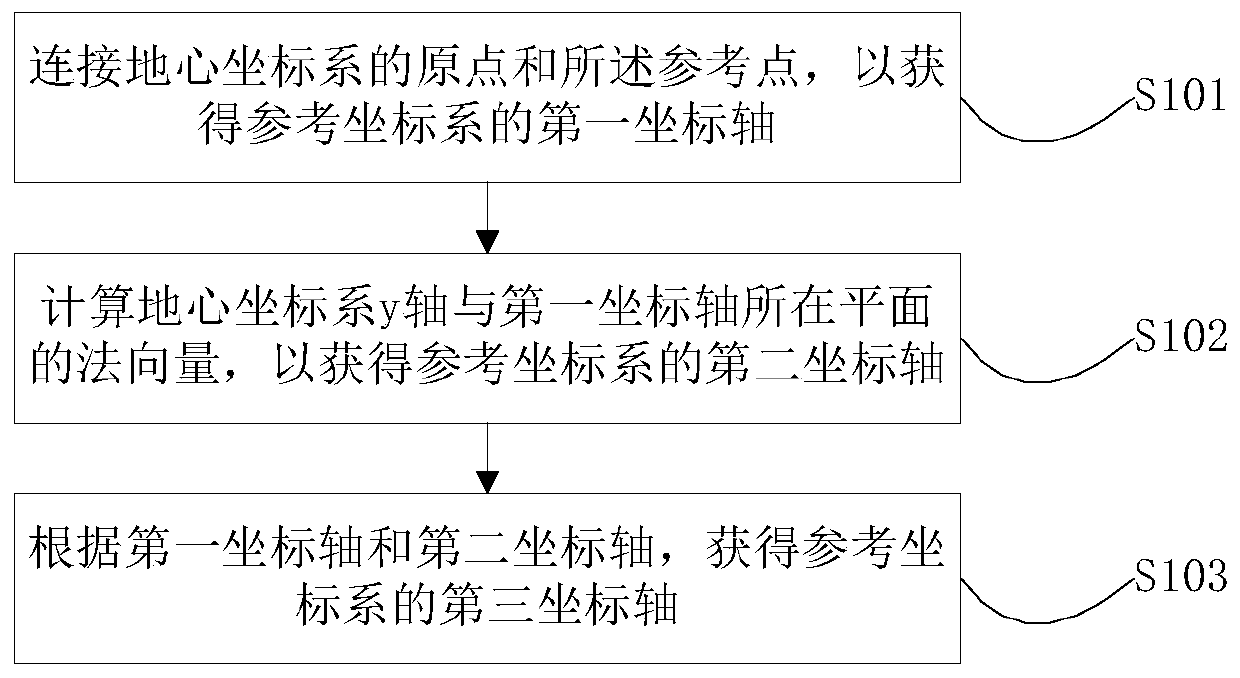
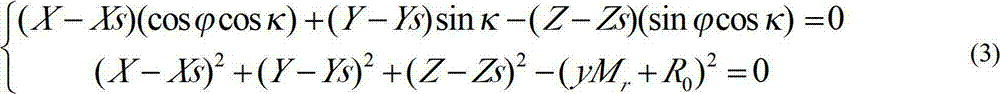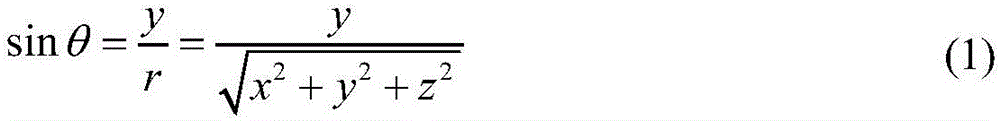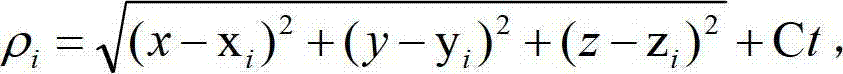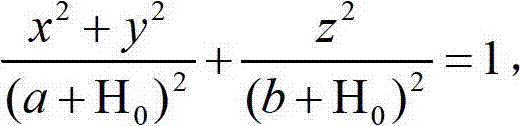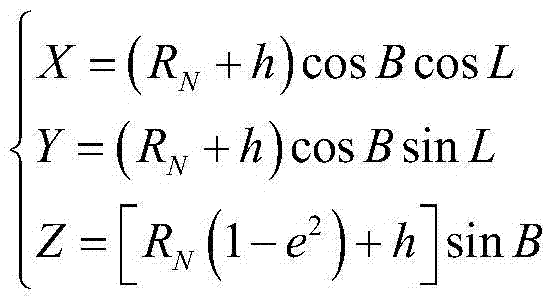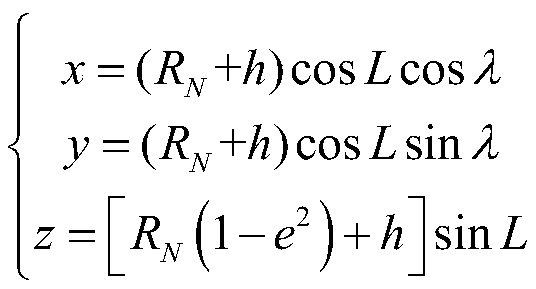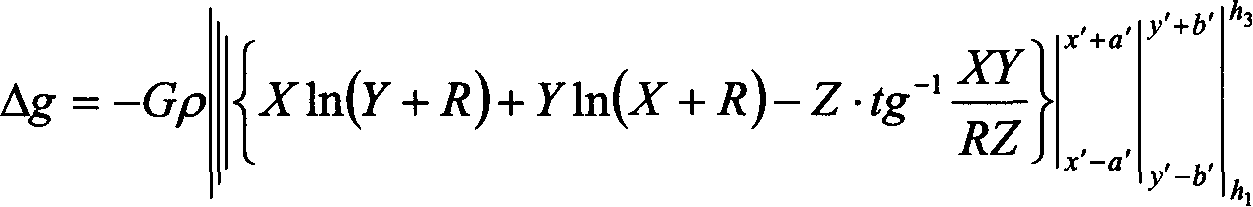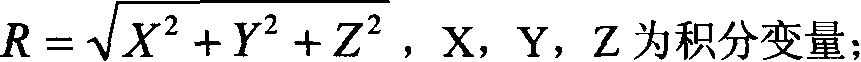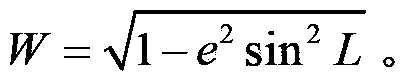Patents
Literature
75 results about "Earth ellipsoid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
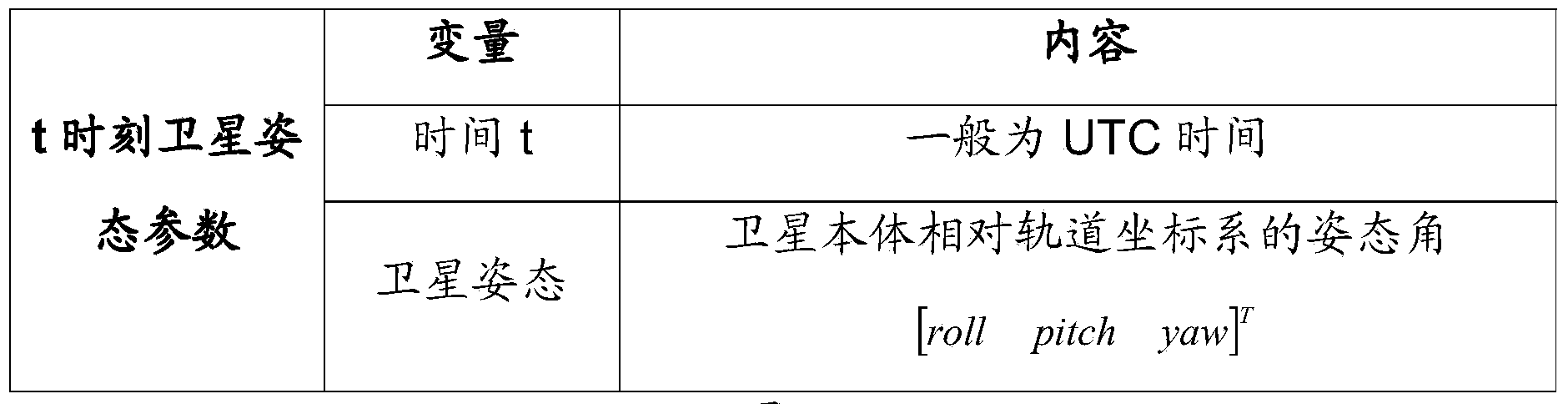
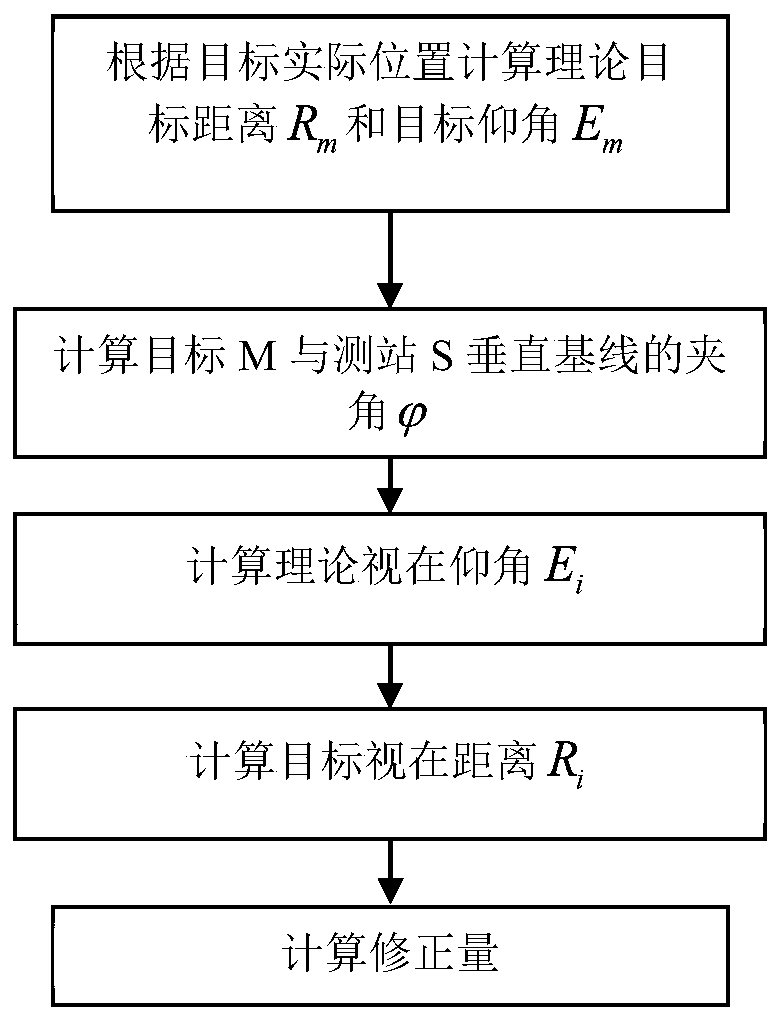
An Earth ellipsoid is a mathematical figure approximating the Earth's form, used as a reference frame for computations in geodesy, astronomy, and the geosciences. Various different ellipsoids have been used as approximations.
Pseudorange differential method based on dual-satellite time difference and frequency difference passive positioning
ActiveCN103645485AHigh positioning accuracyGood precisionSatellite radio beaconingArrival timeMultilateration
The invention provides a pseudorange differential method based on dual-satellite time difference and frequency difference passive positioning. According to the method, the pseudorange difference between two satellites and a reference station is measured successively, the pseudorange correction of the satellites is calculated, the pseudorange difference of an unknown radiation source is corrected through the pseudorange correction to obtain an arrival time difference which is close to the true value, the arrival frequency difference between the reference station and the two satellites is measured, the arrival frequency difference between the reference station and the two satellite which is close to the true value is calculated, the arrival frequency difference between the unknown radiation source and the two satellites is corrected through the frequency correction of the satellites to obtain an arrival frequency difference which is close to the true value, and the high-accuracy positioning of the unknown radiation source is realized through an earth ellipsoid equation and the arrival time difference and the arrival frequency difference which are close to the true value. According to the invention, system positioning errors can be corrected, so that the accuracy of a dual-satellite passive positioning system can be improved.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for processing radar target information in navigating tube automatization system
InactiveCN101206260AReduce projective transformation errorImprove processing precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionJet aeroplaneRectangular coordinates
A processing method for radar target information in an air traffic control (ATC) automatic system includes the following steps: firstly, an ATC radar determines the target information of airplane distance and azimuth; moreover, the target information is shown by the polar coordinate taking the position of the radar as the center; taking the influence of the earth ellipsoid into consideration, the target information which is shown by the polar coordinate is converted to a plane rectangular coordinate taking the radar as the origin from the polar coordinate, thereby providing convenience to Kalman filtering tracking of an airplane target in a plane rectangular coordinate system. Compared with the common algorithm, the method can reduce conversion error and improves precision processing.
Owner:WISESOFT CO LTD
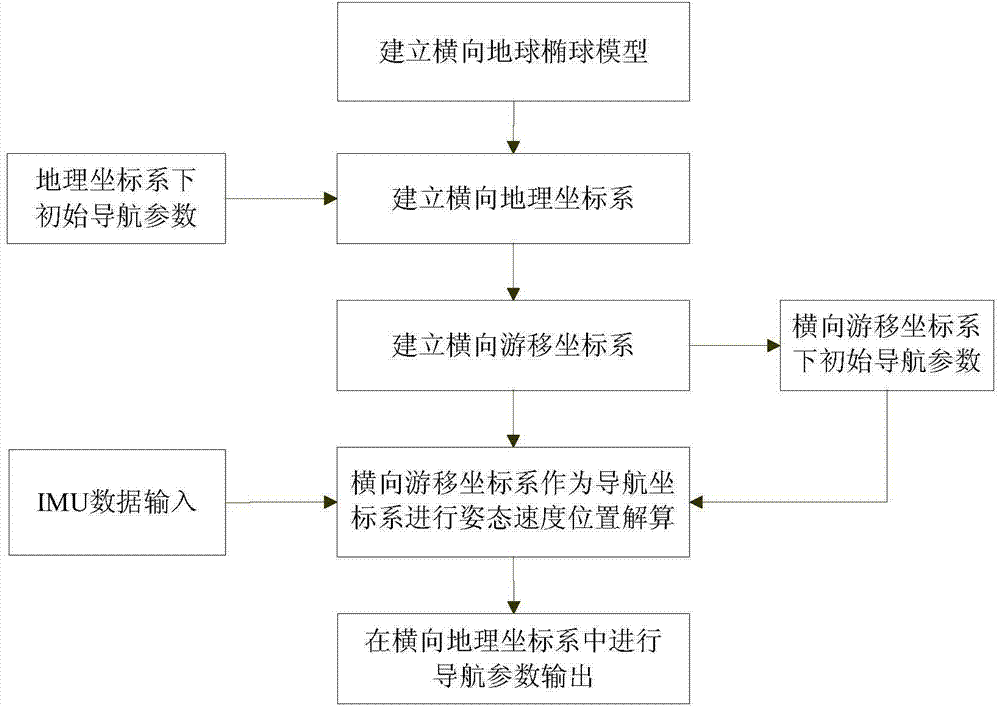
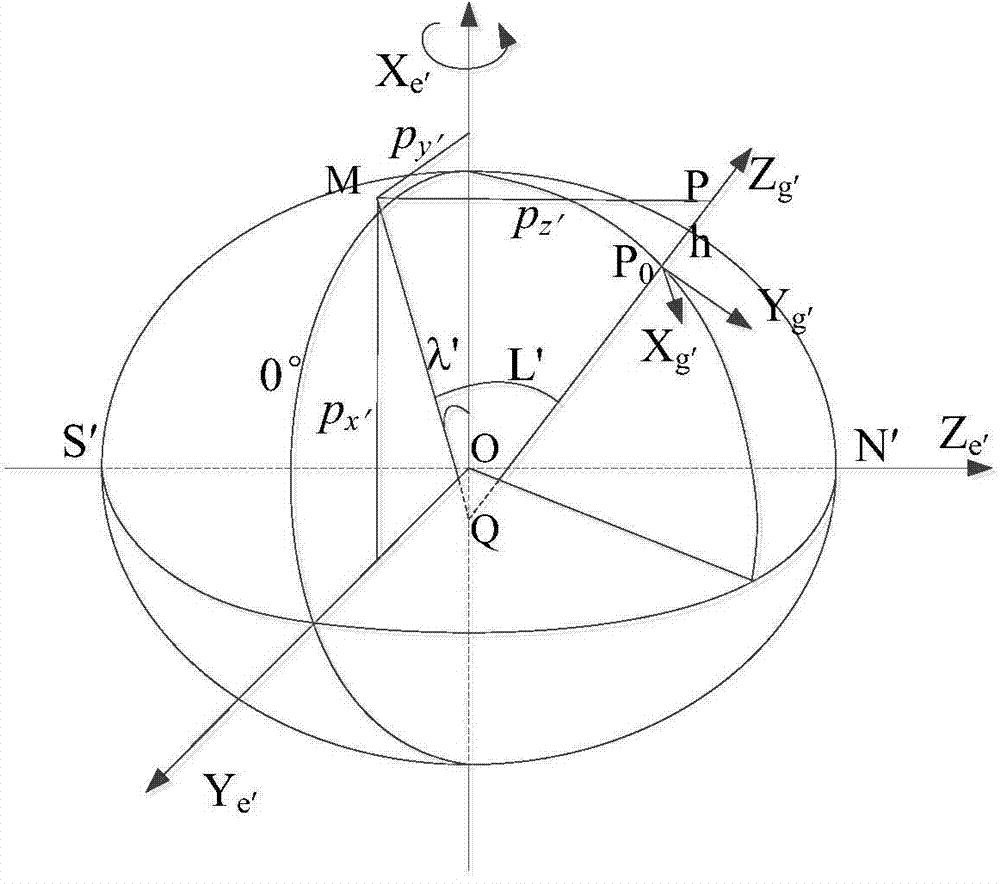
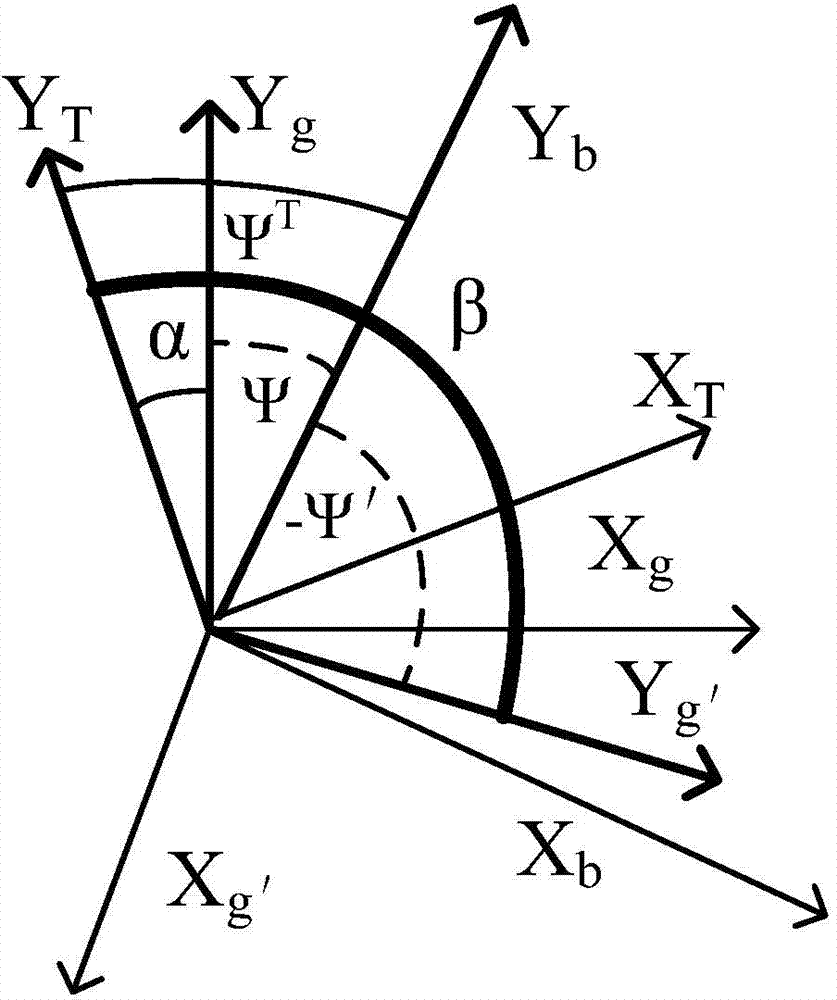
Polar inertial navigation method based on horizontal wandering coordinate system
ActiveCN104215242ASolve non-applicable problemsSatisfy sailing requirementsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsLow latitudeGeographic coordinate system
The invention discloses a polar inertial navigation method based on a horizontal wandering coordinate system. The method includes the steps: building a horizontal earth ellipsoid coordinate system, a horizontal geographic coordinate system and the horizontal wandering coordinate system, setting a traditional geographic coordinate system of initial navigation time as an initial horizontal wandering coordinate system and performing mechanical layout by taking the horizontal wandering coordinate system as a navigation coordinate system of a strap-down inertial navigation system; solving the problem of strap-down algorithm failure based on the geographic coordinate system due to meridian convergence in polar regions based on the inertial navigation layout mode of the horizontal wandering coordinate system. Besides, mechanical layout is performed in wandering azimuth at low latitudes, the internal integrity of a global navigation resolving algorithm is ensured by combining the modes, switching logic design of different latitudes and the transformational relationship between parameters of different navigation coordinate systems are avoided in the strap-down inertial navigation system, and complicated physical platform switching is avoided in a platform inertial navigation system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
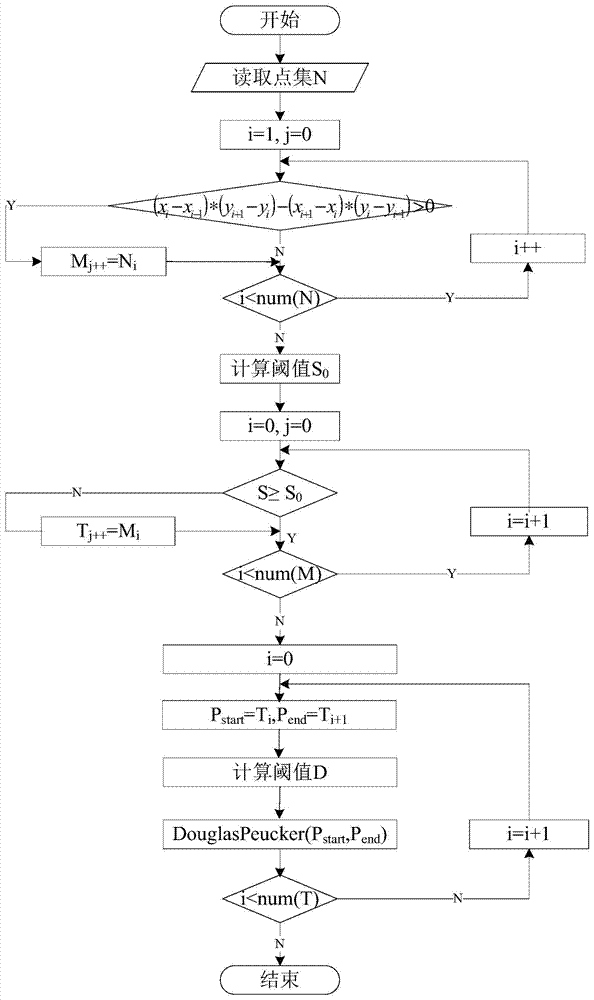
Method for extracting territorial sea baseline based on natural coastline data
InactiveCN104766081AReasonable location distributionImprove computing efficiencyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionRamer–Douglas–Peucker algorithmThinning
A method for extracting a territorial sea baseline based on natural coastline data mainly comprises a natural coastline thinning method based on an improved Douglas-Peucker algorithm and a territorial sea baseline encryption algorithm based on earth spherop geodesic line resolving, and territorial area baseline delimitation is conducted. According to the method for extracting the territorial sea baseline based on the natural coastline data, in the thinning process, natural coastline salient points which have a larger influence on a sea area are extracted and taken as segment points, then two adjacent segment points are taken as a first point and a tail point for data thinning, an optimal distance threshold is selected through a fitting curve based on a least square method, thinning is conducted segment by segment, and the natural maritime rights and interests can be guaranteed under the circumstance that higher precision and compression ratio are guaranteed. The encryption algorithm is based on the earth spherop geodesic line resolving on the ground, a geodesic line is fitted between adjacent territorial sea base points, and therefore encryption calculation is conducted on adjacent base points by using a geodetic theme resolving principle. Improvement is conducted on distance judgment conditions and encryption point positions in the calculation process, the calculation rate is increased, and the position distribution of the territorial sea base points is more reasonable.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Large-angle oblique imaging aerocamera targeted target positioning method
InactiveCN107490364AVerify validitySmall probability errorPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryAviationLongitude
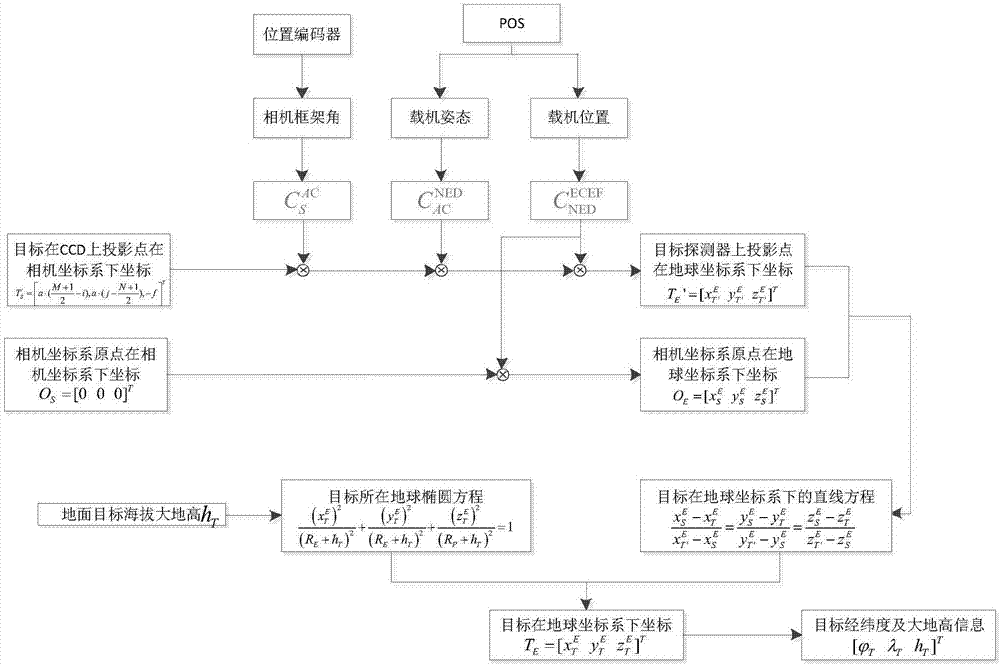
The invention discloses a large-angle oblique imaging aero-camera targeted target positioning method. In accordance with the problems that the shooting distance of a large-angle oblique imaging aero-camera is long, and the operating distance of laser distance measuring equipment is limited, and the invention provides a direct targeted target positioning algorithm which is independent of the distance measuring equipment. According to the position and the attitude information of a carrying aerial vehicle, measured by the carrying aerial vehicle POS ( position and orientation system) and frame angular position information measured by a position encoder in the aero-camera; a homogeneous coordinate conversion method is used for solving the direction of a target under a geodetic coordinate system; and an earth ellipsoid model and a digital elevation model are used for determining latitude and longitude information of the target point. According to the large-angle oblique imaging aero-camera targeted target positioning method disclosed by the invention, flight test data is used for verifying the validity of the target positioning algorithm; and when the flight height is 18000m, and the rolling angle of a shooting frame is smaller than 63 degrees, the target positioning circular probable error is smaller than 70m, so that engineering actual requirements can be met.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
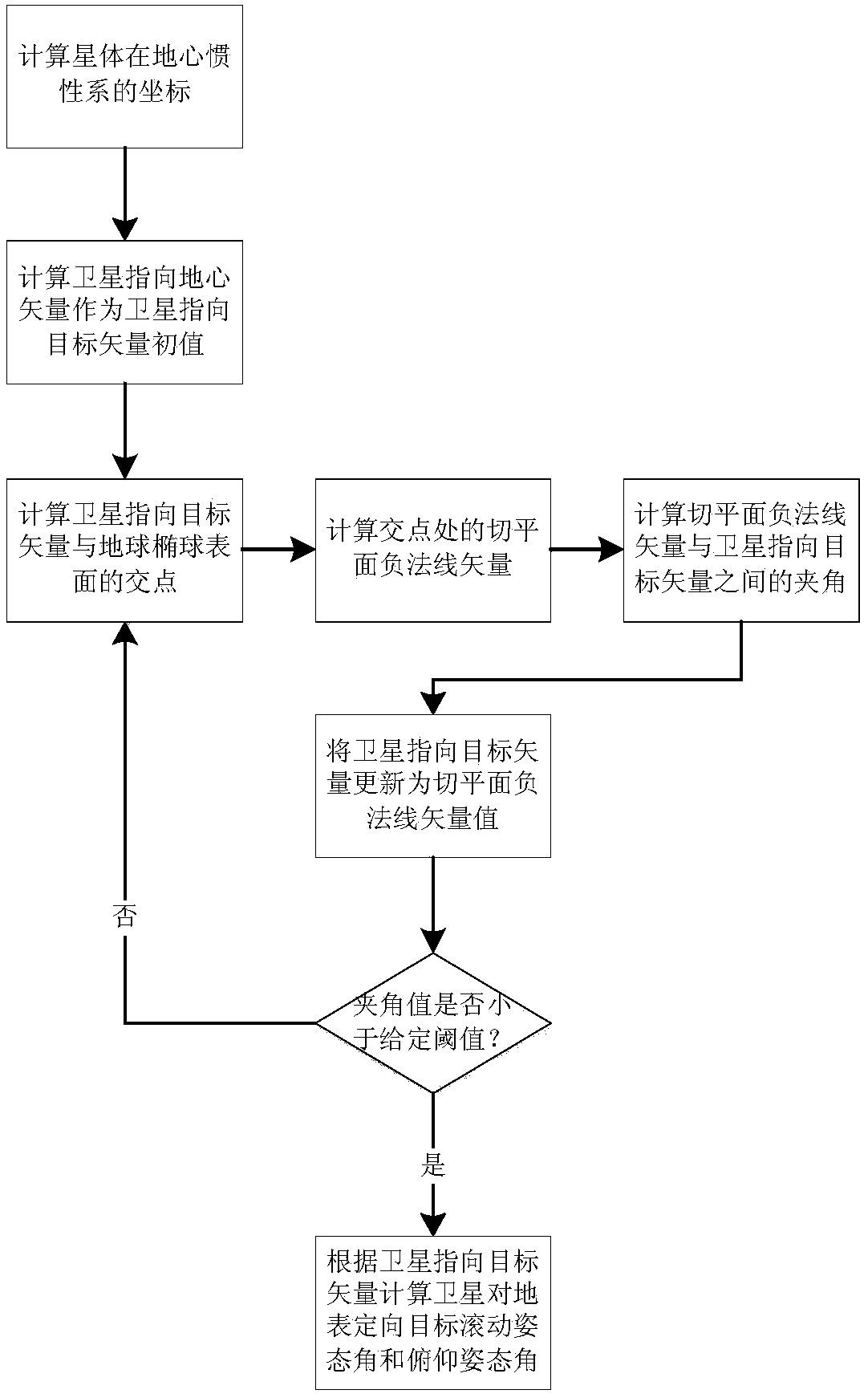
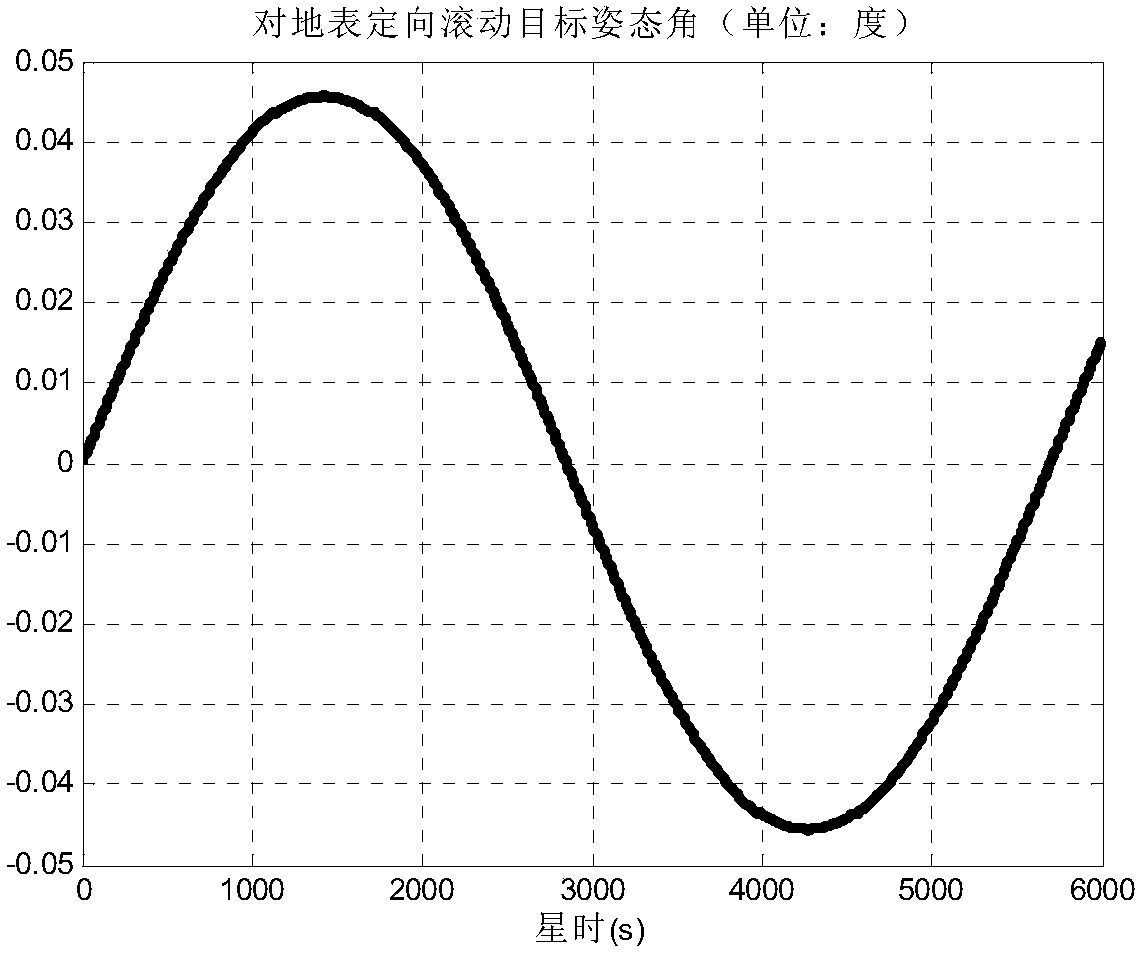
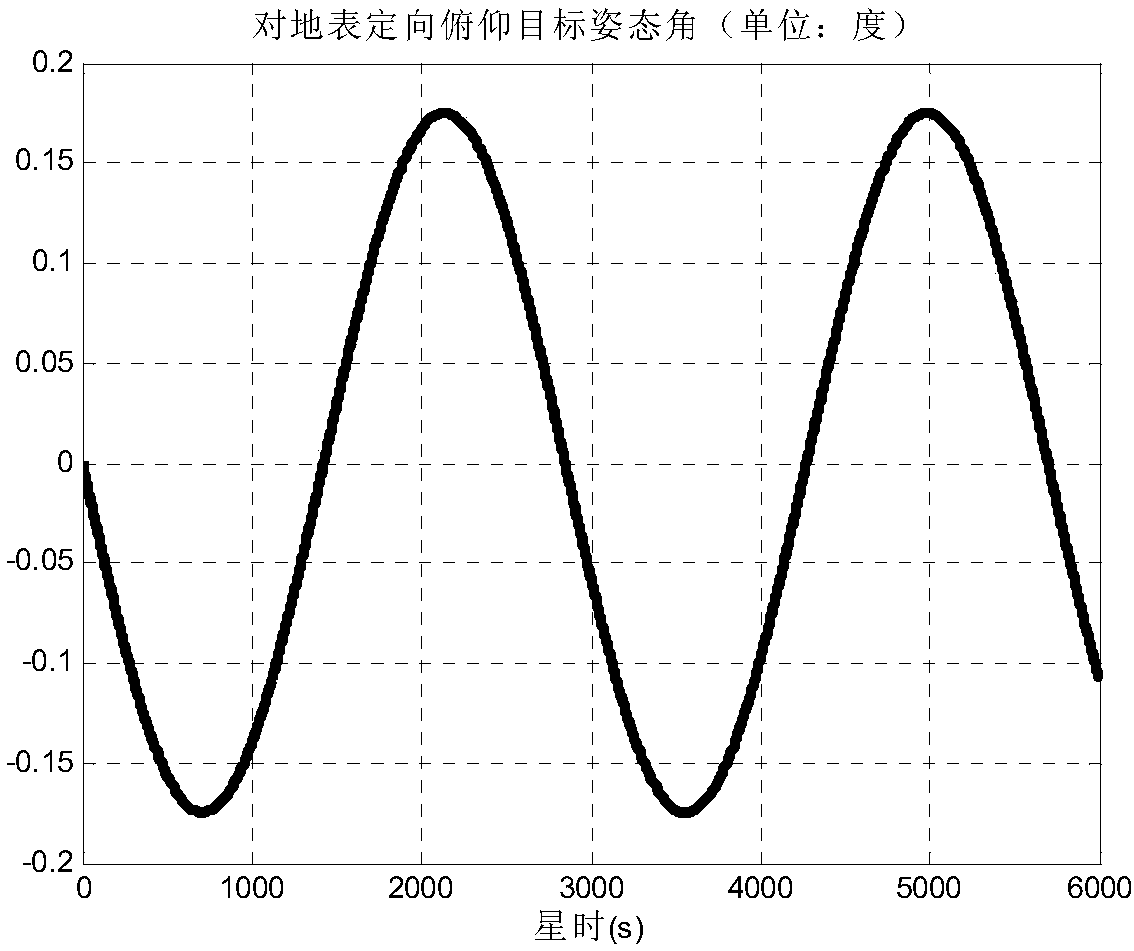
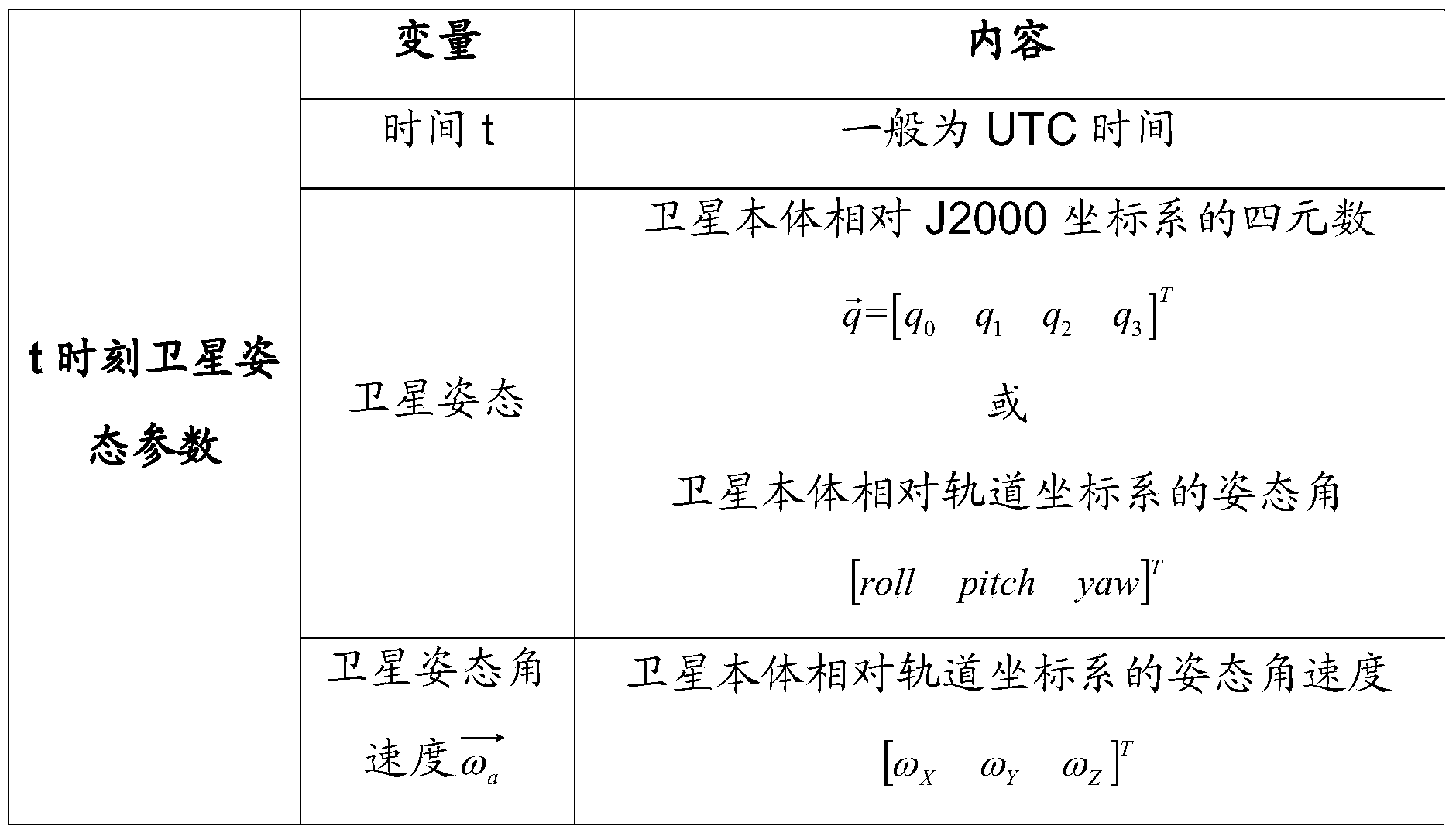
Method for calculating earth's surface-orientated target attitude angle of spacecraft
The invention discloses a method for calculating an earth's surface-orientated target attitude angle of a spacecraft. The method comprises the steps that the position coordinates of a satellite in a geocentric inertial system are computed according to satellite orbital information to obtain a value of a vector of the satellite pointing to the geocenter in the geocentric inertial system to be takenas an initial value of the target-pointed vector of the satellite, the coordinates of an intersection point of the target-pointed vector of the satellite and a spherical surface of an Earth ellipsoidal model are calculated according to the position coordinates of the satellite in the geocentric inertial system to further obtain a negative normal vector of the Earth ellipsoidal model on a tangentplane at the intersection point, and finally the angle between the negative normal vector and the target-pointed vector of the satellite is calculated to conduct optimization on the target-pointed vector of the satellite. According to the method, a vector value of the target-pointed vector of the satellite in a satellite orbital system is obtained by computing according to the target-pointed vector of the satellite and the satellite orbital information to further perform computing to obtain the earth's surface-orientated target attitude angle and an earth's surface-orientated target pitching attitude angle.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
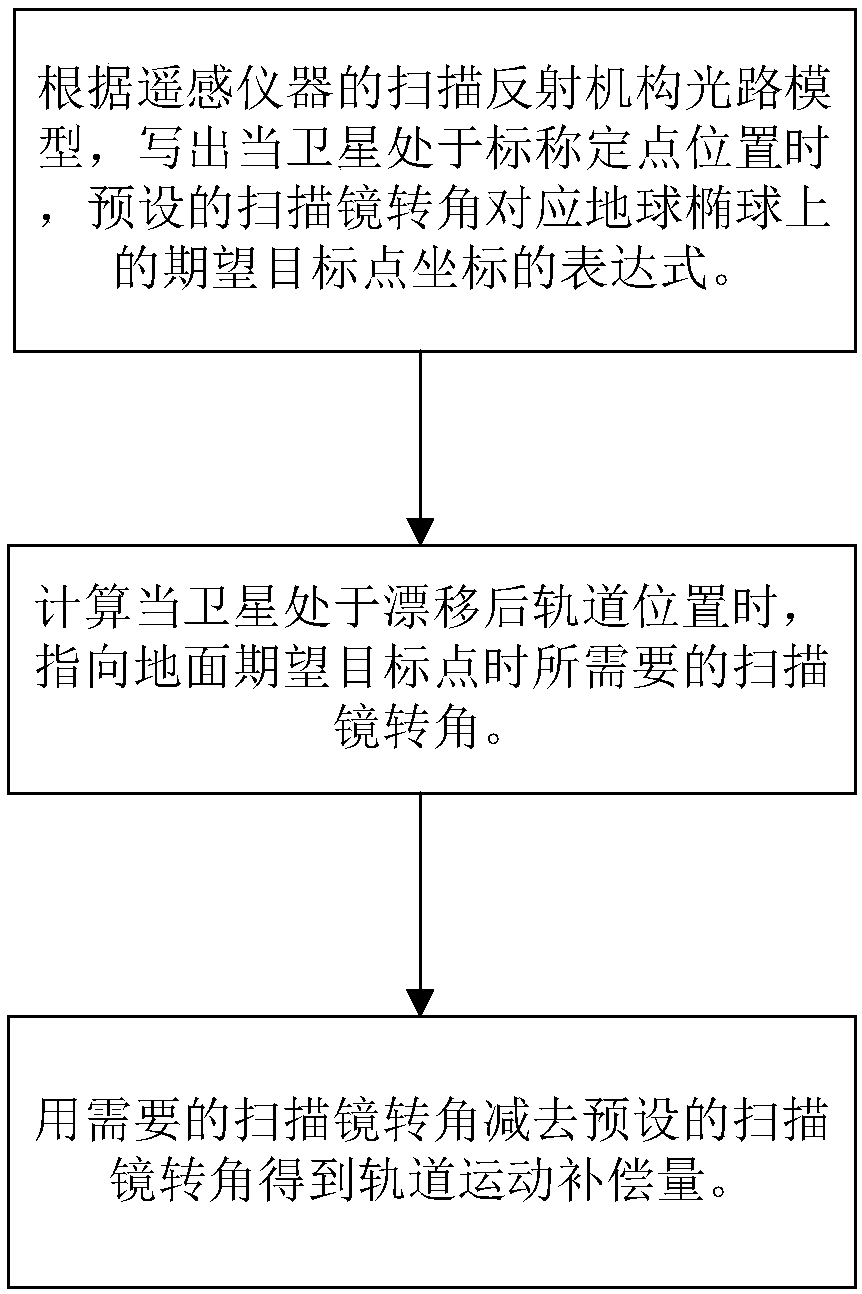
Geostationary satellite imaging navigation and registered orbital motion compensation method
InactiveCN107633108AReduce the difficulty of research and developmentImprove engineering realizabilitySpecial data processing applicationsSatellite imageScanning mirror
The invention provides a geostationary satellite imaging navigation and registered orbital motion compensation method. The method includes the following steps: a first step, writing an expression of adesired target point coordinate on an earth ellipsoid corresponding to a preset scanning mirror rotation angle according to a scanning reflective mechanical optical path model of a remote sensing instrument while a satellite is at a nominal fixed point; a second step, calculating a desired scanning mirror rotation angle while the satellite is at an orbital position after drifting and points to aground desired target point; and a third step, using the desired scanning mirror rotation angle to subtract the preset scanning mirror rotation angle to acquire an orbital motion compensation amount.The acquired image and an earth nominal grid image generated by the satellite at the nominal fixed point are consistent, errors are controlled in an indication range, and the research and developmentdifficulty of a system can be lowered, and the realizability of engineering can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
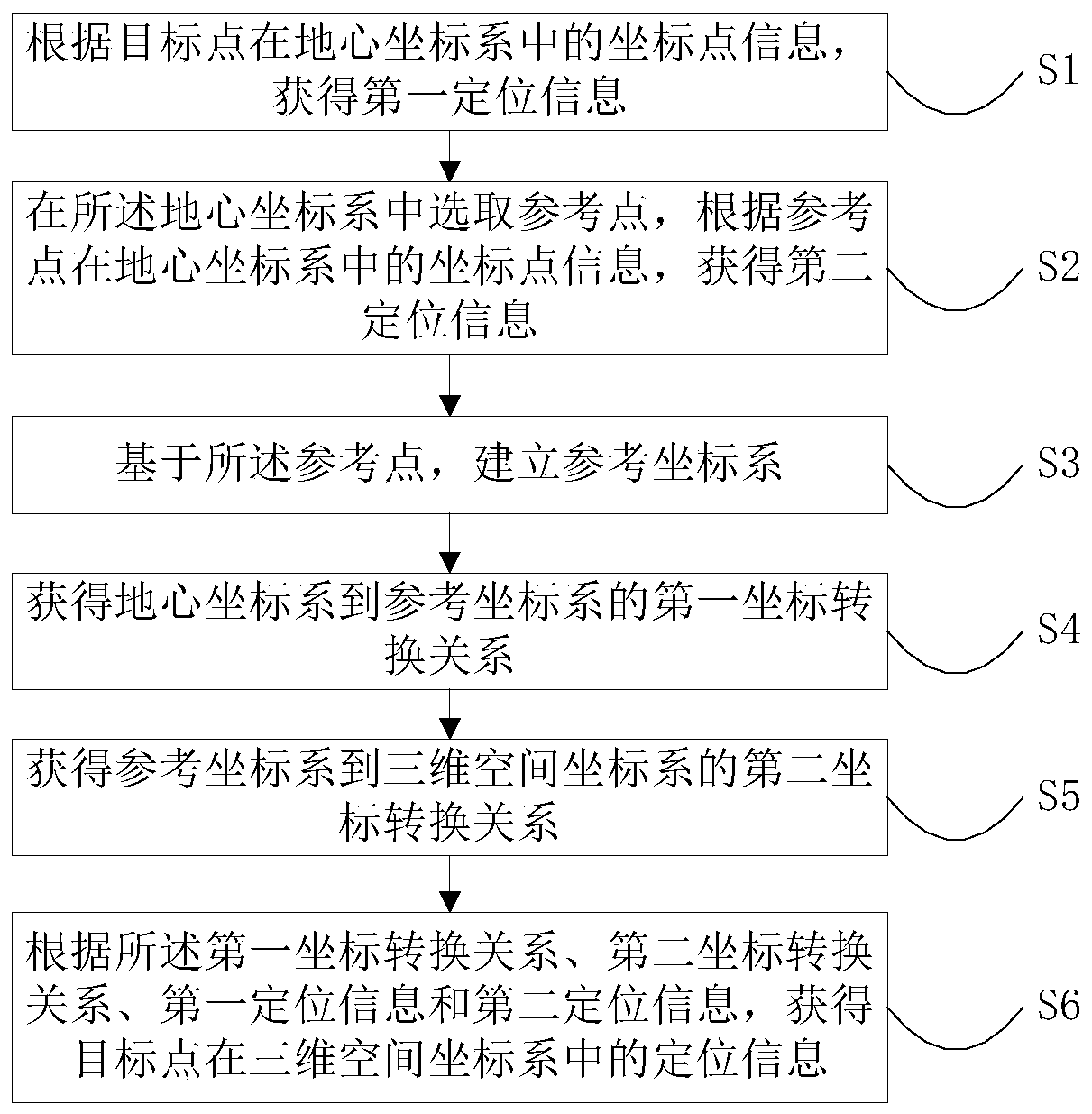
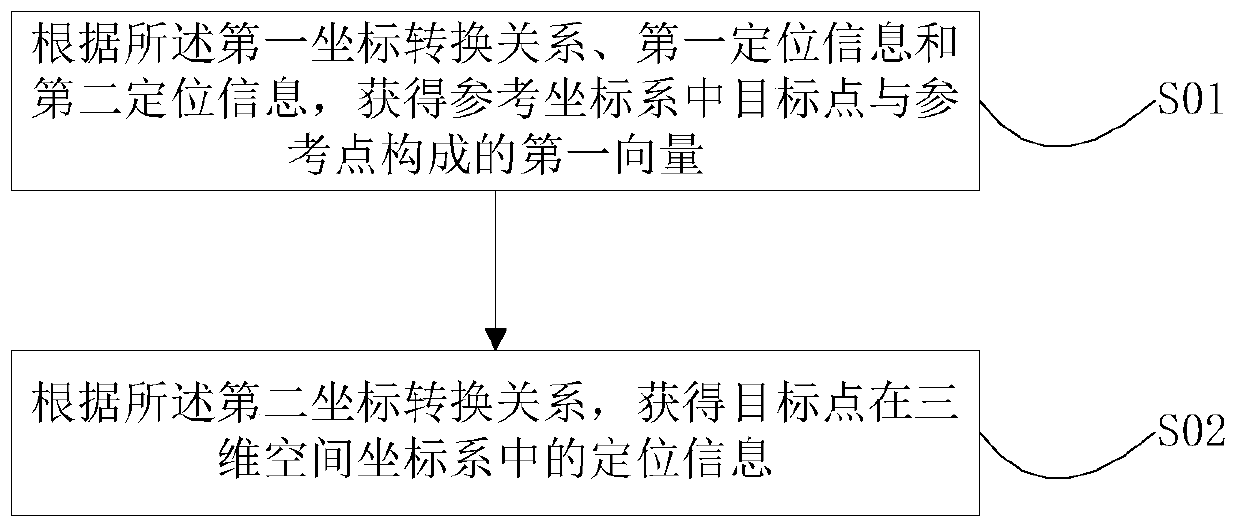
Positioning method, device and terminal of target point on map
ActiveCN109974717AReduce biasSimplify conversion stepsInstruments for road network navigationThree-dimensional spaceComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to the navigation data field and provides a positioning method, device and terminal of a target point on a map. The method comprises the following steps of selecting a referencepoint in a geocentric coordinate system to establish a reference coordinate system; obtaining a first coordinate conversion relationship of the geocentric coordinate system to the reference coordinatesystem; obtaining a second coordinate conversion relationship of the reference coordinate system to a three-dimensional space coordinate system; obtaining vector information of a reference point to the target point in the reference coordinate system according to positioning information of the reference point and the target point in the geocentric coordinate system, and the first coordinate conversion relationship; and converting the vector information through the second coordinate conversion relationship, and acquiring the positioning information of the target point in the three-dimensional space coordinate system. In the method, a coordinate point of the reference coordinate system and the coordinate point of the three-dimensional space coordinate system are converted, and a coordinate system type is unified, a coordinate conversion step is simplified, participation in conversion of constants such as an Earth ellipsoid parameter and the like is avoided, and a deviation of a relativeposition of objects in an adjacent area due to conversion is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GEELY AUTOMOBILE RES INST CO LTD +1
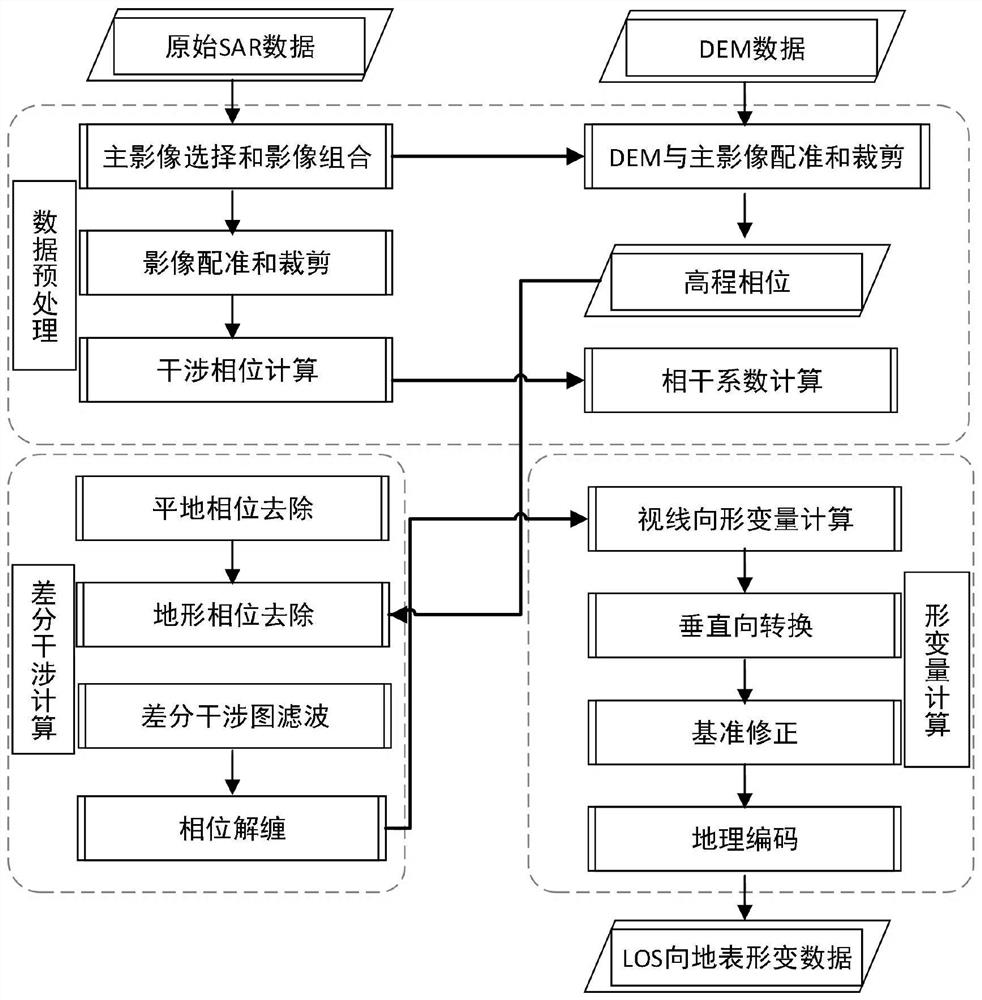
Novel differential InSAR LOS direction deformation quantity estimation method
PendingCN112051571AThe length is smaller than the deformationReasonable and uniform deformation distributionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTerrainRadar
The invention discloses a novel differential InSAR LOS direction deformation quantity estimation method comprising the following steps that: data preprocessing: SAR main image selection and image combination are carried out to generate image pairs on the premise of satisfying space baseline and time baseline requirements, registration is carried out according to DEM and the selected SAR main image, the DEM scope is clipped to be consistent with the SAR main image scope, pre-filtering is carried out on the registered main image and the registered auxiliary image, and calculatinon is conducted to generate an interferogram; differential interference calculation: a flat ground phase is calculated according to space baseline parameters and earth ellipsoid parameters, a terrain phase is calculated by using the registered DEM, a differential interferogram is generated from the interferometric phase, a coherence map is generated by using filtered main and auxiliary image differential interferometric phase pixels, and the phase-wound differential interferogram is unwrapped; lOS direction deformation quantity calculation: unwrapping phases are converted into deformation quantity in the sightline direction according to radar wavelength parameters in combination with external auxiliary data after phase-to-deformation calculation is carried out, and geocoding is carried out through DEM products.
Owner:中冶(北京)交通科技发展有限公司 +1
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) Doppler parameter estimation method based on POS and DEM data
ActiveCN102866393AImprove image qualityImprove estimation accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTerrainSynthetic aperture sonar
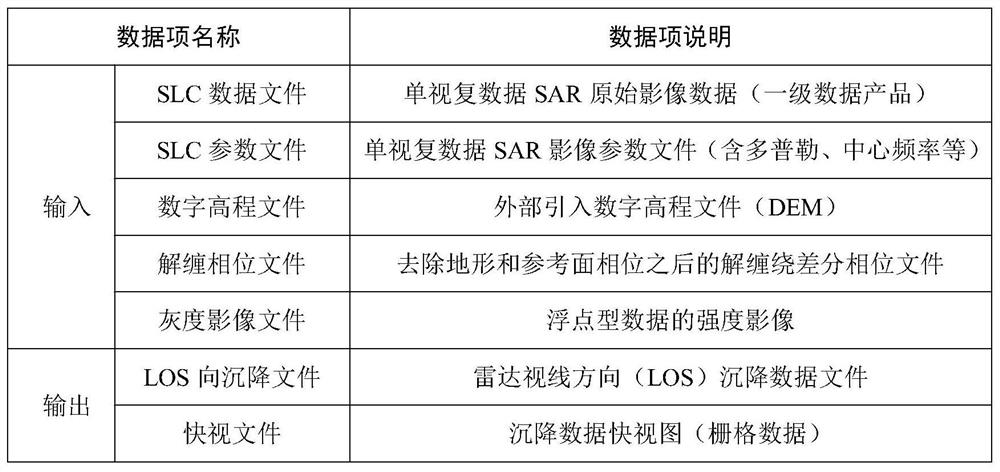
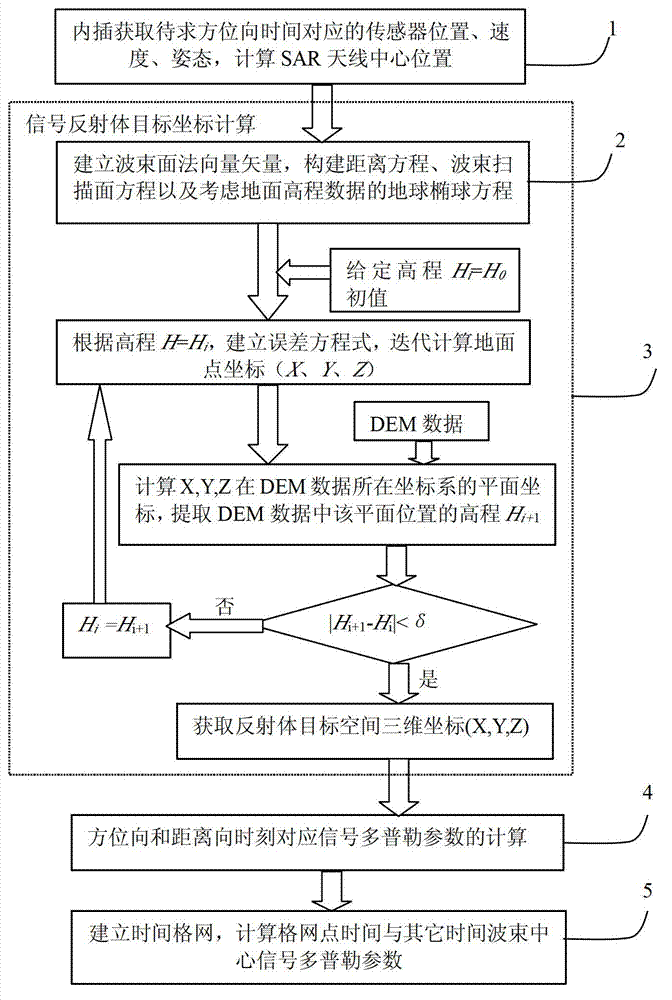
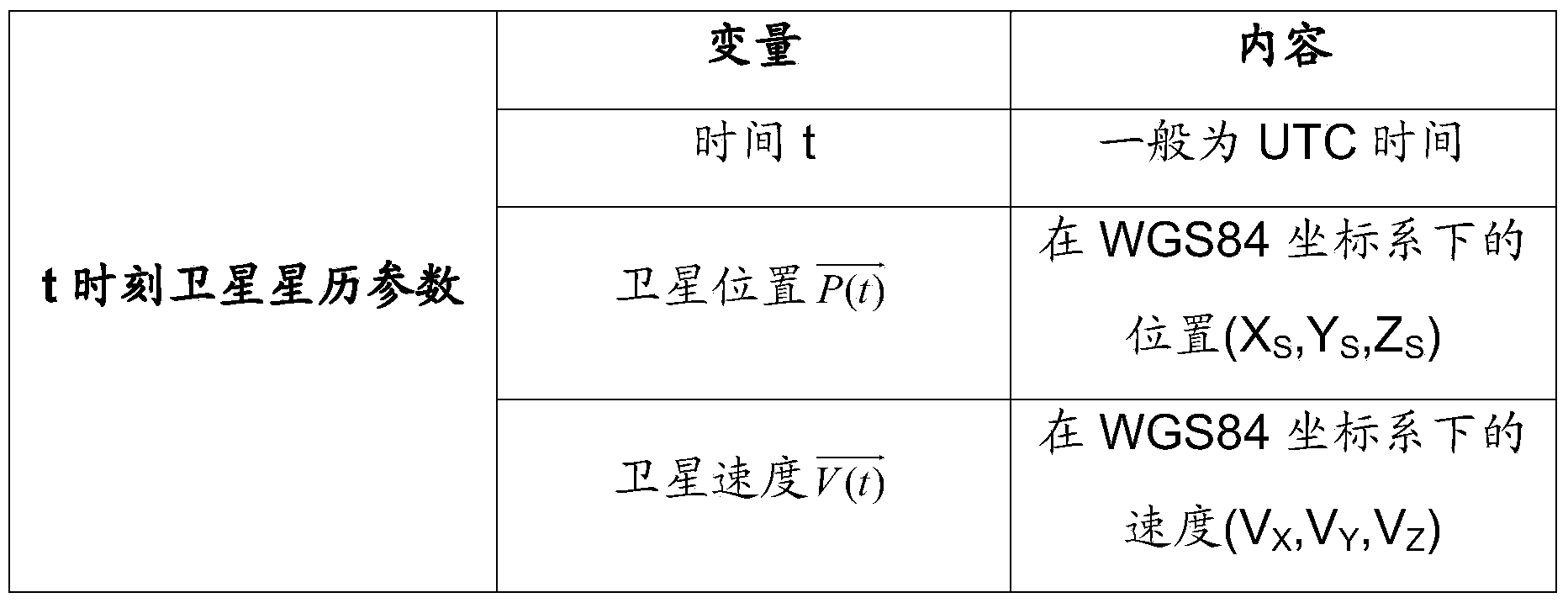
The invention relates to a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) Doppler parameter estimation method based on POS and DEM data. According to the method, onboard GPS navigation data, IMU attitude bases and digital altitude data, target locations of reflected signals are calculated according to a range equation and a coplanarity equation and by considering earth ellipsoid data of ground altitude data, and Doppler information of the wave beam center is estimated according to a sensor state and target location information. According to the method, high-precision estimation can be fully performed on the onboard SAR wave beam center Doppler parameters under non-side-looking, non-stable flying and complex ground terrain conditions, and the method has important effects in the fields of SAR signal processing and imaging.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
High-resolution camera different-field-of-view integral time determination method
ActiveCN104144304AApply exact calculationGuaranteed accuracyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEphemerisImage motion
The invention provides a high-resolution camera different-field-of-view integral time determination method. Firstly, the related parameters of a camera required for accurately calculating integral time are determined, the phi angle and theta angle corresponding to a camera theta field of view are determined, and satellite ephemeris parameters and satellite attitude parameters are prepared respectively; conversion from the camera theta field-of-view visual direction into the WGS84 coordinate system is achieved, the visual direction corresponding to the camera theta field of view is intersected with the earth ellipsoid under the WGS84 coordinate system to determine the geographical coordinates of a photography point, and the photography point slope distance can be obtained according to the photography point geographical coordinates and the satellite position. Furthermore, the motion speed of the corresponding photography point of the camera theta field of view under the J2000 coordinate system is calculated, and the conversion relation from the camera to the WGS84 coordinate system is combined, and the photography point image motion can be determined. Finally, according to the worked out photography point slope distance and the photography point image motion, the integral time of the corresponding photography point of the camera theta field of view can be obtained according to an integral time calculation model in the method.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
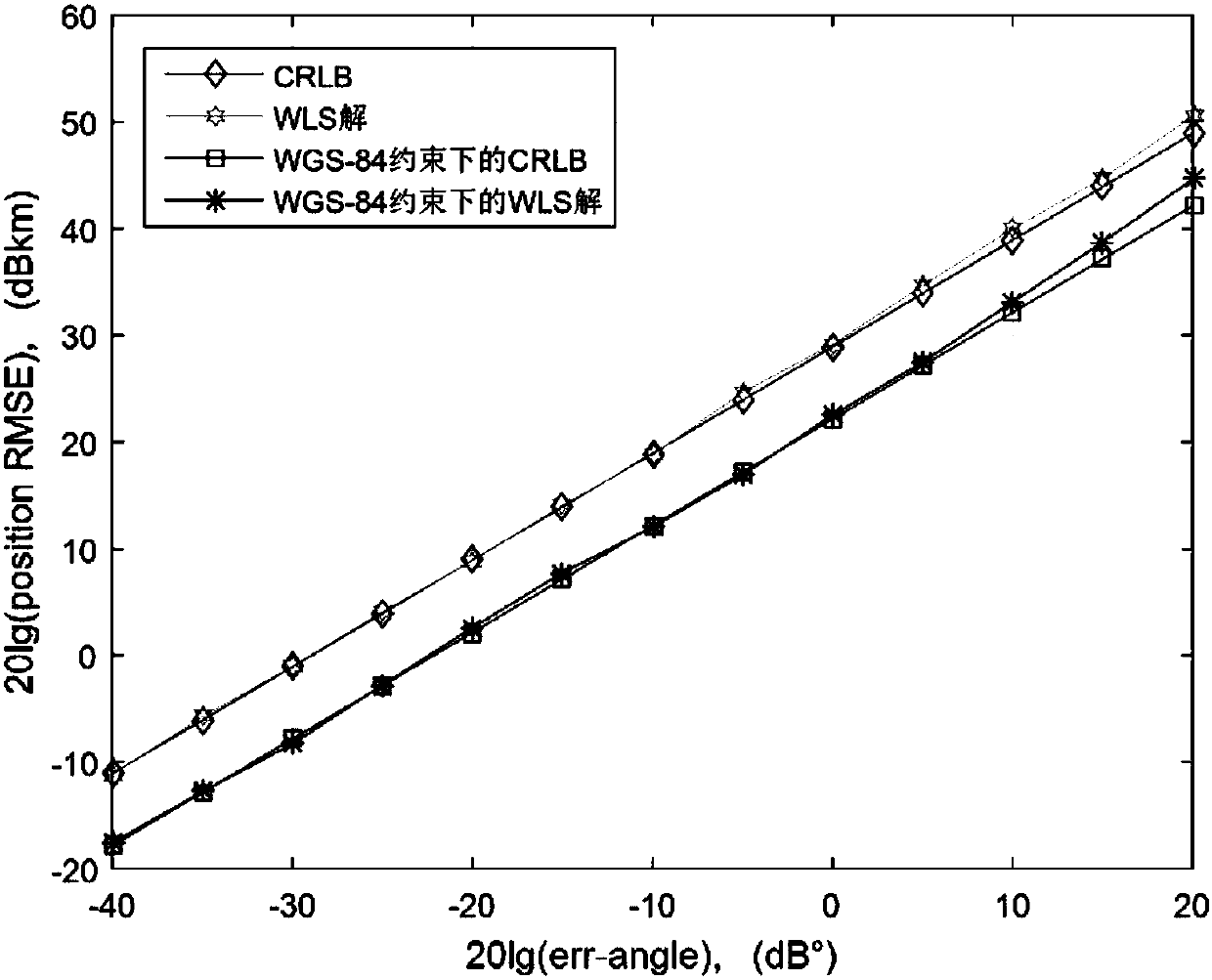
Dual-satellite positioning method based on WGS (World Geodetic System)-84 model
ActiveCN108226978AFlexible configurationNo iterative solutionSatellite radio beaconingSolution analysisEarth surface
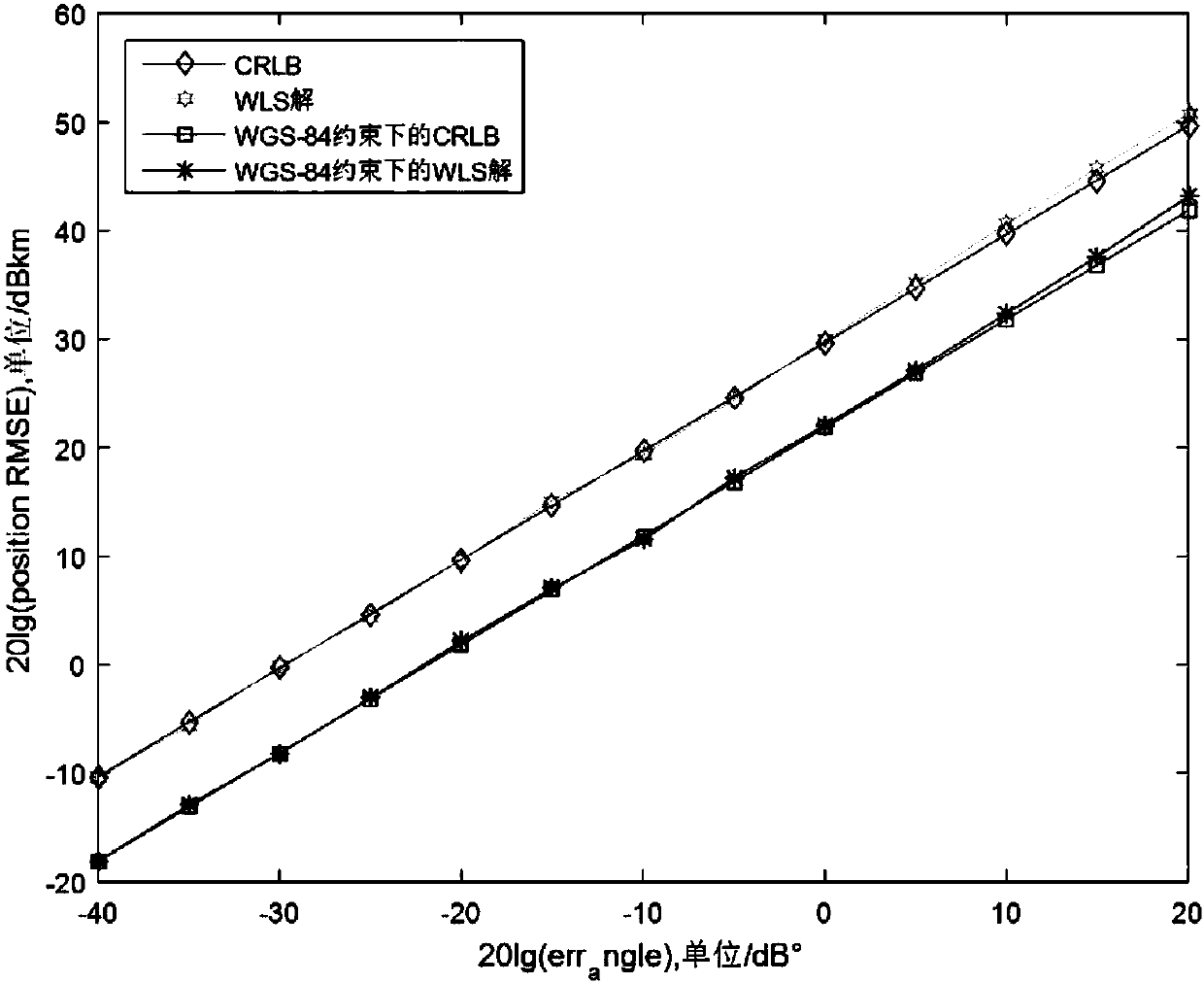
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronic countermeasures, in particular to a dual-satellite positioning method based on a WGS (World Geodetic System)-84 model. A dual-satellite direction-finding positioning closed resolving method based on the WGS-84 model is provided, the dual-satellite direction-finding closed resolving method is provided through the pseudo linearization of anangle measuring equation and combination of WGS-84 earth ellipsoidal model restraint, earth surface target radiation source is positioned and resolved, a weighted least square solution analysis of thetarget under the restraining action of an earth ellipsoidal model is provided; as proved by the simulation, the algorithm can approach the Cramer-Rao low bound (CRLB) of positioning error when the system direction-finding error is not very large; compared with the conventional method of directly resolving a multivariate non-linear equation by an analytical method and using a Newton iteration method to resolve the target position, the method has the advantages that when the two satellites are in the same rail or different rails, the target can be positioned and resolved uniformly, under the method, the configuration of a satellite is flexible, iteration resolution is not required, calculation amount is low, and the problem of inaccurate positioning solution is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for generating line element buffer zone on earth elliposoid based on GIS (geographic information system) component
The invention discloses a method for generating a line element buffer zone on an earth elliposoid based on a GIS (geographic information system) component. The method comprises the following steps of: a, determining vertexes of line elements on an encrypted earth elliposoid; b, calculating out geodetic circles; c, calculating out geodetic rectangles; and d, adopting a CIS component to perform union set generation on the geodetic circles and rectangles established in the step b and step c, so as to obtain a polygon, namely a line element buffer zone on the earth elliposoid. By the method in the invention, the process for generating a line element buffer zone on the earth elliposoid is greatly simplified, and a convenient and efficient method for generating a line element buffer zone on the earth elliposoid on any map projection plane can be provided for users having GIS secondary development capability, an effective technical means for generating high-precision unilateral and bilateral ocean boundaries can be provided for ocean demarcation, and the method has an important significance on protecting national ocean rights and interests according to laws.
Owner:彭认灿
Method suitable for fast spatially-indexing global digital elevation model and remote sensing image data
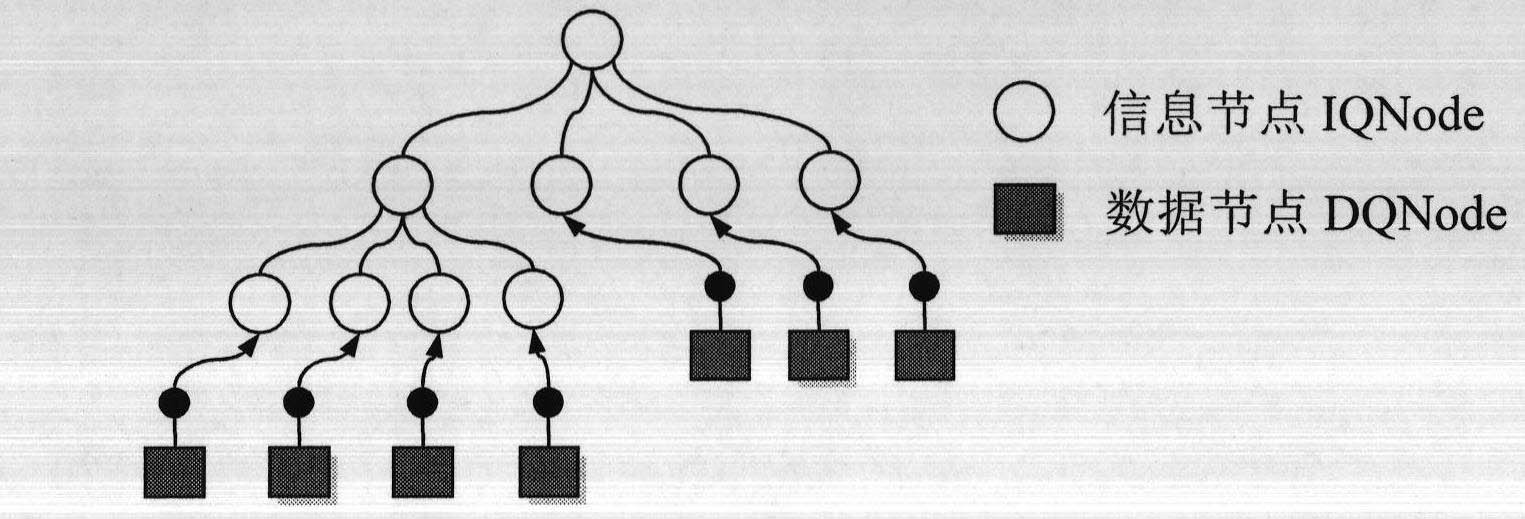
InactiveCN102663028AMask storage locationIncrease flexibilitySpecial data processing applicationsVirtualizationInformation space
The invention relates to a method for indexing a global digital elevation model and remote sensing image data with an ellipsoid quad-tree technology. The method performs quad-tree grid partition to an ellipsoid surface of the earth according to a curvature of the earth, separates a data organization structure and a data storage structure through virtualization for an ellipsoid quad-tree node, and implements multistage seamless integration for mass global data by a sub-tree hooking way. According to the invention, the method overcomes defects of existing spatially-indexing technologies; the spatially-indexing method for global space data provided by the invention is high in efficiency and simple in operation; and the method has good application value in a geographic information space field.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
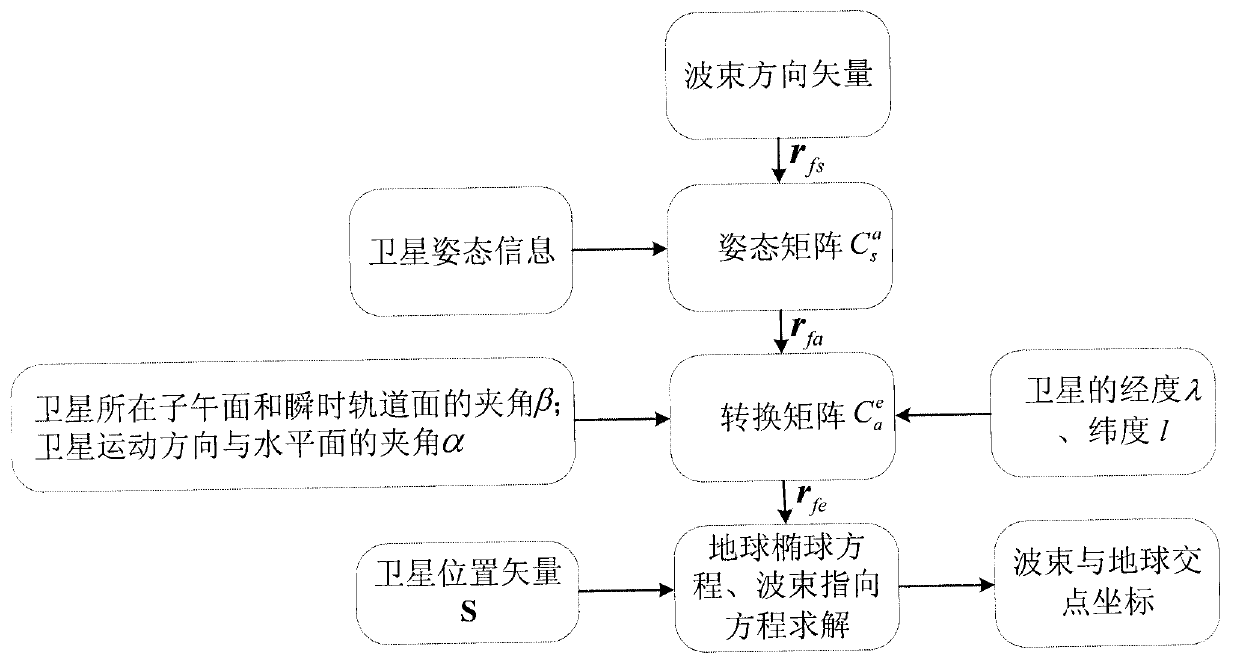
Method for determining intersection coordinates of satellite wave beam and earth
ActiveCN102819019AEasy accessImprove reliabilityIndication/recording movementFluid speed measurementLongitudeGeographic coordinate system
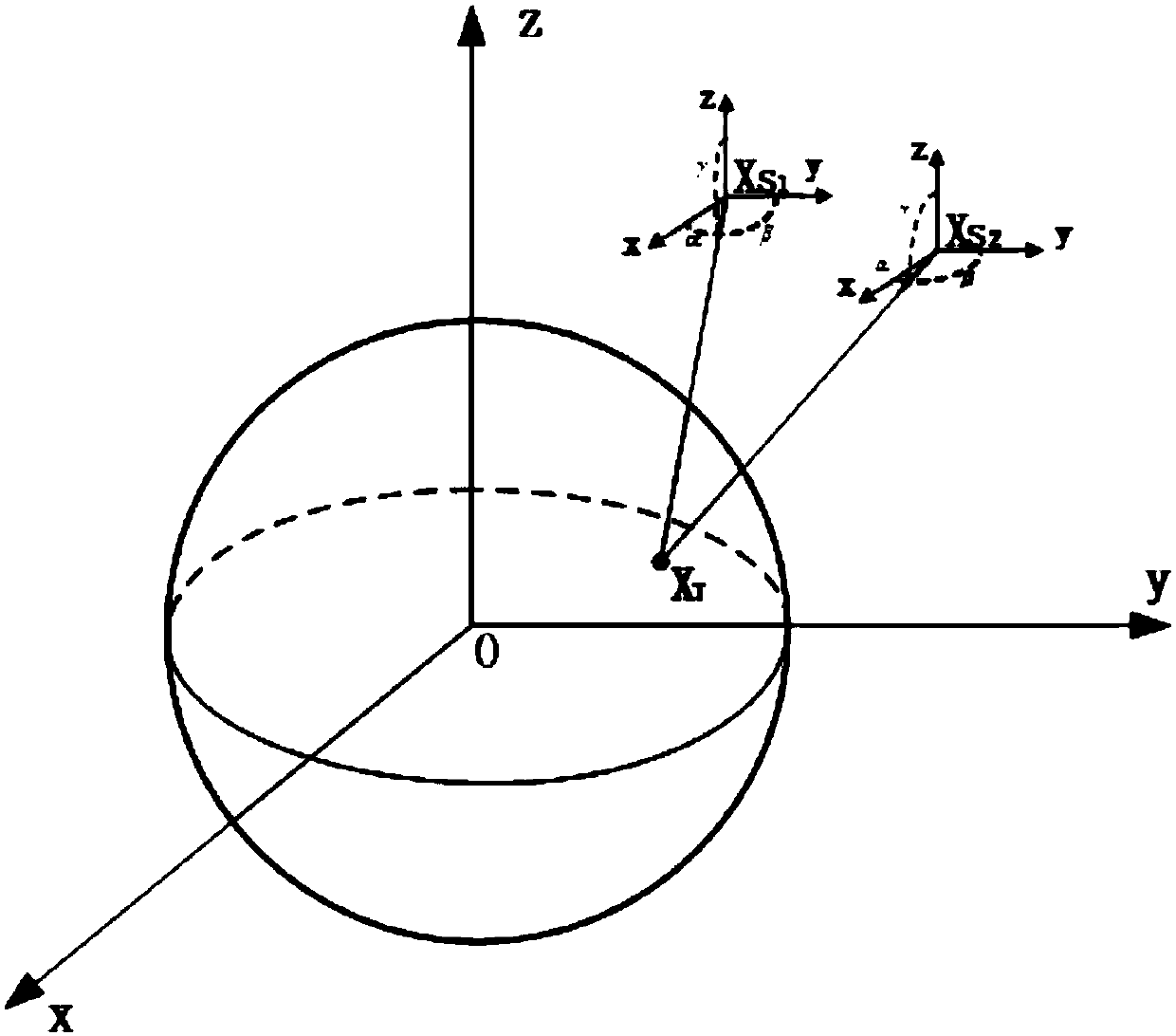
The invention discloses a method for determining intersection coordinates of a satellite wave beam and the earth. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) seeking a unit vector rfs of the satellite wave beam in a satellite body coordinate system; (2) calculating a conversion matrix of the satellite body coordinate system and a satellite track coordinate system by a yaw angle, a pitch angle and a roll angle of a satellite; (3) calculating the conversion matrix of a geographic coordinate system and an earth coordinate system by longitude lambda and latitude I of the satellite; (4) calculating the conversion matrix of an auxiliary coordinate system and the geographic coordinate system by an included angle beta of a meridian plane on which the satellite is and an instantaneous orbit plane of the satellite and an included angle alpha between a movement direction of the satellite and a geographic horizontal plane; (5) converting the unit vector rfs into the earth coordinate system to obtain rfe by coordinate system conversion; (6) associating a linear parameter equation of satellite beam incidence with an earth ellipsoid equation, and calculating two groups of coordinates [xje, yje and zje]T, wherein a group of coordinates near the satellite are coordinates of an intersection point of the satellite wave beam and the earth.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
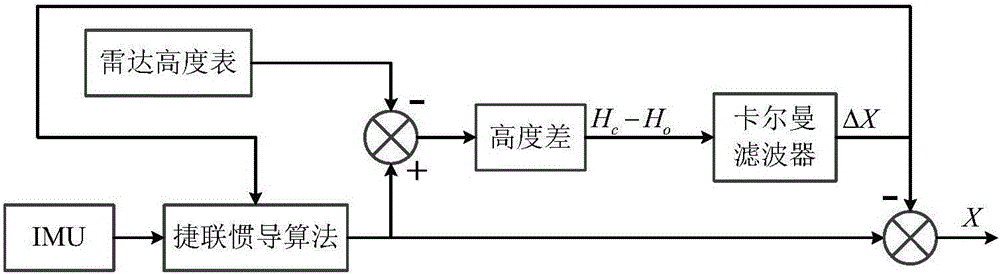
Radar altimeter assistance method aiming to inertial navigation
InactiveCN105841699AHigh positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar altimeterNavigation system
The invention provides a radar altimeter assistance method aiming to inertial navigation. In the method, a measurement quantity is constructed in the manner of calculating earth core altitude of an air vehicle according to position vectors outputted by the inertial navigation, calculating earth core altitude minus earth ellipsoidal radius to obtain the calculated altitude height of the air vehicle, obtaining observed altitude height by means of a measurement value from the radar altimeter with other algorithms, and calculating altitude height minus the observed altitude height to obtain a difference as the measurement quantity, and finally deriving a total differential equation of the measurement quantity. The invention provides a particular embodiment, wherein a strapdown inertial navigation / radar altimeter combined navigation system is formed on the basis of the measurement quantity. Estimation on position error status quantity is achieved, diffusion of position error is inhibited and positioning precision is increased through an indirect method Kalman filtering with feedback compensation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Strict collinearity equation model of satellite-borne SAR image
InactiveCN101571593ASatisfy the ground positioningRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCentral projectionComputer vision
The invention discloses a strict collinearity equation model of a satellite-borne SAR image. In the model, the derivation is carried out aiming at an earth ellipsoid model, a virtual projection center is built at each orientation of the SAR image, and a computing method of external parameter and equivalent focal length of a virtual projection center sensor and a revision method from a slant-distance image to a central projection image are derived. The method solves the following problems: (1), an approximate collinearity equation model is not strict; and (2), a ground control point is required to carry out image geocoding when the external parameter of the sensor is unknown.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
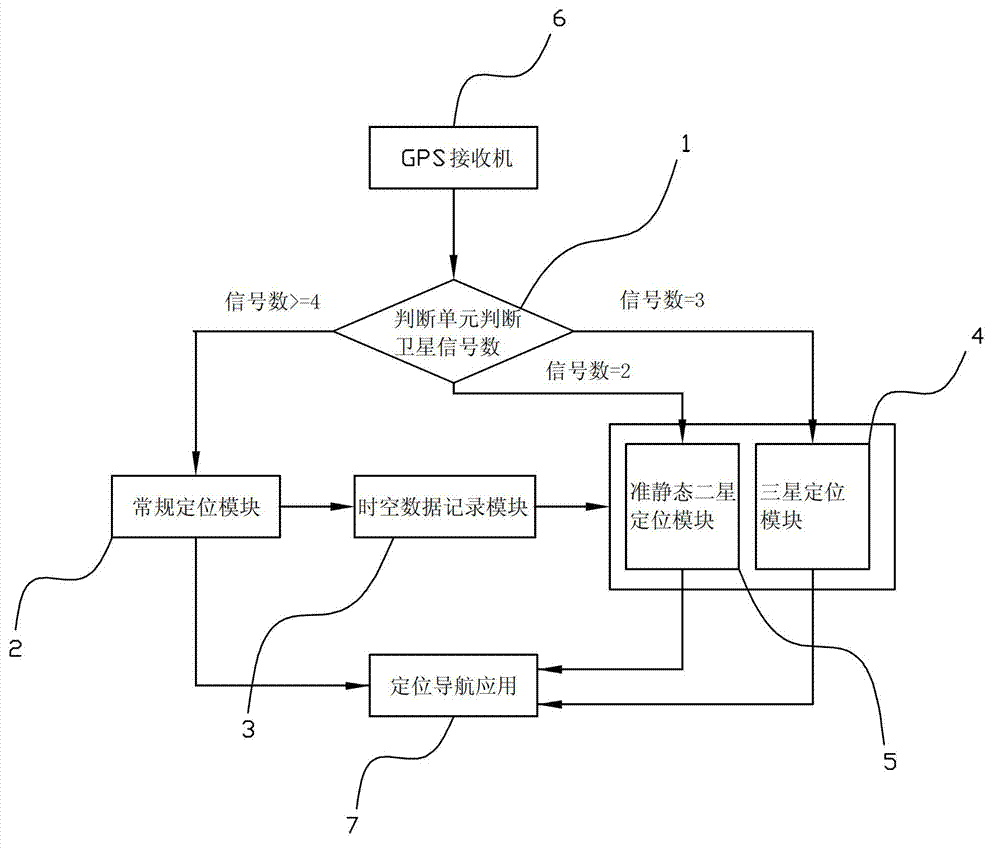
Quasi-state dual-satellite positioning method and application thereof
ActiveCN103713300AReal-time precise positioning capabilityGuaranteed positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingGps receiverTime space
The invention relates to a quasi-state dual-satellite positioning method. A database is used for storing and refreshing conventional positioning spatio-temporal data; when the satellite signal loss phenomenon occurs, the adjacent spatio-temporal data can be searched to establish a precise earth ellipsoid equation to ensure the positioning precision; and because the adjacent spatio-temporal data are used as an iterative initial value, the resolving real-time performance is improved and the wrong positioning solution can be prevented. because Doppler frequency shift amounts are observed continuously, only two satellites are needed to realize real-time and precise positioning based on the positioning equation on the quasi-state condition. According to the invention, under the circumstances that the satellite signal loss phenomenon occurs and the GPS receiver only can receive two or three satellite signals temporarily, the real-time and precise positioning capability can be realized, wherein the error is maintained within ten meters. On the normal motion condition, the precise positioning within 20 minutes can be maintained by using a three-satellite positioning way; and on the quasi-state condition, the precise positioning over 20 minutes can be maintained by using the three-satellite or dual-satellite positioning way.
Owner:XIAMEN YAXON NETWORKS CO LTD
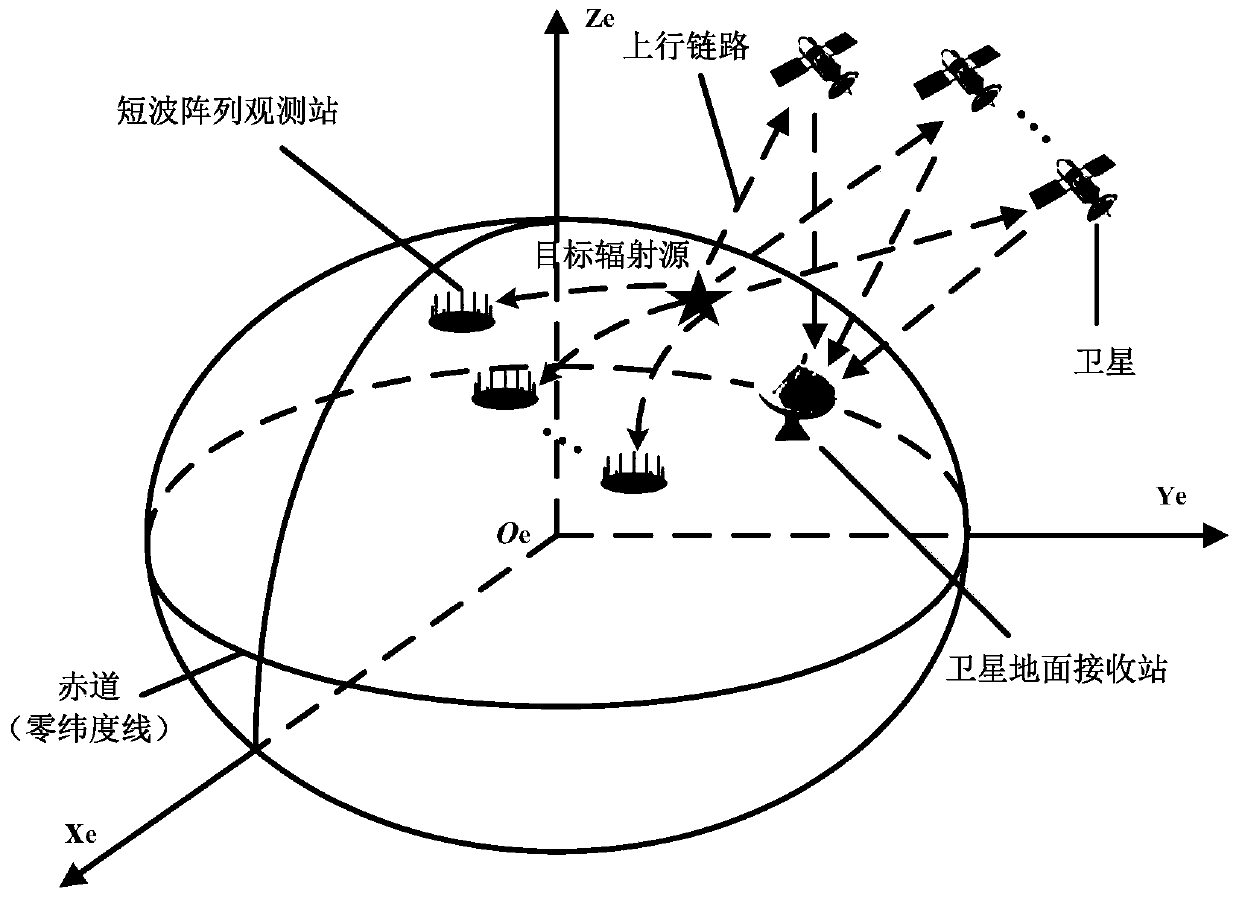
Passive positioning method of employing cooperative short wave and satellite system for over-the-horizon target
ActiveCN110568403AImprove target positioning accuracyRobustPosition fixationAugmented lagrange multiplierHorizon
The invention discloses a passive positioning method of employing cooperative short wave and satellite system for an over-the-horizon target. The method comprises the steps of establishing pseudo-linear observation equations about a plurality of satellite uplink time difference parameters by using an auxiliary variable; establishing a mathematic relation of various short wave observation station arrival azimuths about horizontal coordinate parameters of a target on various stations on the basis of local horizontal coordinate systems of various short wave observation stations, and establishingpseudo-linear observation equations based on a plurality of short wave observation station azimuth parameters by using conversion of the coordinate parameters of the target in horizontal coordinate systems of various stations and earth-centered earth-fixed coordinate parameters; establishing a global least squares optimization model in a quadratic constraint condition by combining the pseudo-linear observation equations of the plurality of satellite uplink time difference parameters with the pseudo-linear observation equations of the plurality of short wave observation station azimuth parameters and combining earth ellipsoid constraints; and designing an augmented Lagrange multiplier algorithm to achieve accurate positioning of the ground over-the-horizon target. According to the passive positioning method, two positioning mechanisms can be cooperatively utilized effectively, so that the positioning accuracy on the target is significantly improved.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Borehole positioning method based on earth ellipse sphere
InactiveCN106991267AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsEllipseMap projection
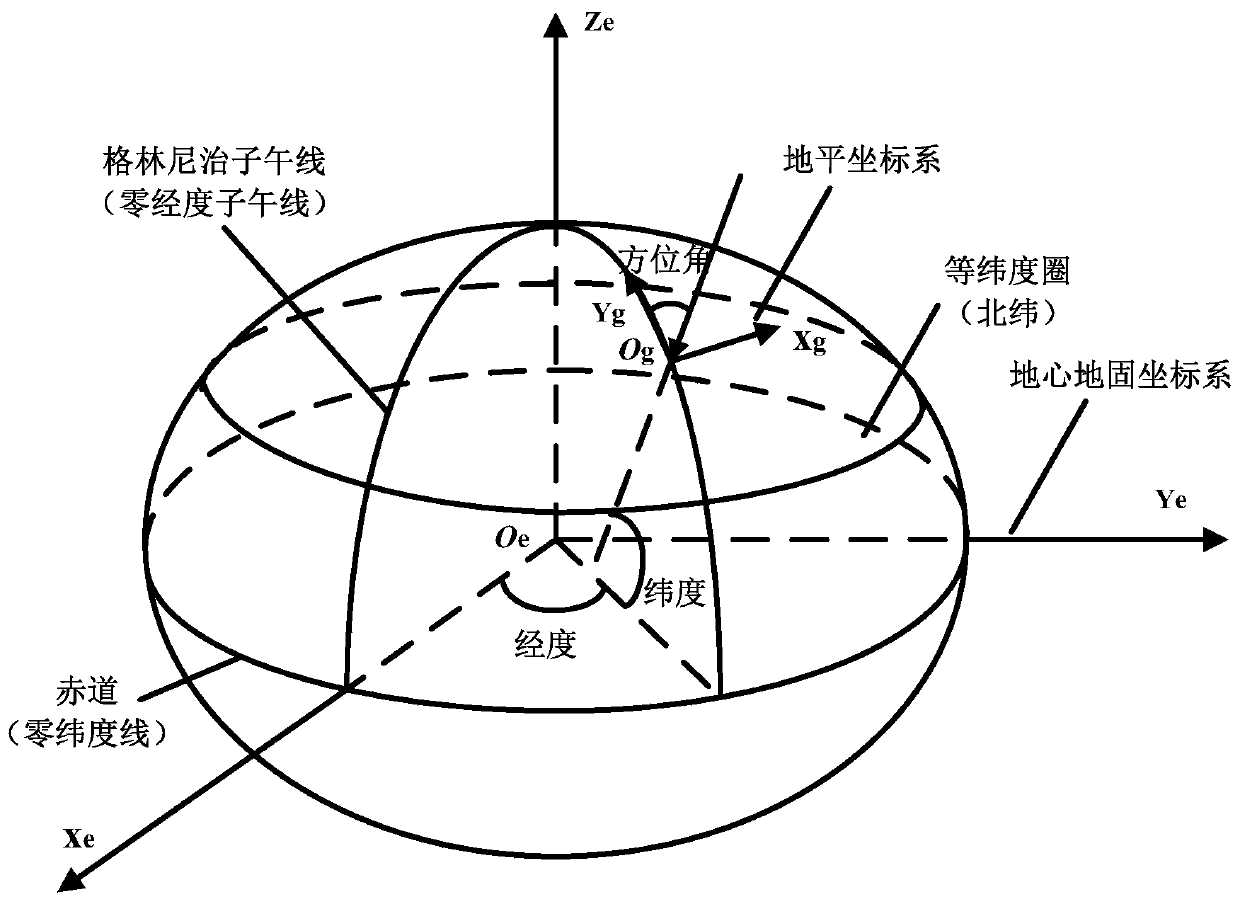
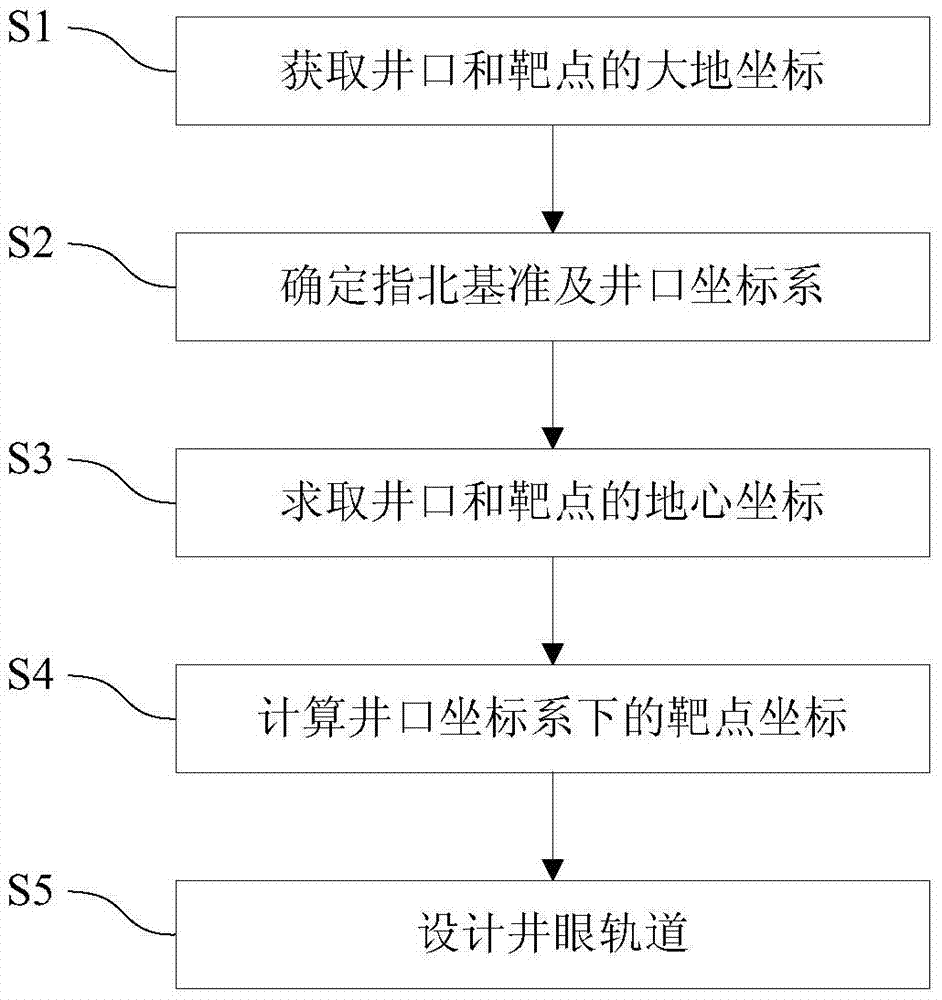
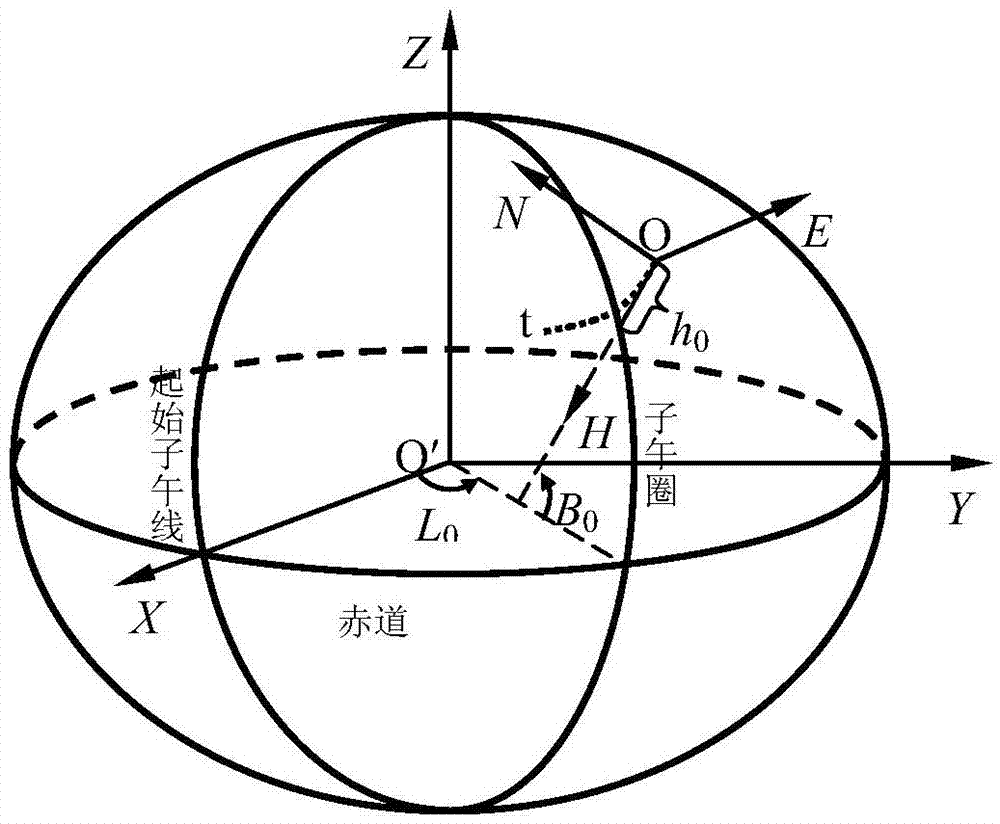
The invention discloses a borehole positioning method based on the earth ellipse sphere. The borehole positioning method comprises obtaining the geodetic coordinates of the wellhead and the target point; determining the north-seeking standard and the wellhead coordinate system; calculating the geocentric coordinates of the wellhead and the target point; calculating the target point coordinate in the wellhead coordinate system; and designing the borehole trajectory. Because the influence of the curve of the earth ellipsoid surface is considered, and map projection and projection transformation problems are not involved, errors caused by map projection deformation and concomitant various error risks are eliminated, and therefore the precision and the reliability of borehole positioning and borehole trajectory designing can be substantially improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for correcting atmospheric refraction for radar measurement
The invention relates to a method for correcting atmospheric refraction when a radar measures the flight path of a space target. The method is mainly applied to radar precision identification, uses astandard track for identifying a target as a correction reference, and changes a ground vertical reference from an earth's core-to-radar position vector in a traditional method to an earth ellipsoid curvature center-to-radar position vector. Thus, the geocentric distance is replaced by curvature center distance and the earth's core intersection angle is replaced by the curvature center intersection angle so as to improve the refractive correction in the space target measurement. The method considers the non-spherical characteristic of the earth, makes the calculation of the refraction error closer to the physical reality, can be directly applied to the precision identification of the space target measurement radar, improves the error separation level of the precision radar, is used in thefields of space debris environment monitoring, in-orbit service and space situational awareness energy, and improves the space target measuring and tracking ability.
Owner:NO 63921 UNIT OF PLA
GNSS computerized ionospheric tomography projection matrix acquisition method based on ellipsoid
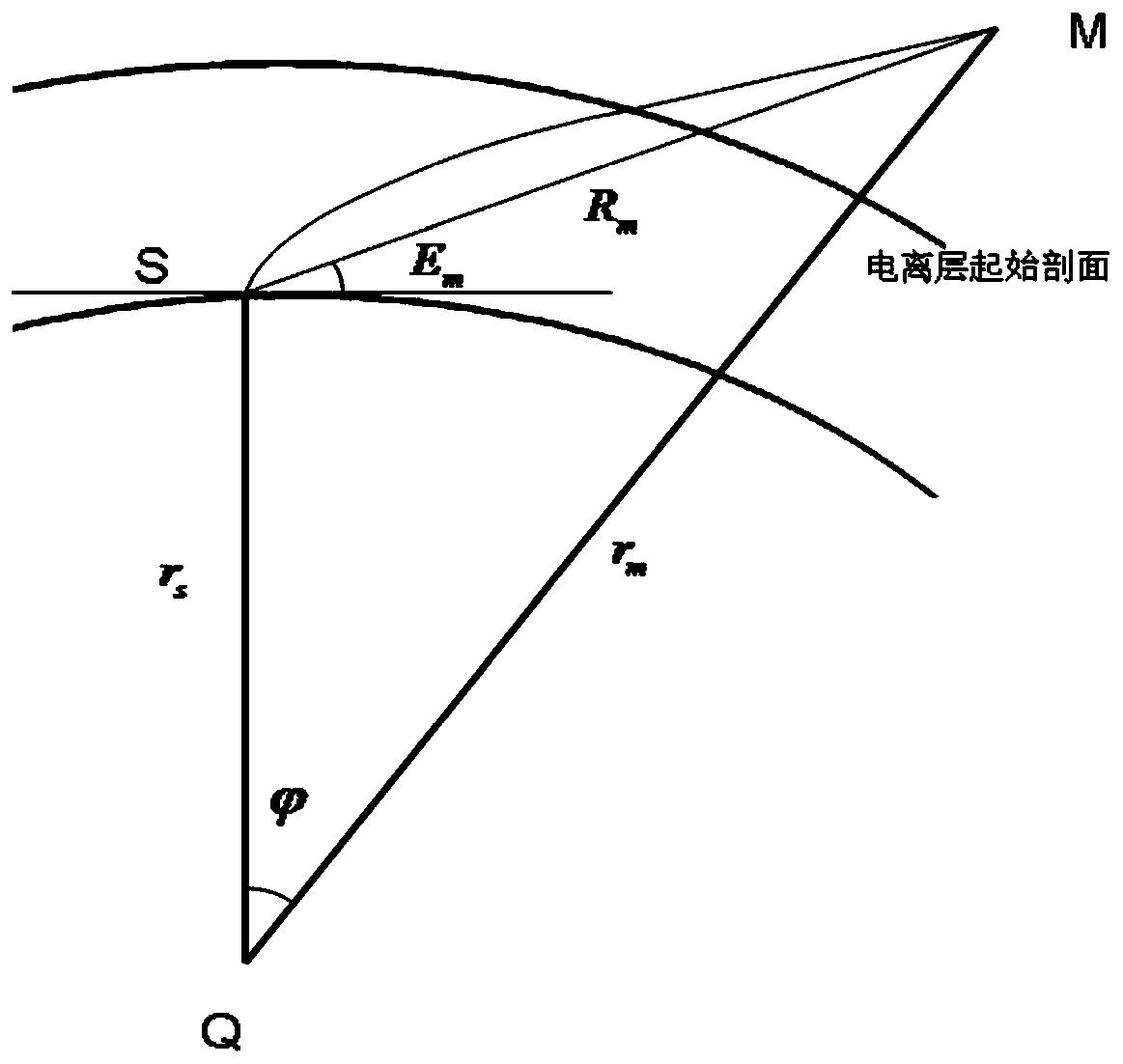
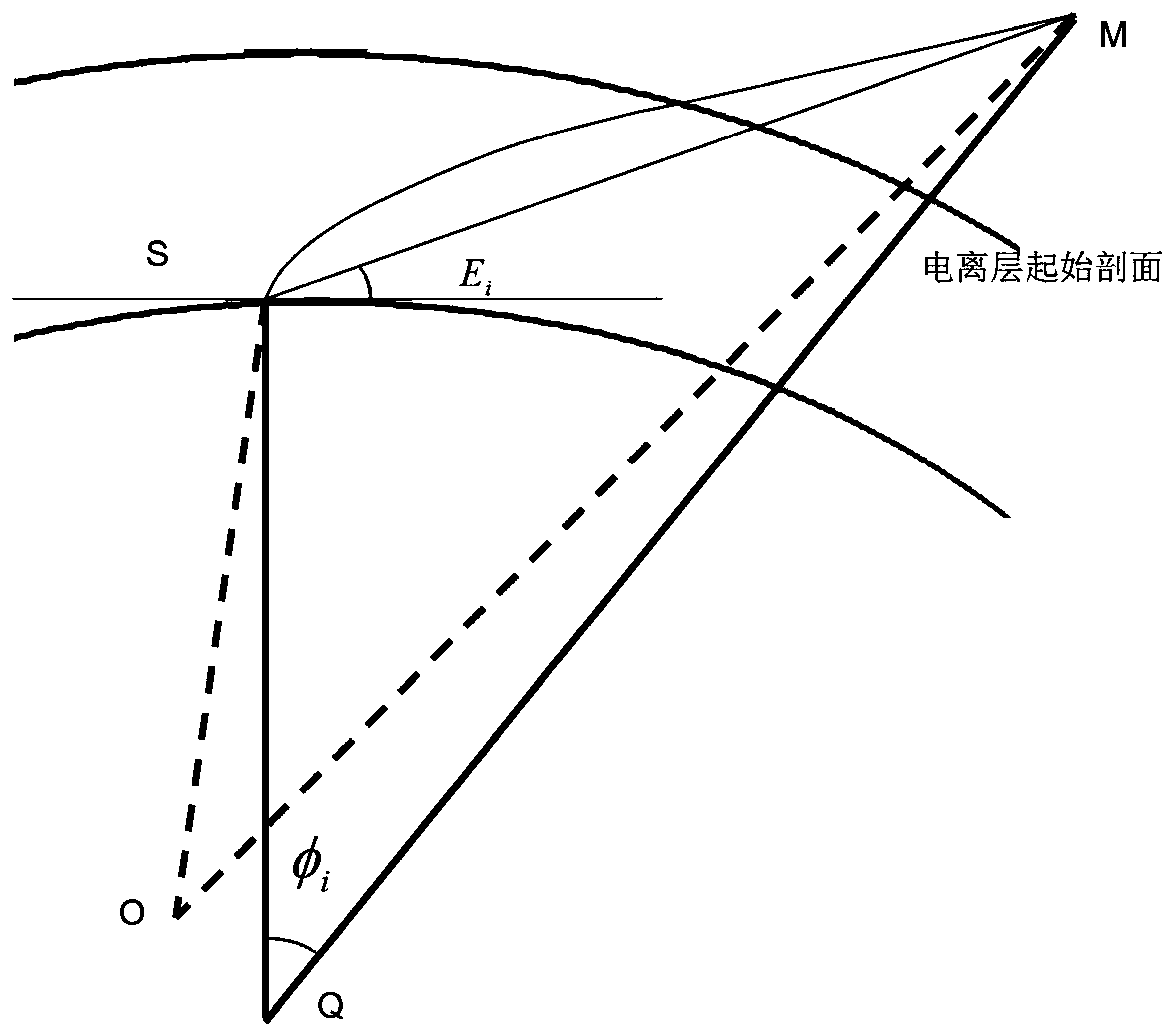
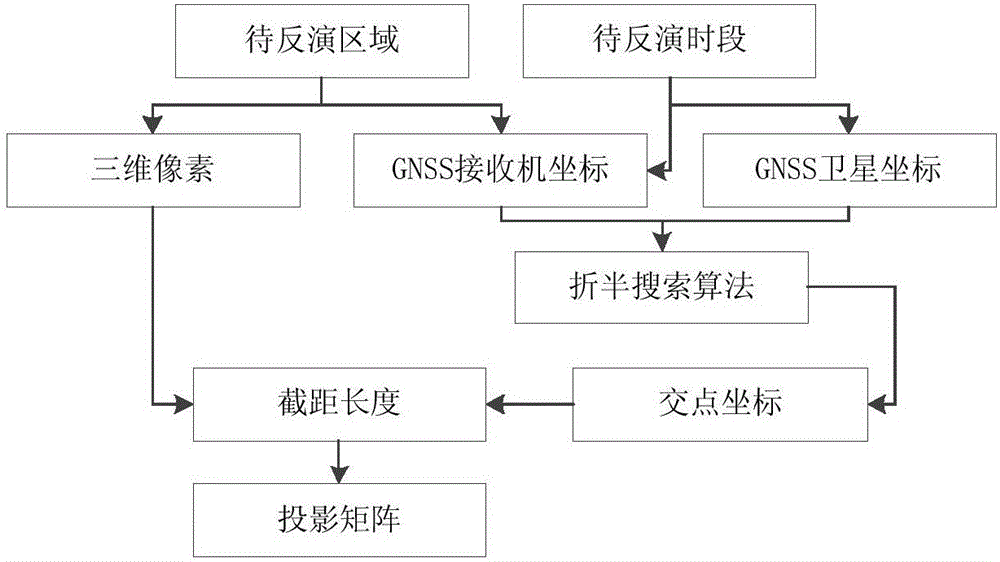
ActiveCN105954764AOvercoming the problem of approximating a sphereTrue Reflects the True InterceptSatellite radio beaconingHat matrixNatural satellite
The invention discloses a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) computerized ionospheric tomography projection matrix acquisition method based on ellipsoid, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, a to-be-inversed area and a to-be-inversed period of the computerized ionospheric tomography are determined; S2, the to-be-inversed area is discretized as a series of 3D voxels; S3, geodetic space rectangular coordinates of a GNSS satellite and a GNSS receiver in the to-be-inversed area and the to-be-inversed period of the computerized ionospheric tomography are prepared; S4, intersection points of signal propagation paths from the GNSS satellite to the GNSS receiver in the to-be-inversed period and each surface of the 3D voxels are calculated; S5, the intercept lengths of the propagation paths of GNSS satellite signals in voxels are calculated; and S6, a projection matrix is formed. According to the invention, a problem that an earth ellipsoid is made to approximate to a ball based on a method for extracting projection matrix from the ball in the prior art is solved, and a condition that an actual intercept of the GNSS signal propagation path in inversed voxels can be faithfully reflected relative to the projection matrix of the earth ellipsoid can be ensured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Geodesic line interpolation method with geodesic line arch height tolerance constrained
ActiveCN107917694ARealize precision displayComplex mathematical operationsProfile tracingRectangular coordinatesAlgorithm
The invention relates to a geodesic line interpolation method with geodesic line arch height tolerance constrained. The geodesic line interpolation method comprises the following steps: reading in longitude and latitude coordinates of a starting point and an end point of a geodesic line; setting the geodesic line arch height tolerance; calculating length, an initial azimuth and midpoints of the longitude and latitude coordinates of each unlabeled broken line section; calculating radium vector of point of tangency of the point on an earth ellipsoid; calculating spatial rectangular coordinates of the starting point and end point of each unlabeled broken line section; calculating geodesic line arch height of each unlabelled broken line section; sequentially judging relation between the geodesic line arch height of each unlabelled broken line section and the geodesic line arch height tolerance, carrying out bipartition encryption interpolation treatment on the broken line section if the geodesic line arch height of the broken line section is higher than the geodesic line arch height tolerance, and carrying out no interpolation treatment on the broken line section if the geodesic line arch height of the broken line section is less than or equal to the geodesic line arch height tolerance. The geodesic line interpolation method provided by the invention has the advantage that preciseplotting of a geodesic line with any length under specified precision and threshold conditions is realized through adaptive adjustment and matching between geodesic line plotting precision and interpolation distance.
Owner:PLA DALIAN NAVAL ACADEMY
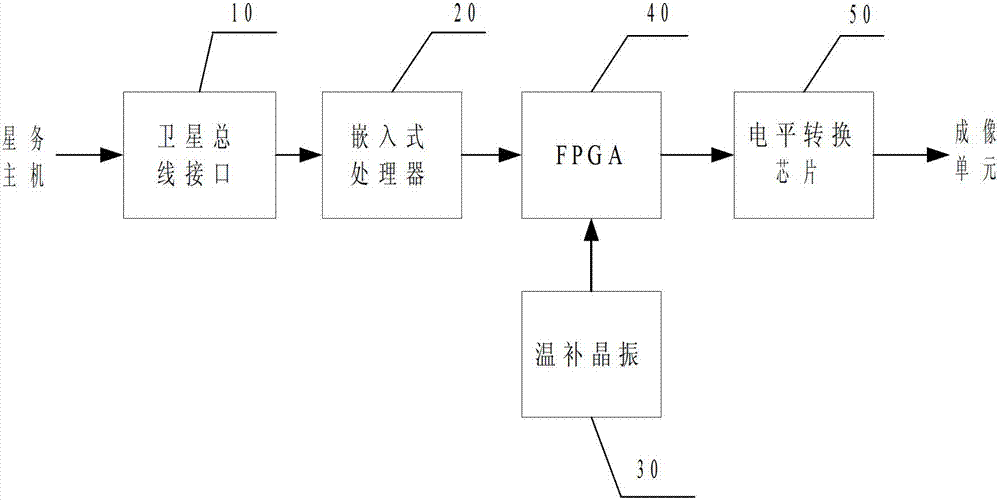
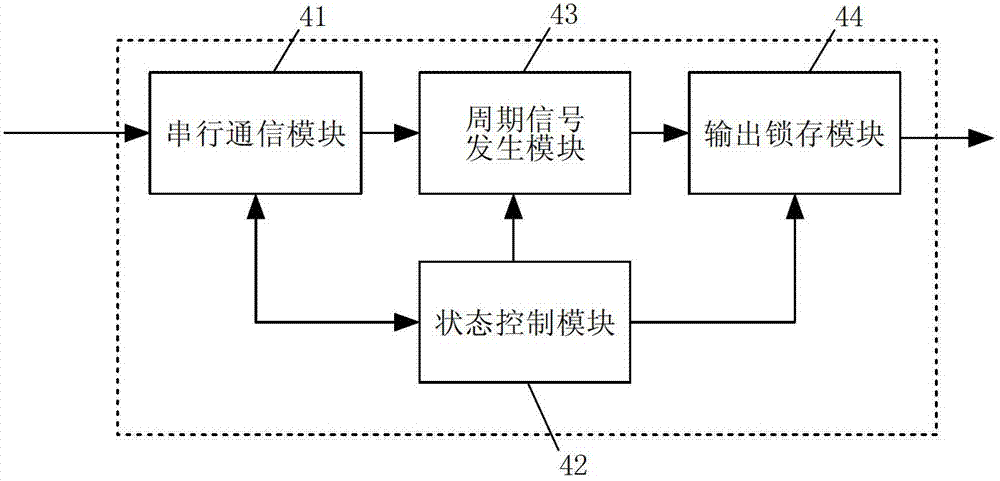
Row cycle real-time adjustment system and method for large-view-field space camera
ActiveCN103245332AIn line with the real situationImprove real-time performancePicture taking arrangementsImage motionTrue Case Status
The invention discloses a row cycle real-time adjustment system and a row cycle real-time adjustment method for a large-view-field space camera, is based on an ellipsoidal model of the earth, considers the image motion velocity differences at different view field positions of the large-view-field space camera, and solves the problems that the existing method is only suitable for small-view-field space cameras, does not consider the compression of the earth, is inconsistent with the true condition and has difficulty in guaranteeing the instantaneity, and the like. The row cycle real-time adjustment system of the large-view-field space camera is composed of a satellite bus interface, an embedded processor, a temperature-compensation crystal oscillator, an FPGA (field programmable gate array) and a level switch chip, wherein the FPGA is used for finishing generation and output enable control of multiple paths of row cycle signals. Compared with the traditional method, the method provided by the invention can effectively reduce the volume, the power consumption of large-view-field space camera controllers, and the machine-hour occupation of embedded processors.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
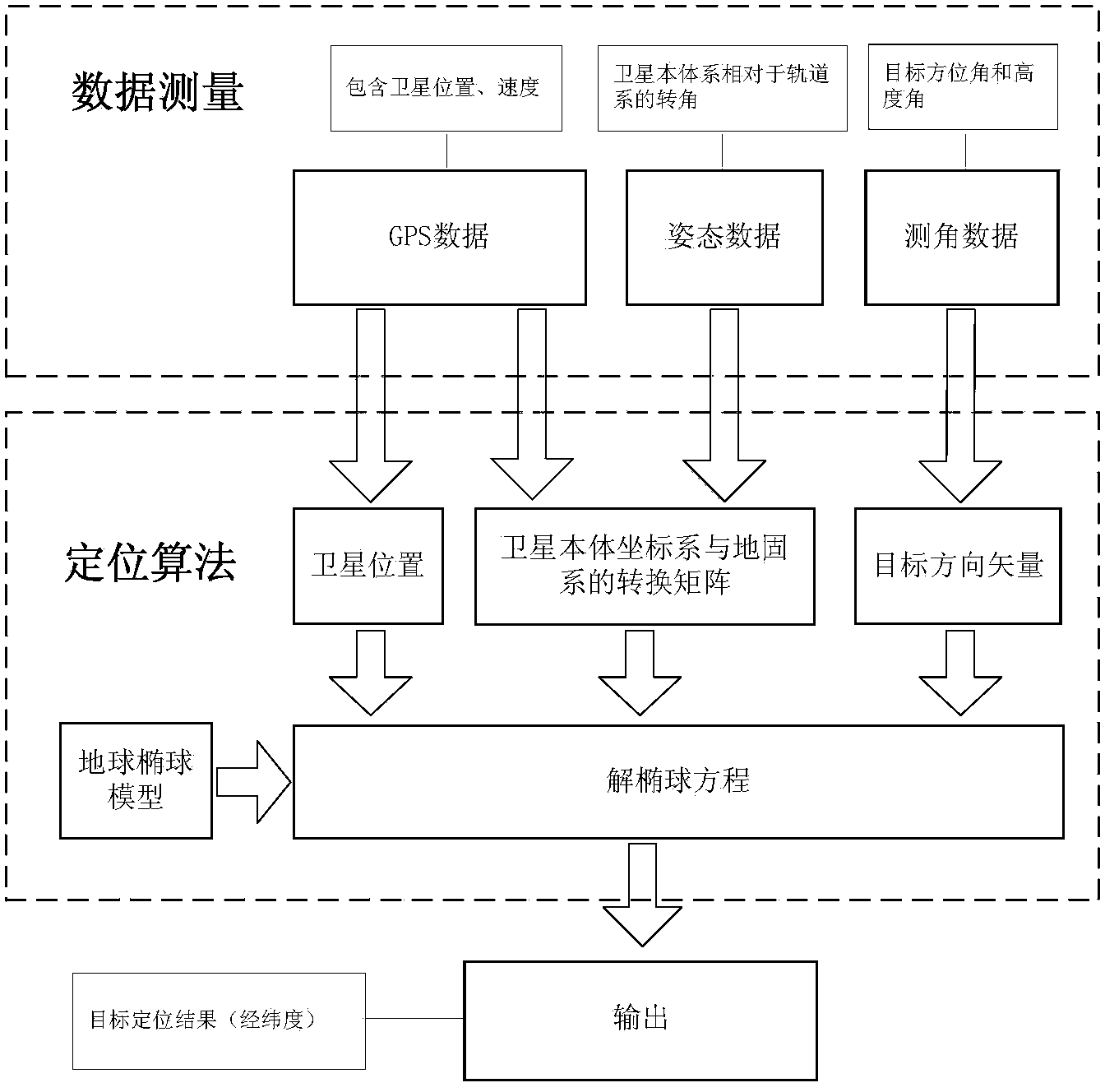
Satellite passive positioning method based on GPS broadcast data
ActiveCN104391311AStrong autonomyHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingSatellite dataBroadcast data
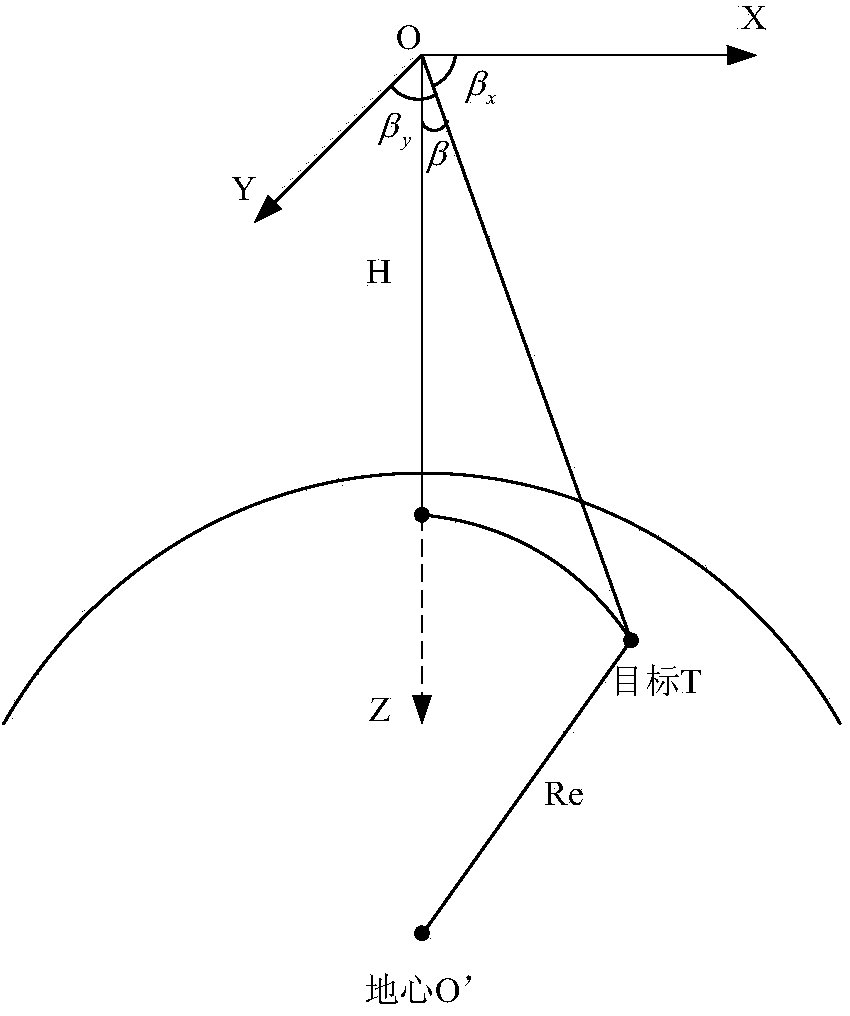
The invention provides a satellite passive positioning method based on GPS broadcast data. The method comprises: acquiring measuring data of a satellite; according to the measuring data, calculating a conversion matrix M from an earth-fixed coordinate system to a satellite local system; selecting an earth ellipsoidal model and obtaining corresponding earth geometrical parameters and an earth ellipsoidal surface equation; and according to the conversion matrix M, solving an object position equation, and solving object position coordinates by simultaneously solving the earth ellipsoidal surface equation. The measuring data comprises the GPS broadcast data including a satellite real-time position P<se><-> and a speed V<se><->, object measurement angles beta<x> and beta<y> and attitude angle data, i.e., a pitch angle phi, a yaw angle yaw angle gamma and a roll angle theta, wherein the GPS broadcast data is obtained through a satellite data bus, the beta<x> and the beta<y> are obtained through a load subsystem, and the attitude angle data is obtained through an attitude orbit control subsystem. According to the invention, the high-precision GPS broadcast data is taken as a system input quality, such that the precision of each parameter during a calculation process is ensured, accordingly, the precision of a positioning result is ensured, at the same time, an offline processing process is unnecessary, and the satellite autonomous calculating capability is enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
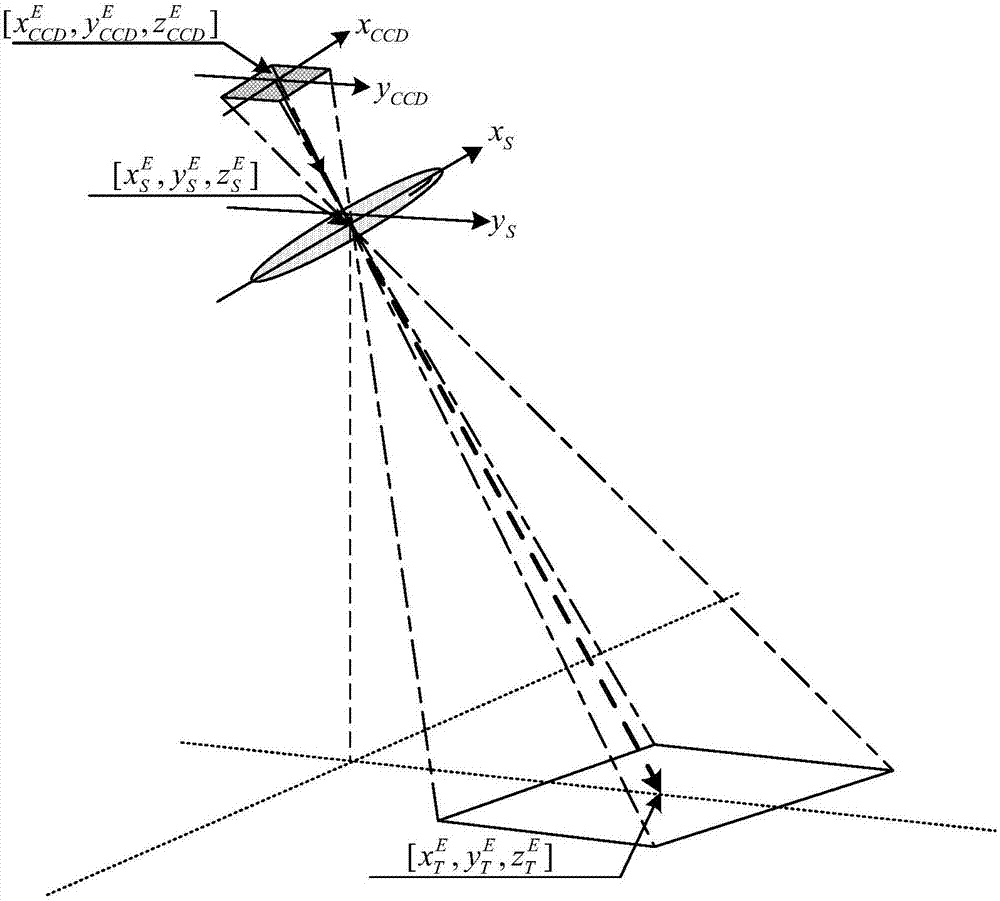
Method for ground positioning by remote sensing image of large side-swaying linear array CCD (Charge Coupled Device)
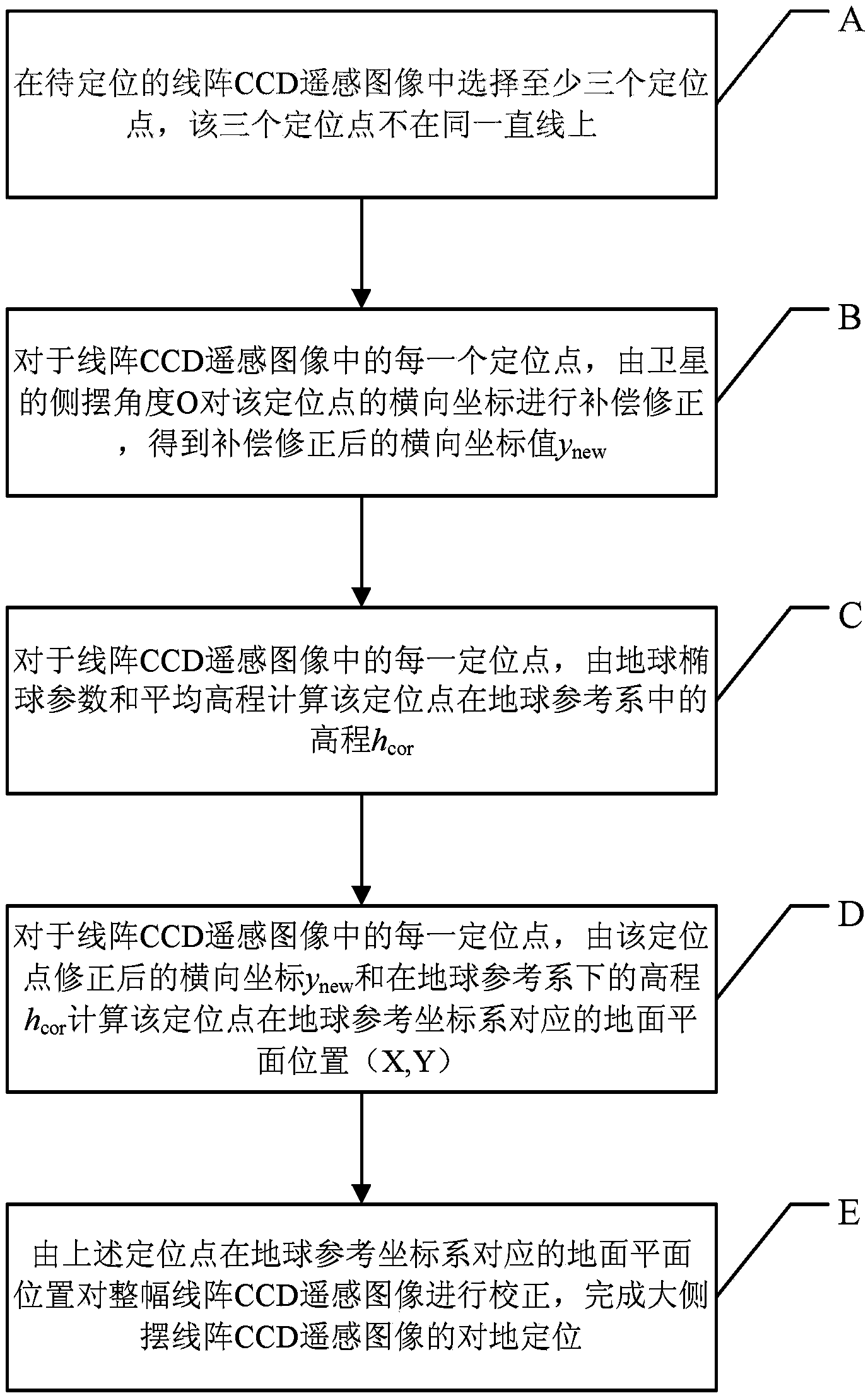
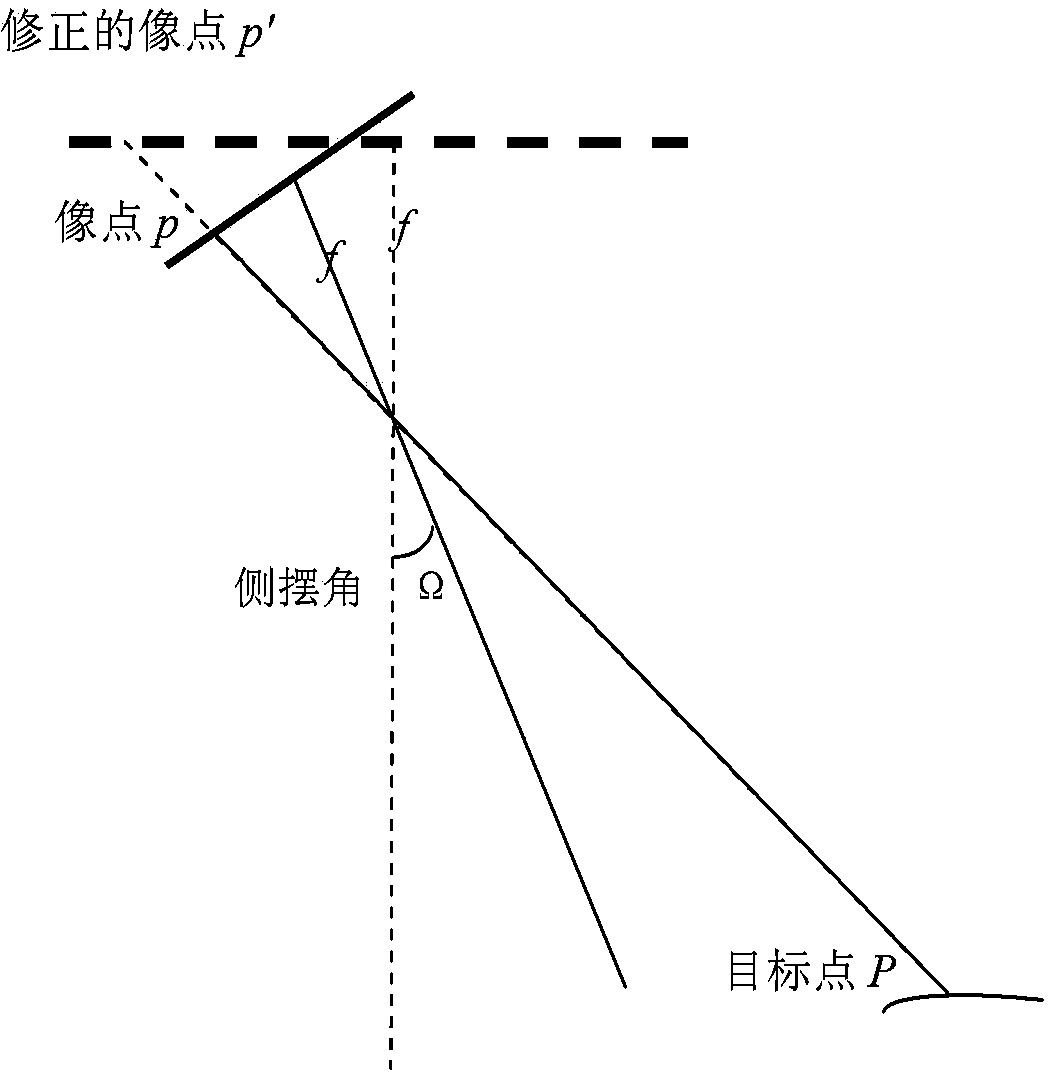
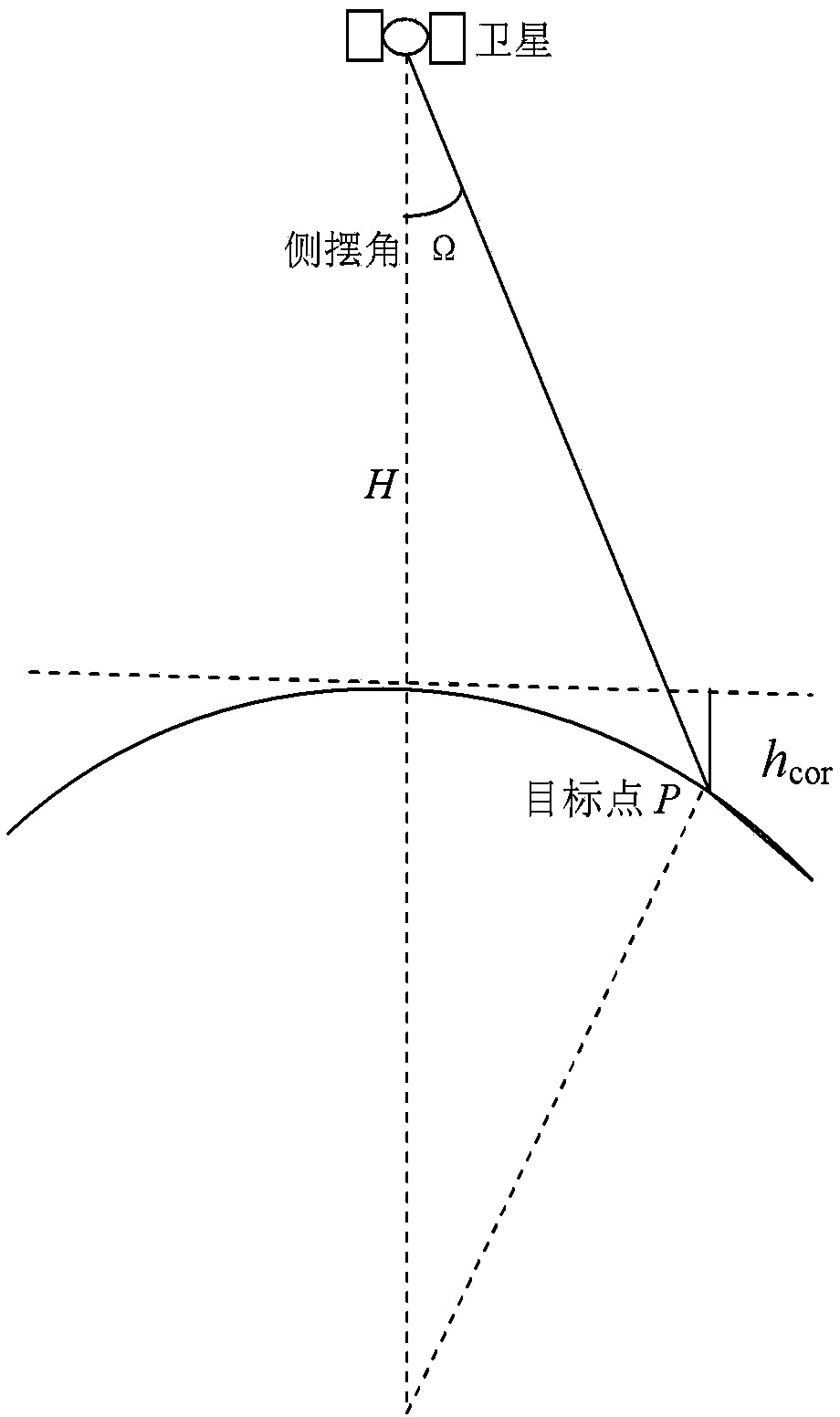
ActiveCN104019800AThe geometric relationship is strictly maintainedCurvature Effect CompensationPicture interpretationGround planeComputer science
The invention provides a method for ground positioning by a remote sensing image of a large side-swaying linear array CCD (Charge Coupled Device). The method comprises the following steps of: (A) selecting at least three positioning points in the remote sensing image to be positioned of the linear array CCD; (B) carrying out compensation and correction on a transverse coordinate of the positioning point by a side-swaying angle Omega for each positioning point; (C) for each positioning point, calculating elevation hcor of the positioning point in a terrestrial reference system on the basis of a terrestrial ellipsoid parameter and an average elevation; (D) for each positioning point, calculating a corresponding ground plane position (X, Y) of the positioning point in the terrestrial reference system; and (E) correcting the whole remote sensing image of the linear array CCD according to the corresponding ground plane positions of at least three positioning points. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the image-space coordinate of the remote sensing image of the linear array CCD is corrected and compensated according to the side-swaying angle of a satellite, and the geometrical relationship of the transverse coordinate of the image is maintained strictly when the satellite sways to one side.
Owner:济钢防务技术有限公司
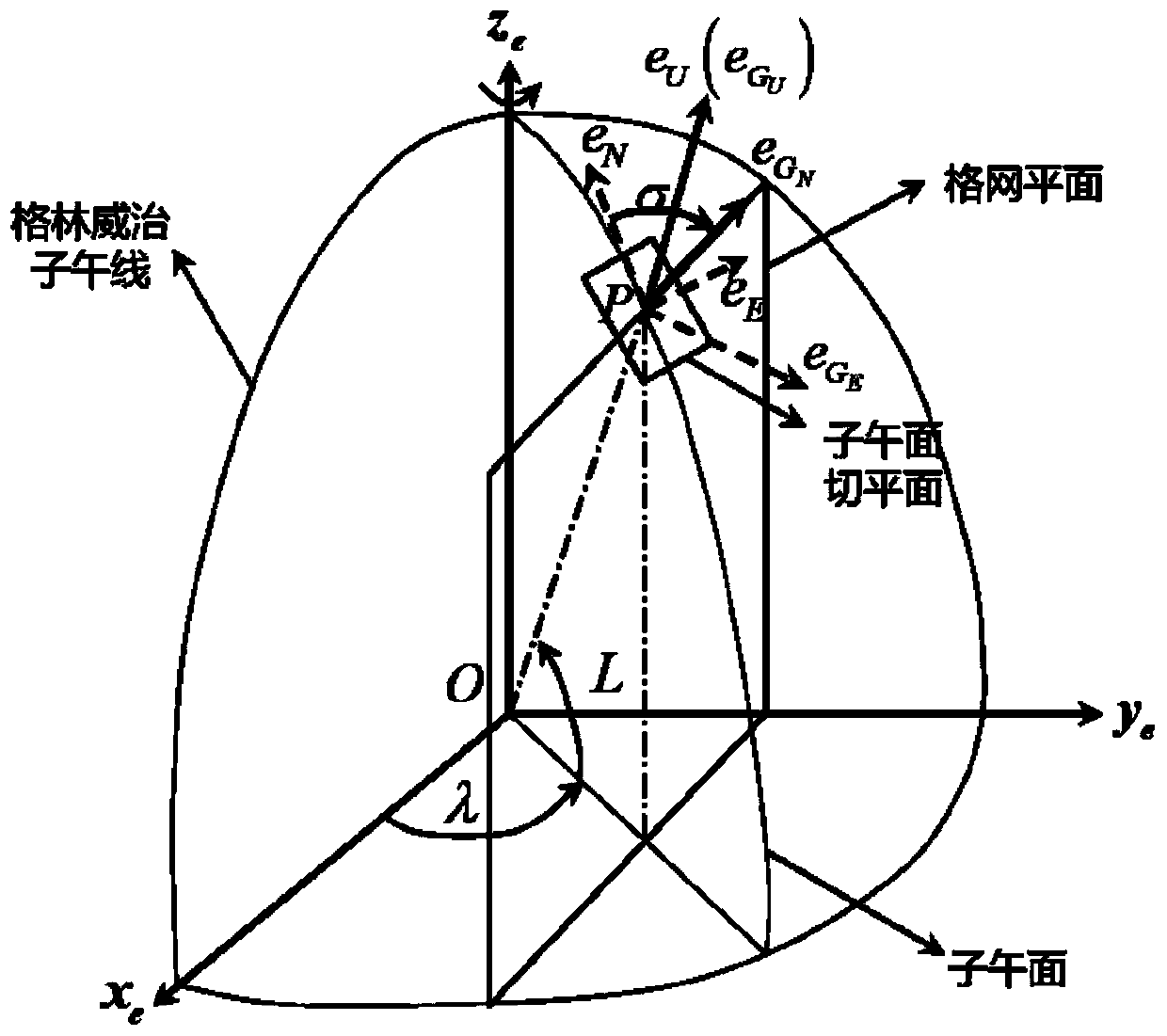
Polar region inertial navigation error acquiring method under earth ellipsoid model
ActiveCN111060140AImprove accuracyReduce the impact of error propagation process accuracyMeasurement devicesComplex mathematical operationsRectangular coordinatesComputational physics
The invention relates to a polar region inertial navigation error acquiring method under an earth ellipsoid model. A calculation error source under the earth ellipsoid model is added into an attitudeerror equation; the grid speed is expressed as a grid speed true value and a grid speed error by a speed error equation, and various error sources are added; and a position error equation adopts a rectangular coordinate system to solve the position, and a grid calculation value containing the grid position true value and the grid position error is added into an error source. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the error model for polar region inertial navigation calculation under the earth ellipsoid model is established, the influence of the earth sphere model on the precision of the error propagation process is reduced, the accuracy of the model is improved, and therefore the precision of polar region integrated navigation and transfer alignment is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Ground motion target measuring method and device based on video satellite
ActiveCN109633720AReduce mistakesExcellent positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterLongitude
The invention discloses a ground motion target measuring method and device based on a video satellite. The method comprises the following steps that S100, real-time solving of a target sight line under a fixed coordinate system of the earth is carried out; S200, real-time solving of the longitude and latitude of an intersection point of the target sight line and the ellipsoid face of the earth iscarried out; and S300, a Kalman filter is adopted, the latitude and longitude of the intersection point serve as input of a target observation equation, and the motion velocity of a motion object andthe earth coordinate of the motion object in a kth frame video image are obtained. By means of the method, the Kalman filter is used for processing video satellite results to obtain the position and velocity of the ground motion target. The invention also provides a ground motion target measuring device based on the video satellite.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Mass space homing sphere gravity external correction method
This invention relates to space homing sphere gravity outer correction method, which adopts right angle coordinate system to represent earth outline curve surface and large earth ellipsoid and adopts sphere outline correction and shell center correction method to make the homing of earth outline quality; separately computing out gravity correction value and middle layer correction. The outer correction method overcomes the correction error of the traditional exploring data process and correction method.
Owner:BGP OF CHINA NAT GASOLINEEUM CORP
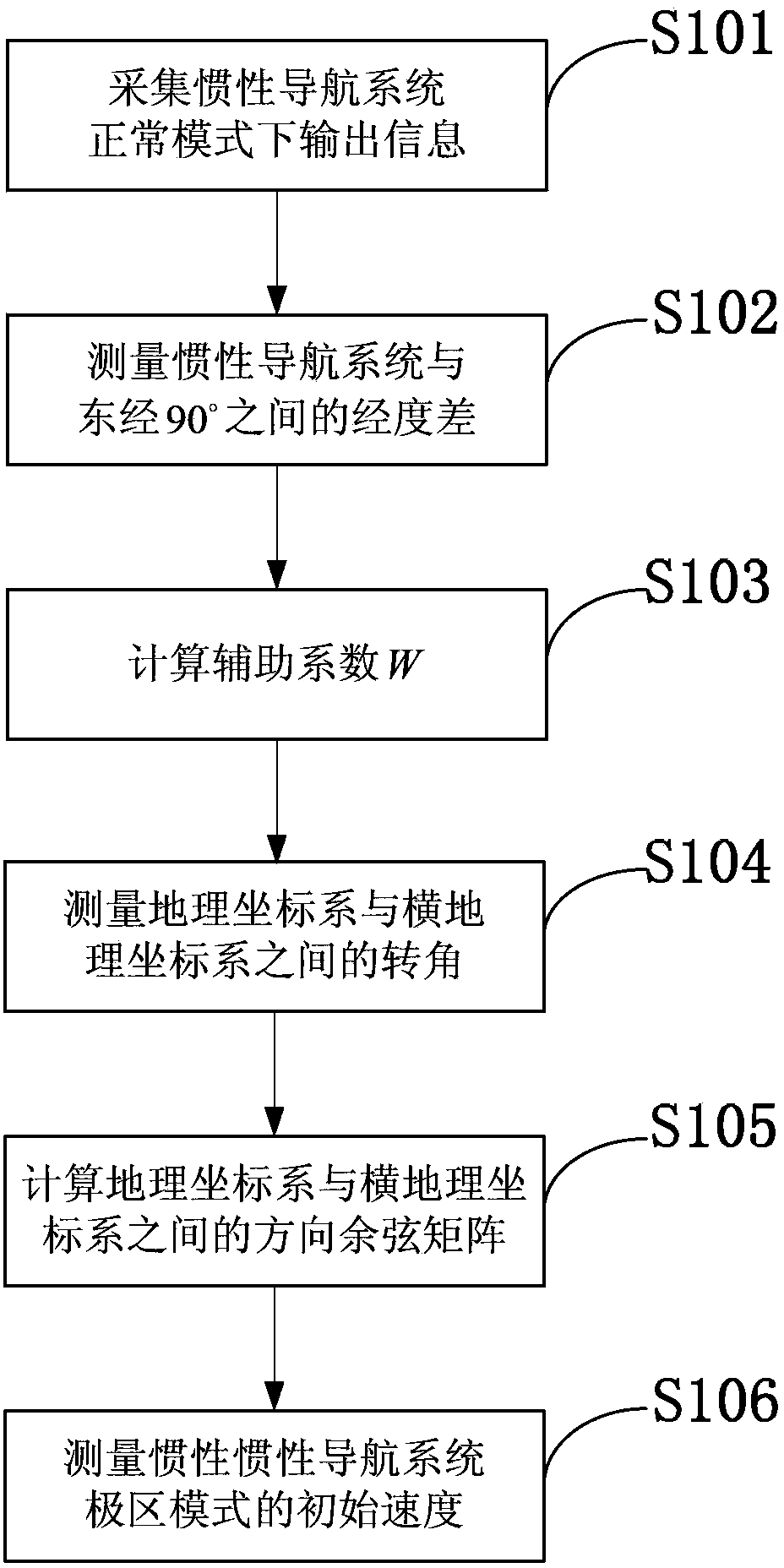
Measurement method for initial speed of polar area navigation mode of inertial navigation system
InactiveCN103389090AAvoid errorsReduce mistakesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNormal modeLongitude
The invention discloses a measurement method for the initial speed of a polar area navigation mode of an inertial navigation system. The measurement method comprises the following steps: collecting output information of the inertial navigation system under a normal mode; measuring the difference of longitude between the inertial navigation system and east longitude 90 degrees; calculating an auxiliary coefficient W; measuring a corner between a geographic coordinate system and a transverse geographic coordinate system; calculating a direction cosine matrix between the geographic coordinate system and the transverse geographic coordinate system; measuring the initial speed of the polar area mode of the inertial navigation system. A conversion matrix between the normal mode of the navigation coordinate system and a polar area mode of the navigation coordinate system is determined on the basis of an earth ellipsoid model; an error of obtaining the conversion matrix when the earth is simply simulated by a conventional sphere is avoided, so that the error of mode conversion of the inertial navigation system is reduced. Initial speed information required by the polar area mode can be measured just by the output information of the inertial navigation system under the normal mode; other external equipment and information are not needed, so that the measurement method is simple and convenient; the practical application is facilitated.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com