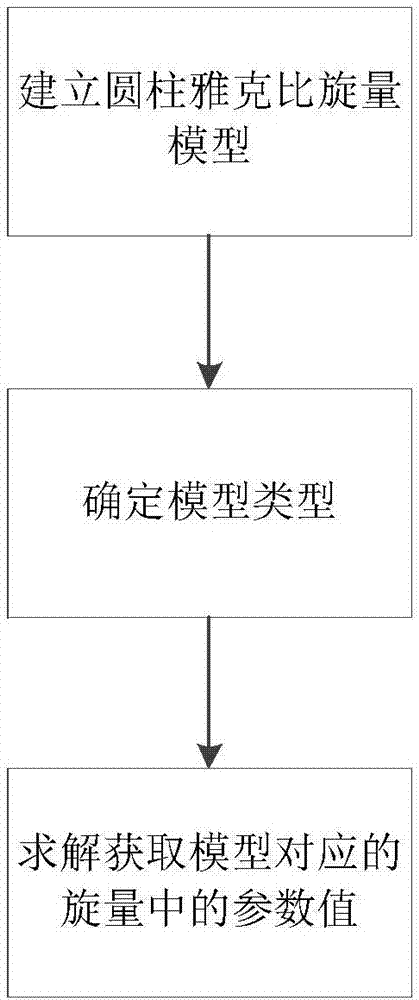
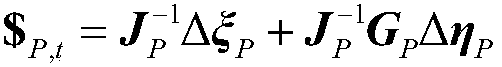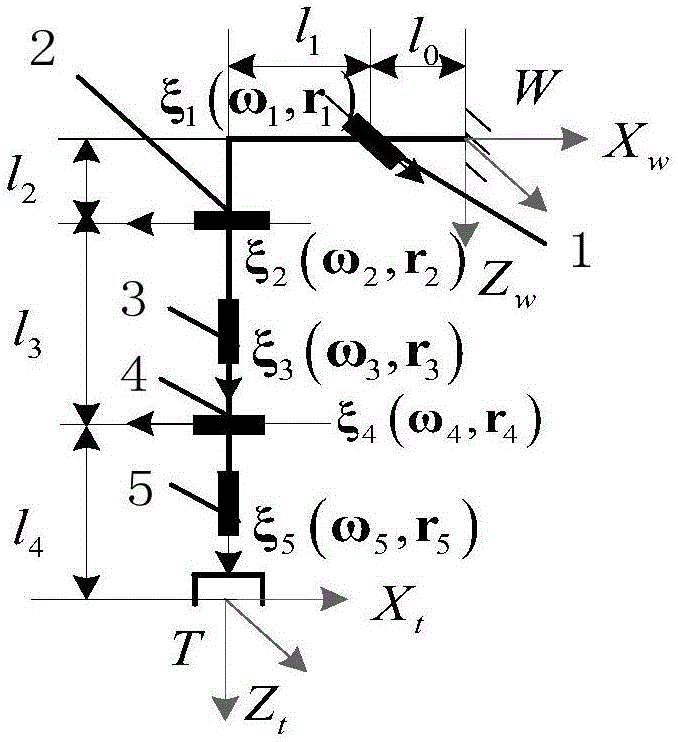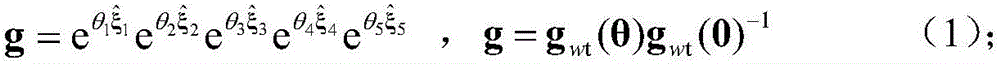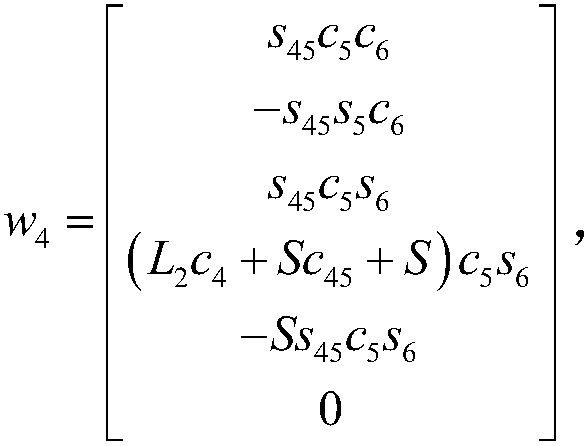Patents
Literature
52 results about "Spinor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
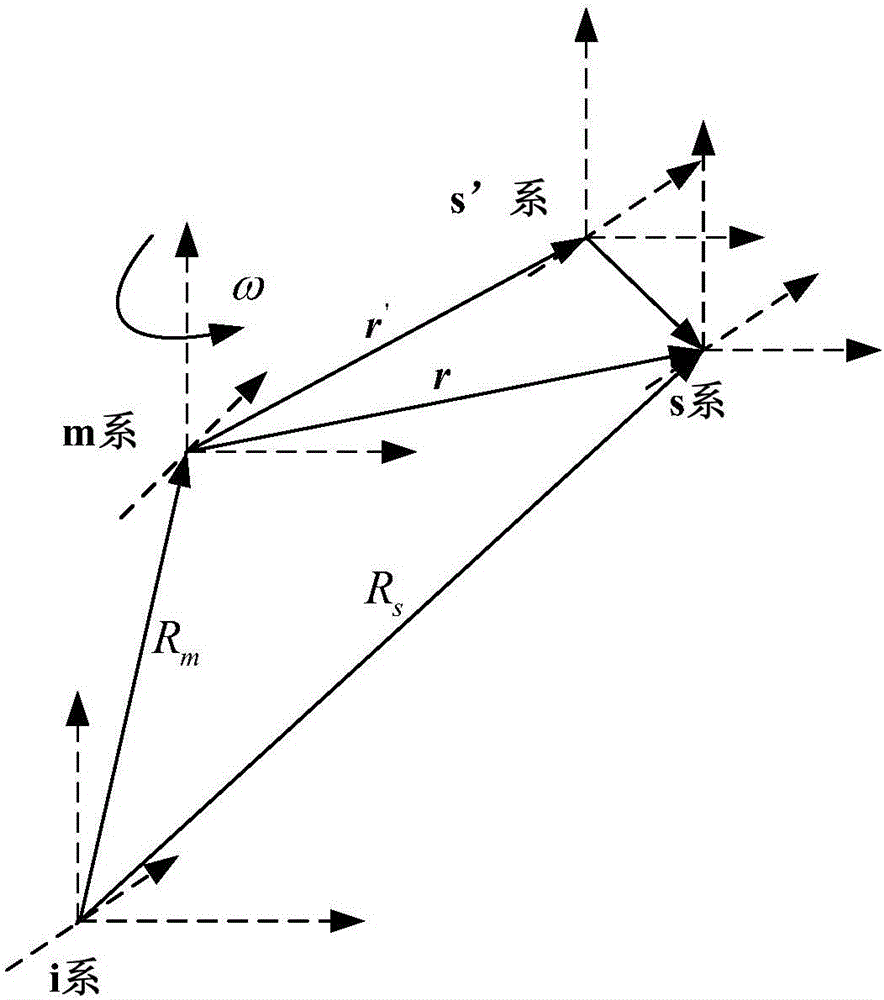
In geometry and physics, spinors /spɪnɔːr/ are elements of a (complex) vector space that can be associated with Euclidean space. Like geometric vectors and more general tensors, spinors transform linearly when the Euclidean space is subjected to a slight (infinitesimal) rotation. However, when a sequence of such small rotations is composed (integrated) to form an overall final rotation, the resulting spinor transformation depends on which sequence of small rotations was used: unlike vectors and tensors, a spinor transforms to its negative when the space is continuously rotated through a complete turn from 0° to 360° (see picture). This property characterizes spinors: spinors can be viewed as the "square roots" of vectors.
Movement flexibility comprehensive evaluation and optimization method of redundant robot
ActiveCN105956297AGood reference valueSpecial data processing applicationsGenetic algorithmsPareto efficiencyStep test
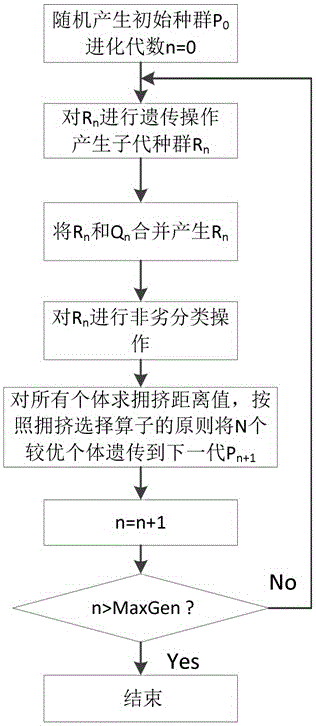
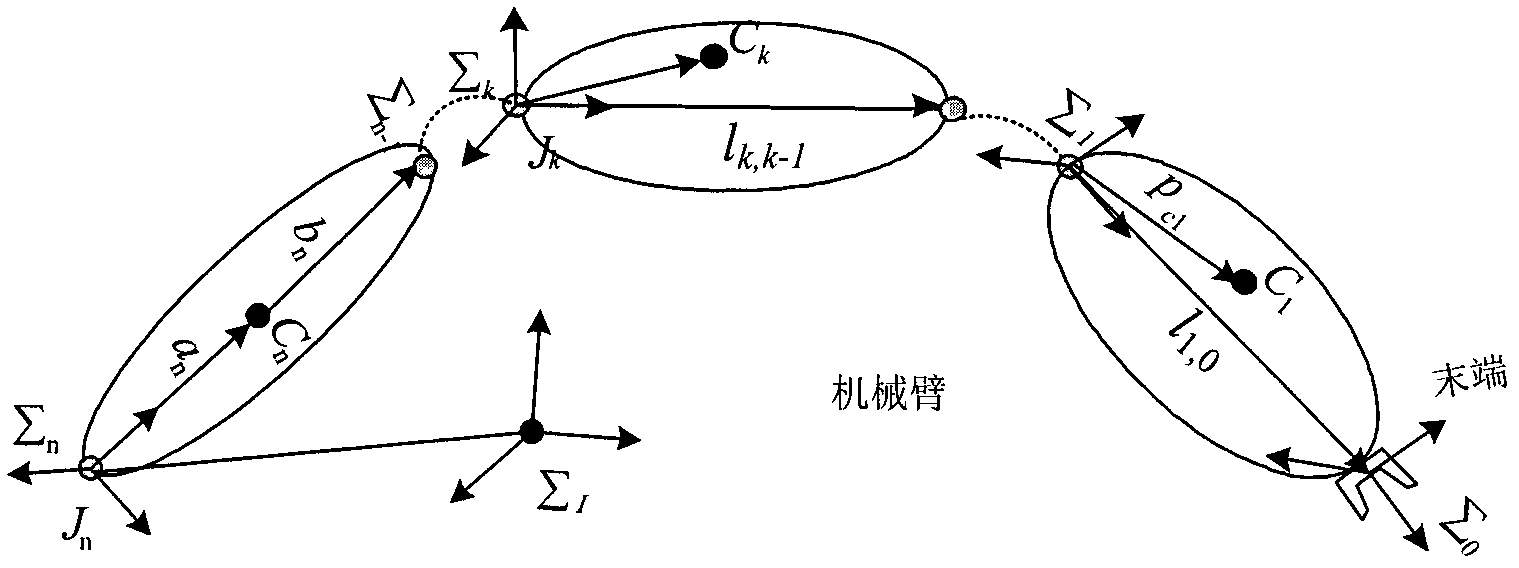
The invention discloses a tow placement robot with a redundant joint. The spinor theory is used for establishing the kinematic jacobian matrix of the robot; for comprehensively evaluating the flexibility index of the robot, three indexes of the condition number, the manipulability and the minimum singular value are modelled as three target functions after being changed, and the target functions are optimized through the adoption of an improved multi-target genetic algorithm and the introduction of Pareto efficiency; performing the data analysis on the optimized Pareto first front-end optimal solution set, describing the relation among the indexes using related coefficients, when finding the performance optimization on the tow placement robot, necessarily considering the mutual relation of the indexes, and finally acquiring the tow placement robot working space region with the optimal comprehensive performance. The simulation result proves that the operation of performing the genetic algorithm optimization and application of the multi-target using the Pareto efficiency is reliable and efficient, and lays the foundation for the next step test research of the tow placement robot; and meanwhile, the operation provides good reference value for the movement flexibility performance analysis and optimization of other serial robots.
Owner:JINLING INST OF TECH
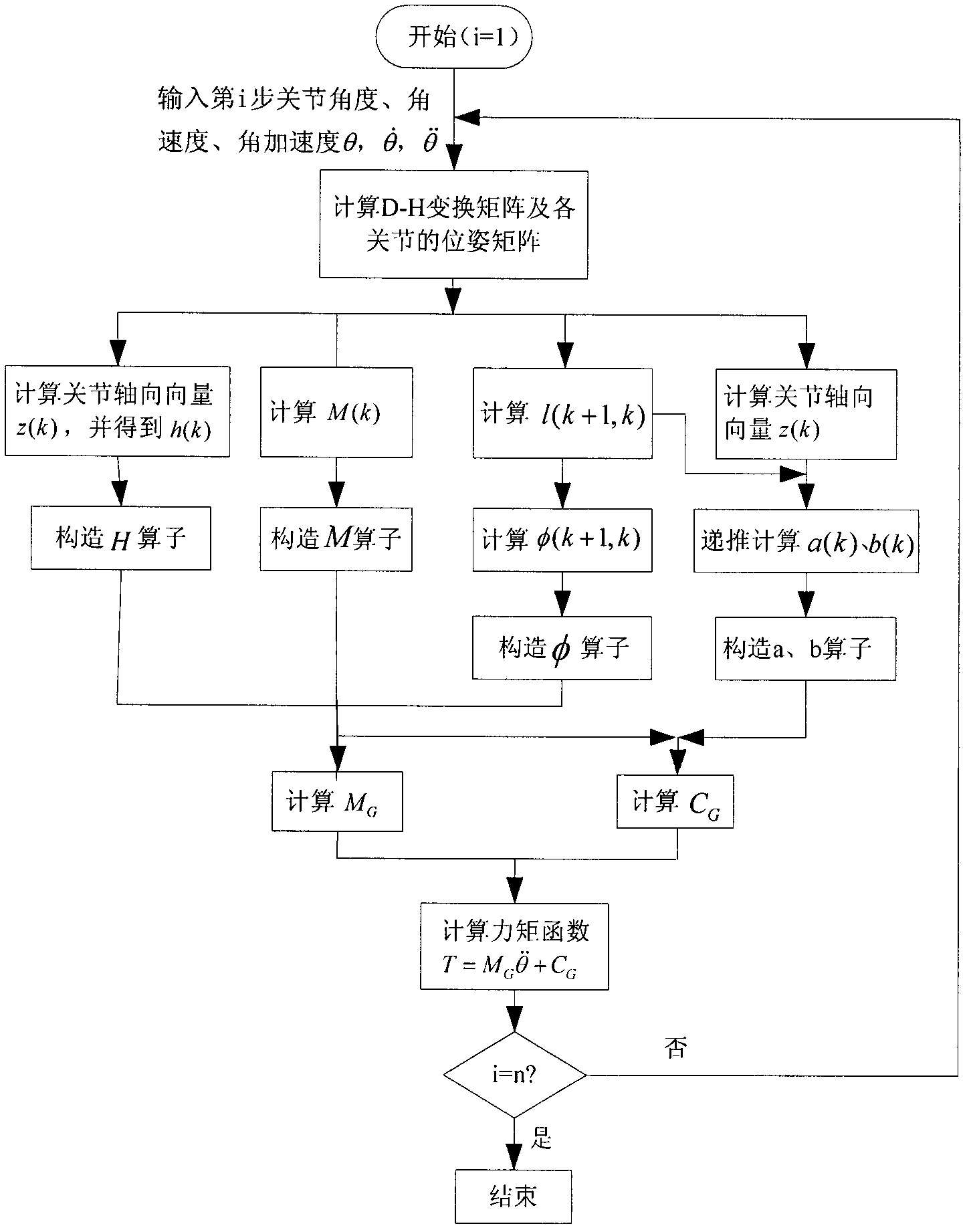
Efficient dynamic modeling method for multi-degree of freedom (multi-DOF) mechanical arm
InactiveCN102207988AReduce computational complexityImproving the efficiency of positive dynamics calculationsSpecial data processing applicationsComputational problemInertial mass
The invention discloses an efficient modeling method for a multi-degree of freedom (multi-DOF) mechanical arm. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: describing speed, acceleration, force and moment of each joint of the mechanical arm by using the screw theory; performing inverse dynamic modeling on the mechanical arm by using the spatial operator algebraic theory; and obtaining a generalized inertial mass matrix of the mechanical arm and a factorization form of the inverse matrix of the mechanical arm by using a Kalman filter smoothing method so as to obtain an efficient lower dynamic model. According to the method, the efficient dynamic calculation problem of the multi-DOF mechanical arm is solved, and the calculation efficiency of the method is first power magnitude order of the degree of freedom of the mechanical arm; meanwhile, the method has strong theoretical property, intuitive expression form and definite physical significance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
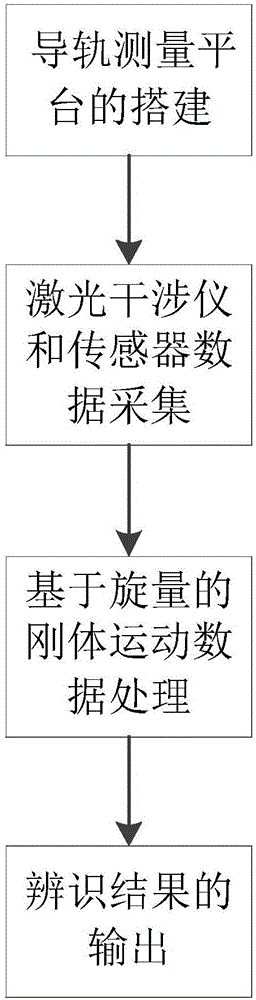
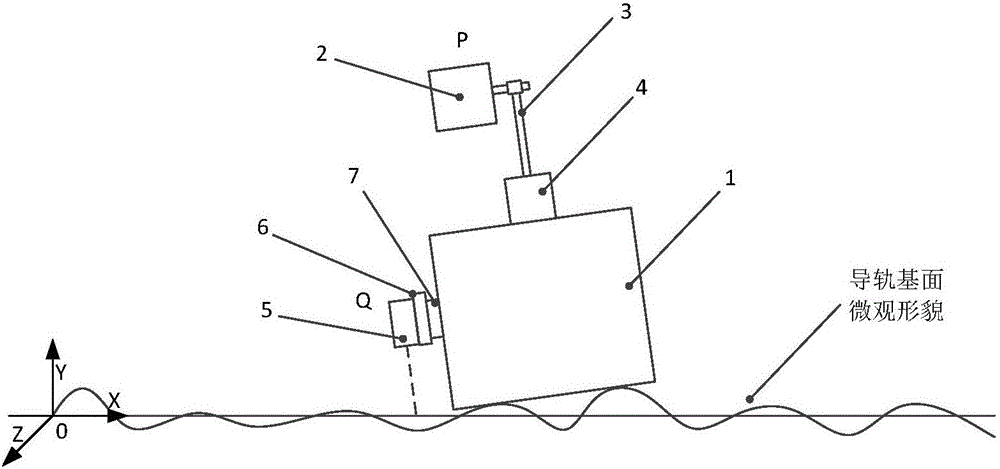
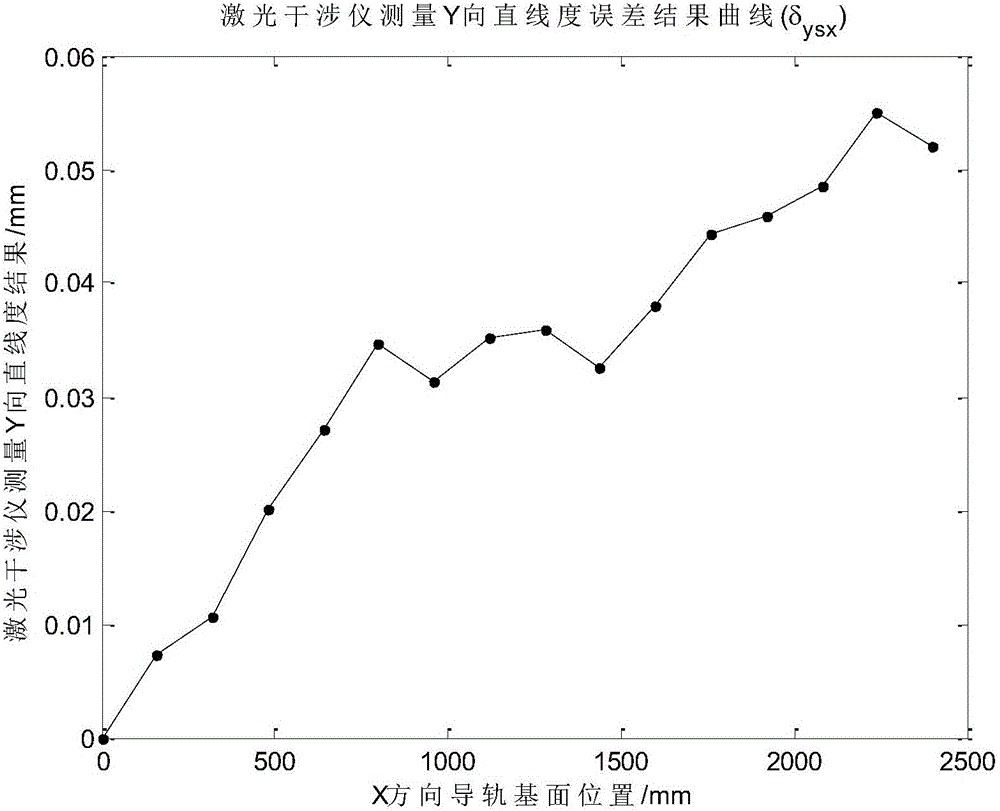
Guide rail basal plane straightness error decoupling and identifying method
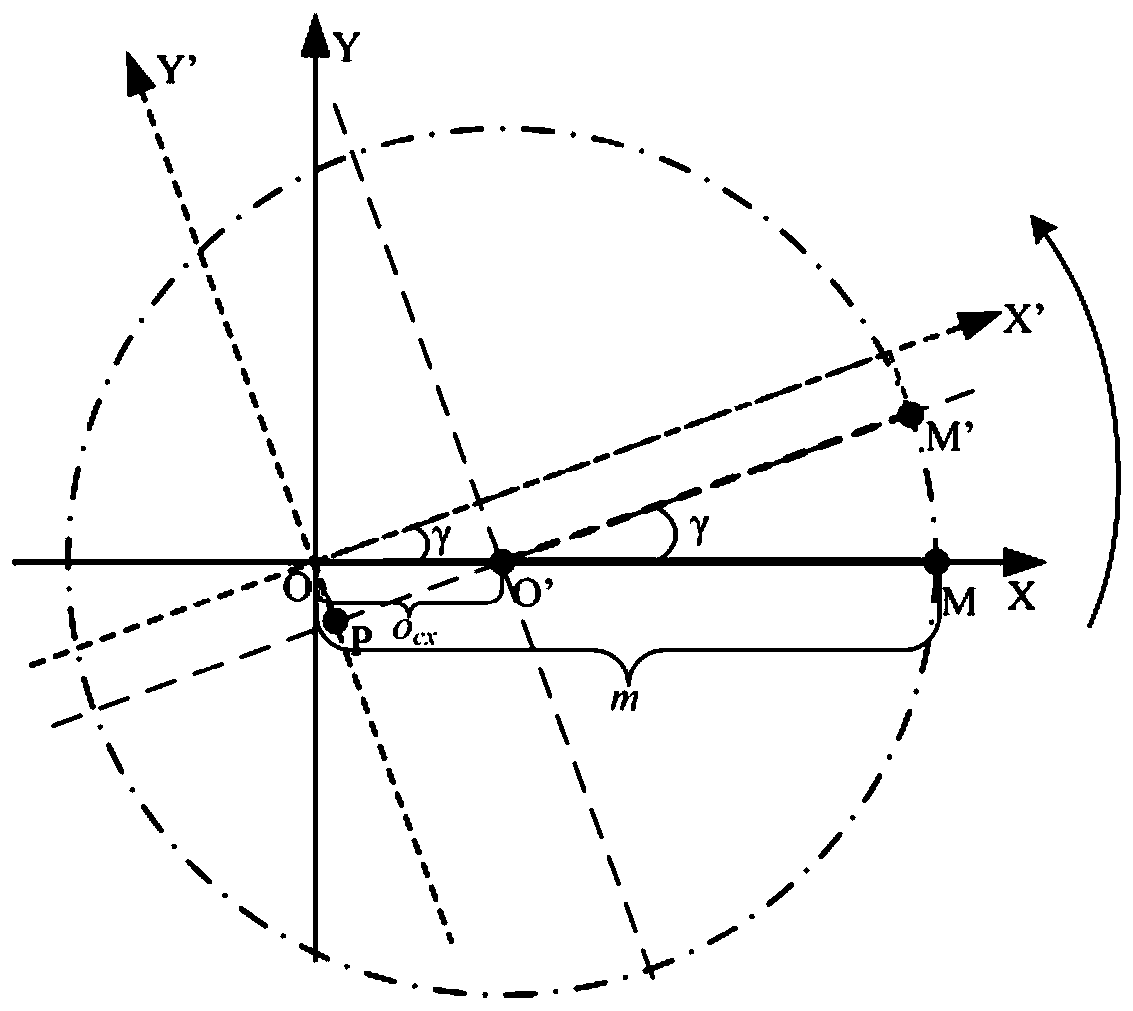
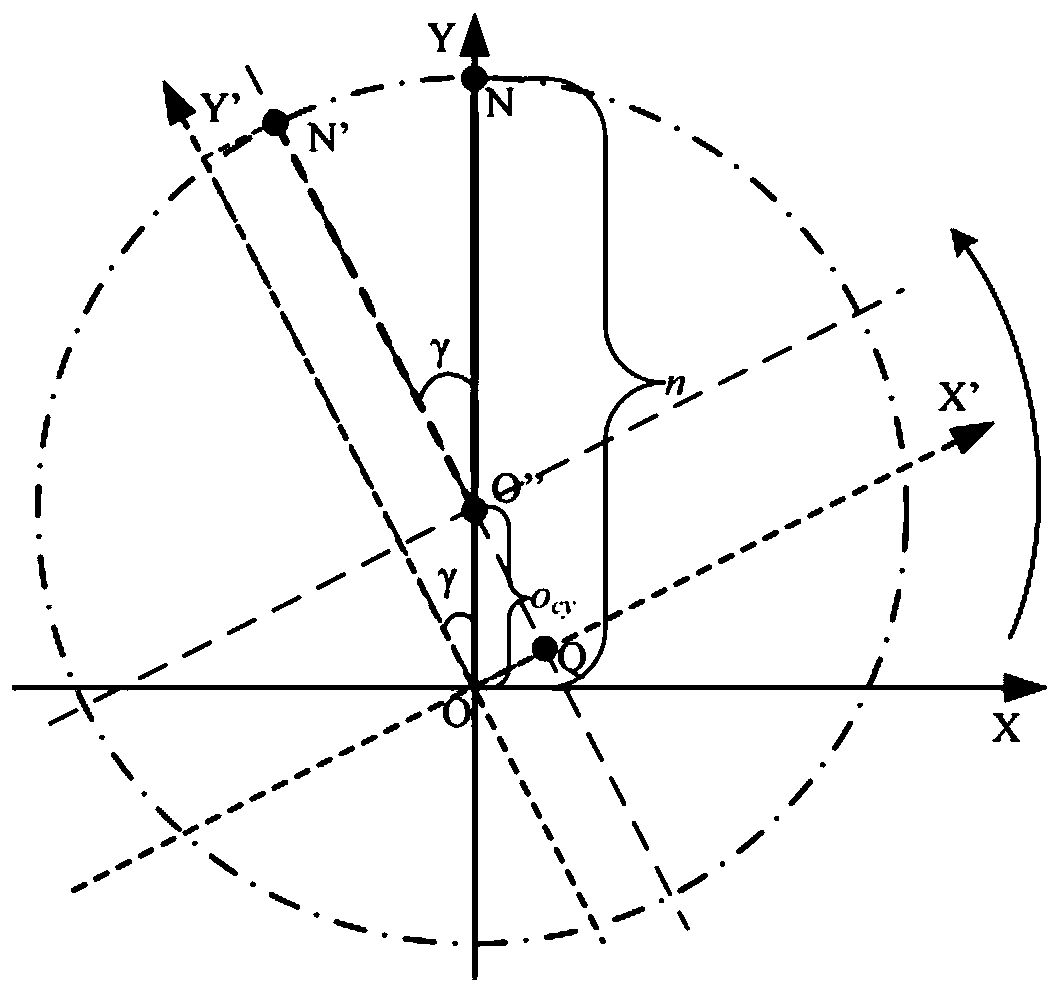
The invention discloses a guide rail basal plane straightness error decoupling and identifying method. According to the method, a laser interferometer is utilized to measure straightness error and angle error of a standard gauge block in sliding and reading error measured by a laser displacement sensor, movement of all parts is expressed based on a spinor theory, and a guide rail basal plane straightness error value can be finally calculated out through an error decoupling data processing method; therefore, the purpose of measuring precise guide rail basal plane straightness error is achieved, and the guide rail basal plane straightness error decoupling and identifying method has an advantage of accuracy and certain practicability, and can be applied to researches of numerical control machine tool production quality detection analysis or machine tool precision analysis.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
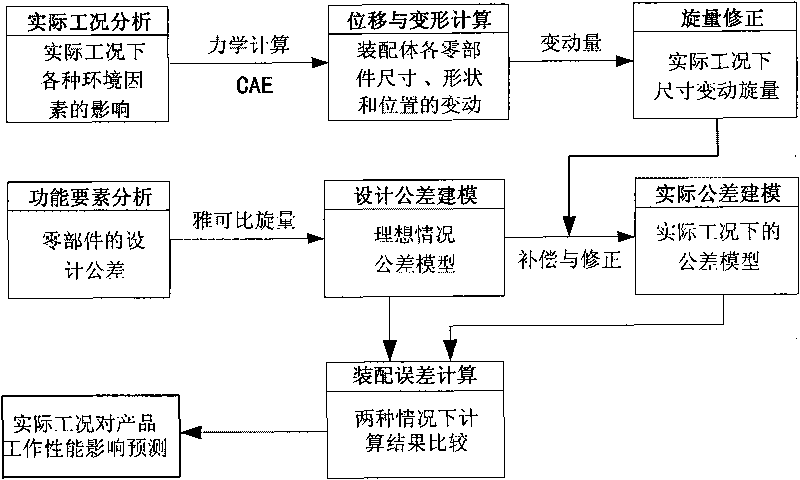
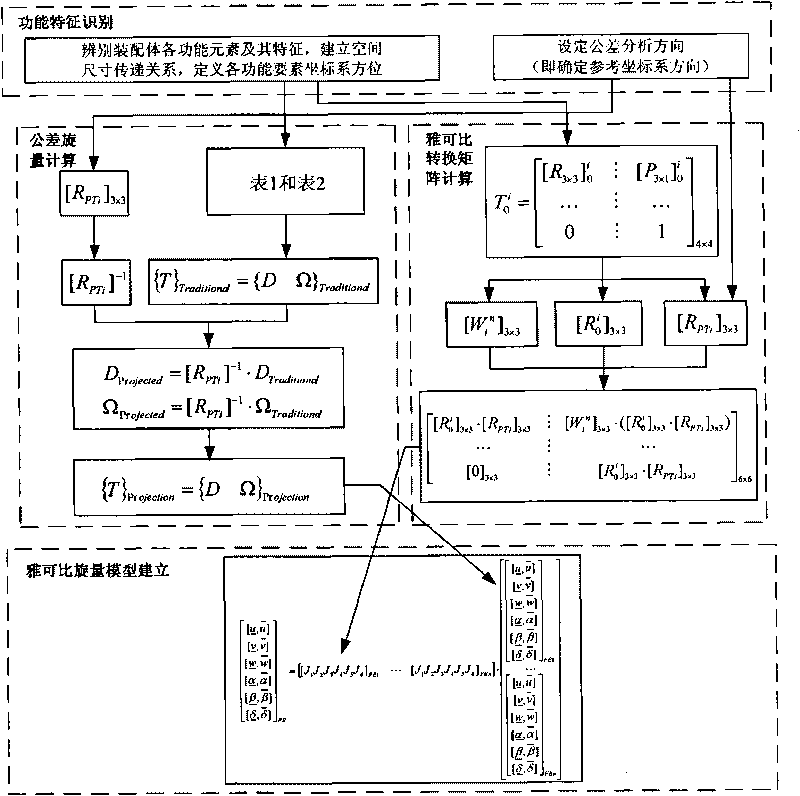
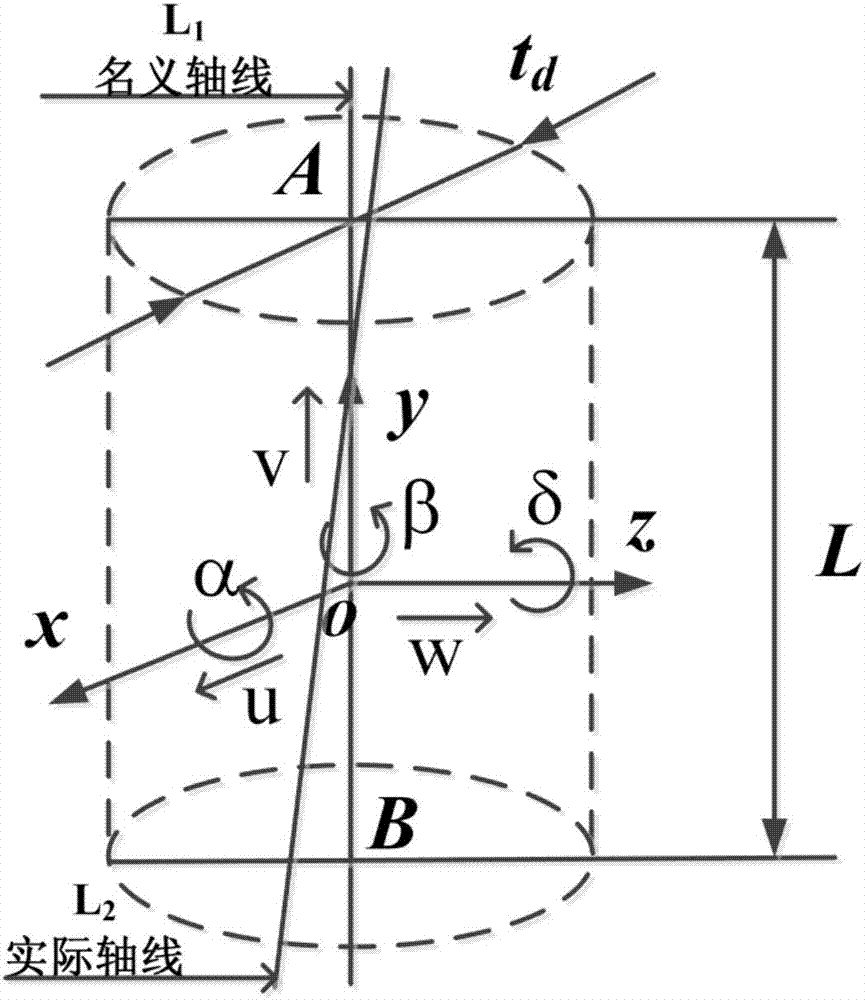
Actual-condition tolerance modeling method based on Jacobian spinors
InactiveCN101710355AMathematical brevityQuantifiable computingSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelSimulation
The invention relates to an actual-condition tolerance modeling method based on Jacobian spinors, belonging to the technical field of mechanical tolerance digitization. By calculating the deformation of a working part during loading, changing to the correction quantity of Jacobian spinors and compensating and correcting a Jacobian spinor tolerance model in an ideal condition, the invention establishes an assembly tolerance mathematical model based on Jacobian spinors and actual conditions. The actual-condition tolerance modeling method is technically characterized by comprising the steps of: firstly establishing an assembly tolerance model in the ideal condition; then considering the influences of environmental factors in the actual conditions, and calculating the changes of the size, the shape and the position of a component caused by the influences; mathematically expressing the changes in a spinor matrix mode as compensation, and combining the compensation with the tolerance model in the ideal conditions; and finally obtaining the assembly tolerance model in the actual conditions accordingly. The invention has the advantages that calculation results can be used for judging the assembling properties in the actual conditions and verifying and checking the tolerance design results, thereby predicting and judging the changes of product performances under different assembling design tolerances.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Kinematics calibration method for series-parallel robot
ActiveCN108015808AImprove recognition accuracyImprove stabilityDesign optimisation/simulationManipulatorGeometric errorKinematics
The invention discloses a kinematic calibration method for a series-parallel robot. The kinematic calibration method comprises the following steps that 1, a series-parallel robot geometric error modelis established based on a rotational amount theory; 2, the pose error of the tail end of the series-parallel robot is obtained based on the spatial position detection information of the laser tracker; 3, a geometric error source is identified on the basis of a Liu estimation method; and 4, error compensation is carried out step by step based on a correction controller output method. The kinematiccalibration method has the advantages of being high in precision and efficiency, convenient for industrial field application, and can be implemented on the basis of the robot tail end full-dimensional or few-dimensional pose error detection information; and according to the kinematic calibration method, an error model capable of meeting the completeness, the minimum and the continuity is established, the physical significance of model variables is definite, the ill-posed problem of the identification matrix is effectively solved, the identification precision of the error source and the stability of the identification result are improved, and therefore the compensation precision is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
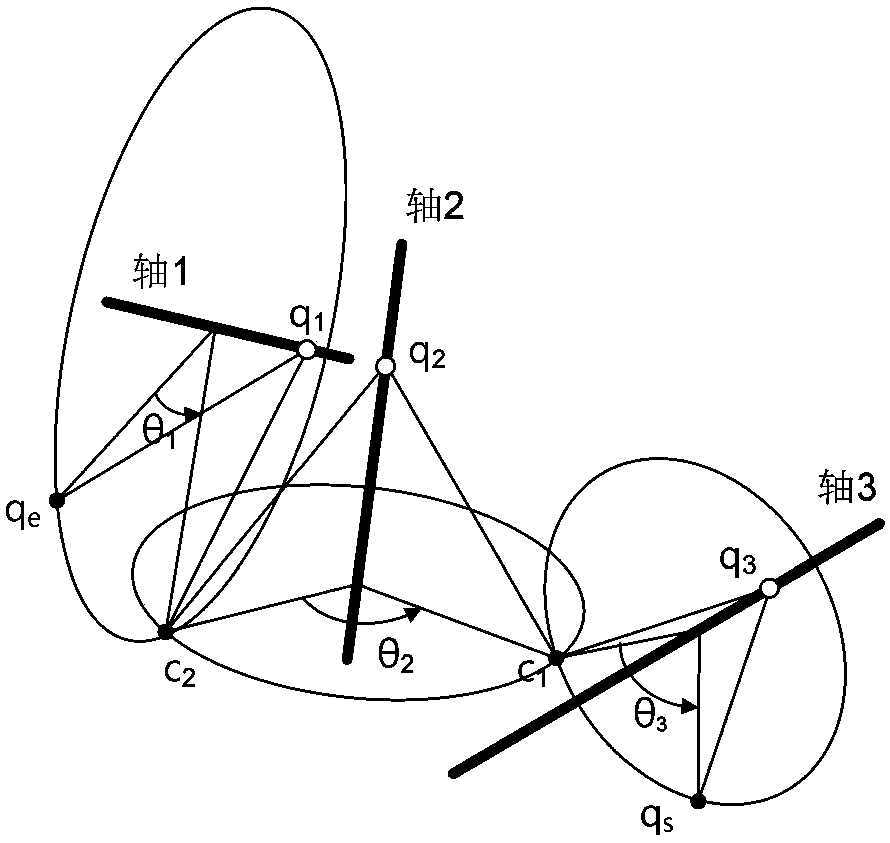
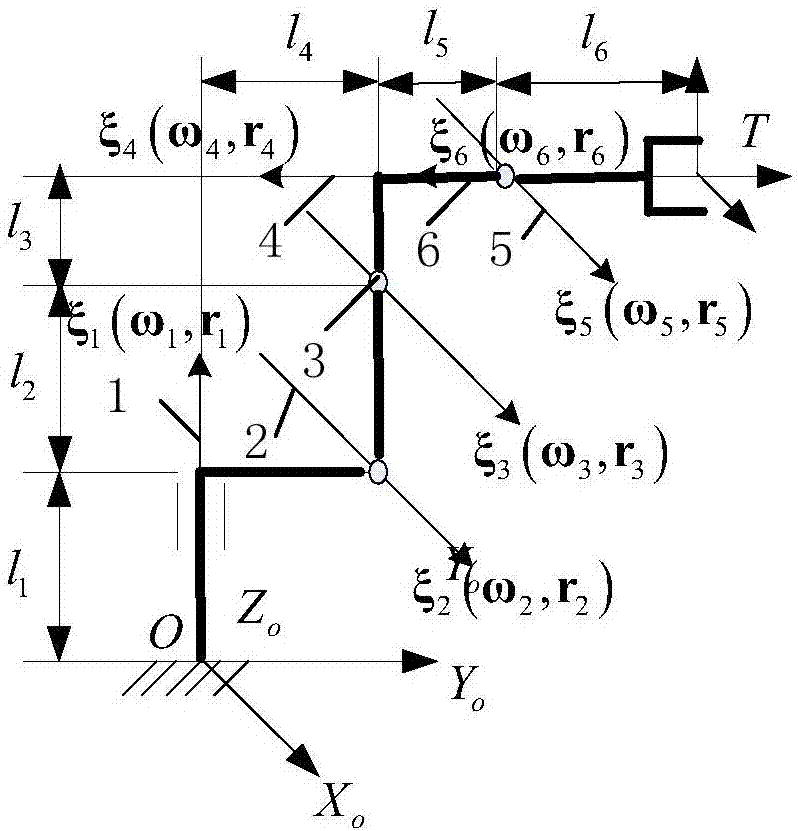
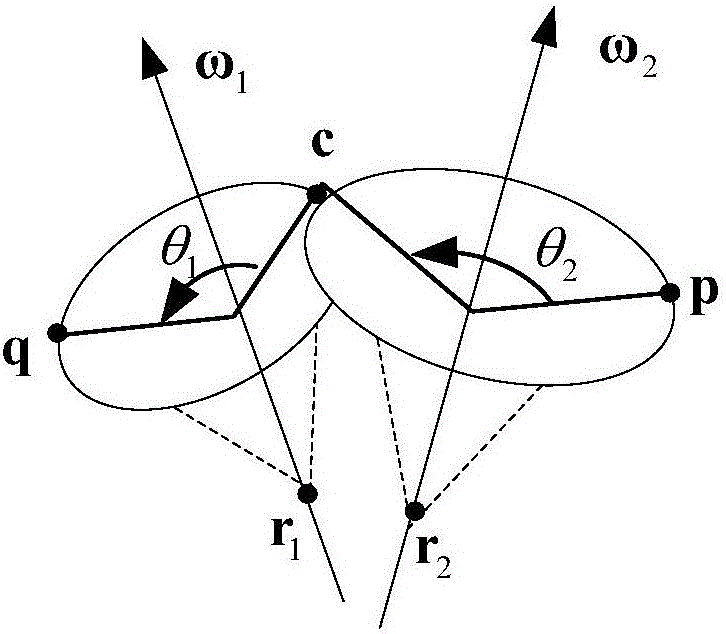
6R robot inverse kinematic geometry solving method based on screw theory
ActiveCN107756400ASimplified inverse modelGeometric meaning is clearProgramme-controlled manipulatorComplex mathematical operationsAlgebraic equationRobot kinematics
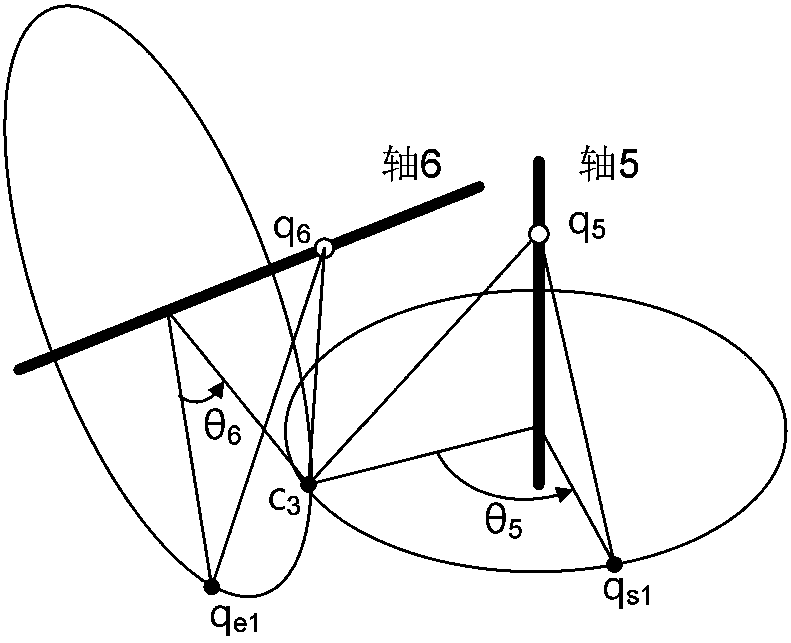
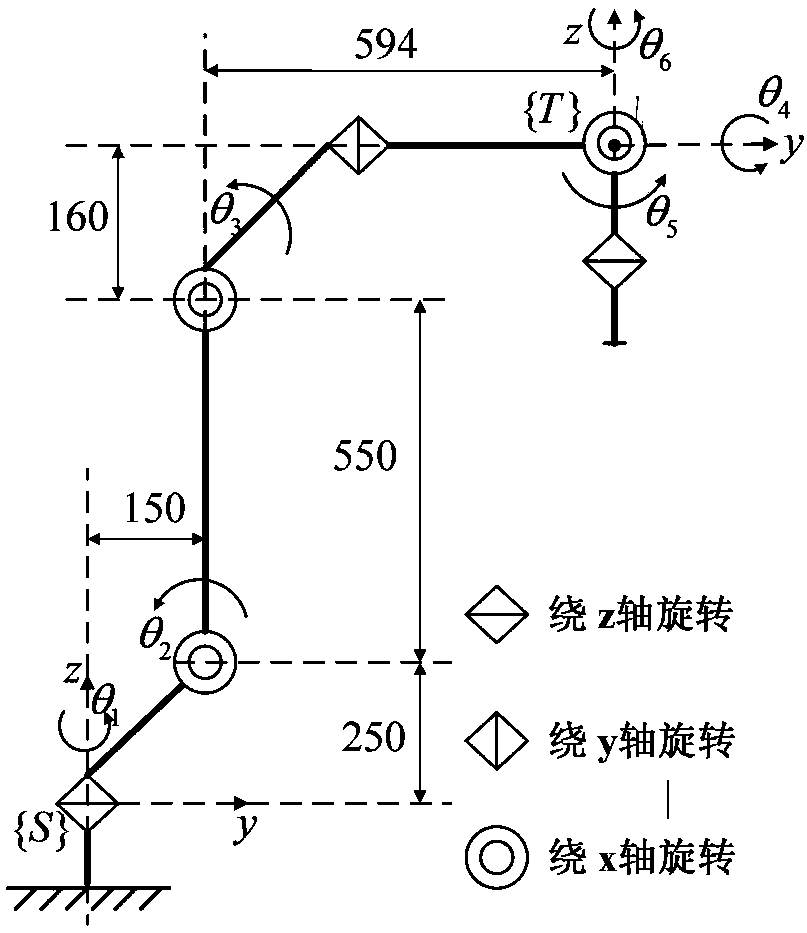
The invention discloses a 6R robot inverse kinematic geometry solving method based on a screw theory and belongs to the field of robot kinematic inverse solution research. A basal coordinate system and a tool coordinate system are established, kinematic parameters of a 6R robot are determined through the basal coordinate system and the tool coordinate system, and a forward kinematic model is established; inverse solution motion of first three joints of the 6R robot is descripted in a decomposed mode, and a six-variable quadratic equation set is established; and a target position qe1 corresponding to an initial position qs1 is solved based on a screw forward kinematic model. Through the method, geometric description is combined with the screw theory, the geometrical significance is more explicit, the algebraic equation set is solved through a simplified inverse kinematic algorithm, the calculation efficiency is effectively improved, and a new inverse kinematics processing method is provided for real-time control over robot movement.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
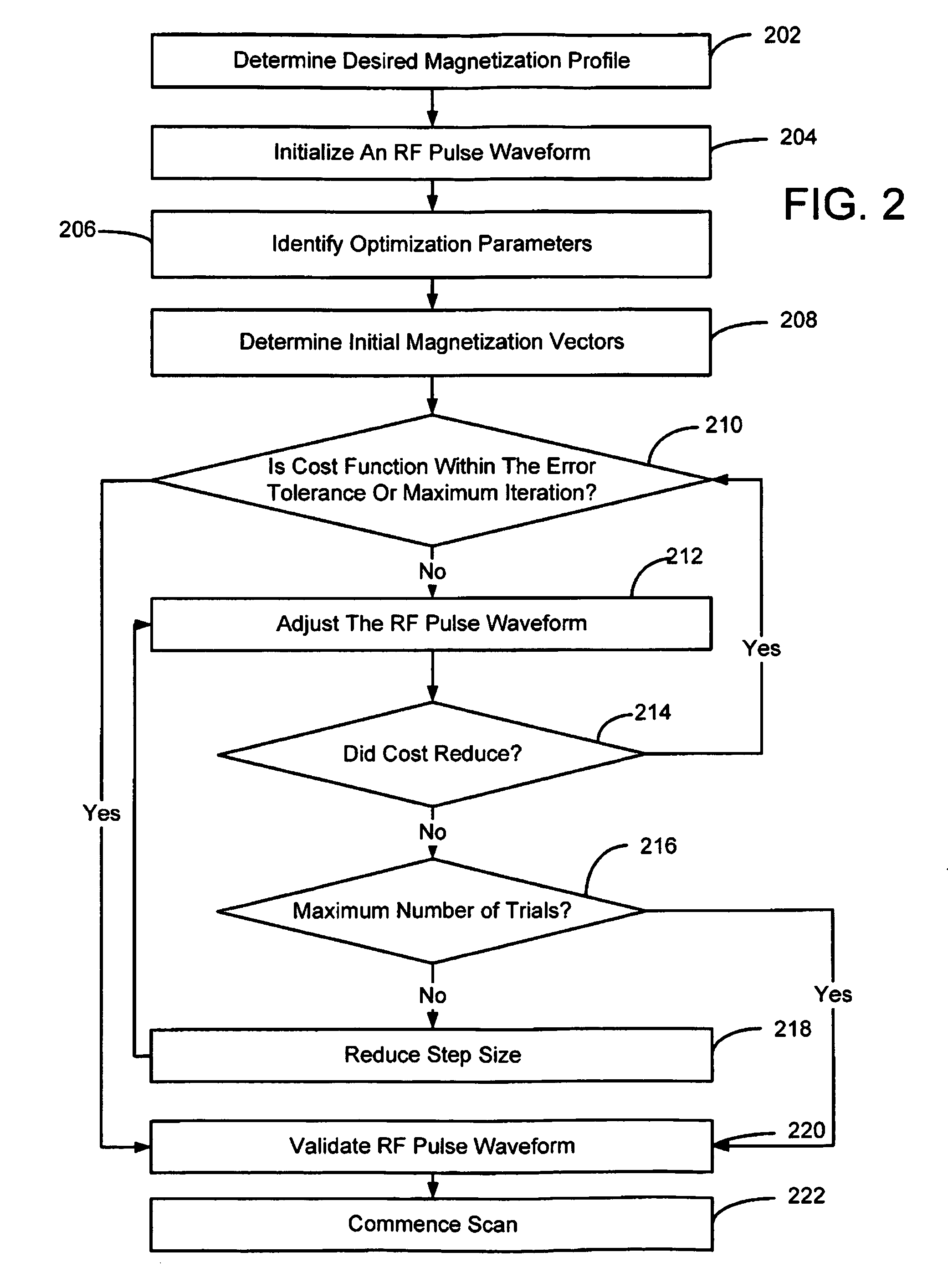
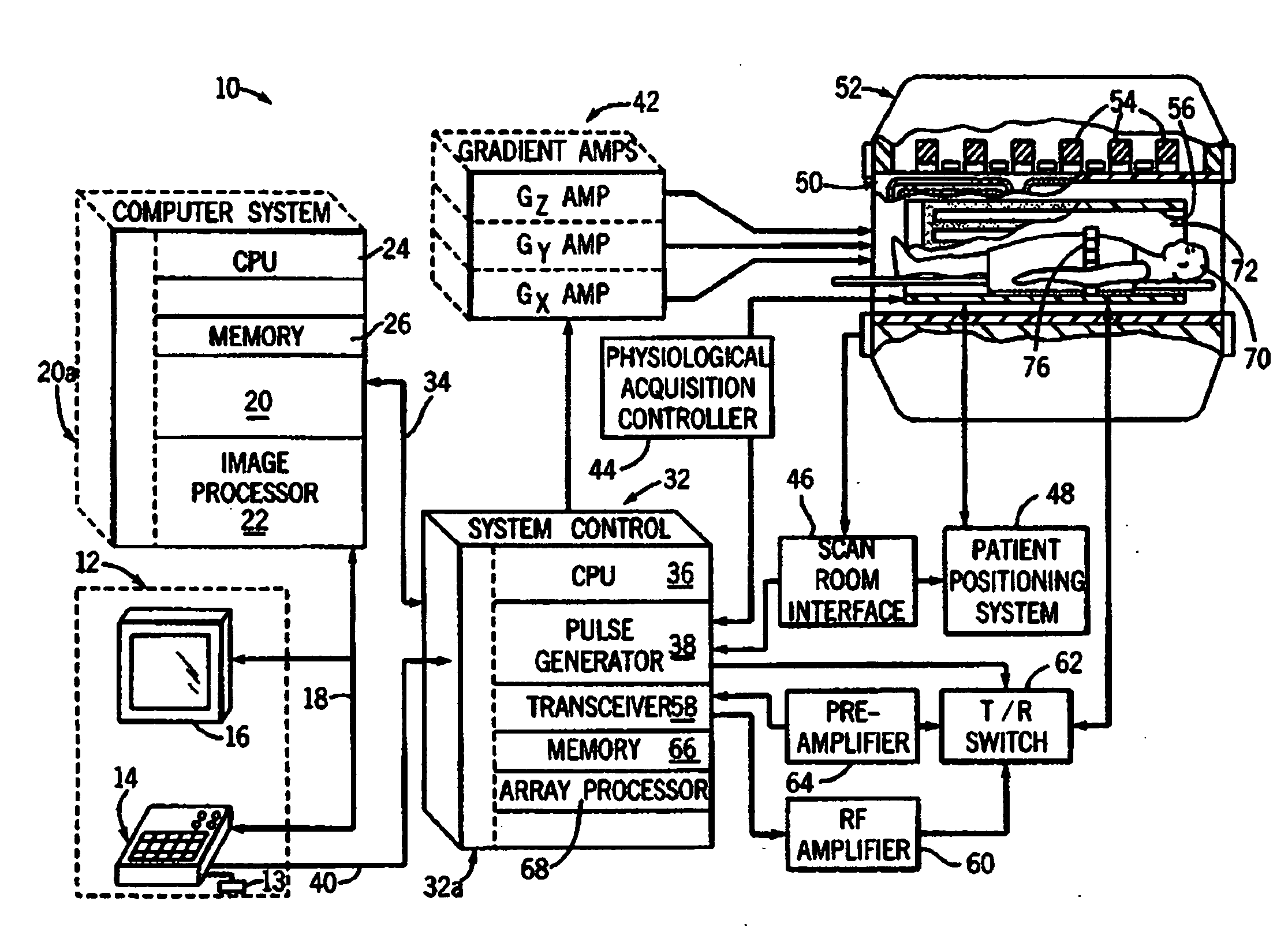
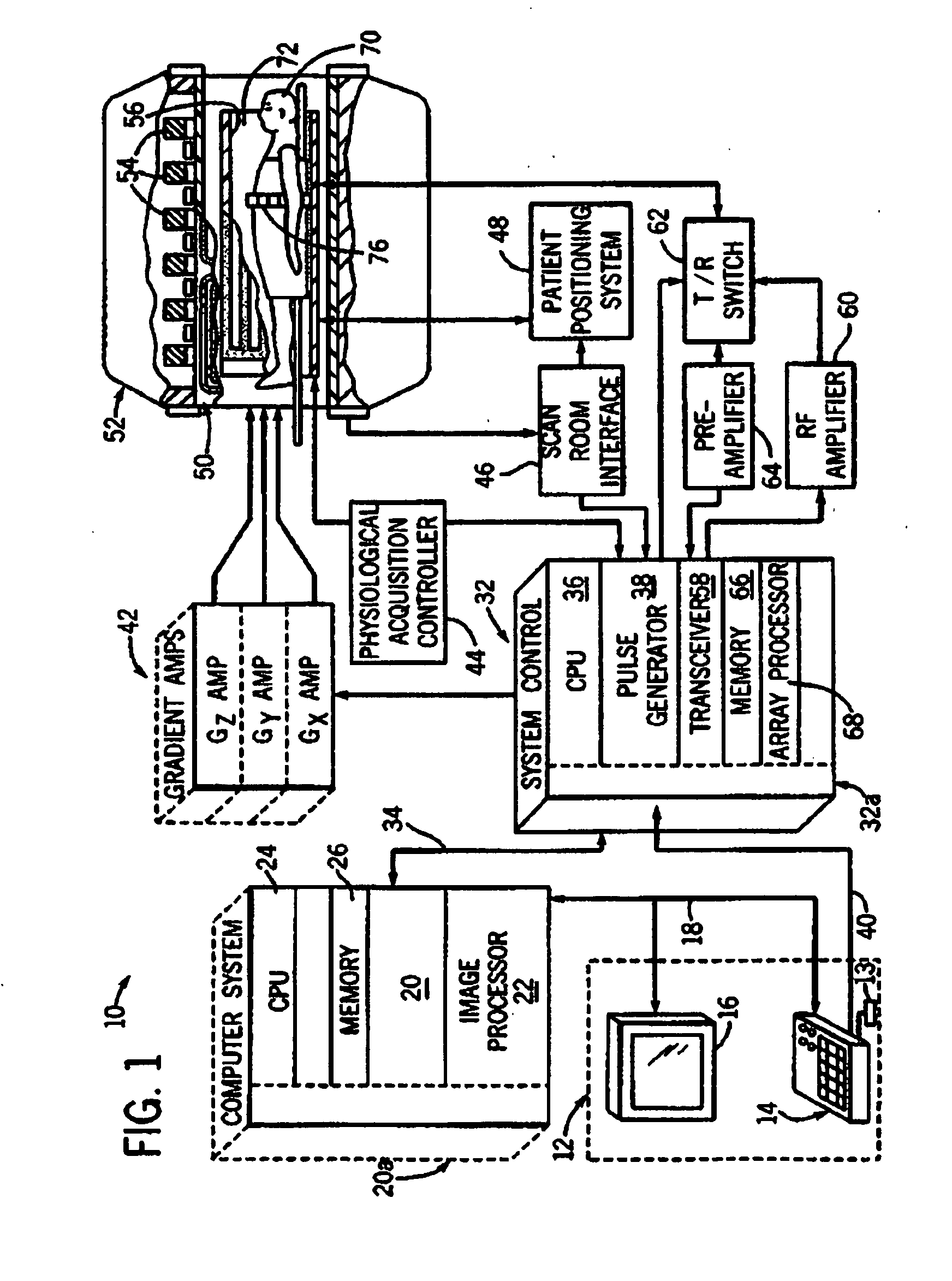
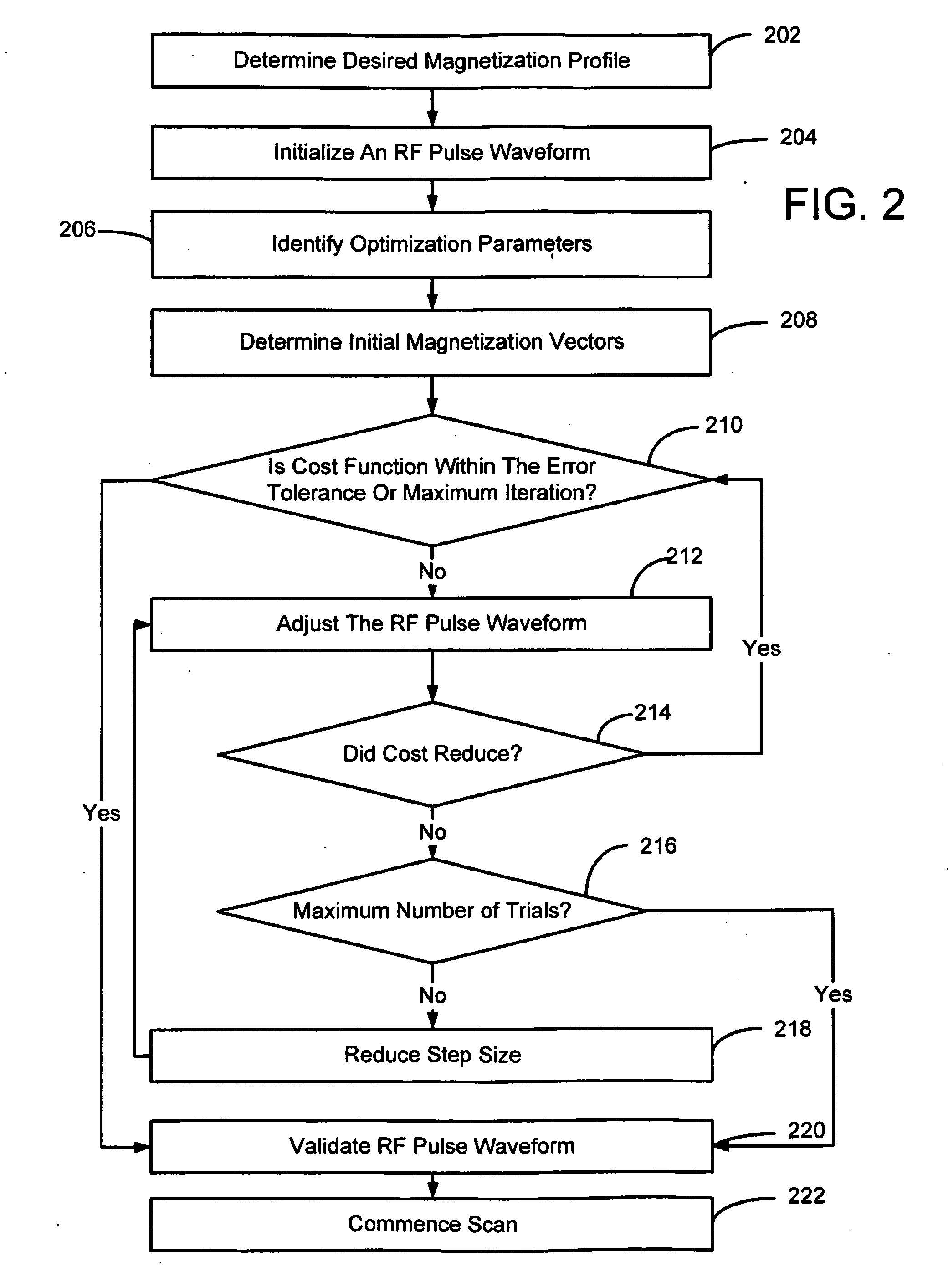
System and method for phase relaxed RF pulse design
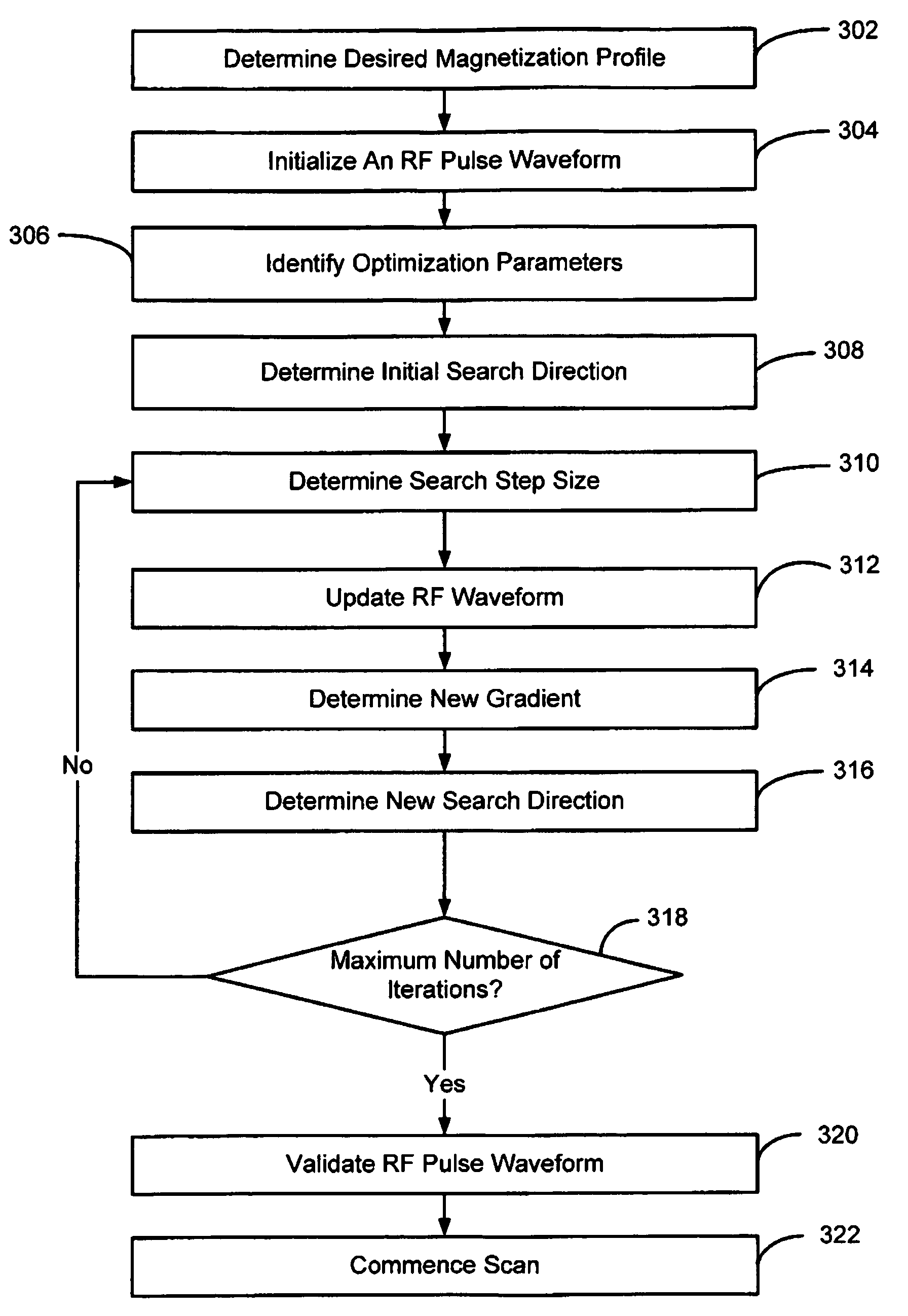
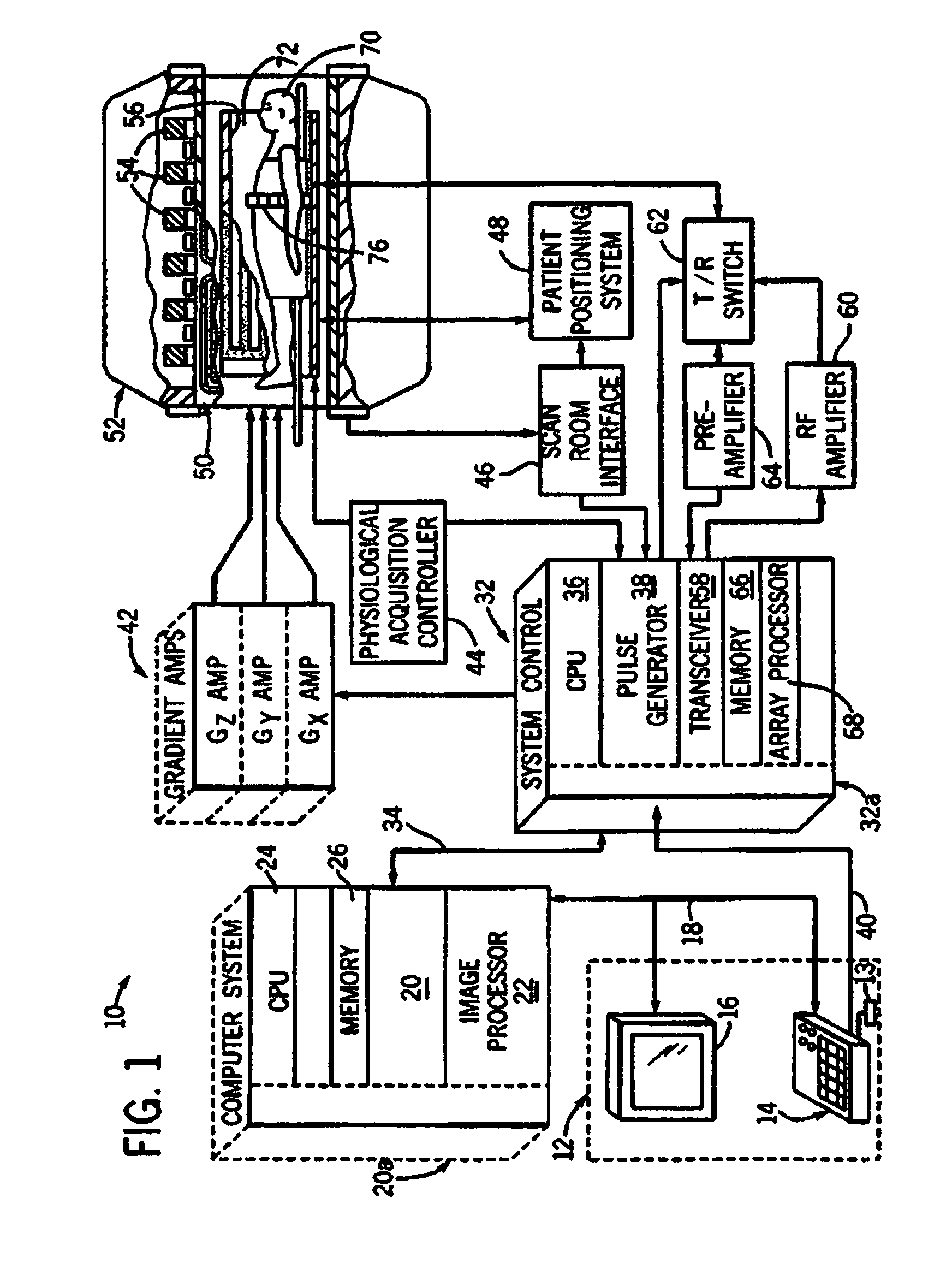
Techniques for designing RF pulses may be configured to produce improved magnitude profiles of the resulting magnetization by relaxing the phase constraint and optimizing the phase profiles. In one embodiment, a spinor-based, optimal control, optimal phase technique may be used to design arbitrary-tip-angle (e.g., large and small tip angle) RF pulses (both parallel transmission and single channel). In another embodiment, small tip angle RF pulses (both parallel transmission and single channel) may be designed using a small-tip-angle (STA) pulse design without phase constraint that is formulated as a parameter optimization problem.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
General inverse kinematic solving method of six-freedom-degree serial robot
ActiveCN107203653ASimple form of expressionSimple and easy to understandDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAngular degreesRodrigues' rotation formula
The invention discloses a general inverse kinematic solving method of a six-freedom-degree serial robot and belongs to the field of inverse kinematics of robots. The closed solving method simple in computational process and easy to achieve is proposed based on an exponential product model. The method mainly utilizes the basic property of a spinor theory, a Rodrigues rotation formula and a special geometric construction to convert a complicated inverse solution problem into a simple trigonometric functional equation for solution, so that six joint angles can be represented only by needing two expressions, and a form is simple and convenient to memorize. The method is wide in practical range, can be applied to any robot conforming to a Pieper principle and having intersected or parallel relation between two adjacent shafts in front three joints and promotes popularization and application of the robots, and the application process is simplified.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Distributed dynamic modeling method for multi-leg robot
ActiveCN110083982AReduce complexityQuick updateSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationDynamic modelsContact force
A distributed dynamics modeling method for a multi-leg robot comprises the following steps that (1) based on virtual model control, a trunk single rigid body serving as an object, simplifying legs into virtual actuator input, performing stress analysis, and establishing a single rigid body dynamics model; (2) adopting an iterative leg dynamics model resolving algorithm to establish a leg dynamicsmodel; the leg dynamic model resolving algorithm comprises the following steps: (1) taking a contact point between the tail end of a limb and the environment as a base coordinate system, and extrapolating to obtain an inertia force and a moment borne by the mass center of each rod piece; and (2) starting from the connection point of the trunk and the limbs, taking the force spinor of the limbs acting on the trunk as a controlled quantity, and performing inward pushing to obtain the interaction force spinor of the internal rod piece for realizing the controlled quantity and the contact force spinor of the limbs and the environment. According to the method, the complexity of model establishment is greatly reduced, the dynamics of the multi-leg robot is quickly updated, and the real-time requirement of control is met.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
System and method for phase relaxed RF pulse design
ActiveUS20100264926A1Magnetic property measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionOptimal controlMagnetization
Techniques for designing RF pulses may be configured to produce improved magnitude profiles of the resulting magnetization by relaxing the phase constraint and optimizing the phase profiles. In one embodiment, a spinor-based, optimal control, optimal phase technique may be used to design arbitrary-tip-angle (e.g., large and small tip angle) RF pulses (both parallel transmission and single channel). In another embodiment, small tip angle RF pulses (both parallel transmission and single channel) may be designed using a small-tip-angle (STA) pulse design without phase constraint that is formulated as a parameter optimization problem.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
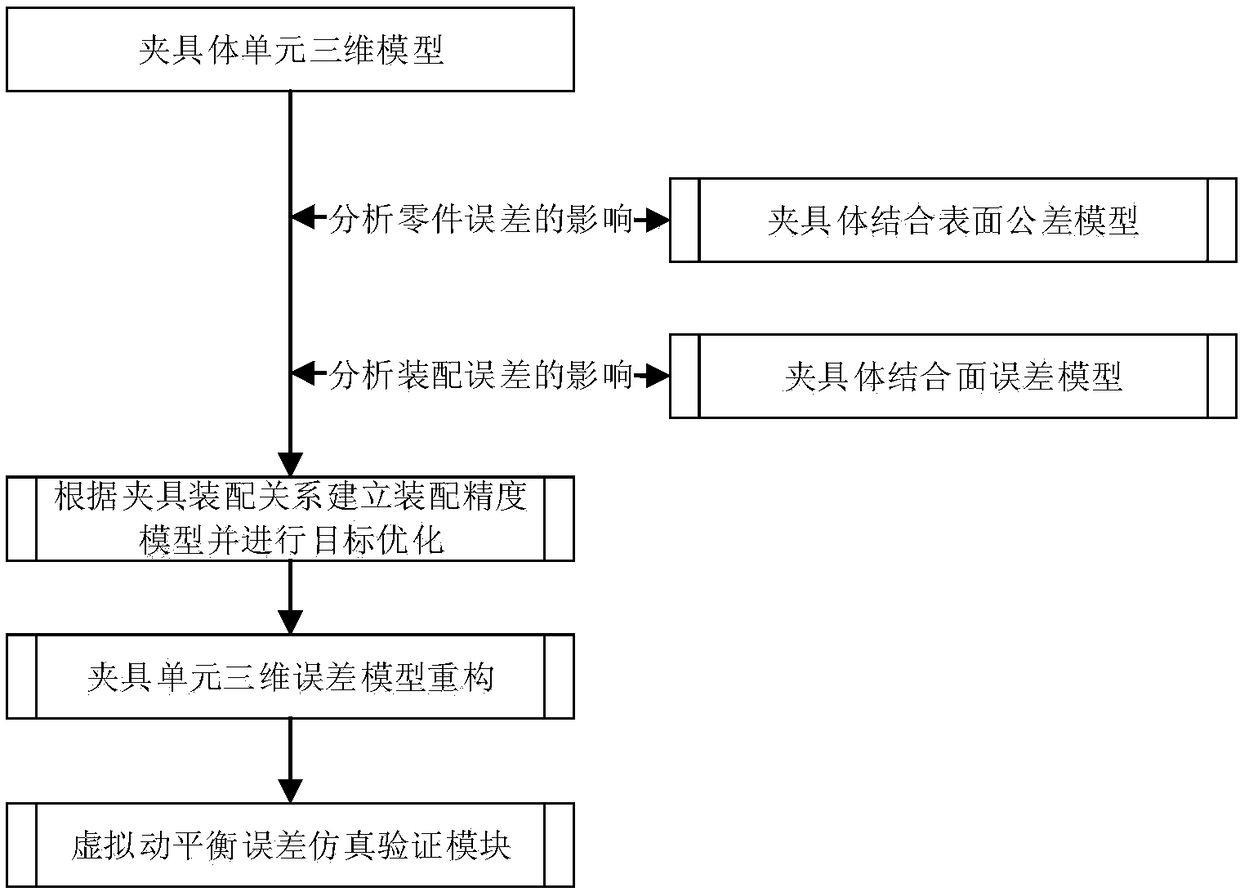
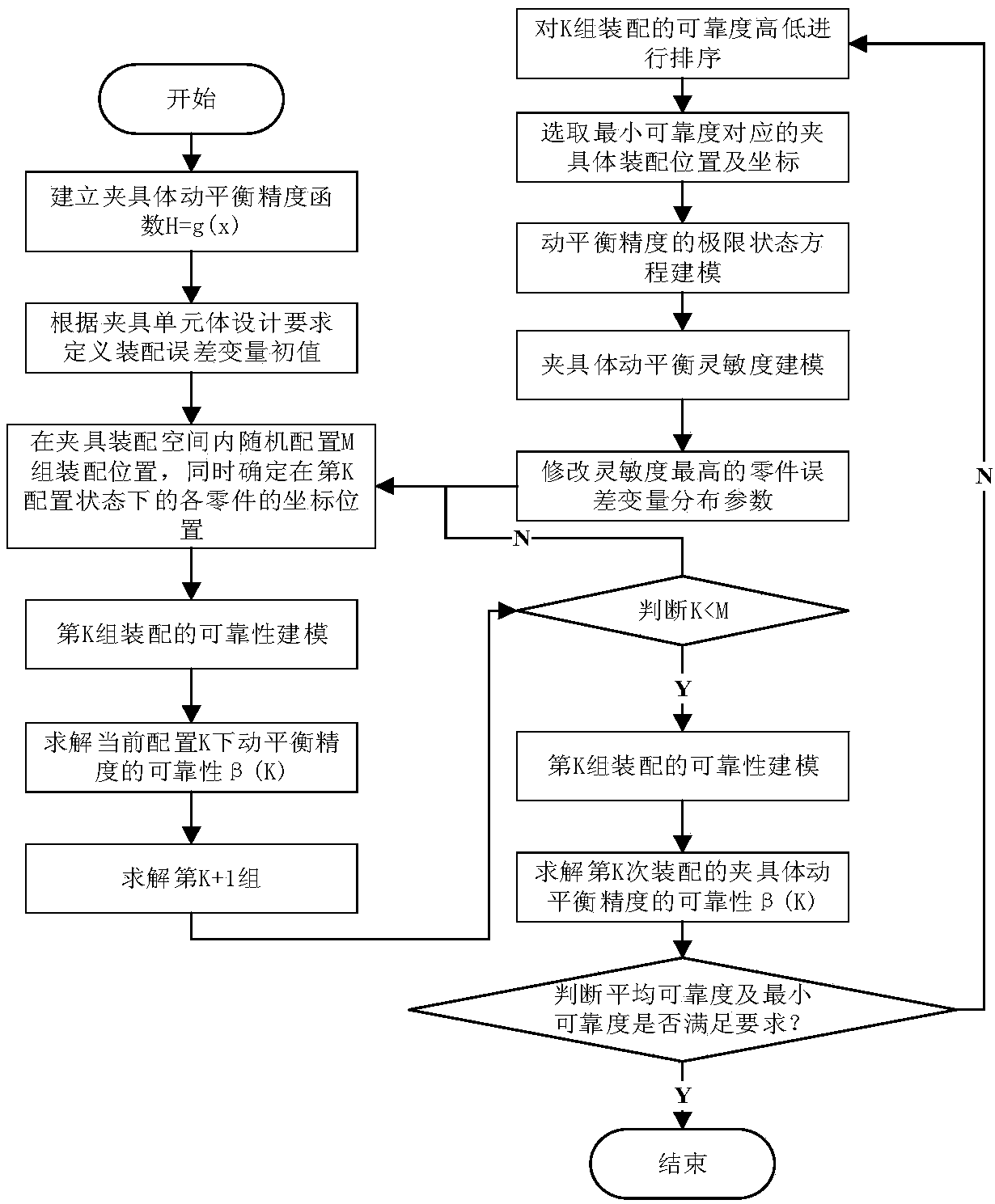
Joint surface error and joint surface tolerance optimization method for machine tool fixture component
InactiveCN108268010ARealize the clamping functionCancel or reduce the passive trim processProgramme controlComputer controlGeometric errorDynamic balance
The invention relates to a joint surface error and joint surface tolerance optimization method for a machine tool fixture component. According to the prior art, the quality characteristics of a machine tool fixture component cannot truly reflect the quality distribution condition of the machine tool fixture component, which can influence calculation accuracy and trimming precision and make automation hard to realize, and therefore, the invention provides the method to solve the problems in the prior art. The method of the invention includes the following steps that: 1, surface tolerance is represented by a homogeneous matrix; 2, joint surface error is represented by a homogeneous matrix; 3, a geometric error transfer model of assembly is constructed; 4, the surface tolerance and joint surface error are optimized according to the nature of error terms; 5, sensitivity is analyzed; 6, a part surface error or surface tolerance parameter optimization method is established with the processing cost of the fixture component adopted as an objective and assembly precision reliability and tolerance selection principles adopted as constraints; and 7, the distribution rule and parameter of theimbalance of a fixture component assembly body are obtained through a simulation experiment after the optimization result of the spinor parameter of the assembly body is obtained, and therefore, the dynamic balance optimization design of the assembly body is realized.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
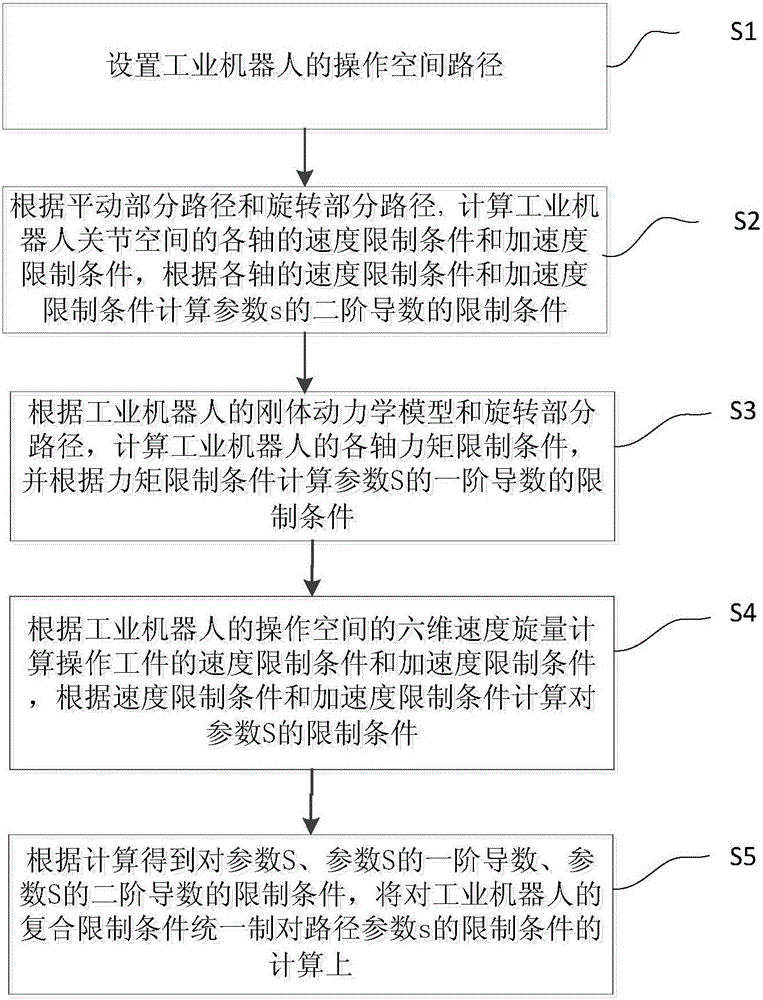
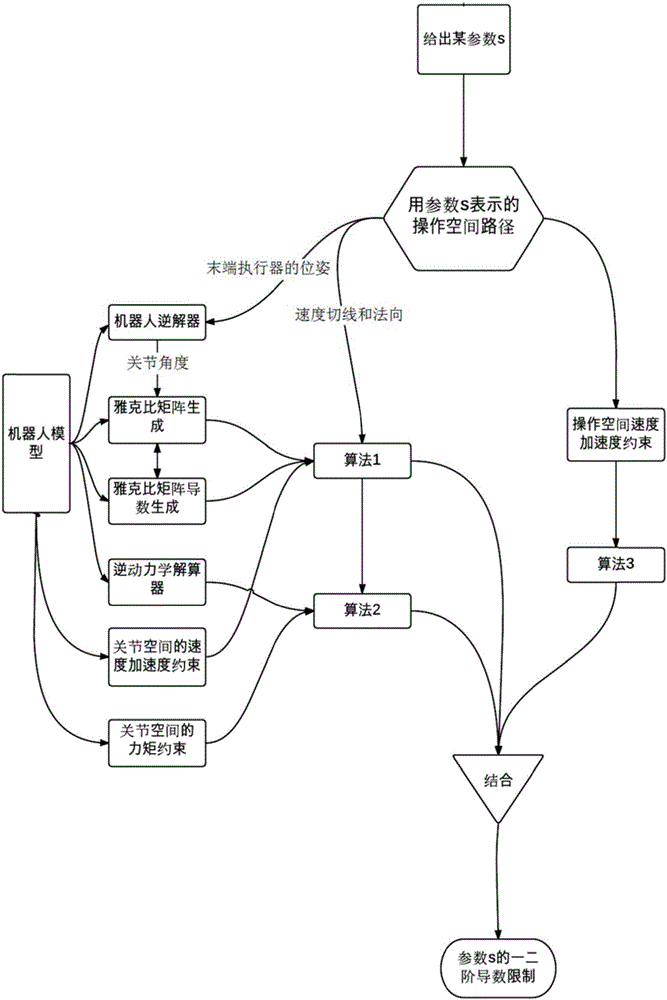
Solving method for composite limitations of operating space paths of industrial robot
ActiveCN105717869AAvoid Path Following ErrorsEfficient solutionNumerical controlControl theoryJoint spaces
The invention provides a solving method for composite limitations of operating space paths of an industrial robot.The method includes the steps that the operating space paths of the industrial robot are set; speed limitation conditions and acceleration limitation conditions of all axes are calculated, and limitation conditions of second derivatives of parameters are calculated according to the speed limitation conditions and acceleration limitation conditions of all the axes; torque limitation conditions of all the axes are calculated according to a rigid body dynamic model and the rotating part paths, and limitation conditions of first derivatives of the parameters are calculated according to the torque limitation conditions; speed limitation conditions and acceleration limitation conditions of operated workpieces are calculated according to the six-dimensional speed spinor of operating space of the industrial robot, and limitation conditions for the parameters are calculated according to the speed limitation conditions and the acceleration limitation conditions; composite limitation conditions for the industrial robot are unified on calculation on limitation conditions of the path parameters.Multiple limitation conditions of joint space and the operating space are effectively solved, and the composite limitations are uniformly shown.
Owner:珞石(北京)科技有限公司
Inertial navigation system transfer alignment modeling method based on dual quaternion
ActiveCN106525034AImprove calculation accuracyImprove computing efficiencyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeAccelerometer
The invention provides an inertial navigation system transfer alignment modeling method based on dual quaternion. A nominal dual quaternion between a main inertial navigation system and an auxiliary inertial navigation system is constructed, the dual quaternion is calculated to describe an auxiliary inertial navigation system carrier system relative to a main inertial navigation system carrier system, rotation and translation motion of the carrier systems are calculated, and a normal dual quaternion differential equation of transfer alignment is constructed by reasoning spinor expressions of relative rotation and translation motion of the main inertial navigation system and the auxiliary inertial navigation system and calculated; a dual quaternion error equation is obtained in combination with an accelerometer parameter error equation and a gyroscope error differential equation; a systematic observation equation is constructed by using the linear velocity of an accelerometer and the angular velocity of rotation of a gyroscope, an initial calibration parameter of the auxiliary inertial navigation system is calculated through kalman filter iteration, the effects of rotation and translation separation calculation on coning errors and sculling errors are eliminated, and the calculation accuracy and the calculation efficiency are effectively improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Extended Fourier amplitude based extraction method of machine tool important geometric error source
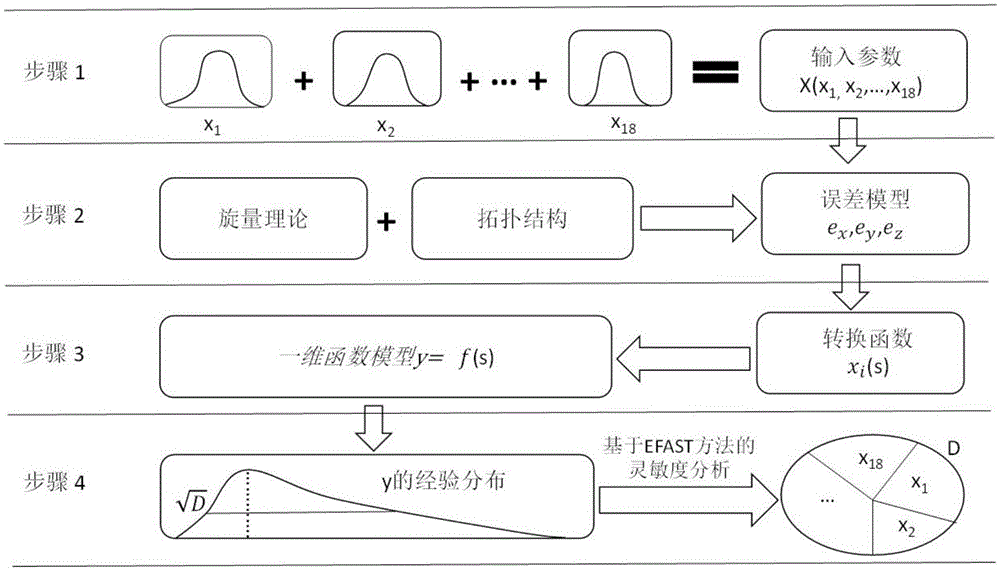
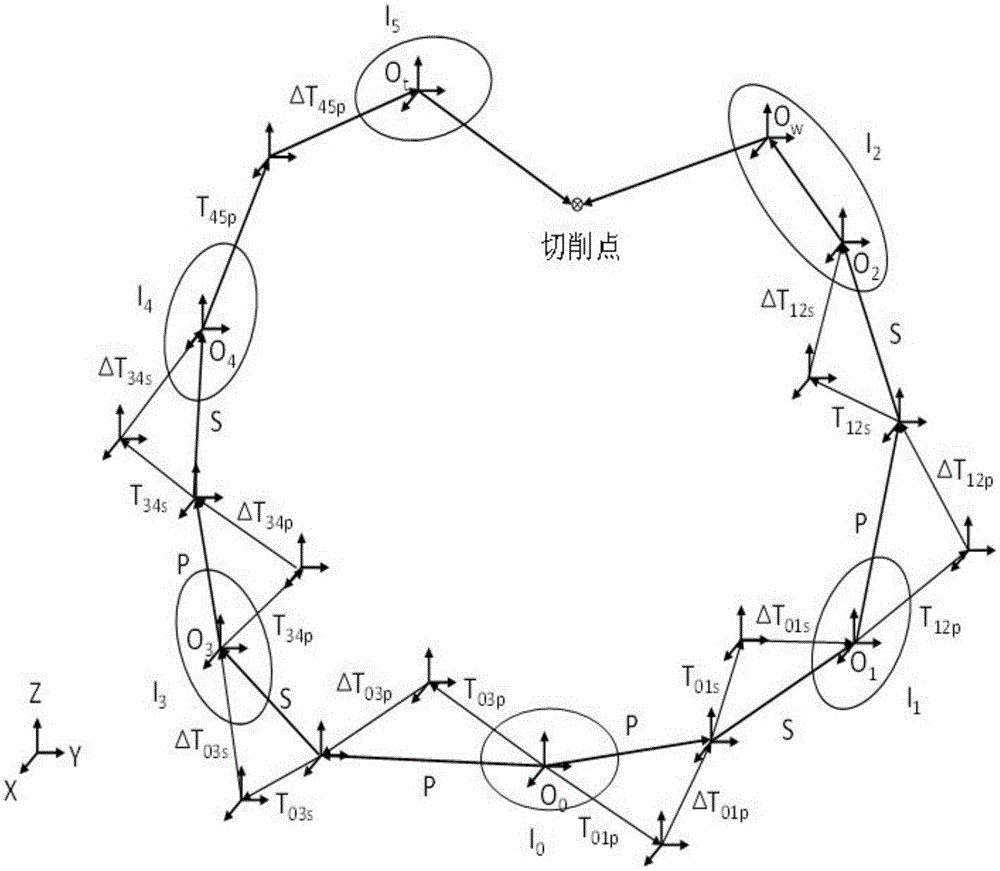
The invention discloses an extended Fourier amplitude based extraction method of a machine tool important geometric error source. Based on error measuring data, by use of an index matrix form of a screw theory, on the basis of the topology structure of a machine tool, an integral space error model of the machine tool is established, a high-order term of the error model is eliminated, and a basis equation of the error model is obtained. According to an EFAST global sensitivity analysis method, through selecting a proper conversion function, the error model is converted into a one-dimensional function from an eighteen-dimensional function, Fourier series expansion is carried out on the one-dimensional function, and a model caused by each parameter and a total variance of model output can be obtained. The EFAST method can simultaneously examine the influences exerted by change of multiple geometric errors on the result of a spinor error model and can also analyze the direct and indirect influences exerted by change of each geometric error on the model result, and the method provided by the invention can be applied to extraction of key geometric error terms having quite large influences on processing precision of the machine tool.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
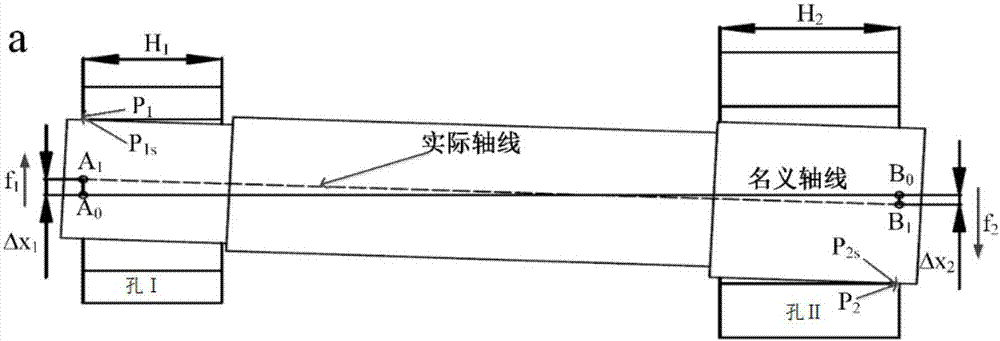
Assembly error acquisition method meeting actual working conditions
InactiveCN107944143AImproving Assembly Error Prediction AccuracyImprove forecast accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSimulationDiscretization
The invention belongs to the field of mechanical manufacturing product assembly error modeling and discloses an assembly error acquisition method meeting actual working conditions. The method comprises the steps that (1) an assembly error spinor model based on a corrected Jacobian spinor model is established; (2) discretization is performed on part surfaces; (3) finite element software is utilizedto load a temperature field and add a stress field load, and part surface deformation is obtained; (4) the part surface deformation meeting the actual working conditions is obtained; and (5) after part surface node deformation meeting the actual working conditions is obtained, subtraction is performed on node coordinate deformation corresponding to upper contact surfaces and lower contact surfaces of combination surfaces, and then surface true assembly errors meeting the actual working conditions can be obtained. Through the method, clearance between corresponding nodes of matching surfaces can be predicted quite precisely, influences of the actual working conditions on the assembly errors are fully considered, and assembly error prediction precision is greatly improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Inverse kinematics general solving method of five-degree-of-freedom serial robot
ActiveCN106845037ASimple form of expressionSimple and easy to understandDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAngular degreesDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses an inverse kinematics general solving method of a five-degree-of-freedom serial robot and belongs to the field of inverse kinematics of the robot. The invention provides the inverse kinematics general solving method, which has a simple form and is easy to calculate, on the basis of an exponential product model; basic properties of a screw theory and Rodrigues rotary expression are mainly combined to simplify an inverse solution solving process; under the condition of meeting Pieper constraints, an angle value of each joint can be directly obtained without the need of considering a relation between former two joint axes; five joint angles can be uniformly expressed through only two expression formulas, and convenience is provided for robots in actual application.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Locally parallel dimension chain error acquisition method influenced by geometric structure
InactiveCN107992647AImprove assembly error accuracyThe method of obtaining spinor is simpleGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationGeometric relationsTransmission equipment
The invention belongs to the field of mechanical manufacturing product assembling error acquisition and discloses a locally parallel dimension chain error acquisition method influenced by a geometricstructure. The method comprises the steps that (a) parallel cooperation of a shaft and two holes is equivalent to a feature of a cylinder, a spinor corresponding to the cylinder is established, and establishment of a Jacobian spinor model is completed; (b) corresponding contact points and analysis points on the shaft and the two holes and an offset size and an offset direction of the analysis points after parallel cooperation of the shaft and the two holes are acquired, and the type of the Jacobian spinor model is determined according to the offset size and the offset direction of the analysispoints; and (c) a geometric relation between all the contact points and the analysis points is obtained, values of a translation vector parameter and a rotation vector parameter in the spinor T are solved and acquired, and the Jacobian spinor model is obtained through the values. Through the method, acquisition of locally parallel dimension chain tolerance information with a leverage effect of the geometric structure is realized, final transmission equipment assembling error precision is improved, an error is lowered, and the method is convenient to use.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
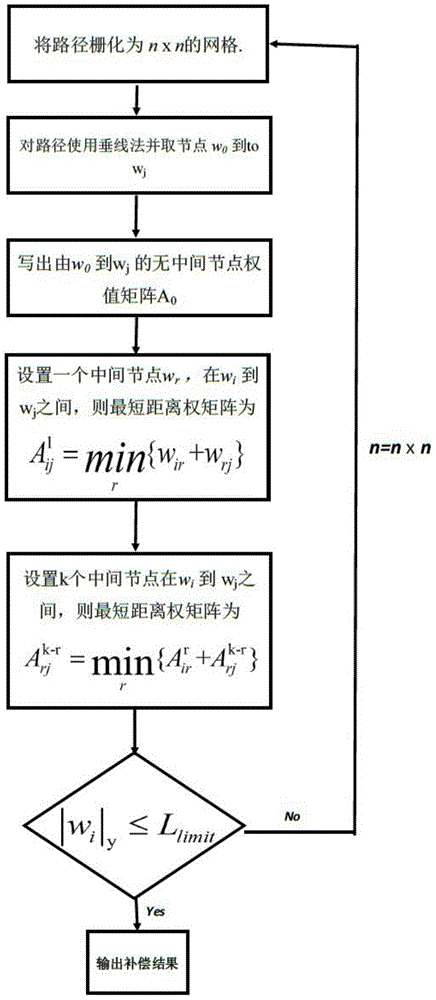
Floyd algorithm-based space error compensation method
The invention discloses a Floyd algorithm-based space error compensation method. The Floyd algorithm-based space error compensation method comprises the steps of building a space error model of a whole machine tool on the basis of a topology structure of the machine tool by utilizing an exponential matrix form of a spinor theory based on error measurement data, cutting down a high-order term of the space error model, and obtaining a basic equation of the space error model; continuously adjusting weight according to a Floyd shortest distance algorithm, iterating the weight to a basic range allowed by accuracy, obtaining an error compensation model, and achieving a compensation result by using lesser computation burden, wherein error compensation can be used for real-time compensation on error of machine tools in various complicated actual machining occasions. Compared with a classic error compensation algorithm ACO-BPN (Ant Colony Algorithm-based Back Propagation Neural Network) in an instance, simulation discovers that compared with the ACO-BPN compensation algorithm, the Floyd compensation algorithm has the characteristics that the compensation effect is good, the execution efficiency is high, the iteration frequency is less, and good robustness of the Floyd compensation algorithm is verified in a temperature changing environment.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH +2
Meta-motion unit part tolerance distribution method based on state space equation
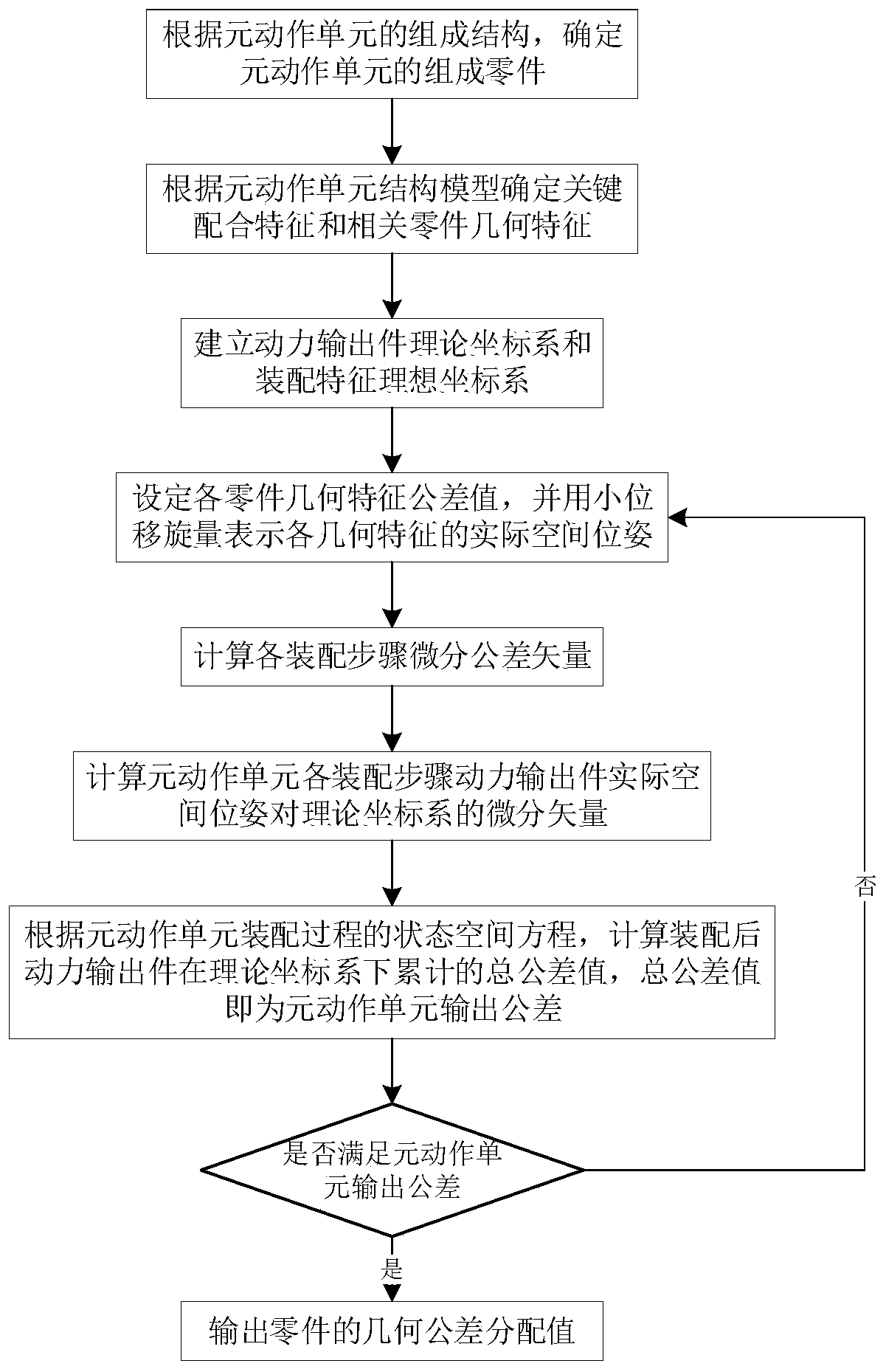
ActiveCN110008433AGuaranteed machining accuracyAccurate and efficient calculationComplex mathematical operationsManufacturing computing systemsDistribution methodCharacteristic space
The invention discloses a meta-motion unit part tolerance distribution method based on a state space equation. The method includes: Analyzing the structure model of the element action unit, and explaining the assembly tolerance transfer of the element action unit as the superposition process of the dimensional tolerance and the form and location tolerance of each part under different matching forms; determining a part assembly sequence of a meta-motion unit and related part geometrical characteristics of each matching characteristic, expressing a geometrical characteristic space pose of each part by using a small displacement spinor according to a tolerance model, and calculating and obtaining micro transformation of an actual pose of the assembly characteristic after each step of assembly; obtaining an output tolerance vector of the assembled power output part according to the assembly tolerance differential vector so as to obtain a state space equation of the element action unit in the assembly process; through iterative calculation, fitting out the part geometric tolerance meeting the requirement, and achieving distribution of the element action unit part tolerance.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Hybrid type automobile electrophoresis coating conveying mechanism dynamics modeling method
ActiveCN105159137AHas coordinate invarianceNeat and concise expressionProgramme controlSimulator controlHybrid typeDynamic models
The invention discloses a hybrid type automobile electrophoresis coating conveying mechanism dynamics modeling method. First of all, the symmetrical structure characteristic of a mechanism is fully utilized, the speed and the accelerated speed of each passive joint in the mechanism are analyzed through an analytical geometry method, and then the speed and the accelerated speed of each active joint of the mechanism are obtained by introducing a screw theory; secondly, based on this, a kinetic equation in a mechanism spinor form is established by use of virtual work principle; and finally, axial driving power of each active joint of the conveying mechanism capable of directly realizing control is obtained through calculation so that construction of a dynamics model capable of realizing high-performance control is completed. According to the invention, the analytical geometry method, the screw theory and the virtual work principle are combined together, so that the problem of coordinate transformation due to lack of coordinate invariance during dynamics modeling of a complex special mechanism is solved, the calculation complexity is reduced, and at the same time, the dynamics modeling method brought forward by the invention is quite simple, is tidy in form and is easy in programmed realization.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method used for determining all singular configurations of 9-freedom-degree mechanical arm
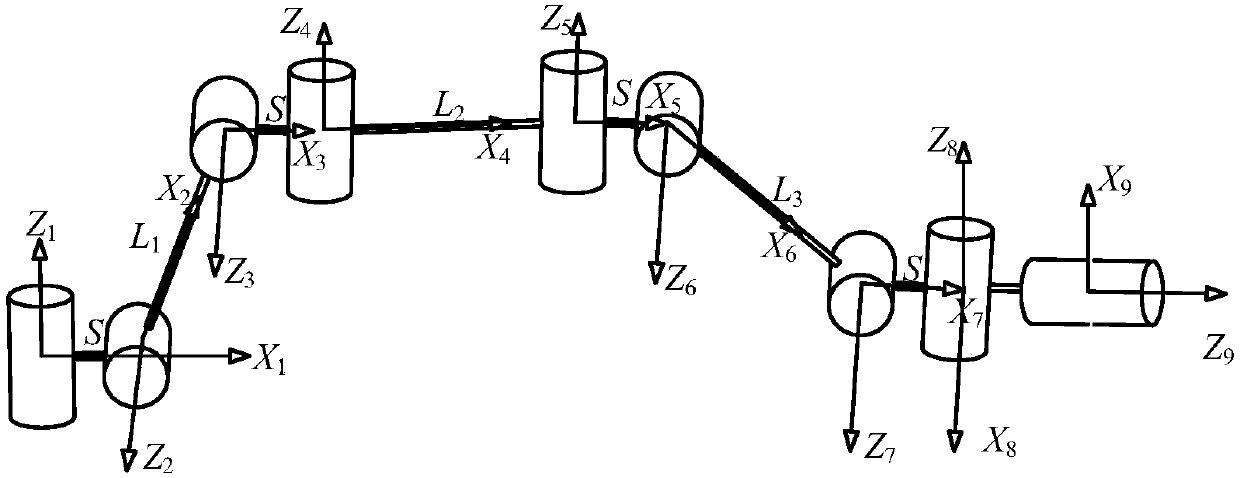
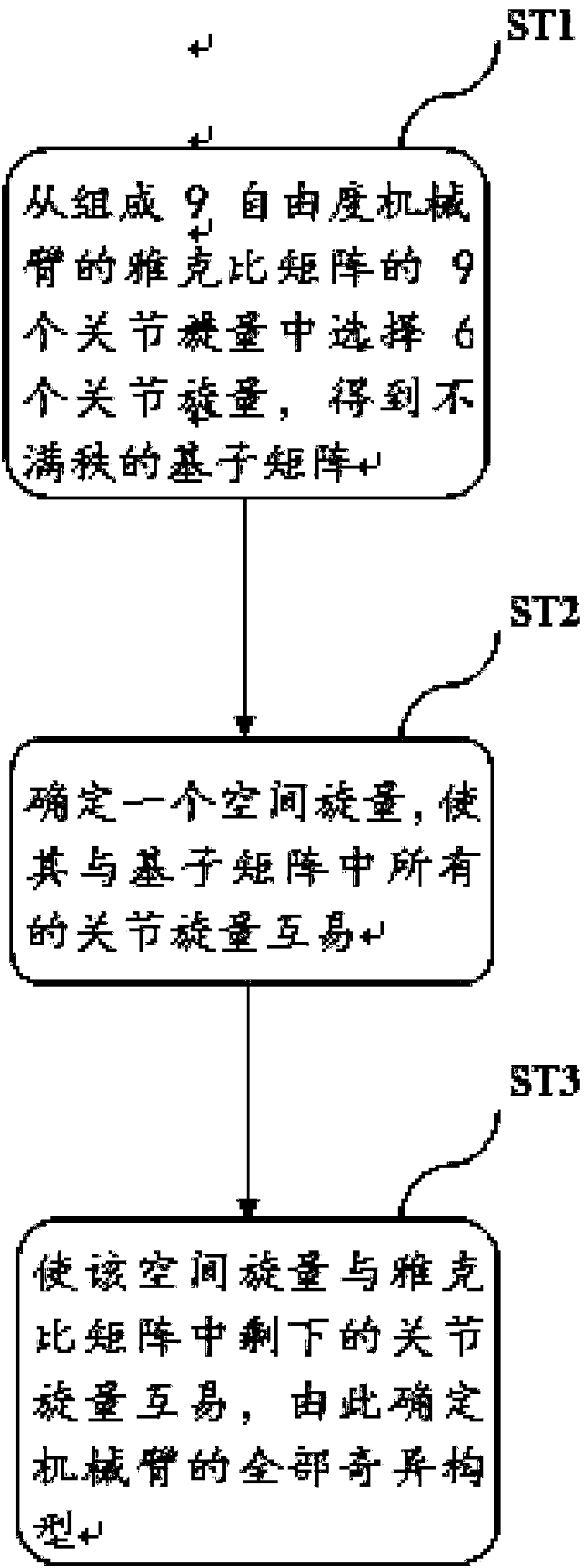
ActiveCN107650120AOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to determine the singular configuration of redundant manipulatorsEasy to analyze and calculateProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringDegrees of freedom
The invention discloses a method used for determining all singular configurations of a 9-freedom-degree mechanical arm. The 9-freedom-degree mechanical arm is composed of 4 same eccentric joints and an independent joint. The method includes the steps that 6 spinors are selected from 9 spinors forming a jacobian matrix [J]=[$[1], $[2],..,$[k]] of the 9-freedom-degree mechanical arm, and a base sub-matrix is obtained, wherein the base sub-matrix is not a full-rank matrix; a space spinor w is determined and is exchanged with all the joint spinors in the base sub-matrix; by using the condition that the 9-freedom-degree mechanical arm is in the singular configurations, w can also be exchanged with the rest of the 3 joint spinors (please see the formula in the specifications), and all the singular configurations of the 9-freedom-degree mechanical arm are determined in this way.
Owner:深圳力合精密装备科技有限公司
Error vector modeling method for rotating shaft position deviation
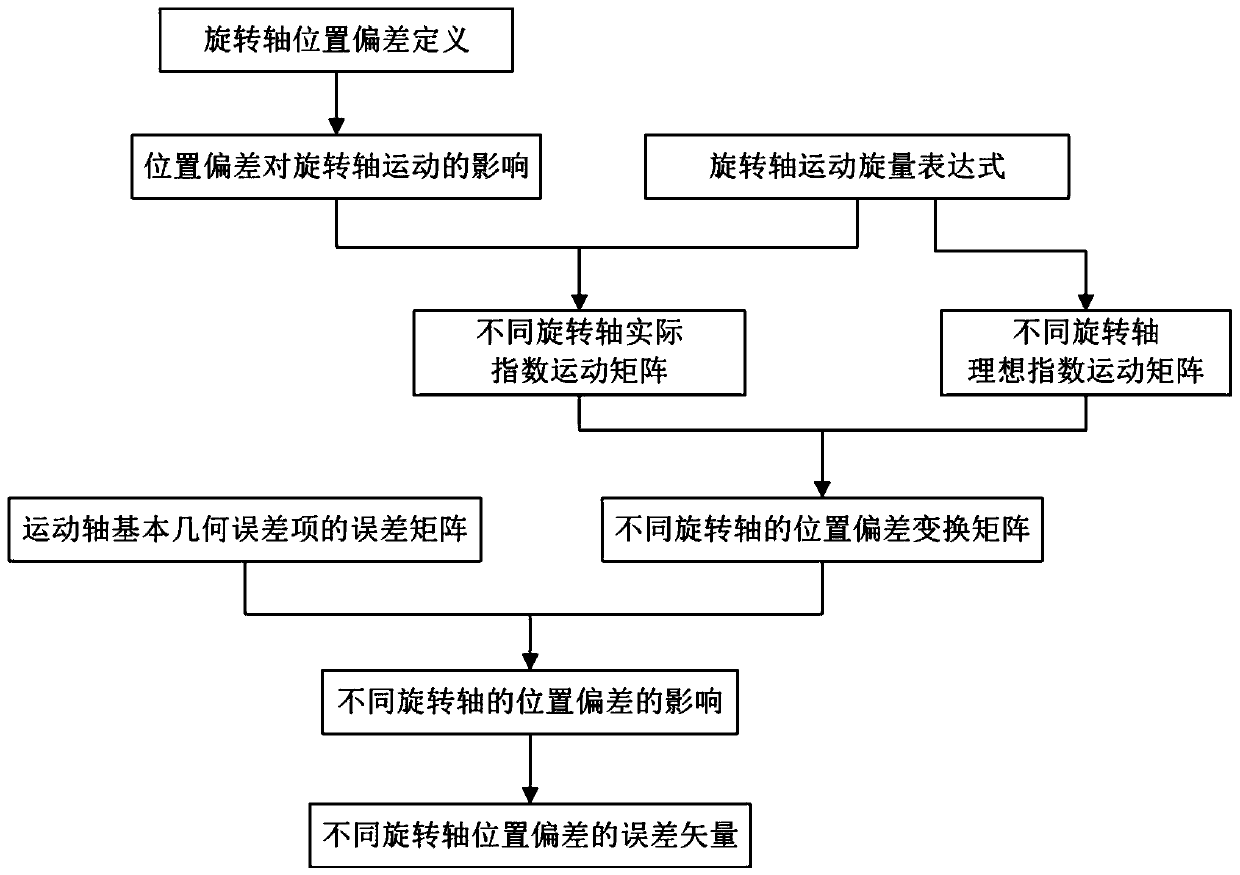
ActiveCN109933920AExact error matrixImprove versatilitySpecial data processing applicationsSimulationPosition bias
The invention discloses an error vector modeling method for rotating shaft position deviation. The method comprises the following steps: S1, defining and analyzing the influence of the position deviation on the movement of the rotating shaft according to the movement property and the position deviation of the rotating shaft; S2, establishing a rotating shaft motion spinor expression according to aspinor definition in an exponential product theory; S3, constructing A-axis, B-axis and C-axis ideal index motion matrixes according to the motion properties of different rotating shafts; S4, constructing an actual exponential motion matrix under the influence of the position deviation of the A axis, the B axis and the C axis by adopting an exponential product theory according to the position deviation distribution of different rotating shafts; S5, constructing position deviation transformation matrixes of different rotating shafts according to the relation among the motion axis error matrix,the ideal motion matrix and the actual motion matrix; S6, comparing the position deviation transformation matrixes of the different rotating shafts with the error matrix of the basic geometric erroritem of the motion shaft to obtain the position deviation influence of the different rotating shafts; and S7, substituting the position deviation influences of different rotating shafts, and constructing error vectors of the position deviations of the different rotating shafts.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
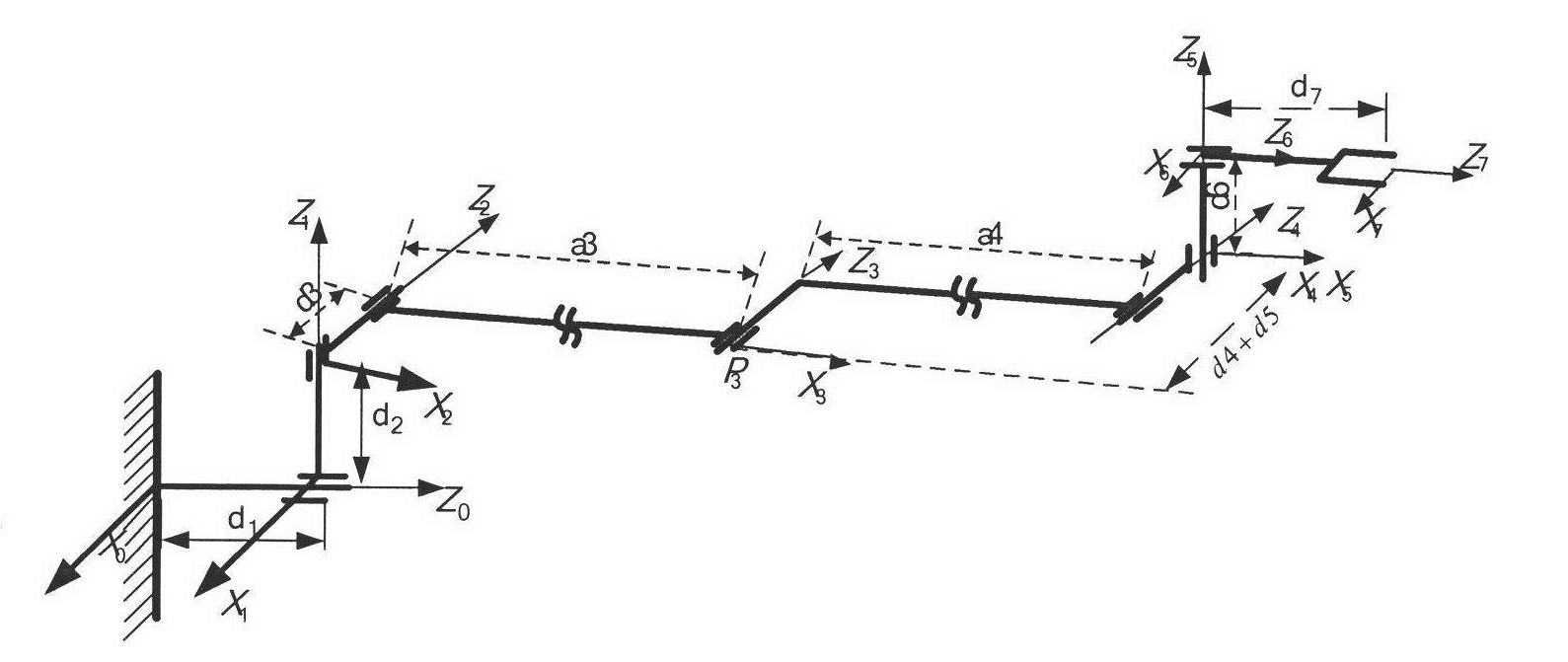
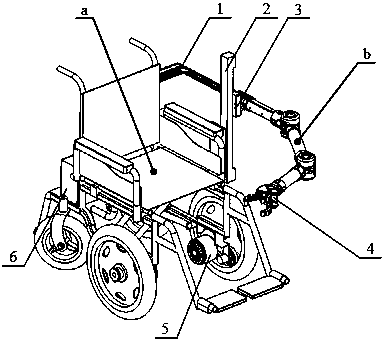
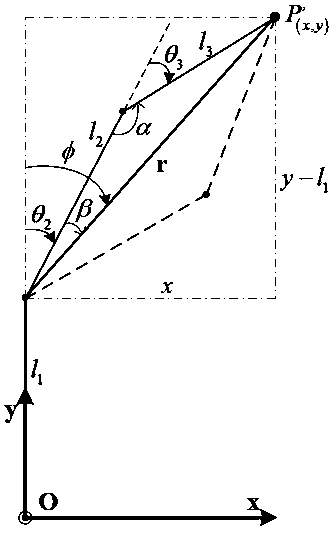
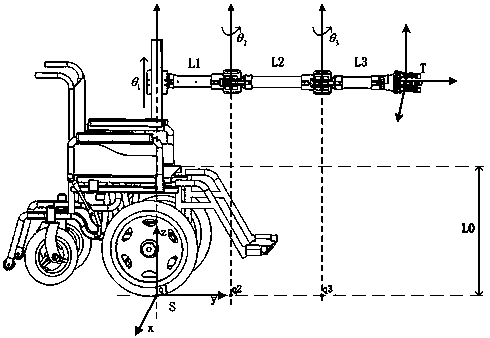
Multi-joint aged and disabled helping wheelchair mechanical arm and kinematical modeling method based on spinor theory
The invention discloses a multi-joint aged and disabled helping wheelchair mechanical arm and a kinematical modeling method based on a spinor theory, and belongs to the field of robot kinematics analysis method research. The kinematical modeling is performed on a wheelchair mechanical arm through an index matrix form of the spinor theory; firstly, a base coordinate system of an initial pose and atool coordinate system are built; and then, kinematics parameters of the wheelchair mechanical arm are determined by the base coordinate system and the tool coordinate system to finish building of a forward kinematics model. According to the structural form of the wheelchair mechanical arm and the motion mode of each joint, the wheelchair mechanical arm is treated as an inverse kinematics form ofa plane two-rod robot to realize the joint motion quantity solving of the mechanical arm to finally finish the inverse kinematics solving analysis. Through the mode of combining the geometric description with the spinor theory, the kinematics solving algorithm is simplified as the algebraic equation set solving process, and a new more-convenient modeling solving method is provided for real-time motion control of the wheelchair mechanical arm.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
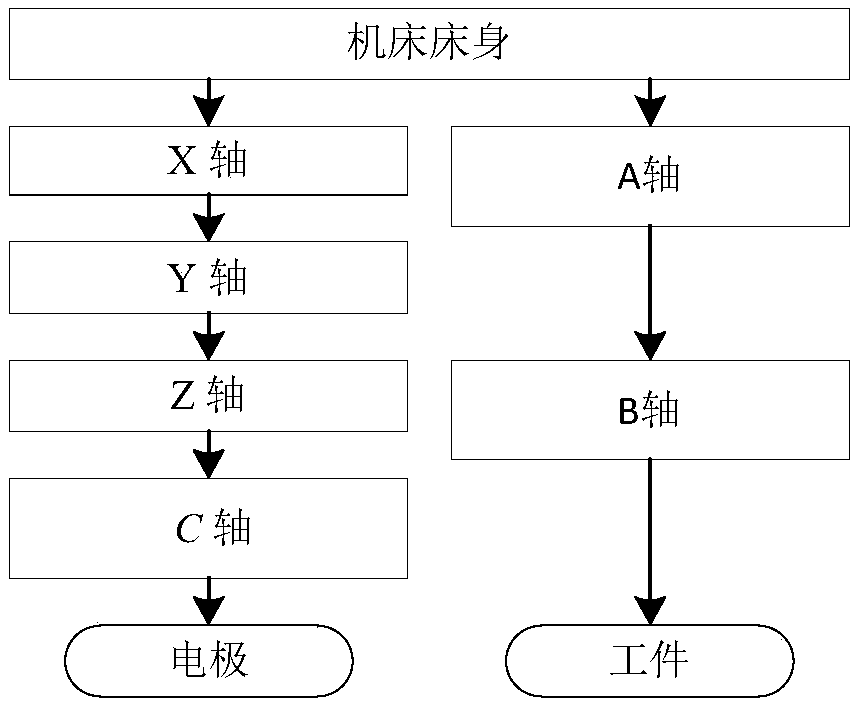
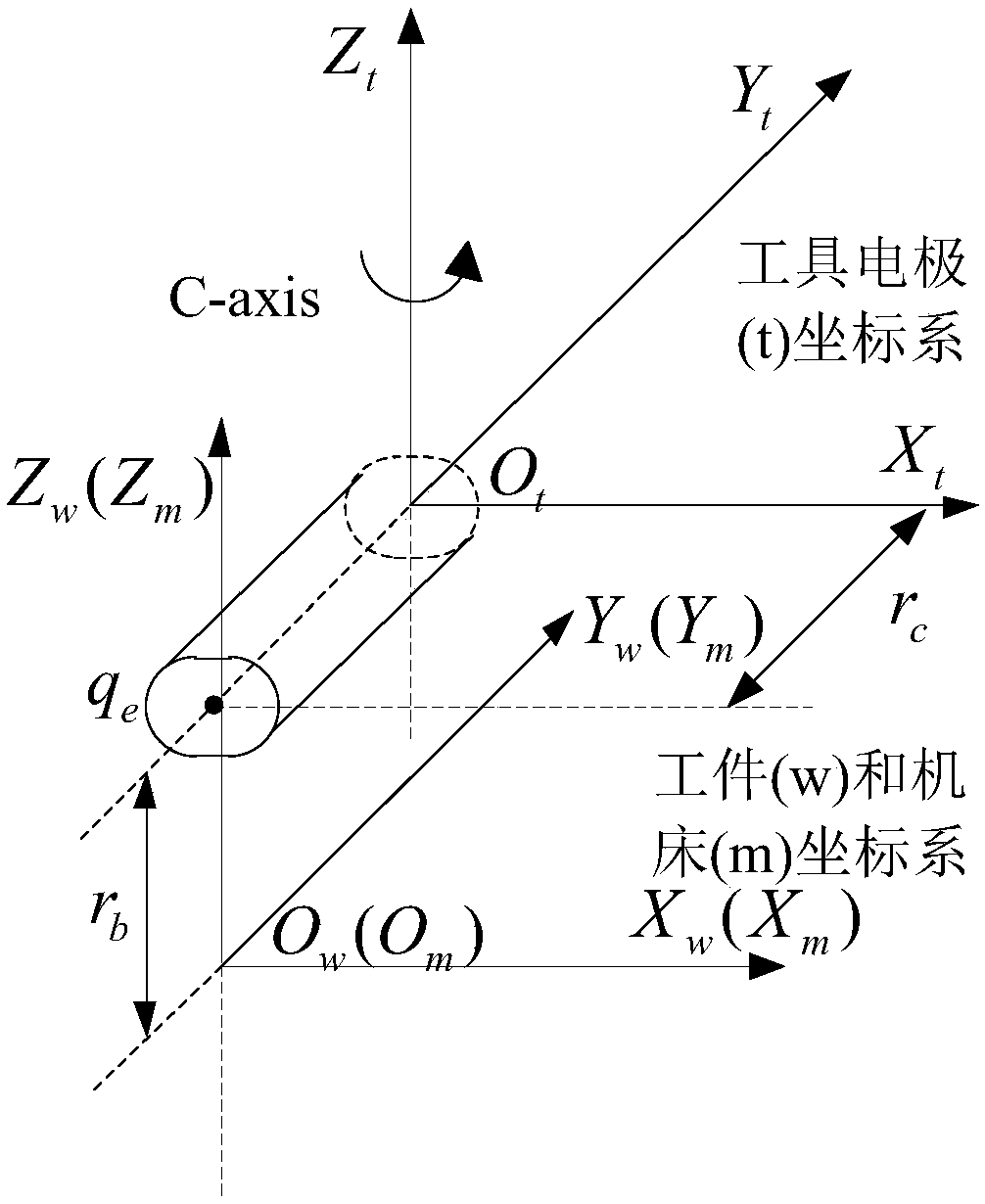
Six-axis linkage electric discharge machining tool kinematic optimization control method based on spinor
ActiveCN108388199AFast processingControl discharge gapNumerical controlRotational axisStabilization control
The invention provides a six-axis linkage electric discharge machining tool kinematic optimization control method based on the spinor theory. The kinematic relational expression between the tool electrode in the six-axis linkage electric discharge machining tool and the workpiece is obtained through the spinor theory and a corresponding spinor is established for each kinematic pair, the kinematicrelation from the machining workpiece to the machine tool body is established by using the product of the spinor power function, and finally a kinematic transfer matrix from the machining tool coordinate system to the workpiece coordinate system is obtained through matrix inversion so that the machining speed in the machining process can be optimized. The discharge state instability caused by theinconsistency of the motion of the rotation axis and the translation axis dimension in the machining process can be avoided so that the problem of speed fluctuation in the machining process can be solved, the discharge gap in the electric discharge machining process can be stably controlled and thus the efficiency of electric discharge machining can be enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Innermost data sharing method of lattice quantum chromodynamics calculation
ActiveUS20170116356A1Design optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingQuantum chromodynamicsData sharing
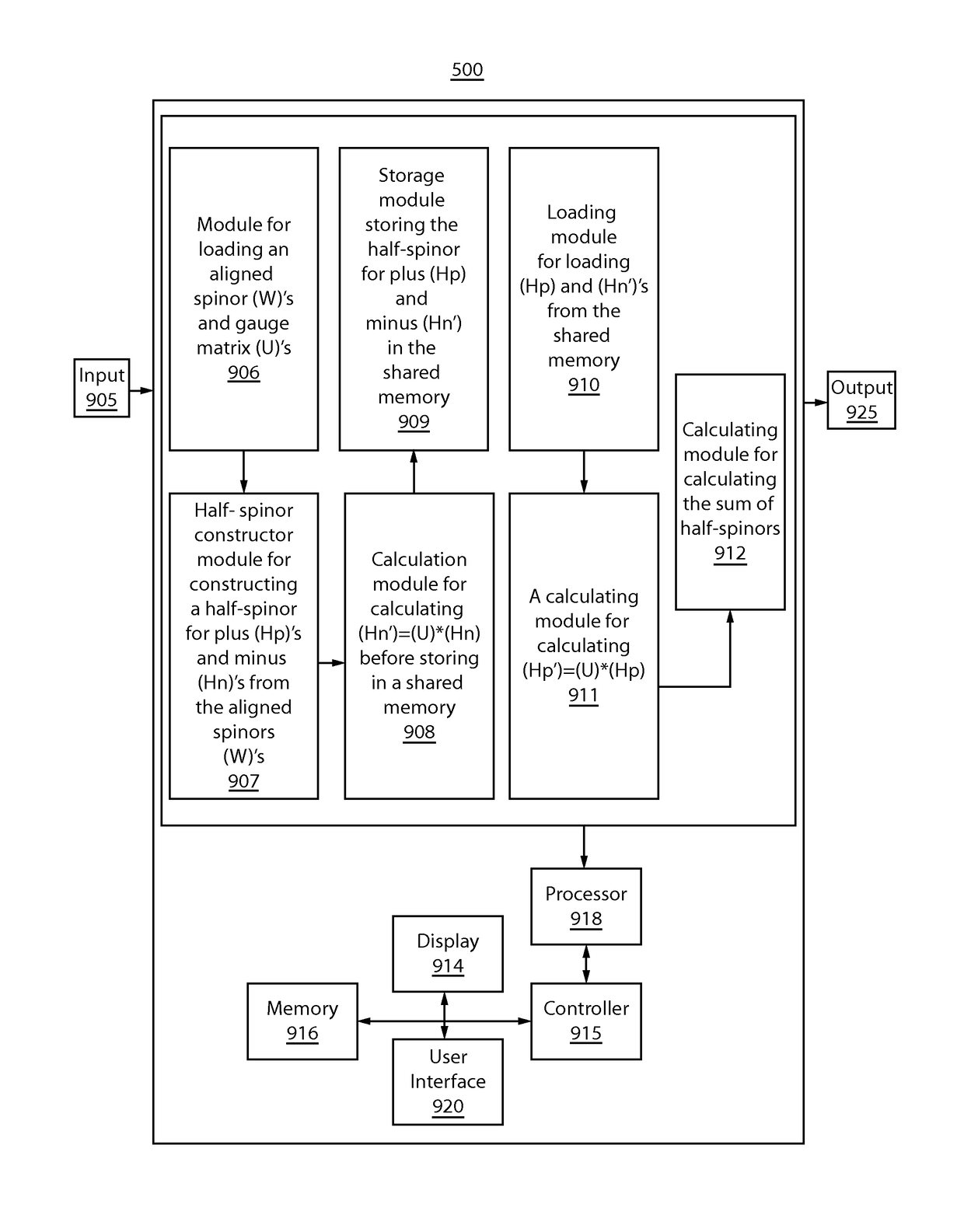
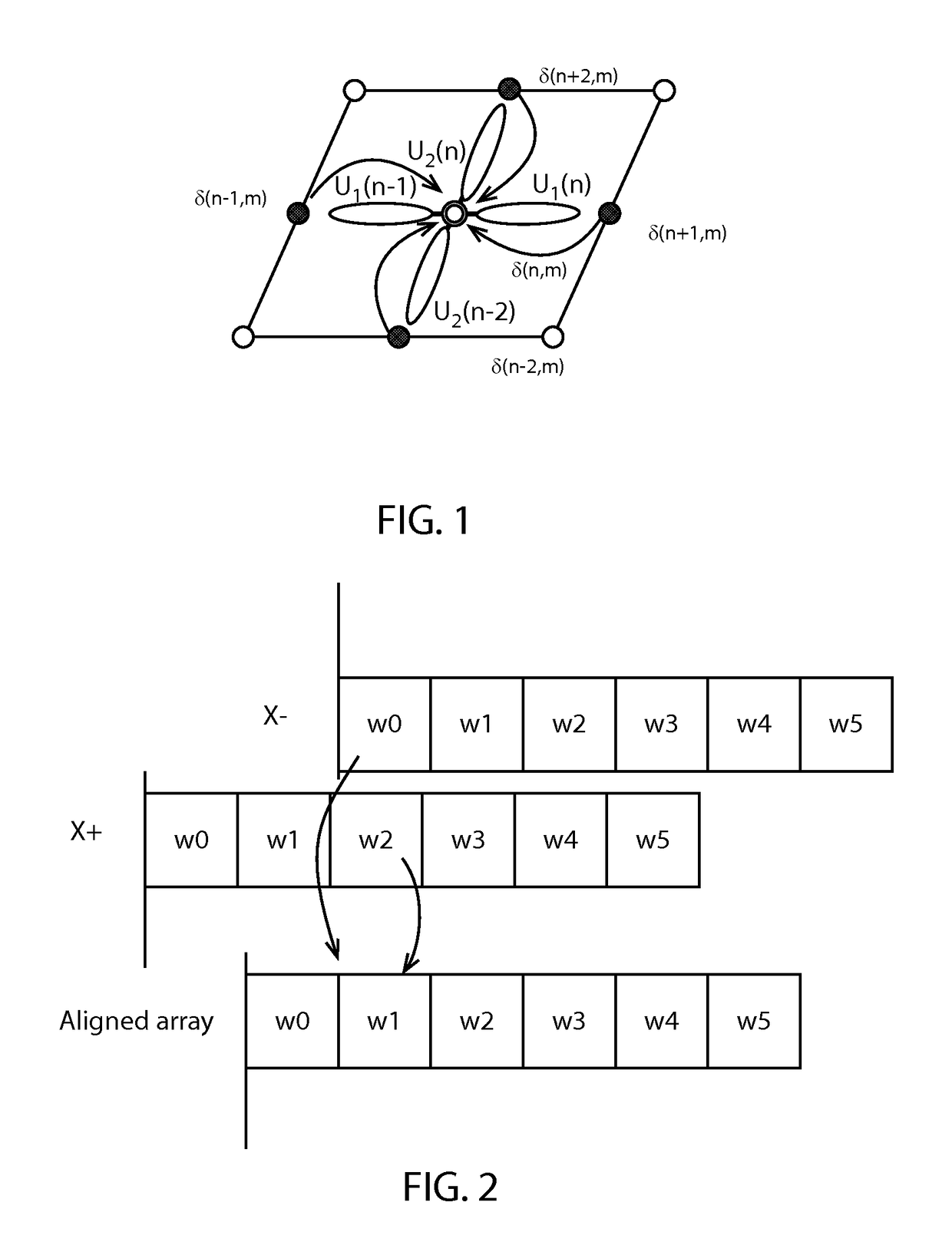
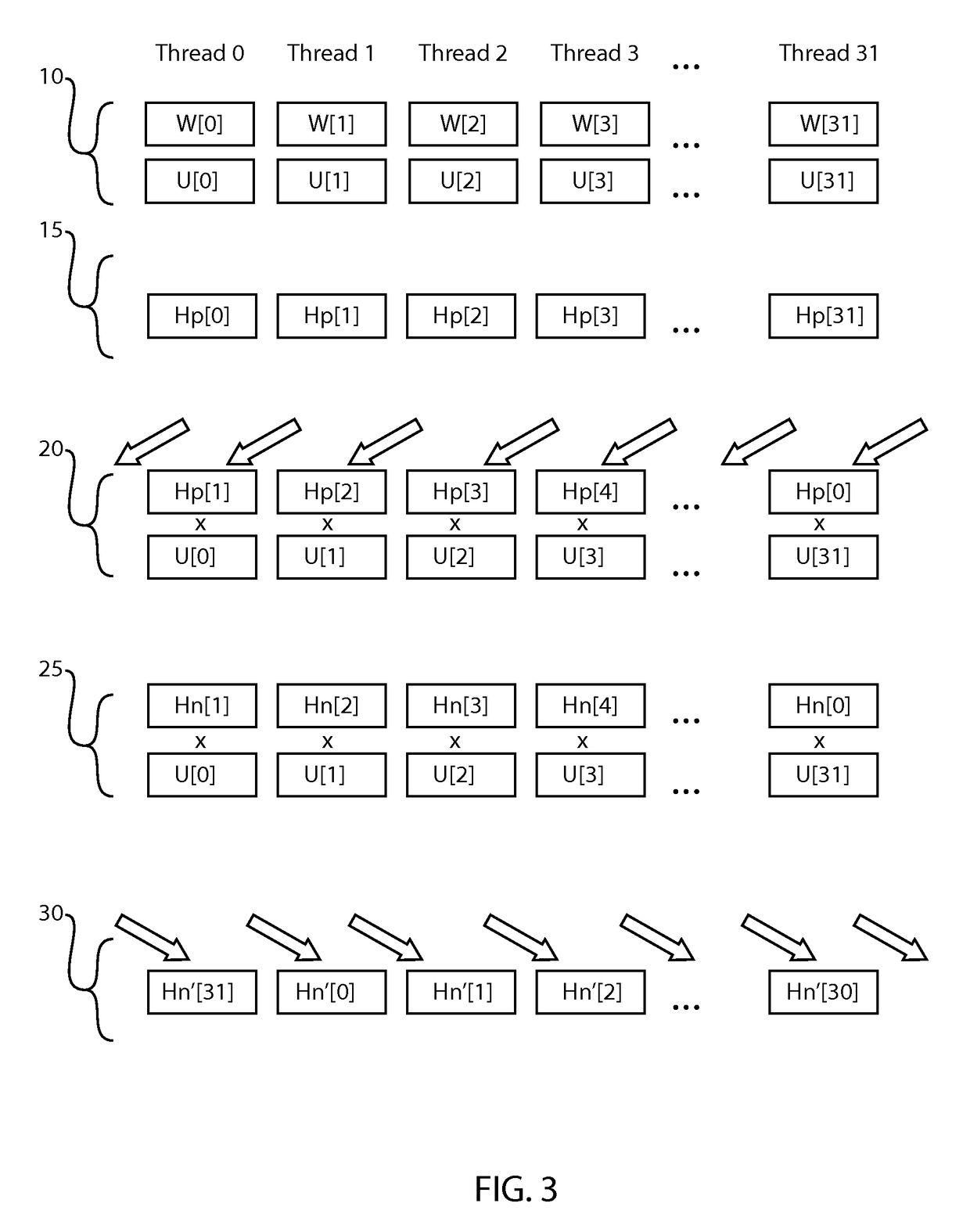
A method for calculating lattice quantum chromodynamics (QCD) that includes loading an aligned spinor and gauge matrix, and constructing a half-spinor for plus and minus from the aligned spinors. In a following step, the method may include calculating a half spinor minus to be transferred to a positive neighbor of the gauge matrix by multiplying the gauge matrix and half-spinor for minus. The half-spinor for plus (Hp) and the half spinor minus may be stored in a shared memory. In a following step, the method may continue with calculating a half spinor plus to be transferred to a negative neighbor of the gauge matrix by multiplying the gauge matrix and the half-spinor for plus. Thereafter, the sum of half-spinors may be calculated.
Owner:IBM CORP
Robot calibration method based on exponent product model
ActiveCN102022989BHigh precisionImprove stabilityMeasurement devicesManipulatorKinematicsMeasuring instrument
Owner:青岛卓信通智能科技有限公司
Focus adjustable method of optical image
InactiveUS7634183B2Good optical performanceImprove focus performanceTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementLight beamComputer science
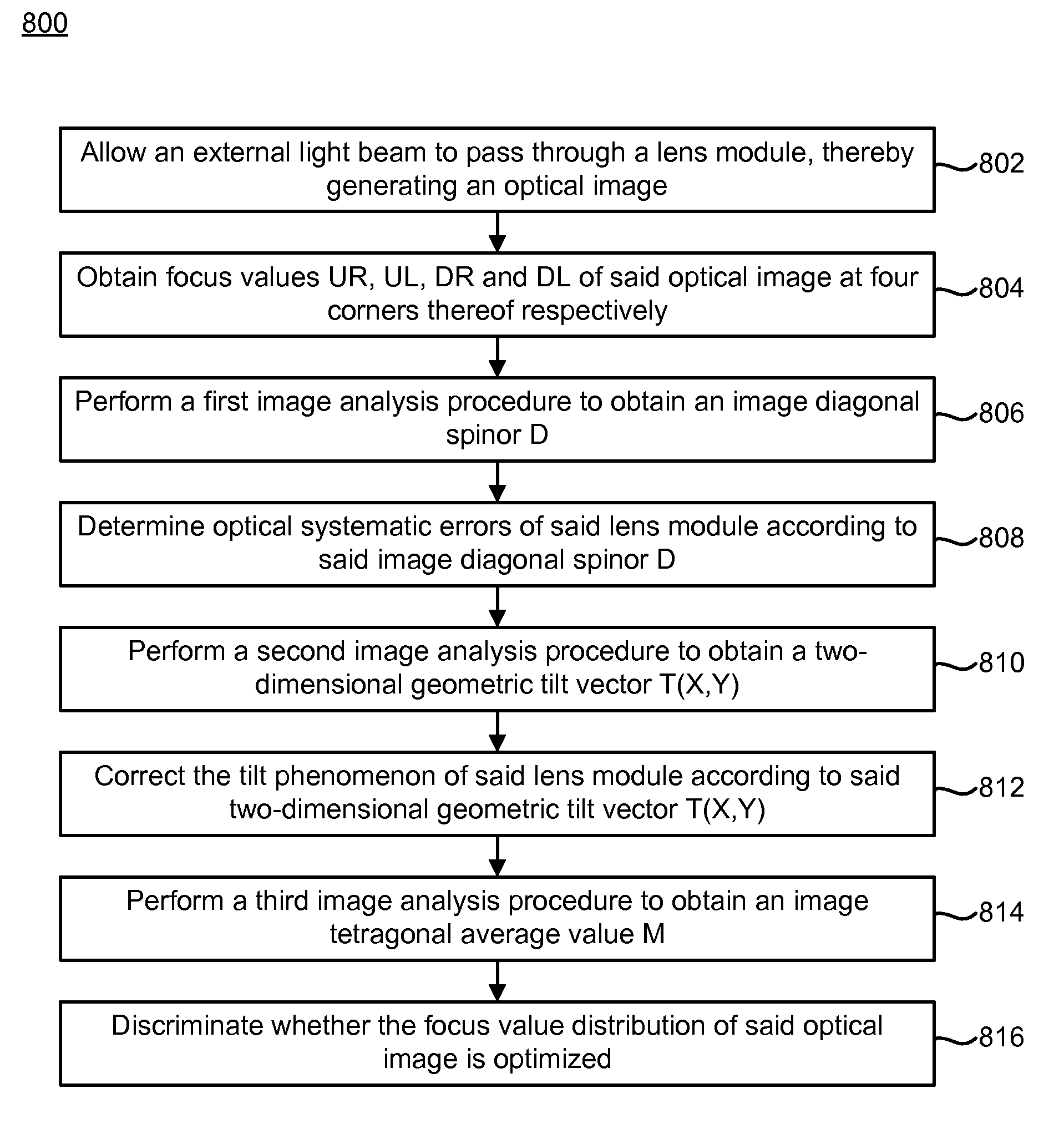
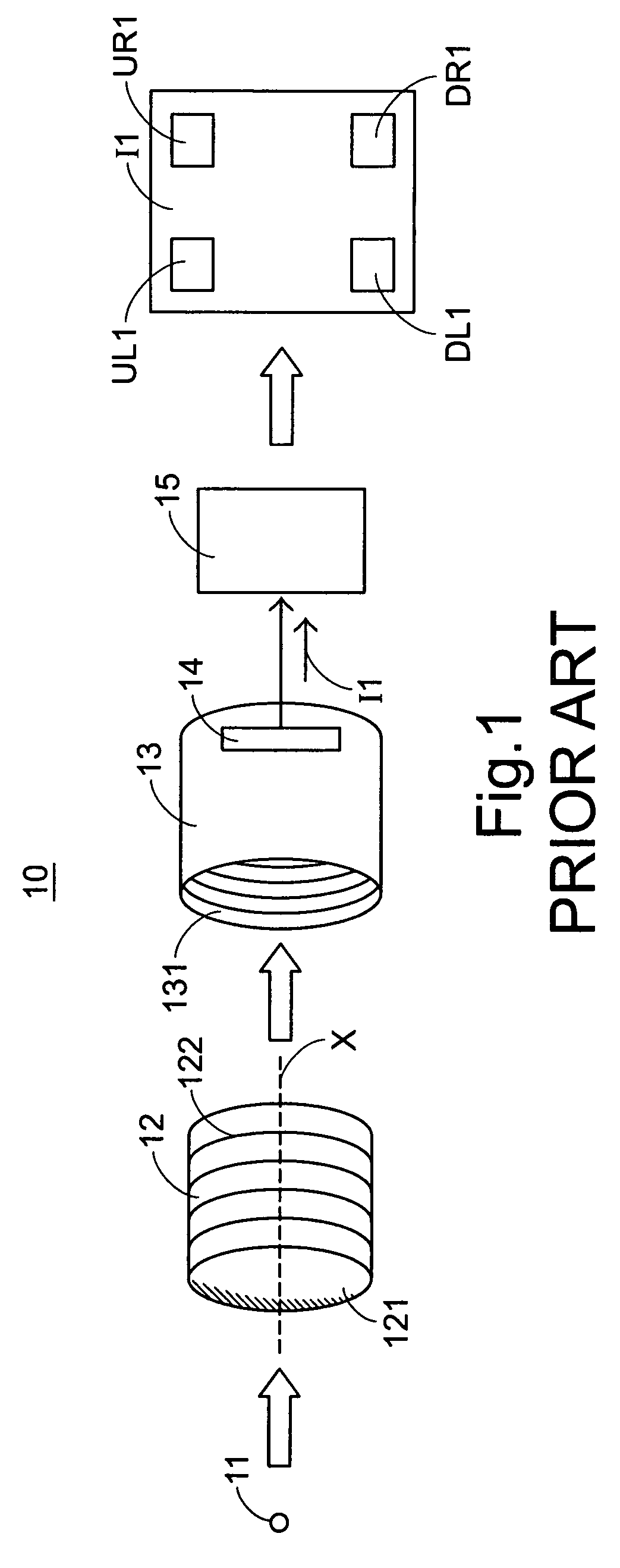
A focus adjustable method of an optical image is implemented by a numerical analysis. An external light beam is allowed to pass through a lens module, thereby generating an optical image. The focus values of the optical image at four corners thereof are computed according to specified formulas to obtain a two-dimensional geometric tilt vector T(X,Y), an image diagonal spinor D and an image tetragonal average value M. According to the values T(X,Y), D and M, the tilt amount and the tilt direction of the lens module are adjusted, the optical quality of the lens module is discriminated and the focus value distribution of the lens module is determined.
Owner:PRIMAX ELECTRONICS LTD
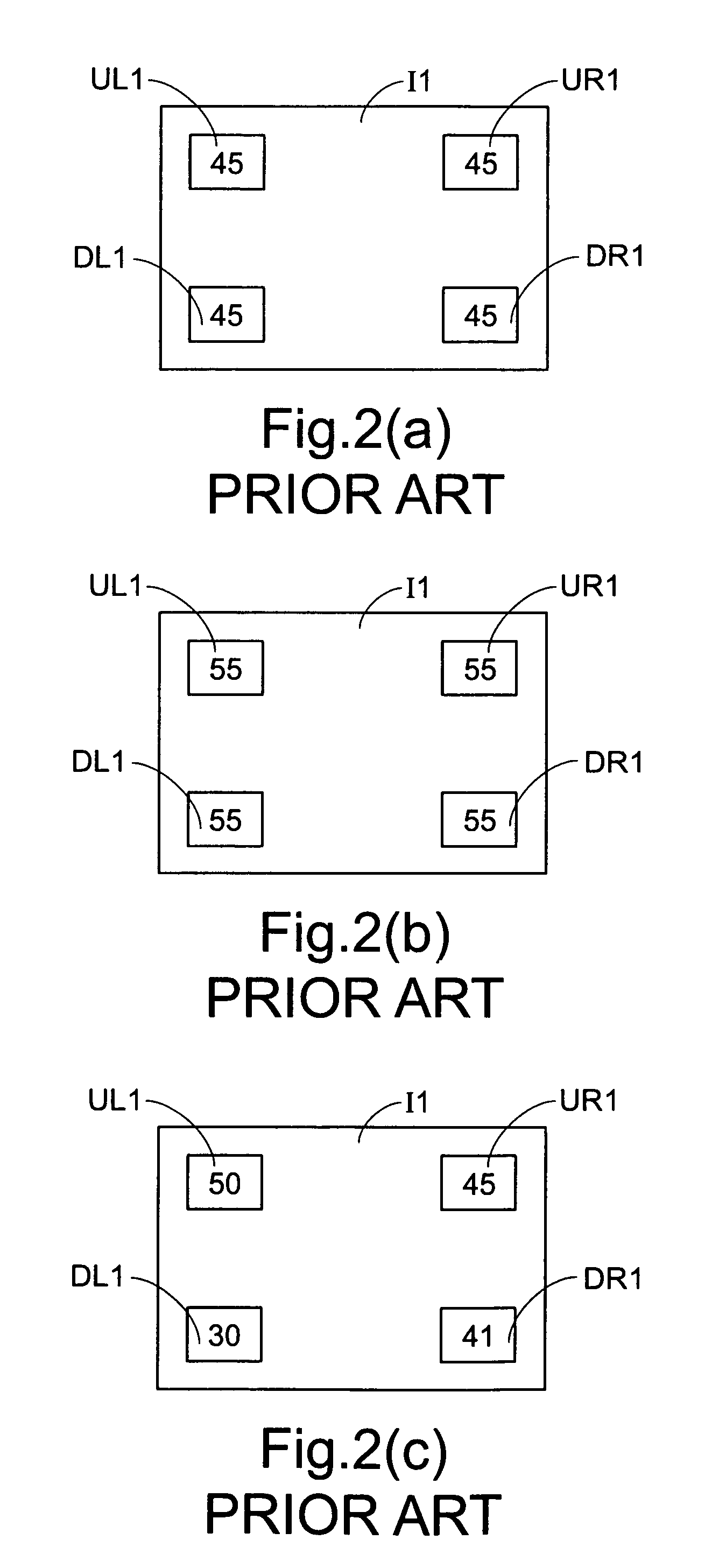
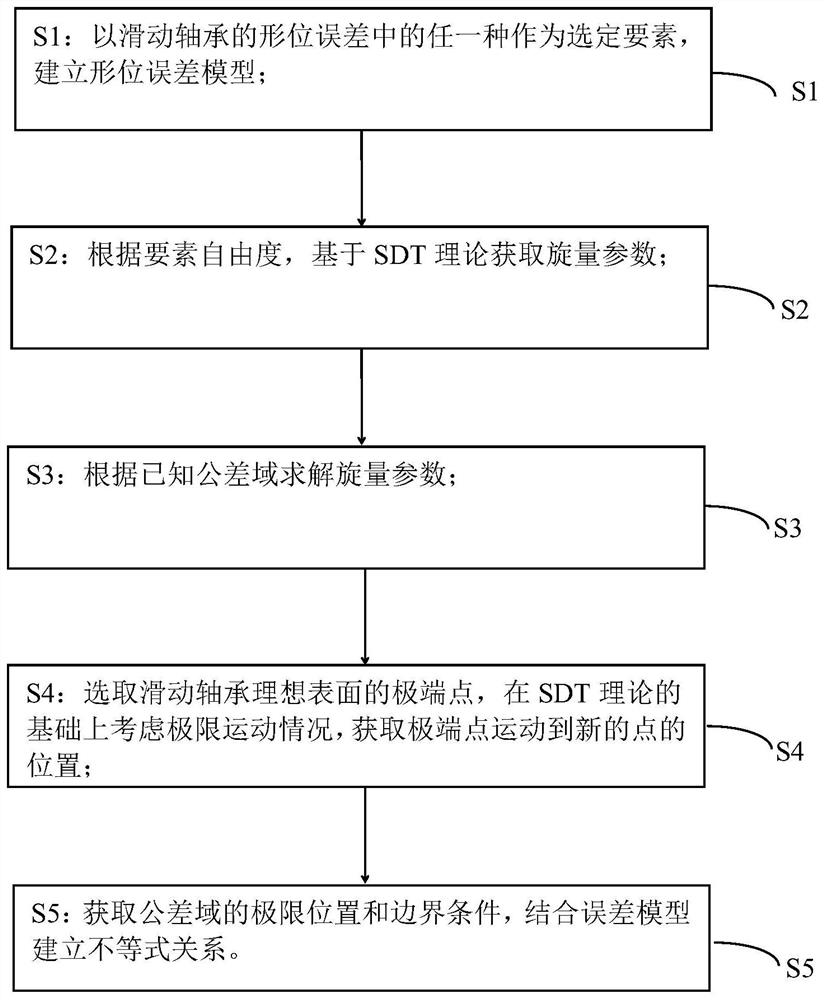
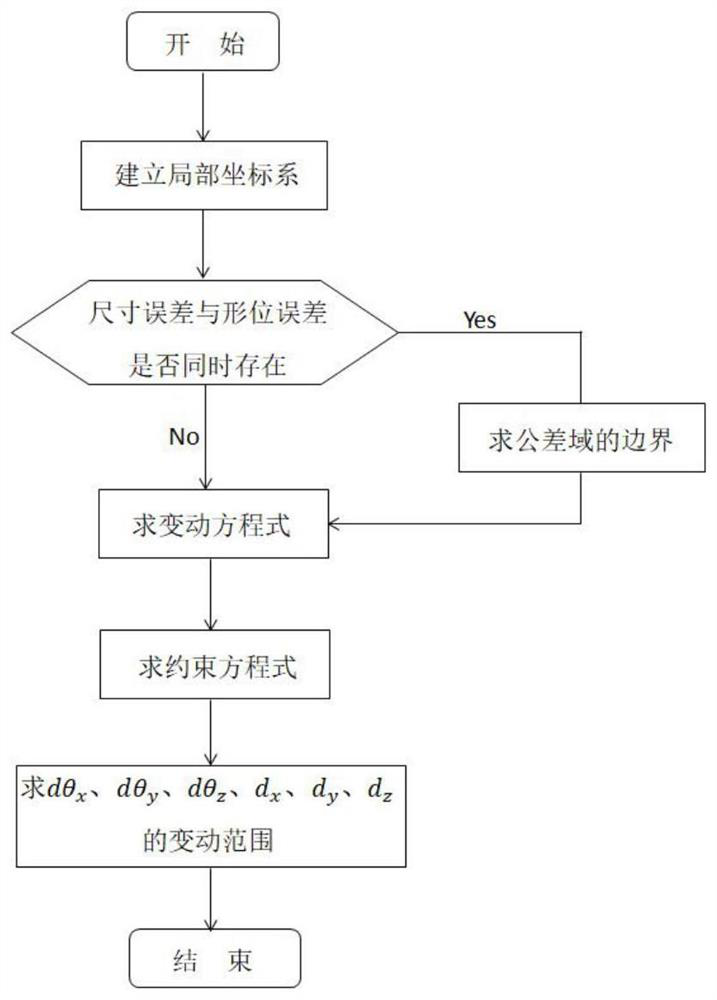
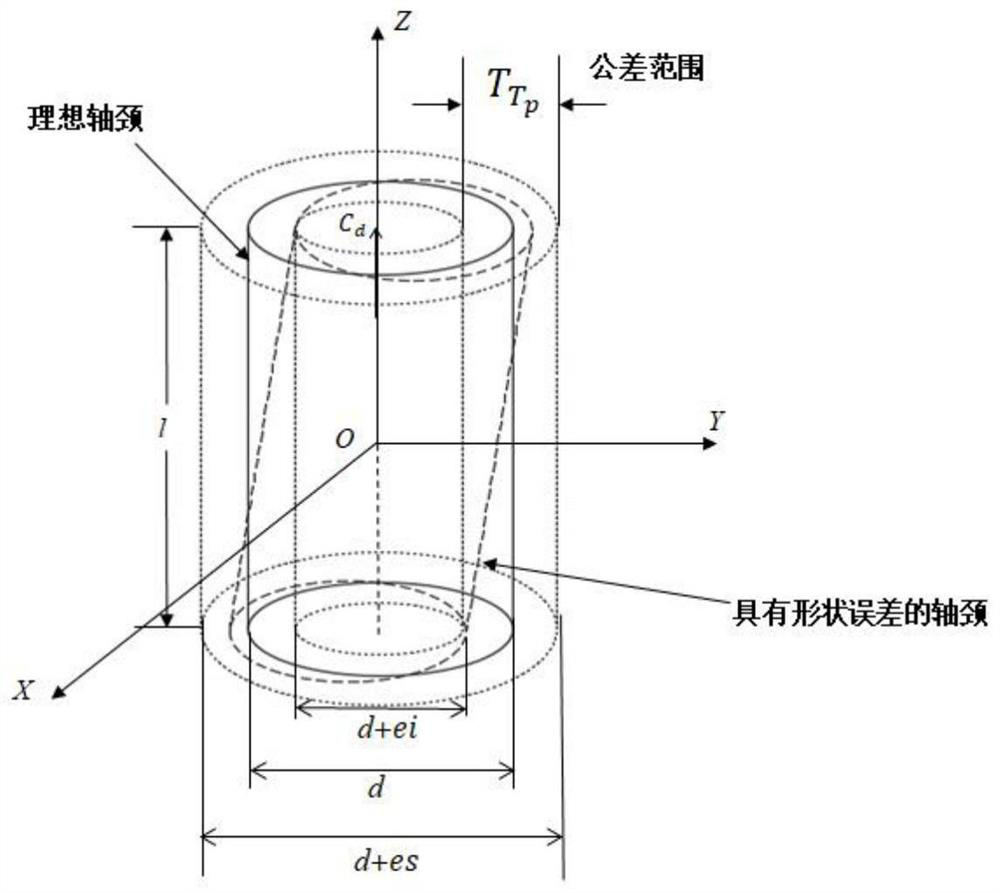
Sliding bearing form and position error modeling method based on SDT theory
ActiveCN112182804AAccurate representationGeometric CADSustainable transportationClassical mechanicsEngineering
The invention discloses a sliding bearing form and position error modeling method based on an SDT theory. The method comprises the steps: S1, building a form and position error model through taking any one of form and position errors of a sliding bearing as a selected element; S2, according to the degree of freedom of the elements, obtaining a spinor parameter based on an SDT theory; S3, solving aspinor parameter according to the known tolerance domain; S4, selecting the extreme point of the ideal surface of the sliding bearing, considering the extreme motion situation on the basis of the SDTtheory, and obtaining the position of the extreme point moving to a new point; and S5, according to the limit position and the boundary condition of the known tolerance domain, establishing an inequality constraint condition in combination with the error model. According to the invention, the generalized equation derived on the basis of the SDT theory not only can represent one form and positionerror, but also can represent any form and position error on the journal.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Wireless communication antenna device
ActiveCN102570041AImprove phase characteristicsImprove linearityWaveguide hornsPhase differenceLoudspeaker
The invention relates to a wireless communication antenna device, which comprises a loudspeaker antenna and a wave guide pipe, wherein the loudspeaker antenna is used for emitting or receiving a polarized radio wave signal, the polarized radio wave signal is provided with a first component electric field and a second component electric field which are orthogonal to each other, the wave guide pipe is connected with the loudspeaker antenna and is used for transmitting the polarized radio wave signal, and in a first opening of the wave guide pipe, the edge length corresponding to the first component electric field, is different from the edge length corresponding to the second component electric field, so a phase difference exists between the first component electric field and the second component electric field when the polarized radio wave signal is transmitted in the wave guide pipe. The wireless communication antenna device has the advantages that the phase characteristics of the polarized radio wave transmission are improved, and in addition, the linear and spinor wave polarized conversion performance can be optimized.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
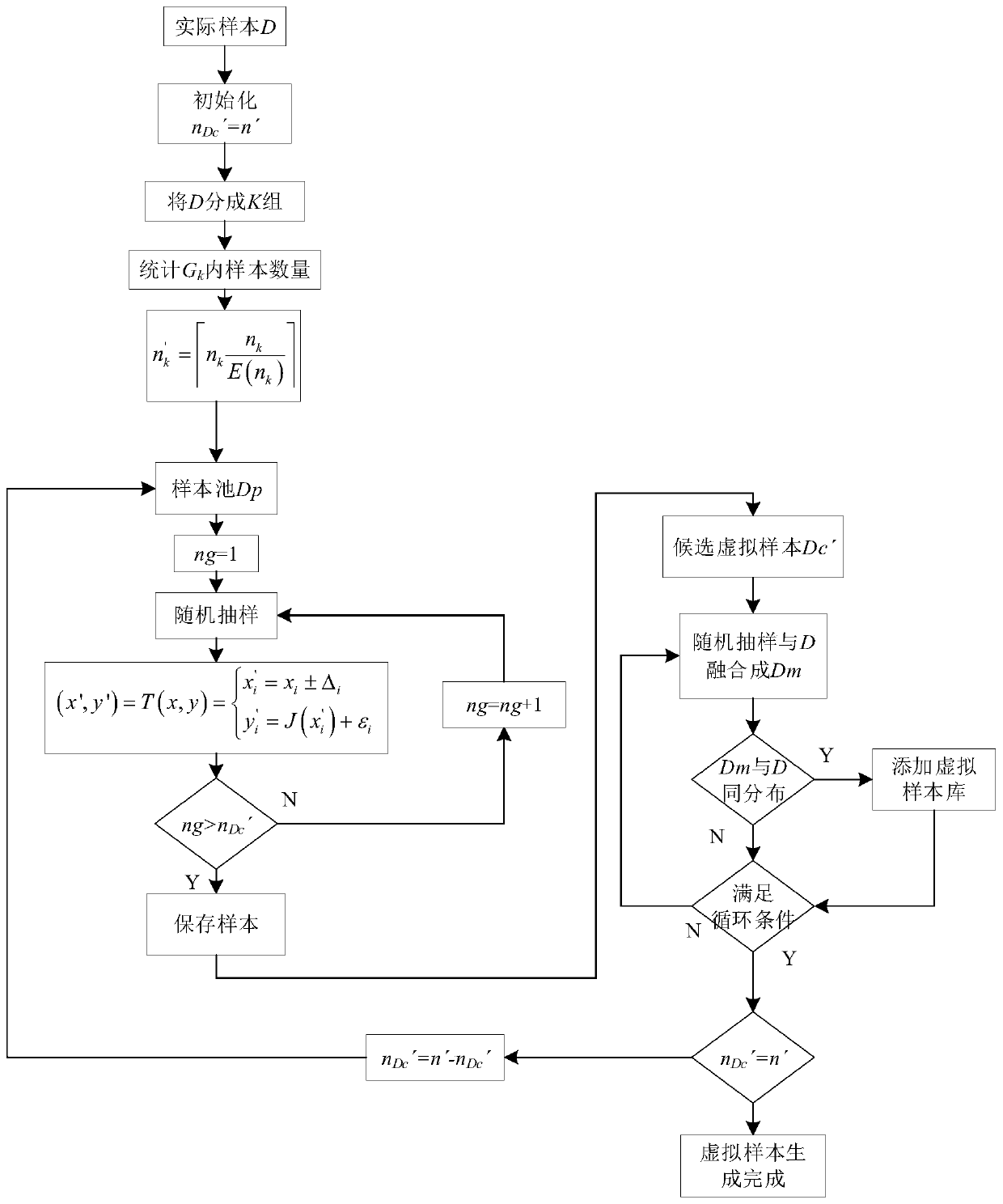
Virtual sample expansion method based on mechanical product historical data
ActiveCN110598243ASolving insufficient sample sizeCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSmall sampleVirtual sample
The invention discloses a virtual sample capacity expansion method based on the mechanical product historical data. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, determining the virtual samplecapacity of a virtual sample in a small sample problem according to the actually measured historical data; constructing a sample pool for generating the virtual samples based on the historical data ofthe mechanical production and the related priori knowledge of the mechanical production; then performing sample sampling based on a roulette sampling thought, and designing a virtual sample generation rule based on an agent model thought and a Jacobian spinor theory; and finally, reserving a feasible expansion sample through a sample rationality judgment condition, so that the small sample regression problem training virtual sample expansion for the mechanical assembly precision prediction is realized. The method can be used for expanding the sample capacity of a small-capacity sample machinelearning training model, can solve the problem that the number of the samples is insufficient in the mechanical assembly precision prediction, and has the important significance for researching the small samples for customizing the product tolerance transfer by using a machine learning regression method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com