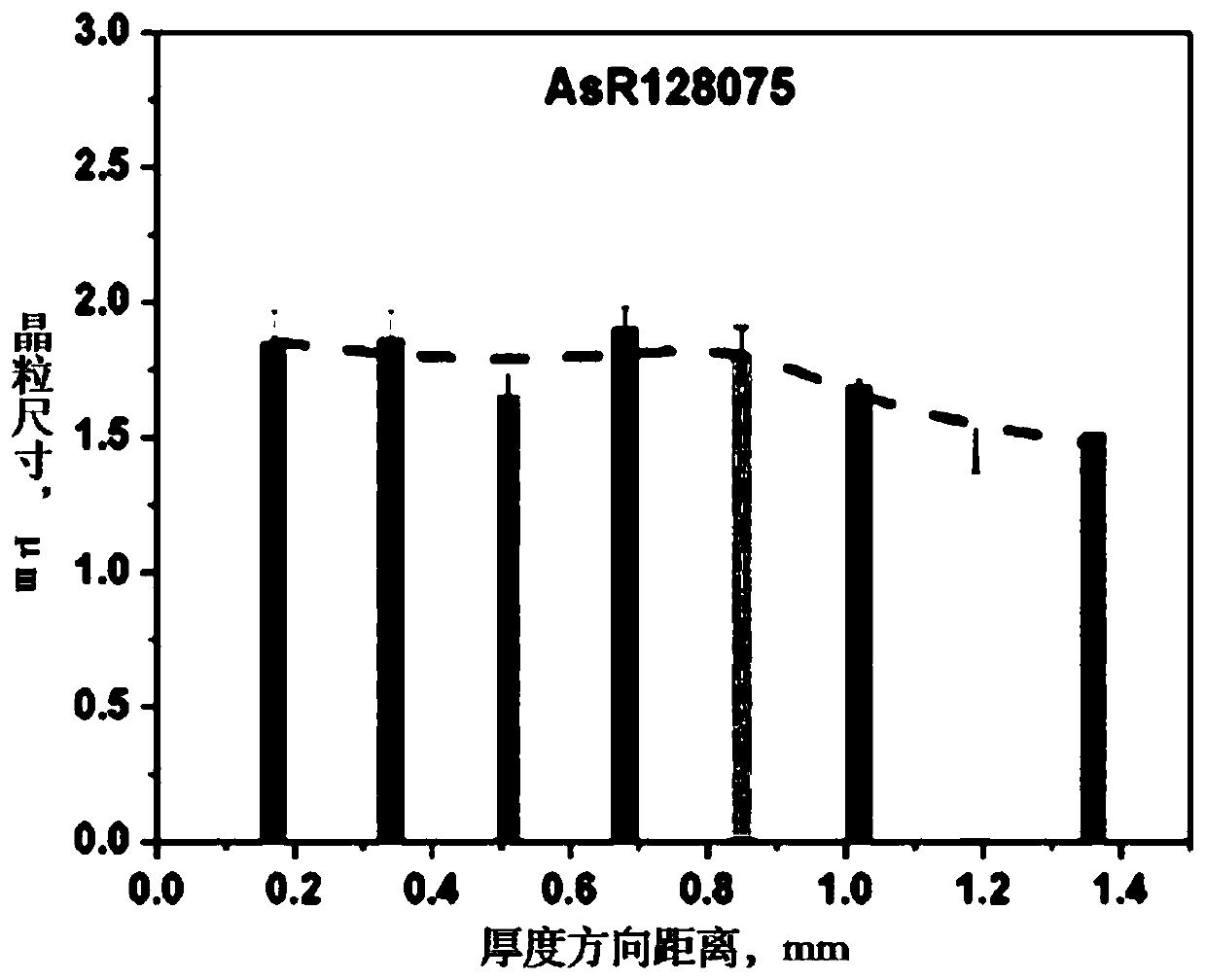
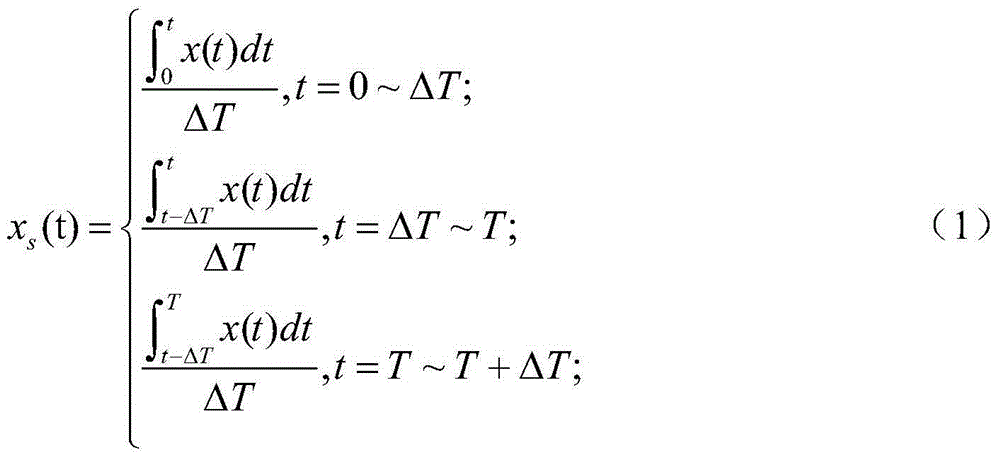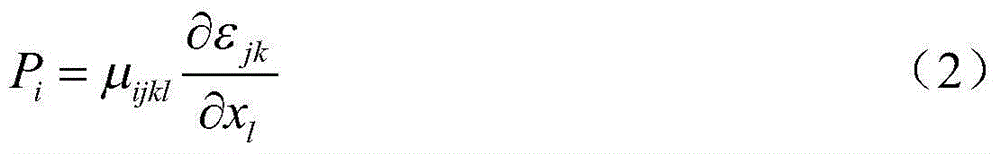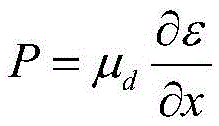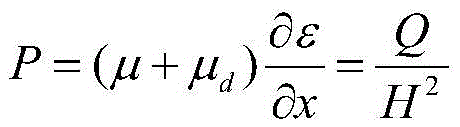Patents
Literature
92 results about "Strain gradient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Answer Wiki. The strain gradient is the rate at which strain changes through a part. A beam in pure tension will have no strain gradient because the whole beam is at the same strain. A beam in pure bending will have maximum strain at the outside of the beam and zero strain in the center.
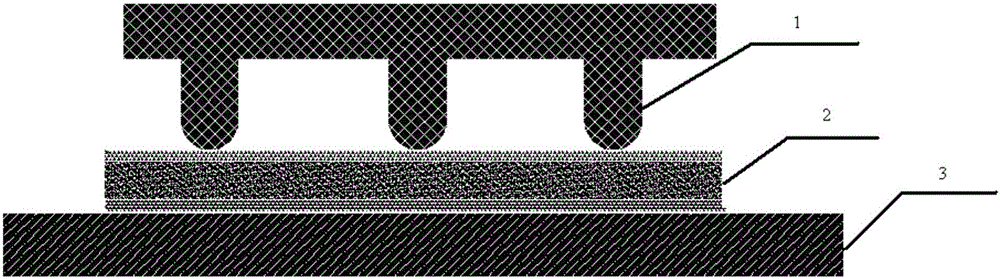
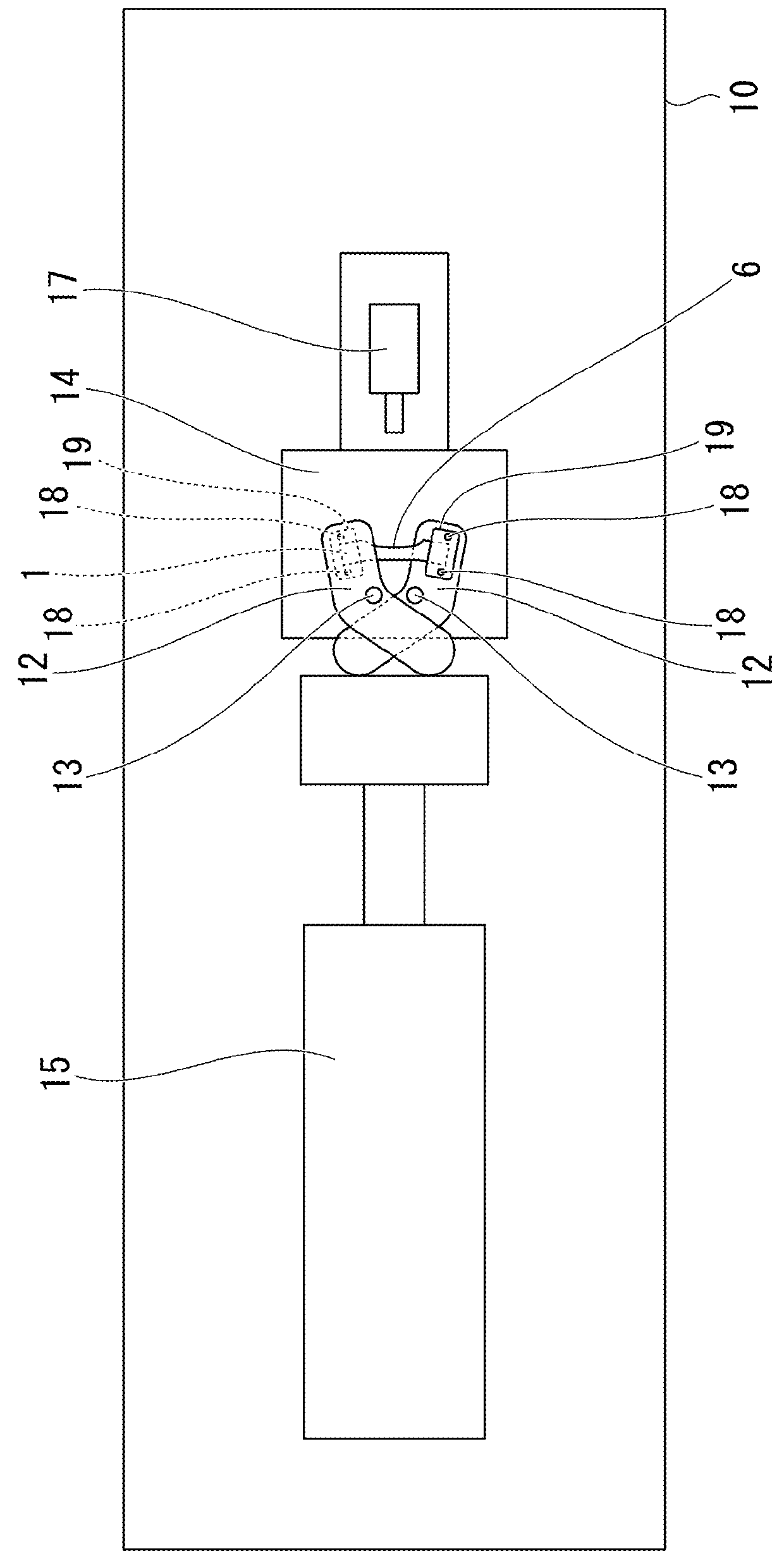
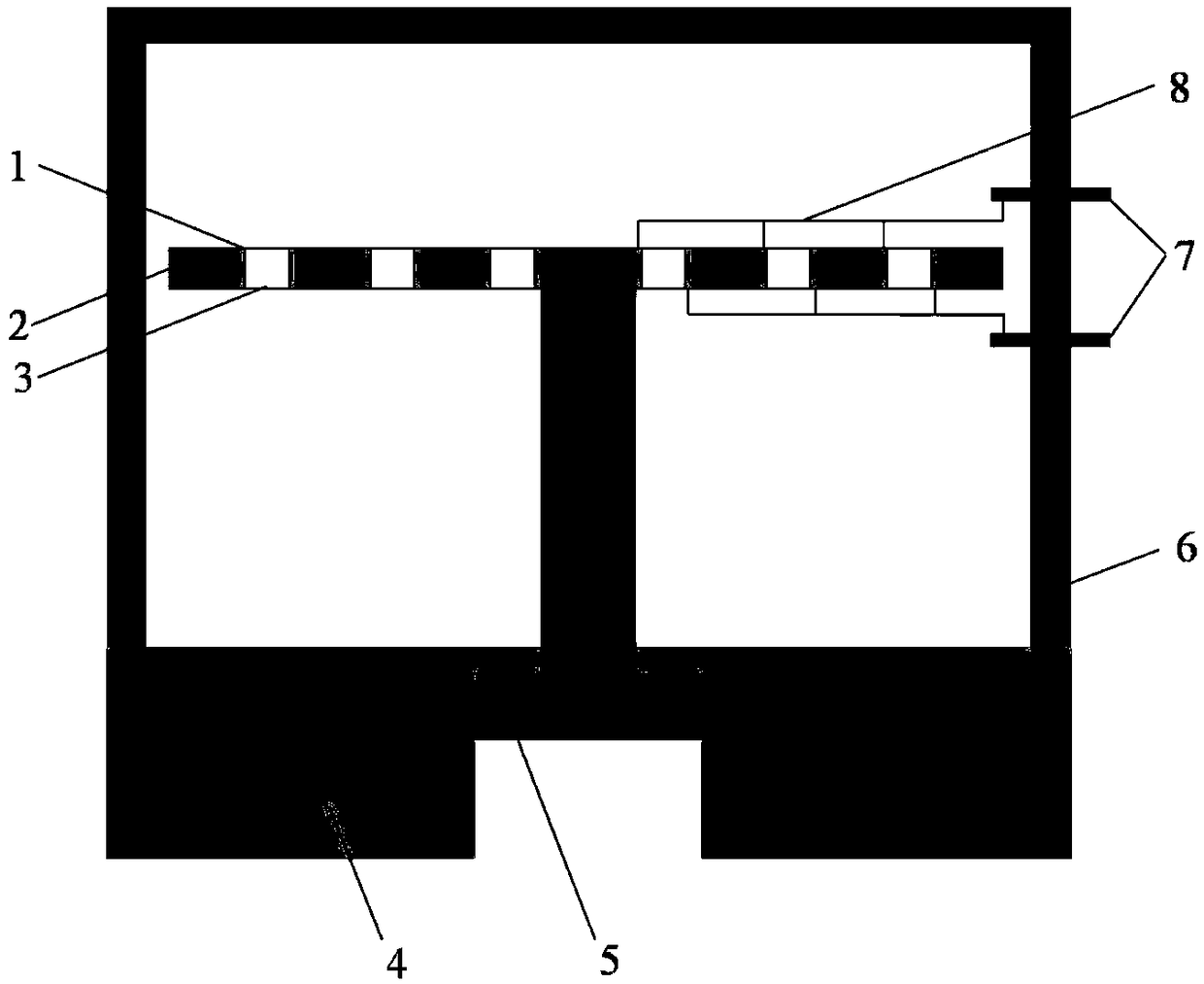
Piezoelectric materials based on flexoelectric charge separation and their fabrication
InactiveUS20090064476A1Easy to makeHigh sensitivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCharge separationPiezoelectricity
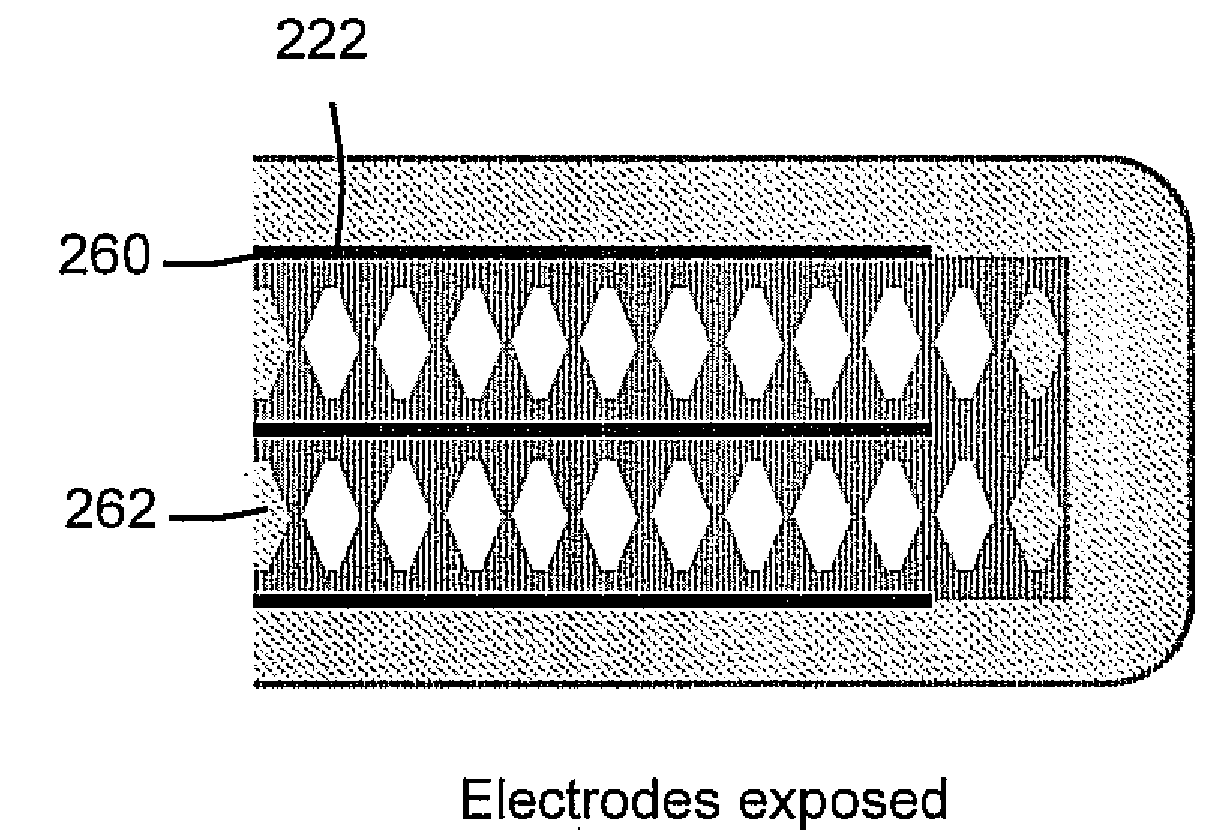
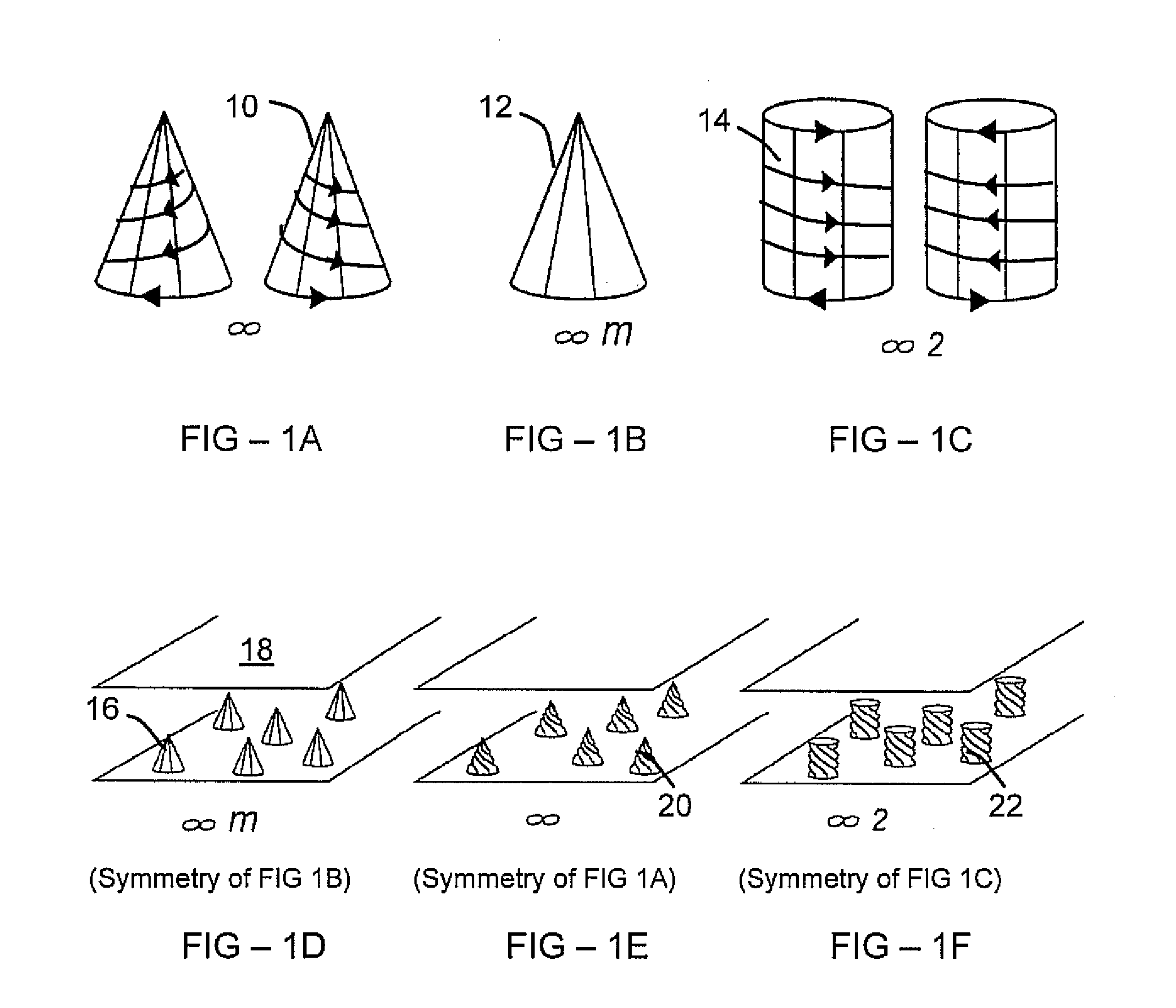
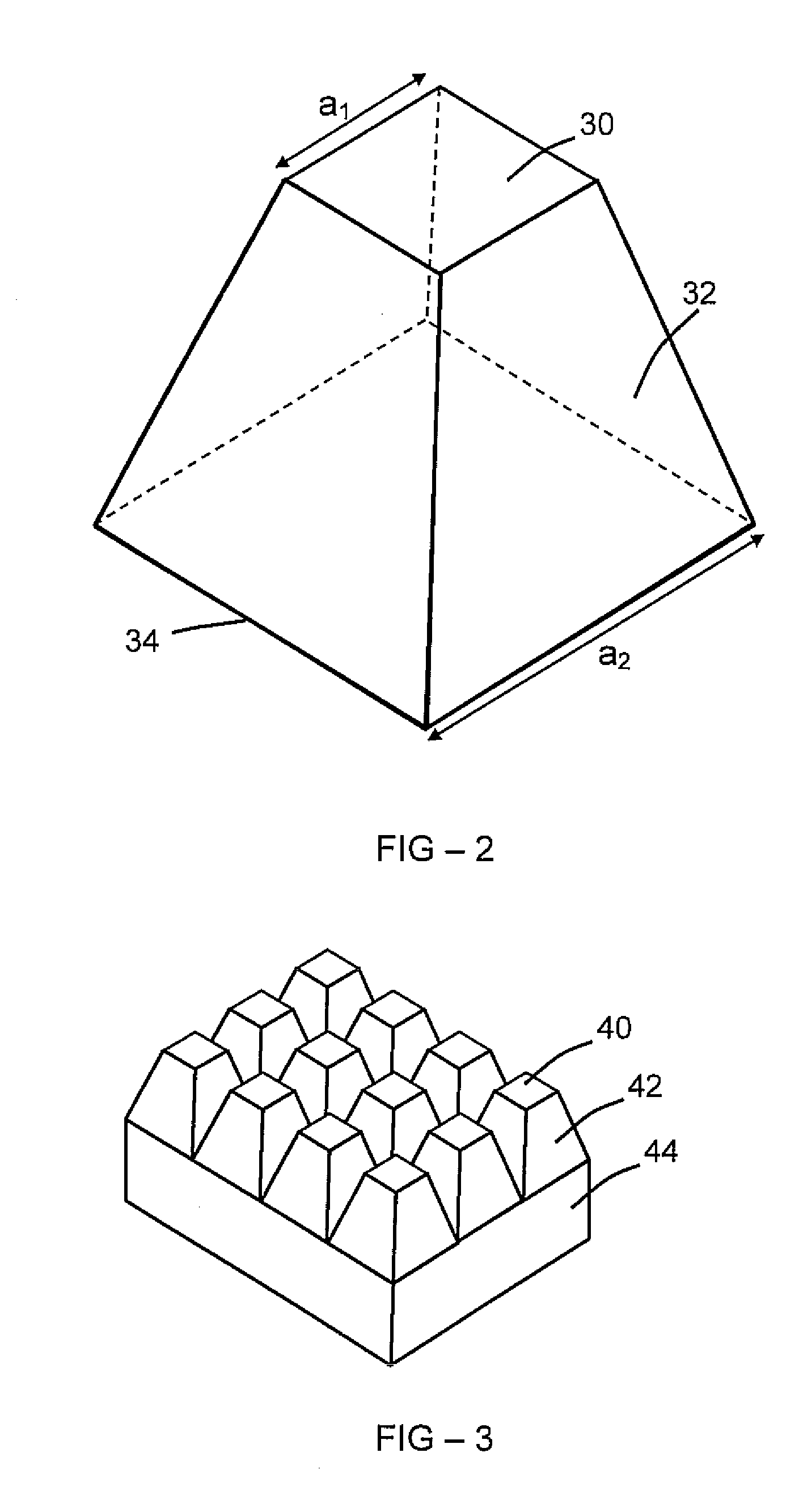
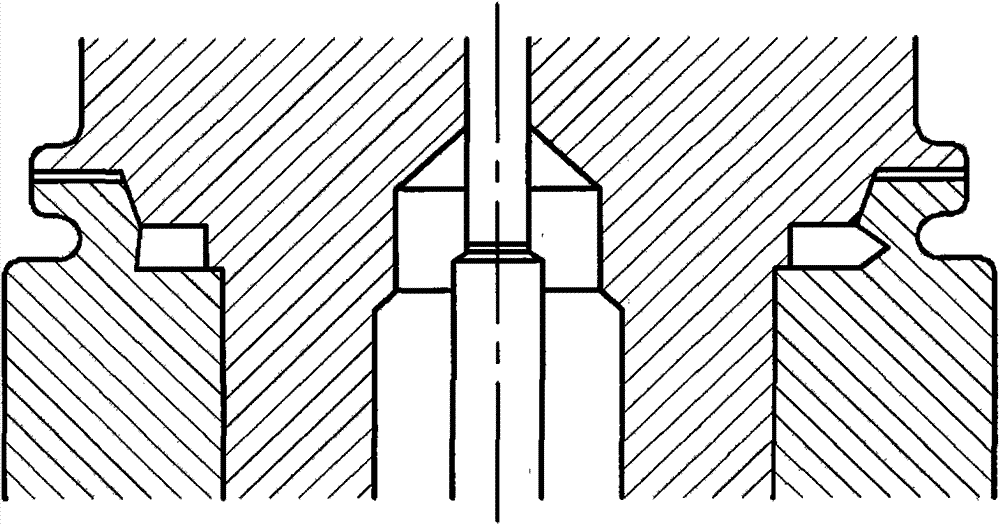
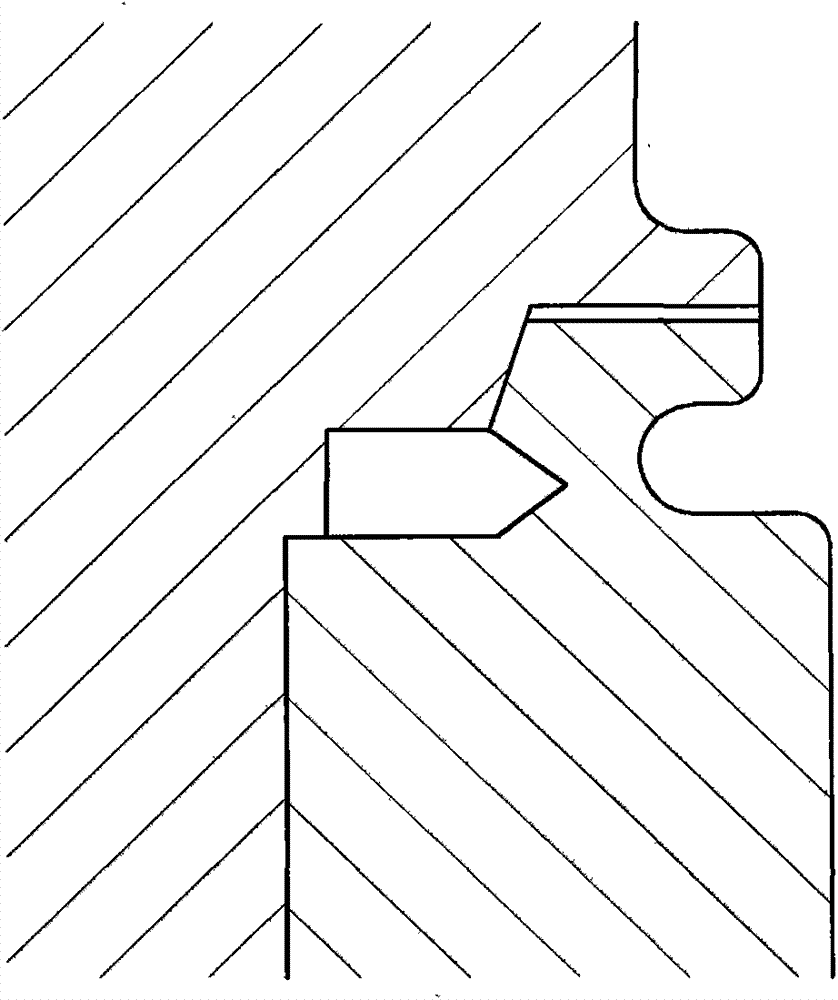
An example flexoelectric piezoelectric material has a piezoelectric response, which may be a direct piezoelectric effect, a converse piezoelectric effect, both effects, or only one effect. A flexoelectric piezoelectric material comprises shaped elements of a material, which may be a substantially isotropic and centrosymmetric material. The shaped elements, such as cones, pyramids, wedges, or other tapered elements, may provide an electrical response in response to stress or strain gradients due to a flexoelectric effect in the material, and may provide a mechanical response in response to electric field gradients. Examples of the present invention include improved methods of fabricating devices comprising such shaped elements, and multi-layer devices having improved properties.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
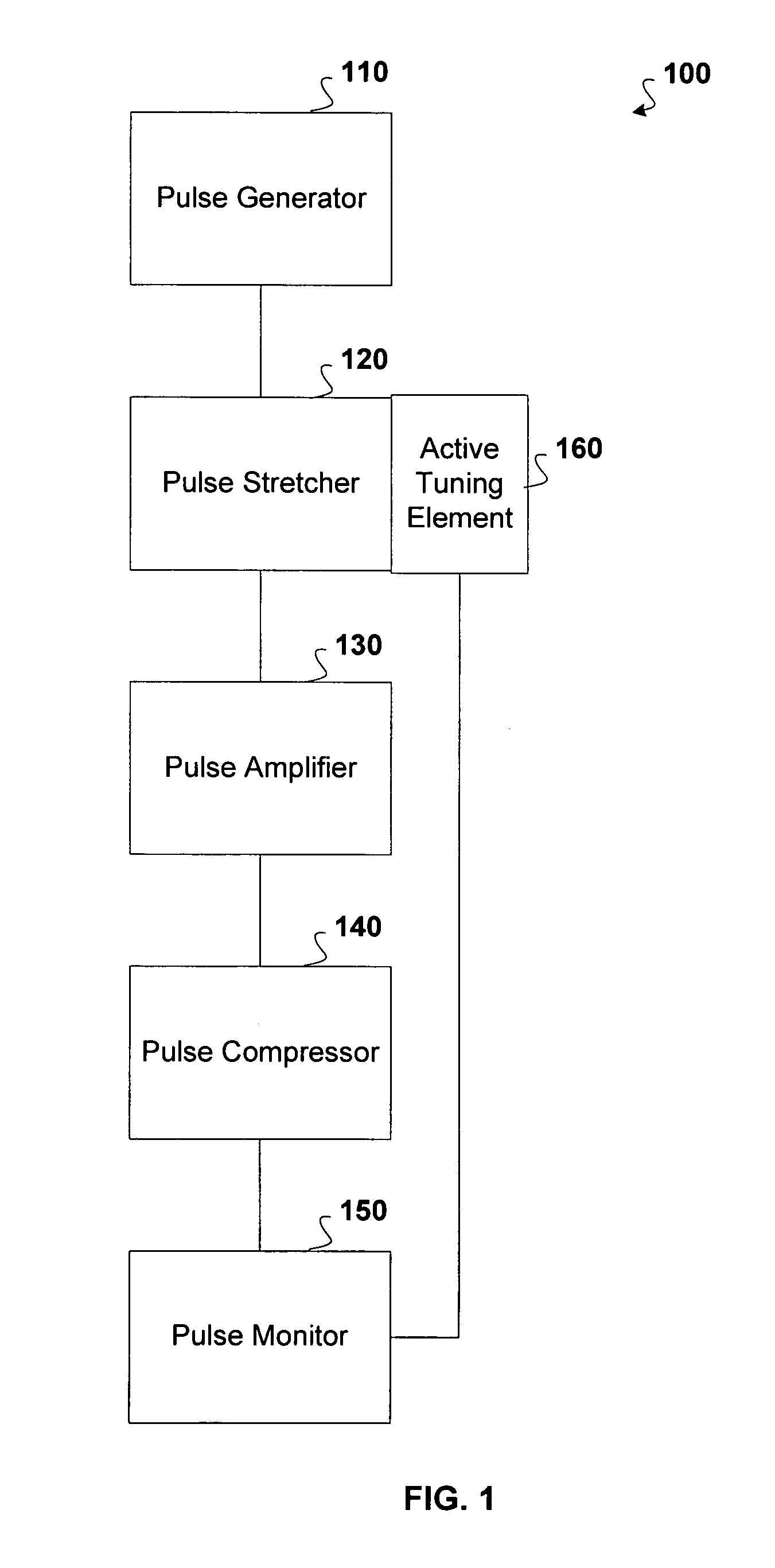
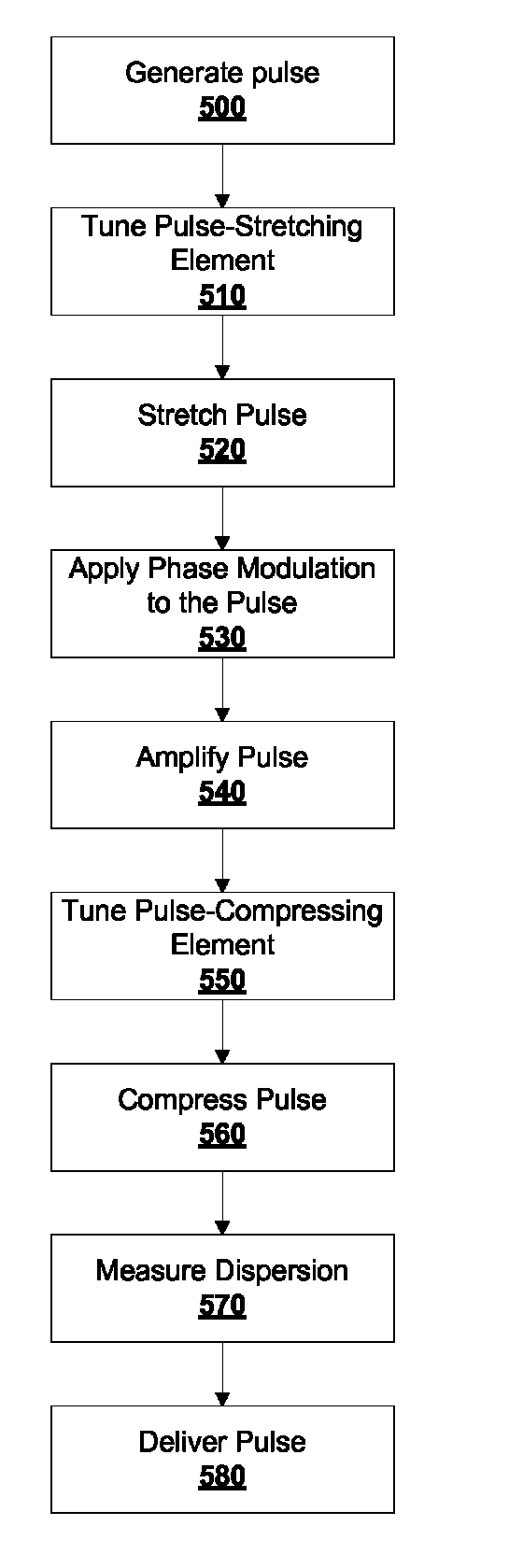
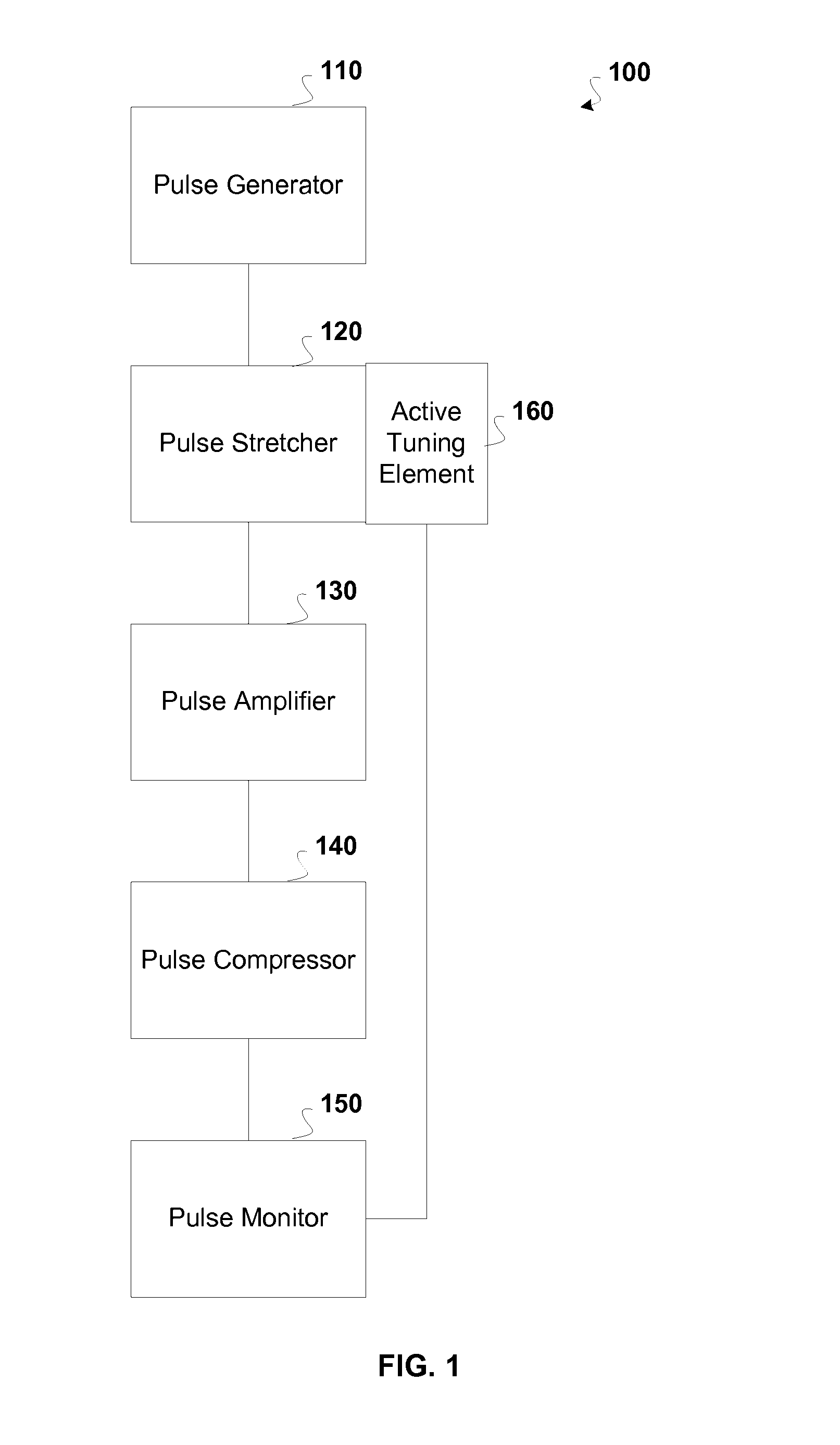
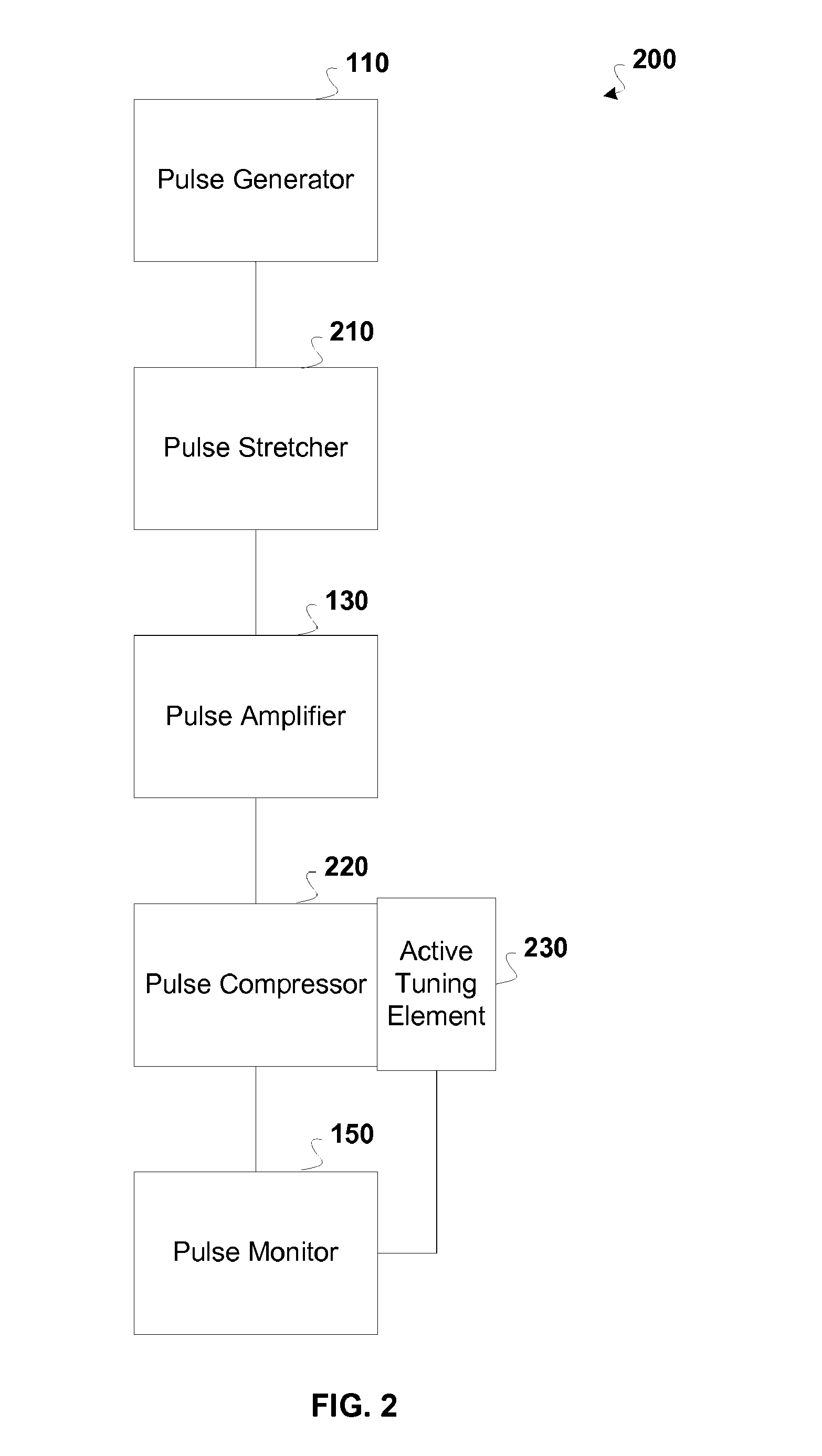
Active tuning of temporal dispersion in an ultrashort pulse laser system
InactiveUS7822347B1Decrease temporal width of output pulseLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmittersChirped pulse amplificationEngineering
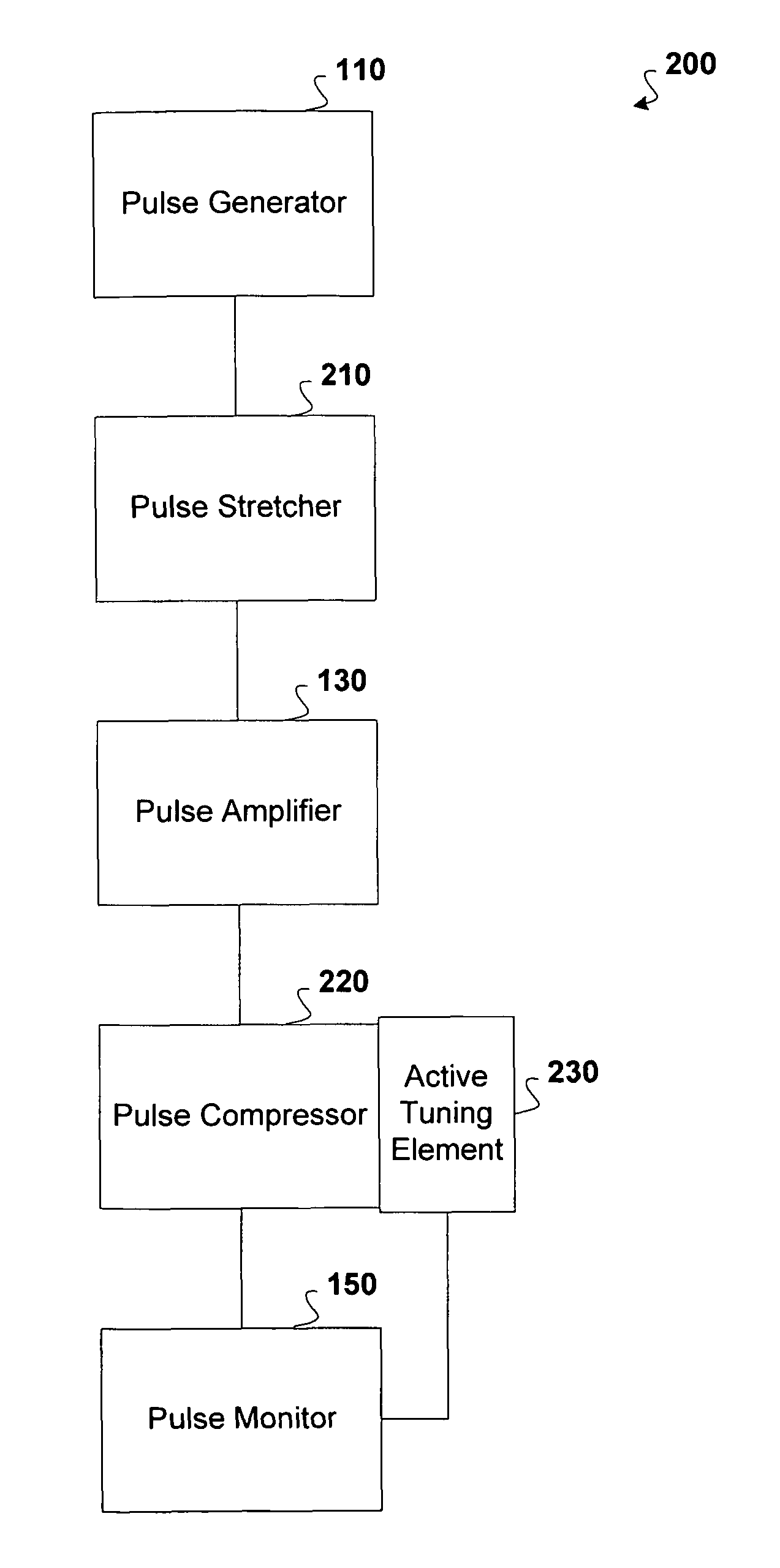
A chirped pulse amplification (CPA) system and method is described wherein the dispersion of the system is tuned by actively tuning one or more system components, for example, using a temperature or strain gradient, or using actinic radiation. In other embodiments, an additional element, such as a modulator, is added to the CPA system to actively to tune the pulse. A pulse monitor is added to the system to measure an output pulse and provide feedback to one or more active tuning elements.
Owner:COHERENT INC
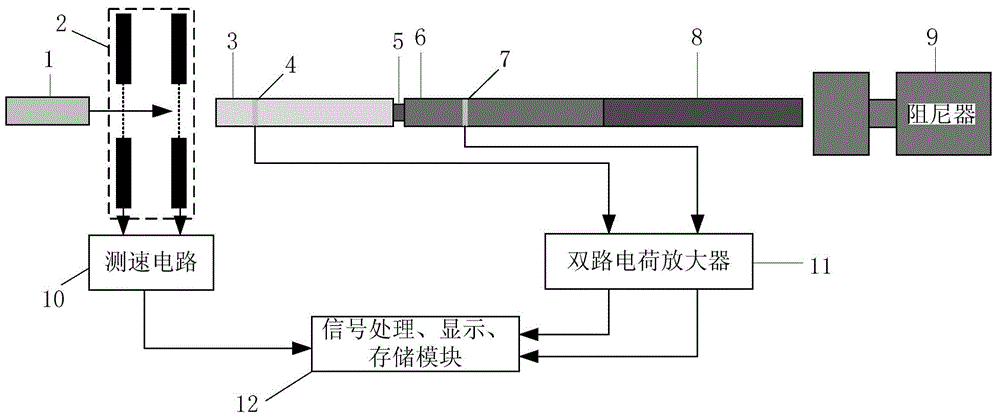
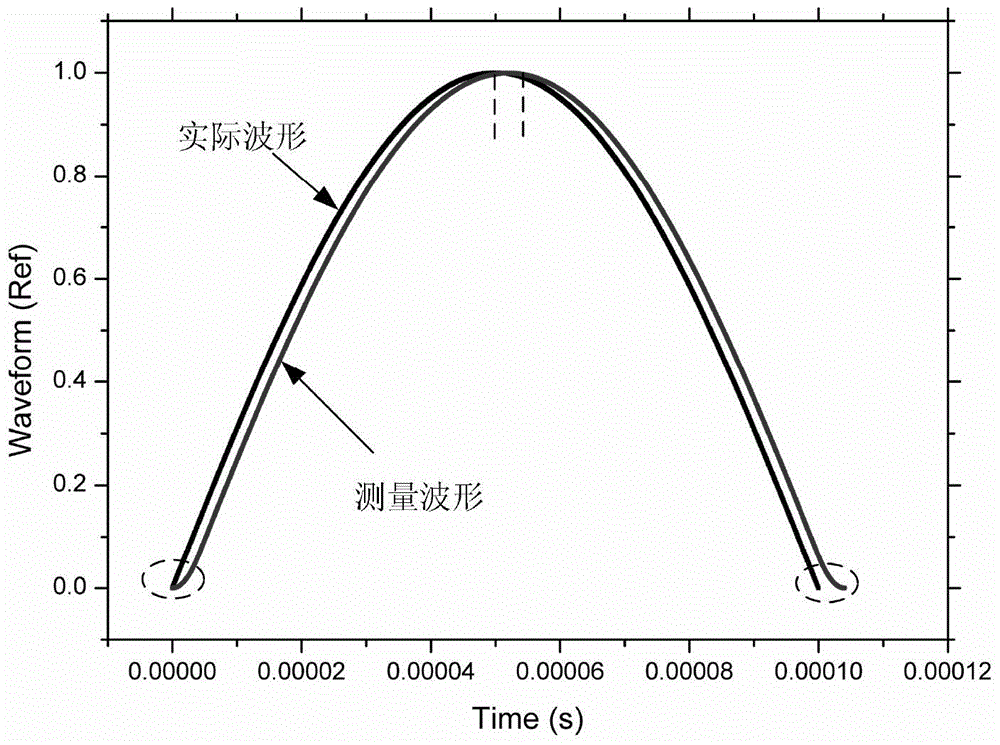
Measurement system and measurement method for stress waves of Hopkinson bars by using flexoelectric effect
ActiveCN104406846AHigh stress waveform measurement accuracyImprove accuracyApparatus for force/torque/work measurementStrength propertiesAudio power amplifierSnubber
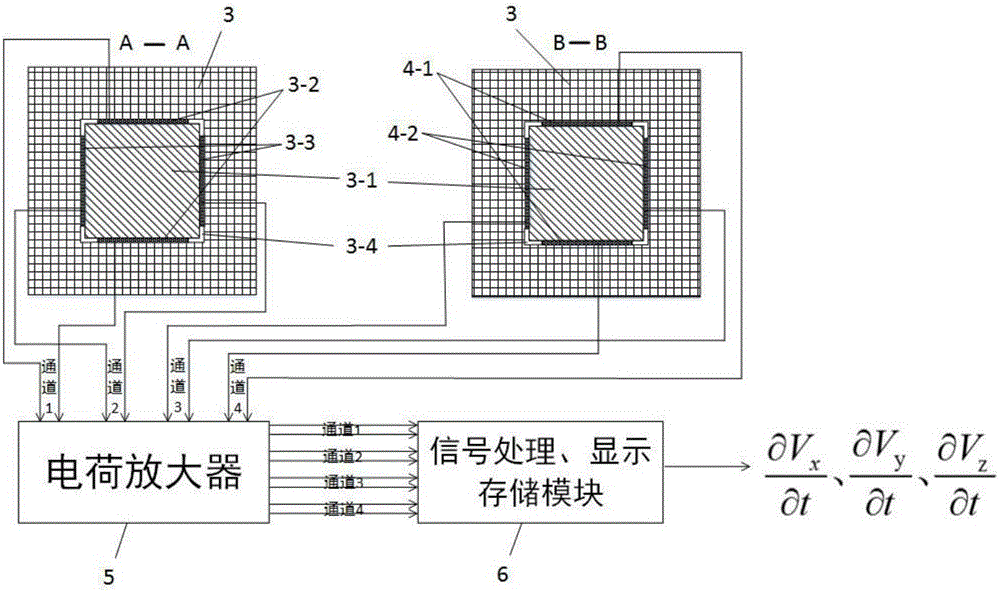
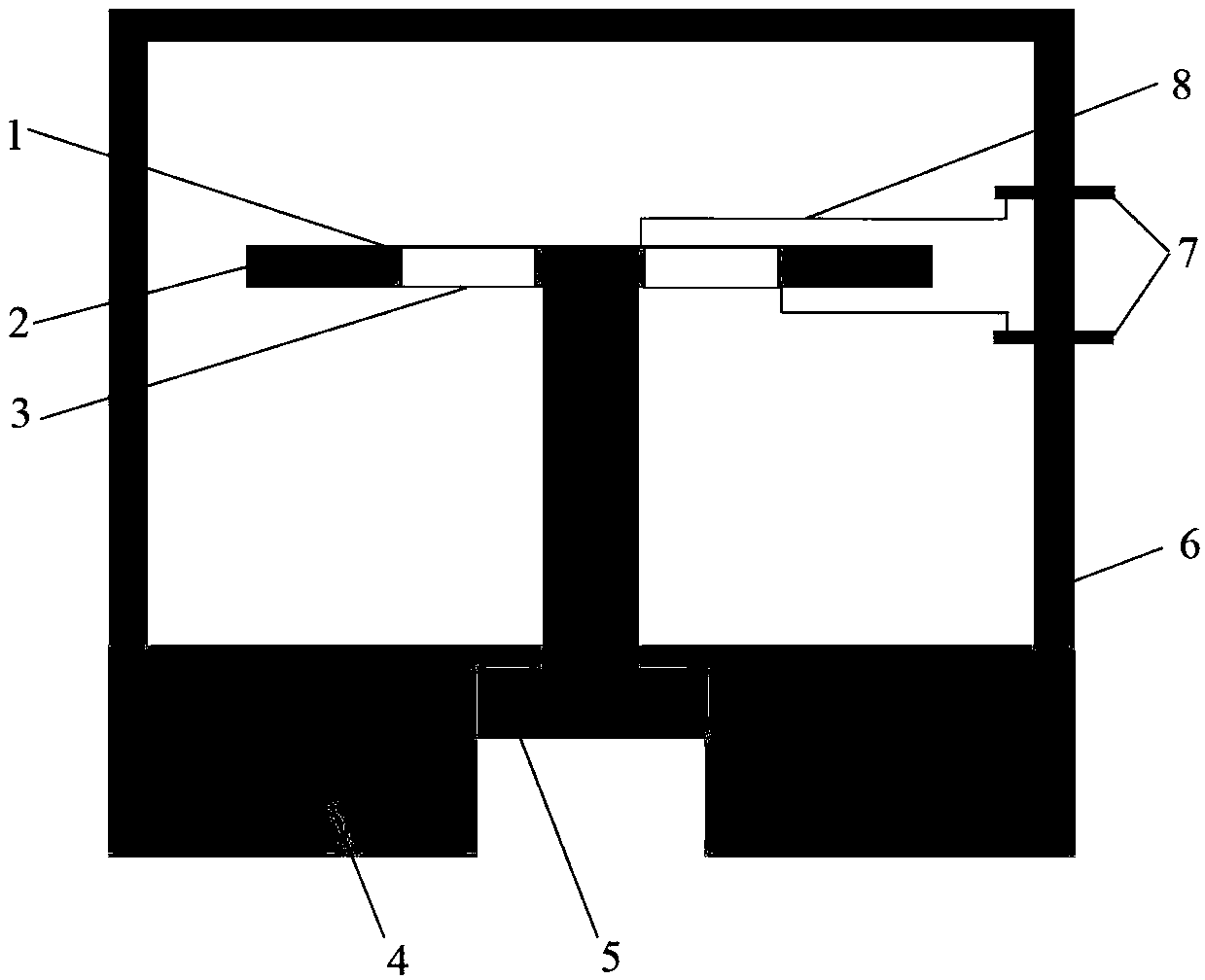
The invention relates to a measurement system and measurement method for stress waves of Hopkinson bars by using a flexoelectric effect. The system comprises a bullet, a laser velocimeter, an input bar, an output bar, an absorbing bar, a damper, a first strain gradient sensor, a second strain gradient sensor, a speed measuring circuit and a two-way charge amplifier, wherein the first strain gradient sensor and the second strain gradient sensor are respectively attached to the input bar and the output bar, the speed measuring circuit is optically connected with the laser velocimeter, and the two-way charge amplifier is electrically connected with the first strain gradient sensor and the second strain gradient sensor; the speed measuring circuit and the output end of the two-way charge amplifier are electrically connected with signal processing, displaying and storing modules. During stress wave measurement, a test piece is fixed between the input bar and the output bar, the absorbing bar and the damper are sequentially arranged behind the output bar, and the bullet and the input bar are respectively arranged on the same horizontal plane on the two ends of the laser velocimeter. As the passive strain gradient sensors based on a flexoelectric principle are arranged, the measurement system can measure the first-order derivative of a real waveform, can directly carry out integral computation for the waveform, and can obtain the more real waveform of the stress waves, and the measurement precision is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Deflection voltage electric composite materials
ActiveCN105024009AImprove carrying capacityImproved apparent piezoelectric responsePiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesElectricityDielectric
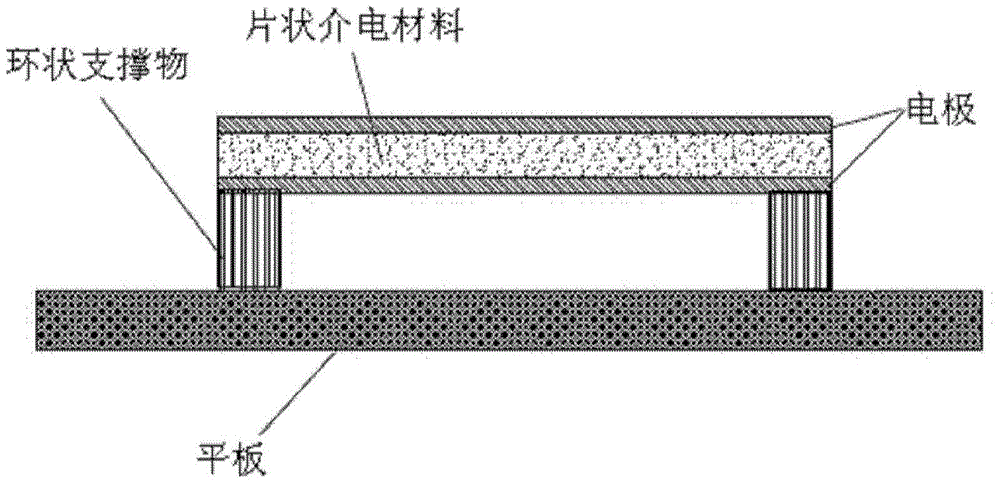
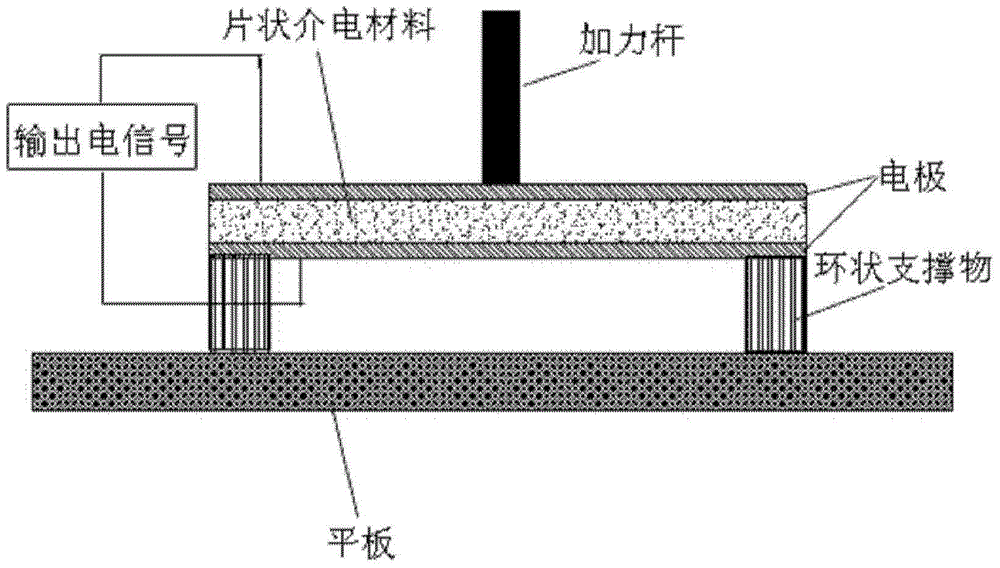
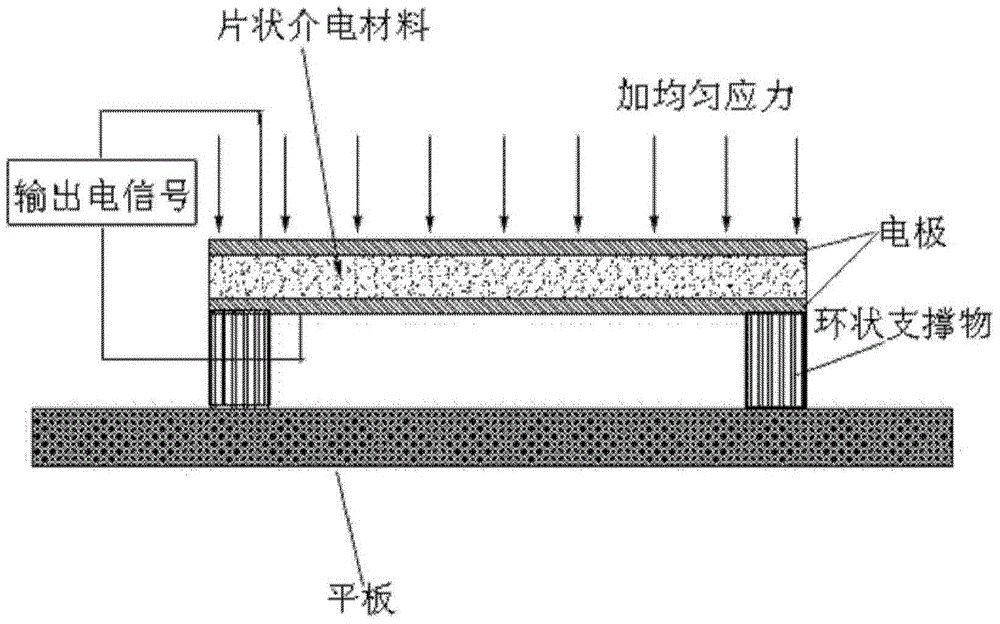
The invention provides one kind of deflection voltage electric composite materials. The composite materials comprise sheet-shape dielectric materials, two electrodes, an annular supporter and a slab. The sheet-shape dielectric materials are clamped between the two electrodes to form sheet-shape dielectric materials provided with the electrodes. The annular supporter is positioned between the slab and the sheet-shape dielectric materials provided with the electrodes, and is in contact with the edges of the lab and the sheet-shape dielectric materials provided with the electrodes. According to the deflection voltage electric composite materials of the invention, by means of applying forces of one side of the sheet-shape dielectric materials, the sheet-shape dielectric materials can be bent or deformed in a bending-like mode. Strain gradient and deflection electric responses are generated on the thickness direction of the sheet-shape dielectric materials so as to generate piezoelectric effects.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
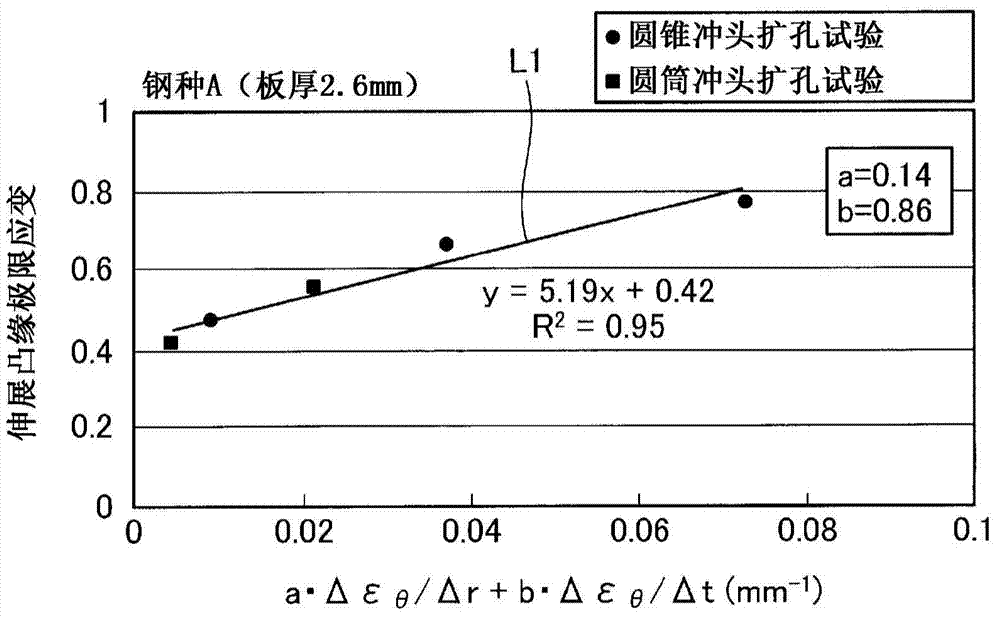
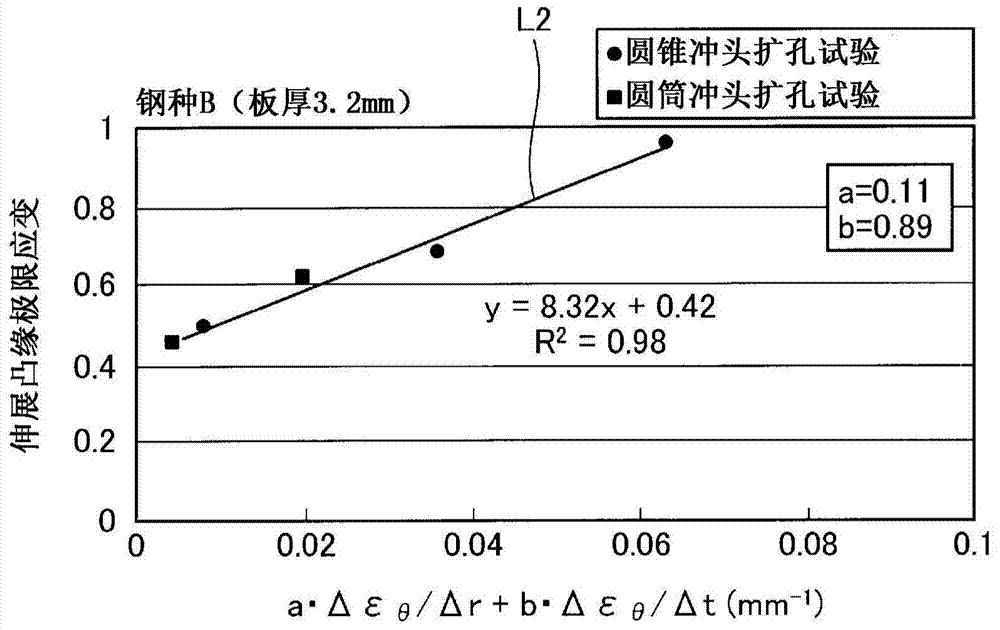
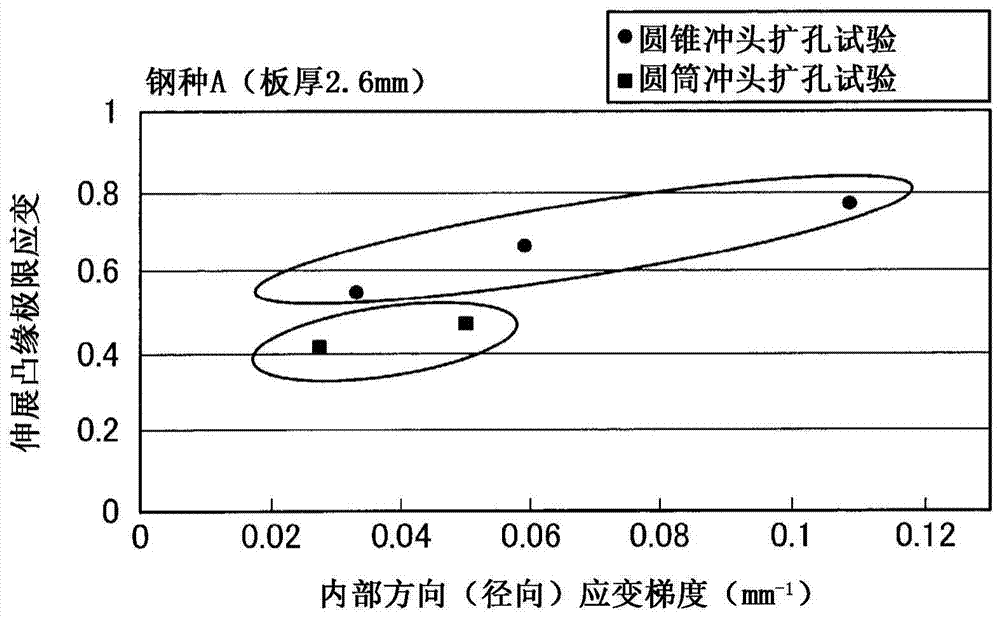
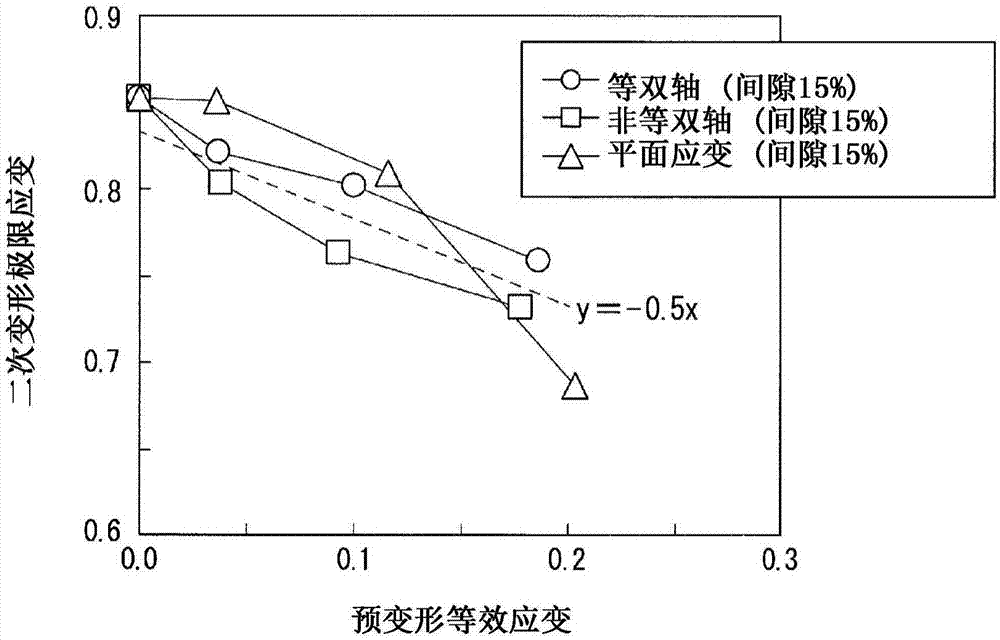
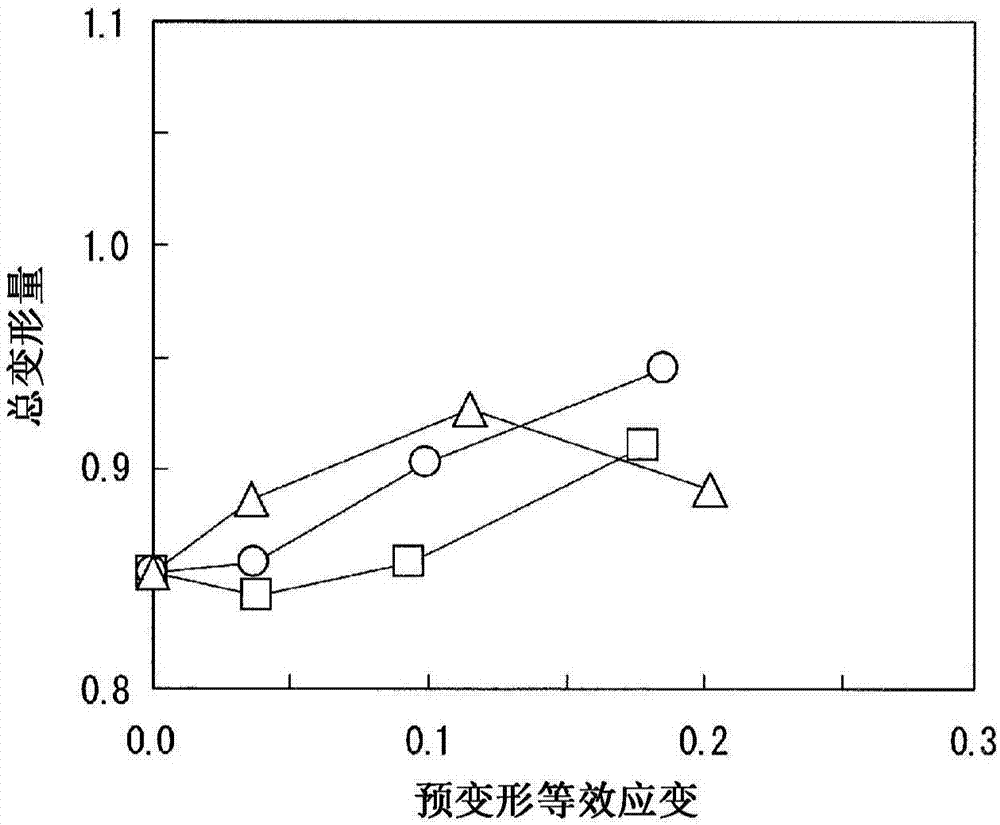
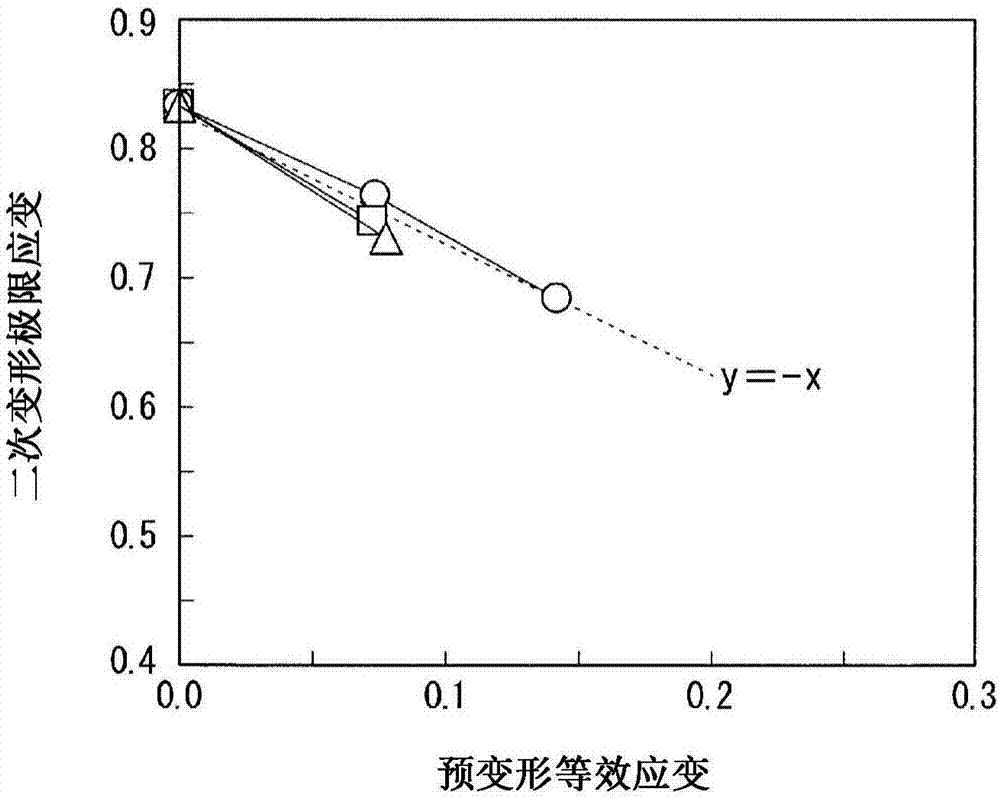
Method for determining stretch flange limit strain and method for assessing press forming feasibility
This method for setting stretch flange limit strain is characterized in that the stretch flange limit strain is set so as to satisfy the relationship in the following equation using the strain gradient from the end part of a metal sheet toward the inside when a press load is added, and the strain gradient in the thickness direction of the metal sheet crossing the loading direction. εθlim = A{a•Δεθ / Δr+b•Δεθ / Δt}+c Provided that: εθlim represents the stretch flange limit strain (tangential to the sheet edge) Δεθ / Δr represents the strain gradient toward the interior Δεθ / Δt represents the strain gradient in the thickness direction A, a, b are influence coefficients c is the limit strain when the strain gradient is zero
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
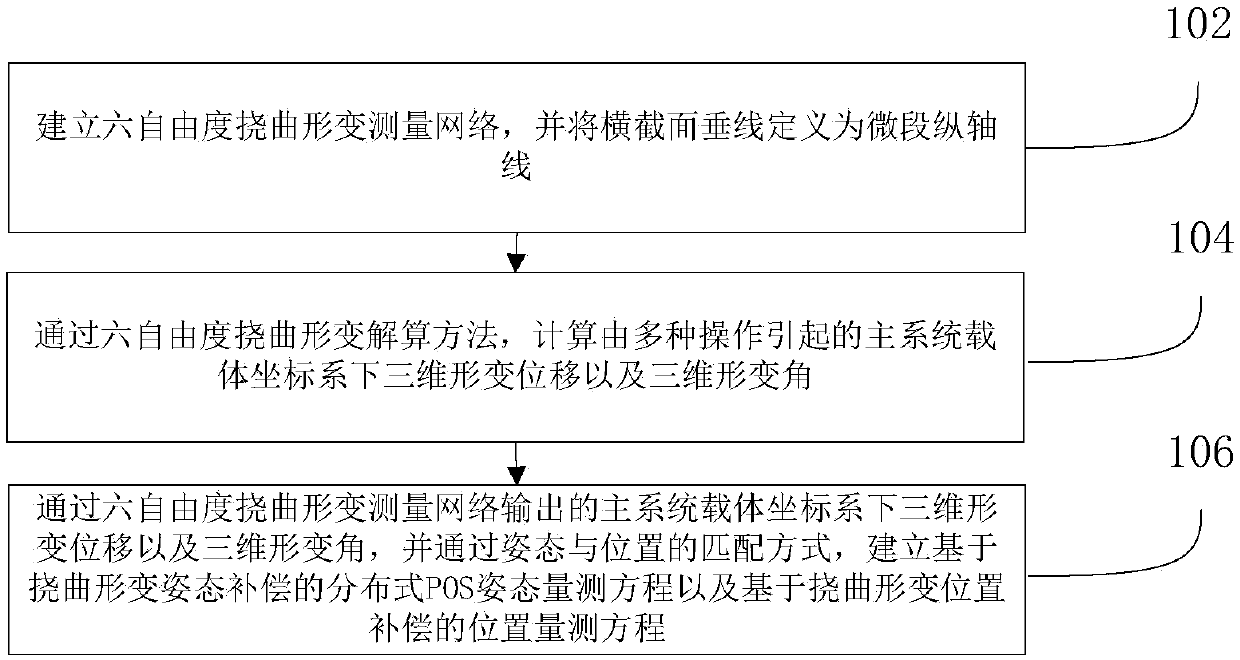
Distributed POS (position and orientation system) transfer alignment modeling method and device of bending deformation measuring network
ActiveCN108398130ANavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsFiberEngineering
The invention discloses a distributed POS (position and orientation system) transfer alignment modeling method and a distributed POS transfer alignment modeling device of a bending deformation measuring network. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a six-degree-of-freedom bending deformation measuring network, and dispersing a flexible rod arm into a plurality of rod arm micro-sections with length not more than 10 cm according to a strain gradient of bending deformation of the distributed POS flexible rod arm; sticking six fiber grating sensors on the surface of each rod armmicro-section, calculating a three-dimensional deformation angle and three-dimensional deformation displacement under a main system carrier coordinate system by adopting a six-degree-of-freedom bending deformation solving method, and providing measuring information for distributed POS transfer alignment; and establishing a distributed POS attitude measuring equation based on bending deformation attitude compensation, and a distributed POS position measuring equation based on bending deformation position compensation so as to establish a transfer alignment system model. The invention also discloses the distributed POS transfer alignment modeling device of the bending deformation measuring network.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
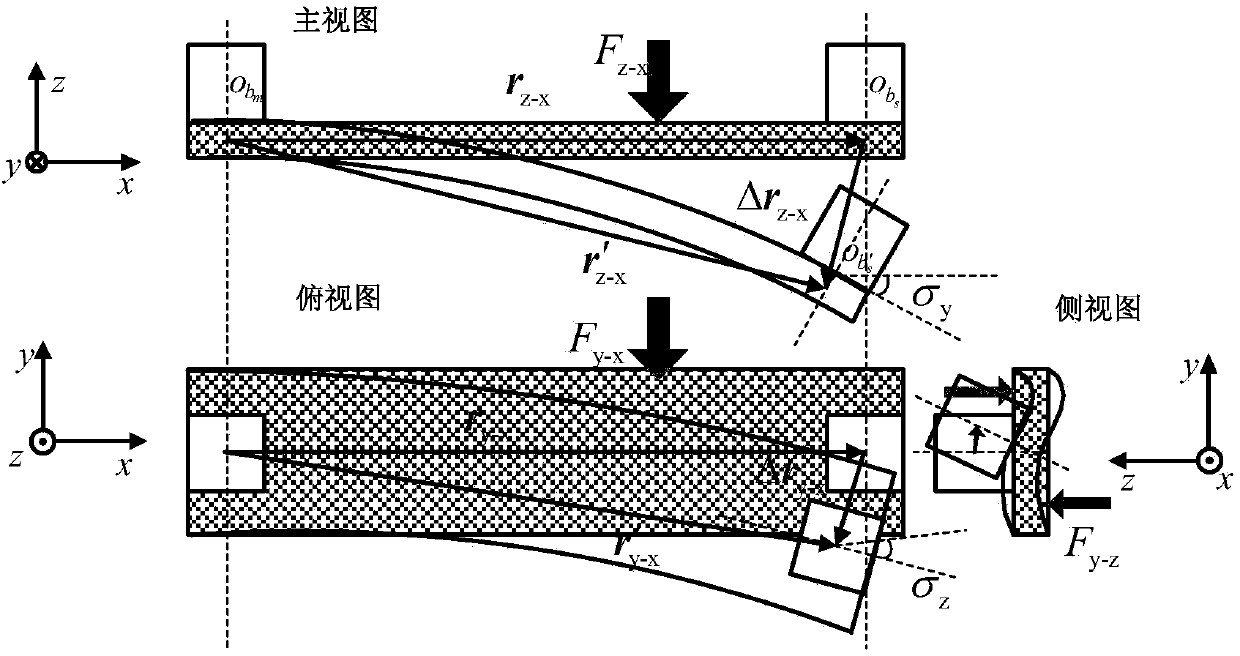
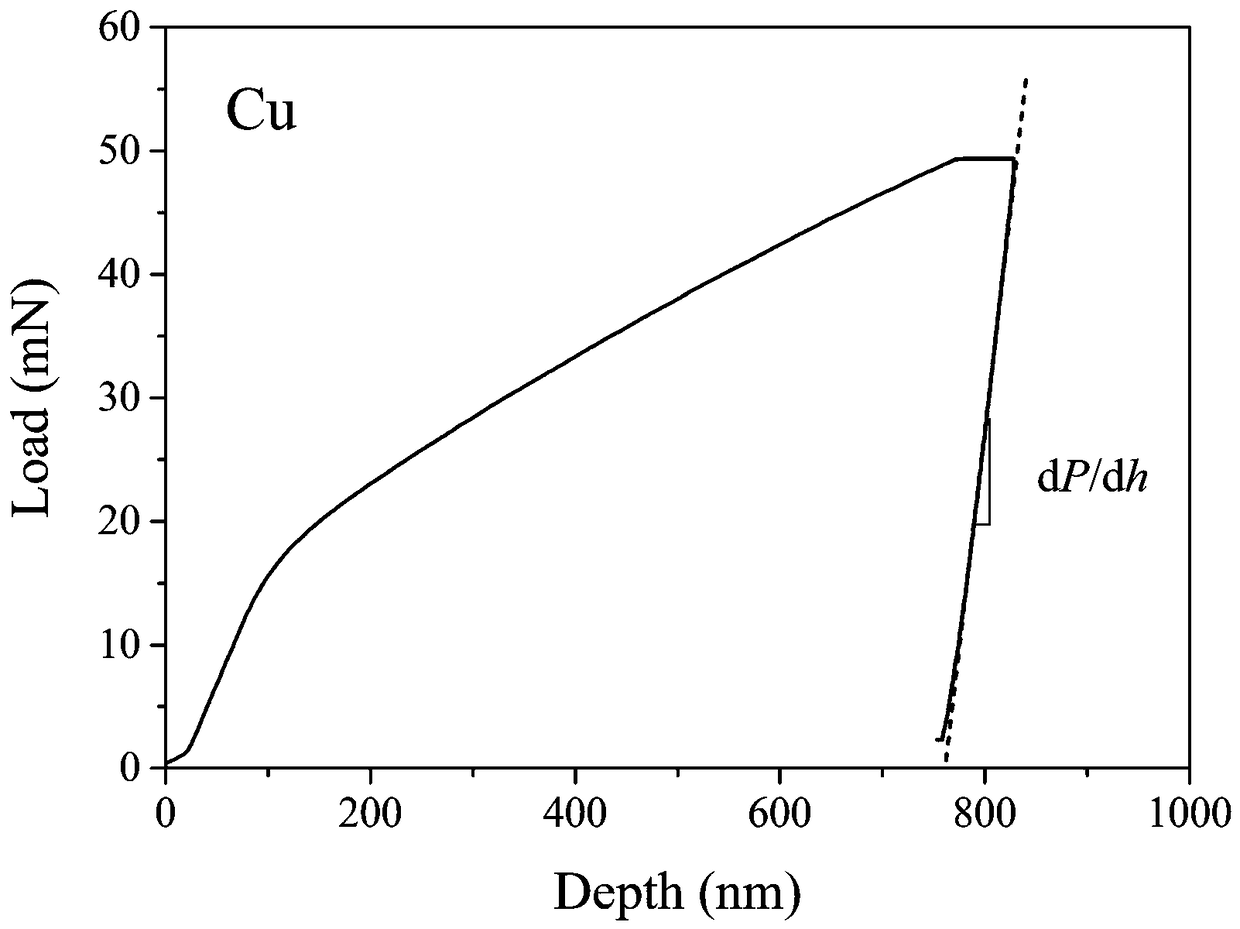
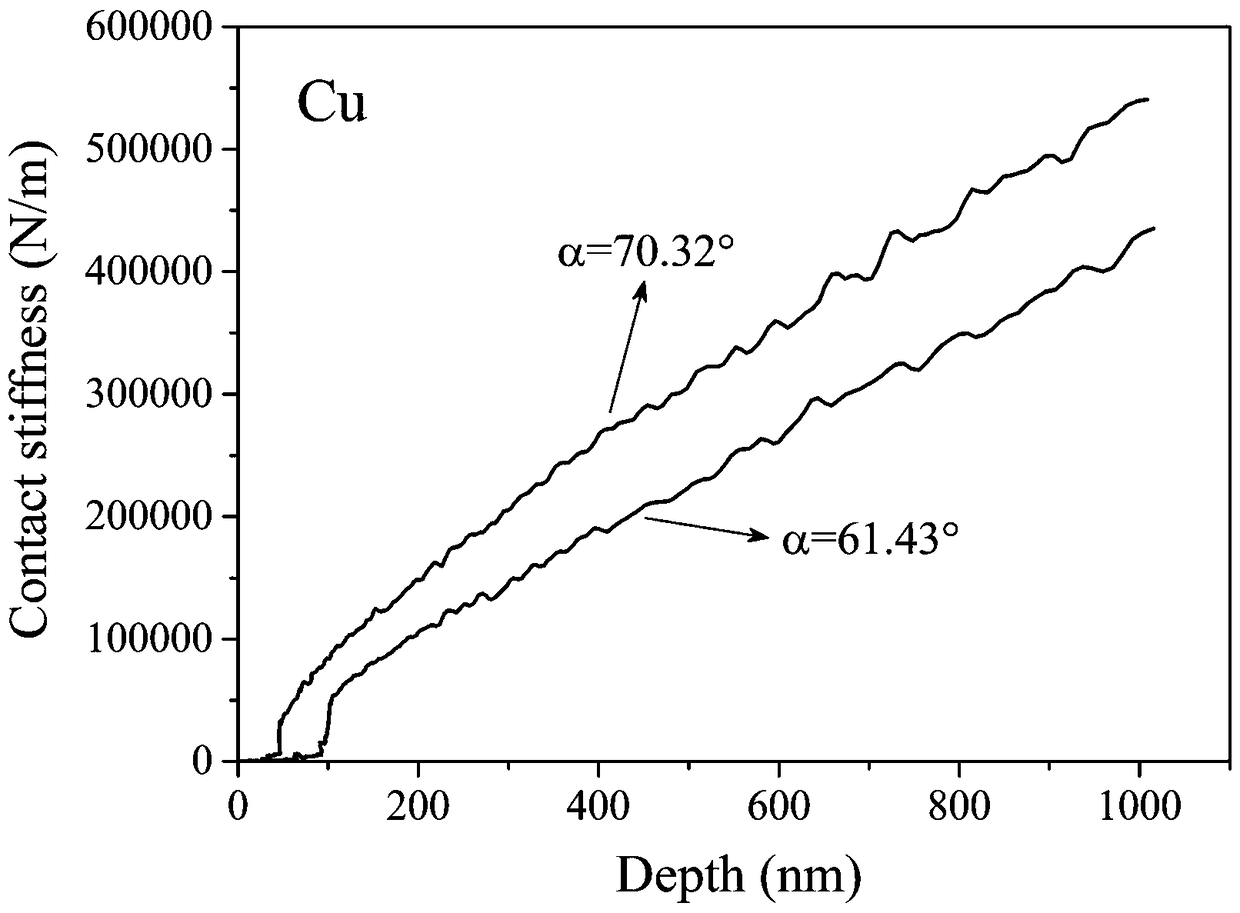
Method for in-situ press-in to test and extract metal elastoplasticity parameters
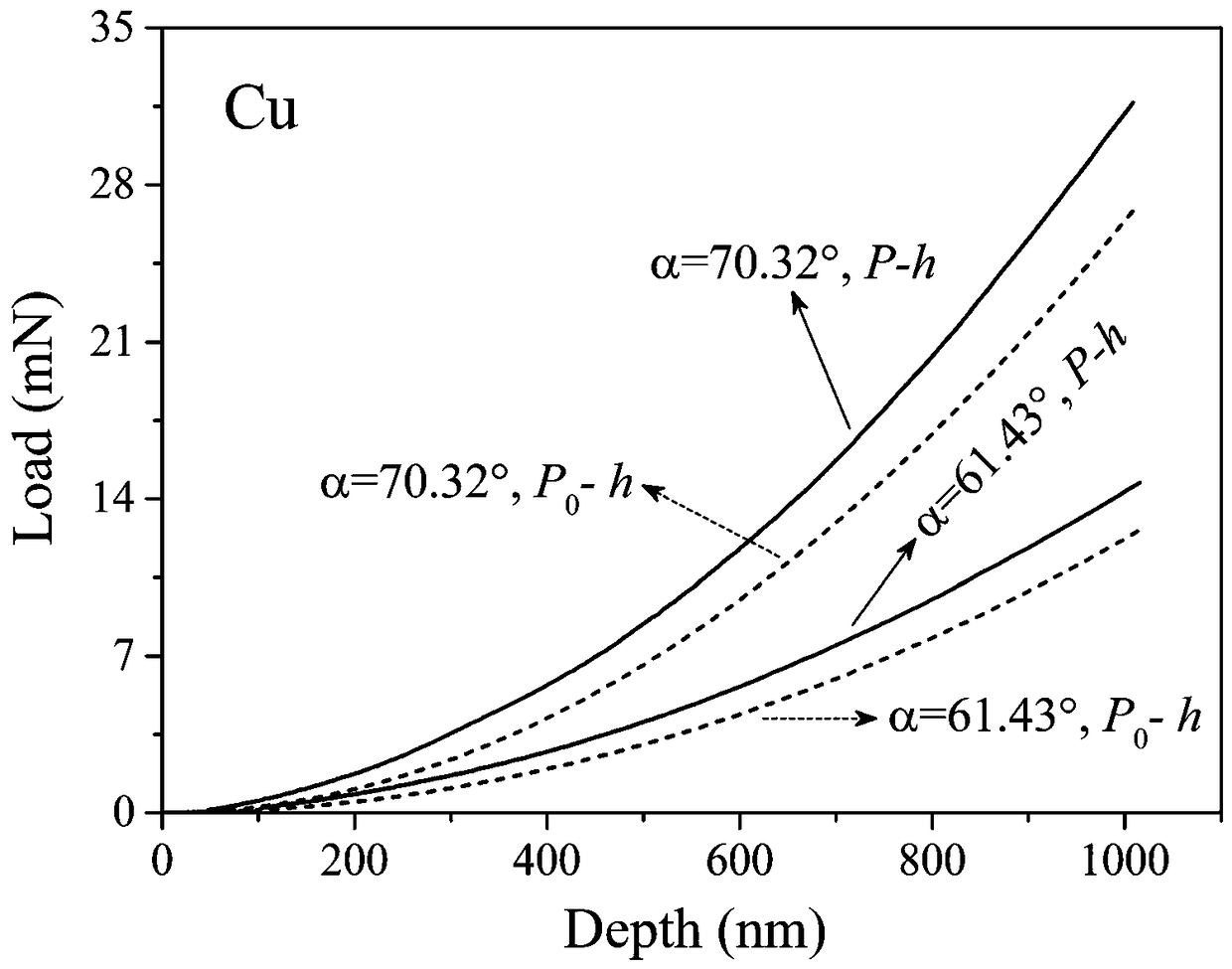
ActiveCN108414379AImprove accuracyUniqueness guaranteedInvestigating material hardnessMicro nanoMetallic materials
The invention discloses a method for in-situ press-in to test and extract metal elastoplasticity parameters. The method includes: adopting a cylindrical pressure head and two pressure heads differentin cone angle for testing to obtain elasticity modulus of metal; combining with plastic strain gradient theory to give out a load-depth curve (P0-h) with press-in gradient effect impact removed; further acquiring feature stress under action of the pressure heads different in cone angle through numerical simulation inversion; combining with feature strain epsilon r under different cone angles; substituting into a power hardening elasticity constitutive relation to acquire yield stress sigma y and hardening index of a tested material. The method is high in accuracy, impact of press-in gradient effect is removed, and uniqueness of the elasticity constitutive relation is ensured mathematically, so that effectiveness of extracting metal material elasticity parameters on the basis of a micro-nano press-in method.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Out-of-plane resonator
ActiveUS20130002363A1Impedence networksOscillations generatorsMicroelectromechanical systemsResonator
A microelectromechanical system (MEMS) device includes a resonator anchored to a substrate. The resonator includes a first strain gradient statically deflecting a released portion of the resonator in an out-of-plane direction with respect to the substrate. The resonator includes a first electrode anchored to the substrate. The first electrode includes a second strain gradient of a released portion of the first electrode. The first electrode is configured to electrostatically drive the resonator in a first mode that varies a relative amount of displacement between the resonator and the first electrode. The resonator may include a resonator anchor anchored to the substrate. The first electrode may include an electrode anchor anchored to the substrate in close proximity to the resonator anchor. The electrode anchor may be positioned relative to the resonator anchor to substantially decouple dynamic displacements of the resonator relative to the electrode from changes to the substrate.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
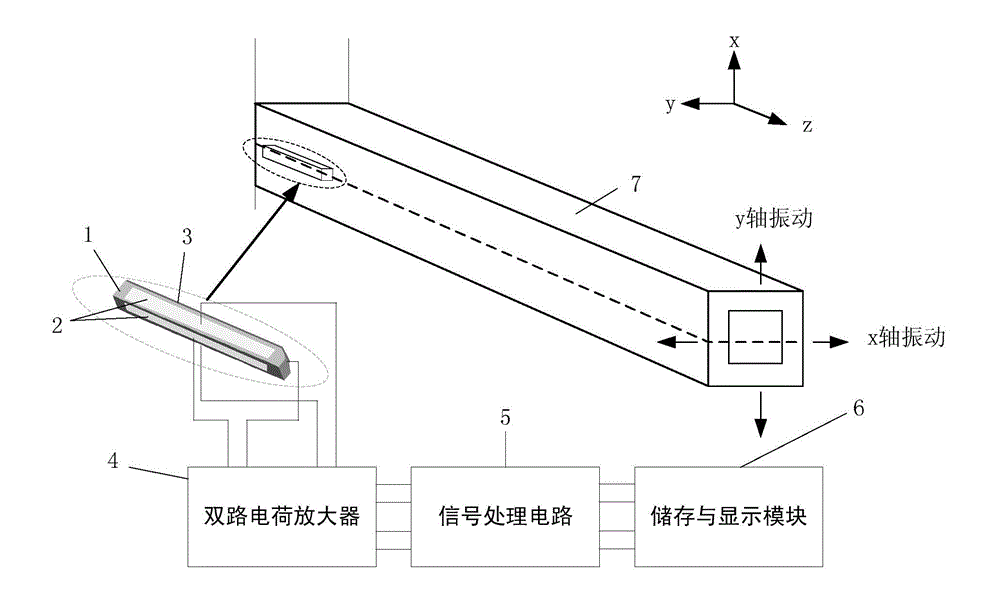
Double-axis vibrating sensor based on flexoelectric principle
ActiveCN104457964AReduce demandNo need to consider the location layoutSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing electrical meansEpoxyAudio power amplifier
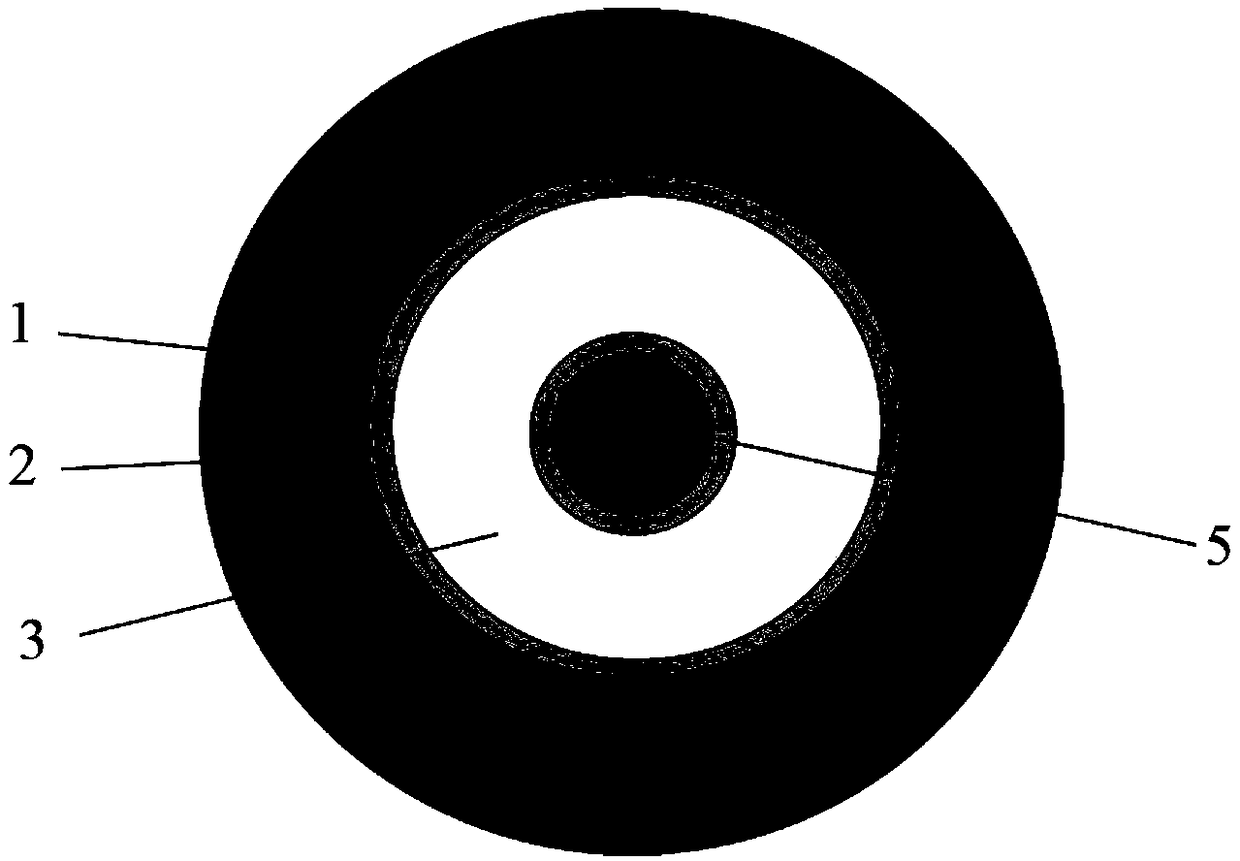
The invention discloses a double-axis vibrating sensor based on the flexoelectric principle. The double-axis vibrating sensor based on the flexoelectric principle comprises a sensing unit with a high flexoelectric coefficient and four electrodes, wherein the four electrodes adhere to the surface in the length direction of the sensing unit and are not connected, the sensing unit is connected to the side face of a structure to be detected through epoxy glue, the electrodes are electrically connected with a double-circuit charge amplifier, the double-circuit charge amplifier is electrically connected with a signal processing circuit, and the signal processing circuit is electrically connected with a storage and display module; when double-axis vibration happens to the structure to be detected, corresponding flexural deflection is generated by the sensing unit located on one side of the structure to be detected, a strain gradient is generated in the deflection direction of the sensing unit, two groups of corresponding polarization charges are output by the passive sensing unit, and the real-time double-axis vibrating condition of the structure to be detected is obtained by measuring and analyzing the charges in real time. According to the double-axis vibrating sensor based on the flexoelectric principle, no power needs to be supplied to the sensing unit, additional arrangement of a sensitive element is not needed, and the real-time double-axis vibrating condition of the structure to be detected can be obtained simply by directly analyzing and processing output charge signals generated through vibration.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
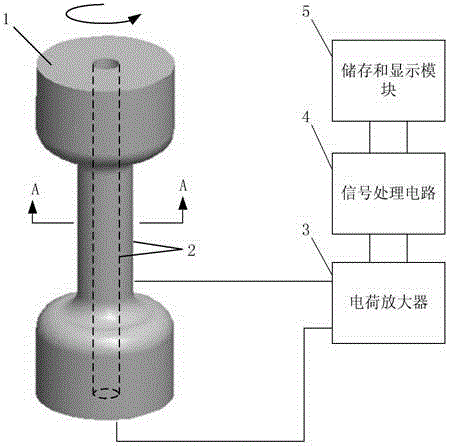
Flexoelectric passive torque sensor
ActiveCN104483054AReduce demandRealize passive torque measurement functionWork measurementTorque measurementElectricitySignal processing circuits
The invention discloses a flexoelectric passive torque sensor, which comprises a sensing unit, electrodes, a charge amplifier, a signal processing circuit and a storage and display unit, wherein the sensing unit is provided with a clamping end and concentric through holes and has a big flexoelectric coefficient; the electrodes are attached to the inner walls of the through holes of the sensing unit and the outer part of the sensing unit; the charge amplifier is electrically connected with the electrodes; the signal processing circuit is electrically connected with the charge amplifier; the storage and display module is electrically connected with the signal processing unit; when the clamping end of the sensing unit loads a torque, the inner wall of each through hole of the sensing unit generates a strain gradient along the radial direction; due to a flexoelectric principle, corresponding polarization charges are directly generated on the sensing unit, and a value of the torque loaded on the clamping end is obtained by a charge signal. The torque loaded on the sensing unit can be measured by being converted into the radial direction strain gradient; meanwhile, since the sensing unit has the big flexoelectric characteristics, sensitive elements do not need to be pasted, the measuring mode of the sensing unit is passive measurement, and the applicable range of the sensor is enlarged.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
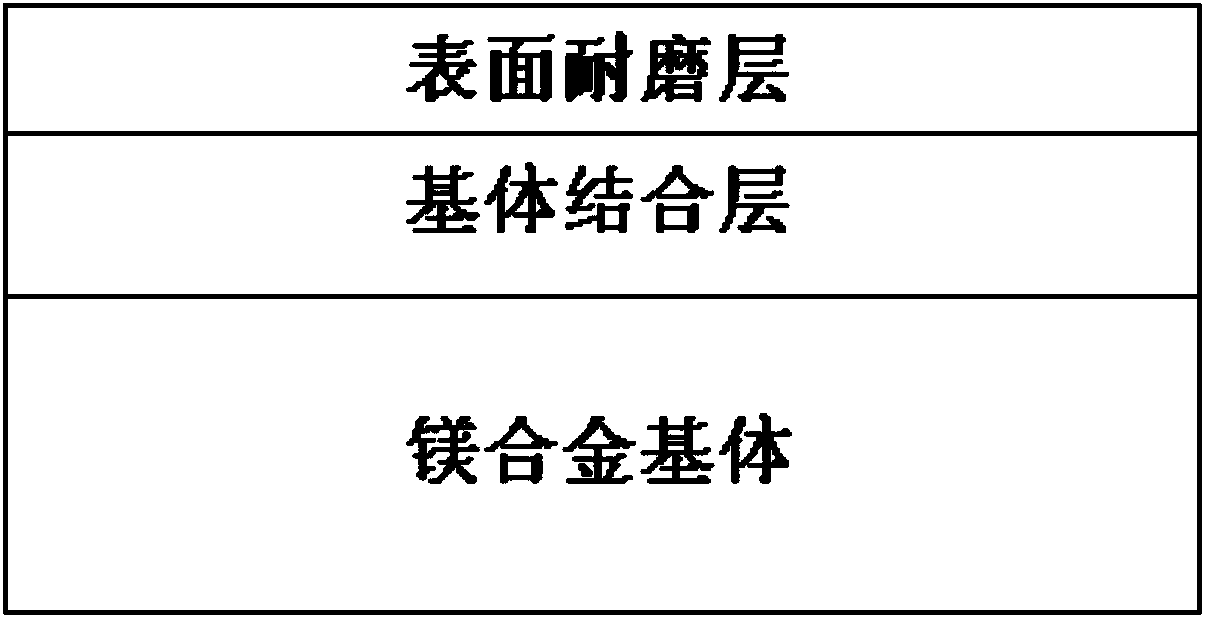
Composite coating on surface of magnesium alloy structural component and preparation method of composite coating
ActiveCN104228183AHigh hardnessImprove corrosion resistanceLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingWear resistantOxygen ions
The invention discloses a composite coating on the surface of a magnesium alloy structural component. The composite coating comprises a matrix bonding layer and a surface wear-resistant layer, wherein the matrix bonding layer is a nitrogen ion implantation layer or an oxygen ion implantation layer; the surface wear-resistant layer is a laser cladding SiC layer, a laser cladding SiO2 layer or a laser cladding SiC and SiO2 composition layer; the ion implantation bonding layer is combined with a magnesium alloy matrix; and the surface wear-resistant layer is combined with the ion implantation bonding layer. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the composite coating. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a matrix bonding layer on the surface of a magnesium alloy matrix in situ by adopting an ion implantation technology; and preparing a surface wear-resistant layer on the matrix bonding layer by adopting a laser cladding method. The magnesium alloy coating prepared by a method disclosed by the invention is tightly combined with the matrix, is excellent in corrosion resistance and wear resistance, flat and dense in surface, uniform in interface transition and small in strain-strain gradient and is not damaged under the action of an alternating load.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
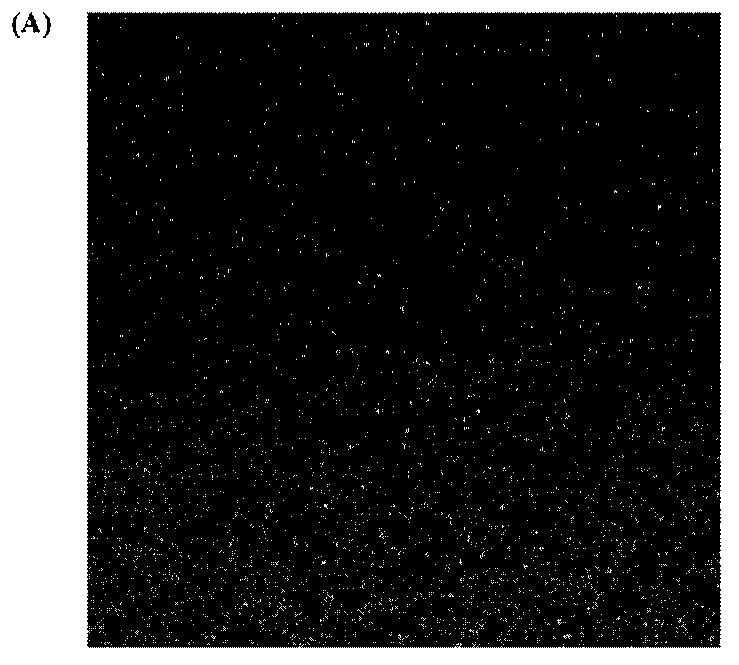
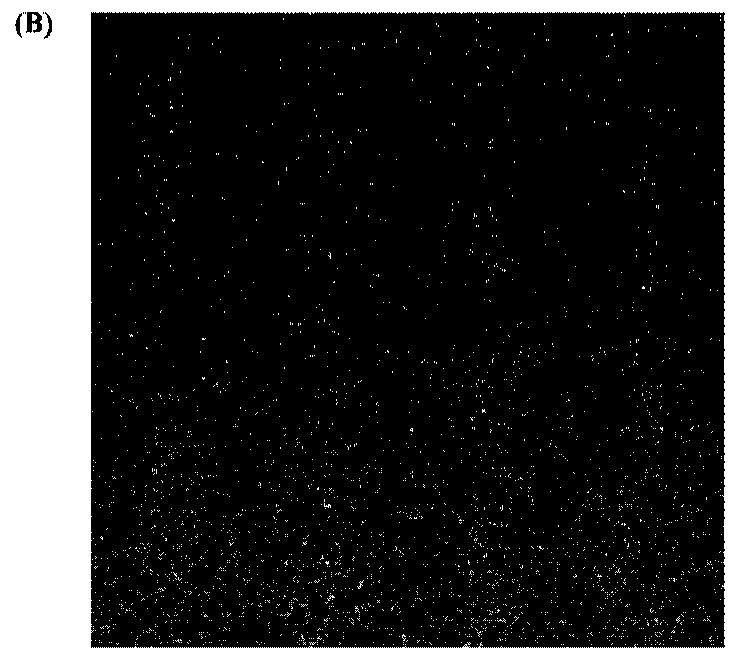
Strain measurement method
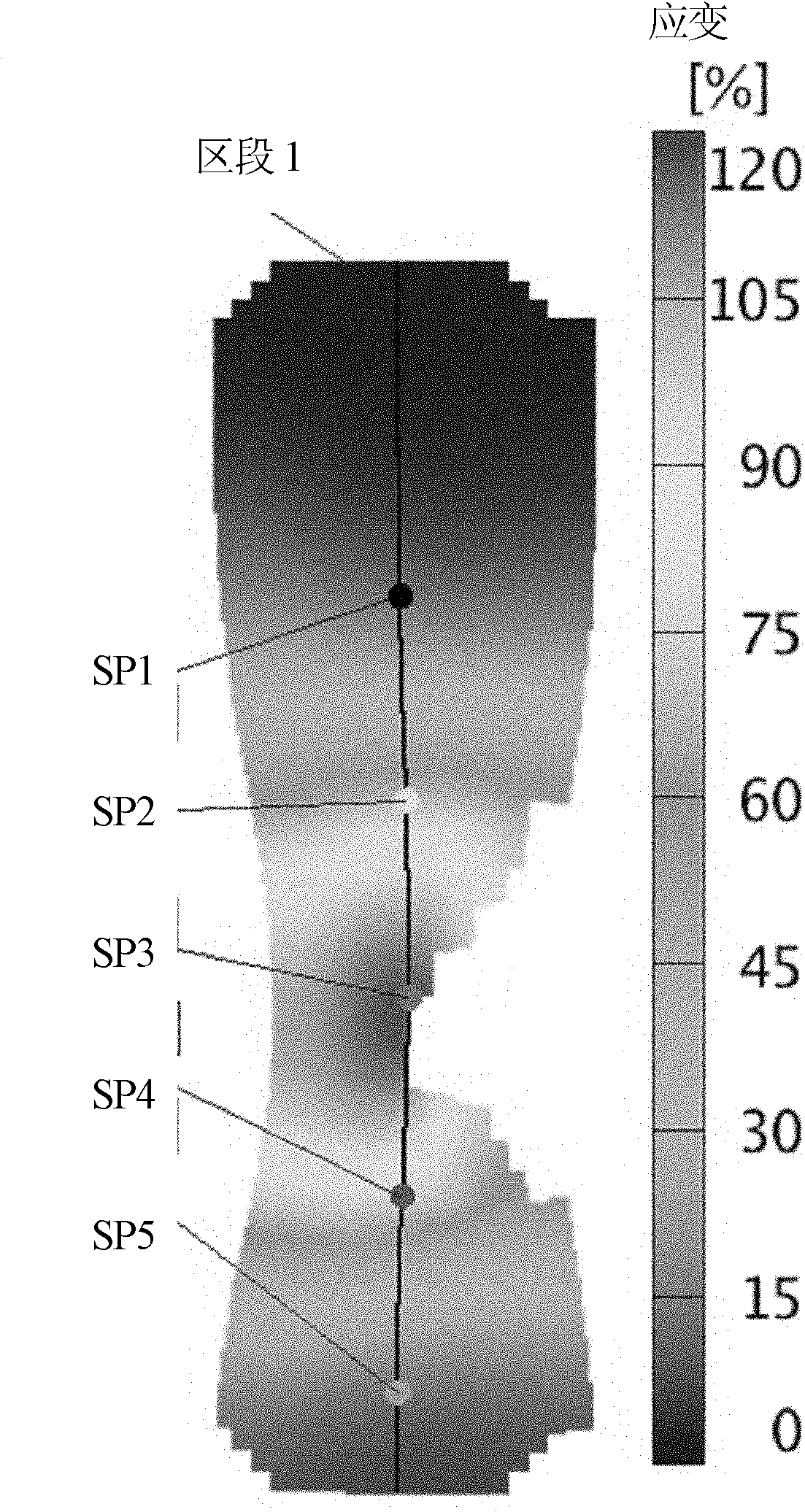
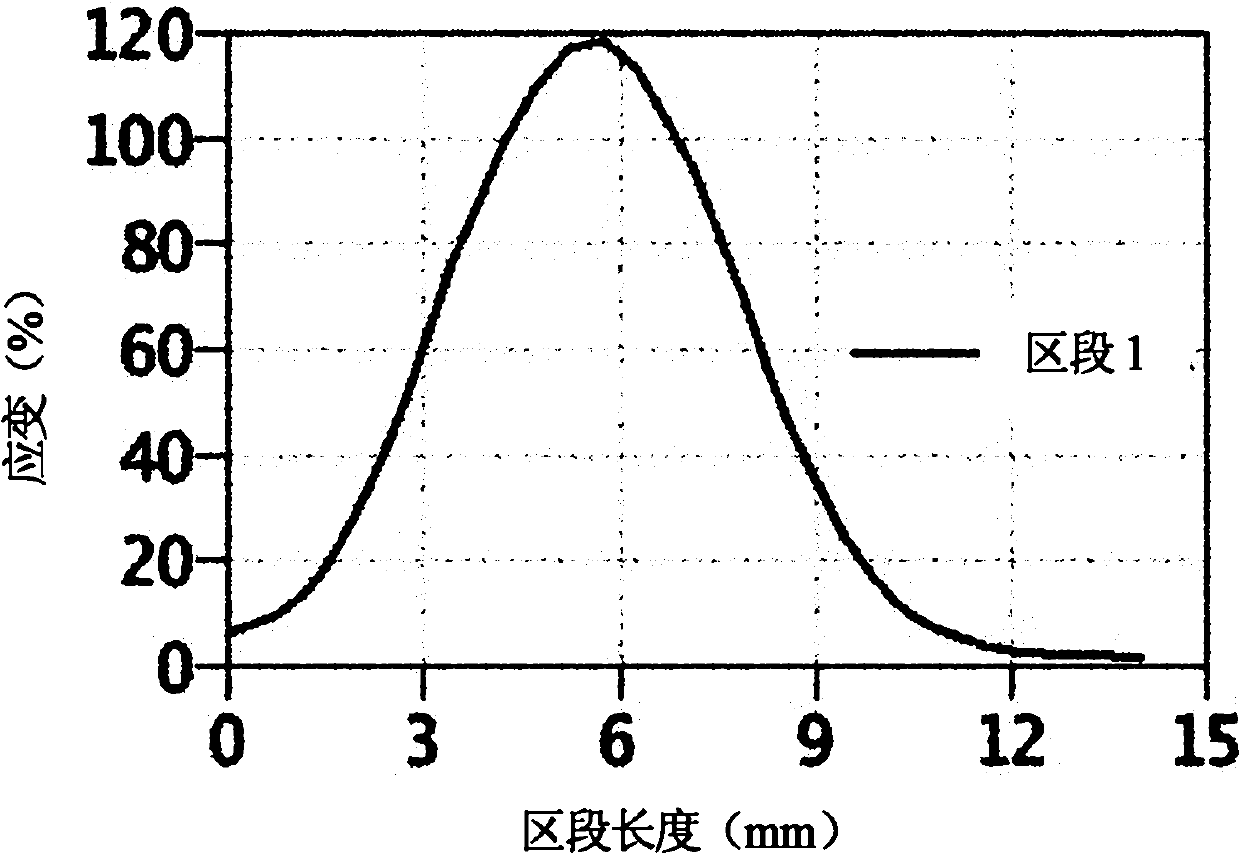
InactiveCN102564282AStrain distribution across the fieldGood impetusMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMechanical solid deformation measurementsMeasurement pointMicrometer
The invention relates to the field of strain measurement, in particular to a method for measuring the strain of a tensile sample, which solves the problem in the prior art that strain cannot reveal the intrinsic characteristics of material strain. The method comprises the following steps: 1, spray paint for speckle measurement is sprayed on the surface of the sample, and the color of the spray paint is in sharp contrast to the surface color of the sample; 2, the sample is mounted and clamped on a tensile testing machine, measuring devices are connected, measurement parameters are set, the test is started, and testing data are recorded; and 3, the size of a speckle measuring point ranges from 0.1 to 50 micrometers, speckles are distributed randomly, the strain distribution of the speckle measuring points is measured, and a measurement report containing strain gradient distribution is formed. The strain distribution provided by the method is important in revealing the intrinsic characteristics of a material. Particularly, to obtain the whole-field strain distribution, the speckle measurement technology is applied to tensile sample surface measurement.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Deflection voltage electrical composite
ActiveCN105140387AFlexoelectric effectPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionPiezoelectric compositeMaterials science
The invention provides a deflection voltage electrical composite which comprises a press head, a dielectric material and a support plate, wherein the press head, the dielectric material and the support plate are successively superimposed. The contact area of the press head and the dielectric material is different from the contact area of the dielectric material and the support plate. Electrode materials are coated on the surface of the side, which contacts the press head, of the dielectric material and the surface of the side, which contacts the support plate, of the dielectric material. The dielectric material is sheet-shaped. According to the invention, the press head presses the deflection voltage electrical composite; due to the structure of the composite, stress on both sides of the composite are asymmetric; strong strain gradient is generated near a force bearing point of the dielectric material; a deflection electrical effect is generated; and an apparent piezoelectric effect is shown.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
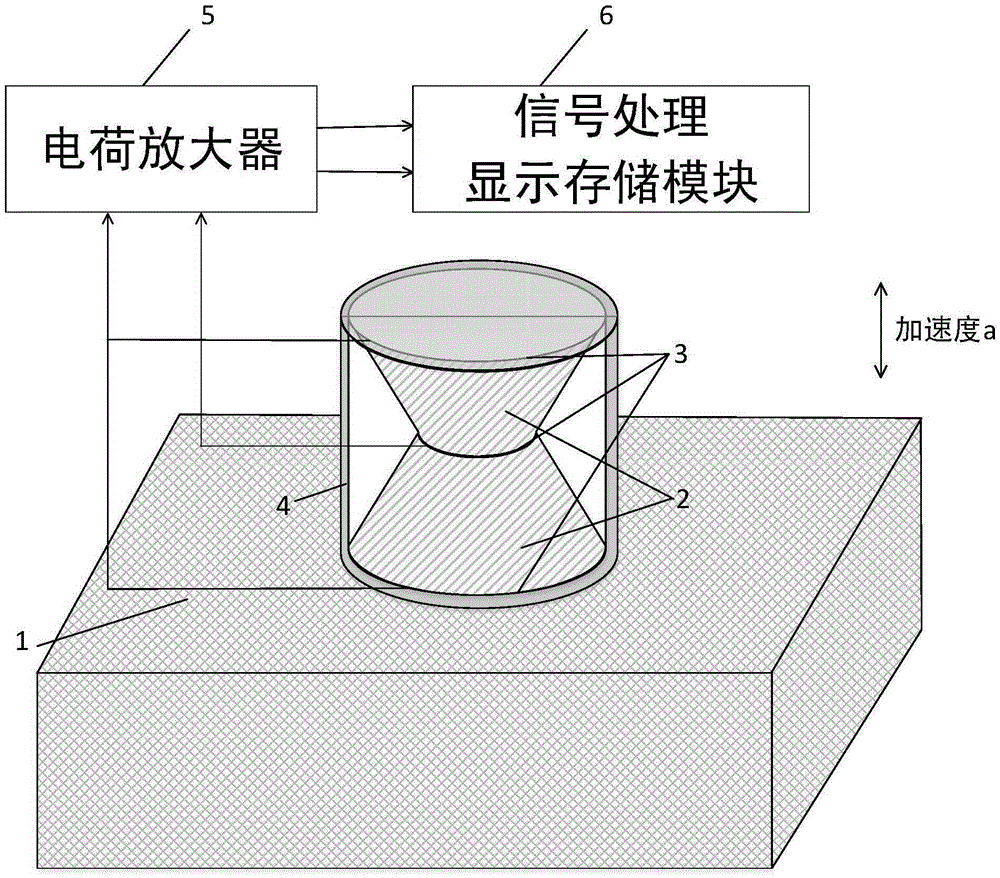
High-g value acceleration sensor based on flexoelectric effects and measurement method
ActiveCN105424978AReduce demandImprove real-time performanceAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAudio power amplifierComputer module
The invention discloses a high-g value acceleration sensor based on flexoelectric effects and a measurement method. The sensor comprises a substrate and an insulated rigid cylindrical shell fixedly connected, wherein two flexoelectric material truncated cones are oppositely arranged in the insulated rigid cylindrical shell; a certain pre-tightening force is provided through the upper cover of the insulated rigid cylindrical shell; electrodes are applied to the upper surface and the lower surface of each flexoelectric material truncated cone; the electrode is connected with the input end of a charge amplifier; and the output end of the charge amplifier is connected with a signal processing, display and storage module. When the high-g value acceleration is measured, the high-g value acceleration exists in the substrate, the high-g value acceleration is transferred to the flexoelectric material truncated cones via the insulated rigid cylindrical shell, the flexoelectric material truncated cones are deformed under an inertia force to generate strain gradient, polarized charges are generated and then transferred to the charge amplifier via the electrodes, and the substrate movement high-g value acceleration change conditions are displayed in real time through processing. No power needs to be provided for the flexoelectric material truncated cones, and the high-g value acceleration sensor based on flexoelectric effects has the advantages that no external mass block exists, the range is wide, the applied frequency band is wide, the real-time performance is good, measurement is direct, and the structure is simple.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Stretch flange crack prediction method, stretch flange crack prediction apparatus, computer program, and recording medium
ActiveUS20180107772A1Accurate predictionDesign optimisation/simulationAerodynamics improvementCircumferential strainEngineering
A stretch flange crack prediction method of predicting initiation of stretch flange cracks that occurs in a flange end section during stretch flange forming of a deformable sheet, includes: a measurement value acquisition process of acquiring, for each of a plurality of sheet-shaped test pieces, a fracture strain measurement value, a normal strain gradient measurement value, and a circumferential strain gradient measurement value; a CAE analysis process of acquiring a maximum major strain maximum element having a highest maximum major strain, a normal strain gradient of the maximum major strain maximum element, and a circumferential strain gradient of the maximum major strain maximum element; a fracture determination threshold acquisition process of acquiring a fracture determination threshold by converting the fracture strain measurement value; and a prediction process of predicting that stretch flange cracks will be initiated, when the maximum major strain is equal to or higher than the fracture determination threshold.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
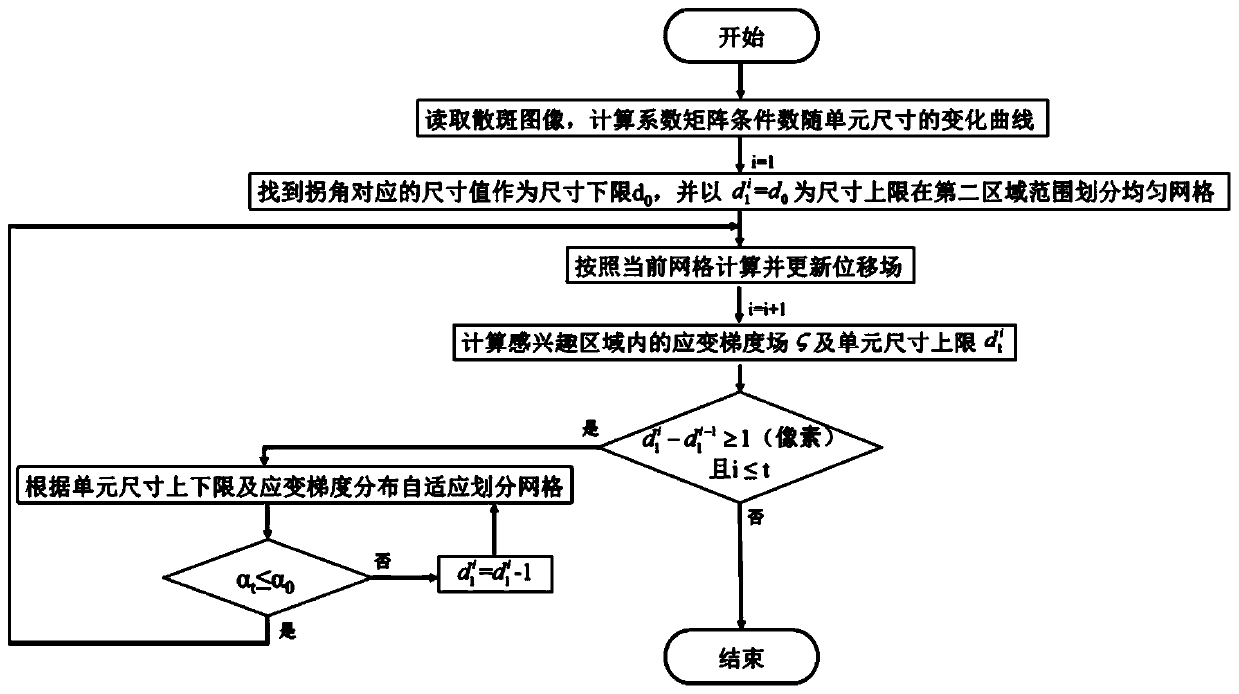
Optical deformation measurement method based on adaptive mesh and electronic equipment
ActiveCN110686610AImprove calculation accuracyImprove robustnessUsing optical meansEngineeringSpeckle pattern
The invention relates to an optical deformation measurement method based on an adaptive mesh and electronic equipment. The measurement method comprises the following steps: acquiring a speckle image containing a region of interest, dividing uniform meshes in the region of interest, and determining an L-shaped curve in which the condition number of a corresponding coefficient matrix changes with the size of a mesh unit; taking the size corresponding to inflection points of the L-shaped curve as a unit size lower limit, taking the same size as an initial upper limit, and dividing uniform meshesin a second region range of the image, the second region including the region of interest; calculating and updating a displacement field according to the uniform meshes divided in the second region; and determining a strain gradient field of the region of interest according to the updated displacement field, determining unit size upper and lower limits according to the strain gradient field, and determining distribution of the unit size through a mapping relationship between strain gradients and unit sizes. According to the measurement method, the mesh size is selected in a self-adaptive mode,so that errors, caused by shape function mismatching, of the large-strain-gradient position and random errors of the small-strain-gradient position are reduced.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
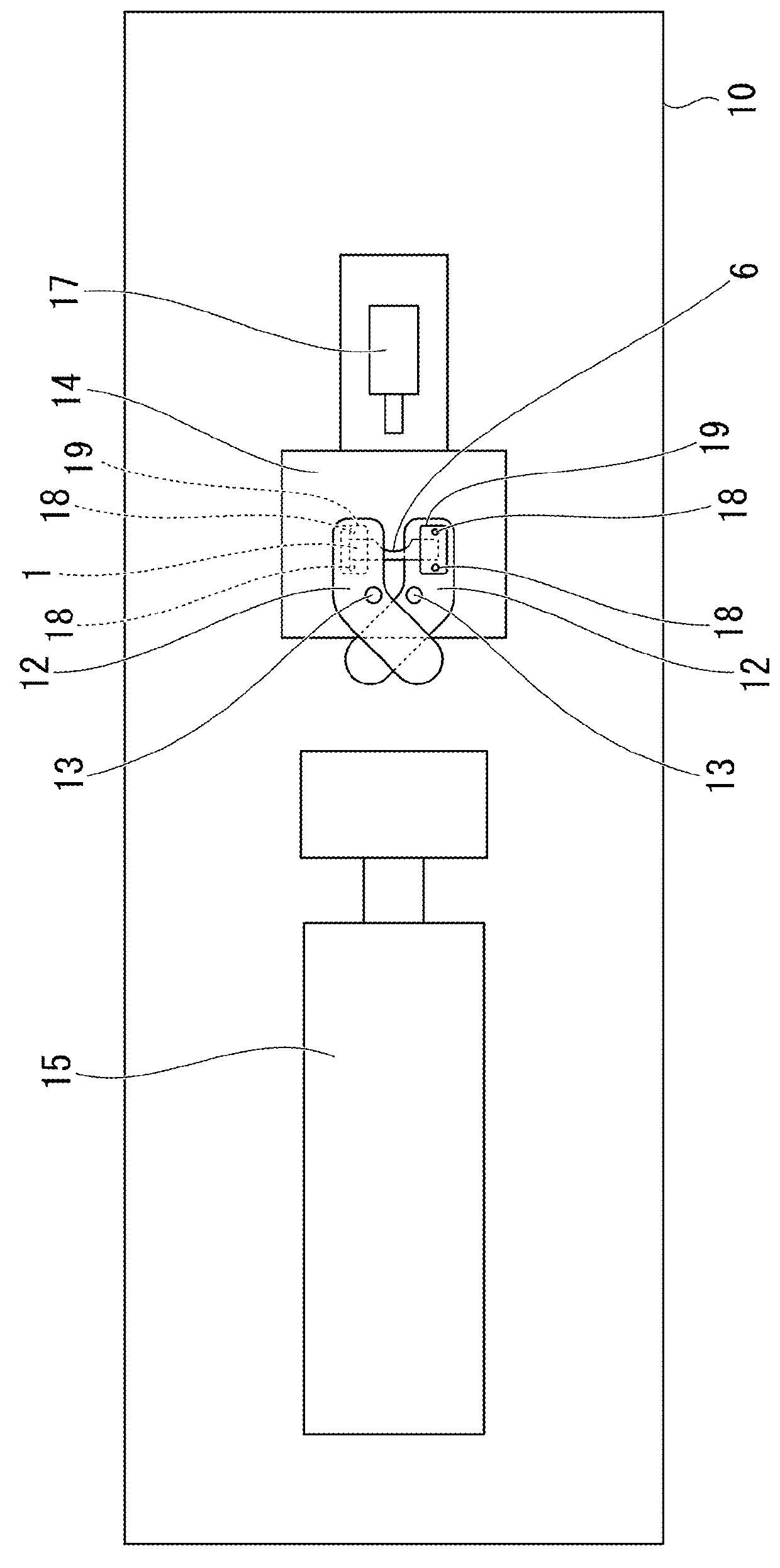
Temperature-insensitive FBG acceleration sensor and method based on strain chirp effect
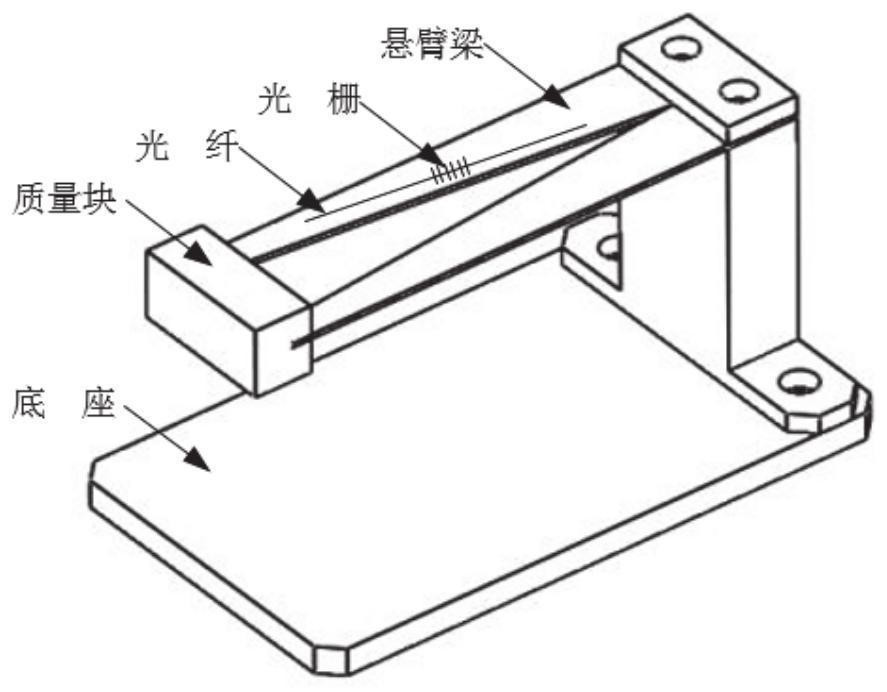
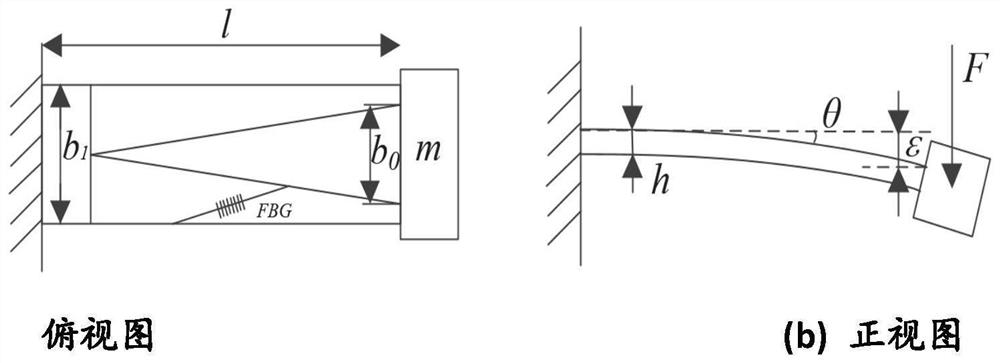
ActiveCN111879970AStrong torsion resistanceWith automatic temperature compensation functionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementCantilevered beamGrating
The invention provides a temperature-insensitive FBG acceleration sensor and method based on a strain chirp effect. The temperature-insensitive FBG acceleration sensor comprises a mass block, an M-shaped cantilever beam, a base and a fiber bragg grating. A supporting rod is vertically fixed to one side of the base, an M-shaped cantilever beam is fixedly installed at one end of the supporting rod,and a mass block is installed at the end, away from the supporting rod, of the M-shaped cantilever beam. The M-shaped cantilever beam is composed of two symmetrical equal-strength triangles, and the fiber bragg grating is obliquely pasted to a non-uniform strain gradient area of the M-shaped cantilever beam. According to the technical scheme, the fiber bragg grating is pasted to the strain non-uniform area of the beam, the fiber bragg grating generates the chirp effect by applying the tensile load, and compared with a single cantilever beam, the sensor has high torsion resistance.
Owner:INST OF DISASTER PREVENTION
High-sensitivity bending electric sensor used for shock wave detection
ActiveCN105571756AWide selectionHas size effectForce measurement using piezo-electric devicesApparatus for force/torque/work measurementEpoxyShock wave
The invention provides a high-sensitivity bending electric sensor used for shock wave detection. The electric sensor comprises a left metal electrode and a right metal electrode which are respectively arranged on the left surface and the right surface of a bending electric dielectric material. The left metal electrode and the right metal electrode are connected with two lead wires for outputting measuring electric charge. Other ends of the lead wires are connected with two externally-connected metal electrodes. The bending electric dielectric material, the metal electrodes and the lead wires are enclosed by epoxy resin. A metal screen is provided with a pressure channel with shock wave imposing pressure. A housing is adhered to the metal screen so as to solidify the epoxy resin therein. According to the invention, based on a linear relation between a strain gradient generated by the bending electric dielectric material under the compression effects of the impact waves and electric charge generated on the basis of the bending electric dynamic effects, size of the pressure of the shock waves is measured.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
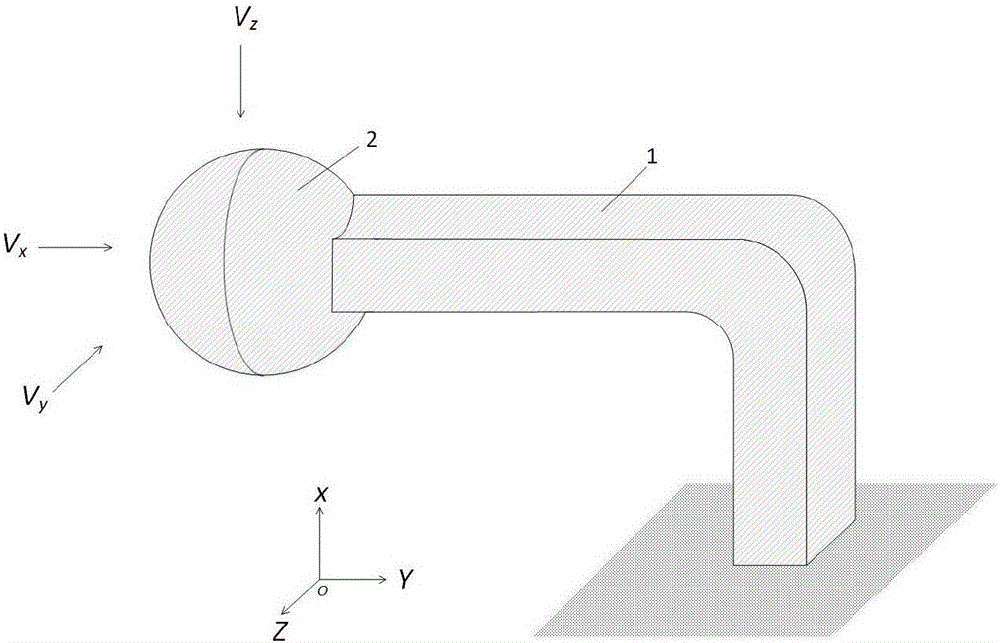
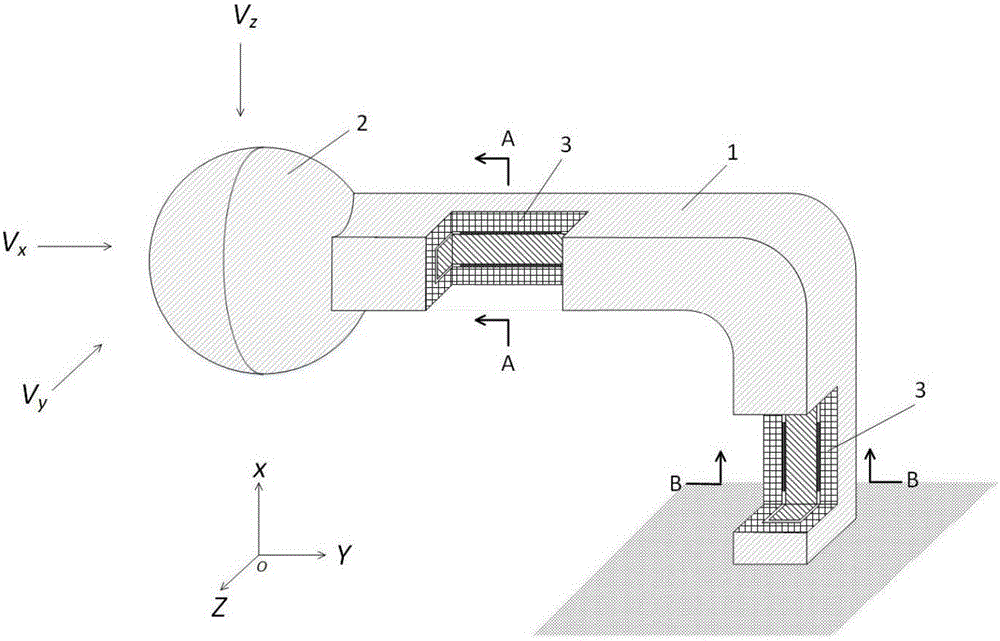
Flexoelectric effect-based three-dimensional flow rate-of-change sensor and measuring method
ActiveCN105158509ADirect measurement of flow rate changeImprove real-time performanceAcceleration measurement using interia forcesAudio power amplifierAdhesive materials
The invention provides a flexoelectric effect-based three-dimensional flow rate-of-change sensor and a measuring method. The sensor comprises an L-shaped three-dimensional body element and a ball-shaped insulating material. The L-shaped three-dimensional body element comprises an insulating layer, an electrode layer and a flexoelectric material layer, wherein the layers are stacked up and the empty part of the L-shaped three-dimensional body element is filled with an insulating adhesive material. The electrode layer is connected with a charge amplifier. The output end of the charge amplifier is connected with a signal processing, display and storage module. During the measurement of the flow change rate, the fluid in a three-dimensional flow field impacts with the ball-shaped insulating material, so that the layers of the L-shaped three-dimensional body element are deformed. The flexoelectric material layer is provided with a strain gradient along the deflection direction thereof to generate four groups of polarization charges. The polarization charges are transferred to the charge amplifier via the electrode layer and then are processed, so that the three-dimensional flow rate of change can be displayed in real time. The sensor has the advantages of small size, little influence on the flow field, no power supply for the flexoelectric material layer, no extra mass block, wide measuring range, good real-time performance, direct measurement, high precision, simple structure and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
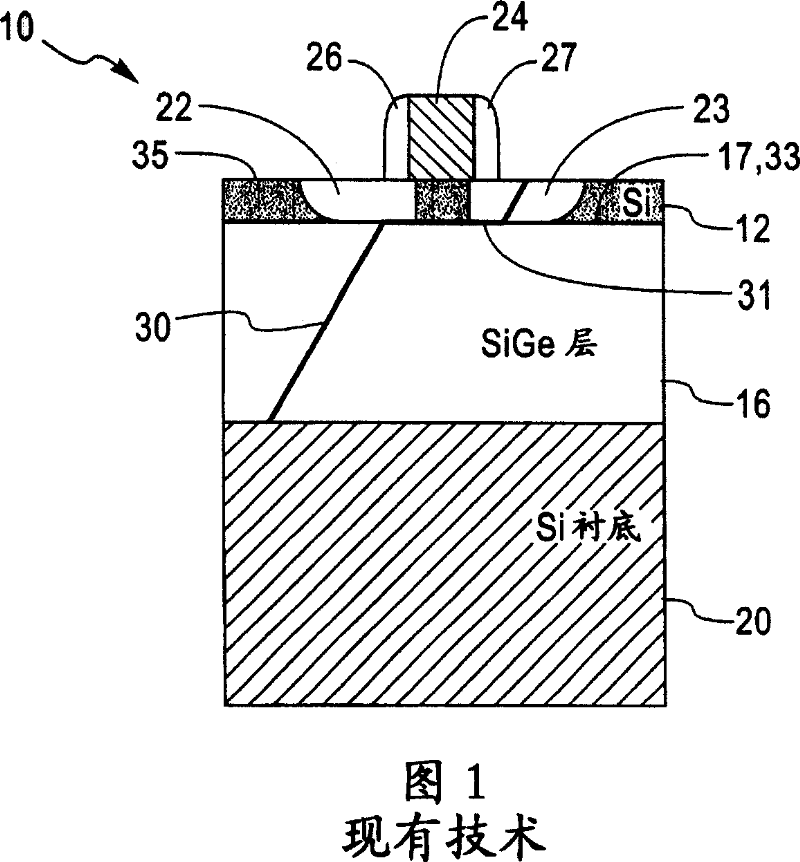
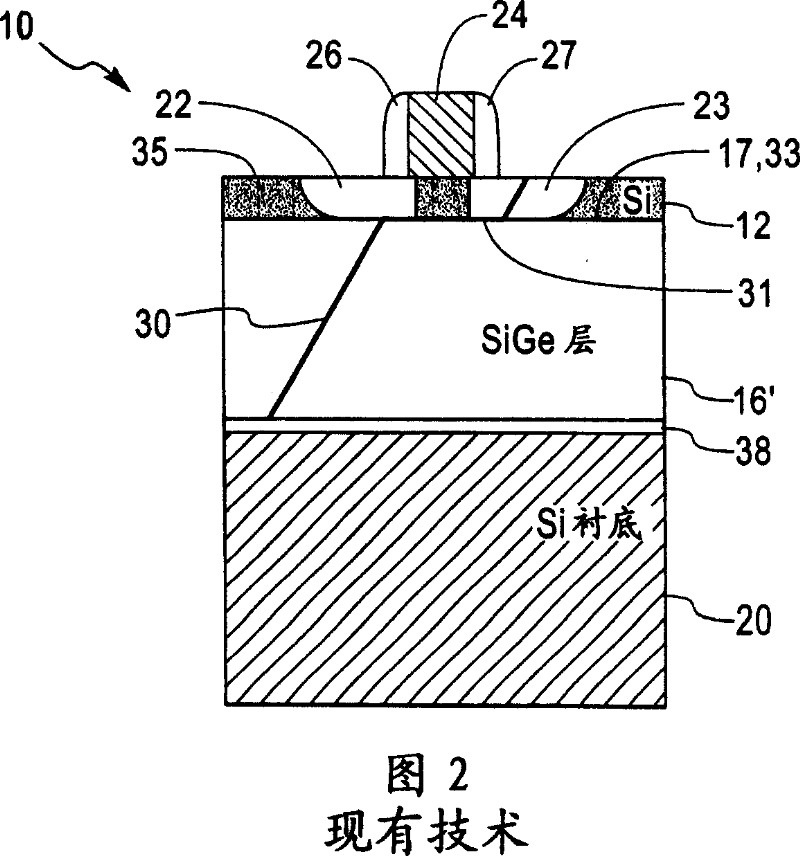
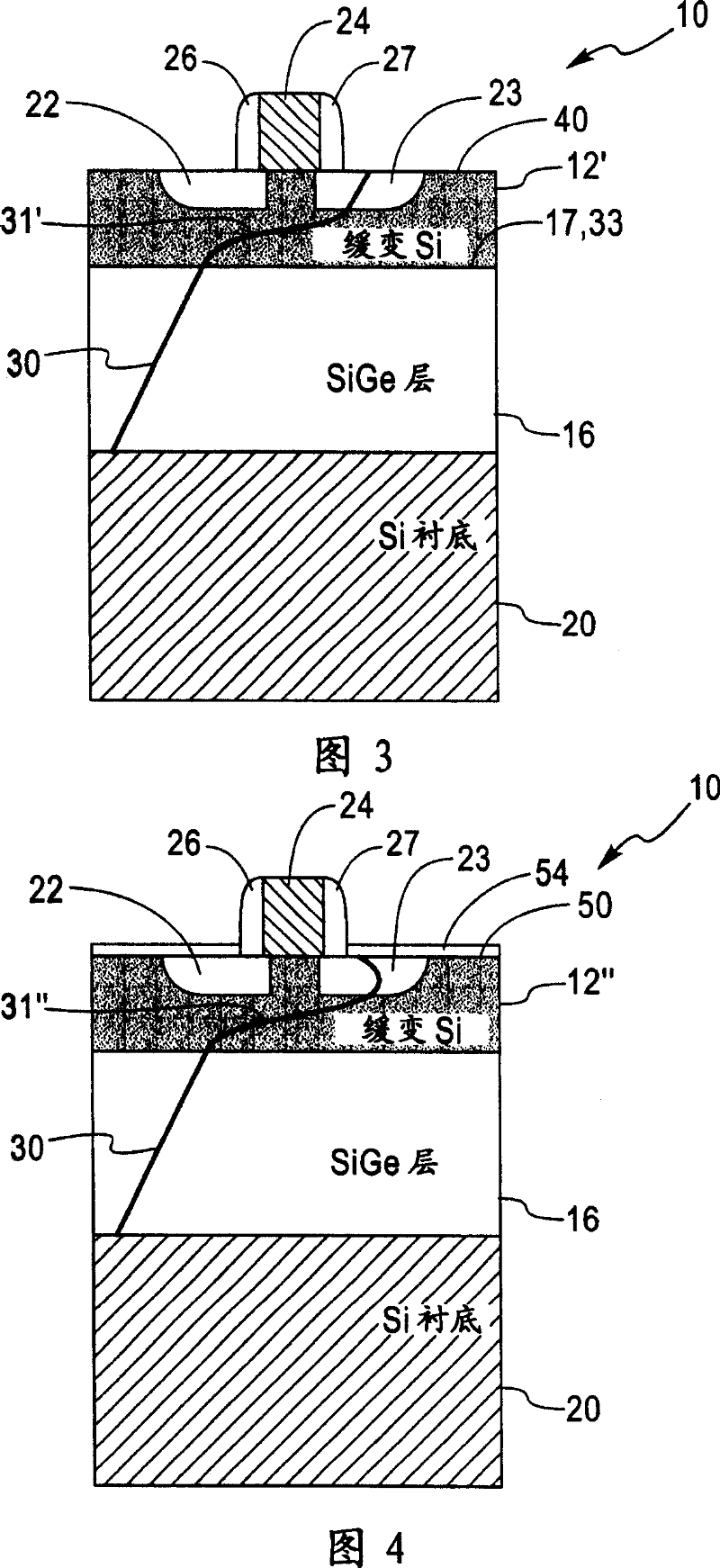
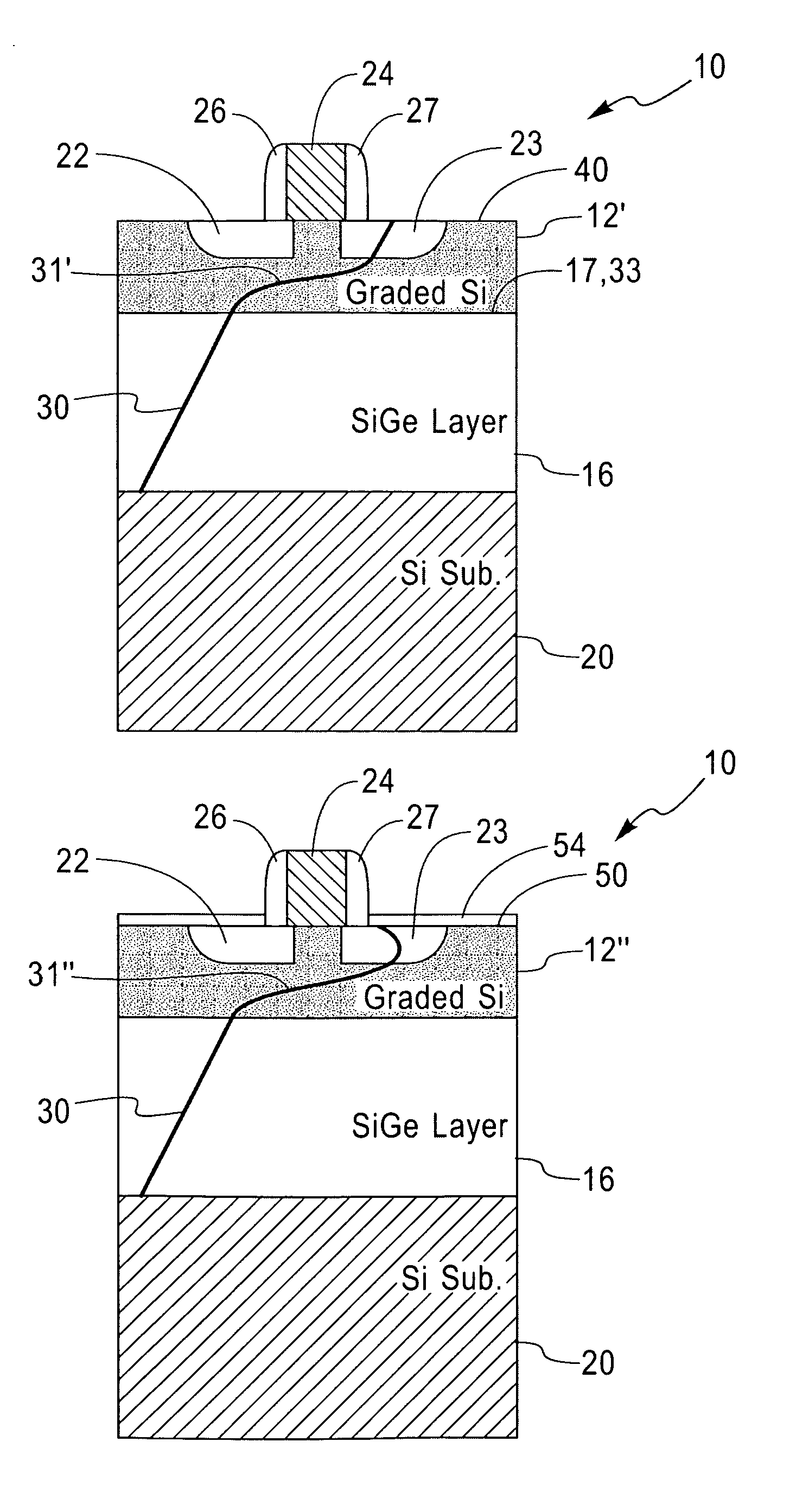
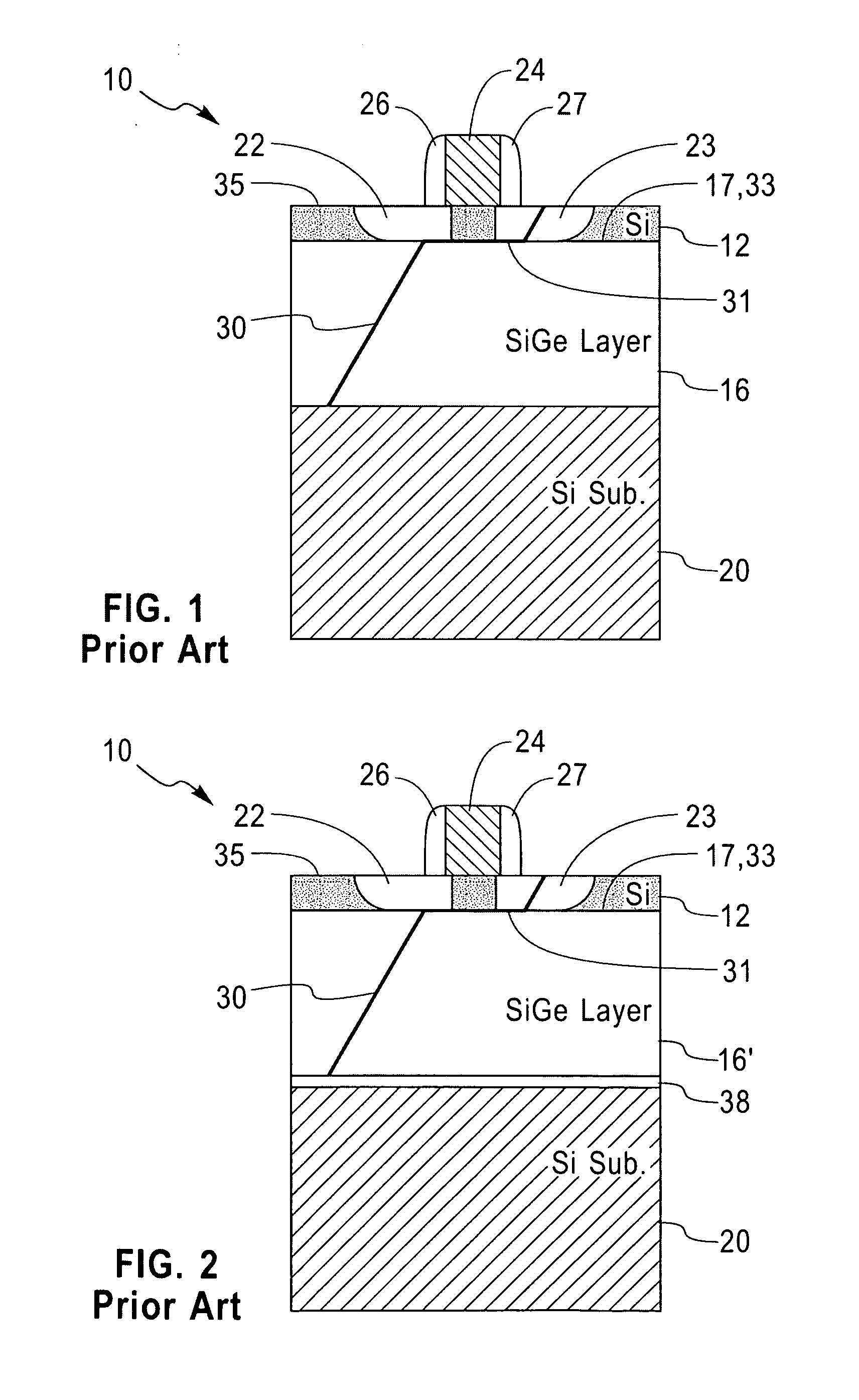
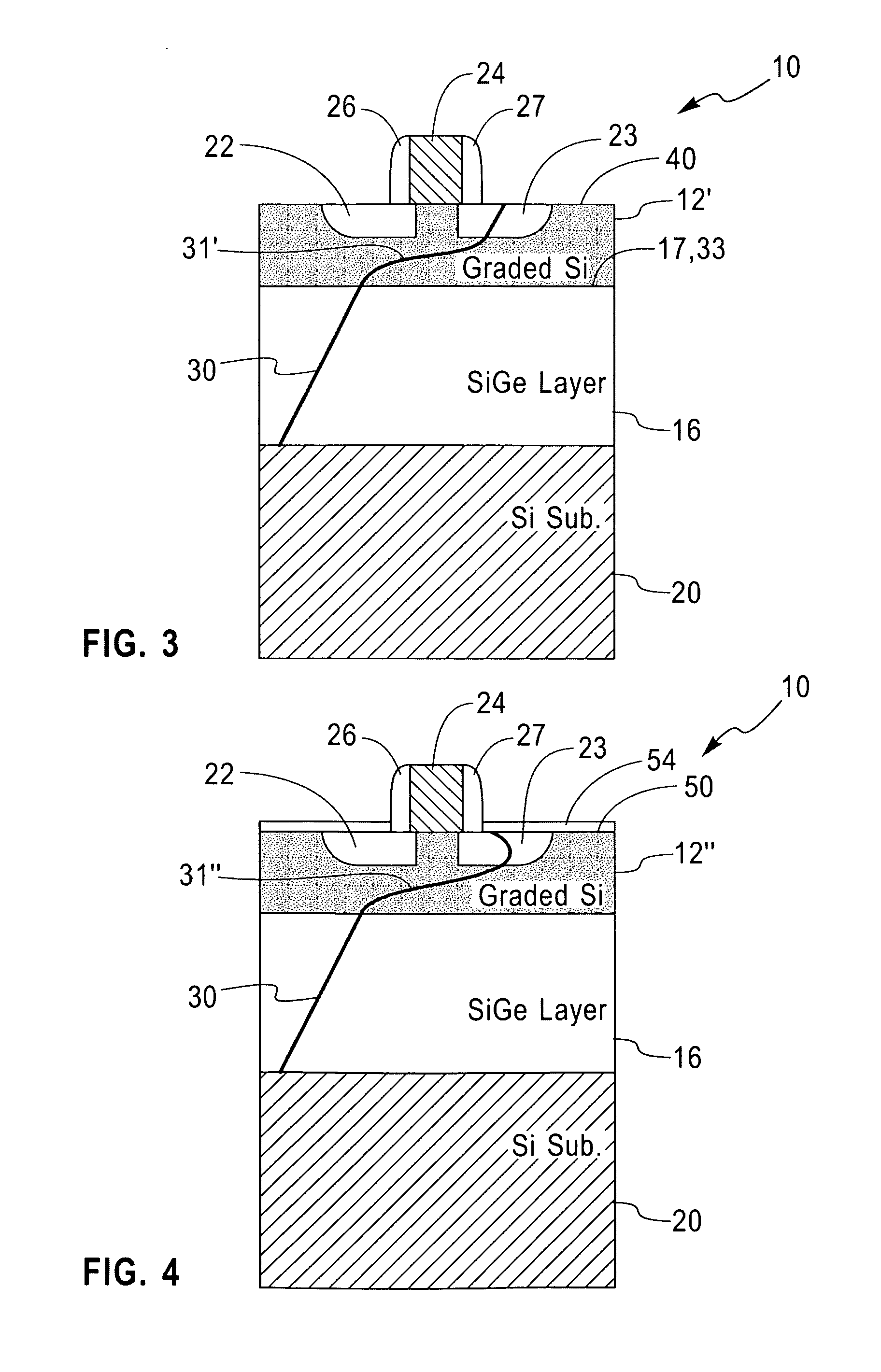
Structure and method for controlling the behavior of dislocations in strained semiconductor layers
InactiveCN101038933ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETOptoelectronics
A structure and method for controlling the behavior of dislocations in strained semiconductor layers is described incorporating a graded alloy region to provide a strain gradient to change the slope or curvature of a dislocation propagating upwards or gliding in the semiconductor layer in the proximity of the source and drain of a MOSFET. The upper surface of the strained semiconductor layer may be roughened and / or contain a dielectric layer or silicide which may be patterned to trap the upper end of dislocations in selected surface areas. The invention solves the problem of dislocation segments passing through both the source and drain of a MOSFET creating leakage currents or shorts therebetween.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Low-carbon micro-alloy steel with gradient ultra-fine grain structure and preparation method for same
Low-carbon micro-alloy steel with a gradient ultra-fine grain structure and a preparation method for the same belong to the technical field of processing and preparation of metal materials. The low-carbon micro-alloy steel with the gradient ultra-fine grain structure comprises, by mass, the ingredients including 0.08%-0.15% of C, 0.5%-1.5% of Mn, 0%-1.0% of Si, 0%-0.05% of Nb, 0%-0.1% of Ti as well as Fe and inevitable impurities. The preparation method comprises steps of smelting, forging, regular hot rolling and asynchronous hot rolling. During the asynchronous hot rolling, a plate is heatedto 950 DEG C-1,200 DEG C and then treated with heat preservation of 10-30 min; and the plate is processed with water quenching and then reaches a room temperature, so the product is obtained. The method is characterized in that an asymmetrical rolling compression-shear composite mechanism and a strain induced ferrite phase change mechanism are combined; a strain gradient and a dynamic phase change gradient are introduced; ultra-fine grains are obtained and an organizational form of gradient distribution of grain sizes along the thickness direction is obtained; and thus, plasticity and tenacity of a metal material are maintained; strength and hardness of the metal material are effectively enhanced; and comprehensive performance of the material is improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
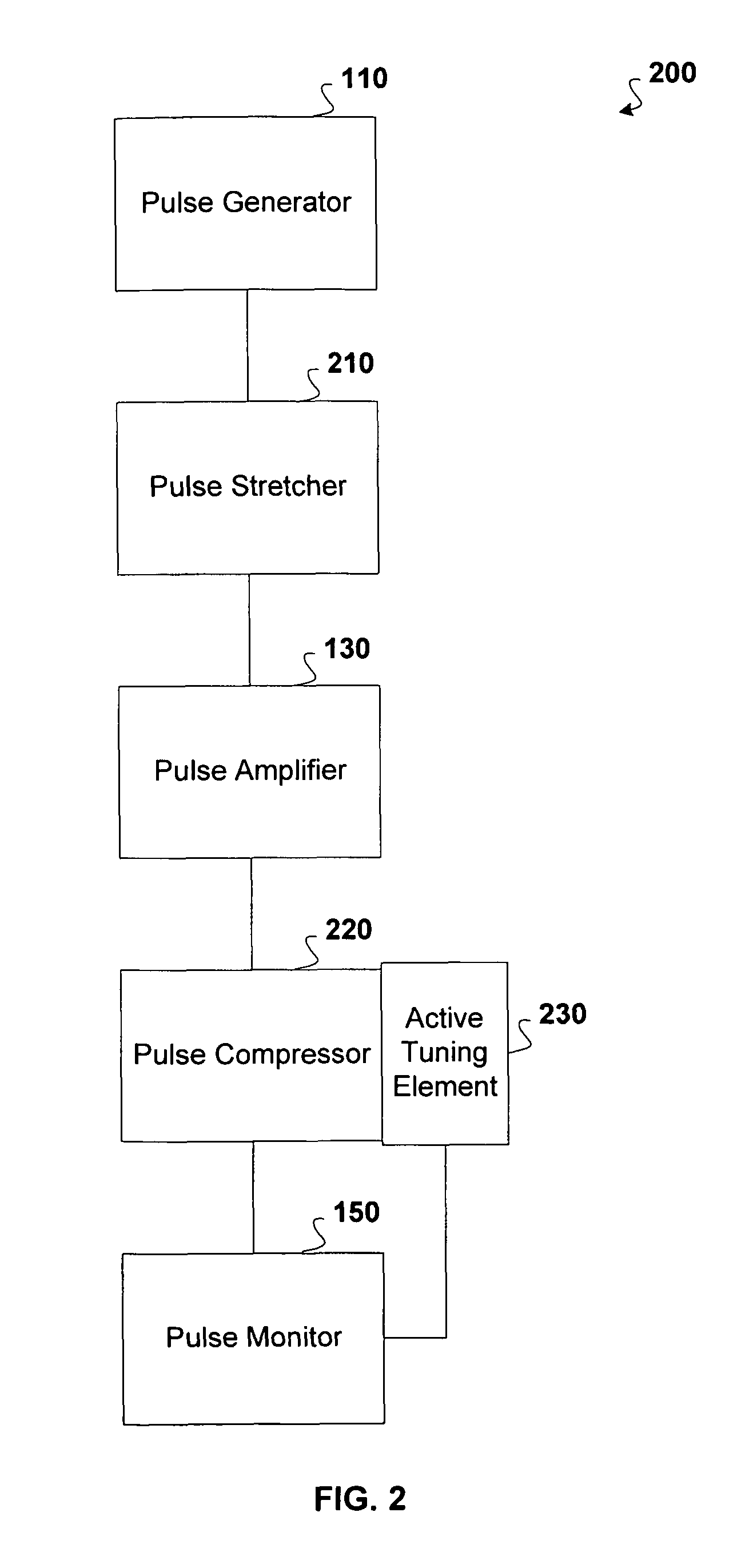
Active tuning of temporal dispersion in an ultrashort pulse laser system
A chirped pulse amplification (CPA) system and method is described wherein the dispersion of the system is tuned by actively tuning one or more system components, for example, using a temperature or strain gradient, or using actinic radiation. In other embodiments, an additional element, such as a modulator, is added to the CPA system to actively to tune the pulse. A pulse monitor is added to the system to measure an output pulse and provide feedback to one or more active tuning elements.
Owner:COHERENT INC
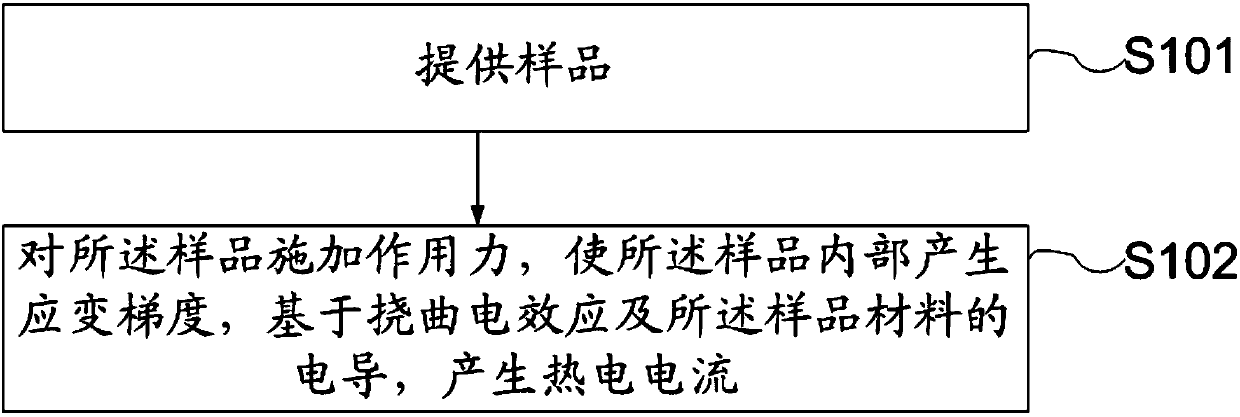
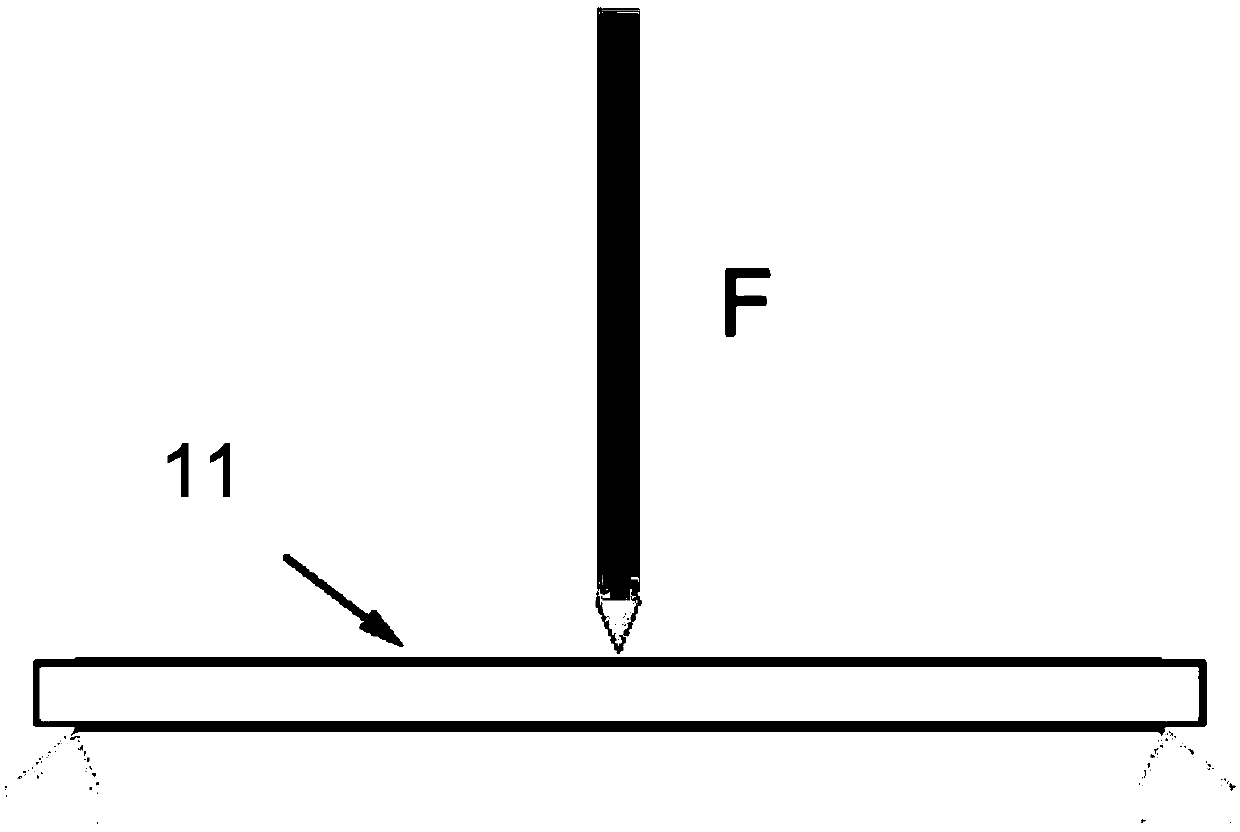
Thermoelectric conversion method
ActiveCN107946453ALow temperature environment requirementsReduce complexityThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentGenerators/motorsElectricityCoupling
The invention provides a thermoelectric conversion method, the thermoelectric conversion method comprises the following steps: providing a sample, wherein material of the sample is a dielectric substance; applying an acting force on the sample, enabling the inside of the sample to generate strain gradient, and generating a thermoelectric current based on flexoelectric effect and electric conductance in the material. The thermoelectric conversion method provided by the invention is based on coupling of the flexoelectric effect and the electric conductance and has no connection with variation ofenvironment temperature and temperature gradient. Uneven strain is generated in the sample material through methods, such as bending, thereby, flexoelectric electric field is generated, electric conductance of the sample material is caused, and the thermoelectric current is generated, relative to a method based on Seebeck effect or pyroelectric effect in the existing technology, the thermoelectric conversion method provided by the invention can generate thermoelectric current without dependence on temperature gradient or temperature variation, thereby can be adapted to more materials, has relatively lower requirement on temperature environment of thermoelectric conversion and consequently can expand application range of thermoelectric conversion.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Fiberoptic raster band width tuning device
InactiveCN1544974AWide reflection bandwidthWide range of bandwidthCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsGratingOptical fiber coupler
The invention relates to an optical fiber grating bandwidth tuning device, specially applying to tune the bandwidths of single or many optical fiber gratings, including optical fiber grating, elastic beam, single mode optical fiber, optical fiber coupler, matching liquid, etc. It pastes the optical fiber Prague grating on a side surface of the adjustable-curvature rectangular elastic beam by special glue in the inclined direction, makes the axis of the grating and the neutral surface of the elastic beam form a certain included angle and ensures the midpoint of the grating precisely situated on the neutral surface of the elastic beam. It has two grating pasting modes: if the elastic beam is a simple strutbeam, the grating is pasted on the side surface in the middle of the beam; if the elastic beam is a cantilever beam, the grating is pasted on the side surface near to the fixed end of the beam. When the elastic beam bends in the elastic range, because the layers at all heights on the beam produce different strains so as to cause the period change of all the grids on two sides of the grating center, it makes the grating generate strain gradient axially, accordingly resulting in the width change of the optical fiber grating. By changing the curvature of the elastic beam, it can implement the high-precision tuning of the optical fiber grating.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for measuring strain of connecting piece of pull rod linkage mechanism
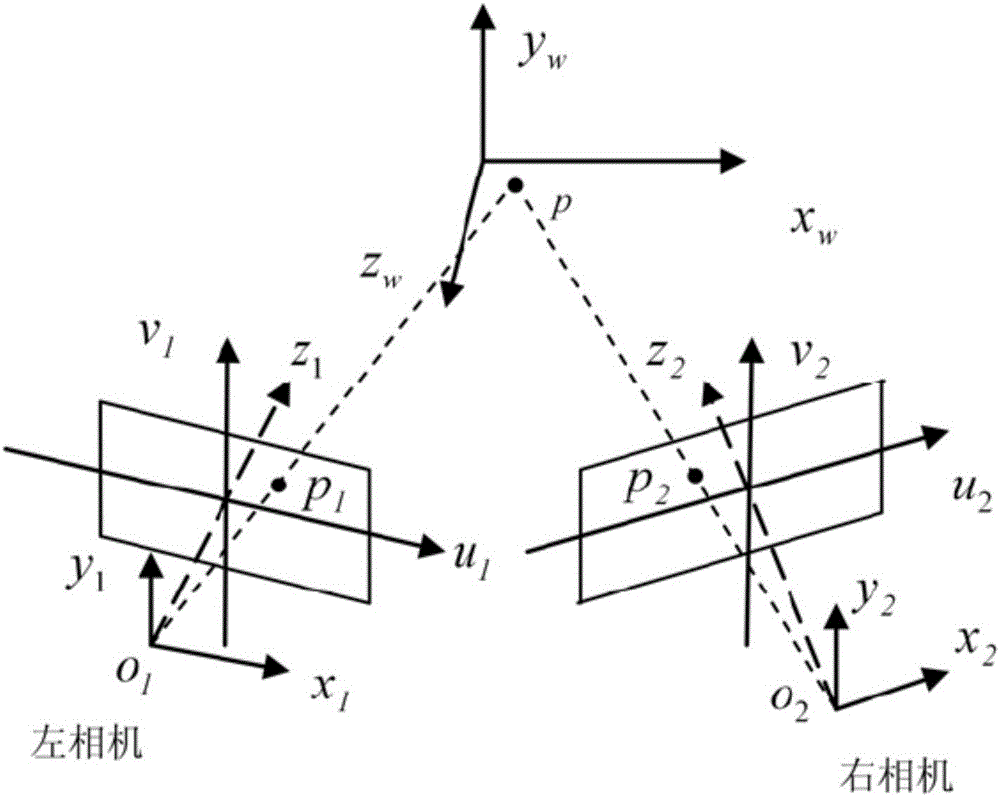
InactiveCN106091964AOvercoming the disadvantages of measurement methodsShorten the development cycleUsing optical meansParallaxFull field strain
The invention relates to a method for measuring the strain of the connecting piece of a pull rod linkage mechanism. The method captures a sensed image of a connection position by using double cameras, may measure the strain gradient of the curved connecting piece, and comprises a step 1 of establishing a non-contact measurement coordinate system; a step 2 of discretizing a curved structure to be measured in order to divide the curved structure to be measured into a plurality of area units, observing the area units by using the double cameras at two different points of sight in order to obtain the sensed images, and obtaining the 3D morphological information of the surface of an object by computing and analyzing the parallax of the area units in different sensed images; a step 3 of computing the spatial positions, in the measurement coordinate system, of measuring points in the curved surface to be measured; and a step 4 of performing subarea point-by-point fitting on a displacement field by using a fitting process to obtain full-field strain. The method for measuring the strain of the connecting piece of a pull rod linkage mechanism overcomes the defects of a conventional strain gage measurement method, shortens a development period, and reduces development cost.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Valve stress dispersion based welding method
InactiveCN103752995AGuaranteed to be smooth and tidyImprove fatigue resistanceArc welding apparatusWorkpiece edge portionsStress concentrationMachining
The invention discloses a valve stress dispersion based welding method. The method comprises machining a semi-spherical opening at the corresponding positions of bonnet and valve body connection portions through a machining method on the basis of conventional bonnet and valve body welding processes respectively to form a corresponding spherical opening, wherein the size and the position of the opening is adjusted according to the valve model, utilization condition and application place particular actual conditions; performing welding connection on the bonnet and the valve body through pulse TIG welding to enable the weld joint root gap sharpness to be reduced to the minimum. According to the method, the weld joint root gap sensitivity is reduced by reducing the weld toe gap sharpness; when a valve is under the external load action, the stress concentration factor and the strain gradient at the weld toe are reduced apparently, so that the weld joint root stress concentration problem is solved, the weld joint quality and the anti-fatigue performance are improved, and the valve service life is prolonged.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Annular shear type deflection electric acceleration sensor and laminated structure acceleration sensor
ActiveCN109212264ASimple designReduced Sensitivity EffectsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDielectricLinear relationship
The invention discloses an annular shear type deflection electric acceleration sensor and a laminated structure acceleration sensor. The annular shear type deflection electric acceleration sensor comprises a support rod, output terminals, an annular mass block and an annular sensing module made of a deflection dielectric material; the inner ring and the outer ring of the annular sensing module areplated with a metal film; the inner ring of the annular sensing block is arranged at the upper end of the support rod; the inner ring of the annular mass block is fixed at the outer ring of the annular sensing block; and the metal films of the inner ring and the outer ring of the annular sensing block are connected with two output terminals respectively through wires. As the acceleration is measured by using a linear relationship between a strain gradient which is generated by the deflection dielectric material along the axial direction and electric charge which is generated based on the deflection electric effect under the action of a shearing stress generated by the annular mass block, measurement of vibration is accordingly realized.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Method for evaluating propriety of molding sheared edge
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a technique for more precisely evaluating the propriety of forming a sheared material edge after preforming. Through a hole enlargement test on a metal plate after preforming, a strain gradient at a sheared edge is changed and a plurality of data of the deformation limit equivalent strain amount with respect to the strain gradient are calculated,and a relationship of a stretch flange deformation limit equivalent strain to the strain gradient is calculated from the plurality of data and the amount of pre-deformation equivalent strain. The propriety of forming a sheared edge for a metal plate subjected to pre-deformation by preforming is evaluated from a forming limit line L or formable region R of the sheared edge from the calculated relationship.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
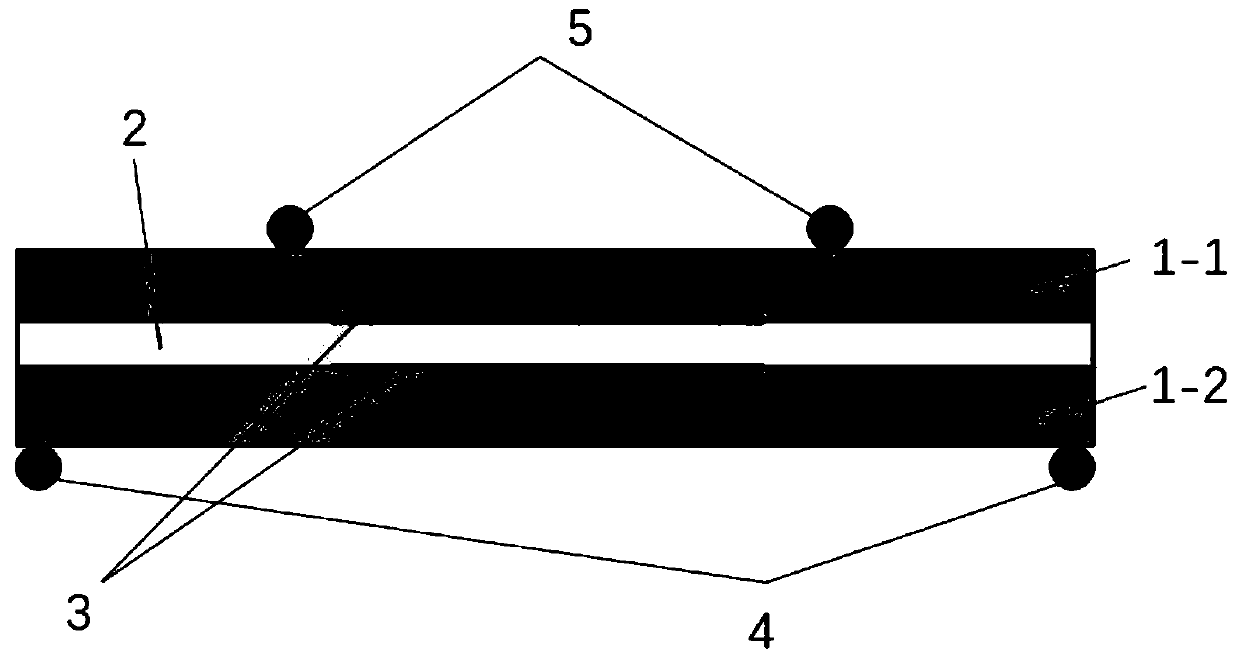
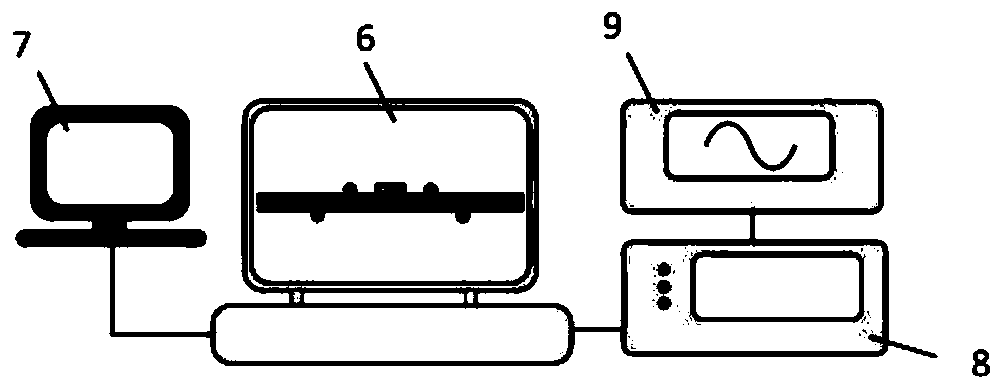
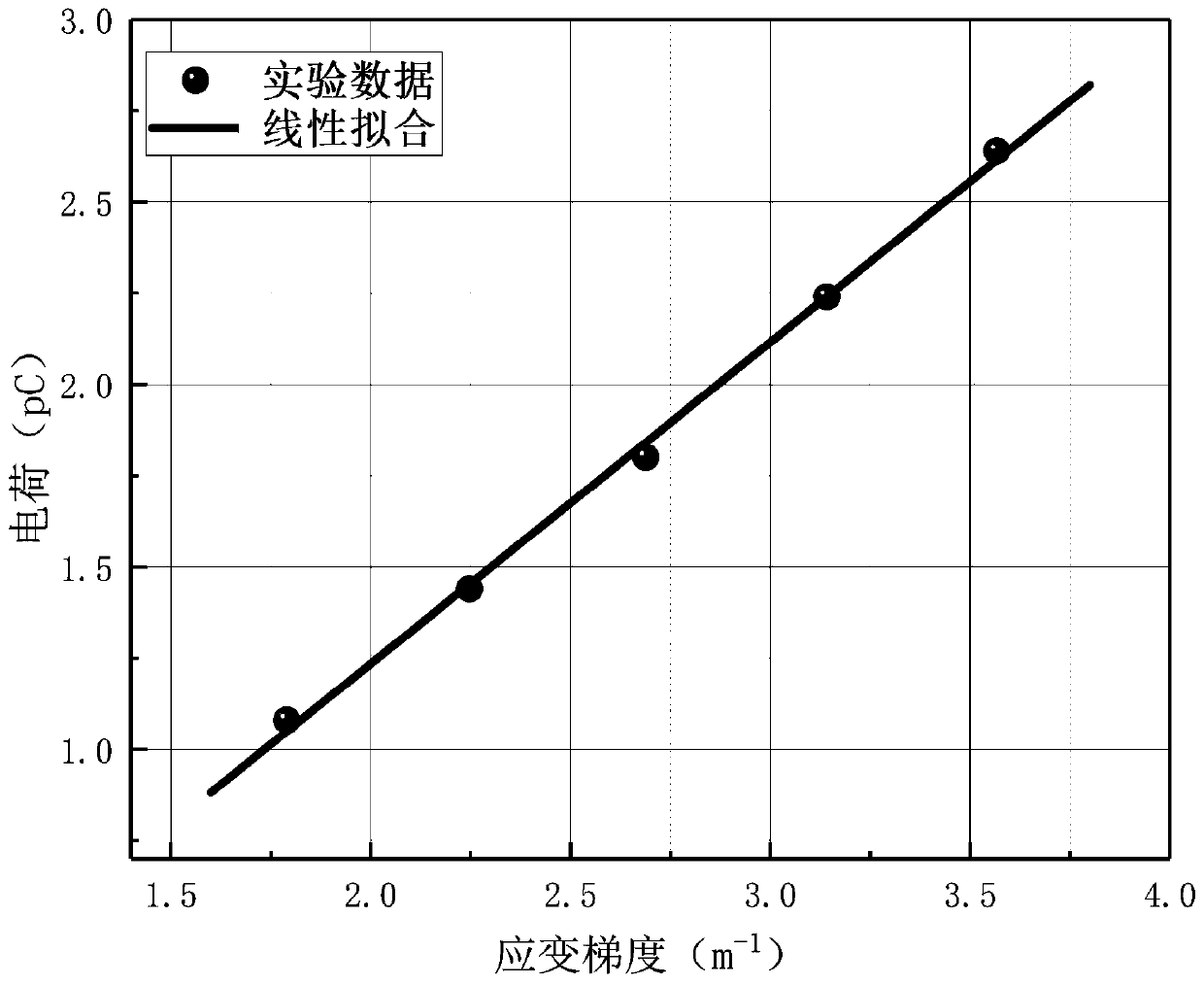
Thin film material flexoelectric coefficient measuring device capable of regulating and controlling strain gradient and method thereof
ActiveCN110988494AAvoid the problem of measuring non-uniform strain gradientsWith regulationElectrical measurementsThin membraneStructural engineering
The invention discloses a thin film material flexoelectric coefficient measuring device capable of regulating and controlling strain gradient and a method thereof. The device having a sandwich structure formed by two layers of matrix beams with the same lengths, widths and thicknesses and a test film which is arranged between the two layers of beams and has the same length and width as the beams comprises a four-point 1 / 4 bending clamp including two upper pressing heads and two stress supporting pieces, a small-load loading instrument for loading the four-point 1 / 4 bending clamp, a controllerbeing connected with the small-load loading instrument and being used for controlling the loading force and loading frequency, and a charge amplifier and an oscilloscope sequentially connected with the small-load loading instrument. Under loading control of four-point 1 / 4 bending clamp force application points, namely two upper pressing heads, regulation and control of strain gradient in flexoelectric coefficient measurement are realized; the method is simple, the structural model is low in cost and easy to implement, the difficulty of strain gradient control in flexoelectric coefficient measurement is reduced, and the difficulty of flexoelectric coefficient measurement of the thin film material is reduced.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Structure and method for controlling the behavior of dislocations in strained semiconductor layers
InactiveUS20070218597A1Reduce probabilityMitigating dopant diffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETSalicide
A structure and method for controlling the behavior of dislocations in strained semiconductor layers is described incorporating a graded alloy region to provide a strain gradient to change the slope or curvature of a dislocation propagating upwards or gliding in the semiconductor layer in the proximity of the source and drain of a MOSFET. The upper surface of the strained semiconductor layer may be roughened and / or contain a dielectric layer or silicide which may be patterned to trap the upper end of dislocations in selected surface areas. The invention solves the problem of dislocation segments passing through both the source and drain of a MOSFET creating leakage currents or shorts therebetween.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com