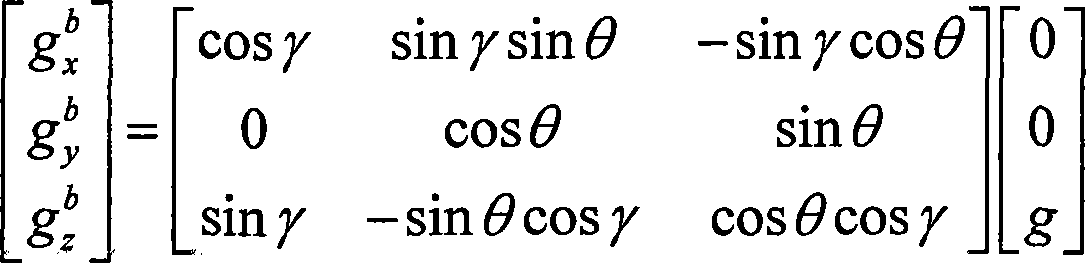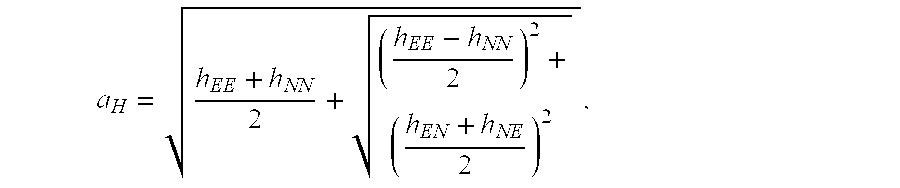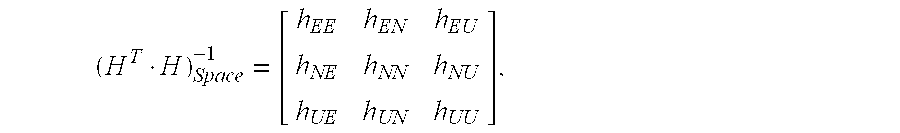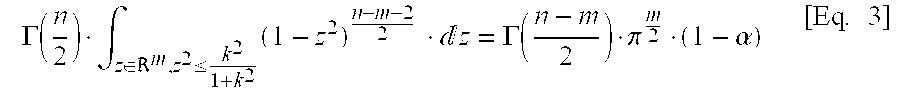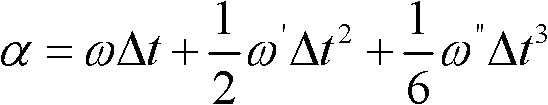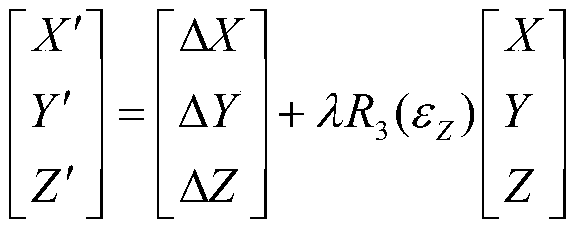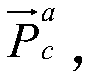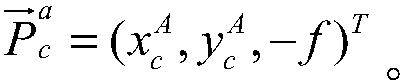Patents
Literature
105 results about "Horizontal coordinate system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
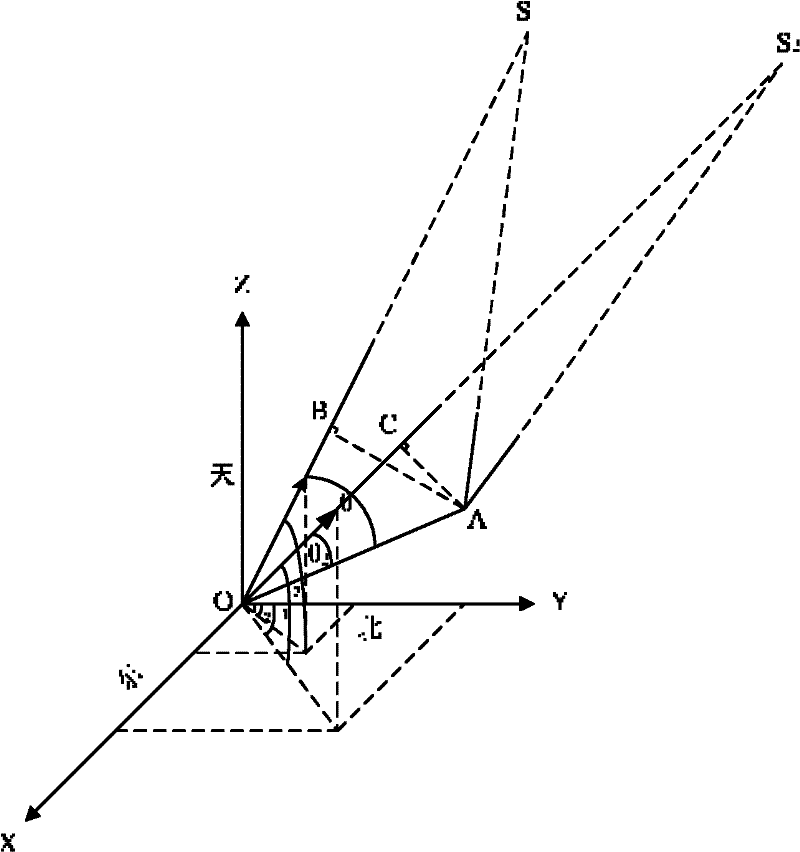
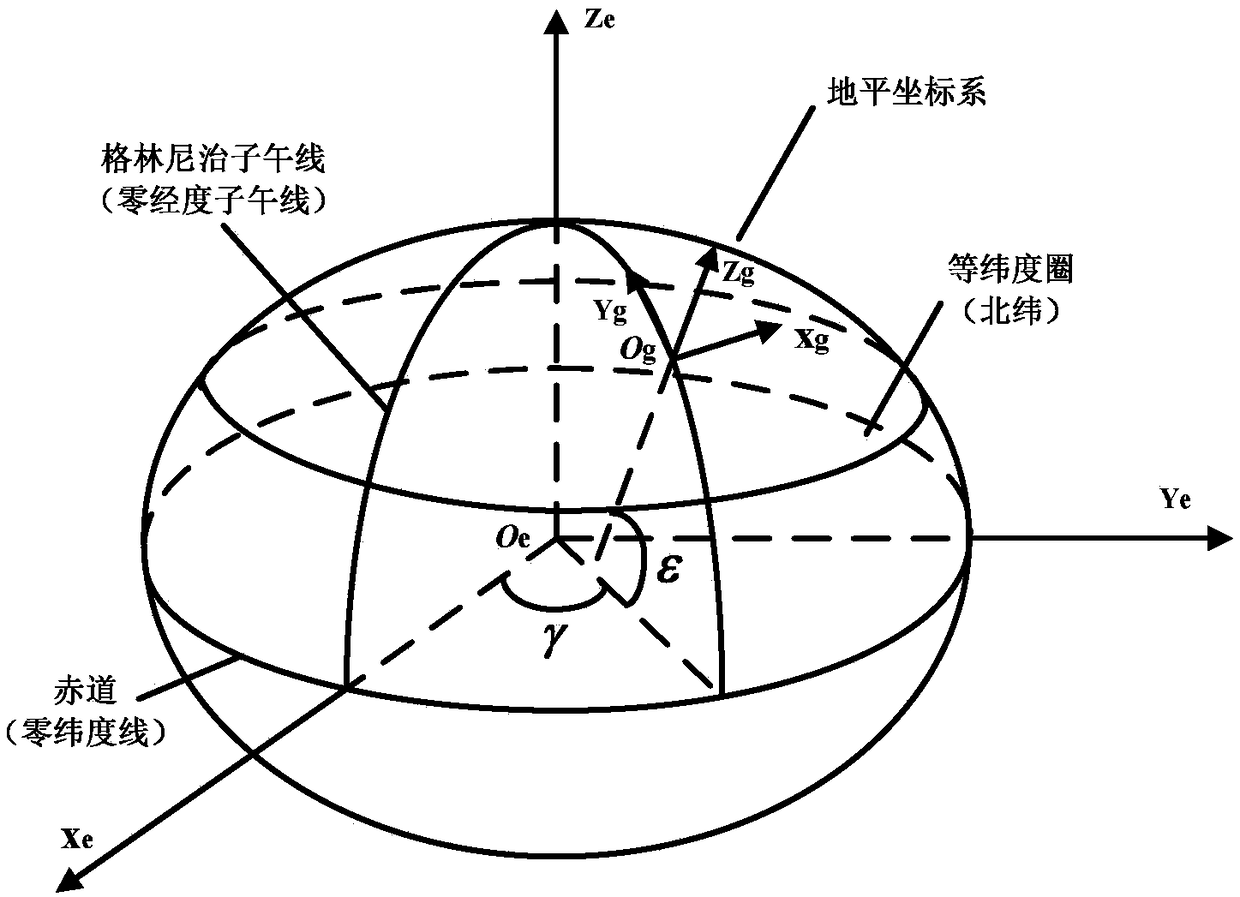
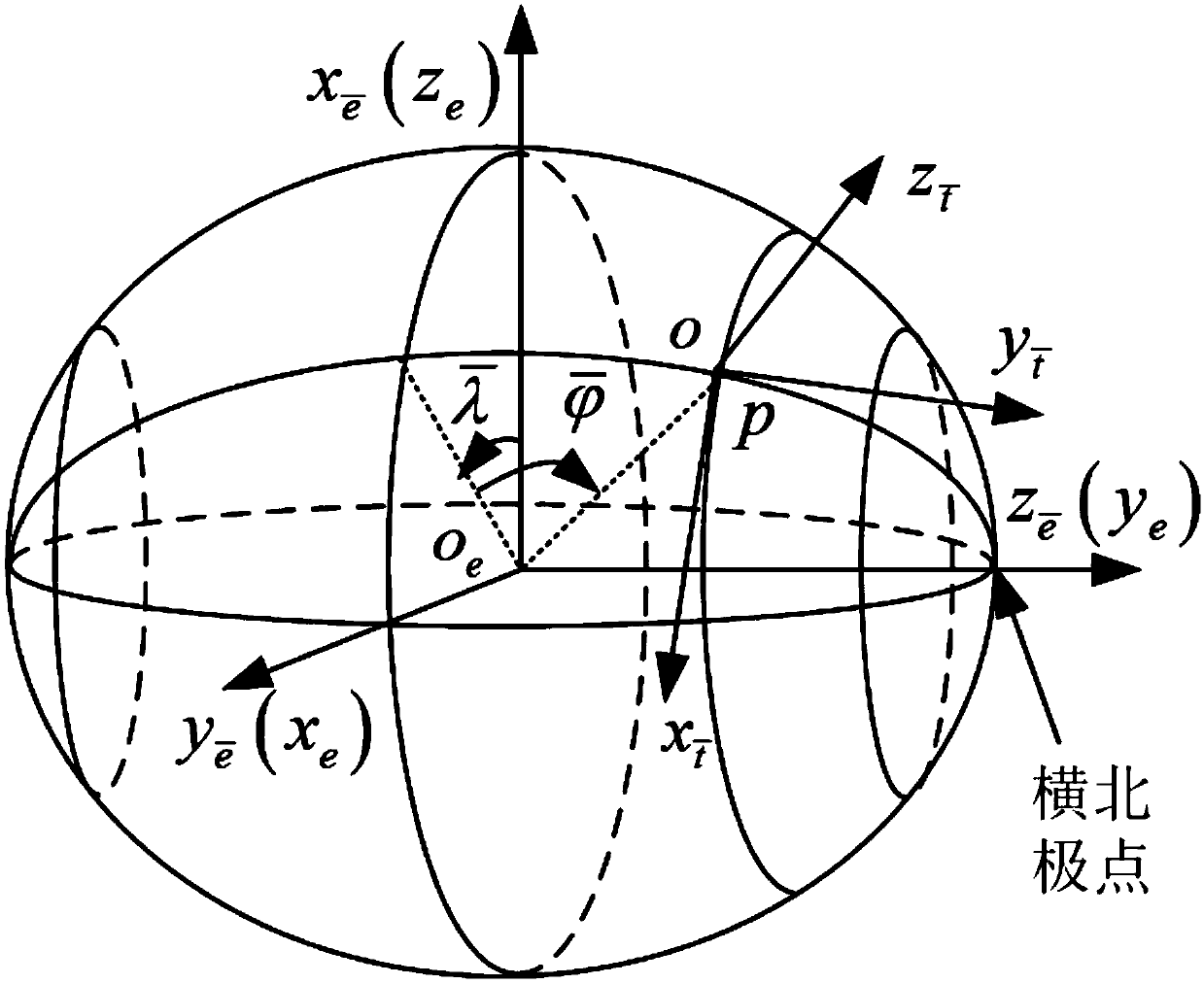
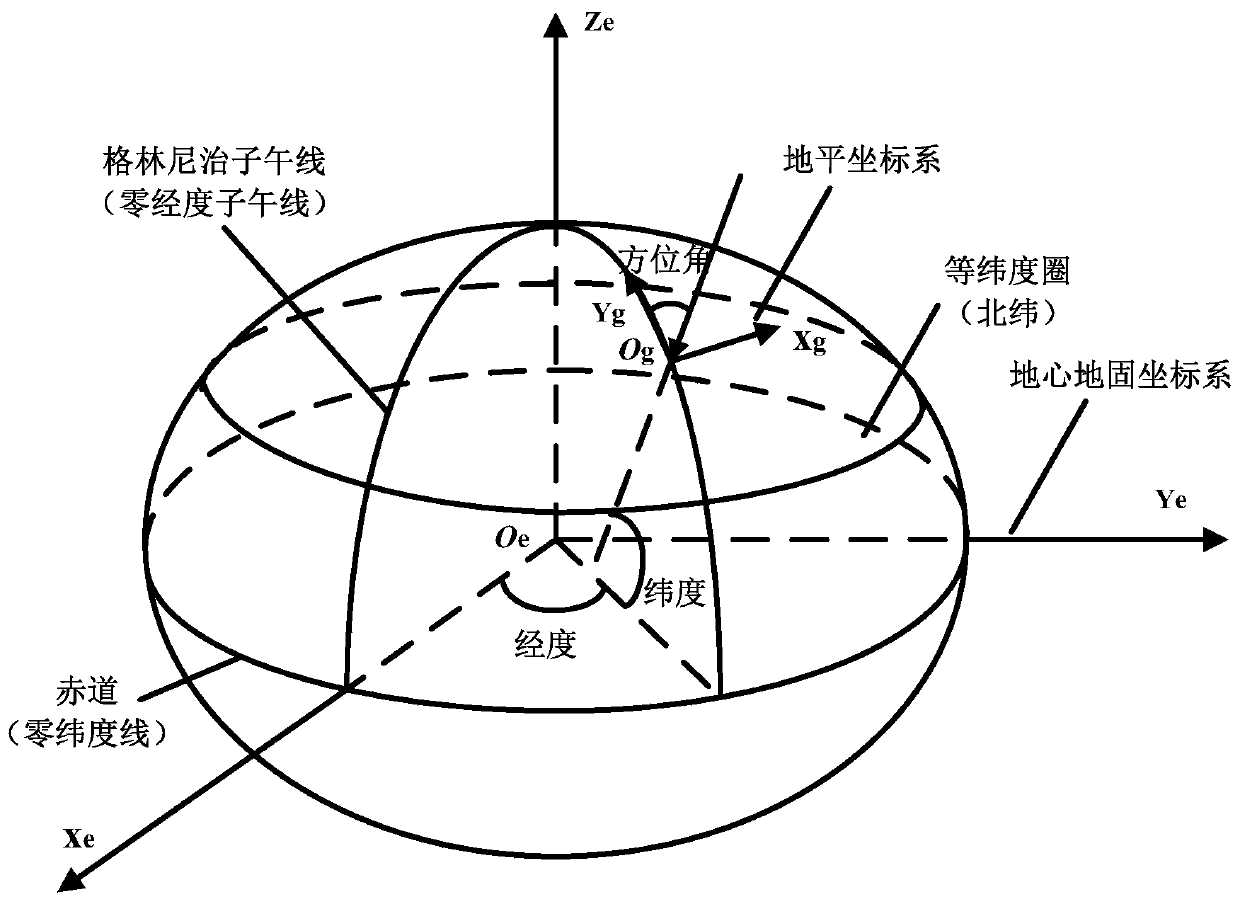
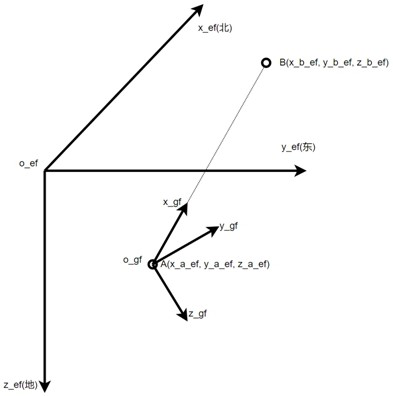
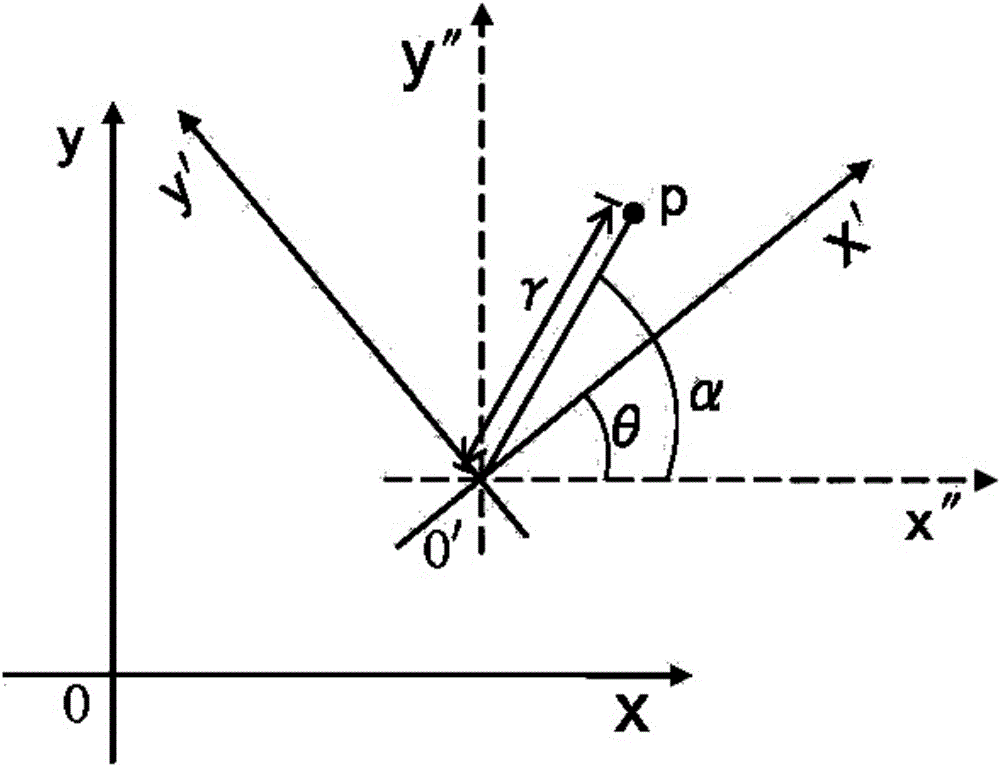
The horizontal coordinate system, also known as topocentric coordinate system, is a celestial coordinate system that uses the observer's local horizon as the fundamental plane. Coordinates of an object in the sky are expressed in terms of altitude (or elevation) angle and azimuth.
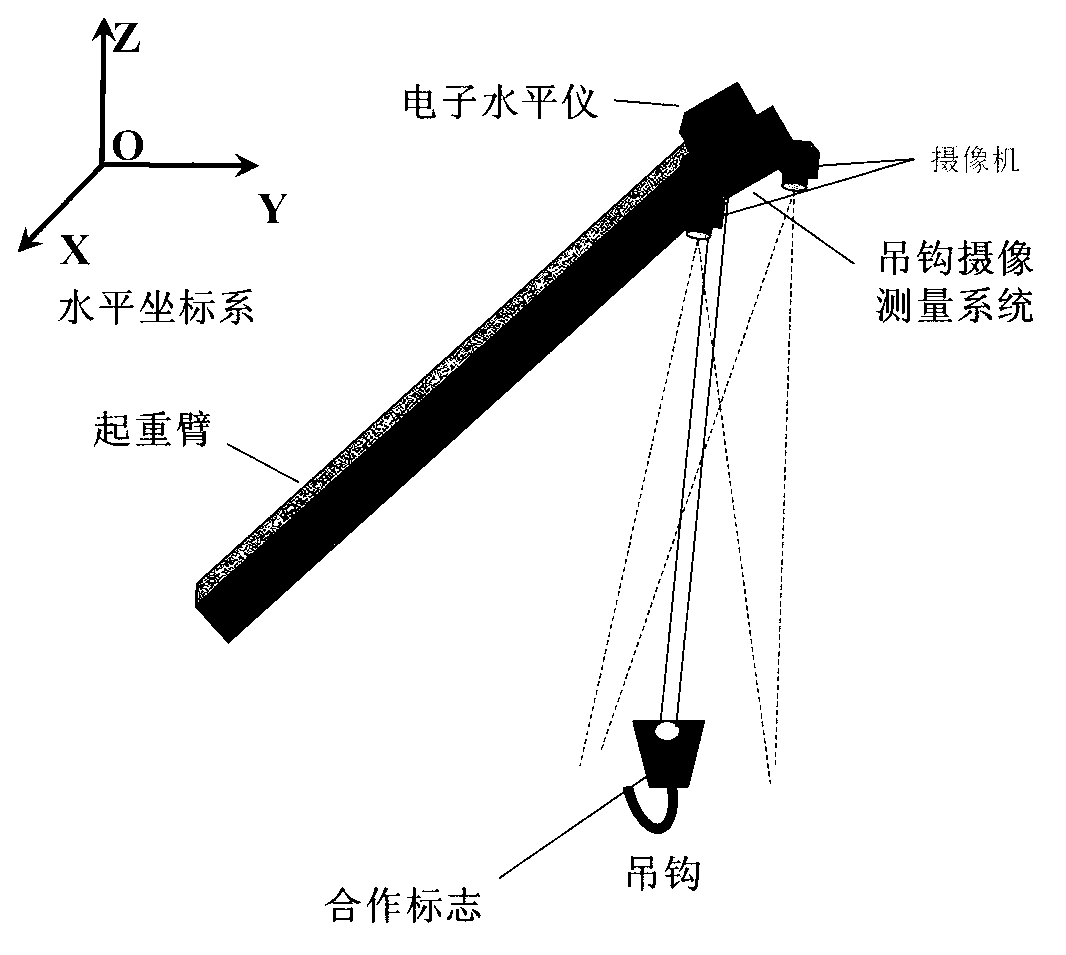
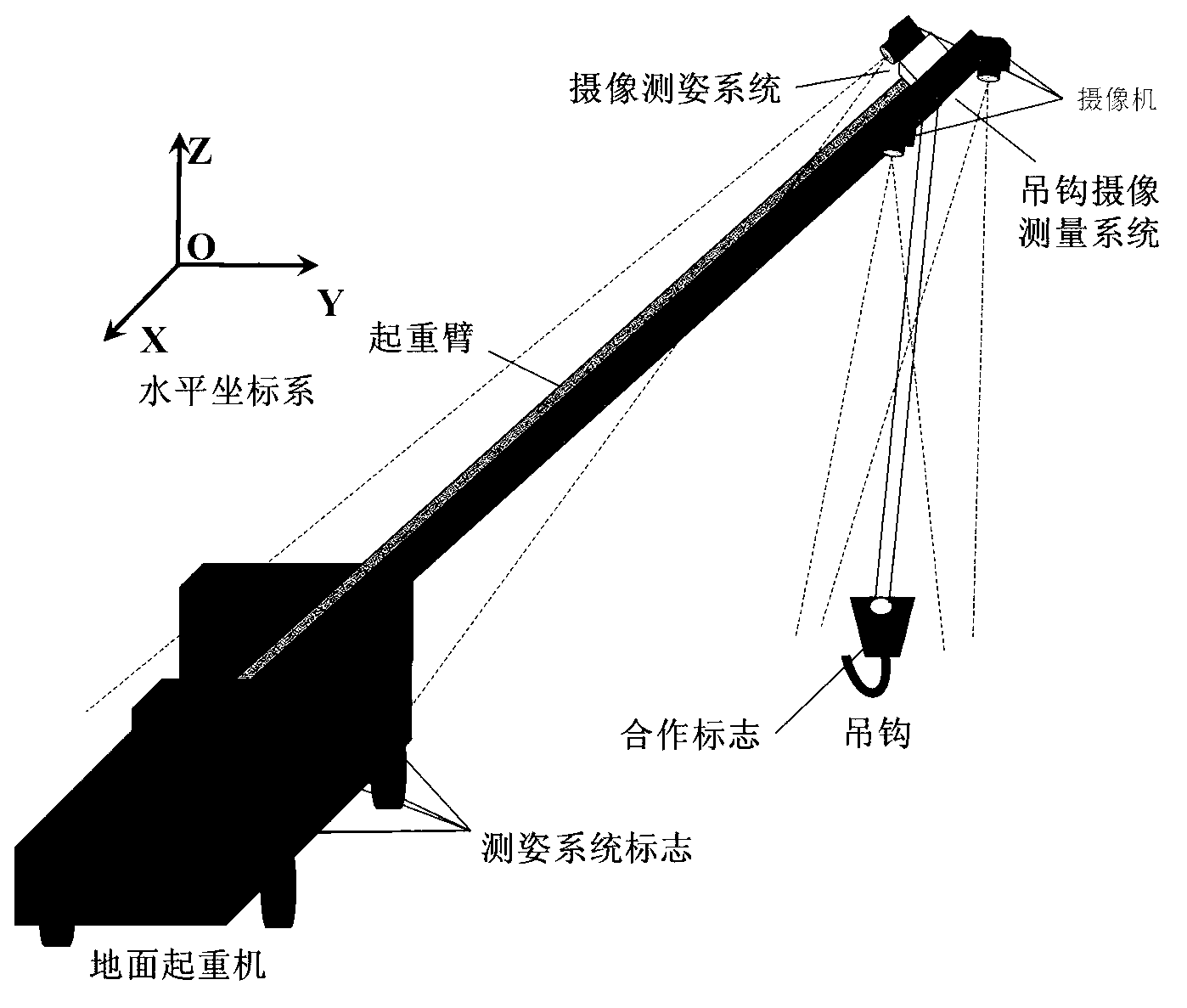
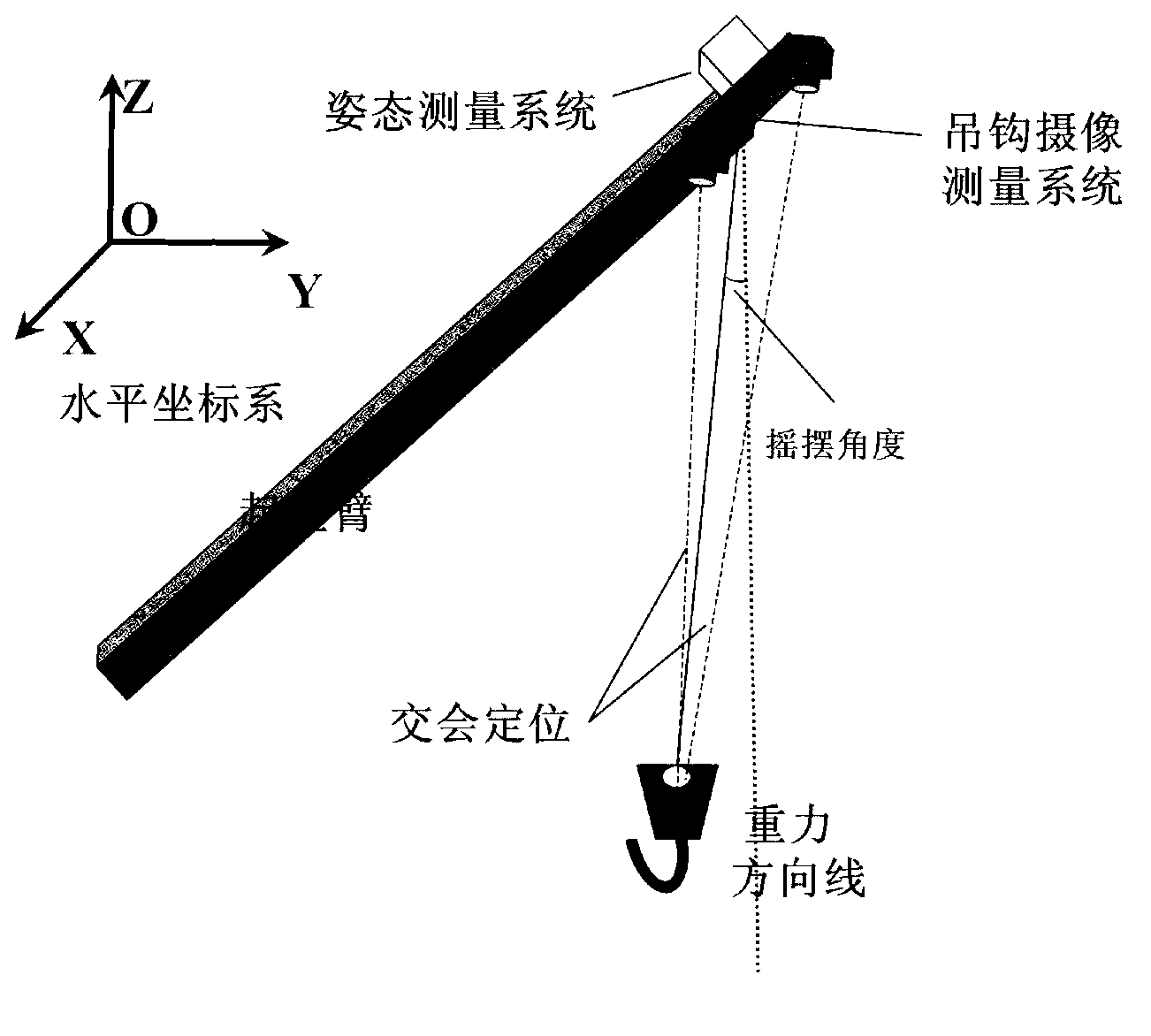
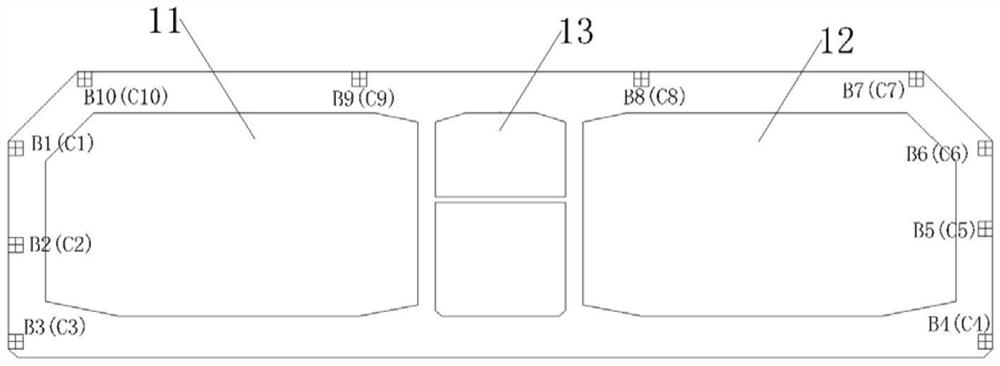
Real-time photographic measuring method of position and swing angle of lifting hook of crane
InactiveCN102795547AFix the angle problemProcessing calculations are easy to implementLoad-engaging elementsEngineeringHorizontal coordinate system
The invention relates to a photographic measuring method of a position and a swing angle of a lifting hook of a crane. The method comprises the steps of: mounting a set of gesture measuring system and a set of lifting hook photographic measuring system at the top end of an arm rest of a crane, which is close to a lifting rope rolling wheel; mounting a cooperation mark on the lifting hook; measuring inclination gesture of the lifting hook photographic measuring system in real time through a gesture measuring system; measuring the position of the cooperation mark on the lifting hook, with respect to the lifting hook photographic measuring system in real time and in an intersecting manner through double cameras of the lifting hook photographic measuring system; representing the position of the lifting hook by using a horizontal coordinate system based on the inclination gesture; and calculating a swing angle of the lifting hook in real time by utilizing the position of the lifting hook represented by the horizontal coordinate system. As the photographic measuring method is utilized to solve the measurement problem of the position and swing angle of the lifting hook of the crane, the photographic measuring method of the position and the swing angle of the lifting hook of the crane, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of easy implementation of relevant treatment and calculation and high real-time capability, and can be applied to measurement of positions and swing angles of lifting hooks of multiple cranes.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
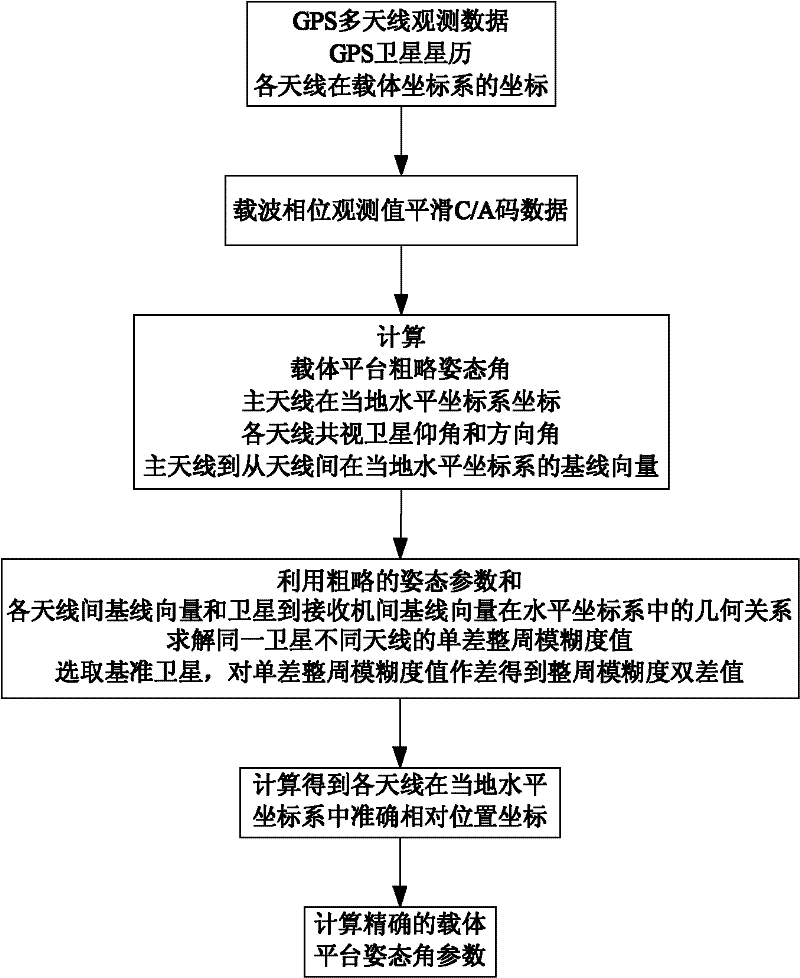
GPS multi-antenna attitude determination method
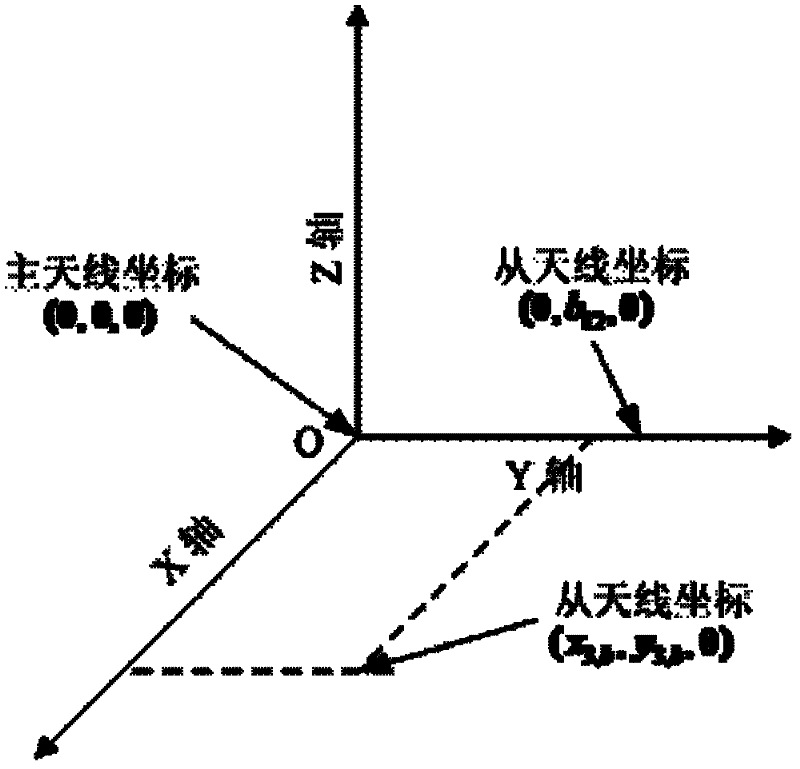
The invention aims at providing a GPS multi-antenna attitude determination method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly GPS multi-antenna observation data, a GPS satellite ephemeris and the coordinates of antennas on a carrier coordinate system are collected; a smoothing procedure is carried out to C / A code observation data with a carrier wave phase observed value; a carrier platform rough attitude angle, the coordinate of the main antenna in a local horizontal coordinate system, the shared vision satellite elevation angles and direction angles of the antennas and the baseline vector from the main antenna to subordinated antennas in the local horizontal coordinate system are calculated; based on the geometry relations of the baseline vectors among the antennas and the baseline vectors from the satellite to a receiver in the horizontal coordinate system, the single difference integer cycle fuzziness value of different antennas of the same satellite is solved; a reference satellite is selected and a difference operation is carried out to the single difference integer cycle fuzziness value to obtain an integer cycle fuzziness double difference value; the integer cycle fuzziness double difference value obtained is substituted into a carrier wave phase double difference model to obtain accurate coordinate components of the antennas and based on the coordinate components of the antennas, accurate attitude parameters are solved so as to realize GPS multi-antenna attitude determination.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
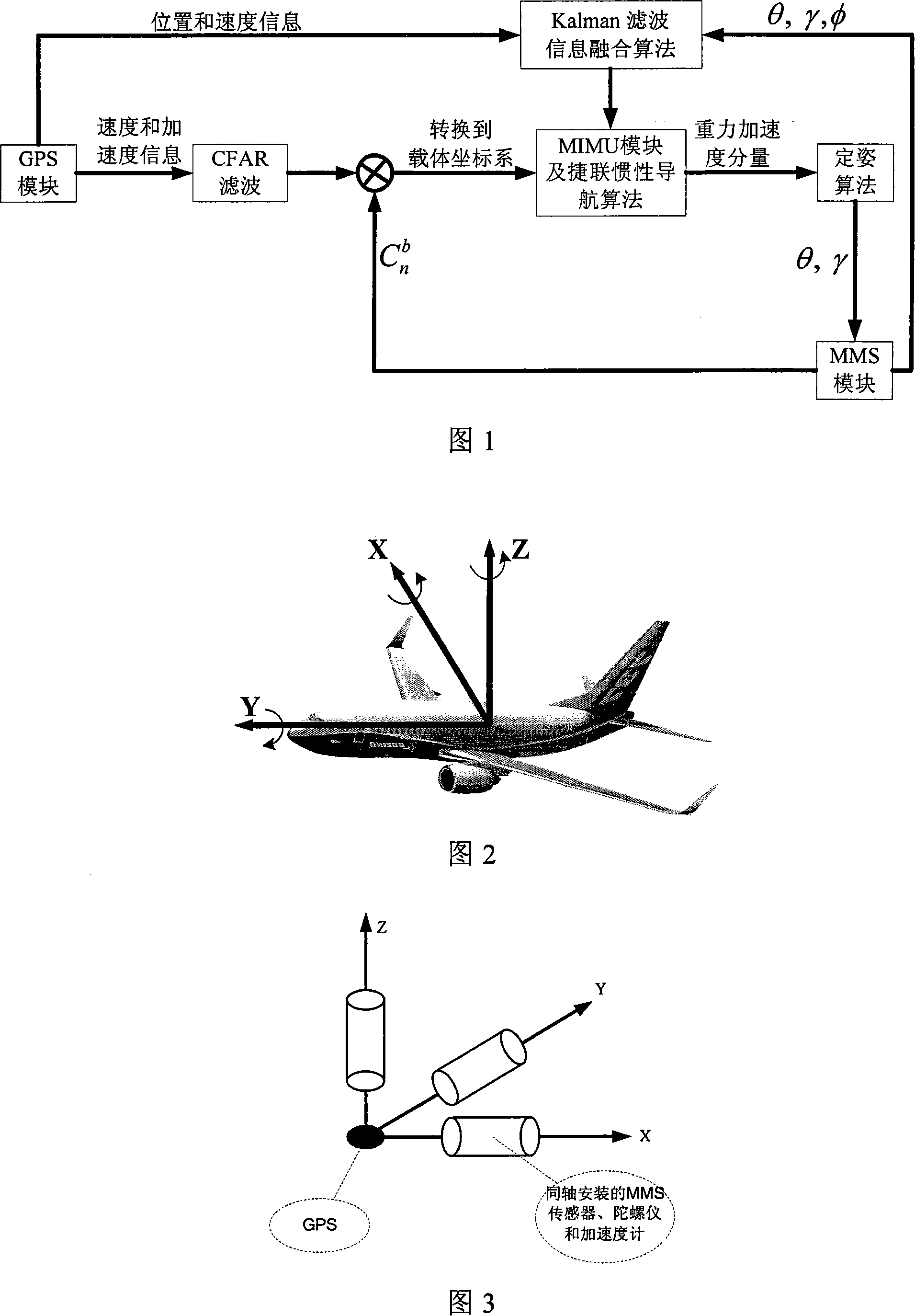
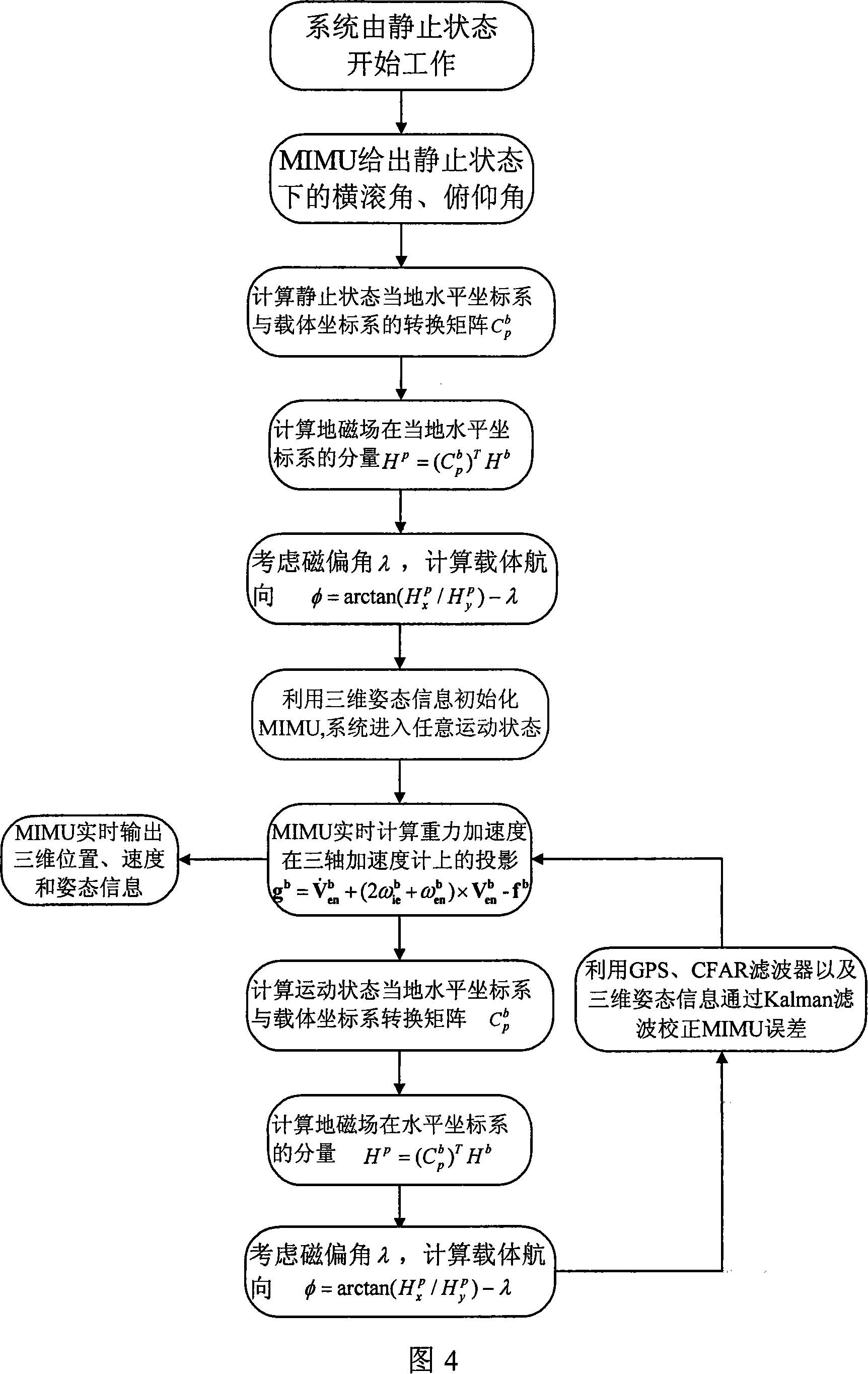
Attitude determining system of mini system suitable for any motion
A posture-fixing system for the mini-system which can realize the arbitrary movement; the system is characterized in that comprises a micro-magnetic sensor MMS module, a micro-inertia measurement unit MIMU module, a GPS module and a Kalman filtering module. Under the arbitrary state of motion of the mini-system, the MIMU module can work out the gravitational acceleration of the mini-system via the strapping of the output data and the navigation algorithm; the MMS module revolves the roll maneuver angle, the pitch angle and the 3D attitude information of the course angle for the mini-system via the real-time posture-fixing algorithm; also, the constant false alarm CFAR wave filter is adopted to filter the noise in the output speed and the acceleration information of the GPS. On one hand, the 3D posture information is sent to the Kalman filtering module for combination with the position and velocity information of the GPS, so as to correct the MIMU error from time to time via the information mixing algorithm, on the other hand, 3D posture information is adopted to replace the Cnb coordinate transfer matrix in real time; the Cnb coordinate transfer matrix will be delivered to the MIMU module and the GPS module, so that the horizontal coordinate system information is transferred to the carrier coordinates. The utility model introduces the iterative solution among the GPS, the MIMU and the MMS, so as to ascertain the direction of the moving vehicle under arbitrary state of motion. Therefore, the wide application prospects are available.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
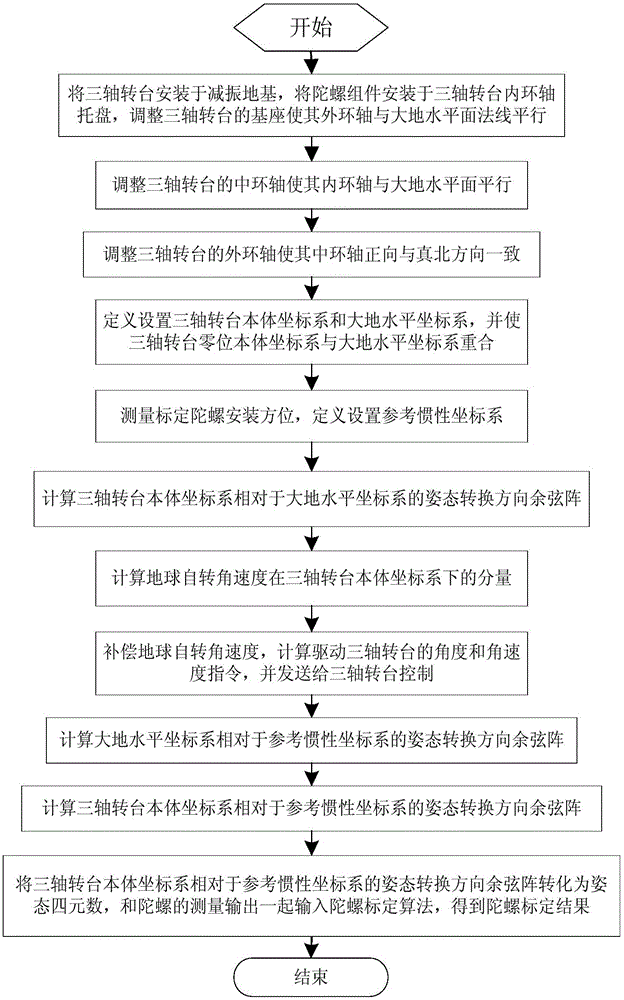
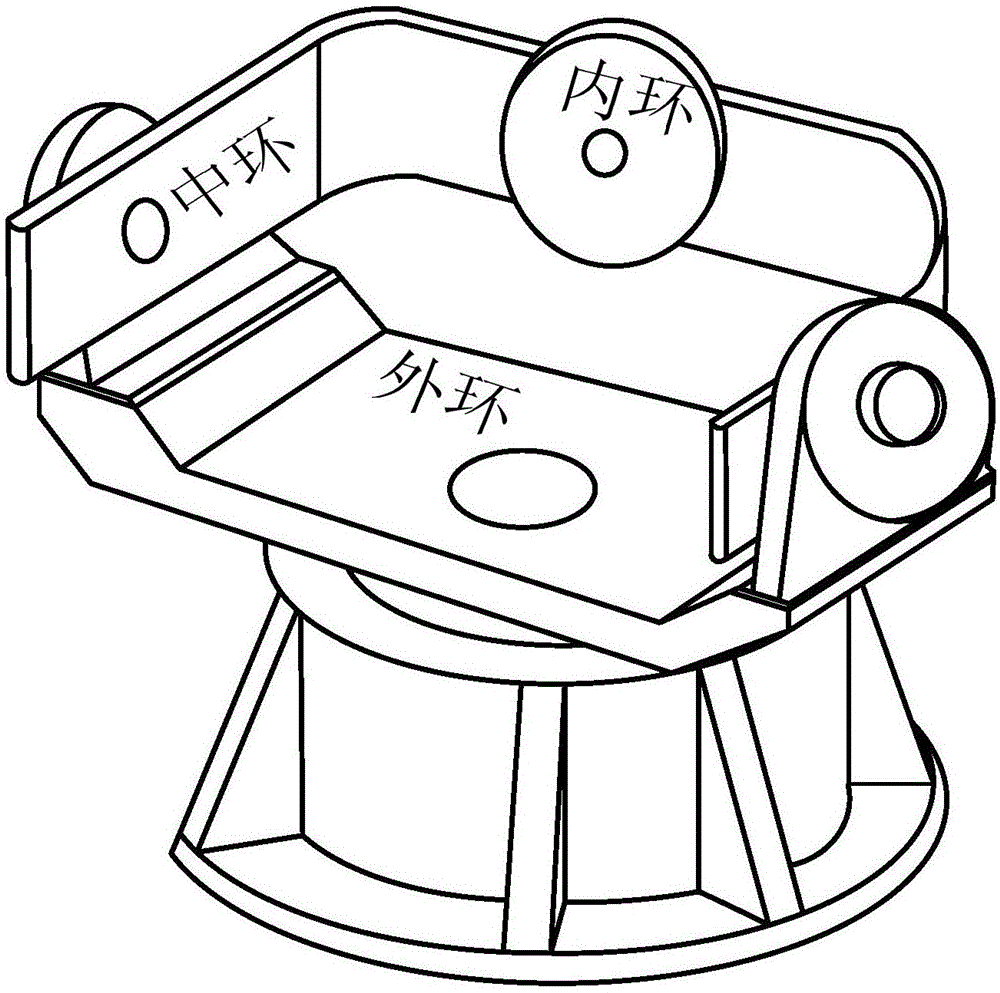
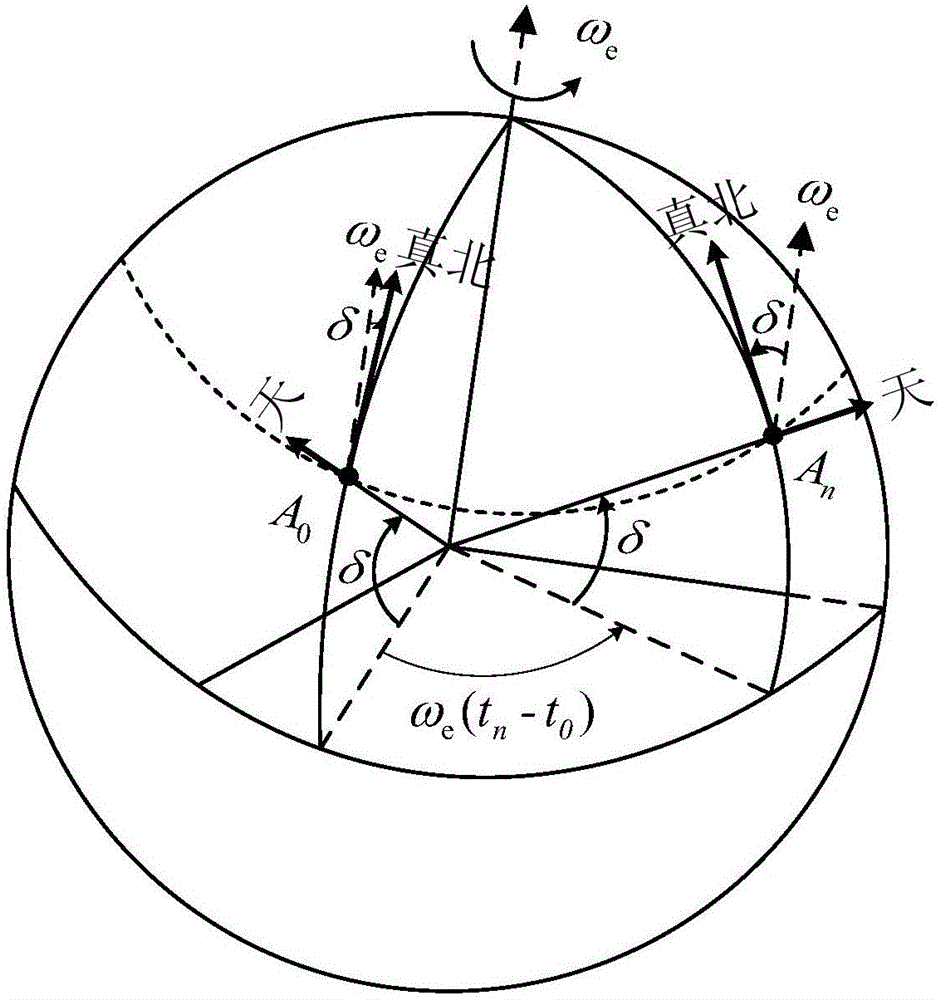
Inertial space gyro calibration test method based on three-shaft turntable
ActiveCN106525073AThe result is validHigh precisionMeasurement devicesSpace constantEarth's rotation
The invention relates to an inertial space gyro calibration test method based on a three-shaft turntable; while a gyro assembly attitude rotation is provided by the three-shaft turntable, the compensation dosage of the earth autorotation angular velocity is calculated according to the real-time rotating angle output of three rotating shafts of the three-shaft turntable, so that the influence of earth autorotation on the gyro measurement output is eliminated, and the inertial space constant angular velocity required for a gyro calibration algorithm is ensured. At the same time, based on attached rotation characteristics of the three rotation shafts of the three-shaft turntable, the method defines a rotation sequence rule of the three rotation shafts and a three-shaft turntable body coordinate system and a reference inertial coordinate system having the initial zero coinciding with the ground horizontal coordinate system, and provides a reference benchmark for determining the inertial system angle increment according to the gyro output and for determining the inertial system attitude according to the rotation angle output of the three rotation shafts of the three-shaft turntable. The method can significantly improve the precision of a ground gyro calibration test, can guarantee the ground to perform effective calibration and test result calibration on a gyro assembly, can establish a good foundation for performing relevant calibration tests of satellites in orbit, and improves the determination precision of the gyro attitude.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
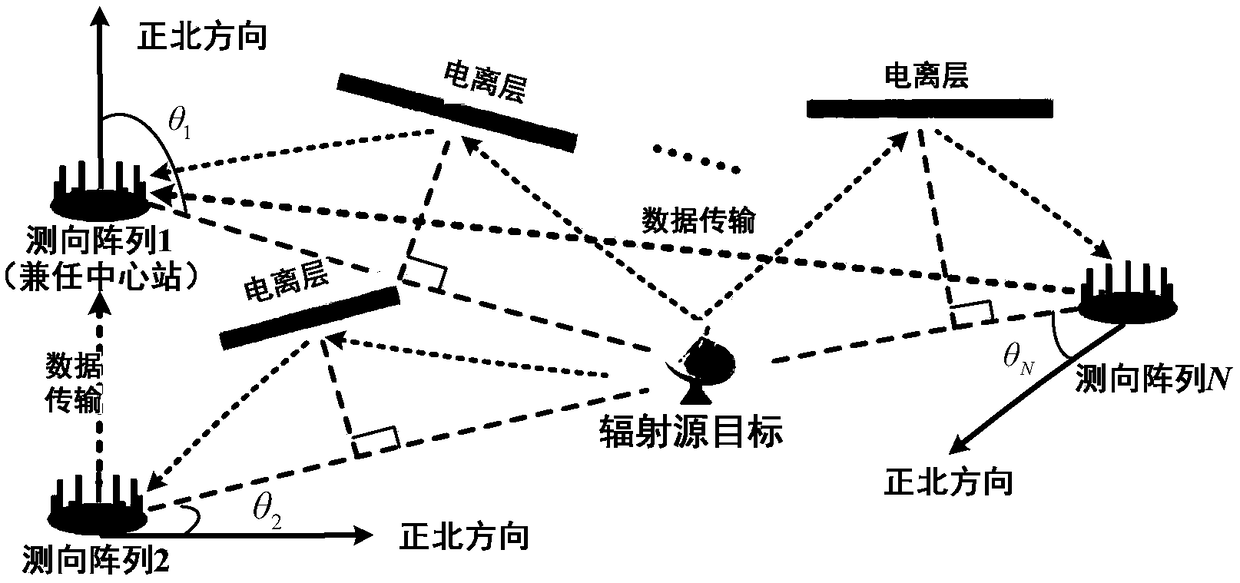
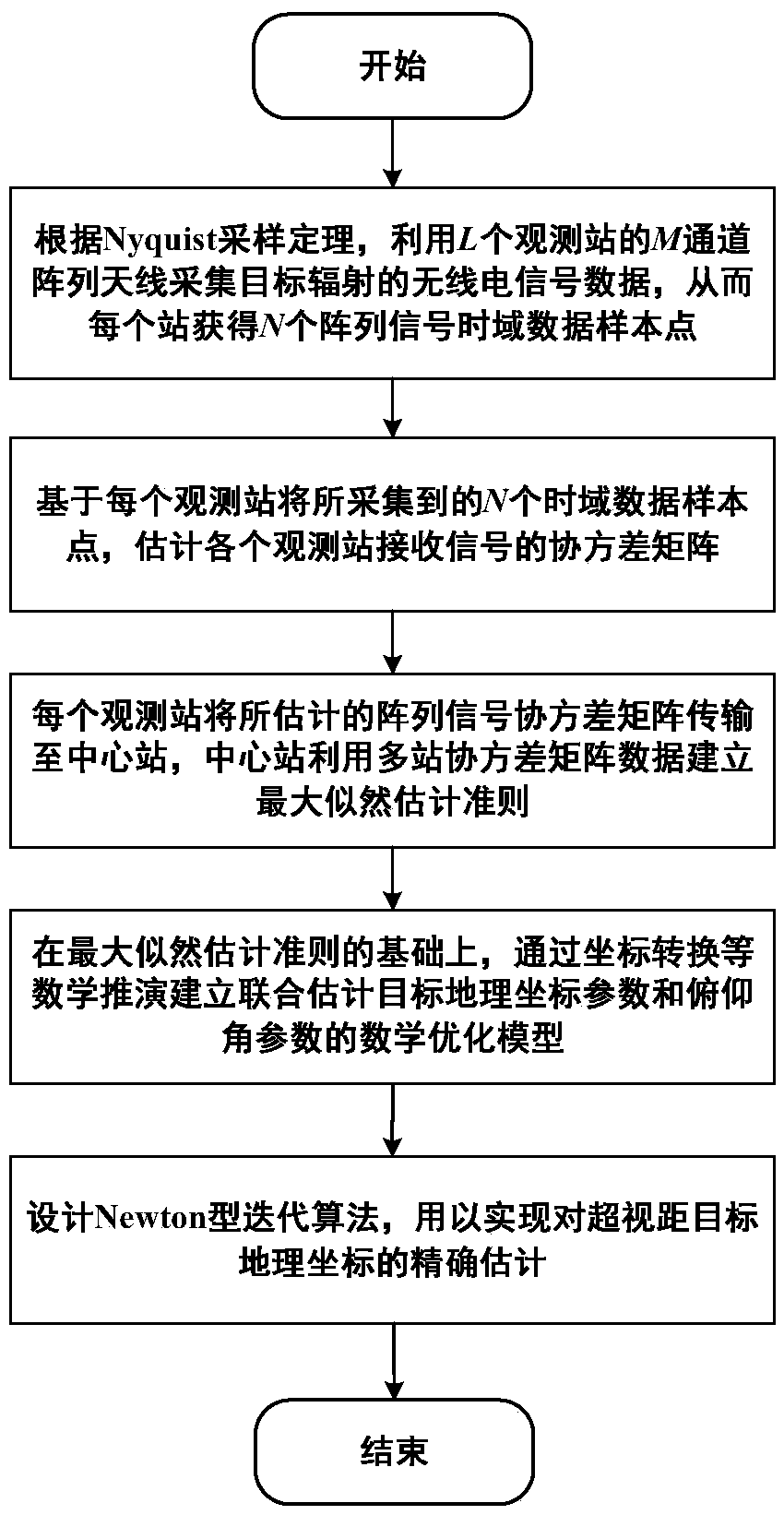
Azimuth information-based beyond-visual-range target geographic coordinate direct estimation method
ActiveCN109298388AImprove estimation accuracyImprove target positioning accuracyPosition fixationMathematical modelAngular degrees
The invention belongs to the technical field of radio signal positioning, in particular to an azimuth information-based beyond-visual-range target geographic coordinate direct estimation method; the method comprises the following steps of establishing a two-dimensional angle array signal model of each observation station, wherein the two-dimensional angles comprise an azimuth angle and a pitch angle, and calculating respective covariance matrixes; based on a ground plane coordinate system of each observation station, establishing a mathematical model of each station arrival azimuth angle relative to the target geographic coordinate parameters; utilizing the covariance matrix of each station, and establishing a mathematical optimization model for jointly estimating the target geographic coordinate parameters and the pitching angle parameters according to the maximum likelihood estimation criterion; and solving the mathematical optimization model through iteration, and obtaining a targetaddress coordinate. By adoption of the method, the target positioning precision under a low signal-to-noise ratio can be remarkably improved, the estimation precision of the target pitch angle is improved, and the convergence speed is relatively high, high-dimensional searching is not needed, and the calculation amount of real-time positioning can be effectively reduced; and the method is relatively high in practical application value, stable and reliable in performance, and efficient.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
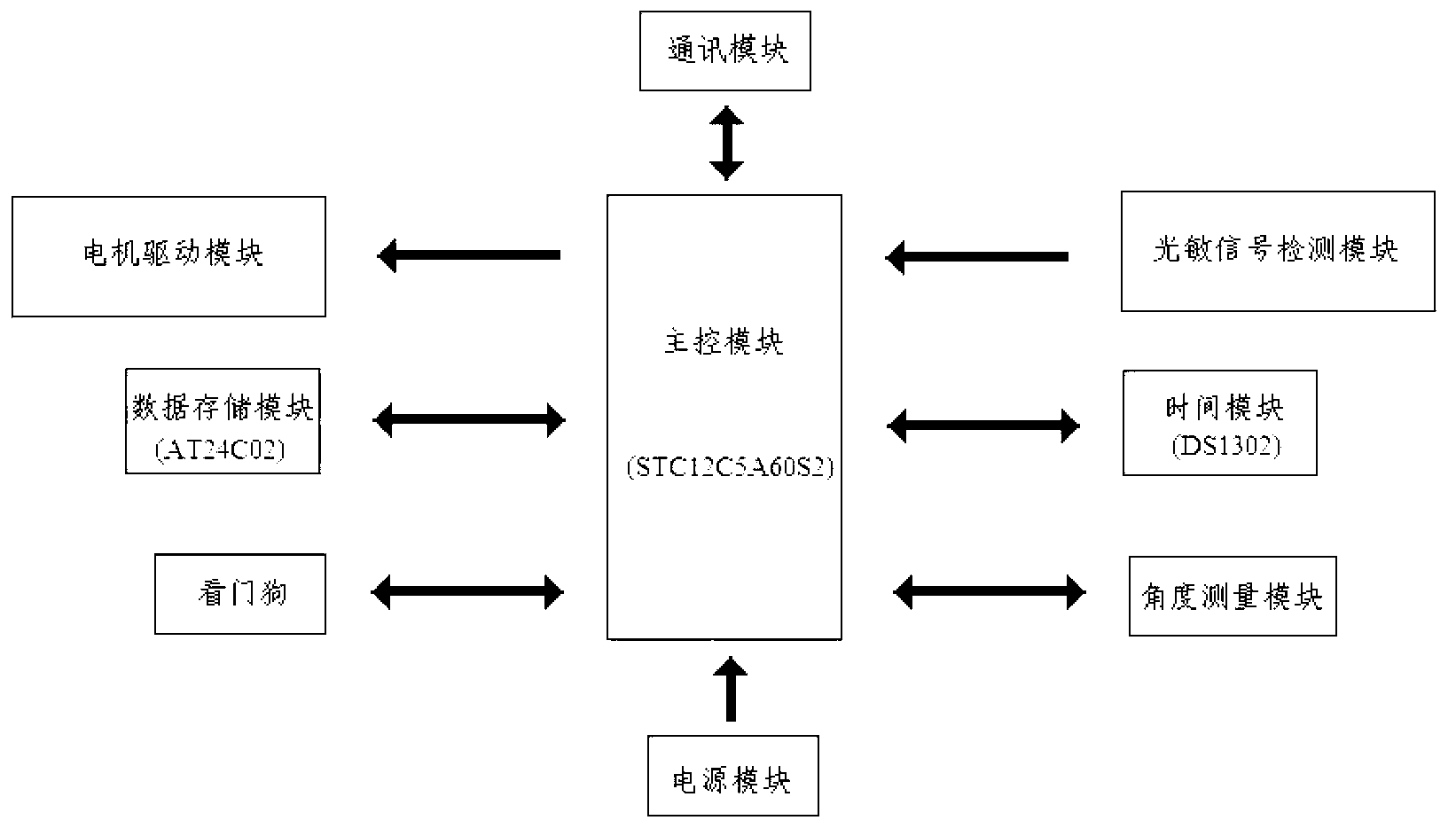
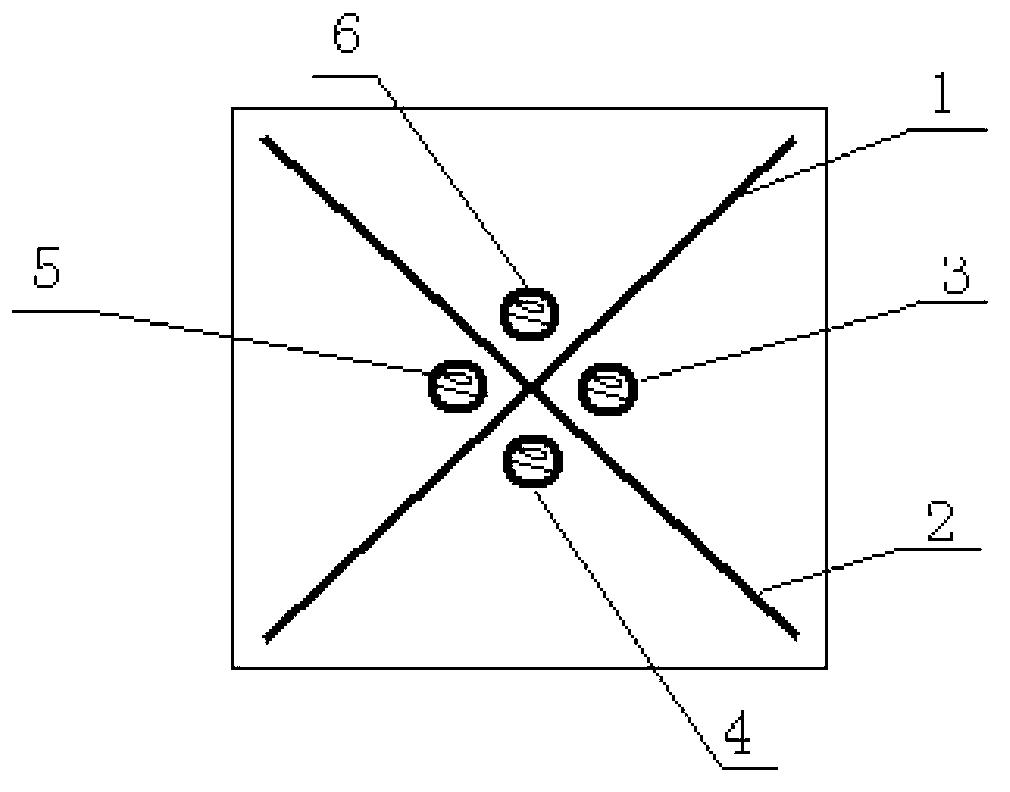
Automatic sun tracking device and control method
InactiveCN103235603AImplement automatic trackingStable jobSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersMotor driveComputer module
The invention discloses an automatic sun tracking device and a control method, mainly solves the problems that a mono-shaft tracking method is large in tracking error although being simple in implementation, and a dual-shaft tracking method is complex in structure and larger in technical difficulty although being high in tracking precision, and provides an automatic tri-freedom-degree sun tracking device under a horizontal coordinate system. The device comprises a tri-freedom-degree moving platform on which a circuit part is mounted. The circuit part is formed by a main control module, a posture measuring module, a time module, a motor driving module, an optical signal detecting module, a data storage module, a communication module, a power supply module and a watchdog circuit. The main control module is used for the work of operation, processing, commanding, coordinating and managing of the whole equipment and is of a core part of the equipment. The automatic sun tracking device and the control method realize the automatic tracking on the sun, and have the advantages of reasonable product structure, stable circuit work, high efficiency, being less influenced by external conditions and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
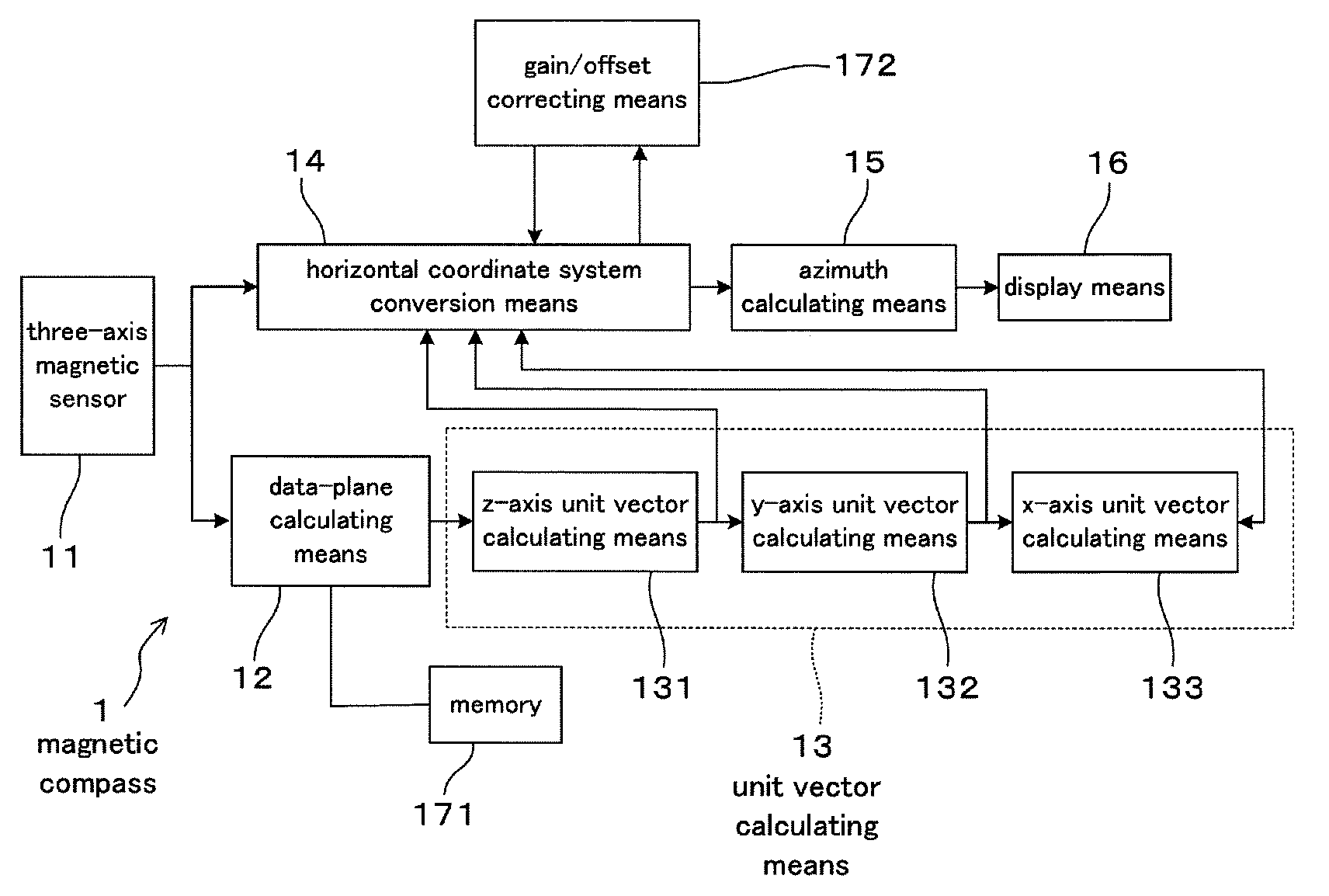
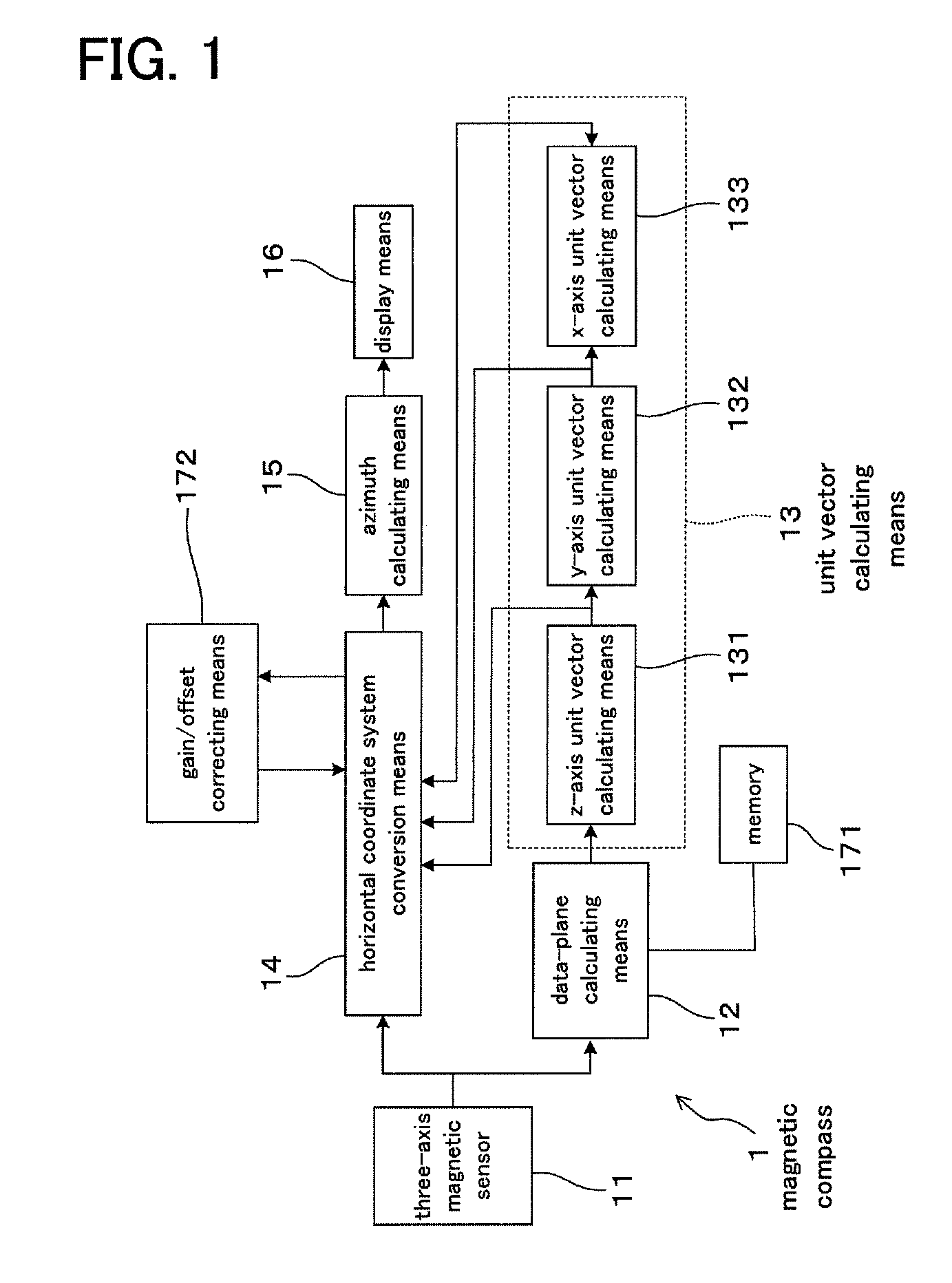
Magnetic compass
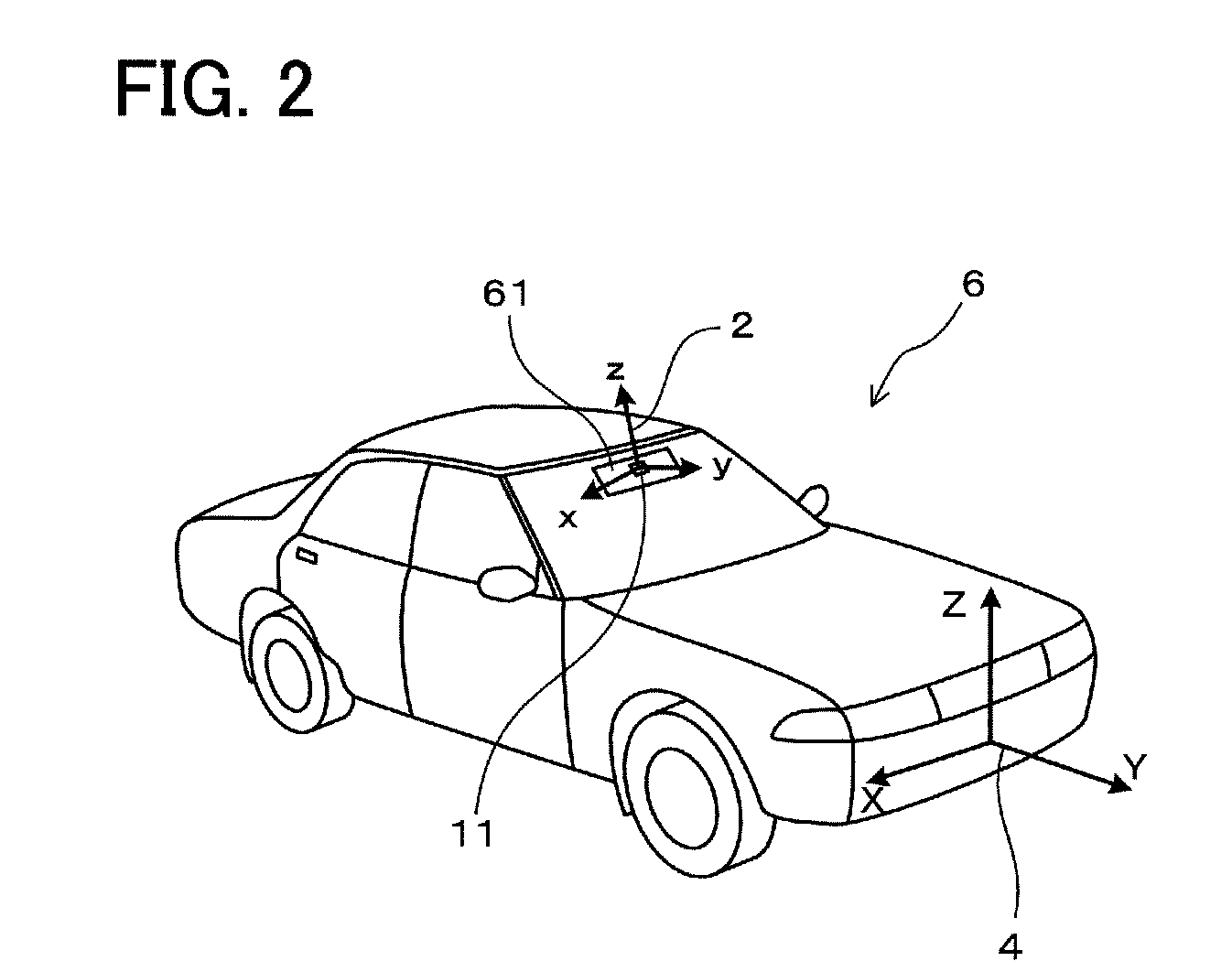
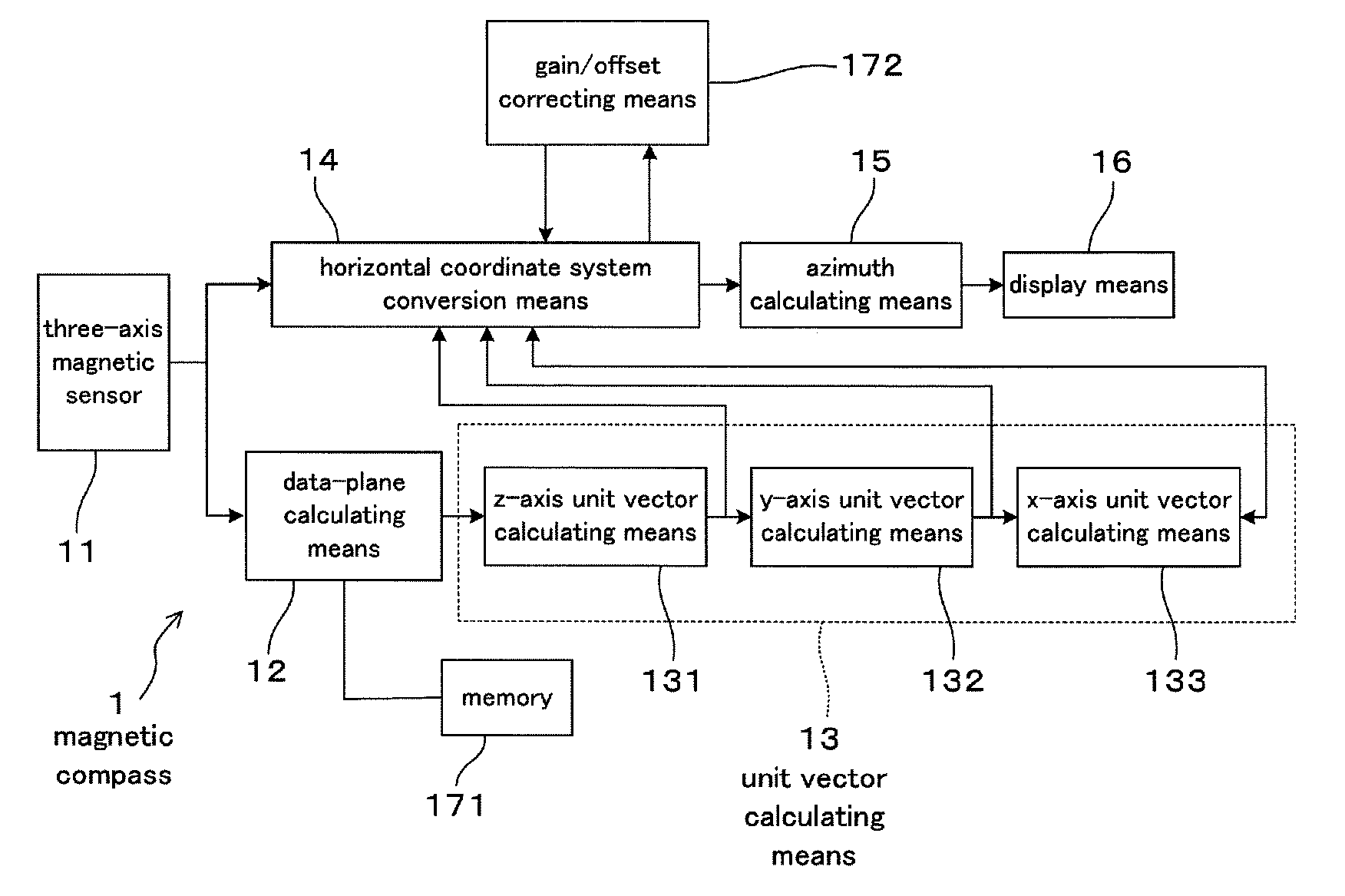
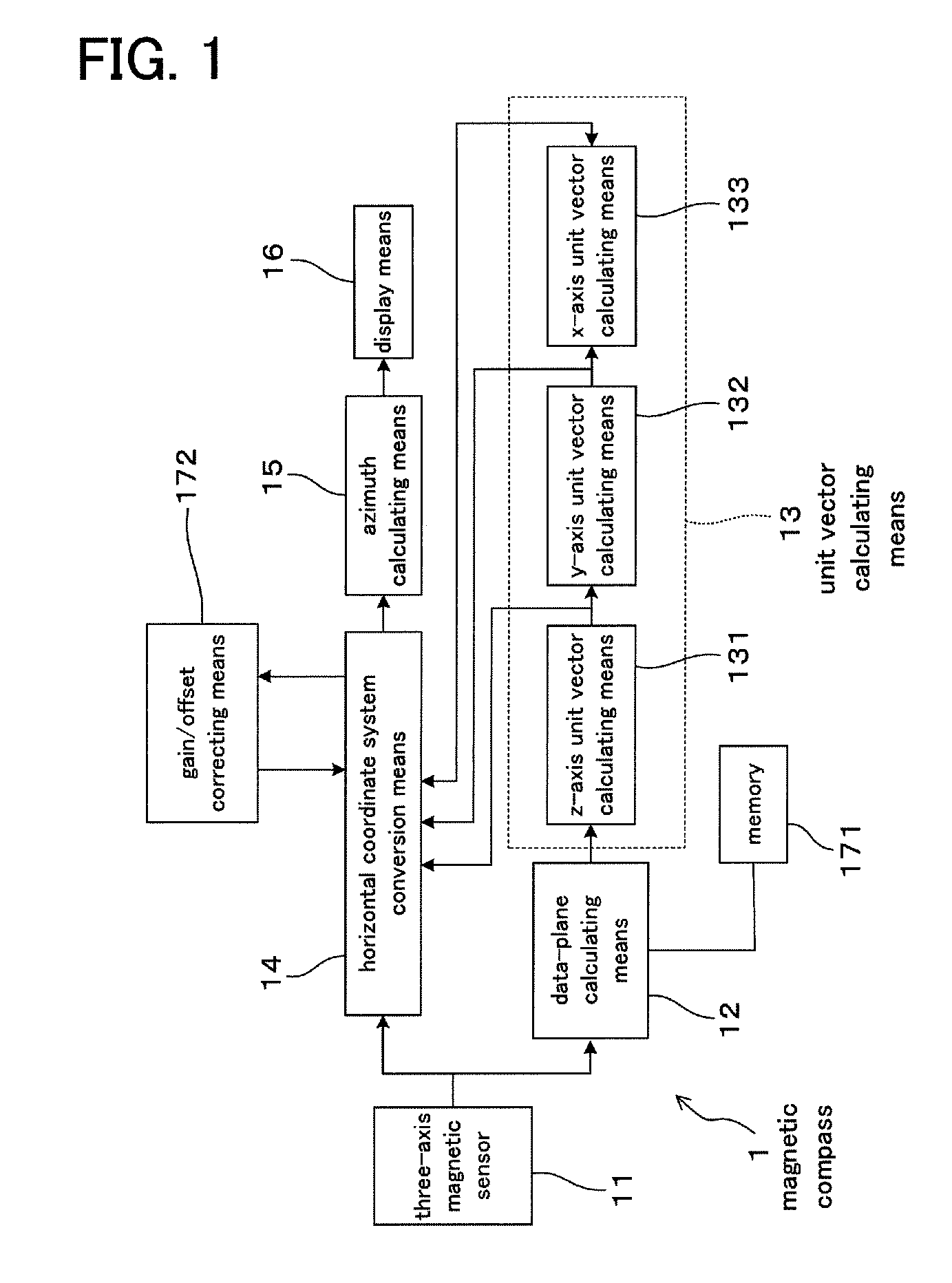
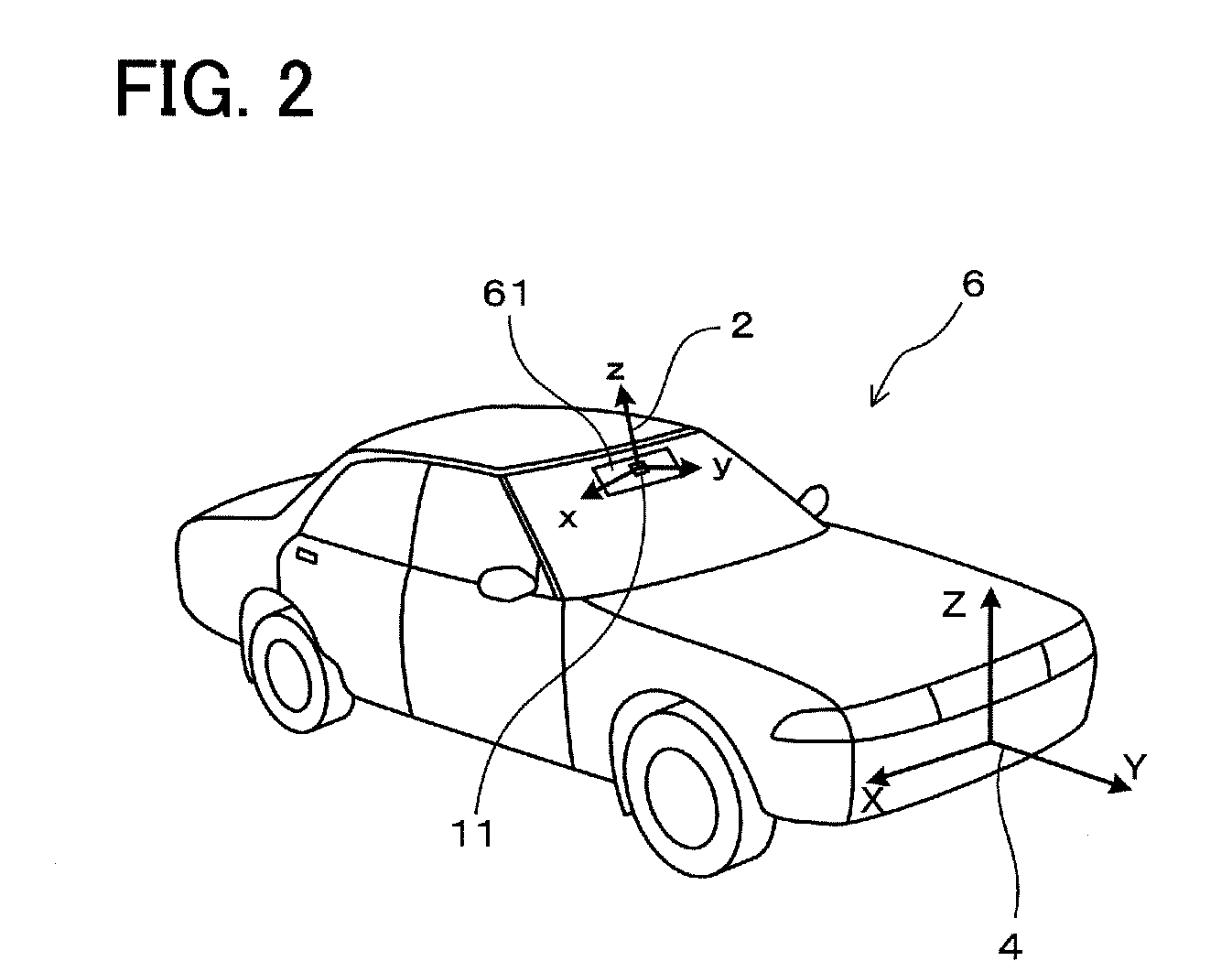
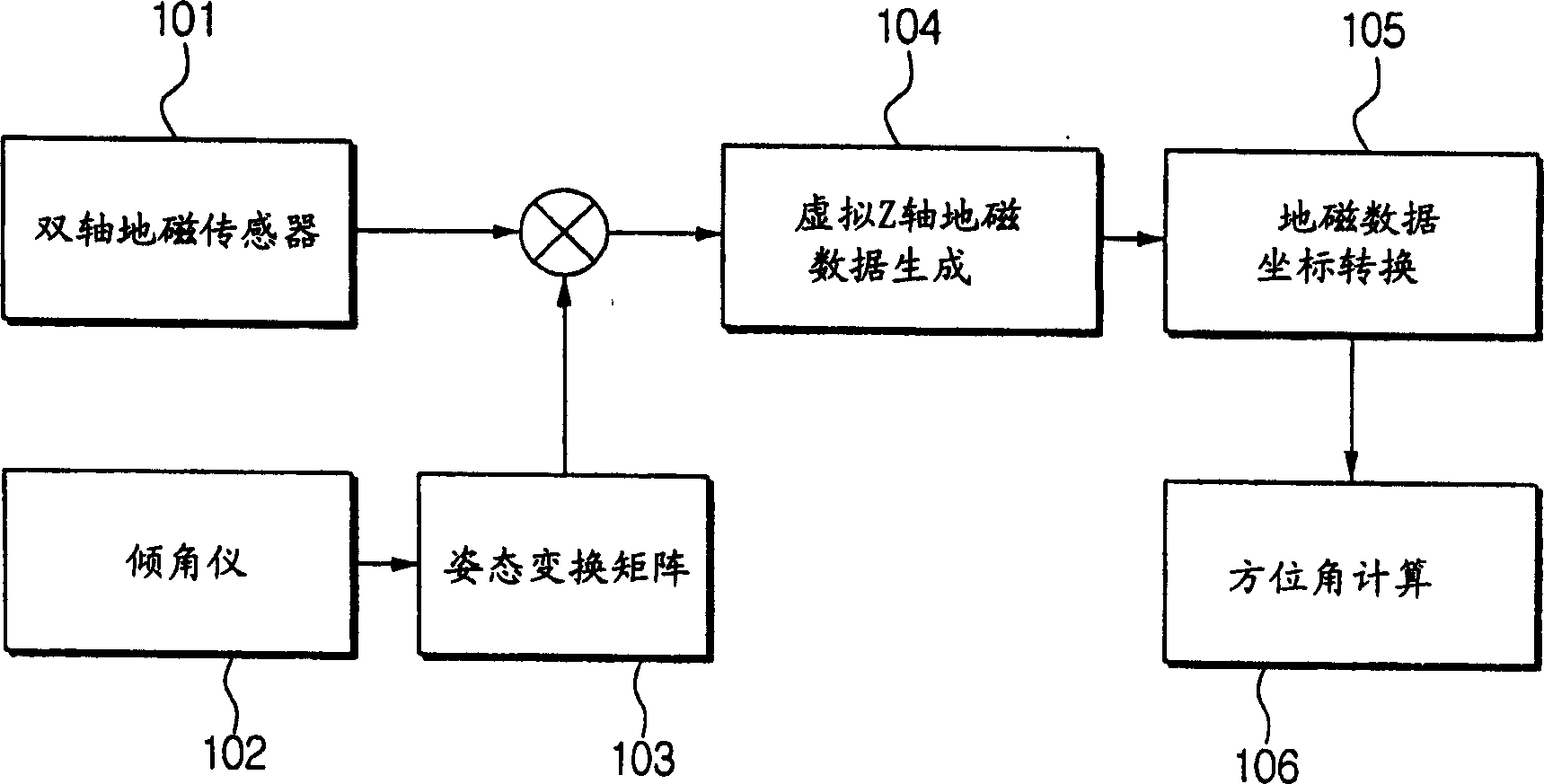
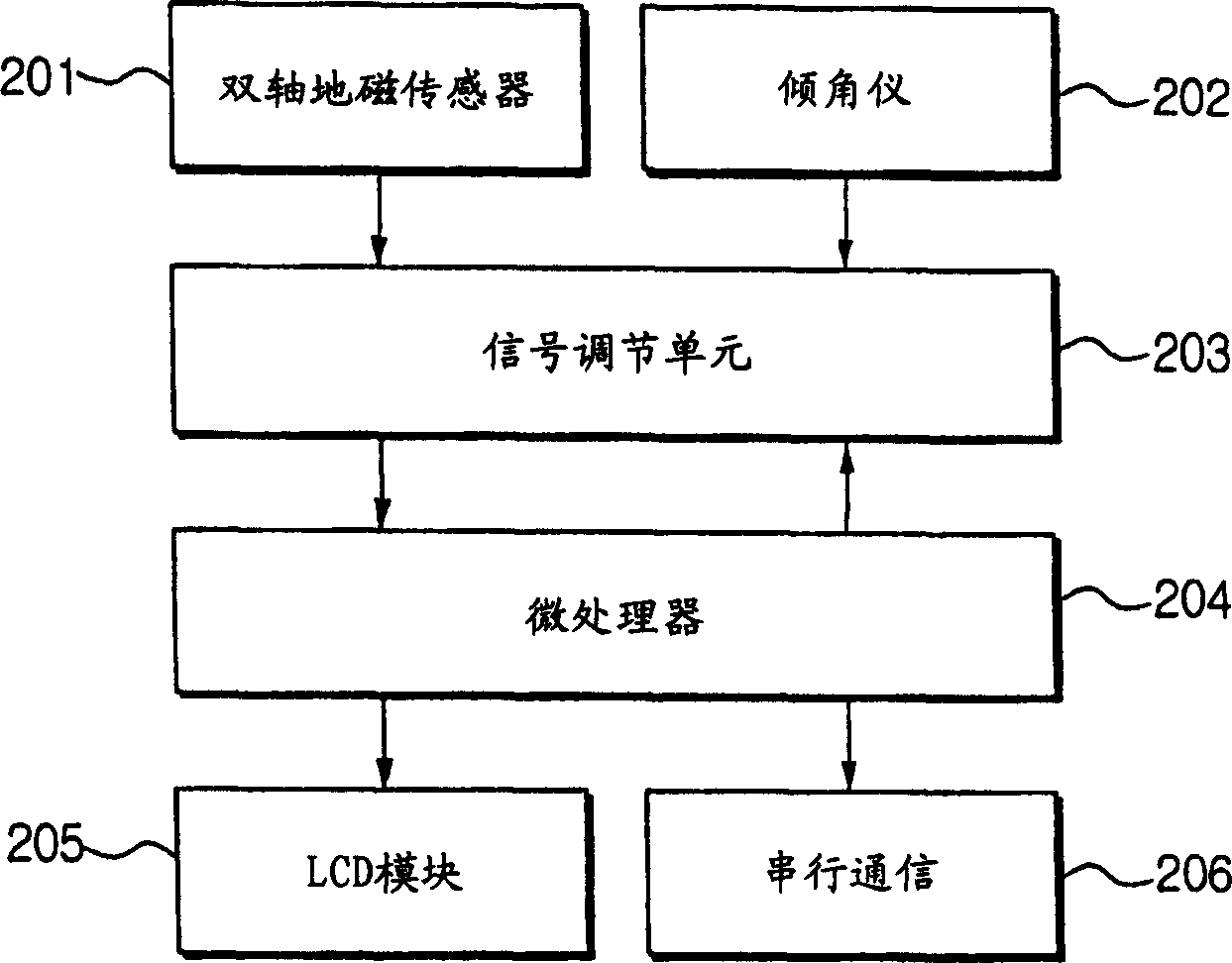
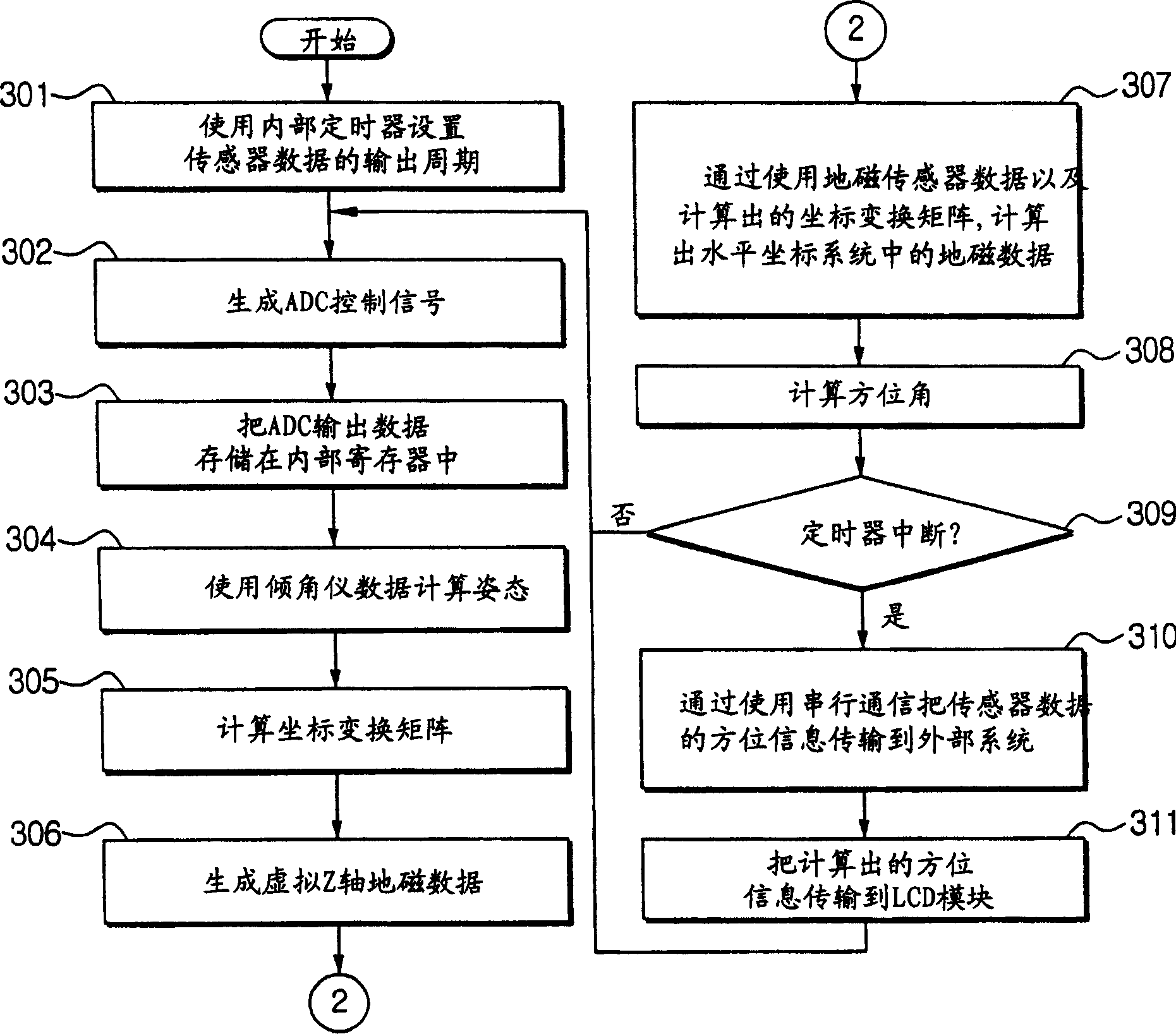
A magnetic compass includes: a three-axis magnetic sensor for detecting geomagnetic vector as geomagnetic components in directions of three orthogonal axes x, y, and z; a data-plane calculating unit for calculating a data plane on which output data of the three-axis magnetic sensor are present in a sensor coordinate system of the three axes x, y, and z; a unit vector calculating unit for calculating unit vectors of a horizontal coordinate system of three orthogonal axes X, Y, and Z whose Z-axis runs vertically and X-Y plane defines a horizontal plane relative to the earth; a horizontal coordinate system conversion unit for converting geomagnetic components in the sensor coordinate system detected by the three-axis magnetic sensor into geomagnetic components in the horizontal coordinate system; an azimuth calculating unit for calculating azimuth based on the converted geomagnetic components in the horizontal coordinate system; and a display unit for displaying the calculated azimuth.
Owner:AICHI MICRO INTELLIGENT
Magnetic compass
InactiveUS20070084070A1Easy and accurate azimuth measurementLow costCompassesClassical mechanicsCompass
A magnetic compass includes: a three-axis magnetic sensor for detecting geomagnetic vector as geomagnetic components in directions of three orthogonal axes x, y, and z; a data-plane calculating unit for calculating a data plane on which output data of the three-axis magnetic sensor are present in a sensor coordinate system of the three axes x, y, and z; a unit vector calculating unit for calculating unit vectors of a horizontal coordinate system of three orthogonal axes X, Y, and Z whose Z-axis runs vertically and X-Y plane defines a horizontal plane relative to the earth; a horizontal coordinate system conversion unit for converting geomagnetic components in the sensor coordinate system detected by the three-axis magnetic sensor into geomagnetic components in the horizontal coordinate system; an azimuth calculating unit for calculating azimuth based on the converted geomagnetic components in the horizontal coordinate system; and a display unit for displaying the calculated azimuth.
Owner:AICHI MICRO INTELLIGENT
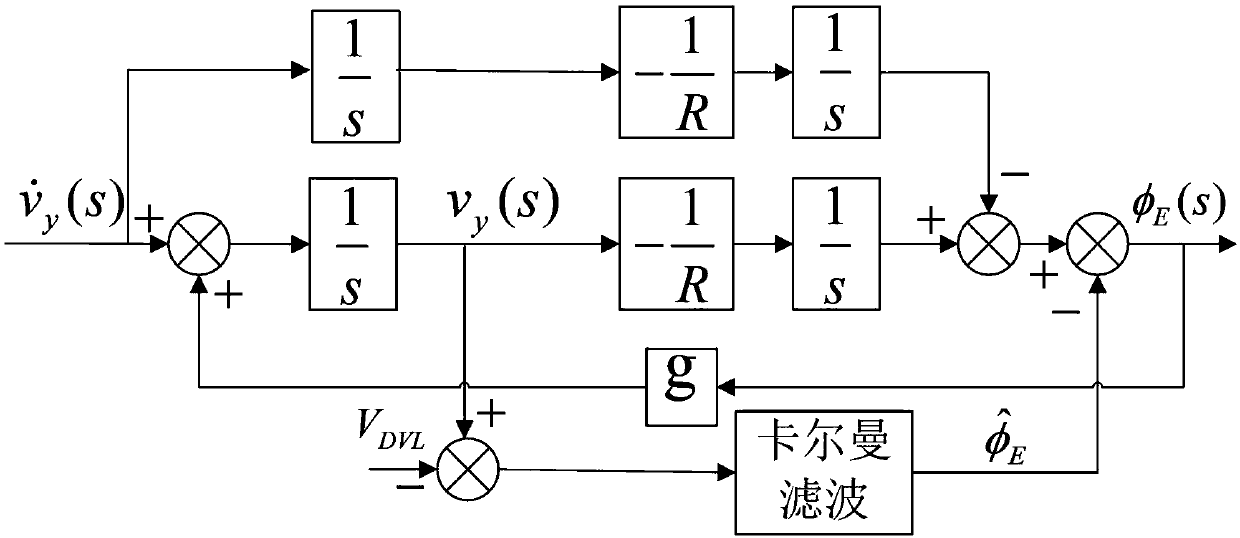
Kalman filtering-based horizontal coordinate system strapdown inertial navigation system damping algorithm
InactiveCN109029454AEliminate Schuler oscillationsAchieving external horizontal dampingNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition errorComputer science
The invention provides a kalman filtering-based horizontal coordinate system strapdown inertial navigation system damping algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of polar region navigation. A kalman filtering error model in the horizontal coordinate system is established, a horizontal attitude error angle is estimated, and the horizontal attitude error angle is continuously corrected by means of feedback correction, so that Schuler oscillation in posture, speed and position errors is inhibited, and outer horizontal damping of the kalman filtering is realized. The reliability of the outerspeed information is judged according to the outer speed validity criterion; and the running state of the current strapdown inertial navigation system is determined according to the judgment result,and when the outer speed information is effective, the system switches from the non-damping state to the damping state; finally, after the kalman filtering is stable, the estimated horizontal attitudeerror angle is continuously fed back and corrected, so that that Schuler oscillation in posture, speed and position errors is inhibited, and outer horizontal damping of the polar region kalman filtering is realized. According to the algorithm, the outer horizontal damping of the polar region can be realized, and the overshoot error generated in the damping switching process also can be inhibited.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Apparatus and method of compensating for the attitude change of an earth magnetic sensor
InactiveCN1501050ASolve the real problemNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by terrestrial meansDual axisInclinometer
Owner:朴赞国 +1
Initial alignment method of strap-down inertial navigation system based on low-precision micro electro mechanical system
ActiveCN103217174ANavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsInertial navigation systemHorizontal coordinate system
The invention relates to an initial alignment method of a strap-down inertial navigation system and particularly relates to the initial alignment method of the strap-down inertial navigation system based on a low-precision micro electro mechanical system (MEMS) under the condition of only utilizing GPS (Global Position System) auxiliary equipment. The initial alignment method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a direction cosine matrix from a carrier coordinate system to a horizontal coordinate system; establishing a coarse alignment Kalman filtering state equation of the strap-down inertial navigation system of the low-precision micro electro mechanical system; establishing a Kalman filtering measurement equation of coarse alignment of the strap-down inertial navigation system of the low-precision micro electro mechanical system; carrying out first-time correction on a carrier posture; establishing a Kalman filtering state equation and a measurement equation of fine alignment of the strap-down inertial navigation system; carrying out second-time Kalman filtering; and carrying out second-time correction on the carrier posture to obtain an accurate strap-down matrix of the strap-down inertial navigation system of the micro electro mechanical system. According to the initial alignment method disclosed by the invention, a method of estimating an error of the strap-down inertial navigation system of the low-precision MEMS by two times of Kalman filtering is utilized to finish the initial alignment of the system, so that the application is convenient.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for autonomous determination of protection levels for GNSS positioning based on navigation residuals and an isotropic confidence ratio
Method for the computation of horizontal and vertical protection levels, HPL VPL, that bound up to a given confidence level 1-α the horizontal and vertical components, respectively, of the position estimation error δ of a least squares-based GNSS navigation solution, wherein the HPL and VPL are computed as follows:HPL=k·∥r∥·aH, VPL=k·∥r∥aV,where:∥r∥ is the Euclidean norm of the least squares estimation residuals vector r;aH is defined as:aH=hEE+hNN2+(hEE-hNN2)2+(hEN+hNE2)2,andaV is defined as: aV=√{square root over (hUU)}, wherehEE, hNN, hEN, hNE, hEU, hUE, hUU, hNU, hUN are the spatial components of the dilution of precision matrix DoP (HT·H)−1 of the least squares estimation expressed in the local horizontal coordinate system of the estimated position:(HT·H)Space-1=[hEEhENhEUhNEhNNhNUhUEhUNhUU],H being the n×m observation matrix of the least squares-based navigation solution;and wherek is an isotropic confidence ratio computed by numerically solving the following expression Eq. 3 which links k with n, m and a, n and m being the number of observations and of estimated parameters, respectively, of the least squares estimation:Γ(n2)·∫z∈ℜm,z2≤k21+k2(1-z2)n-m-22·z=Γ(n-m2)·πm2·(1-α)[Eq.3]where Γ is Euler's Gamma function; and m denotes a standard m-dimensional real vector space.
Owner:GMV AEROSPACE & DEFENCE
Star simulation system based shipborne theodolite calibration method
InactiveCN106500731ASupport day and night observationSmall amount of calculationTheodolitesTheodoliteTechnological convergence
The invention relates to a GPS (global positioning system) carrier phase difference and bivector attitude determination technique fusion, belongs to the field of navigation, and provides a star simulation system based shipborne theodolite calibration method. The method includes the following steps: firstly, performing project construction by utilizing an airborne optical cooperative target to simulate the spatial direction of a star calibration shipborne theodolite; secondly, performing GPS baseline correction including airborne and shipborne terminal correction; thirdly, performing bivector attitude determination, utilizing relative coordinate data of two ends of a corrected GPS baseline to compute spatial direction of the theodolite under the horizontal coordinate system. Influences brought by self-axis parameter error of the theodolite, inertial navigation equipment attitude error and unknown deformation conduction can be isolated, and angle measurement accuracy of the shipborne theodolite is improved highly.
Owner:UNIT 63680 OF PLA
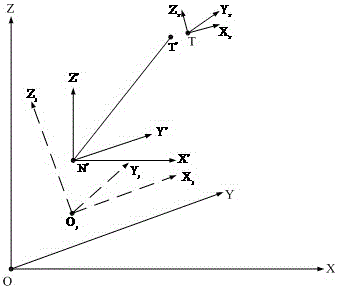
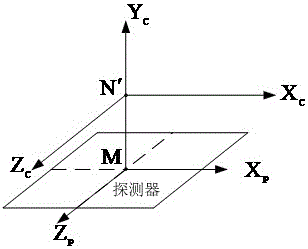
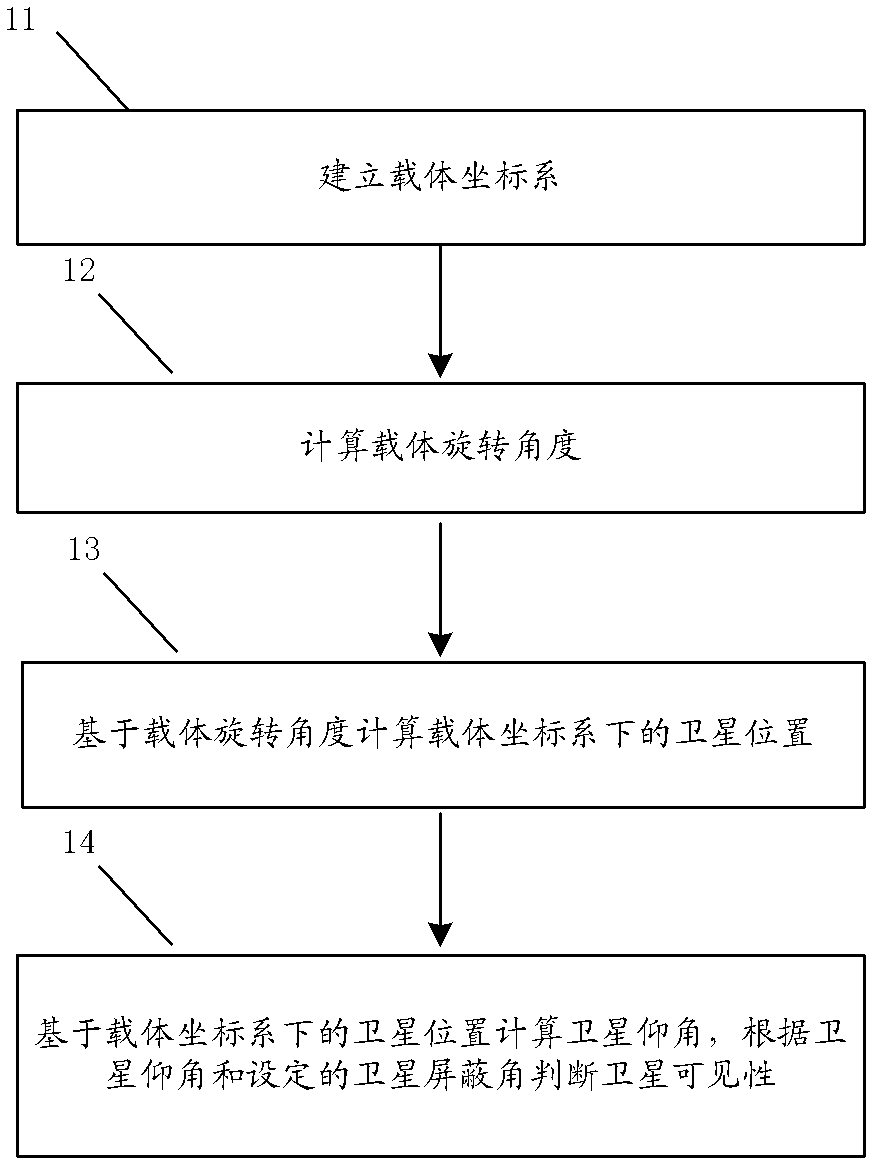
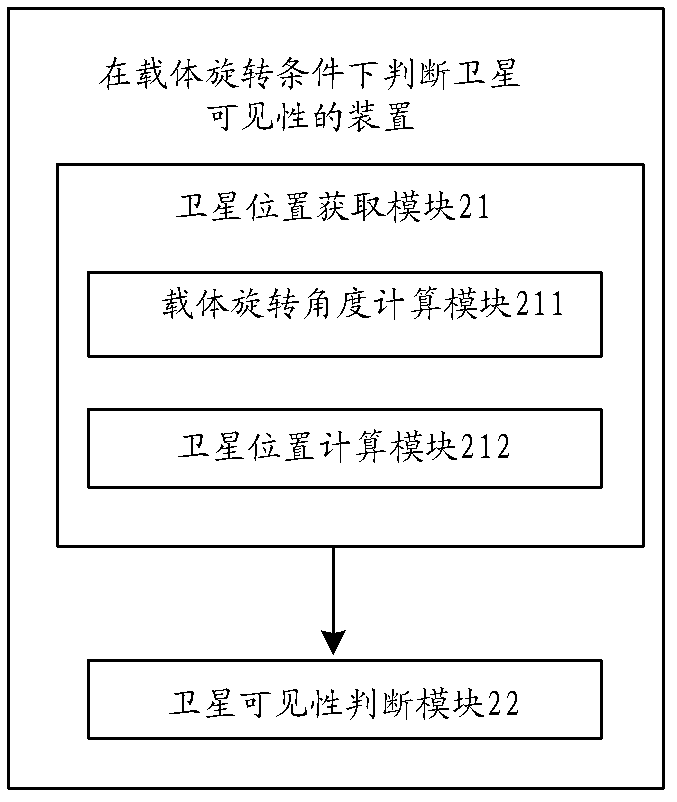
Method and device for judging satellite visibility under carrier rotating condition
The invention relates to a method and a device for judging satellite visibility under carrier rotating condition. The method mainly includes: building a carrier coordinate system, calculating carrier rotating angles, and calculating satellite positions in the carrier coordinate system according to the carrier rotating angles; and calculating satellite elevation angles according to the satellite positions in the carrier coordinate system, comparing the satellite elevation angles and satellite screening angles, and judging satellite visibility according to comparison results. In an embodiment of the method and the device, the carrier coordinate system is built, positions of satellites in a horizontal coordinate system are shifted into the carrier coordinate system and the satellite elevation angles are calculated, and accordingly the satellite visibility can be effectively judged according to the satellite elevation angles under carrier rotating condition.
Owner:华力智芯(成都)集成电路有限公司
Combined navigation posture measurement method based on polarized light and geomagnetism
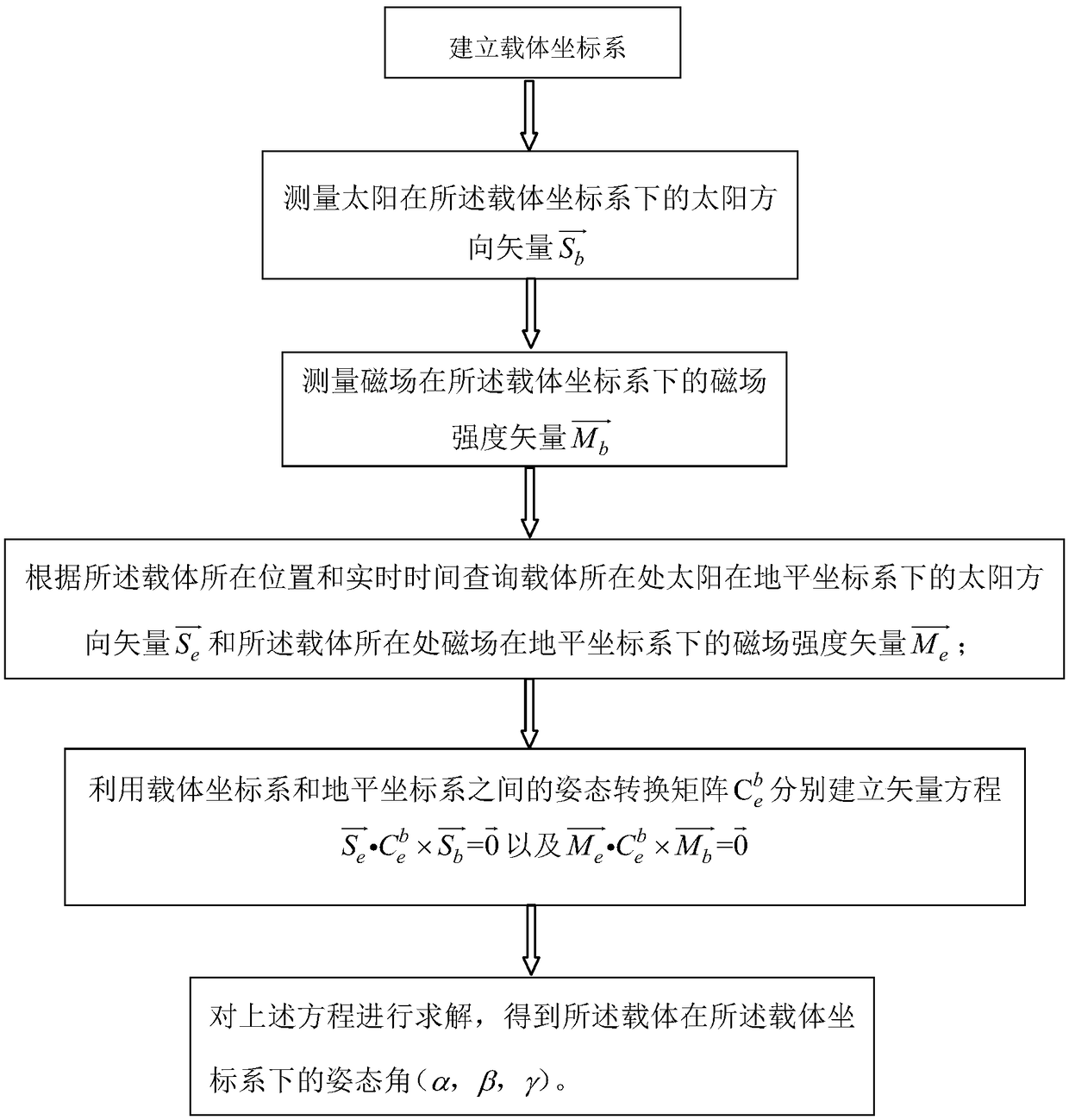
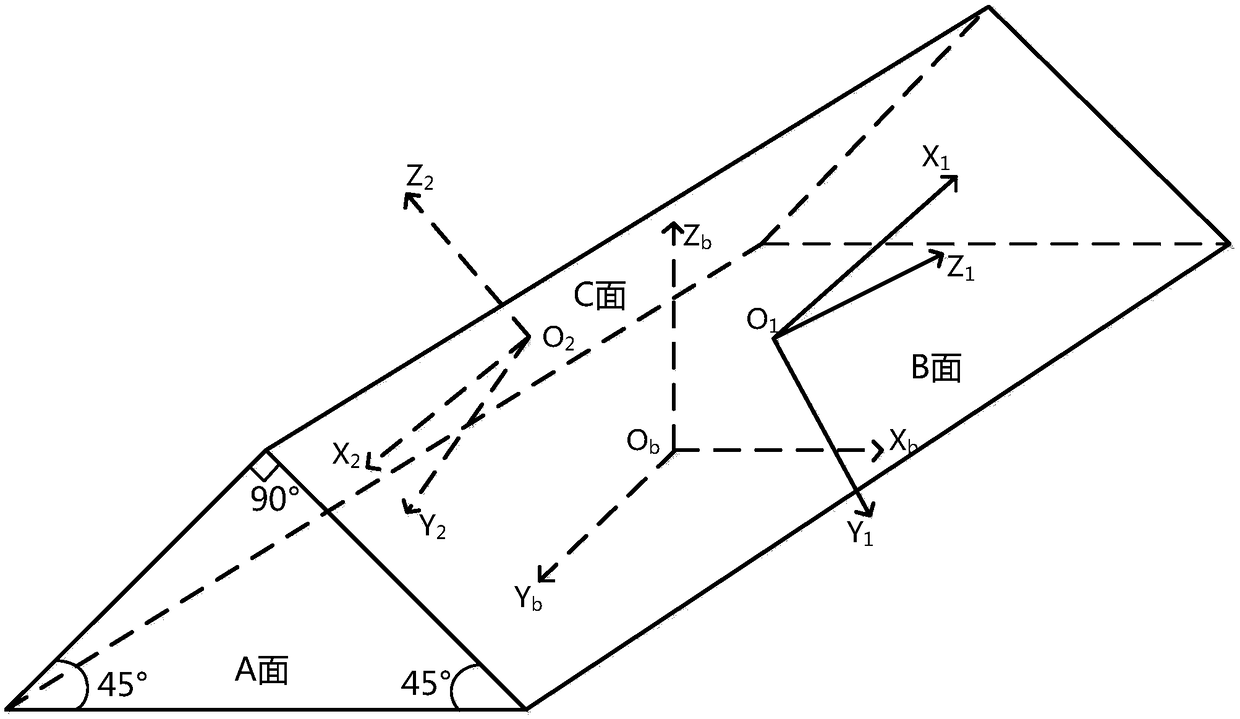
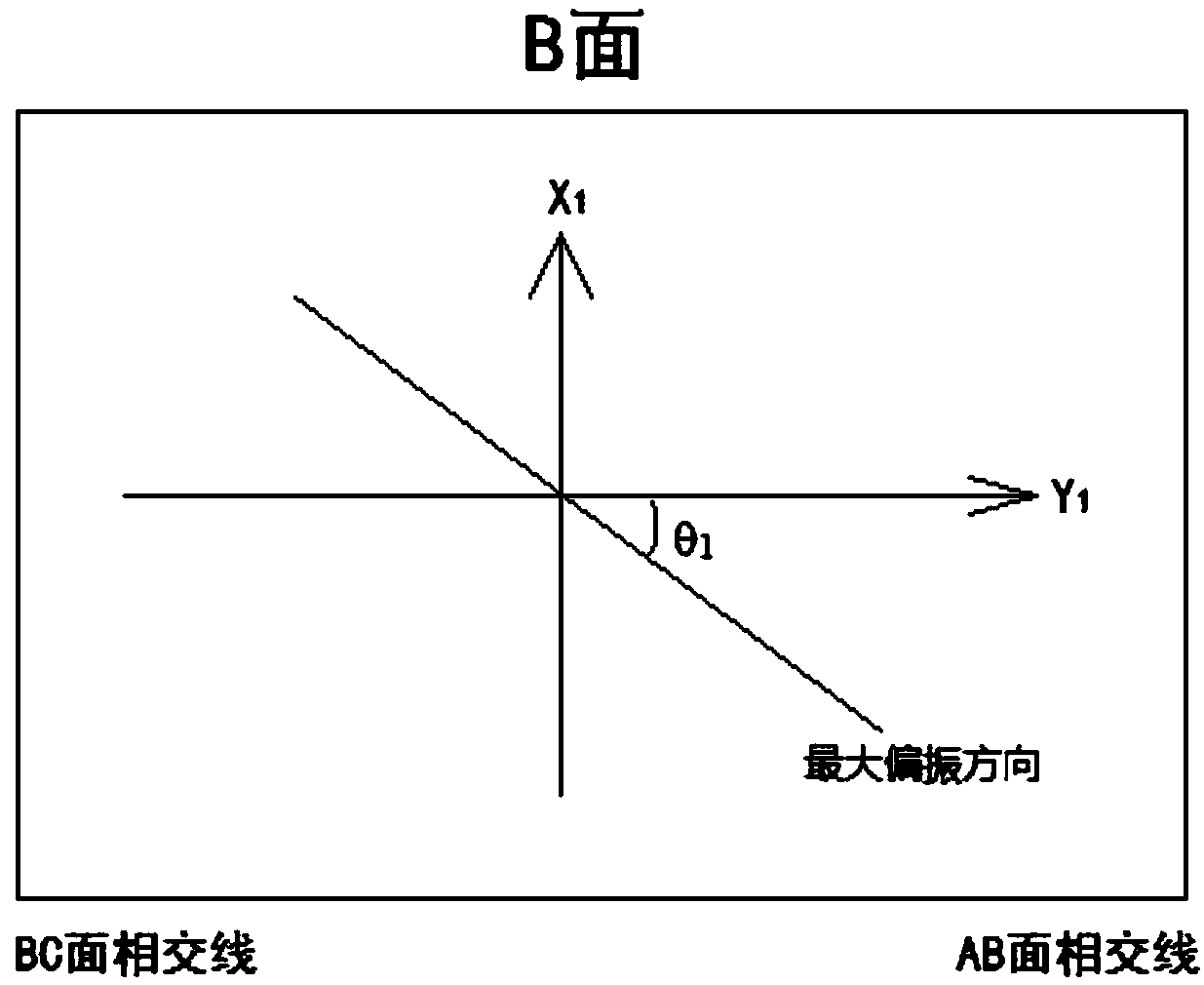
The invention discloses a combined navigation posture measurement method based on polarized light and geomagnetism. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a carrier coordinate system ObXbYbZb; S2, measuring a sun direction vector as shown in description of the sun under the carrier coordinate system; S3, measuring the magnetic field strength vector as shown in description of the magnetic field under the carrier coordinate system; S4, querying the sun direction vector as shown in description of the sun under the horizontal coordinate system of the carrier location and the magnetic field strength vector as shown in description of the carrier under the horizontal coordinate system of the carrier location; S5, respectively establishing a vector equation as shown in description by utilizing the posture conversion matrix between the carrier coordinate system and the horizontal coordinate system; and S6, solving the equation in the step S5 to obtain attitude angles alpha,beta and gamma. The invention provides a method for combining the geomagnetism measurement with the polarized light measurement technology, the complete attitude information can be provided, and the method has the feature of not accumulating and diverging along the time.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
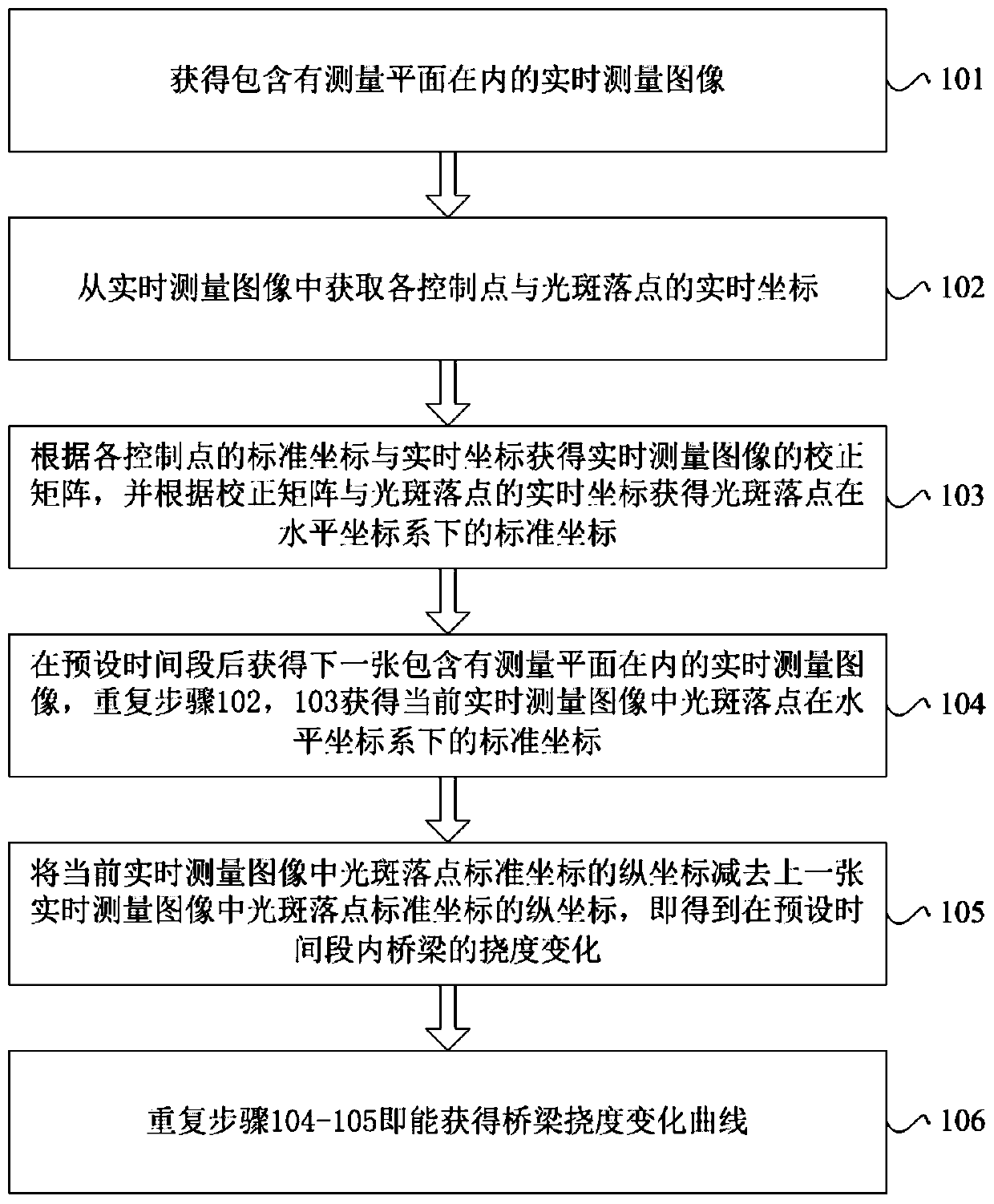
Bridge deflection change measuring method, device and equipment
ActiveCN110285770AFlexible measurement of deflection changesAvoid environmental problemsUsing optical meansElasticity measurementVertical planeImaging processing
The invention discloses a bridge deflection change measuring method, device and equipment. A vertical plane is selected or arranged at any position of the bridge as a measuring plane; at least four positioning pieces containing control point images are arranged in the measuring plane; the control point images in all control pieces are not collinear at the same time; the method includes the steps of measuring the standard coordinates of the control points in the control point images in the positioning pieces under a horizontal coordinate system, placing a laser at any position, enabling laser spots emitted by the laser to fall into the measuring plane, placing a camera at any position, and enabling the measuring plane to be located in a shooting view field of the camera. A mode of combining laser indication with camera short-distance imaging is adopted, so that the problems that long-distance imaging is influenced by the atmospheric environment and measurement precision is influenced by postures of the camera can be avoided; through control point imaging processing, the influence of camera shaking on the measurement can be eliminated, and deflection measurement can be flexibly carried out on bridges on the water surface, canyons and other positions. The method is applied to the technical field of measurement.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
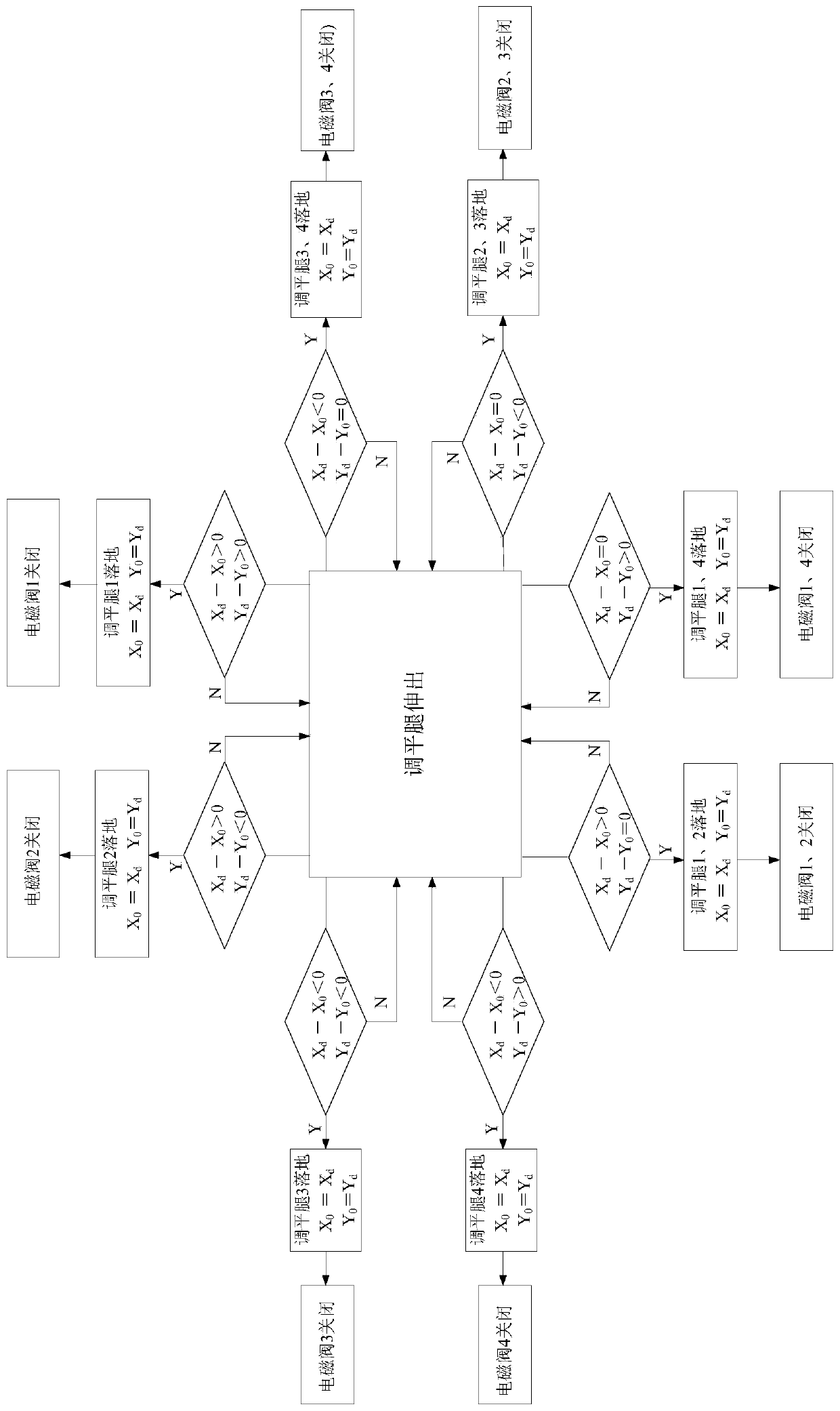
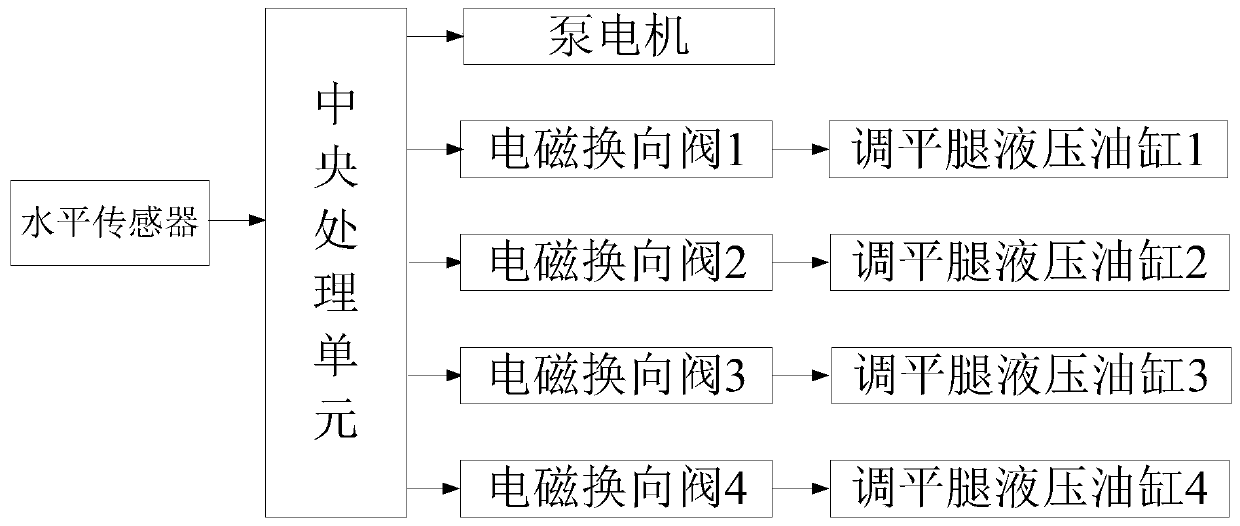
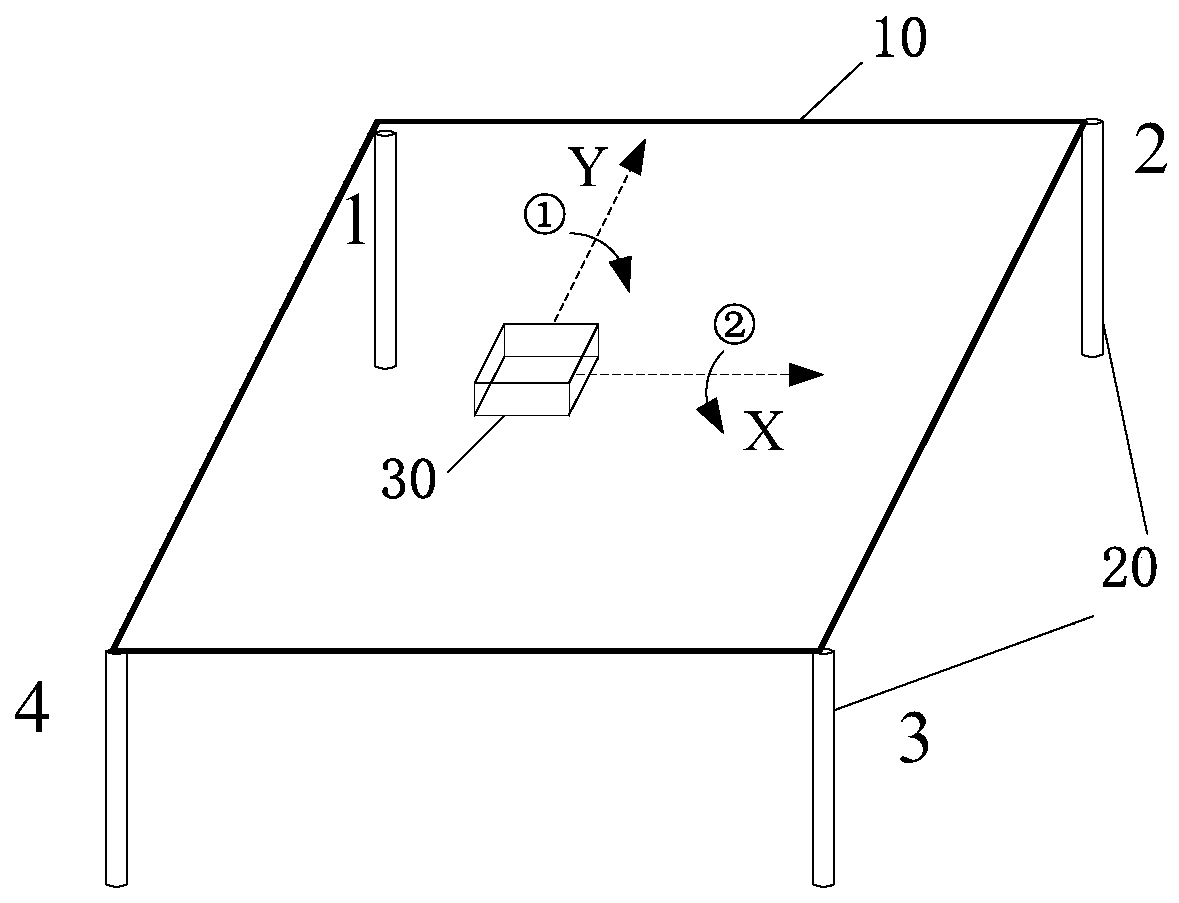
Leveling leg landing detection method
ActiveCN110985465ARealization of landing detectionNovel methodServomotor componentsServomotorsControl theoryMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a leveling leg landing detection method. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a two-dimensional horizontal coordinate system XOY by taking a platform supported by a plurality of points as a horizontal plane, and installing a horizontal sensor at an original point O of a coordinate system; assuming that X0 and Y0 represent an initial X-direction horizontal angle value and a Y-direction horizontal angle value of the horizontal sensor, and Xd and Yd represent a real-time X-direction horizontal angle value and a Y-direction horizontal angle value of thehorizontal sensor; and when one or more leveling legs extend out, determining whether the leveling leg falls to the ground and plays a supporting role by judging the angle values of Xd-X0 and Yd-Y0 of the leveling leg and a size of a change characteristic threshold value till that all the leveling legs are detected to fall to the ground. In the landing detection method, hydraulic detection is notneeded, a sliding block limiting structure does not need to be additionally arranged, landing detection of the leveling leg can be achieved through software control, and the method is novel, simple,reliable, free of influences of factors such as an external environment and the like, and high in detection precision.
Owner:ANHUI BOWEI CHANGAN ELECTRONICS
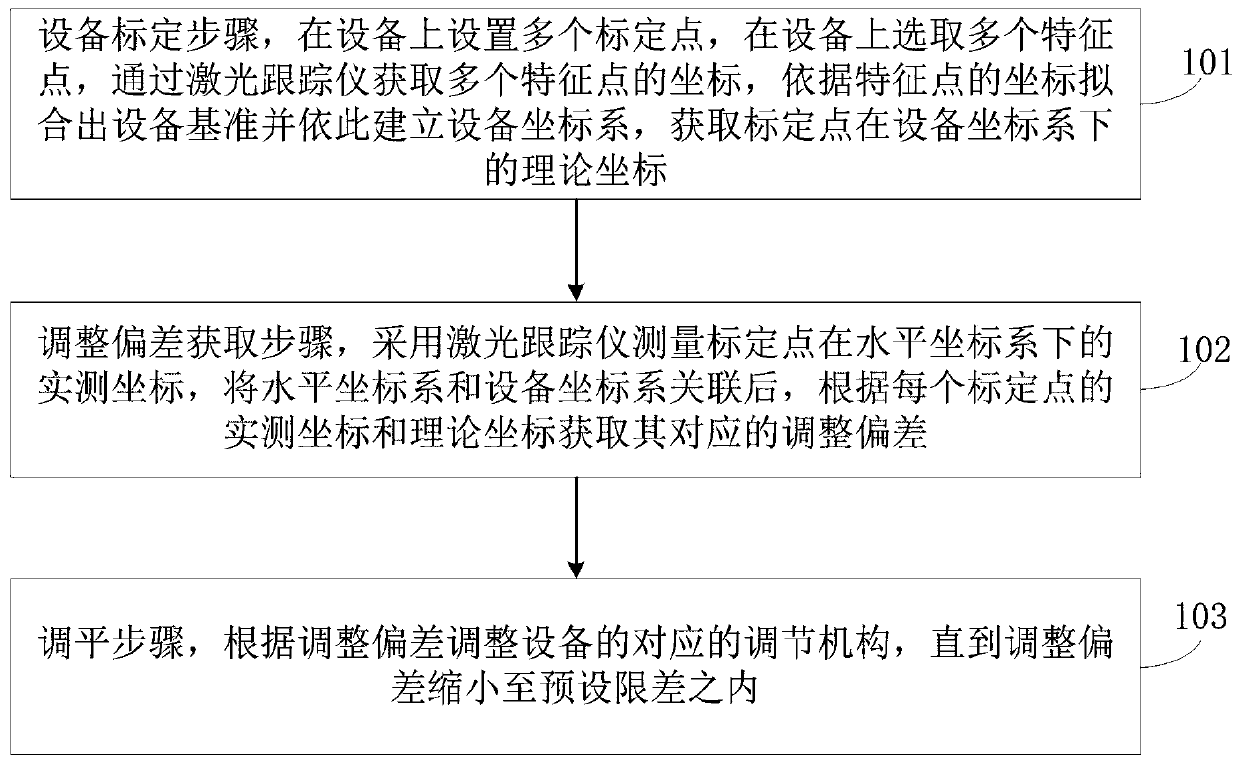
Equipment reference rapid leveling method
The invention relates to the technical field of measuring equipment, in particular to an equipment reference rapid leveling method. The method comprises the steps: calibrating equipment, and setting aplurality of calibration points on the equipment; selecting a plurality of feature points on the equipment, and acquiring coordinates of a plurality of feature points through a laser tracker; fittingan equipment reference according to the coordinates of the feature points and establishing an equipment coordinate system according to the equipment reference; after the theoretical coordinates of the calibration point under the equipment coordinate system and the actually measured coordinates of the calibration point under the horizontal coordinate system are obtained, acquiring the adjustment deviation of the calibration point after coordinate conversion, and guiding the adjustment equipment to be leveled according to the adjustment deviation, so the leveling method is intuitive and effective, and the equipment can be leveled quickly.
Owner:CHINA SPALLATION NEUTRON SOURCE SCI CENT +1
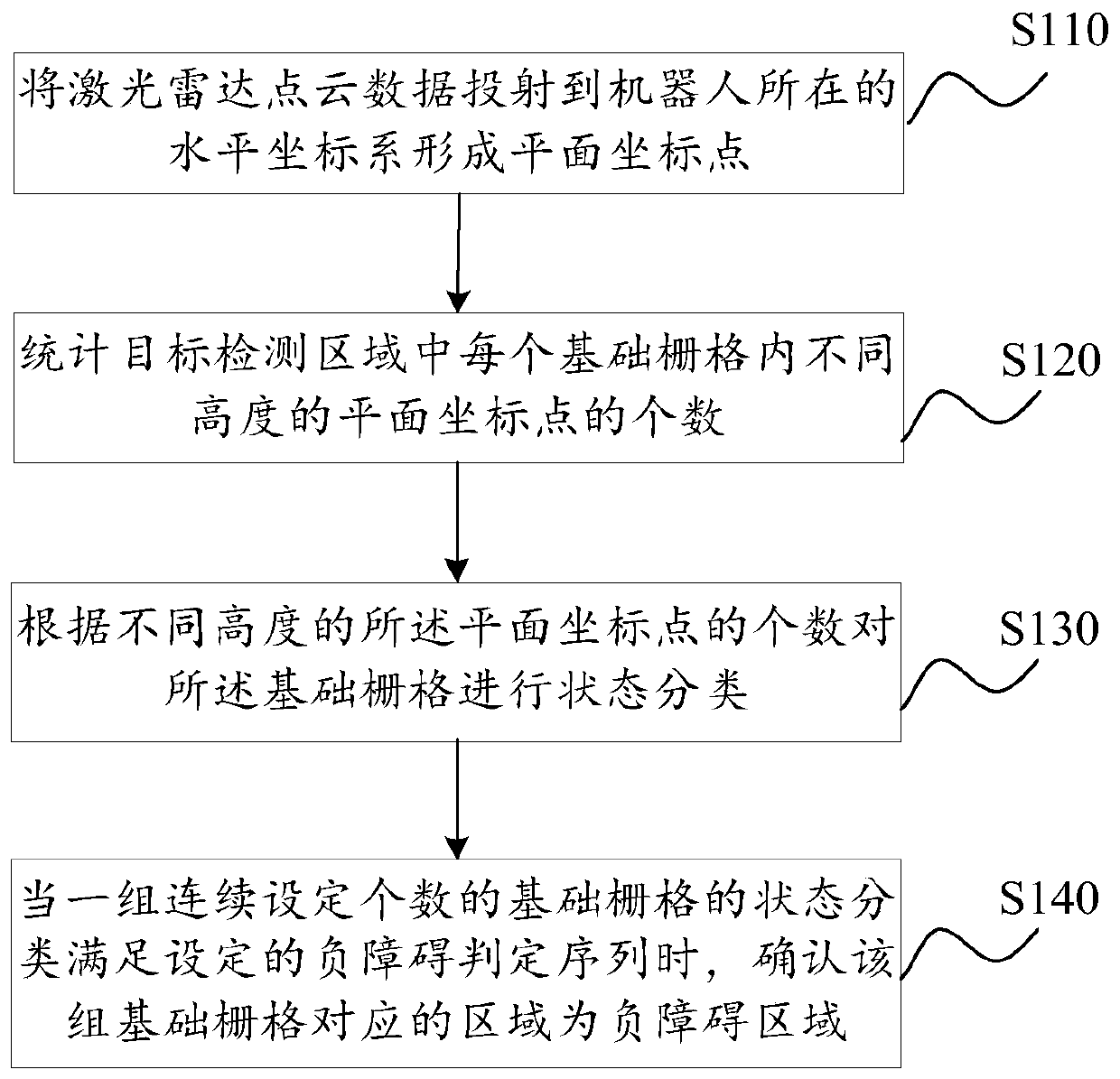
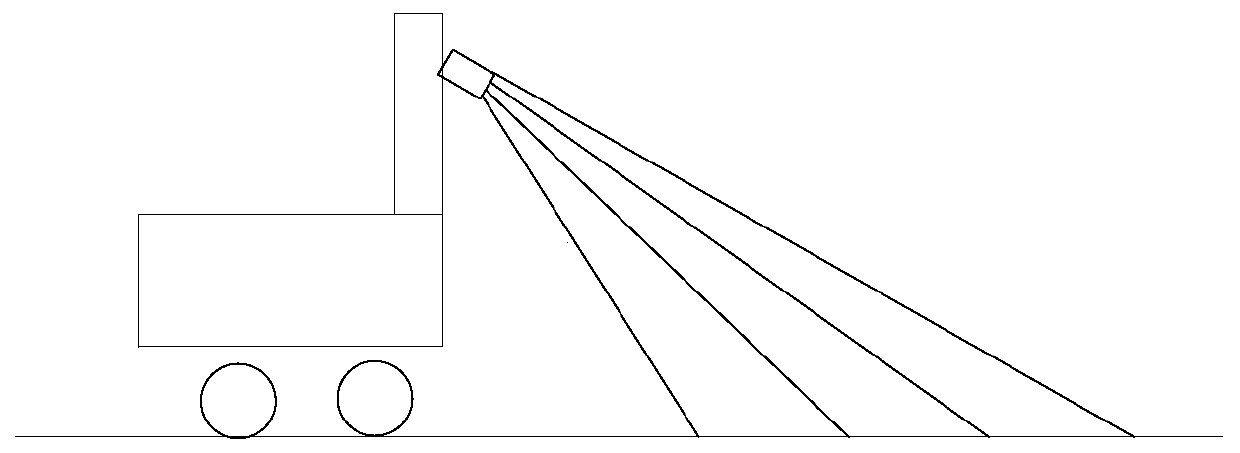
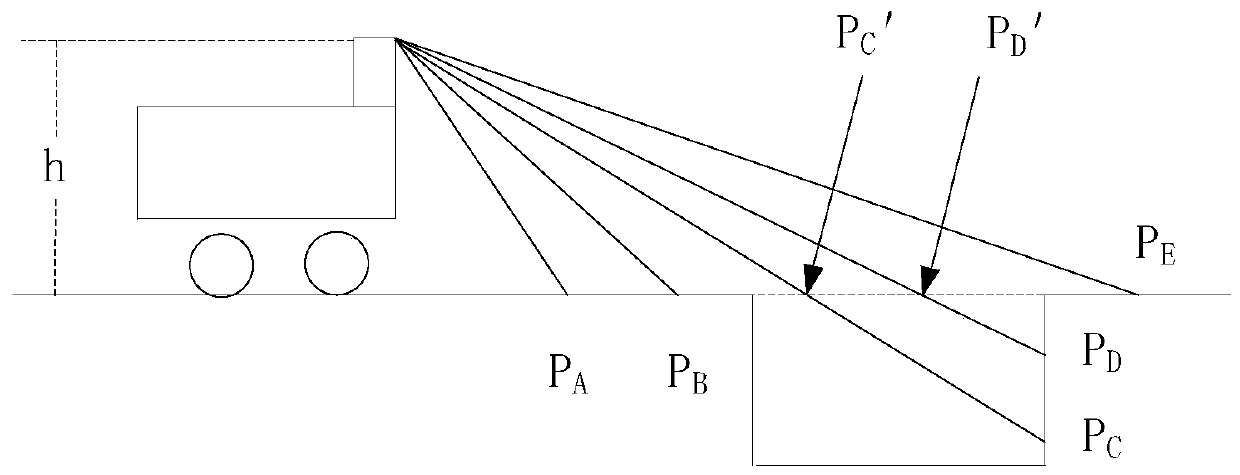
Negative obstacle detection method and device, terminal equipment and storage medium
PendingCN111429520AAvoid dealing with issues with lower precisionReduce processingImage enhancementImage analysisTerminal equipmentLidar point cloud
The embodiment of the invention discloses a negative obstacle detection method and device, terminal equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of projecting laser radar point clouddata to a horizontal coordinate system where a robot is located to form plane coordinate points; counting the number of plane coordinate points with different heights in each basic grid in a target detection area, the target detection area being located in the horizontal coordinate system, and a grid formed by the basic grids covering the target detection area; performing state classification onthe basic grids according to the number of the plane coordinate points with different heights; and when the state classification of a group of continuously set number of basic grids meets a set negative obstacle judgment sequence, determining that an area corresponding to the group of basic grids is a negative obstacle area. According to the method for segmenting the negative obstacle from the original point cloud by fusing multiple frames of data, the problem of low processing precision of single-frame data can be avoided, the negative obstacle is detected through arrangement characteristics,and computing resources can be effectively saved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHIYUAN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ground detection method for IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) collimation axis errors of area array camera
The invention discloses a ground detection method for IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) collimation axis errors of an area array camera. The ground detection method for the IMU collimation axis errors of the area array camera, disclosed by the invention, comprises the following steps: generating a parallel-light light beam; imaging in a direction vertical to the parallel-light light beam by adoptingthe area array camera to obtain a picpointed coordinate of the parallel-light light beam in an image space coordinate system plane; converting a direction vector of the parallel-light light beam in an image space coordinate system to a direction vector under a local horizontal coordinate system, and solving a pitch angle and a roll angle of the image space coordinate system relative to a navigation coordinate system; acquiring an azimuth angle of the image space coordinate system; acquiring an IMU collimation axis error angle. The ground detection method for the IMU collimation axis errors ofthe area array camera, provided by the invention, has the advantages of low cost, simplicity in operation and easiness for implementation.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
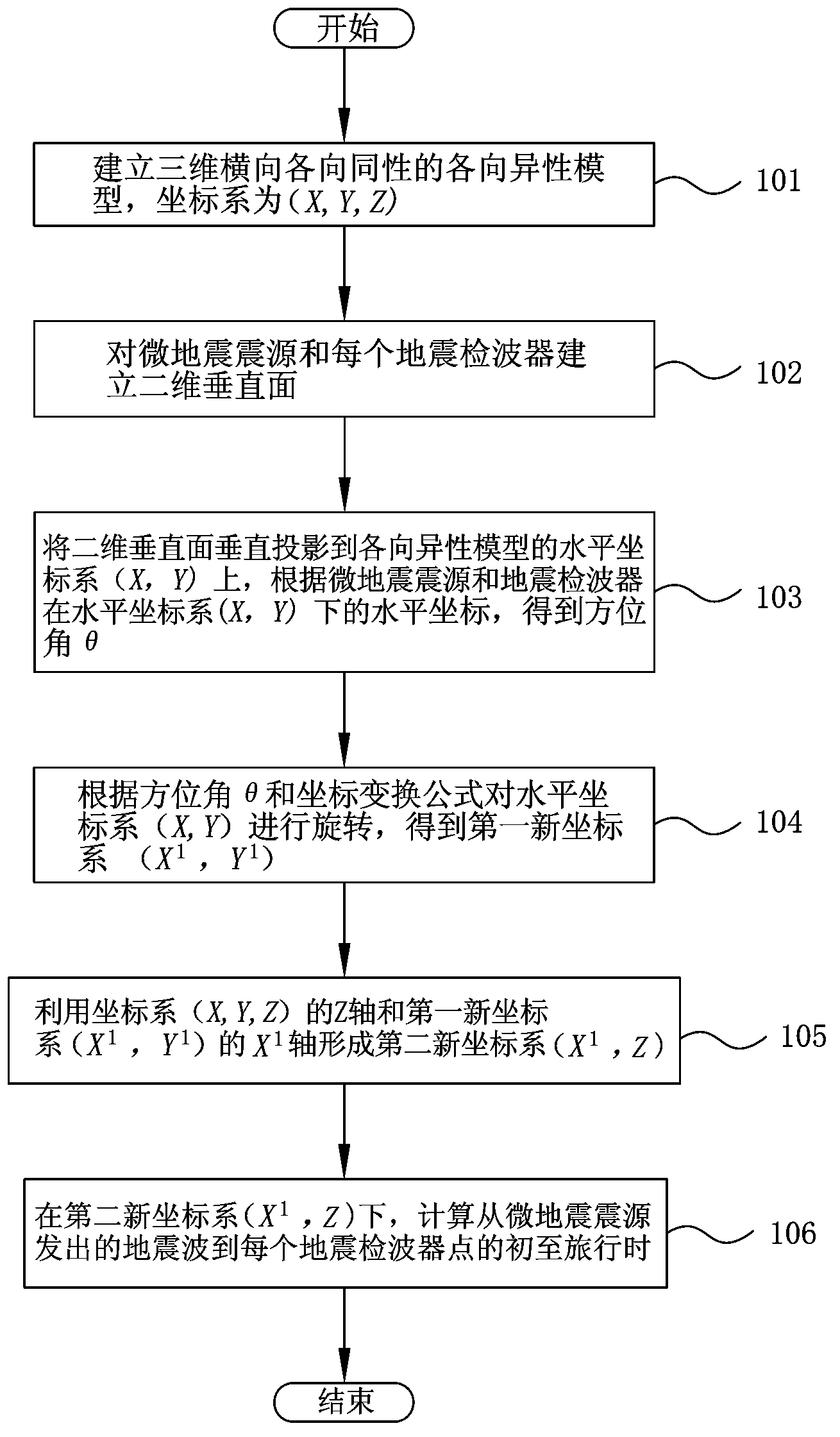
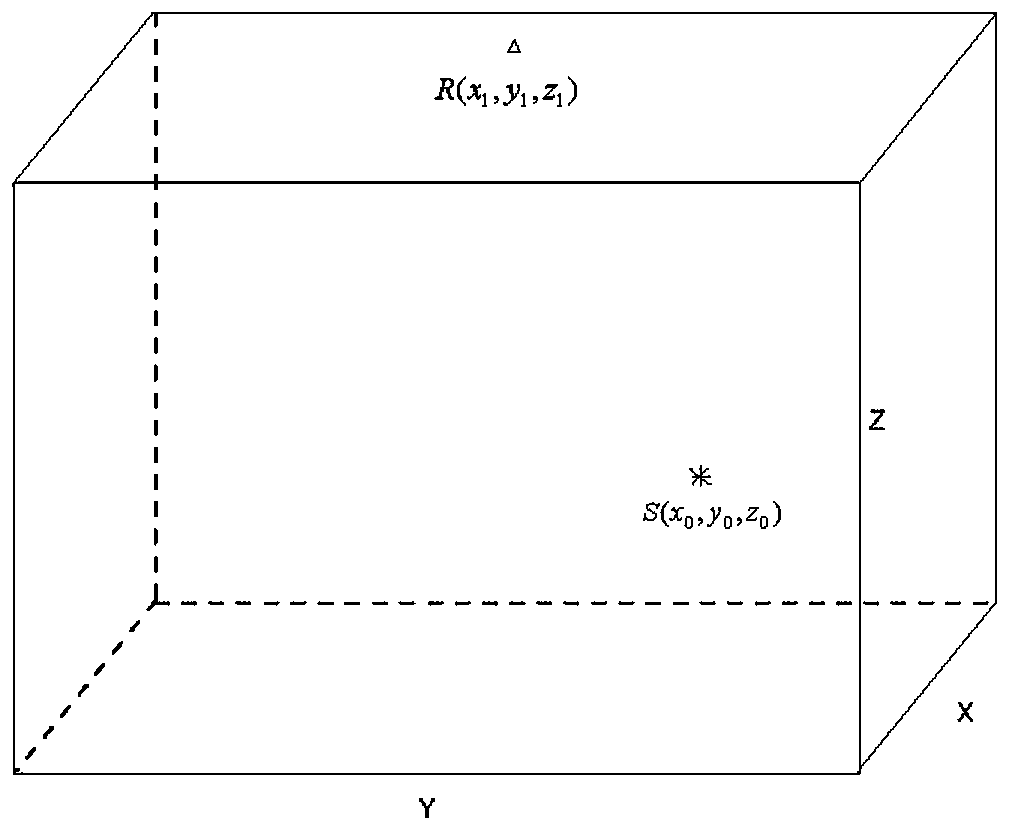
Pseudo three-dimensional fast microseism forward modeling method based on scanning surface forward modeling
A pseudo three-dimensional fast microseism forward modeling method based on scanning surface forward modeling includes that a three-dimensional (3D) horizontal isotropic anisotropic model is set up and provided with a coordinate system (X, Y, Z), a microseism origin is disposed inside the anisotropic model, and a plurality of seismic geophones are arranged on the upper surface of the anisotropic model; a two-dimensional (2D) vertical plane is set up for the microseism origin and the seismic geophones so that the microseism origin and the seismic geophones are all arranged on the 2D vertical plane; the 2D vertical plane is vertically projected in a horizontal coordinate system (X, Y) of the anisotropic model, and according to horizontal coordinates of the microseism origin and the seismic geophones in the horizontal coordinate system (X, Y), an azimuth angle theta is obtained; according to the azimuth angle theta and the coordinate transformation formula, the horizontal coordinate system (X, Y) is rotated and then a first new coordinate system X<1> Y<1> is obtained; a Z-axis of the coordinate system (X, Y, Z) and an X<1>-axis of the first new coordinate system X<1> Y<1> are used to form a second new coordinate system (X1, Z); and first arrival travel-times of microseismic waves generated from the microseism origin to every seismic geophone are calculated in the second new coordinate system (X<1>, Z).
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
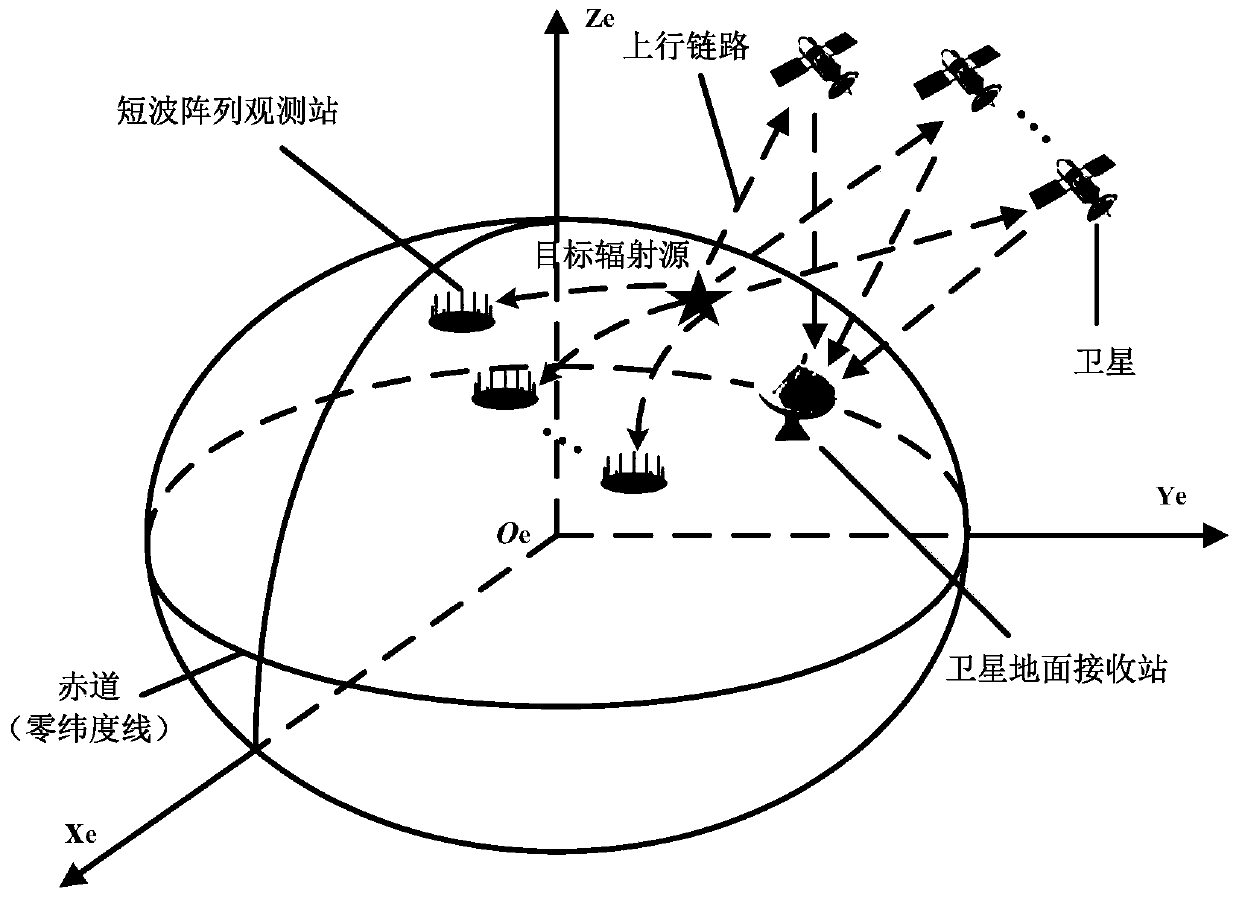
Passive positioning method of employing cooperative short wave and satellite system for over-the-horizon target
ActiveCN110568403AImprove target positioning accuracyRobustPosition fixationAugmented lagrange multiplierHorizon
The invention discloses a passive positioning method of employing cooperative short wave and satellite system for an over-the-horizon target. The method comprises the steps of establishing pseudo-linear observation equations about a plurality of satellite uplink time difference parameters by using an auxiliary variable; establishing a mathematic relation of various short wave observation station arrival azimuths about horizontal coordinate parameters of a target on various stations on the basis of local horizontal coordinate systems of various short wave observation stations, and establishingpseudo-linear observation equations based on a plurality of short wave observation station azimuth parameters by using conversion of the coordinate parameters of the target in horizontal coordinate systems of various stations and earth-centered earth-fixed coordinate parameters; establishing a global least squares optimization model in a quadratic constraint condition by combining the pseudo-linear observation equations of the plurality of satellite uplink time difference parameters with the pseudo-linear observation equations of the plurality of short wave observation station azimuth parameters and combining earth ellipsoid constraints; and designing an augmented Lagrange multiplier algorithm to achieve accurate positioning of the ground over-the-horizon target. According to the passive positioning method, two positioning mechanisms can be cooperatively utilized effectively, so that the positioning accuracy on the target is significantly improved.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Method and system for autonomously compensating inclined angle of base without leveling
ActiveCN106289165AAvoid adjustment operationsReduce preparation timeIncline measurementComputer scienceResponse ability
The invention relates to a method and a system for autonomously compensating an inclined angle of a base without leveling. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a transmitting coordinate system, and calculating coordinates of an object under the transmitting coordinate system; establishing a horizontal coordinate system, and transforming the coordinates of the object under the transmitting coordinate system into coordinates of the object under the horizontal coordinate system according to the inclined angle of the base; resolving firing data under the horizontal coordinate system according to the coordinates of the object under the horizontal coordinate system; calculating and transforming the firing data under the horizontal coordinate system into firing data under the transmitting coordinate system. The system is provided with an inclined angle sensor fixed on the base and a control computer connected with the inclined angle sensor through a communication bus. According to the method and the system, regulating operation of equipment on an unprepared position is avoided, preparation time of unfolding the equipment is shortened, and quick response ability of the equipment is improved.
Owner:BEIJING MECHANICAL EQUIP INST
Large-curvature immersed tube one-time calibration method in high and cold environment
PendingCN114440844ASolve the technical problems of large measurement errorsImprove calibration accuracySurveying instrumentsHeight/levelling measurementEngineeringImmersed tube
The invention relates to a one-time calibration method for a large-curvature immersed tube in a high and cold environment. The one-time calibration method comprises the following steps that control points are arranged, wherein a plurality of control points are arranged on the outer surface of the top of the immersed tube and near the immersed tube; establishing coordinate systems: establishing a horizontal coordinate system and a vertical coordinate system; measuring coordinates of the control points: measuring horizontal coordinates and elevations of the control points by utilizing the position relationship among the control points; feature points are selected from the end faces of the head end and the tail end of the immersed tube, the interior of a middle gallery of the immersed tube and the outer surface of the top of the immersed tube; and immersed tube feature point calibration: performing feature point calibration by using the control point coordinates obtained by measurement to obtain three-dimensional coordinates of each feature point so as to obtain a relative position relationship of each feature point. According to the method provided by the invention, calibration can be completed outside the immersed tube, the calibration precision is improved, and the calibration integrity is ensured.
Owner:CCCC FIRST HARBOR ENG +1
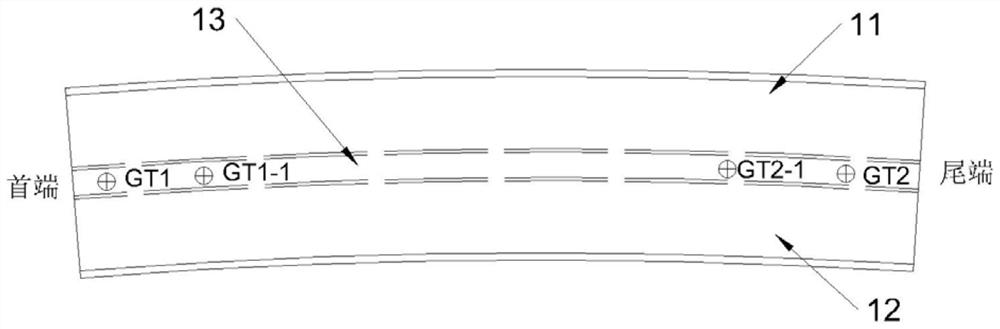
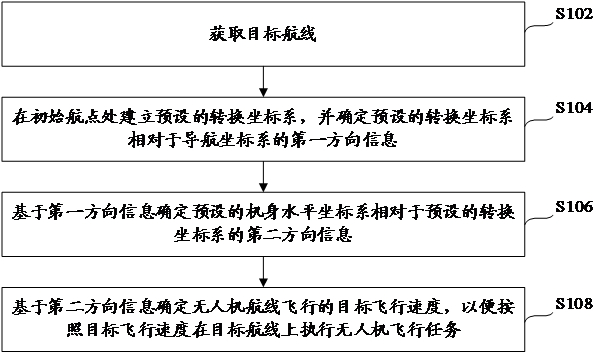
Anti-yaw control method and device for unmanned aerial vehicle, control equipment and unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN112666964AImprove accuracyImprove controlAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsUncrewed vehicleFlight velocity
The invention provides an anti-yaw control method and device for an unmanned aerial vehicle, control equipment and the unmanned aerial vehicle, and relates to the technical field of unmanned aerial vehicles. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a targe route, wherein the target route comprises an initial waypoint; establishing a preset conversion coordinate system at the initial waypoint, and determining first direction information of the preset conversion coordinate system relative to the navigation coordinate system; determining second direction information of a preset fuselage horizontal coordinate system relative to a preset conversion coordinate system based on the first direction information; and determining a target flight speed of unmanned aerial vehicle route flight based on the second direction information so as to execute an unmanned aerial vehicle flight task on the target route according to the target flight speed. According to the invention, the anti-yawing control effect of the unmanned aerial vehicle is better improved, so that the flight accuracy of the unmanned aerial vehicle along the target route is improved.
Owner:北京云圣智能科技有限责任公司
Horizontal robot camera coordinate system calibration method
ActiveCN105773613AEasy to set upImprove calibration efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobot controlComputer vision
The invention relates to the technical field of visual robots, in particular to a horizontal robot camera coordinate system calibration method. The steps of coordinate calibration are as follows: a horizontal robot controls a calibration board to move in an X direction until a location target is aligned with a reference position in the X direction, and the horizontal robot controls the calibration board to move in a Y direction until the location target is aligned with the reference position in the Y direction; X and Y coordinates of a horizontal coordinate system of the horizontal robot are set to zero; and the horizontal robot controls the calibration board to rotate forwards or reversely around a center point until the angle of deflection of the calibration board in a pixel coordinate system is zero, and direction coordinates of the horizontal coordinate system of the horizontal robot are set to zero. The horizontal robot camera coordinate system calibration method has the advantages of no programming, simple setting and automatic calibration; after the position or direction of a camera is changed, an on-site maintenance engineer can solve a position calibration problem; and the calibration efficiency is high, and the maintenance cost is low.
Owner:DONGGUAN SUMIDA AUTOMATION CO LTD
Inertia/visual integrated attitude determination device and method for rocker arm of coal mining machine
ActiveCN110411443AReal-time automatic monitoring of absolute altitudeHelp with automatic height adjustmentNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsInformation processingVisual perception
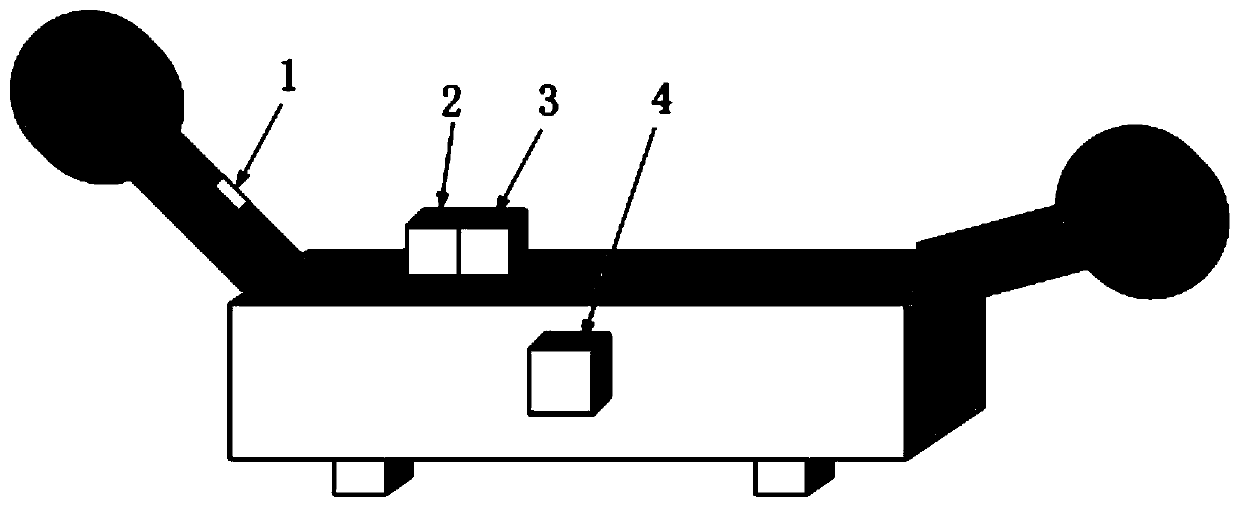
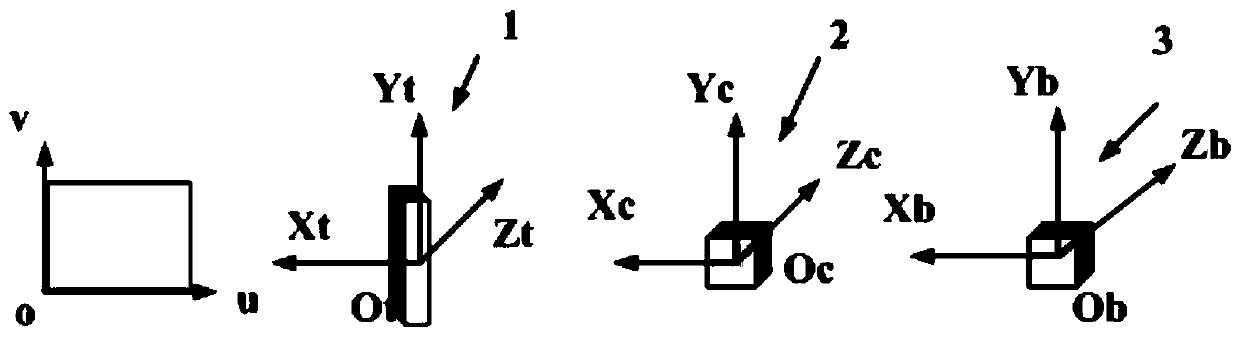
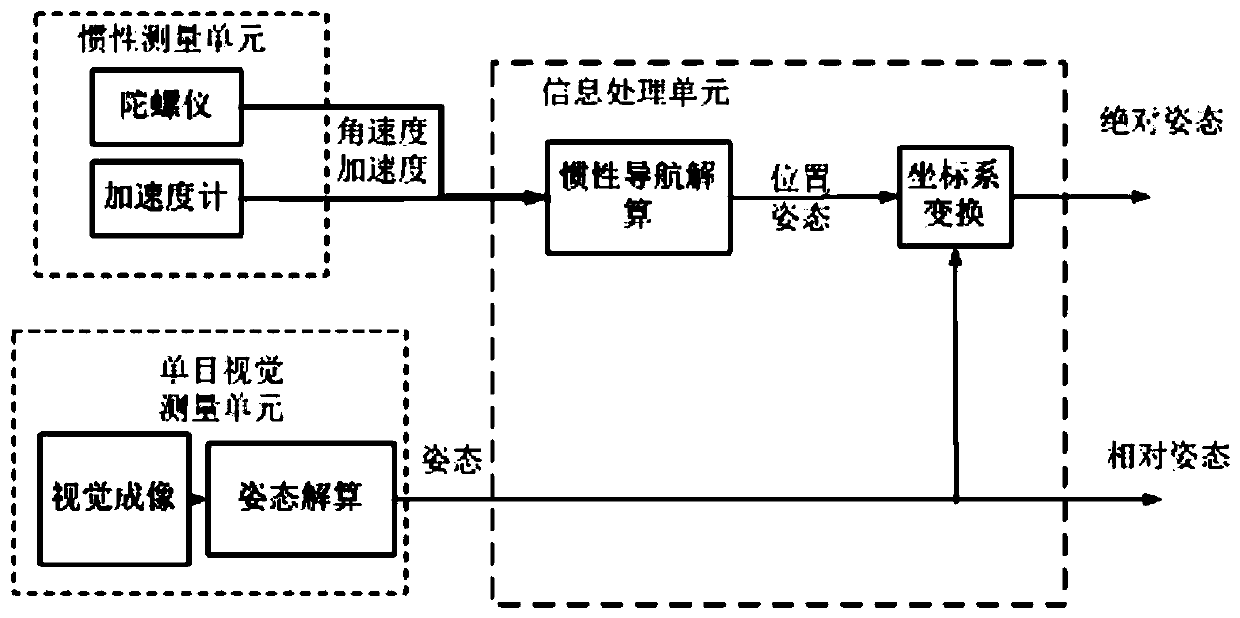
The invention discloses an inertia / visual integrated attitude determination device and method for a rocker arm of a coal mining machine. The device comprises a target feature point, an inertial measurement unit and a monocular vision measurement unit and an information processing unit, wherein the target feature point unit is installed on the rocker arm of the coal mining machine; the inertial measurement unit and the monocular vision measurement unit are rigidly connected and are arranged on the coal mining machine; the information processing unit is arranged in an electrical control box of the coal mining machine; and the monocular vision measurement unit is used for measuring the relative attitude of the rocker arm relative to the coal mining machine, and the inertia measurement unit isused for measuring the absolute attitude of the coal mining machine relative to a local horizontal coordinate system. By simultaneously calculating the attitude of the rocker arm relative to the coalmining machine and the attitude of the rocker arm relative to the local horizontal geographic coordinate system, a problem of high-precision attitude determination of the rocker arm of the coal mining machine is solved. The device has the advantages of simple system structure, easy camera calibration and calibration, adaptability to a rocker arm strong vibration environment, complete attitude information and high precision, and is particularly suitable for near-distance high-precision attitude determined of a fully-mechanized mining face.
Owner:XIJING UNIV
Deformation amount and servo angle detection method for large precision industrial equipment
ActiveCN109297426AEasy to graspHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansIndustrial equipmentTotal station
The invention discloses a deformation amount and servo angle detection method for large precision industrial equipment, and belongs to the technical field comprising industrial measurement and geodetic measurement. The invention uses a technology combining an industrial photogrammetry system, a laser tracker and a high precision total station. The invention mainly comprises the contents of the following aspects: (1) on the basis of a reference ruler, the lengths of two line segments measured by a laser tracker are also used as a length reference of the photogrammetry, and spatial scale accuracy of the photogrammetry can be improved while a mutual check can be performed; (2)the measuring camera can shoot any position of a target at any angle by a self-made shooting assist telescopic rod, thereby solving an observation problem of large equipment; (3)the high precision conversion of a photogrammetry coordinate system to a geodetic coordinate system is realized by using a local gravity horizontal coordinate system established by the laser tracker as a transition.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE SURVEYING & MAPPING ENG INST
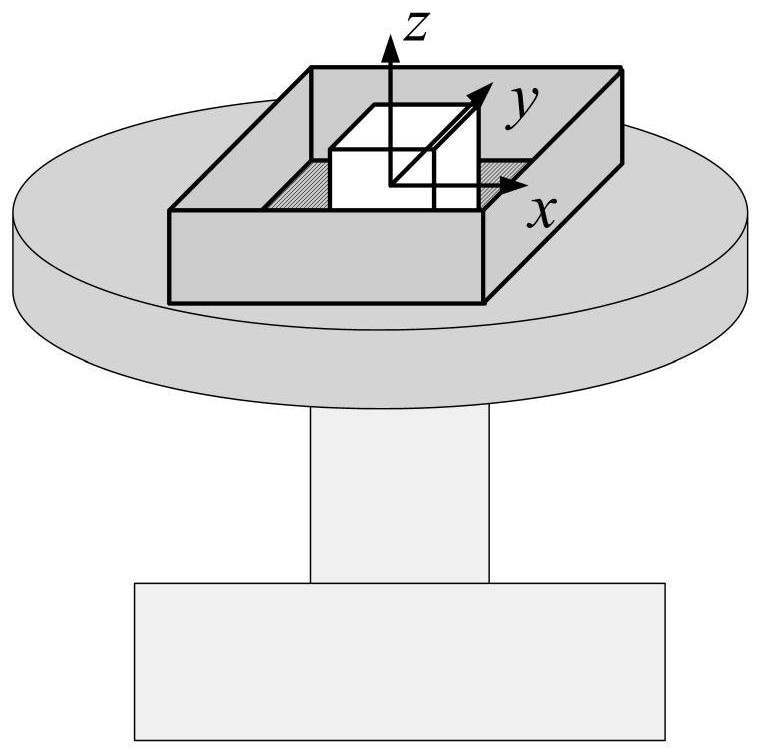
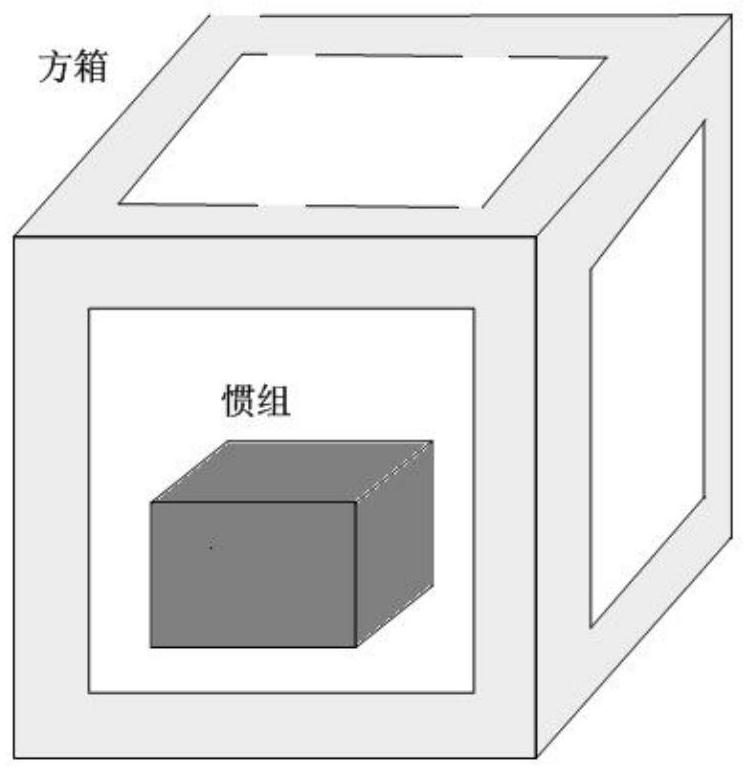
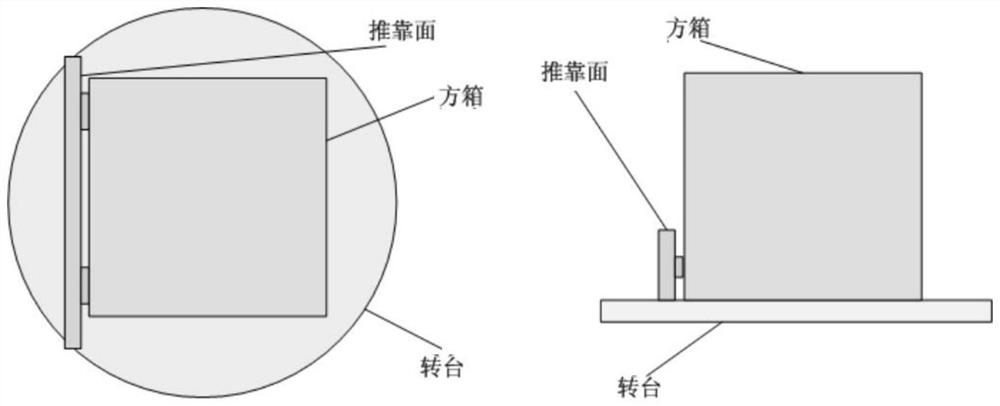
Inertial measurement unit field calibration method based on single-axis turntable
InactiveCN112611400AReduce restrictionsEasy to install and apply on siteMeasurement devicesAccelerometerClassical mechanics
The invention relates to an inertial measurement unit field calibration method based on a single-axis turntable, wherein the method is technically characterized by comprising the steps: establishing a single-axis turntable model, and establishing the following coordinate systems according to the frame structure of the single-axis turntable: a ground horizontal coordinate system, a turntable rotating shaft coordinate system, a turntable plane coordinate system, a gyro three-axis coordinate system and an accelerometer three-axis coordinate system; establishing a gyro accelerometer inertial component model; and establishing a square box coordinate system, wherein three coordinate axes of the square box coordinate system are perpendicular to one another, and the directions of the three axes are parallel to the pointing directions of a gyro and an accelerometer; the square box provided with an inertial measurement unit is mounted on the single-axis turntable, and then inertial measurement unit field calibration is carried out. The calibration method is reasonable in design, the calibration function of the inertial measurement unit can be achieved only through the single-axis position turntable and the hexahedron square box which are small in size, meanwhile, no leveling requirement exists for installation of the turntable, limitation to the calibration site is small, field installation and application are facilitated, and thus a large amount of time is saved.
Owner:TIANJIN NAVIGATION INSTR RES INST
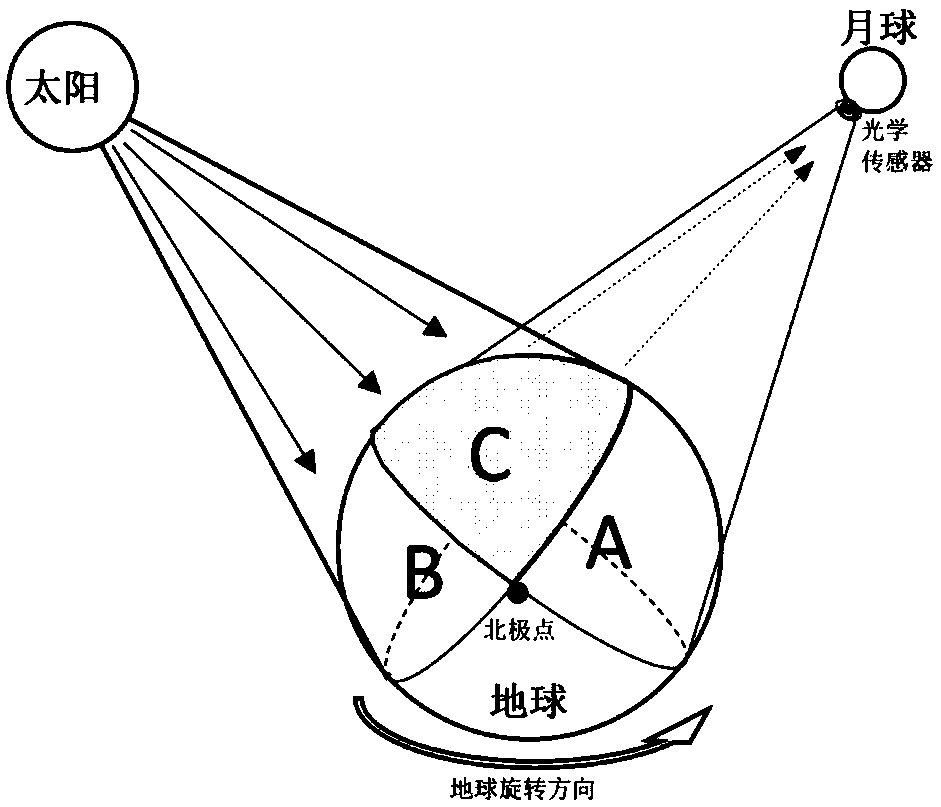
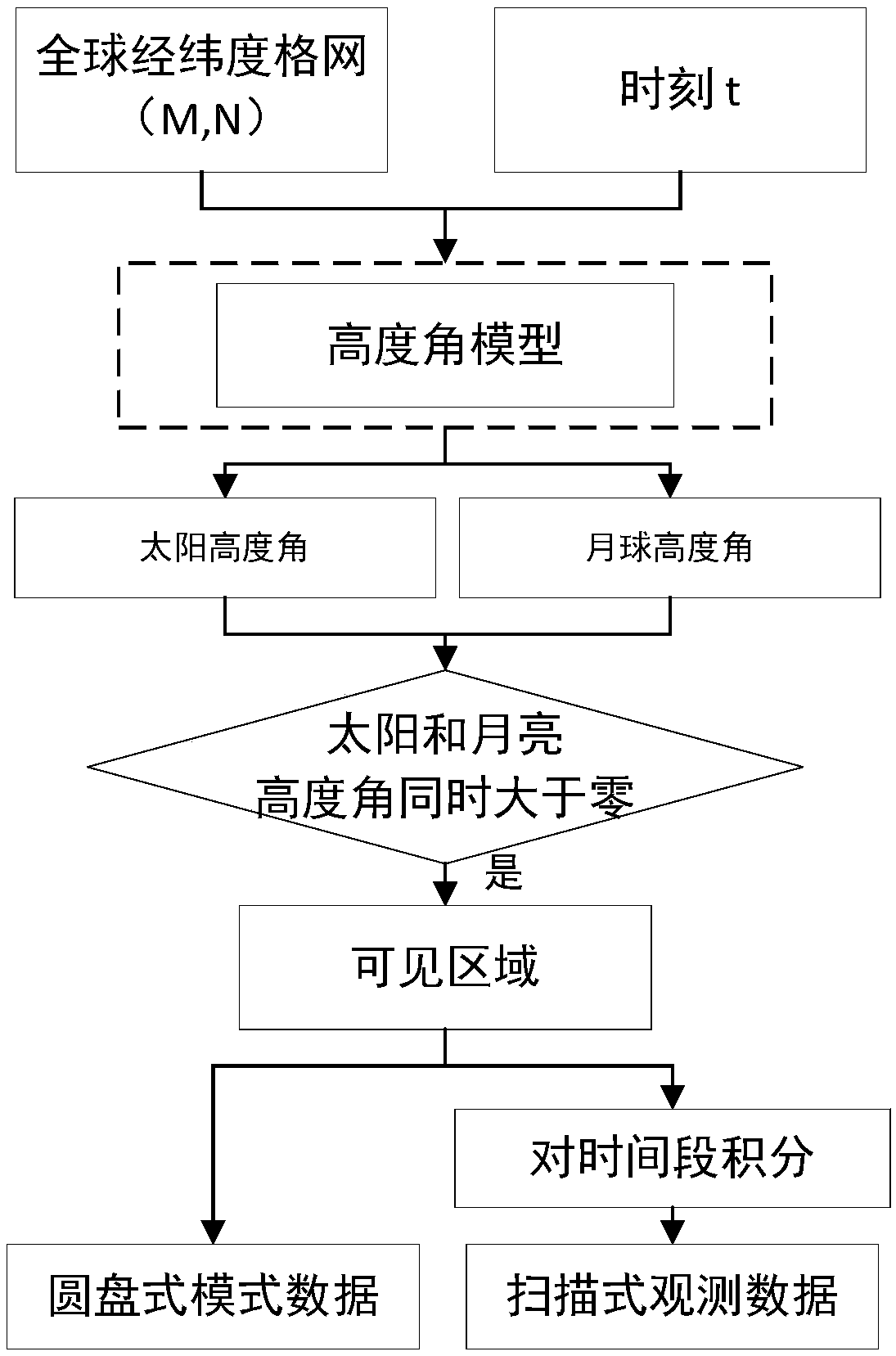
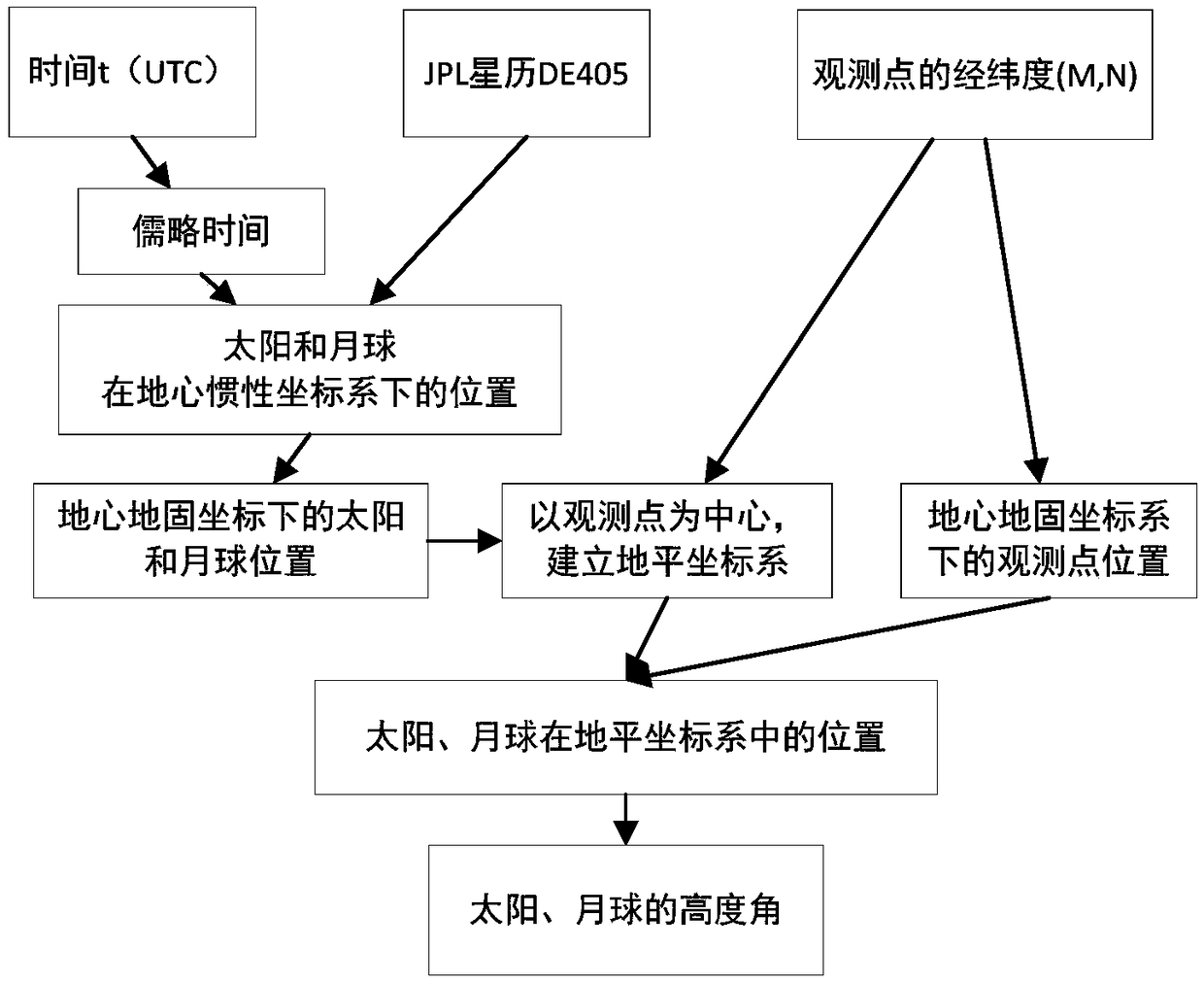
Imaging method for lunar based optical sensor
ActiveCN108896038AContinuous observation dataContinuous observationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansECEFObservation point
The invention discloses an imaging method for a lunar based optical sensor. The imaging method comprises the following steps: (1) setting an optical sensor on moon; (2) confirming an imaging moment and respectively acquiring the positions of moon centroid and sun centroid under a geocentric inertial coordinate system at the imaging moment on the basis of the ephemeris data; (3) converting the positions under the geocentric inertial coordinate system into the positions under a geocentric fixed coordinate system; (4) converting the position of an observation point i on the earth under a WGS84 coordinate system into the position under the geocentric fixed coordinate system; (5) establishing a horizontal coordinate system by taking the observation point i on the earth as an original point andcalculating the positions of moon centroid and sun centroid under the horizontal coordinate system; (6) calculating a moon elevating angle and a sun elevating angle of the observation point i on the earth under the horizontal coordinate system; (7) extracting the moon elevating angle and the sun elevating angle while taking an area more than 0 as a lunar disc type observation imaging area. According to the method, the large-scale instant image and the global image in slow change of scale can be observed.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com