Low-carbon micro-alloy steel with gradient ultra-fine grain structure and preparation method for same
A technology of ultra-fine grain and alloy steel, applied in the field of low-carbon micro-alloy steel with gradient ultra-fine grain structure and its preparation, can solve the problems of complex process control, unfavorable steel materials, and inability to undergo phase transformation of samples, and achieve the production process The effect of simplicity, excellent mechanical properties, excellent work hardening ability and formability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036]A low-carbon microalloy steel plate with a gradient ultra-fine grain structure, which contains chemical components and the mass percentages of each chemical component are: C is 0.12%, Mn is 1.35%, Si is 0.49%, Nb is 0.035%, and Ti is 0.019% %, the balance is Fe and unavoidable impurities.
[0037] A method for preparing a low-carbon microalloy steel plate with a gradient ultrafine grain structure, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0038] (1) Melting: according to the chemical composition and ingredients of the above-mentioned low-carbon microalloy steel plate with gradient ultra-fine grain structure, it is added to a vacuum induction melting furnace, melted at a temperature of 1650 ° C, and cast to obtain a 50 kg round ingot;
[0039] (2) Forging: heat a 50kg round ingot at 1150°C for 3 hours, forge it, and air-cool it to room temperature to obtain a 100mm×100mm square ingot. Cut the square ingot into 30mm×100mm×100mm to obtain a cut square ingot;
[0040] ...
Embodiment 2
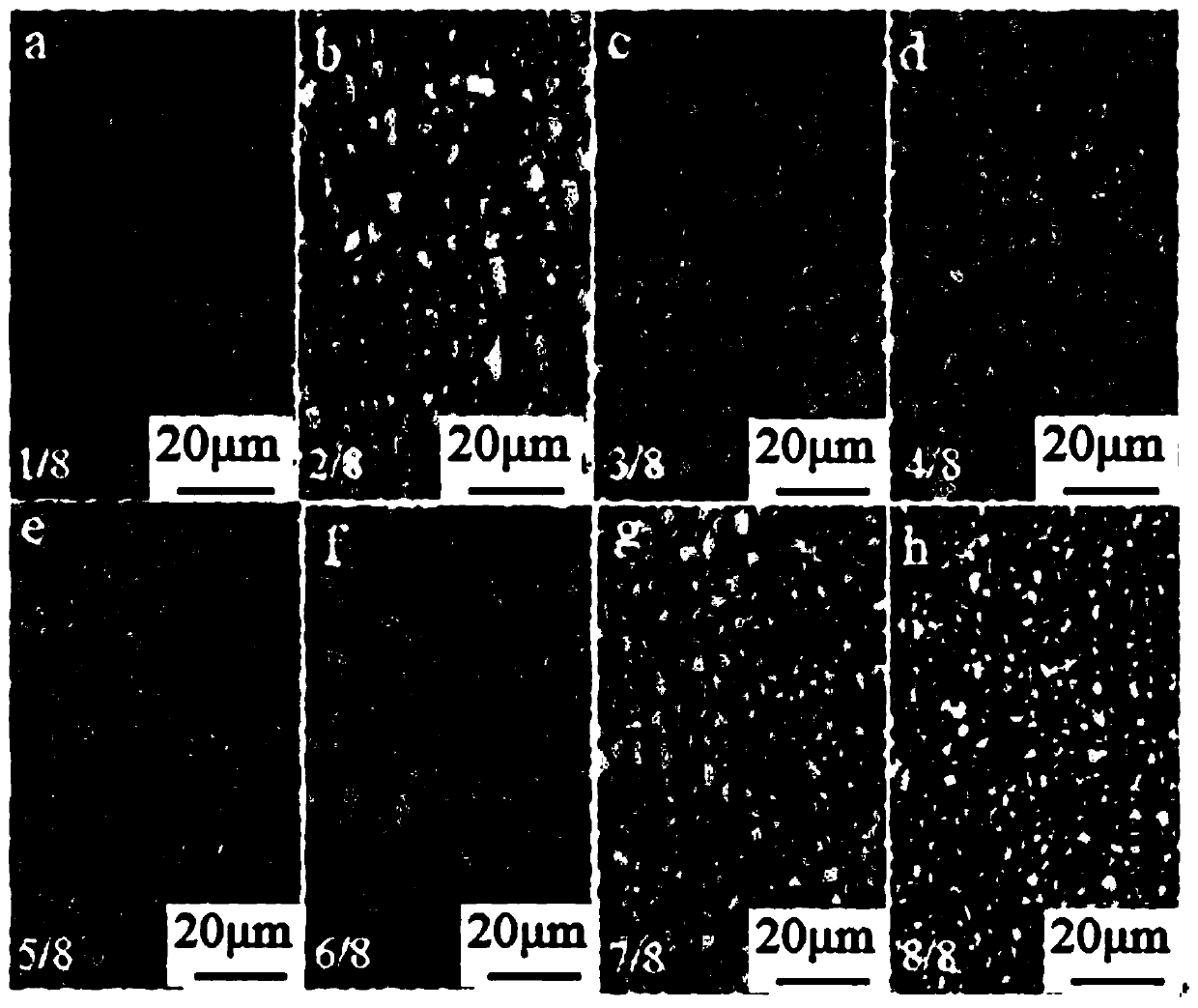
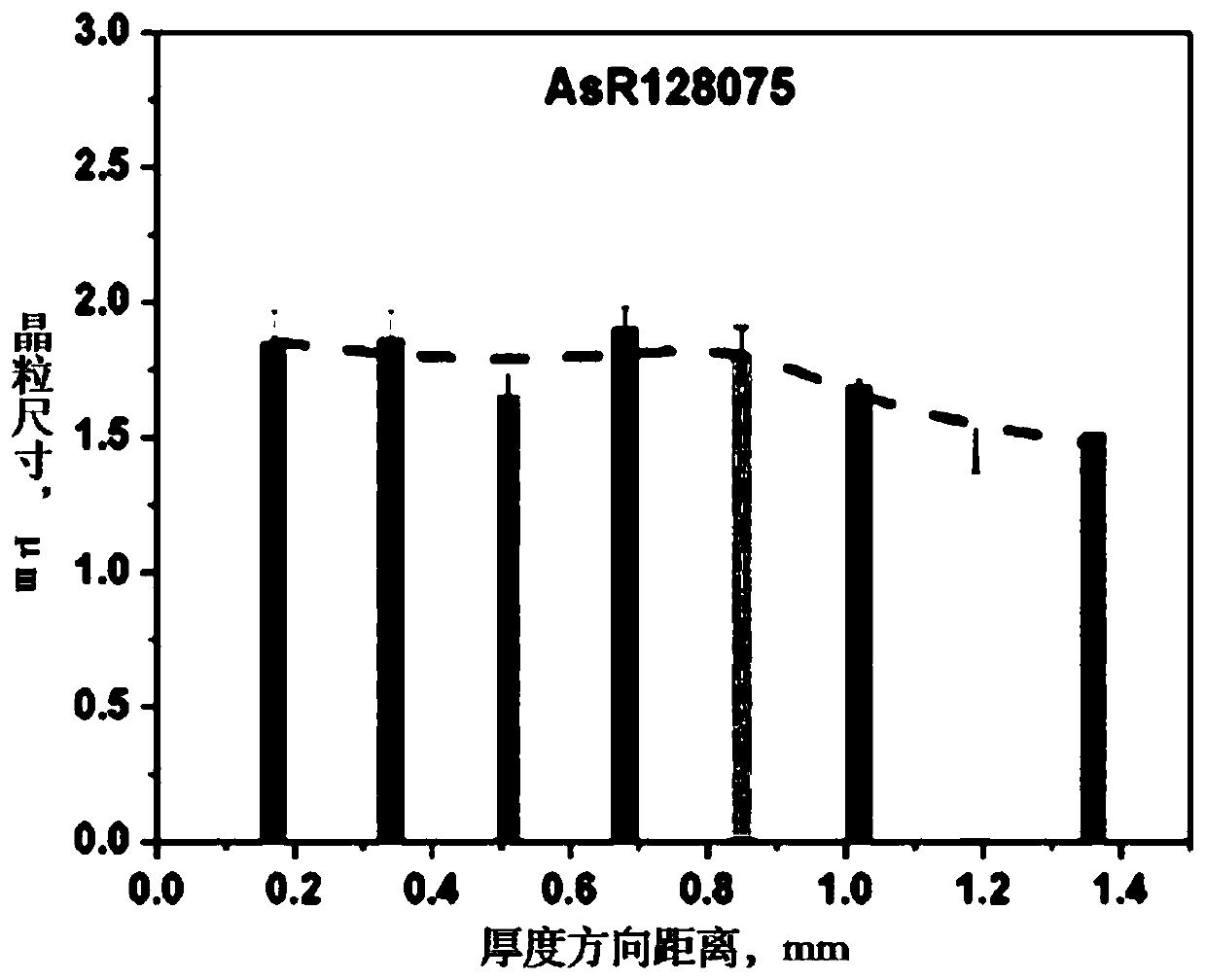
[0047] A kind of low-carbon microalloy steel plate with gradient ultra-fine grain structure. After the same smelting, forging, and conventional hot rolling as in Example 1, the hot-rolled steel plate is heated at 950 ° C, kept for 15 minutes, and asynchronously rolled at 800 ° C. The ratio is 2:1, the reduction is 75%, and a steel plate with a thickness of 1.50 mm is obtained, and then water quenched to room temperature to obtain a low-carbon microalloy steel plate with a gradient ultrafine grain structure. Its mechanical performance parameters are: tensile strength is 937MPa, yield strength is 662MPa, elongation is 21.6%, uniform elongation is 18%, and yield ratio is 0.71. The low-carbon microalloy steel plate with gradient ultra-fine grain structure prepared in this embodiment is along the thickness direction 1 / 8 (a), 2 / 8 (b), 3 / 8 (c), 4 / 8 (d), 5 / 8 ( The metallographic microstructure corresponding to the regions e), 6 / 8(f), 7 / 8(g) and 8 / 8(h) are shown in image 3 , the grai...
Embodiment 3
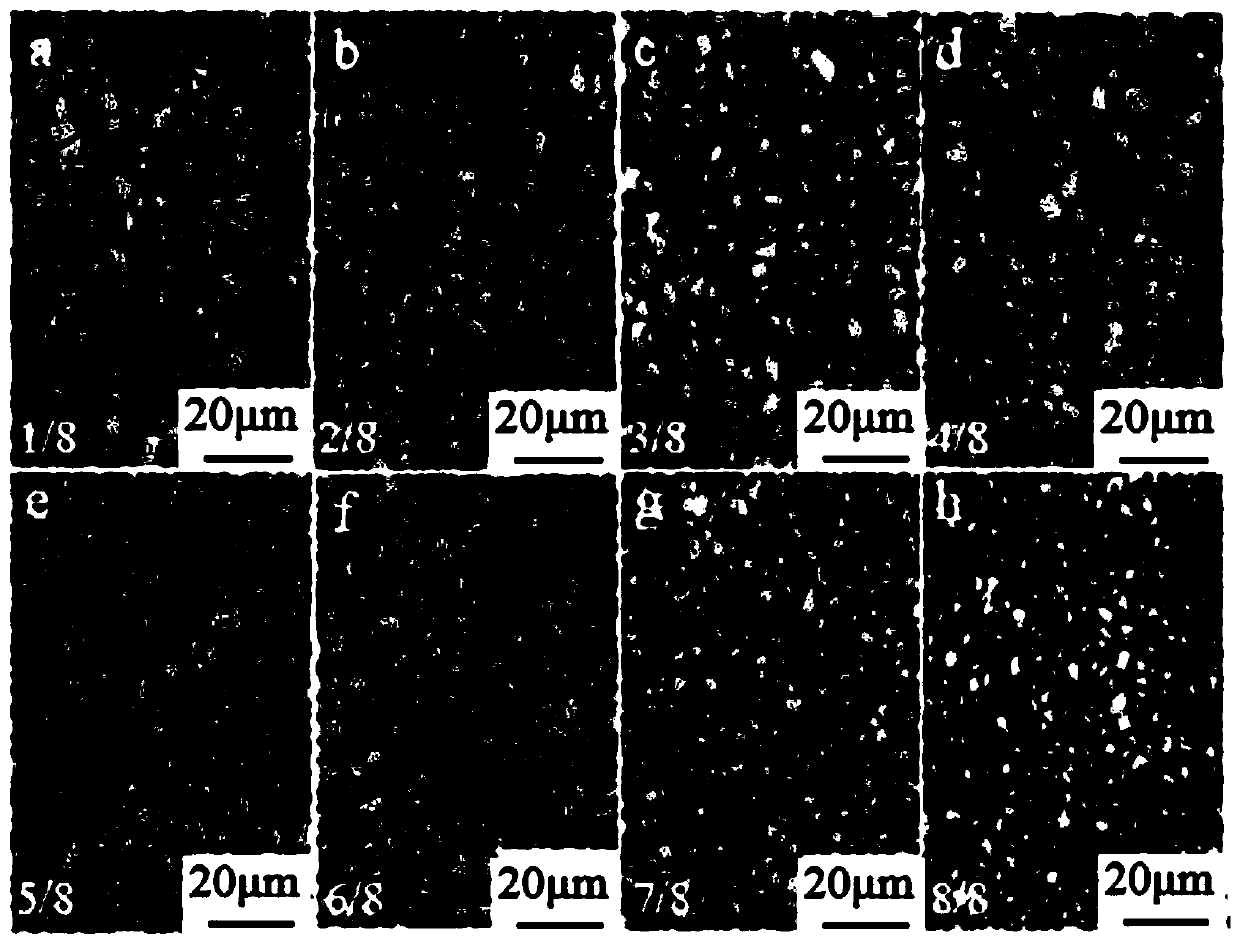
[0049] A kind of low-carbon microalloy steel plate with gradient ultra-fine grain structure. After the same smelting, forging, and conventional hot rolling as in Example 1, the hot-rolled steel plate is heated at 950°C, kept for 15 minutes, and asynchronously rolled at 750°C. The ratio is 2:1, the reduction is 75%, and a steel plate with a thickness of 1.50 mm is obtained, and then water quenched to room temperature to obtain a low-carbon microalloy steel plate with a gradient ultrafine grain structure. Its mechanical performance parameters are: tensile strength is 905MPa, yield strength is 628MPa, elongation is 16.8%, uniform elongation is 13.4% and yield ratio is 0.73. The low-carbon microalloy steel plate with gradient ultra-fine grain structure prepared in this embodiment is along the thickness direction 1 / 8 (a), 2 / 8 (b), 3 / 8 (c), 4 / 8 (d), 5 / 8 ( The metallographic microstructure corresponding to the regions e), 6 / 8(f), 7 / 8(g) and 8 / 8(h) are shown in Figure 5 , the grain ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com