Patents
Literature
260 results about "Earth's rotation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Earth's rotation is the rotation of Planet Earth around its own axis. Earth rotates eastward, in prograde motion. As viewed from the north pole star Polaris, Earth turns counterclockwise. The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. This point is distinct from Earth's North Magnetic Pole. The South Pole is the other point where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface, in Antarctica.
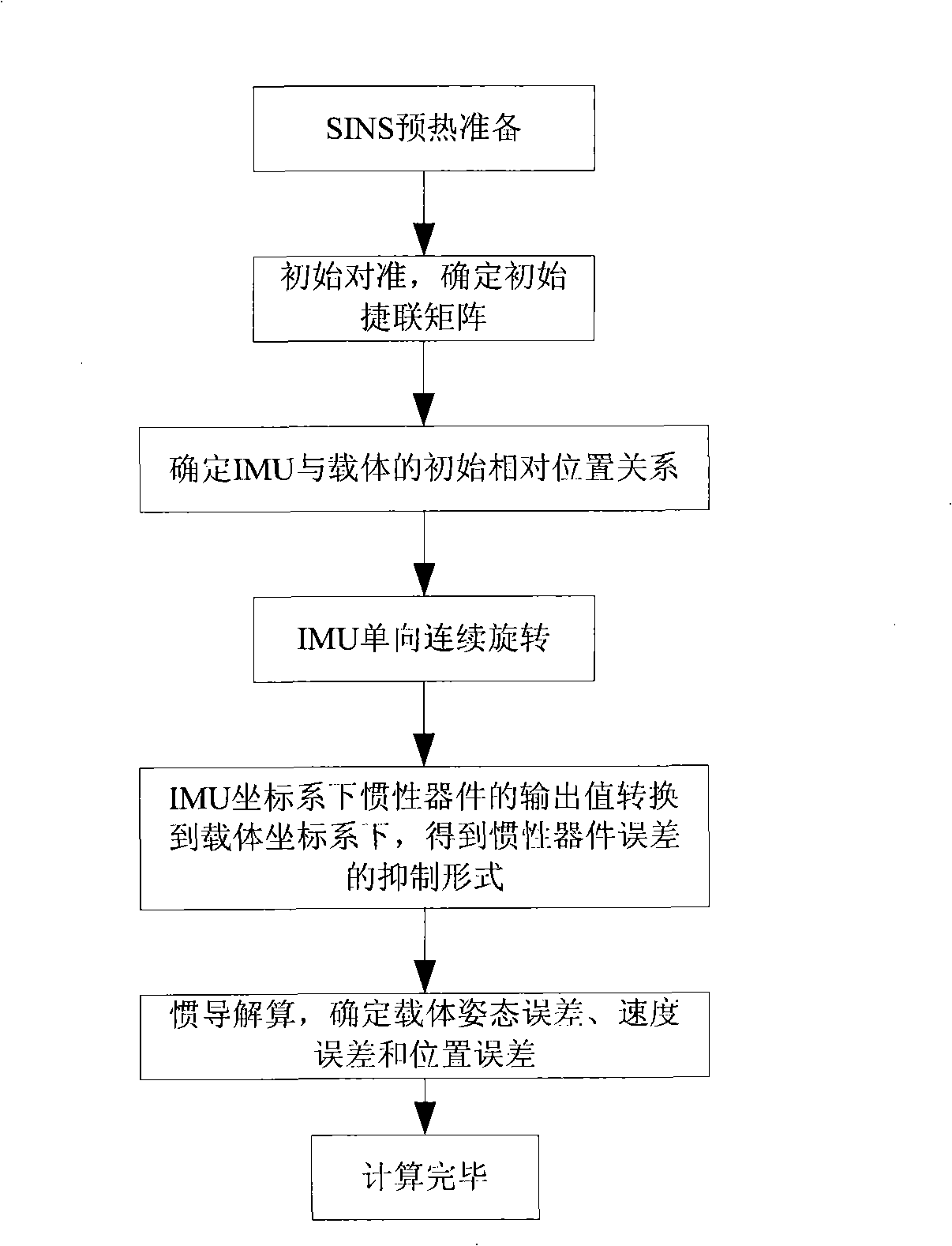
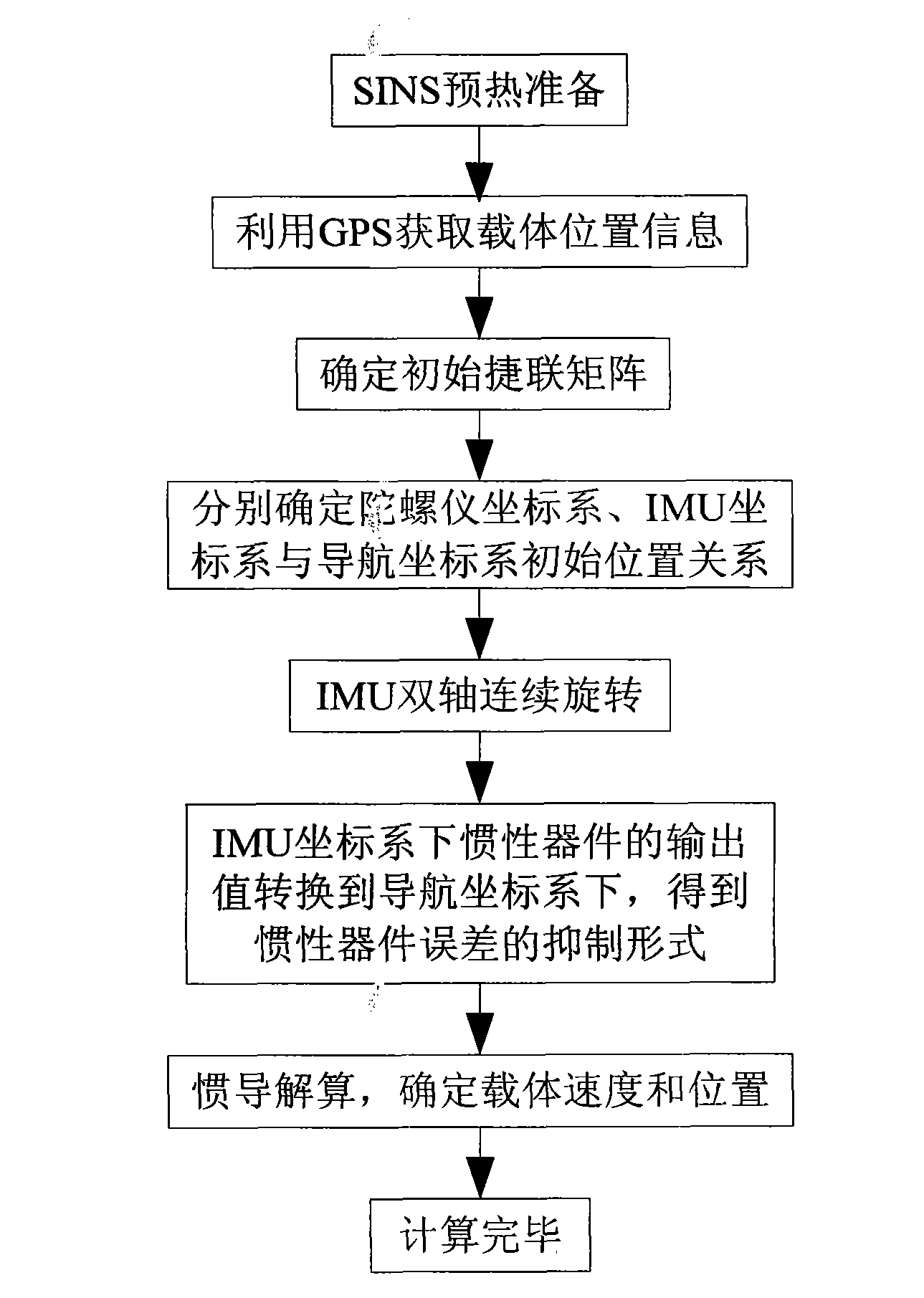
Optical fibre gyro strapdown inertial navigation system error inhibiting method based on single-shaft rotation
InactiveCN101514899AImprove navigation and positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerEarth's rotation
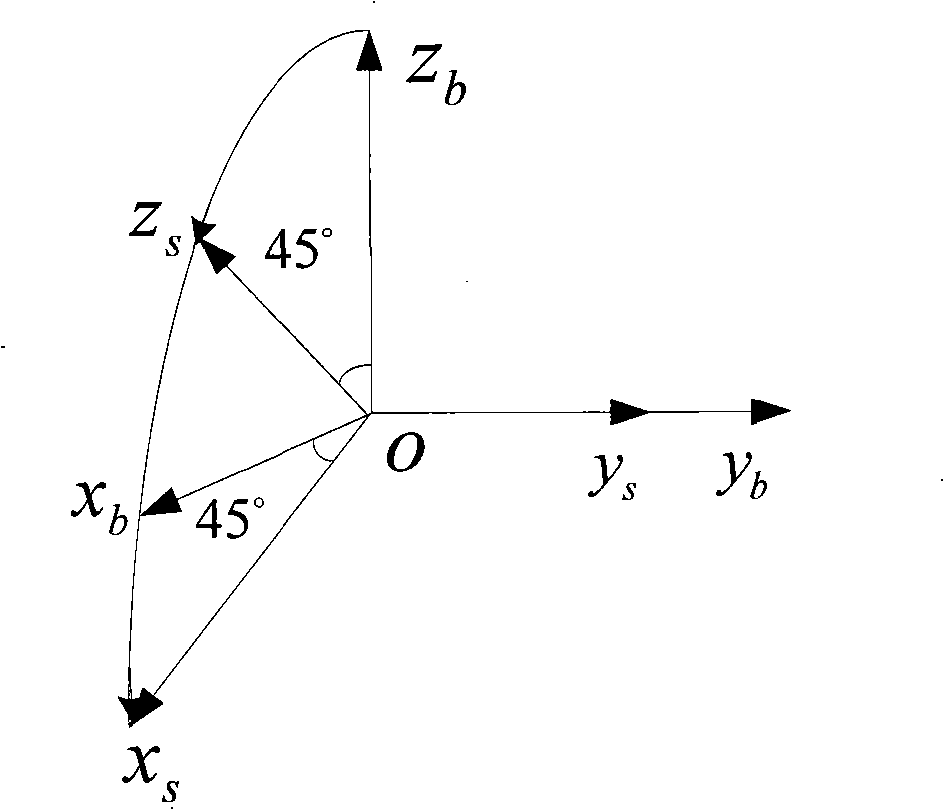
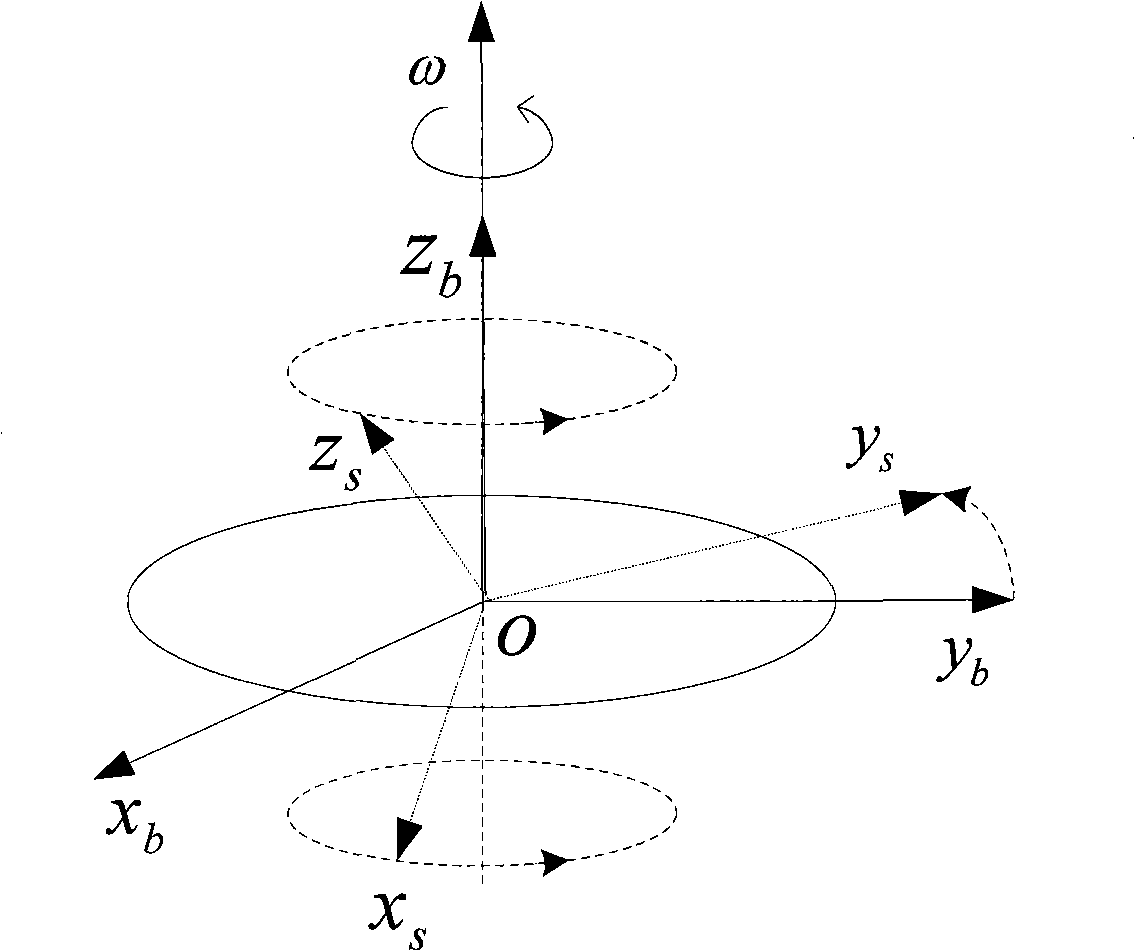
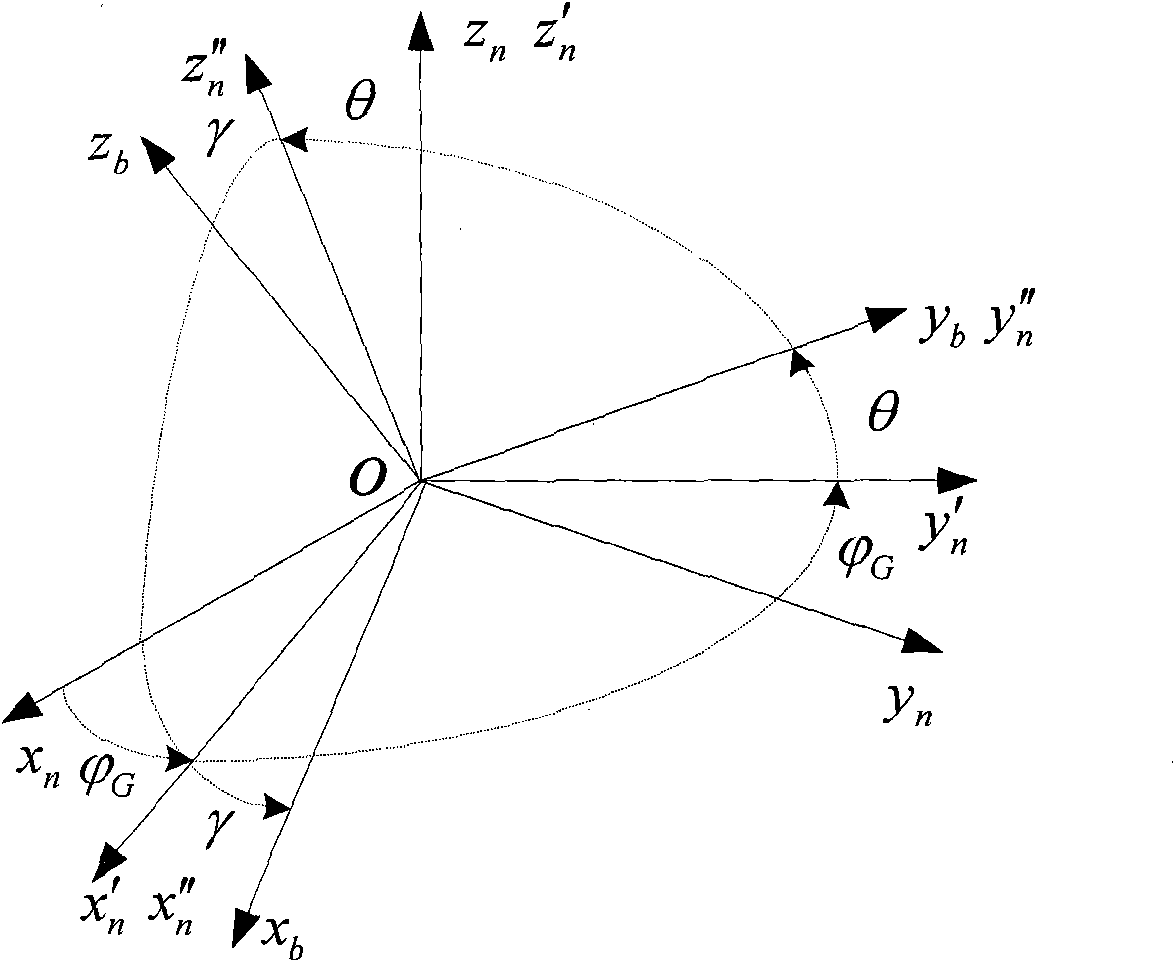
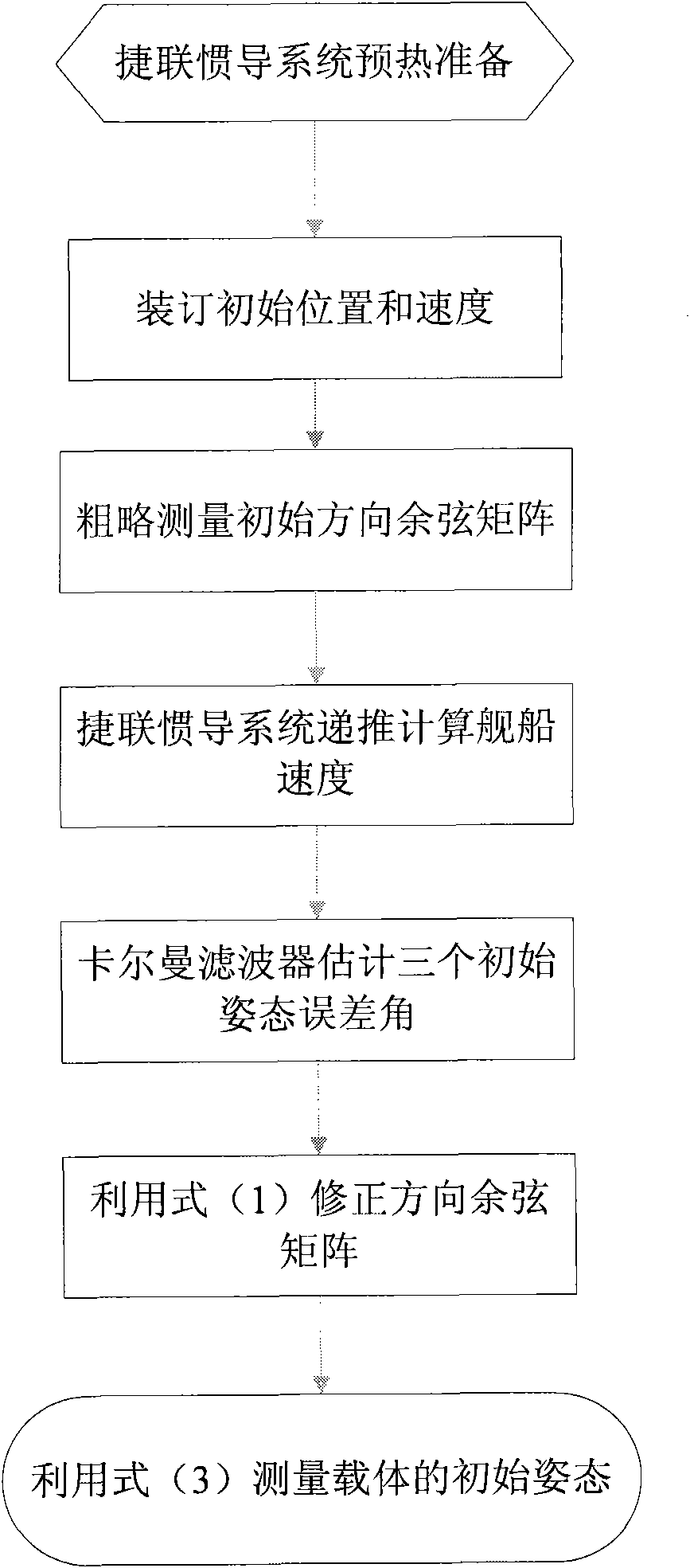
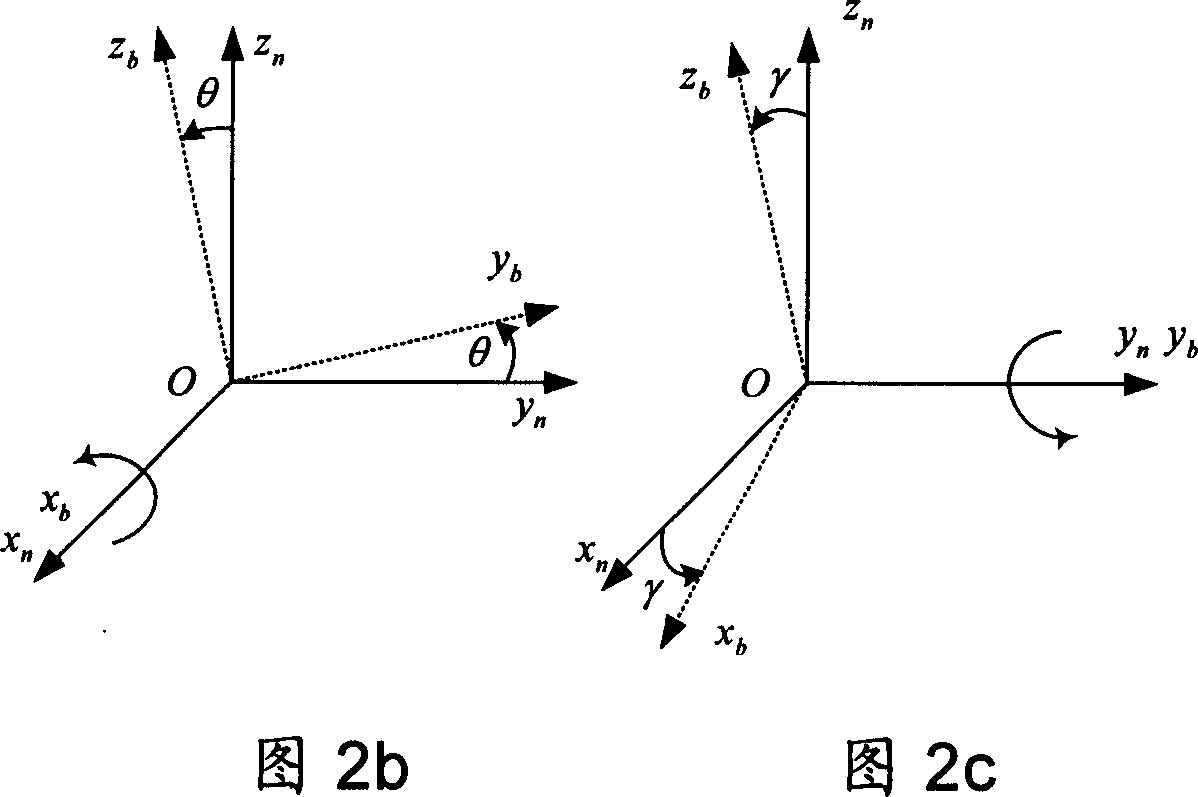
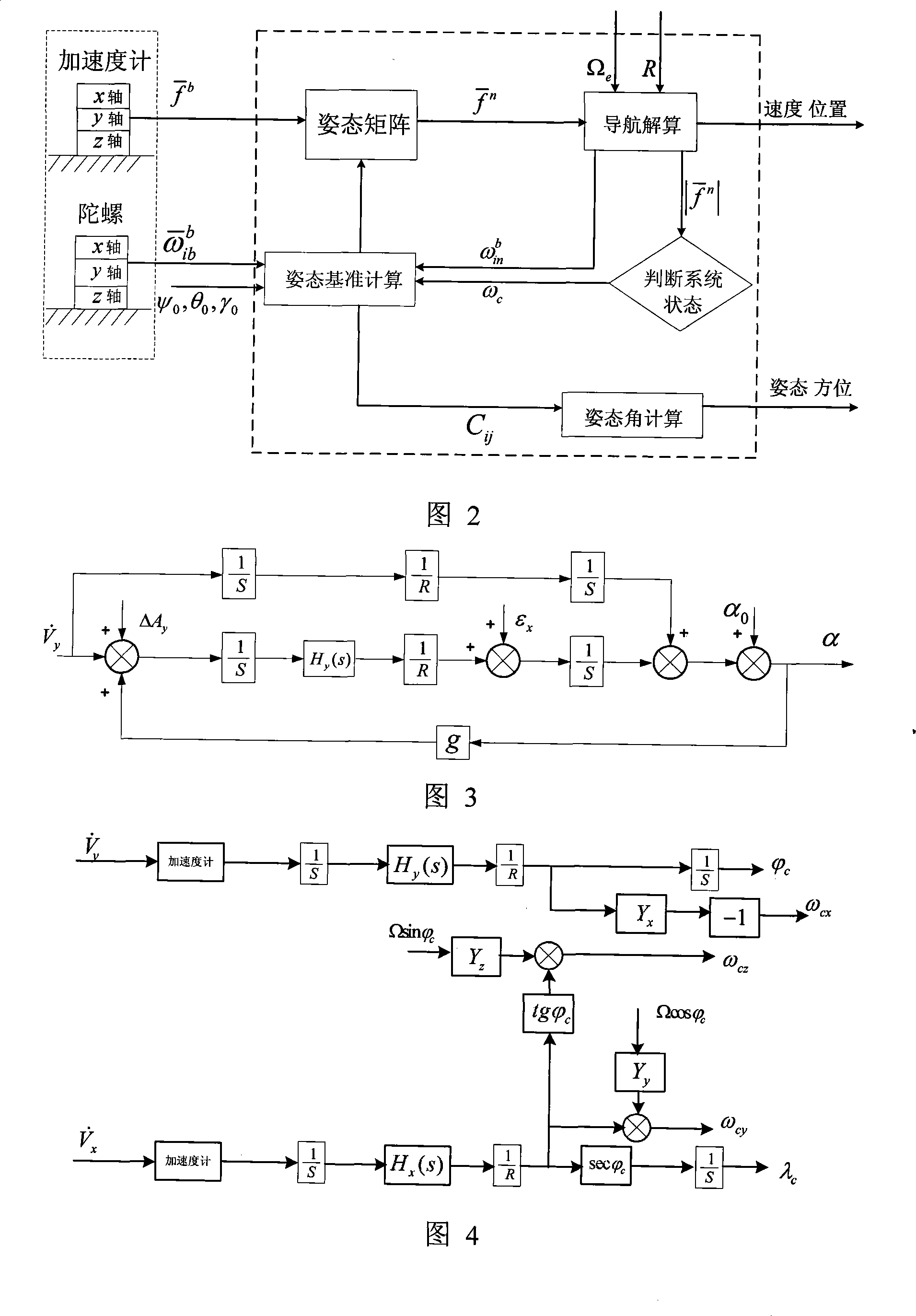
The invention provides an optical fibre gyro strapdown inertial navigation system error inhibiting method based on single-shaft rotation. The initial position parameters of a carrier are confirmed; the data outputted by an optical fibre gyroscope and a quartz accelerometer are collected; the pose information of the carrier is confirmed by the relation between the output of the accelerometer and an acceleration of gravity as well as the relation between the output of the gyroscope and the earth rotation rate; and the initial aligning of the system is finished; an inertial measuring unit coordinate system rotates by 45 degrees along the front direction of the shaft oyb of a carrier coordinate system and the initial opposite position between the two coordinate systems is confirmed; IMU continuously rotates along the front direction of the orientation shaft ozb of the carrier coordinate system by an angular velocity that Omega is equal to 6 degrees / s. The data generated by the optical fibre gyroscope and the quartz accelerometer after the rotation of the IMU is converted under the carrier coordinate system to obtain the modulating form of the constant deviation of an inertial apparatus. The output vale Omega ib of the optical fibre gyroscope is used to update a strapdown matrix Tb; the speed and the position of the carrier after the IMU is rotated and modulated are calculated. The invention modulates the constant deviation of the inertial device on the directions of three shafts to improve the navigation and location precisions.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for determining initial attitude of fiber strapdown inertial navigation system based on rotating mechanism
InactiveCN101571394APrecise initial poseNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition fixationFiberGyroscope
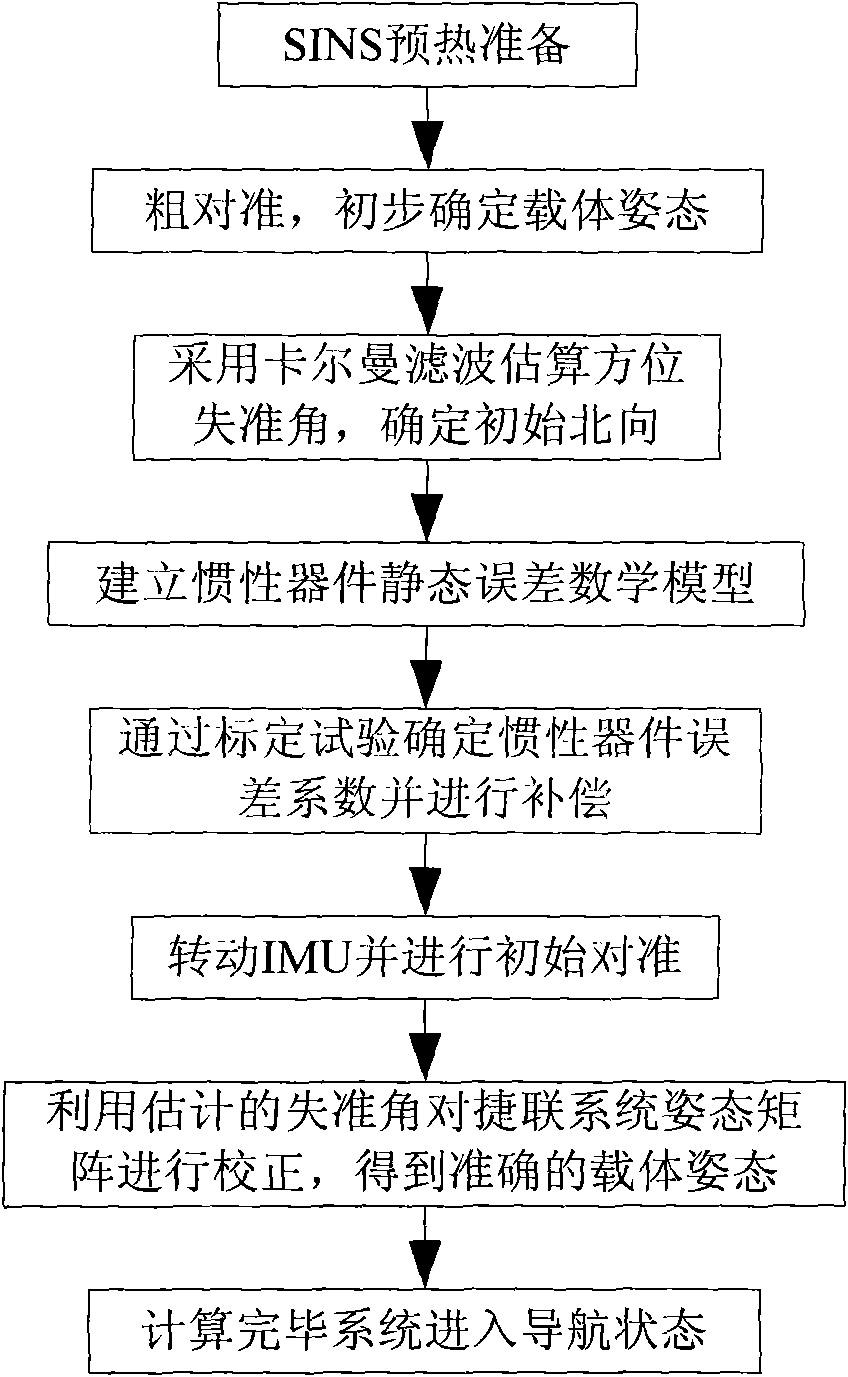
The invention provides a method for determining the initial attitude of a fiber strapdown inertial navigation system based on a rotating mechanism. The method comprises the following steps: according to the relation between the SINS output and the rotational angular velocity and the acceleration of gravity of the earth, initially determining the SINS initial attitude, and utilizing the Kalman filtering method to estimate a misalignment angle so as to determine the local north orientation; establishing an error model of a fiber optic gyroscope to estimate the north orientation gyroscope drift under the navigation system; after an inertial measurement unit (IMU) clockwise rotates for 90 degrees, estimating the south orientation gyroscope drift under the navigation system; after the IMU horizontal gyroscope drift is obtained, the operation of compensation is carried out; and the technical scheme of initial alignment under the state that the inertial measurement unit rotates around a carrier azimuth axis is adopted for the system after error compensation, so as to determine the initial strapdown matrix of the system and to obtain the attitude of the carrier at the initial time by calculation. The method has the characteristics of automation and high precision, and is suitable for various medium and high precision strapdown inertial navigation systems.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
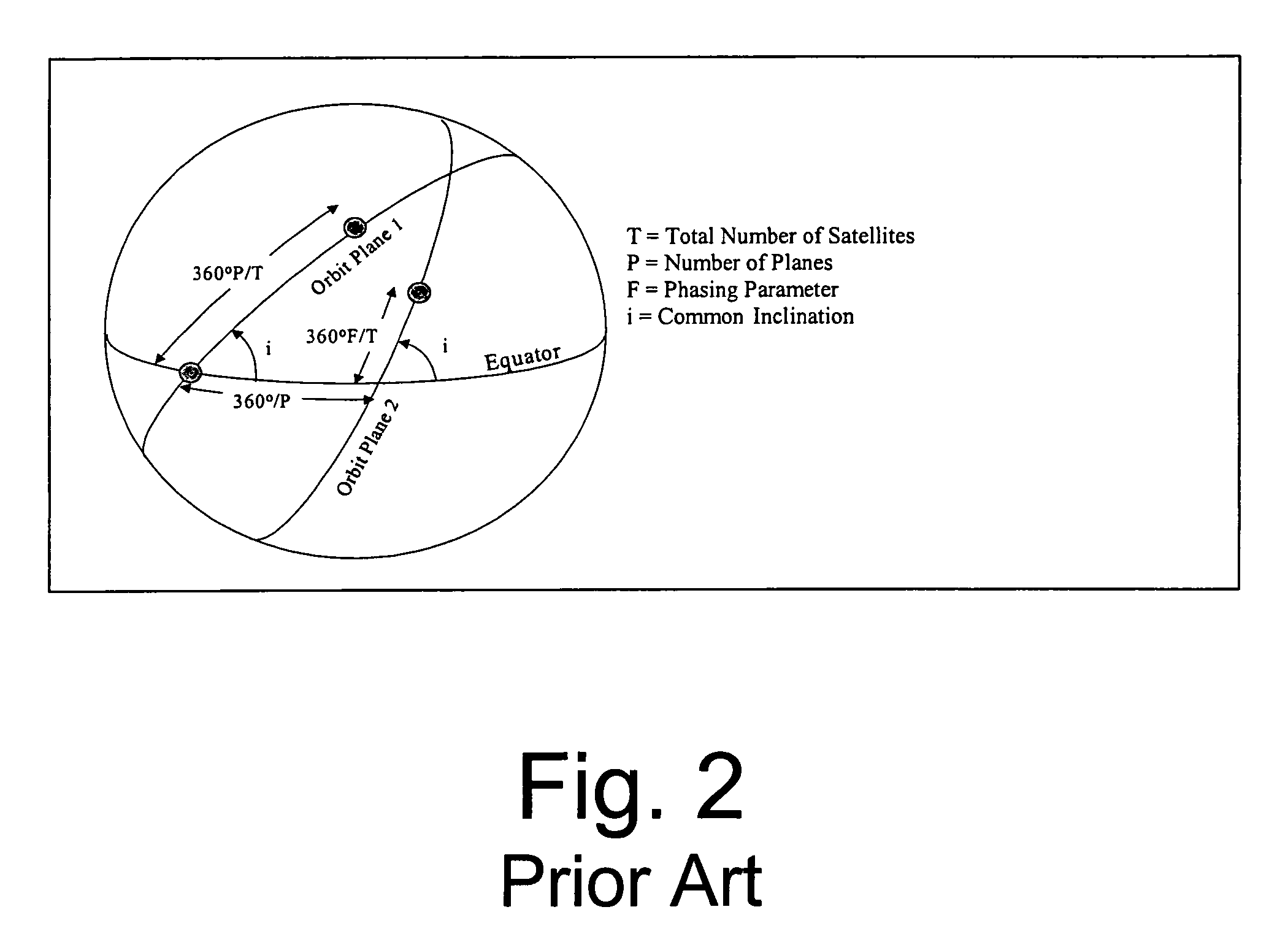
Space based change detection using common ground track constellations
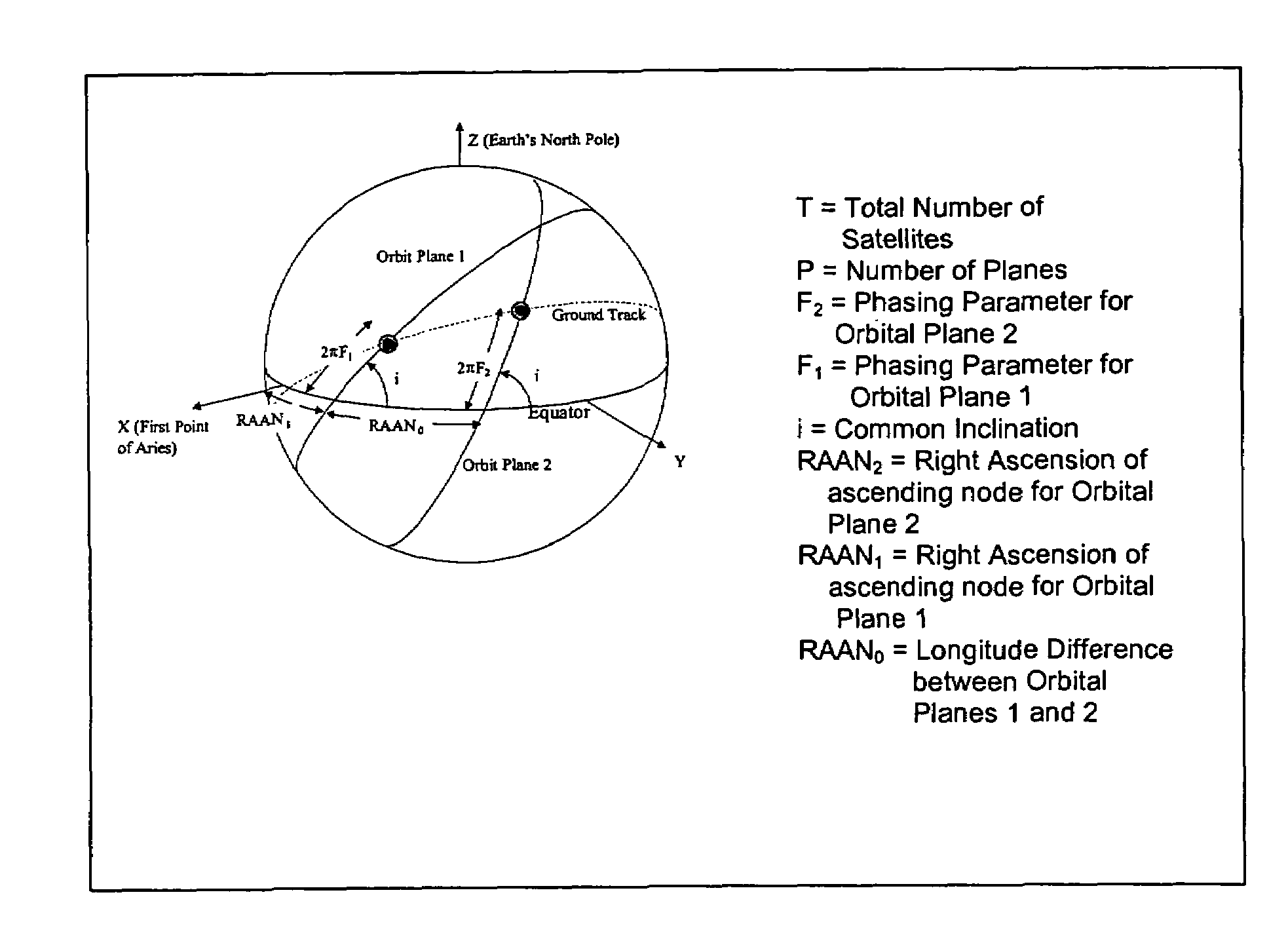
InactiveUS7270299B1Minimal image blurring and distortionReduce in quantityCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesEarth's rotationPhase angle difference
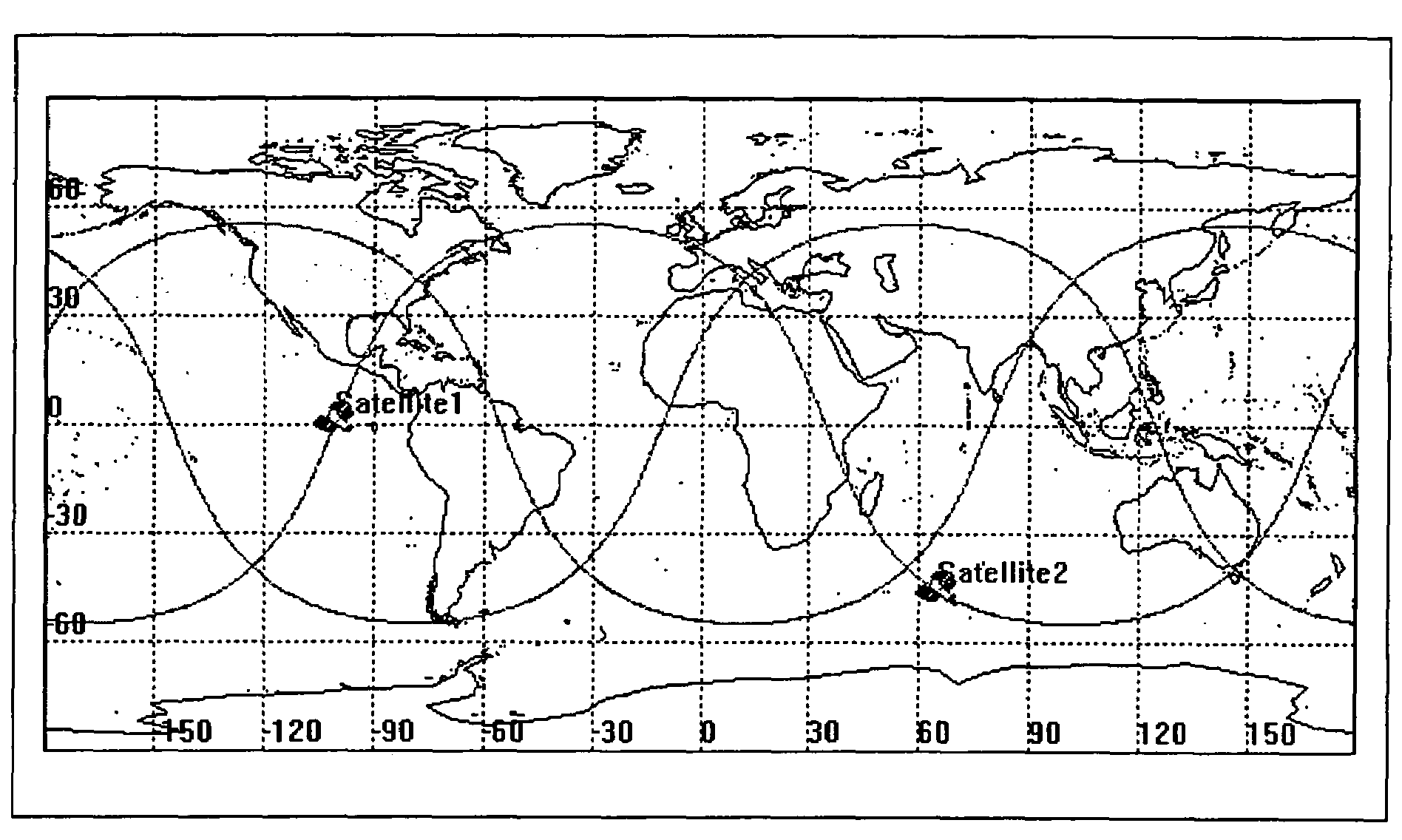
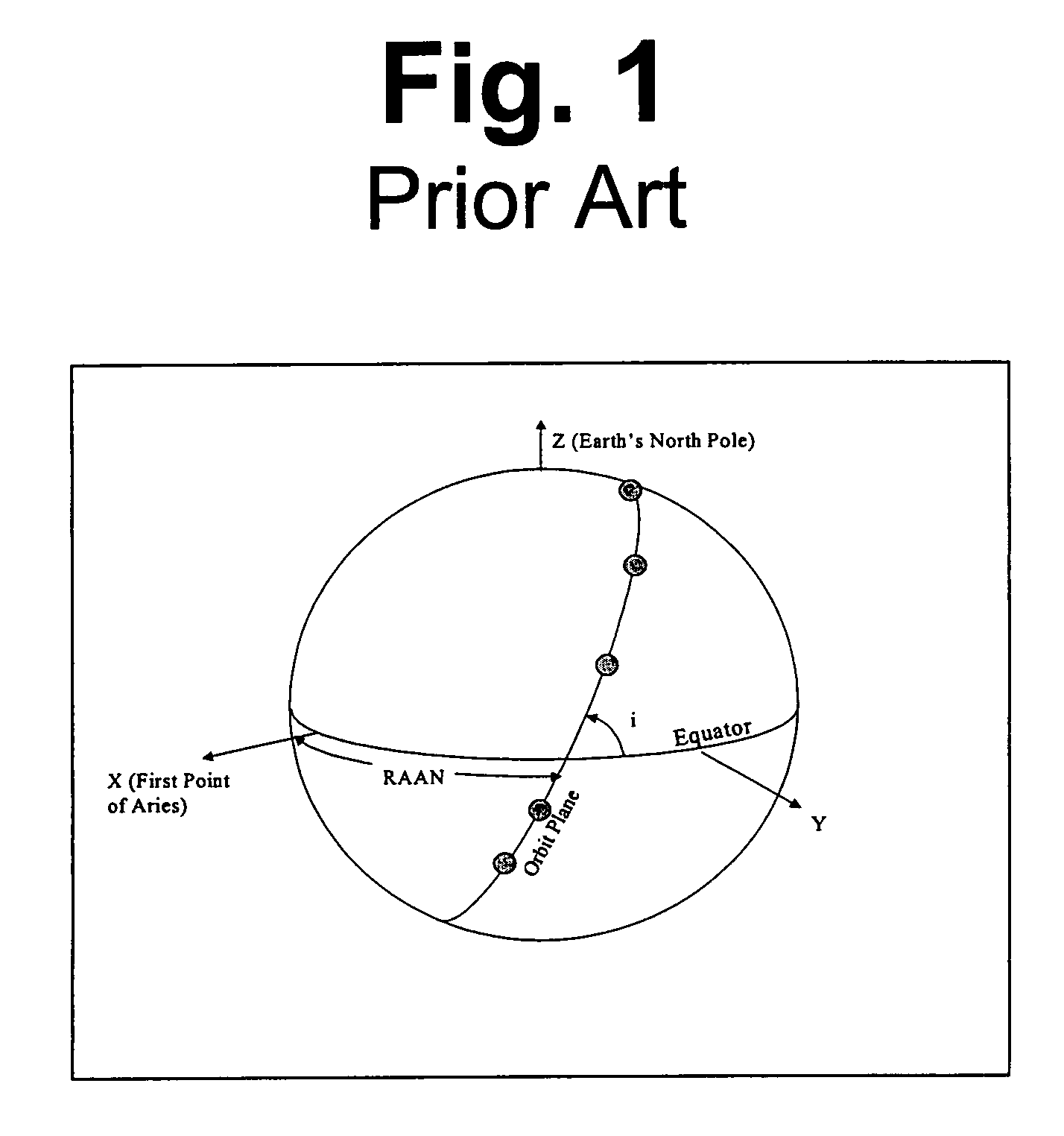
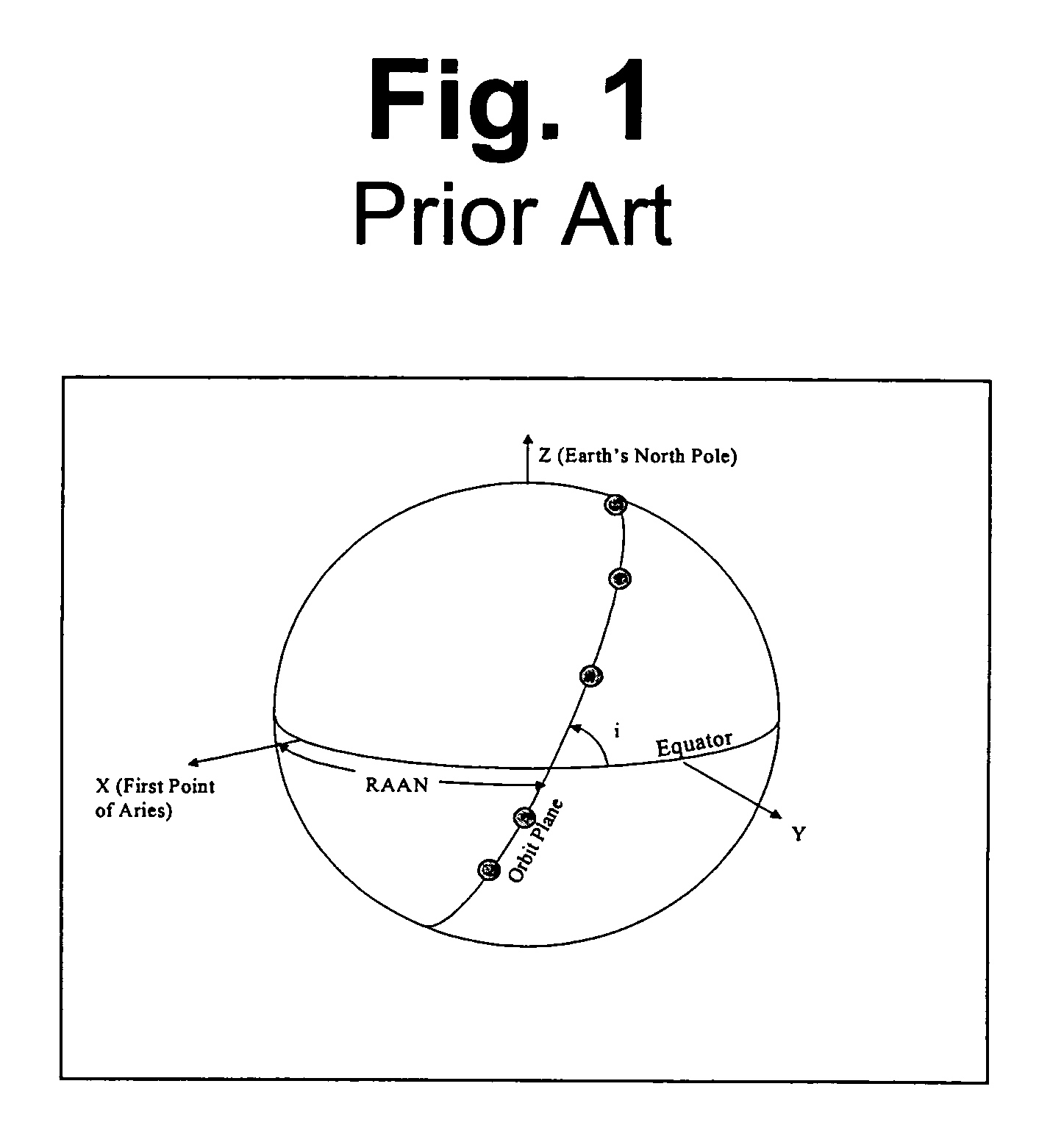
A new approach for designing satellite constellations whereby each satellite follows a common ground track is being proposed for performing high-precision change detection imagery for long periods of time. By precisely prescribing the orbital parameters, i.e., the relationship between the right ascension of the ascending nodes (RAAN) and the phase angle difference between successive satellites, for example, sharpened change detection images may be taken from successive satellites in the constellation without the need to process out blurring by any special image re-working software. The relationship between the orbital parameters of the satellites is precisely tuned to the earth's rotation rate for the altitude of the satellites. A reduction in the total satellite count is achievable due to tiling the satellite coverage in near optimal arrangements. Such high-precision change detection imaging by successive satellites in orbit around the earth is at least useful in the detection of underground facilities activities and the detection of slow moving objects.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
High-lift-to-drag-ratio hypersonic stable gliding reentry guidance method based on drag profile
ActiveCN107941087AHigh precisionWell formedGeometric CADCosmonautic vehiclesEarth's rotationFlight vehicle
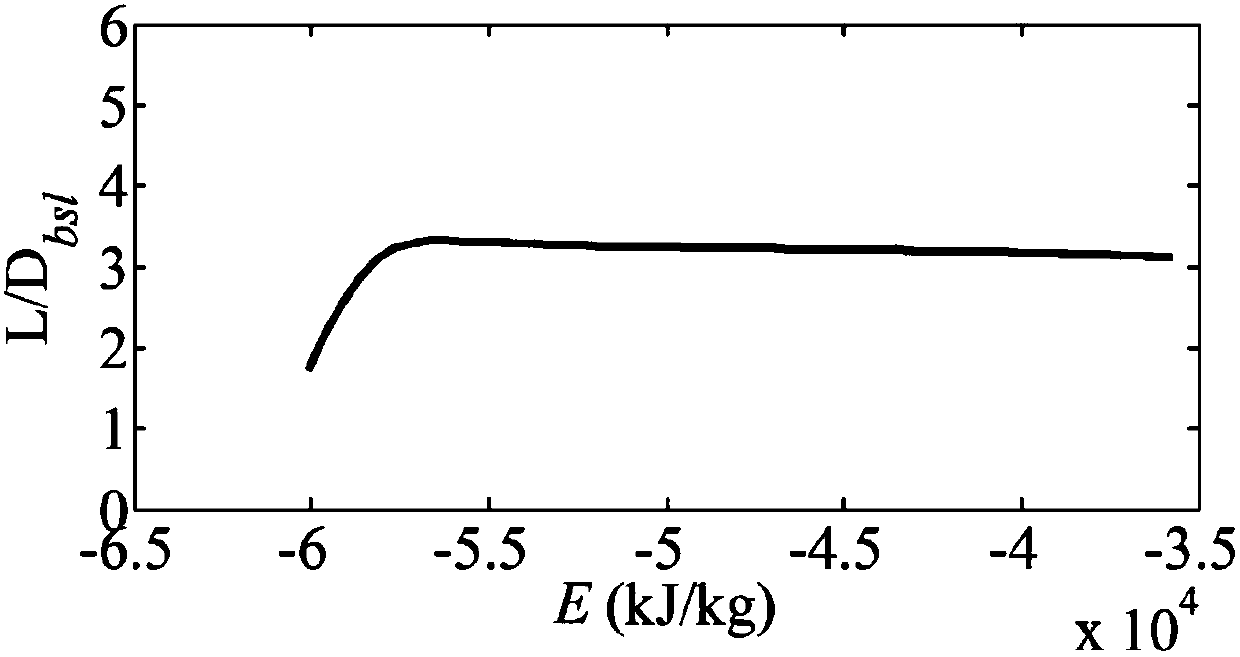
The invention relates to a high-lift-to-drag-ratio hypersonic stable gliding reentry guidance method based on a drag profile. The method comprises the following steps that the first step, modeling ofa hypersonic flight vehicle is conducted; the second step, gliding distance analytic solution derivation is conducted; the third step, reentry track planning and tracking guidance are conducted; and the fourth step, a stable gliding trajectory tilt angle based on an earth rotation model is derived. The high-lift-to-drag-ratio hypersonic stable gliding reentry guidance method based on the drag profile has the advantages that a gliding distance analytic solution which is higher in accuracy and is based on energy is obtained, the form is simple, and application is convenient; the drag profile isplanned by using the energy as an independent variable, the drag profile is converted into the longitudinal lift-to-drag ratio under the rotating earth background, then a heeling angle is adjusted, tracking is conducted under the condition of the maximum lift-to-drag ratio, and transverse movement is controlled by a course error threshold; and in order to solve the reentry trajectory oscillation problem, the stable gliding trajectory tilt angle based on the earth rotation model is derived, and a trajectory damping technology using the stable gliding trajectory tilt angle as the feedback item is adopted to restrain oscillation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
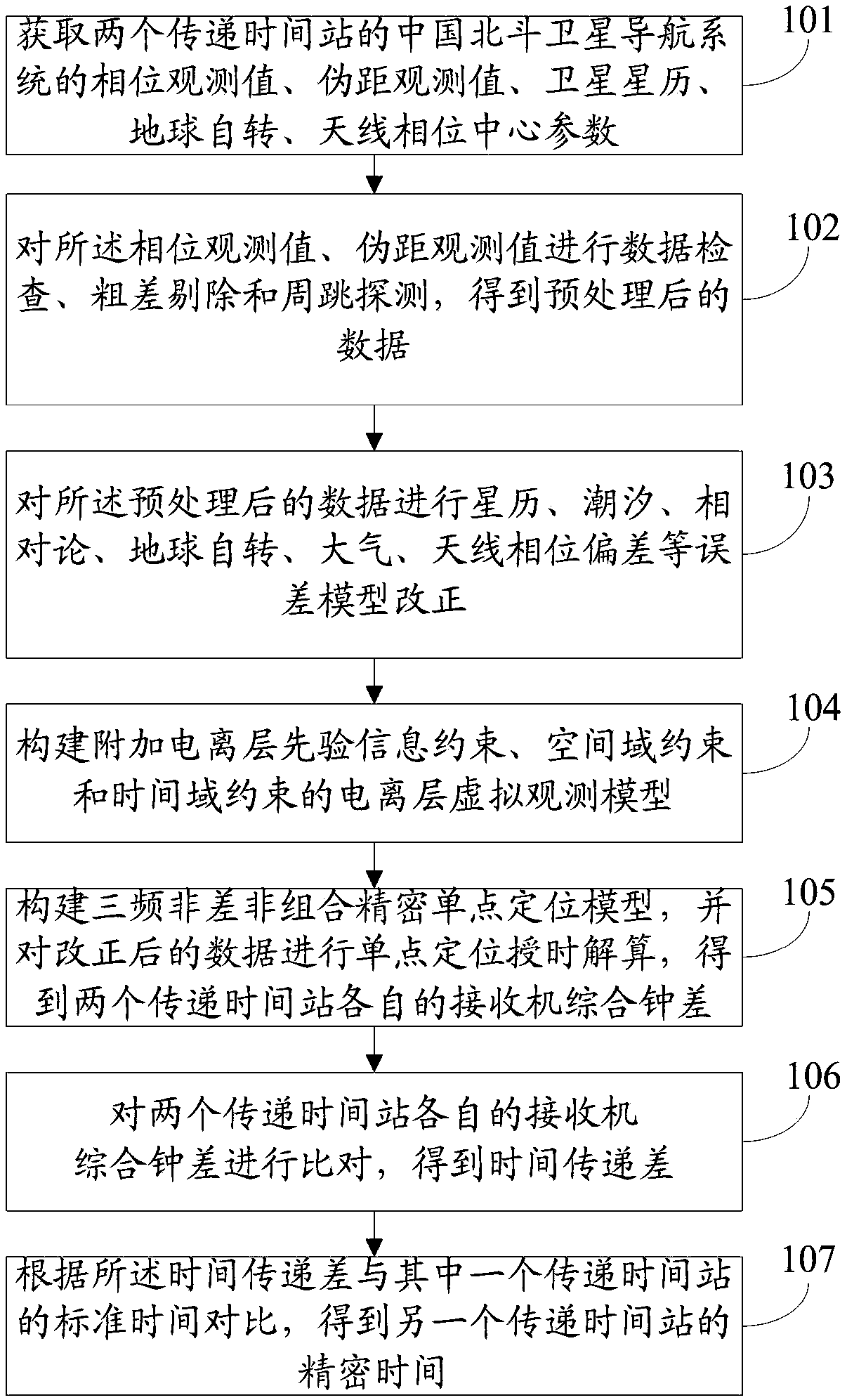
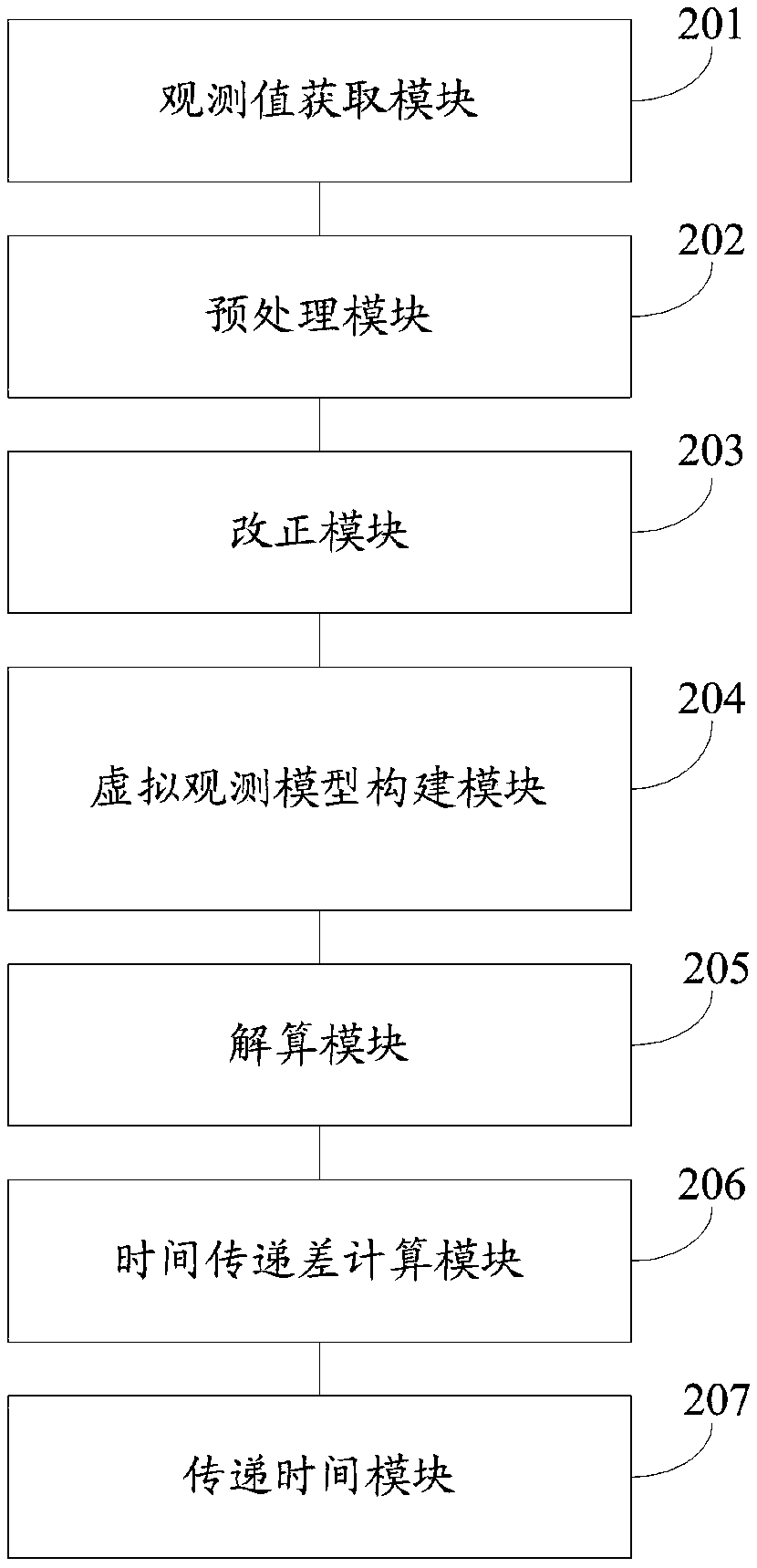
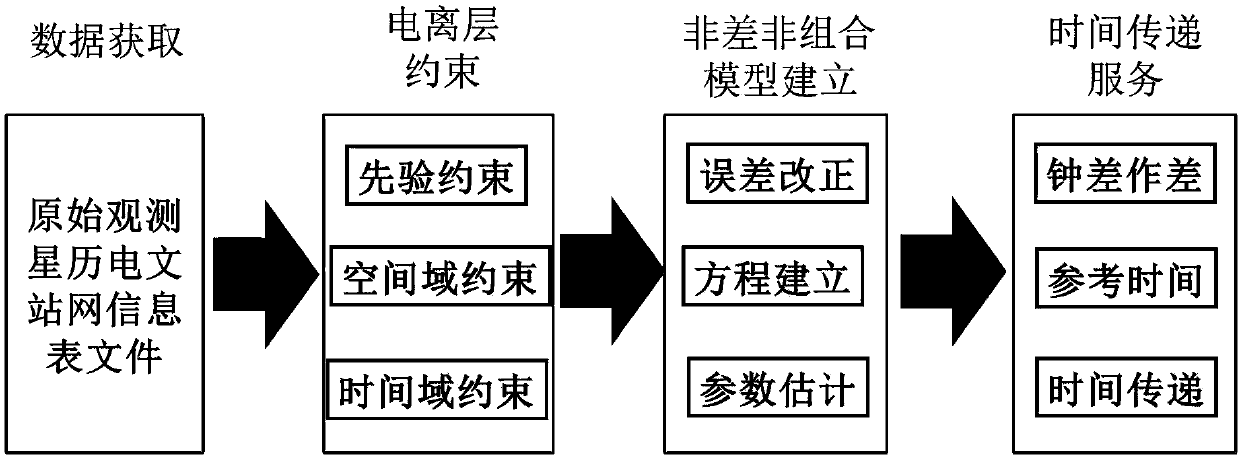
Beidou three-frequency non-differential non-combined observation value time transmission system and method
ActiveCN108919634AReduce observation noiseImprove time transfer accuracyRadio-controlled time-piecesEarth's rotationClock correction
The invention discloses a Beidou three-frequency non-differential non-combined observation value time transmission system and method. The method includes the steps that phase observation value, pseudo-range observation value, satellite ephemeris, earth rotation, antenna phase center and other parameters of China Beidou satellite navigation systems at two time transmission stations are obtained; data check, gross error reject and cycle slip detection are carried out, error models of ephemeris, tide, relativity, the earth rotation, atmosphere and antenna phase deviation are corrected; an ionospheric virtual observation model with additional ionospheric prior information constraints, spatial domain constraints and time domain constraints is constructed; and a three-frequency non-differentialnon-combinatorial precise single-point positioning model is constructed, a single-point positioning timing solution is carried out on corrected data, and comprehensive clock corrections of receivers of the two transmission time stations are obtained and compared to obtain a time transmission difference; and compared with standard time of one of the two transmission time stations, precise time of the other one of the two transmission time stations is obtained. According to the Beidou three-frequency non-differential non-combined observation value time transmission system and method, the observation noise can be reduced, and the accuracy and reliability of time transmission are improved.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for acquiring initial course attitude of fiber optic gyro strapdown inertial navigation system
InactiveCN102486377AAccurate estimateImprove alignment accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEarth's rotationAngular velocity
The invention relates to a method for acquiring an initial course attitude of a fiber optic gyro strapdown inertial navigation system. The method is characterized by: extracting gravitational acceleration information from an acceleration meter through filtering processing and compensation, projecting an earth gravitational vector to an inertial coordinate system, with rotational-angular velocity information of the earth included in a projecting component, taking the earth gravitational vector in the inertial coordinate system as reference information, and making use of the output of a gyro and the acceleration meter to estimate an initial attitude angle. On the basis of ensuring that an initial horizontal angle satisfies a precision requirement, the method of the invention substantially improves the precision of an initial course angle of the fiber optic gyro strapdown inertial navigation system.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for determining initial status of strapdown inertial navigation system
ActiveCN1908584AImprove ObservabilityImprove filtering effectNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEarth's rotationGyroscope
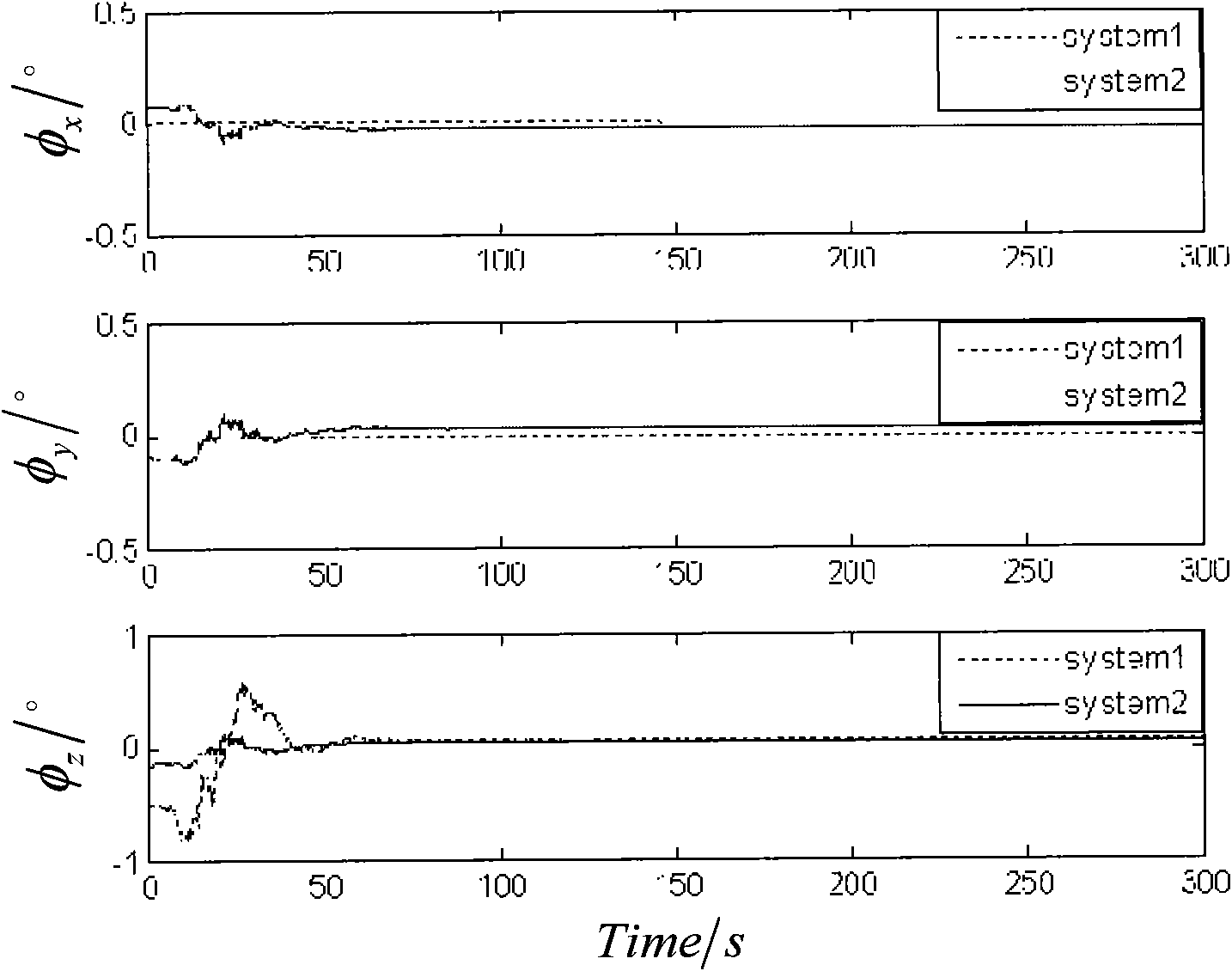
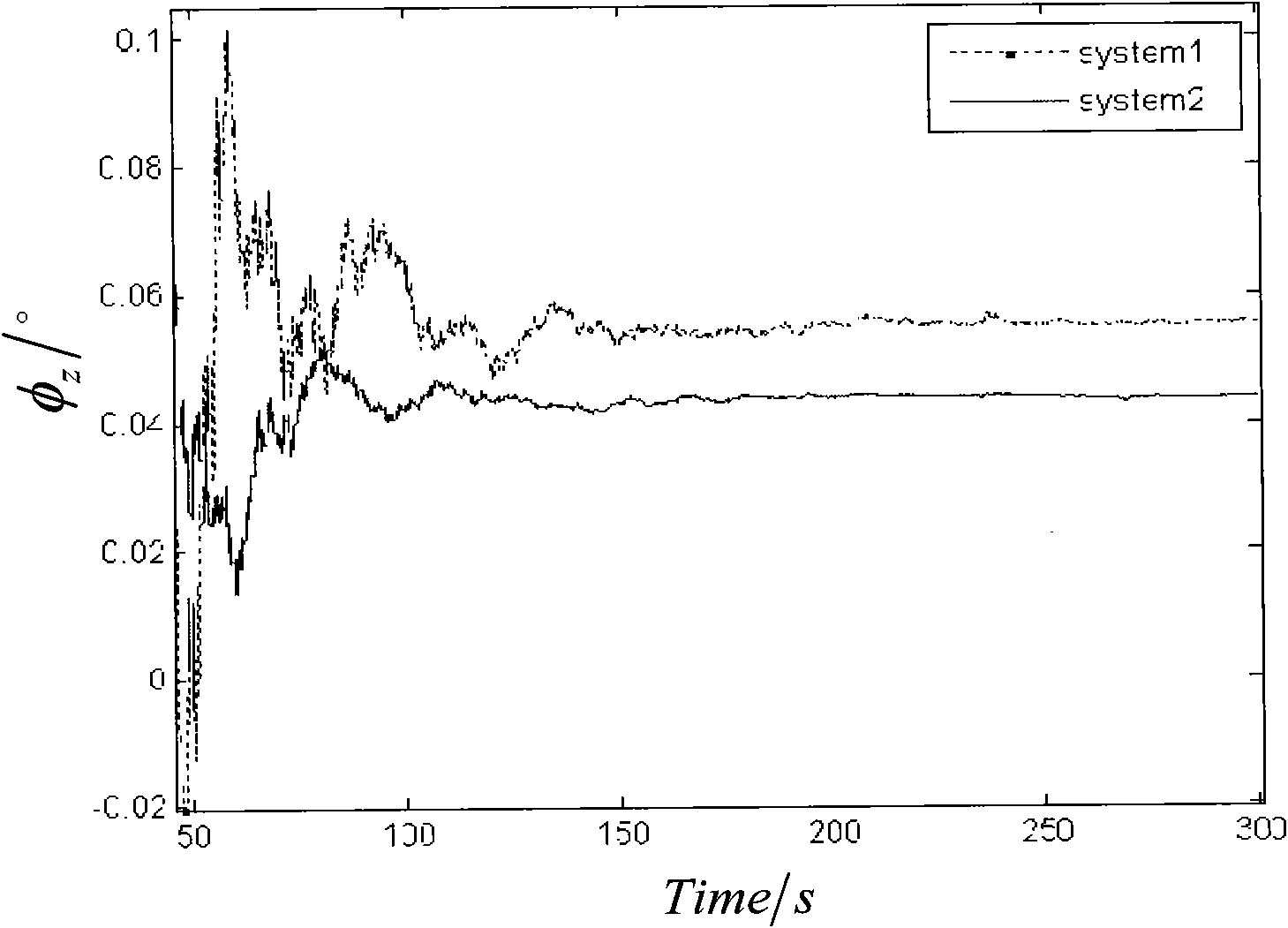
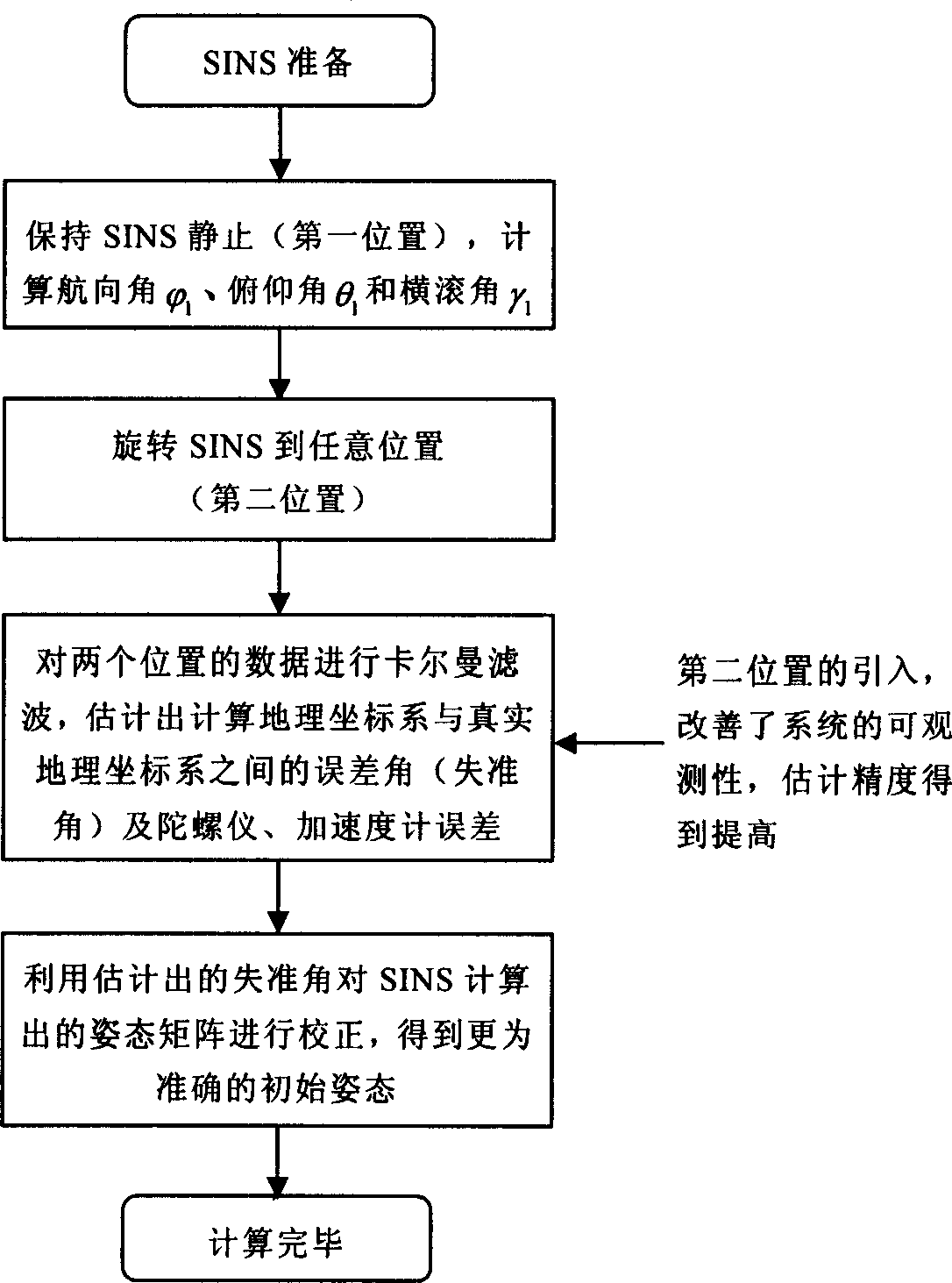
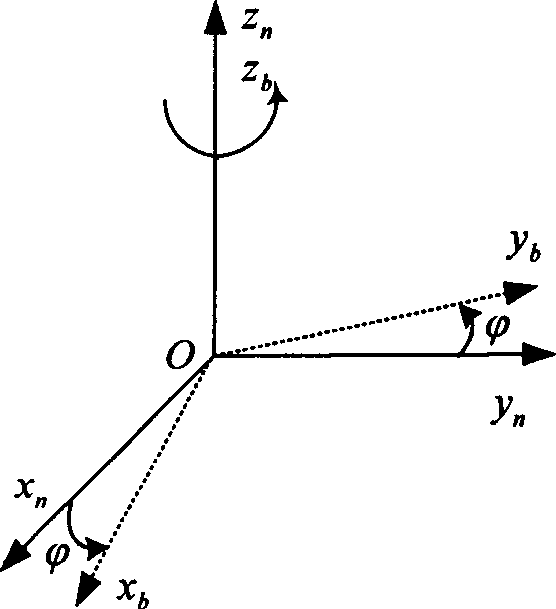
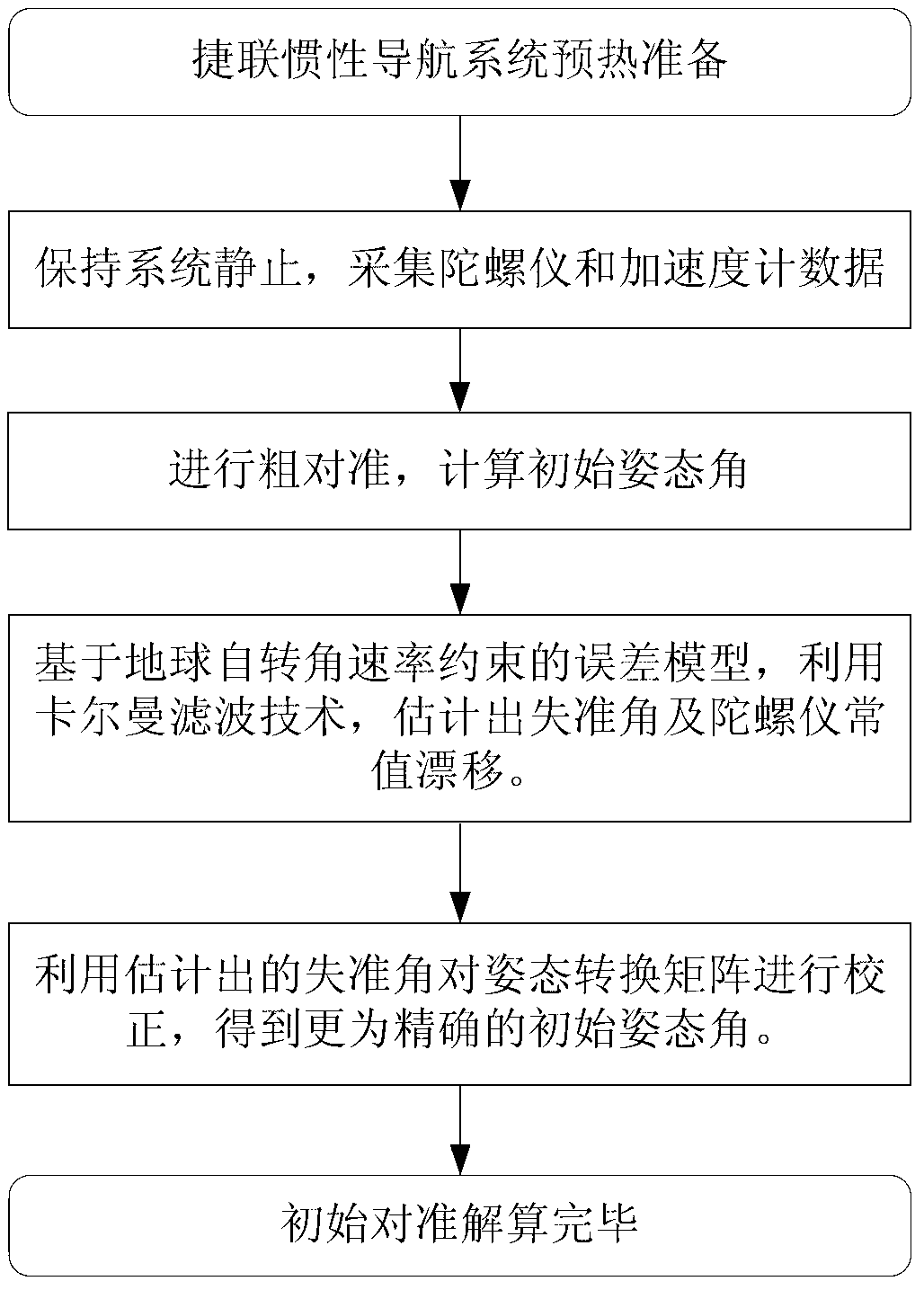
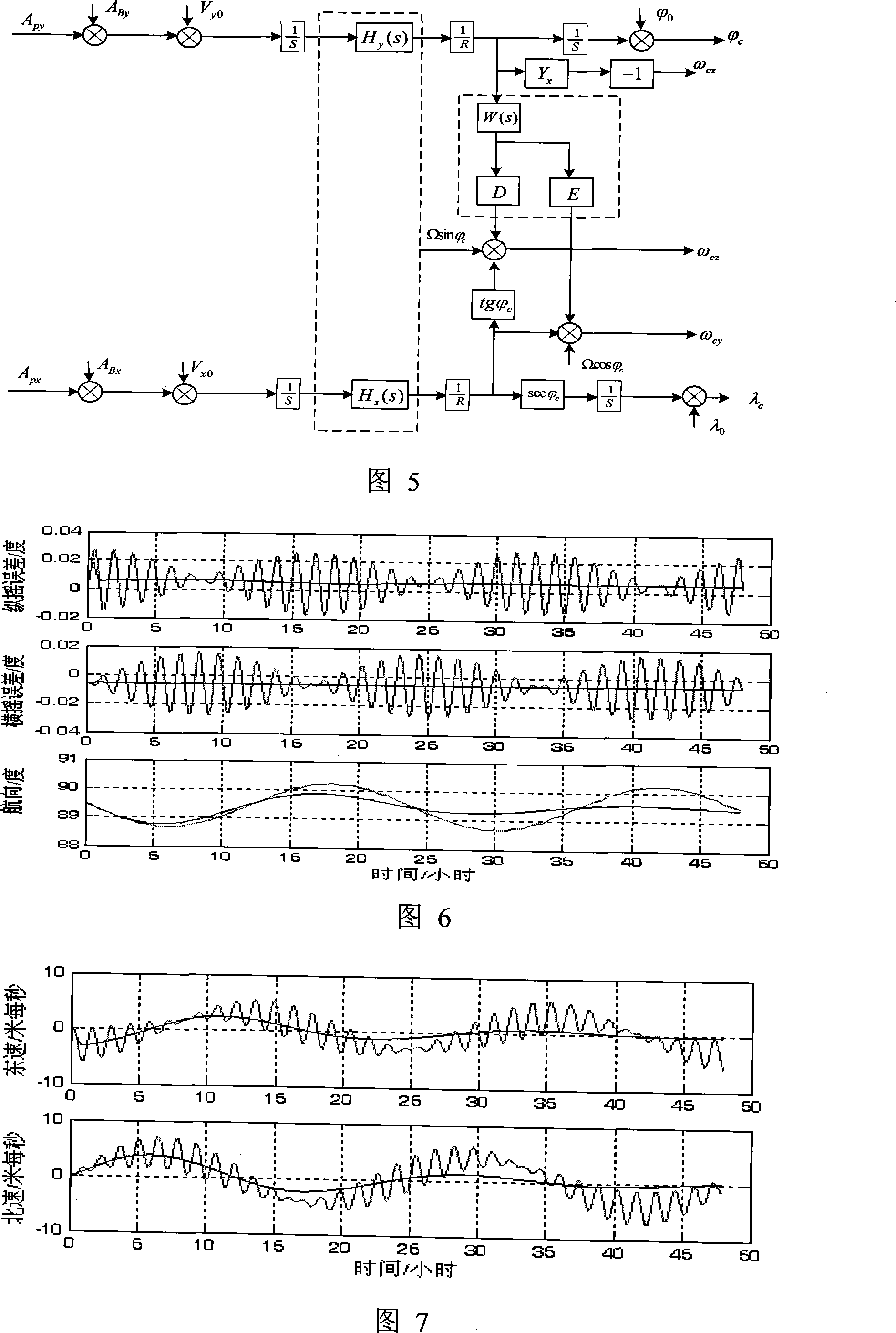
The initial attitude determination method for SINS comprises: rotating the SINS from initial position to any one position round arbitrary 3D axis; according to SINS output on first position and the relation of earth rotational angular velocity and acceleration of gravity, determining the initial attitude primarily; then, using Kalman filter to estimate the gyro constant drift and other values for more accurate initial attitude. This invention improves observability and precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
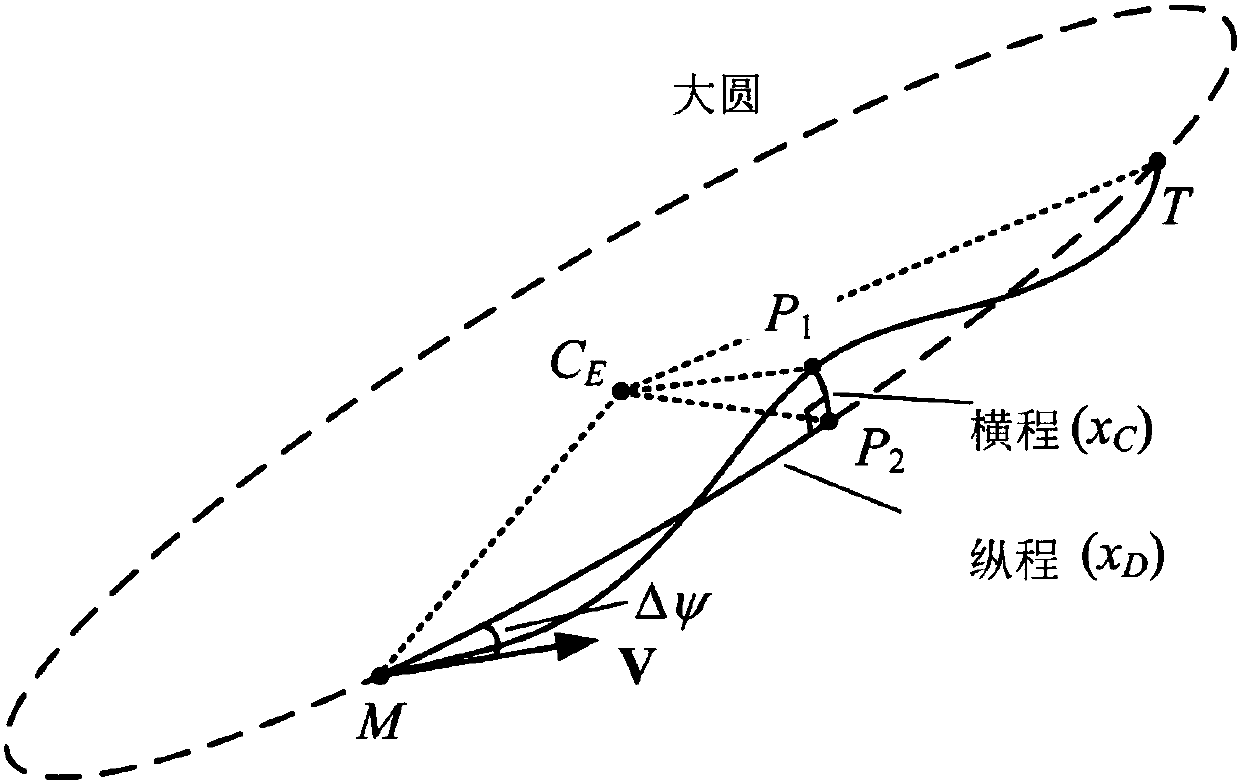
Full-firing-direction autonomous reentry guidance method based on three-dimensional reentry trajectory analytical solution
ActiveCN108036676AOscillation suppressionReduce peakGeometric CADSustainable transportationHeat fluxEarth's rotation
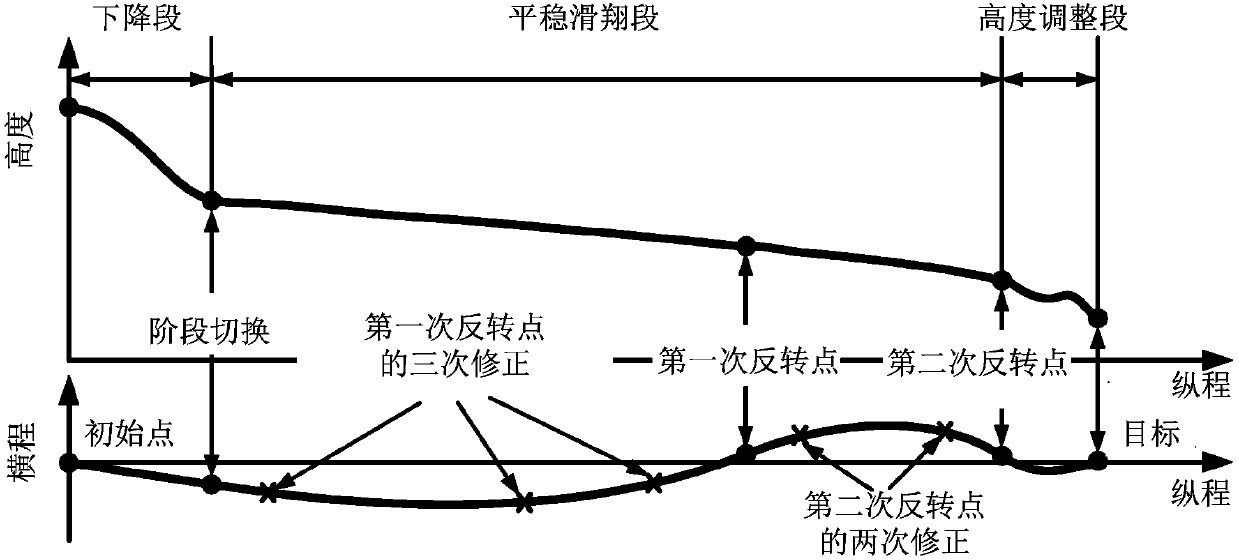
The invention discloses a full-firing-direction autonomous reentry guidance method based on a three-dimensional reentry trajectory analytical solution. The full-firing-direction autonomous reentry guidance method comprises the following steps of 1, building of a kinematical equation and a dynamical equation, 2, summarizing of the reentry guidance method, 3, descent stage guidance strategies, 4, steady gliding stage guidance strategies and 5 height-adjustment stage guidance strategies. The full-firing-direction autonomous reentry guidance method has the advantages that reentry guidance of an aircraft with the large lift-drag ratio can be guided effectively, low-damping and long-period trajectory oscillation caused by the high lift-drag ratio can be restrained effectively, the peak value ofthe heat flux density is reduced, and tracking of a reference track is facilitated; inertia force caused by earth rotation and actual aerodynamic force are combined into equivalent aerodynamic force,an equivalent aerodynamic section is planned through the analytical solution, and thus the aircraft has the omni-directional reentry task processing capability; and an equivalent aerodynamic section fitting formula based on the inverse proportional function is put forward, the reentry trajectory analytical solution based on the complex equivalent aerodynamic section form is further deduced, and thus high precision, all-dimensional applicability and high robustness are achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
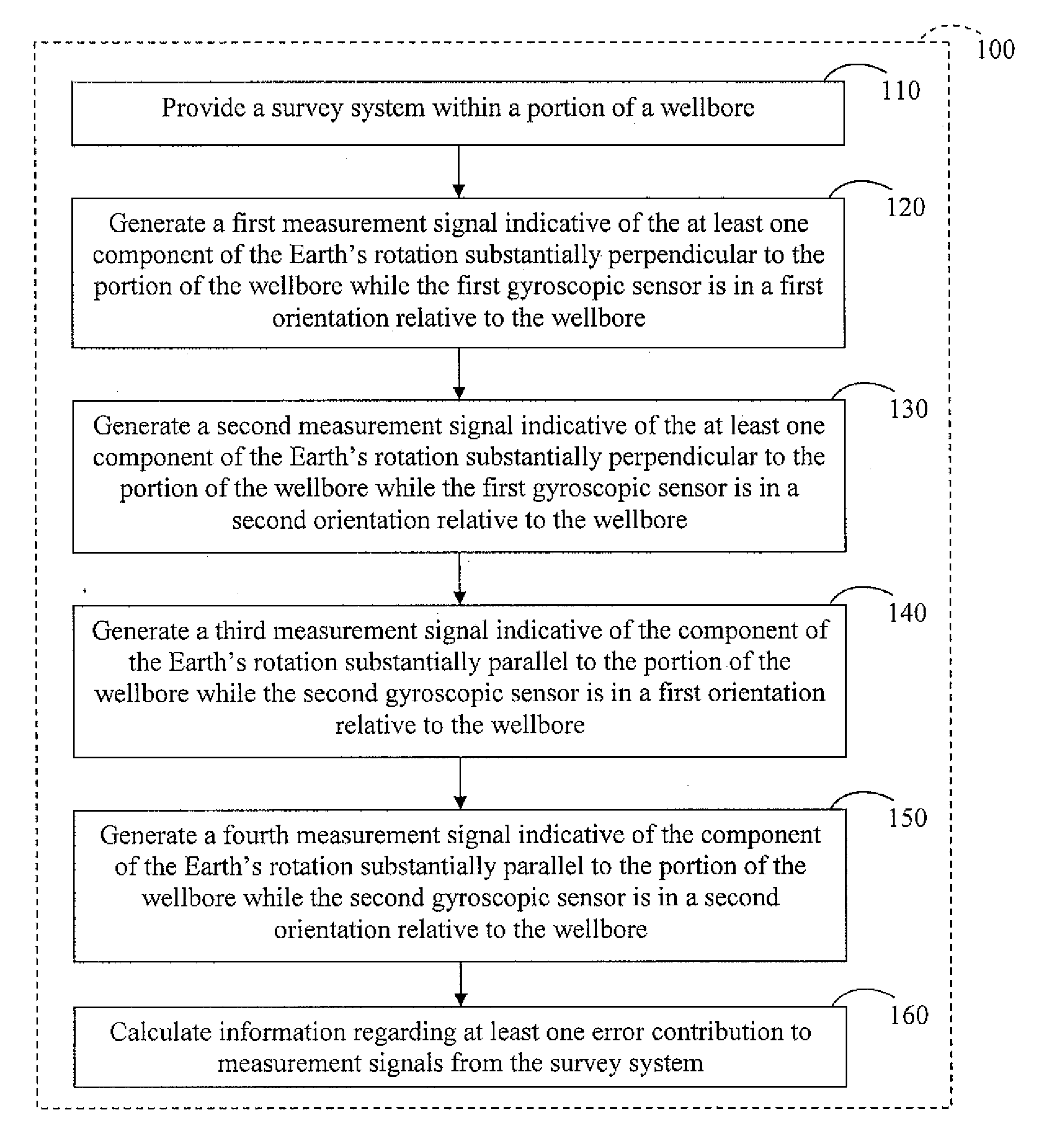
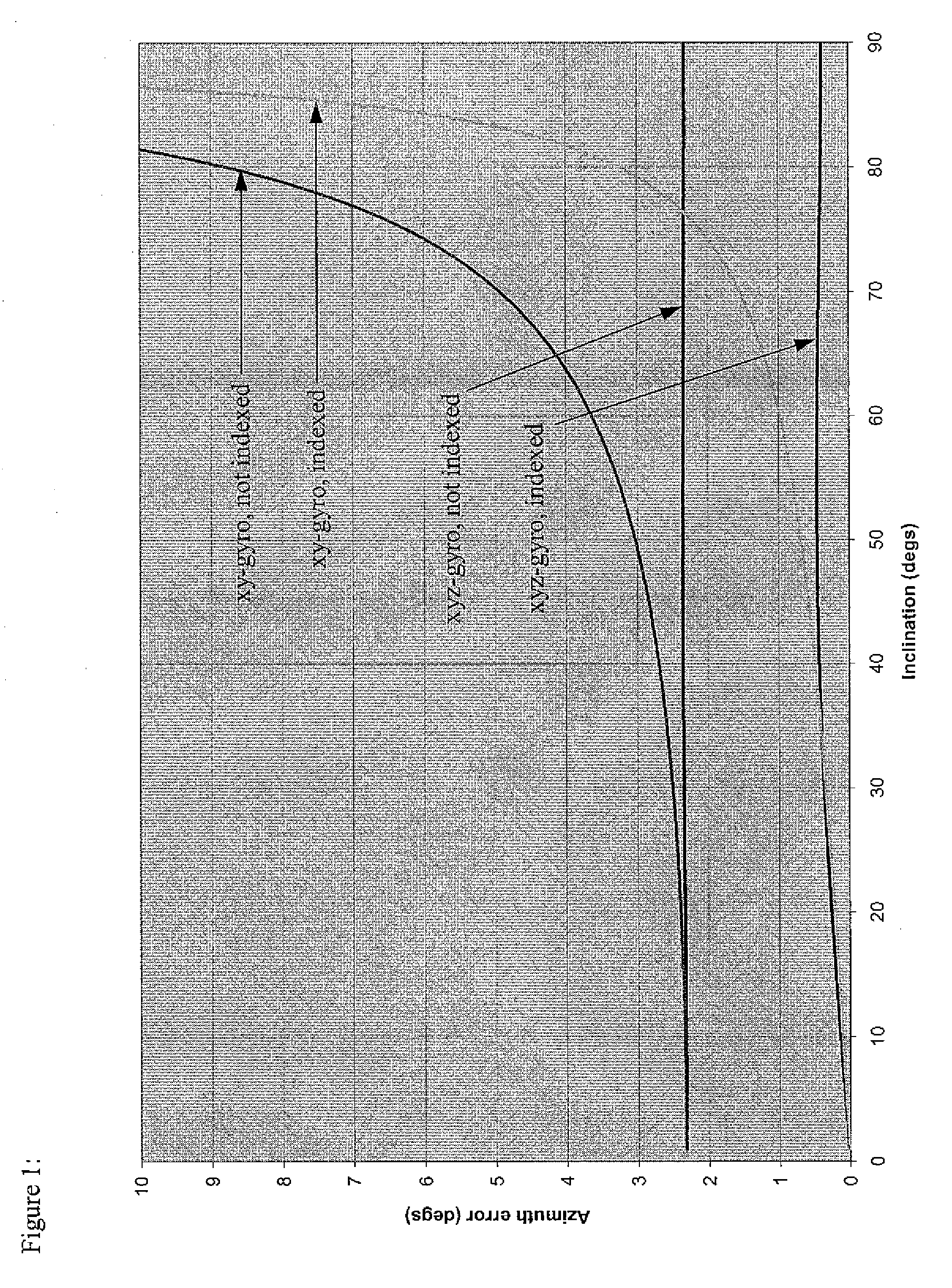
Reducing error contributions to gyroscopic measurements from a wellbore survey system
ActiveUS20100198518A1Reduces error contributionReducing error contributionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyEarth's rotationGyroscope
A method reduces error contributions to gyroscopic measurements from a wellbore survey system having two gyroscopic sensors adapted to generate signals indicative of at least one component of the Earth's rotation substantially perpendicular to the wellbore and indicative of a component of the Earth's rotation substantially parallel to the wellbore. The method includes generating a first signal indicative of the at least one substantially perpendicular component while the first sensor is in a first orientation; generating a second signal indicative of the at least one substantially perpendicular component while the first sensor is in a second orientation; generating a third signal indicative of the substantially parallel component while the second sensor is in a first orientation; and generating a fourth signal indicative of the substantially parallel component while the second sensor is in a second orientation. The method further includes calculating information regarding at least one of a mass unbalance offset error and a quadrature bias error using the first, second, third, and fourth signals.
Owner:GYRODATA
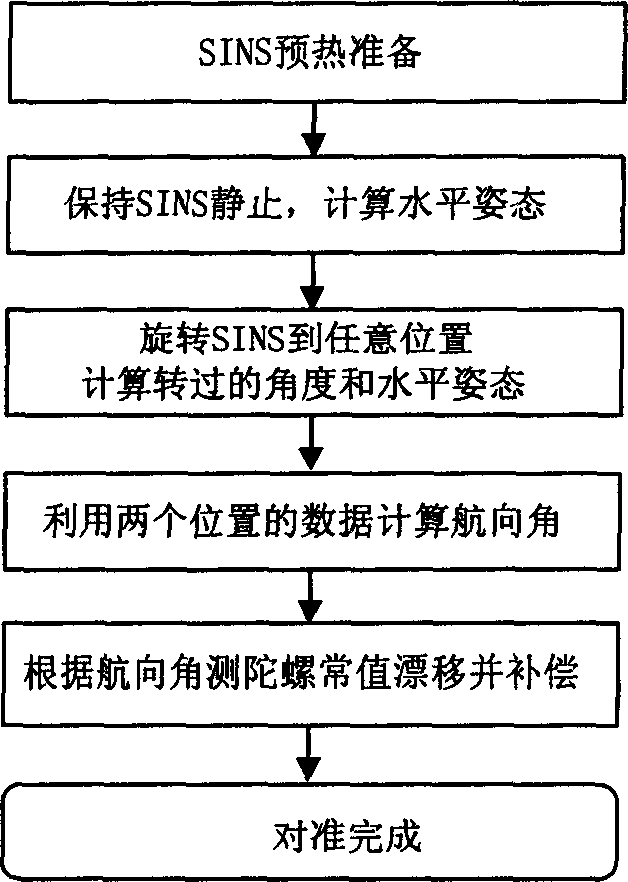
SINS (strapdown inertial navigation system) initial alignment method based on earth rotation angular rate constraint
InactiveCN102706366AImprove measurement errorImprove ObservabilityMeasurement devicesGyroscopeEarth's rotation
The invention relates to an SINS (strapdown inertial navigation system) initial alignment method based on earth rotation angular rate constraint. The method adopts a Kalman filtering technique for alignment. On the basis of the traditional speed error measuring model, earth rotation angular rate is added as a constraint condition to obtain an improved initial alignment error model. The error model improves the observability of a system during stationary base alignment. By conducting Kalman filtering based on the model to estimate the attitude misalignment angle, the speed error, the gyroscope constant drift and the accelerometer constant bias of the system, the initial attitude and skyward gyroscope drift of the SINS can be obtained more rapidly and accurately. The SINS initial alignment method based on earth rotation angular rate constraint has the characteristics of autonomous navigation, high accuracy, high flexibility, simplicity and convenience, and is suitable for all kinds of medium-accuracy and high-accuracy SINSs.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Real time precision rail fixing method of navigational satellite
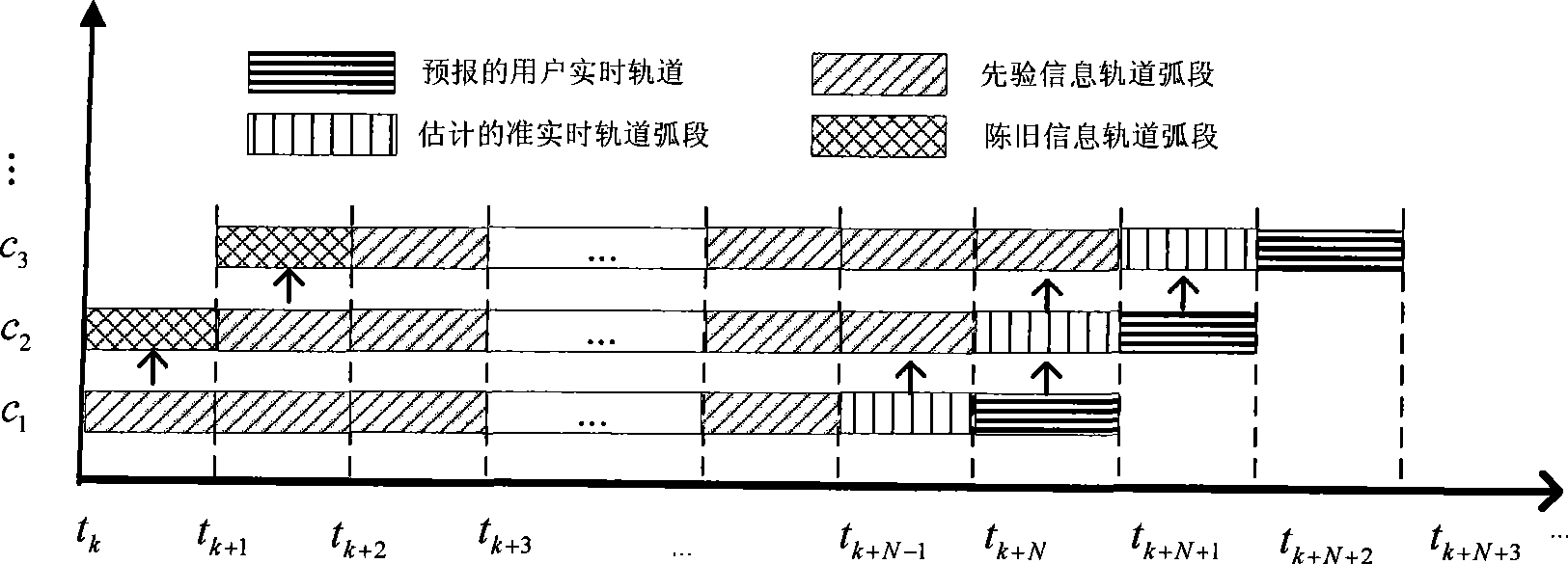
InactiveCN101435863AProcessing speedOvercoming the problem of reduced or even wrong estimation accuracyBeacon systems using radio wavesEarth's rotationSlide window
The invention discloses a method for precisely determining an orbit of a navigational satellite in real time based on a sliding data window. The main concept of the method is that when an estimation is carried out on a state Xk including an initial state of the satellite, a force model parameter, an earth rotation parameter, an atmospheric parameter, a station coordinate and the like; only first N measurements which are closest to k moment are utilized, while other measurements are completely abandoned, wherein N is a predetermined length of the sliding window; a precise satellite orbit initial value and the precise force model parameter of the Nth segmental arc can be acquired through establishing, combining, solving a normal equation and other steps; and a predicted orbit of the next moment can be acquired through an orbit integral and taken as a real-time orbit to be transmitted to a user. The method for determining the orbit of the satellite has the advantages of high speed of data processing, high orbit precision, stable numerical value and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
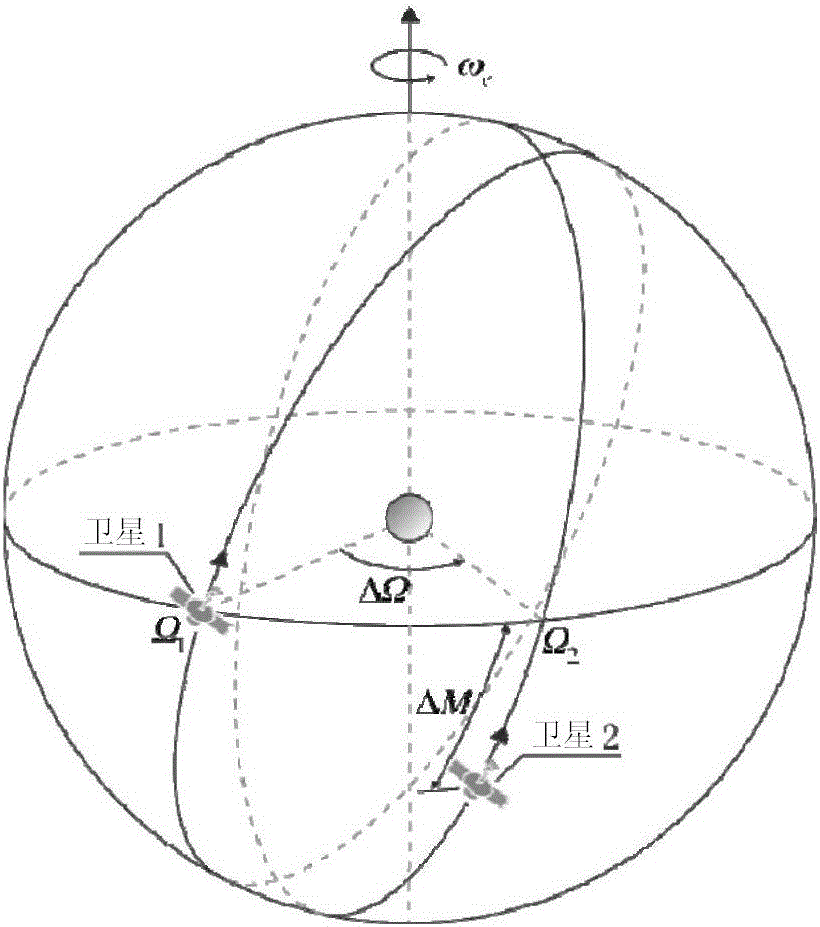
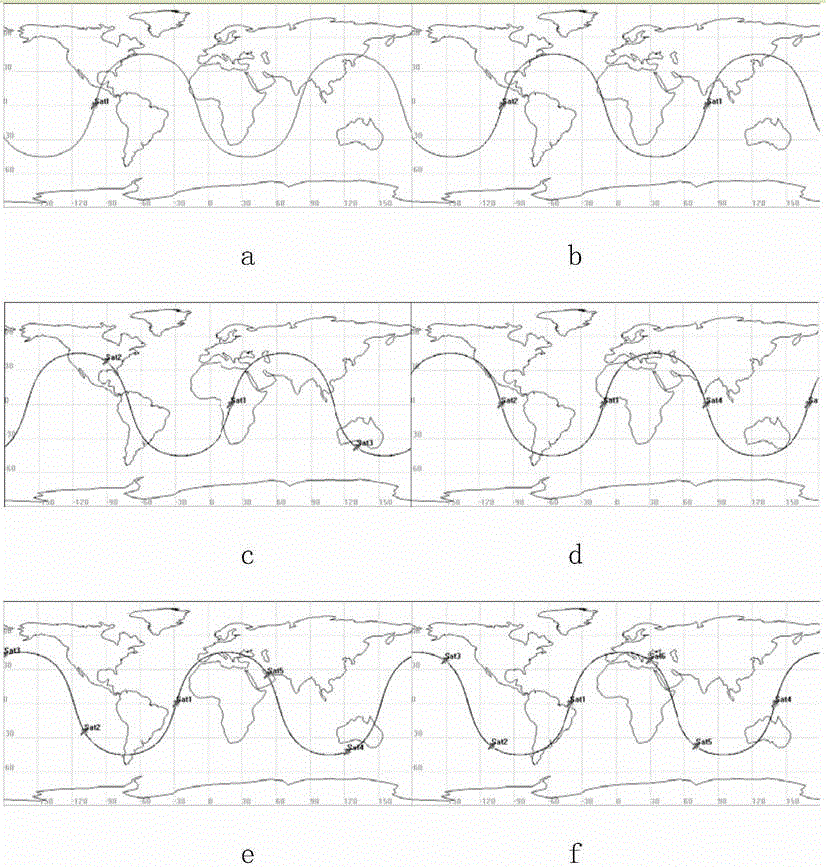
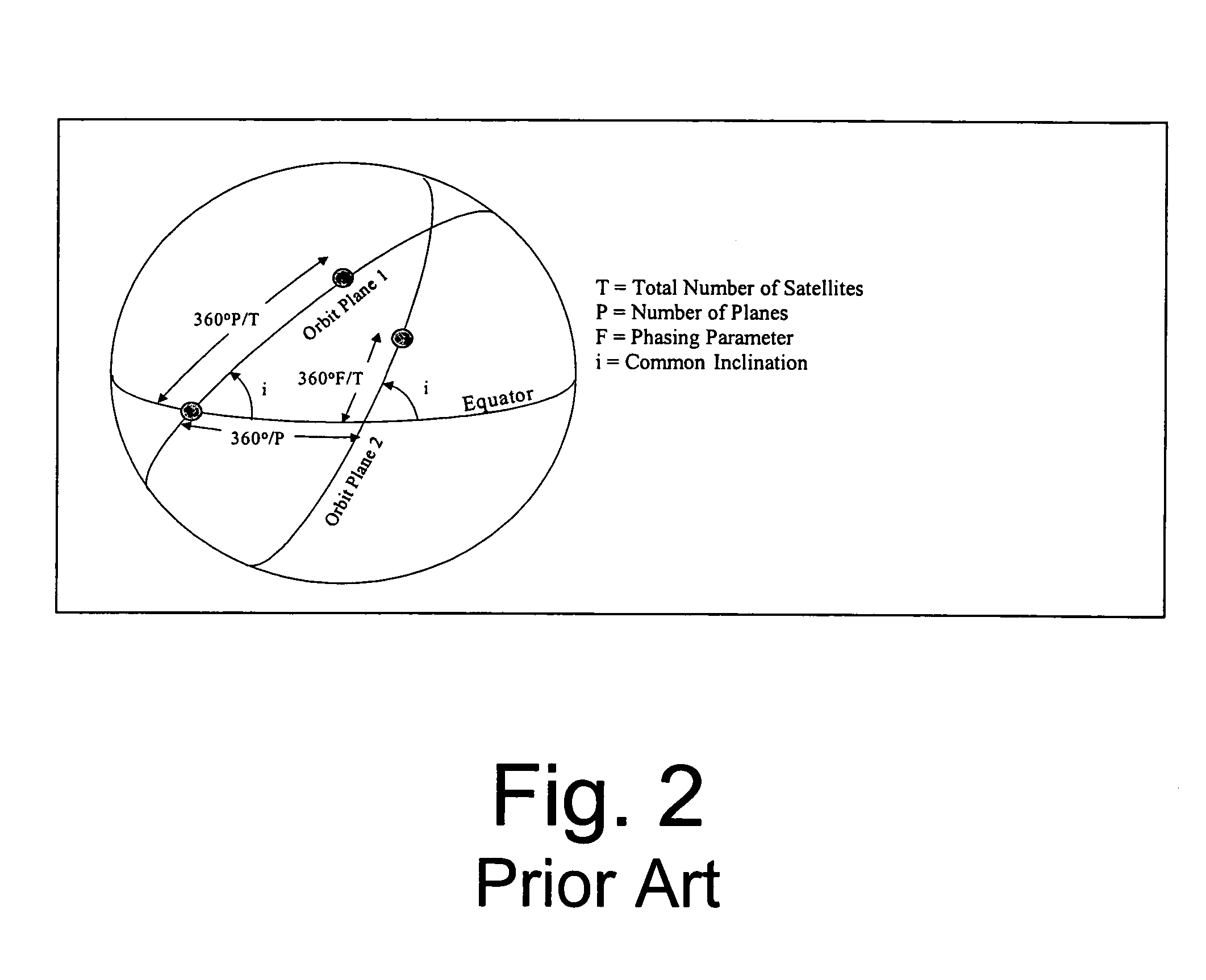
Global communication constellation designing method for realizing on-demand coverage of key areas
ActiveCN106209205AReduce the numberReduce complexityRadio transmissionHigh elevationEarth's rotation
The invention belongs to the technical field of satellite communication, and particularly relates to a global communication constellation designing method for realizing on-demand coverage of key areas. In particular, a constellation comprises a plurality of orbital planes which are uniformly distributed along an equator; only one satellite exists on each orbital plane; an orbital period of each satellite is one integer of a rotation period of the earth; and sub-satellite point tracks of all satellites in the constellation coincide. The constellation can provide a high-elevation communication coverage service for the key areas as required according to a task demand by adjusting design parameters of the constellation such as a regression period, an orbit inclination, an eccentricity ratio, an argument of perigee, an ascending node geographic longitude of a first satellite and a mean anomaly. Area coverage can be realized through the constellation designed by the method; a sub-satellite point track repeating and high-elevation communication service can be provided specific to specific areas of a southern / northern hemisphere by adjusting constellation designing parameters; the number of satellites required by a coverage demand is reduced; the complexity of space and ground systems is lowered; and the systems are more economical.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
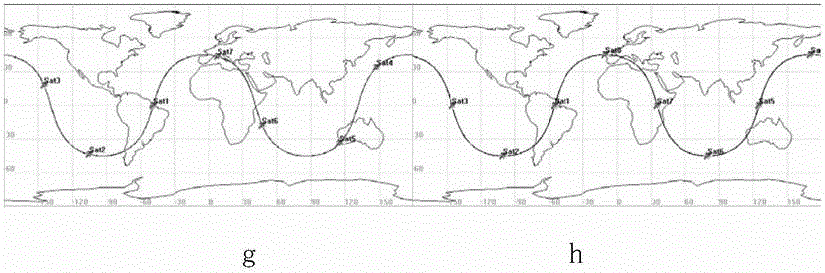
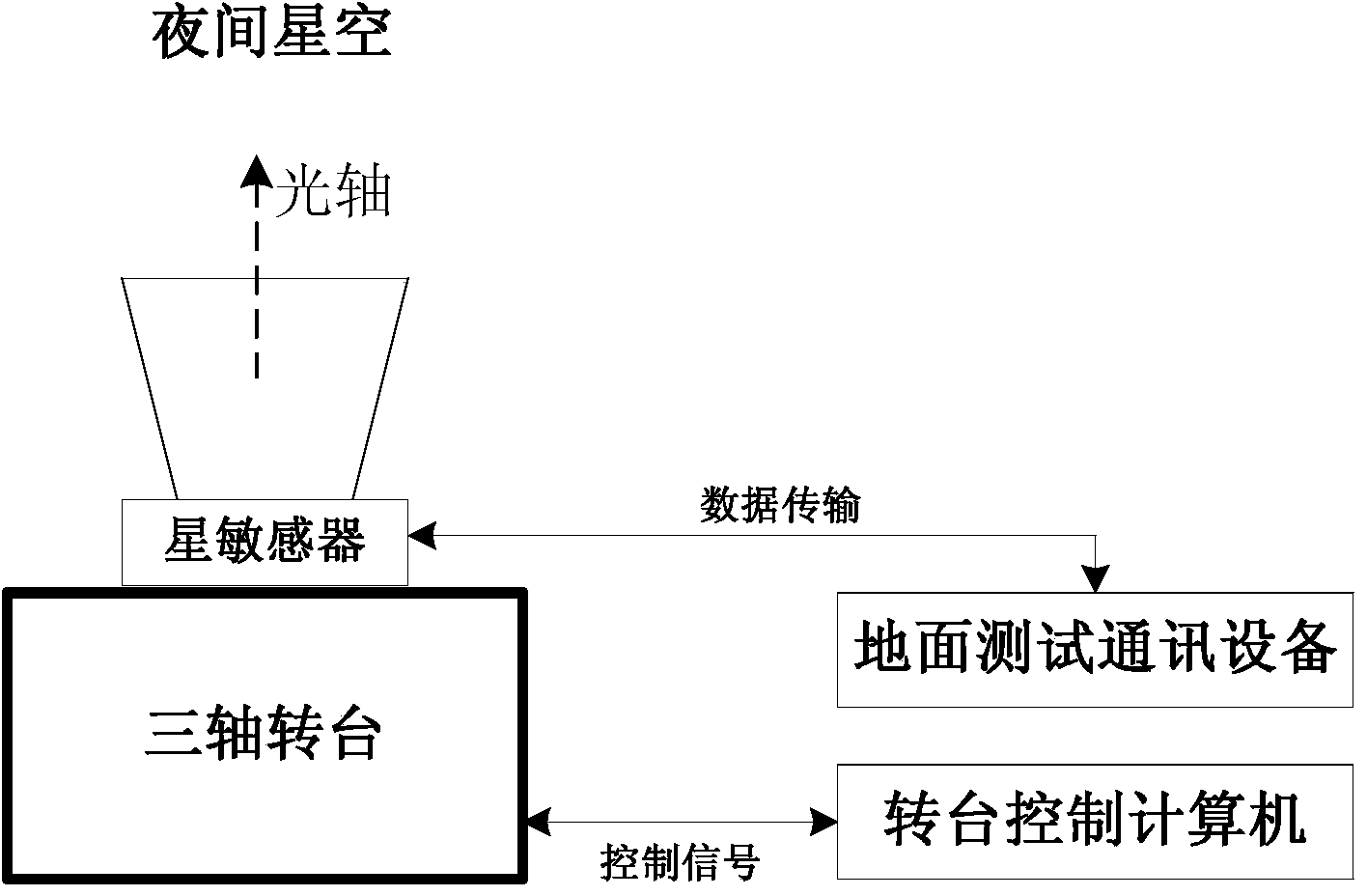
Outfield precision testing method for high-precision star sensor
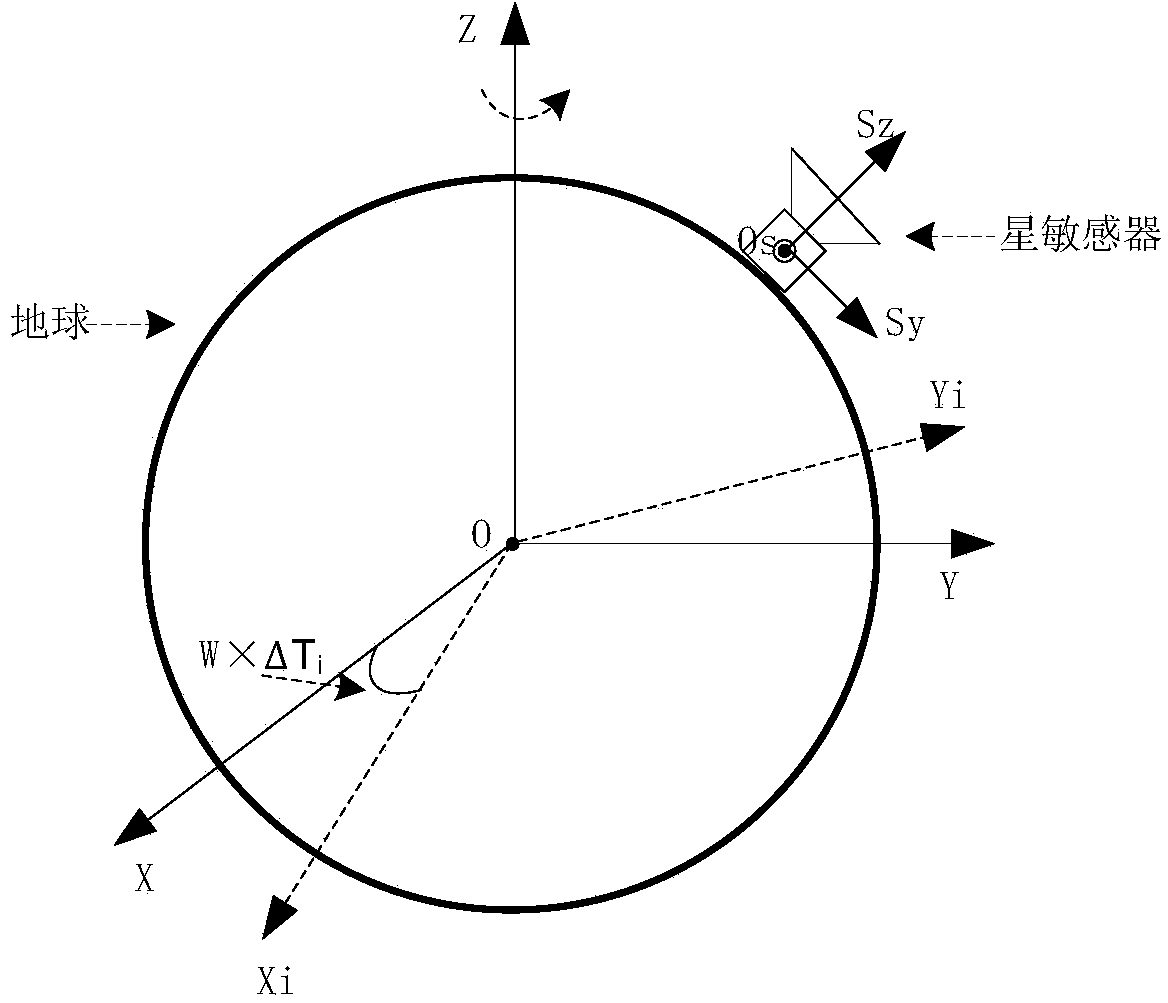
ActiveCN104280049AAchieving Frequency Domain StrippingAccurate calculationNavigation by astronomical meansStar patternObservational error
The invention discloses an outfield precision testing method for a high-precision star sensor. Accuracy in calculation of a star pattern posture of the star sensor and frequency domain stripping of short-period error terms of the posture are realized by utilizing a procession correction formula, an earth rotation model, an atmosphere correction model and a power spectral density formula, and the posture measuring error of the star sensor can be rapidly and effectively analyzed and evaluated. According to the method, the hardware resource is not occupied, the method is realized by utilizing software and does not need the ground intervention. According to the method, by combining the posture identification principle of the star sensor and adopting a data smoothing method, the posture truth value of each frame star pattern moment is calculated, so that a foundation is established for the subsequent analysis on the posture measuring error; by adopting the method for combining the time domain and the frequency domain, the short-period error term is decomposed into an airspace low-frequency error, a high-frequency error and a time-domain error by virtue of the power spectral density analysis, so that reasonable data support is provided for further evaluation of the precision indexes of the star sensor, and the index performance of the star sensor can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
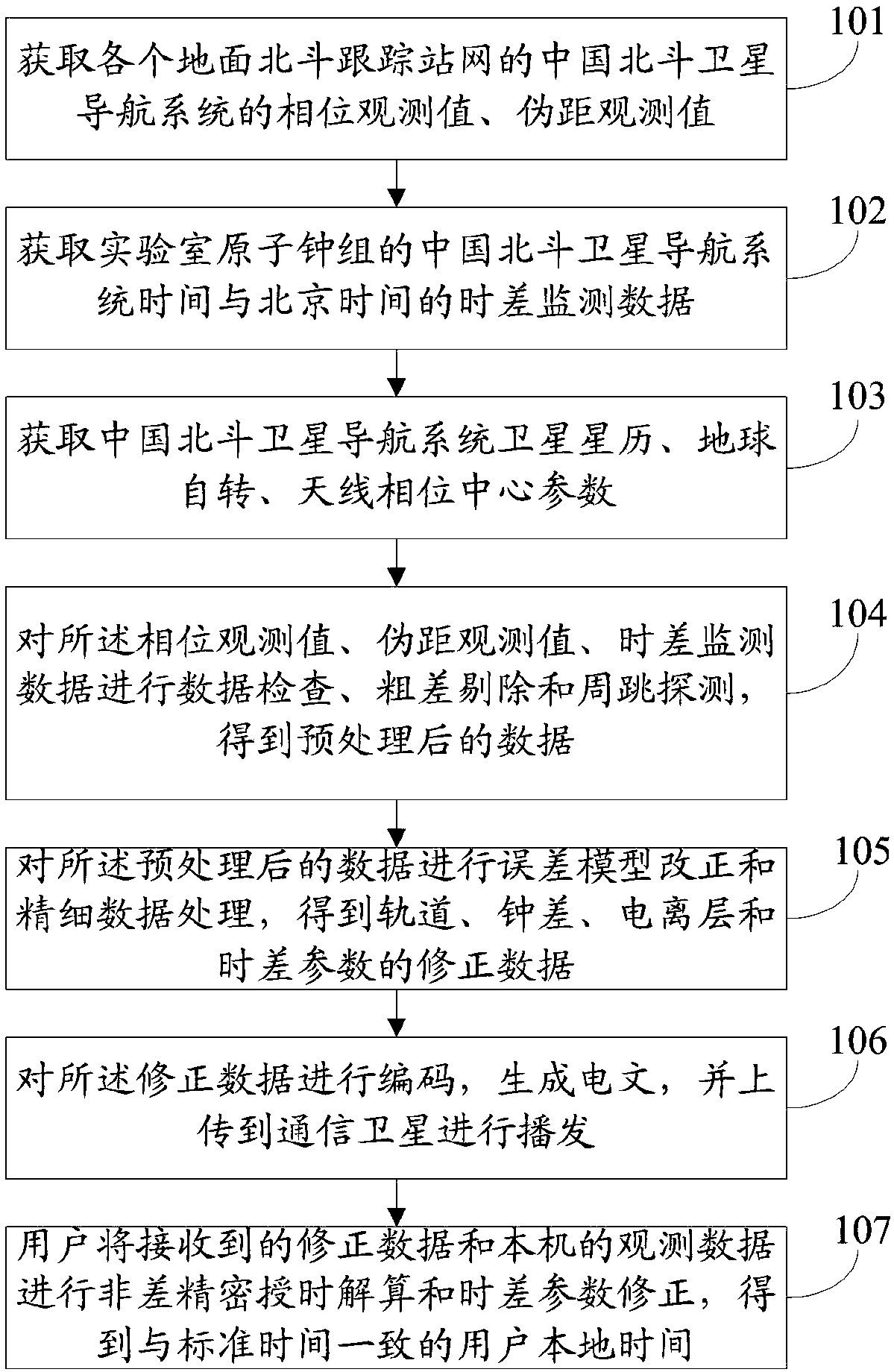
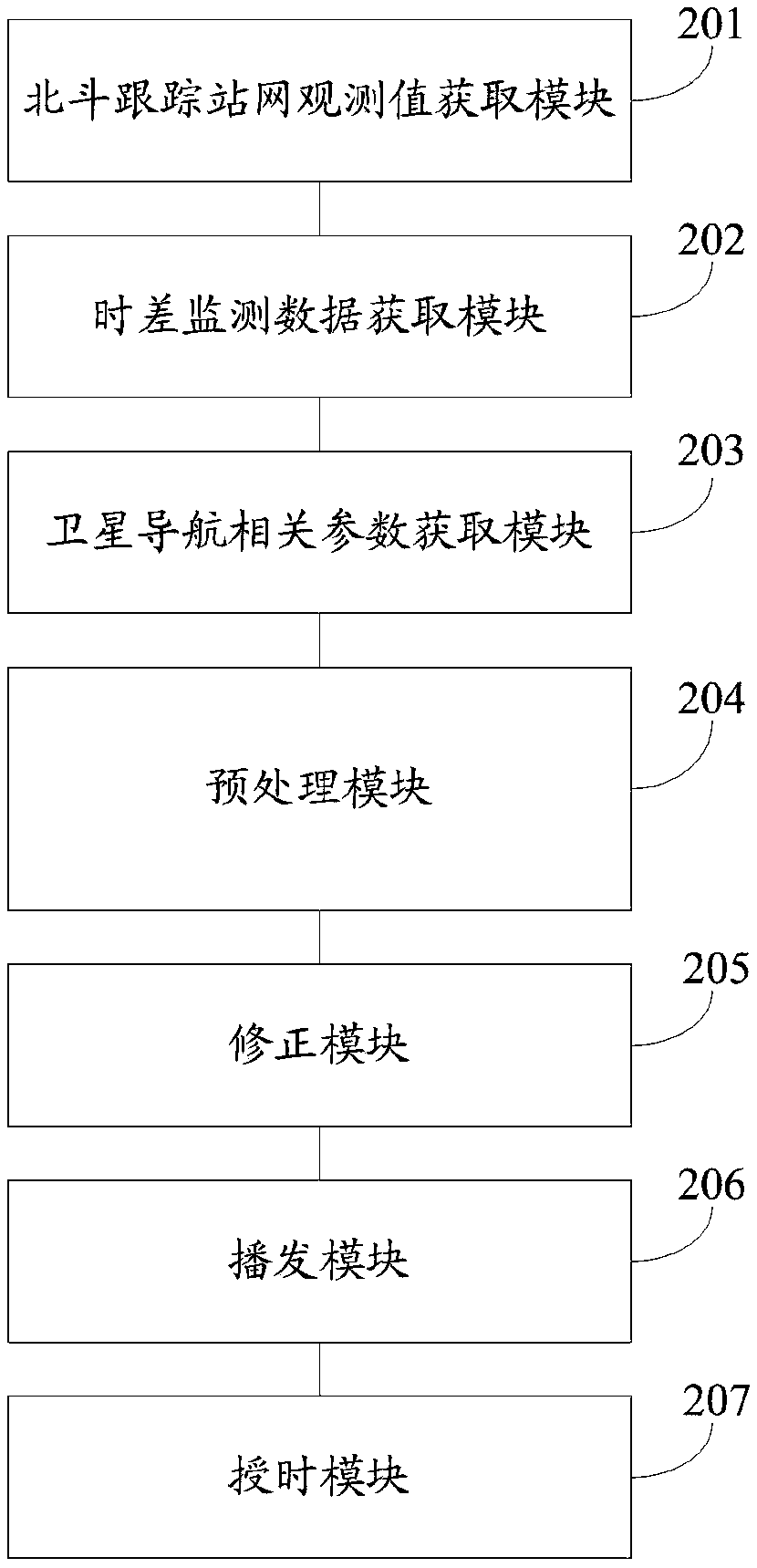
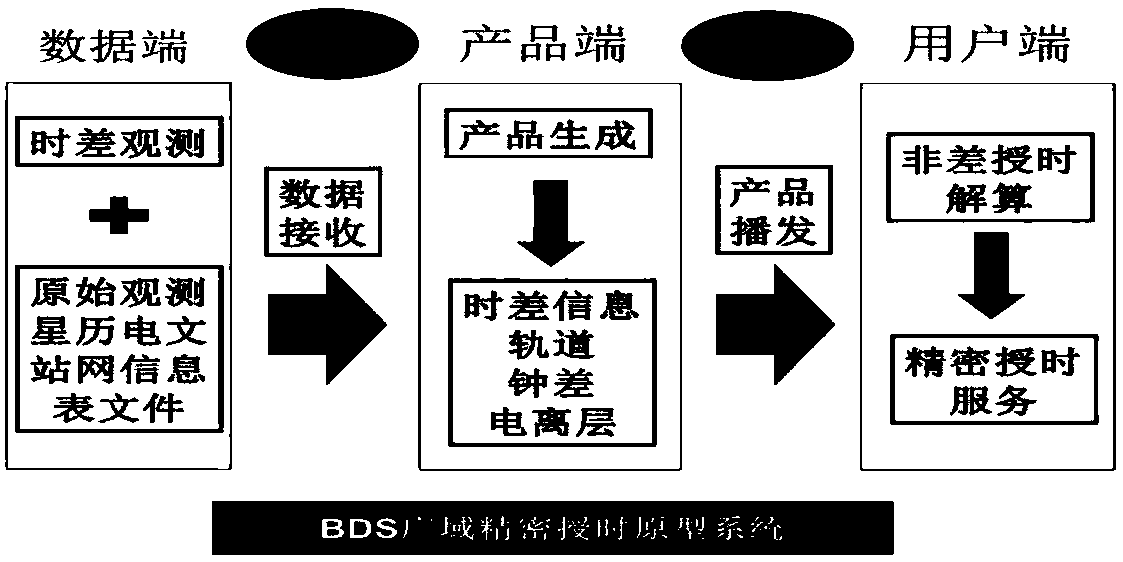
Beidou wide area timing system and method
ActiveCN109001972ALimited number of solutionsHigh precisionRadio-controlled time-piecesWide areaEarth's rotation
The invention discloses a Beidou wide area timing system and method. The Beidou wide area timing method comprises the following steps: obtaining a phase observation value and a pseudo-range observation value of a China Beidou satellite navigation system of each ground Beidou tracking station network, time difference monitoring data of the time of the China Beidou satellite navigation system and the Beijing time of a laboratory atomic clock group, a satellite ephemeris of the China Beidou satellite navigation system, earth rotation and antenna phase center parameters; performing preprocessing of data check, gross error elimination and cycle slip detection on the obtained data; performing error model correction and fine data processing on the preprocessed data; encoding the corrected data togenerate a telegraph text, and uploading the telegraph text to a communication satellite for broadcasting; and performing, by a user, non-difference precise timing solution and time difference parameter correction on the received corrected data and the local observation data to obtain a user local time consistent with the standard time. By adoption of the Beidou wide area timing system and methoddisclosed by the invention, single-station wide area timing service can be achieved, the timing precision is high, the operability is high and the action range is limited.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for initial aiming of arbitrary double position of strapdown inertial navigation system
InactiveCN1786666AEfficient use ofGuaranteed accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeEarth's rotation
The invention relates to random two position aiming method of strapping inertial navigation system. It is the method used to confirm strapping inertial navigation system (SINS) initial appearance. Its features are rotated the SINS from the initial position to random, utilized the relation ship of the two position SINS output and rotational angular velocity of the earth and gravity acceleration to confirm SINS initial appearance and measure out gyroscope constant drift. The invention has high precision. And it is simple and practical, and can be applied in various strapping inertial navigation system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
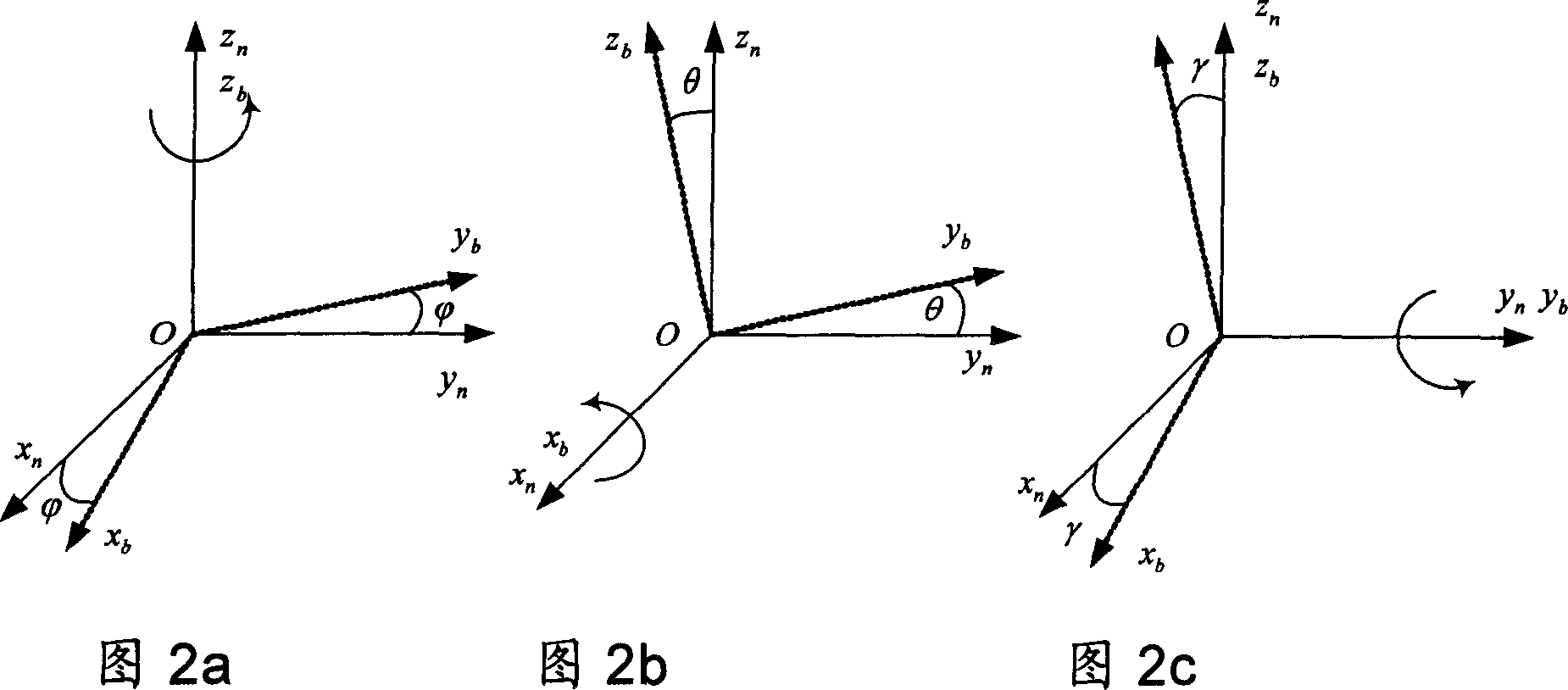
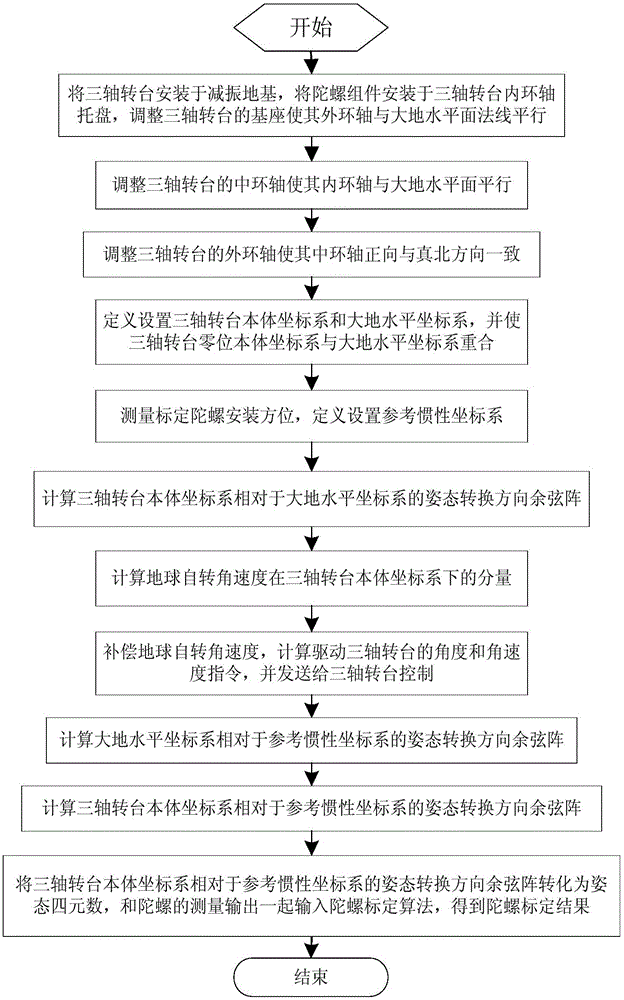
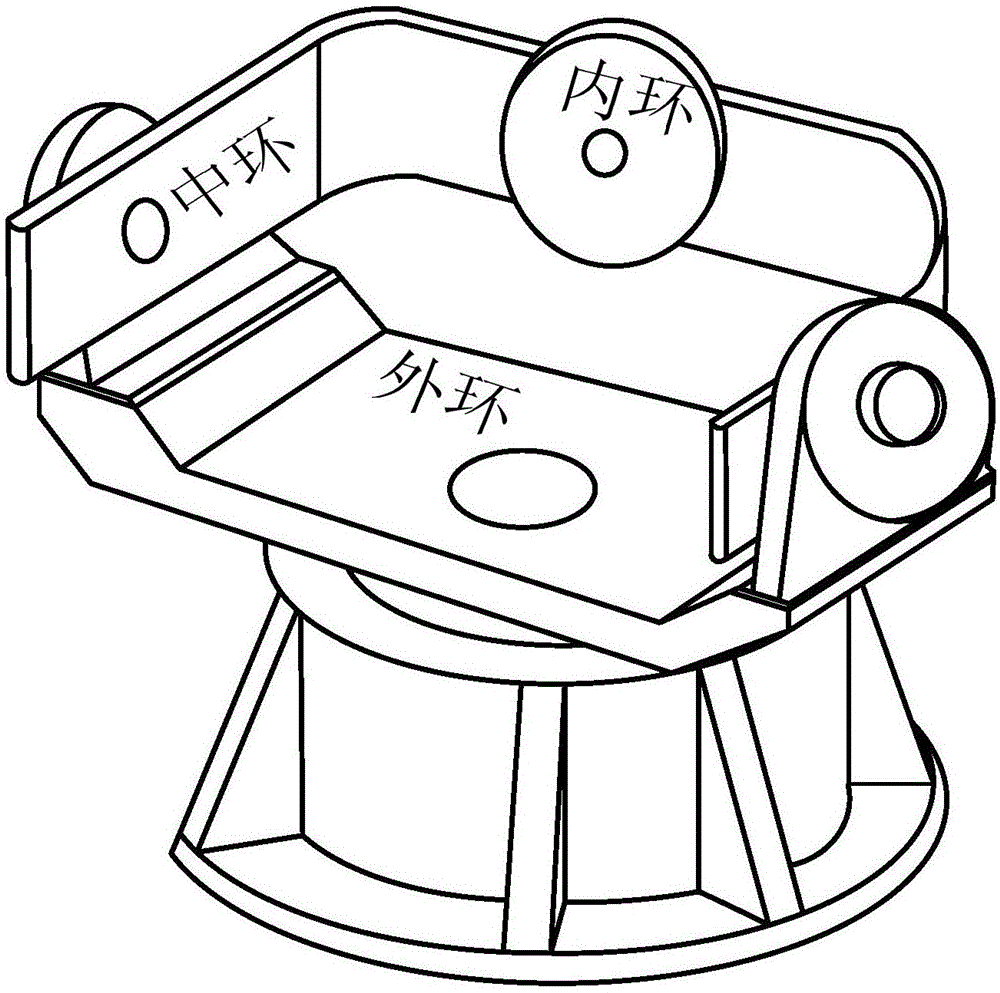
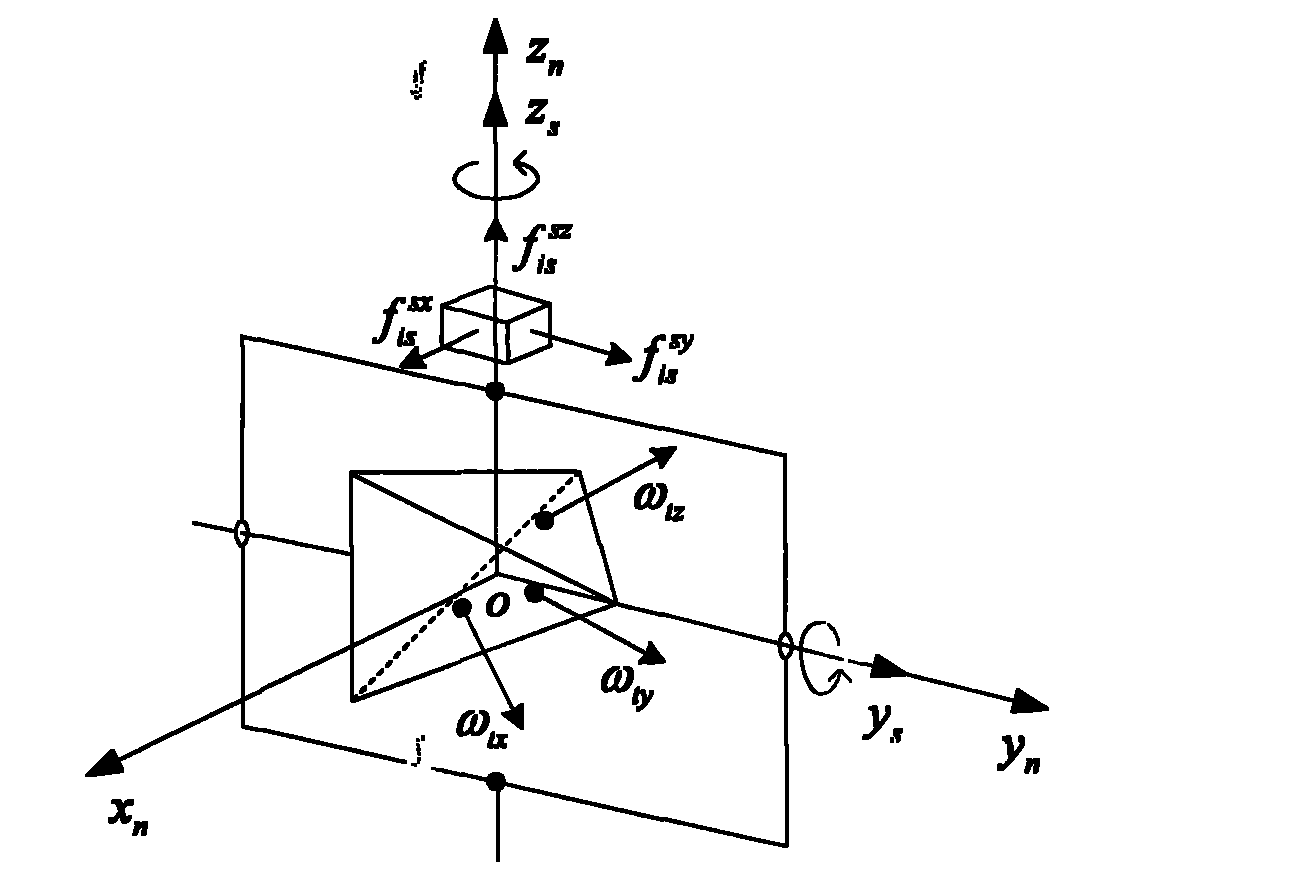
Inertial space gyro calibration test method based on three-shaft turntable
ActiveCN106525073AThe result is validHigh precisionMeasurement devicesSpace constantEarth's rotation
The invention relates to an inertial space gyro calibration test method based on a three-shaft turntable; while a gyro assembly attitude rotation is provided by the three-shaft turntable, the compensation dosage of the earth autorotation angular velocity is calculated according to the real-time rotating angle output of three rotating shafts of the three-shaft turntable, so that the influence of earth autorotation on the gyro measurement output is eliminated, and the inertial space constant angular velocity required for a gyro calibration algorithm is ensured. At the same time, based on attached rotation characteristics of the three rotation shafts of the three-shaft turntable, the method defines a rotation sequence rule of the three rotation shafts and a three-shaft turntable body coordinate system and a reference inertial coordinate system having the initial zero coinciding with the ground horizontal coordinate system, and provides a reference benchmark for determining the inertial system angle increment according to the gyro output and for determining the inertial system attitude according to the rotation angle output of the three rotation shafts of the three-shaft turntable. The method can significantly improve the precision of a ground gyro calibration test, can guarantee the ground to perform effective calibration and test result calibration on a gyro assembly, can establish a good foundation for performing relevant calibration tests of satellites in orbit, and improves the determination precision of the gyro attitude.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
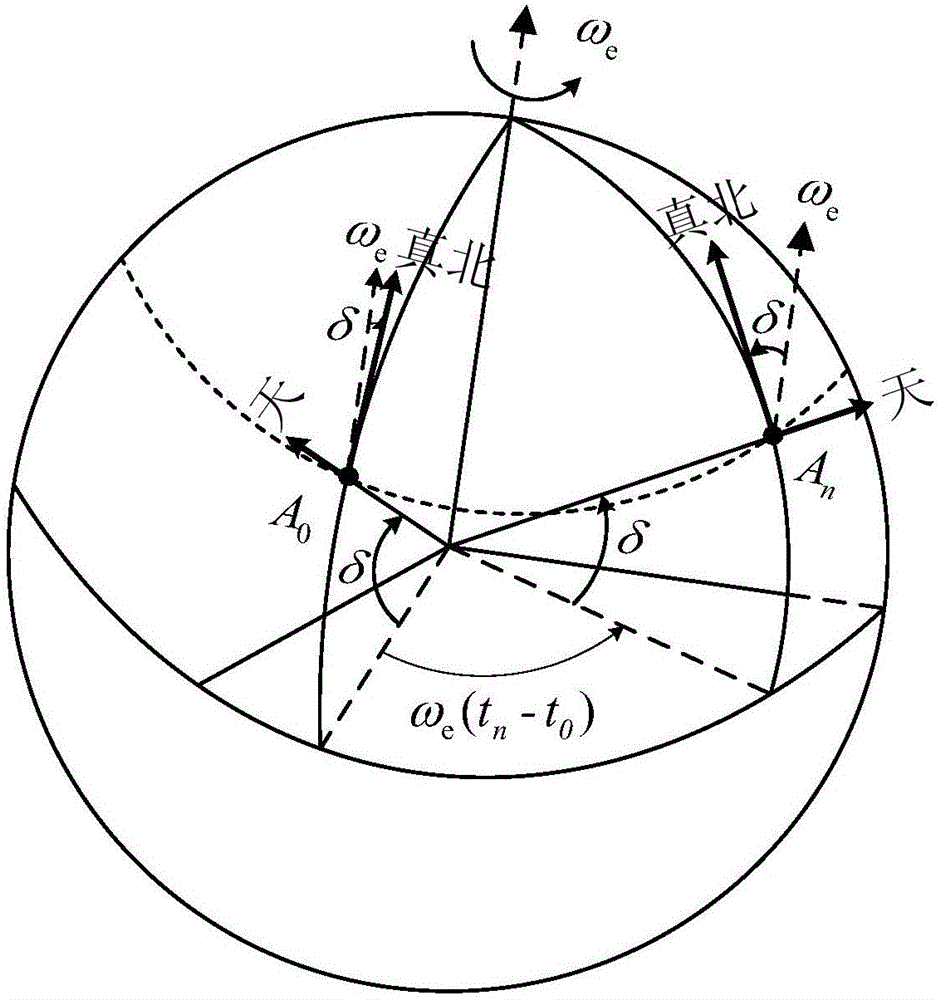
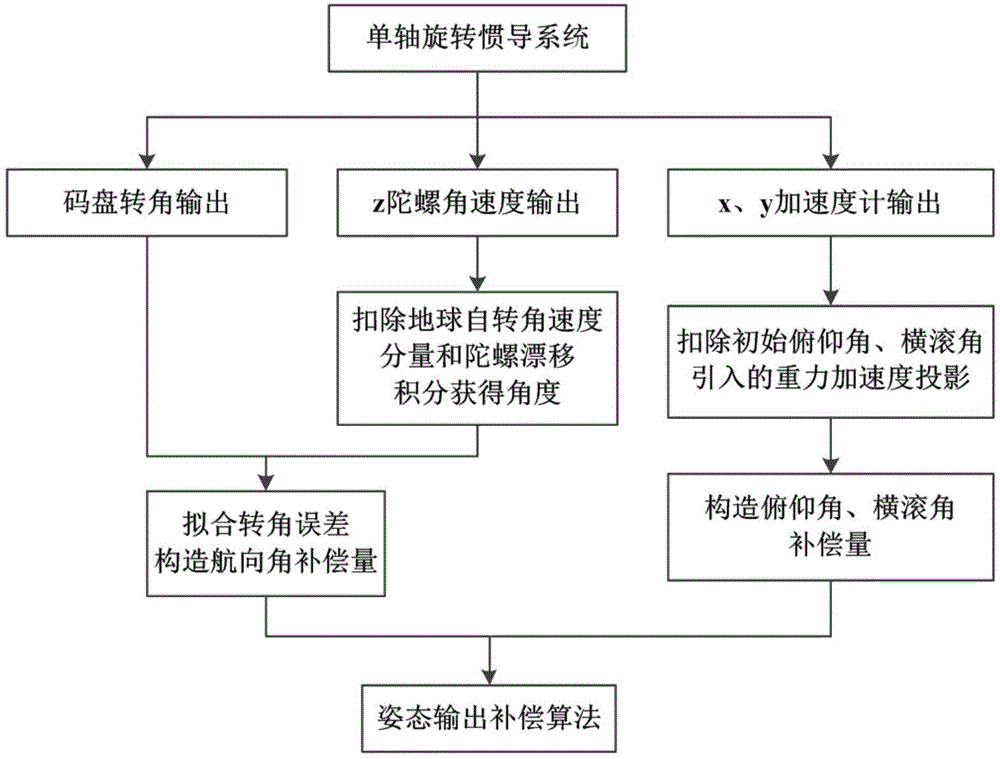
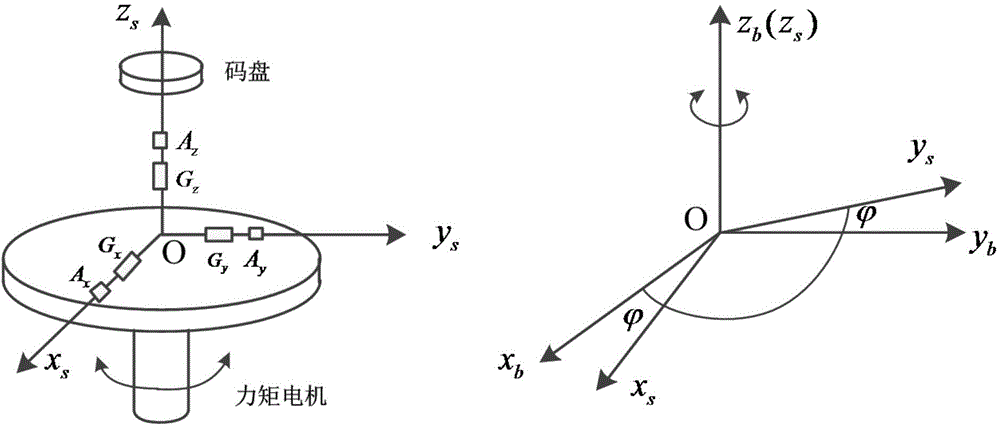
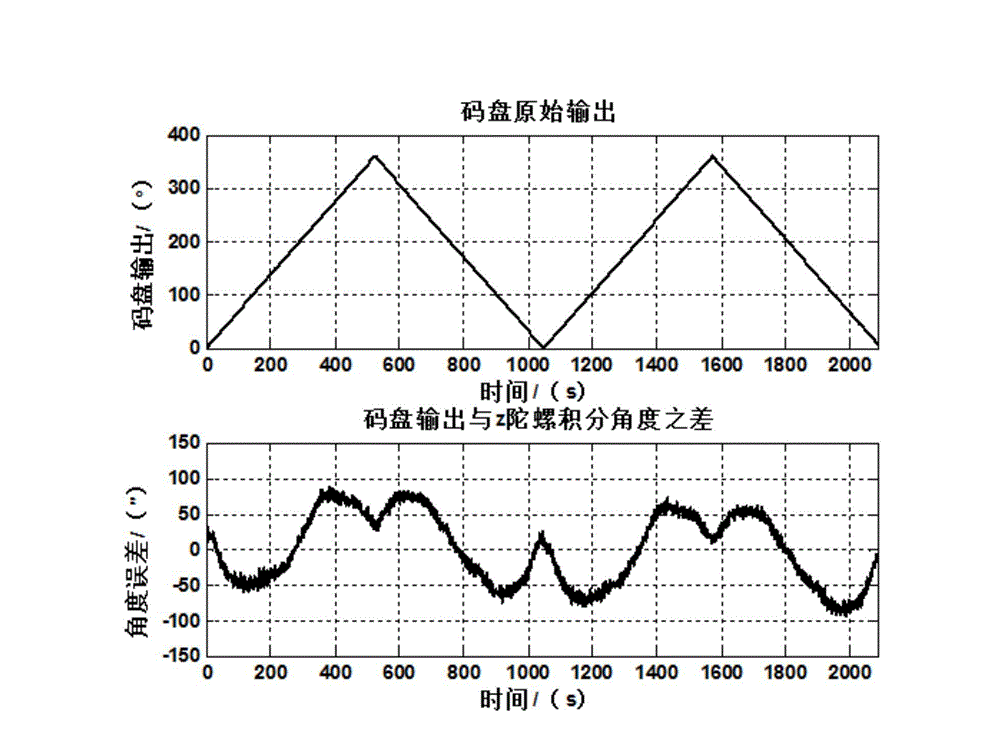
Gesture output compensation method of single-axial rotary inertial navigation system
ActiveCN104596546AAttitude output implementationImprove attitude accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerEarth's rotation
The invention discloses a gesture output compensation method of a single-axial rotary inertial navigation system. The method comprises the following steps: deducting the rotational angular velocity of the earth and gyroscopic drift from angular velocity output by a top z and integrating to obtain an angle; making a difference between the angle of the integral of the top z and a rotating angle output by a coded disc and fitting the difference value to configure compensation quantity of the course angle; deducting gravity acceleration projection from output of x and y accelerometers and angle of pitch and roll angle obtained by initial alignment so as to configure compensation quantity of the angle of pitch and the roll angle; and compensating the gesture output of the single-axial rotary inertial navigation system according to a gesture output compensation algorithm. The gesture output compensation algorithm is easy to implement, and not only can satisfy the real-time requirement of project application, but also can greatly enhance the gesture output precision of the single-axial rotary inertial navigation system, so that the method is of important meaning to improvement of navigation performance of the single-axial rotary inertial navigation system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Satellite formation realizing method for earth ultra-width imaging
ActiveCN109240322AStable flightAchieve ultra-wide imagingAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsEarth's rotationSingle star
The invention discloses a satellite formation realizing method for earth ultra-width imaging, relates to a formation technique of satellite stable imaging, and belongs to the technical field of control and regulation. The method is applied to the problem of distributed ultra-width imaging, which breaks the single-star lower-point imaging mode of traditional satellite imaging and enables the satellite to achieve high-precision ultra-width imaging in the manner of formation imaging by carrying high-precision imaging load and combined with distributed satellite control technology, thereby greatlyenhancing the efficiency of satellite search imaging. The method proposes a distributed satellite formation ultra-width imaging mode based on J2 stability, which solves the problem that the satelliteis unable to achieve continuous imaging on the adjacent areas of the ground caused by small satellite gaze range, narrow imaging width, and the earth rotation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
Attitude compensation method of agile satellite imagery in reverse push-broom mismatch
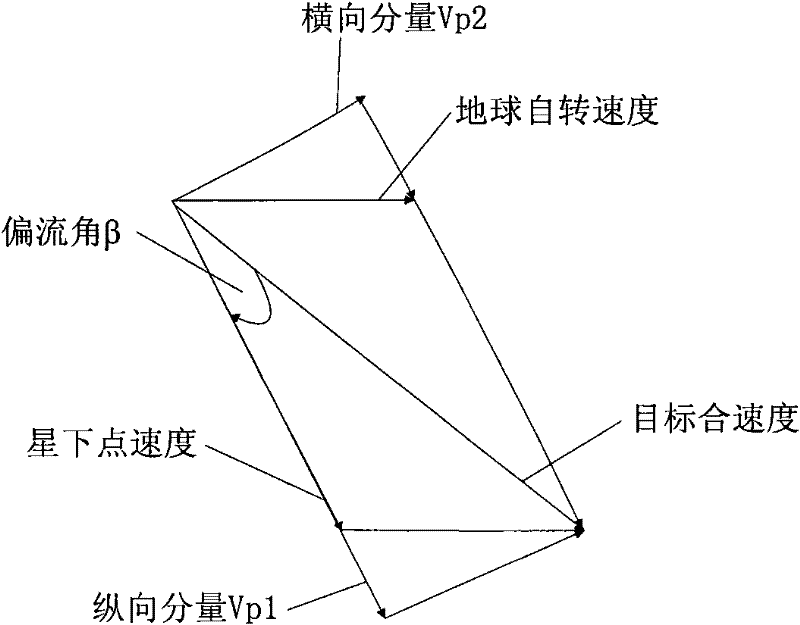
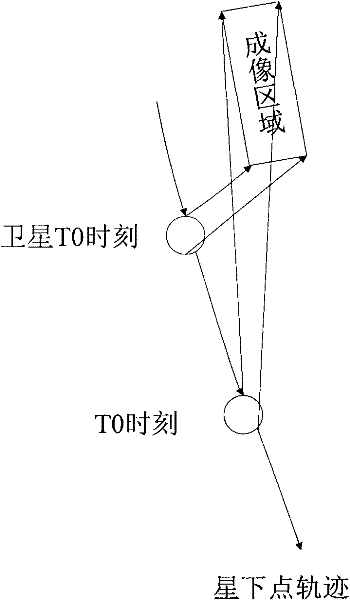
ActiveCN102229362ASolve task planning and scheduling problemsImprove mission performanceImage analysisSpacecraft guiding apparatusEarth's rotationBroom
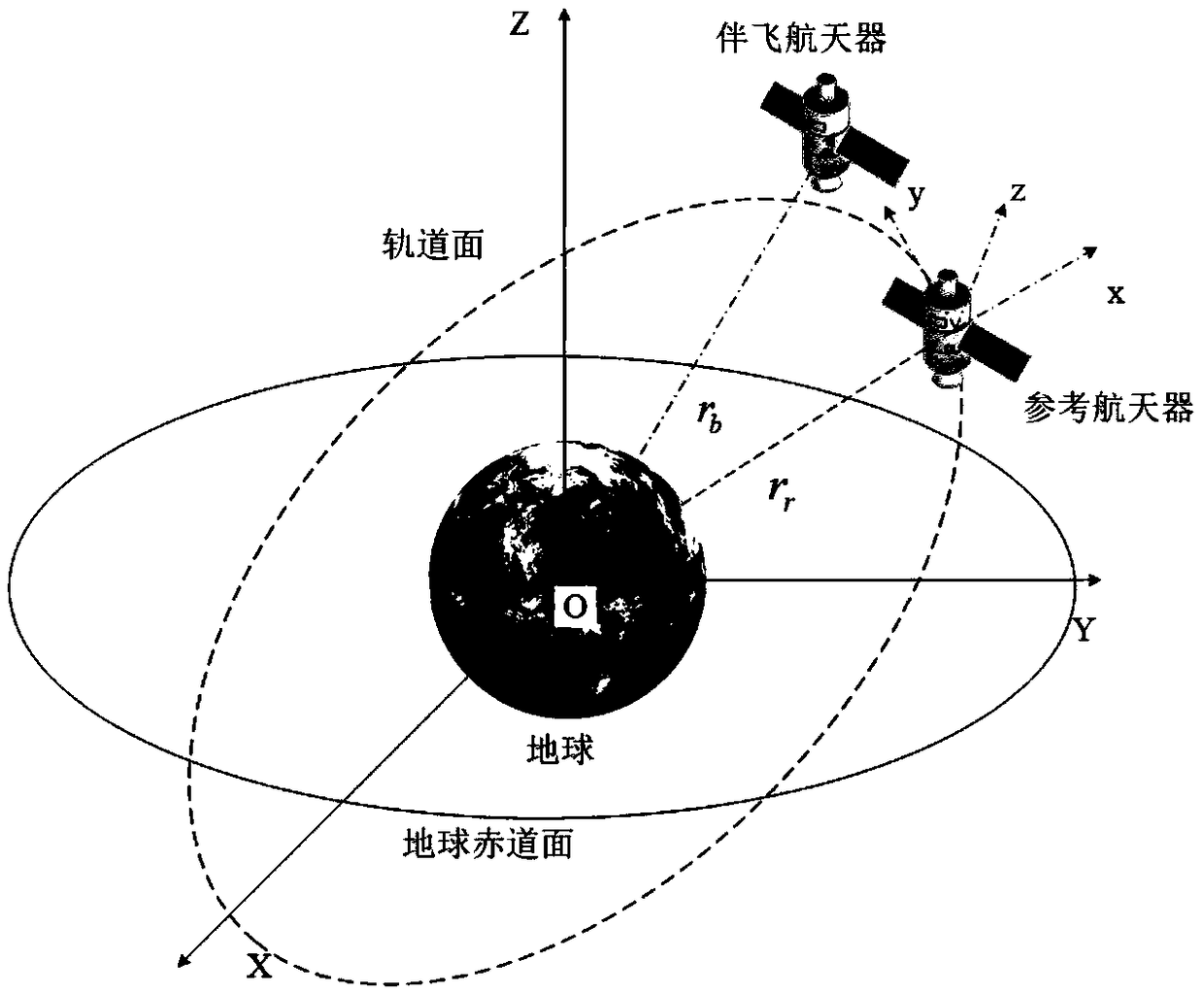
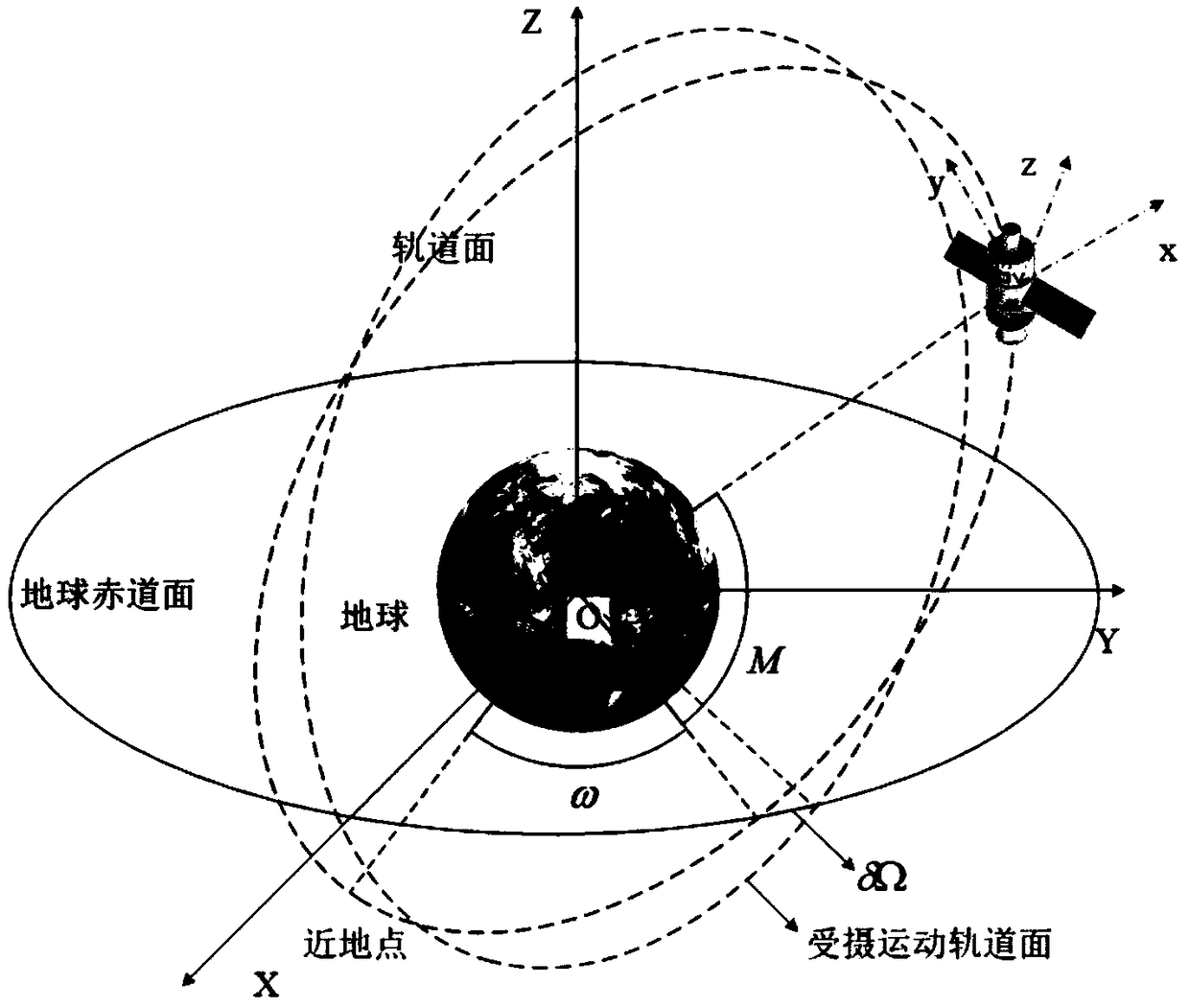
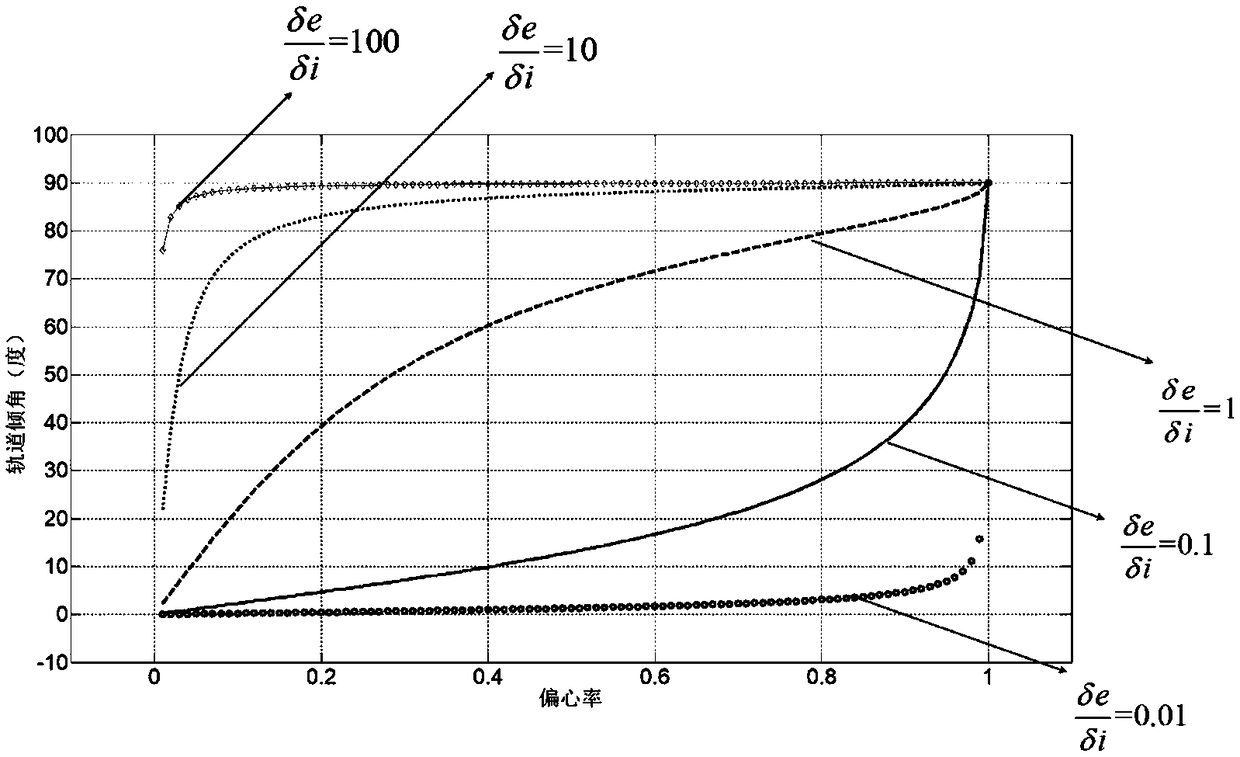
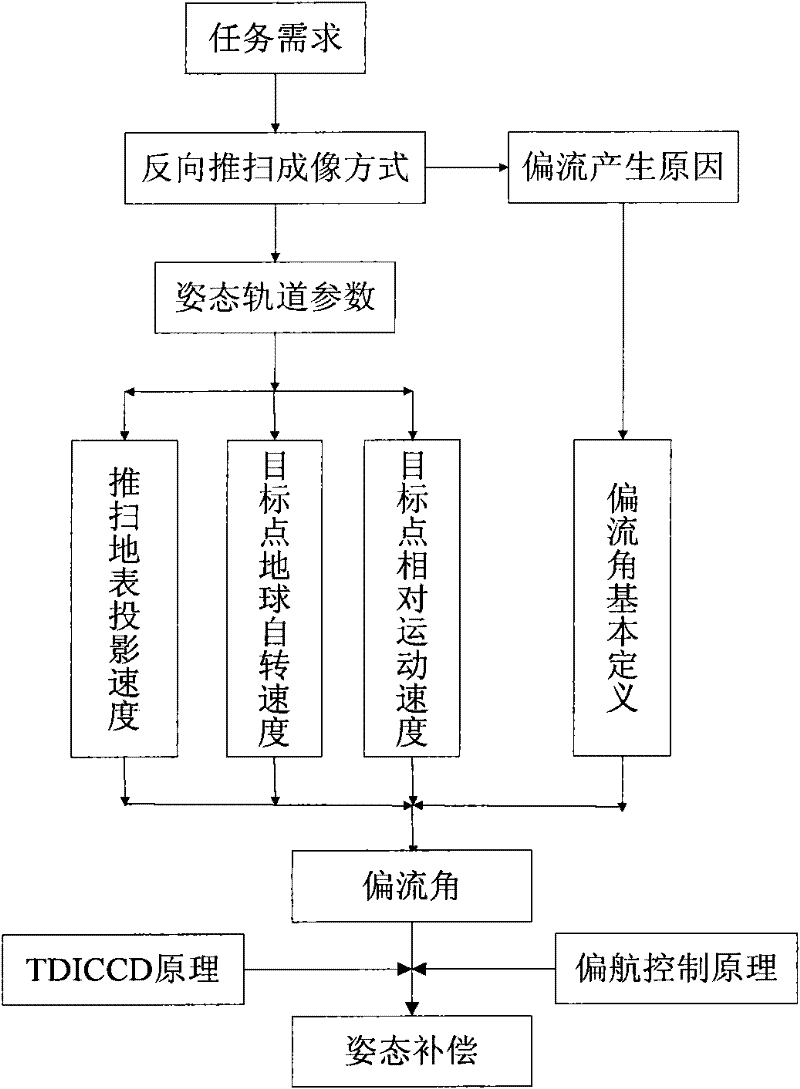
The invention discloses an attitude compensation method of agile satellite imagery in reverse push-broom mismatch. Aiming at the defect (only considering the drift current effect brought by earth rotation) of the attitude compensation method in the traditional imagery mode (the satellite directing over the ground is fixed), through analyzing the generation reason of a drift angle under the imagery mode of constantly changing satellite reverse push-broom attitude directing over the ground (constantly changing attitude directing over the ground under the condition of mismatch between the substellar point speed and the camera push-broom speed), the drift current effect of imagery is considered from three aspects (orbital motion, earth rotation and camera push-broom speed), a drift current angle calculation formula under the mode is obtained according to the orbital attitude parameters combining the basic definition of the drift angle, on the basis, the satellite attitude compensation method is obtained by combining the basic principle of TDICCD (time delayed and integration charge coupled device) imagery and the yaw control principle, and the imagery requirement of agile satellite reverse push-broom can be satisfied.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
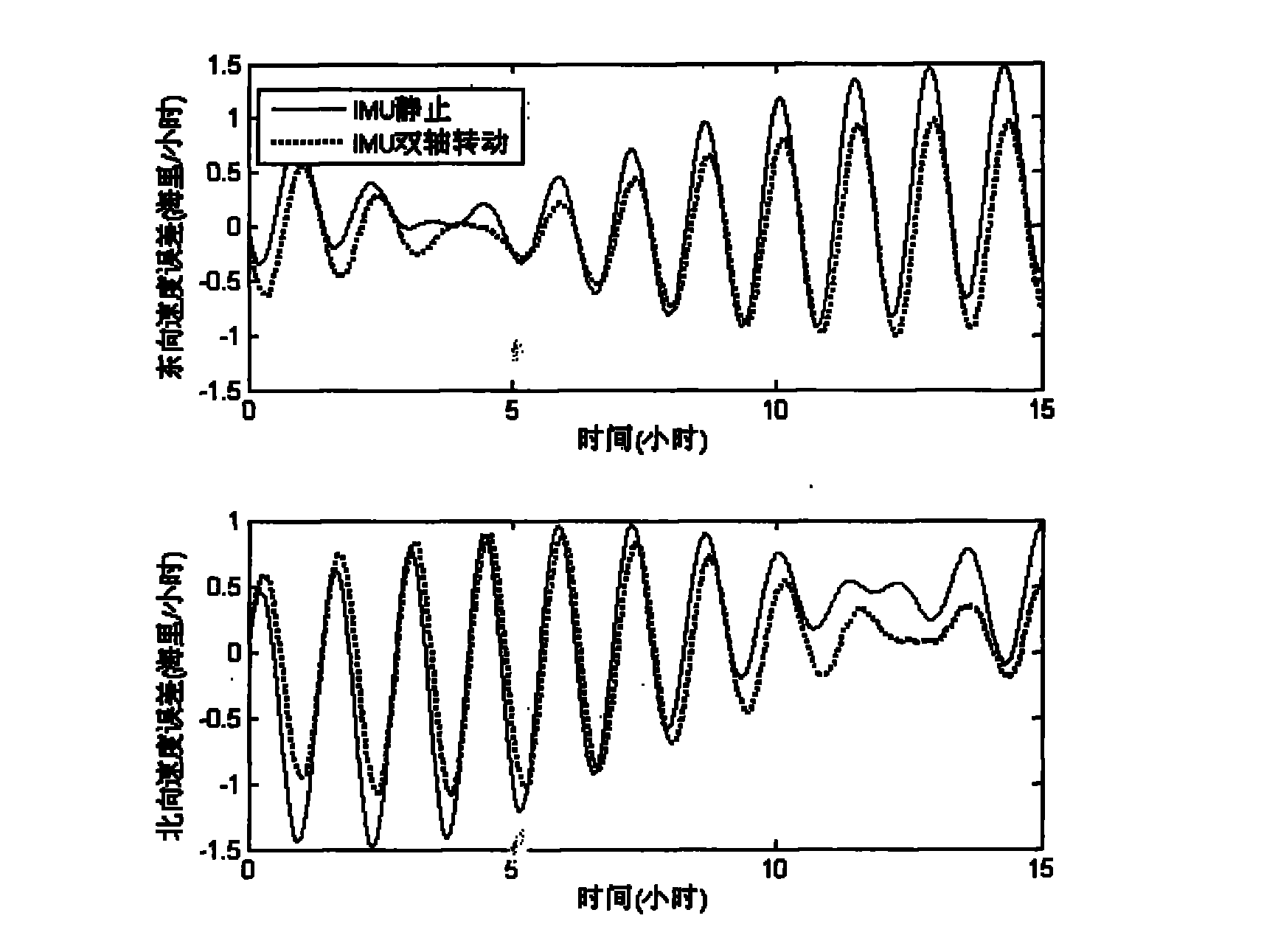
SINS error inhibiting method based on biaxial rotation scheme
The invention provides an SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System) error inhibiting method based on a biaxial rotation scheme. A global positioning system (GPS) is used for determining the parameters of the initial position of a carrier, and the parameters are input into a navigation computer; after preheating preparation, an SINS collects the data output by a fiber optic gyroscope and a quartz accelerometer and processes the data; primarily determining the attitude information of an inertial measurement unit (IMU) at the time according to the relationship between the output of the accelerometer and acceleration of gravity and the relationship between the output of the gyroscope and the rotational angular velocity of the earth so as to complete the initial alignment of the system; the IMU continuously rotates around the azimuth axis and the pitch axis; and the data generated by the fiber optic gyroscope and the quartz accelerometer after the rotation of the IMU is converted under a navigation coordinate system to get the modulation manner with deviated constants of inertia instruments. According to the invention, the SINS error inhibiting method based on a biaxial rotation scheme can be used for modulating the drift of the gyroscope in three directions and the zero offset of the accelerometer in the horizontal direction so as to improve the positioning precision of navigation.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
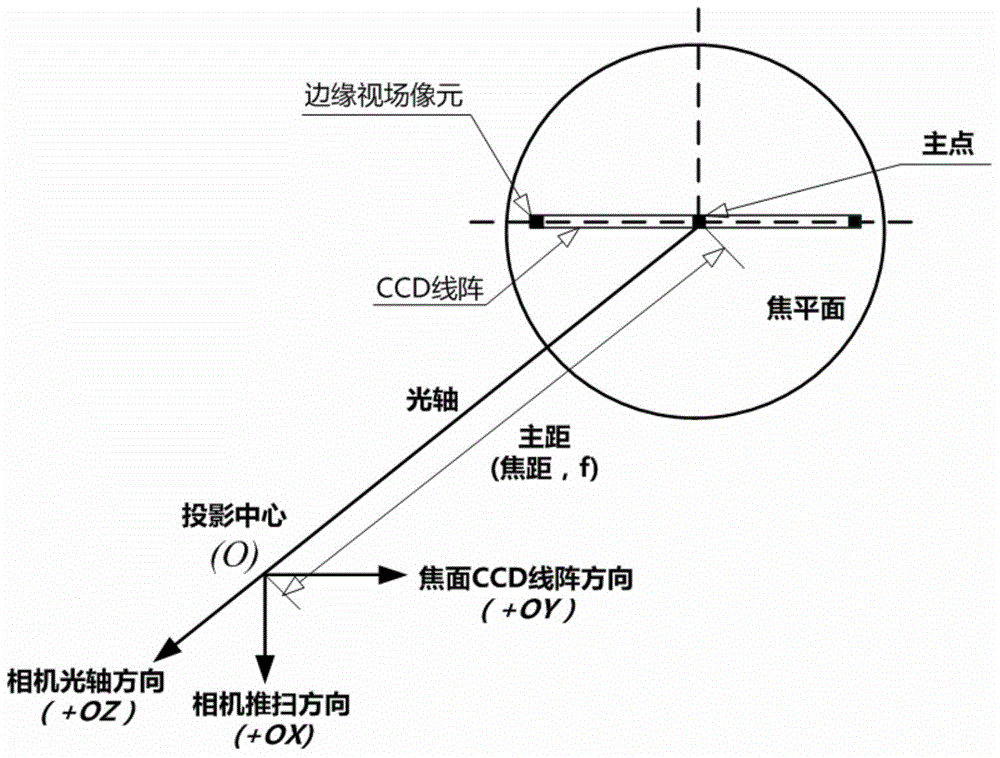
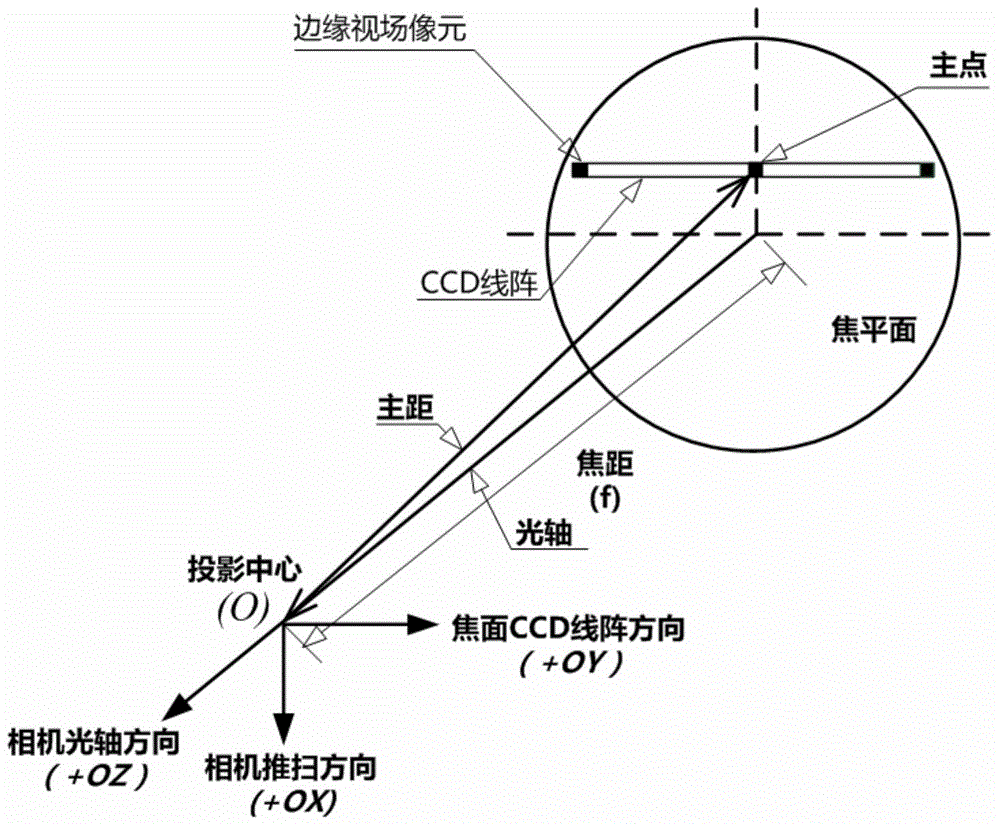
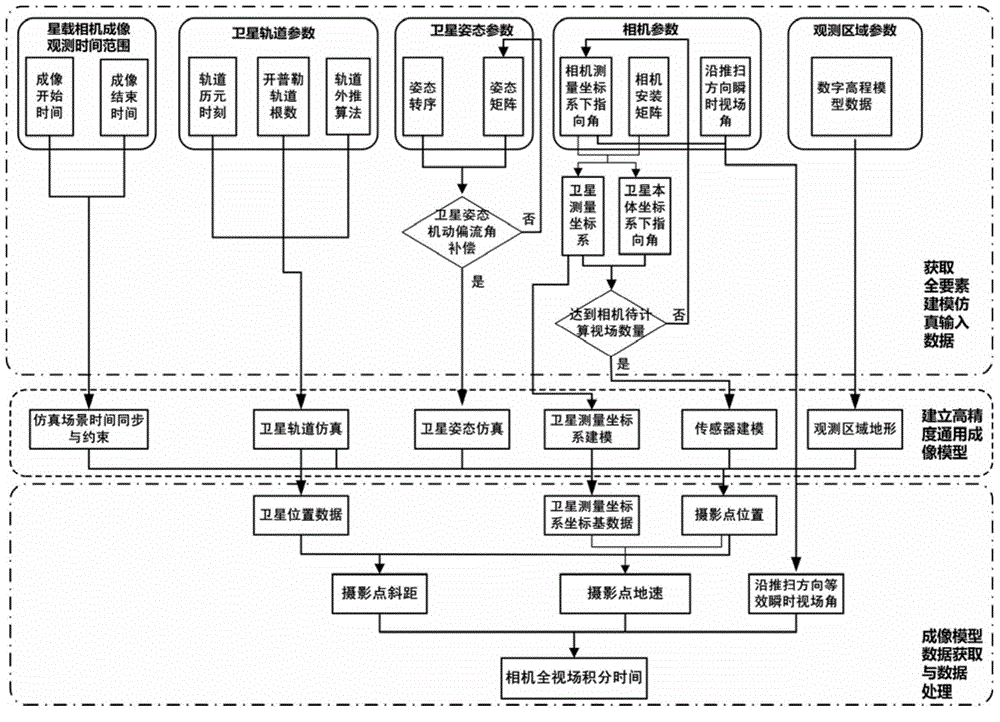
Full-field integral time determining method for satellite-borne linear array push broom camera
ActiveCN104581144AComprehensive modeling elementsComprehensive Computational Modeling ElementsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEarth's rotationFull field
The invention relates to a full-field integral time determining method for satellite-borne linear array push broom camera. The full-field integral time determining method for the satellite-borne linear array push broom camera comprises the following steps:1, acquiring a simulation input data of a total factor modeling; 2, building a generalized imaging model with high precision, the imaging model parameter comprises an observation time range of a scene imaging, an orbit of a satellite, a posture, a satellite measurement coordinate system, a directional angle of a single pixel in a satellite system and an altitude data of an imaging region; 3, data obtaining and data processing of the imaging model; 4, repeating steps 1 to 3, calculating the integral time of pixels at different positions of the focal plane of a remote sensor one by one, and determining the full-field integral time of the camera. According to the full-field integral time determining method for the satellite-borne linear array push broom camera, the earth rotation, the curvature of the earth and the hypsograpgy are comprehensively considered, the integral time of pixels at different positions of the focal plane of a remote sensor are accurately calculated, and providing evidence for analyzing the influence of different integral time packet mode of the full-field camera to the imaging quality and setting out reasonable strategy for the integral time adjustment.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
Low-orbit satellite real-time orbital determination method
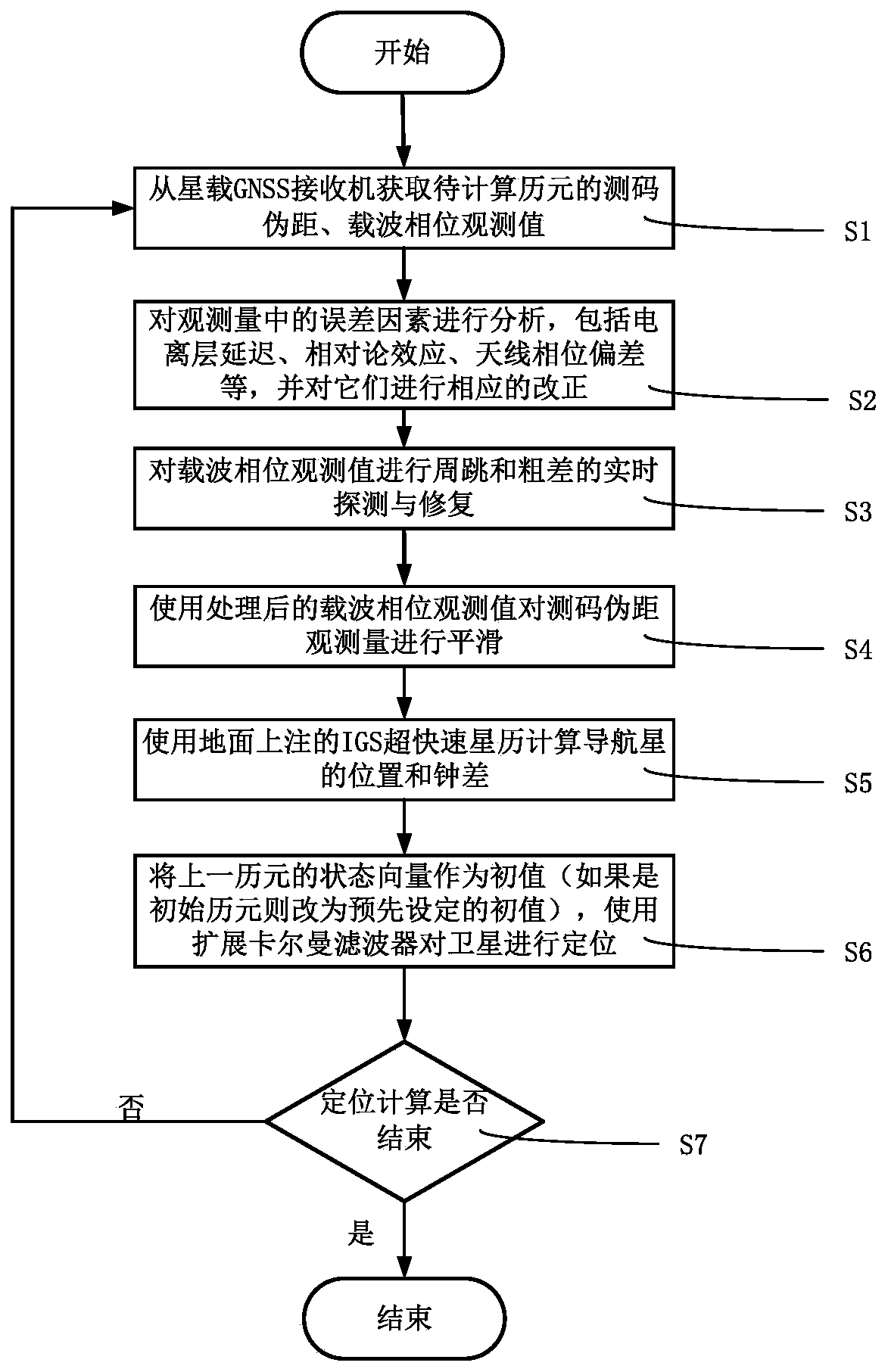
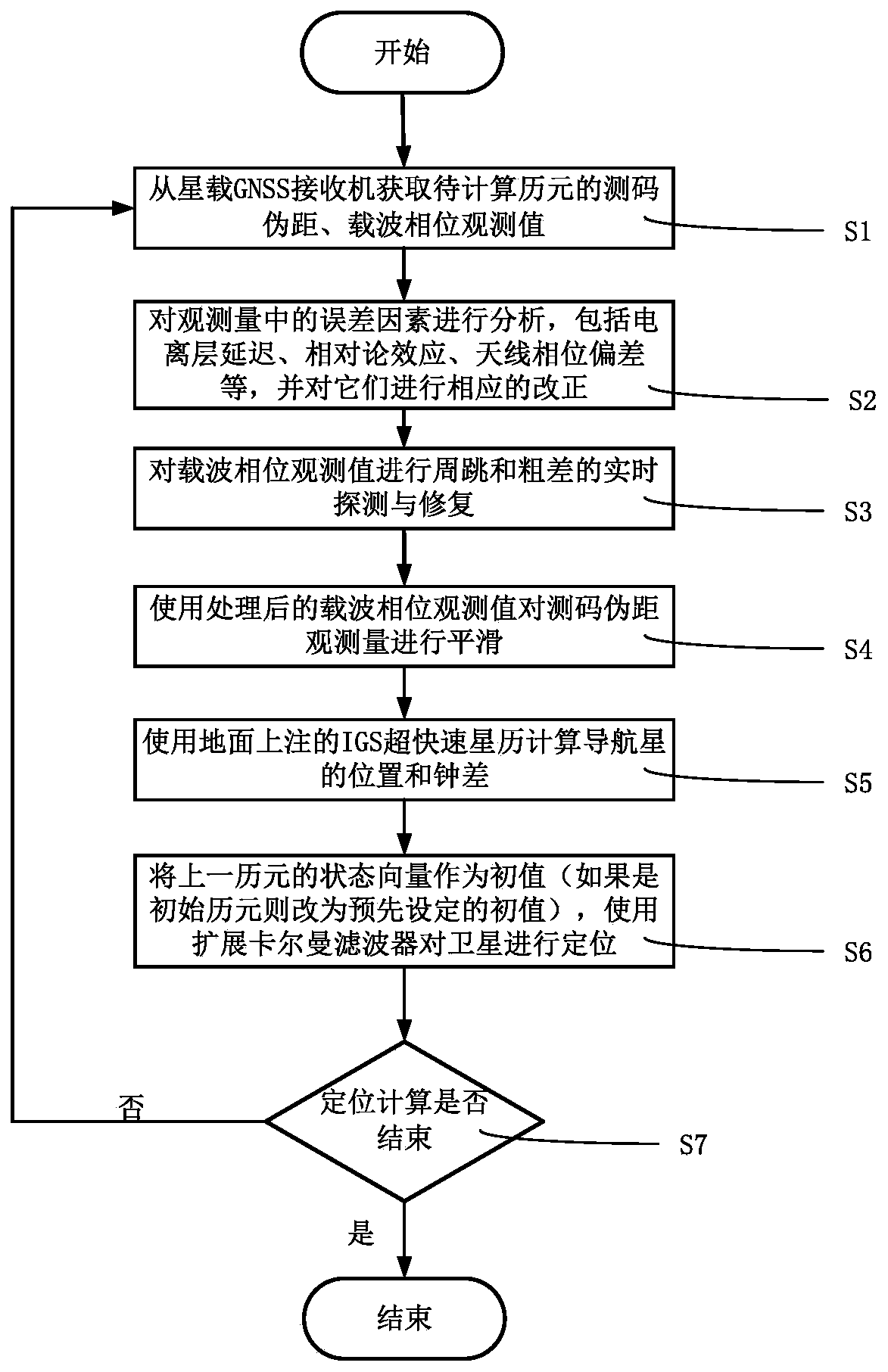
The invention discloses a low-orbit satellite real-time orbital determination method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring double-frequency code measurement pseudo-range and carrier phase observed quantity of a to-be-positioned epoch from a satellite-borne GNSS receiver; performing error correction on the acquired double-frequency code measurement pseudo-range and carrier phase observed quantity, wherein the error correction comprises ionized layer delay, relativity theory effect, antenna phase center error, and earth rotation effect; performing cycle-slip and gross error real-time detection and restoration on the carrier phase observed quantity after error correction; performing smoothing on the code measurement pseudo-range observed quantity by using processed carrier phase observed value; computing location and clock difference information of a navigation satellite by using an IGS ultra-fast ephemeris marked on the ground; taking a positioning result of the previous epoch as initial value, and computing a low-orbit satellite positioning result of the current epoch by using an extended Kalman filter; judging whether the positioning task is ended or not; and returning to the first step to continuously compute if the positioning task is not ended. The method disclosed by the invention can achieve high positioning precision in adaptive to the on-board processor finite computing resources.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Solar dominated satellite constellations capable of having repeating common ground tracks
InactiveUS7255308B1High revisit rateMinimal battery requirementCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesEarth's rotationSynchronous orbit
A new method of constellation design based on combining repeating ground tracks with common ground tracks and / or sun-synchronous orbits is used for performing high-precision change detection imagery for longer periods of time while minimizing battery usage. By precisely prescribing the orbital parameters, sharpened change detection images may be taken without the need to process out blurring by any special image re-working software. The relationship between the orbital parameters of the satellites is precisely tuned to the earth's rotation rate for the altitude of the satellites. The unique set of earth orbits minimizes satellite battery requirement while optimizing the ability to perform coherent change detection (CCD).
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
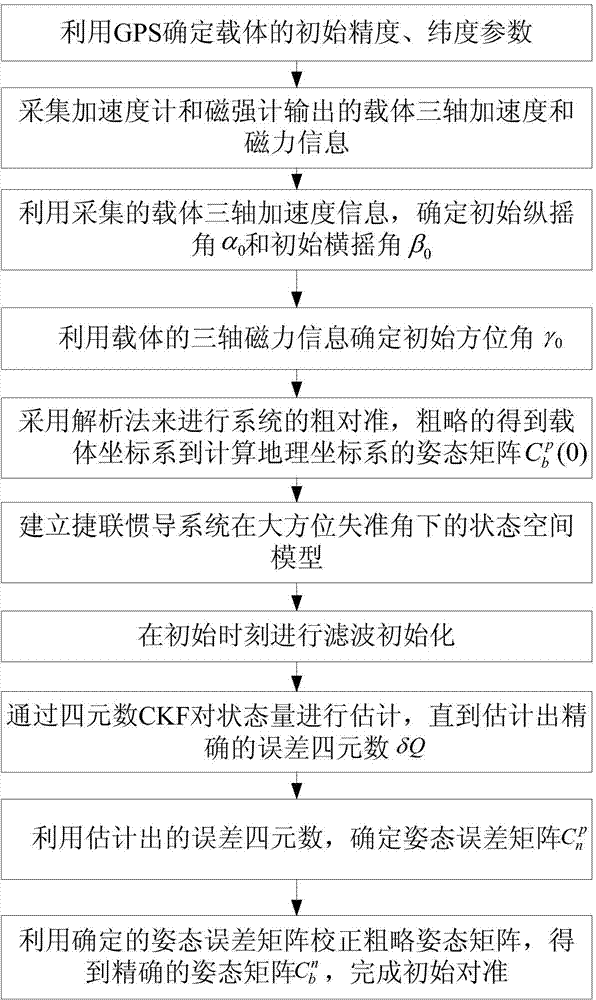
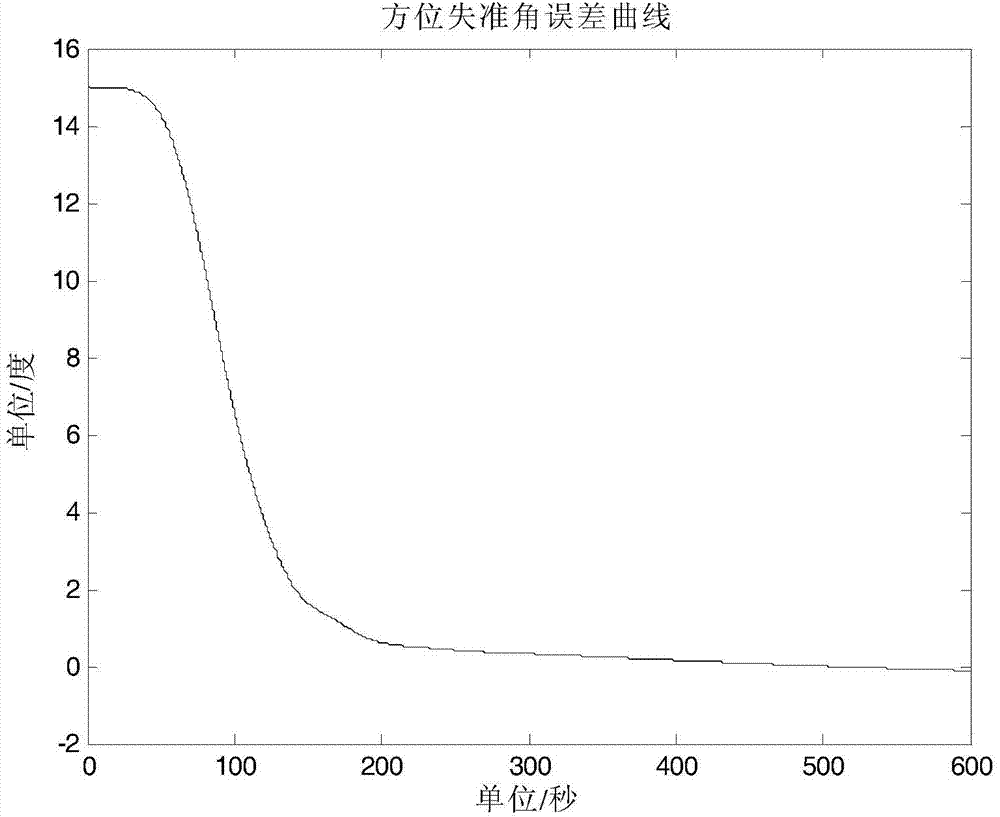
Low-precision inertial navigation initial alignment method based on quaternion CKF
InactiveCN103900608AReduced alignment accuracyEasy alignmentMeasurement devicesGyroscopeEarth's rotation
The invention provides a low-precision inertial navigation initial alignment method based on a quaternion CKF. The low-precision inertial navigation initial alignment method comprises the following steps: carrying out coarse alignment by utilizing measured values of an accelerometer and a magnetometer to obtain a coarse attitude matrix; taking a position and a speed error as value measurement by using accurate outside information provided by a GPS (Global Position System); carrying out nonlinear filtering by the quaternion CKF to obtain an attitude error matrix; and finally, correcting by using the attitude error matrix to obtain an accurate attitude matrix. According to the low-precision inertial navigation initial alignment method, the value measurement of the gravitational acceleration and the magnetic force, which is carried out by the accelerometer and the magnetometer, is subjected to the coarse alignment. The problems that the gyroscope performance is low under the condition of a low-precision inertial device, the rotation angle speed of the earth can not be accurately sensed and a traditional coarse alignment method can not be applied are solved; furthermore, the quaternion CKF provided by the method can be used for a non-linear model of a large angle error, can still finish alignment under the condition of a large orientation misalignment angle and has high alignment precision.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
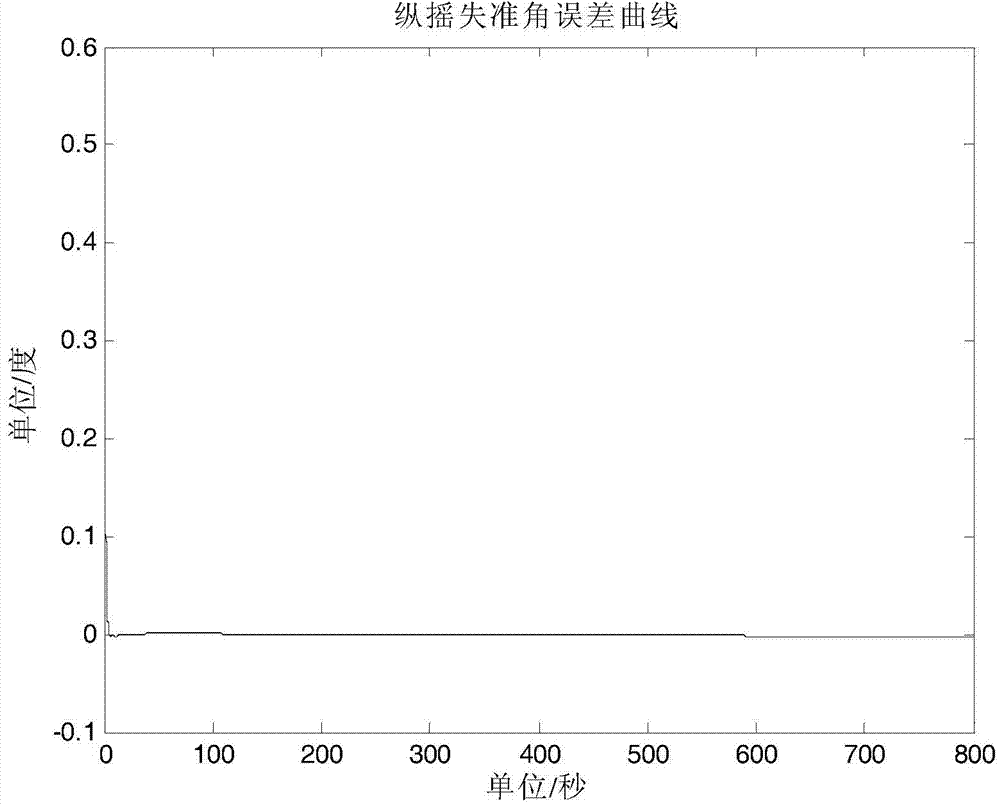
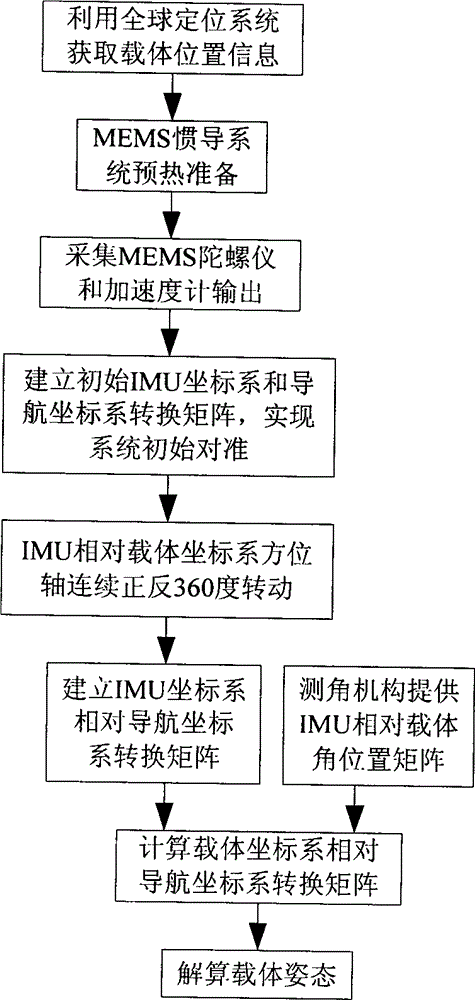
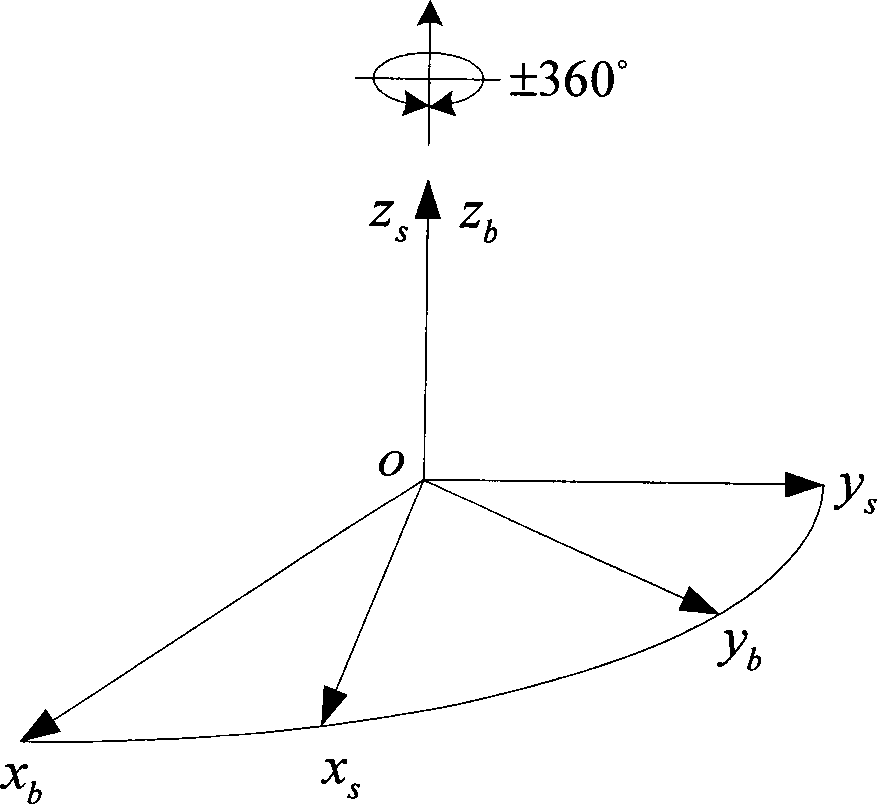
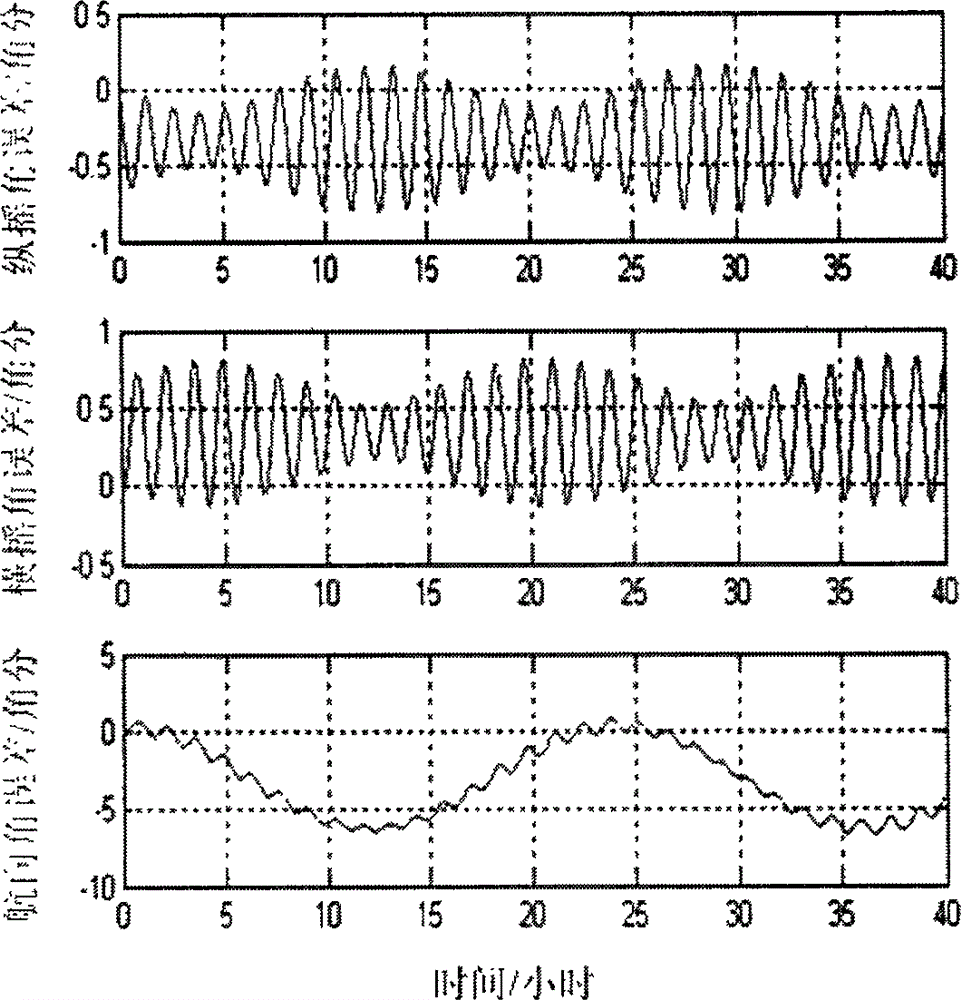
Attitude measurement method of micro-electro mechanical system (MEMS) inertial navigation system based on single-shaft forward revolution and reverse revolution
InactiveCN103148854AAccurate extractionAccurate acquisitionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEarth's rotationAccelerometer
The invention provides an attitude measurement method of a micro-electro mechanical system (MEMS) inertial navigation system based on single-shaft forward revolution and reverse revolution. Initial position parameters of a carrier are determined by means of a global position system and are input into a navigational computer; after being pre-heated, an MEMS inertial navigation system collects output data of an MEMS gyroscope and output data of an MEMS accelerometer; according relationship between carrier motion acceleration information measured by the MEMS accelerometer and local gravity acceleration and relationship between carrier angular speed information output by the MEMS gyroscope and the earth rotation angular rate, angle information between an inertial measurement unit (IMU) coordinate system and a navigation coordinate system is determined, and an initial alignment process of the system is completed; the revolution scheme is that an IMU alternately revolves for 360 degrees forwards and reversely around a carrier coordinate system (b coordinate system) and a cycle is completed; an output value of the MEMS gyroscope under the revolution state of the IMU is plugged into the inertial navigation system, and a strapdown matrix is updated by quaternion algorithm; and according to a real-time revolution angle position of the IMU relative to the carrier provided by an angle measurement mechanism, a transfer matrix of the carrier coordinate system and the IMU coordinate system is built, and by means of combination of the transfer matrix and an attitude matrix, a transfer matrix of the carrier coordinate system relative to the navigation coordinate system is calculated. According to the method, modulation for constant deviation of an inertial component is carried out, and attitude precision of the system is improved.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
Accurate Telescope Tracking System with a Calibrated Rotary Encoder
InactiveUS20130265639A1Improve accuracyExpensive encoderComputer controlTelescopesMicrocontrollerEarth's rotation
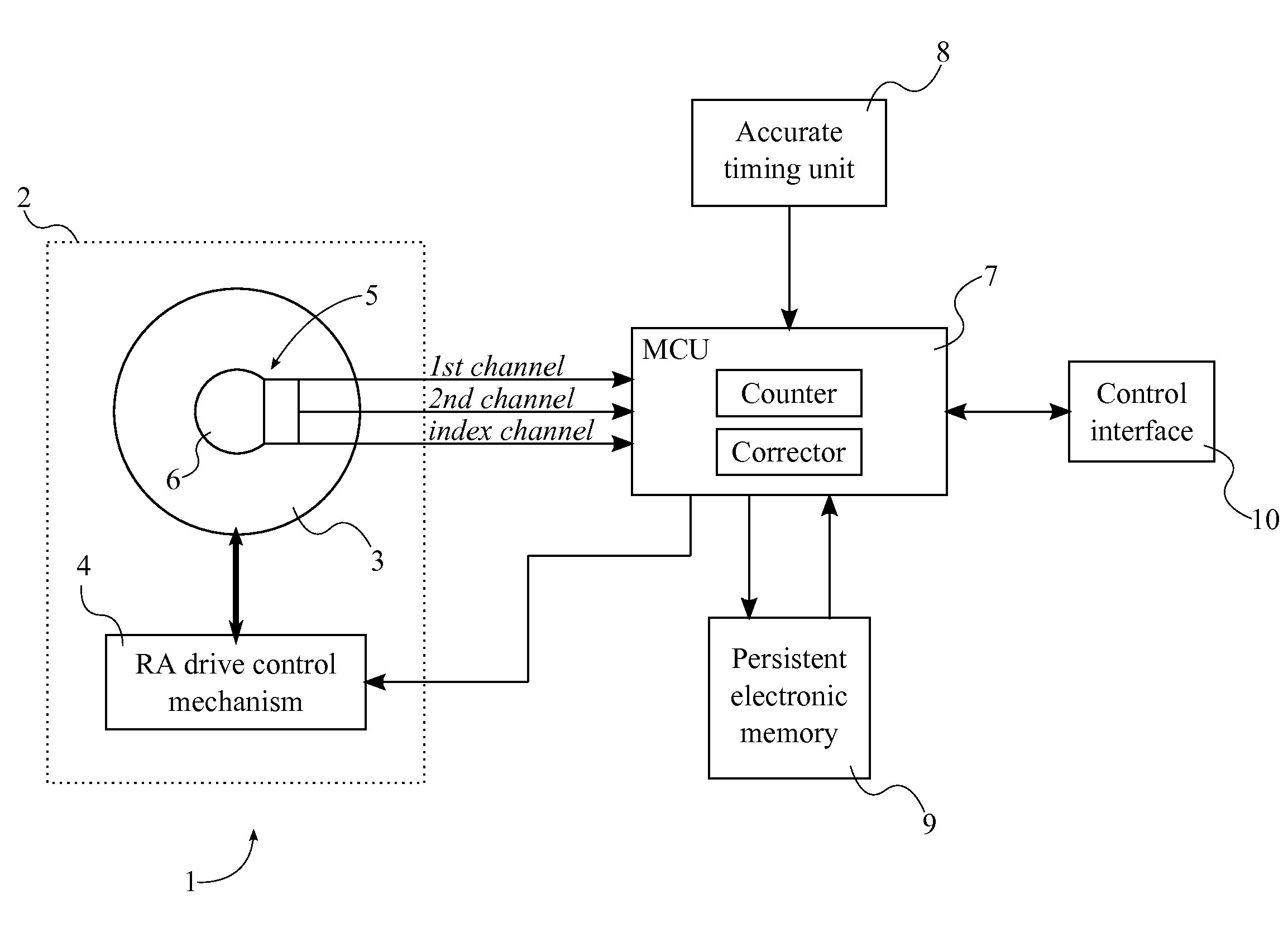
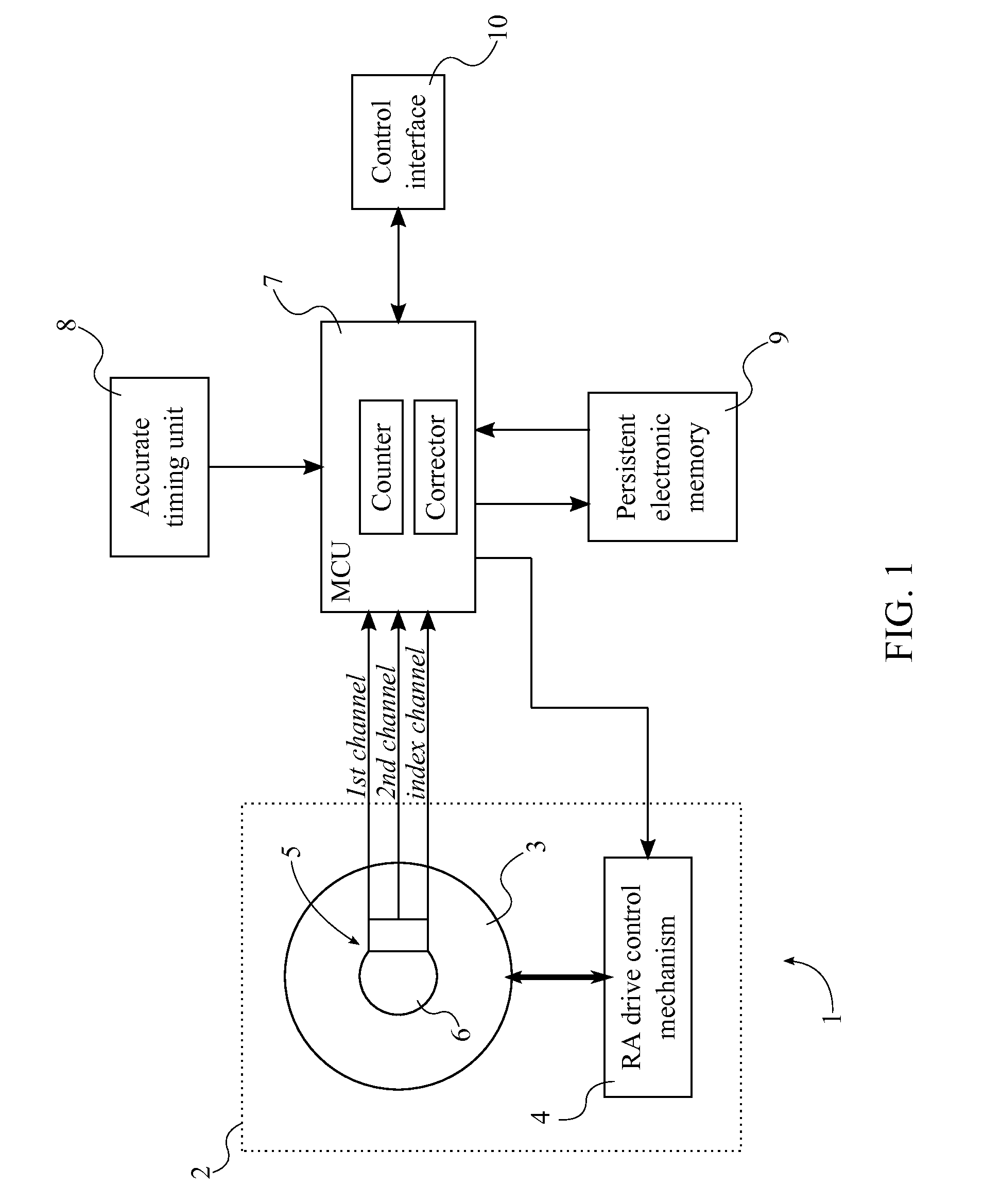
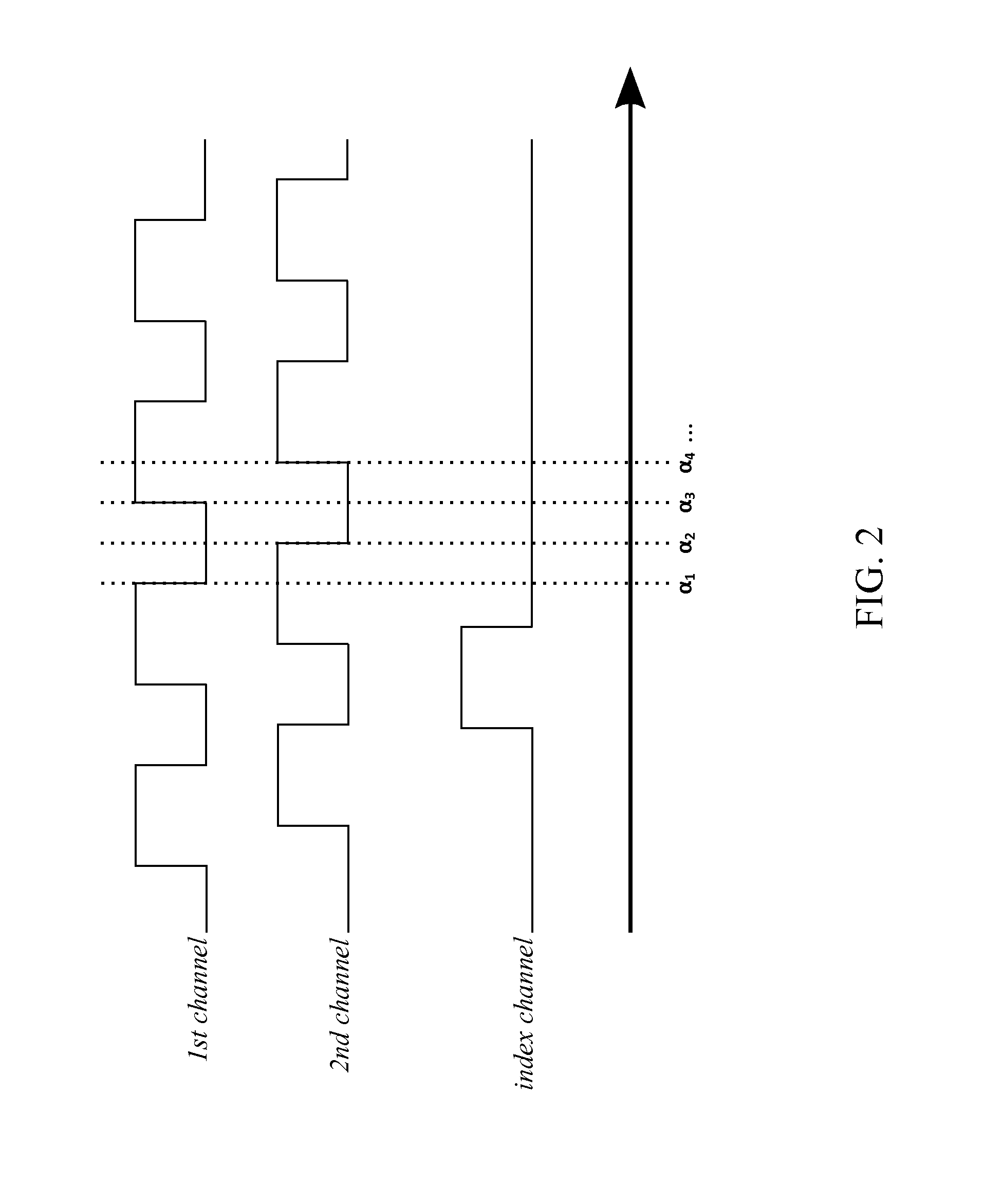
A system with a calibrated rotary encoder can be used for accurate telescope tracking along the Right Ascension (RA) rotation axis. The system includes an incremental quadrature optical encoder, a microcontroller unit (MCU), a timer, an electronic memory, and a control interface. The rotor of the encoder is coaxially attached to the RA drive shaft of the telescope mount in order to send angular position data for the RA drive shaft to the MCU. The MCU evaluates the angular position data for errors and send corrections to the control mechanism of the RA drive shaft. The electronic memory stores calibrated reference data, which is compared to the angular position data by the MCU. The calibrated reference data can be found by measuring the movement of a reference star across an image. The system can also calculate an accurate visible speed for the Earth's rotation in a desired direction.
Owner:BATCHVAROV ANDREY BORISSOV
Method for online real-time removing oscillation error of optical fibre gyroscope SINS system
InactiveCN101183004ADoes not change the installation structureNot affectedNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEarth's rotationInertial navigation system
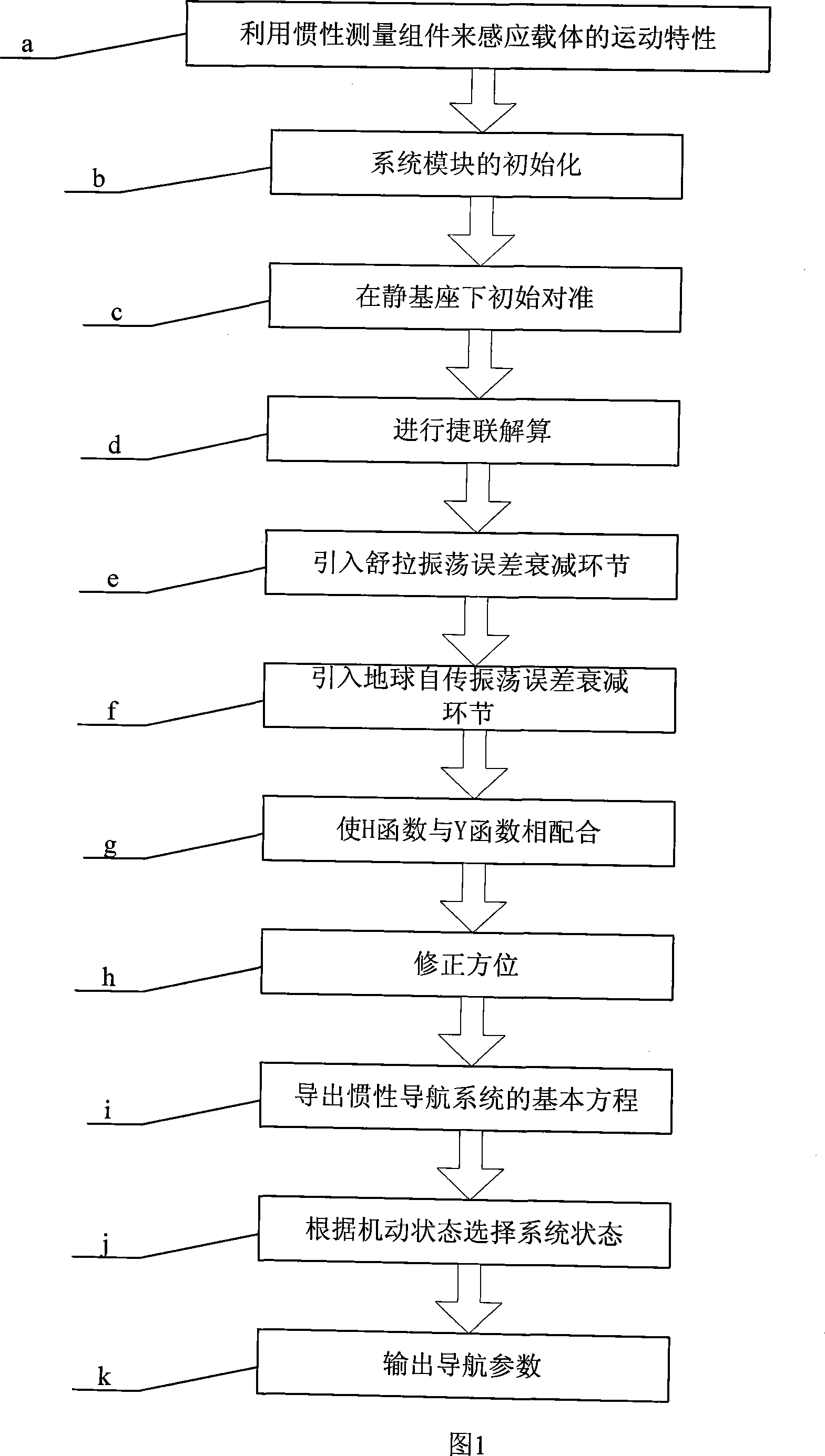
The invention provides an online method which can eliminate the oscillation error of a fiber optic gyroscope strap-down inertial navigation system in real time and relates to an error compensation method of a strap-down inertial navigation system, moreover, the method belongs to the technical field of strap-down inertial navigation technology and data process. The invention aims at solving the shortcoming of the prior method of improving the navigation accuracy of the fiber optic gyroscope strap-down inertial navigation system which leads to increasing the system cost and decreasing reliability and system autonomy, etc. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: step a, an inertial measuring component is adopted to sense kinetic characteristics of the carrier; step b, the system module is initialized; step c, initial adjustment is conducted; step d, strap-down solving is conducted; step e, a sula oscillation error decay link is drawn into the invention; step f, an earth rotation oscillation error decay link is drawn into the invention; step g, the invention results in that Y function is compatible with H function; step h, orientation is revised; step i, the basic mathematical equation of the inertial navigation system is derived from the invention; step j, the system state is selected according to the flexible state; step k, the navigation parameter is output.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for controlling glide flying ballistic curve damping
ActiveCN104176268AAchieve stabilizationSuppression of ballistic long-period oscillationsSpecial data processing applicationsGround installationsLow speedLongitudinal plane
The invention discloses a method for controlling glide flying ballistic curve damping. The method comprises the following three major steps: step 1: taking into consideration influence of earth curvature, ignoring influence of earth rotation, studying three degree-of-freedom kinematical equation of gliding of an aircraft, and acquiring condition of furthest distance of powerless gliding of the aircraft; step 2: based on the atmosphere model and the aircraft aerodynamic force model already known, performing force analysis on the longitudinal plane of the aircraft under stable gliding condition, and acquiring stable gliding ballistic curve angle of inclination gamma*; step 3: adding feedback to the control instruction, introducing ballistic curve damping control. The method is a guidance method enabling stable gliding of the aircraft, and is applicable to aircrafts having a glide ballistic curve, including a cannonball of a low speed and a short range as well as a long-distance, reentry, and hypersonic-velocity aircraft.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Reducing error contributions to gyroscopic measurements
InactiveUS20130211723A1Reducing error contributionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyEarth's rotationGyroscope
A method and system for reducing error contributions to gyroscopic measurements is provided. The method includes receiving a plurality of signals indicative of at least one component of the Earth's rotation substantially perpendicular to a portion of a wellbore and a component of the Earth's rotation substantially parallel to the portion of the wellbore. The plurality of signals is generated by one or more gyroscopic sensors within the portion of the wellbore. The method further includes calculating, using the plurality of signals and using one or more signals indicative of the Earth's rotation rate and one or more signals indicative of the latitude of the one or more gyroscopic sensors within the portion of the wellbore, a mass unbalance offset for the one or more gyroscopic sensors.
Owner:GYRODATA
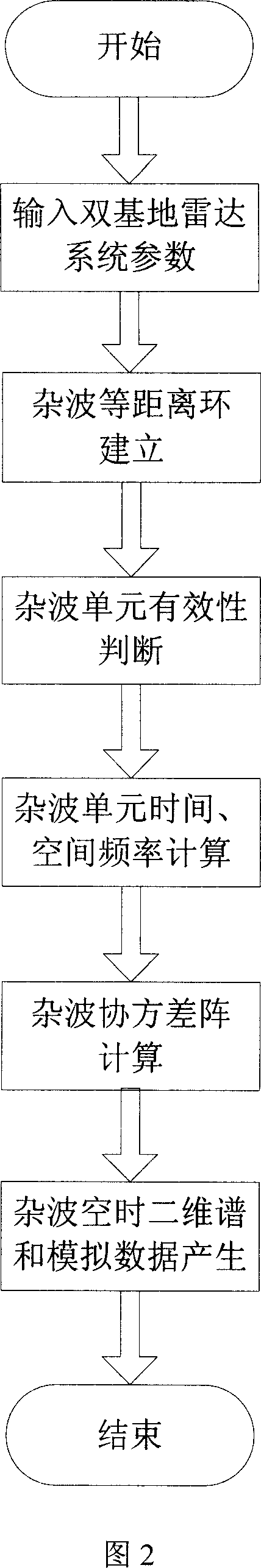
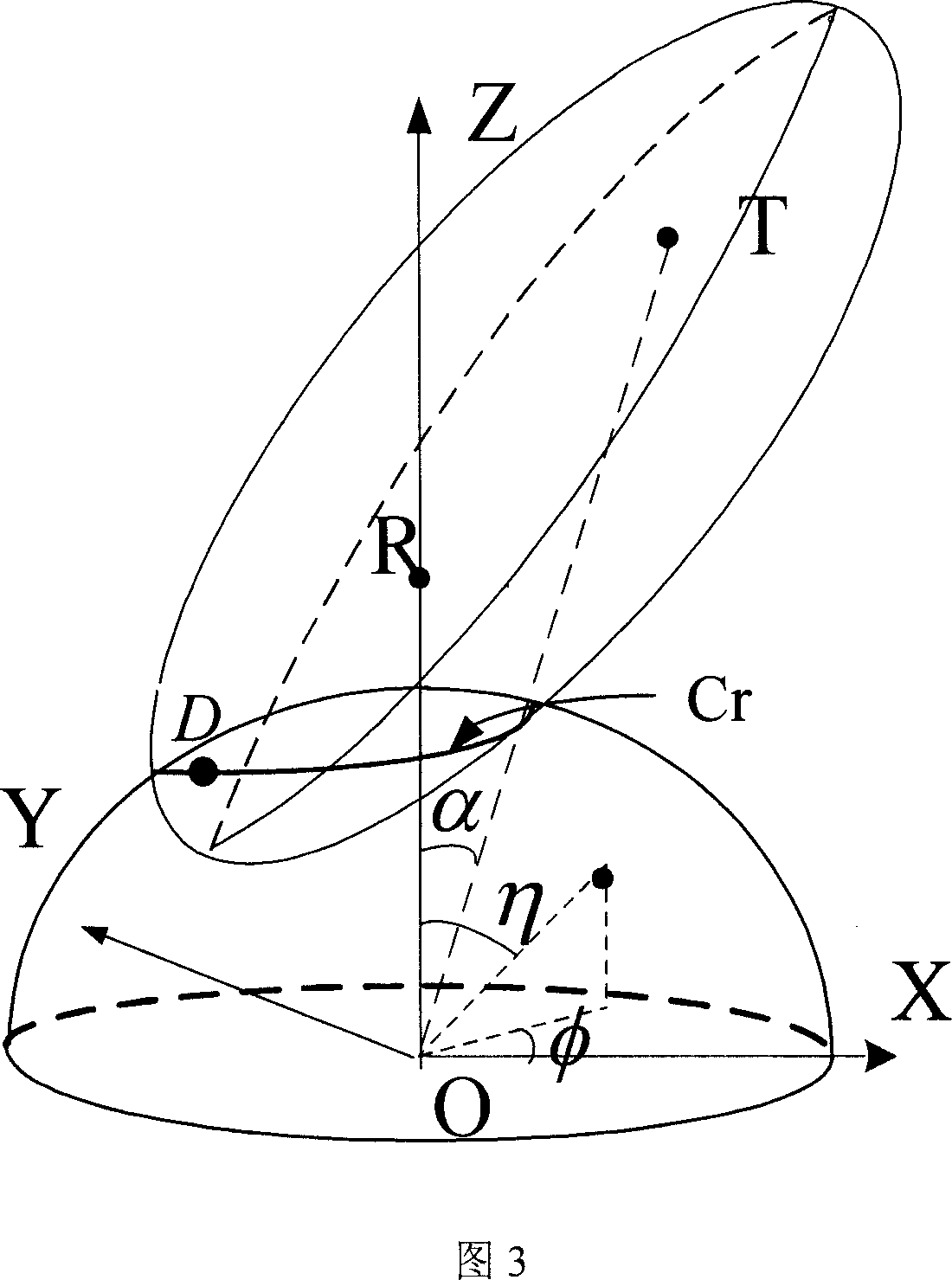
Method for producing noise wave base belt analog signals of space-borne two-foundation radar
The related clutter baseband signal generation method for satellite-carried bistatic radar comprises: setting initial condition, building the clutter equidistance ring model; deciding the clutter unit validation, calculating the clutter unit motion vector led by earth rotation; then, according to satellite position and orbit parameters, calculating satellite velocity vector and the corresponding time frequency and space frequency for clutter unit; summarizing all clutter unit space-time 2D fast-beat to calculate clutter covariance matrix and clutter data for succeeding algorithm processing.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com