Patents
Literature
617 results about "Ct scanners" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
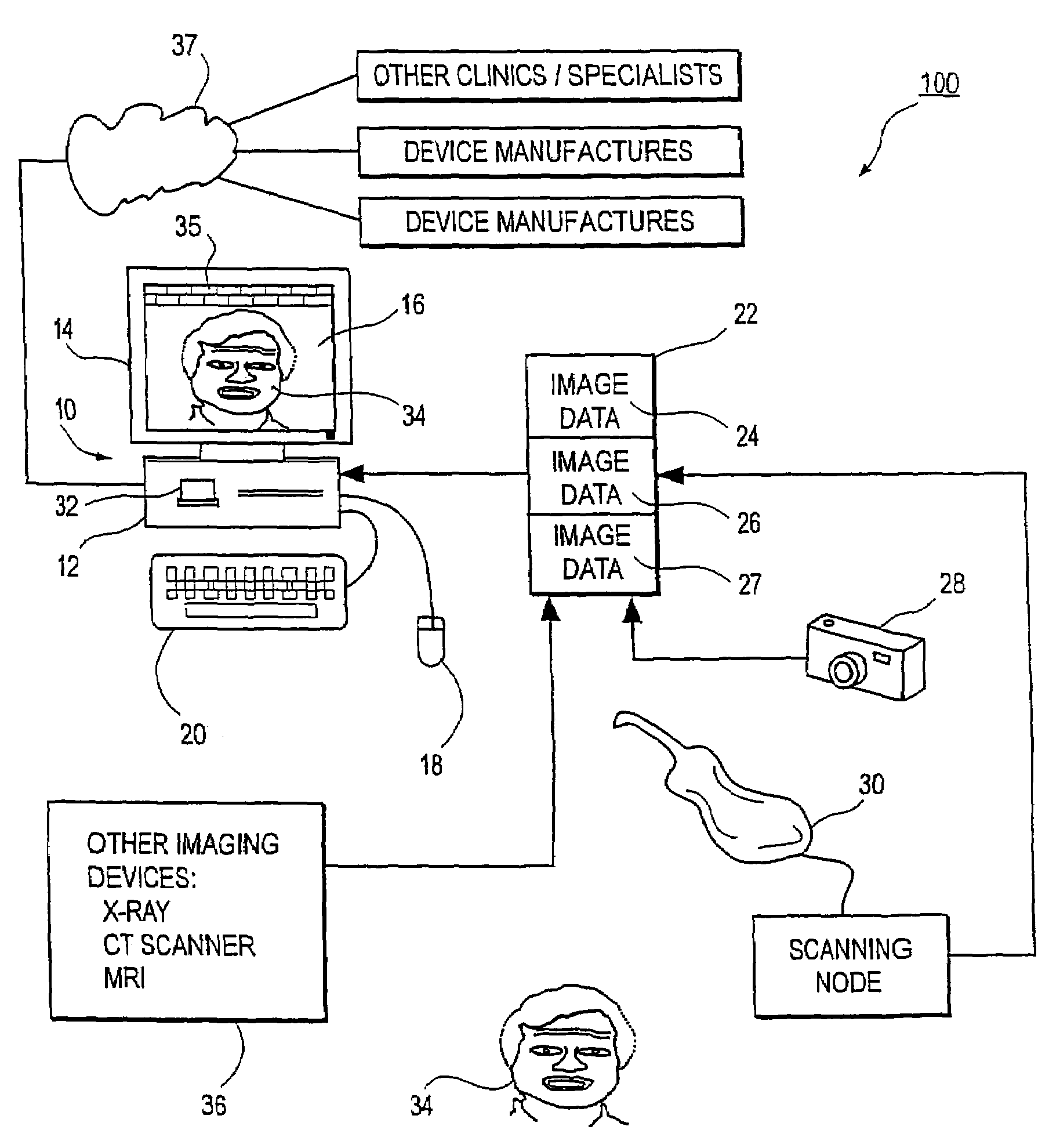
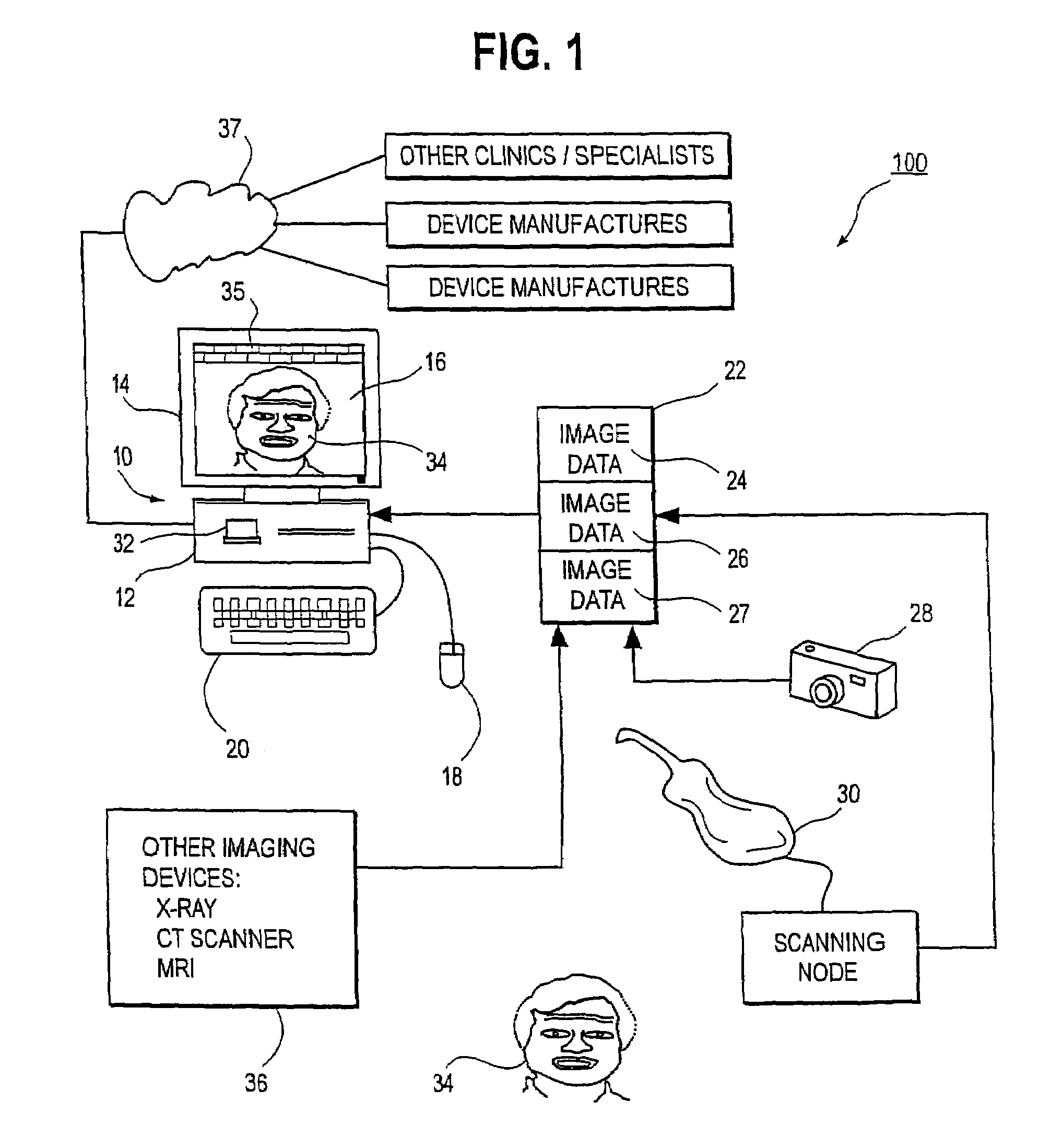
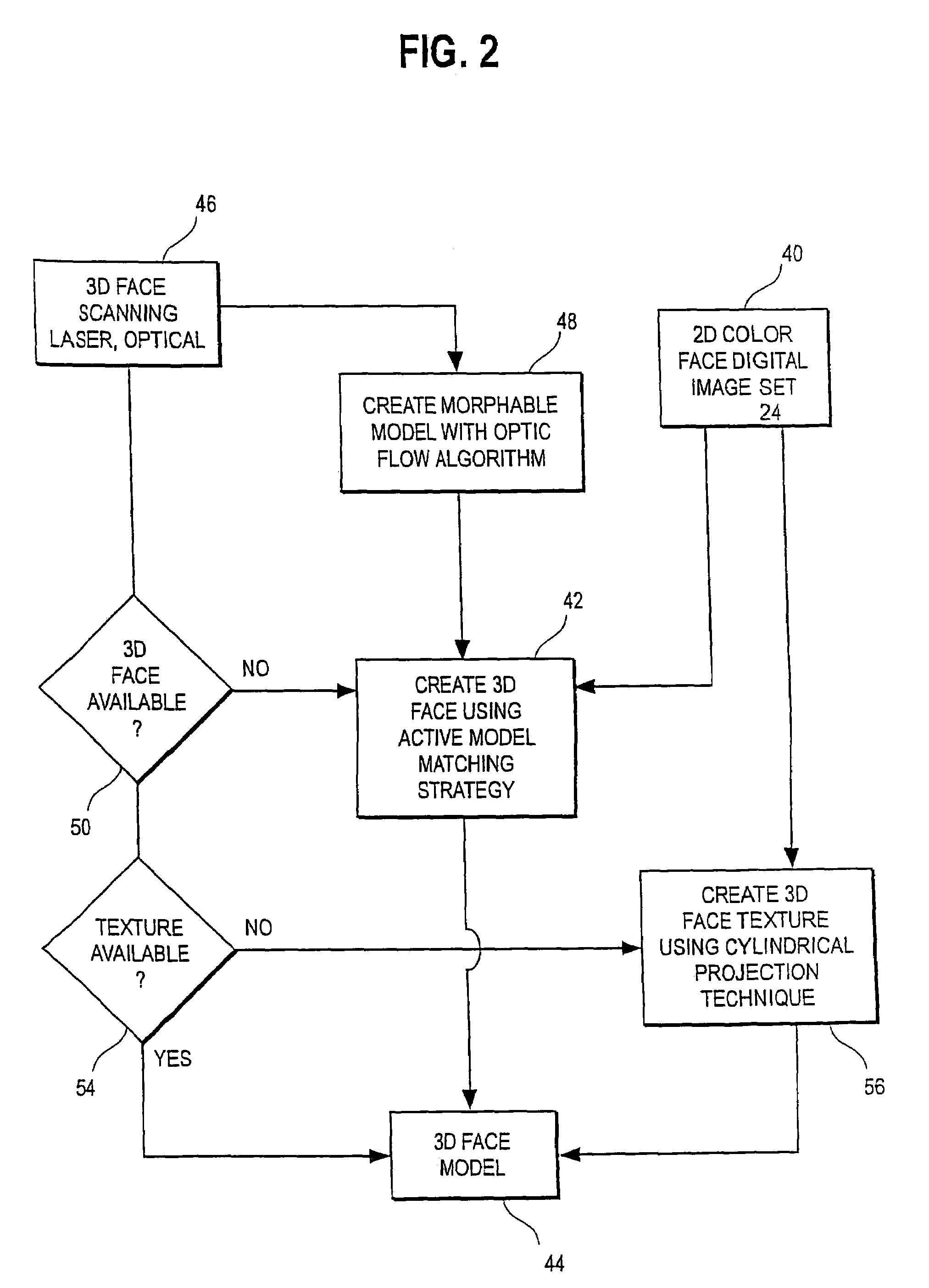
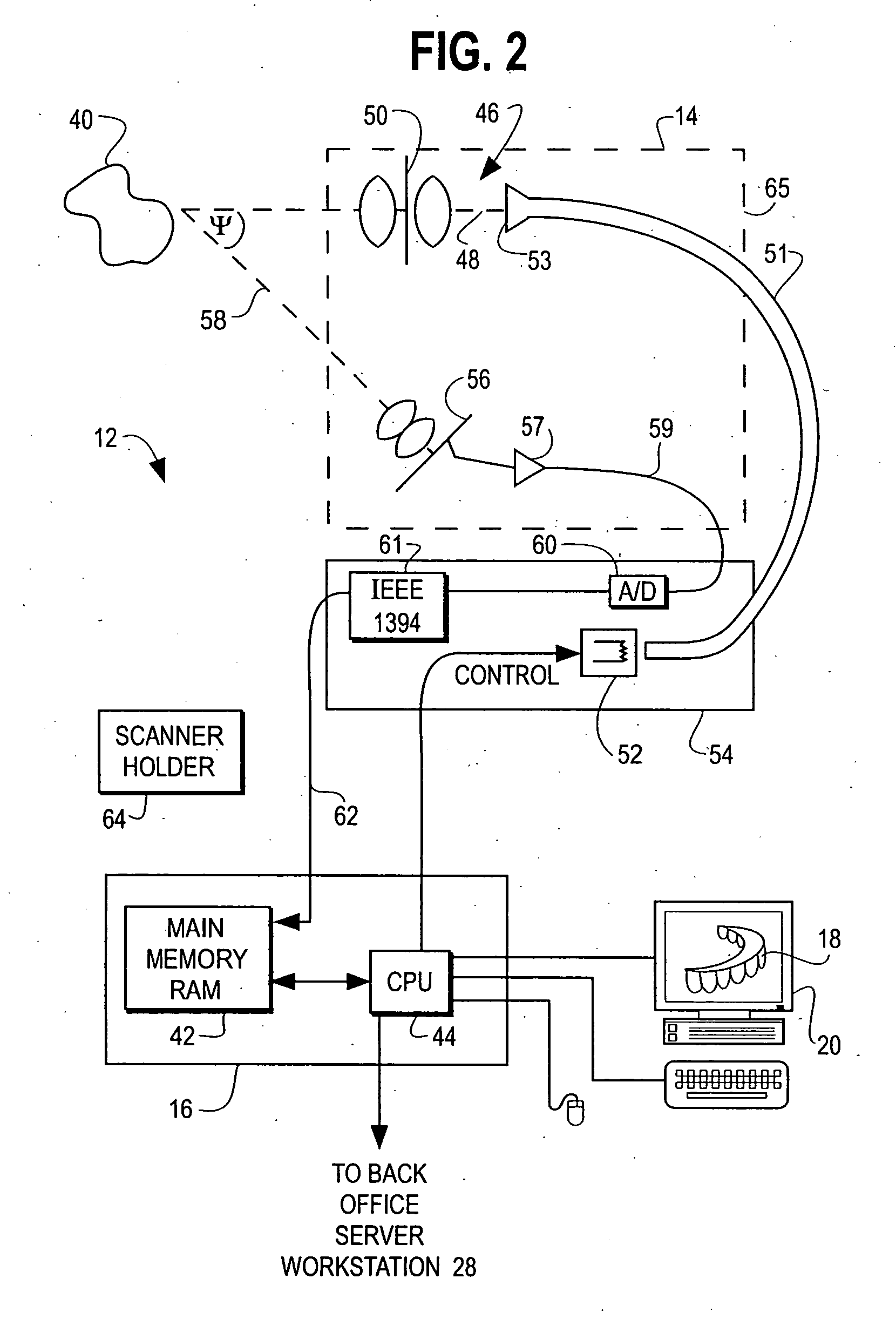
Unified workstation for virtual craniofacial diagnosis, treatment planning and therapeutics
InactiveUS7234937B2Quick analysisPowerful toolDental implantsImpression capsPlan treatmentPatient model
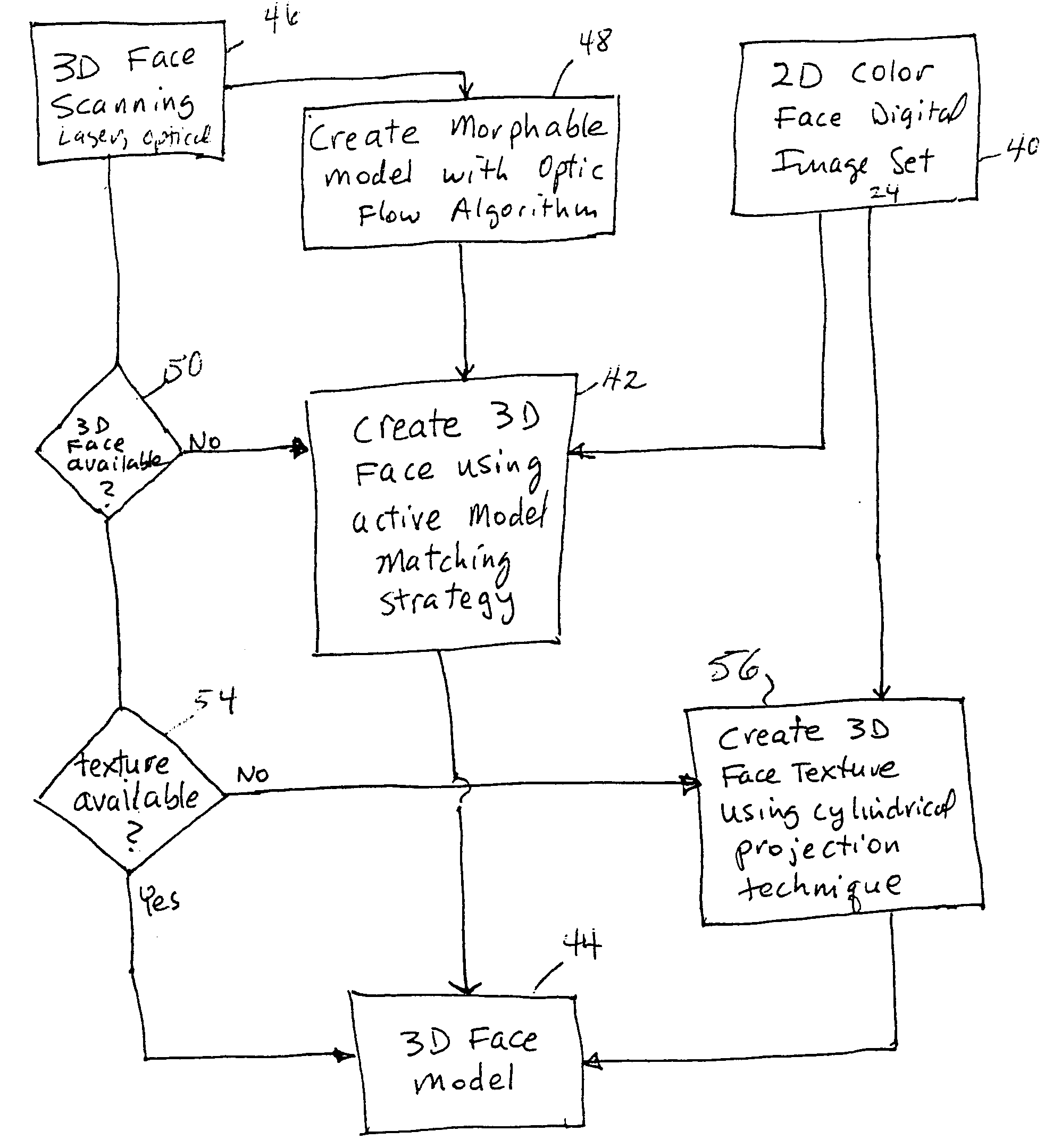
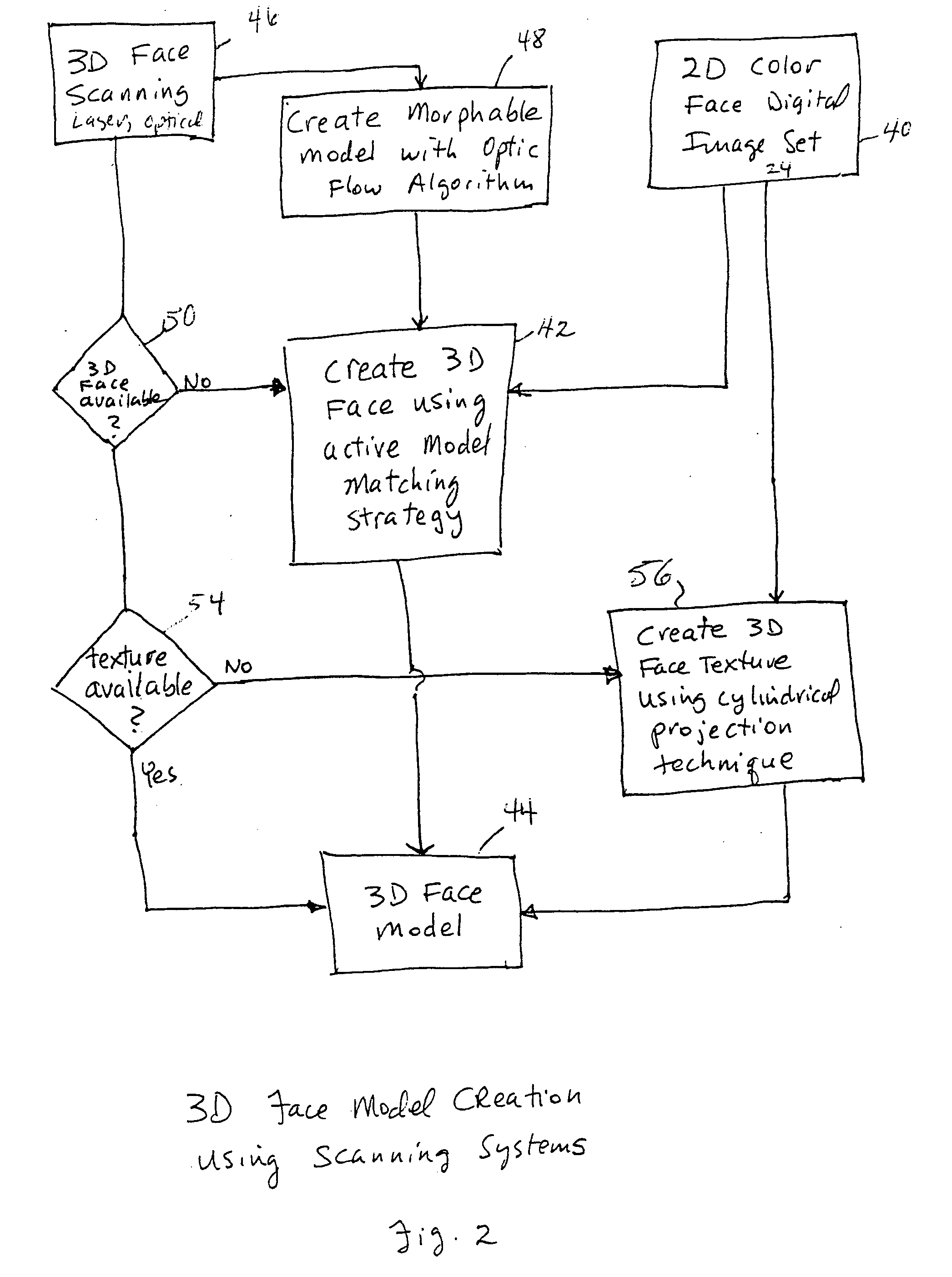
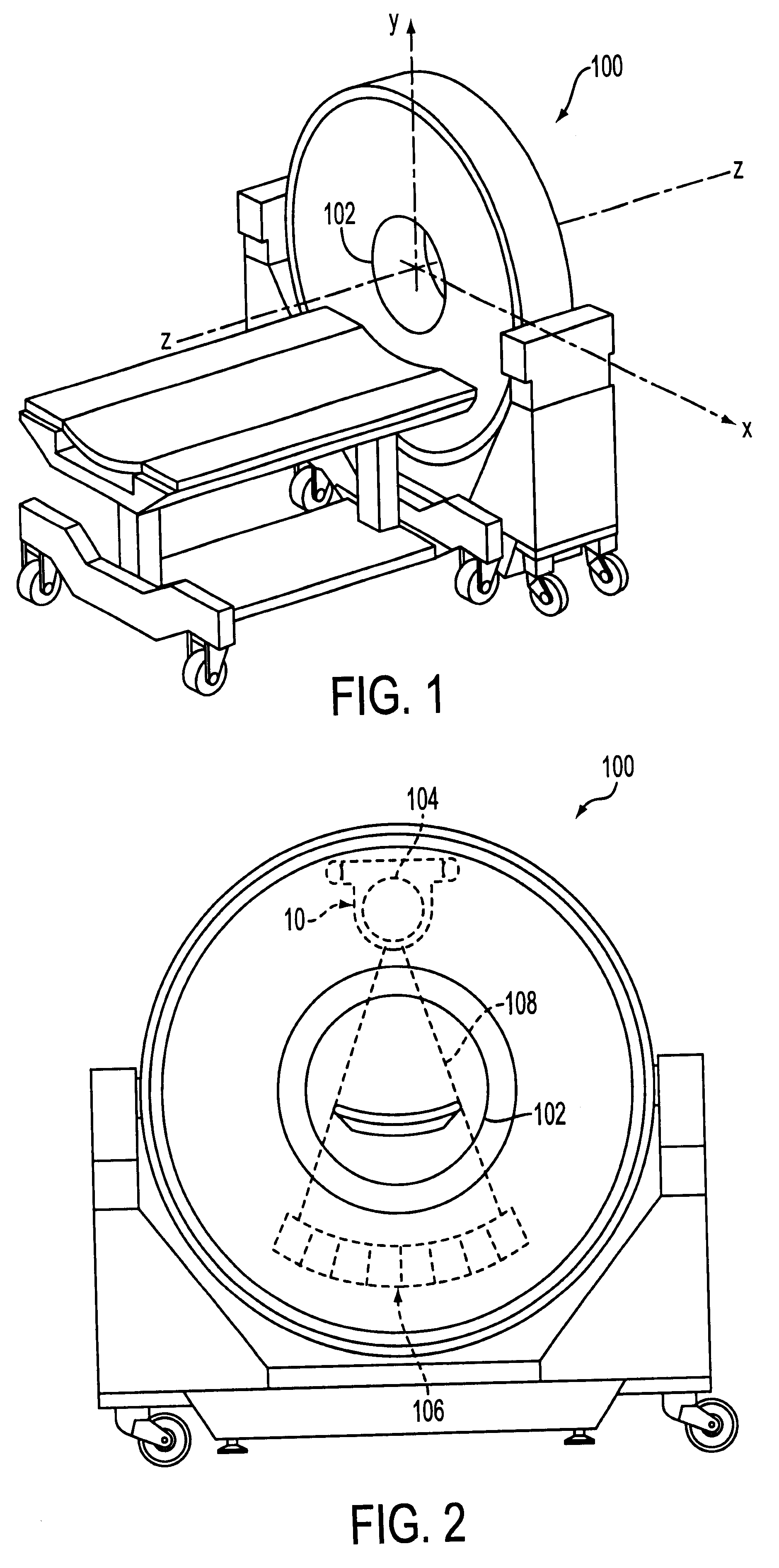
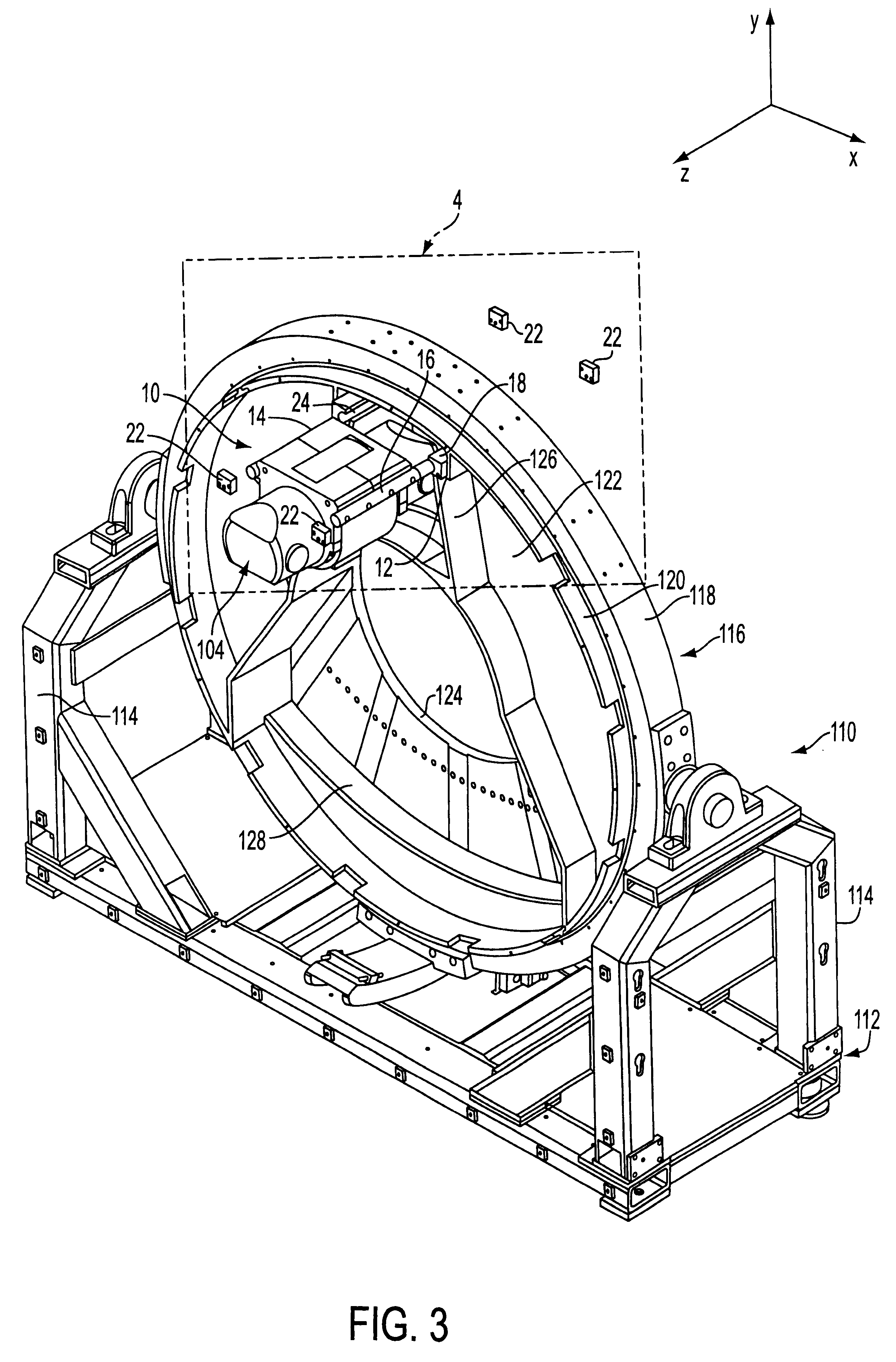
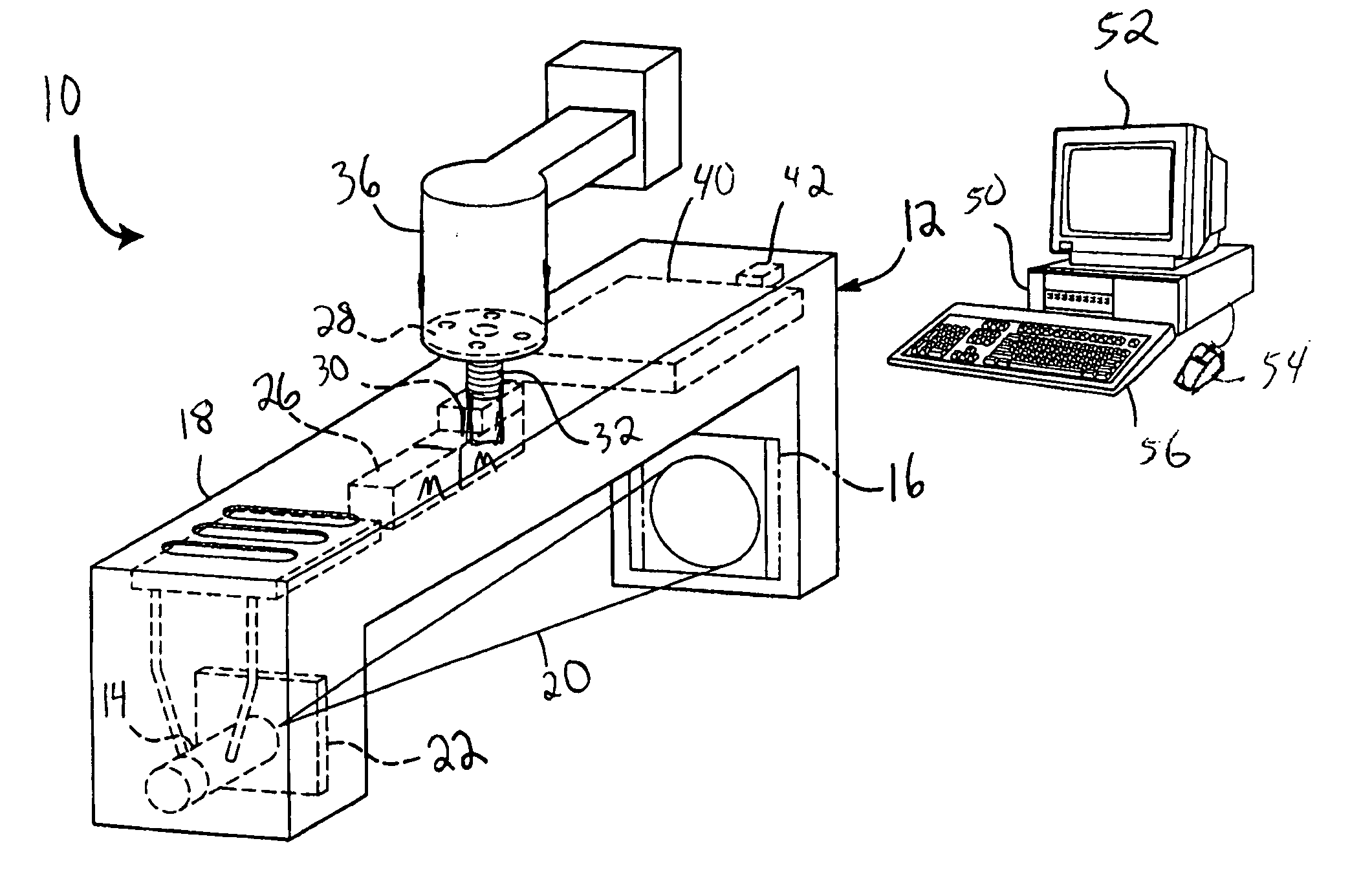
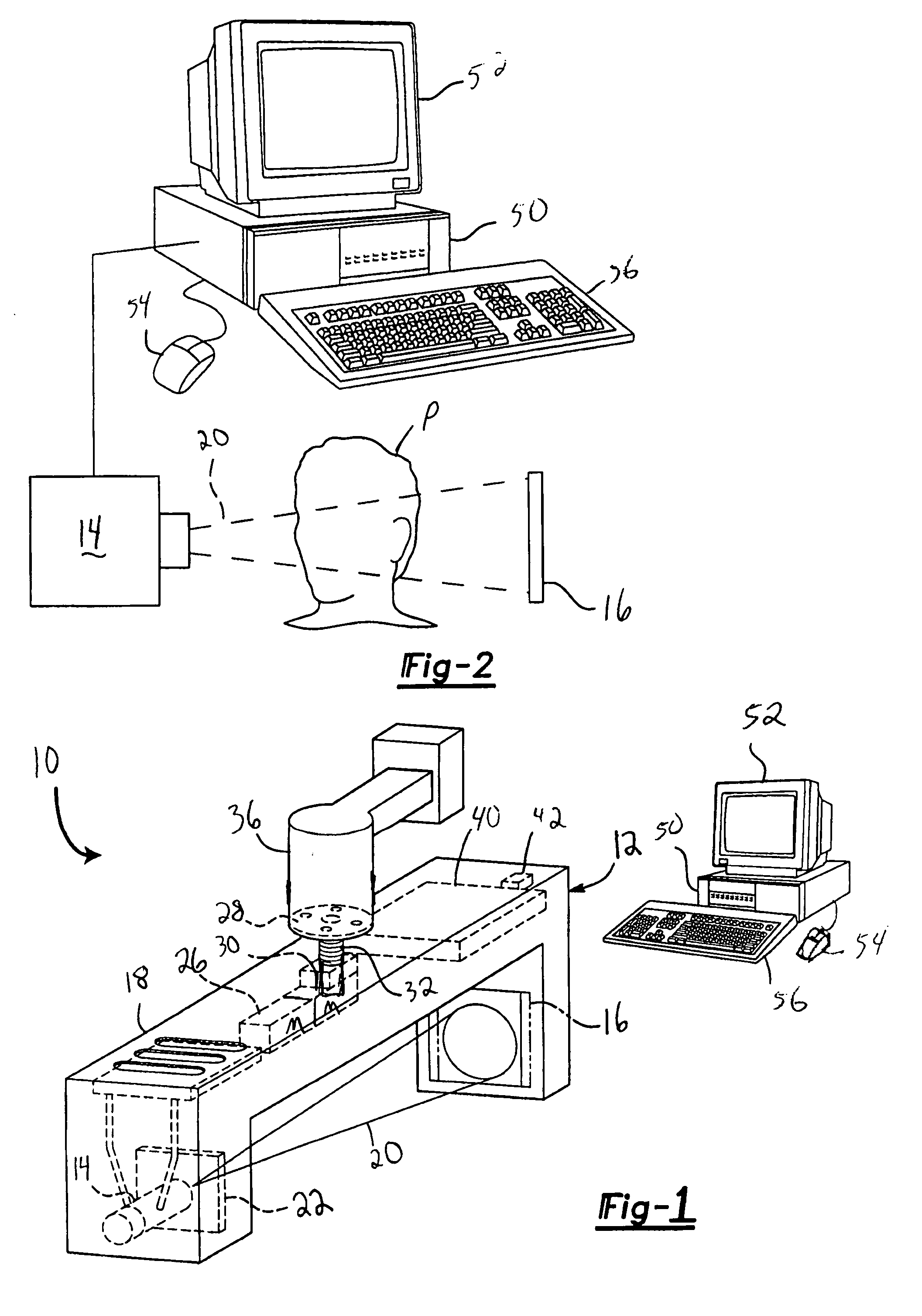
An integrated system is described in which digital image data of a patient, obtained from a variety of image sources, including CT scanner, X-Ray, 2D or 3D scanners and color photographs, are combined into a common coordinate system to create a virtual three-dimensional patient model. Software tools are provided for manipulating the virtual patient model to simulation changes in position or orientation of craniofacial structures (e.g., jaw or teeth) and simulate their affect on the appearance of the patient. The simulation (which may be pure simulations or may be so-called “morphing” type simulations) enables a comprehensive approach to planning treatment for the patient. In one embodiment, the treatment may encompass orthodontic treatment. Similarly, surgical treatment plans can be created. Data is extracted from the virtual patient model or simulations thereof for purposes of manufacture of customized therapeutic devices for any component of the craniofacial structures, e.g., orthodontic appliances.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
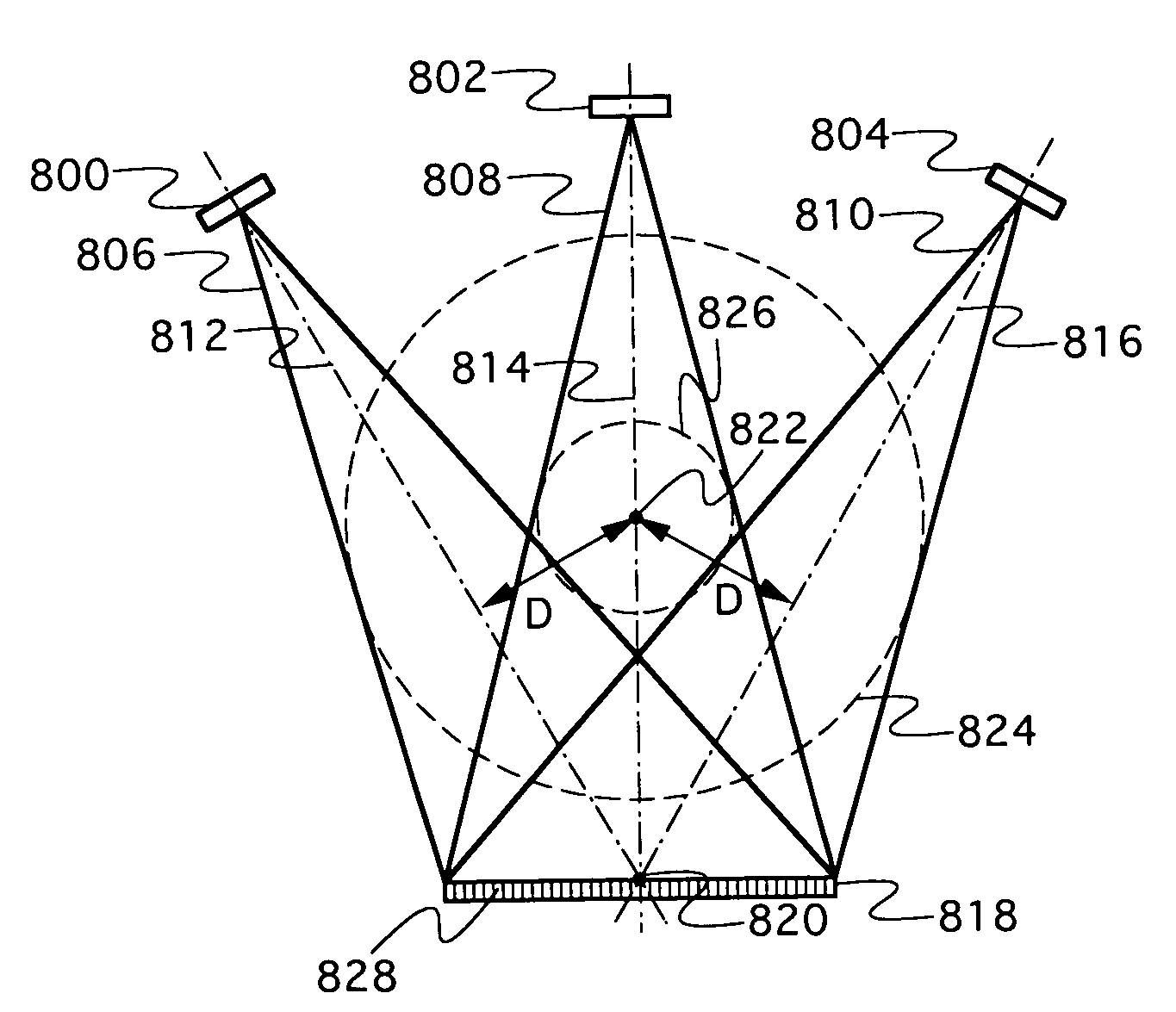
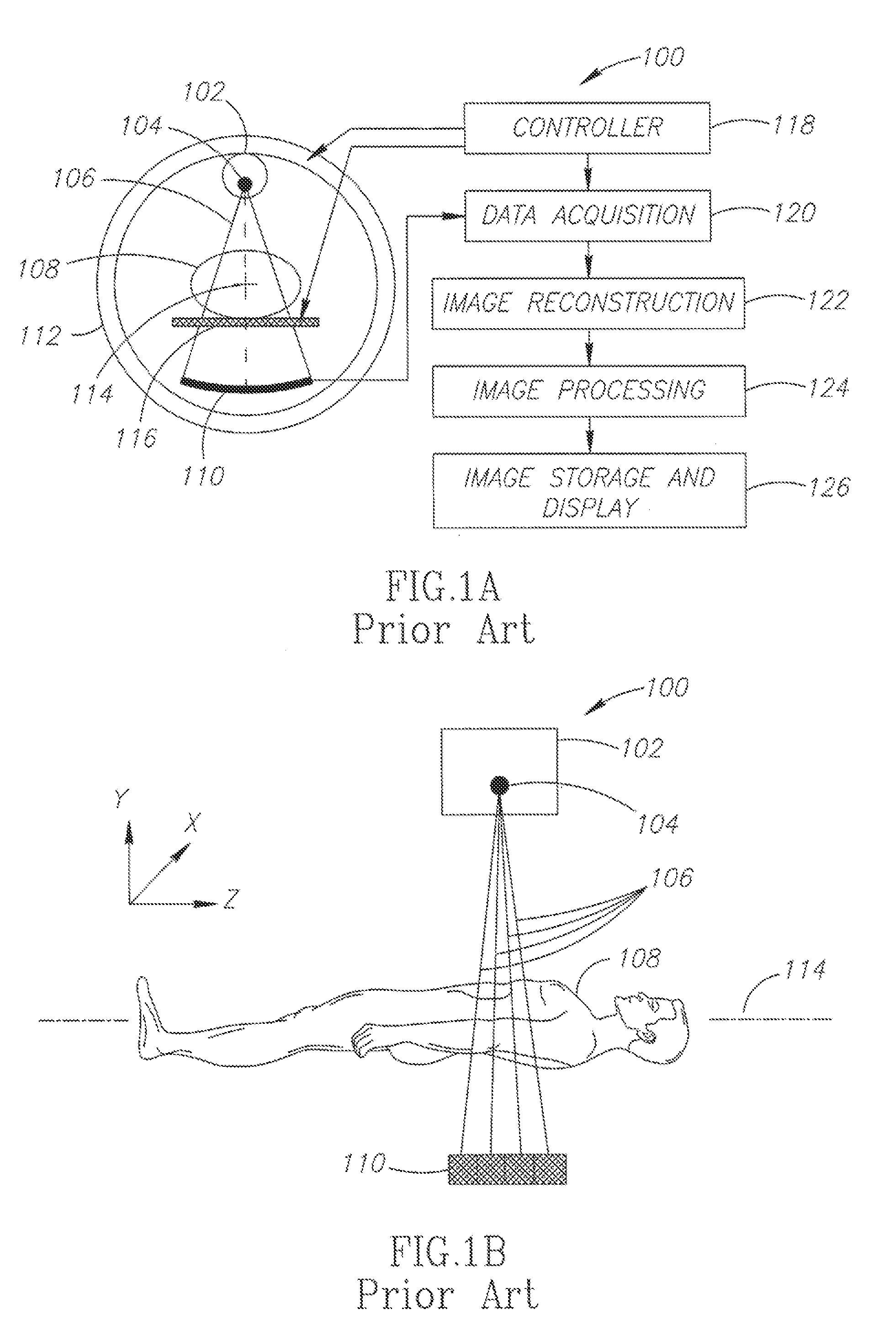
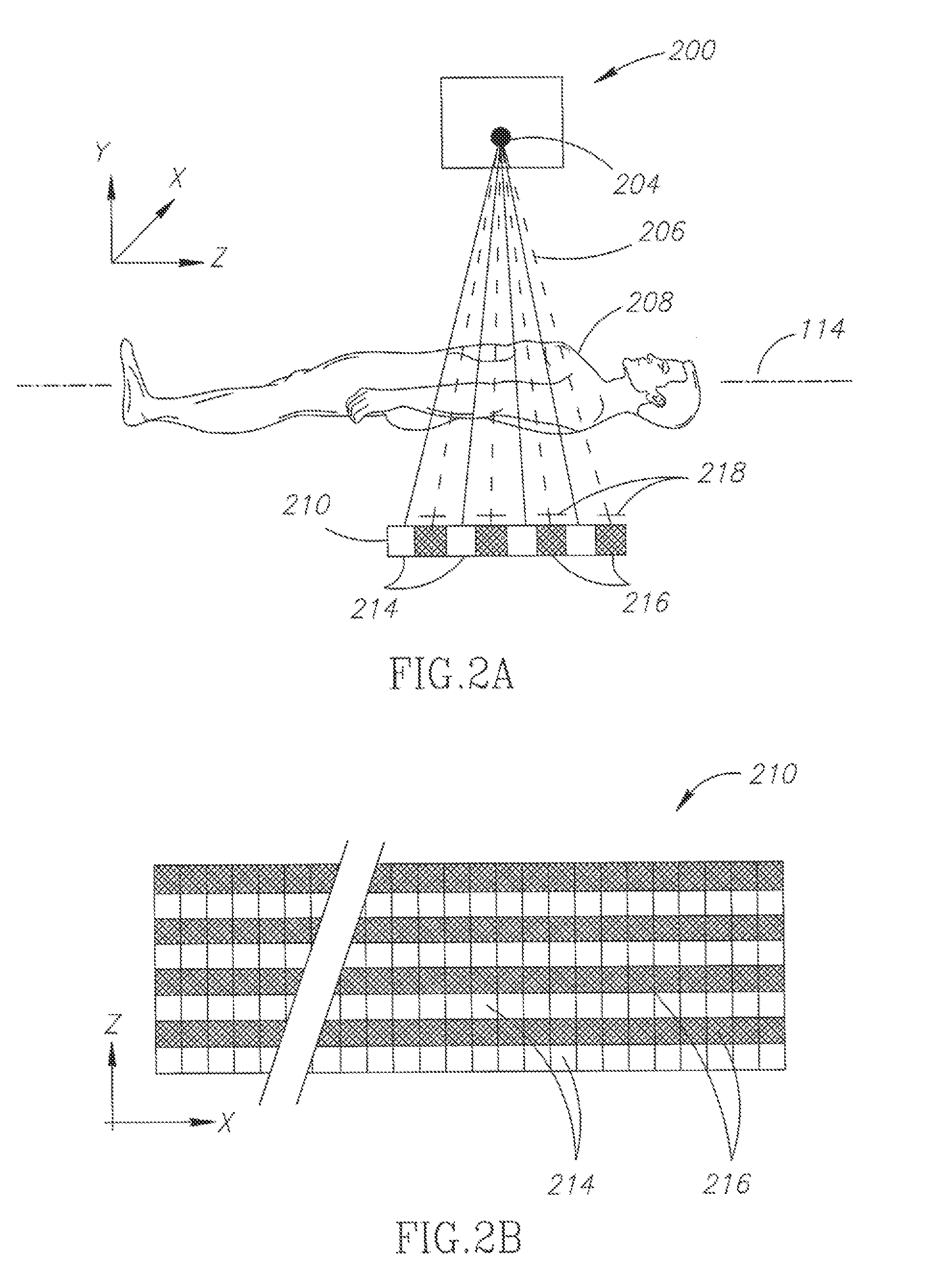
Computed tomography with increased field of view
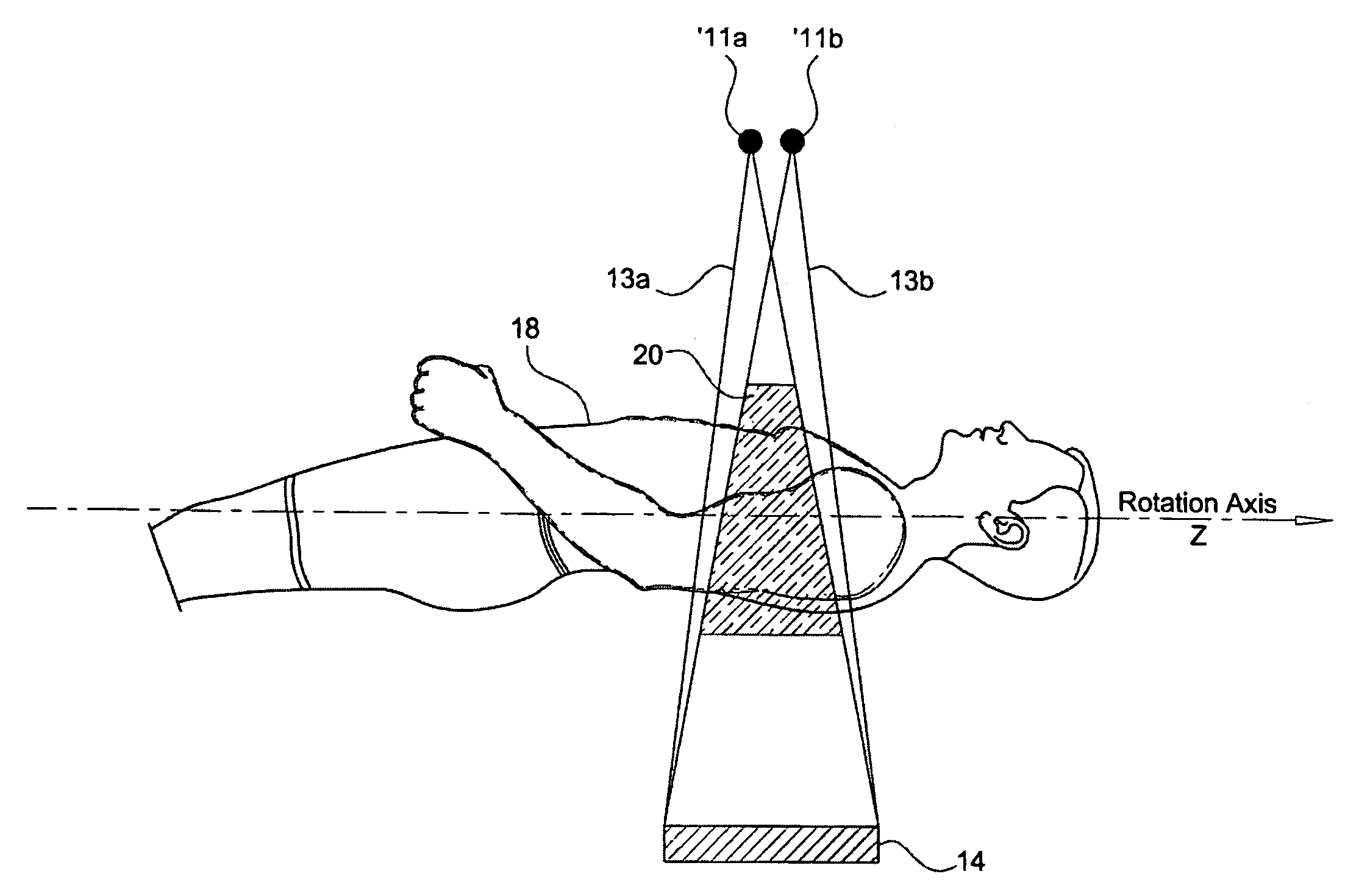
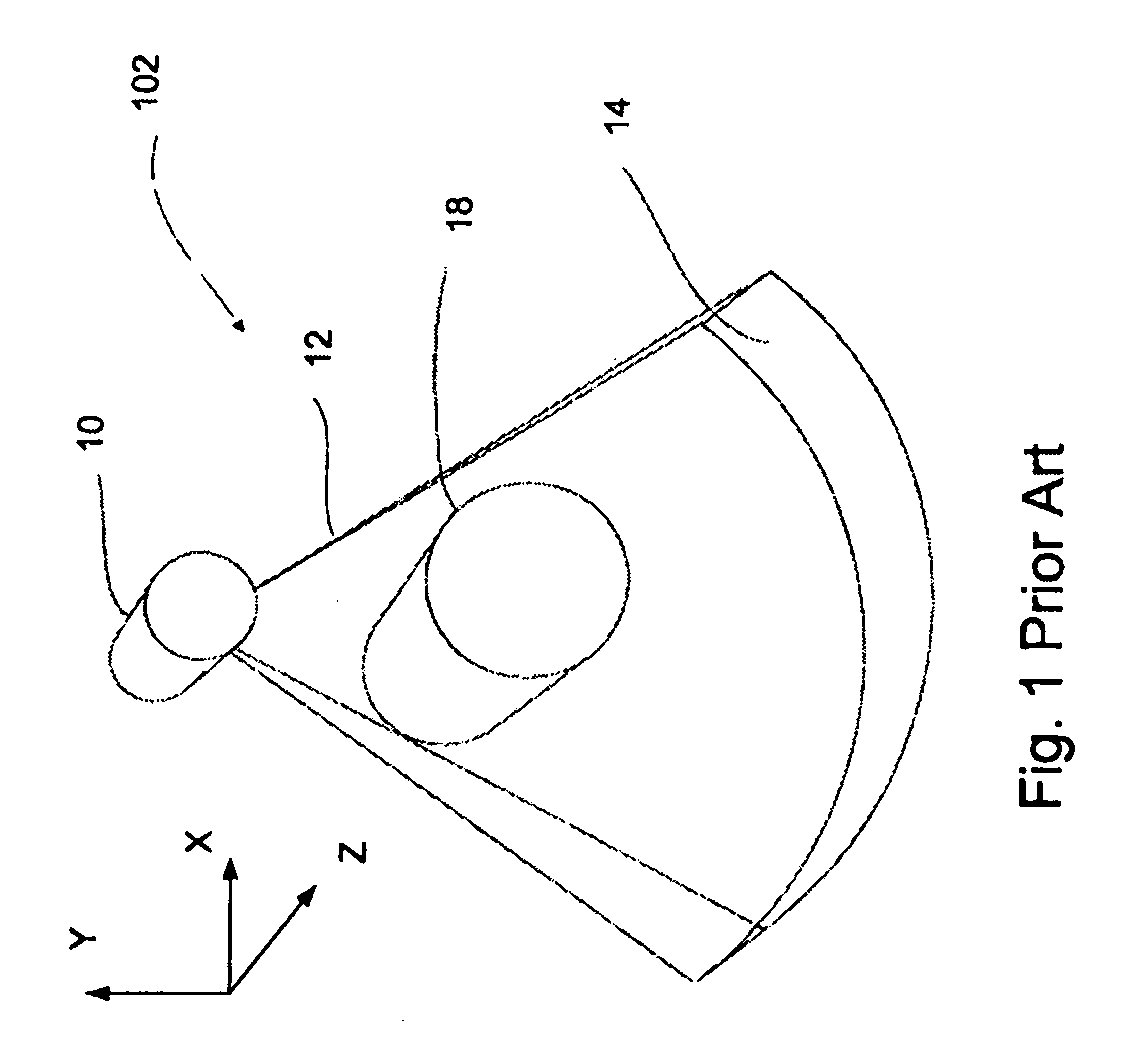
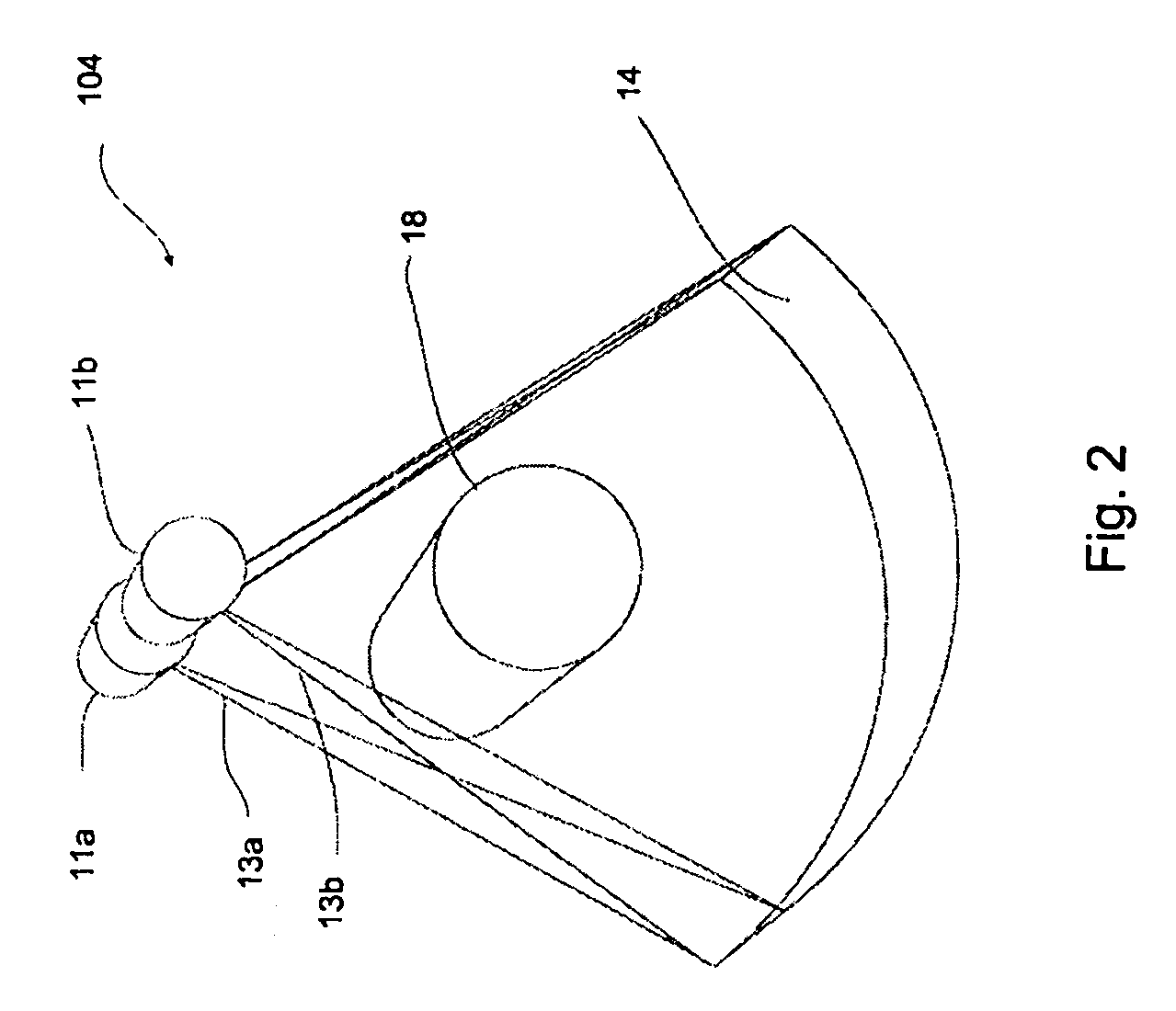
ActiveUS7062006B1Expand field of viewLarge array sizeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingIn planeOffset distance
A volumetric computed tomography system with a large field of view has, in a forward geometry implementation, multiple x-ray point sources emitting corresponding fan beams at a single detector array. The central ray of at least one of the fan beams is radially offset from the axis of rotation of the system by an offset distance D. Consequently, the diameter of the in-plane field of view provided by the fan beams may be larger than in a conventional CT scanner. Any number of point sources may be used. Analogous systems may be implemented with an inverse geometry so that a single source array emits multiple fan beams that converge upon corresponding detectors.
Owner:AIRDRIE PARTNERS I LP +1
Imaging and display system for guiding medical interventions
An imaging and display system for guiding medical interventions includes a wearable display, such as a goggle display, for viewing by a user. The display presents a composite, or combined image that includes pre-operative surgical navigation images, intraoperative images, and in-vivo microscopy images or sensing data. The pre-operative images are acquired from scanners, such as MRI and CT scanners, while the intra-operative images are acquired in real-time from a camera system carried by the goggle display for imaging the patient being treated so as to acquire intraoperative images, such as fluorescence images. A probe, such as a microscopy probe or a sensing probe, is used to acquire in-vivo imaging / sensing data from the patient. Additionally, the intra-operative and in-vivo images are acquired using tracking and registration techniques to align them with the pre-operative image and the patient to form a composite image for display by the goggle display.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Geometry calibration algorithm for large flat module detector CT scanner
ActiveUS9398890B2The process is simple and effectiveSmall sizeComputerised tomographsTomographyCt scannersComputer science
A method for geometric calibration of a CT scanner, including, for each row of at least one row of detector cells, establishing a complete geometric description of the CT scanner, including at least one unknown geometric parameter, establishing a description of a forward projection function using the complete geometric description, acquiring actual projection coordinates of a calibration phantom placed in a scanning field of view (SFOV) on a current row of detector cells and corresponding to a plurality of angles, acquiring calculated projection coordinates of the calibration phantom on the current row of detector cells and corresponding to the plurality of angles using the description of the forward projection function, and acquiring a calibrated value for the at least one unknown geometric parameter by evaluating the at least one unknown geometric parameter based on the acquired actual projection coordinates and calculated projection coordinates via a nonlinear least square fitting algorithm.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
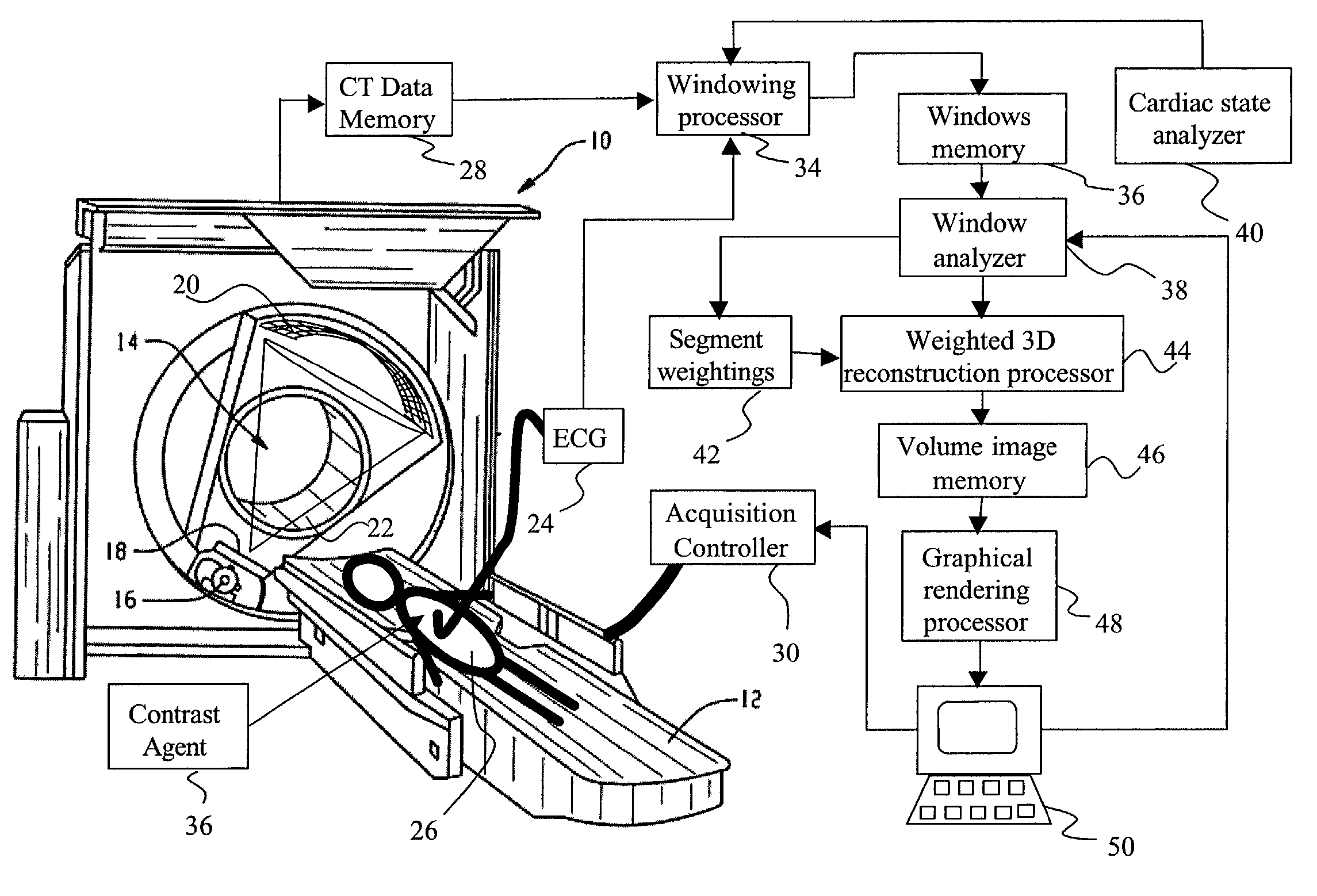
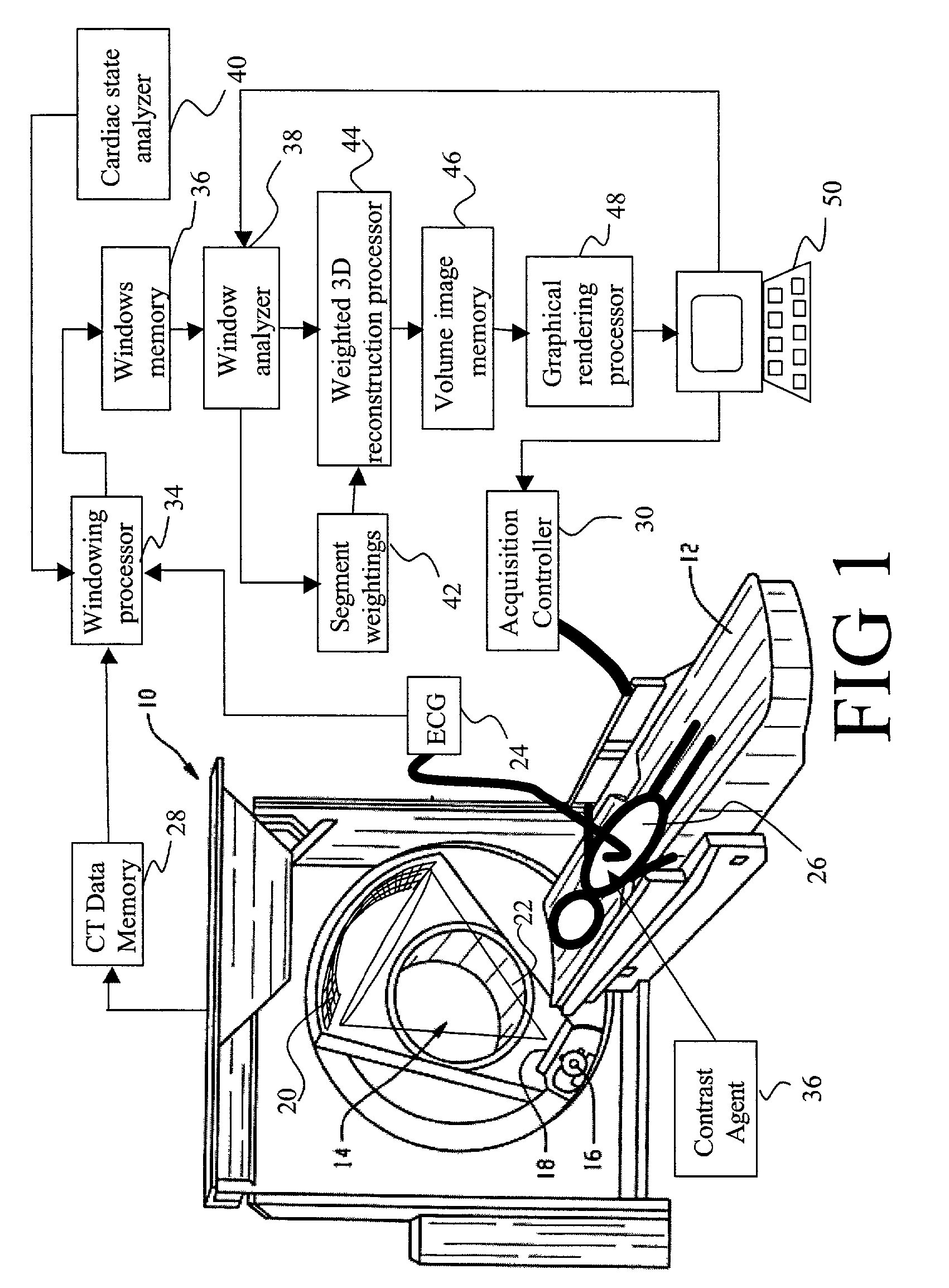
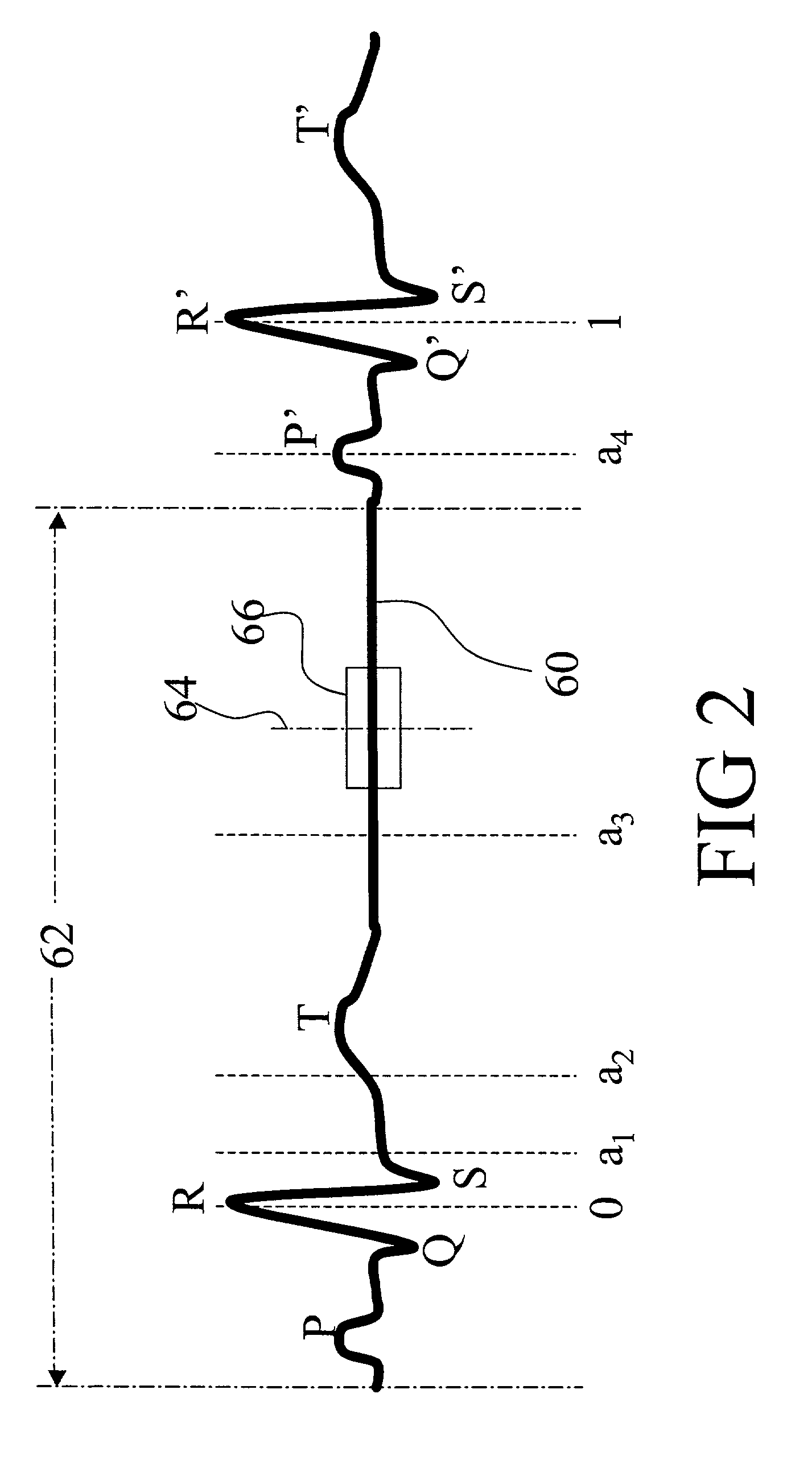
Dynamic computed tomography imaging using positional state modeling
InactiveUS7058440B2Improves temporalImprove spatial resolutionElectrocardiographyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData segmentData set
An apparatus for computed tomography (CT) imaging of a cyclically moving organ includes a positional state monitor (24, 40) that monitors a positional state of the cyclically moving organ such as the heart. A cone-beam CT scanner (10) acquires image data at least within a plurality of time windows. Each time window is centered about an occurrence of a selected positional state of the organ. A window analyzer (38) selects a data segment within each time window such that the data segments combine to form a complete data set covering a selected angular range. A reconstruction processor (44) reconstructs the selected data segments into an image representation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method of and system for intravenous volume tomographic digital angiography imaging
InactiveUS6075836AQuality improvementEfficient contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersData acquisition
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
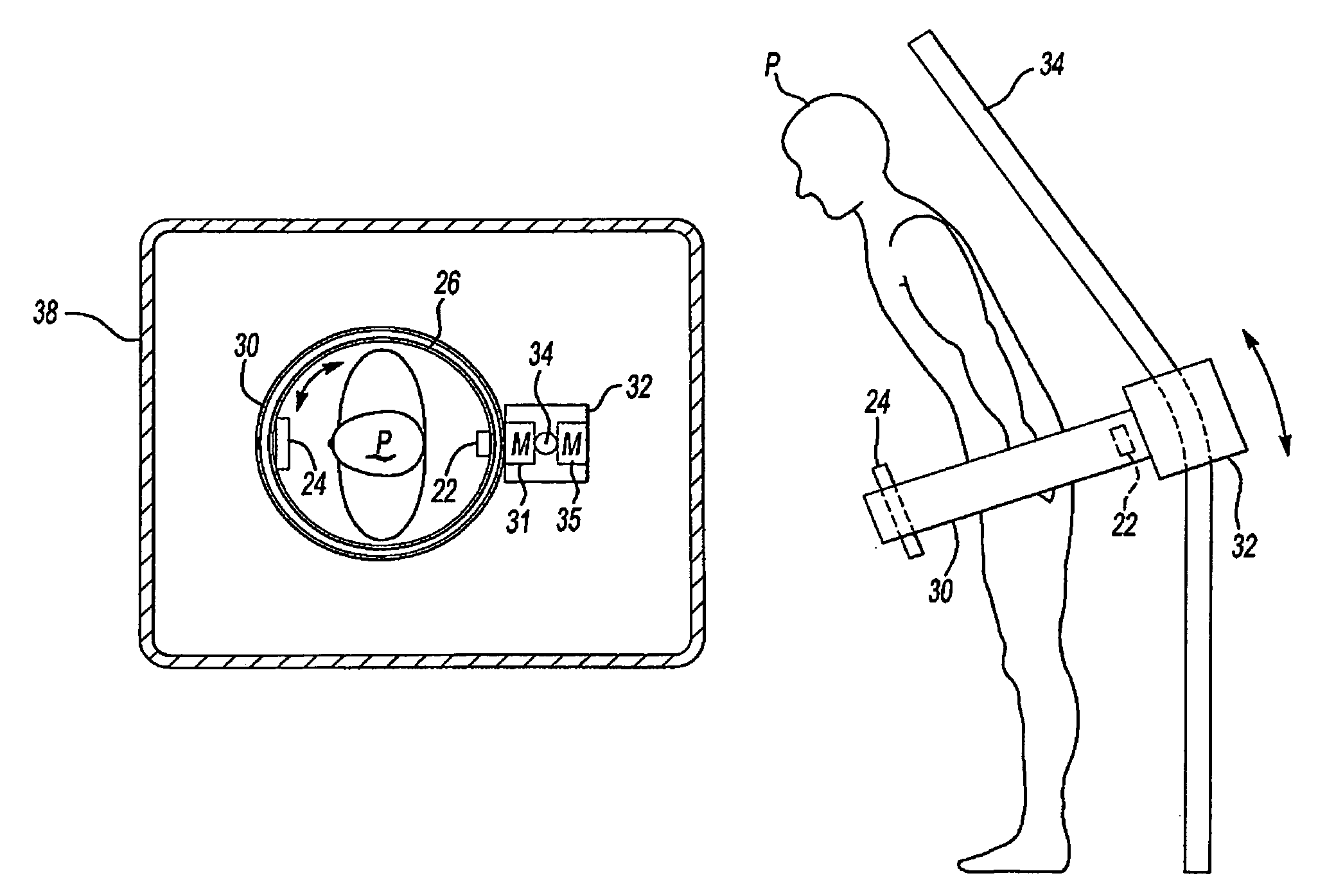
CT extremity scanner
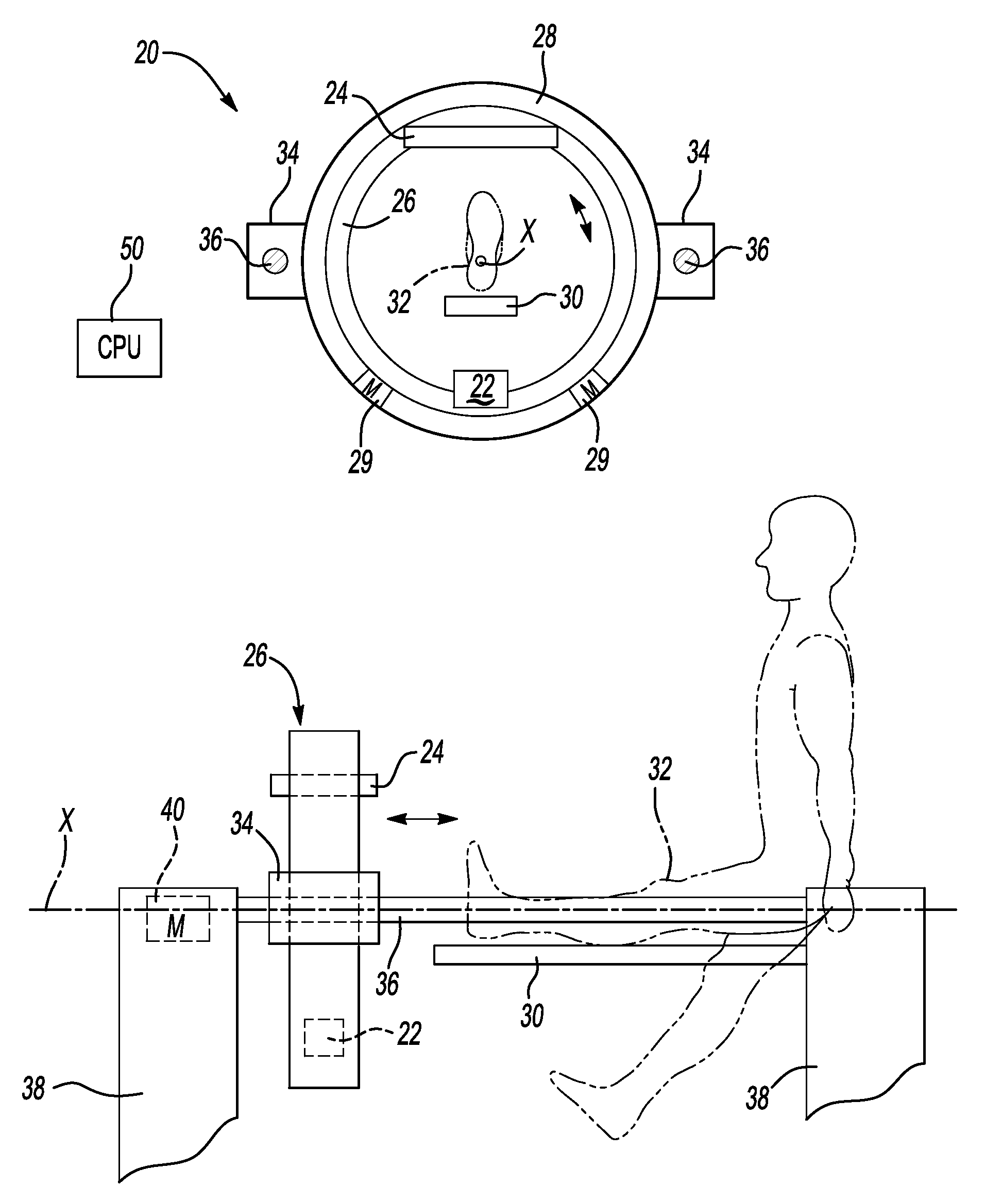
ActiveUS7388941B2Easy to useRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsHelical scanCt scanners
A CT scanner according to the present invention is particularly adapted for scanning the extremities of a patient. The CT scanner includes an x-ray source and x-ray detector mounted for rotation and translation along an axis parallel to a table for supporting the patient's extremity. The source and detector are mounted opposite one another on an inner circumference of an inner ring. The inner ring is rotatable about the axis within an outer ring mounted on at least one carriage. The carriage is movable parallel to the axis. During scanning, the inner ring rotates within the outer ring while the rings and carriage move along the axis, thereby producing a helical scan of the extremity.
Owner:XORAN TECH
Cone beam volume CT angiography imaging system and method
InactiveUS6298110B1Quality improvementEfficient contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersX-ray
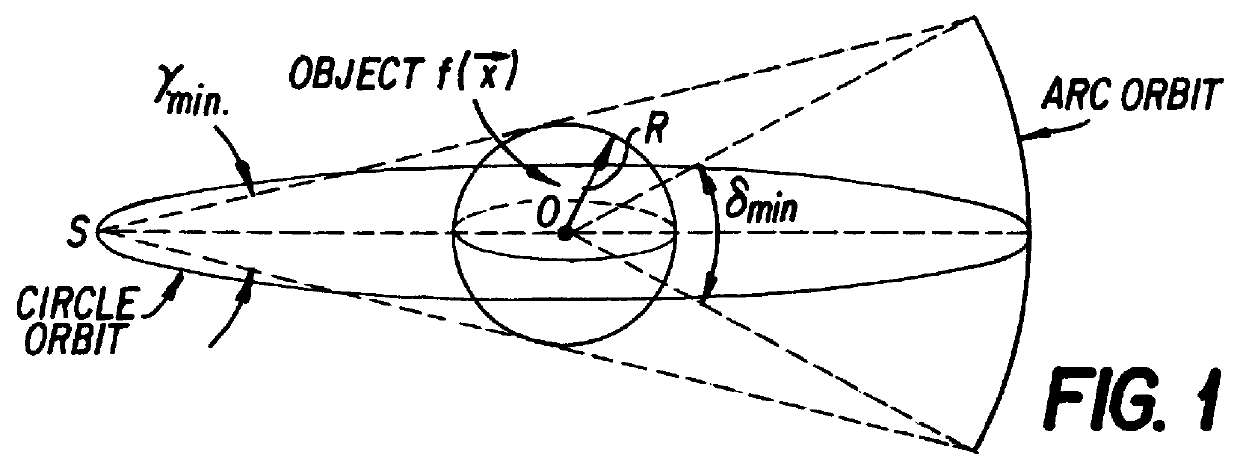
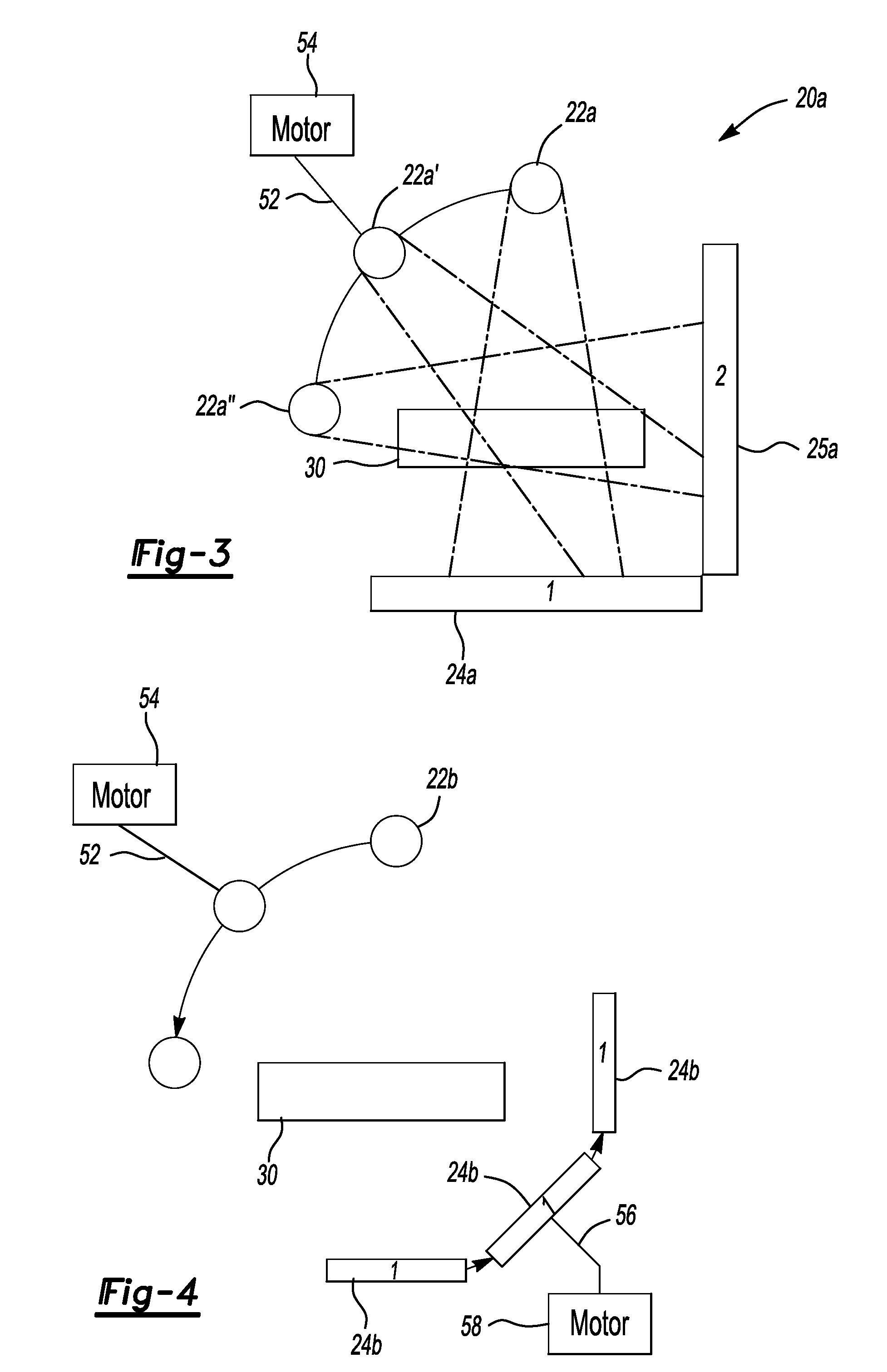
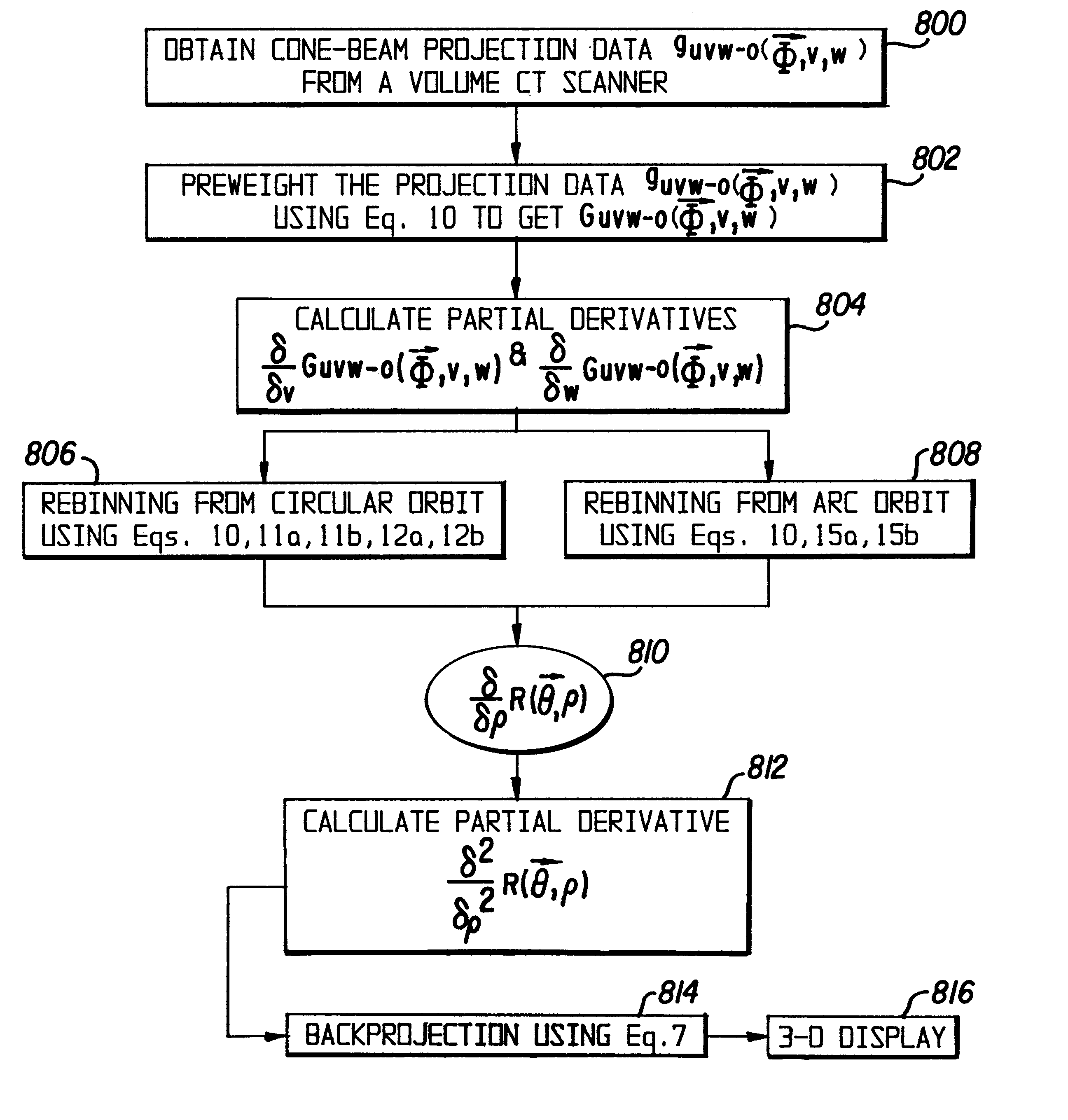
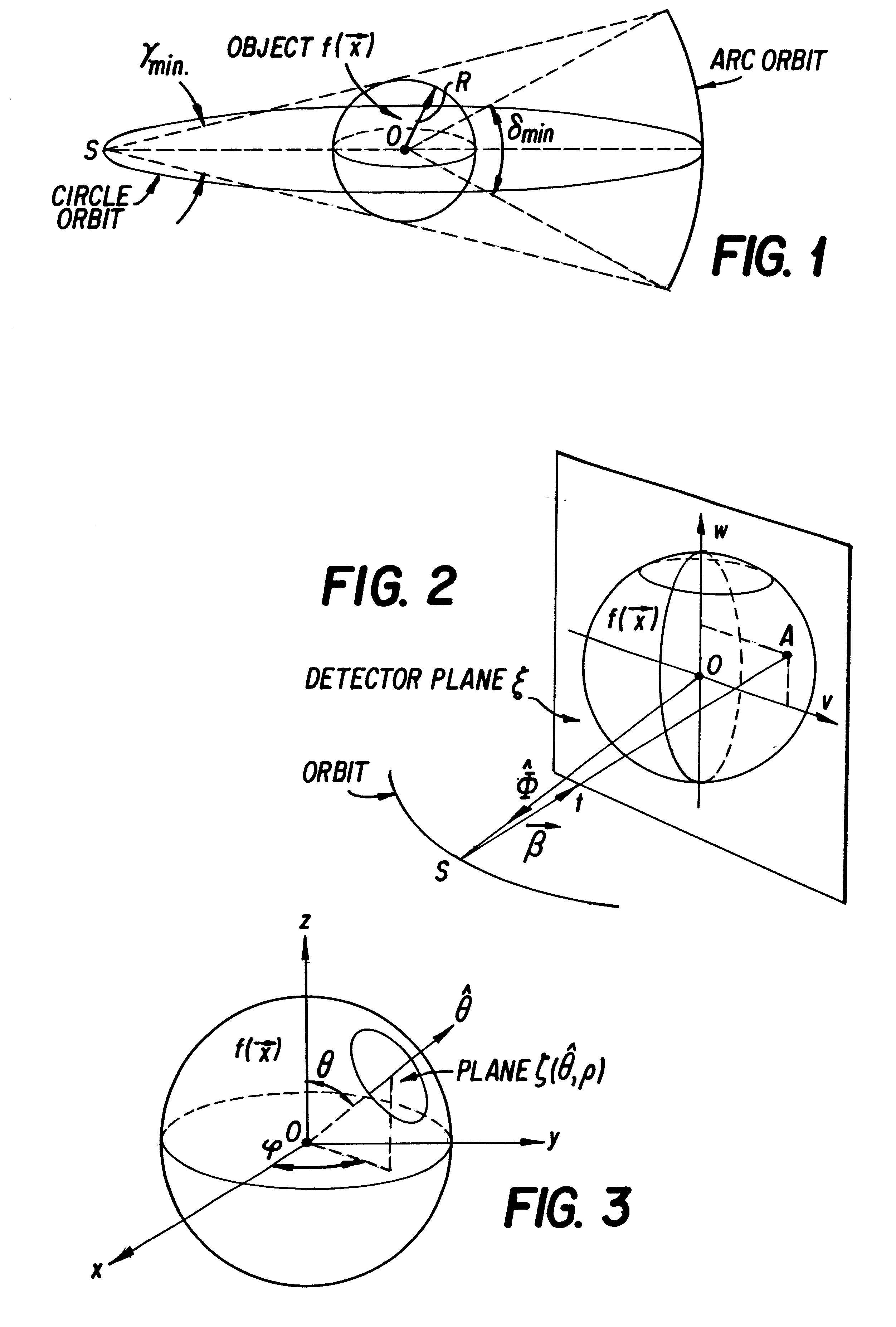
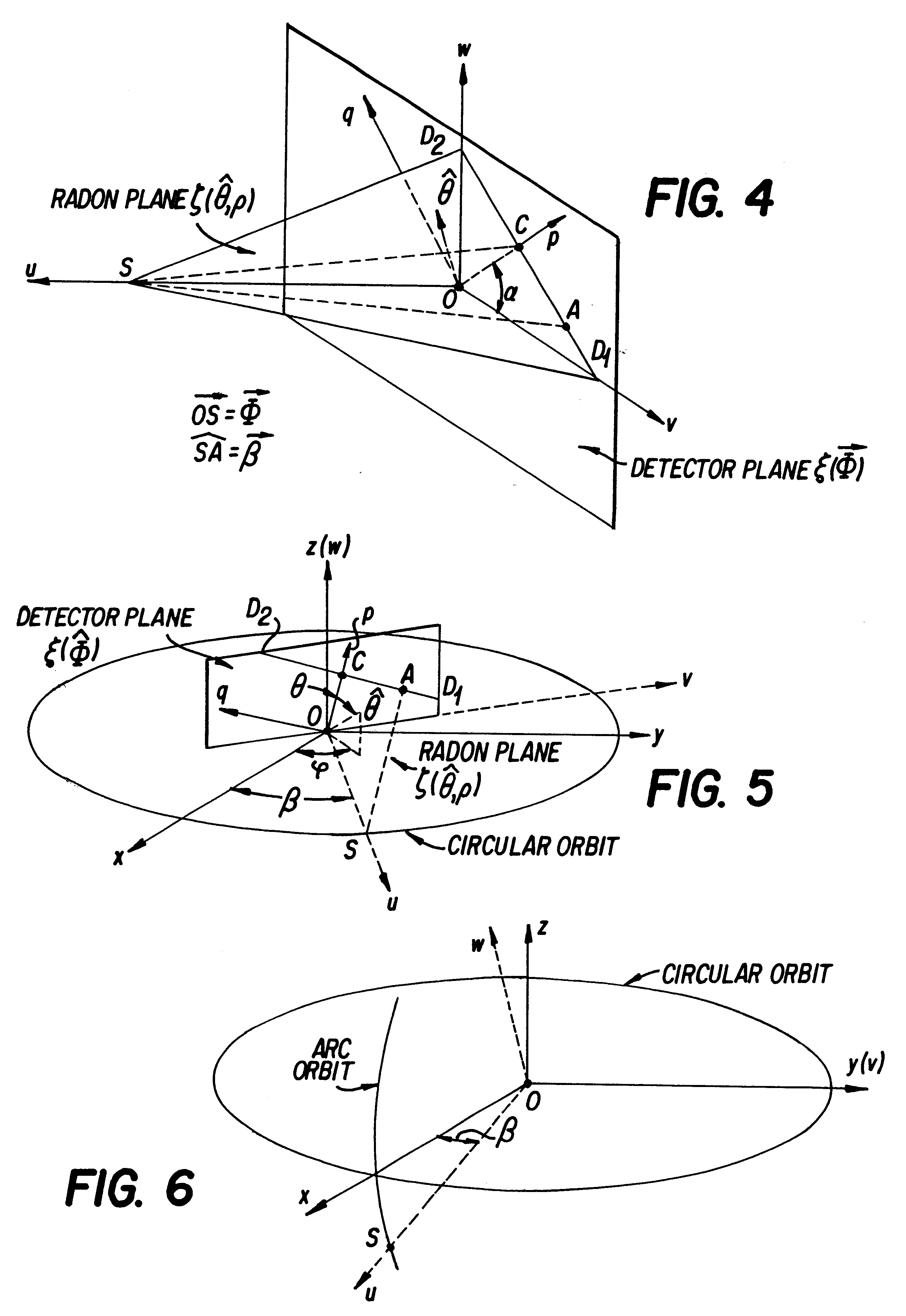
Only a single IV contrast injection with a short breathhold by the patient is needed for use with a volume CT scanner which uses a cone-beam x-ray source and a 2-D detector for fast volume scanning in order to provide true 3-D descriptions of vascular anatomy with more than 0.5 lp / mm isotropic resolution in the x, y and z directions is utilized in which one set of cone-beam projections is acquired while rotating the x-ray tube and detector on the CT gantry and then another set of projections is acquired while tilting the gantry by a small angle. The projection data is preweighted, partial derivatives are calculated and rebinned for both the circular orbit and arc orbit data The second partial derivative is then calculated and then the reconstructed 3-D images are obtained by backprojecting using the inverse Radon transform.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
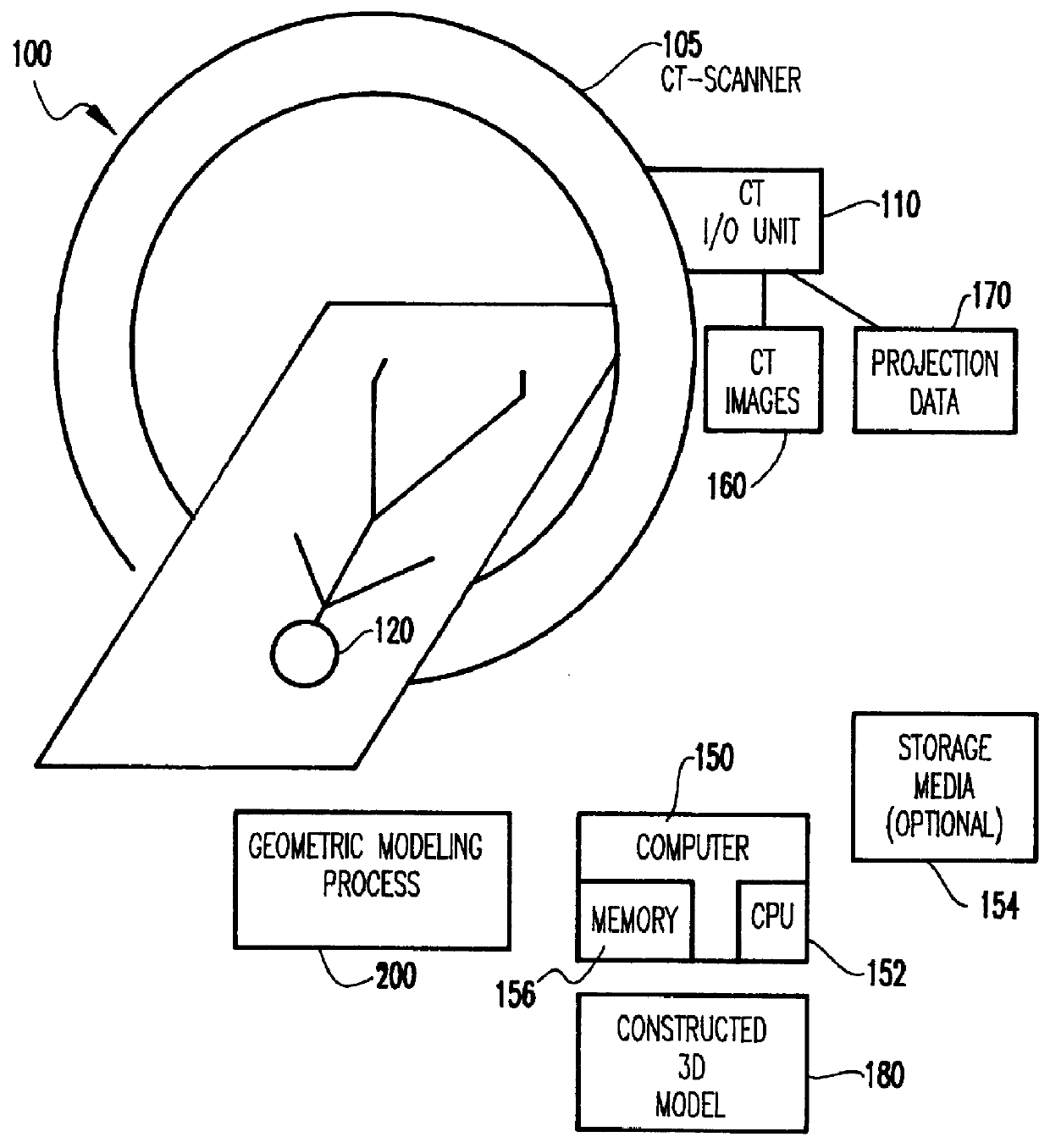
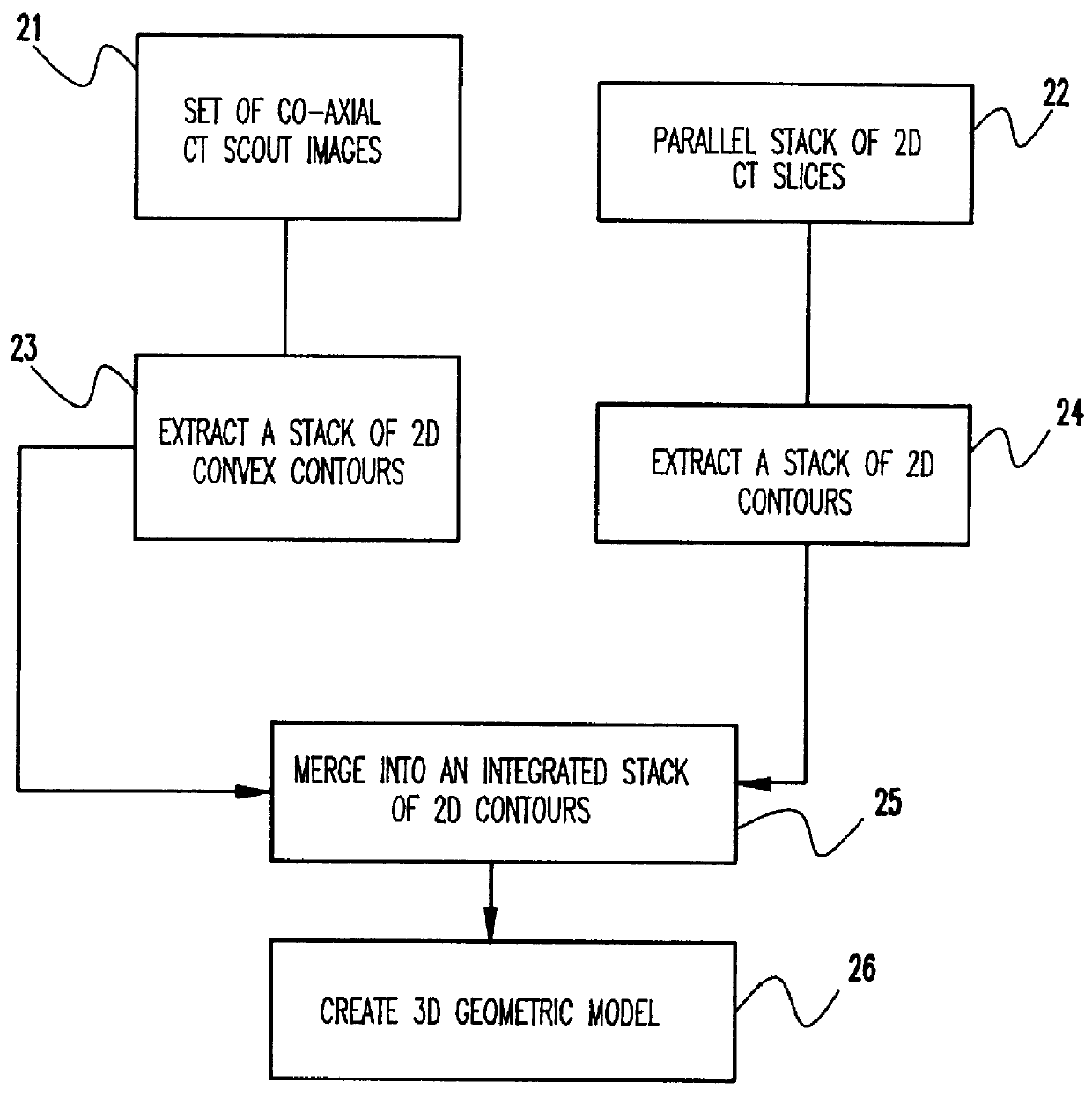
System and method for three-dimensional geometric modeling by extracting and merging two-dimensional contours from CT slice data and CT scout data
InactiveUS6028907AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersGeometric modeling
A computer system and method solve the problem of getting a useful three-dimensional representation of an object like the spine using a small amount of data. This is done by gathering three-dimensional data in the form of a set of 2D computer tomography (CT) slices of a patient's bones and a coaxial set of 2D CT scout images, which are digital two-dimensional X-ray images that can be produced by a CT scanner; extracting from each of these three-dimensional data sets a corresponding stack of 2D contours; and constructing a 3D geometric model of the object. The main features of spinal deformation are captured by integrating these two sets of three-dimensional data, and constructing from them a three-dimensional geometric model of the spine. Scouts are usually used to monitor CT scan acquisition. Here, they are also used as an essential source of data.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
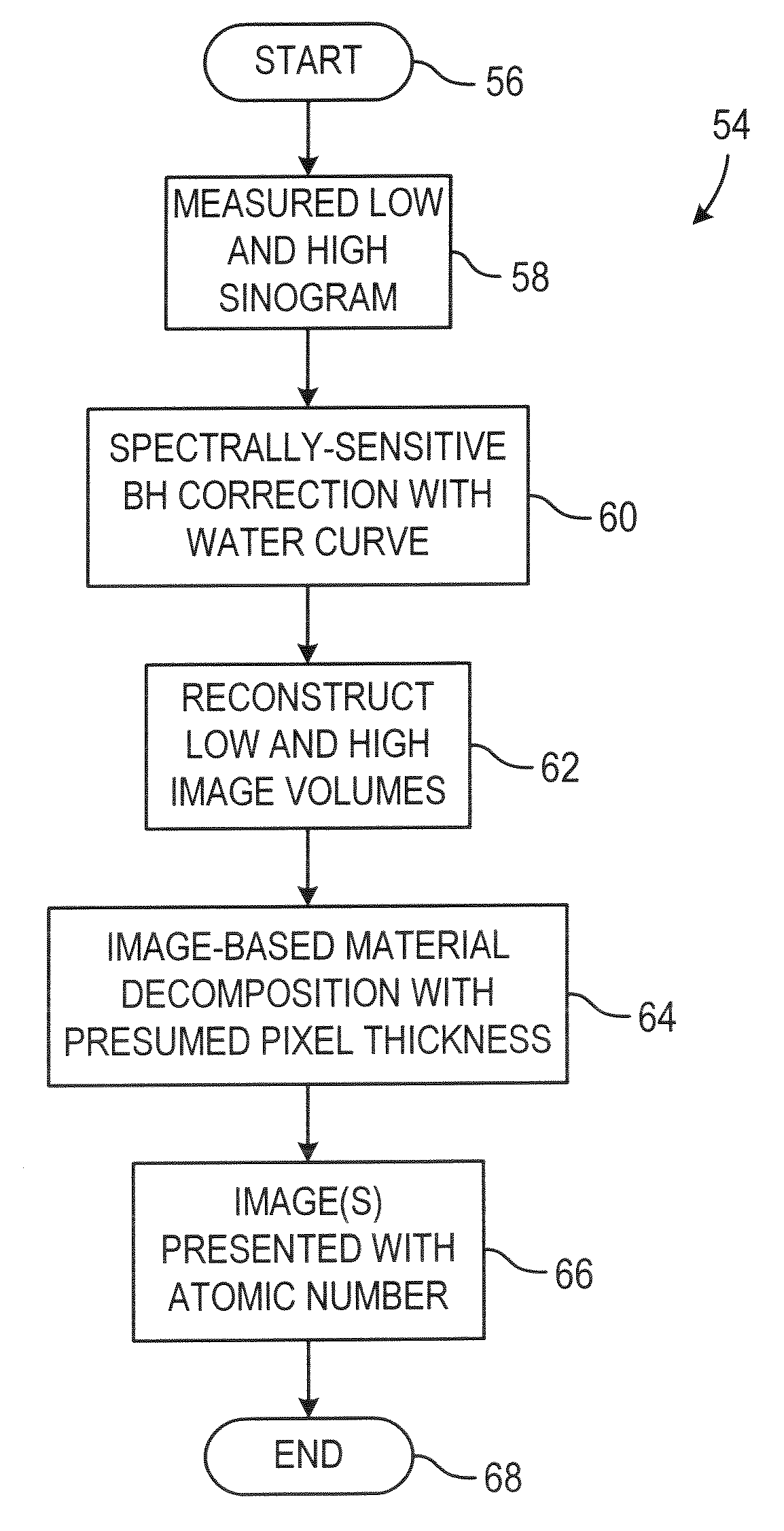
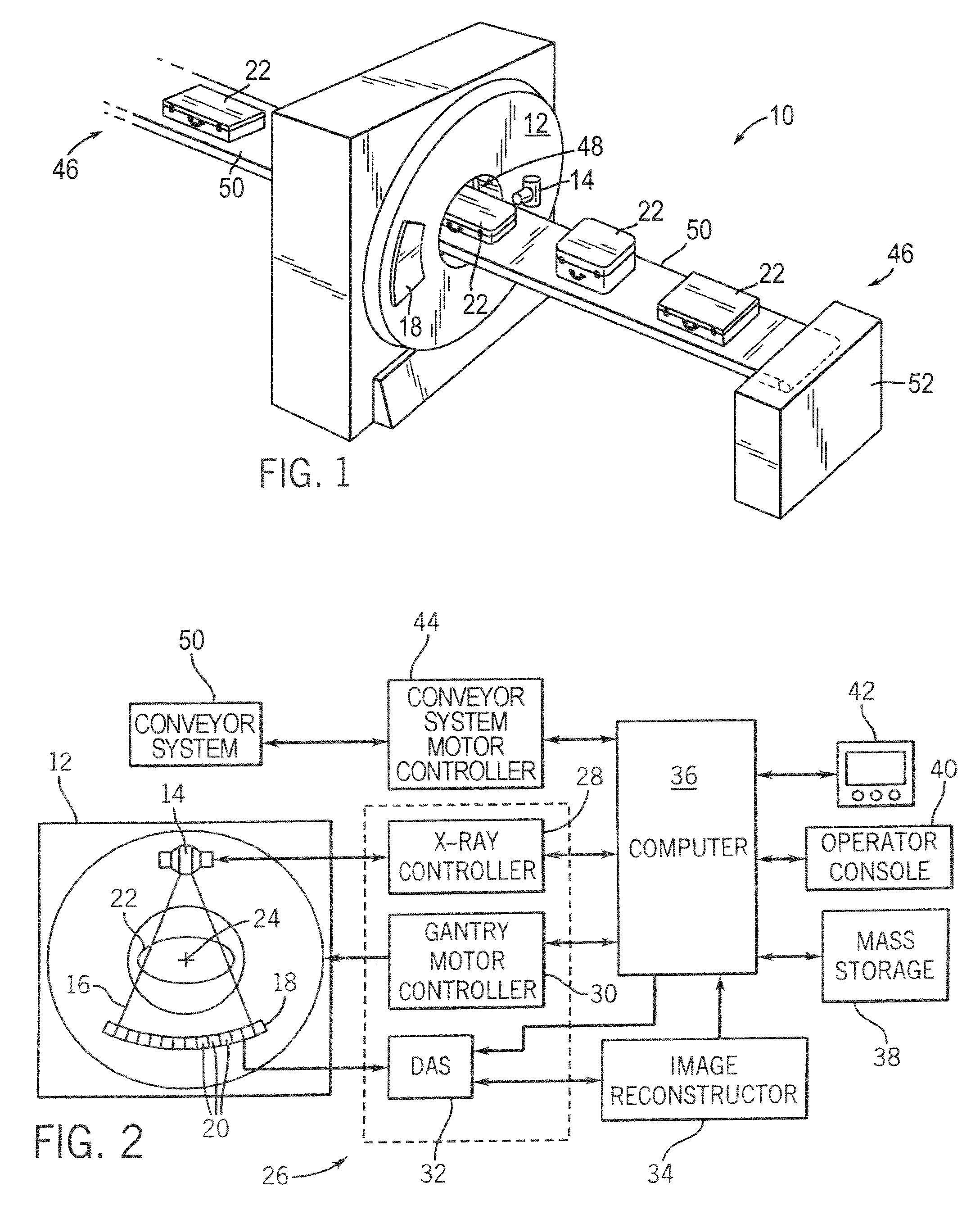
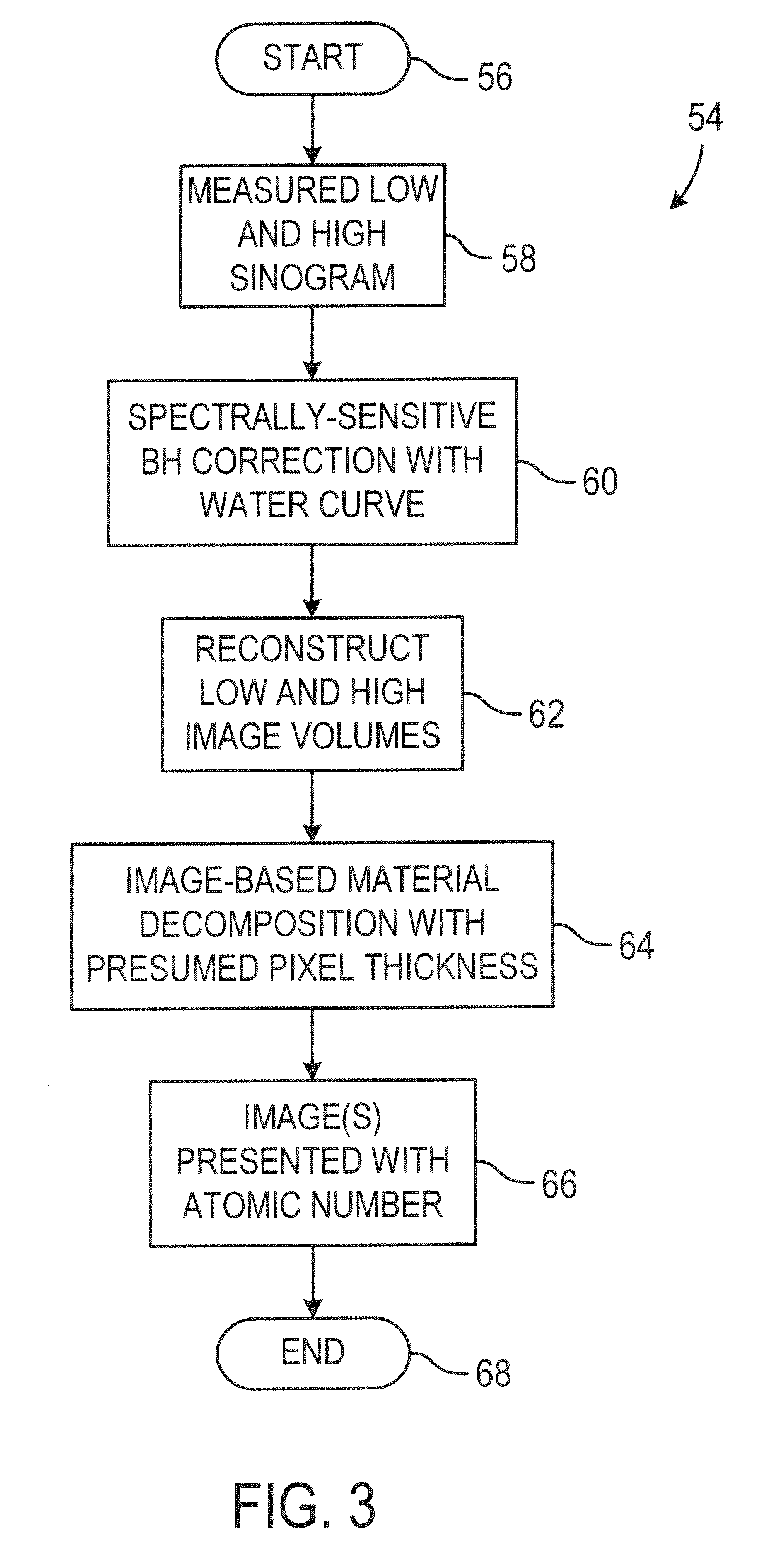
Image-based material decomposition
ActiveUS7298812B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam Hardening ArtifactCt scanners
A CT scanner acquires CT images at different energy levels and registers those images to provide a composite image that is substantially free of beam hardening artifacts and conspicuously provides atomic information of that imaged.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
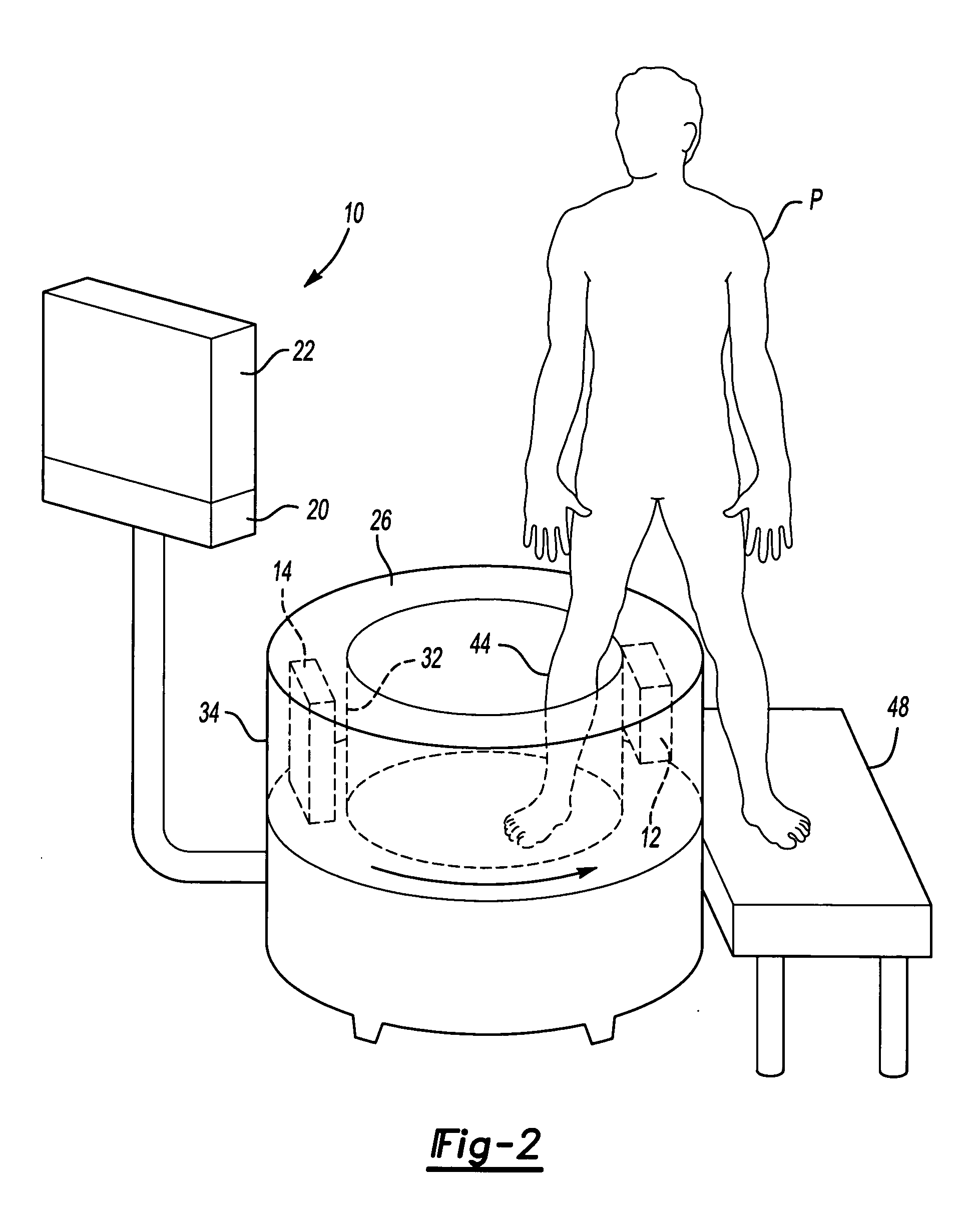
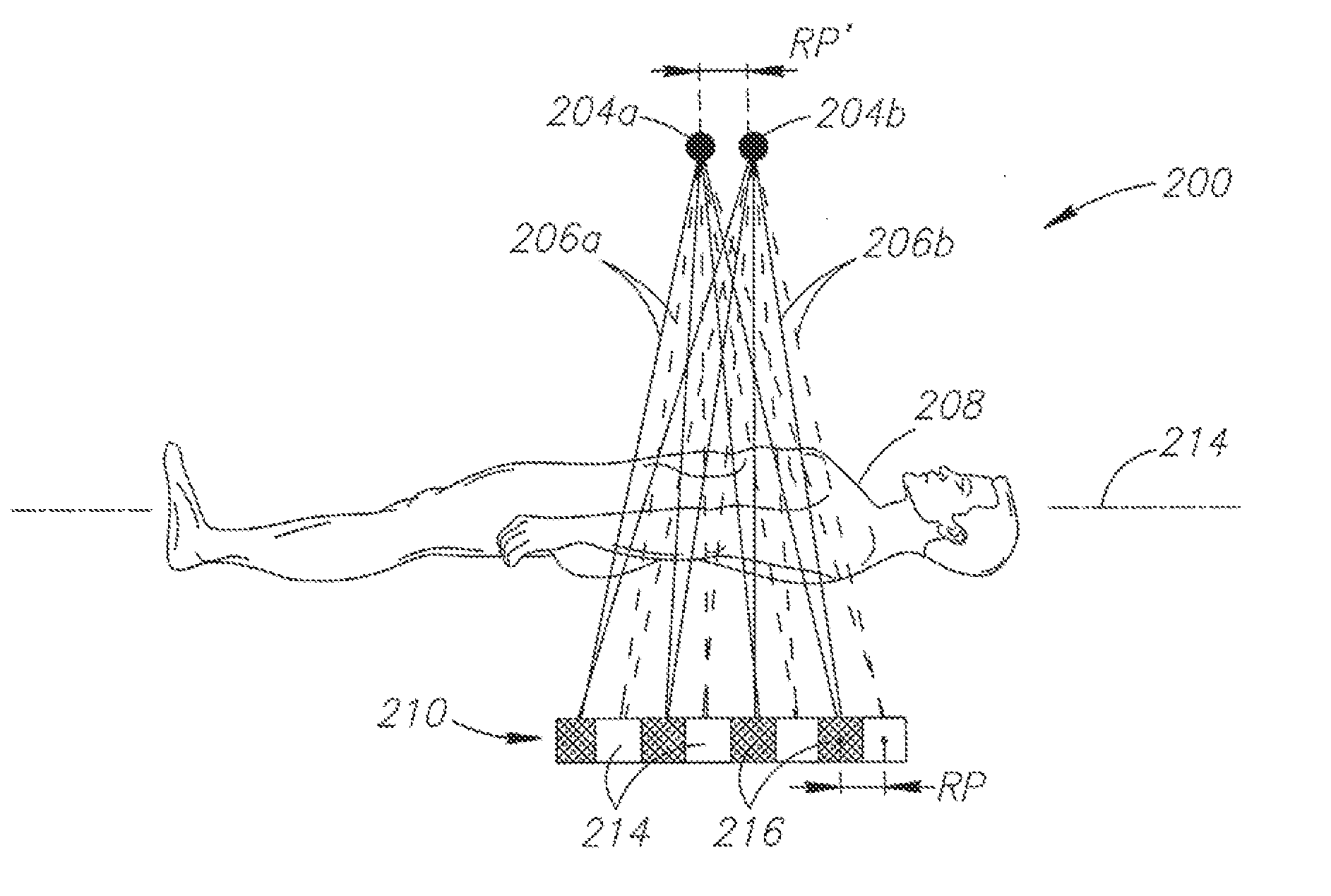
Large bore pet and hybrid pet/ct scanners and radiation therapy planning using same
ActiveUS20100040197A1Quick responseReduced radially inward extentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPatient positioning for diagnosticsLines of responseRadiation planning
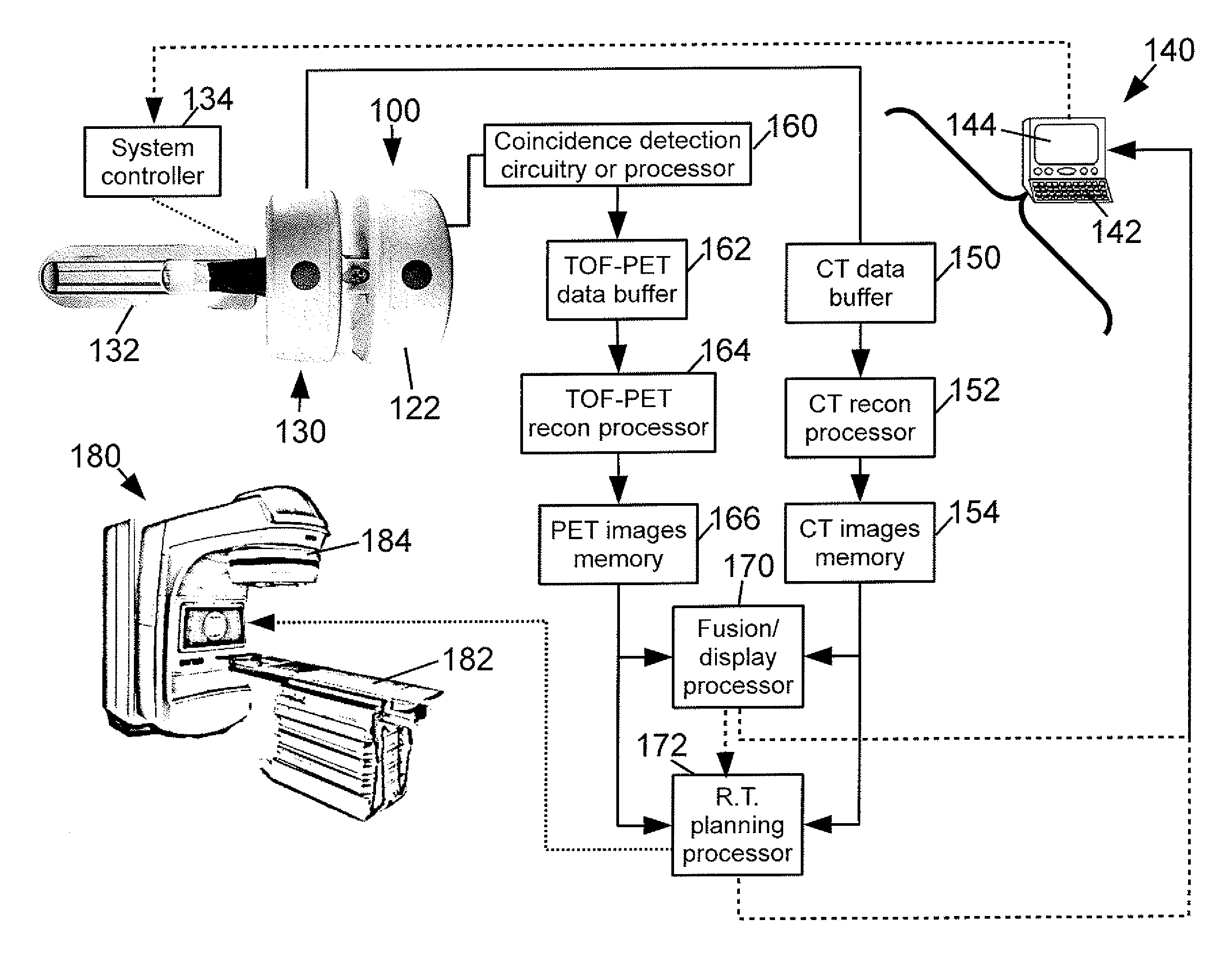
An imaging system comprises: a ring of positron emission tomography (PET) detectors; a PET housing at least partially surrounding the ring of PET detectors and defining a patient aperture of at least 80 cm; a coincidence detection processor or circuitry configured to identify substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events corresponding to electron-positron annihilation events; and a PET reconstruction processor configured to reconstruct into a PET image the identified substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events based on lines of response defined by the substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events. Radiation planning utilizing such an imaging system comprises: acquiring PET imaging data for a human subject arranged in a radiation therapy position requiring a patient aperture of at least about 80 cm; reconstructing said imaging data into a PET image encompassing an anatomical region to undergo radiation therapy; and generating a radiation therapy plan based on at least the PET image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for acquiring PET and CT images
InactiveUS7603165B2Easy to correctAccurate scatter correctionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingDiagnostic Radiology ModalityData set
A combined PET and X-Ray CT tomograph for acquiring CT and PET images sequentially in a single device, overcoming alignment problems due to internal organ movement, variations in scanner bed profile, and positioning of the patient for the scan. In order to achieve good signal-to-noise (SNR) for imaging any region of the body, an improvement to both the CT-based attenuation correction procedure and the uniformity of the noise structure in the PET emission scan is provided. The PET / CT scanner includes an X-ray CT and two arrays of PET detectors mounted on a single support within the same gantry, and rotate the support to acquire a full projection data set for both imaging modalities. The tomograph acquires functional and anatomical images which are accurately co-registered, without the use of external markers or internal landmarks.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Apparatus and method for tracking feature's position in human body
ActiveUS20090257551A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHuman bodyFluoroscopic image
A CT scanner for scanning a subject is provided, the scanner comprising: a gantry capable of rotating about a scanned subject; at least two cone beam X-Ray sources displaced from each other mounted on said gantry; at least one 2D detector array mounted on said gantry, said detector is capable of receiving radiation emitted by said at least two X-Ray sources and attenuated by the subject to be scanned; a first image processor capable of generating and displaying CT images of a volume within the subject; a second image processor capable of generating projection X-Ray images of said volume, wherein the images are responsive to X-Ray separately emitted by each of said at least two cone beam X-Ray sources; and a third image processor capable of generating and displaying fluoroscopic images composed of said projection X-Ray images, wherein said fluoroscopic images are spatially registered to said CT images.
Owner:ARINETA
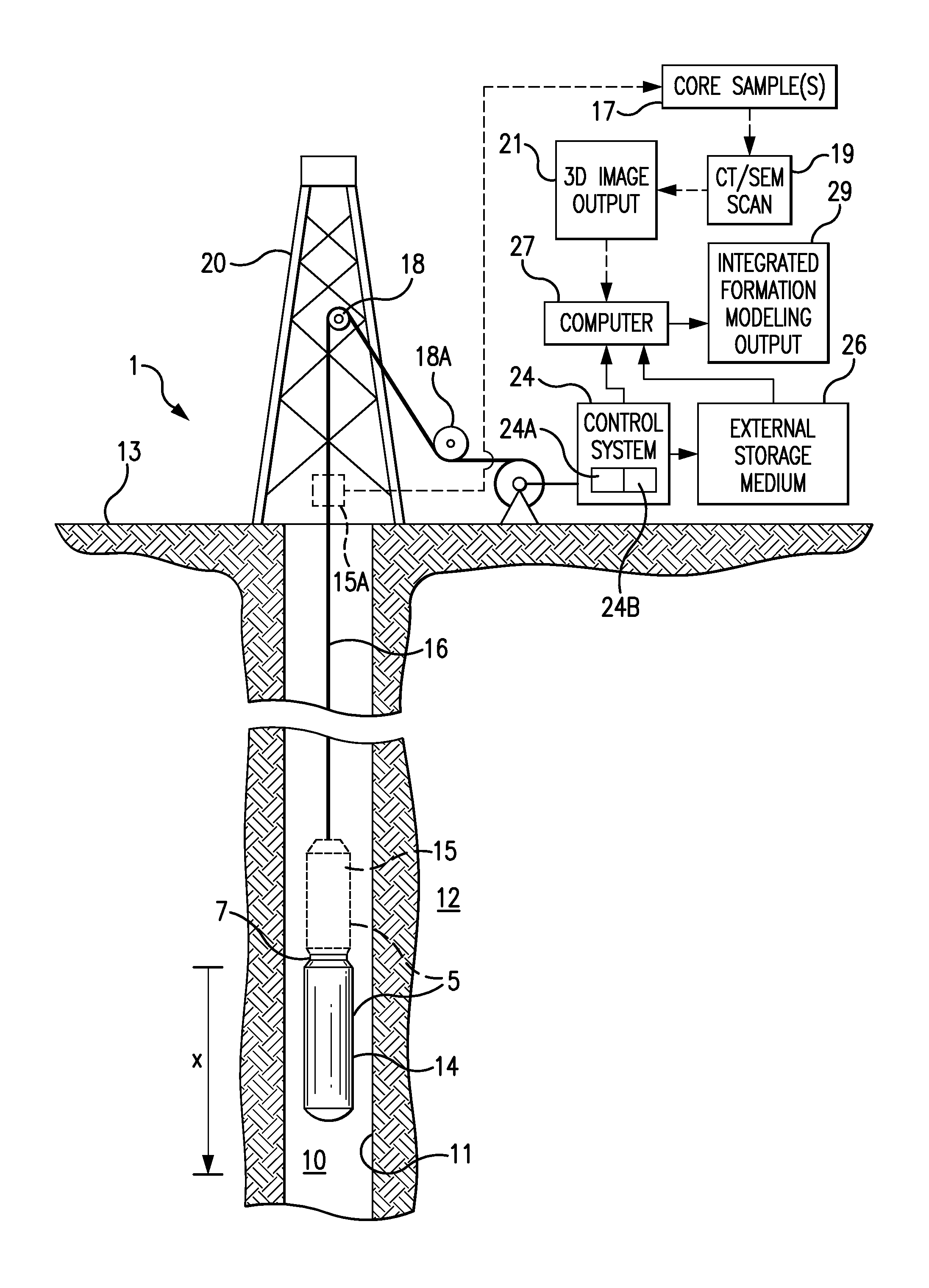
Method and system for integrating logging tool data and digital rock physics to estimate rock formation properties
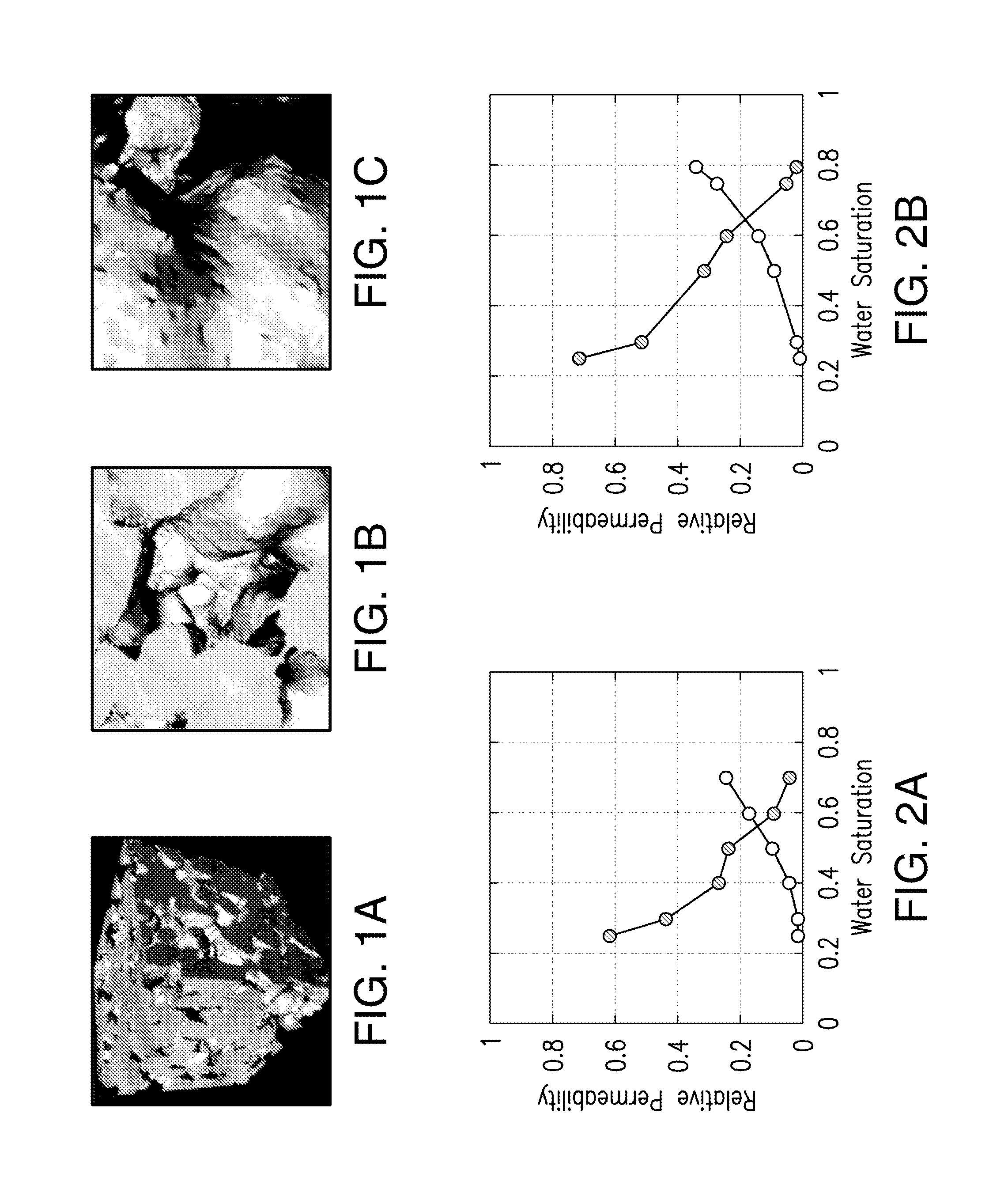
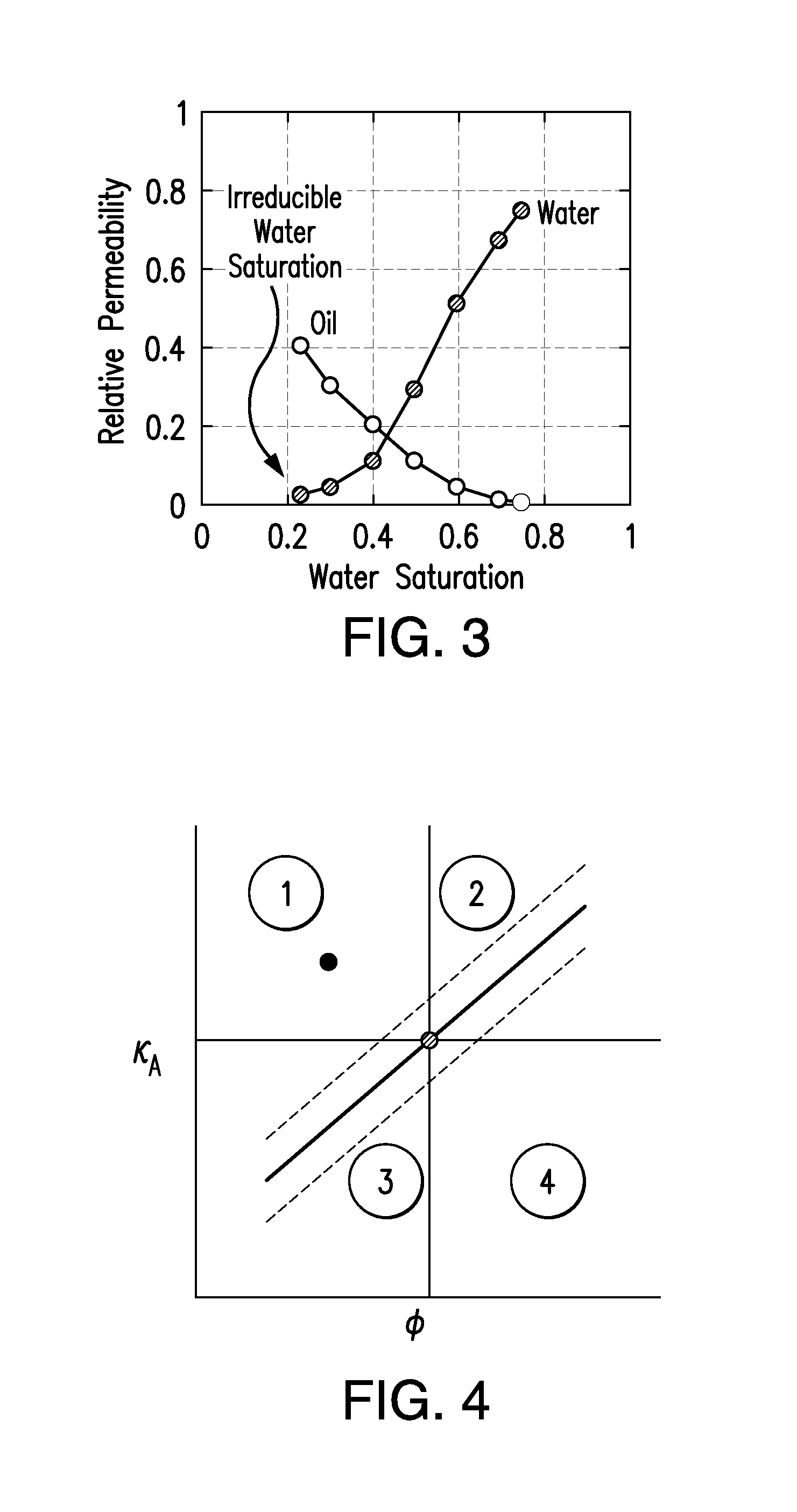
ActiveUS9507047B1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationNuclear radiation detectionPorosityCt scanners
The present invention relates to a method and system for integrating logging tool data and digital rock physics to estimate rock formation properties. A rock sample from a logging tool such as a sidewall plug or large enough cutting can be extracted by the logging tool at approximately the same well bore location that the logging tool measures fluid properties. The rock samples thus obtained is scanned using a CT scanner, scanning electron microscope or other suitable scanning device. The resulting scanned rock image can be segmented and rock properties comprising porosity, absolute permeability, relative permeability, capillary pressure and other relevant rock properties are calculated. The resulting digital calculations are integrated with logging tool data and rock property estimates to improve the accuracy and timeliness of the logging tool data.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
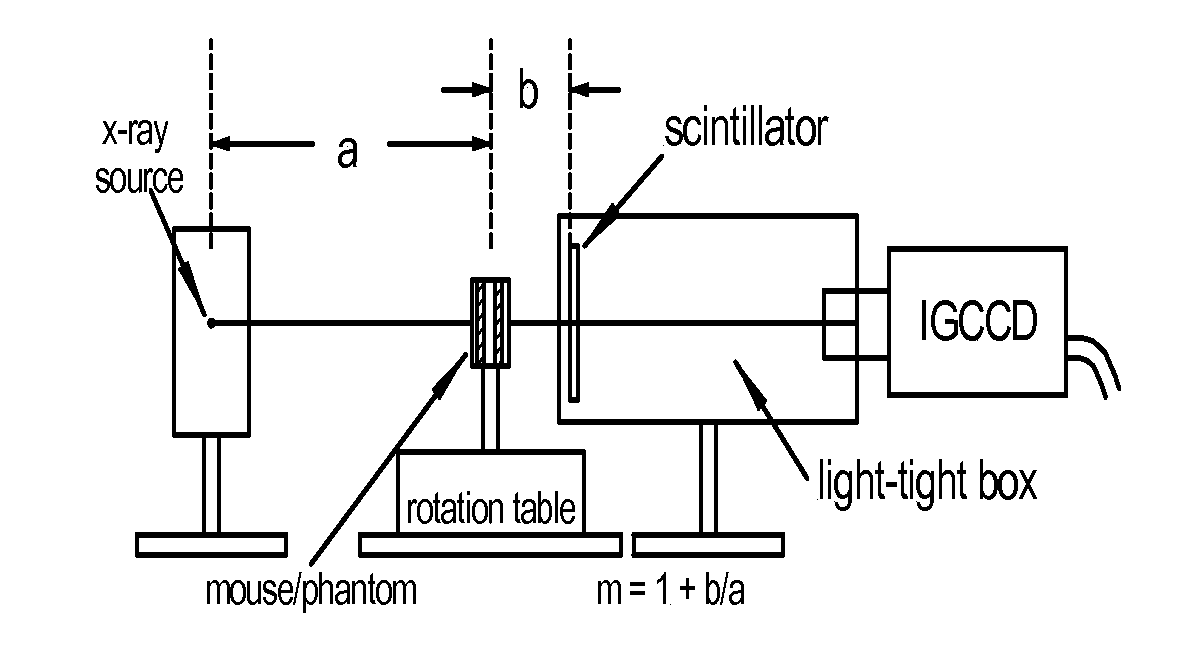
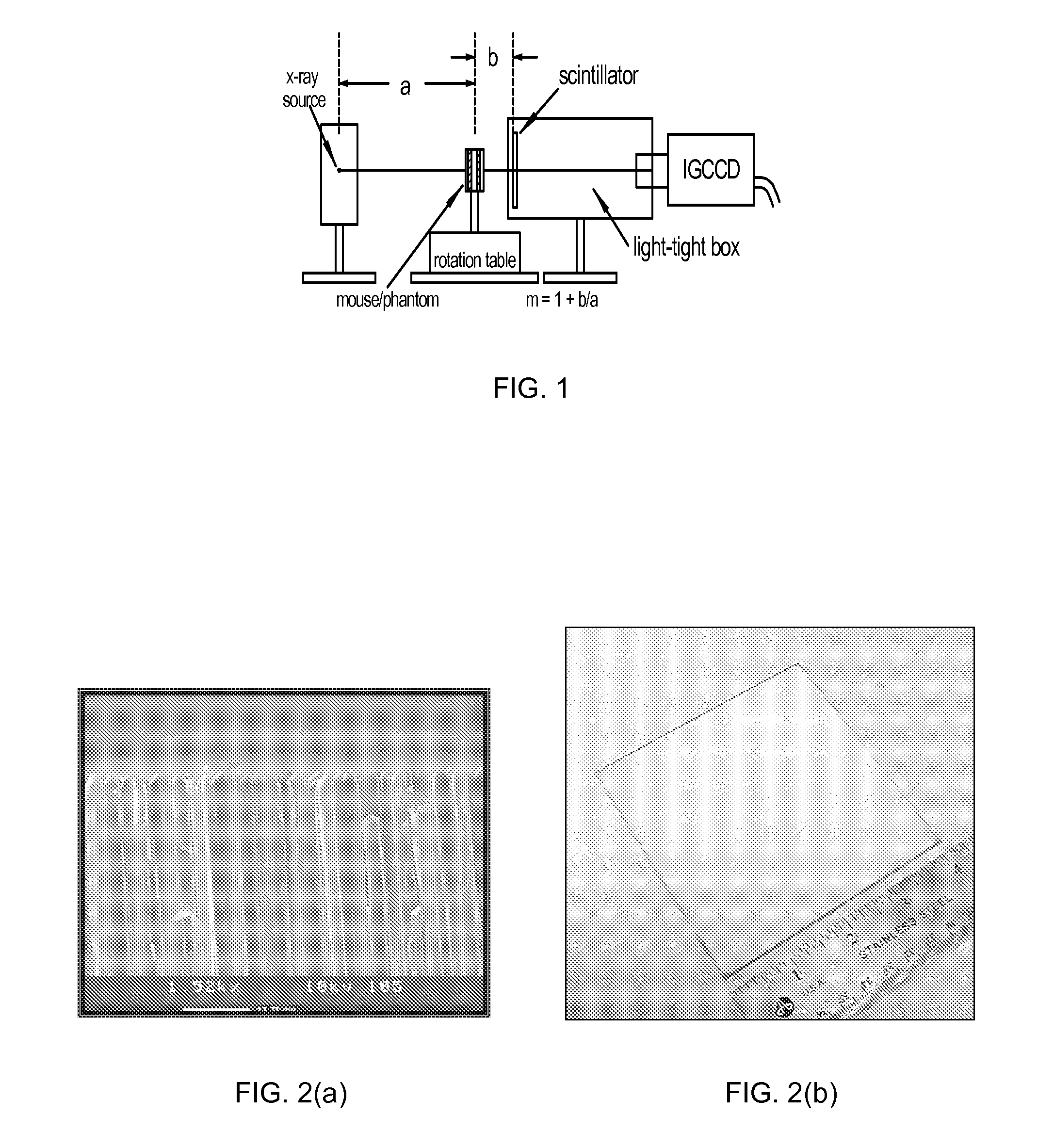
Micro CT scanners incorporating internal gain charge-coupled devices
ActiveUS7352840B1Improve rendering capabilitiesTake advantageTelevision system detailsRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersEngineering
The present invention provides internal gain charge coupled devices (CCD) and CT scanners that incorporate an internal gain CCD. A combined positron emission tomography and CT scanner is also provided.
Owner:RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES
Folded array CT baggage scanner
A reduced size CT scanner for baggage inspection has a wide angle x-ray source and multiple sets of detectors at different distances from the x-ray source. The detectors in each set are sized and positioned to maintain consistent pitch and flux levels among all detectors. Conventional reconstruction processes can be used to process the data from the CT scanner. The scanner may also be incorporated into a check-in desk in a network of scanners.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING TECH
Unified workstation for virtual craniofacial diagnosis, treatment planning and therapeutics
An integrated system is described in which digital image data of a patient, obtained from a variety of image sources, including CT scanner, X-Ray, 2D or 3D scanners and color photographs, are combined into a common coordinate system to create a virtual three-dimensional patient model. Software tools are provided for manipulating the virtual patient model to simulation changes in position or orientation of craniofacial structures (e.g., jaw or teeth) and simulate their affect on the appearance of the patient. The simulation (which may be pure simulations or may be so-called “morphing” type simulations) enables a comprehensive approach to planning treatment for the patient. In one embodiment, the treatment may encompass orthodontic treatment. Similarly, surgical treatment plans can be created. Data is extracted from the virtual patient model or simulations thereof for purposes of manufacture of customized therapeutic devices for any component of the craniofacial structures, e.g., orthodontic appliances.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
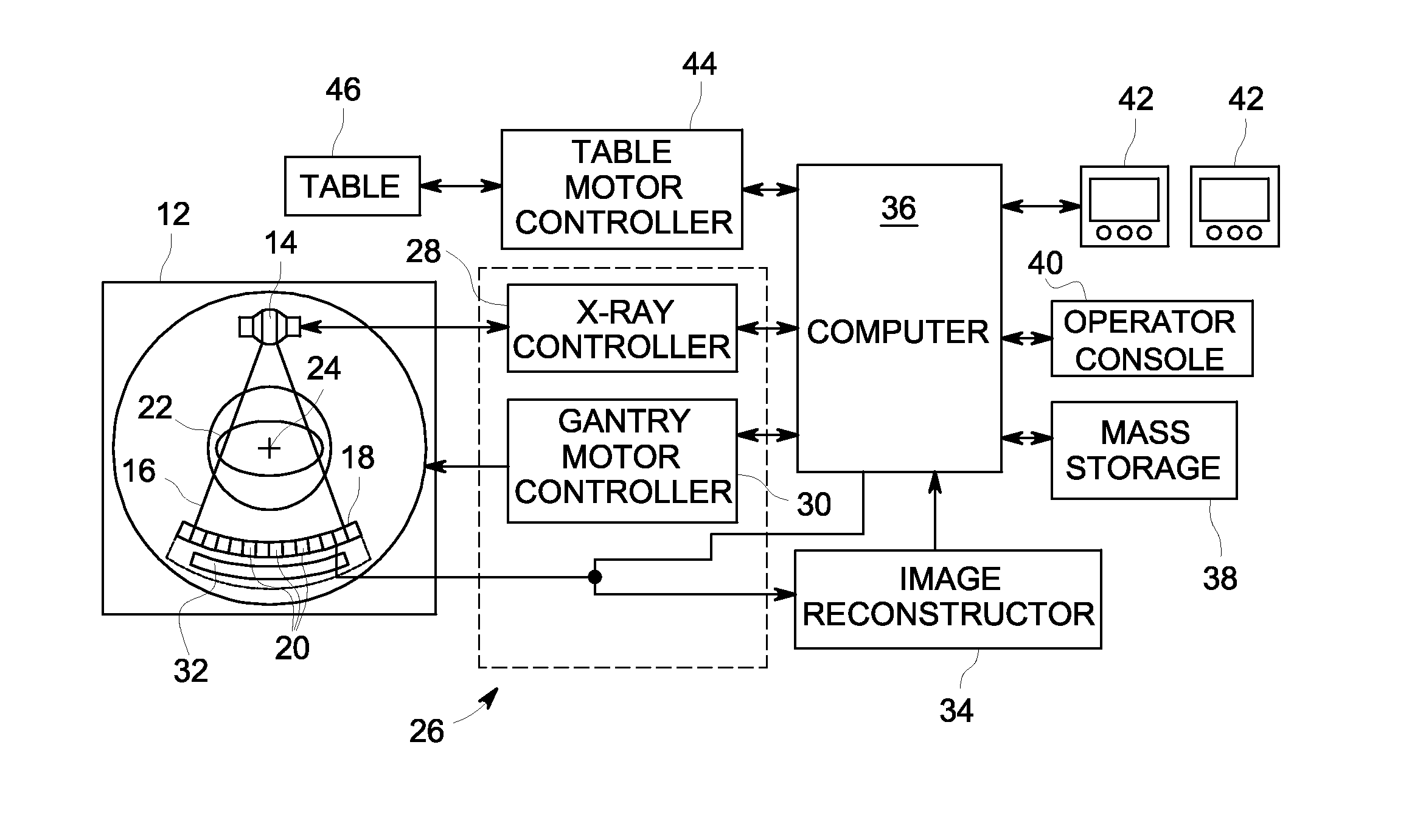
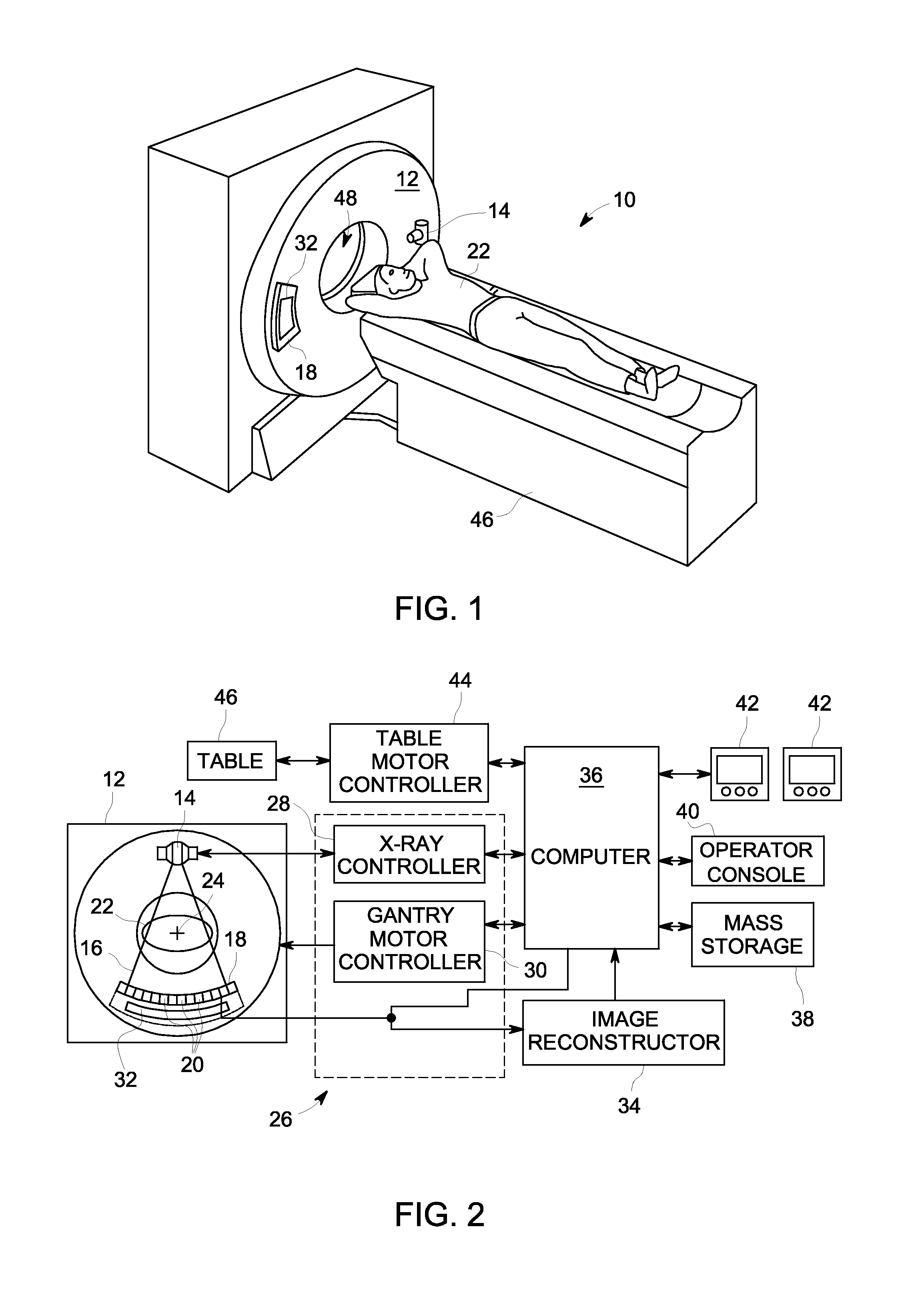
System and method for mounting x-ray tube in CT scanner
InactiveUS6519312B1Easy to liftEasy to handleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayCt scanners
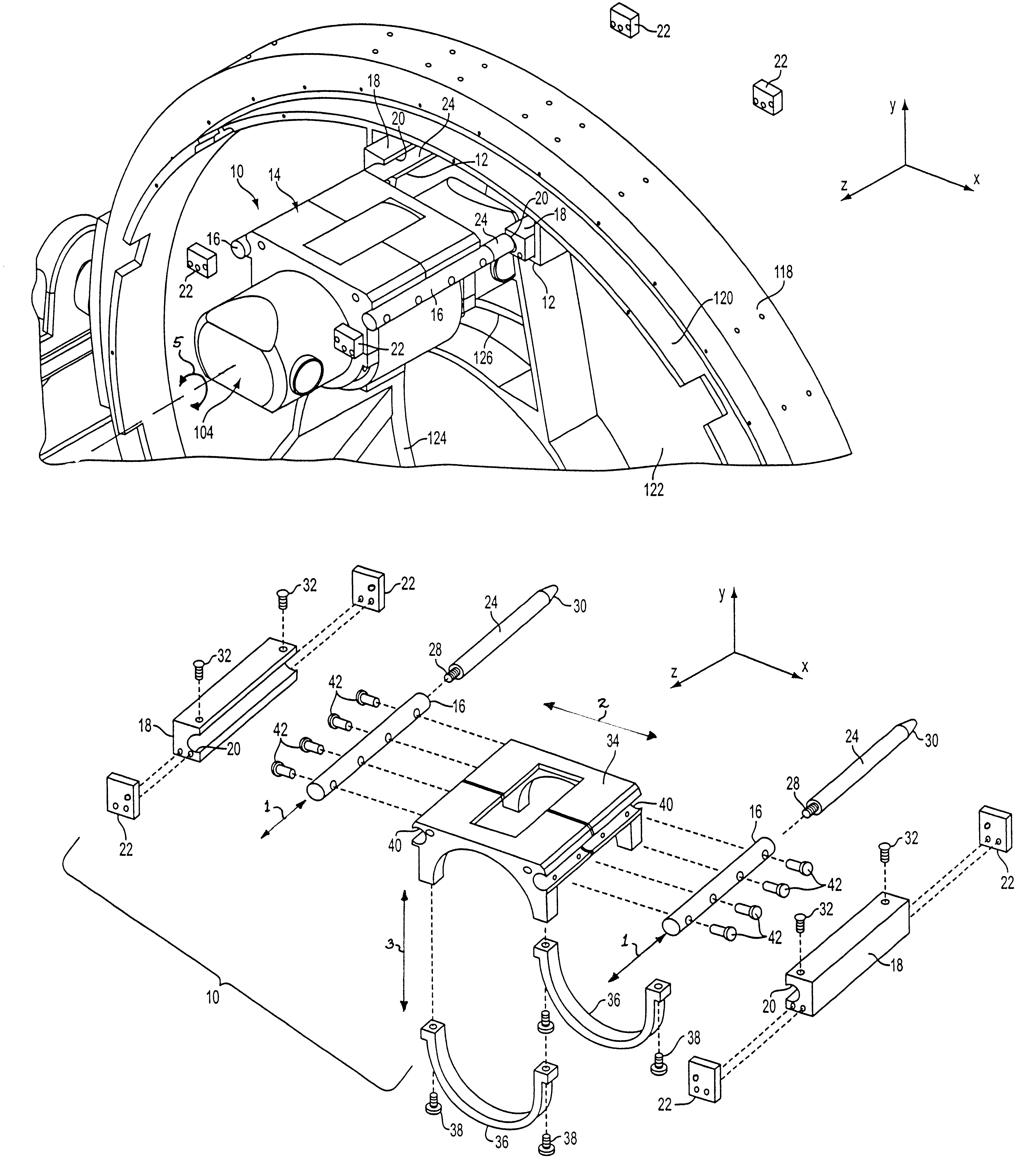
The present disclosure provides a system for mounting an x-ray tube to a gantry disk of a CT scanner. The system is designed to make lifting and handling a heavy and cumbersome x-ray tube easier for a person removing or replacing the x-ray tube in a CT scanner. The system includes a harness adapted to be secured to the x-ray tube, at least two elongated rods secured to the harness, and two elongated tracks adapted to be secured to the gantry disk such that the tracks extend generally parallel with a z-axis of the CT scanner. Each track includes a channel for slidingly receiving one of the rods. The present disclosure also provides a method of mounting an x-ray tube in a gantry of a CT scanner. The method includes securing a harness to the x-ray tube, securing elongated rods to the harness such that the rods extend parallel to an axis of the x-ray tube, attaching elongated guides to ends of the rods, inserting distal ends of the guides into channels of elongated tracks in the gantry of the x-ray scanner, and sliding the guides and the rods into the channels of the tracks. Then the guides are removed from the rods, and stops are secured to ends of the tracks to retain the rods within the channels.
Owner:ANLOGIC CORP (US)
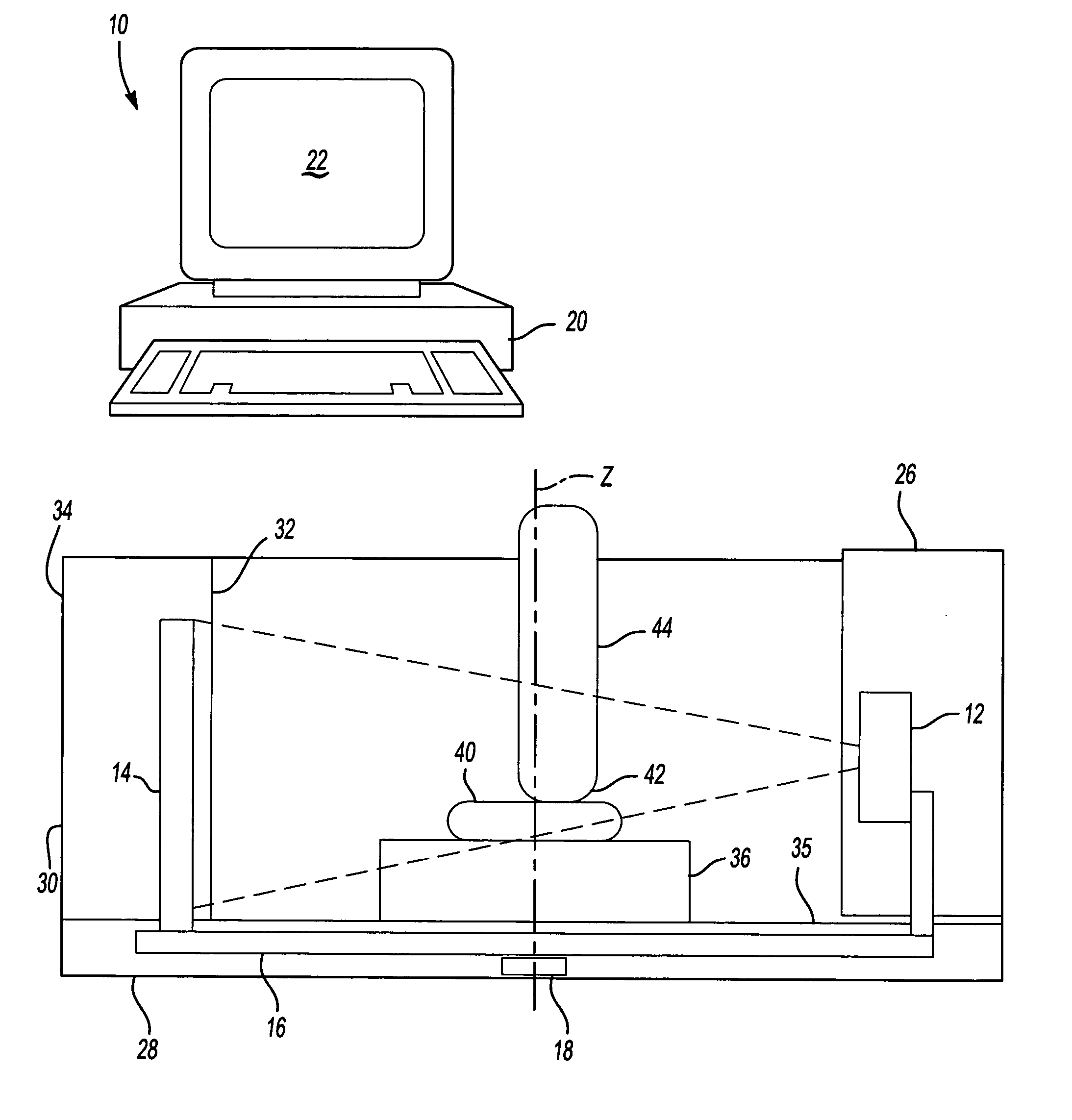
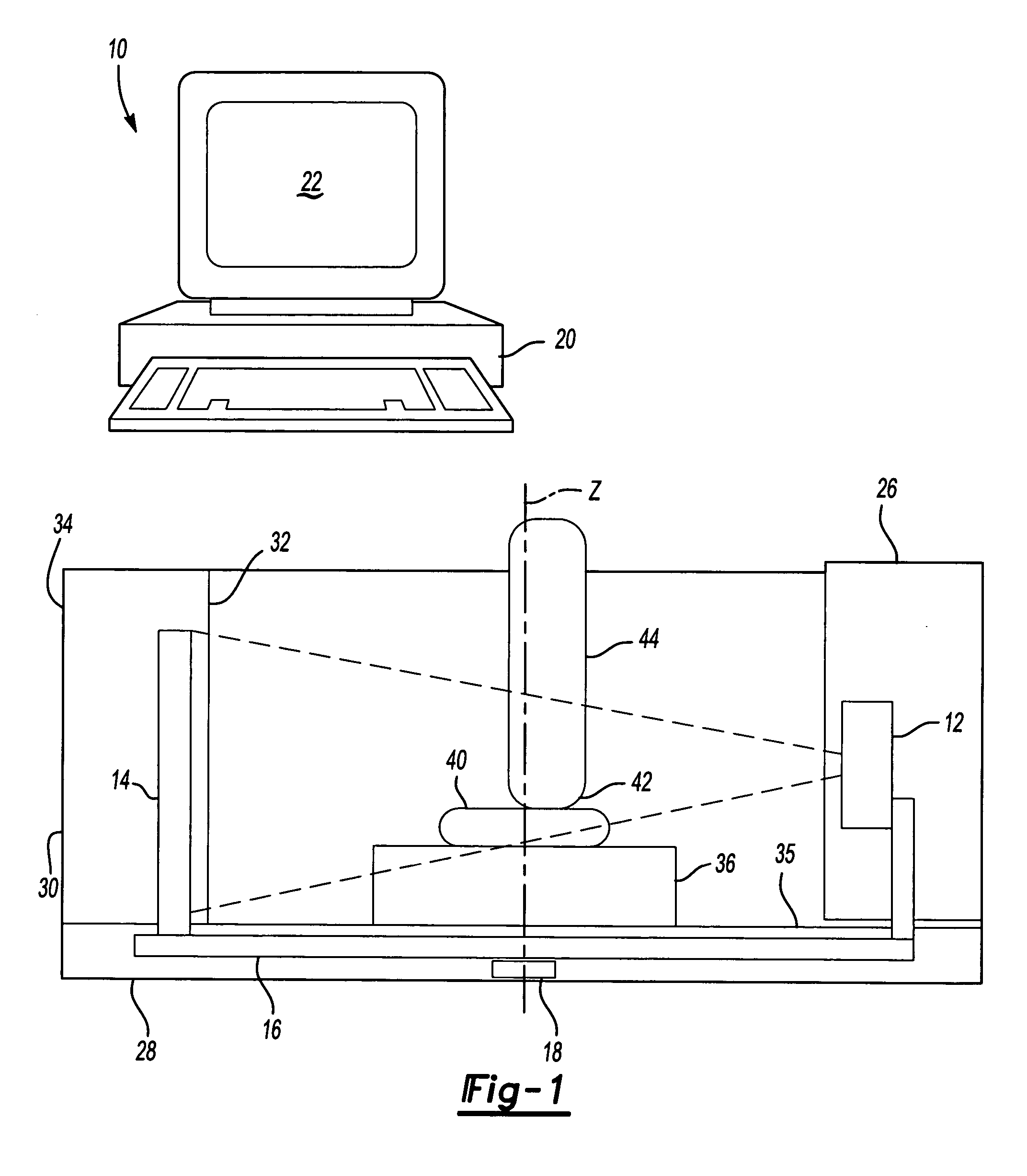
Methods for registration of three-dimensional frames to create three-dimensional virtual models of objects
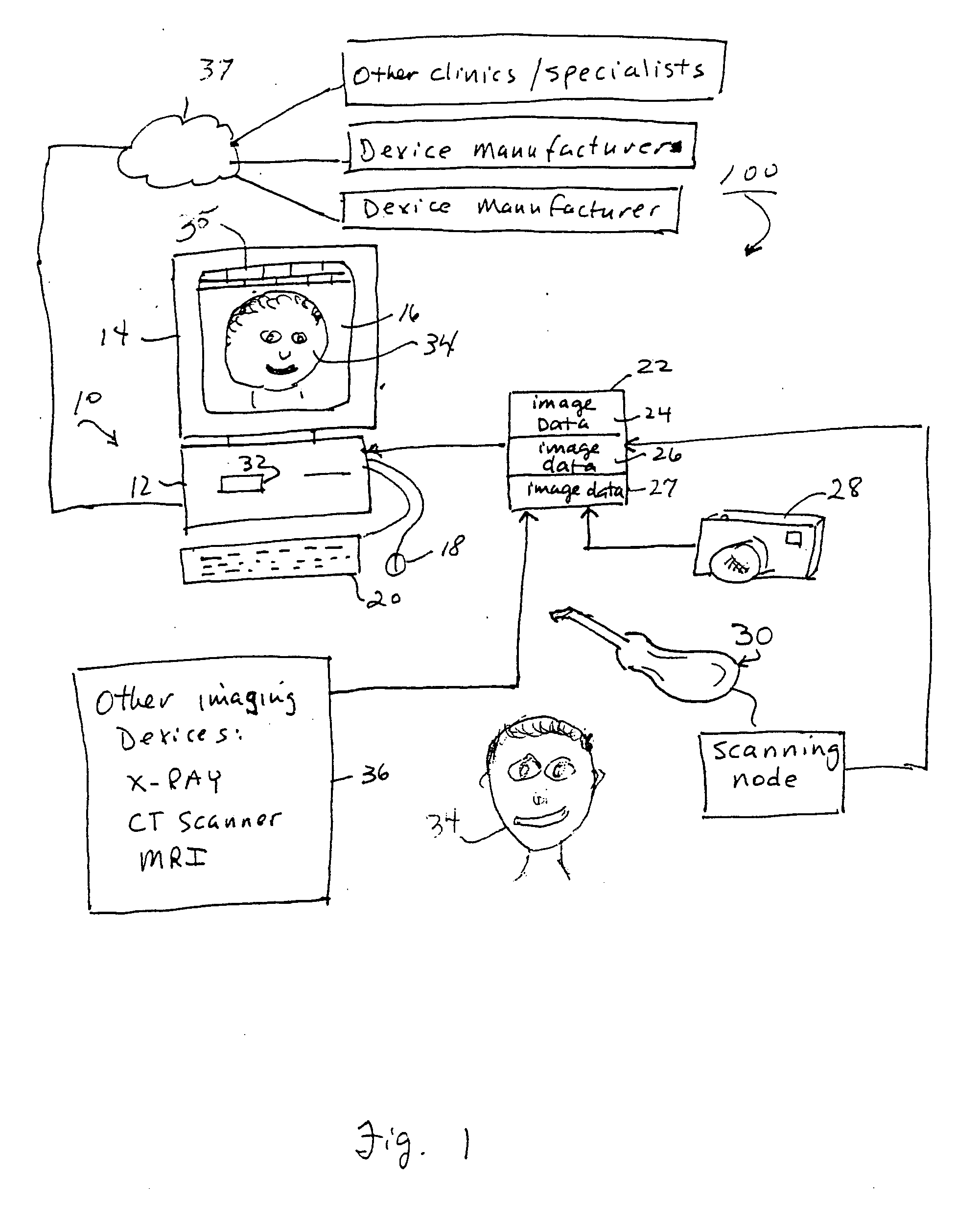
A method and system are provided for constructing a virtual three-dimensional model of an object using a data processing system, and at least one machine-readable memory accessible to said data processing system. A set of at least two digital three-dimensional frames of portions of the object are obtained from a source, such as a computing system coupled to an optical or laser scanner, CT scanner, Magnetic Resonance Tomography scanner or other source. The at least two frames comprise a set of point coordinates in a three dimensional coordinate system providing differing information of the surface of the object. The frames provide a substantial overlap of the represented portions of the surface of the object, but do not coincide exactly for example due to movement of the scanning device relative to the object between the generation of the frame. Data representing the set of frames are stored in the memory. The data processing system processes the data representing the set of frames with said data processing system so as to register the frames relative to each other to thereby produce a three-dimensional virtual representation of the portion of the surface of the object covered by said set of frames. The registration is performed without using pre-knowledge about the spatial relationship between the frames. The three-dimensional virtual model or representation is substantially consistent with all of the frames.
Owner:ORAMETRIX
CT scanner for lower extremities
ActiveUS20060245539A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersX-ray
A CT scanning system provides the ability to scan a patient's lower extremities while the patent is upright, i.e. either standing on the foot, or at least putting some load on the foot, or with the ankle at a given angle. The CT scanning system provides a generally horizontal upper support surface on which the patient's foot is supported. A gantry supporting an x-ray source and x-ray detector are rotated about a z-axis through the support surface. With the CT scanning system, the patient's lower extremities can be scanned while under load.
Owner:XORAN TECH
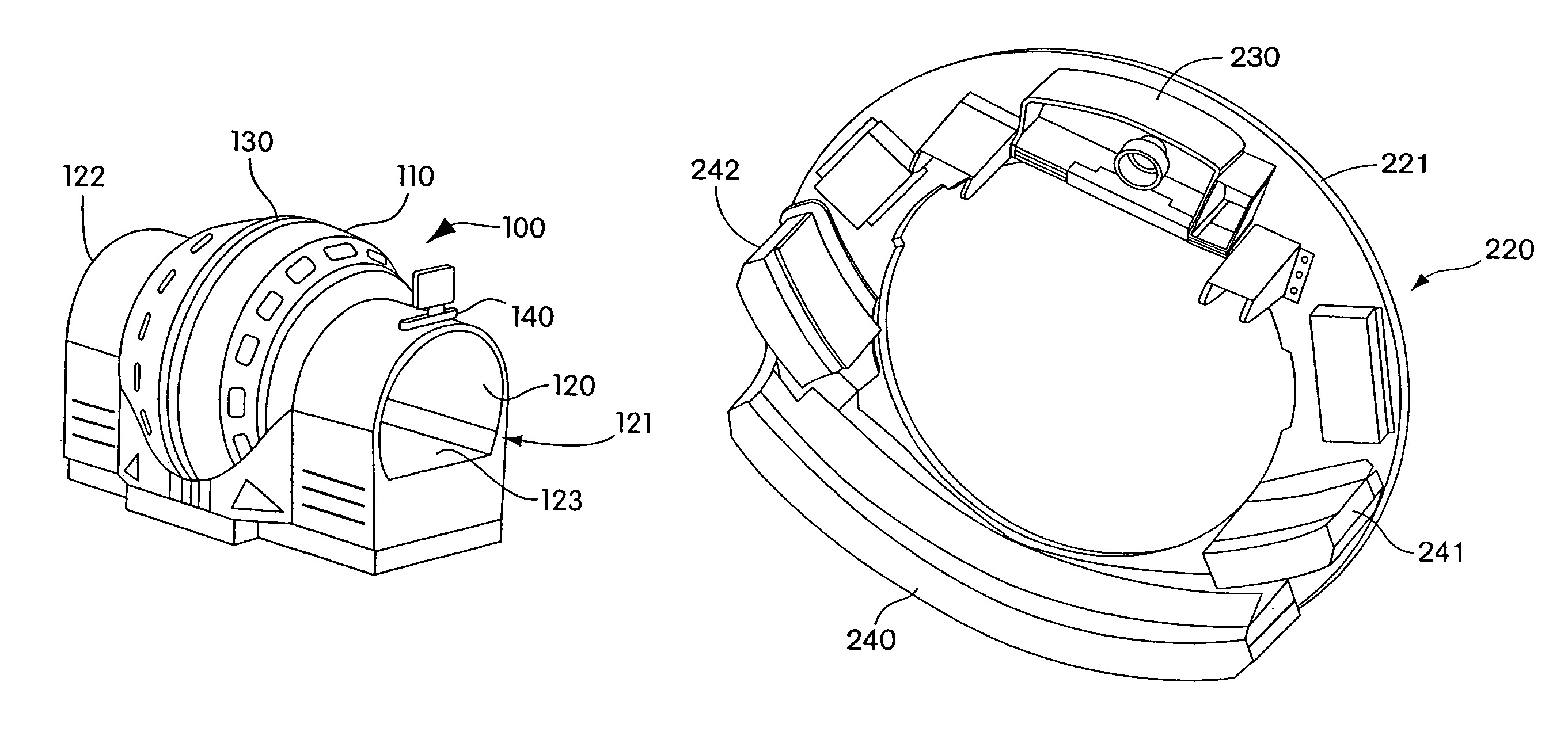
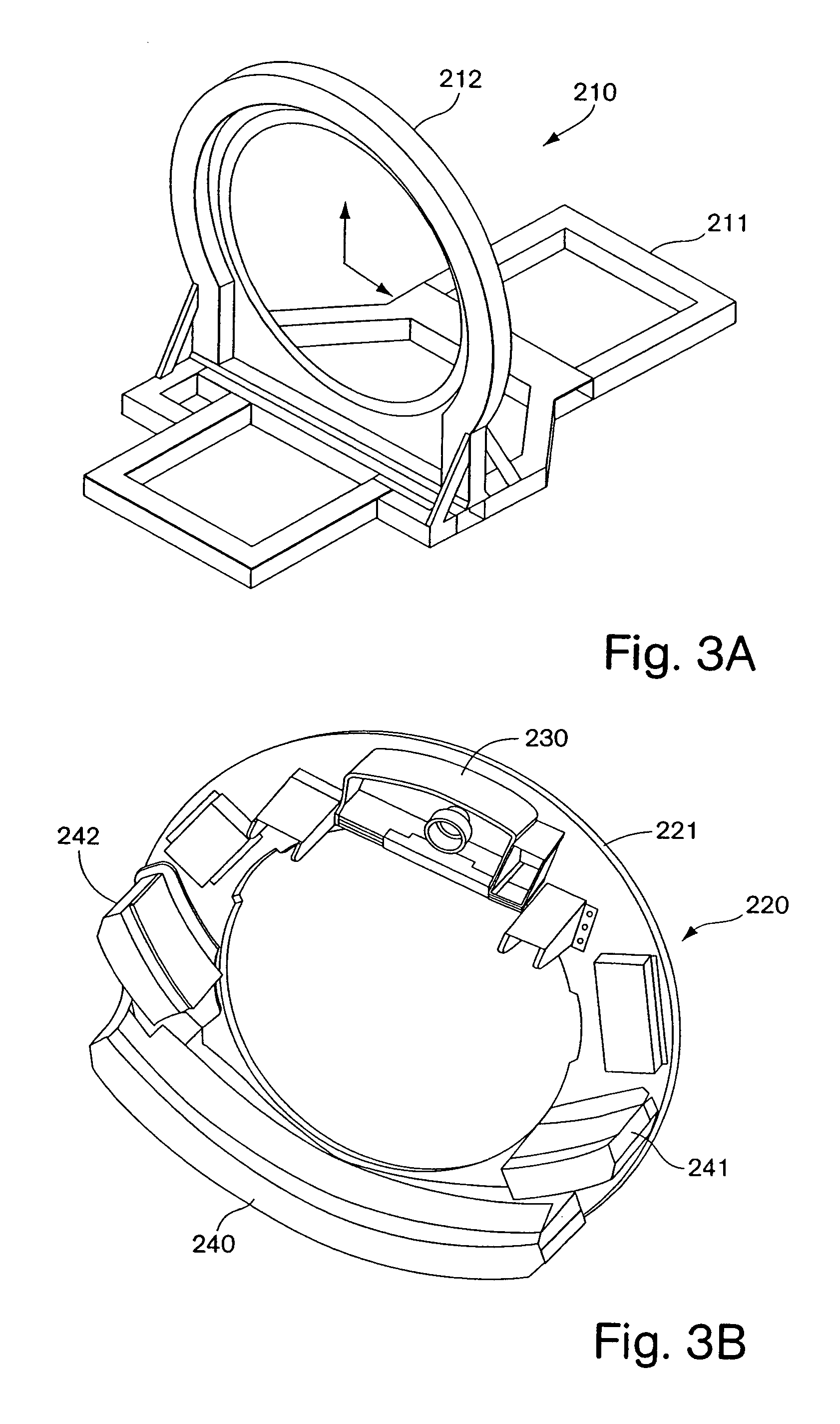
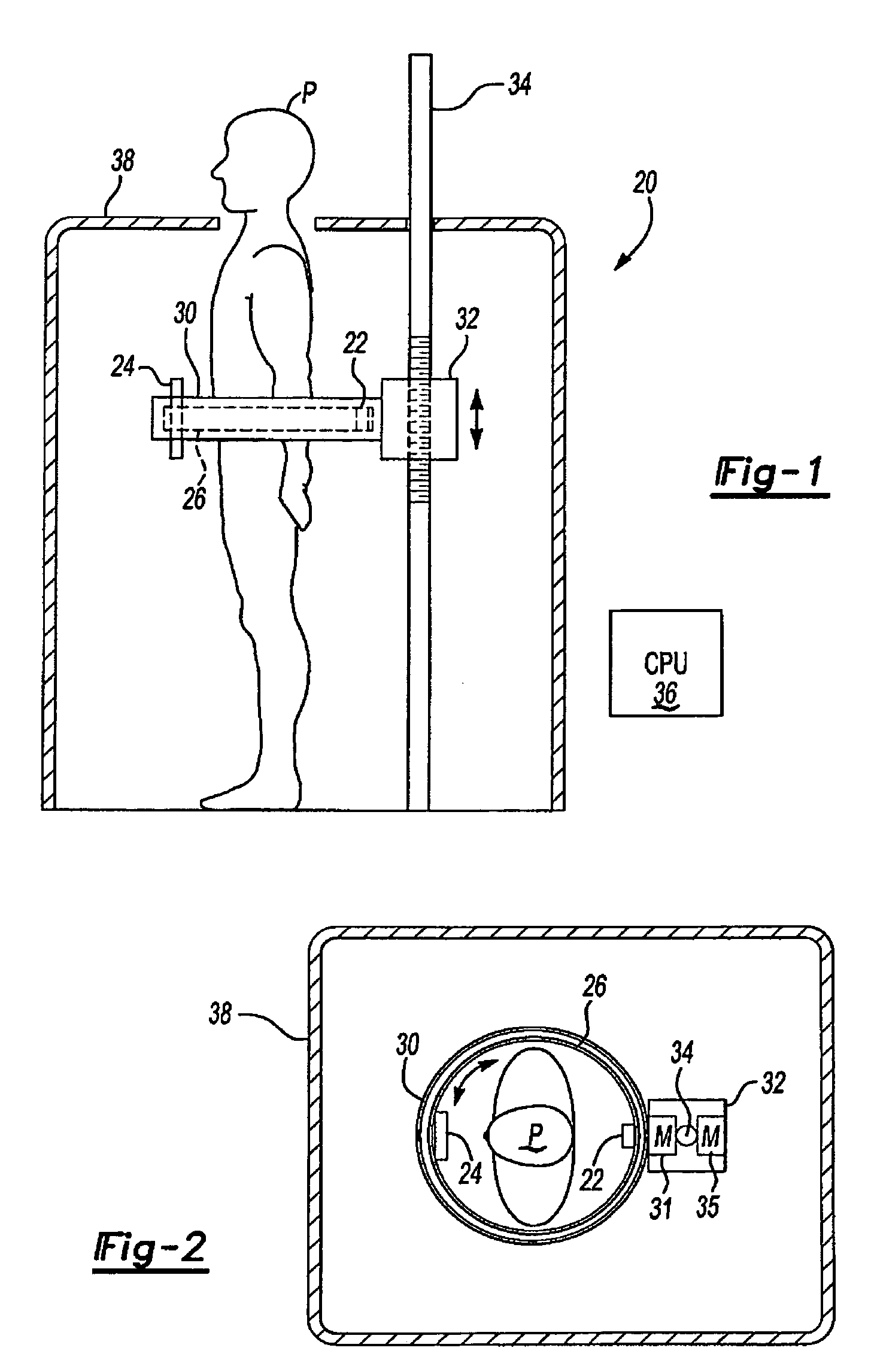
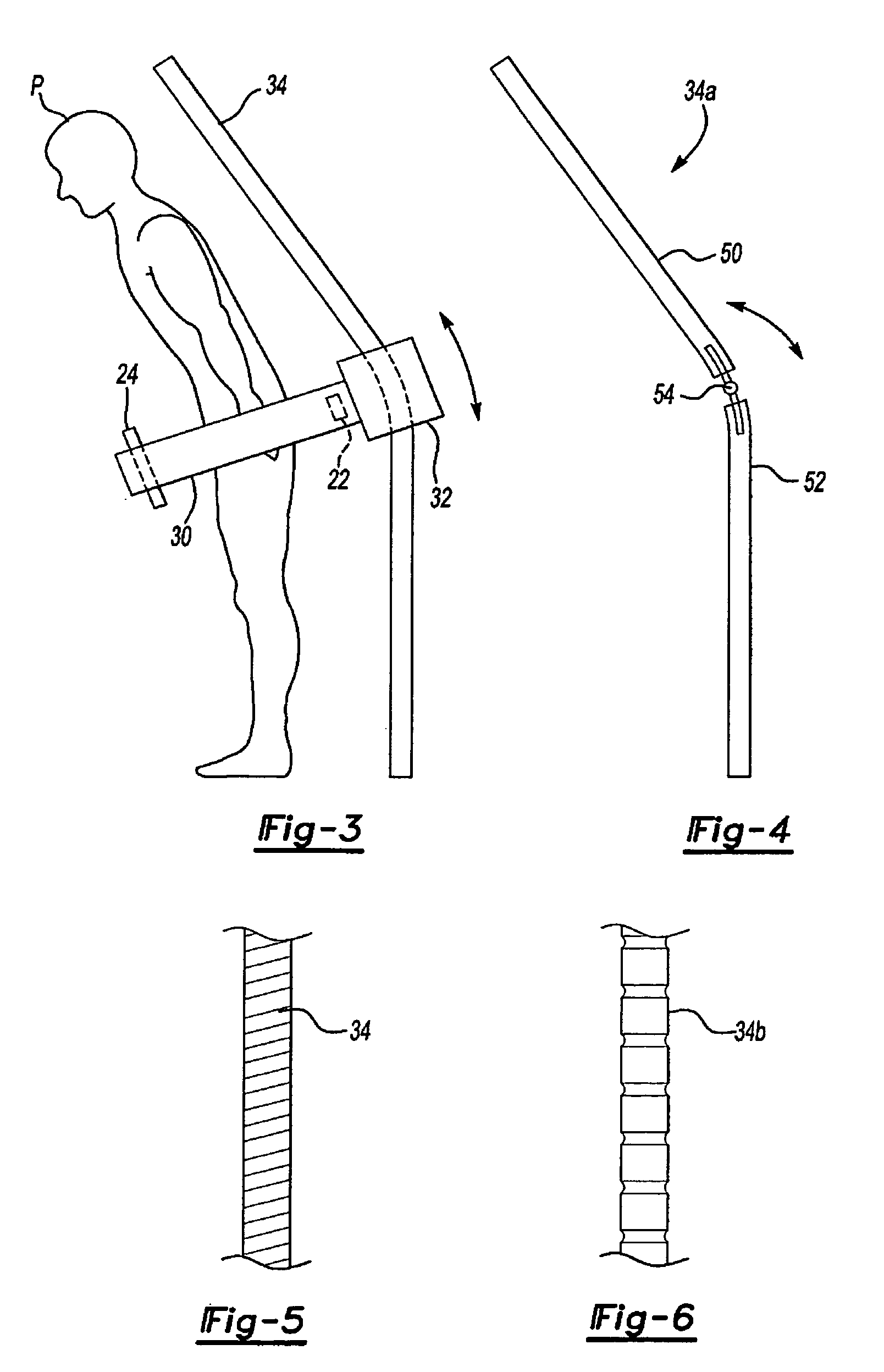
Stand-up CT scanner
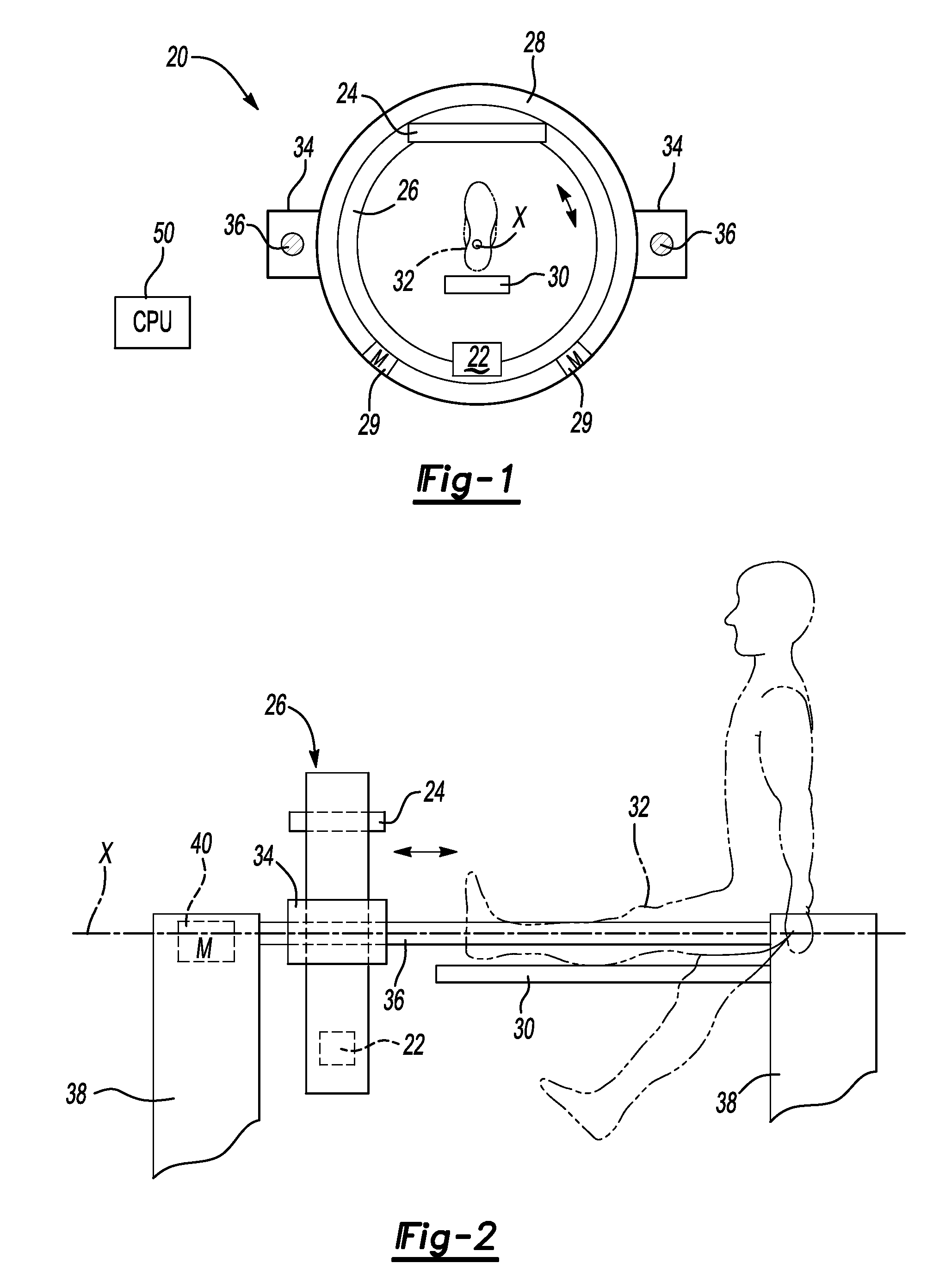
ActiveUS7224764B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHelical scanCt scanners
A CT scanner according to the present invention is particularly useful for scanning the spine and extremities, such as knees, and ankles, especially while the patient is in an upright position. The CT scanner generally includes a source and detector that are rotatable about a generally upright axis. The source and detector are also moved along the upright axis during rotation to perform a helical scan. The source and detector are mounted to an inner ring, which is rotatably mounted within an outer ring. The outer ring is fixedly mounted to a carriage that is movable along an upright rail.
Owner:XORAN TECH
Multiple energy ct scanner
InactiveUS20120236987A1Radiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsUltrasound attenuationSoft x ray
A CT scanner for multiple energy CT scanning of a subject having an X-Ray source adapted to rotate about the subject; and a detector array, having a plurality of detector elements, adapted to acquire attenuation data for X-Rays that have been attenuated by a subject disposed between said X-Ray source and said detector array, said detector array comprising at least two types of detector element, which are differ by their spectral response. The scanner is adapted to generate images associated with the different X-Ray energy spectra.
Owner:RUIMI DAVID +2
Stand-up CT scanner
ActiveUS20050053186A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHelical scanCt scanners
A CT scanner according to the present invention is particularly useful for scanning the spine and extremities, such as knees, and ankles, especially while the patient is in an upright position. The CT scanner generally includes a source and detector that are rotatable about a generally upright axis. The source and detector are also moved along the upright axis during rotation to perform a helical scan. The source and detector are mounted to an inner ring, which is rotatably mounted within an outer ring. The outer ring is fixedly mounted to a carriage that is movable along an upright rail.
Owner:XORAN TECH
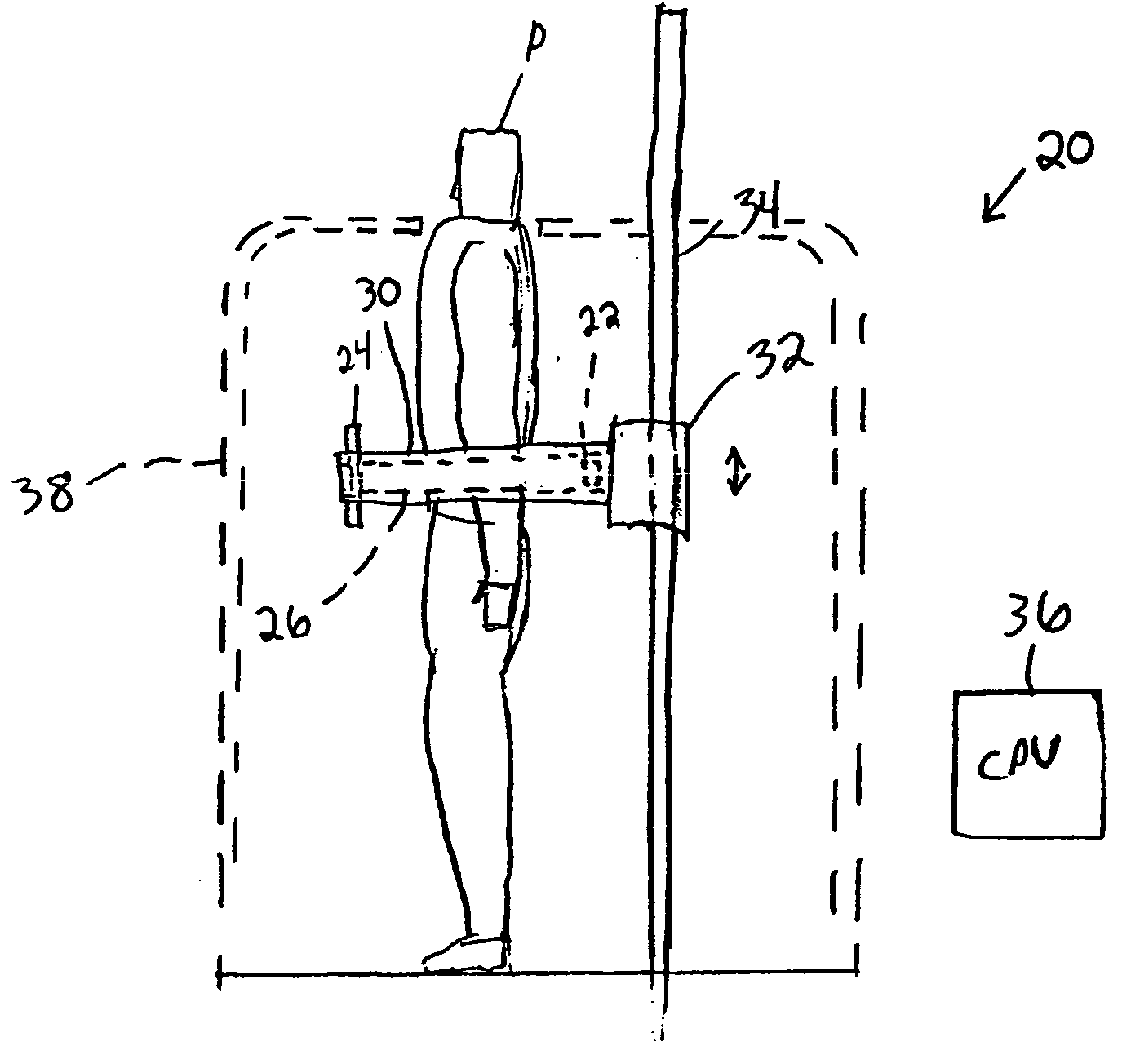
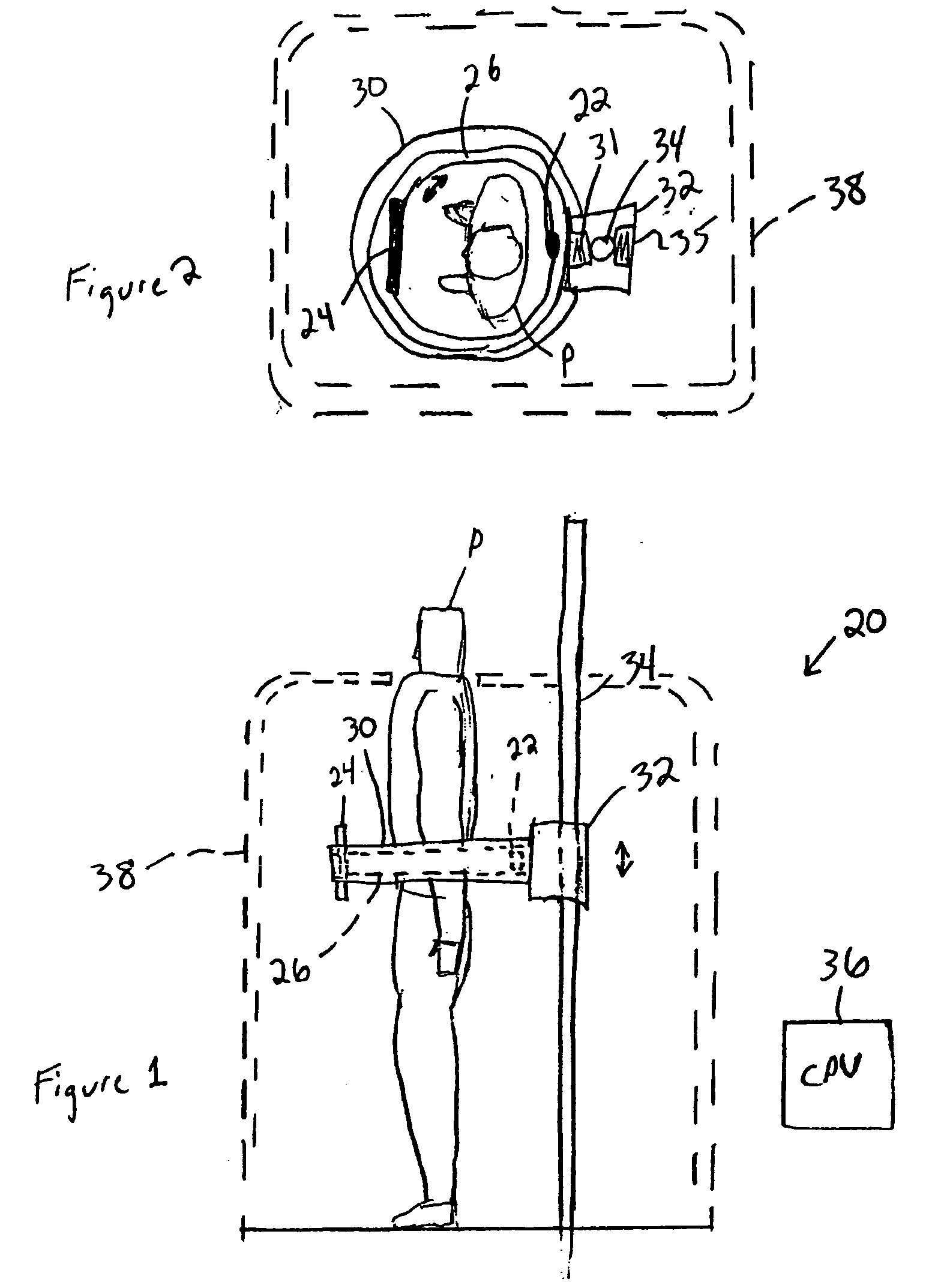
Particle beam irradiation system
InactiveUS7659528B2Simple structureImprove precision controlPhotometryDiagnostic recording/measuringParticle beamCt scanners
A particle beam irradiation system includes a particle beam irradiation apparatus, which is free of a gantry structure, having a particle beam irradiator for irradiating an affected area of a patient with a particle beam, the particle beam irradiator being housed in a chamber, a CT scanner installed in the chamber, for positionally confirming the affected area of the patient, a drive unit for moving the patient from a detection range to an irradiation range, a patient fixing device for fixing the patient in position, the device being mounted on the drive unit for rotation, and a housing unit having a structure housing the drive unit with the patient fixing device mounted and the CT scanner, the housing unit being rotatable about an axis perpendicular to a plane including a direction in which the particle beam is applied and a direction in which the drive unit moves.
Owner:UEMATSU MINORU +2
Dual display ct scanner user interface
ActiveUS20140098933A1Consistency of qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersDisplay device
A CT user interface includes first and second displays that enable an operator to perform set-up and scanning tasks associated with performing CT scans and enable the operator to perform image post-processing tasks associated with the CT scans. A plurality of distinct display zones are selectively displayed on the first and second displays, with the first display displaying a zone enabling the operator to create a record for each of a plurality of patients, a task list zone displaying all steps and sub-steps of a CT scan to be performed for a selected patient based on a selected scan protocol, a settings zone and a scanning zone displaying and enabling operator selection of scan parameters related to the selected scan protocol for the selected patient, and a dose area zone displaying a relationship between the selected scan parameters and a radiation dosage experienced by the patient based thereon.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
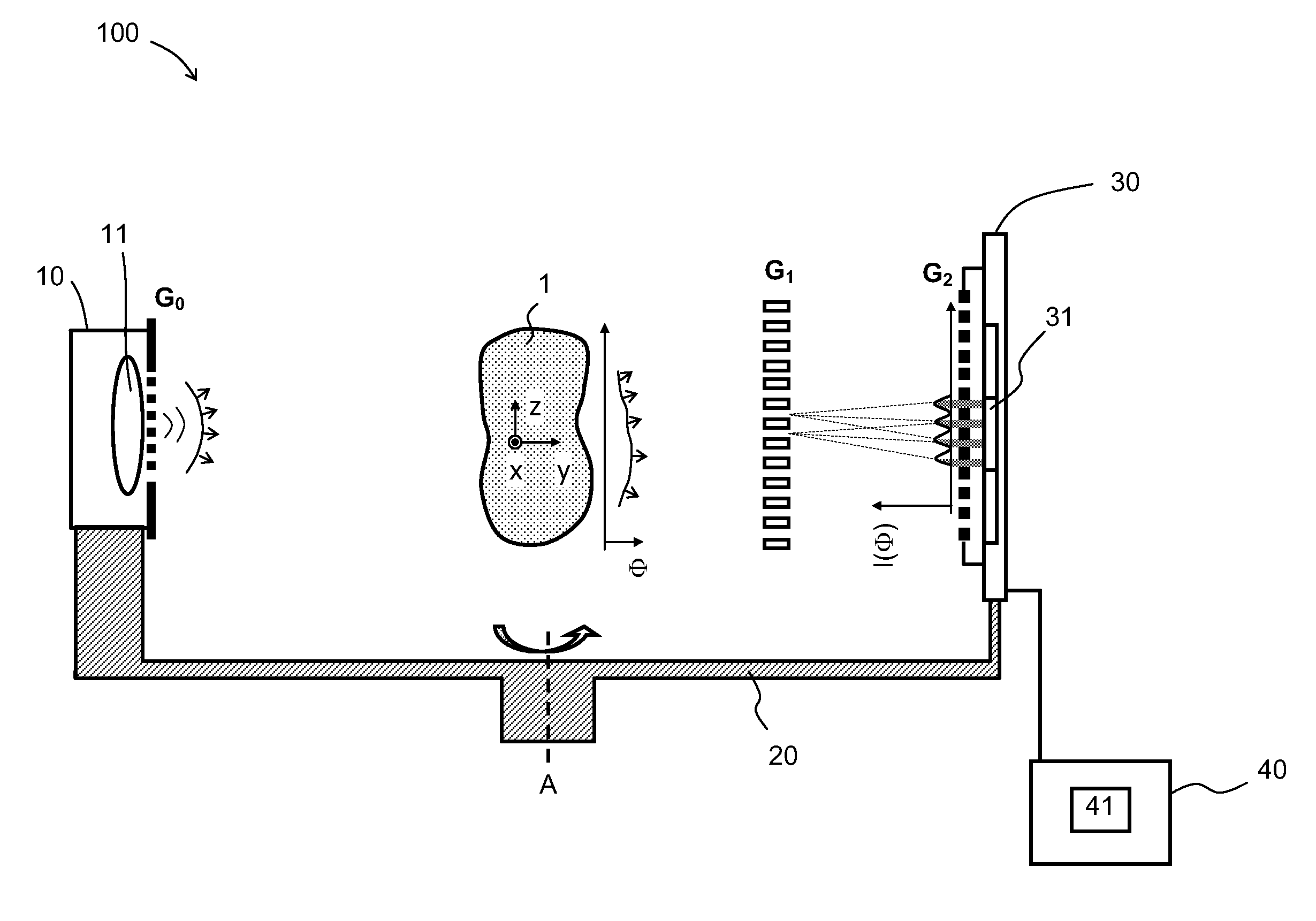
Rotational X ray device for phase contrast imaging
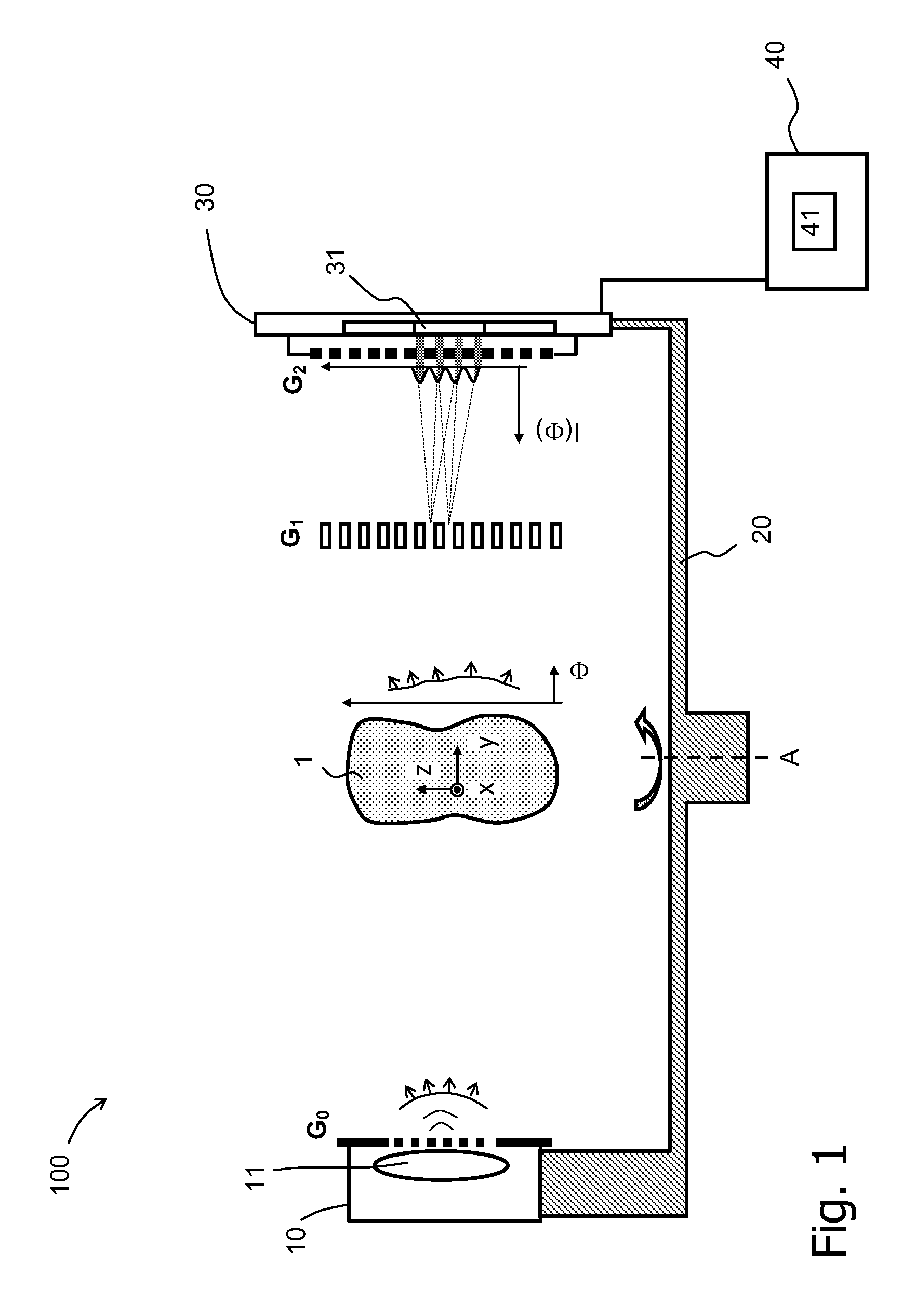
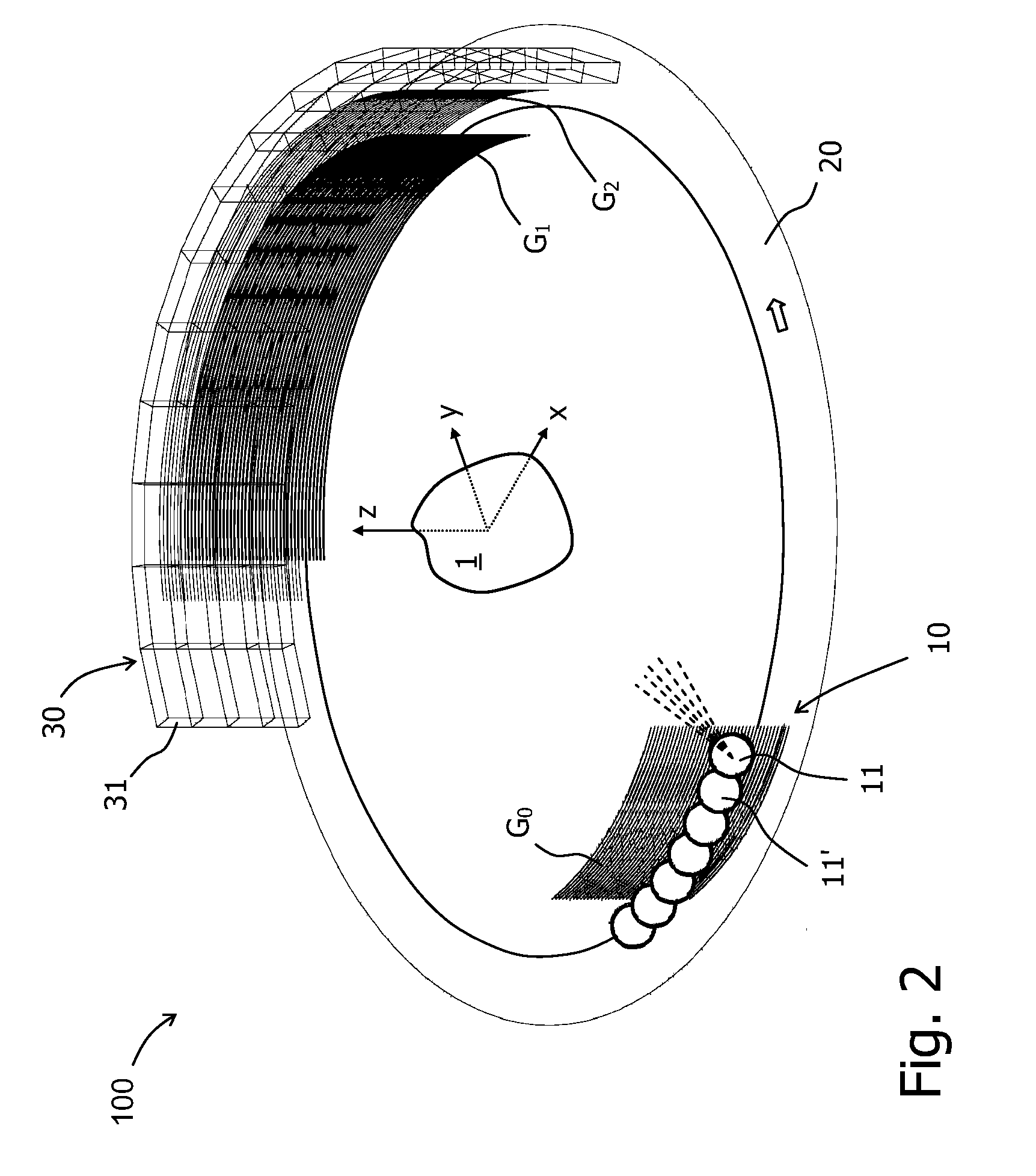
InactiveUS8565371B2Reduce lossesImaging devicesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayPhase grating
The invention relates to a rotational X-ray device (100), for example a CT scanner, for generating phase contrast images of an object (1). In a particular embodiment of the device (100), a plurality of X-ray sources (11), an X-ray detector (30), and an analyzer grating (G2) are attached to a rotatable gantry (20), while a ring-shaped phase grating (G1) is stationary. The X-ray sources are disposed such that X-rays first pass an object under study before traversing the phase grating (G1) and subsequently the analyzer grating (G2). This is achieved by either shifting the X-ray sources axially with respect to the ring-shaped phase grating (G1) or by disposing the X-ray sources in the interior of the ring. Moreover, the phase grating (G1) and the analyzer (G2) shall have spatially varying relative phase (and / or periodicity), for example realized by line grids that are tilted with respect to each other. During the rotation of the gantry (20), the synchronized activation of X-ray sources (11) allows to generate projection images of an object (1) from the same viewing angle with different relative positions (and therefore phases) between the phase grating (G1) and the analyzer (G2).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
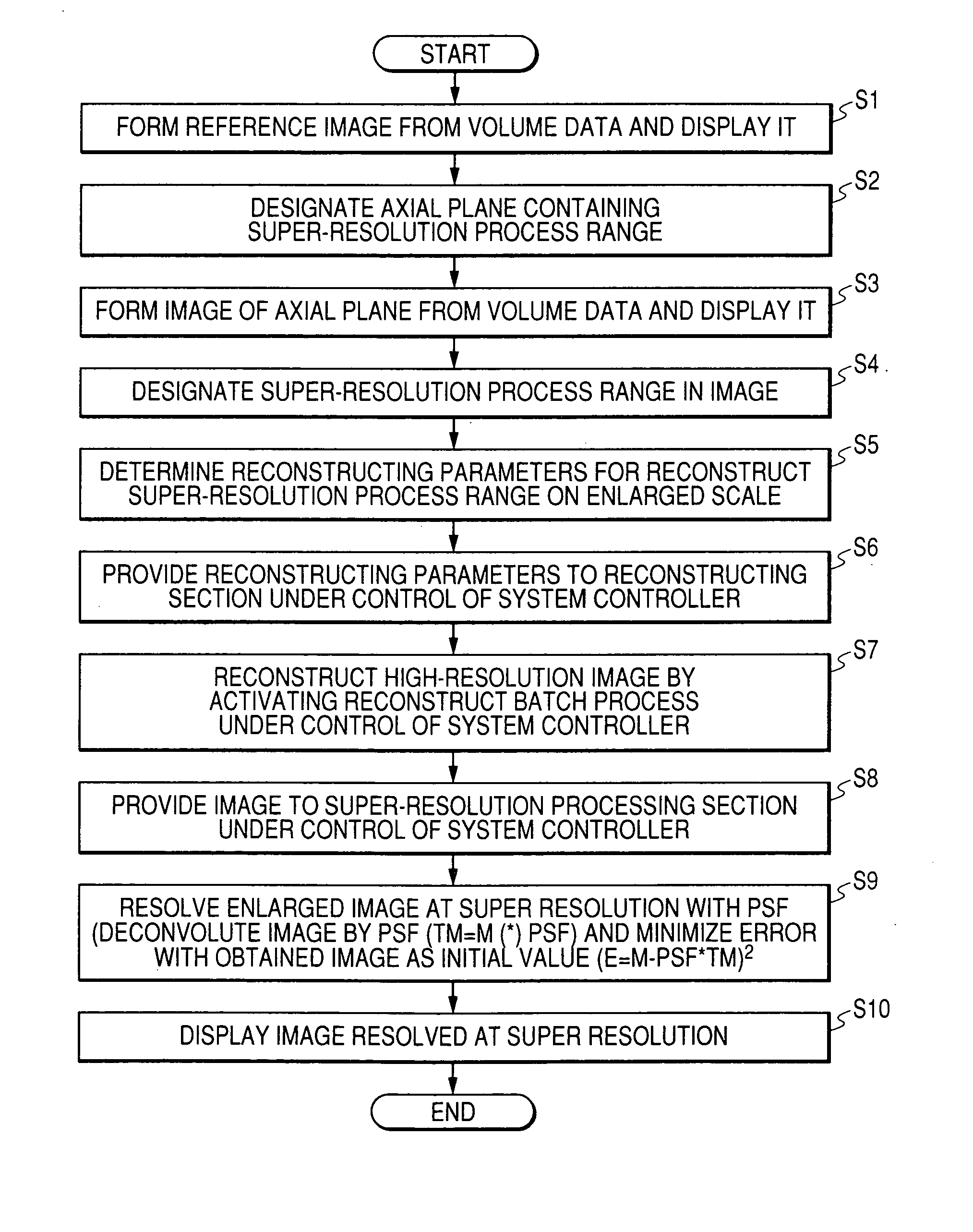
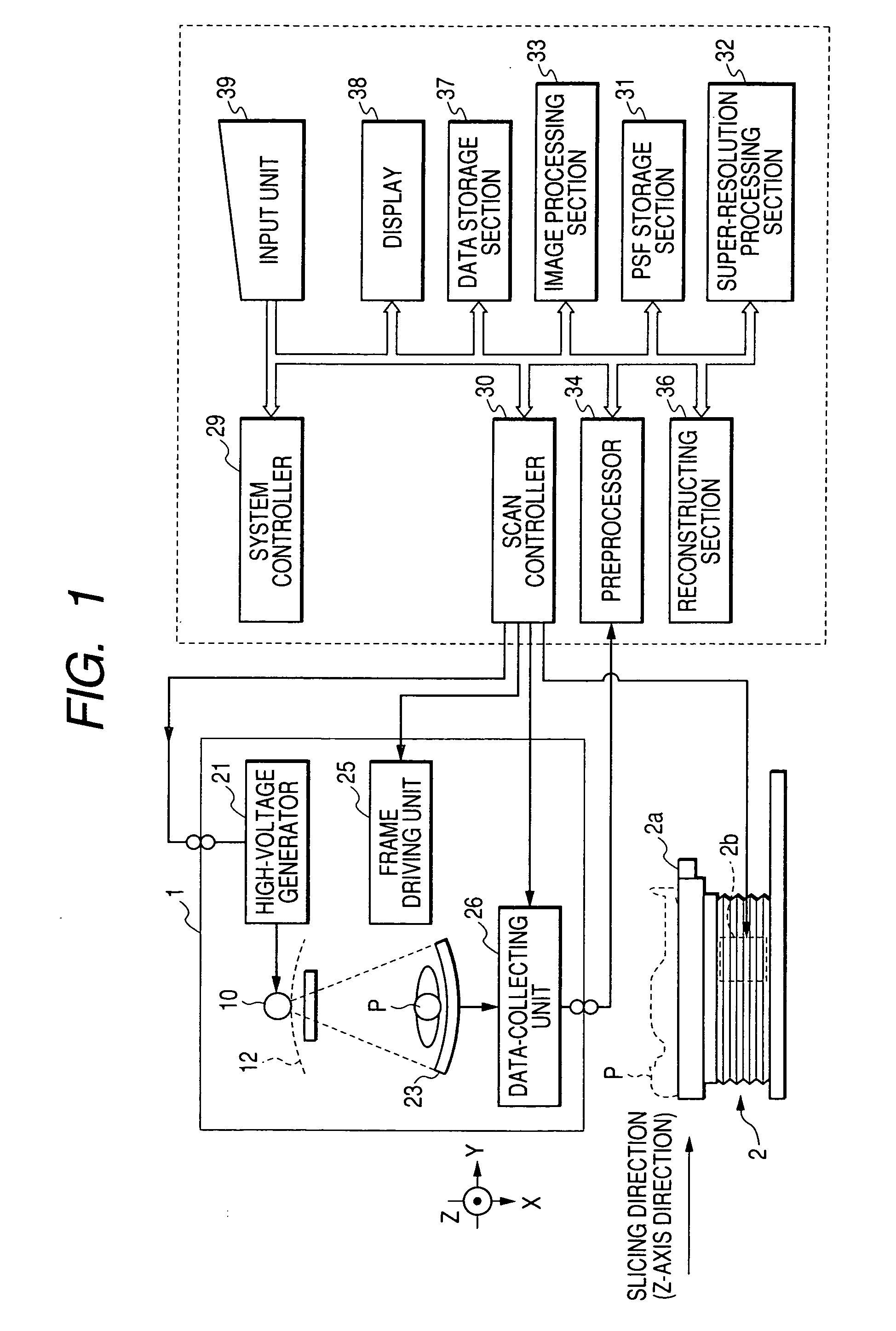
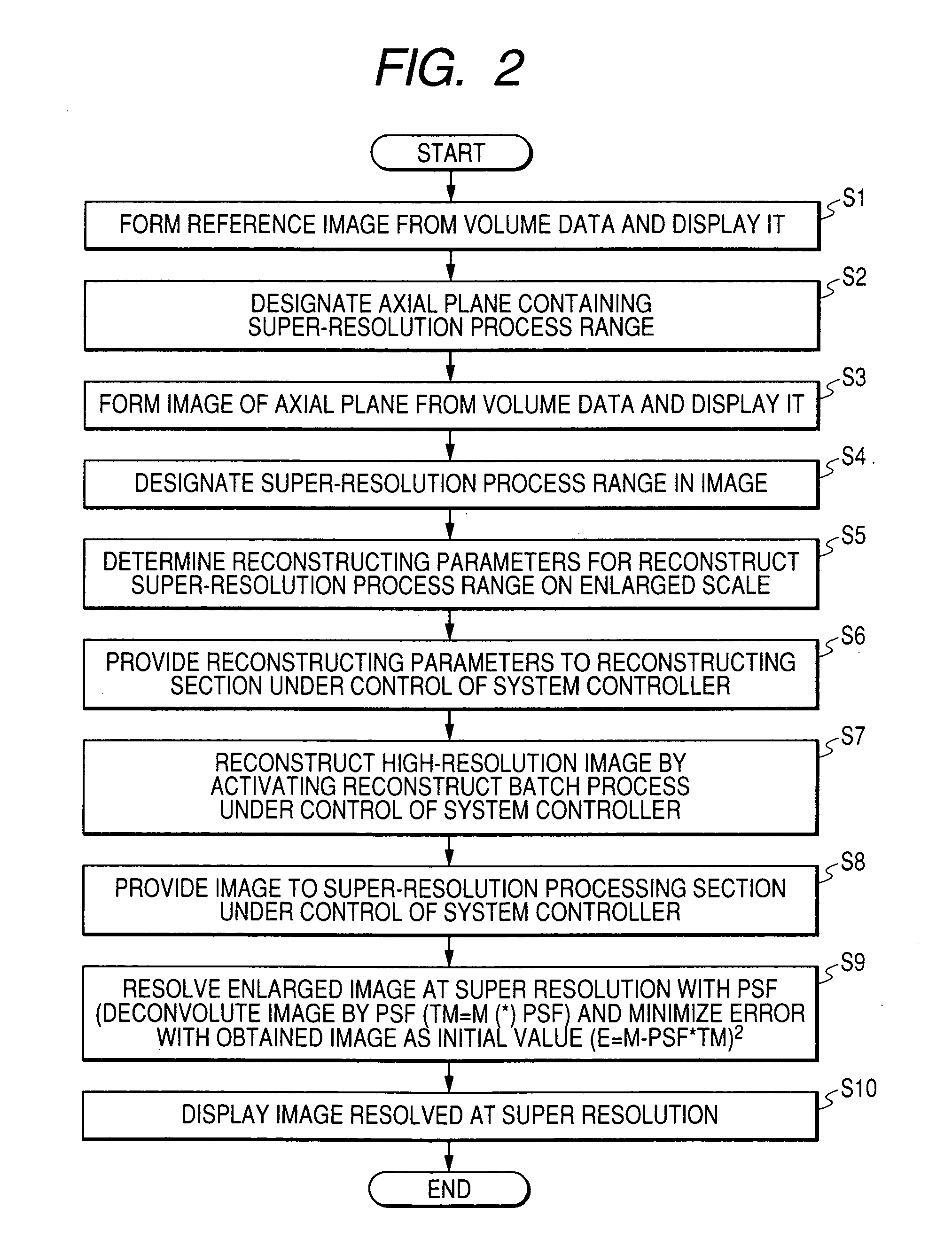
Super-resolution processor and medical diagnostic imaging apparatus
A super-resolution processor includes a storage section for storing data of point spread functions of an X-ray CT scanner which are acquired using a phantom and a super-resolution processing section performing super-resolution of image data of a sample generated by the X-ray CT scanner using the stored point spread functions.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Mobile computed tomography (CT) scanner and operation method thereof
InactiveCN102697517AExtended service lifeReduce operating costsComputerised tomographsTomographyCt scannersImaging quality
The invention discloses a mobile computed tomography (CT) scanner. The mobile CT scanner comprises a bottom plate platform, a machine frame, a rotary plate, an X-ray emitting source, and a detector and data acquisition system. The bottom plate platform is provided with a linear guide rail; and one end of the machine frame is provided with a guide rail sliding block which is slidably connected with the linear guide rail, and the other end of the machine frame is connected with the rotary plate. The rotary plate can rotate relative to the machine frame. The X-ray emitting source and the detector and data acquisition system are arranged on the rotary plate and are respectively positioned at two ends of the same diameter of the rotary plate. The X-ray emitting source comprises a grid controlled carbon nano tube-based field emission cathode X-ray tube. The invention also provides an operation method for the mobile CT scanner. The mobile CT scanner is simple in structure, low in radiation dosage, and high in imaging quality, and has two purposes.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH
CT system with synthetic view generation
ActiveUS20060239400A1Reduce doseQuality improvementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputer graphics (images)Ct scanners
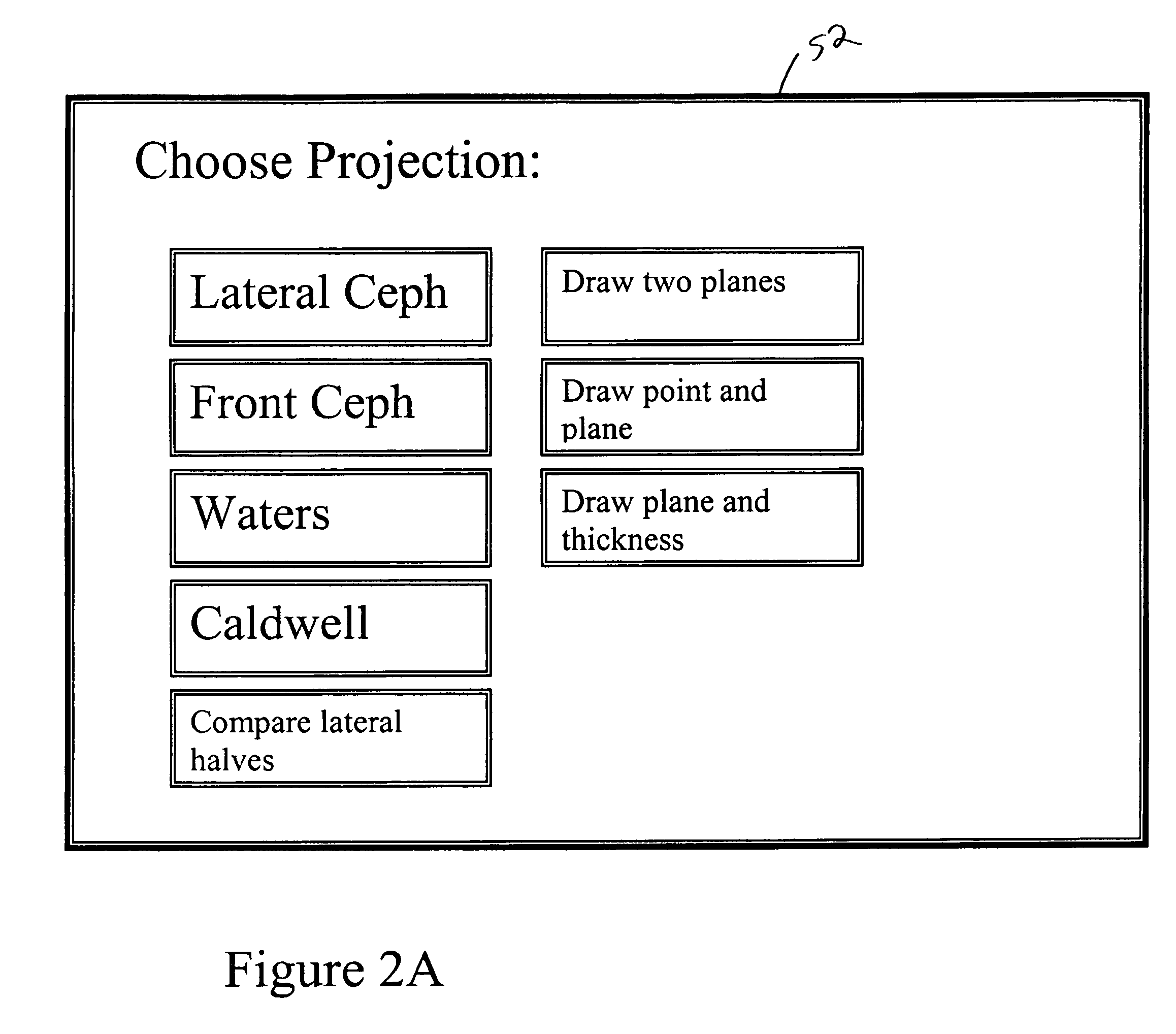
A CT scanner system provides projection-like images of a patient volume. After a CT scan is obtained and a three-dimensional model of the patient is created, any synthetic view can be generated by choosing any array of projection lines, e.g. between a point and a surface (a flat plane, curved plane, spherical, etc) or between two surfaces (parallel or not) and summing across the projection lines. The synthetic projections can mimic certain traditional views, such as a ceph scan, Water's view, Caldwell's projection, etc or can provide a new view that is impossible or impractical with traditional x-ray equipment, such as a perfect parallel projection, or a projection that does not pass all the way through the patient.
Owner:XORAN TECH
Large bore PET and hybrid PET/CT scanners and radiation therapy planning using same
ActiveUS8063376B2Quick responseReduced radially inward extentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPatient positioning for diagnosticsLines of responseRadiation planning
An imaging system comprises: a ring of positron emission tomography (PET) detectors; a PET housing at least partially surrounding the ring of PET detectors and defining a patient aperture of at least 80 cm; a coincidence detection processor or circuitry configured to identify substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events corresponding to electron-positron annihilation events; and a PET reconstruction processor configured to reconstruct into a PET image the identified substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events based on lines of response defined by the substantially simultaneous 511 keV radiation detection events. Radiation planning utilizing such an imaging system comprises: acquiring PET imaging data for a human subject arranged in a radiation therapy position requiring a patient aperture of at least about 80 cm; reconstructing said imaging data into a PET image encompassing an anatomical region to undergo radiation therapy; and generating a radiation therapy plan based on at least the PET image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com