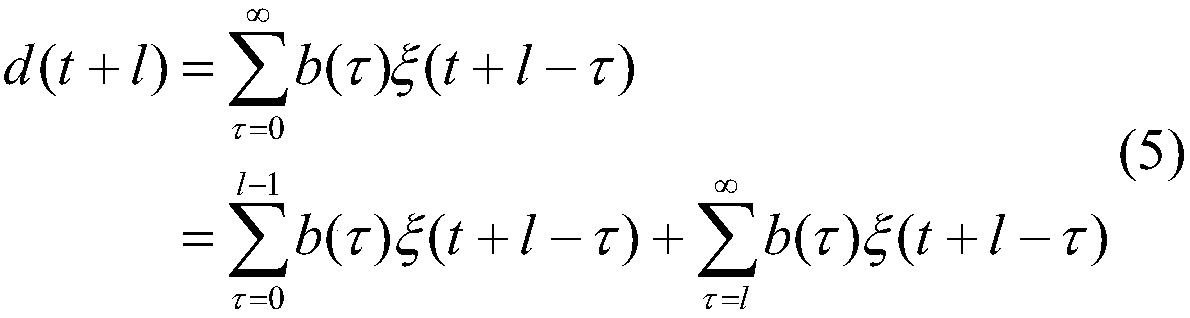Patents
Literature
34 results about "Inverse radon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of and system for intravenous volume tomographic digital angiography imaging
InactiveUS6075836AQuality improvementEfficient contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersData acquisition
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Cone beam volume CT angiography imaging system and method
InactiveUS6298110B1Quality improvementEfficient contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersX-ray
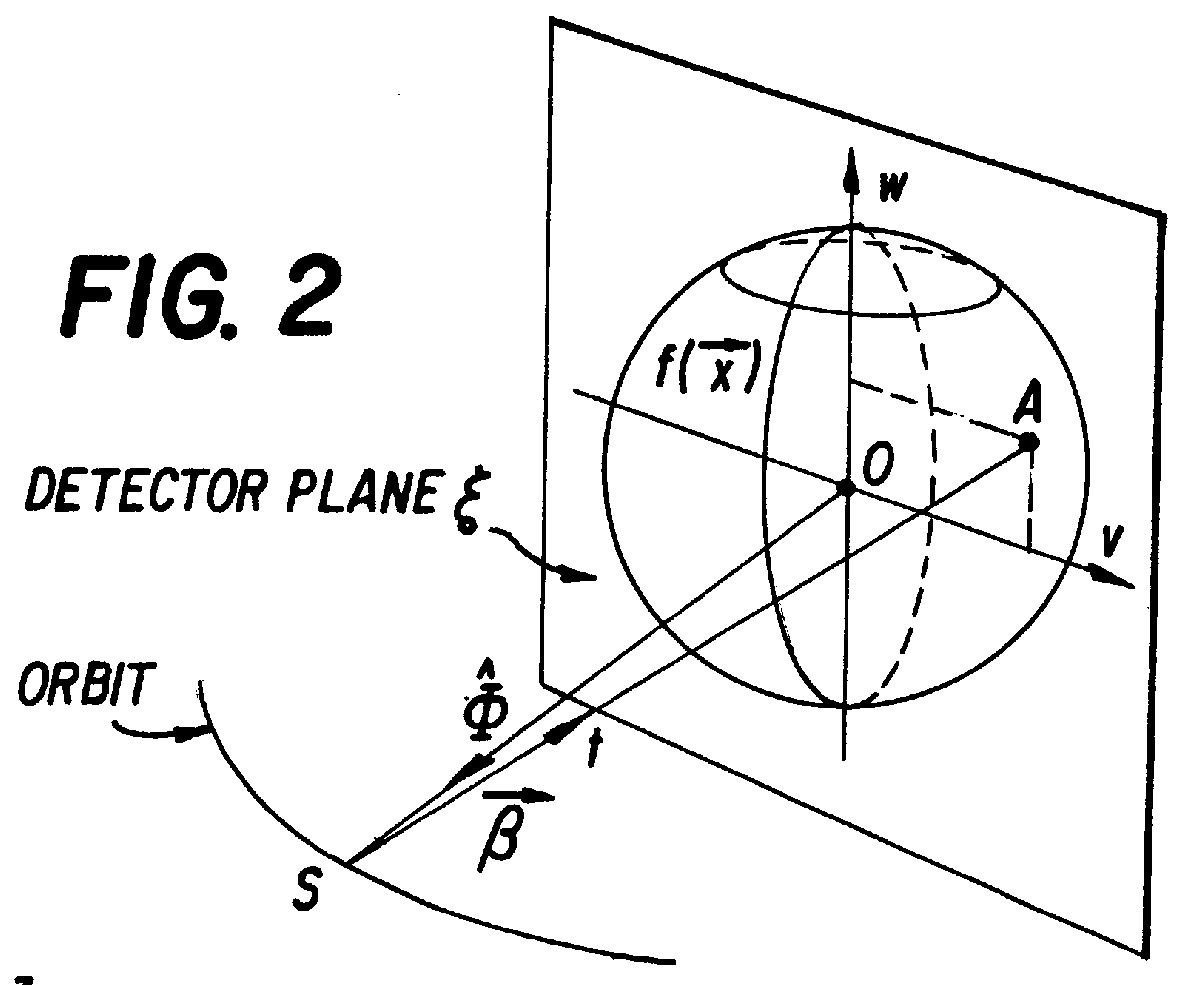
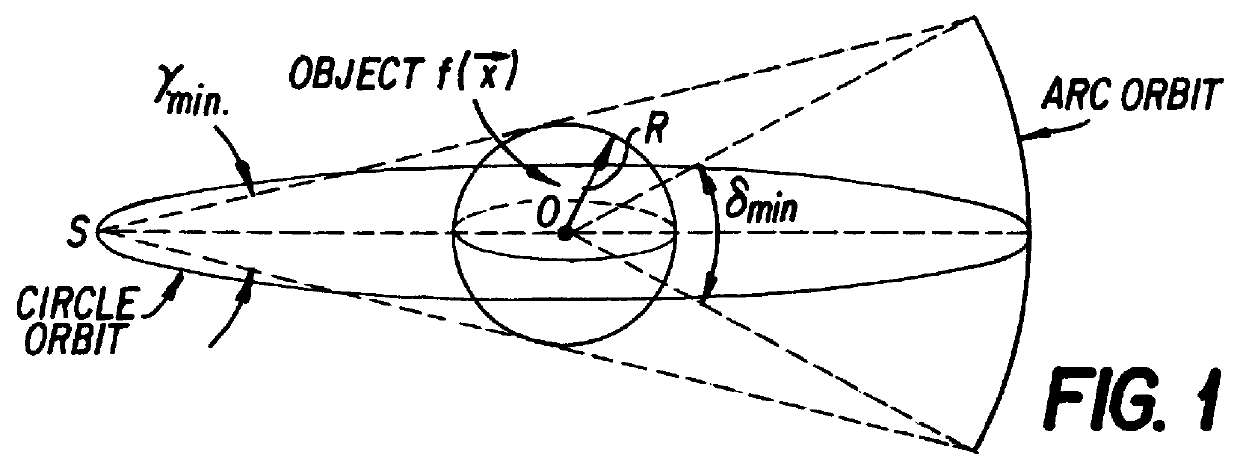
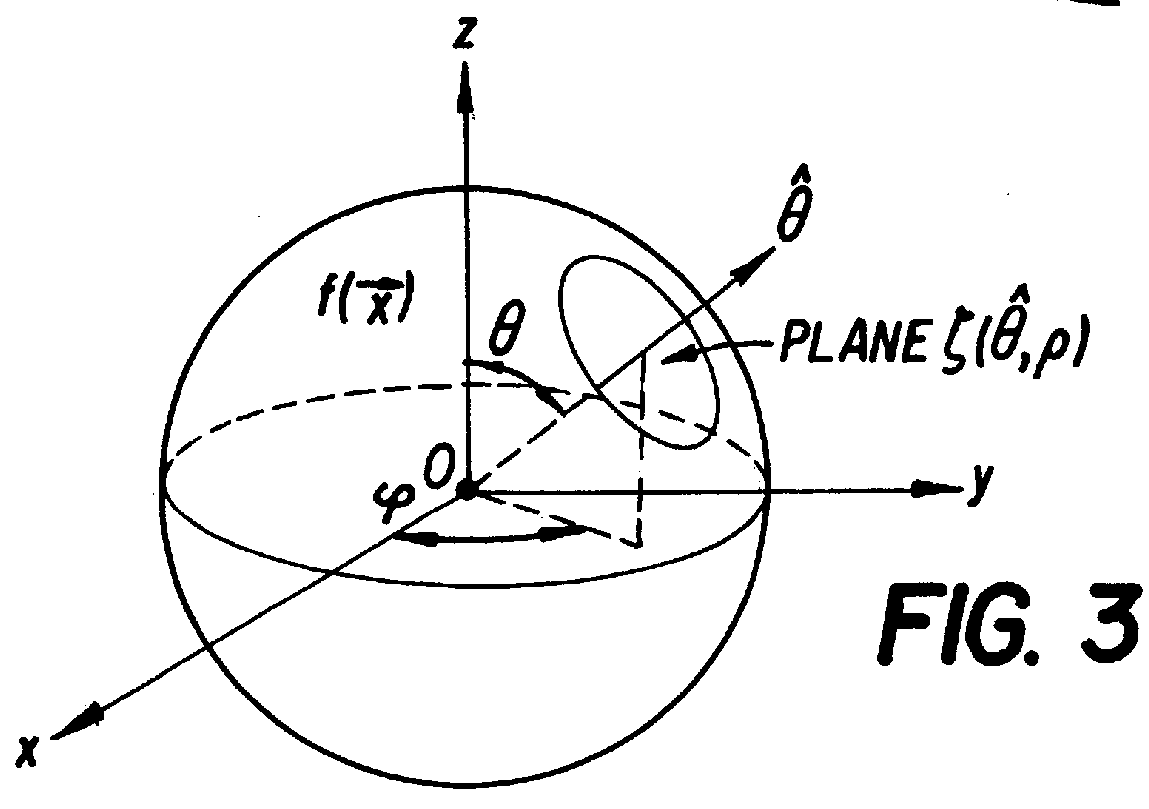
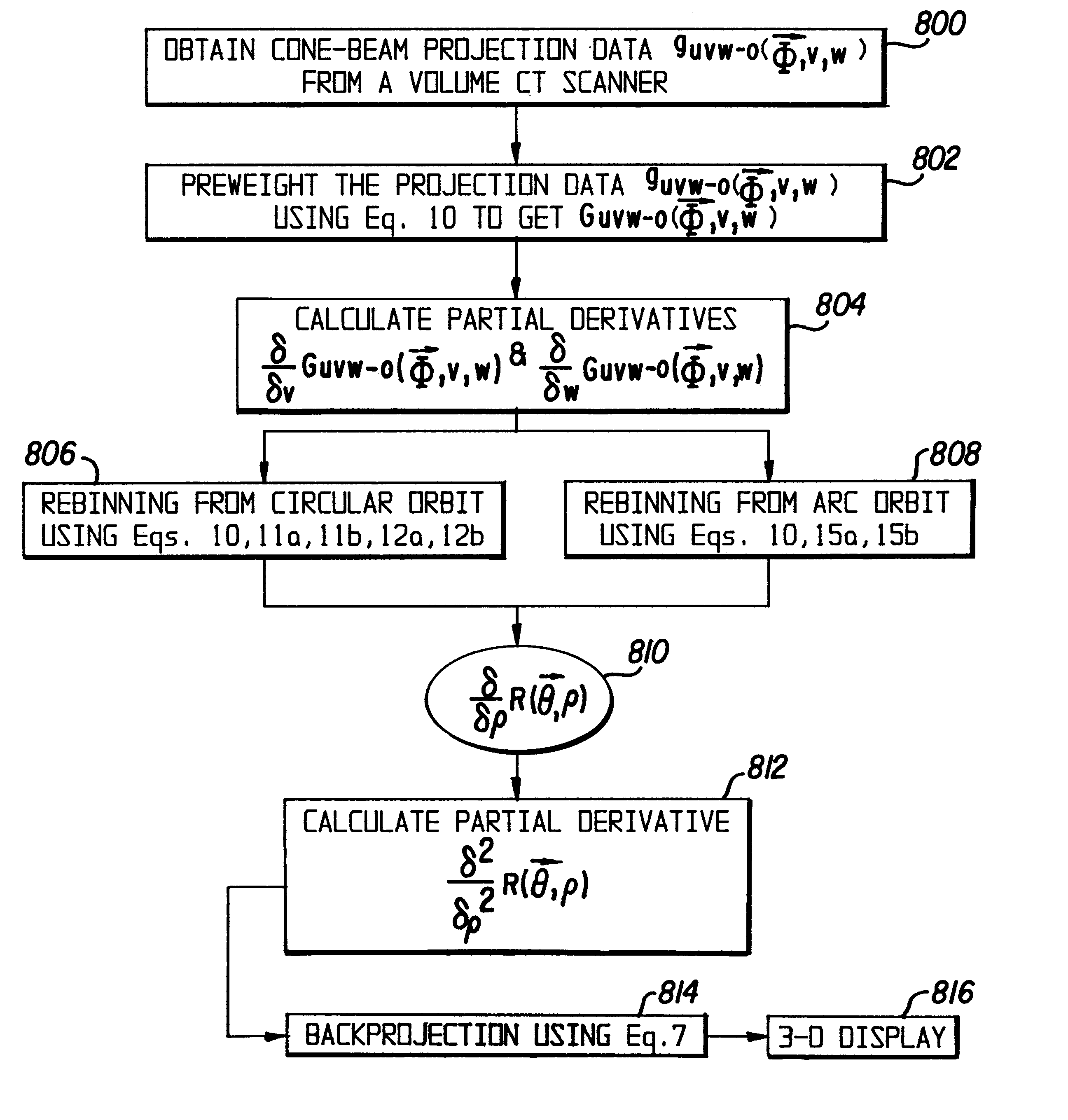
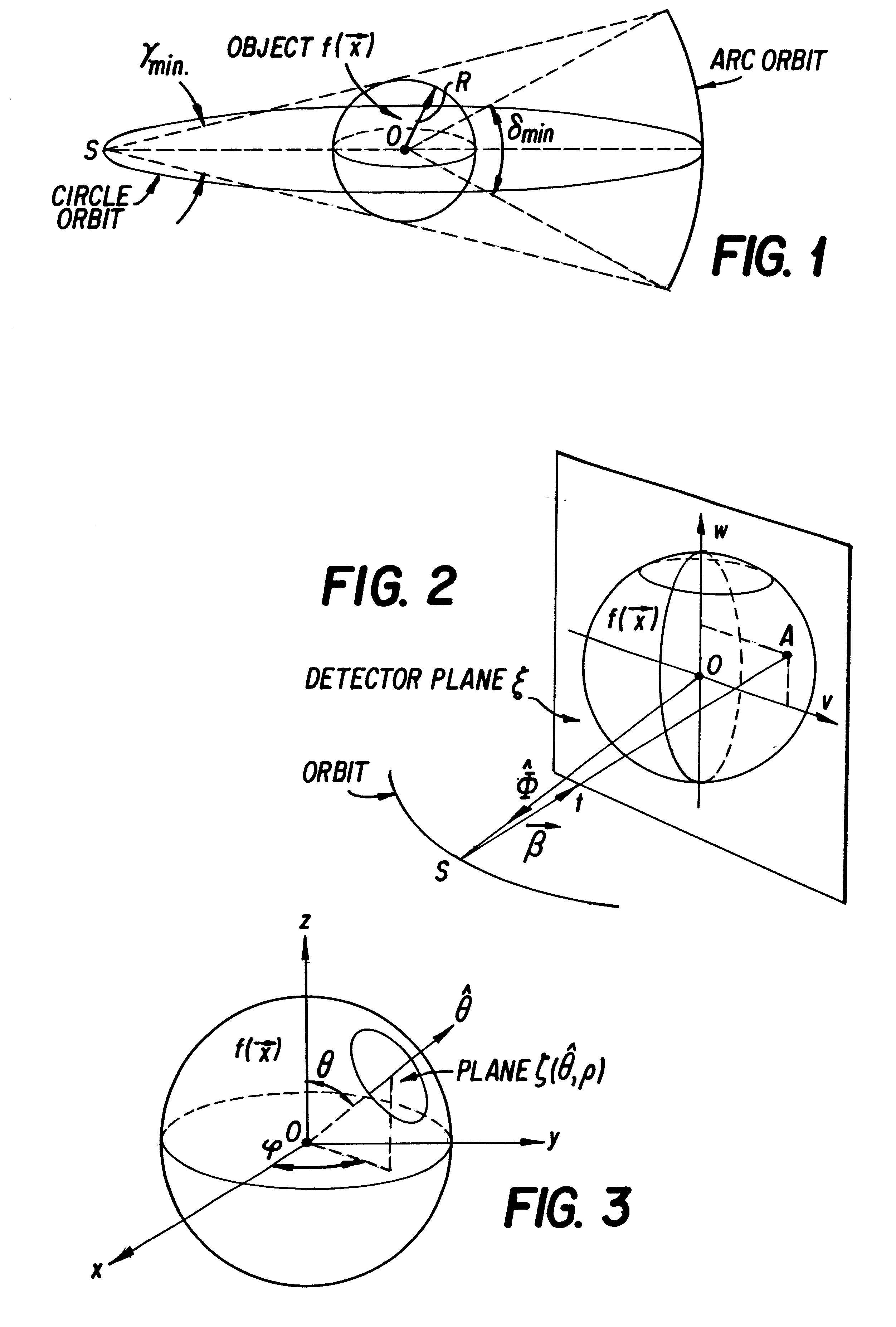
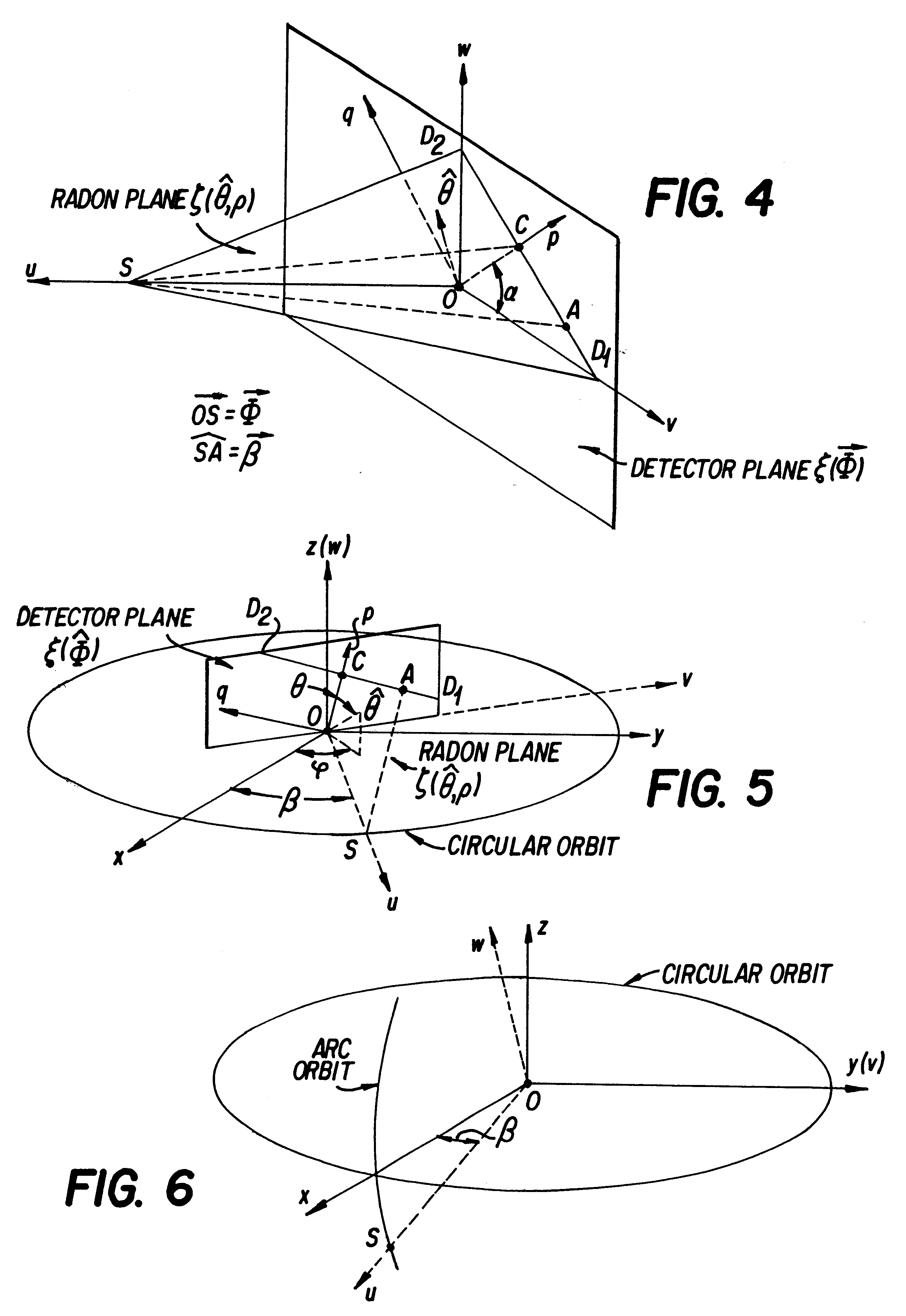
Only a single IV contrast injection with a short breathhold by the patient is needed for use with a volume CT scanner which uses a cone-beam x-ray source and a 2-D detector for fast volume scanning in order to provide true 3-D descriptions of vascular anatomy with more than 0.5 lp / mm isotropic resolution in the x, y and z directions is utilized in which one set of cone-beam projections is acquired while rotating the x-ray tube and detector on the CT gantry and then another set of projections is acquired while tilting the gantry by a small angle. The projection data is preweighted, partial derivatives are calculated and rebinned for both the circular orbit and arc orbit data The second partial derivative is then calculated and then the reconstructed 3-D images are obtained by backprojecting using the inverse Radon transform.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
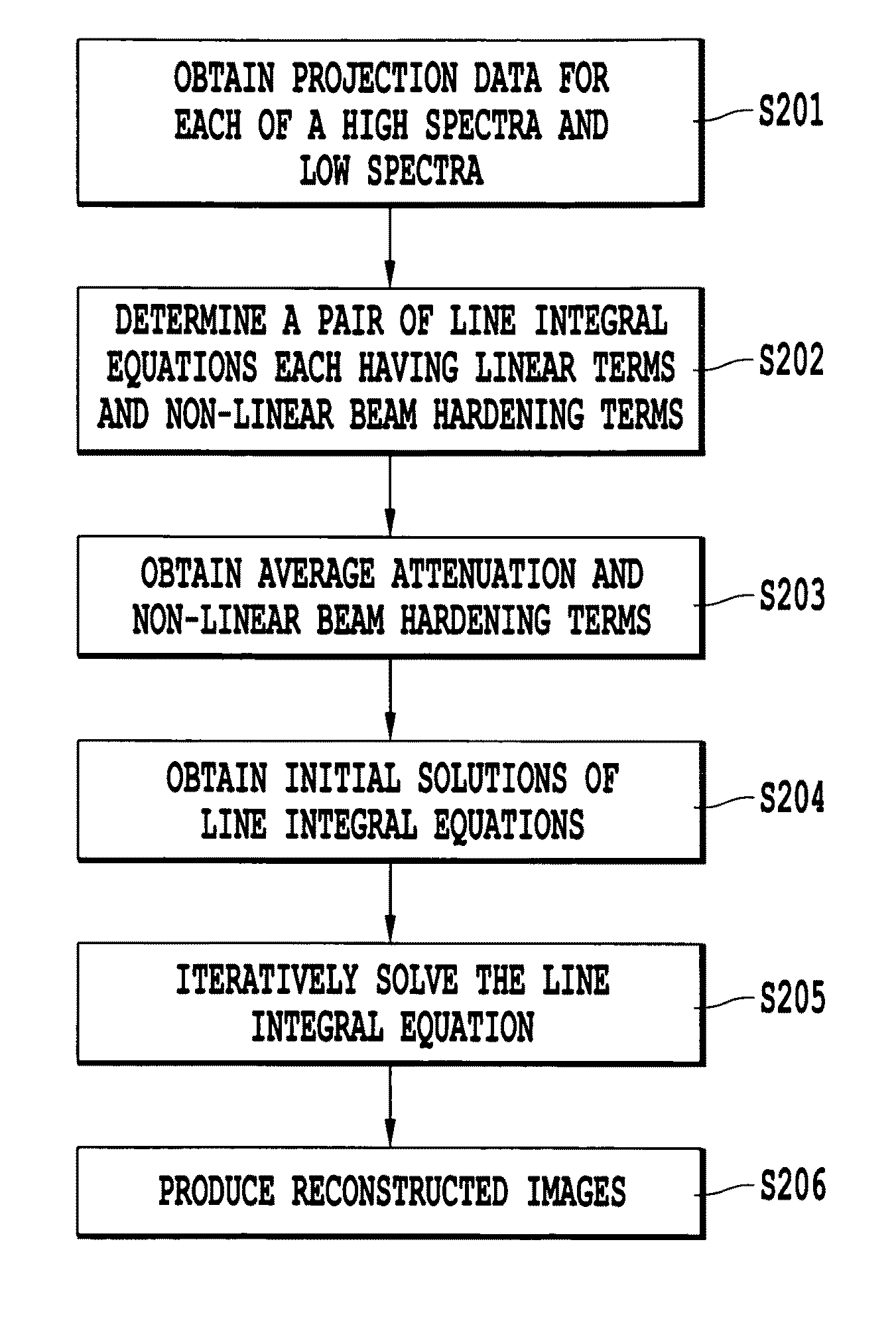
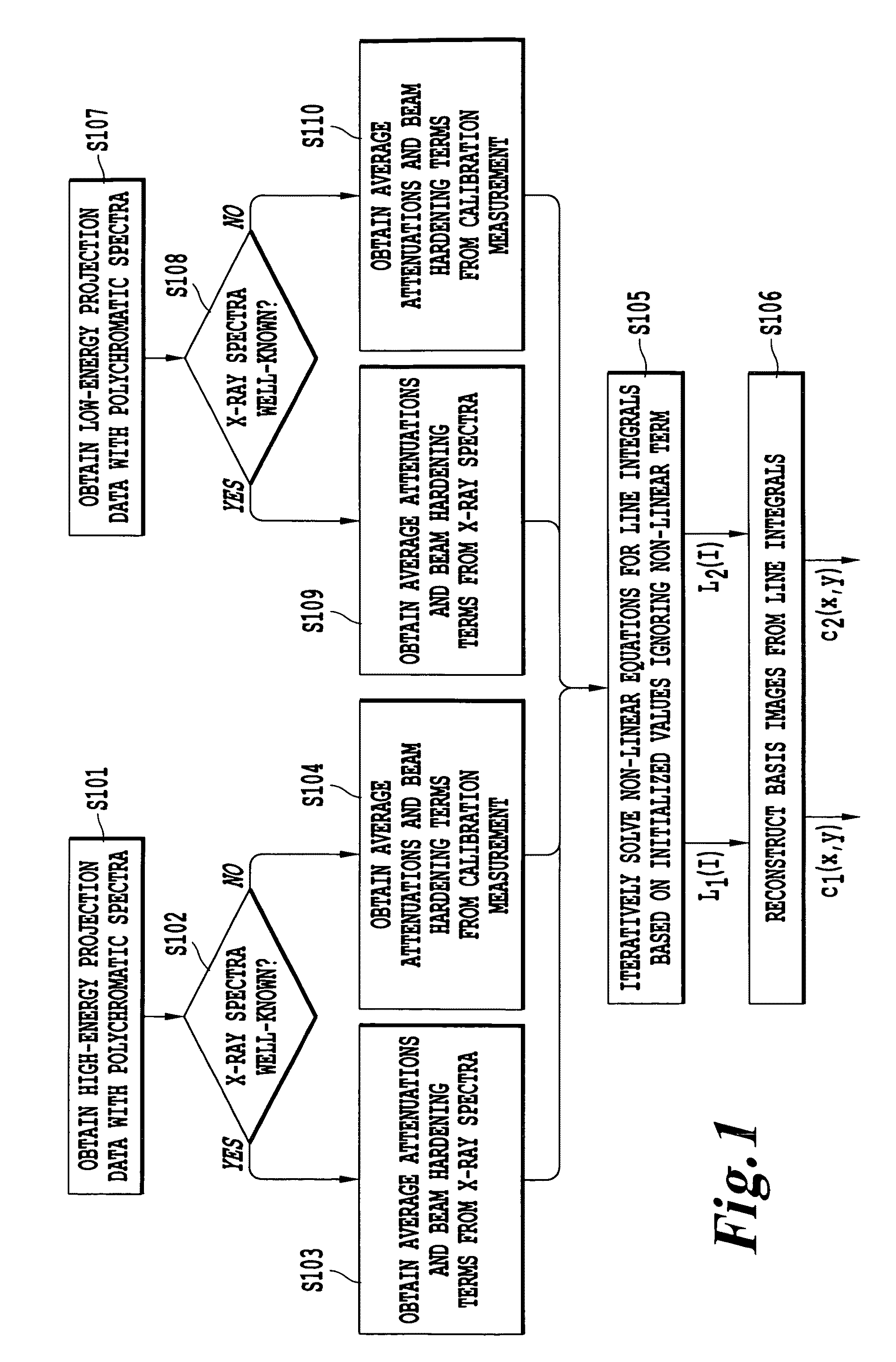
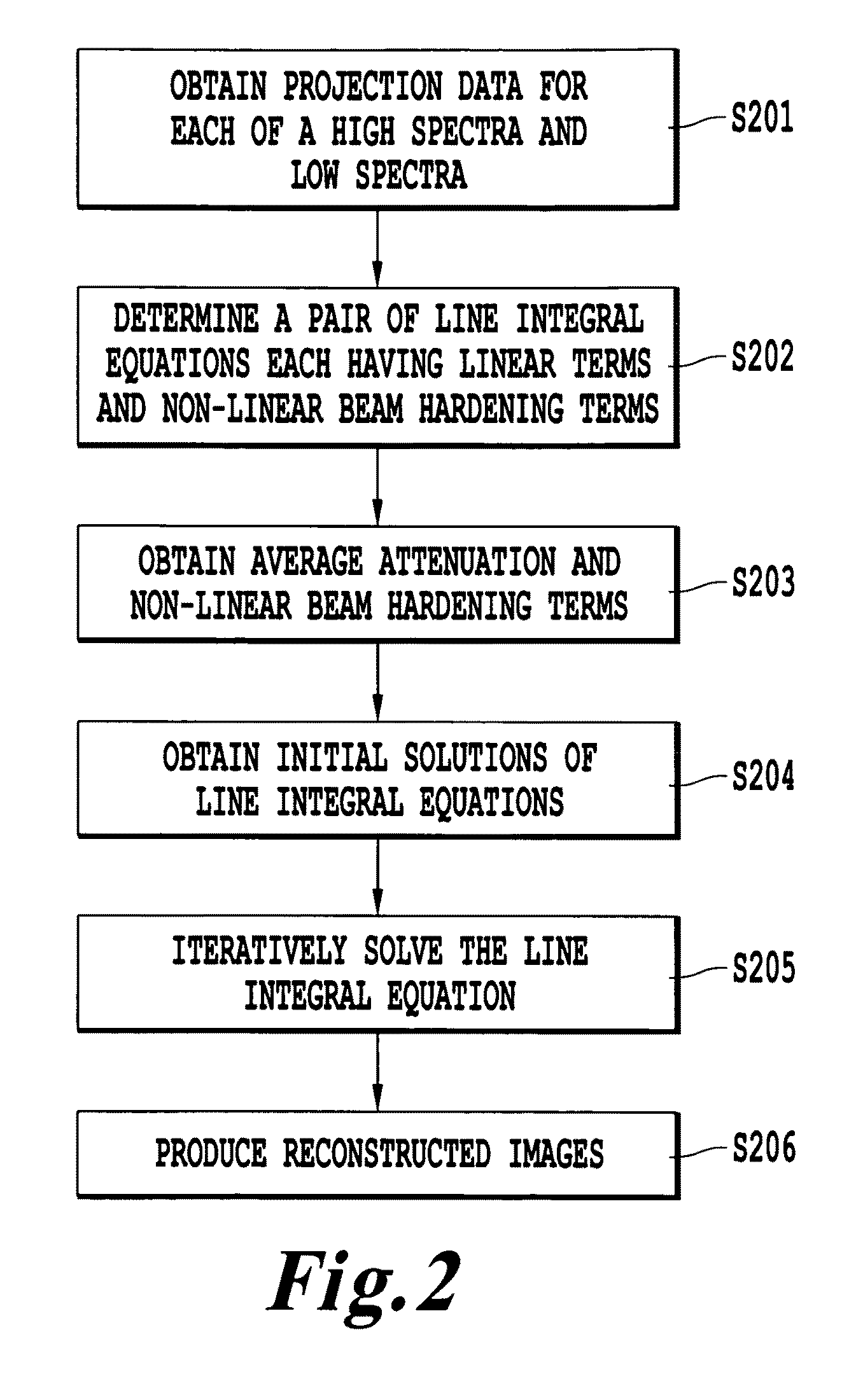
Method, apparatus, and computer-readable medium for pre-reconstruction decomposition and calibration in dual energy computed tomography
ActiveUS20090262997A1Easy to handleReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDecompositionDual energy
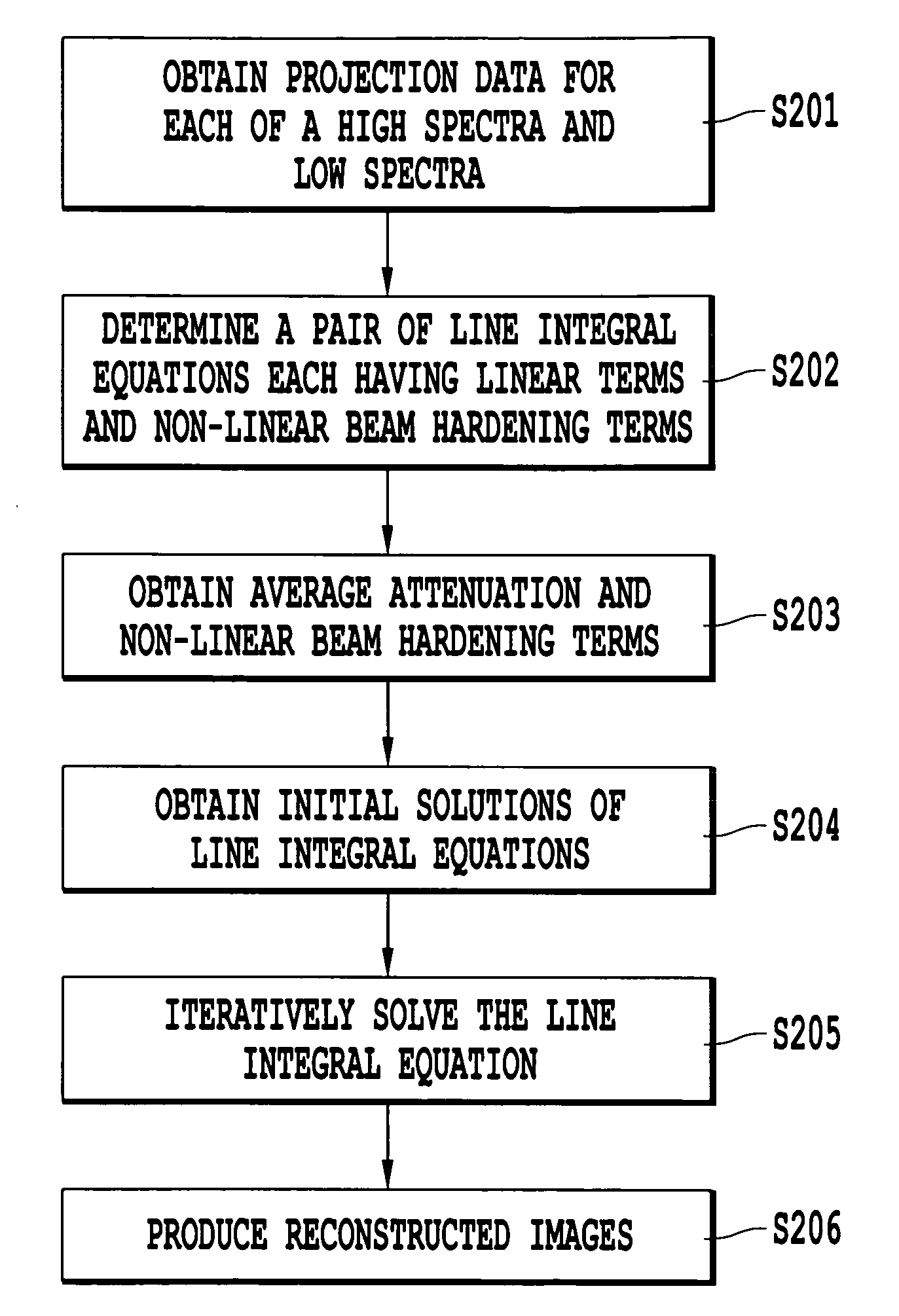
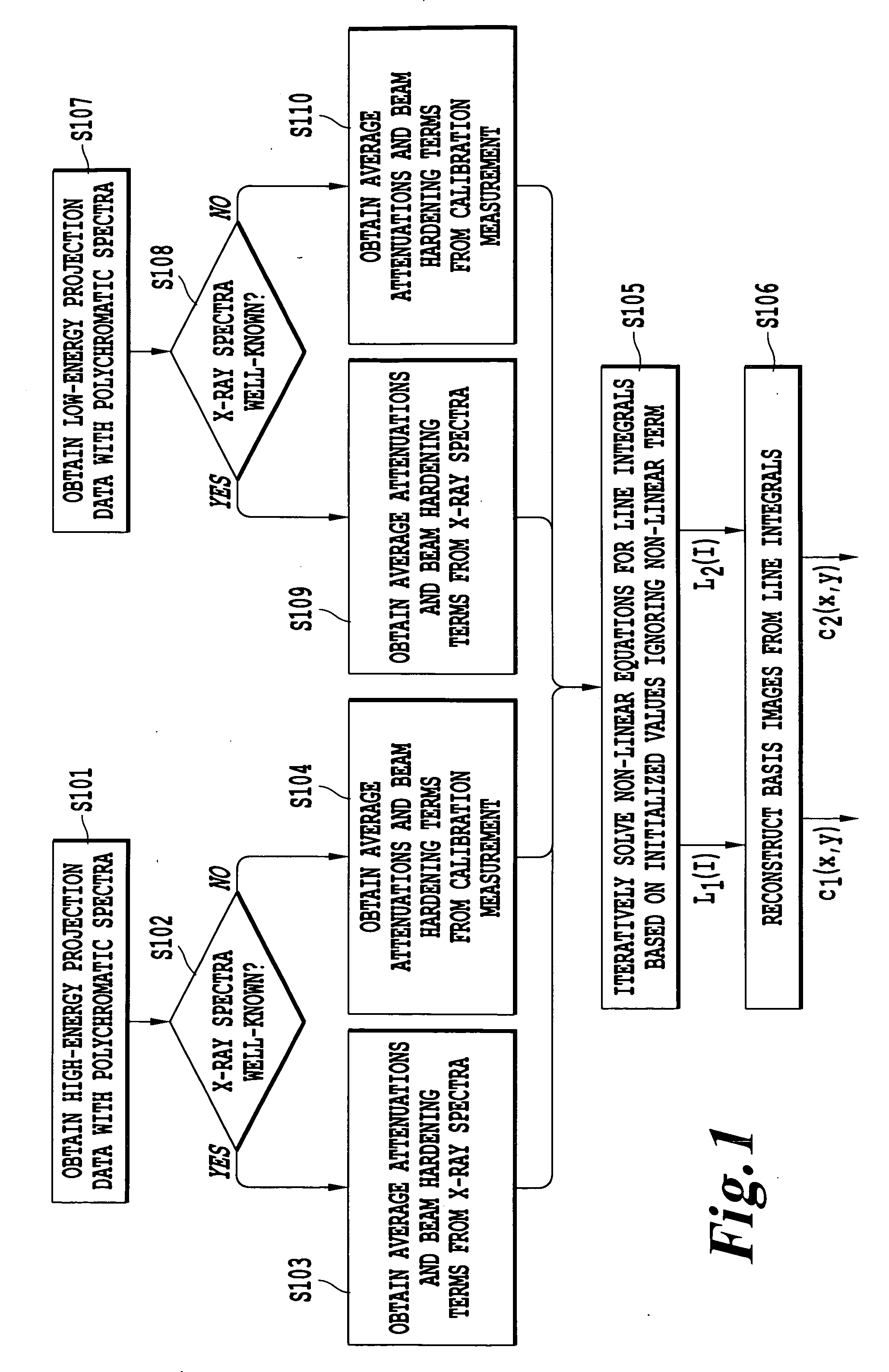
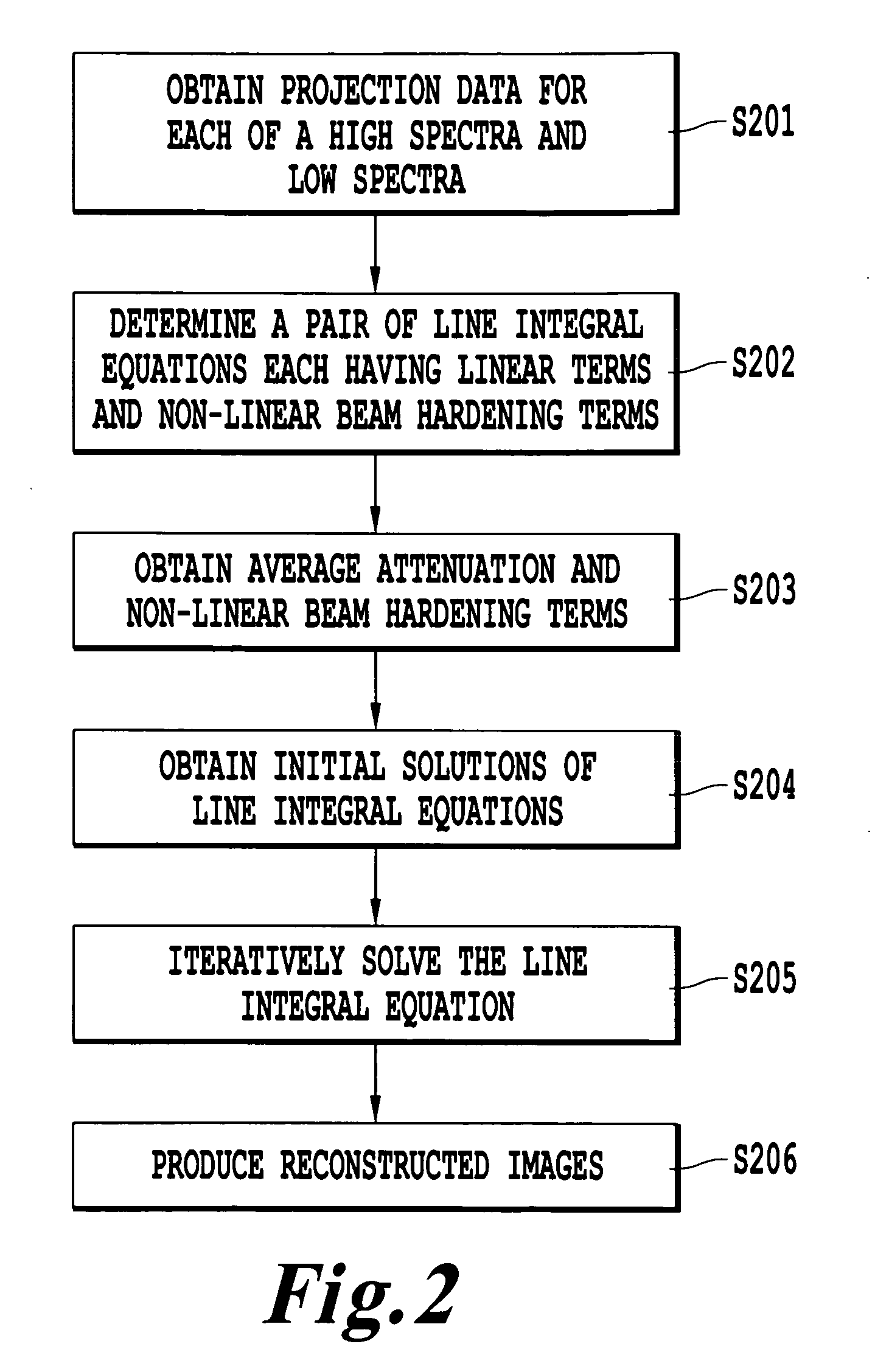
A method of obtaining a computed tomography image of an object includes determining linear terms and non-linear beam hardening terms in a pair of line integral equations for dual-energy projection data from inserting average and difference from average attenuation terms, obtaining an initial solution of the line integral equation by setting the non-linear beam hardening terms to zero, and iteratively solving the line integral equations to obtain one line integral equations for each basis material. Attenuation by the first basis material corresponds to a photoelectric attenuation process, and attenuation by the second basis material corresponds to a Compton attenuation process. The line integral equations can be inverted by an inverse Radon procedure such as filtered backprojection to give images of each basis material. The images of each basis material can then be optionally combined to give monochromatic images, density and effective atomic number images, or photoelectric and Compton processes images.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
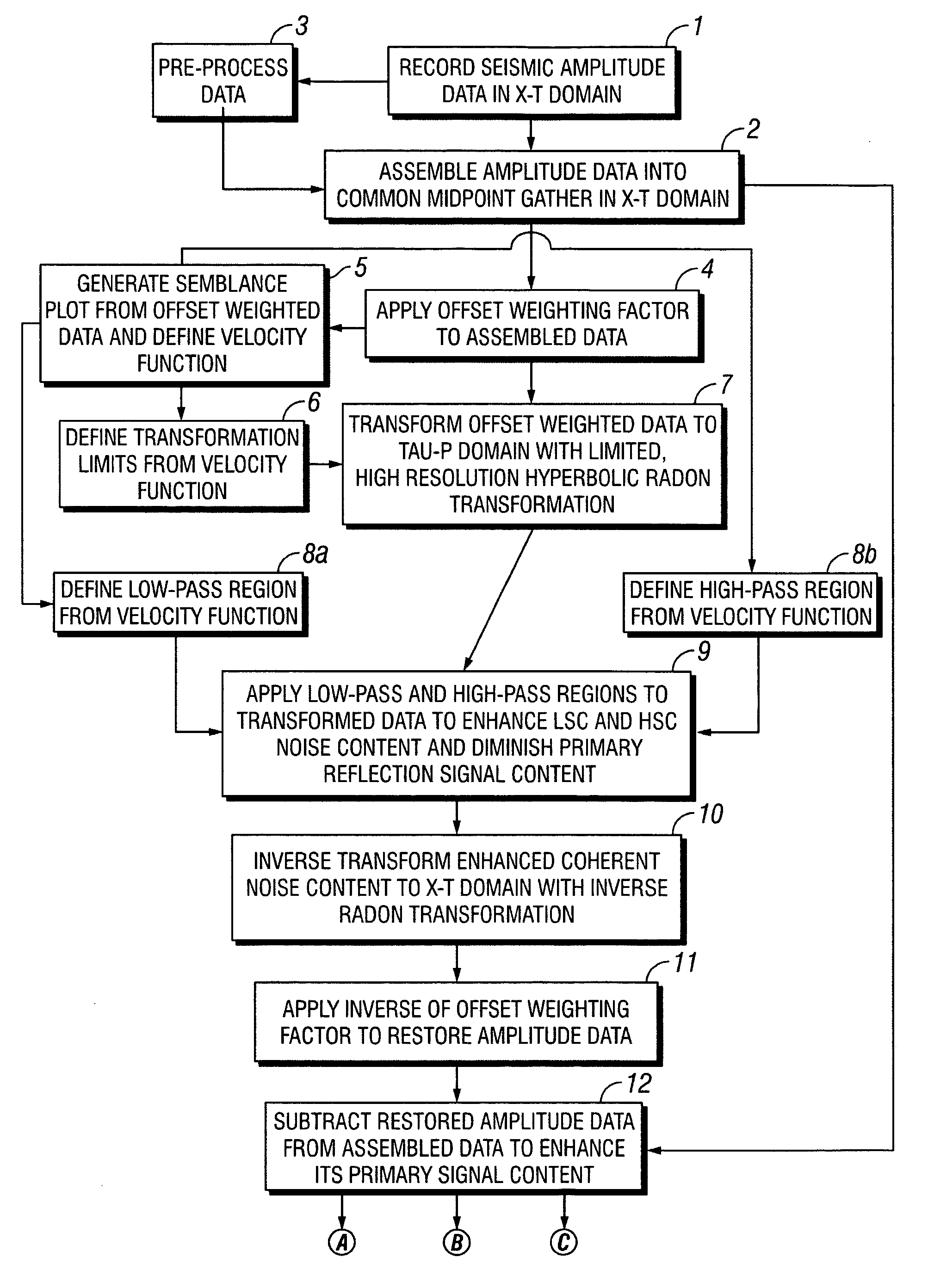
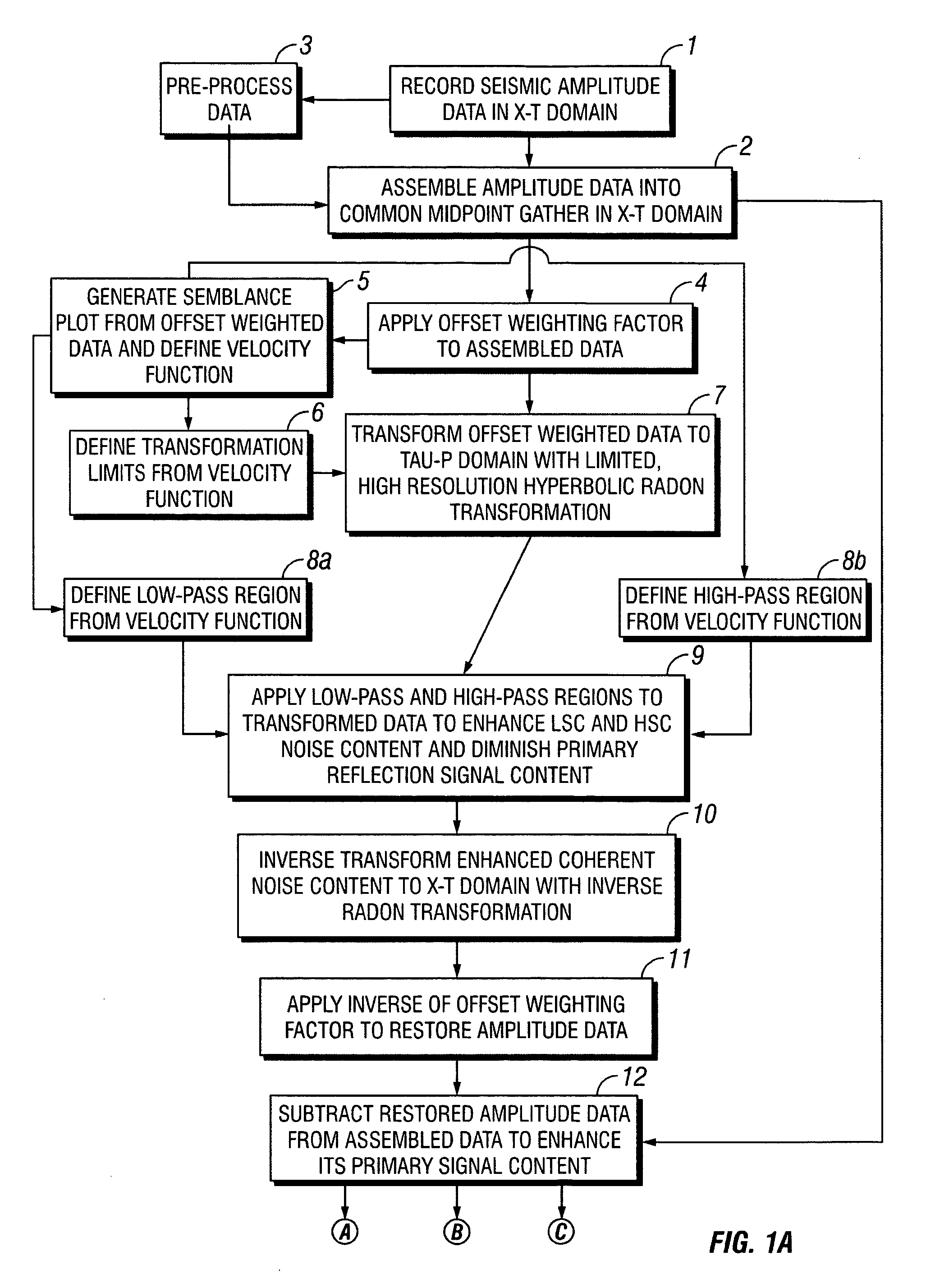
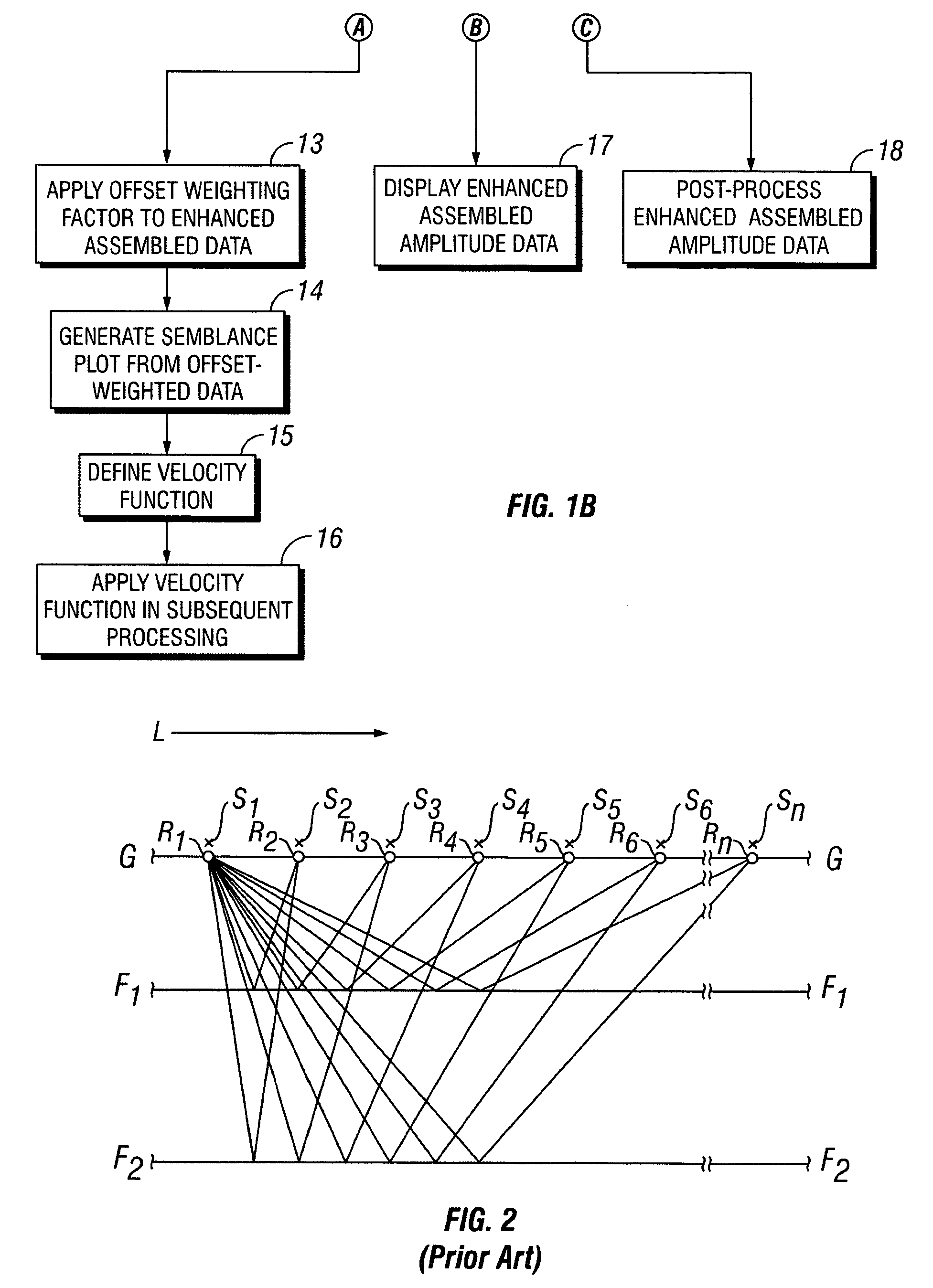
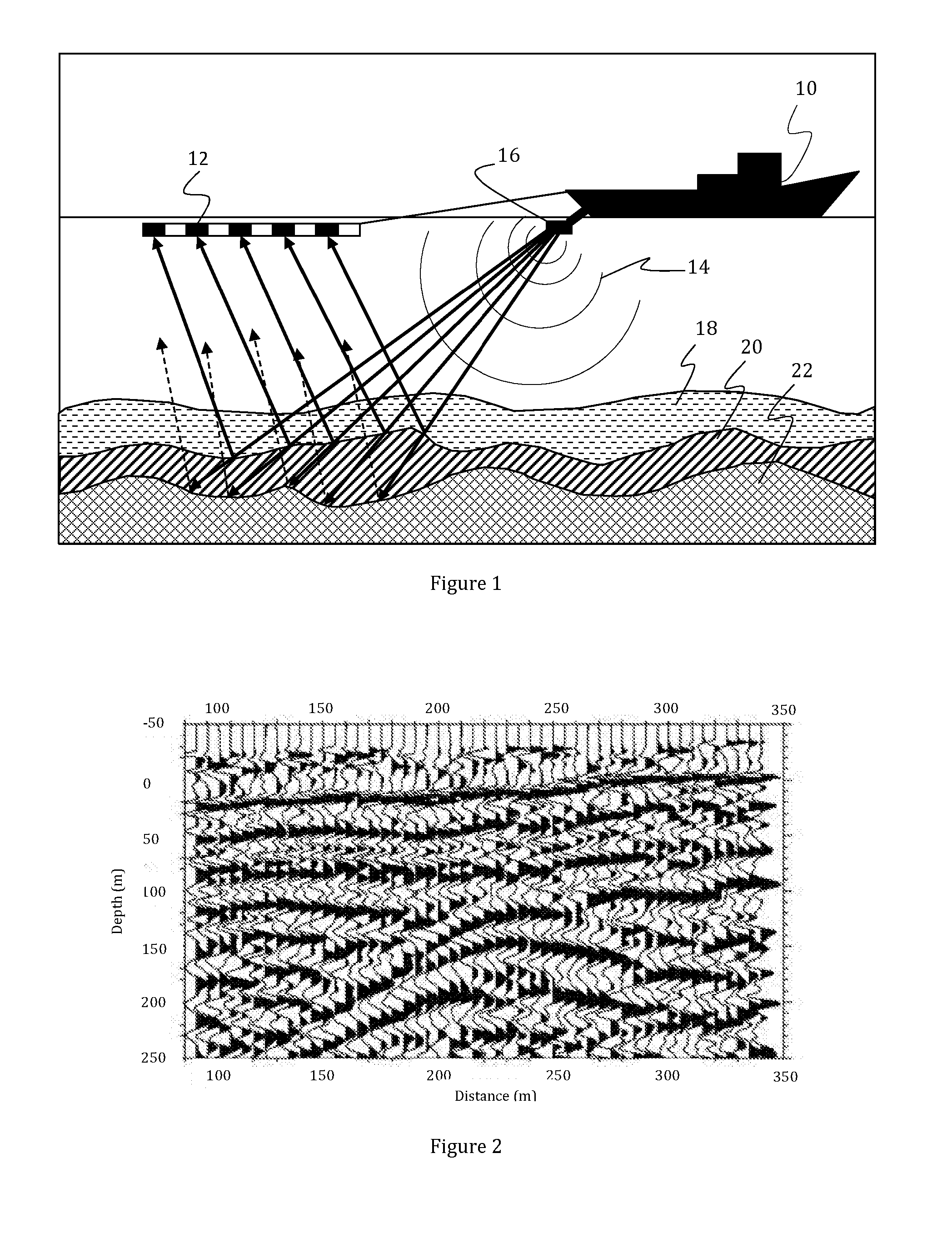
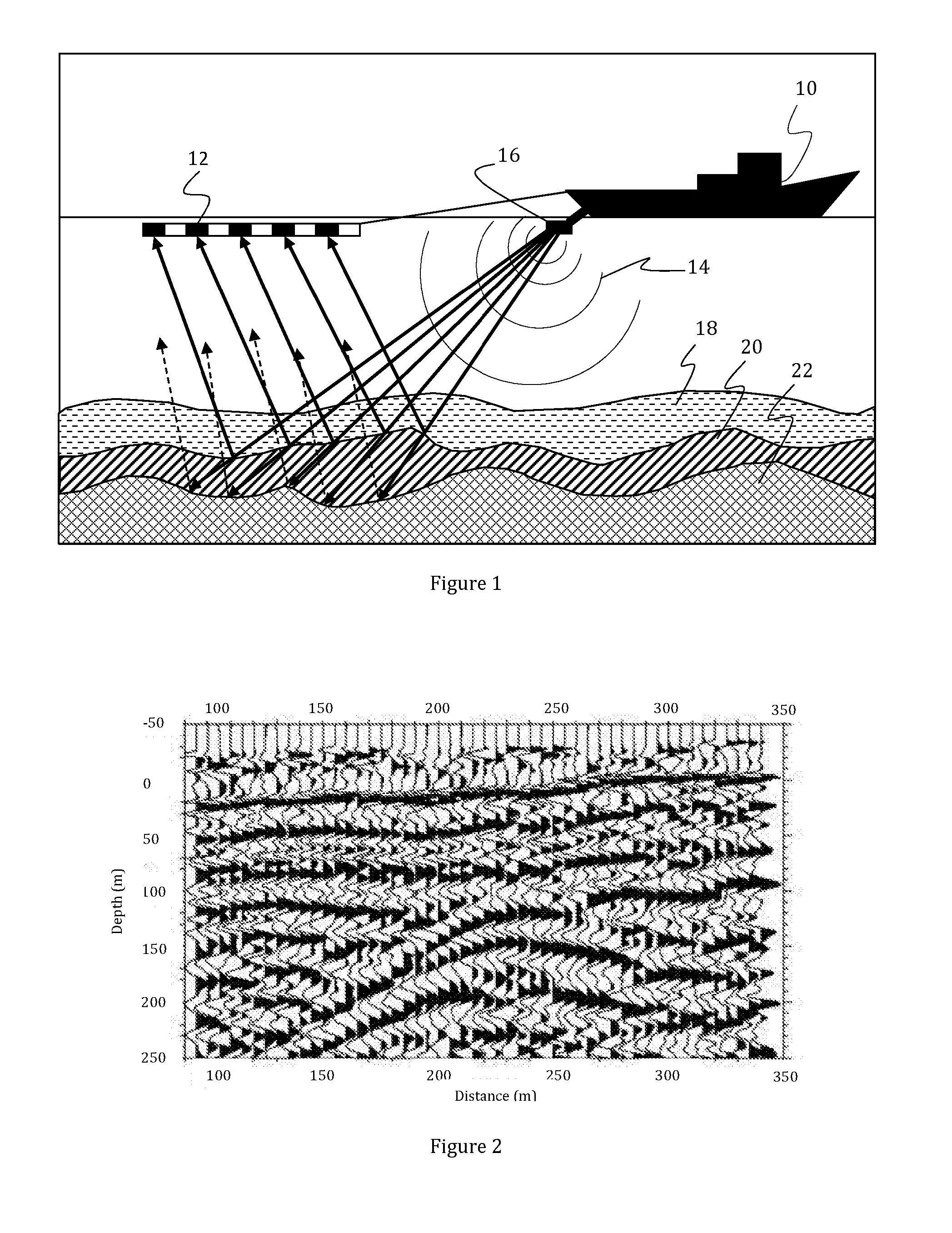
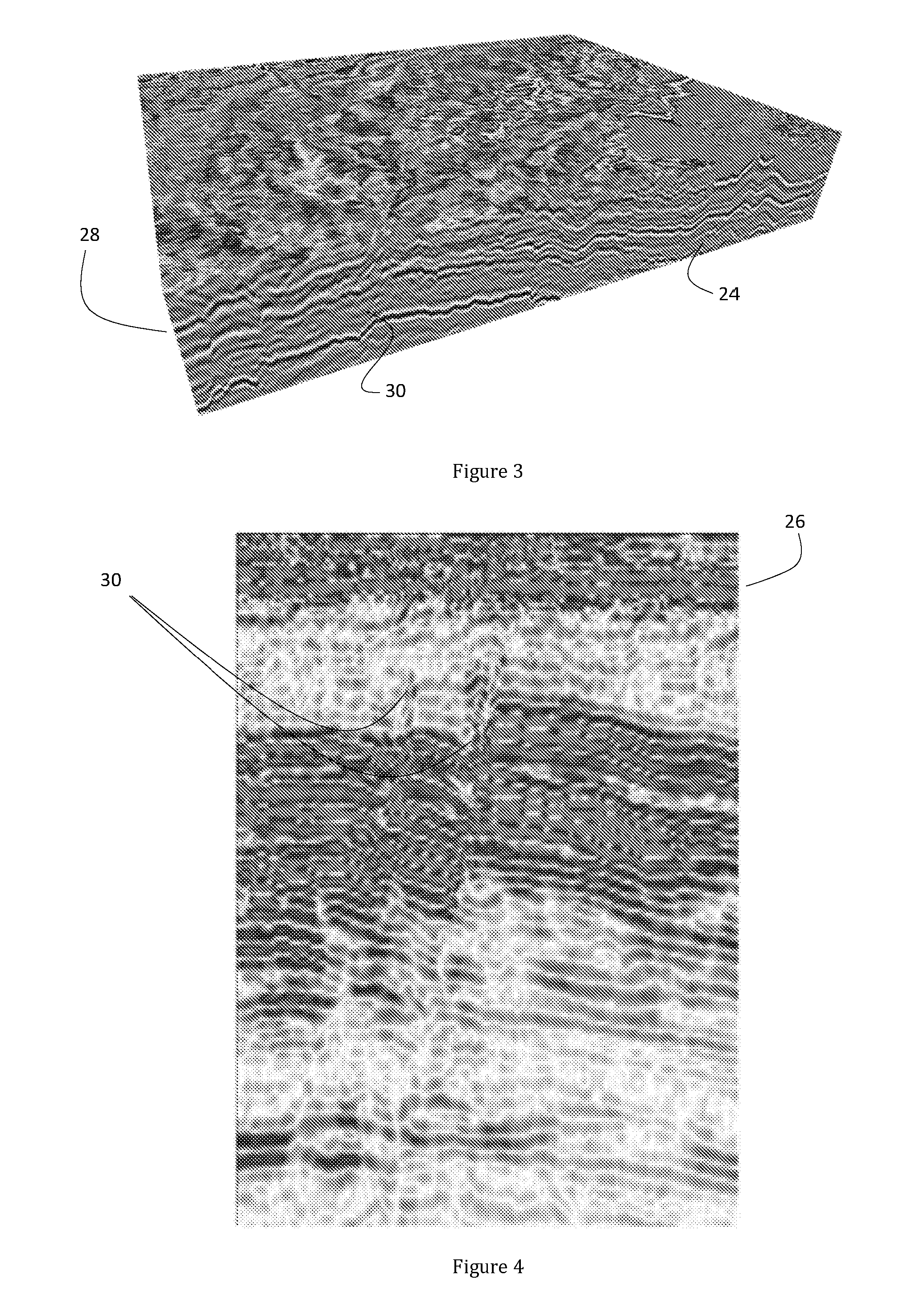
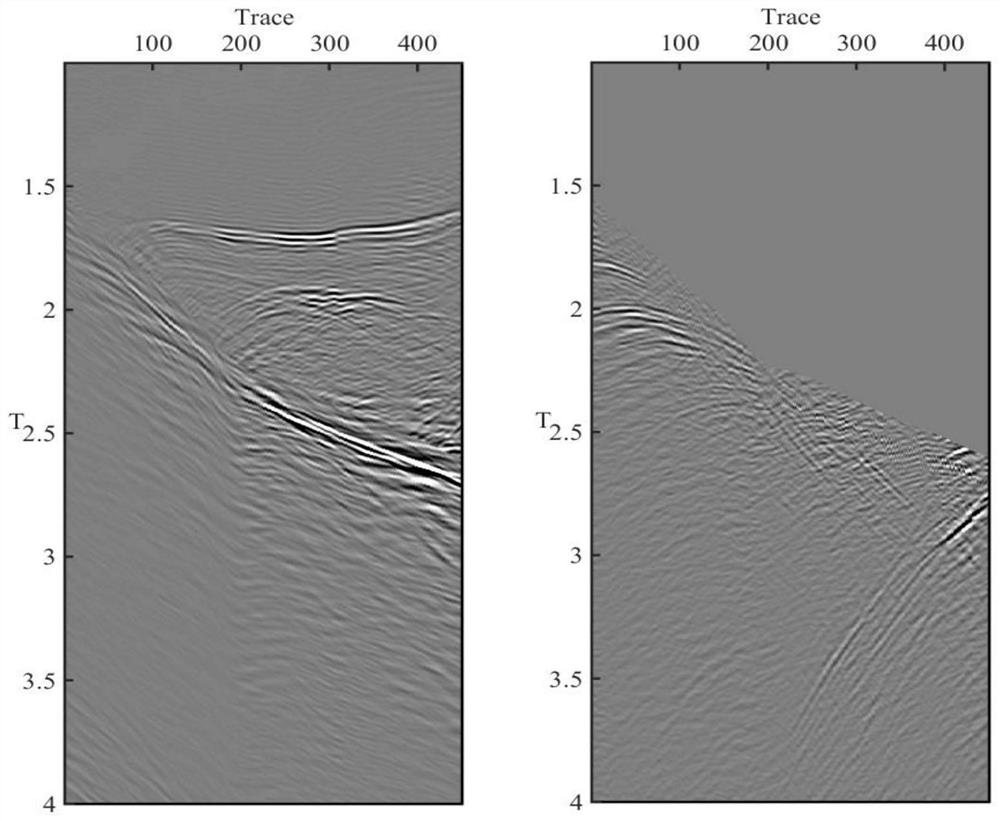
Removal of noise from seismic data using radon transformations
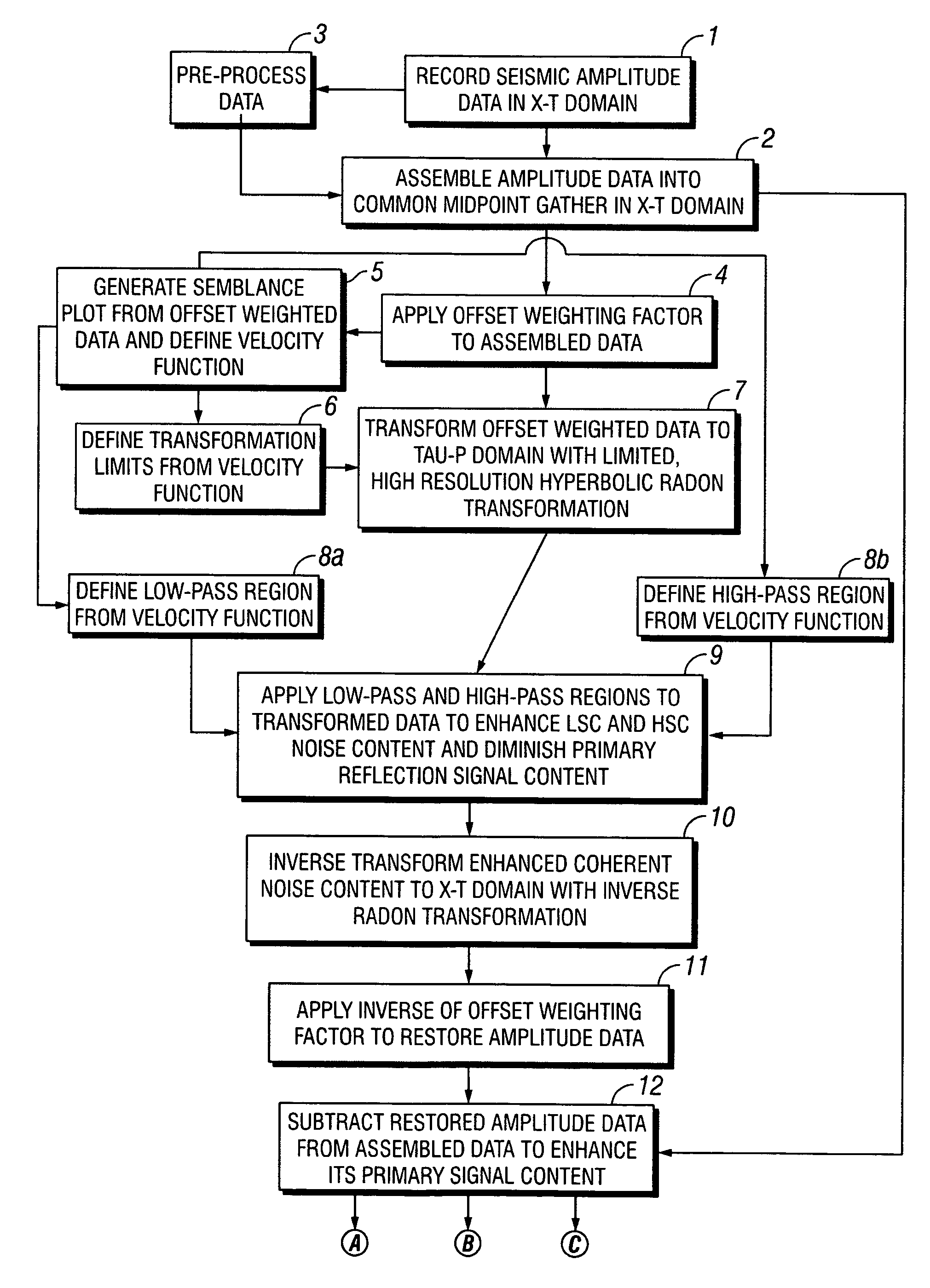
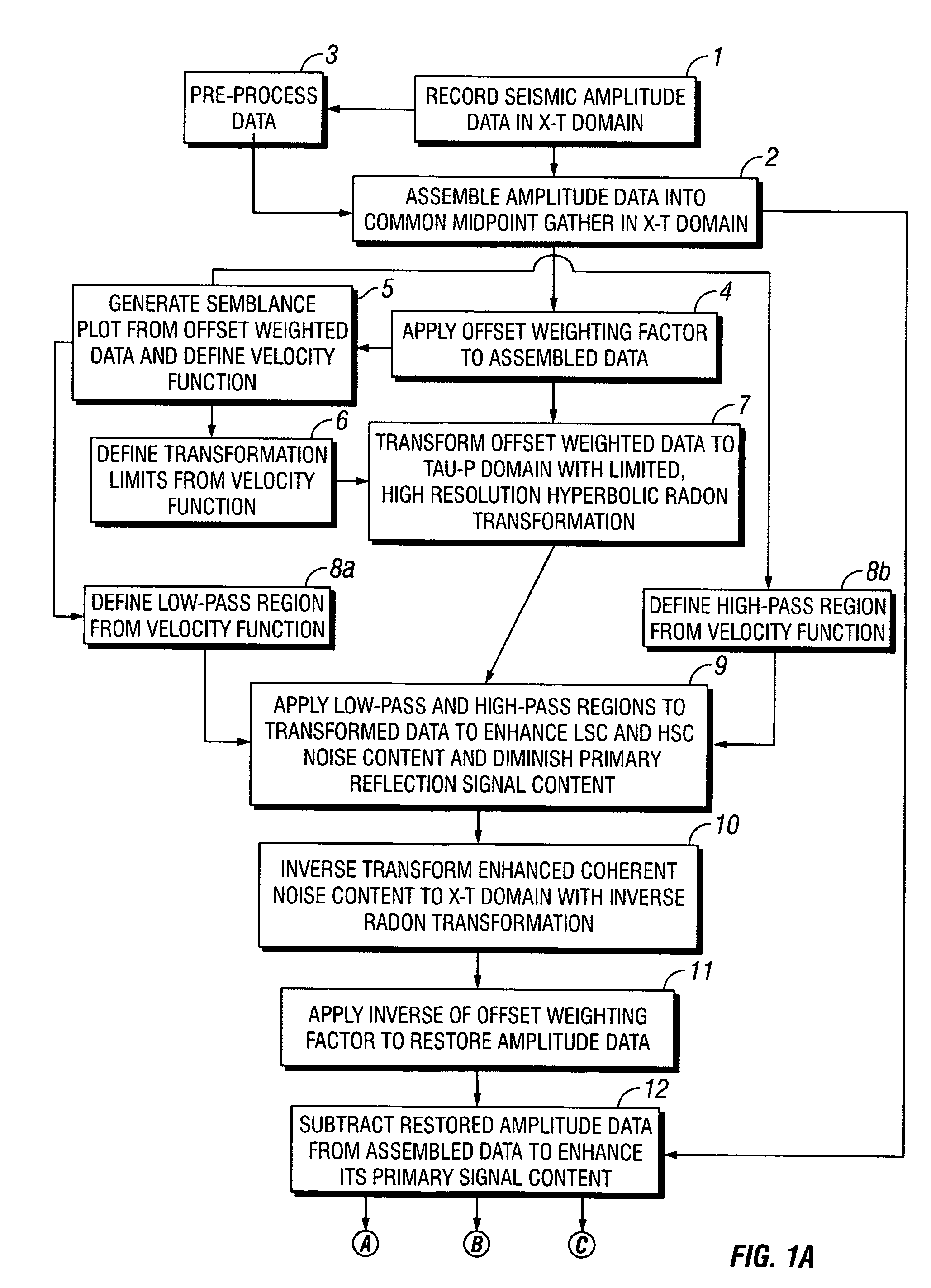
ActiveUS20050180262A1Diminish primary reflection signal contentImprove noiseSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainNormal moveout
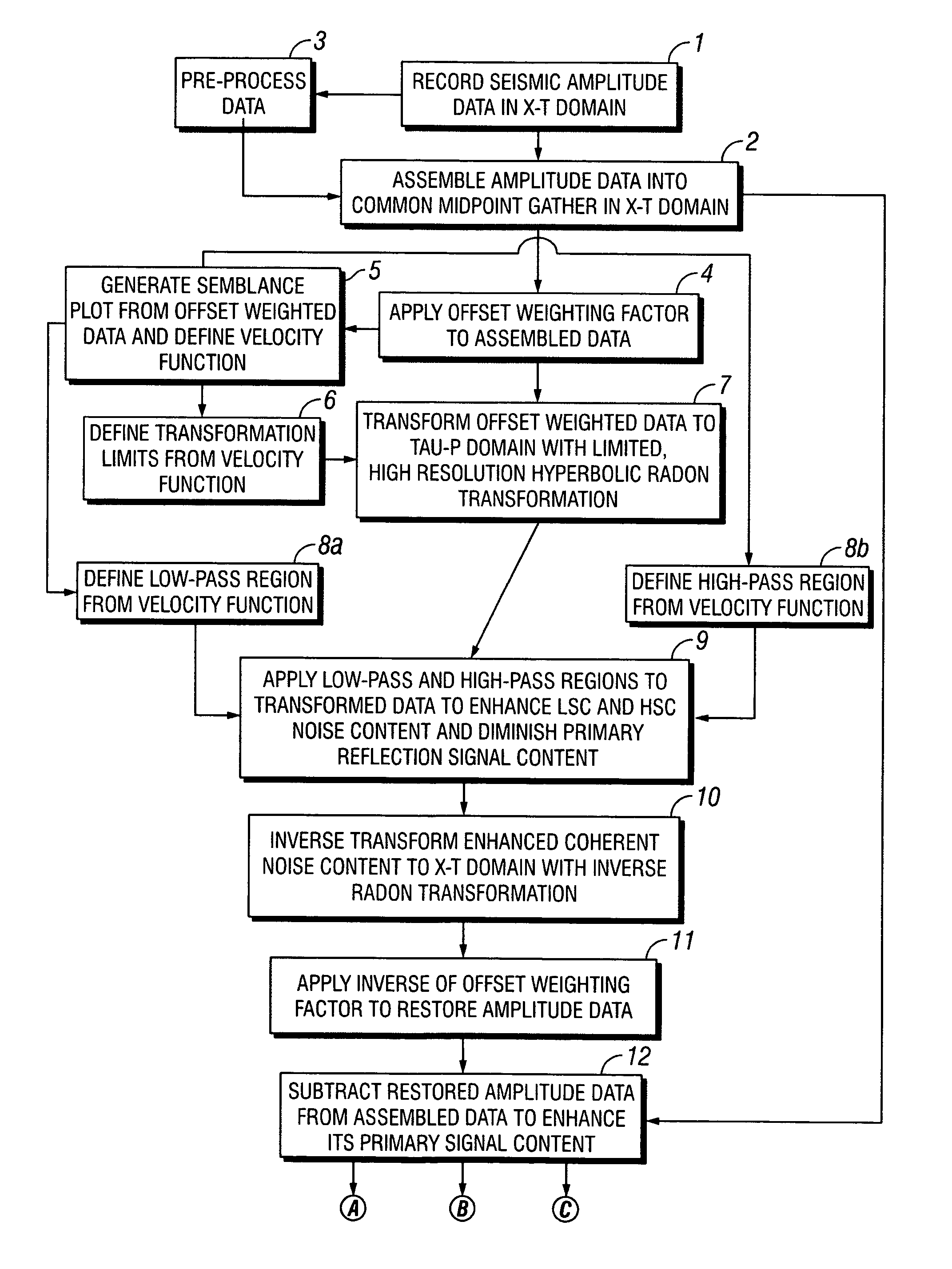
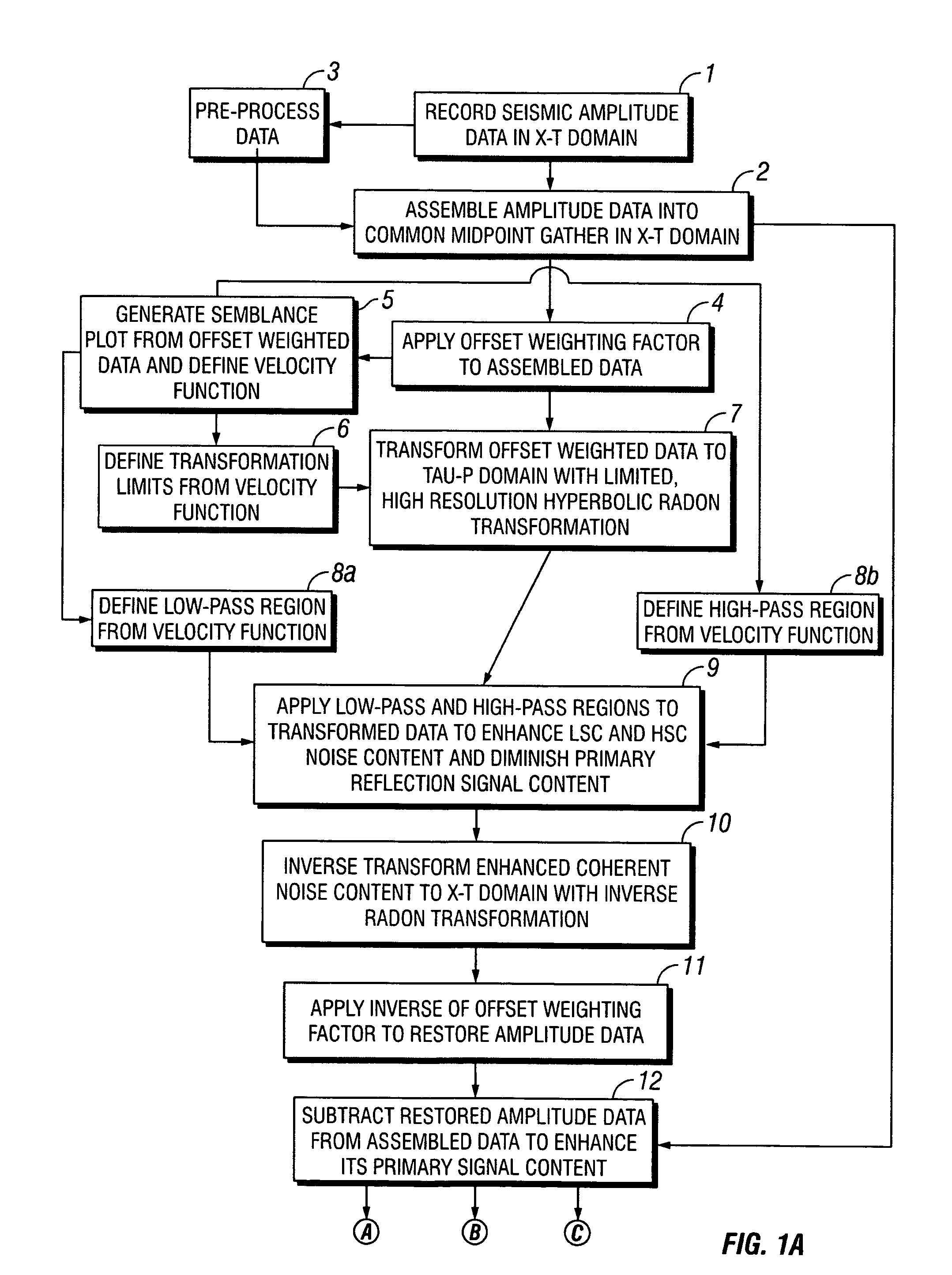
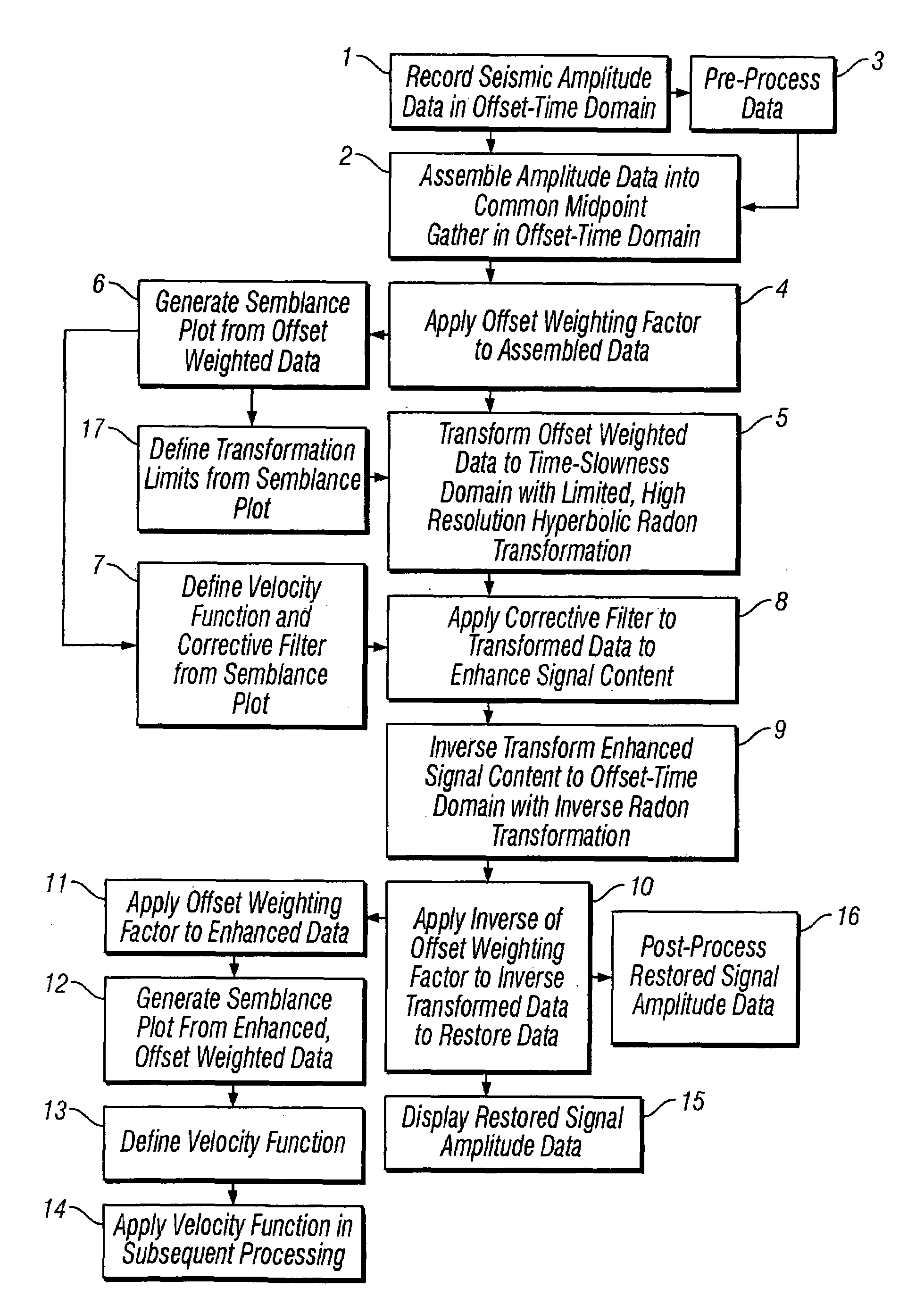
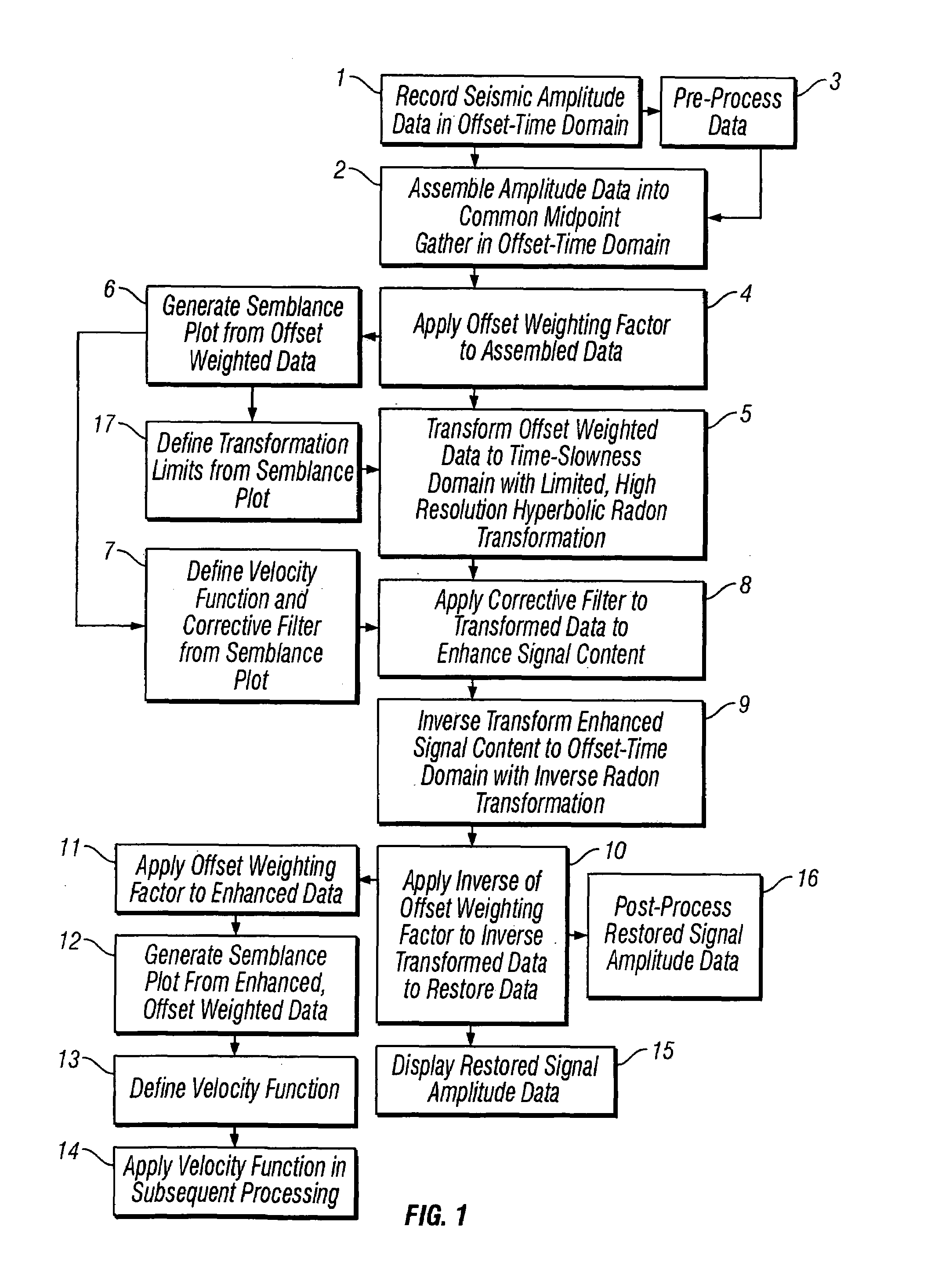
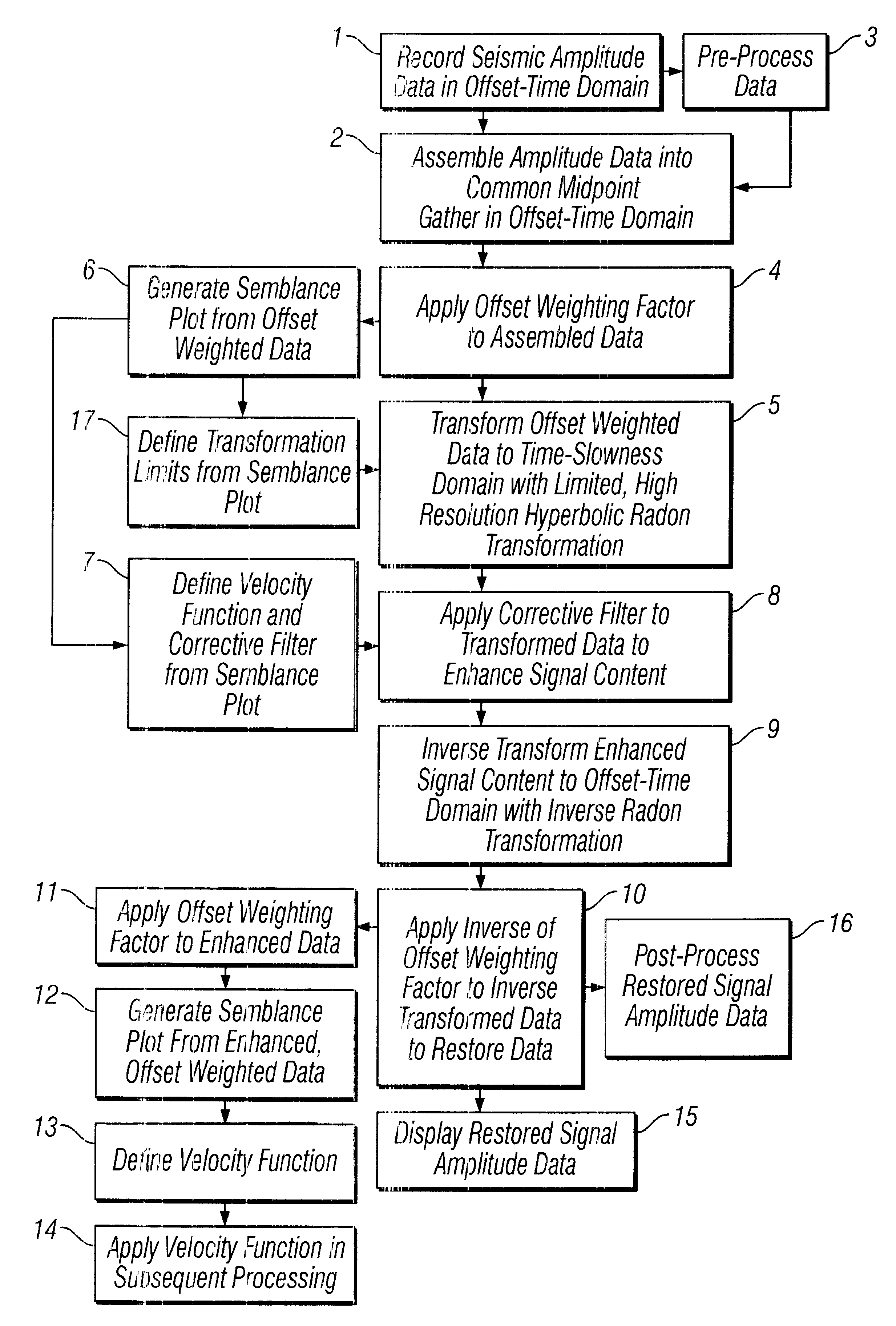
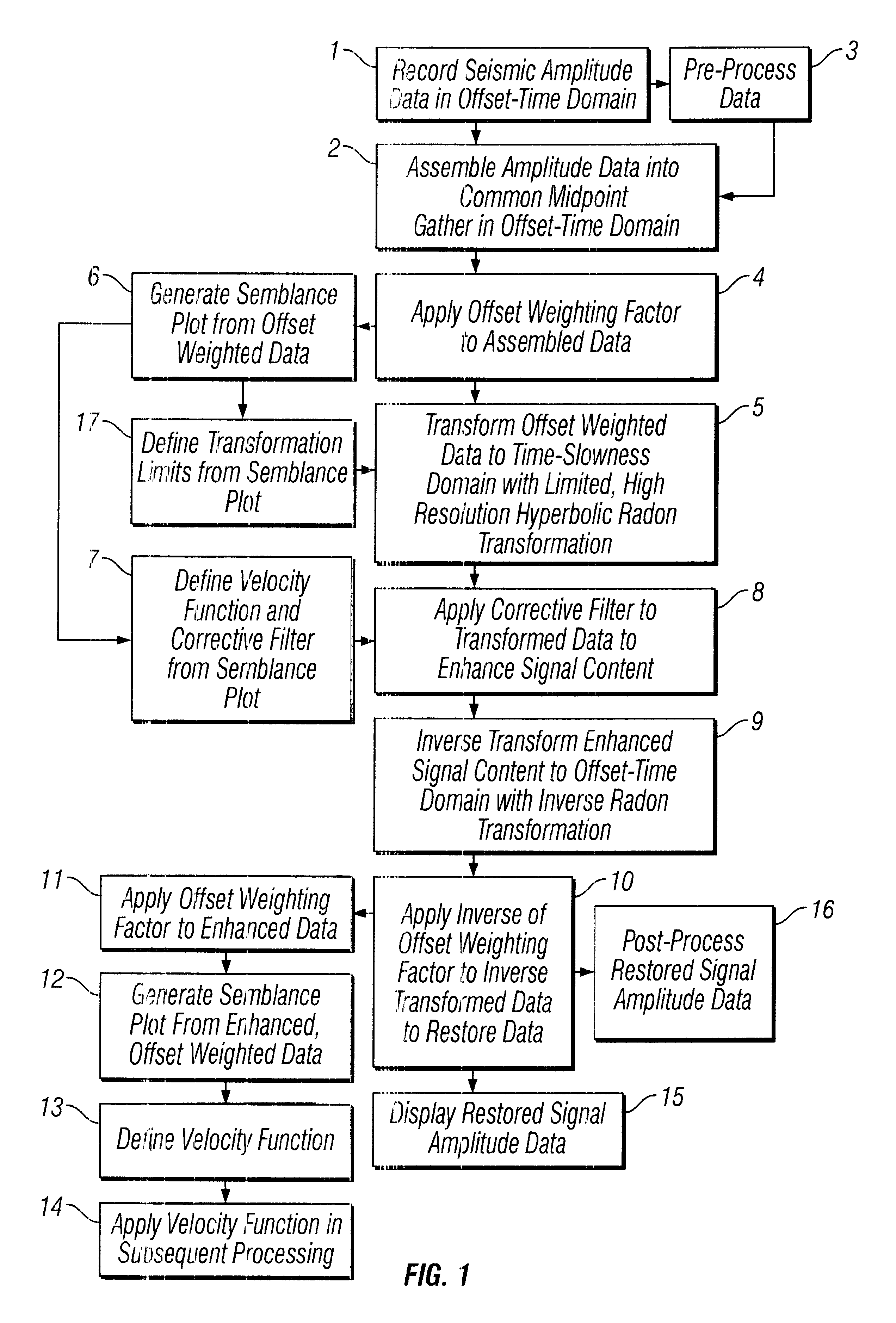
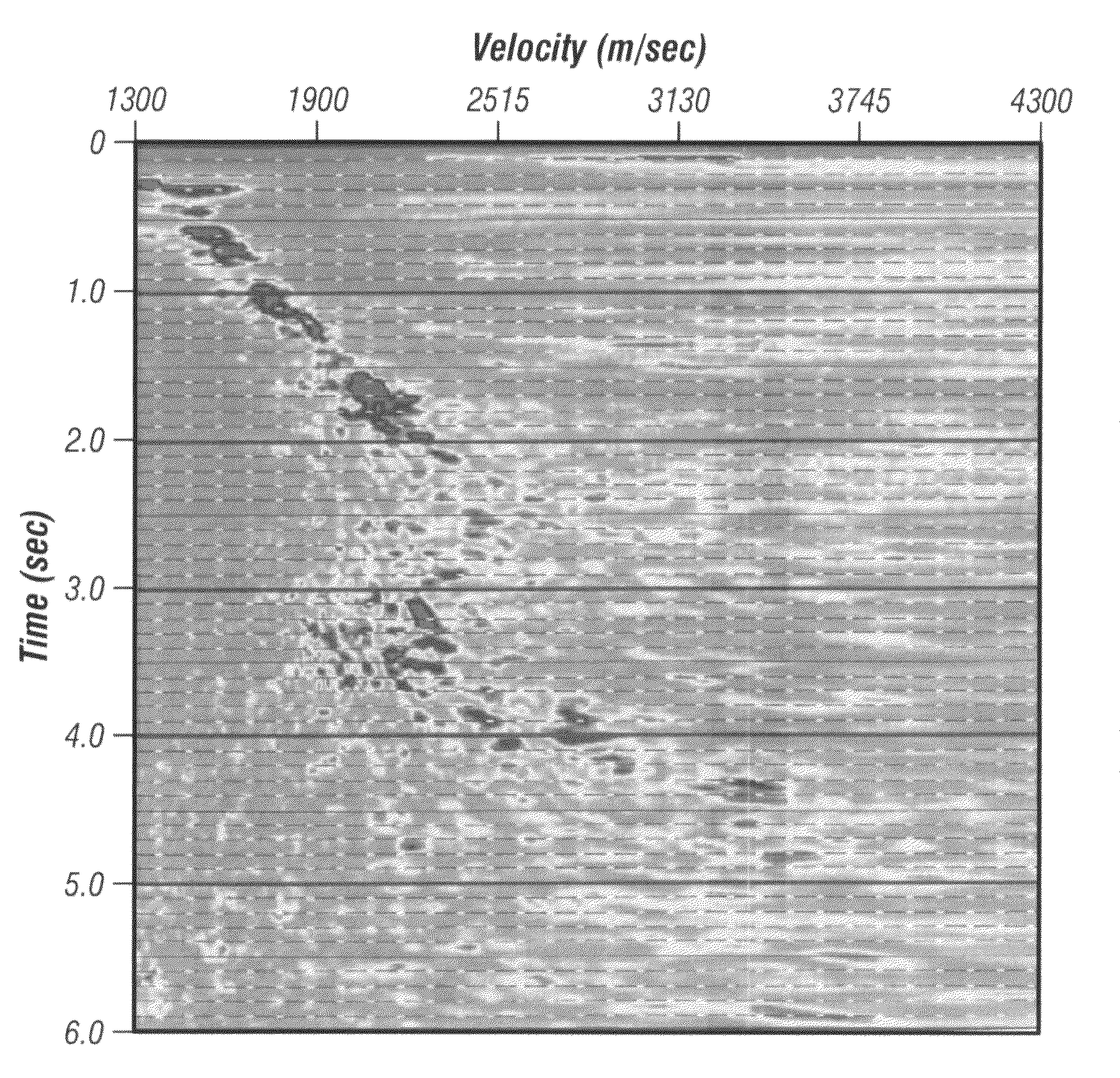
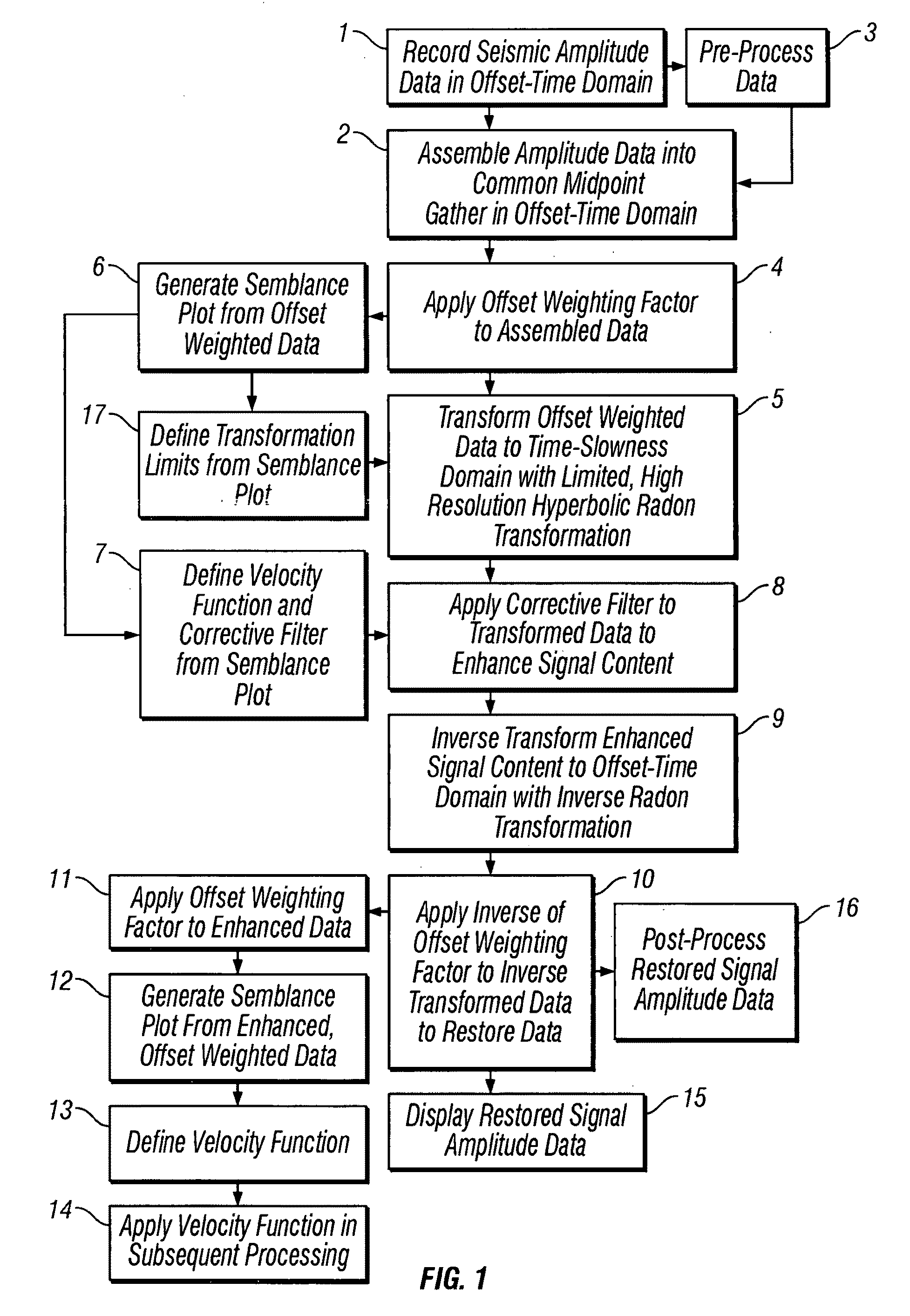
Methods of processing seismic data to remove unwanted noise from meaningful reflection signals are provided for. The methods comprise the steps of assembling seismic data into common midpoint geometry gathers in an offset-time domain without correcting the data for normal moveout. The amplitude data are then transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a Radon transformation. At least of subset of the transformed data is filtered to enhance its coherent noise content and to diminish its primary reflection signal content by defining a slowness high-pass region and, preferably, a slowness low-pass region. The low-pass region is defined to enhance the low slowness coherent noise content and to diminish the primary reflection signal content thereof, thereby generating a first subset of said transformed data having enhanced low slowness coherent noise content. The high-pass region is defined to enhance the high slowness coherent noise content and to diminish the primary reflection signal content thereof, thereby generating a second subset of said transformed data having enhanced high slowness coherent noise content. After filtering, the first and second subsets of transformed data are inverse transformed from the time-slowness domain back to the offset-time domain using an inverse Radon transformation to restore the data. The restored signal amplitude data of the first and second subsets of data are then subtracted from the assembled data, thereby enhancing its primary reflection signal content.
Owner:E S & A ROBINSON
Tau-P filters for removal of noise from seismic data
InactiveUS7366054B1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencySeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainNormal moveout
Methods of processing seismic data to remove unwanted noise from meaningful reflection signals are provided for. The methods comprise the steps of assembling seismic data into common geometry gathers in an offset-time domain without correcting the data for normal moveout. The amplitude data are then transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a Radon transformation. A corrective filter is then applied to enhance the primary reflection signal content of the data and to eliminate unwanted noise events. The corrective filter has a pass region with a lower pass limit and a higher pass limit. The higher pass limit is set within 15% above the slowness of the primary reflection signals and, preferably, it is more closely set to the slowness of the primary reflection signals. The lower pass limit is also preferably set within 15% below the slowness of the primary reflection signals. The tau-P filter preferably is defined by reference to the velocity function of the primary reflection signals, and preferably is expressed as:1vs(1+r2)≤p≤1vs(1-r1)where r1 and r2 are percentages expressed as decimals. After filtering, the enhanced signal content is inverse transformed from the time-slowness domain back to the offset-time domain using an inverse Radon transformation.
Owner:ROBINSON JOHN M
Removal of noise from seismic data using high resolution radon transformations
InactiveUS6987706B2Enhance primary reflection signal contentRemove noiseSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainComputer science
Methods of processing seismic data to remove unwanted noise from meaningful reflection signals are provided for. The seismic data is transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a high resolution Radon transformation. That is, the Radon transformation is performed according to an index j of the slowness set and a sampling variable Δp; wherein j=pmax-pmin+1 µ sec / mΔ p,Δp is from about 0.5 to about 4.0 μsec / m, pmax is a predetermined maximum slowness, and pmin is a predetermined minimum slowness. A corrective filter is then applied to enhance the primary reflection signal content of the data and to eliminate unwanted noise events. After filtering, the enhanced signal content is inverse transformed from the time-slowness domain back to the offset-time domain using an inverse Radon transformation.Suitable forward and reverse Radon transformations incorporating an offset weighting factor xn and its inverse pn, where 0<n<1, include the following continuous transform equations, and discrete versions thereof that approximate the continuous transform equations: u(p,τ)= ∫-∞∞ ⅆx∫-∞∞ ⅆt d(x,t)xnδ[f(t,x,τ,p)] (forward transform)d(x,t)= ∫-∞∞ ⅆp∫-∞∞ ⅆ τ pnρ(τ)*u(p,τ)δ[g(t,x,τ,p)] (inverse transform)
Owner:JOHN M ROBINSON +1
Removal of noise from seismic data using radon transformations
ActiveUS7239578B2Diminish primary reflection signal contentEnhanced low slowness coherent noise contentSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainNormal moveout
Methods of processing seismic data to remove unwanted noise from meaningful reflection signals are provided for. The methods comprise the steps of assembling seismic data into common geometry gathers in an offset-time domain without correcting the data for normal moveout. The amplitude data are then transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a Radon transformation. At least of subset of the transformed data is filtered to enhance its coherent noise content and to diminish its primary reflection signal content by defining a slowness high-pass region and, a slowness low-pass region. The low-pass region is defined to enhance the low slowness coherent noise content and to diminish the primary reflection signal content thereof, thereby generating a first subset of said transformed data having enhanced low slowness coherent noise content. The high-pass region is defined to enhance the high slowness coherent noise content and to diminish the primary reflection signal content thereof, thereby generating a second subset of said transformed data having enhanced high slowness coherent noise content. After filtering, the first and second subsets of transformed data are inverse transformed from the time-slowness domain back to the offset-time domain using an inverse Radon transformation to restore the data. The restored signal amplitude data of the first and second subsets of data are then subtracted from the assembled data, thereby enhancing its primary reflection signal content.
Owner:E S & A ROBINSON
Method and device for wave fields separation in seismic data
ActiveUS20130021873A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasHydrophoneWave field
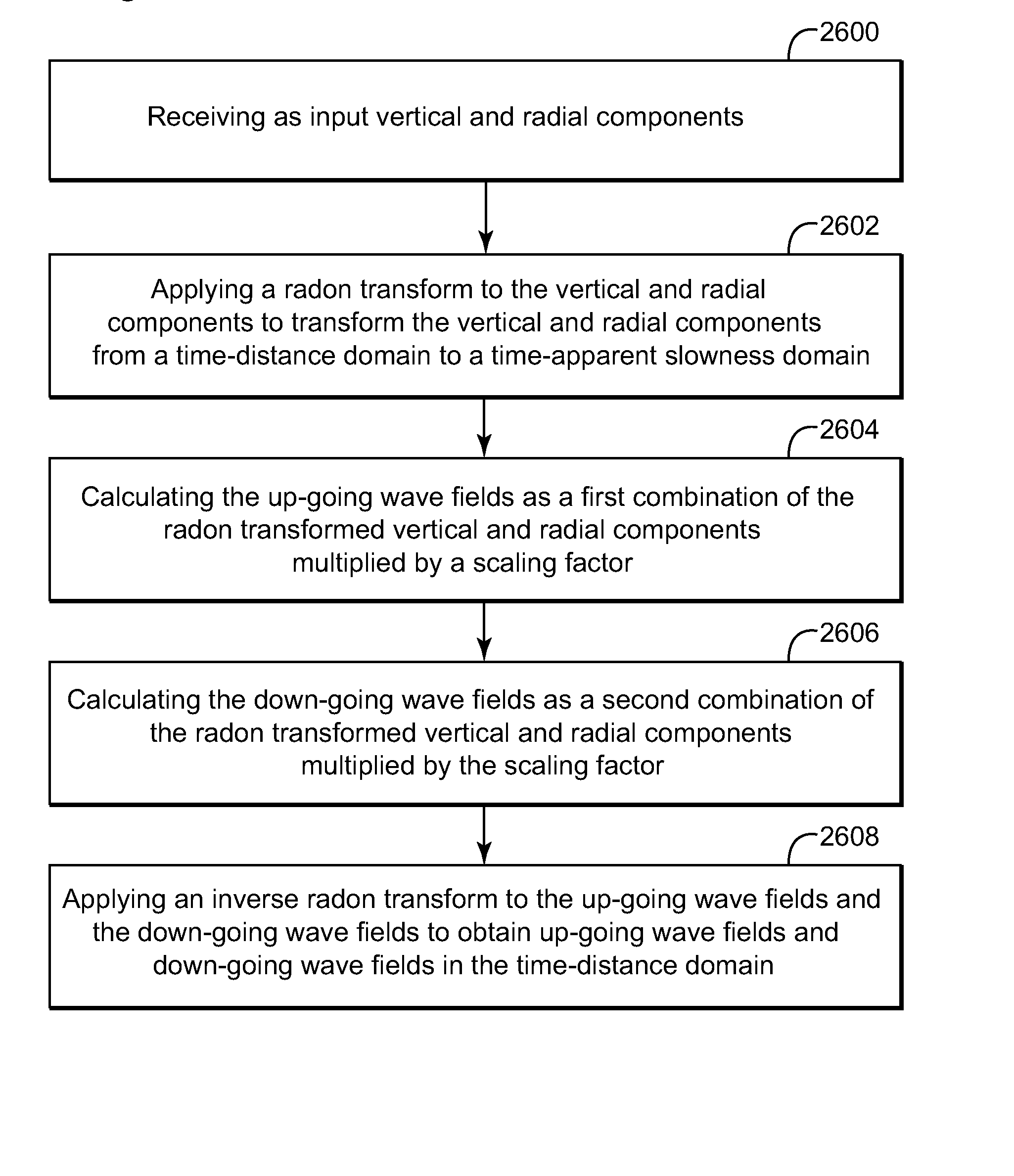
Apparatus, computer instructions and method for processing seismic data related to a subsurface of a body of water. The method includes receiving input data for a vertical direction and radial direction and / or from a hydrophone, applying a radon transform to the input data, separating primary signals from ghosts signals based on the vertical and radial components, applying an inverse radon transform to determine up-going and down-going wave fields in a time-distance domain, and separating interfering up-going and down-going wave fields that are recorded by the same receivers.
Owner:CGG SERVICES U S
Radon transformations for removal of noise from seismic data
InactiveUS7561491B2Diminish primary reflection signal contentImprove noiseSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasTime domainComputer science
Methods of processing seismic data to remove unwanted noise from meaningful reflection signals are provided for. Assembled seismic data are transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a Radon transformation. Preferably, an offset weighting factor xn is applied to the amplitude data, wherein 0<n<1, and the Radon transformation is applied within defined slowness limits pmin and pmax that will preserve coherent noise, and according to an index j of the slowness set and a sampling variable Δp; whereinj=pmax-pmin+1µsec / mΔp,Δp is from about 0.5 to about 4.0 μsec / m. The coherent noise content of the transformed data is then enhanced, and the primary reflection signal content diminished by filtering at least a subset of the transformed data. The filtered data are inverse transformed from the time-slowness domain back to the offset-time domain using an inverse Radon transformation, and, if necessary, an inverse of the offset weighting factor pn is applied to the inverse transformed data, wherein 0<n<1, to restore the amplitude data. The restored amplitude data of the filtered data are then subtracted from the originally assembled amplitude data. The coherent noise content of the assembled amplitude data is thereby diminished and the primary reflection signal content enhanced.
Owner:E S & A ROBINSON
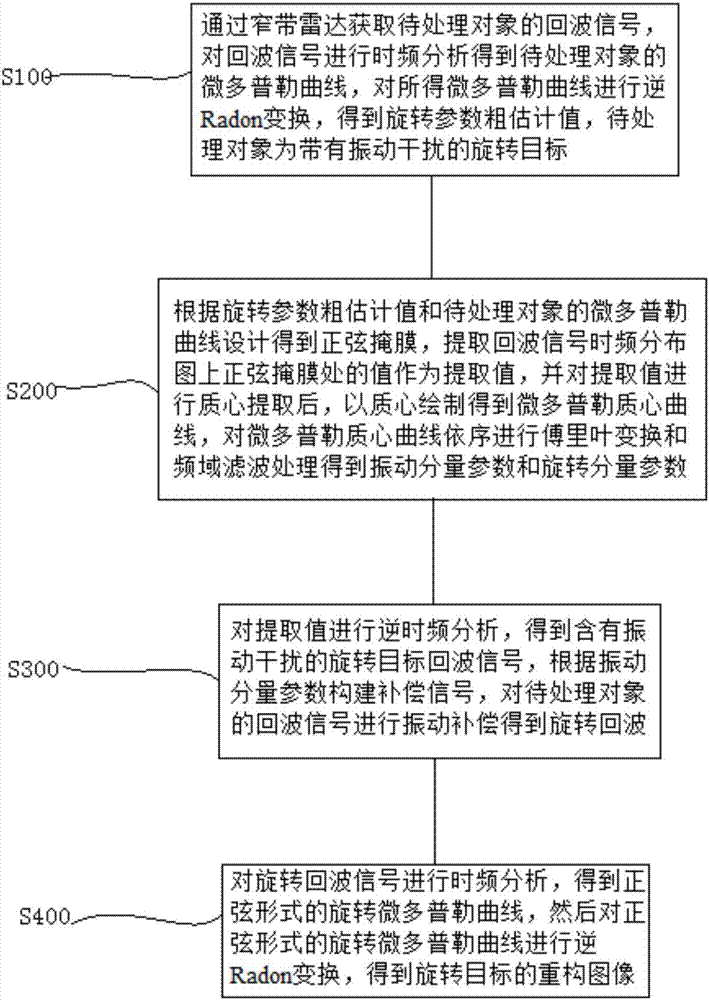
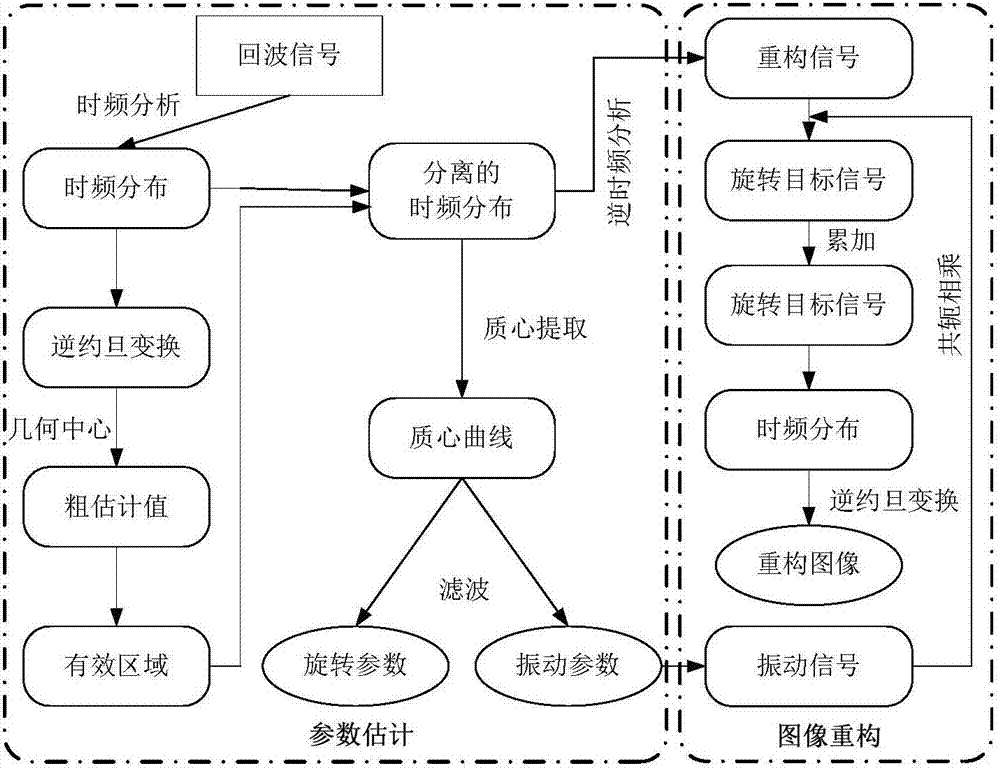
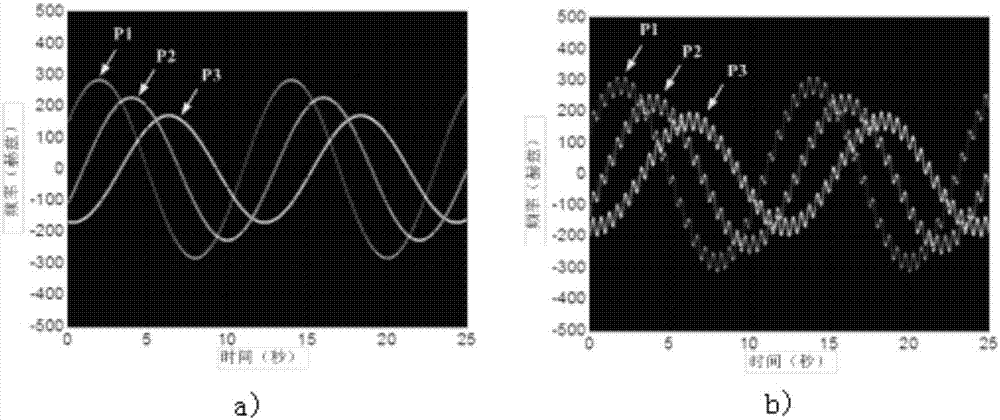
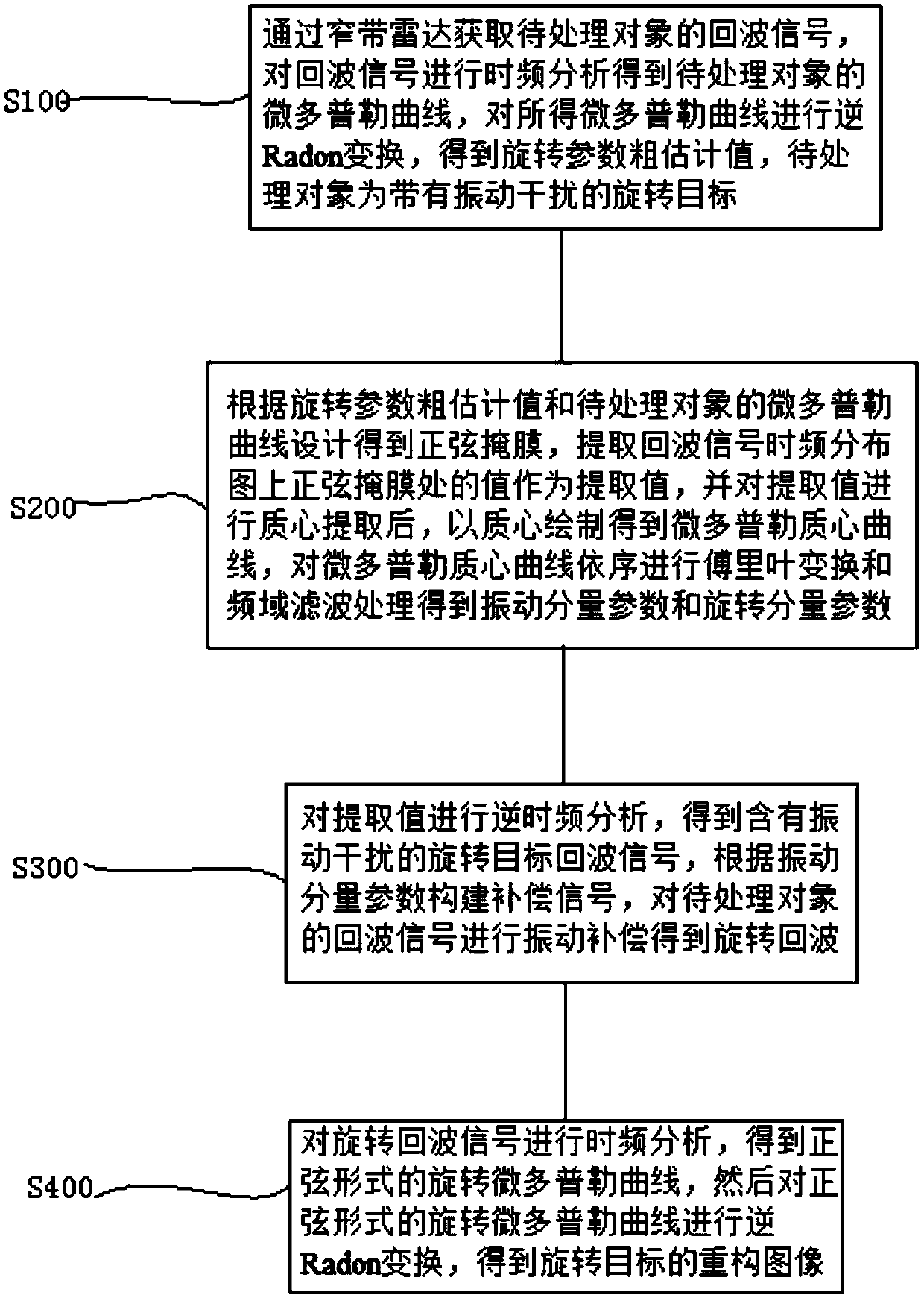
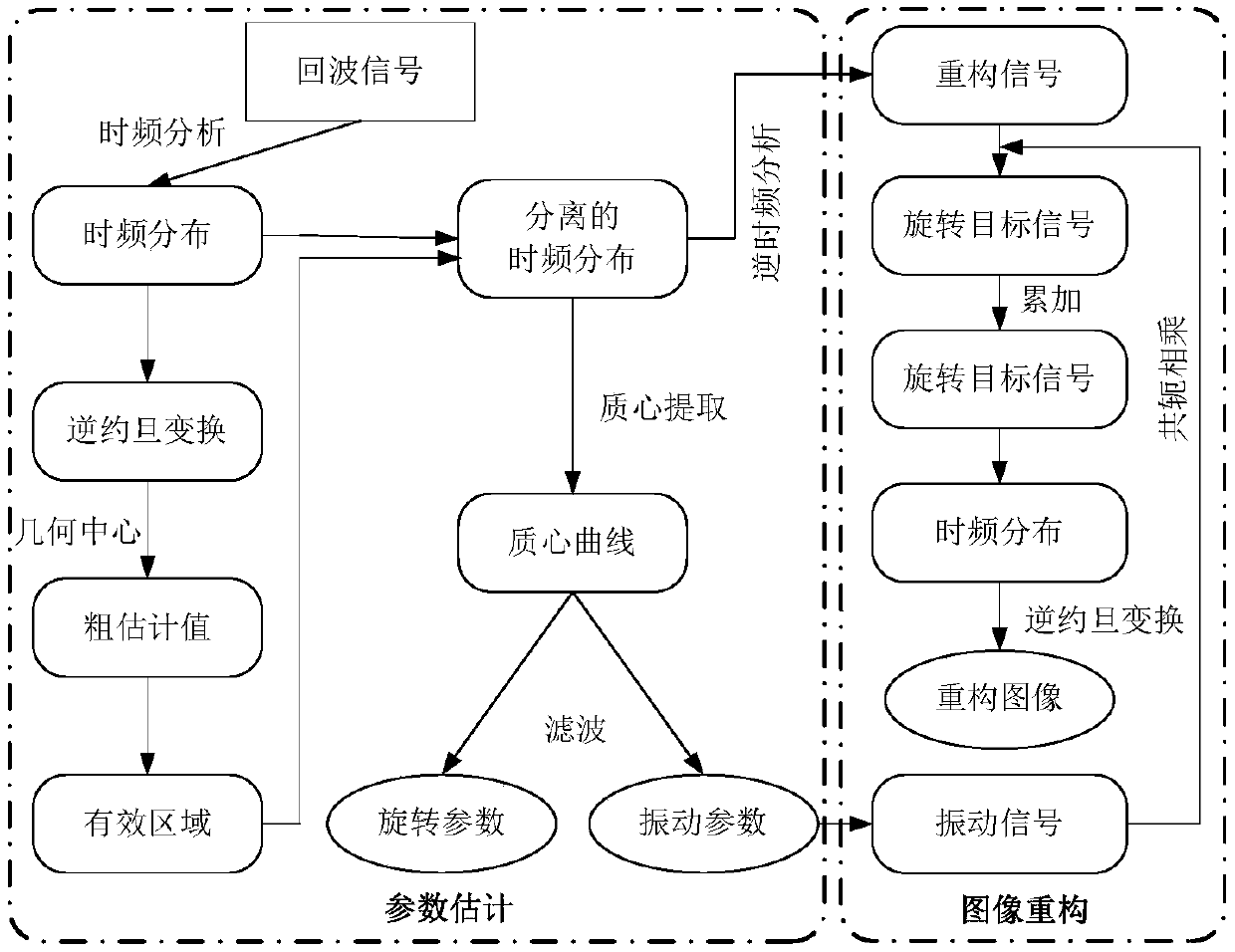
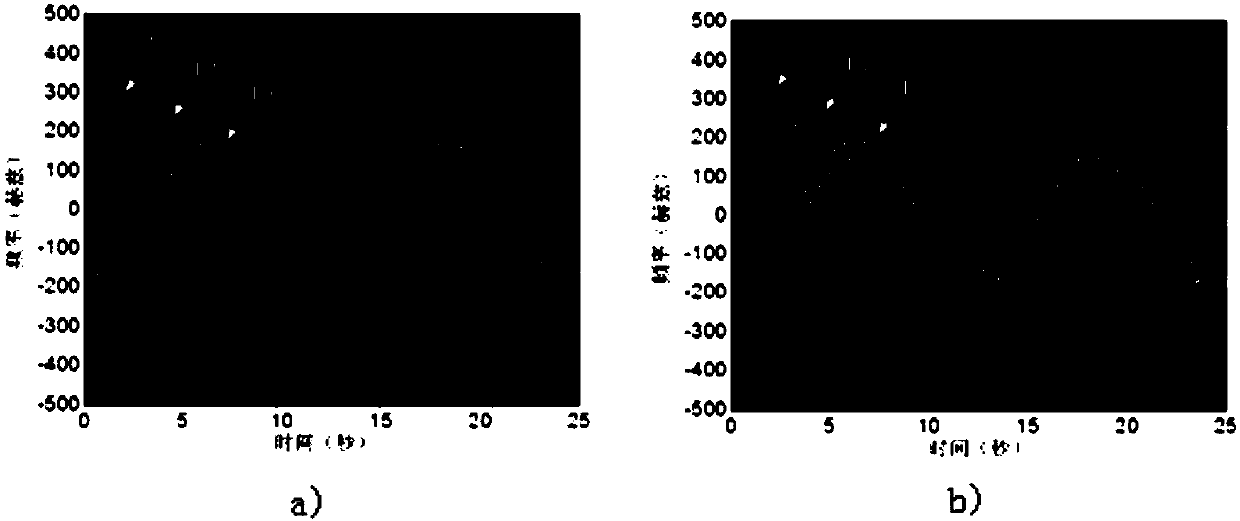
Method for estimating rotation target parameter under vibration disturbance condition
ActiveCN106950554AEffective observationIncreased complexityWave based measurement systemsMicrowaveRadar systems
The invention provides a method for estimating a rotation target parameter under a vibration disturbance condition. The method is characterized by introducing a narrowband terahertz radar system with a frequency band between those of a microwave and a laser; providing a fast and effective signal processing method by means of signal processing means such as inverse Radon transform, time-frequency analysis and inverse transform thereof, and the like; and achieving the separation estimation and compensation of vibration disturbance and the parameter estimation and image reconstruction of the rotation for the rotation target accompanied by vibration disturbance. The method is highly efficient and stable, and does not enhance system complexity.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
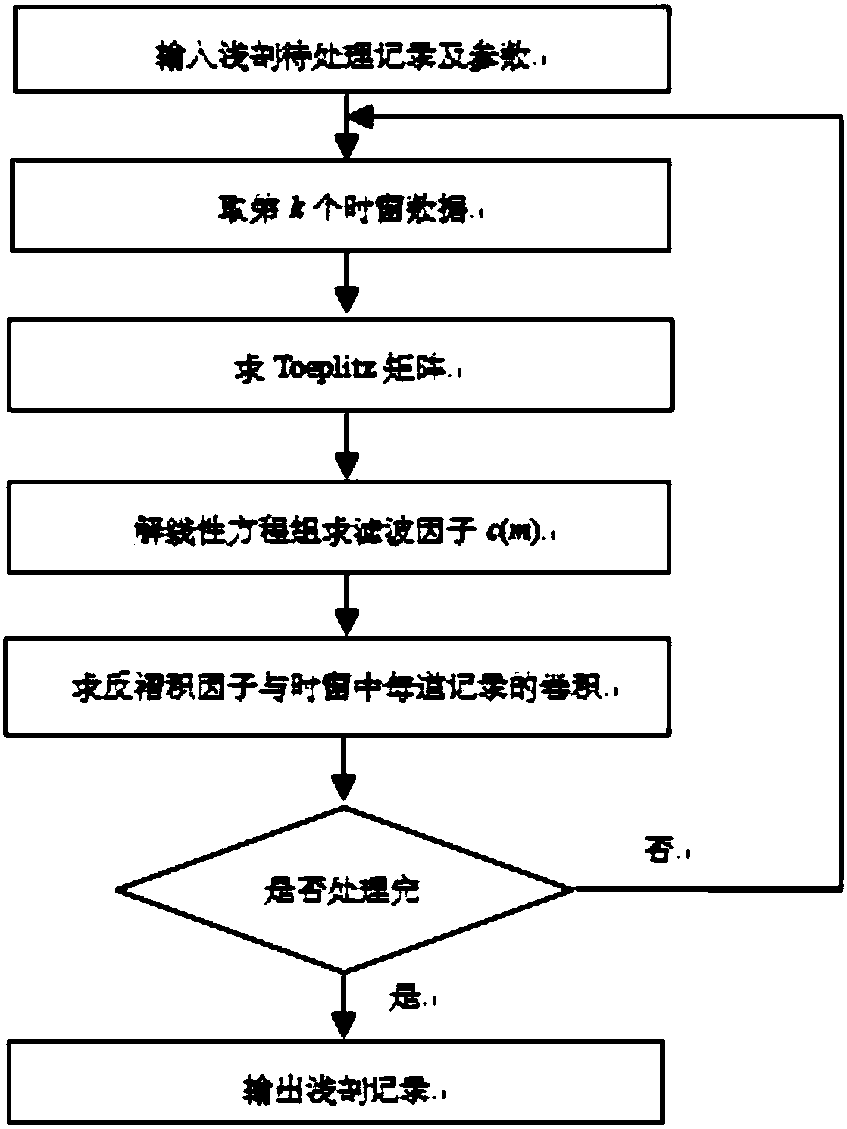
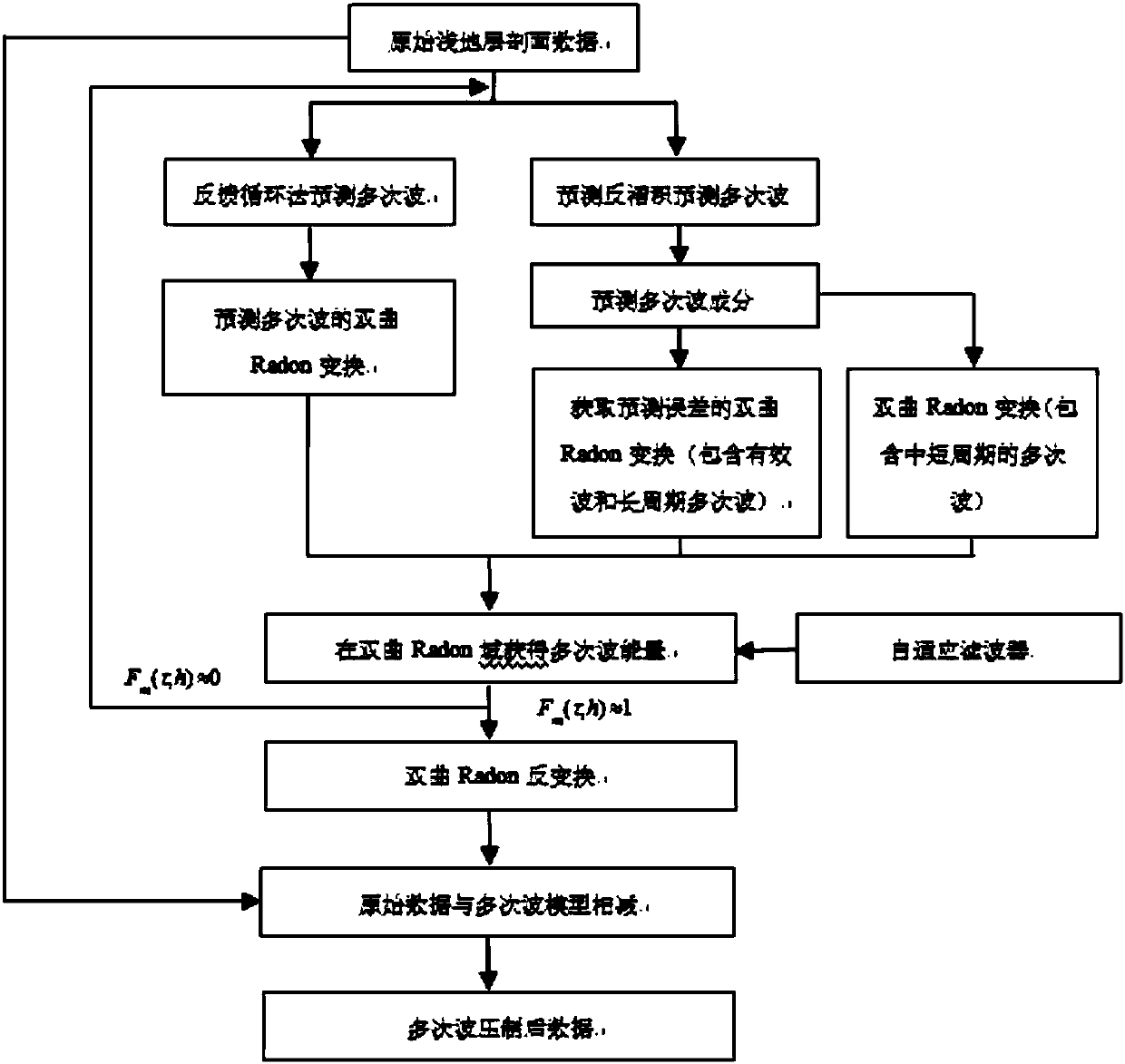
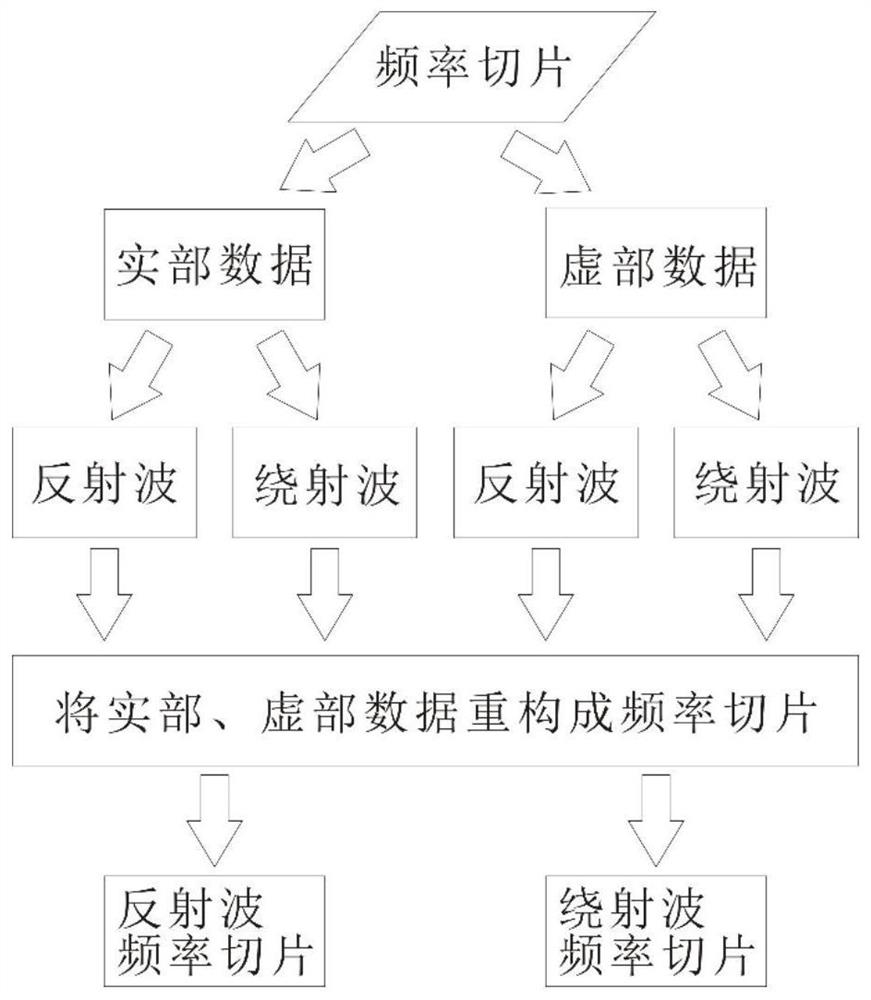
Modeling method integrating predictive deconvolution and feedback loop method to suppress multiples in hyperbolic Radon domain
InactiveCN107678062AImprovement ingredientsMultiple suppressionSeismic signal processingOcean bottomAdaptive filter
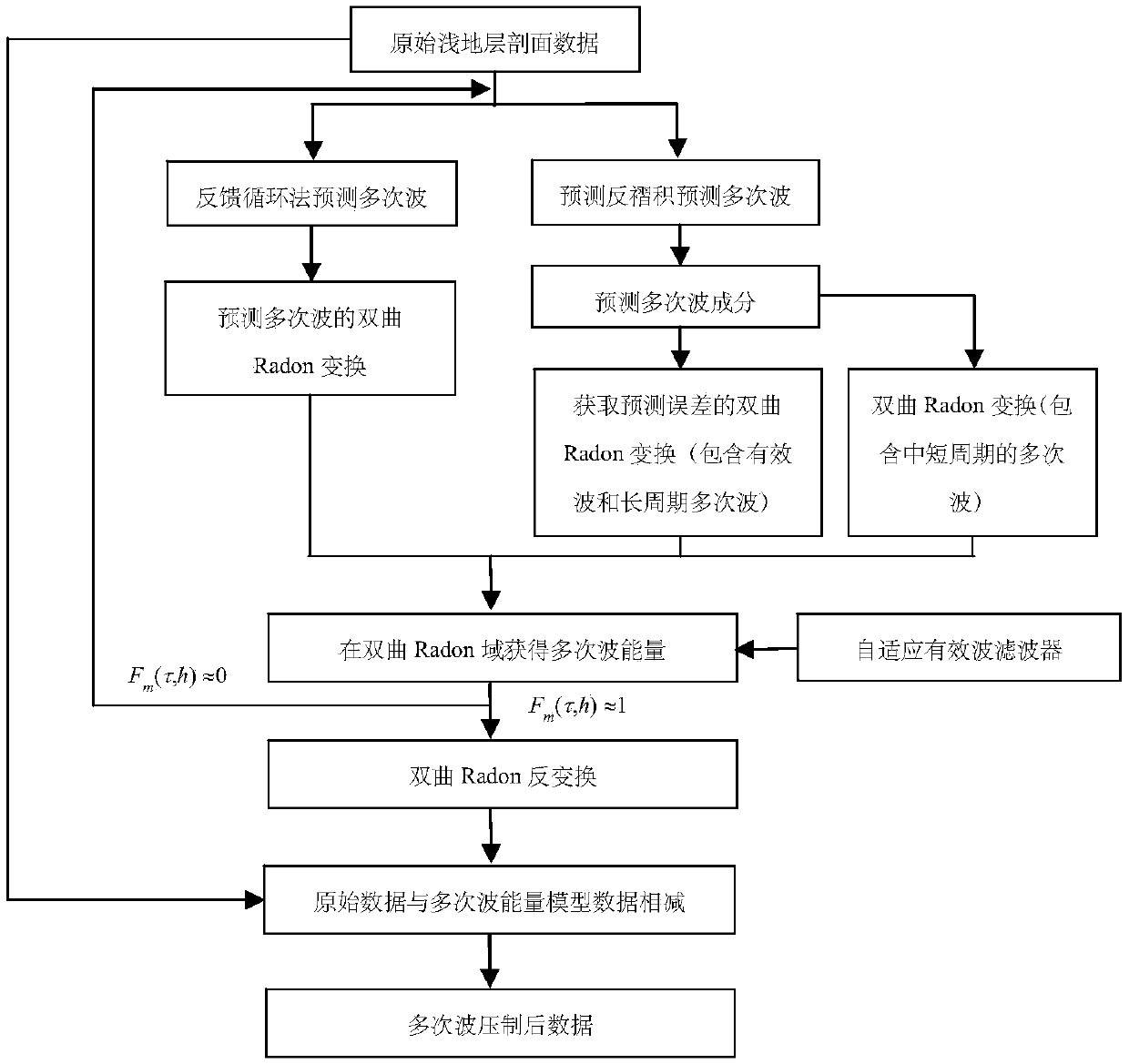
The invention provides a modeling method integrating the predictive deconvolution and the feedback loop method to suppress multiples in the hyperbolic Radon domain. According to the method, after original shallow profile data are read in, the original shallow profile data are processed by using the predictive deconvolution and the feedback loop method, and then, hyperbolic Radon transform is performed; an adaptive filter is constructed, and when the output value Fm (tau, h) of the adaptive filter is approximate to 0, it is considered that valid reflected waves still exist, and iteration processing should be performed on the data until Fm (tau, h) is approximate to 1; inverse Radon transform is performed on a multiple energy model in the hyperbolic Radon domain; and multiple energy model data are subtracted from the original shallow profile data, and finally, multiple-suppressed high-reliability shallow formation profile data can be obtained. With the method of the invention adopted, multiples on free interfaces and inter-layer multiples can be effectively suppressed; valid waves will not be damaged; the multiples can be effectively separated from primary waves; and a more reliablebasis is provided for later-stage submarine underground medium interpretation.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Limited radon transformations for removal of noise from seismic data
InactiveUS20090005999A1Enhance primary reflection signal contentRemove noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionSeismic signal processingPattern recognitionTime domain
Methods of processing seismic data to remove unwanted noise from meaningful reflection signals are provided for. The methods comprise the steps of assembling seismic data into common geometry gathers in an offset-time domain without correcting the data for normal moveout. The amplitude data are then transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a limited Radon transformation. That is, the Radon transformation is applied within defined slowness limits pmin and pmax, where pmin is a predetermined minimum slowness and pmax is a predetermined maximum slowness. A corrective filter is then applied to the transformed data enhance the primary reflection signal content of the data and to eliminate unwanted noise events. After filtering, the enhanced signal content is inverse transformed from the time-slowness domain back to the offset-time domain using an inverse Radon transformation.
Owner:E S & A ROBINSON
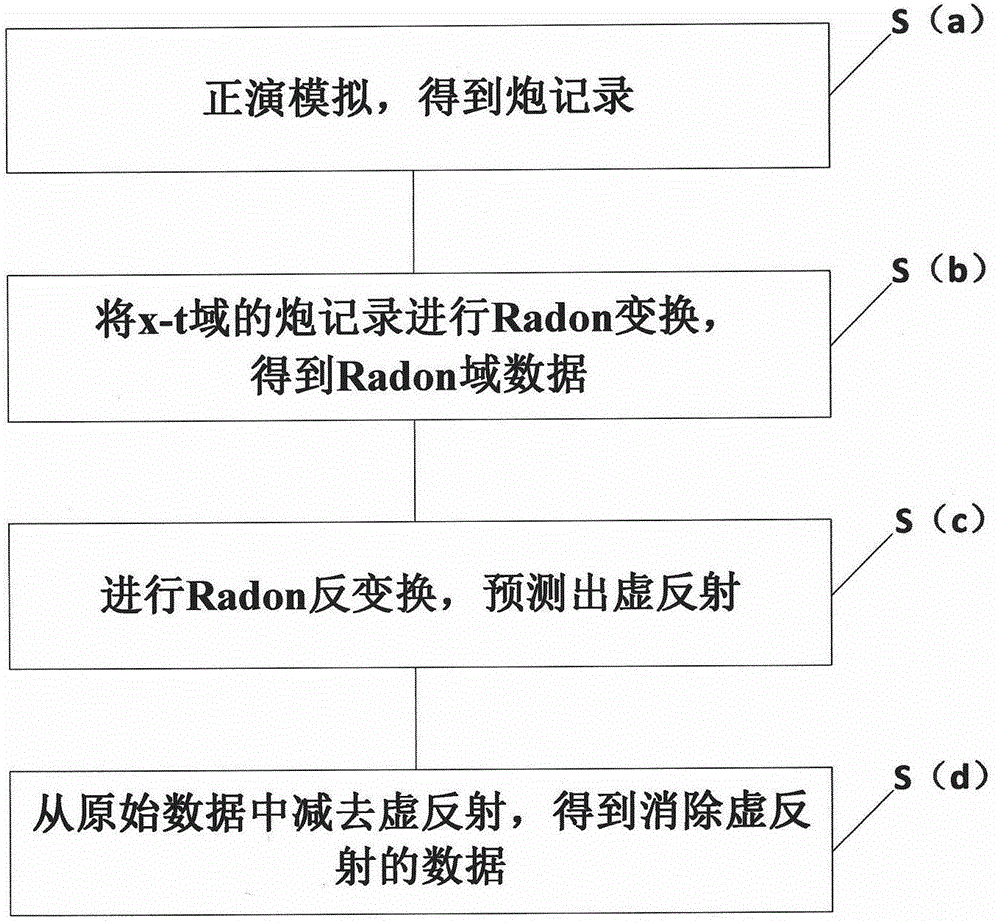
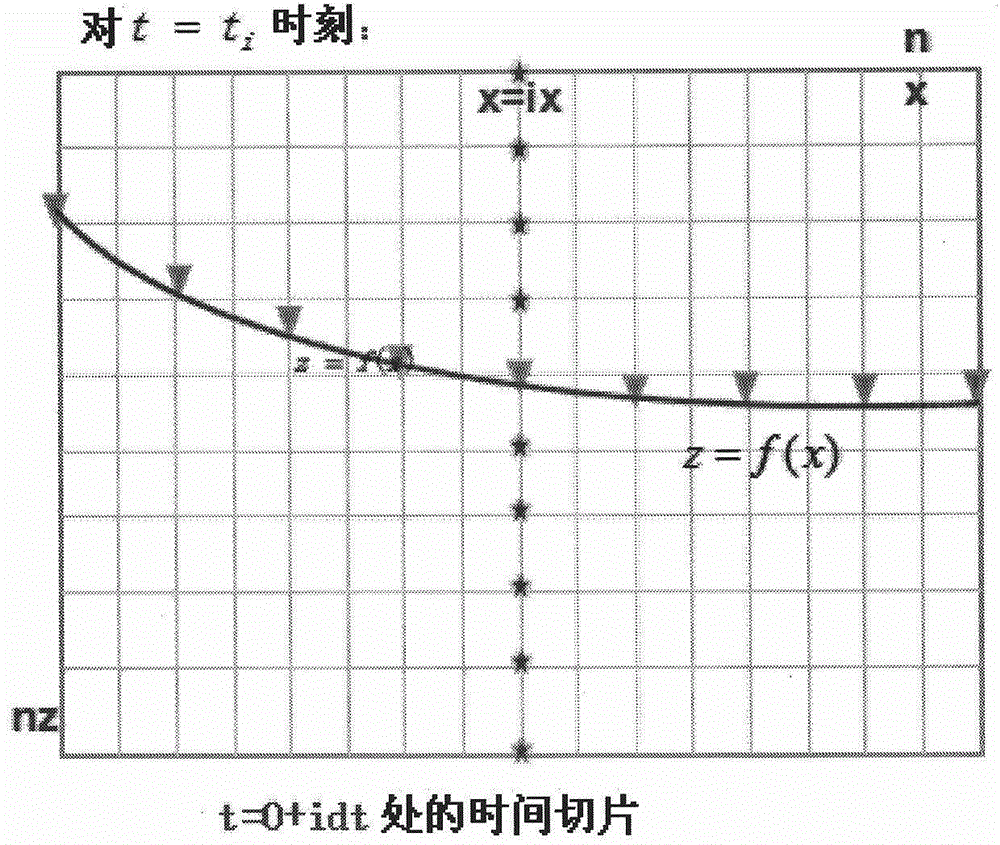
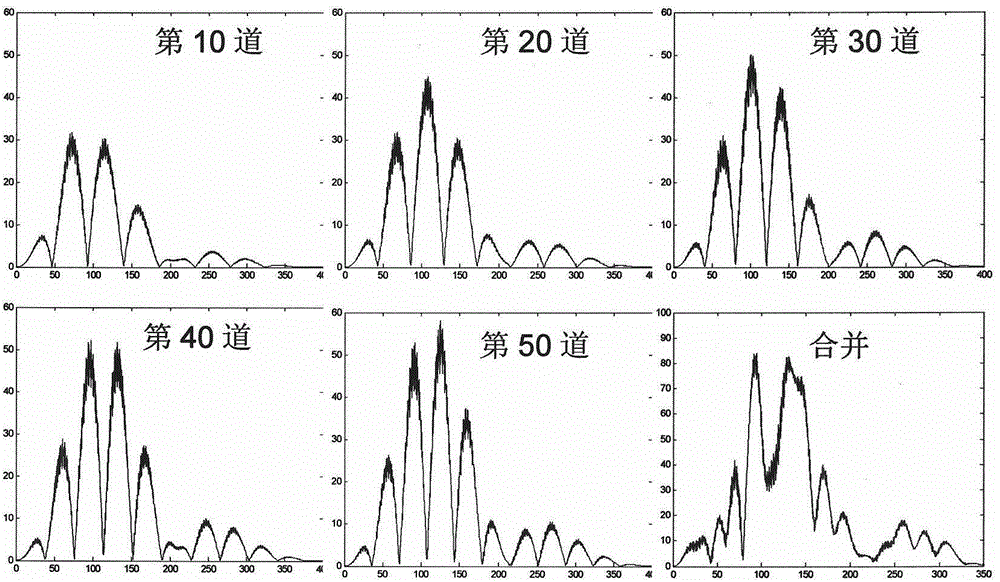
Method for eliminating pseudo-reflection of inclined cable based on Radon conversion
The invention provides a method for eliminating pseudo-reflection of an inclined cable based on Radon conversion. The method comprises the following steps: (a) carrying out forward simulation to obtain a shot record; (b) performing Radon conversion on the shot record in an x-t domain to obtain Radon domain data; (c) performing inverse Radon conversion to forecast the pseudo-reflection; (d) subtracting the pseudo-reflection from original data to obtain data subjected to pseudo-reflection elimination. According to the method, all detection points in the inclined cable are calculated by an interpolation method, trapped wave points are mutually compensated, so that the aim of expanding the frequency band is finally fulfilled; by Radon conversion, the inclined cable is corrected into a horizontal cable, and then inverse conversion is realized, namely data of the sea surface is converted to the original position of the inclined cable, and a sea surface earthquake record is reduced to the pseudo-reflection at the position of the inclined cable, so that the pseudo-reflection at the position of the inclined cable is forecast; pseudo-reflection waves are subtracted from the original data, so that the data subjected to pseudo-reflection elimination is obtained, and the resolution of the record is improved.
Owner:李姗
Method, apparatus, and computer-readable medium for pre-reconstruction decomposition and calibration in dual energy computed tomography
ActiveUS8194961B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDecompositionVolumetric Mass Density
A method of obtaining a computed tomography image of an object includes determining linear terms and non-linear beam hardening terms in a pair of line integral equations for dual-energy projection data from inserting average and difference from average attenuation terms, obtaining an initial solution of the line integral equation by setting the non-linear beam hardening terms to zero, and iteratively solving the line integral equations to obtain one line integral equations for each basis material. Attenuation by the first basis material corresponds to a photoelectric attenuation process, and attenuation by the second basis material corresponds to a Compton attenuation process. The line integral equations can be inverted by an inverse Radon procedure such as filtered backprojection to give images of each basis material. The images of each basis material can then be optionally combined to give monochromatic images, density and effective atomic number images, or photoelectric and Compton processes images.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
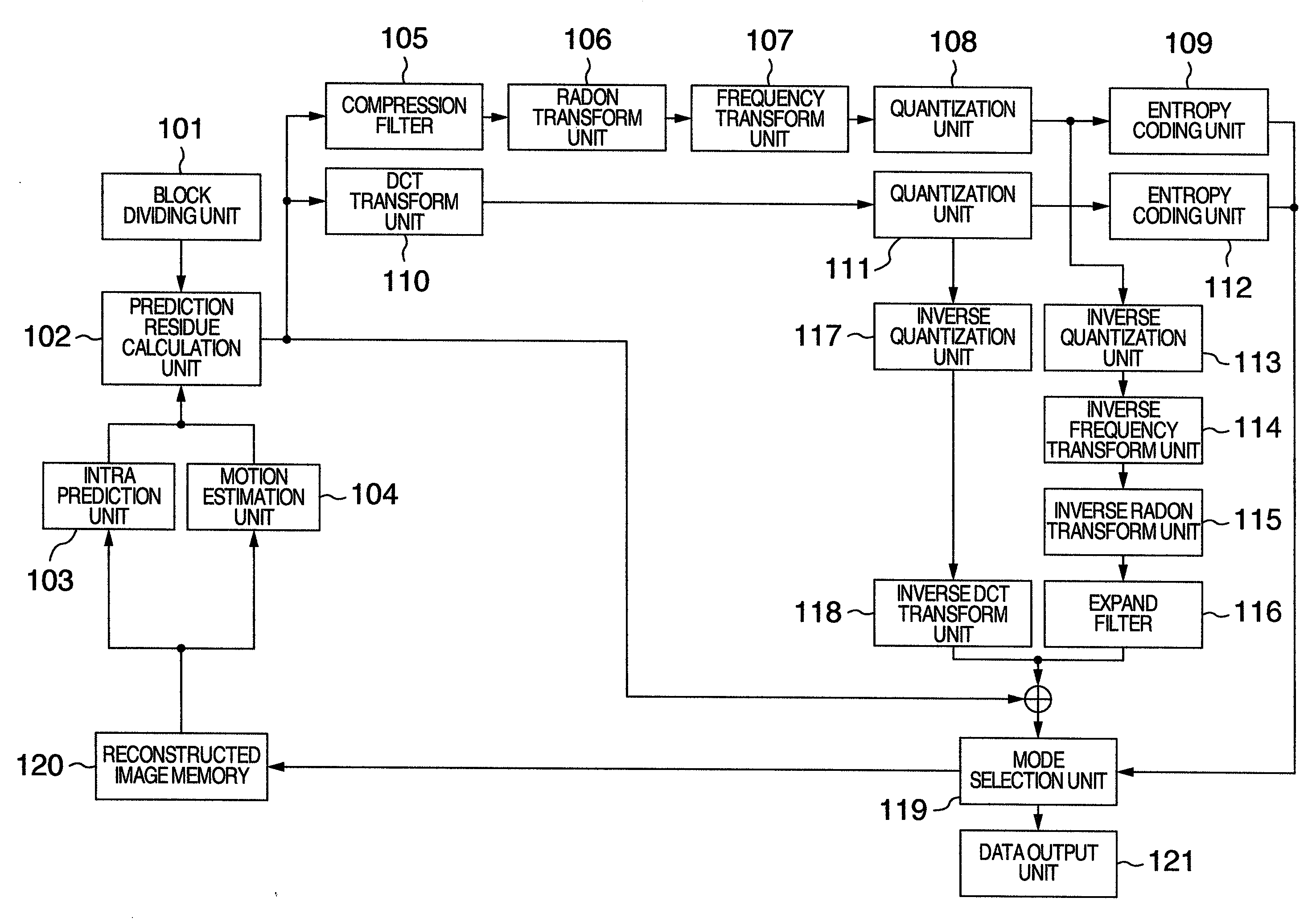
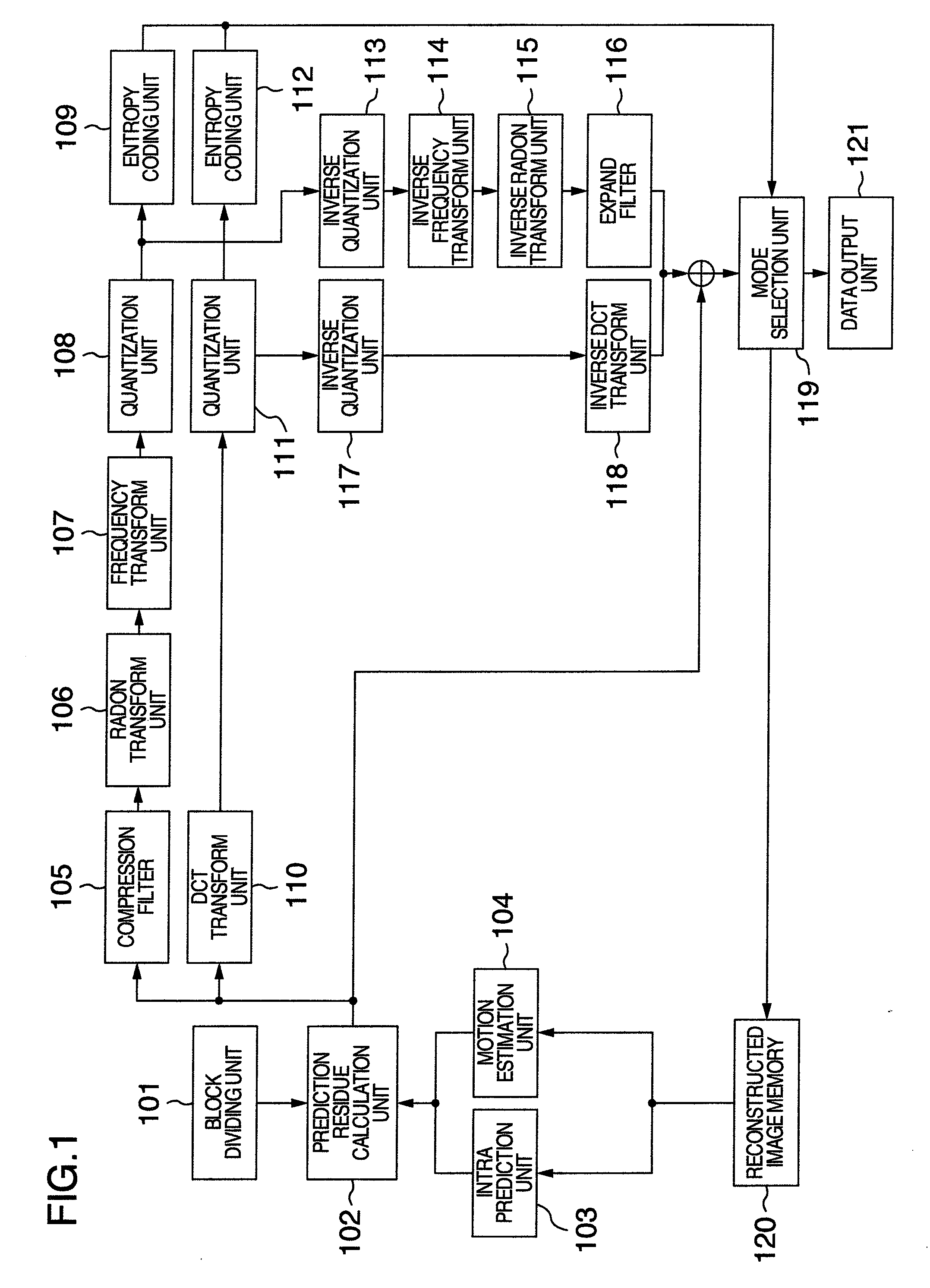
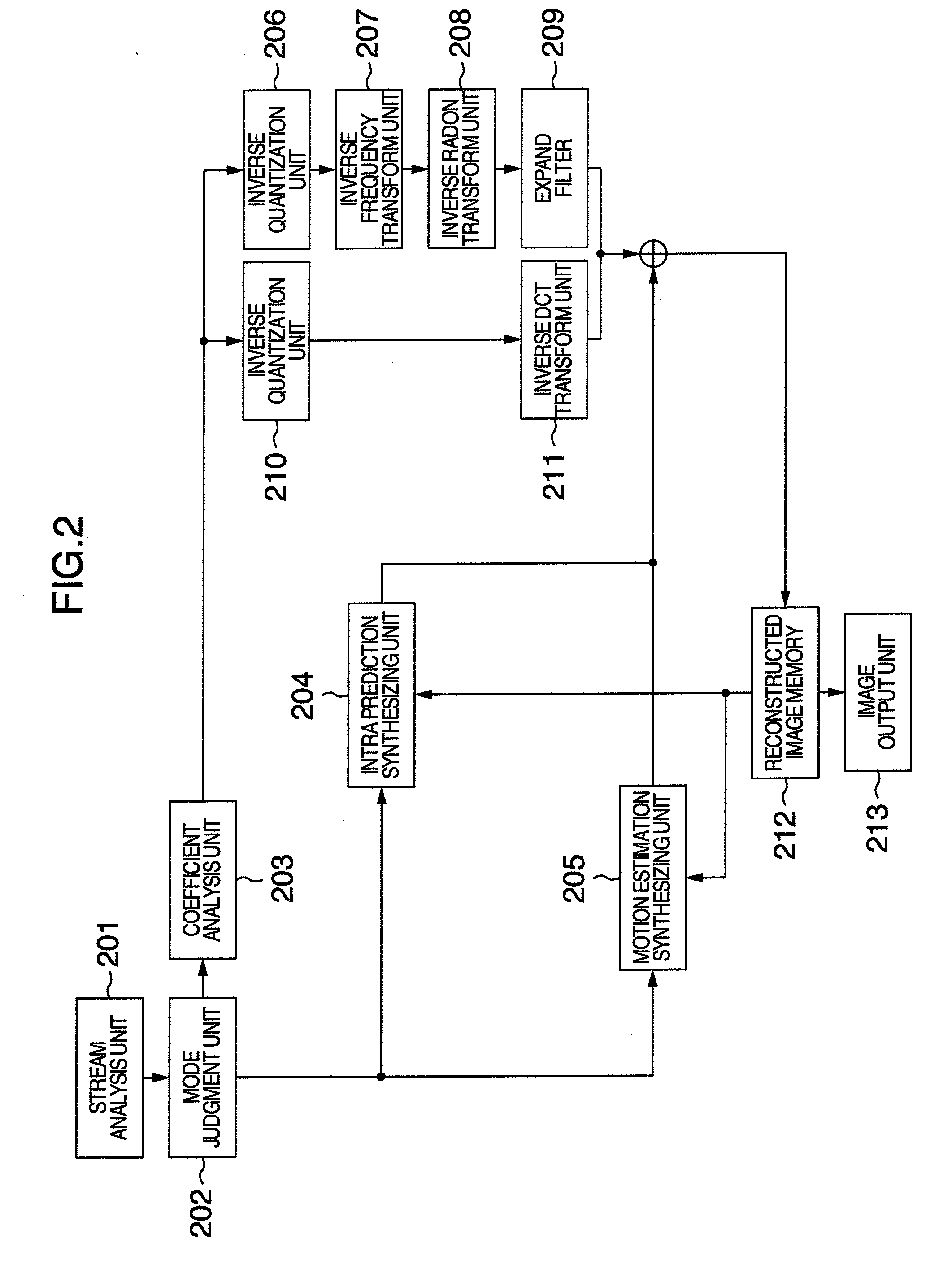
Image Coding Method, Image Coding Apparatus, Image Decoding Method and Image Decoding Apparatus
InactiveUS20080304572A1Inhibit deteriorationReduce the amount of codeTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesImage codeInverse quantization
An image coding and decoding apparatus includes functions, in which an image of every block including either an entire input image or an image divided from the input image is compressed, a Radon transform is applied to the compressed image to generate a coefficient, the generated coefficient is transformed in a frequency, and the frequency transformed coefficient is quantized to generate coding data to generate a coding stream, in the encoding, and an inverse quantization is applied to a coding coefficient included in the coding stream to generate a coefficient, an inverse frequency transform is applied to the generated coefficient, an inverse Radon transform is applied to the inversed frequency transformed coefficient to generate a decompress image, an expand process is applied to the decompression image to decode a residual component, and a predicted image is synthesized with the residual component to generate a reconstructed image, in the decoding.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
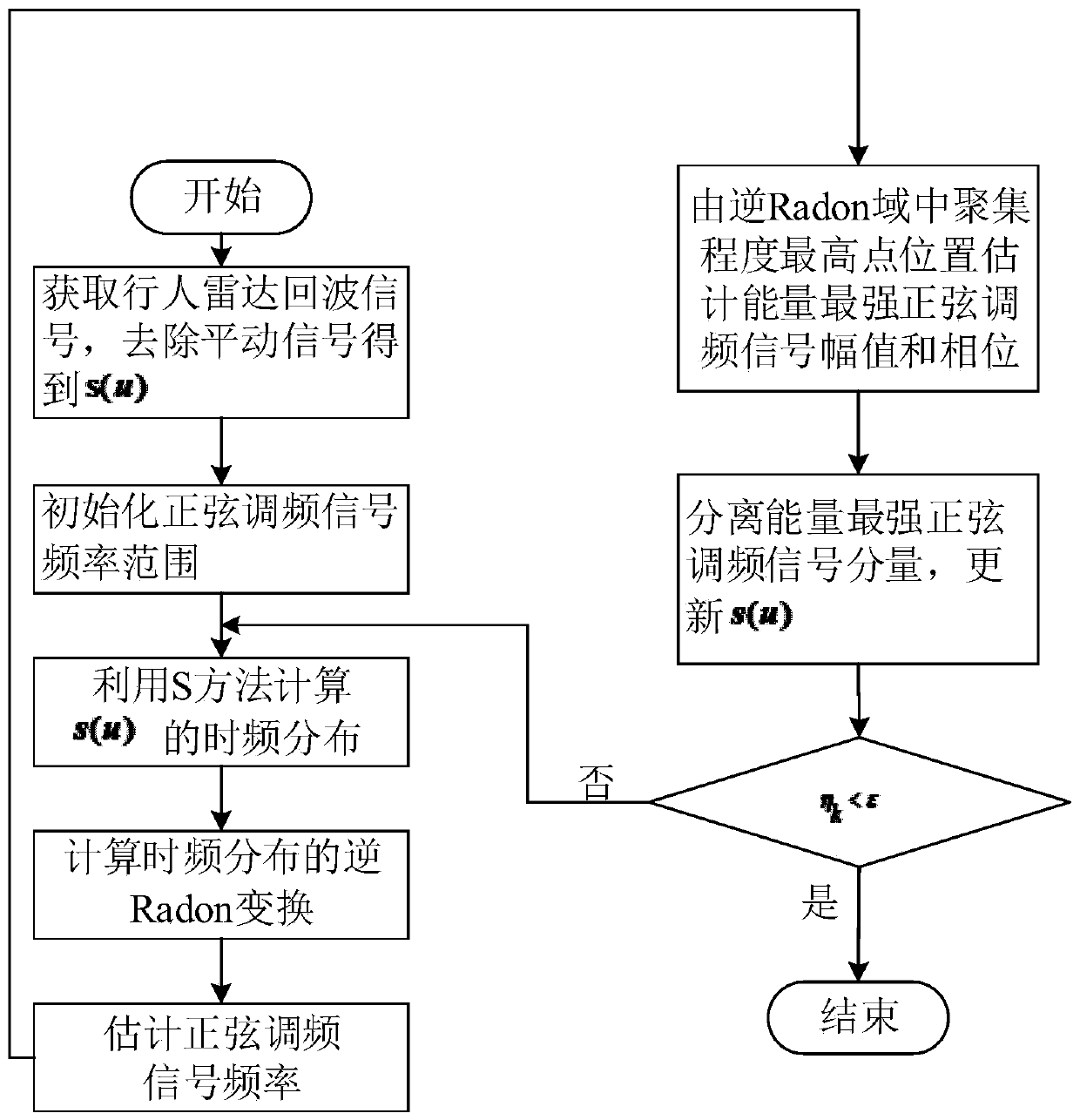
Human body micro-Doppler component extraction method based on inverse Radon transform
PendingCN110146872AGood component separationEasy to separateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHuman bodyHigh energy
The invention discloses a human body micro-Doppler component extraction method based on inverse Radon transform. The method is characterized by carrying out time-frequency transform and the inverse Radon transform on a pedestrian radar echo signal to acquire a point with the highest aggregation degree, wherein the point is a mapping point of a frequency component signal with highest energy in an inverse Radon domain; then, estimating a frequency and an amplitude of a sine frequency modulation signal through the mapping point so as to obtain the sine frequency modulation signal with the highestenergy; separating the signal from the pedestrian radar echo signal so as to complete extraction of the first micro-Doppler component; continuously separating the signal till that signal component energy is less than or equal to a signal separation threshold, then stopping the separation, and extracting the plurality of micro-Doppler components. In the invention, micro-motion signal components ofdifferent parts of pedestrians can be accurately estimated and fine separation of pedestrian micro-motion signals is achieved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
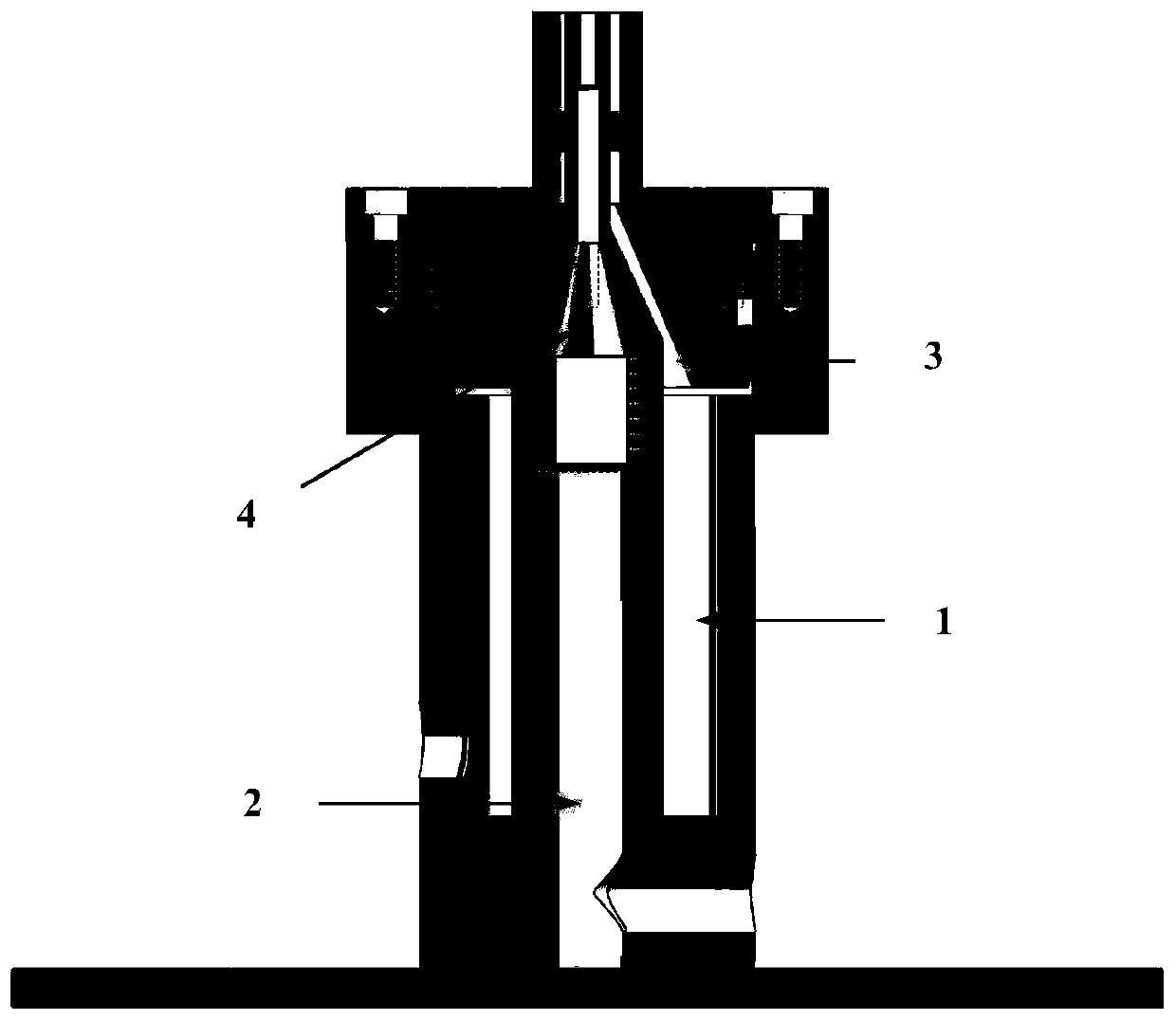
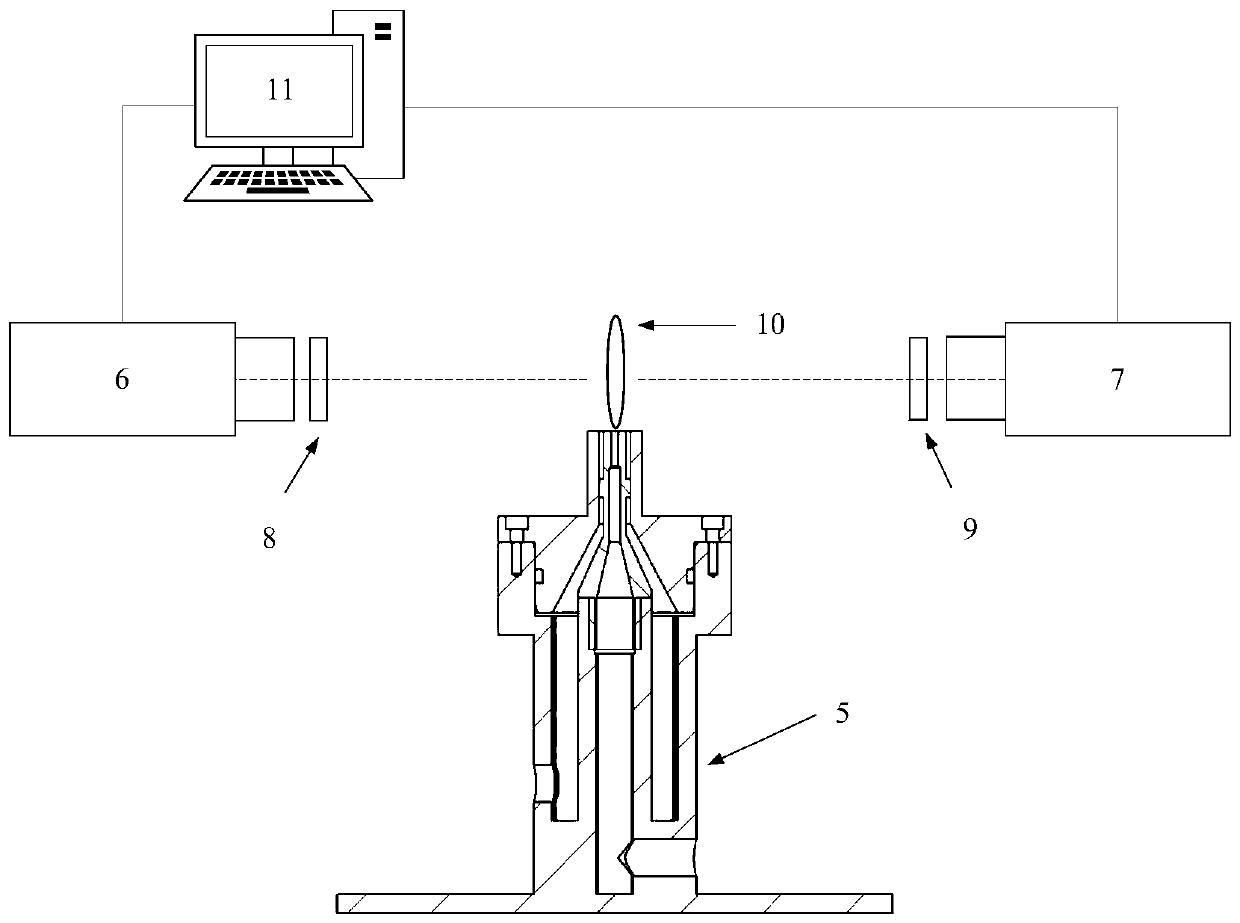
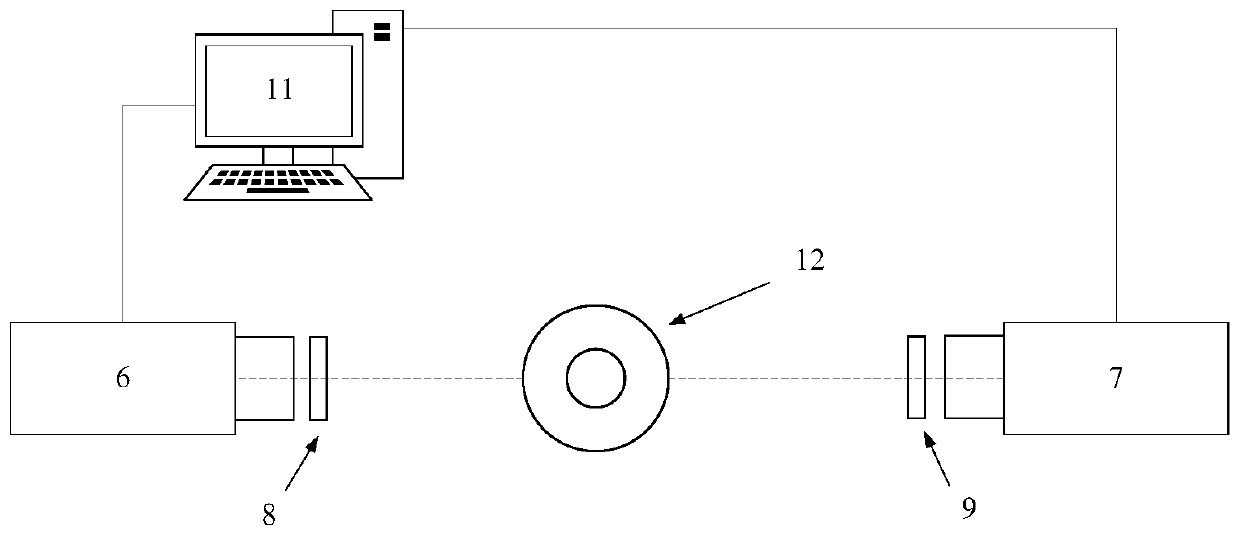
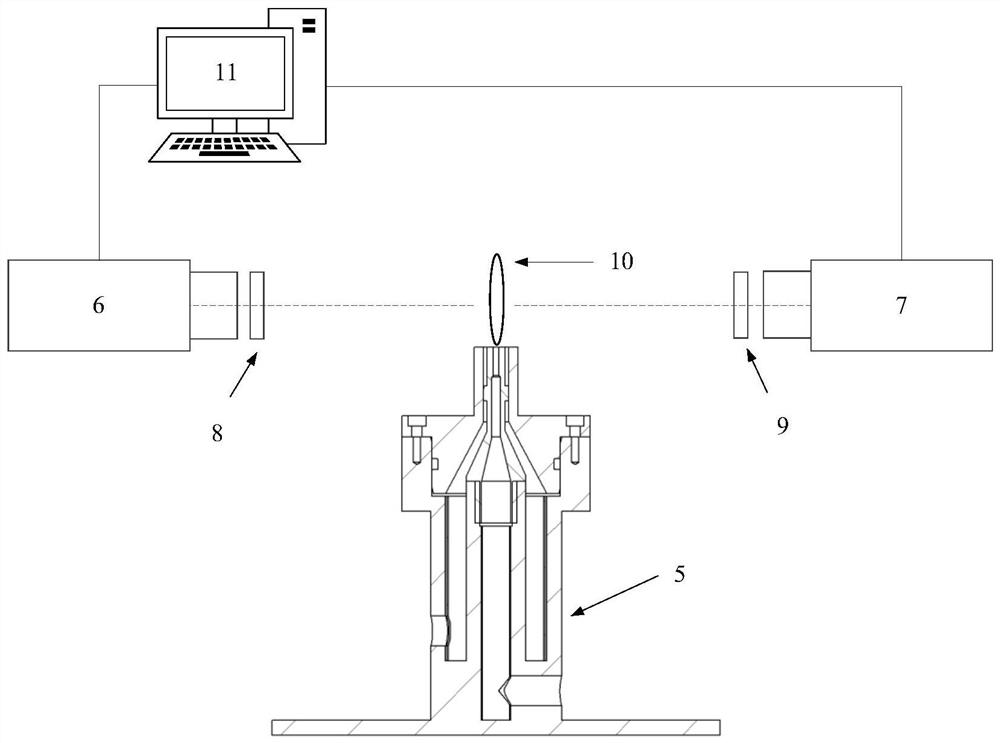
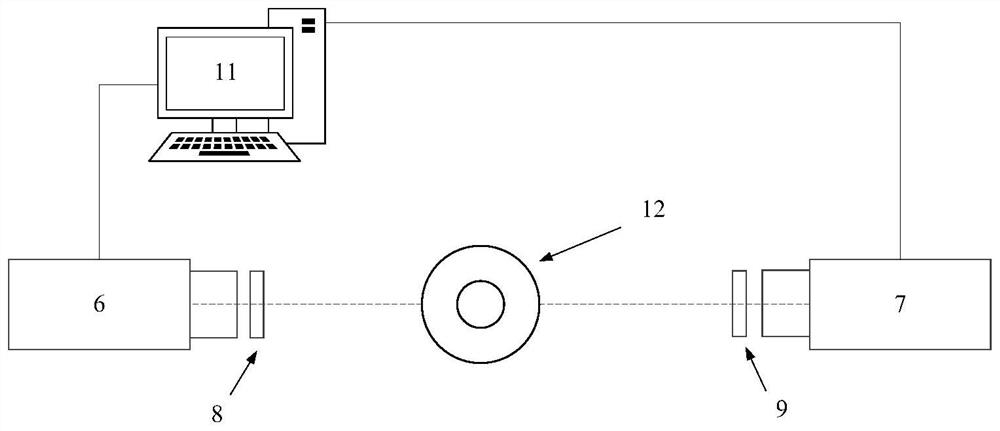
Flame excited state particle radiation rate measurement method based on uniform light source
The invention discloses a flame excited state particle radiation rate measurement method based on a uniform light source. A jet diffusion burner, an integrating sphere uniform light source, two ICCD cameras, an Edmud 34980 filter plate, an Edmud 65198 filter plate and a computer are utilized to build a test system. On the basis of OH * chemiluminescence initial images and CH * chemiluminescence initial images which are obtained by shooting jet diffusion flame generated by combustion of a jet diffusion combustor through two cameras, OH * chemiluminescence radial distribution and CH * chemiluminescence radial distribution are obtained through inverse Radon transformation, the luminous intensity of the uniform light shot by the two cameras is obtained based on the images of the uniform lightsources respectively obtained by the integrating sphere uniform light sources shot by the two cameras, the radiation rate of the OH * excited state particles is obtained based on the OH * chemiluminescence radial distribution and the luminous intensity of the uniform light source shot by the corresponding camera, and the radiation rate of the CH * excited state particles is obtained based on the CH * chemiluminescence radial distribution and the luminous intensity of the uniform light shot by the corresponding camera. The method is low in cost, simple and efficient.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
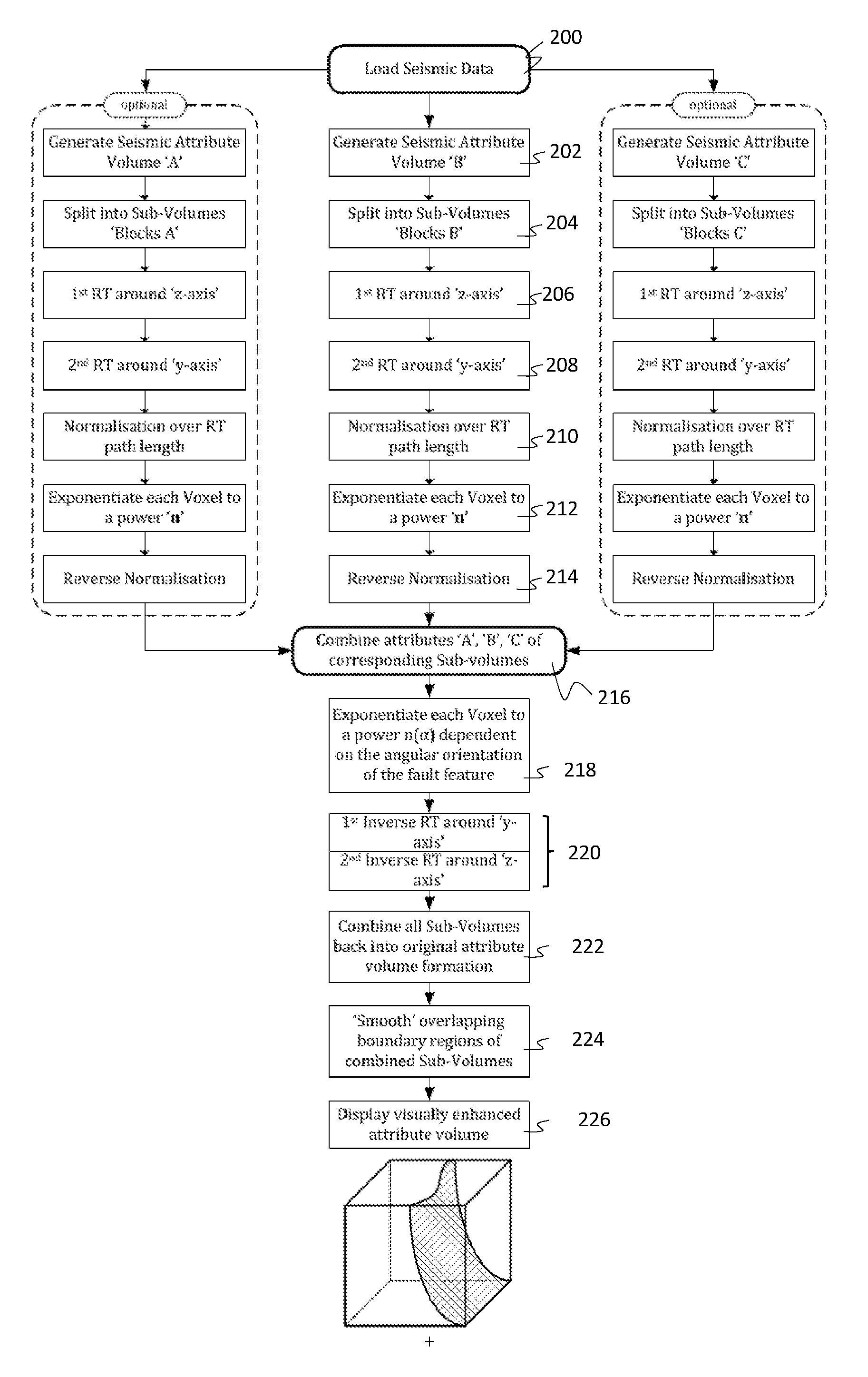
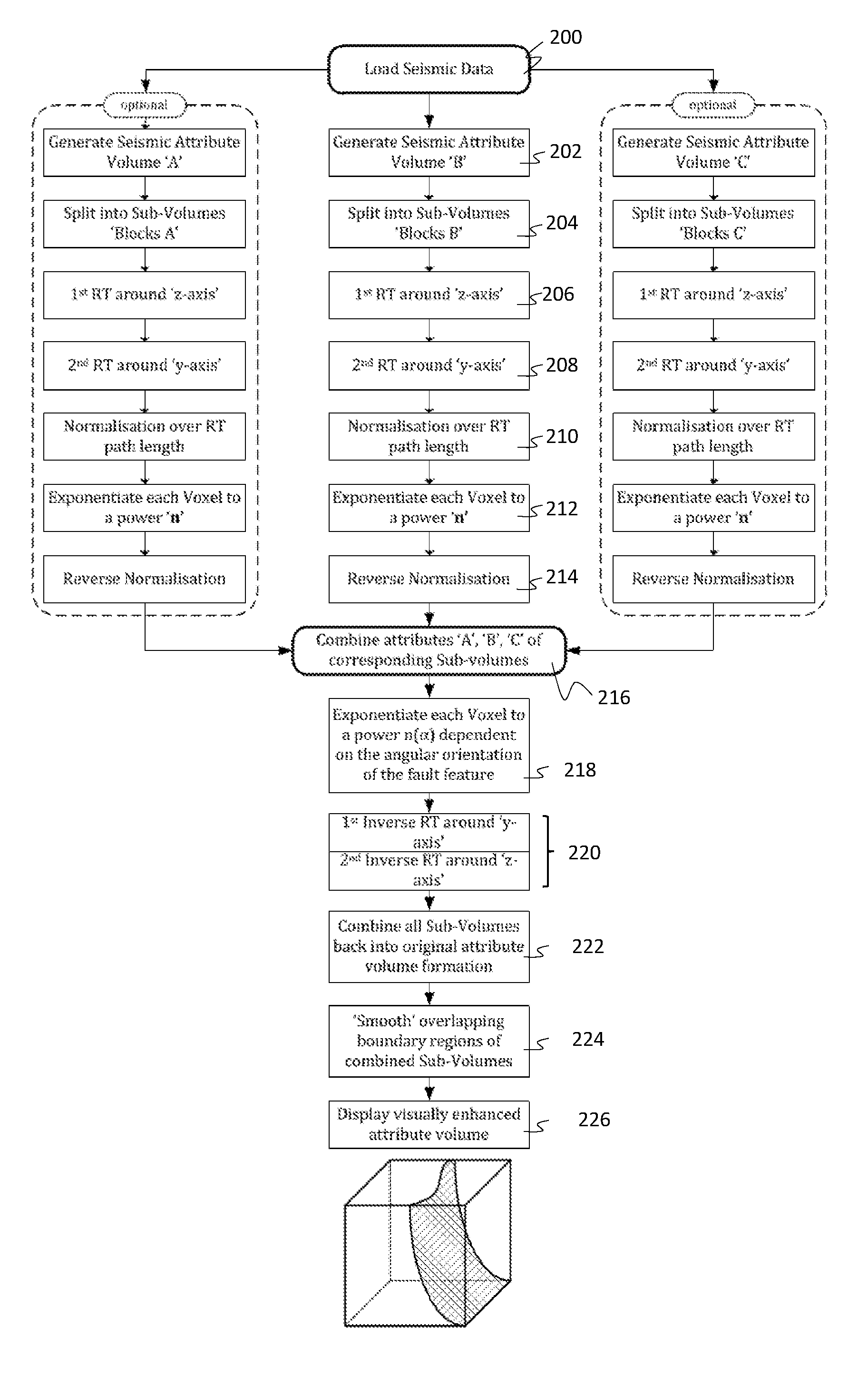
Enhanced Visualisation of Geologic Features in 3D Seismic Survey Data
ActiveUS20160003956A1Add featureEliminate offsetSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic surveyVoxel
A method of visually enhancing at least one geologic feature in 3D seismic survey data, comprising the steps of: (a) generating at least one attribute volume definable in Cartesian space and comprising at least one attribute derivable from said 3D seismic survey data; (b) generating a first Radon data volume from data resulting from a transaxial Radon Transform of said at least one attribute volume with respect to a first Cartesian axis; (c) generating a second Radon data volume from data resulting from a transaxial Radon Transform of said first Radon data volume with respect to a second Cartesian axis; (d) generating a third Radon data volume from data resulting from exponentiating a characteristic parameter of each one of a plurality of voxels forming said second Radon data volume to a predetermined first power value, and (e) applying a first Inverse Radon Transform to said third Radon data volume with respect to said second Cartesian axis, and a subsequent second Inverse Radon Transform to the resulting data from said first Inverse Radon Transform with respect to said first Cartesian axis.
Owner:FOSTER FINDLAY ASSOCS
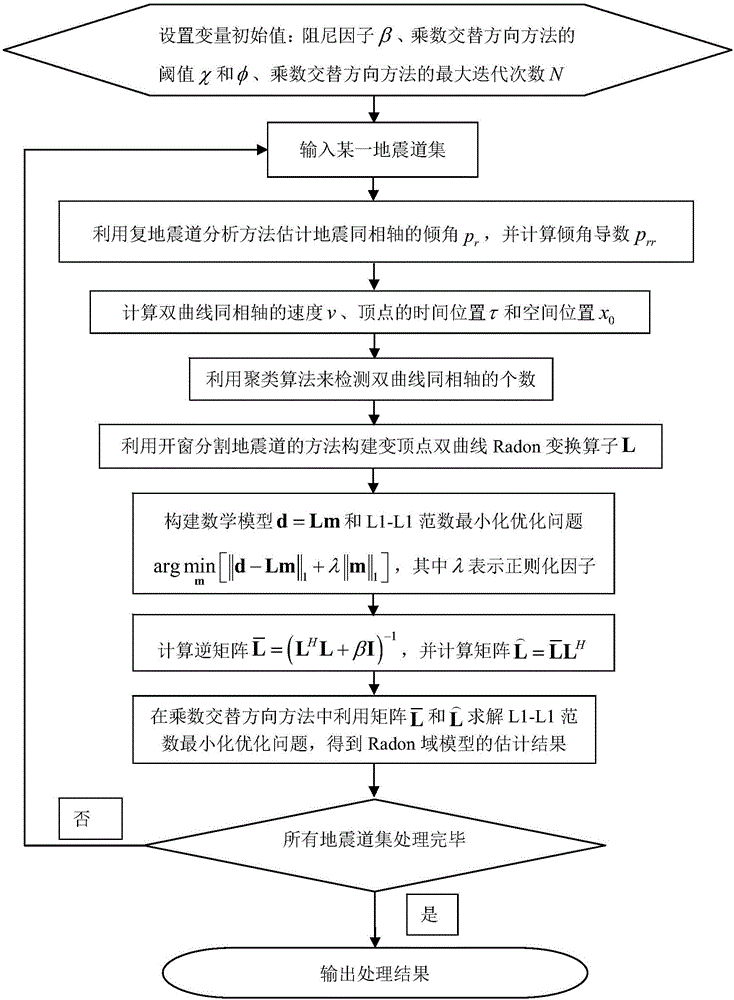
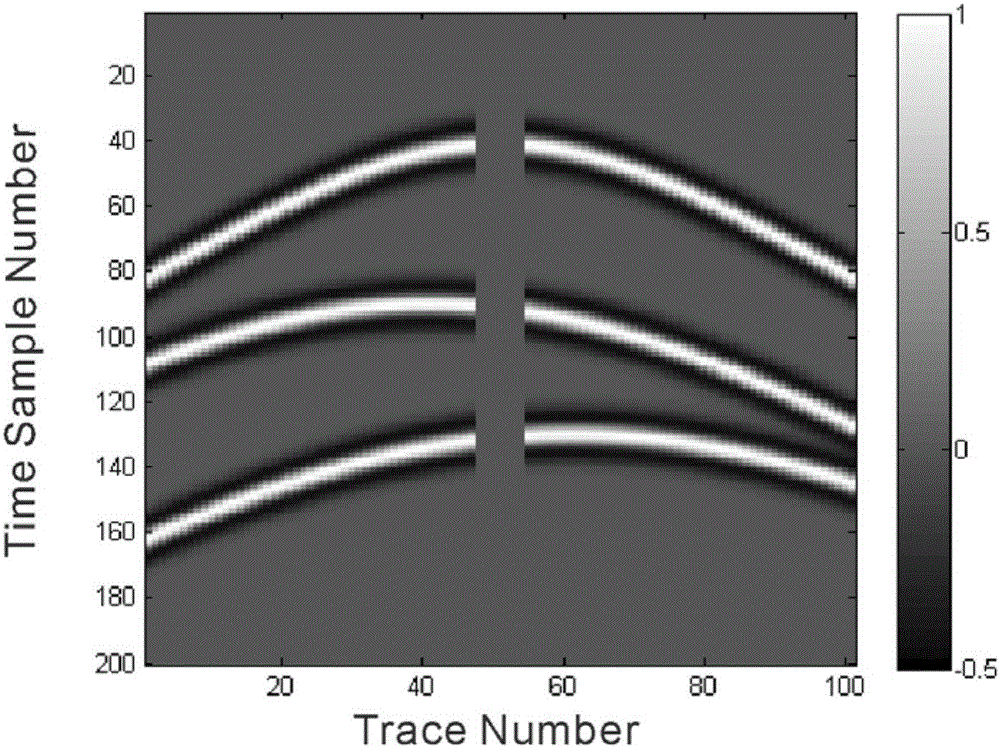
Vertex variable sparse hyperbolic Radon transform method considering seismic wavelet stretching effect
ActiveCN105929447AReduce the numberEliminate wave stretching effectsSeismic signal processingCluster algorithmDomain model
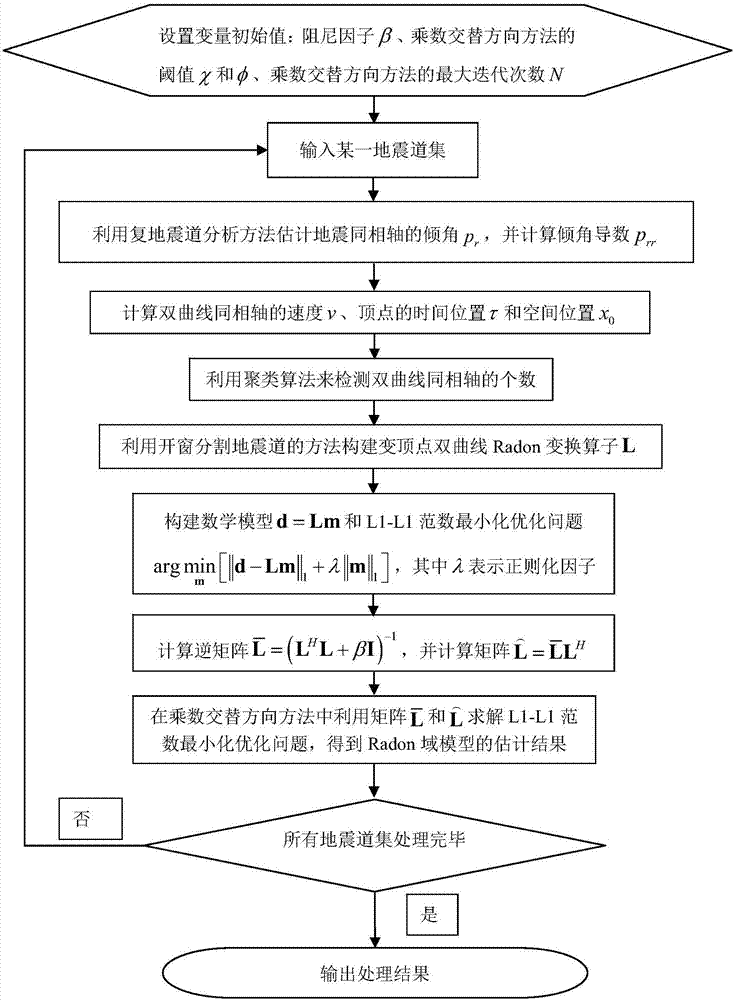
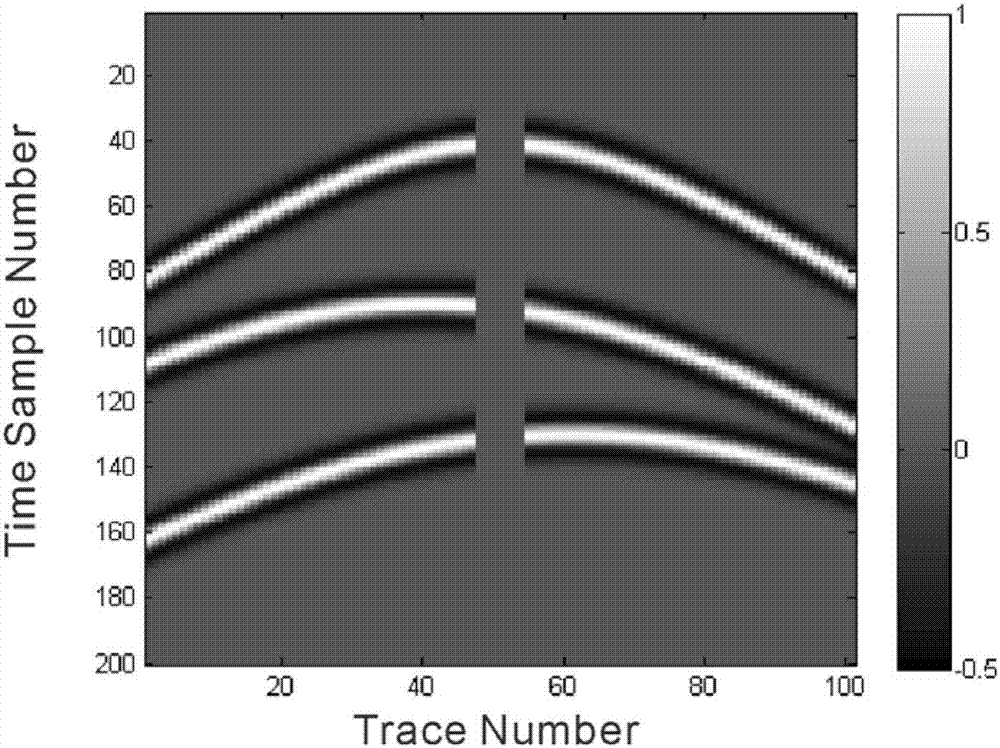
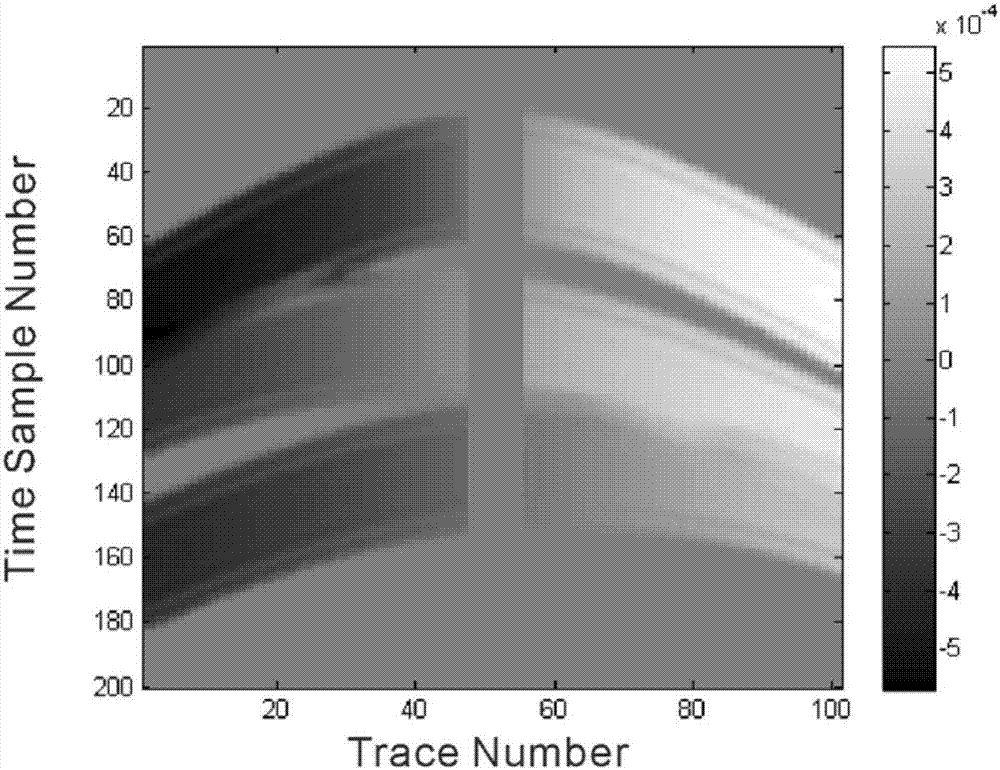
The invention discloses a vertex variable sparse hyperbolic Radon transform method considering a seismic wavelet stretching effect. According to the method, the vertex positions and velocities of hyperbolic events are calculated by using the dip angles and the derivatives thereof of seismic events; the number of the hyperbolic events is determined through using a clustering algorithm, and the number of parameters of the estimated events is decreased; based on the calculated vertex positions and velocities of the events, a vertex variable hyperbolic Radon transform operator is constructed by using a method according to which windowing is adopted to segment a seismic channel, and the seismic wavelet stretching effect generated by inverse Radon transform is eliminated; a Radon domain model and the L1 norm minimization constrain of a data fitting term are introduced into an optimization problem, so that the sparsity of the Radon domain model and the adaptability of the Radon domain model to non Gaussian fitting error can be improved; a multiplier alternating direction method is utilized to solve an L1-L1 norm minimization problem; and in a whole iterative process, matrix inversion is only needed to be carried out for once, so that computational complexity is low.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Passive sonar multi-target azimuth trace extraction method, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN111882585AImprove extraction abilityExtract fineImage analysisComplex mathematical operationsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
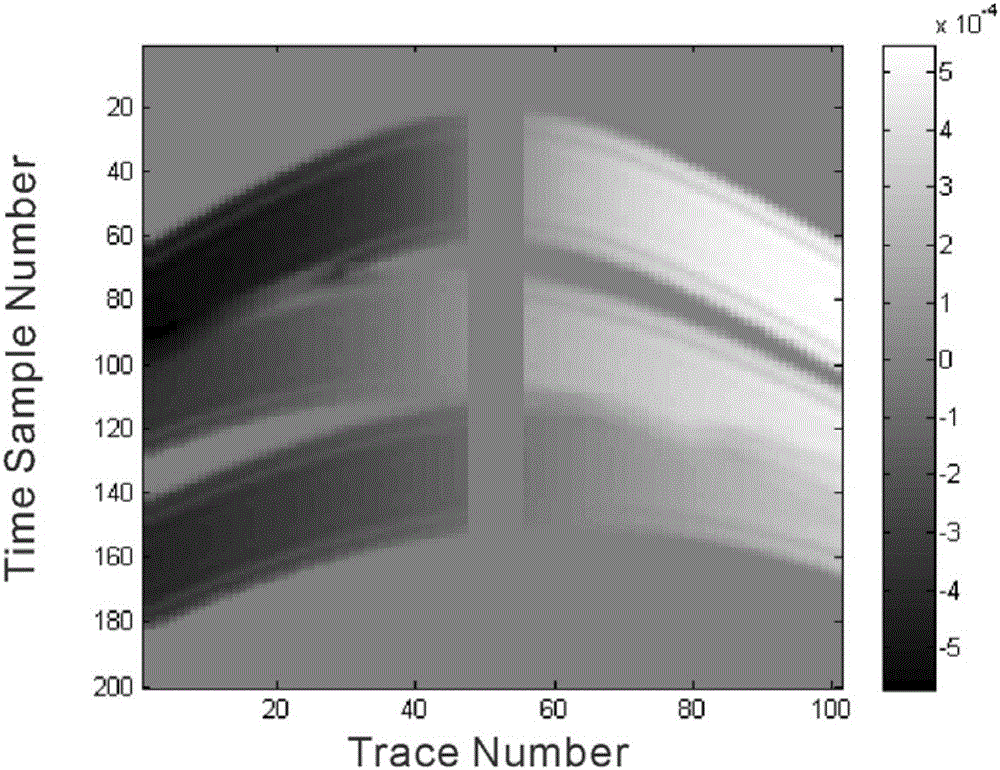
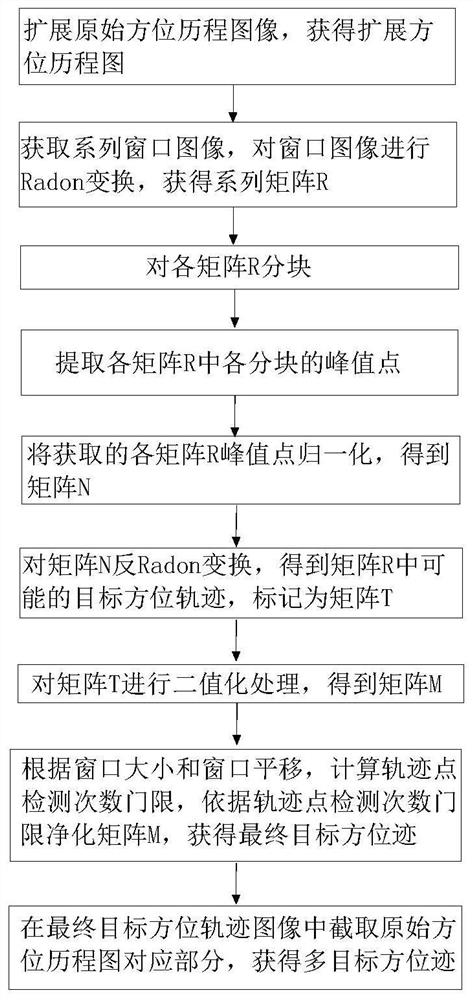
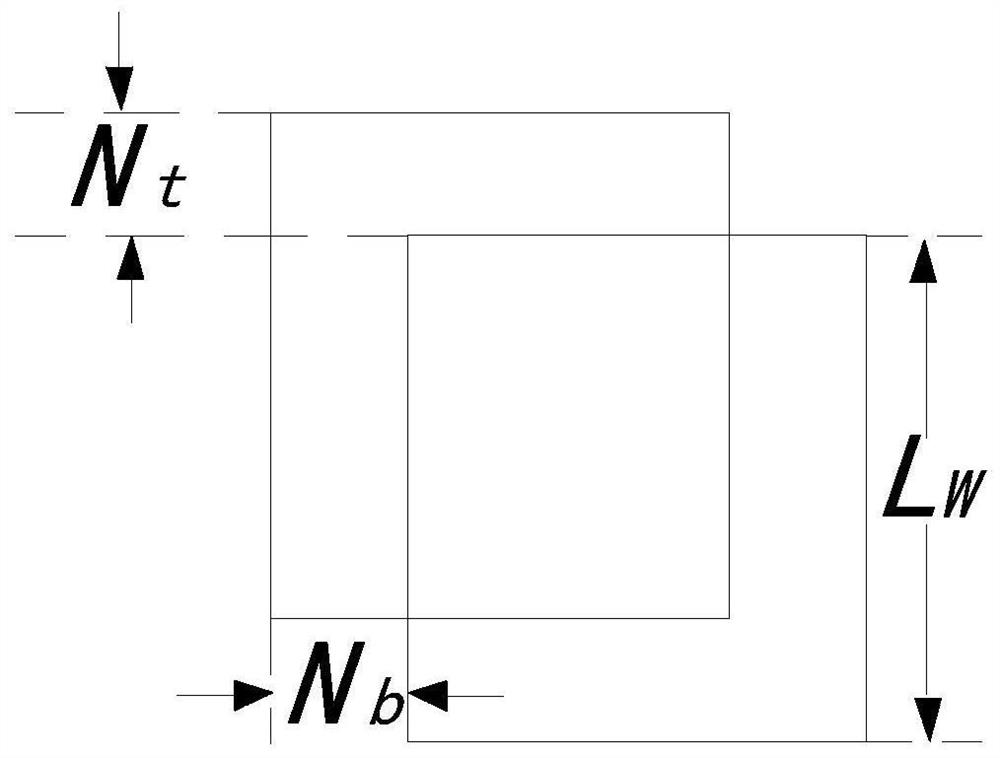
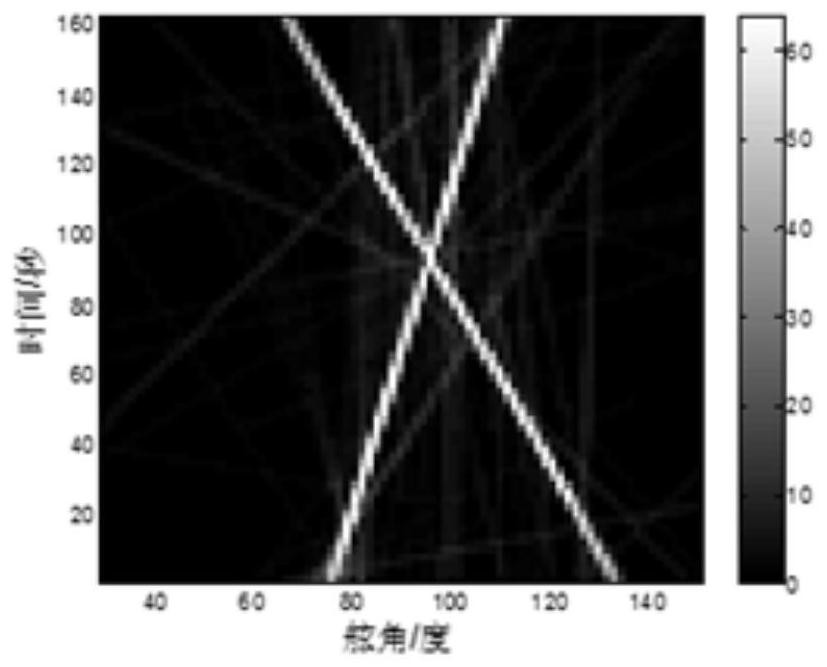
The invention relates to the technical field of sonar image processing, in particular to a passive sonar multi-target azimuth trace extraction method, electronic equipment and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: expanding an original azimuth course image to obtain an expanded azimuth course image; setting a window, sequentially obtaining a series of windowimages on the extended azimuth course image, and performing Radon transformation on each window image to obtain a coefficient matrix R; partitioning each matrix R into blocks; extracting a peak pointof each block in each matrix R; normalizing the obtained peak points of each matrix R to obtain a matrix N; performing inverse Radon transformation on the matrix N to obtain an initial target azimuthtrace in the matrix R, and marking the initial target azimuth trace as a matrix T; performing binarization processing on the matrix T to obtain a matrix M; calculating an azimuth trace point detection frequency threshold according to the window size and the window translation pixel point number, and purifying the matrix M according to the azimuth trace point detection frequency threshold to obtain a final target azimuth trace; and intercepting a corresponding part of the original azimuth course graph to obtain an extracted multi-target azimuth trace.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
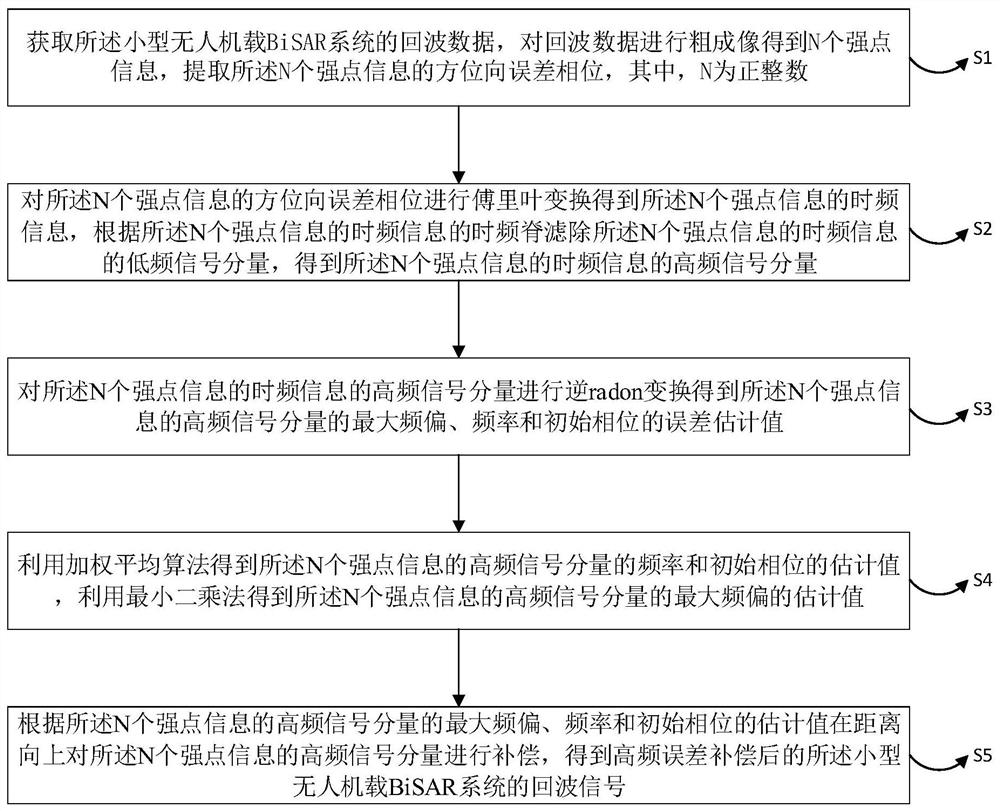
High-frequency motion error compensation algorithm of small unmanned aerial vehicle BiSAR system
ActiveCN113221062AAchieving space-variant motion compensationFocusComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmUncrewed vehicle
According to the high-frequency motion error compensation algorithm of the small unmanned aerial vehicle-mounted BiSAR system, the azimuth error phases of N pieces of strong point information are obtained by performing coarse imaging on echo data of the small unmanned aerial vehicle-mounted BiSAR system, and N is a positive integer; fourier transform is carried out on the azimuth error phase of the strong point information to obtain time-frequency information of the strong point information, and low-frequency signal components of the time-frequency information of the strong point information are filtered out according to a time-frequency ridge of the time-frequency information of the strong point information to obtain high-frequency signal components of the time-frequency information; inverse radon transformation is performed on the high-frequency signal component to obtain error estimation values of the maximum frequency offset, the frequency and the initial phase of the high-frequency signal component; estimated values of the frequency and the initial phase are obtained by using a weighted average algorithm, and an estimated value of the maximum frequency offset is obtained by using a least square method; and the high-frequency signal component in the distance direction is compensated according to the estimated value of the high-frequency signal component. Space-variant motion compensation and low-frequency motion compensation of high-frequency errors of a BiSAR system are achieved, and good focusing of SAR images is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Enhanced visualisation of geologic features in 3D seismic survey data
ActiveUS9366773B2Eliminate offsetSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsVoxelSeismic survey
A method of visually enhancing at least one geologic feature in 3D seismic survey data, comprising the steps of: (a) generating at least one attribute volume definable in Cartesian space and comprising at least one attribute derivable from said 3D seismic survey data; (b) generating a first Radon data volume from data resulting from a transaxial Radon Transform of said at least one attribute volume with respect to a first Cartesian axis; (c) generating a second Radon data volume from data resulting from a transaxial Radon Transform of said first Radon data volume with respect to a second Cartesian axis; (d) generating a third Radon data volume from data resulting from exponentiating a characteristic parameter of each one of a plurality of voxels forming said second Radon data volume to a predetermined first power value, and (e) applying a first Inverse Radon Transform to said third Radon data volume with respect to said second Cartesian axis, and a subsequent second Inverse Radon Transform to the resulting data from said first Inverse Radon Transform with respect to said first Cartesian axis.
Owner:FOSTER FINDLAY ASSOCS
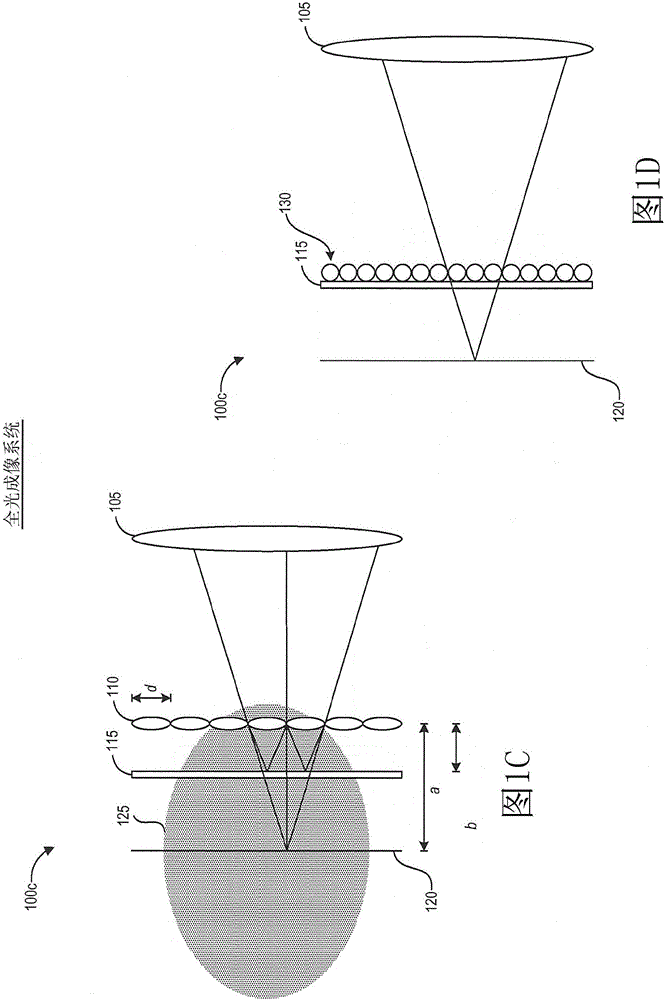
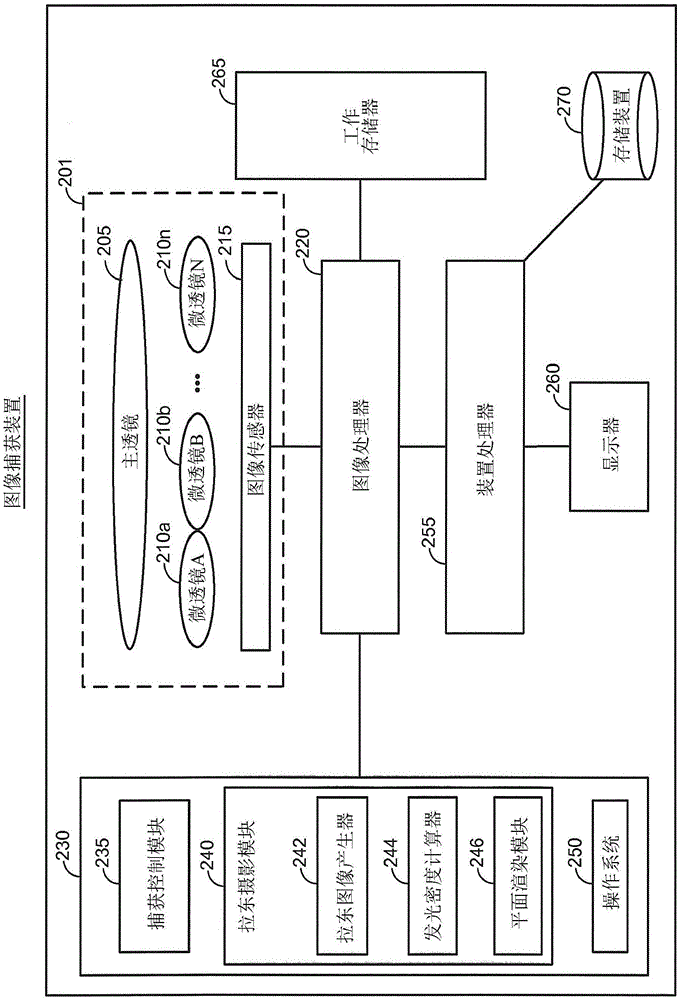
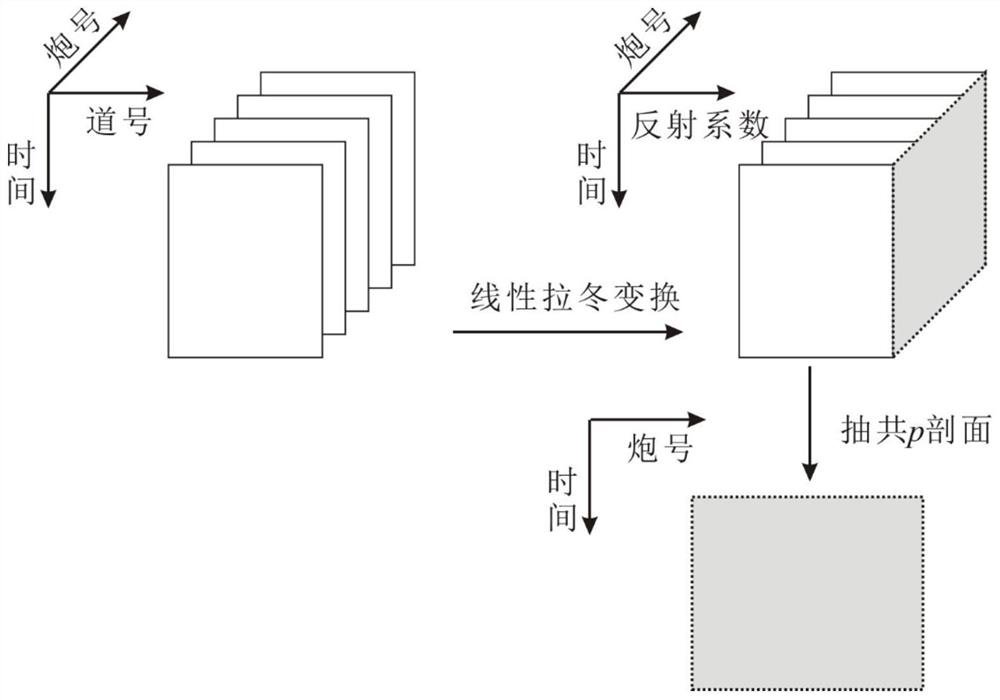
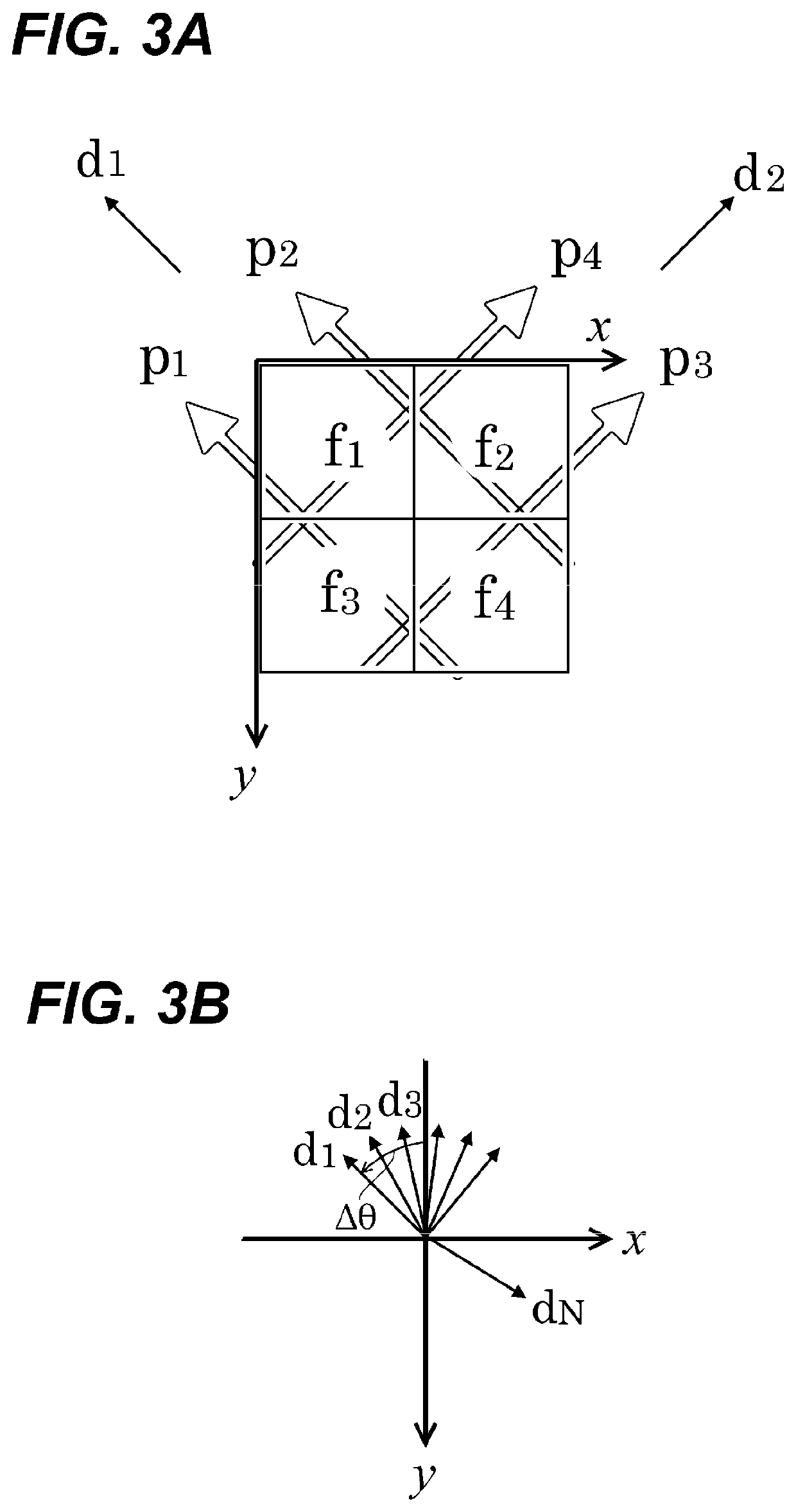
Generation and use of a 3d radon image
Certain aspects relate to systems and techniques for efficiently recording captured plenoptic image data and for rendering images from the captured plenoptic data. The plenoptic image data can be captured by a plenoptic or other light field camera. In some implementations, four dimensional radiance data can be transformed into three dimensional data by performing a Radon transform to define the image by planes instead of rays. A resulting Radon image can represent the summed values of energy over each plane. The original three-dimensional luminous density of the scene can be recovered, for example, by performing an inverse Radon transform. Images from different views and / or having different focus can be rendered from the luminous density.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Processing methodology for full-waveform sonic wavefield separation
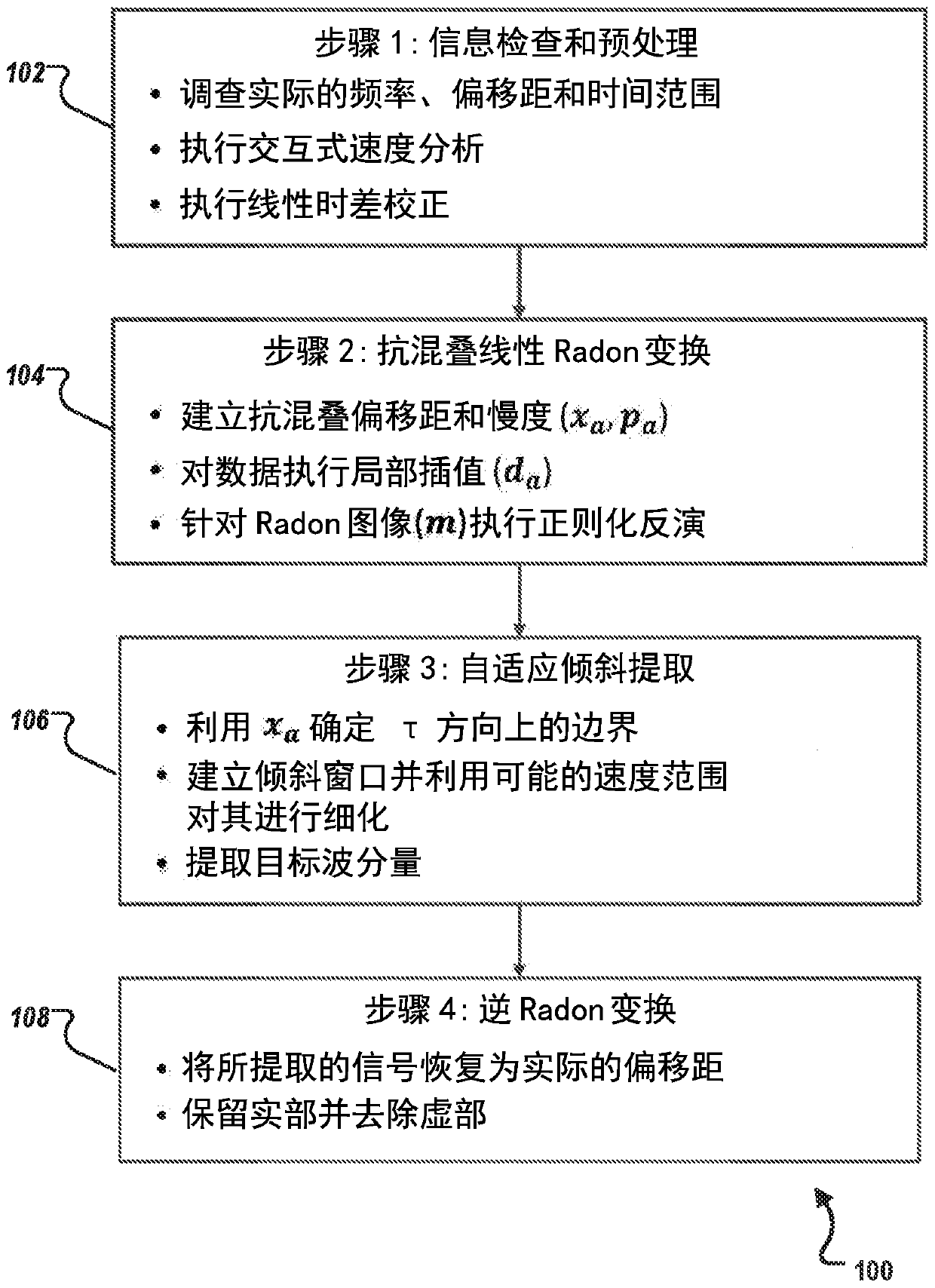
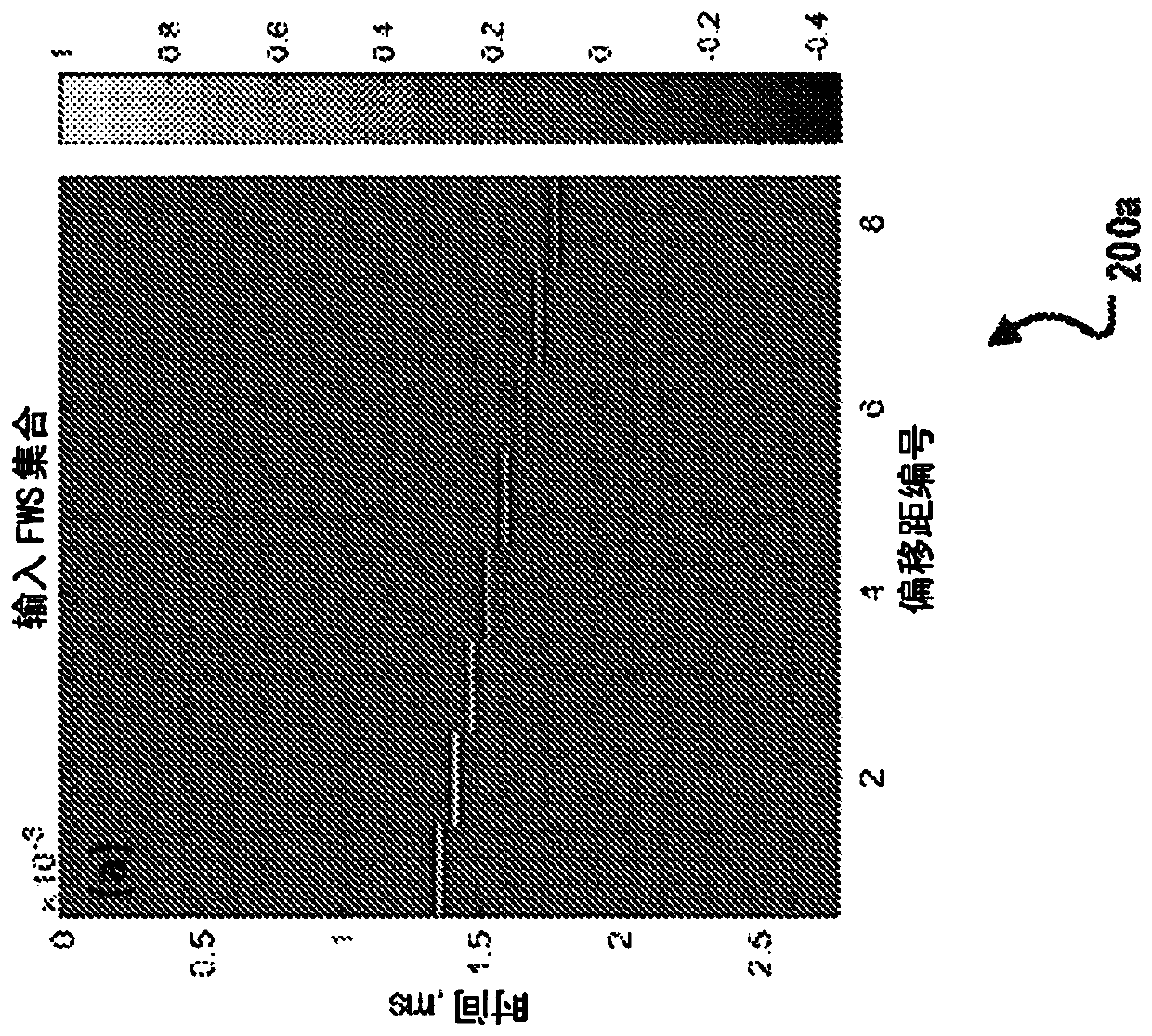
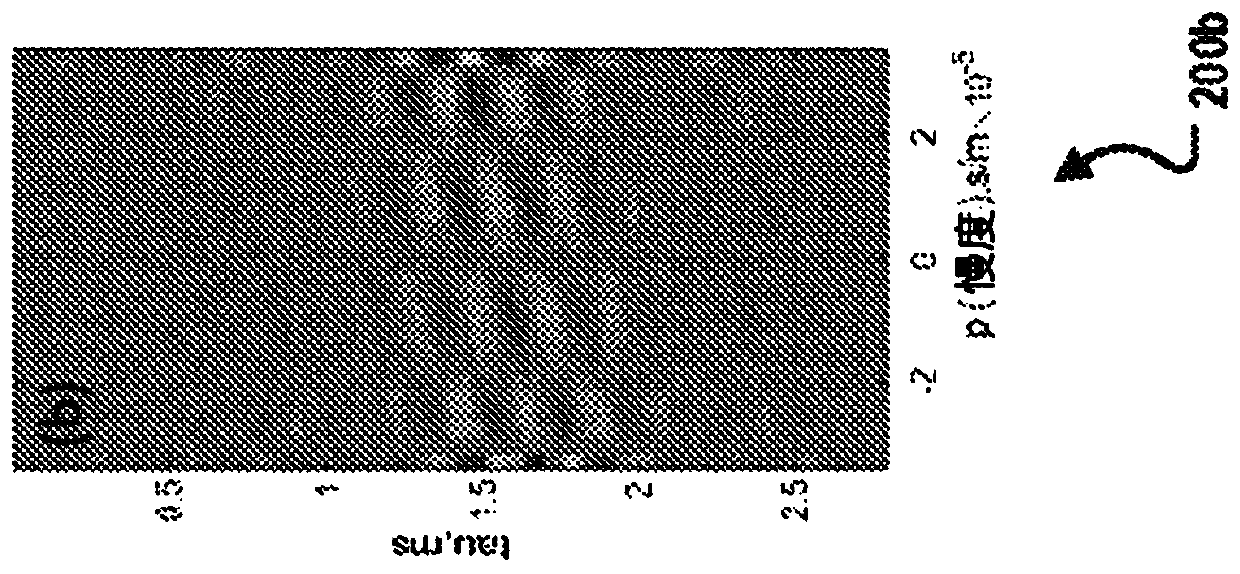
ActiveCN110832355AEfficient separationEfficient local interpolationSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingWave shapeWave field
A method for full-waveform sonic (FWS) wavefield separation includes receiving FWS data; performing an anti-aliasing linear Radon transform on the received FWS data; extracting Radon-transformed FWS data corresponding to a wave component using a slanted window; and determining signals of the wave component by performing an inverse Radon transform on the extracted Radon-transformed FWS data.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
A Variable Vertex Sparse Hyperbolic Radon Transform Method Considering Seismic Wavelet Stretch Effect
ActiveCN105929447BReduce the numberEliminate wave stretching effectsSeismic signal processingDomain modelComputation complexity
The invention discloses a vertex variable sparse hyperbolic Radon transform method considering a seismic wavelet stretching effect. According to the method, the vertex positions and velocities of hyperbolic events are calculated by using the dip angles and the derivatives thereof of seismic events; the number of the hyperbolic events is determined through using a clustering algorithm, and the number of parameters of the estimated events is decreased; based on the calculated vertex positions and velocities of the events, a vertex variable hyperbolic Radon transform operator is constructed by using a method according to which windowing is adopted to segment a seismic channel, and the seismic wavelet stretching effect generated by inverse Radon transform is eliminated; a Radon domain model and the L1 norm minimization constrain of a data fitting term are introduced into an optimization problem, so that the sparsity of the Radon domain model and the adaptability of the Radon domain model to non Gaussian fitting error can be improved; a multiplier alternating direction method is utilized to solve an L1-L1 norm minimization problem; and in a whole iterative process, matrix inversion is only needed to be carried out for once, so that computational complexity is low.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Diffraction Multiple Wave Suppression Method Based on Wavefield Decomposition
ActiveCN111505719BAccurate calculationImprove robustnessSeismic signal processingOriginal dataReflected waves
The present invention involves a multi -wave suppression method based on the decomposition of the wave field. The seismic data is arranged to the concentration form of the concentration and the linear pulled winter transformation.The graphic wave data of the incident is separated from the difference between the reflection and the dextering of the same phase shaft according to the graphic wave incident.The form of the Taoism and reflecting the winter transformation, obtaining the separation wave field data and the reflection wave field data, subtracting the separated data from multiple wave prediction methods, and obtaining multiple waves of earthquake data.This method does not require the types of multiple waves in the original data. It can effectively distinguish the multiple waves of different types of waves, and the hierarchical multiple wave prediction results have been greatly improved, which improves the robustness of multiple wave suppression results, and reduces the robustness of multiple wave suppression results.The complexity of the predictive model and the difficulty of subsequent waves of subsequent waves.
Owner:ZHANJIANG BRANCH OF CHINA NATIONAL OFFSHORE OIL CORP
Acquisition method, acquisition device, and control program for tomographic image data by means of angular offset
ActiveUS20210228167A1Increase speedLittle computational resourceReconstruction from projectionComputerised tomographsAngular scanComputer graphics (images)
In an embodiment of the present disclosure, in order to raise the reproducibility of a reconstructed tomographic image without increasing a calculation load, any one among two directions adjacent to two boundaries that demarcate an angular scan range is offset from any one among coordinate axes of a two-dimensional tomographic image of N pixels×N pixels, and the angle of the offset is made to be above 0 degrees and under 90 degrees or above −90 degrees and under 0 degrees. A detection device, which includes N detection elements, performs detection in each detection direction, and a first vector having N×N elements is obtained from a detection signal obtained by the detection device in a detection operation. A discrete Inverse Radon transform matrix is applied to the first vector to obtain a second vector having N×N elements. The second vector is de-vectorized to obtain image data for a two-dimensional tomographic image of N pixels×N pixels. An inverse matrix of a system matrix for an offset is obtained and used as the discrete Inverse Radon transform matrix.
Owner:RIKEN +1
Hyperbolic radon domain comprehensive prediction deconvolution and feedback loop method to suppress multiple wave model construction method
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
A Method for Parameter Estimation of Rotating Target Under Vibration Disturbance Condition
ActiveCN106950554BEffective observationIncreased complexityWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsMicrowave
The invention provides a method for estimating a rotation target parameter under a vibration disturbance condition. The method is characterized by introducing a narrowband terahertz radar system with a frequency band between those of a microwave and a laser; providing a fast and effective signal processing method by means of signal processing means such as inverse Radon transform, time-frequency analysis and inverse transform thereof, and the like; and achieving the separation estimation and compensation of vibration disturbance and the parameter estimation and image reconstruction of the rotation for the rotation target accompanied by vibration disturbance. The method is highly efficient and stable, and does not enhance system complexity.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Measurement method of flame excited state particle radiation rate based on uniform light source
A method for measuring the radiation rate of flame excited state particles based on a uniform light source, using a jet diffusion burner, an integrating sphere uniform light source, two ICCD cameras, Edmund 34980 filters, Edmund 65198 filters and a computer to build a test system, based on two cameras shooting The initial image of OH* chemiluminescence and the initial image of CH* chemiluminescence obtained from the jet diffusion flame generated by the combustion of the jet diffusion burner, and the radial distribution of OH* chemiluminescence and the radial distribution of CH* chemiluminescence were obtained by using the inverse Radon transform. The luminous intensity of the uniform light captured by the two cameras is obtained based on the images of the uniform light source obtained by shooting the integrating sphere uniform light source respectively by the two cameras. Based on the radial distribution of OH* chemiluminescence and the luminous intensity of the uniform light source captured by the corresponding camera, the radiation rate of OH* excited state particles is obtained, and the CH* excitation is obtained based on the radial distribution of CH* chemiluminescence and the luminous intensity of the uniform light captured by the corresponding camera The radiation rate of the particles in the state. The invention is low in cost, simple and efficient.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com