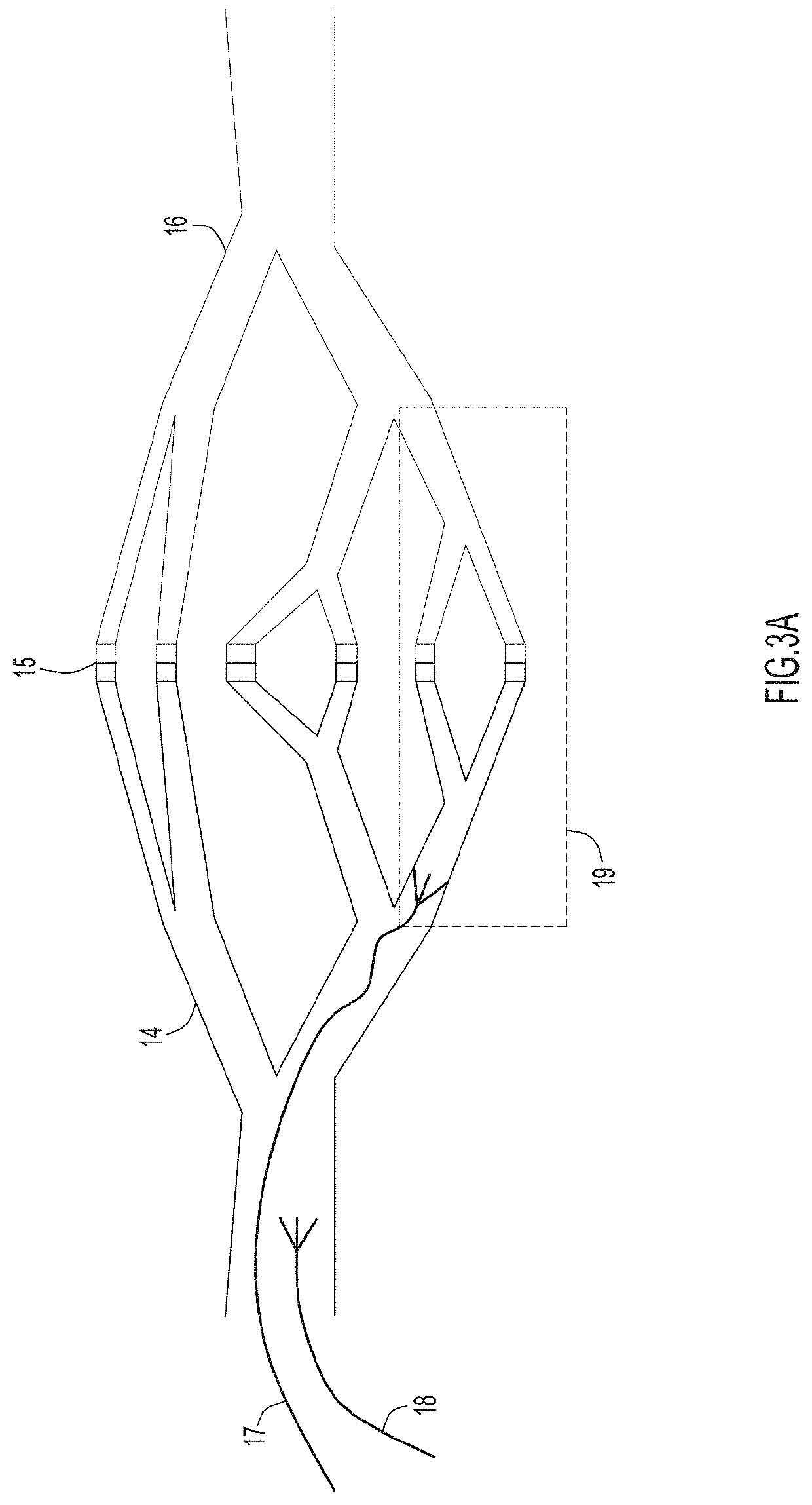
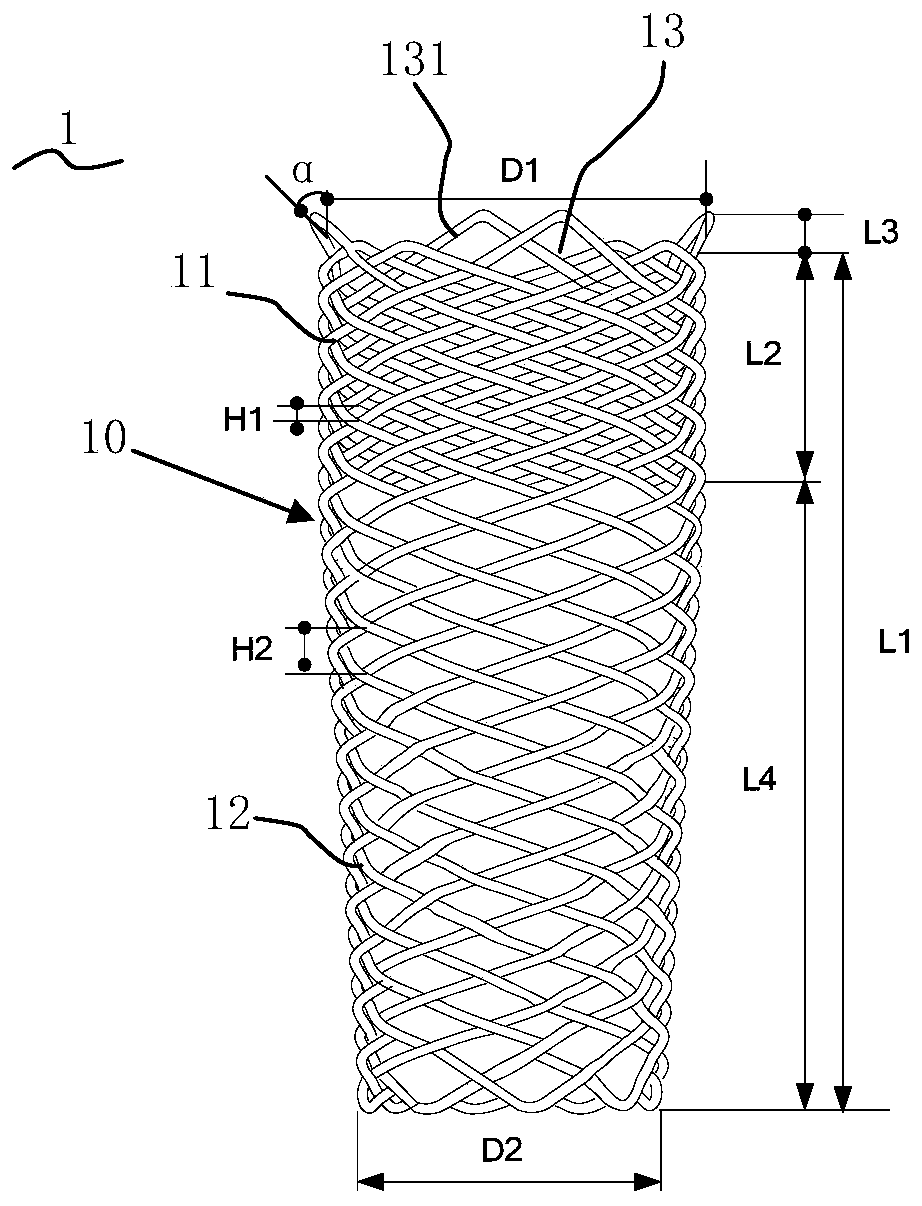
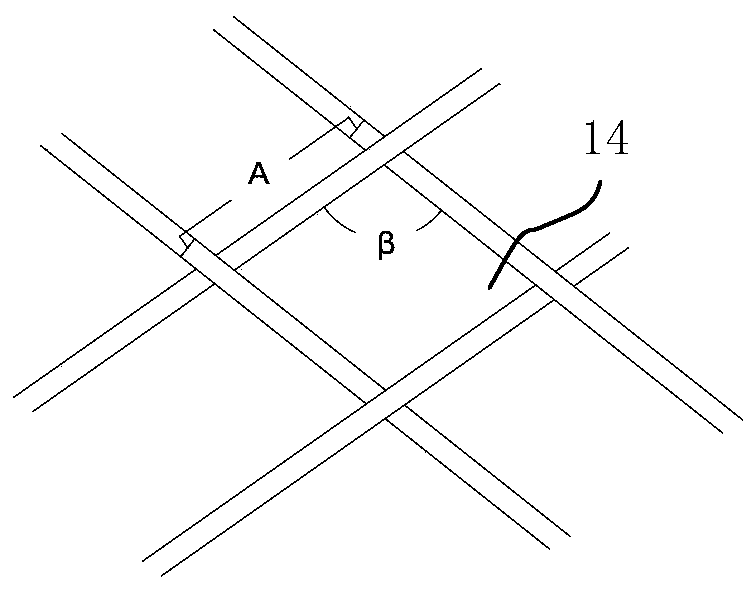
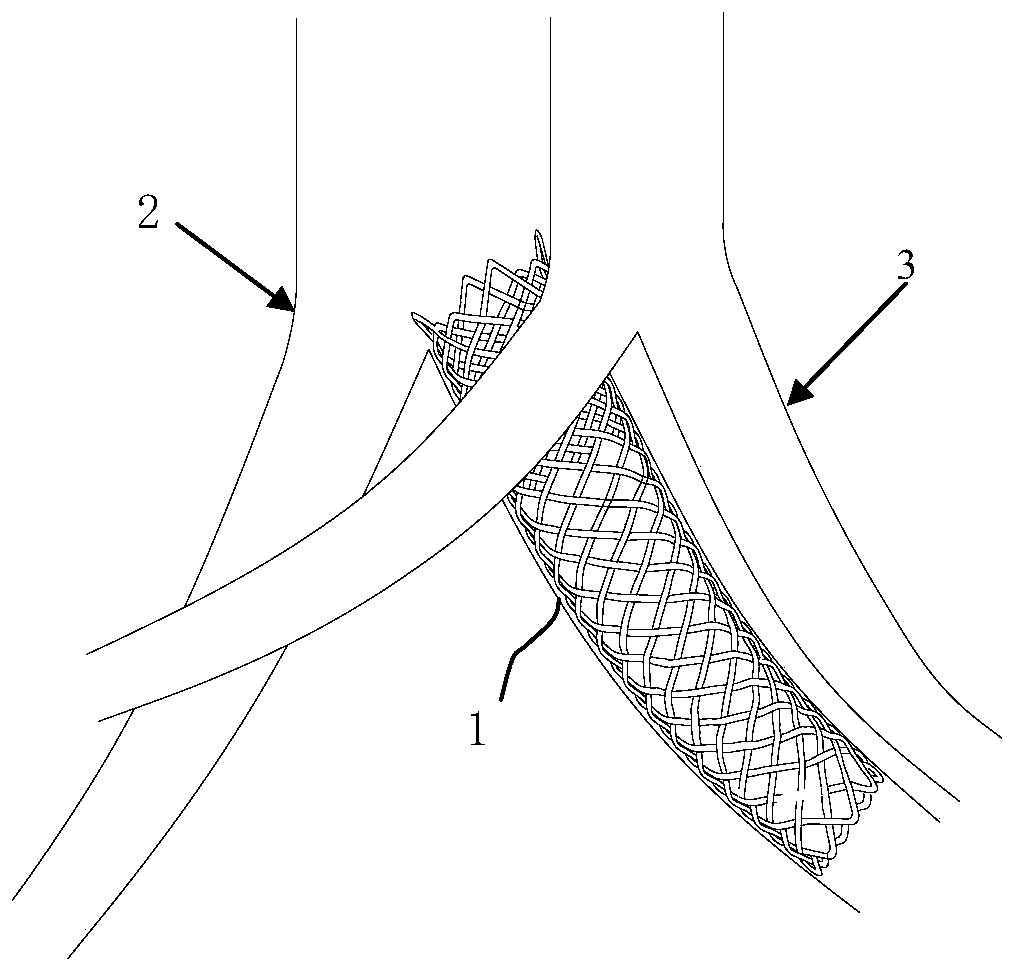
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Vascular anatomy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
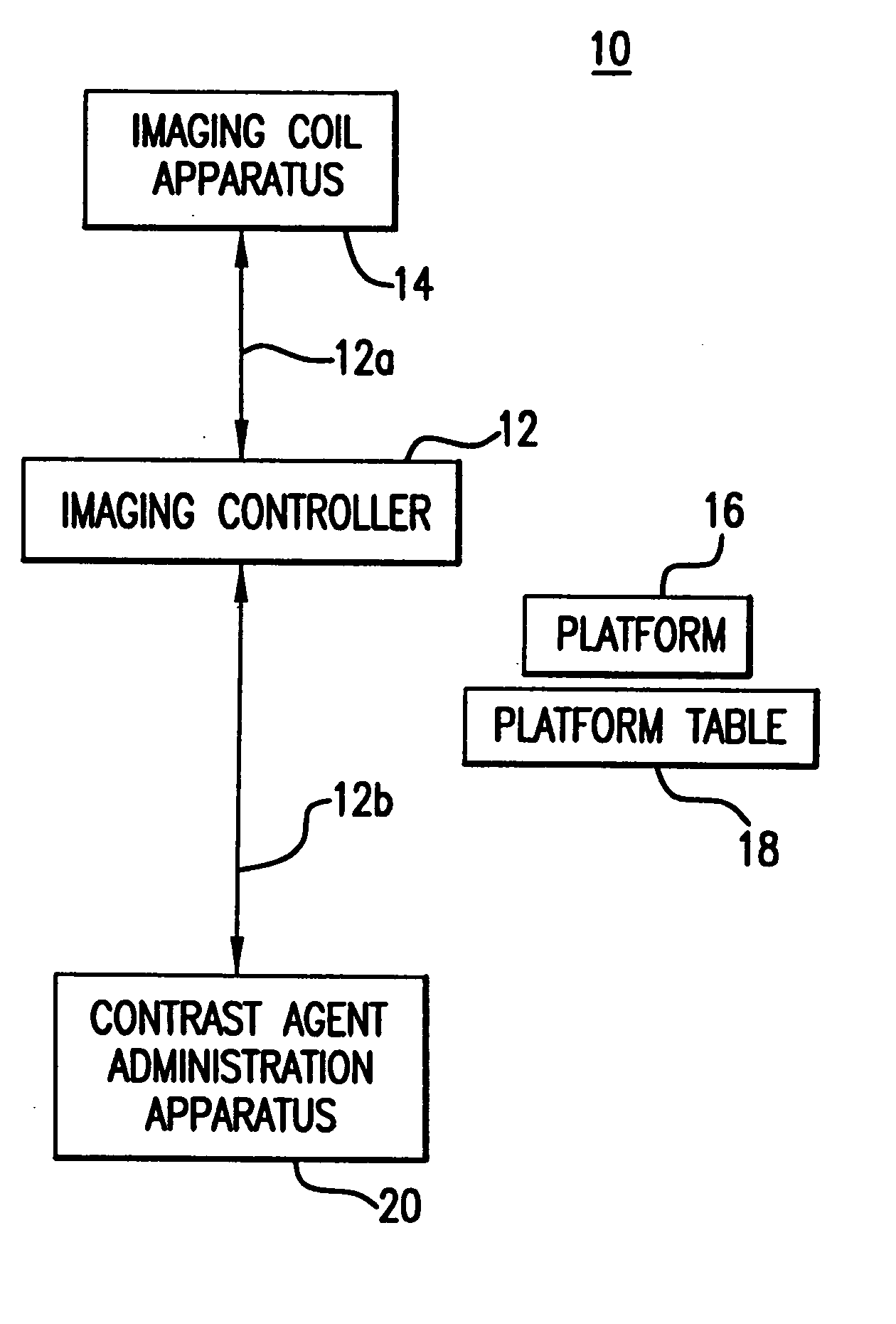
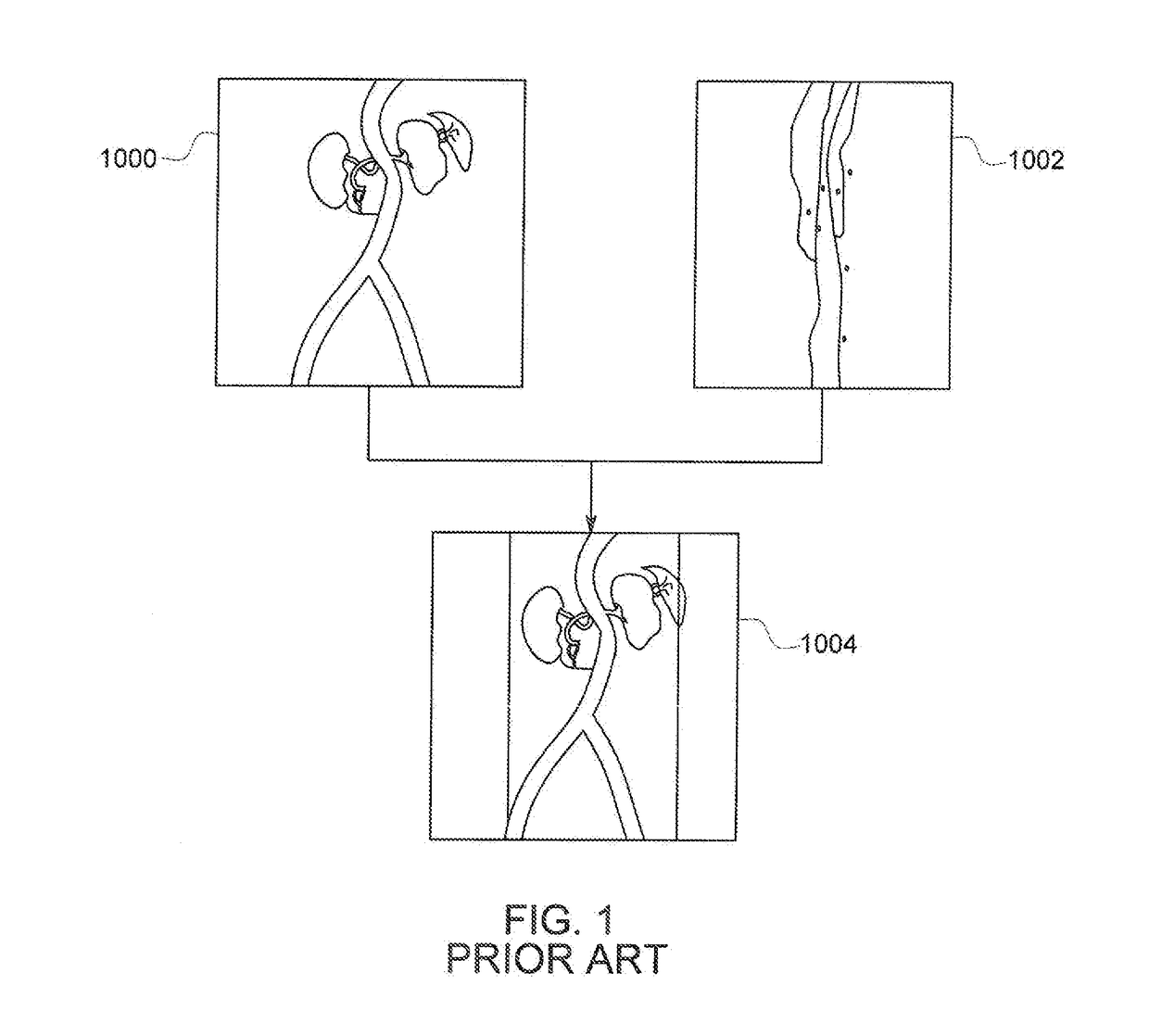
Method of and system for intravenous volume tomographic digital angiography imaging
InactiveUS6075836AQuality improvementEfficient contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersData acquisition
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Method and apparatus for visualizing anatomical structures
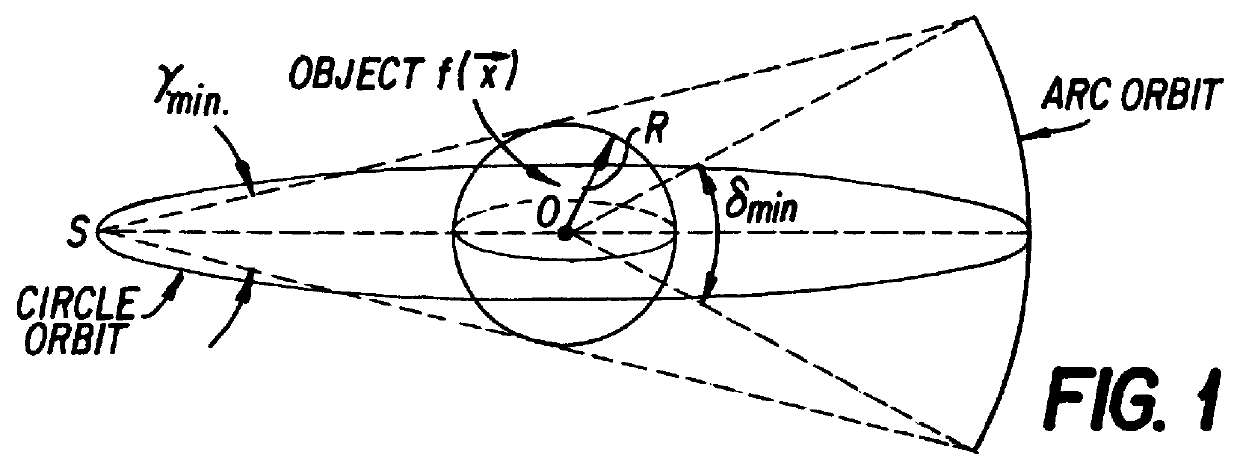
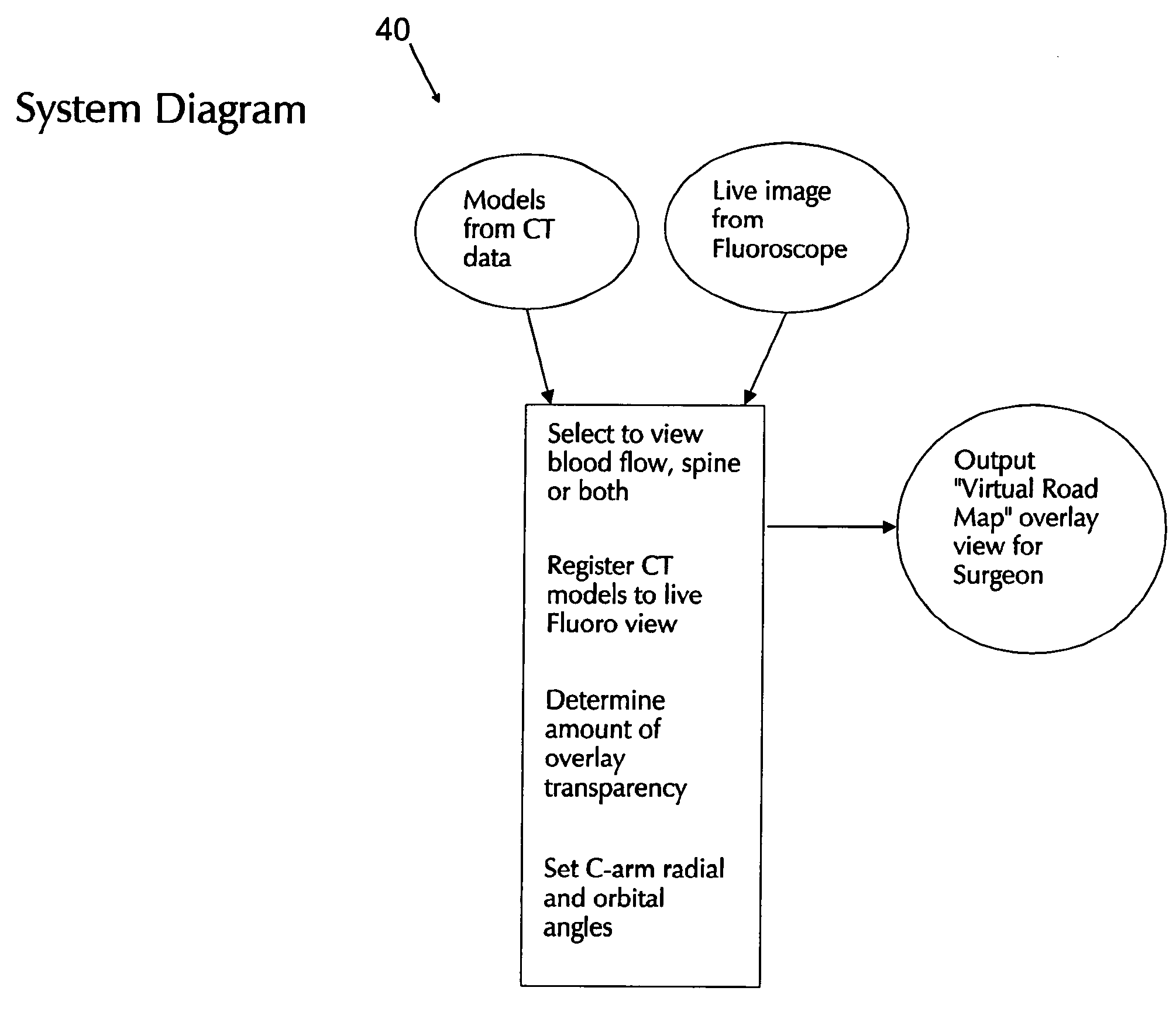
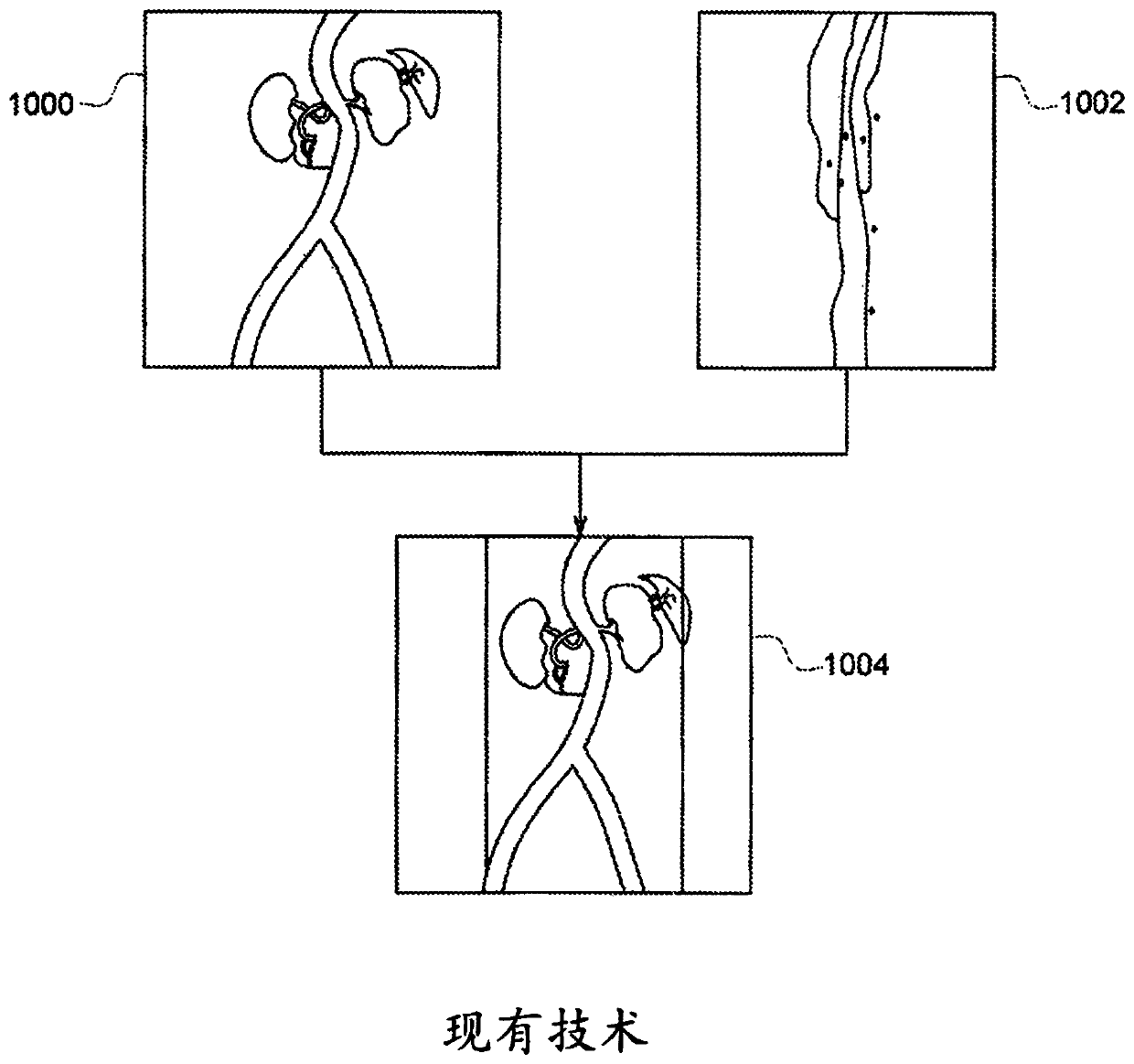
Apparatus and method for producing a virtual road map of a patient's vascular anatomy comprising a virtual 3D model of the patient's vascular and bony structure in proper registration with one another, a fluoroscope for providing real-time images of the bony structure of the patient, registration apparatus for placing the virtual 3D model in proper registration with the patient space of the fluoroscope, bone mask subtraction apparatus for generating a bone mask of the bony structure, and subtracting the same from the real-time images, whereby to create modified fluoroscope images omitting bony structure, and image generating apparatus for generating the virtual road map comprising a composite image combining (i) images of the virtual 3D structure representing the vascular structure, and (ii) modified fluoroscope images omitting bony structure, wherein the images of the virtual 3D structure representing vascular structure are in proper registration with the modified fluoroscope images omitting bony structure.
Owner:ASTUTE IMAGING LLC
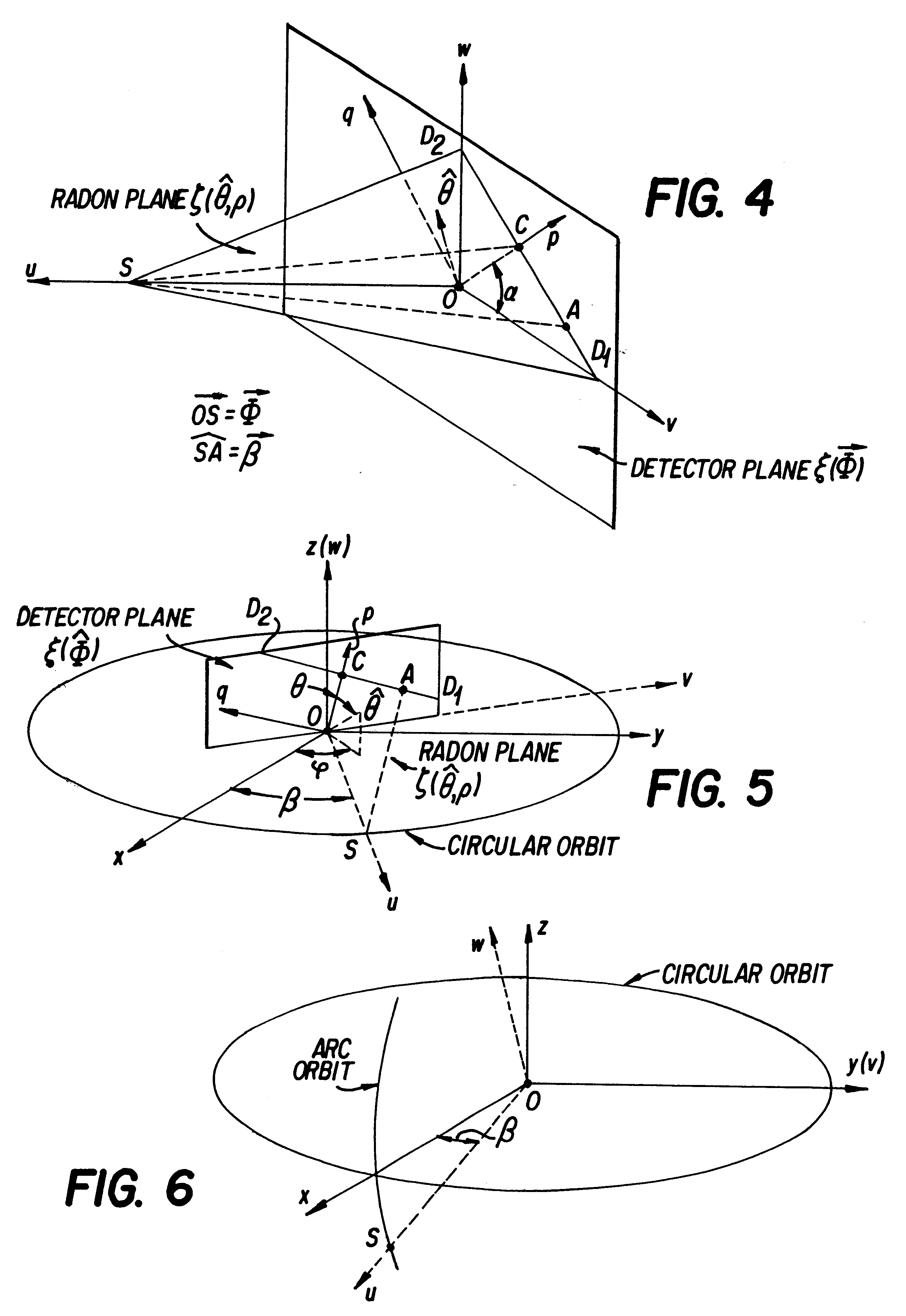
Cone beam volume CT angiography imaging system and method
InactiveUS6298110B1Quality improvementEfficient contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersX-ray
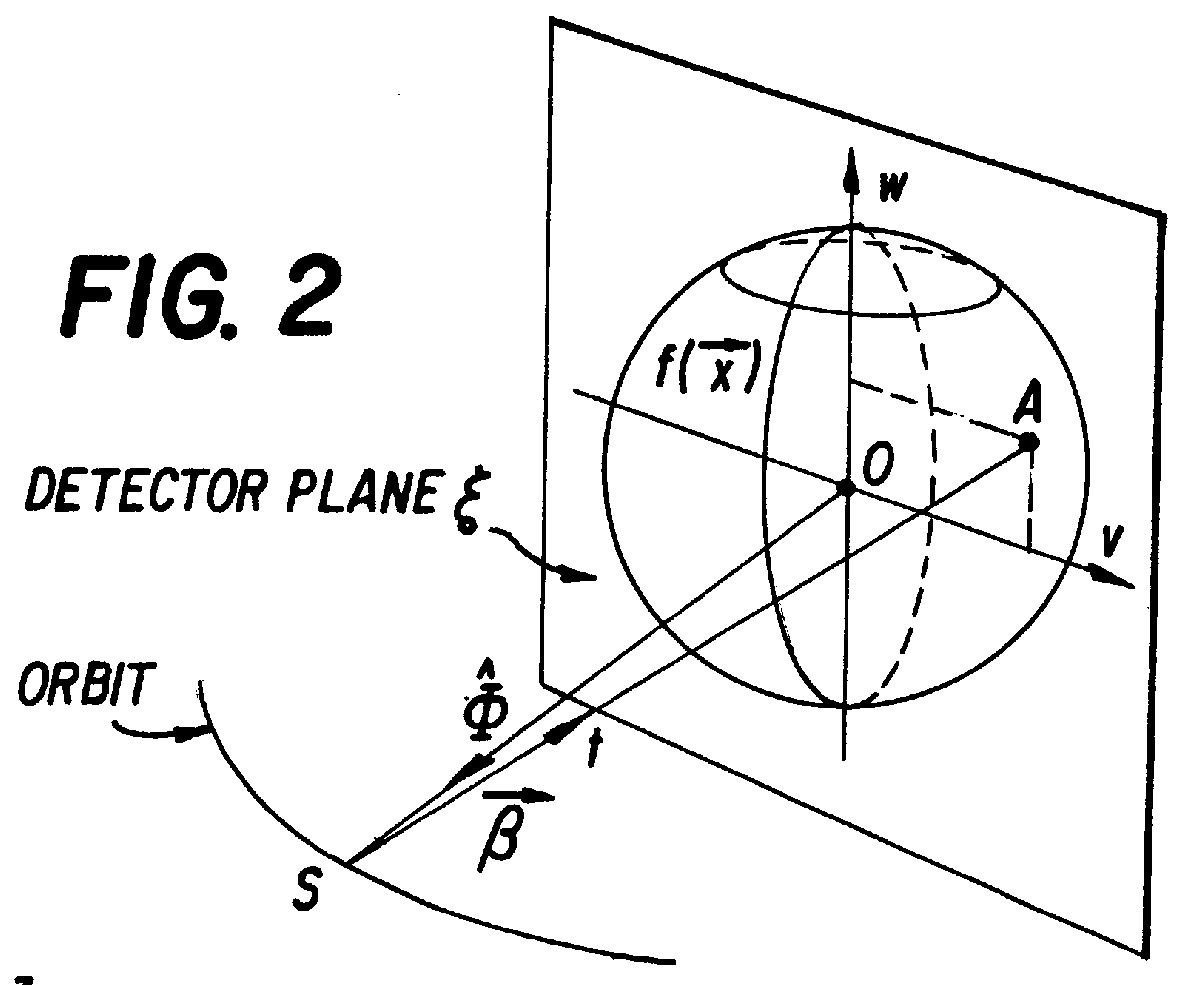
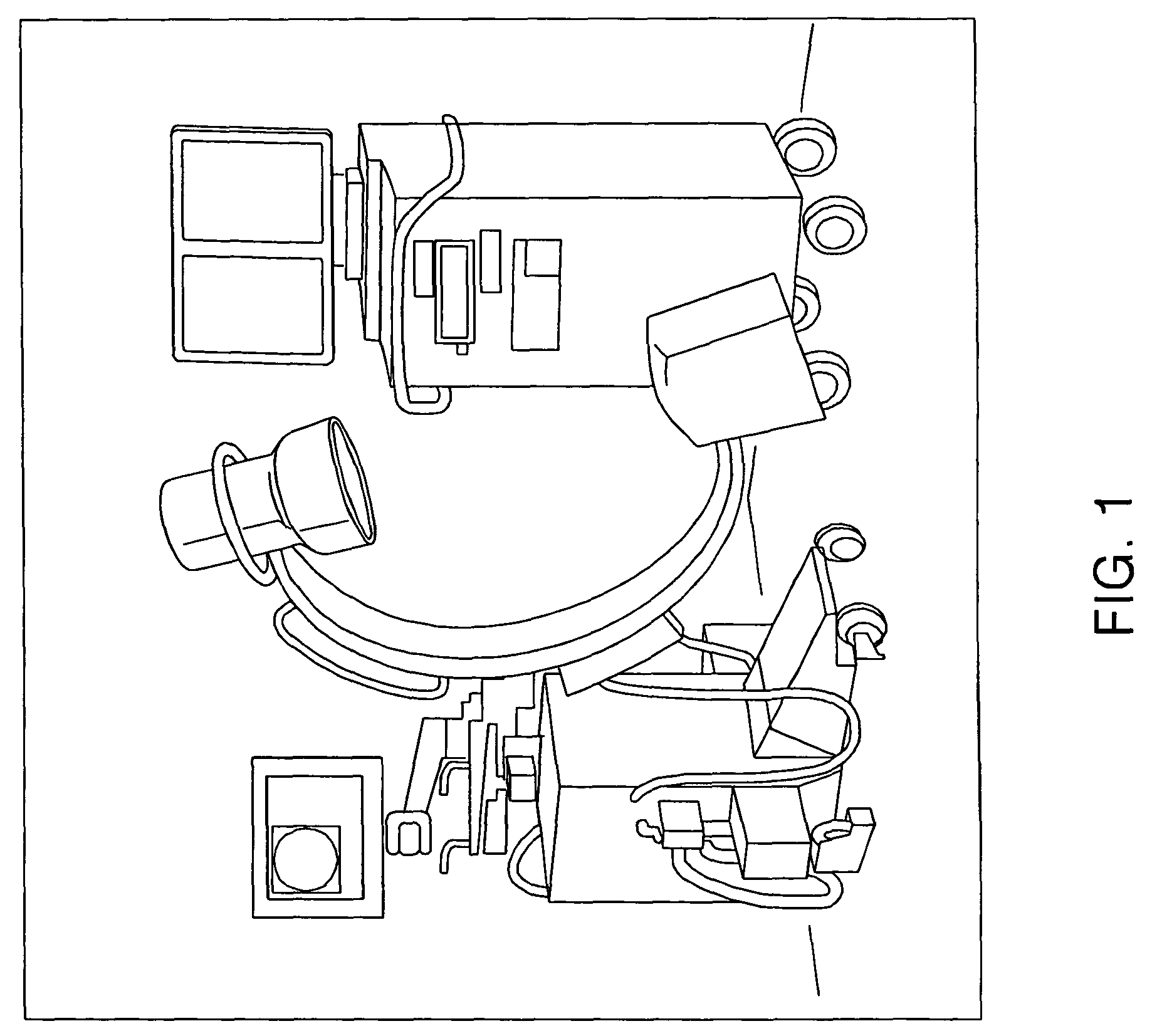
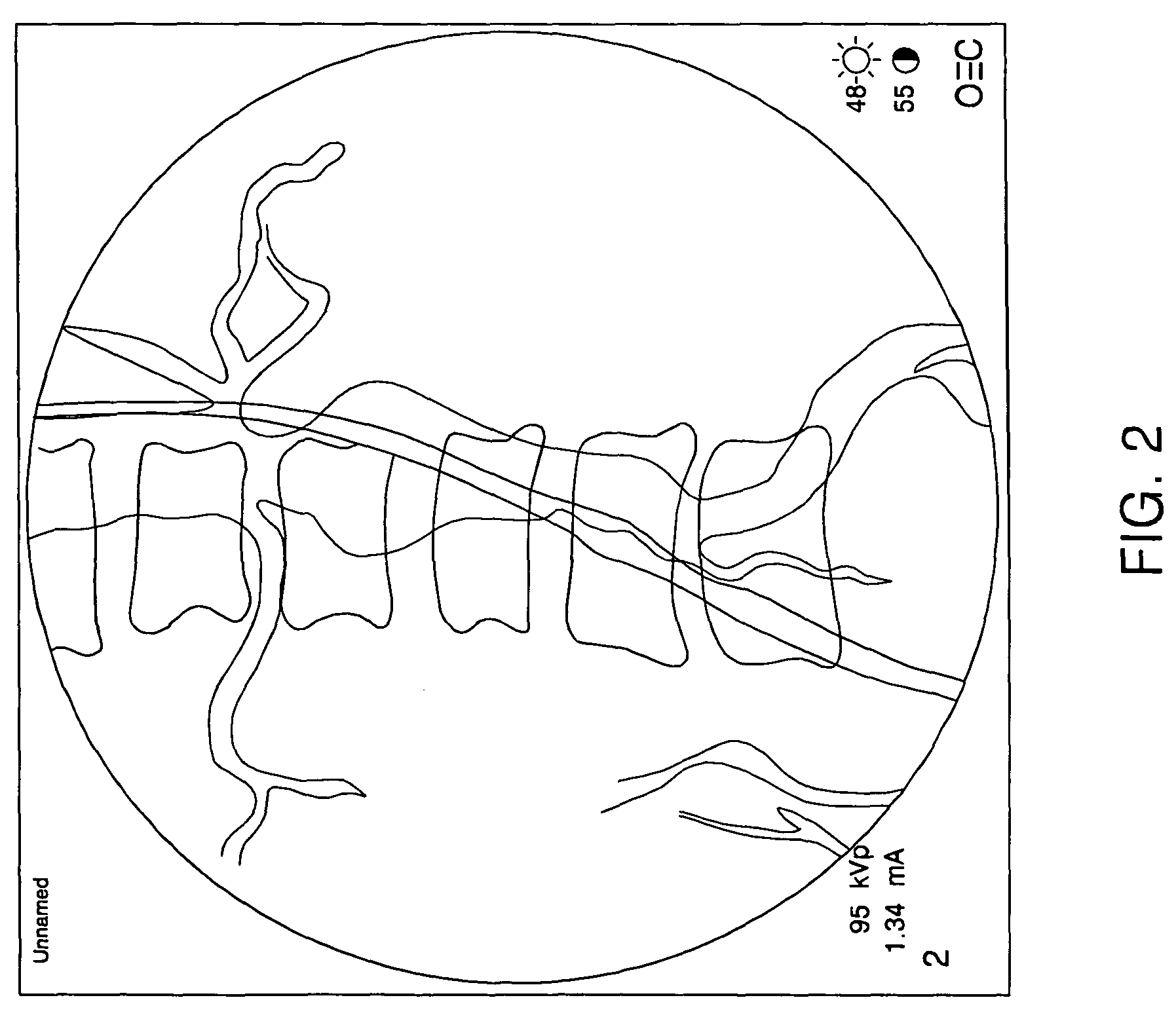
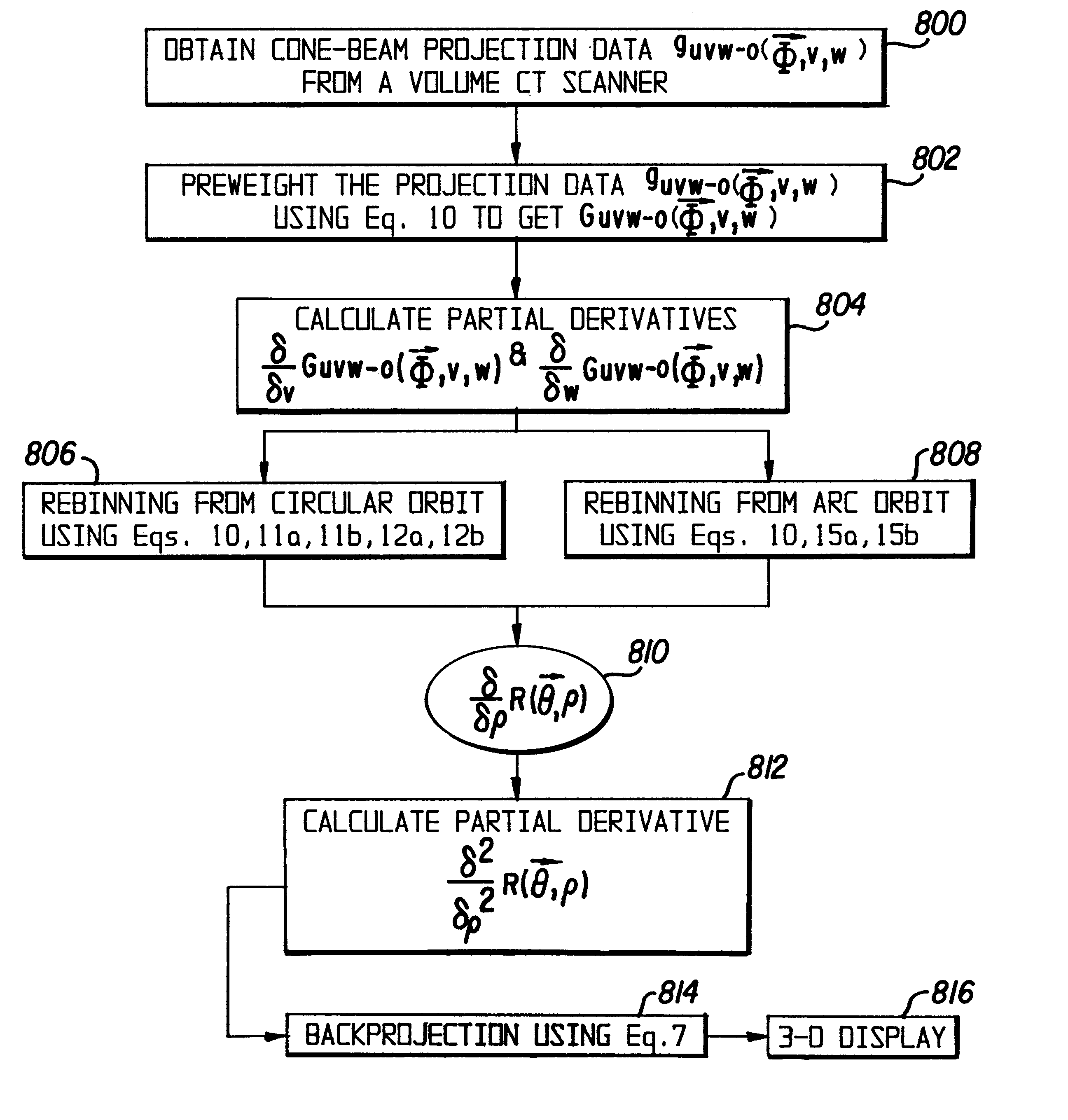
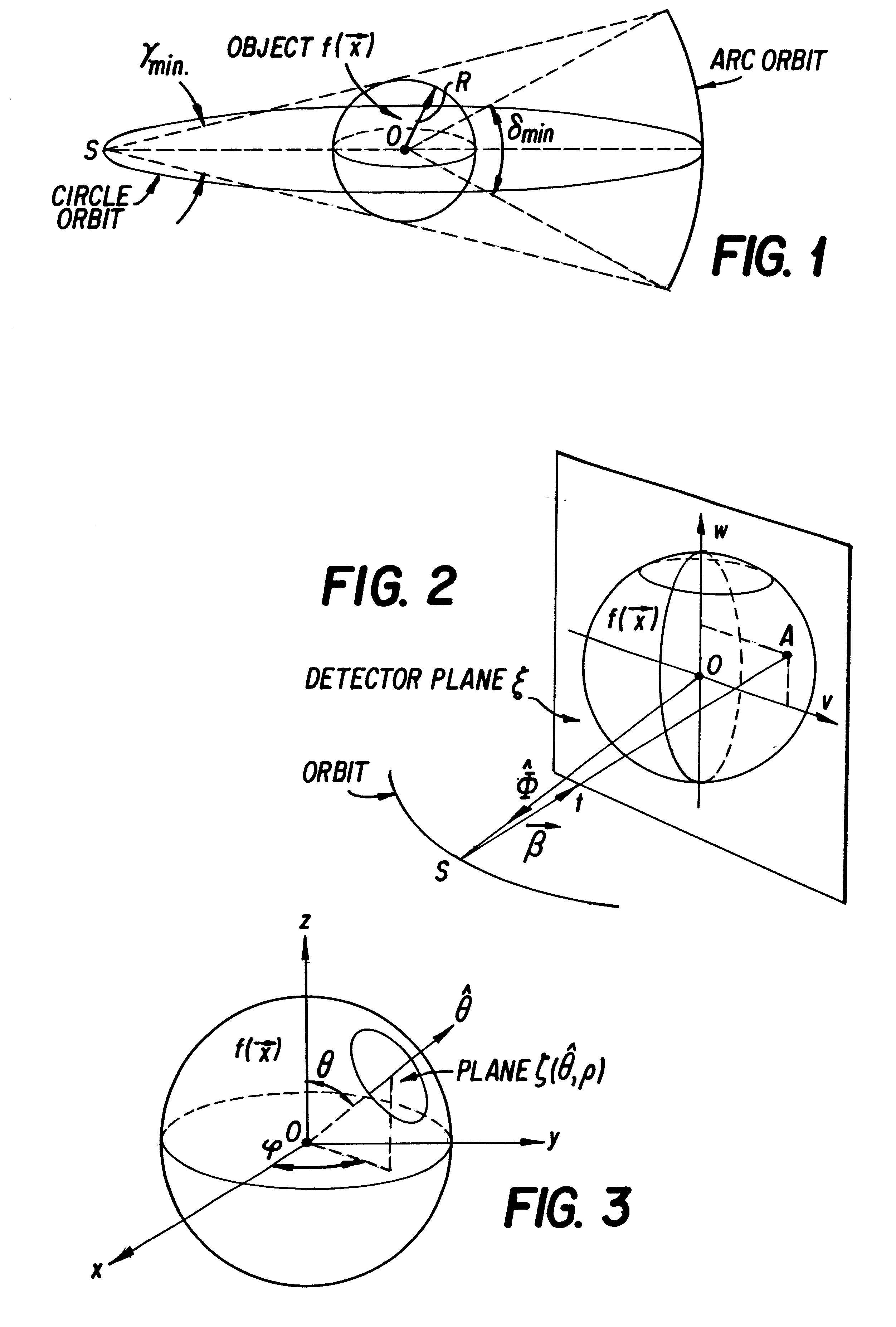
Only a single IV contrast injection with a short breathhold by the patient is needed for use with a volume CT scanner which uses a cone-beam x-ray source and a 2-D detector for fast volume scanning in order to provide true 3-D descriptions of vascular anatomy with more than 0.5 lp / mm isotropic resolution in the x, y and z directions is utilized in which one set of cone-beam projections is acquired while rotating the x-ray tube and detector on the CT gantry and then another set of projections is acquired while tilting the gantry by a small angle. The projection data is preweighted, partial derivatives are calculated and rebinned for both the circular orbit and arc orbit data The second partial derivative is then calculated and then the reconstructed 3-D images are obtained by backprojecting using the inverse Radon transform.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Two-step/dual-diameter balloon angioplasty catheter for bifurcation and side-branch vascular anatomy
The present invention tackles the challenging anatomic characteristics of the coronary artery disease in the bifurcation point and the origin of side-branch. The invention has a specifically designed angioplasty balloon catheter, particularly the balloon shape and profile, to be used in the diseased vessels at these difficult anatomic locations. In stent implanting into a coronary artery, a balloon catheter application is an inseparable requirement. A stent is a passive device that cannot be deployed in a diseased or stenosed artery without a pre-stent, with-stent and / or post-stent balloon dilatation. In majority (more than 95%) of available coronary stents, a stent is deployed by balloon expandable mode, meaning that the stent is delivered and expanded inside a vessel lumen by expanding a delivery balloon. This is done by crimping a stent over a folded balloon for delivery into a coronary artery. When expanded by balloon inflation, a stent is expanded and shaped passively by the inflated balloon shape and profile. The balloon catheter is designed to do angioplasty in the bifurcation and side-branch anatomy of coronary arteries, while minimizing the side effect. This specially designed balloon catheter is not only for balloon angioplasty dilatation of the bifurcation and side-branch anatomy, but is also for delivering and deploying specially designed bifurcation or side-branch stents into these difficult anatomic locations, as a stent delivery system.
Owner:JANG G DAVID
Intraoperative C-ARM fluoroscope datafusion system
In one form of the present invention, there is provided an apparatus for producing a virtual road map of a patient's vascular anatomy for use by a surgeon while conducting a procedure on the patient's vascular anatomy, the apparatus comprising: a virtual 3D model of the patient's anatomy, wherein the virtual 3D model comprises a virtual 3D structure representing bony structure of the patient and a virtual 3D structure representing vascular structure of the patient, with the virtual 3D structure representing bony structure of the patient being in proper registration with the virtual 3D structure representing vascular structure of the patient; a fluoroscope for providing real-time images of the bony structure of the patient and a surgical device being used in the procedure; registration apparatus for placing the virtual 3D model in proper registration with the patient space of the fluoroscope; bone mask subtraction apparatus for (i) generating a bone mask of the bony structure of the patient, and (ii) subtracting the same from the real-time images provided by the fluoroscope, whereby to create modified fluoroscope images omitting bony structure; and image generating apparatus for generating the virtual road map, wherein the virtual road map comprises a composite image combining (i) images of the virtual 3D structure representing vascular structure of the patient, and (ii) modified fluoroscope images omitting bony structure, wherein the images of the virtual 3D structure representing vascular structure of the patient are in proper registration with the modified fluoroscope images omitting bony structure.
Owner:ASTUTE IMAGING LLC
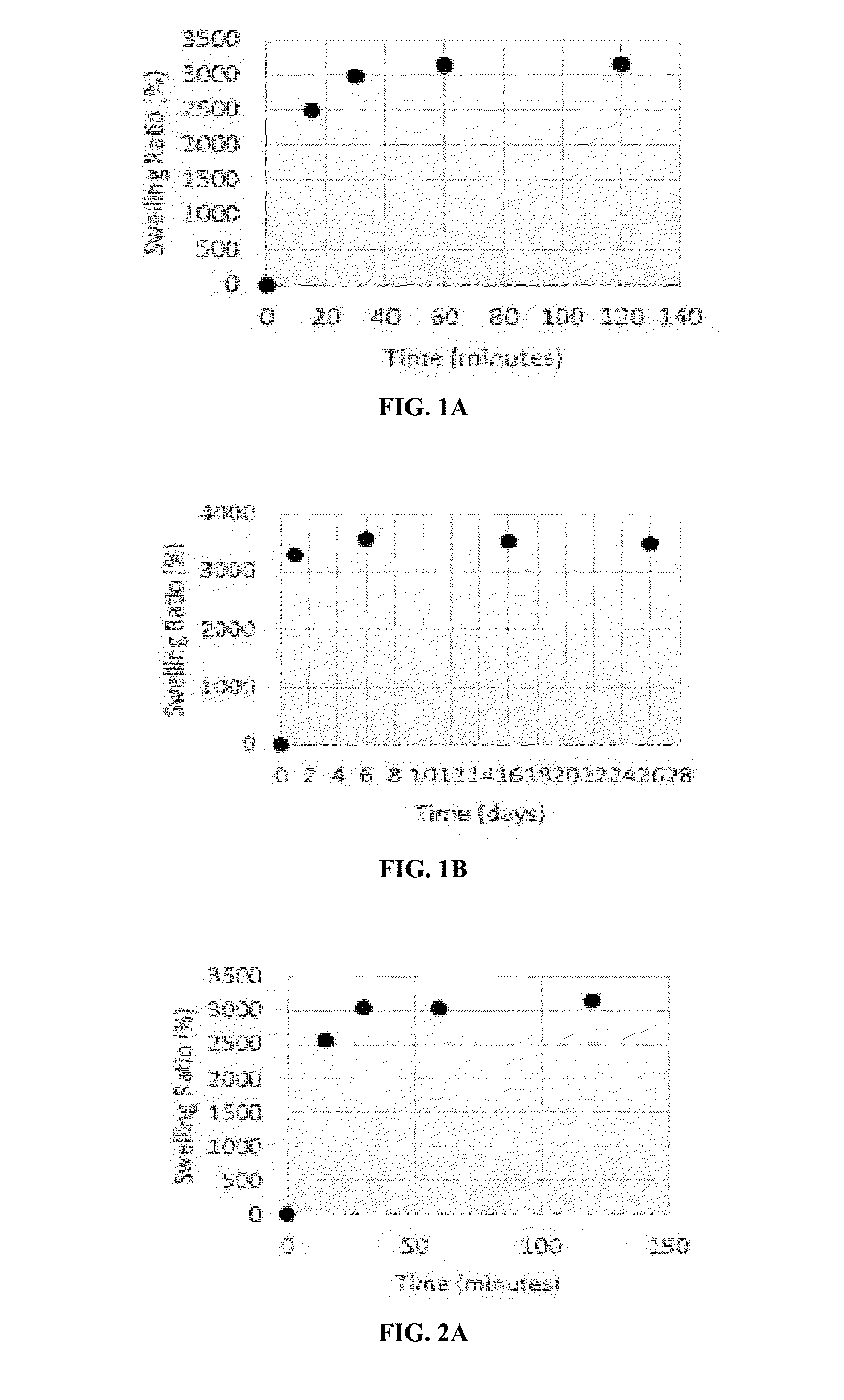
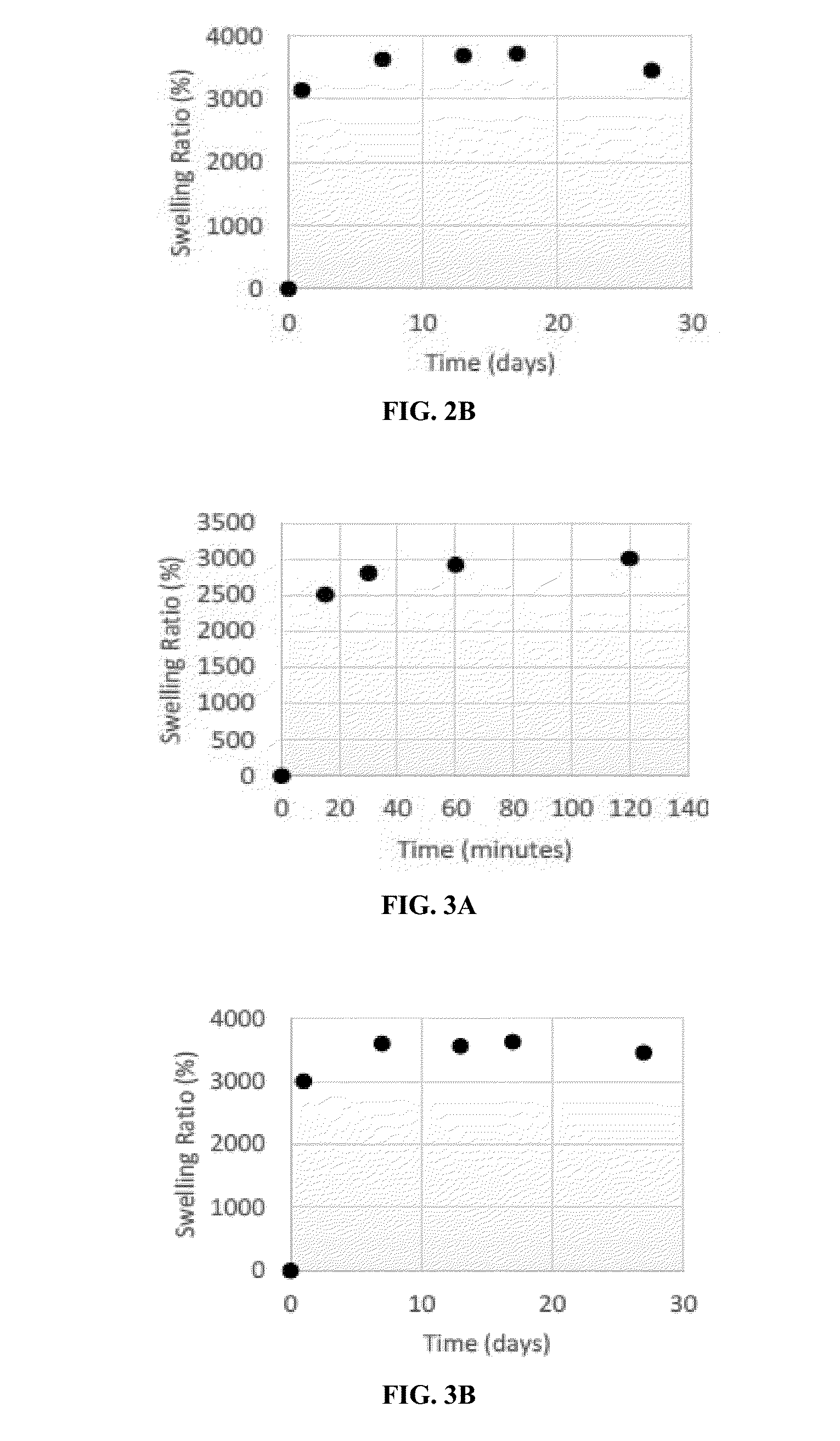
Highly expandable hydrogels in medical device sealing technology
Highly expandable materials have been developed for filling an aneurysm sac and for sealing of endoluminal devices vessel walls. The expandable materials have appropriate chemical and physical properties to withstand radiation, sterilization, or storage in sterilizing solution, without loss of expandable characteristics. The expandable materials may contain protectants, prophylactic, diagnostic, therapeutic, or imaging agents. The expandable materials form a seal that actively conforms to vascular anatomy sealing any leaks that may occur after device implantation. In one embodiment, the technology is used to prevent leaks associated with abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair, especially for complex AAA repair.
Owner:ENDOLUMINAL SCI
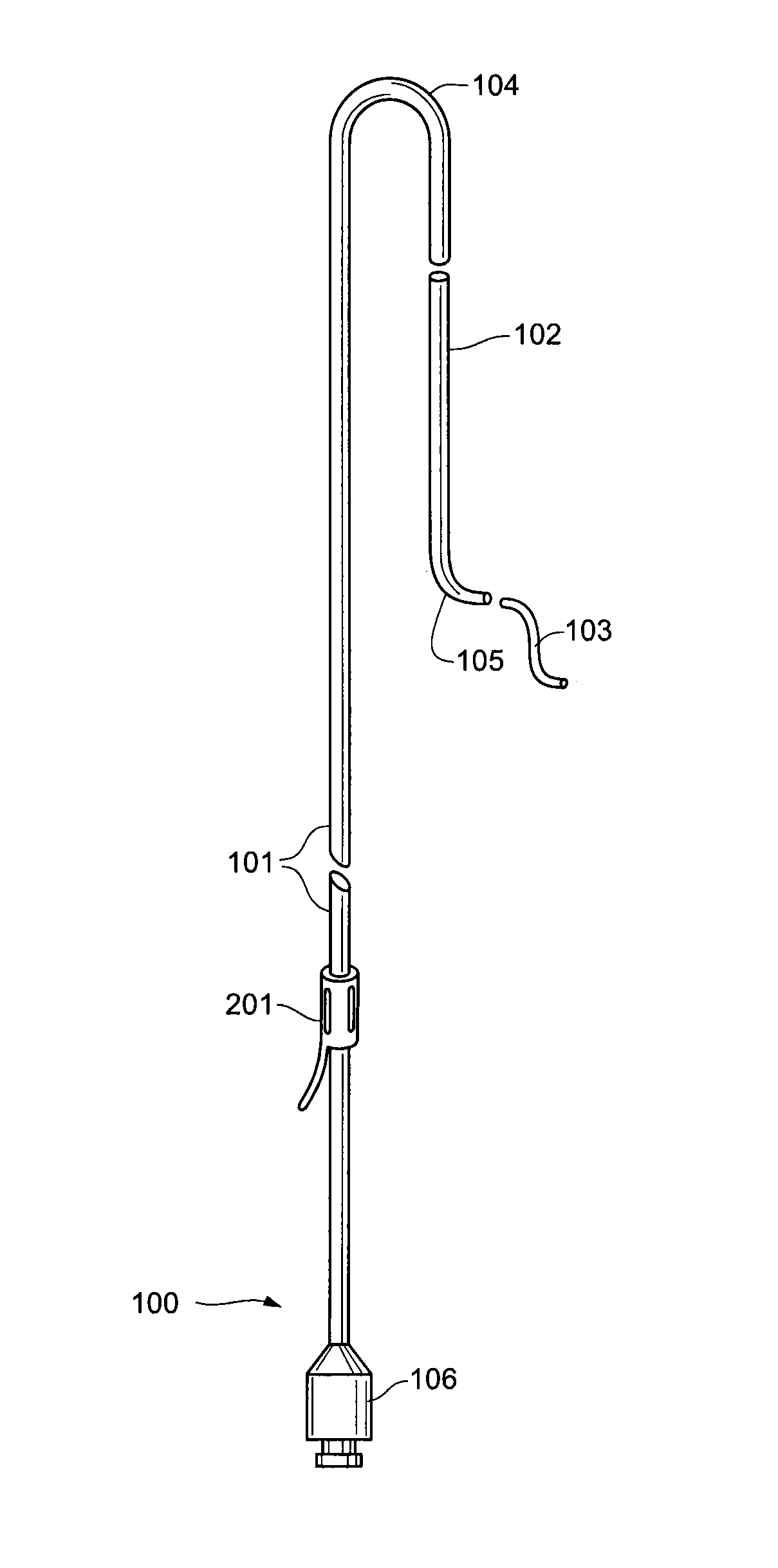
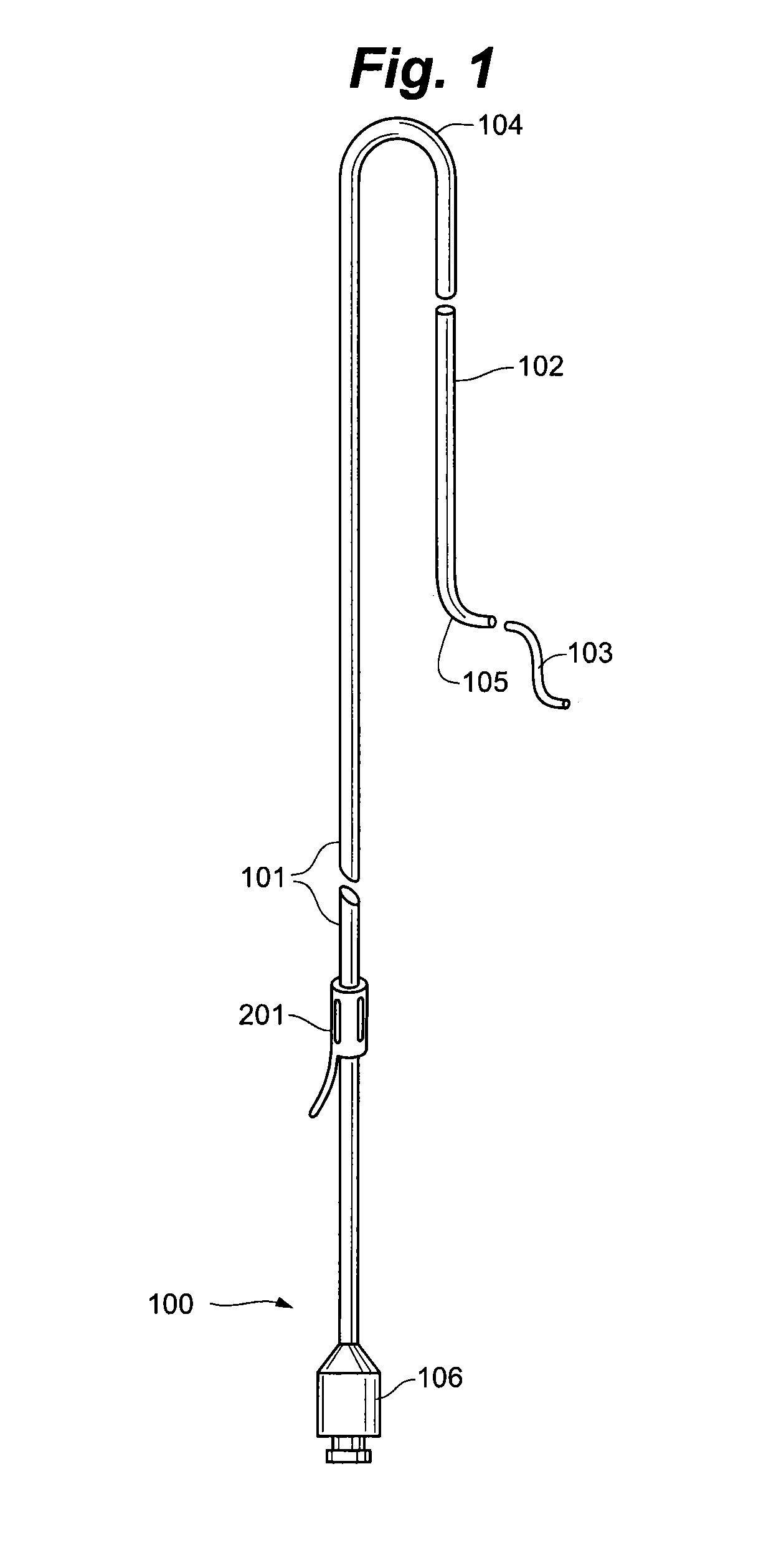
Pelvic arterial catheter
ActiveUS20050113801A1Minimal traumaHigh trafficCatheterRadiation diagnosticsArterial catheterTherapeutic intent
An improved angiographic catheter that allows selective catheterization of the bilateral pelvic arteries via a unilateral single common femoral arterial entry site for the purpose of introducing radioopaque iodinated contrast solutions for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. The catheter has an optimal length, specific tapered and curved regions, and a progressively tapering diameter along its length. The catheter is made from a hybrid of soft, flexible hydrophilic and reinforced materials to allow for conformational changes in order to accommodate to the variety of vascular anatomy encountered in clinical angiographic practice.
Owner:VASCULAR SOLUTIONS LLC
Two-step/dual-diameter balloon angioplasty catheter for bifurcation and side-branch vascular anatomy
The present invention tackles the challenging anatomic characteristics of the coronary artery disease in the bifurcation point and the origin of side-branch. The invention has a specifically designed angioplasty balloon catheter, particularly the balloon shape and profile, to be used in the diseased vessels at these difficult anatomic locations. In stent implanting into a coronary artery, a balloon catheter application is an inseparable requirement. A stent is a passive device that cannot be deployed in a diseased or stenosed artery without a pre-stent, with-stent and / or post-stent balloon dilatation. In majority (more than 95%) of available coronary stents, a stent is deployed by balloon expandable mode, meaning that the stent is delivered and expanded inside a vessel lumen by expanding a delivery balloon. This is done by crimping a stent over a folded balloon for delivery into a coronary artery. When expanded by balloon inflation, a stent is expanded and shaped passively by the inflated balloon shape and profile. The balloon catheter is designed to do angioplasty in the bifurcation and side-branch anatomy of coronary arteries, while minimizing the side effect. This specially designed balloon catheter is not only for balloon angioplasty dilatation of the bifurcation and side-branch anatomy, but is also for delivering and deploying specially designed bifurcation or side-branch stents into these difficult anatomic locations, as a stent delivery system.
Owner:JANG G DAVID
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance arteriography using contrast agents
The present invention is a technique of, and system for, imaging vascular anatomy over distance considerably greater than the maximum practical field of view of a magnetic resonance imaging system while using substantially one contrast agent injection. The technique and system of the present invention acquires image data of a plurality of image volumes which are representative of different portions of the patient's body. The image data of each image volume includes image data which is representative of the center of k-space. The acquisition of image data which is representative of the center of k-space is correlated with a concentration of contrast agent in the artery(ies) residing in the image volume being substantially greater than the concentration of contrast agent in veins and background tissue adjacent to the artery(ies). This provides preferential enhancement of arteries relative to adjacent veins and background tissue for each acquisition, wherein each acquisition is representative of a different portion of the arterial system (e.g., abdominal aorta, femoral, popliteal, and tibial arteries).
Owner:PRINCE MARTIN R
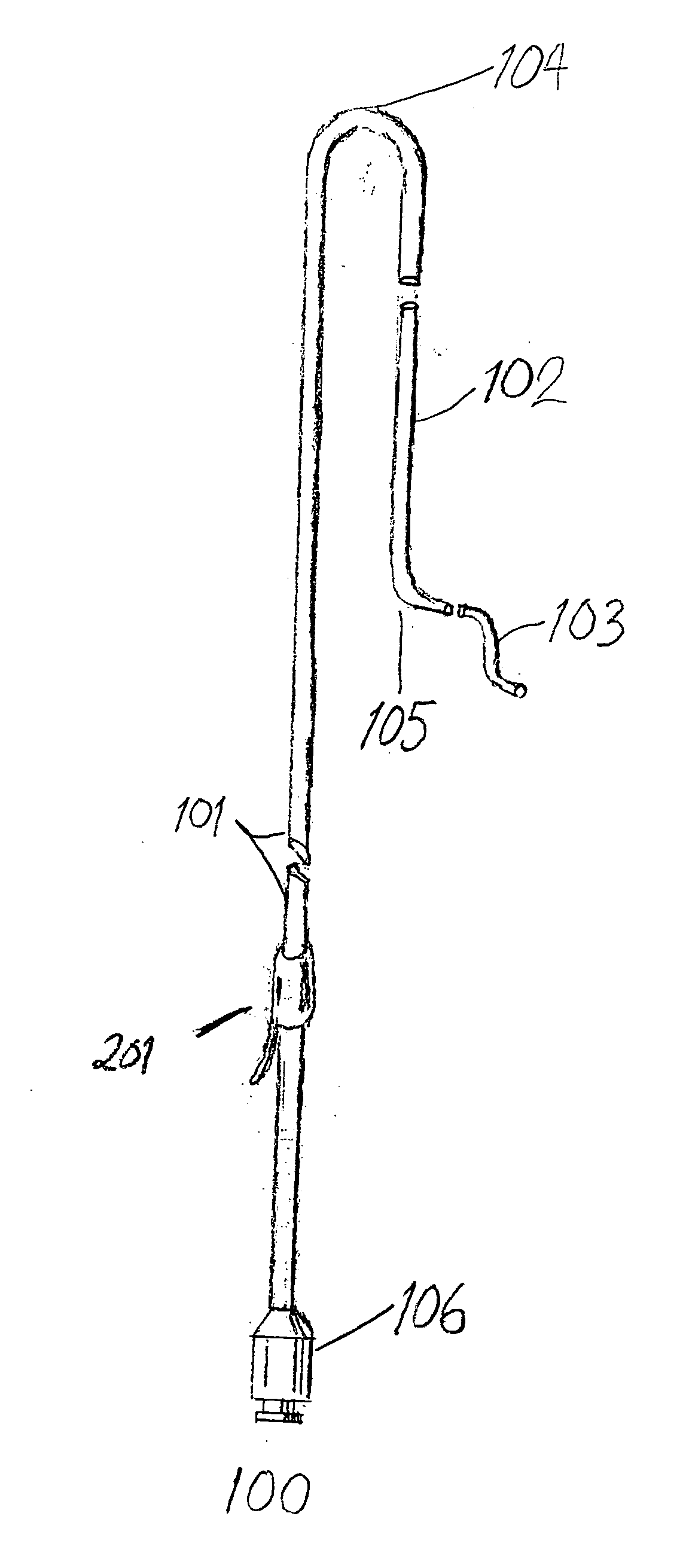
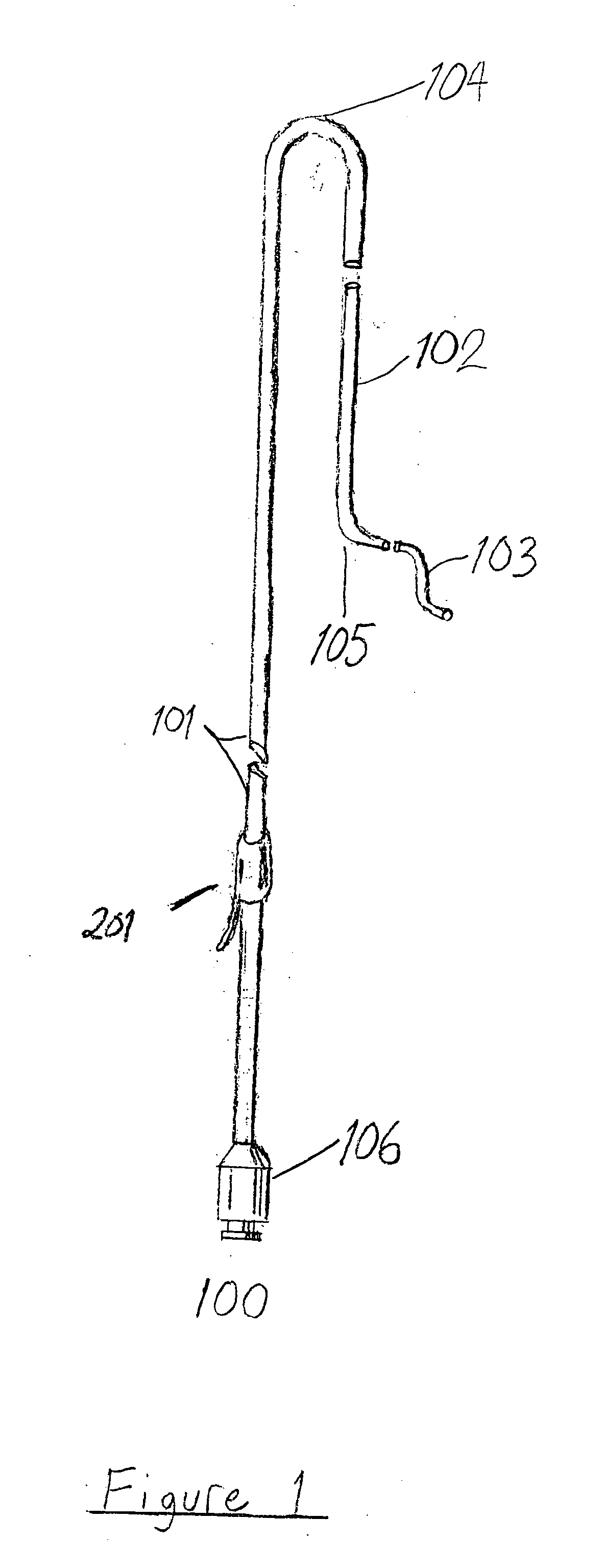
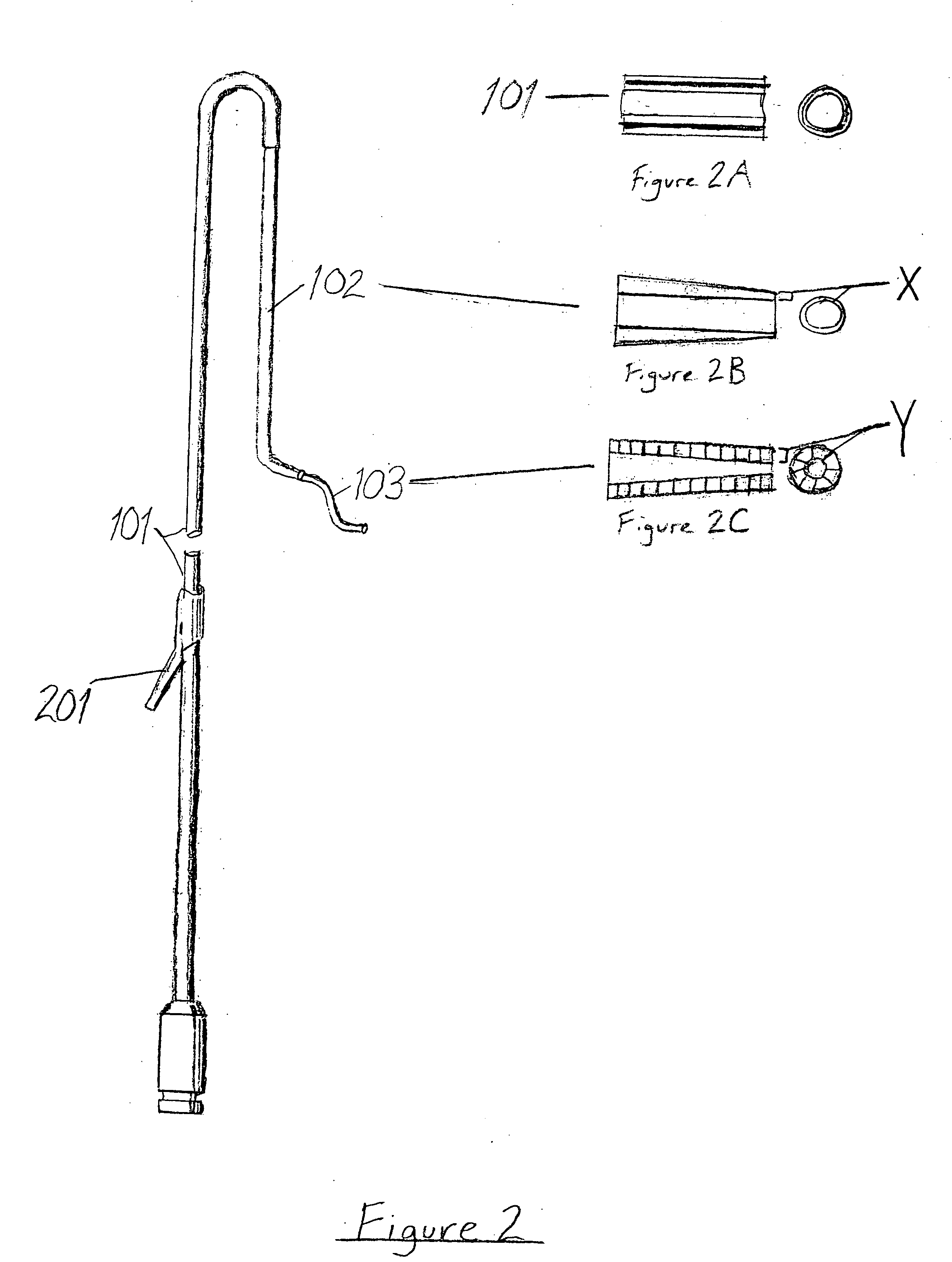
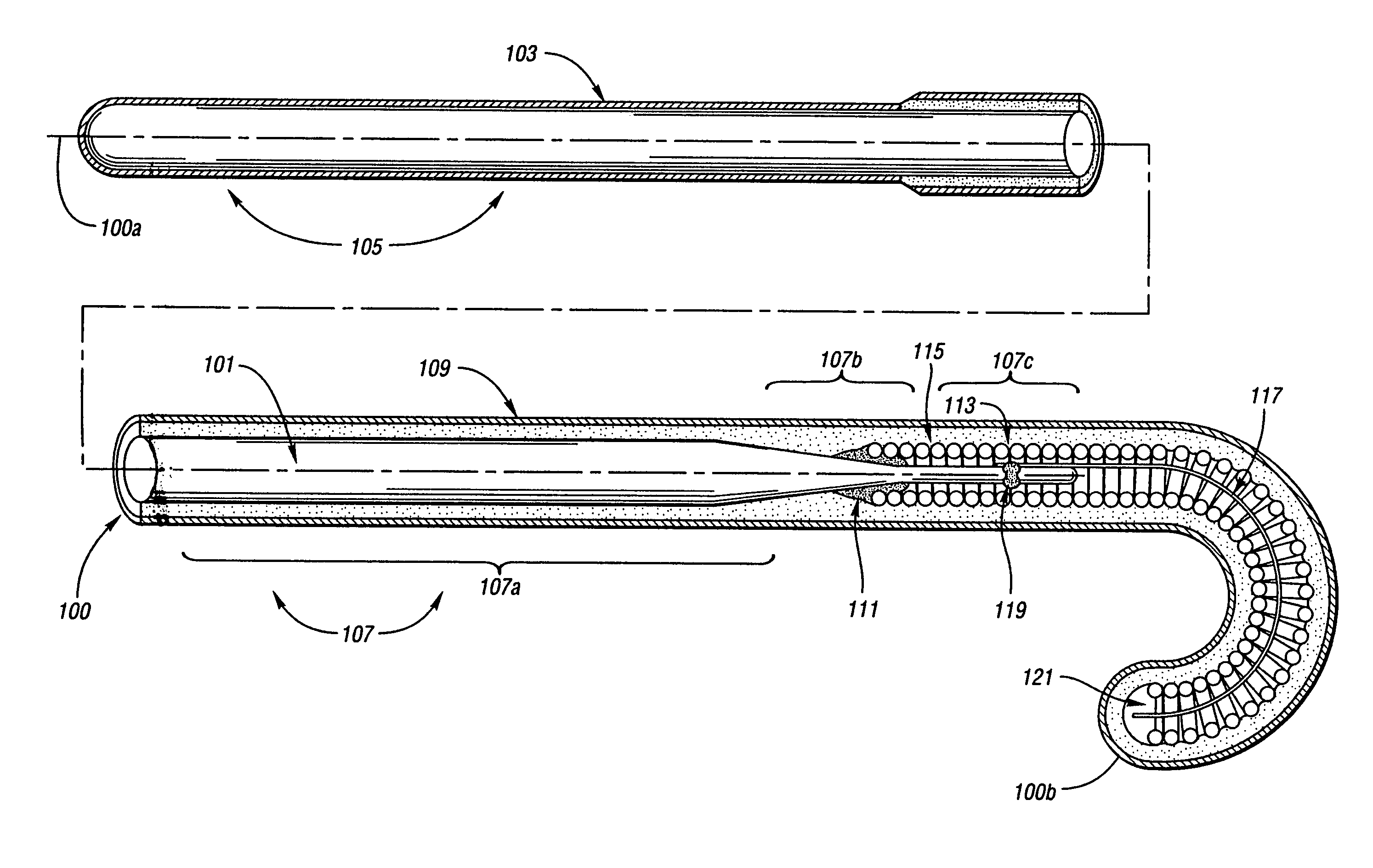
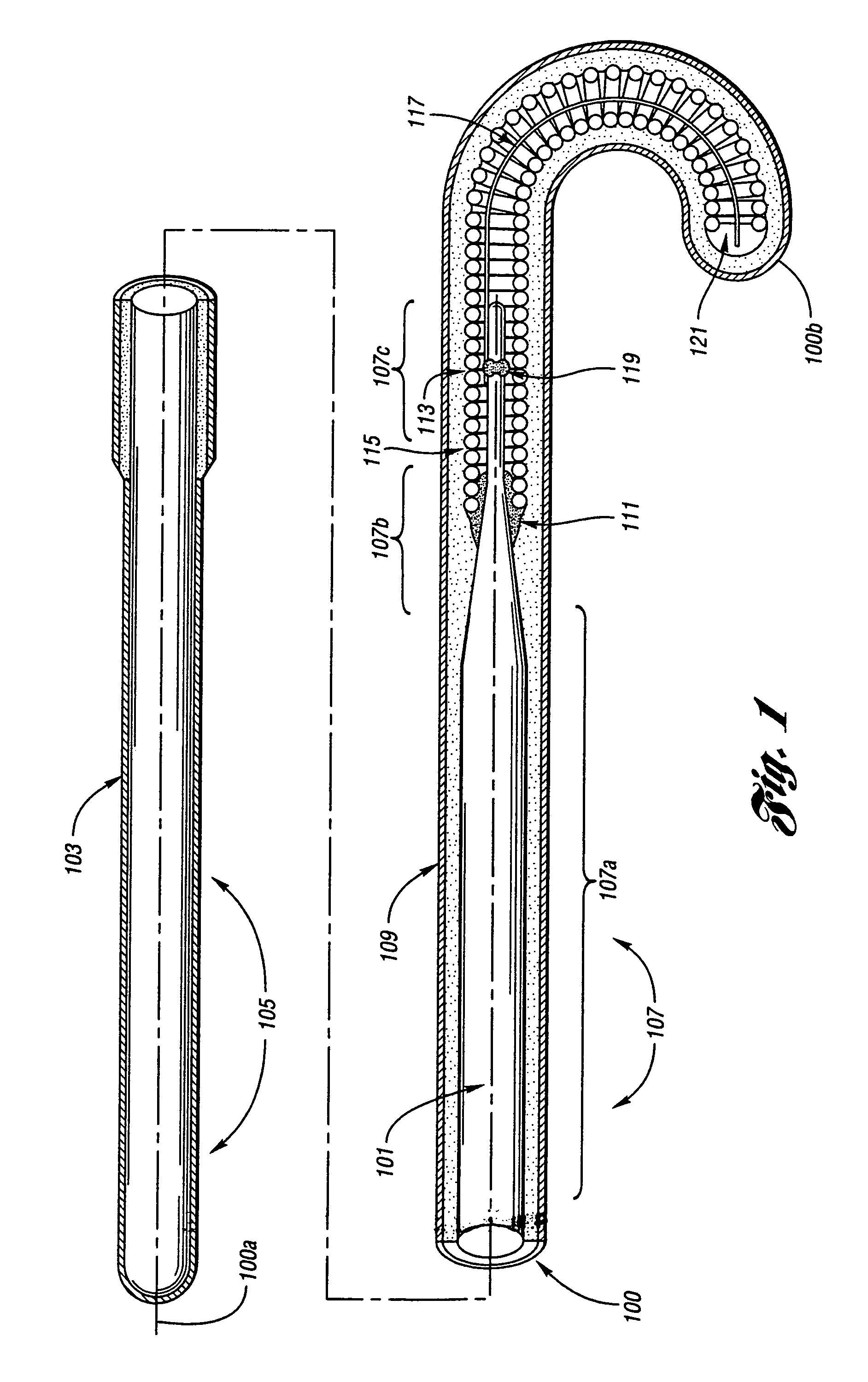
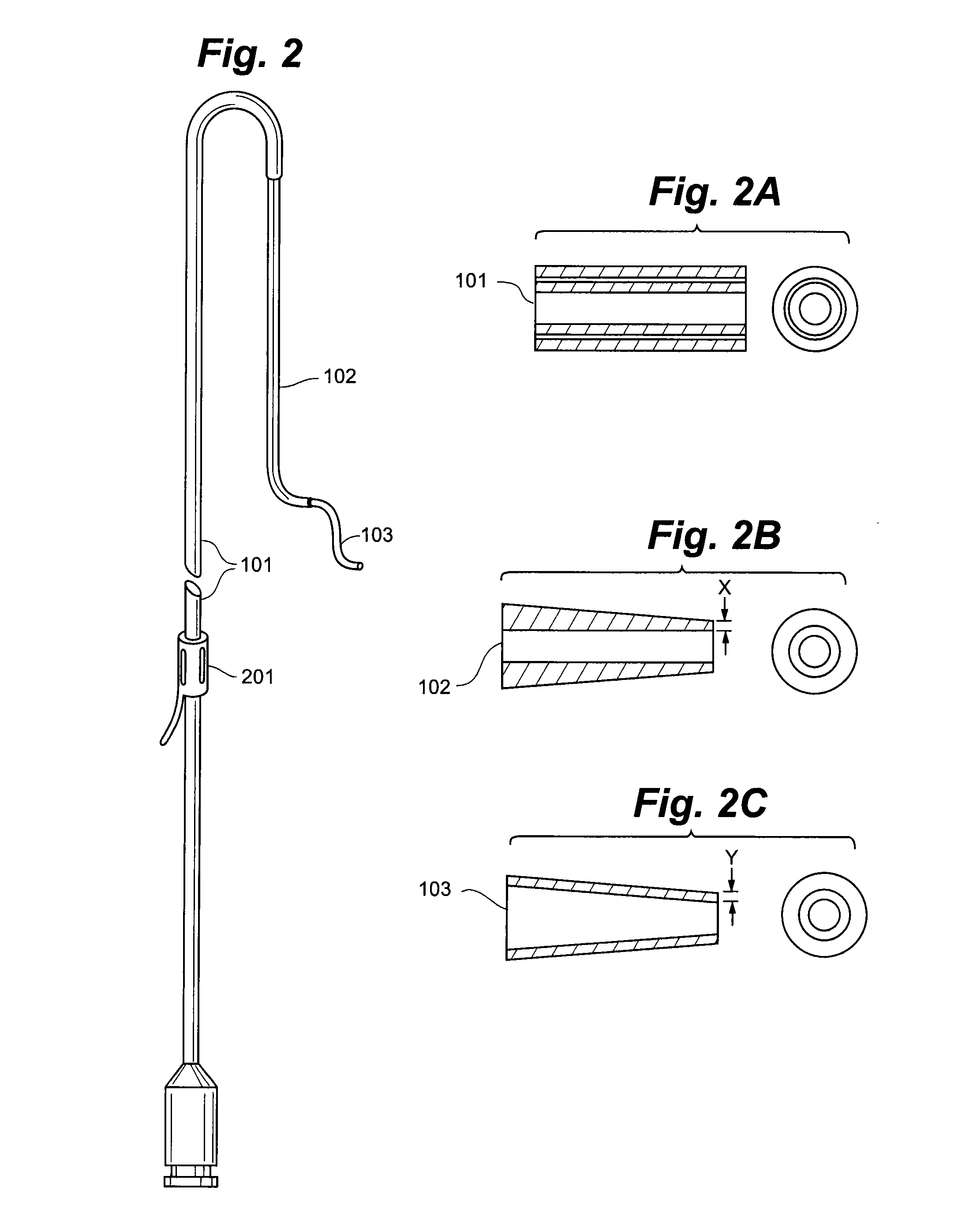
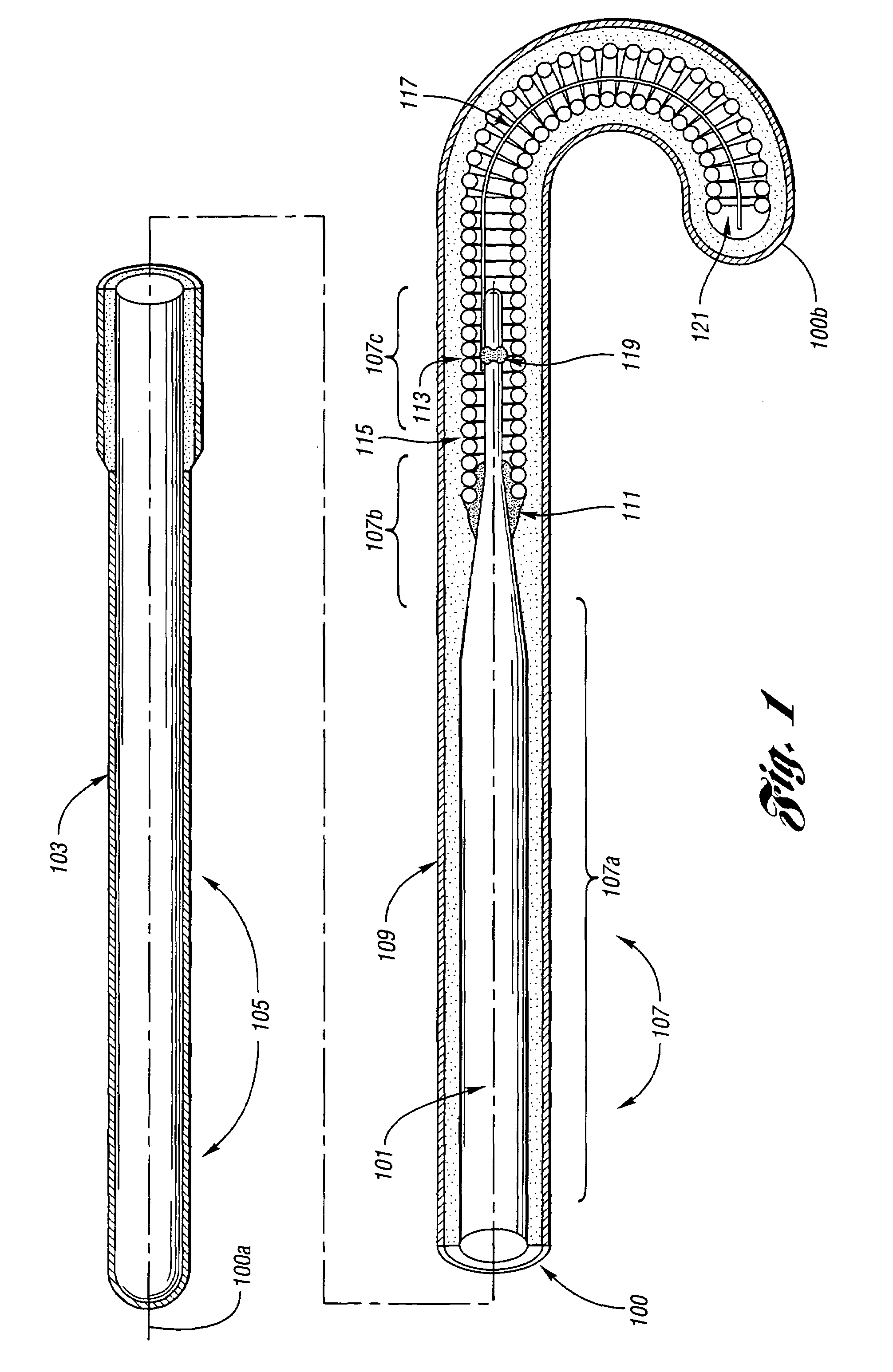
Wire guide
InactiveUS7001345B2Easy to handleEasy to operateGuide wiresDiagnostic recording/measuringDistal portionEngineering
A wire guide includes a mandrel that has a proximal portion and a distal portion. A first coating with a low coefficient of friction is disposed on the proximal portion of the mandrel. A second coating is disposed on the distal portion of the mandrel, where the second coating provides a sub-structure. A third coating is disposed on the second coating, where the third coating comprises a surface that allows for easy maneuverability of the wire guide. The first coating on the proximal portion provides enough lubricity to keep the wire guide from becoming bound or stuck in a catheter or medical device while still allowing a user to have a good grip of the wire guide. The second coating on the distal portion provides lubricity for the wire guide, which allows the user to easily maneuver the wire guide through a vascular anatomy.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Pelvic arterial catheter
ActiveUS7799013B2Minimal traumaMinimize longitudinal traumaCatheterRadiation diagnosticsAngiographic cathetersArterial catheter
Owner:VASCULAR SOLUTIONS LLC
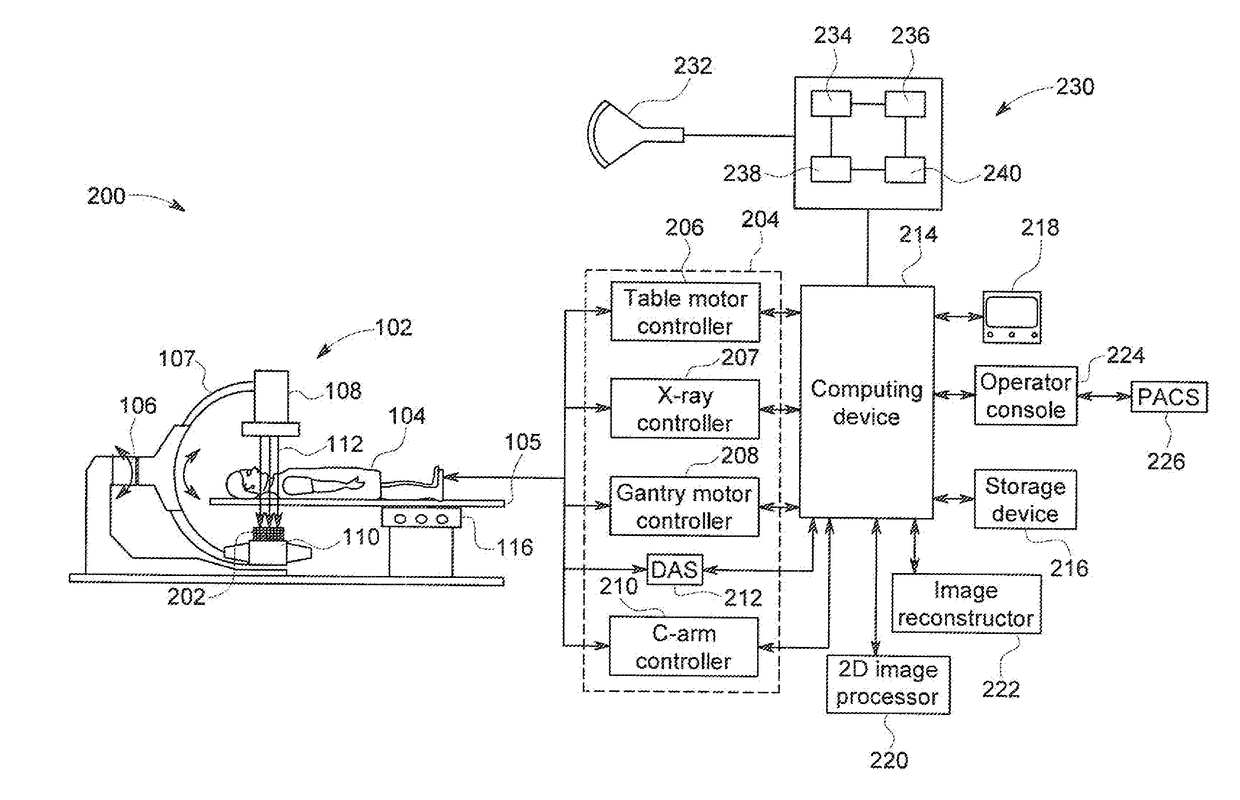
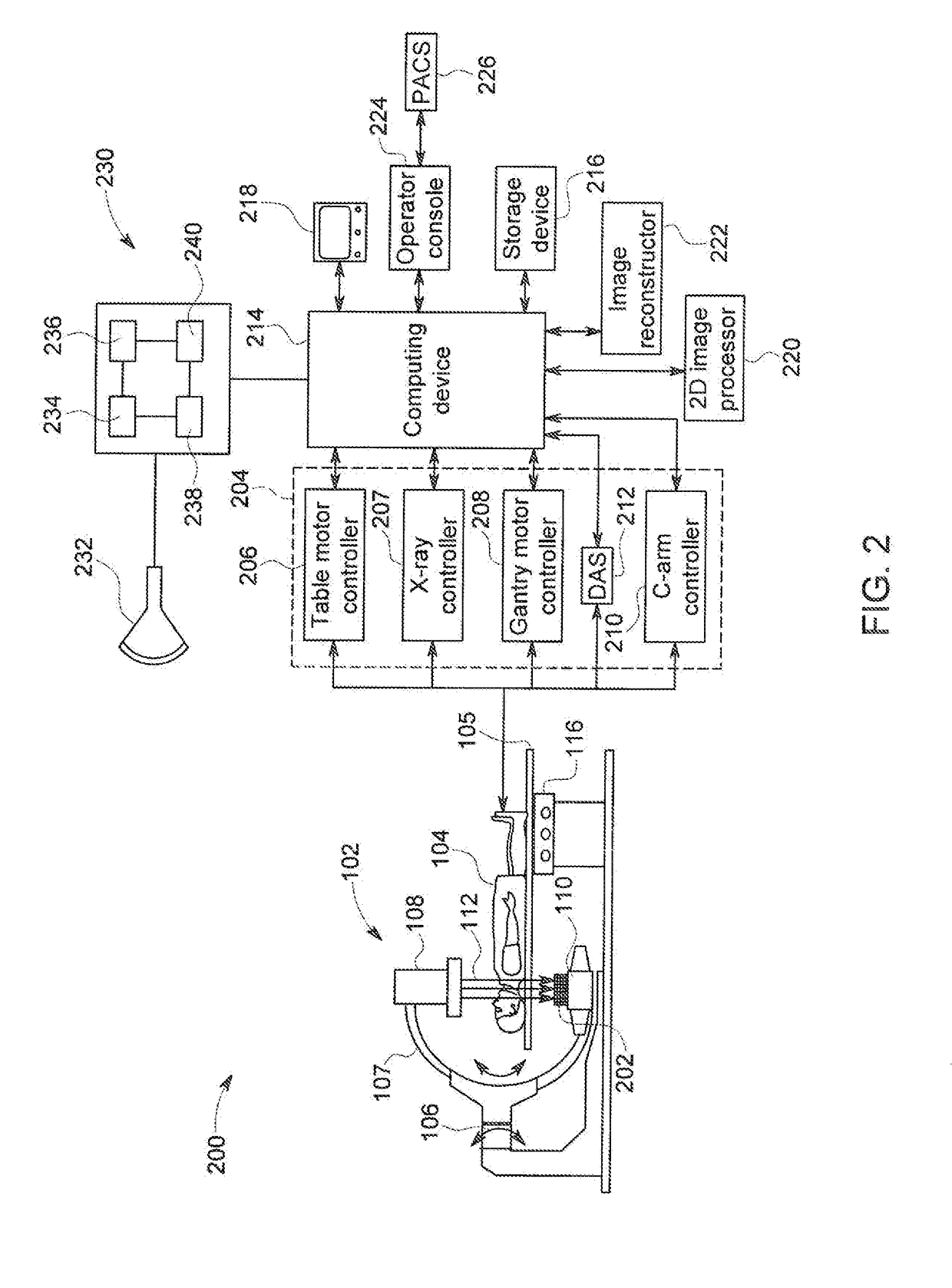
Combination Of 3D Ultrasound And Computed Tomography For Guidance In Interventional Medical Procedures
ActiveUS20180168732A1Correction of deformationImprove matchOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical navigation systemsComputing tomographyPre operative
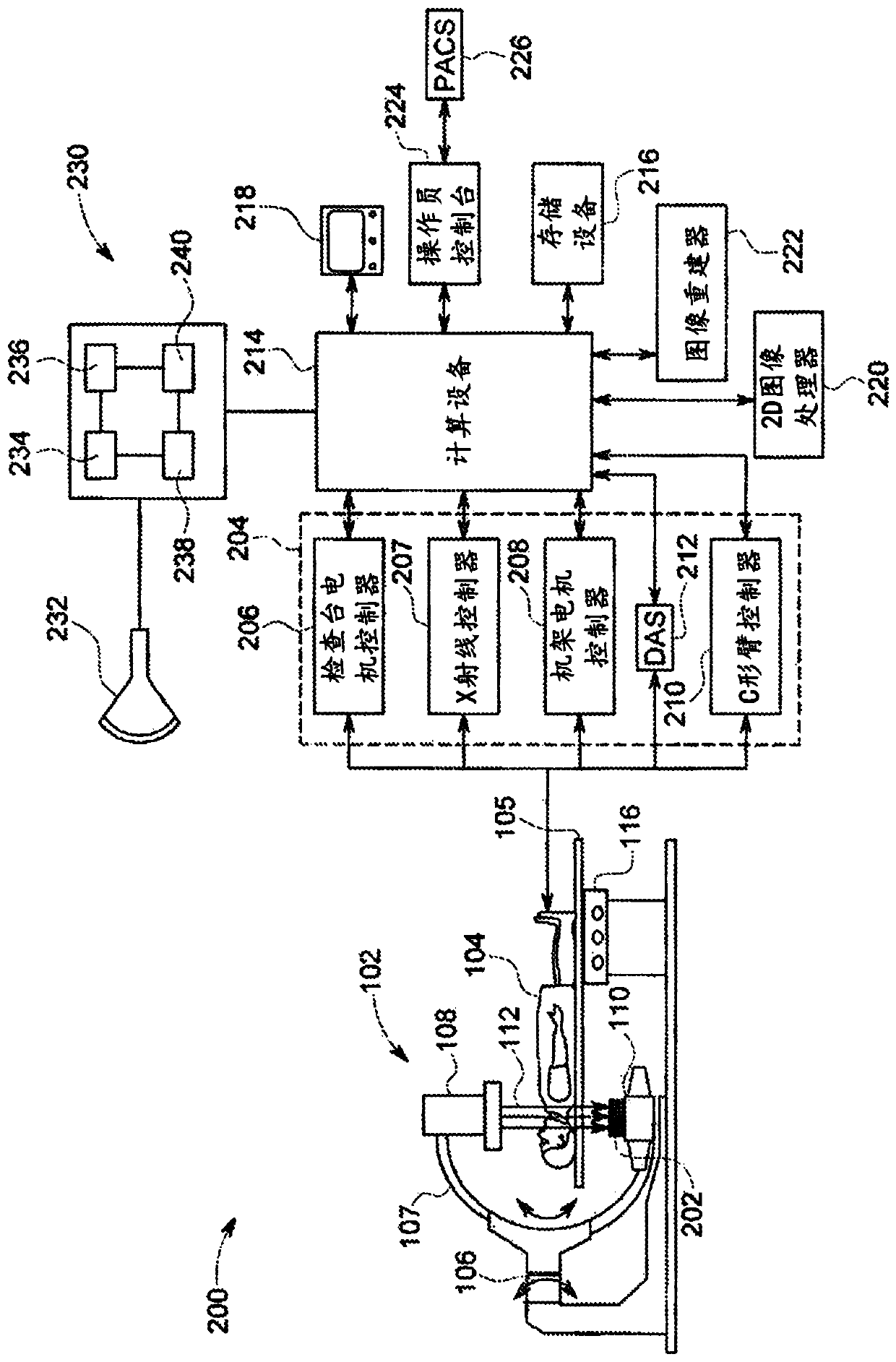
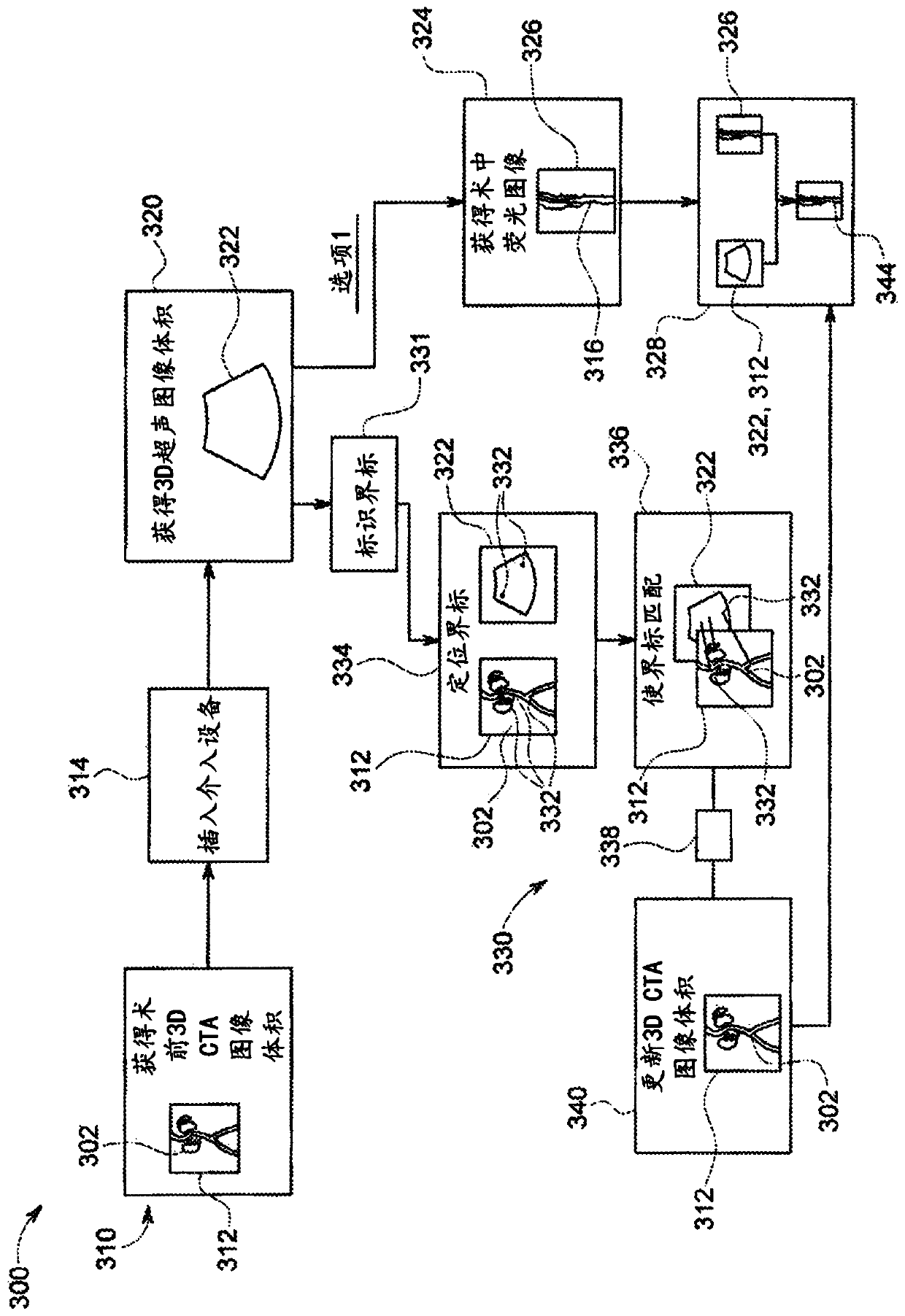
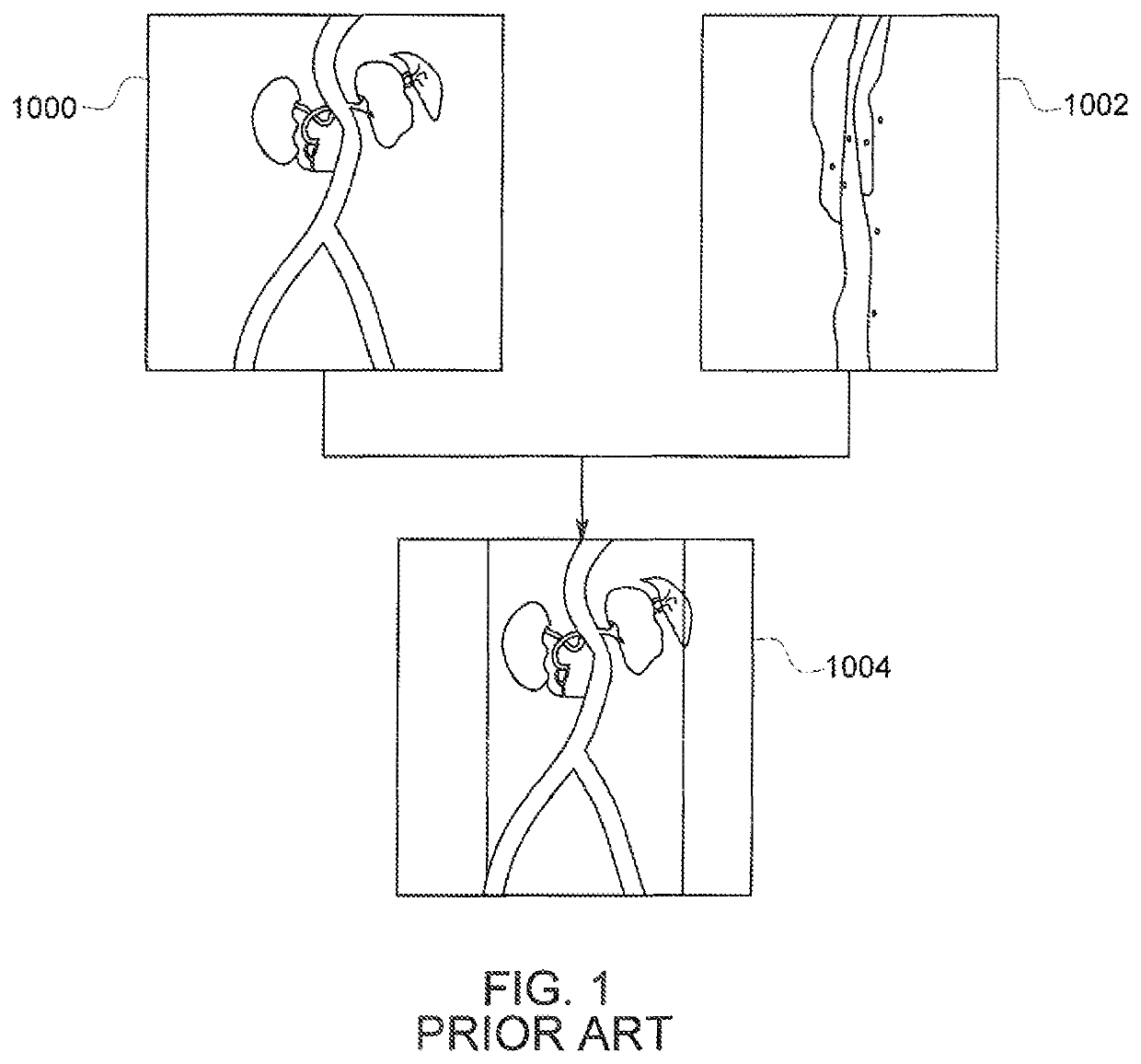
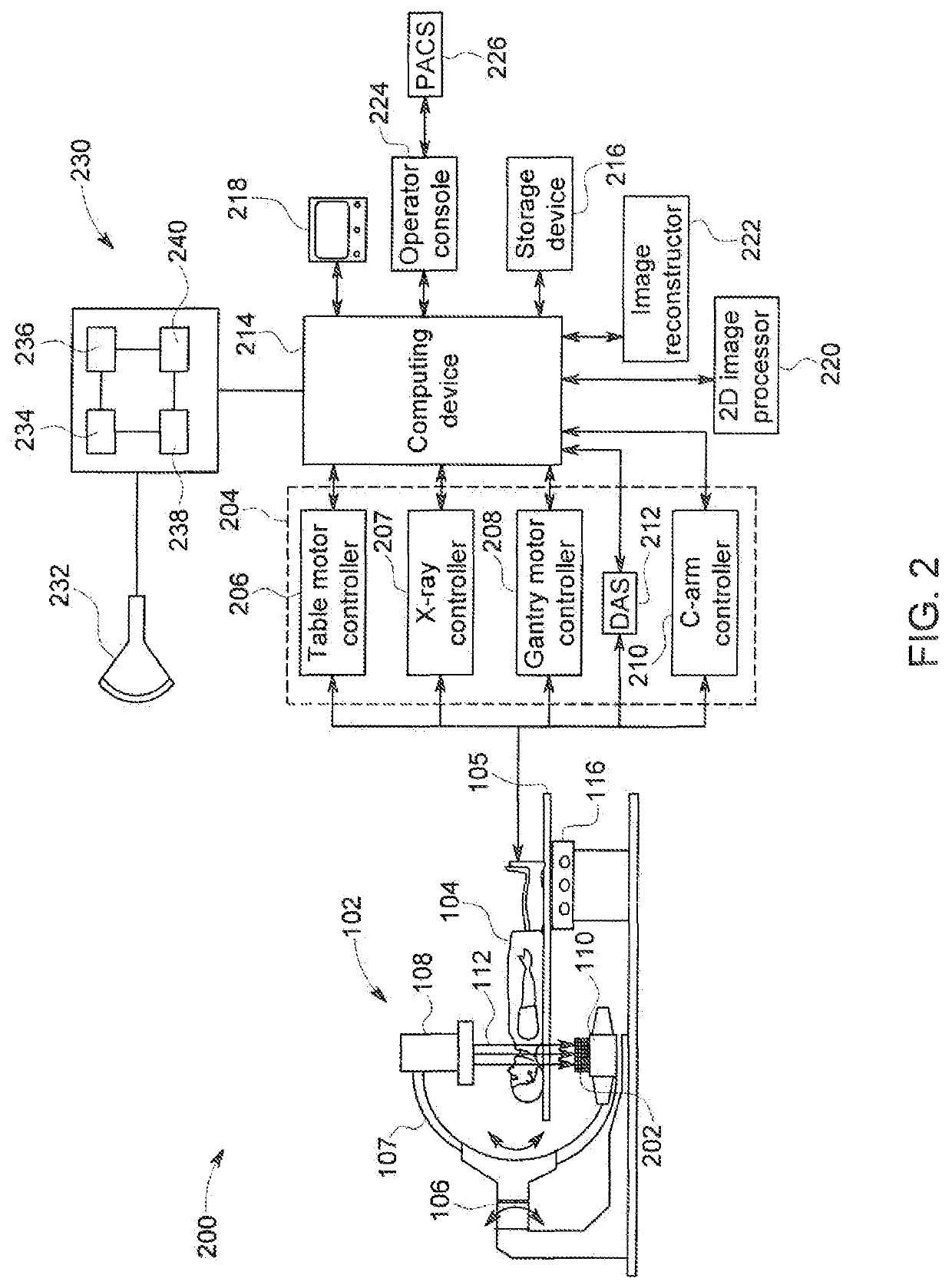
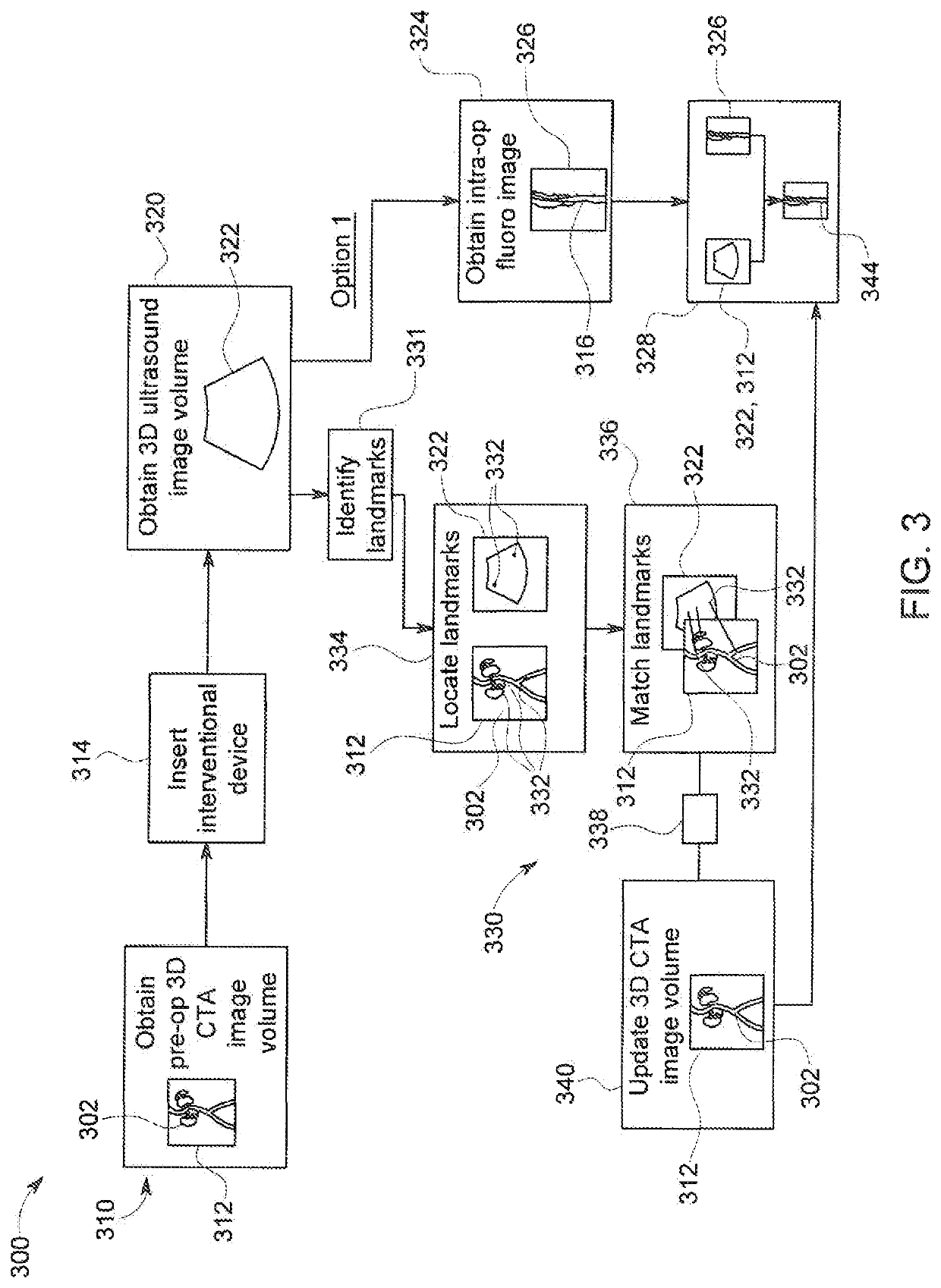
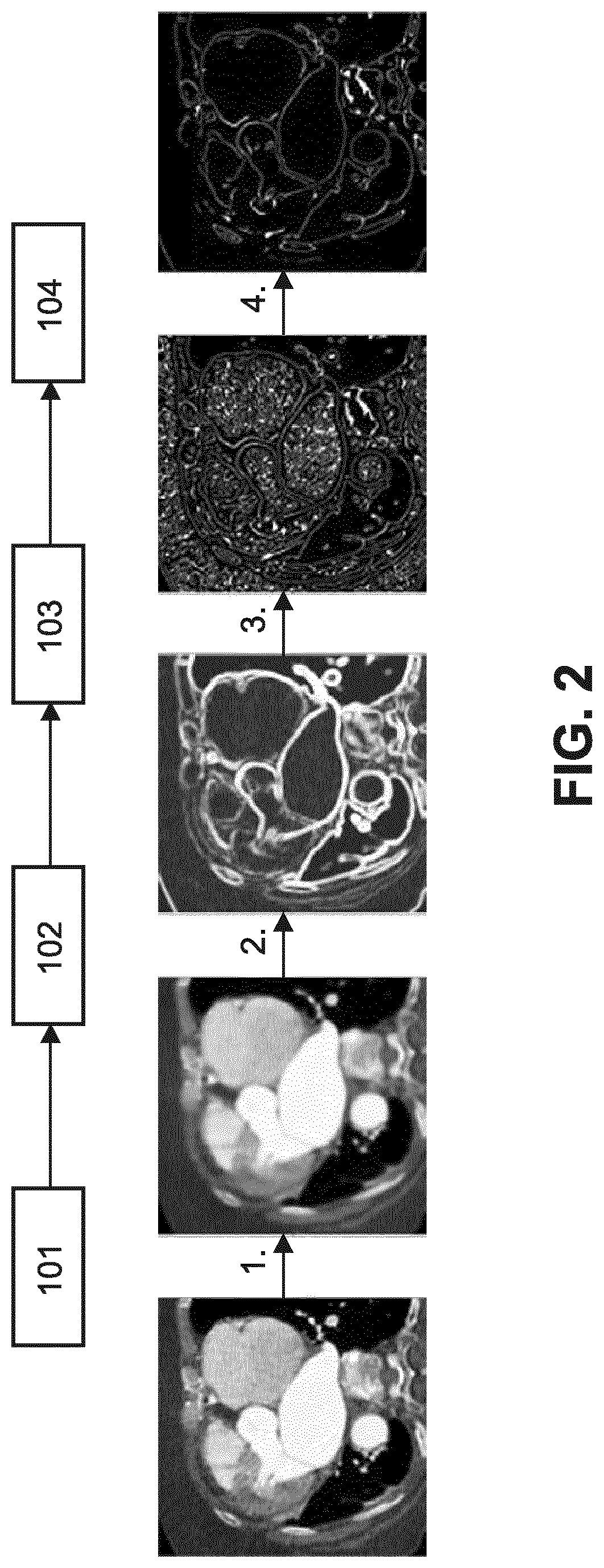
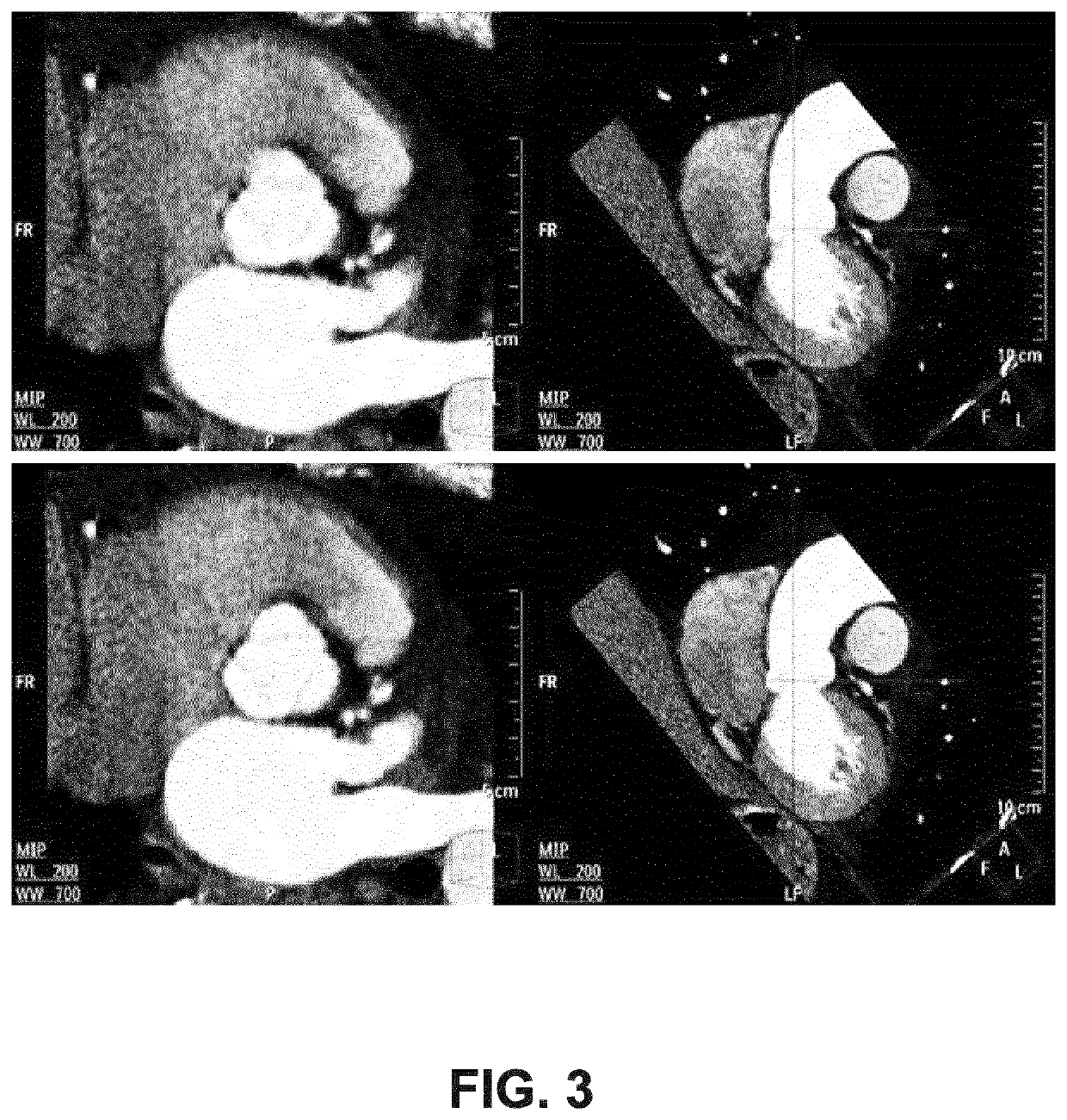
In the present invention, an imaging system and method is provided to obtain a fusion image of a patient anatomy used as a navigational 3D roadmap to guide an interventional device into the anatomy. The fusion image fuses in real-time, fluoroscopy images taken during the interventional procedure with pre-operative CTA images, so that the operator can see the anatomy in the fluoroscopy image without having to inject contrast agent. To correct for the deformation in the anatomy from the pre-op CTA images form the insertion of interventional devices during the procedure, a 3D ultrasound image is obtained after the insertion of the devices. The 3D ultrasound images are then utilized to correct the pre-op CTA images and provide the current vascular anatomy of the patient. This updated CTA image is fused with the intra-op fluoro images to provide an accurate 3D roadmap image that matches the deformed anatomy.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Composite aortic arch reconstruction system and using method thereof
The invention provides a composite aortic arch reconstruction system and a using method thereof. The system comprises a quadrifurcation vascular prosthesis and a cross arch covered stent; the vascularprosthesis comprises a vascular body, an arch upper branch communicated with the vascular body and a perfusion branch, the arch upper branch is sequentially divided into an anonyma branch, a left common carotid branch and a left collarbone lower branch, and blood vessel lumina are communicated with each other. The cross arch covered stent comprises an inner layer metal stent and an outer layer vascular cover, and conical and preflex designs which more conform to the physiological structure of an aorta of a human body are adopted. When an aortic arch surgery is carried out, deep hypothermic circulatory arrest can be avoided by means of the system to reduce the difficulties of vascular anatomy and vascular anastomosis, shorten the surgical operating time and improve the success rate of thesurgery.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Composite type intraoperative stent system and using method thereof
ActiveCN106388972AReduce the effects of coagulationShorten operation timeStentsBlood vesselsAv graftLinear control
The invention provides a composite type intraoperative stent system which comprises an artificial vessel capable of being anastomosed, a linear control released left subclavian artery covered stent vessel and a balloon-expandable type descending aorta covered stent artificial vessel; the artificial vessel is connected with the balloon-expandable type descending aorta covered stent artificial vessel; the left subclavian artery covered stent vessel is arranged at the connecting part of the artificial vessel and the balloon-expandable type descending aorta covered stent artificial vessel and communicates with the artificial vessel and the balloon-expandable type descending aorta covered stent artificial vessel; and the balloon-expandable type descending aorta covered stent artificial vessel is internally provided with a balloon. The composite type intraoperative stent system can shorten the operation time, reduces influence of deep hypothermic circulatory arrest on the coagulation function of a patient, lowers the difficulties of vascular anatomy and anastomosis and increase the success rate of an operation.
Owner:FUJIAN PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL
Covered stent and using method thereof
ActiveCN105213074AReduce the need for technical expertiseAvoid displacementStentsProximal pointBlood vessel
The embodiment of the invention discloses a covered stent and a using method thereof. The covered stent comprises an inverted-Y-shaped iliac branch main body, a first main body and a second main body. The iliac branch main body comprises a cylindrical metal support and a film covering the metal support, so do the first main body and the second main body. The far-end of the first main body is connected to the iliac branch main body, and the far-end of the second main body is connected to the near-end of the first main body. The iliac branch main body has a three-way structure, and comprises an aorta chimney and two iliac branches. The aorta chimney is connected to the far-end of the first main body. By employing the covered stent, risks of stent movement and inner-leakage caused by the butt connection of a conventional iliac stent and a bifurcation stent short leg can be avoided; the operation time is shortened; the operation difficulty is reduced, risks of complications such as blood vessel erosion, perforation and laceration can be reduced; the approach application occurrence rate can be substantially reduced; and the operation difficulty for a patient whose unilateral approach is badly tortuous and narrow is reduced. The covered stent can be placed based on a blood vessel anatomy configuration, the original iliac artery bifurcation is retained, and the contralateral intervention in a later period can be carried out more easily.
Owner:APT MEDICAL HUNAN INC
Vasculature modeling
InactiveUS20160284080A1Effective evaluationReduce computing timeImage enhancementImage analysisVascular structureComputer science
The present invention relates to modeling of vascular structures, and in particular to extracting a vessel tree from medical-images of vascular anatomy. A respective method comprises among others the steps of providing an image of at least one vessel, obtaining multiple measurements from the image for a first point of the image, and fitting a four-dimensional tensor to the measurements. Based on said four-dimensional tensor fitted to the measurements, a vessel direction in a vessel tree is determined and a model of the vascular structures is generated based on at least the determined vessel direction.
Owner:SABANCI UNIVERSITY
Wire guide
ActiveUS7595082B2Easy to handleEasy to operateGuide wiresPharmaceutical containersDistal portionEngineering
A wire guide includes a mandrel that has a proximal portion and a distal portion. A first coating with a low coefficient of friction is disposed on the proximal portion of the mandrel. A second coating is disposed on the distal portion of the mandrel, where the second coating provides a sub-structure. A third coating is disposed on the second coating, where the third coating comprises a surface that allows for easy maneuverability of the wire guide. The first coating on the proximal portion provides enough lubricity to keep the wire guide from becoming bound or stuck in a catheter or medical device while still allowing a user to have a good grip of the wire guide. The second coating on the distal portion provides lubricity for the wire guide, which allows the user to easily maneuver the wire guide through a vascular anatomy.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Methods for angiography
PendingUS20200245961A1Low toxicityReducing and preventing contrastImage enhancementImage analysisBlood vesselContrast medium
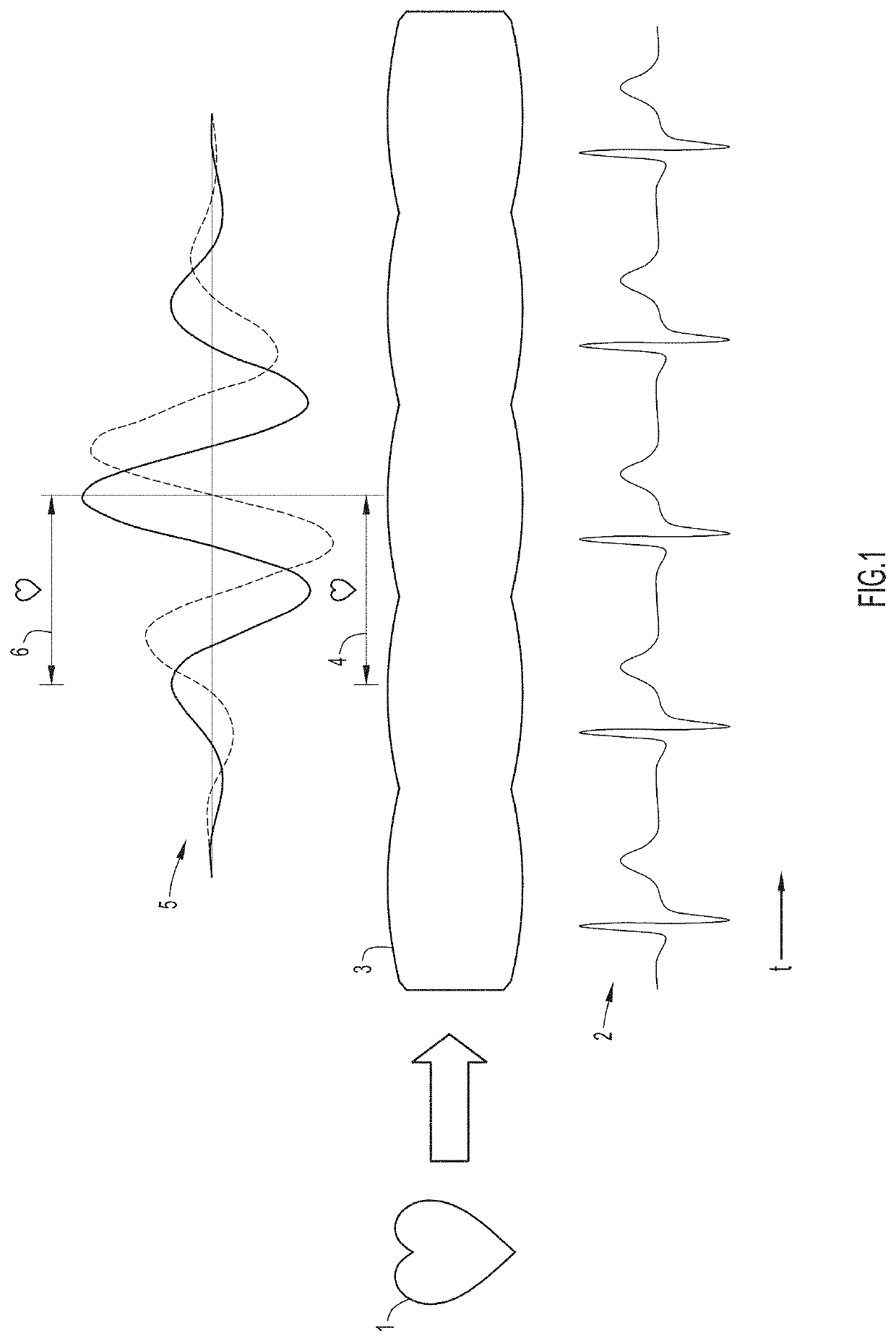
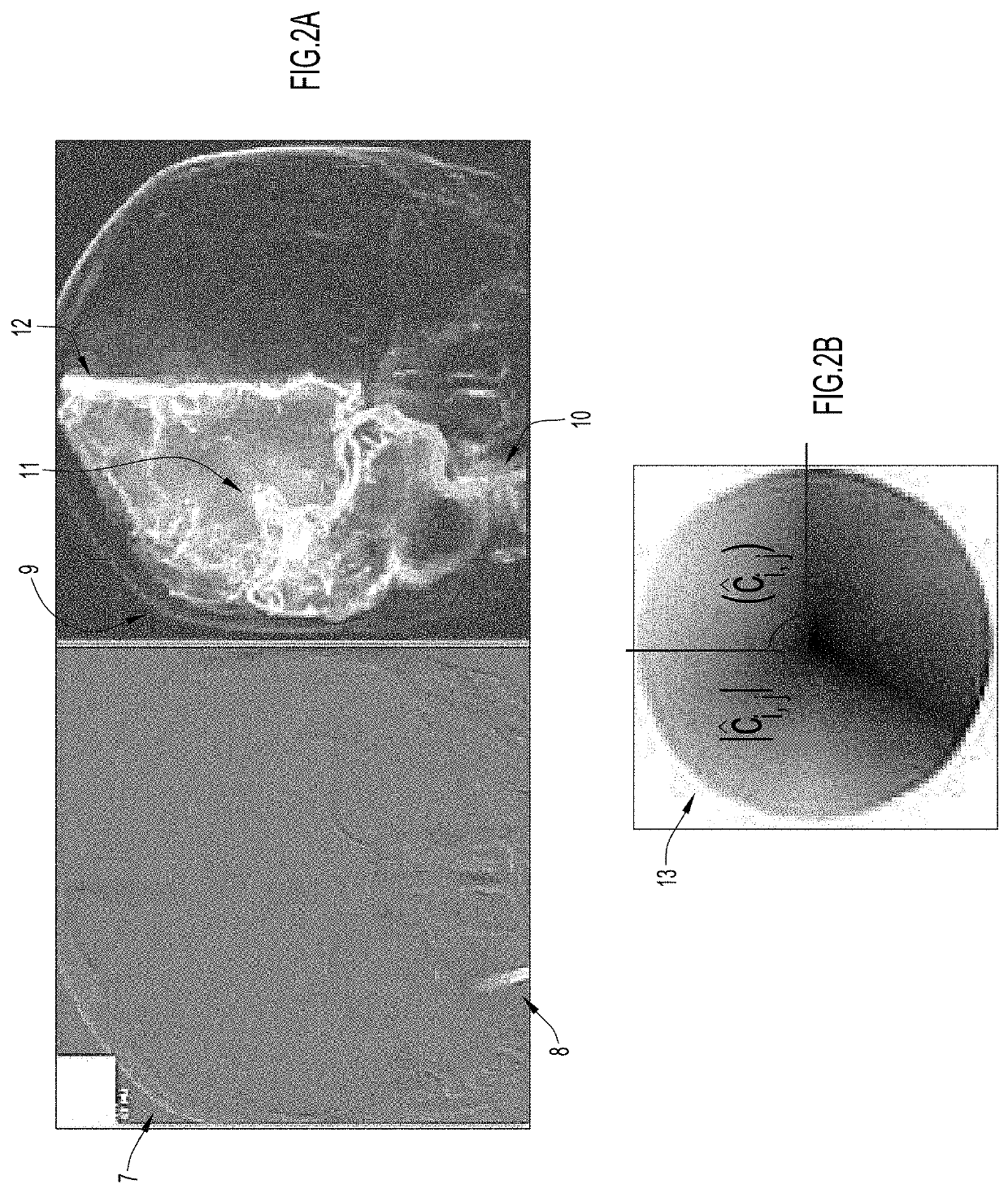
An angiogram is a study of blood vessels where an angiographic chemical contrast agent is injected while a sequence of images (typically x-rays) are obtained. The contrast pattern on the sequence of images provides information about the vascular anatomy and physiology. The discovery that contrast in blood vessels varies at cardiac frequency in magnitude and phase, which may be visualized as a spatiotemporal reconstruction of cardiac frequency angiographic phenomena, enables a set of processes for increasing the signal to noise ratio or equivalently the informational content of an angiogram. In this invention, the organization of cardiac frequency magnitude and phase enables equivalent information on anatomy and physiology to be obtained with less dose of injected chemical contrast agent, less x-ray dose, and / or less navigation of the injecting catheter within blood vessels. The cardiac frequency magnitude and phase is organized so that the arterial and venous subsystems of circulation have coherence at cardiac frequency. This enables processes for diagnosing deficits of circulation that involve alterations in the transit of blood from the arterial to the venous subsystems of circulation. Furthermore, the discovery of cardiac frequency magnitude and phase organization enables the design and manufacture of lighter and more portable angiography equipment.
Owner:BUTLER WILLIAM E
Blood vessel stent
PendingCN110731843AIntegrity guaranteedImprove bending performanceStentsSurgeryVeinTherapeutic effect
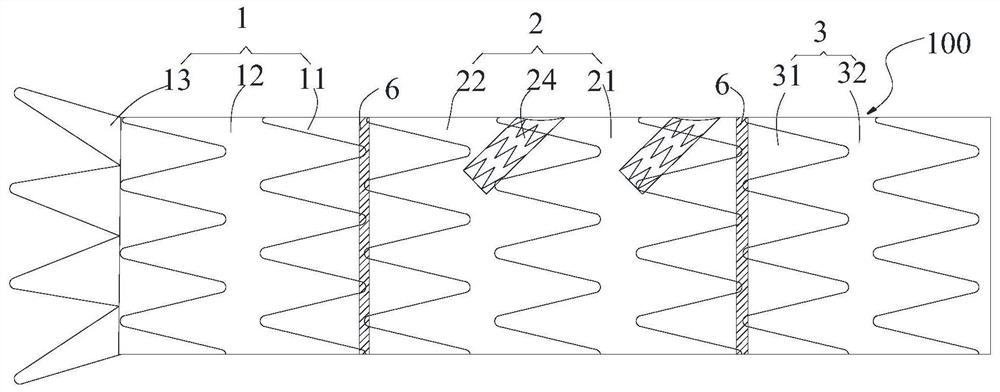
The invention discloses a blood vessel stent. The blood vessel stent includes a stent main body which is of a mesh-tube-shaped structure woven by metal wires, wherein the stent main body includes a first stent segment and a second stent segment which are connected in an axial direction, and the mesh density of the first stent segment is different from that of the second stent segment. By adoptingthe blood vessel stent, regarding phlebostenosis involving inferior vena cava and iliofemoral veins, naked segments are arranged so that therapeutic effects can be improved; regarding compressed parts, a dense mesh structure with larger mesh density is arranged so that support strength and anti-extrusion performance can be improved; regarding bent parts, a sparse mesh structure with smaller mesh density is arranged so that flexibility performance and adherence performance can be improved; and regarding blood vessel anatomic forms, a variable-diameter structure is arranged and can adapt to theblood vessel forms, and therefore the blood vessel stent is suitable for blood vessels of various diameters.
Owner:SHANGHAI BLUEVASCULAR MEDTECH CO LTD
Microscopic anastomosis training model and vascular model preparation process for model
PendingCN112309217AImprove accuracyEasy to understandCosmonautic condition simulationsManufacturing driving meansHuman bodyHematological test
The invention discloses a microscopic anastomosis training model and a vascular model preparation process for the model. The training model comprises a vascular model, a pipeline connecting system, ablood circulating pump, a base and a supporting platform; the blood circulating pump is arranged in a sealed cavity; a plurality of openings are formed in the supporting platform; the vascular model is communicated with the pipeline connecting system through a joint; and the pipeline connecting system is communicated with the blood circulating pump. The vascular model adopts a specific material and a specific manufacturing process, so that the touch feeling and the structure are close to those of real blood vessels of a human body; the microscopic anastomosis operation training model is helpful for better understanding blood vessel anatomy and anastomosis angles, directions, positions and effects, and the model is used for assisting a trainee to improve the accuracy of blood vessel anatomyseparation and suture. Moreover, after the model is displayed to the patient, the patient can visually and deeply understand physiology, anatomy, characteristics, operation schemes and the like of the neurosurgery operation.
Owner:宁波创导三维医疗科技有限公司 +1
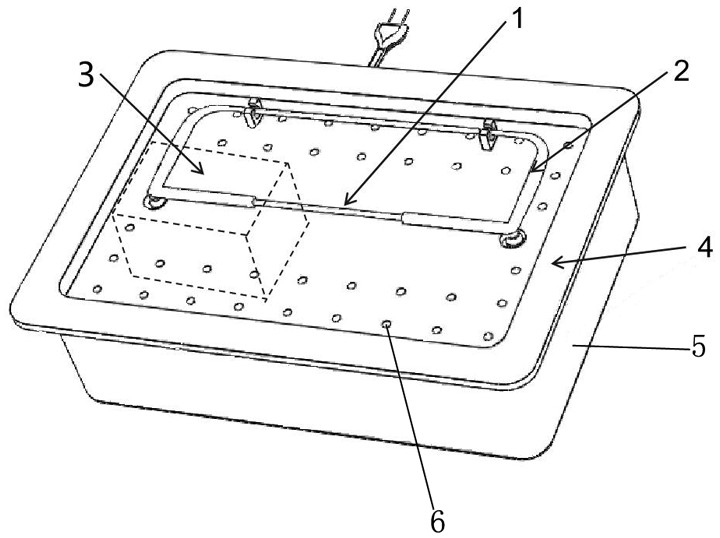
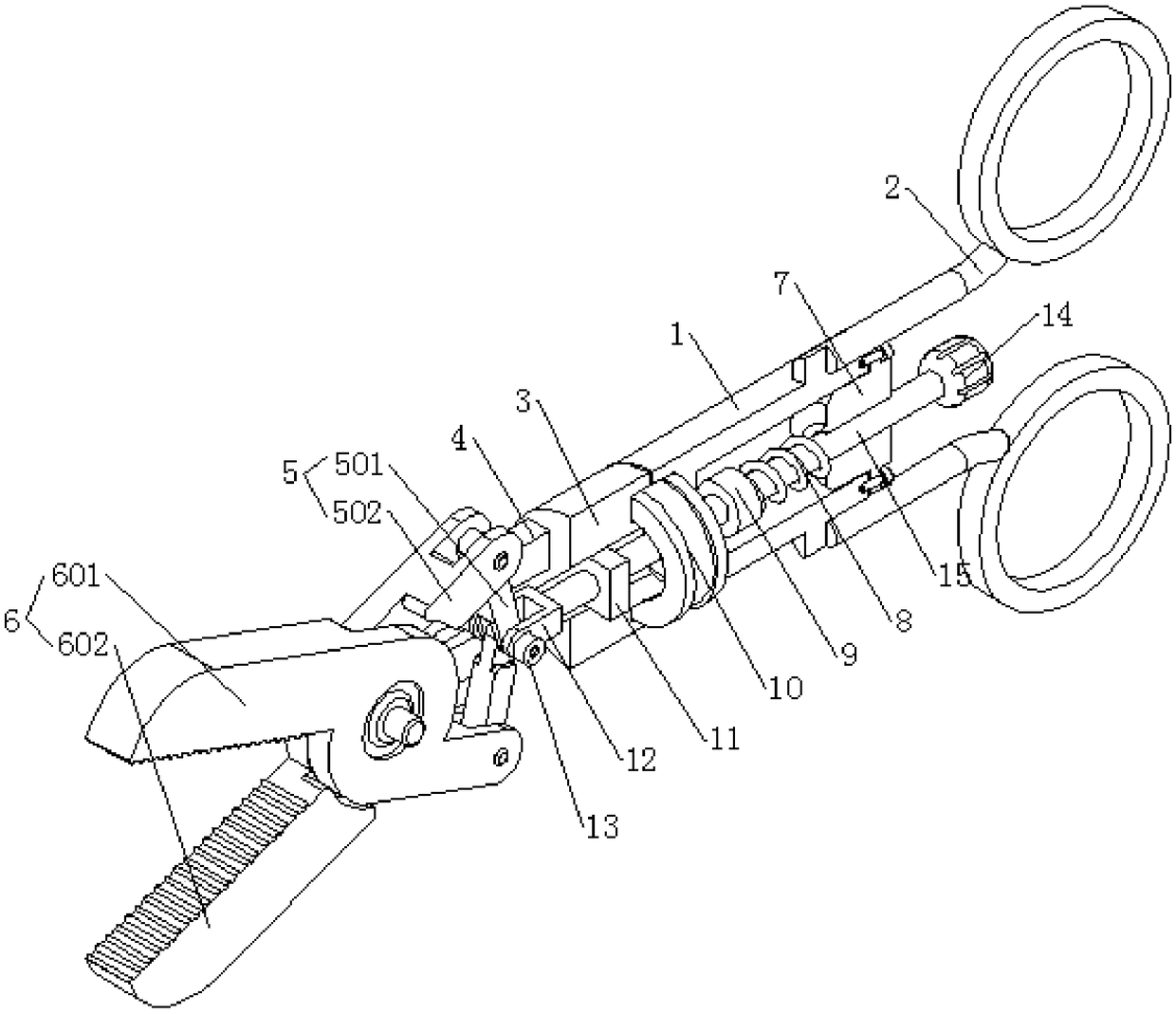
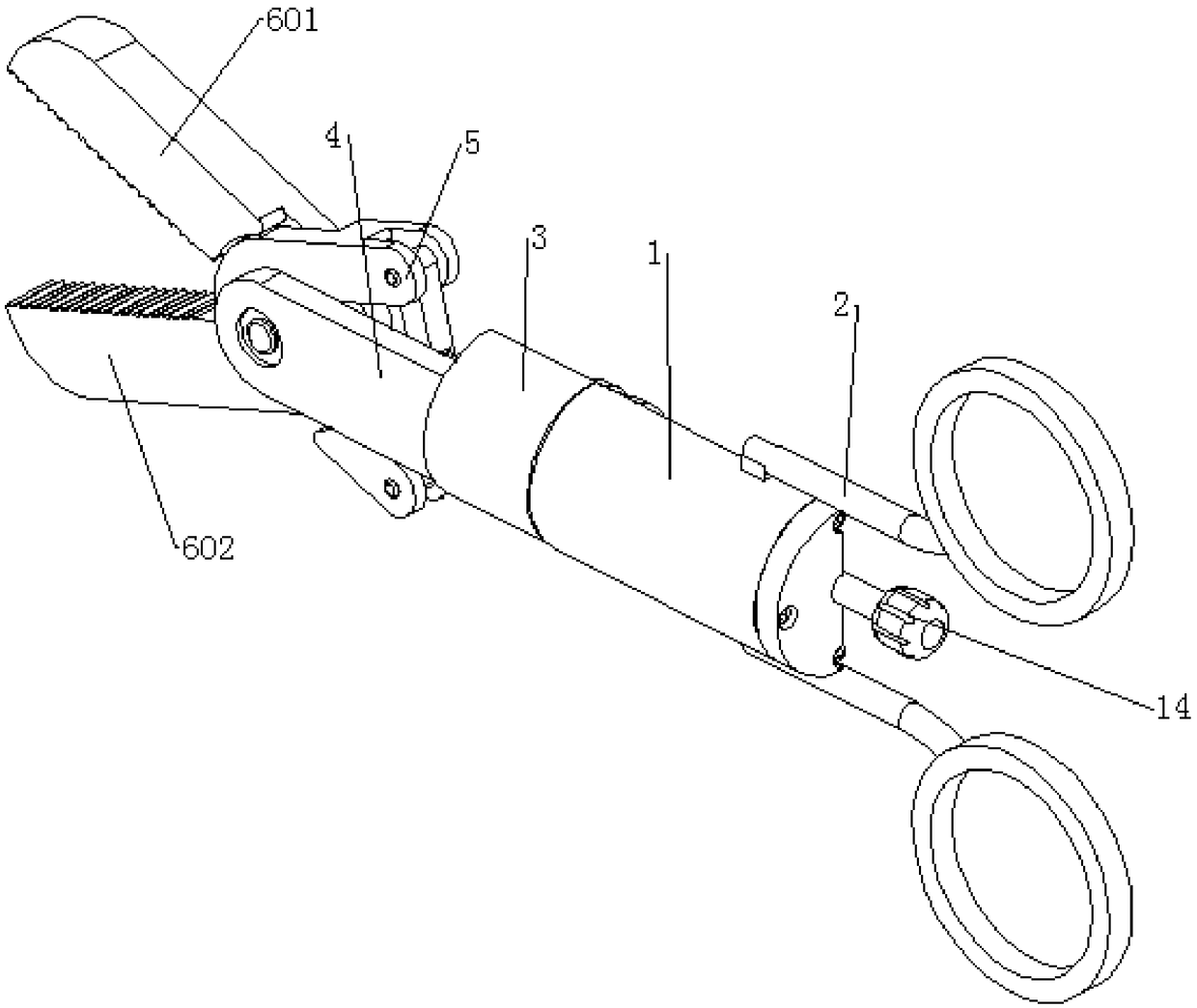
Inferior vena cava root blood vessel anatomic separating forceps applied to laparotomy
The invention belongs to the field of medical apparatuses, and relates to a pair of anatomic separating forceps for separating vena cava root blood vessels in laparotomy. The pair of anatomic separating forceps comprises a head end separating portion, a forceps rod, a connecting device, a holding device, connecting rods, a rotating wheel and a punching piece; the pair of anatomic separating forceps is characterized in that the main bodies of two forceps blades of the head end separating portion form a right angle, and the entire separating portion forms a 120-degree arc-shaped included angle with the forceps rod; the forceps rod is hollowed and is composed of two sections, and the connecting device is arranged in the forceps rod; two flexible steel wires are arranged in the first section, and the flexible steel wires are connected to the separating portion and a spring in the second section; the two symmetrical connecting rods are hinged with the second section of the forceps rod and the holding device; the rotating wheel is arranged on the forceps rod, so that the separating portion is rotated; and the punching device is arranged on the rotating wheel and communicates with the interior of the rotating wheel and the connecting device. The pair of anatomic separating forceps provided by the invention is reasonable in structural design and strong in practicability, and the safety and the efficiency of separating the inferior vena cava root blood vessels can be improved.
Owner:李楠 +1
Vein vascular stent
The invention discloses a vein vascular stent, which comprises a stent body, the stent body is of a mesh tubular structure formed by weaving metal wires, the stent body comprises a first stent sectionand a second stent section which are connected in the axial direction, and the mesh density of the first stent section is different from that of the second stent section. According to the intravenousstent provided by the invention, the treatment effect can be improved for bare sections involving inferior vena cava and iliac femoral vein stenosis, and the supporting strength and extrusion resistance can be improved for a dense net structure with relatively high mesh density at a compression part; a sparse net structure with small mesh density is arranged at a bent part, so that the flexibility and the adherence performance can be improved; the variable-diameter structure can conform to the blood vessel form aiming at the blood vessel anatomical form, and the product is suitable for various blood vessel diameters.
Owner:SHANGHAI BLUEVASCULAR MEDTECH CO LTD
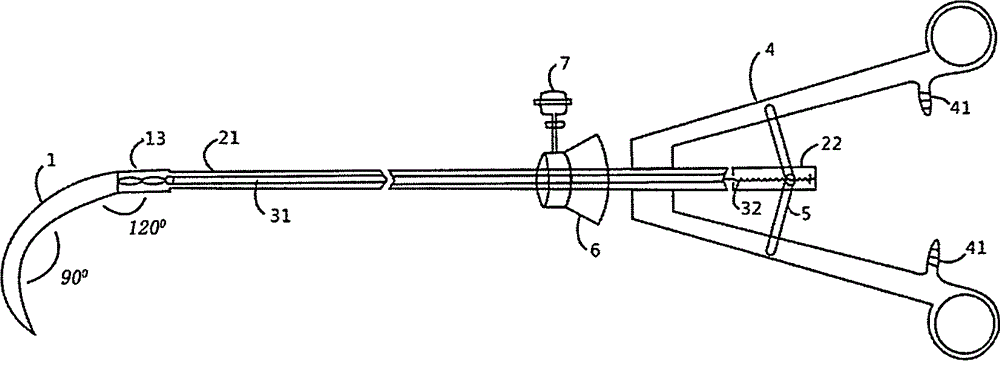
Inferior vena cava root vascular anatomical dissecting forceps for liver surgery
ActiveCN109009328ARealize opening and closingAchieve angle adjustmentSurgical forcepsAgainst vector-borne diseasesVeinForceps
The invention discloses an inferior vena cava root vascular anatomical dissecting forceps for liver surgery. The dissecting forceps comprises a forceps body, two forceps handles and a forceps head, wherein the forceps body is a cylinder; the inside of the cylinder is a cavity structure; and the two forceps handles are connected to the rear end of the forceps body and are symmetrically distributedabout the forceps body. The dissecting forceps drives a pull rod to rotate and stretch by a driving structure so as to open and close the forceps head and rotate the forceps head, and to adjust the angle of the forceps head. During inferior vena cava root vascular dissection, a surgeon can operate without twisting his / her wrist, improves operation precision, and avoids a danger caused by twistingthe wrist. The inferior vena cava root vascular anatomical dissecting forceps is convenient to use.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RAILWAY VOCATIONAL & TECH COLLEGE
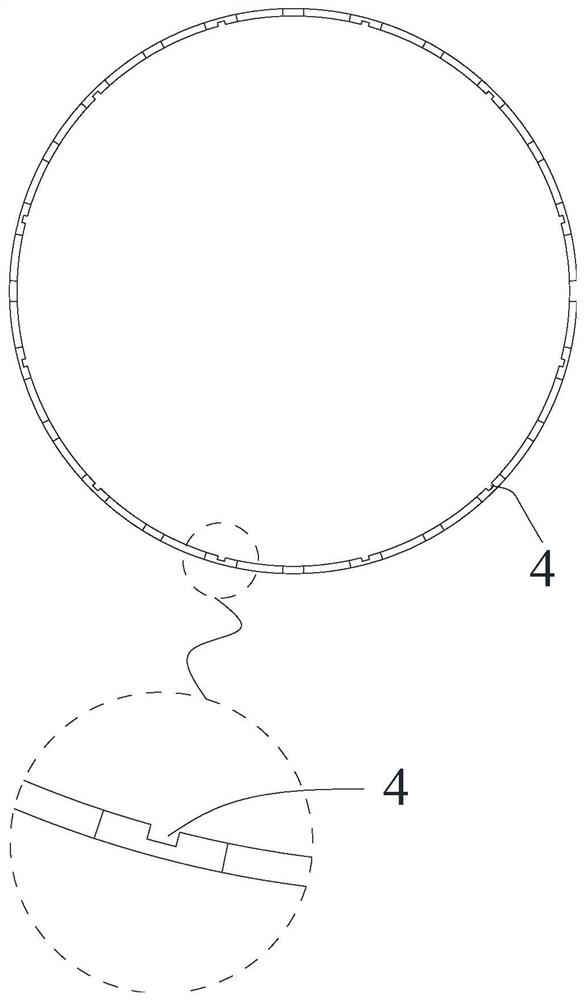
Covered stent system
ActiveCN111407463ASufficient anchor lengthEasy accessStentsHaemostasis valvesExtracorporeal circulationSurgical operation
The invention provides a covered stent system. The covered stent system is simple in structure, clear in principle, flexible and diverse in combinations and relatively few in required stent specifications, achieves limited stent specifications and meets the requirements for different vascular anatomical structures. Various stents in a stent sub-system are fast in release, and blood flow, deep hypothermic circulatory and extracorporeal circulation do not need to be blocked, so that the surgical operation difficulty is greatly reduced, the operation time is shortened, and the perioperative mortality and complication can be greatly reduced. In addition, the operation time is shortened and the operation difficulty is reduced, so that the amount of a contrast medium can be reduced, and meanwhile, the irradiation time that a doctor and a patient are exposed to radioactive rays is significantly shortened. The covered stent system provided by the invention can achieve endovascular exclusion treatment from single-branched vessels to multibranched vessels, for example, endovascular exclusion treatment from arcus aortae and celiac trunks to renal arteries.
Owner:APT MEDICAL HUNAN INC
Devices, systems, and methods to optimize annular orientation of transcatheter valves
In various embodiments, provided herein are methods, devices and systems to optimize annular orientation of transcatheter valves and thereby facilitate transcatheter aortic valve replacement in the setting of challenging cardiovascular anatomy. These methods, devices and systems are used to treat patients with valvular diseases. To solve these problems, described herein is a Device to Optimize aNnUlar orientation of Transcathether valves (DONUT). DONUT can correct large differences between a native valve's anatomical dimensions and the external dimensions of a transcatheter valve stent frame.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Spliced intravascular stent
The invention discloses a spliced intravascular stent. The spliced intravascular stent comprises a first stent and a second stent, the first stent comprises a first body pipe, and a first connecting structure is arranged at the second end of the first body pipe. The second stent comprises a second main body pipe, and a second connecting structure is arranged at the first end of the second main body pipe; the first connecting structure and the second connecting structure are arranged in a matched mode so that the first support and the second support can be spliced into a whole. According to the technical scheme provided by the spliced intravascular stent, the first stent and the second stent can be selected to be matched and spliced according to the condition of a patient, and the spliced stent is implanted into a diseased region of the patient, so that disease treatment of the patient is realized. Therefore, the splicing type intravascular stent can adapt to blood vessel anatomical structures or different diseased regions of different patient individuals, the types and specifications of the stent are reduced, and the universality of the splicing type intravascular stent is improved.
Owner:胡佳
Combination of 3D ultrasound and computed tomography for guidance in interventional medical procedures
ActiveCN110248603AOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical navigation systemsAnatomical structuresContrast medium
In the present invention, an imaging system and method are provided to obtain a fusion image of a patient anatomy used as a navigational 3D roadmap to guide an interventional device into the anatomy. The fusion image fuses in real-time, fluoroscopy images taken during the interventional procedure with pre-operative CTA images, so that the operator can see the anatomy in the fluoroscopy image without having to inject contrast agent. To correct for the deformation in the anatomy from the pre-op CTA images formed by the insertion of interventional devices during the procedure, a 3D ultrasound image is obtained after the insertion of the devices. The 3D ultrasound images are then utilized to correct the pre-op CTA images and provide the current vascular anatomy of the patient. This updated CTA image is fused with the intra-op fluoro images to provide an accurate 3D roadmap image that matches the deformed anatomy.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Combination of 3D ultrasound and computed tomography for guidance in interventional medical procedures
ActiveUS10524865B2Correction of deformationImprove matchOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical navigation systemsAnatomical structuresContrast medium
In the present invention, an imaging system and method is provided to obtain a fusion image of a patient anatomy used as a navigational 3D roadmap to guide an interventional device into the anatomy. The fusion image fuses in real-time, fluoroscopy images taken during the interventional procedure with pre-operative CTA images, so that the operator can see the anatomy in the fluoroscopy image without having to inject contrast agent. To correct for the deformation in the anatomy from the pre-op CTA images form the insertion of interventional devices during the procedure, a 3D ultrasound image is obtained after the insertion of the devices. The 3D ultrasound images are then utilized to correct the pre-op CTA images and provide the current vascular anatomy of the patient. This updated CTA image is fused with the intra-op fluoro images to provide an accurate 3D roadmap image that matches the deformed anatomy.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Motion compensated cardiac valve reconstruction
ActiveUS11308660B2Reduce Motion ArtifactsReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsHeart valve reconstructionRat heart
Motion compensated reconstruction is currently not well-suited for reconstructing the valve, the valve leaflets and the neighboring vascular anatomy of the heart. Blurring of the valve and the valve leaflets occurs. This may lead to wrong diagnosis. A new approach for motion compensated reconstruction of the valve and the related anatomy is presented in which an edge-enhancing step is performed to suppress blurring.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
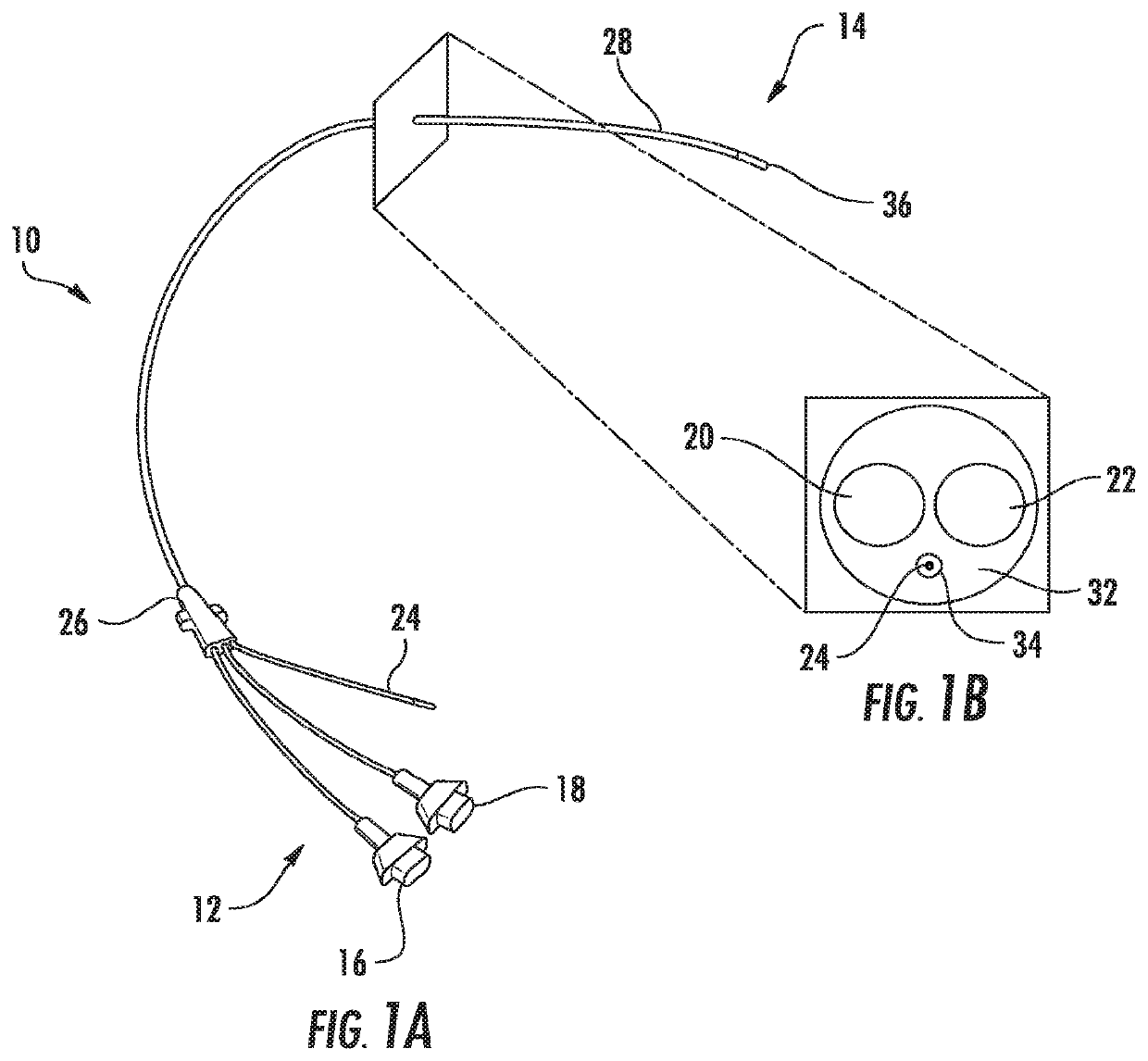
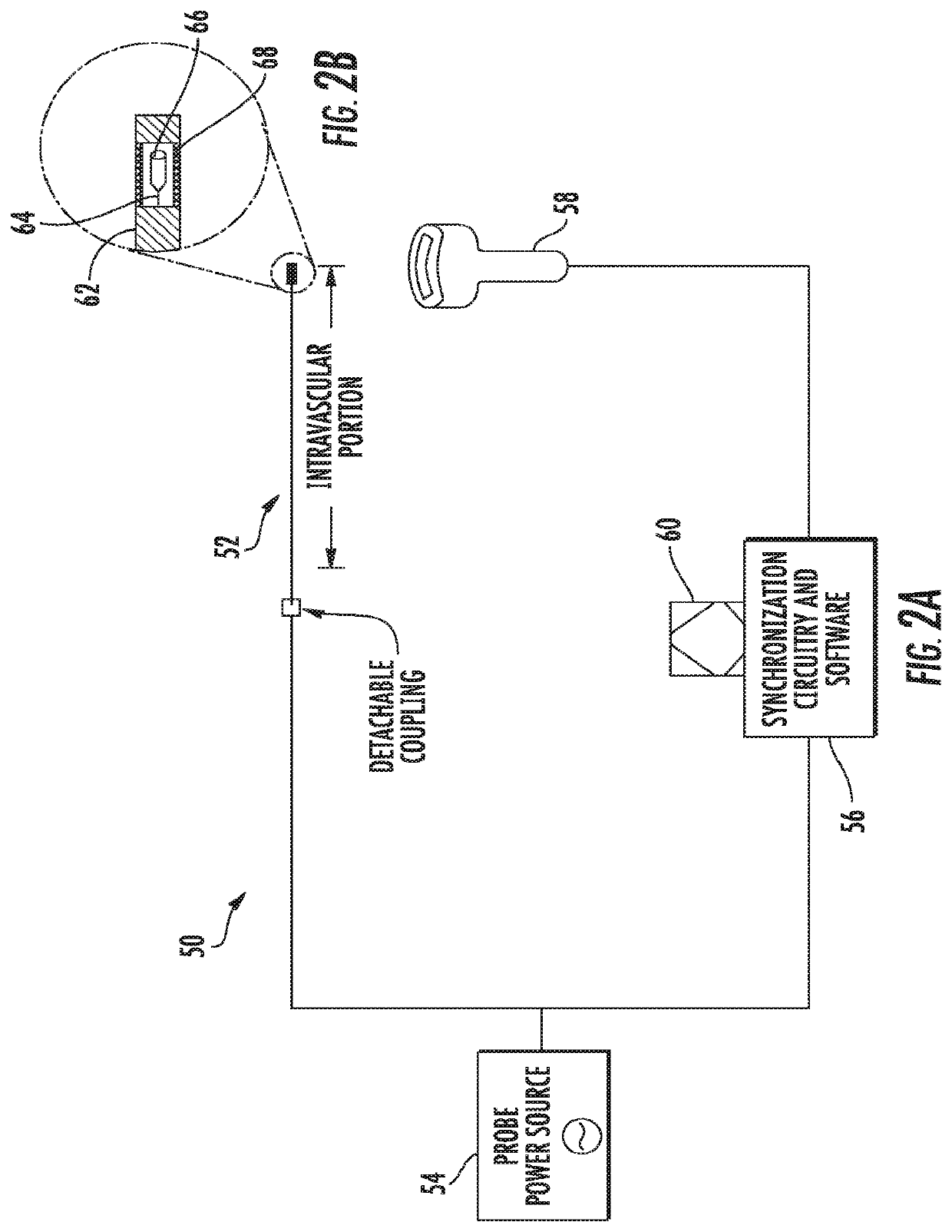
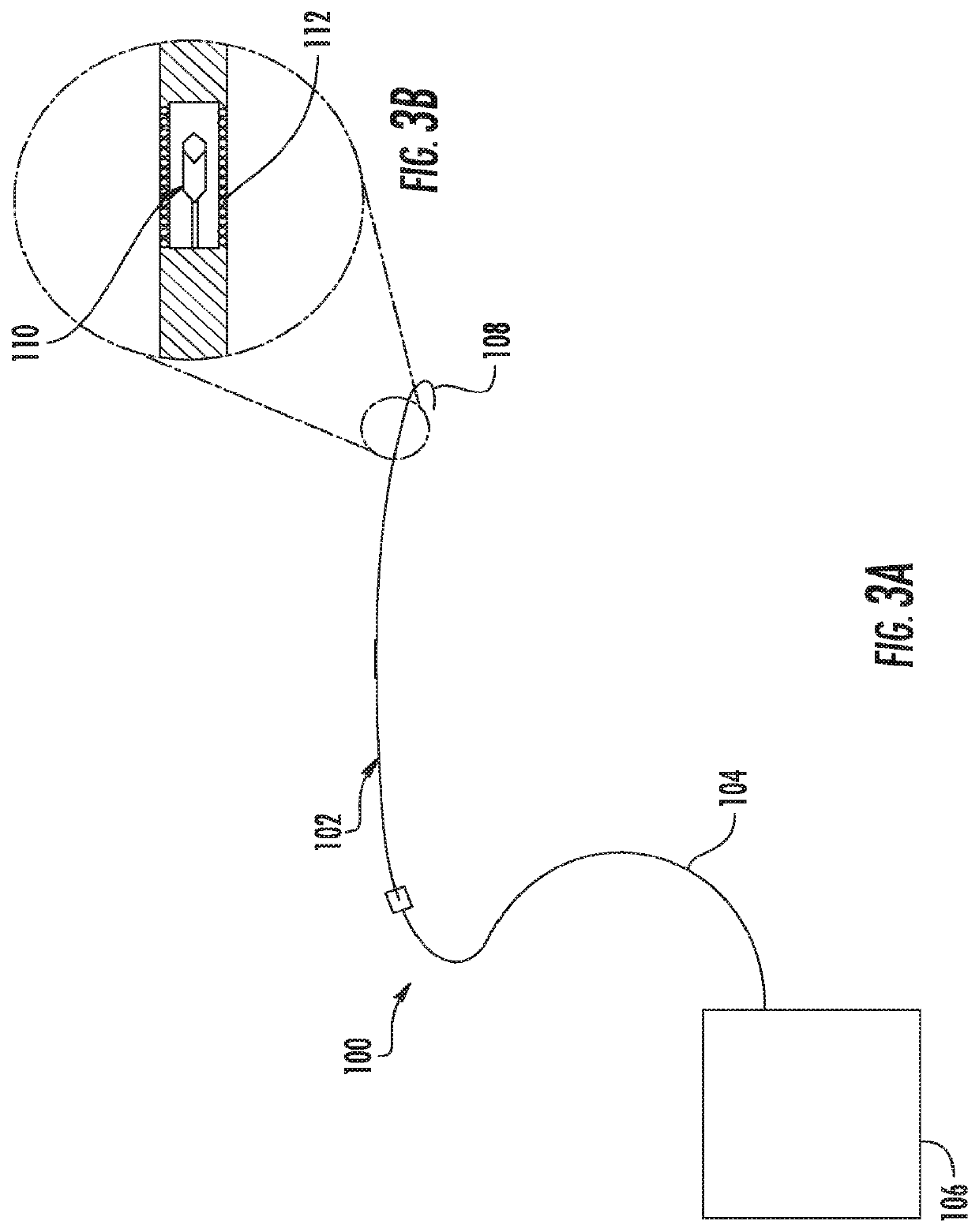
Device for utilizing transmission ultrasonography to enable ultrasound-guided placement of central venous catheters
ActiveUS20190380678A1Organ movement/changes detectionSurgeryIntravascular probeDiagnostic Radiology Modality
Ultrasound is typically performed with the use of an external transcutaneous probe that emits ultrasonic energy and measures the timing of reflected waves, thus allowing measurement of fluid flow or formation of a two-dimensional image. Clinically, the modality is limited by attenuation of the signal with increasing depth of penetration of the ultrasound into tissues, as well as by similarities in echo-genicity between different tissues. The present invention includes a system in which an intravascular probe actively transmits ultrasound that can then be detected by in-line piezoelectric transducers without reflection. This signal can be overlaid onto traditional B-mode or Doppler representation. Furthermore, the present invention includes a signal processing system that will display a real-time graphical representation of the vascular anatomy in order to assist the surgeon or procedural radiologist in the placement of central venous catheters.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com