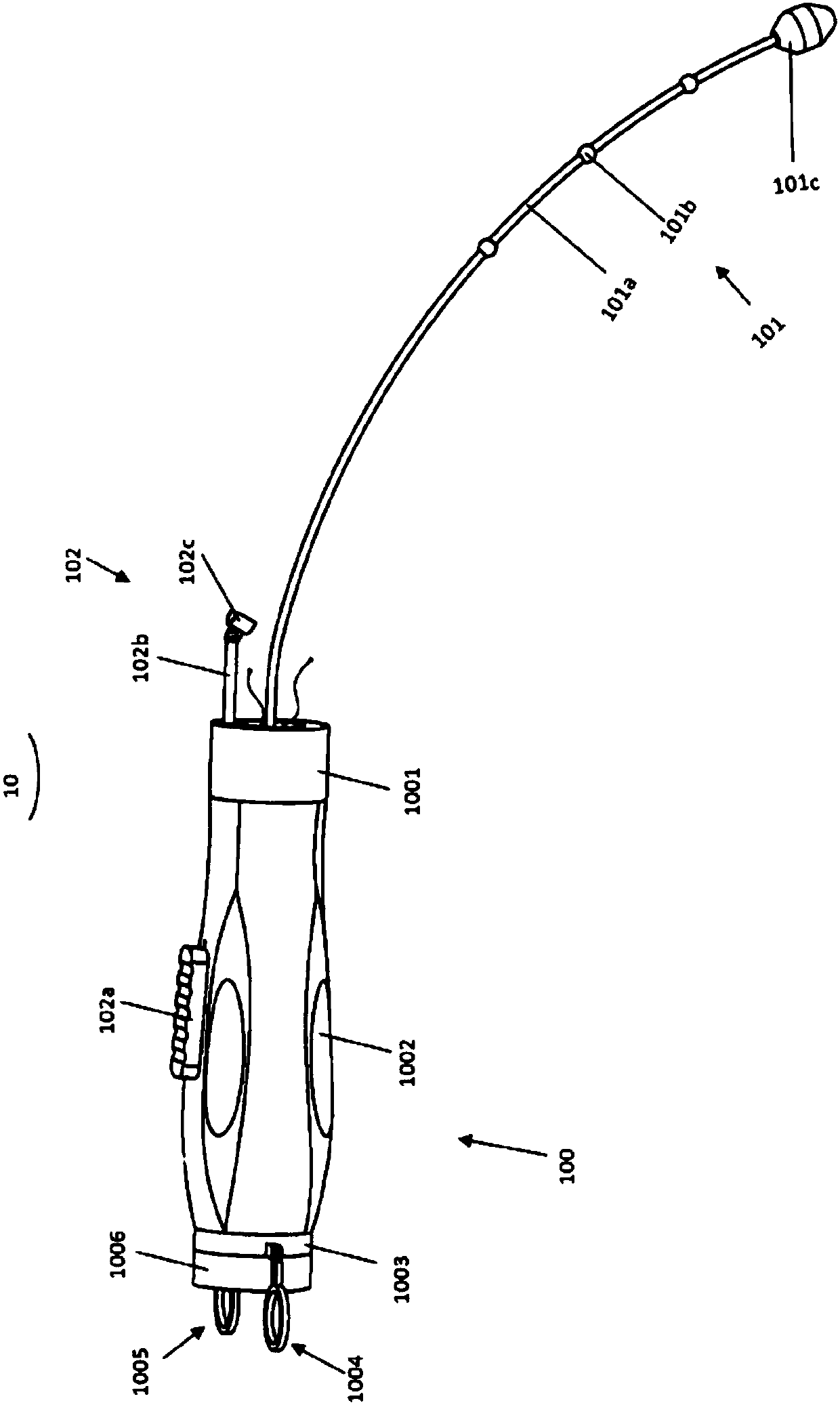
Methods and devices for treating aortic atheroma
InactiveUS20060161241A1Precise positioningAvoid obstructionStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryAortic atheroma
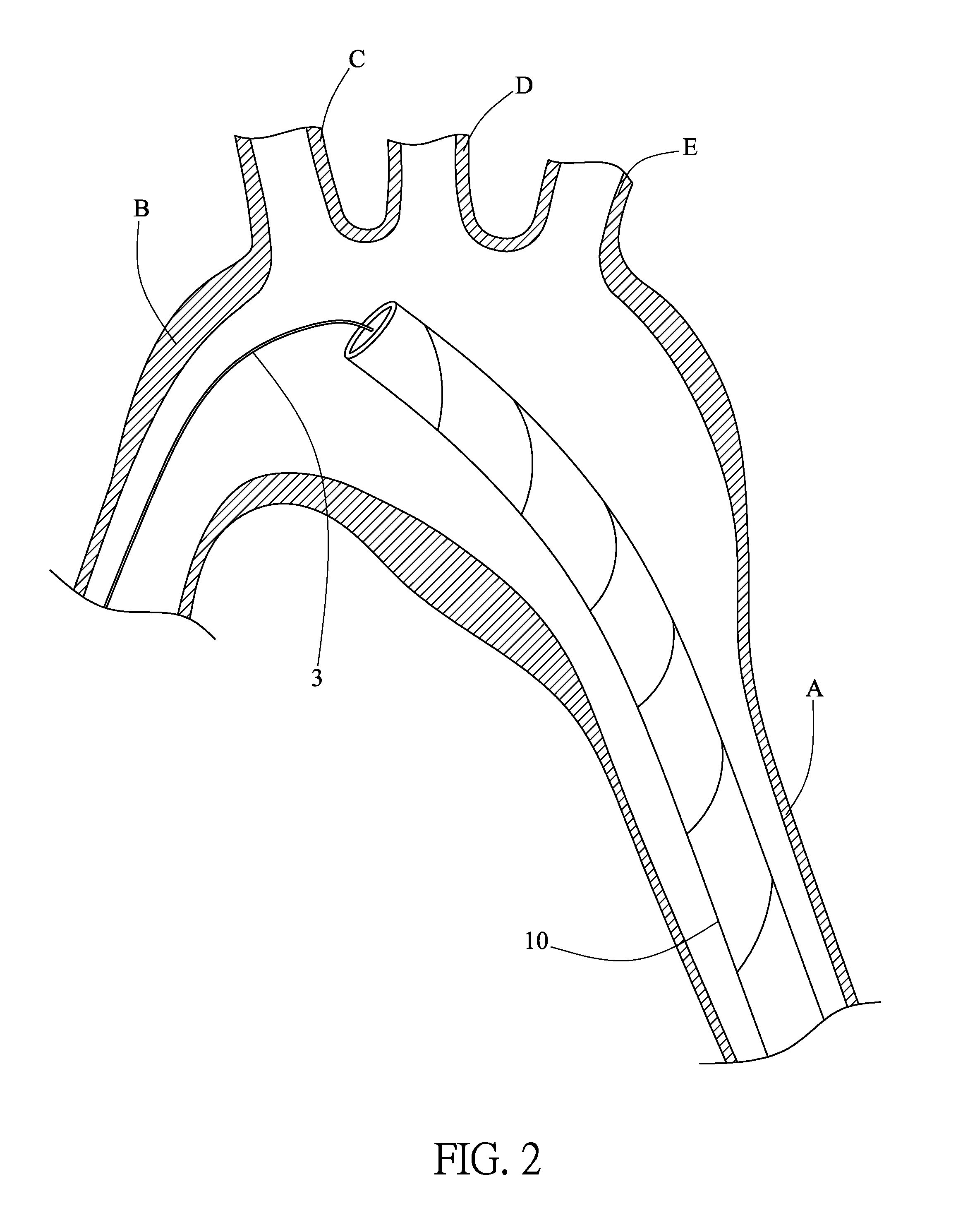
A method for treating both sessile and mobile aortic atheroma is described. A radially expanding device, such as a stent or compliant cast, comprising a generally cylindrical member expandable between a compressed state and an enlarged state is provided. The cylindrical member has a proximal opening, a distal opening, a lumen therebetween, and at least one side opening in the wall of the generally cylindrical member. The methods comprise imaging the aorta to identify position and extent of atheroma. The stent is then advanced into the aortic arch and positioned so that the at least one side-opening is aligned with the takeoff of one or more of the right brachiocephalic artery, the left common carotid artery, or the left subclavian artery. The stent is expanded into contact with the endoluminal surface of the aorta and atheroma is trapped between the stent and the endoluminal surface of the aorta.
Owner:SAGE MEDICAL TECH
Methods and devices for treatging aortic atheroma
InactiveUS20080004687A1Avoid obstructionPrecise positioningStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryAortic atheroma
A method for treating both sessile and mobile aortic atheroma is described. A radially expanding device, such as a stent or compliant cast, comprising a generally cylindrical member expandable between a compressed state and an enlarged state is provided. The cylindrical member has a proximal opening, a distal opening, a lumen therebetween, and at least one side opening in the wall of the generally cylindrical member. The methods comprise imaging the aorta to identify position and extent of atheroma. The stent is then advanced into the aortic arch and positioned so that the at least one side-opening is aligned with the takeoff of one or more of the right brachiocephalic artery, the left common carotid artery, or the left subclavian artery. The stent is expanded into contact with the endoluminal surface of the aorta and atheroma is trapped between the stent and the endoluminal surface of the aorta.
Owner:SAGE MEDICAL TECH
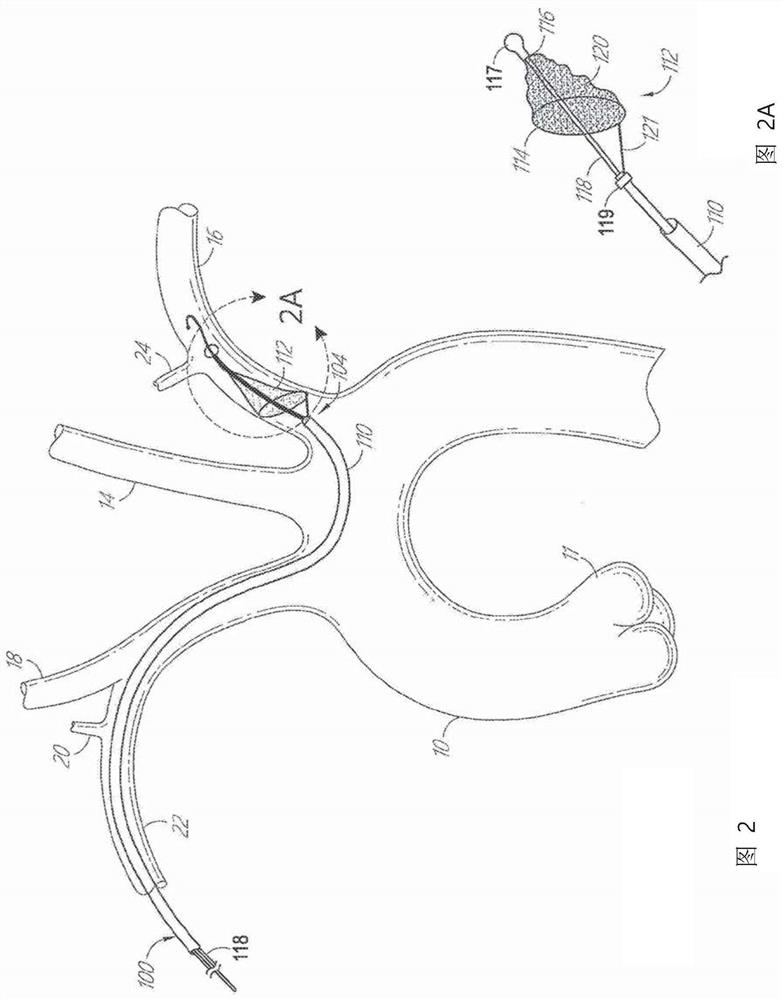
Embolic protection device and method
An embolic protection device adapted for placement in a left subclavian artery, a right subclavian artery and to cover a left and a right carotid artery, the device having a reduced state and an expanded state, the device comprising an expandable support structure, the expandable support structure comprising a frame, the frame further comprising a porous material, the frame defining the circumference of the porous material in the expanded state.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Fluoroscopy-independent, endovascular aortic occlusion system
ActiveUS20130102926A1Quick measurementIncrease perfusionBalloon catheterOther printing matterArterial occlusionsLeft subclavian artery
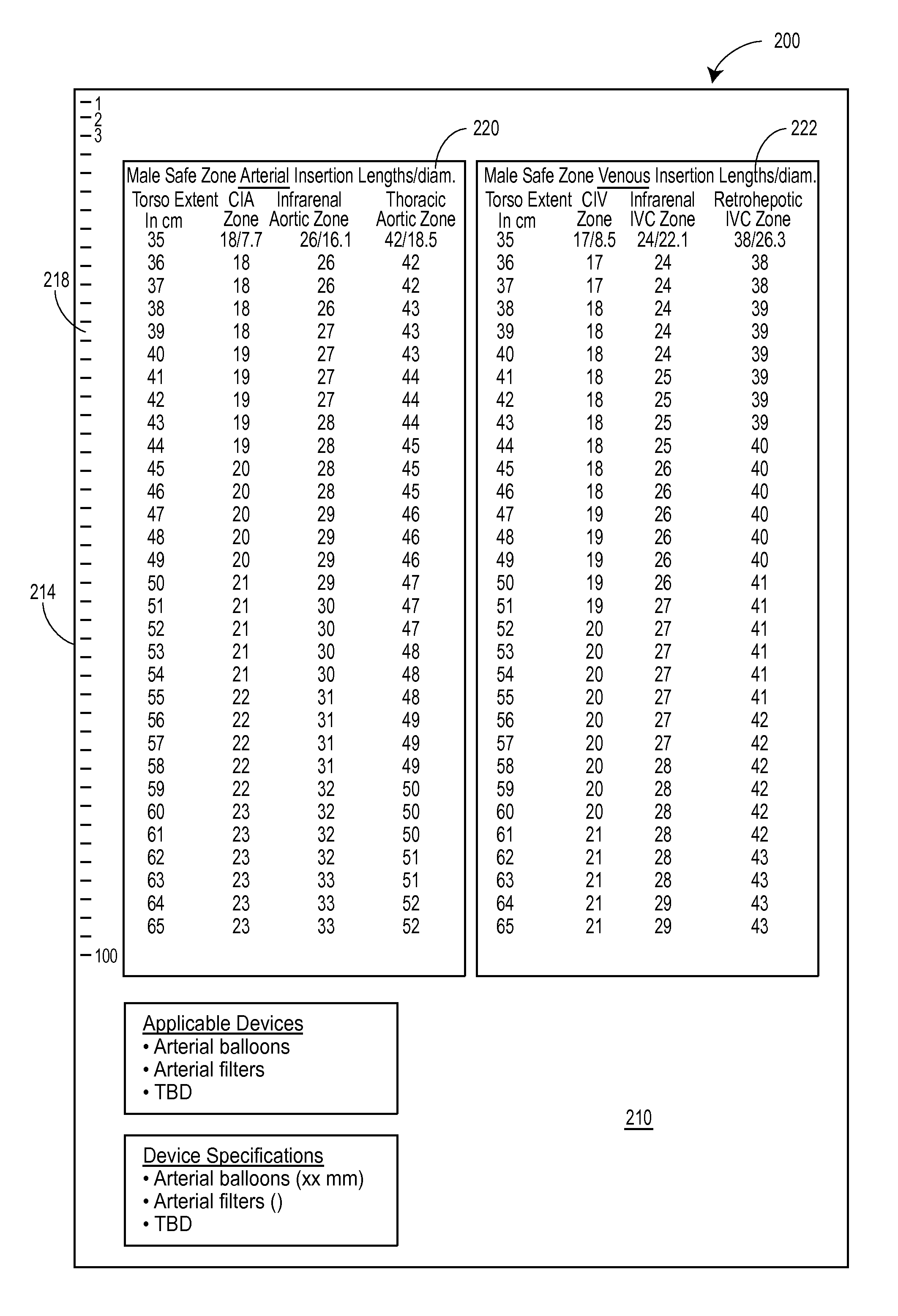
A system for deploying and selectively inflating a thoracic aortic balloon at a desired location within the thoracic aorta for resuscitative aortic occlusion, inferior to the left subclavian artery, without the aid of fluoroscopy is described. Using CT imaging data, a distance between readily identifiable and consistently located external landmarks of torso extent is measured. Next, using the same data, a second distance from the femoral artery to a desired aortic occlusion location inferior to the left subclavian artery is determined. A correlation between the external measure of torso extent and the desired intra-arterial (i.e. endovascular) distance within the torso is made. Using a nomogram, a calibrated endovascular resuscitative thoracic aortic occlusion system can be positioned to this desired location on any injured individual with end-stage shock and impending cardiovascular collapse or death without the aid of fluoroscopy for delivery or balloon inflation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Branch artificial blood vessel bracket applied in surgery
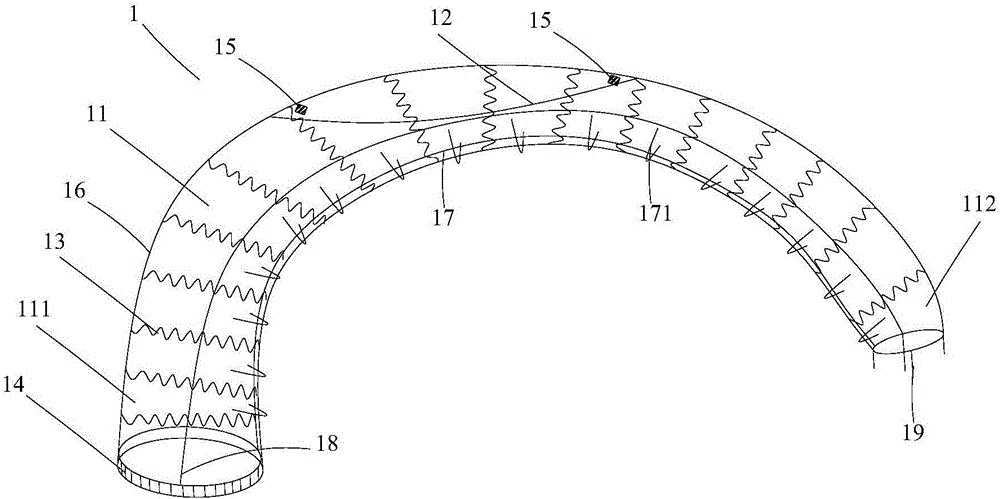
The invention relates to a branch artificial blood vessel bracket applied in surgery, which is provided with a terylene fabric blood vessel and a large bracket lined with a harder memory alloy wire; an artificial blood vessel of 1cm long without alloy wires is arranged at the near end and taken as a sewing ring; the branch artificial blood vessel bracket is characterized in that the near end of the large bracket is sewed by a small bracket; and the small bracket consists of the terylene fabric blood vessel and the lined soft memory alloy wire. The branch artificial blood vessel bracket creatively adds a branch bracket used for supporting the true lumen of left subclavian artery so as to keep smooth and complete left subclavian artery and the distal end of thoracic descending aorta, overcome the defects of the current surgery and avoid the coincidence of the left subclavian artery; and the distal end coincident hole is arranged between the innominate artery and the left common carotid artery, thus solving the most difficult point of the technique.
Owner:陈良万 +2
Three-collateral bracket vascellum for arcus aortae
InactiveCN101152109AReduce the incidence of injuryReduce the chance of bleedingStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryBlood vessel
The present invention relates to aortic arch three collateral support blood vessels comprising an aorta support vascular that comprises an aorta ascenden section, an aortic arch section and an aorta section; the aorta support vascular also comprises three collateral artery support vasculars which are fixed respectively on an aortic arch section arc surface of the aorta support vascular and are formed into an five-way type. The three collateral artery support vasculars are corresponding respectively to an arteria anonyma, a left common carotid artery and a left subclavian artery. The invention is capable of greatly simplifying an operation process and greatly shortens the time of a deep hypothermia and a circulation arrest, which is characterized by not only omitting an inosculation between an artificial vascular graft and three branches of the aortic arch but also reducing bleeding rate and operation risk. In an operation, the invention changes an operation method from a partial blood vessel replacement plus partial endovascular repair to a complete endovascular repair.
Owner:黄方炯
Covered stent for aortic dissection surgery, delivery device and use method thereof
InactiveCN105832447AAvoid punctureFacilitates a tight fitStentsBlood vesselsAortic dissectionLeft subclavian artery
The invention discloses a covered stent for an aortic dissection surgery, a delivery device and a use method thereof. The stent comprises a main body, wherein the main body decreases progressively from the heart near end with a large diameter to a far end with a small diameter, and the superior border of the middle piece of the main body is a rotary island; a tectorial membrane is arranged except the rotary island, and the two ends of the main body and the rotary island are provided with positioning marks. The delivery device comprises a delivery sheathing canal, a suture and a traction guide wire, wherein the suture is sewn on the outer side surface of the covered stent, and the two side edges of the covered stent at the near end of the left subclavian artery are sewn up by the suture; the stent is closed up to be in a semi-contraction state by the traction guide wire through the suture, and the covered stent is closed up and wrapped in the delivery sheathing canal; the delivery sheathing canal is provided with a steeple, and the far end of the traction guide wire penetrates through the handle of the delivery sheathing canal and is fixed. The covered stent for the aortic dissection surgery is used for a dissecting aneurysm surgery of the lesser curvature side of aortic arch and an interventional minimally invasive surgery of an aortic dissection near the brachiocephalic trunk, so that the trauma of a thoracotomy is avoided, and the athe lumen crevasse occlusion is directly implemented.
Owner:杨威
Implant for aortic dissection and methods of use
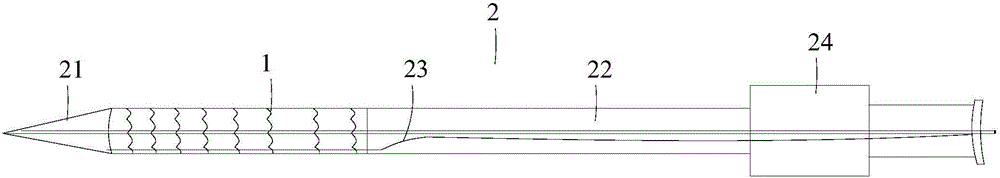
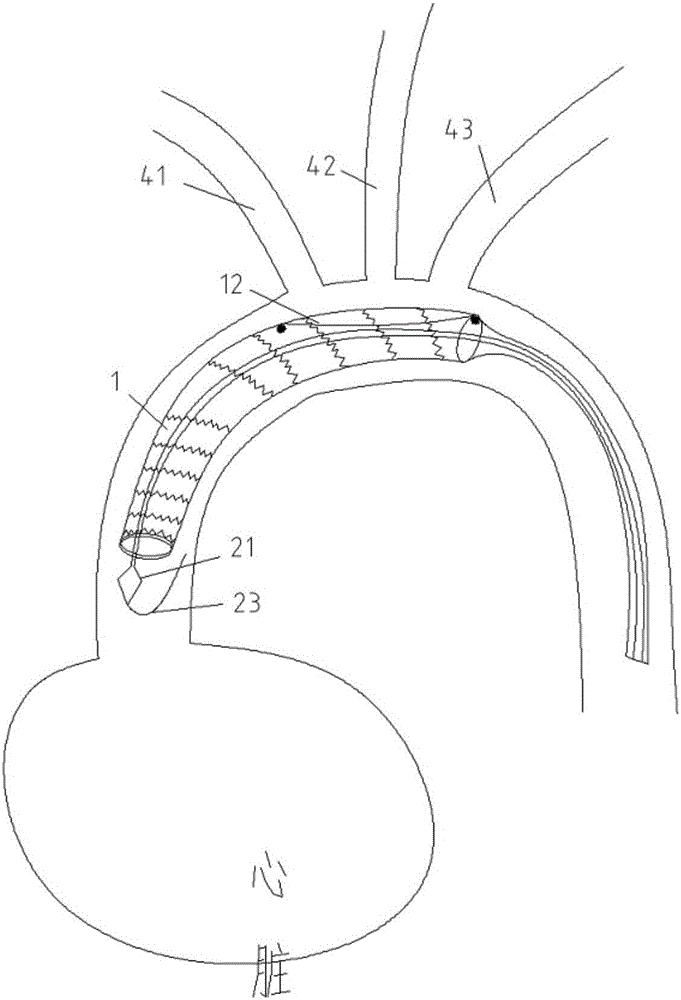
Methods and devices for treating an aortic dissection having an entry point downstream of the takeoff of the left subclavian artery. The devices include a catheter that carries an endoluminal implant at a distal region of the catheter. The implant is a self-expanding tubular mesh or strutted stent. A capture sheath holds the stent in a compressed state for percutaneous delivery. The catheter is advanced to position the stent adjacent the entry point of the dissection. The stent is released by withdrawing the capture sheath. The stent expands to engage the intimal lining and press the intima into contact with the outer layers of the aorta and thereby promote healing of the dissection.
Owner:SAGE MEDICAL TECH
Method of implanting an aortic stent
A method of implanting an aortic stent comprising steps of: putting a main tube on a metal guide wire; moving the main tube along the metal guide wire to the descending aorta, the main tube is constrained by a first cover, and first and second tube bifurcations are branched from the main section; removing the first cover; inserting a second and third metal guide wire through the first tube bifurcation into the ascending aorta and branchiocephalic artery respectively; a first and a second tube branch moving into the ascending aorta and the branchiocephalic artery respectively; inserting a fourth and fifth metal guide wire through the first tube bifurcation into the ascending aorta and branchiocephalic artery respectively; a third and a fourth tube branch moving into left common carotid artery and the left subclavian artery respectively; removing a second cover constraining said tube branches.
Owner:VICTOR ACTION LTD
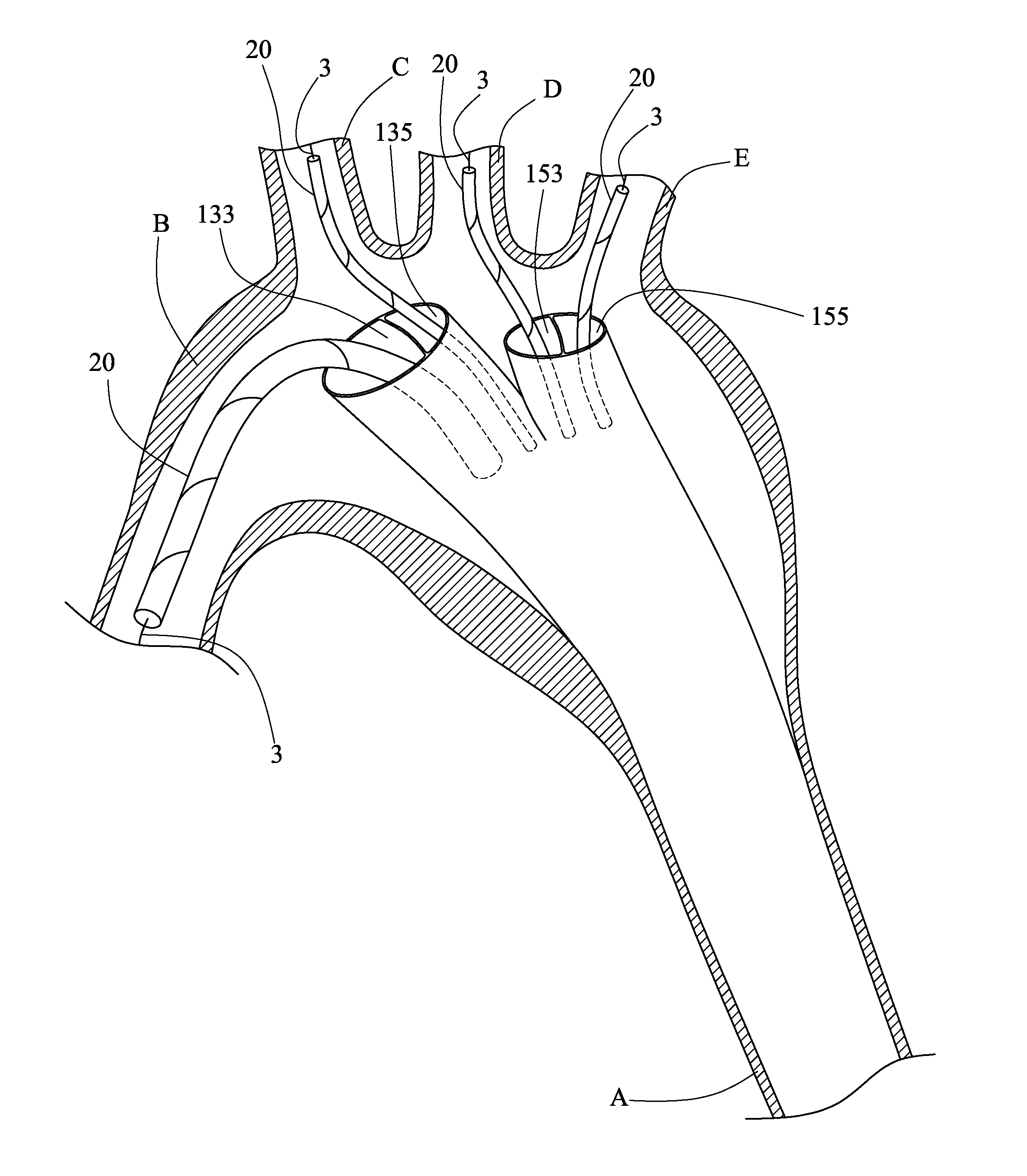
Total aortic arch reconstruction graft
A total aortic arch reconstruction graft, includinga) a first, hollow cylindrical segment in the shape of an aortic arch and adapted to be joined to a patient's ascending aorta, and including three side hollow cylindrical branches in communication therewith and adapted to be joined to a patient's left subclavian artery, left common carotid artery and innominate artery, respectively, and a fourth hollow cylindrical branch adapted to be joined to a heart-lung machine;b) a second, hollow cylindrical segment having a first end being joined to the second end of the first segment, and a second end adapted to be inserted into the descending aorta of a patient, the second segment having an expandable outer wall covered with an expandable open-mesh stent having means for attaching the second segment to an internal surface of a patient's descending aorta,c) a collar having a diameter slightly larger than the diameter of said first segment, the collar located at a juncture where the first end of the second segment is joined to the second end of the first segment, with the collar having means for attachment to the open end of a patient's descending aorta. A surgical procedure for total replacement of the aortic arch of a patient is also disclosed.
Owner:SHERIF HISHAM M F
Integrated multiple-branch interventional aorta arch covered stent
The invention discloses an integrated multiple-branch interventional aorta arch covered stent. The covered stent is of a crank-shaped structure and comprises a front arch zone, an arch portion zone and a rear arch zone. The front arch zone is formed by a section of tubular covering membrane extending along one end of the stent, the covering membrane extends from the tail end of the front arch zone in an arched-bent mode to form the arch portion zone, and the covering membrane continuously extends from the tail end of the arch portion zone to form the rear arch zone. The greater-curvature side of the arch portion zone is an ellipsoidal protrusion, a fixed branch matched with the brachiocephalic trunk of a human body is arranged on the protrusion, and two holes matched with the left common carotid artery and left subclavian artery are sequentially formed in one side of the fixed branch. Multiple rows of metal frames for supporting the covering membrane and the fixed branch are arranged in the covering membrane and the fixed branch in a lined mode. The integrated multiple-branch interventional aorta arch covered stent has the advantages of being capable of conforming to the characteristics of the aorta arch portion of human anatomy, completely covering the aorta arch of the human body by utilizing different models of main body supports and movable branched stents in a combined mode and having aortic artery protection and continuous angiectasis and angiorrhexis prevention effects.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Adjustable human body aorta vessel model device
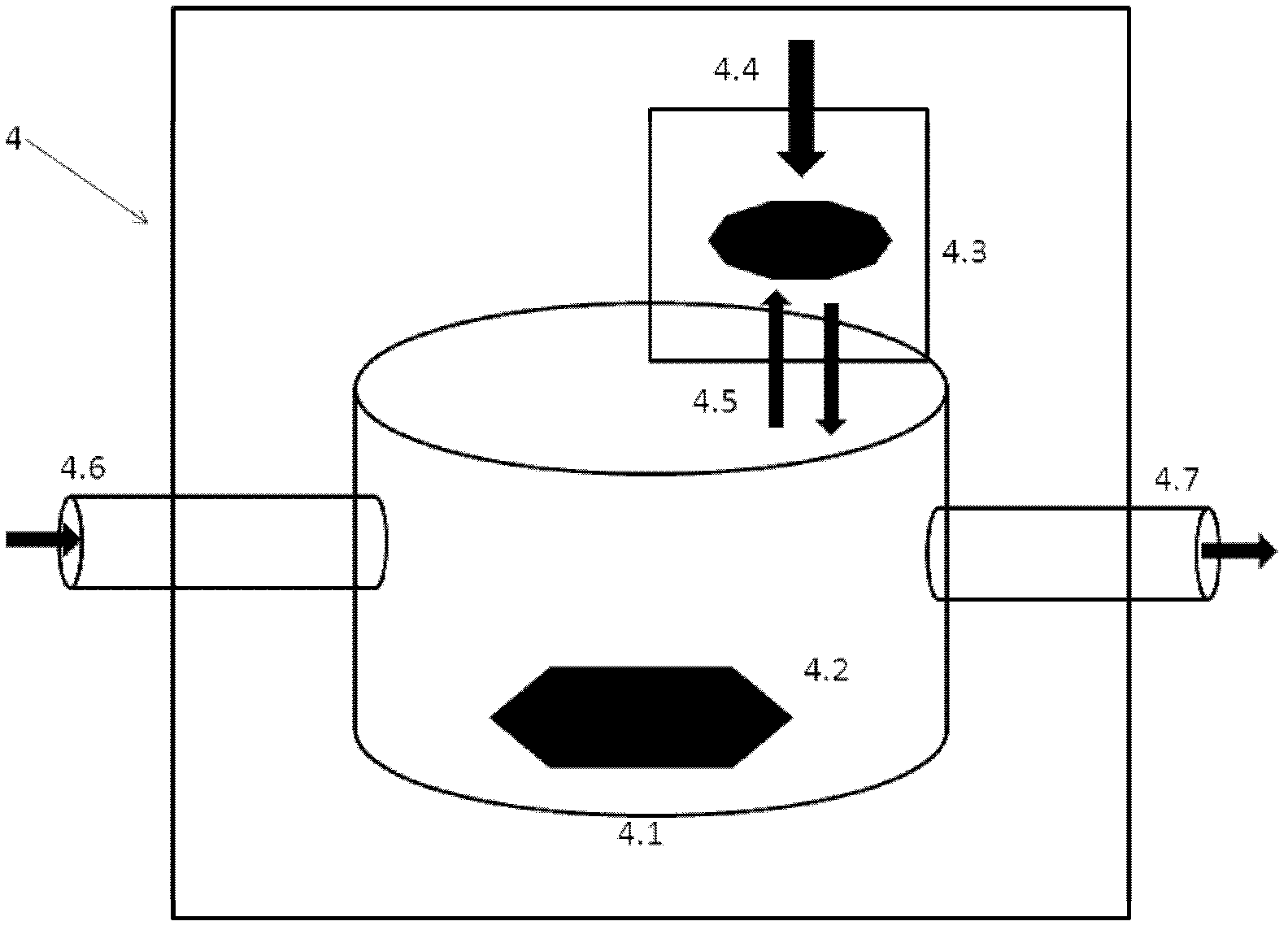
The invention relates to an adjustable human body aorta vessel model device. A aorta primary loop, three branch brachiocephalic trunk arteries of aortic arches, left common carotid artery and left subclavian artery are respectively provided with a pressure regulator (with built-in pressure gauge and regulating valve) which can regulate the loop pressure by regulating the vessel diameter size; an adjustable liquid heater and a pressure gate control channel are arranged in a liquid storage pool and can control the liquid in the pool to exchange with the outside according to the pressure magnitude; the aorta primary loop is connected with a vessel bypass in parallel; and the vessel bypass is provided with a pressure gate control channel which can automatically regulating the internal pressure in the whole vessel model. The invention can respectively regulate the pressure, temperature and circulation volume in the aorta loop to simulate the blood circulation and dynamic blood variations of human aorta under physiologic or pathological conditions in the aorta model in a more realistic way, thereby laying the foundation for clinical and scientific research related studies.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Fluoroscopy-independent, endovascular aortic occlusion system
ActiveUS9131874B2Quick measurementIncrease perfusionOther printing matterBalloon catheterLeft subclavian arteryArterial occlusions
A system for deploying and selectively inflating a thoracic aortic balloon at a desired location within the thoracic aorta for resuscitative aortic occlusion, inferior to the left subclavian artery, without the aid of fluoroscopy is described. Using CT imaging data, a distance between readily identifiable and consistently located external landmarks of torso extent is measured. Next, using the same data, a second distance from the femoral artery to a desired aortic occlusion location inferior to the left subclavian artery is determined. A correlation between the external measure of torso extent and the desired intra-arterial (i.e. endovascular) distance within the torso is made. Using a nomogram, a calibrated endovascular resuscitative thoracic aortic occlusion system can be positioned to this desired location on any injured individual with end-stage shock and impending cardiovascular collapse or death without the aid of fluoroscopy for delivery or balloon inflation.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES SEC OF THE AIR FORCE +2
Intraoperative support conveying system and intraoperative support system
ActiveCN106618822AEasy to adjustEasy alignmentStentsBlood vesselsSupporting systemPostoperative complication
The invention provides an intraoperative support conveying system and an intraoperative support system. An intraoperative support comprises a main support and a side supporting support arranged on the main support and stretching outwards. The intraoperative support conveying system comprises a main lining and a side supporting lining arranged on the main lining. The side supporting support is configured to be arranged on the side supporting support in a sleeving mode, the main support is configured to be arranged on the main lining in a sleeving mode, and the side supporting lining is arranged on the main lining in a swing mode to synchronously drive the side supporting support to swing relative to the main support. By the arrangement of the side supporting lining capable of swinging relative to the main lining, the side supporting support can synchronously swing relative to the main support, the side supporting support is aligned with the left subclavian artery to be easily implanted during an operation, it is avoided that the time of freeing and suturing the left subclavian artery in thoracotomy operation is too long, so that postoperative complications are increased, then the operating difficulty of the operation is reduced, the operating time of the operation is shortened, and the adaptation disease range of the operation is widened.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT ENDOVASCULAR MEDTECH (GRP) CO LTD
Composite type intraoperative stent system and using method thereof
ActiveCN106388972AReduce the effects of coagulationShorten operation timeStentsBlood vesselsAv graftLinear control
The invention provides a composite type intraoperative stent system which comprises an artificial vessel capable of being anastomosed, a linear control released left subclavian artery covered stent vessel and a balloon-expandable type descending aorta covered stent artificial vessel; the artificial vessel is connected with the balloon-expandable type descending aorta covered stent artificial vessel; the left subclavian artery covered stent vessel is arranged at the connecting part of the artificial vessel and the balloon-expandable type descending aorta covered stent artificial vessel and communicates with the artificial vessel and the balloon-expandable type descending aorta covered stent artificial vessel; and the balloon-expandable type descending aorta covered stent artificial vessel is internally provided with a balloon. The composite type intraoperative stent system can shorten the operation time, reduces influence of deep hypothermic circulatory arrest on the coagulation function of a patient, lowers the difficulties of vascular anatomy and anastomosis and increase the success rate of an operation.
Owner:FUJIAN PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL
Arcus aortae stent graft vascular structure for department of surgery and application
The invention discloses an arcus aortae stent graft vascular structure for the department of surgery. The structure comprises a first artificial blood vessel, a connecting ring and a second artificial blood vessel. The connecting ring is embedded into the exterior of one side of the first artificial blood vessel. A reflection portion is reserved at the connecting ring and the end of the first artificial blood vessel. The reflection portion is turned outwards to wrap the connecting ring to form the compound end. One end of the second artificial blood vessel is embedded at the compound end to form a connecting portion. A threading hole is formed in the peripheral side wall of the connecting ring. A first branch and a second branch are arranged on the periphery of the first artificial blood vessel. The first branch comprises a first forked portion for being connected with an innominate artery and a second forked portion for being connected with the left common carotid artery. The second branch is connected with a pump blood vessel and then disconnected with the left subclavian artery. The second artificial blood vessel is the stent graft artificial blood vessel, and the far end of the second artificial blood vessel is used for being connected with the thoracic descending aorta.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL
Method of implanting an aortic stent
A method of implanting an aortic stent comprising steps of: putting a main tube on a metal guide wire; moving the main tube along the metal guide wire to the descending aorta, the main tube is constrained by a first cover, and first and second tube bifurcations are branched from the main section; removing the first cover; inserting a second and third metal guide wire through the first tube bifurcation into the ascending aorta and branchiocephalic artery respectively; a first and a second tube branch moving into the ascending aorta and the branchiocephalic artery respectively; inserting a fourth and fifth metal guide wire through the first tube bifurcation into the ascending aorta and branchiocephalic artery respectively; a third and a fourth tube branch moving into left common carotid artery and the left subclavian artery respectively; removing a second cover constraining said tube branches.
Owner:VICTOR ACTION LTD
Stent for treating type B aortic dissection
InactiveCN108553202AAvoid customizationReduce and reduce complicationsStentsBlood vesselsAnatomical structuresLeft subclavian artery
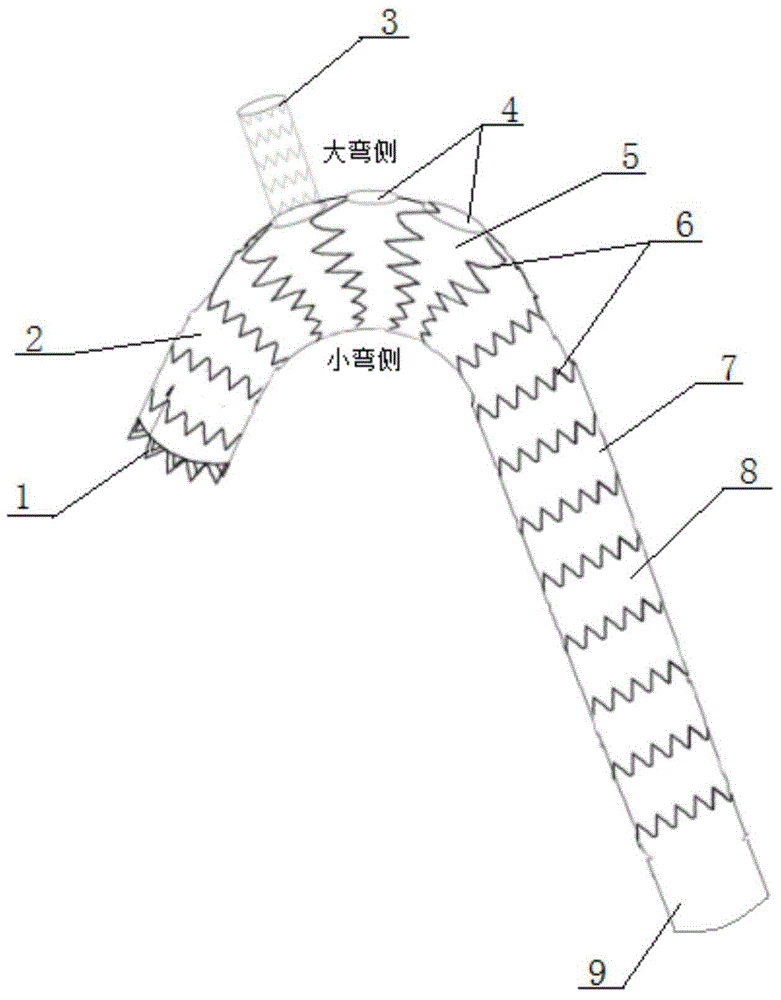
The invention belongs to the crossed field of medicine and engineering, and relates to the production and manufacturing of a novel stent for treating type B aortic dissection. An aortic stent is of aconical structure; the proximal end is completely covered by a film coating stent; no metal bare stent is used; a material capable of slowly expanding when meeting blood covers the outer side of the film coating stent; the 1 to 2cm position, near the big bent side, of the stent is formed by small woven V-shaped stent units through connection; the remote end of the big bent side is formed by big woven V-shaped stent units through connection; the small bent side of the stent is formed by small V-shaped stent units through connection. The aortic film coating stent system can adapt to the anatomical structure of the Stanford type B aortic dissection, particularly the Stanford type B aortic dissection involving with left subclavian artery due to proximal anchoring area deficiency; a breaking opening of the aortic dissection can be completely isolated; the application to various normal and deformation blood vessels can be realized; the application range is wide; the stent customization is avoided; the mass production can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
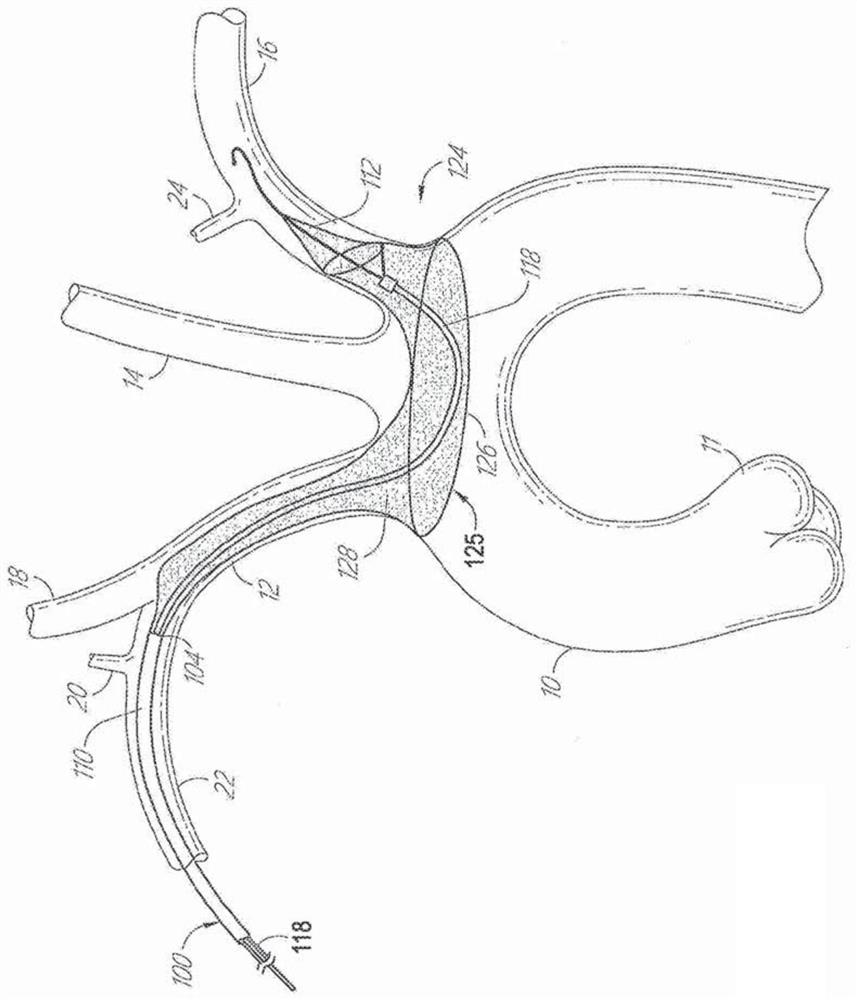
Self-protuberant aortic intracavity implant
An aortic intracavity implant, which is provided with an anchoring zone at the near-end to reliably fix the implant and prevent the inner leakage, is provided. A membrane braid is used for replacing partial overlay film of the aortic intracavity implant, in the operation, a central region of the membrane braid is opposite to a left subclavian artery opening, under the pressure of aortic blood pressure the central region is inserted into the left subclavian artery, the top is sparse under the pressure effect to form an opening, thus the blood supply of the left subclavian artery can be maintained. A main body structure of the membrane braid is elliptic, and is divided into a central region and a peripheral region, no absolute boundary line is arranged between the central region and the peripheral region, the braid from the peripheral to the central region is gradually sparse. No leakage is provided at the peripheral region, and the central region is provided with an opening in the opening process. The membrane braid has no supporting effect on the aortic intracavity implant, and has the main effects: (1) guaranteeing the blood supply of main branch blood vessel after the implant isopened, and adding the anchoring zone; and (2) having no leakage at the peripheral region of the membrane braid, thus preventing the inner leakage.
Owner:景在平 +1
Systems for protecting the cerebral vasculature
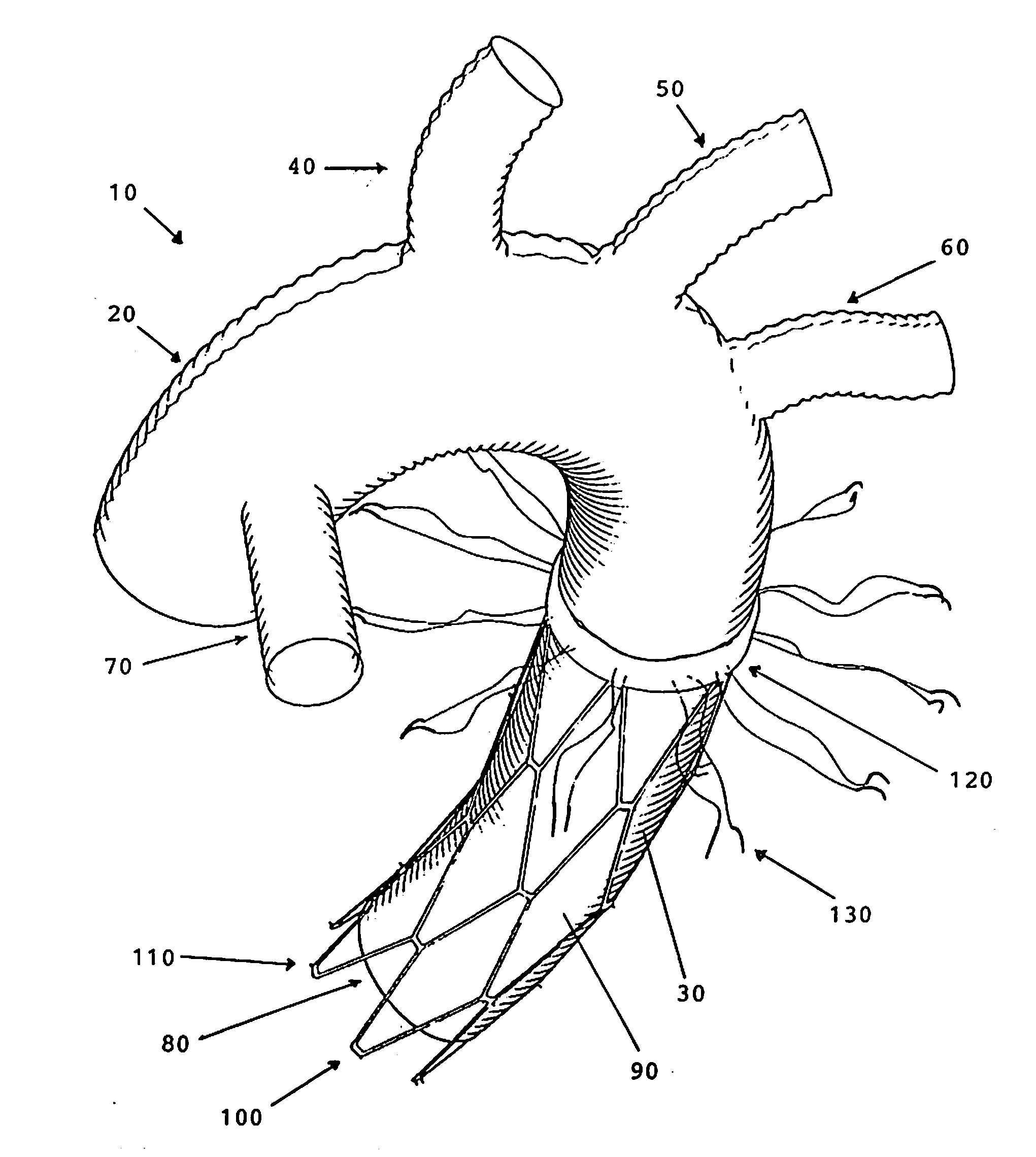
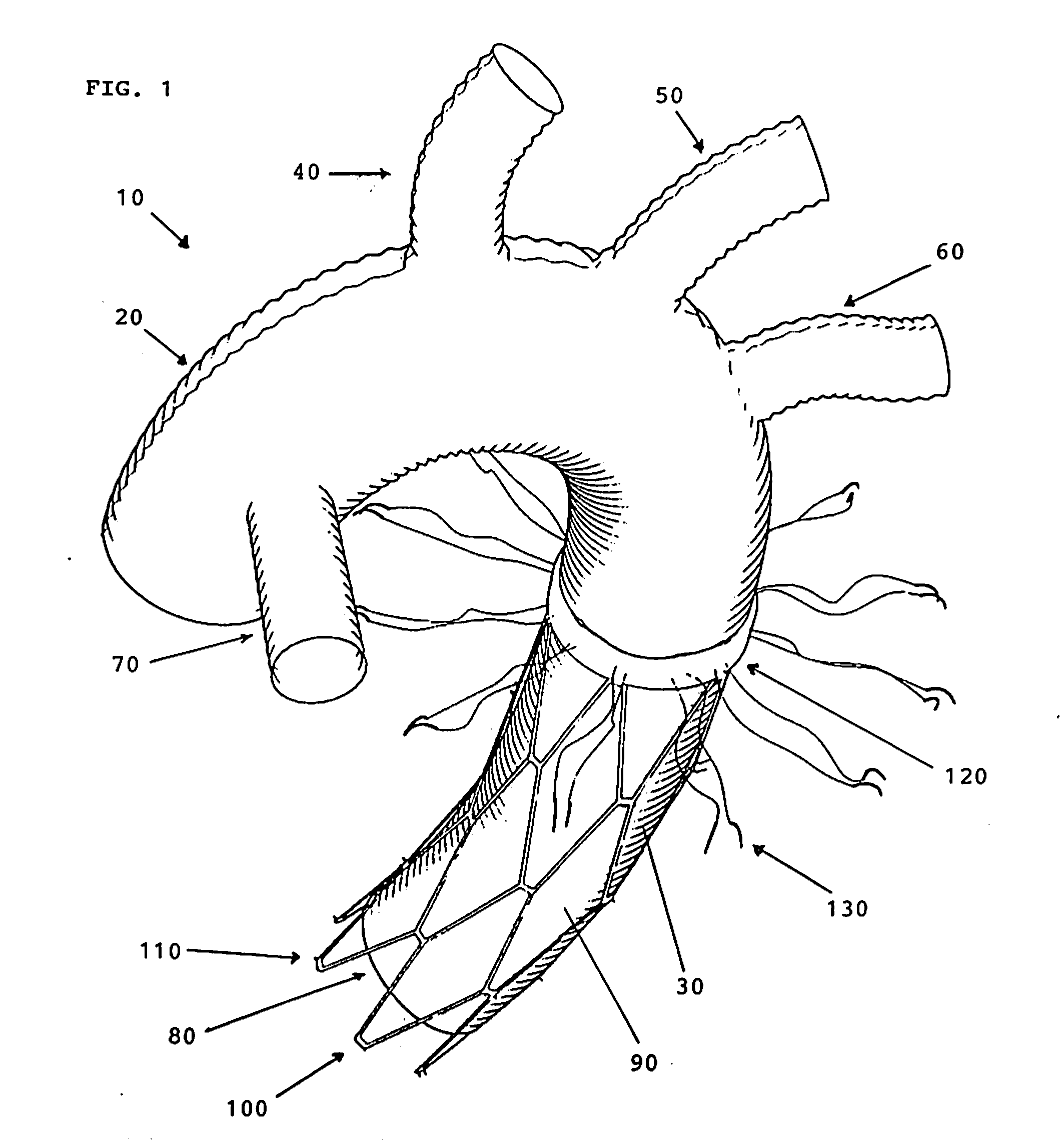
Disclosed are methods and devices for isolating all three of the left subclavian, left common carotid and brachiocephalic arteries from embolic debris that might flow through the aortic arch, via a single access point. A system may include an elongate flexible tubular sheath, having a proximal end and a distal end, and an inner member extending through the sheath and moveable relative to the sheath. A left subclavian element may be supported by the inner member. A filter membrane may be configured to isolate the aorta from the brachiocephalic, left common carotid and left subclavian arteries when the left subclavian element is expanded within the left subclavian artery and the sheath is retracted to expose the membrane. The left subclavian element may include a self expandable frame, whichmay carry a left subclavian filter.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Intraoperative stent delivery system and use method thereof
The invention provides an intraoperative stent delivery system and an use method thereof. The intraoperative stent delivery system is used for loading and delivering the intraoperative stent. The intraoperative stent delivery system comprises a main body operating handle, a main body lining bar and a branch swing mechanism; the main body lining bar is arranged at the front end of the main body operating handle; the branch swing mechanism is also arranged at the front end of the main body operating handle; the main body operating handle comprises a front end cover, a middle handle, a rear end cover, a main body stent release portion, a branch support release portion and a lock cover; the main body lining bar comprises a bending bar, a limit ball and a guide head; and the branch swing mechanism comprises a sliding block , a transmission bar and a U-shaped ring. The invention also includes a method by using the system to deliver the intraoperative stent. The system can be used for delivering and releasing the single branch intraoperative stent so that the single branch intraoperative stent can solve the problem that the intraoperative stent is difficult to be matched with branch vessels, especially for the anastomosis with the left subclavian artery, accordingly the dissociation, the blocking and the anastomosis of the super-aortic branch vessels can be reduced or avoided so as toreduce the difficulty of surgery as well as the trauma of the surgery.
Owner:北京有卓正联医疗科技有限公司
Aortic arch-thoracic aorta slide regulation pre-fenestration covered stent
The invention discloses an aortic arch-thoracic aorta slide regulation pre-fenestration covered stent. The aortic arch-thoracic aorta slide regulation pre-fenestration covered stent is characterized by comprising a cylindrical tubular first covered stent body, a second covered stent body, a rotating stent, a truncus brachiocephalicus branch vessel port covered stent body and a left subclavian artery branch vessel port covered stent body; the rotating stent is formed by connecting a cylindrical front covered stent segment, a front bare stent segment, a covered stent segment, a rear bare stent segment and a rear covered stent segment coaxially. A left common carotid artery branch vessel port is arranged on the side wall of the covered stent segment, the truncus brachiocephalicus branch vessel port covered stent body is inserted in the front bare stent segment, and the left subclavian artery branch vessel port covered stent body is inserted in the rear bare stent segment. The proximal endof the rotating stent is slidably connected with an annular rear sliding track of the first covered stent body through a circular front slide in a sleeving mode, and the distal end of the rotating stent is slidably connected with an annular front sliding track of the second covered stent body through an annular rear slide in a sleeving mode. The aortic arch-thoracic aorta slide regulation pre-fenestration covered stent has the advantages such as novel structure, simple manufacturing process, short operation time and small technical difficulty during the operation.
Owner:侯红军
Integrated thoracic aortic branch support
InactiveCN103300940AReduce surgical riskReduce medical costsStentsBlood vesselsTectorial membraneLeft subclavian artery
The invention relates to an integrated thoracic aortic branch support which comprises a main support and a first branch support arranged on the sidewall of the main support, wherein the main support is communicated with the first branch support; the main support and the first branch support are composed of memory alloy wire frames and tectorial membranes fixedly coating the frames. The first branch support is arranged on the main support, a most important branch artery channel is reserved when the important arteries are coated, so as to enable the thoracic aortic support to achieve the left side of the right brachiocephalic trunk opening, the first branch support carried by the main support is placed in the left common carotid artery, or conducting bridging to the right common carotid artery and the left common carotid artery, and conducting bridging to the left common carotid artery and the left subclavian artery firstly and then covering all the arcus aortas by the support, the first support is placed in the right brachiocephalic trunk, so that the support can also be used for lesion near the aortic arch, exaggerated thoracic surgery is avoided, and the surgical risk and medical cost of a patient are decreased accordingly.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Intraoperative brain protection device
PendingCN114469438AReduces the effects of co-occupancy of the femoral arteryImprove fitBlood vessel filtersLeft subclavian arteryHead artery
The invention discloses an intraoperative brain protection device which comprises an elastic support and a filter screen. The elastic support can expand on the inner wall of a blood vessel of the aortic arch and is attached to the inner wall of the blood vessel of the aortic arch, the elastic support is of a ring-like structure defined by elastic metal materials, and the far end and the near end, in the axial direction, of the ring-like structure tilt upwards so that the intra-operative brain protection device can be fixed in the aortic arch; the filter screen is located in an area defined by the elastic support, and the two ends of the filter screen are connected with the far end and the near end of the ring-like structure respectively so as to prevent thrombus generated in the operation from entering the head artery. The protection device adopts the left subclavian artery approach, and compared with a traditional femoral artery protection device, the influence that other femoral artery approach instruments jointly occupy the femoral artery is reduced, the operation effect is guaranteed, and popularization and application of the intraoperative brain protection device in the technical field of medical instruments are facilitated.
Owner:CHENXING (NANTONG) MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Compound type human great artery intraoperative stent system
PendingCN107822741AProsthetic prosthesisAccelerate the remodeling processStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryGreat artery
The invention provides a compound type human great artery intraoperative stent system. The compound type human great artery intraoperative stent system comprises an anastomosable artificial blood vessel, a release-by-wire left subclavian artery covered stent blood vessel, and a balloon-expanding type descending aorta covered stent artificial blood vessel provided with a balloon inside. The distalend of the balloon-expanding type descending aorta covered stent artificial blood vessel extends outwards to form an extending portion covering the spinal cord area. The extending portion and the balloon-expanding type descending aorta covered stent artificial blood vessel are integrally formed. A plurality of rows of through holes are evenly distributed in the tube wall of the extending portion,and the diameters of the through holes are 2-3 mm. By adding the extending portion and arranging the through holes, namely openings, it is possible to extend the balloon-expanding type descending aorta covered stent artificial blood vessel while avoiding completely covering the opening of the spinal artery, thereby reducing the possibility of paraplegia due to spinal cord ischemia.
Owner:FUJIAN PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL
Aortic pump devices
ActiveCN110022912ASmall sizeSize can be adjustedBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesLeft subclavian arteryBlood pump
A disclosed apparatus or method can include or use a non-transluminally implantantable blood pump housing, which can be sized and shaped to be implanted at an aortic valve of a human subject, the pumphousing can include: a pump housing cross-sectional profile size that is larger than is passable via a blood vessel of the human subject; and a power connection, configured for being electrically connected to an intravascular lead that is sized and shaped to extend from the pump housing through a subclavian artery of the human subject.
Owner:BERLIN HEART GMBH
Perfusion-type aorta blocking double-balloon
The invention provides a perfusion-type aorta blocking double-balloon. The perfusion-type aorta blocking double-balloon has the advantages that by the sectional-type double-balloon, a first balloon islocated in an upper half portion region between the lower edge of the left subclavian artery and the celiac trunk, so that the near-end aorta can be blocked, and hemorrhage can be controlled to the greatest extent; a second balloon is located in a lower half portion region between the lower edge of the renal artery and the iliac artery bifurcation, so that hemorrhage between the celiac trunk andthe renal artery is blocked, and vital organs such as bilateral lower limbs are perfused selectively; selective liquid perfusion to related damage-free regions is realized, and the problem of ischemiaof visceral organs and limbs is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGHAI HOSPITAL
Scaffold for treating aortic arch diseases
The invention provides a scaffold for treating aortic arch diseases, and relates to the technical field of medical instruments. The scaffold mainly solves the technical problem that the varieties and / or types of scaffolds for treating the aortic arch diseases in the prior art are too many. The scaffold comprises a main scaffold body, an anti-blocking opening groove and branch scaffold bodies, theanti-blocking opening groove is formed in one end of the main scaffold body, the branch scaffold bodies are communicated with the main scaffold body, and the branch scaffold bodies and the anti-blocking opening groove are located on the same side of the main scaffold body. Due to the arrangement of the anti-blocking opening groove, the range of the distance between the left common carotid artery and the left subclavian artery of the human body can be enlarged, then the scaffold can be suitable for more patients, the size of the scaffold is uniformed, and the aim of reducing the varieties and / or types of the scaffolds is achieved.
Owner:魏民新
Four-branch artificial blood vessel for arcus aortae portion replacement perfusion
InactiveCN107468374APerfusion assuranceReduce complicationsBlood vesselsExtracorporeal circulationLeft subclavian artery
The invention provides a four-branch artificial blood vessel for arcus aortae portion replacement perfusion. The artificial blood vessel comprises a body artificial blood vessel for introducing blood for perfusion and a brachiocephalic artery branch artificial blood vessel, a left common carotid artery branch artificial blood vessel and a left subclavian artery branch artificial blood vessel which are communicated with the body artificial blood vessel. An arterial perfusion branch artificial blood vessel communicated with extracorporeal circulation is further arranged on the body artificial blood vessel. Perfusion can be performed on the bilateral whole brain and the whole body during operation, the brain perfusion during operation during profound hypothermia circulation arrest is ensured to the maximum extent, postoperative neurological complications can be reduced, the operation technique can be simplified, and the operation time is shortened, so that the purposes of improving the operation success rate and reducing related operation complications are achieved.
Owner:马路遥
Quick connecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel for irrigation
PendingCN110584830AImprove survival rateIngenious structureBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryNervous system
The invention relates to a quick connecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel for irrigation. The quick connecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel comprises a main body artificial blood vessel, a brachiocephalic artery branch artificial blood vessel, a left common carotid secondary branch artificial blood vessel and a left subclavian artery secondary branch artificial blood vessel,wherein the brachiocephalic artery branch artificial blood vessel, the left common carotid secondary branch artificial blood vessel and the left subclavian artery secondary branch artificial blood vessel are connected with the main body artificial blood vessel in a communicating manner. The quick connecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel is characterized in that left-hand threaded typeconnectors are respectively arranged at the far end of the left common carotid secondary branch artificial blood vessel and the far end of the left subclavian artery secondary branch artificial bloodvessel; and an intra-arterial infusion branch artificial blood vessel which communicates with the outer circulation of a connector is also arranged on the main body artificial blood vessel. The quickconnecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel disclosed by the invention is ingenious in structure and reasonable in design, so that the problem that in the prior art, in an aortic arch replacement operation, cerebral perfusion is insufficient, and nervous system complications are liable to generate can be solved; the quick connecting type four-branch artificial blood vessel can be quickly and reliably fixed, the situation that time is consumed for suturing is not needed, the operation is quick and convenient, the operation time can be greatly saved, the operation procedure difficulty isreduced, and the survival rate of a patient is increased.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL WITH NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com