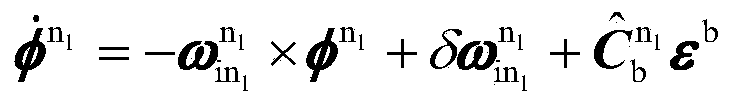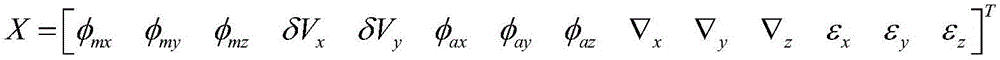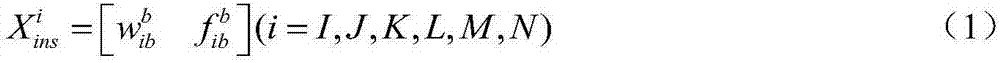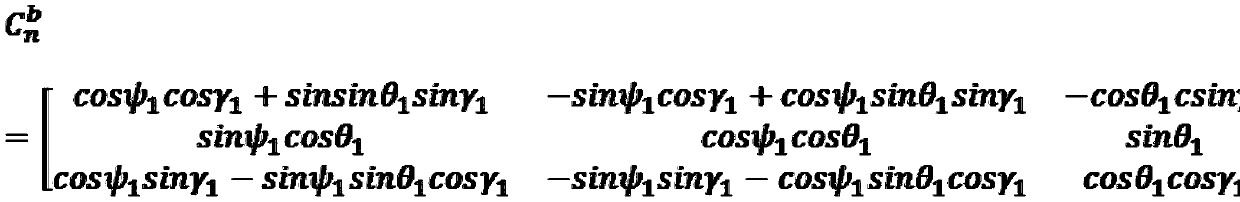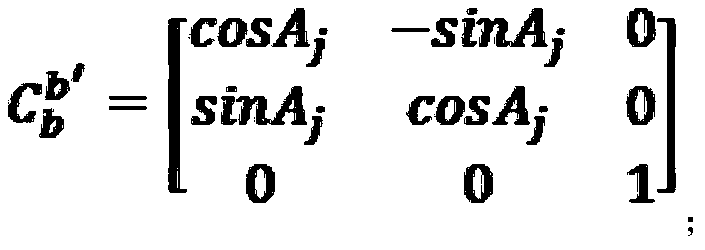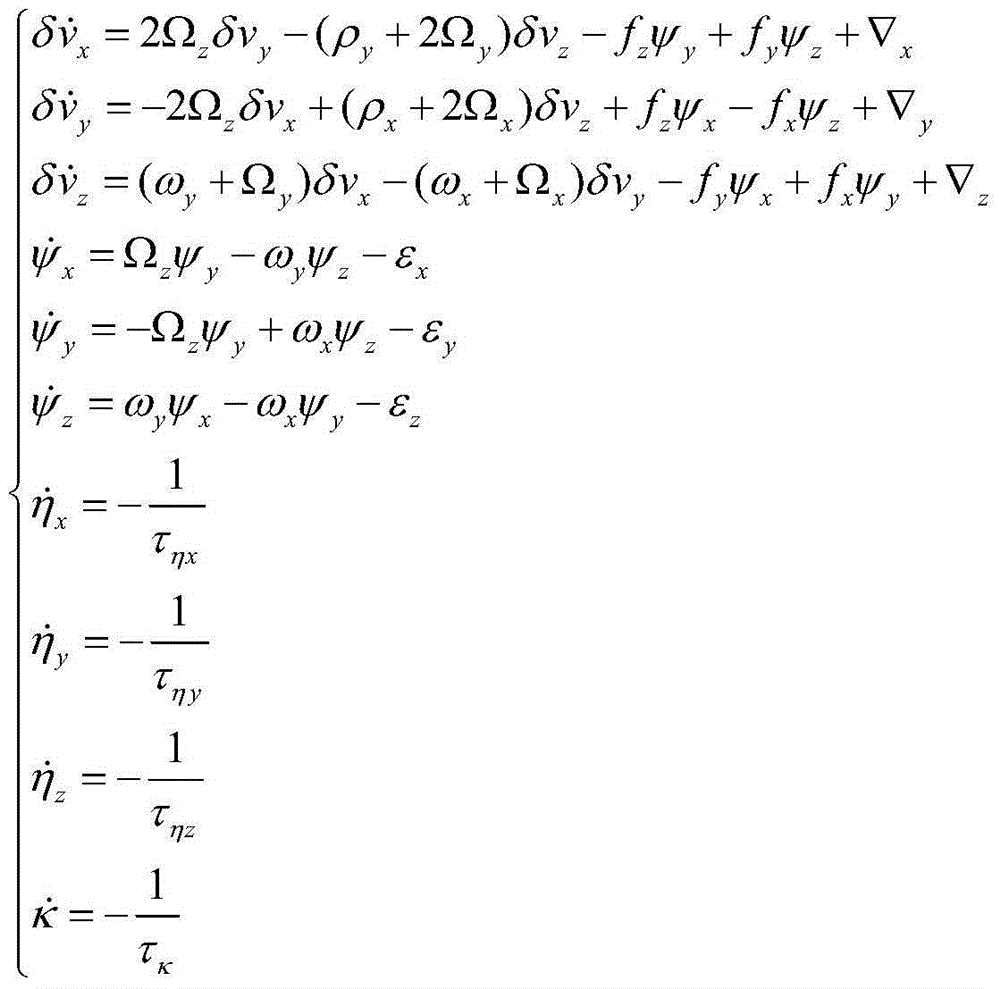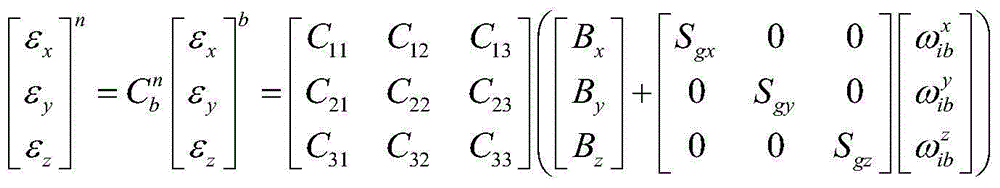Patents
Literature
155 results about "Transfer alignment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
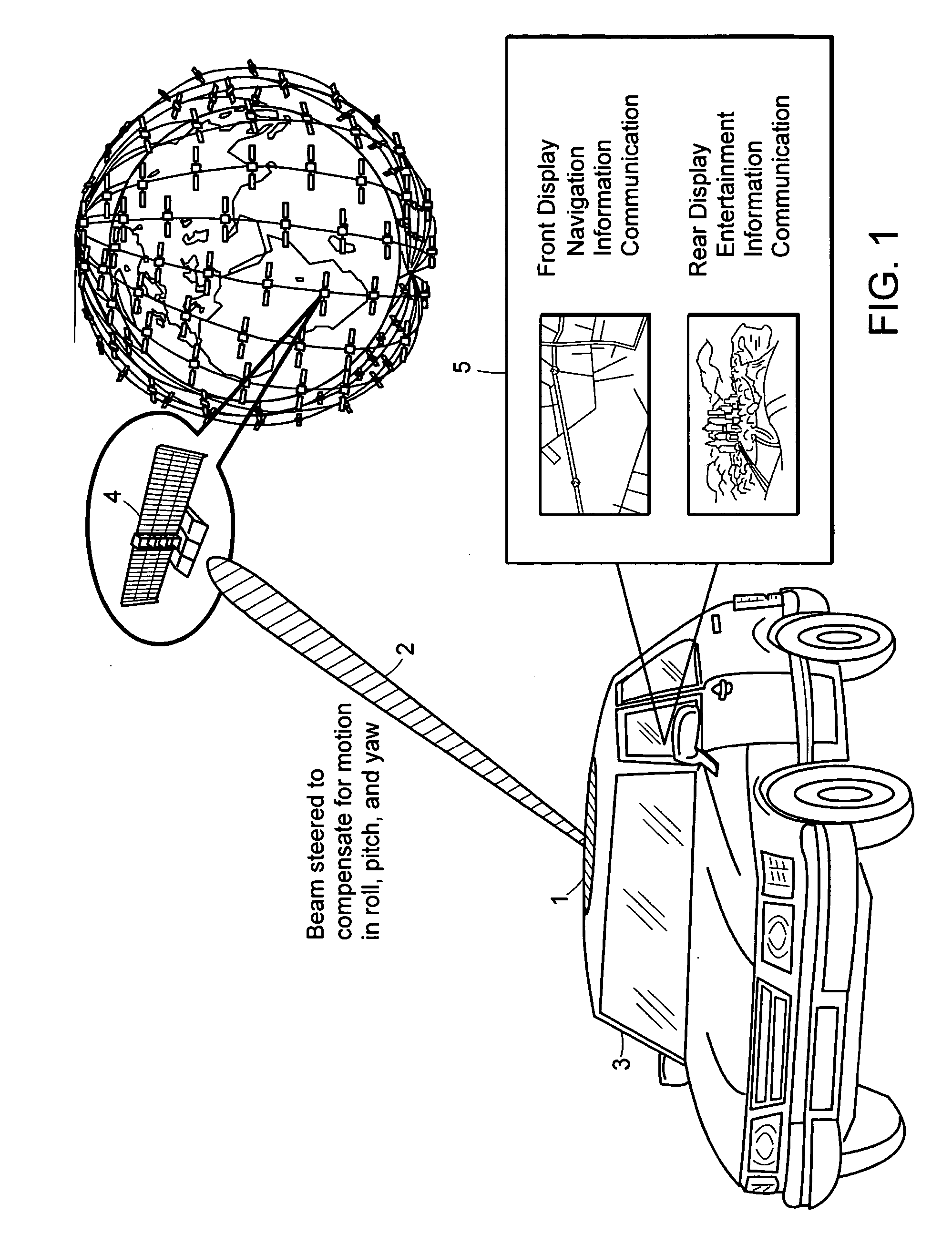
Transfer alignment is the process of initializing and calibrating a missile or torpedo inertial navigation system using data from the host carrier's navigation system. The inertial navigation systems on missiles and torpedoes are limited by weight, volume and cost. Initialization of such systems must be rapid and accurate. Different matching methods, such as velocity matching and position matching, are designed to improve the speed and accuracy of the alignment.
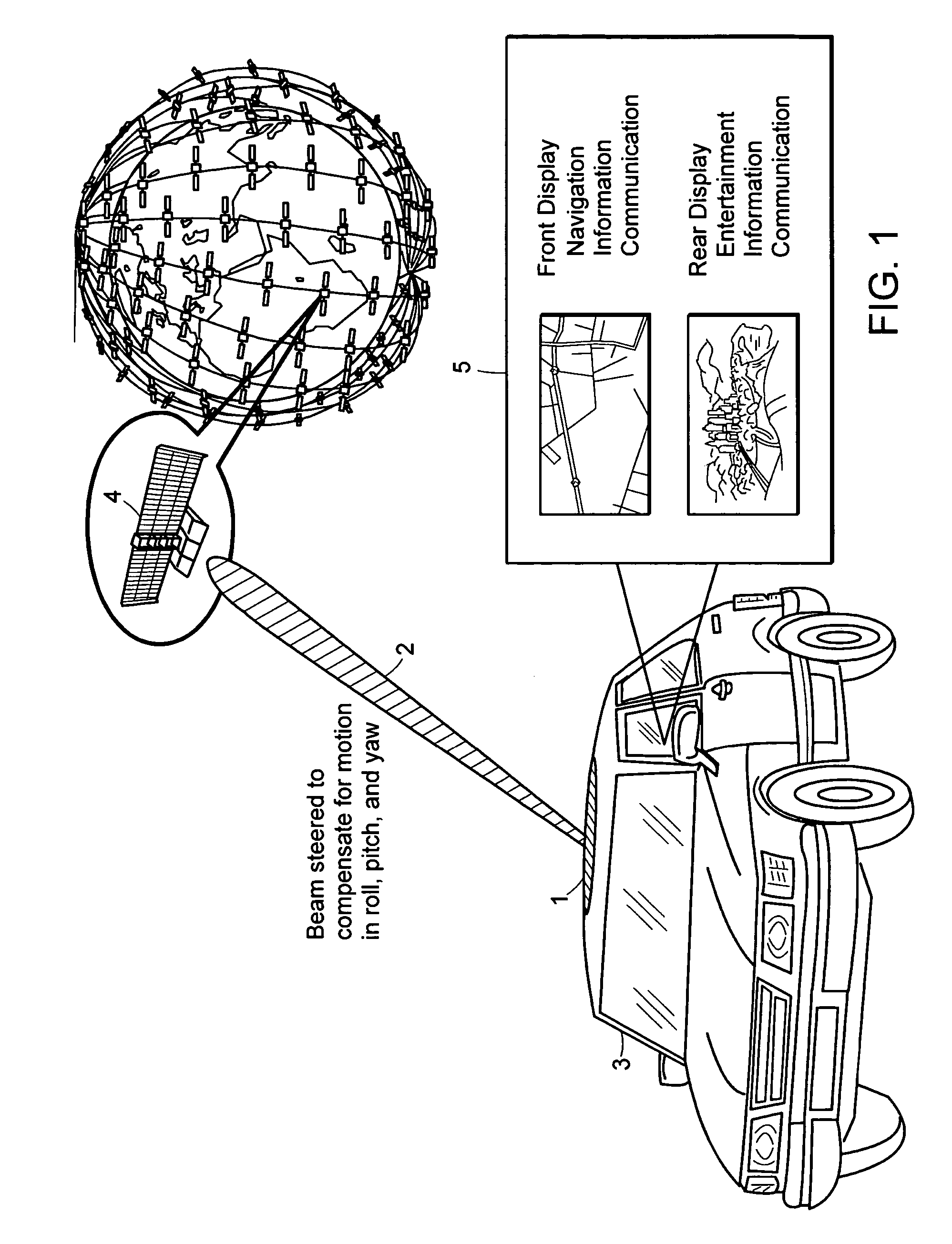
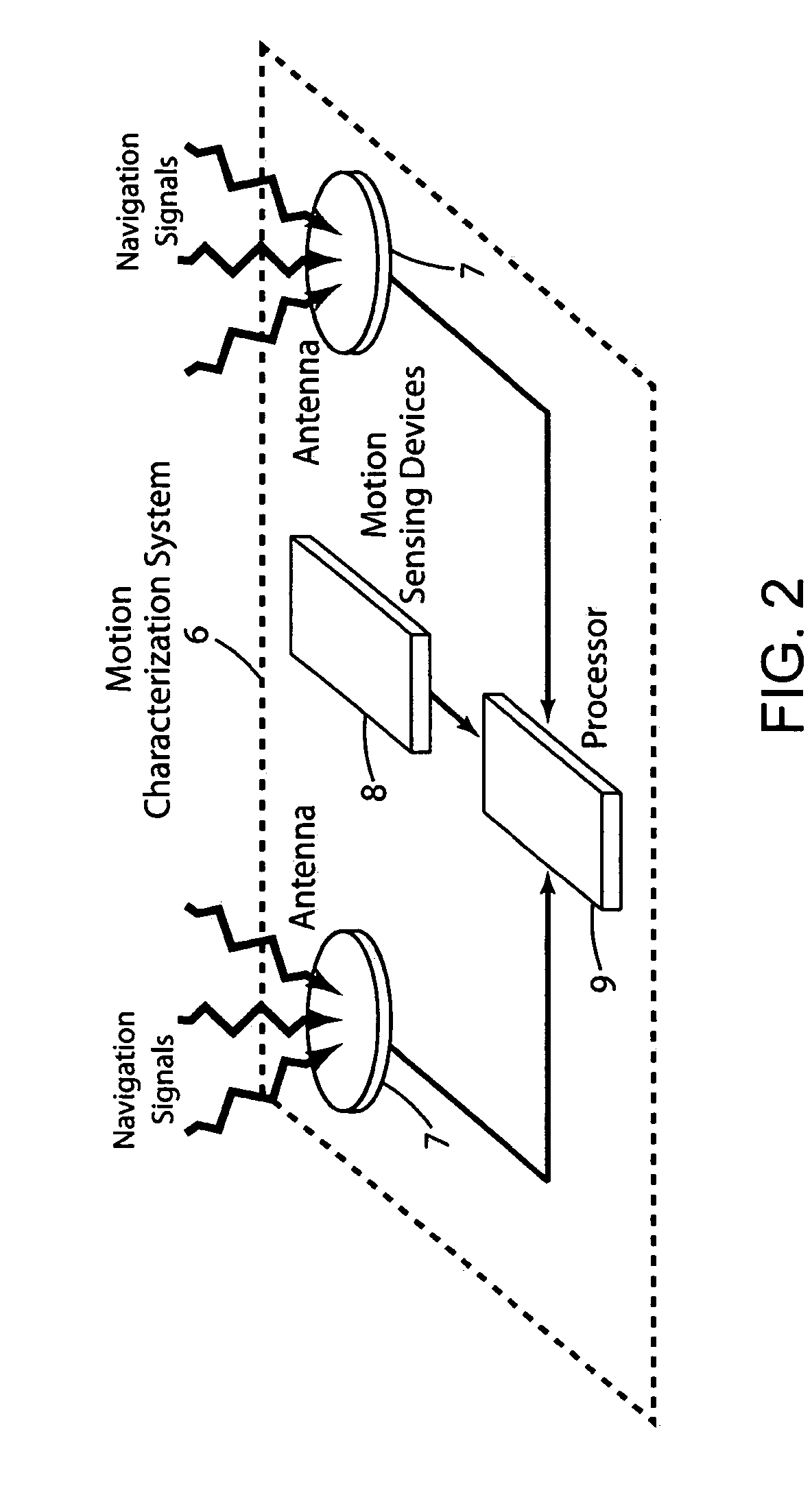
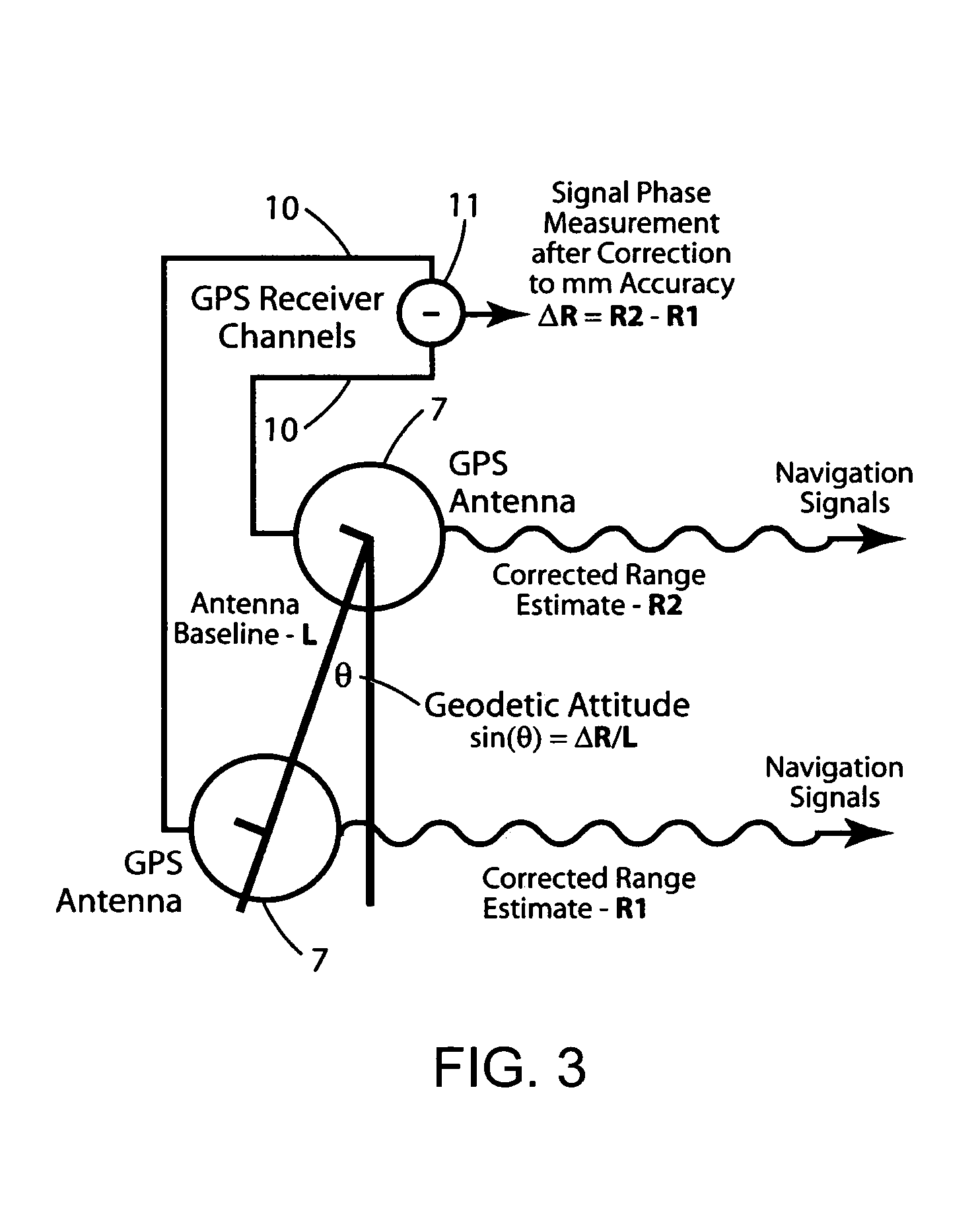
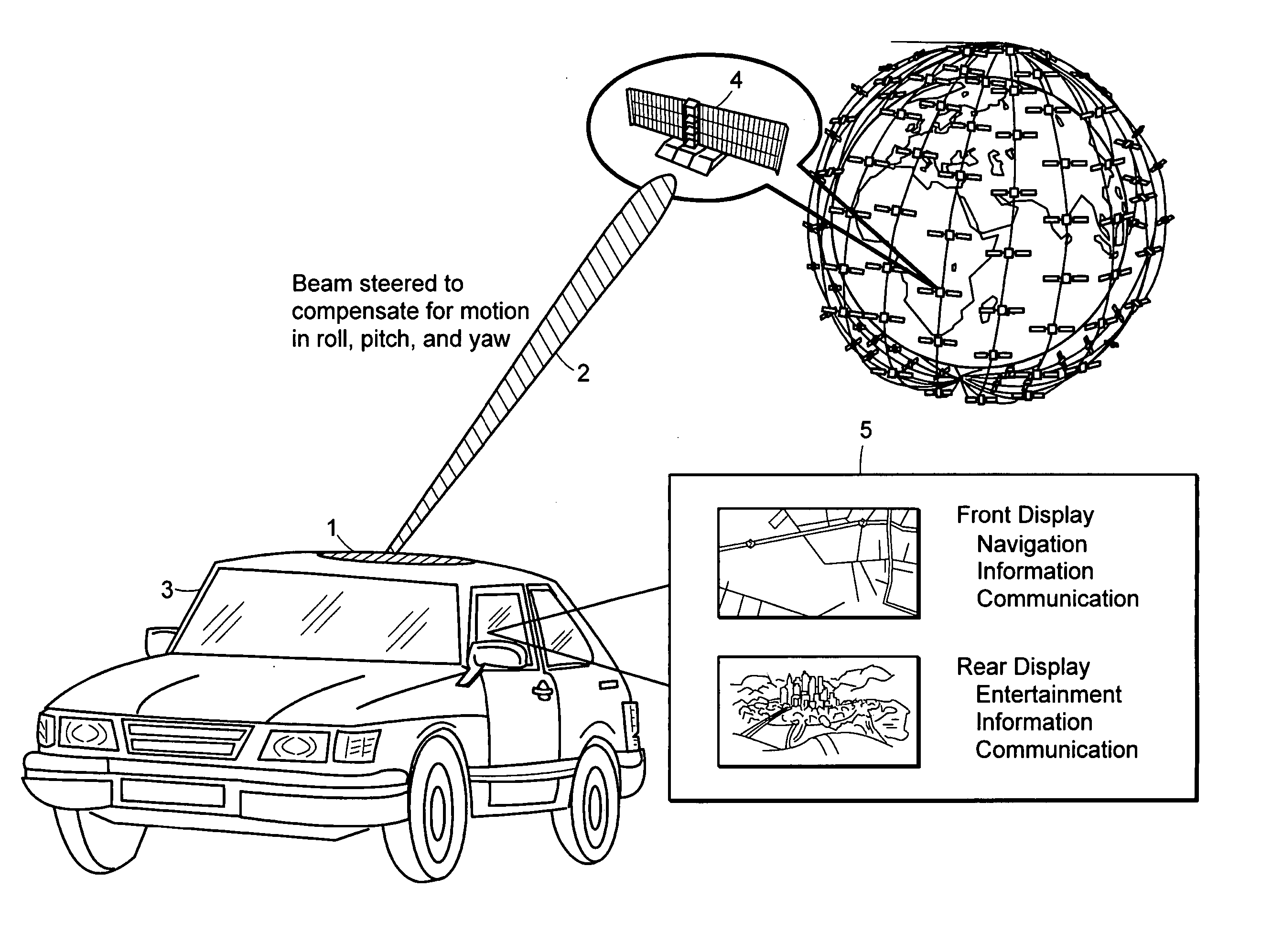
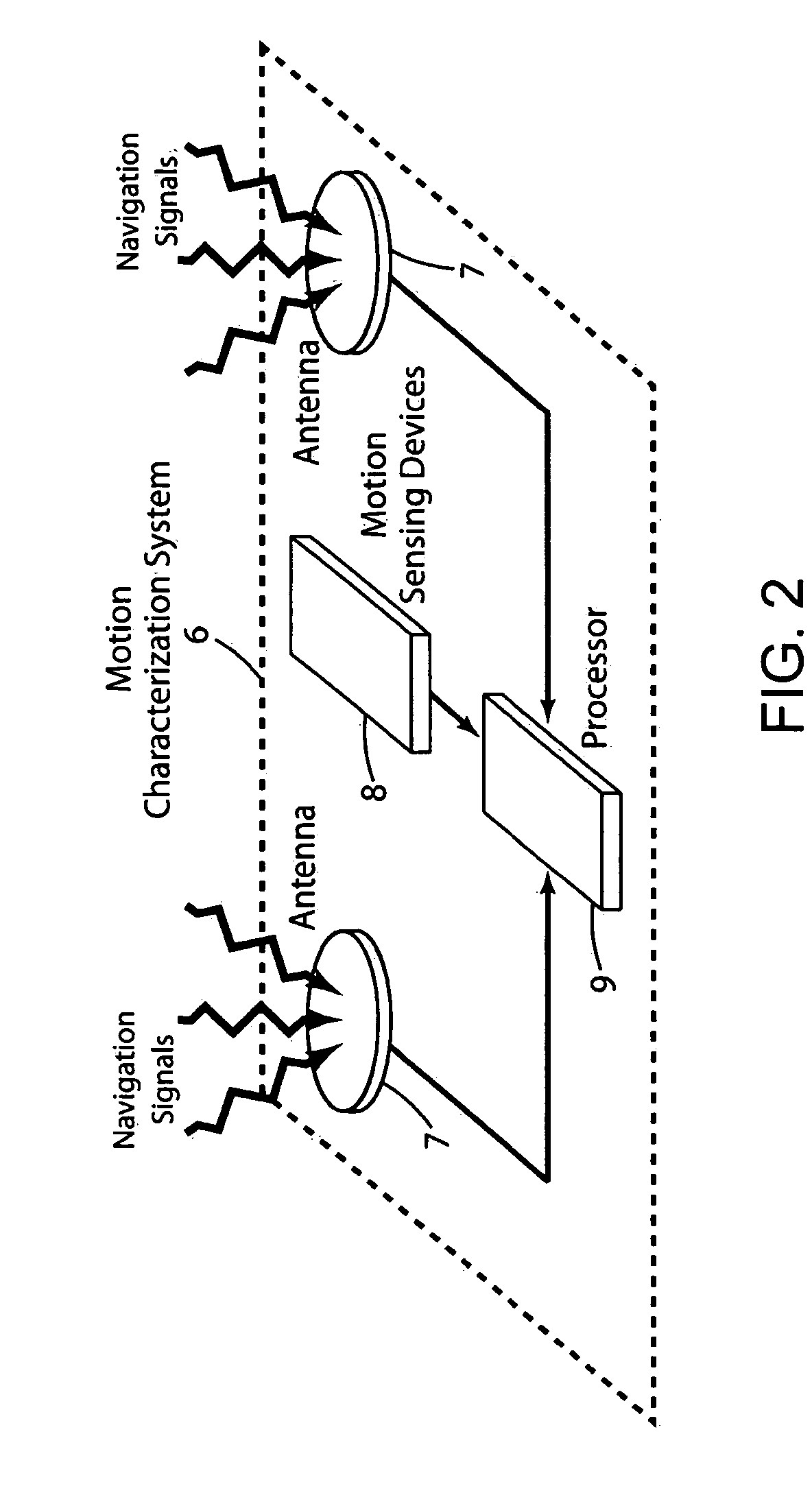
Attitude measurement using a GPS receiver with two closely-spaced antennas
InactiveUS7136751B2Low costCost advantageDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesAccelerometerAmbiguity
A system determines three-dimensional attitude of a moving platform using signals from two closely spaced Global Positioning System (GPS) antennas. The system includes three rate gyroscopes and three accelerometers rigidly mounted in a fixed relationship to the platform to aid in determining the attitude. The system applies signals from one of the two GPS antennas to sufficient channels of a GPS receiver to support navigation. The system applies signals from a second of the two GPS antennas to the additional receive channels to support interferometry. The system resolves the ambiguity normally associated with the interferometric heading solution by having closely spaced GPS antennas, and uses interferometry to refine a coarse heading estimate from a GPS plus Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) transfer alignment solution. The system achieves sub-meter spacing of the two GPS antennas by merging many temporal interferometric measurements and the attitude memory provided by the IMU time-history solution.
Owner:ENPOINT
Attitude measurement using a single GPS receiver with two closely-spaced antennas
InactiveUS20050004748A1Simple packagingLess space involvementInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationAccelerometerAmbiguity
A system determines three-dimensional attitude of a moving platform using signals from two closely spaced Global Positioning System (GPS) antennas. The system includes three rate gyroscopes and three accelerometers rigidly mounted in a fixed relationship to the platform to aid in determining the attitude. The system applies signals from one of the two GPS antennas to sufficient channels of a GPS receiver to support navigation. The system applies signals from a second of the two GPS antennas to the additional receive channels to support interferometry. The system resolves the ambiguity normally associated with the interferometric heading solution by having closely spaced GPS antennas, and uses interferometry to refine a coarse heading estimate from a GPS plus Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) transfer alignment solution. The system achieves sub-meter spacing of the two GPS antennas by merging many temporal interferometric measurements and the attitude memory provided by the IMU time-history solution.
Owner:ENPOINT
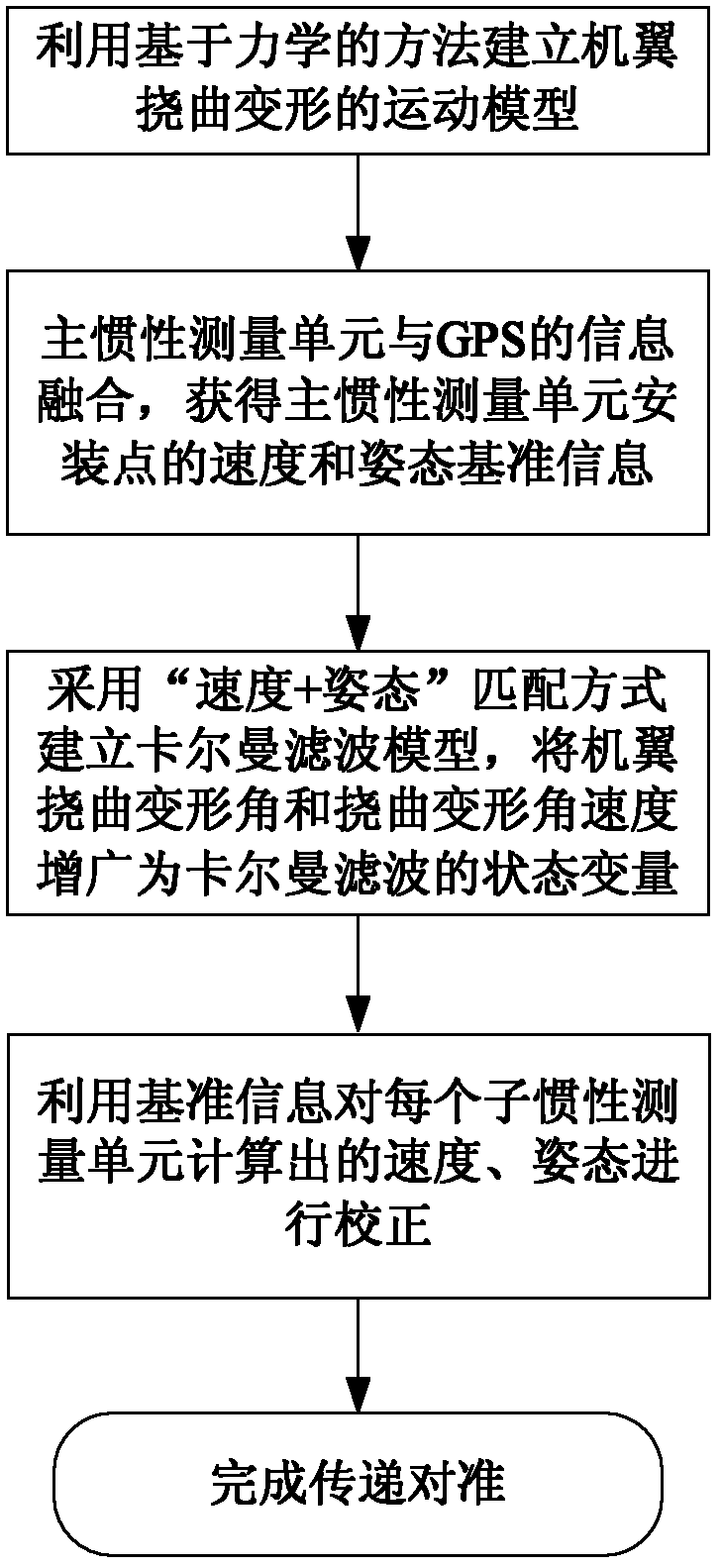
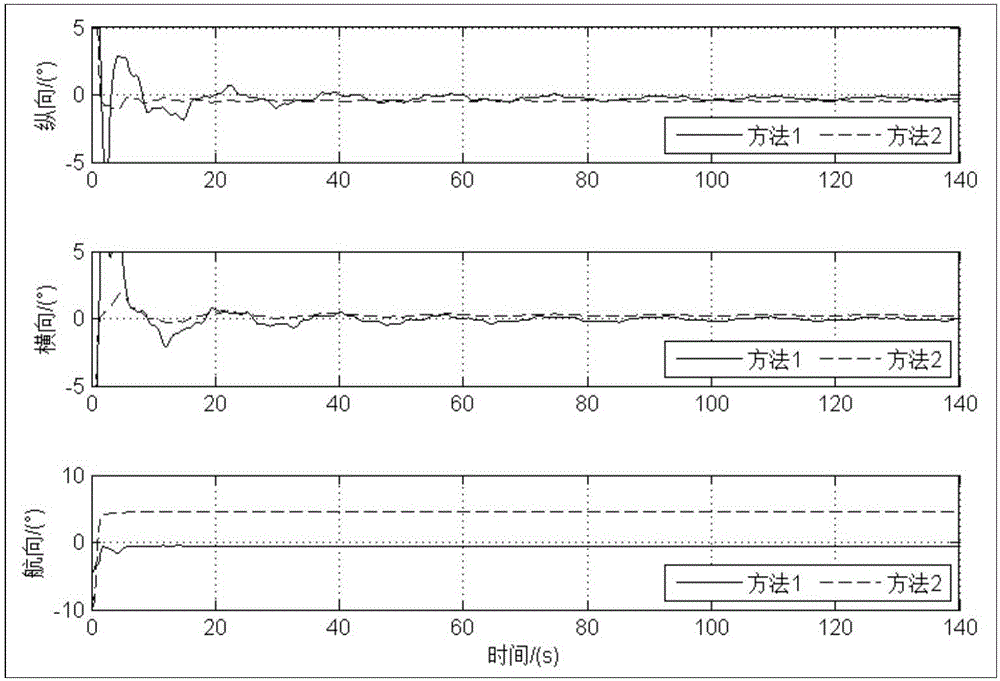
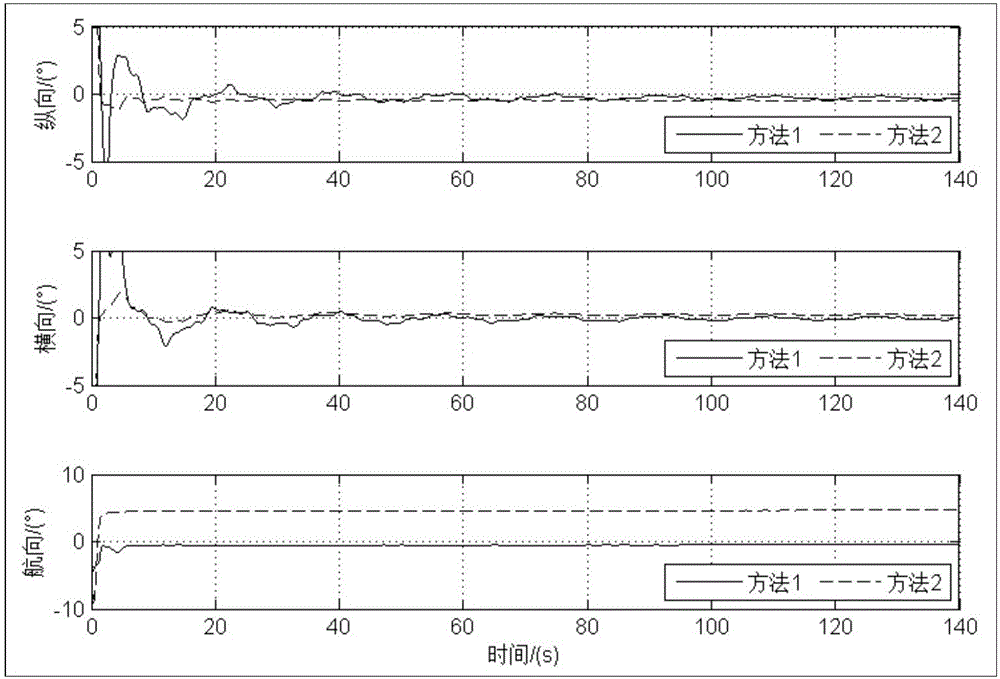
Transfer aligning method of airborne distributed POS (Position and Orientation System)
The invention provides a transfer aligning method of an airborne distributed POS (Position and Orientation System). The method comprises the following steps of: modeling deflecting motion of an aircraft wing by using a mechanical method; augmenting a deflection deformation angle and deflection deformation angular velocity generated by the deflecting motion of the aircraft wing into state variables of Kalman filter; on this basis, designing a Kalman filter by using a velocity+posture matching method; carrying out transfer alignment on a sub inertial measuring unit by using velocity and posture reference information obtained after carrying out information fusion by using a main inertial measuring unit and a GPS (Global Positioning System); and finally obtaining corrected velocity and posture information of each sub inertial measuring unit mounting point. The transfer aligning method provided by the invention has the advantages of strong independency and high accuracy and can be used for improving the transfer alignment accuracy of the distributed POS when deflection deformation exists in the aircraft.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Near-space missile-borne strap-down inertial navigation system transfer alignment method based on star sensor
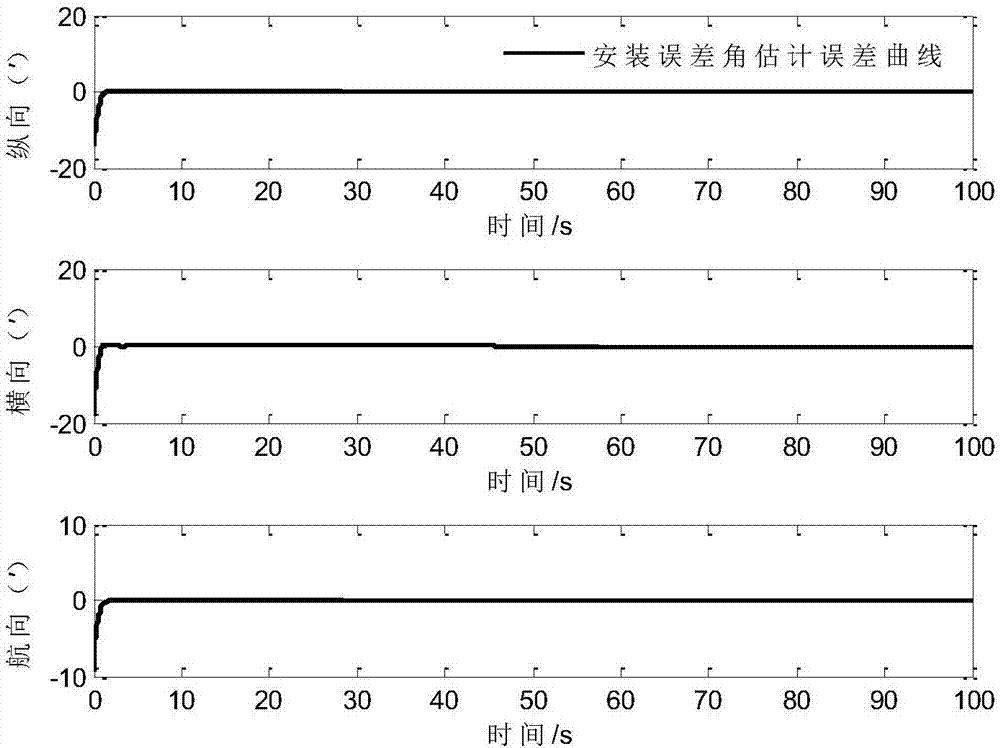
ActiveCN104165640AAttitude Error Estimation High AccuracyComply with flight altitudeMeasurement devicesInertial coordinate systemInstallation Error
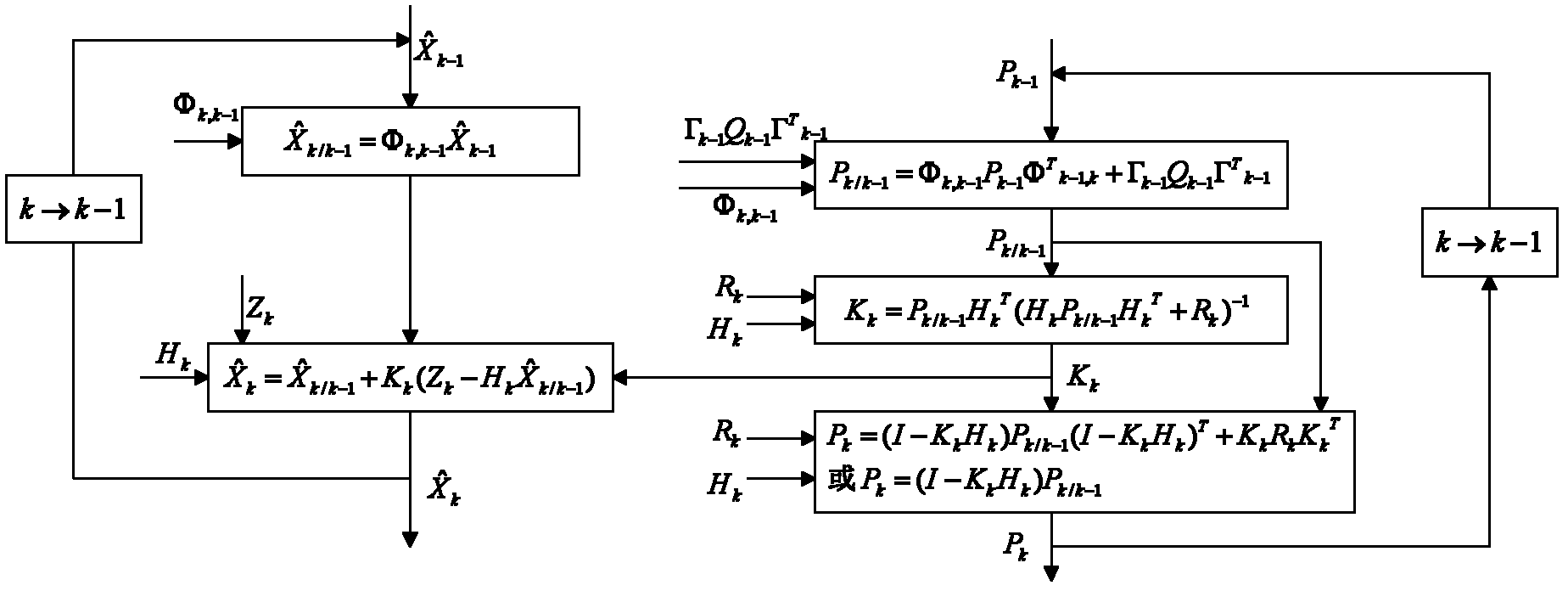
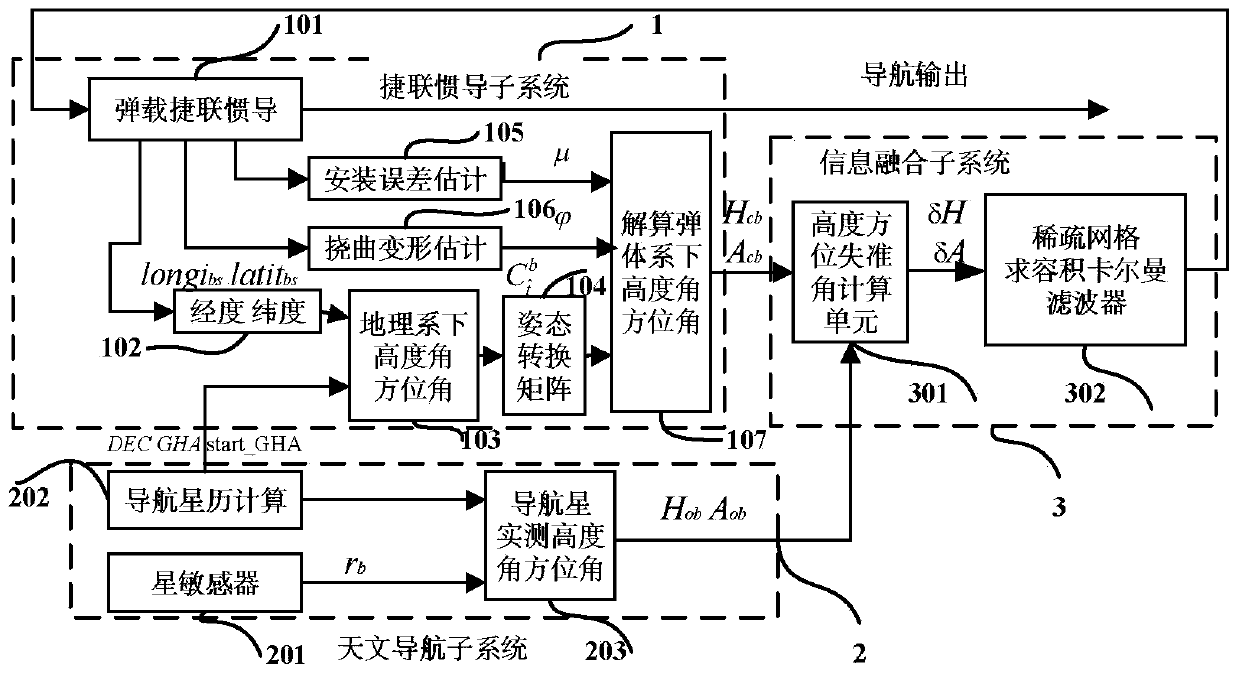
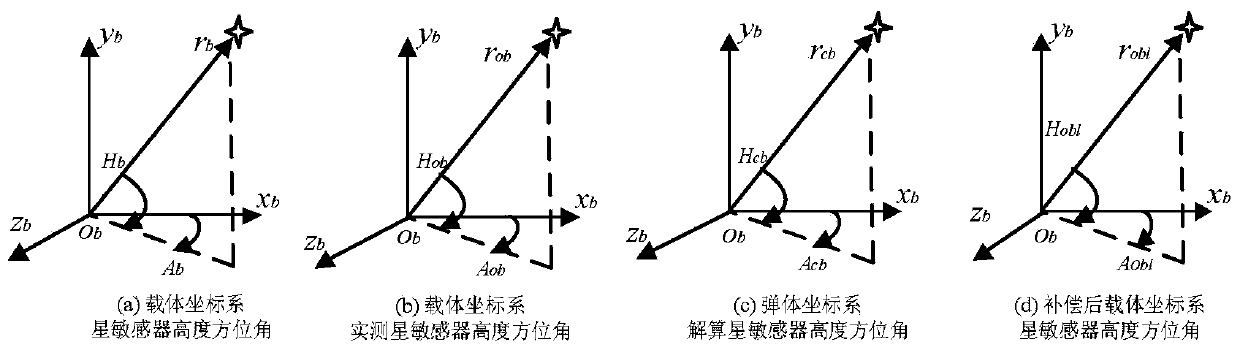
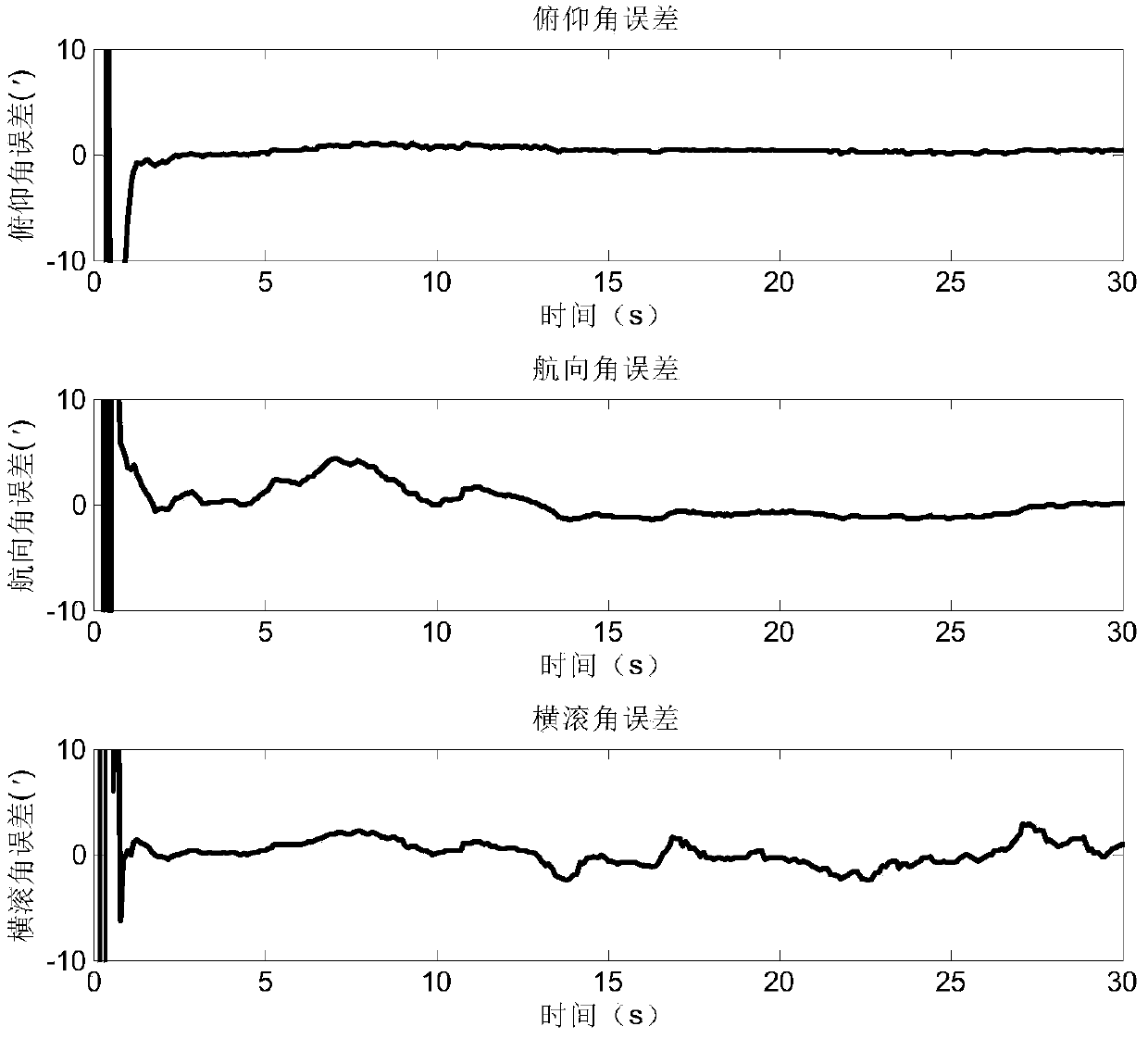
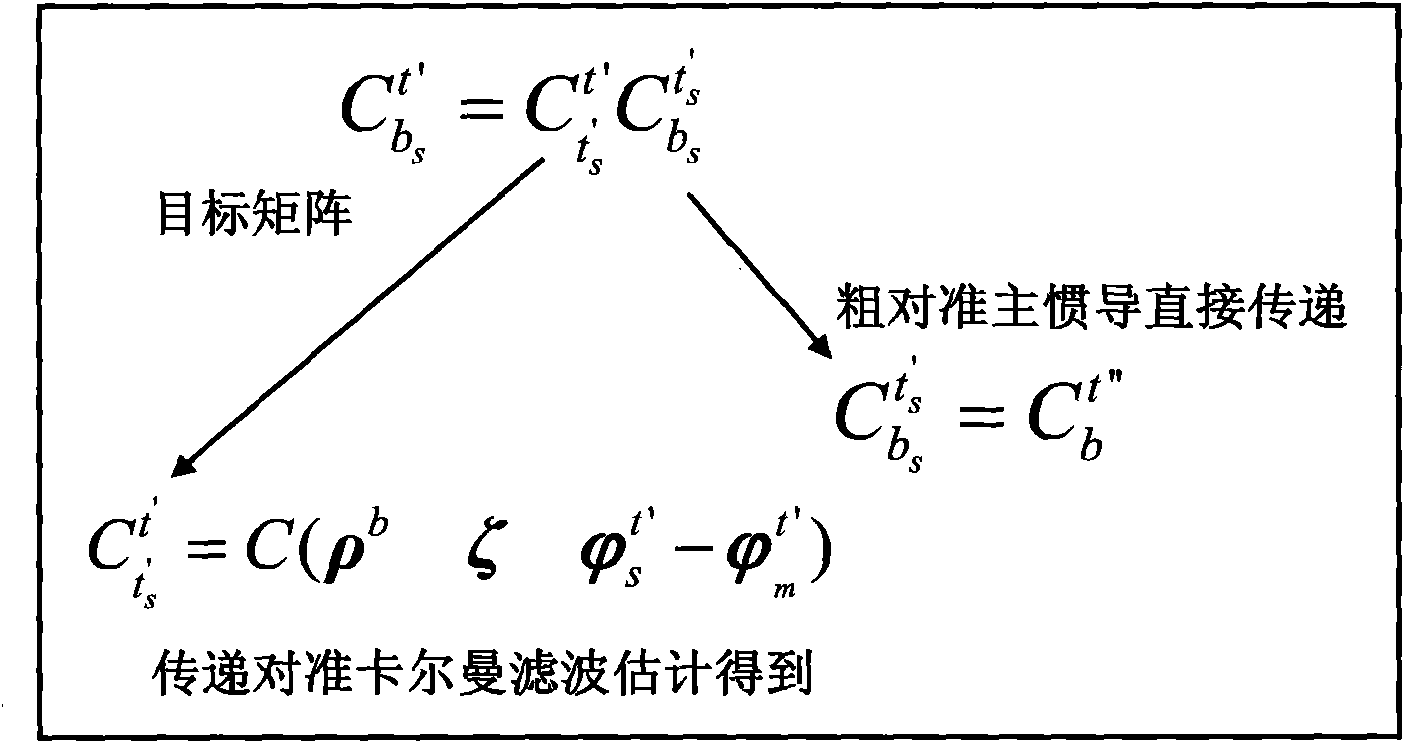
The invention discloses a near-space missile-borne strap-down inertial navigation system transfer alignment method based on a star sensor. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a missile-borne strap-down inertial navigation system transfer alignment state equation by taking an inertial coordinate system (launching point coordinate system for short) on a carrier launching point as a navigation coordinate system and a strap-down inertial navigation system (SINS) on a missile to be launched as sub-inertial navigation; 2) calculating navigation information and observed quantity of the missile-borne strap-down inertial navigation system; 3) establishing a measurement equation; 4) by depending on the state equation and the measurement equation established, estimating a mathematics platform misalignment angle, a speed error, a position error and an installation error of the missile as well as flexural deflection of the carrier through a sparse grid integral kalman filter, and correcting a sub-inertial navigation system, thus finishing a transfer alignment process.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Airborne distribution type POS (position and orientation system) transfer alignment method based on parameter identification
ActiveCN103913181ARealize online identificationImprove accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsTime changesMathematical model
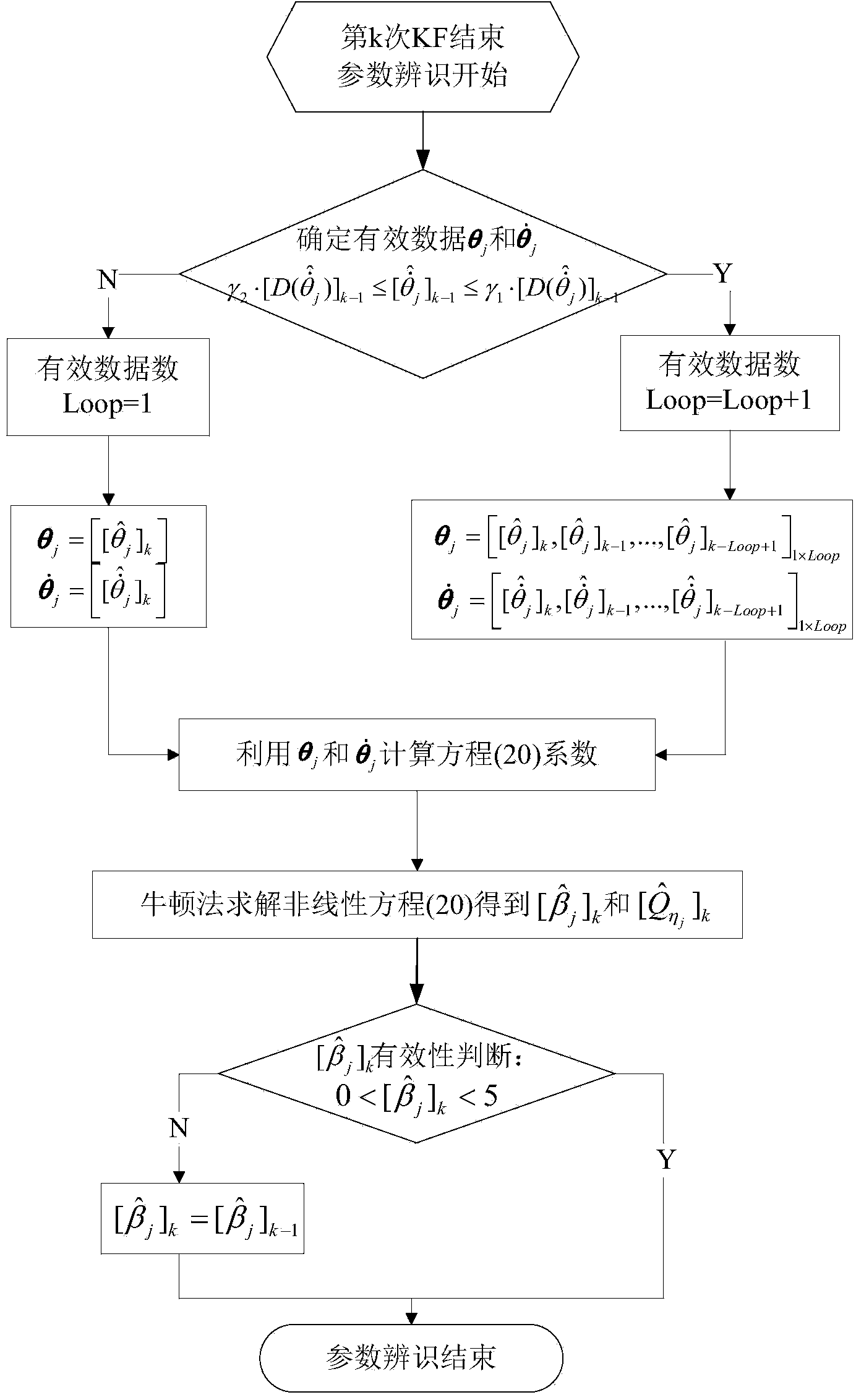
The invention discloses an airborne distribution type POS (position and orientation system) transfer alignment method based on parameter identification. An airborne distribution type POS comprises a high-precision master POS and a plurality of sub IMUs (inertial measurement units). Aiming at the problems of unknown elastic deformation and time change of a machine body, the elastic deformation angle of the machine body is regarded as a second-order Markoff process, the elastic deformation angle and the elastic deformation angle speed are expanded into state variables, the differences between the speeds and the postures of the master POS and the sub IMUs are measured, and a mathematic model of sub IMU transfer alignment is built; then, the Kalman filtering is performed and parameters of the second-order Markoff process are calculated and updated by virtue of the estimated elastic deformation angle and elastic deformation angle speed; at last, the updated second-order Markoff process parameters serve as initial filtering values at next moment to estimate the relatively accurate posture errors, speed errors and position errors of the sub IMUs, strapdown calculation results of the sub IMUs are corrected by virtue of the errors, and the relatively accurate positions, speeds and postures of the sub IMUs are calculated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Airborne distributed POS transfer alignment method based on H infinity and CKF hybrid filtering
ActiveCN106352876AReduce precisionReduced stabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsFilter algorithmSelf adaptive
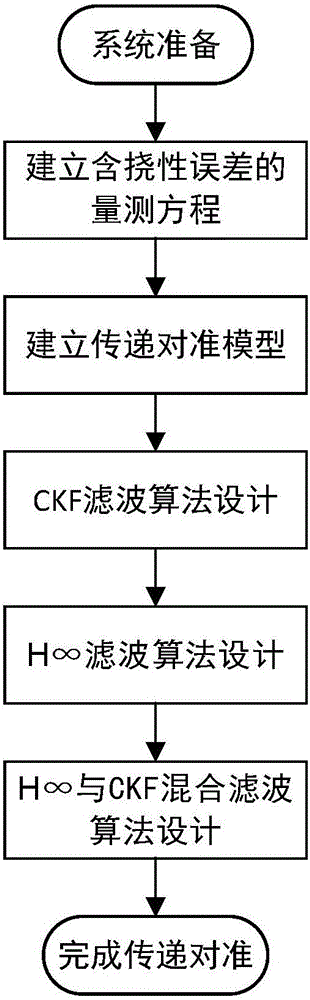
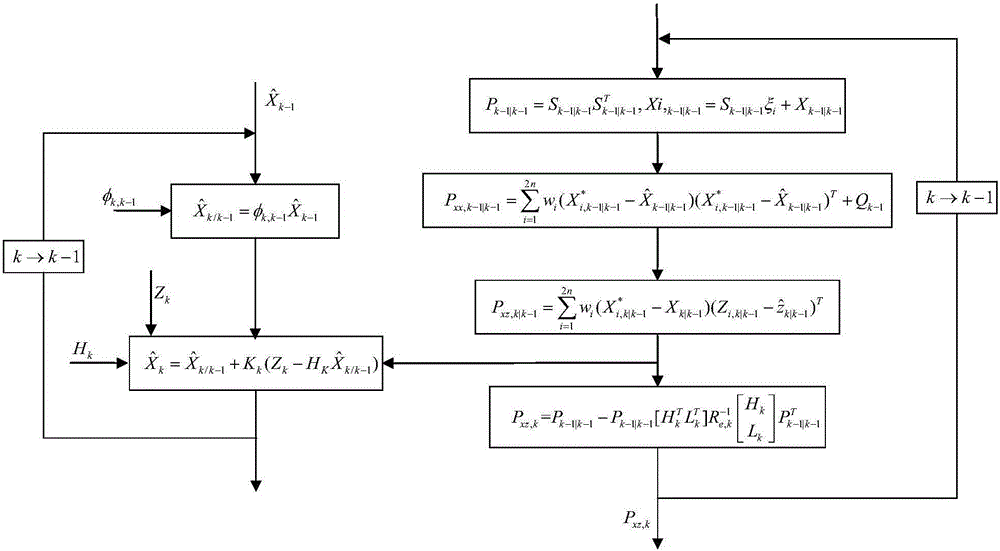
The invention relates to an airborne distributed POS transfer alignment method based on H infinity and CKF (Capacity Kalman Filtering) hybrid filtering. The method comprises the following steps: first, incorporating a deflection deformation error into measurement noise, determining a speed match measurement equation and an attitude match measurement equation, and primarily establishing a transfer alignment model of a system; designing nonlinear filtering, namely a CKF algorithm with high precision based on Kalman filtering; finally, achieving the purposes of weakening and eliminating the deflection deformation and a dynamic lever arm by utilizing good robust adaptive ability of H infinity filtering, designing an H infinity filtering algorithm, combining an H infinity filtering module and the CKF filtering, and designing a new H infinity and CKF hybrid filtering algorithm so as to estimate more accurate position, speed and attitude information of a slave inertial navigation system to complete transfer alignment. According to the airborne distributed POS transfer alignment method based on the H infinity and CKF hybrid filtering, the problem that the position, speed and attitude information of the slave inertial navigation system cannot be estimated accurately under the situation that the deflection deformation is difficult to model is solved, so that the airborne distributed POS transfer alignment method based on the H infinity and CKF hybrid filtering has the characteristics of high precision and strong anti-interference capacity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Airborne distributed inertial attitude measurement system and transfer alignment method of airborne distributed inertial attitude measurement system
ActiveCN103196448ALow costReduce volumeNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsLN-3 Inertial Navigation SystemControl area
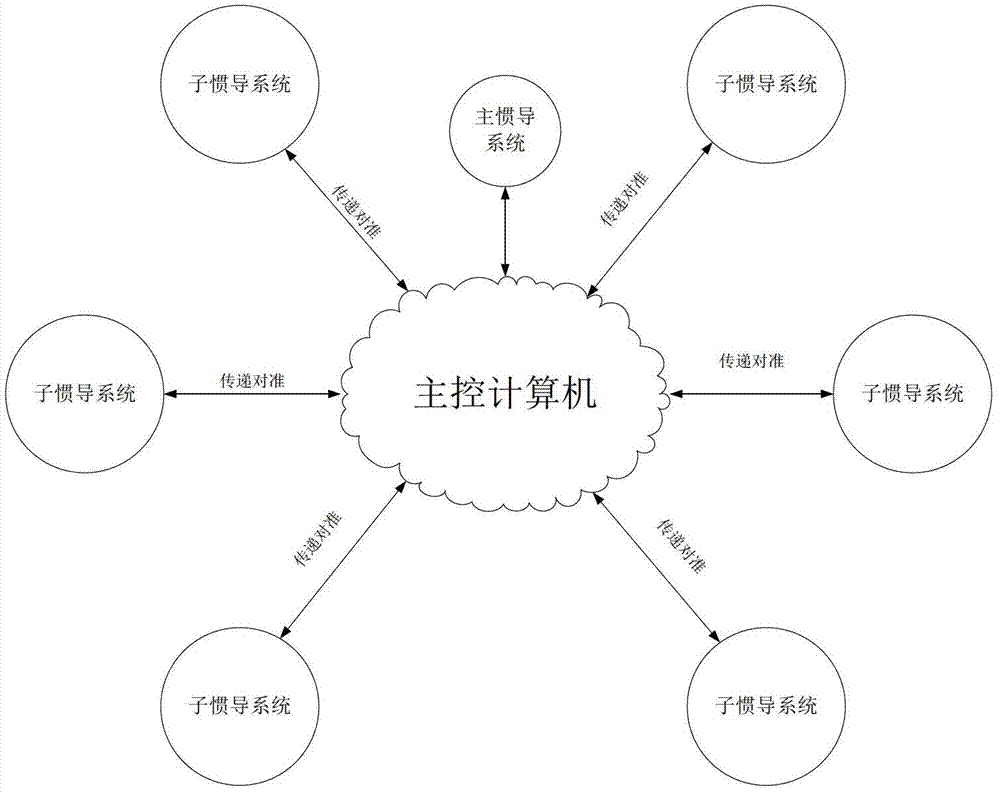
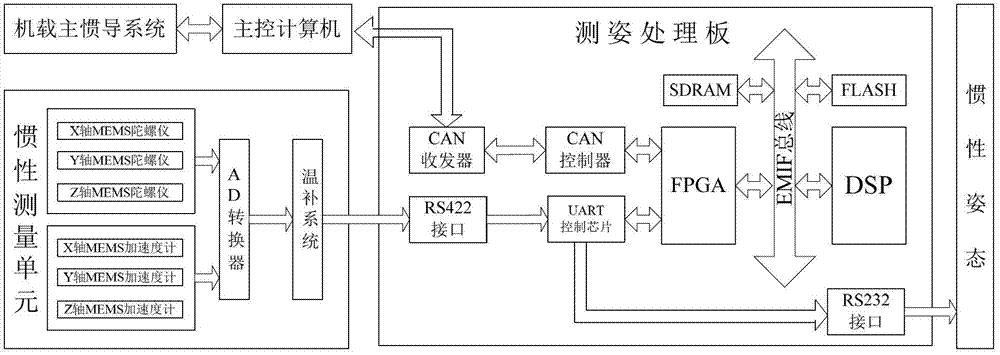
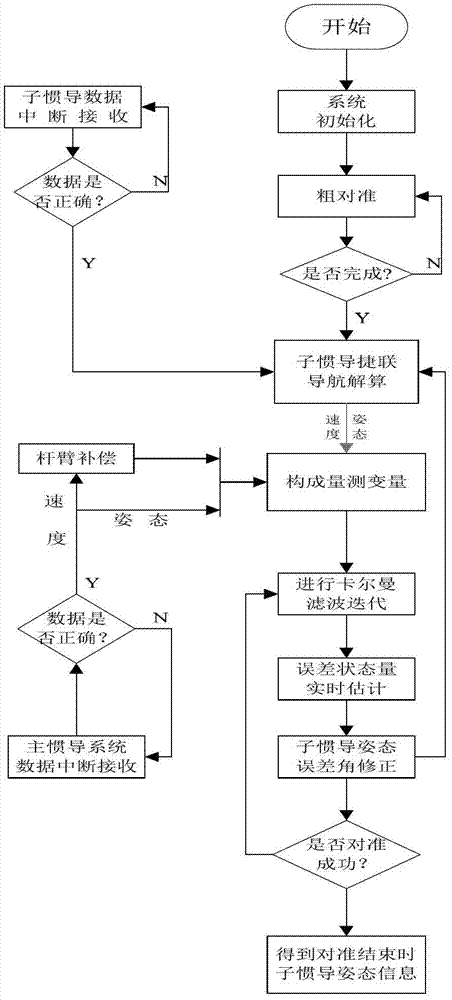
The invention relates to an airborne distributed inertial attitude measurement system and a transfer alignment method of the airborne distributed inertial attitude measurement system. The airborne distributed inertial attitude measurement system comprises a master inertial navigation system, a main control computer, and six slave inertial navigation systems connected with the main control computer, wherein each slave inertial navigation system respectively comprises an inertial measurement unit and an attitude measurement processing board, each inertial measurement unit is connected with an RS_422 interface of the corresponding attitude measurement processing board, each RS_422 interface is connected with an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) chip through a UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver / Transmitter) control chip, each FPGA chip is connected with a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) chip through an EMIF (External Memory Interface) bus and also connected with the master inertial navigation system through a CAN (Control Area Network) controller and a CAN transceiver, and the main control computer is connected with the master inertial navigation system. The transfer alignment method between the master inertial navigation system and each slave inertial navigation system of the airborne distributed inertial attitude measurement system comprises the steps of: by taking the speed information error and the attitude information error of the master inertial navigation system and the slave inertial navigation systems as measuring variables, correcting speed information and attitude information calculated by the slave inertial navigation systems after carrying out Kalman filtering iteration, and finally obtaining stable and accurate navigation attitude information.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
SINS dynamic base transfer alignment method based on satellite positioning
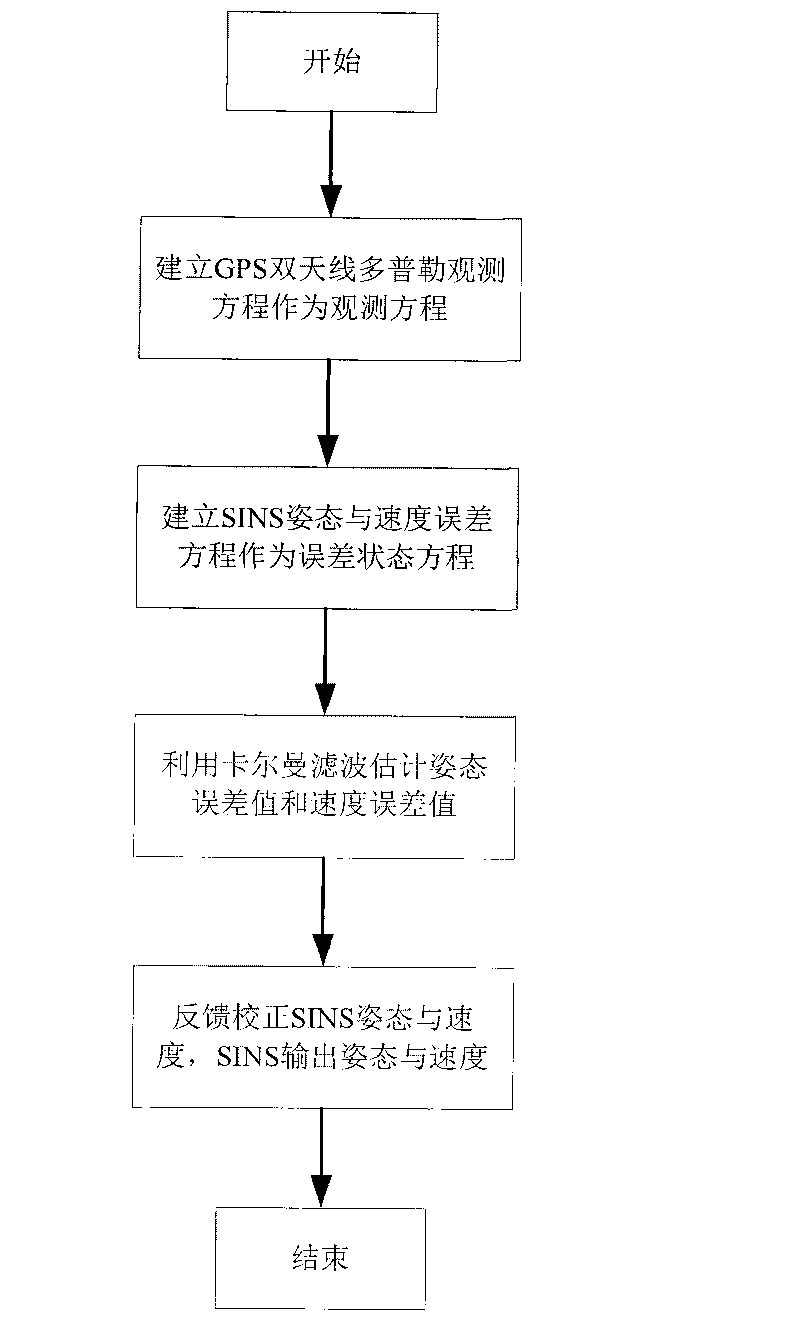
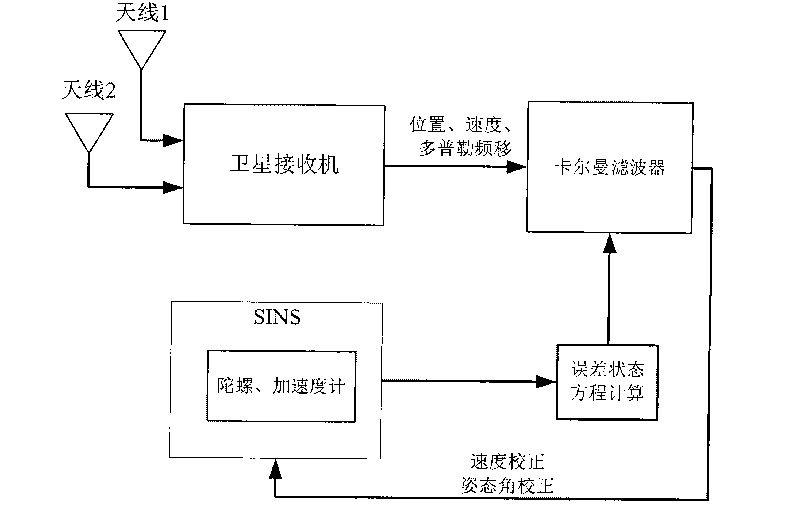
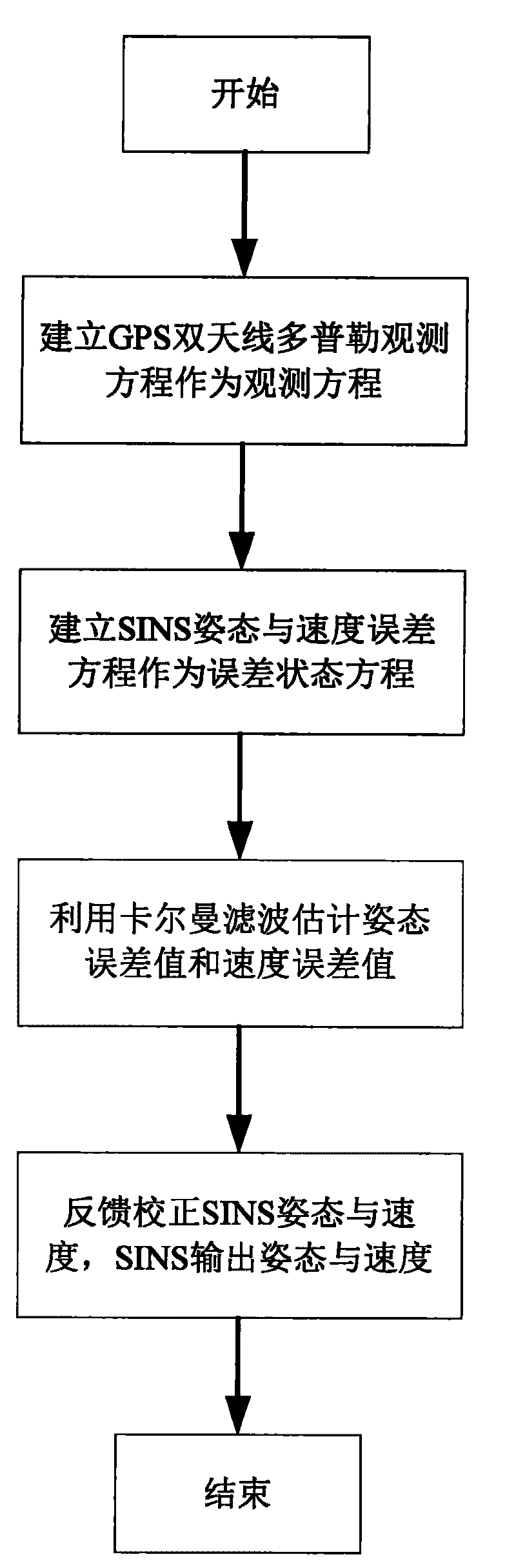
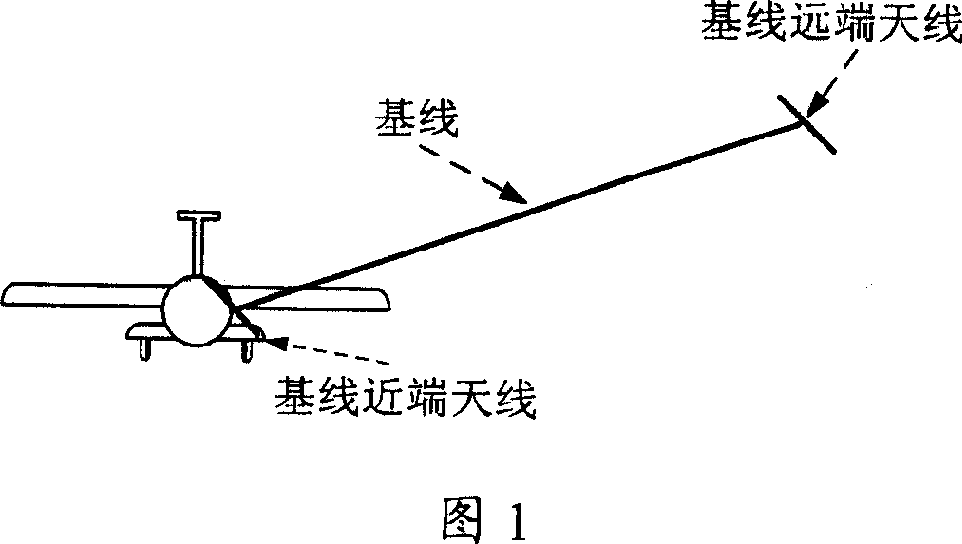
ActiveCN101750066AThe difficulty of avoiding ambiguityHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterFault tolerance
A SINS dynamic base transfer alignment method based on satellite positioning includes the following steps: (1) the baseline vector direction of the GPS dual-antenna is in accordance with the navigation direction of the SINS, wherein one antenna is positioned at a carrier and the other antenna is positioned at the sub-carrier of the SINS, a GPS dual-antenna Doppler observational equation is used to establish the observational equation of SINS dynamic base transfer alignment method, and the position and speed information received by the GPS receiver are used as the position and speed of the initial state SINS; (2) an attitude error equation and an speed error equation of the SINS are established and used as the error state equation of the alignment method; (3) a kalman filter is adopted for attitude error and speed error estimation; (4) the feedback correction on attitude and speed are carried out for the SINS, and the SINS output the attitude and speed information of the carrier to the user. The SINS dynamic base transfer alignment method based on satellite positioning has high processing speed, high accuracy, small computation quantity, strong fault tolerance and is not affected by the deflection deformation of the carrier.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Airborne double-antenna double-measuring device interference SAR base linc motion measuring method
InactiveCN101067657AHigh precisionAvoid divergenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionObservational errorMeasurement device
The invention discloses a measuring method used piggyback twin antenna double measuring devices to interfere SAR base line motion. It includes the following steps: using twin antenna interference phase to gain carried machine roll angle; increasing observed quantity for base line near end antenna motion measurement integrated navigation system by co-ordinate transformation to restrain attitude measurement error diversity for routine inertial navigation and GPS integrated navigation system to increase base line near end antenna motion measurement precision; using the base line as strengthener to realize rough transfer alignment; using silicon MEMS inertial navigation output data and local relative navigation technique to correct the rough transfer alignment result to increase base line far end antenna motion measurement precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
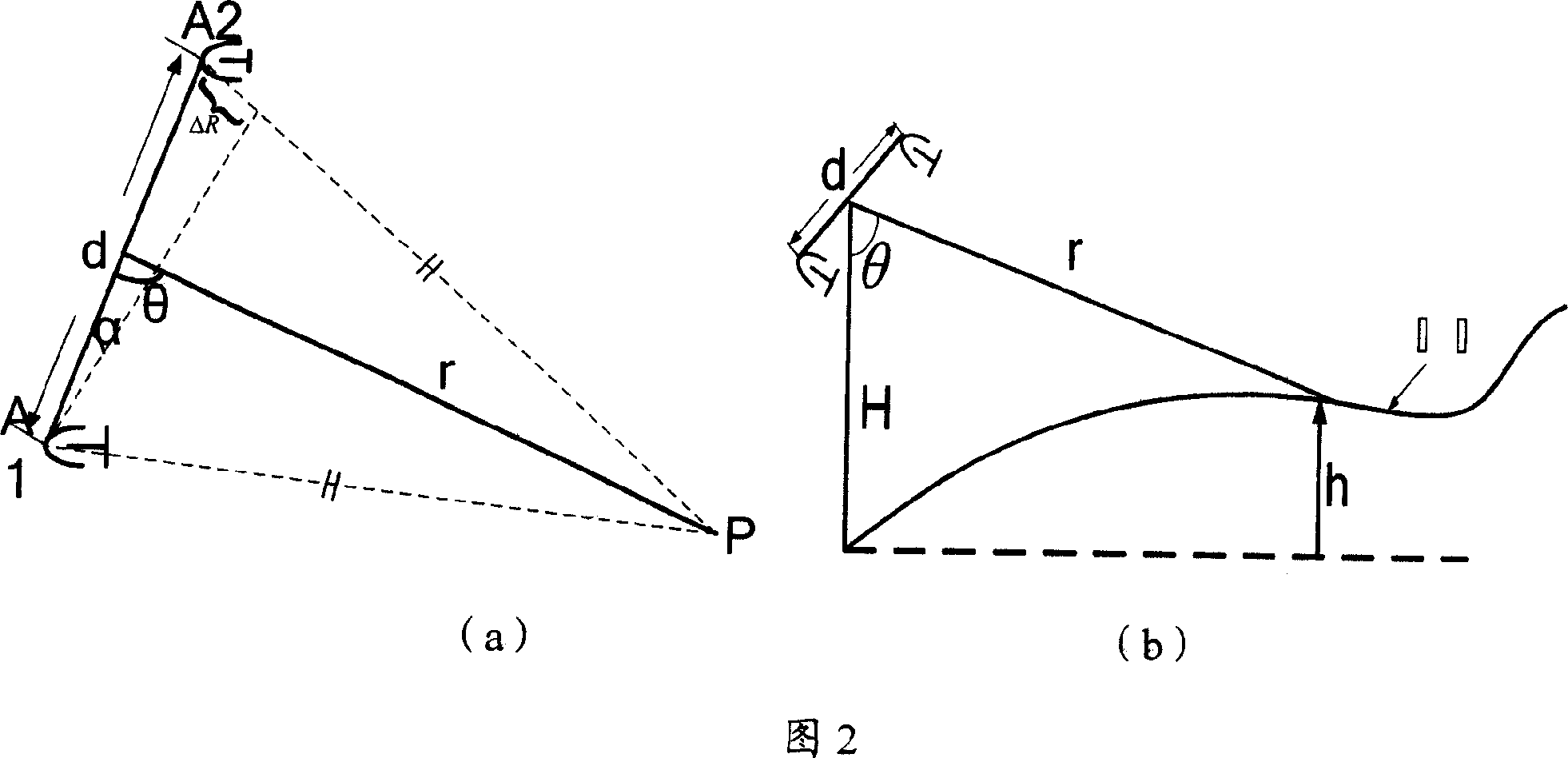
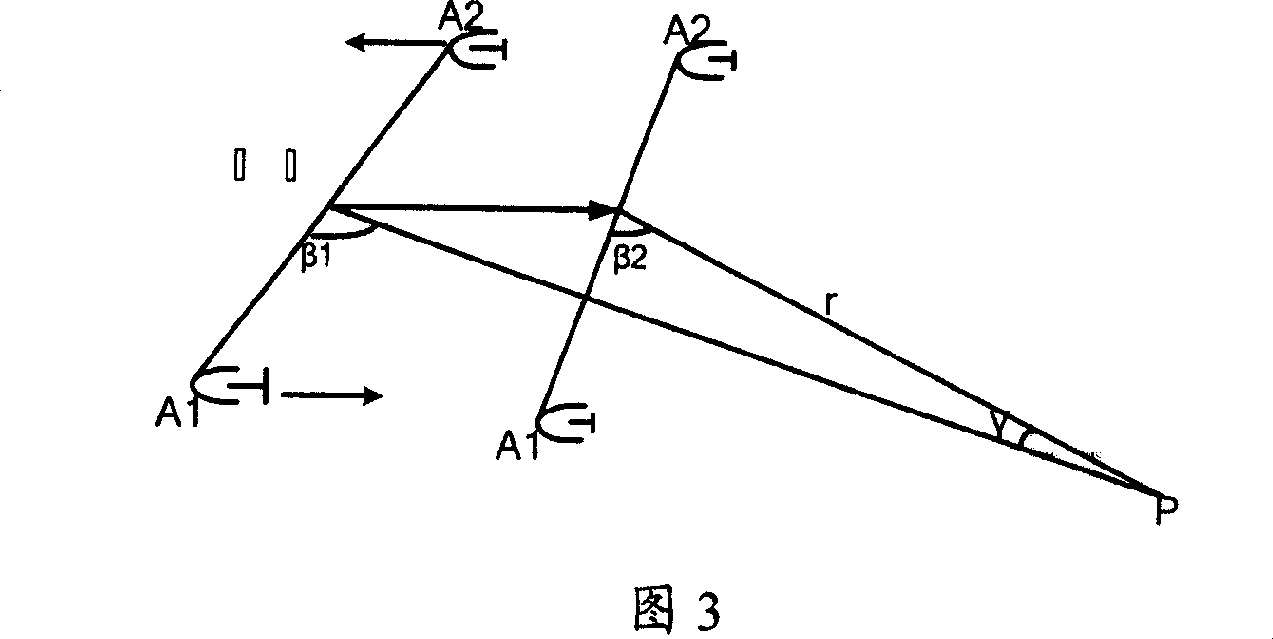
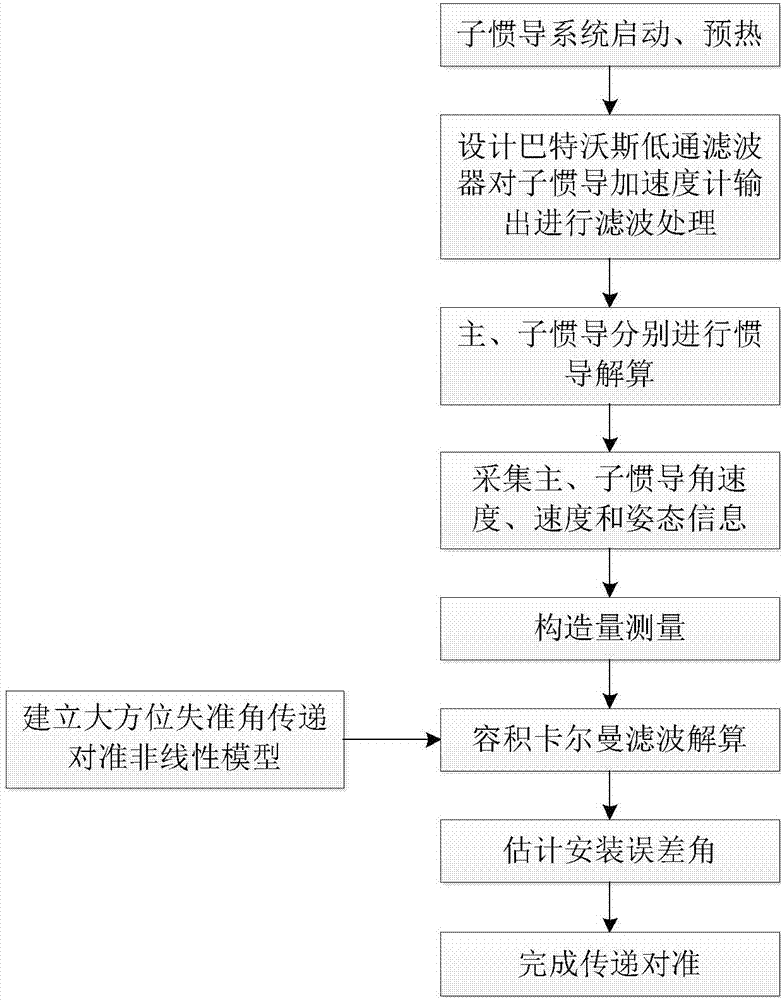
Ship large azimuth misalignment angle transfer alignment method based on volumetric Kalman filtering
The invention discloses a ship large azimuth misalignment angle transfer alignment method based on volumetric Kalman filtering. The ship large azimuth misalignment angle transfer alignment method comprises the following steps: firstly, converting a specific force output of a secondary inertial navigation accelerometer to a navigation coordinate system; carrying out filtering processing on the specific force by utilizing a Butterworth digital low-pass filter; secondly, carrying out inertial navigation calculation on primary and secondary inertial navigation respectively; transmitting speed, posture and angular speed information of the primary inertial navigation to a navigation computer of the secondary inertial navigation; constructing measurement by utilizing speed error, posture error and angular speed error between primary and secondary inertial navigation system; then establishing a state equation and a measurement equation under a large azimuth misalignment angle condition by adopting a matching manner of a speed, a posture and an angular speed; finally, carrying out volumetric Kalamn filtering calculation by utilizing the established state equation and measurement equation and estimating a mounting error angle between the secondary inertial navigation system and the primary inertial navigation system, so as to finish transfer alignment. By adopting the ship large azimuthmisalignment angle transfer alignment method, the rapid and high-precision alignment problem of a ship under a condition of a large azimuth misalignment angle and a large lever arm error is solved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Specific differential integration matched transfer alignment of stabilized sighting pod and combination navigation method thereof
InactiveCN101603833ARealize full-time navigation and positioning functionMeet positioning accuracy requirementsInstruments for comonautical navigationMarine navigationTransfer alignment
The invention discloses a specific differential integration matched transfer alignment of a stabilized sighting pod and a combination navigation method thereof, belonging to inertial navigation system. The alignment method comprises collecting signals of an inertial measurement unit; performing fast and accurate transfer alignment of the stabilized sighting pod; resolving inertial navigation based on pod stabilized sighting platform; performing error analysis, model establishment and supplementation of inertial navigation system and inertial components; and performing main inertial navigation / sub inertial navigation / GPS multi information variable structure combination navigation under the condition of pod flexible and rigid connection. The invention solves the problems of fast transfer alignment and navigation positioning of the stabilized sighting pod when taking off and flying in the air.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Inertial navigation alignment performance evaluation method based on main inertial navigation attitude variation quantity assistance
InactiveCN104807479AAccurate and precise estimateReduced maneuvering requirementsMeasurement devicesLinear motionTransfer alignment
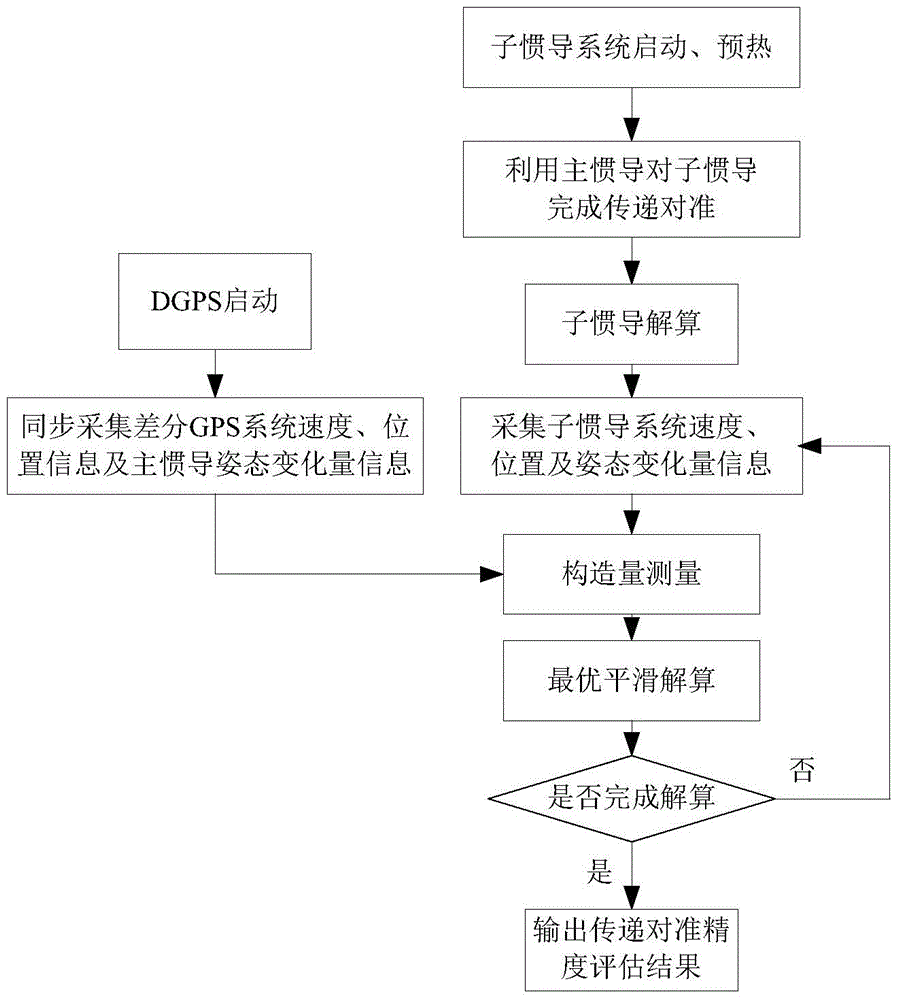
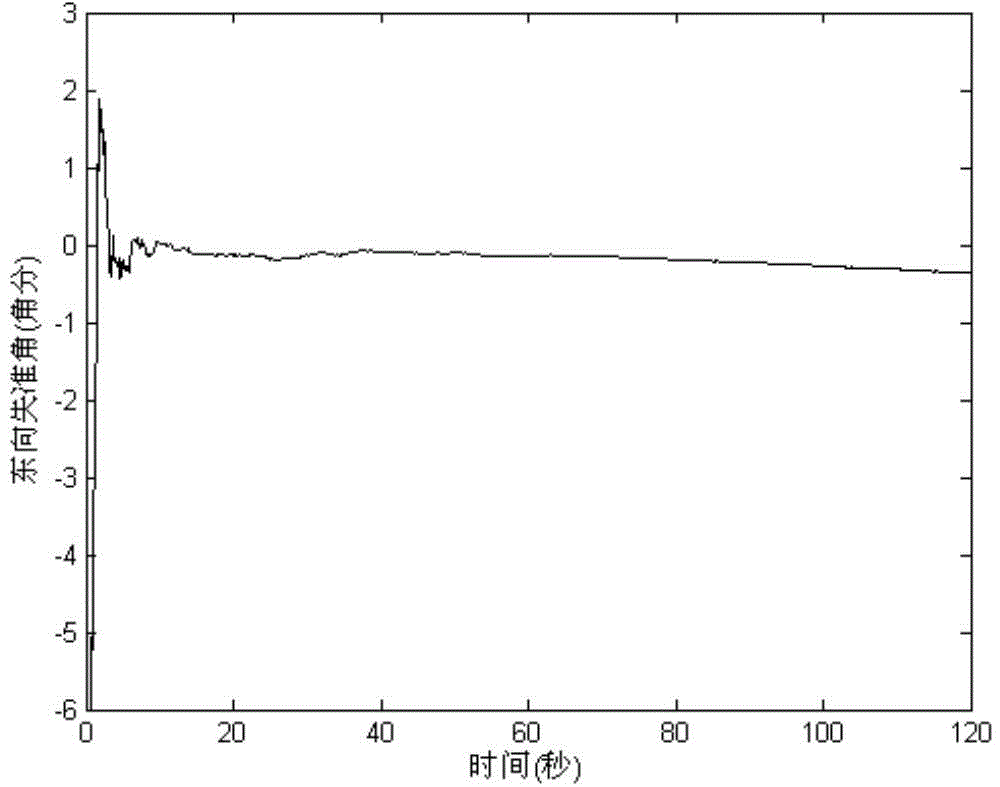
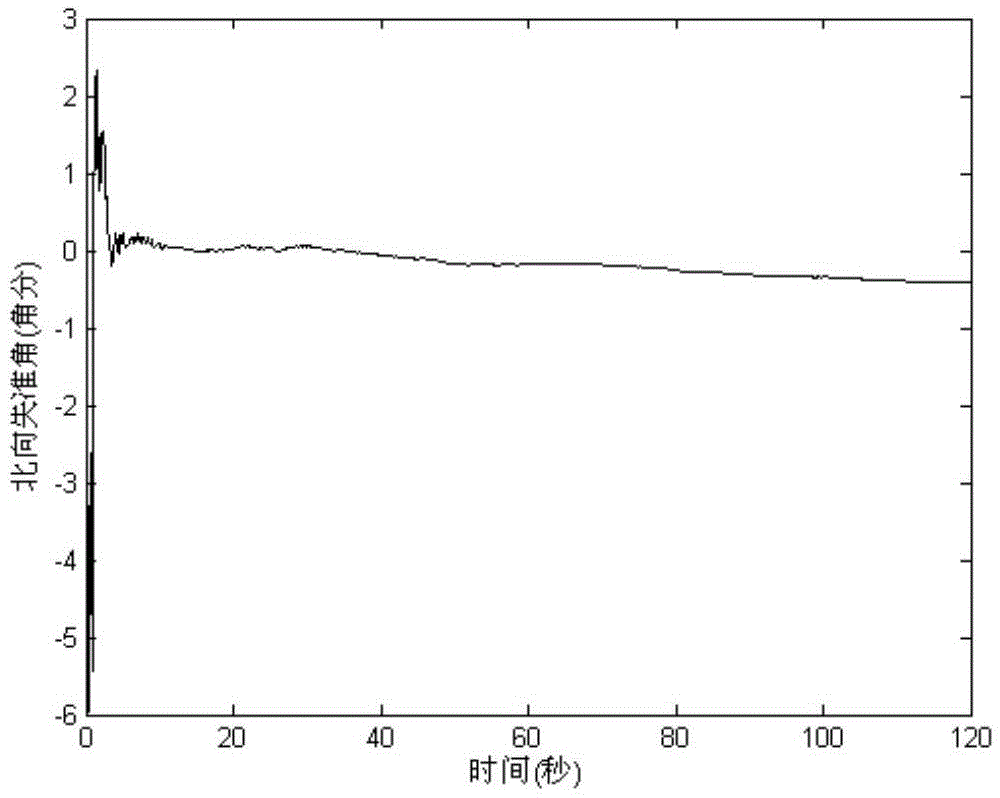
The invention discloses an inertial navigation alignment performance evaluation method based on main inertial navigation attitude variation quantity assistance. The method comprises the following steps of implementing preheating preparation; performing navigation solution on a main inertial navigation system and a secondary inertial navigation system respectively; constructing a measurement equation of attitude variation quantity; constructing a performance evaluation measurement equation; performing Kalman filtration solution; performing reverse smoothing estimation; acquiring an attitude misalignment angle at a transfer alignment ending moment so as to realize alignment precision evaluation of transfer alignment of the inertial navigation system of a ship-borne weapon. The invention designs the inertial navigation alignment performance evaluation method based on the main inertial navigation attitude variation quantity assistance, linear motion information of GDPS position and speed is taken as main reference information, and the main inertial navigation attitude variation quantity is taken as auxiliary reference information, so that the requirements of accuracy evaluation on mechanical strength of a carrier can be reduced; integral output based on angular rate is taken as an observed value, so the influences on the inertial navigation alignment performance evaluation effect caused by external environmental interferences can be effectively inhibited, and the inertial navigation alignment accuracy evaluation performance of the ship-borne weapon can be improved.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAHAO MARINE ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE
Method for performing transfer alignment on large azimuth misalignment angle of ship in polar region environment based on unscented Kalman filtering
InactiveCN105783943AAchieving transfer alignmentHigh precisionMeasurement devicesMarine navigationTransfer alignment
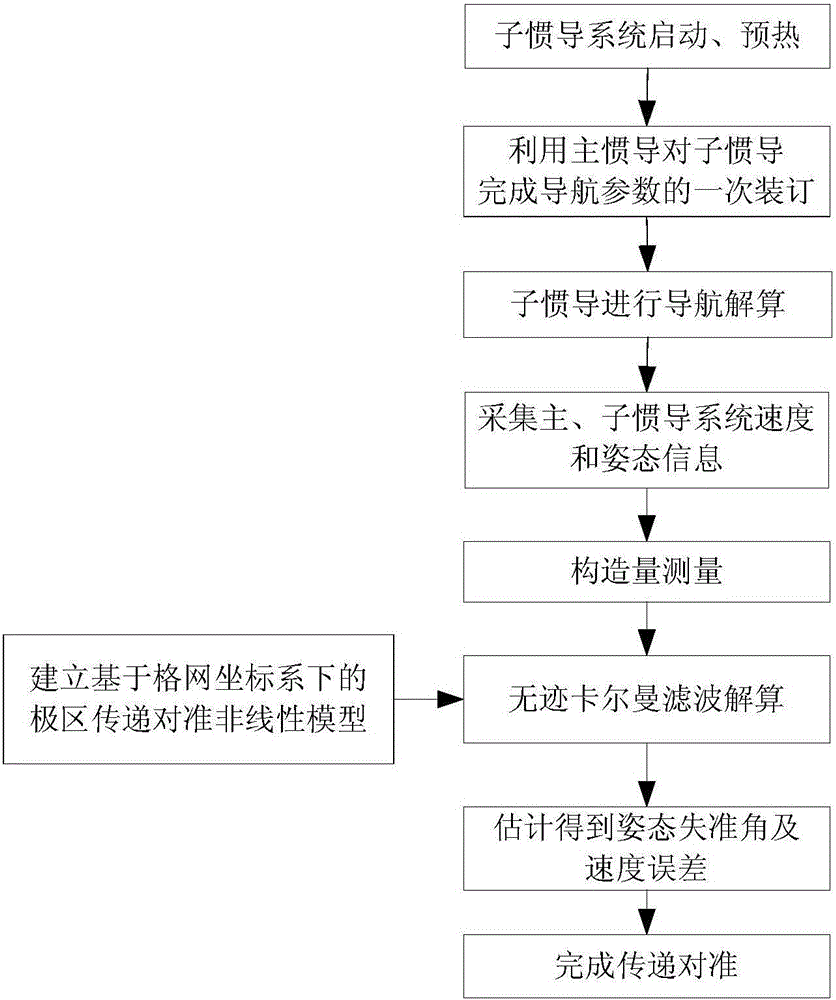
The invention discloses a method for performing transfer alignment on a large azimuth misalignment angle of a ship in a polar region environment based on unscented Kalman filtering. The method comprises the following steps: I, completing starting and preheating preparation of a slave inertial navigation system, wherein the slave inertial navigation system completes primary binding by utilizing navigation parameters transmitted by a master inertial navigation system; II, performing inertial navigation calculation on the slave inertial navigation system, and synchronously acquiring the speed and attitude information of the master and slave inertial navigation systems output in a grid system to obtain speed and attitude errors so as to constitute and measure Z; III, according to navigation mechanics arrangement in the grid system, combining a grid navigation error equation, adopting a 'speed + attitude' matching manner, and establishing a system state equation and a measurement equation in the grid system; and IV, performing unscented Kalman filtering calculation, estimating the attitude misalignment angle of the slave inertial navigation system and the speed state estimated value, and completing transfer alignment. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the problem that the large azimuth misalignment angle cannot be subjected to transfer alignment in the polar region environment is solved, and the transfer alignment accuracy and applicability of the polar region are improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
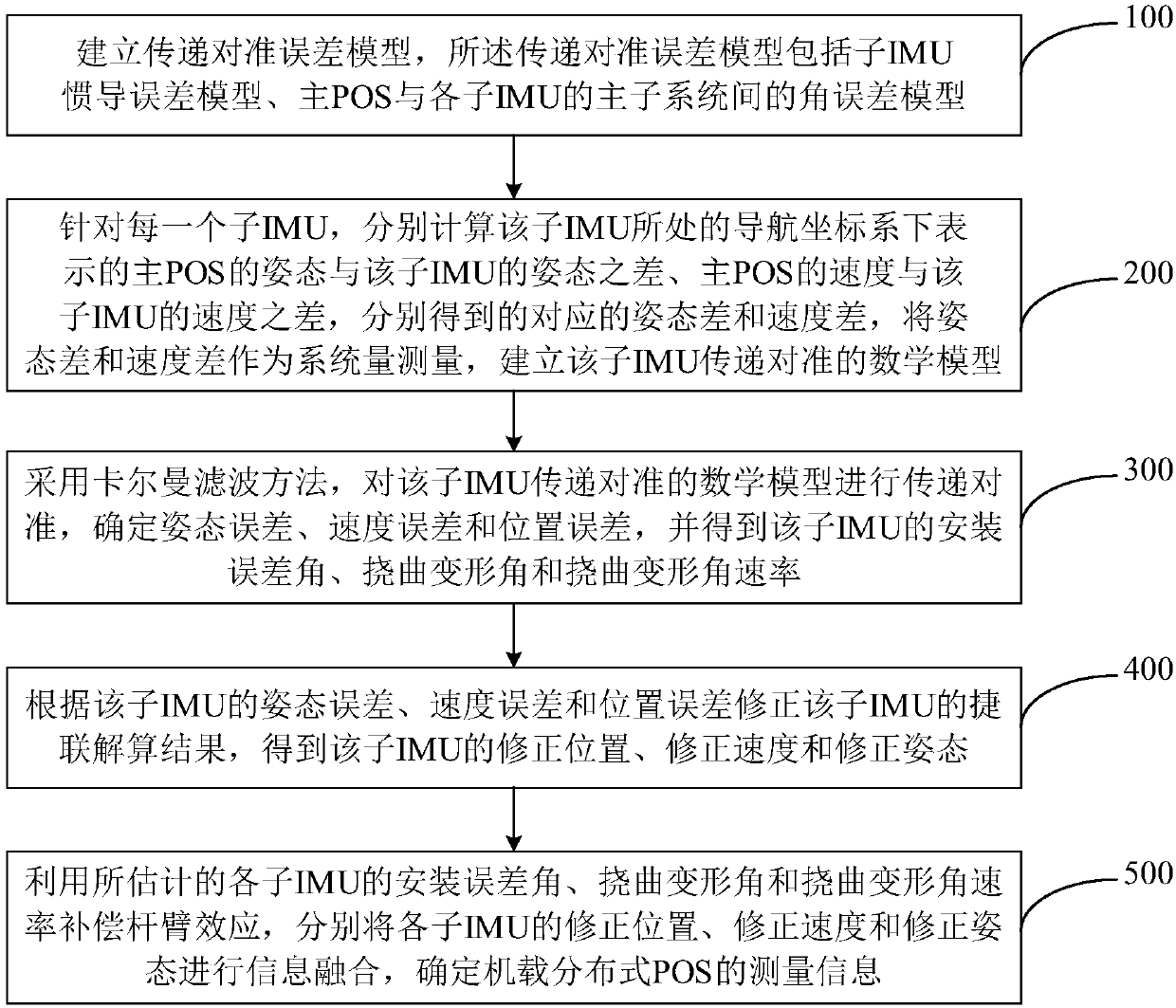
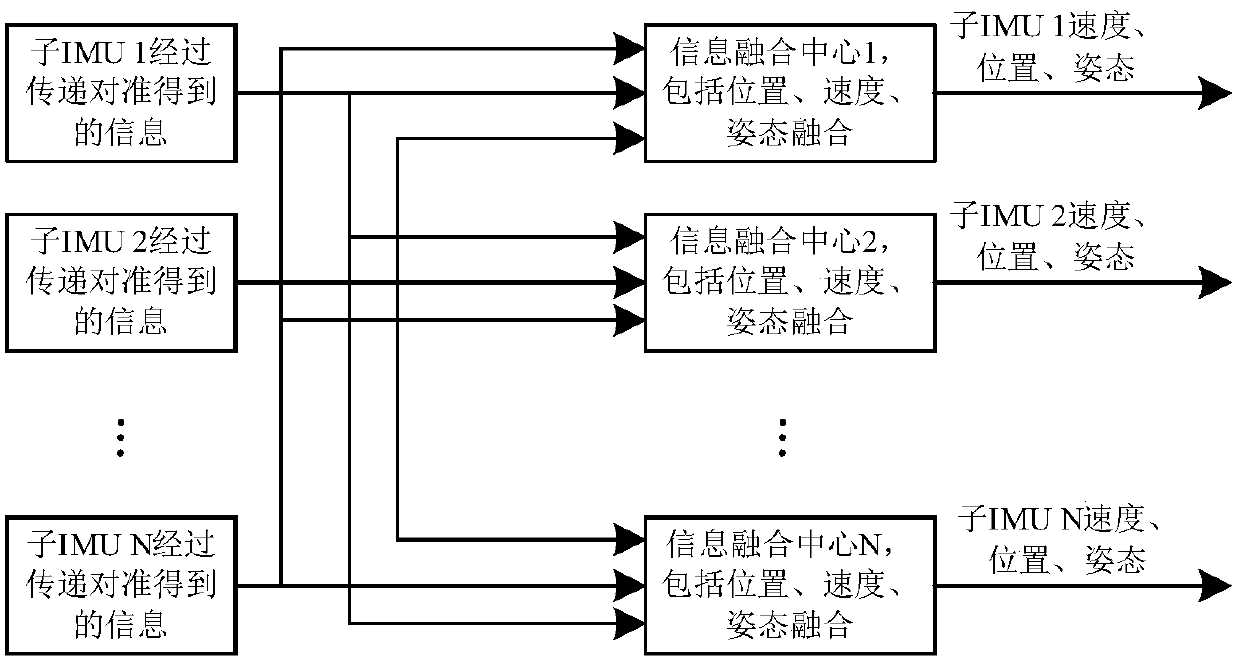
Multi-node information fusion method and system of airborne distributed POS (Position and Orientation System)
ActiveCN108387227AAccurate measurement informationHigh measurement accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsMathematical modelInformation integration
The invention provides a multi-node information fusion method and system of an airborne distributed POS (Position and Orientation System). The method comprises the following steps: establishing a transfer alignment error model; aiming at each sub-IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), calculating the difference between a posture of a main POS represented by a navigation coordinate system of the sub-IMUand the posture of the sub-IMU, and the difference between the speed of the main POS and the speed of the sub-IMU and establishing a mathematical model of transfer alignment of the sub-IMU; carrying out the transfer alignment on the mathematical model of the transfer alignment of the sub-IMU, and determining a posture error, a speed error and a position error and obtaining a mounting error angle,a deflection deformation angle and a deflection deformation angle speed; revising a strapdown solving result of the sub-IMU to obtain a revised position, a revised speed and a revised posture of the sub-IMU; compensating a lever arm effect by utilizing the estimated mounting error angle, deflection deformation angle and deflection deformation angle speed of each sub-IMU and carrying out information fusion on the revised position, the revised speed and the revised posture of each sub-IMU; determining measurement information of the airborne distributed POS so as to improve the overall measurement precision of a distributed POS system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
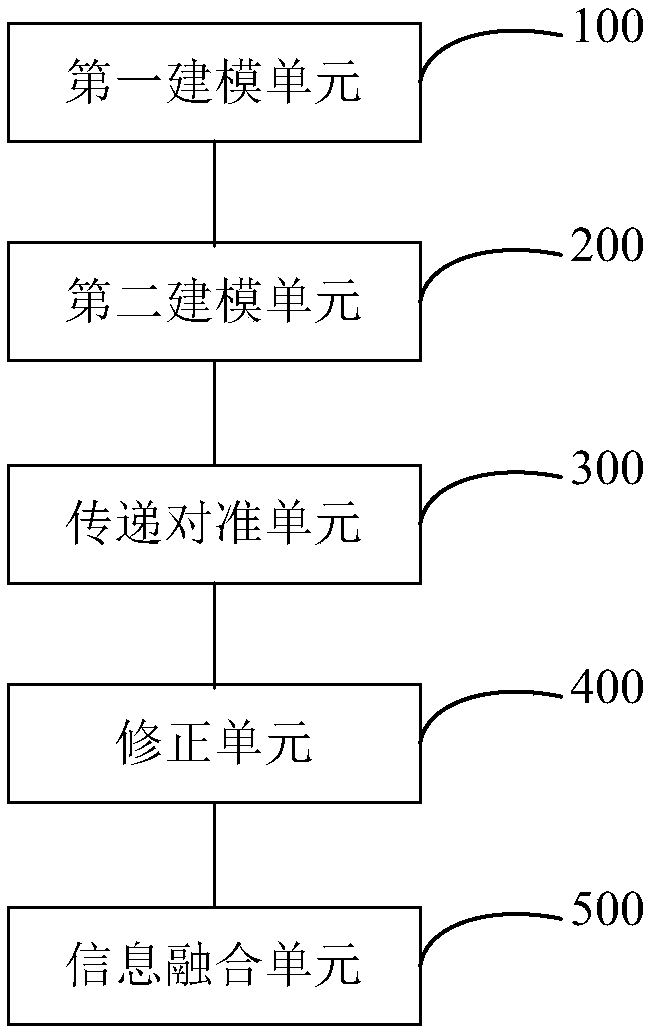
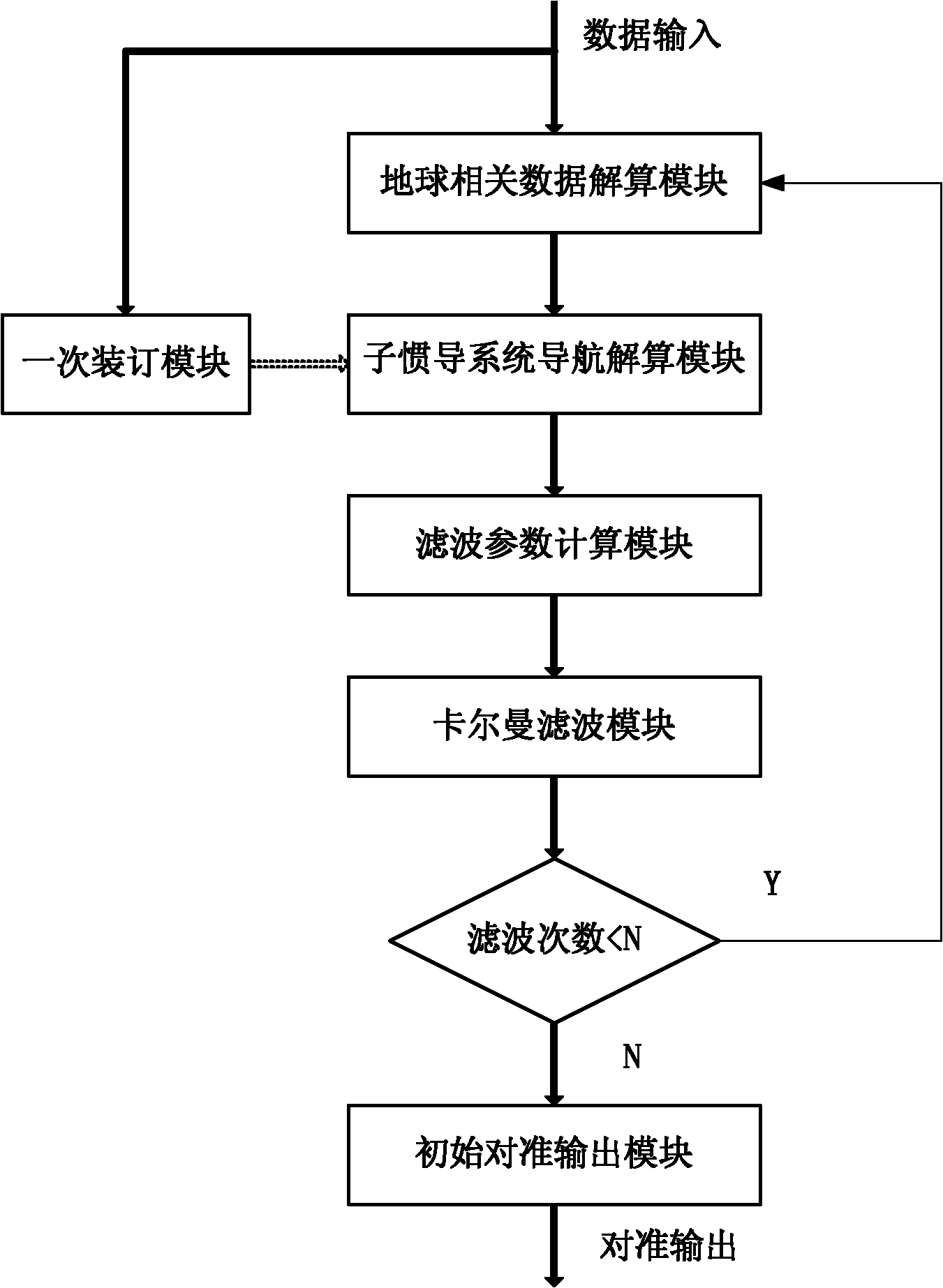
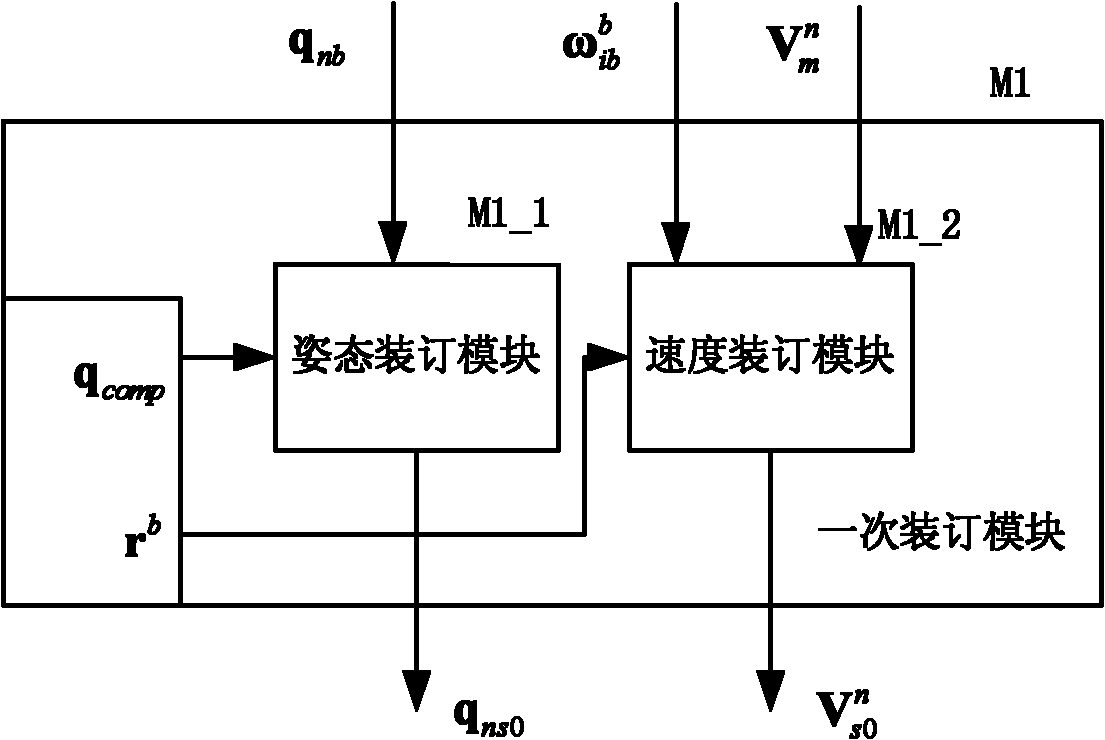
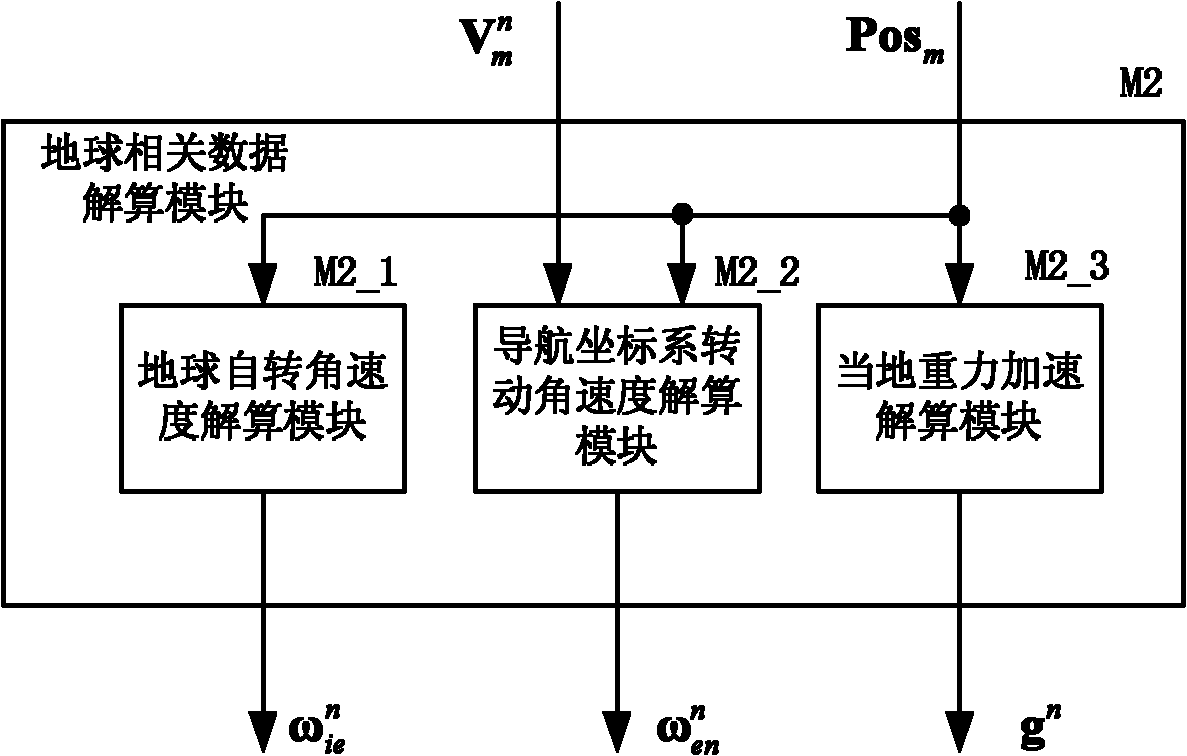
Strap-down inertial navigation transfer alignment algorithm parallel implementation method
The invention discloses a strap-down inertial navigation transfer alignment algorithm parallel implementation method. A primary binding module, a globe related parameter calculating module, a sub inertial navigation system navigation calculating module, a filter parameter calculating module, a Kalman filter module and an alignment output module are adopted in the method; the primary binding module receives data information of a first frame main inertial navigation system, and the data information is subjected to compensating calculation and then used as an initial value of initial alignment navigation calculation of a sub inertial navigation system; the globe related parameter calculating module, the sub inertial navigation system navigation calculating module, the filter parameter calculating module and the Kalman filter module form a fine alignment process of transfer alignment, and the fine alignment process is circularly executed till reaching the set cycle times; and the alignment output module performs one-time correction on the attitude information of the sub inertial navigation system after the fine alignment process is finished, and outputs attitude, speed and position initial values required by navigation calculation of the sub inertial navigation system. By the method, the calculation velocity of the strap-down inertial navigation transfer alignment algorithm is quickened, and the alignment precision of transfer alignment is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of digitally constructing a prosthesis
ActiveUS20140188260A1Efficient rateSpecial data processing applicationsProsthesisProsthetic limbBiomedical engineering
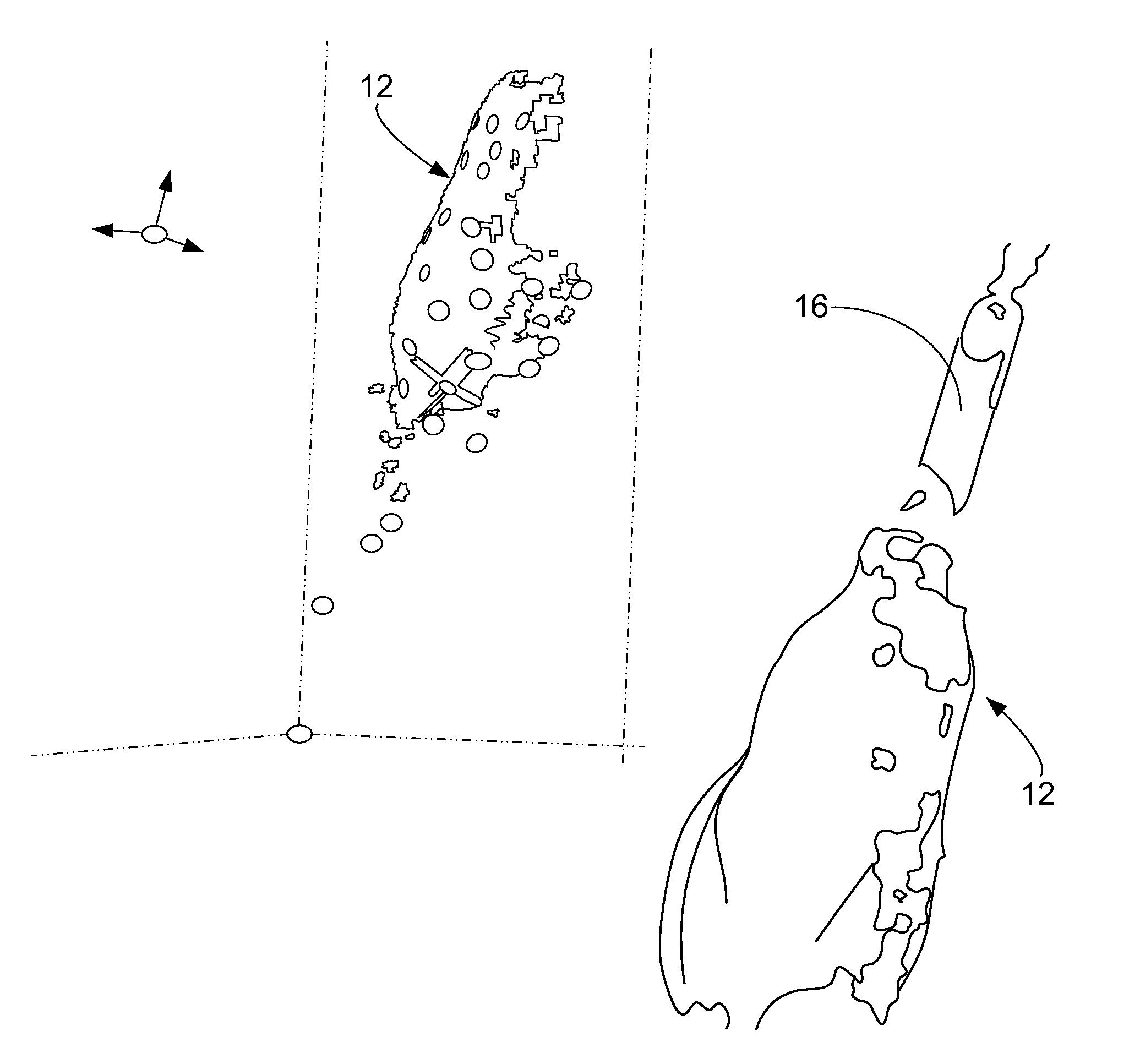
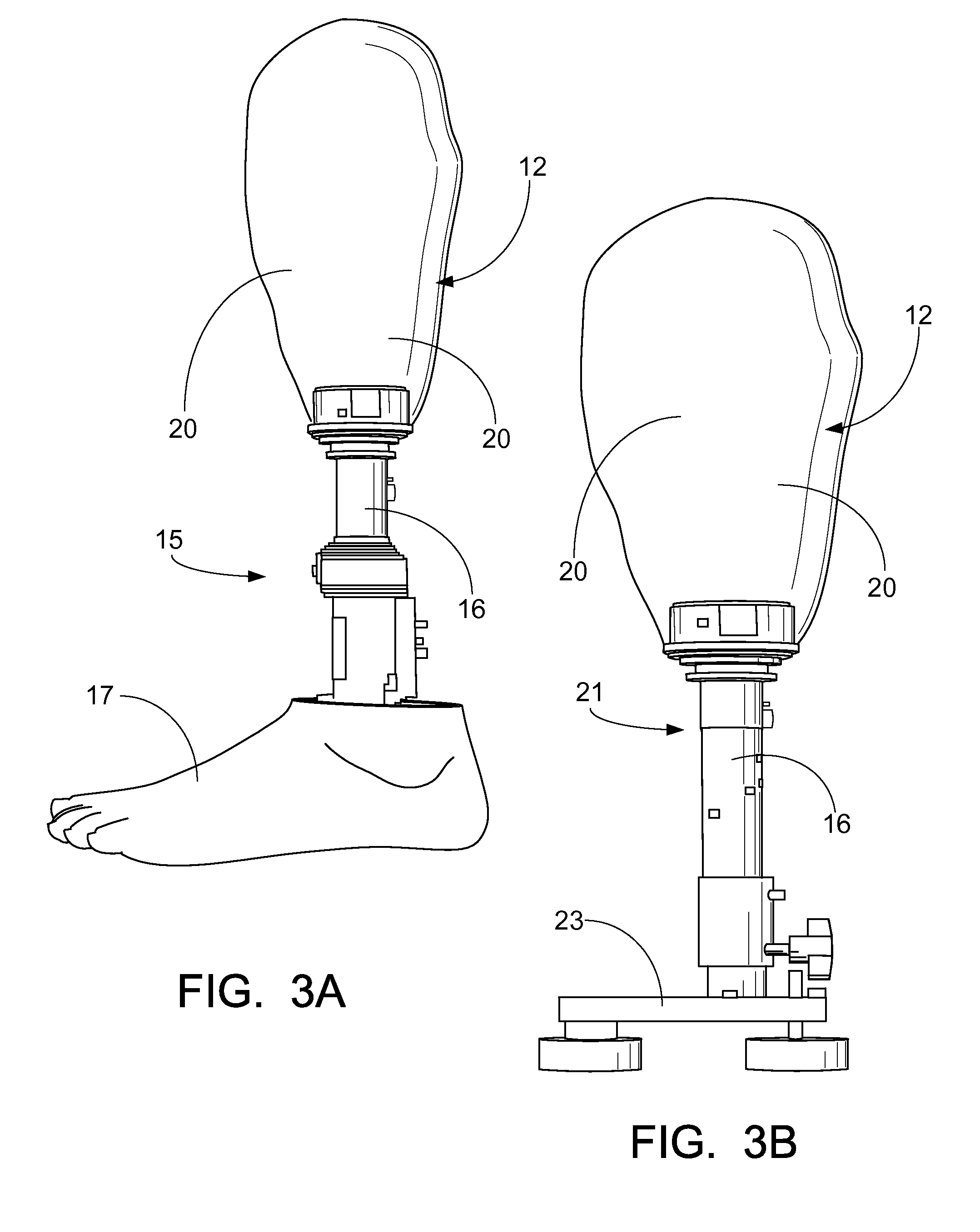
A prosthetic limb and process to digitally construct a prosthetic limb which includes first, digitally producing a modified mold of a residual limb via 3d scanners and software; constructing a test socket from the digitally modified mold and be equipped with an alignable system; accurately scanning the test socket, along with finalized alignment that has been recorded and adjusted by a certified practitioner to provide a 3-D Image of the finalized prosthetic alignment; transferring the finalized digital alignment of the test socket to the finalized digitally modified mold; once the modified model has received the transferred alignment, fabricating the type of hookup in the socket; i.e., plug fit, four hole, support drop lock, or any other type of industry standard connection or accommodation via basic 3D software; and once the desired prosthetic attachment is finalized, sending finished file to a 3-D printer to produce the definitive prosthetic device.
Owner:LAYMAN WILLIAM STRATFORD +1
Co-base installation-based transfer alignment accuracy quantitative evaluation method
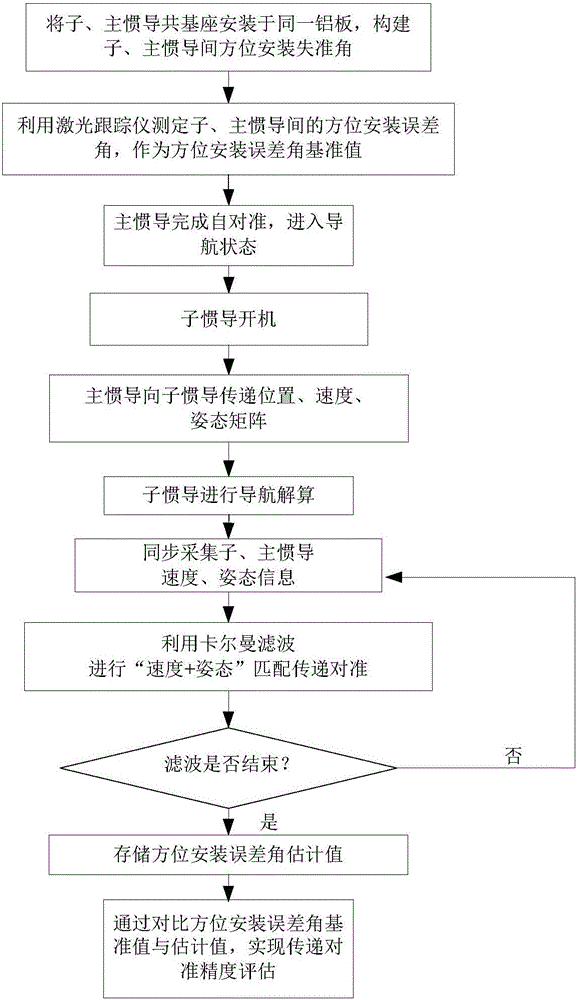
ActiveCN105973268AAlignment Accuracy EvaluationAlignment assessmentMeasurement devicesComputation complexityAutocollimation
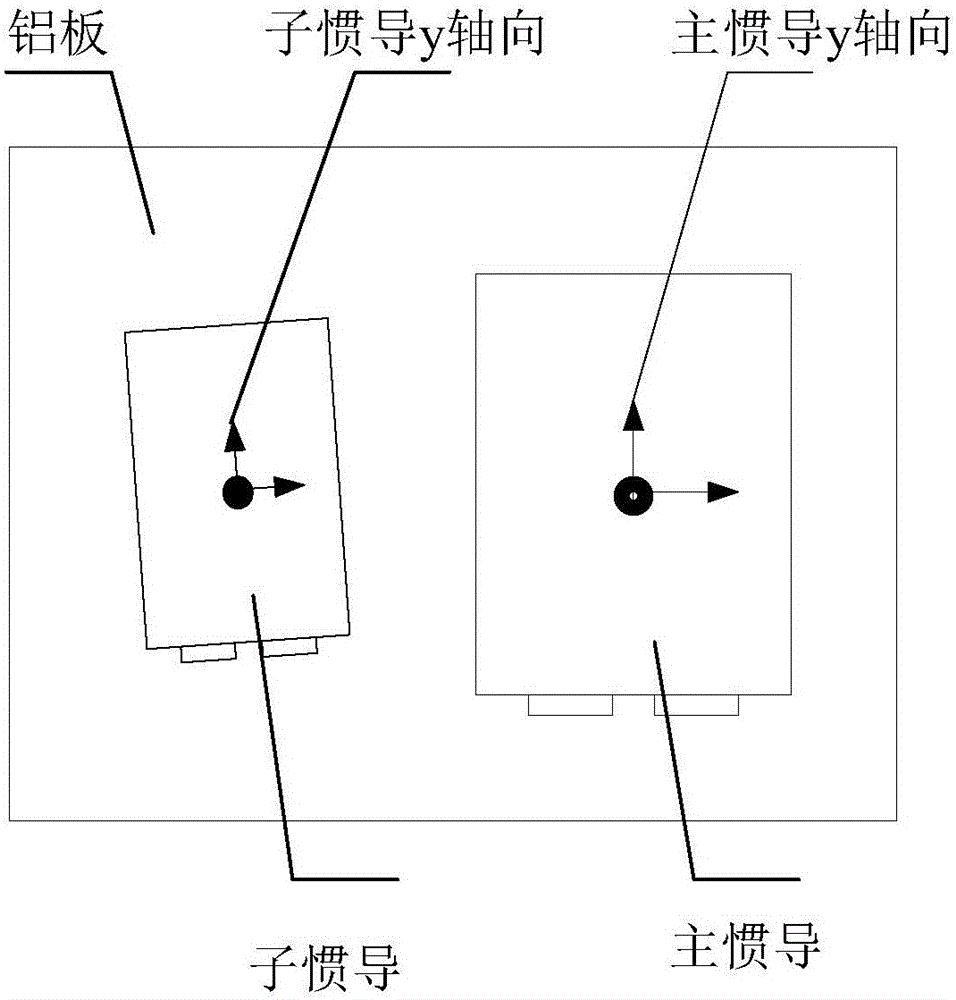
The invention belongs to the field of inertial navigation system performance assessment and relates to a co-base installation-based transfer alignment accuracy quantitative evaluation method aiming at strapdown inertial navitation system transfer alignment accuracy. The method comprises installing slave and main inertial navigation devices sharing a base on an aluminum plate, constructing slave and main inertial navigation device orientation installation misalignment angles, putting the aluminum plate with the slave and main inertial navigation devices on a high precision rotary table, guiding the y axis of the main inertial navigation device to point to the true north direction through an optical sighting telescope, measuring slave and main inertial navigation device y axis orientation installation error angles as orientation installation error angle reference values through a laser tracker and starting the main inertial navigation device to carry out autocollimation. The method can acquire alignment accuracy evaluation reference before transfer alignment and through comparison between the reference value and the evaluation value, alignment accuracy quantitative evaluation is realized. The method is free of slave inertial navigation device navigation calculation and smooth calculation after alignment, greatly reduces computation complexity and data storage demands and realizes repeated tests in short time.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
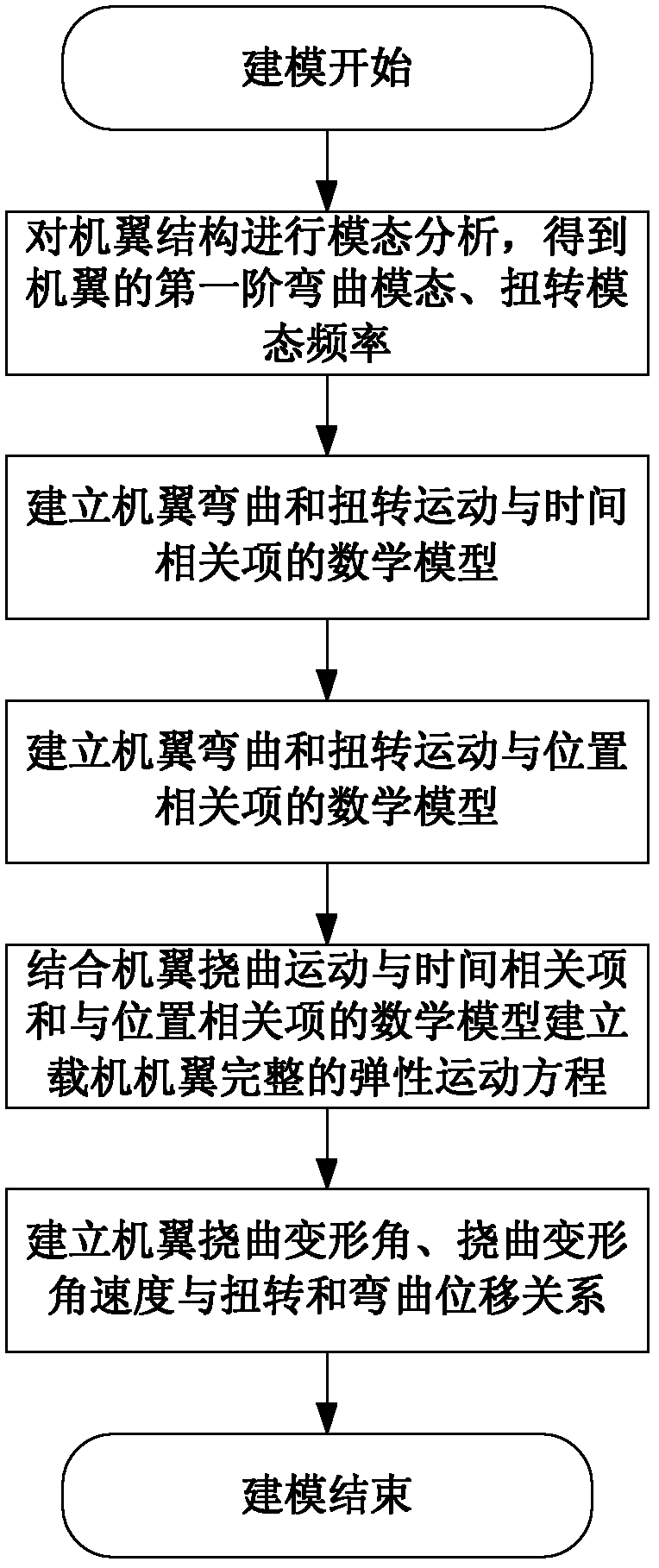
Method for analyzing influences of wing deformation and vibration on aircraft transfer alignment
InactiveCN103995918AImprove combat capabilityShorten the timeSustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsStructural dynamicsAnalysis method
The invention belongs to the field of aircraft structural dynamics, and relates to a method for analyzing influences of wing deformation and vibration on aircraft transfer alignment. The method is characterized by including the following steps: (1) building a full-aircraft structure dynamical model, (2) building a full-aircraft unsteady aerodynamic model, (3) building a transfer relationship between plug-ins and inertial navigation, and (4) obtaining a primary-secondary inertial navigation error fitting empirical formula. The method has the advantages that speed errors and angular speed errors generated between the primary inertial navigation and the secondary inertial navigation of an aerial movable platform are analyzed through the built aircraft structure dynamical model, then the errors are eliminated through filtering, and in this way, the transfer alignment time of the primary inertial navigation and the secondary inertial navigation during guided missile launching can be shortened to a great degree.
Owner:SHENYANG AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
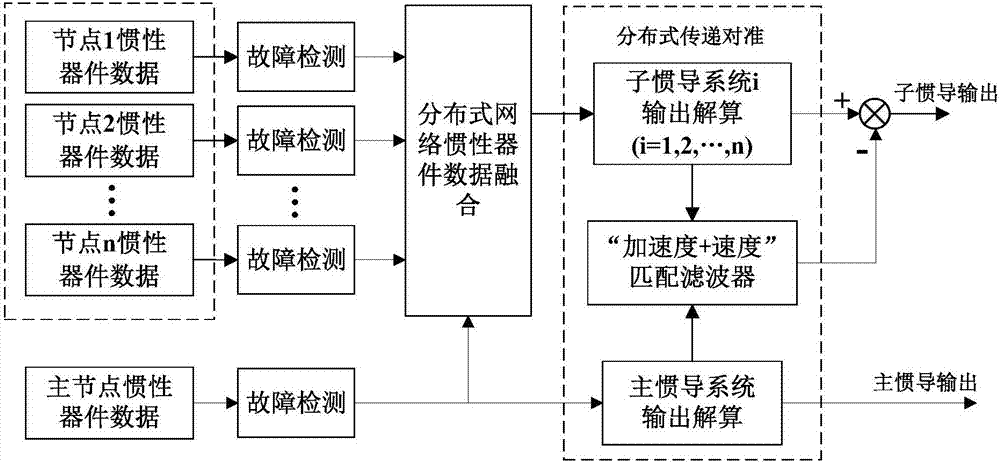
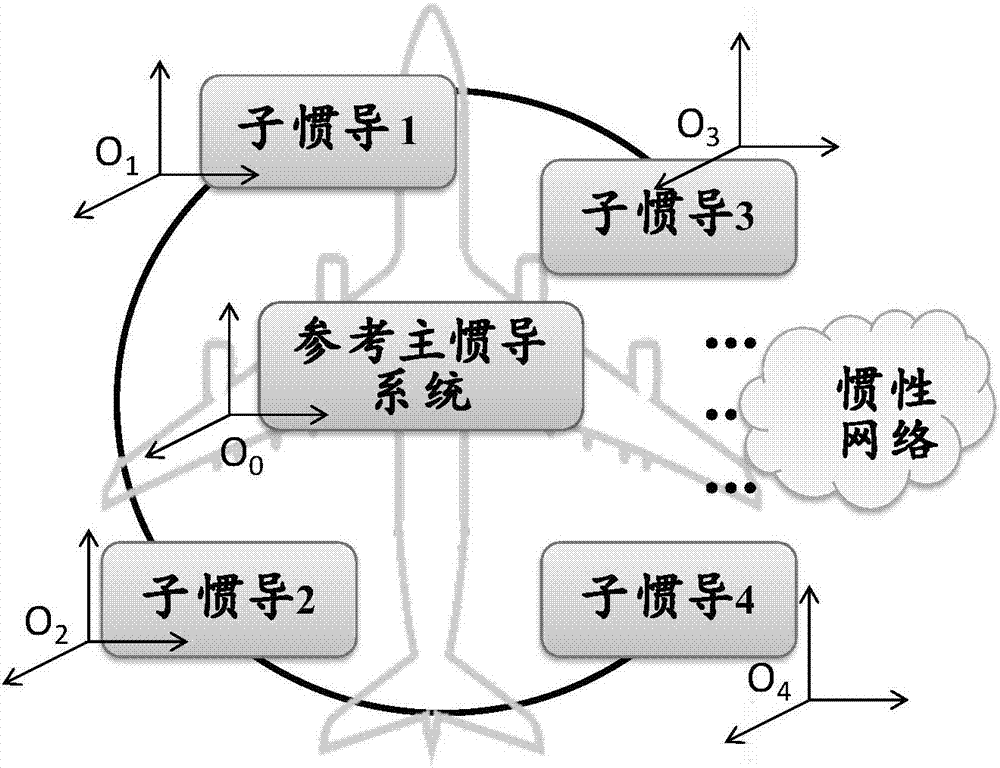
Distributed inertial network-based high accuracy transfer alignment method
ActiveCN106979781AAchieve sharingHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsRadarTransfer matrix
The invention discloses a distributed inertial network-based high accuracy transfer alignment method, belonging to the application category of the technical fields of inertial navigation and transfer alignment. According to the method, a distributed inertial network is established according to the demands and the actual situation, and a plurality of inertial systems are configured at the different parts of a carrier (such as an aircraft, a ship or the like), so that information of a plurality of inertial nodes can be obtained. The reliability of the data output of an inertial device is guaranteed by means of fault detection and isolation; the information of all the nodes is transferred to a certain sub-node for performing data fusion according to a transfer matrix, and inertial measurement information at the certain sub-node is obtained. On the basis of error modeling, a filtering equation is established so as to realize the transfer alignment between the inertial navigation main nodes and the inertial navigation sub-nodes. After the scheme is adopted, external equipment does not need to be additionally arranged, effective redundant inertial information can be provided for the carrier, and local measurement is provided for carrier equipment such as radar tracking and weapon load, so that the accuracy and reliability of the transfer alignment are guaranteed; furthermore, the method has the characteristics of being low in cost, high in autonomy, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
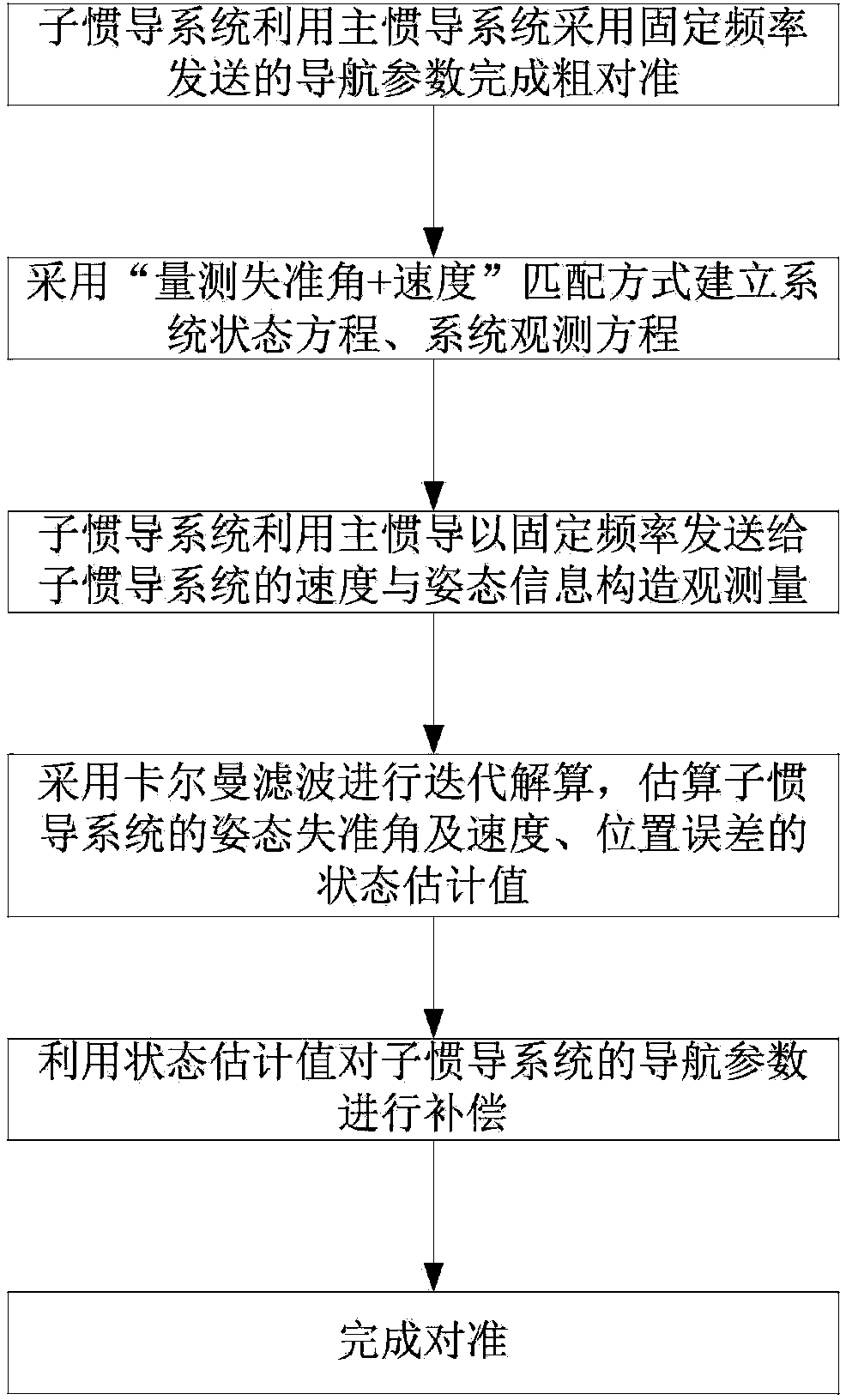
Moving base transfer alignment method based on measurement of misalignment angle
The invention provides a moving base transfer alignment method based on measurement of a misalignment angle. The moving base transfer alignment method comprises the following steps: step (1), completing coarse alignment by a sub-inertial navigation system by use of navigation parameters sent by a main inertial navigation system at fixed frequency, wherein the navigation parameters comprise speed, attitude and position information; step (2), establishing a system state equation and a system observation equation in a'measurement of misalignment angle and speed' matching way; step (3), constructing observables by the sub-inertial navigation system by used of the speed and posture information which is sent from the main inertial navigation system to the sub-inertial navigation system at fixed frequency; and step (4), performing iterative solution by virtue of Kalman filtration, estimating state estimated values of attitude misalignment angle, speed and position errors of the sub-inertial navigation system and correcting navigation information of the sub-inertial navigation system correspondingly so as to complete transfer alignment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Communication-in-motion antenna multi-platform heading and attitude determination method based on transfer alignment
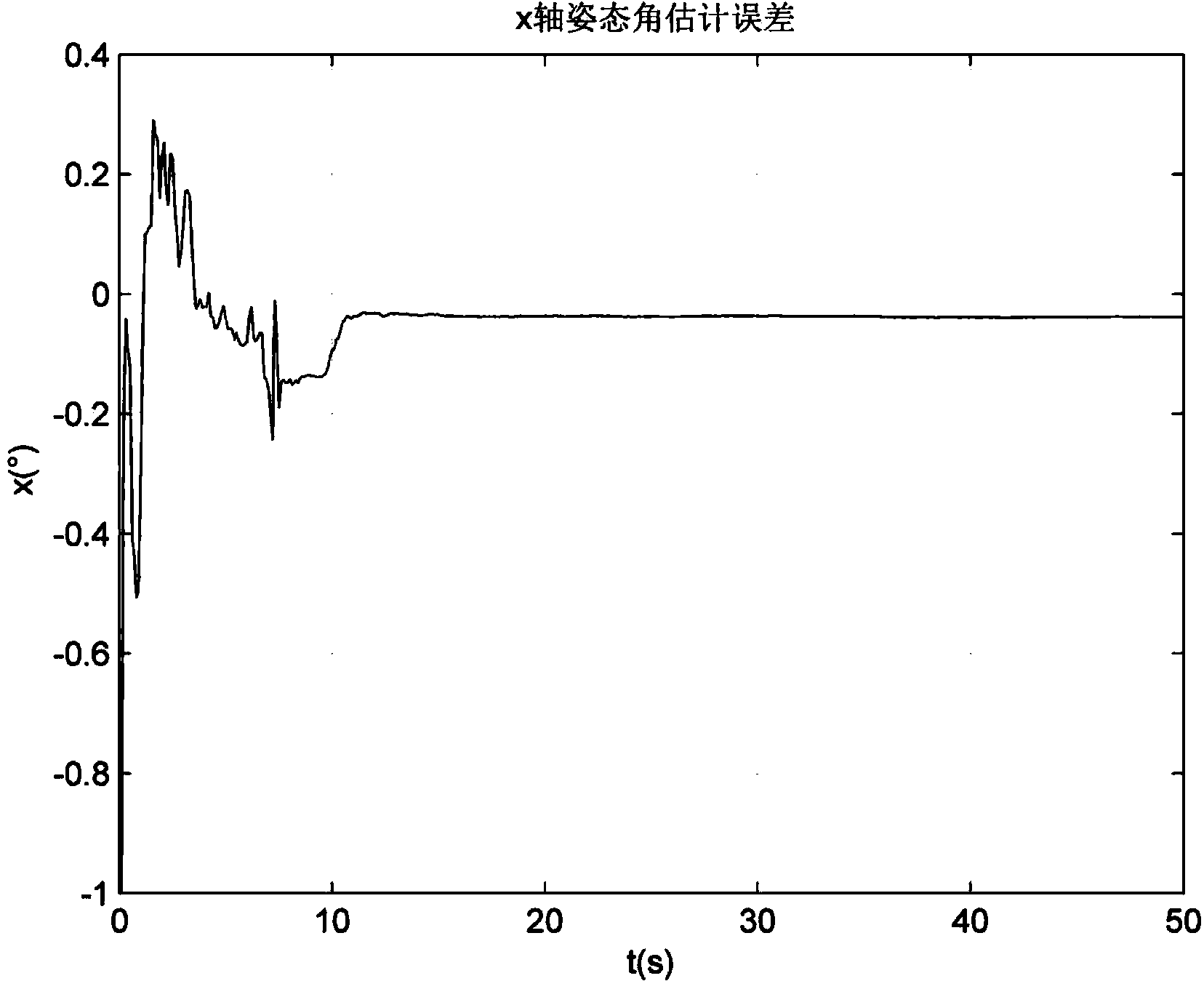
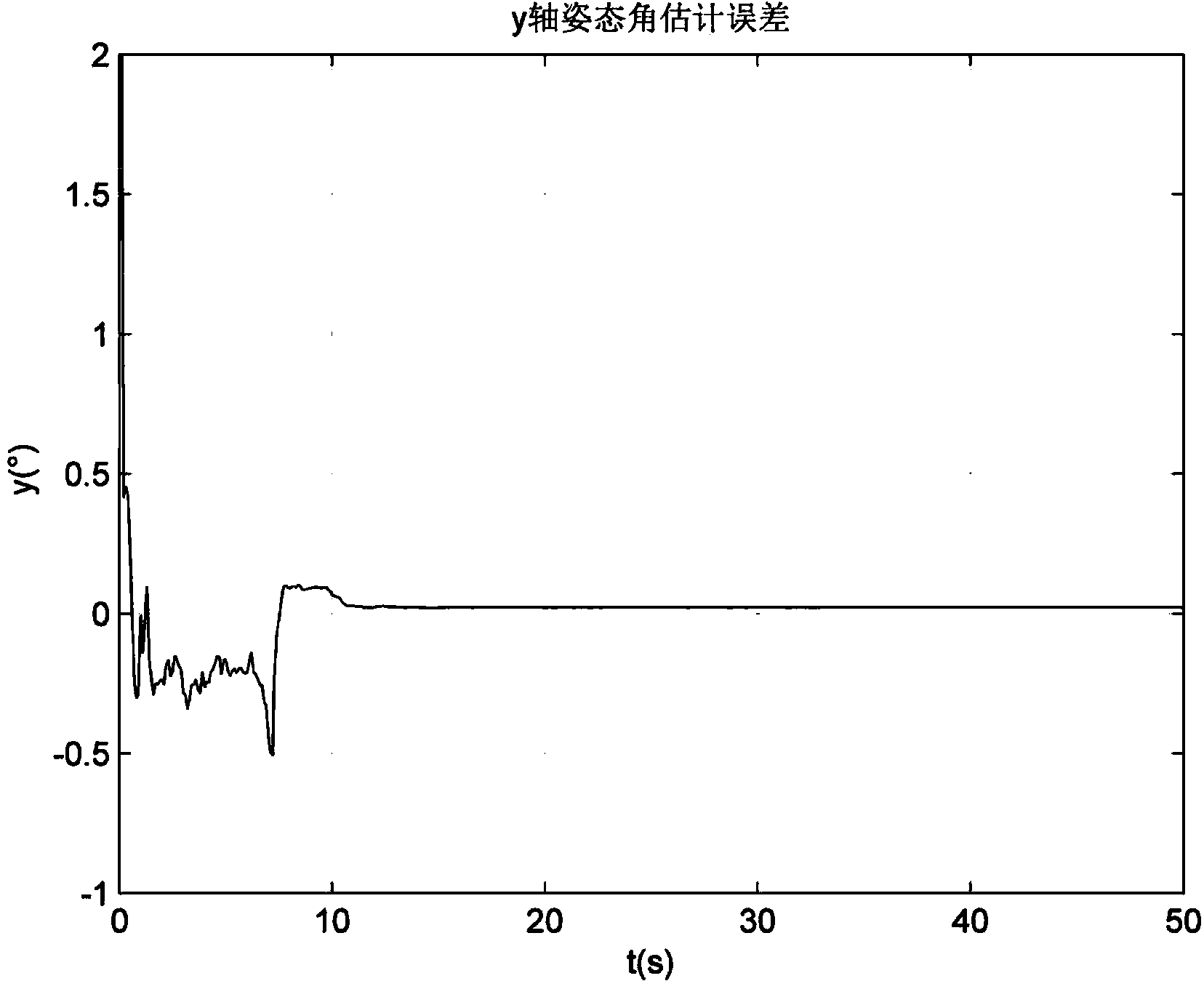
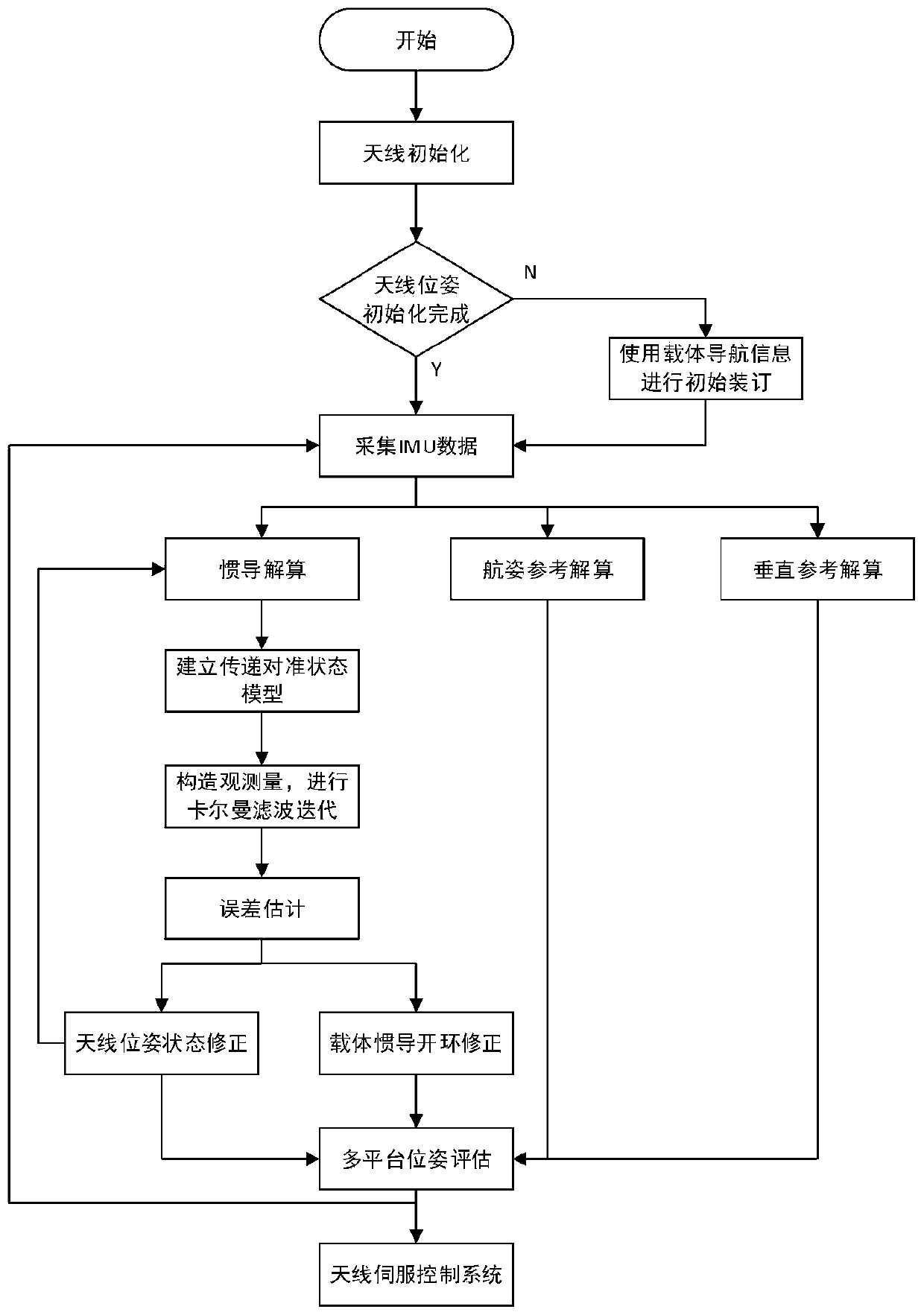
ActiveCN110926468AOvercoming Antenna Pointing ErrorsReduce workloadNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsControl theorySignal strength
The invention discloses a communication-in-motion antenna multi-platform heading and attitude determination method based on transfer alignment. According to the method, an inertial measurement unit isinstalled on a satellite communication-in-motion antenna, multi-platform navigation calculation is carried out, and error compensation is carried out on a strapdown navigation algorithm result of theinertial measurement unit by using output information of navigation equipment on an antenna installation carrier and a transfer alignment algorithm; and finally, a multi-platform heading and attitudedata validity evaluation method is used to obtain heading and attitude information beneficial to improving the tracking performance of the antenna. The multi-platform heading and attitude determination method is established by combining the azimuth angle and signal intensity information of the antenna, the tracking performance of the antenna is improved, and the method has the advantages of no need of manual operation, simple implementation and wide application range.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
Method for transfer alignment of speed and specific force matching
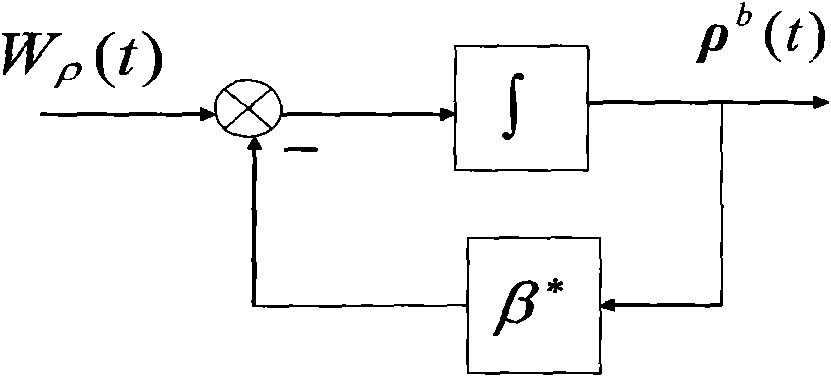
InactiveCN103424127ADifferent transfer alignment methodsHigh speedNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEquation of stateSpecific force
The invention provides a method for transfer alignment of speed and specific force matching. According to the method, precise estimation is conducted on the misalignment angle of a platform in a short time under the dynamic environment. The method comprises the steps that according to the work principle and characteristics of a platform inertial navigation system, a speed error model and an attitude error model between main inertial navigation and sub inertial navigation are established; according to the obtained system error models, a state equation of system filtering is established and an observing equation of the filtering is established, wherein speed and specific force serve as the observed quantity; the system state is estimated through the Kalman filtering, so that the platform misalignment angle relative to the sub platform inertial navigation is finally obtained. The method is suitable for transfer alignment of the platform inertial navigation system under the dynamic condition.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
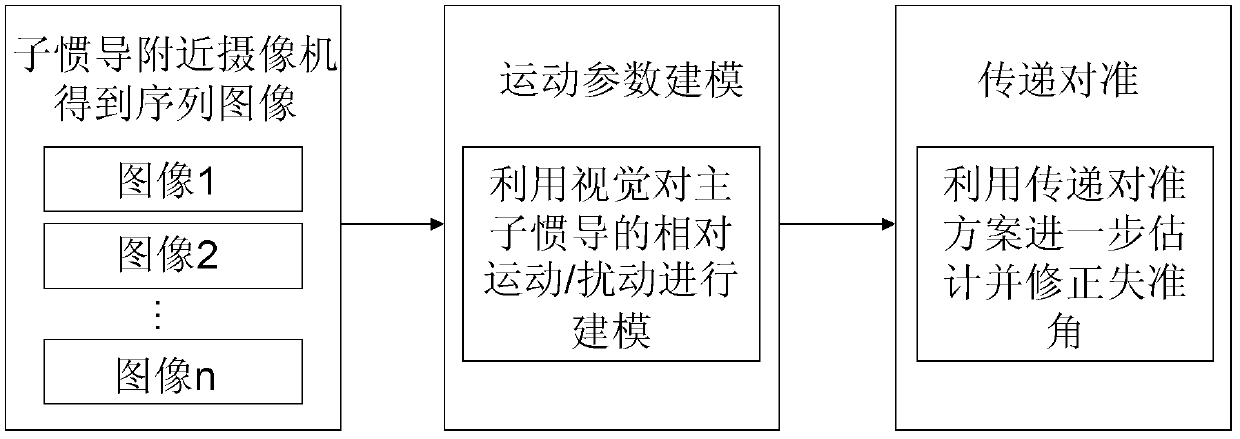
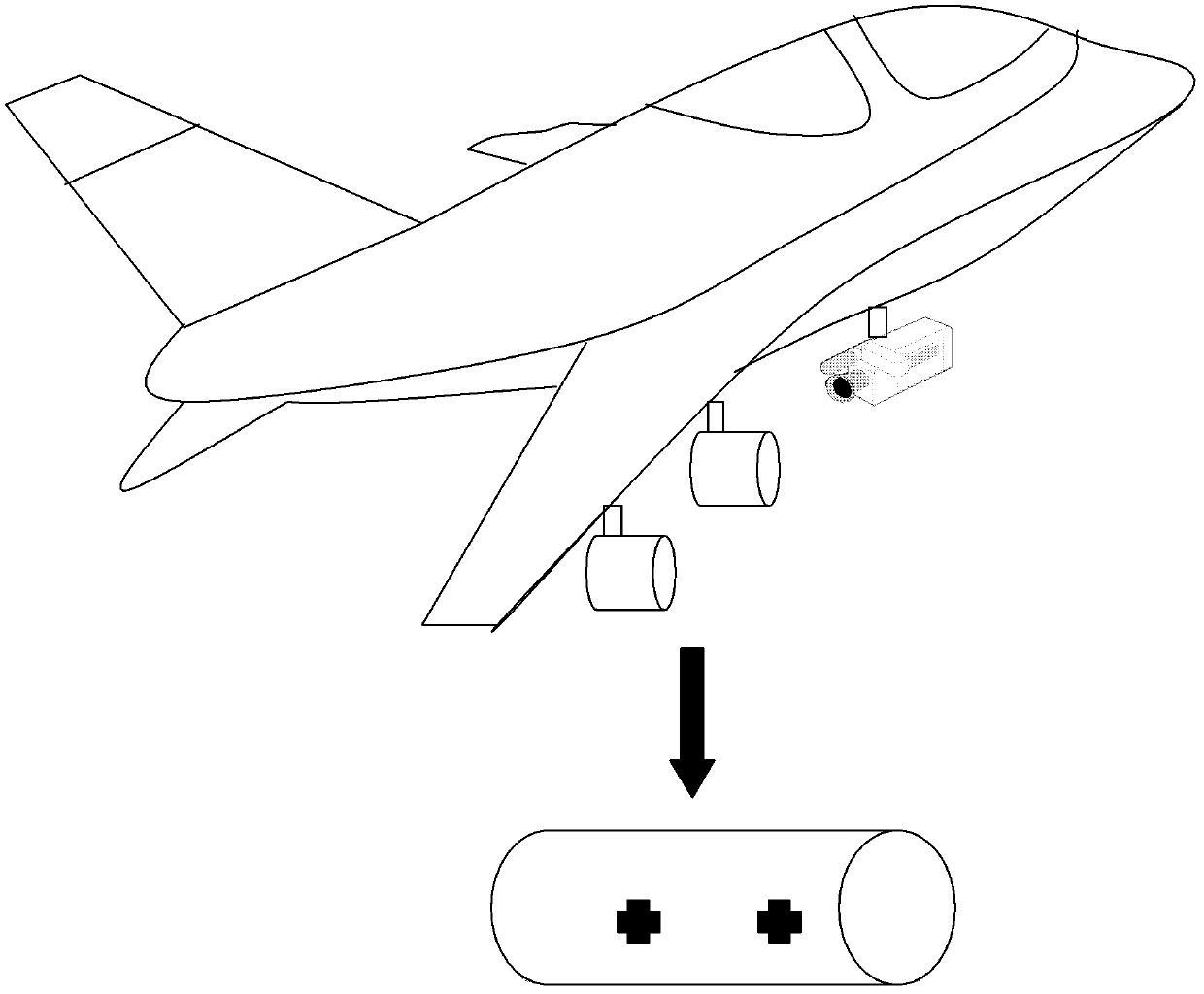
Transfer alignment method and device based on visual movement modeling
ActiveCN102636081ATransfer alignment facilitatesQuick responseAiming meansVisual field lossDynamic models
The invention discloses a transfer alignment method and device based on visual movement modeling and belongs to application fields of visual navigation and transfer alignment fields. According to the requirements and the actual conditions, a high-speed camera is pre-arranged adjacently to a secondary inertial navigation so that the secondary inertial navigation to be detected is located in a photographing visual field of the camera; and the camera is fixedly connected with a primary inertial navigation. High-accuracy and high-precision characteristic point information of mark points of inertial navigation equipment is collected by the camera and image sequences obtained by a visual camera are used for carrying out dynamic parameter modeling on relative movement of the primary and secondary inertial navigations, even relative disturbance. On the basis of quickly establishing a dynamic model, the transfer alignment of the primary and secondary inertial navigations is realized by utilizing the transfer alignment to establish a Kalman filtering equation. The transfer alignment method and device based on the visual movement modeling can be used for the field needing to carry out alignment on the primary and secondary inertial navigations and solve the high-precision transfer alignment problem.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
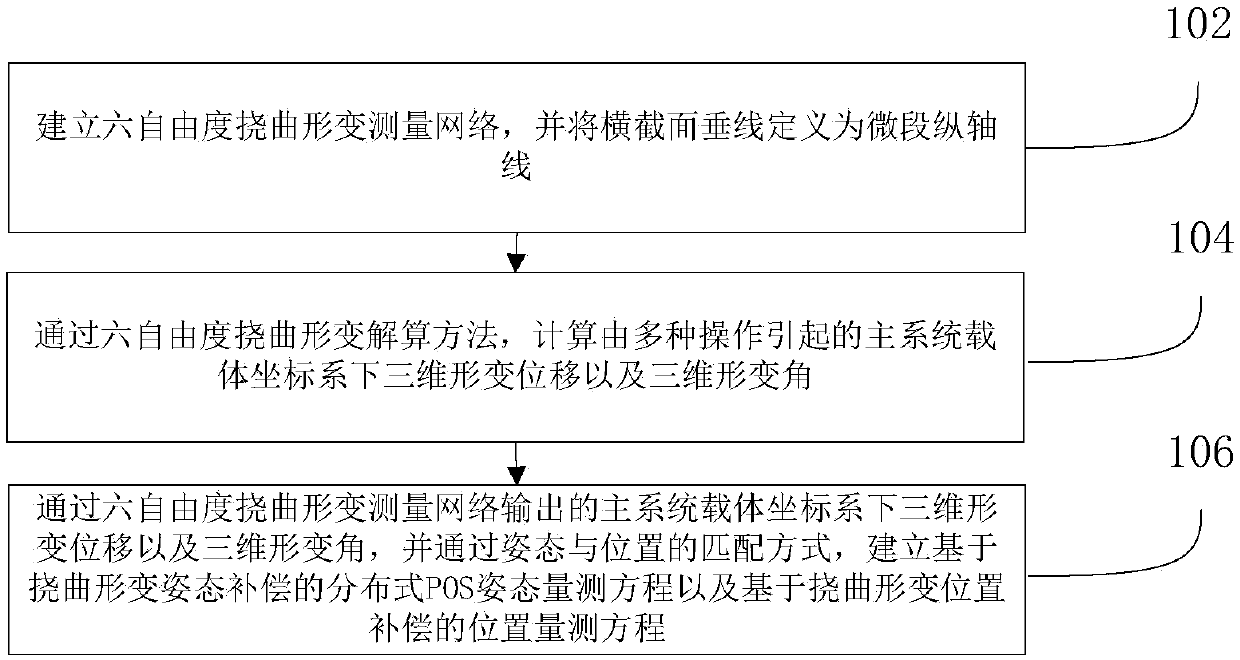
Distributed POS (position and orientation system) transfer alignment modeling method and device of bending deformation measuring network
ActiveCN108398130ANavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsFiberEngineering
The invention discloses a distributed POS (position and orientation system) transfer alignment modeling method and a distributed POS transfer alignment modeling device of a bending deformation measuring network. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a six-degree-of-freedom bending deformation measuring network, and dispersing a flexible rod arm into a plurality of rod arm micro-sections with length not more than 10 cm according to a strain gradient of bending deformation of the distributed POS flexible rod arm; sticking six fiber grating sensors on the surface of each rod armmicro-section, calculating a three-dimensional deformation angle and three-dimensional deformation displacement under a main system carrier coordinate system by adopting a six-degree-of-freedom bending deformation solving method, and providing measuring information for distributed POS transfer alignment; and establishing a distributed POS attitude measuring equation based on bending deformation attitude compensation, and a distributed POS position measuring equation based on bending deformation position compensation so as to establish a transfer alignment system model. The invention also discloses the distributed POS transfer alignment modeling device of the bending deformation measuring network.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
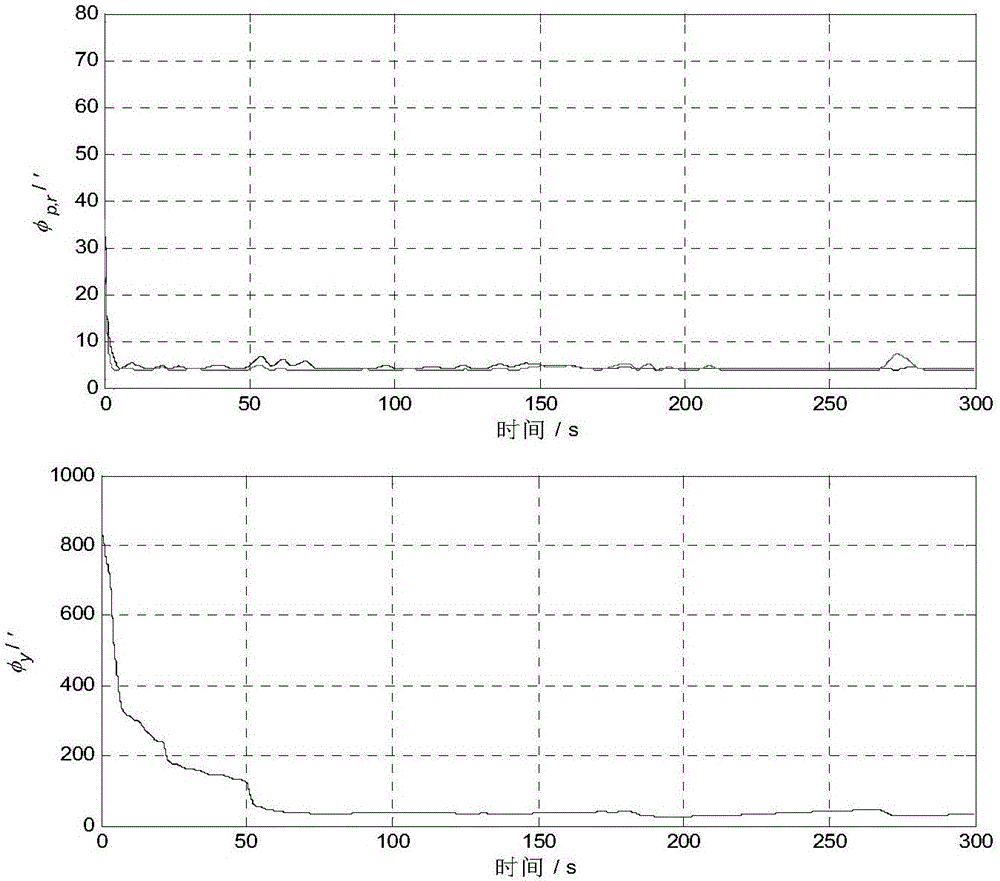
Transfer-alignment time-delay estimation method based on matching of speed and specific force
InactiveCN103344251AFast deliveryTransfer alignment fastNavigational calculation instrumentsDelay DurationState variable
The invention discloses a transfer-alignment time-delay estimation algorithm based on matching of speed and specific force. The method is realized by: carrying out coarse alignment of a sub inertial navigation system by using an aligned main inertial navigation system, then taking the speed difference and the specific force difference of the sub inertial navigation system relative to the main inertial navigation system as filtering observed quantities, expanding the time delay amount of main inertial navigation information into a filtering system state variable, combining an error model of the sub inertial navigation system, using Kalman filtering algorithm to estimate the time delay, and to estimate a platform error angle of the sub inertial navigation relative to the main inertial navigation. The method is applicable in the conditions that the main inertial navigation and the sub inertial navigation are both platform type navigation systems, and the transfer alignment based on the matching of the speed and the specific force has a shorter time delay.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Transfer alignment time delay estimation and compensation method based on velocity plus attitude matching
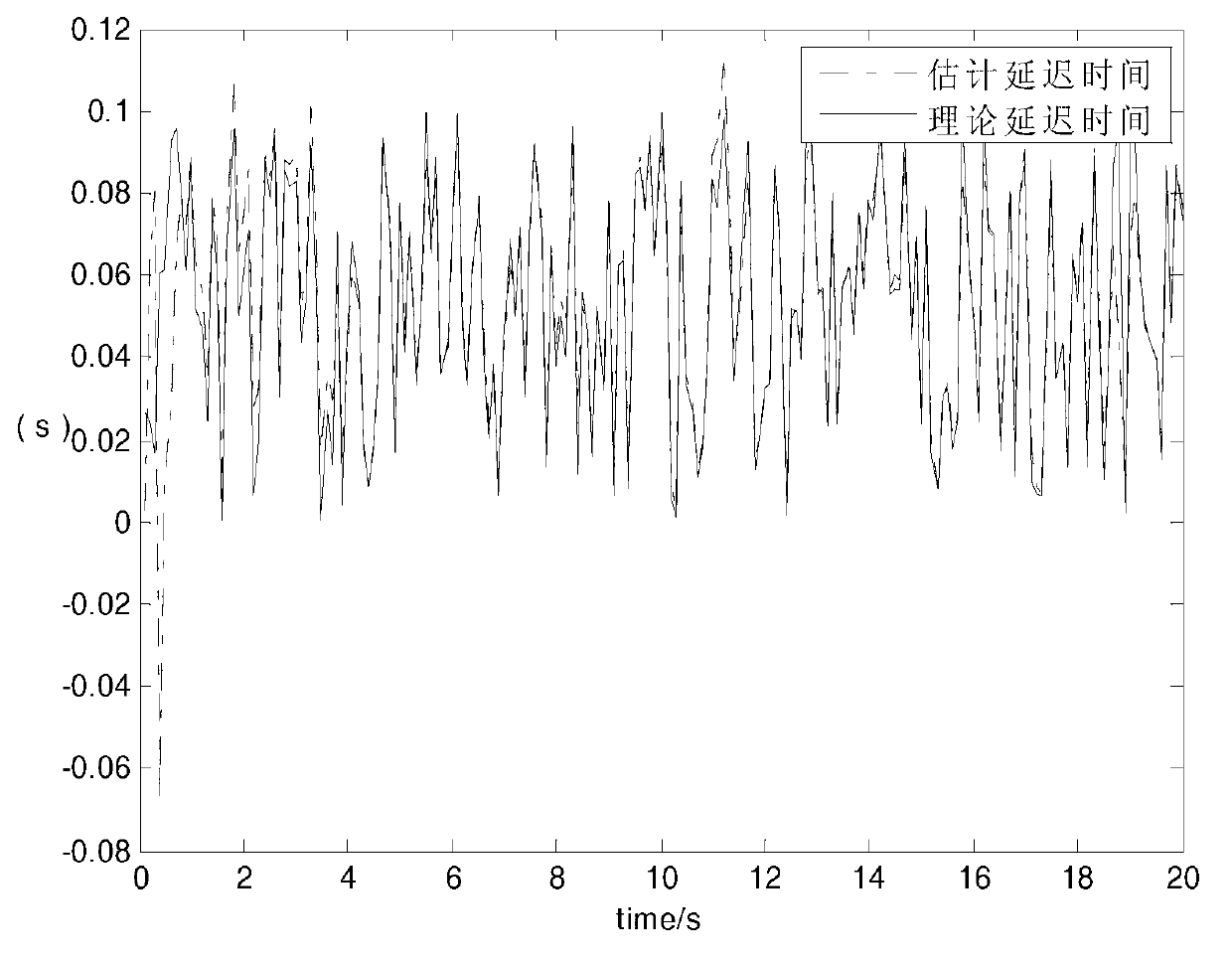
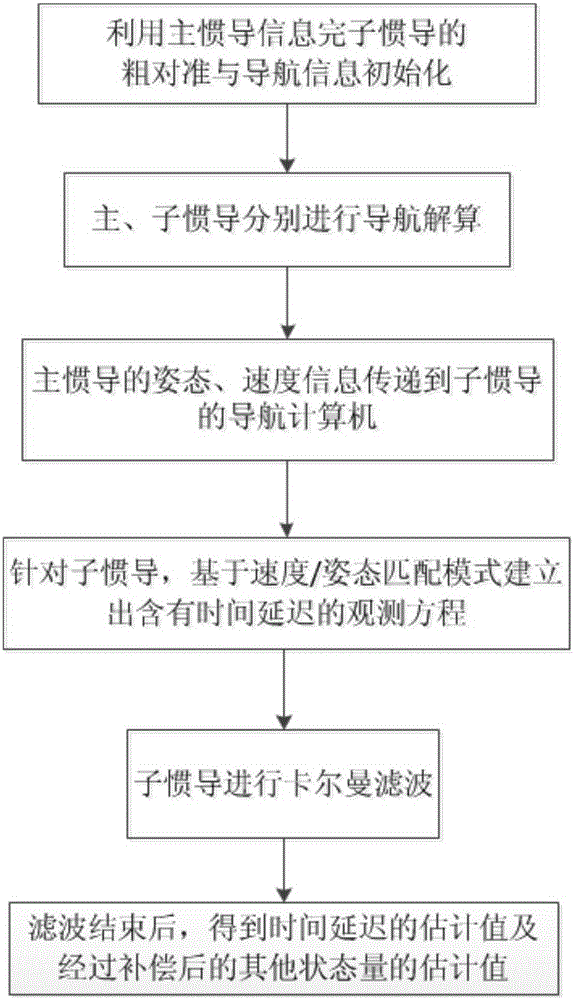
InactiveCN105157724ASuppresses the effect of error estimation accuracyMeasurement devicesDiscrete kalman filterTime delays
The invention discloses a transfer alignment time delay estimation and compensation method based on velocity plus attitude matching. The method comprises the following four steps: 1, utilizing aligned master inertial navigation system information to finish coarse alignment of a slave inertial navigation system and initialization of navigation information; 2, performing navigation calculation respectively on the master and the slave inertial navigation systems, and transmitting the velocity and attitude information of the master inertial navigation system to a navigation computer of the slave inertial navigation system; 3, in the navigation computer of the slave inertial navigation system, deriving a filter observation model based on a common velocity / attitude matching mode, establishing an observation equation containing time delay, and performing standard discrete Kalman filter iterative calculation; and 4, after filtering is finished, obtaining an estimation value of time delay and estimation values of other state quantities subjected to compensation. The filtering method helps to accurately estimate time delay error and also helps to effectively inhibit influence of time delay on transfer alignment and inertial device error estimate precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and device for measuring airborne distribution type POS (point of sale) flexibility base line assisted by multiple cameras
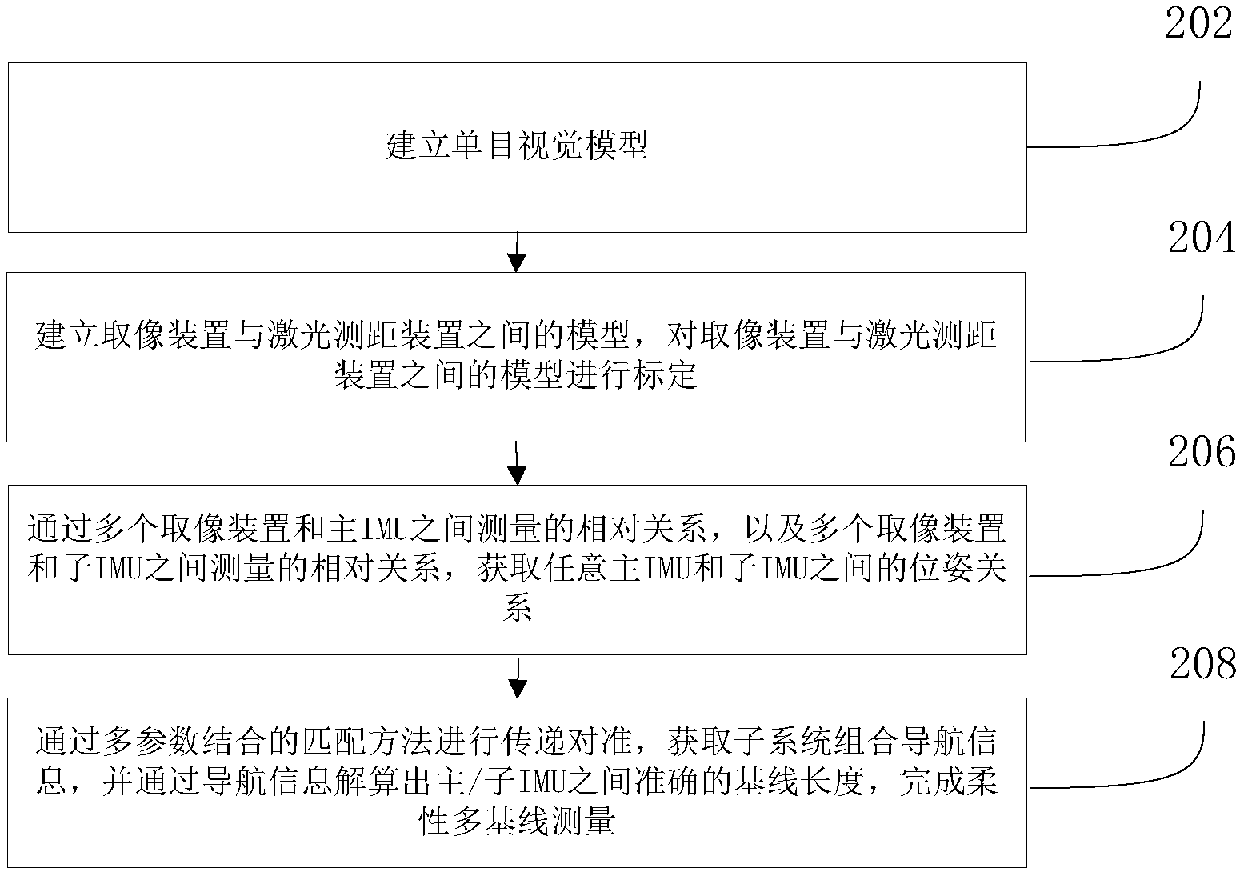
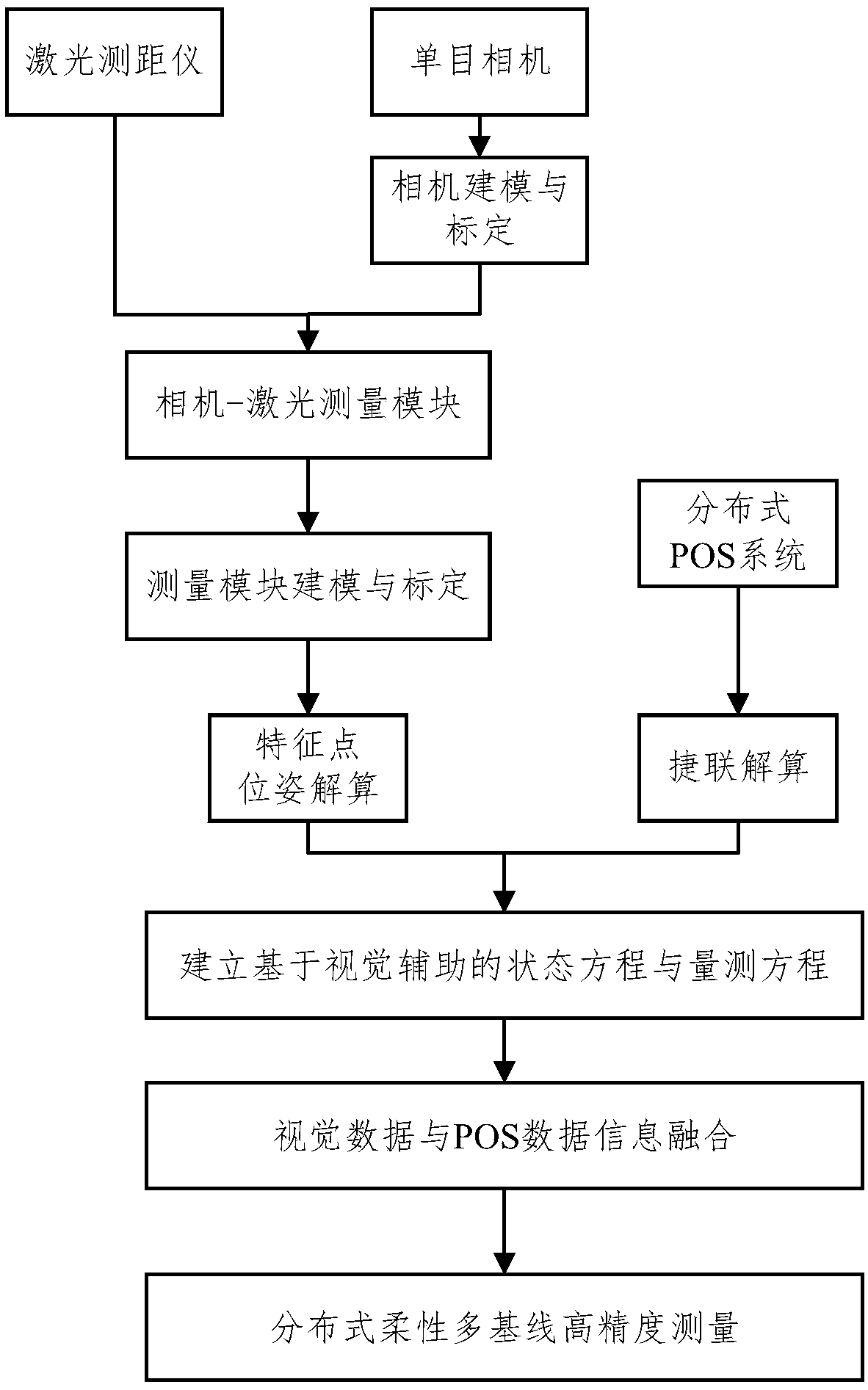
ActiveCN108375383AHigh precisionImprove anti-interference abilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsComputer scienceTransfer alignment
The invention discloses a method for measuring an airborne distribution type POS (point of sale) flexibility base line assisted by multiple cameras. The method comprises the following steps: performing transfer alignment on a low-accuracy sub-inertial measurement unit (sub-IMU) with the help of relative position posture information between a main IMU and the sub-IMU measured by the cameras by using a high-accuracy main inertial measurement unit (main IMU) to complete flexible multi-base line measurement. The method has the characteristics of high accuracy and strong anti-interference capacity,can be used for measuring flexible base line lengths between multiple loads when a carrier aircraft has flexural deflection, and improves the accuracy of the relative position posture between multiple loads. The invention further discloses a device for measuring the airborne distribution type POS flexibility base line assisted by the multiple cameras.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for measuring hull deformation angle based on inertia instruments and iterative filtering algorithm
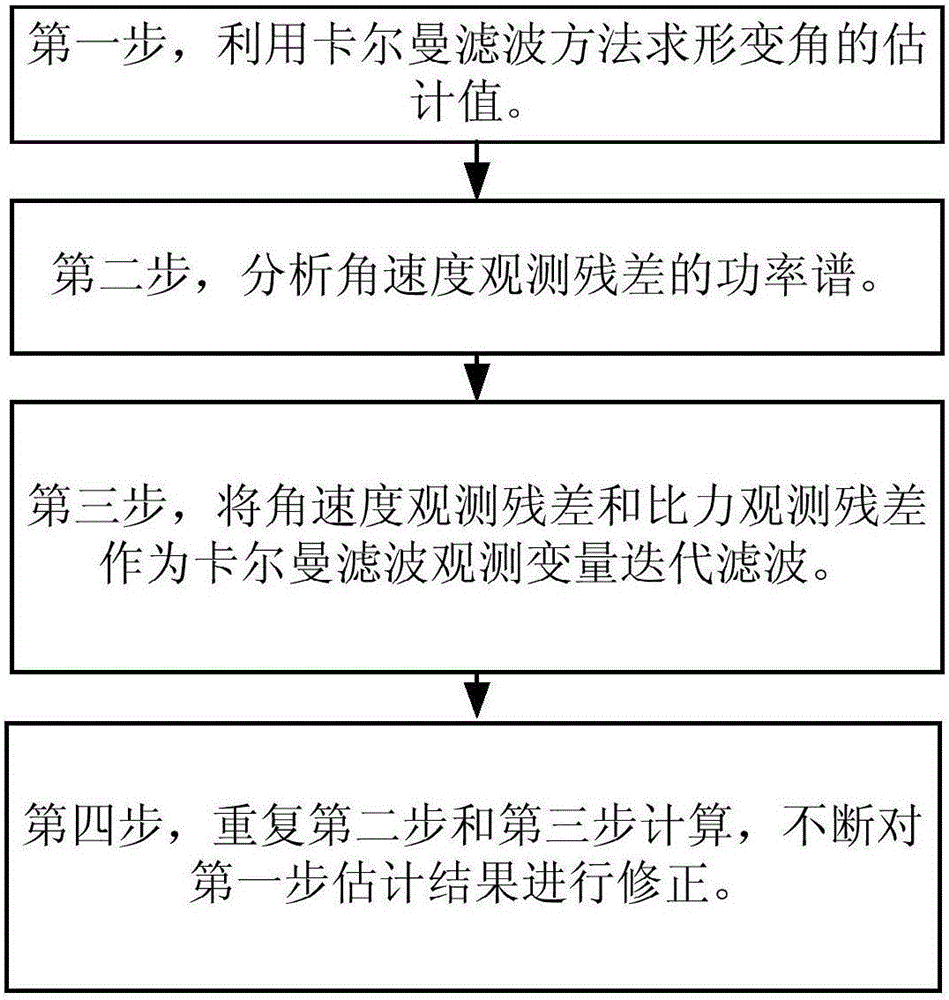
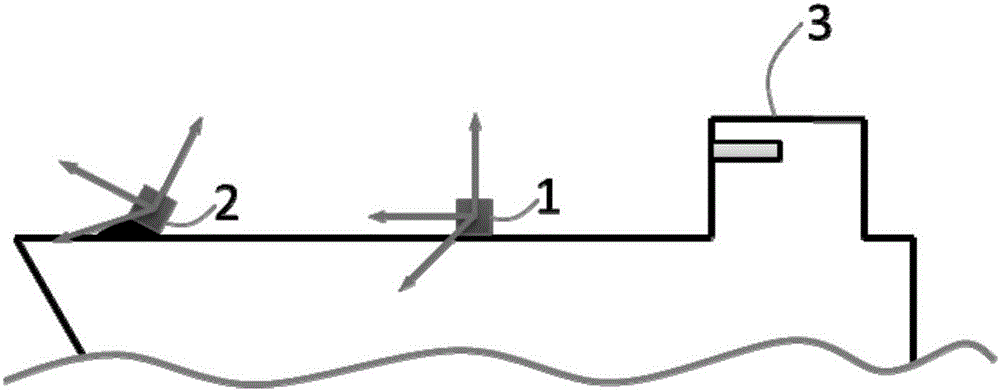
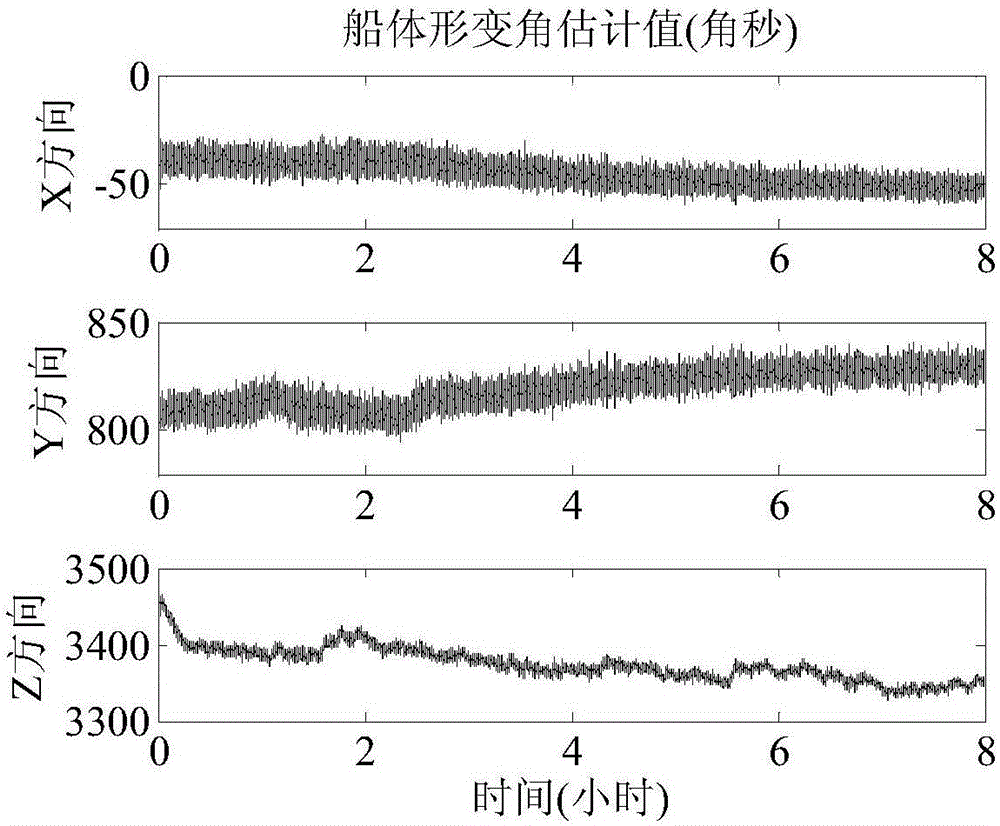
ActiveCN106802143AImprove robustnessHigh precisionAngle measurementNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
The invention belongs to the technical field of transfer alignment in inertial navigation, and particularly relates to a method for measuring hull deformation angle based on inertia instruments, such as a gyroscope, an accelerometer and the like, and an iterative filtering algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: 1, evaluating an estimated value (FORMULA) of the deformation angle by utilizing a Kalman filtering method; 2, analyzing the power spectrum of an angular velocity observation residual; 3, using the angular velocity observation residual and a specific force observation residual as Kalman filtering observation variables for iterative filtering; 4, through calculation repetition of the second step and the third step, constantly correcting an estimated result in the first step till a corrected value (FORMULA) of the deformation angle is close to but not equal to a true value (FORMULA). By the method, in allusion to the environmental characteristics that a large ship is low in speed and swings weakly, the measurement accuracy of the deformation angle in a vertical direction can be significantly improved; meanwhile, the method is relatively small in calculation amount, and is suitable for online real-time measurement.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
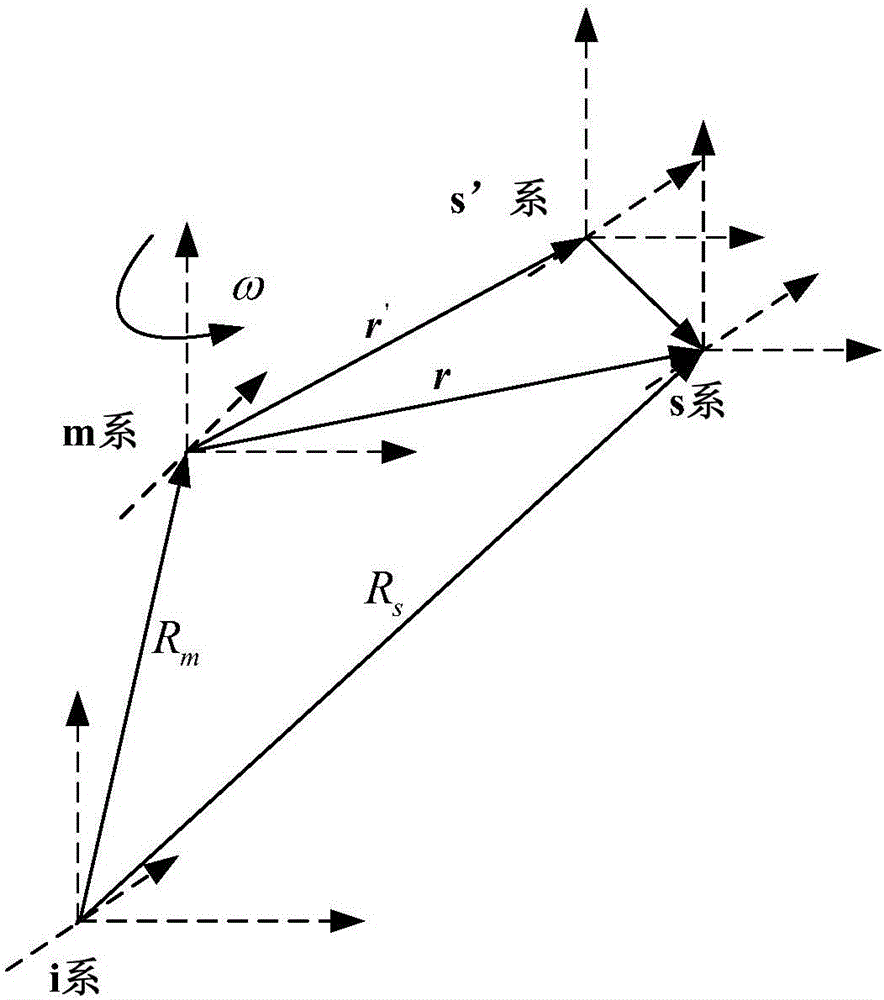
Inertial navigation system transfer alignment modeling method based on dual quaternion
ActiveCN106525034AImprove calculation accuracyImprove computing efficiencyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeAccelerometer
The invention provides an inertial navigation system transfer alignment modeling method based on dual quaternion. A nominal dual quaternion between a main inertial navigation system and an auxiliary inertial navigation system is constructed, the dual quaternion is calculated to describe an auxiliary inertial navigation system carrier system relative to a main inertial navigation system carrier system, rotation and translation motion of the carrier systems are calculated, and a normal dual quaternion differential equation of transfer alignment is constructed by reasoning spinor expressions of relative rotation and translation motion of the main inertial navigation system and the auxiliary inertial navigation system and calculated; a dual quaternion error equation is obtained in combination with an accelerometer parameter error equation and a gyroscope error differential equation; a systematic observation equation is constructed by using the linear velocity of an accelerometer and the angular velocity of rotation of a gyroscope, an initial calibration parameter of the auxiliary inertial navigation system is calculated through kalman filter iteration, the effects of rotation and translation separation calculation on coning errors and sculling errors are eliminated, and the calculation accuracy and the calculation efficiency are effectively improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Transfer alignment method in polar region based on inverse coordinate system
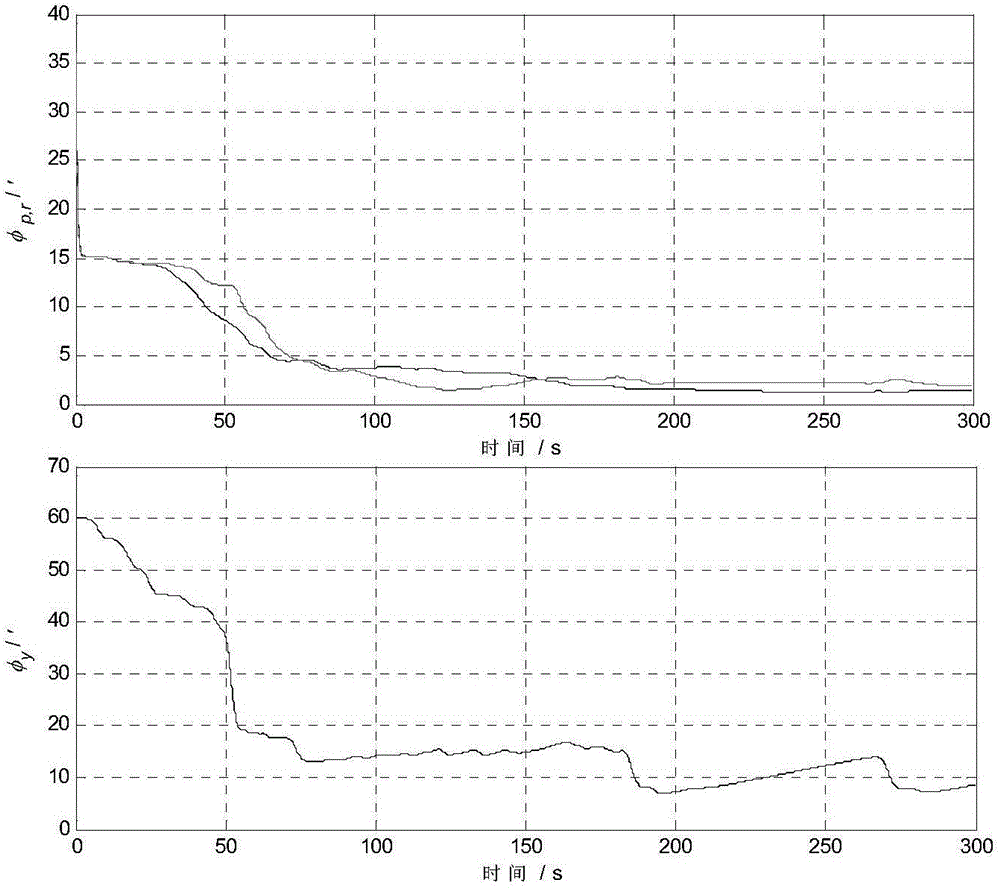
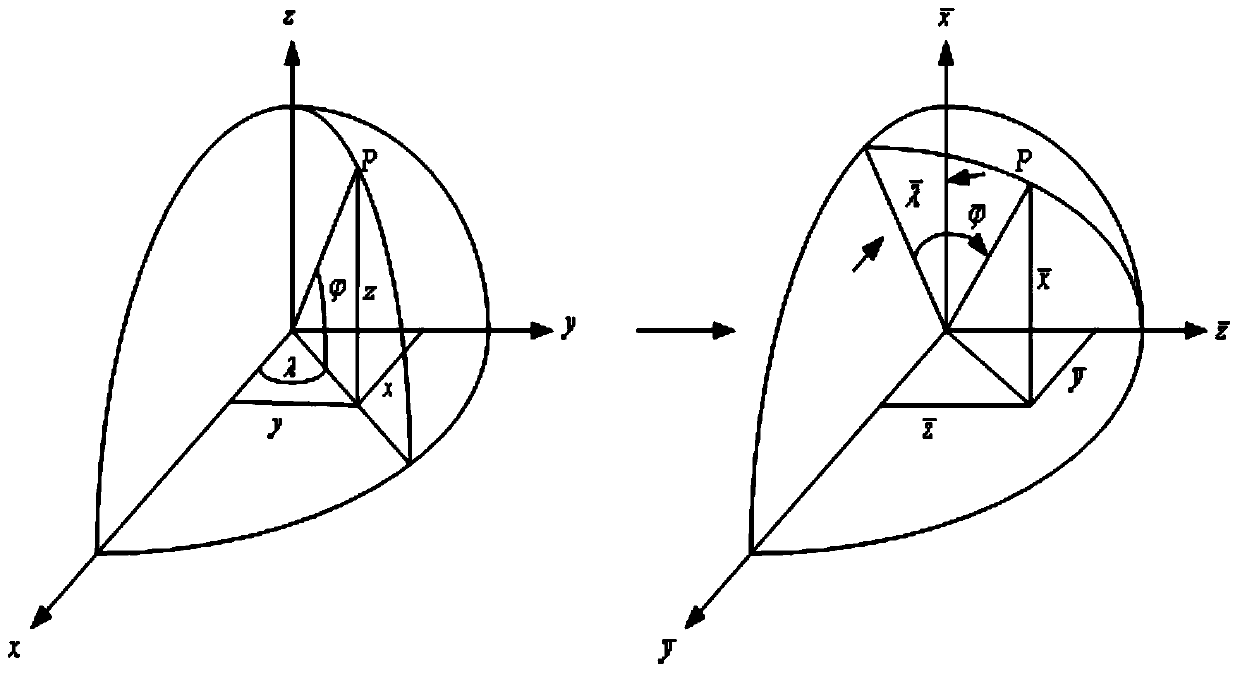
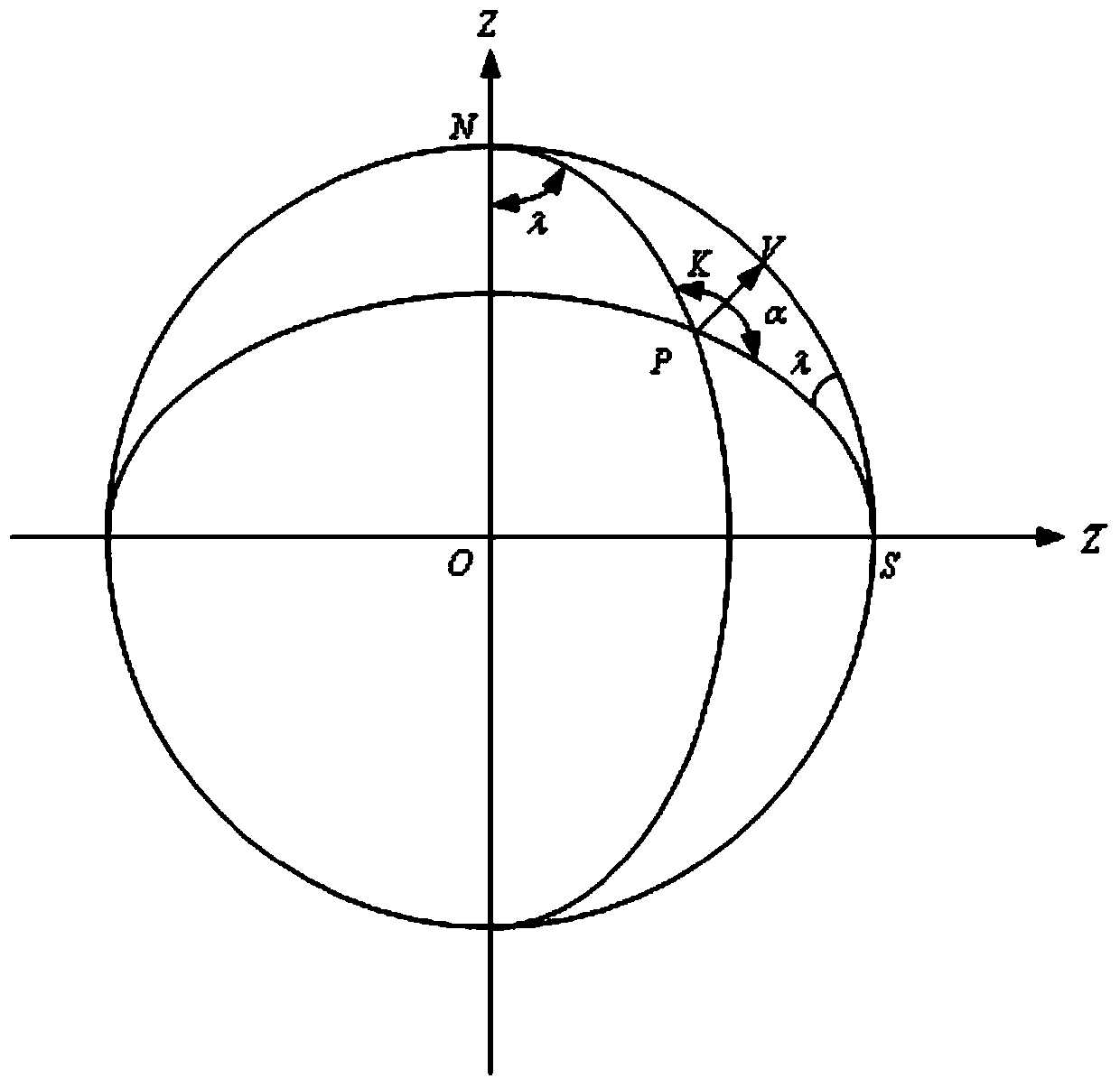
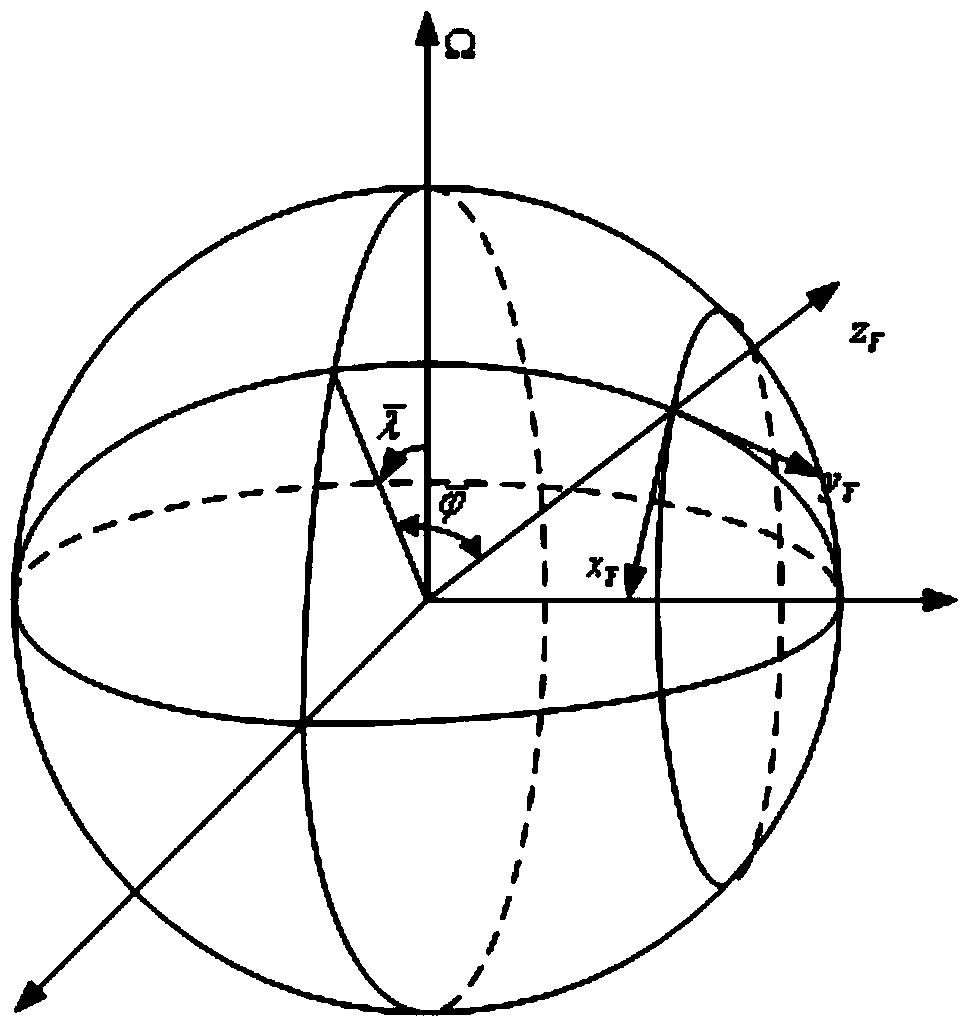
InactiveCN103471614ASolve the defect that transfer alignment cannot be performed effectivelyMeasurement devicesHigh latitudeGeographic coordinate system
The invention discloses a transfer alignment method in a polar region based on an inverse coordinate system. The method comprises the steps of taking the earth as a sphere, converting carrier navigation information under the traditional coordinate system into the inverse coordinate system by establishing the inverse coordinate system, obtaining carrier navigation information under a new coordinate system, establishing a new geographic coordinate system based on the inverse coordinate system, establishing a state equation and a measurement equation of transfer alignment under the new coordinate system by establishing a quick velocity and posture transfer alignment matching method, establishing a Kalman filtering equation to estimate a misalignment angle of primary and secondary inertial navigation, and judging the feasibility of the transfer alignment in the polar region. The method solves the problem that the transfer alignment method based on the traditional geographic coordinate system cannot be used during navigation of a ship in the polar region. The method has the characteristics of independence, flexibility, simplicity and certain navigation accuracy, and is more applicable to launch of shipborne weapons in high latitudes and the polar region.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com