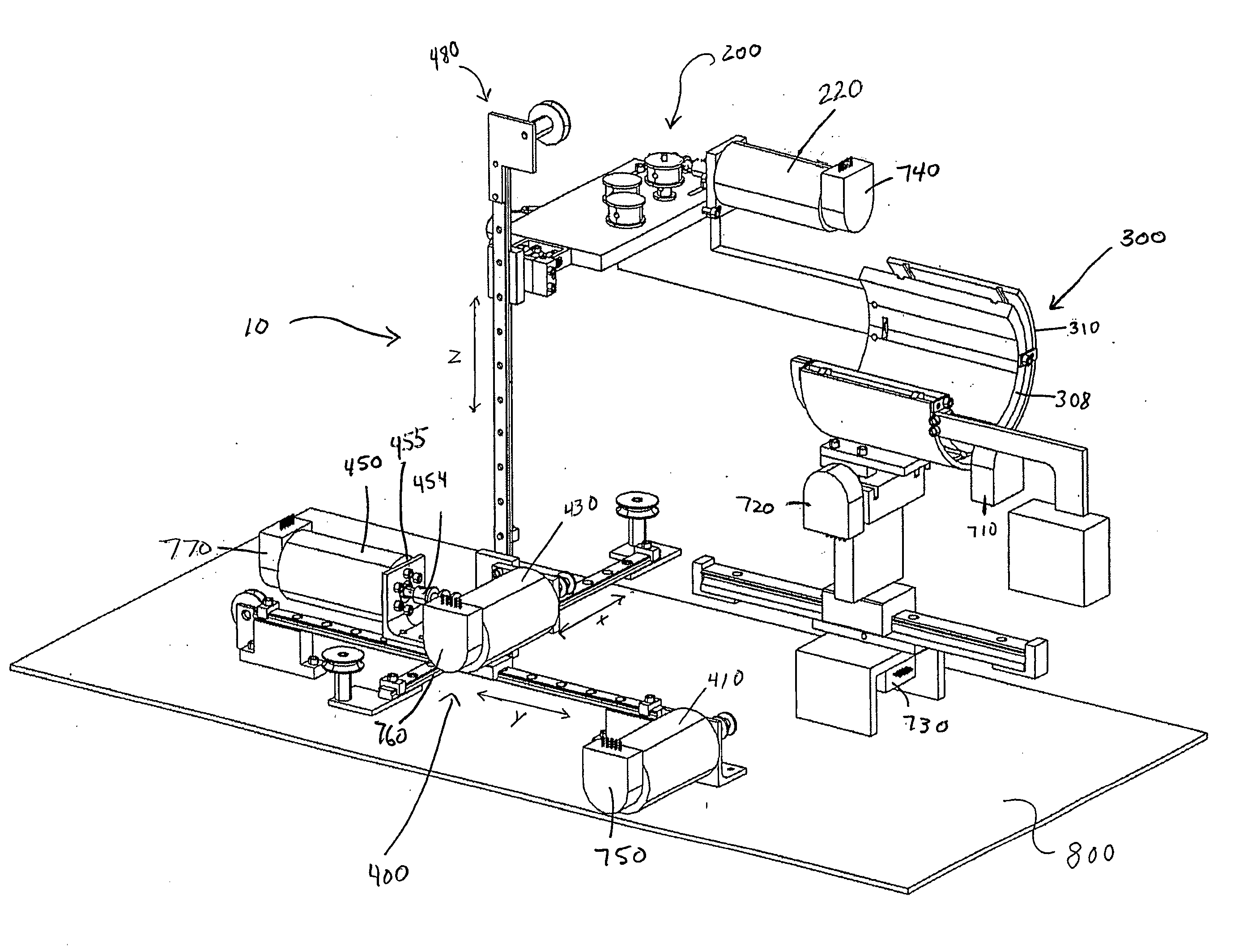
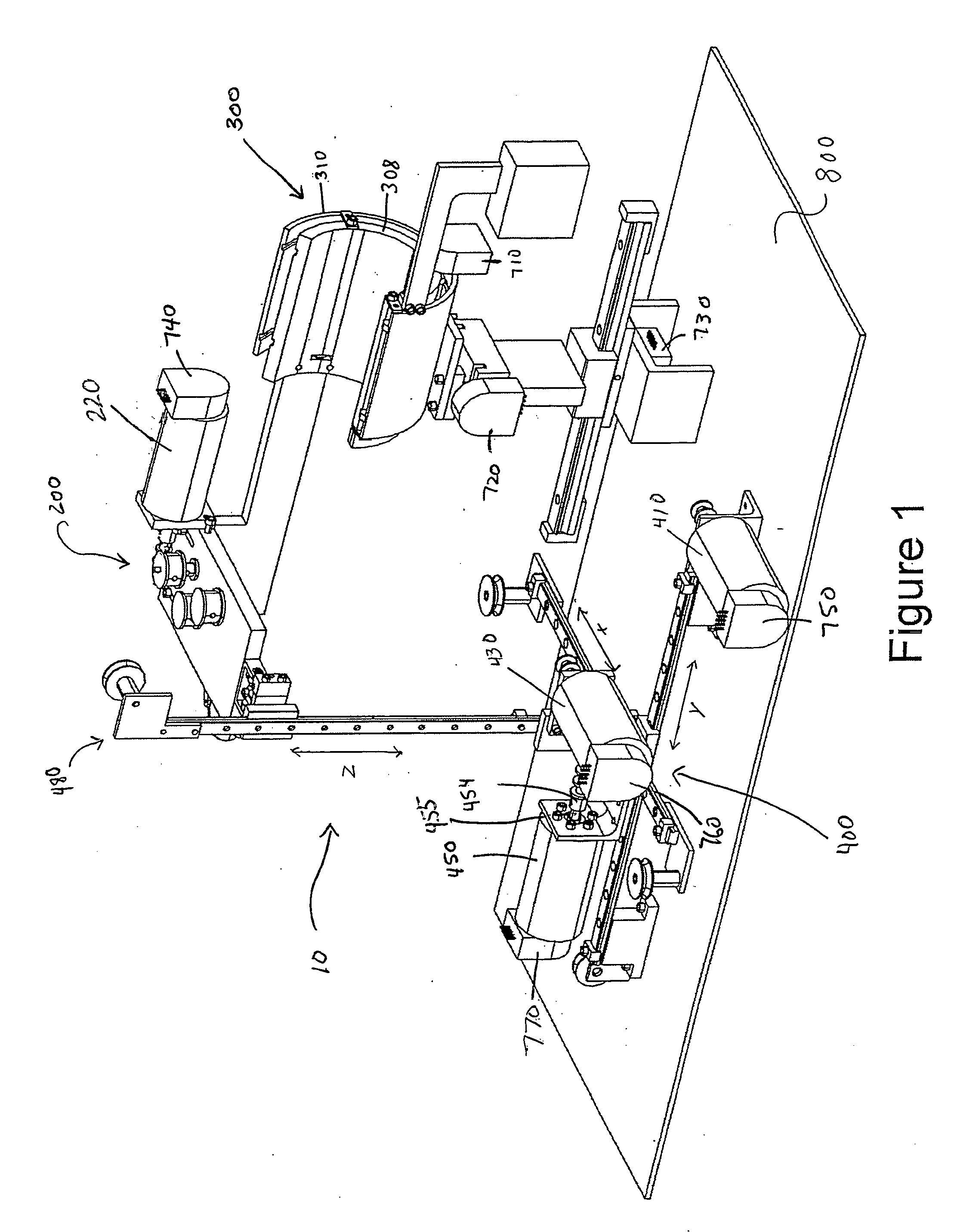
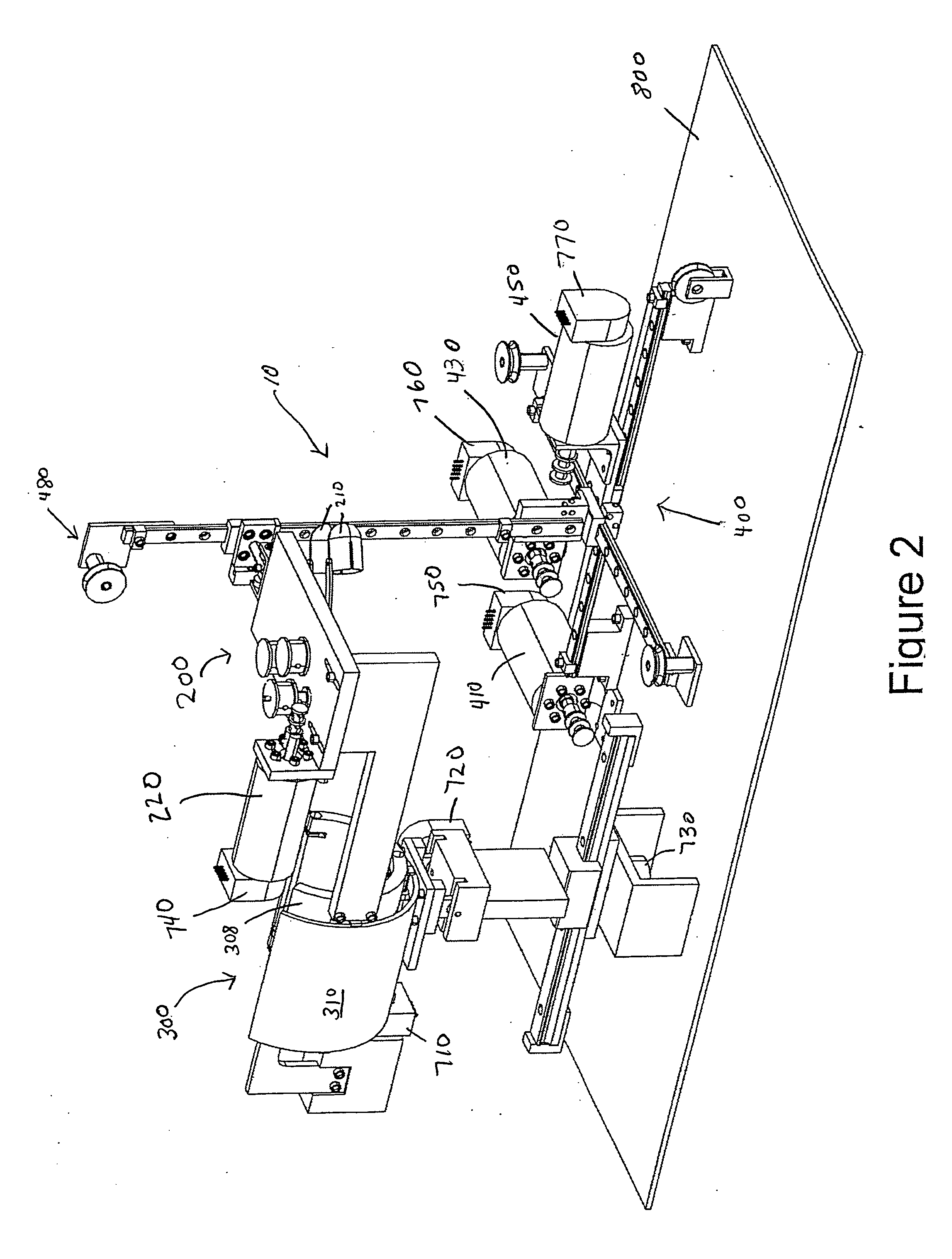
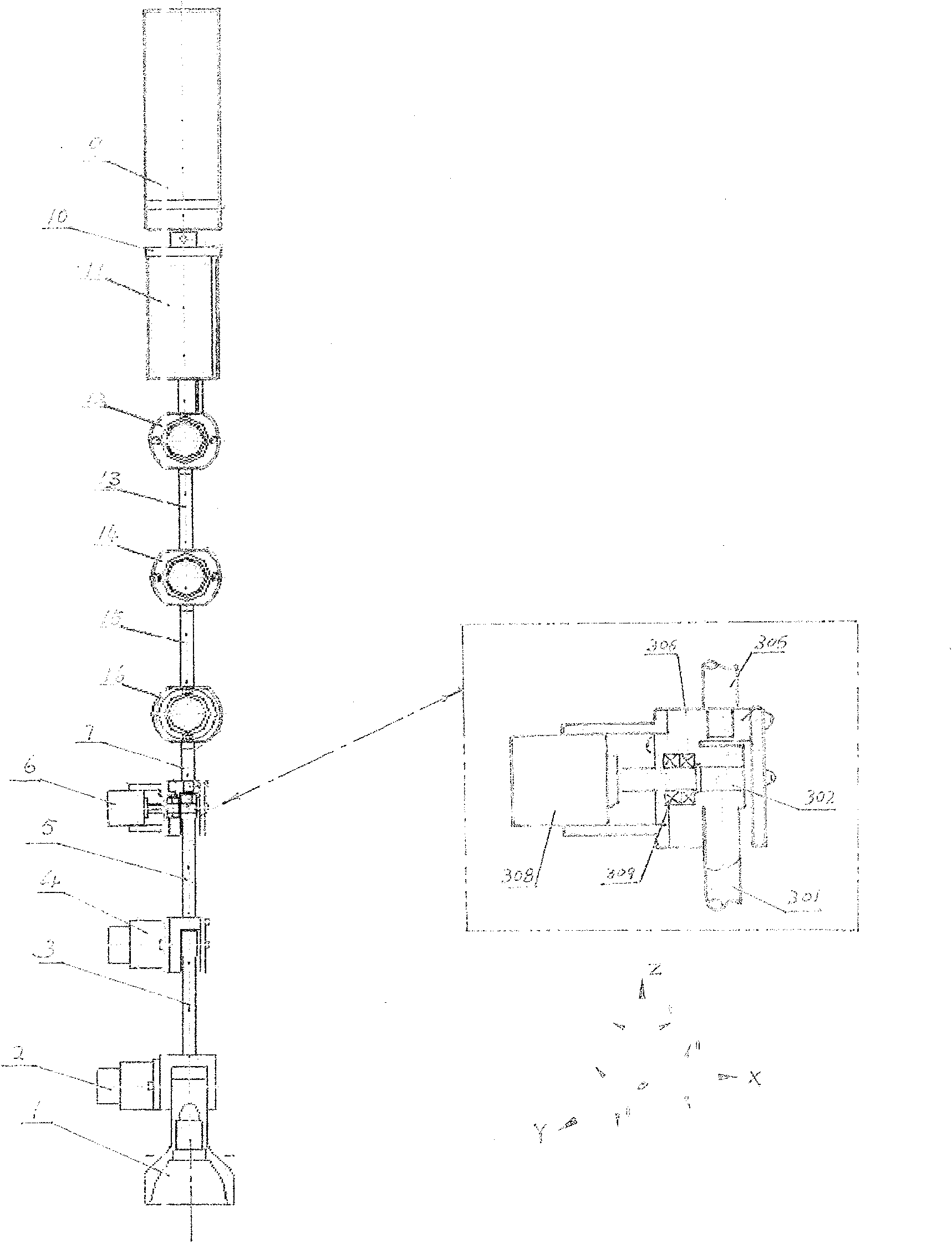
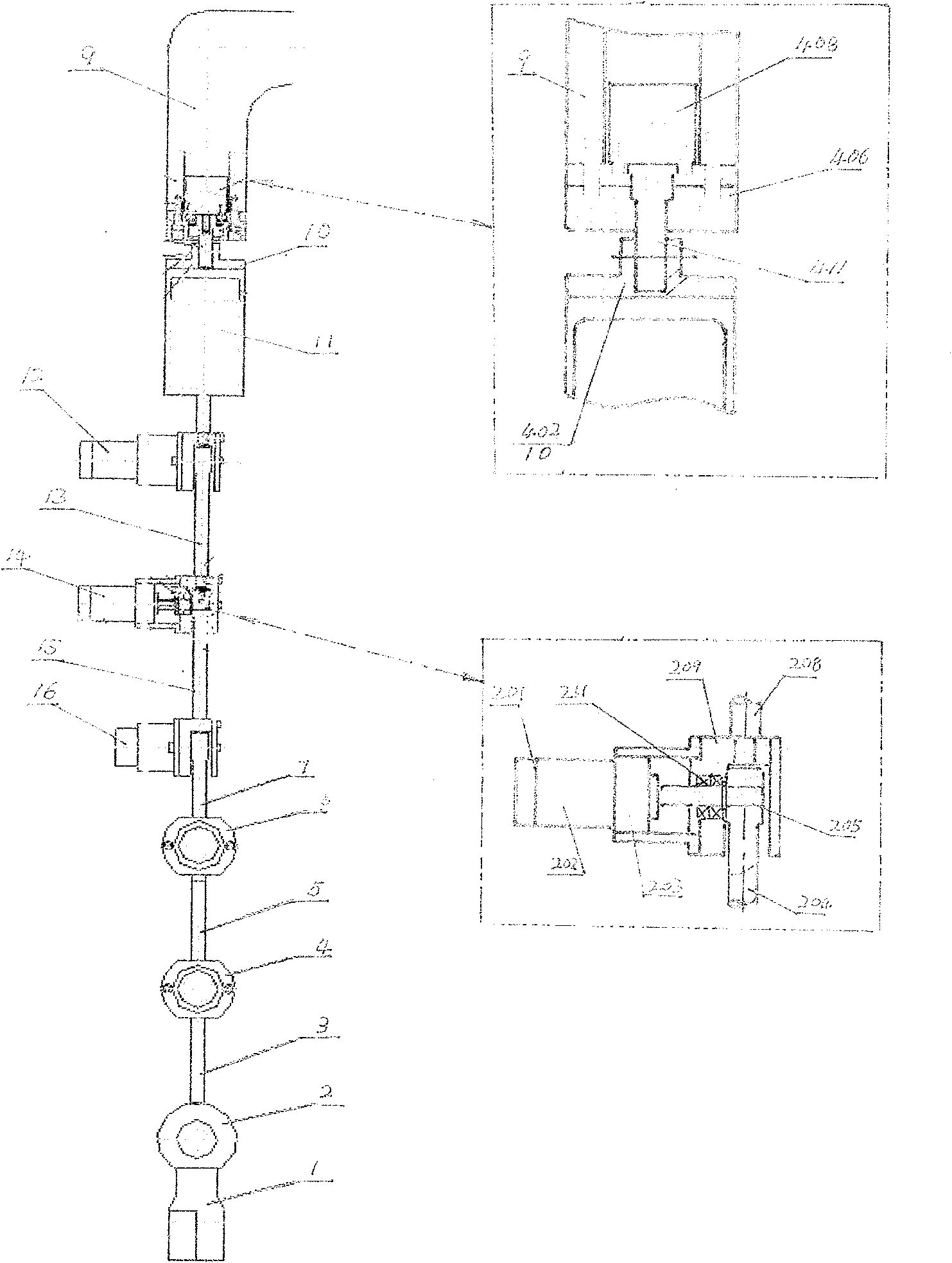
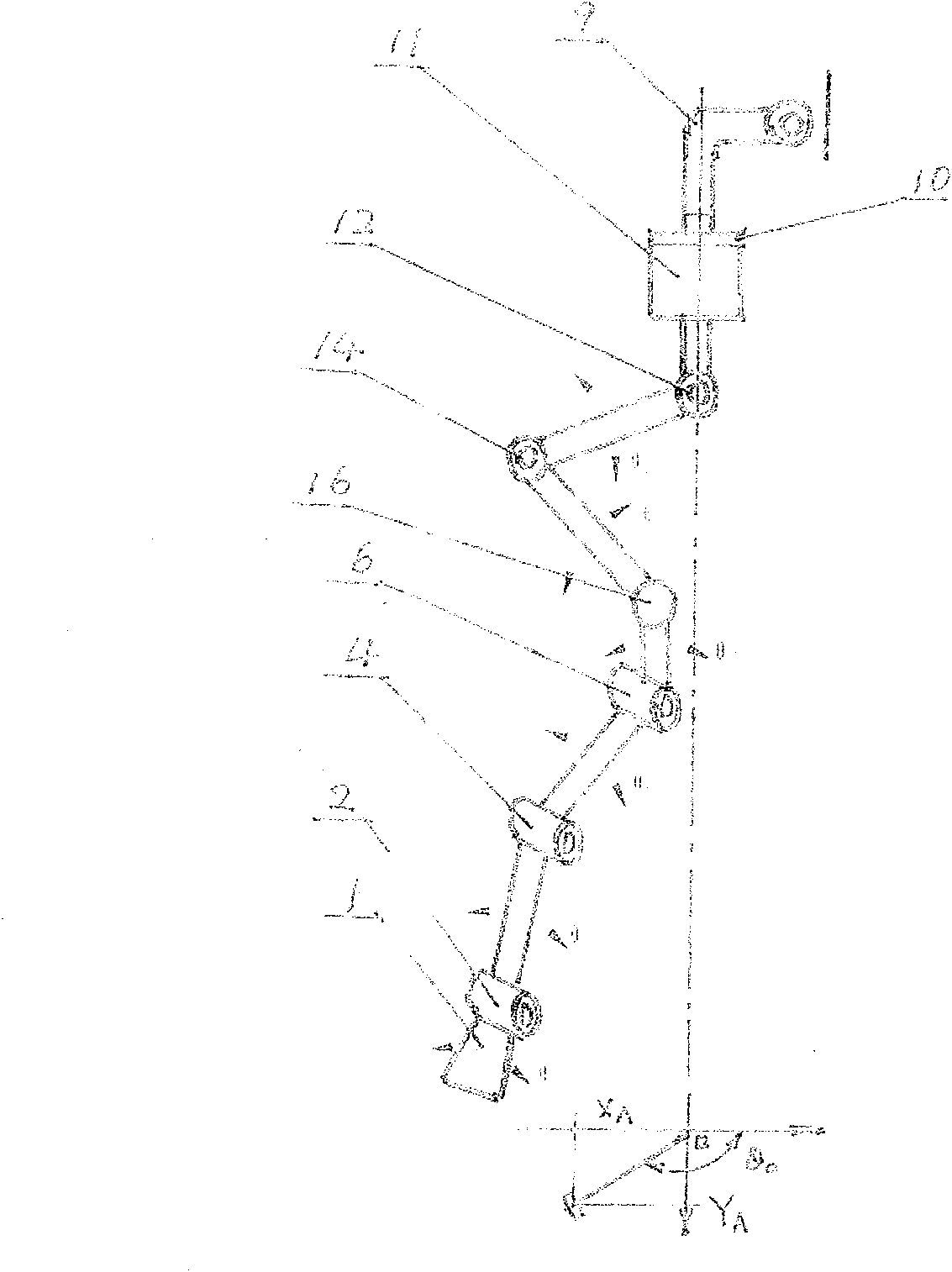
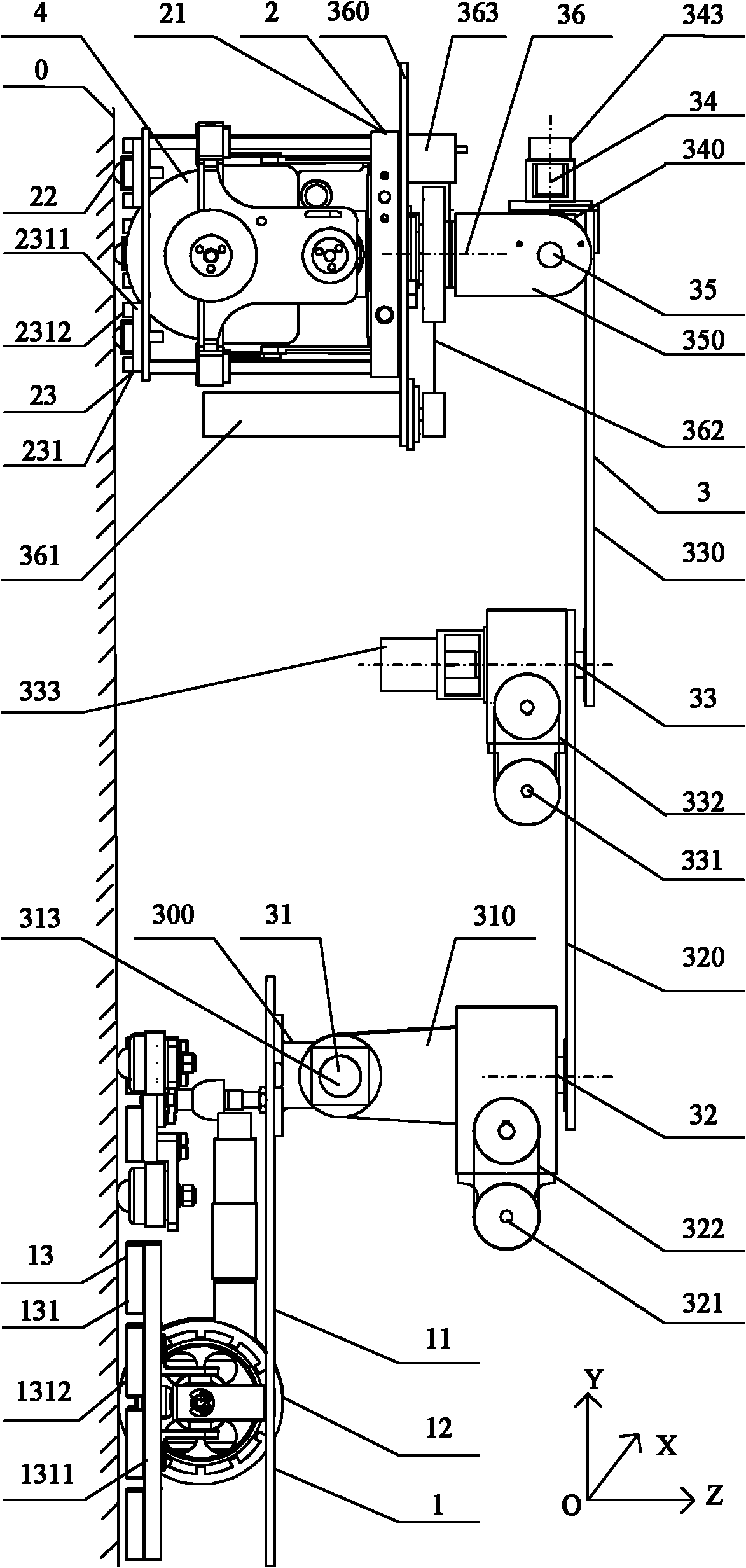
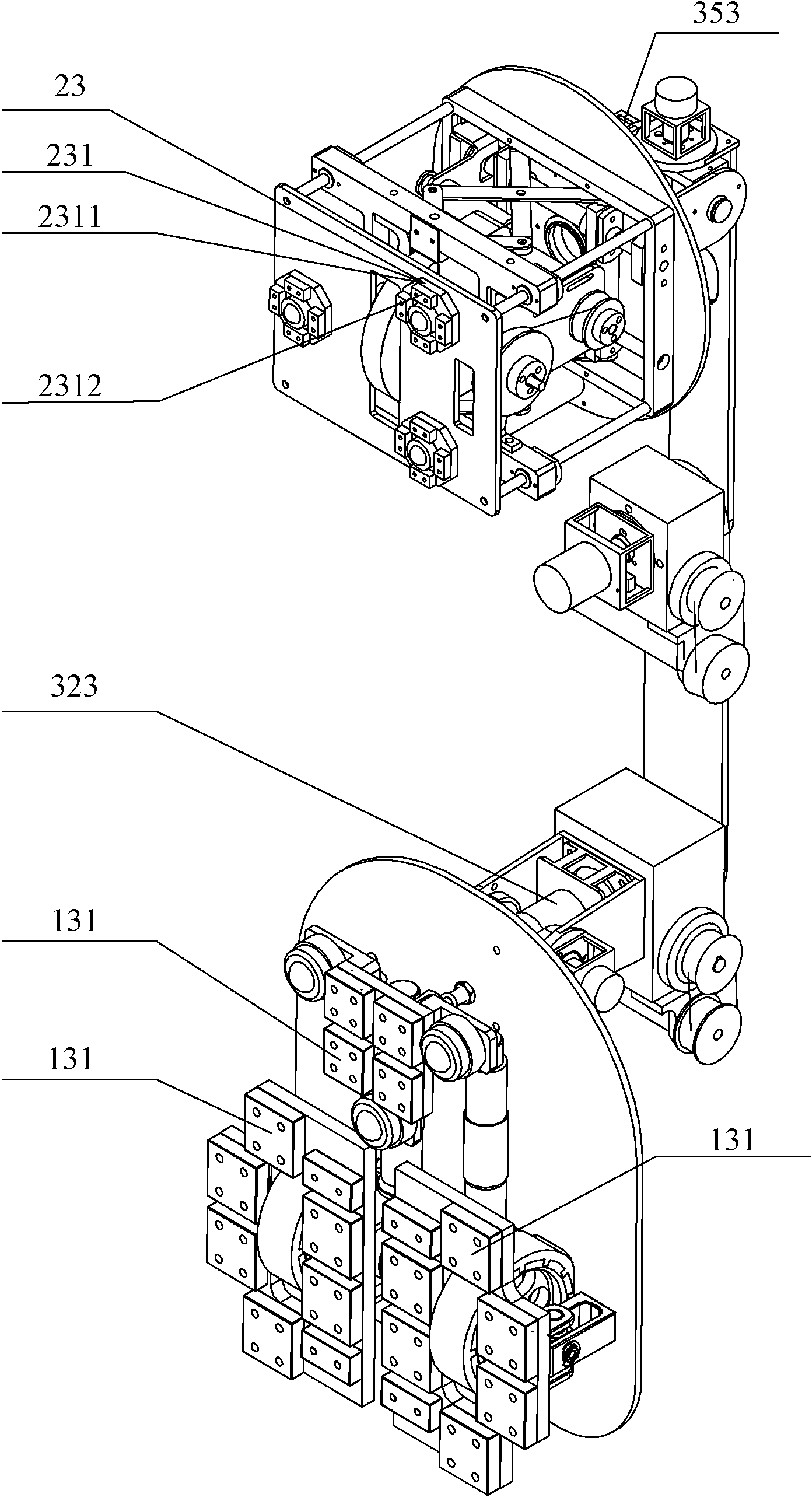
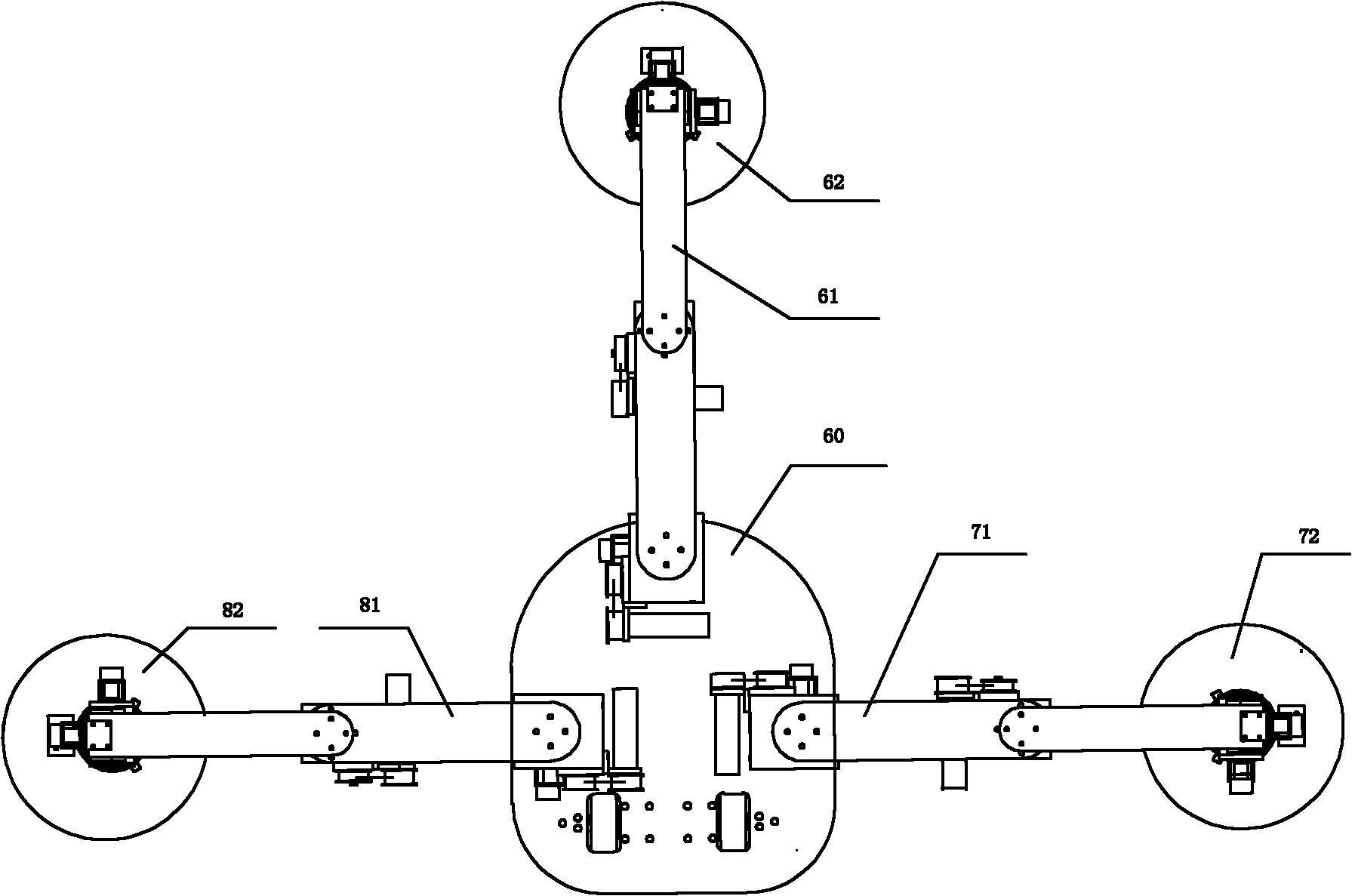
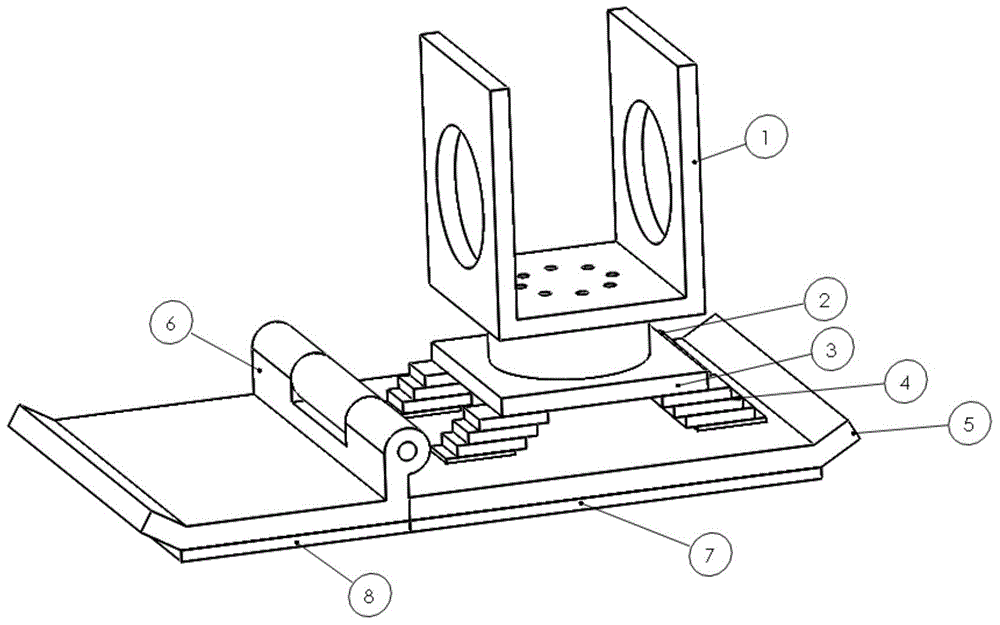
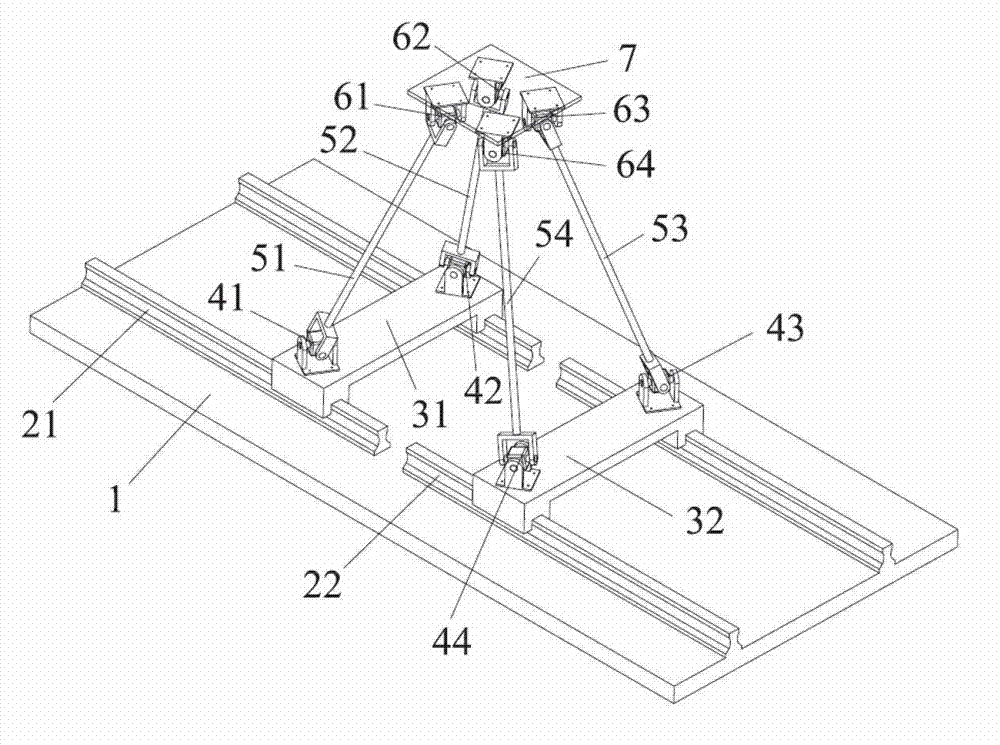
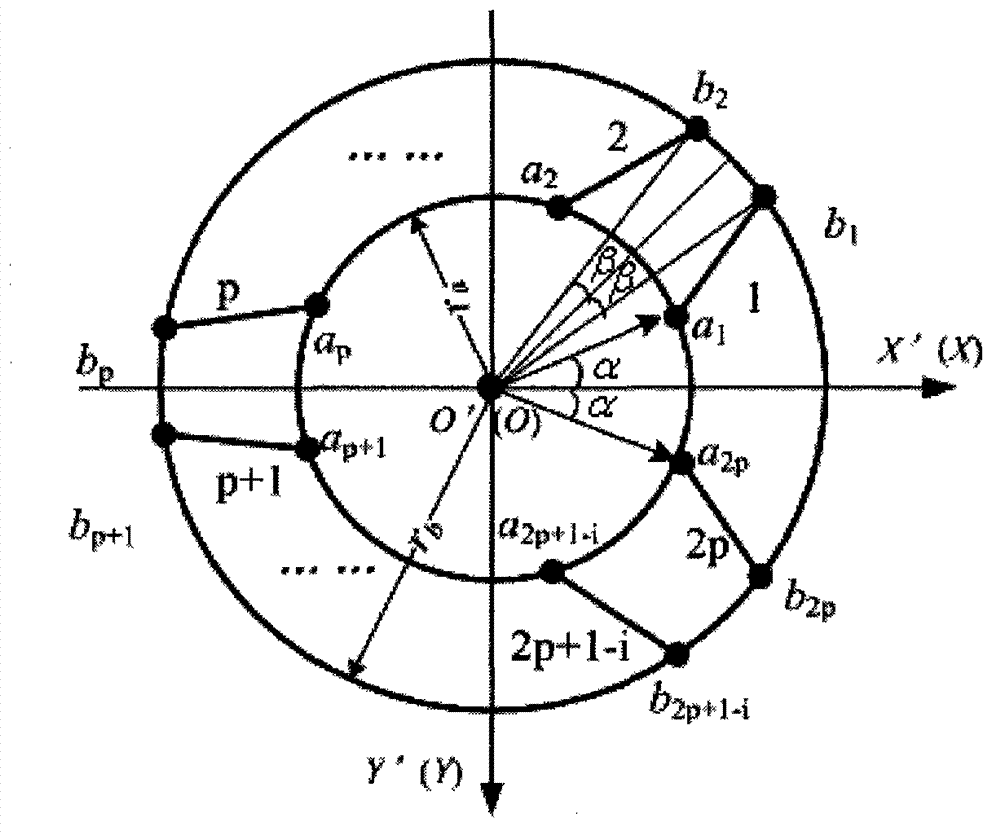
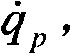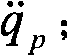Patents
Literature
89 results about "Passive joint" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
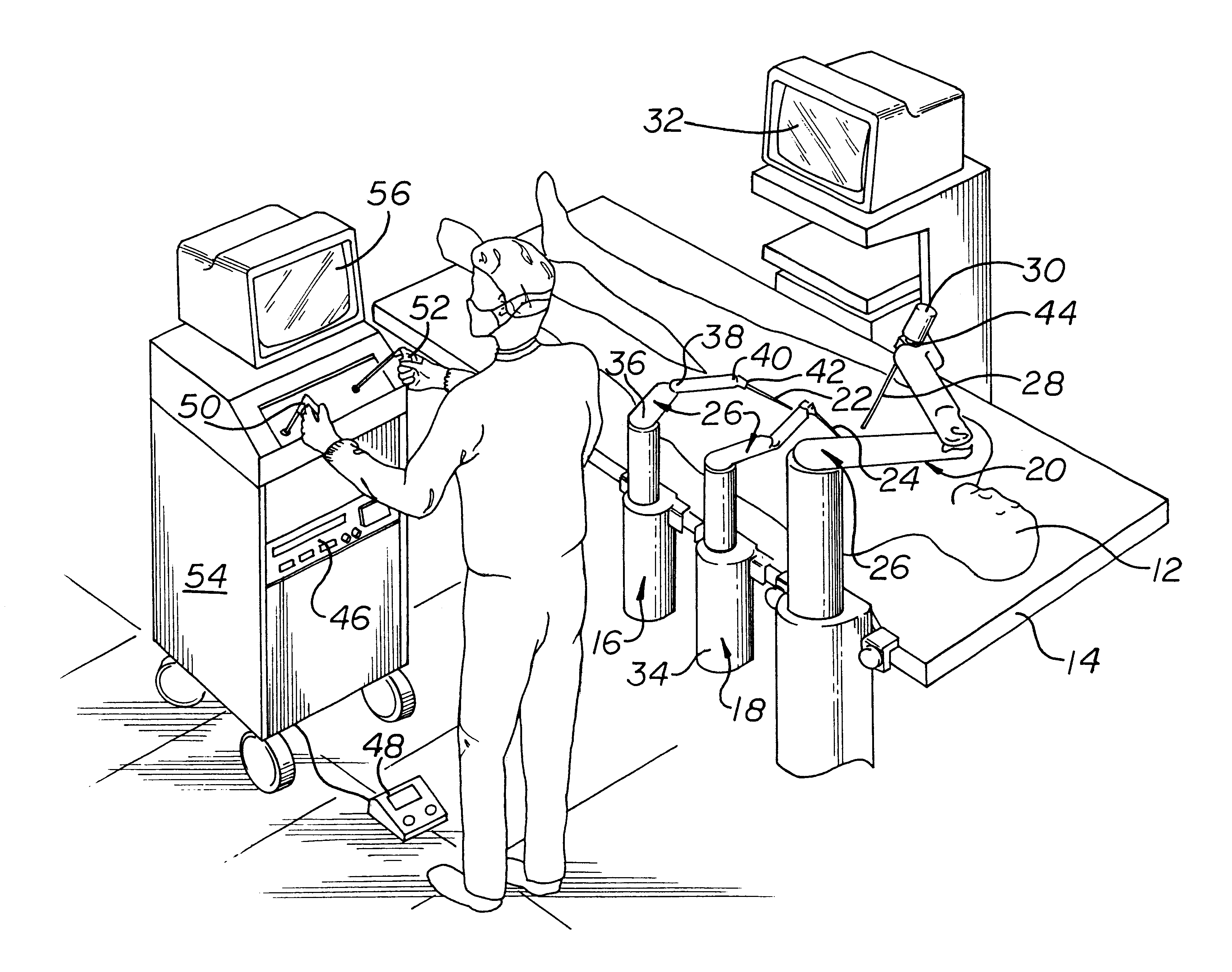
Haptic interface for force reflection in manipulation tasks
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
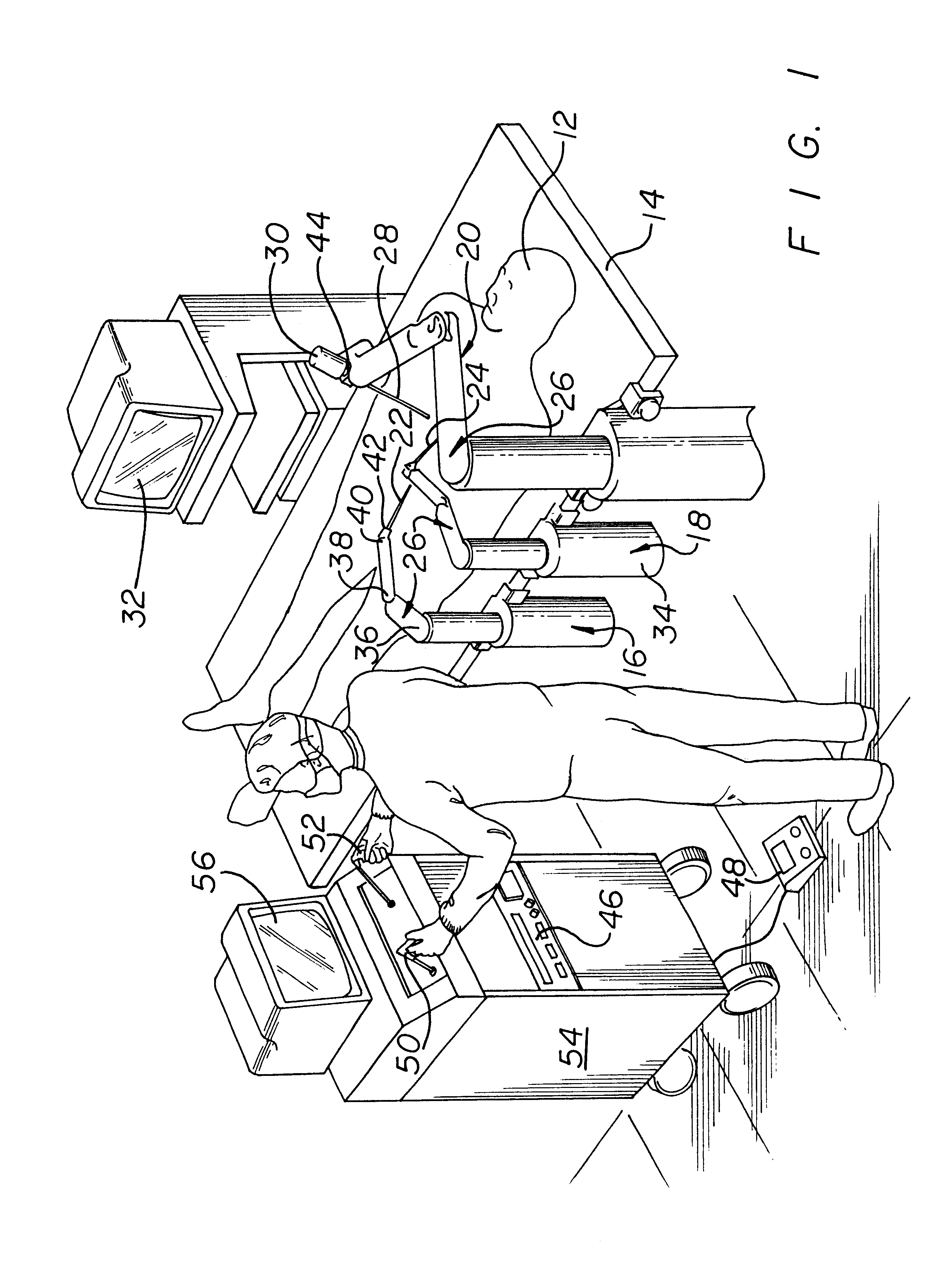
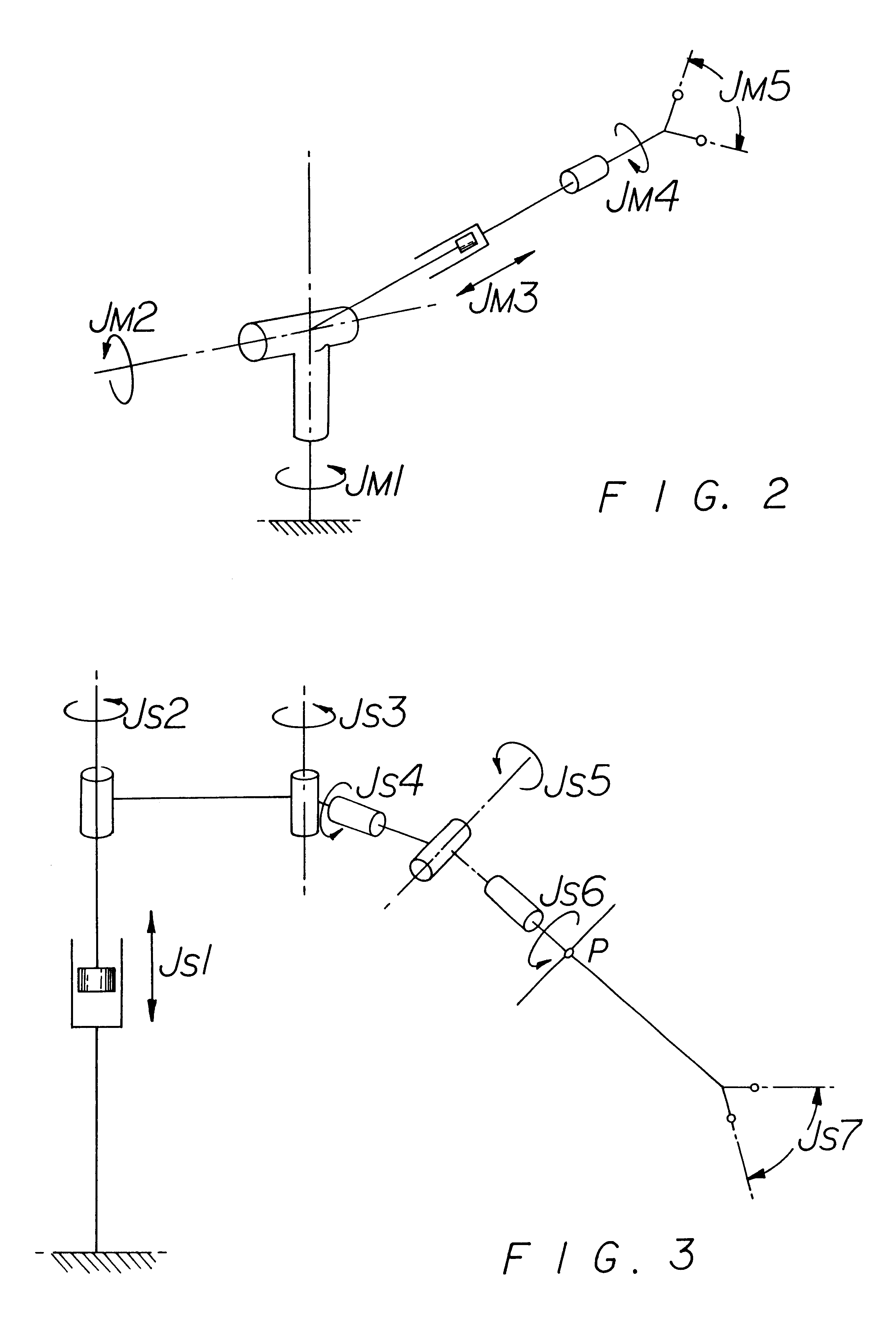
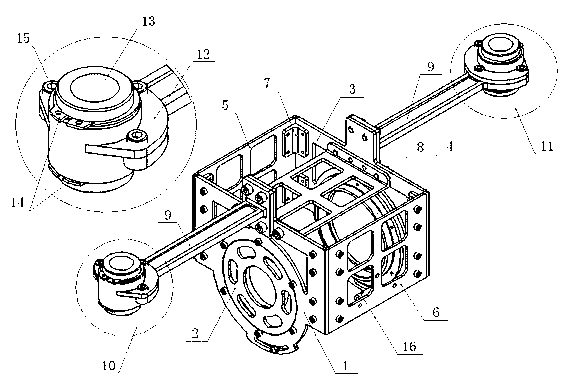
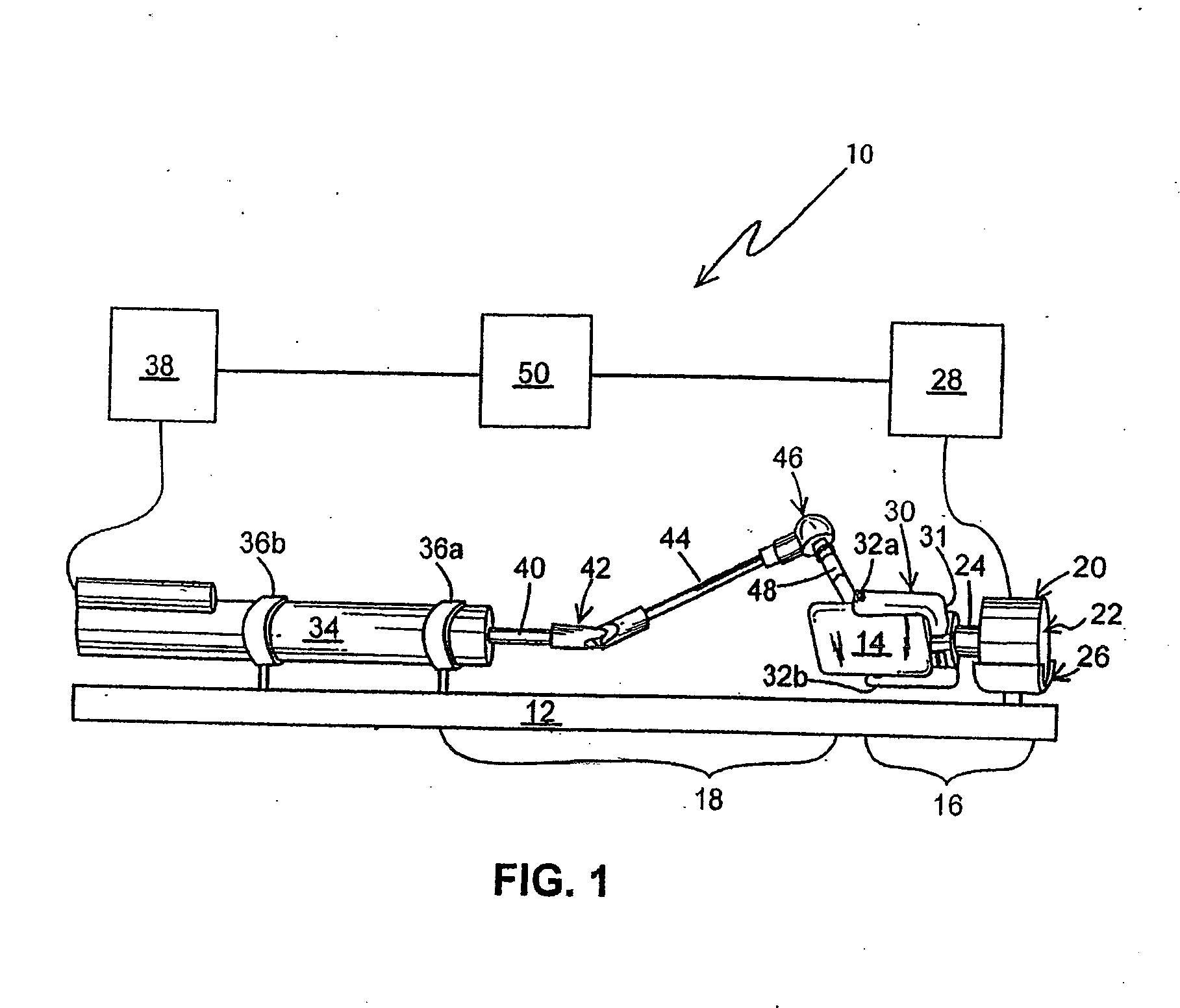
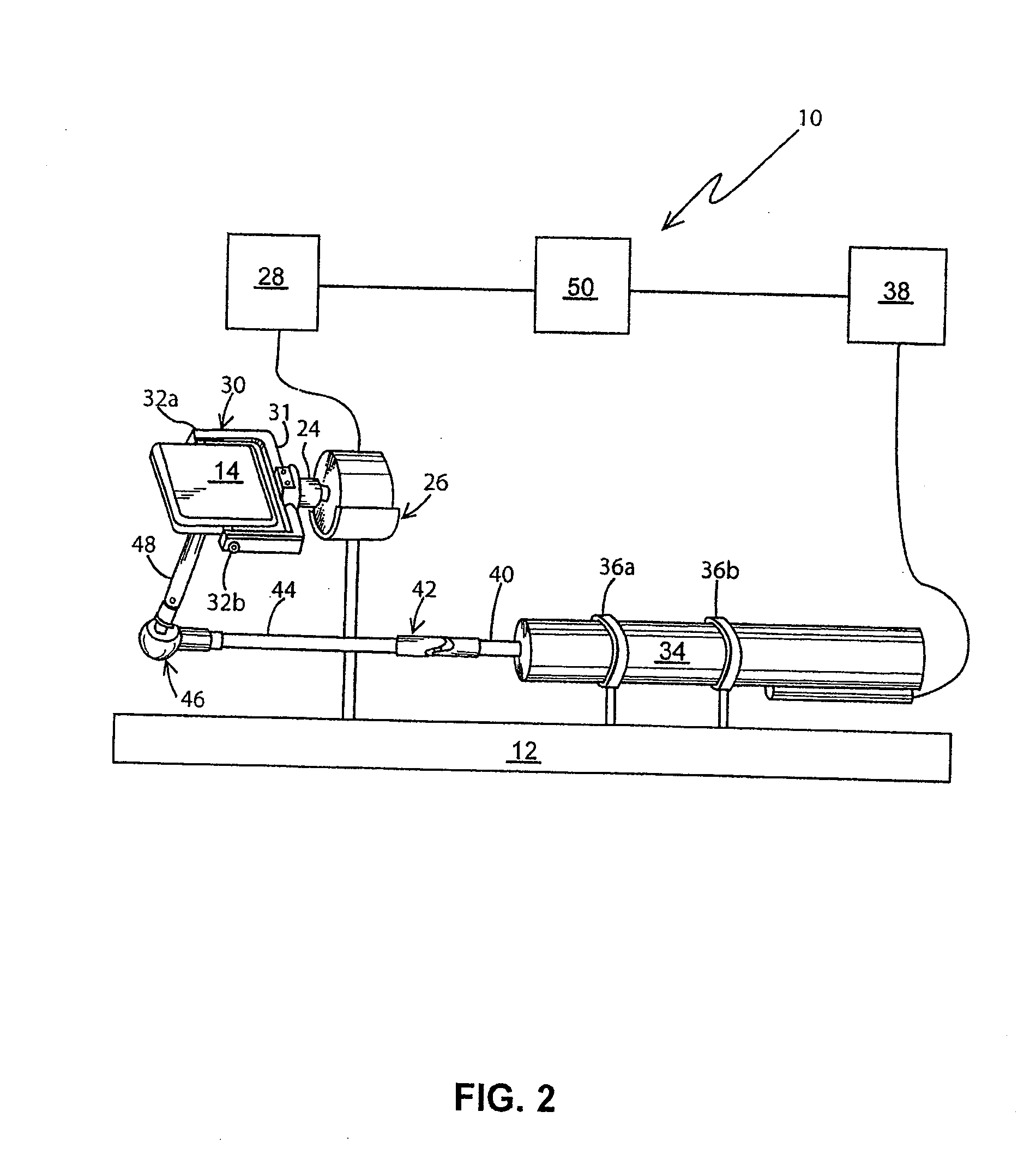
Apparatus for performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures with a robotic arm that has a passive joint and system which can decouple the robotic arm from the input device
InactiveUS6905491B1Minimally invasiveComfortable postureSuture equipmentsProgramme controlRobotic armEngineering
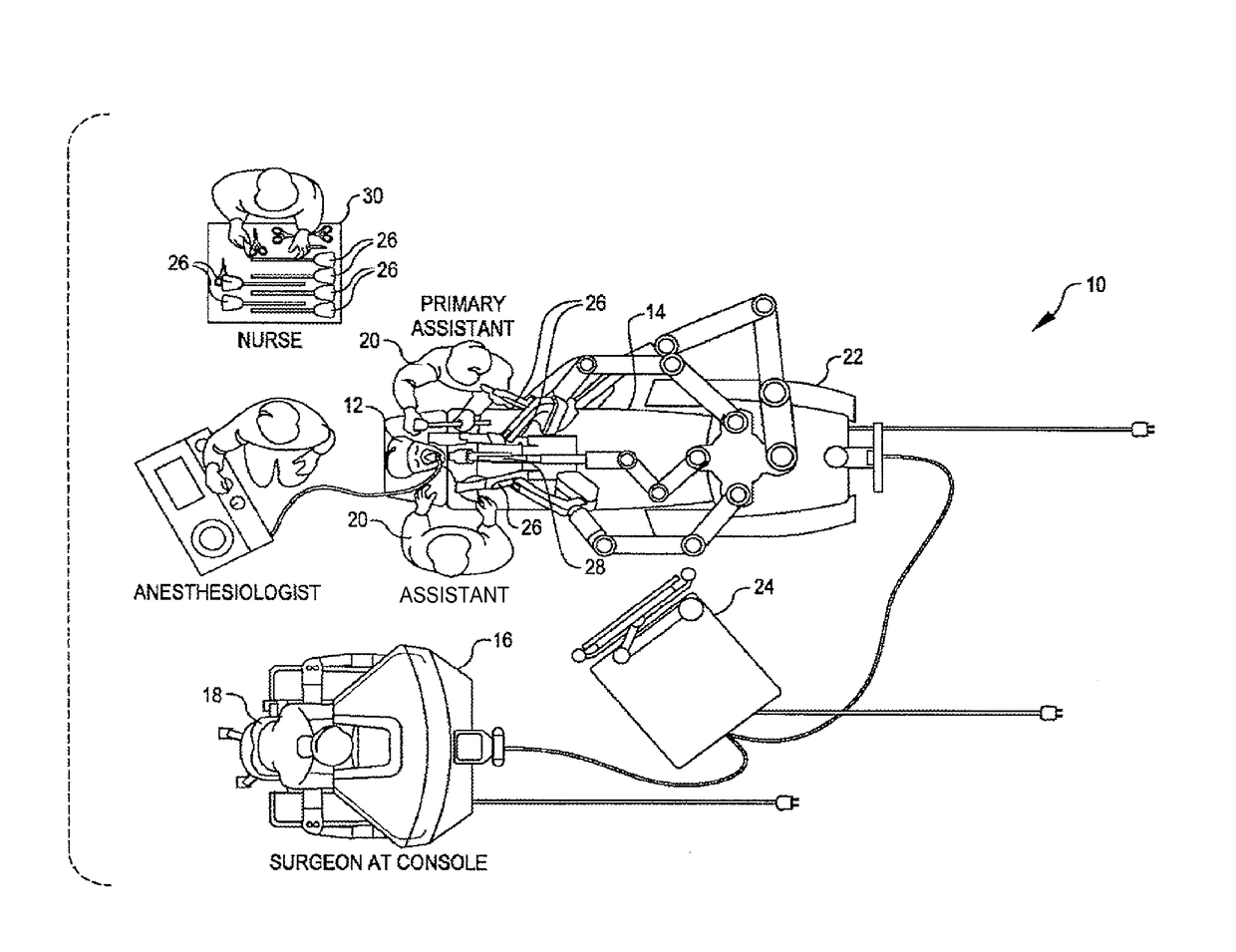
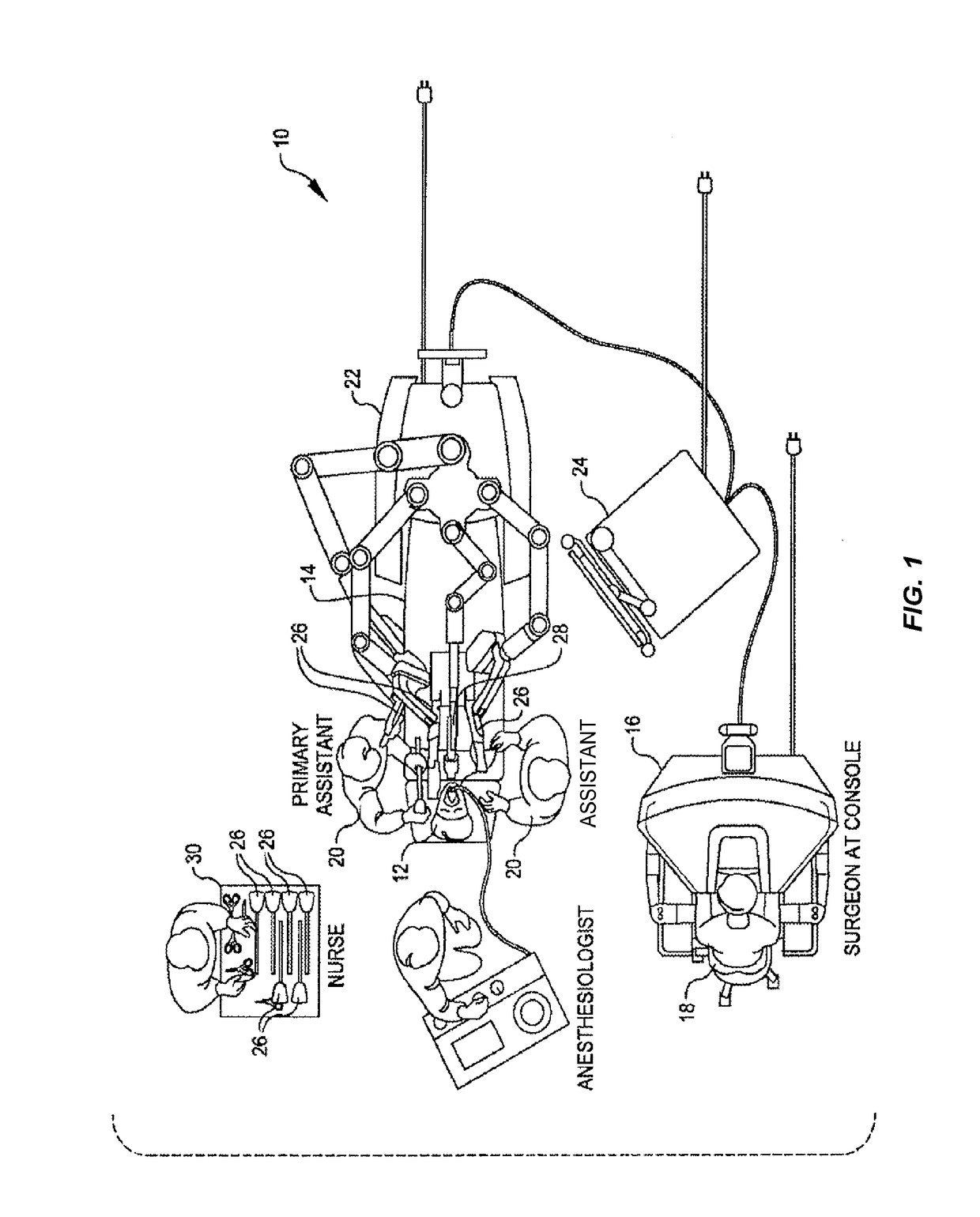
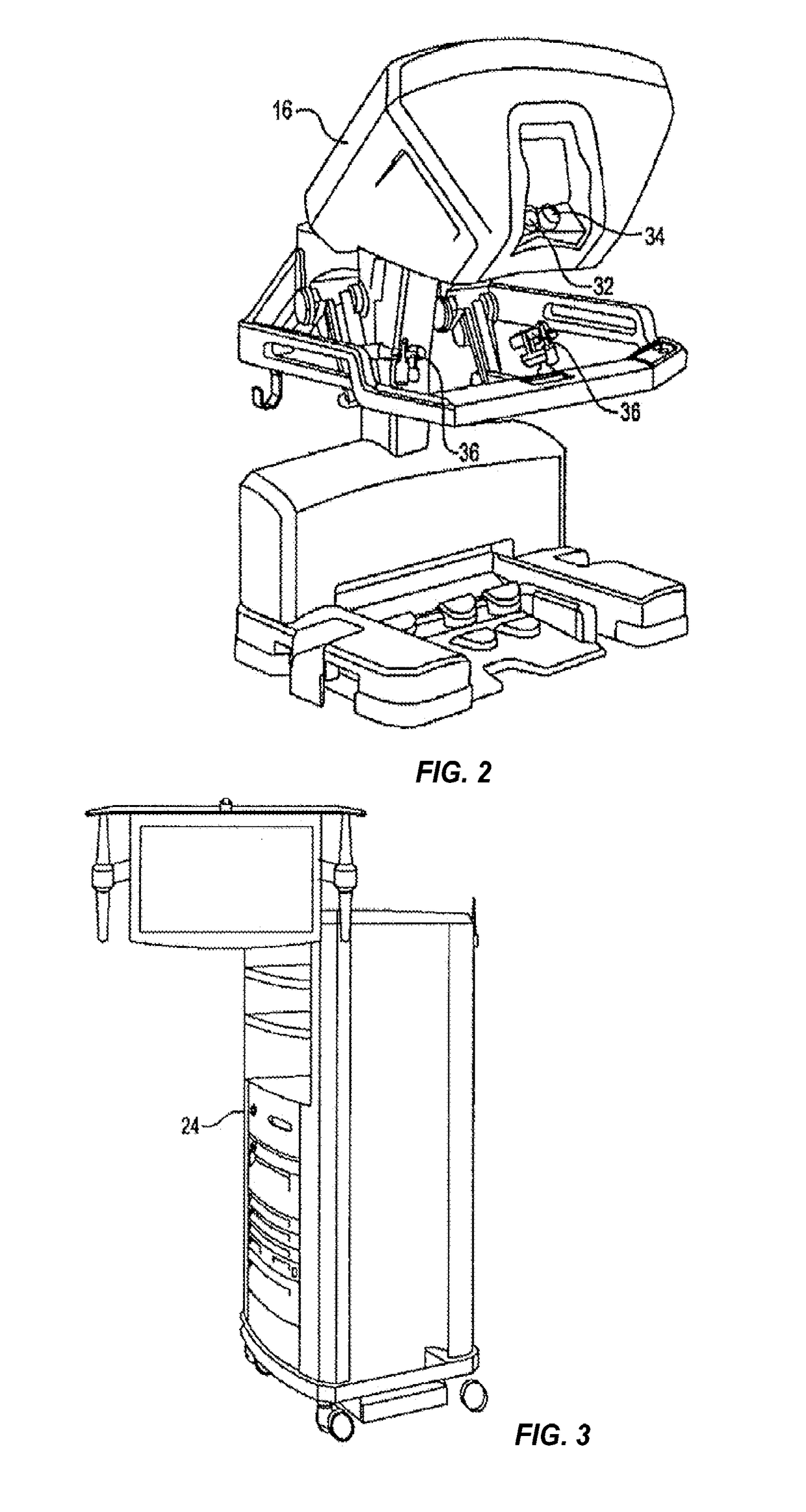
A system for performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures. The system includes a pair of surgical instruments that are coupled to a pair of robotic arms. The instruments have end effectors that can be manipulated to hold and suture tissue. The robotic arms are coupled to a pair of master handles by a controller. The handles can be moved by the surgeon to produce a corresponding movement of the end effectors. The movement of the handles is scaled so that the end effectors have a corresponding movement that is different, typically smaller, than the movement performed by the hands of the surgeon. The scale factor is adjustable so that the surgeon can control the resolution of the end effector movement. The movement of the end effector can be controlled by an input button, so that the end effector only moves when the button is depressed by the surgeon. The input button allows the surgeon to adjust the position of the handles without moving the end effector, so that the handles can be moved to a more comfortable position. The robotic arm may contain a passive joint that provides an additional degree of freedom. Additionally, the system may include a disconnect input device that decouples the arm from an input device such as the handles.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Active-passive joint-arm type measuring robot
InactiveCN101024286ACompensation accuracyMake up for the deficiency of only passive data collectionMeasurement devicesManipulatorGeometric relationsMeasuring output
The invention relates to active passive knuckle arm type measuring robot. It includes I, II, III, IV, and V shaft assemblies. Its features are that each shaft assembly is set actuator and active passive switching unit; encoder used to measure output corner is connected with the output axis. The invention has high measuring accuracy, can actively process trace plan. The encoder can collect final moving corner for each knuckle axis to avoid mechanical error between step motor and harmonic reducer. The invention can be widely used in various products measuring and detecting.
Owner:廊坊智通机器人系统有限公司
Underactuated lower limb assistance exoskeleton robot based on rope-pulley mechanism
ActiveCN107137207AReduce consumptionReduce the numberProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesExoskeleton robotCoxal joint
The invention provides an underactuated lower limb assistance exoskeleton robot based on a rope-pulley mechanism, and relates to an underactuated lower limb assistance exoskeleton robot. The robot aims to solve the problems that a prior active joint-driving exoskeleton has large self-mass, large drive energy consumption, and a passive joint exoskeleton cannot provide effective assistance. The robot comprises a harness device, a drive control power system, two thigh bar devices, two leg bar devices, two ankle devices, two drive devices and two strings; wherein each drive device includes a motor shell bracket, a first motor shell, a waist frame, a planetary reducer, a second motor shell, a servo motor, a third motor shell, a hip joint spline shaft, a drive pulley, an elastic actuator, a first shaft sleeve, a small bevel gear, a large bevel gear, a second shaft sleeve, a fourth motor shell, a fifth motor shell, a sixth motor shell, a fixing plate and two first bearing end covers with bearings. The underactuated lower limb assistance exoskeleton robot based on the rope-pulley mechanism is used for the field of assistance exoskeleton robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Methods of Controlling Motion of Under-Actuated Joints in a Surgical Set-up Structure
ActiveUS20170079731A1Less timeEasy alignmentProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsControl systemEngineering
Robotic and / or surgical devices, systems, and methods include kinematic linkage structures and associated control systems configured to control movement of passive or under-actuated joints by coordinated joint braking of the under-actuated joints concurrent with driving of one or more driven joints. In one aspect, the methods include driving a set-up structure by pivoting an orienting platform supporting multiple manipulators back-and-forth in opposite directions while selectively braking the under-actuated joints to inhibit passive joint movement away from a reference joint state and releasing braking to facilitate movement of the joints toward the reference until each of the under-actuated joints of the multiple manipulators are at the respective reference states. In an other aspect, a joint brake controller is provided that receives a motor torque input and converts the input to a brake control input by determining an impulse applied variable braking to deplete the impulse over time.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
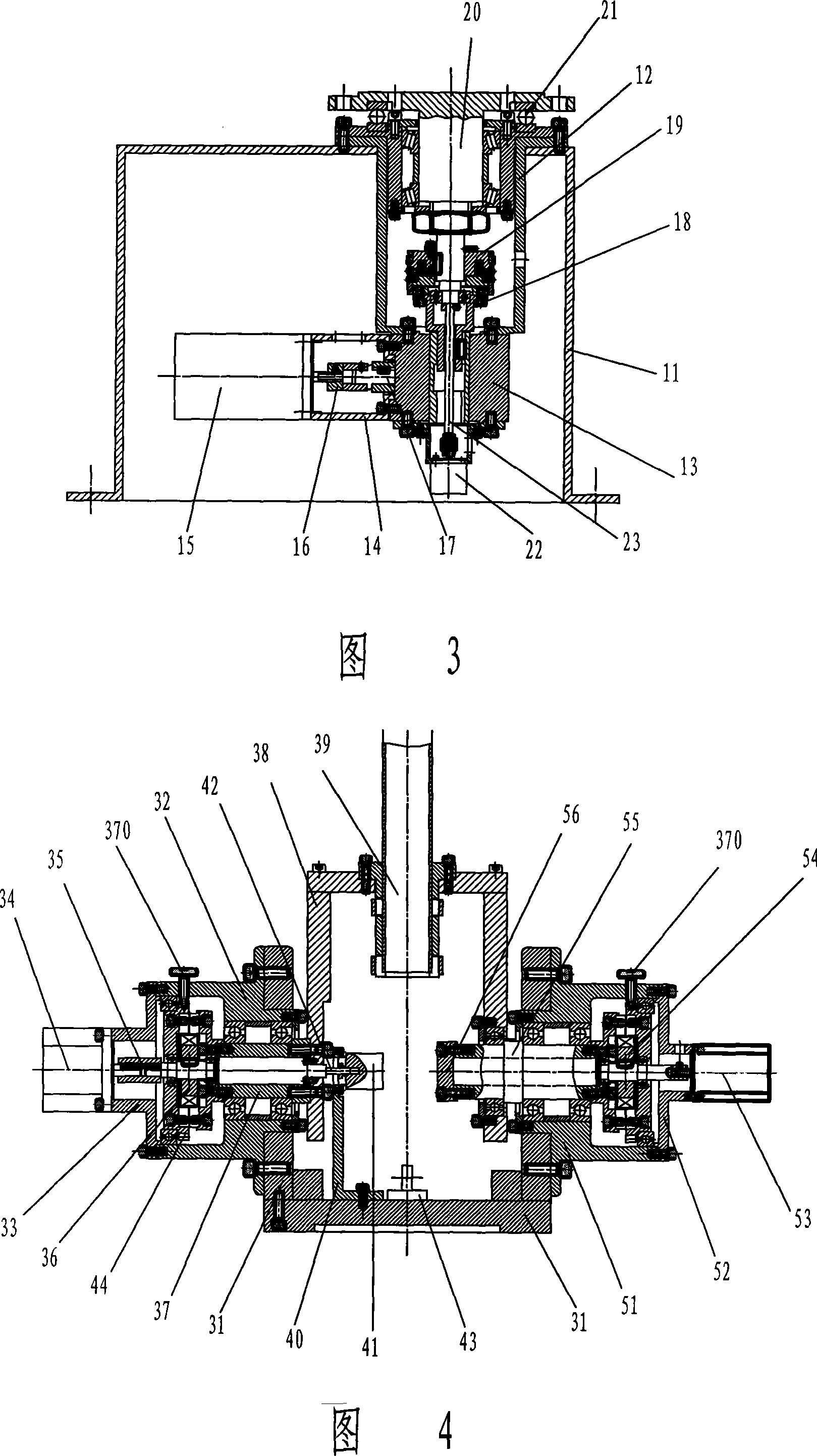
Lower half body module of bipedal walking robot
ActiveUS7498758B2Heavy loadImprove rigidityProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsDegrees of freedomEngineering
Owner:TMSUK CO LTD +1
Lower Half Body Module of Bipedal Walking Robot
ActiveUS20080150465A1Right and left to operatePower right and leftProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsEngineeringDegrees of freedom
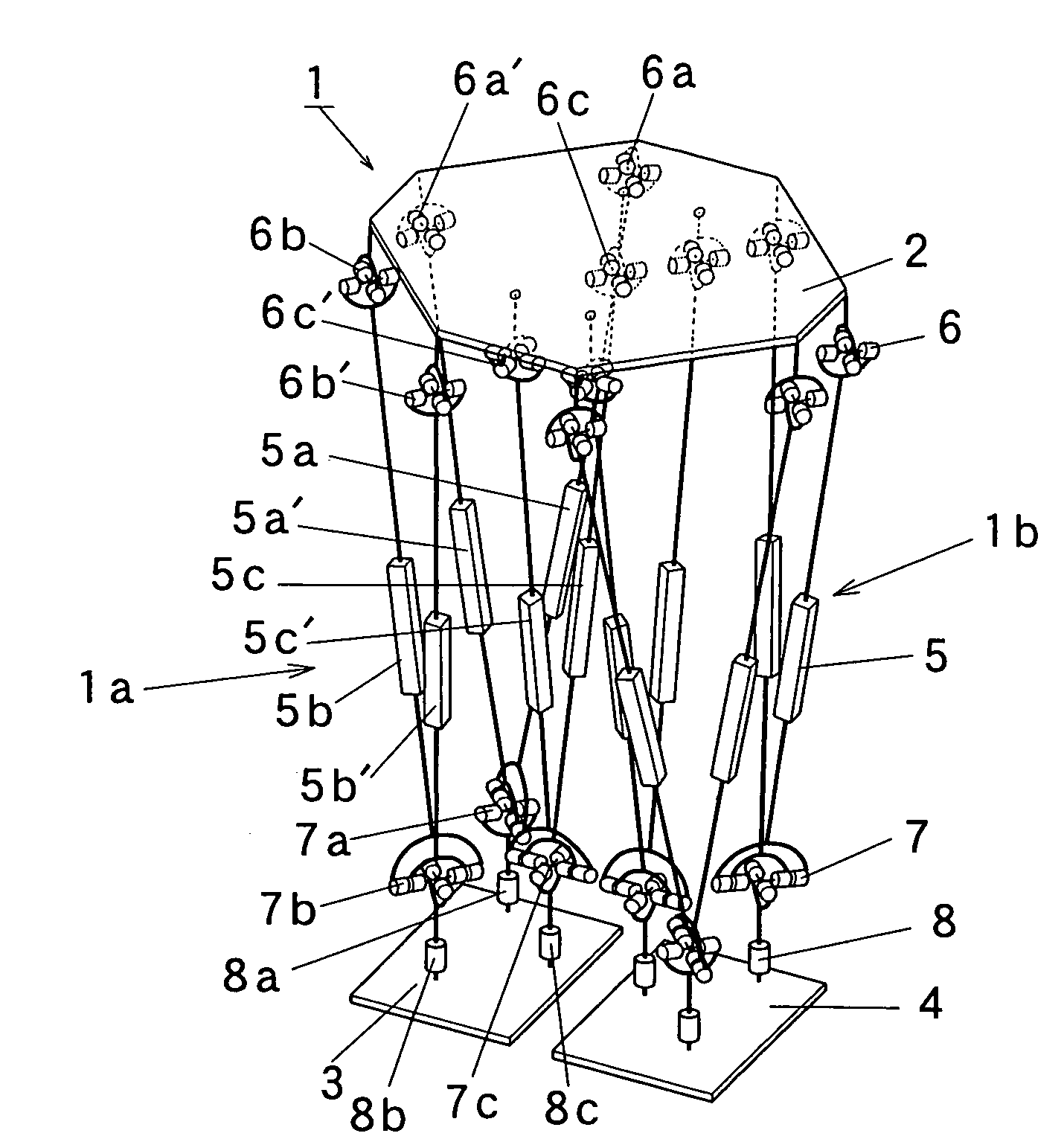
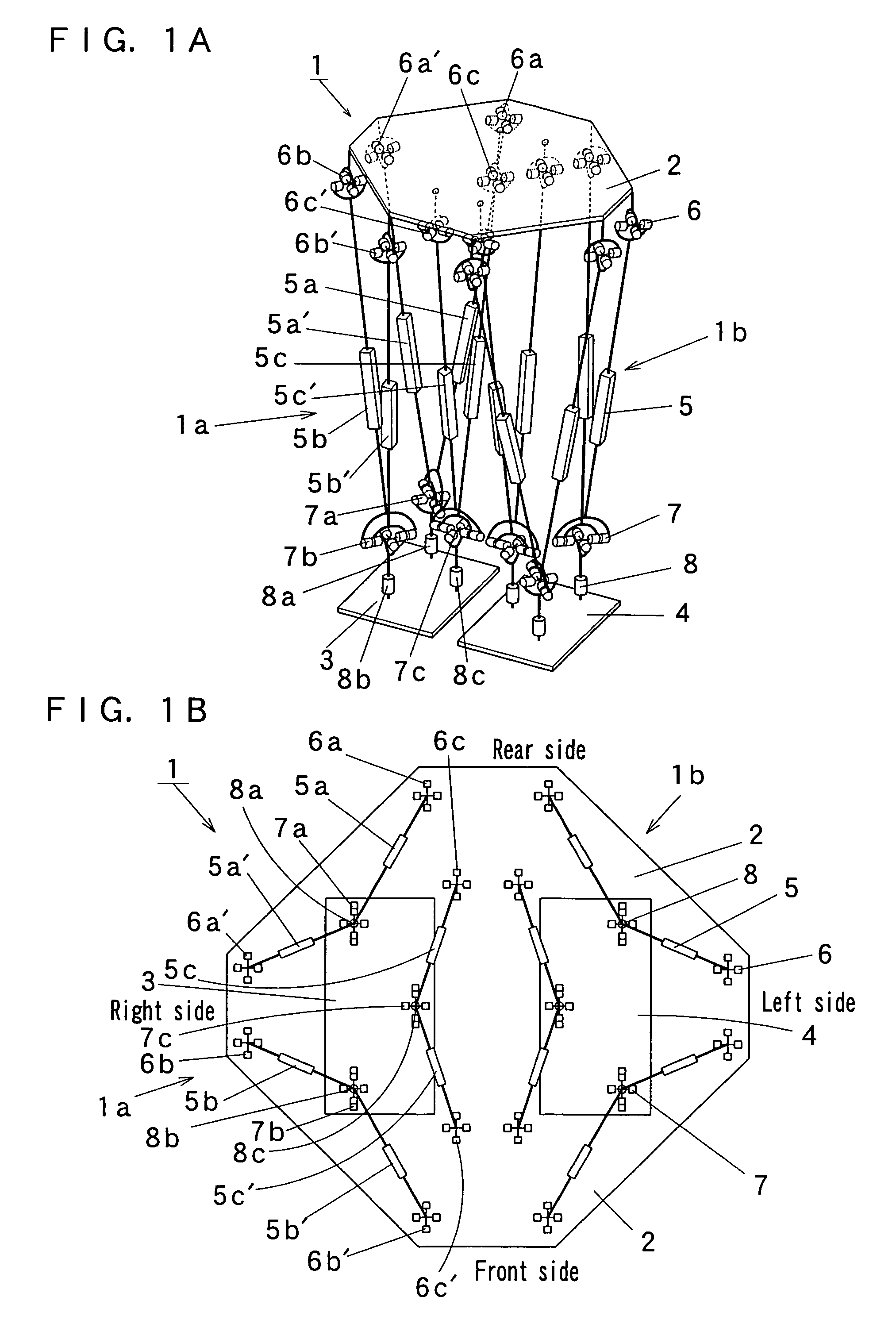
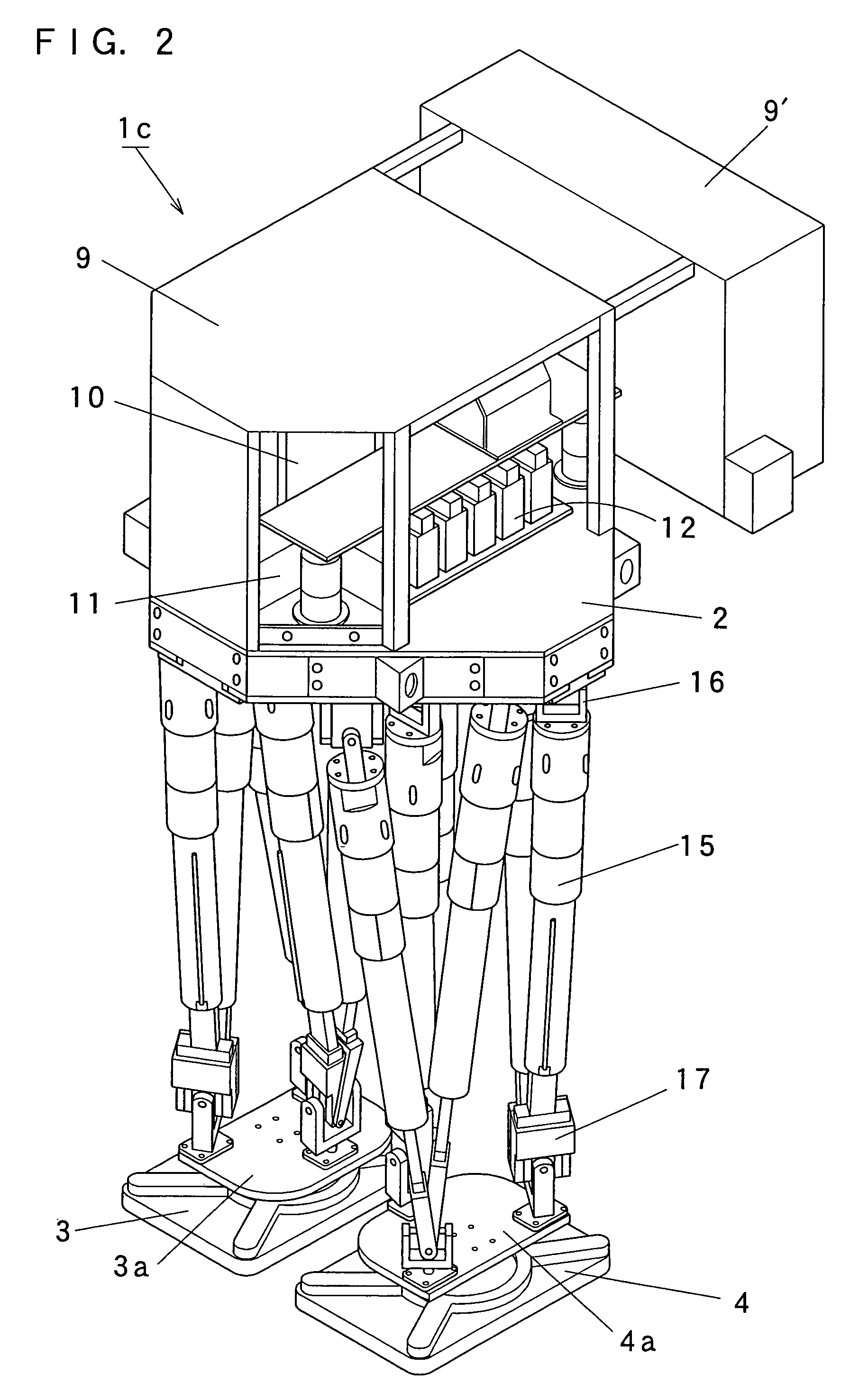
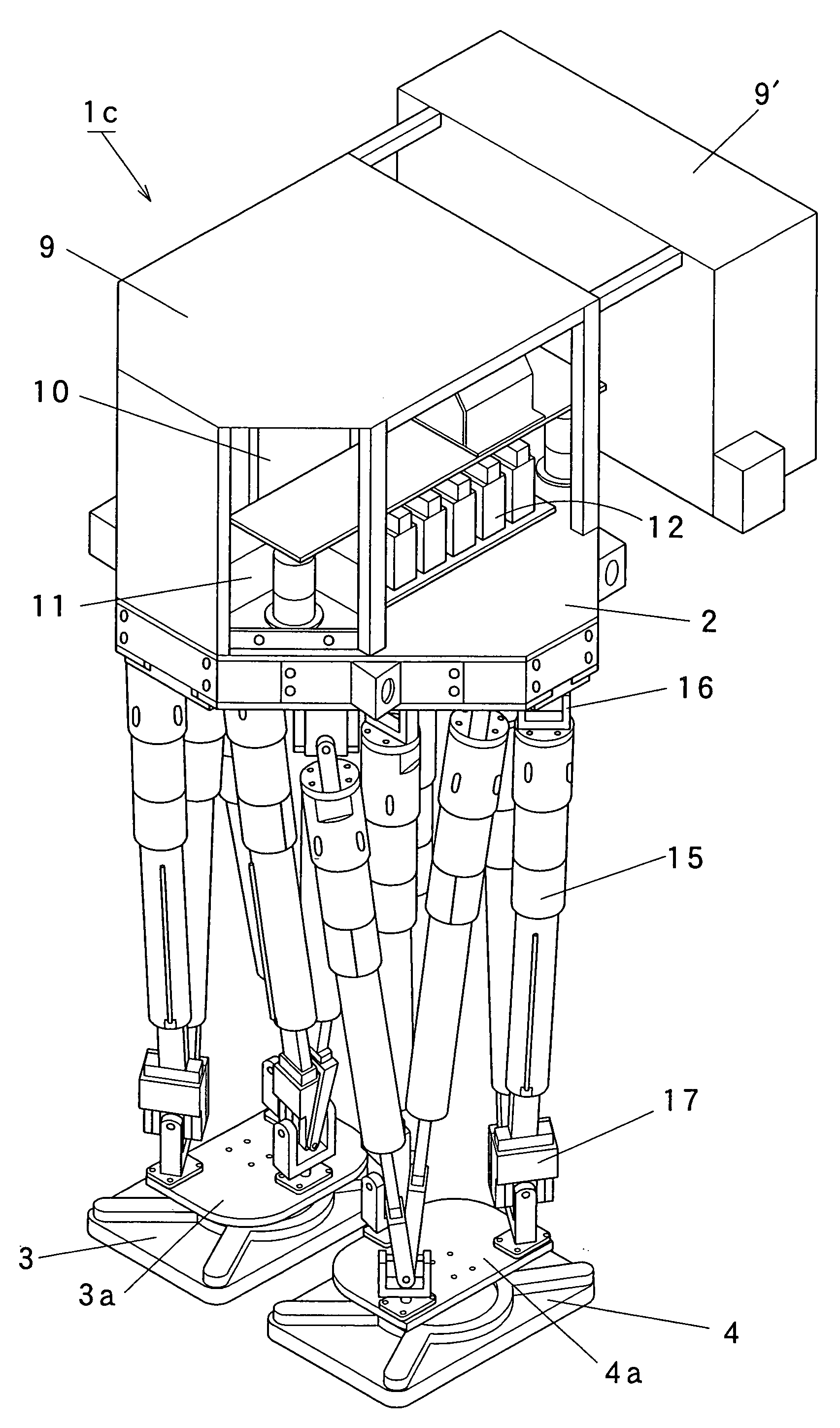
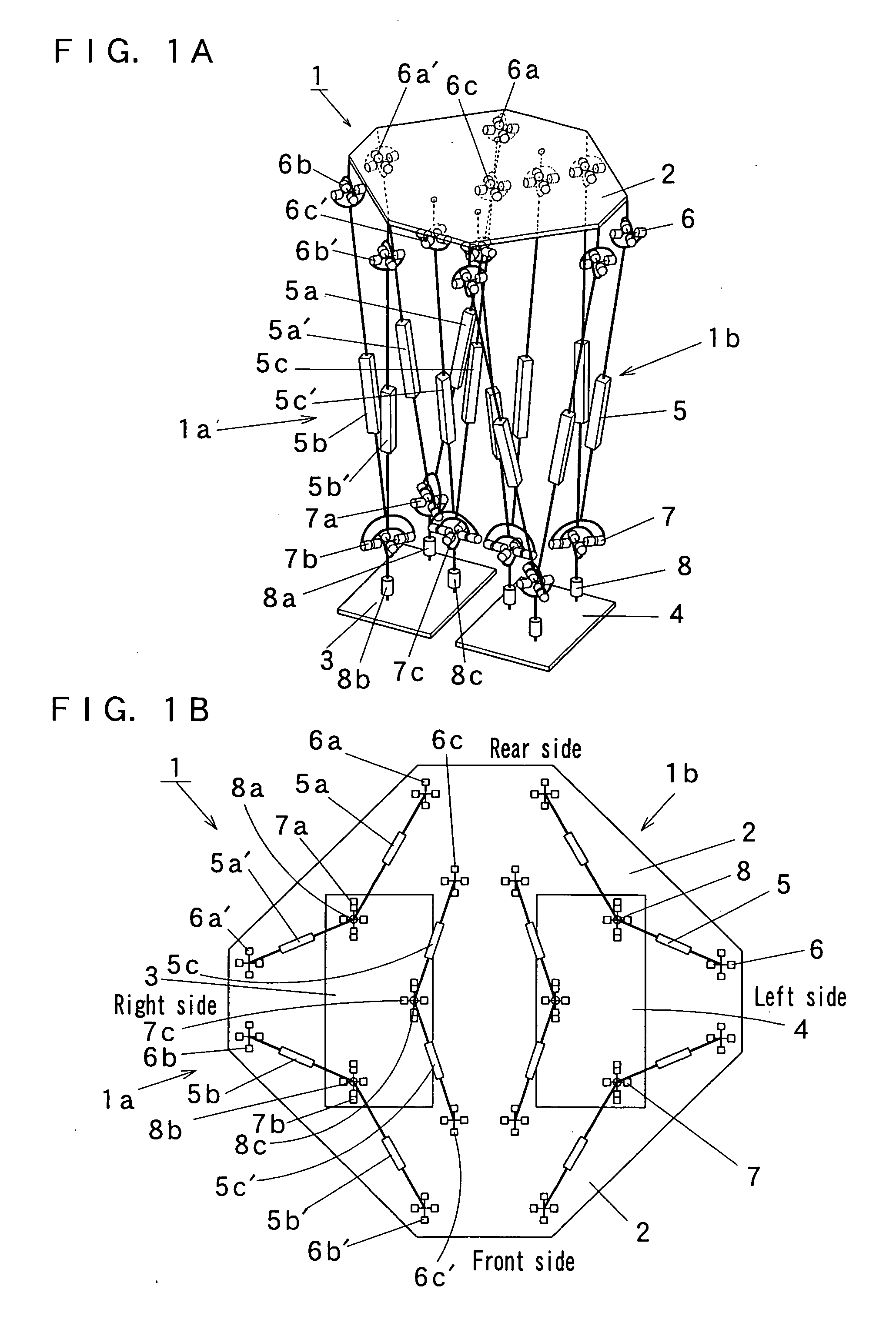
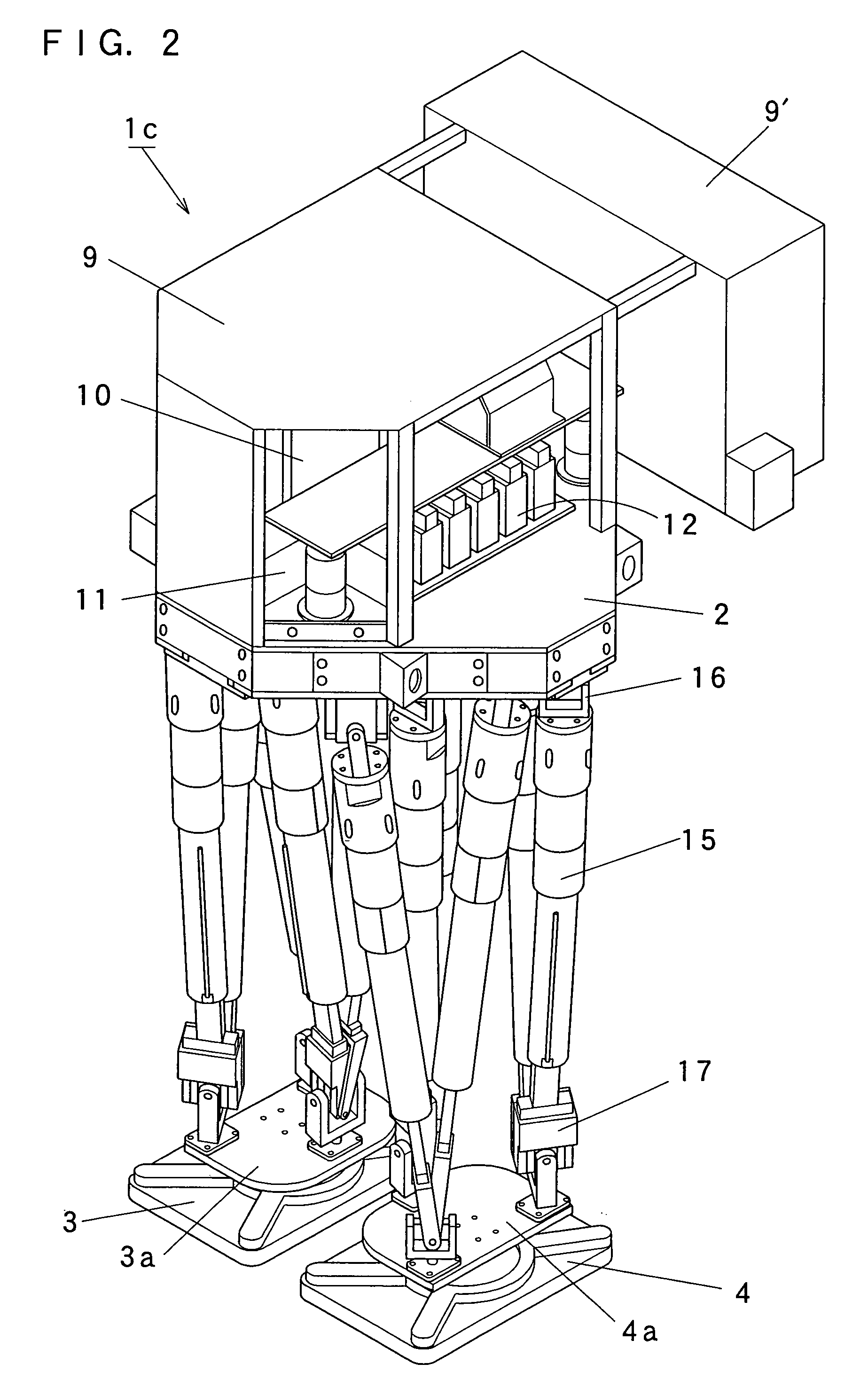
It is an object of the present invention to provide a lower half body module of a bipedal walking robot which is excellent in practicality in the point that it is possible to transport a heavy load, and which is excellent in the degree of freedom in designing in the point that it is possible to mount or incorporate an upper half body having a large weight. Therefore, this is why legs of the lower half body module are constituted by a parallel link mechanism to sustain a large load. The lower half body module (1) of the present invention includes a base (2), aright foot (3) and a left foot (4), a plurality of passive joints (6, 7, 8) which are respectively provided on the base (2), the right foot (3) and the left foot (4), and parallel link mechanism portions (1a, 1b) which are respectively provided between the passive joint (6) provided on the base (2) and the passive joints (7, 8) provided on the right foot (3) and between the passive joint (6) provided on the base (2) and the passive joints (7, 8) provided on the left foot (4).
Owner:TMSUK CO LTD +1
Humanoid robot feet
InactiveCN103802907ARealize three degrees of freedom movementReduce shockVehiclesEngineeringPassive joint
The invention discloses humanoid robot feet. Each humanoid robot foot comprises a humanoid sole and a robot shank connected onto the sole through an ankle joint, wherein the sole comprises toes, an arch body and a sole plate; the toes are connected onto the arch body through a passive joint; the arch body comprises an upper arch body, an inner arch motion block and a lower arch part; flexible cushion blocks are arranged between the upper arch body and the inner arch motion block as well as between the inner arch motion block and the lower arch part; the upper arch body is hinged onto the sole plate; and the lower arch part is fixed on the sole plate. The humanoid robot feet are compact in structure, impact generated in a stage of contact between the feet and the ground during walking can be cushioned, greater push force is generated when the feet leave the ground, and the robot can walk on a complicated ground.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MFG TECH
Wire order test method
ActiveCN102012465ALow costRealize measurementElectrical testingPhase sequence/synchronism indicationElectrical resistance and conductancePassive joint
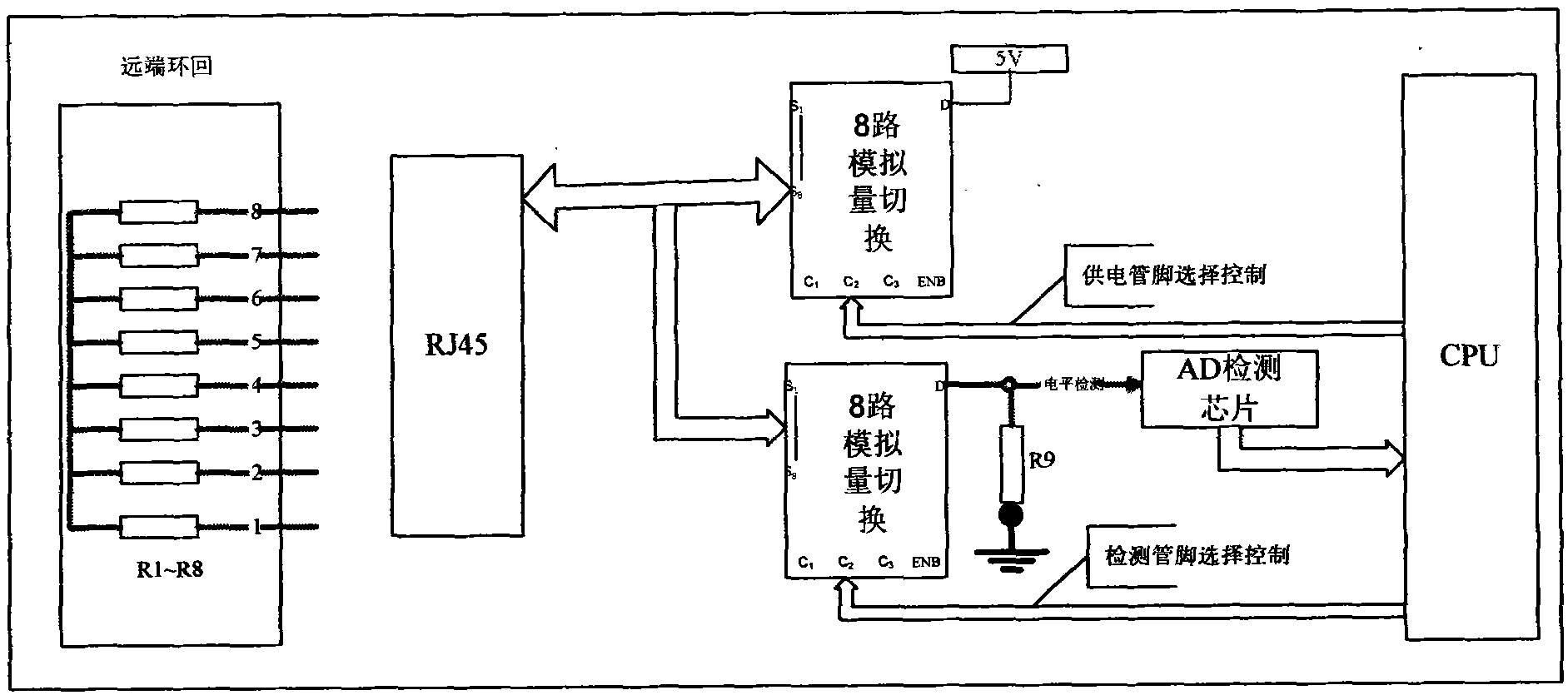
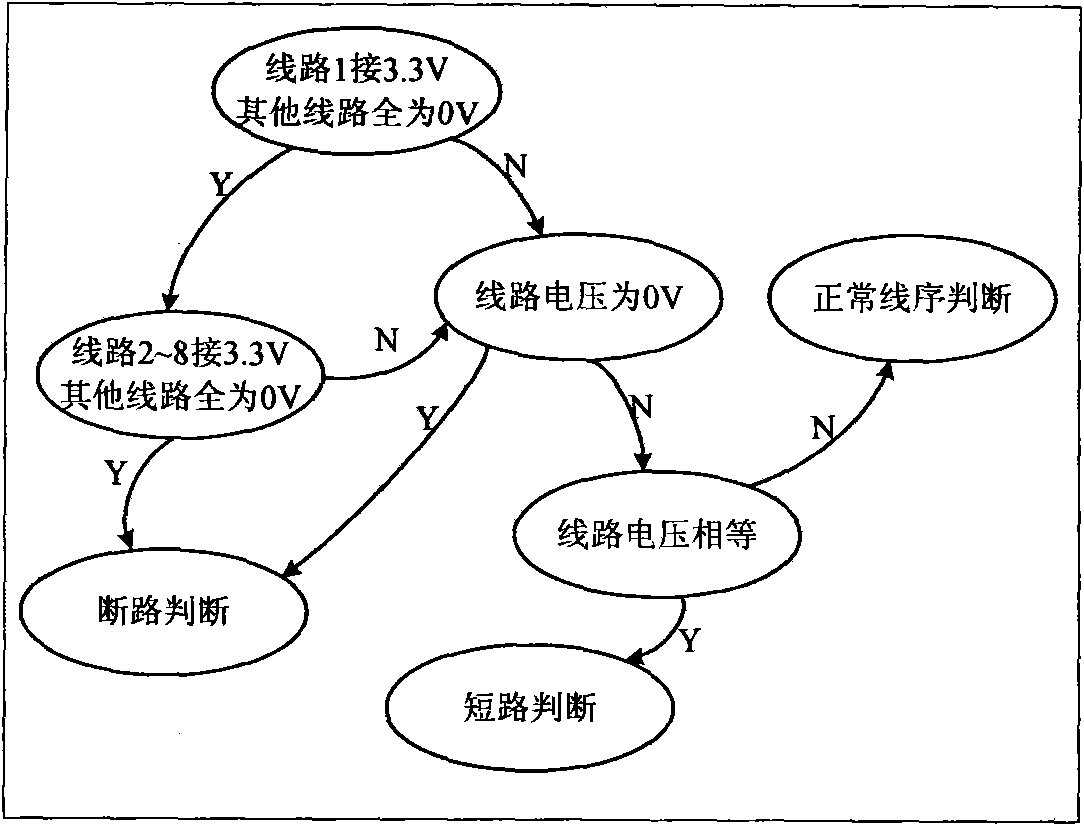
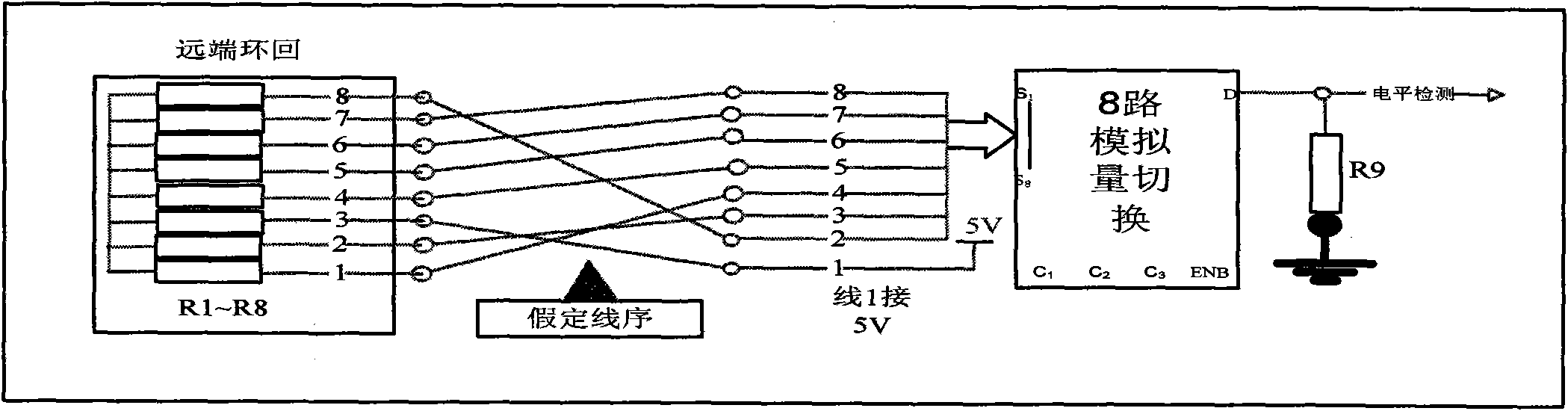
The invention discloses a wire order test method for testing cable wire order. The method is as follows: a first N-path analog quantity switch selector is placed at the side of a cable to be tested, and a far-end loopback line is arranged; the far-end loopback line is respectively connected with resistors R1-RN in series, and the requirement of selecting far-end loopback resistors is that the sumof any two resistors is not equal; local 5 V high level is output through the line and then delivered to a far-end loopback passive joint; the 5 V high level is looped back to the local through the tandem resistors in the line and then through the tandem resistors on the other line; and because the sum of any two far-end resistors is not equal, the partial pressure value on any loopback line is not equal, thus the connection manner of the wire order can be judged. In the invention, a single port device is used to achieve measurement and the cost of the test device can be saved. By using the method, the measurement of any wire order can be realized. The method can be used in more occasions owing to the any wire order judgment function.
Owner:LIUZHOU DADI TELECOMM EQUIP
Single-leg robot in-place jumping mechanism with power energy storage function
ActiveCN103264733AImprove the level of security protectionJump in placeVehiclesKnee JointEngineering
The invention discloses a single-leg robot in-place jumping mechanism with a power energy storage function and belongs to the technical field of robots. A robot is composed of five portions including a body, a hip joint, a knee joint, a pelma and a thigh and a shank, the body and the thigh are connected through the hip joint, the thigh and the shank are connected through the knee joint, the hip joint is composed of elements like a motor, a harmonic speed reducer, a coder and a hip spring, has a function of actively outputting joint moment and provides active moment output for the knee joint through a synchronous belt, a knee spring is mounted on a knee rotary shaft of the knee joint, the knee joint stores and complements energy for jumping of the robot by converting gravitational potential energy of the robot into elastic potential energy of the knee spring, and a force sensor is mounted on the pelma and used for detecting ground-touching information of the robot. By reasonably arranging the joints and combining an active and passive joint control technology to store and complement the energy for jumping of the robot, improving of quickness and efficiency in moving of the robot is facilitated.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUNSHENCHU TECH CO LTD
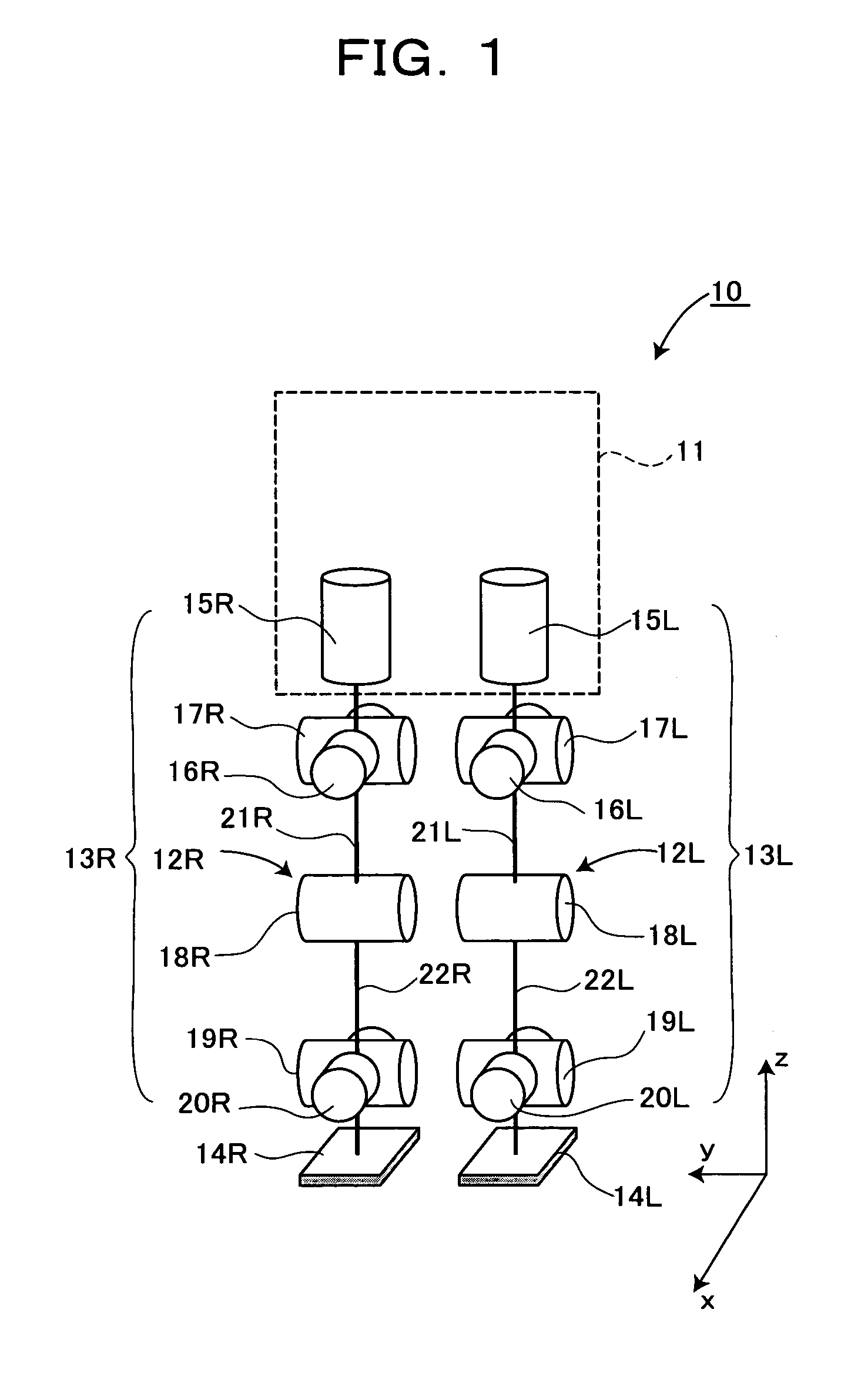
Biped walking mobile system, its walk controller, and walk control method therefor
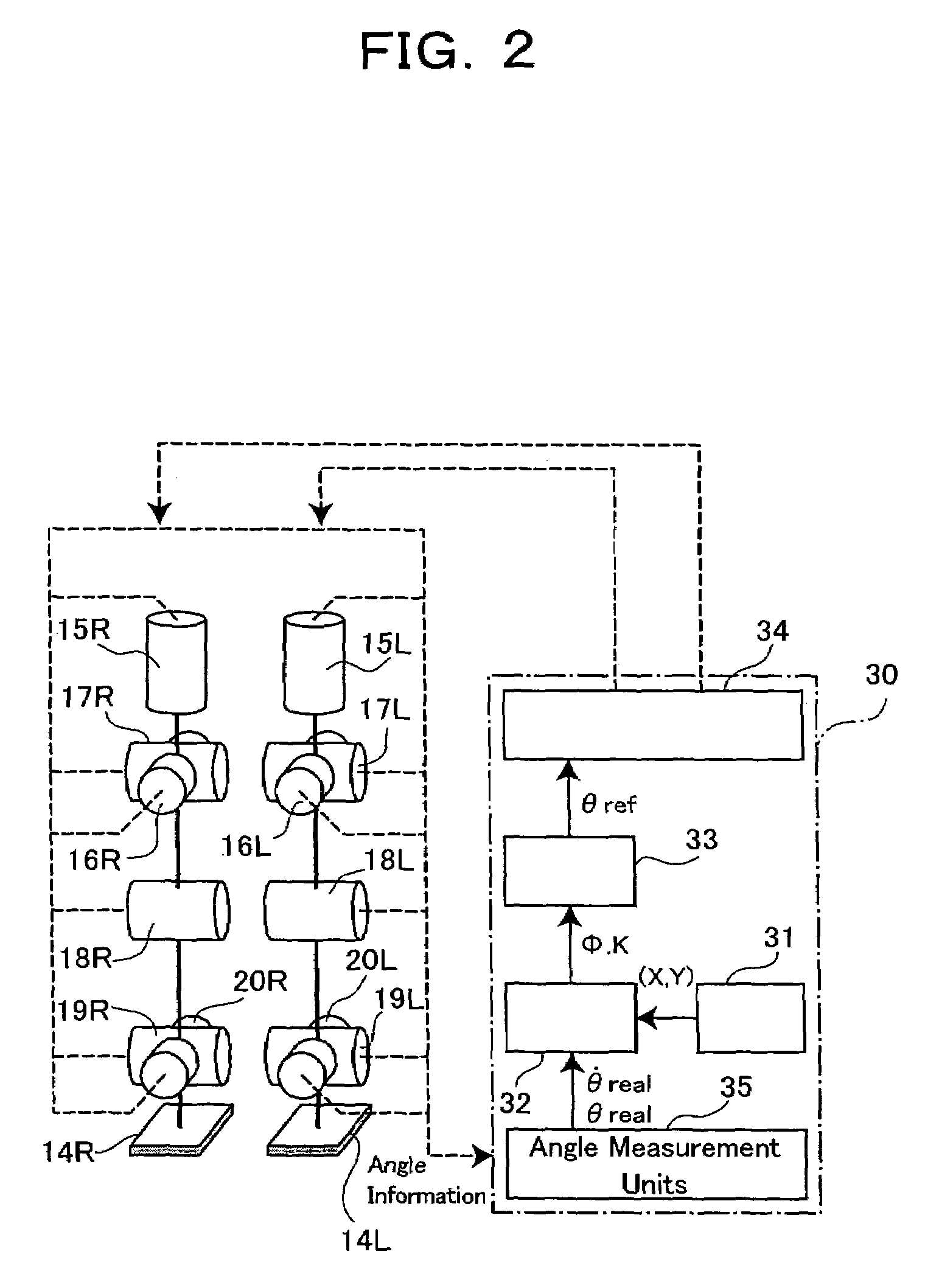
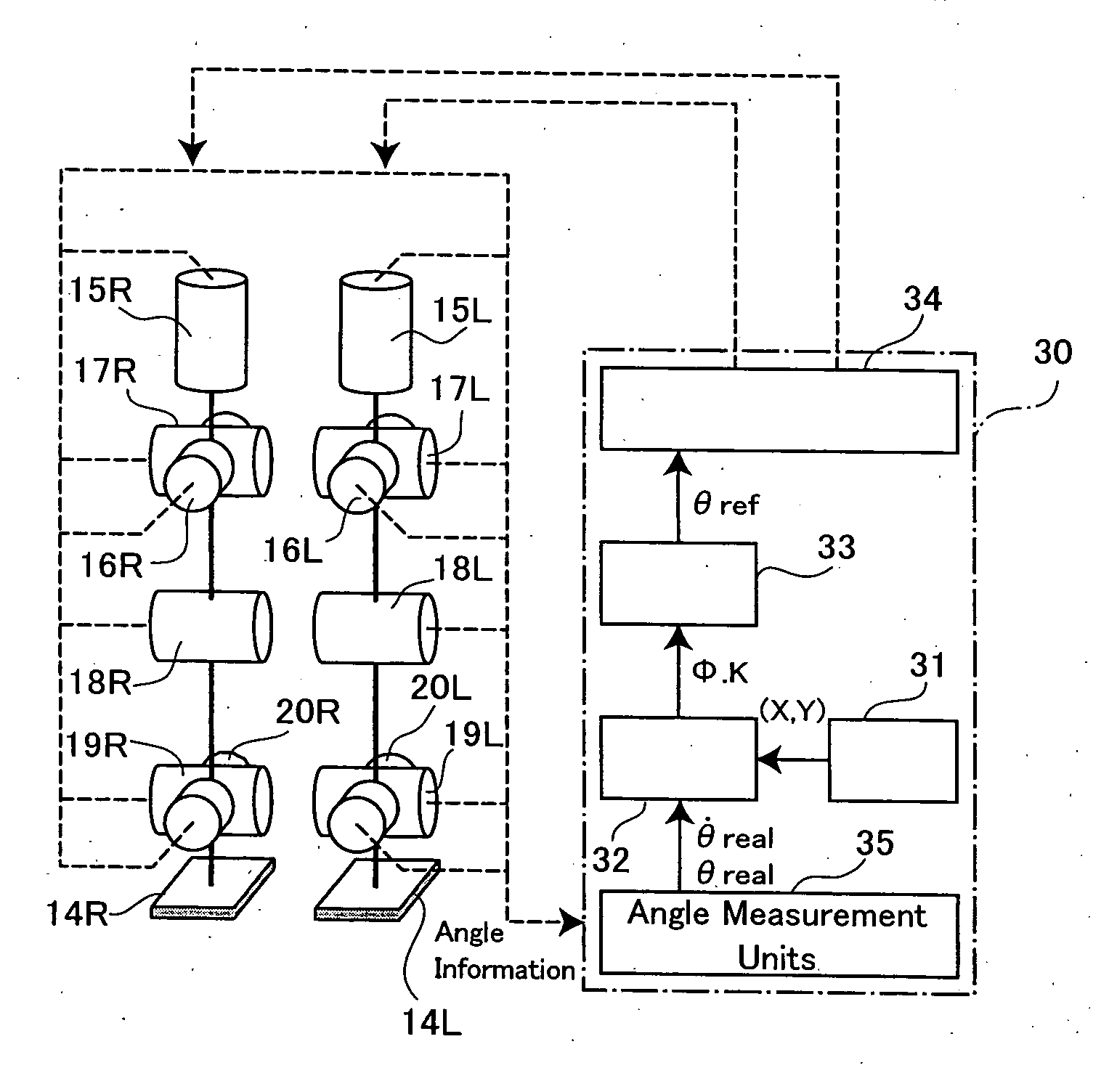
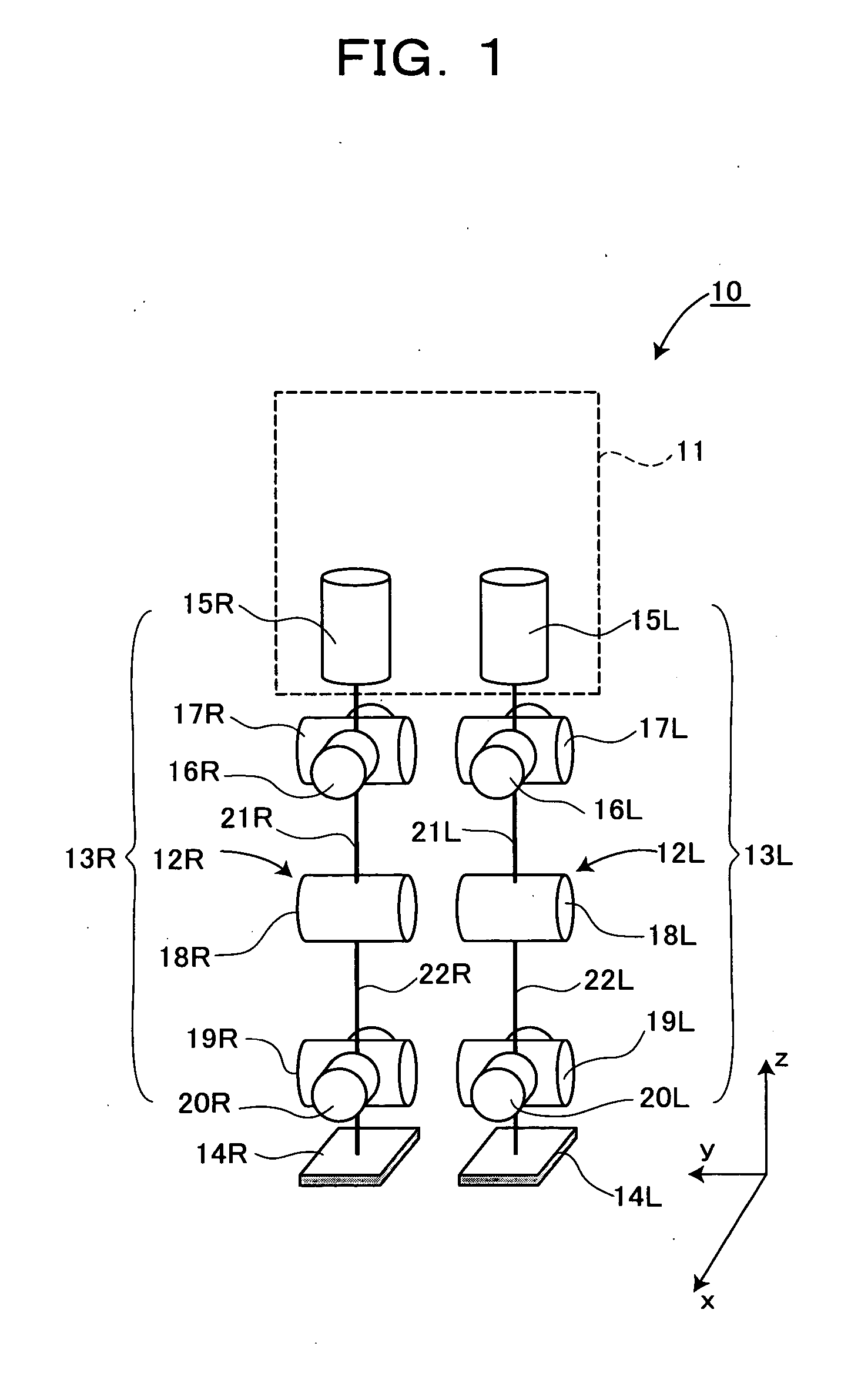
InactiveUS6992456B2Improve walking stabilityDefects can be eliminatedProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlPower modeEngineering
The present invention provides a biped (two-footed) walking mobile system, its walk controller, and walk control method therefore, which are to realize enhancing an walk stability, as well as a consumed energy saving. A walk controller (30) of a biped walking mobile system forms a gait data by a gait forming part (33) based on parameters from a gait stabilizing part (32), and drive-controls drive means of respective joint portions (15L, 15R–20L, 20R) of each leg portion based on said gait data. In this case, the walk controller (30) is so constituted as to selectively witch a powered mode to conduct ordinary drive-control and a passive mode to drive-control the drive means similarly with passive joints, whereby drive-controlling respective joint portions. The walk controller (30) preferably switches the drive and passive modes with respect to, for example, joint portions of knee and foot portions, or switches to the powered mode for kick-up and landing during walking motion, and to the passive mode for a free foot state.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Working robot, actuator and control method thereof
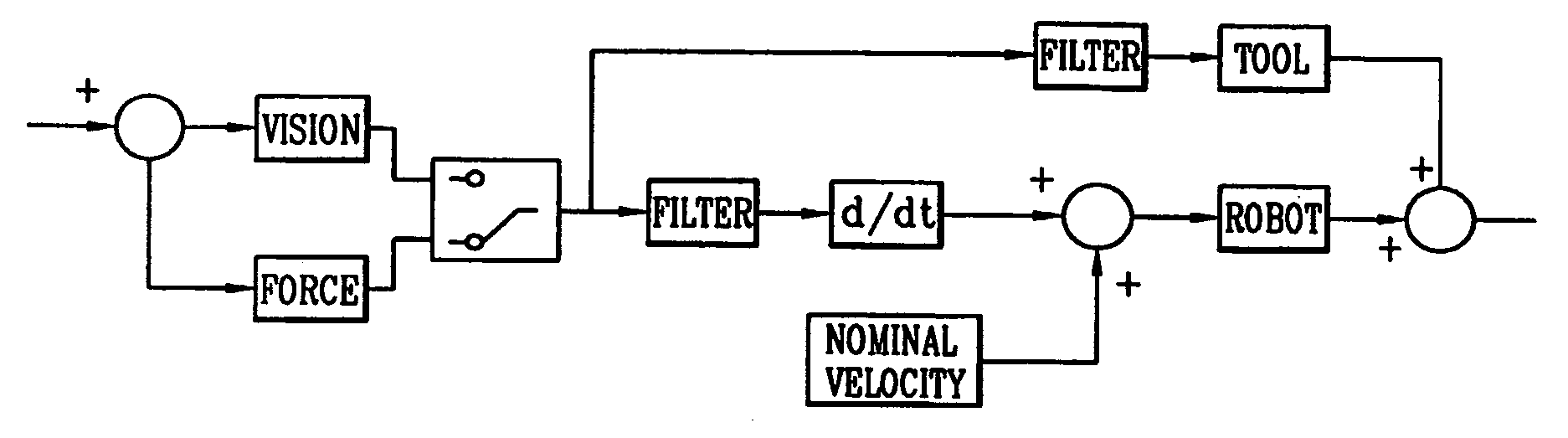
InactiveUS20060111810A1Quick responseHigh frequencyProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorDegrees of freedomActuator
A working robot, which is able to perform a required operation by locating a tool on a working position of a moving object, comprises a robot body moving with the object according to the movement of the object with more than one degree of freedom; an actuator mounted on a free end of the robot body and including a tool mounting unit, on which the tool is mounted, connected by a passive joint which reacts passively to small displacement of the object for locating the tool on the working position; and a control device for controlling the robot body, the actuator, and the tool.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for navigating and positioning multi-joint arm mechanical sensing type ultrasonic image
InactiveCN101612062AOptimize data processingFast data processingDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsSemi activeControl theory
The invention relates to a method for navigating and positioning a multi-joint arm mechanical sensing type ultrasonic image, which mainly comprises a mechanical sensing component combining method, and a navigating and positioning method, wherein the method adopts a six-joint arm with a sensor to directly measure the real-time position of an ultrasonic probe; the multi-joint arm adopts the combination form that rotating shafts of two electric joints and four passive joints are mutually perpendicular; the x-direction displacement only depends on the intersection angle of the electric joint group and is unrelated to the intersection angle of the passive joint group when the probe position is measured and controlled; and the y-direction displacement of a probe pedestal only depends on the intersection angle of the passive joint group and is unrelated to the intersection angle of the electric joint group. The method adopts a semi-active structure mode that the electric joint group is matched with the passive joint group mutually. The method has the advantages of simple and compact structure, safety and stability.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Multi-body magnetic adsorption type adaptive wall climbing robot
ActiveCN102039592AExpand the scope of processingIncrease load capacityArmsCarrying capacityEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-body magnetic adsorption type adaptive wall climbing robot and belongs to the technical field of special robots. The robot comprises a main body device, at least one slave body device, at least one mechanical arm and a working tool arranged on each slave body device, wherein the main body device comprises a main body frame, a movable mechanism and a main body magnetic adsorption device; the slave body device comprises a slave body frame, a slave body magnetic adsorption device and at least one auxiliary supporting wheel; and each mechanical arm comprises at least five connecting rods, at least two active joints and at least two passive joints. The invention provides a wall climbing robot which flexibly moves and steers on a magnetized wall surface at full positions spatially, is adaptive to a spatial curved surface and can perform welding, gouging, cutting, grinding, milling, detecting, cleaning or spraying work. The robot has wide processing range, high carrying capacity, high flexibility of movement and high working efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Bionic foot for bionic robot
The invention provides a bionic foot for a bionic robot. The bionic foot comprises a sole base, a bionic arch, an anti-sliding foot pad and a moveable sole, wherein the bionic arch has an arch-shaped structure, simulates a human arch and comprises four bionic arch plate spring stacking modules which are formed by successively staggering and stacking a plurality of plate spring blocks; the bionic arch has a buffering function when the robot walks and climbs stairs and can greatly reduce the ground impact force; the moveable sole is in pivoted connection with the sole base through a rotating shaft; the moveable sole and the sole base has a same degree of freedom; a spring is used for applying a pre-tightening force in the rotating shaft, so that a passive joint is formed; when the robot walks, the moveable sole is clung to the ground, so that the flexibility of the foot is increased and the moving posture of the foot while walking is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Surgical robot passive joint based on motor drive locking
InactiveCN103622751AAvoid the disadvantages of easy leakageAvoid noiseJointsDiagnosticsControl theoryPassive joint
The invention discloses a surgical robot passive joint based on motor drive locking, and relates to the surgical robot passive joint which aims at solving the problems that the current hydraulic drive locking joint has a complex design and needs a hydraulic power unit and hydraulic oil easily leaks; a pneumatic drive locking joint needs an air pump so that noises are high; according to an electromagnetic power locking mode, the calorific value is large, the electromagnetic interference is strong and the joint volume large. The surgical robot passive joint based on motor drive locking is characterized in that the upper end of a lower shell can be rotatably embedded into the lower part of an upper shell, and a stepping motor is arranged in a motor base; the output end of the stepping motor is sequentially connected with an input shaft, a harmonic reducer and an output shaft from bottom to top; an elastic coupling is sheathed on the output shaft and the input shaft of the stepping motor, and a gear is arranged on the output shaft; a shell connecting piece, a lower bearing shell and upper bearing shell are sequentially installed on the motor base from bottom to top, and a gear screw is installed in the lower shell; a wedge-shaped friction piece is installed on a support piece, and a coder is installed on a coder connecting piece. The surgical robot passive joint based on motor drive locking is used for surgical robots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
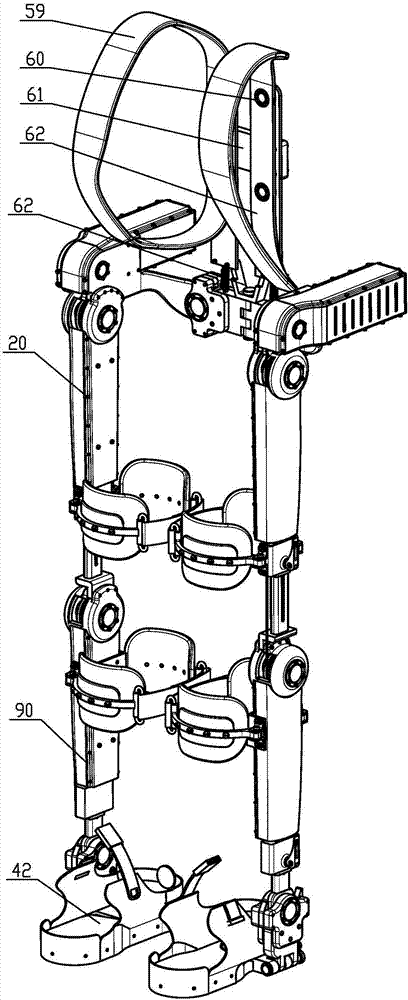
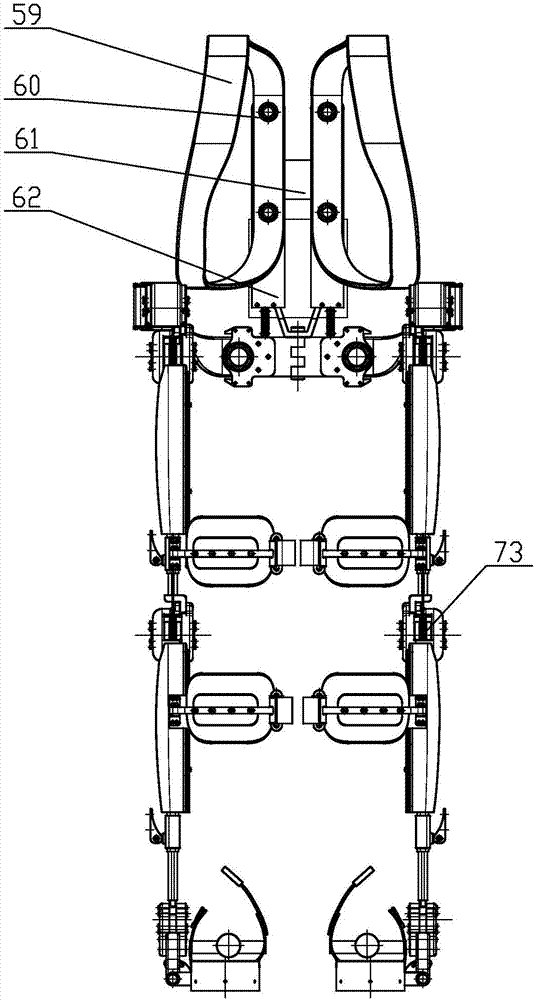
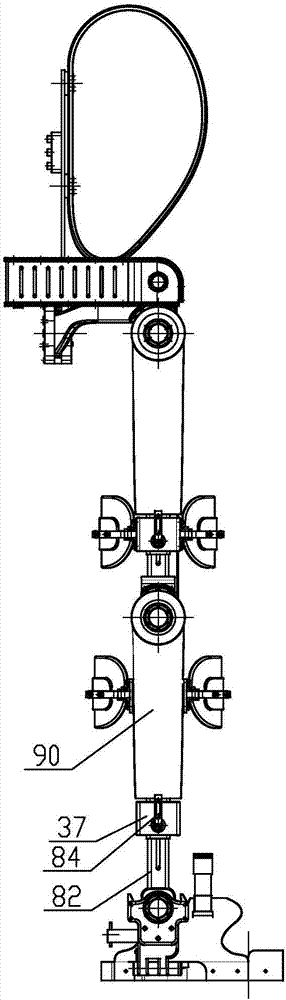
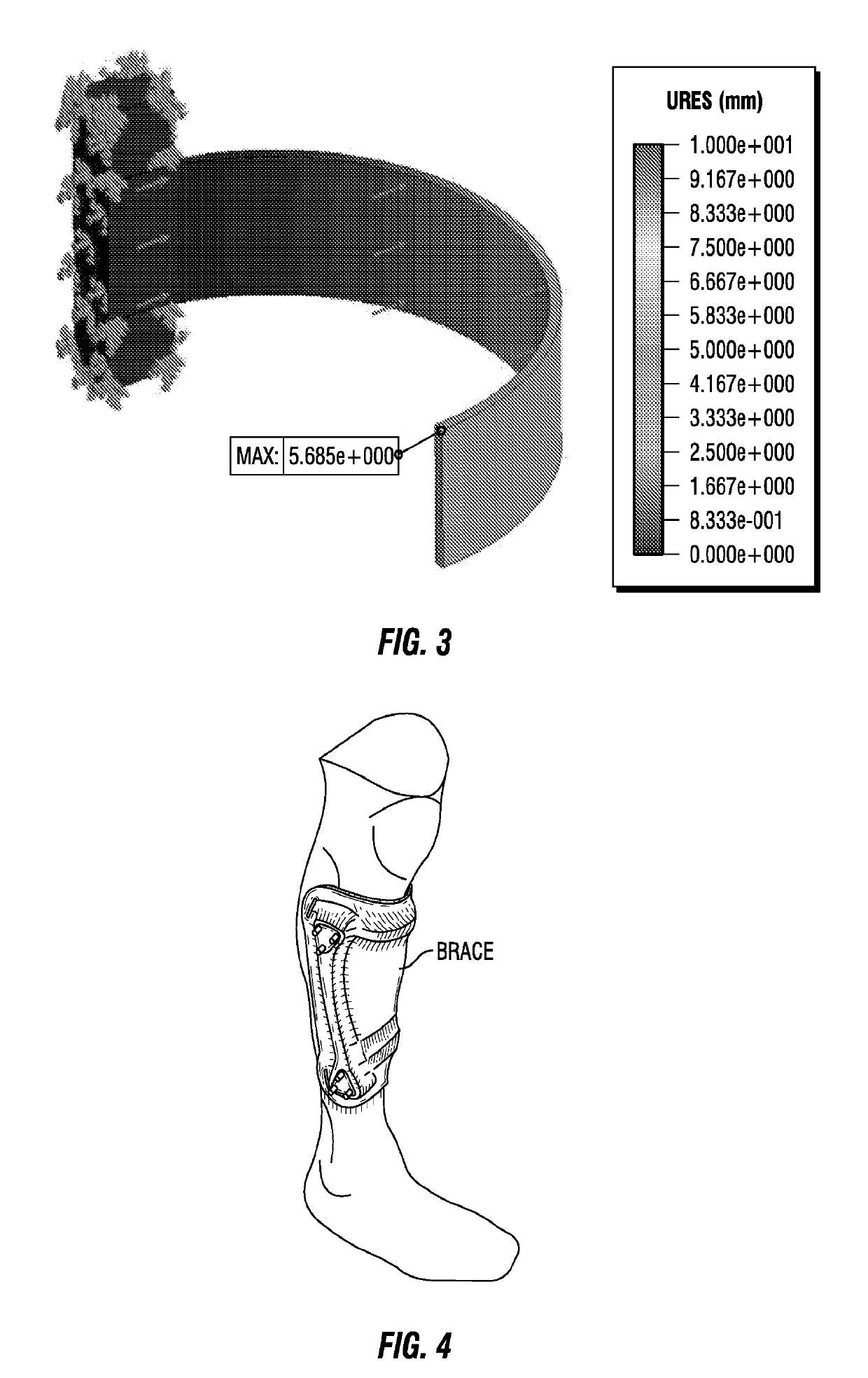
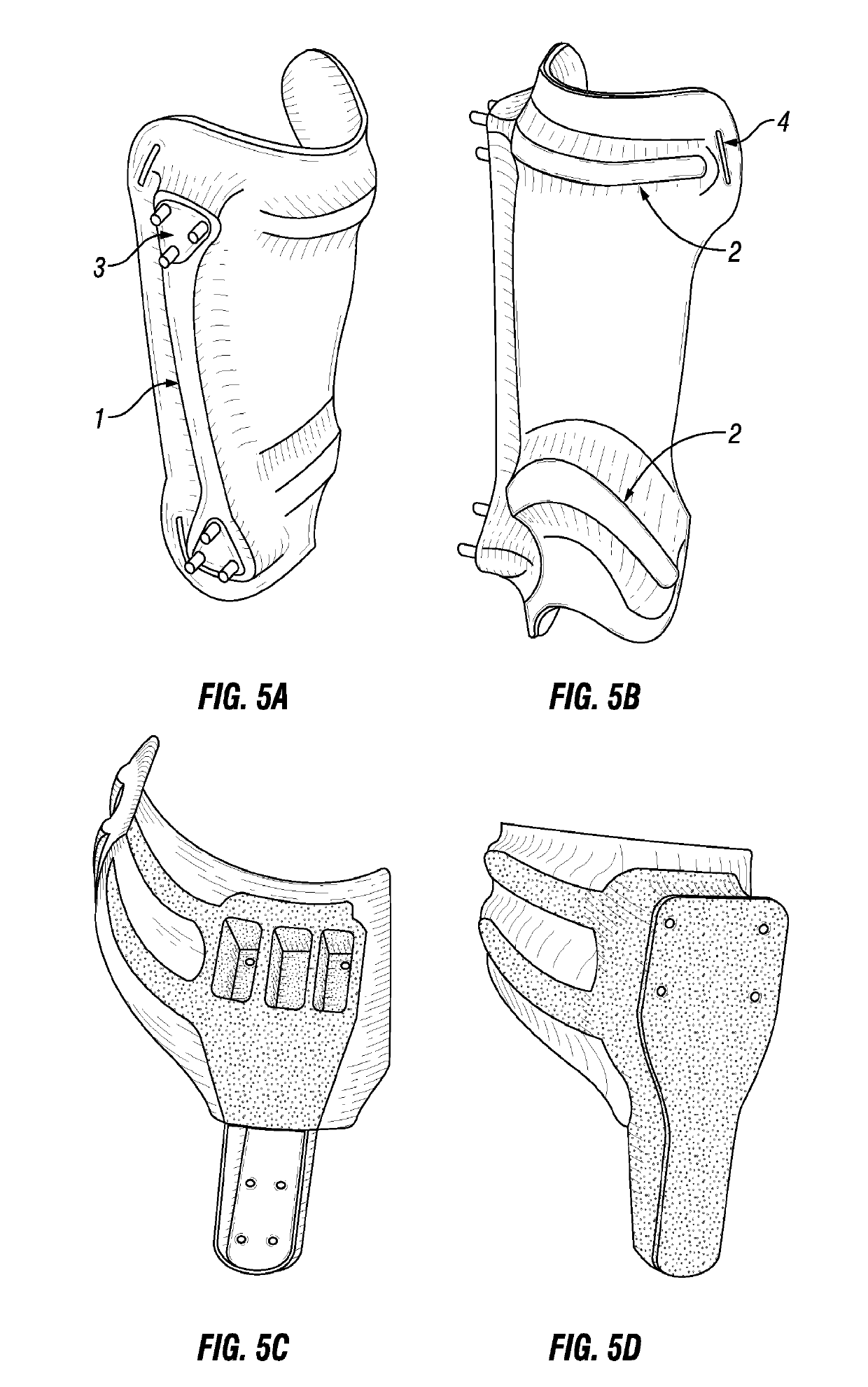
Customizable orthotic/prosthetic braces and lightweight modular exoskeleton
Improved customizable orthotic / prosthetic braces and a lightweight modular exoskeleton may aid individuals with lower limb motor impairment, including children. These customizable orthotic / prosthetic braces improve the strength and rigidity of such braces without a weight penalty. A structural frame is embedded between an inner shell and outer shell, which comprise materials that are easily moldable to conform to a user's limb. The lightweight modular exoskeleton system provides six (6) joint actuators, which are designed to be modular, that act as the active joints (e.g. hips, knees, and ankles) of the exoskeleton. Additionally, the exoskeleton may also provide four (4) passive joints for inversion / eversion of the legs and feet. Foot, crutch, and hip assemblies may also be provided IN for the exoskeleton. Further, the six joint actuators may be utilized between the hip brace assembly and thigh brace assembly, the thigh and shank brace assembly, and the shank brace assembly and foot assembly, where the braces may correspond to the customizable orthotic / prosthetic design. The modularity of the actuators and braces allows for exoskeleton assemblies that can be tailored to patient specific needs.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Instrument holding mechanical arm used for minimally-invasive robot
InactiveCN105012023AReduce occupancyEasy to decoupleDiagnosticsSurgeryOperative instrumentTarsal Joint
The invention provides an instrument holding mechanical arm used for a minimally-invasive robot, and relates to the instrument holding mechanical arm. The instrument holding mechanical arm solves the problems that the number of passive joints is large when an existing mechanical arm is arranged in a concentrated mode and the existing mechanical arm is large in overall size and low in rigidity when a passive arm is too long. The instrument holding mechanical arm comprises vertical horizontally-moving safety brake devices, passive joints, first joints, second joints and an integrated operative instrument drive device. One ends of the passive joints are arranged on the upper portions of the vertical horizontally-moving safety brake devices in a rotatable mode. One ends of the first joints are connected to the passive joints in a rotatable mode. One ends of the second joints are connected with the other ends of the first joints in a rotatable mode. The integrated operative instrument drive devices are arranged at the other ends of the second points. The instrument holding mechanical arm is used for operative instrument drive of the micro operative instruments of the robot.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Bipedal moving device, and device and method for controlling walking of the bipedal moving device
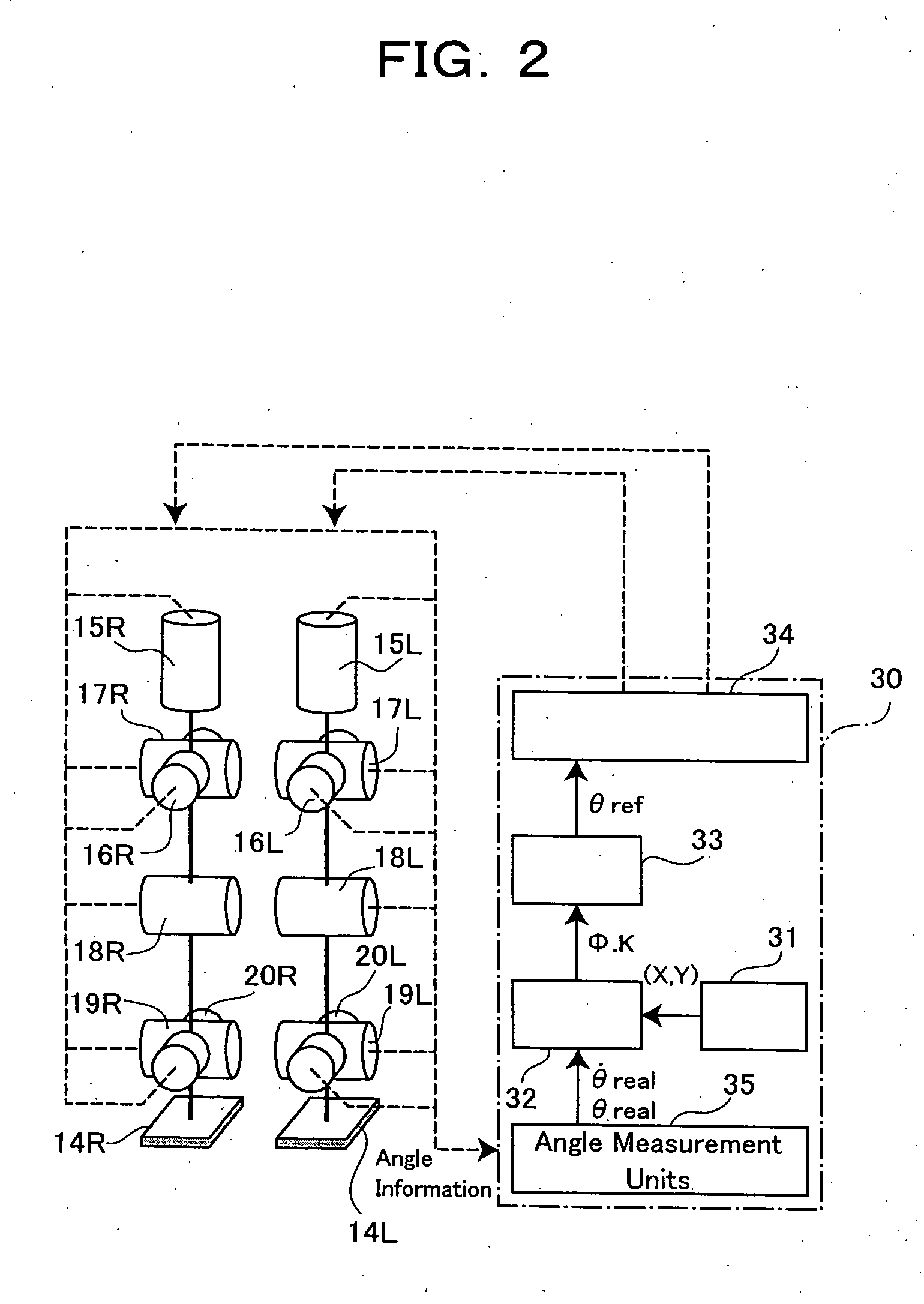
InactiveUS20050001575A1Improve walking stabilityDefects can be eliminatedProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlPower modeControl theory
The present invention provides a biped (two-footed) walking mobile system, its walk controller, and walk control method therefore, which are to realize enhancing an walk stability, as well as a consumed energy saving. A walk controller (30) of a biped walking mobile system forms a gait data by a gait forming part (33) based on parameters from a gait stabilizing part (32), and drive-controls drive means of respective joint portions (15L, 15R-20L, 20R) of each leg portion based on said gait data. In this case, the walk controller (30) is so constituted as to selectively witch a powered mode to conduct ordinary drive-control and a passive mode to drive-control the drive means similarly with passive joints, whereby drive-controlling respective joint portions. The walk controller (30) preferably switches the drive and passive modes with respect to, for example, joint portions of knee and foot portions, or switches to the powered mode for kick-up and landing during walking motion, and to the passive mode for a free foot state.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Working robot, actuator and control method thereof
InactiveUS7236850B2Quick responseHigh frequencyProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorDegrees of freedomActuator
A working robot, which is able to perform a required operation by locating a tool on a working position of a moving object, comprises a robot body moving with the object according to the movement of the object with more than one degree of freedom; an actuator mounted on a free end of the robot body and including a tool mounting unit, on which the tool is mounted, connected by a passive joint which reacts passively to small displacement of the object for locating the tool on the working position; and a control device for controlling the robot body, the actuator, and the tool.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Prismatic/revolute orienting apparatus
ActiveUS20120103123A1The process is fast and accurateVibrationProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusDegrees of freedomActuator
A two degree-of-freedom parallel device for orienting or pointing an end effector with vibration suppression is described. The two end effector degrees-of-freedom are decoupled by connecting fast actuators to the effector by passive joints. The stiffness of the linkages and the high speed of the revolute and prismatic actuators employed permit the application of large feedback useful for disturbance rejection.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
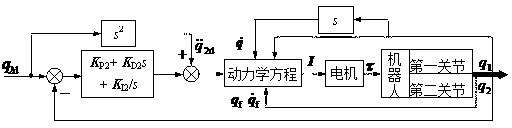
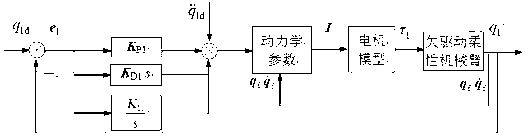
Method for controlling position of 2R under-actuated plane flexible mechanical arm
The invention provides a method for controlling a position of a 2R under-actuated plane flexible mechanical arm. The method comprises the following steps: an assumed mode method is adopted to establish a dynamic model synthetically considering joint passivity, rod piece flexibility and joint friction, of the 2R under-actuated plane flexible mechanical arm; and aiming at the characteristics of flexibility and under-actuating which simultaneously exist in the system, and on the base of a time-scale and PID control method, a segmented control strategy is designed so as to realize the position control of an active joint and a passive joint, thereby finishing the tail-end operation of a whole robot. Compared with a conventional full-drive rigidity system, the under-actuated plane flexible mechanical arm provided by the invention has the advantages of light weight, low energy consumption and compact structure; by the segmented control design, complex operation and control for the robot can be realized by using the simple method; a nonlinear theory and a nonlinear theory solving method are avoided; and the purpose of simple method and easiness in realization are achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Joint movement rehabilitation instrument
InactiveCN104606029AIncrease elasticityReduce swellingGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesCold compressesActive exercise
The invention discloses a joint movement rehabilitation instrument used for guaranteeing sufficient joint recovery training of fracture patients. The rehabilitation instrument is characterized in that an elbow joint rehabilitation assembly and a knee joint rehabilitation assembly which are driven through a drive assembly are arranged on a base assembly, and angle of passive joint training can be optionally adjusted. A temperature adjusting mechanism is arranged on each of the elbow joint rehabilitation assembly and the knee joint rehabilitation assembly, elbow joints and knee joints can be adjusted in temperature, namely early cold compress and later thermal therapy, training effect can be enhanced, and rehabilitation time can be shortened. An elbow joint movement unit and the elbow joint rehabilitation assembly can be used in connection or separation, and passive training is performed when the elbow joint movement unit and the elbow joint rehabilitation assembly are used in connection; when the elbow joint movement unit and the elbow joint rehabilitation assembly are used in separation, the patient wears the instrument for active training, and active training and the passive training are performed alternatively so as to enhance the rehabilitation effect. A carrying-angle adjusting structure is arranged on the elbow joint movement unit so as to meet requirements of different patients and alleviate pains of the same in training, and comfortableness is increased.
Owner:SHANDONG PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL
Active and passive joint prosthesis
The invention provides an active and passive joint prosthesis mechanism, which comprises an active driving mechanism, a passive constraining mechanism, a knee joint shaft, an overrun clutch and the like. The active driving mechanism consists of a direct current servo motor, a reducer and a gear. The passive constraining mechanism consists of a direct current servo motor and a bevel gear shaft. The knee joint shaft is mounted on a U-shaped block consisting of a left side plate, a right side plate and a top plate. The knee joint shaft is provided with the bevel gear; a star wheel of the one-way overrun clutch and the shaft are fixedly connected by key connection; and the external ring of the clutch is fixedly connected with a cylindrical gear. The relationship between the active driving mechanism and the passive constraining mechanism is established by the mesh of two cylindrical gears, namely, one of the active driving mechanism and the passive constraining mechanism drives the star wheel of the clutch and the other one drives the external ring of the clutch. When a user of the prosthesis walks, under the control and coordination of a prosthesis control system, the active driving mechanism conducts an active driving function and the passive constraining mechanism conducts a passive constraining function.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
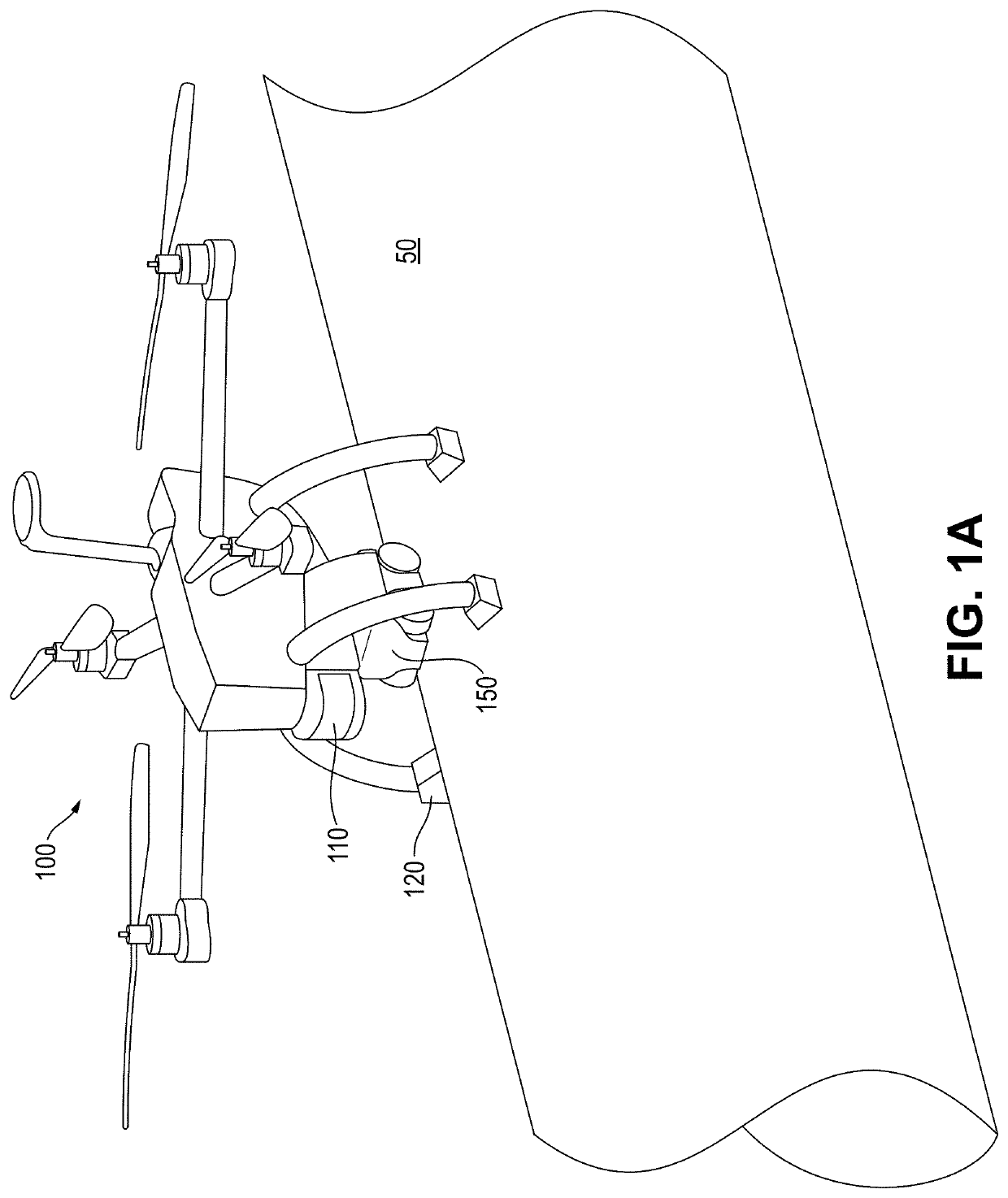
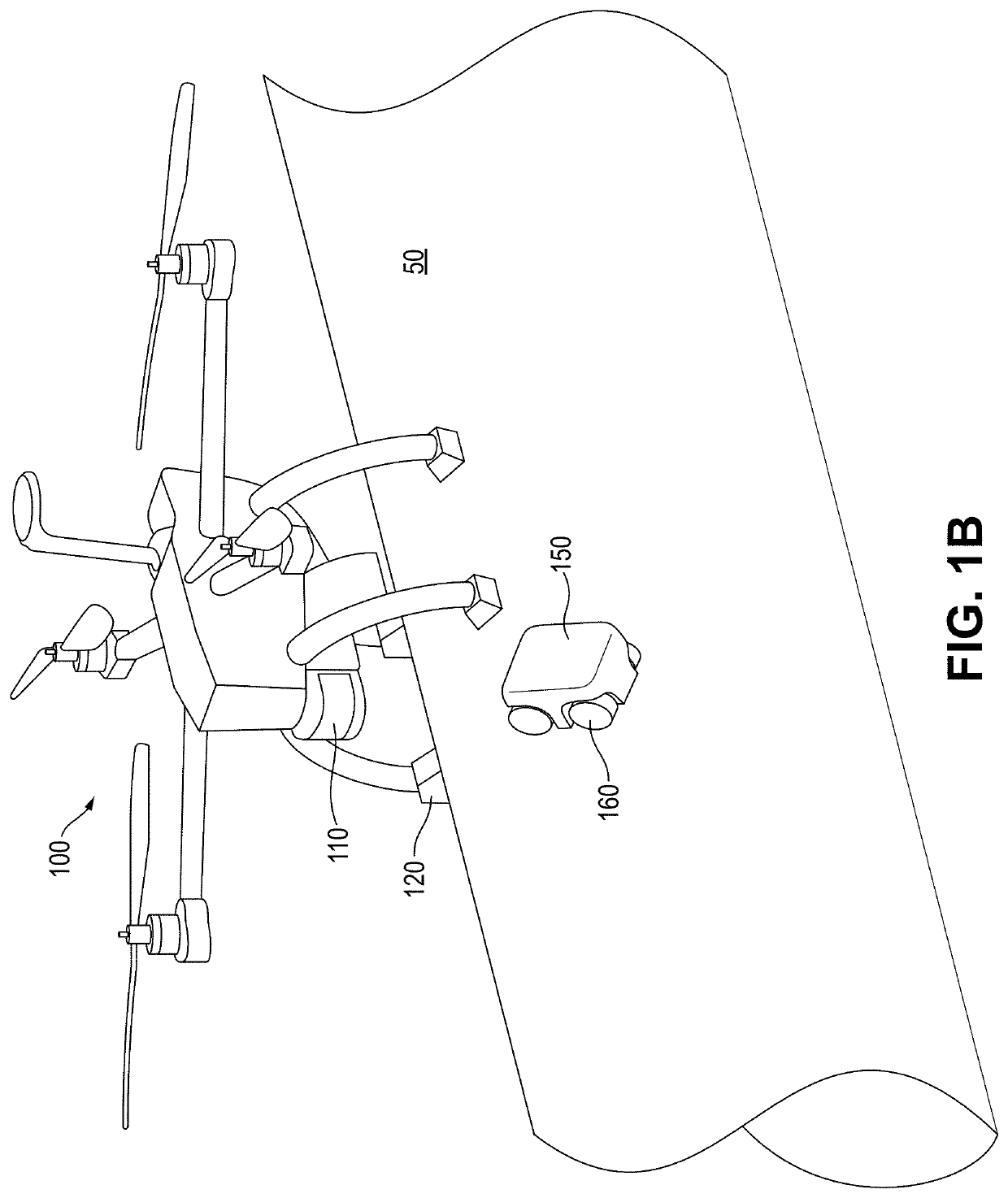
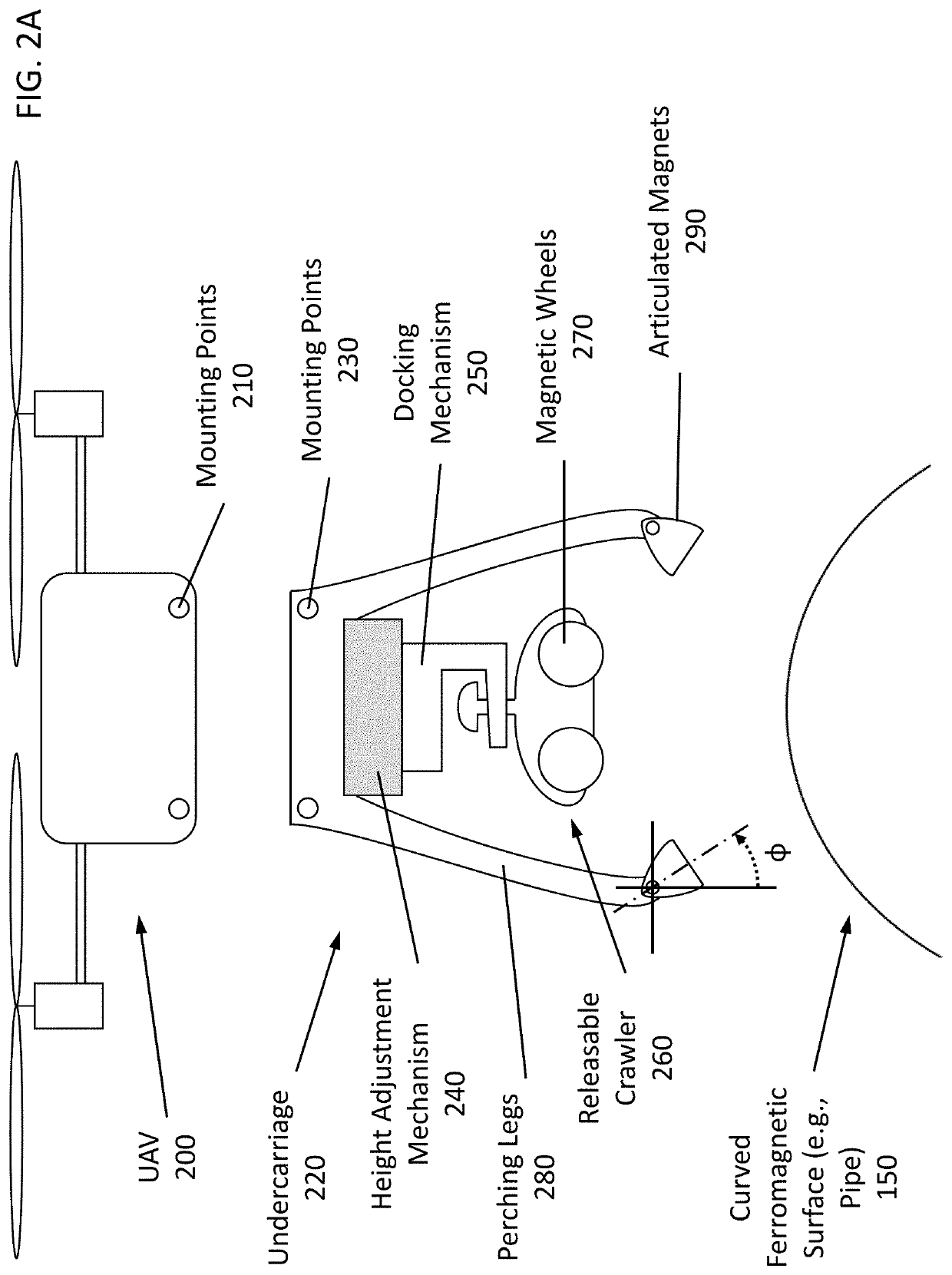
Perching UAV with releasable crawler
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) includes a body constructed to enable the UAV to fly and three or more legs connected to the body and configured to land and perch the UAV on a curved ferromagnetic surface. Each leg includes a first portion connected to the body, a second portion including a magnet and configured to magnetically attach and maintain the magnetic attachment of the leg to the ferromagnetic surface during the landing and perching, and a passive articulation joint connecting the first and second portions and configured to passively articulate the second portion with respect to the first portion in response to the second portion approaching the ferromagnetic surface. The UAV further includes a releasable crawler including magnetic wheels which detach the crawler from the body during the perching and maneuver the crawler on the ferromagnetic surface while magnetically attaching the crawler to the ferromagnetic surface after detachment.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Translation parallel mechanism with two degrees of freedom and hooke joints as passive joints
ActiveCN102848376AThe overall structure is simple and reliableIncrease lateral stiffnessProgramme-controlled manipulatorSide chainStructural engineering
The invention discloses a translation parallel mechanism with two degrees of freedom and hooke joints as passive joints. The parallel robot mechanism comprises a moving platform, a fixed platform, two pairs of guide rails and two moving side chains, and the moving side chains are connected between the fixed platform and the moving platform in parallel. One or two secondary constraint side chains and a moving slider are serially connected to form each moving side chain, the moving sliders are directly connected with the guide rails, the corresponding hooke joint, a corresponding connecting rod and another corresponding hooke joint are serially connected to form each secondary constraint side chain, and the secondary constraint side chains are connected between the moving platform and the moving sliders in parallel. The translation parallel mechanism with the two degrees of freedom is simple in structure and does not have an over-constraint structure; and the hooke joints are used as the passive joints, so that stress states of the connecting rods are improved, and lateral rigidity of the mechanism is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Remote exercise rehabilitation system
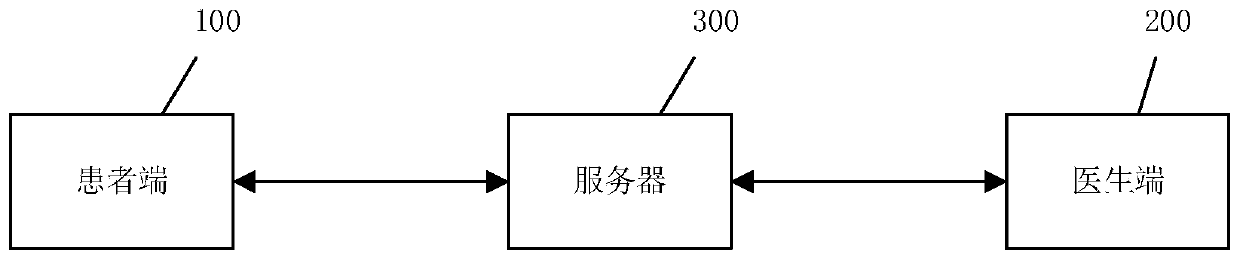
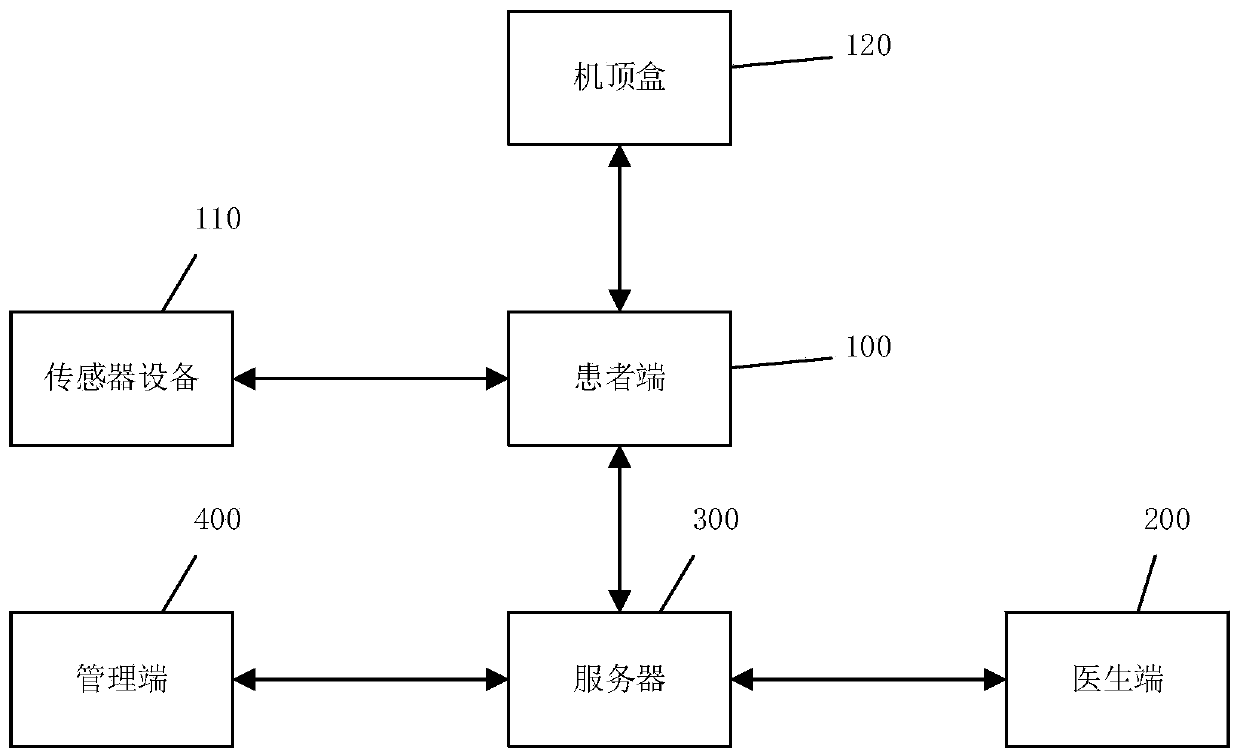
PendingCN110808092APhysical therapies and activitiesMedical communicationPersonalizationPassive joint
The invention discloses a remote exercise rehabilitation system. The system comprises a patient terminal (100), a doctor terminal (200) and a server (300). The patient terminal is matched with a wearable sensor device to evaluate and train the joint activity, and transmits the active and passive joint evaluation information to the doctor terminal through the server. The doctor terminal creates andmaintains the patient information, formulates a personalized evaluation and rehabilitation training scheme for the patient terminal, and facilitates the direct introduction at the patient terminal for rehabilitation training. Based on a micro sensor technology and a network transmission technology, a patient can also accept professional evaluation and training guidance at home and in a community,and the problem that medical treatment is inconvenient is effectively solved. A patient can achieve evaluation and rehabilitation training by using a television or a computer at home through a mobiledevice.
Owner:南京茂森电子技术有限公司
Parameter optimization method for six-degree of freedom parallel mechanism for modal space control
The invention provides a parameter optimization method for six-degree of freedom parallel mechanisms for modal space control. The six-degree of freedom parallel mechanism is similar to a viscous proportion damping system by changing structural parameters on the premise of not ignoring passive joint damping, so that a modal space decoupling controller can still give full play to the advantage of greatly improving the control characteristics of the system. By the method, the application range of the modal space controller is greatly increased.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
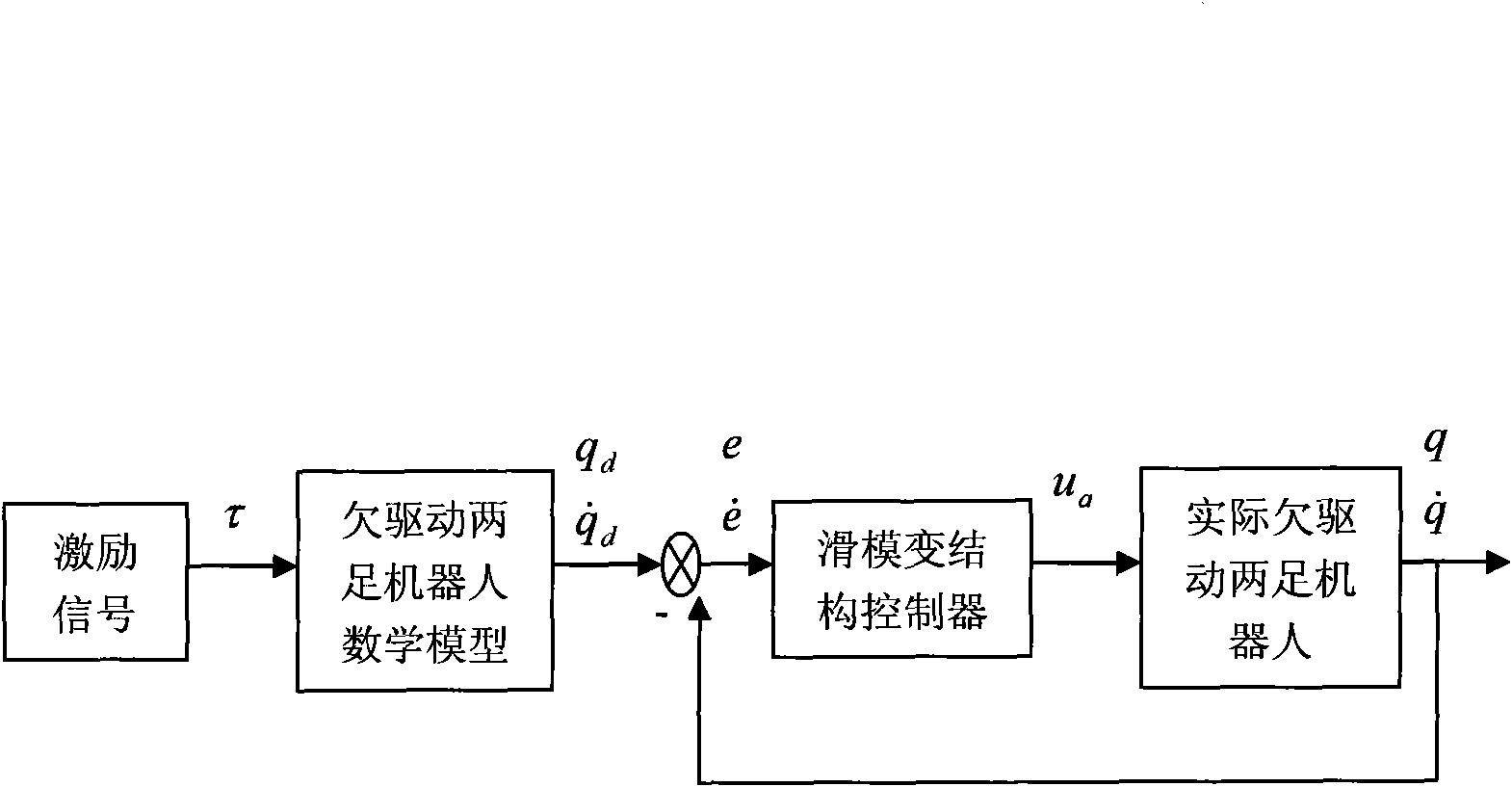
Underactuated biped robot excitation planning and control method
InactiveCN101799663AImprove real-time performanceStrong engineering practicabilityAdaptive controlExcitation signalPassive joint
The invention discloses an underactuated biped robot excitation planning and control method, which has the advantages of high real-time property and strong engineering practicability. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a mathematic model and converting the mathematic model into a system state equation; (2) selecting an excitation signal; (3) inputting the excitation signal; (4) taking joint angle positions, joint angle speeds and joint angle acceleration obtained in the step (3) as given values, recording an angle excitation plan for a passive joint to be qpd and recording an actual output angle of an underactuated joint to be qp; (5) performing sampling according to a sampling period and calculating an actual underactuated joint angle qp, an underactuated joint angle speed and underactuated joint angle acceleration by using a sensor; (6) comparing qpd with qp in each sampling period to obtain an error, determining the error with an expression and performing sliding mode variable structure control correction so as to make e tend to zero; (7) outputting an active joint control variable ua after the operation of the sliding mode variable structure control correction; and (8) repeating the steps (3) to (7) to obtain the active joint control variables of each sampling period.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
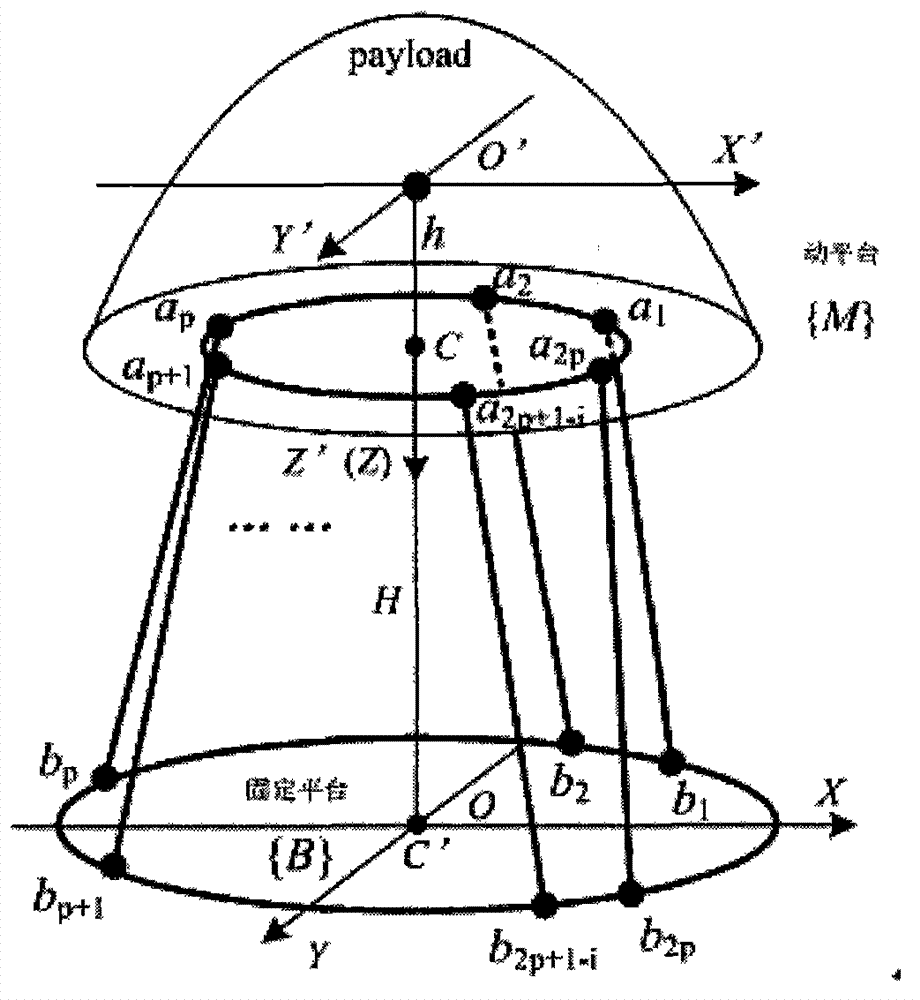
Hybrid type automobile electrophoresis coating conveying mechanism dynamics modeling method
ActiveCN105159137AHas coordinate invarianceNeat and concise expressionProgramme controlSimulator controlHybrid typeDynamic models
The invention discloses a hybrid type automobile electrophoresis coating conveying mechanism dynamics modeling method. First of all, the symmetrical structure characteristic of a mechanism is fully utilized, the speed and the accelerated speed of each passive joint in the mechanism are analyzed through an analytical geometry method, and then the speed and the accelerated speed of each active joint of the mechanism are obtained by introducing a screw theory; secondly, based on this, a kinetic equation in a mechanism spinor form is established by use of virtual work principle; and finally, axial driving power of each active joint of the conveying mechanism capable of directly realizing control is obtained through calculation so that construction of a dynamics model capable of realizing high-performance control is completed. According to the invention, the analytical geometry method, the screw theory and the virtual work principle are combined together, so that the problem of coordinate transformation due to lack of coordinate invariance during dynamics modeling of a complex special mechanism is solved, the calculation complexity is reduced, and at the same time, the dynamics modeling method brought forward by the invention is quite simple, is tidy in form and is easy in programmed realization.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com