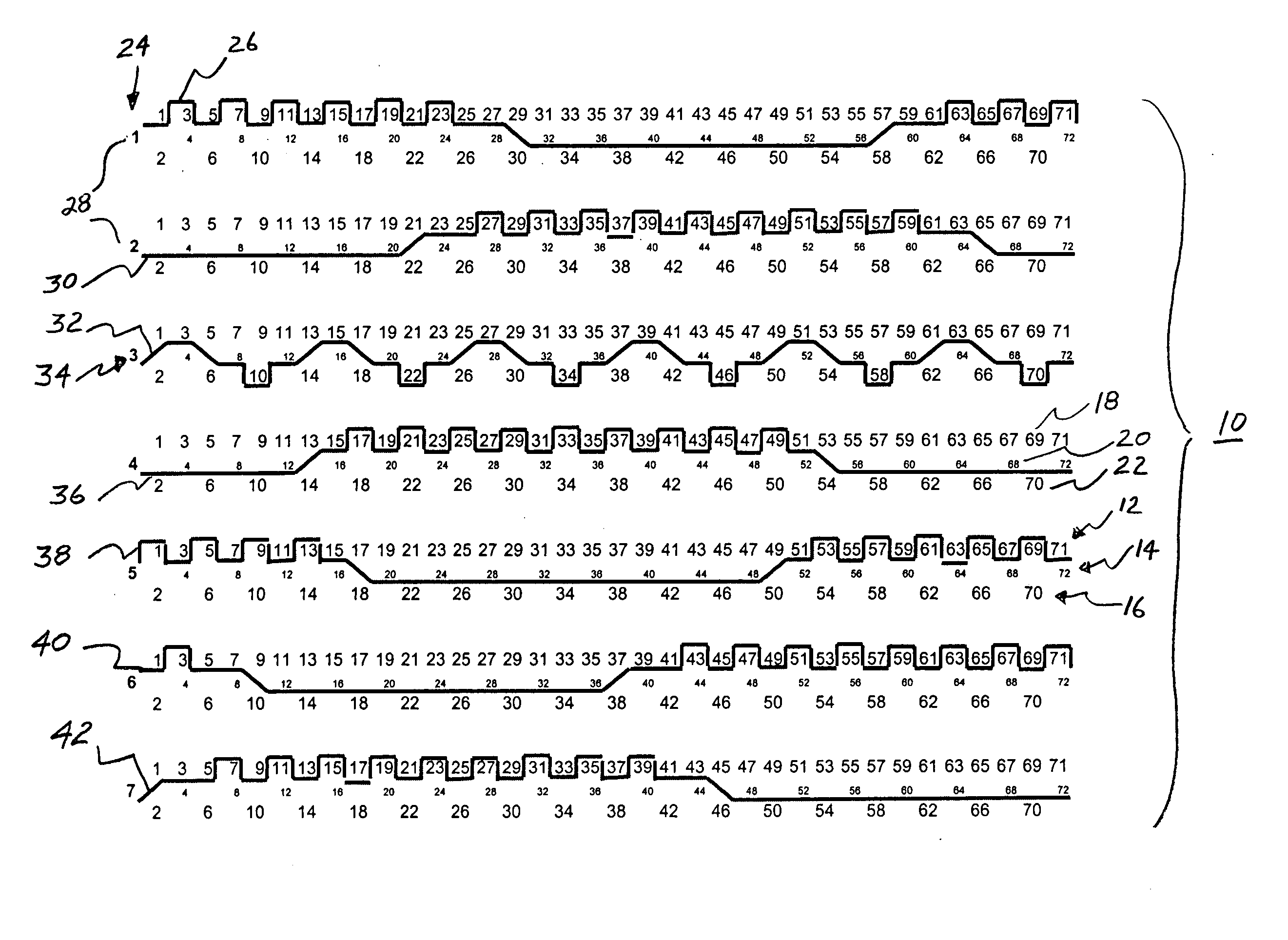
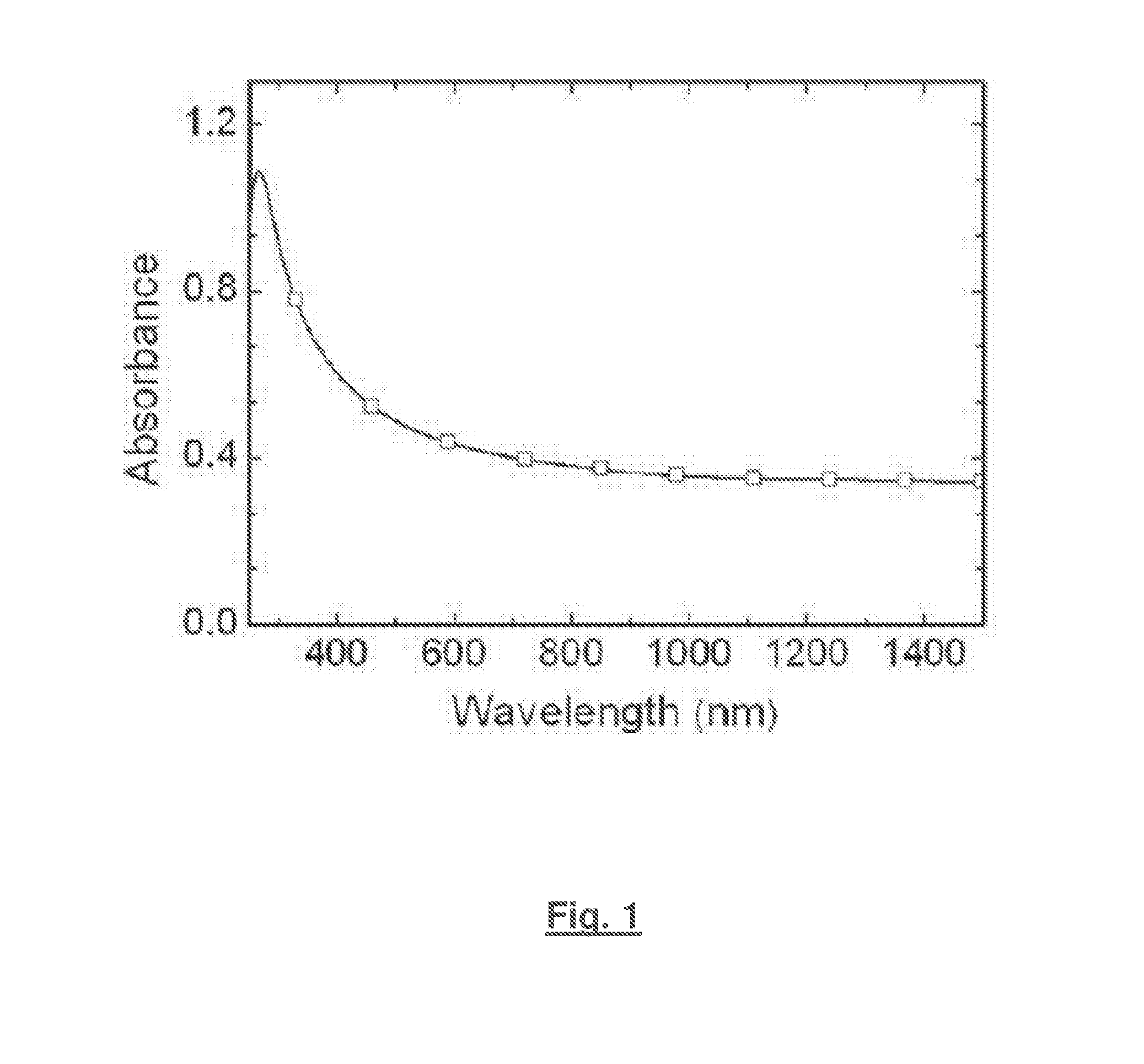
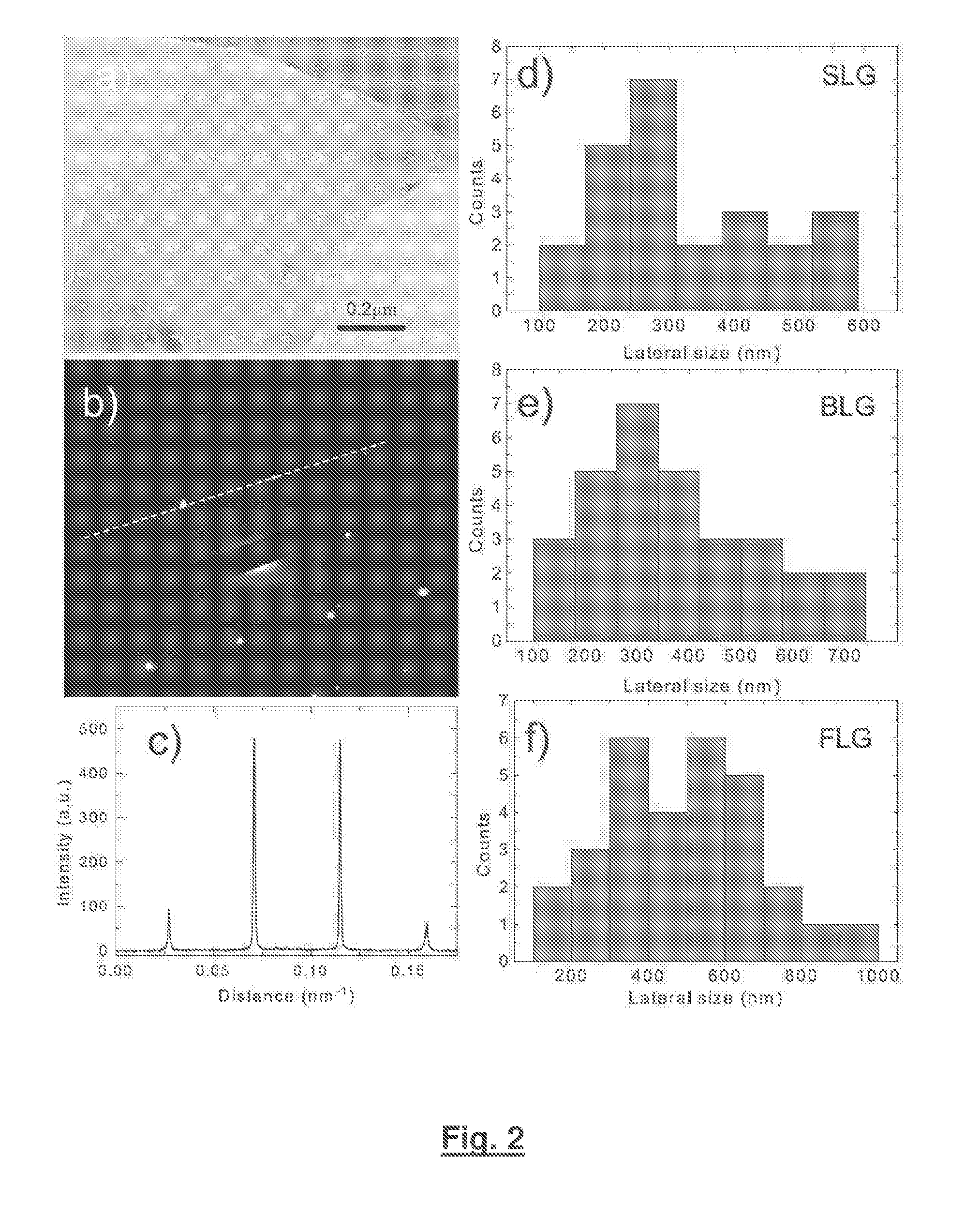
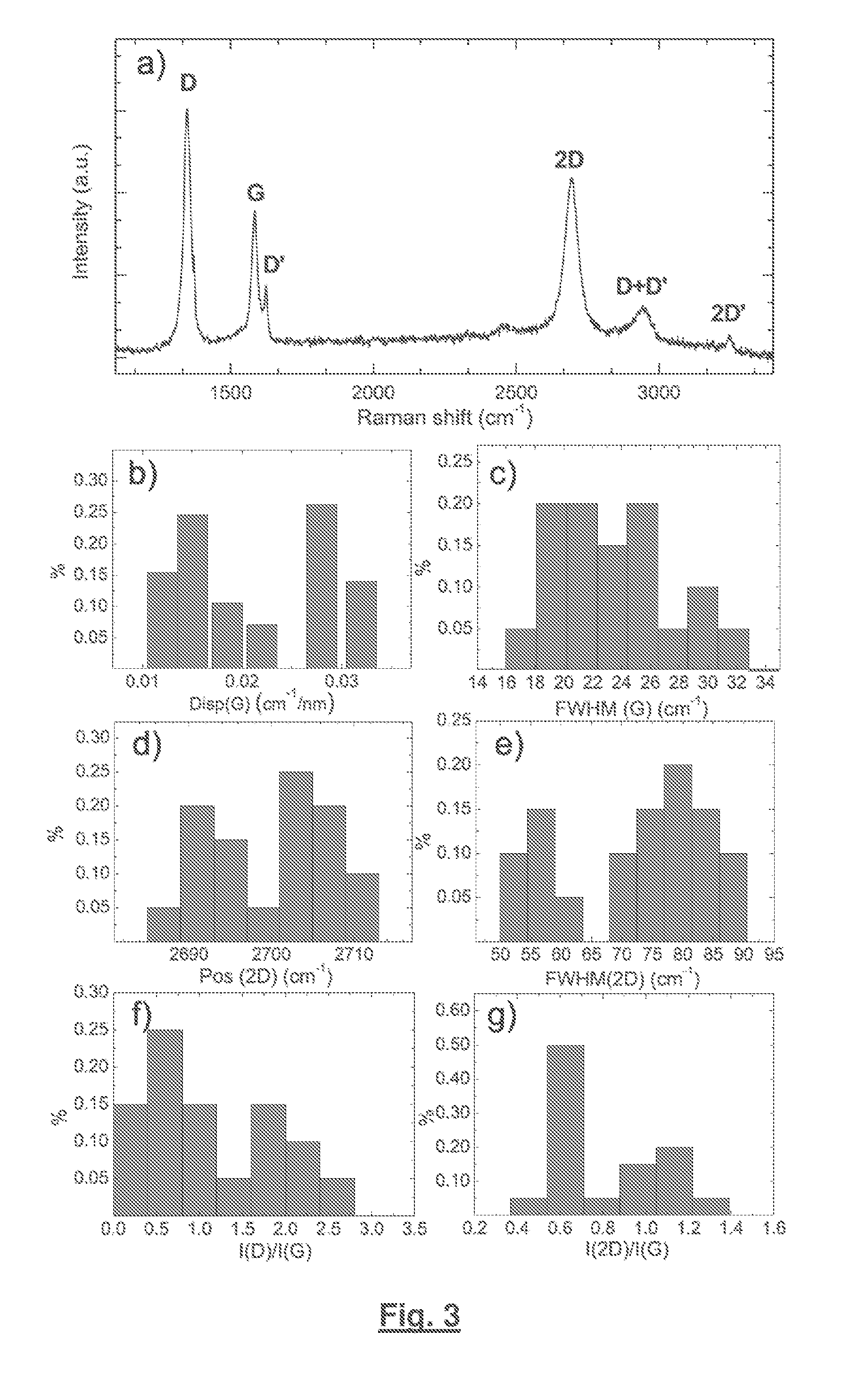
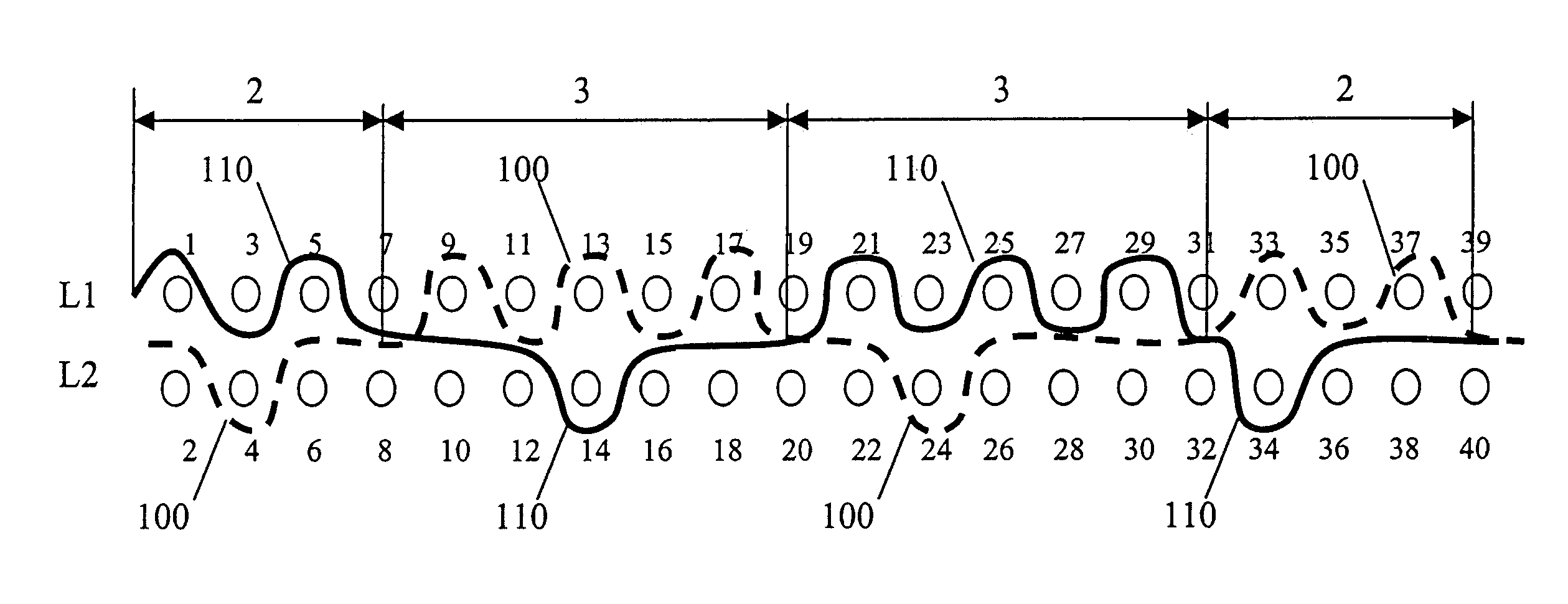
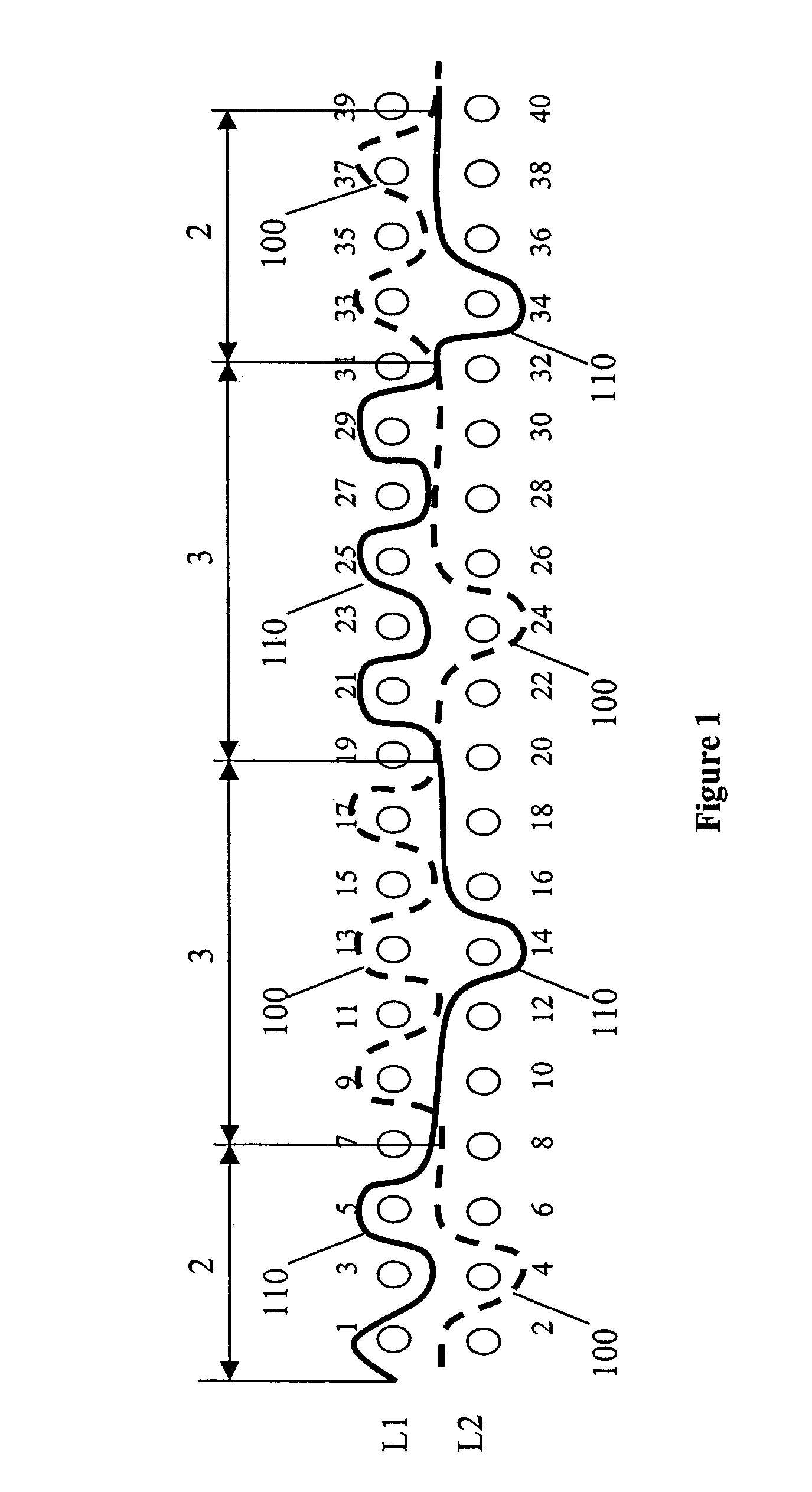
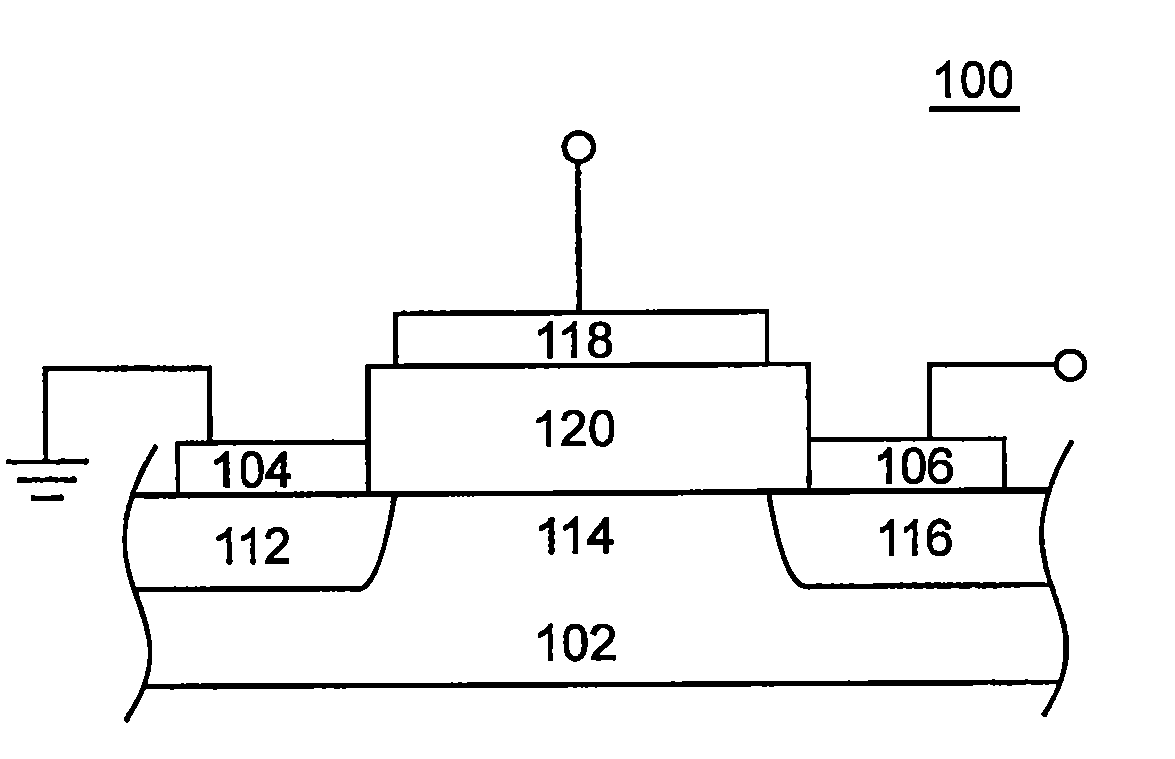
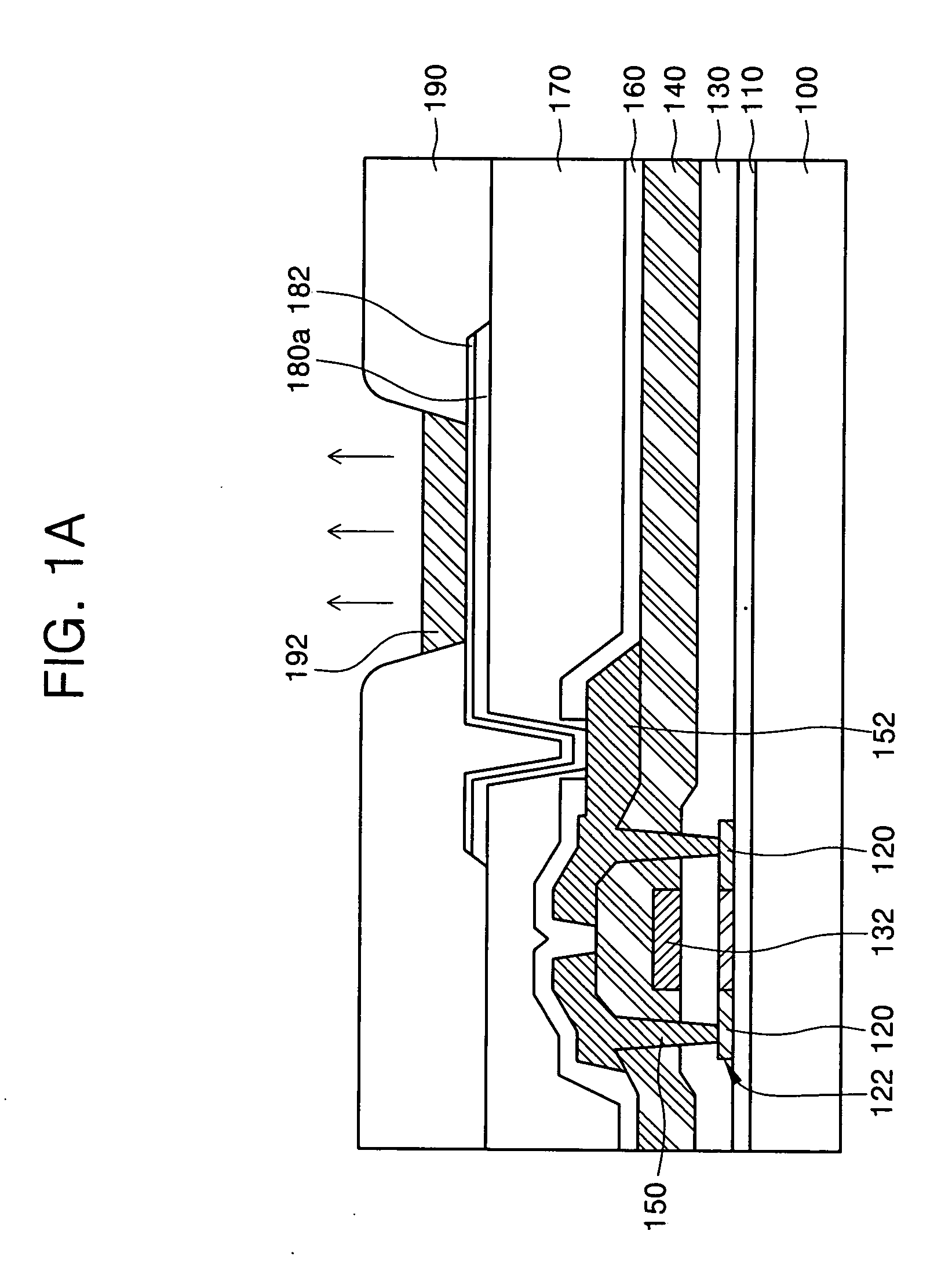
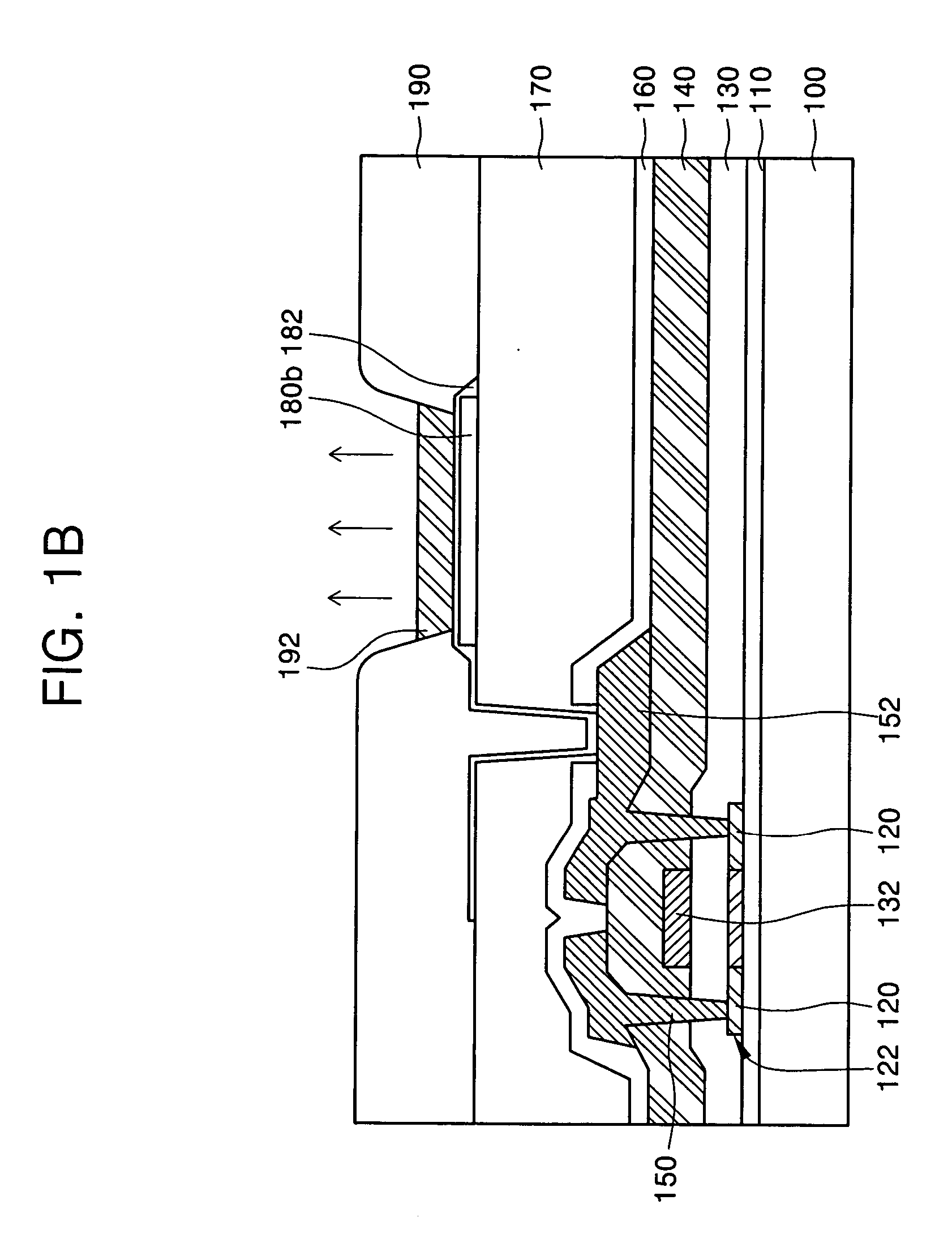
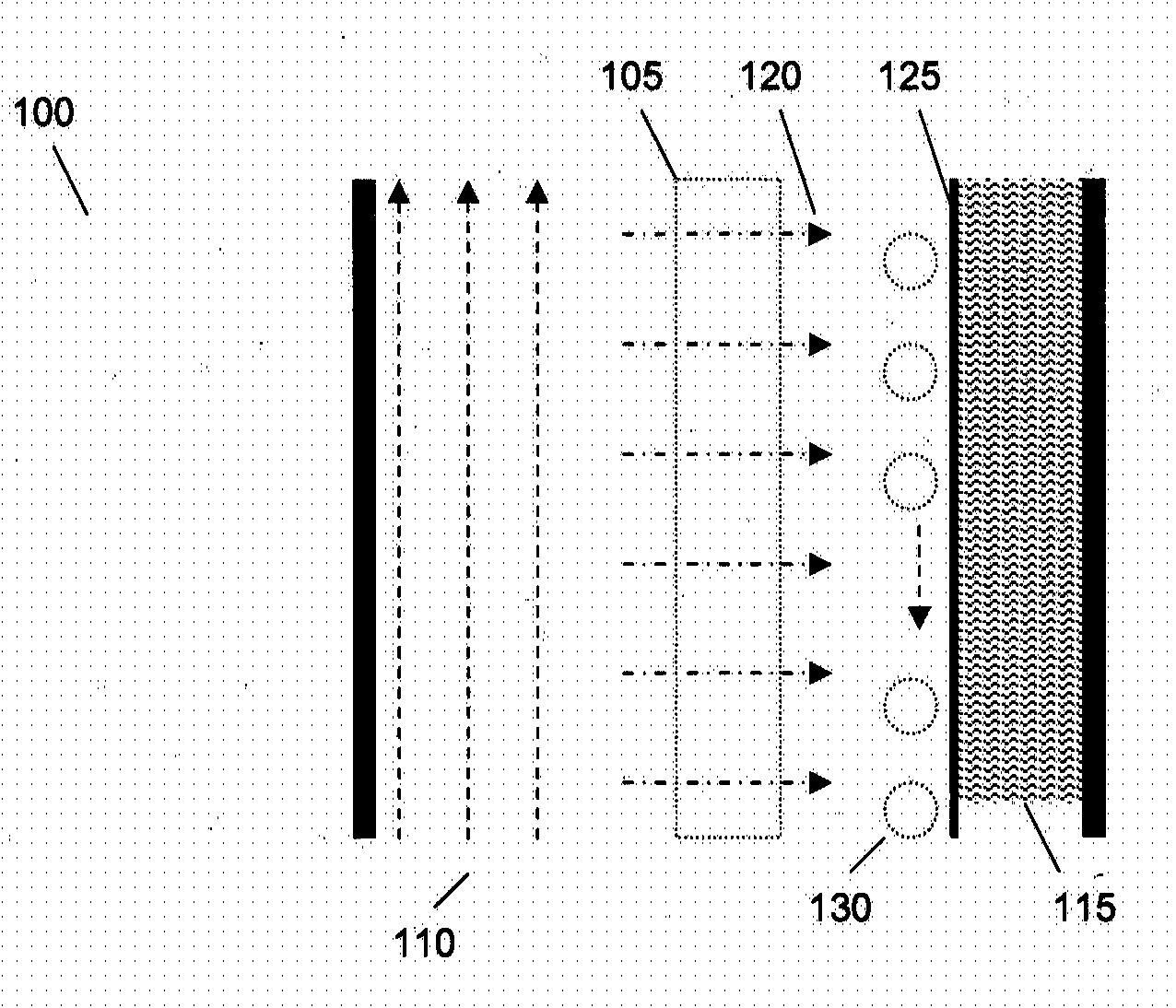
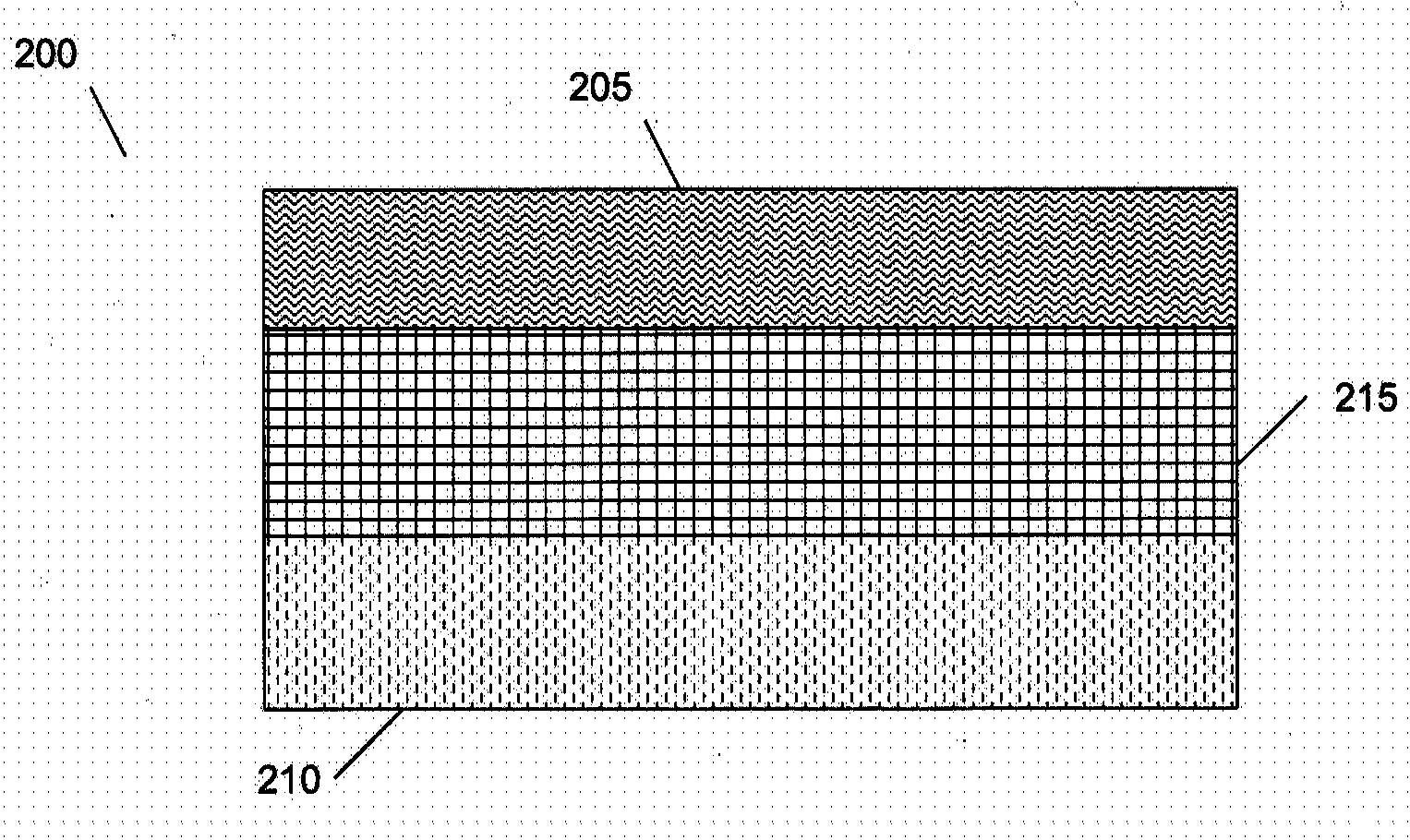
Patents
Literature
164 results about "Triple layer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
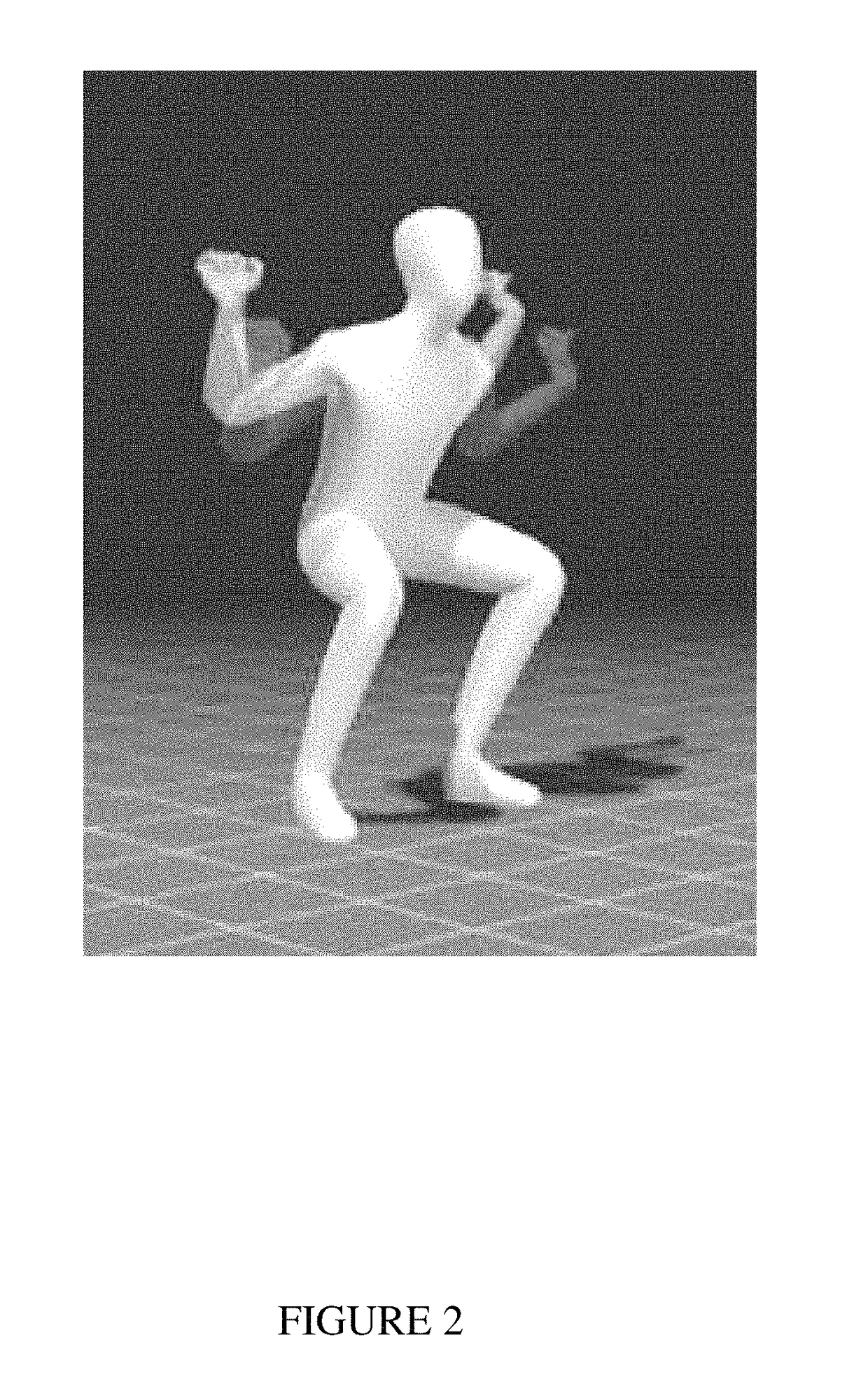
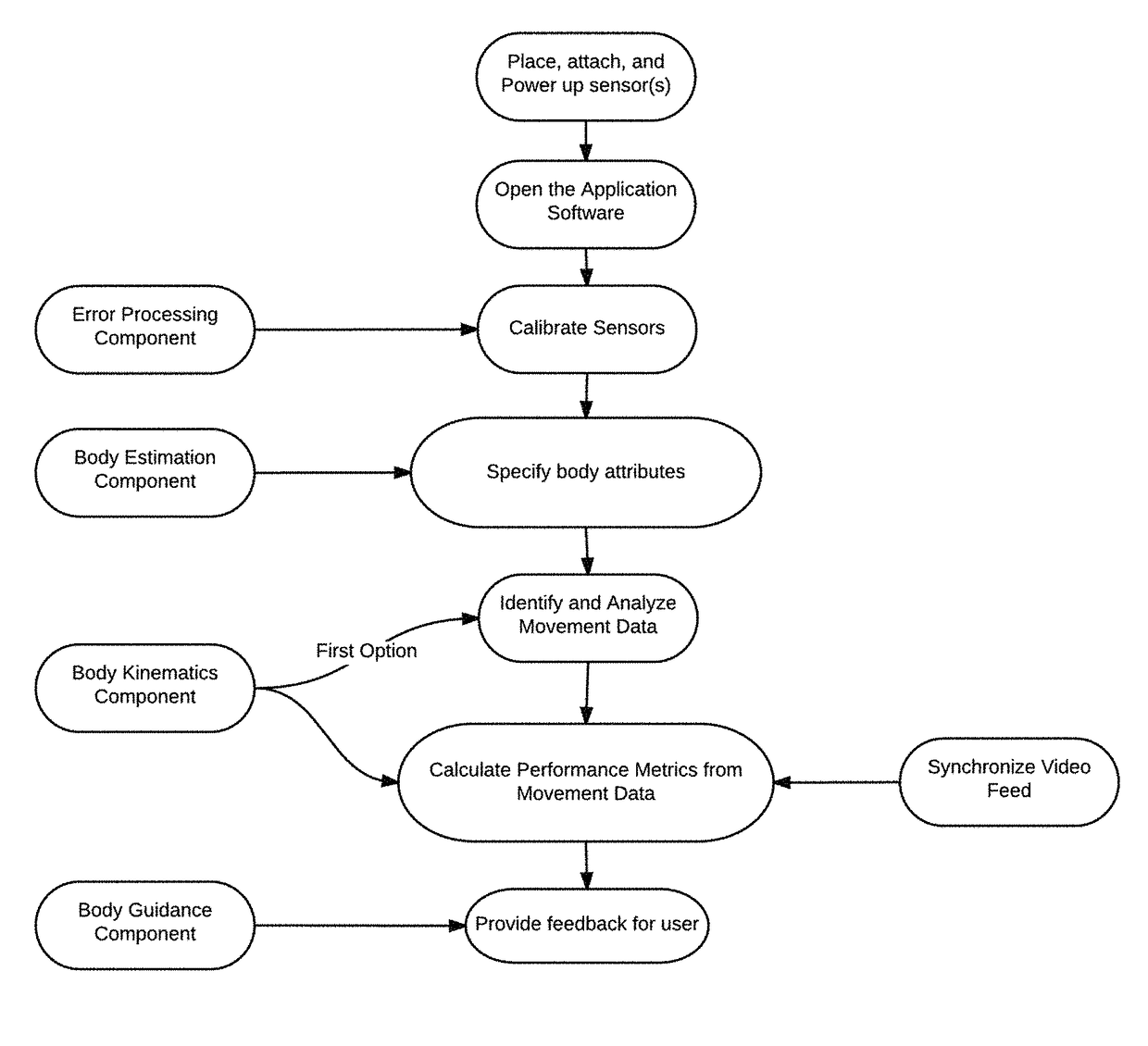
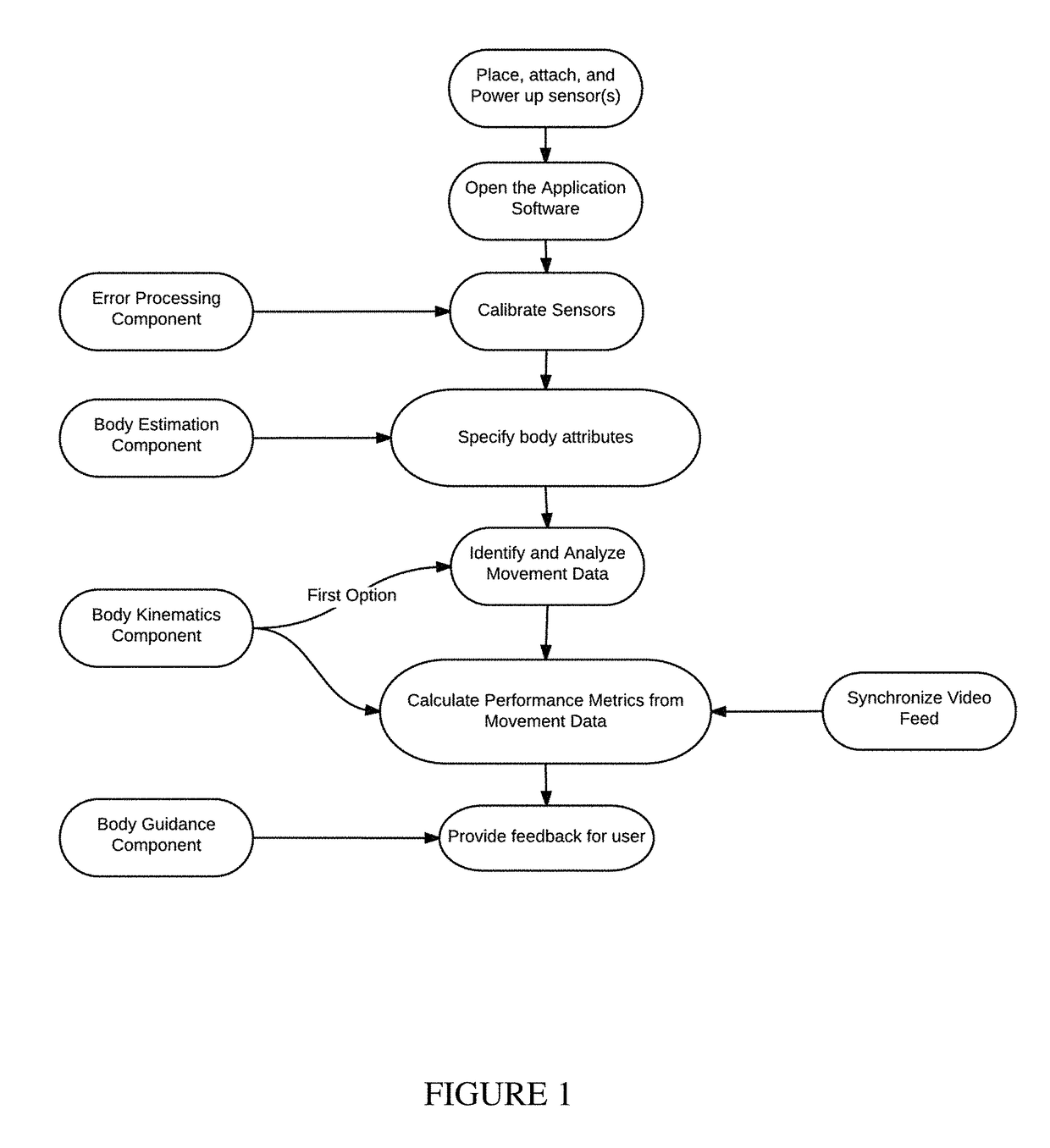
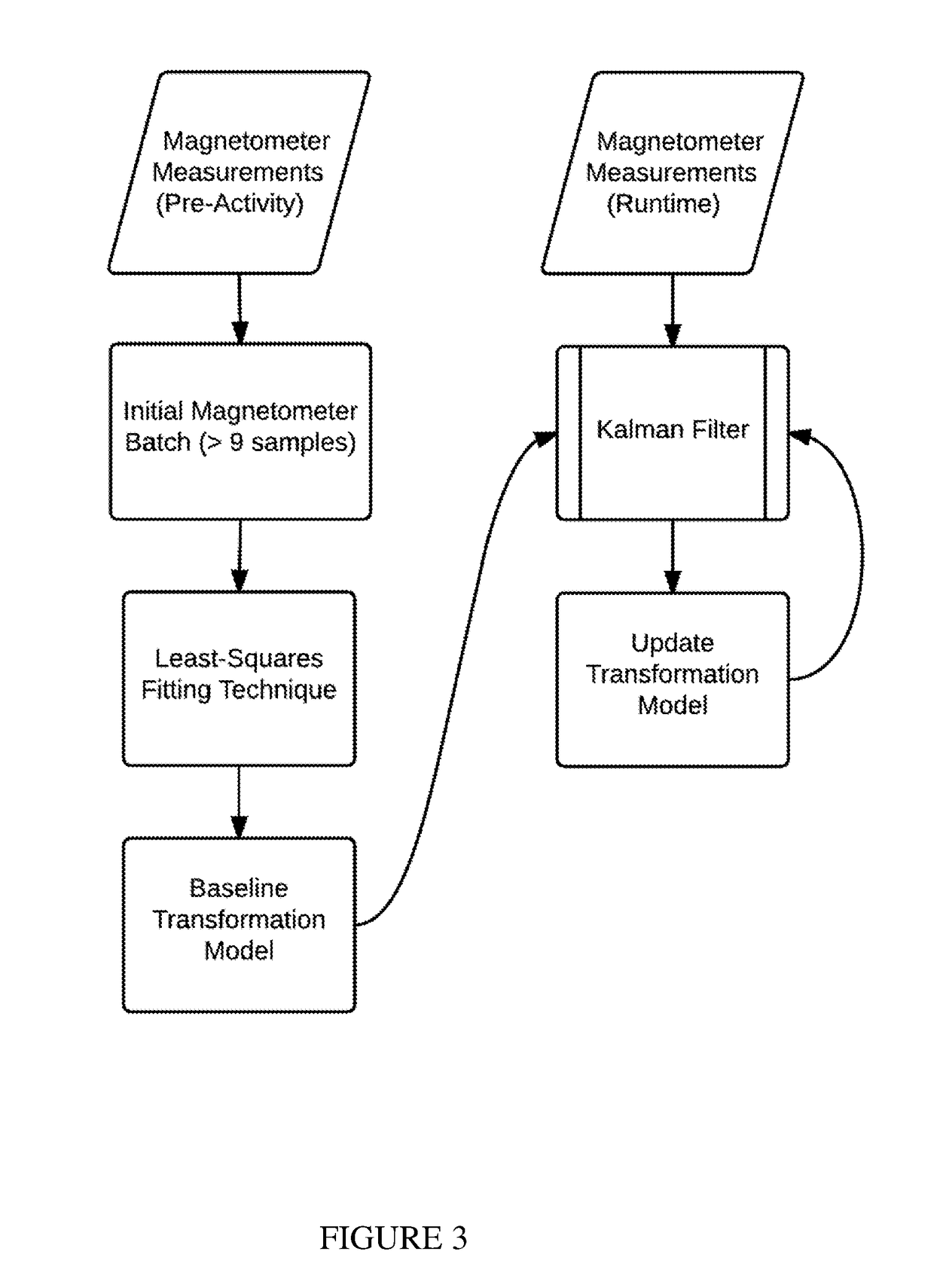
Training systems with wearable sensors for providing users with feedback
InactiveUS10065074B1Accelerated trainingEnhance coachingPhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationMultiple sensorHuman motion
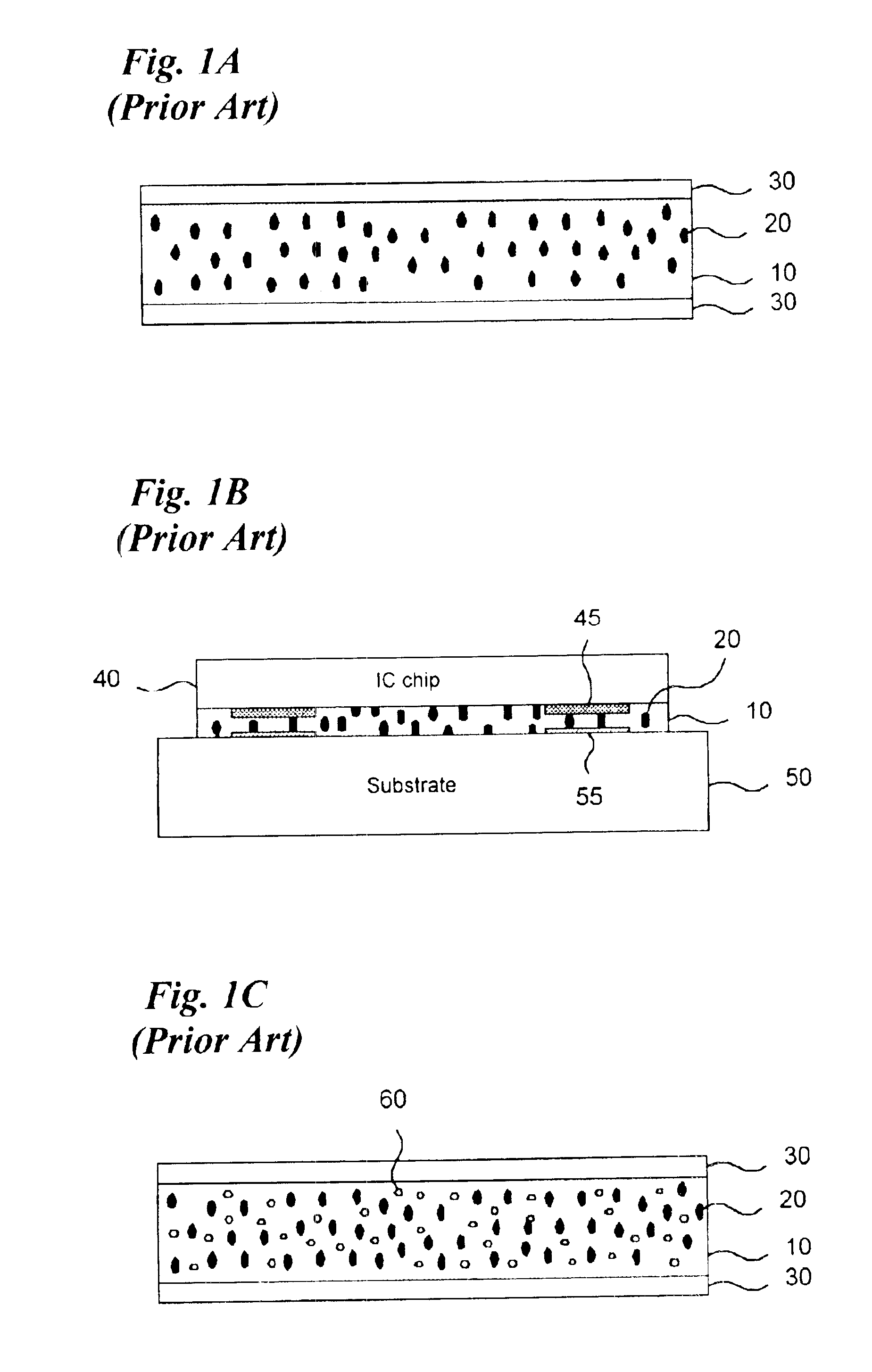
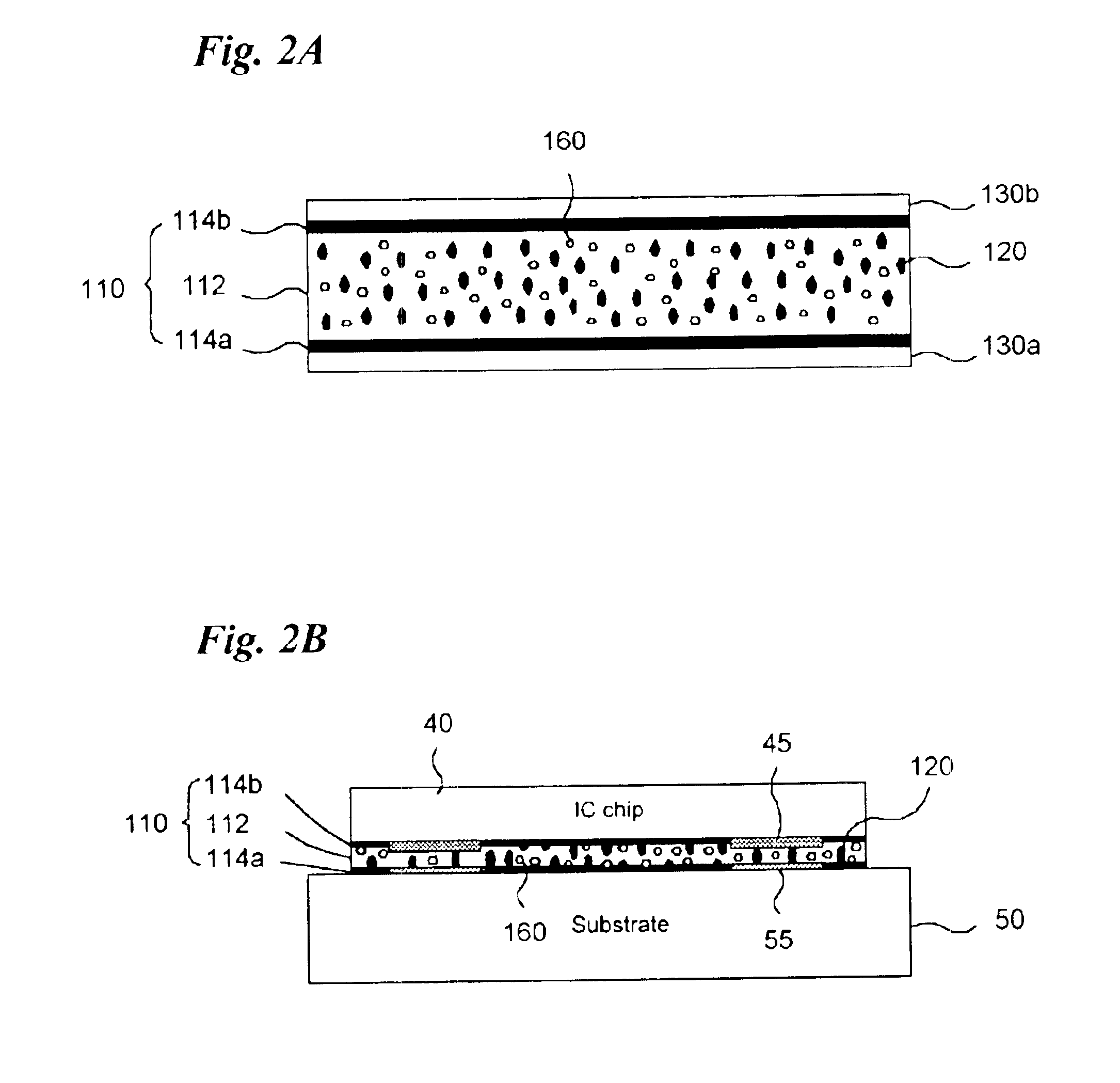
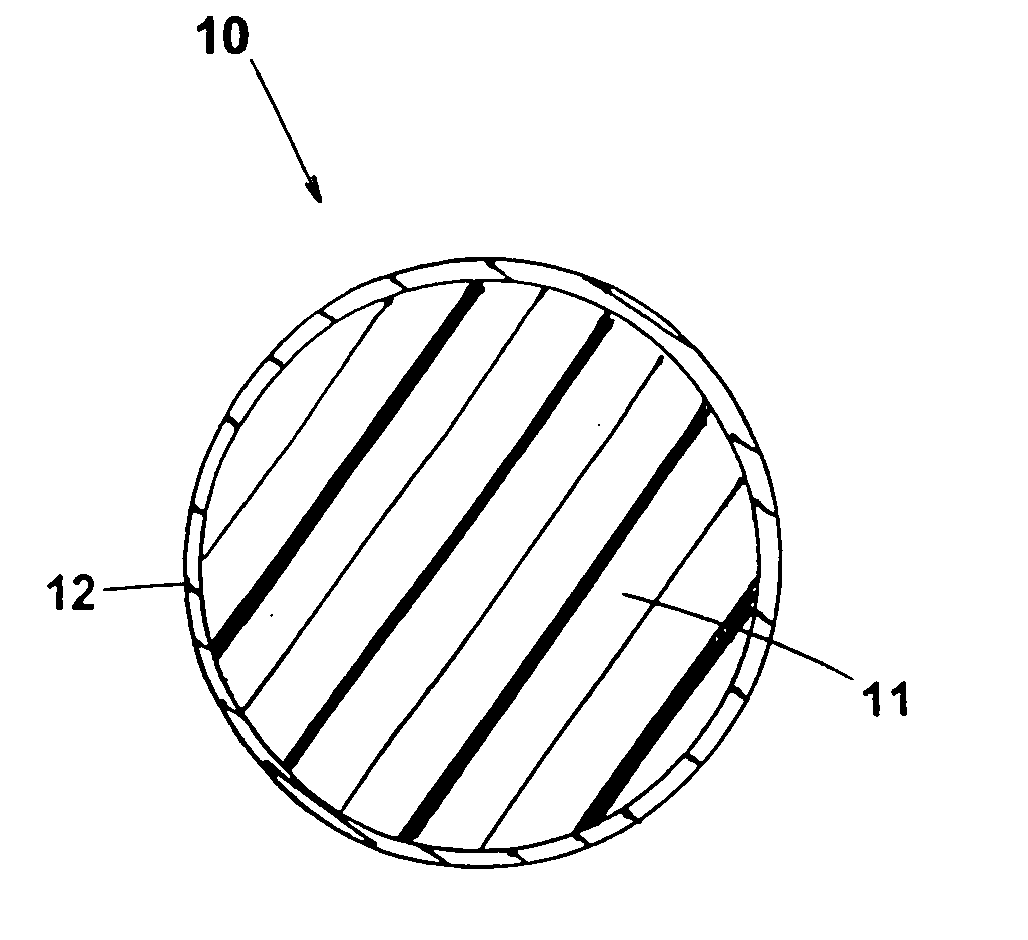
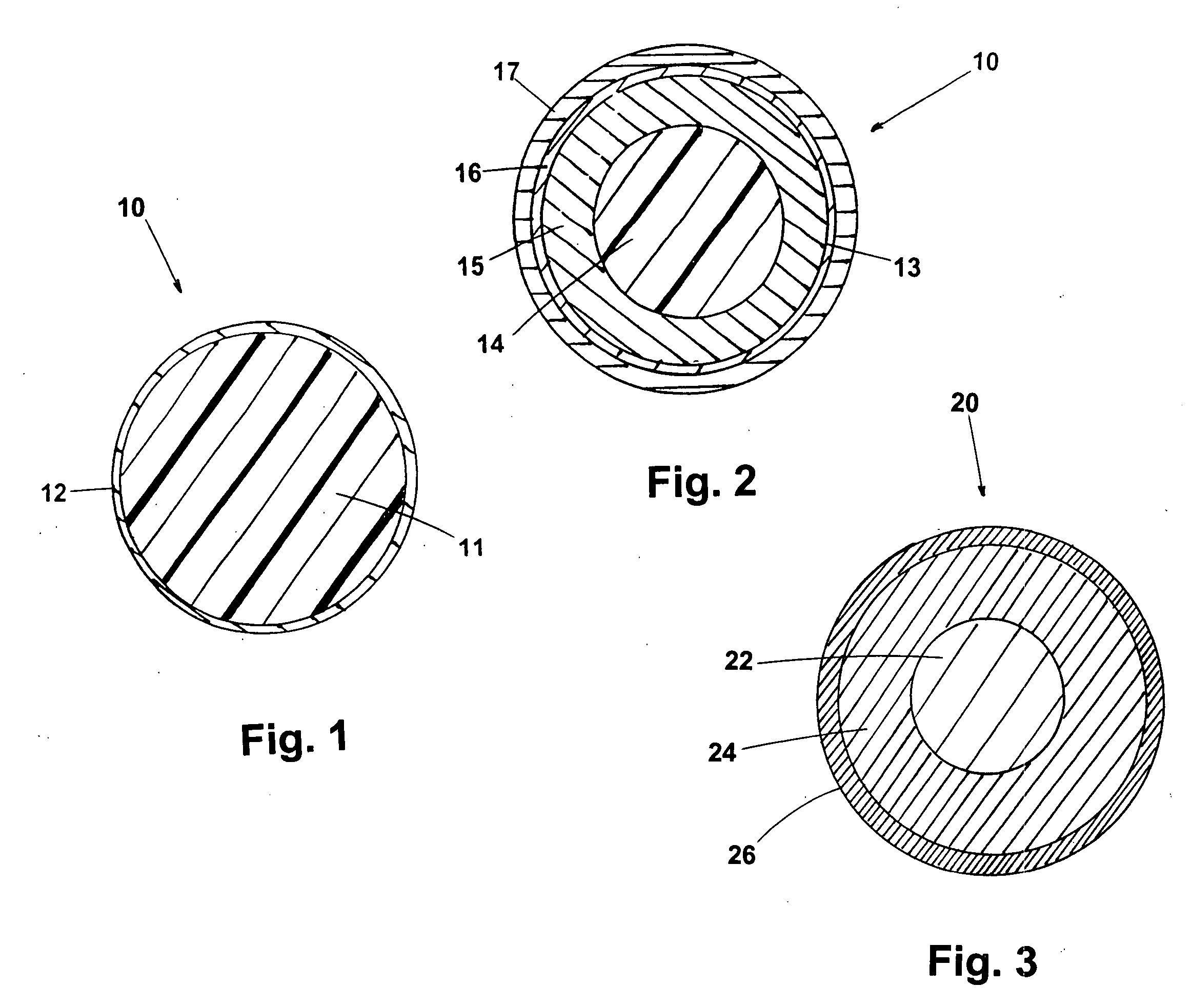
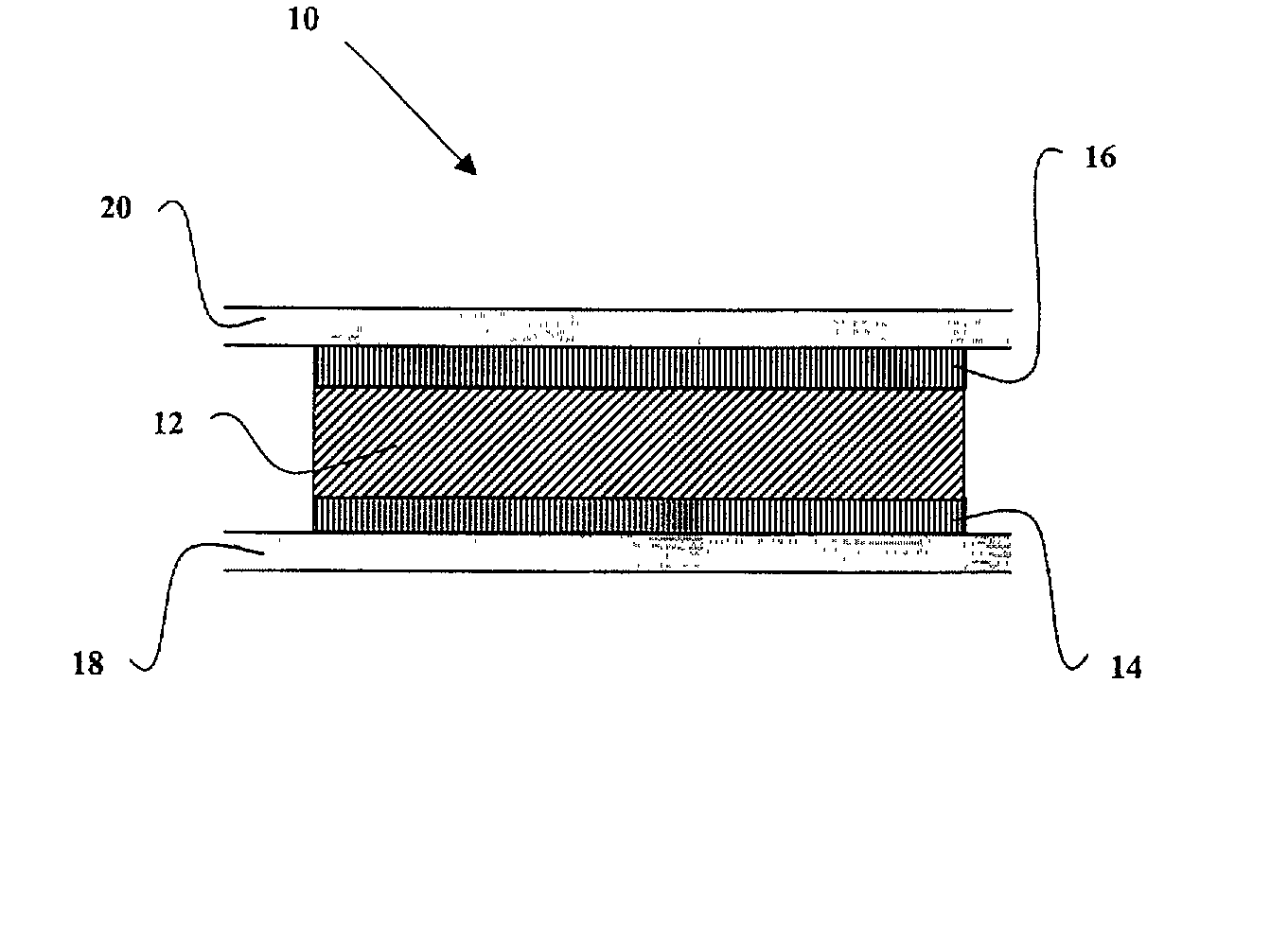
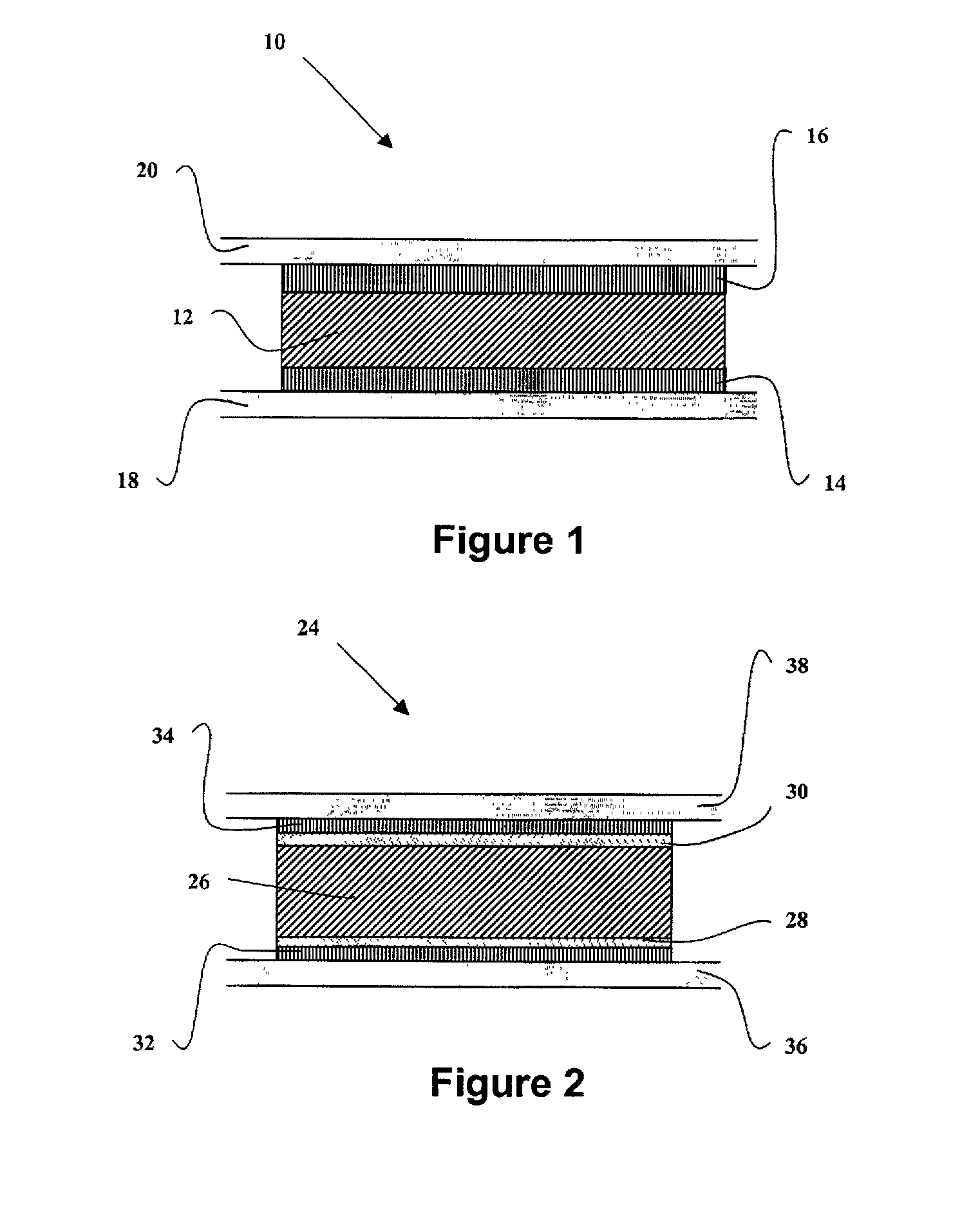
A training system based on mobile technology and kinematics of human motion characterizes, analyzes, and supplies feedback to a user based on the user's movements. The training system includes a garment having a sensor control module connected to multiple sensor nodes via electrically-conductive fabric running along parts portions of the garment. The sensor module / nodes can communicate through the conductive fabric. The sensor nodes acquire motion and / or physiologic readings that are wirelessly transmitted to a mobile computing device that runs an application that analyzes the data and provides visual (e.g., graphs, 3D avatar) and audio feedback (e.g., voice prompts). Vibration motors and LEDs / electroluminescent fabric in the garment also provide notifications and alerts. The triple layer of garment, conductive fabric, and sensor module / sensor node are sealed against contaminants, allowing the garment to be washable.
Owner:ENFLUX INC
Electron blocking layers for electronic devices
InactiveUS20080150003A1Improve performanceEnhancement of charge retention propertySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCharge retentionHafnium
Methods and apparatuses for electronic devices such as non-volatile memory devices are described. The memory devices include a multi-layer control dielectric, such as a double or triple layer. The multi-layer control dielectric includes a combination of high-k dielectric materials such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3), hafnium oxide (HfO2), and / or hybrid films of hafnium aluminum oxide. The multi-layer control dielectric provides enhanced characteristics, including increased charge retention, enhanced memory program / erase window, improved reliability and stability, with feasibility for single or multistate (e.g., two, three or four bit) operation.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
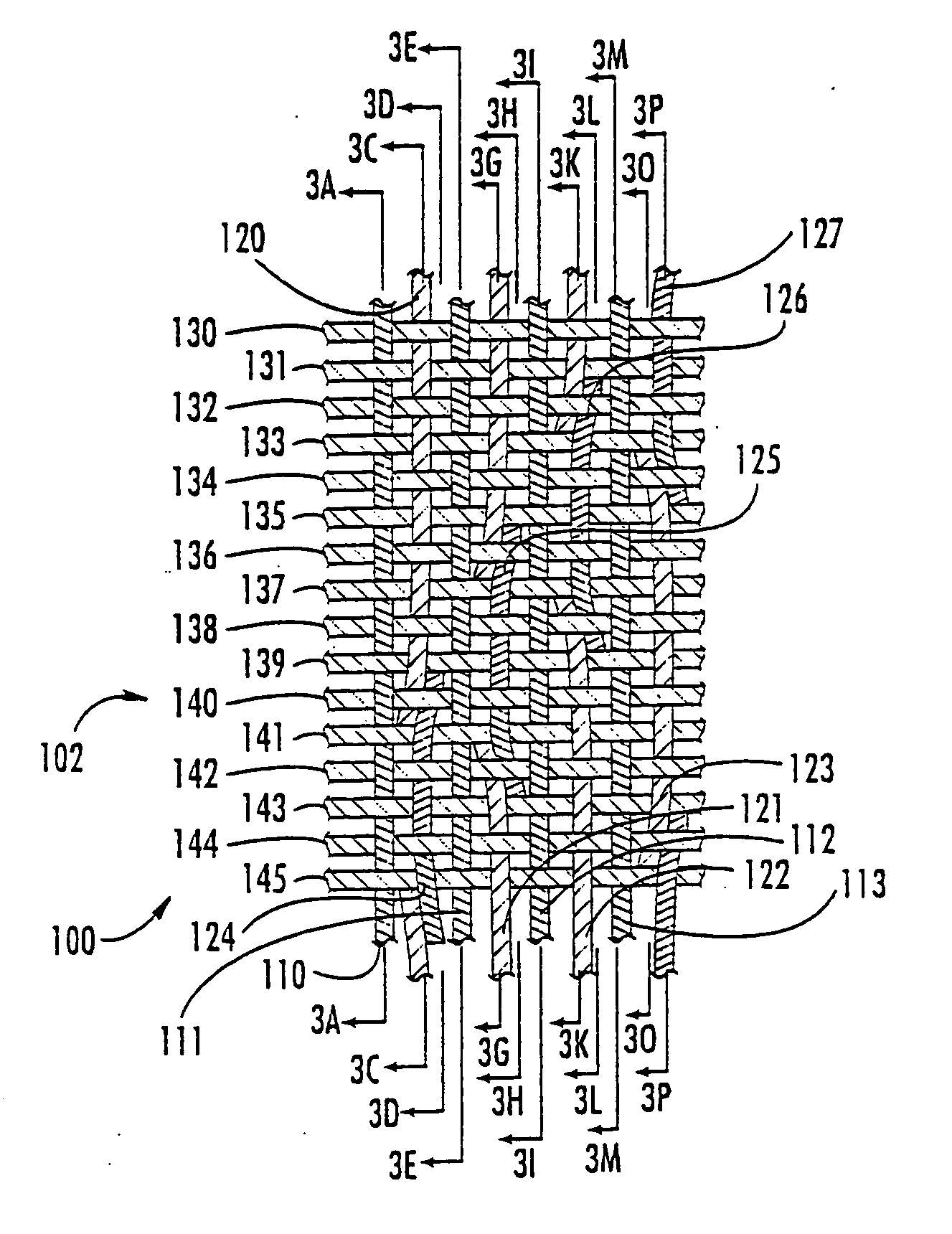
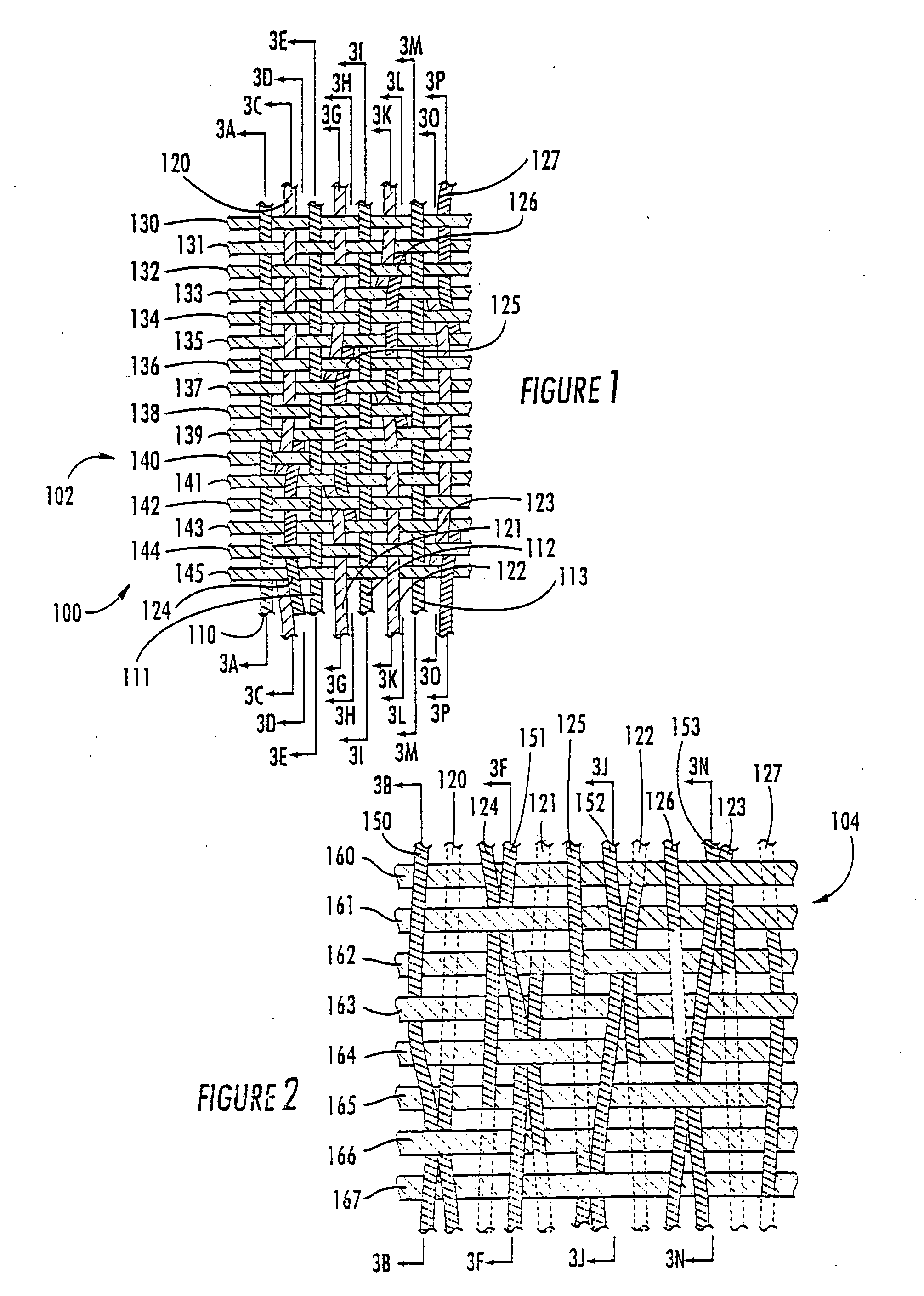
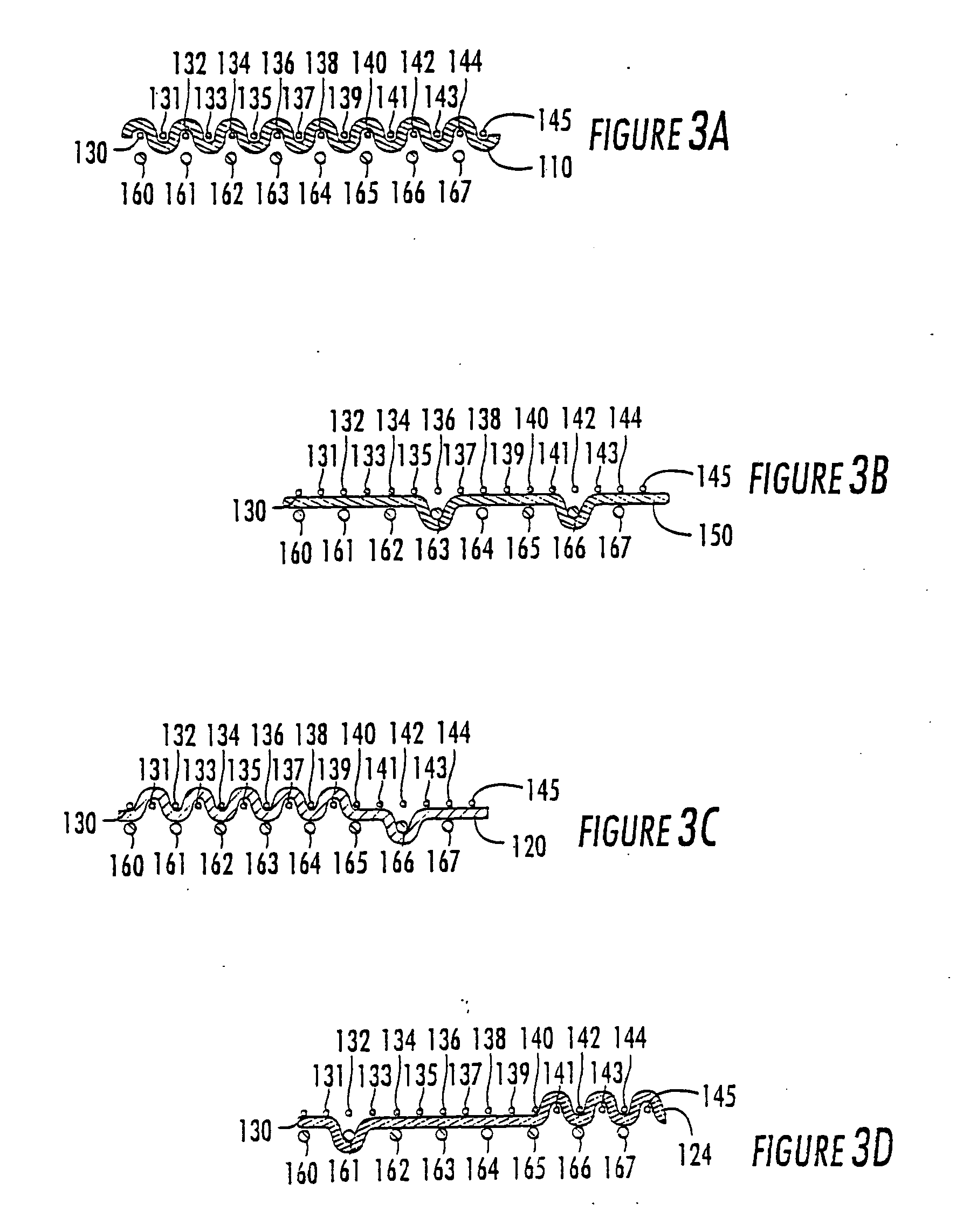
Machine direction yarn stitched triple layer papermaker's forming fabrics
InactiveUS6896009B2Excellent characteristicsImprove permeabilityPaper/cardboardMachine wet endYarnEngineering
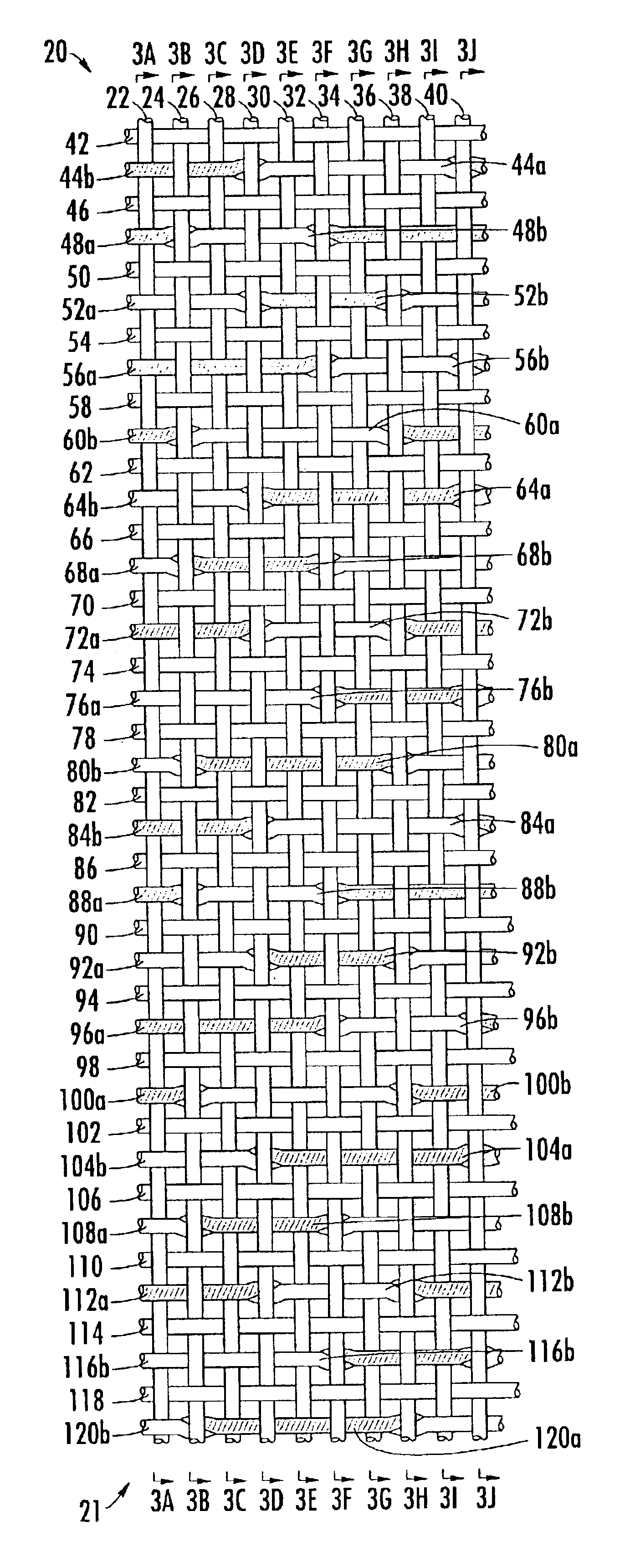
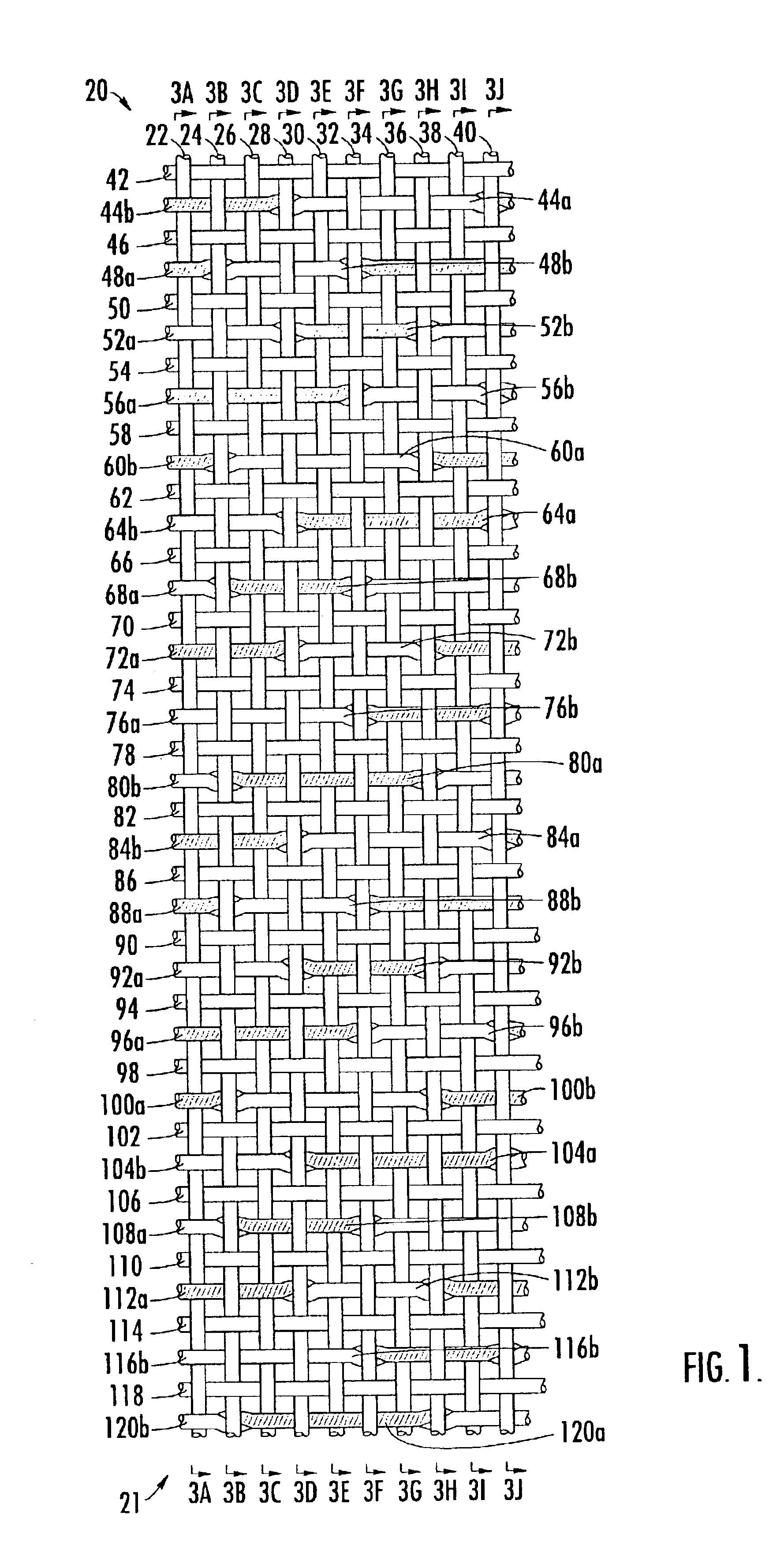
Triple layer papermaker's forming fabrics having a set of top MD yarns that are interwoven exclusively with a set of top CMD yarns to form at least part of a top fabric layer and a set of bottom MD yarns that are interwoven exclusively with a set of bottom CMD yarns to form at least part of a bottom fabric layer are provided. These fabrics further include a set of stitching MD yarn pairs. The stitching MD yarns that comprise each such pair weave in both the top fabric layer and the bottom fabric layer such that at locations where the first yarn in the pair weaves in the top fabric layer the second yarn in the pair drops down into the bottom fabric layer. In embodiments of the present invention, each stitching MD yarn may also be woven so as to form side-by-side machine direction knuckles on the bottom surface of the bottom fabric layer with a bottom MD yarn. In other embodiments of the invention, at least some of the top CMD yarns that the stitching MD yarns of the stitching MD yarn pairs pass over immediately before dropping down into the bottom fabric layer have a larger diameter and / or a higher modulus than the remainder of the top CMD yarns.
Owner:WEAVEXX
High adhesion triple layered anisotropic conductive adhesive film
InactiveUS6878435B2High bonding strengthImprove adhesionNon-insulated conductorsSolid-state devicesEpoxyAnisotropic conductive film
Disclosed is a triple layered ACA film adapted for enhancing the adhesion strength of a typical single layer Anisotropic Conductive Film or for enhancing the adhesion strength of the ACA film in flip chip bonding. The triple layered ACA film of the invention comprises: a main ACA film based upon epoxy resin and containing conductive particles having a particle size of 3 to 10 μm and optionally non-conductive particles having a particle size of 0.1 to 1 μm; and adhesion reinforcing layers based upon epoxy resin and formed at both sides of the main ACA film.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Papermaker's forming fabric
The bottom machine direction yarns and the bottom cross machine direction yarns of a triple layer fabric are interwoven in a series of repeat units in which the bottom machine direction yarns pass below multiple nonadjacent bottom cross machine direction yarns to form bottom machine direction knuckles, and in which pairs of bottom machine direction yarns separated from one another by one bottom machine direction yarn form bottom machine direction knuckle pairs under a common bottom cross machine direction yarn. Each bottom machine direction knuckle pair forms two imaginary diagonal lines with a nonadjacent bottom machine direction knuckle pair such that each bottom machine direction knuckle pair in the diagonal lines is offset by two cross machine direction yarns and one bottom machine direction yarn.
Owner:WEAVEXX
Infrared heating method for creating cure gradients in golf balls and golf ball cores
This invention is directed to a method for creating a triple layer like golf ball core out of a single material. A thermoset material is cured for only a partial period of time in a compression mold, therein creating a short-cured core wherein the innermost region of the core is substantially softer than the outer region. Subsequently, the short-cured core is heated with infrared radiation to create a cure gradient in the skin of the core. This results in a relatively hard skin, which is at least 2 Shore D points harder than the rest of the core. The hardness gradients created in the skin are in the range of about 0.005 inches to about 0.040 inches.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Carton and handle in multi-ply carton material
ActiveUS20110233091A1High strengthImprove structural supportFlexible coversWrappersMajor and minorTriple layer
A carton blank is assembled into a carton for beverage containers, the blank having a number of panels including a top panel, a bottom panel and a pair of side panels each joined by a fold line to an adjacent one of the panels. A number of end flaps are each joined by an end flap fold line to one of the panels and the end flaps are adapted to be folded upon selected other end flaps to form composite end panels of the carton. A carrying handle is formed in a selected one of the panels and adapted to be grasped by a user to carry the erected carton filled with the beverage containers. The blank includes a primary reinforcing panel joined to one of the panels such that the primary reinforcing panel may be folded into face to face juxtaposition with the selected one of the panels. A secondary reinforcing panel is joined to one of the panels via a secondary reinforcing panel fold line about which the secondary reinforcing panel may be folded into face to face juxtaposition with at least one of the primary reinforcing panel and the selected one of the panels. When the primary and secondary reinforcing panels are folded into position, at least portions of the selected one of the panels surrounding the handle have a triple layer of thickness.
Owner:C W ZUMBIEL
Devices related to electrode pads for p-type group iii nitride compound semiconductors
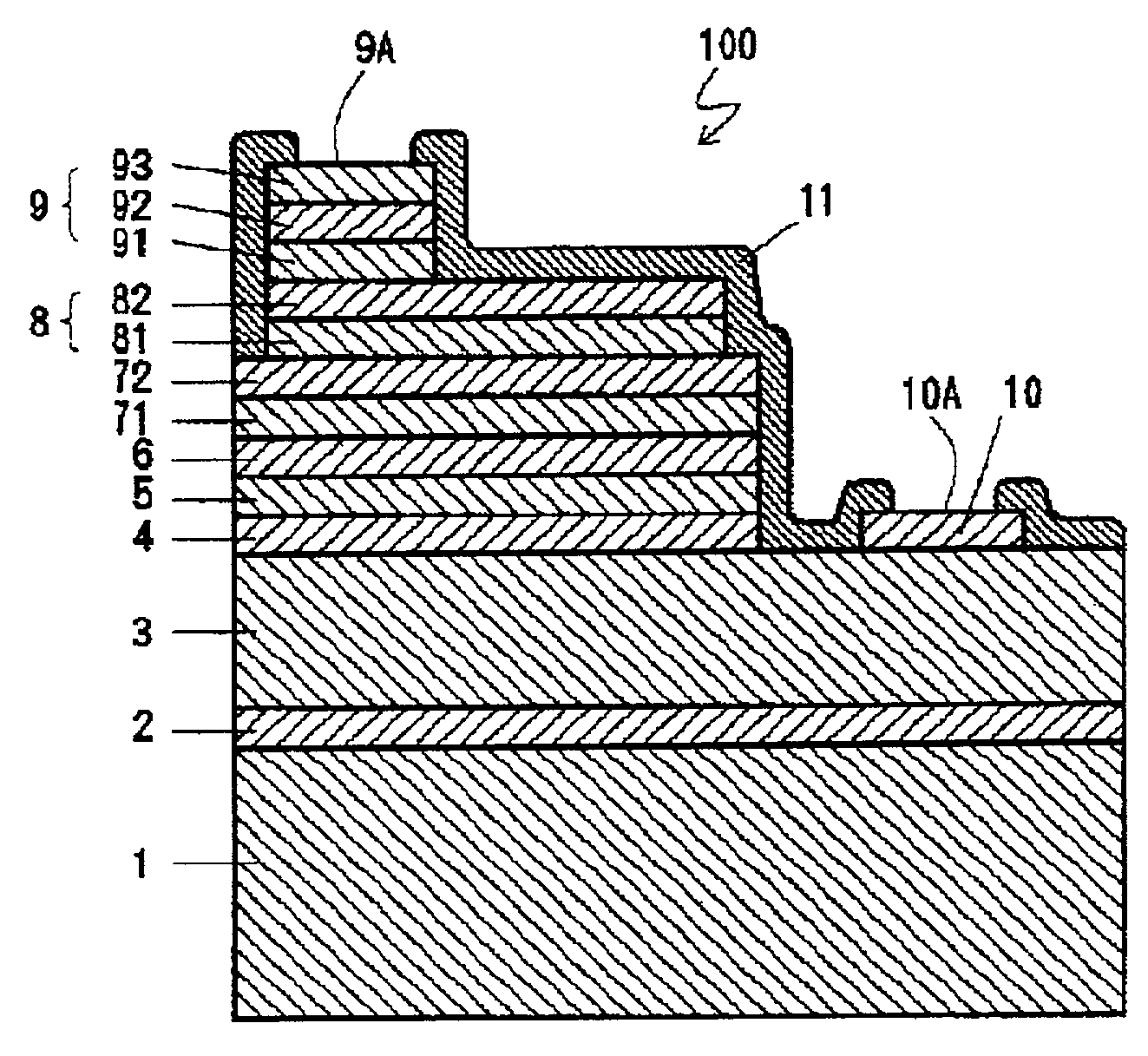
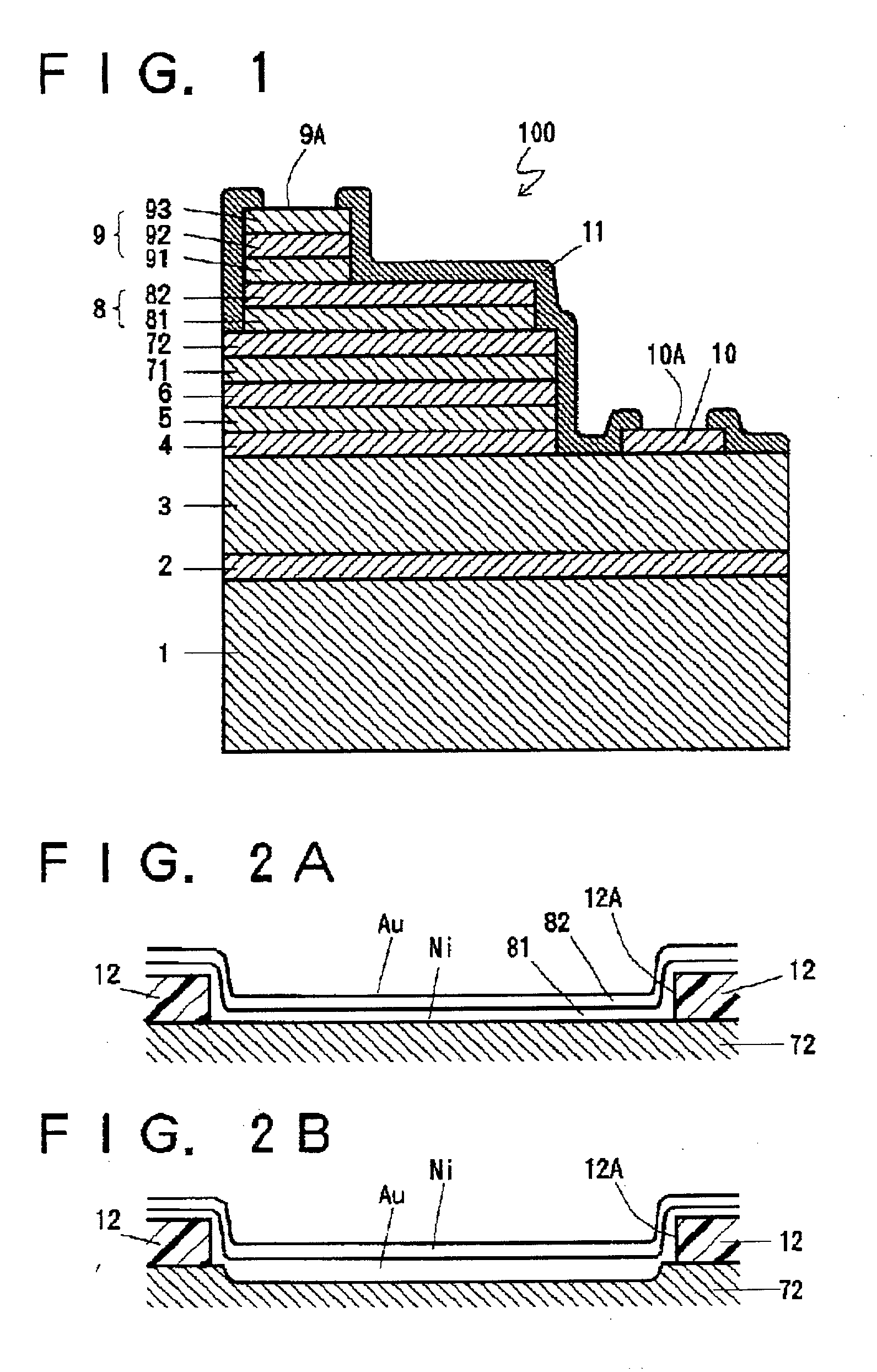
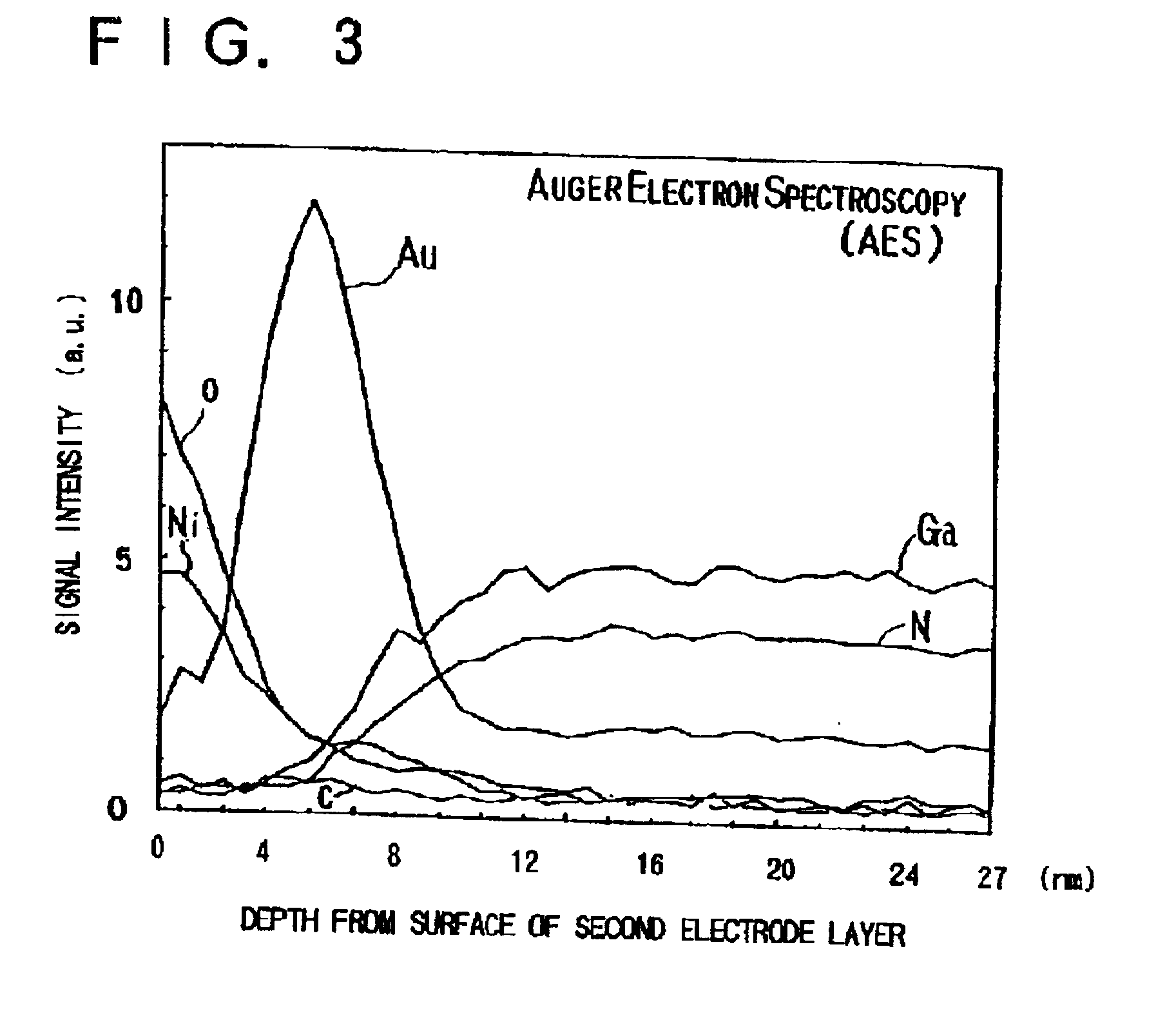
InactiveUS20020000643A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTectorial membraneEtching
An electrode pad for a Group III nitride compound semiconductor having p-type conduction includes a triple layer structure having first, second, and third metal layers, formed on an electrode layer. A protection film with a window exposing a central portion of the third metal layer is formed by etching on the third metal layer and covers the sides of the first, second, and third metal layers. The second metal layer is made of gold (Au). The first metal layer is made of an element which has ionization potential lower than gold (Au). The third metal is made of an element which has adhesiveness to the protection film stronger than that of gold (Au). Consequently, this structure of the electrode pad improves the adhesive strength between the protection layer and the third meal layer and prevents the etching of the sides of the protection film. Furthermore, the contact resistance between the semiconductor and the electrode pad is lowered and, thus, ohmic characteristic of the electrode pad is improved.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
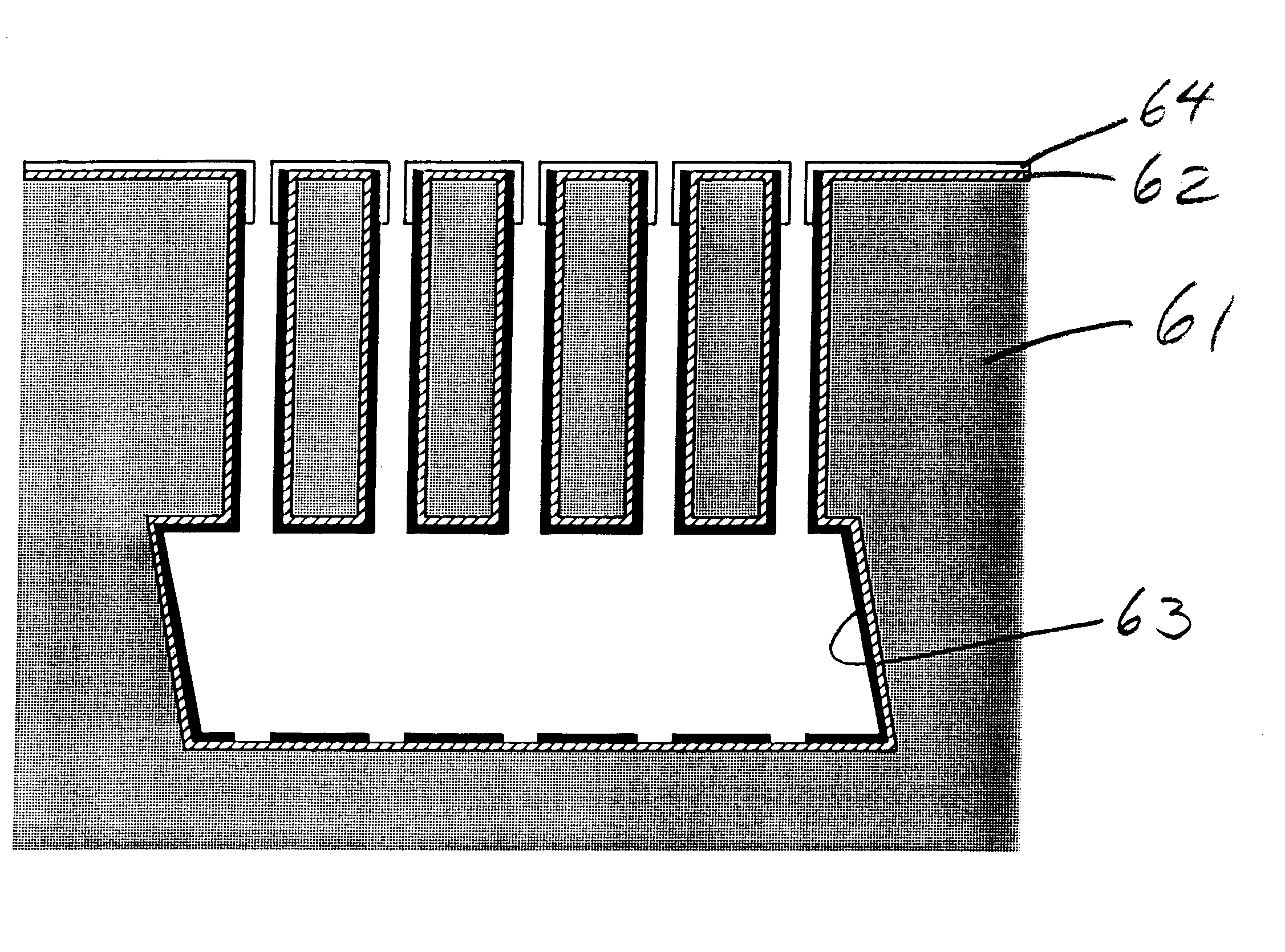
Paired warp triple layer forming fabrics with optimum sheet building characteristics
InactiveUS7048012B2Less complexMinimizes drainage and topographical markingsLoomsMachine wet endYarnEngineering
A papermaker's fabric, usable in the forming section of a paper machine, having two layers of cross-machine-direction (CD) yarns. Interwoven with the CD yarns is a system of MD yarns. At least some of the MD yarns are grouped into alternating pairs comprising a crossing pair having a first MD yarn and a second MD yarn and a second pair having a third MD yarn and a fourth MD yarn. The first MD yarn and the second MD yarn combine to weave each CD yarn in the first layer and cross between the first layer and the second layer. The left and right warp yarns in the pairs are aligned in such a way that like adjacent yarns from adjacent pairs have MD cell lengths greater than or less than the MD cell lengths from non-like adjacent yarns from adjacent pairs. The third MD yarn is interwoven with the first layer of CD yarns and the fourth MD yarn is interwoven with the second layer of CD yarns. In this manner, a paired warped triple layer forming fabric may be produced which minimizes drainage and crossover point topographical markings.
Owner:ALBANY INT CORP
Transistors, methods of manufacturing a transistor and electronic devices including a transistor
A transistor, a method of manufacturing a transistor, and an electronic device including a transistor are provided, the transistor may include a channel layer having a multi-layer structure. The channel layer may have a double layer structure or a triple layer structure. At least two layers of the channel layer may have different oxygen concentrations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wire structure, a thin film transistor substrate of using the wire structure and a method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6969889B2Low resistivityImprove reliabilityTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesAlloyTriple layer
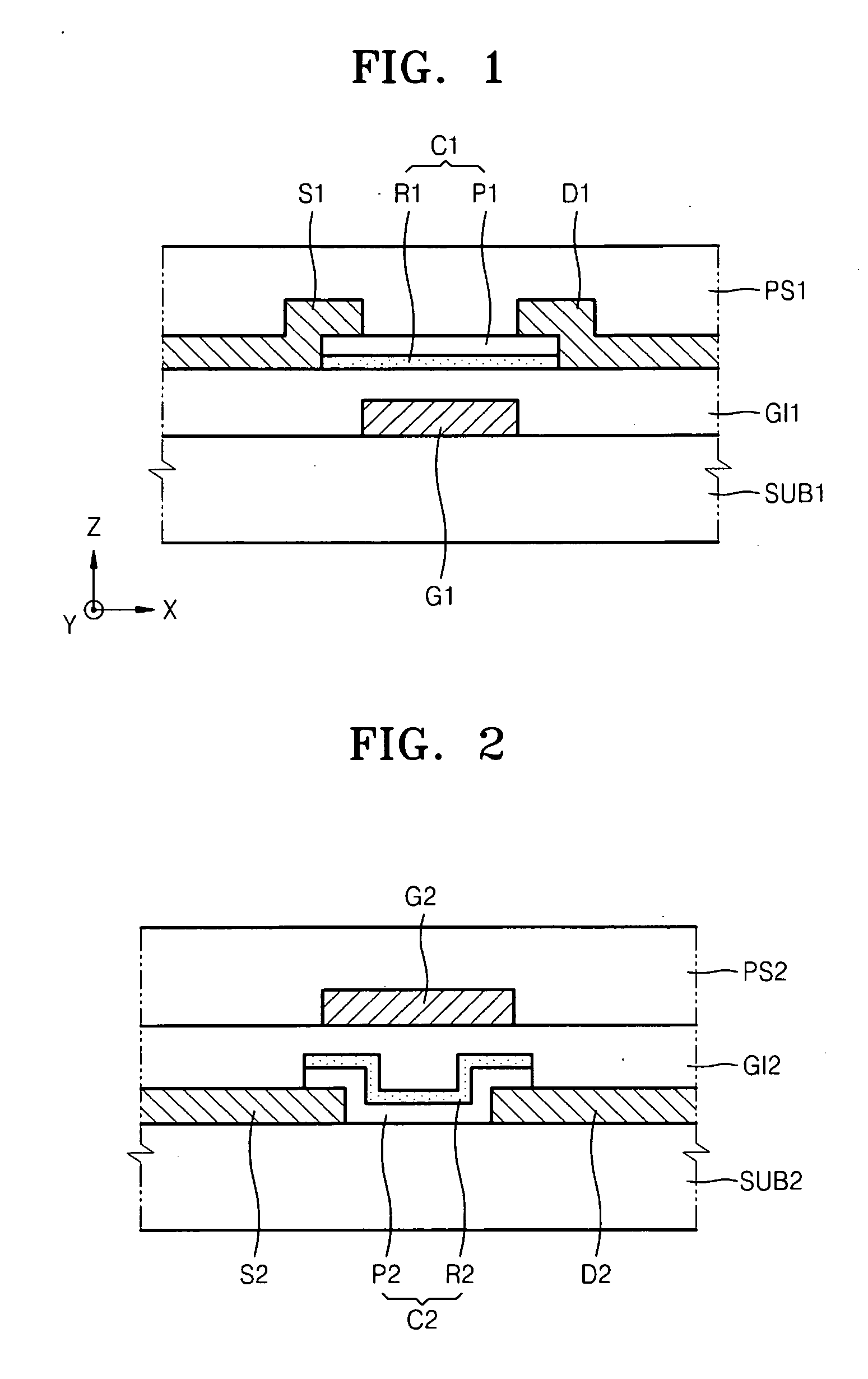
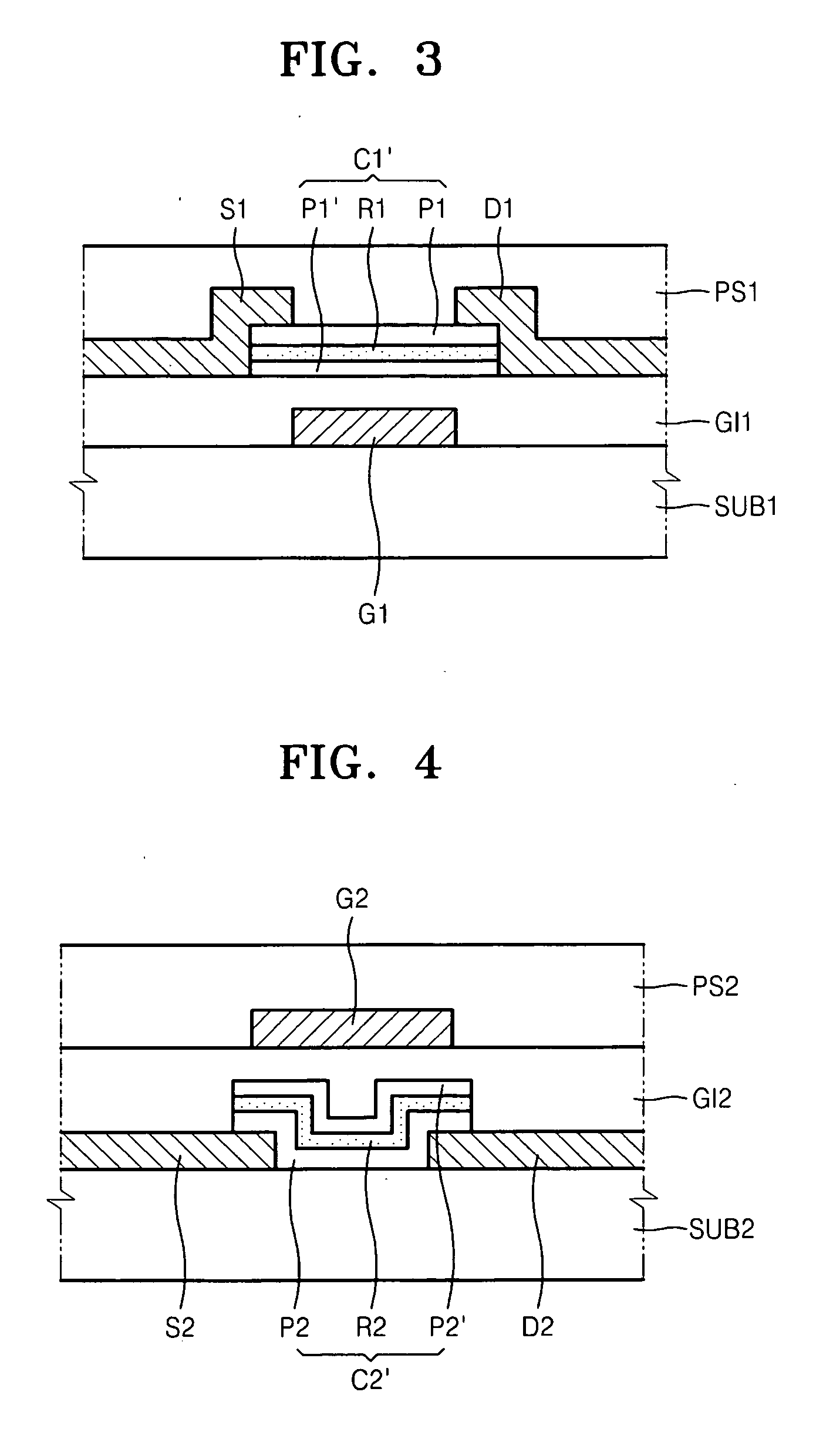
A thin film transistor array panel includes an insulating substrate, a gate wire formed on the insulating substrate. A gate insulating layer covers the gate wire. A semiconductor pattern is formed on the gate insulating layer. A data wire having source electrodes, drain electrodes and data lines is formed on the gate insulating layer and the semiconductor pattern. A protective layer is formed on the data wire. Pixel electrodes connected to the drain electrode via contact holes are formed on the protective layer. The gate wire and the data wire include triple layers of an adhesion layer, a Ag containing layer and a protection layer. The adhesion layer includes one of Cr, Cr alloy, Ti, Ti alloy, Mo, Mo alloy, Ta, Ta alloy, the Ag containing layer includes Ag or Ag alloy, and the protection layer includes one of IZO, Mo, Mo alloy, Cr and Cr alloy.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Paired warp triple layer forming fabrics with optimum sheet building characteristics
InactiveUS6953065B2Less complexMinimizes drainage and topographical markingsMachine wet endMulti-ply fabricsYarnEngineering
A papermaker's fabric, usable in the forming section of a paper machine, having two layers of cross-machine-direction (CD) yarns. Interwoven with the CD yarns is a system of MD yarns. The MD yarns are grouped into alternating pairs comprising a crossing pair having a first MD yarn and a second MD yarn and a second pair having a third MD yarn and a fourth MD yarn. The first MD yarn and the second MD yarn combine to weave each CD yarn in the first layer and cross between the first layer and the second layer. The left and right warp yarns in the pairs are aligned in such a way that like adjacent yarns from adjacent pairs have MD cell lengths equal to or less than the MD cell lengths from non-like adjacent yarns from adjacent pairs. The third MD yarn is interwoven with the first layer of CD yarns and the fourth MD yarn is interwoven with the second layer of CD yarns. In this manner, a paired warped triple layer forming fabric may be produced which minimizes drainage and crossover point topographical markings.
Owner:ALBANY INT CORP
Barrier structures for integration of high K oxides with Cu and AI electrodes
InactiveUS20020167086A1Improve the immunityImprove barrier propertiesTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTriple layerOxygen
An integrated circuit barrier structure disposed between high dielectric constant metal oxide and Cu or Al electrodes, for preventing diffusion of species such as oxygen, bismuth, or lead from the high dielectric constant metal oxide into the Cu or Al electrodes. Such barrier structure also protects the Cu or Al electrodes against oxidization during deposition of the high dielectric constant metal oxide. The barrier structure can be formed as (1) a single layer of Pt, Ir, IrO2, Ir2O3, Ru, RuO2, CuO, Cu2O, Al2O3, or a binary or ternary metal nitride, e.g., TaN, NbN, HfN, ZrN, WN, W2N, TiN, TiSiN, TiAlN, TaSiN, or NbAlN, or (2) double or triple layers of such materials, e.g., Pt / TiAlN, Pt / IrO2, Pt / Ir, Ir / TiAlN, Ir / IrO2, IrO2 / TiAlN, IrO2 / Ir, or IrO2 / Ir2O3 / Ir. Such barrier structures enable Cu or Al electrodes to be used in combination with high dielectric constant metal oxides in microelectronic structures such as ferroelectric stack and trench capacitors, non-volatile ferroelectric memory cells, and dynamic random access memory (DRAM) cells.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Training systems with wearable sensors for providing users with feedback
InactiveUS20180369637A1Accelerated trainingEnhance coachingPhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationMultiple sensorEngineering
A training system based on mobile technology and kinematics of human motion characterizes, analyzes, and supplies feedback to a user based on the user's movements. The training system includes a garment having a sensor control module connected to multiple sensor nodes via electrically-conductive fabric running along parts portions of the garment. The sensor module / nodes can communicate through the conductive fabric. The sensor nodes acquire motion and / or physiologic readings that are wirelessly transmitted to a mobile computing device that runs an application that analyzes the data and provides visual (e.g., graphs, 3D avatar) and audio feedback (e.g., voice prompts). Vibration motors and LEDs / electroluminescent fabric in the garment also provide notifications and alerts. The triple layer of garment, conductive fabric, and sensor module / sensor node are sealed against contaminants, allowing the garment to be washable.
Owner:ENFLUX INC
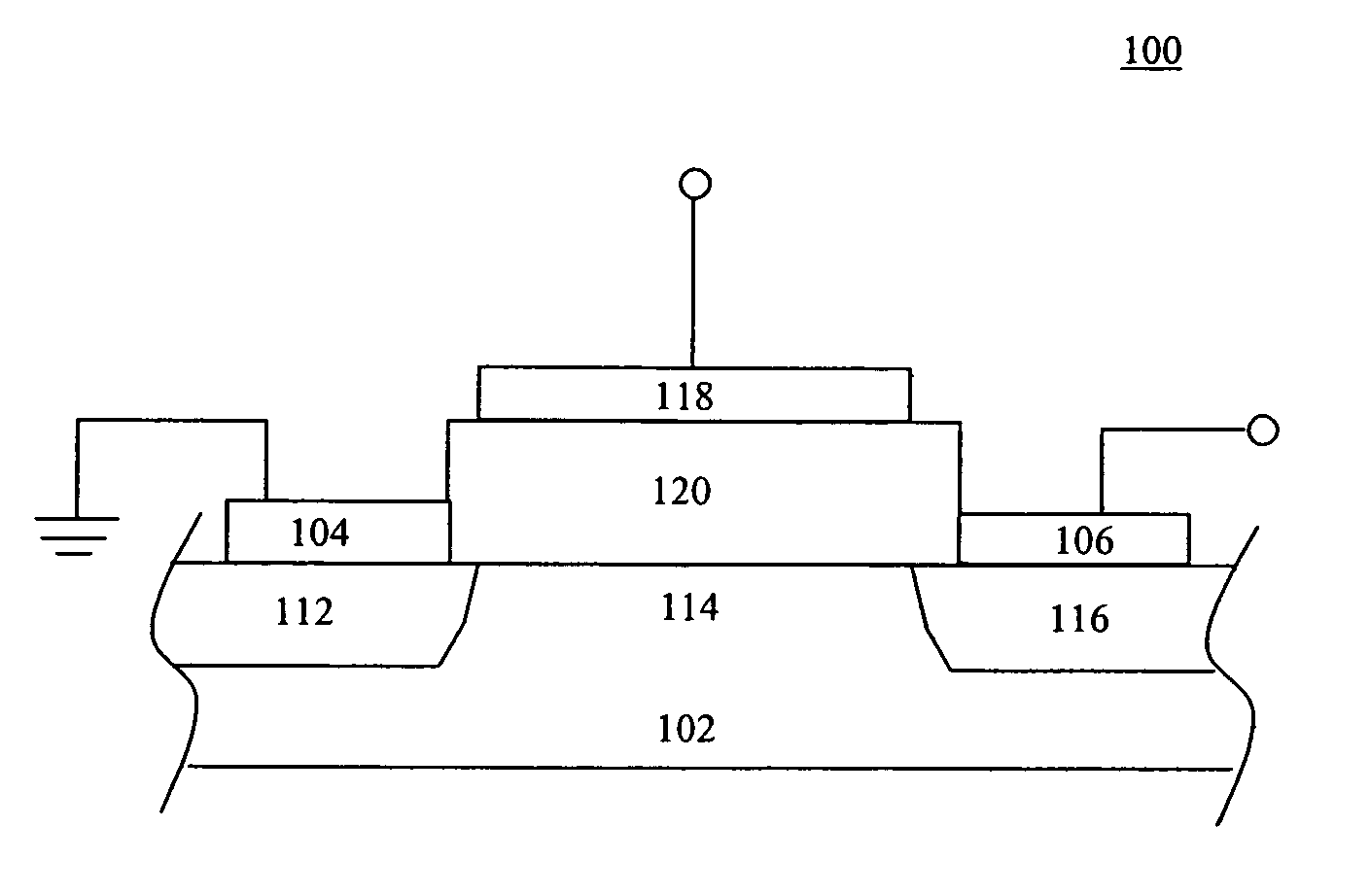
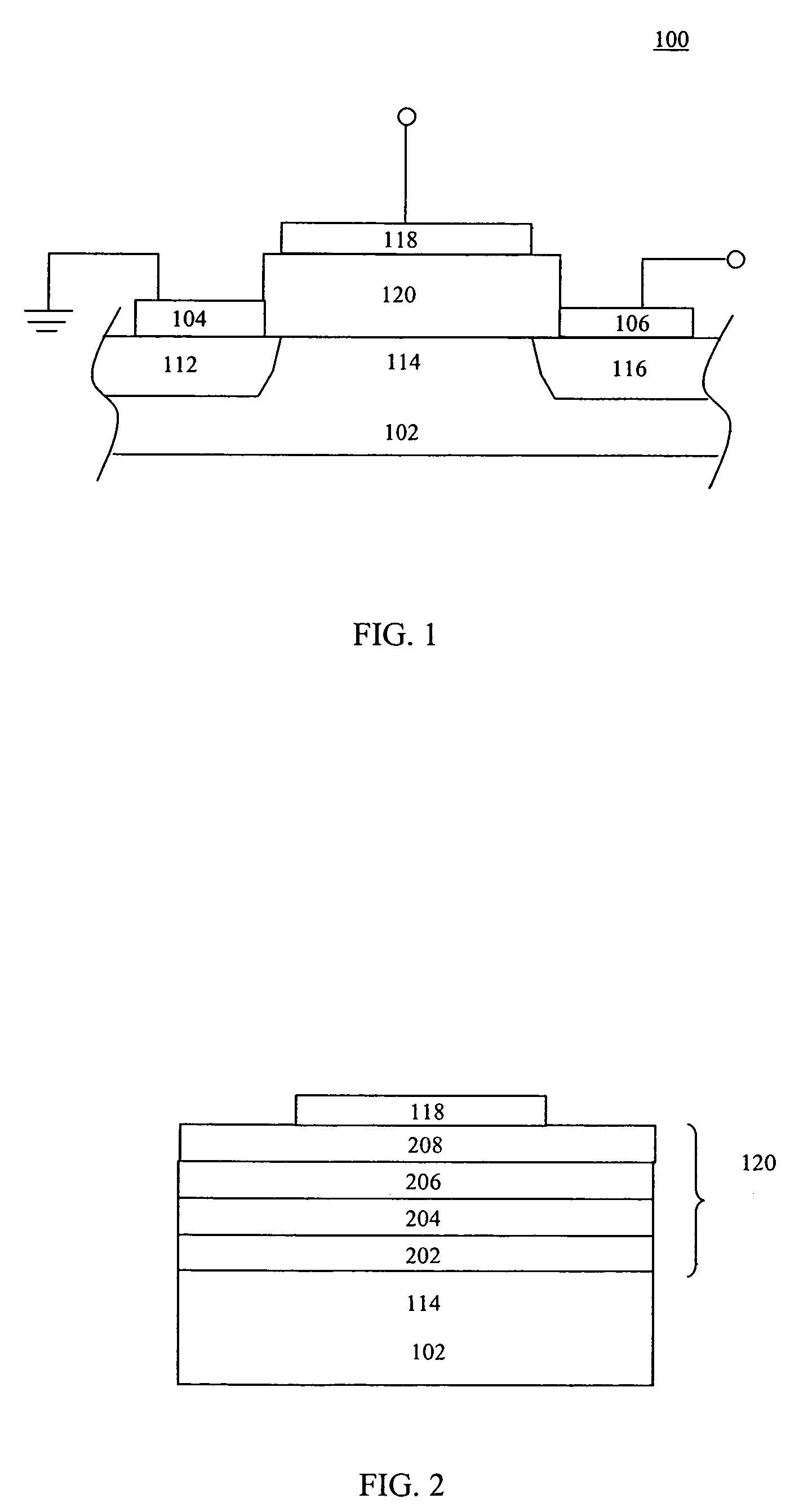
Semiconductor device with floating trap type nonvolatile memory cell and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050023604A1Reduce processing timeSlow changeTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialImpurity doping
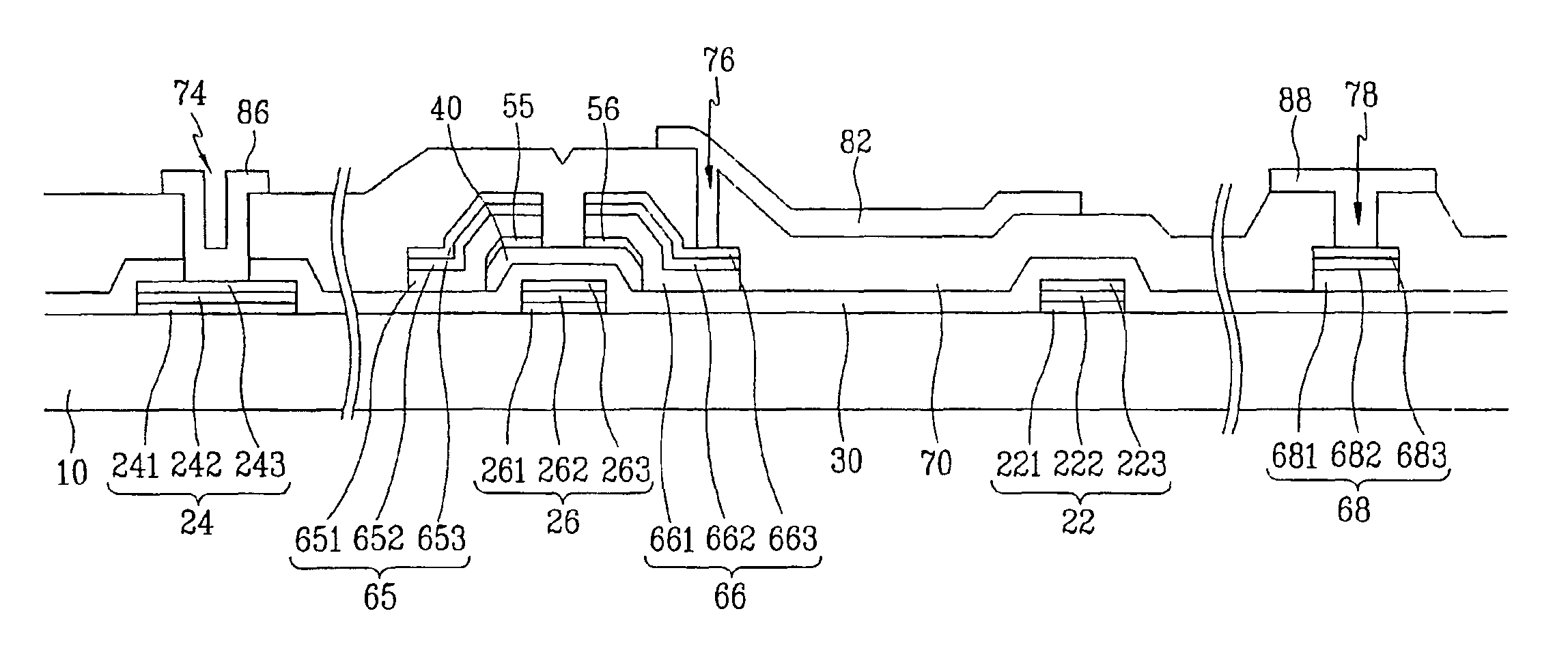
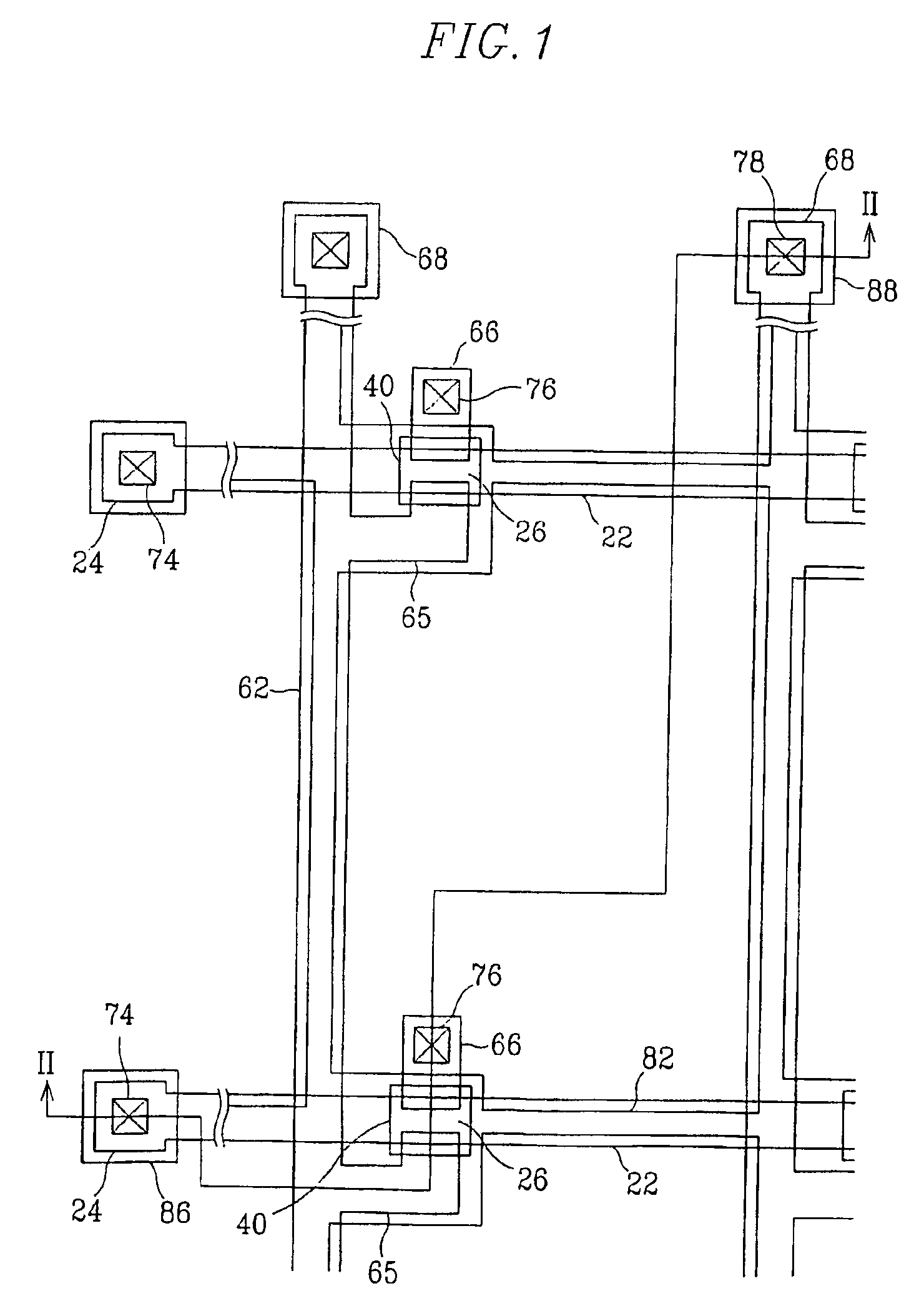
The present invention discloses a semiconductor device having a floating trap type nonvolatile memory cell and a method for manufacturing the same. The method includes providing a semiconductor substrate having a nonvolatile memory region, a first region, and a second region. A triple layer composed of a tunnel oxide layer, a charge storing layer and a first deposited oxide layer on the semiconductor substrate is formed sequentially. The triple layer on the semiconductor substrate except the nonvolatile memory region is then removed. A second deposited oxide layer is formed on an entire surface of the semiconductor substrate including the first and second regions from which the triple layer is removed. The second deposited oxide layer on the second region is removed, and a first thermal oxide layer is formed on the entire surface of the semiconductor substrate including the second region from which the second deposited oxide layer is removed. The semiconductor device can be manufactured according to the present invention to have a reduced processing time and a reduced change of impurity doping profile. The thickness of a blocking oxide layer and a high voltage gate oxide layer can be controlled.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hybrid warp exchange triple layer forming fabric
InactiveUS20060278294A1High modulusLarge caliberMachine wet endWoven fabricsYarnPulp and paper industry
A fabric for papermaking usable in the forming section of a paper making machine, having a first weft system, a second weft system and a third weft system; and a plurality of warp systems, each warp system having at least one warp yarn, each warp yarn binding with one of the first weft system, the third weft system, the first and second weft systems, and the second and third weft systems; wherein a first warp system is an exchange warp system.
Owner:VOTH FABRICS PATENT GMBH
Functional Inks Based on Layered Materials and Printed Layered Materials
An ink disclosed herein comprises a carrier liquid with a dispersion of flakes derived from a layered material. The thickness of each flake depends on the number of layers of the layered material in the flake. The thickness distribution of the flakes includes: at least 20% by number of single layer flakes; at least 40% by number cumulatively of single, double and triple layer flakes; or not more than 40% by number of flakes having ten or more layers. The layered material is selected from one or more of elemental materials such as graphene (typically derived from pristine graphite), metals (e.g., NiTe2, VSe2), semi-metals (e.g., WTa2, TcS2), semiconductors (e.g., WS2, WSe2, MoS2, MoTe2, TaS2, RhTe2, PdTe2), insulators (e.g., h-BN, HfS2), superconductors (e.g., NbS2, NbSe2, NbTe2, TaSe2) and topological insulators and thermo-electrics (e.g., Bi2Se3, Bi2Te3). Also disclosed are methods of manufacturing suitable inks and uses of the inks.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
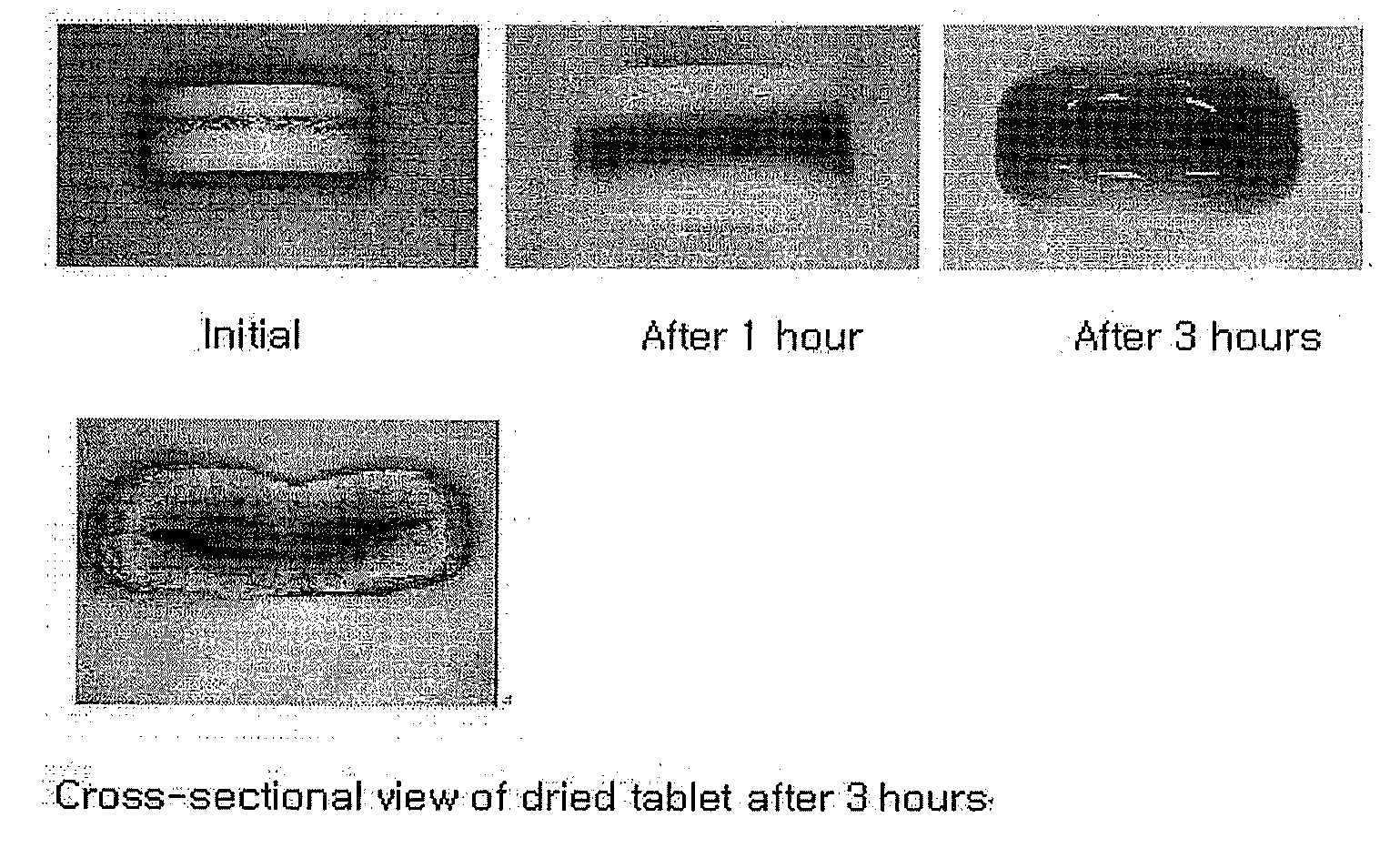
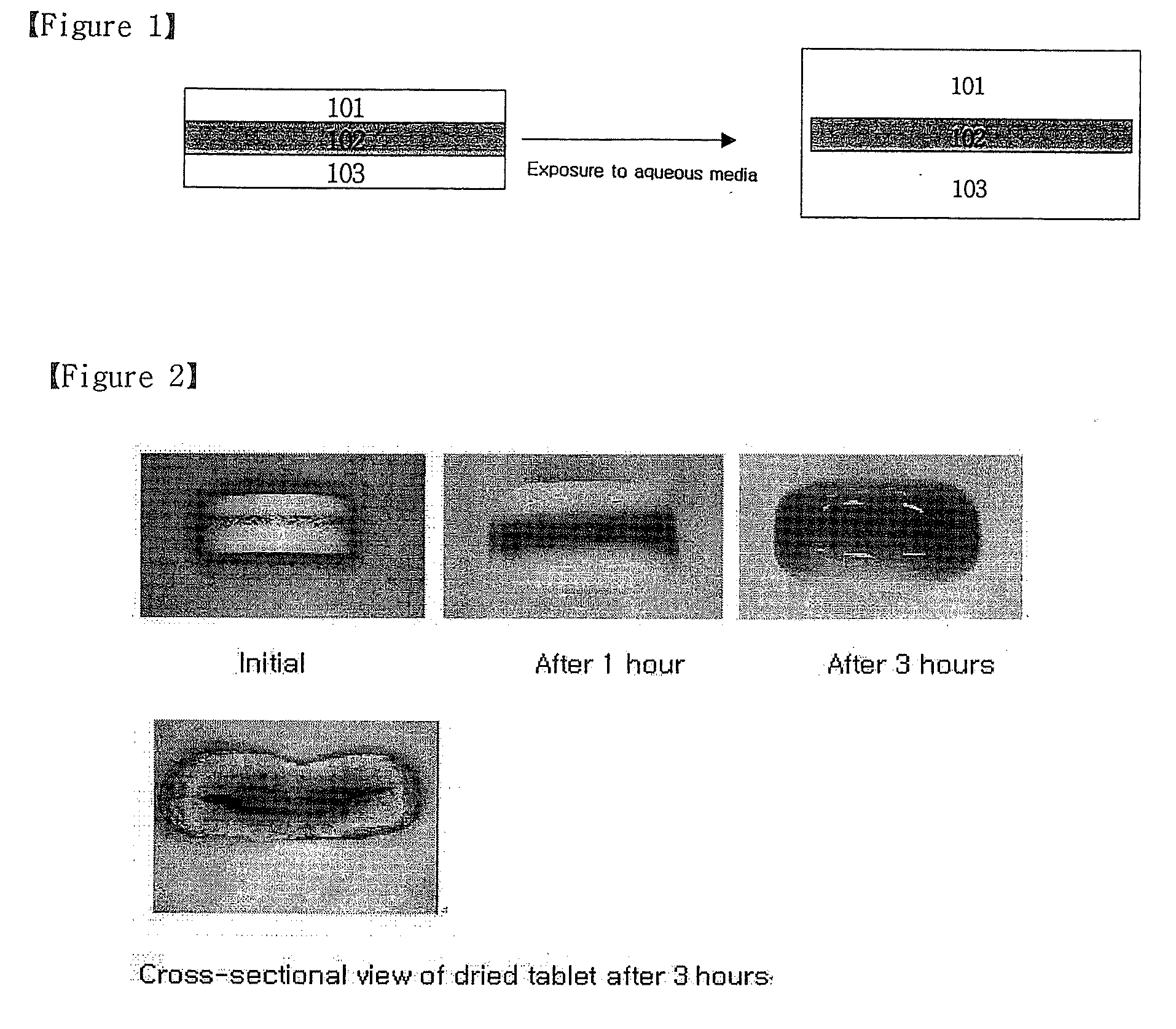
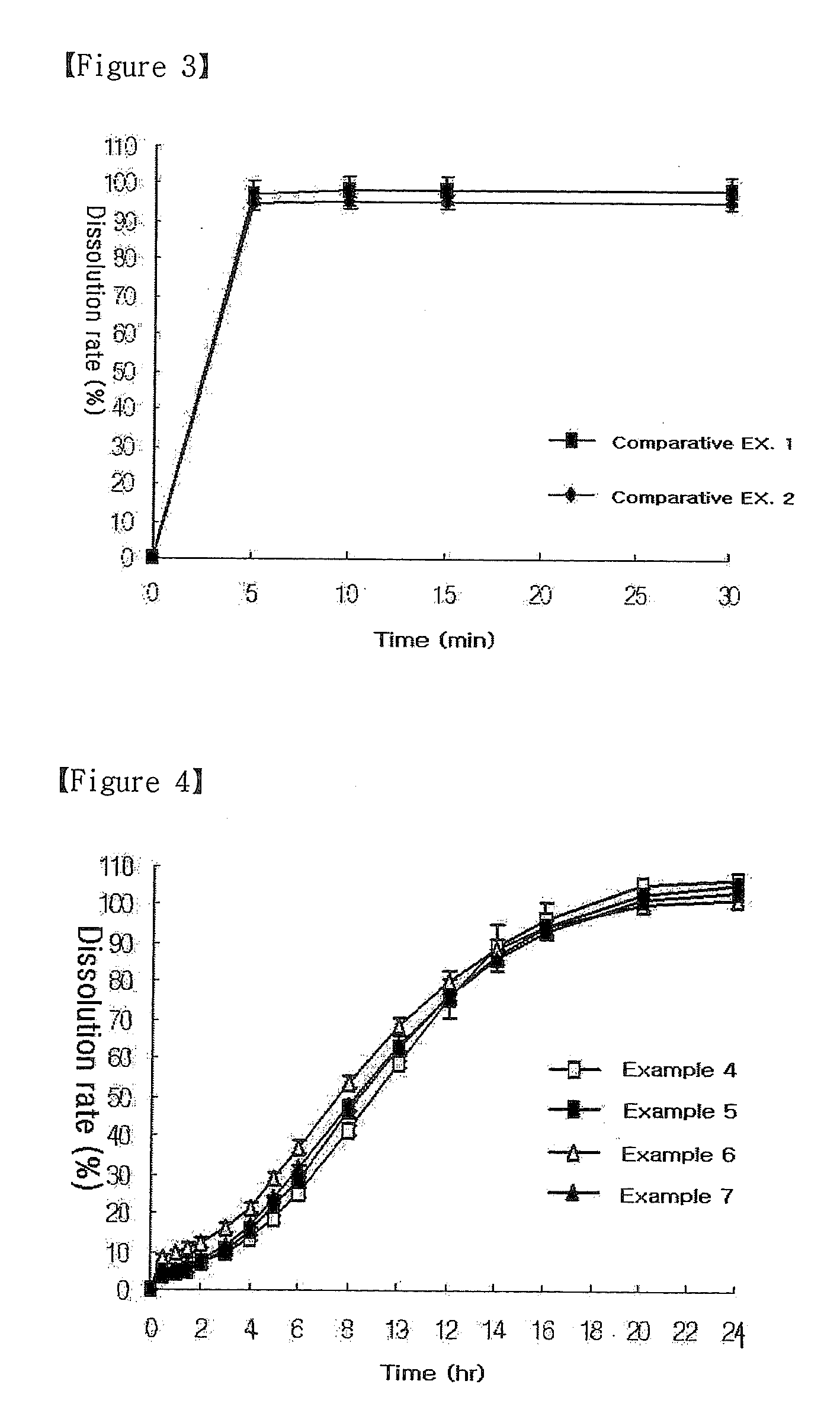
Oral Sustained-Release Triple Layer Tablet
ActiveUS20100040681A1Reduce initial burstControl releaseOrganic active ingredientsPill deliveryImmediate releaseBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to an oral sustained-release triple layer tablet, more particularly, a triple layer tablet consisting of an inner immediate-release layer containing a pharmaceutically active ingredient and two outer layers containing swellable polymers. Upon exposure to aqueous media, the two outer layers swell to form gelled layers surrounding the lateral side of the inner layer rapidly, thereby control effectively the release of the pharmaceutically active ingredient from the inner immediate-release layer.
Owner:GL PHARMTECH
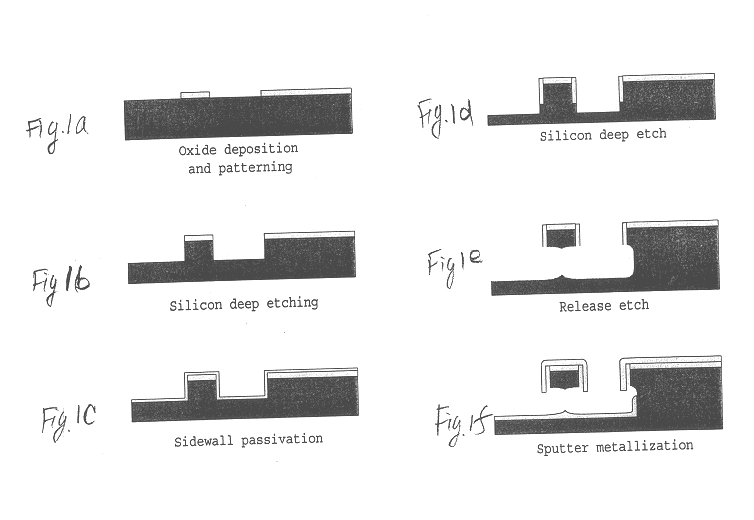
Gate electrodes for millimeter-wave operation and methods of fabrication
ActiveUS20100276698A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesResistManufacturing technology
A transistor device having a tiered gate electrode fabricated with methods using a triple layer resist structure. The triple layer resist stack is deposited on a semiconductor structure. An exposure pattern is written onto the resist stack using an e-beam writer, for example. The exposure dose is non-uniform across the device. Portions of the three resist layers are removed with a sequential development process, resulting in tiered resist structure. A conductive material is deposited to form the gate electrode. The resulting “Air-T” gate also has a three-tiered structure. The fabrication process is well-suited for the production of gates small enough for use in millimeter wave devices.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Paired warp triple layer forming fabrics with optimum sheet building characteristics
InactiveUS20050139281A1Minimizes drainageMinimizes topographical markingMachine wet endPress sectionYarnEngineering
A papermaker's fabric, usable in the forming section of a paper machine, having two layers of cross-machine-direction (CD) yarns. Interwoven with the CD yarns is a system of MD yarns. At least some of the MD yarns are grouped into alternating pairs comprising a crossing pair having a first MD yarn and a second MD yarn and a second pair having a third MD yarn and a fourth MD yarn. The first MD yarn and the second MD yarn combine to weave each CD yarn in the first layer and cross between the first layer and the second layer. The left and right warp yarns in the pairs are aligned in such a way that like adjacent yarns from adjacent pairs have MD cell lengths greater than or less than the MD cell lengths from non-like adjacent yarns from adjacent pairs. The third MD yarn is interwoven with the first layer of CD yarns and the fourth MD yarn is interwoven with the second layer of CD yarns. In this manner, a paired warped triple layer forming fabric may be produced which minimizes drainage and crossover point topographical markings.
Owner:ALBANY INT CORP
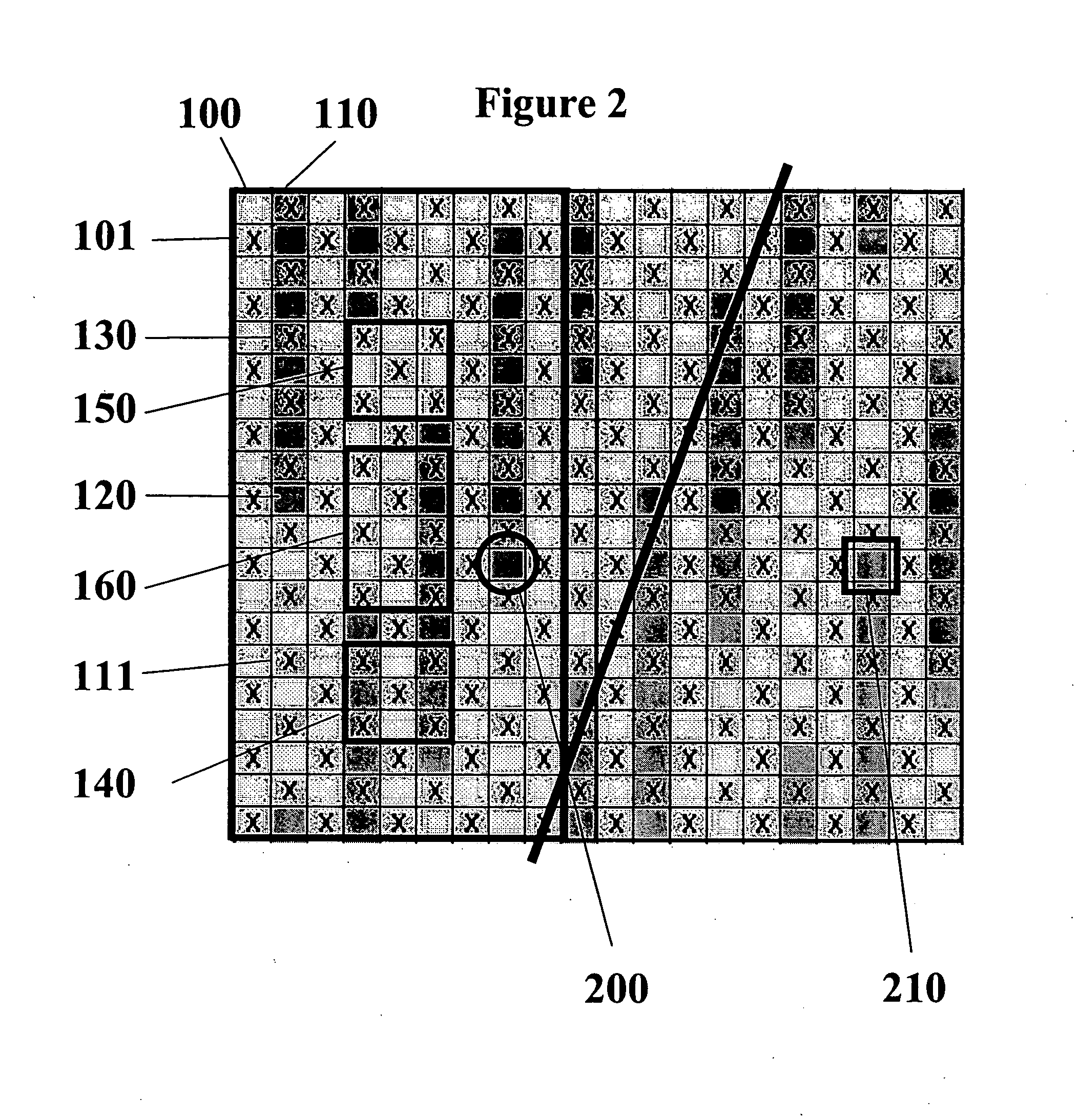
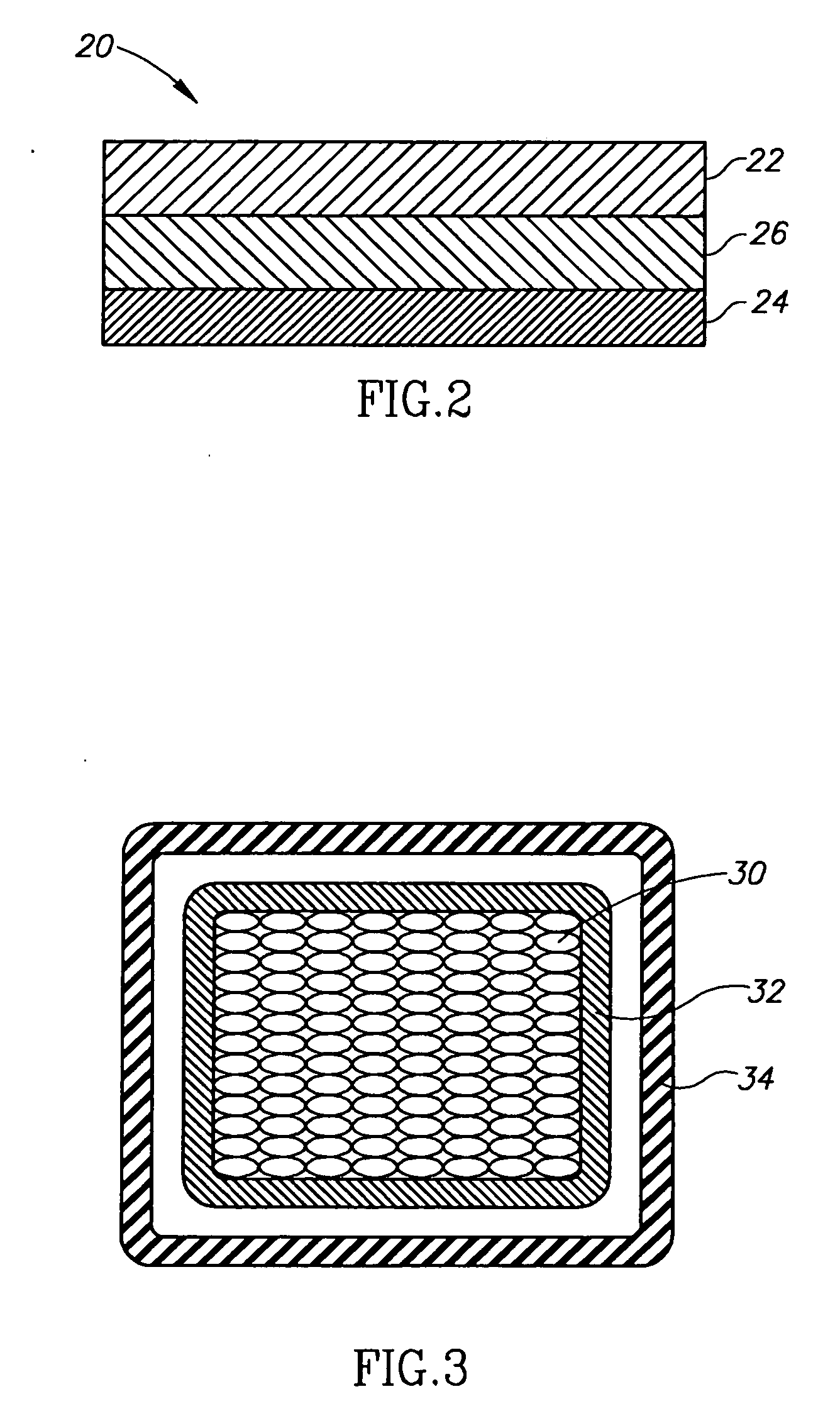
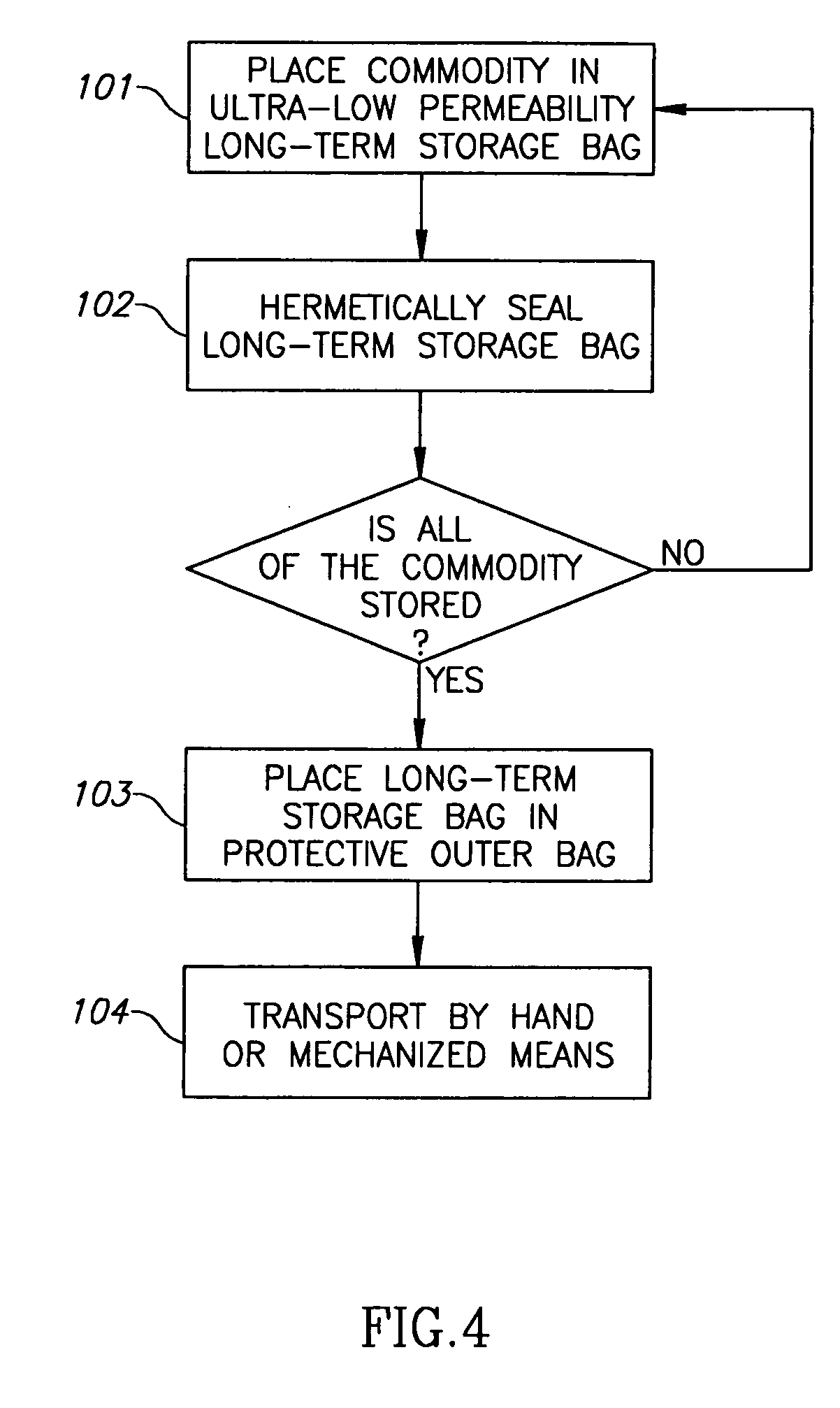
Flexible ultra-low permeability transport system and method
A system and method for long-term storage of a commodity in a weight range of 10-2000 kilograms includes hermetic sealing of an ultra-low permeability, easily transportable, flexible long-term storage container. The long-term storage container may also be treated using non-toxic insect repellents of botanical origin or using a synthetic pyrethroid. The long-term storage container includes a triple layer co-extruded film having an outer layer, an inner layer, and a middle layer. The middle layer is comprised of ultra-low permeability material or materials. After hermetic sealing, the long-term storage container having the commodity therein is placed into an outer container for protection during transport.
Owner:GRAINPRO
Multiple contour binders in triple layer fabrics
A multi-layer fabric which may be utilized in a papermaking process. Such fabric has a first layer of machine direction (MD) yarns, a second layer of MD yarns and a first system of cross-direction (CD) yarns having first binder yarns weaving a first contour pattern and second binder yarns weaving a second contour pattern different from the first contour pattern. The first binder yarns and the second binder yarns are each intrinsic to the first layer and each bind with the second layer. Moreover, the binder yarns each weave in sequence in the first layer more than once in a pattern repeat of the fabric. The binder yarns also weave plural contour patterns in the first layer in the weave pattern repeat.
Owner:ALBANY INT CORP
Electron blocking layers for electronic devices
Methods and apparatuses for electronic devices such as non-volatile memory devices are described. The memory devices include a multi-layer control dielectric, such as a double or triple layer. The multi-layer control dielectric includes a combination of high-k dielectric materials such as aluminum oxide, hafnium oxide, and / or hybrid films of hafnium aluminum oxide. The multi-layer control dielectric provides enhanced characteristics, including increased charge retention, enhanced memory program / erase window, improved reliability and stability, with feasibility for single or multi state (e.g., two, three or four bit) operation.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
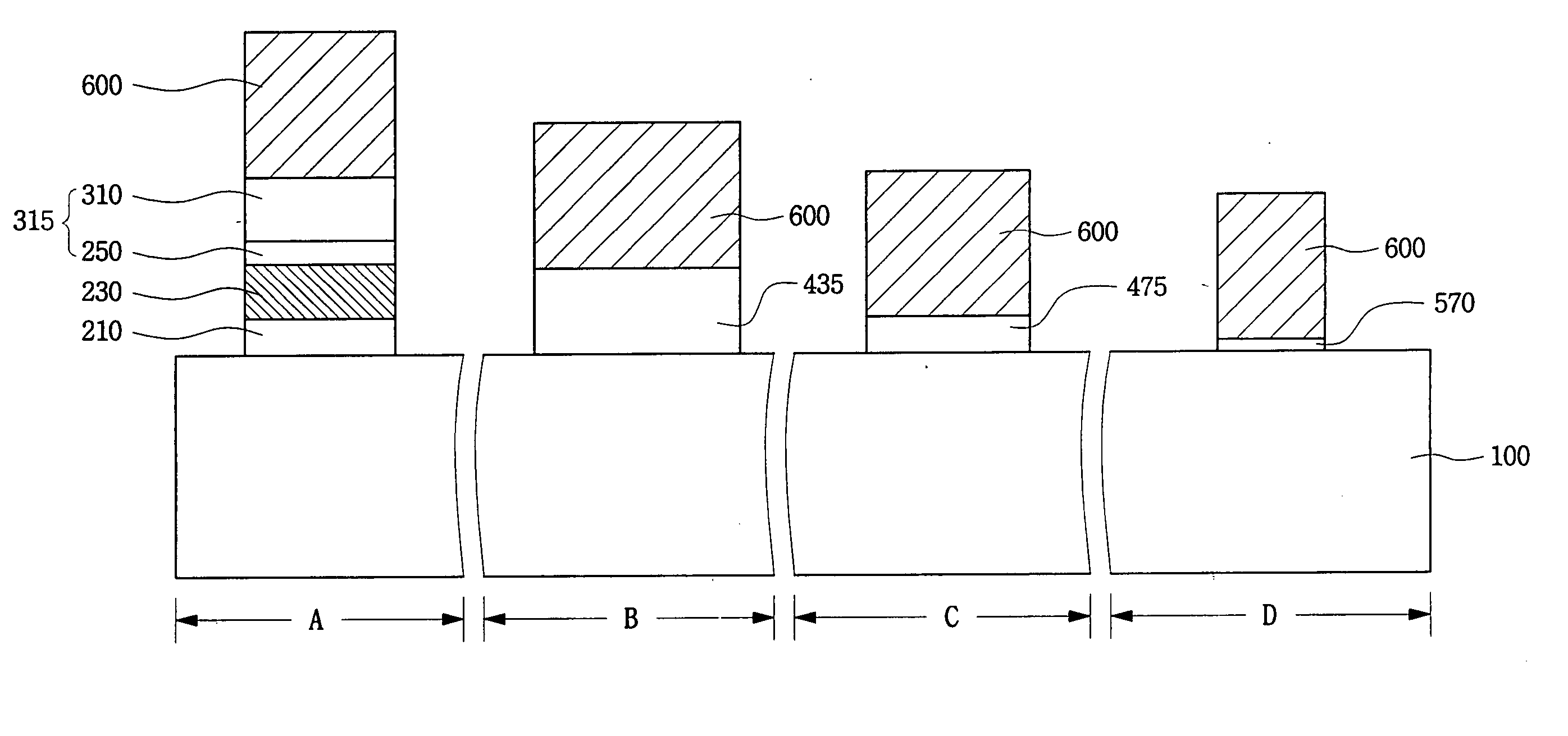
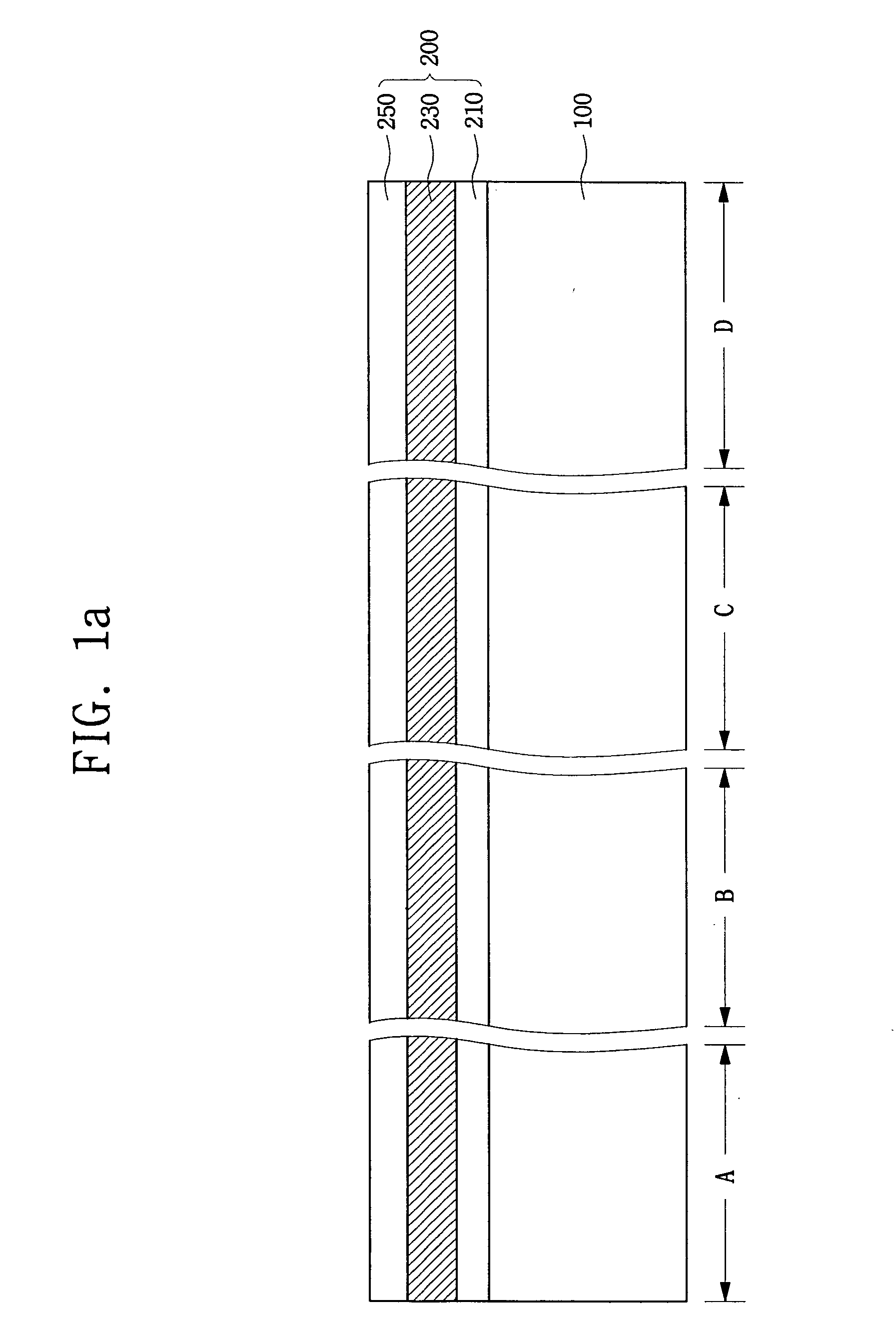
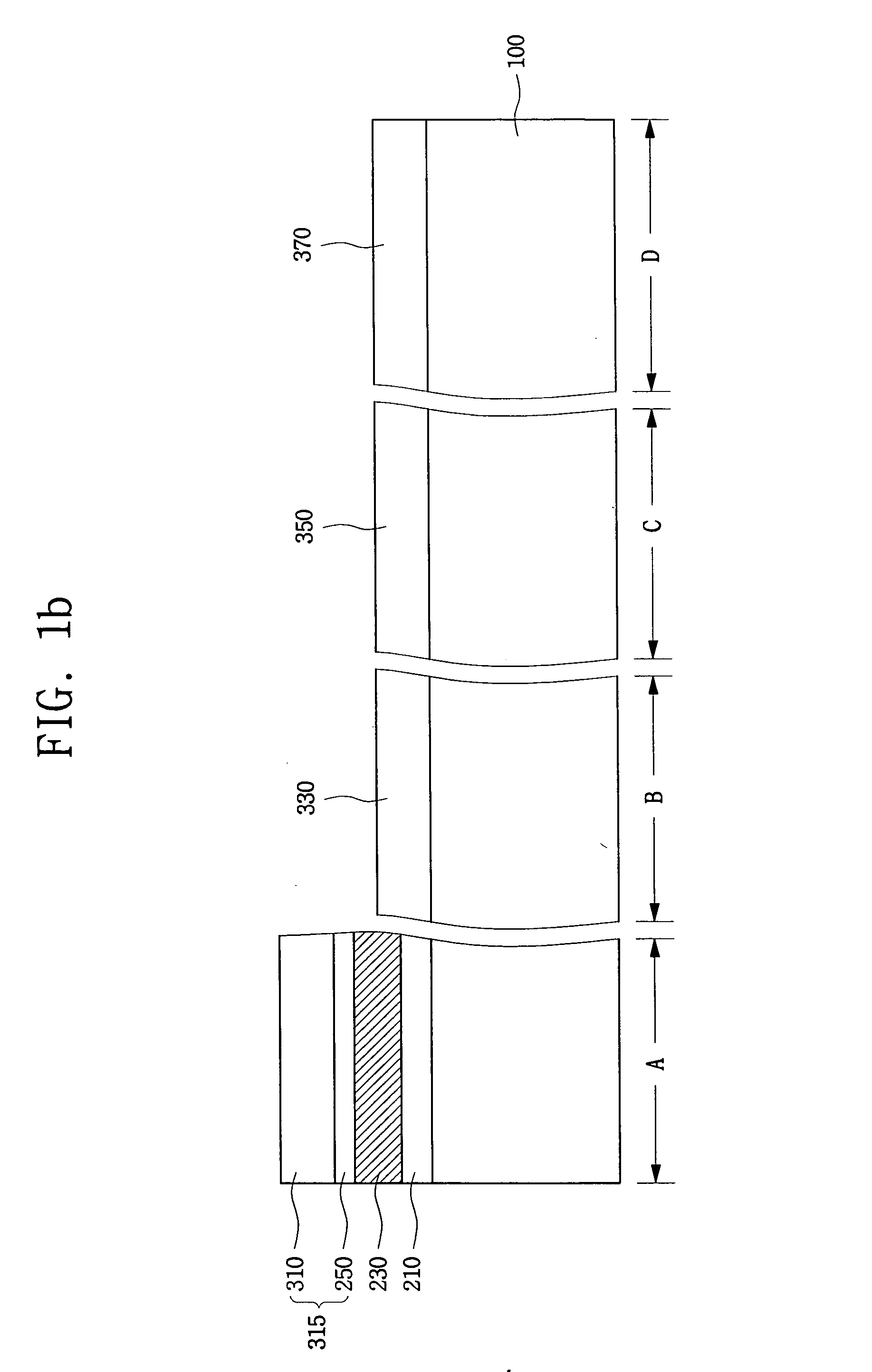
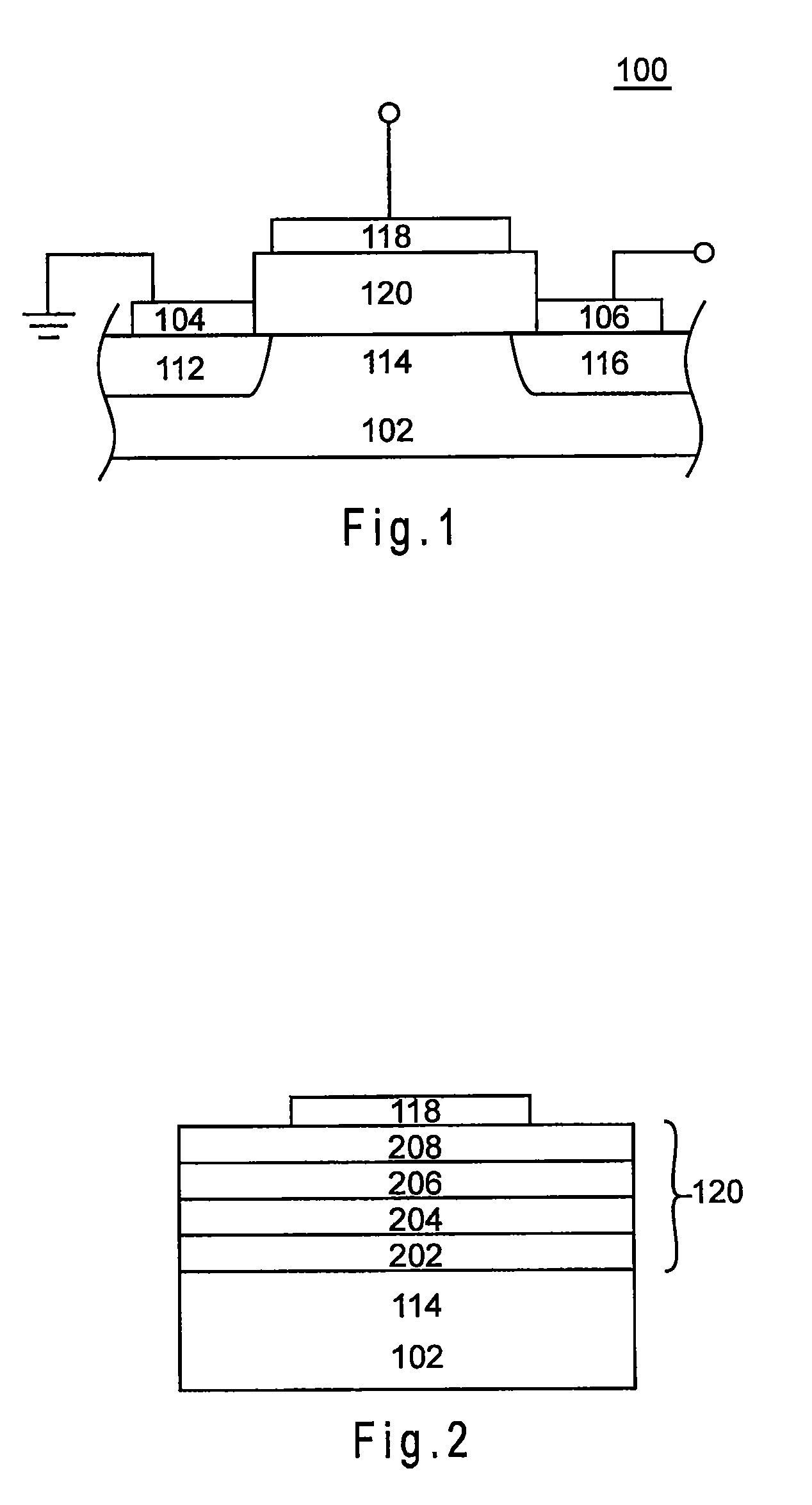
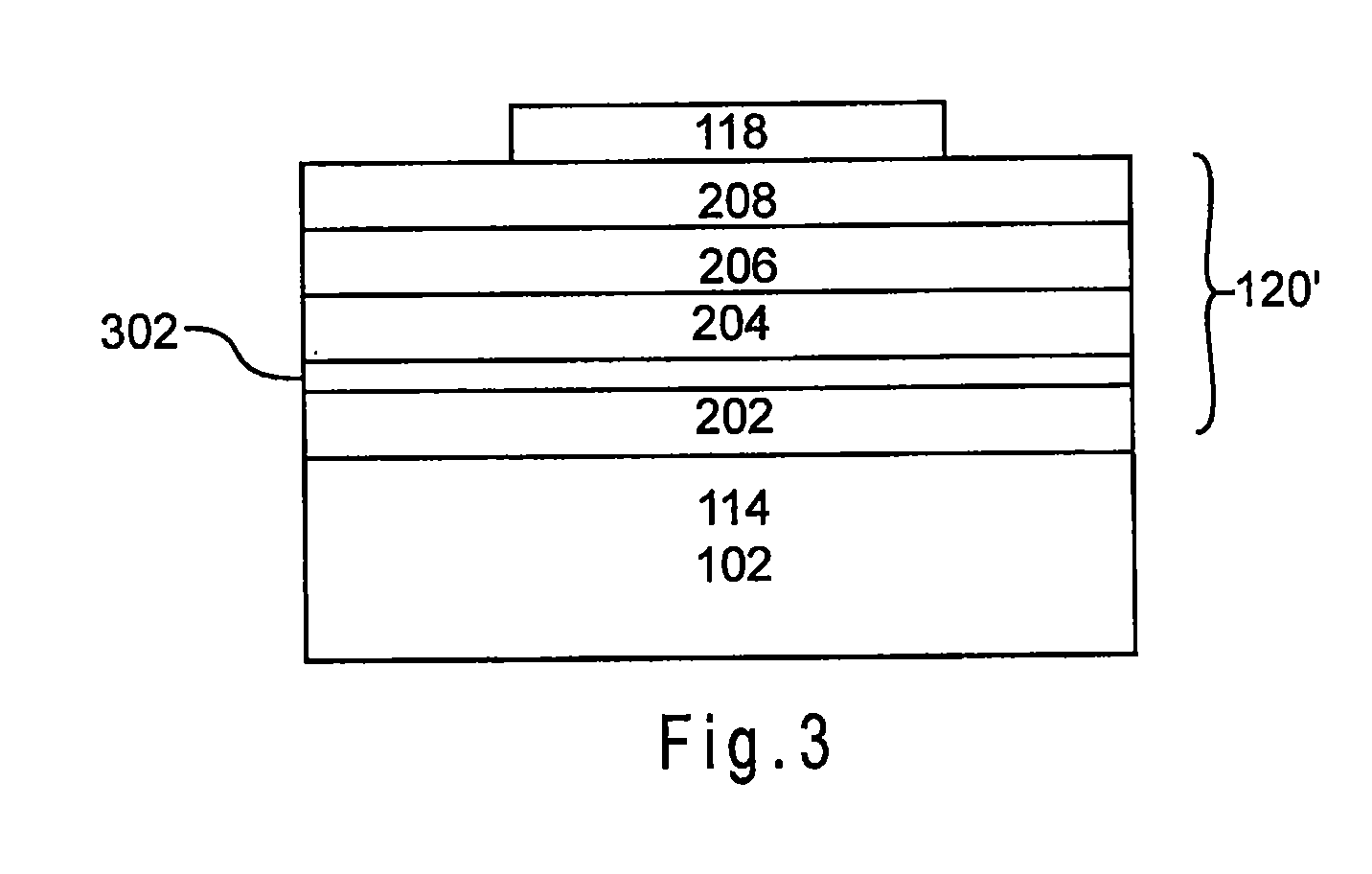
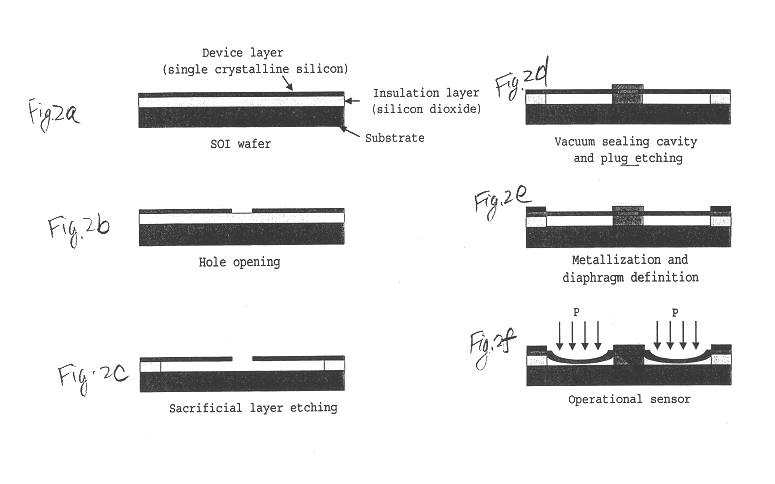
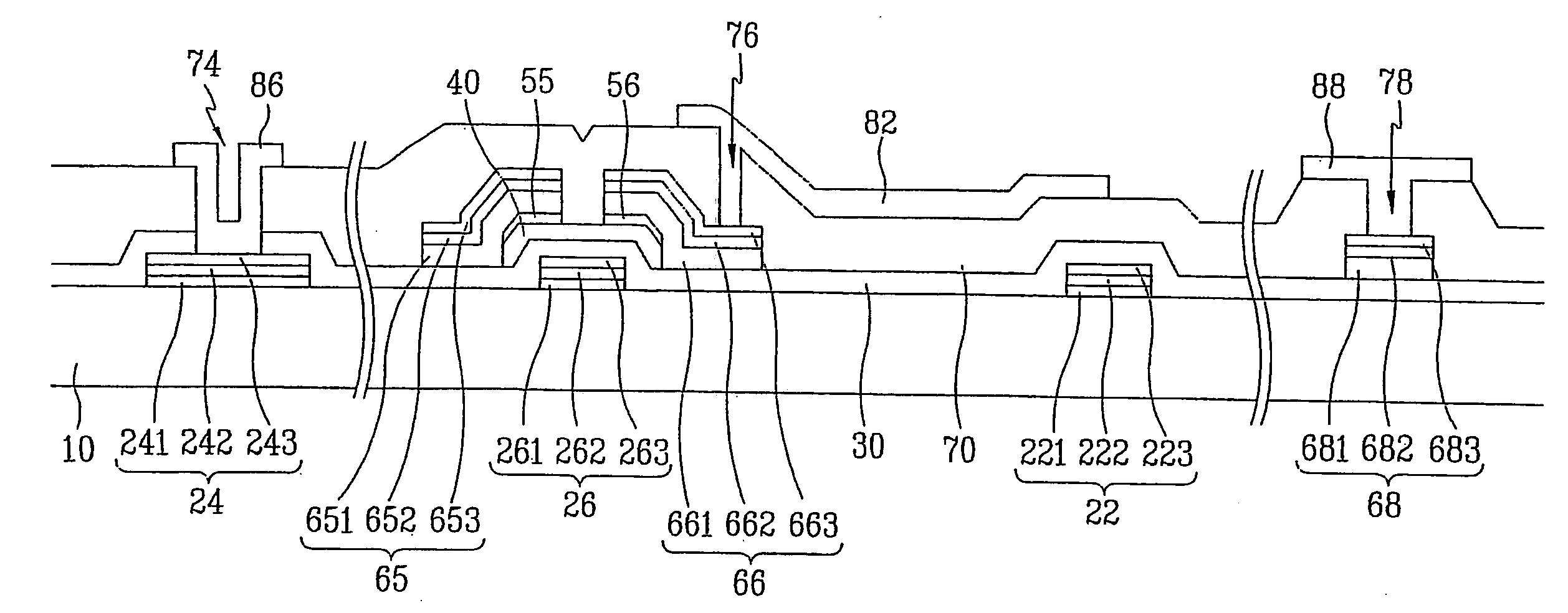
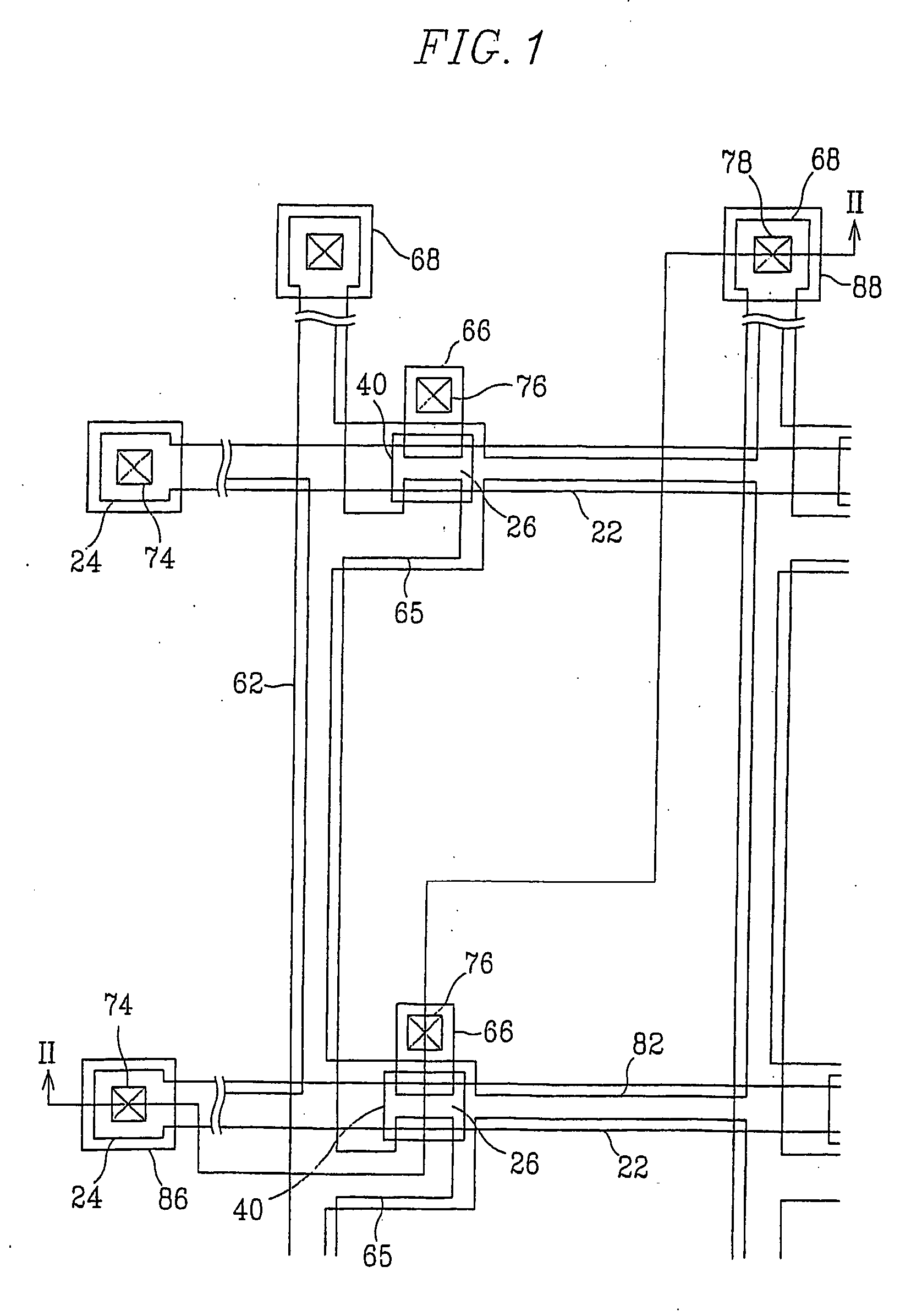
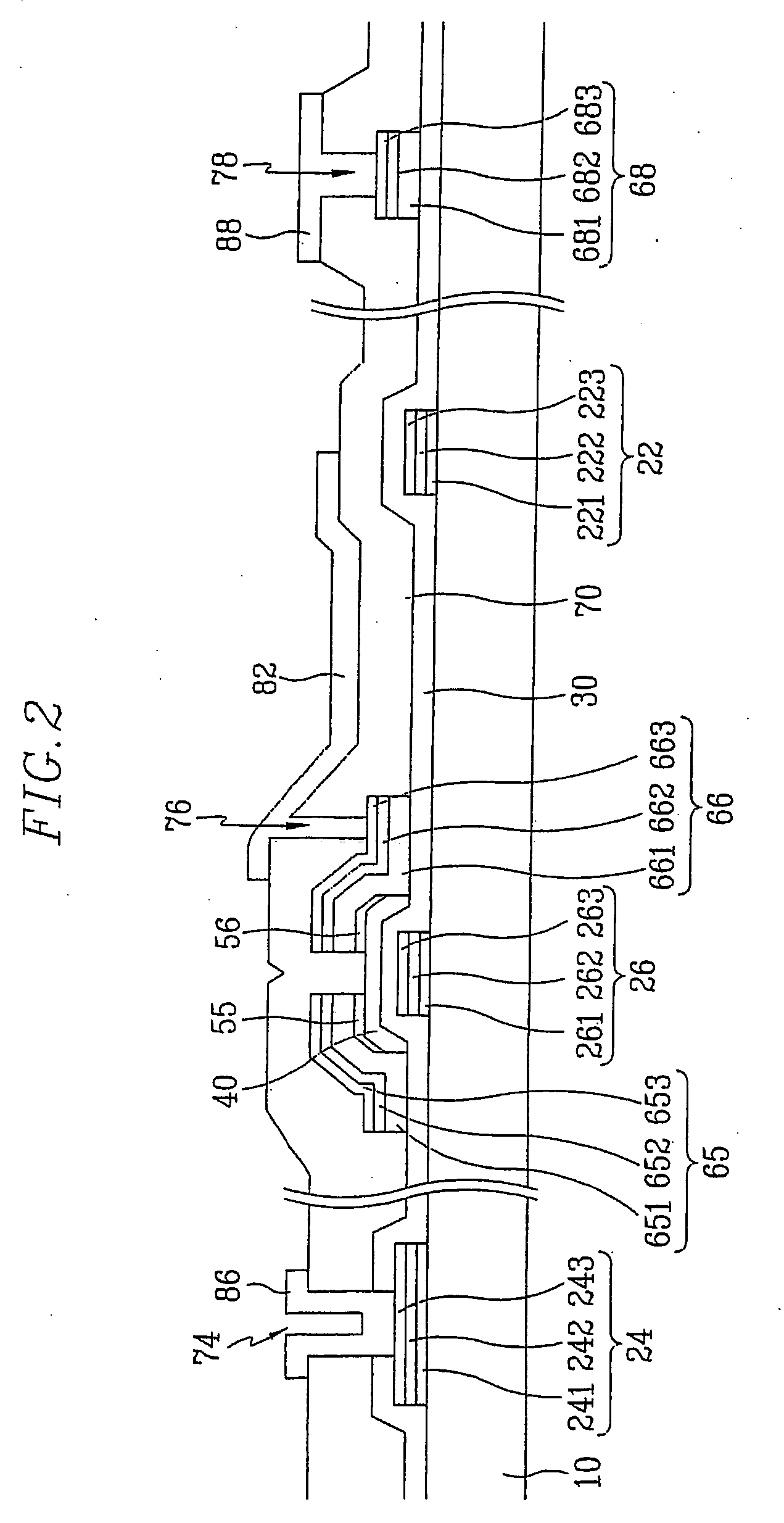
Triple layer isolation for silicon microstructure and structures formed using the same
InactiveUS6569702B2Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerTriple layer
An isolation method for a single crystalline silicon microstructure using a triple layer structure is disclosed. The method includes forming the triple layer composed of an insulation layer formed over an exposed surface of the silicon microstructure, a conductive layer formed over the entire insulation layer, and a metal layer formed over a top portion of the microstructure; and partially etching the conductive layer to form electrical isolation between parts of the microstructure. The method does not require a separate photolithography process for isolation, and can be effectively applied to microstructures having high aspect ratios and narrow trenches. Also disclosed are single crystalline silicon microstructures having a triple layer isolation structure formed using the disclosed method.
Owner:BARUN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wire structure, a thin film transistor substrate of using the wire structure and a method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050242401A1Low resistivityImprove reliabilityTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesAlloyTriple layer
A thin film transistor array panel includes an insulating substrate, a gate wire formed on the insulating substrate. A gate insulating layer covers the gate wire. A semiconductor pattern is formed on the gate insulating layer. A data wire having source electrodes, drain electrodes and data lines is formed on the gate insulating layer and the semiconductor pattern. A protective layer is formed on the data wire. Pixel electrodes connected to the drain electrode via contact holes are formed on the protective layer. The gate wire and the data wire include triple layers of an adhesion layer, a Ag containing layer and a protection layer. The adhesion layer includes one of Cr, Cr alloy, Ti, Ti alloy, Mo, Mo alloy, Ta and Ta alloy, the Ag containing layer includes Ag or Ag alloy, and the protection layer includes one of IZO, Mo, Mo alloy, Cr and Cr alloy.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Machine direction yarn stitched triple layer papermaker's forming fabrics
InactiveUS20050121097A1Excellent characteristicsImprove permeabilityMachine wet endPaper/cardboardYarnTriple layer
Triple layer papermaker's forming fabrics having a set of top MD yarns that are interwoven exclusively with a set of top CMD yarns to form at least part of a top fabric layer and a set of bottom MD yarns that are interwoven exclusively with a set of bottom CMD yarns to form at least part of a bottom fabric layer are provided. These fabrics further include a set of stitching MD yarn pairs. The stitching MD yarns that comprise each such pair weave in both the top fabric layer and the bottom fabric layer such that at locations where the first yarn in the pair weaves in the top fabric layer the second yarn in the pair drops down into the bottom fabric layer. In embodiments of the present invention, each stitching MD yarn may also be woven so as to form side-by-side machine direction knuckles on the bottom surface of the bottom fabric layer with a bottom MD yarn. In other embodiments of the invention, at least some of the top CMD yarns that the stitching MD yarns of the stitching MD yarn pairs pass over immediately before dropping down into the bottom fabric layer have a larger diameter and / or a higher modulus than the remainder of the top CMD yarns.
Owner:WEAVEXX
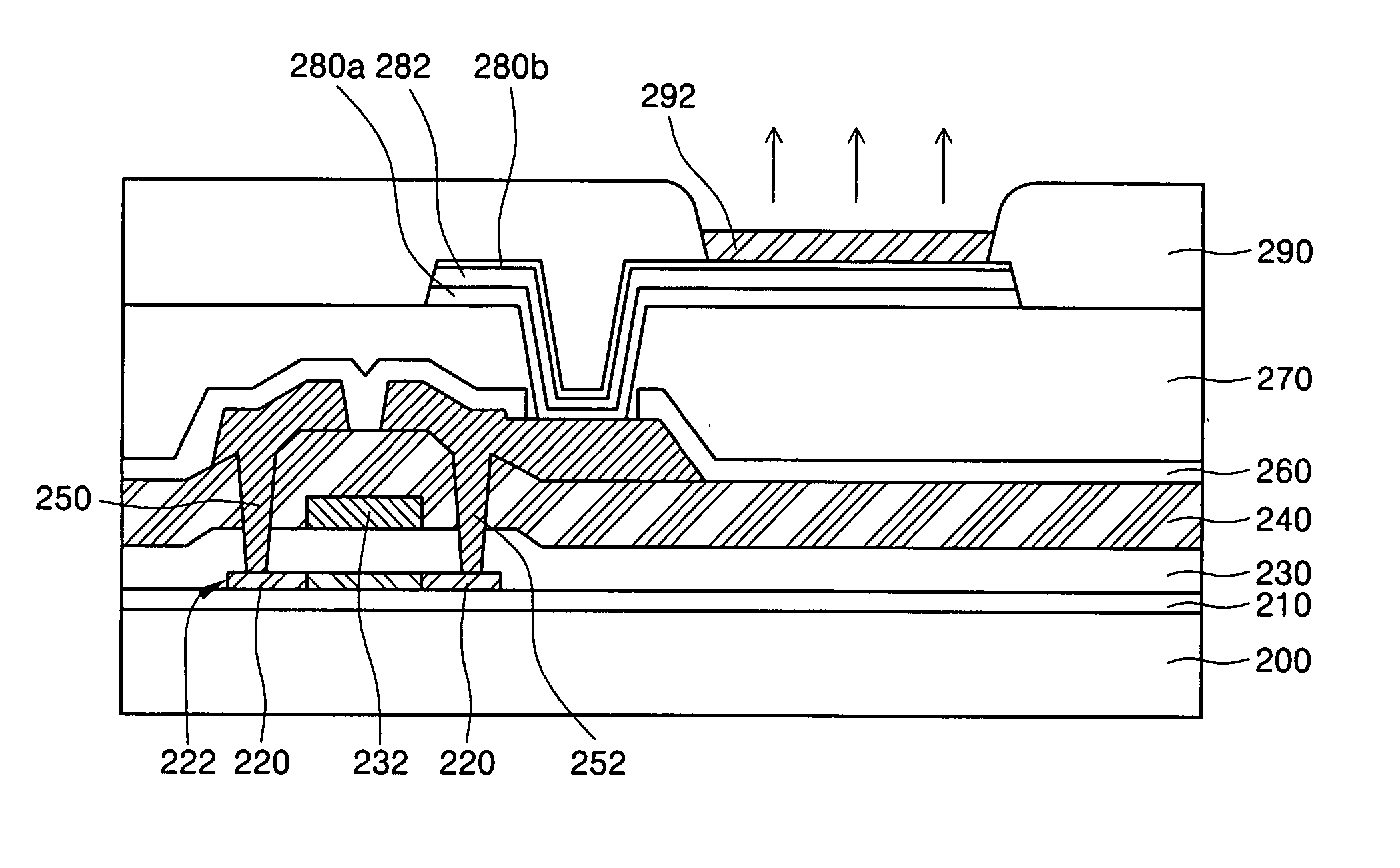
Organic light emitting device and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20050275339A1Improving electrical characteristic and optical characteristicDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic light emitting deviceOrganic layer
An organic light emitting device (OLED) and a method of fabricating the same are provided, wherein the OLED includes a thin film transistor having a gate electrode, and source and drain electrodes on a substrate; a triple-layered pixel electrode connected to one of the source and drain electrodes through a via-contact hole formed in an insulating layer on the t substrate, and having a lower pixel electrode, a reflective layer pattern and an upper pixel electrode; an organic layer disposed on the upper pixel electrode and having at least an emission layer; and an opposite electrode disposed on the organic layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
A triple layer hydrophobic-hydrophilic membrane for membrane distillation applications
InactiveCN103998115AAvoid cloggingImprove permeabilityMembranesSynthetic resin layered productsFiberComposite nanofibers
This invention relates to a triple layer composite nanofiber membrane for Membrane Distillation (MD) applications. The triple layer membrane has an extremely hydrophobic nanofiber layer, a hydrophobic microporous middle layer and a hydrophilic backing layer for MD applications.
Owner:NGEE ANN POLYTECHNIC
Electron Blocking Layers for Electronic Devices
InactiveUS20080150004A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCharge retentionHafnium
Methods and apparatuses for electronic devices such as non-volatile memory devices are described. The memory devices include a multi-layer control dielectric, such as a double or triple layer. The multi-layer control dielectric includes a combination of high-k dielectric materials such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3), hafnium oxide (HfO2), and / or hybrid films of hafnium aluminum oxide. The multi-layer control dielectric provides enhanced characteristics, including increased charge retention, enhanced memory program / erase window, improved reliability and stability, with feasibility for single or multistate (e.g., two, three or four bit) operation.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Steel cord for tire and pneumatic tire using the steel cord
InactiveUS20100300592A1Strong penetrating powerLow tensile strengthPneumatic tyre reinforcementsTyre beadsFrettingEngineering
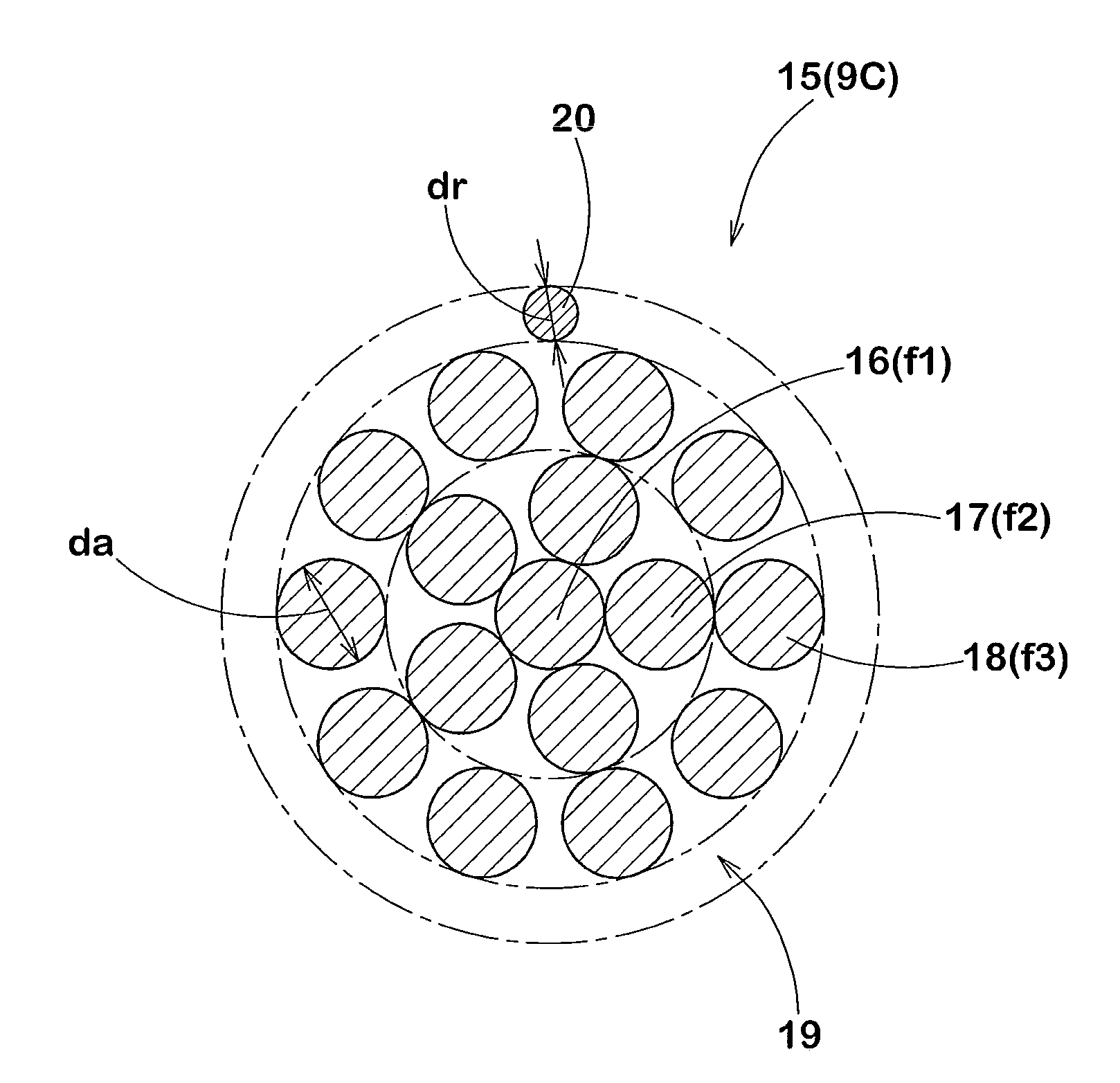
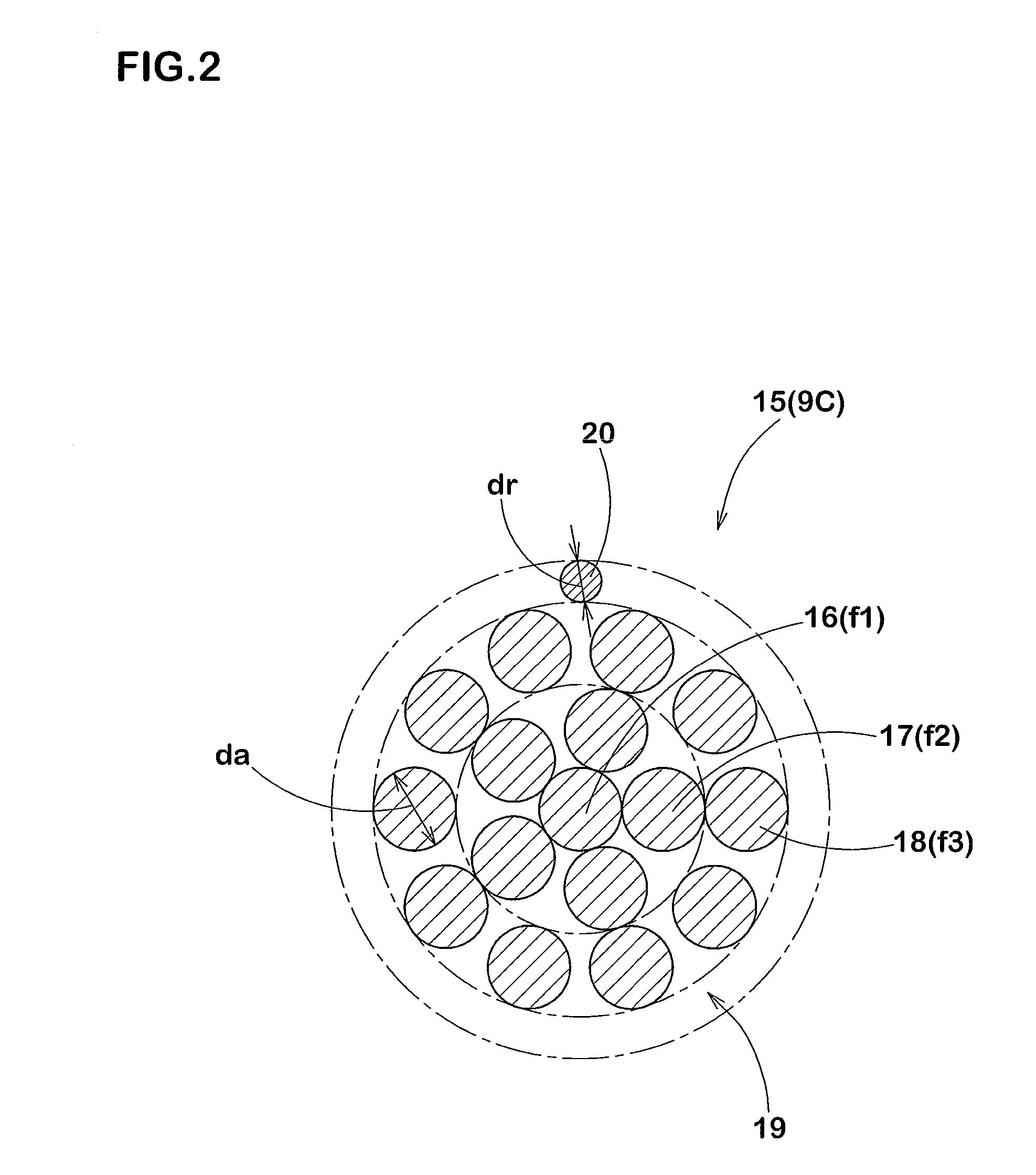
It is an object of the present invention to reduce fretting between strands in a steel cord, to suppress reduction in cord strength caused by running, to enhance rubber penetrability, and to improve tire durability. The steel cord includes a cord main portion 19 of a triple layer-stranding structure including: a core 16 formed from one core strand f1, an inner sheath 17 including N (2 to 5) inner sheath strands f2 stranded with a stranding pitch Pi around the core; and outer sheath 18 formed from M (6 to 11) outer sheath strands f3 stranded with a stranding pitch Po around the inner sheath. Diameters of the strands f1, f2 and f3 are equal to each other, and stranding directions of the sheaths 17 and 18 are the same. A difference (|Ai−Ao|) between a stranding angle Ai of the inner sheath strand f2 and a stranding angle Ao of the outer sheath strand f3 is greater than 1° and smaller than 3°.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com