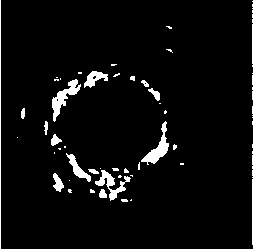Patents
Literature
58 results about "Velocity function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
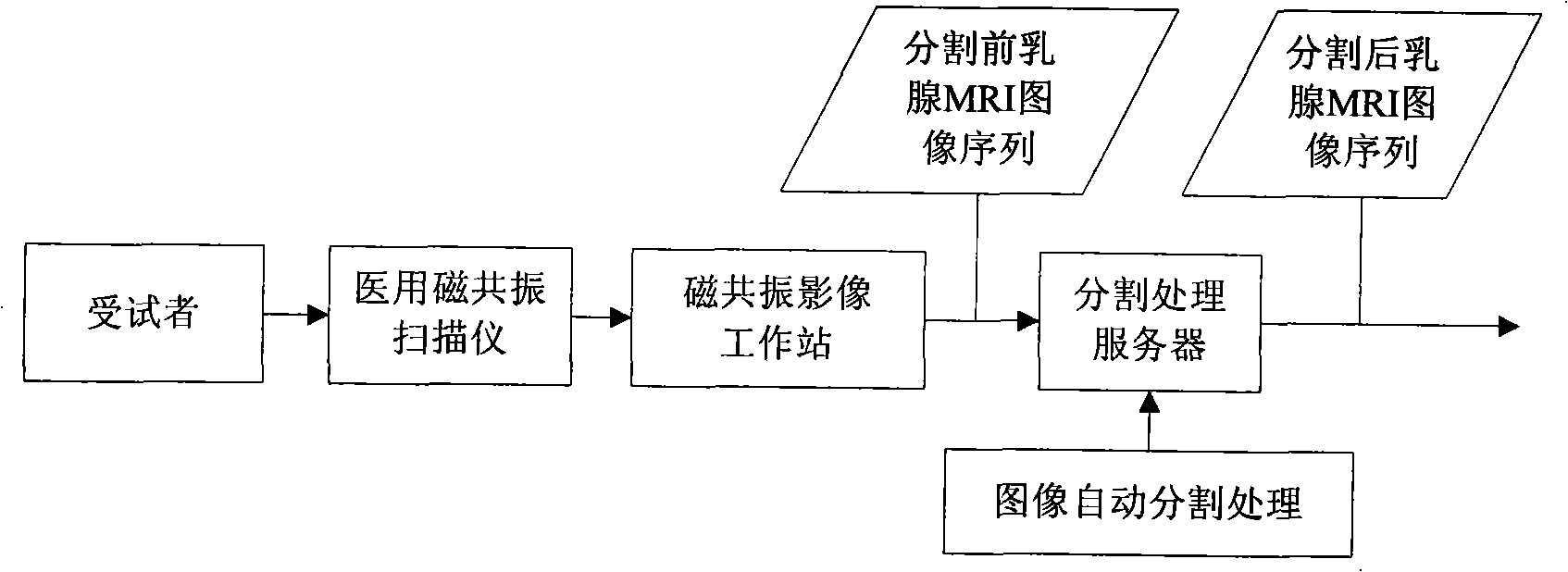
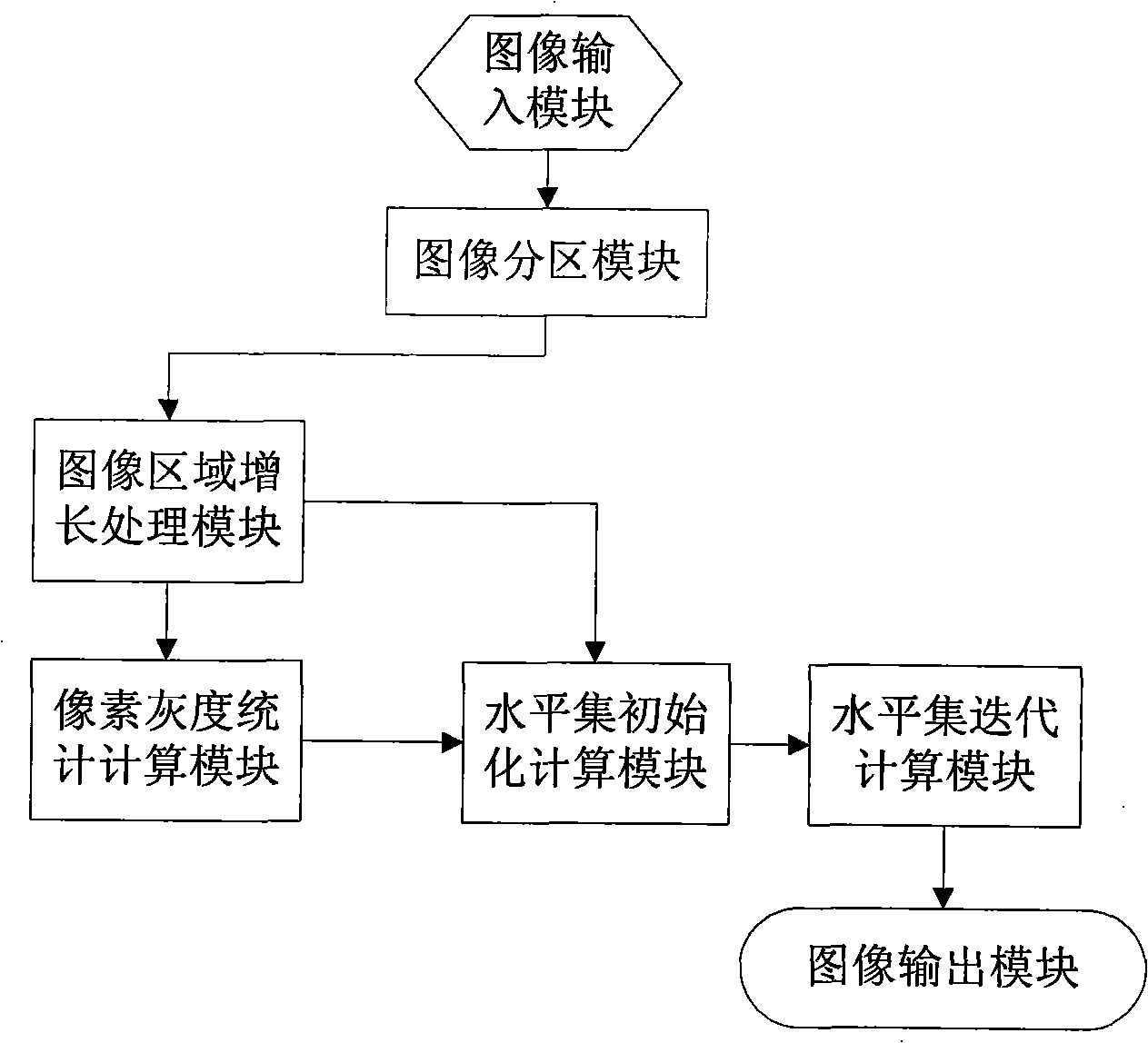
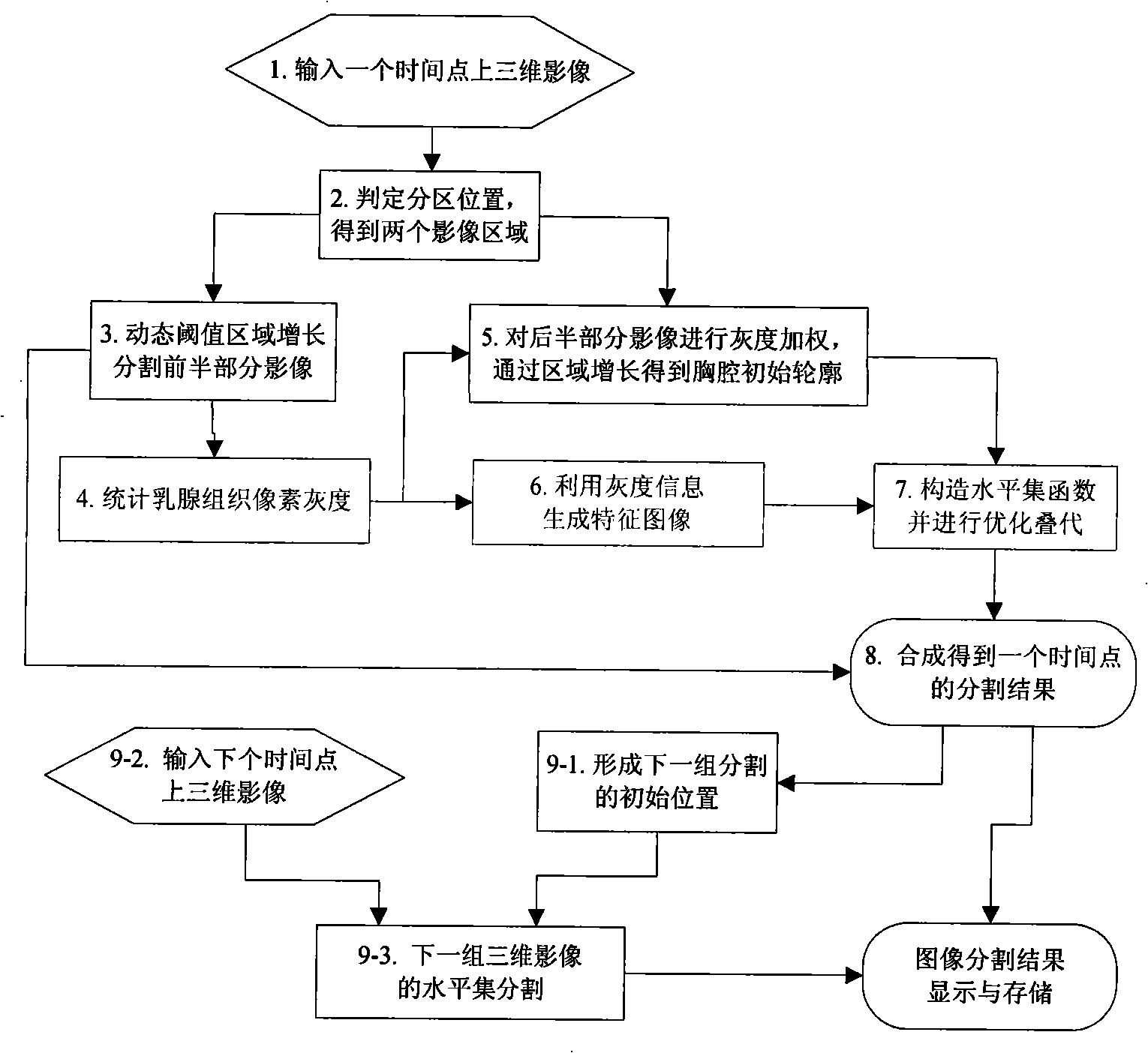
Image division method aiming at dynamically intensified mammary gland magnetic resonance image sequence
InactiveCN101334895ASolve the automatic segmentation problemImprove stabilityImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringAutomatic segmentationDynamic contrast
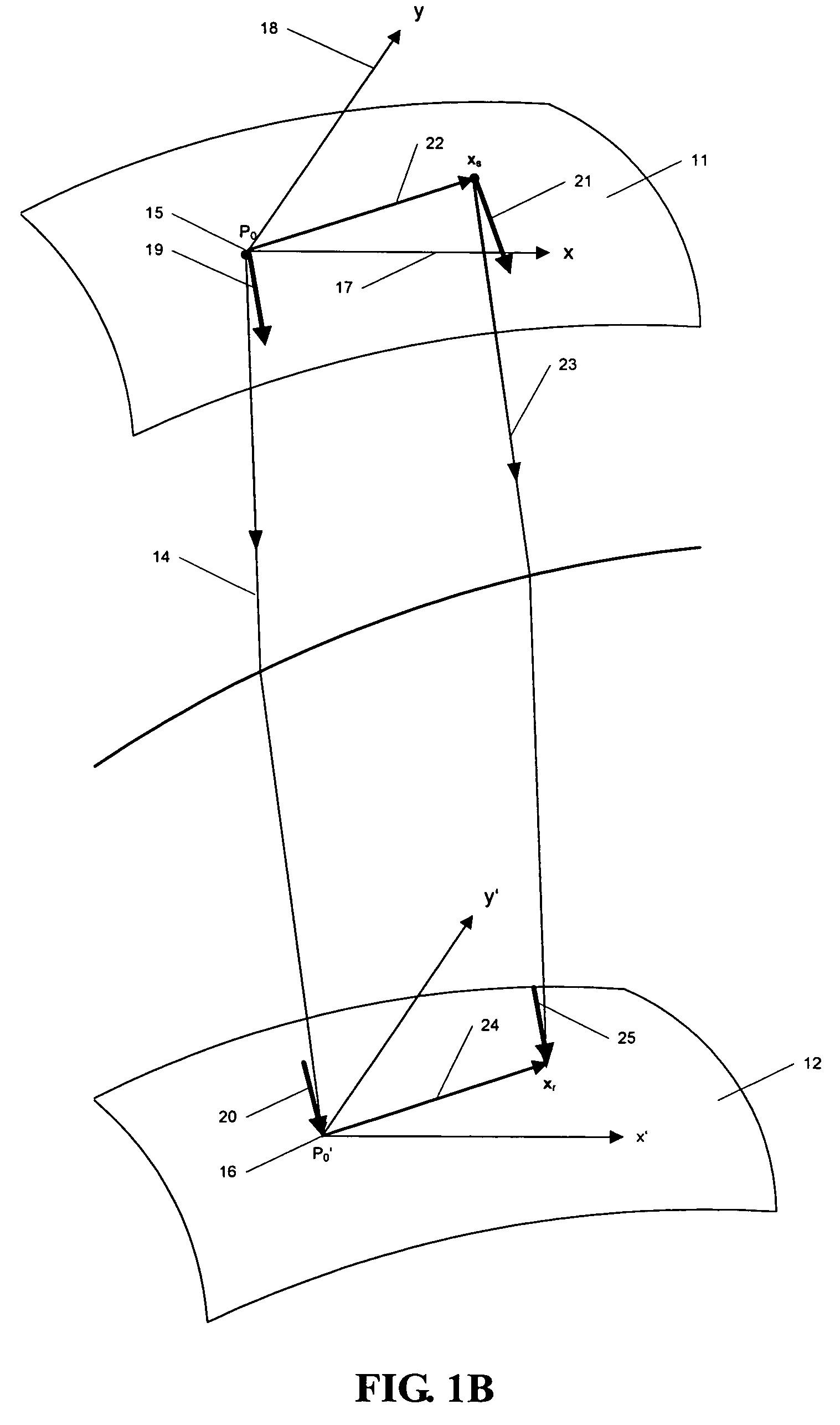
The invention discloses an image segmentation method for a dynamic contrast-enhanced mammary gland MRI sequence, pertaining to the field of magnetic resonance image processing techniques, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: a three-dimensional magnetic resonance image sequence of the section of the mammary gland is put into a computer; the image is divided into two parts including a mammary gland-air interface and a mammary gland-chest interface; a breast-air boundary is obtained by a splitting transaction in which a dynamic threshold controls the regional growth; an initial profile of the mammary gland and the chest is obtained in the same way, the complex profile of the breast and the chest is obtained with a method of controlling a level set; a three-dimensional magnetic resonance image sequence of a point-in-time is obtained by split jointing the segmentation results and taken as an initial position of the next group three-dimensional image segmentation. The image segmentation method of the invention increases the segmentation speed, solves the problem that a level set algorithm can not easily determine the initial profile and the velocity function and realizes an automatic segmentation of the complex dynamic contrast-enhanced mammary-gland magnetic resonance image with plenty of data.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
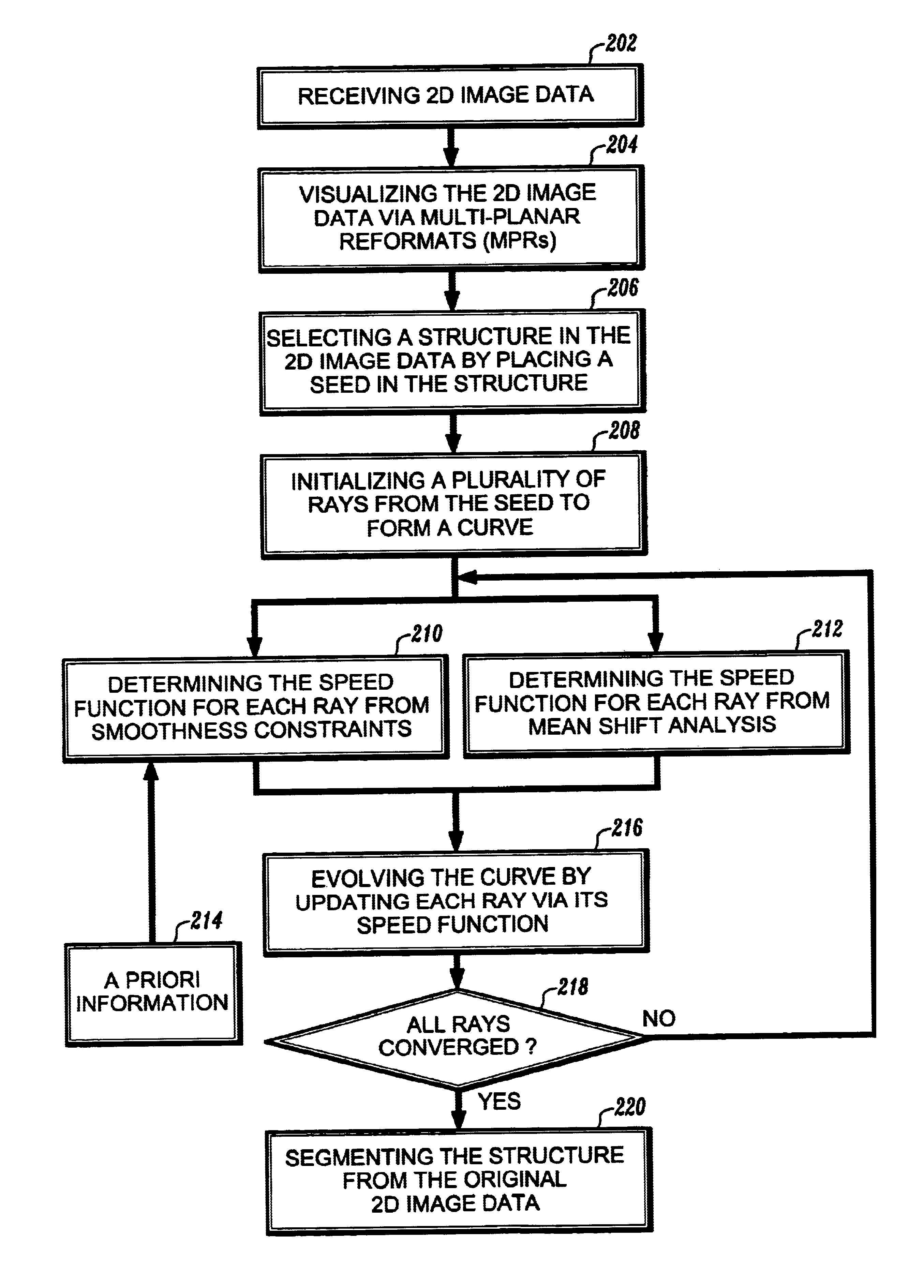
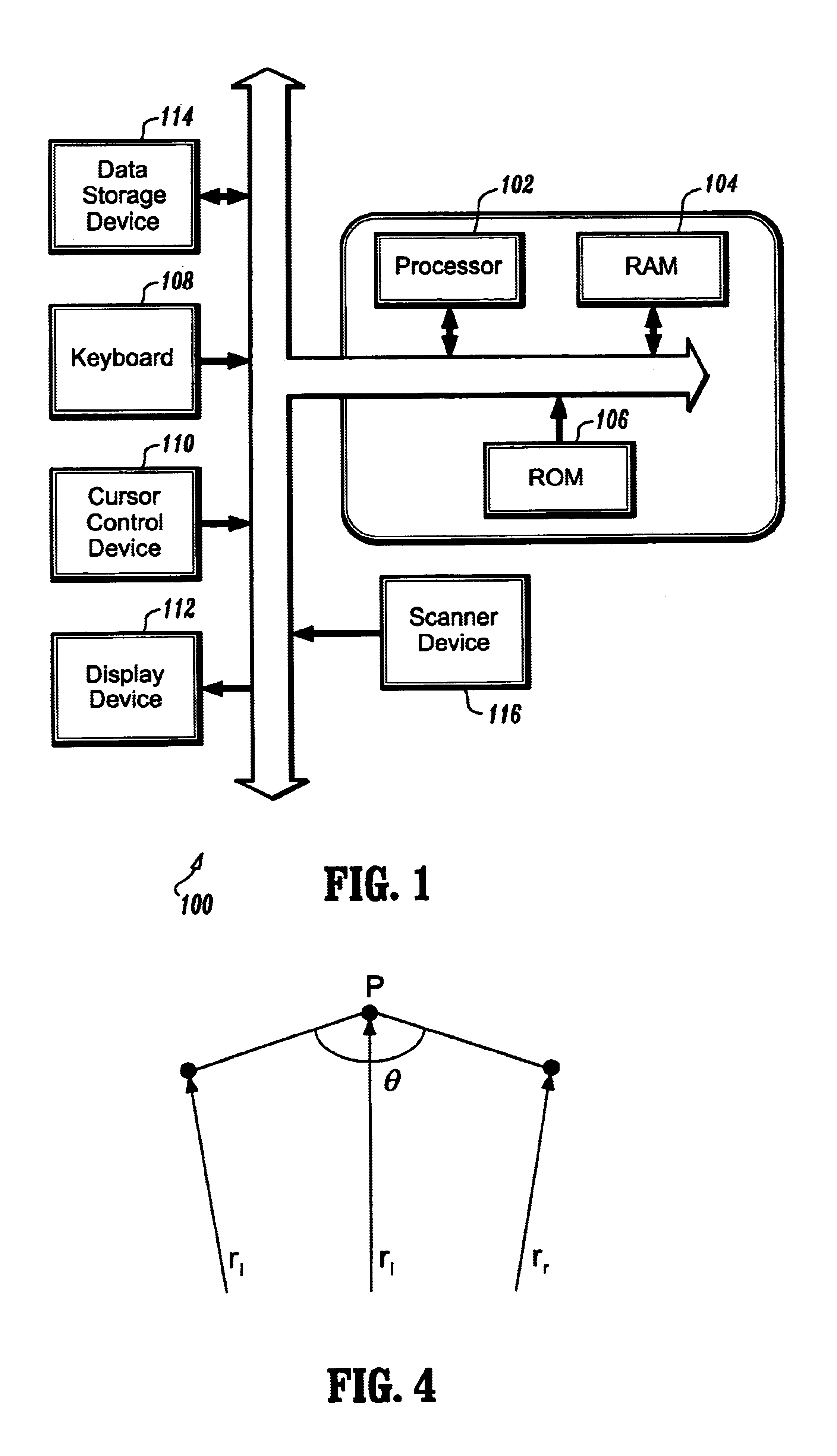
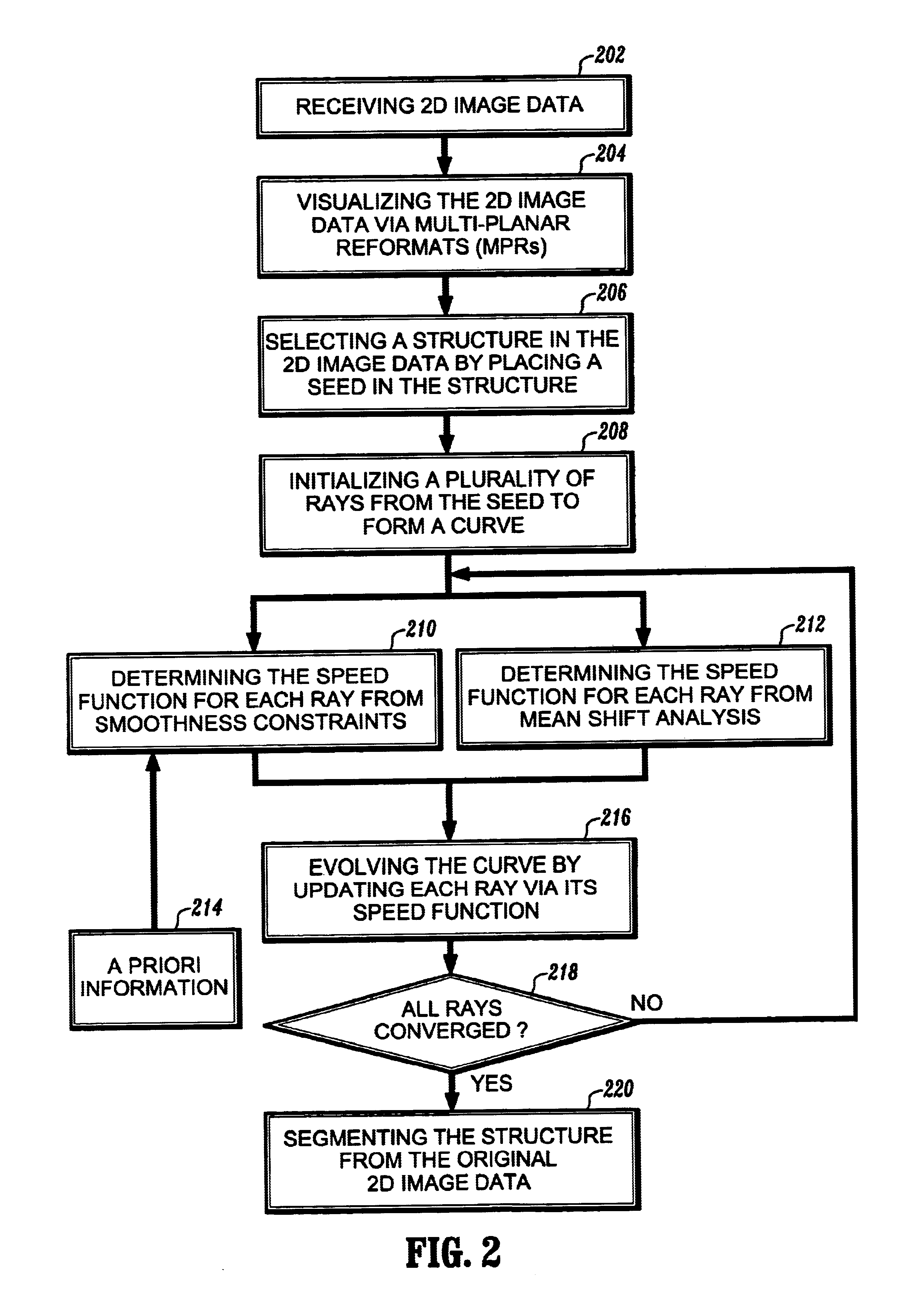
Vessel detection by mean shift based ray propagation
InactiveUS6947040B2Efficient and robustEnhance the imageImage enhancementImage analysisMean-shiftDisplay device
A method for segmentation of 2D structures in CT and MR images is provided. The method is based on 2D ray propagation by mean-shift analysis with a smoothness constraint. Ray propagation is used to guide an evolving curve due to its computational efficiency and shape priors are incorporated for robust convergence. The method includes the steps of receiving 2D image data; visualizing the 2D image data on a display device; selecting a structure in the 2D image data by placing a seed in the structure; initializing a plurality of rays from the seed to form a curve; determining a speed function of each of the rays; evolving the curve by propagating the rays based on the speed function of each of the rays; converging the rays on a boundary of the structure; and segmenting the structure when all of the rays have converged on the structure's boundary.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
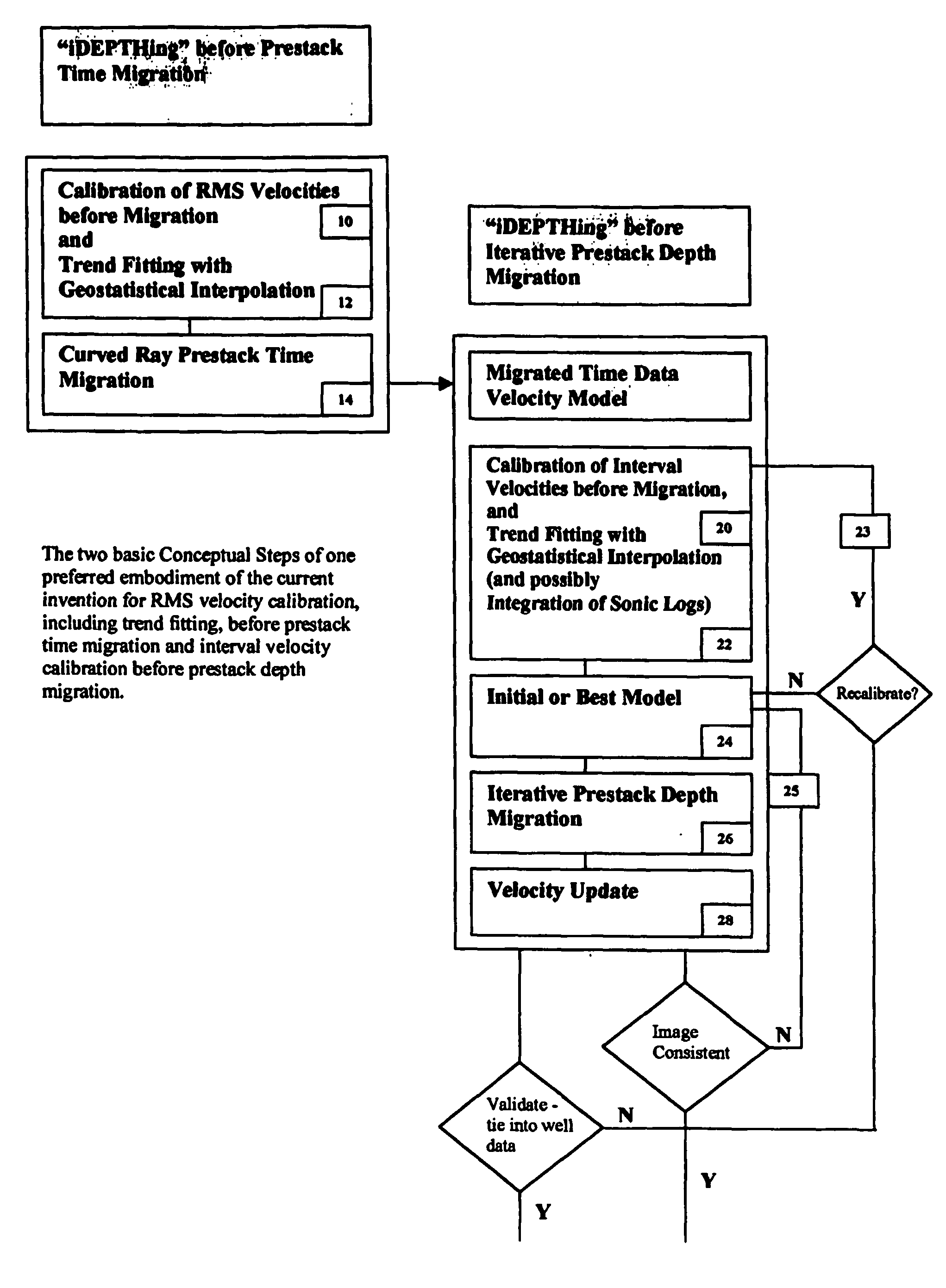
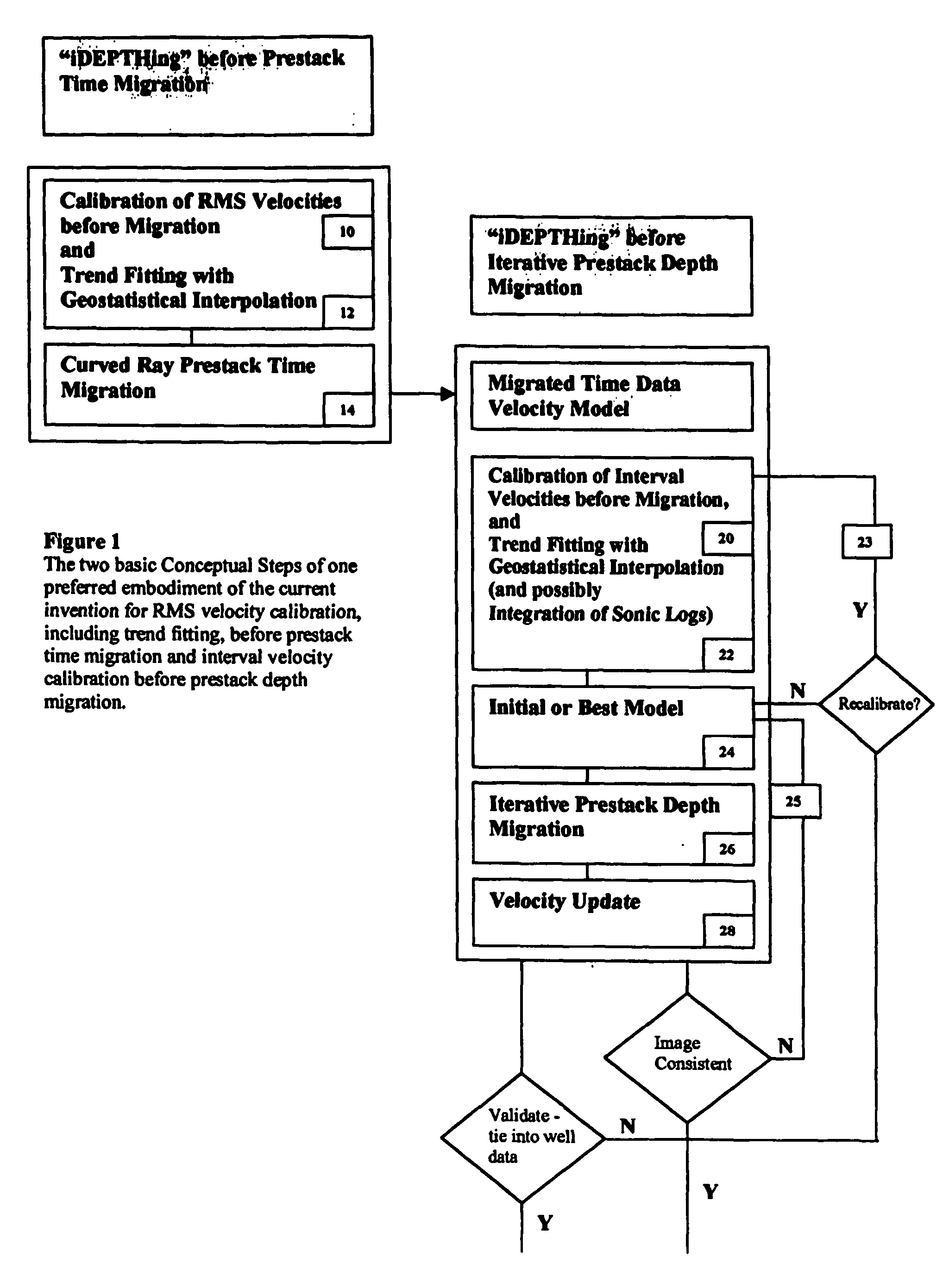
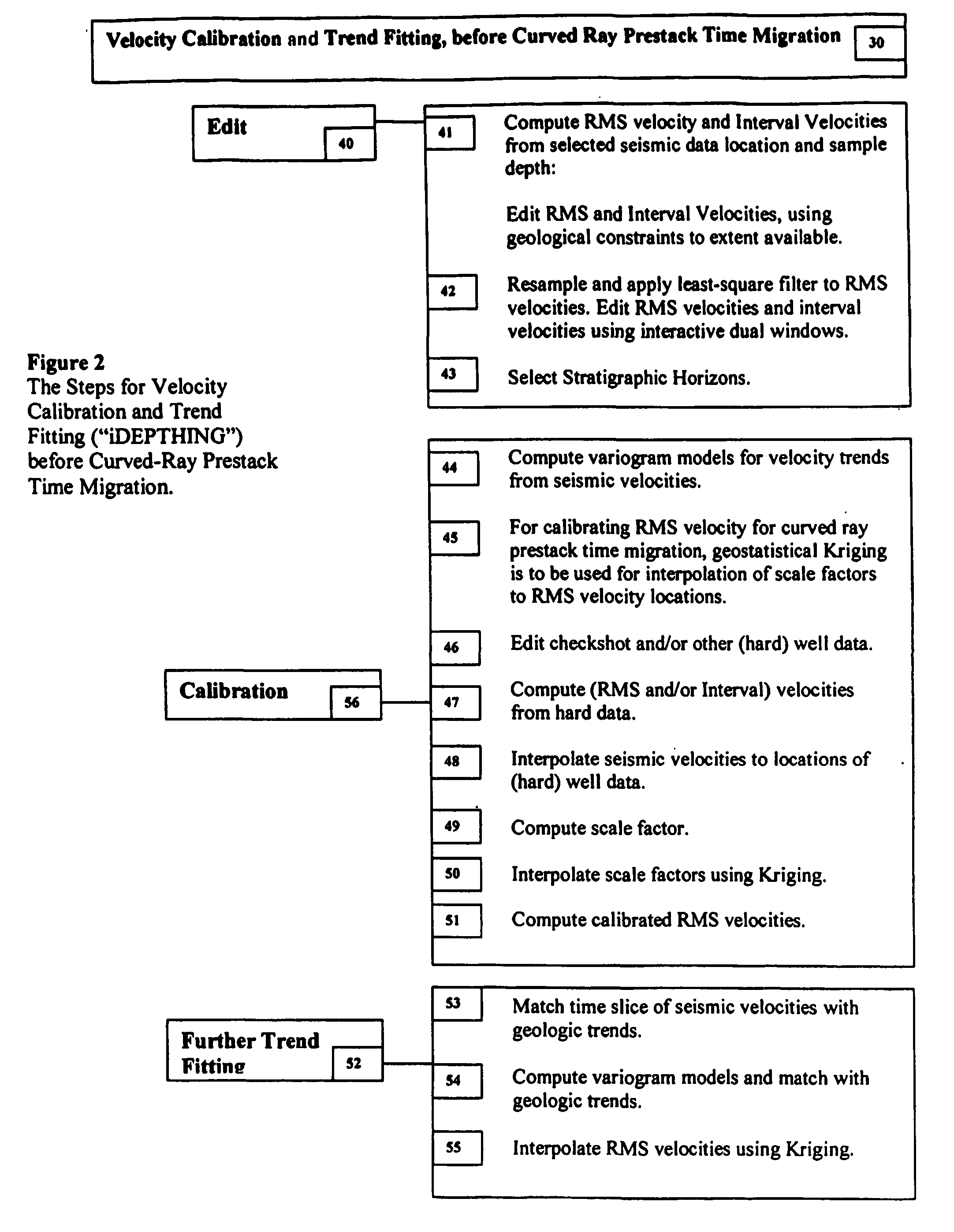
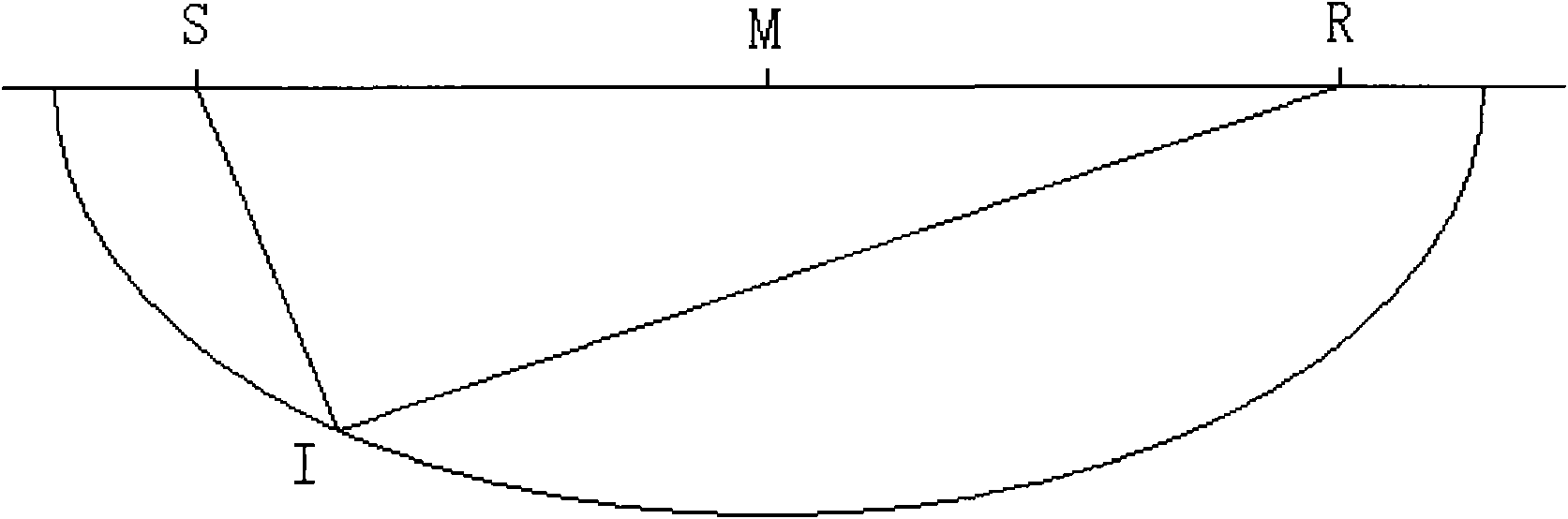
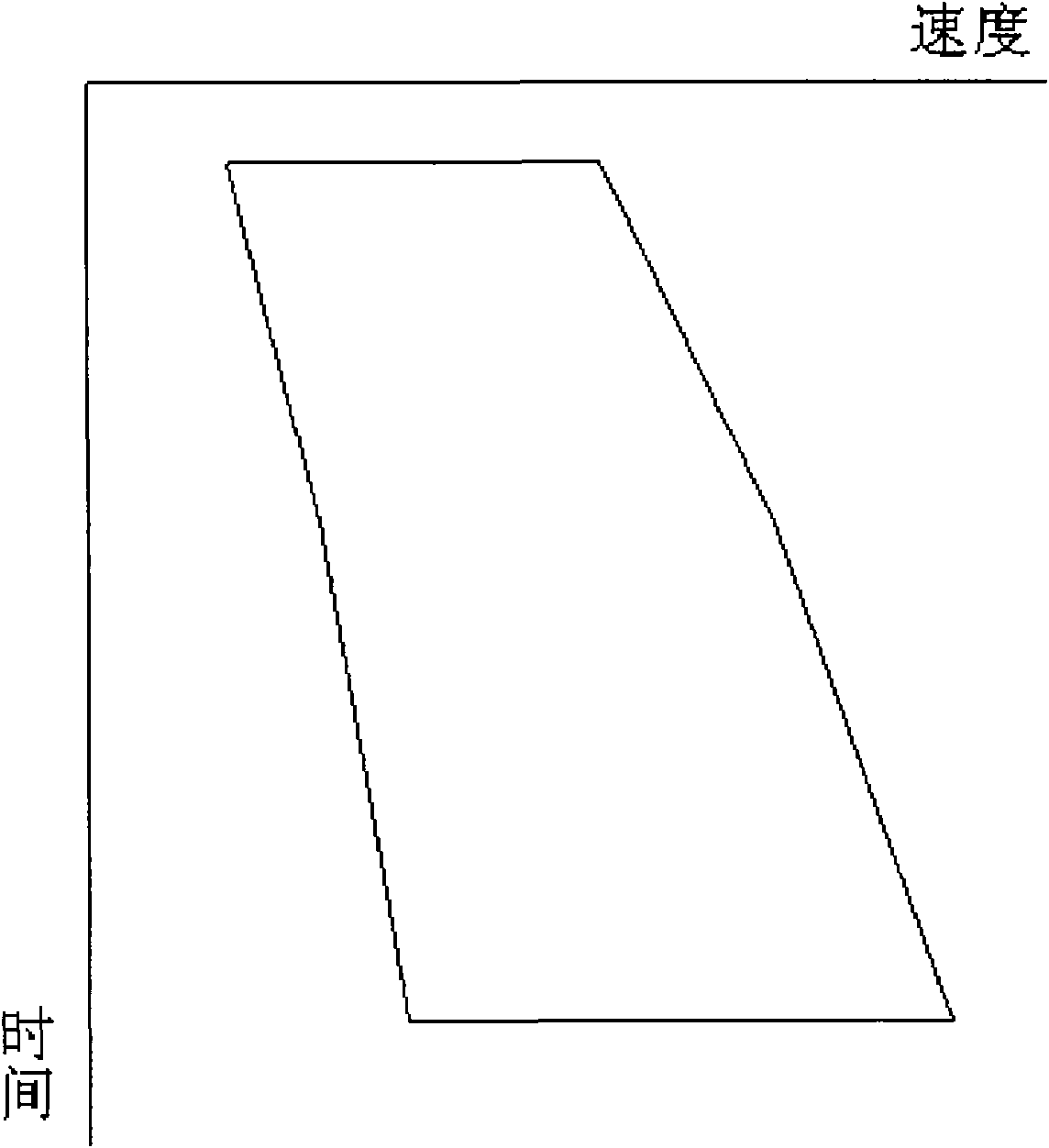
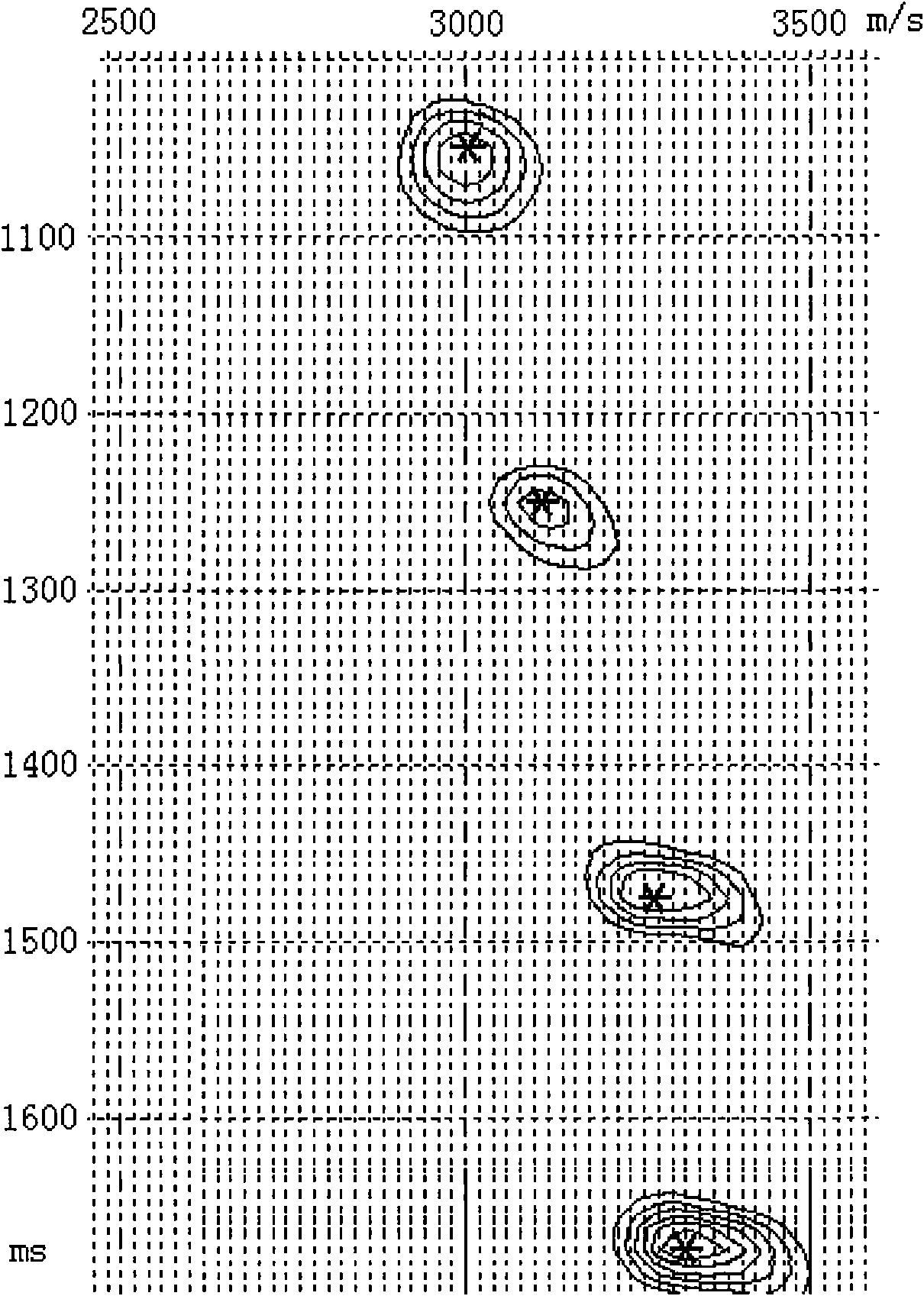
3D velocity modeling, with calibration and trend fitting using geostatistical techniques, particularly advantageous for curved for curved-ray prestack time migration and for such migration followed by prestack depth migration
InactiveUS20070021951A1Efficient and accurate prestack imagingReducing resource-intensive interpretation effortComputation using non-denominational number representationSeismic signal processingSeismic attributeVelocity function
A method of constructing a 3D geologically plausible velocity model for efficient and accurate prestack imaging wherein embodiments of the invention provide: (1) a method of calibrating velocity functions, appropriately and effectively taking into account well (hard) and seismic (soft) data as well as geological features, and trend fitting (“iDEPTHing”) RMS velocities before curved-ray prestack time migration; (2) a method of calibrating and trend fitting (“iDEPTHing”) interval velocities before prestack depth migration, appropriately and effectively taking into account well (hard) and seismic (soft) data as well as geological features; and (3) a method of constructing a geologically plausible velocity model using the previous steps of velocity calibration and trend fitting RMS and interval velocities, for efficient sequential use in prestack time migration followed by prestack depth migration. Advantages of the embodiments include providing a quick turnaround of prestack time and depth migration to interpreters and cutting back resource-intensive interpretation efforts for 3D seismic data The invention has significant implications for improving aspects of oil and gas exploration and production technologies, including pore pressure prediction, prospect evaluation and seismic attribute analysis.
Owner:LEE WOOK B
Method for determining optimum velocity section for pre-stack time migration
ActiveCN101839999ASmall amount of calculationImprove practicalitySeismic signal processingVelocity spectrumVelocity function
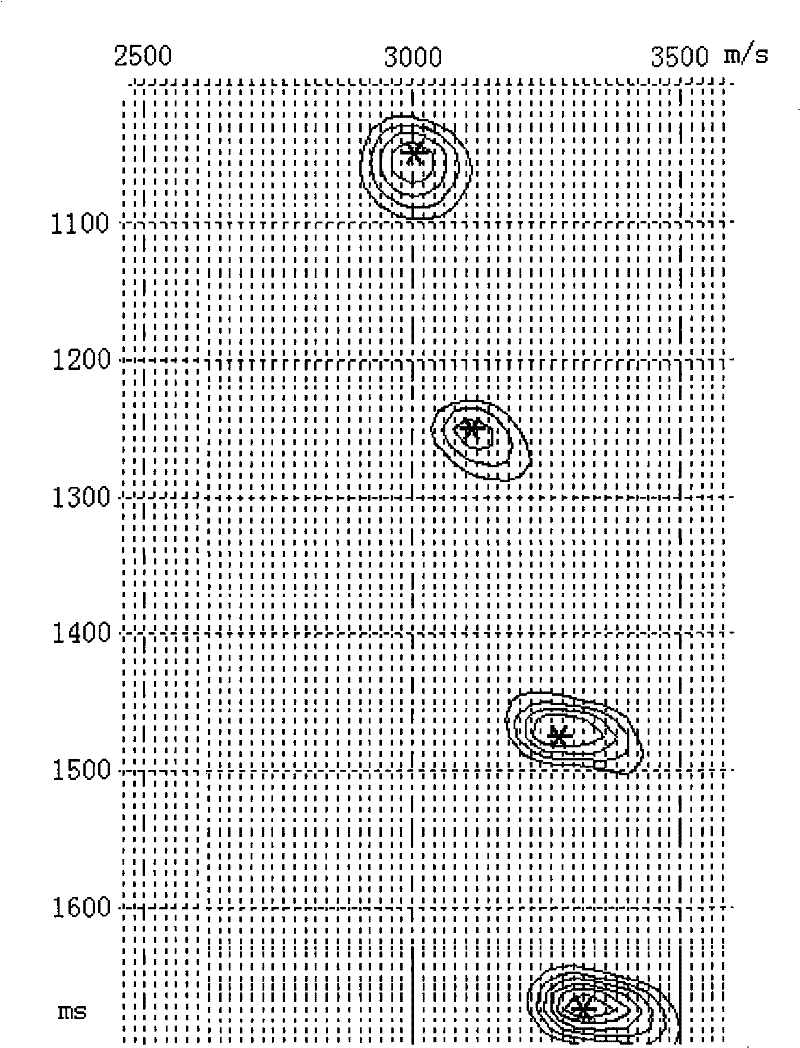
The invention discloses a method for determining an optimum velocity section for pre-stack time migration in the processing of petroleum earthquake data. The method comprises the following steps of: forming a group of functions of the velocity which varies along with the reflection time of the earthquake wave for the central velocity by taking the velocity which varies along with the reflection time of earthquake wave as the central velocity and the velocity interval which varies along with the reflection time of the earthquake wave as the varying step length; performing pre-stack migration on the acquired earthquake data, wherein the result varies along with the velocity and is listed in the form of velocity spectrum; and generating the determined pre-stack time migration on a common reflection point into the optimum velocity section for the pre-stack time migration according to the strength and distribution of an energy ball on the velocity spectrum, and the optimum velocity of the re-stack time migration on a gather. By calculating the information needing to be output on a velocity analysis point in a valid velocity range, the method obviously reduces the calculation amount and improves the practicability.
Owner:BGP OF CHINA NAT GASOLINEEUM CORP
Tau-P filters for removal of noise from seismic data
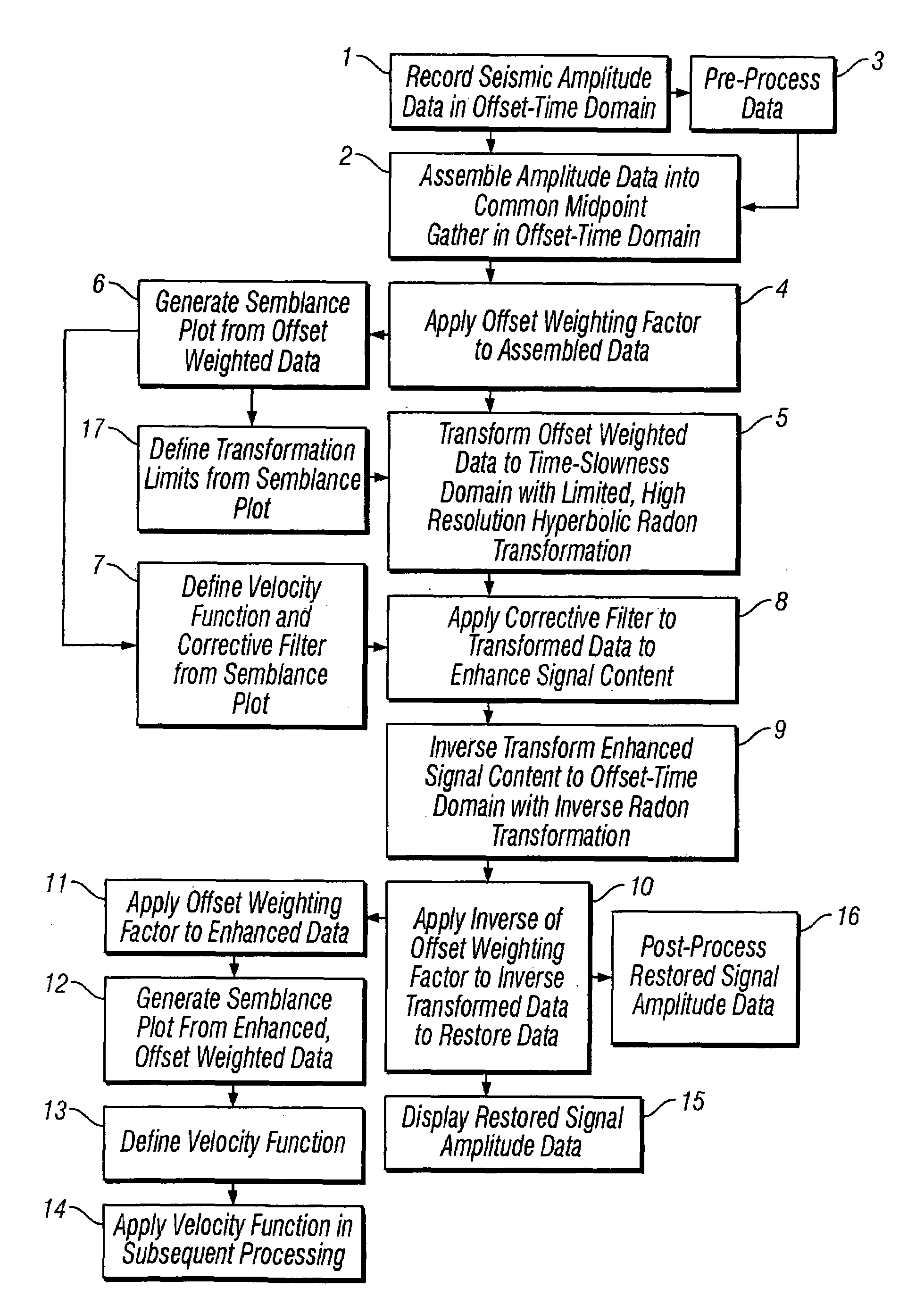
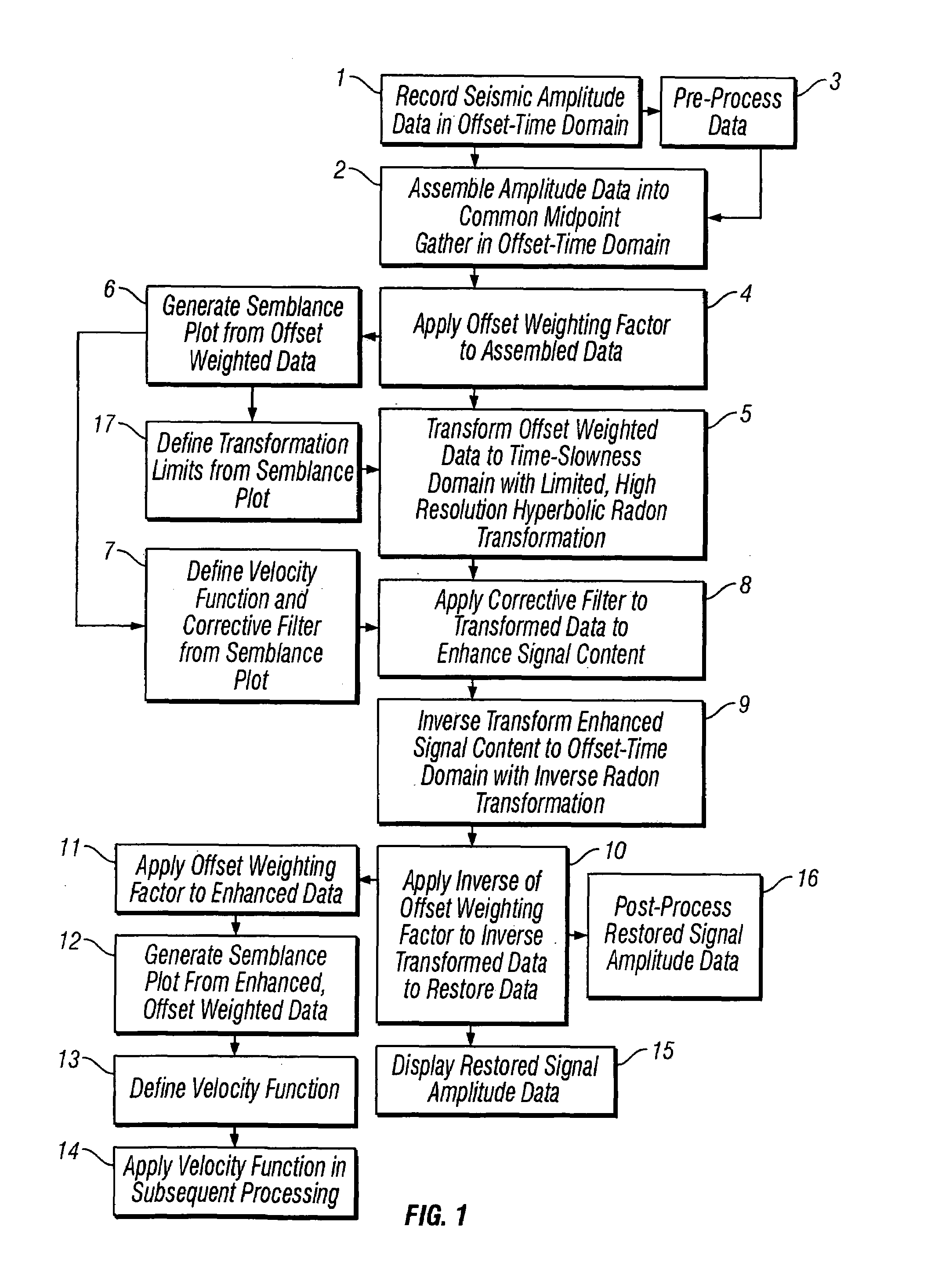
InactiveUS7366054B1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencySeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainNormal moveout
Methods of processing seismic data to remove unwanted noise from meaningful reflection signals are provided for. The methods comprise the steps of assembling seismic data into common geometry gathers in an offset-time domain without correcting the data for normal moveout. The amplitude data are then transformed from the offset-time domain to the time-slowness domain using a Radon transformation. A corrective filter is then applied to enhance the primary reflection signal content of the data and to eliminate unwanted noise events. The corrective filter has a pass region with a lower pass limit and a higher pass limit. The higher pass limit is set within 15% above the slowness of the primary reflection signals and, preferably, it is more closely set to the slowness of the primary reflection signals. The lower pass limit is also preferably set within 15% below the slowness of the primary reflection signals. The tau-P filter preferably is defined by reference to the velocity function of the primary reflection signals, and preferably is expressed as:1vs(1+r2)≤p≤1vs(1-r1)where r1 and r2 are percentages expressed as decimals. After filtering, the enhanced signal content is inverse transformed from the time-slowness domain back to the offset-time domain using an inverse Radon transformation.
Owner:ROBINSON JOHN M
Method for multi-azimuth prestack time migration for general heterogeneous, anisotropic media
ActiveUS20080137478A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsAzimuth directionIndependent parameter
Three data subsets are obtained in three selected azimuthal directions from seismic data in heterogeneous, anisotropic media. Azimuthal velocities are determined for each of the data subsets. A linear system of equations in the three selected azimuthal directions and the three determined azimuthal velocities is solved for three independent parameters. An azimuthal time migration velocity function is constructed from the three solved independent parameters. A time migration traveltime function is constructed from the constructed azimuthal time migration velocity function.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Level set surface editing operators
InactiveUS7542036B2Fast computerCharacter and pattern recognition3D modellingInteractive editingShortest distance
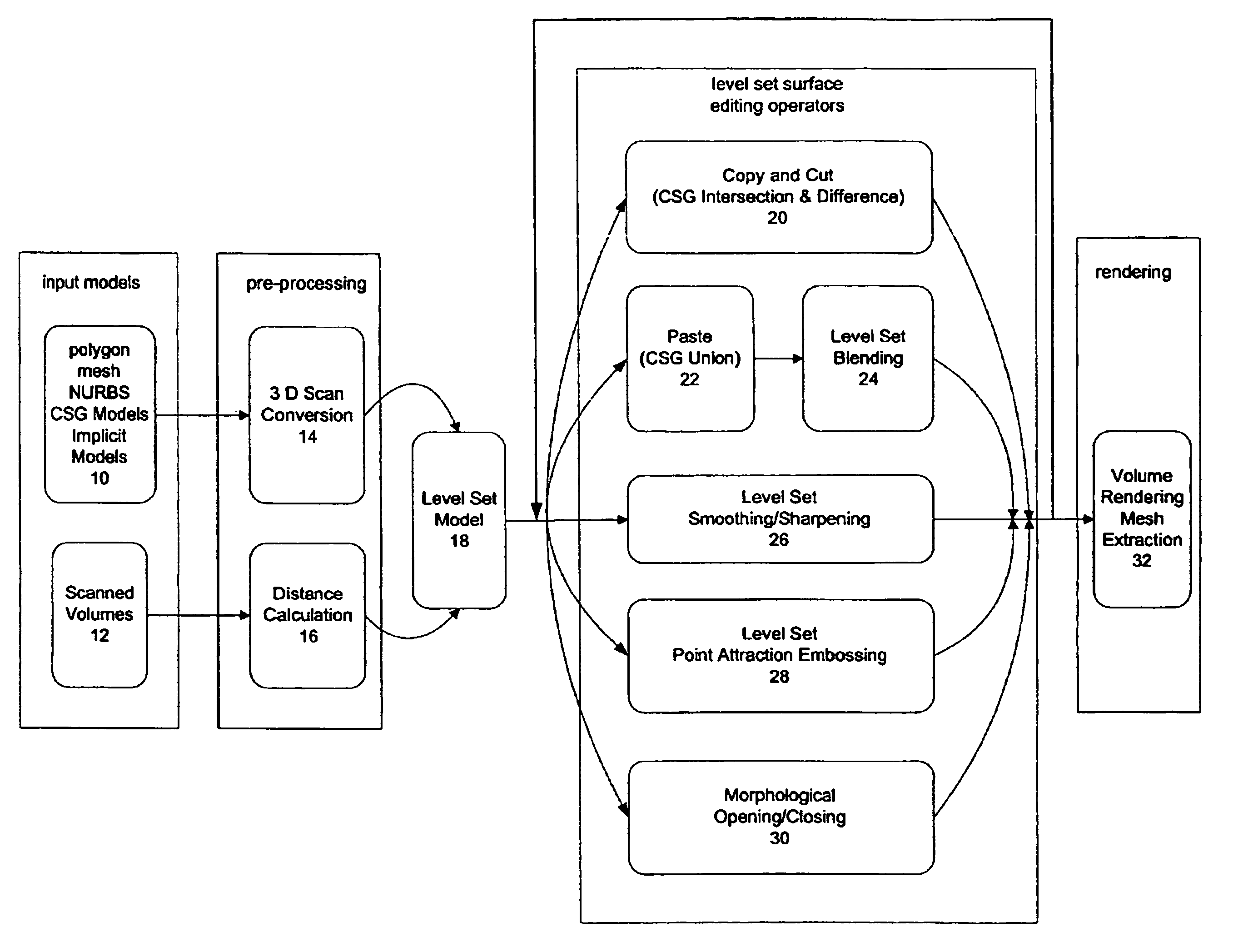
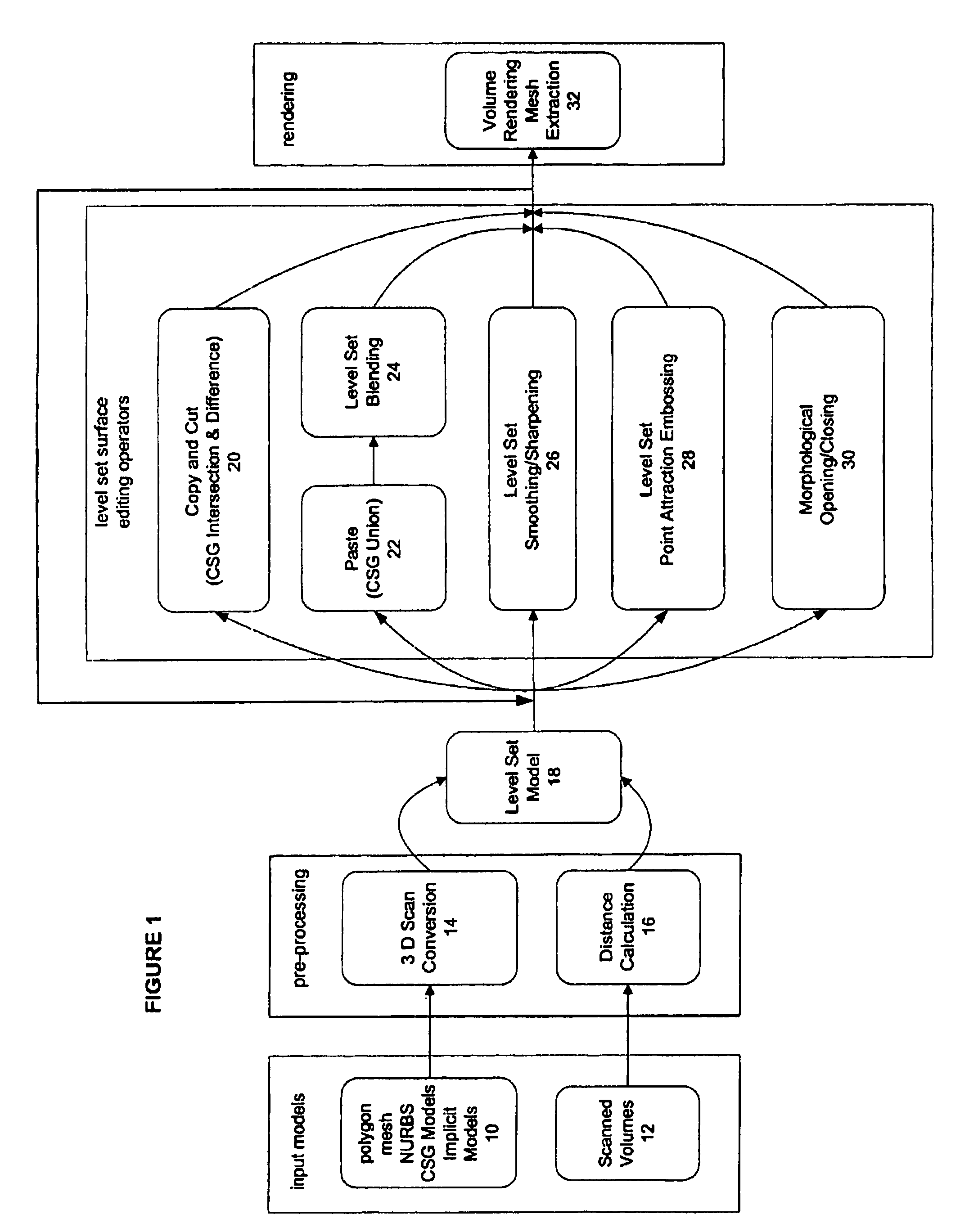
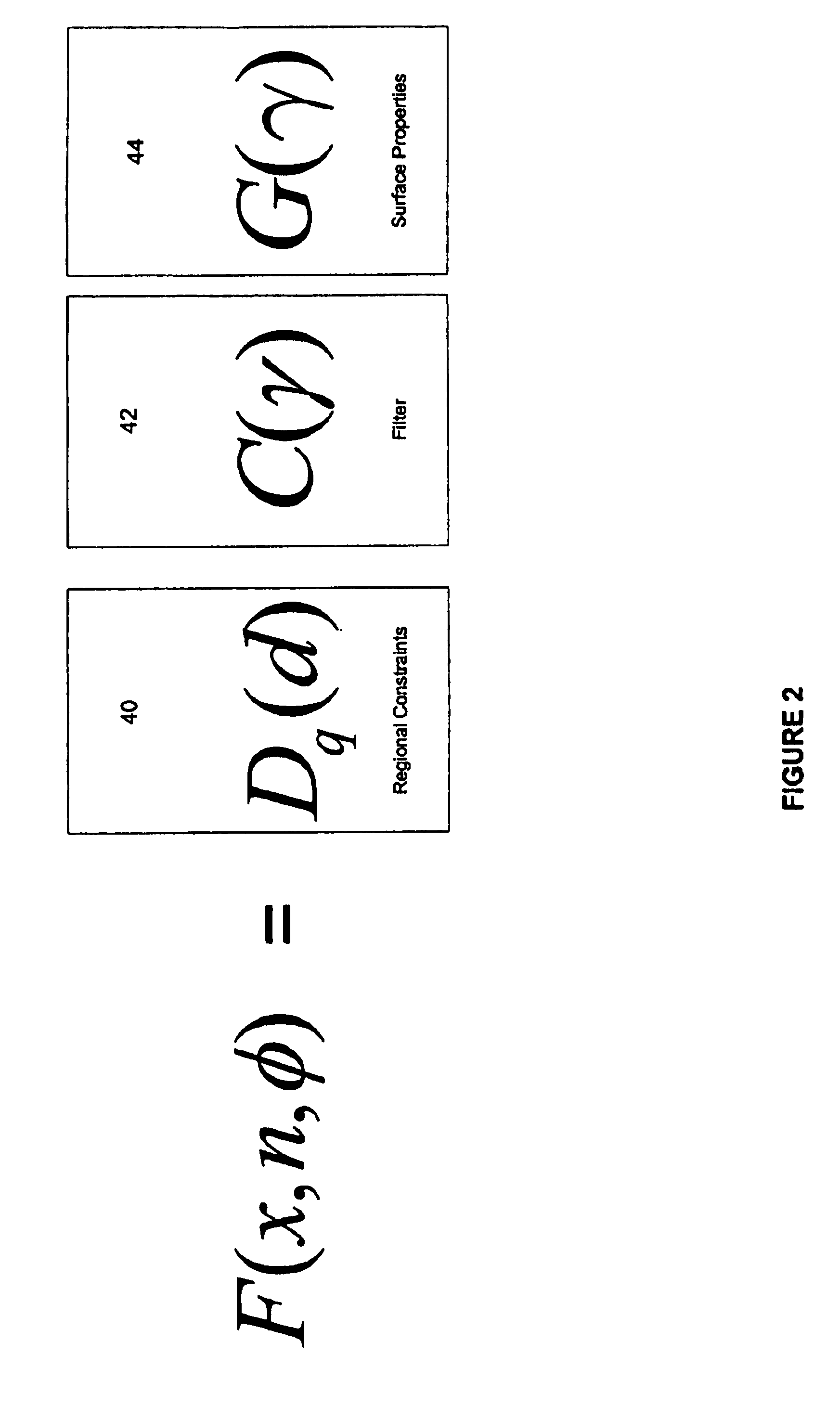
The present invention is level set system for implementing interactive editing operators for surfaces. Level set models are deformable implicit surfaces where the deformation of the surface (editing operation) is controlled by a speed function in the level set partial differential equation. The level set system overcomes the self-interaction problems associated with mesh models. One embodiment takes scan converts input models such as polygon mesh, NURBS, CSGS models into level set models. An interface is provided by which models can be edited with editing operators such as blending, smoothing, embossing, etc. One embodiment utilizes several methods to optimize computations related to the editing operators. For example, shortest distance calculations, bounding boxes, numerical integration, and the sparse-field methods are disclosed for the implementation of the level set deformation operator embodiments including blending, smoothing sharpening, and embossing. The resulting level sets model can be volume rendered or extracted to a polygon mesh.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Mould cavity numerical control machining spiral curve track planning method
InactiveCN101452284AControl residual heightImprove processing efficiencyProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlVelocity function
The invention relates to a method for programming a spiral curve track through die cavity numerical control machining .The boundary of a die cavity is embedded into a level set function of a high one-dimensional space; a zero level set of the level set function is the boundary of the die cavity; and the level set function is initialized to a sign distance function. Bias of the boundary of the die cavity is obtained through the solution of a level set equation; and a speed function of the level set equation is corrected so that a high-curvature region can be smooth in generating a bias line. The distance between the bias lines is controlled through the control of time for boosting the boundary; in the process of boosting the boundary of the die cavity, the complex topological change is naturally treated; and the spiral curve track is programmed in different regions respectively. The method is suitable for programming a cutter track of a numerical control machining system with a common die cavity and a complex die cavity; the cutter track is continuous and smooth; and for the complex die cavity with island, the method can realize automatic division in regions and carry out spiral curve track programming in different regions.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
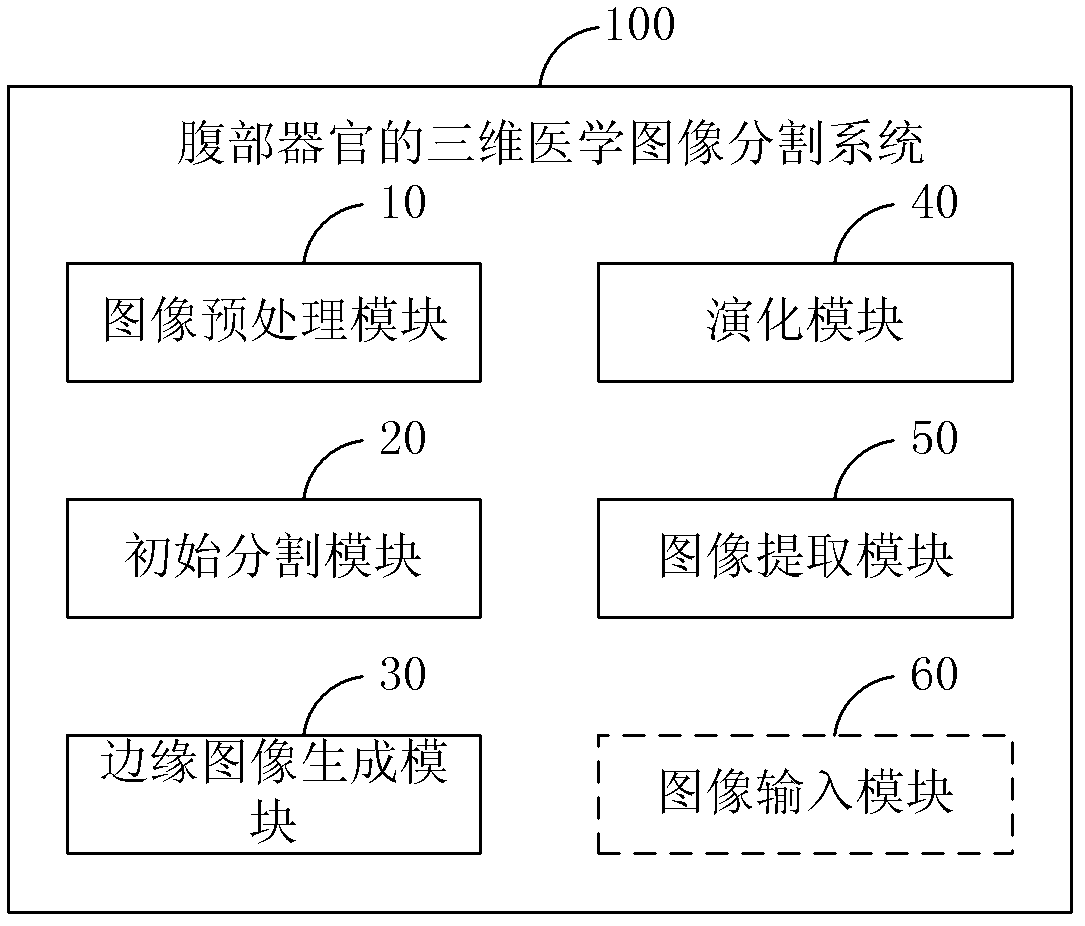
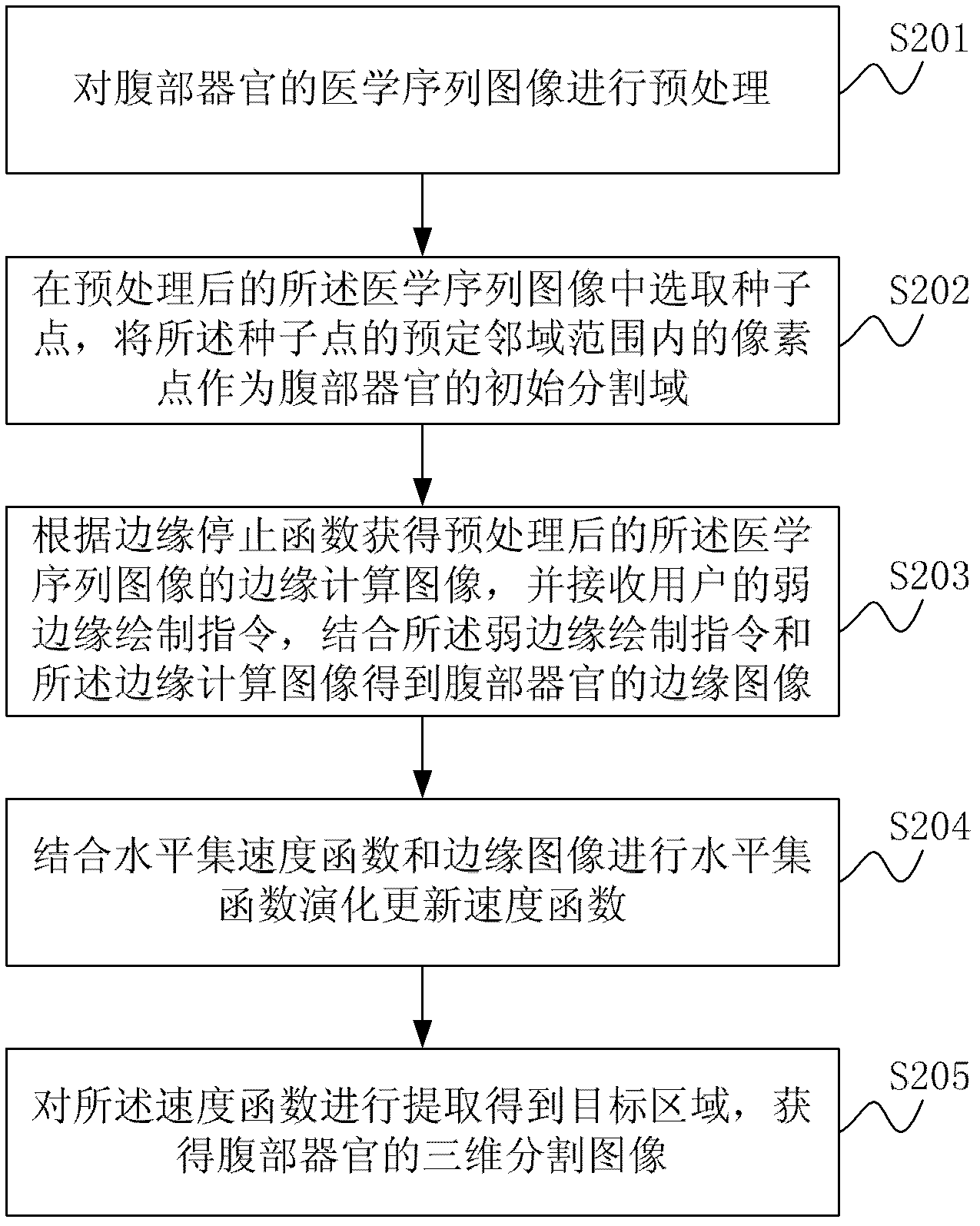
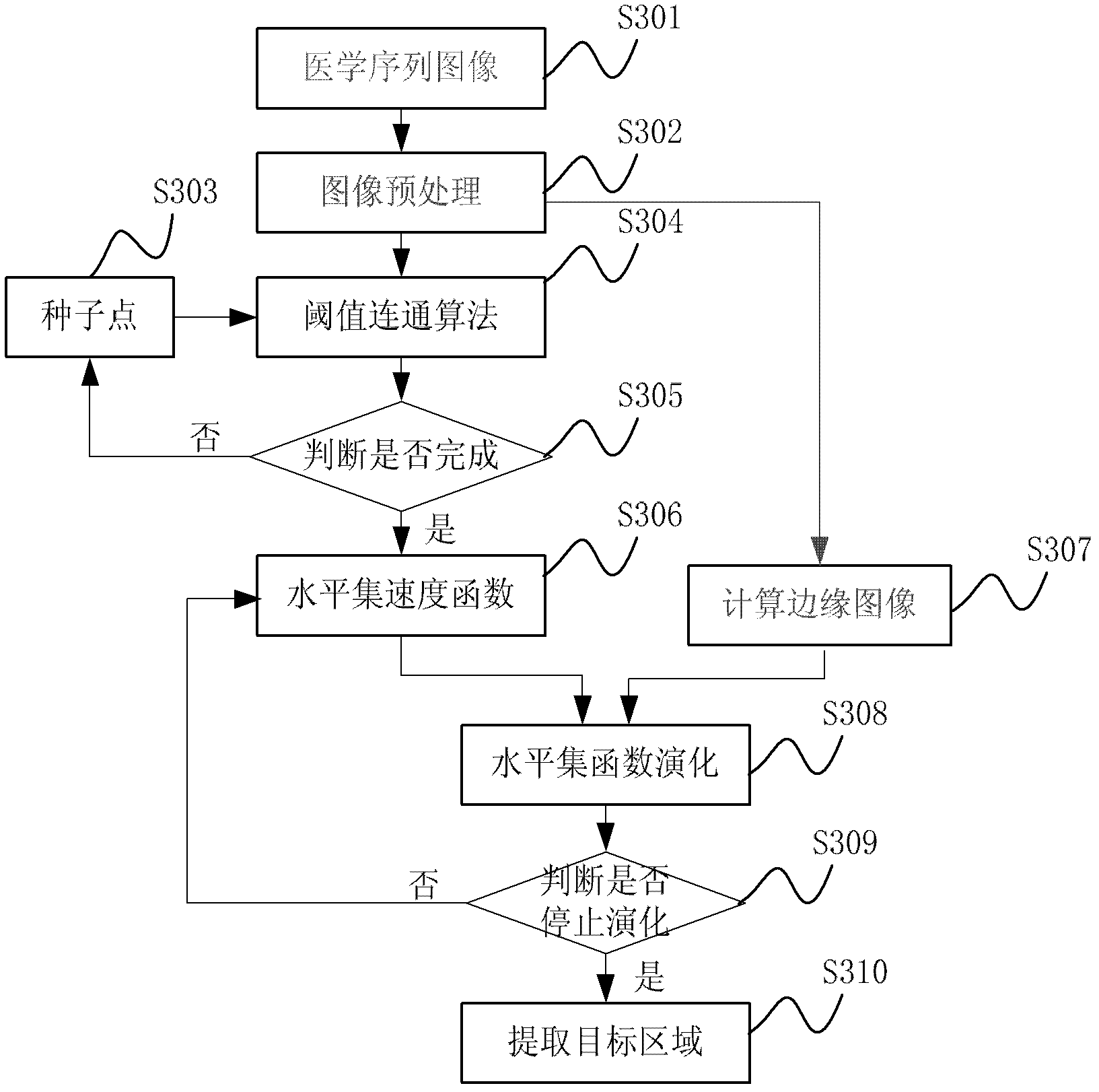
Method and system for dividing up three-dimensional medical image of abdominal organ
InactiveCN102306373AQuality improvementEasy to analyzeImage enhancementImage segmentationVelocity function
The invention discloses a method and a system for dividing up a three-dimensional medical image of an abdominal organ. The method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing a medical sequence image of the abdominal organ; selecting a seed point from the preprocessed medical sequence image, and using a pixel point in a preset neighborhood range of the seed point as an initial division region of the abdominal organ; acquiring an edge calculation image of the preprocessed medical sequence image according to an edge stop function, and receiving a feebleness edge drawing instruction of a user to obtain an edge image of the abdominal organ by combining the feebleness edge drawing instruction with the edge calculation image; performing level set function evolution to update a velocity function by combining a level set velocity function with the edge image; and extracting the velocity function to obtain a target region. Therefore, according to the invention, the problem of fuzzy boundary in medical image division is solved by using a user interaction type input boundary fuzzy boundary, and the quality of the three-dimensional division image of the abdominal organ is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YORATAL DMIT
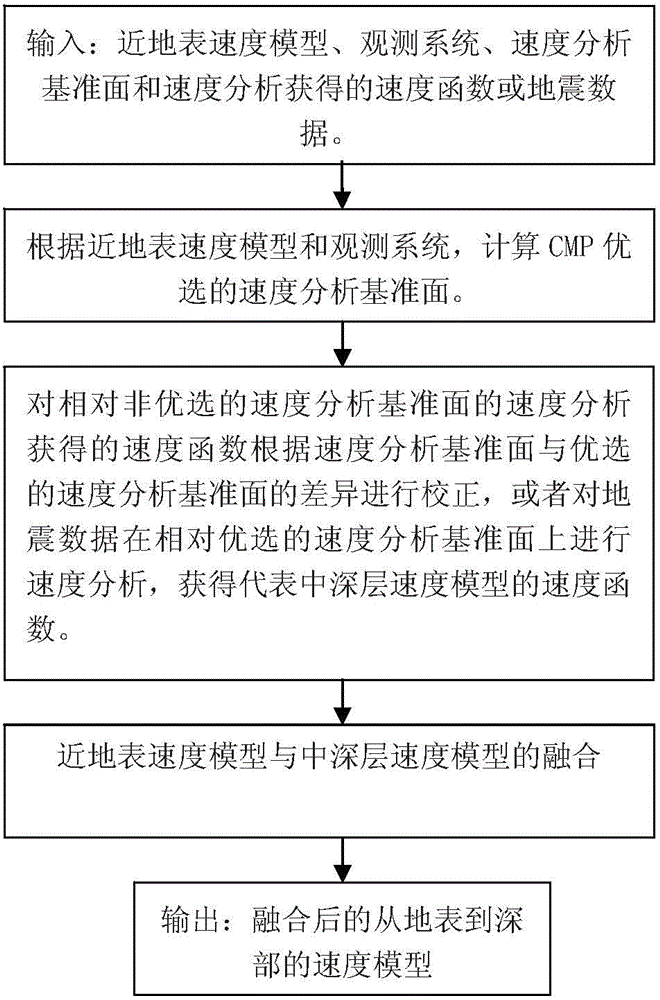
Method for combining near-surface velocity model with middle-deep stratum velocity model
The invention provides a method for combining a near-surface velocity model with a middle-deep stratum velocity model, and belongs to the field of seismic exploration data processing. The method comprises the following steps: (1) the near-surface velocity model, an observation system, a velocity analysis reference surface and speed functions or seismic data obtained through velocity analysis are input; (2) a preferable velocity analysis reference surface of a CMP (common midpoint) is calculated according to the near-surface velocity model and the observation system; (3) velocity analysis is conducted relative to the preferable velocity analysis reference surface obtained in the steps (2) to obtain a velocity function representing the middle-deep stratum velocity model, or a speed function obtained through velocity analysis relative to a non-preferable velocity analysis reference surface is corrected according to the difference of the velocity analysis reference surface and the preferable velocity speed analysis reference surface to obtain the velocity function representing the middle-deep stratum velocity model; (4) the near-surface velocity model is combined with the middle-deep stratum velocity model.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Servo-motor acceleration-deceleration control method for servo pressure machine
ActiveCN102522944AContinuous changeAvoid Flex ShockElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlTriangular functionAcceleration deceleration
The invention discloses a servo-motor acceleration-deceleration control method for a servo pressure machine, comprising the following steps of: constructing an acceleration function of a servo motor at an acceleration stage; establishing a speed expression of the servo motor at the acceleration stage; establishing a rotary displacement expression of the servo motor at the acceleration stage; constructing an acceleration function of the servo motor at a deceleration stage; establishing a speed expression of the servo motor at the deceleration stage; establishing a rotary displacement expression of the servo motor at the deceleration stage; and determining total acceleration time and total deceleration time. According to the servo-motor acceleration-deceleration control method, two triangular functions with different periods are adopted as acceleration-deceleration constructed functions of the servo motor, so that the change of the speed, the acceleration and the accelerated acceleration is continuous, the soft shock of the acceleration-deceleration process on the machine body is avoided, the operation stability of the pressure machine is improved and the softness of acceleration-deceleration control of the pressure machine is higher; and by full utilization of the constant and maximum output torque of the server motor under the rated rotating speed, the operation period of the servo pressure machine can be shortened and the takt time of stamping production is improved.
Owner:DALIAN DESIGN INST CO LTD CHINA FIRST HEAVY IND +1
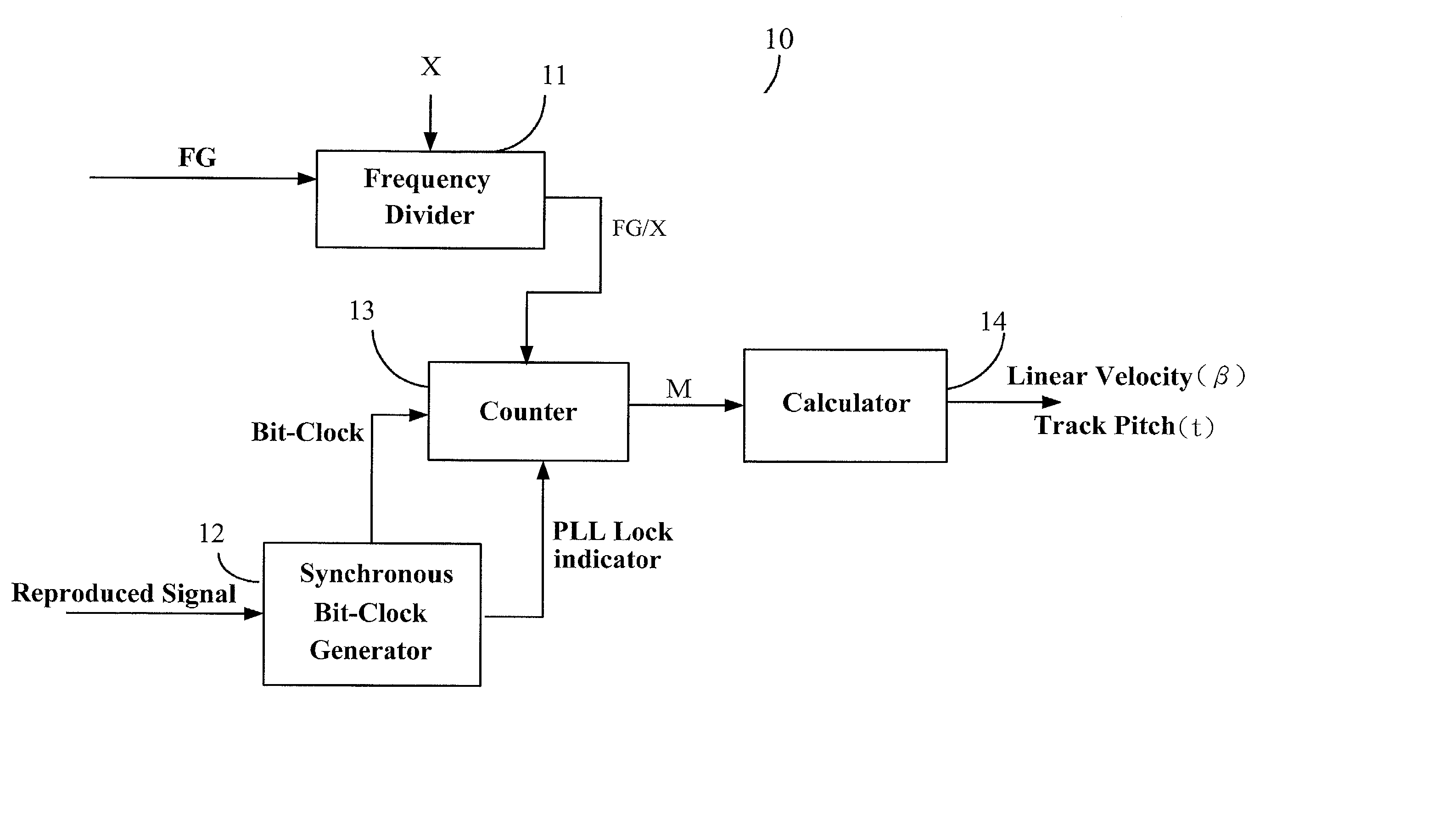
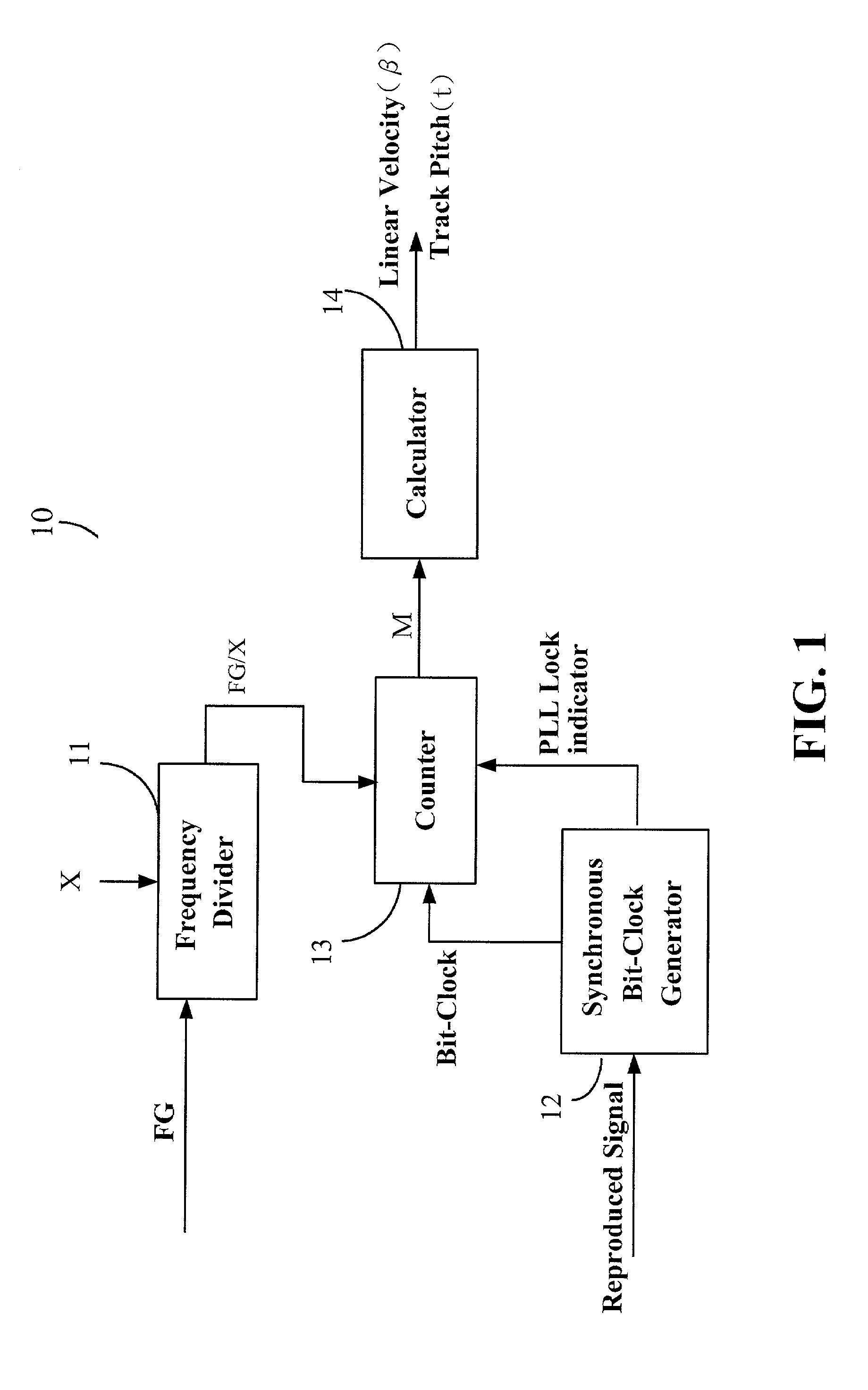
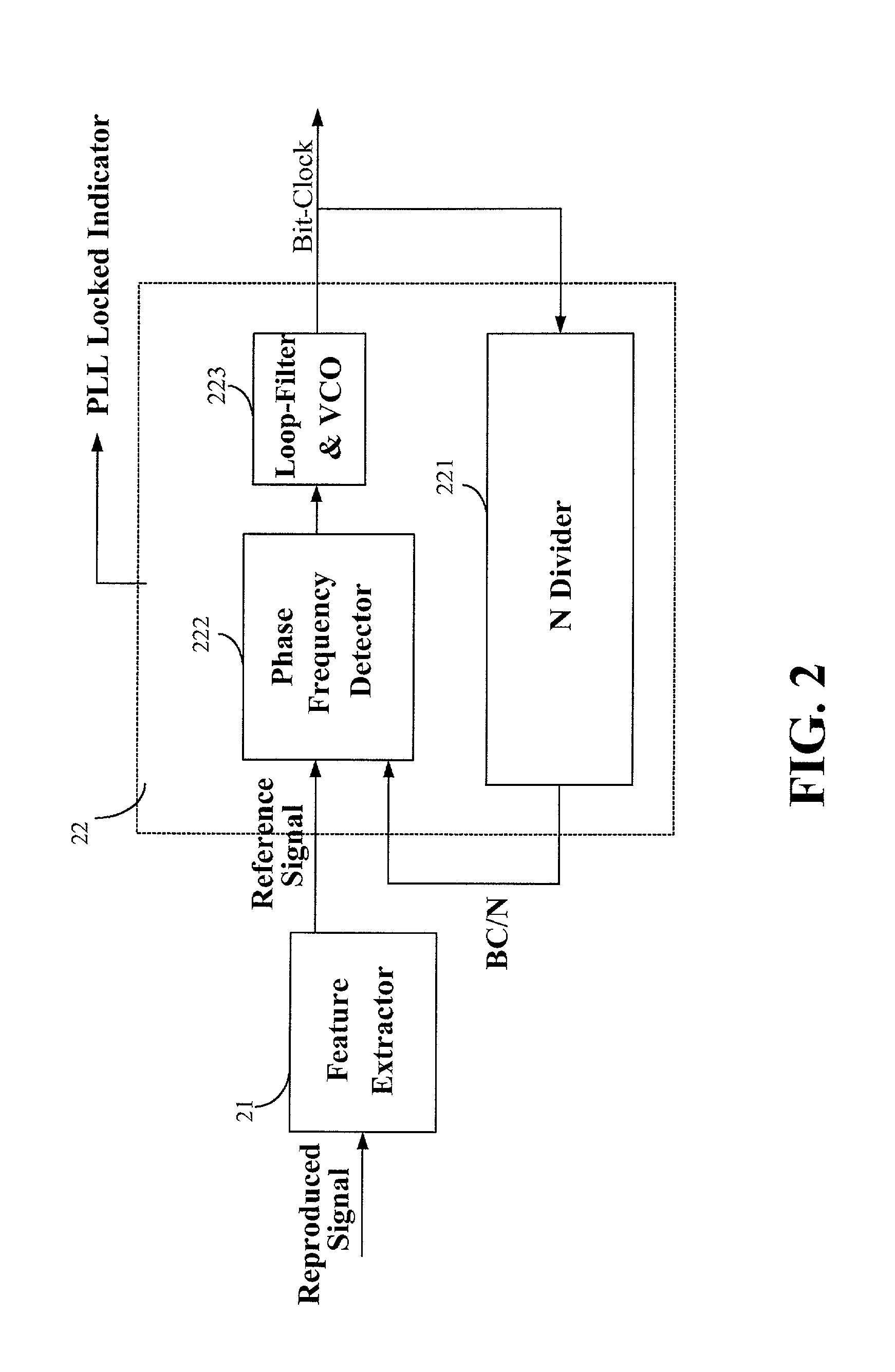
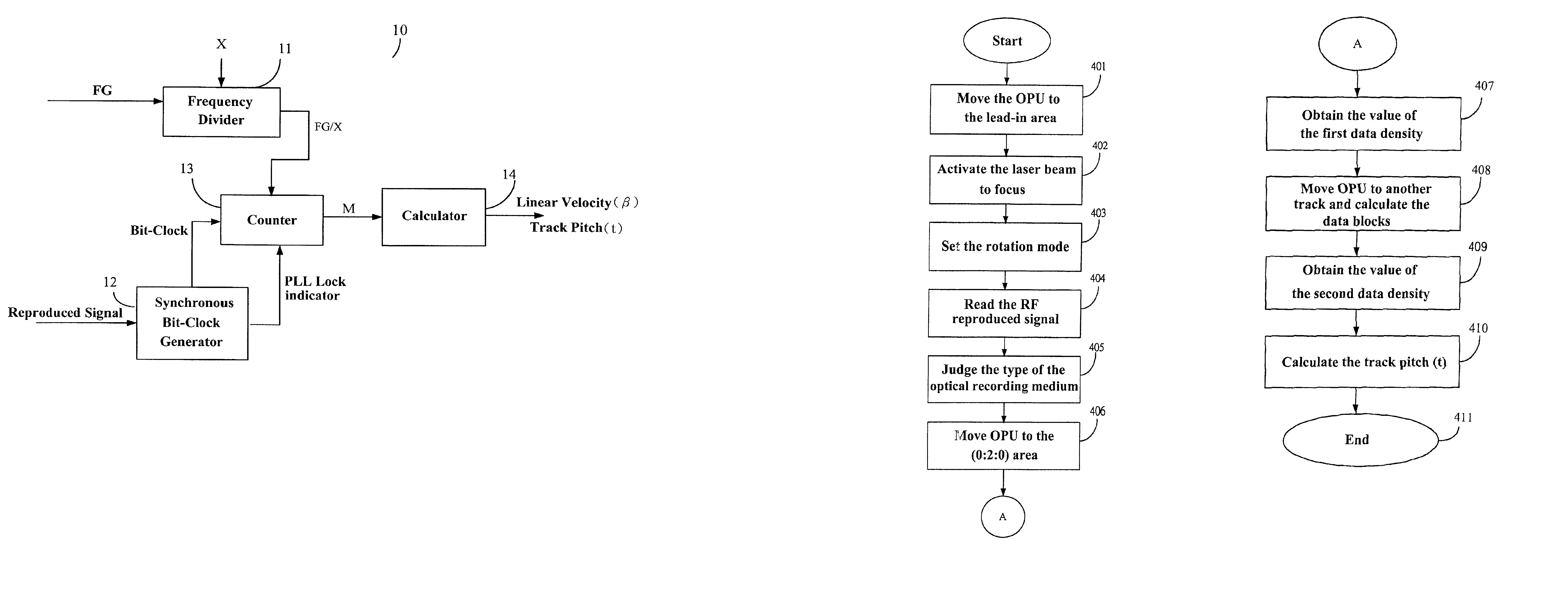
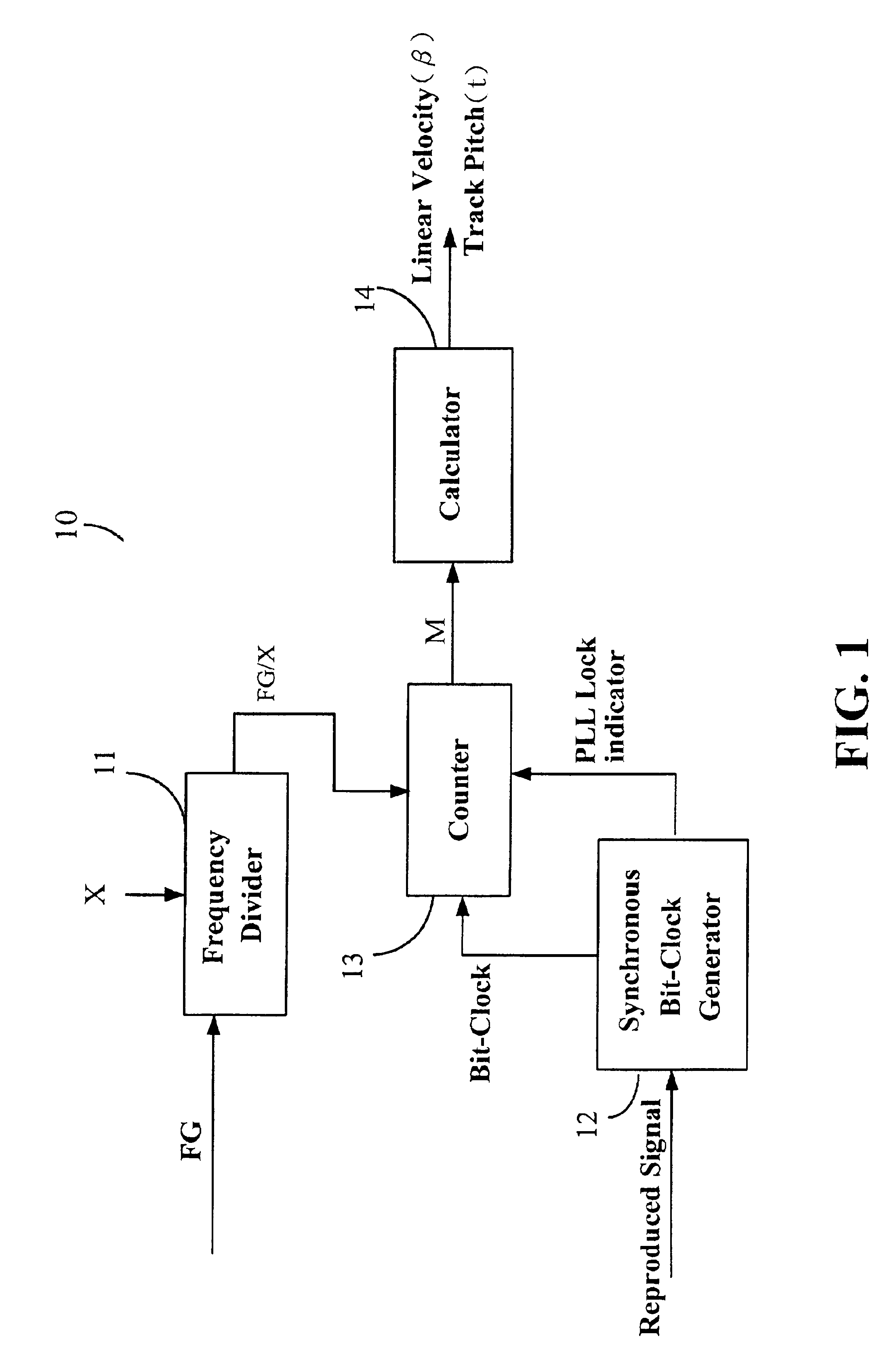
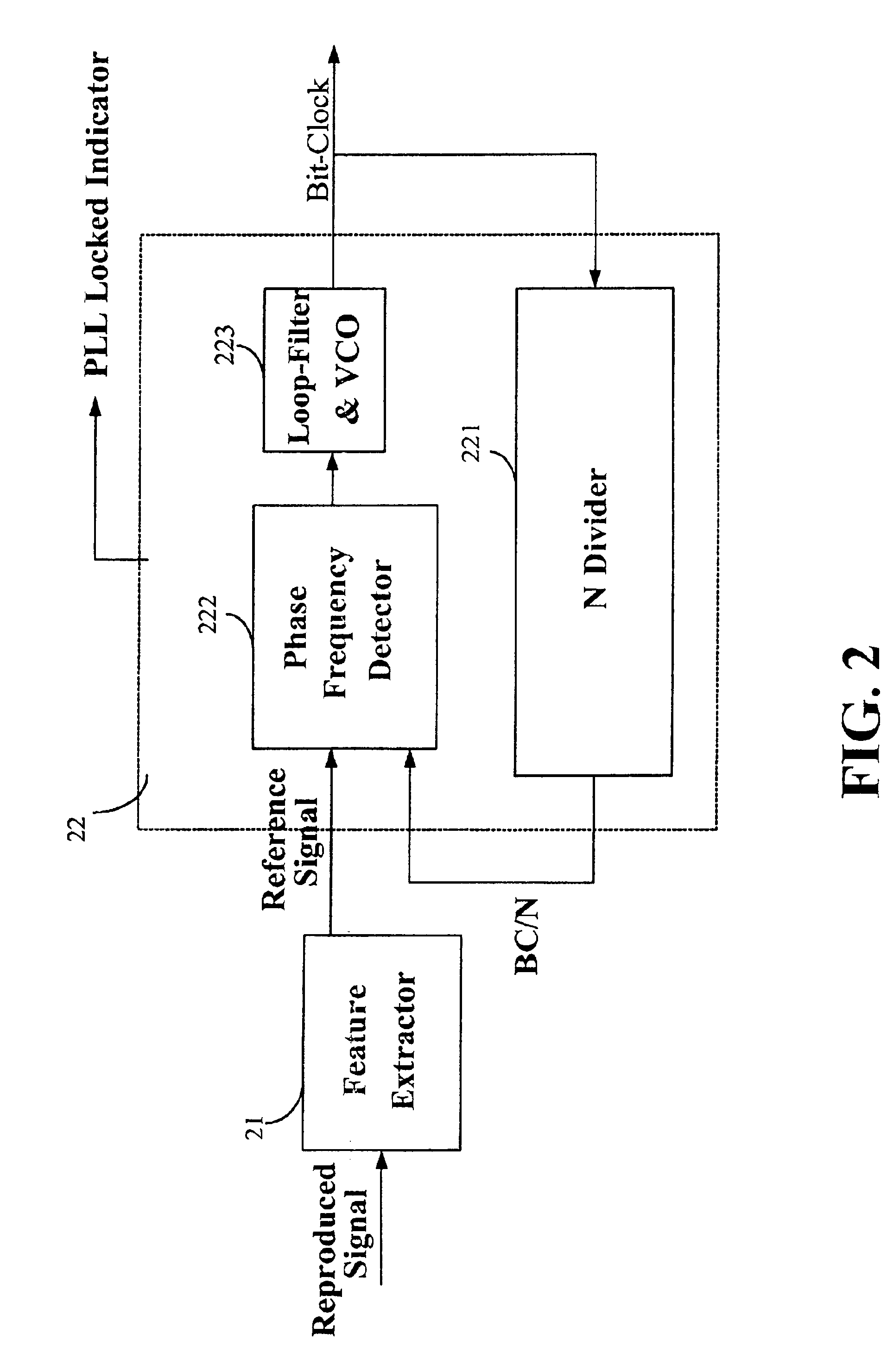
Device and method for calibrating linear velocity and track pitch for optical disc drive
ActiveUS20020145961A1Improve accuracyCombination recordingRecord information storageClock generatorOptical disc drive
A device and method for calibrating linear velocity and track pitch for an optical disc is disclosed. The device comprises a frequency divider, a synchronous bit-clock generator, a counter and a linear velocity and track pitch calculator. The frequency divider receives a motor frequency generator (FG) pulse and generates a motor rotation period signal (FG / X). The synchronous bit-clock generator generates a high frequency bit-clock according to a reproduced signal read from disc. The bit counter counts the pulse of the bit-clock for each period of the motor rotation period signal to generate the data amount M. The linear velocity and track pitch calculator calculates the linear velocity by a linear velocity function with the information of the data amount M and the motor rotation period. Then, the linear velocity and track pitch calculator calculates the track pitch by a pitch function with the information of the data amount, radius and linear velocity at different tracks.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
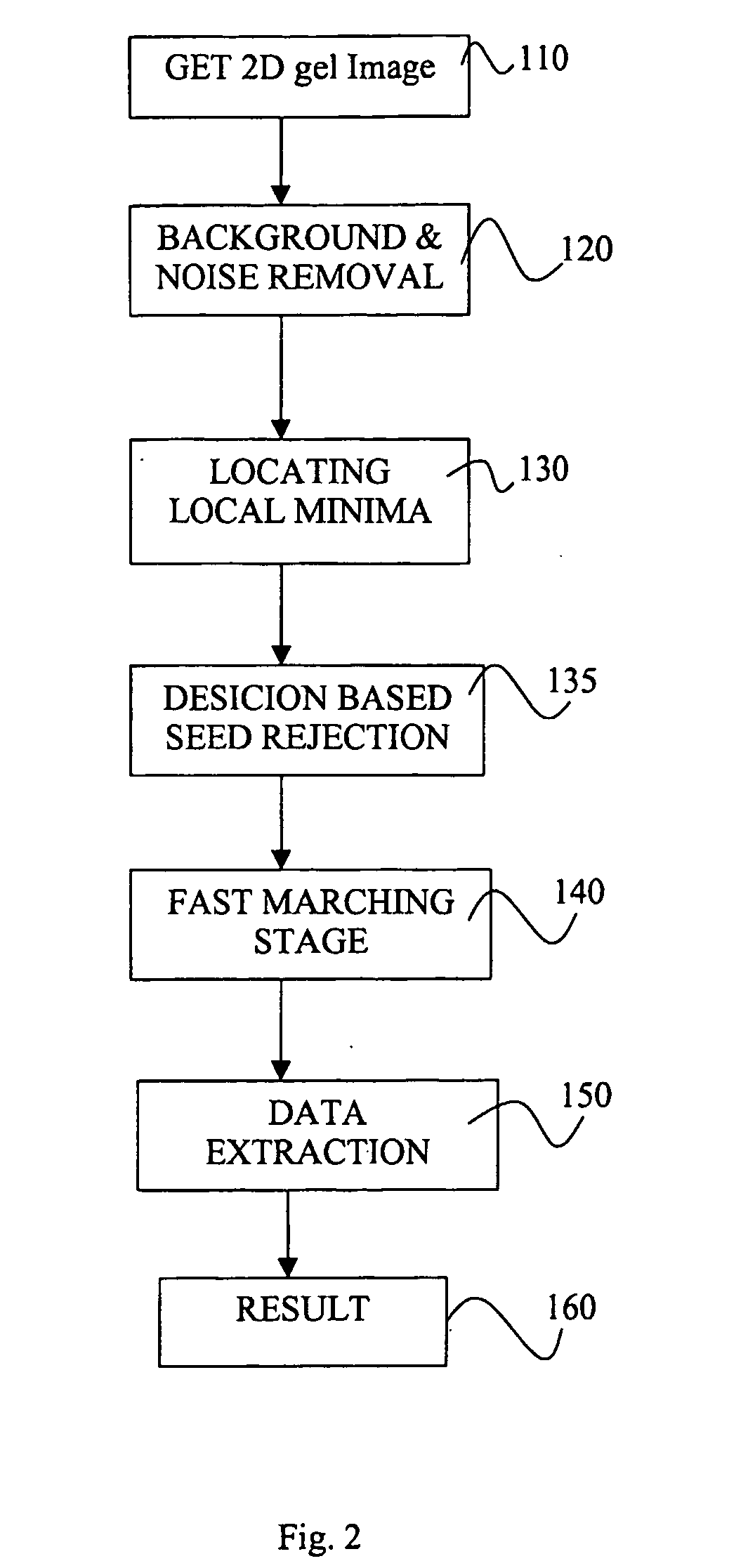
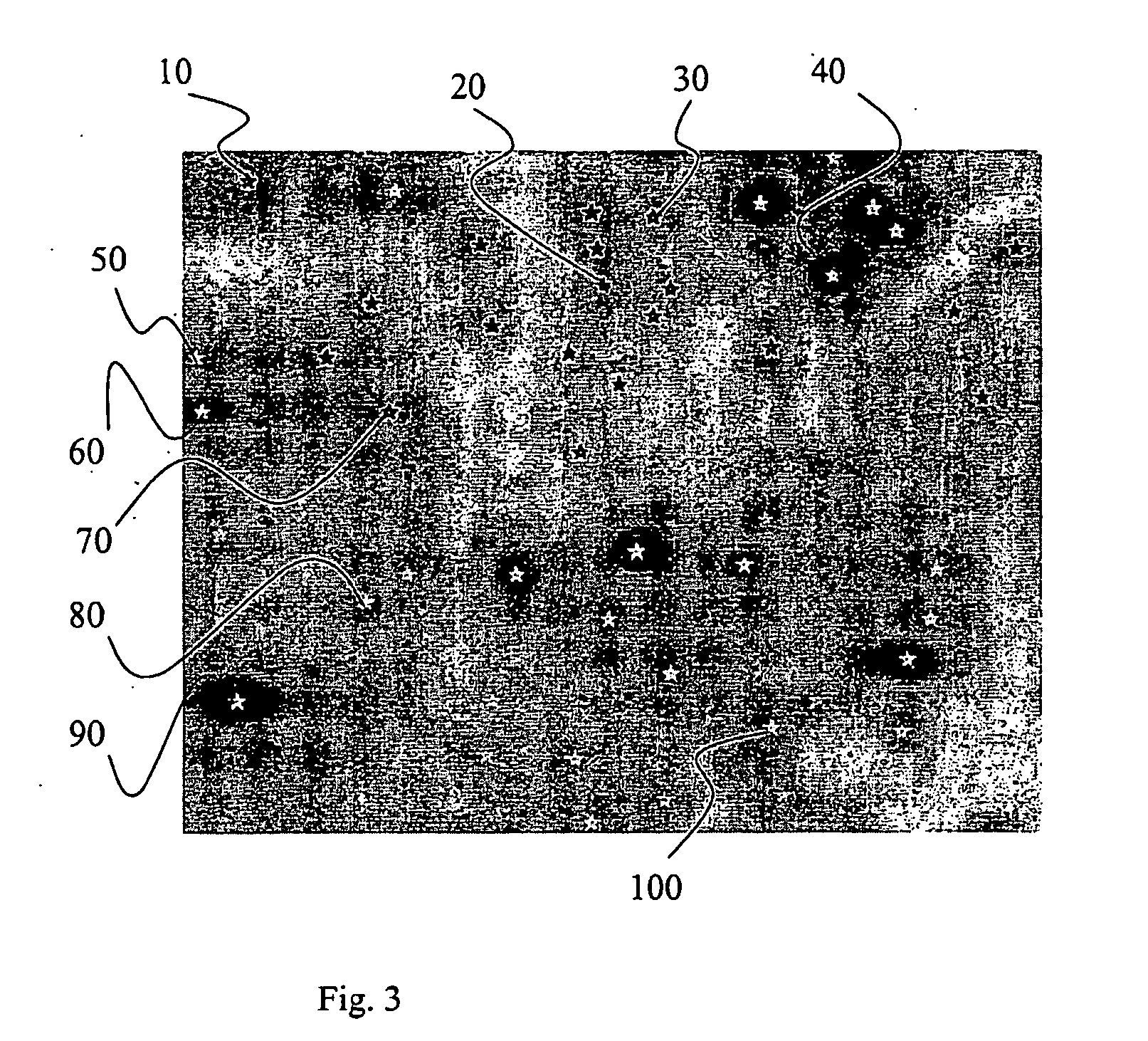
Method and means for 2d-gel-image segmentation
InactiveUS20060153435A1Interpretation result accurateEffective segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisElectrophoresisImage segmentation
The present invention relates to the segmentation of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis images (2D images). The method according to the invention associates an initial protein seed candidate with an interface circumscribing said seed and thereafter brings said interface to evolve in accordance with a defined speed function F(x, y). The evolution of the interface is halted by a stopping criterion, C. According to the invention, the speed function can depend on a wide variety of parameters such as the pixel intensity, the curvature of the pixel intensity, the distance to the initial seed, the curvature and / or shape and / or normal direction and / or position of the evolving interface. The stopping criterion depends e.g. on the speed function F and / or the time of arrival T(x, y) and / or the departure time Td for said interface. The invention provides criteria for a specific treatment of saturated spots and to mike sure that interfaces never overlap.
Owner:LUDESI
Device and method for calibrating linear velocity and track pitch for optical disc drive
A device and method for calibrating linear velocity and track pitch for an optical disc is disclosed. The device comprises a frequency divider, a synchronous bit-clock generator, a counter and a linear velocity and track pitch calculator. The frequency divider receives a motor frequency generator (FG) pulse and generates a motor rotation period signal (FG / X). The synchronous bit-clock generator generates a high frequency bit-clock according to a reproduced signal read from disc. The bit counter counts the pulse of the bit-clock for each period of the motor rotation period signal to generate the data amount M. The linear velocity and track pitch calculator calculates the linear velocity by a linear velocity function with the information of the data amount M and the motor rotation period. Then, the linear velocity and track pitch calculator calculates the track pitch by a pitch function with the information of the data amount, radius and linear velocity at different tracks.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Mutually-coupled fractional-order chaos electromechanical transducer acceleration adaptive fuzzy control method
ActiveCN110501906AImprove featuresIncreased Design FreedomAdaptive controlDifferentiatorFeedback controller
The invention discloses a mutually-coupled fractional-order chaos electromechanical transducer acceleration adaptive fuzzy control method. The method comprises the following steps: a) creating a smallnetwork formed by three same electromechanical transducers, wherein each electromechanical transducer has a nearest neighbor coupling structure, and building an electromechanical coupled transducer model with a nearest neighbor based on the small network; and b) designing a controller composed of a feedforward fuzzy controller and an adaptive optimal feedback controller, wherein the feedforward fuzzy controller is integrated by a regression non-single-valued type-2 sequence fuzzy neural network, a velocity function and a tracking differentiator in an inversion control framework, and the adaptive optimal feedback controller is formed by the regression non-single-valued type-2 sequence fuzzy neural network, policy iteration and an execution-evaluation reinforcement learning algorithm, and can solve a Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equation. The method not only guarantees boundedness of all signals, realizes chaos suppression and synchronous and accelerated convergence, but also minimizes a cost function.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Sliding method for touch control
InactiveUS20090225049A1Simple processHigh sensitivityInput/output processes for data processingVelocity functionComputer science
The present invention discloses a sliding method for touch control comprising the following steps. First, an input module is used to touch a first position and a second position on a touch display interface, and the touch display interface generates a time signal while being touched. The time signal is compared with a preset time signal to determine stopping actuation or sliding. In case of a sliding motion, first direction actuation is performed when a first direction function is larger than a second direction function, whereas second direction actuation is performed. Next, a velocity function signal is derived according to the distance and the time signal, and then compared with the first and second preset velocity functions to determine first, second or third velocity actuation.
Owner:MITAC INT CORP
Acceleration control method of vehicle follow gallop sports
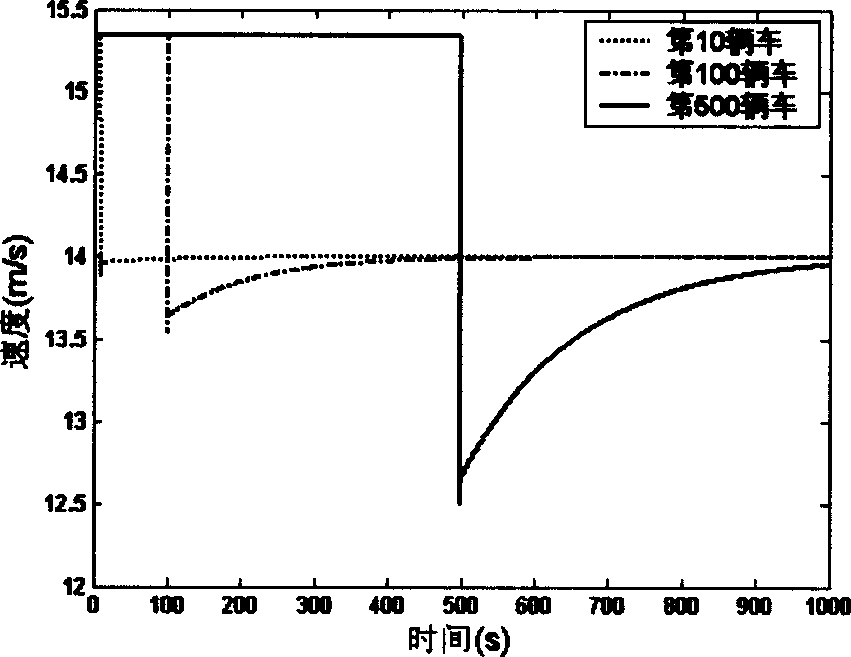
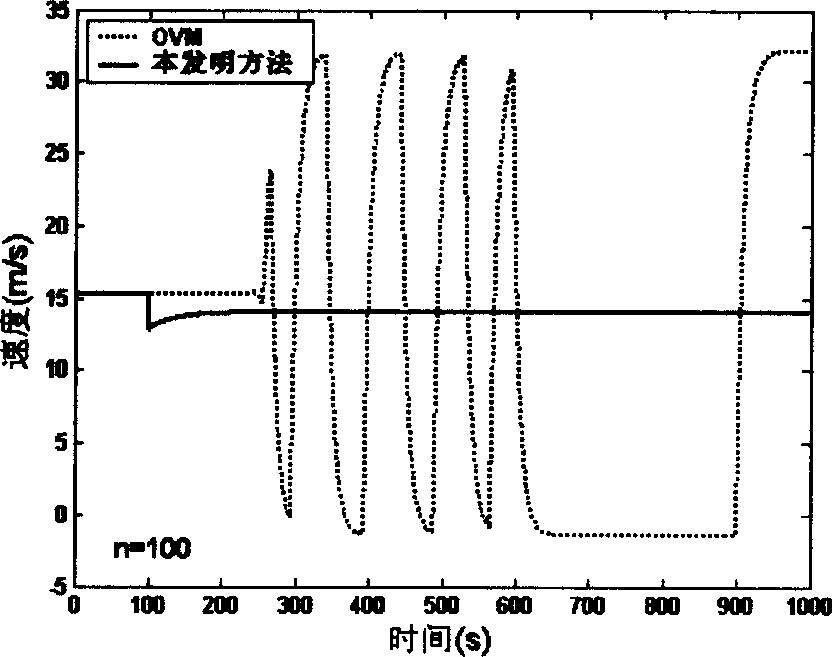
InactiveCN1719354AThere will be no speed shocks or even vehicle collisionsEasy to understandSpeed/accelaration controlAdaptive controlTraffic accidentEngineering
The present invention relates to an acceleration control method for car following movement in the field of vehicle engineering technology. Said method includes the following steps: (1). Setting traffic condition; (2). Selecting parameter value; (3) obtaining initial state of all the vehicles; and (4). Observing running state of vehicle queue when t is greater than O. said invention is mainly aimed at preventing traffic accident.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Fast-marching fiber tracking method based on topology preservation
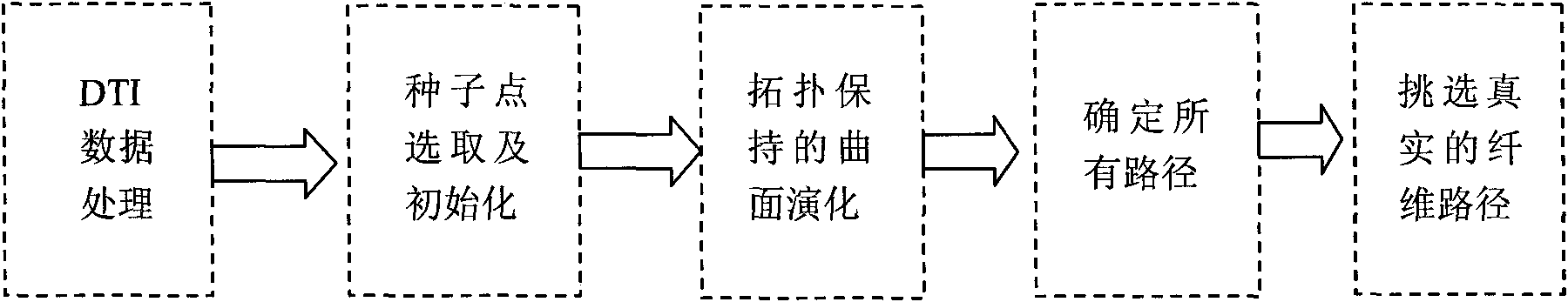
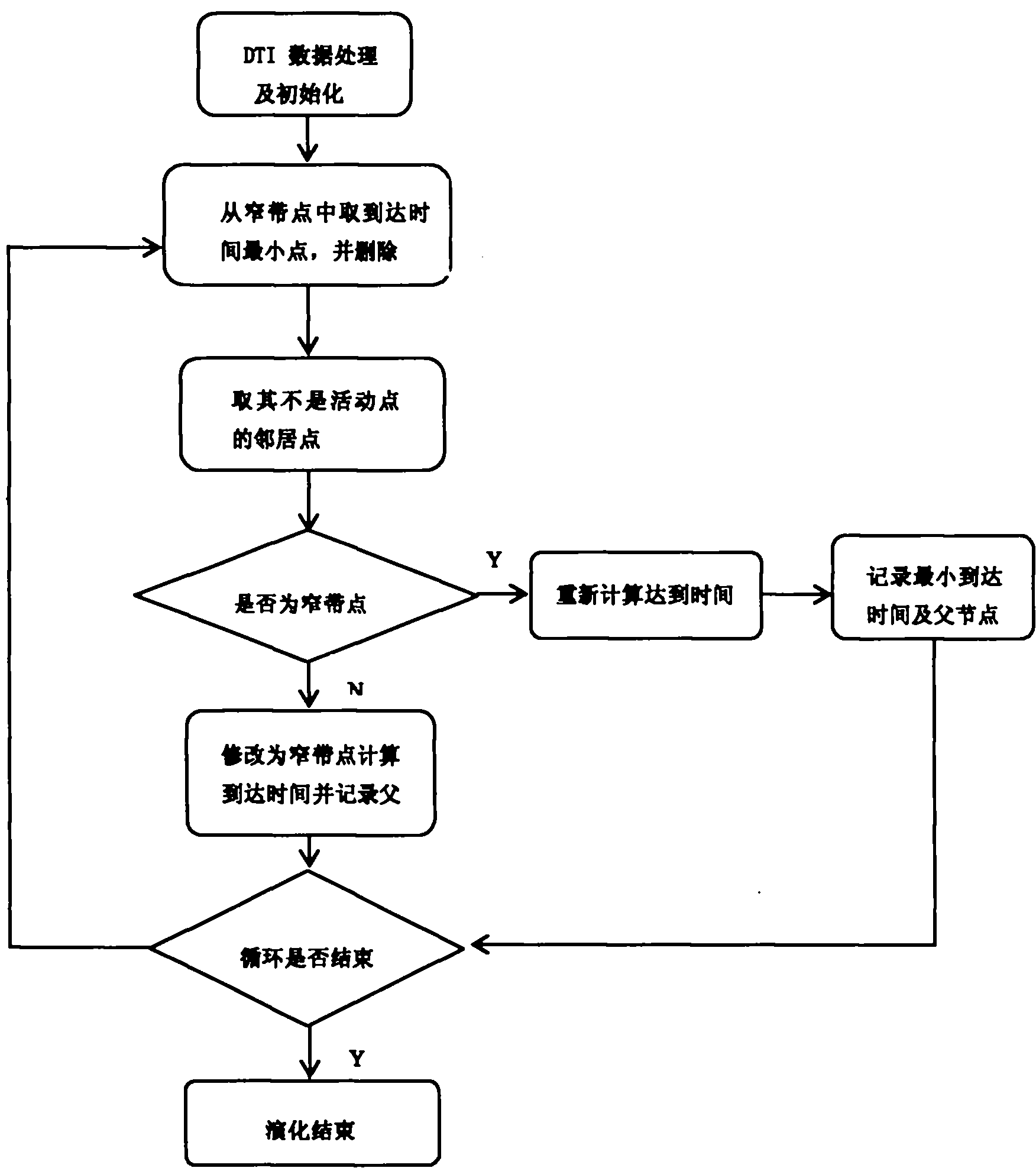
ActiveCN101872385AReact fork infoTracking results are accurateSpecial data processing applicationsDiffusionFiber
The invention belongs to the field of resonance diffusion imaging, in particular to a fast-marching fiber tracking method based on topology preservation, comprising the steps of: reading DTI (Diffusion Tensor Imaging) data; manually selecting a seed point and initializing; evoluting from the seed point to peripheral neighbor points by using a fast-marching method and adopting a curvature weighting speed function, recording topology information in an evolution process, i.e. a source node of each evoluting point; calculating all paths by adopting a time gradient descent method; and selecting a real fiber path by a link matrix. The invention has the advantages of more according with the real fiber path by fiber tracking and reducing urious positive branches; and the obtained fiber is smooth and better reflects the fiber direction.
Owner:苏州盛泽科技创业园发展有限公司
Method for determining optimum velocity profile of converted-wave pre-stack time migration during seismic data processing process
InactiveCN103675900ASmall amount of calculationImprove practicalitySeismic signal processingVelocity spectrumLongitudinal wave
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
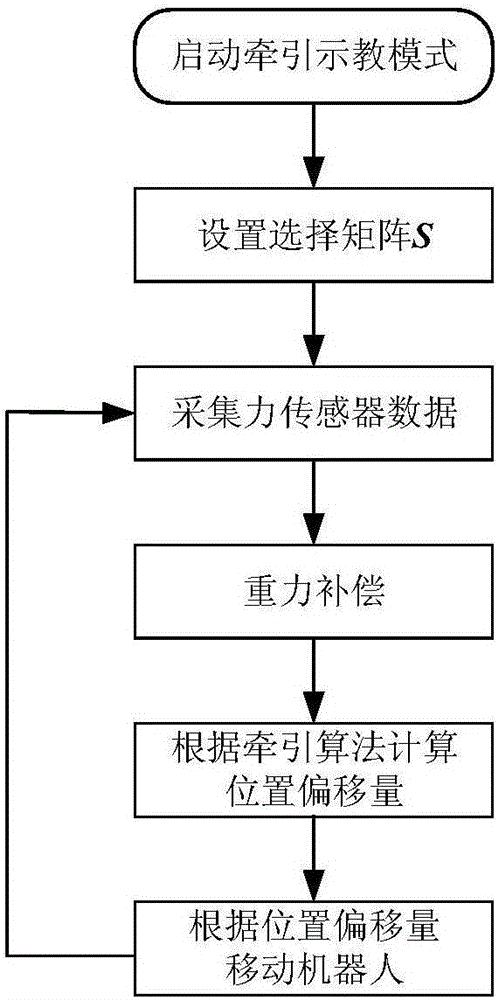
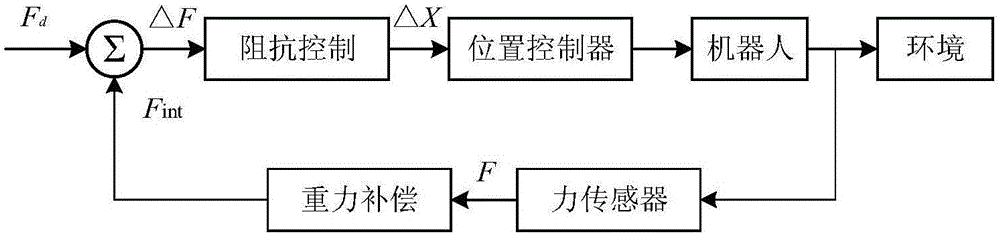
Speed control method for high-accuracy traction teaching robot based on impedance model
ActiveCN106774181AImprove real-time follow-up effectSmooth motionNumerical controlInverse kinematicsServo drive
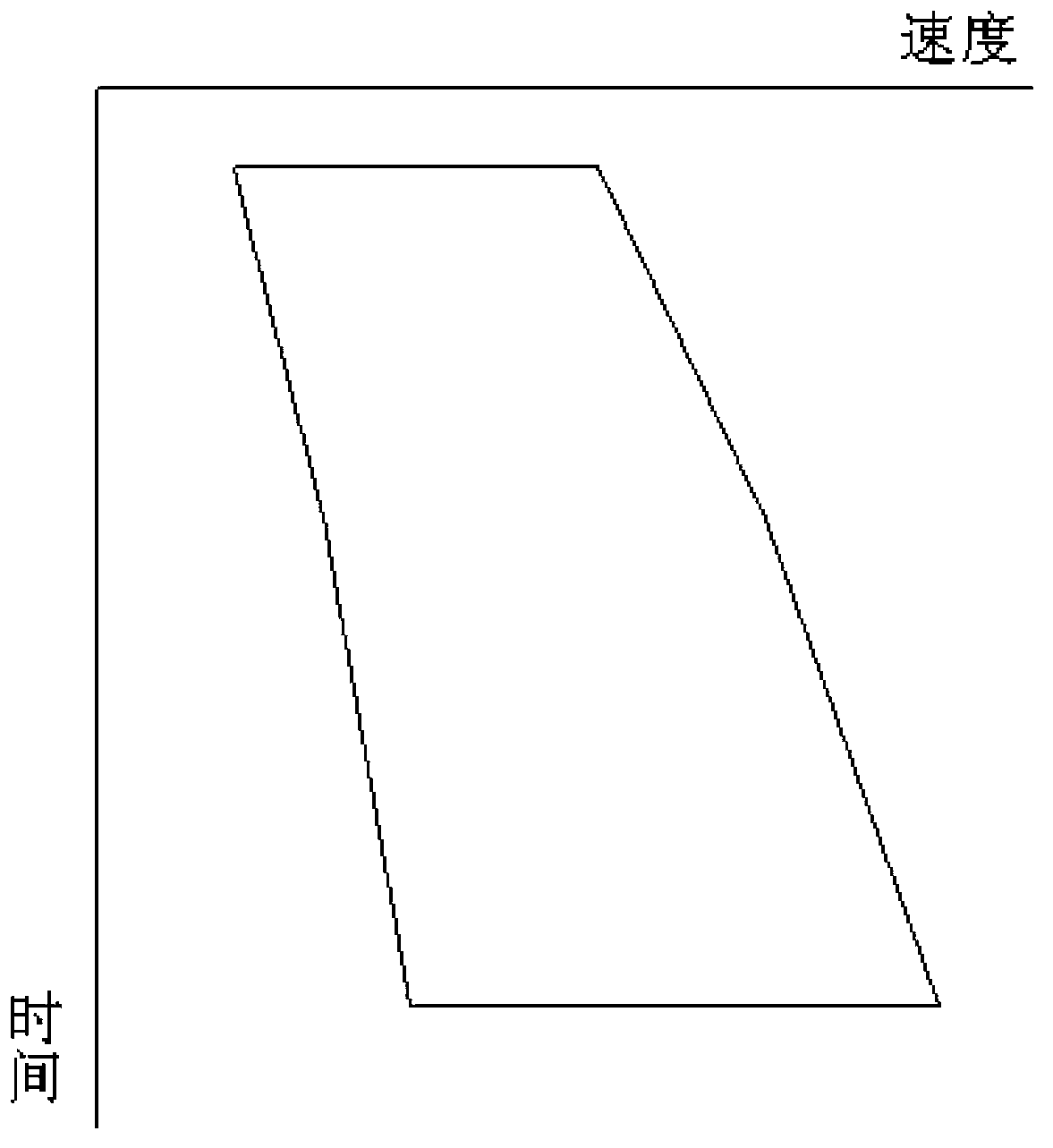
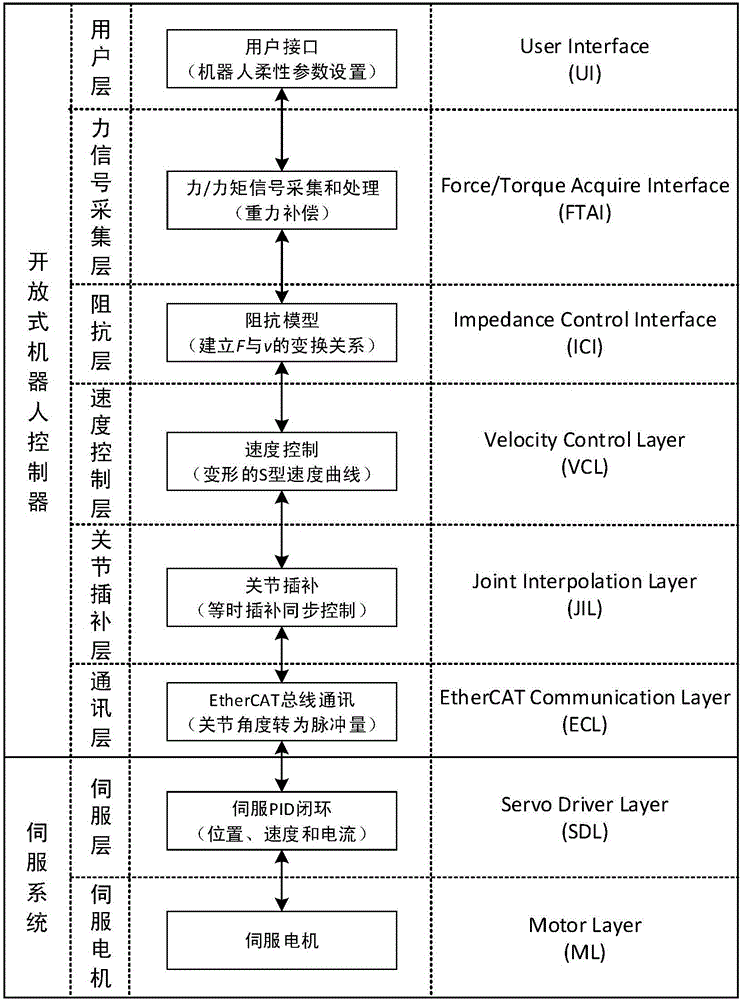
The invention discloses a speed control method for a high-accuracy traction teaching robot based on an impedance model. The speed control method includes the steps: S1 acquiring information of a six-dimensional force sensor by the robot: firstly, performing filter processing for acquired information, secondly, performing gravity compensation, and finally, acquiring deviation data of expected force or an expected torque value; S2, transforming the deviation data of the force or the deviation data of the torque value into moving speed of the tail end of the robot in the Cartesian space and angle speed rotating around an axis according to the impedance model; S3 performing smooth interpolation for motion according to a deformed S-shaped speed control curve to obtain a corresponding position function, a speed function and an acceleration function; S4 calculating a joint angle function in joint space according to inverse kinematics; S5 performing isochronous interpolation of the joint space for the joint angle function, and transmitting the joint angle function to a servo driver by a bus of a controller to control actions of the robot. According to the speed control method, traction accuracy is effectively improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for multi-azimuth prestack time migration for general heterogeneous, anisotropic media
ActiveUS7830747B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsAzimuth directionVelocity function
Three data subsets are obtained in three selected azimuthal directions from seismic data in heterogeneous, anisotropic media. Azimuthal velocities are determined for each of the data subsets. A linear system of equations in the three selected azimuthal directions and the three determined azimuthal velocities is solved for three independent parameters. An azimuthal time migration velocity function is constructed from the three solved independent parameters. A time migration traveltime function is constructed from the constructed azimuthal time migration velocity function.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Method for designing wind and solar hybrid system
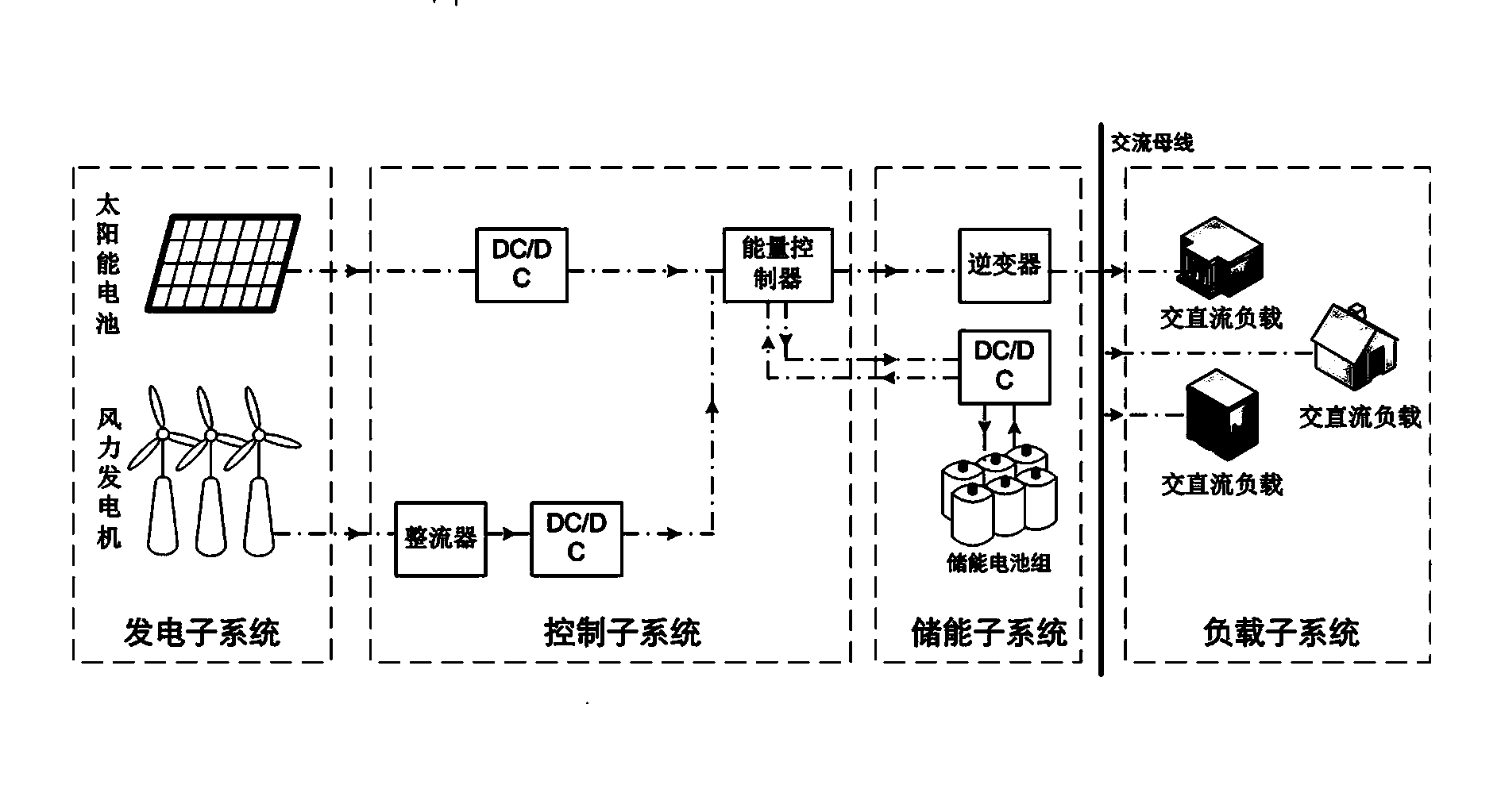
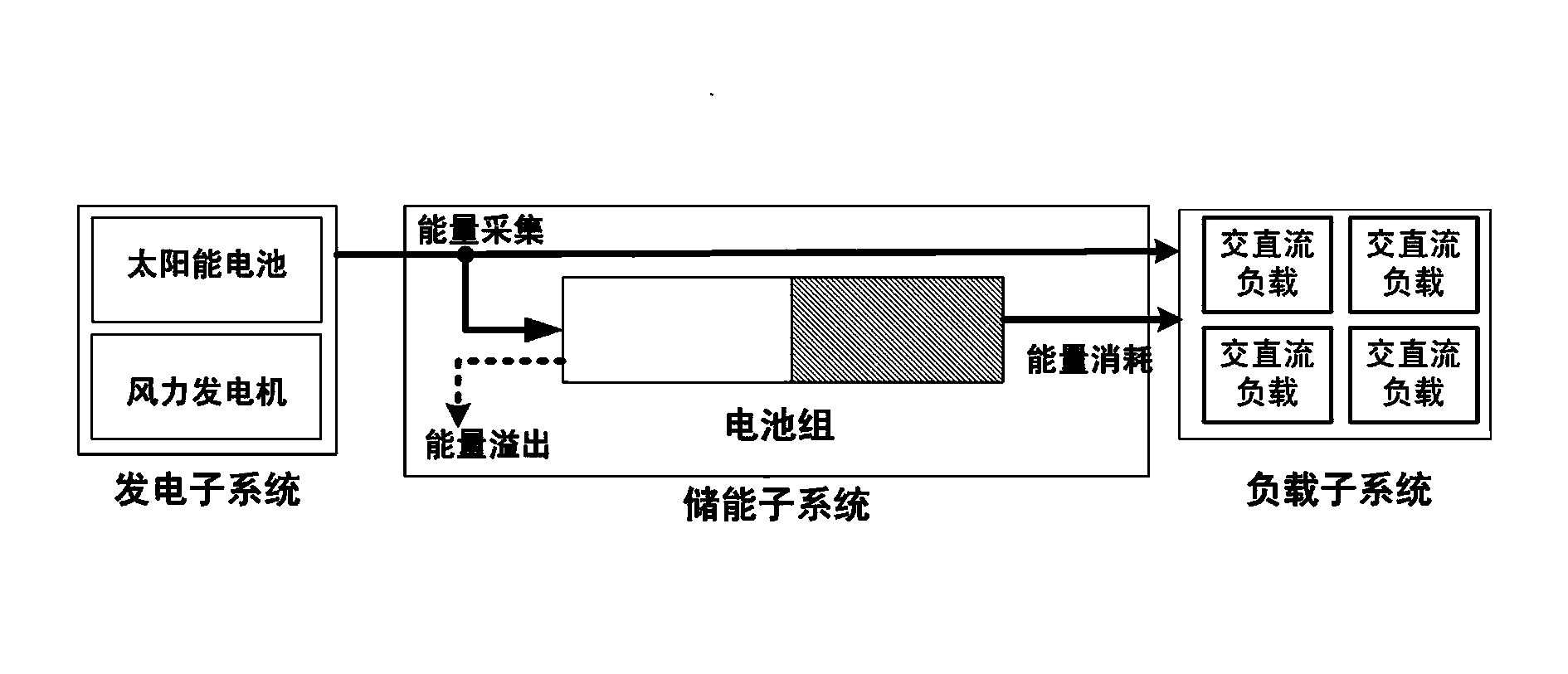
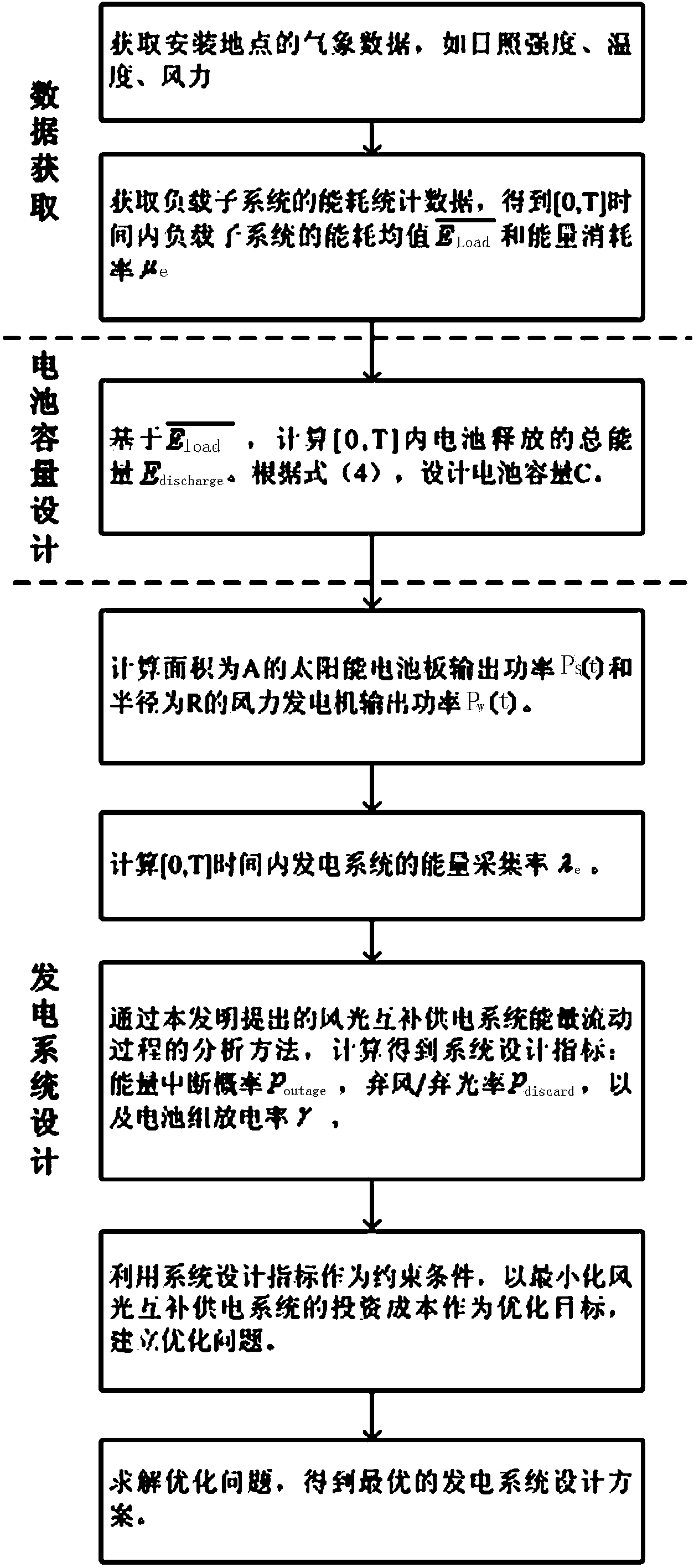
InactiveCN103684213AGuaranteed reliabilityGuaranteed robustnessPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationSystems designNew energy
The invention relates to the new energy technology and the wind and solar hybrid power generation system, in particular to a method for designing a wind and solar hybrid system. The method includes the following steps of firstly, measuring energy consumption data of support loads of a place where the wind and solar hybrid system is located; secondly, obtaining a sunlight intensity function S(t), a temperature function T(t) and a wind velocity function vw(t) within the time period [0,T] by conducting statistics on solar radiation intensity data, temperature data and wind power data of the place where the wind and solar hybrid system is located; thirdly, obtaining an energy consumption mean value and an energy consumption rate mue of load subsystems within the time period [0,T] according to the energy consumption data of supporting loads of the place where the wind and solar hybrid system is located and sunlight intensity function S(t) and the temperature function T(t) of the place where the wind and solar hybrid system is located, wherein T takes one day as a unit. The method is reasonable in design, and required cost of the optimized wind and solar hybrid system is determined on the premise that the energy outage probability poutage and the wind / solar discard probability pdiscard are lowered and it is ensured that a battery pack works in the optimal low-charging and low-discharging working state.
Owner:山西绿色光电产业科学技术研究院(有限公司)
Burn-back energy matching control method used for digital welding machine
ActiveCN109590578AAvoid affecting the success rate of arc strikingFlexible adjustment of welding energy outputArc welding apparatusControl engineeringEngineering
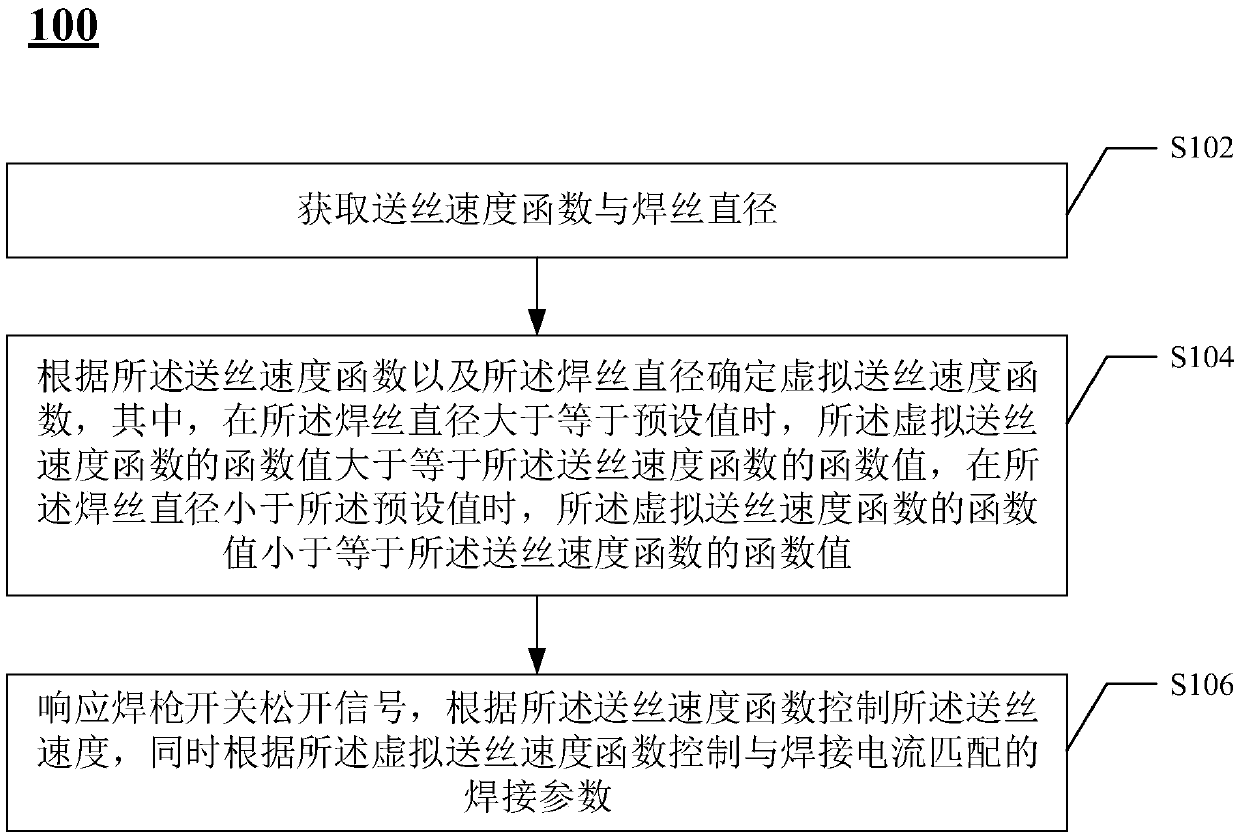
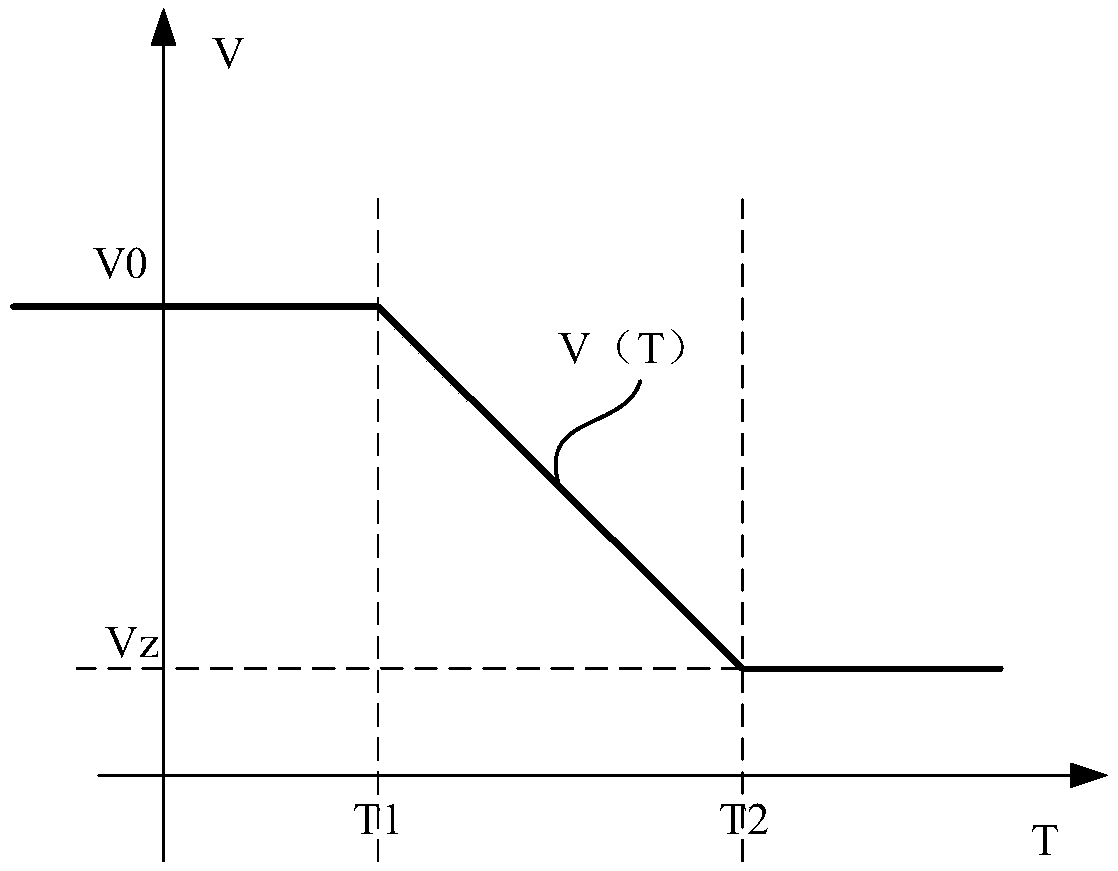
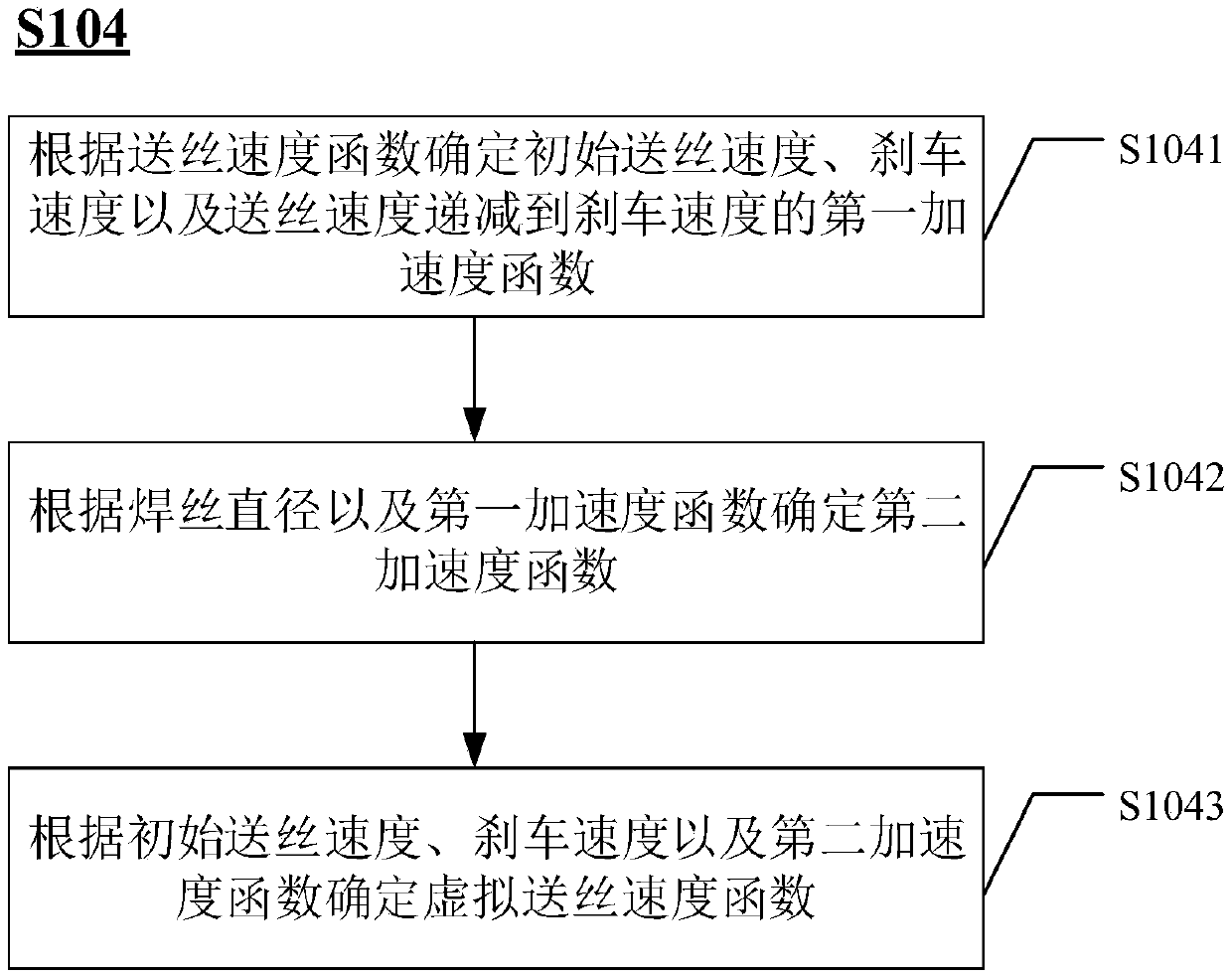
The invention provides a burn-back energy matching control method used for a digital welding machine. The burn-back energy matching control method used for the digital welding machine mainly includesthe steps that a wire feed speed function and a welding wire diameter are obtained; a virtual wire feed speed function is determined according to the wire feed speed function and the welding wire diameter, wherein when the welding wire diameter is larger than or equal to a preset value, the function value of the virtual wire feed speed function is larger than or equal to the function value of thewire feed speed function, and when the welding wire diameter is smaller than the preset value, the function value of the virtual wire feed speed function is smaller than or equal to the function valueof the wire feed speed function; and a response is made to a welding gun switch releasing signal, the wire feed speed is controlled according to the wire feed speed function, and the welding parameter matched with the welding current is controlled according to the virtual wire feed speed function. By means of the burn-back energy matching control method used for the digital welding machine, the welding quality can be effectively improved.
Owner:PANASONIC WELDING SYST TANGSHAN
Intravascular ultrasound image based automatic adventitia detection method
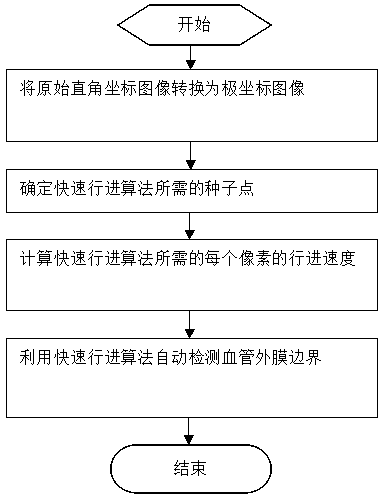
ActiveCN104361554AEasy to keepGuaranteed validityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging conditionSonification
The invention discloses an intravascular ultrasound image based automatic adventitia detection method. The method includes processes: transforming an intravascular ultrasound image from rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates; determining seed points needed by a Fast Marching algorithm; determining marching speed of each pixel needed by the Fast Marching algorithm according to image grayscale and gradient; automatically detecting the adventitia by the aid of the Fast Marching algorithm. The seed points, a termination point and a valid marching speed function are detected automatically, so that automaticity in the detection process is guaranteed; by the Fast Marching algorithm based processing method, simpleness and effectiveness of the detection method are guaranteed, and complexity of an existing algorithm model and dependence on imaging conditions are avoided.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for restarting a robot
ActiveUS20090198378A1Improve coating qualityQuality improvementProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlCurrent velocityMotion parameter
A method for restarting a robot after a premature interruption of a processing program, which controls it, at an interruption point. The robot has an atomiser apparatus for automatic coating of workpieces, and the processing program is used to preset a nominal movement of the atomiser apparatus with respect to a workpiece, which is to be coated and can be moved by means of a feed device, and to preset the associated nominal atomiser parameters. After the interruption of the processing program, the atomiser apparatus is first of all moved to a restarting point, which is located on the nominal movement path and is located ahead of the interruption point. After this, the atomiser apparatus is then moved on the nominal movement path, corresponding to a predeterminable velocity function, to a transfer point which is located on the nominal movement path and is located behind the interruption point. The atomiser apparatus is switched on again between the restarting point and the transfer point. The nominal atomiser parameters which are provided by the processing program are matched and are applied at least once, between the restarting point and the transfer point, to the respective current velocity of the atomiser apparatus, in relation to the nominal velocity preset, and all of the nominal movement parameters and nominal atomiser parameters in the processing program are used when the transfer point is reached.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
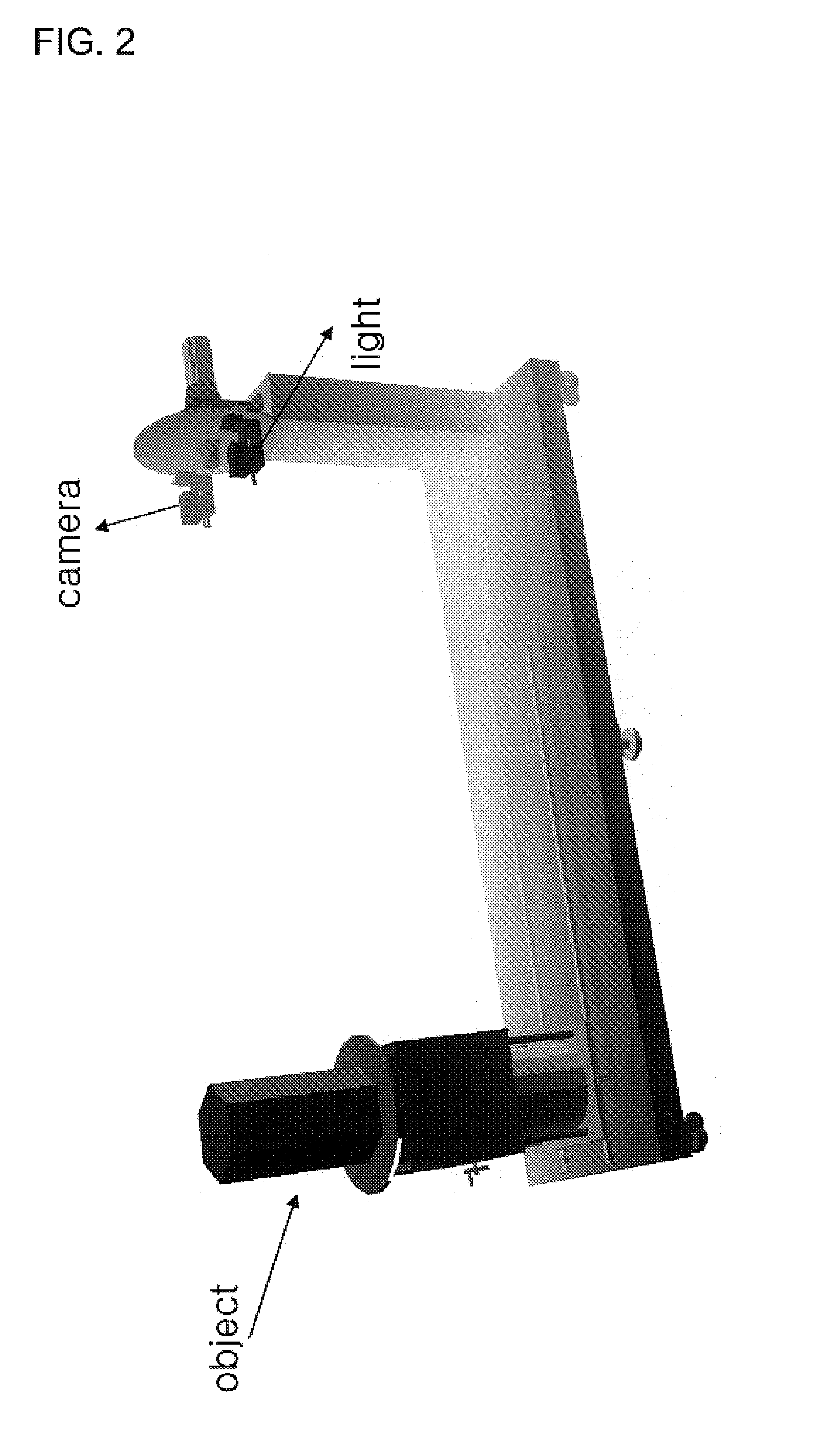
Method for modeling three dimensional shape of objects using level set solutions on partial differential equation derived from helmholtz reciprocity condition
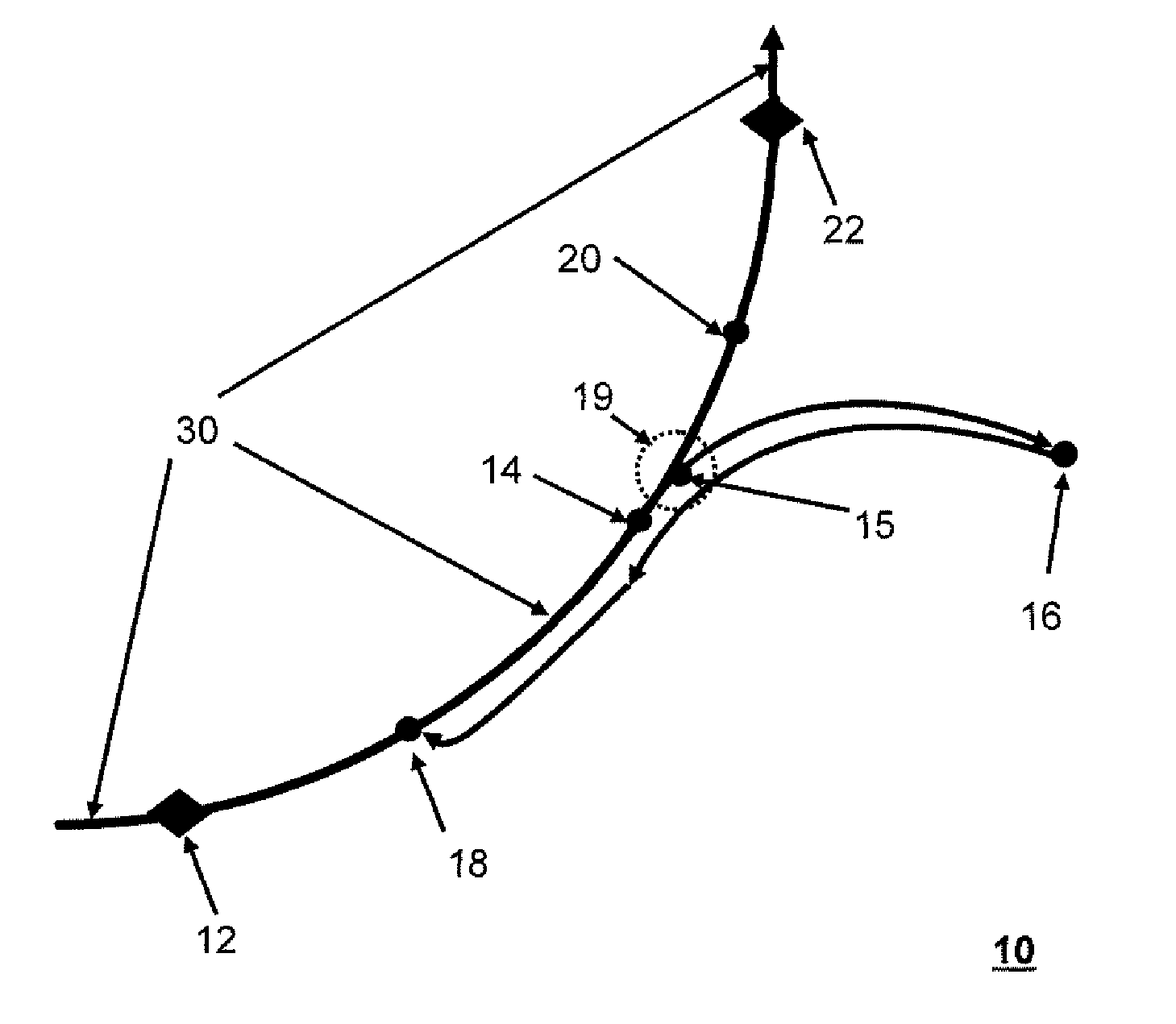
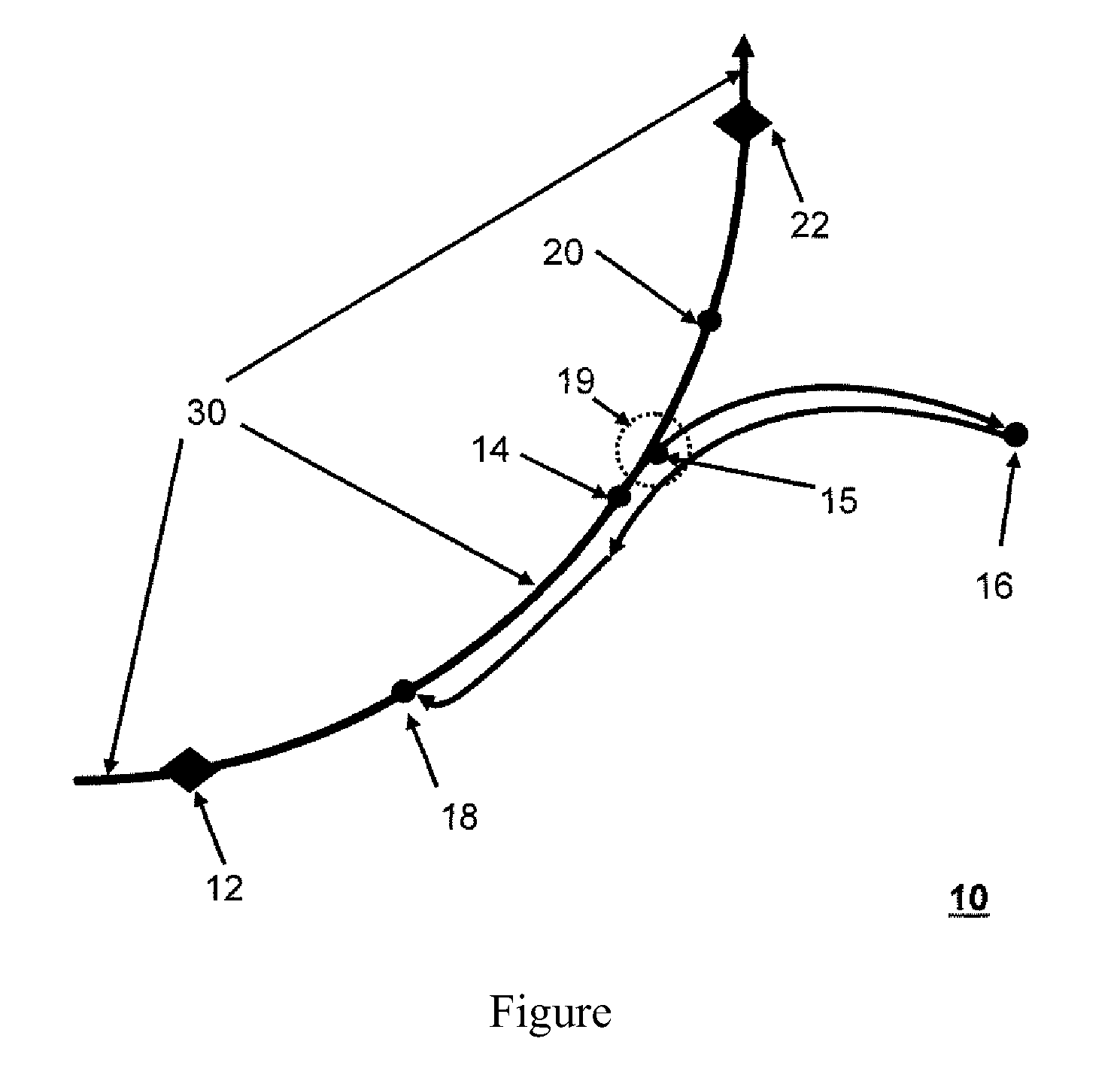
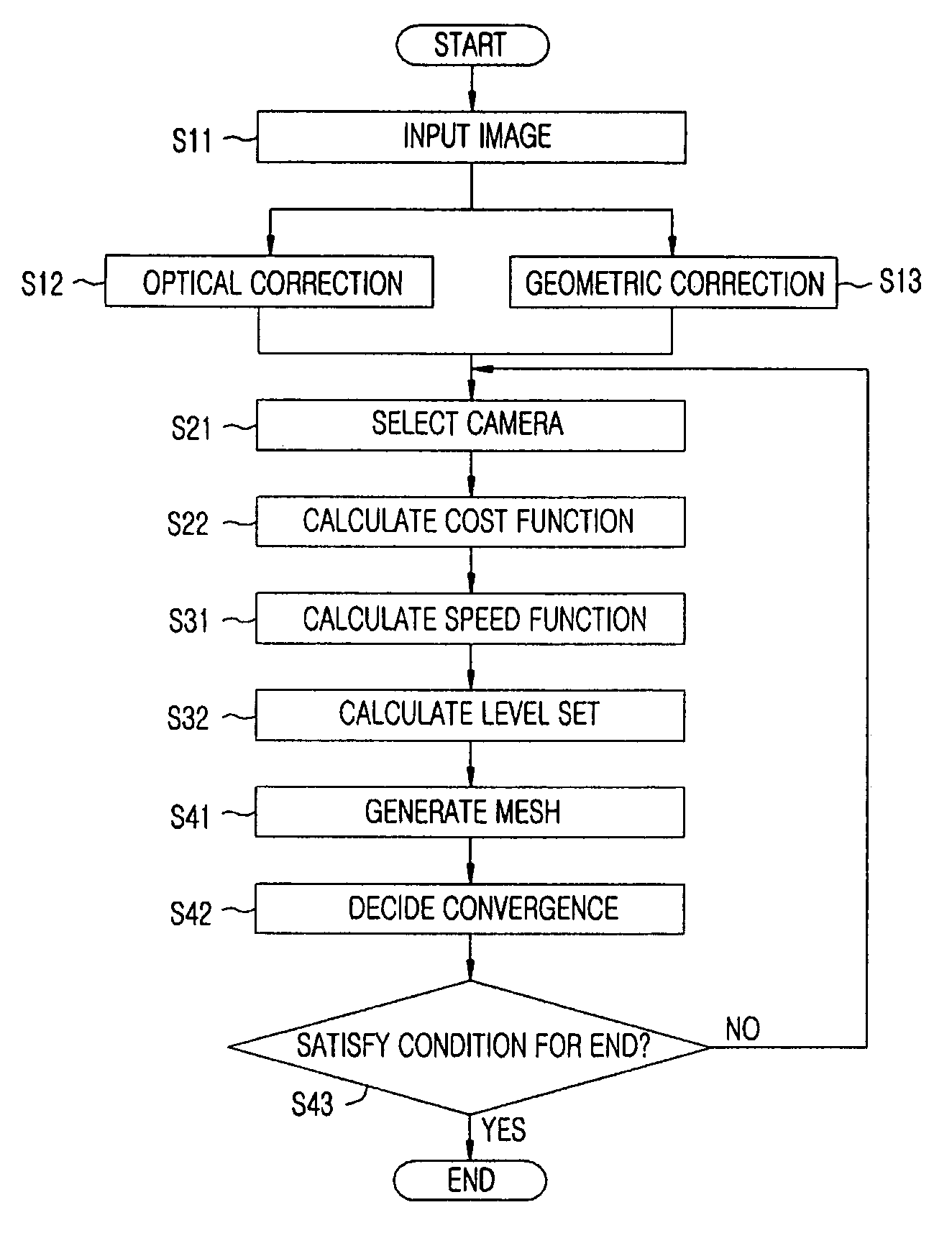
InactiveUS7684614B2Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionThree dimensional shapeFirst-order partial differential equation
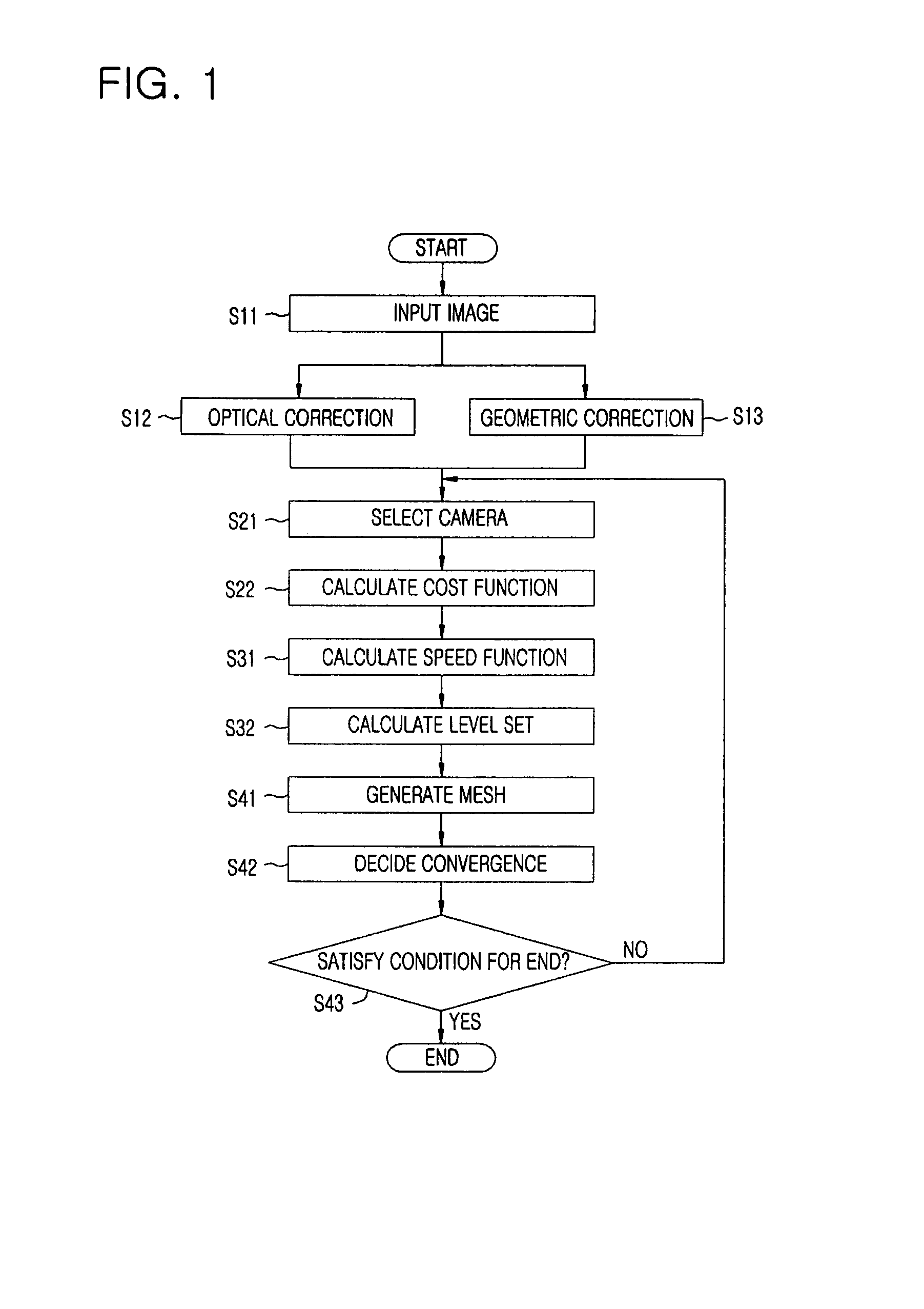
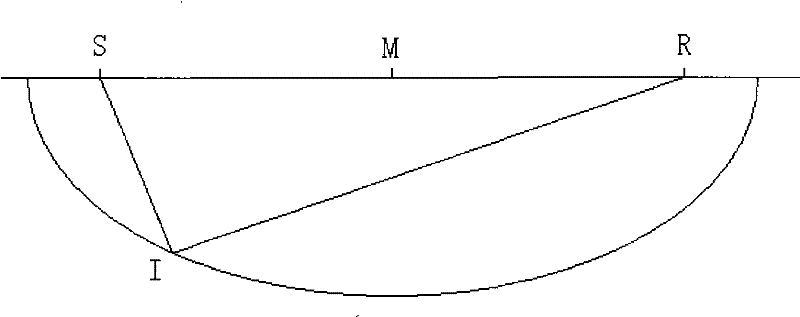
A method for modeling a three dimensional shape of object using a level set solution on a partial differential equation derived from a Helmholtz reciprocity condition is provided. The method includes the steps of: a) inputting an image pair satisfying a Helmholtz reciprocity condition; b) performing an optical correction and simultaneously performing a geometric correction; c) performing a camera selection to select cameras capable of seeing a point (X, Y, Z), and defining and calculating a cost function by the Helmholtz reciprocity condition; d) calculating a speed function of a PDE that minimizes the cost function obtained in the step c); and e) generating a three dimension mesh model from a set of points configuring the object surface provided from the step d), and deciding a final three dimension mesh model by comparing cost function values.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
A Method for Determining the Optimal Velocity Profile for Prestack Time Migration
ActiveCN101839999BSmall amount of calculationImprove practicalitySeismic signal processingVelocity spectrumUsability
The invention is a method for determining the optimal velocity profile of pre-stack time migration for petroleum seismic data processing. The procedure is to take the velocity that changes with the seismic wave reflection time as the central velocity, and the velocity interval that varies with the seismic wave reflection time as the change step, form a set of velocity functions with the seismic wave reflection time for the central velocity, and then pre-stack the collected seismic data. Migration, the results are listed in the form of velocity spectrum as the velocity changes, according to the energy mass intensity and distribution position on the velocity spectrum, and the optimal velocity used for prestack time migration on the gather, the prestack time determined on the common reflection point Migrating Optimal Velocity Generates a prestack time-migrated optimal velocity profile. The invention calculates the information that needs to be output at the speed analysis point within the effective speed range, which significantly reduces the calculation amount and improves the practicality.
Owner:BGP OF CHINA NAT GASOLINEEUM CORP
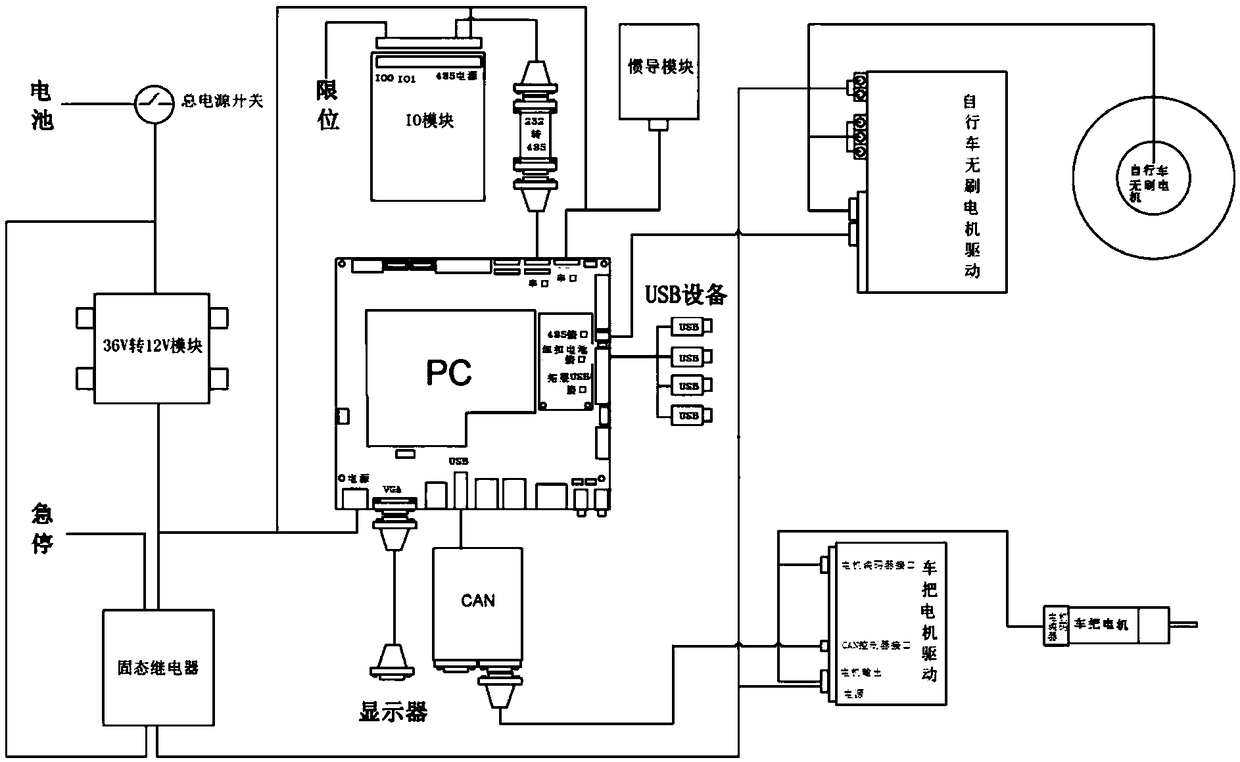
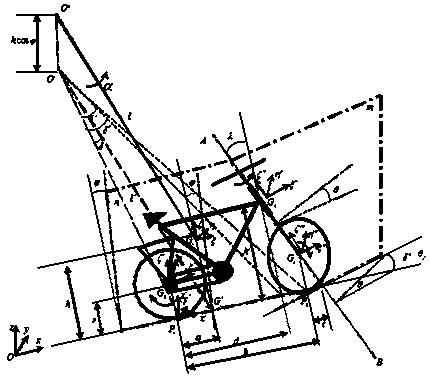
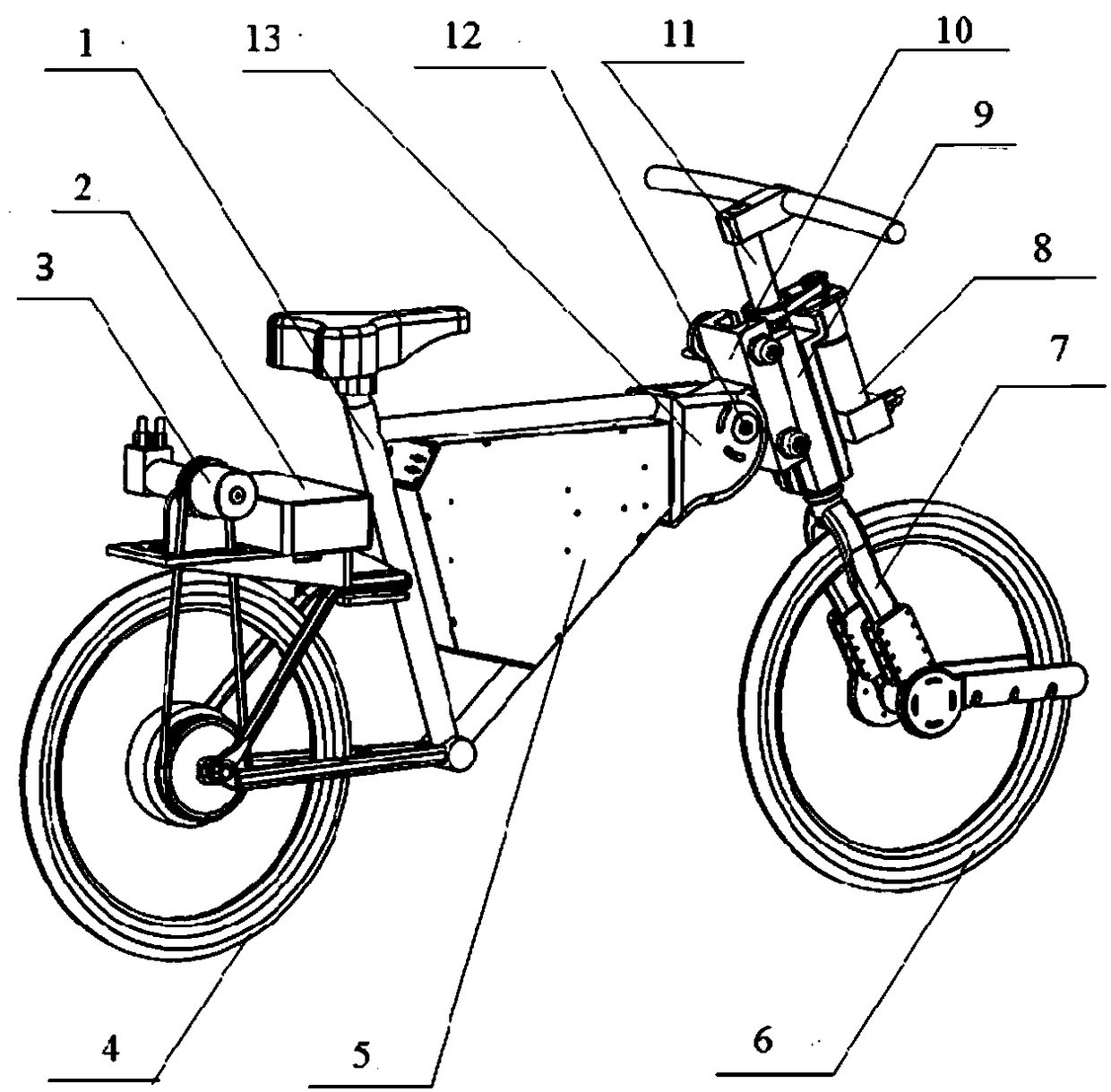
Autonomous balance bicycle mechanical power system and a multi-rigid-body dynamic model thereof
The invention relates to an autonomous balance riding bicycle mechanical power system and a multi-rigid-body dynamic model thereof, the mechanical power system comprises a mechanical system and an electrical control system, and the mechanical system comprises a bicycle body, a rear wheel, a front fork and a front wheel; the electric control system comprises an industrial personal computer, a direct-current power supply and an electronic gyroscope, a front fork tail adjusting device is arranged at the joint of a front fork and the vehicle body, a servo driving motor is arranged on a rear wheel,and a direction adjusting servo driving motor is arranged on the front wheel and connected with the industrial personal computer through a bus; a Kane method is adopted to establish a multi-rigid-body dynamic model of the autonomous balance riding bicycle. The method has the beneficial effects that a reliable theoretical basis is provided for the structure, parameter optimization and control system design of the autonomous balance riding bicycle; an autonomous balance running bicycle state space model is established by means of a multi-rigid-body dynamics model, and autonomous balance runningof the bicycle is achieved based on a cascade stage optimal control algorithm of a speed function.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIV ZHUHAI +1
Acceleration self-adaptive stabilization method of fractional order mechanical centrifugal speed regulator system
ActiveCN109634116AOvercome the iterative derivation problemGuaranteed boundednessAdaptive controlBacksteppingDifferentiator
The invention discloses an acceleration self-adaptive stabilization method of a fractional order mechanical centrifugal speed regulator system. The accelerated self-adaptive stabilization method of the system comprises the following steps that a, the convergence speed of the system state is accelerated in a preset time by introducing a speed function; b, learning or approximating unknown nonlinearterms are carried out in a system mathematical model by using Chebyshev neural network, the expansion state tracking differentiator is designed to estimate the derivative of the virtual control input, and then the accelerated self-adaptive stability controller is constructed under the backstepping control framework. According to the acceleration self-adaptive stabilization method, the stability problem of the fractional order mechanical centrifugal speed regulator system under the condition of unknown parameters and disturbance, the acceleration stability problem at a given convergence rate and the problem of repeated derivation of a traditional inversion method are overcome, so that the problem of chaotic oscillation of the fractional order mechanical centrifugal speed regulator system is effectively solved.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com