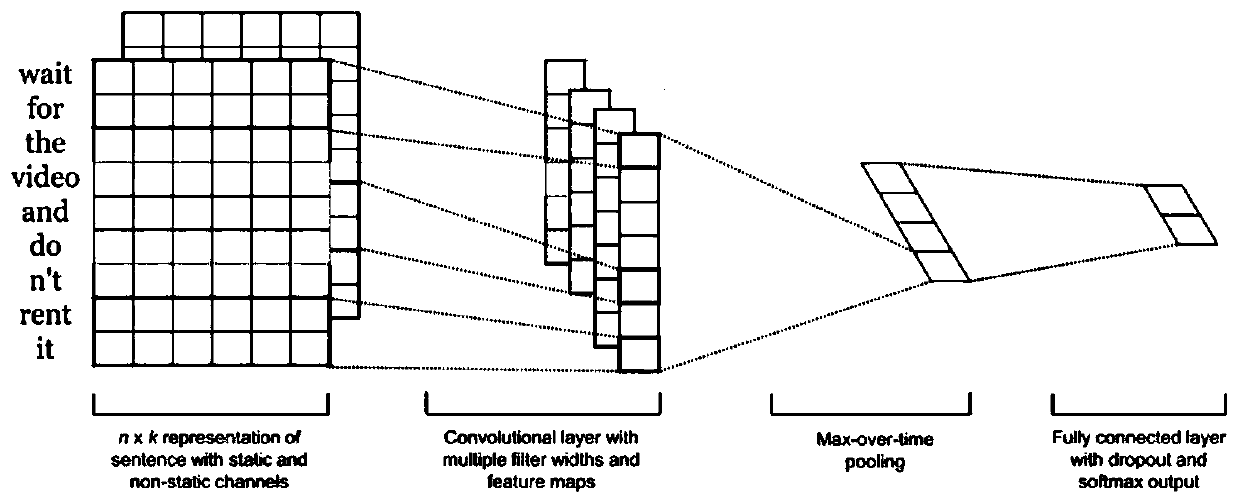
Patents
Literature
510 results about "Domain model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In software engineering, a domain model is a conceptual model of the domain that incorporates both behaviour and data. In ontology engineering, a domain model is a formal representation of a knowledge domain with concepts, roles, datatypes, individuals, and rules, typically grounded in a description logic.
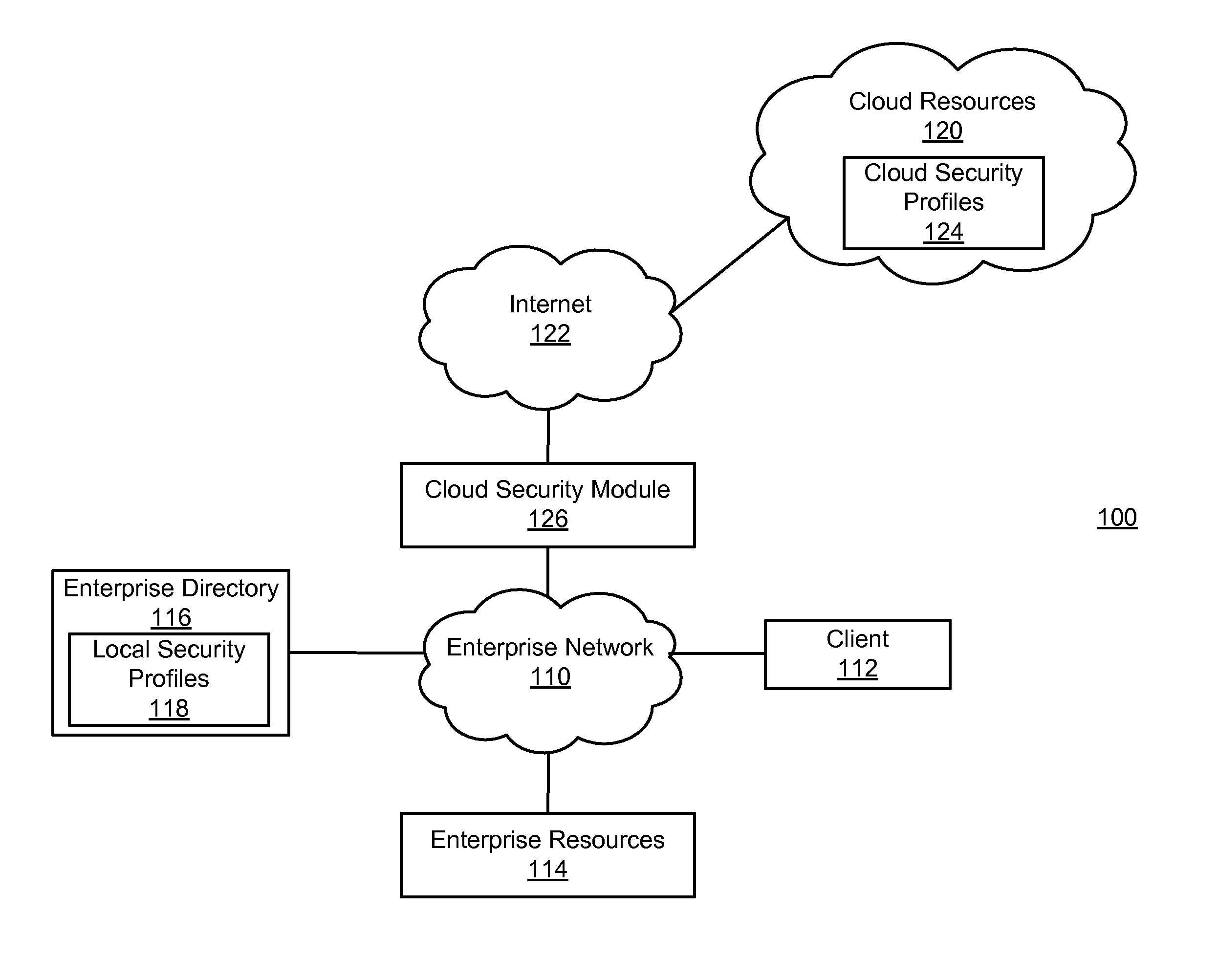
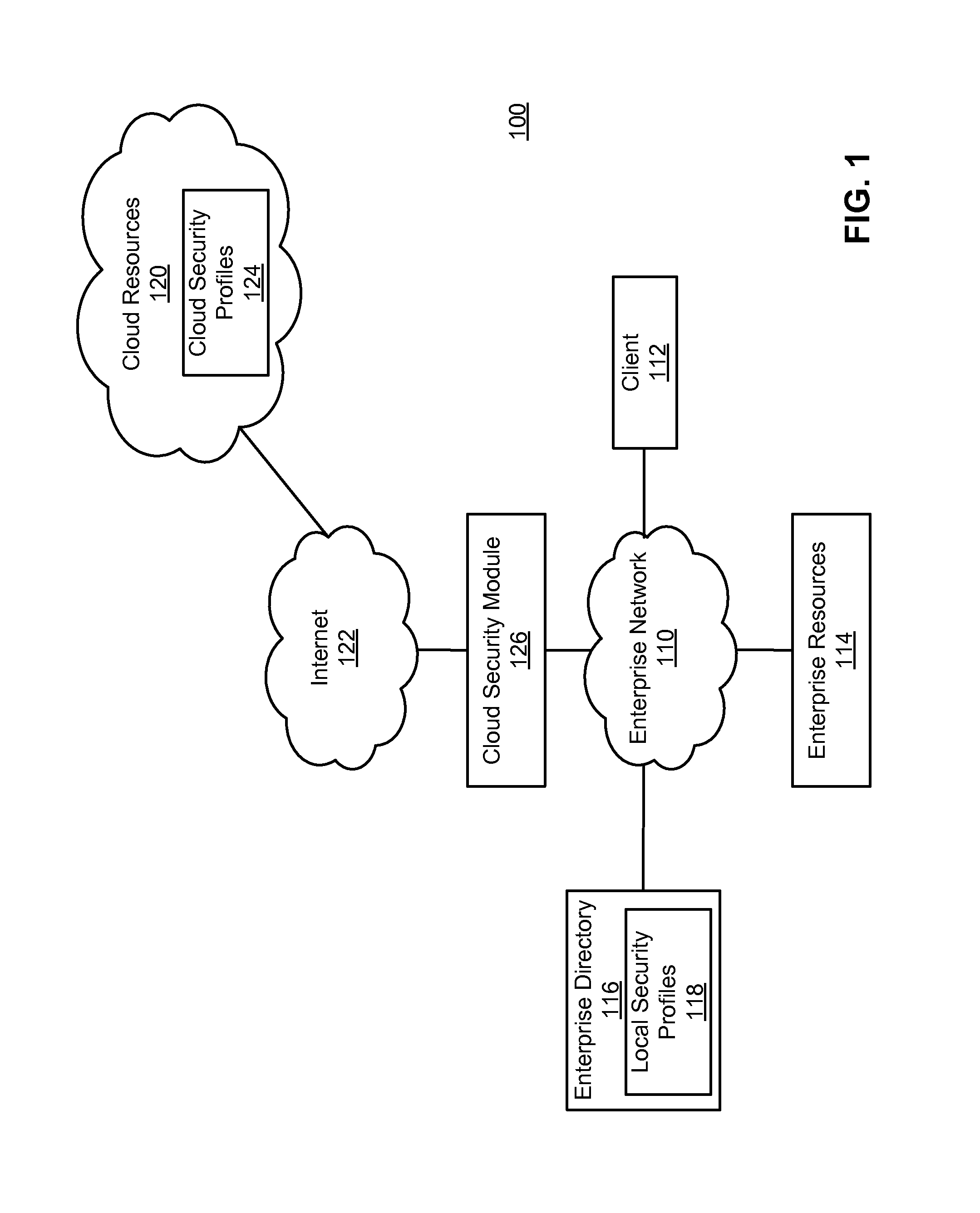
Enforcing consistent enterprise and cloud security profiles
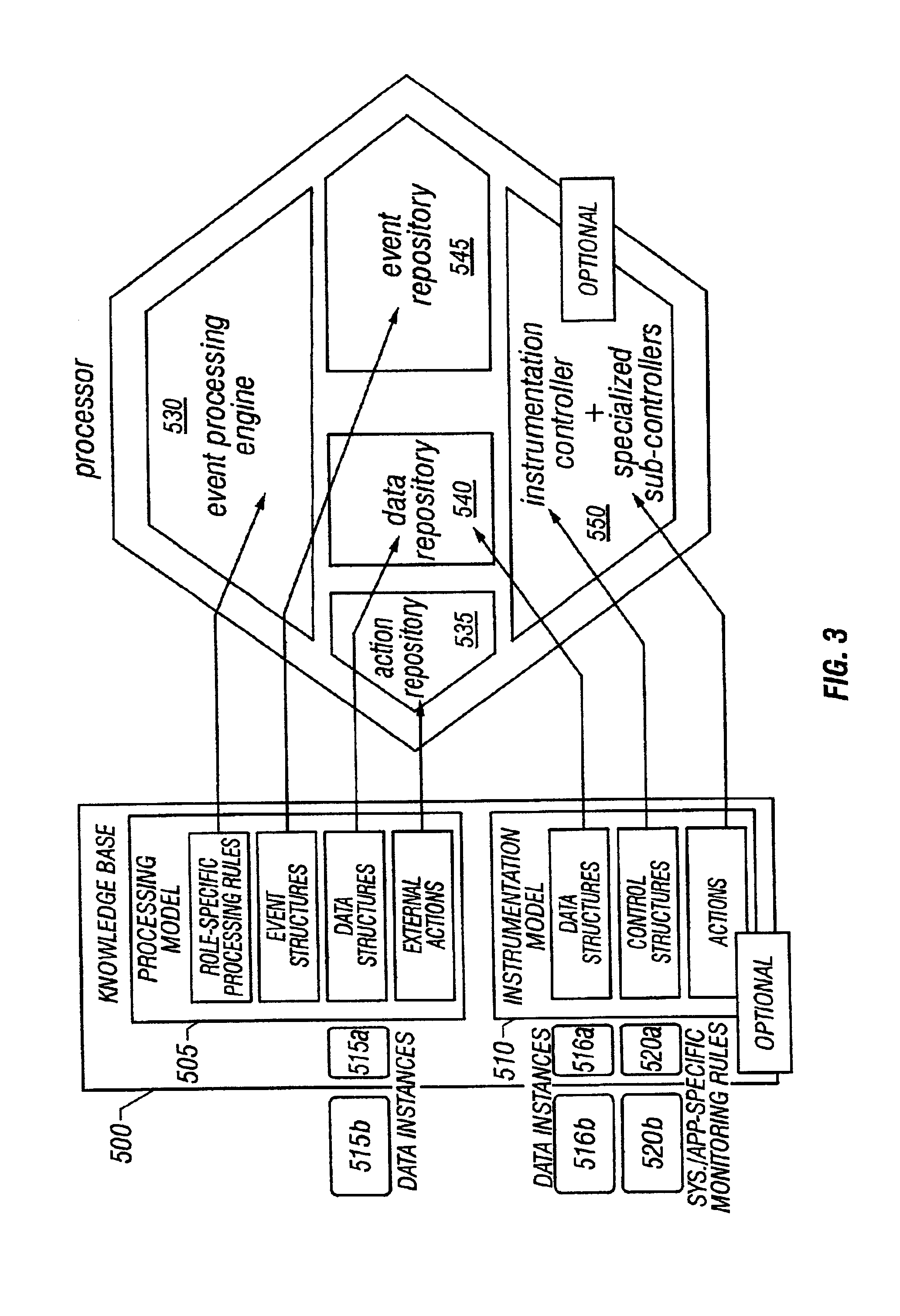
Consistent enterprise and cloud security profiles are enforced. A domain model describing cloud resource objects associated with an enterprise is defined. Further, a relationship map describing relationships between the objects of the domain model and roles of enterprise users described by local security profiles maintained by the enterprise is specified. The domain model and relationship map collectively form an access policy for the cloud resource objects. Network traffic is monitored to detect network traffic attempting to configure a cloud security profile describing permissions of an enterprise user with respect to cloud resource objects in a manner inconsistent with the access policy. Detected network traffic attempting to configure the cloud security profile in the manner inconsistent with access policy is remediated.
Owner:CA TECH INC
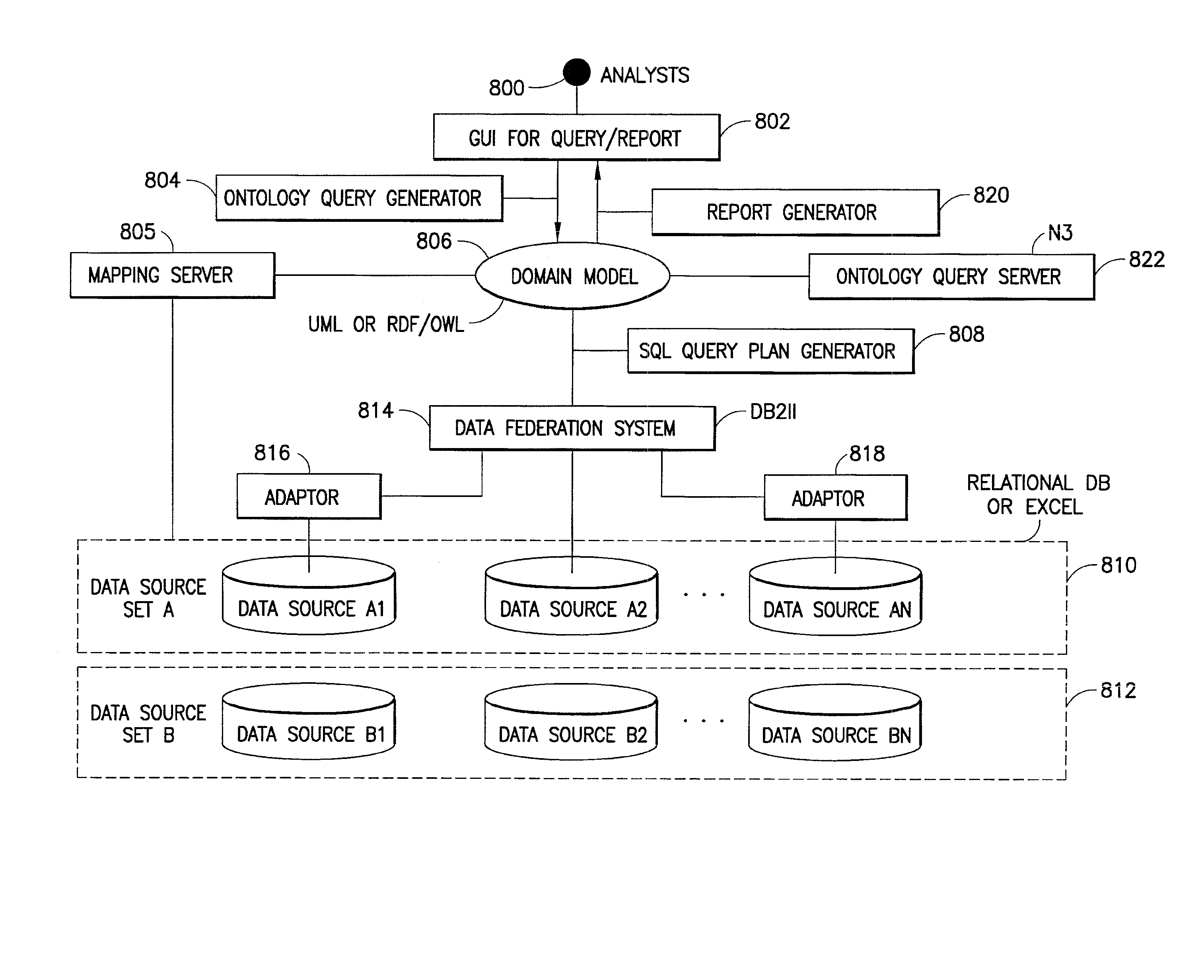
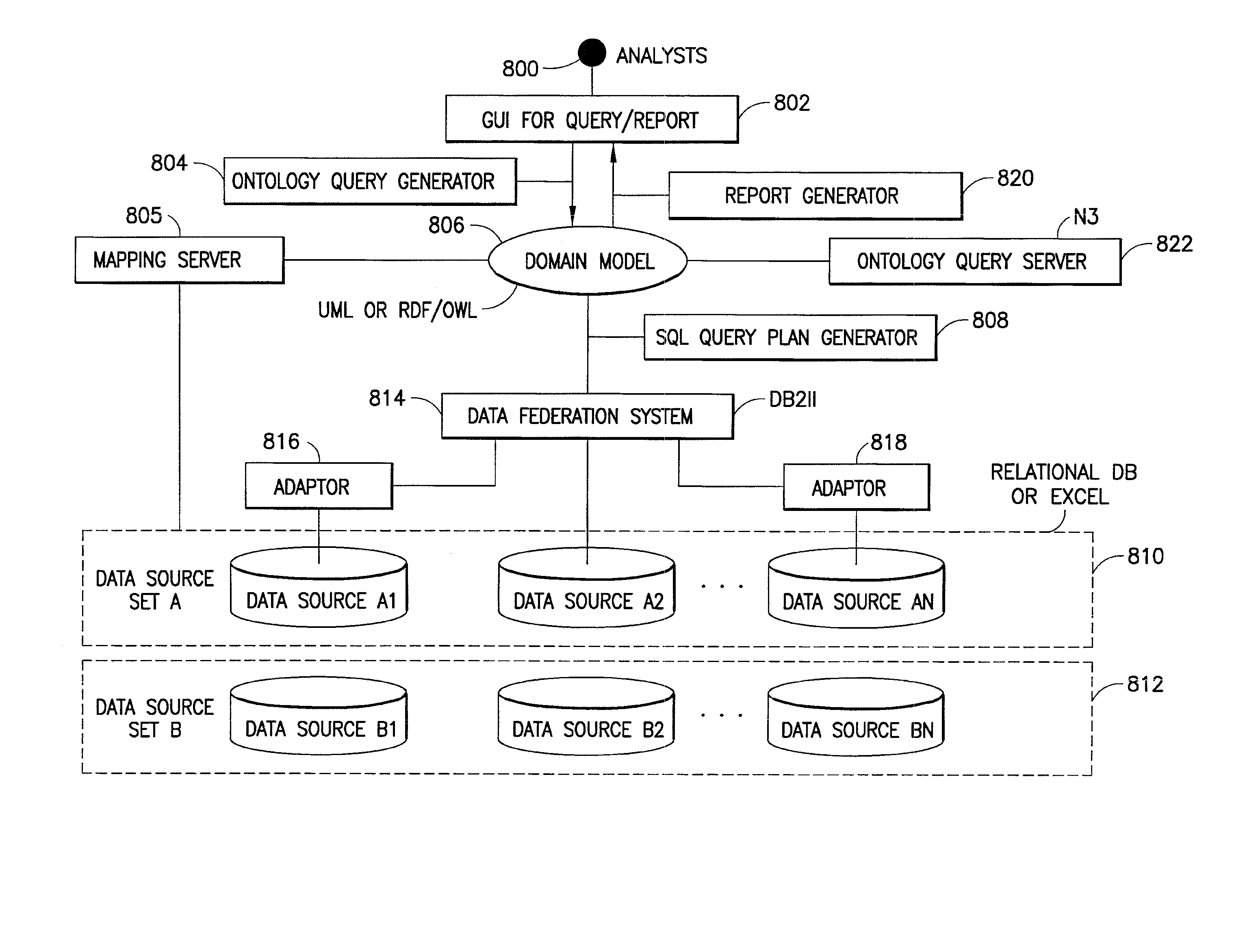
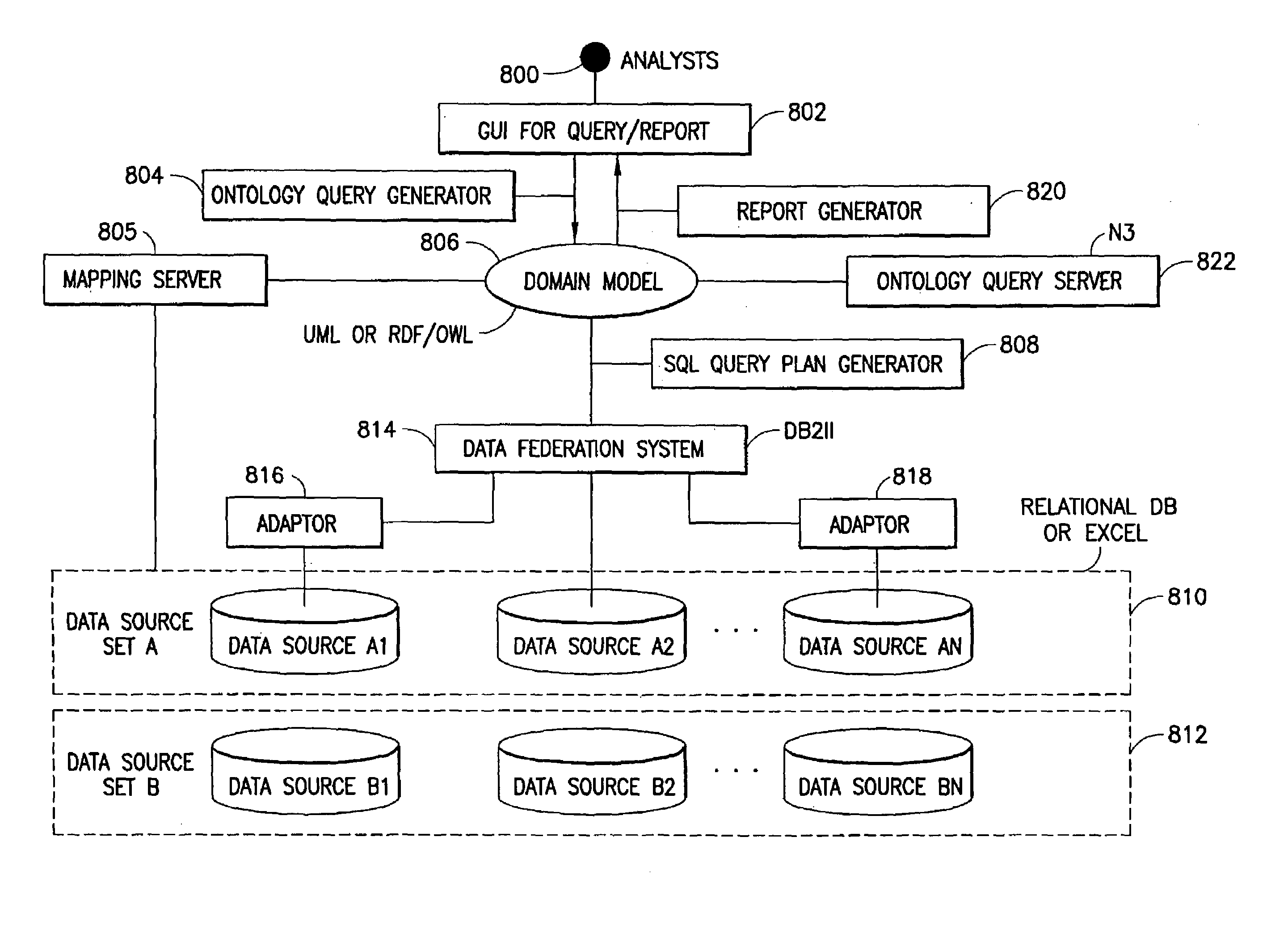
System and Method for Planning and Generating Queries for Multi-Dimensional Analysis using Domain Models and Data Federation
InactiveUS20080046422A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDomain modelData warehouse
Data integration and data analysis using computing equipment, software as well as hardware, includes a system and method for integrating data from various data sources, structured and unstructured, without physically creating a data warehouse and automatically generating queries for analysis of the integrated data from a multitude of different views.
Owner:SERVICENOW INC
System and method of enterprise systems and business impact management
InactiveUS6983321B2Faster and accurate analysisAvoid lot of costDigital computer detailsPayment architectureBusiness managementPotential impact
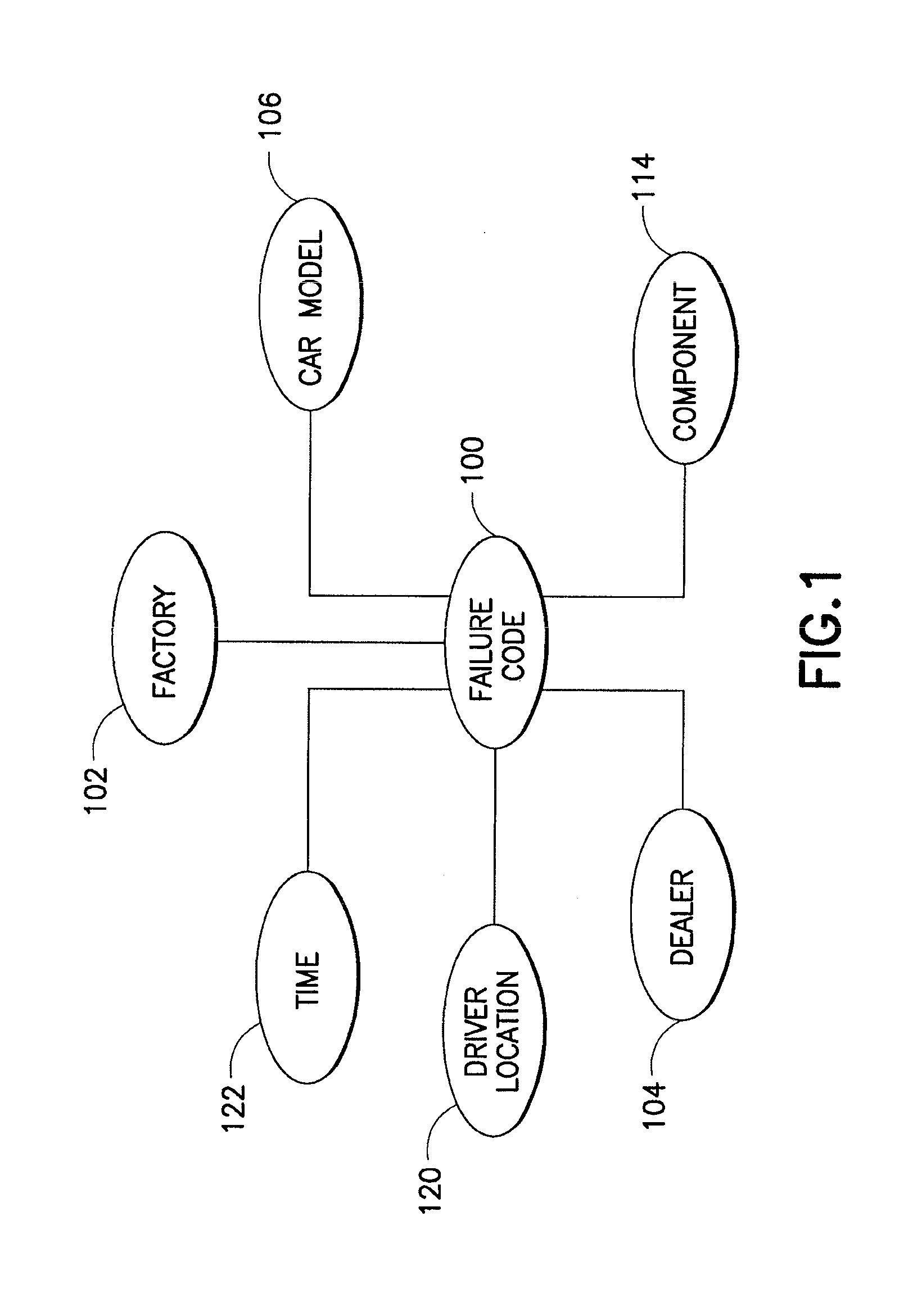
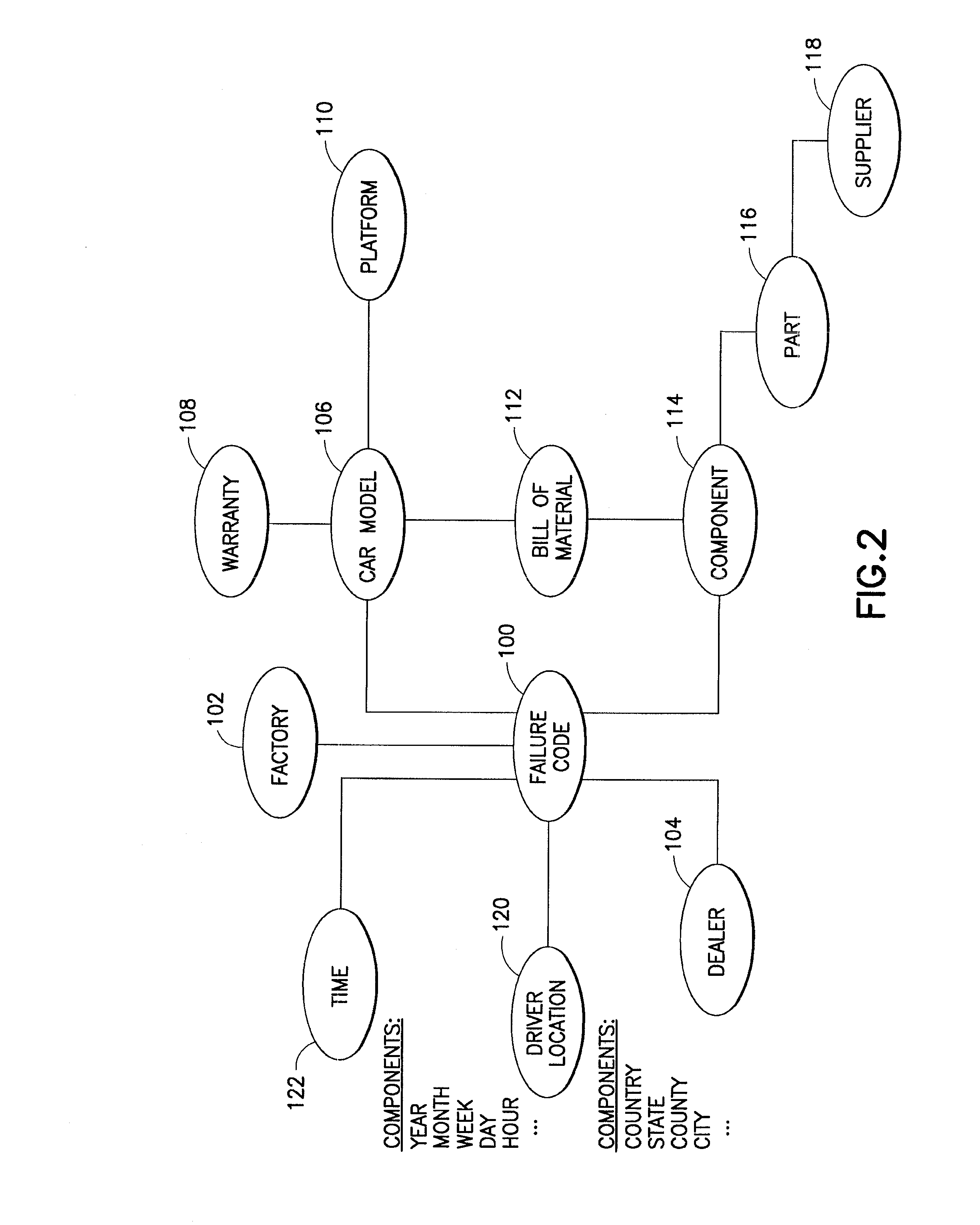
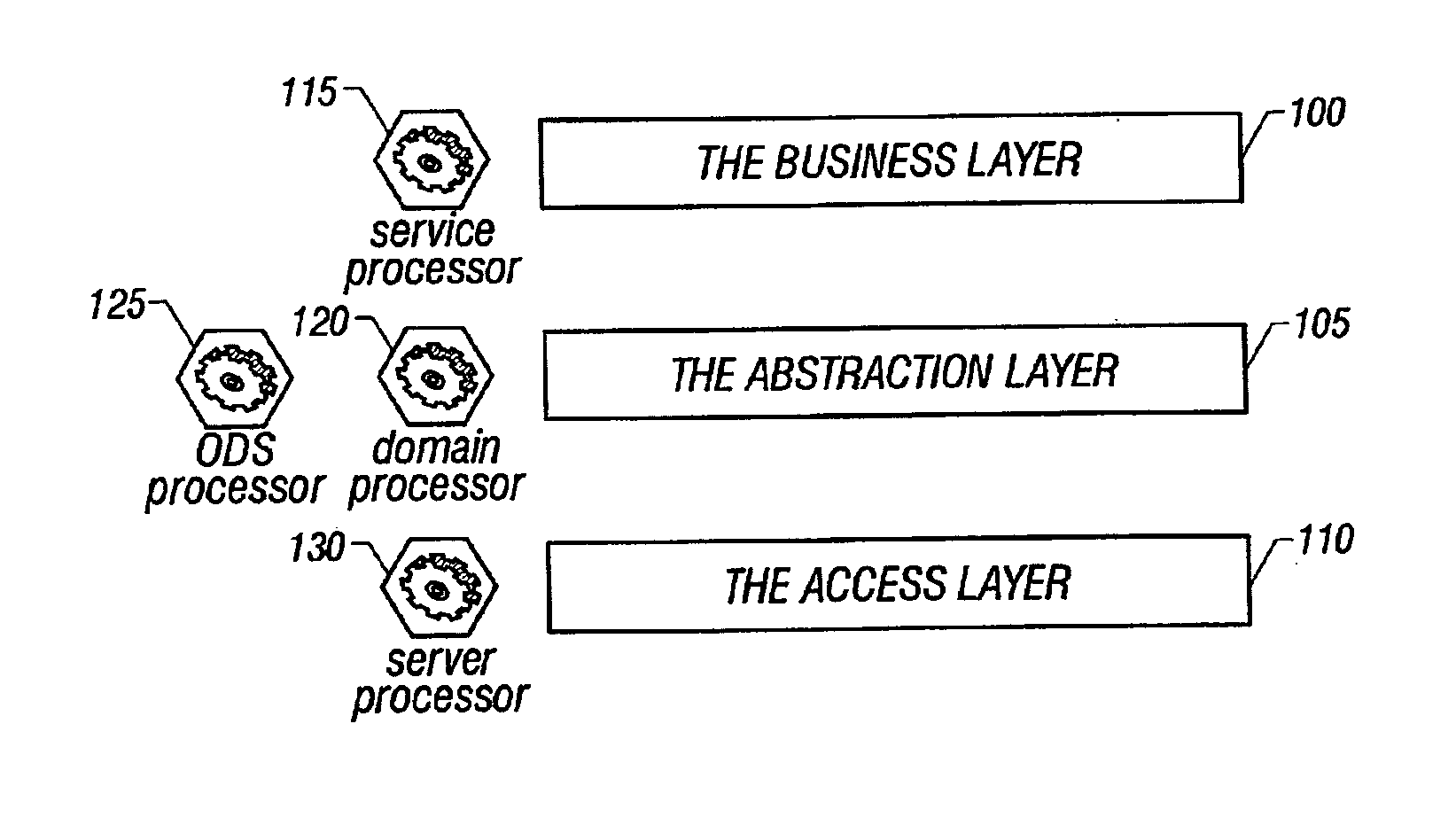
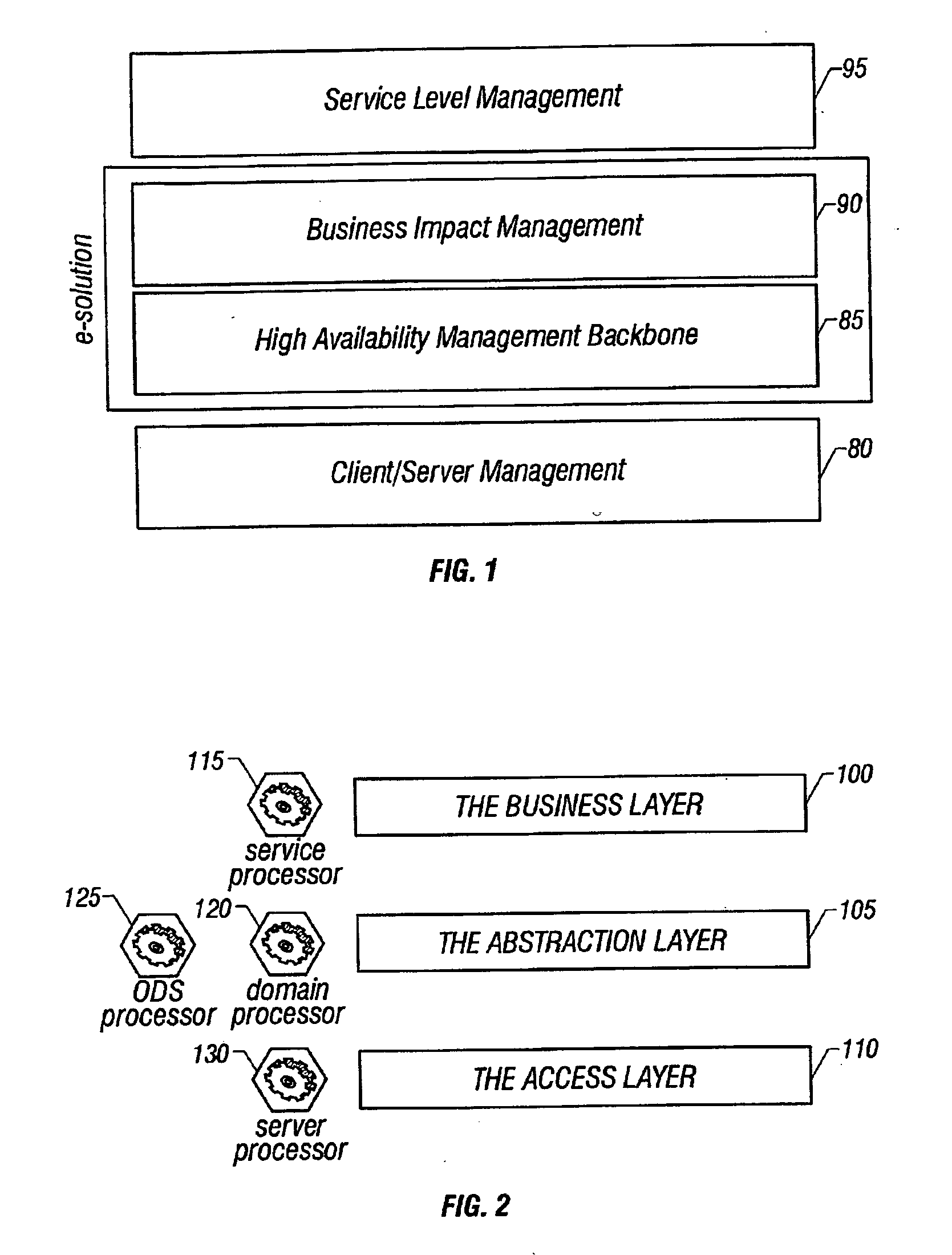
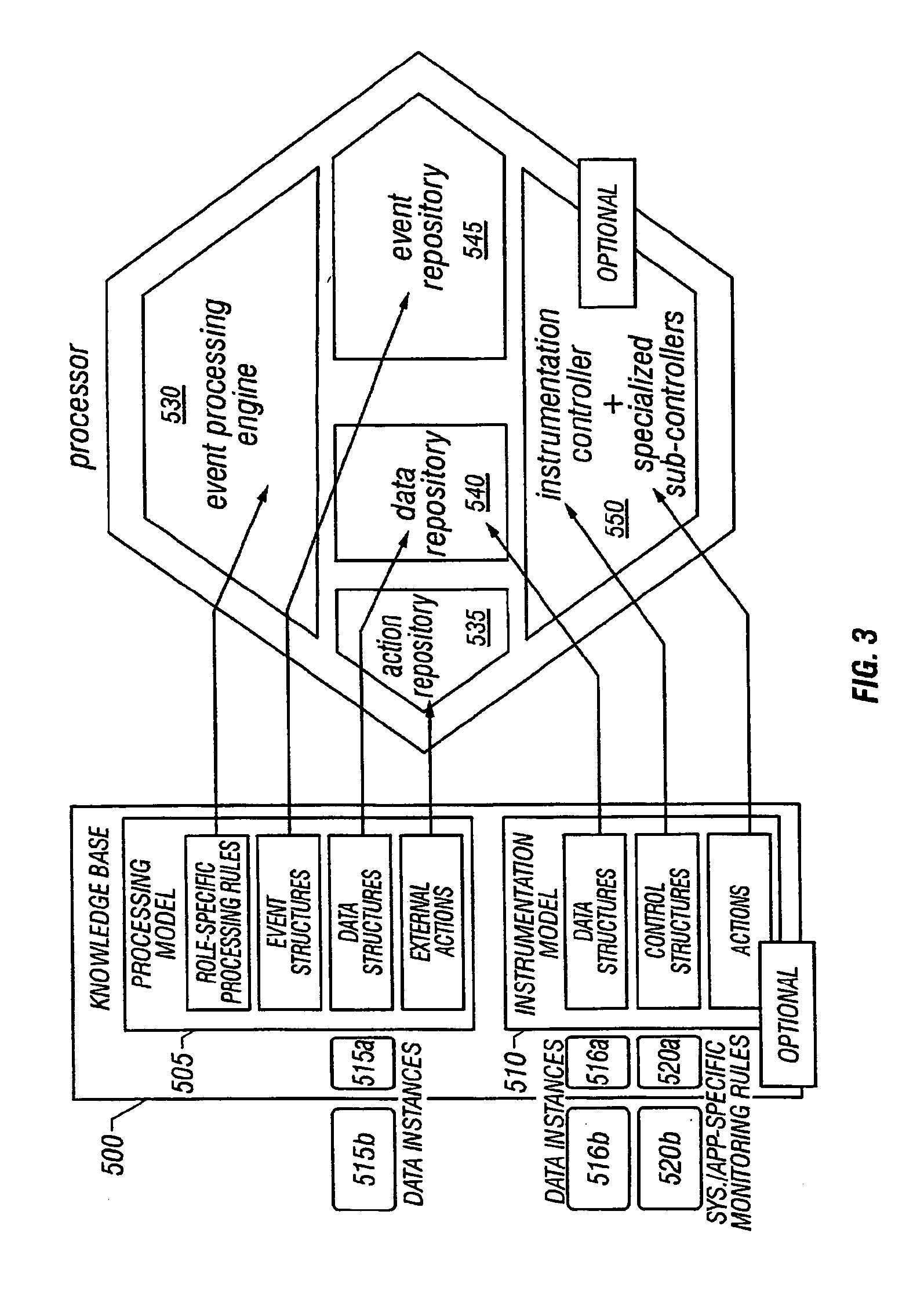
A system architecture and a method for management using a cellular architecture to allow multi-tier management of events such as the managing of the actual impact or the potential impact of IT infrastructure situations on business services. A preferred embodiment includes a high availability management backbone to frame monitoring operations using a cross-domain model where IT Component events are abstracted into IT Aggregate events. By combining IT Aggregate events with transaction events, an operational representation of the business services is possible. Another feature is the ability to connect this information to dependent business user groups such as internal end-users or external customers for direct impact measurement. A web of peer-to-peer rule-based cellular event processors preferably using Dynamic Data Association constitutes management backbone crossed by event flows, the execution of rules, and distributed set of dynamic inter-related object data rooted in the top data instances featuring the business services.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
Interactive tool for semi-automatic creation of a domain model
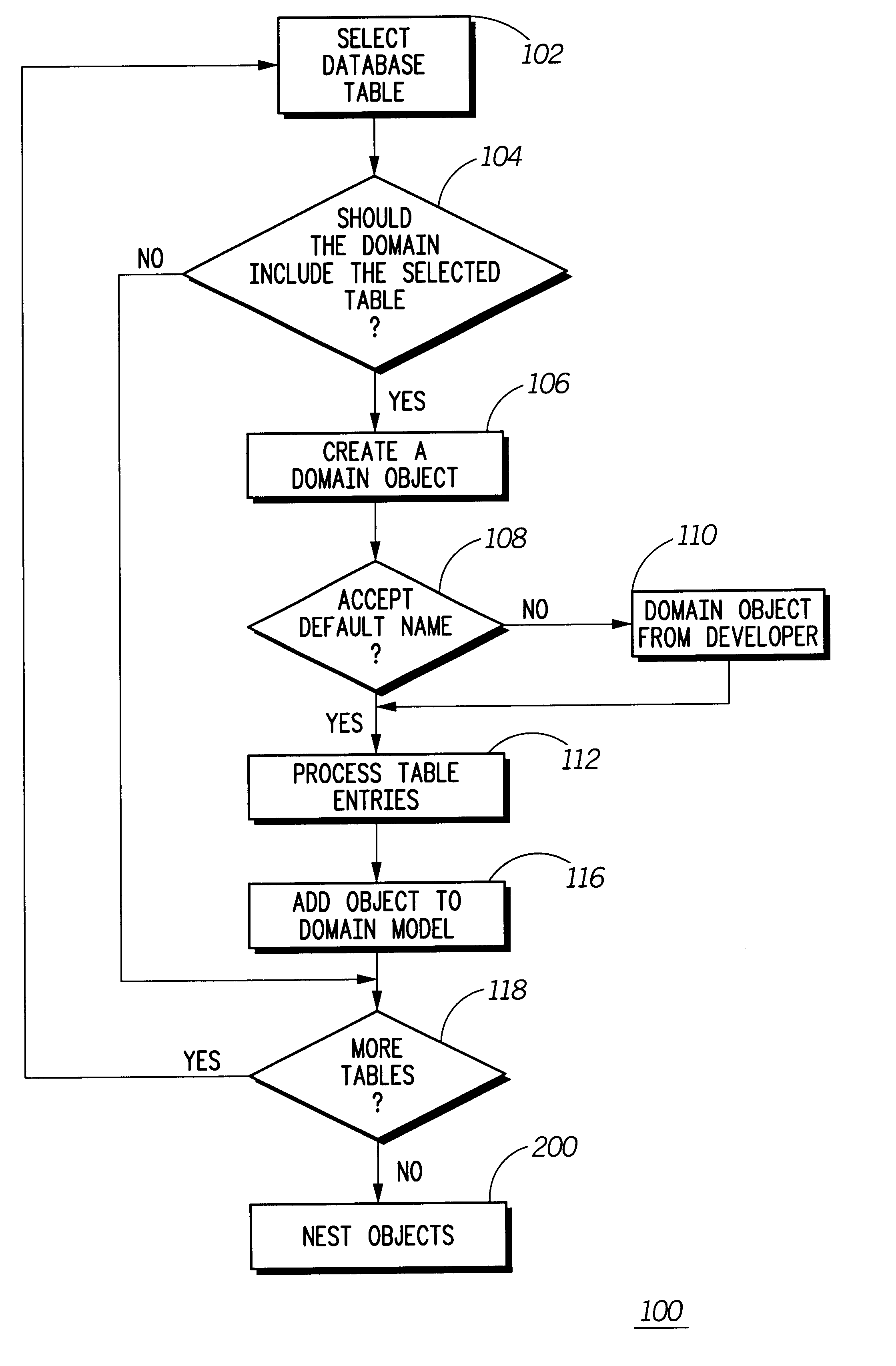
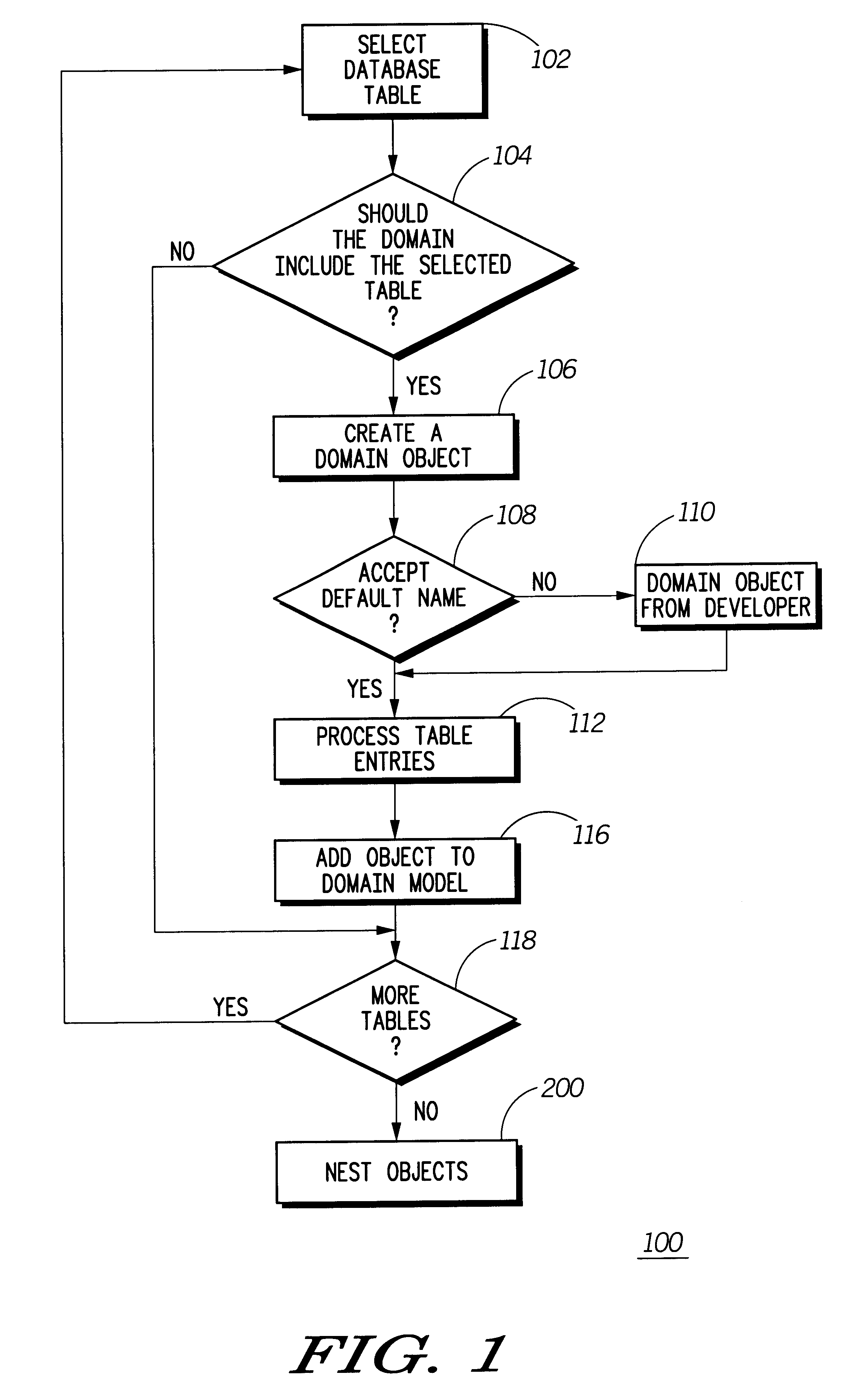
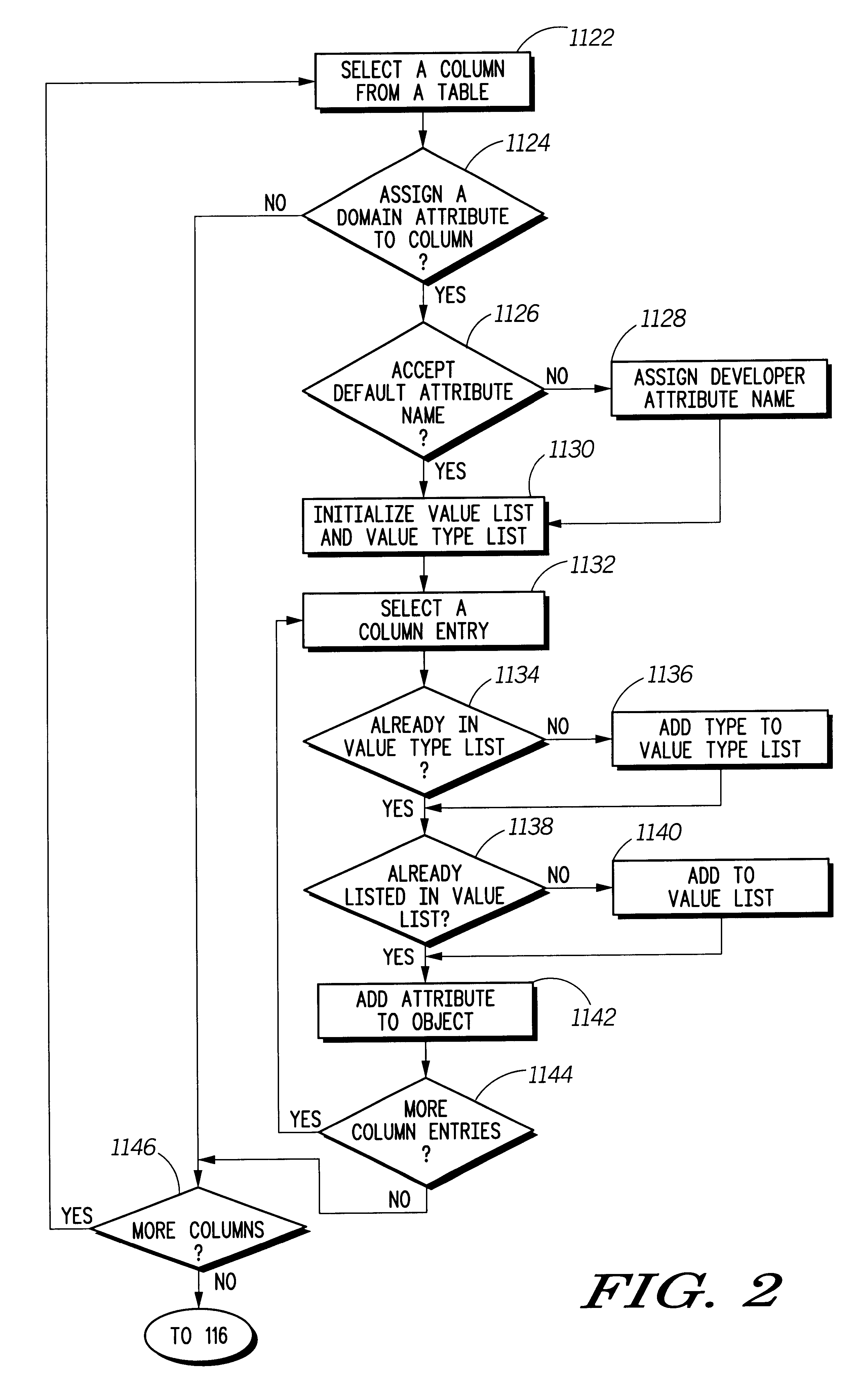
A method, system and program product 100 usable by domain developers having any experience level in creating domain models. A representation of domain model knowledge is derived from a domain specification. The domain specification includes multiple potential domain objects, e.g., tables of APIs functional arguments, and each of the potential domain objects include one or more attributes. Potential domain objects are selected one at a time 102 from the specification and offered to the developer. The developer decides 104 whether or not to include the potential domain object in the domain model. If the developer decides to include the potential domain object 106, then the system provides a default name 108, i.e., the table name or argument name, and allows the developer to rename the selected domain object 110. Then, after having selected the object, potential attributes 112, e.g., table columns 1122, are selected from the object and offered to the developer 116. If the developer decides to include a potential attribute, then a default name, i.e., the column name or name extracted from an API function, is offered 1126 for the selected attribute and the developer is allowed to rename attributes 1128. Once all the potential domain objects have been offered 118 to the developer and the developer has either decided to include the potential objects or not, the system checks the domain model for nesting structure 200. If domain objects include attributes that are shared with other domain objects 2006, then those domain objects may be reorganized such that some domain objects include instances of identically named attributes from other domain objects.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
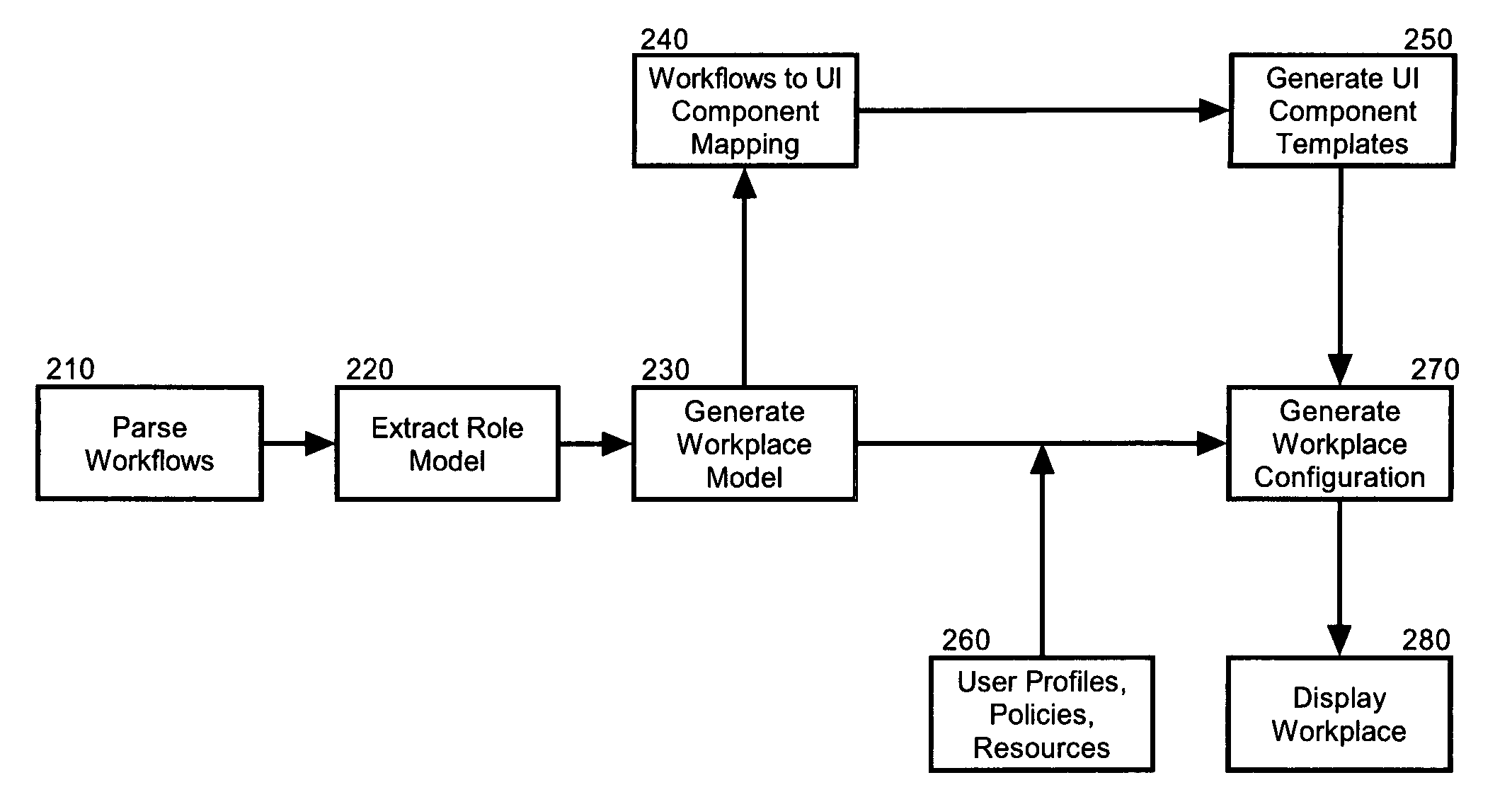
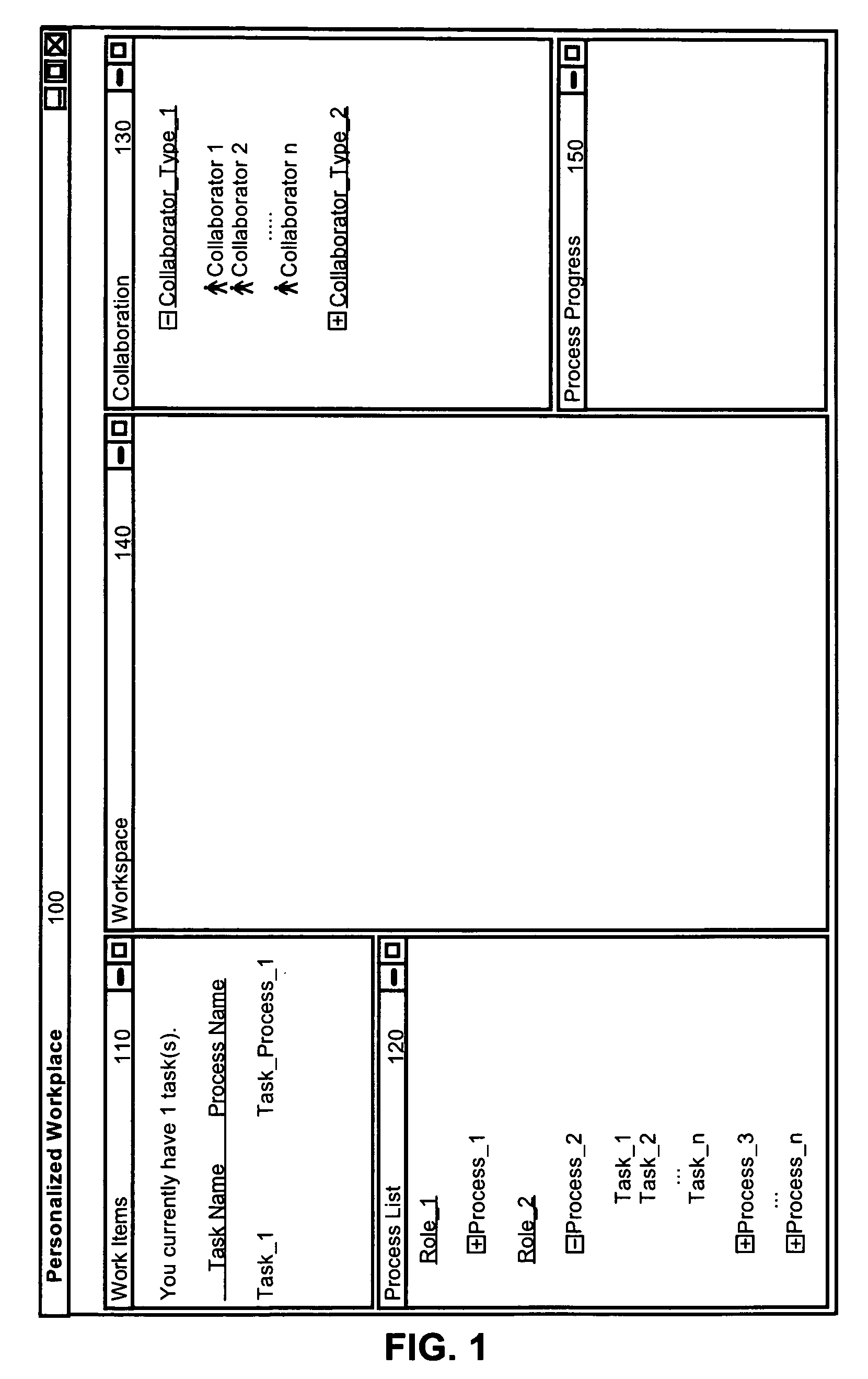
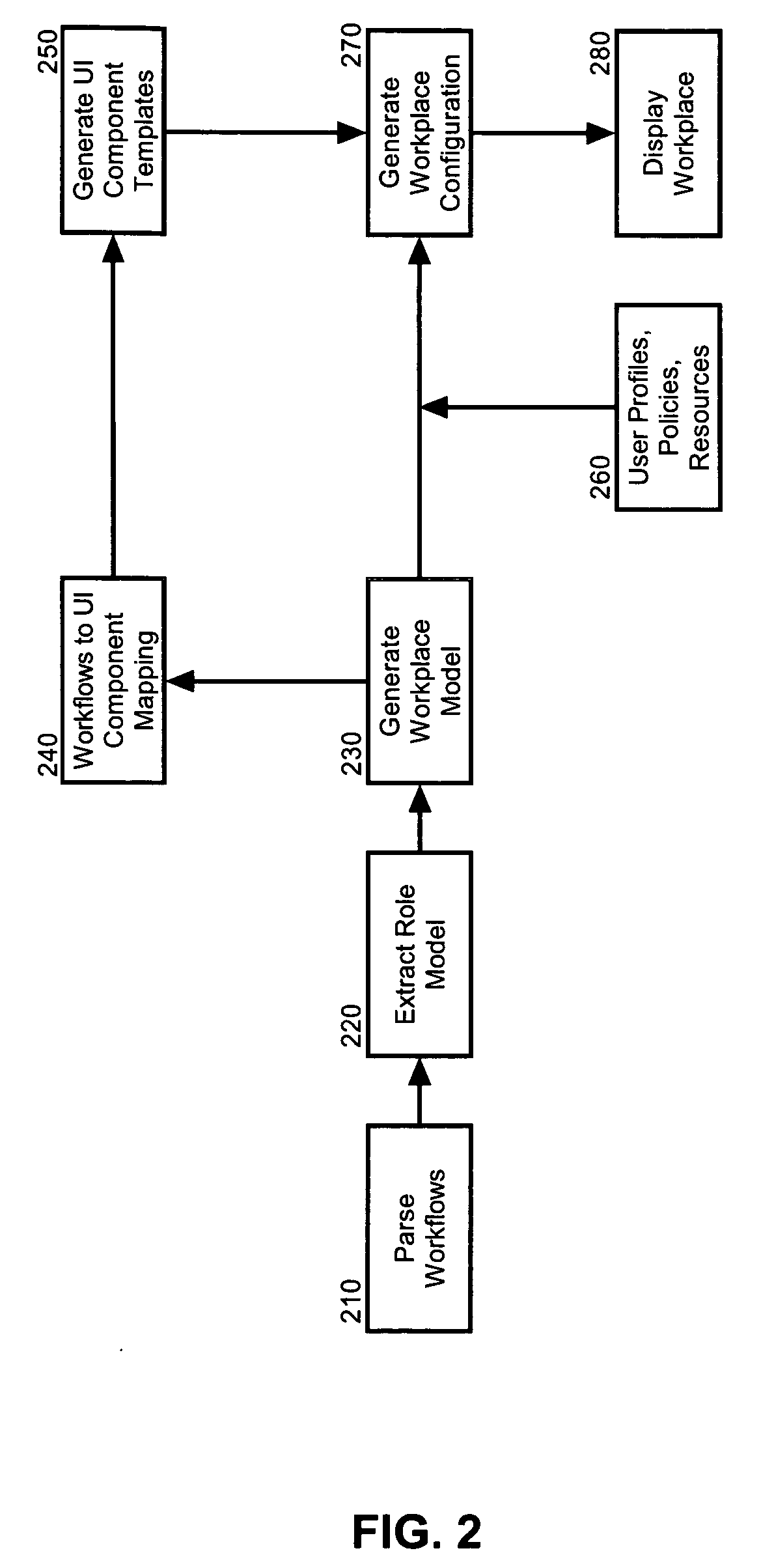
Dynamically configuring a role-based collaborative space
A method for role-based personalization of a collaborative space can include generating a collaborative space utilizing role information for an interacting user that has been defined by an underlying business process model in a workflow. For example, the step of generating a collaborative space can include parsing the workflow to extract a role model, generating a collaborative space domain model from the role model, selecting a plurality of user interface components based upon the role model, organizing the selected user interface components in the collaborative space, and rendering the collaborative space.
Owner:IBM CORP
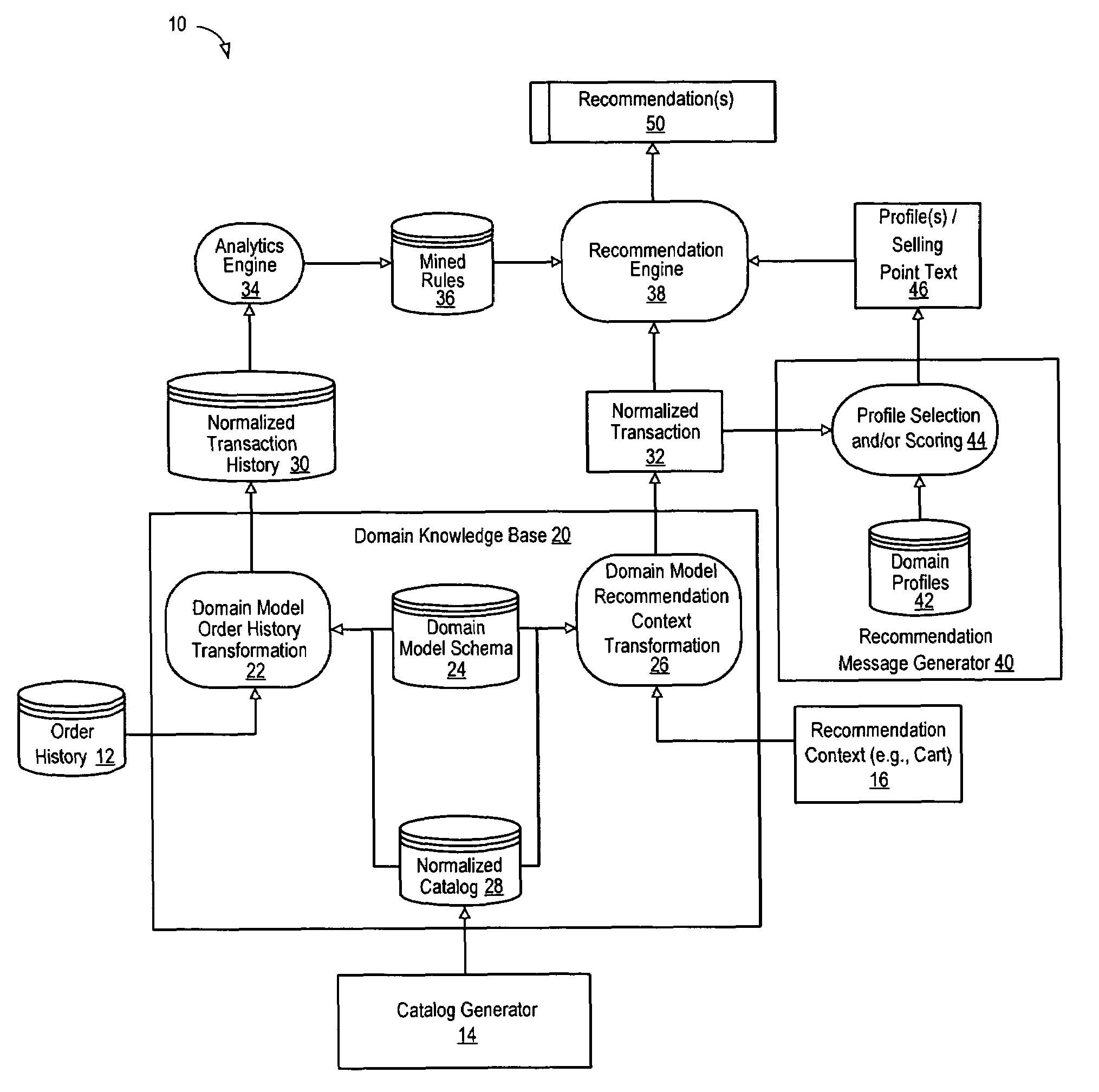
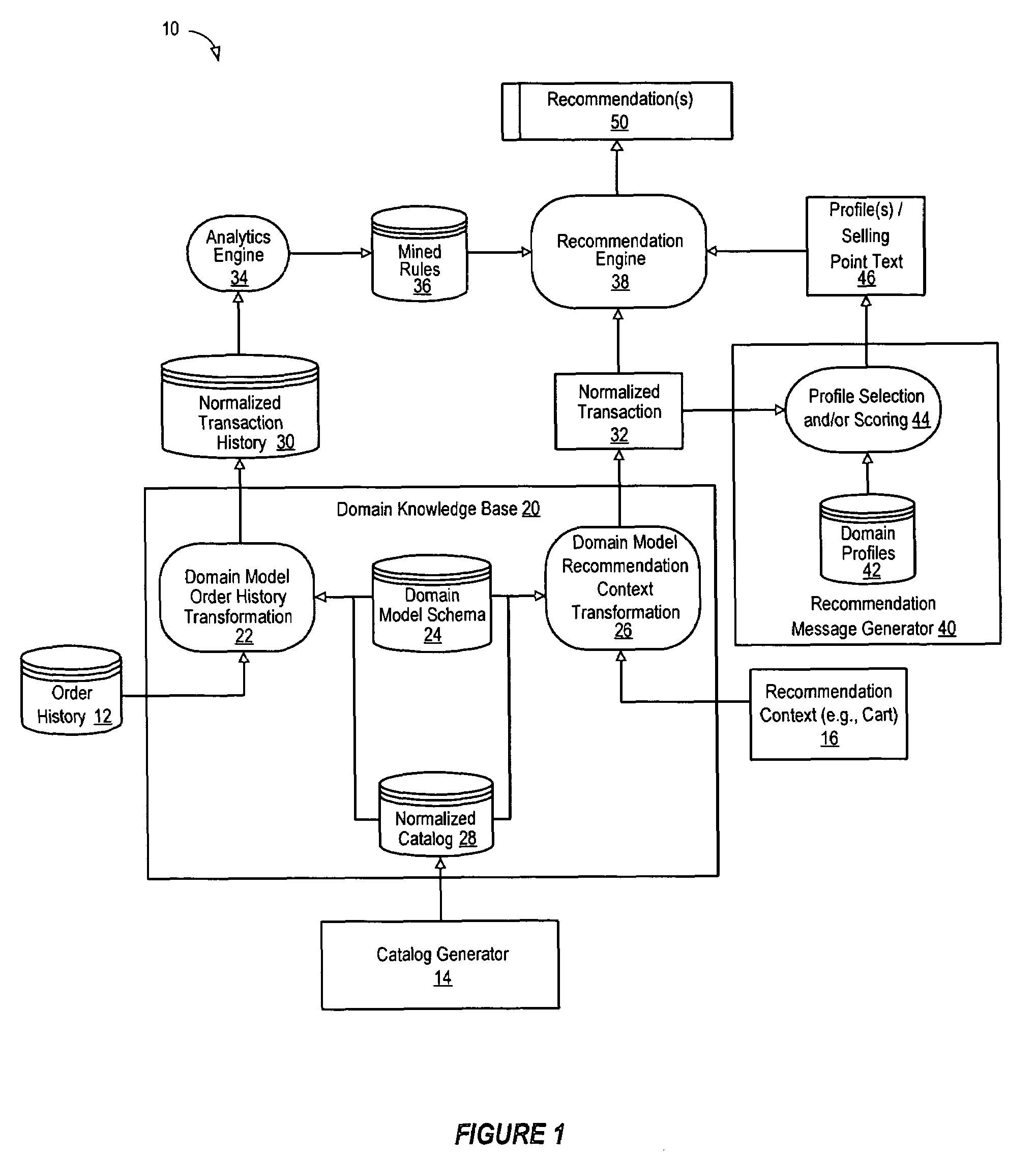
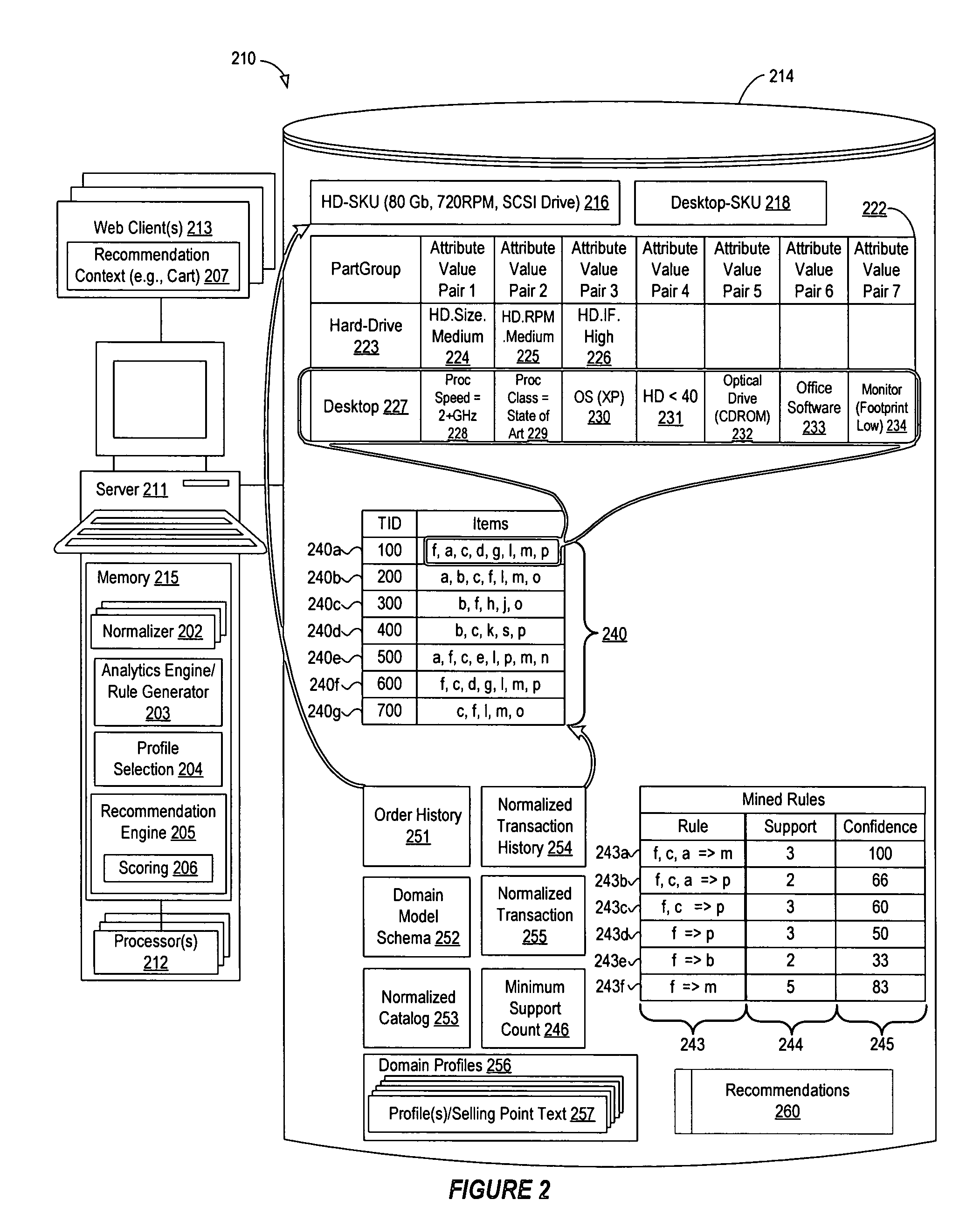
Retail recommendation domain model
A data processing system normalizes data sets (such as low-resolution transaction data) into high-resolution data sets by mapping generic information into attribute-based specific information that is stored in a database. By establishing a shared domain model for representing items in the recommendation context, catalog and quote history with common terms and concepts, a recommendation engine operating in the shared domain may process the attribute-based representations to make specific and relevant recommendations to the customer. In addition, when certain attribute values are normalized over time, recommendations derived from past order history can be intelligently applied to current orders. The normalized representation of elements in the shared domain may also be used to generate compelling selling point text for each recommendation that is specific to the marketing objectives of the seller and identifies the objectives of the buyer.
Owner:VERSATA DEV GROUP
System And Method For Planning And Generating Queries For Multi-Dimensional Analysis Using Domain Models And Data Federation
InactiveUS20080046427A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDomain modelData warehouse
Owner:SERVICENOW INC
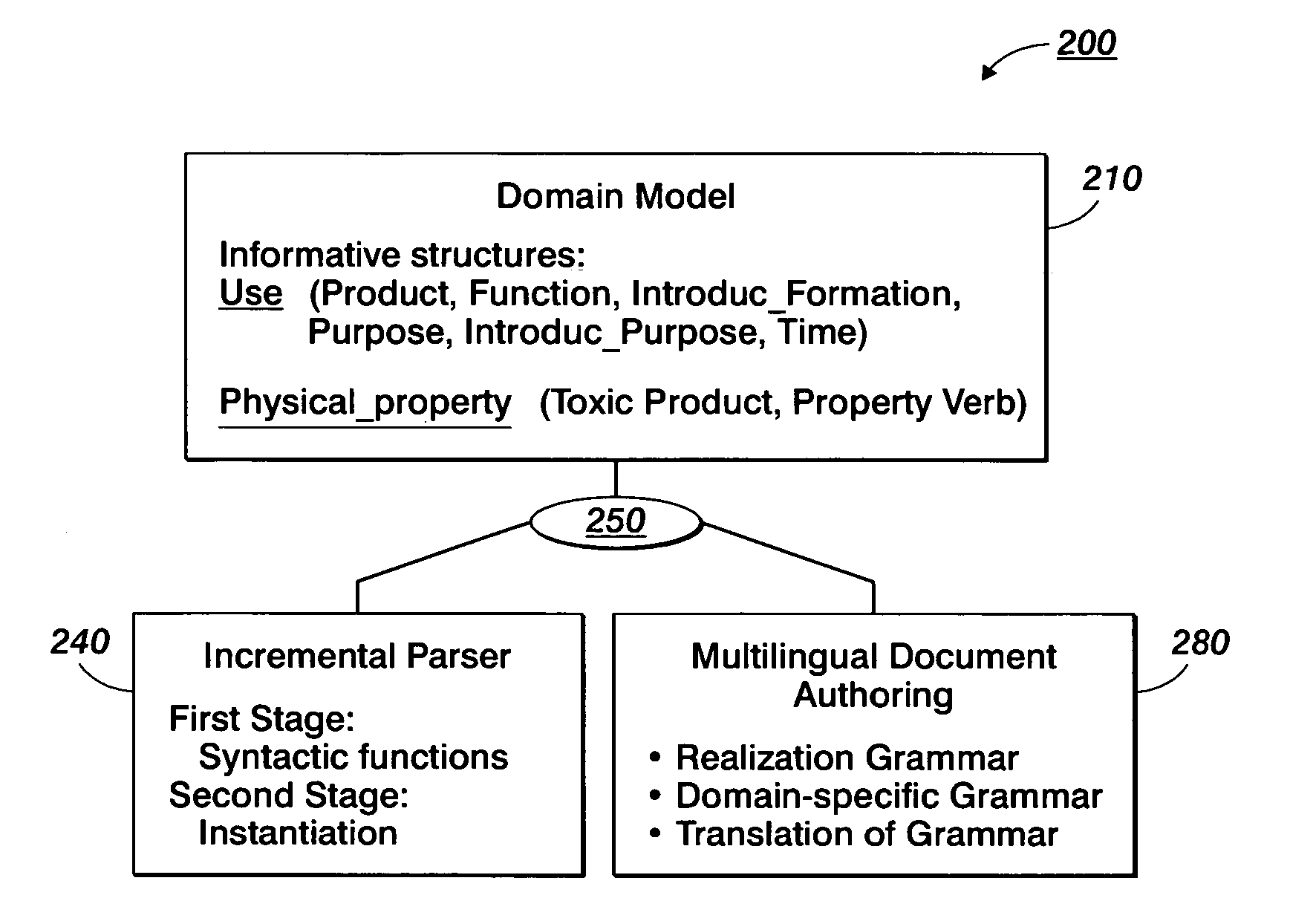
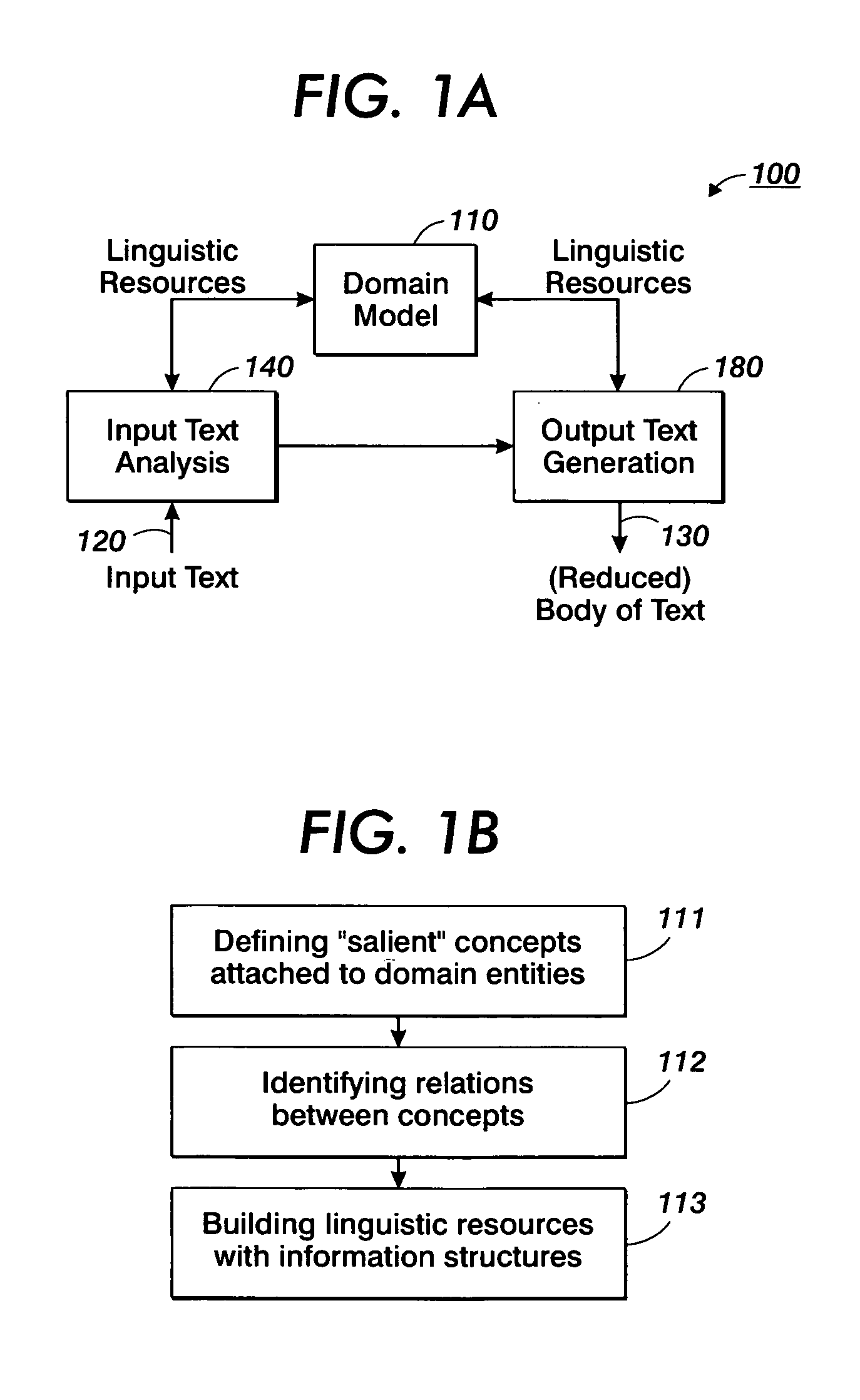
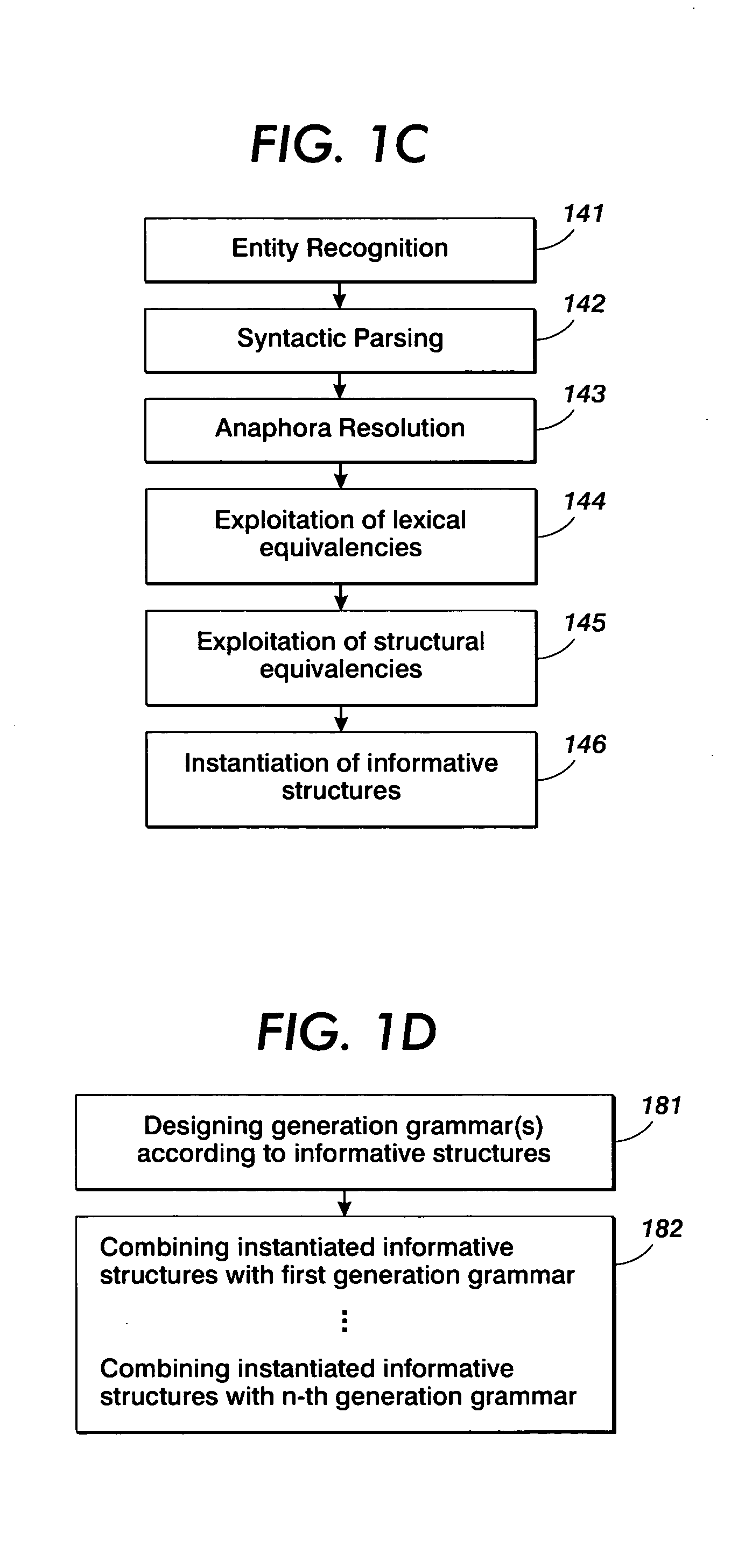
Creation of normalized summaries using common domain models for input text analysis and output text generation
InactiveUS20050138556A1Digital data information retrievalNatural language data processingDomain modelHuman language
Normalized output texts, such as rundowns or summaries, from raw texts belonging to a given domain are produced. The normalized output text may be generated in different languages and may take into account a user's interest. To this end, linguistic resources associated with a model of the domain are used both for input text analysis and output text generation.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Model training method for cross-domain sentiment analysis based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN109753566ASolving the Sentiment Classification ProblemGood lifting effectCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsWeight trainDomain model
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
System, method, and computer program product for anticipatory hypothesis-driven text retrieval and argumentation tools for strategic decision support
InactiveUS20070018953A1Effective and accurate decision makingImprove accuracyDigital data information retrievalCathode-ray tube indicatorsDomain modelStrategic decision support
Provided are systems, methods, and computer programs for facilitating strategic decision support that include providing a domain model, receiving a hypothesis or query, using the domain model and hypothesis or query with a related prediction, and searching for evidentiary results related to a prediction obtained from the hypothesis or from the query and domain model. A method may search and extract evidentiary results based on the hypothesis, query, or prediction. Evidentiary results may be associated with domain concepts and ranked according to relevancy to the associated domain concepts. And a user may select certain evidentiary results as being relevant, and these relevant evidentiary results may be used to create a report.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
System and method for quantifying material properties
InactiveUS20020157478A1Simple processOptimize economyForce measurementMeasurement arrangements for variableElement analysisComputational model
A materials characterization method models dynamic, non-linear, temperature-dependent stress, strain, hysteresis, creep, and loss of elasticity at high strain, both in test samples and in Finite Element Analysis (FEA). Incorporating universal properties of statistical mechanics and adapting domain models from ferromagnetics to the higher-dimensional realm of stress tensors, the model is applicable to polymers, rubbers, liquids, and metals in elastic and plastic deformation. The model quantifies the dynamics of both plastic and brittle failure. Apparatus and methods are shown for testing material samples and matching the computational model to sample characteristics, leading to a set of characterizing parameters and predictive simulations using those parameters. Though apparatus and testing protocols of the invention yield optimum characterizations, pre-existing data from conventional testing yield useful results.
Owner:SEALE JOSEPH B
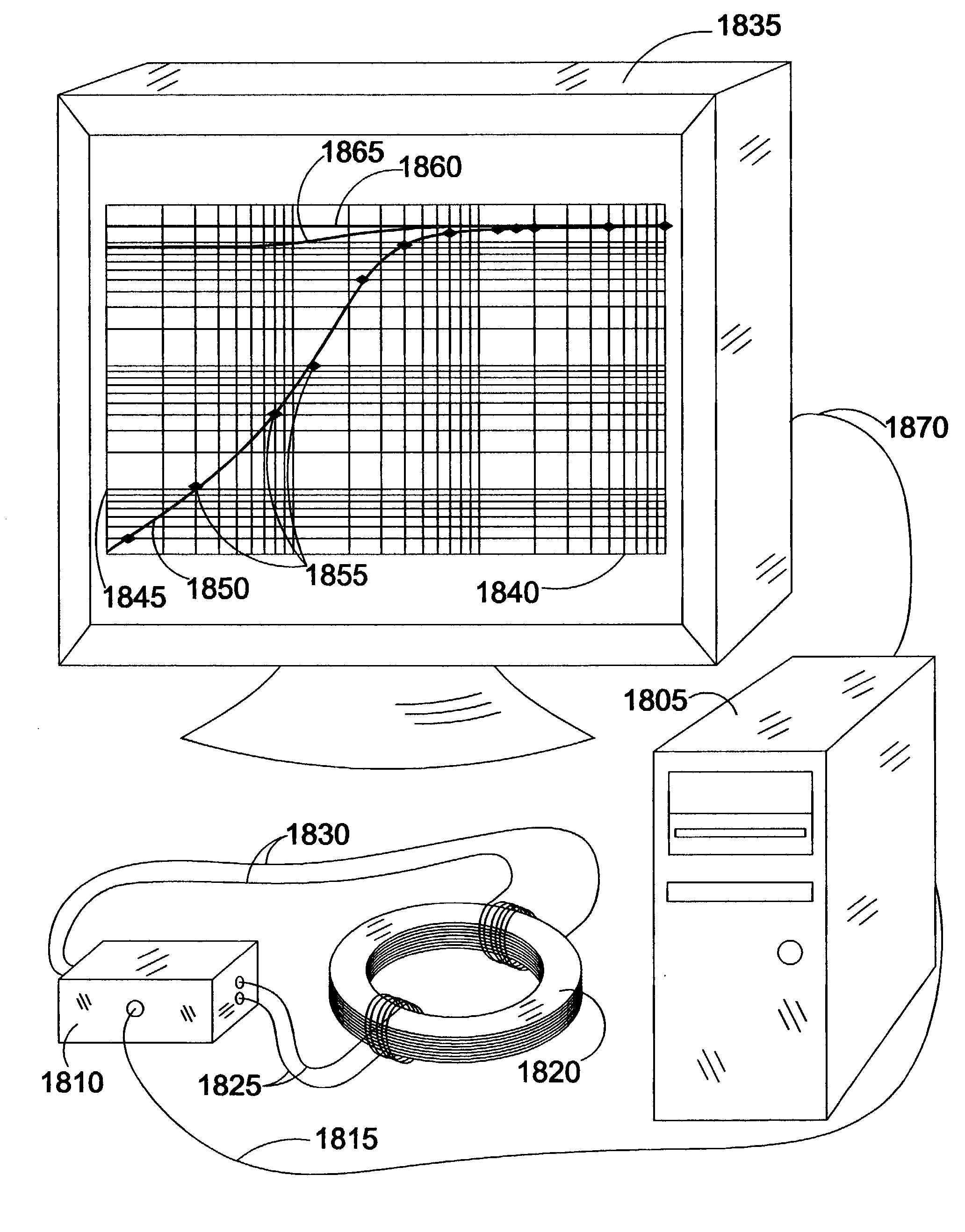
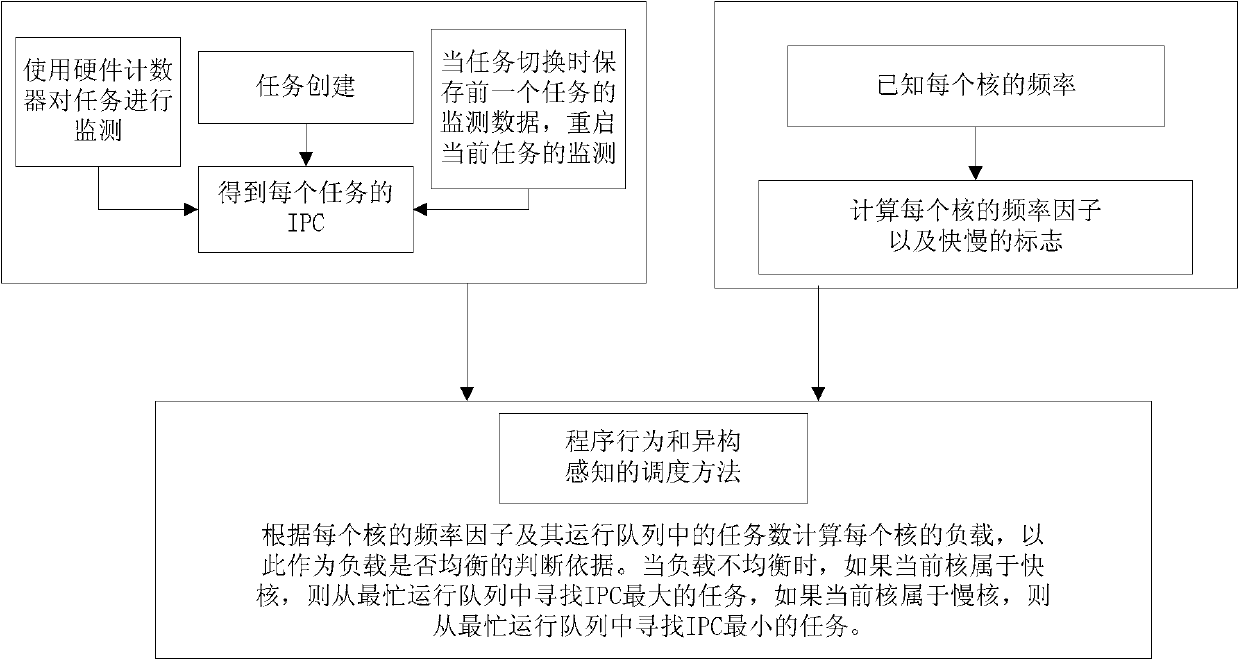
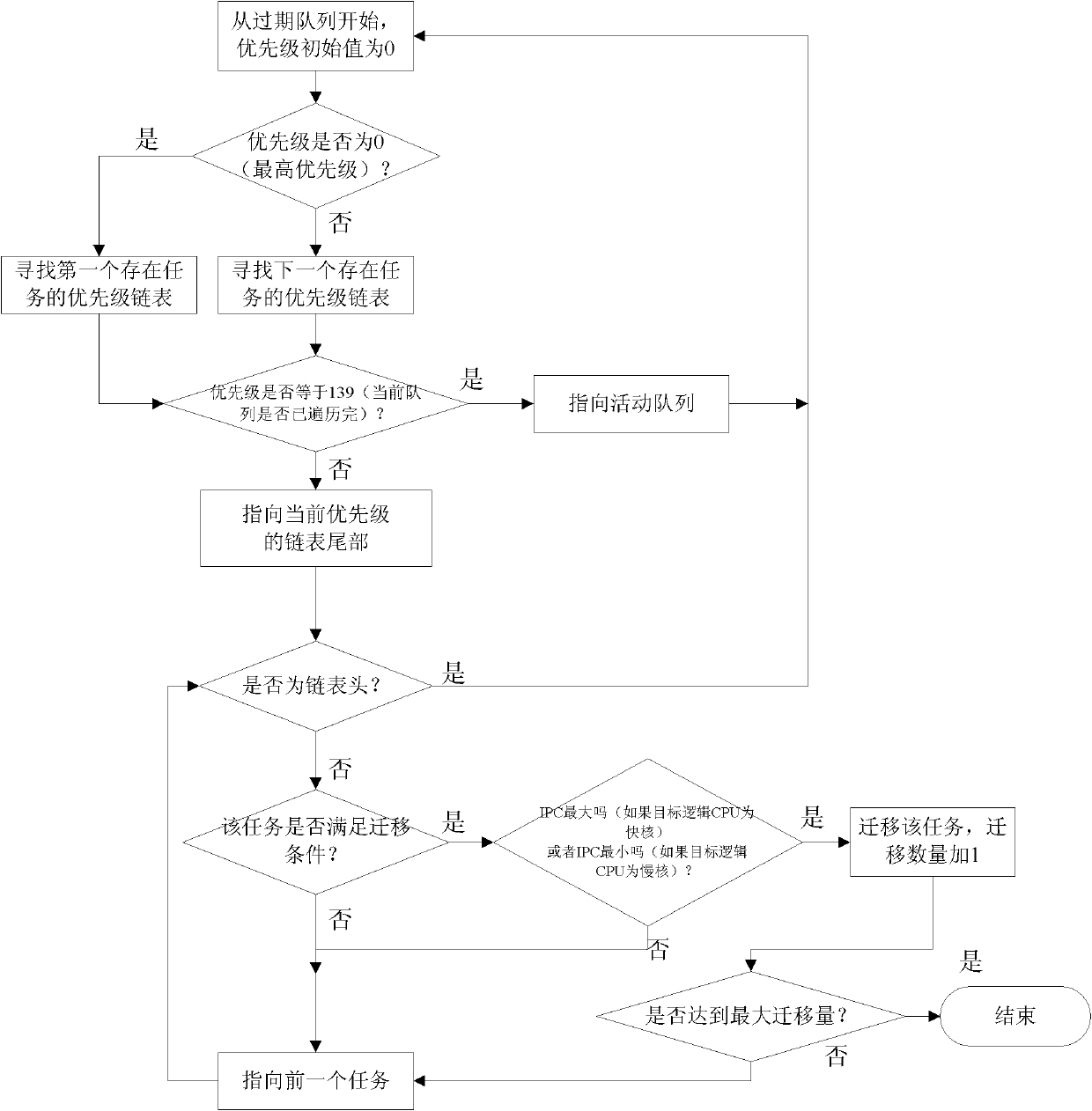
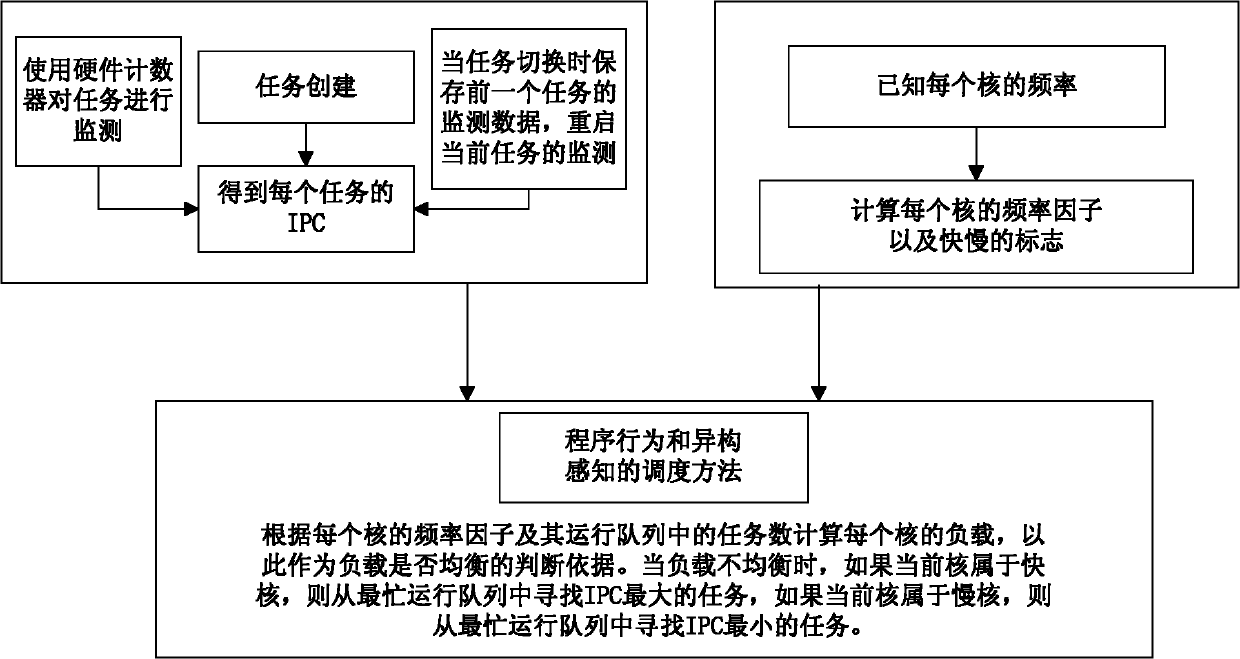
Load balancing method based on program behaviour online analysis under heterogeneous multi-core environment
InactiveCN102184125AHigh frequencyBear moreResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsDomain modelOperational system
The invention discloses a load balancing method based on program behaviour online analysis under a heterogeneous multi-core environment, which comprises the steps of: being compatible with a heterogeneous multi-core environment of the traditional scheduling domain model, dynamically monitoring task characteristics, calculating a logic CPU load, and balancing loads of program behaviour perception. The load balancing method is completely compatible with the traditional operating system scheduling strategy, is simple and efficient, and is suitable for popularization; and an algorithm is tested on an actual software and hardware platform.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
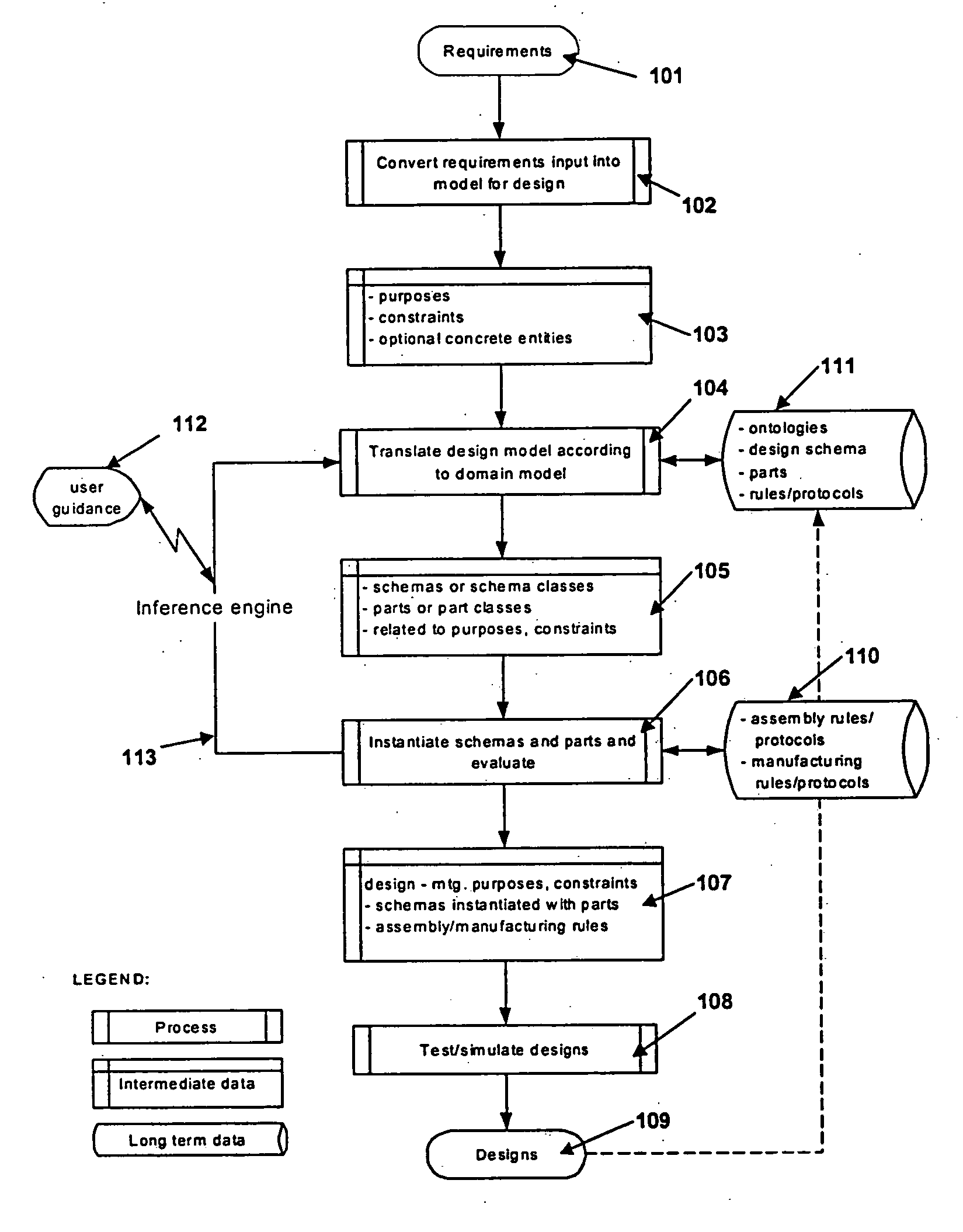
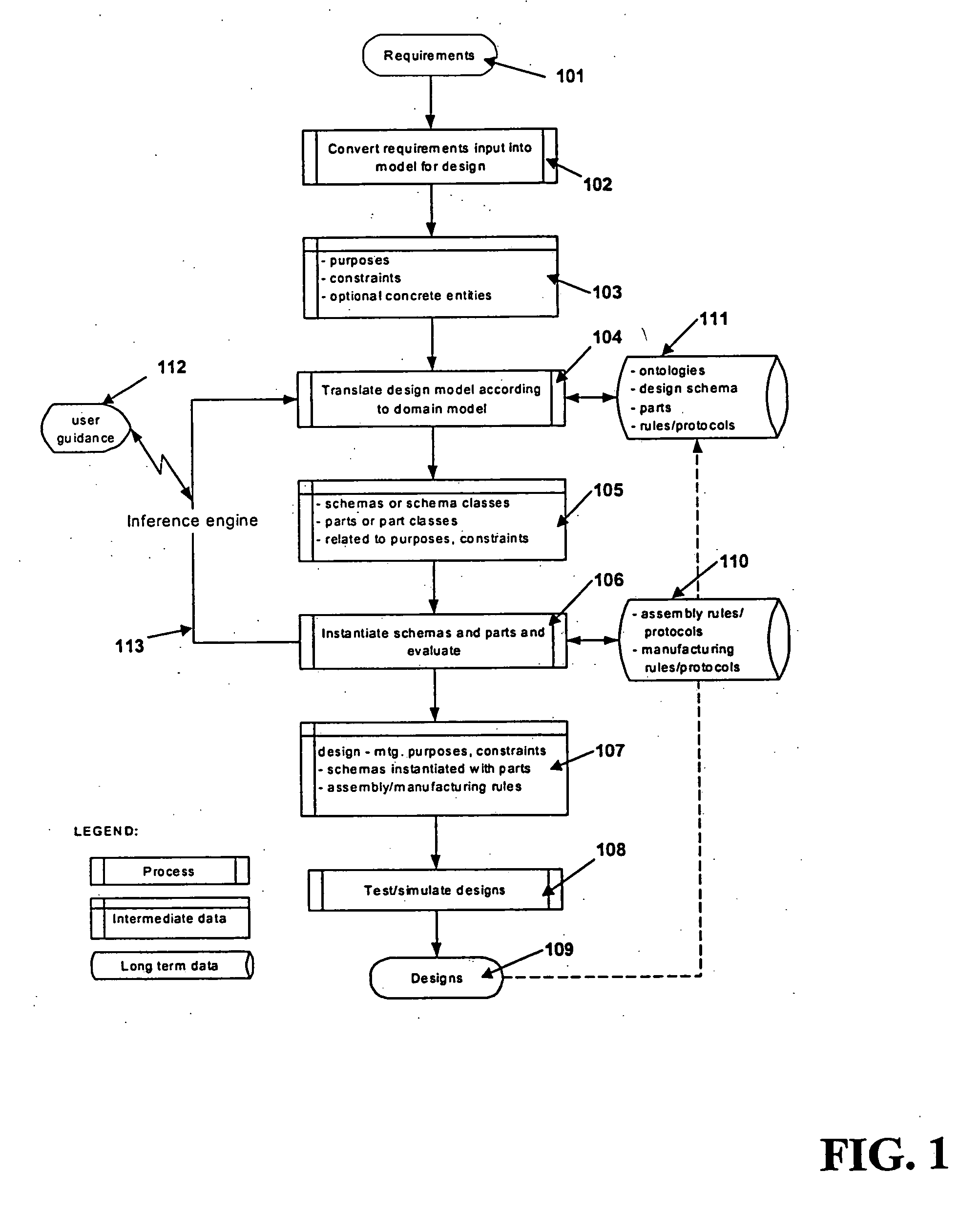
Methods and systems for designing machines including biologically-derived parts
InactiveUS20060178862A1Analogue computers for chemical processesComputer aided designDomain modelOperability
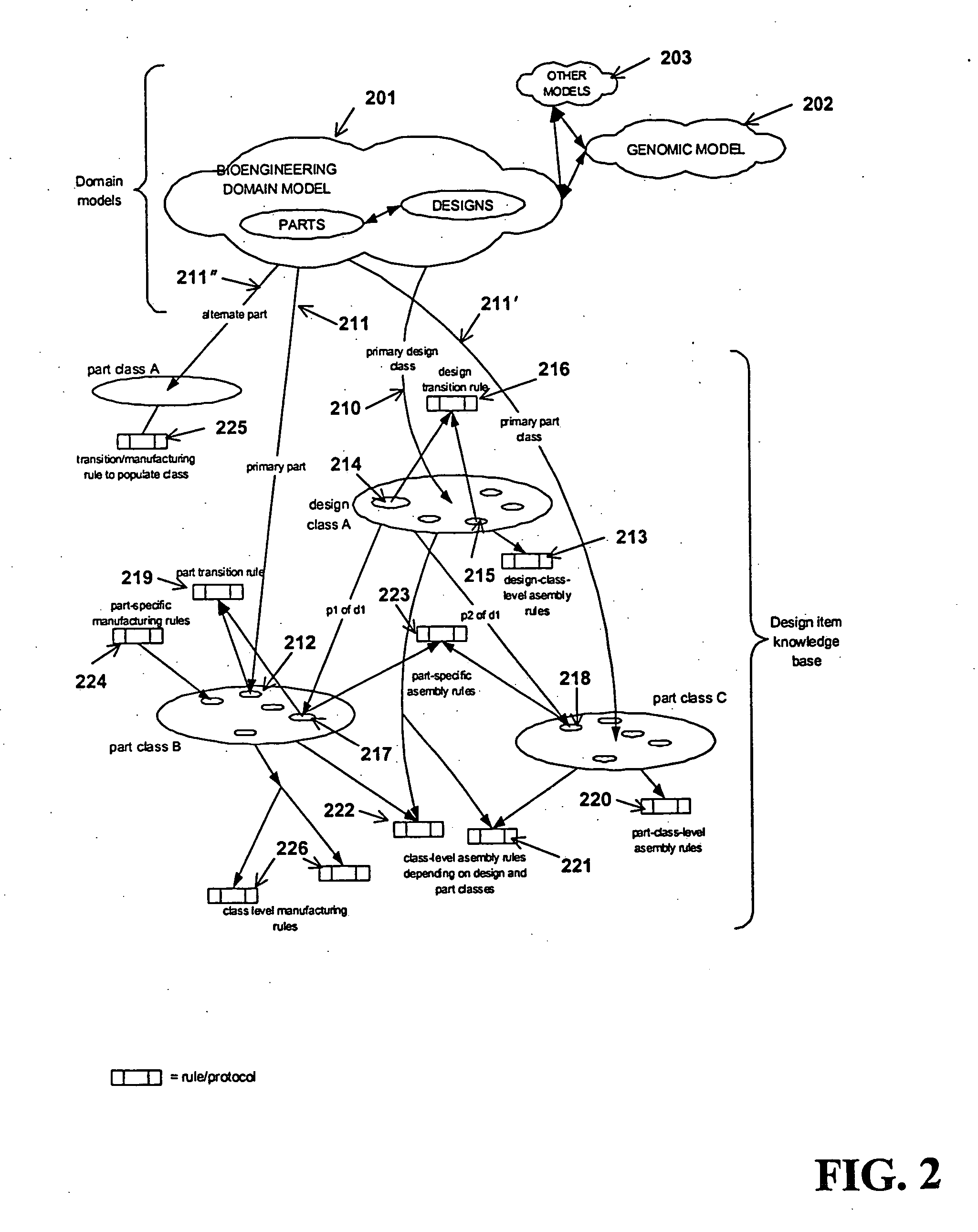
A preferred embodiment of the present invention comprises computer-implemented methods for providing user assistance in biomachine design that, first, retrieve one or more digitally-represented candidate design items stored in a bioengineering knowledge base by translating requirements provided for a biomachine according to a bioengineering domain model into queries to the knowledge base for design items capable of implementing the biomachine according to the domain model; then second, construct one or more digitally-represented candidate biomachines from the candidate design items by arranging part information represented in the candidate design items according to a selected structure, and next evaluate the candidate biomachines according to bioengineering operability knowledge associated with the candidate design items, wherein operability knowledge associated with a design item specifies requirements for that item to inter-operate with other design items. The methods may backtrack. If at least one candidate biomachine has not been satisfactorily evaluated, the methods backtracking to one or more of these steps. The invention further encompasses variations of these methods, systems and program products performing these methods, data products including digital representations of design knowledge used by these methods, data products with digital representations of designed biomachines. Also encompassed are further steps of constructing or synthesizing biomachines along with the actual biomachines themselves.
Owner:ENGENEOS
System and method for quantifying material properties
InactiveUS6631647B2Optimize overall economy and utilityThe testing process is simpleForce measurementMeasurement arrangements for variableHysteresisModel dynamics
A materials characterization method models dynamic, non-linear, temperature-dependent stress, strain, hysteresis, creep, and loss of elasticity at high strain, both in test samples and in Finite Element Analysis (FEA). Incorporating universal properties of statistical mechanics and adapting domain models from ferromagnetics to the higher-dimensional realm of stress tensors, the model is applicable to polymers, rubbers, liquids, and metals in elastic and plastic deformation. The model quantifies the dynamics of both plastic and brittle failure. Apparatus and methods are shown for testing material samples and matching the computational model to sample characteristics, leading to a set of characterizing parameters and predictive simulations using those parameters. Though apparatus and testing protocols of the invention yield optimum characterizations, pre-existing data from conventional testing yield useful results.< / PTEXT>
Owner:SEALE JOSEPH B
System and method of enterprise systems and business impact management
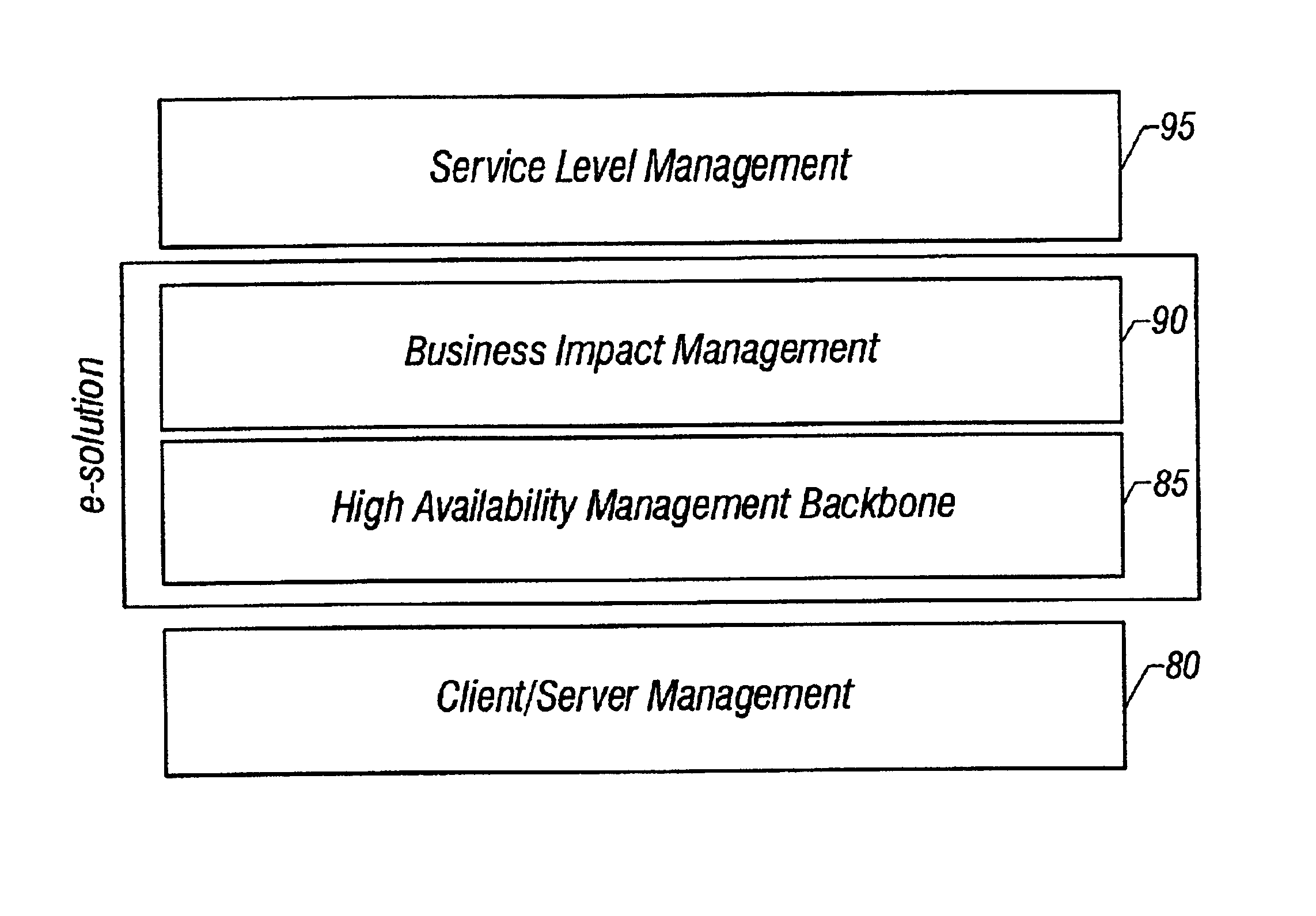
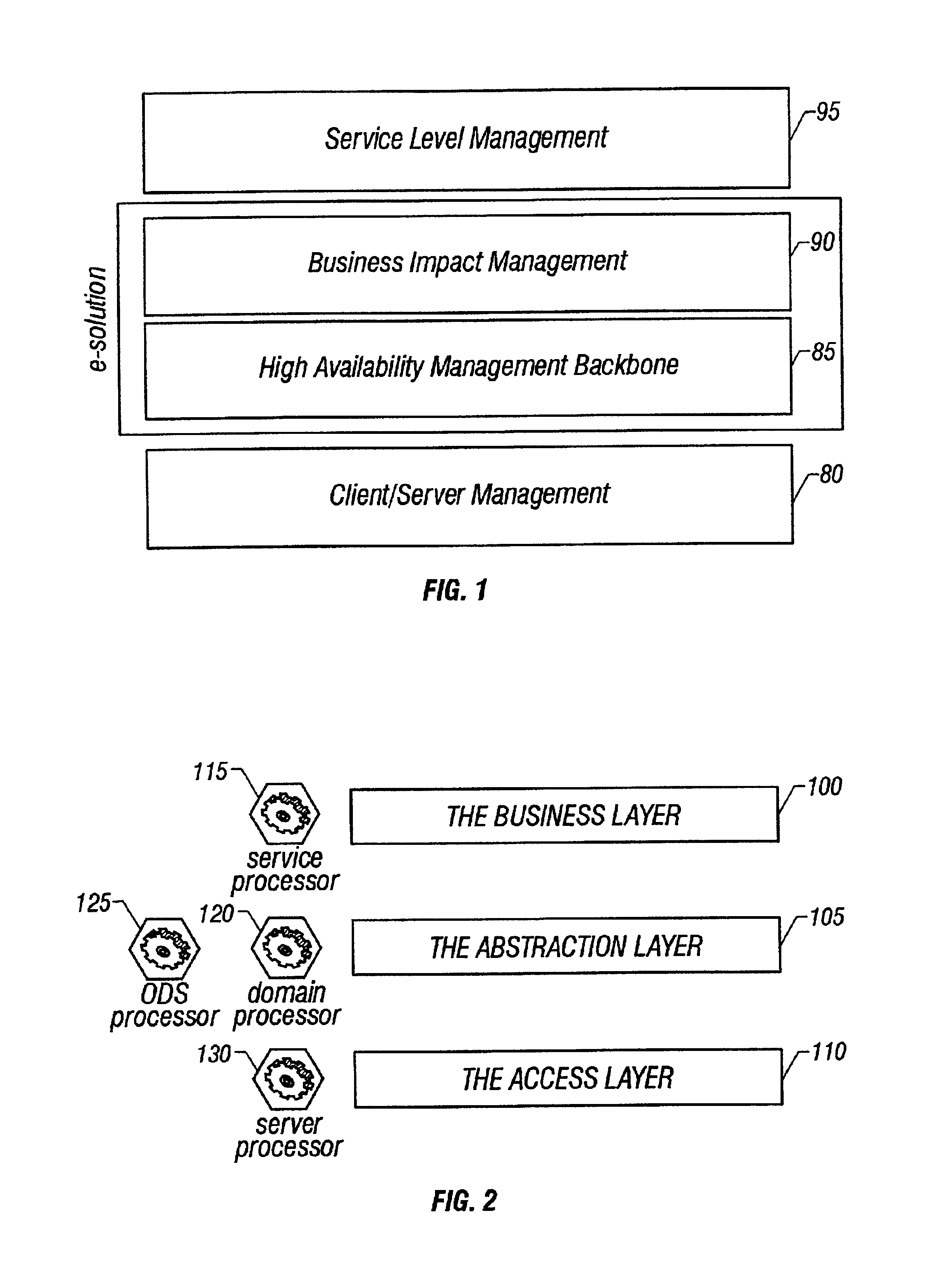
ActiveUS20050283445A1Faster and accurate analysisAvoid lot of costDigital computer detailsPayment architectureDomain modelCellular architecture
A system architecture and a method for managing using a cellular architecture to allow multi-tier management of events such as the managing of the actual impact or the potential impact of IT infrastructure situations on business services. A preferred embodiment includes a high availability management backbone to frame monitoring operations using a cross-domain model where IT component events are abstracted into IT Aggregate events. By combining IT Aggregate events with transaction events, an operational representation of the business services is possible. Another feature is the ability to connect this information to dependent business user groups such as internal end-users or external customers for direct impact measurement. A web of peer-to-peer rule-based cellular event processors preferably using Dynamic Data Association constitutes management backbone crossed by event flows, the execution rules, and distributed set of dynamic inter-related object data rooted in the top data instances featuring the business services.
Owner:BMC SOFTWARE
System and method for developing and deploying sensor and actuator applications over distributed computing infrastructure
InactiveUS20090106011A1Geometric CADAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDomain modelDistributed computing infrastructure
The present invention discloses a method for coordinating zero or more modelings, zero or more implementations and zero or more deployments of a computer system, including but not limited to computer systems involving sensors, actuators, or both and a system providing assistance to designers, implementers, and deployers of computer systems. The method and system including: defining one or more interfaces of one or more components; creating models for the one or more components, each of which is either a composite component model or a atomic component, model, creating the one or more composite components as instances of the composite component models creating the one or more atomic components as instances of the atomic component models creating a domain model by specifying the computational resources; and creating a deployment model by specifying one or more component-model instances and specifying which the component-model instances should be executed on which the computational resources of the domain model.
Owner:IBM CORP
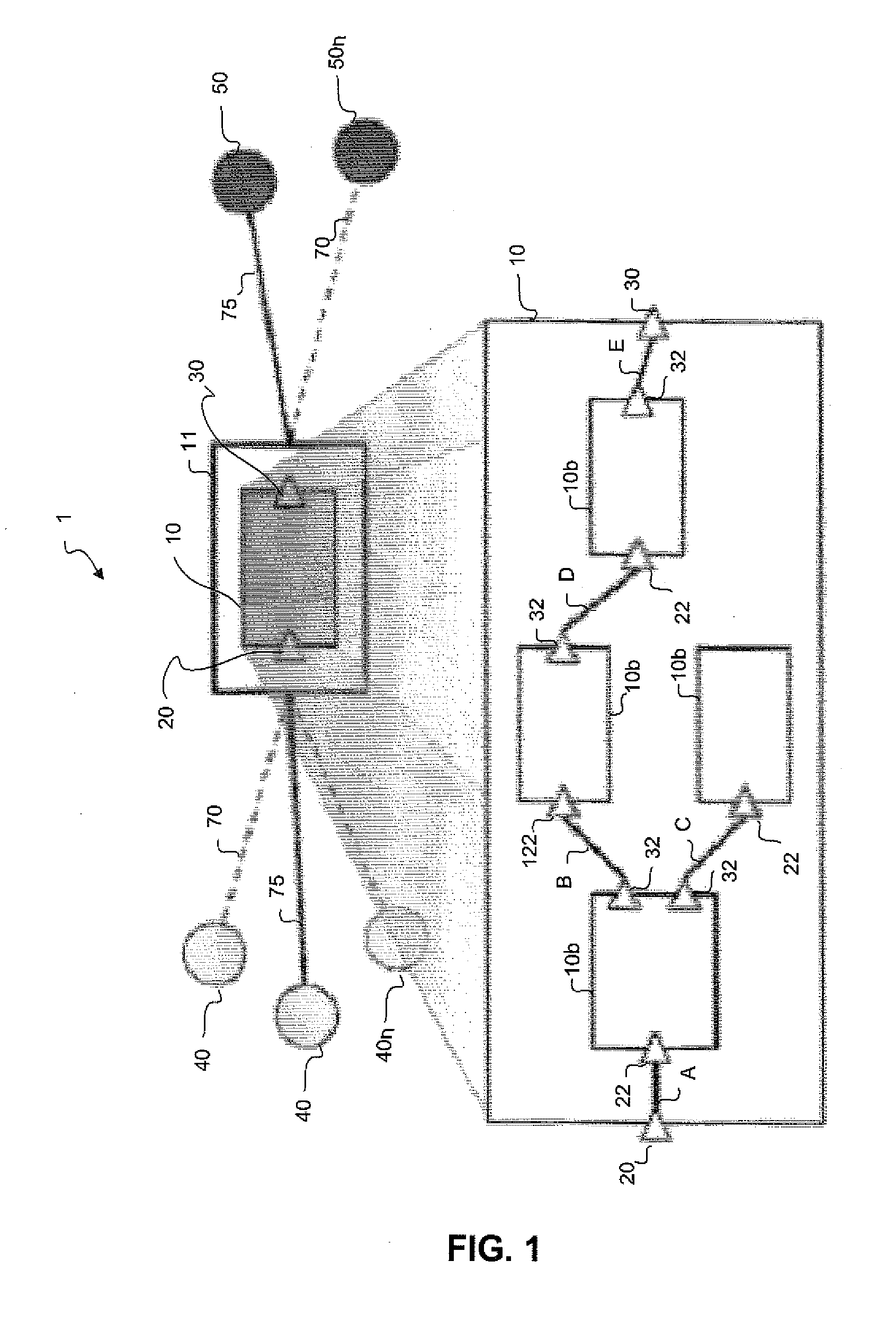
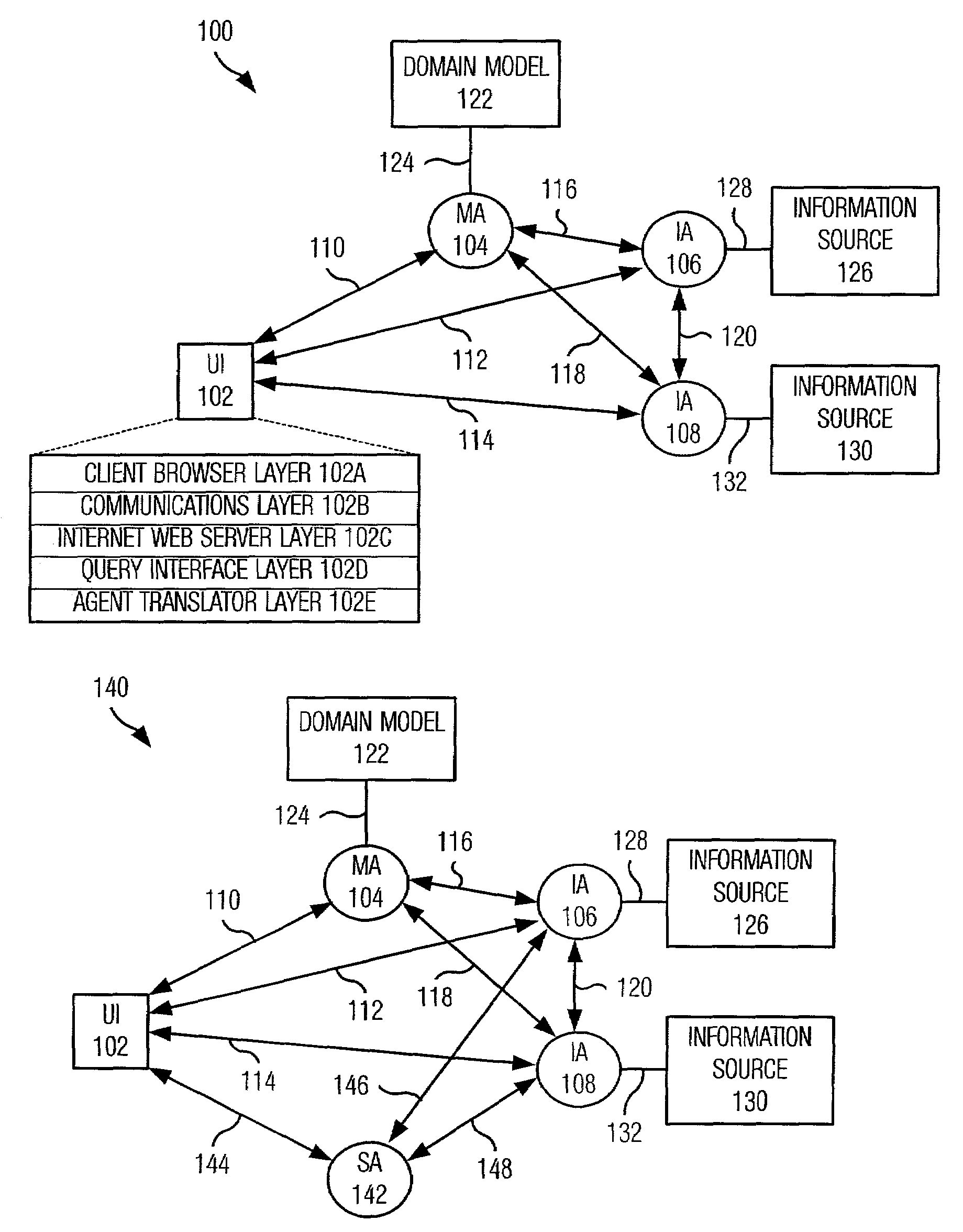
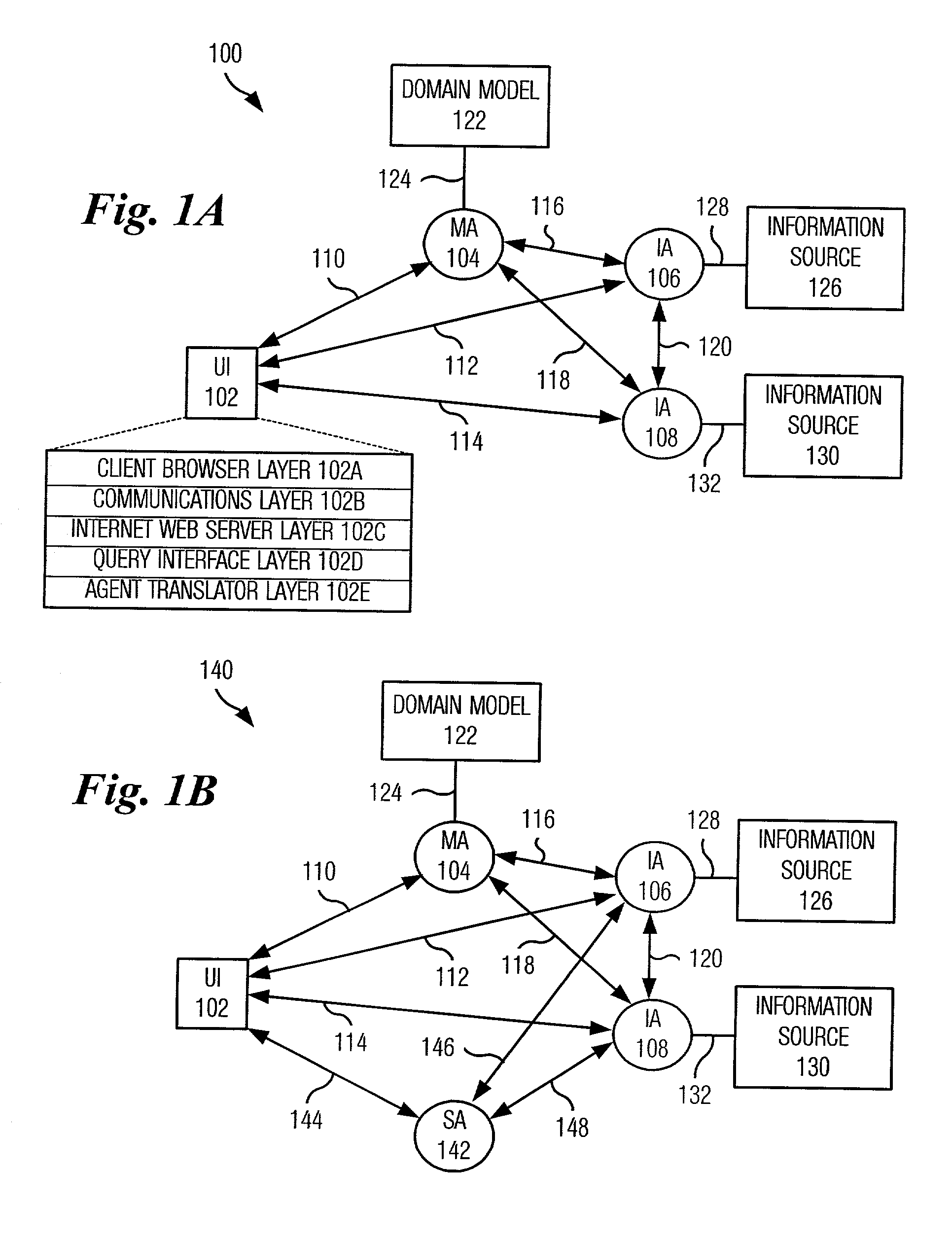
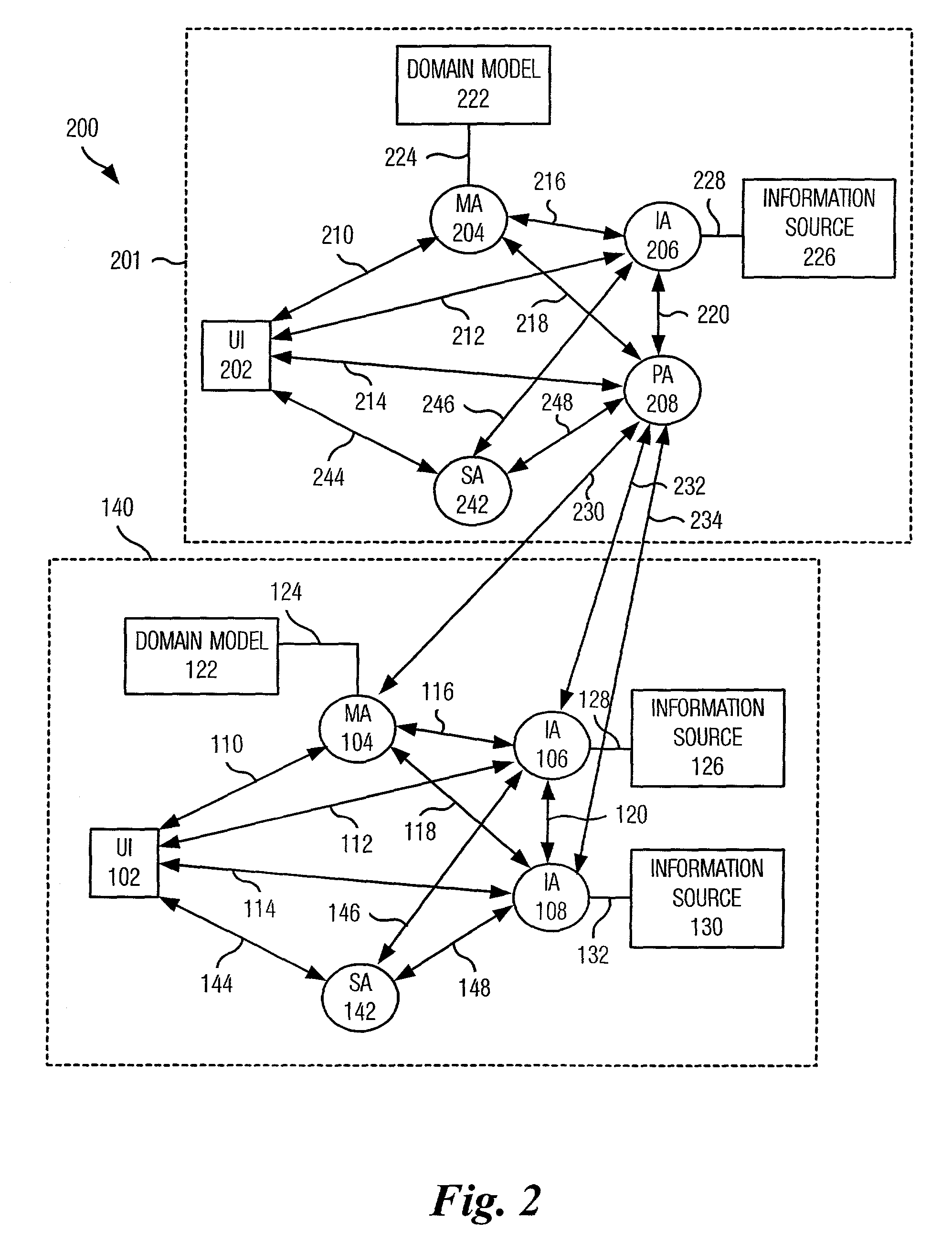
System and method for retrieving information from disparate information sources in a decentralized manner and integrating the information in accordance with a distributed domain model/ontology
A system and method are provided for retrieving and integrating disparate, heterogeneous information such as structured data, unstructured text, and images from different information sources in real-time. The system includes a plurality of client applications a model agent and a plurality of integration agents. Queries are written in terms of the classes, attributes, and relationships of the domain model as provided by the model agent. These queries for information are sent from a requesting client application to an appropriate integration agent based upon the data source it is responsible for. If the requested information is split among a plurality of integration agents that are each tied to a data source, the agent will broker the query by sending sub-queries to those agents directly, perform transformations on the data to match the model, and combine the information together for transmission to the requester. In this fashion, each integration agent can act as a broker and thus no centralized brokering system is required.
Owner:DEAN CHRISTOPHER JAMES
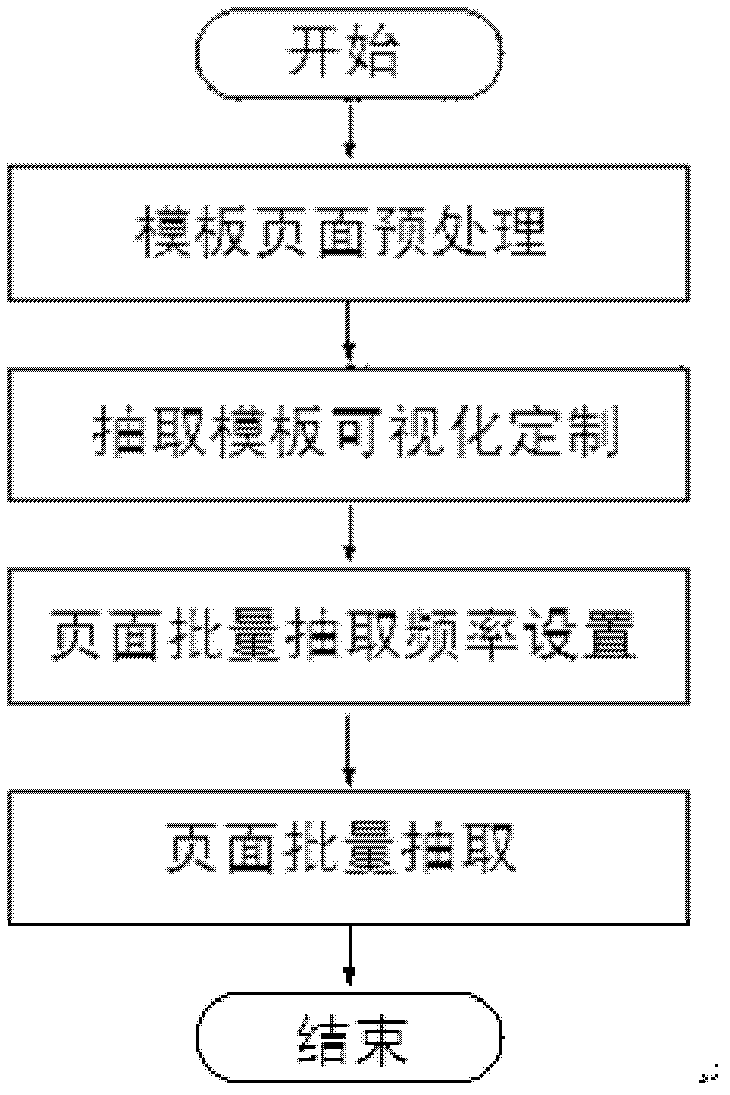
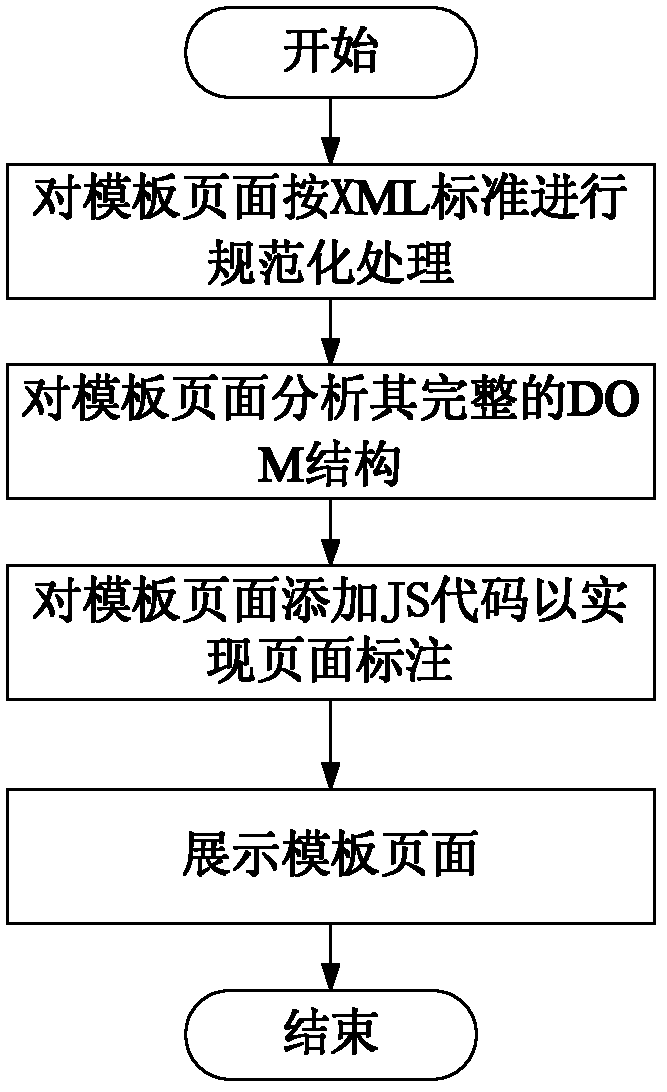
Web data extraction method based on visual customization of extraction template
ActiveCN102360368AFriendly interaction abilityImprove applicabilitySpecial data processing applicationsDomain modelSemi-structured data
The invention discloses a Web data extraction method based on visual customization of an extraction template. The Web data extraction method comprises the following steps: A. pretreatment of template pages: converting and showing source codes of the template pages; B. visual customization of the extraction template: providing a drag selection function on a user interface, setting the corresponding relationship between attribute tags and data values on the template pages and attributes in a domain model by a user, and establishing the extraction template; C. setting of mass extraction frequency of the pages: extracting the crawled HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) pages in large quantity once every 8 hours; and D. mass extraction of the pages: extracting the crawled HTML pages in large quantity by the corresponding extraction template, converting semi-structured data into structured data and then storing the structured data in a local database.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
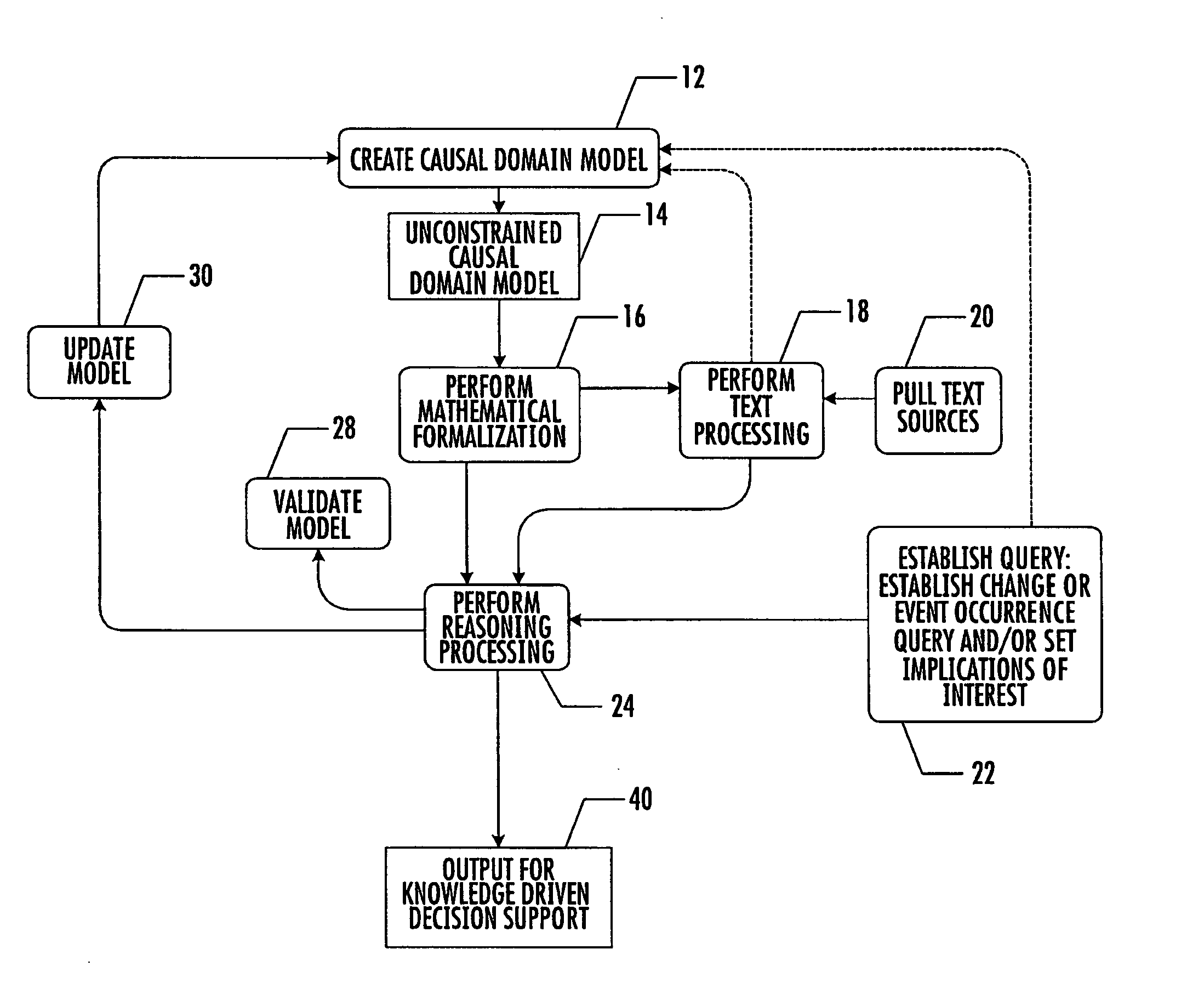
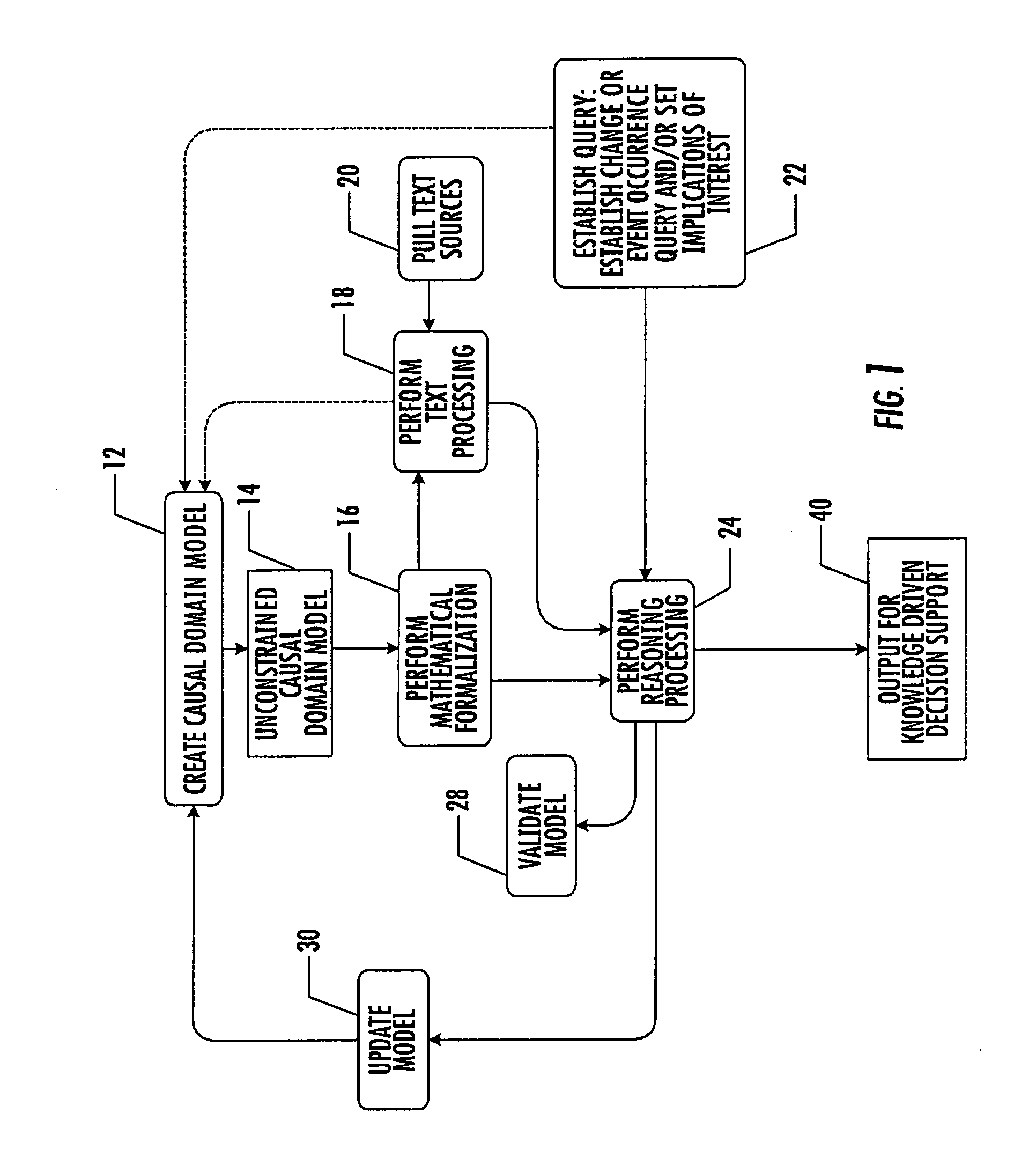
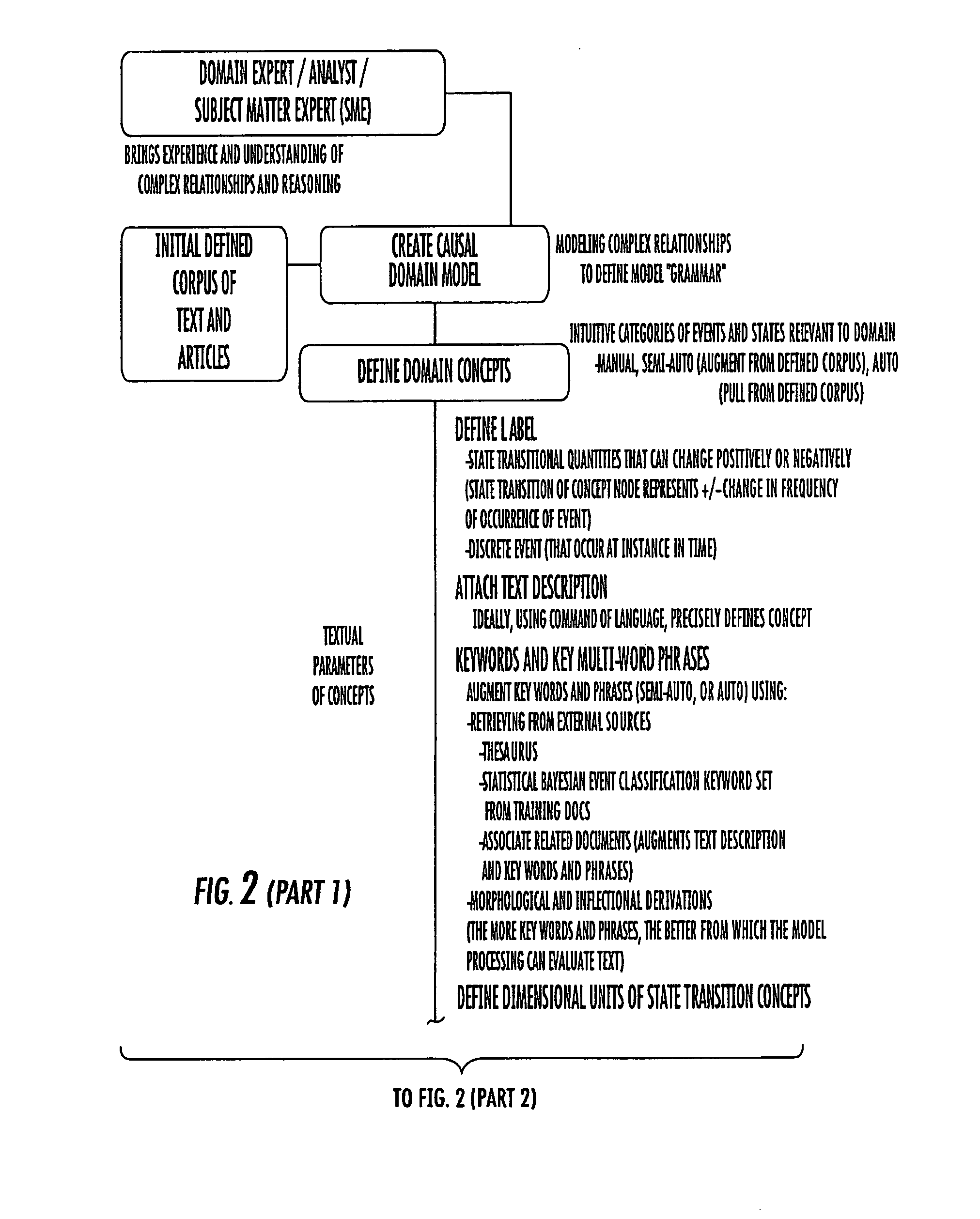
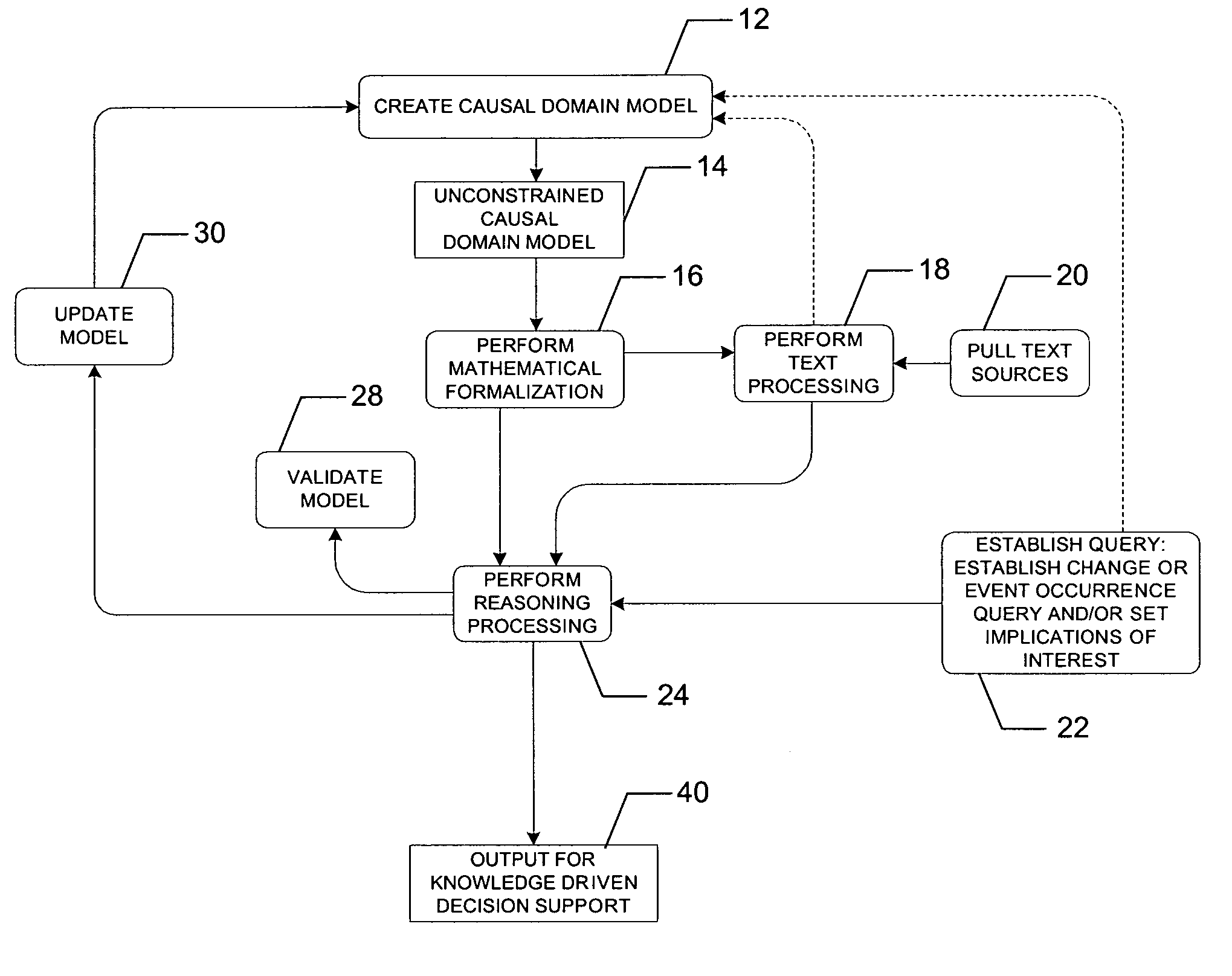
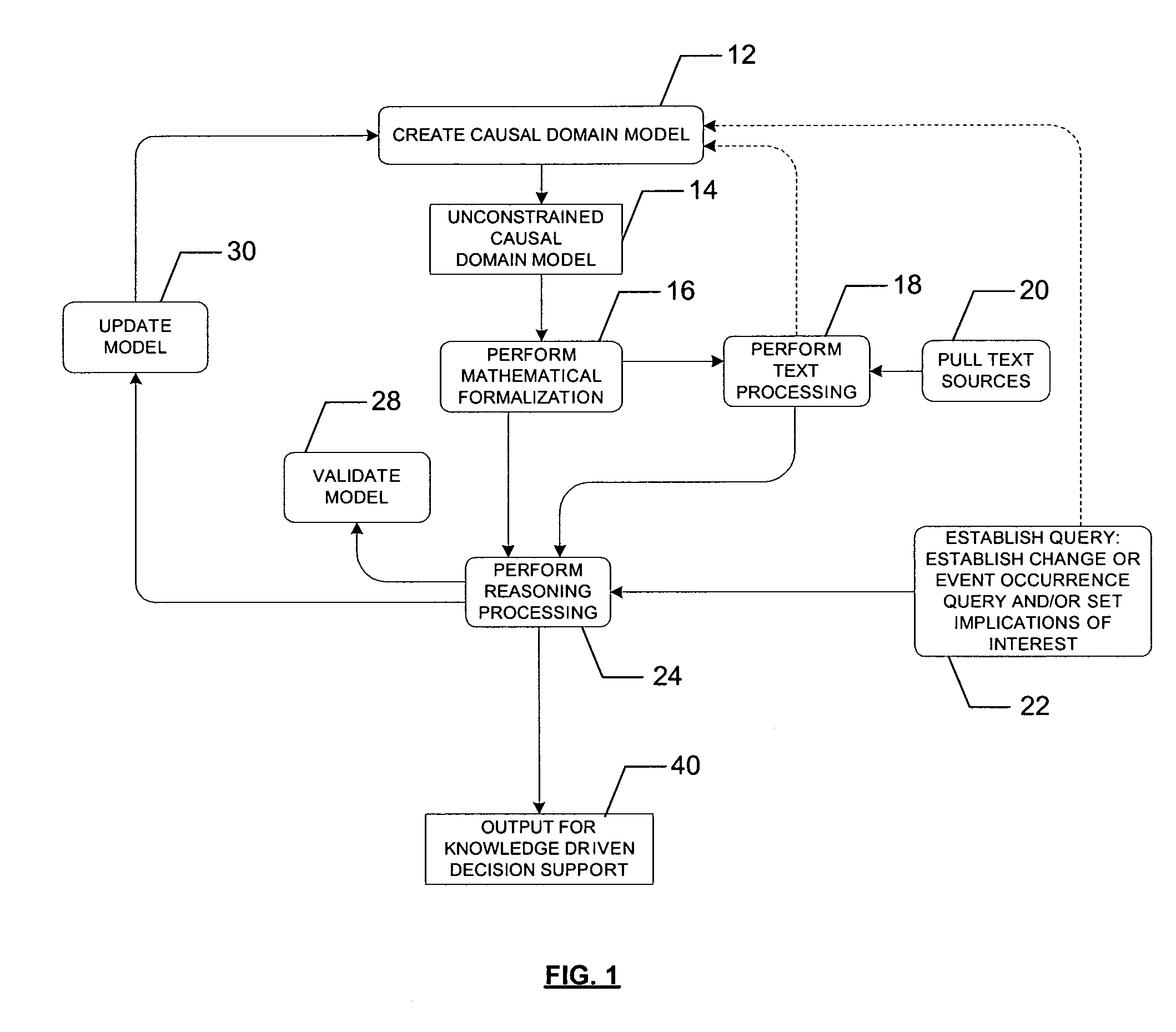
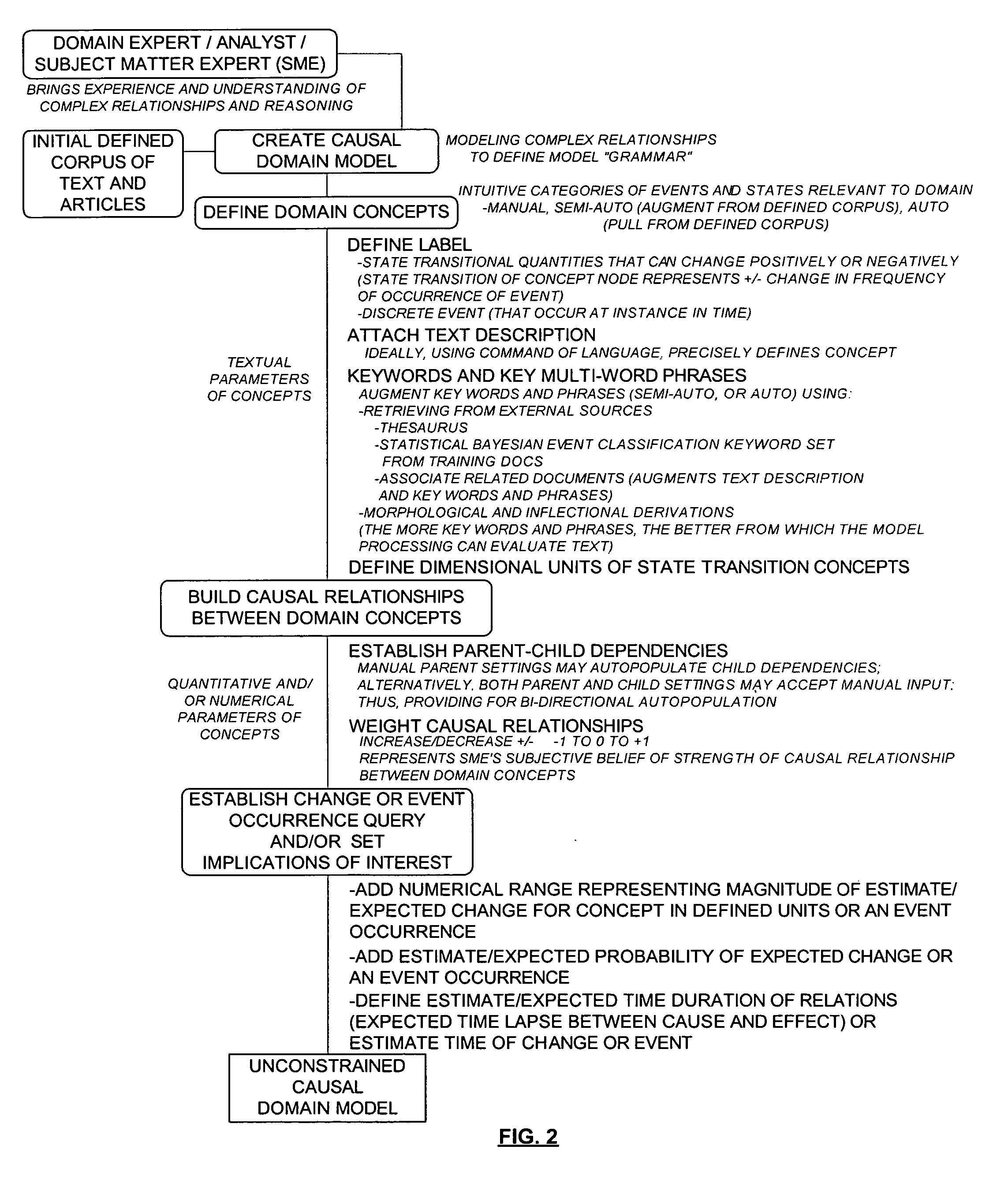
System, method, and computer program product for combination of cognitive causal models with reasoning and text processing for knowledge driven decision support
ActiveUS20050197992A1Increase or decrease weightImprove relevanceDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisDomain modelProcessing element
A system, method, and computer program product for combining causal domain models with reasoning and text processing for knowledge driven decision support are provided. A knowledge driven decision support system is capable of creating a domain model, extracting and processing quantities of text according to the domain model, and generating understanding of the content and implications of information sensitive to analysts. An interface may be used to receive input to model complex relationships of a domain, establish implications of interest or request a query, and update the causal model. A processing element can capture and process text into text profiles by incorporating the domain model and process the text profiles in accordance with the domain model by applying formal reasoning to the information to derive trends, predict events, or arrive at other query results. An output element can provide a user the resulting information related to the domain model.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
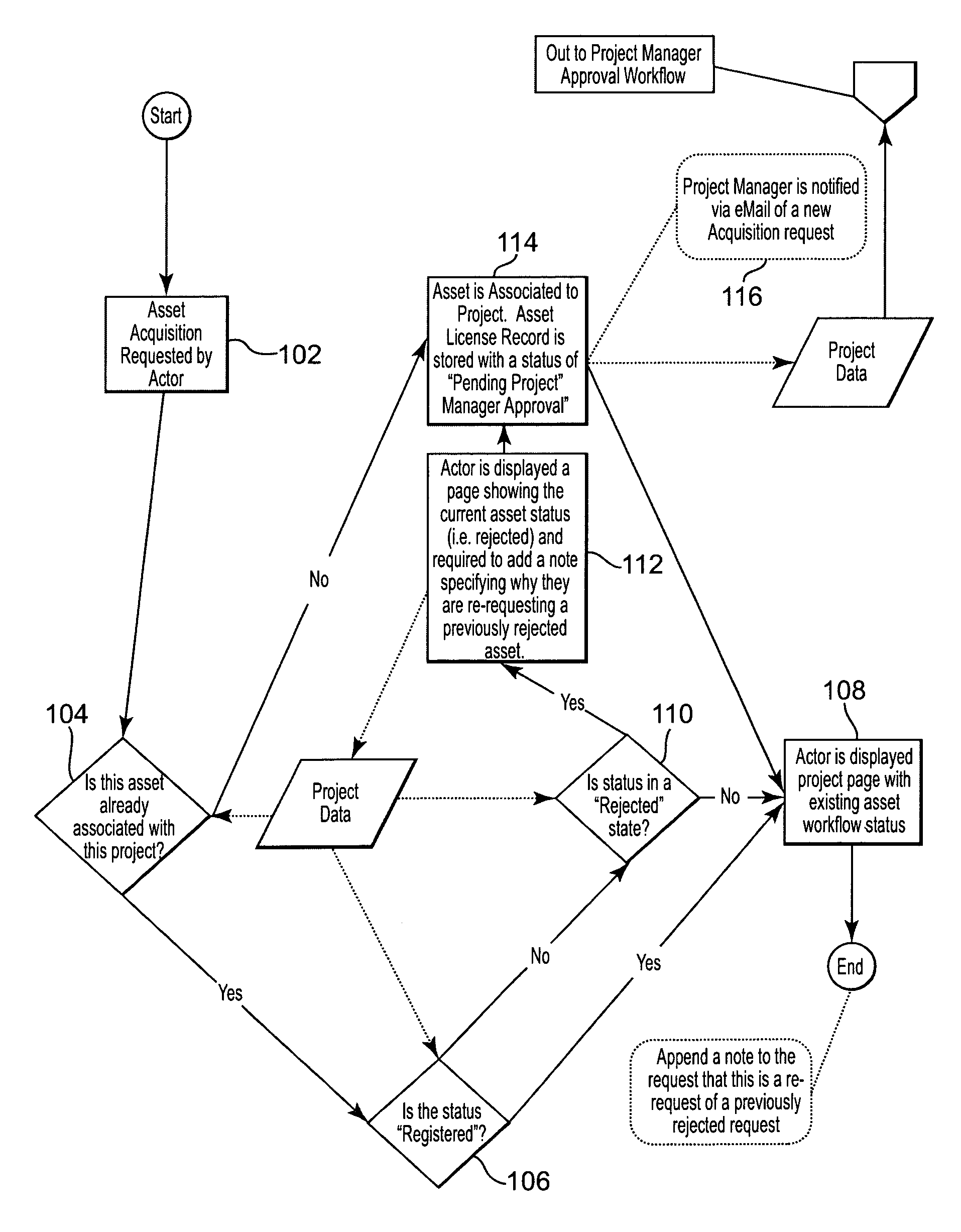
Targeted asset capture, identification, and management
A targeted asset capture system that maps software resources to a domain model, and search and management tools for retrieving asset information and controlling asset acquisition. The domain model may include a process-centered organization and / or a structural organization of model tasks, functions, and data types. Capture includes mapping to the model functions and data types, and preferably also includes capturing other information about the asset and about the quality of mapping. The domain model may be used to build a search specification for searching for available assets that meet some or all of a set of functional (and / or nonfunctional) requirements. The search specification may also be published in part or in whole as a development specification.
Owner:AKANA
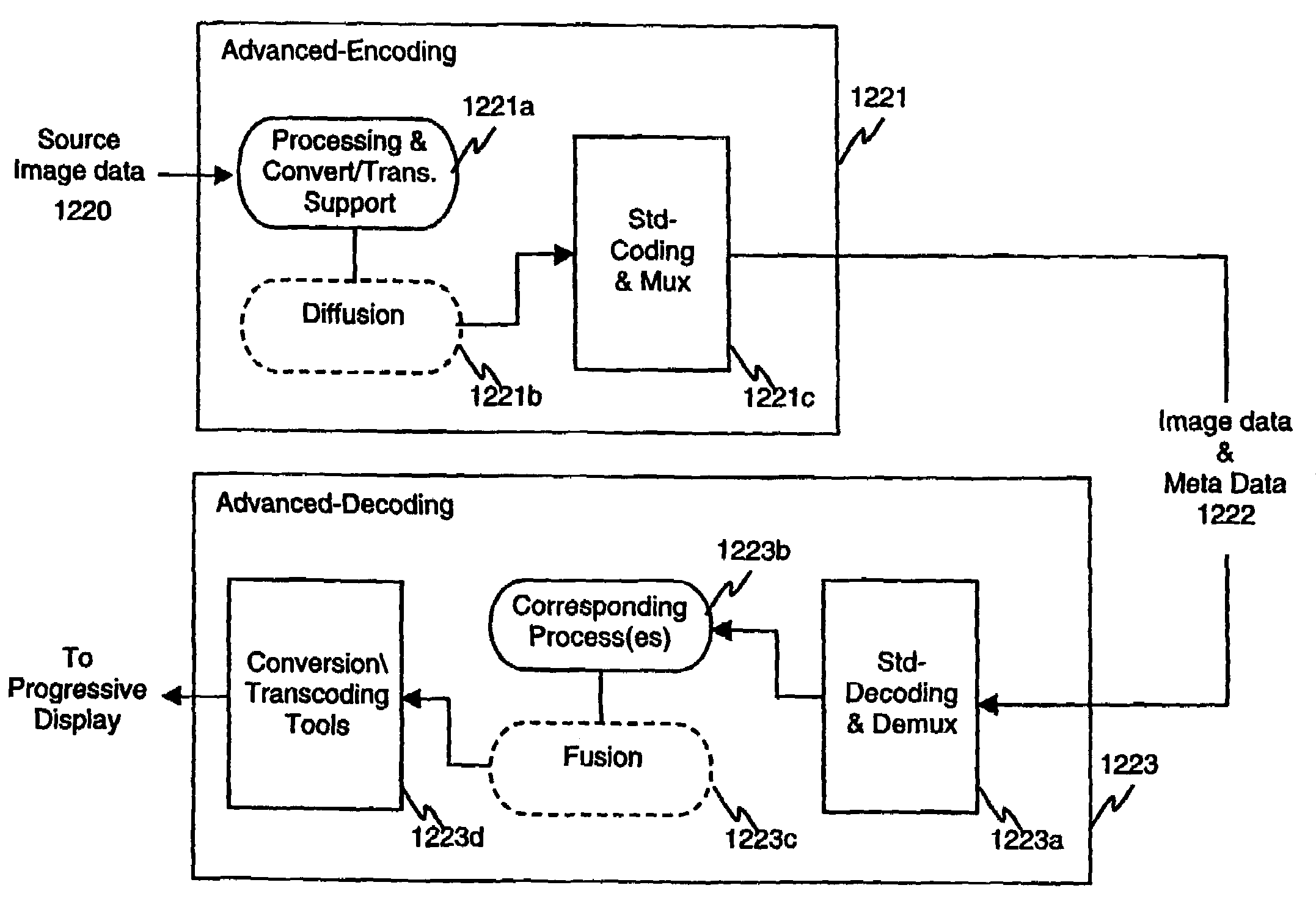
Video coding reconstruction apparatus and methods
InactiveUS7496236B2Reduced operating requirementsAdapt effectivelyTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDiffusionDomain model
The present invention provides advanced encoding and advanced reconstruction apparatus and methods enabling low bitrate, enhanced coding and quality-enhanced reconstruction, among other aspects. Preferably operating in accordance with a super-domain model, the invention enables the superimposed use of advanced coding tools such as for determining the susceptibility of image data to optimization and degradation avoidance. Other preferred tools also include multi-dimensional diffusion, registration, meta data utilization, advanced constructs, image representation optimization and efficiency optimization. Advanced decoding further enables maximized utilization of received enhanced image data and other information, also preferably in accordance with a super-domain model. Advanced encoding preferably comprises reverse-superresolution encoding and advanced decoding preferably comprises advanced superresolution decoding, which can further be conducted in a distributed and / or cooperative manner.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
System and method for planning and generating queries for multi-dimensional analysis using domain models and data federation
ActiveUS7337170B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDomain modelData warehouse
Data integration and data analysis using computing equipment, software as well as hardware, includes a system and method for integrating data from various data sources, structured and unstructured, without physically creating a data warehouse and automatically generating queries for analysis of the integrated data from a multitude of different views.
Owner:SERVICENOW INC
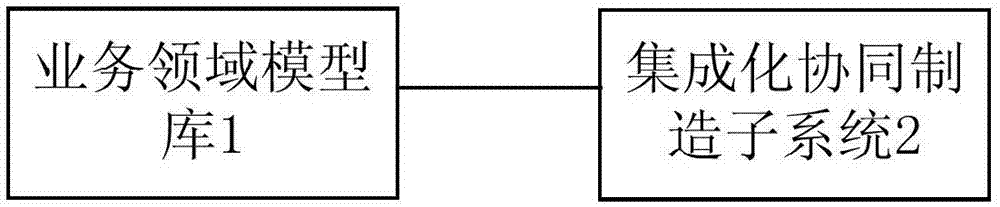
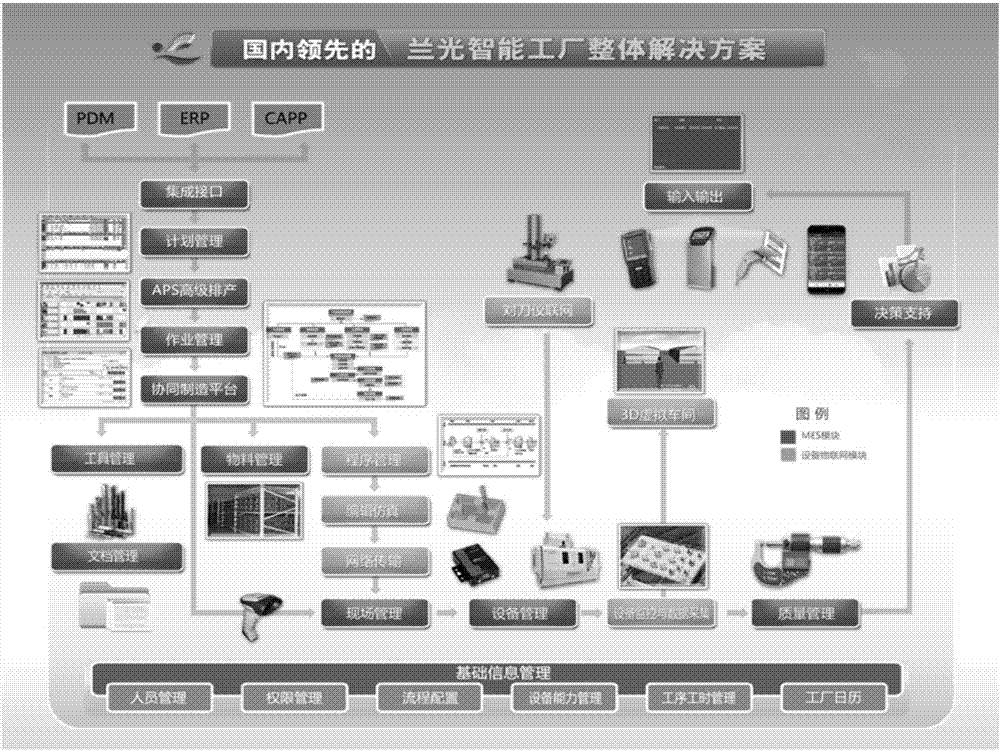
Platform-based intelligent MES
The invention provides a platform-based intelligent MES (Manufacturing Execution System). The system includes a business domain model base and an integrated collaborative manufacturing subsystem. The business domain model base is used for storing a business model, a domain model and a database model. The business model includes the corresponding requirements and associations of personnel, technology, materials, equipment, tooling and test. The domain model includes the work dependence and decomposition relations, the association between work and material and production units, and a field problem component. The database model stores relevant data and data associations in the business model and in the domain model. The integrated collaborative manufacturing subsystem makes an operation plan based on the data and data association in the business domain model base, and manages and schedules the whole operation process. Through a business domain model, all kinds of basic models can be specified, and the association relation can be established. The integrated collaborative manufacturing subsystem executes production planning and management scheduling.
Owner:北京兰光创新科技有限公司
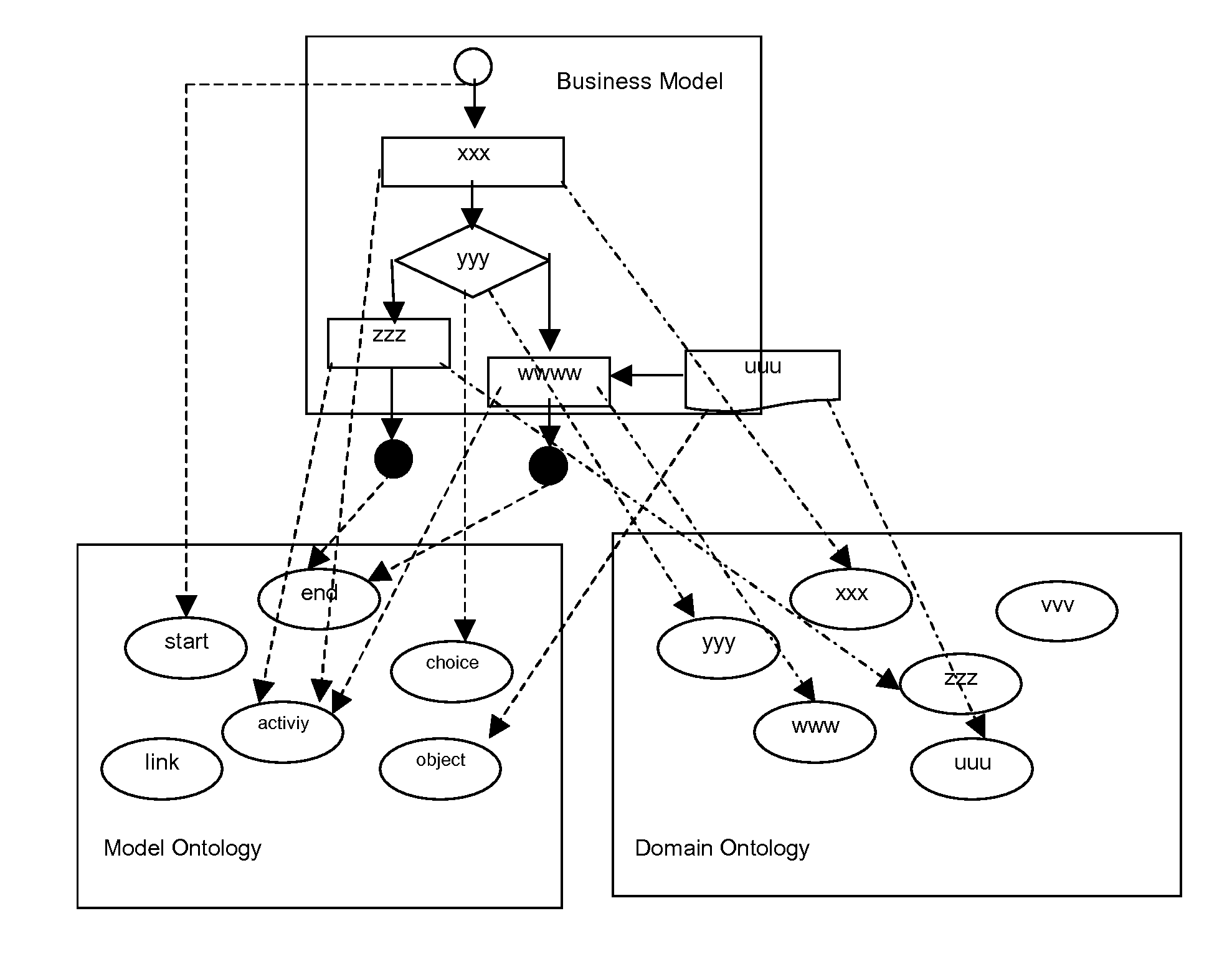
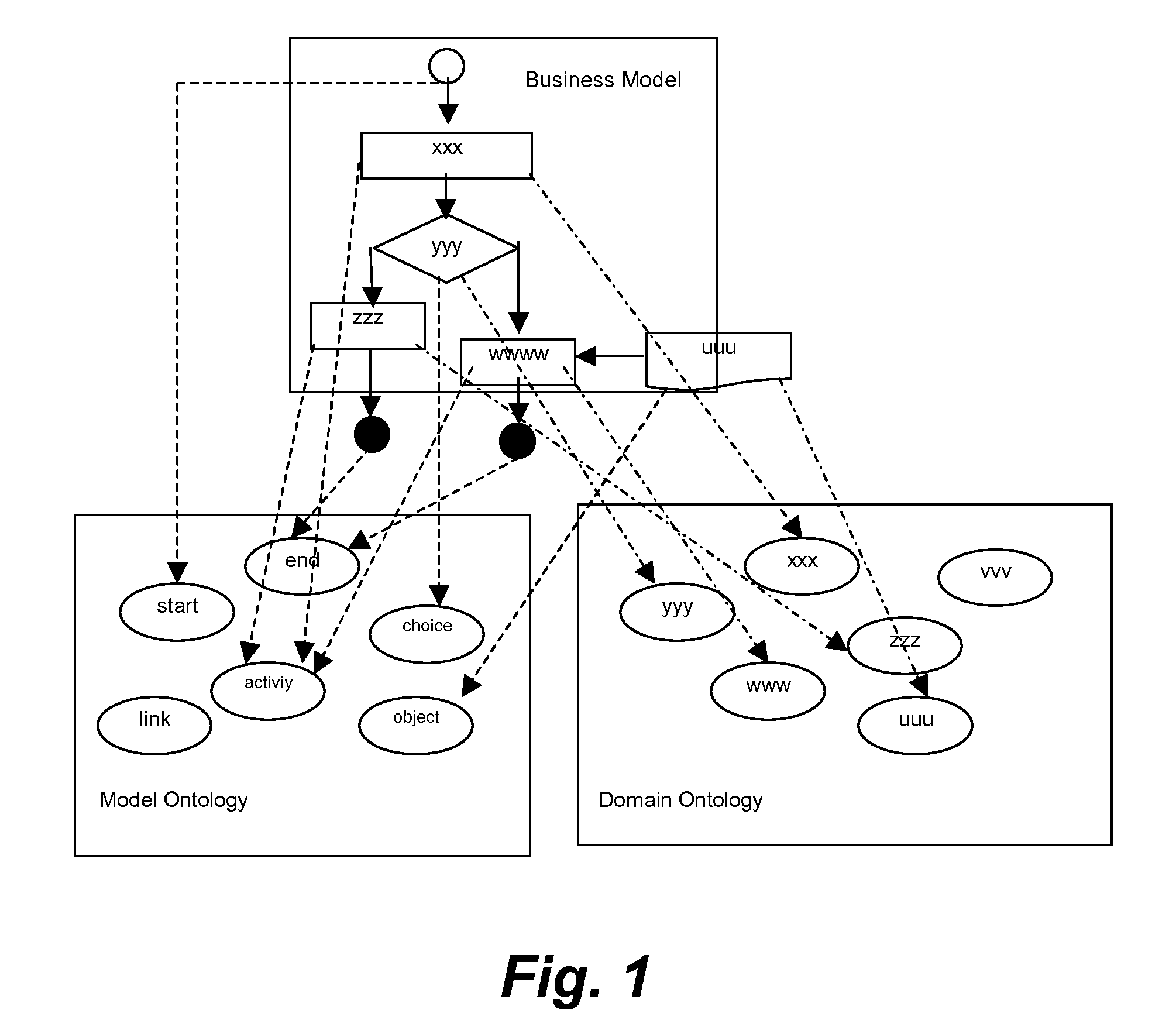
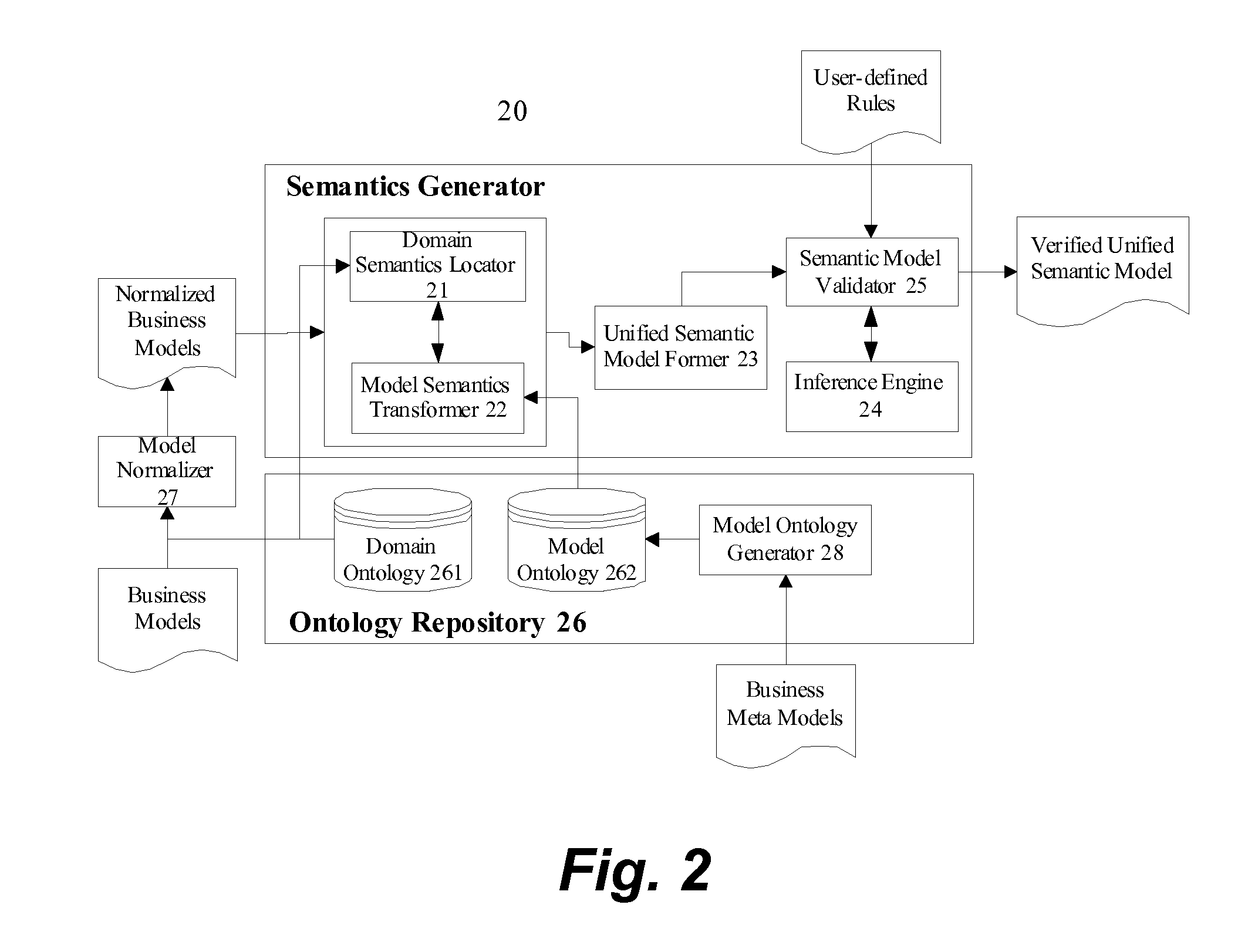
Method and apparatus to enable integrated computation of model-level and domain-level business semantics
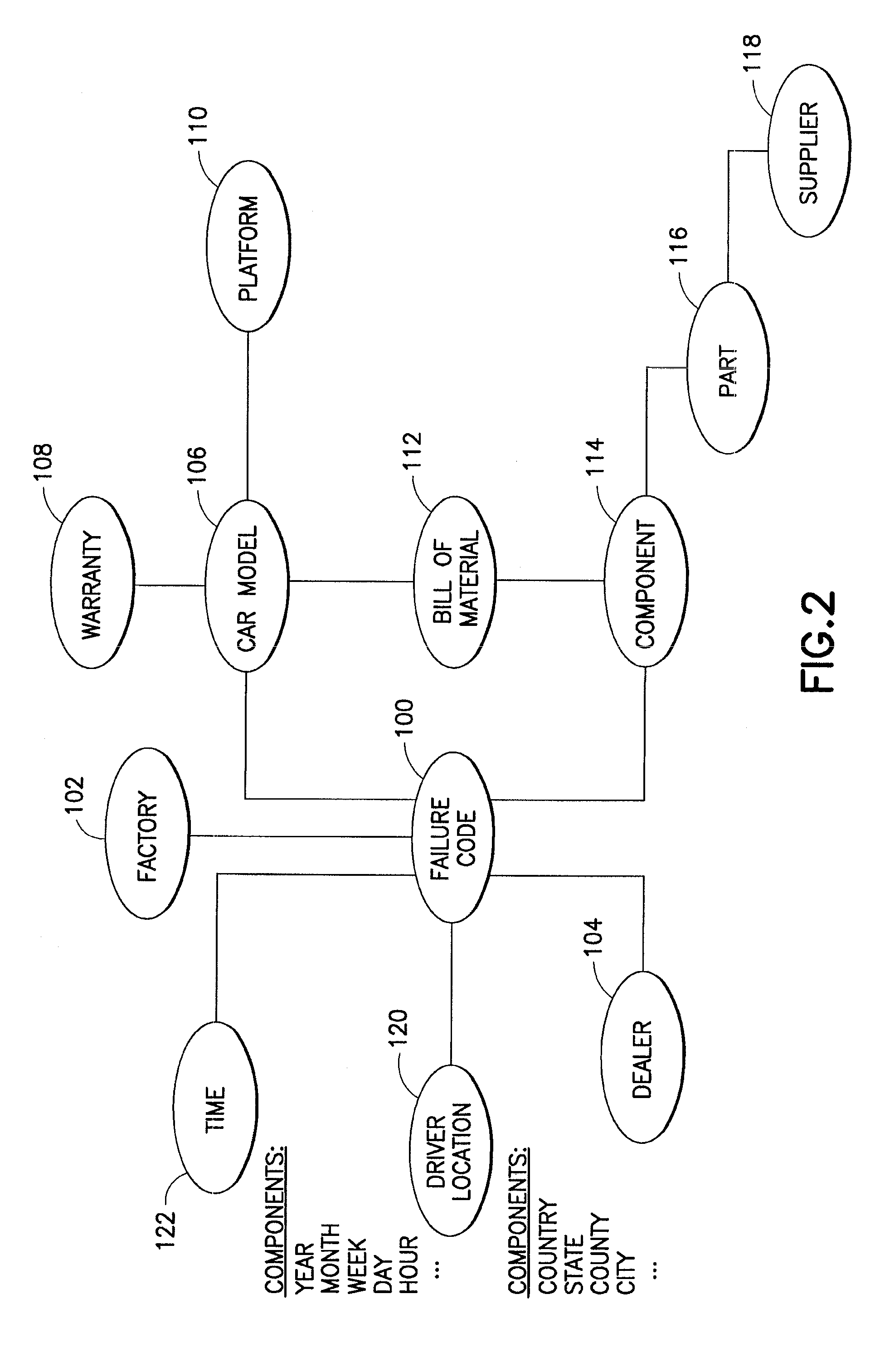
InactiveUS20070112718A1Business value is tremendousKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsDomain modelDomain level
A method is provided for integrating model and domain semantics in business models. The method includes a business model inputting step for inputting the business model to be realized; a domain semantics locating step for locating the domain semantics of the modeling element of the business model within the domain ontology and outputting the corresponding domain model semantics; a model semantics transforming step for transforming the modeling element of the business model into business model semantics that are represented by a model ontology; and a unified semantic model forming step for combining the aforesaid business model semantics and domain model semantics and then outputting a unified semantic model. The teachings disclosed are directed to facilitate the integration and utilization of the semantics embedded in business models.
Owner:IBM CORP
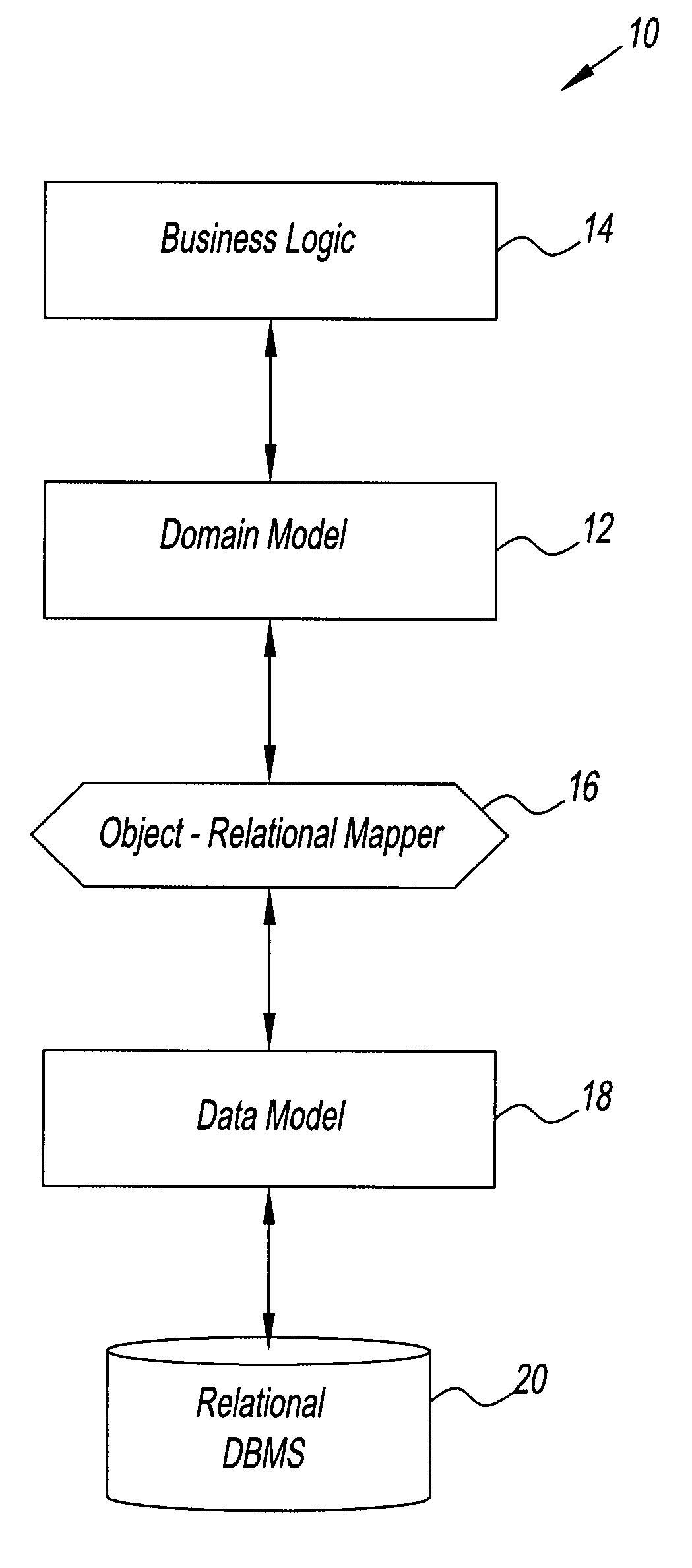
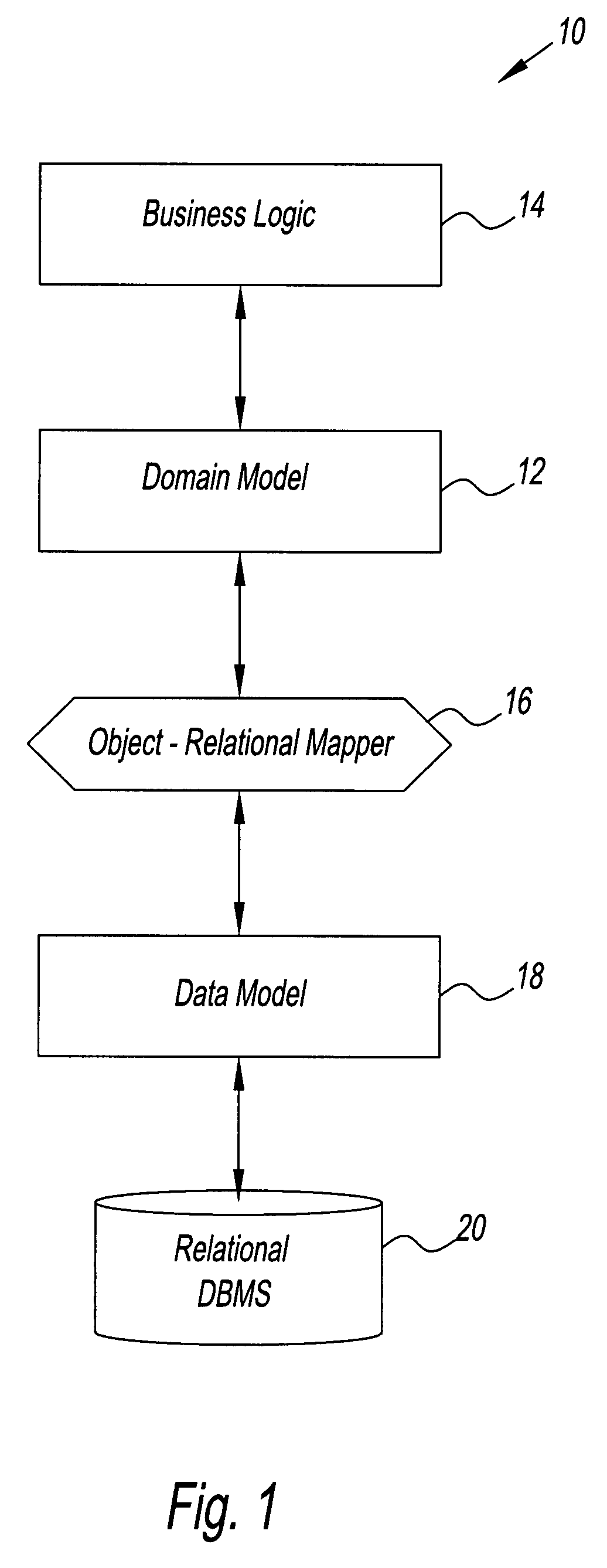
System and method for creating an object model
InactiveUS7734659B2Digital data processing detailsRelational databasesTemporal informationDomain model
A method for creating a dynamic domain model of an object. The method includes storing and organizing temporal information about the object in a bitemporal database that includes both a valid time and a transaction time for the information. The information is inserted into a plurality of tables in the database and a key is assigned to each of the plurality of tables. A composite representing the object is formed to represent a state of the object at the current time or at any previous time by dynamically linking the information by key, based on a business logic and a request made by a user.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
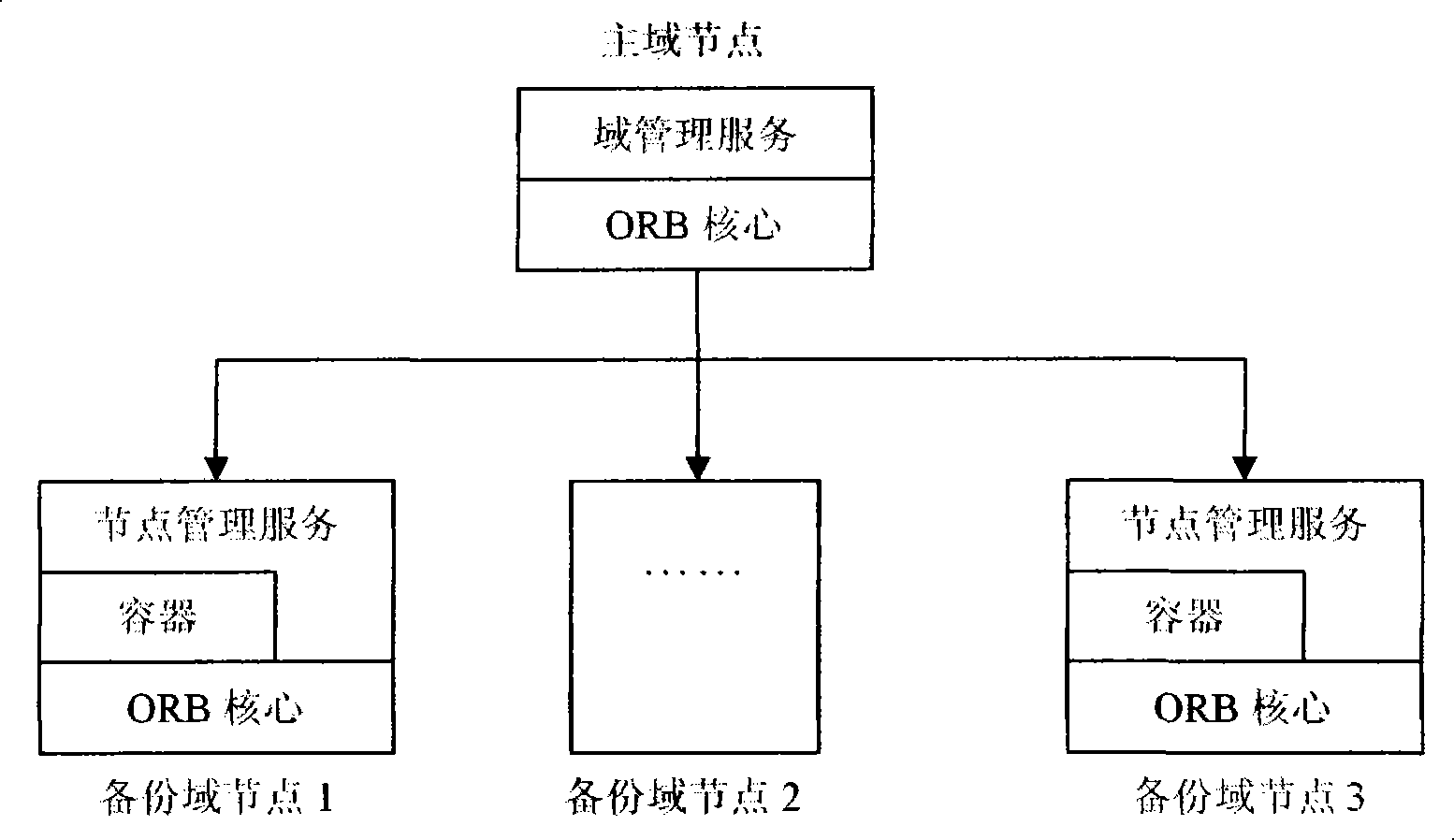
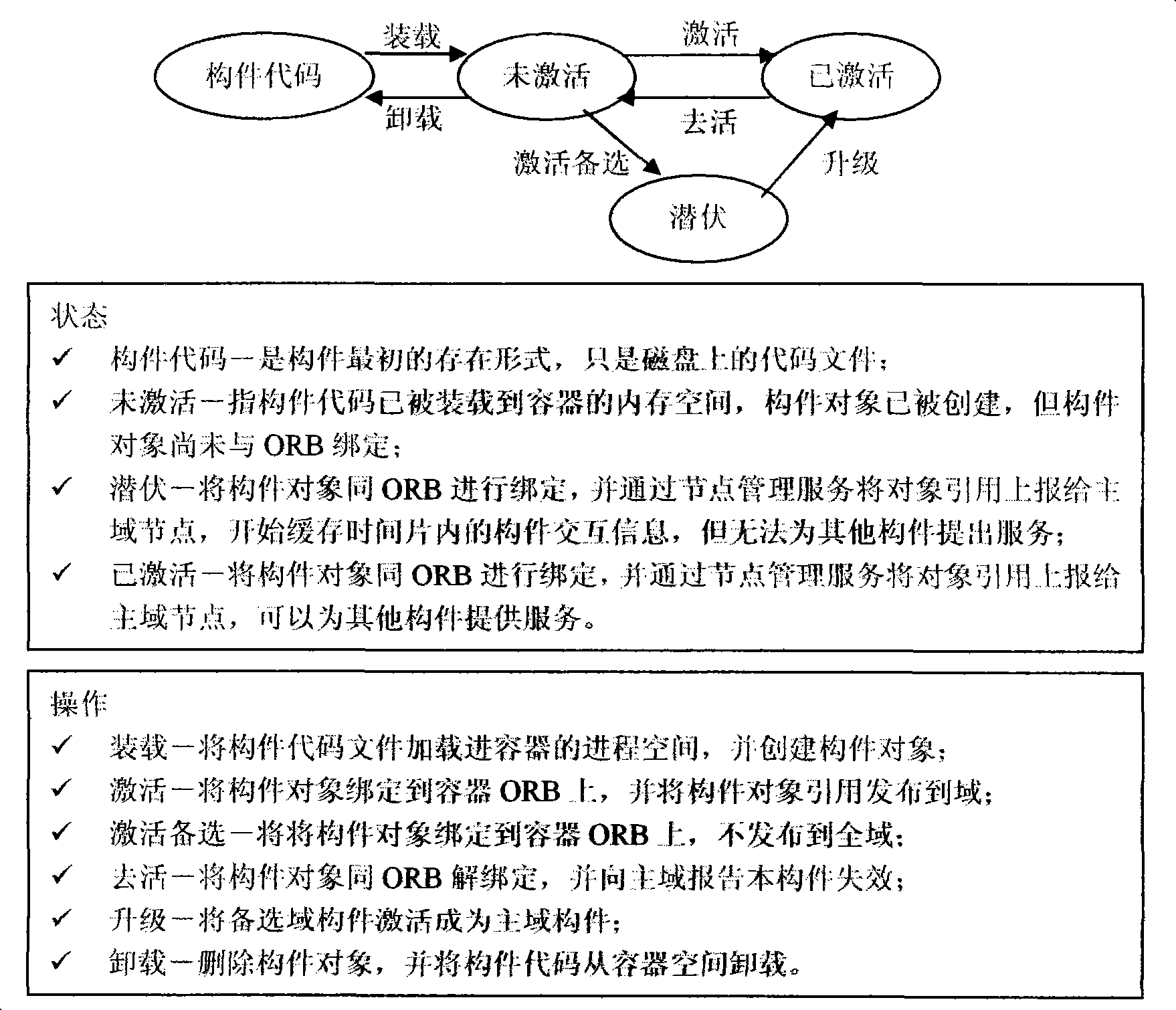
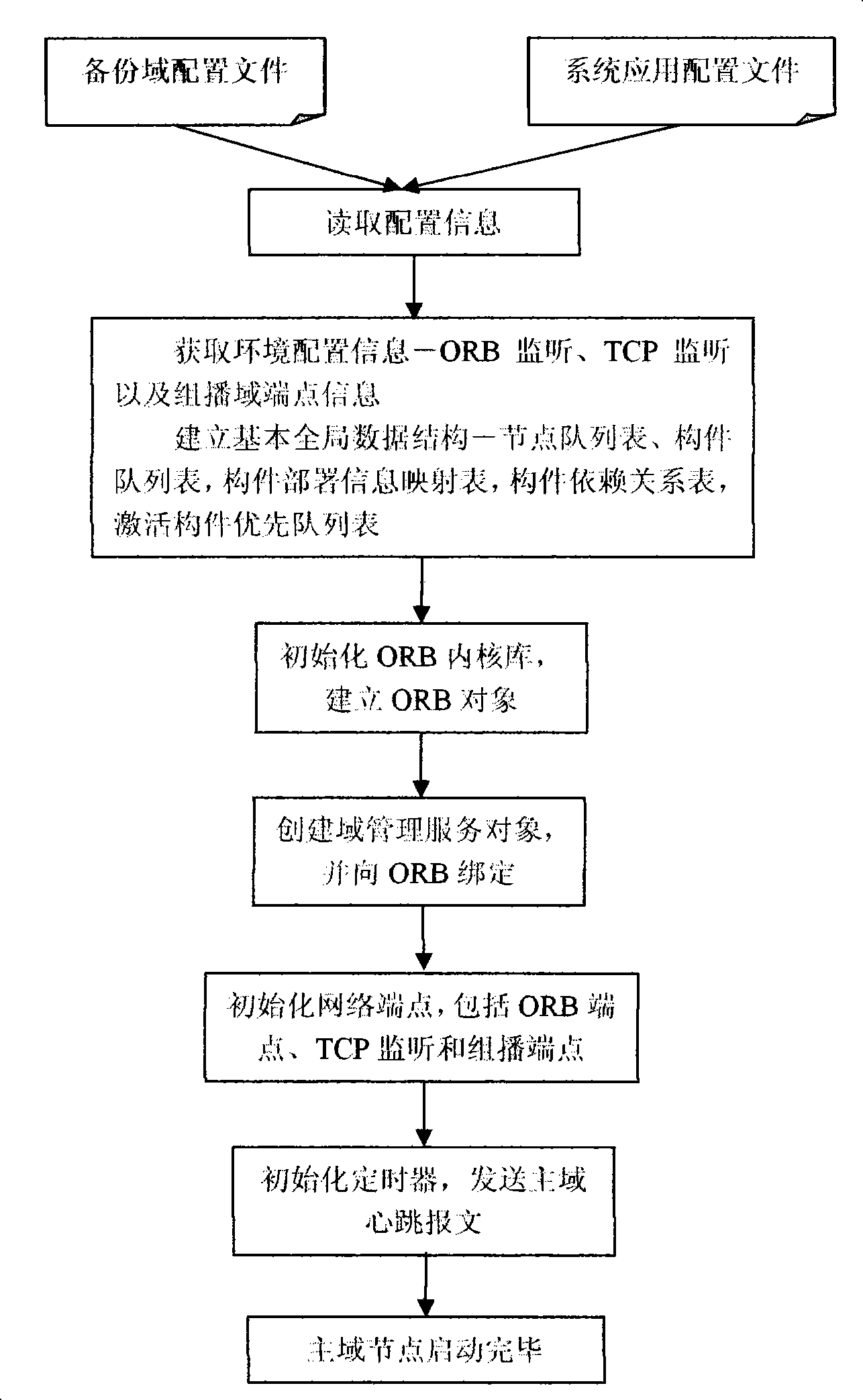
Element real time initiative transferring method based on domain model
InactiveCN101251797AEliminate loadingEliminate timeSpecific program execution arrangementsTime responseDomain model
The present invention provides a method for carrying out component migration in a component-based distributed system, belonging to the software component-based technical field. The method comprises the following steps that: 1) nodes of a distributed system are divided into domain nodes and non-domain nodes; the domain nodes manage the global strategy, and the non-domain nodes are responsible for the specific execution on a present node; 2) creating an interaction management protocol between the domain nodes and the non-domain nodes for controlling the migration management; 3) creating multi-point redundancy, failure active discovery and real-time migration algorithm of the component. The component migration method of the present invention has as follows: 1) real-time; the component loading and environment binding time during the migration process is eliminated and the real-time response degree during the migration process is improved through the simplification and optimization of the global information and the component activation queue based on priority; 2) accuracy; the integrity of the information and correctness of the running state of the system are ensured by realizing the function of the backup of 'latency' state of the domain component.
Owner:NO 709 RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
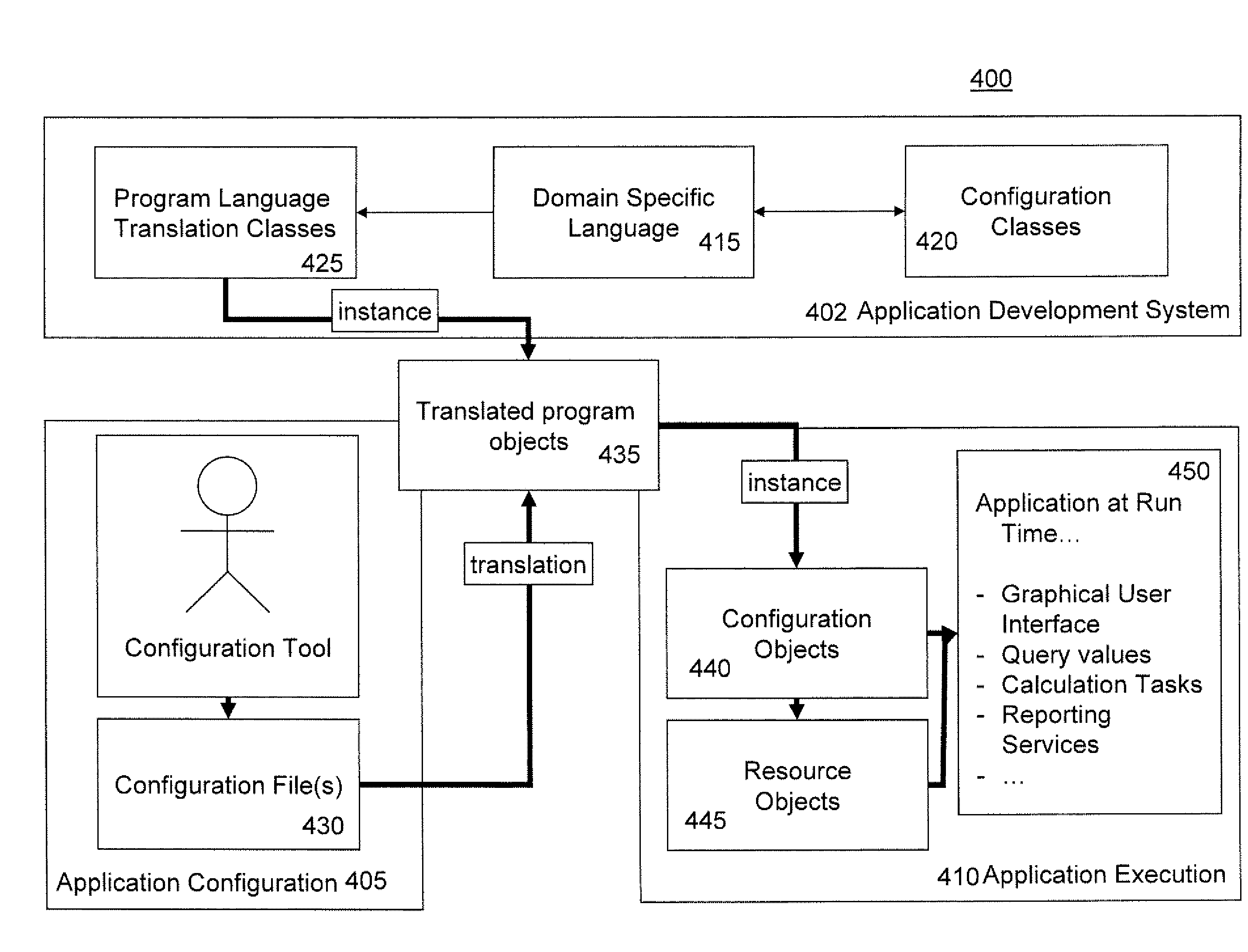
Domain model concept for developing computer applications
Methods and systems for developing a computer application wherein a domain specific language is provided that allows for the developing of computer applications based on a configuration. In particular, the domain specific language pertains to calculation tasks. The developing of a computer application is performed at different levels or phases. In particular, these phases are the providing of an application development system in the design phase, performing the application configuration and executing the application. The design phase provides the application design environment and provides the abstract basis for the application development in the sense of configuration classes and domain-specific language. For the specific configuration of an application in a particular project, i.e. for the development of a specific application, resources as elements and their associations are defined. This configuration is stored in a configuration file. At run time, an application is generated which instantiates the resources and configured elements. Within the generated graphical user interfaces of the application the instantiated resource objects are provided and the calculation is performed according to the configured element assignment.
Owner:FACTON
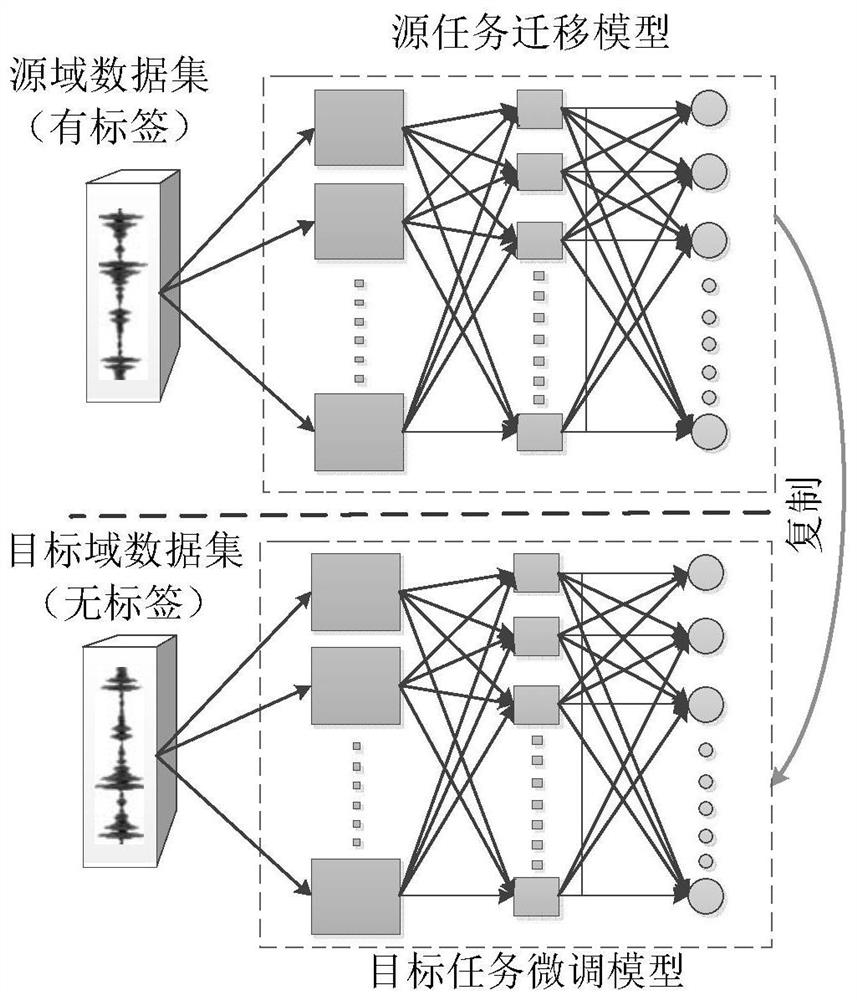
Unsupervised model parameter migration rolling bearing life prediction method
ActiveCN112101220AAchieve lifeRealize multi-state recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesHealth indexProbability estimation
The invention discloses an unsupervised model parameter migration rolling bearing life prediction method, and belongs to the technical field of rolling bearing state identification and residual life prediction. The method is provided for solving the problems that in practice, rolling bearing labeled vibration data under a certain working condition is difficult to obtain, health indexes are difficult to construct, and the service life prediction error is large. The method comprises the steps that firstly, extracting root-mean-square features from rolling bearing full-life-cycle vibration data,and introducing a new bottom-to-top time sequence segmentation algorithm to segment a feature sequence into three states composed of a normal period, a degradation period and a recession period; marking the state information of an amplitude sequence of the vibration signal subjected to fast Fourier transform, taking the amplitude sequence as an input of an improved full convolutional neural network, extracting deep features, and constructing a source-domain model and a state recognition model subjected to fine adjustment through training to realize rolling bearing multi-state recognition; andestablishing a rolling bearing life prediction model by using a state probability estimation method. Experiments prove that the method provided by the invention does not need to construct health indexes, can realize rolling bearing state identification and life prediction under different working conditions under an unsupervised condition, and obtains a better effect.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
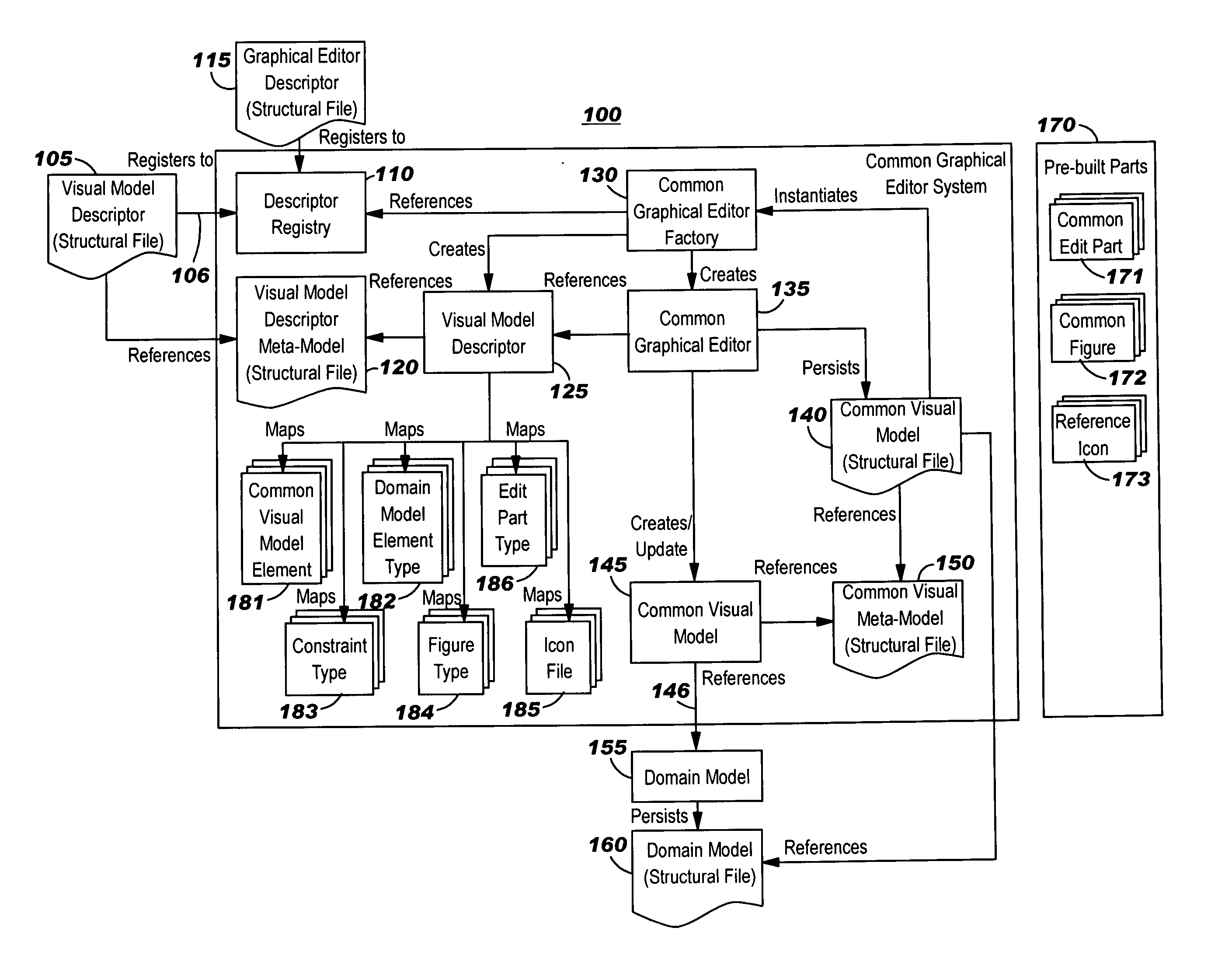
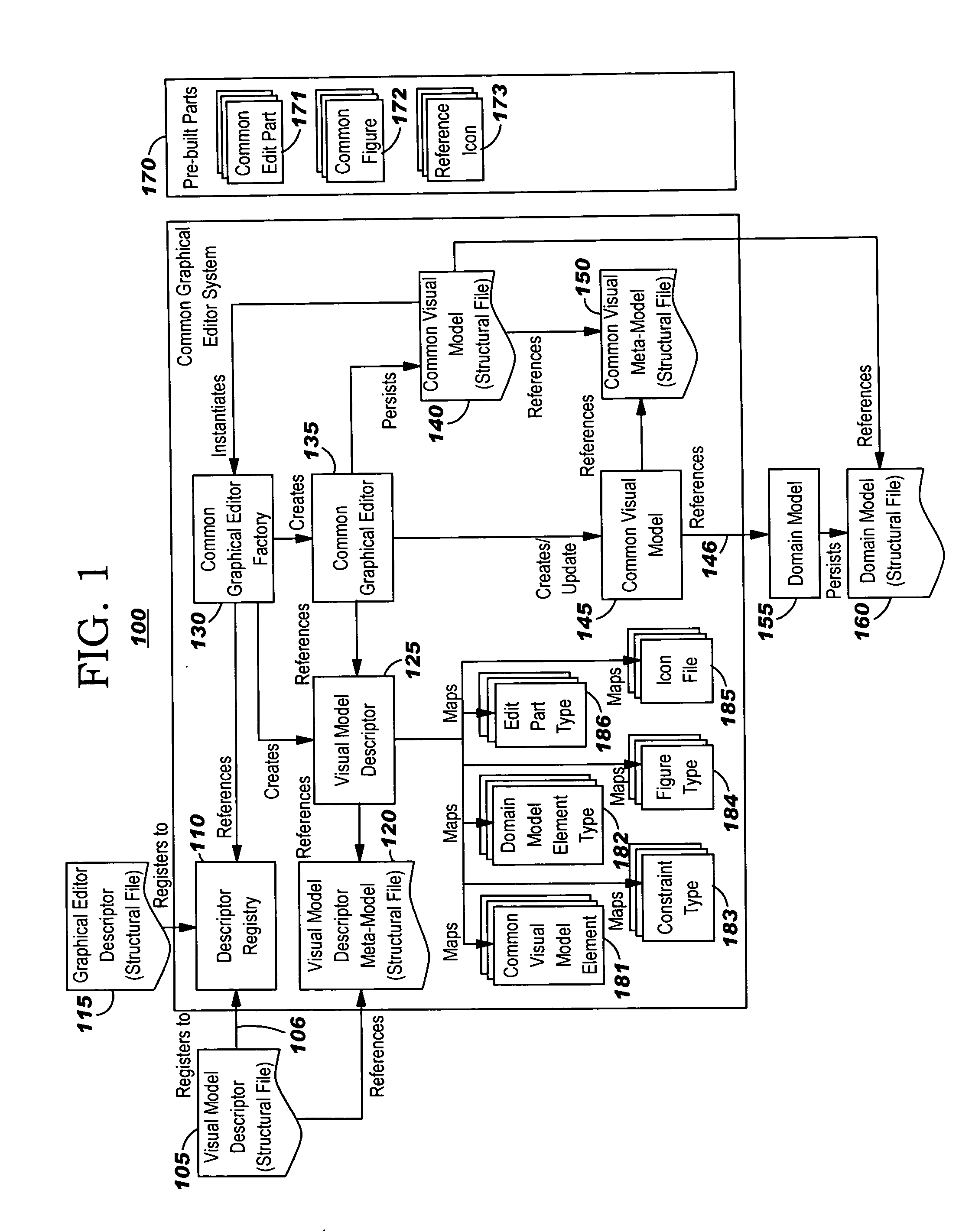
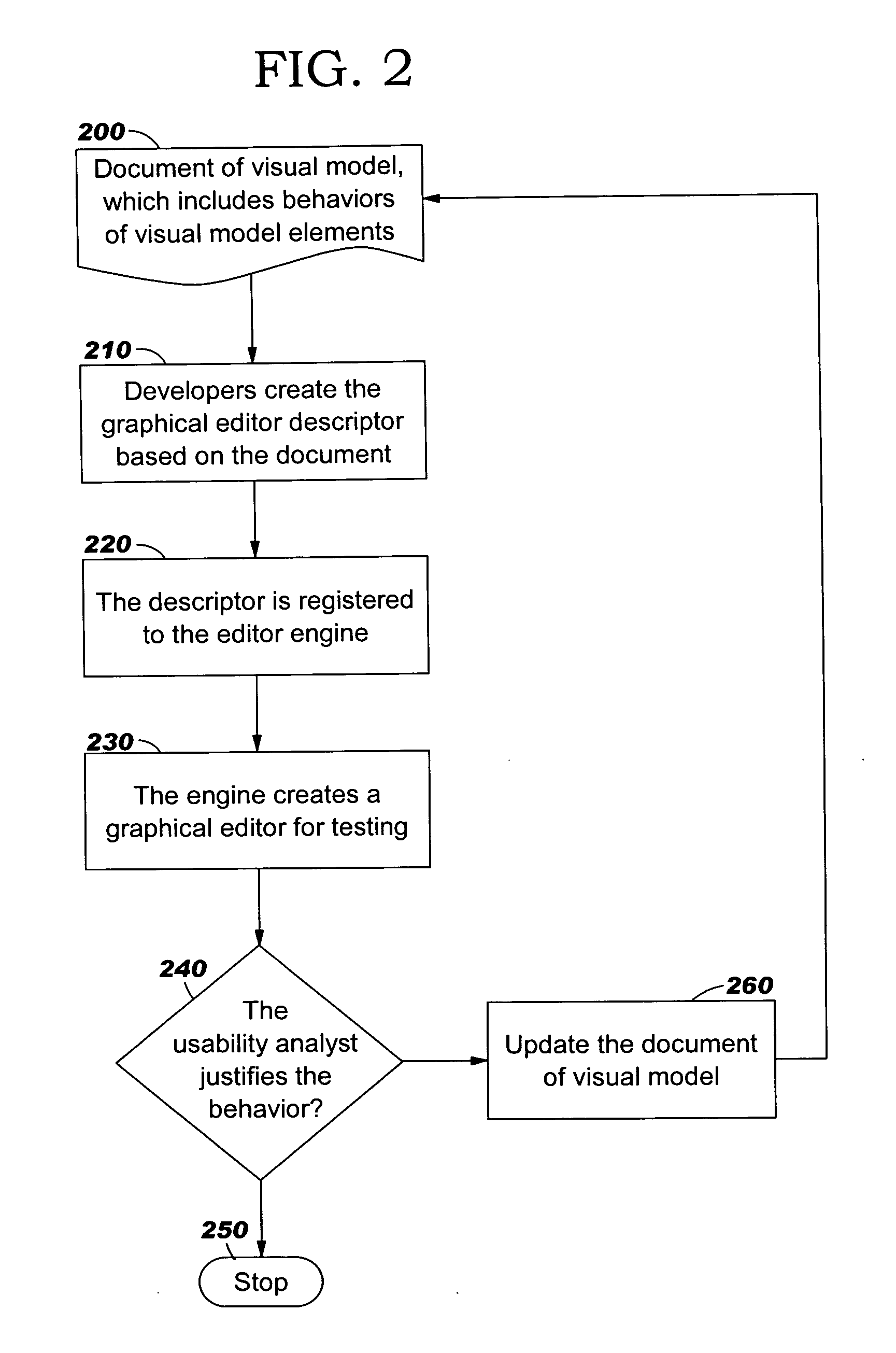
Graphical editor with incremental development
InactiveUS20060271909A1Create quicklyLow costVersion controlSpecific program execution arrangementsGraphicsDomain model
Techniques for developing a graphical editor using an incremental development approach. Externally-stored descriptors are used to specify information on which a graphical editor engine operates to create a graphical editor. Developers can thus redefine the look and feel of the graphical editor by modifying these descriptors, effectively re-configuring the elements of visual models without changing the code of the graphical editor engine. Visual models for modeling a domain can be created and used, without first requiring the domain model to be defined.
Owner:IBM CORP
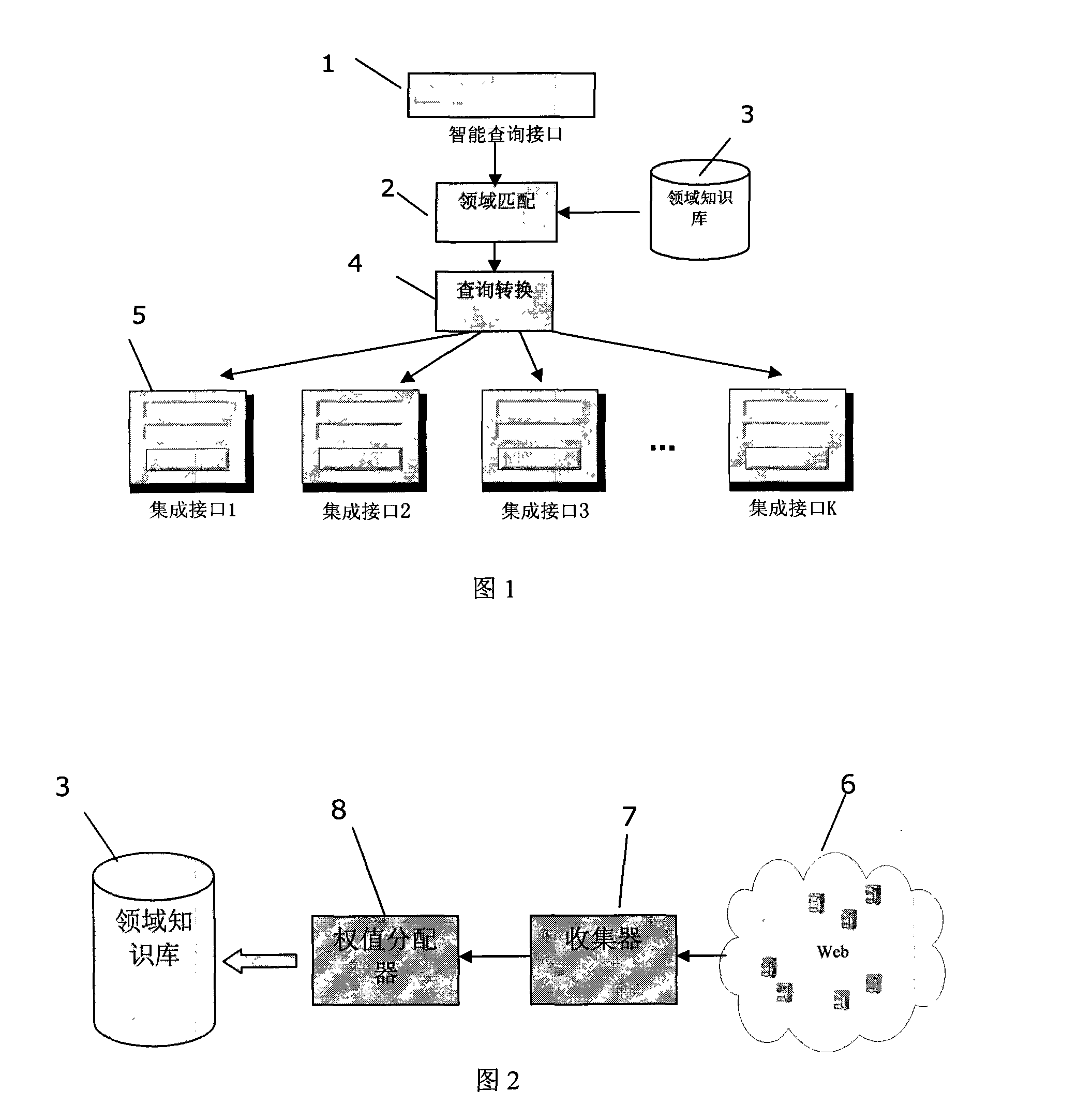
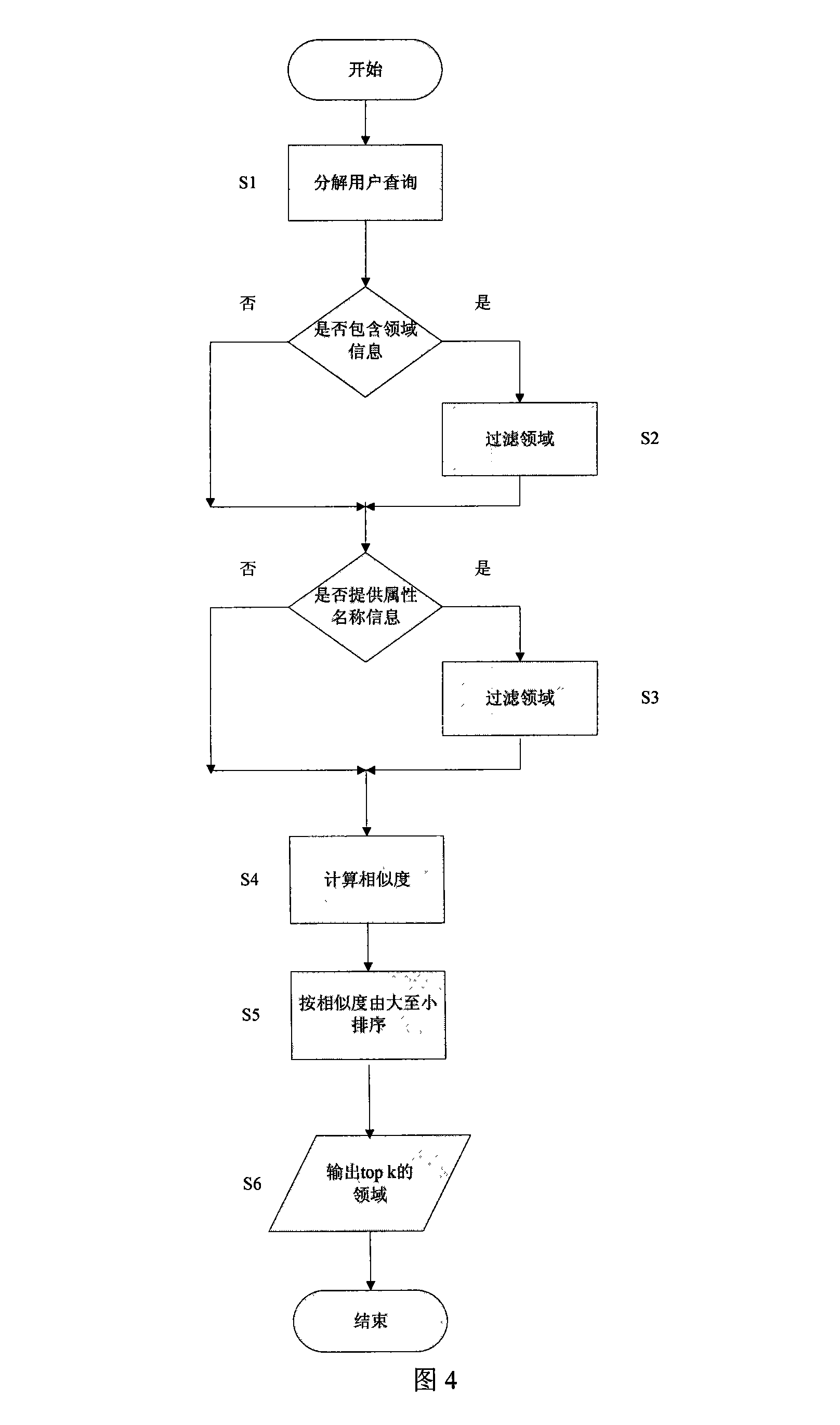
Intelligent web enquiry interface system and its method
The invention discloses an intelligent query interface system and a method, wherein the system comprises a domain knowledge base for storing the domain model of each candidate domain, an intelligent query interface, which the users fill in the query condition unit on and which decomposes each query of users into a plurality of query condition units, a domain matching module for calculating the matching degree between the query of users and each candidate domain according to the information stored in the domain knowledge base and selecting the most relevant domain for users reference and a query conversion module for establishing a correspondence between the user query condition units and query interface attributes and sending the generated final query to the complex integrated interface of corresponding domain.
Owner:孟小峰
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com