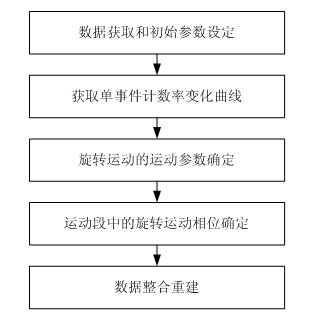
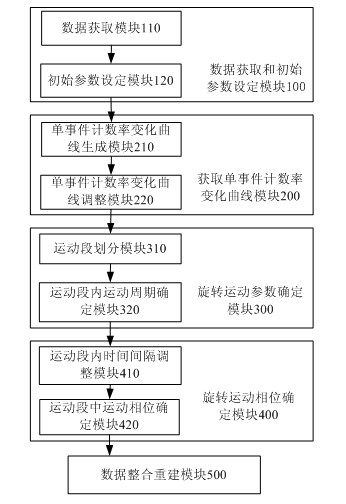
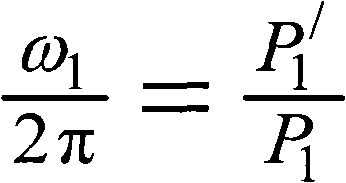Patents
Literature
277 results about "Rotation period" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In astronomy, the rotation period of a celestial object (e.g., a star, gas giant, planet, moon, astroid, etc.) is the time that the object takes to complete a single revolution around its axis of rotation relative to the background stars. It differs from the object's solar day, which may include an extra fractional rotation needed to accommodate the portion of the object's orbital period during one day.
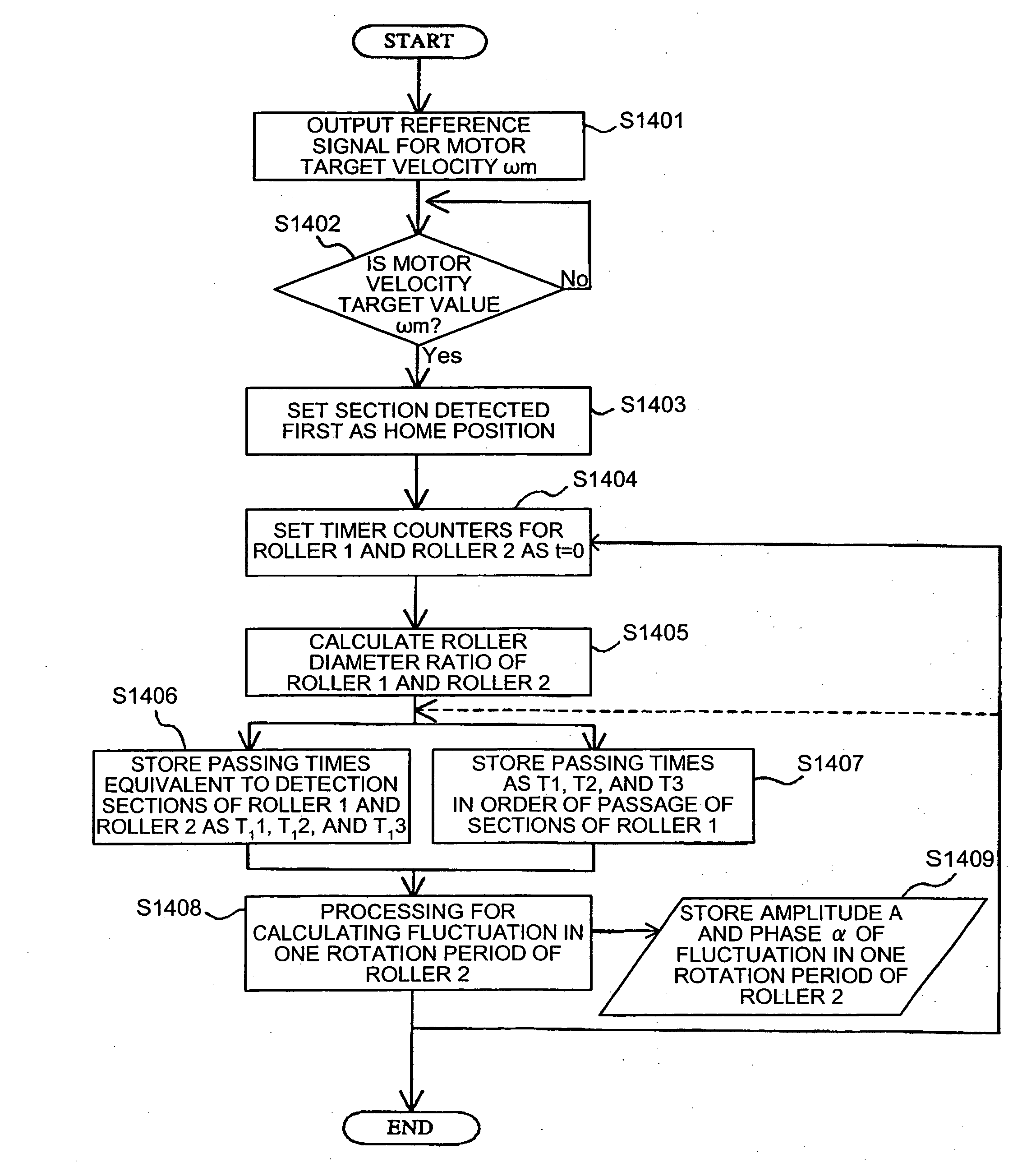
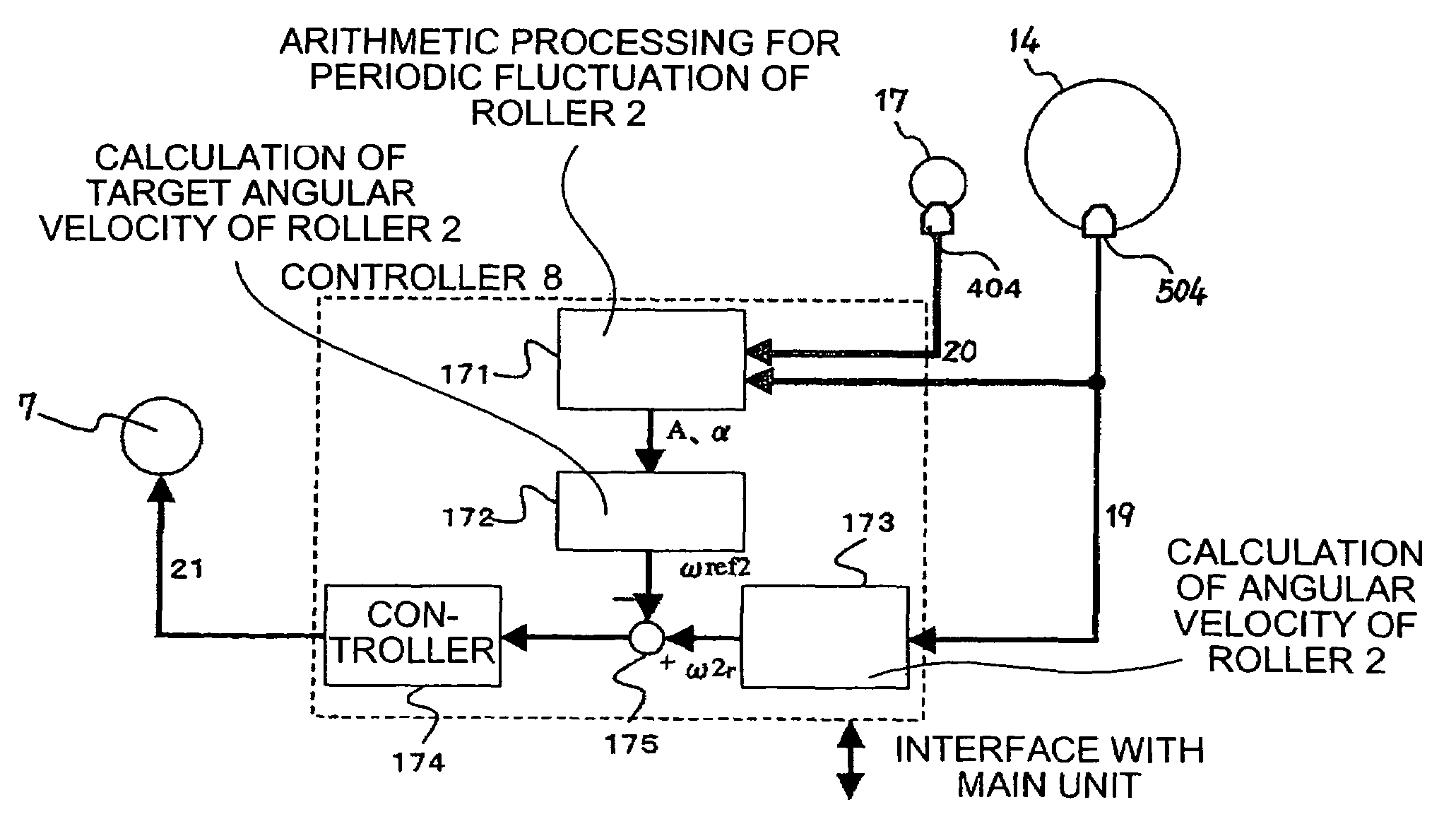
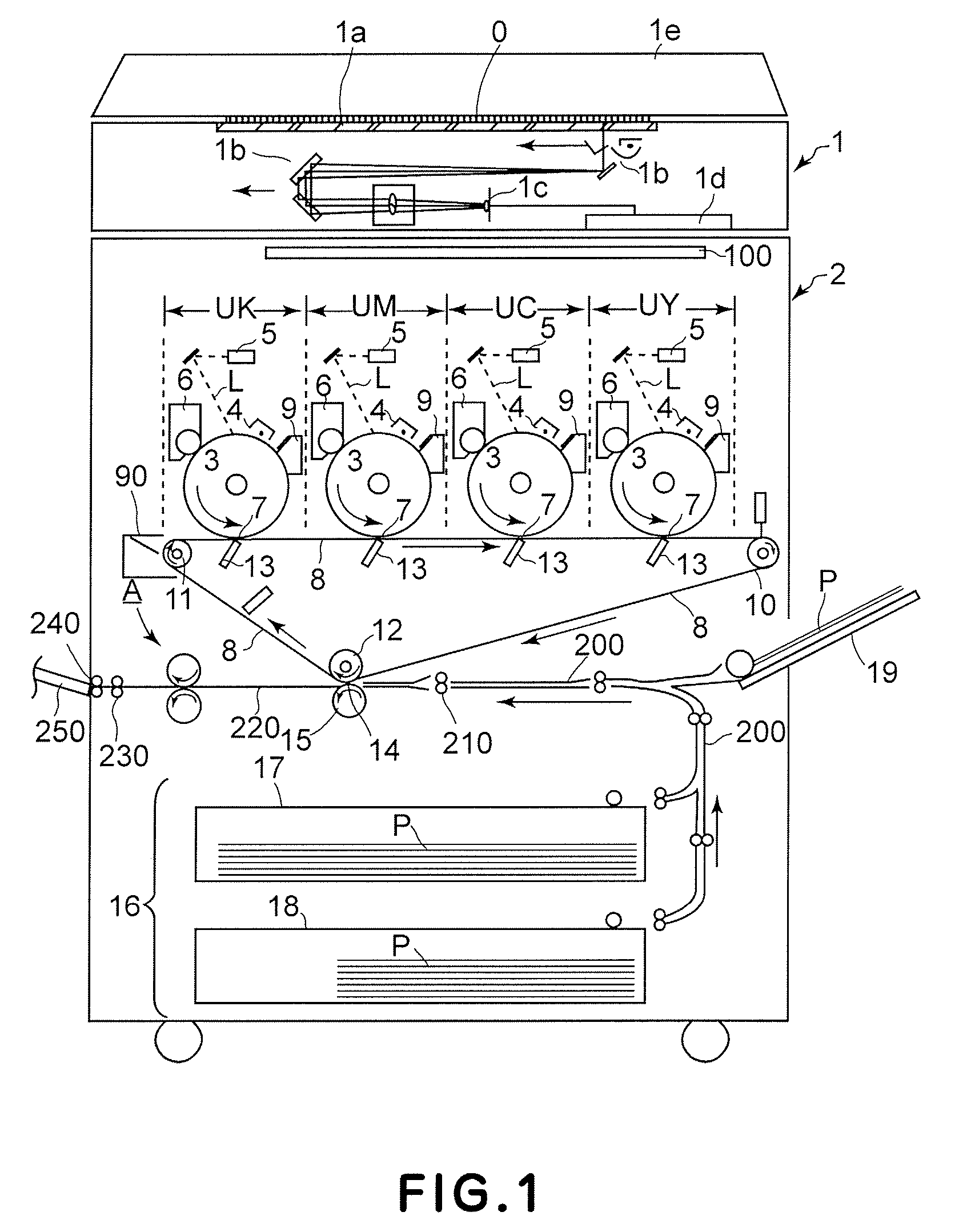
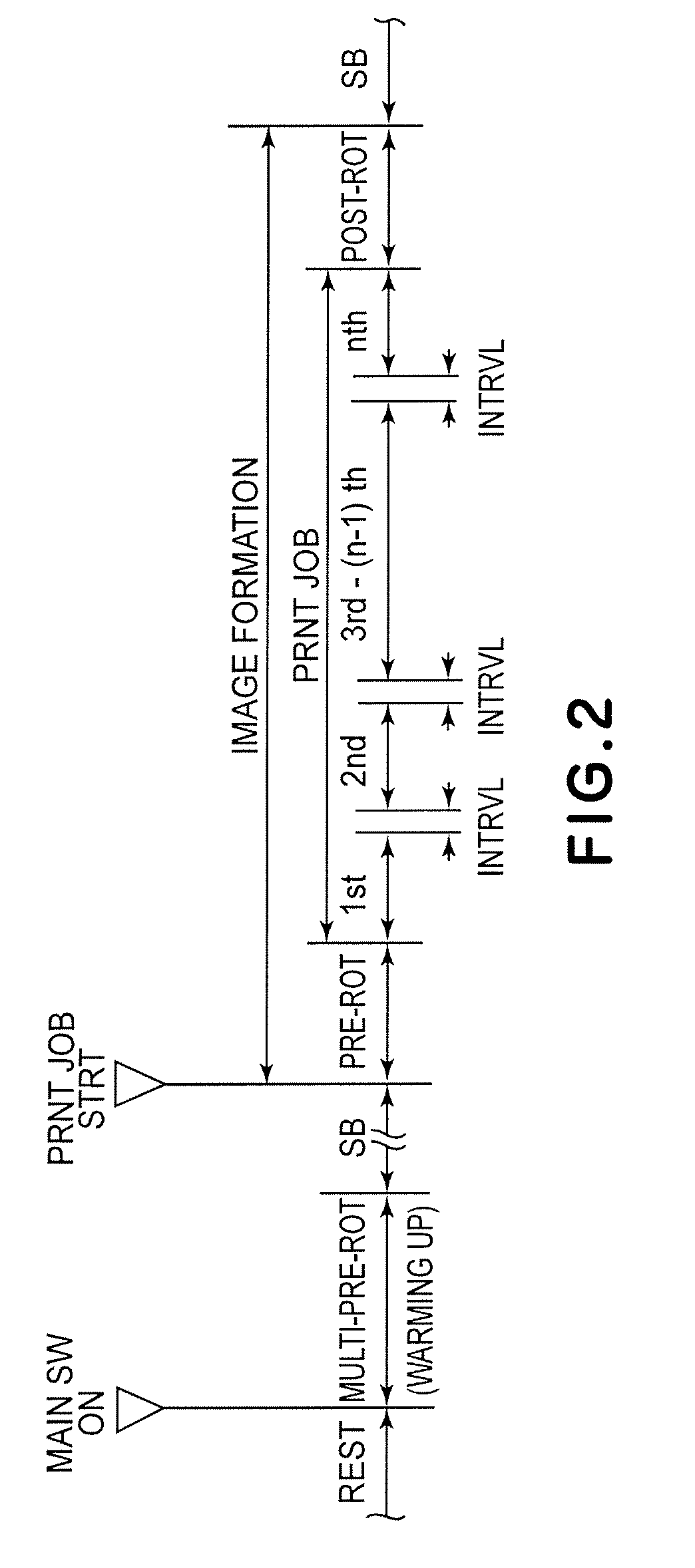
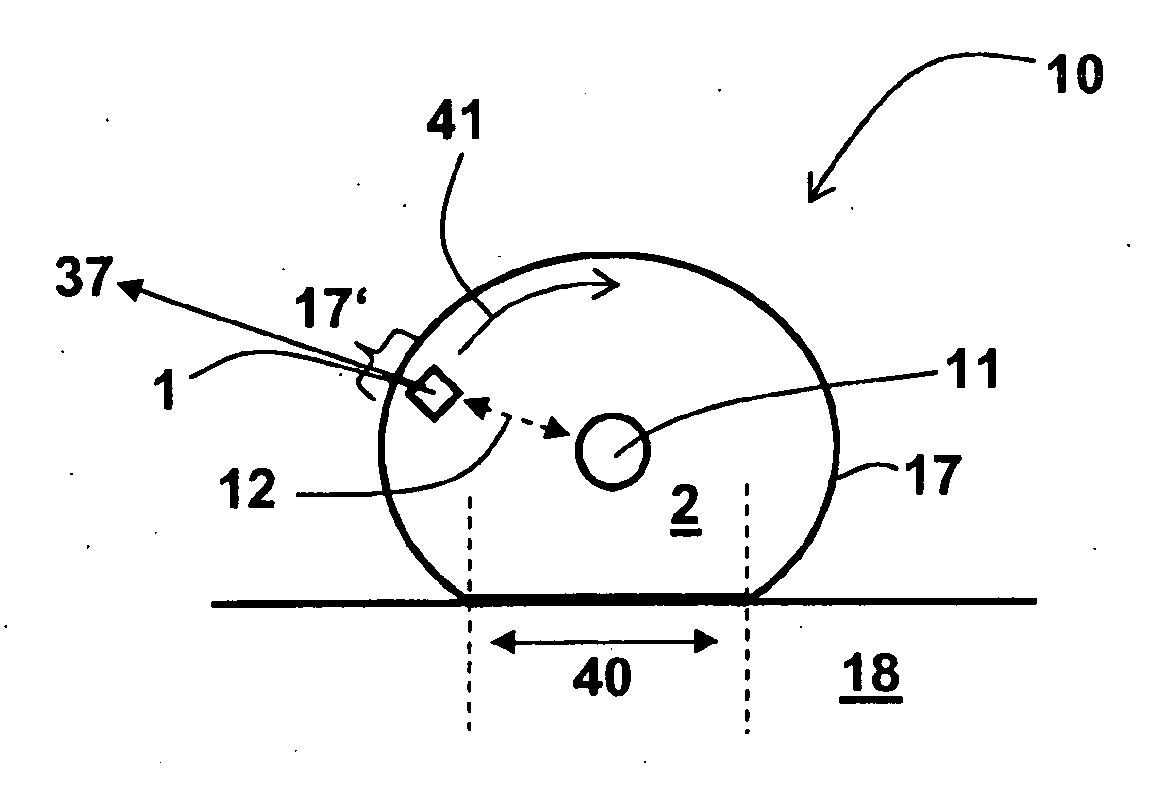
Belt drive control method, belt-drive control device, and image forming apparatus
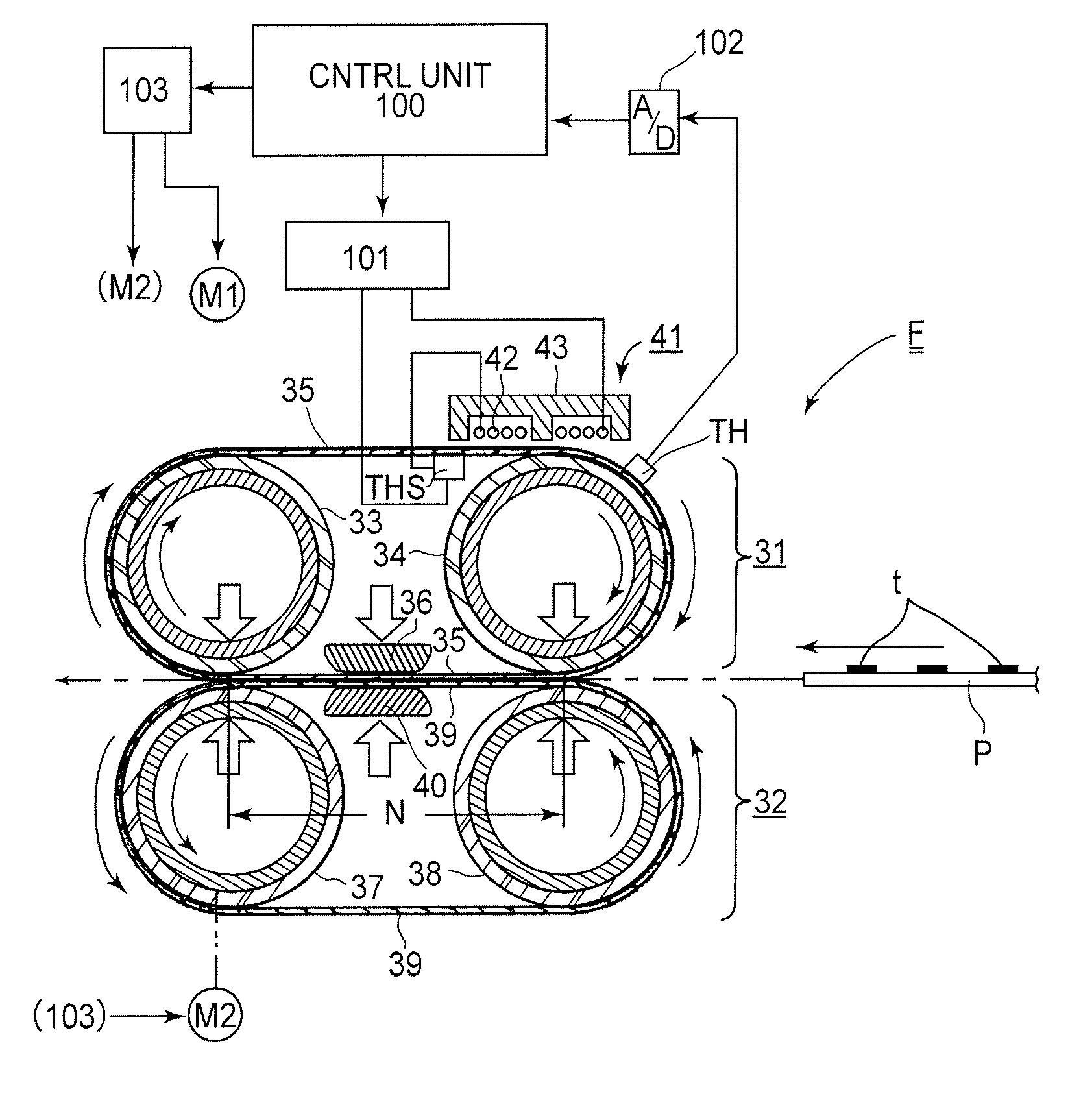
A rotational speed of a first roller and a time required for a second roller to make one rotation are measured. A controller calculates an amplitude and a phase of fluctuation in a rotational speed in one rotation period of the first roller while the first roller is rotated by a predefined angle based on the speed and the time. The controller corrects measured speed of the first roller based on the amplitude and the phase, and controls a driving roller based on corrected speed.
Owner:RICOH KK
Analysis method of gear train noise based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition and support vector machine
InactiveCN106778694AEfficient extractionHigh recognition accuracy and fastMachine gearing/transmission testingCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineFeature vector
The invention provides an analysis method of gear train noise based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition and support vector machine. Firstly, the method of ensemble empirical mode decomposition stepwise decomposes the different time scale wave or trend of gear train noise signals and a set of intrinsic mode functions IMF. Gear train noise useful signals are extracted and the signals including mesh frequency are found from the result of ensemble empirical mode decomposition and conducted reconsitution. time synchronous averaging is operated according to gear rotation period and the signal irrelevant to gear rotation frequency is weaken through time expansion treatment. The characteristic parameter of treated gear train noise signals is calculated and a set of characteristic parameters with large differences is selected as characteristic vector. The characteristic vector as sample is divided into two groups, wherein the two groups have the same numbers and are used as a training sample and a testing sample. The method has little man-made operation and ensures the accuracy of analysis. The intelligent analysis method is based on support vector machine and has high and fast recognition accuracy of gear train prosperity.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
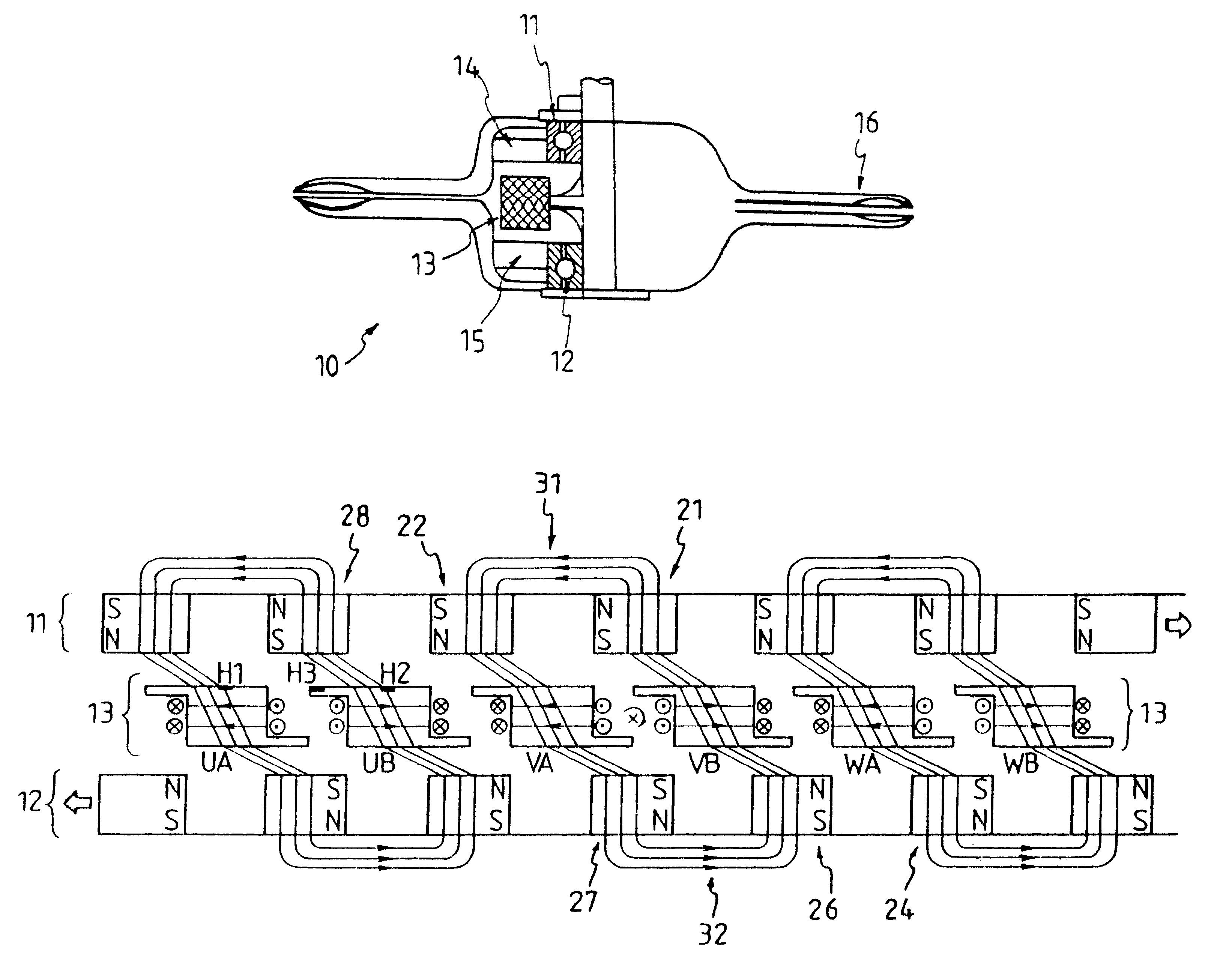
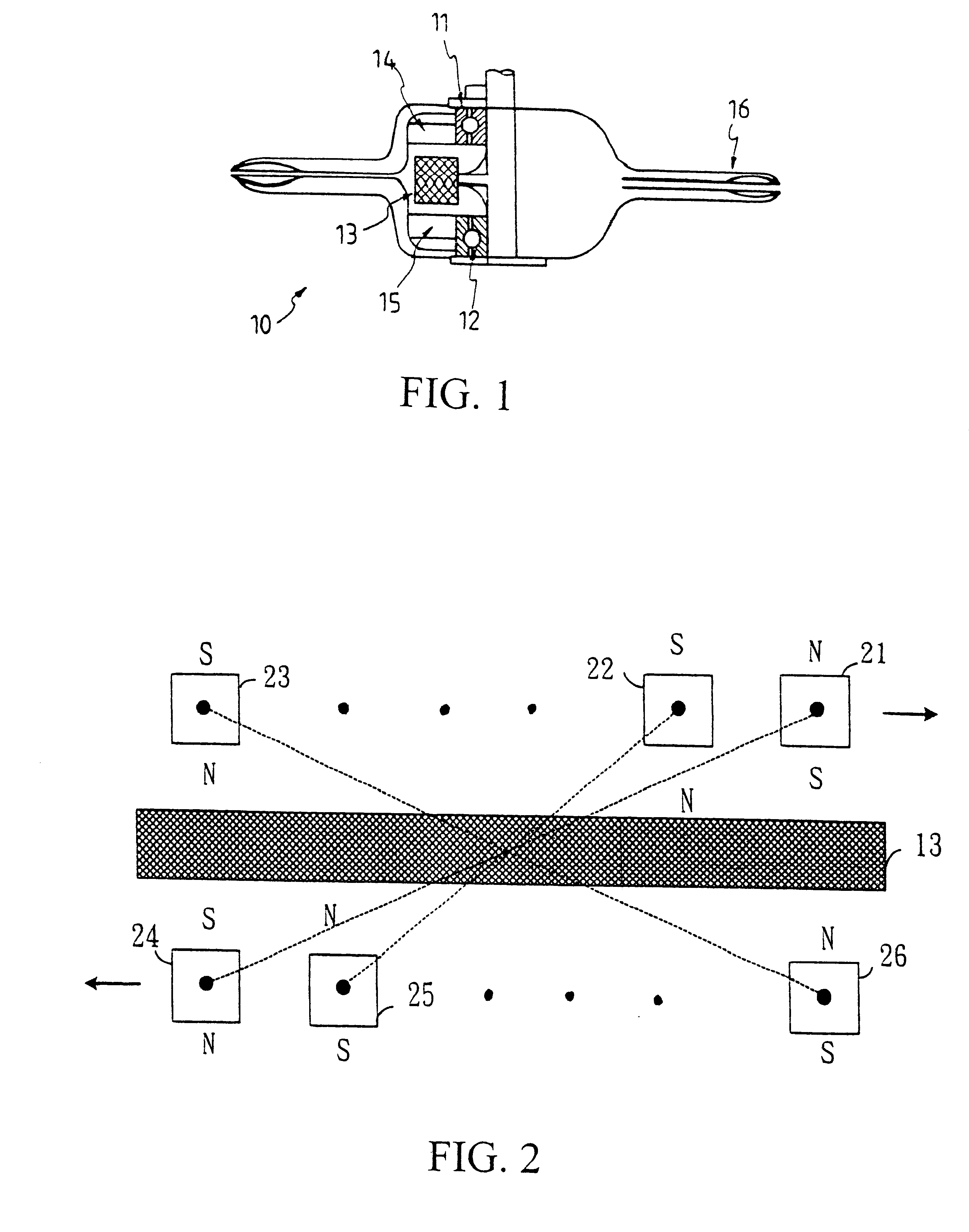
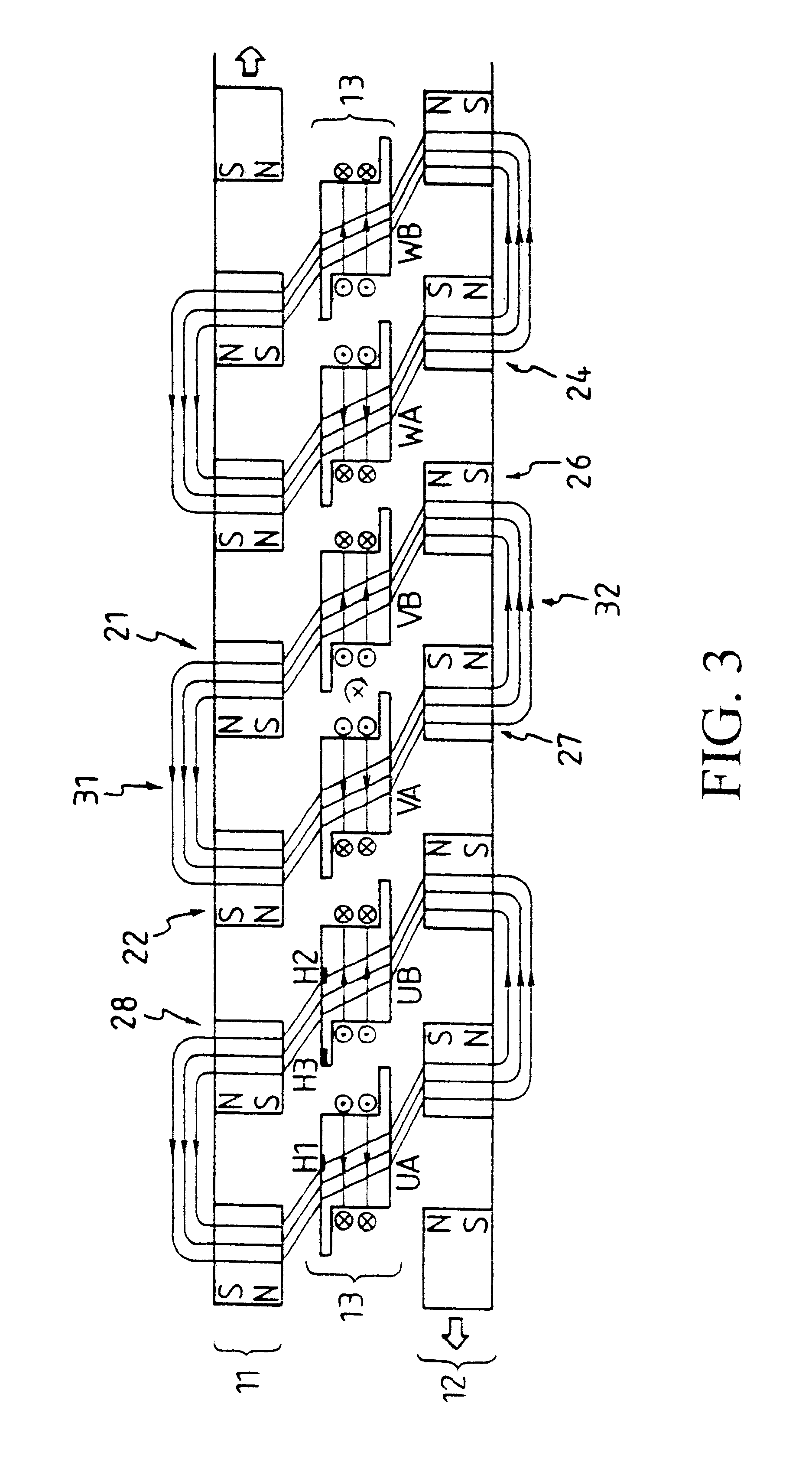
Multiple layer double rotor single stator skew symmetry permanent magnet rotating motor
InactiveUS6455969B1Simple structureHigh-efficient powerMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsMagnetic polesRotation cycle
A single-stator-double-rotor rotating motor has one upper-layer rotor, one intermediate-layer armature and one lower-layer rotor. The upper-layer rotor and lower-layer rotor are embedded with the same number of magnets to form a magneto type magnetic pole, stator electrodes of the same number as the number of magnets are disposed on the intermediate-layer armature to form an electro type magnetic pole. A skew symmetry exists between an upper-layer rotor and a corresponding lower-layer rotor, and the upper-layer rotor and the lower-layer rotor are rotated in opposite directions by commutation of the current flowing through exciting coils of the stator electrodes every T / N of time, wherein T is a rotation period of the upper-layer rotor, and N is the number of the magnets.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
Nakedness-eye holographic display device based on persistence-of-vision effect and method for nakedness-eye holographic display device
ActiveCN105845050ATo achieve the display effectStatic indicating devicesIdentification meansPersistence of visionImage resolution
The invention discloses a nakedness-eye holographic display device based on a persistence-of-vision effect. The nakedness-eye holographic display device comprises a plurality of LED (Light Emitting Diode) lamp strips and a rotating disk, wherein the inner ends of the LED lamp strips are fixedly connected with the rotating disk; the LED lamp strips are uniformly distributed along a rotating center of the rotating disk and comprise lamp poles and RGB (Red, Green and Blue) lamp beads; the RGB lamp beads are linearly fixed on the lamp poles. A display method of the nakedness-eye holographic display device comprises the following steps in sequence: determining a display area and resolution; calculating a rotation period; calculating refresh time; displaying picture data processing. According to the nakedness-eye holographic display device disclosed by the invention, by using the principle of point-into-line and line-into-plane, the RGB lamp beads are arranged in a line form and move according to certain trajectory to form a trajectory plane; the picture can be displayed according to pixel points (the RGB lamp beads) corresponding to a lightening trajectory plane required by the picture; due to the motion of the lamp strips, a realistic background can be transmitted through the trajectory plane of lamp strip motion, and a display picture theme is displayed in the realistic environment in a floating way.
Owner:CHENGDU BAIYUN SCI & TECH
Belt drive control method, belt-drive control device, and image forming apparatus
A rotational speed of a first roller and a time required for a second roller to make one rotation are measured. A controller calculates an amplitude and a phase of fluctuation in a rotational speed in one rotation period of the first roller while the first roller is rotated by a predefined angle based on the speed and the time. The controller corrects measured speed of the first roller based on the amplitude and the phase, and controls a driving roller based on corrected speed.
Owner:RICOH KK
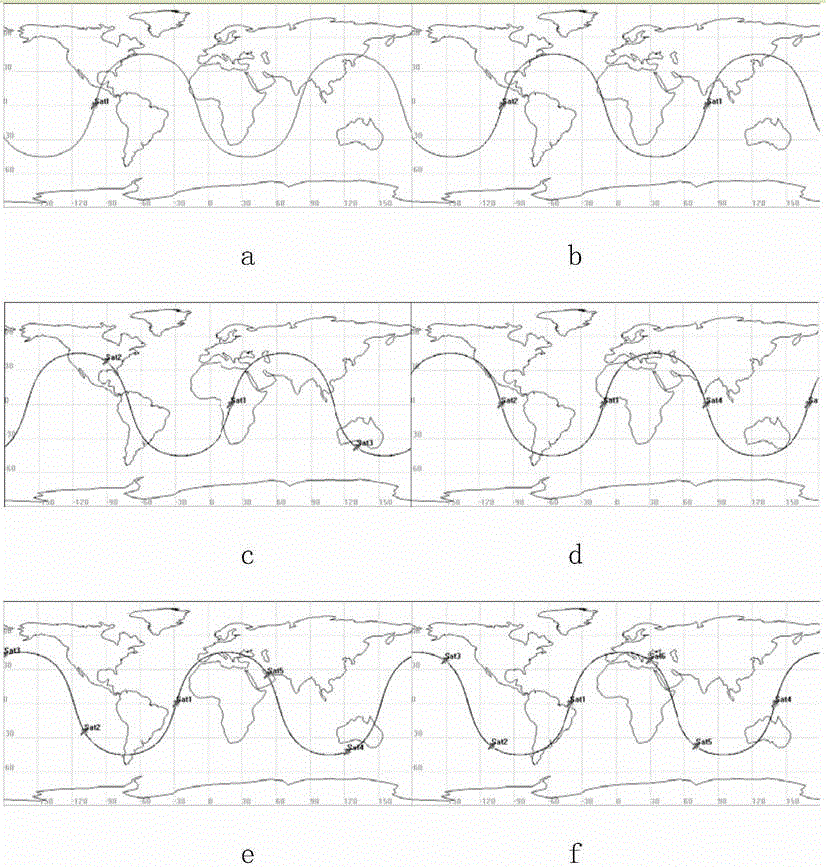
Global communication constellation designing method for realizing on-demand coverage of key areas
ActiveCN106209205AReduce the numberReduce complexityRadio transmissionHigh elevationEarth's rotation
The invention belongs to the technical field of satellite communication, and particularly relates to a global communication constellation designing method for realizing on-demand coverage of key areas. In particular, a constellation comprises a plurality of orbital planes which are uniformly distributed along an equator; only one satellite exists on each orbital plane; an orbital period of each satellite is one integer of a rotation period of the earth; and sub-satellite point tracks of all satellites in the constellation coincide. The constellation can provide a high-elevation communication coverage service for the key areas as required according to a task demand by adjusting design parameters of the constellation such as a regression period, an orbit inclination, an eccentricity ratio, an argument of perigee, an ascending node geographic longitude of a first satellite and a mean anomaly. Area coverage can be realized through the constellation designed by the method; a sub-satellite point track repeating and high-elevation communication service can be provided specific to specific areas of a southern / northern hemisphere by adjusting constellation designing parameters; the number of satellites required by a coverage demand is reduced; the complexity of space and ground systems is lowered; and the systems are more economical.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
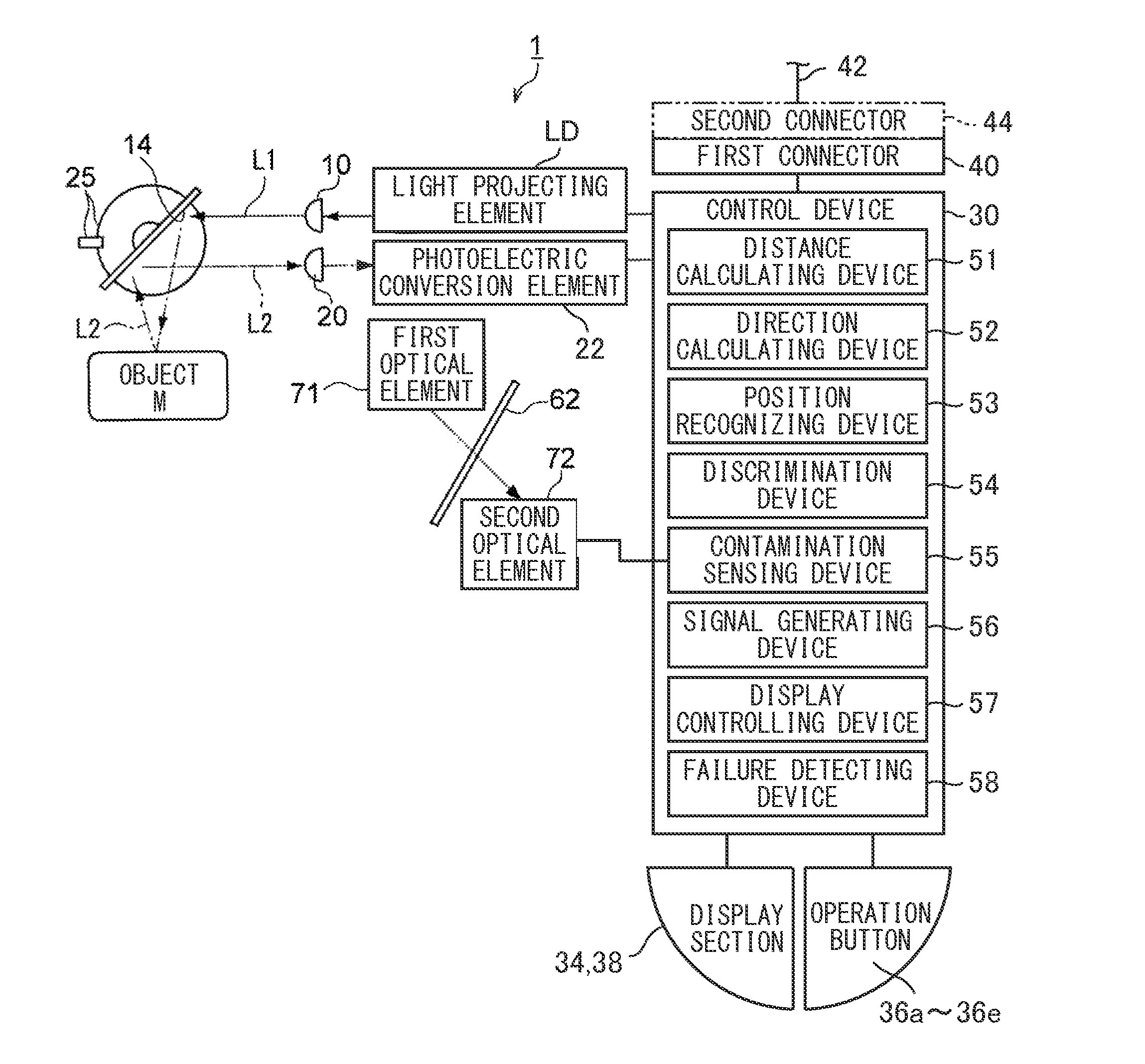
Safety photoelectric switch
ActiveUS8330095B2Avoid interferenceSolve the real problemOptical rangefindersInvestigating moving sheetsPhotoswitchOptical axis
There is provided an optical scanning type photoelectric switch capable of preventing interference with another photoelectric switch by use of its own capability, wherein, as for light projection pulse periods of the first and second optical scanning type photoelectric switches, the period is set to 30 μs in the first optical scanning type photoelectric switch while the period is set to 33 μs in the second optical scanning type photoelectric switch 1B, the light projection pulses have the same pulse width, and by setting the light projection periods different between the first and second optical scanning type photoelectric switches, even if mutual interference occurs between any optical axes, a phase difference of 36 degrees in rotation period is generated therebetween in a next scan, thereby preventing occurrence of the interference in succession in a plurality of times of scanning.
Owner:KEYENCE
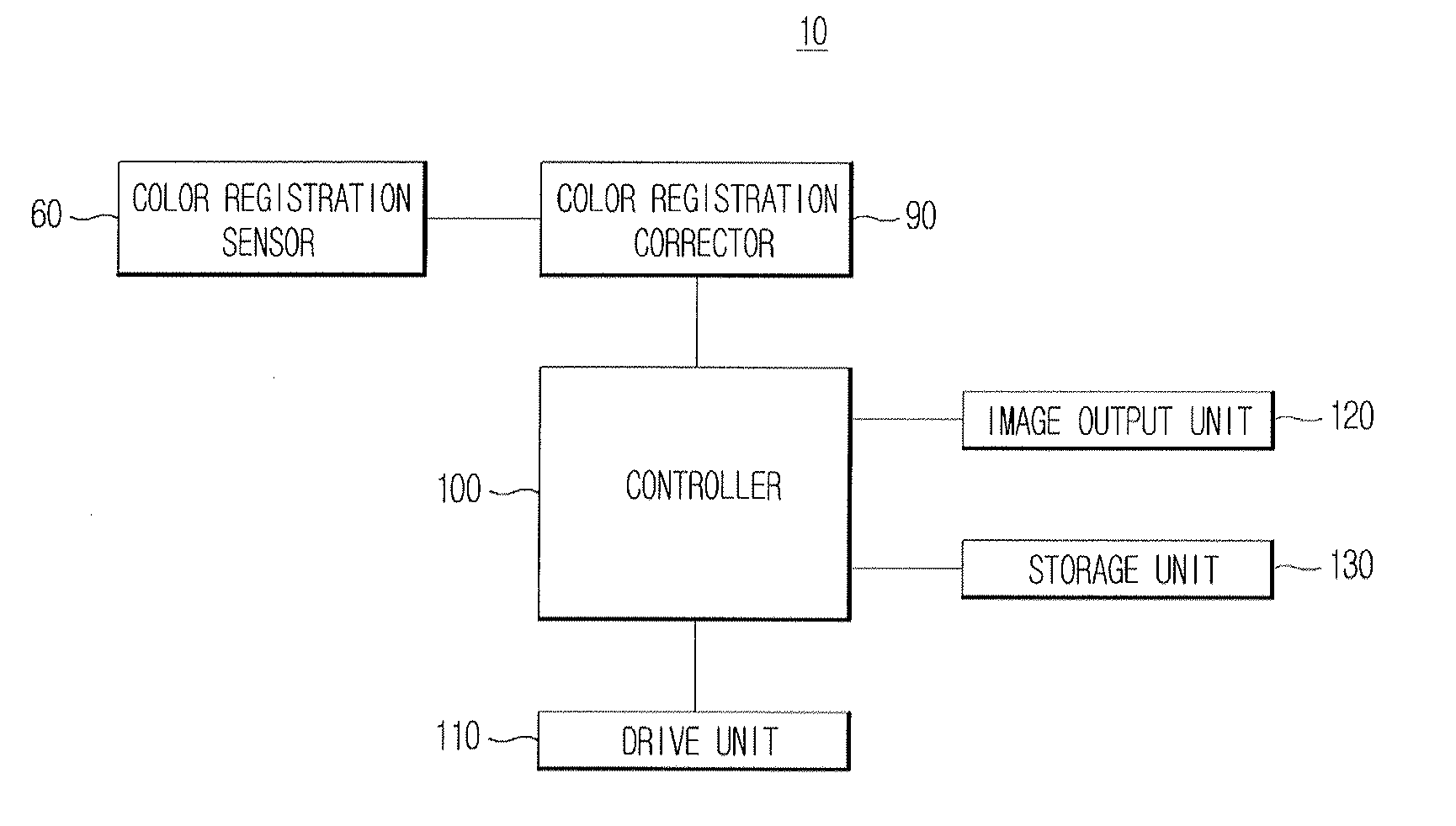
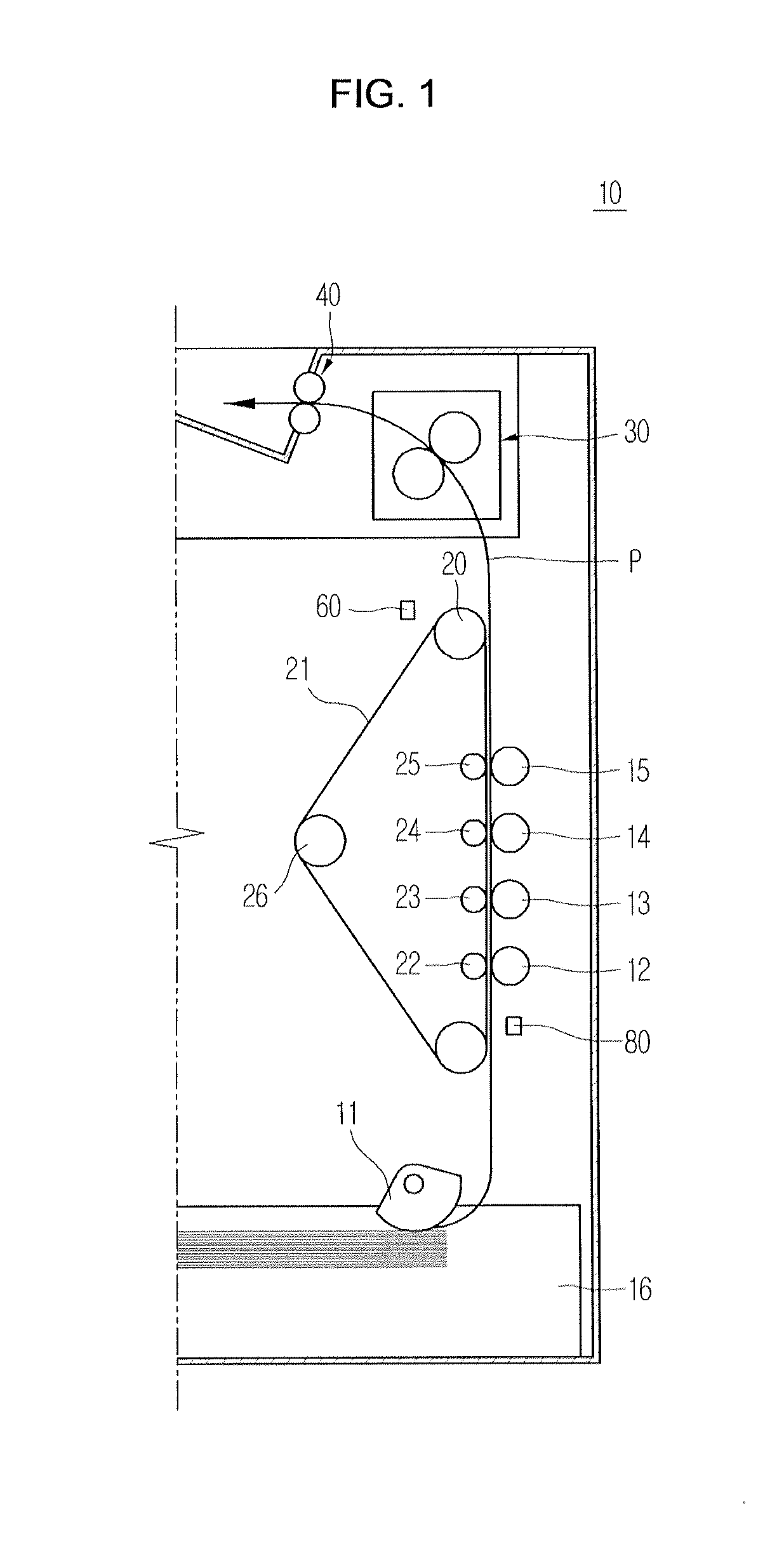
Image forming apparatus and auto color registration method thereof
ActiveUS20100178084A1Accurate correctionImprove image qualityDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImage formationRotation cycle
An image forming apparatus and an auto color registration method thereof. The image forming apparatus performs an auto color registration (ACR) operation by excluding or minimizing the influence caused by variation in speed of a drive unit driving a transfer member. The image forming apparatus includes a controller, which prints a test pattern of each color according to a rotation period of the drive unit, and controls an operation for outputting an image in which each color registration error is corrected on the basis of the test pattern, such that a reliability of the ACR operation is increased and a quality of an image output from the image forming apparatus is also increased.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
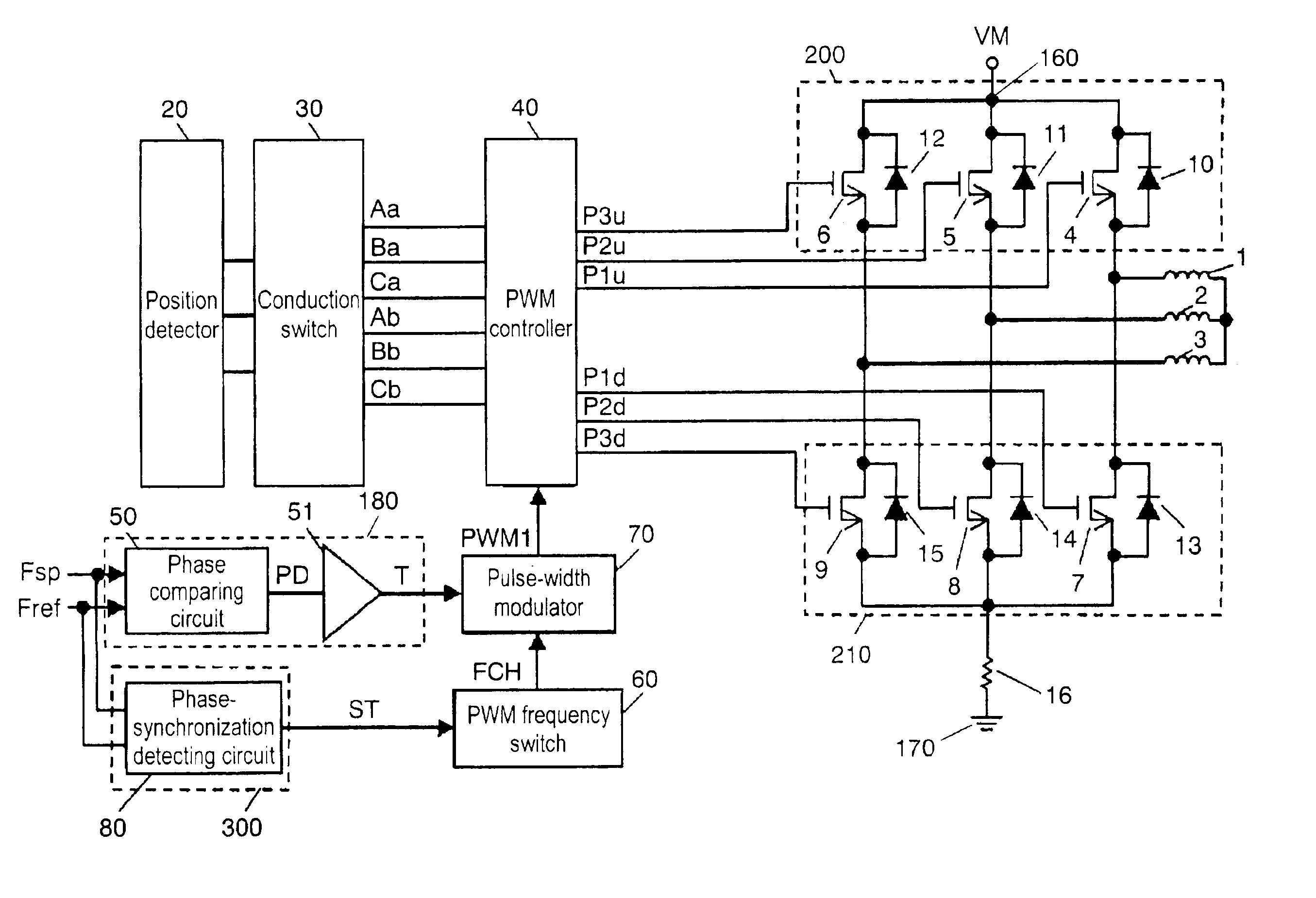
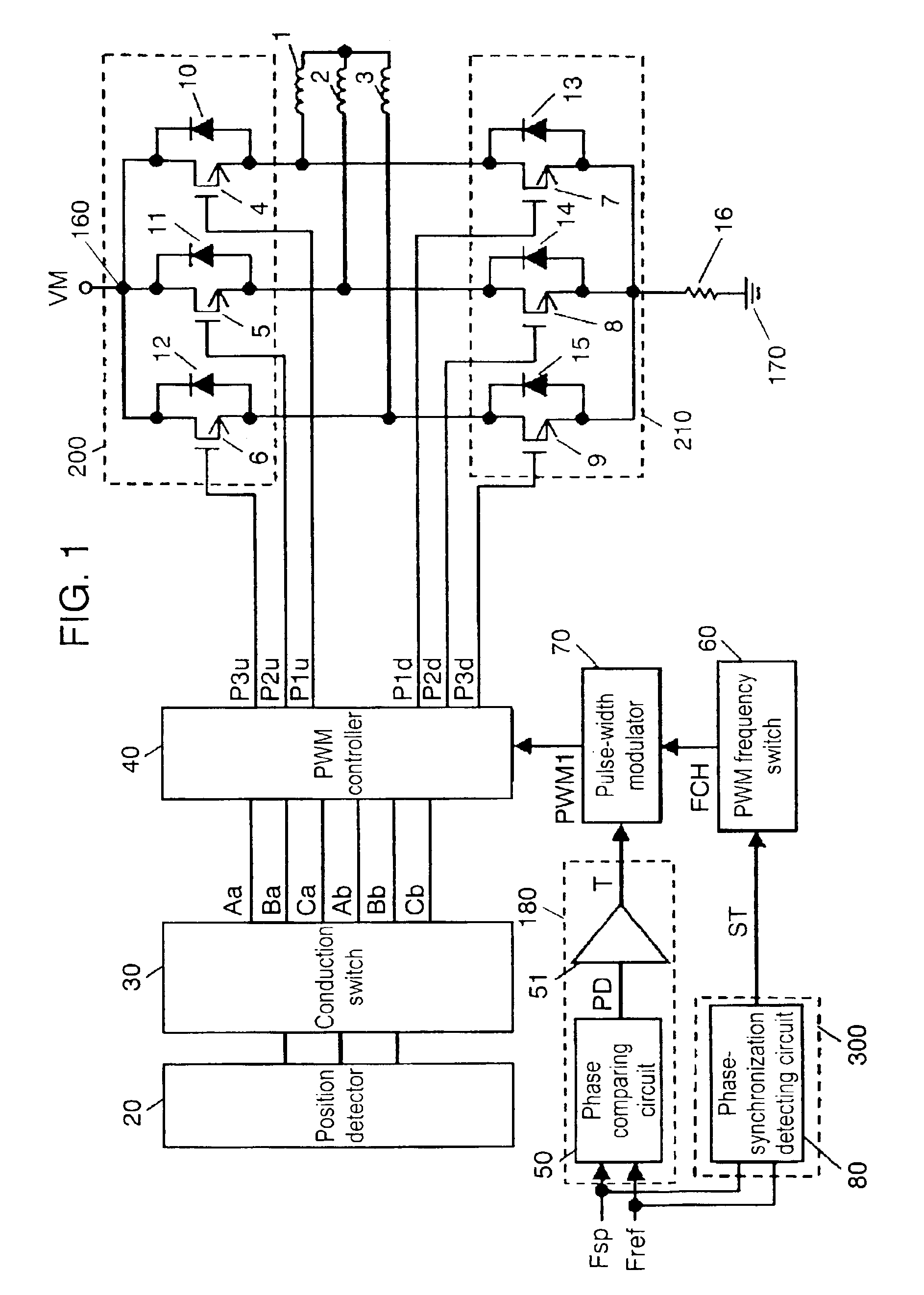
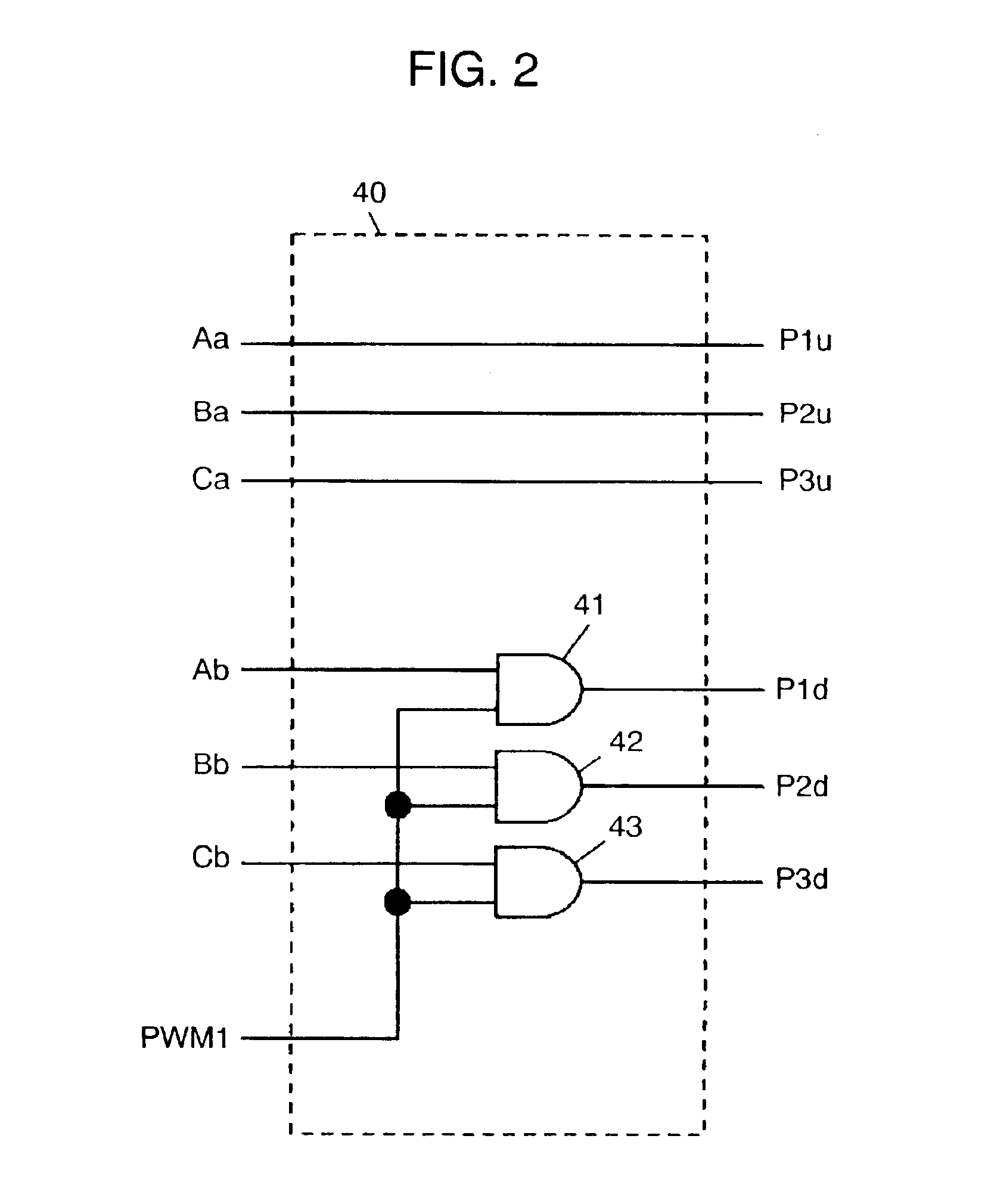
Motor driving apparatus and motor using the same
InactiveUS6873125B2Reduce power lossHigh rotation accuracyMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersMotor driveElectric machine
A motor driving apparatus includes a pulse-width modulator and a PWM frequency switch for switching a carrier frequency of the modulator. The PWM frequency switch changes a carrier frequency in a start-up period of the motor to another frequency when the motor enters into a regular rotation. The carrier frequency in the start-up period is set at a lower level than that in the regular rotation period, so that the driving apparatus can reduce power-loss generated in the start-up period by switching actions of respective driving elements forming a first and a second drivers. In the regular rotation period, the driving apparatus performs PWM-driving with a high enough carrier frequency, so that the motor driven by this driving apparatus can realize accurate rotation.
Owner:MINEBEA MOTOR MFG
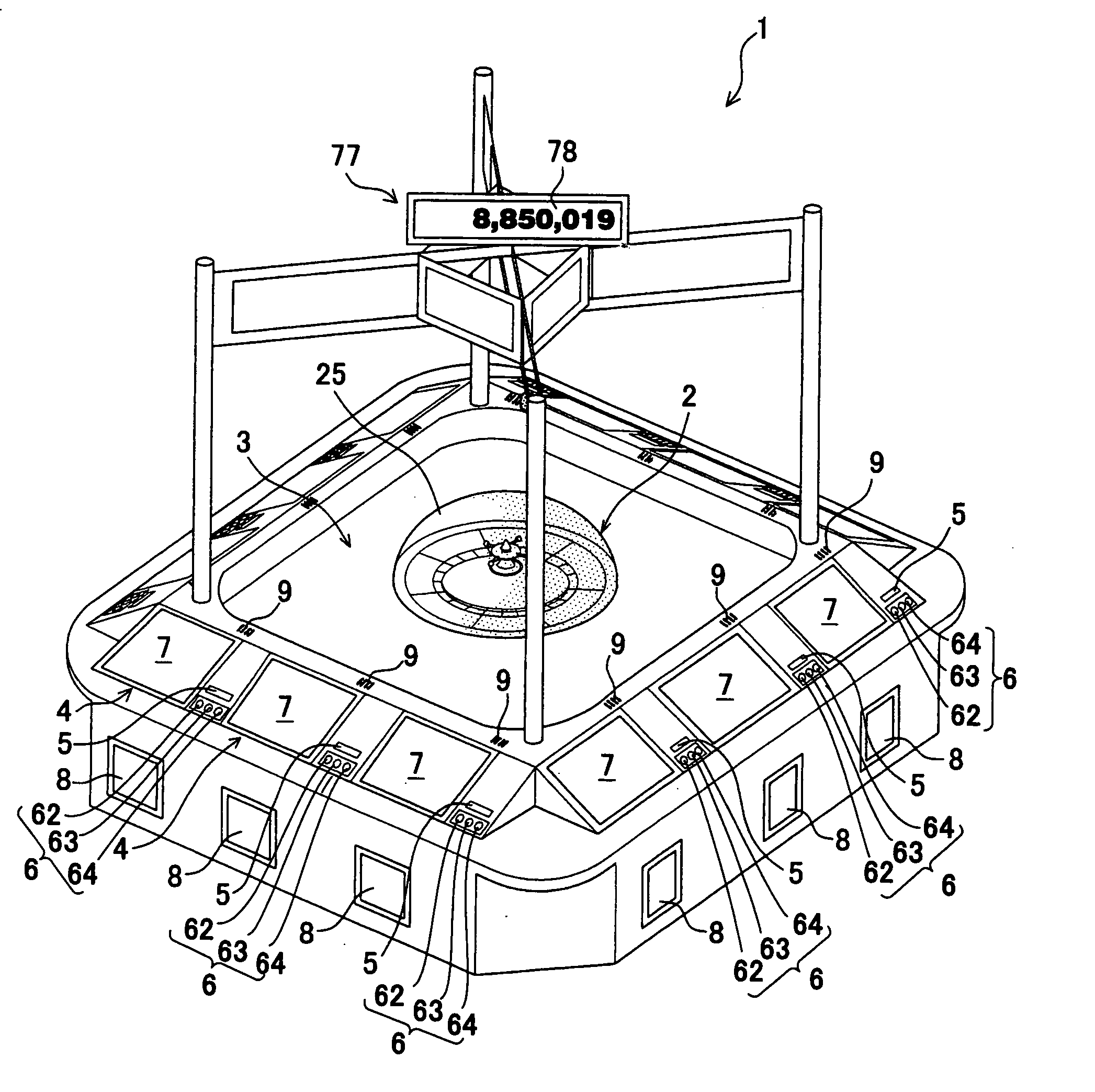
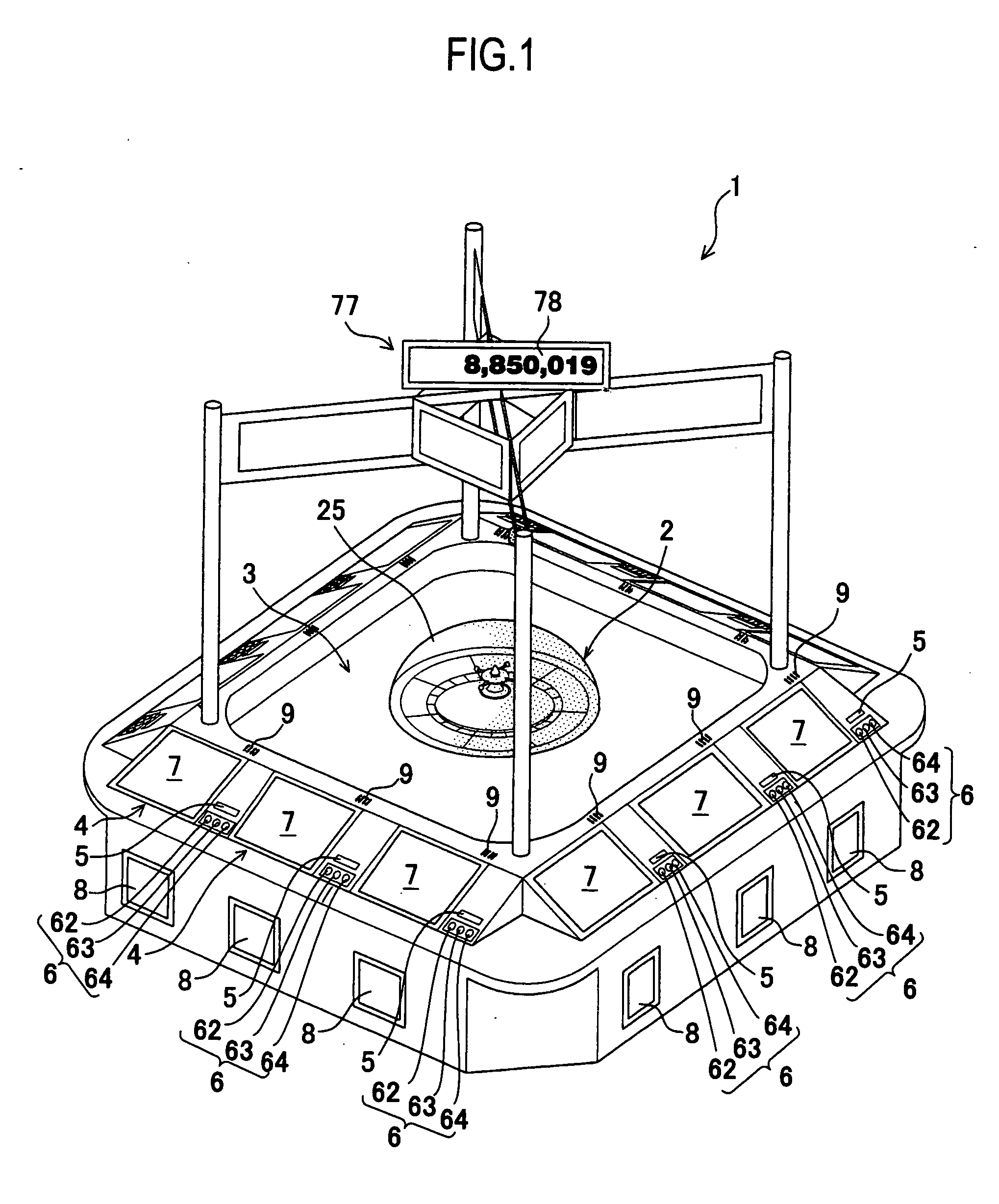
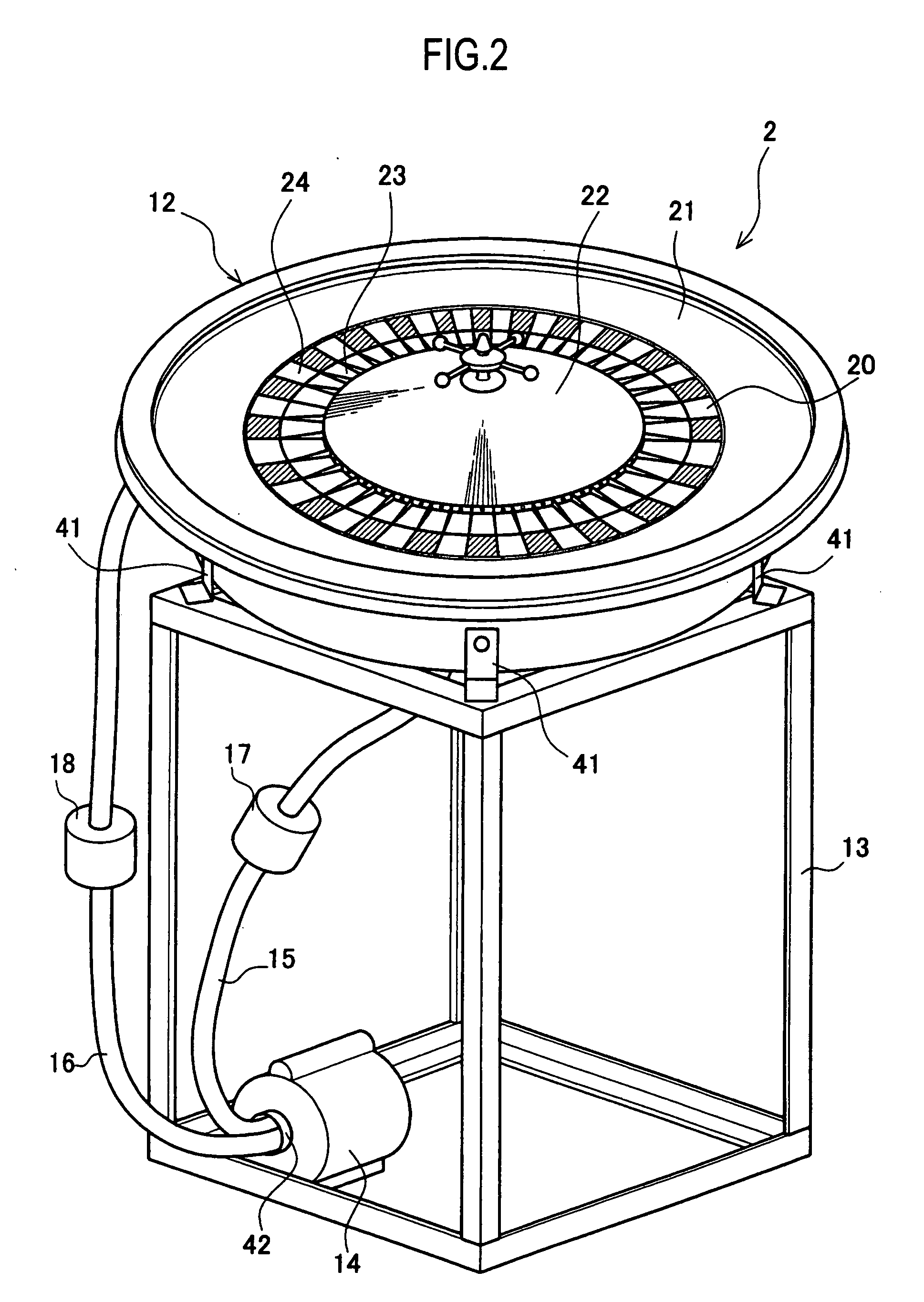
Roulette gaming machine and method for selecting constant rotation period
ActiveUS20070010312A1Easily and surely preventEasily and surely preventingRoulette gamesVideo gamesEngineeringDrive motor
A roulette gaming machine comprises a roulette board, a ball, a rotatable portion, ball receiving parts, numerals, a driving motor and a main control CPU. The rotatable portion is rotatably provided at a center portion of the roulette board. The ball receiving parts receives the ball and circularly arranged on an inner periphery side of the rotatable portion. The numerals are circularly arranged on an outer periphery side of the rotatable portion so as to be opposed to the ball receiving parts respectively. The driving mortor rotates the rotatable portion in a certain direction. The main control CPU selects a drive control pattern. The main control CPU varies a constant speed rotation period for rotating the rotatable portion at a certain rotation speed according to the drive control pattern, and controls the driving unit according to the constant speed rotation period and the certain rotation speed.
Owner:UNIVERSAL ENTERTAINMENT CORP
Tension control method
The invention discloses a tension control method which comprises the steps: 1, unreeling a tape coil by an unreeling roll, and winding the unreeled tape coil onto a reeling roll through a tension roll; 2, acquiring the original roll diameters of the unreeling roll and the reeling roll; 3, acquiring time-varying real-time roll diameter(s) of the unreeling roll and / or the reeling roll in a tape coil winding process; 4, integrating input information in the steps 2 and 3, carrying out an interpolation operation on the input information, respectively working out rotation positions of motors of the unreeling roll and the reeling roll once the tape coil is wound by a distance L, and respectively outputting the rotation positions to the motor of the unreeling roll and the motor of the reeling roll through an information output unit; and 5, running the motor of the unreeling roll and the motor of the reeling roll according to the position information output in the step 4, wherein the interpolation operation in the step 4 is that an interpolator carries out calculation on pulses required by the rotation of the motors or a bus controller carries out the calculation on the positions of the rotation periods of the motors. The tension control method disclosed by the invention is simple in control manner, easy to realize, high in control precision and good in system operation stability.
Owner:ADTECH SHENZHEN TECH
Image heating apparatus and image forming apparatus
An image heating apparatus comprising an endless belt for heating an image on a recording material; heating means for heating a part of the endless belt; driving means for rotating the belt; a first contact member for contacting an inner surface of the belt; stand-by control means operable in a stop period in which the heating means effects heating with the belt at rest and in a rotation period in which the belt is rotated; and drive stop control means for stopping, upon stoppage of rotation of the in the rotation period, the endless belt at such a position that contact member contacts at least a part of such a portion of the endless belt as has been opposed to the heating means in a previous stop period.
Owner:CANON KK
X-ray ct device
ActiveUS20060140337A1Reduces noise level differenceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayComputer science
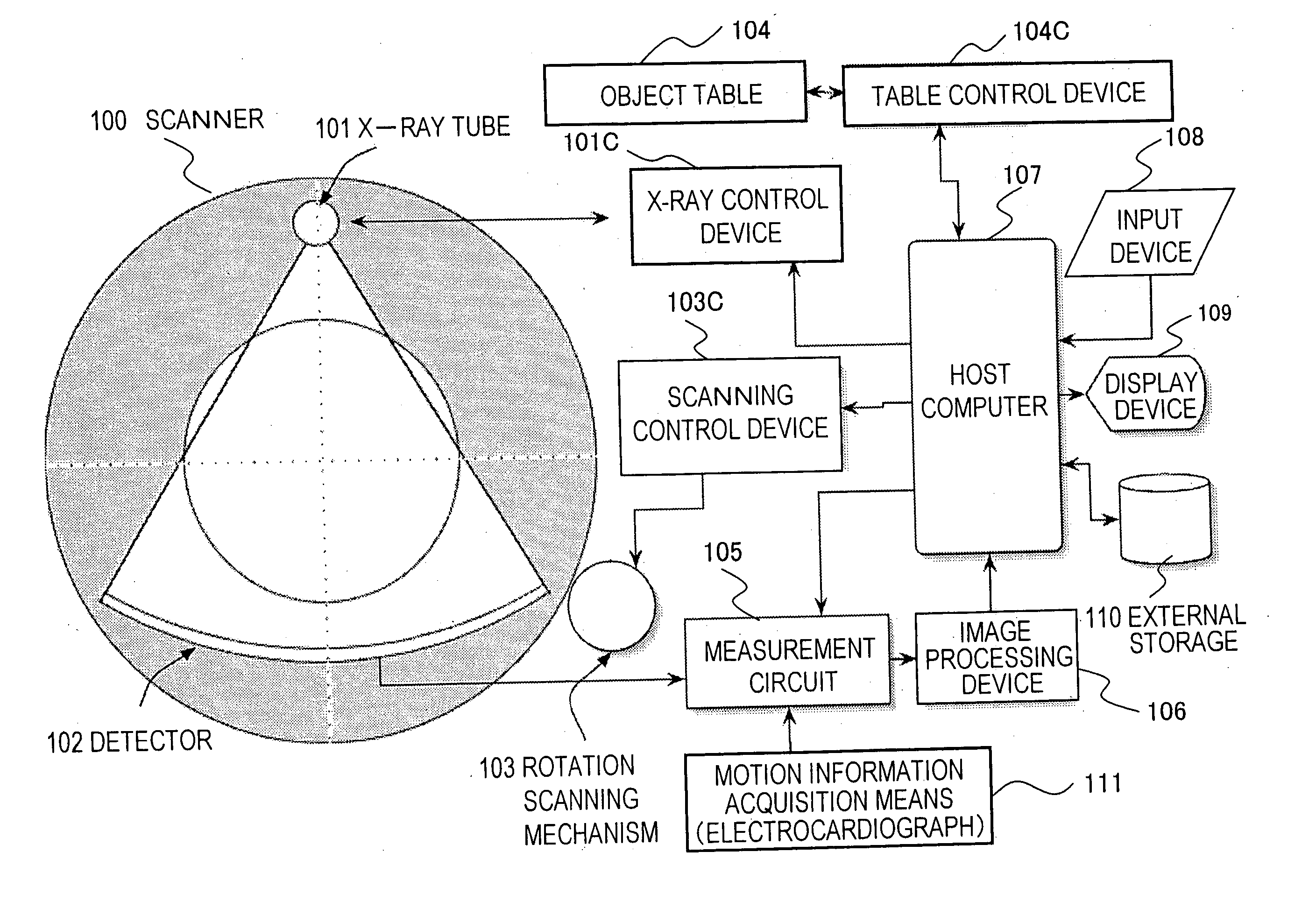
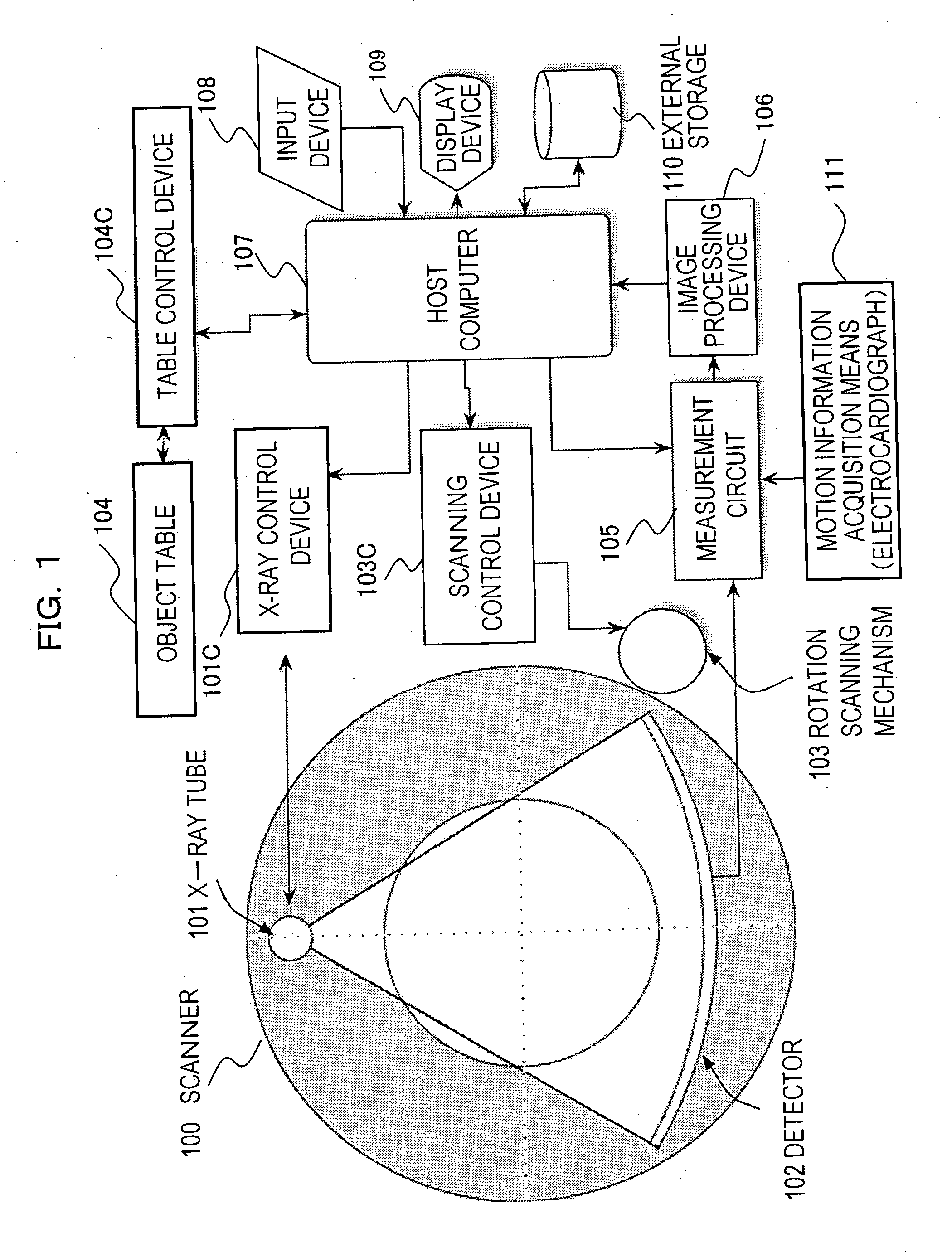
An X-ray CT apparatus comprises: motion information acquisition means that acquires periodical motion information on a motion portion of an object to be examined; a detector that rotates together with an X-ray source and detects X-rays applied to the object from the X-ray source to acquire projection data per collection region; and reconstruction means that processes the projection data resulting from the detector to reconstruct a tomogram of the object, wherein the X-ray CT apparatus further includes delay time determination means that determines a delay time by adding a time width of the collection region and a processing delay time in the X-ray CT apparatus and a time interval from the moment when the phase of the measured periodical motion information is matched with the phase of the rotation period of the X-ray CT apparatus to the moment when they are matched next time, and collection means that correlates, with the periodical motion information obtained by the motion information acquisition means, and successively collects the projection data obtained from the detector, with the reconstruction means starting reconstruction of the tomogram after the delay time.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Electronic device with variable chopping signal and duty ratio selection for strong braking
InactiveUS6483276B1Low costSimple configurationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlElectric power systemClosed loop
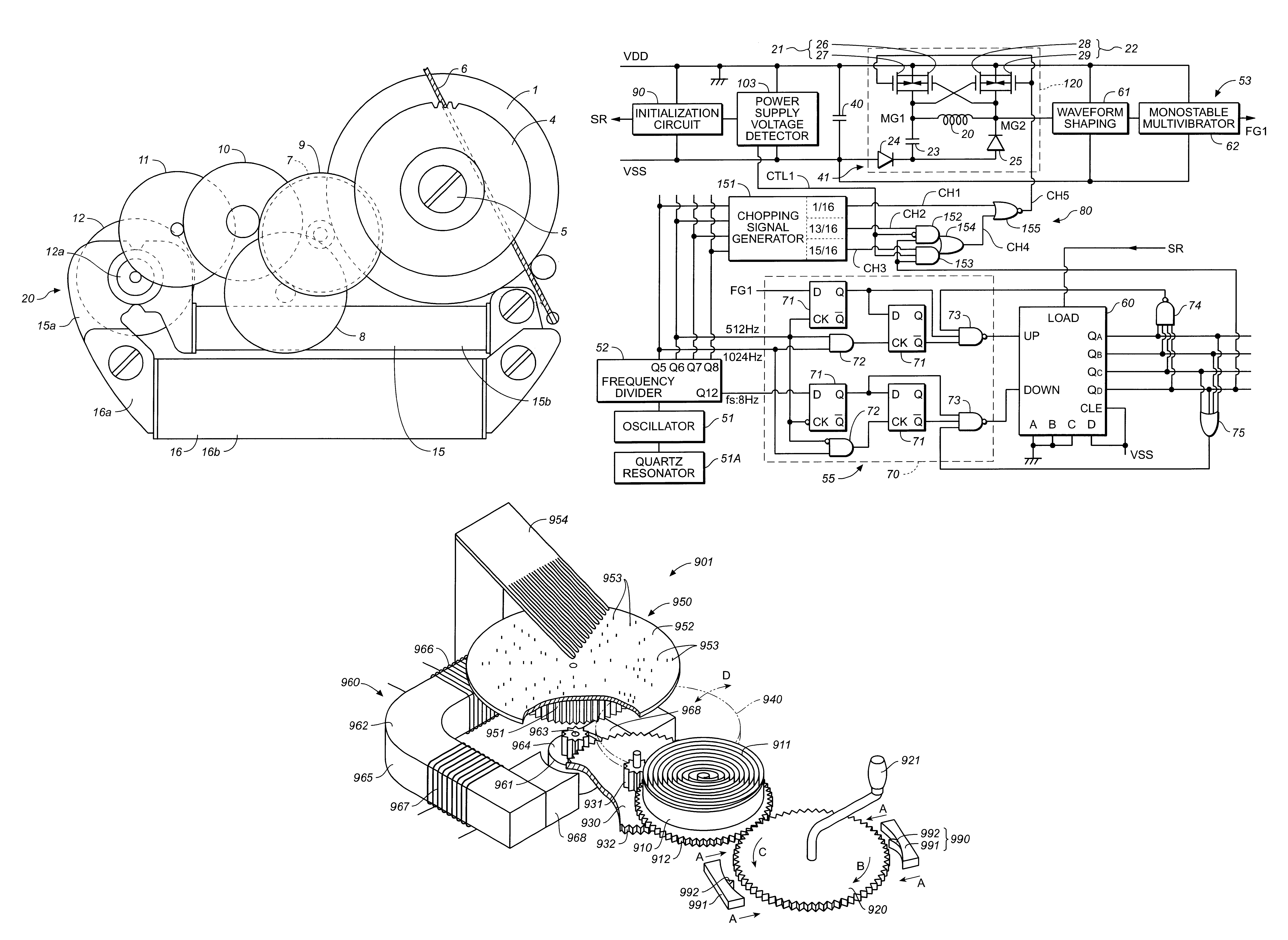
An electronic device capable of increasing the braking torque applied to an electric power generator without causing a significant reduction in electric power generated by the electric power generator. The electronic device, which may be embodied in an electronically controlled mechanical clock, includes an electric power generator for converting mechanical energy transmitted from a spring via a wheel train to electrical energy, and a rotation controller for controlling the rotation period of the electric power generator. The rotation controller includes switches capable of connecting two terminals of the electric power generator in a closed-loop state, a chopping signal generator for generating two or more types of chopping signals which are different in duty ratio or frequency for use in a strong braking operation, and chopping signal selector that selects one of the chopping signals, wherein, in the strong braking operation, the selected chopping signal is applied to the switches so as to control the electric power generator in a chopping fashion. The strong braking operation is performed in one of two modes such that a higher priority is given to generation of electric power or the braking torque depending on the mode, thereby achieving an increase in the braking torque of the electric power generator without causing a significant reduction in the voltage generated by the electric power generator.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Resonance demodulation double isolate frequency spectrum method for detecting crack of gear shaft
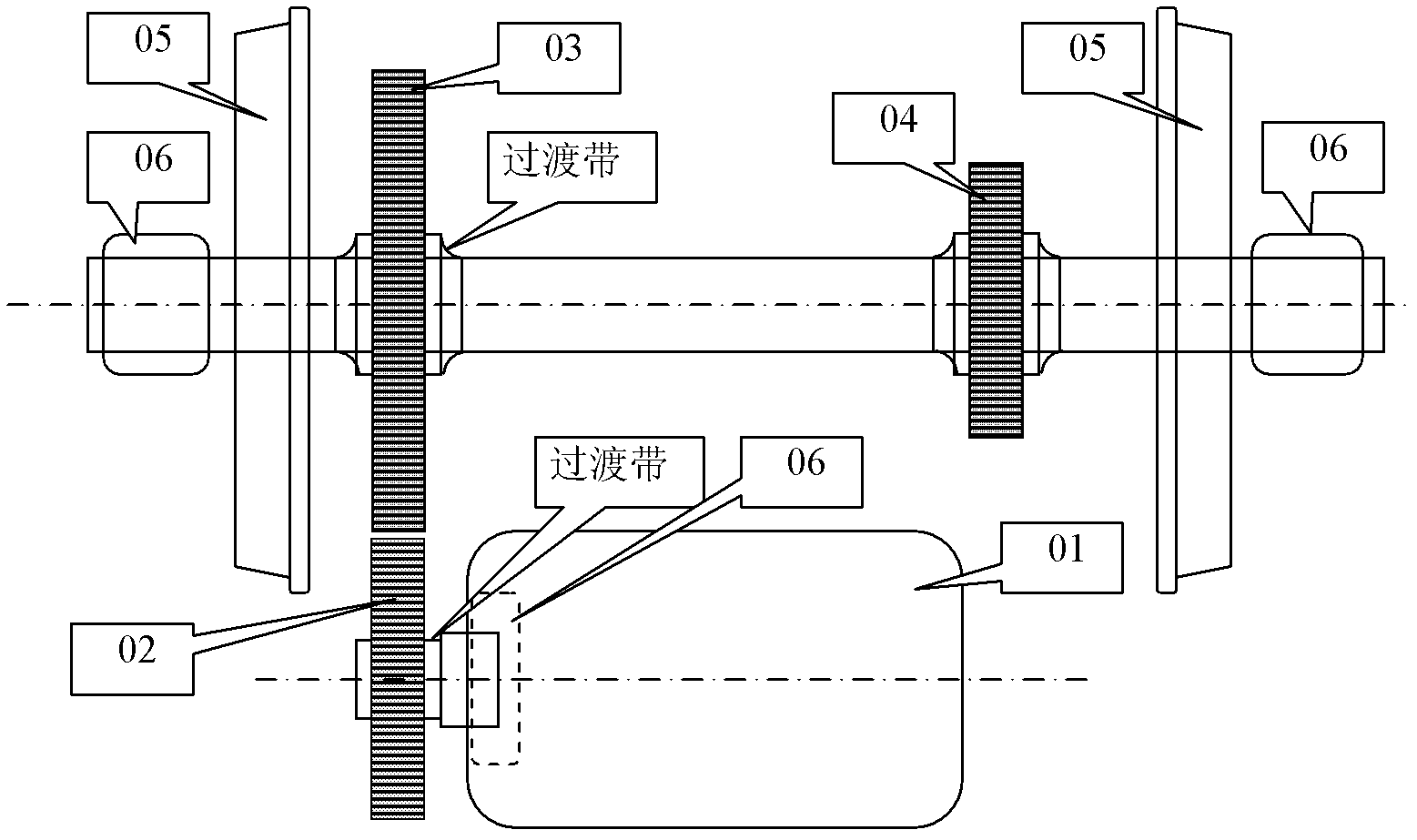
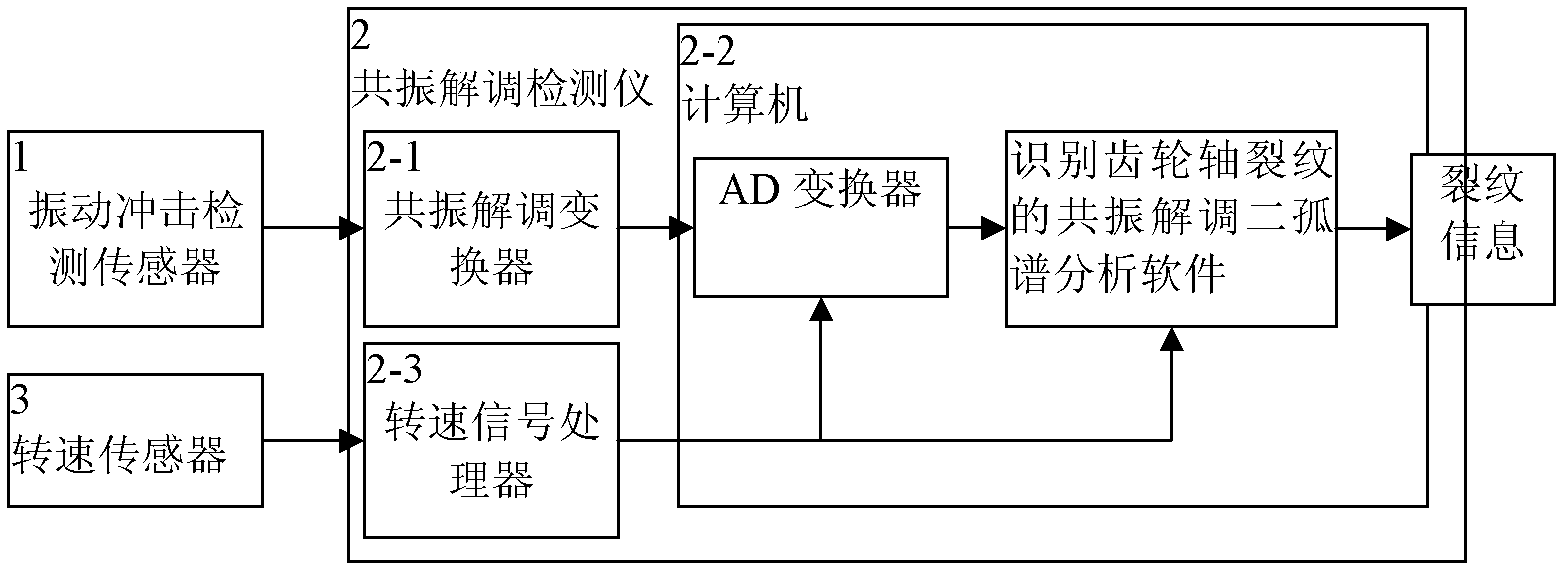
ActiveCN102426102AAvoid downtime lossesAvoid damageMachine gearing/transmission testingFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a resonance demodulation double isolate frequency spectrum method for detecting crack of a gear shaft. Analysis of resonance demodulation wave is obtained by performing resonance demodulation separation processing and AD (Analog-Digital) converter sampling on a vibration impact signal detected on a bearing close to a gear; and if discovering that the resonance demodulationtime domain waveform occurs two clusters of basically symmetric meshing impact waves in each rotation period of a shaft where the gear is positioned, a meshing impact spectrum of the gear occurs in an FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) analytical spectrum of the resonance deformation time domain waveform and double isolate frequency spectrum equal to rotation speed frequency of the gear shaft occurs, it is reported that the shaft has the crack. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of low cost, low loss and capability of on-line frequent detection, and plays an important role in guaranteeing safety of equipment, particularly personal safety.
Owner:TANGZHI SCI & TECH HUNAN DEV CO LTD
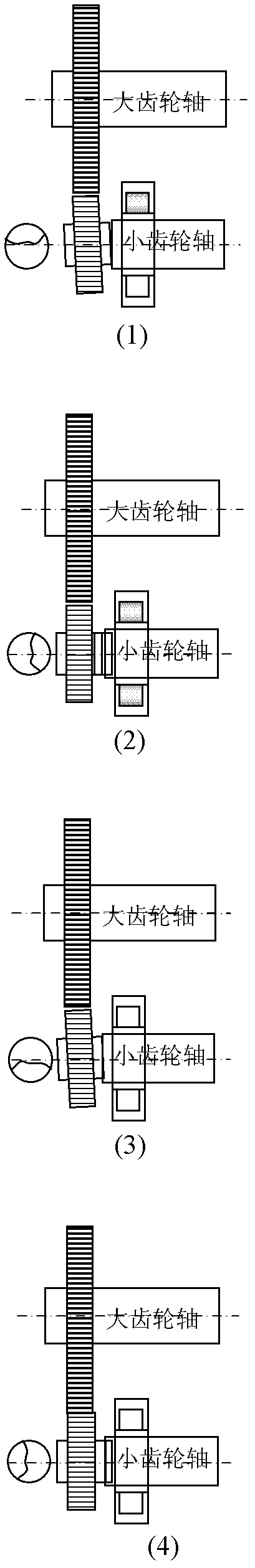
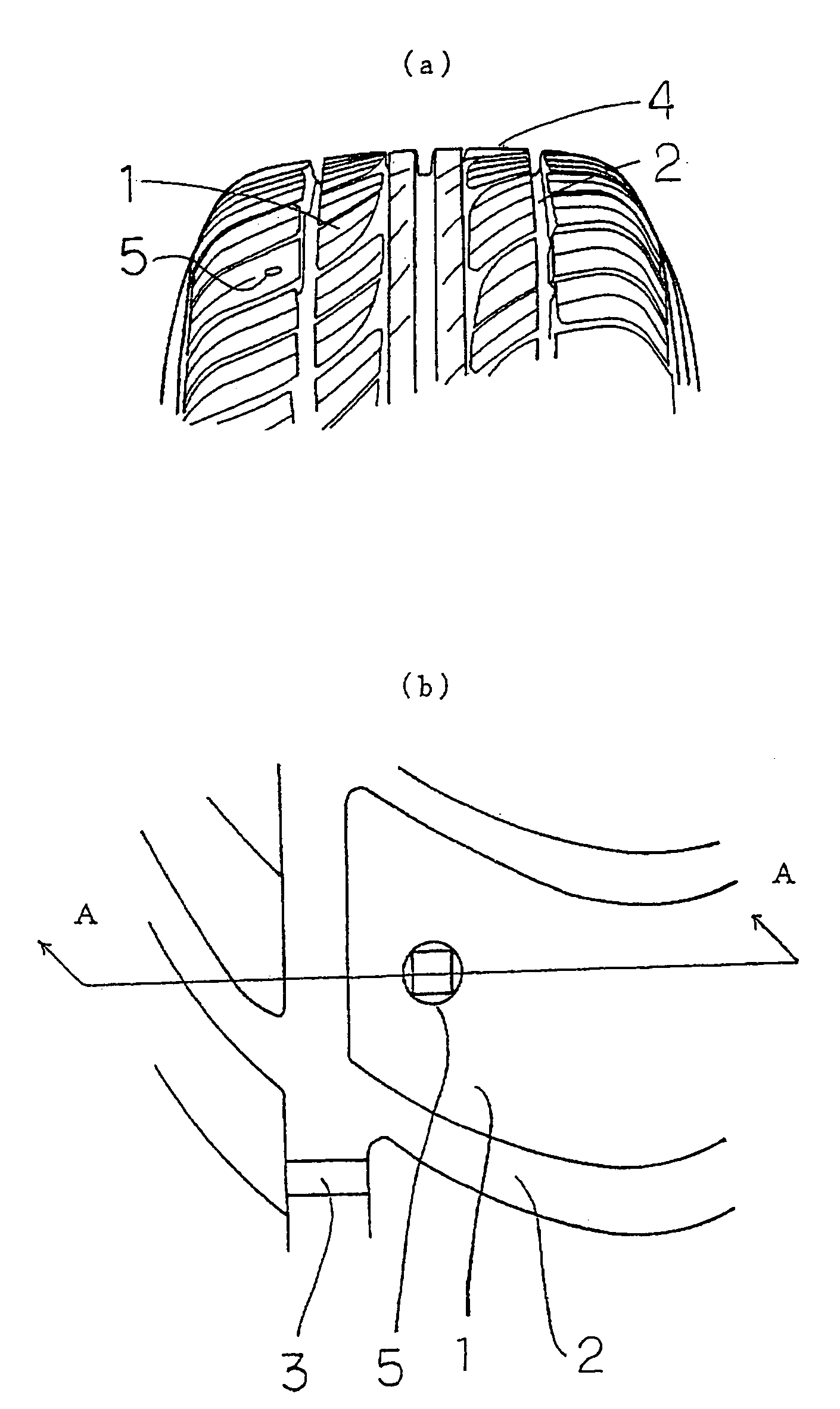
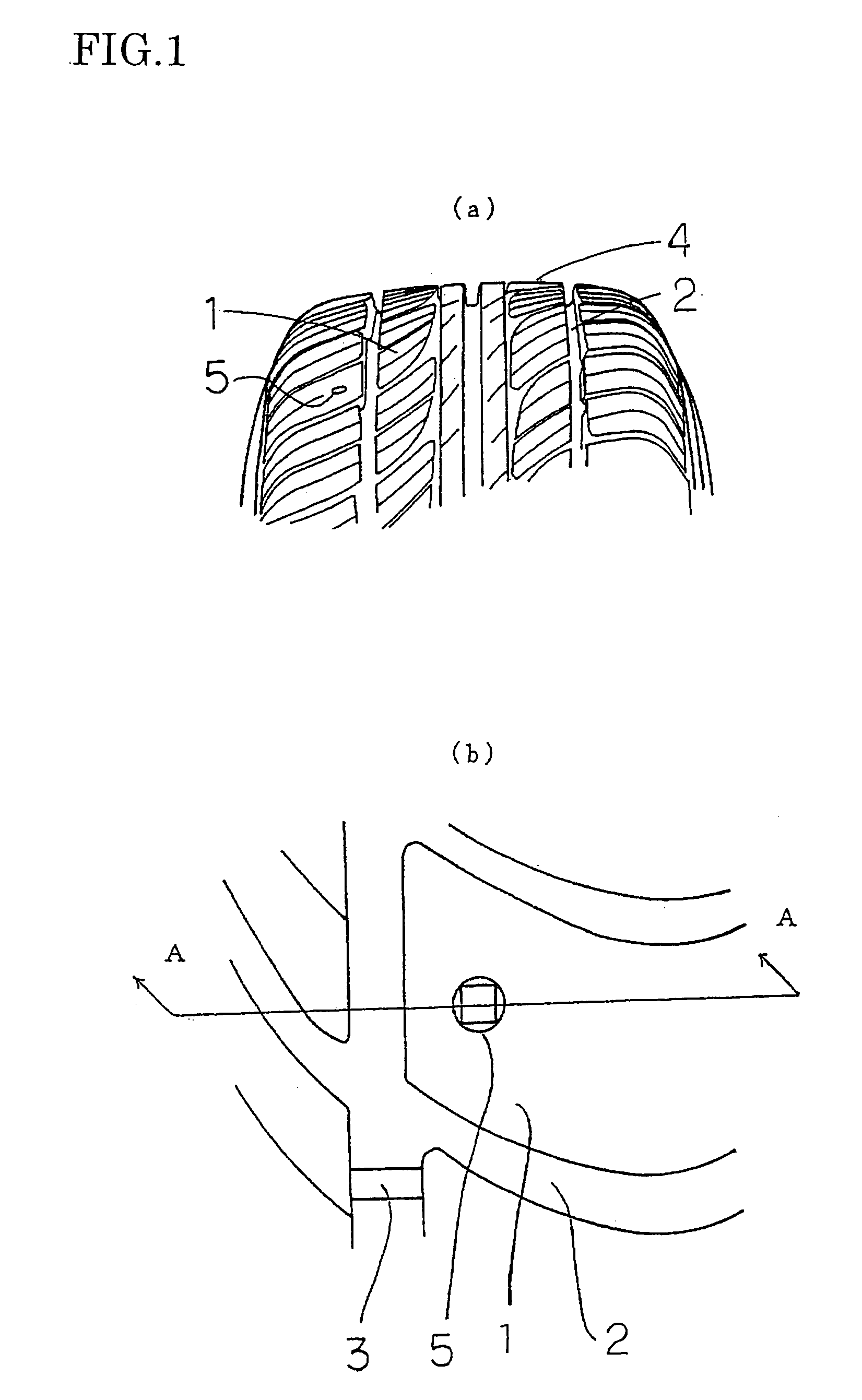
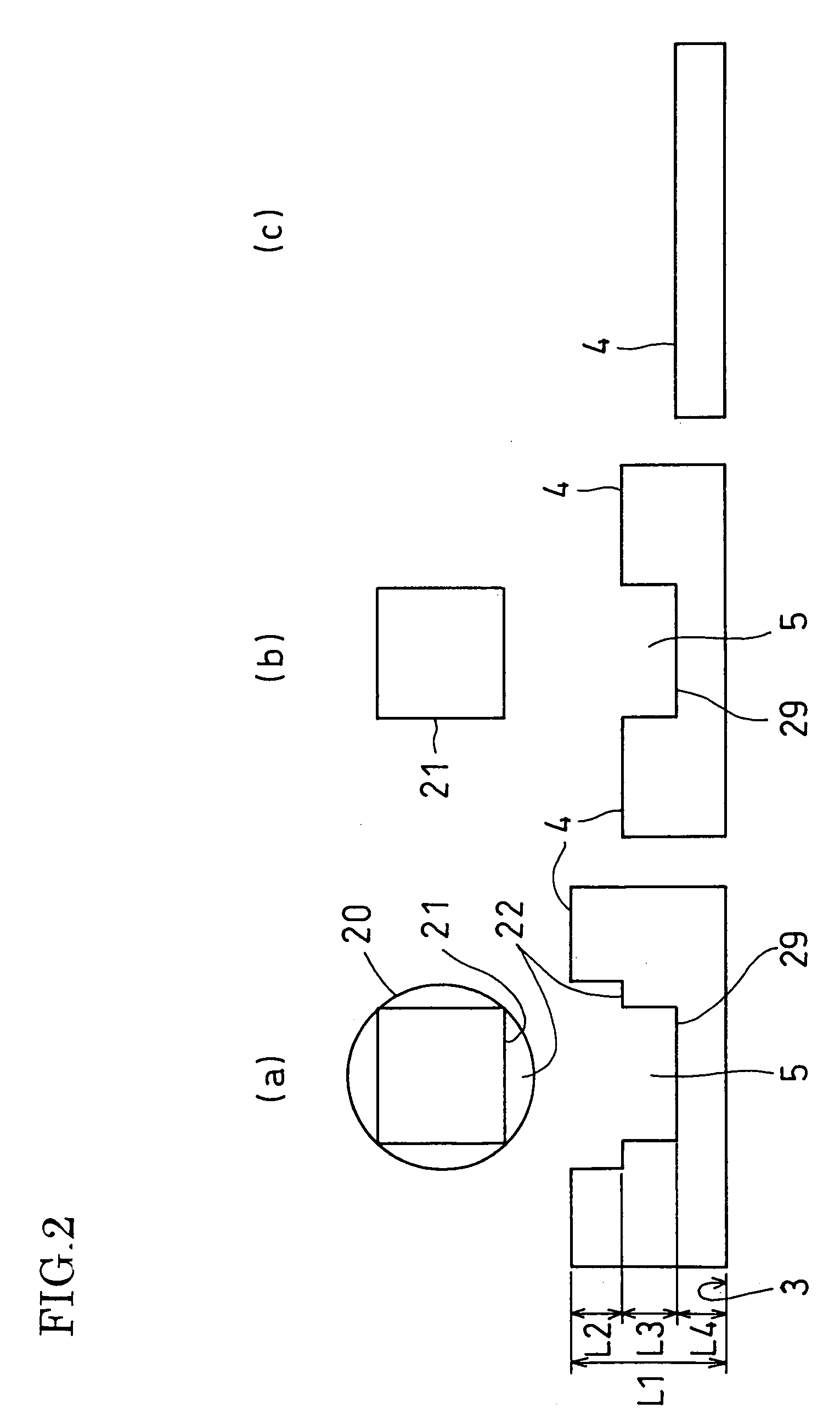
Tire with rotation period indication hole, and method of indicating tire rotation period
InactiveUS20050269003A1Easy to identifyAccurately indicatedTyre measurementsTyre tread bands/patternsTire rotationRotation period
A tire having a rotation timing indication hole of the invention has a rotation timing indication hole comprising a multi-step hole provided in a tire tread, and respective steps of the hole have different contours from each other. Since the contour of the hole changes when the tire is worn, the rotation timing of the tire can be recognized.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
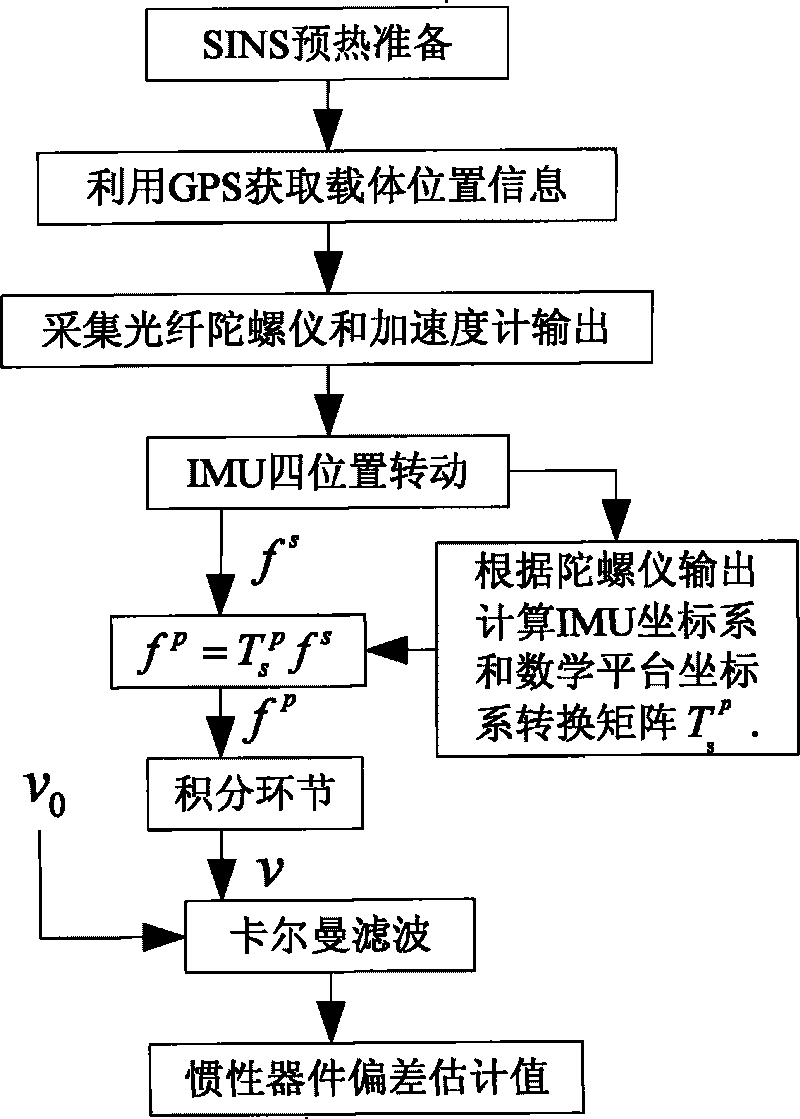
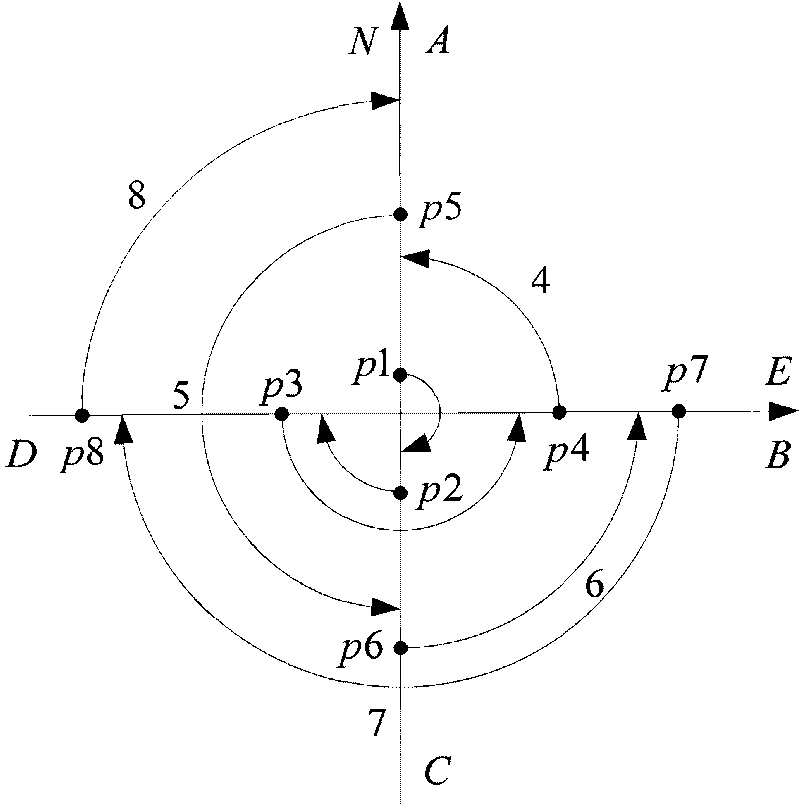
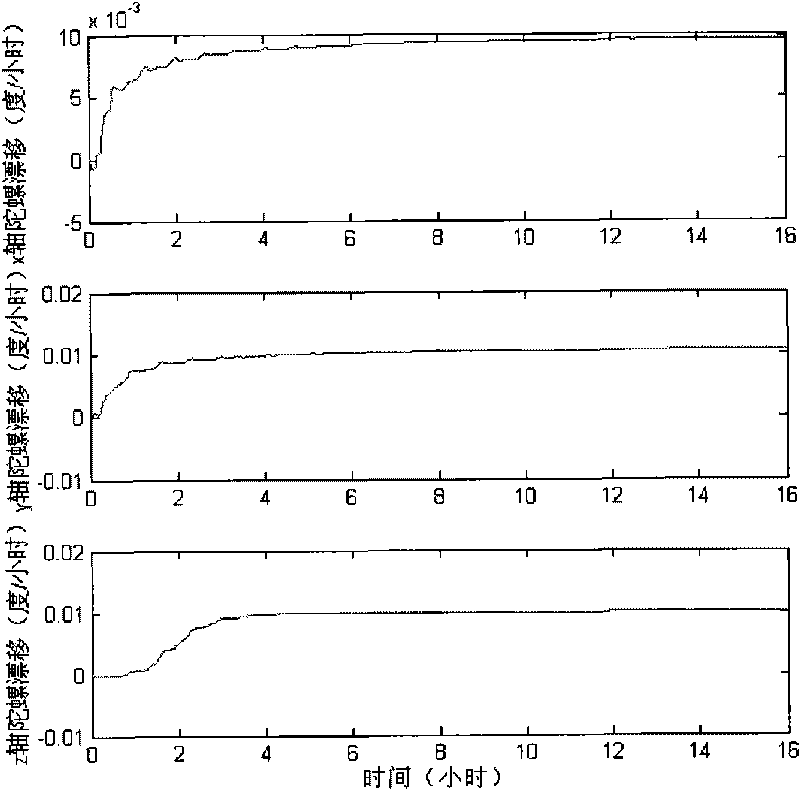
Single-shaft rotation-stop scheme-based mooring and drift estimating method
The invention provides a single-shaft rotation-stop scheme-based mooring and drift estimating method, which comprises the following steps: determining an initial position parameter through GPS; acquiring output of an optical fiber gyroscope and data output by and an accelerometer and processing the data; adopting 8 rotation-stop sequences as a transposition scheme of one rotation period by an IMU; performing real-time update on a strapdown matrix according to the output of the gyroscope under the rotation state of the IMU, and simultaneously performing coordinate conversion on acceleration information acquired under the rotation state of the IMU and converting the acceleration information to a mathematic platform coordinate system; establishing a Kalman drift estimation module of a separation position loop in a mooring state of a load according to a load moving base error model; and processing constant errors of inertial apparatuses obtained after Kalman filtering by an average filtering method to obtain a relatively stable estimated mean value. When the load is in a mooring state, the drift estimating method provided by the invention can accurately estimate the constant errors of the inertial apparatuses by the Kalman filtering technology.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for Aligning and Starting a BLDC Three Phase Motor
InactiveUS20110291597A1Keep energy smallOperate efficiently and effectivelyMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersThree-phaseEngineering
System and method for aligning and initiating rotation of a rotor in a motor. The motor may include the rotor and a plurality of pairs of electromagnets. The energy needed for alignment of the rotor of the motor may be used to generate the first movement in forced commutation. The energy needed for alignment may be combined with the initial energy to start the motor. The logic may be configured to align the rotor of the motor by energizing the three coils of the motor. Pulse width modulation may be applied to the first coil to control current on the coils; when a maximum PWM duty cycle is reached, the coil not required to rotate the correct direction may be released, thereby initiating motion in a rotor of the three phase motor. A rotation period may be determined. One or more pairs of electromagnets of the plurality of pairs of electromagnets may be excited at a first excitation level. The excitation level may be increased, over a second period of time, to a second excitation level. The second excitation level may be a higher excitation level than the first excitation level. The rotation period may be decreased over the first and second periods of time.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
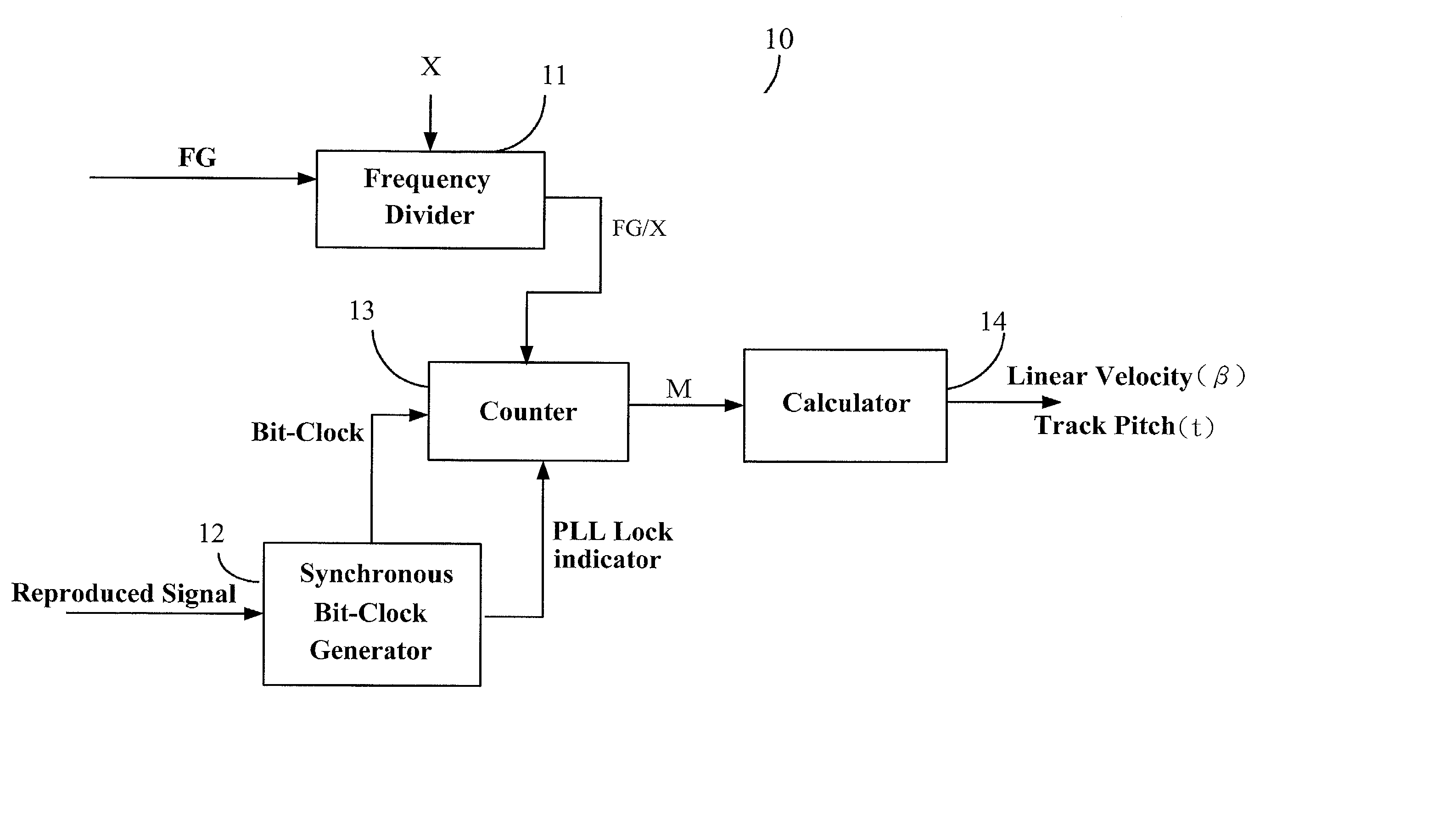
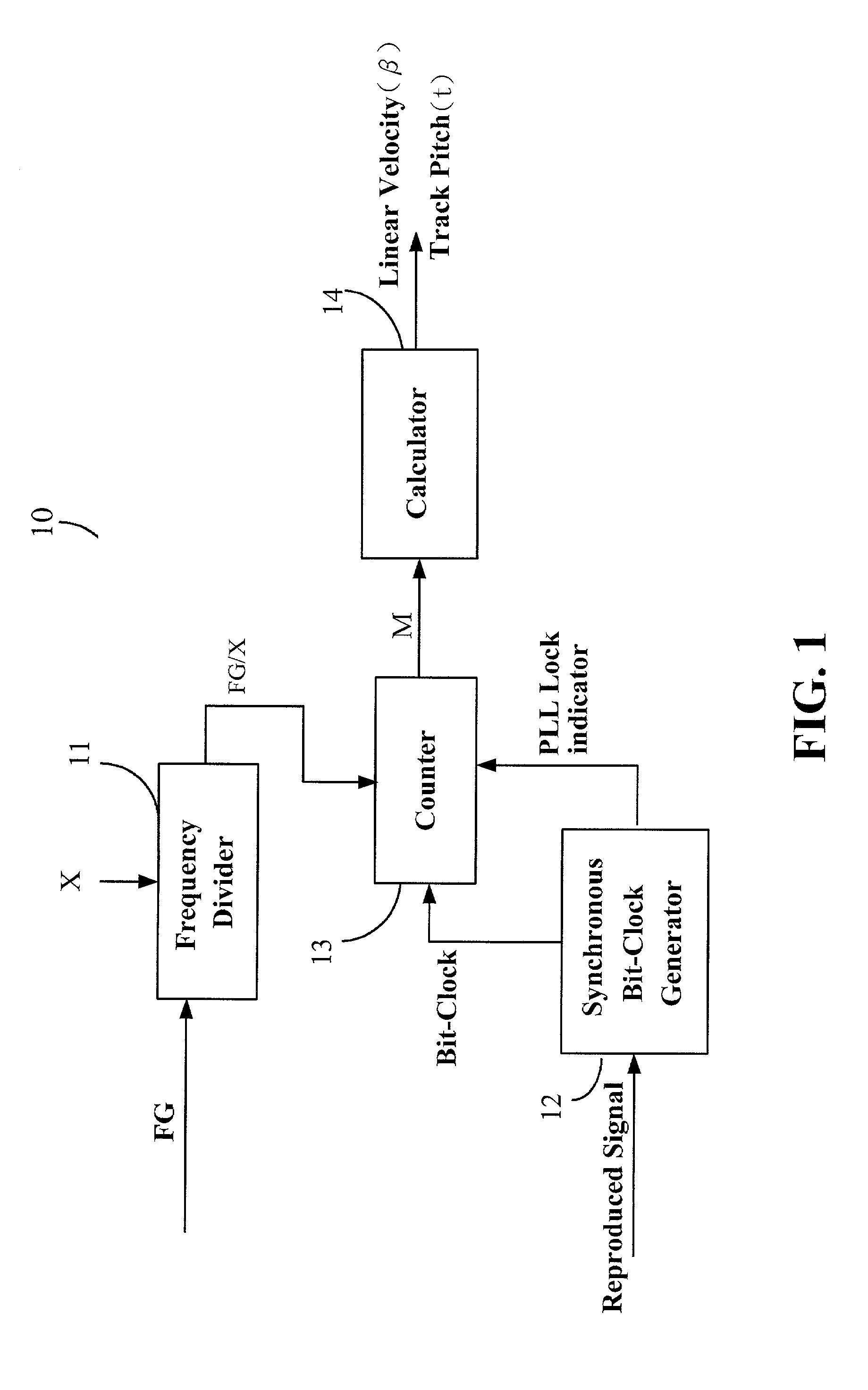
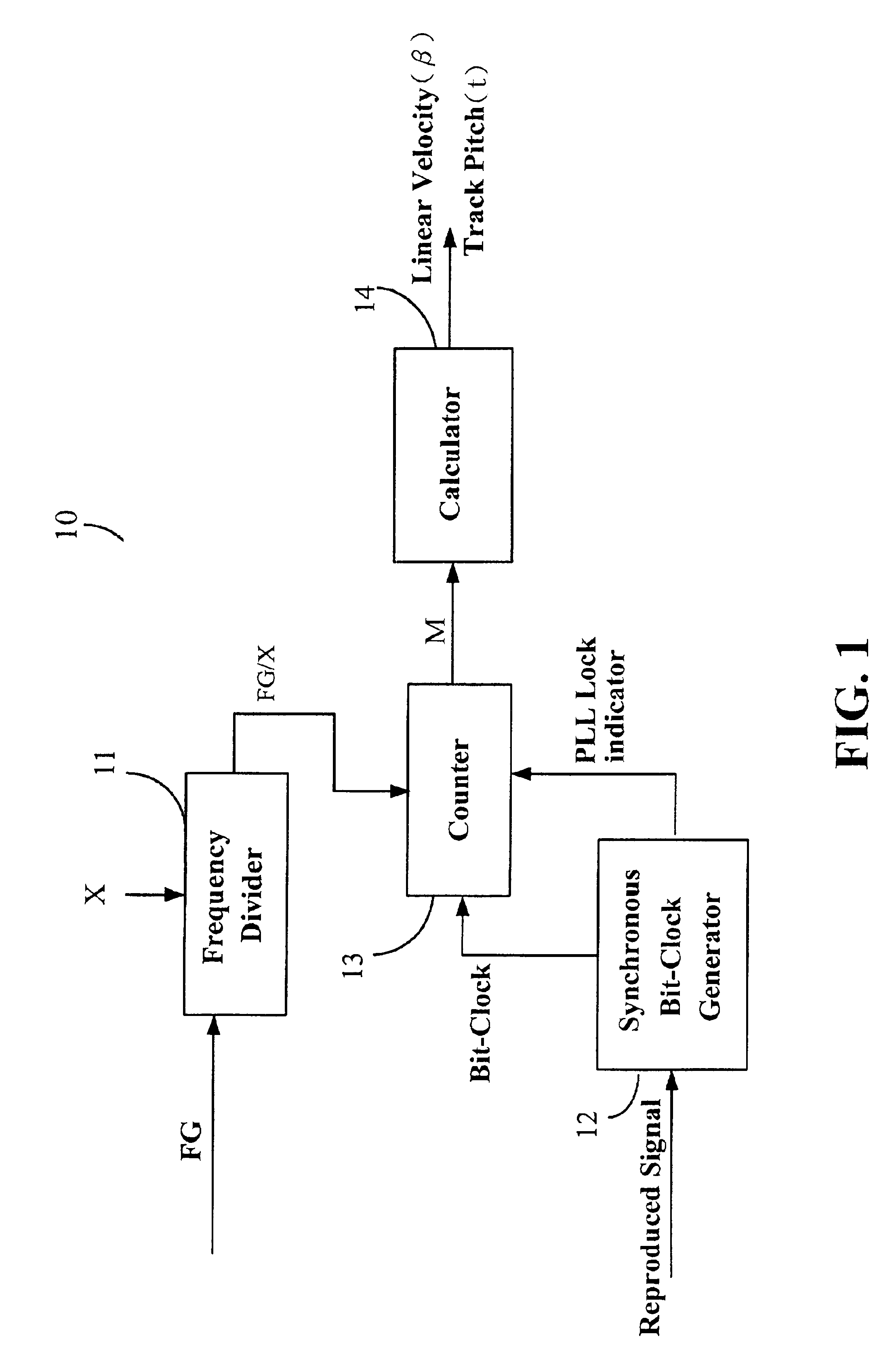
Device and method for calibrating linear velocity and track pitch for optical disc drive
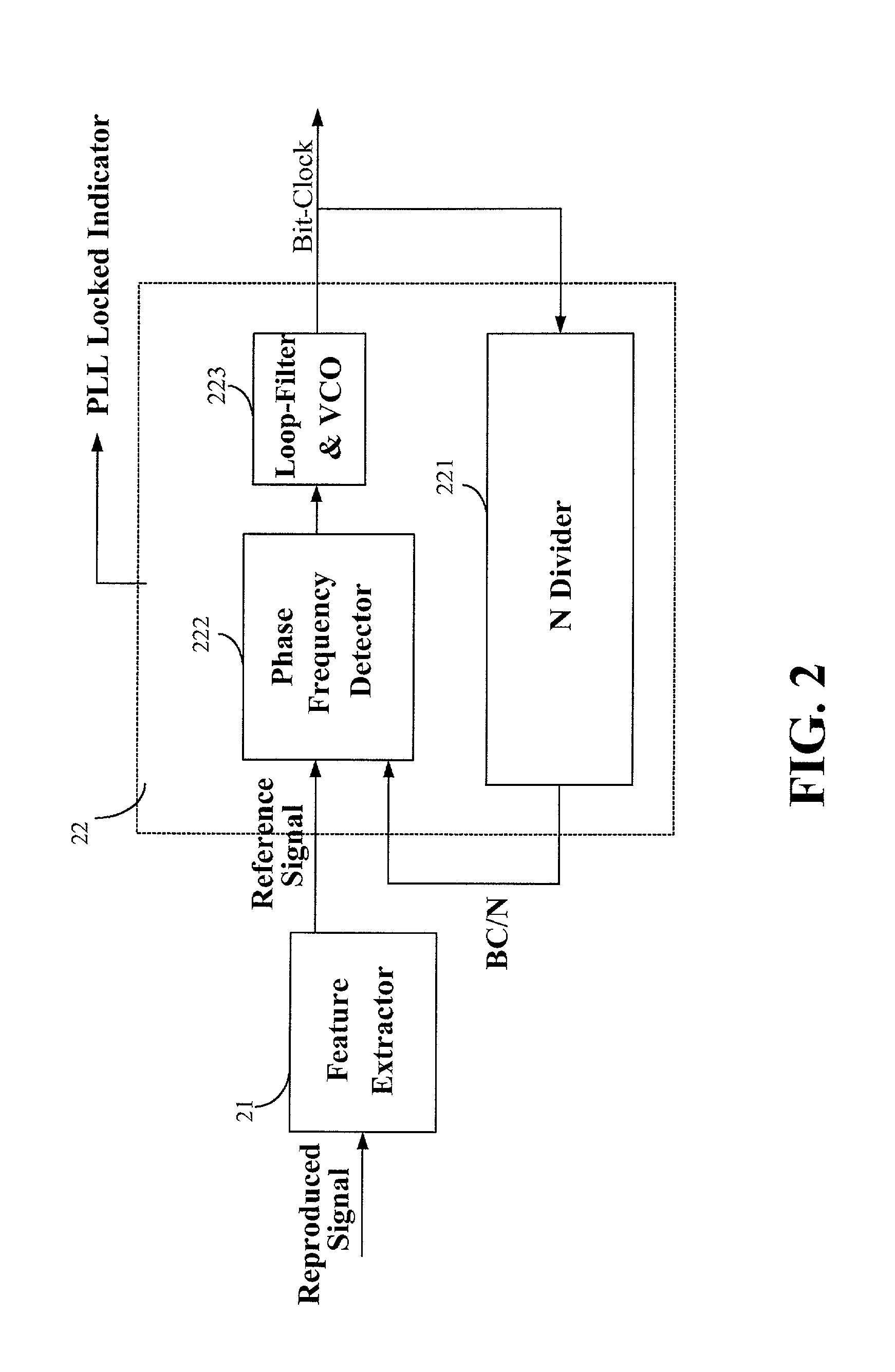
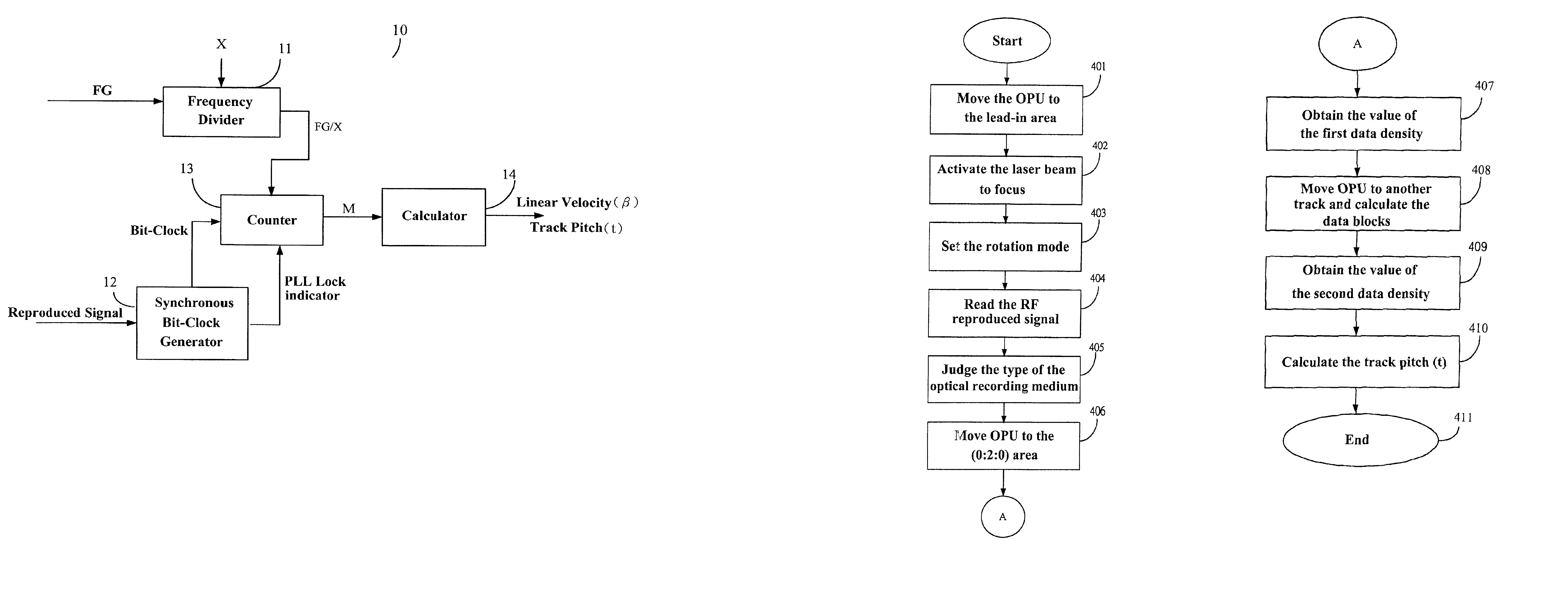
ActiveUS20020145961A1Improve accuracyCombination recordingRecord information storageClock generatorOptical disc drive
A device and method for calibrating linear velocity and track pitch for an optical disc is disclosed. The device comprises a frequency divider, a synchronous bit-clock generator, a counter and a linear velocity and track pitch calculator. The frequency divider receives a motor frequency generator (FG) pulse and generates a motor rotation period signal (FG / X). The synchronous bit-clock generator generates a high frequency bit-clock according to a reproduced signal read from disc. The bit counter counts the pulse of the bit-clock for each period of the motor rotation period signal to generate the data amount M. The linear velocity and track pitch calculator calculates the linear velocity by a linear velocity function with the information of the data amount M and the motor rotation period. Then, the linear velocity and track pitch calculator calculates the track pitch by a pitch function with the information of the data amount, radius and linear velocity at different tracks.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
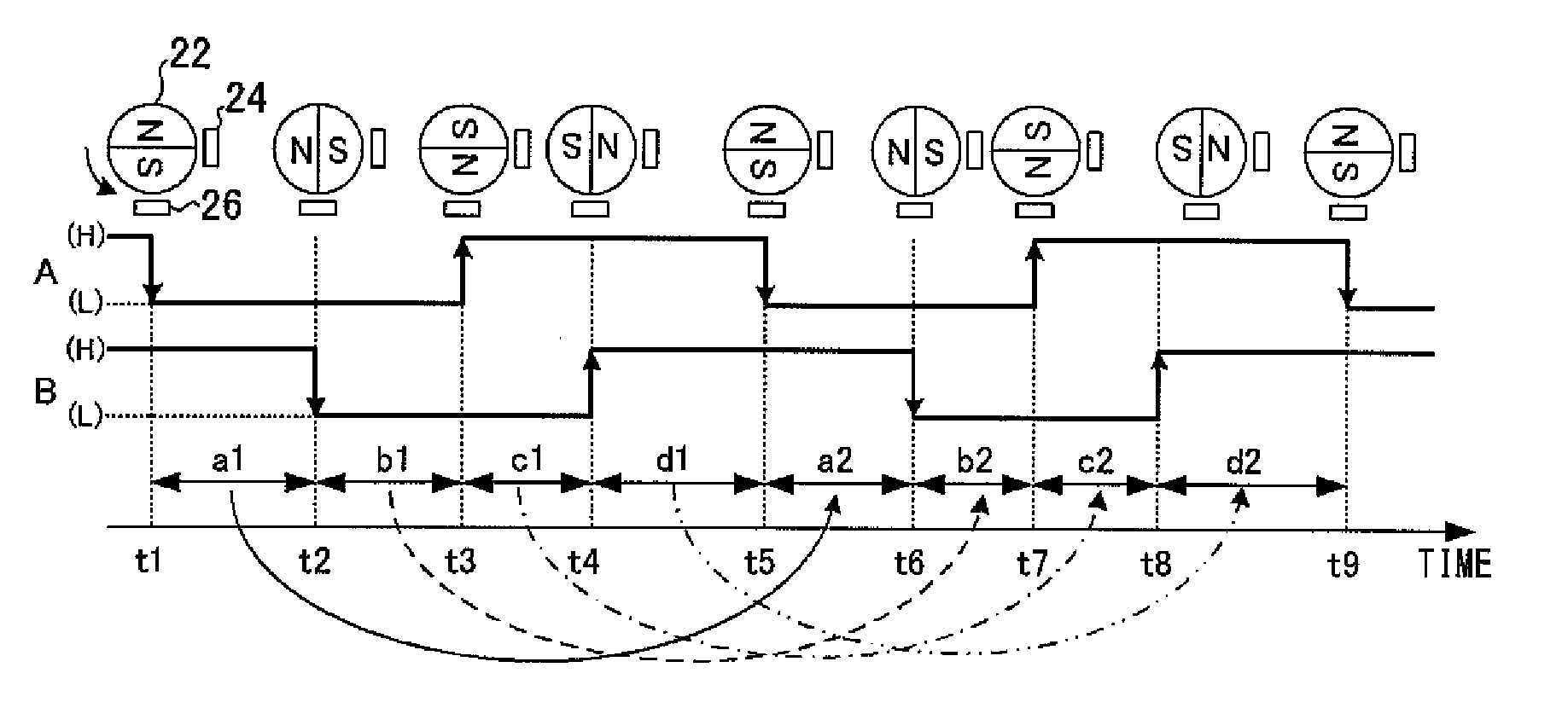
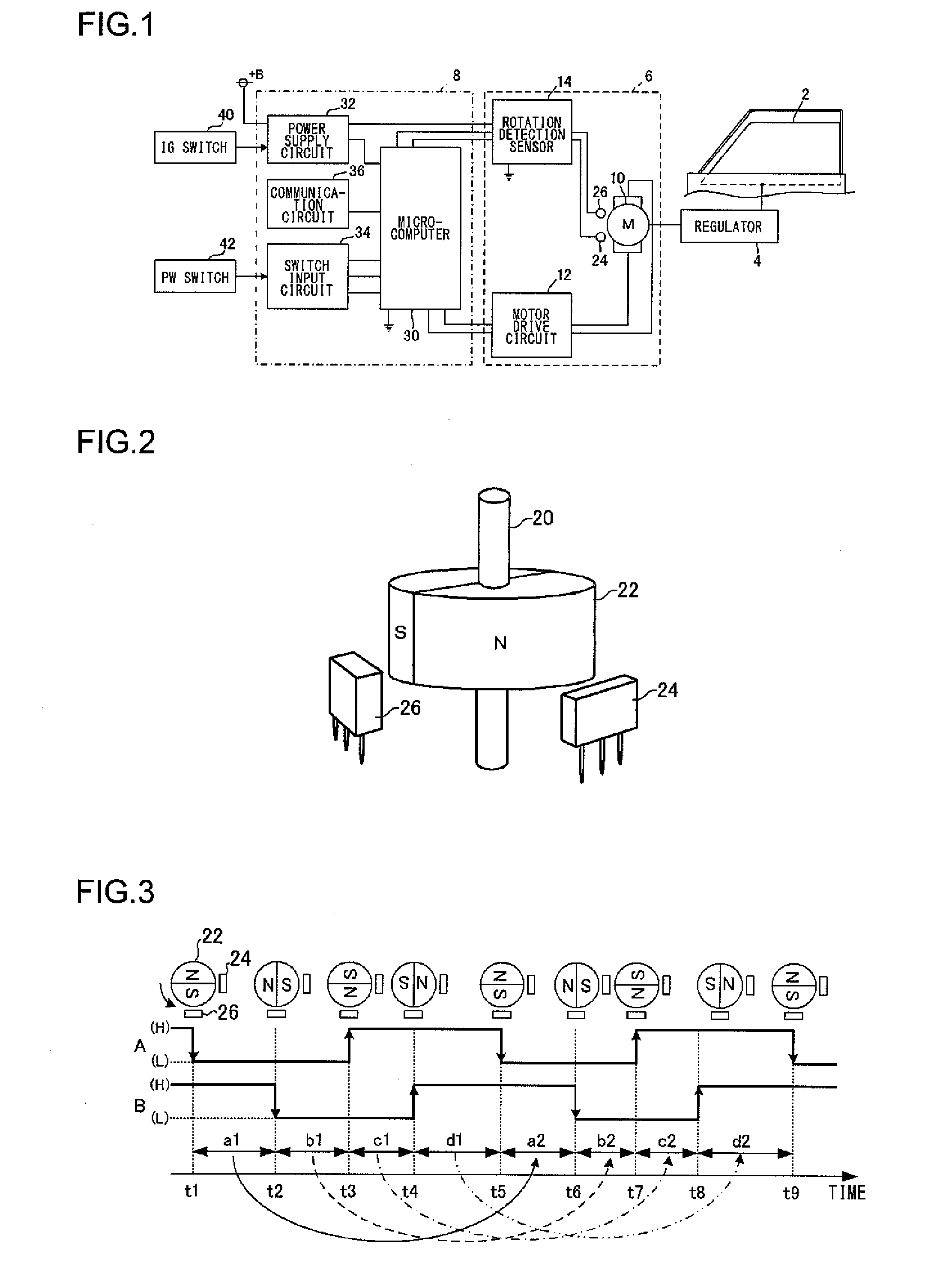
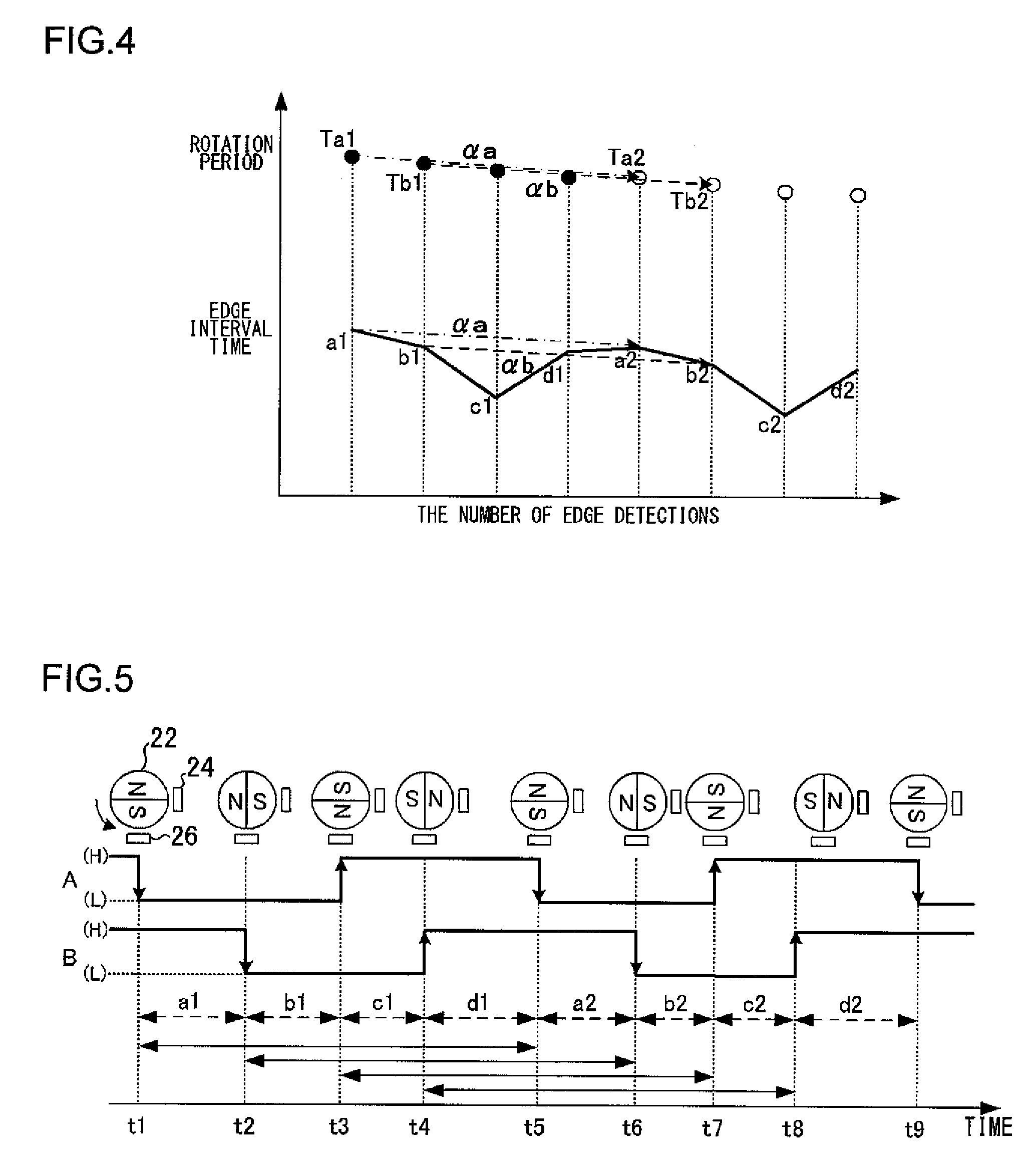
Motor characteristics acquiring apparatus, control apparatus using the acquired motor characteristics, and power window control apparatus
InactiveUS20090162038A1DC motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motors startersReference PeriodEngineering
The rotation period of a motor is subdivided by edge interval times and a rate of change between a currently calculated edge interval time and an edge interval time calculated one rotation of the motor previously is calculated at the detection of each edge. Then the rotation period of the motor is calculated by multiplying a set reference period by the calculated rate of change.
Owner:MABUCHI MOTOR
Motion door control method and system in positron emission tomography
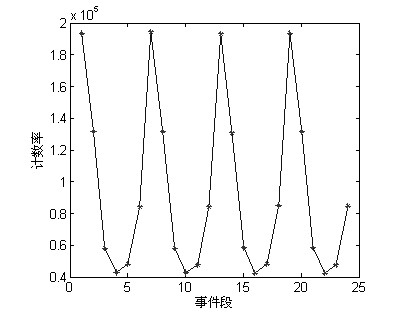
InactiveCN102151142AReduce artifactsHigh-resolutionComputerised tomographsTomographyObject motionCompanion animal
The invention discloses a motion door control method in positron emission tomography (PET), which comprises the following steps of: dividing the acquired PET list type single event data into a plurality of data frames; generating a single event data change curve by counting the counting rate of the single event data of data frames in detection modules; regulating the single event data change curve to make the single event data change curve have obvious local interval periodicity, dividing motion sections of rotary motion by utilizing the local interval periodicity, and calculating the rotation period in each motion section; obtaining a motion phase corresponding to the data frames in each motion section by using the rotation period and the number of the data frames; and integrating the data frames with the same phase for reconstructing an image. The invention also discloses a motion door control system in PET. Under the condition of not increasing any hardware equipment, the rotary motion of an object is monitored, image artifact brought by the motion of the object can be well reduced, and the resolution of the image is greatly improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Device and method for calibrating linear velocity and track pitch for optical disc drive
A device and method for calibrating linear velocity and track pitch for an optical disc is disclosed. The device comprises a frequency divider, a synchronous bit-clock generator, a counter and a linear velocity and track pitch calculator. The frequency divider receives a motor frequency generator (FG) pulse and generates a motor rotation period signal (FG / X). The synchronous bit-clock generator generates a high frequency bit-clock according to a reproduced signal read from disc. The bit counter counts the pulse of the bit-clock for each period of the motor rotation period signal to generate the data amount M. The linear velocity and track pitch calculator calculates the linear velocity by a linear velocity function with the information of the data amount M and the motor rotation period. Then, the linear velocity and track pitch calculator calculates the track pitch by a pitch function with the information of the data amount, radius and linear velocity at different tracks.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
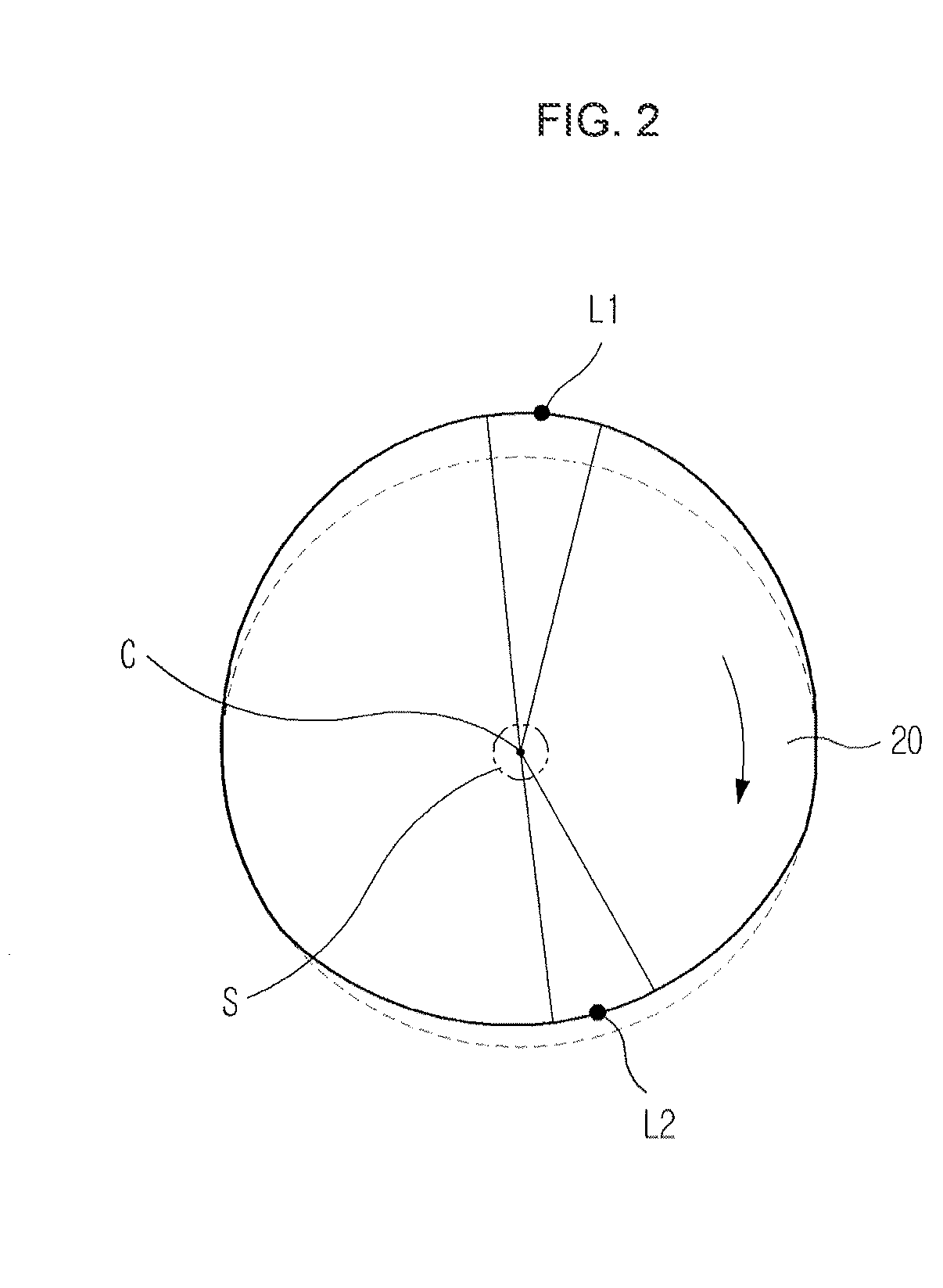
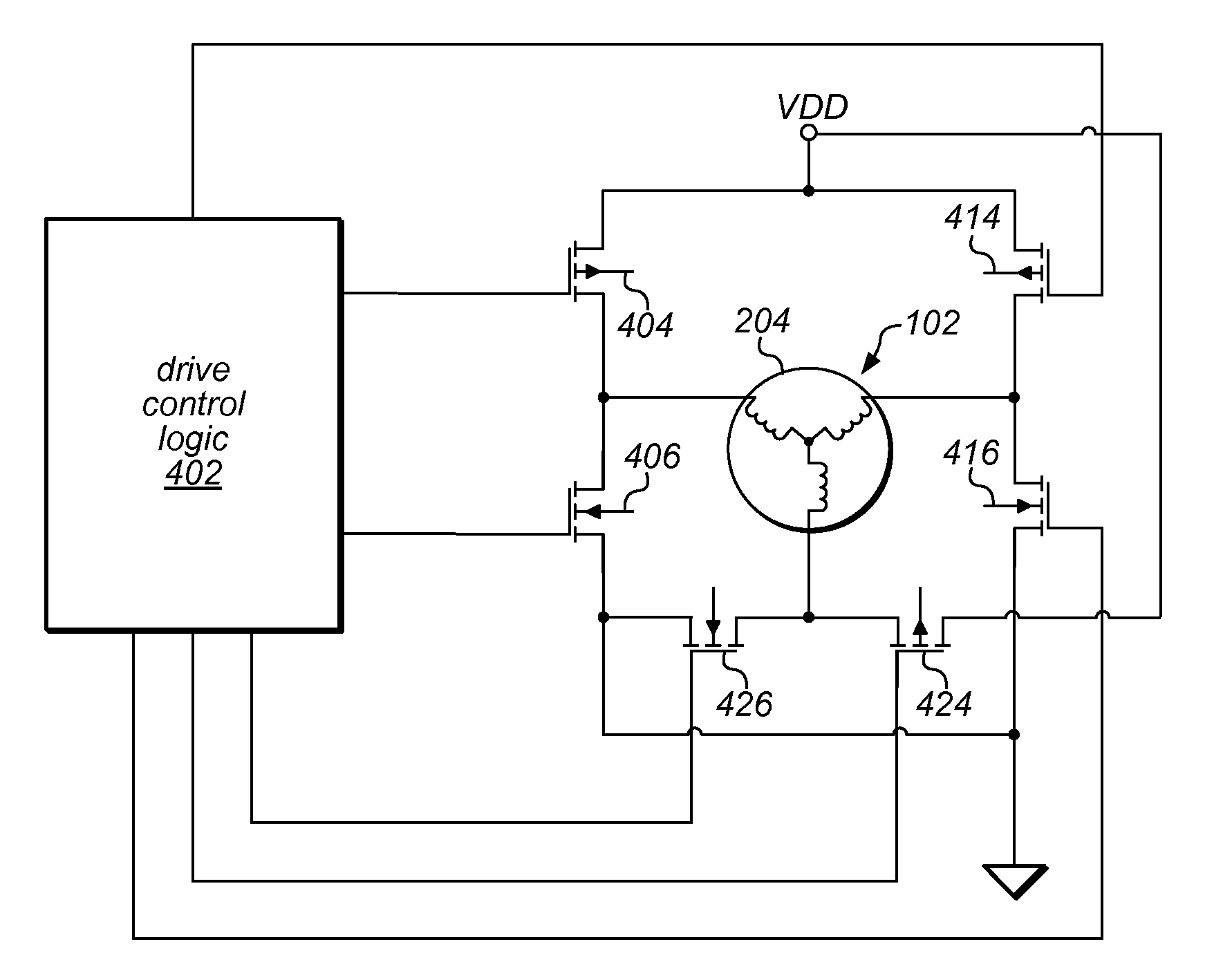
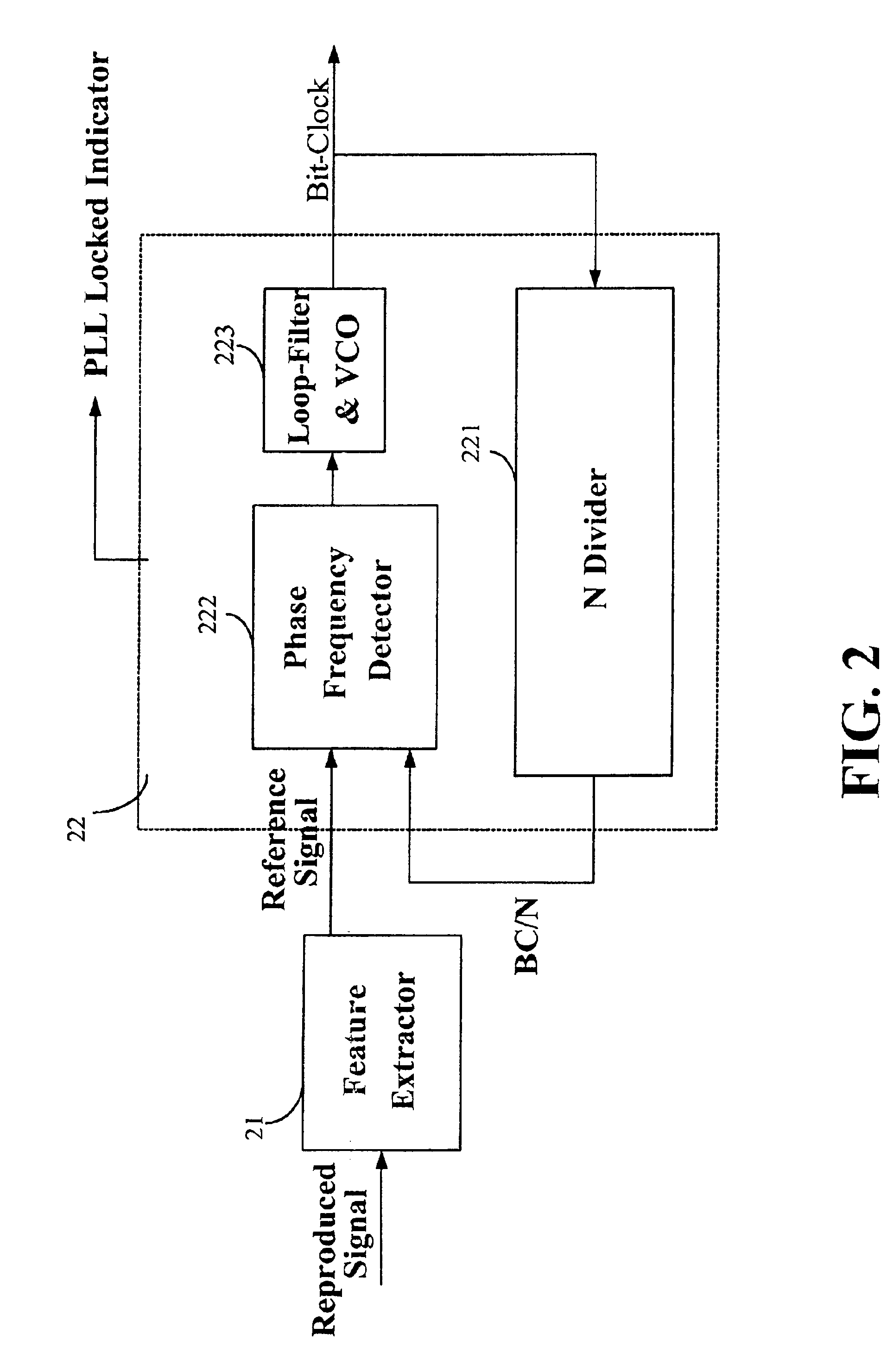
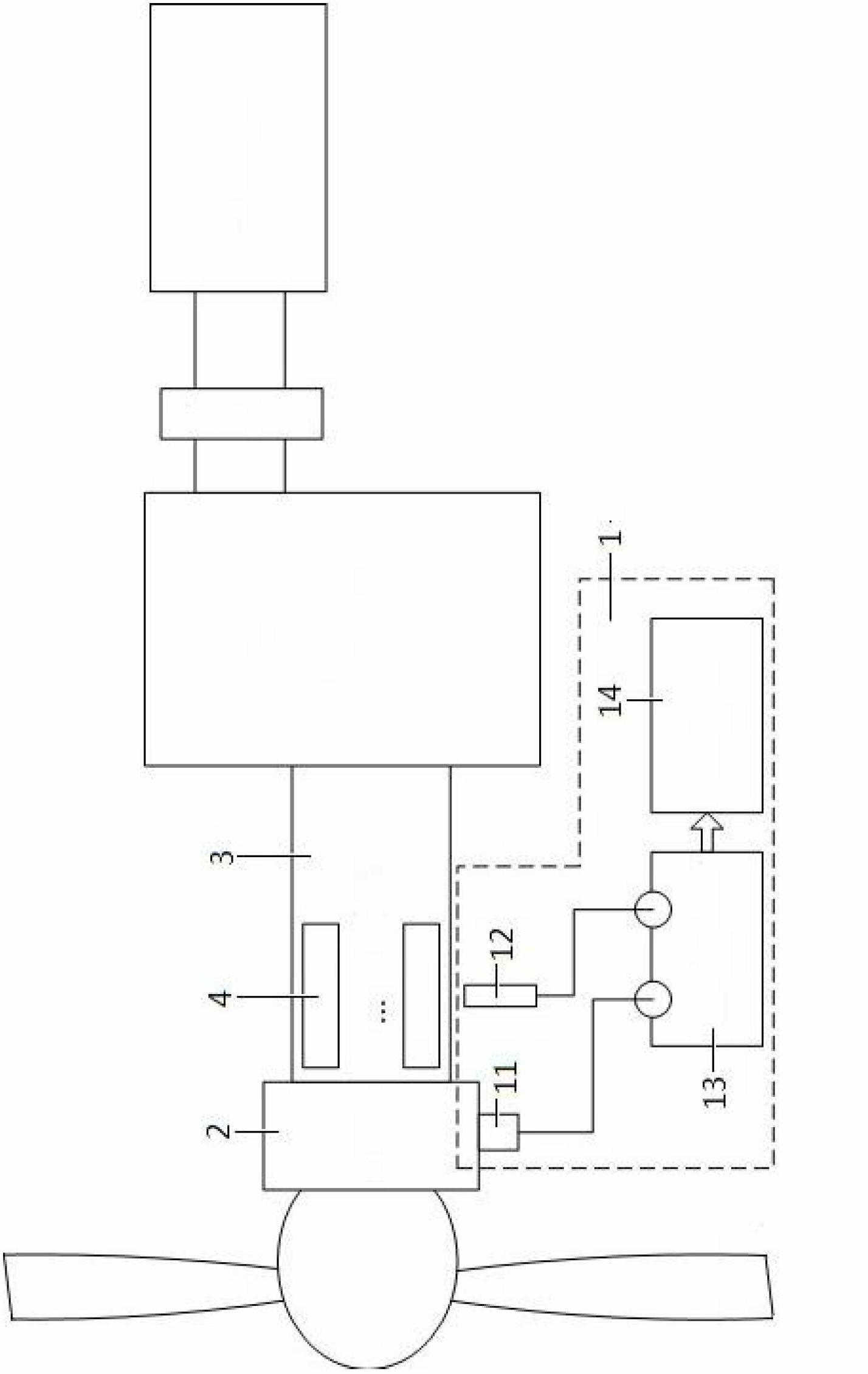
Rotor Driving Control Device and Image Forming Apparatus
InactiveUS20080231223A1Structural economyHigh detection sensitivityTorque ripple controlAC motor controlColor imageEngineering
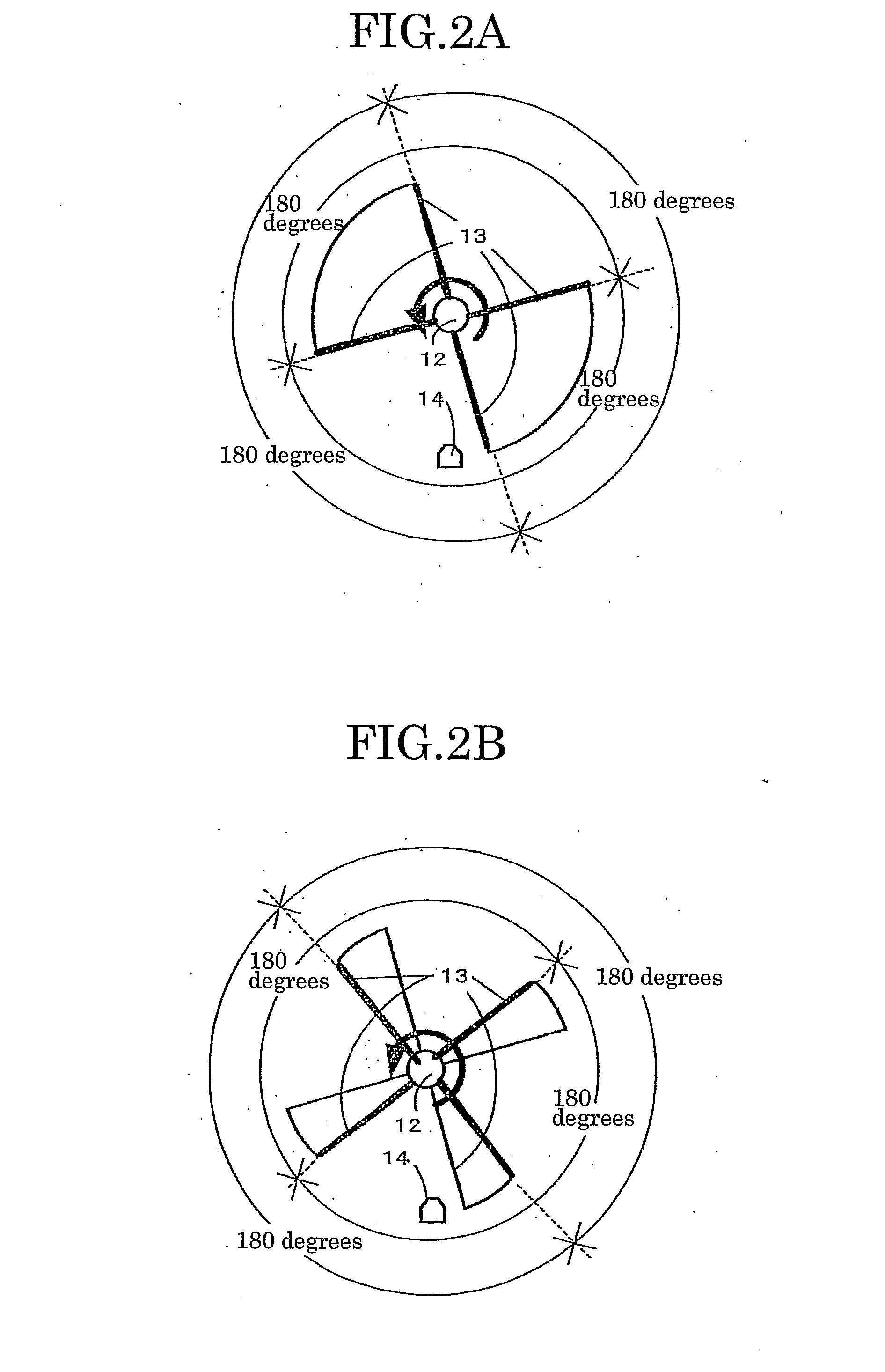
A device of a motor with a rotation control means that decreases the fluctuation of its rotation period. The control is carried out based on the amplitude and the phase generated by amplitude-and-phase generating devices, detecting passage time of detected portions (13) in different zones. And a color image forming apparatus of tandem type with such motors.
Owner:RICOH KK
Air gap eccentric checking device and method for single-phase inductor
ActiveCN1905330AGood effectJudgment of air gap eccentric stateAsynchronous induction motorsCentering/balancing rotorsAir gap eccentricityInductor
By measuring the air gap eccentricity and eccentric direction during the rotor rotation, it is possible to accurately determine whether the air gap is qualified or not. It can adjust the AC current flowing through the above-mentioned main coil or auxiliary coil and use a rotating magnetic field in which the magnetic flux induced by the main coil in the air gap is larger than the magnetic flux induced by the auxiliary coil in the air gap or by the auxiliary coil in the air gap. The magnetic flux induced in the gap is larger than the magnetic flux induced by the main coil in the air gap. The rotating magnetic field causes the rotor to rotate at a rotation period smaller than the period of the alternating current. The vibration detection sensor is installed in the direction perpendicular to the winding direction of the coil whose magnetic flux is larger than the other, and by detecting the amplitude or shape of the vibration waveform of the vibration obtained during rotational driving, the above-mentioned change according to the phase of the rotor can be calculated. Air gap eccentricity and air gap eccentric direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
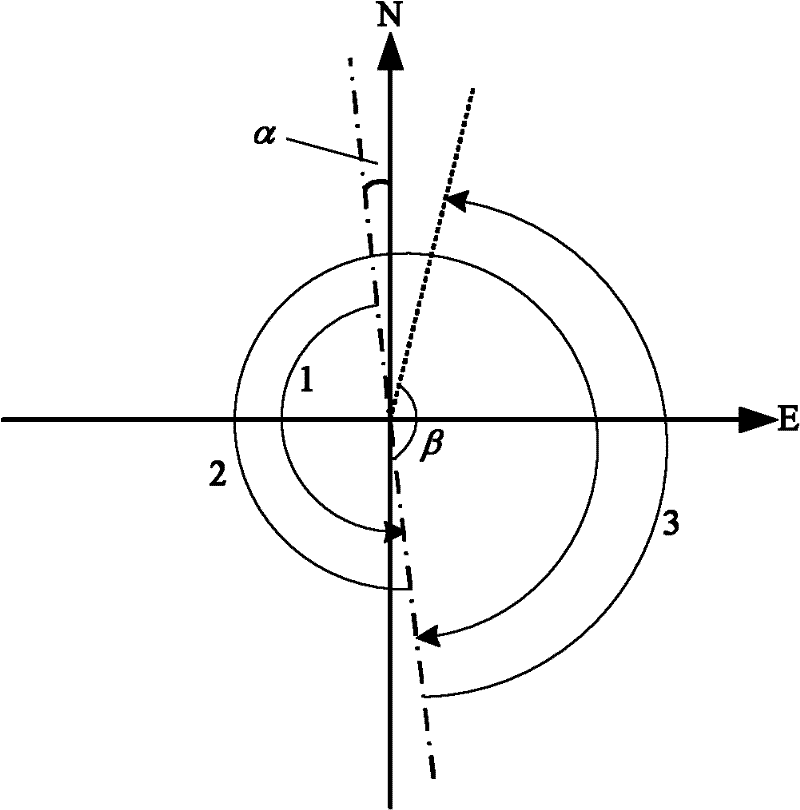
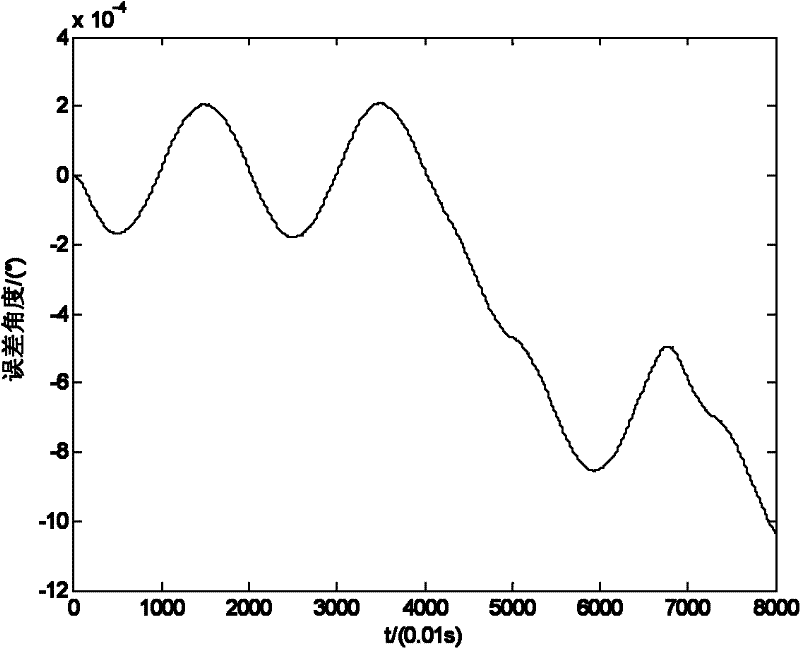
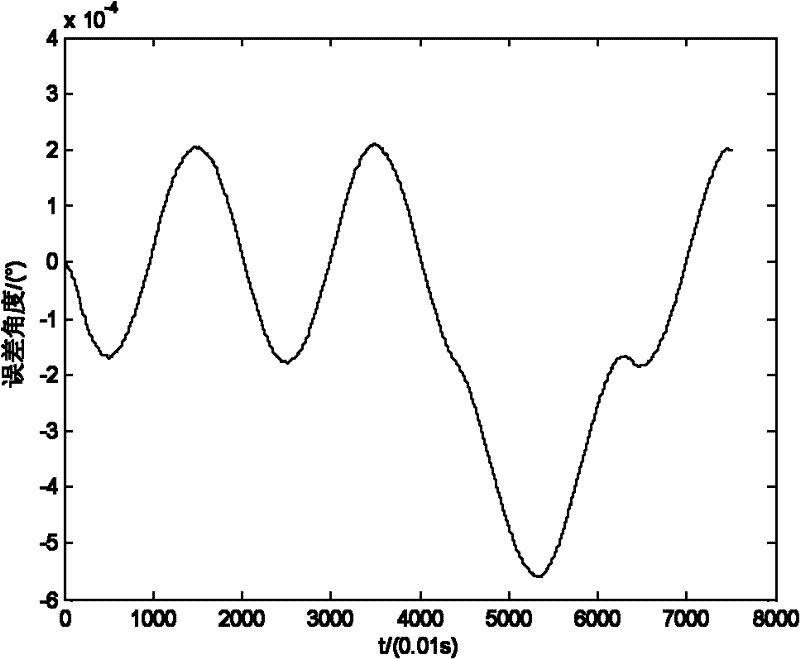
Single-axis rotation type strapdown inertial navigation system transposition method
InactiveCN102221364AHigh precisionThe method steps are simpleNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMarine navigationInertial navigation system
The invention relates to a single-axis rotation type strapdown inertial navigation system transposition method and belongs to the technical field of inertial navigation. A carrier of an inertial navigation system serves as a reference coordinate system, inertial navigation is controlled to rotate in a certain period, each rotation period comprises three rotation processes, and an error caused by carrier motion in the third-time rotation of each rotation period is compensated in the next rotation period. The method has simple steps, a constant drift error which cannot be completely compensateddue to non-isolated carrier motion can be made up, the accuracy of the inertial navigation system is greatly improved, and a rotary system arranged on a moving carrier can be subjected to constant drift compensation on land and in water.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for operating a sensor on or in a vehicle tire, and a sensor system
ActiveUS20100294032A1Less energyLow query rateInflated body pressure measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsEngineeringRotation cycle
A method is proposed for operating a sensor on or in a vehicle tyre, in particular an acceleration sensor and in particular for detecting a tyre rotation period and / or a tyre contact period, wherein the sensor is operated with a first sampling rate in a first time interval of a rotation of a tyre, and with a second sampling rate in a second time interval of the rotation of the tyre.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
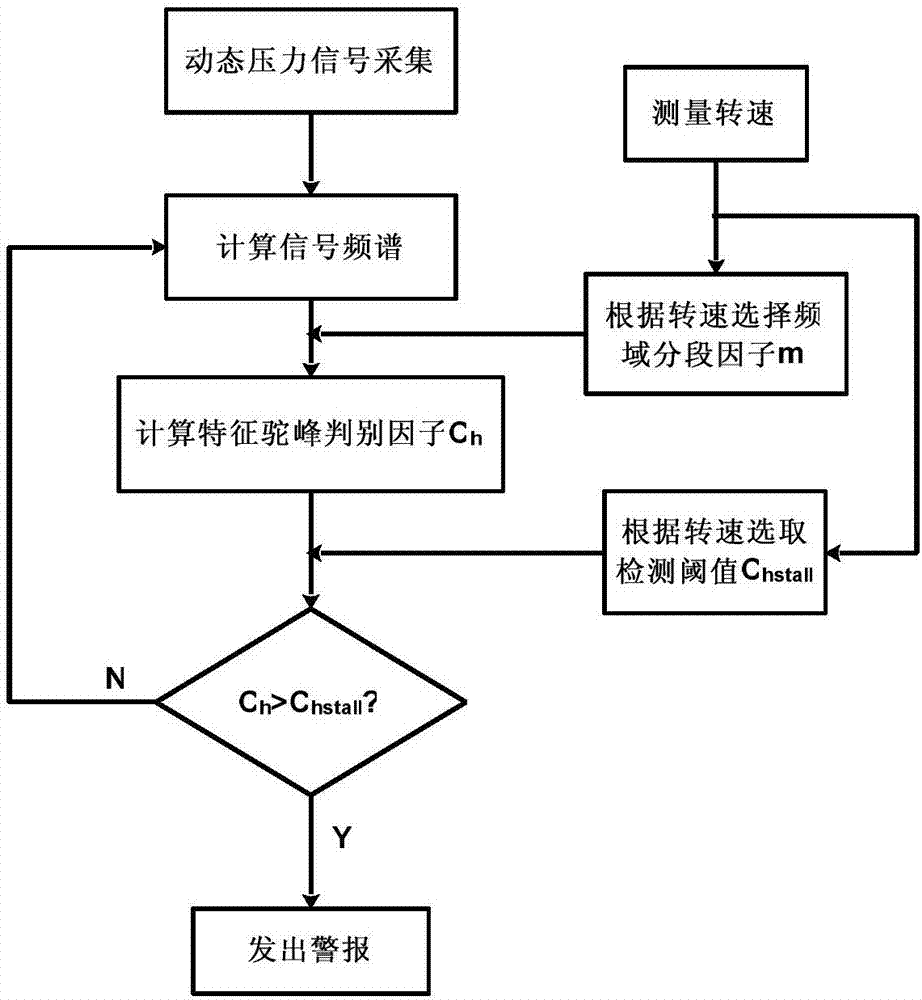
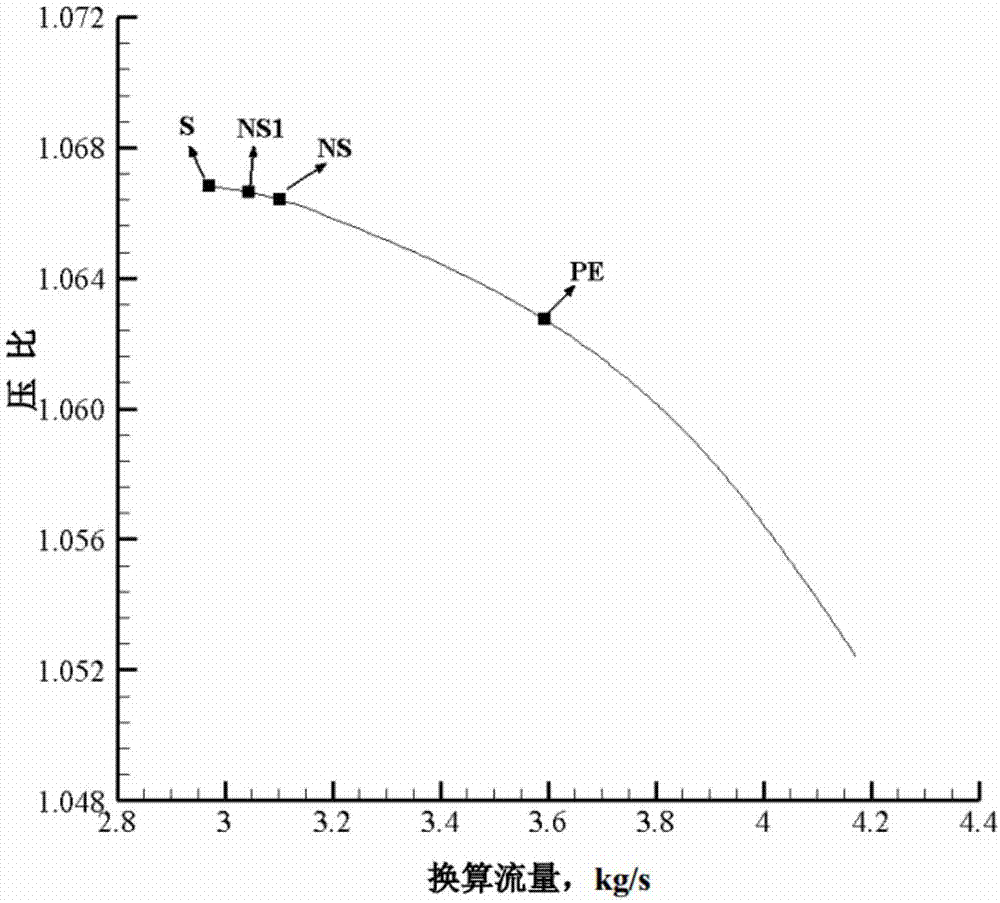
Early warning method for rotating stall of axial-flow air compressor based on frequency domain hump identification
ActiveCN107165850ACalculation speedReduce intermediate processCharacter and pattern recognitionPump controlFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an early warning method for rotating stall of an axial-flow air compressor based on frequency domain hump identification. The method comprises the following steps: continuously and dynamically acquiring a pressure signal; continuously calculating the frequency spectrum of the pressure signal within one air compressor rotation period by utilizing fast Fourier transform; calculating a characteristic hump distinguish factor Ch corresponding to the frequency spectrum; and judging whether the air compressor is close to the rotating stall boundary by comparing the characteristic hump distinguish factor Ch with a detection threshold value Chsta11. The characteristic hump distinguish factor Ch defined by the early warning method for rotating stall of the axial-flow air compressor has definite physical significations and is used for implementing real-time on-line detection on a frequency domain hump appearing earlier than rotating stall so as to give an early warning when the work situation of the air compressor is close to the rotating stall boundary, and the early warning method is reliable. By requiring a simplex signal sensor only and adopting fast Fourier transform, the early warning method for rotating stall of the axial-flow air compressor has few middle procedures, realizes high calculation speed and provides sufficient response time for active control.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
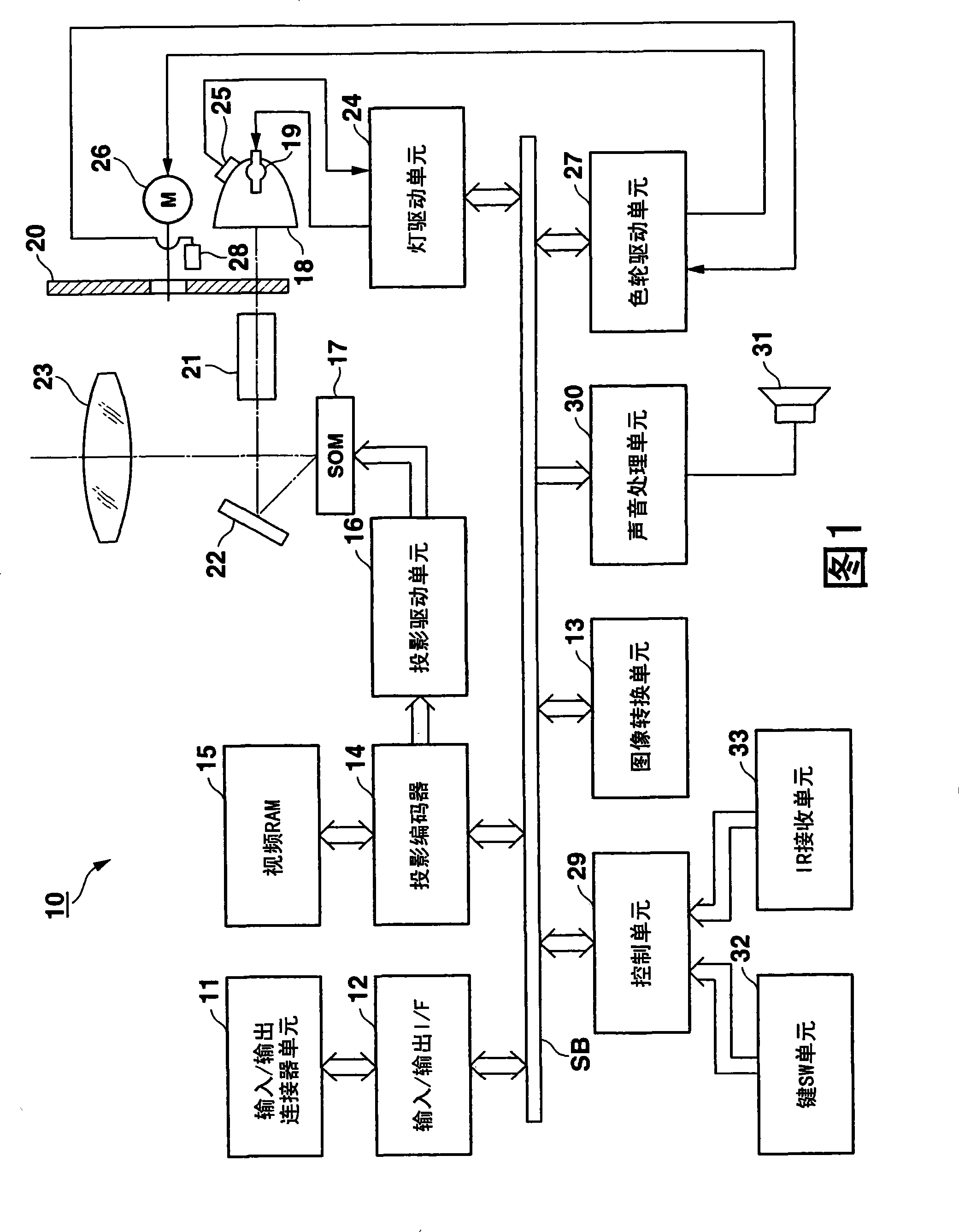
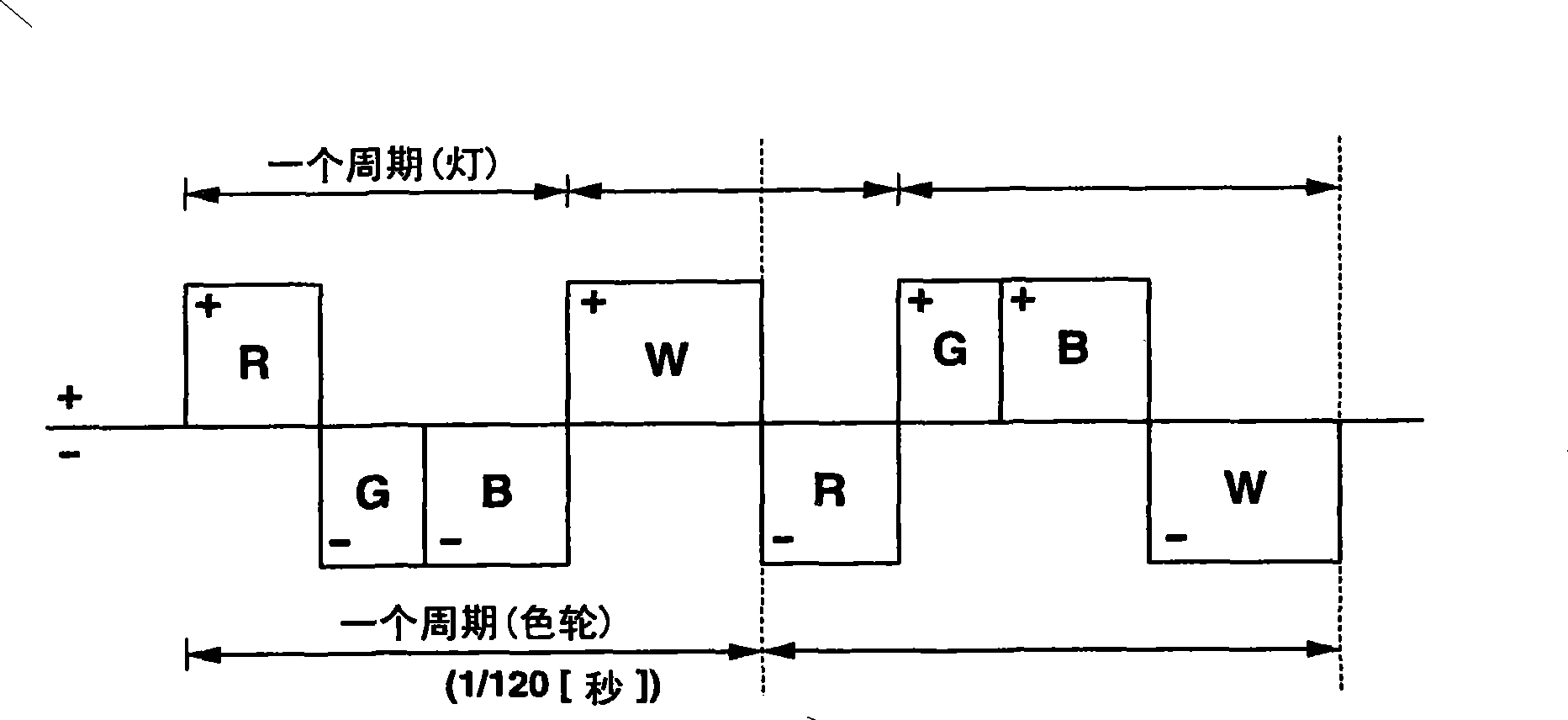
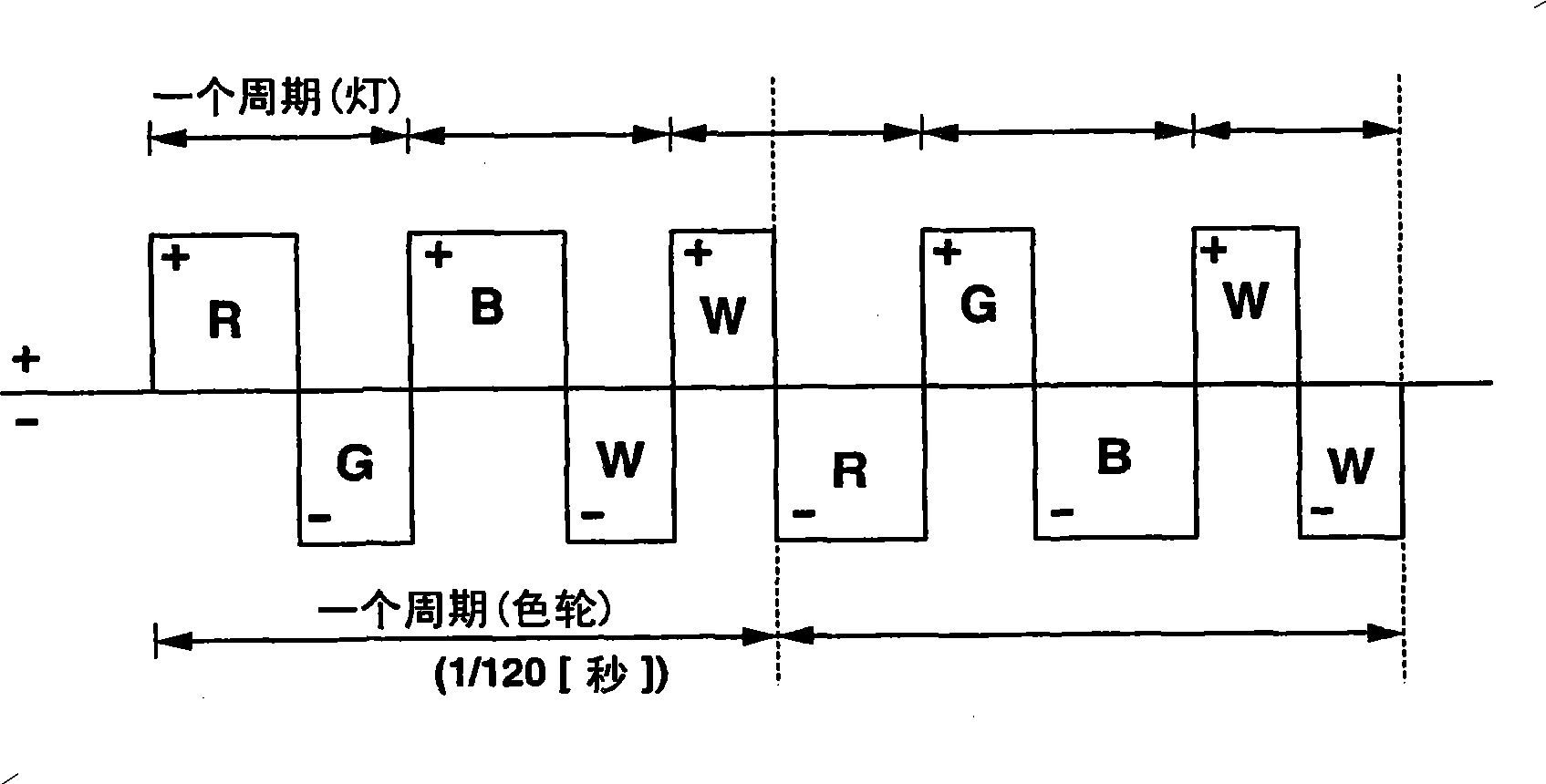
Projection device and projection method
A projection device comprises a light source, a color wheel which is inserted into an optical path of the light source and in which a plurality of color segments are formed along a peripheral direction of the color wheel. The color segments are configured to transmit a plurality of wavelength band components in the white light in a time division manner during a rotation of the color wheel. A light source driving unit alternating-current discharges the light source at a period shorter than a rotation period of the color wheel while reverses a polarity at a timing to switch the segment of the color wheel inserted into the optical path.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
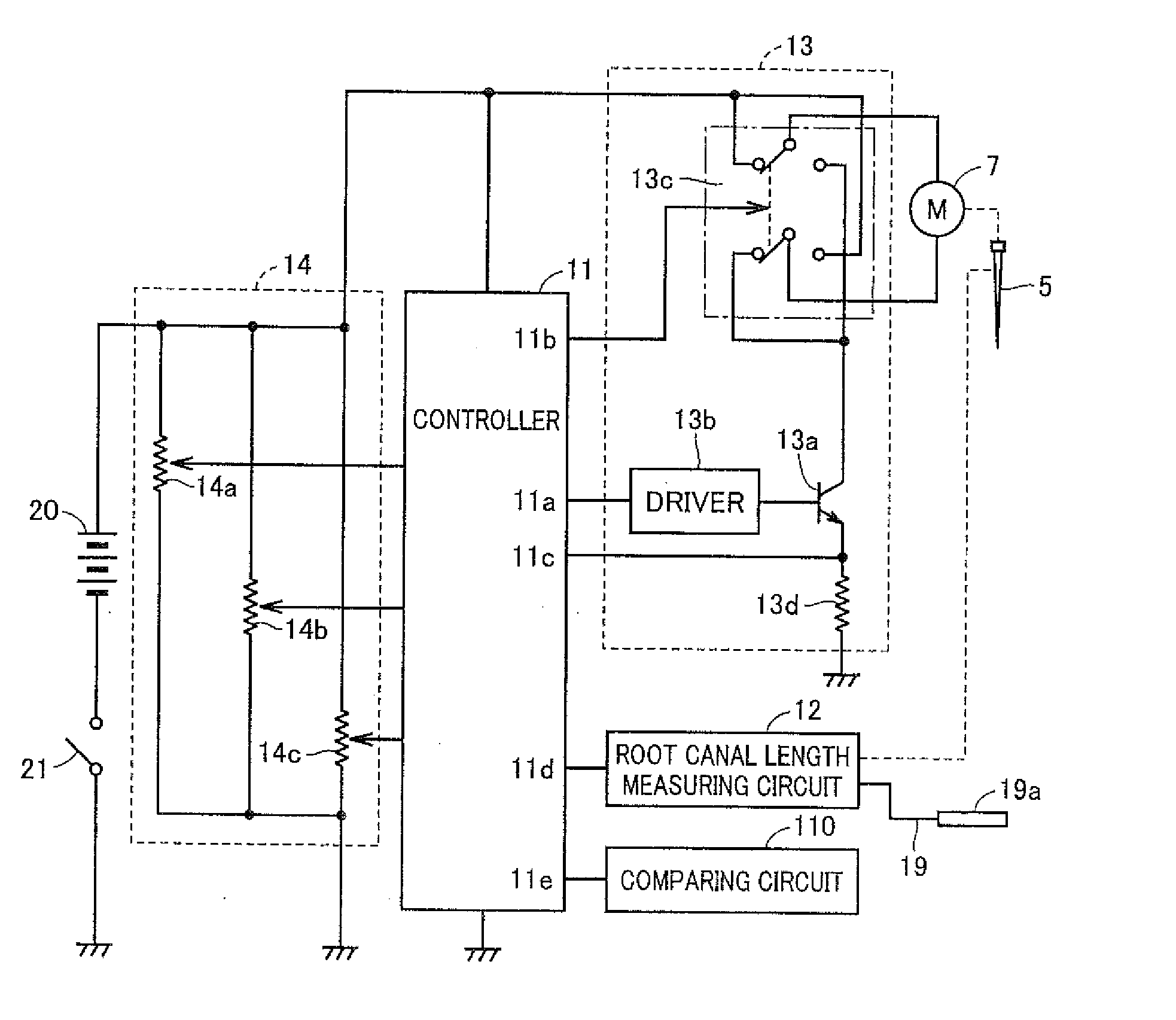
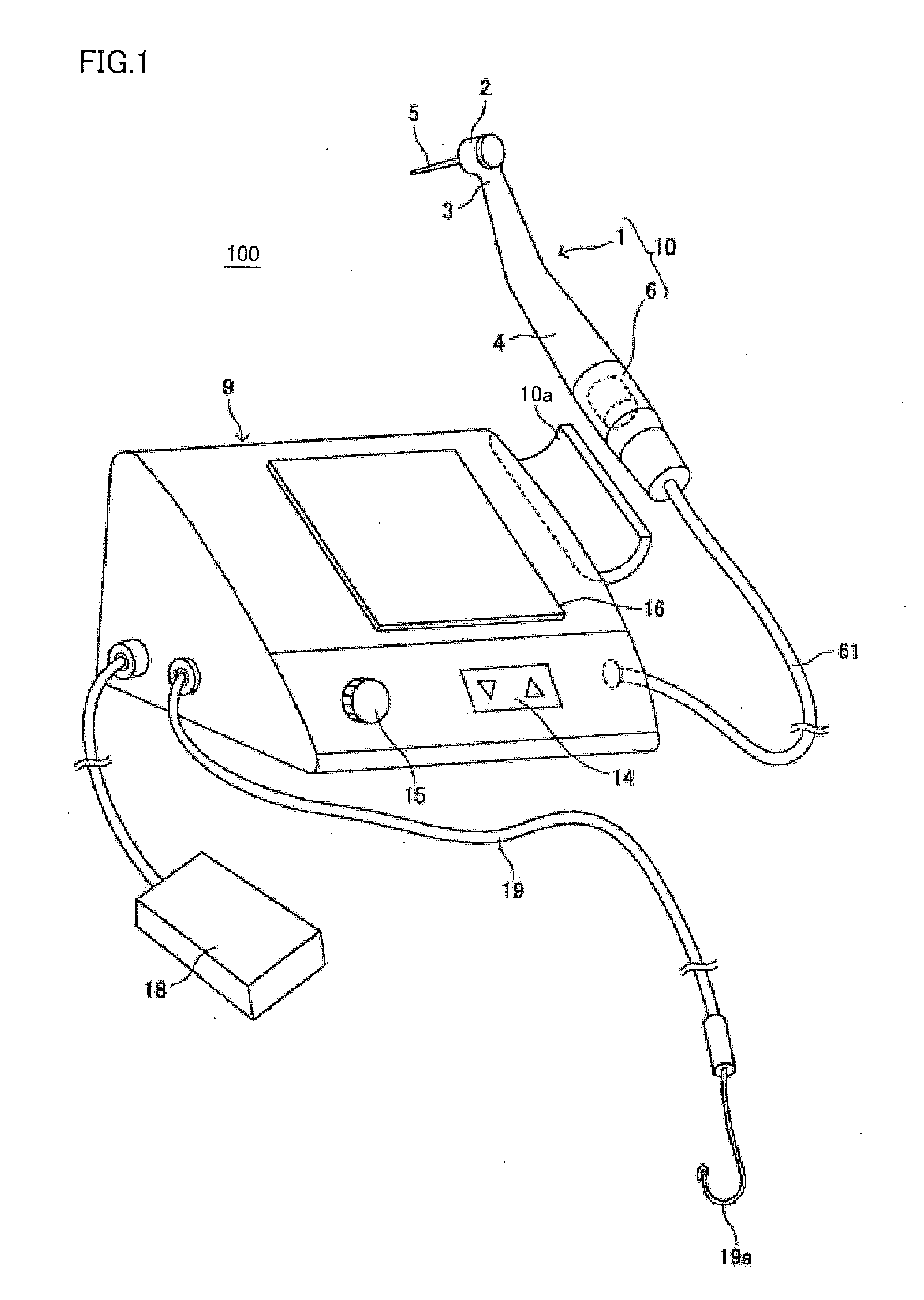
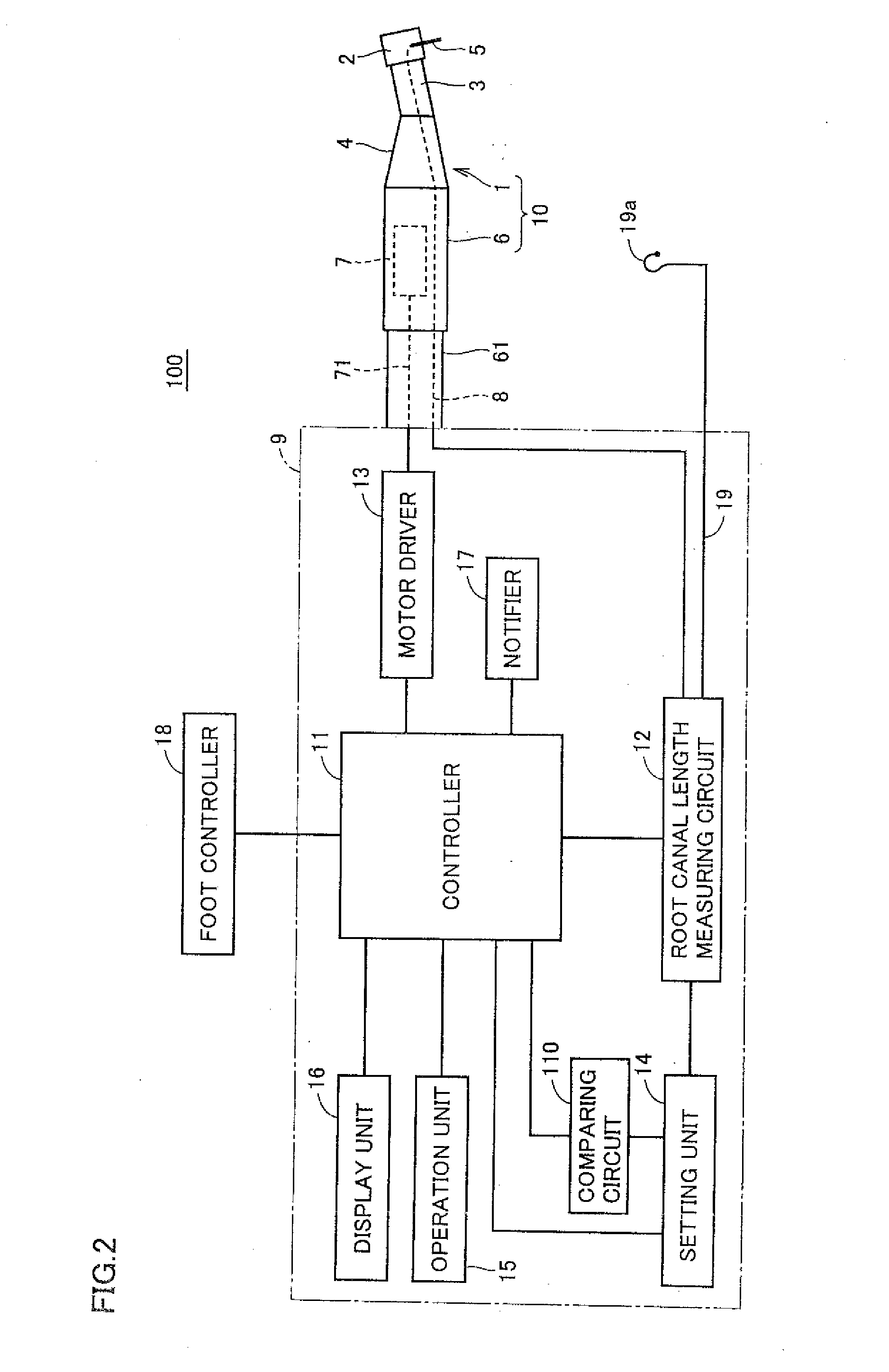
Dental treating apparatus and driving method for the same
ActiveUS20150086937A1Enhance tooth cutting efficiencyAvoid breakingDental toolsNerve needlesRotation cycleMechanical engineering
A dental treating apparatus according to the present invention includes: a hand piece; a head unit; a driving unit; a control unit; a load specifying unit; and a load comparing unit. The hand piece drivably holds a cutting tool on the head unit. The driving unit drives the cutting tool in a normal rotation direction or in a reverse rotation direction. The load comparing unit compares a load detected and a reference load. During a normal rotation period until driving for rotating the cutting tool in the normal rotation direction by the driving unit satisfies a predetermined first condition, the control unit maintains a rotation direction of the cutting tool in the normal rotation direction, and when a result of comparison by the load comparing unit attains a predetermined result during the normal rotation period, the control unit controls the rotation direction to the reverse rotation direction.
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
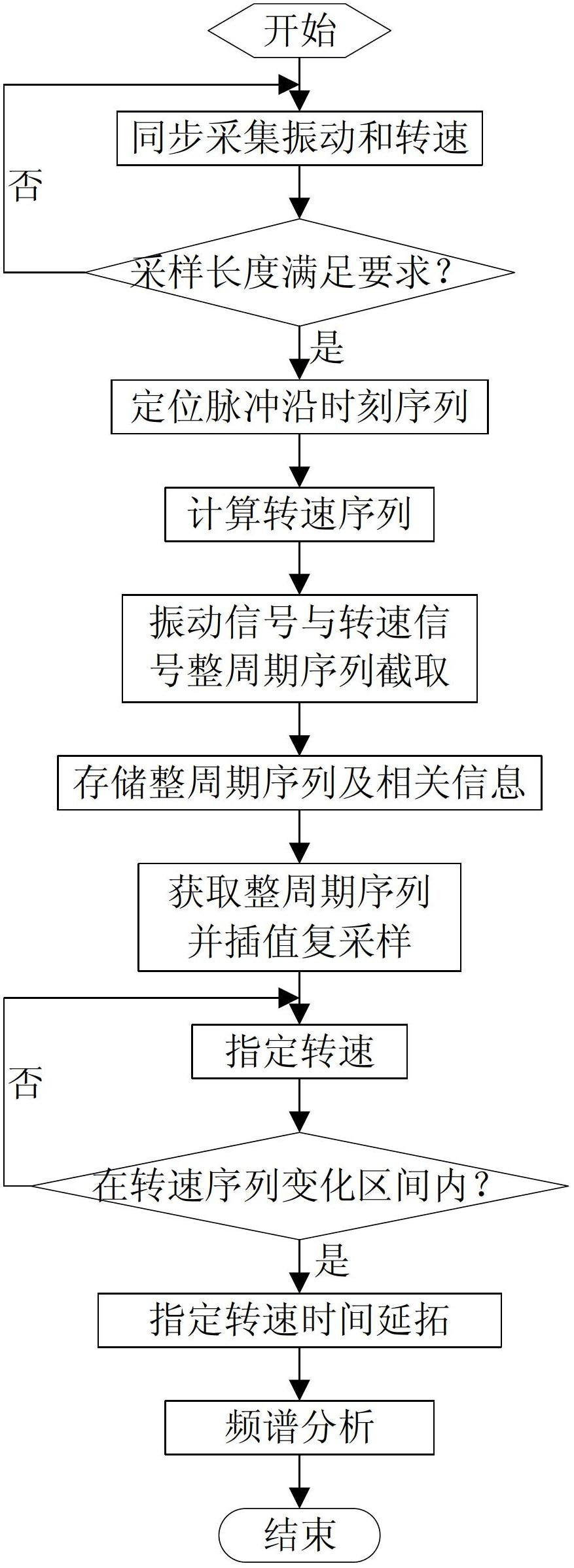
Method and device for acquiring and analyzing rotor vibration signal of variable-rotation wind generation set
ActiveCN102661786ARealize the interception of the whole cycle signal sequenceMeet subsequent analysis requirementsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementElectricityFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a method and a device for acquiring and analyzing a rotor vibration signal of a variable-rotation wind generation set. The device comprises a vibration sensor, a rotation sensor, an acquisition unit and an analysis module. The method comprises the following steps of: synchronously acquiring rotation a pulse signal and an vibration signal at equal time interval; positioning the time sequence of a pulse rising or falling edge, calculating a rotation sequence based on the time sequence, dividing the corresponding vibration signal into vibration signal ranges according tothe pulse sequence and intercepting vibration signal sequence of the full rotation period of an wind wheel; and performing the interpolation complex sampling of vibration signal sequences of all fullperiods, prolonging the time of the vibration signal obtained by complex sampling at a specified rotation speed, obtaining the continuous vibration signal of the full period at the specified rotationspeed, and performing spectrum analysis. By the method and the device, a waveform spectrum which can facilitate analysis can be obtained, and basis is provided for the rotor vibration signal analysisand fault clearance of the wind generation set.
Owner:GUODIAN UNITED POWER TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com