Patents
Literature
3860 results about "Knuckle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
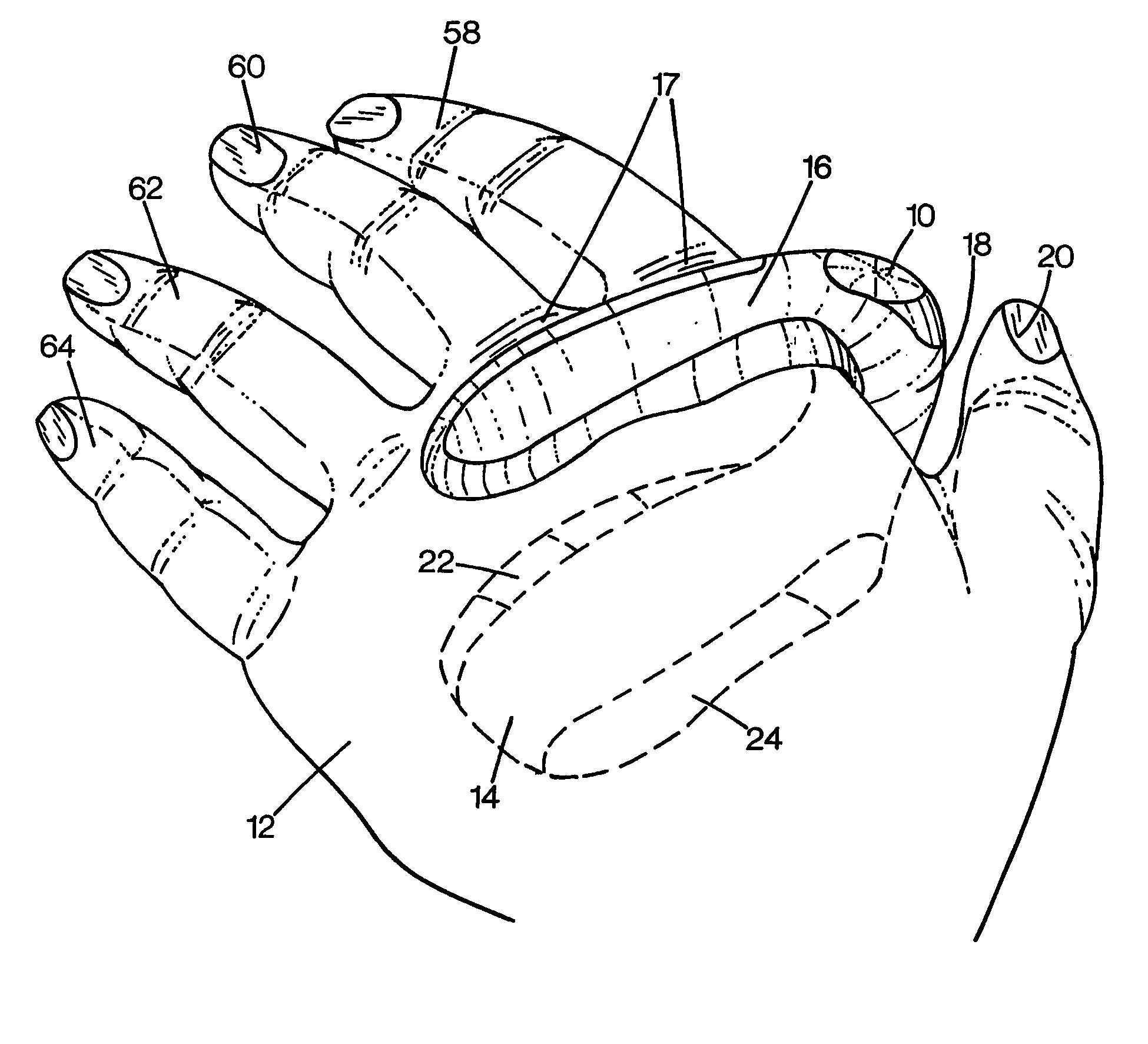
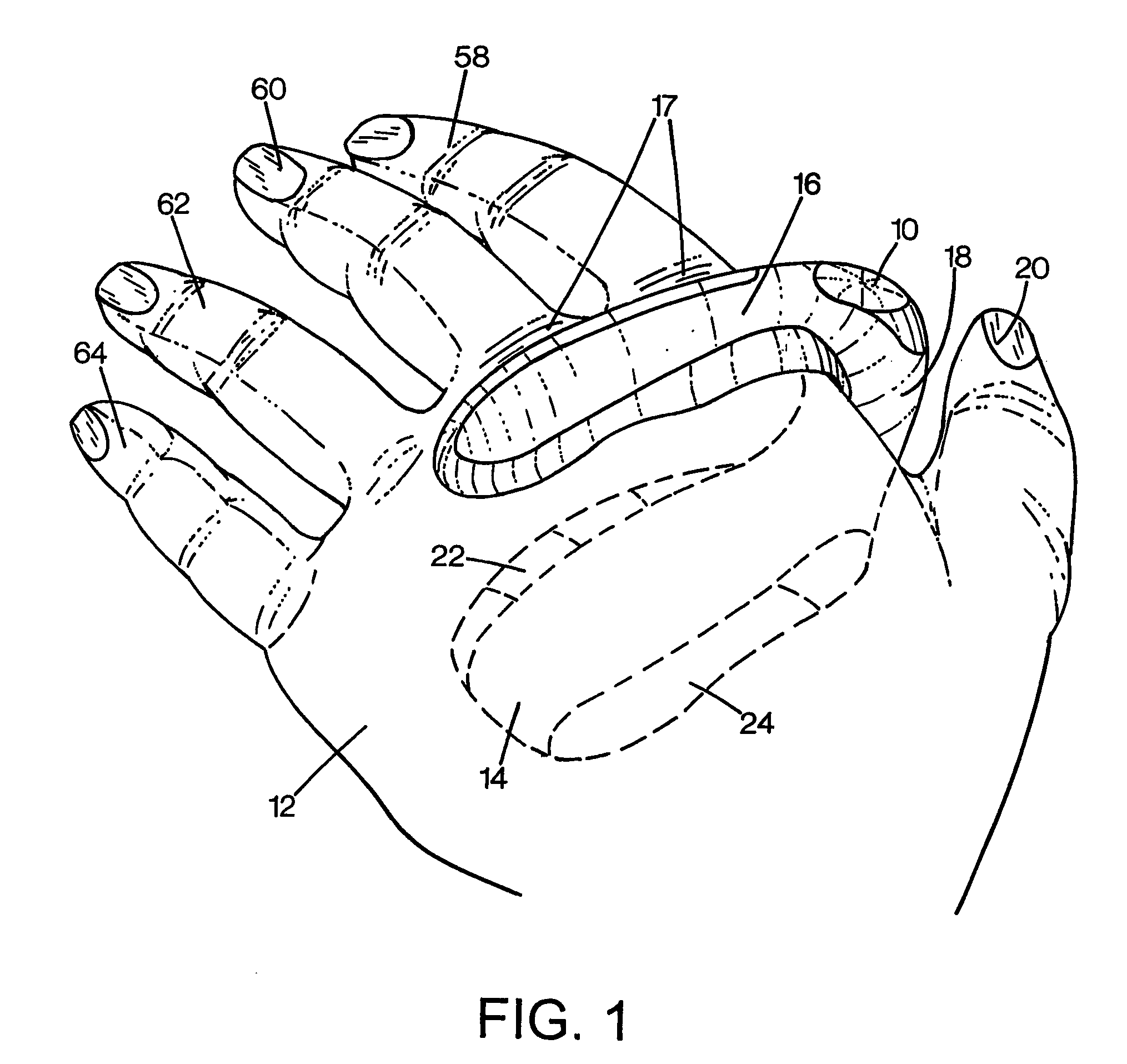
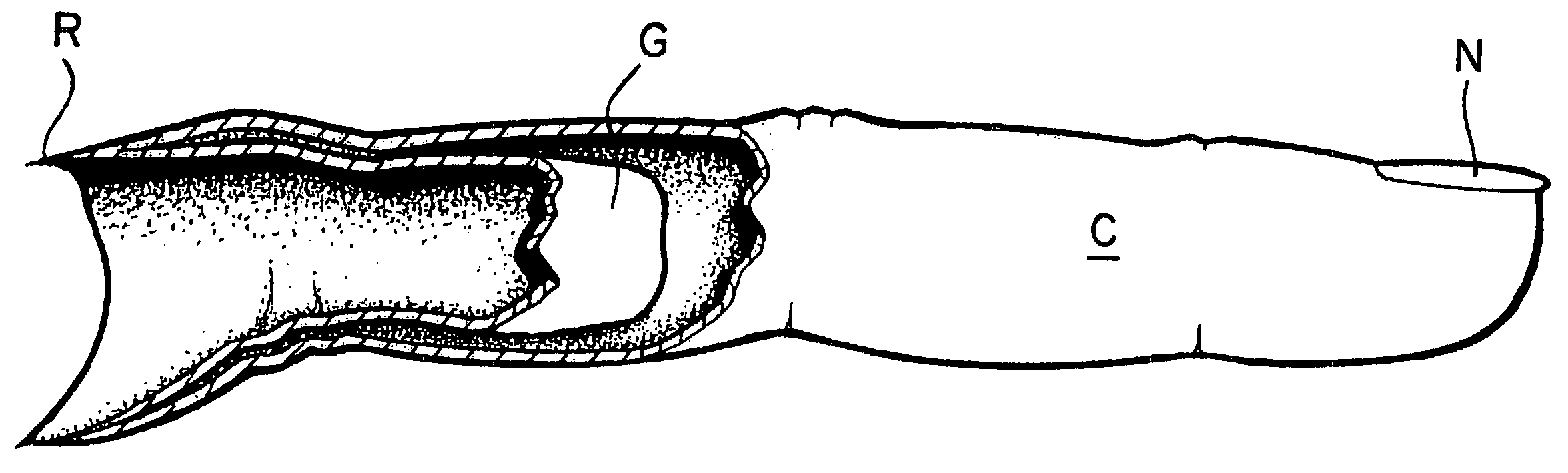
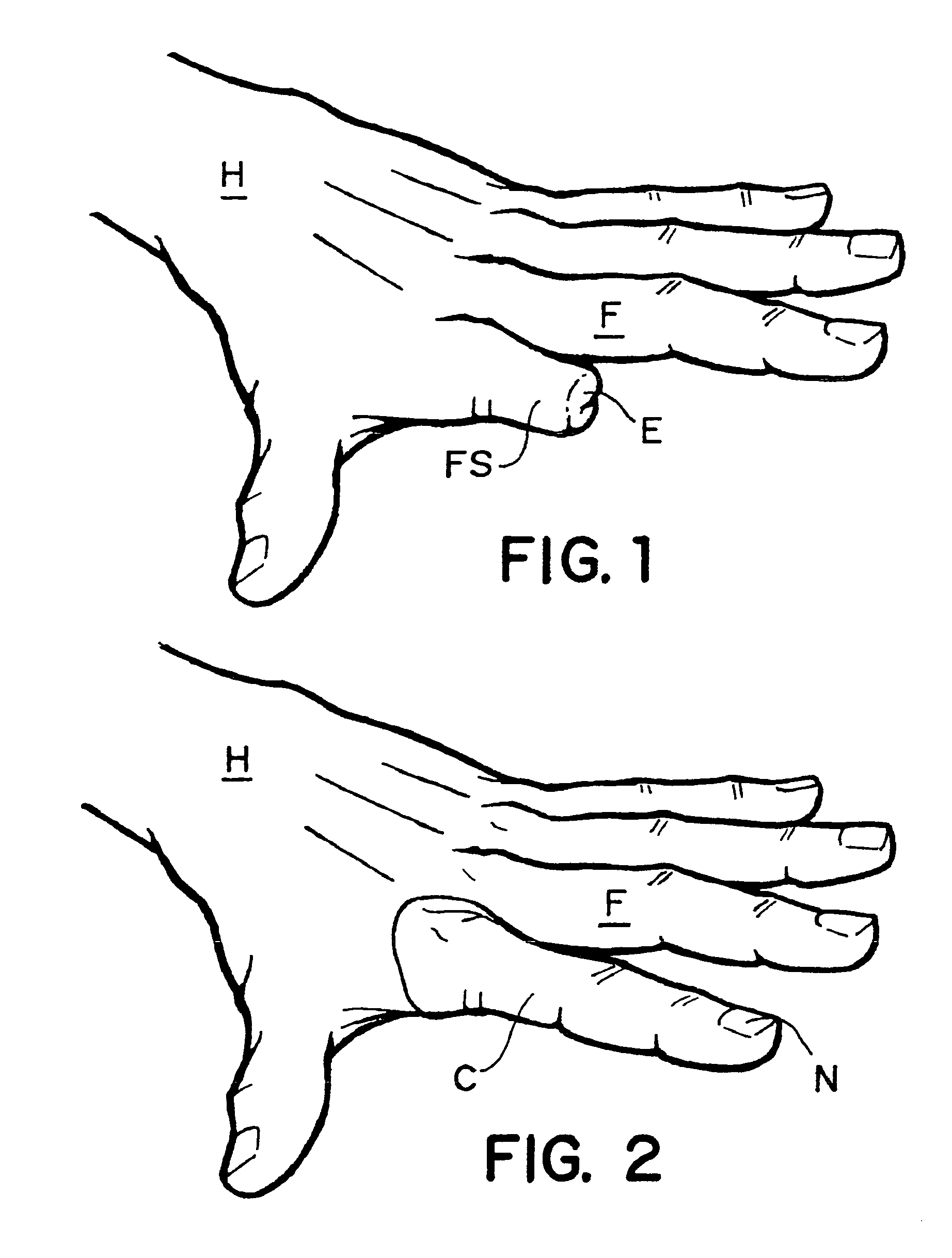
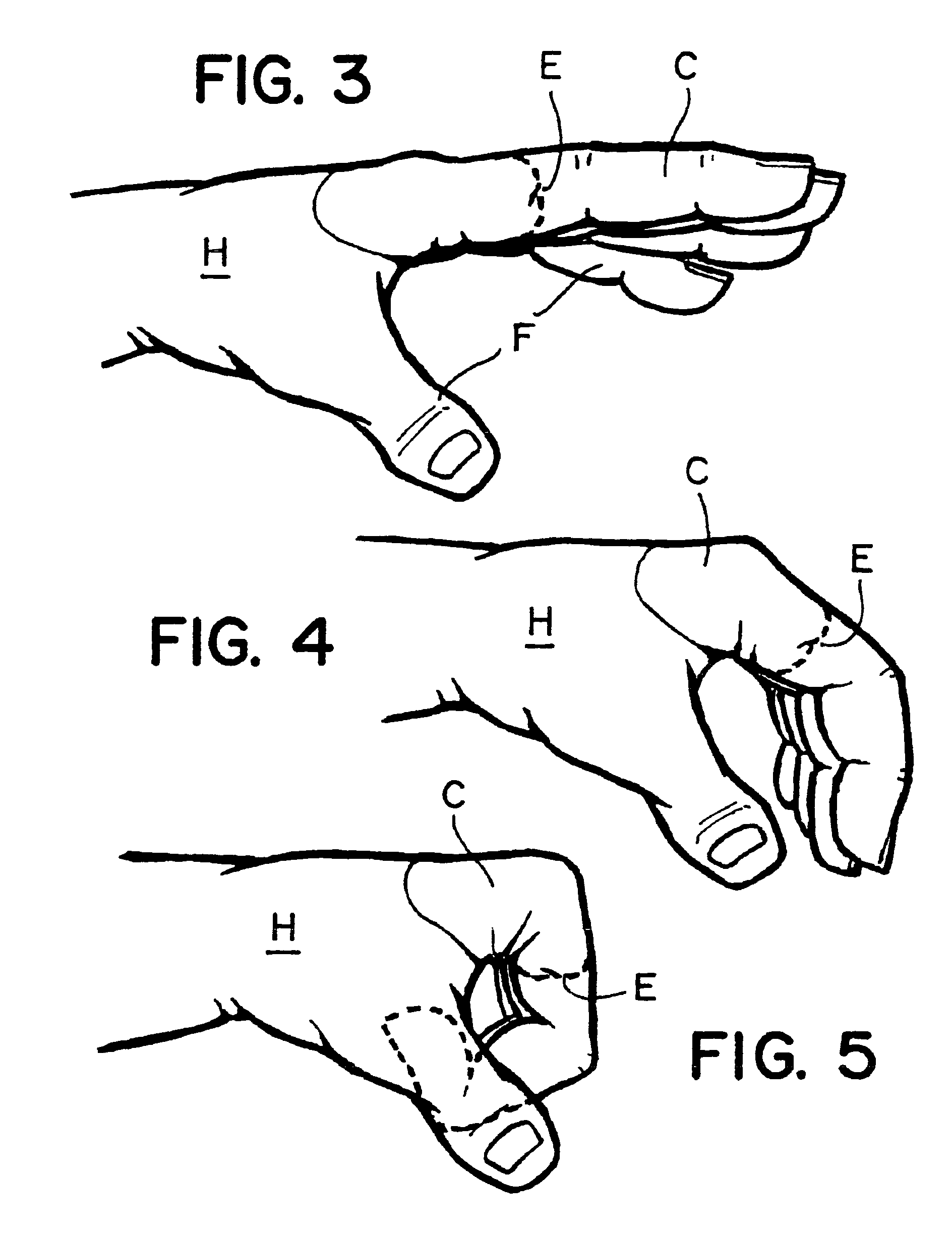
The knuckles are the joints of the fingers. The word is cognate to similar words in other Germanic languages, such as the Dutch "knokkel" (knuckle) or German "Knöchel" (ankle), i.e., Knöchlein, the diminutive of the German word for bone (Knochen). Anatomically, it is said that the knuckles consist of the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and interphalangeal (IP) joints of the finger. The knuckles at the base of the fingers may be referred to as the 1st or major knuckles while the knuckles at the midfinger are known as the 2nd and 3rd, or minor, knuckles. However, the ordinal terms are used inconsistently, and can be found referring to any of the knuckles.
Articulable surgical instrument
Owner:MICROLINE SURGICAL INC
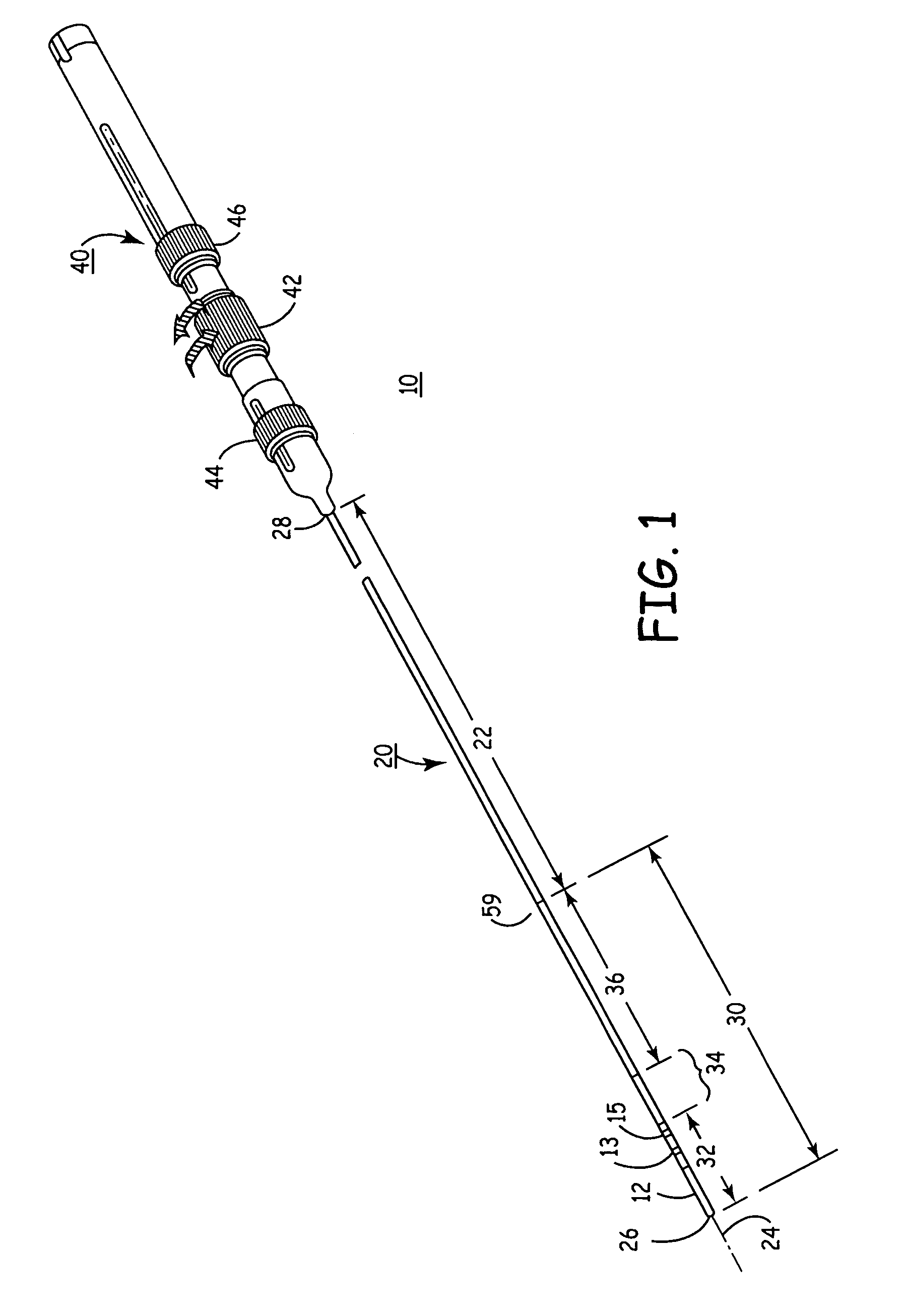
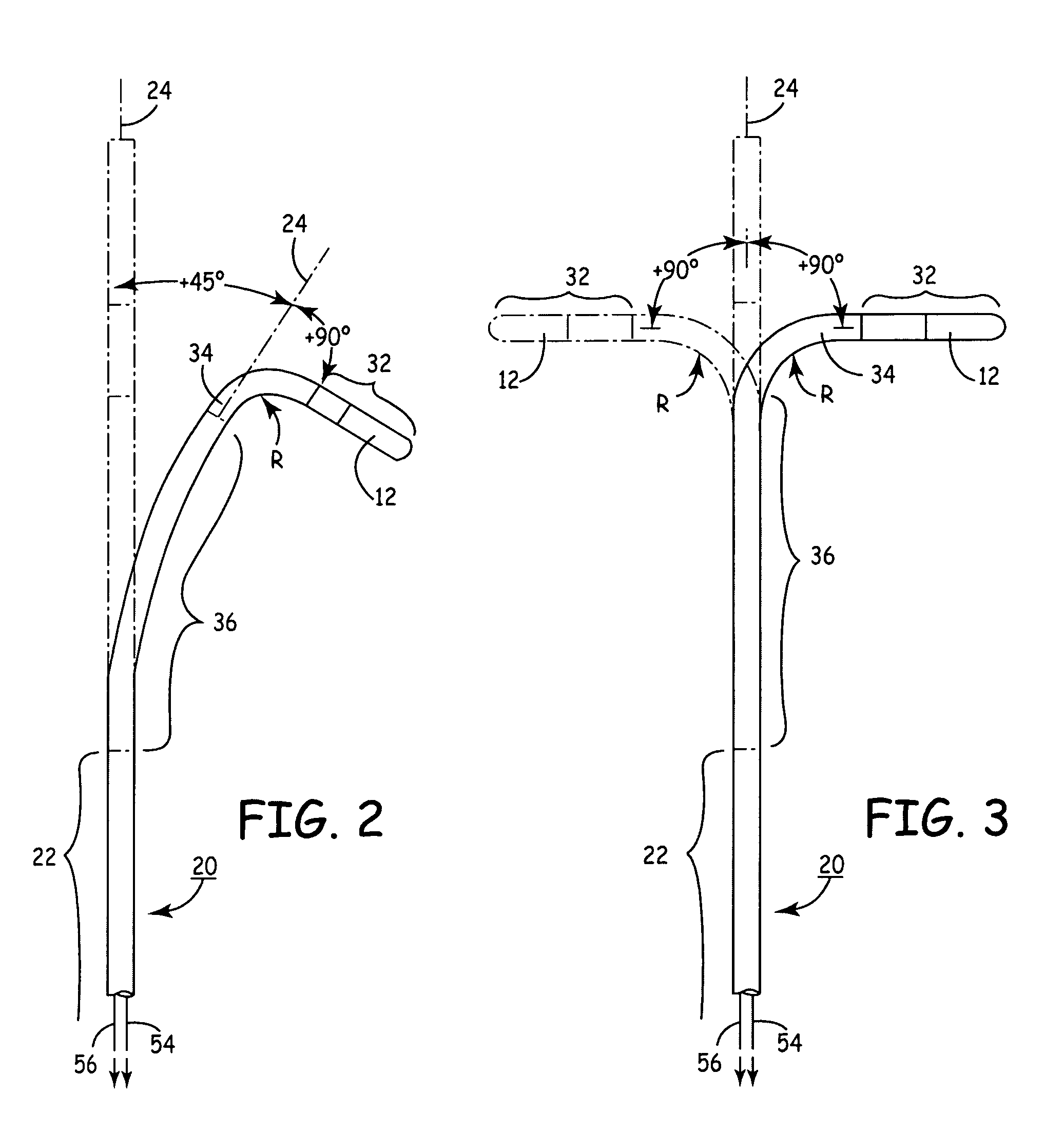
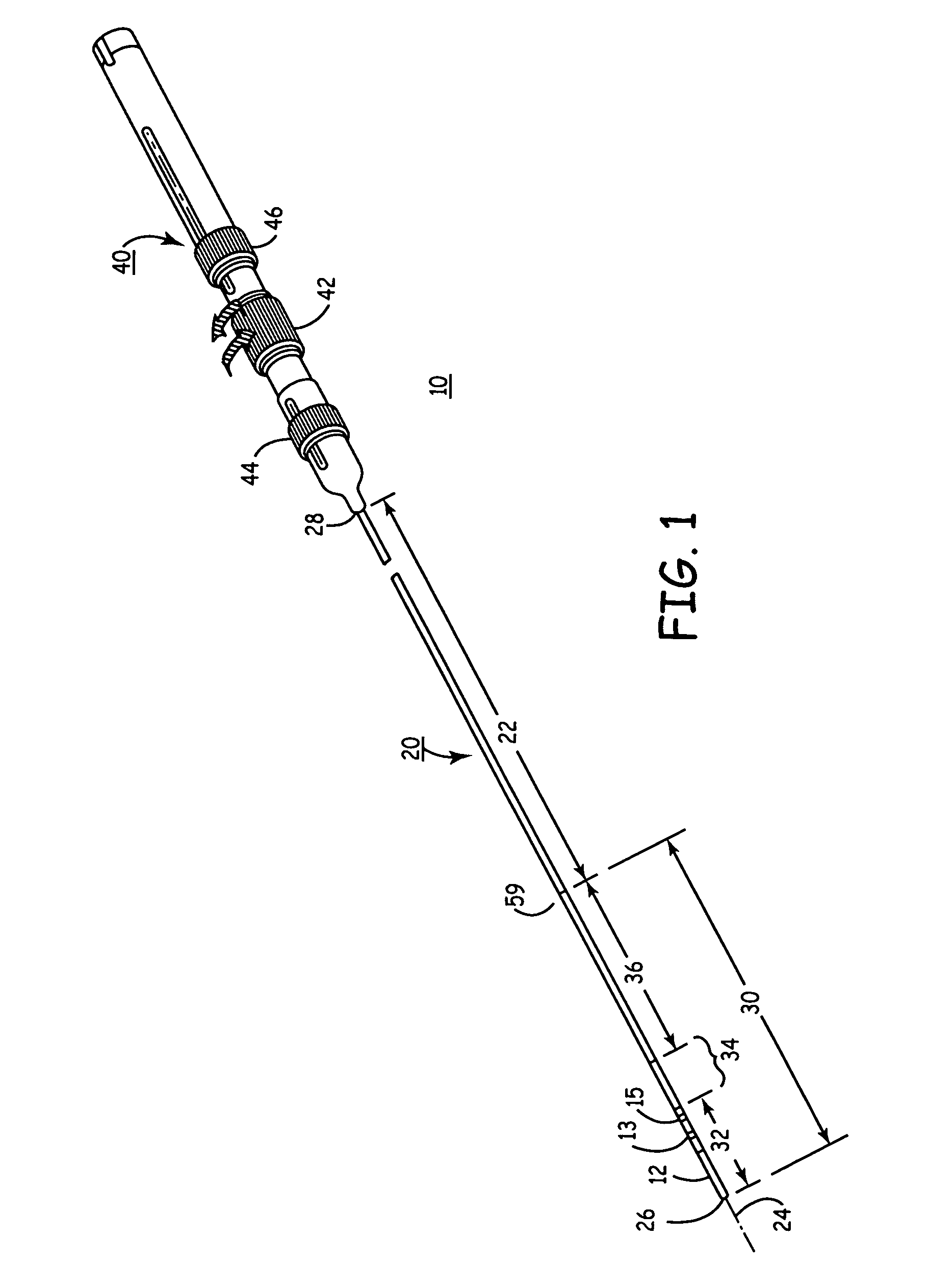
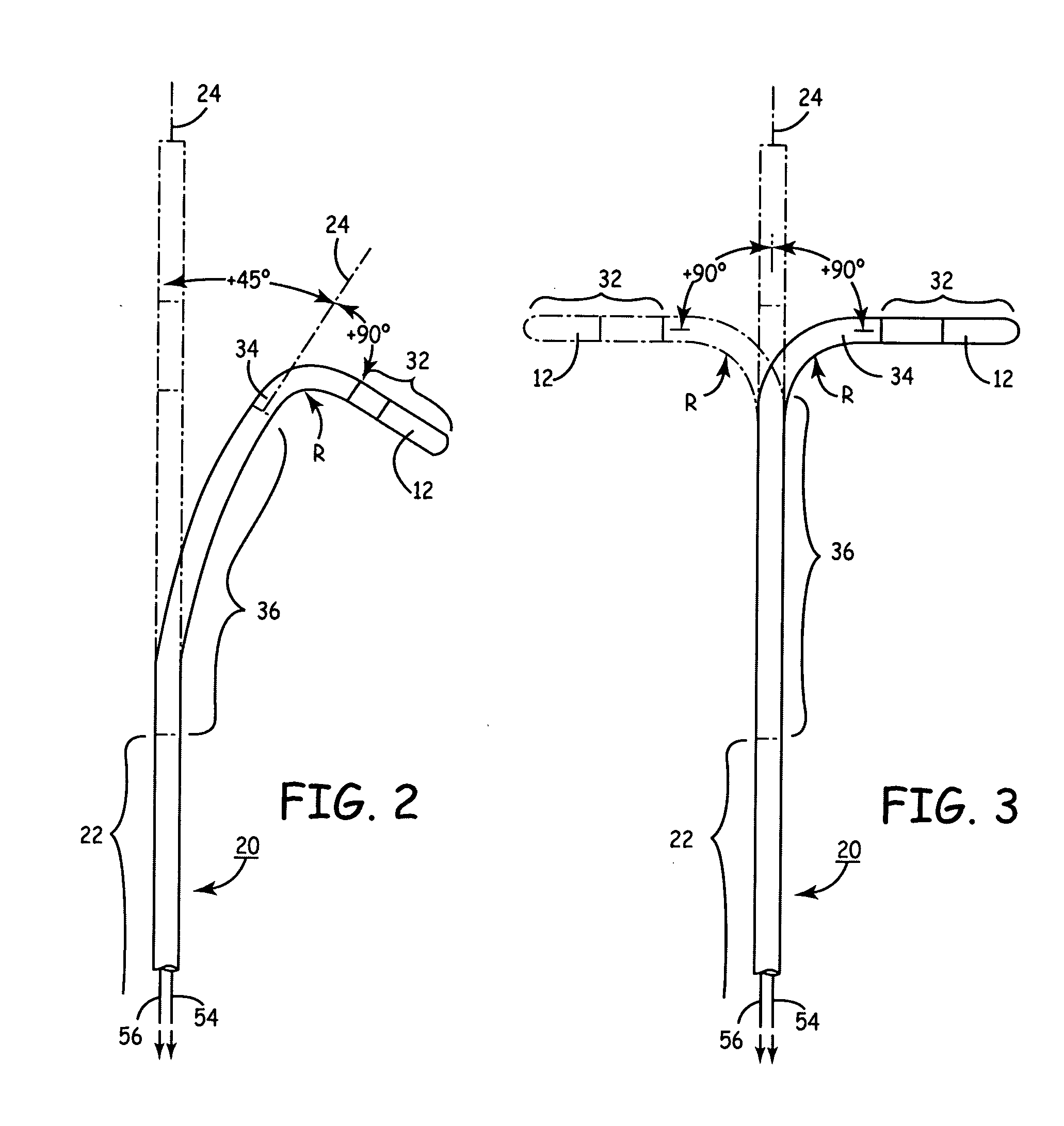
Heart wall ablation/mapping catheter and method
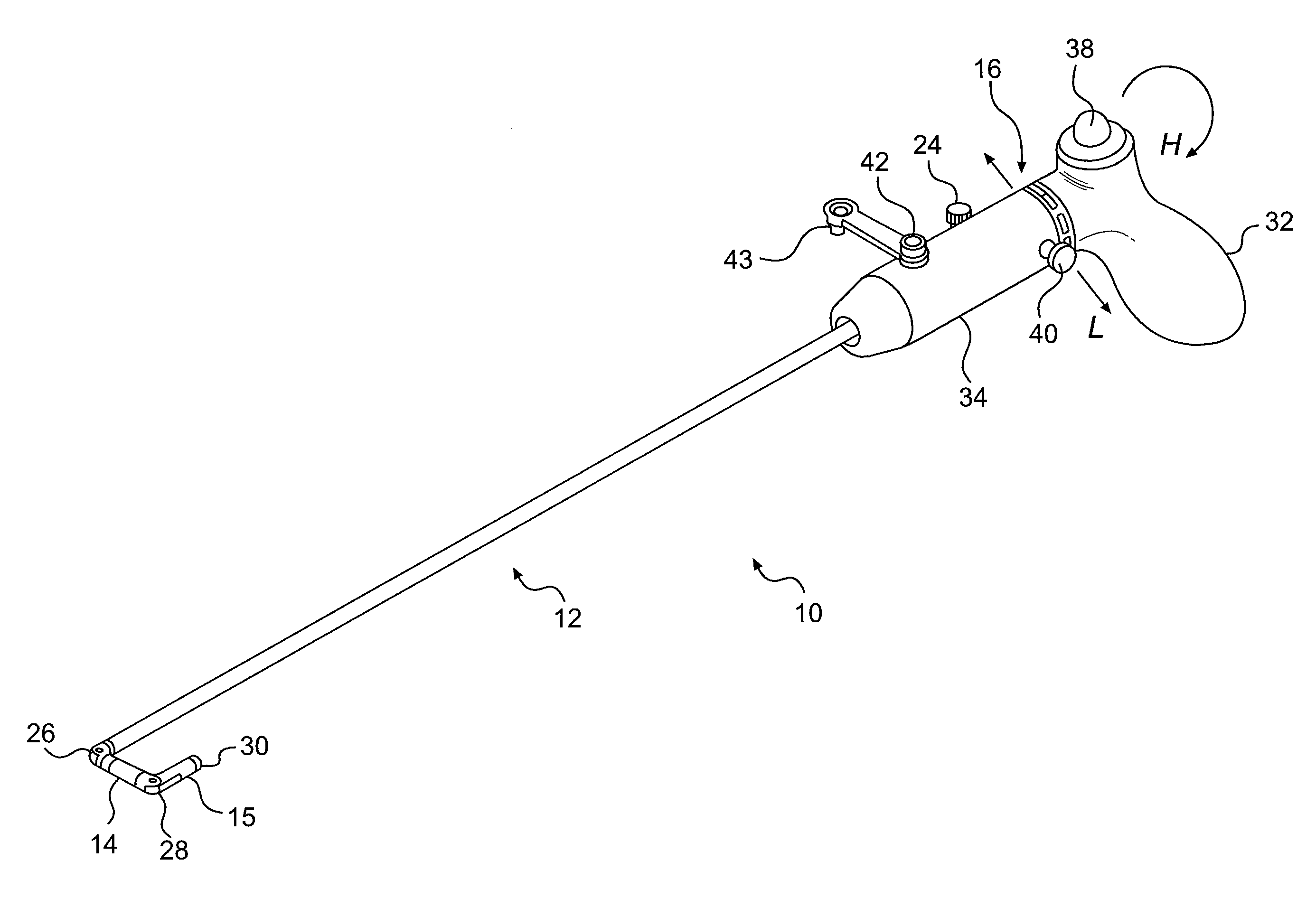
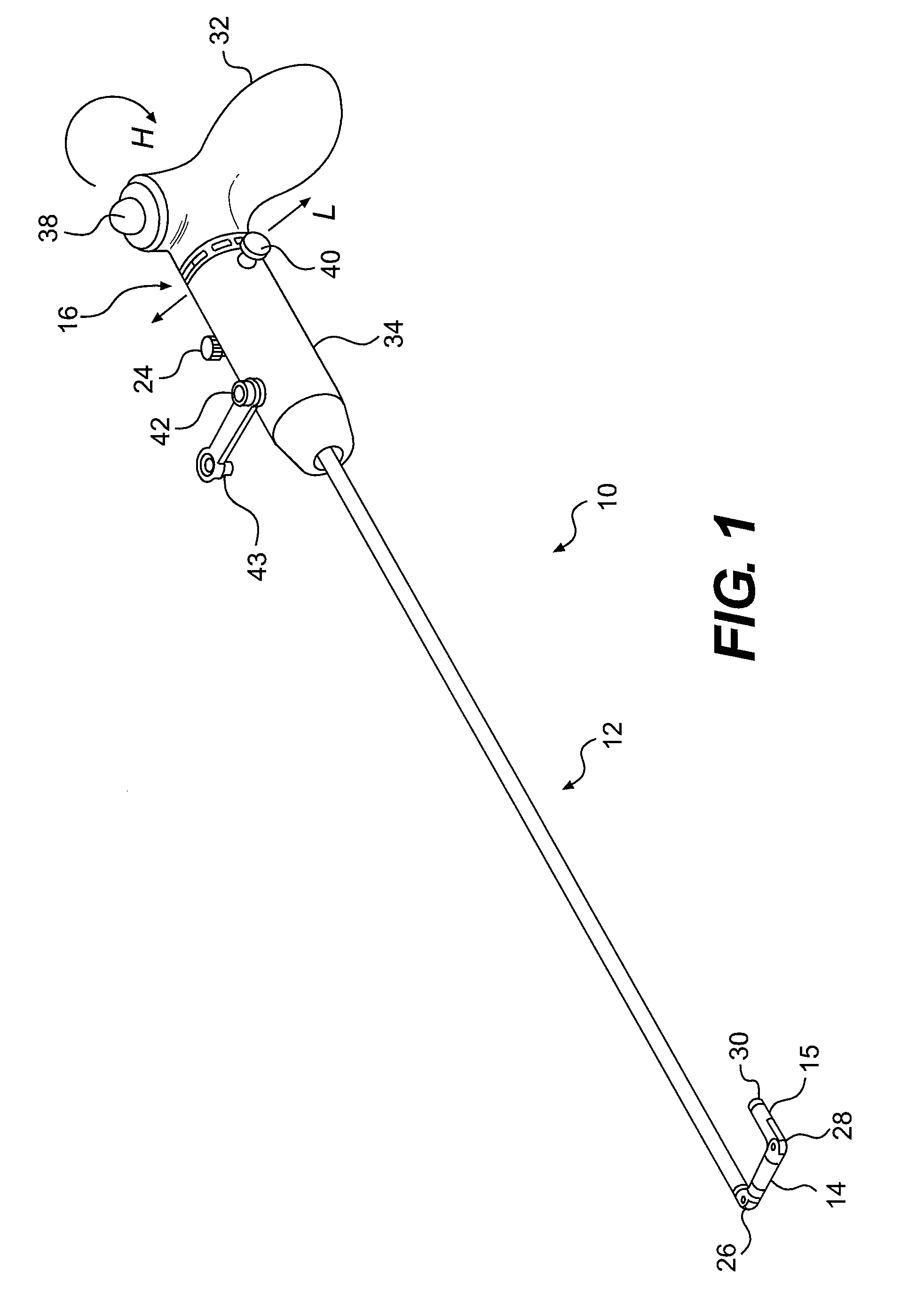
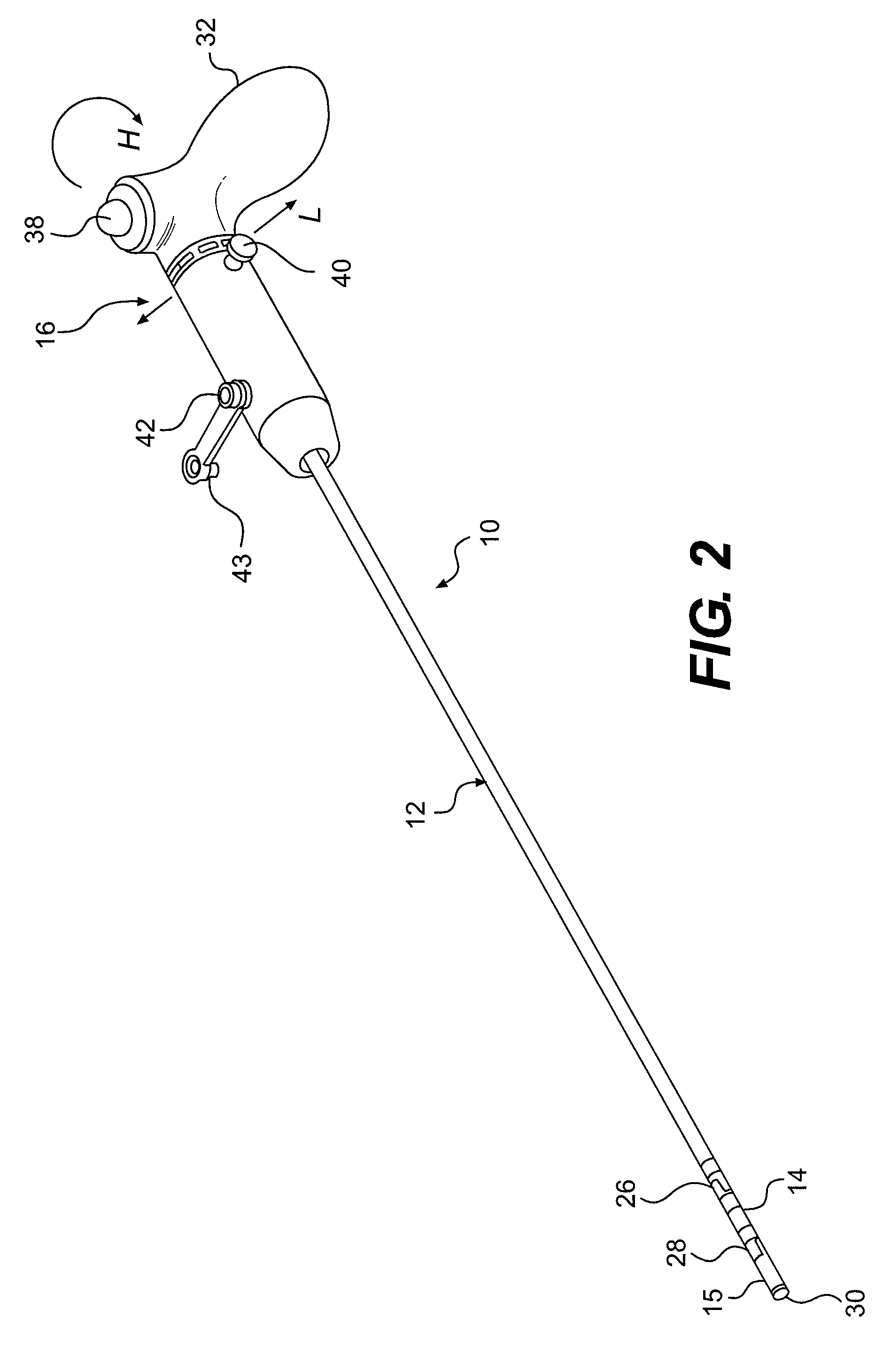
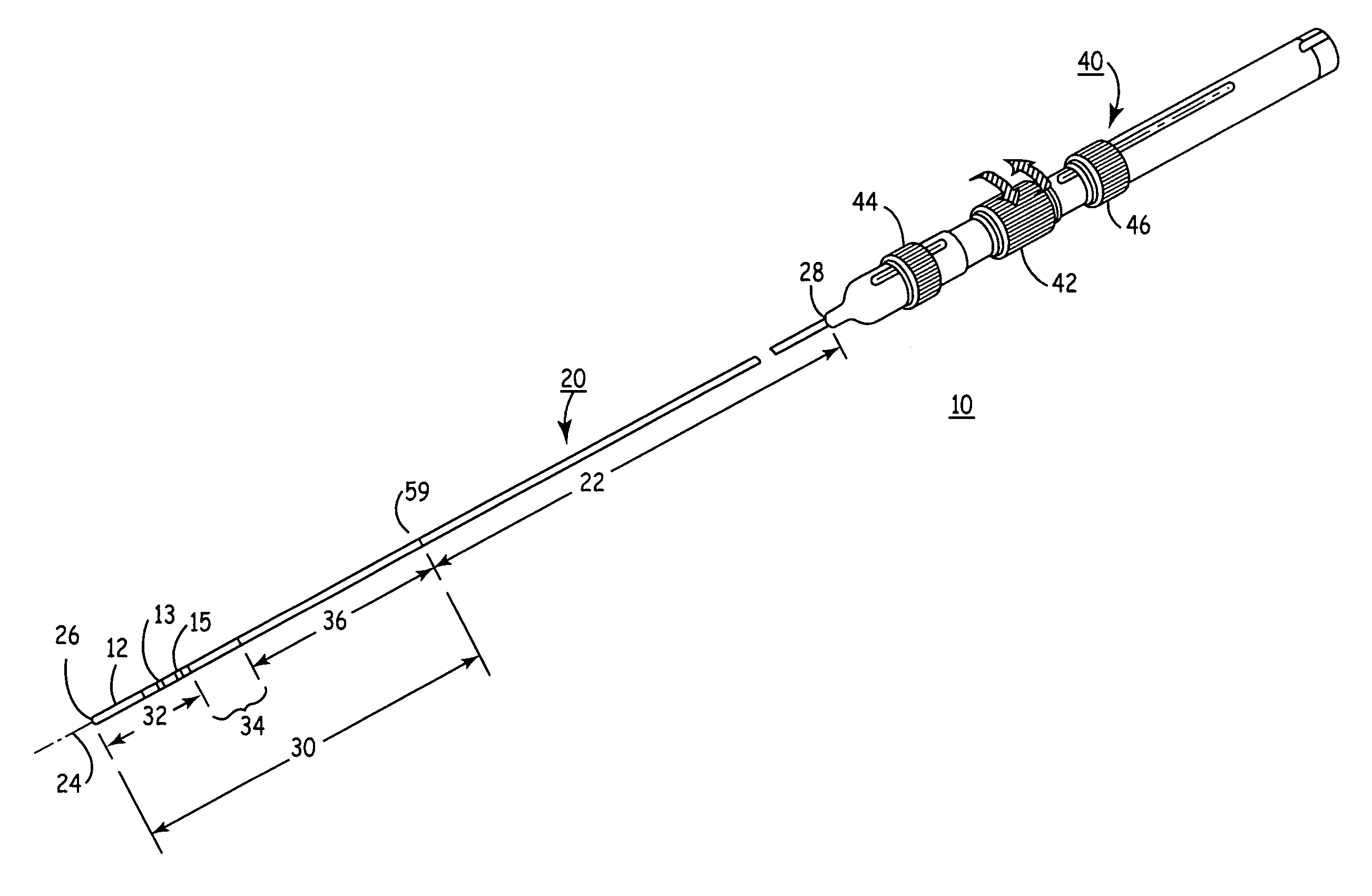
InactiveUS6926669B1Wide angleSmall knuckle curveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesCardiac wallAngular orientation
Steerable electrophysiology catheters for use in mapping and / or ablation of accessory pathways in myocardial tissue of the heart wall and methods of use thereof are disclosed. The catheter comprises a catheter body and handle, the catheter body having a proximal section and a distal section and manipulators that enable the deflection of a distal segment of the distal tip section with respect to the independently formed curvature of a proximal segment of the distal tip section through a bending or knuckle motion of an intermediate segment between the proximal and distal segments. A wide angular range of deflection within a very small curve or bend radius in the intermediate segment is obtained. At least one distal tip electrode is preferably confined to the distal segment which can have a straight axis extending distally from the intermediate segment. The curvature of the proximal segment and the bending angle of the intermediate segment are independently selectable. The axial alignment of the distal segment with respect to the nominal axis of the proximal shaft section of the catheter body can be varied between substantially axially aligned (0° curvature) in an abrupt knuckle bend through a range of about −90° to about +180° within a bending radius of between about 2.0 mm and 7.0 mm and preferably less than 5.0 mm. The proximal segment curve can be independently formed in a about +180° through about +270° with respect to the axis of the proximal shaft section to provide an optimum angular orientation of the distal electrode(s). The distal segment can comprise a highly flexible elongated distal segment body and electrode(s) that conform with the shape and curvature of the heart wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Data input device
InactiveUS20050179644A1Input/output for user-computer interactionProgramme controlTransducerEngineering
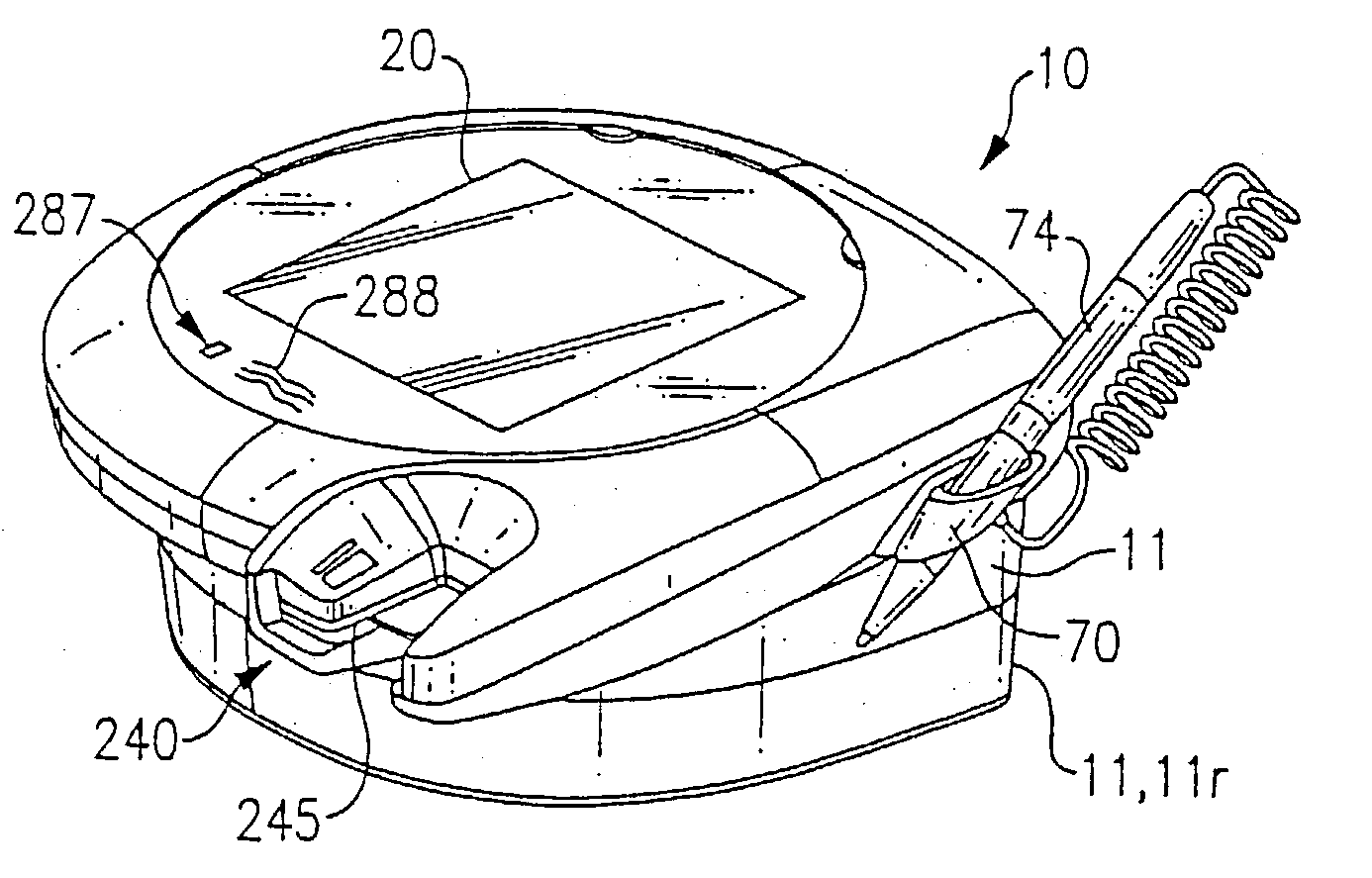
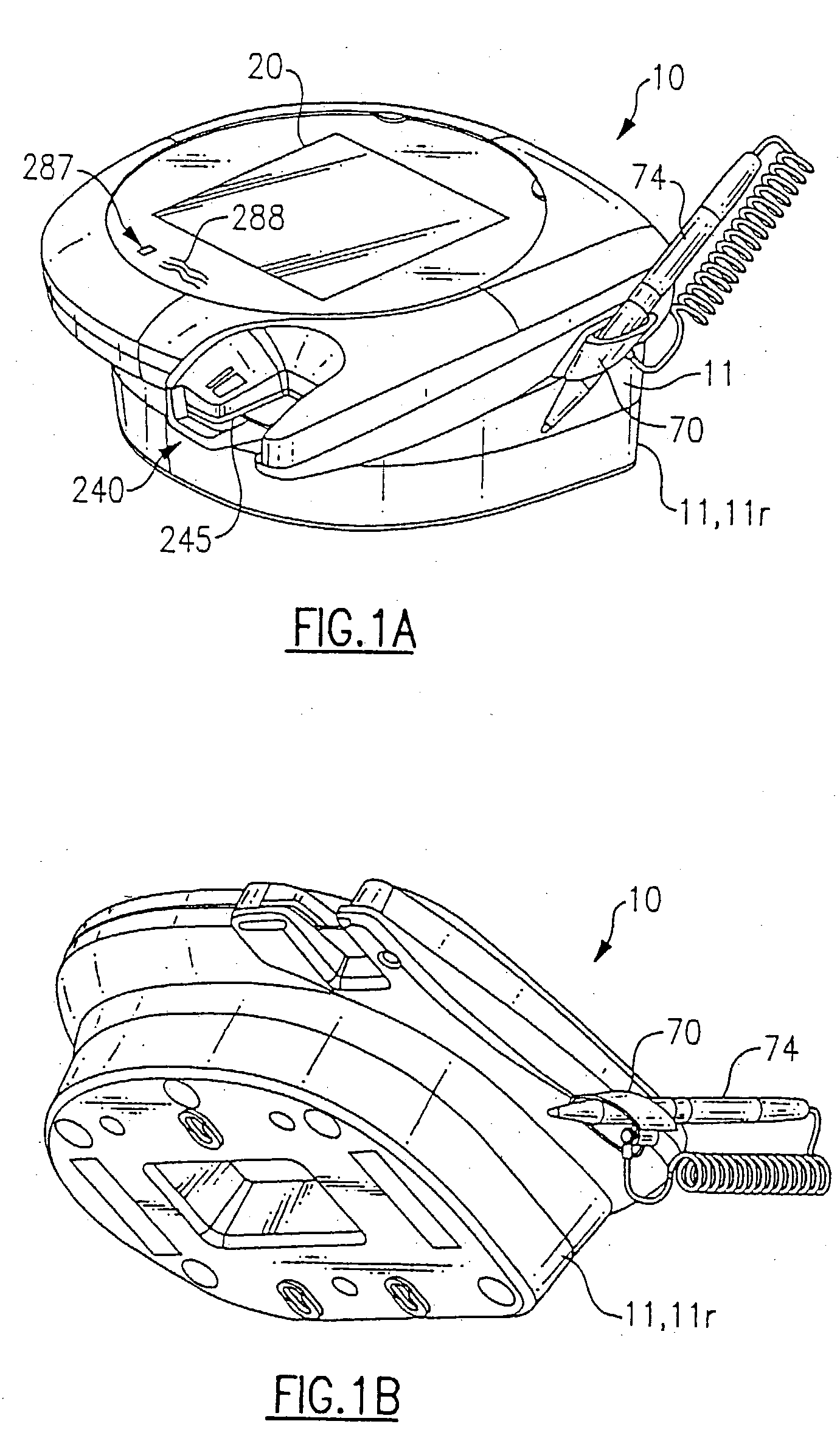
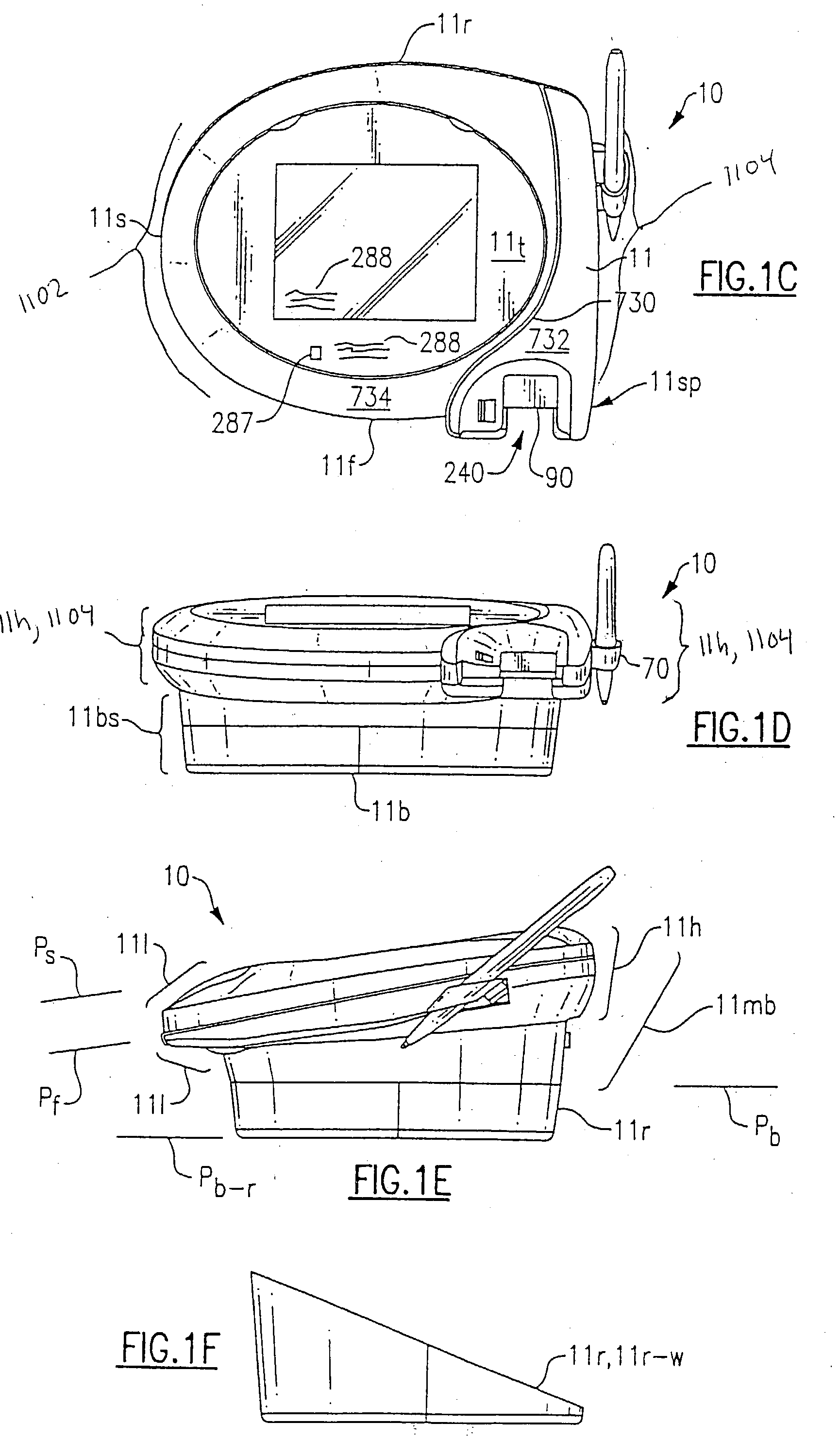
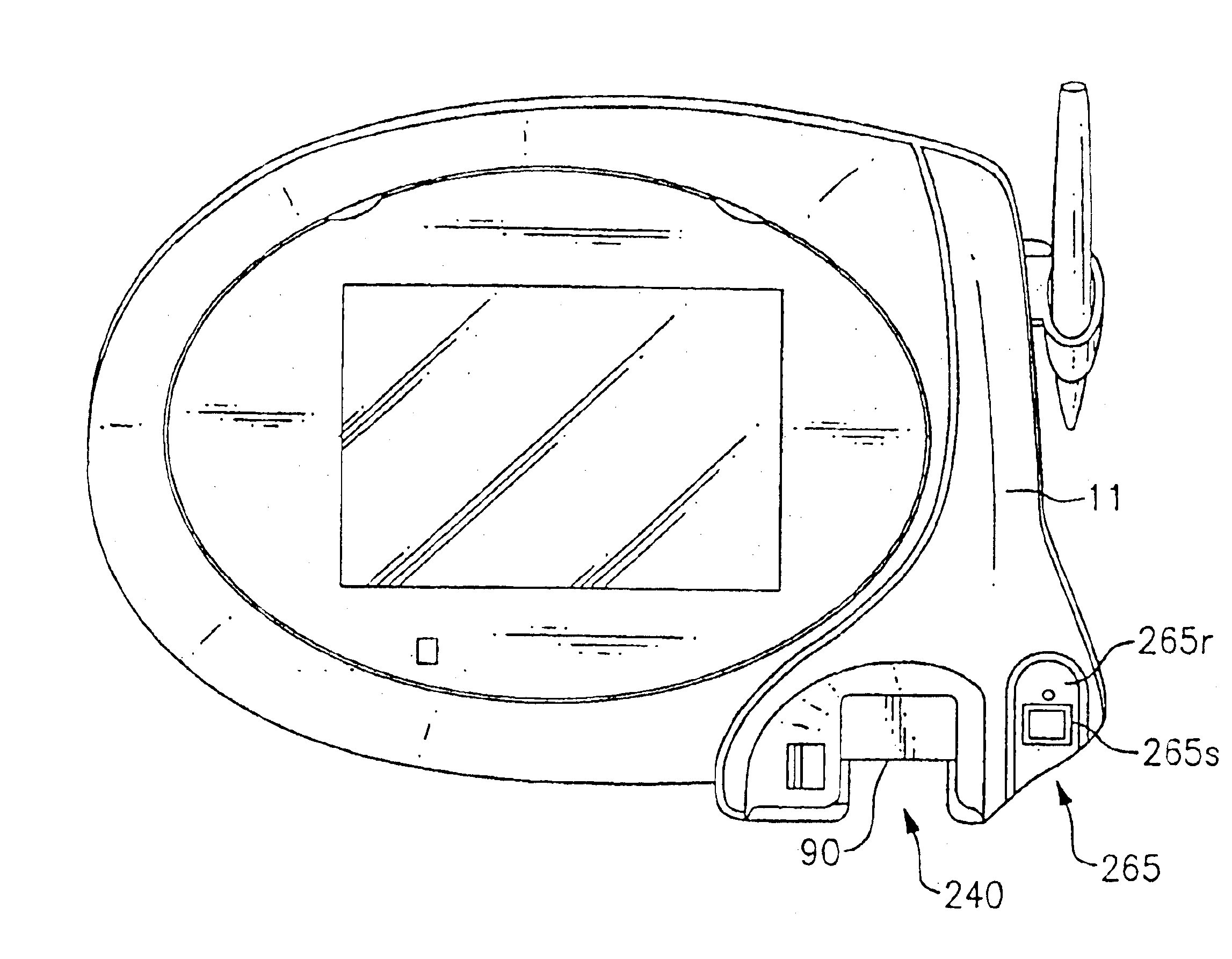
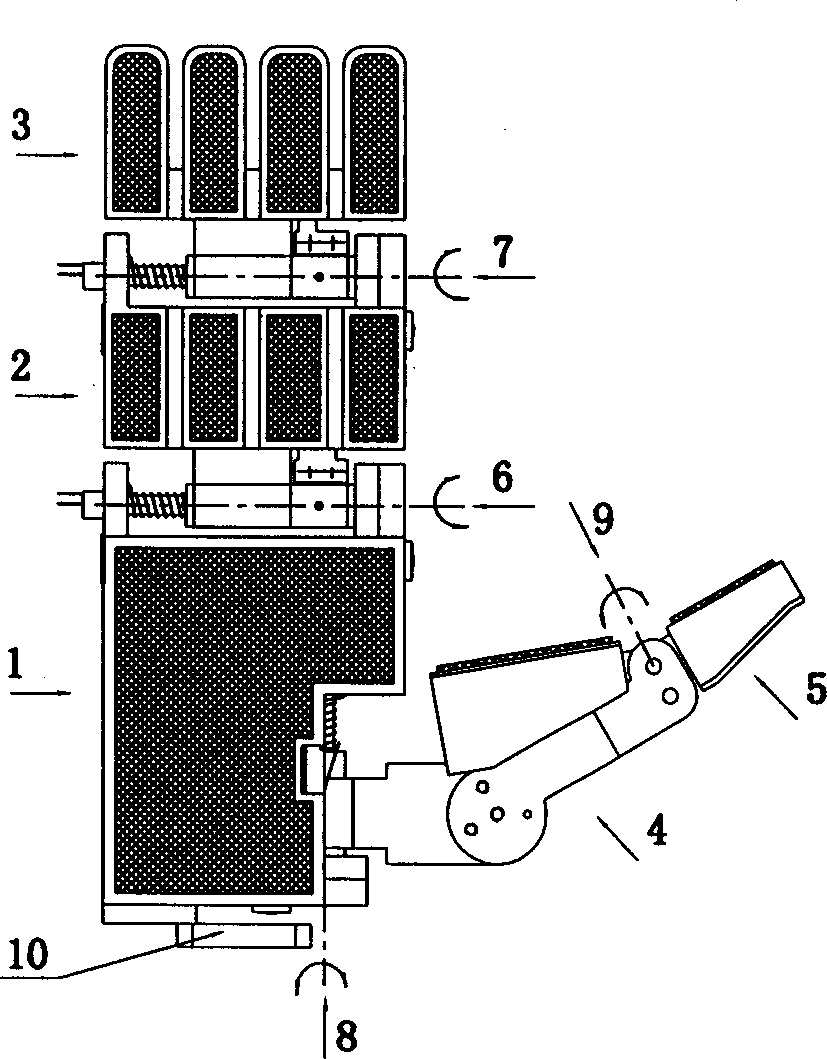
The method is for entering data into a computer device. A wearable device (10) is attaching to a hand (212). The device (10) has a lower unit (14) placed in a palm (106) of the hand and an upper unit (16) placed behind knuckles (17) of the hand and connected to the lower unit (14). A sensor (202) has transducers (260, 262, 264, 266, 268) in operative engagement with fingers (250, 252, 254, 256, 258). The sensor (202) has a position sensor (210) associated with an electronic cursor or sign (211) displayed on a screen (213). The fingers and / or hand are moved to switch the sensor (202) from a keyboard mode to a mouse mode. The hand (212) is shifted in a first direction to move the cursor (211) in the first direction on the screen (213).
Owner:ALSIO GUNILLA
Antenna system for a communication device
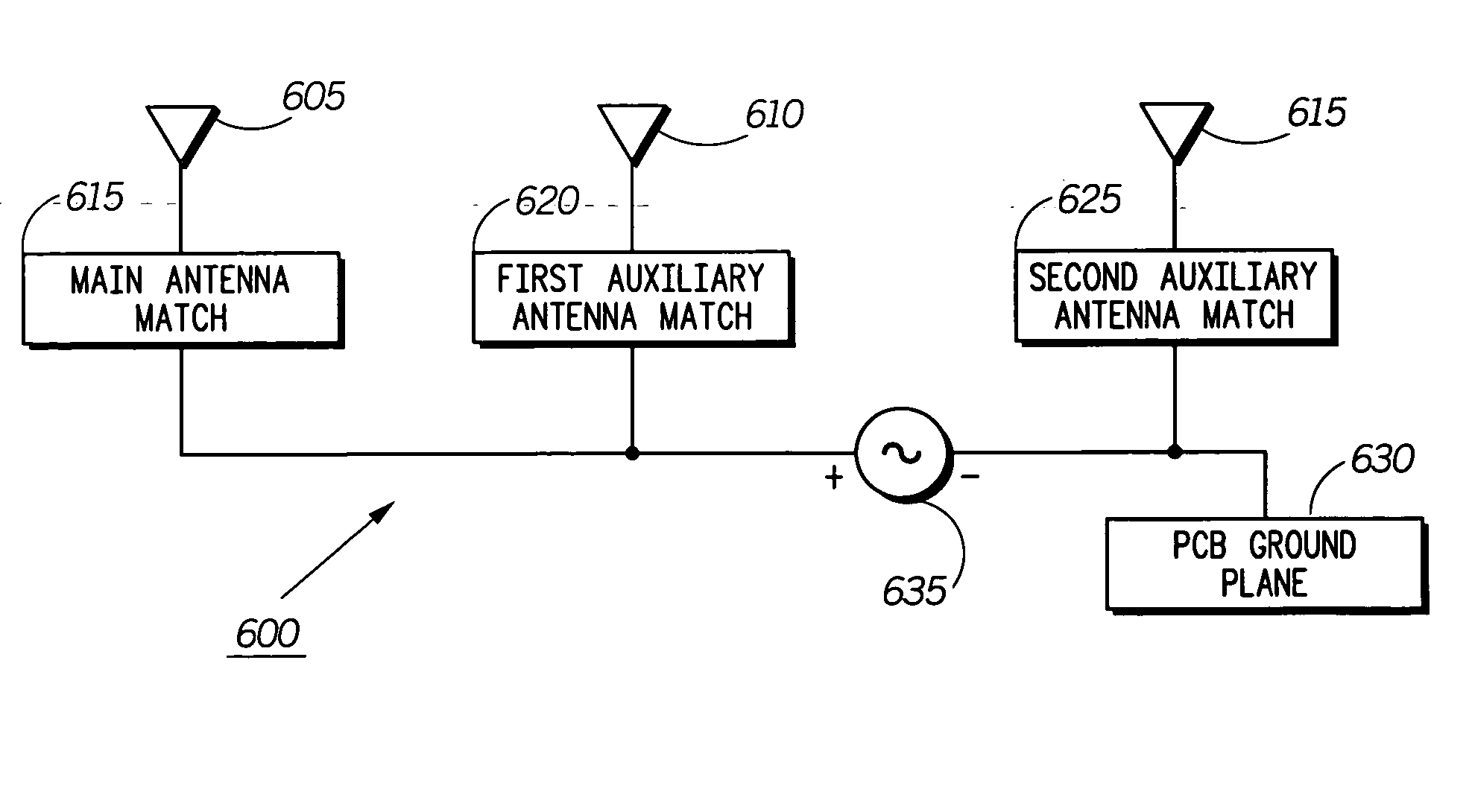
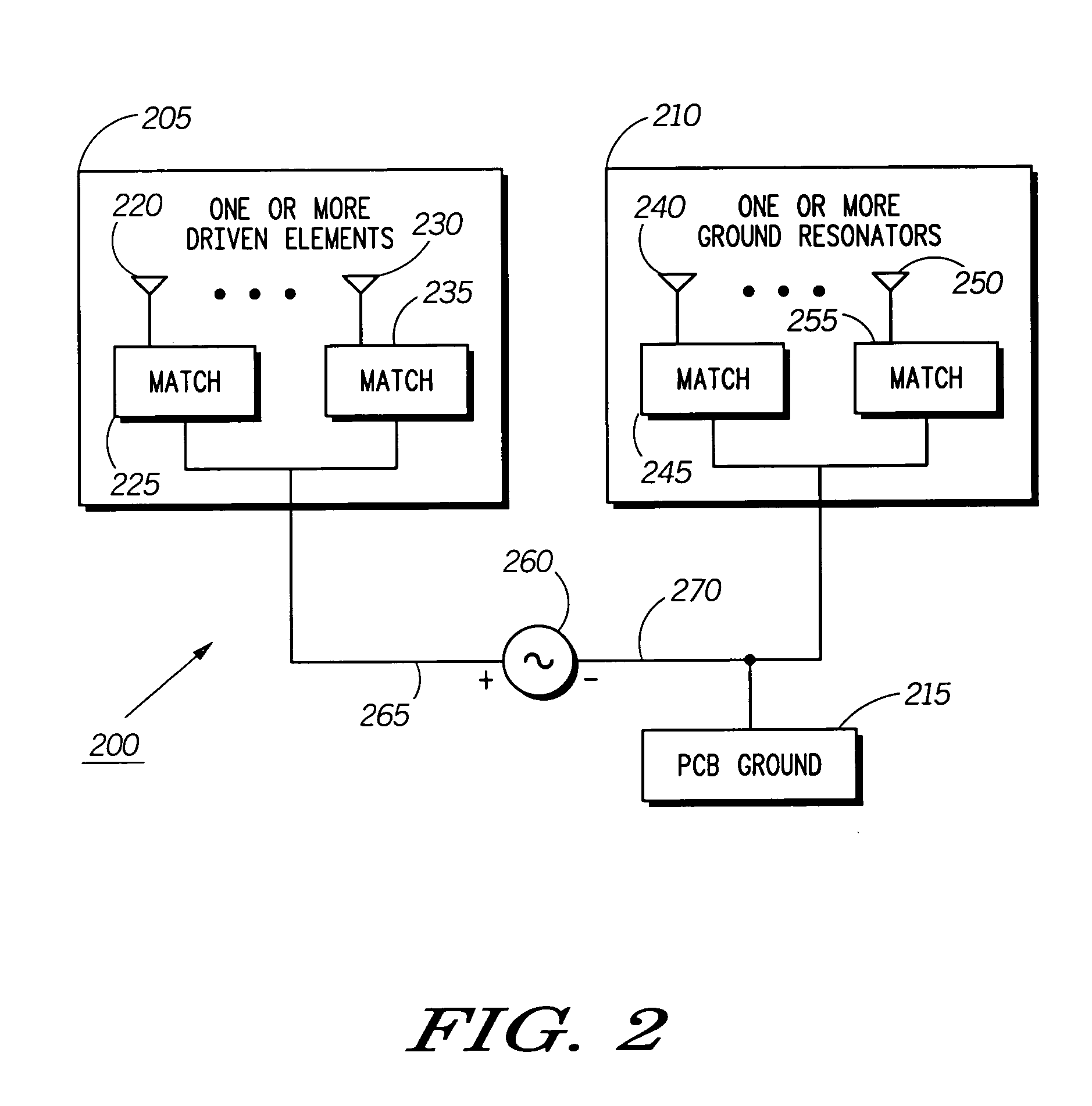
An antenna system (200,400,500,600) for use within a communication device (100) is disclosed. The communication device (100) including a signal source (260,425,635), a main housing (105) and a movable flip housing (110) moveably coupled to the main housing (105) through a hinge assembly (125). The hinge assembly (125) being comprised of a hinge shaft, a first knuckle (805) coupled to one side of the hinge shaft, and a second knuckle (810) coupled to an opposing side of the hinge shaft. The antenna system (200,400,500,600) includes at least one of the knuckles of the hinge assembly (125).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Transaction terminal having elongated finger recess
A transaction terminal includes a housing, an elongated finger recess defined by the housing, and a finger scanner sensor disposed in the recess. The elongated finger recess may include a length of at least approximately a two knuckle distance. An outer surface region of the housing and the finger recess may define a web receiving area adapted to receive a web of a hand. The transaction terminal can include a card cavity formed integral with the elongated finger recess.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Transaction terminal having elongated finger recess
A transaction terminal includes a housing, an elongated finger recess defined by the housing, and a finger scanner sensor disposed in the recess. The elongated finger recess may include a length of at least approximately a two knuckle distance. An outer surface region of the housing and the finger recess may define a web receiving area adapted to receive a web of a hand. The transaction terminal can include a card cavity formed integral with the elongated finger recess.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Drive mechanism for vehicle
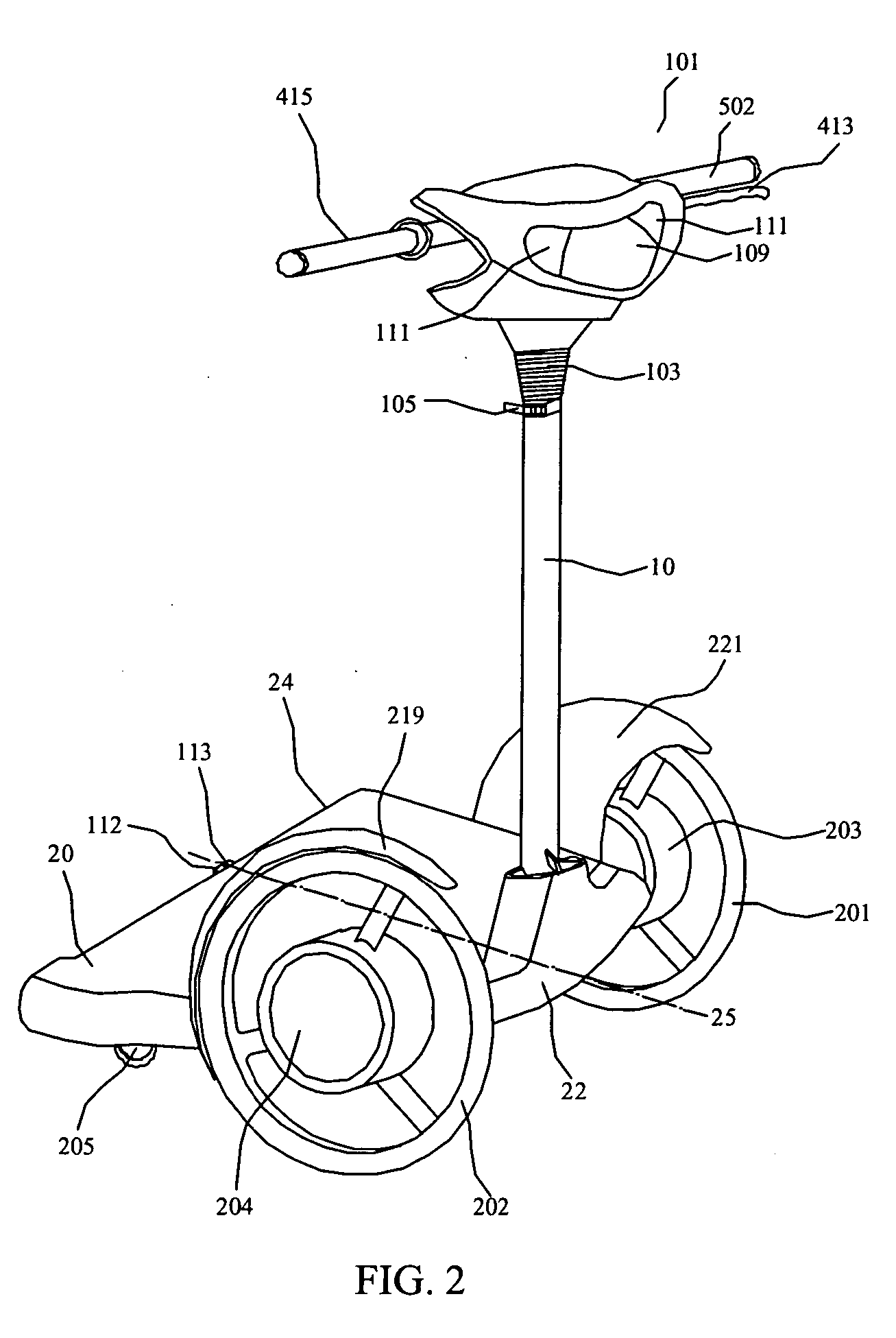
InactiveUS20050134014A1Simple structureImprove stabilitySteering linkagesFluid steeringSteering wheelDrive wheel
The present invention provides an electric-driven vehicle, which comprises a supporting platform and an upright tube, wherein the supporting platform has first and second ends and a longitudinal axis perpendicular to the first and second ends, the upright tube is fitted at the first end of the supporting platform and operatively connected with the supporting platform, a handle frame is provided on a top end of the upright tube. The electric-driven vehicle further includes two driving wheels operatively mounted at opposite sides of the first end of the supporting platform, at least one steering wheel operatively mounted on a bottom of the second end of the supporting platform, a driving means for the driving wheels, and a power supply means mounted on the bottom of the supporting platform and electrically connected with the driving means. The present invention also provides a support platform structure for an electric-driven vehicle, which comprises a first portion and a second portion, wherein the first portion having sleeves for operatively mounting the driving wheels, and a first side; the second portion having a steering knuckle for operatively mounting the steering wheels, and a second side corresponding to the first side; the first side and the second side are connected via a connecting member, and at least one of the first side and the second side can rotate about the bond-linkage element.
Owner:XIE SHOUCHUN
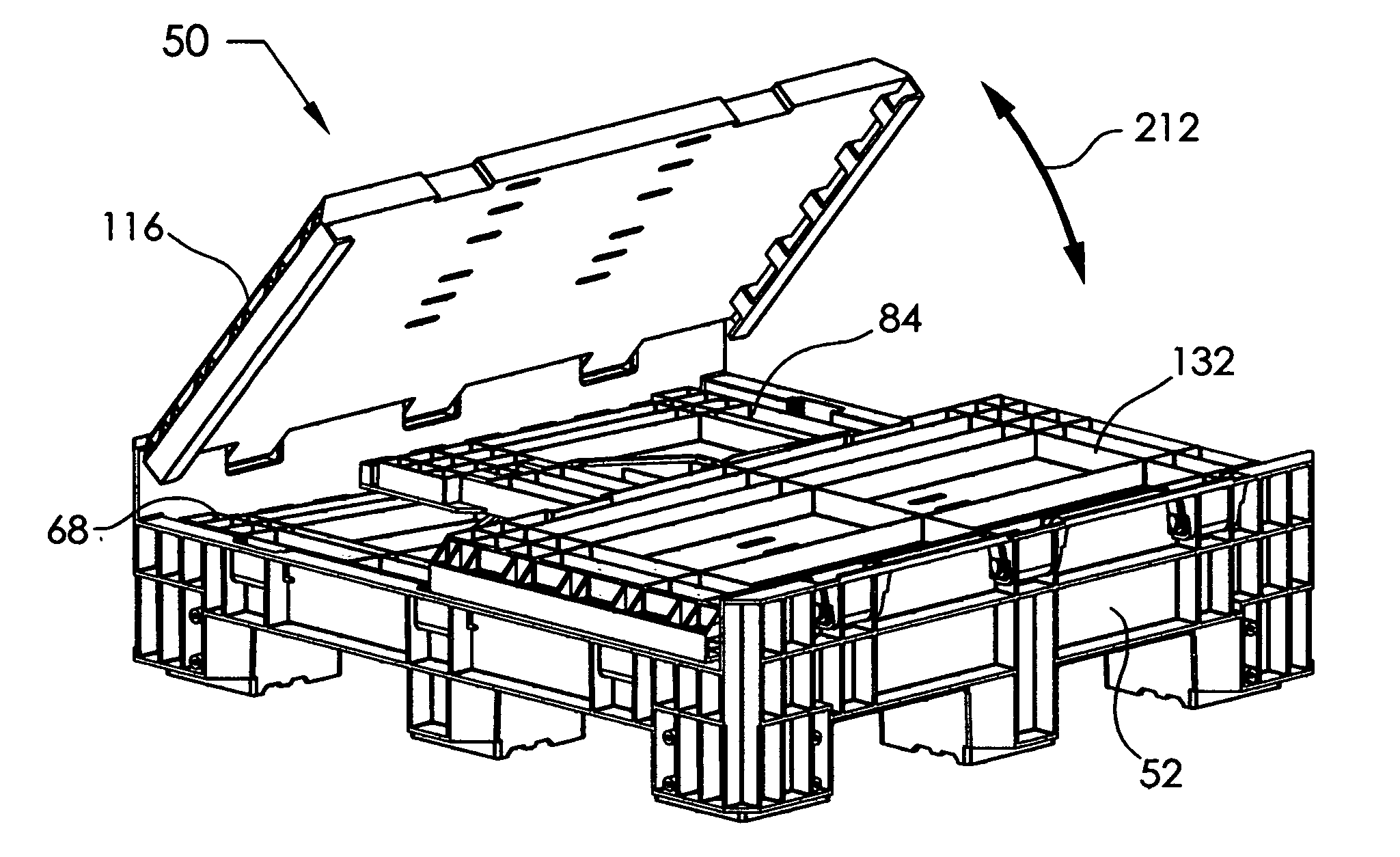
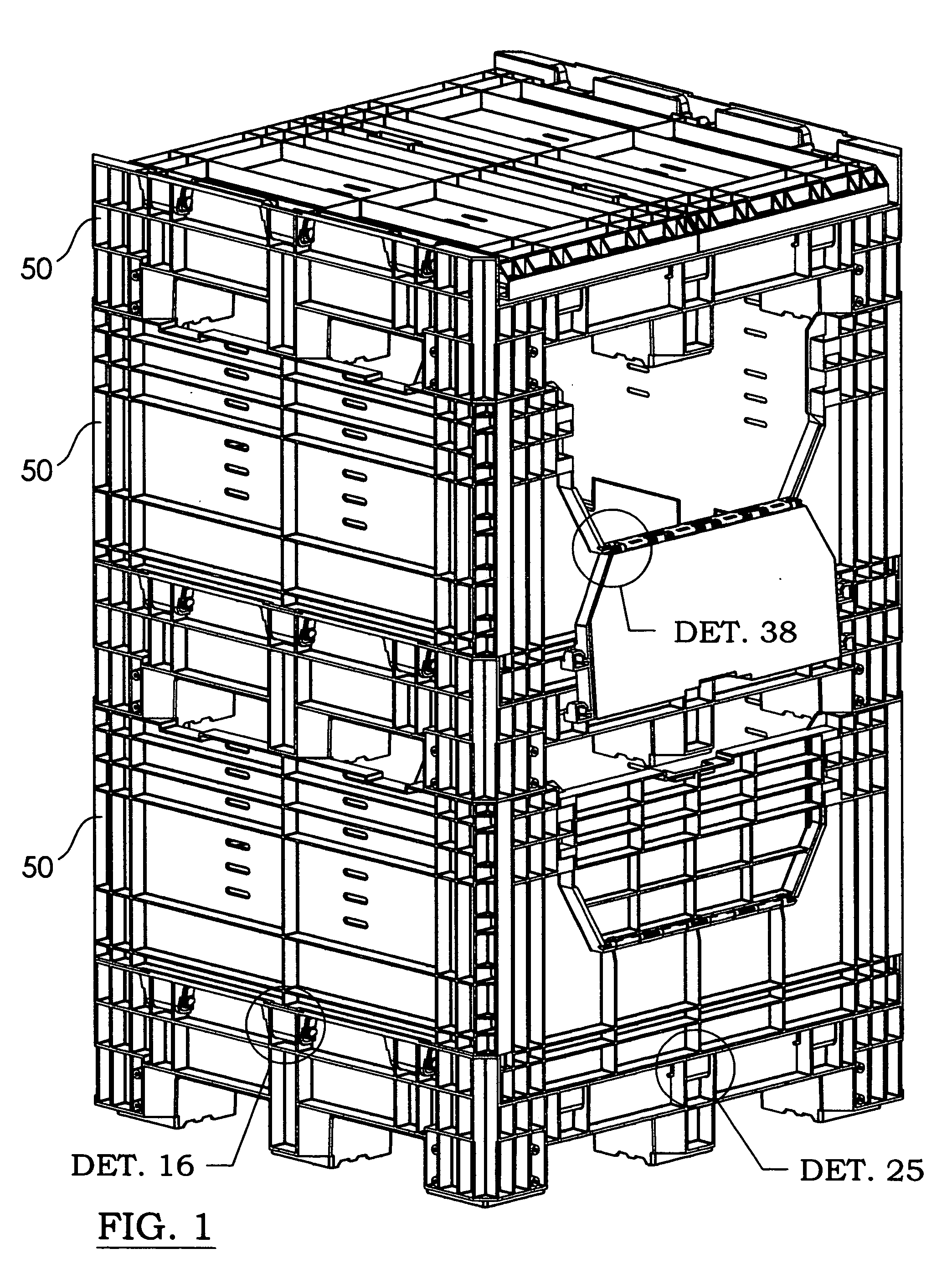
Collapsible container
A collapsible container has four panels that fold down on a base for storage. The base has slide sockets with vertical slots. Front and rear panels pivot on the base with slide hinges received in the slide sockets. The panels are able to slide up and down. A hinge pin has a narrowed waist portion to engage a latch. Left and right panels pivot with snap hinges received in snap sockets on the base. Trunnions, disposed in the snap sockets, are eccentric to increase or decrease the backlash between the snap hinge and the snap socket as the panels pivot. The left and right panels have edge pockets that receive edge fingers on the front and rear panels to hold the container open. The front and rear panels each have an access opening with access doors. Links pivot the access doors on two hinge rods. Locking members wedge the hinge rods in the hinge knuckles. The base has feet with bumper plates having flanges that prevent the container from shifting on an adjacent lower stacked container.
Owner:MARAZITA NICK +1
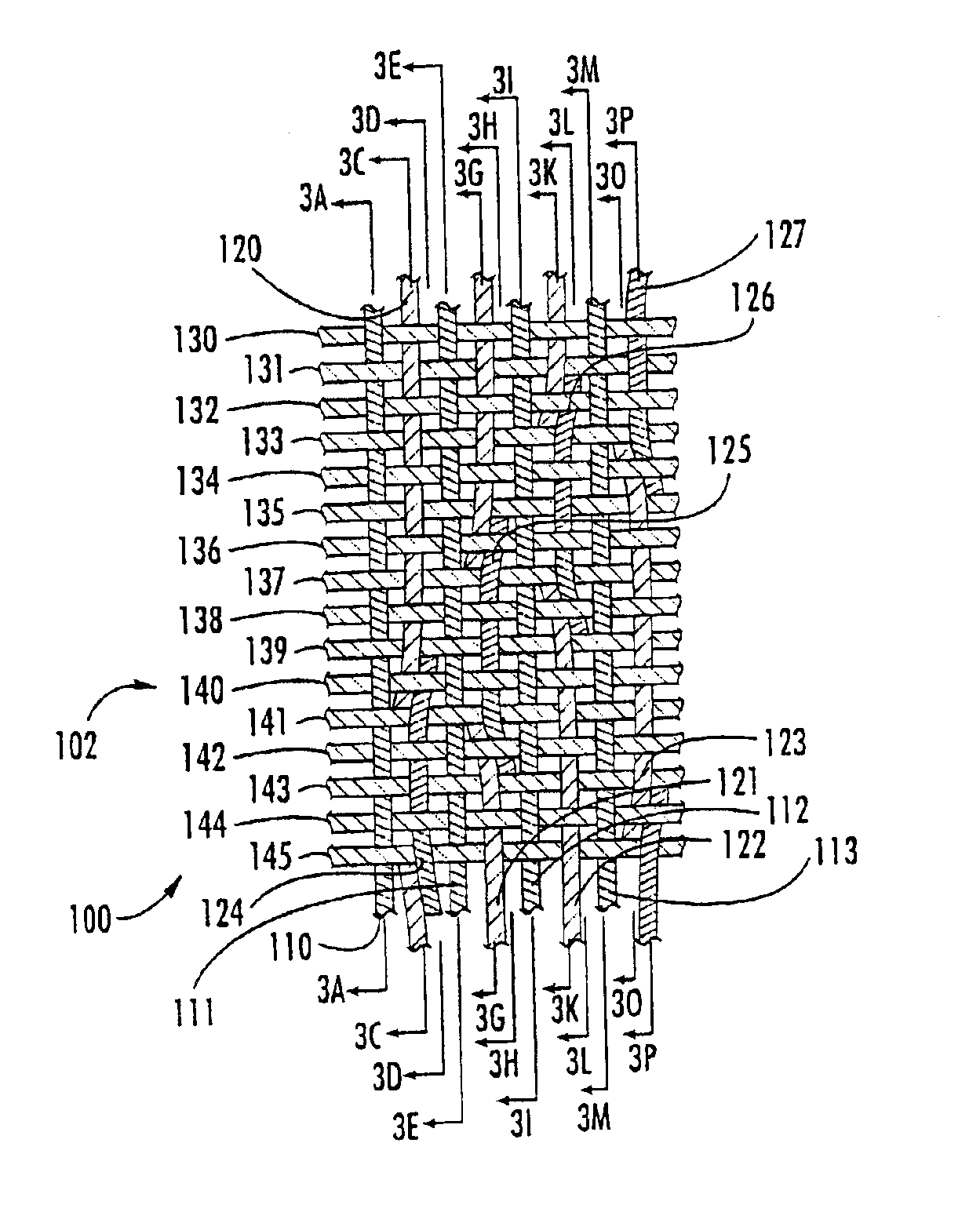
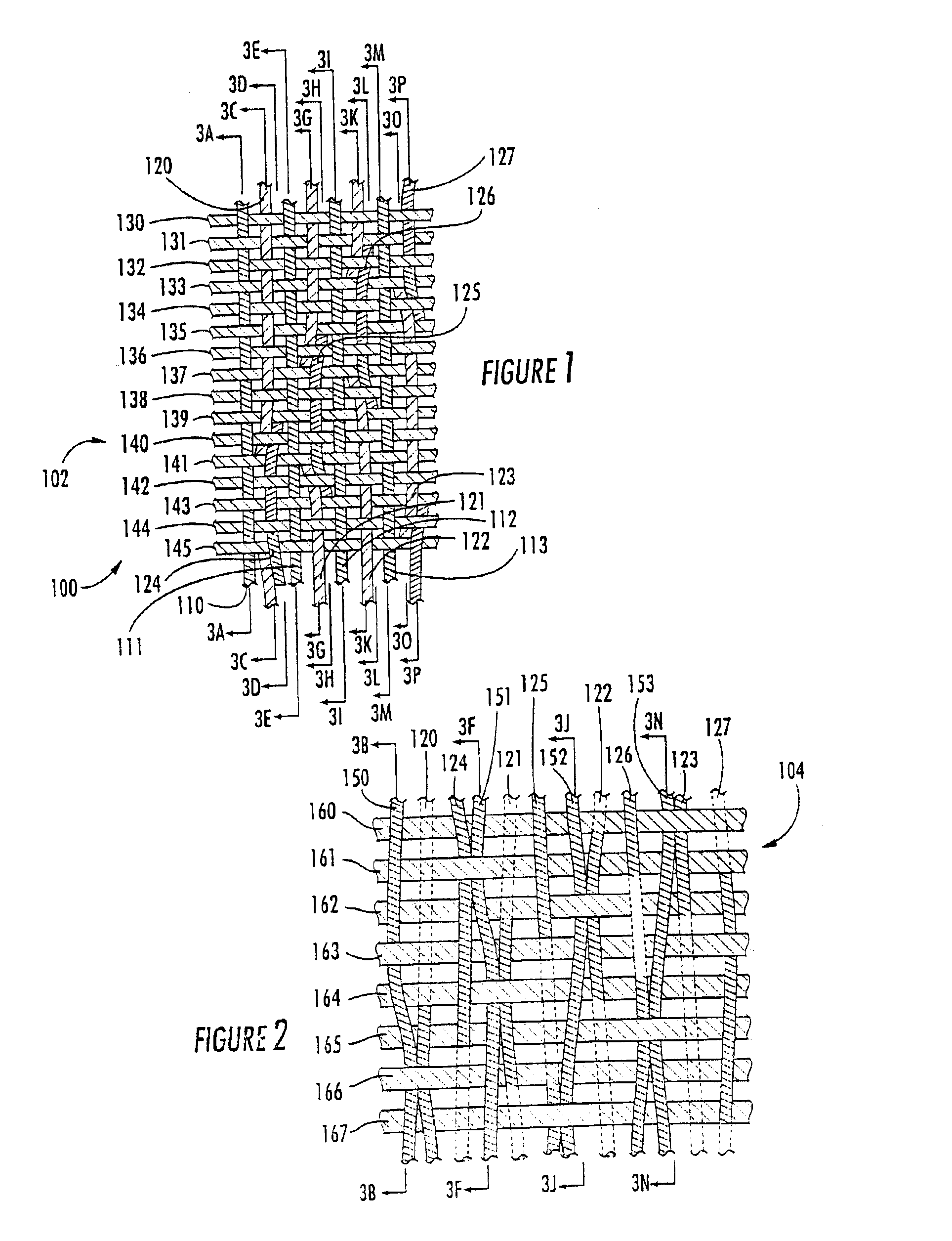
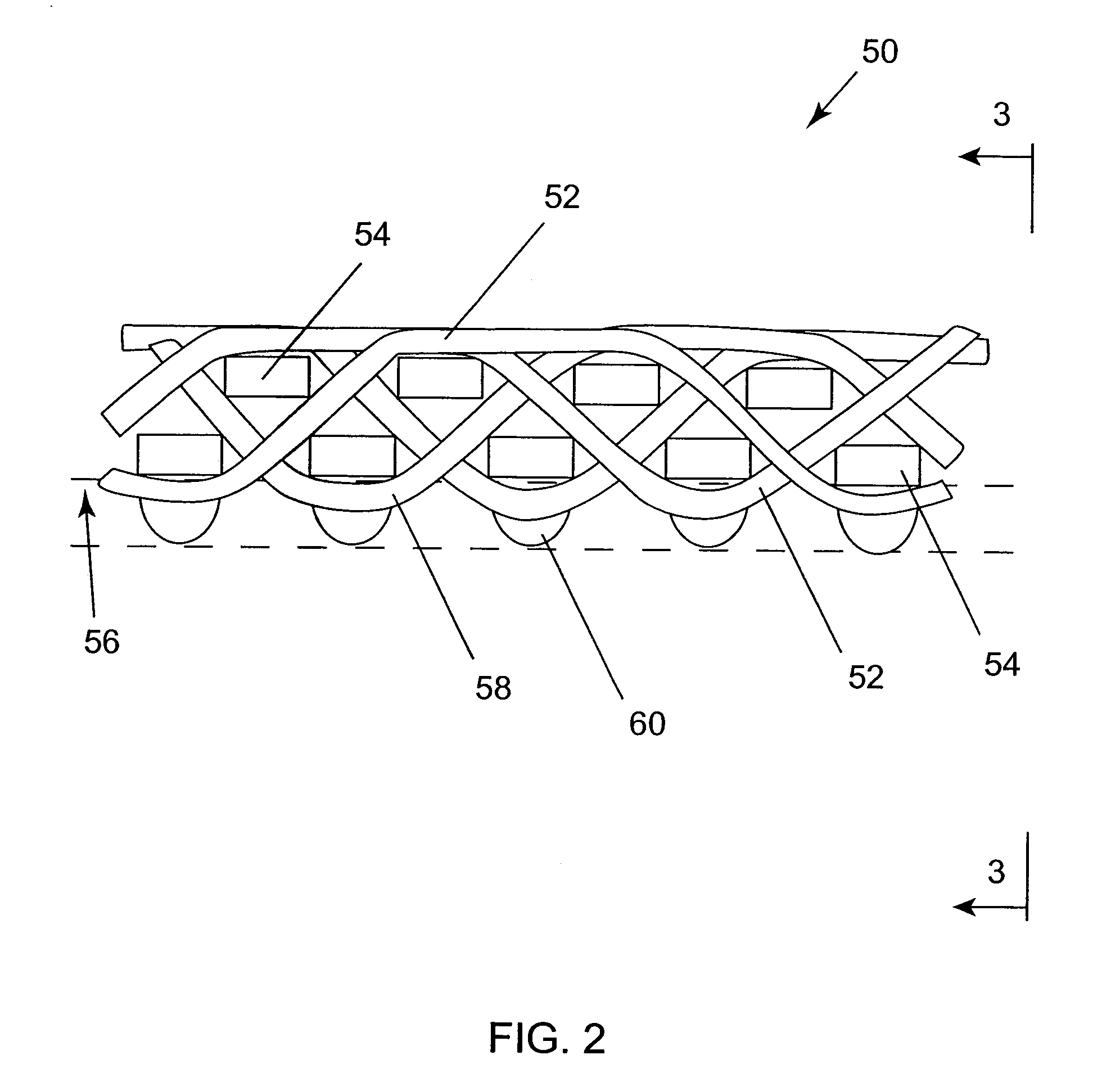
Machine direction yarn stitched triple layer papermaker's forming fabrics
InactiveUS6896009B2Excellent characteristicsImprove permeabilityPaper/cardboardMachine wet endYarnEngineering
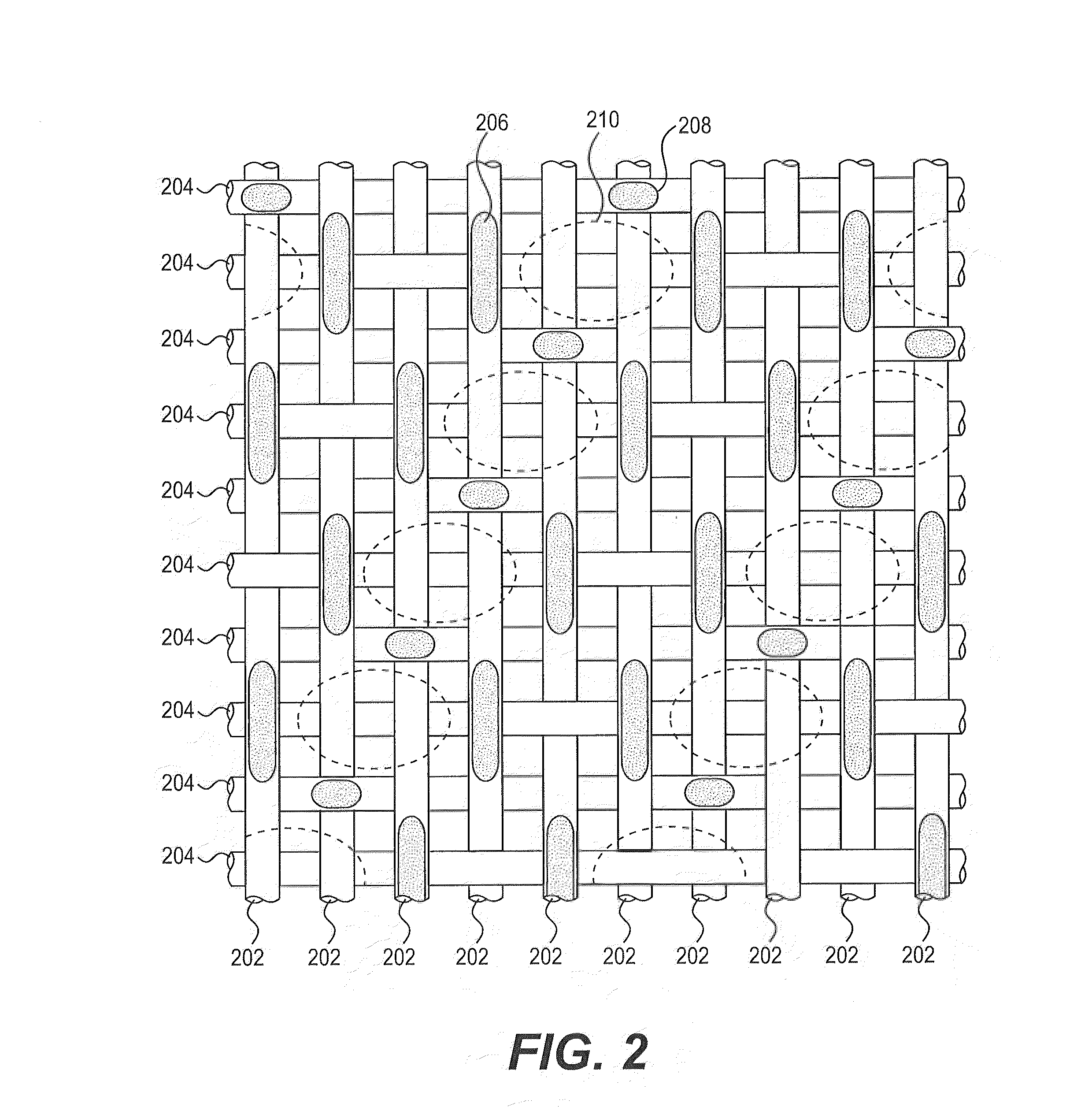
Triple layer papermaker's forming fabrics having a set of top MD yarns that are interwoven exclusively with a set of top CMD yarns to form at least part of a top fabric layer and a set of bottom MD yarns that are interwoven exclusively with a set of bottom CMD yarns to form at least part of a bottom fabric layer are provided. These fabrics further include a set of stitching MD yarn pairs. The stitching MD yarns that comprise each such pair weave in both the top fabric layer and the bottom fabric layer such that at locations where the first yarn in the pair weaves in the top fabric layer the second yarn in the pair drops down into the bottom fabric layer. In embodiments of the present invention, each stitching MD yarn may also be woven so as to form side-by-side machine direction knuckles on the bottom surface of the bottom fabric layer with a bottom MD yarn. In other embodiments of the invention, at least some of the top CMD yarns that the stitching MD yarns of the stitching MD yarn pairs pass over immediately before dropping down into the bottom fabric layer have a larger diameter and / or a higher modulus than the remainder of the top CMD yarns.
Owner:WEAVEXX
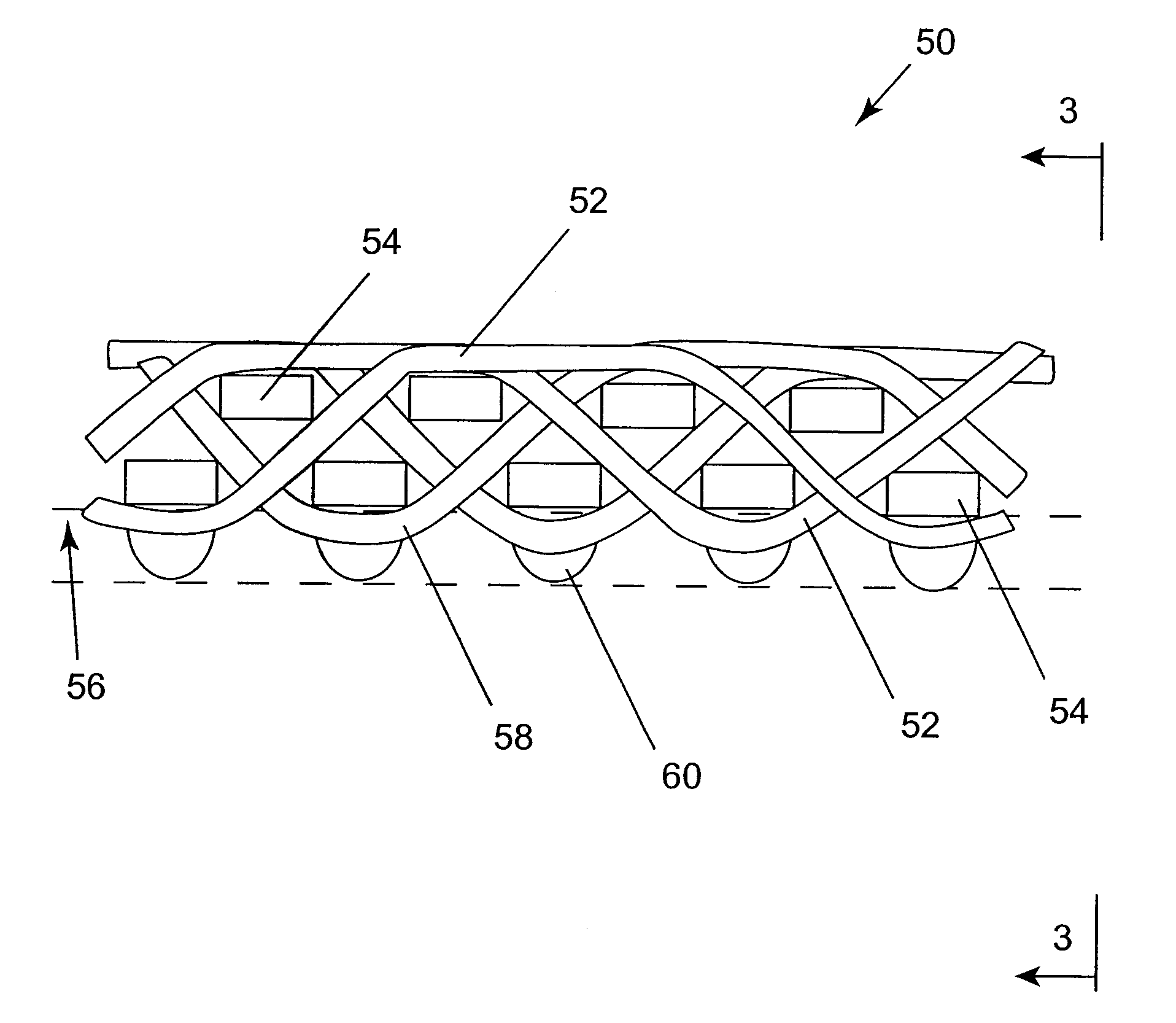
Method of fabrication of a dryer fabric and a dryer fabric with backside venting for improved sheet stability
InactiveUS7005043B2Reduce decreaseSimpler and less-costly to manufacture and seamNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperYarnPolymer resin
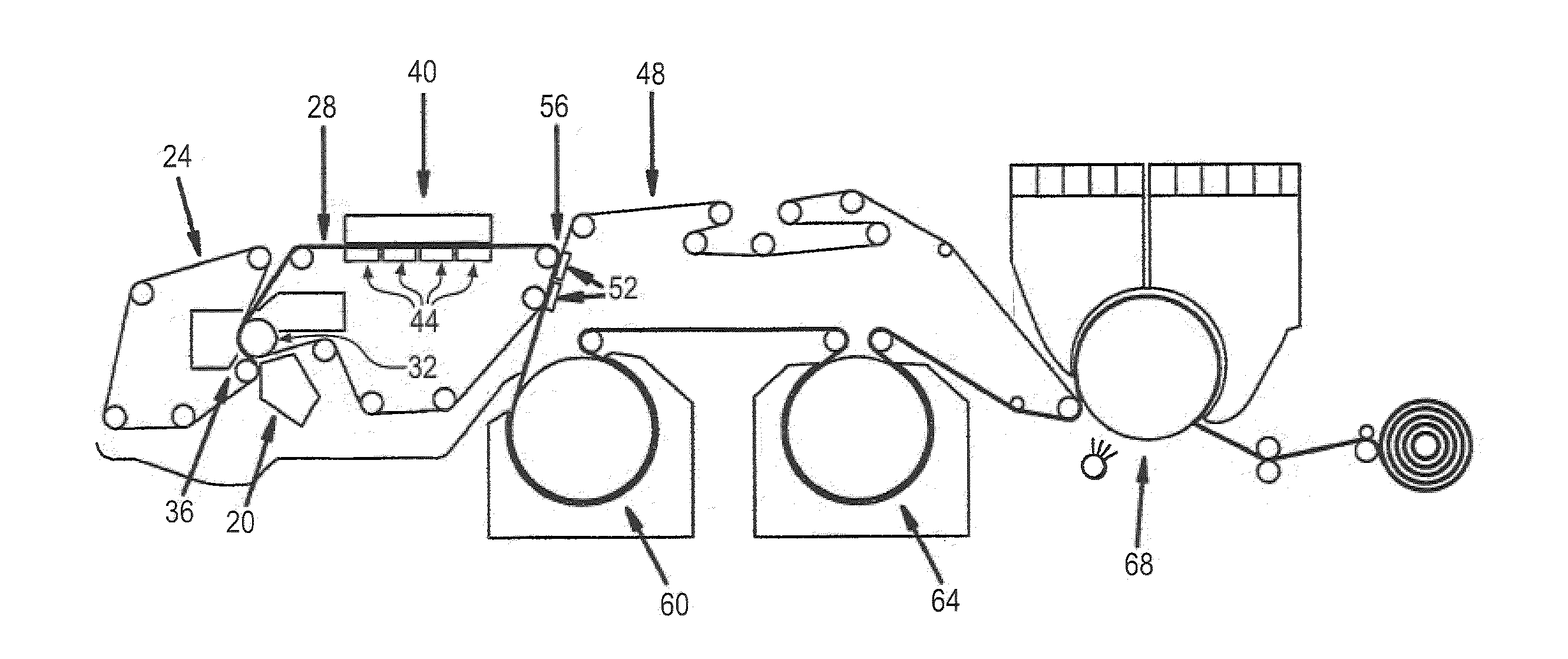
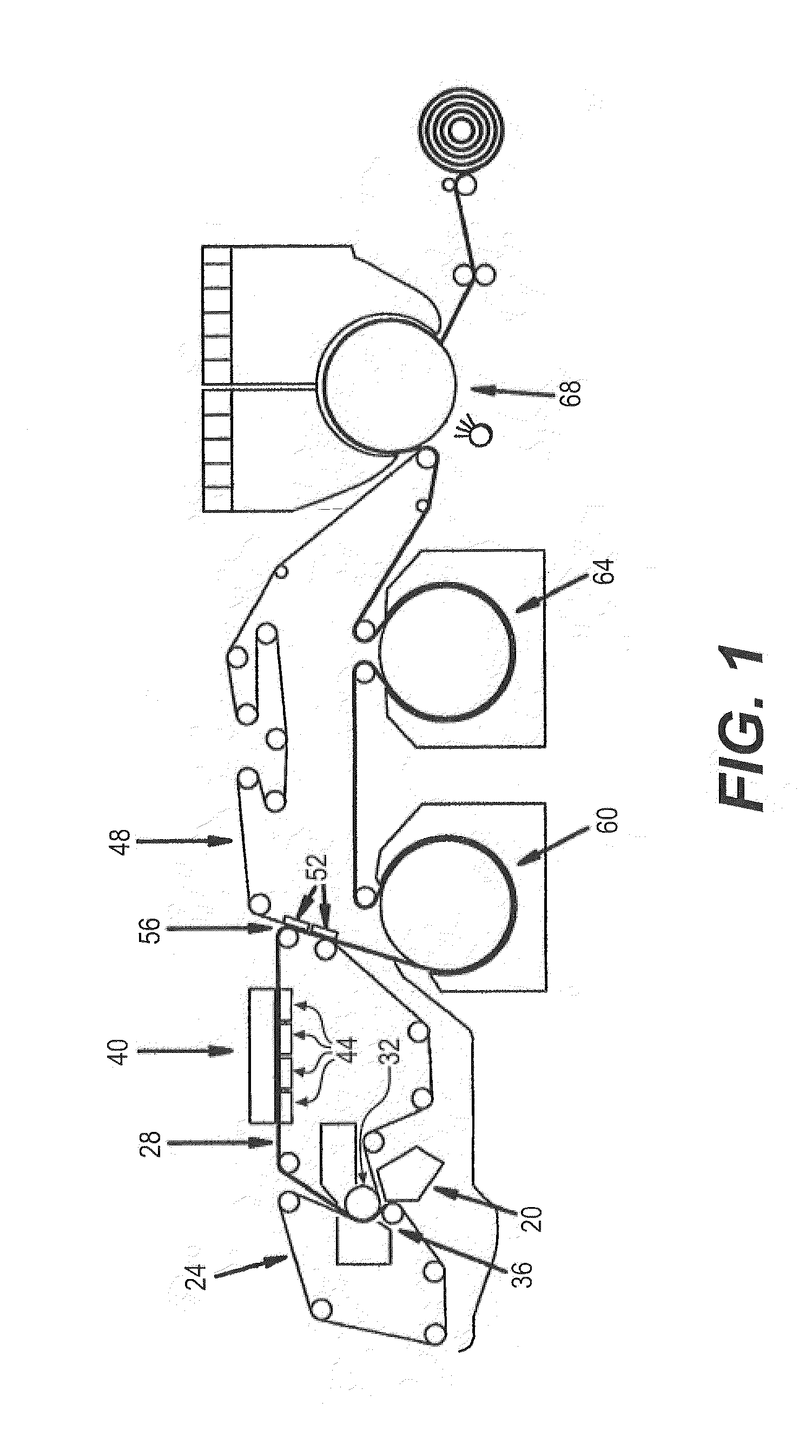
A method of manufacturing and a papermaker's or industrial fabric, such as a dryer fabric for the dryer section of a paper machine, includes the application of a polymeric resin material onto preselected locations on the backside of a base substrate using a piezojet array which deposits the polymeric resin material in droplets having an average diameter of 10μ (10 microns) or more to build up discrete, discontinuous deposits of the polymeric resin material having a height of about 0.5 mm at the preselected locations. The preselected locations may be the knuckles formed by the interweaving of the yarns making up the fabric. The purpose of the deposits is to separate the backside of the dryer fabric from a surface, such as that of a dryer cylinder or turning roll, to enable air trapped between the dryer fabric and the surface to escape in lengthwise and crosswise directions parallel to the surface, instead of being forced through the fabric, possibly causing “drop off”. The polymeric resin material is set by means appropriate to its composition, and, optionally, and, if necessary, may be abraded to provide the deposits with a uniform height above the surface plane of the base substrate.
Owner:ALBANY INT CORP
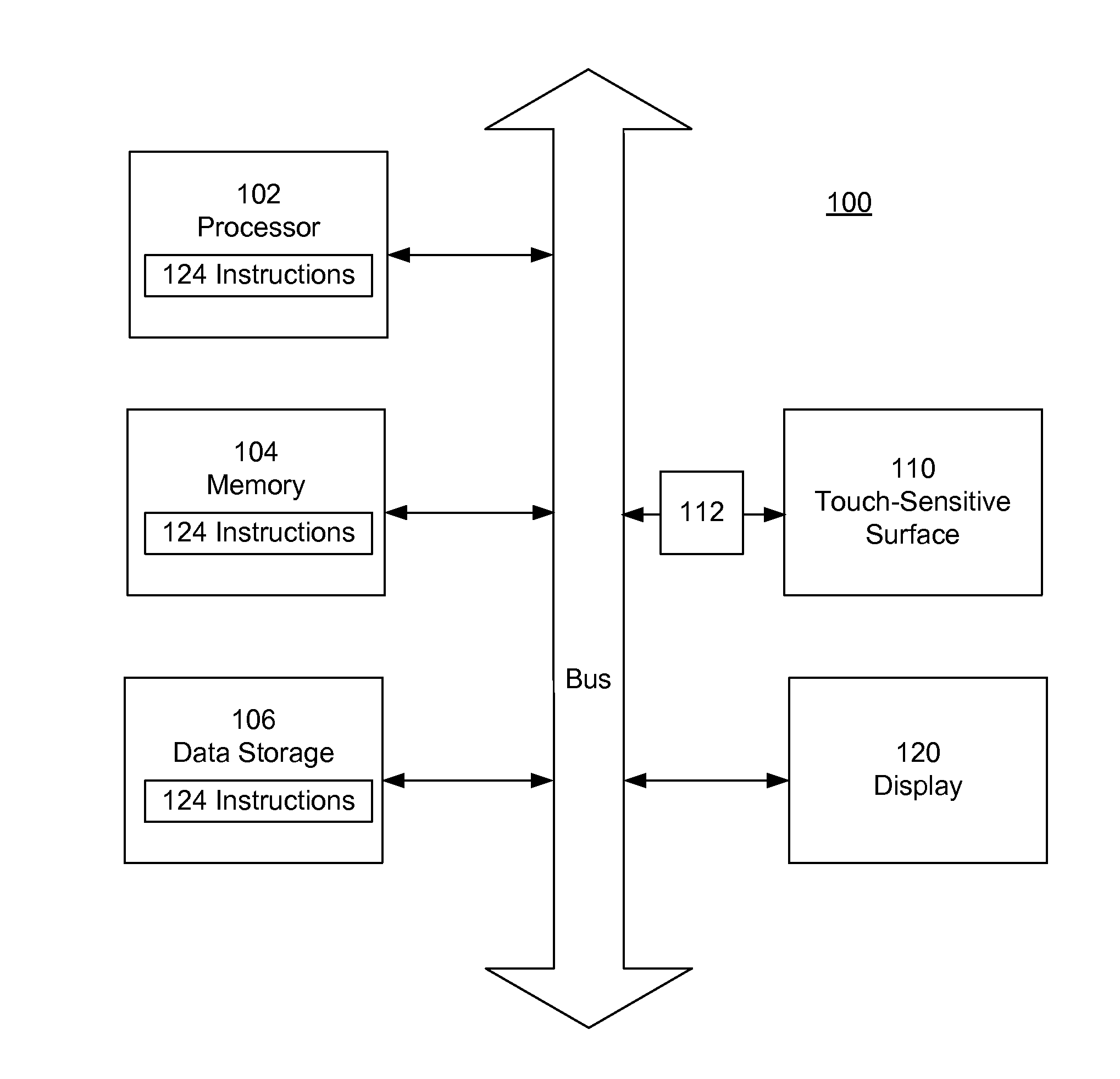
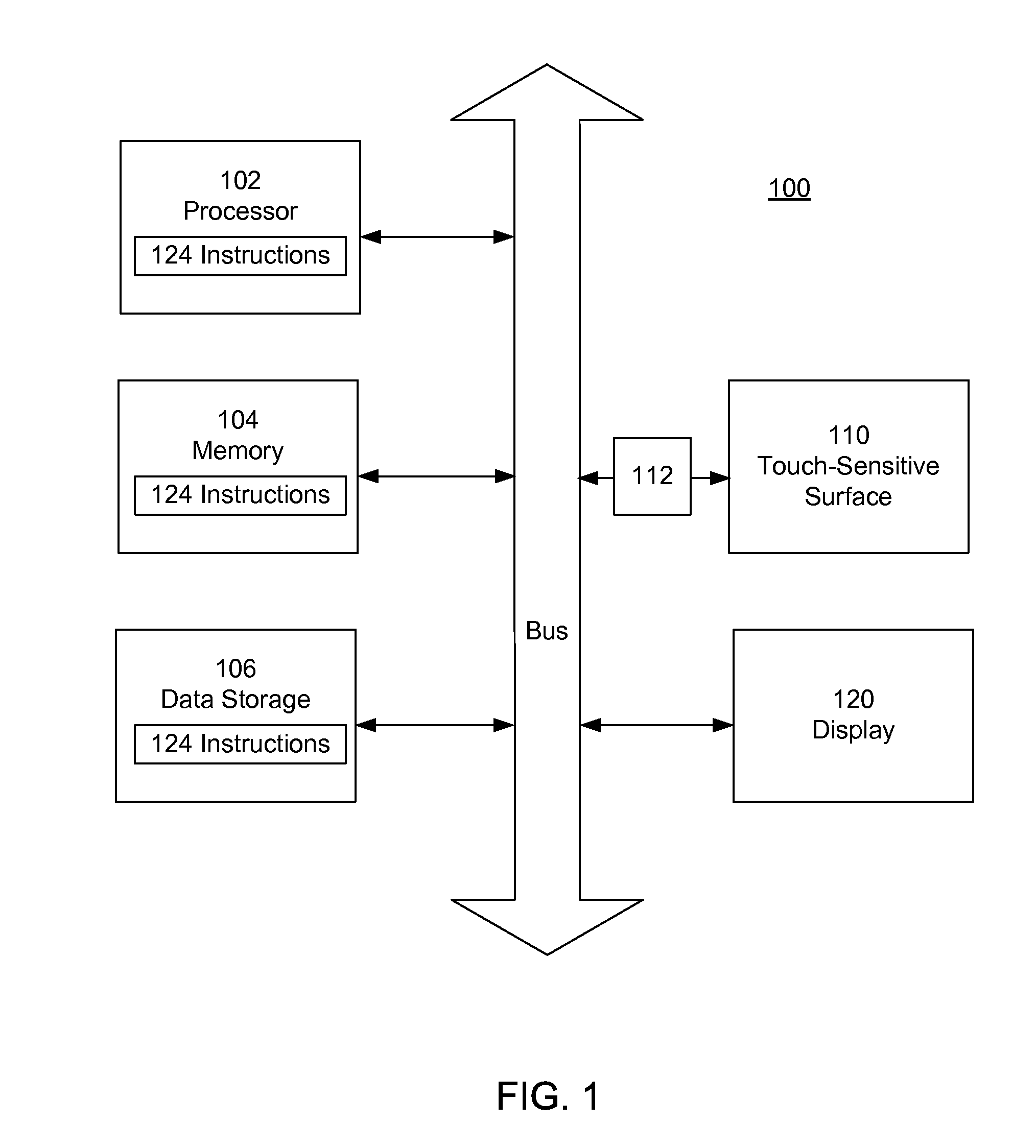
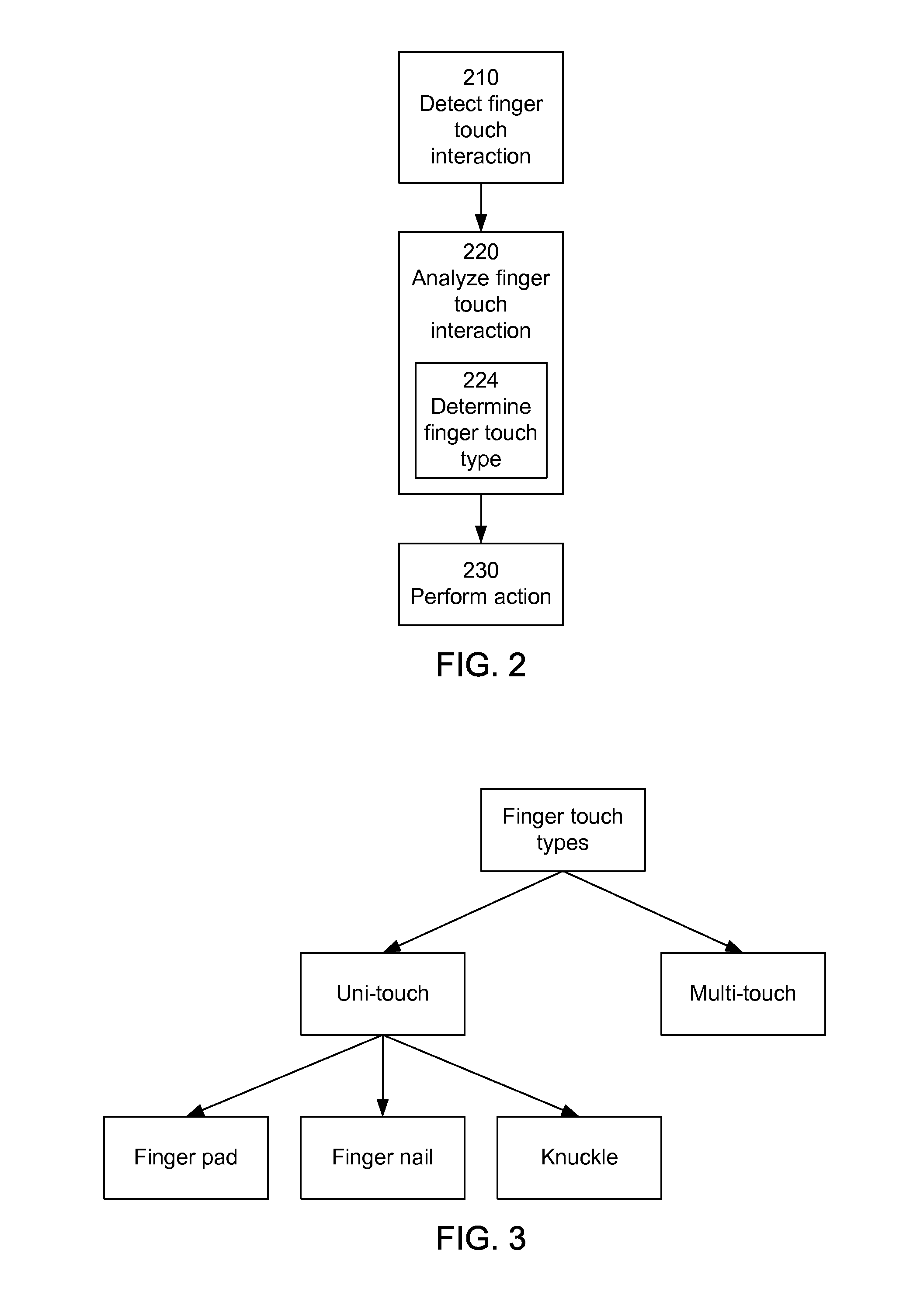
Using Finger Touch Types to Interact with Electronic Devices
An electronic device includes a touch-sensitive surface, for example a touch pad or touch screen. The user interacts with the touch-sensitive surface, producing touch interactions. The resulting actions taken depend at least in part on the touch type. For example, the same touch interactions performed by three different touch types of a finger pad, a finger nail and a knuckle, may result in the execution of different actions.
Owner:QEEXO
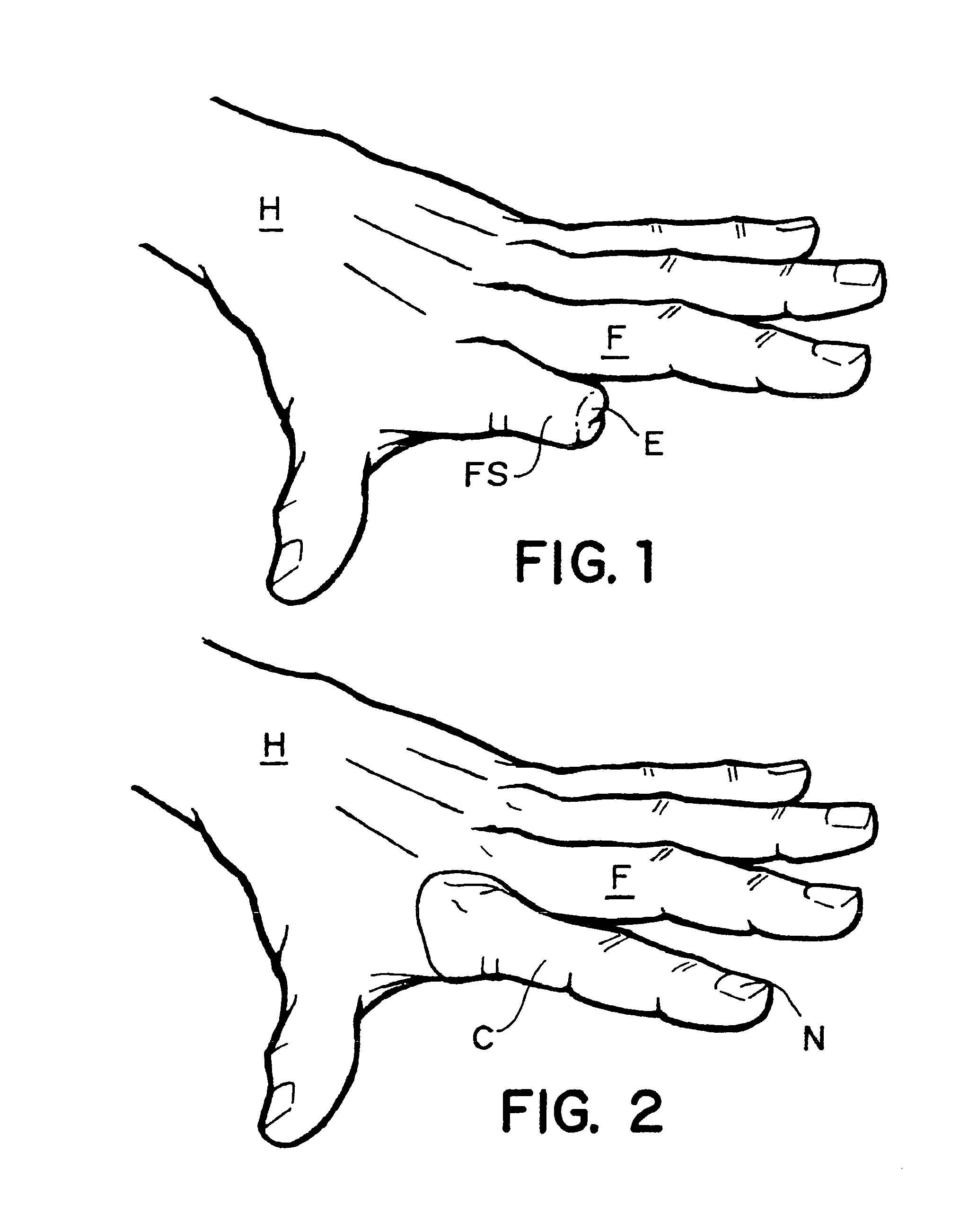
Articulated artificial finger assembly
Disclosed is an articulated artificial finger assembly, which can be controlled by the remaining portion of an amputated finger. An adjacent finger is used to manipulate the device when no finger is present. When the stump or adjacent finger begins to bend at the first knuckle, the rest of the device will react to the movements and articulate in the natural manner of a human finger. There are two embodiments shown which, can accommodate a variety of cases. The first embodiment relates to an amputated finger with a portion of the finger remaining. The second is used when a total finger is absent. In either case, the first embodiment uses a ring that is placed over the remaining stub of the finger and the second embodiment a ring is placed over an adjacent finger. The ring, in either embodiment, actuates upper and or lower actuation drives, which are reciprocally and transversely attached to a pivoting block. The pivoting block is fastened to an adjustable middle phalangeal section. The transversely connected upper and lower actuation drives cause the middle phalangeal section to curl under when articulated. The middle phalangeal section is comprised of two main body parts. The first is an outer phalangeal section and the second phalangeal section is placed inside the outer phalangeal section and fastened thereto. A forward fingertip section is pivotally fastened to a forward end of the inner phalangeal section. A forward end of the upper actuating drive is pivotally connected to the forward fingertip section. A supple cover is placed over the device once it is assembled. An inner supple cover is inserted into the device and sealed along the edges of the outer supple cover. To complete the device a screw is inserted into the fingertip, passing through the supple cover and is then hidden by an artificial fingernail placed thereon.
Owner:DIDRICK MEDICAL
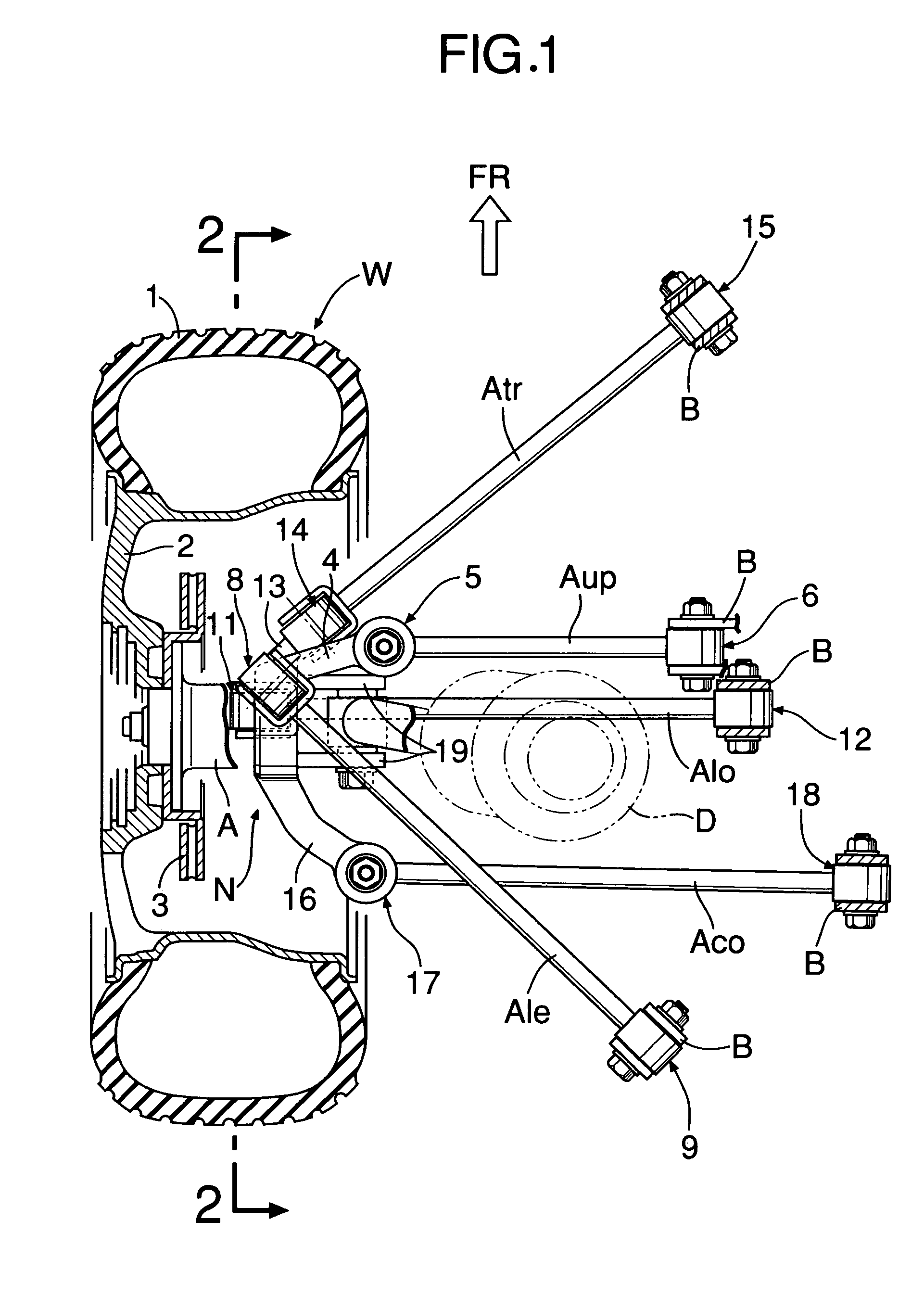
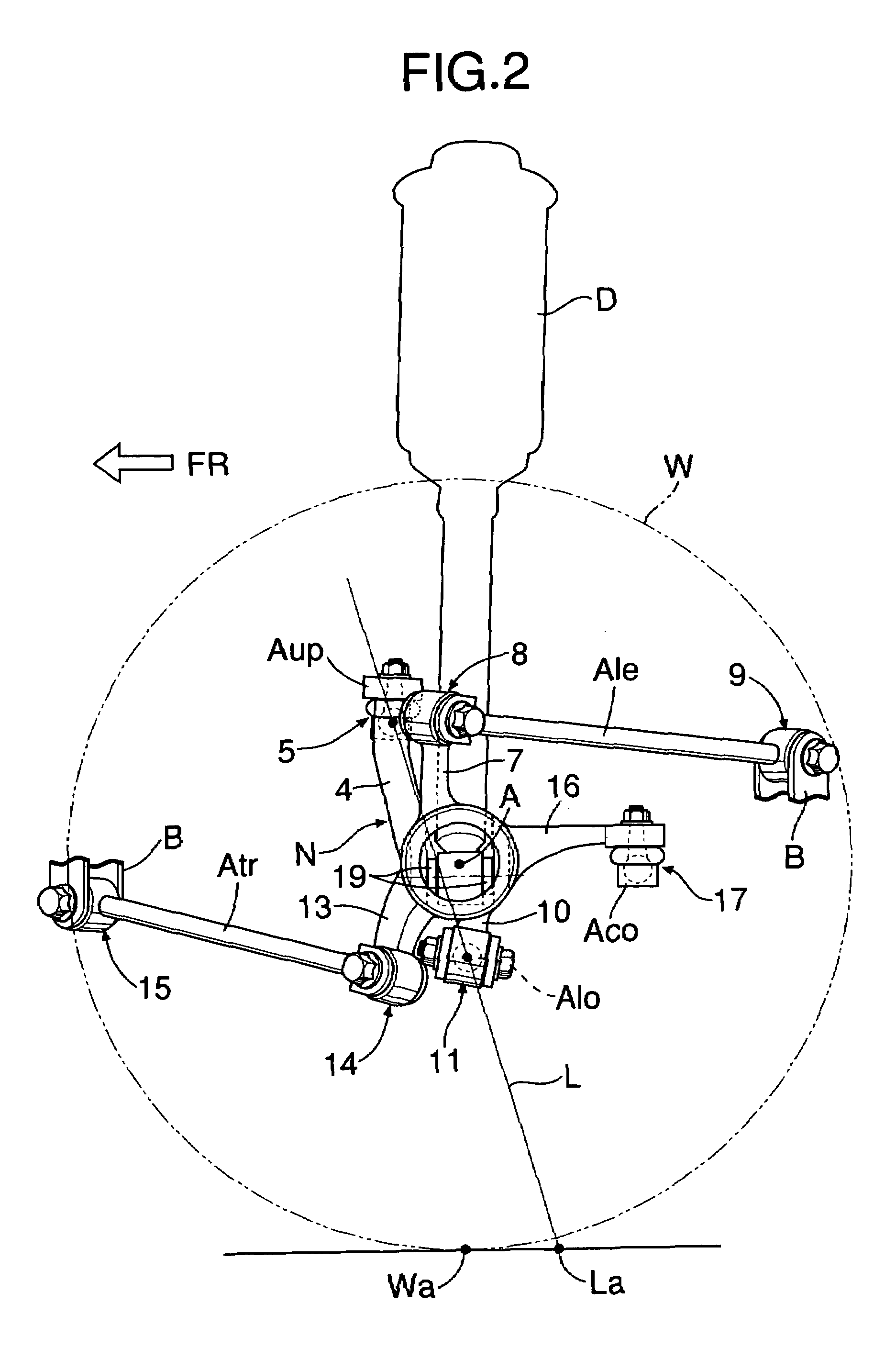
Vehicular rear suspension system
InactiveUS7258355B2Improve vehicle stabilityIncrease lateral stiffnessInterconnection systemsResilient suspensionsGround contactControl arm
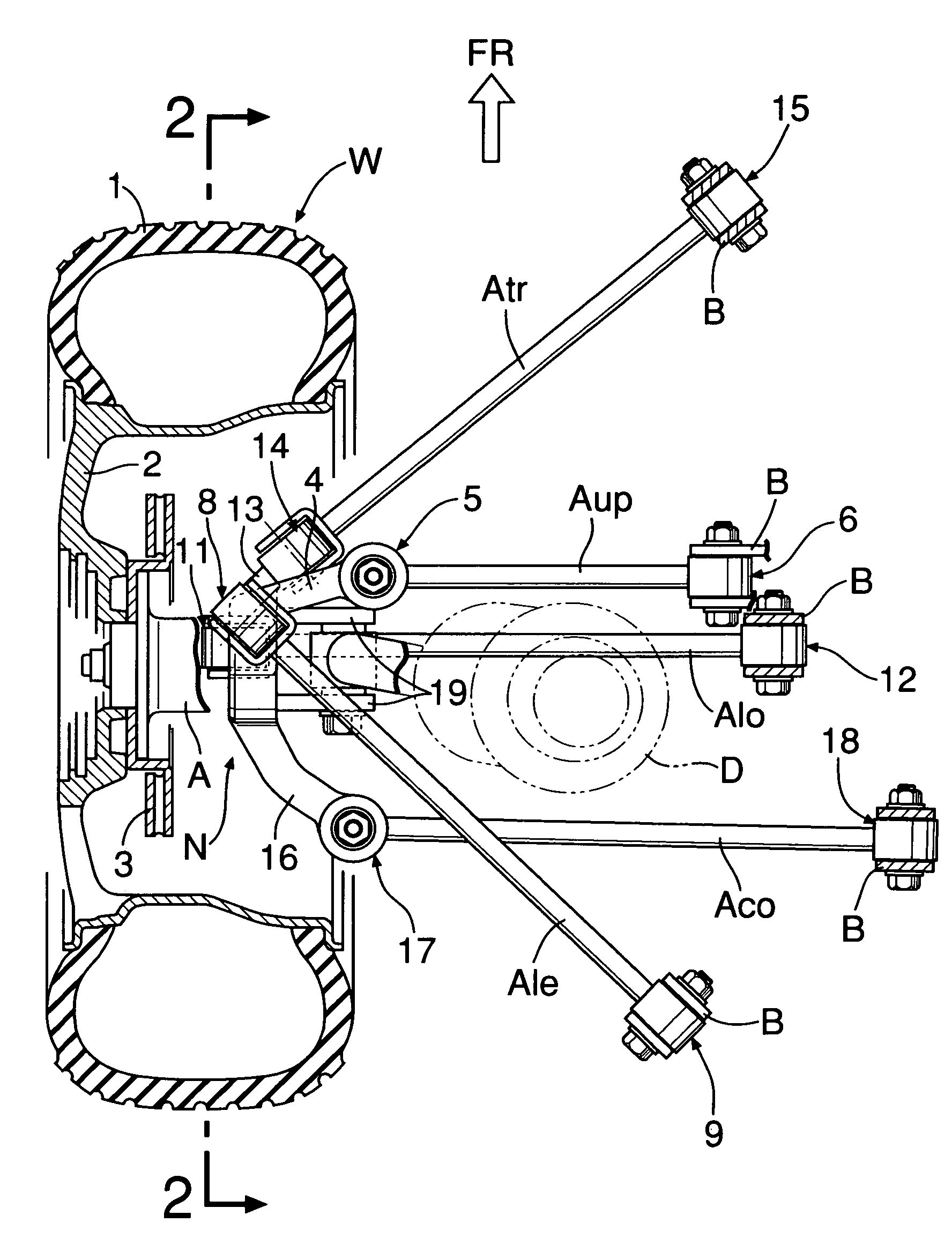
A vehicular rear suspension system includes an upper arm, a lower arm, and a control arm, each of which is connected to a knuckle. A straight line passing through a ball joint and a rubber bushing joint intersects the road surface at an intersection point that is positioned behind a ground contact point of the rear wheel in the longitudinal direction of the vehicle body. The ball joint connects the upper arm to the knuckle, and the rubber bushing joint connects the lower arm to the knuckle. Longitudinal elastic coefficients of the three arms are set in a predetermined relationship. Therefore, the intersection point at which an elastic kingpin intersects the road surface is positioned without fail behind a point of action of a lateral force when turning in the longitudinal direction of the vehicle body to achieve a lateral force toe-in and enhanced steering stability of the vehicle.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
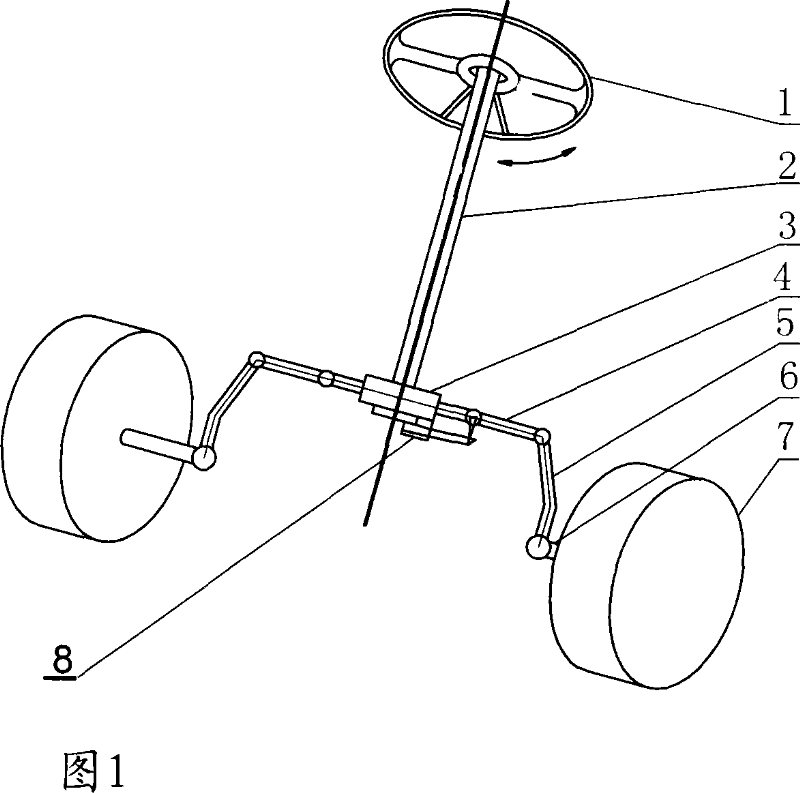
Device for displaying the turning angel of the turning wheel of automobile
InactiveCN101037117AVisual display of steering angleReduce incidenceSteering partsJoystickDriver/operator
A steering wheel steering angle display device for an automobile, belonging to the automobile instrument device, is used for displaying the steering angle when the automobile steering wheel is steering. The purpose of the invention is to provide a device capable of displaying the steering angle of the steering wheel of the automobile, thus to help the driver accurately to control the automobile to steer and improve running safety. An angle sensor is installed on the automobile steering mechanism, the specific installation position can be any position on the joystick, steering post, steering engine, pull rod, steering knuckle arm, steering knuckle and steering wheel, if only the angle sensor at the position is capable of directly or indirectly sensing the steering information of the automobile steering wheel. The angle sensor transforms variations of the steering angle of the steering wheel into variations of the electric quantity signal and output the signals to a signal processing circuit, the signal processing circuit processes the signals inputted by the angle sensor and output the signals to the display circuit to display.
Owner:王粤江
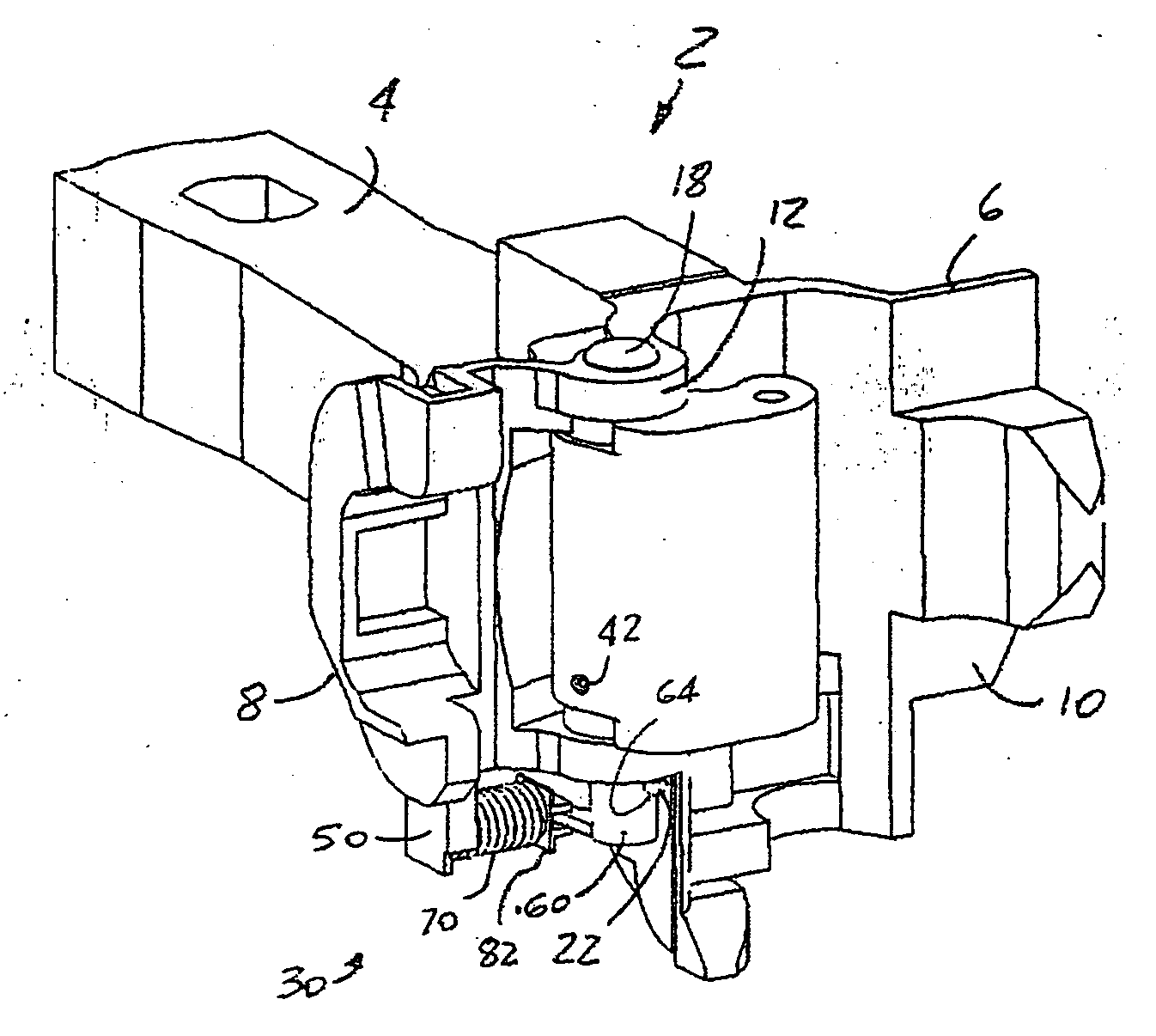
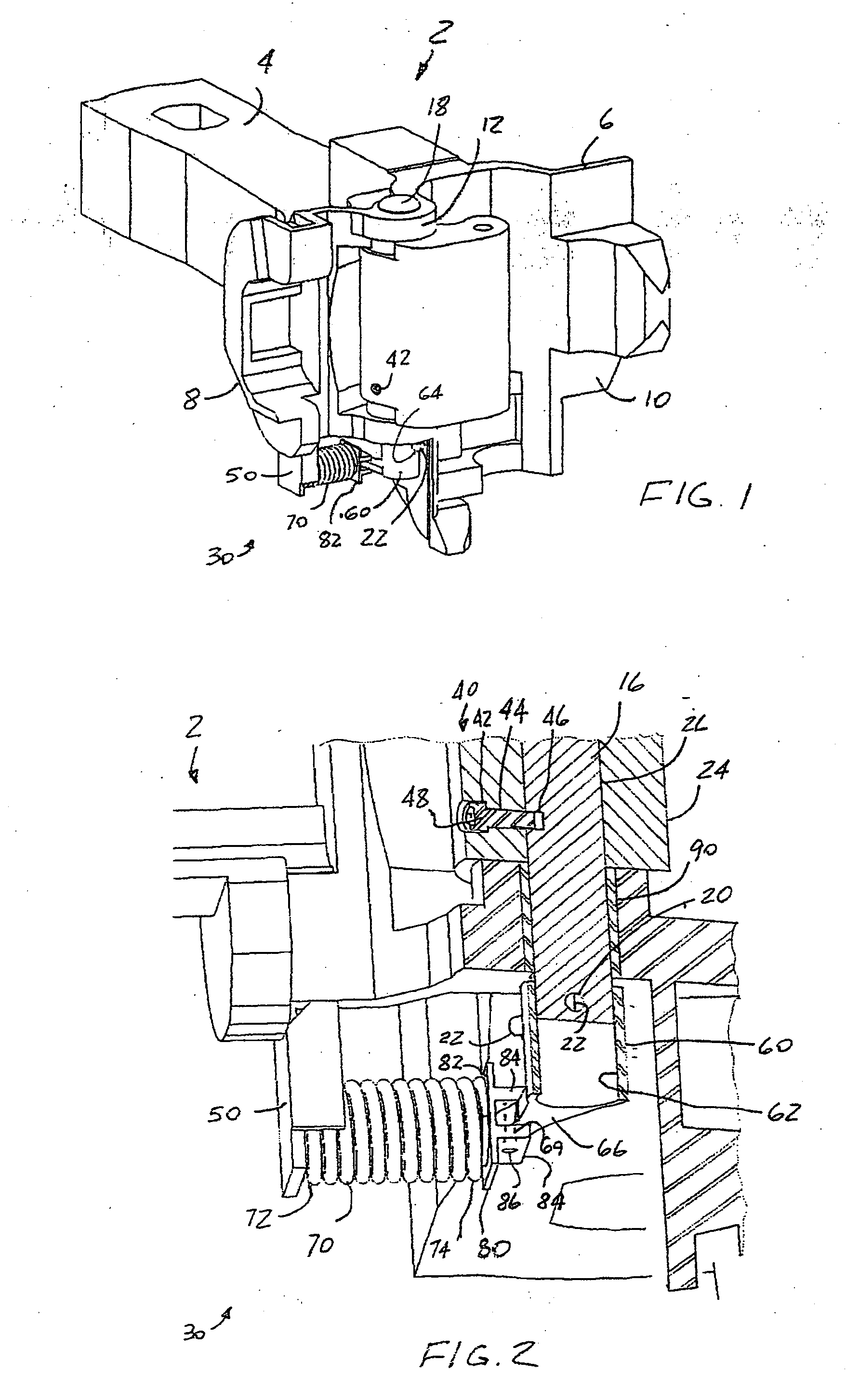
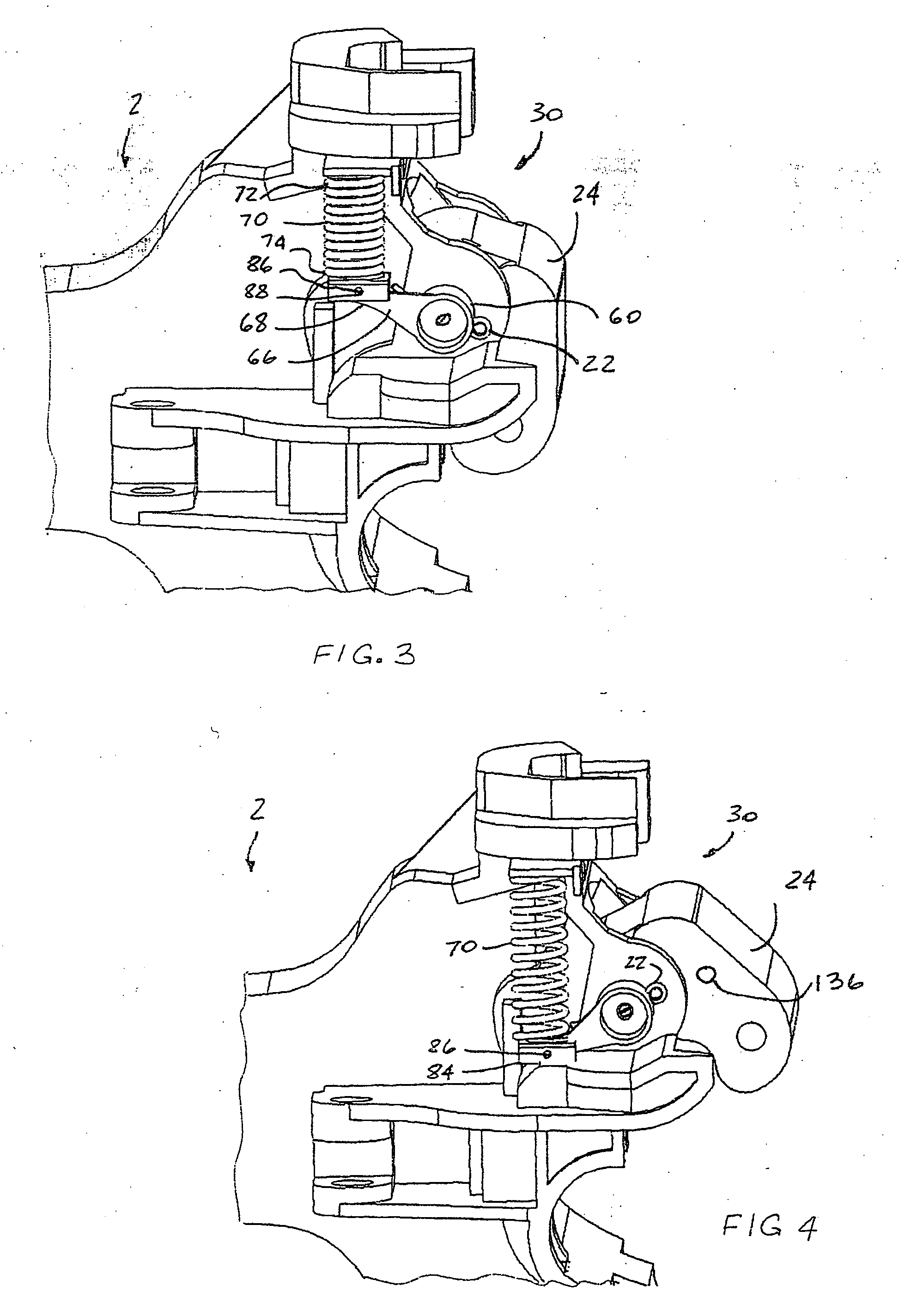
Railway car coupler knuckle having improved bearing surface
InactiveUS7337826B2Enhanced bearing surface areaIncrease surface areaFoundry mouldsFoundry coresEngineeringBearing surface
Owner:MCCONWAY & TORLEY LLC
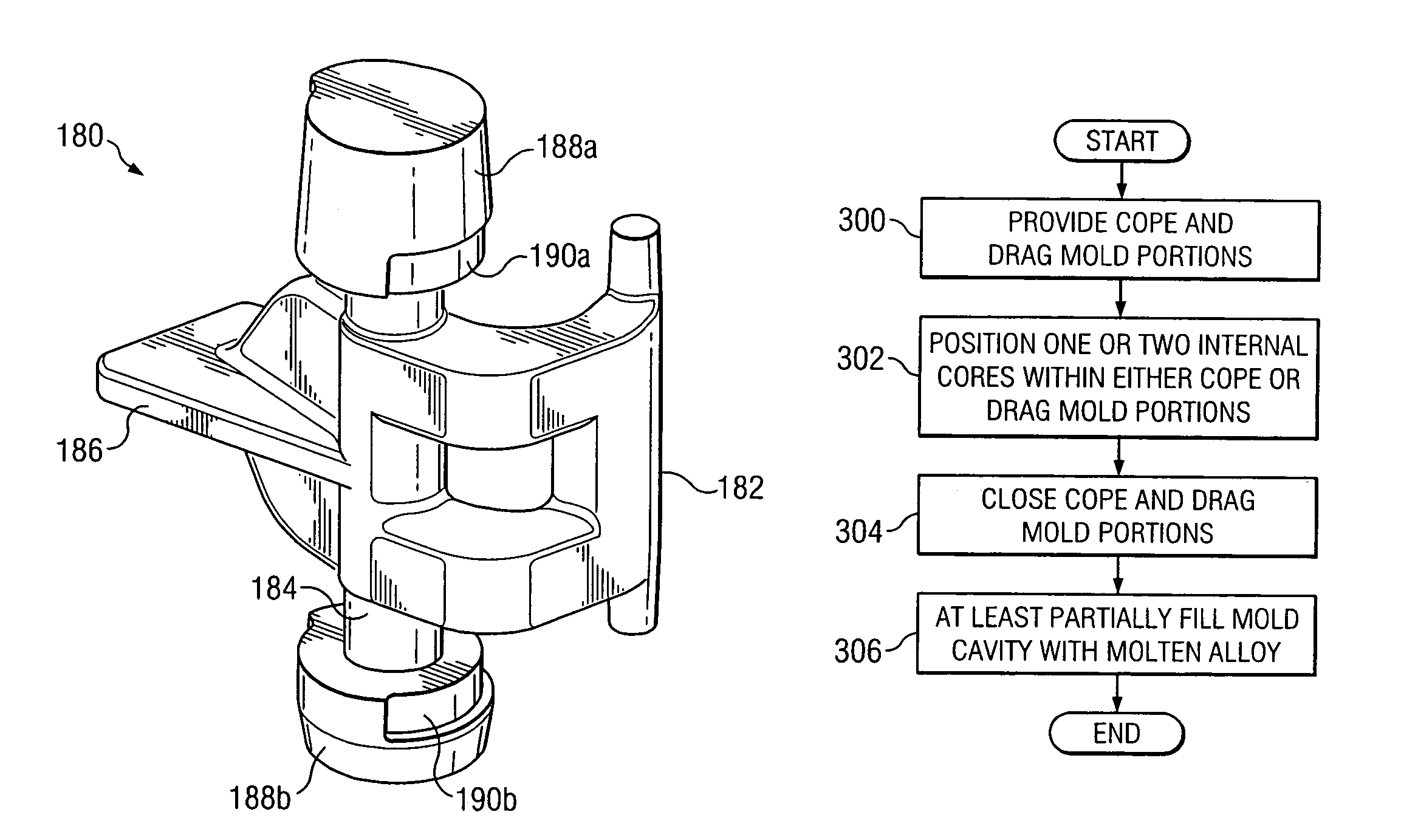
Method and system for manufacturing a coupler knuckle
A method for manufacturing a railcar coupler knuckle includes providing a cope mold portion and a drag mold portion. The cope and drag mold portions have internal walls defining at least in part perimeter boundaries of a coupler knuckle mold cavity. The method includes positioning one or two internal cores within either the cope mold portion or the drag mold portion. The one or two internal cores are configured to define a kidney cavity, a finger cavity and a pivot pin cavity of a coupler knuckle. The method includes closing the cope and drag mold portions with the one or two internal cores therebetween and at least partially filling the mold cavity with a molten alloy, the molten alloy solidifying after filling to form the coupler knuckle.
Owner:MCCONWAY & TORLEY LLC
Heart wall ablation/mapping catheter and method
InactiveUS20050273006A1Wide angleSmall knuckle curveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyCardiac wallAngular orientation
Steerable electrophysiology catheters for use in mapping and / or ablation of accessory pathways in myocardial tissue of the heart wall and methods of use thereof are disclosed. The catheter comprises a catheter body and handle, the catheter body having a proximal section and a distal section and manipulators that enable the deflection of a distal segment of the distal tip section with respect to the independently formed curvature of a proximal segment of the distal tip section through a bending or knuckle motion of an intermediate segment between the proximal and distal segments. A wide angular range of deflection within a very small curve or bend radius in the intermediate segment is obtained. At least one distal tip electrode is preferably confined to the distal segment which can have a straight axis extending distally from the intermediate segment. The curvature of the proximal segment and the bending angle of the intermediate segment are independently selectable. The axial alignment of the distal segment with respect to the nominal axis of the proximal shaft section of the catheter body can be varied between substantially axially aligned (0° curvature) in an abrupt knuckle bend through a range of about −90° to about +180° within a bending radius of between about 2.0 mm and 7.0 mm and preferably less than 5.0 mm. The proximal segment curve can be independently formed in a range of about −180° through about +270° with respect to the axis of the proximal shaft section to provide an optimum angular orientation of the distal electrode(s). The distal segment can comprise a highly flexible elongated distal segment body and electrode(s) that conform with the shape and curvature of the heart wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Articulated artificial finger assembly
Disclosed is an articulated artificial finger assembly, which can be controlled by the remaining portion of an amputated finger. An adjacent finger is used to manipulate the device when no finger is present. When the stump or adjacent finger begins to bend at the first knuckle, the rest of the device will react to the movements and articulate in the natural manner of a human finger. There are two embodiments shown which, can accommodate a variety of cases. The first embodiment relates to an amputated finger with a portion of the finger remaining. The second is used when a total finger is absent. In either case, the first embodiment uses a ring that is placed over the remaining stub of the finger and the second embodiment a ring is placed over an adjacent finger. The ring, in either embodiment, actuates upper and or lower actuation drives, which are reciprocally and transversely attached to a pivoting block. The pivoting block is fastened to an adjustable middle phalangeal section. The transversely connected upper and lower actuation drives cause the middle phalangeal section to curl under when articulated. The middle phalangeal section is comprised of two main body parts. The first is an outer phalangeal section and the second phalangeal section is placed inside the outer phalangeal section and fastened thereto. A forward fingertip section is pivotally fastened to a forward end of the inner phalangeal section. A forward end of the upper actuating drive is pivotally connected to the forward fingertip section. A supple cover is placed over the device once it is assembled. An inner supple cover is inserted into the device and sealed along the edges of the outer supple cover. To complete the device a screw is inserted into the fingertip, passing through the supple cover and is then hidden by an artificial fingernail placed thereon.
Owner:DIDRICK MEDICAL
Separated steering device for vehicular four wheels and its control method
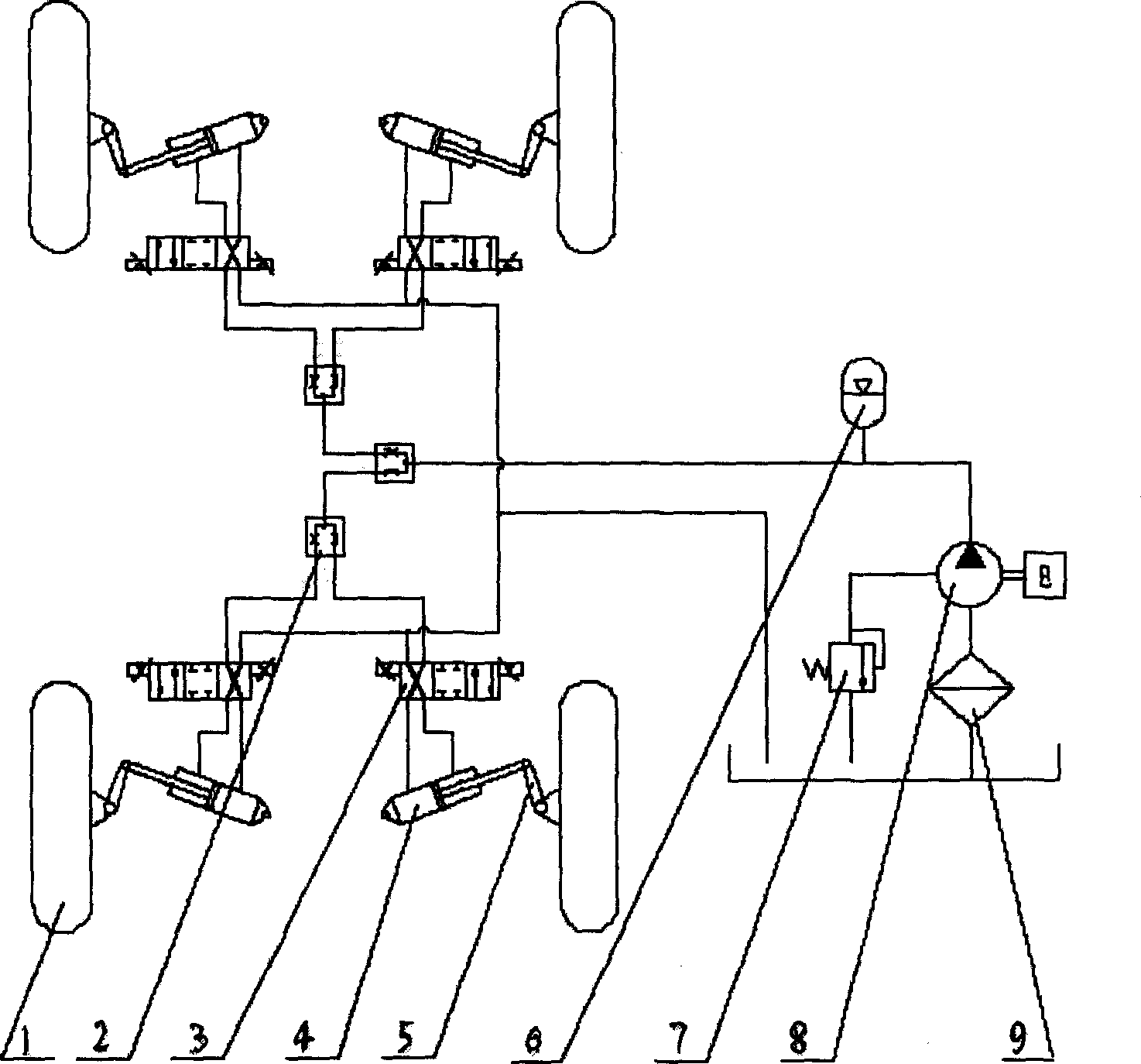
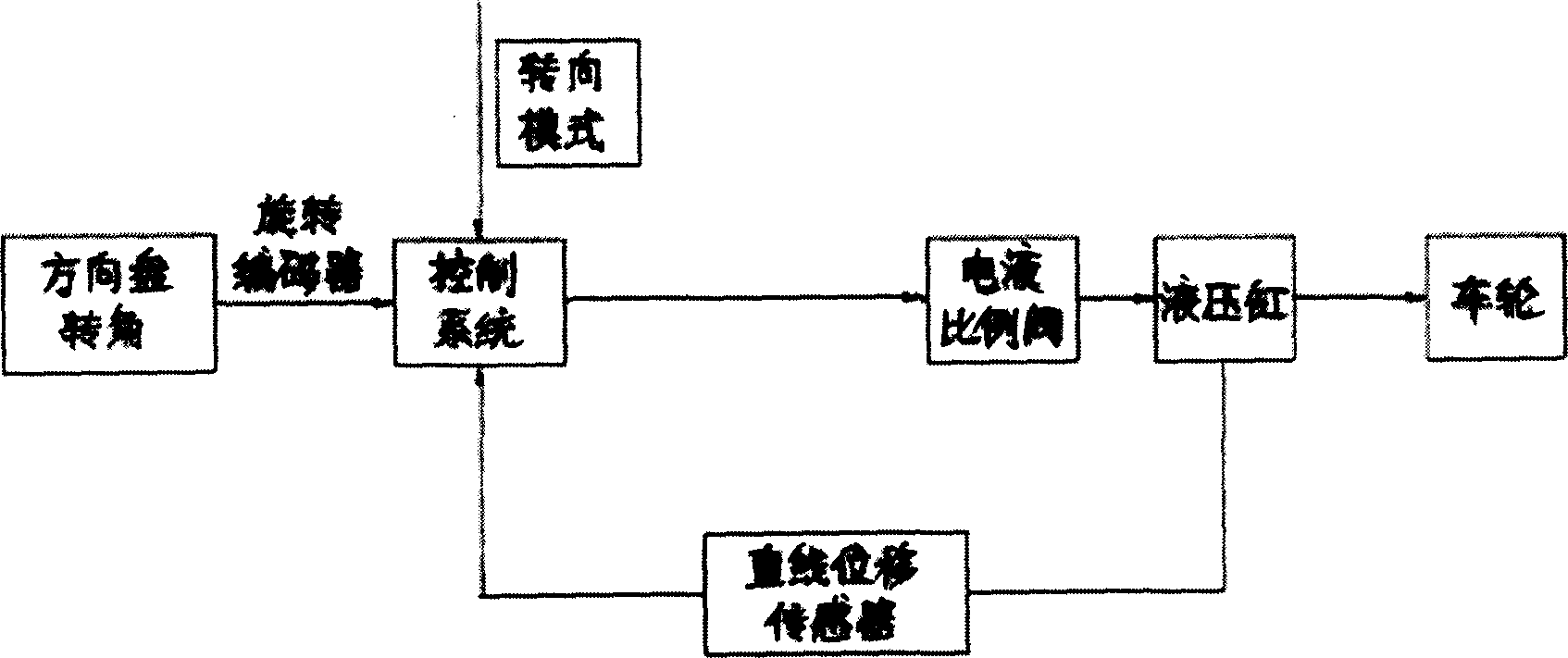
The invention relates to domain of special purpose vehicle and especially to a separate four-wheel steering device of vehicle and controlling means, which is mainly used in steering system of special purpose vehicle to guarantee steering behavior. The device comprises steering knuckle arm, steering hydraulic cylinder, electro-hydraulic proportional control valves, and accumulator, easing valve, hydraulic pump, clarifier and electronic control system. The invention is characterized in that every wheel is controlled by independent oil-hydraulic cylinder, electronic control system comprises steering emulator, signal processor and measuring apparatus of displacement line and hydraulic pump driven by engine in steering hydraulic system controls hydraulic cylinder of steering system via electro-hydraulic proportional control valves of steering system. Hydraulic cylinder connects with linear movement pickup to feed variable of displacement line of hydraulic cylinder back to CPU. System adopts closed-loop control. Control circuit equips system failure diagnosis element to realize alarm when system steering error occurs and steering mode switching control unit to complete steering mode switching of vehicle.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Joint fusion device
A device and method are disclosed for the fusion of joints (particularly finger joints or toe joints) in a bent (or angled) position. In certain embodiments, a device for the fusion of joints preferably allows for one or more of various angled positions, and the particular angle may differ for different joints. The device is preferably a bendable implant device for fusing together bones or a joint.
Owner:EXSOMED CORP
Modular monitor support assembly
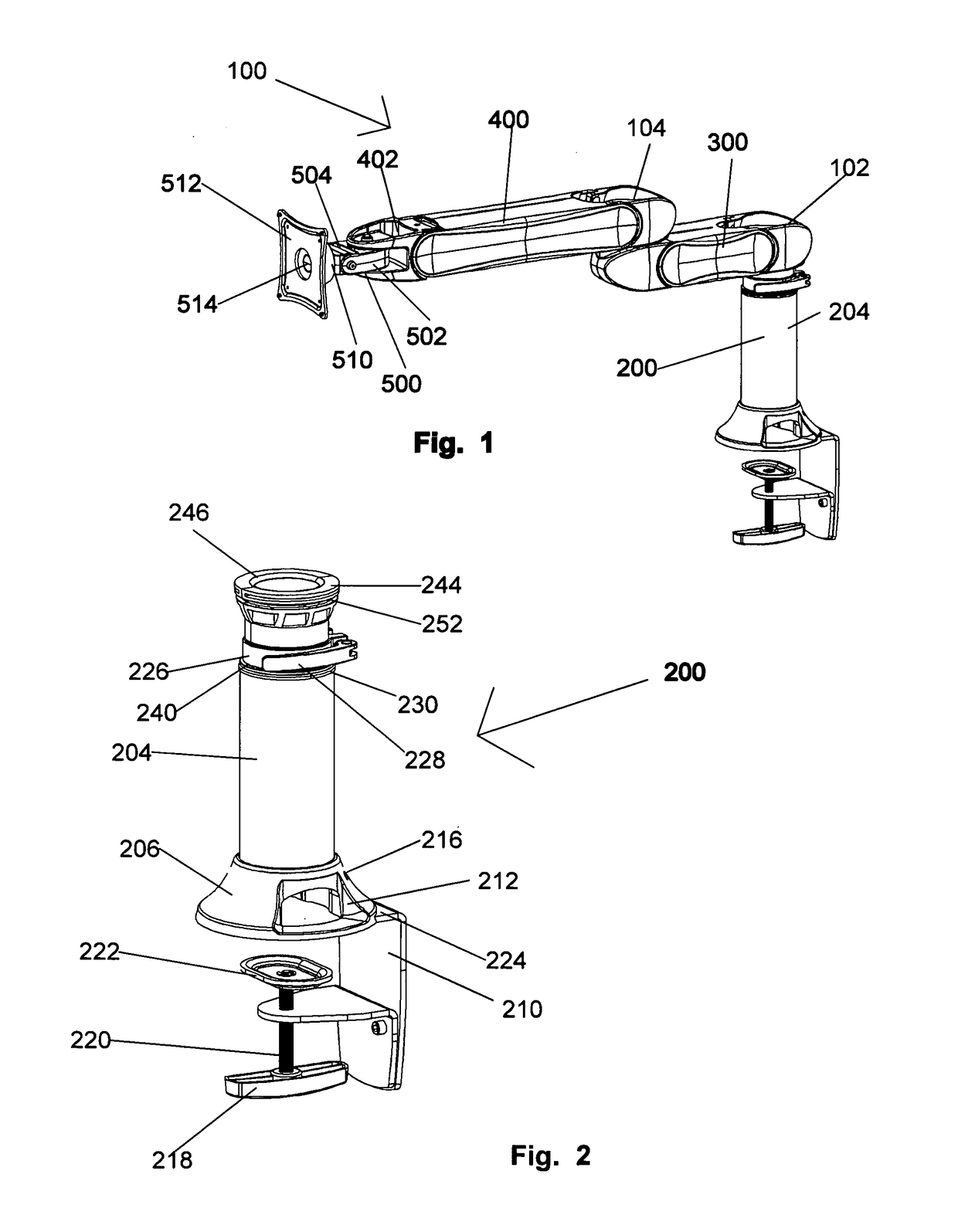
InactiveUS8469323B1Sufficient dimensionDigital data processing detailsStands/trestlesModularityDisplay device
A monitor support assembly having an internal cable raceway. The support assembly includes a pole mount that can be secured to a desk or table top or to a vertical wall or furniture panel, a rotatable knuckle joint at the upper end of the pole mount, and a quick-release mount for a monitor or other peripheral device. The assembly may also include nonarticulatable and vertical members, connected to each other and to the pole mount with knuckle joints that include internal sleeves. One or more cables, with plugs attached, can be inserted into the cable raceway and joints without disassembling the monitor support. The assembly may have interchangeable parts to provide different lengths for the nonarticulatable and vertical members.
Owner:ATOMDESIGN
Strut suspension with pivoting rocker arm
InactiveUS7185902B1Improves camber gainImproves roll center controlSteering partsInterconnection systemsEngineeringRocker arm
A strut suspension can include a shock-absorber / spring assembly having a lower portion mountable at one end to an upper portion of the steering knuckle. A transverse link can be connectible to the steering knuckle at a location opposite from the shock-absorber / spring assembly. A rocker arm can be supportable for pivotal movement from the vehicle body and can be pivotally connectible to the shock-absorber / spring assembly from the steering knuckle. A push rod can be pivotally connectible to the rocker arm and can extend between the rocker arm and the transverse link. The upper end of the shock-absorber / spring assembly can be connected to either an inboard or outboard portion of the rocker arm, while an upper end of the push rod is connected to the other of the outboard or inboard portion of the rocker arm.
Owner:ALTAIR ENGINEERING
Collapsible potty
A collapsible potty comprises a one piece, rigid seat with a central hole through it. A pair of opposed tracks on the seat lower surface extend from front to rear. Left and right support panels are pivotally attached, by means of support hinge knuckles, to seat hinge knuckles on the seat left and right ends, respectively. Hinge pins engage hinge holes in the knuckles. The support panels are able to pivot from a folded position adjacent the seat lower surface, to an open position extending downward.A flexible, sealable waste bag hangs beneath the seat to receive waste. A tray has a plurality of hooks, arrayed around a central hole, that engage holes in the waste bag. The tray slides into the seat tracks to position the tray central hole directly beneath the seat central hole. A zip-lock closure seals the waste bag.A resilient locking arm on the seat hinge knuckle expands into a notch in the support hinge knuckle when the support panel is rotated into the open position, to hold the support panel open. A pushbutton release member moves the locking arm out of the notch to release the support panel for folding.
Owner:SELL TIMOTHY L
Apparatus for railway freight car coupler knuckle
InactiveUS20070084818A1Eliminate dangerEliminate hazardous routineRailway couplingsLocking mechanismCombined use
In combination with a railway freight car coupler. A coupler has a knuckle side, and includes a knuckle, knuckle pin, and an apparatus for automatically pivoting and maintaining the knuckle full open position. The improvement comprises a coiled torsion spring which is capable of continuously exerting a predetermined force. A sleeve in combination with a flange is secured to the bottom end of the knuckle pin for attaching the torsion spring onto the coupler head. A support member is attached to the knuckle and cages one arm of the torsion spring which exerts a continuous force on the knuckle to rotate and maintain the knuckle full open position. A compression spring may be employed in place of the torsion spring in combination with a locking mechanism which, rigidly secures the knuckle and knuckle pin therebetween to prevent independent movement.
Owner:SHARMA & ASSOCS
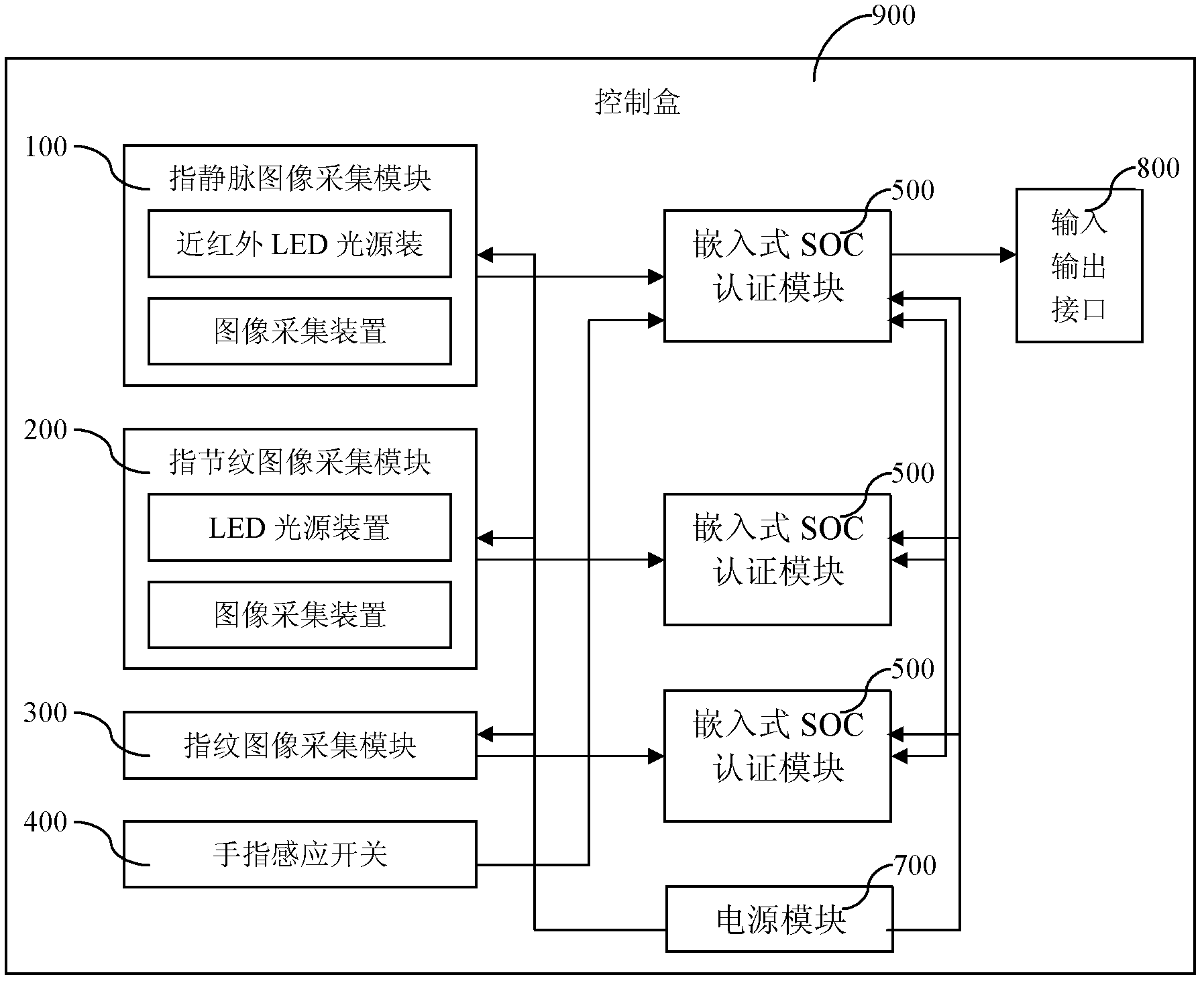
Multi-mode identity authentication method and device based on biological characteristics of fingers
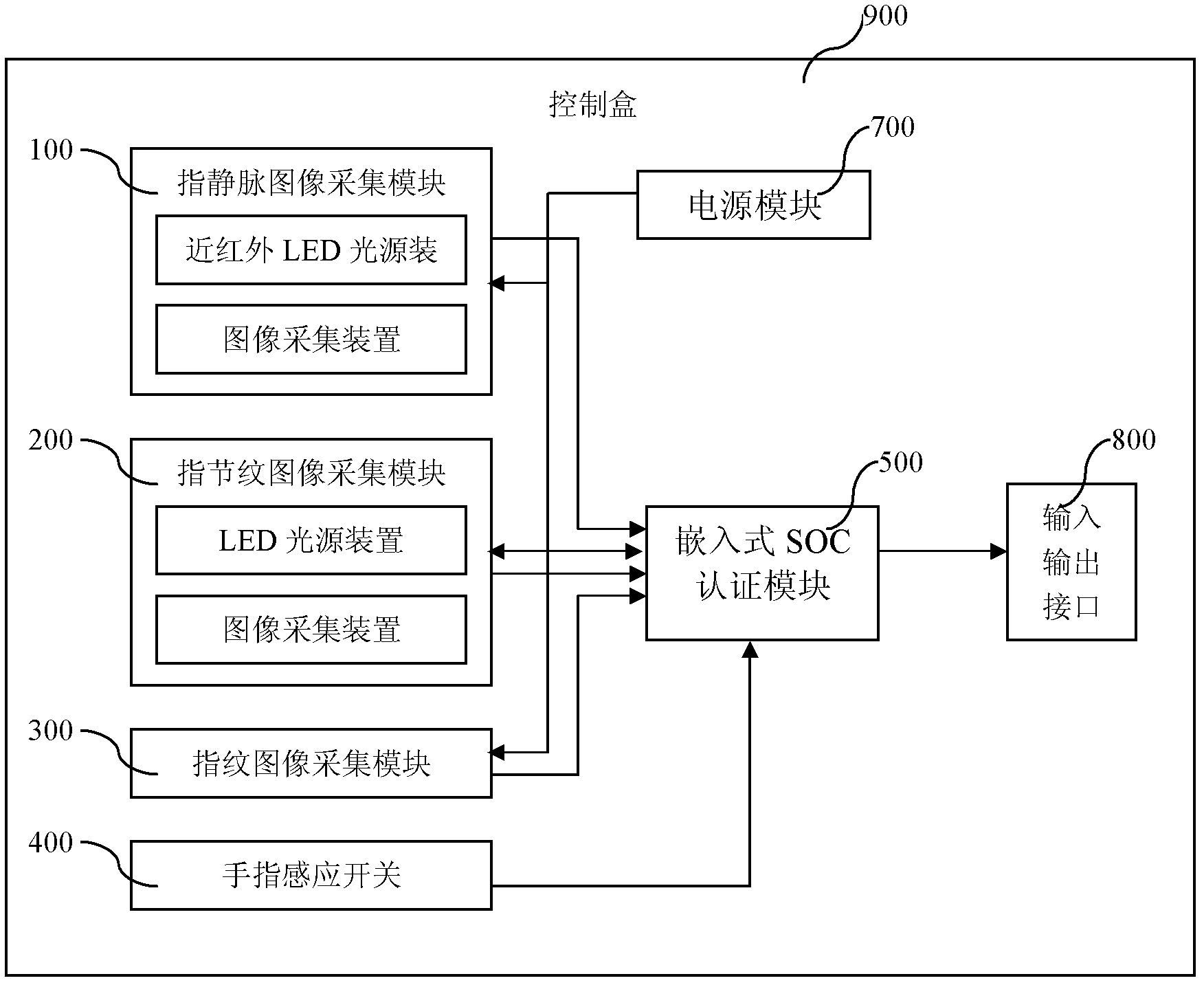
InactiveCN102542263AEfficient integrationImprove collection qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionVeinComputer module
The invention relates to a multi-mode identity authentication device based on the biological characteristics of fingers, which comprises a finger vein image collection module, a finger knuckle stripe image collection module, a fingerprint image collection module, a finger induction switch, an embedded type start of conversion pulse (SOC) authentication module, a control box, an input / output interface and a power supply module; the modules, the finger induction switch and the input / output interface are all installed on the control box, the finger vein image collection module, the finger knuckle stripe image collection module and the fingerprint image collection module are connected with an image input interface of the embedded type SOC authentication module so as to realize the collection of the biological characteristics of veins, finger knuckle stripes and fingerprints, and the finger induction switch is connected with a GPIO (General Purpose Input / Output) interface of the embedded type SOC authentication module so as to realize the detection of the placement of the fingers; and the power supply module is connected with each module so as to provide a power supply required for working. The invention relates to a multi-mode identity authentication method based on the biological characteristics of the fingers, which comprises characteristic registration and characteristic comparison comprising nine steps respectively. According to the multi-mode identity authentication device and the method based on the biological characteristics of the fingers, the safety of identity identification is effectively enhanced. The multi-mode identity authentication device and the method based on the biological characteristics of the fingers have extensive application prospect.
Owner:北京鑫光智信软件技术有限公司
Motion-decoupled rope-driven non-individual body mechanical arm and robot
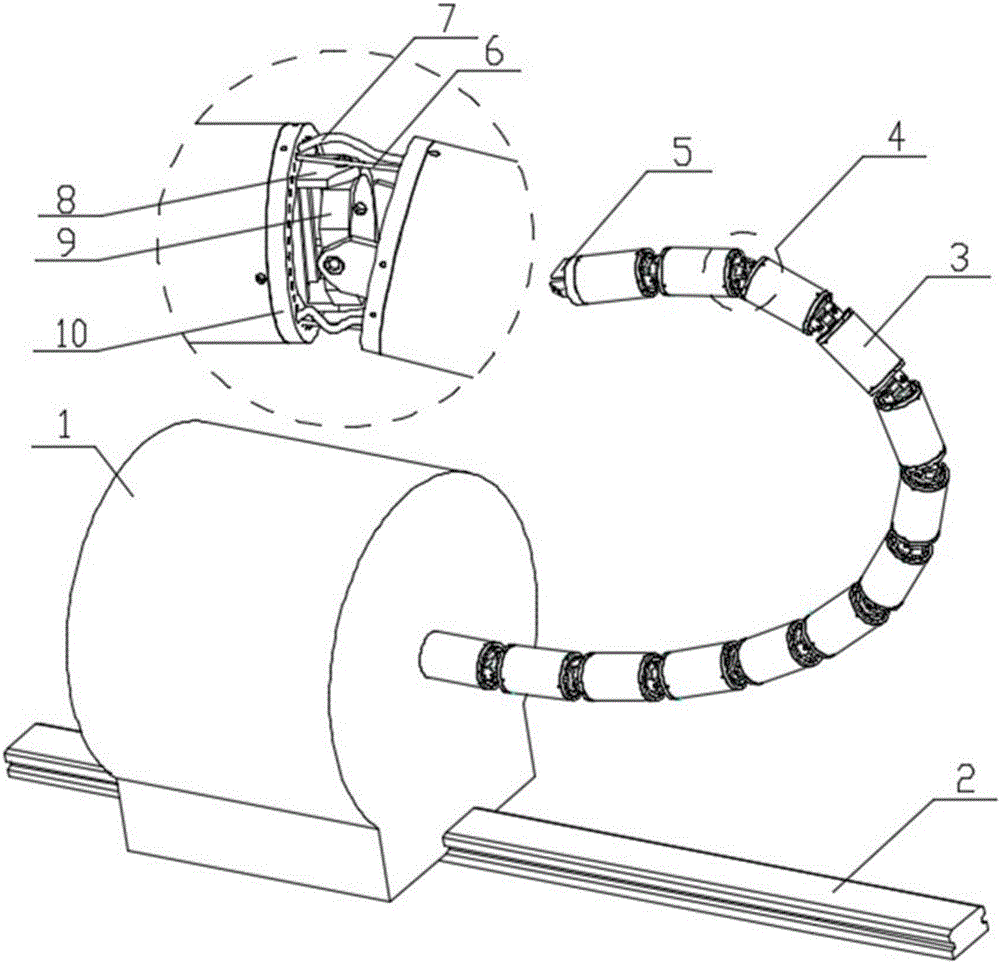
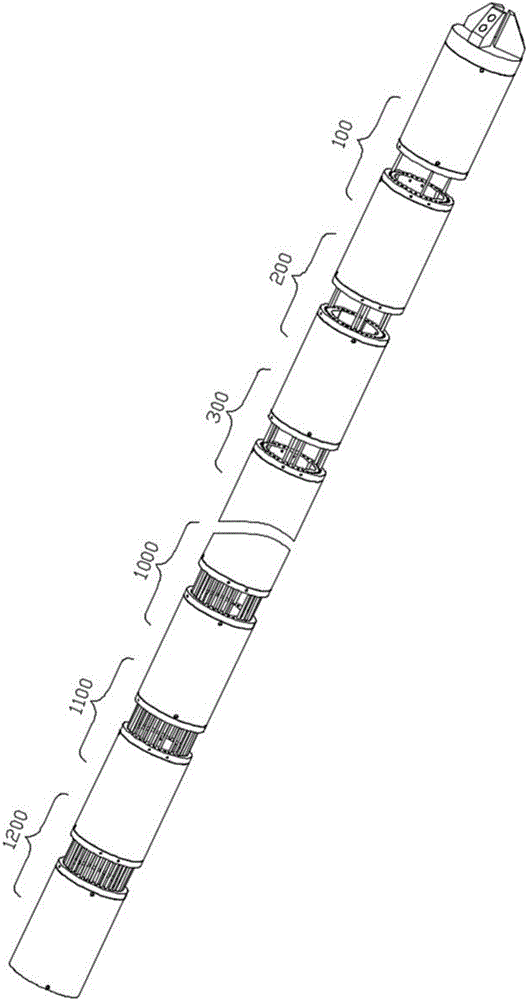
InactiveCN105014689ADoes not affect changes in rope lengthAchieving Motion DecouplingProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsEngineeringSacroiliac joint
The invention provides a motion-decoupled rope-driven non-individual body mechanical arm and a robot. The mechanical arm comprises mechanical arm sleeves, traction rope sets and knuckles, wherein the number of the mechanical arm sleeves, the number of the traction rope sets and the number of the knuckles are more than one. The mechanical arm sleeves are sequentially arranged, and the adjacent mechanical arm sleeves are hinged to form a mechanical arm body through the knuckles. The front end of the mechanical arm body is used for being connected with a rope-driven base. The traction rope sets are used for driving the corresponding knuckles. The traction rope sets and the knuckles are in one-to-one correspondence. One end of each traction rope set is connected with the corresponding knuckle, and the other end of each traction rope set is used for being connected with the rope-driven base after sequentially penetrating through through-holes in multiple knuckle rope guiding discs arranged on the front side of the corresponding knuckle. The mechanical arm has multiple degrees of freedom, is thin and long in body type and suitable for survey and operation in narrow spaces, and has large application potential.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Hinge for extended grabber tool
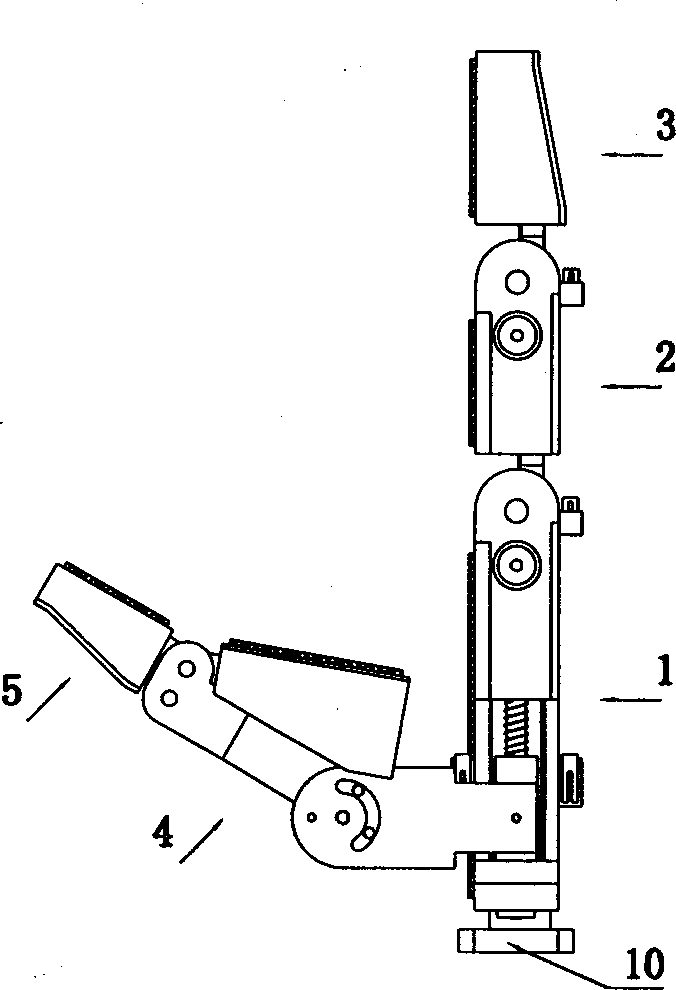
An elongate engagement tool that has engagement elements located on a distal end of a first rod, a handle on the proximate end of second rod, a controller on the handle to control the engagement elements, and a linkage between the controller and engagement elements to control the engagement elements is disclosed. The rods are connected together by a locking hinge. A locking pin is received by the knuckles of the hinges has a plurality of axial segments. The profiles of the axial segments alternate from round disks to aster shaped disks that closely fit into the apertures formed by the knuckles. When the locking pin is moved to a first locked position where the aster shaped profiled sections are aligned with the apertures in the corresponding knuckles to the hinge is locked. Movement of the pin to a second free position where the round axial sections are aligned with the apertures in the knuckles provides for limited rotational movement.
Owner:ONTEL PRODS
Apparatus, system, and process for determining characteristics of a surface of a papermaking fabric
Apparatuses, processes, and systems for implementing techniques for determining characteristics of a papermaking fabric. The techniques include forming a representation of a portion of the surface of the fabric, with the representation showing the knuckles and pockets in the surface. The representation can be formed, for example, in pressure measurement film, in wax paper, or as a photograph. An image is generated from the representation, and the image is analyzed to determine characteristics of the surface of the fabric, such as knuckle sizes and pocket sizes. The depth of pockets in the fabric can also be determined. The techniques can be used in processes for analyzing wear of a fabric, and for obtaining a fabric for making a paper product with a particular three-dimensional structure.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Multi-finger hand simulating human hand for robot
An anthropometric multi-finger hand of robot is composed of palm, the first and the second knuckles of thumb and forefinger, and the first and the second joints of thumb and forefinger. The said palmand knuckles are hollow for installing joint and motor driver in them. Its advantages include fewer number of drivers, easy control small size, light weight and several actions.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Pointing device with solid-state roller
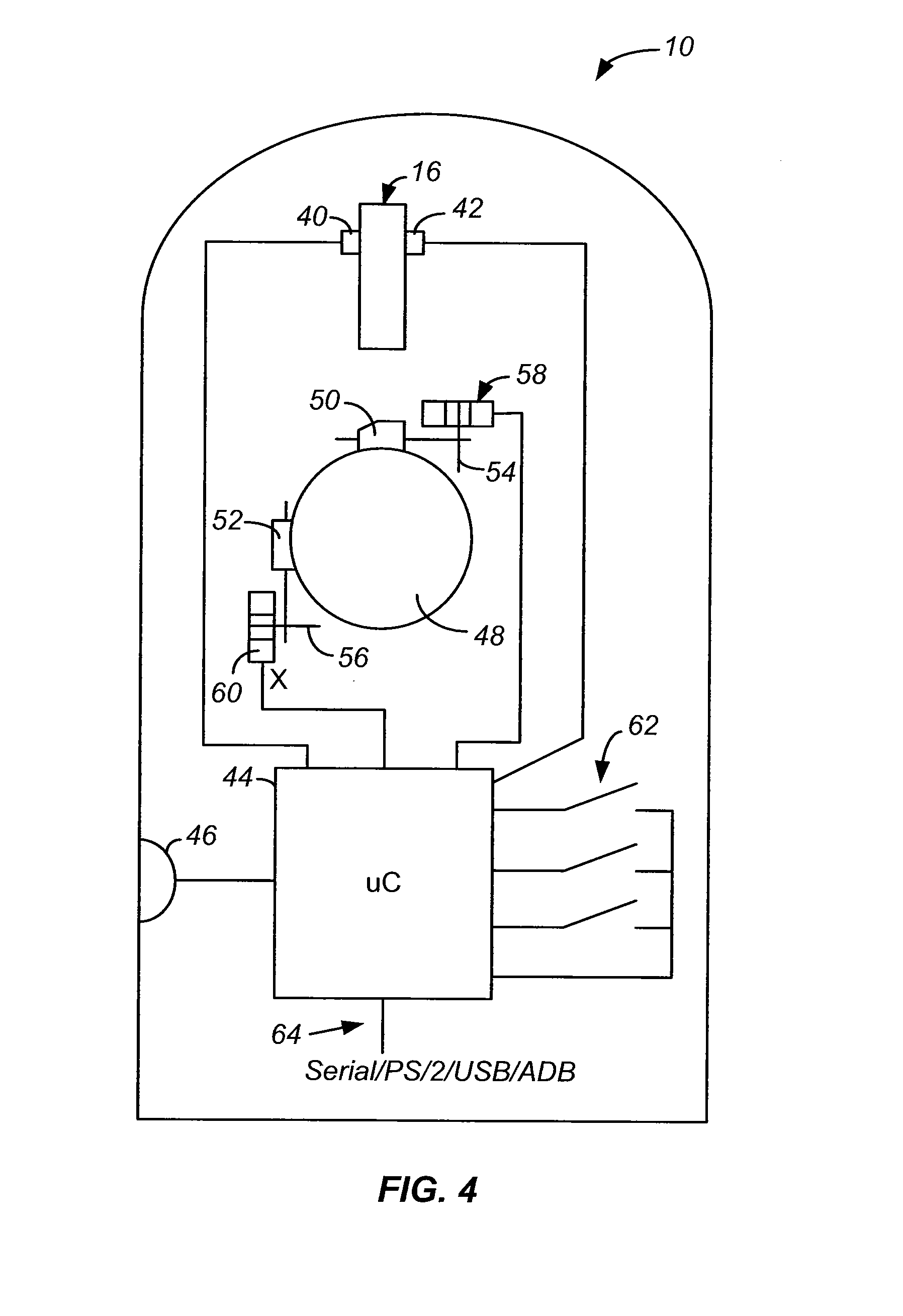
InactiveUS7170488B2Add featureCompensate for interferenceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringPointing device
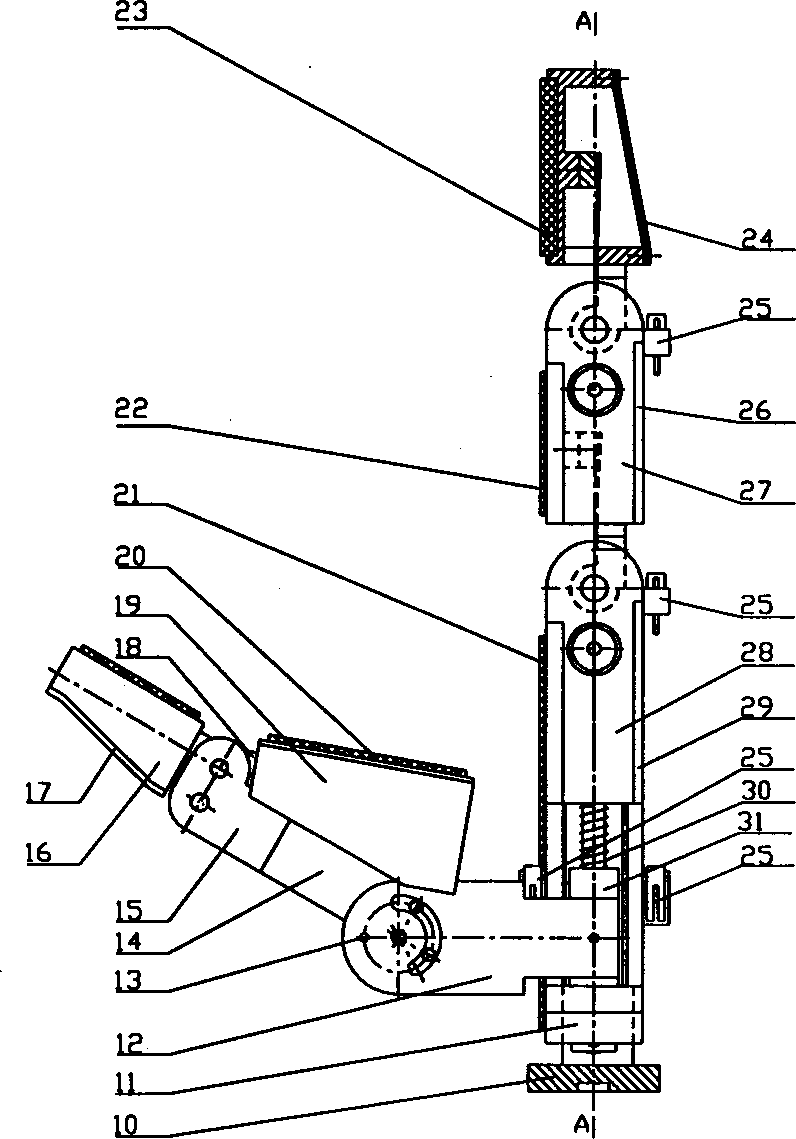
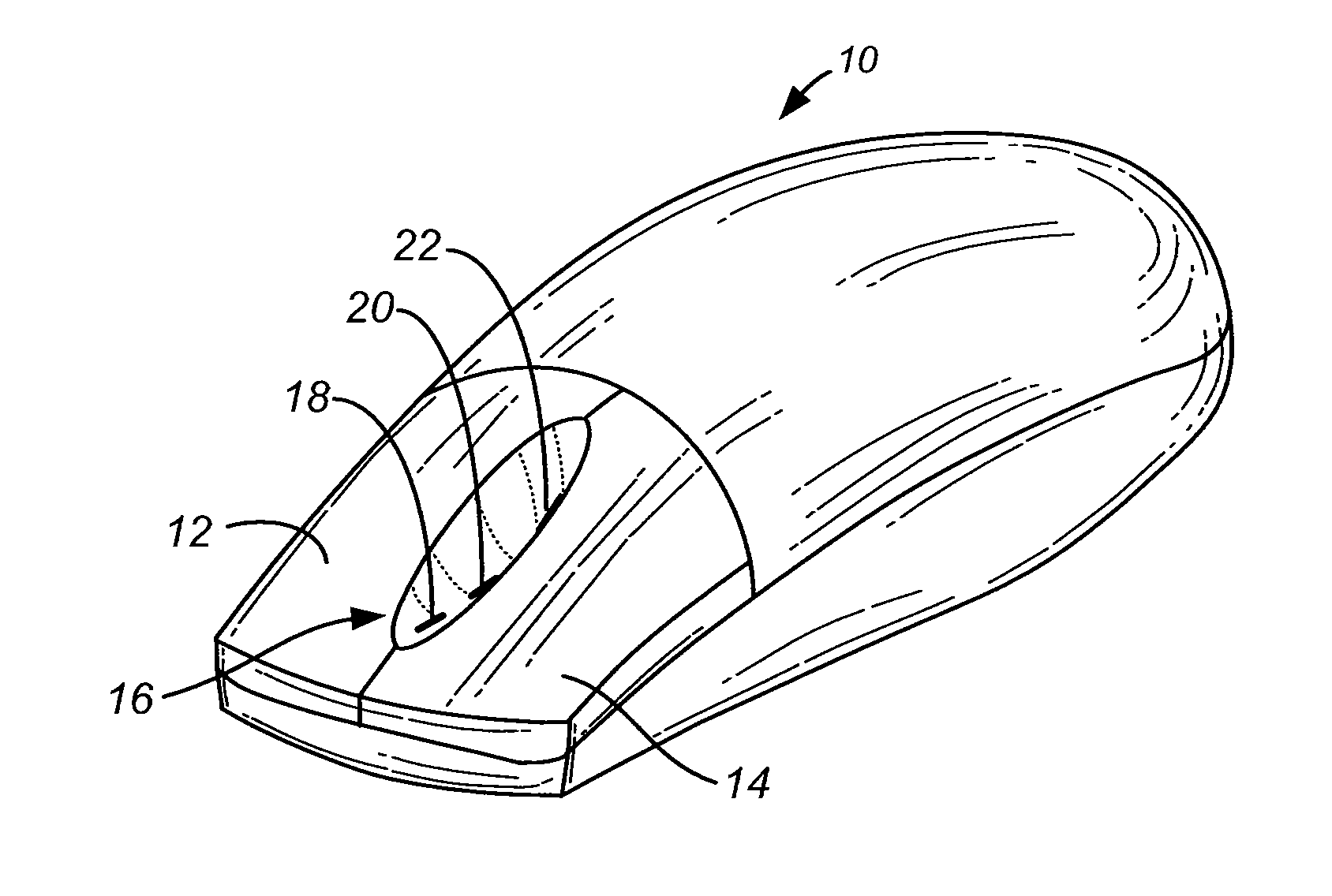
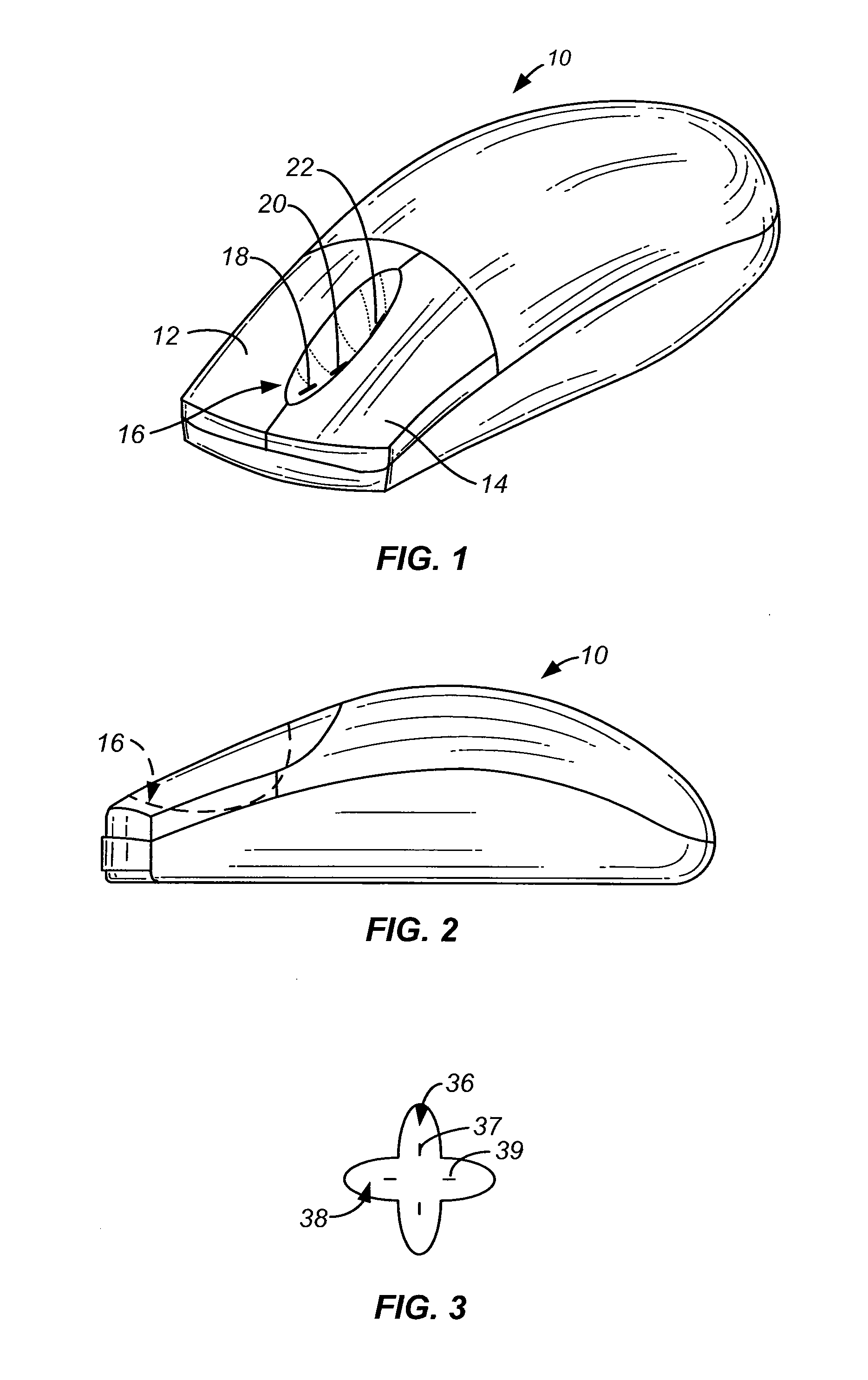
A solid-state roller on a pointing device with enhanced features. The solid-state design described herein allows the sensor to be placed on any shape of surface, such as one that has curvature in two directions. In one embodiment, a trench or downward curve contains sensors for detecting finger movement. The user's finger can thus bend about a knuckle in a curved motion to activate the sensor, requiring little or no movement of the finger up and down. The solid-state sensors can be of one of a number of designs. In one embodiment, multiple electrodes are contacted by a finger as it moves. Each electrode is coupled to a capacitive detection circuit, for detecting the change in capacitance as the electrode is contacted by the finger.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com