Patents
Literature
913results about How to "Accelerated training" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
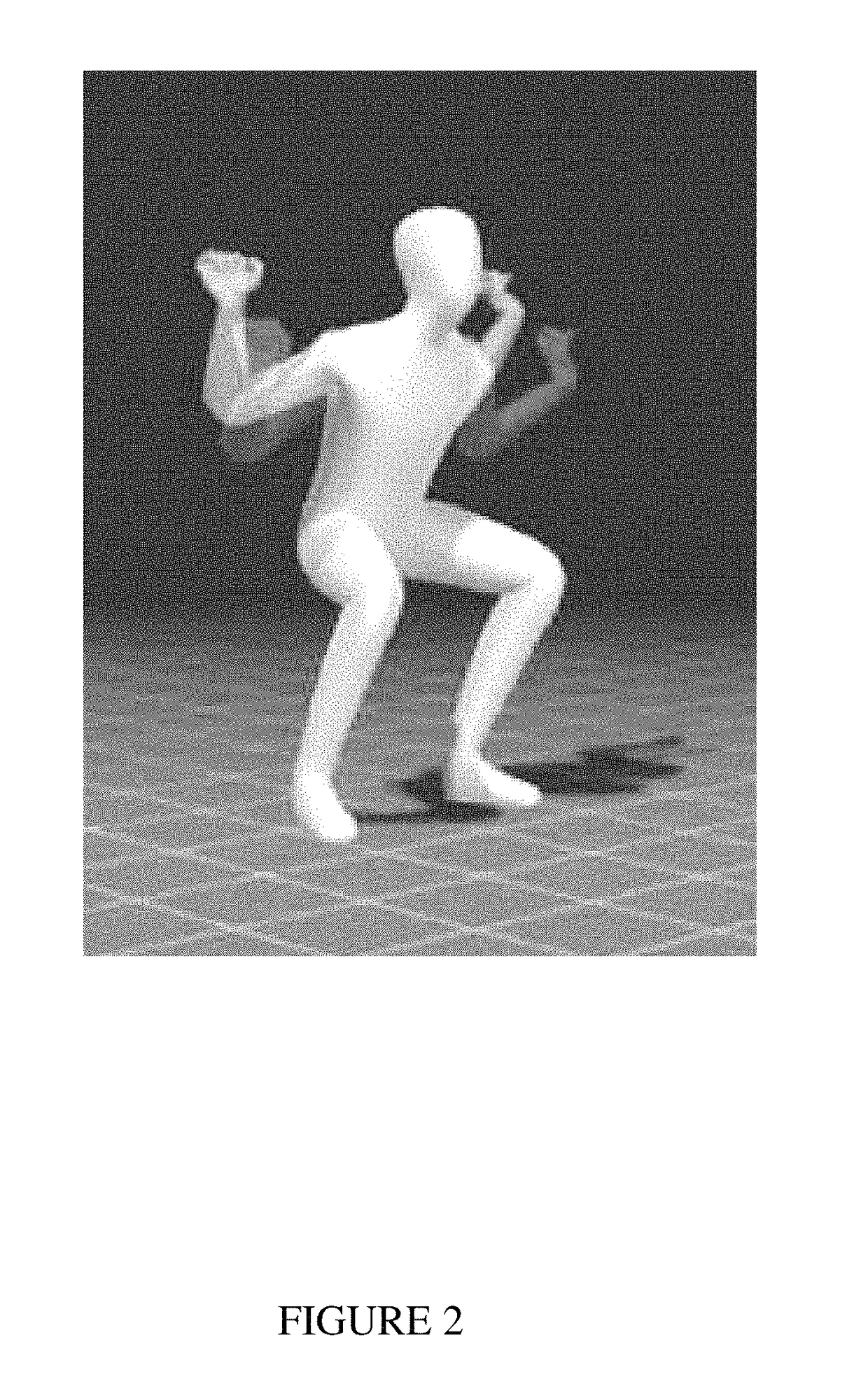
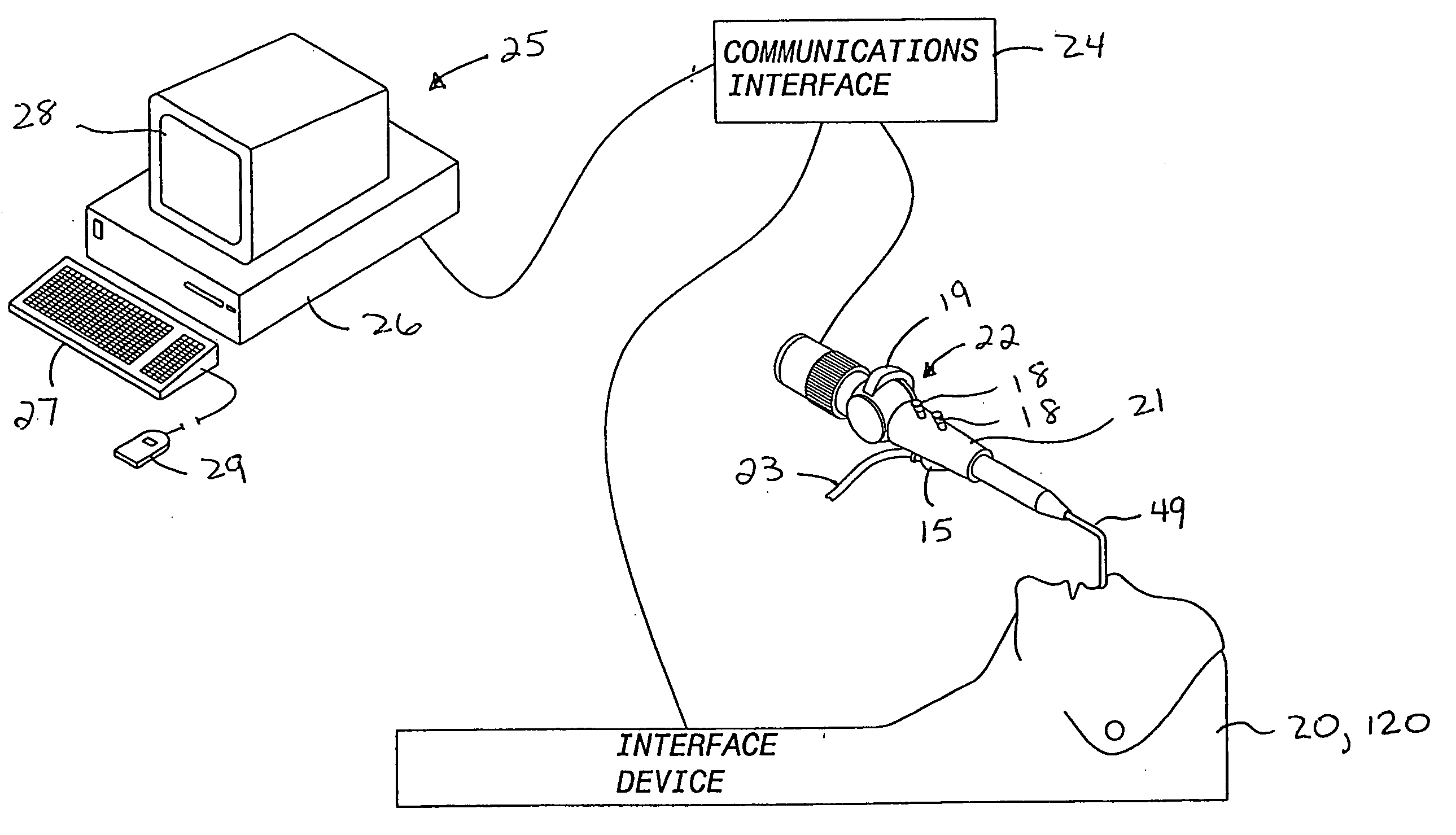
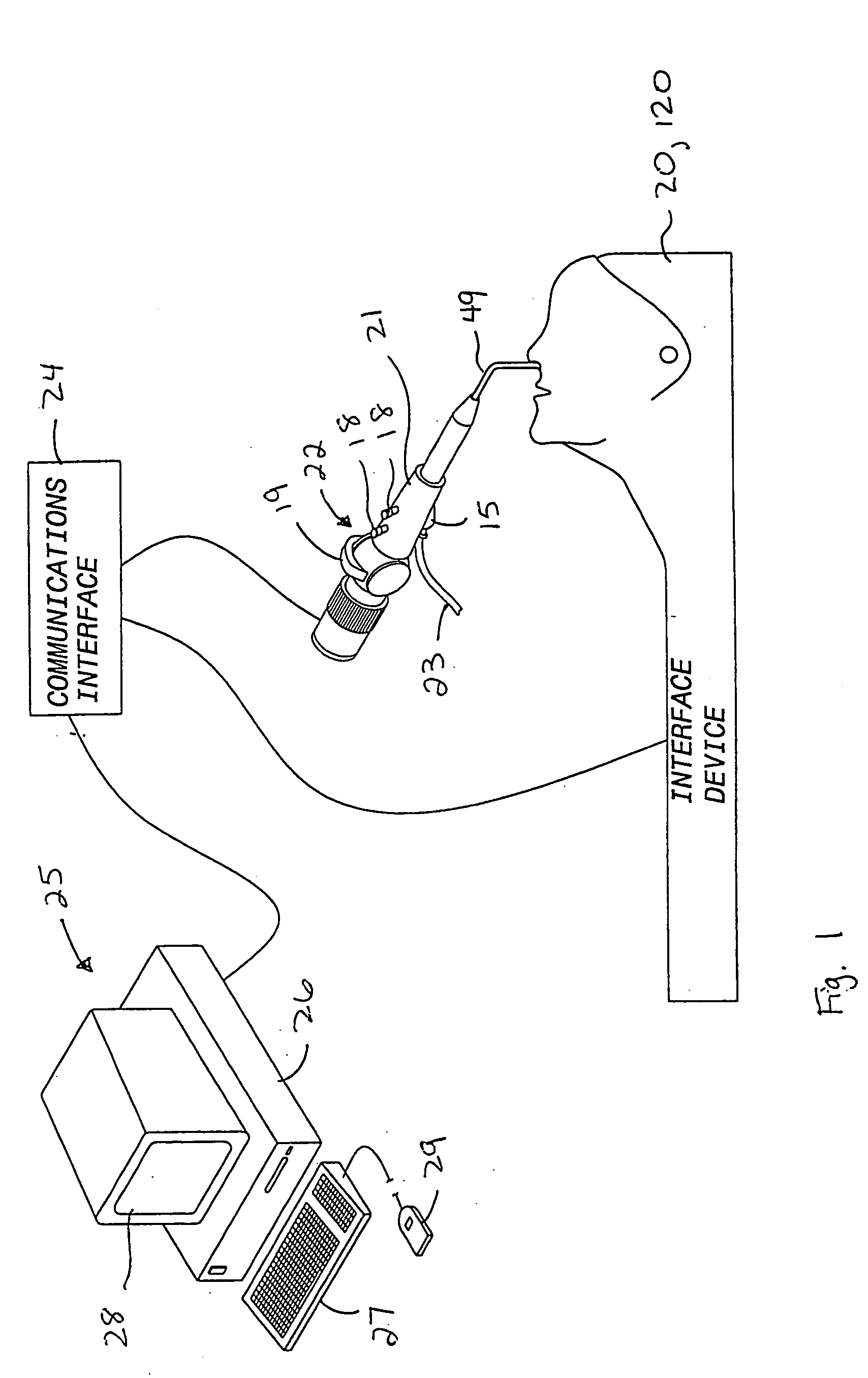
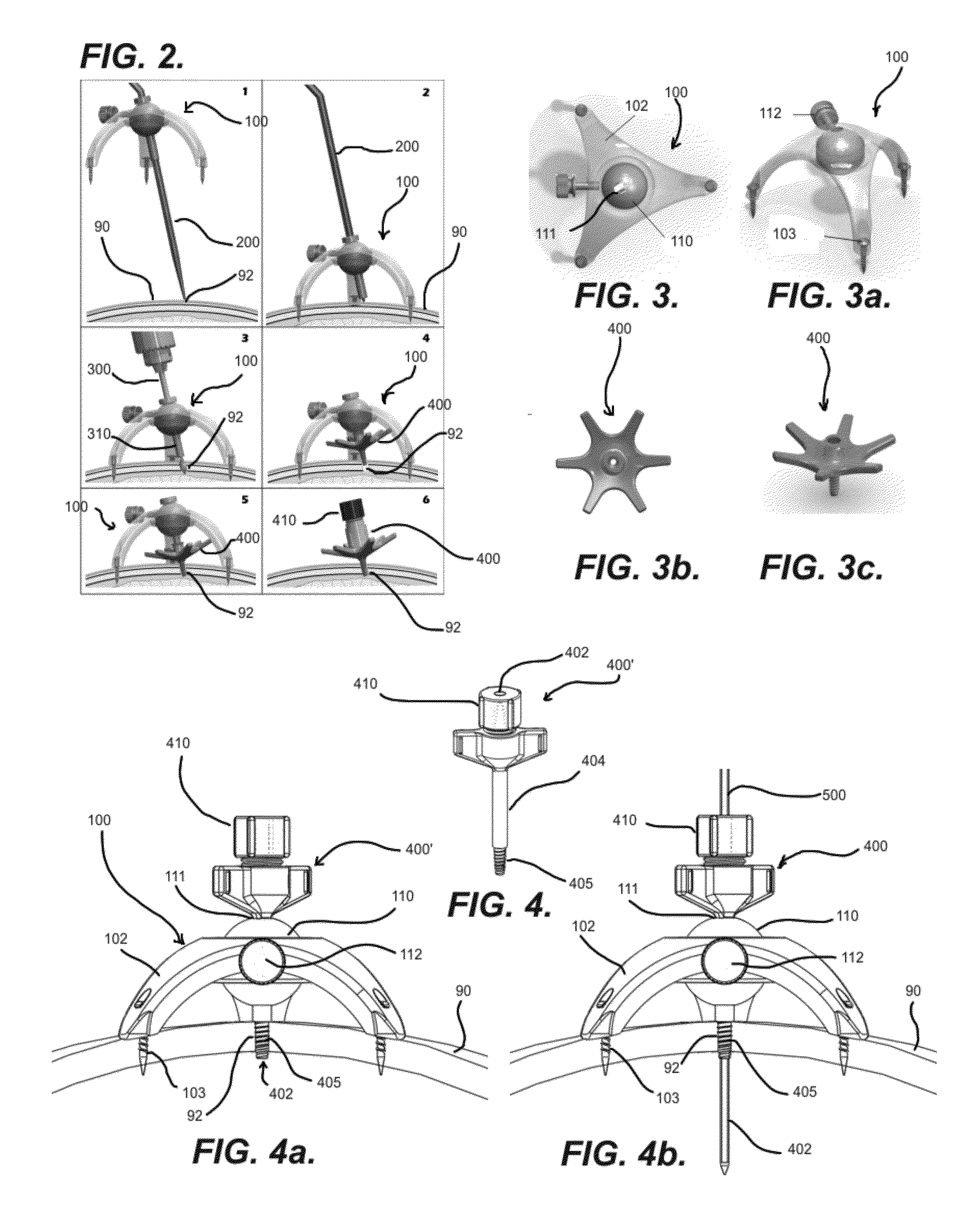
Interface device and method for interfacing instruments to medical procedure simulation systems
InactiveUS6929481B1Improve realismSimulate the realEducational modelsMeasuring instrumentDisplay device
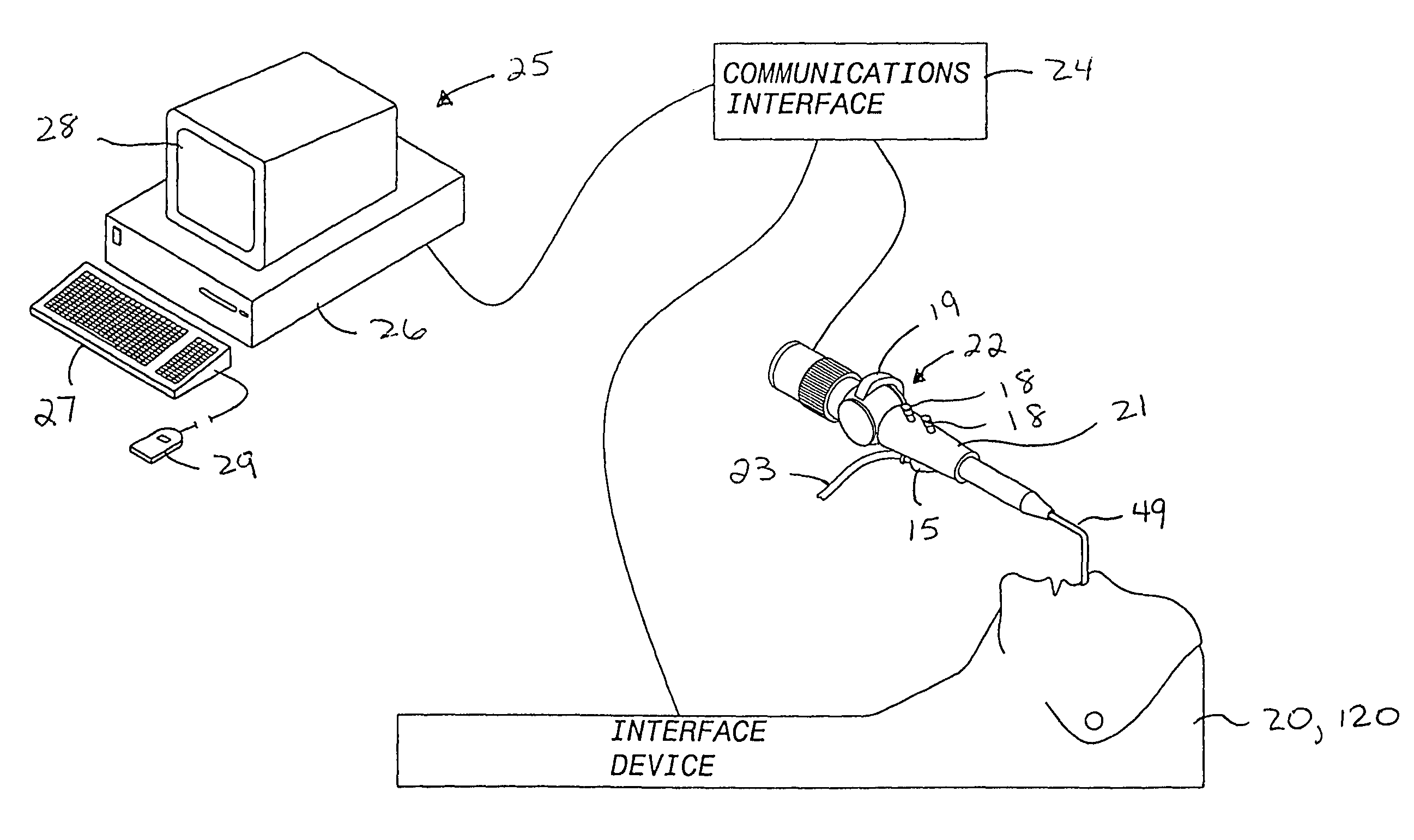
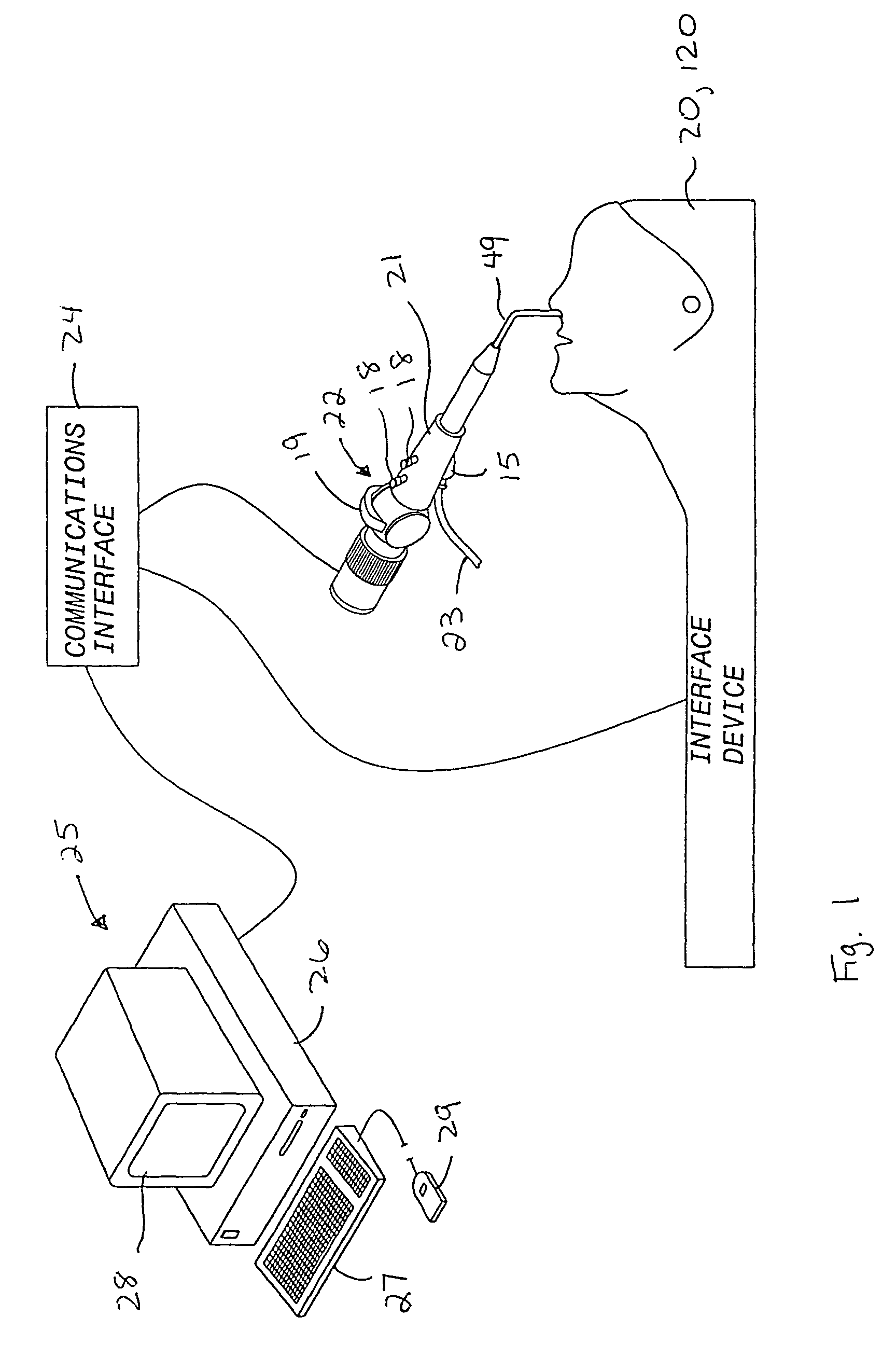
An interface device and method for interfacing instruments to a medical procedure simulation system serve to interface peripherals in the form of mock medical instruments to the medical procedure simulation system computer to enable simulation of medical procedures. The interface device includes a housing having a mock bodily region of interest to facilitate insertion of a mock instrument, such as an endoscope tube, into the interface device. The mock bodily region of interest may be pivotable to simulate various patient orientations. The instrument is engaged by a capture mechanism in order to measure rotational and translational motion of the instrument. An actuator is disposed within the interface device to provide force feedback to the instrument. The measured motion is provided to the computer system to reflect instrument motion on the display during the simulation. Alternatively, the interface device may be configured to accommodate instrument assemblies having a plurality of nested instruments (e.g., sheath, catheter and wire), whereby the interface device individually grasps, measures manipulation of and provides force feedback to the nested instruments. In addition, the interface device may be configured to simultaneously accommodate a plurality of independently inserted instruments.
Owner:IMMERSION MEDICAL
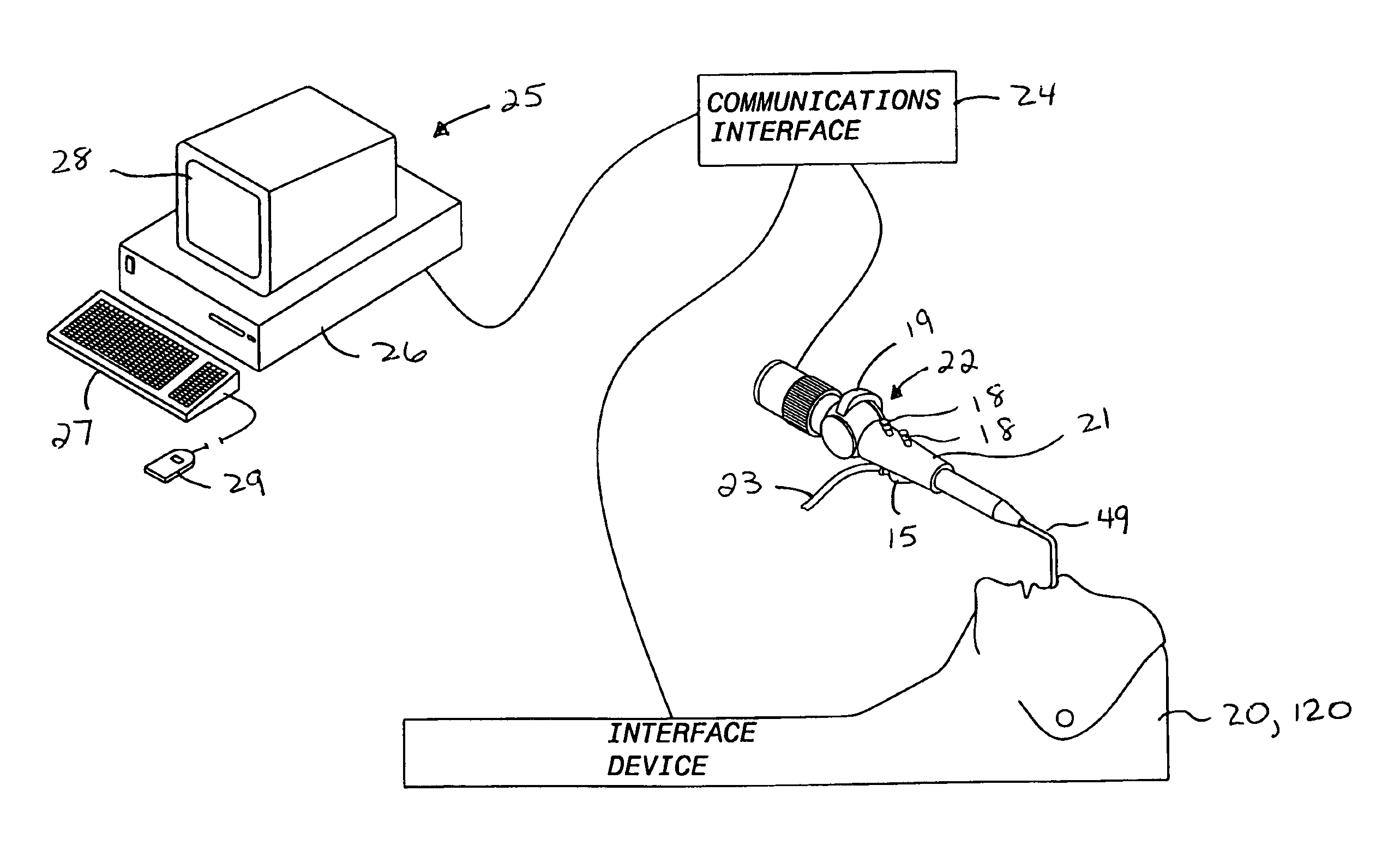
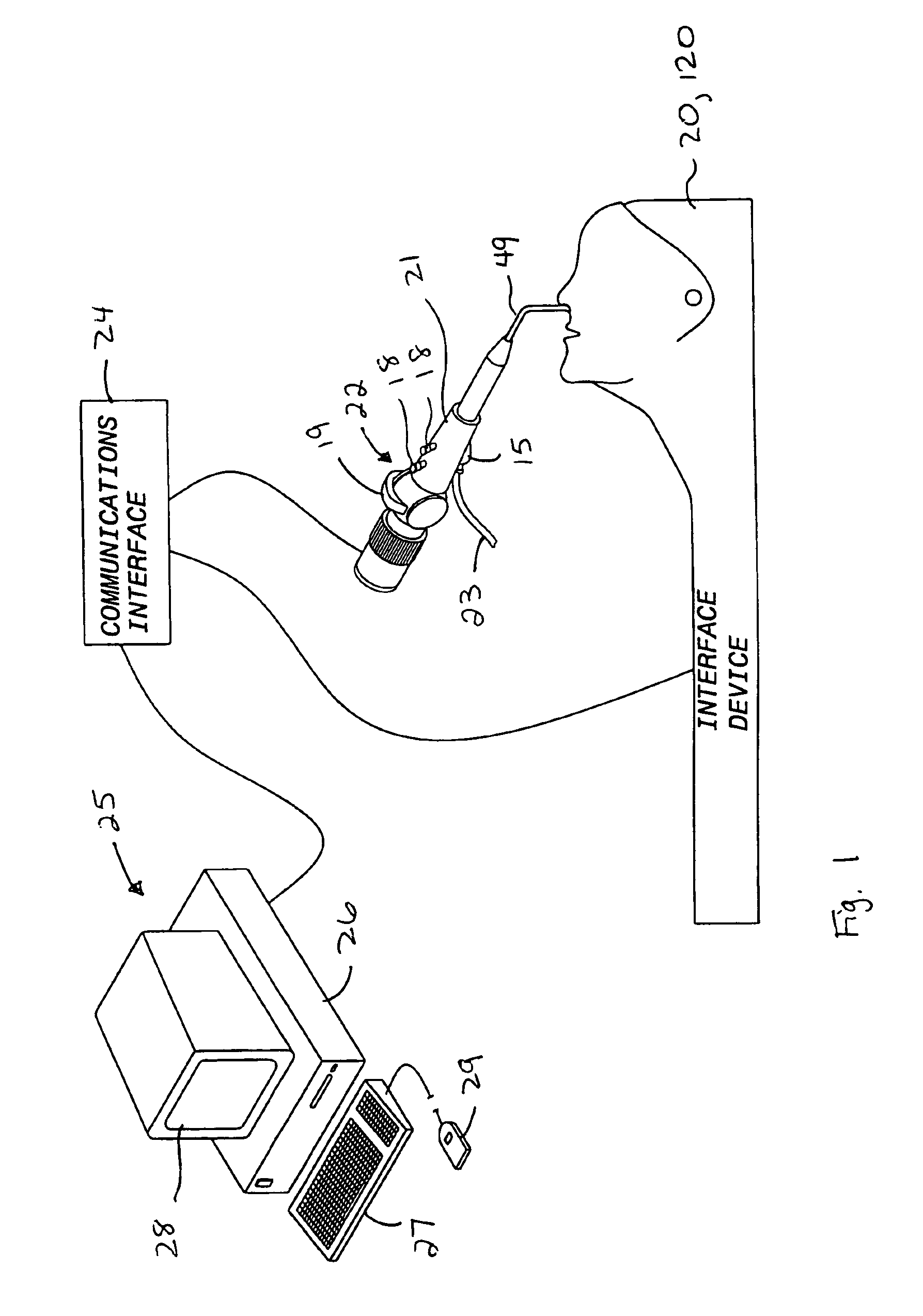
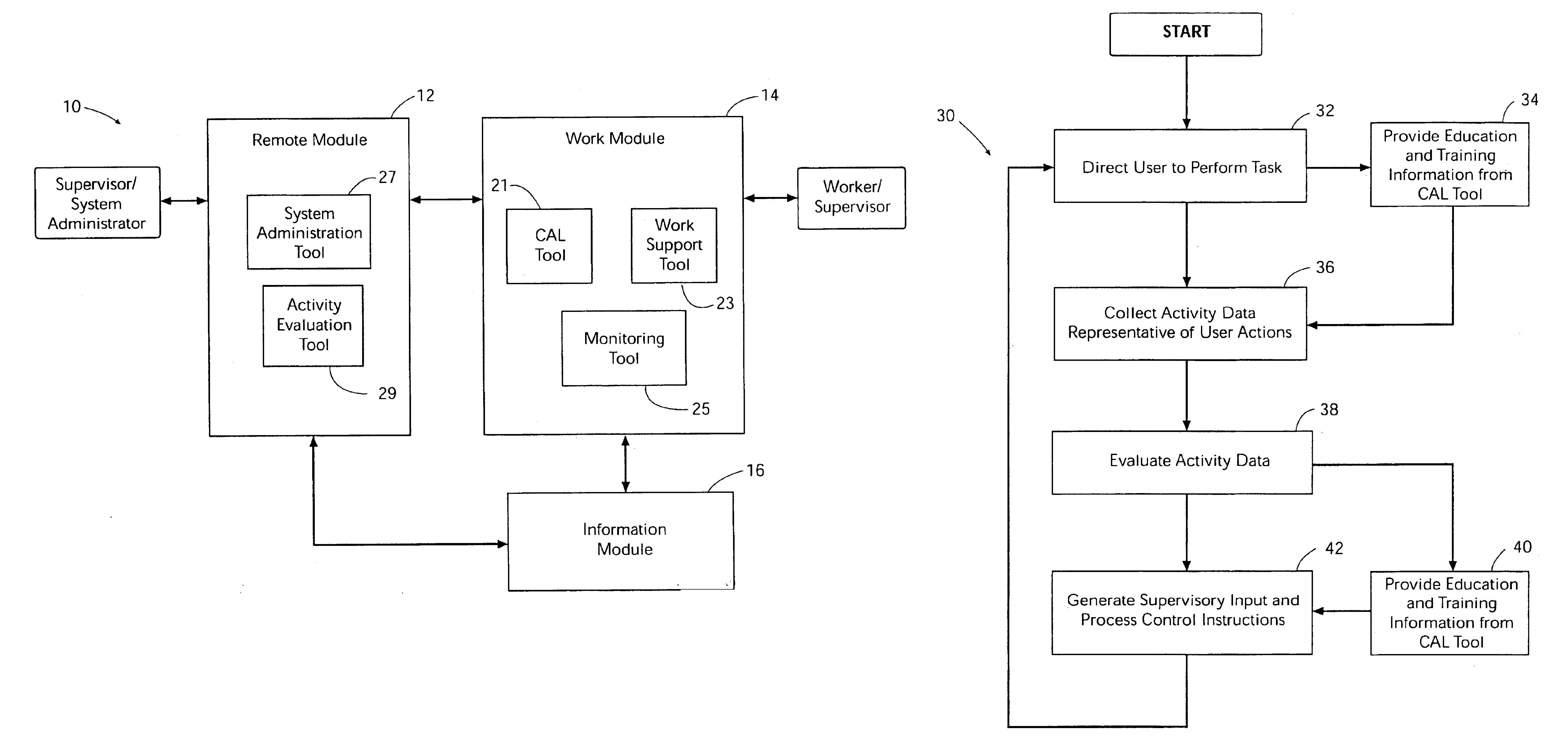
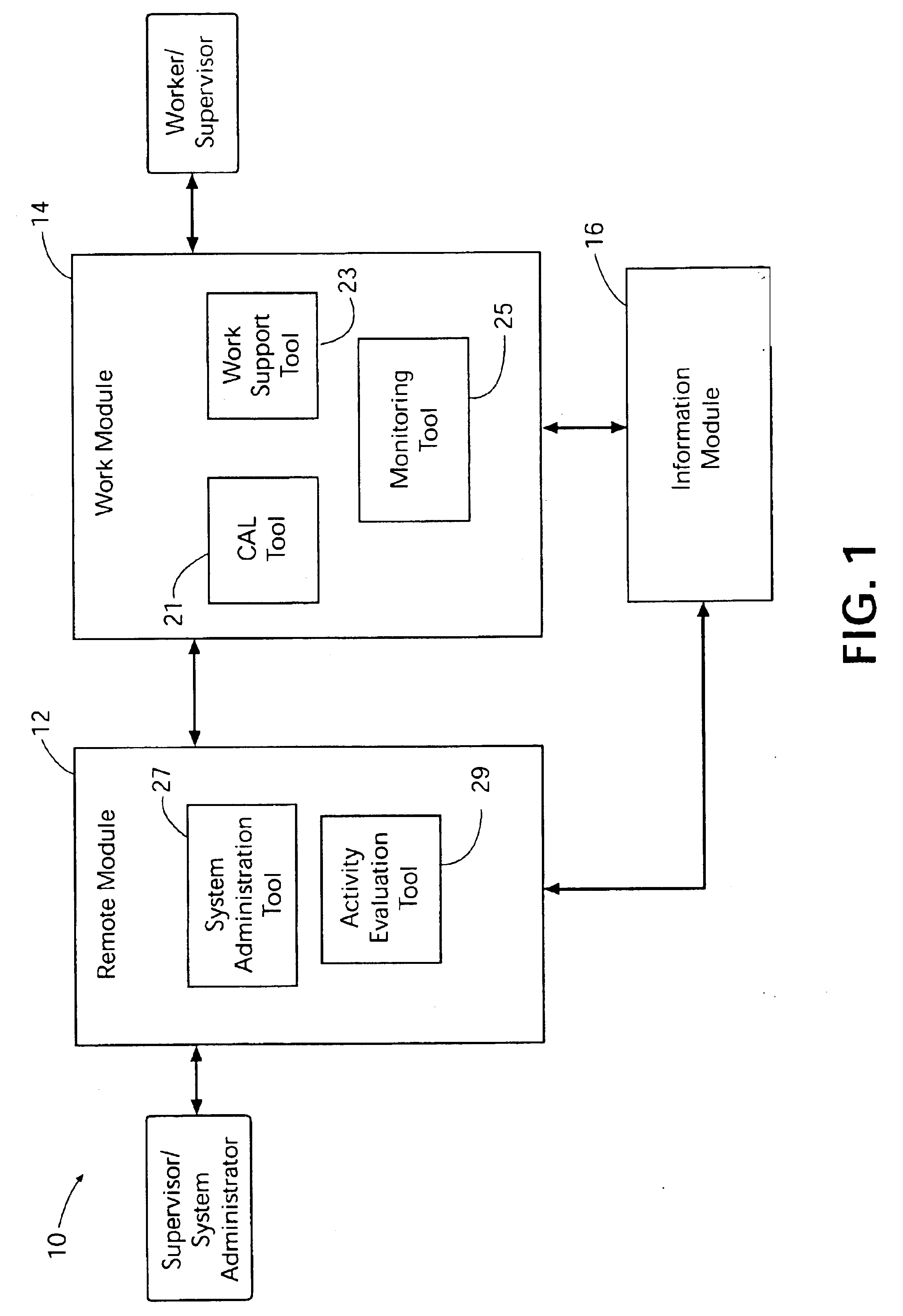
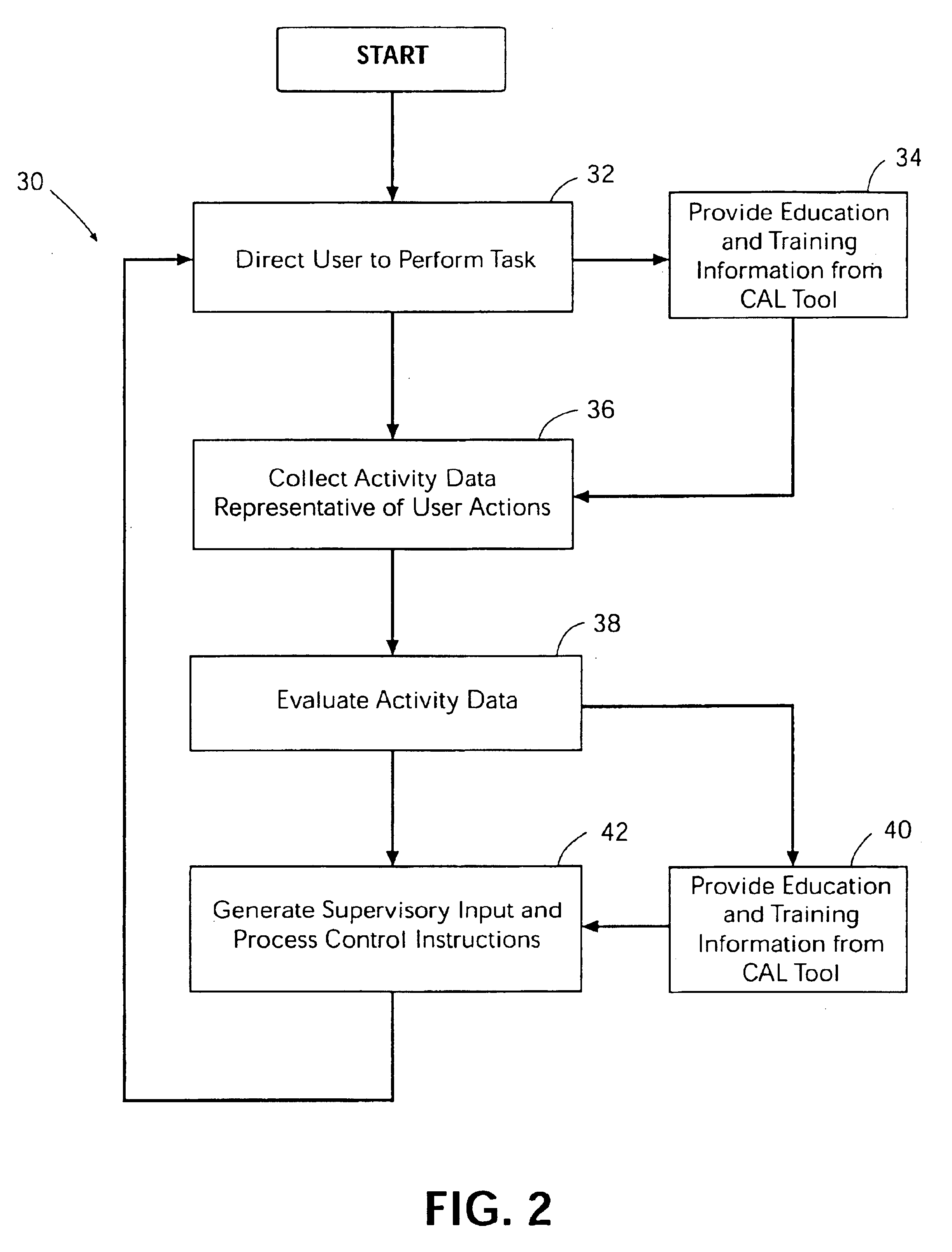
Method and system for remote electronic monitoring and mentoring of computer assisted performance support
InactiveUS6871195B2Easy to updateAccelerated trainingDigital computer detailsDigital dataProduction rateComputer-aided
Method and system for computer assisted performance support include remote electronic monitoring and mentoring to provide for supervision, control and instruction of the worker while the worker performs directed tasks. Activity data representative of worker activities are collected at the work site and can be accessed by a supervisor located remote from the work site. The remote supervisor generates and transmits to the worker feedback based on the activity data. The remote supervisor can evaluate an activity trail of a worker's performance of directed tasks and development of skills through educational training to permit timely identification and correction of worker deficiencies. The ability of the remote supervisor to transmit feedback to the worker while the worker is performing directed tasks enhances rapid development of the worker's skills and workplace safety and productivity.
Owner:E PROMENTOR
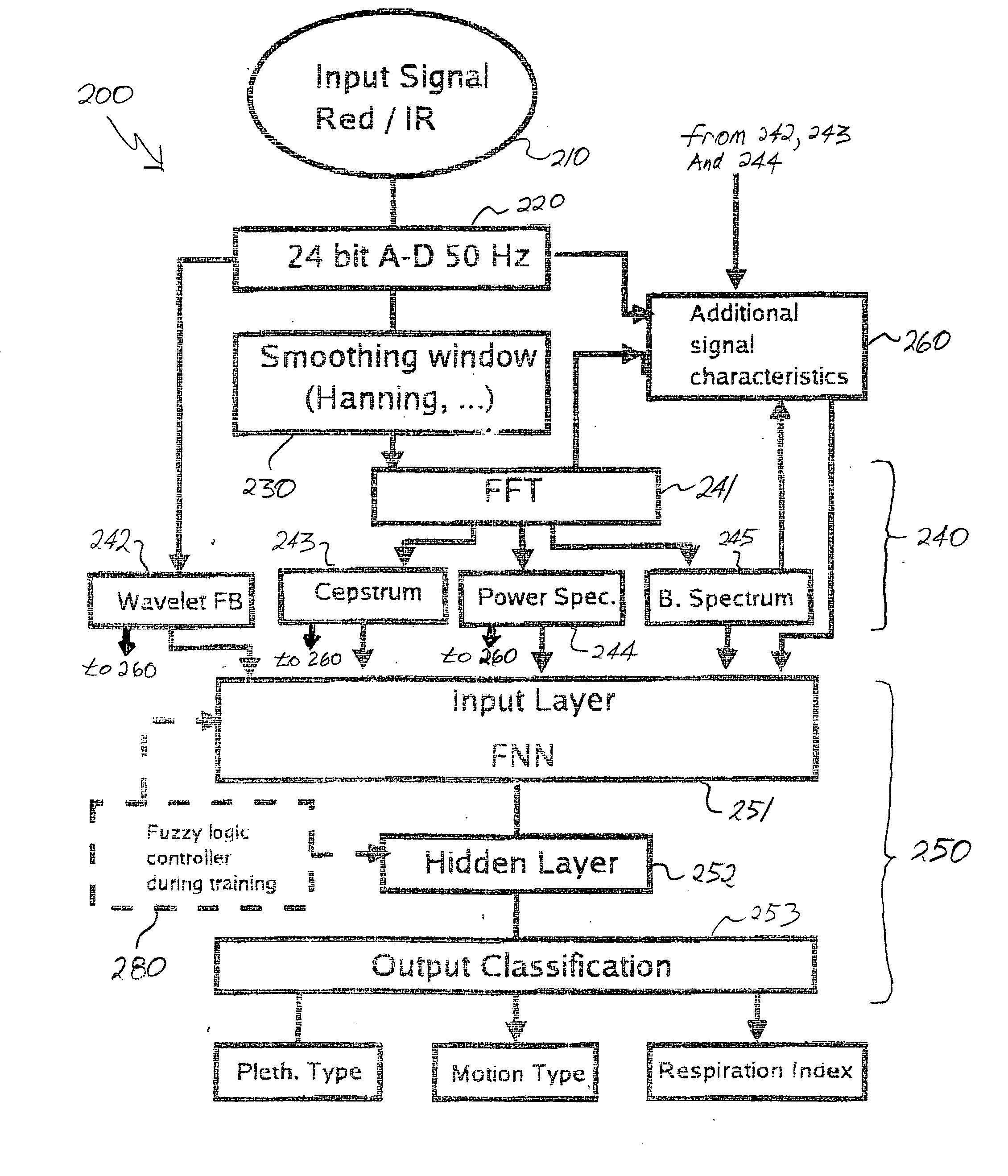
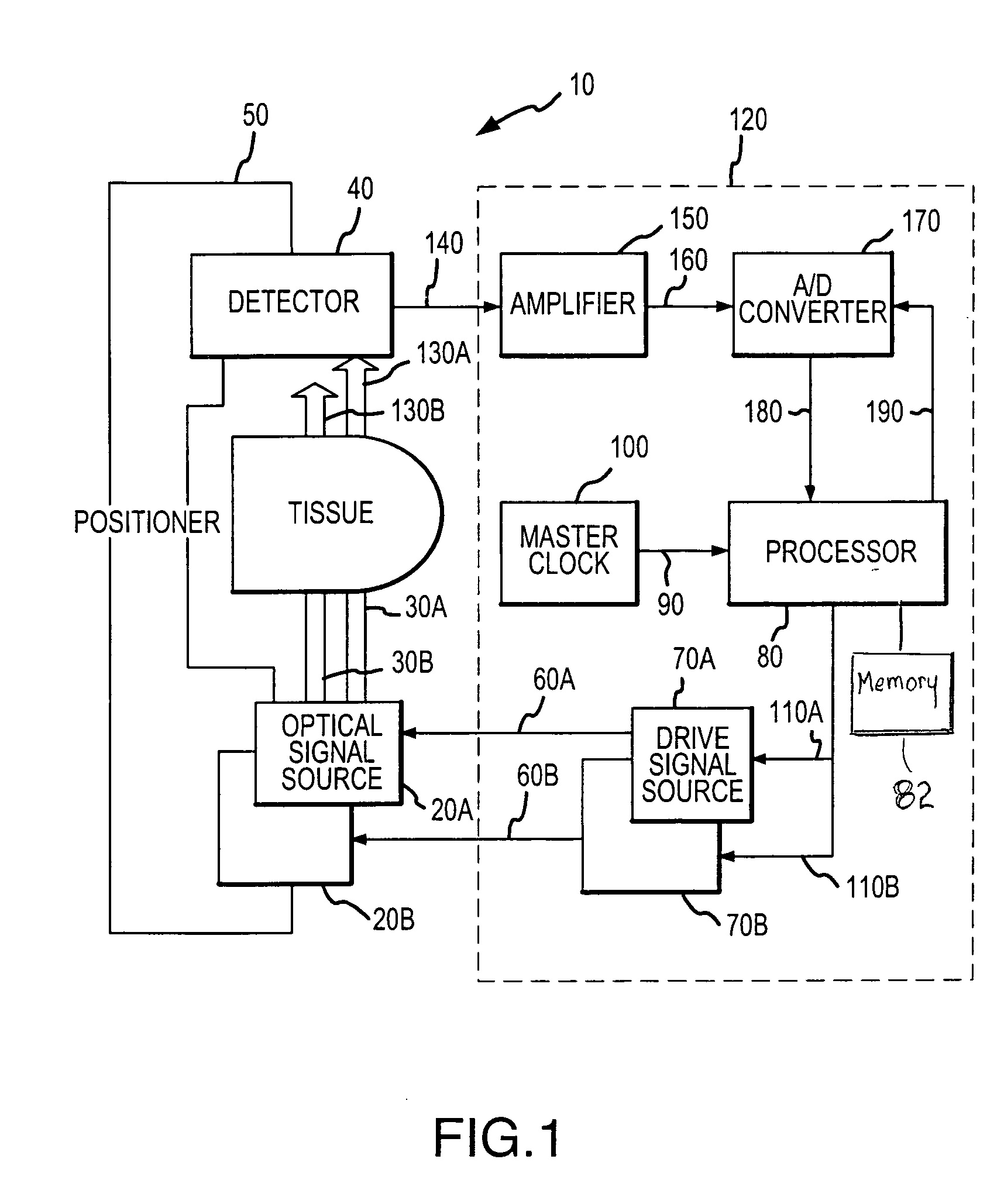
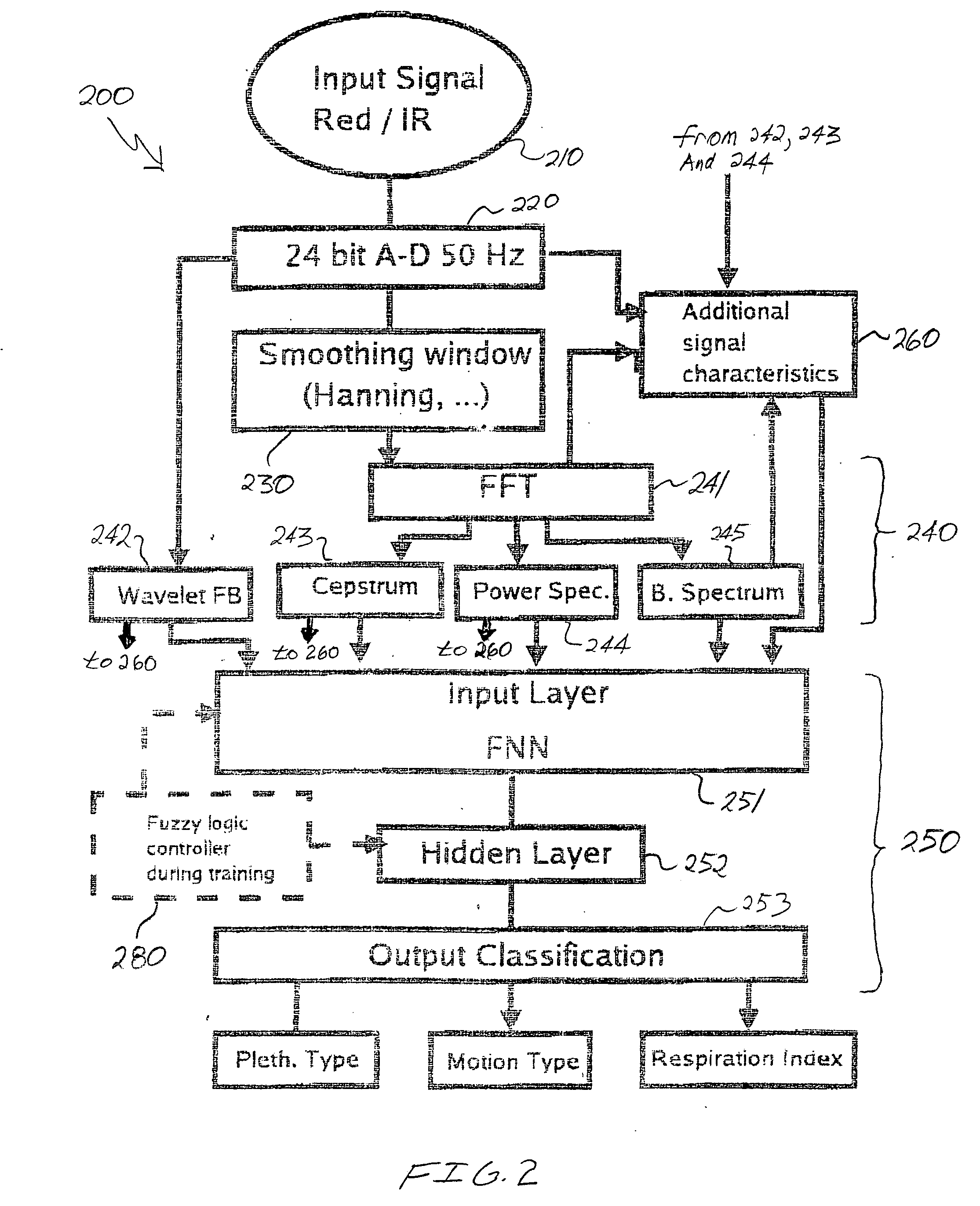
Multi-domain motion estimation and plethysmographic recognition using fuzzy neural-nets
ActiveUS20050049470A1Improve signal extractionLess abilitySurgeryCatheterSignal transformationWavelet filter
Pulse oximetry is improved through classification of plethysmographic signals by processing the plethysmographic signals using a neural network that receives input coefficients from multiple signal domains including, for example, spectral, bispectral, cepstral and Wavelet filtered signal domains. In one embodiment, a plethysmographic signal obtained from a patient is transformed (240) from a first domain to a plurality of different signal domains (242, 243, 244, 245) to obtain a corresponding plurality of transformed plethysmographic signals. A plurality of sets of coefficients derived from the transformed plethysmographic signals are selected and directed to an input layer (251) of a neural network (250). The plethysmographic signal is classified by an output layer (253) of the neural network (250) that is connected to the input layer (251) by one or more hidden layers (252).
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
Interface device and method for interfacing instruments to medical procedure simulation systems
InactiveUS20060046235A1Improve realismSimulate the realEducational modelsMeasuring instrumentDisplay device
An interface device and method for interfacing instruments to a medical procedure simulation system serve to interface peripherals in the form of mock medical instruments to the medical procedure simulation system computer to enable simulation of medical procedures. The interface device includes a housing having a mock bodily region of interest to facilitate insertion of a mock instrument, such as an endoscope tube, into the interface device. The mock bodily region of interest may be pivotable to simulate various patient orientations. The instrument is engaged by a capture mechanism in order to measure rotational and translational motion of the instrument. An actuator is disposed within the interface device to provide force feedback to the instrument. The measured motion is provided to the computer system to reflect instrument motion on the display during the simulation. Alternatively, the interface device may be configured to accommodate instrument assemblies having a plurality of nested instruments (e.g., sheath, catheter and wire), whereby the interface device individually grasps, measures manipulation of and provides force feedback to the nested instruments. In addition, the interface device may be configured to simultaneously accommodate a plurality of independently inserted instruments.
Owner:IMMERSION MEDICAL
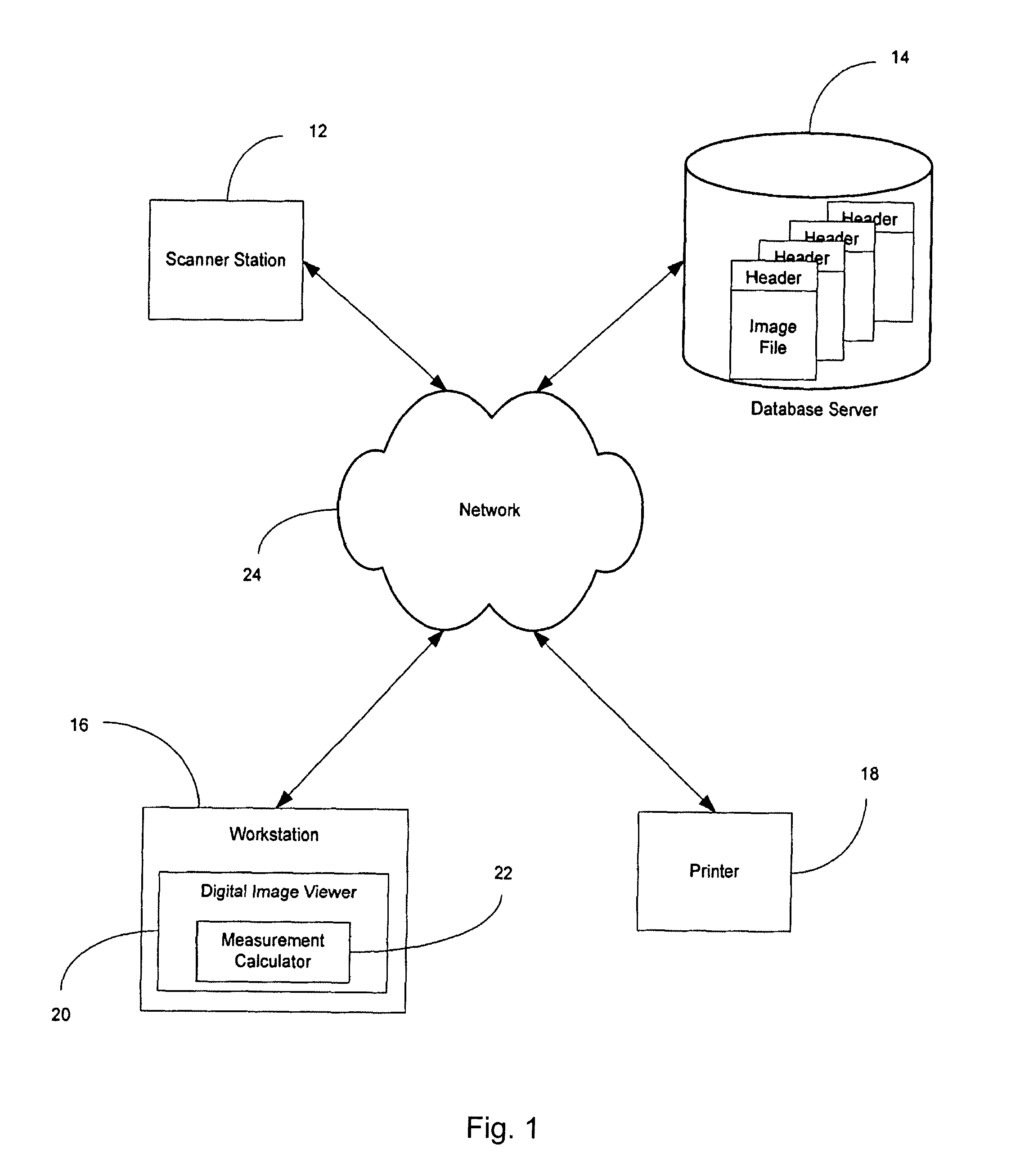
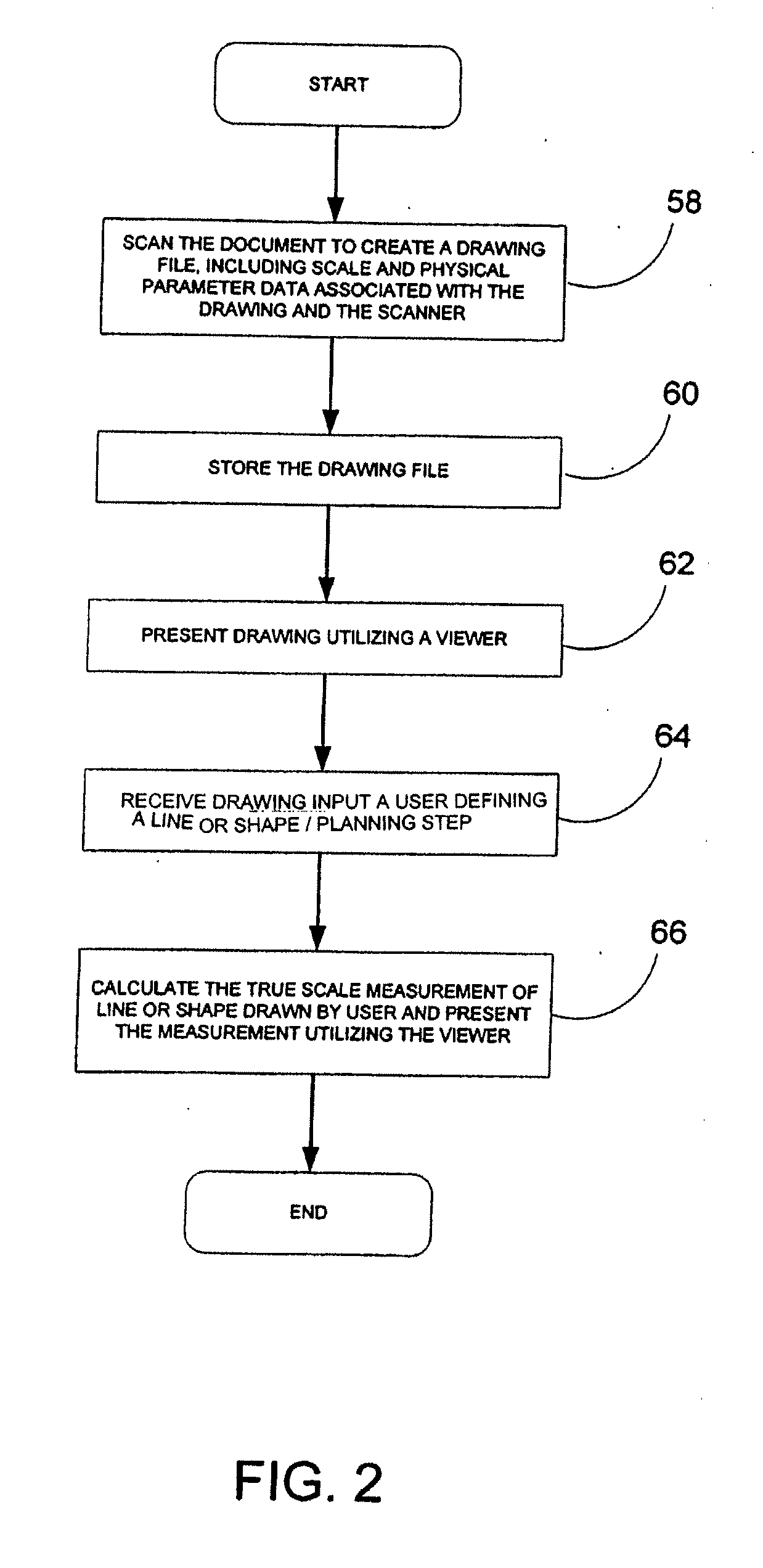
System and method for simultaneously viewing, coordinating, manipulating and interpreting three-dimensional and two-dimensional digital images of structures for providing true scale measurements and permitting rapid emergency information distribution
InactiveUS20100066559A1Security riskEase of evacuationCharacter and pattern recognitionElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingTime informationComputer graphics (images)
The present invention provides a true-scale, coordinate-matched, linked in real-time, dual three-dimensional / two-dimensional visual display / viewer. The display simultaneously shows a 3D digital image and an associated 2D digital image of a selected drawing. The display of the present invention allows a user to visualize an asset's location, surrounding environment and hazards and true scale structural details for interior or external structural scenes. Using the display and associated tools, the user can obtain real-time information of an environment, true-scale measurement, plan ingress / egress paths, shortest paths between points and the number of doorways in a structure and track objects within the displayed environment. The intelligence gained using the tools and 3D / 2D display may be used and further manipulated by a single user or may be distributed to other users.
Owner:SACAL HLDG LTD
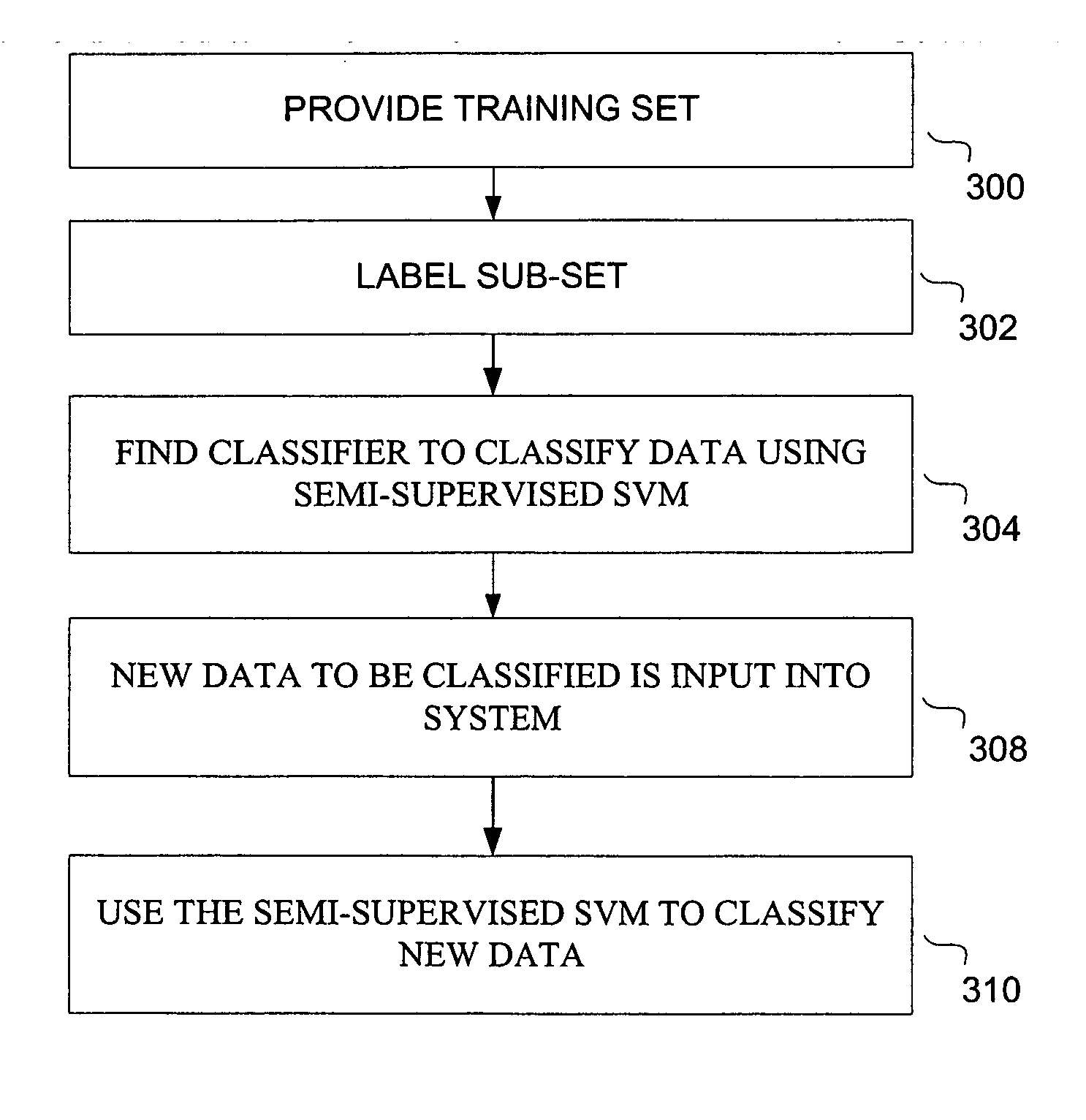
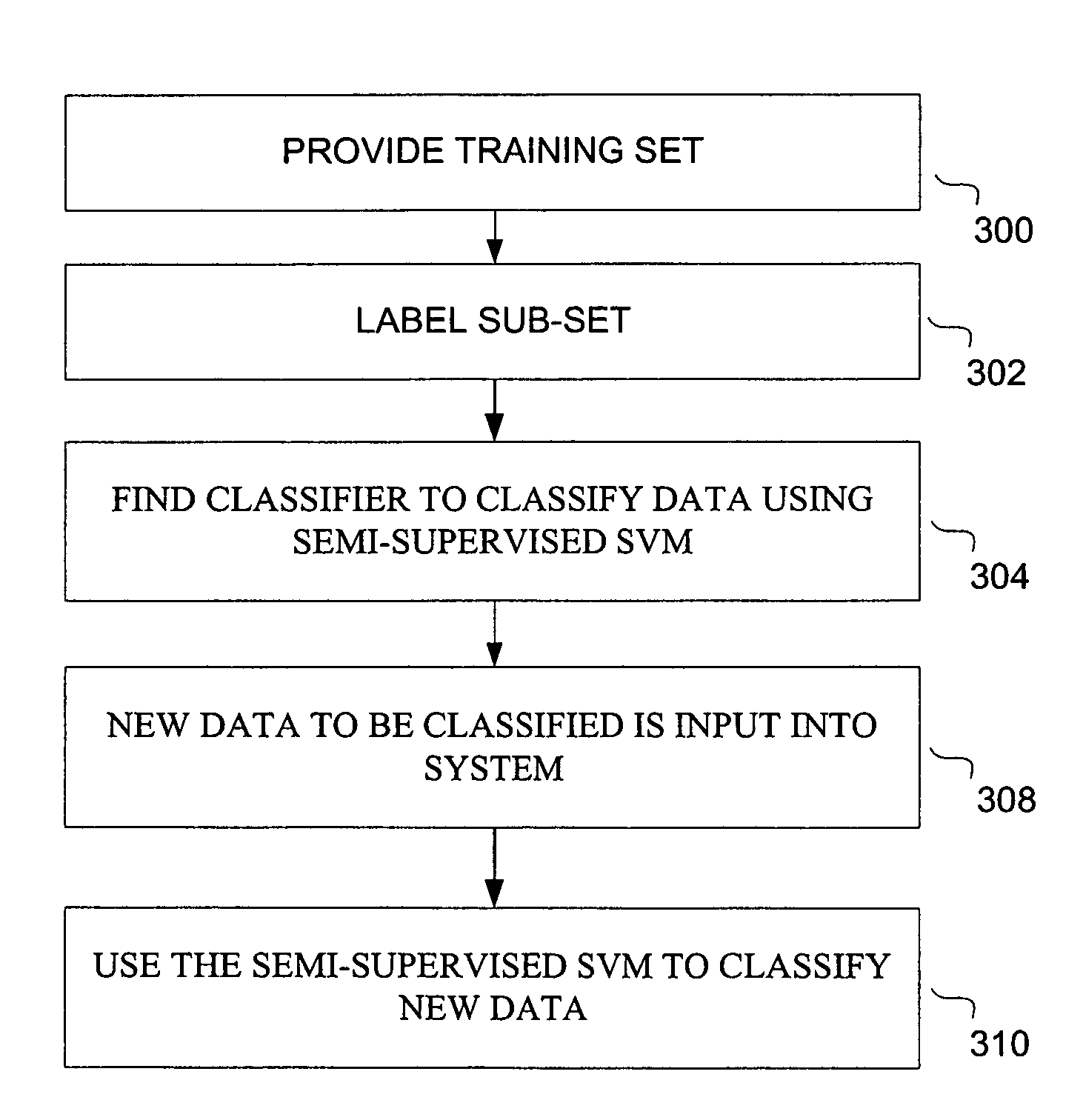
Large scale semi-supervised linear support vector machines
InactiveUS20070239642A1Improve good performanceAccelerated trainingDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerized systemMean field annealing
A computerized system and method for large scale semi-supervised learning is provided. The training set comprises a mix of labeled and unlabeled examples. Linear classifiers based on support vector machine principles are built using these examples. One embodiment uses a fast design of a linear transductive support vector machine using multiple switching. In another embodiment, mean field annealing is used to form a very effective semi-supervised support vector machine. For both these embodiments, the finite Newton method is used as the base method for achieving fast training
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
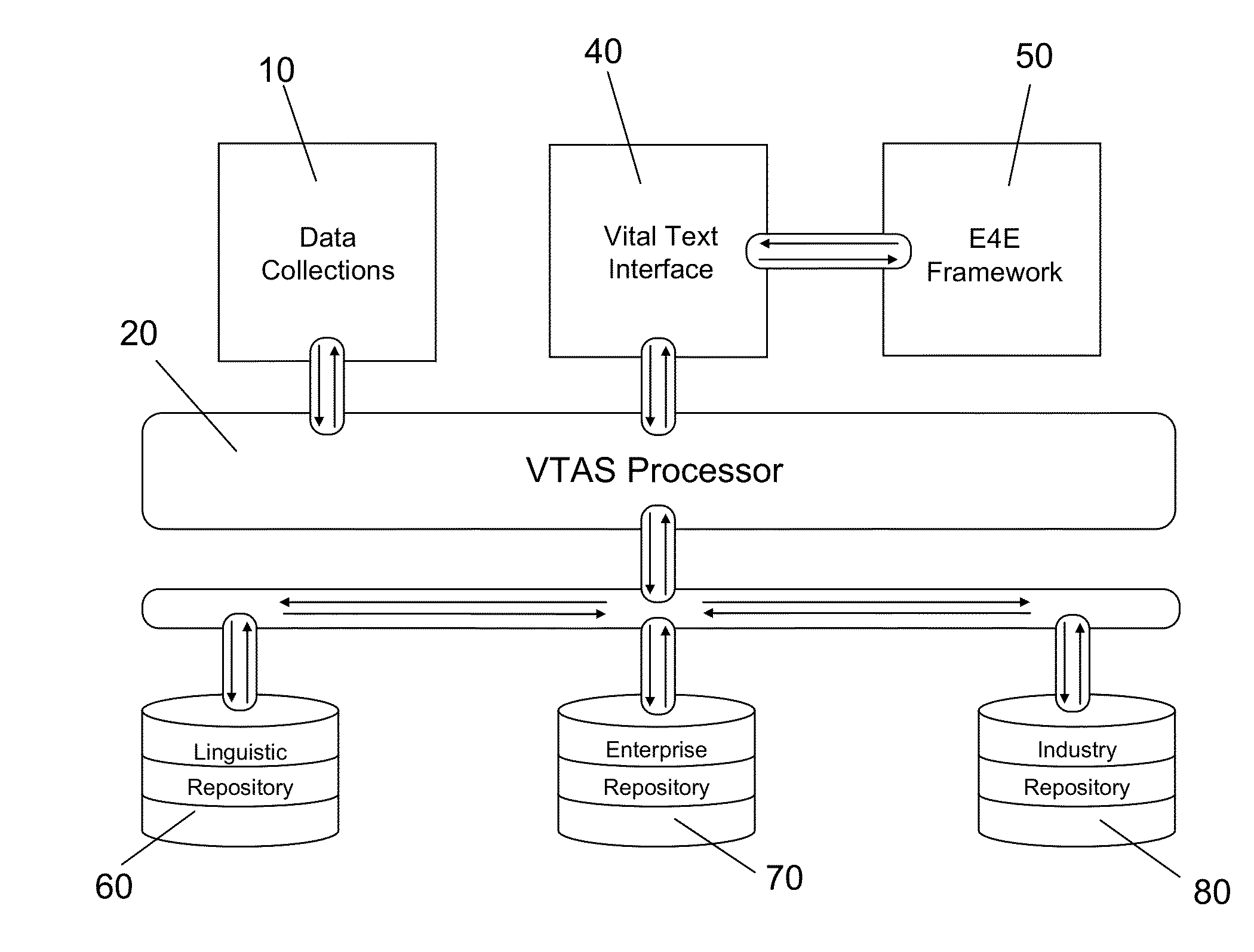
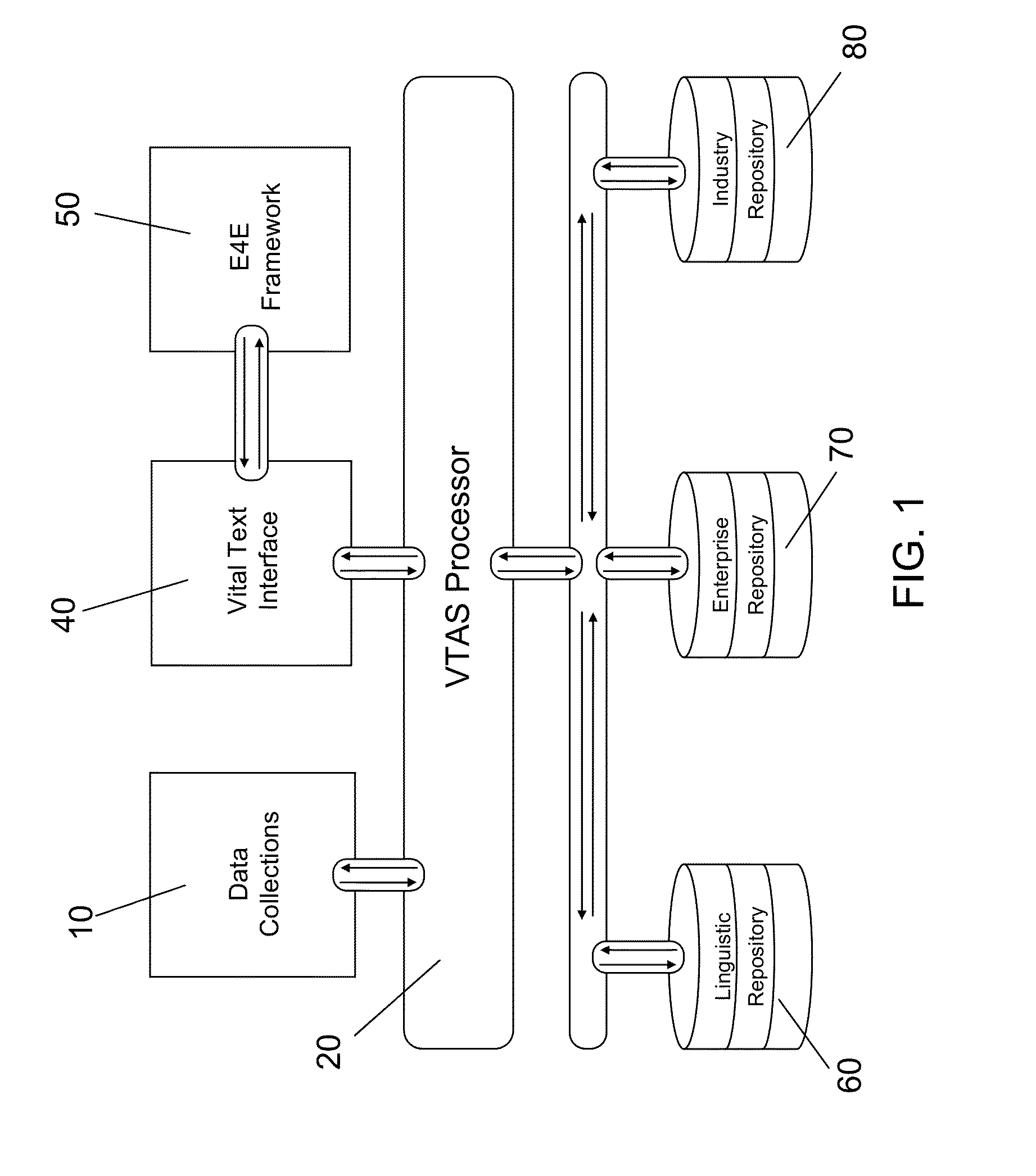
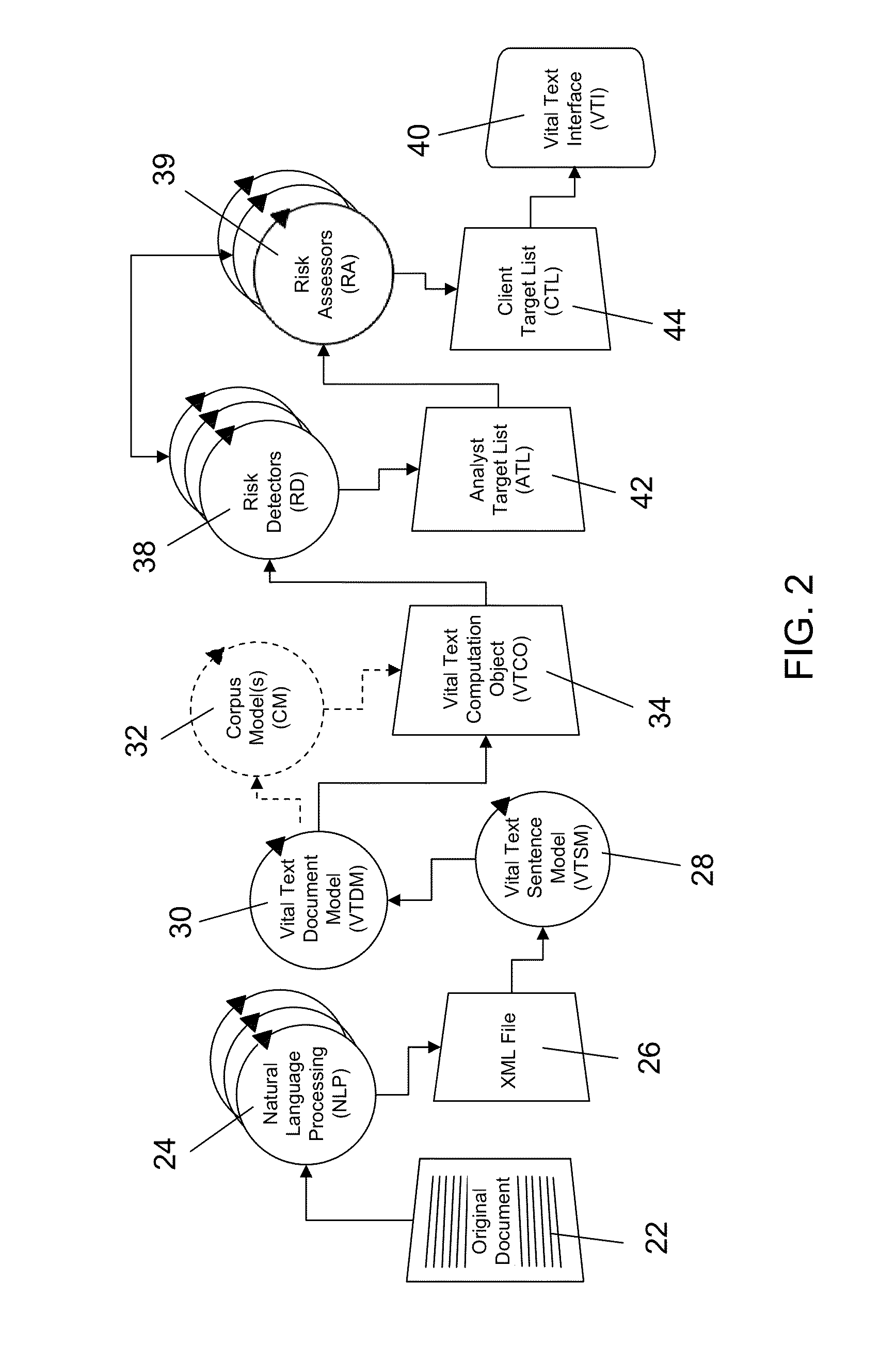
Vital text analytics system for the enhancement of requirements engineering documents and other documents
ActiveUS20140172417A1Improve efficiencyReduce defectsSemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsDocumentation procedureTechnical specifications
A Vital Text Analytics System (VTAS), incorporating a repository of enterprise terms or concepts, is one that improves the readability and fidelity of technical specifications, instructions, training manuals requirements engineering documents and other related engineering documents, typically from a single organization or workgroup. The system stresses ontological analysis of a corpus of related documents, and applies a suite of computational tools that supports the identification and assessment of risk in evaluating the content of the documents, as well as providing statistical measures reflecting the frequency and severity of document features that threaten comprehension.
Owner:CLOUD 9 LLC DBA VITAL TEXT SYST
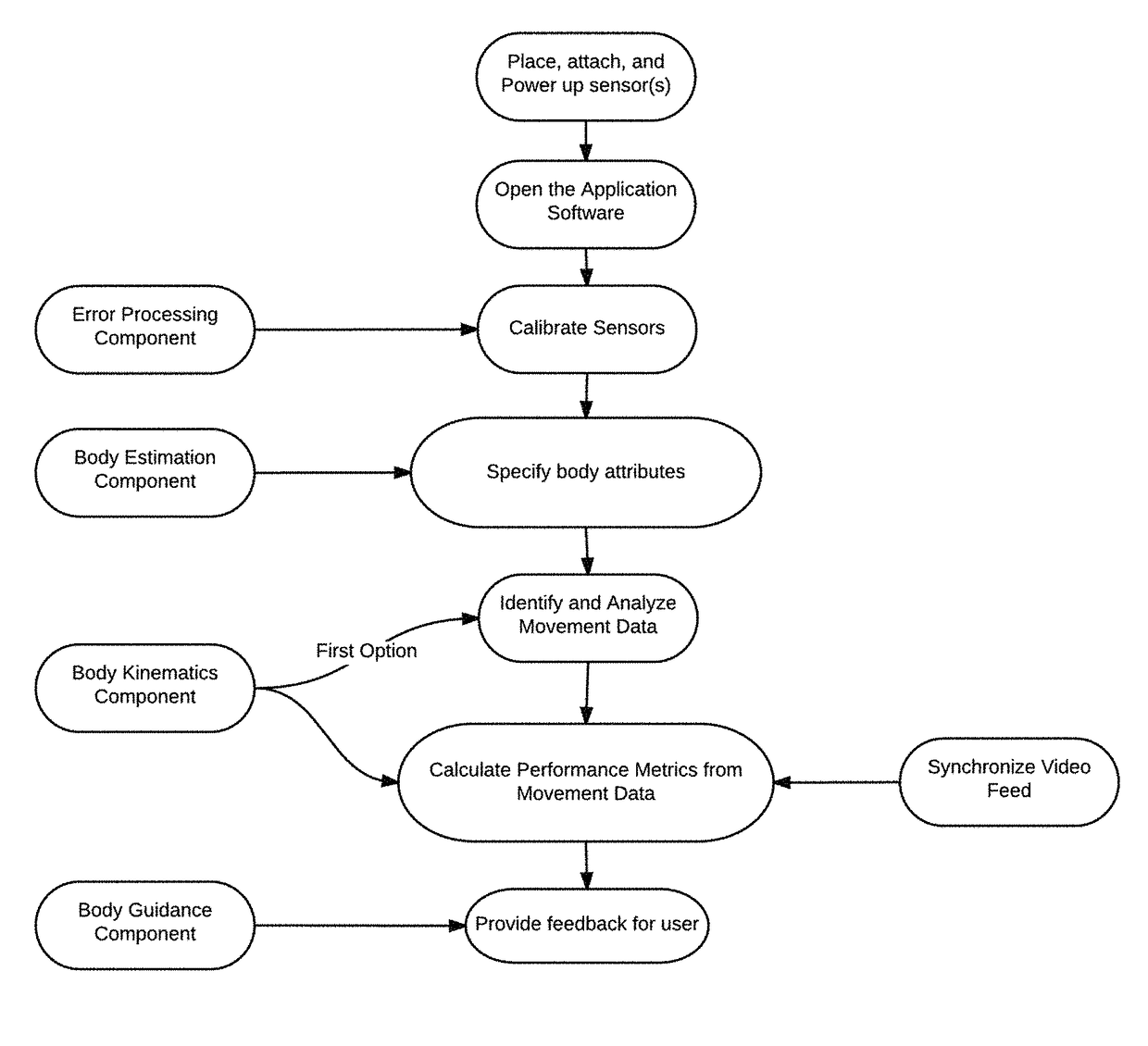
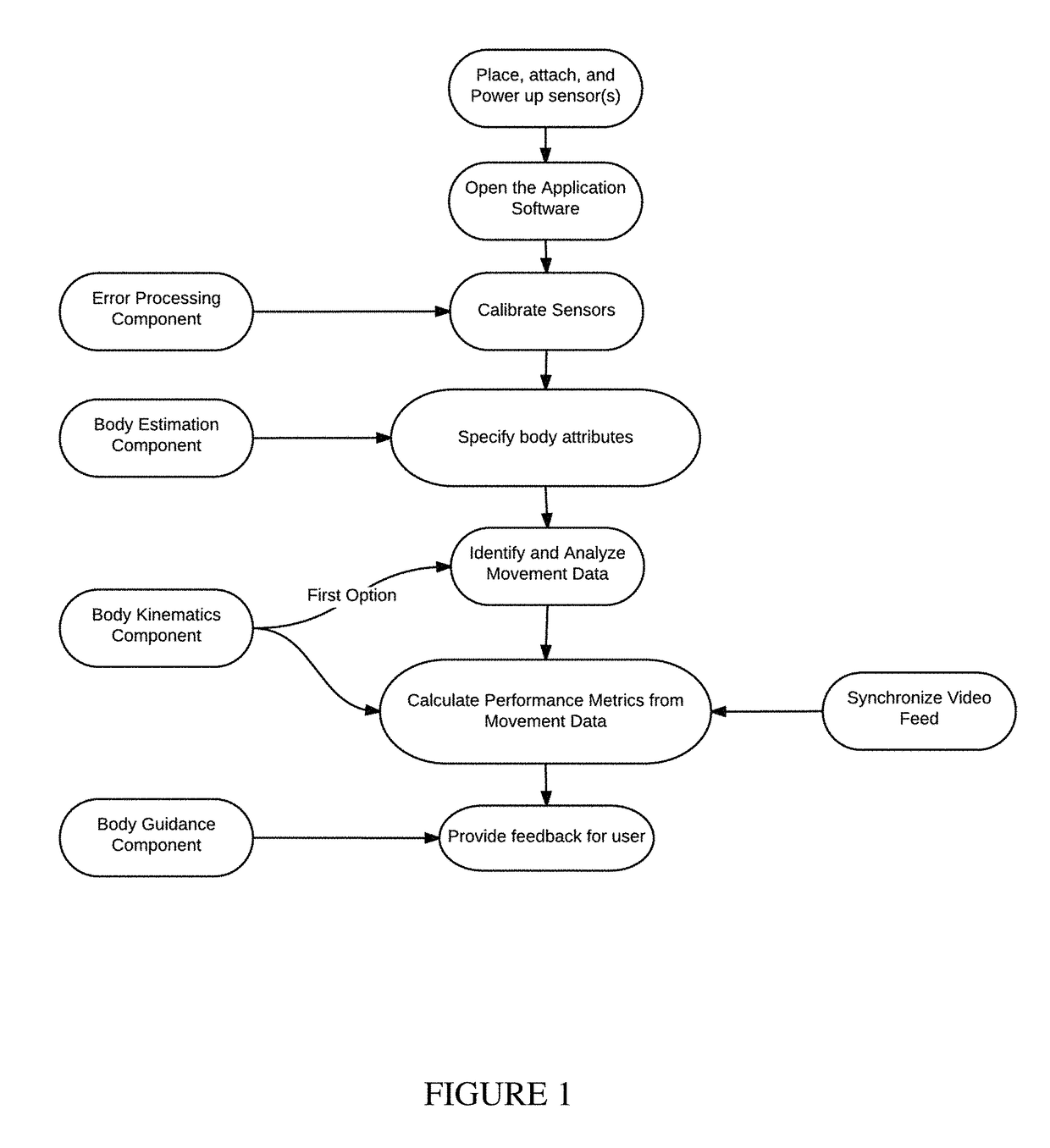
Training systems with wearable sensors for providing users with feedback
InactiveUS10065074B1Accelerated trainingEnhance coachingPhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationMultiple sensorHuman motion
A training system based on mobile technology and kinematics of human motion characterizes, analyzes, and supplies feedback to a user based on the user's movements. The training system includes a garment having a sensor control module connected to multiple sensor nodes via electrically-conductive fabric running along parts portions of the garment. The sensor module / nodes can communicate through the conductive fabric. The sensor nodes acquire motion and / or physiologic readings that are wirelessly transmitted to a mobile computing device that runs an application that analyzes the data and provides visual (e.g., graphs, 3D avatar) and audio feedback (e.g., voice prompts). Vibration motors and LEDs / electroluminescent fabric in the garment also provide notifications and alerts. The triple layer of garment, conductive fabric, and sensor module / sensor node are sealed against contaminants, allowing the garment to be washable.
Owner:ENFLUX INC
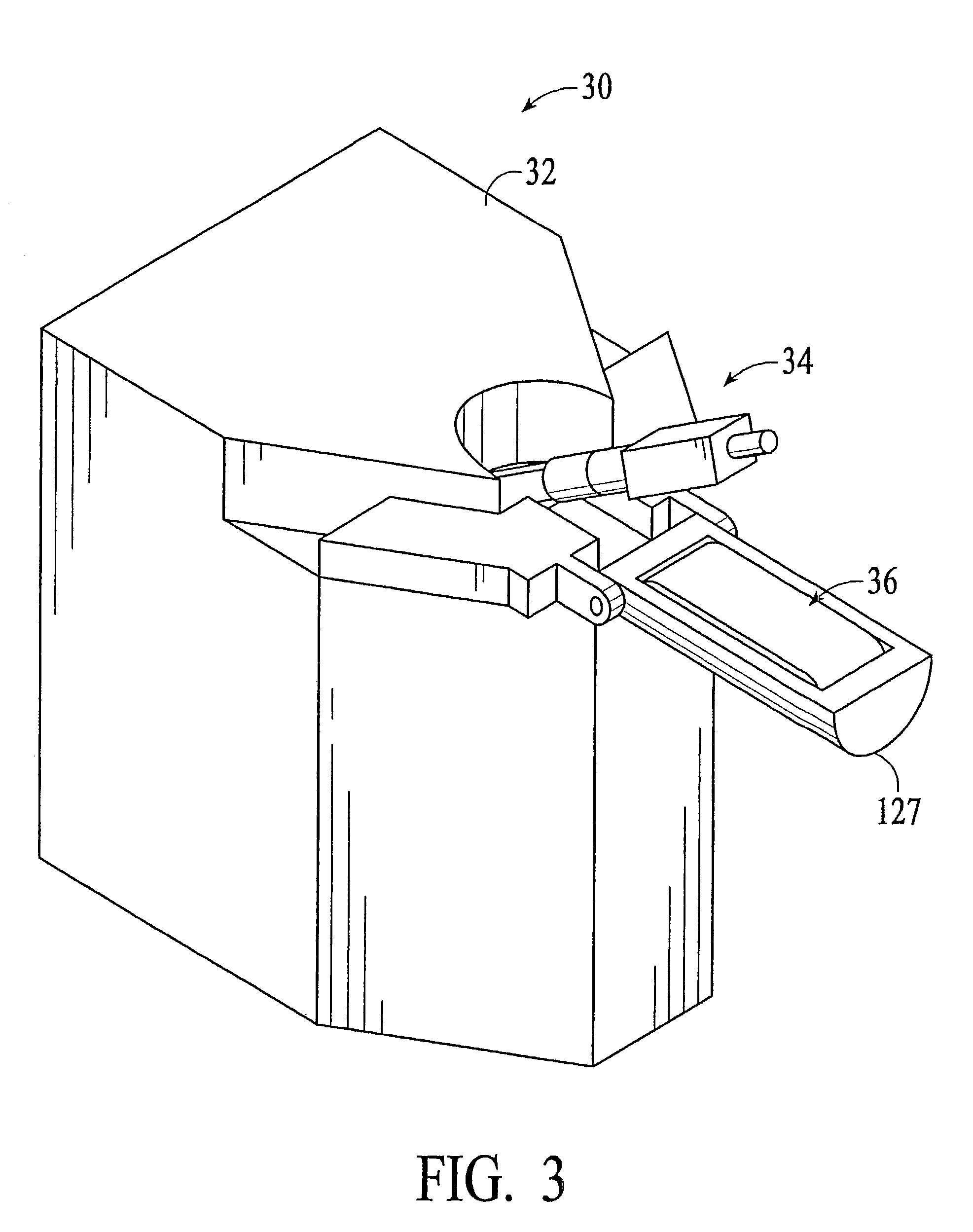
Interface device and method for interfacing instruments to vascular access simulation systems
InactiveUS7308831B2Improve realismSimulate the realCosmonautic condition simulationsData processing applicationsControl signalSkin traction
An interface device and method for interfacing instruments to a vascular access simulation system serve to interface peripherals in the form of mock or actual medical instruments to the simulation system to enable simulation of medical procedures. The interface device includes a catheter unit assembly for receiving a catheter needle assembly, and a skin traction mechanism to simulate placing skin in traction or manipulating other anatomical sites for performing a medical procedure. The catheter needle assembly and skin traction mechanism are manipulated by a user during a medical procedure. The catheter unit assembly includes a base, a housing, a bearing assembly and a shaft that receives the catheter needle assembly. The bearing assembly enables translation of the catheter needle assembly, and includes bearings that enable the shaft to translate in accordance with manipulation of the catheter needle assembly. The shaft typically includes an encoder to measure translational motion of a needle of the catheter needle assembly, while the interface device further includes encoders to measure manipulation of the catheter needle assembly in various degrees of freedom (e.g., translation, pitch and yaw) and the skin traction mechanism. Alternatively, the shaft may include an additional encoder to measure translational motion of an instrument inserted through the catheter needle assembly. The simulation system receives measurements from the interface device encoders and updates the simulation and display, while providing control signals to the force feedback device to enable application of force feedback to the catheter needle assembly.
Owner:IMMERSION MEDICAL
Systems and Methods for Deep Model Translation Generation
ActiveUS20190080205A1Low costAccelerated trainingCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesPattern recognitionGenerative adversarial network
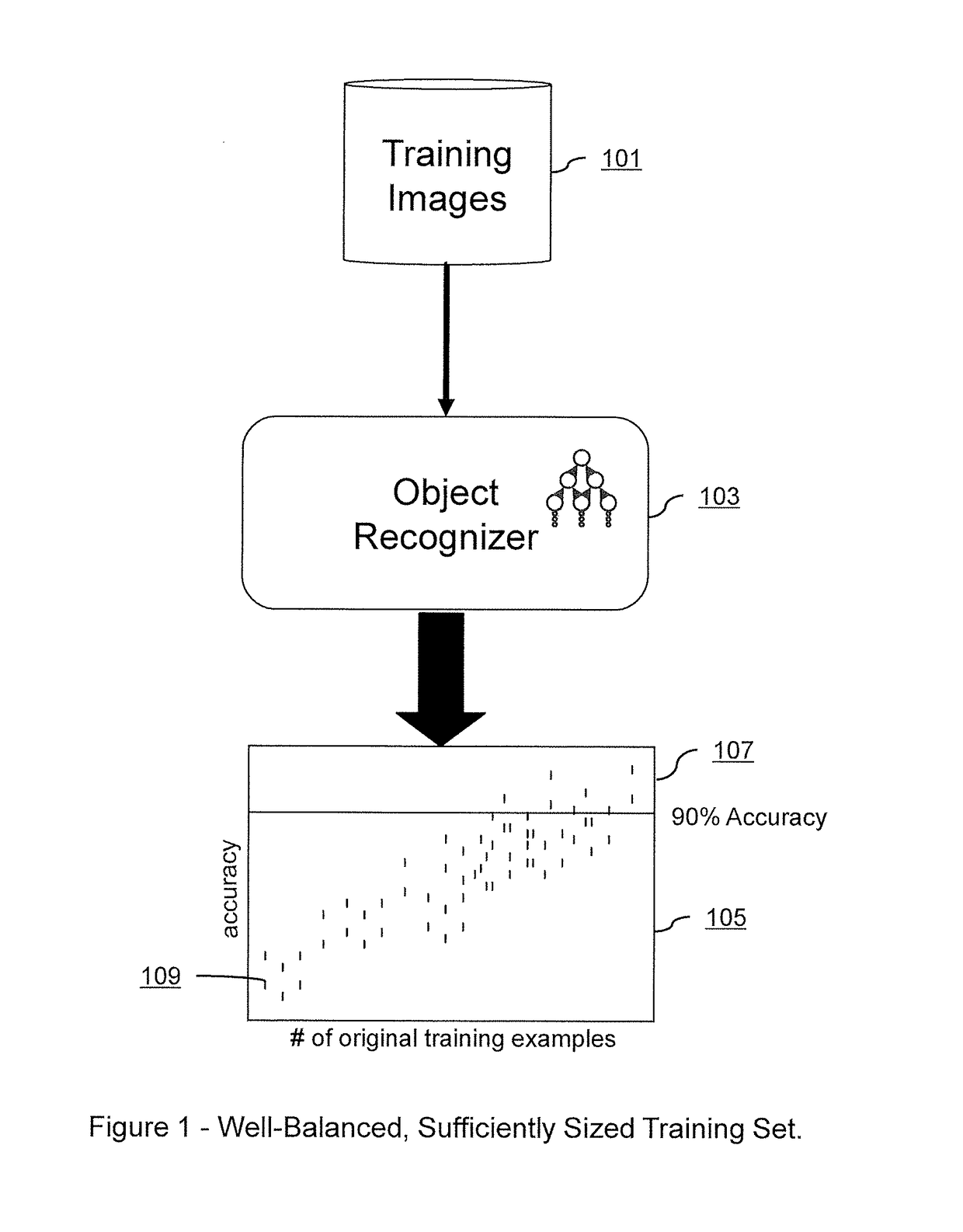
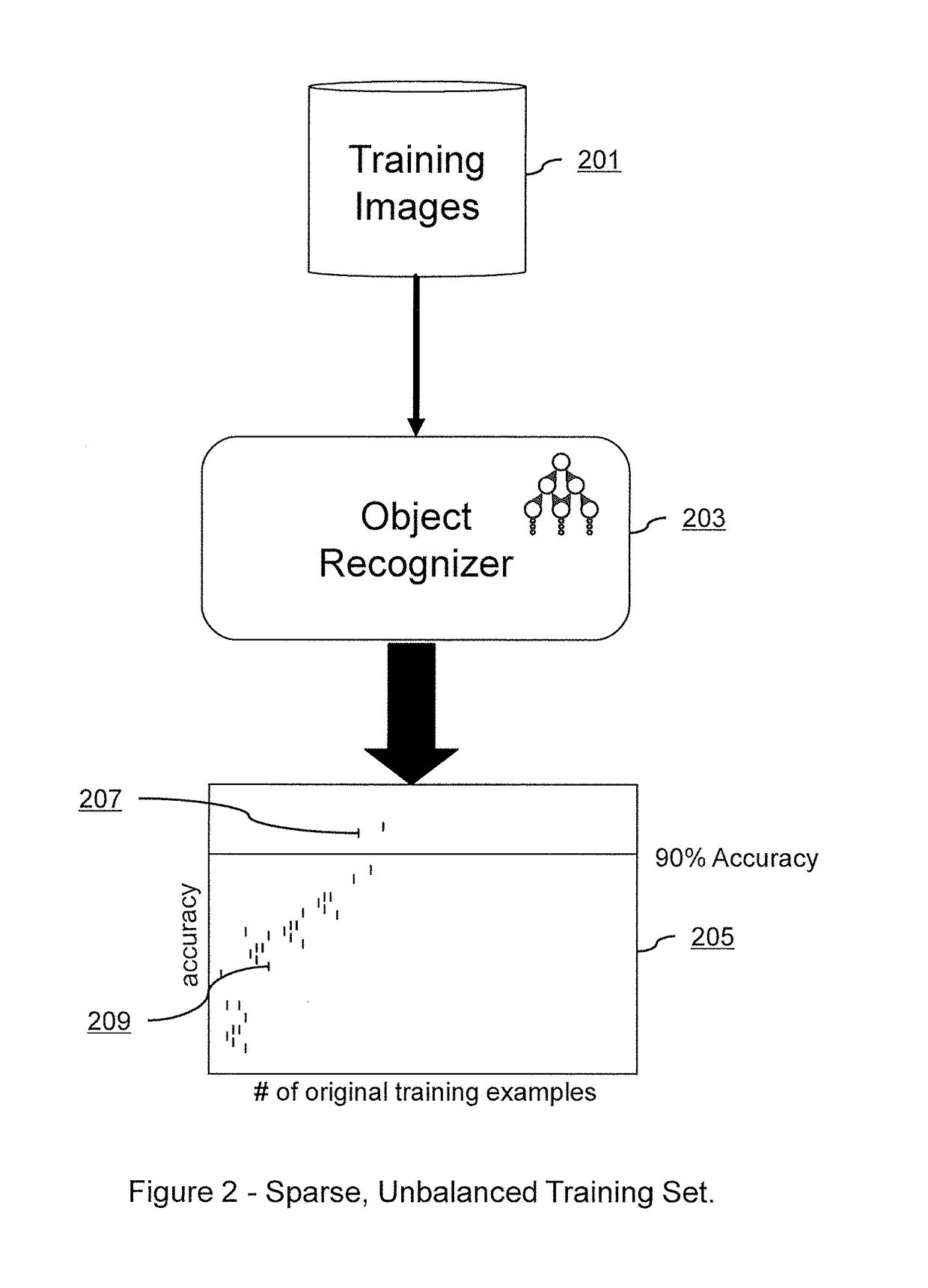
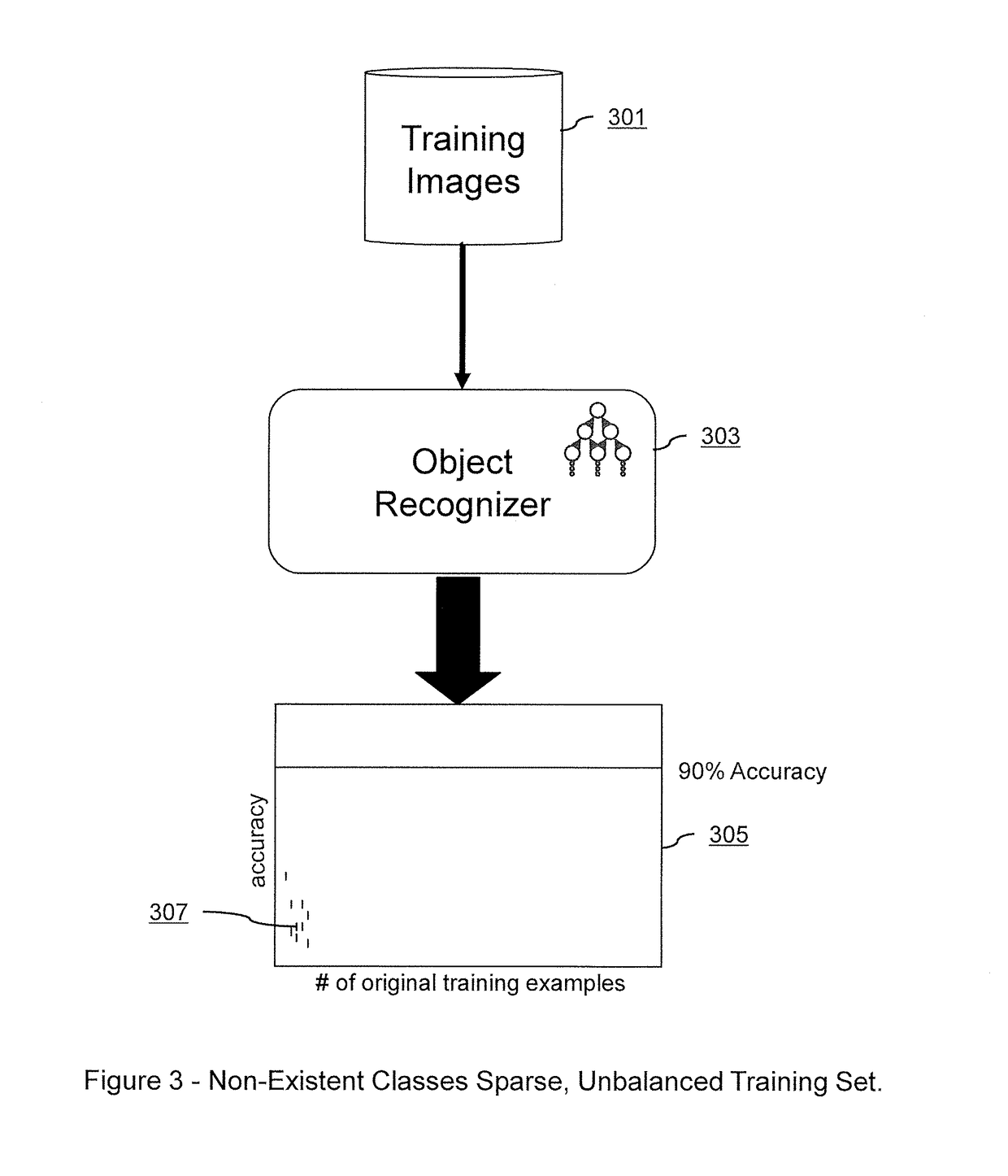
Embodiments of the present invention relate to systems and methods for improving the training of machine learning systems to recognize certain objects within a given image by supplementing an existing sparse set of real-world training images with a comparatively dense set of realistic training images. Embodiments may create such a dense set of realistic training images by training a machine learning translator with a convolutional autoencoder to translate a dense set of synthetic images of an object into more realistic training images. Embodiments may also create a dense set of realistic training images by training a generative adversarial network (“GAN”) to create realistic training images from a combination of the existing sparse set of real-world training images and either Gaussian noise, translated images, or synthetic images. The created dense set of realistic training images may then be used to more effectively train a machine learning object recognizer to recognize a target object in a newly presented digital image.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
Augmented cognitive training
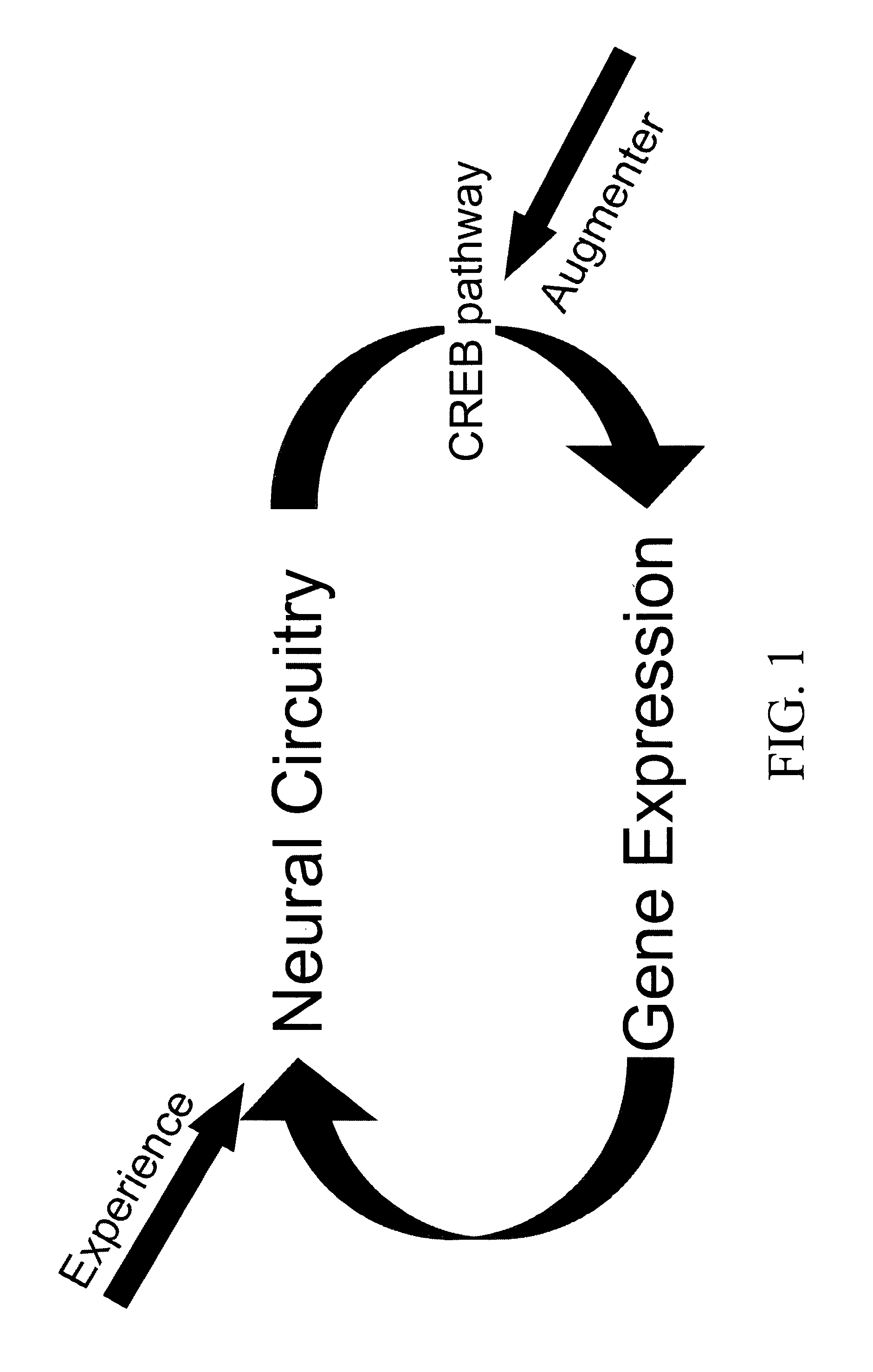
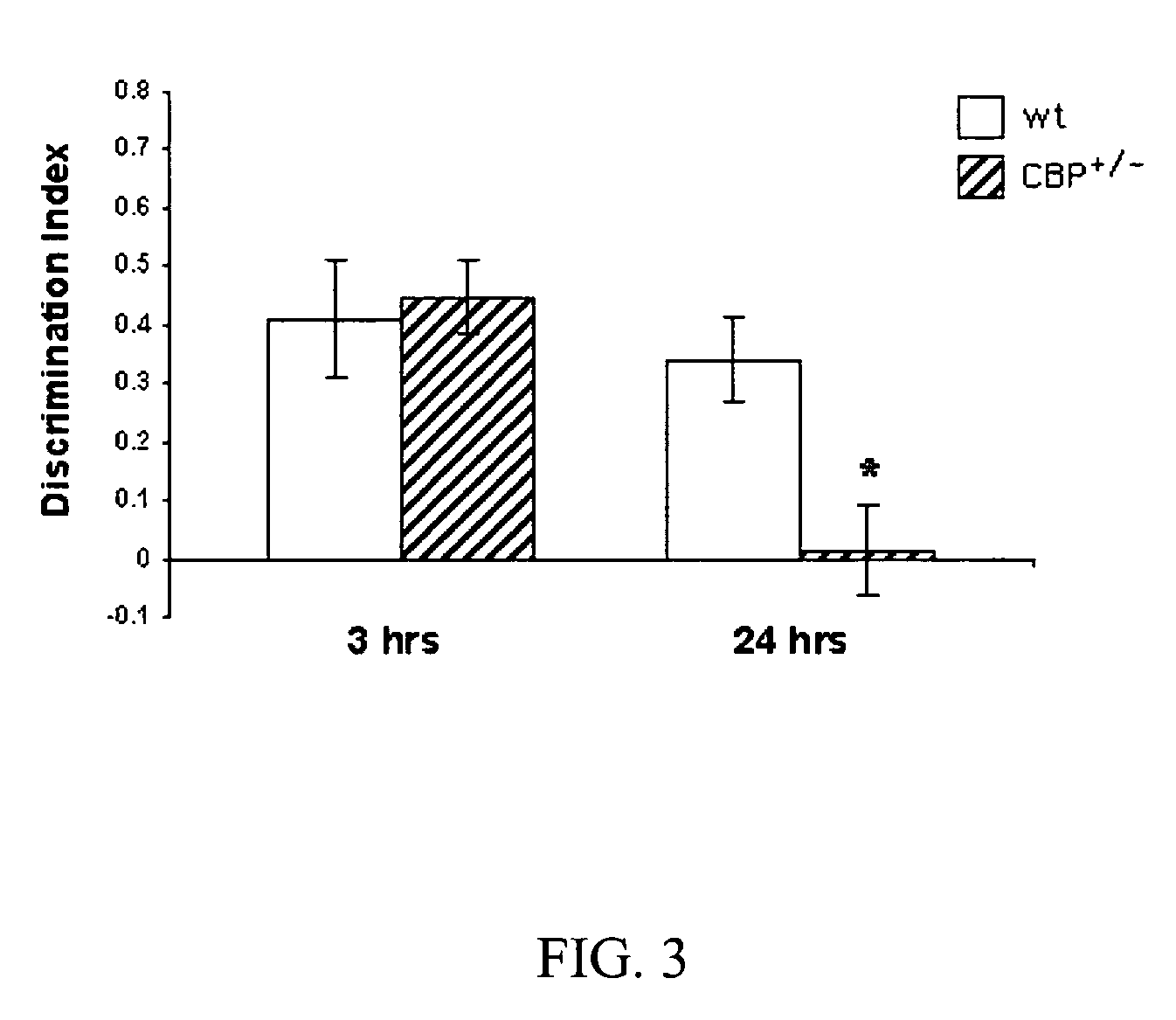
InactiveUS7947731B2Improve performanceNormally performanceBiocideNervous disorderNeuronal circuitsClinical psychology
The present invention provides methods of therapy of cognitive deficits associated with a central nervous system disorder or condition, methods of enhancing cognitive performance and methods for repeated stimulation of neuronal activity or a pattern of neuronal activity, such as that underlying a specific neuronal circuit(s). The methods comprise combining cognitive training protocols and a general administration of CREB pathway-enhancing agents.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
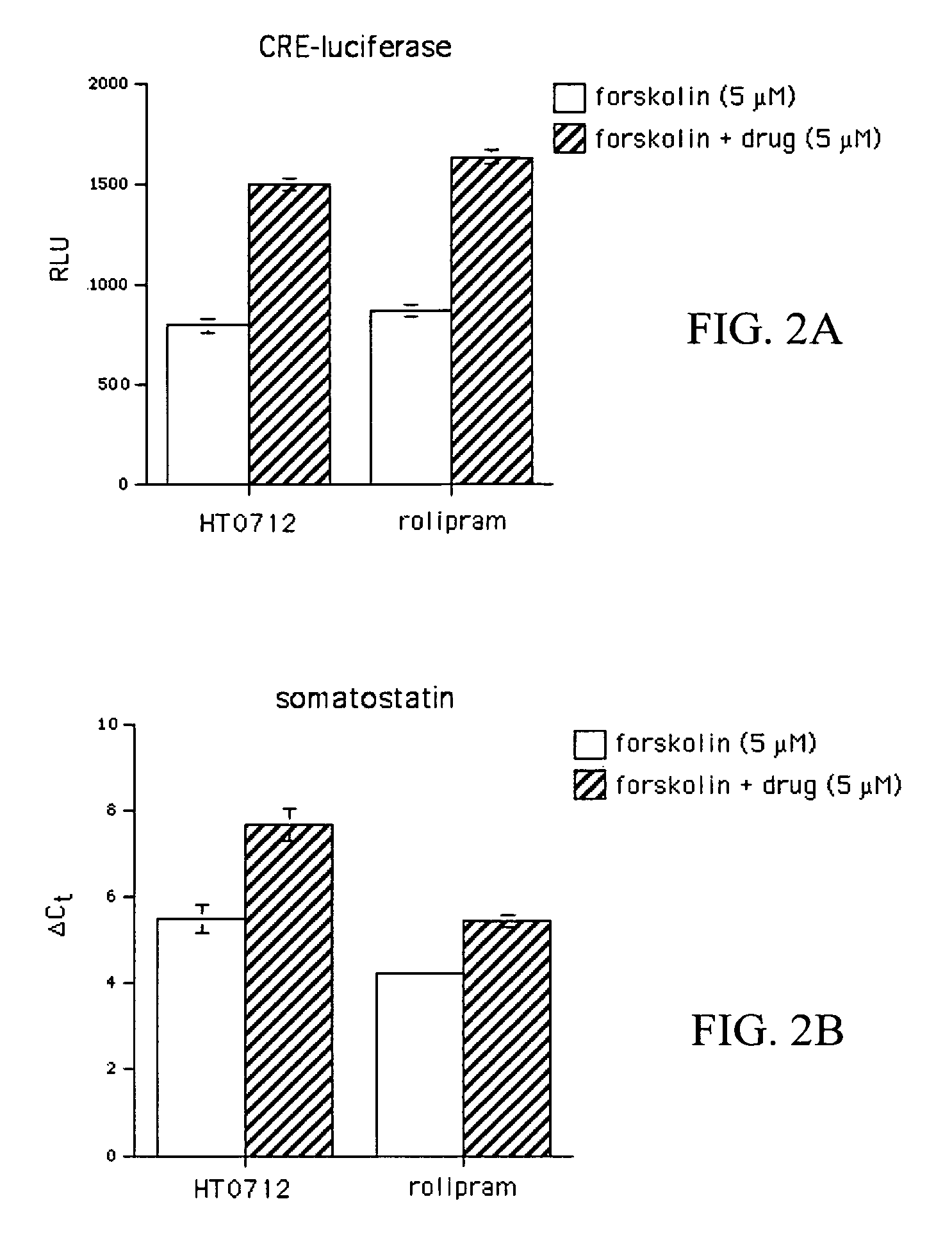
Phosphodiesesterase 4 inhibitors for the treatment of a cognitive deficit
InactiveUS7868015B2Normally performanceVarious formsPhysical therapies and activitiesBiocidePhosphodiesterase-4Psychiatry
The present invention provides methods of treating cognitive deficits associated with mental retardation. The methods comprise combining cognitive training protocols and a general administration of phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
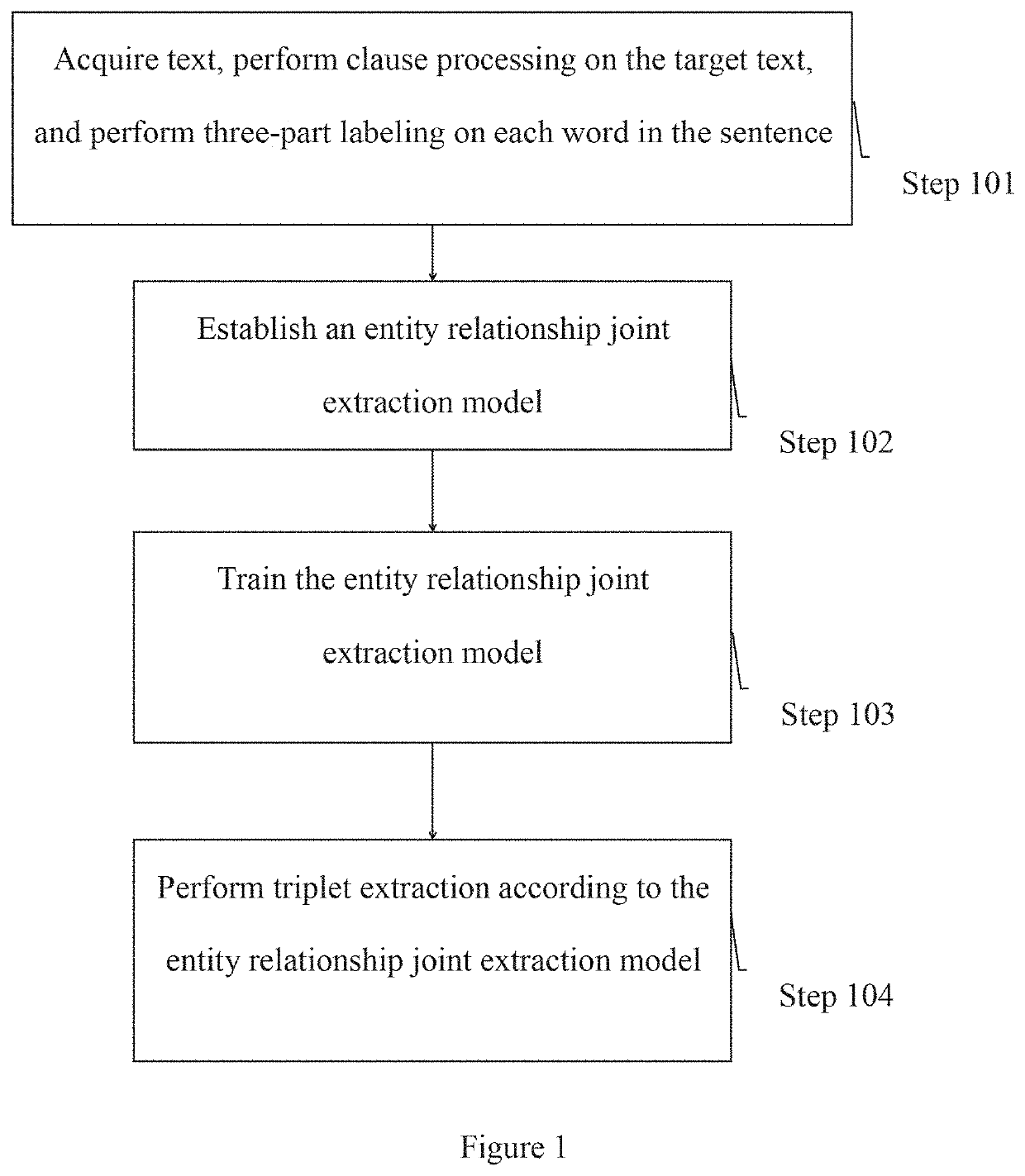
Multi-triplet extraction method based on entity-relation joint extraction model
PendingUS20200073933A1Efficient extractionImprove accuracyNatural language data processingNeural architecturesPattern recognitionTarget text
The invention discloses a multi-triplets extraction method based on the entity relationship joint extraction model, comprises: performing segmentation processing on the target text, and tagging position, type and whether is involved with any relation or not of each word in the sentence; the joint extraction model of the entity relationship is established; the joint extraction model of the entity relationship is trained; the triple extraction is performed according to the joint extraction model of the entity relationship; the tri-part tagging scheme designed by the present invention is in the process of joint extraction of the entity relationship an entity that is not related to the target relationship can be excluded; the multi-triplets extraction method based on the entity relationship joint extraction model can be used to extract multiple triplets, and based on the model of the triplet extraction method of the present invention other models have stronger multi-triplets extraction capabilities.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and device for generative adversarial network training
ActiveUS20190130221A1Improved neural network trainingAccelerated trainingKernel methodsCharacter and pattern recognitionGenerative adversarial networkMachine learning
An electronic device for neural network training includes at least one processor and one or more memories configured to provide or train: a generative adversarial network (GAN) using a generator and a discriminator for: receiving a plurality of training cases; and training the generative adversarial network, based on the plurality of training cases, to classify the training cases; wherein the generator generates hard negative examples for the discriminator.
Owner:ROYAL BANK OF CANADA
Method of managing interference during delay recovery on a train system
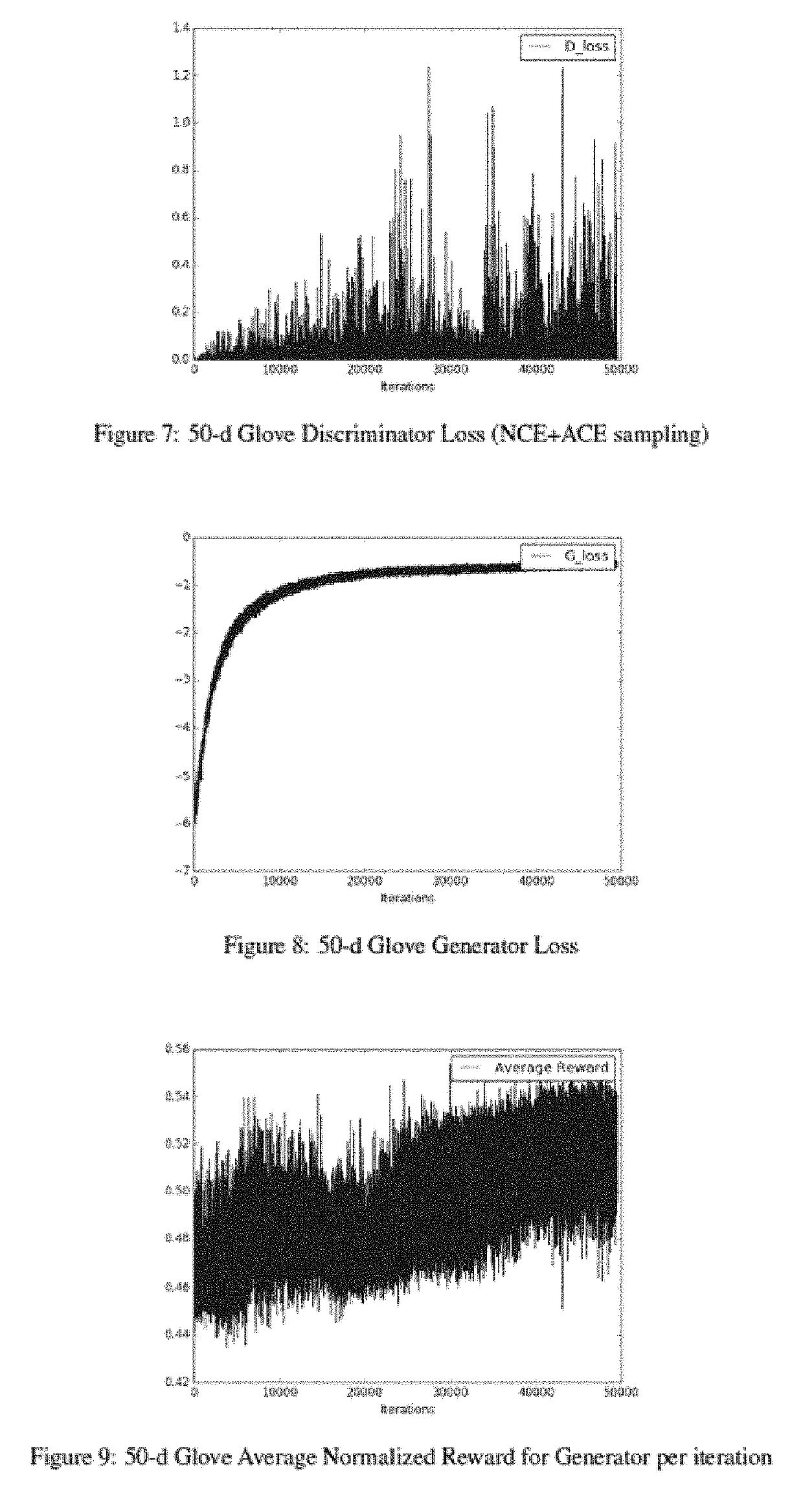
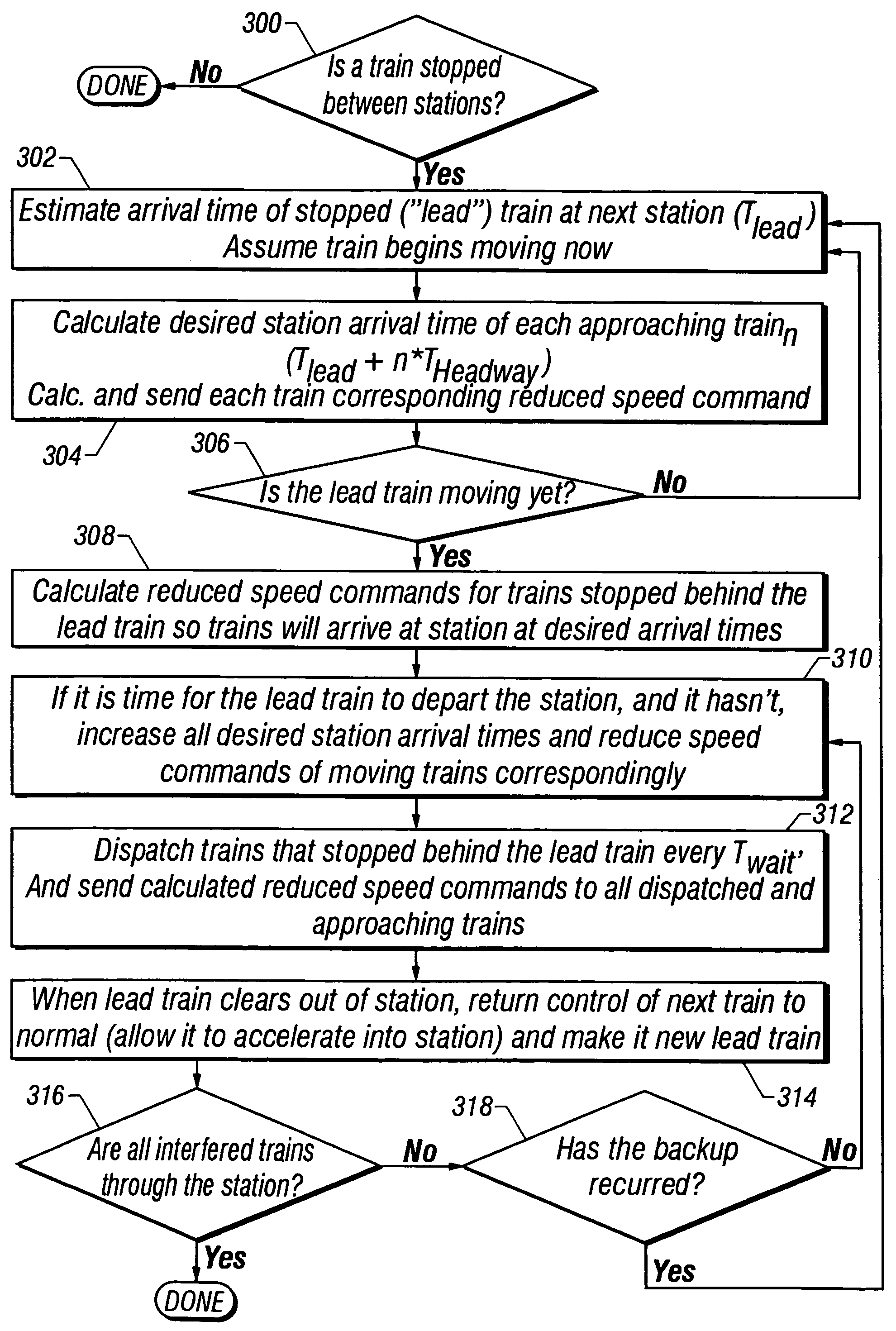
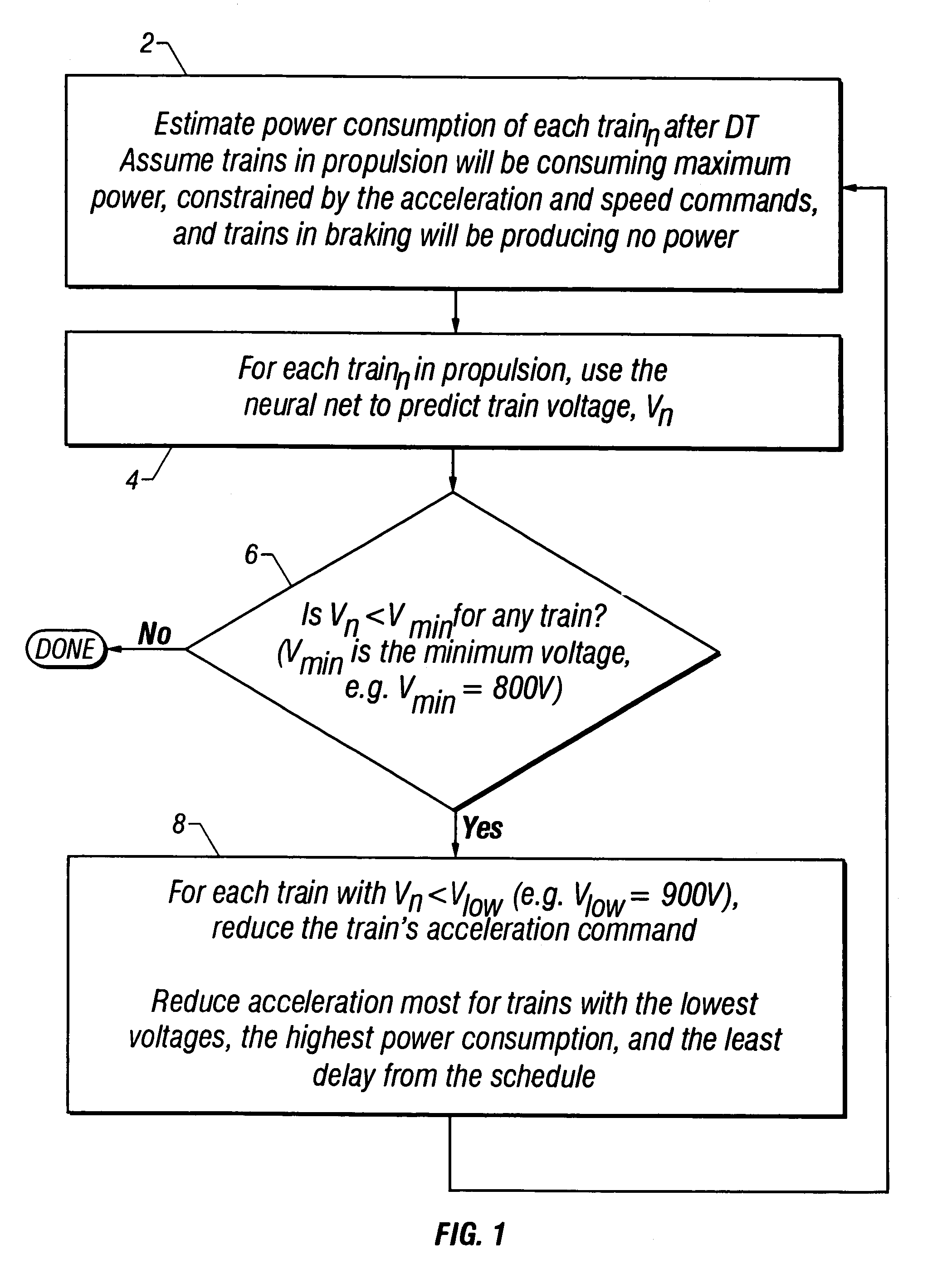
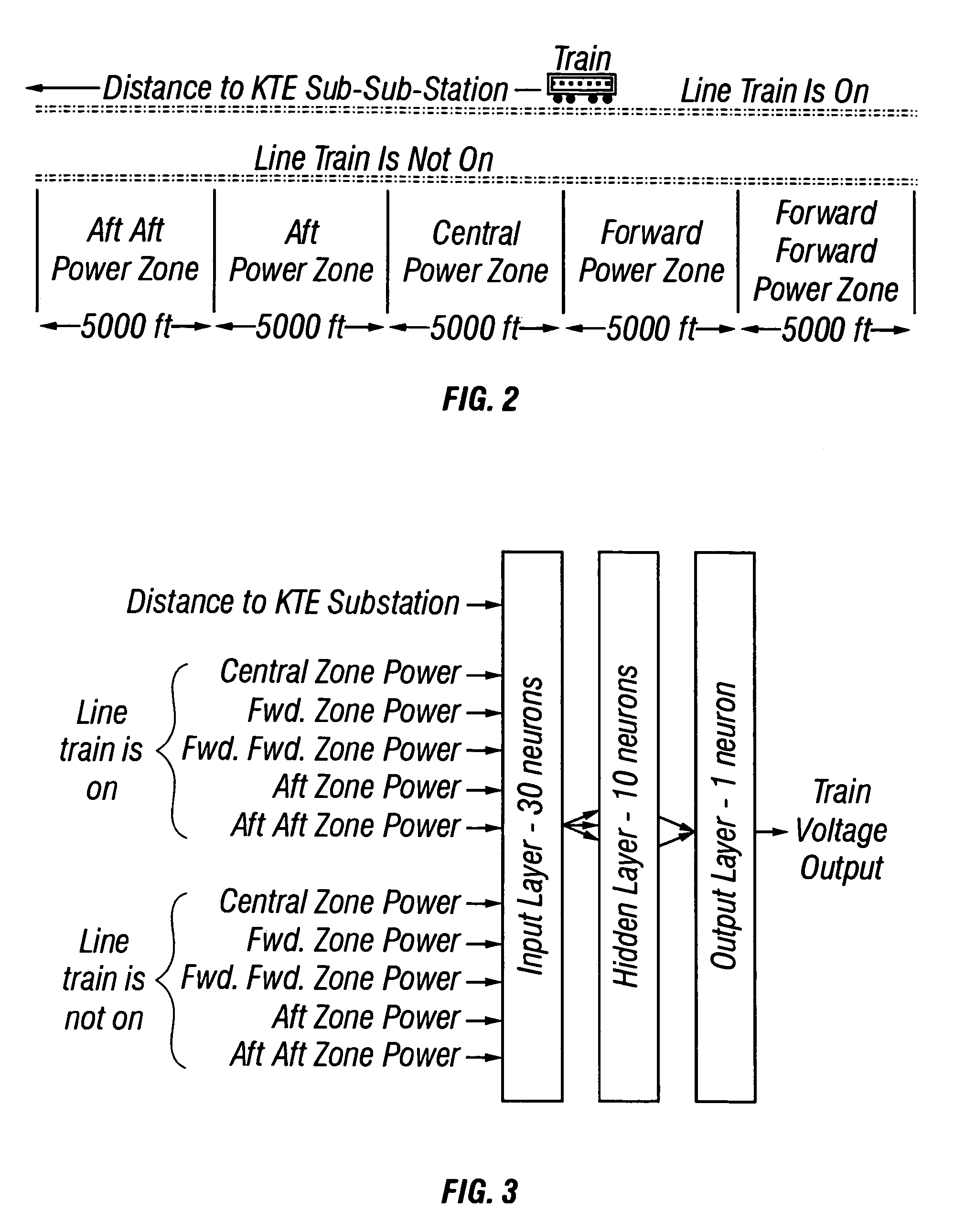
InactiveUS6980894B1Minimizing trip timeAvoiding low train voltageSpeed controllerElectric devicesSystem requirementsLow voltage
The present invention provides methods for preventing low train voltages and managing interference, thereby improving the efficiency, reliability, and passenger comfort associated with commuter trains. An algorithm implementing neural network technology is used to predict low voltages before they occur. Once voltages are predicted, then multiple trains can be controlled to prevent low voltage events. Further, algorithms for managing inference are presented in the present invention. Different types of interference problems are addressed in the present invention such as “Interference During Acceleration”, “Interference Near Station Stops”, and “Interference During Delay Recovery.” Managing such interference avoids unnecessary brake / acceleration cycles during acceleration, immediately before station stops, and after substantial delays. Algorithms are demonstrated to avoid oscillatory brake / acceleration cycles due to interference and to smooth the trajectories of closely following trains. This is achieved by maintaining sufficient following distances to avoid unnecessary braking / accelerating. These methods generate smooth train trajectories, making for a more comfortable ride, and improve train motor reliability by avoiding unnecessary mode-changes between propulsion and braking. These algorithms can also have a favorable impact on traction power system requirements and energy consumption.
Owner:SAN FRANCISCO BAY AREA RAPID TRANSIT DISTRICT
Interface device and method for interfacing instruments to medical procedure simulation systems
An interface device and method for interfacing instruments to a medical procedure simulation system serve to interface peripherals in the form of mock medical instruments to the medical procedure simulation system computer to enable simulation of medical procedures. The interface device includes a housing having a mock bodily region of interest to facilitate insertion of a mock instrument, such as an endoscope tube, into the interface device. The mock bodily region of interest may be pivotable to simulate various patient orientations. The instrument is engaged by a capture mechanism in order to measure rotational and translational motion of the instrument. An actuator is disposed within the interface device to provide force feedback to the instrument. The measured motion is provided to the computer system to reflect instrument motion on the display during the simulation. Alternatively, the interface device may be configured to accommodate instrument assemblies having a plurality of nested instruments (e.g., sheath, catheter and wire), whereby the interface device individually grasps, measures manipulation of and provides force feedback to the nested instruments. In addition, the interface device may be configured to simultaneously accommodate a plurality of independently inserted instruments.
Owner:IMMERSION MEDICAL
Tactile feedback man-machine interface device
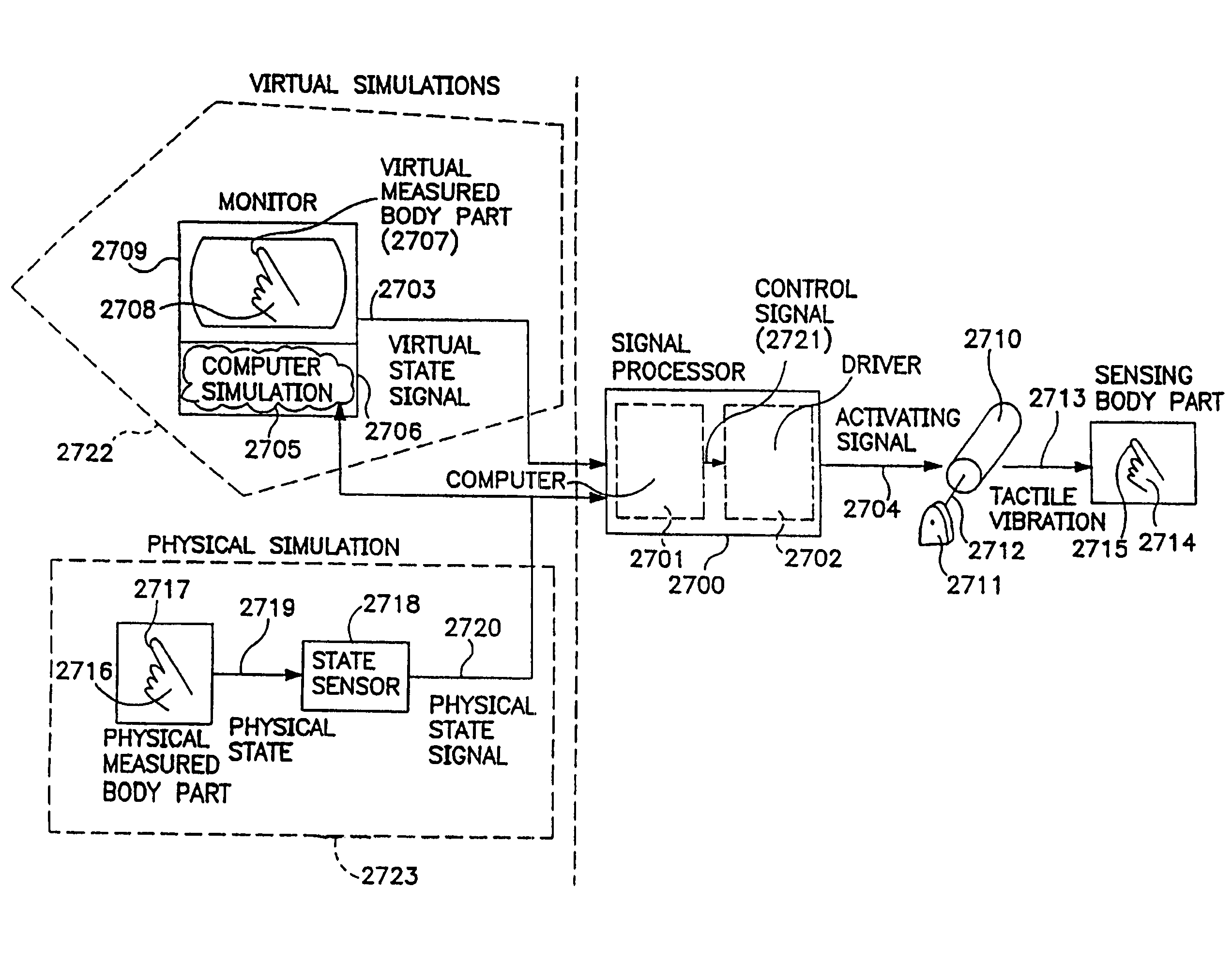
InactiveUS7755602B2Accelerated trainingLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionElectrophonic musical instrumentsHuman–machine interfaceMan machine
A man-machine interface which provides tactile feedback to various sensing body parts is disclosed. The device employs one or more vibrotactile units, where each unit comprises a mass and a mass-moving actuator. As the mass is accelerated by the mass-moving actuator, the entire vibrotactile unit vibrates. Thus, the vibrotactile unit transmits a vibratory stimulus to the sensing body part to which it is affixed. The vibrotactile unit may be used in conjunction with a spatial placement sensing device which measures the spatial placement of a measured body part. A computing device uses the spatial placement of the measured body part to determine the desired vibratory stimulus to be provided by the vibrotactile unit. In this manner, the computing device may control the level of vibratory feedback perceived by the corresponding sensing body part in response to the motion of the measured body part. The sensing body part and the measured body part may be separate or the same body part.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
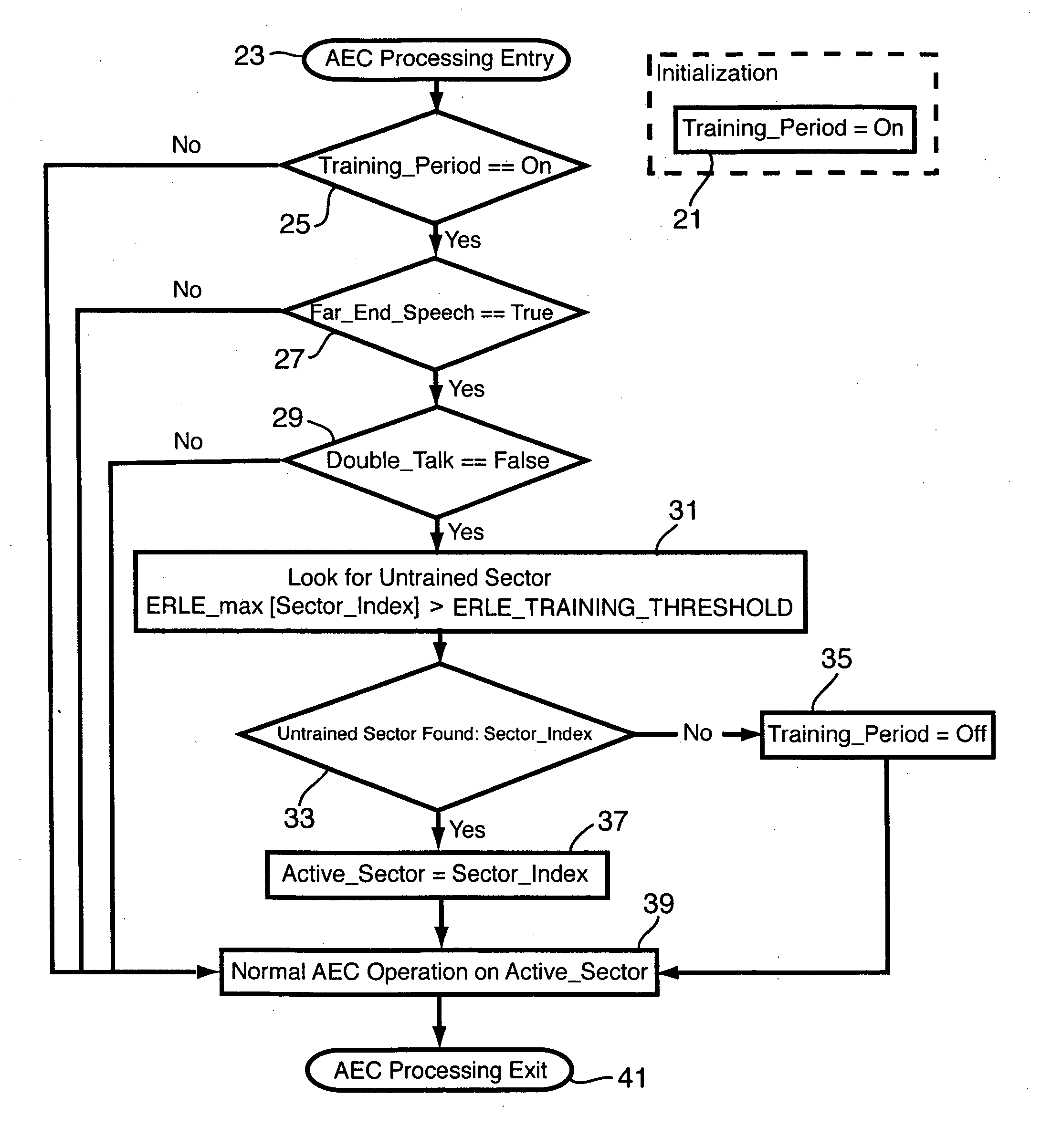
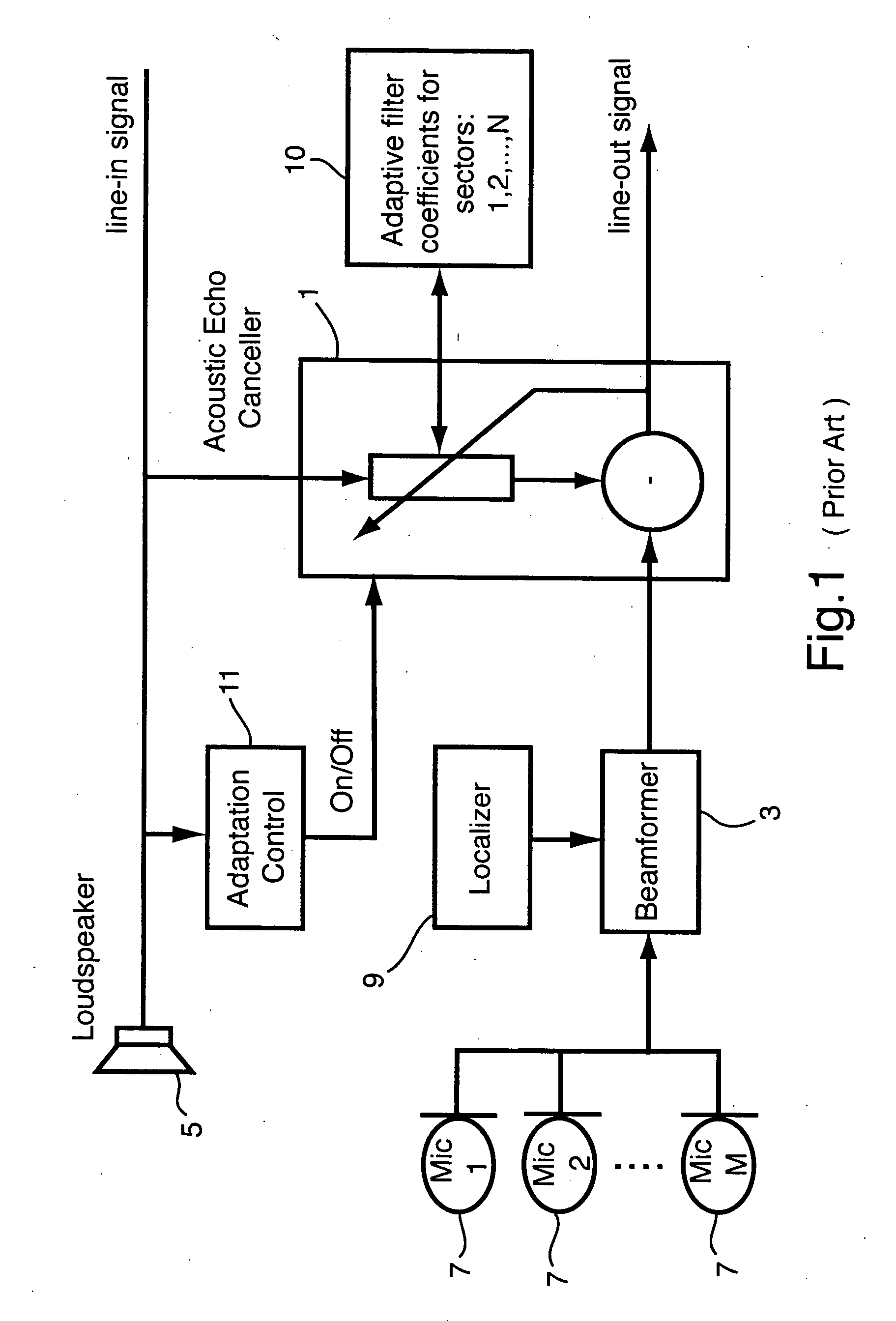
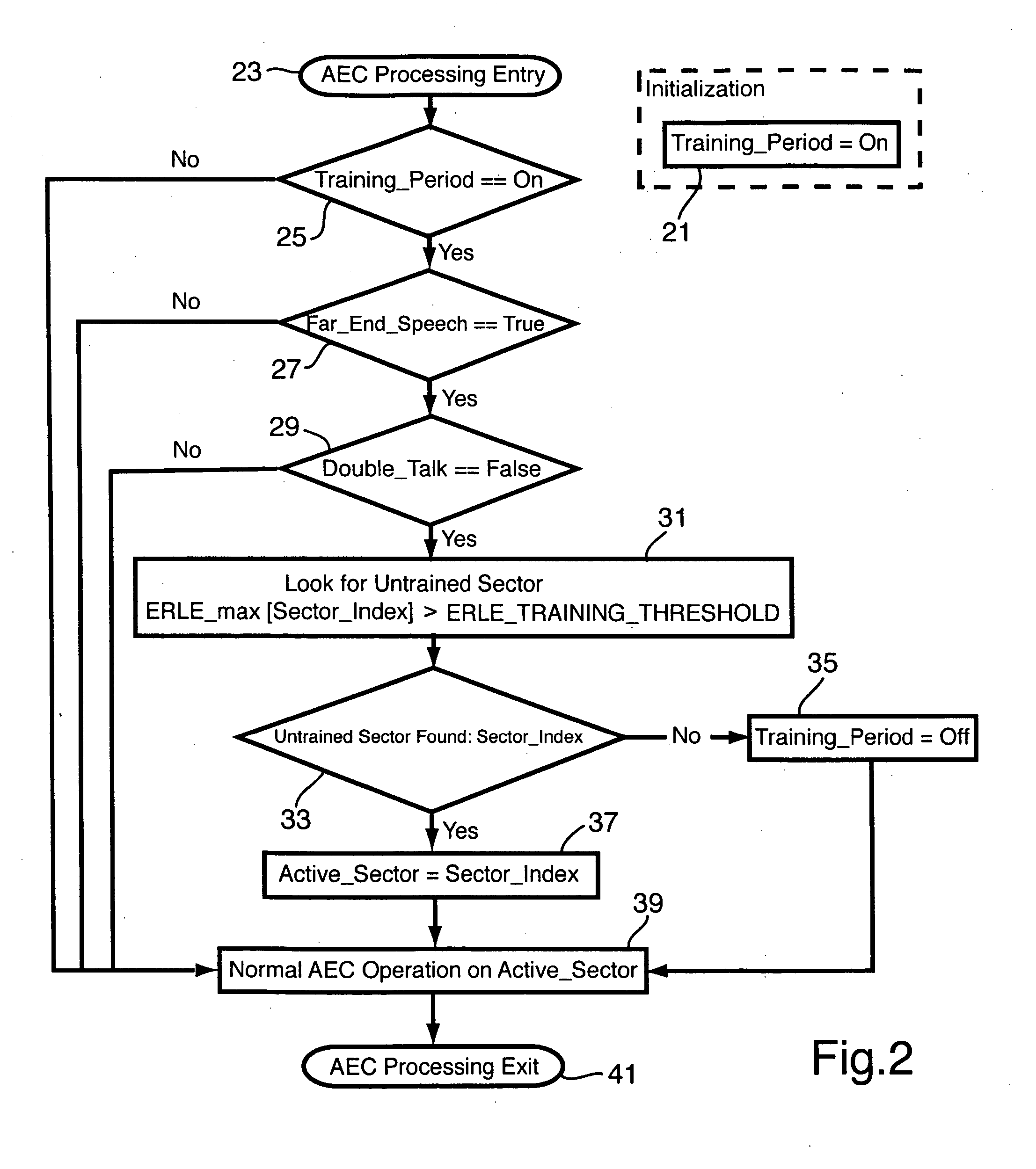
Method of accelerating the training of an acoustic echo canceller in a full-duplex beamforming-based audio conferencing system
ActiveUS20060233353A1Accelerated trainingTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstation/switching arrangement detailsEngineeringSpeech sound
A method and apparatus is set forth for accelerating the total acoustic echo cancellation convergence time in a microphone array full-duplex conferencing system with beamformer. The invention is based on sequentially switching the beamformer to untrained sectors during periods of far-end speech activity and performing real-time cancellation of far-end echo signals from the near-end signals to consecutively adapt and store filter coefficients for the echo canceller corresponding to each sector.
Owner:MITEL
Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors for cognitive and motor rehabilitation
InactiveUS20080188525A1Function increaseImprove performanceBiocideNervous disorderMotor rehabilitationMedicine
The present invention provides methods of improving cognitive and motor deficits associated with central nervous system (CNS) disorder or condition in an animal. The methods comprise a general administration of phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors and optionally training the animal under conditions sufficient to produce an improvement in performance.
Owner:DART NEUROSCIENCE CAYMAN LTD
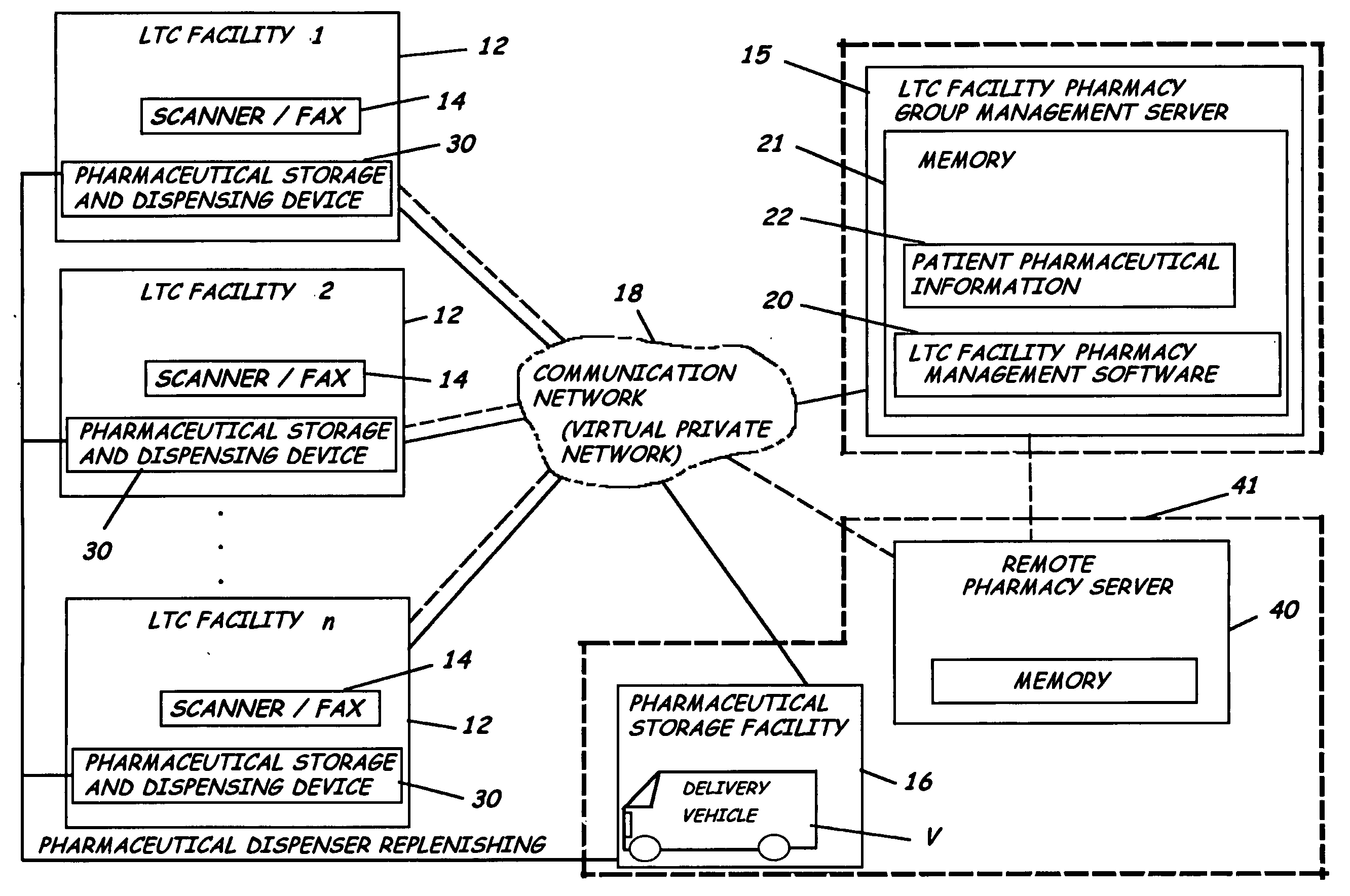
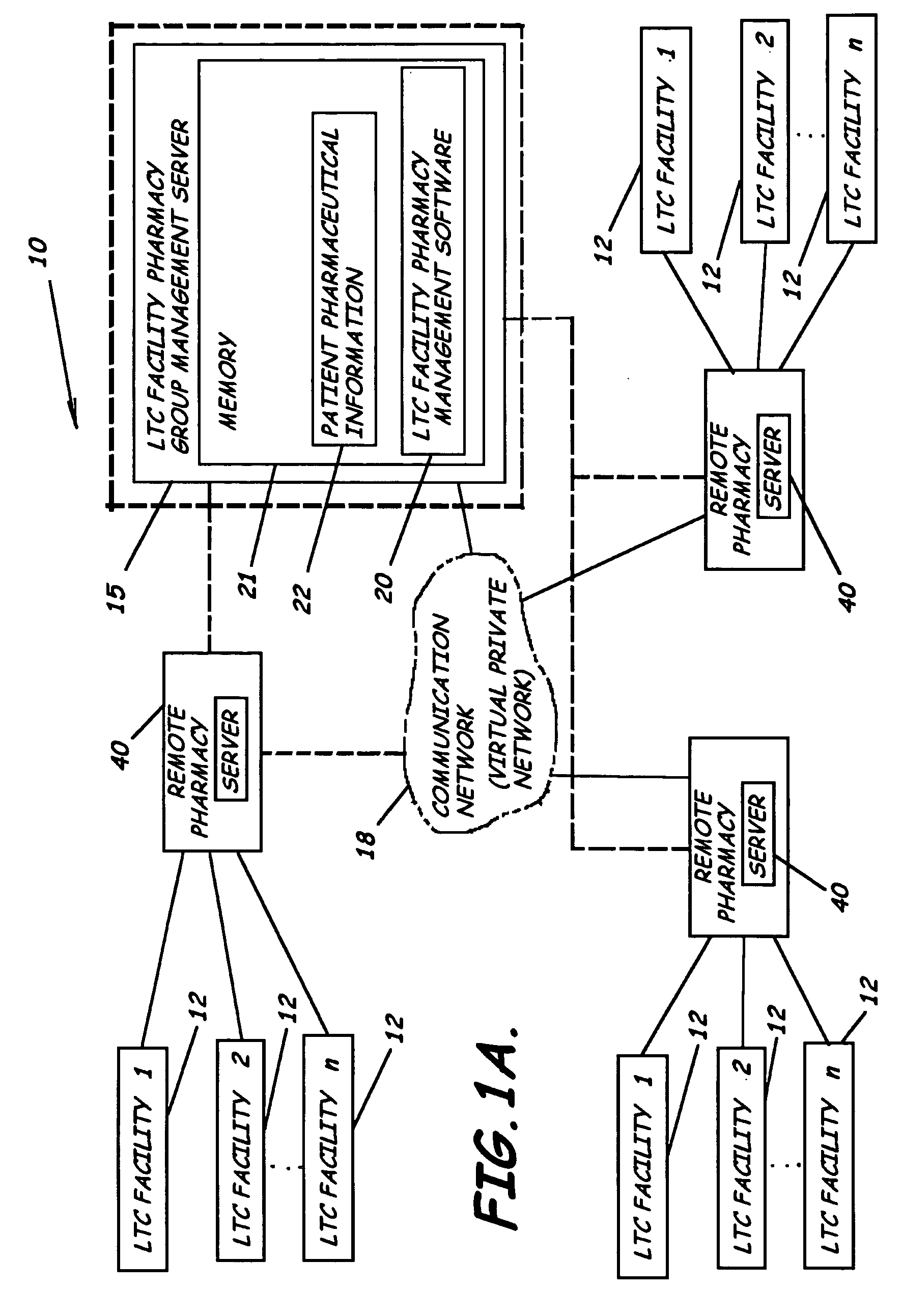
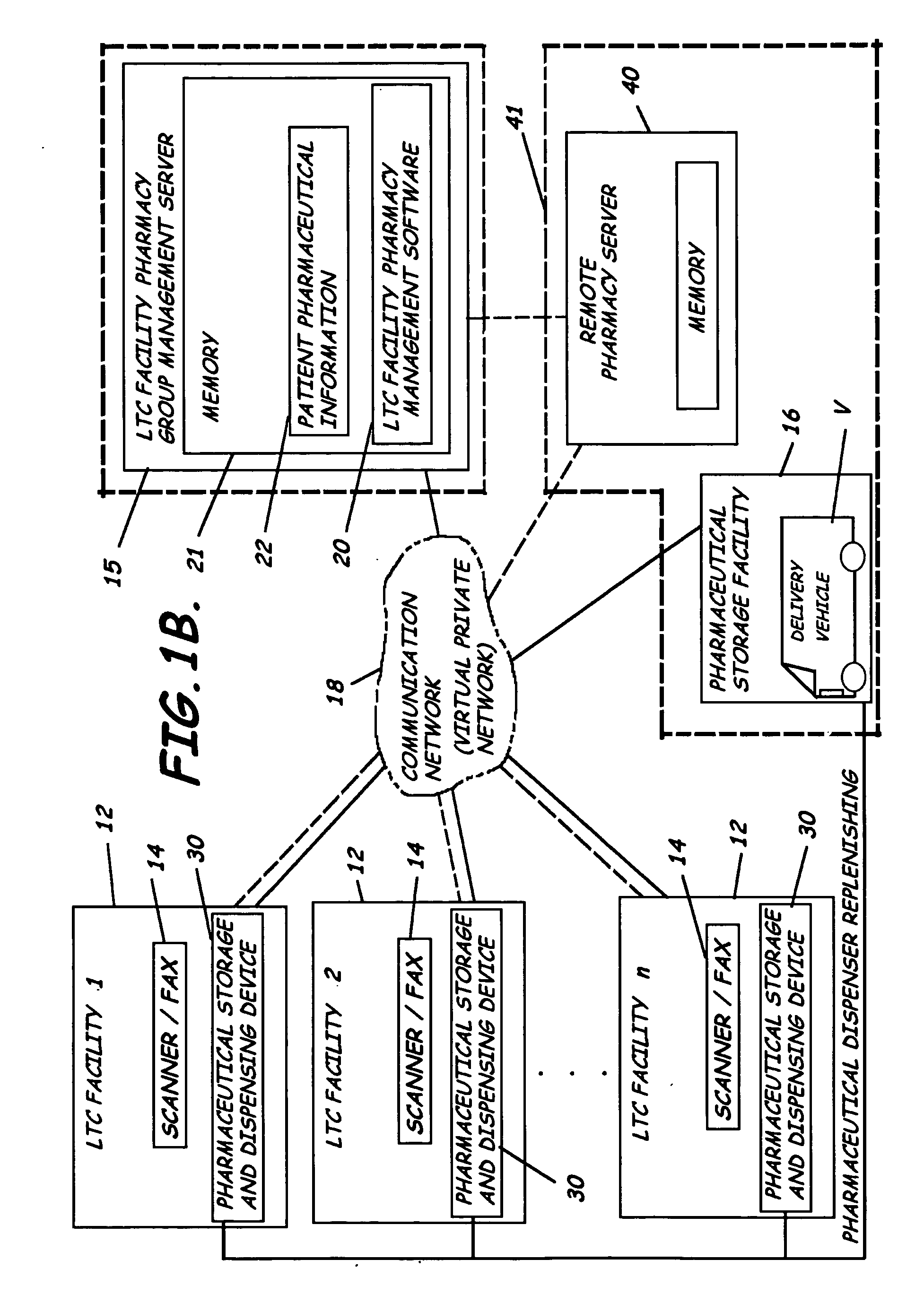
System and software of enhanced pharmaceutical operations in long-term care facilities and related methods
ActiveUS20050096785A1Ass performanceFacilitate communicationFinanceDrug and medicationsPharmacyLong-term care
A system, software and related methods of enhanced pharmaceutical operations in long term care facilities are provided. An embodiment of a system includes a long-term care facility pharmacy group management server, long-term care facility pharmacy management software associated with the long-term care facility pharmacy group management server to manage pharmacological operations in a plurality of long-term care facilities, a plurality of pharmaceutical storage and electronic dispensing carts each positioned in a long-term care facility remote from the long-term care facility pharmacy group management server and in communication therewith, a remote pharmacy group server in communication with the long-term care facility pharmacy group management server, and a plurality of pharmaceutical prescription document processors each positioned in a long-term care facility and in communication with the remote pharmacy group server or the long-term care facility pharmacy group management server.
Owner:DFW ASSOC III LLC +1
Large scale semi-supervised linear support vector machines
InactiveUS7562060B2Improve good performanceAccelerated trainingDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmMean field annealing
A computerized system and method for large scale semi-supervised learning is provided. The training set comprises a mix of labeled and unlabeled examples. Linear classifiers based on support vector machine principles are built using these examples. One embodiment uses a fast design of a linear transductive support vector machine using multiple switching. In another embodiment, mean field annealing is used to form a very effective semi-supervised support vector machine. For both these embodiments the finite Newton method is used as the base method for achieving fast training.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Stereotactic access devices and methods
ActiveUS20130053867A1Wide range of usesAccelerated trainingDiagnosticsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryStereotaxisMedical device
This invention is directed to devices and methods for stereotactic access, and particularly to a frameless stereotactic access device for accessing a body cavity and methods therefor. In general, a stereotactic device may include portions or features for fixing the device to a portion of a patient's body, such as, for example, a skull, such that the device may be generally spatially fixed in relation to the patient's body or part thereof. The stereotactic device may also generally include portions or features for guiding a medical device or other device at a particular trajectory in relation to the patient's body or part thereof.
Owner:VISUALASE
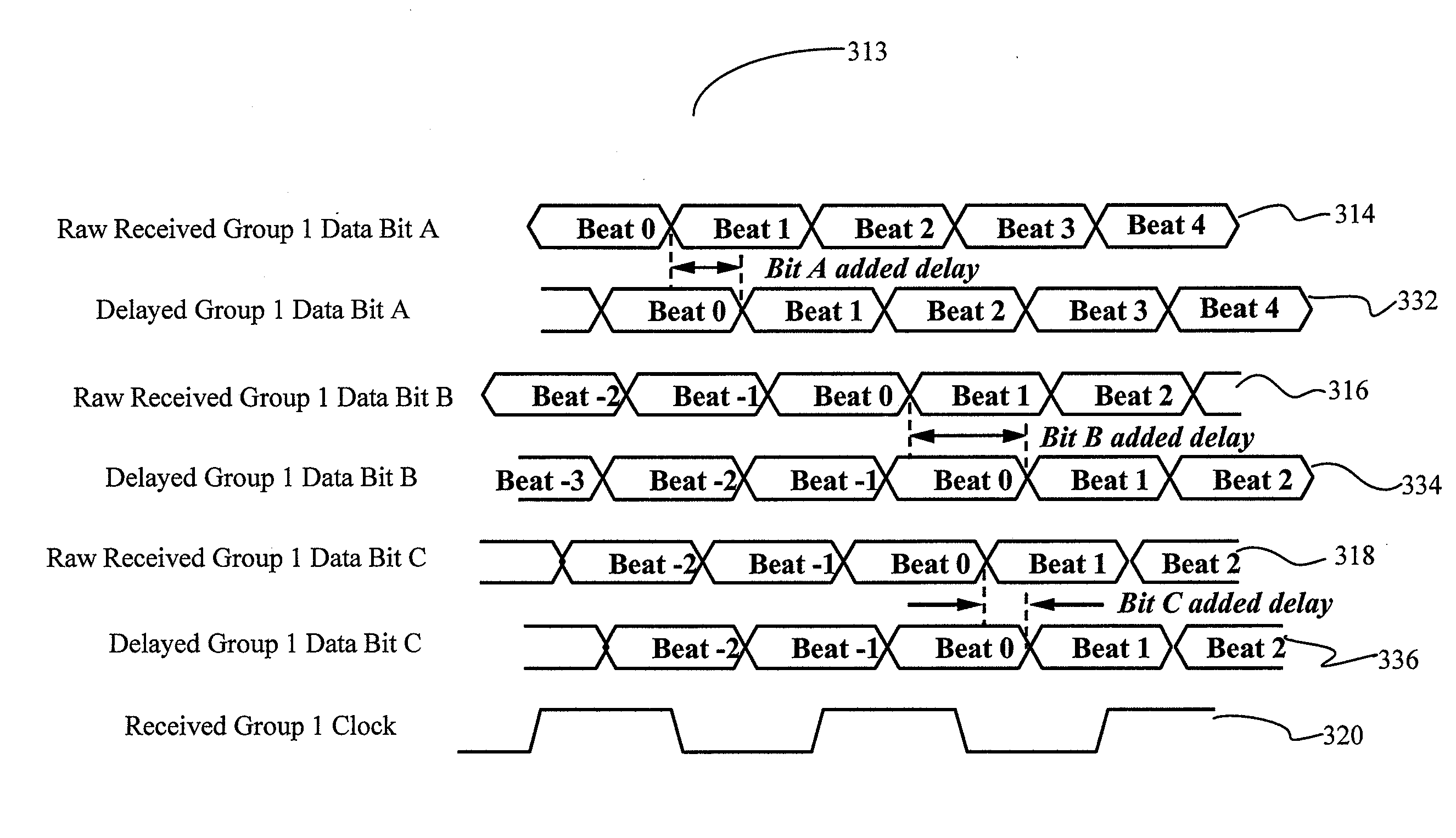
Combined alignment scrambler function for elastic interface
InactiveUS20080201599A1Accelerated trainingImprove performanceChannel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsLogic stateComputer science
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Sewage-disposal soft measurement method on basis of integrated neural network
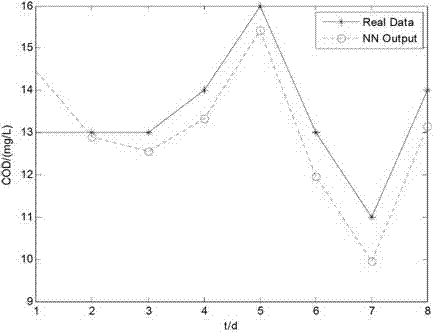
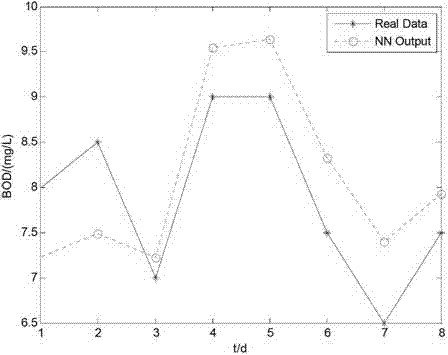
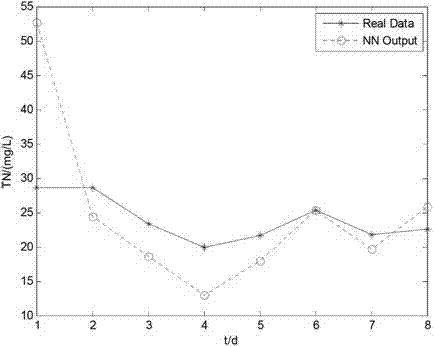
ActiveCN102854296APrediction is accurateAccelerated trainingBiological neural network modelsTesting waterWater qualityEngineering
The invention discloses a sewage-disposal soft measurement method on the basis of an integrated neural network, and belongs to the field of sewage disposal. A sewage disposal process is high in nonlinearity, time-varying characteristics and complexity, and measurement for key water quality indexes is crucially significant in control of water pollution. In order to improve precision of simultaneous soft measurement for various key water quality parameters in a sewage-disposal soft measurement process by the sewage-disposal soft measurement method, an integrated neural network model is provided for measuring COD (chemical oxygen demand) of outlet water, BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) of the outlet water and TN (total nitrogen) of the outlet water, coupling relation between the three key water quality parameters is sufficiently utilized in the model, the integrated neural network model contains three feedforward neural sub-networks, and the various neural sub-networks are trained by particle swarm optimization, so that the optimal structure of each neural sub-network can be obtained. The COD of the outlet water, the BOD of the outlet water and the TN of the outlet water are predicted by the trained neural network finally, and prediction results are accurate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
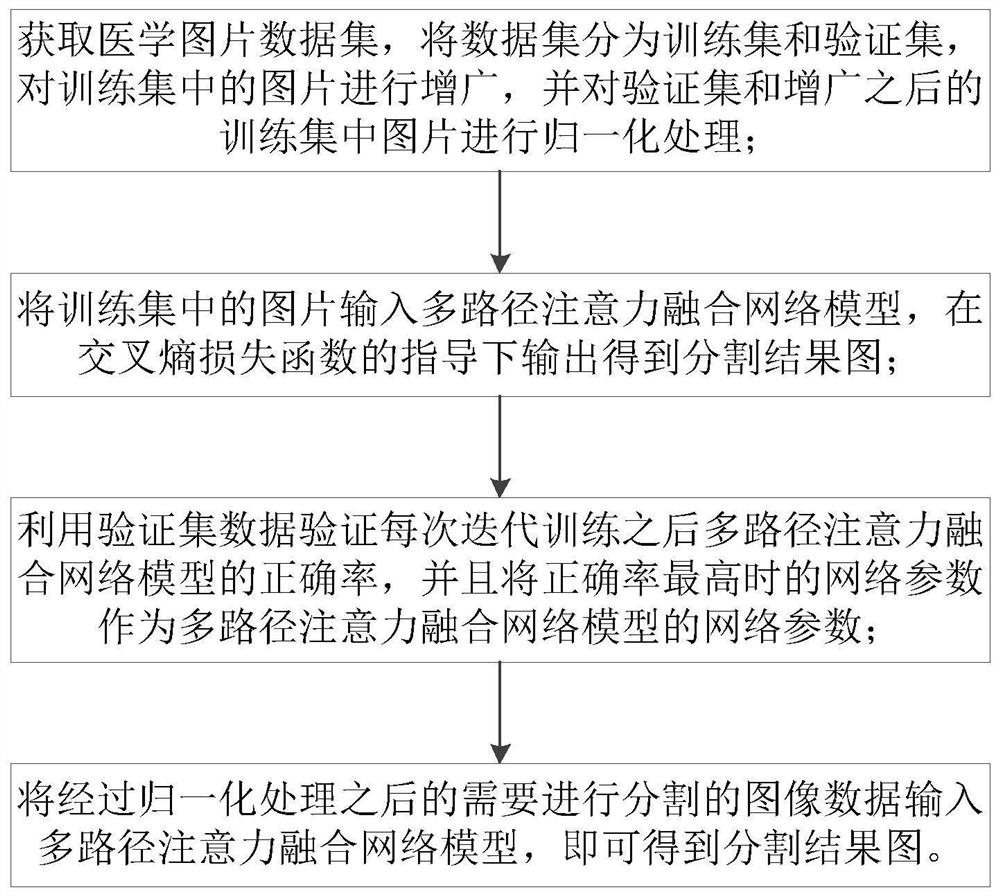
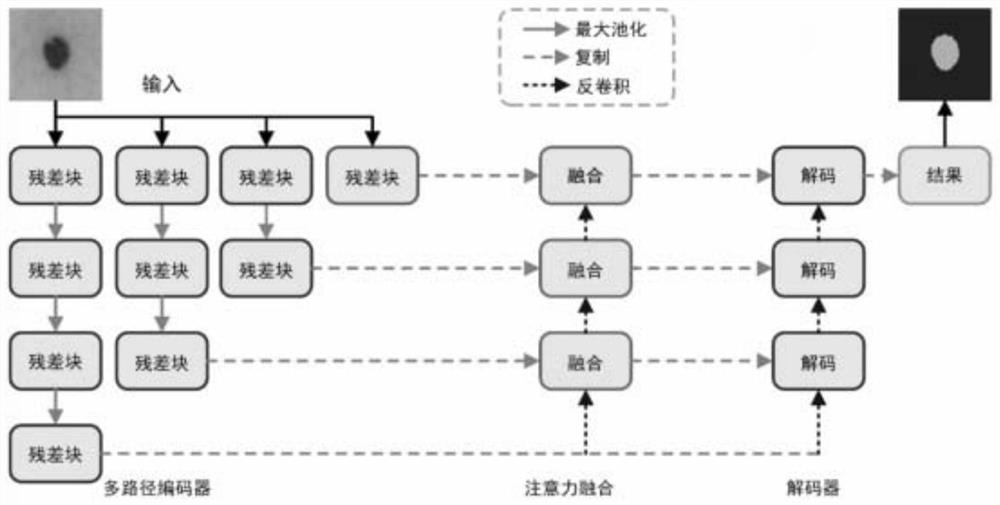
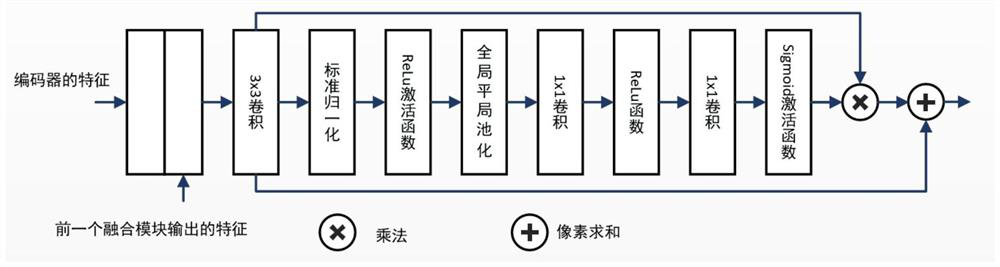
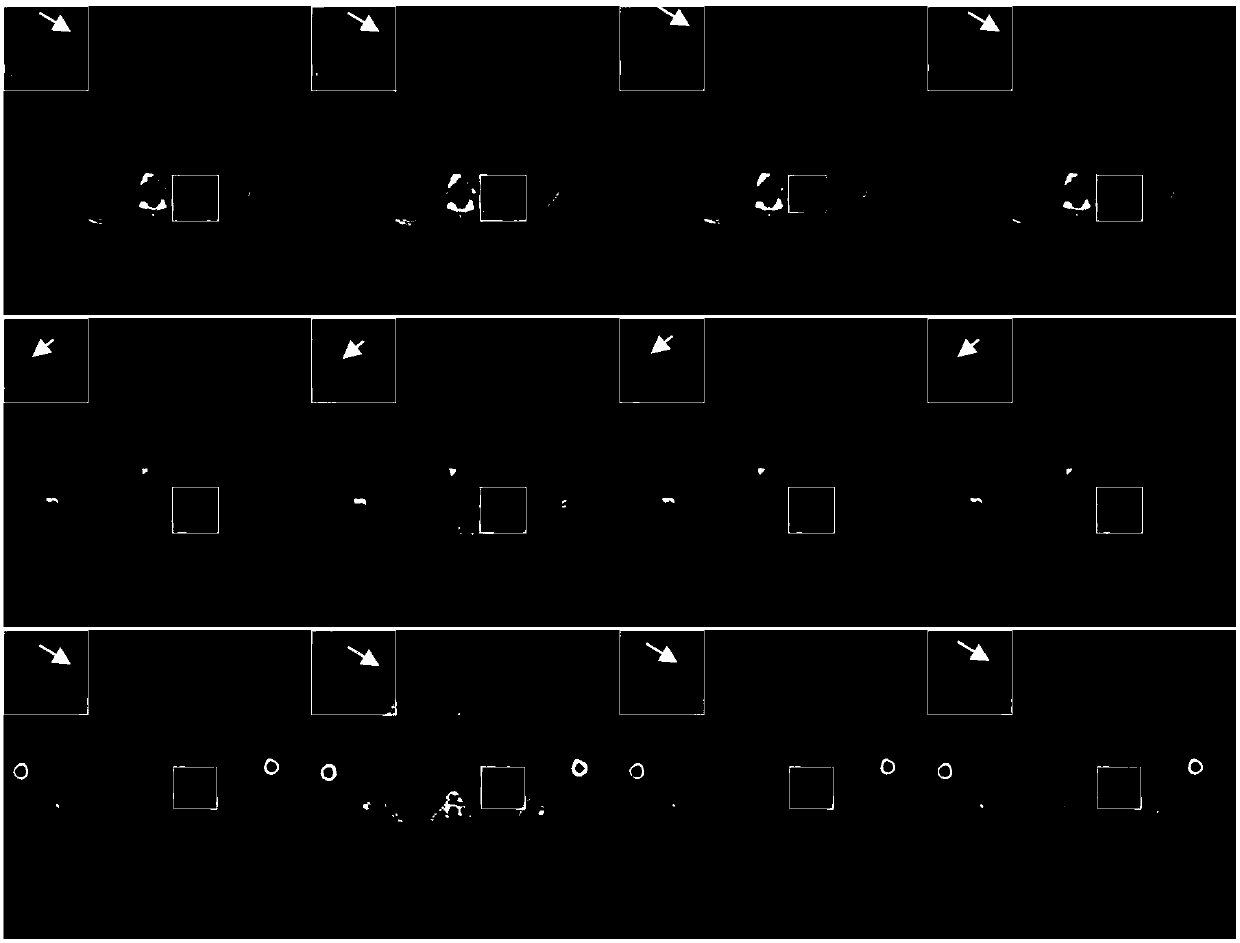
Medical image automatic segmentation method based on multi-path attention fusion
ActiveCN111681252AIncrease the number of picturesImprove feature qualityImage enhancementImage analysisNetwork modelData set
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical image processing and computer vision, in particular to a medical image automatic segmentation method based on multi-path attention fusion, whichcomprises the following steps: obtaining a medical image data set, dividing the data set into a training set and a verification set, augmenting images in the training set, and normalizing images of the verification set and the augmented images in the training set; inputting the pictures in the training set into a multi-path attention fusion network model, and outputting under the guidance of a cross entropy loss function to obtain a segmentation result picture; selecting a model with the highest accuracy of the verification set, inputting the test set into a multi-path attention fusion network loading the model, and outputting to obtain a segmentation result graph of the image. According to the method, the problems that in the medical image segmentation process, an existing network cannoteffectively improve the feature quality under different scales through an encoder, interlayer dependence between network low-level structure features and high-level semantic features is difficult tocontrol, and consequently the segmentation result is poor are solved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
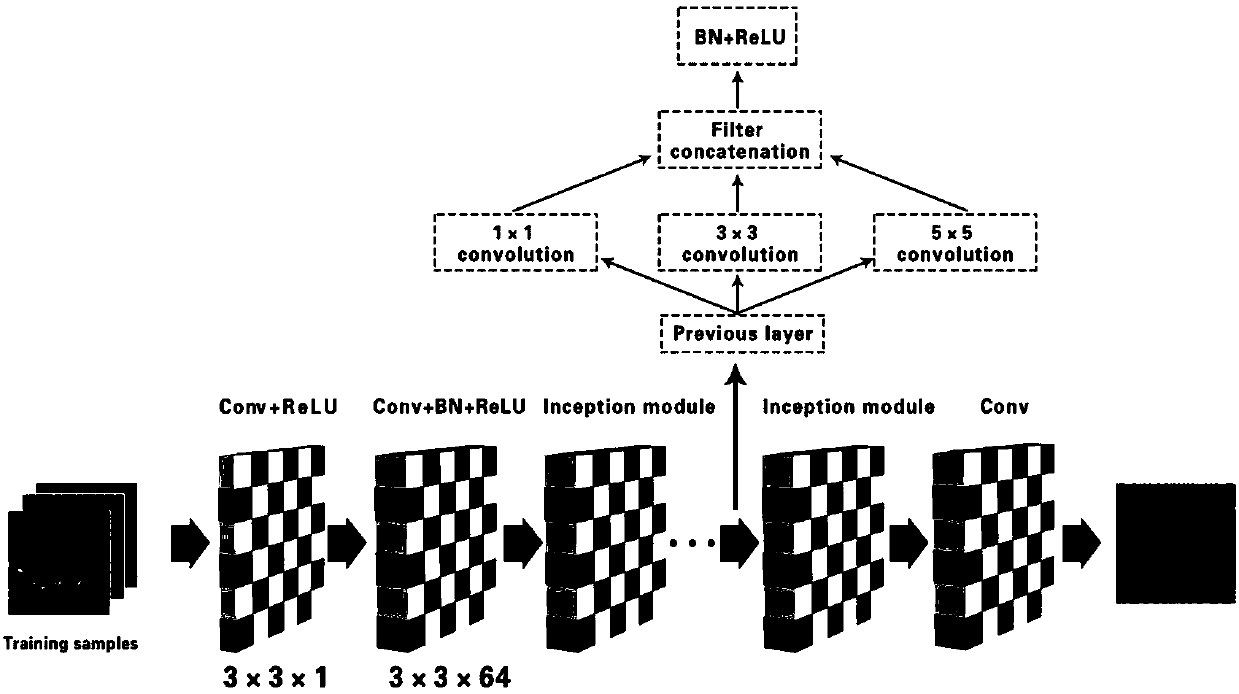
Residual error learning-based CT sparse reconstruction artifact correction method and system
InactiveCN107871332AReduce training timeSpeed up the training processImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionCorrection methodFilter back projection
The invention discloses a residual error learning-based CT sparse reconstruction artifact correction method and system. The method comprises the steps of firstly, reconstructing sparse projection datagenerated by CT through an FBP (Filtered Back-Projection) method, wherein a image after reconstruction has a serious artifact; secondly, learning features of the artifact by establishing a residual error neural network structure to obtain an artifact image; and finally, recovering a clear CT image by performing residual error operation on the sparse reconstruction image and the artifact image. Based on sparse reconstruction, a residual error learning-based convolutional neural network structure framework is introduced; by adopting GPU acceleration, the training time is shortened, the trainingprocess of an experiment is accelerated, and very high CT reconstruction image quality can be realized at a very low CT projection angle; and therefore, the unnecessary injury of radiation to a humanbody is effectively reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Systems for augmented reality visual aids and tools
InactiveUS20180144554A1Improved eccentric viewing capabilityImprovement in visual adaptationInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementRetinaSelf adaptive
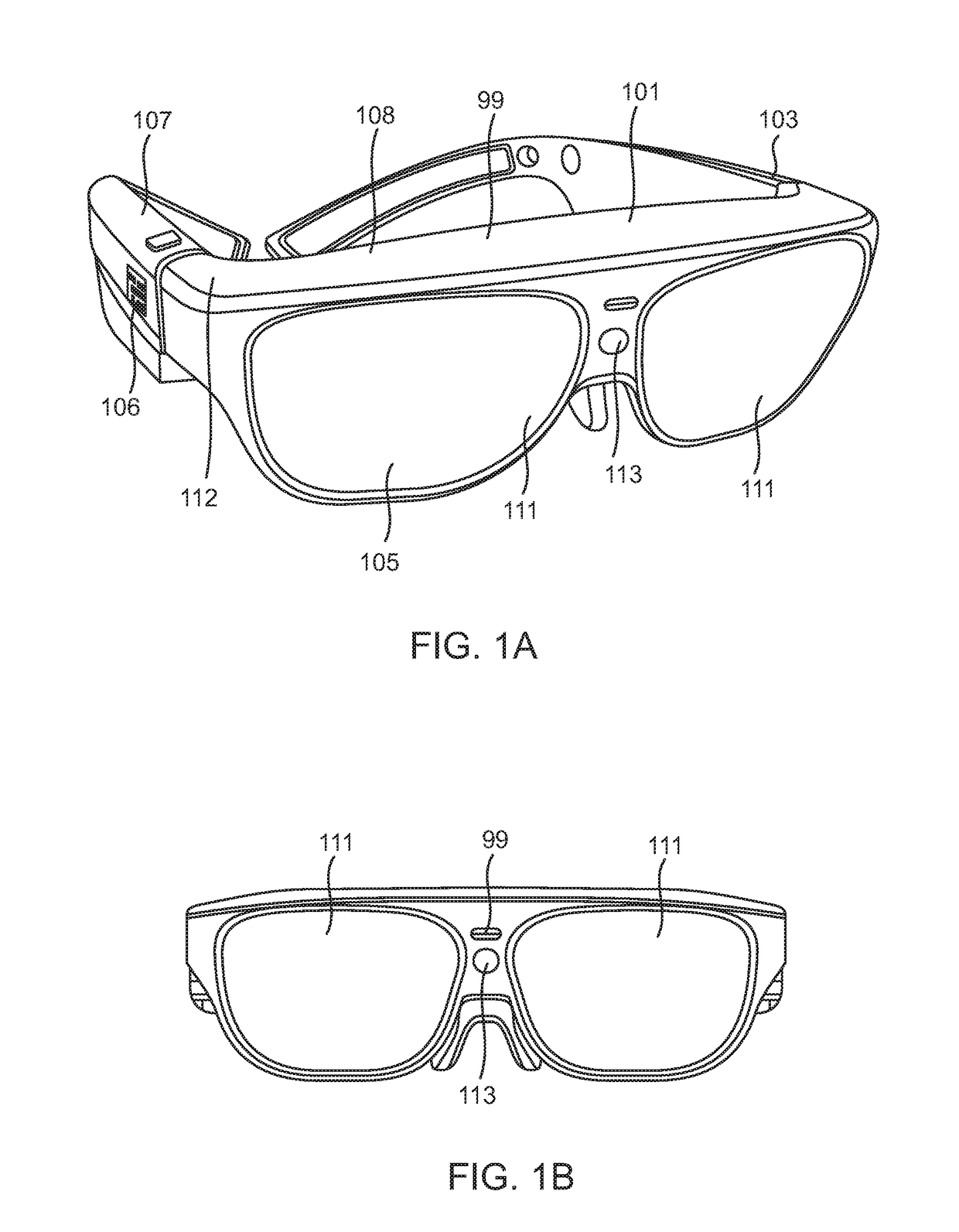
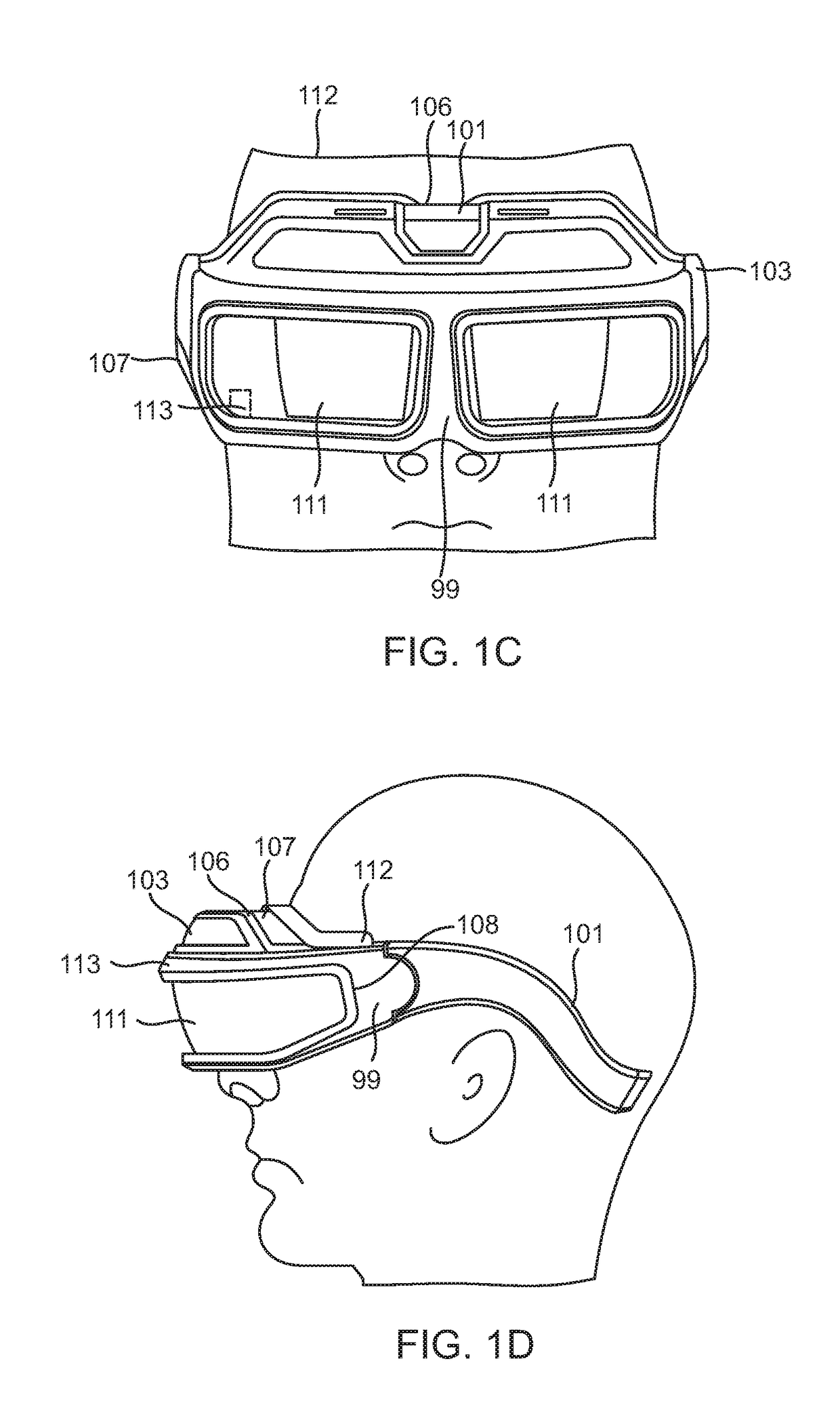
Adaptive Control Driven System / ACDS 99, supports visual enhancement, mitigation of challenges and with basic image modification algorithms and any known hardware from contact lenses to IOLs to AR hardware glasses, & enables users to enhance vision with user interface based on a series of adjustments that are applied to move, modify, or reshape image sets and components with full advantage of the remaining useful retinal area, thus addressing aspects of visual challenges heretofore inaccessible by devices which learn needed adjustments.
Owner:EYEDAPTIC INC
Equipment for volleyballer training use
InactiveCN1861233AChanges are flexible and accurateAccelerated trainingSport apparatusEngineeringTraining level
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
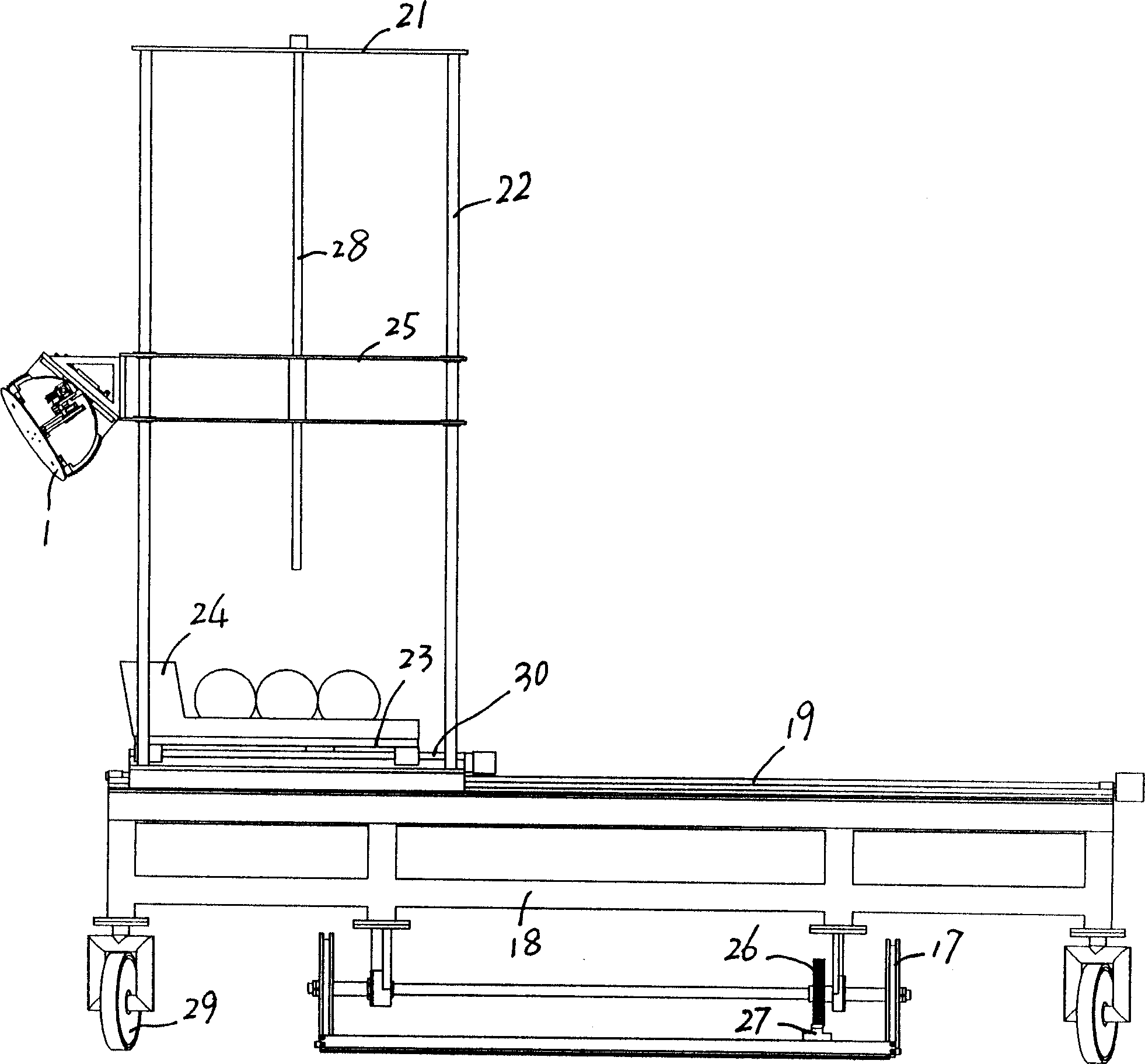
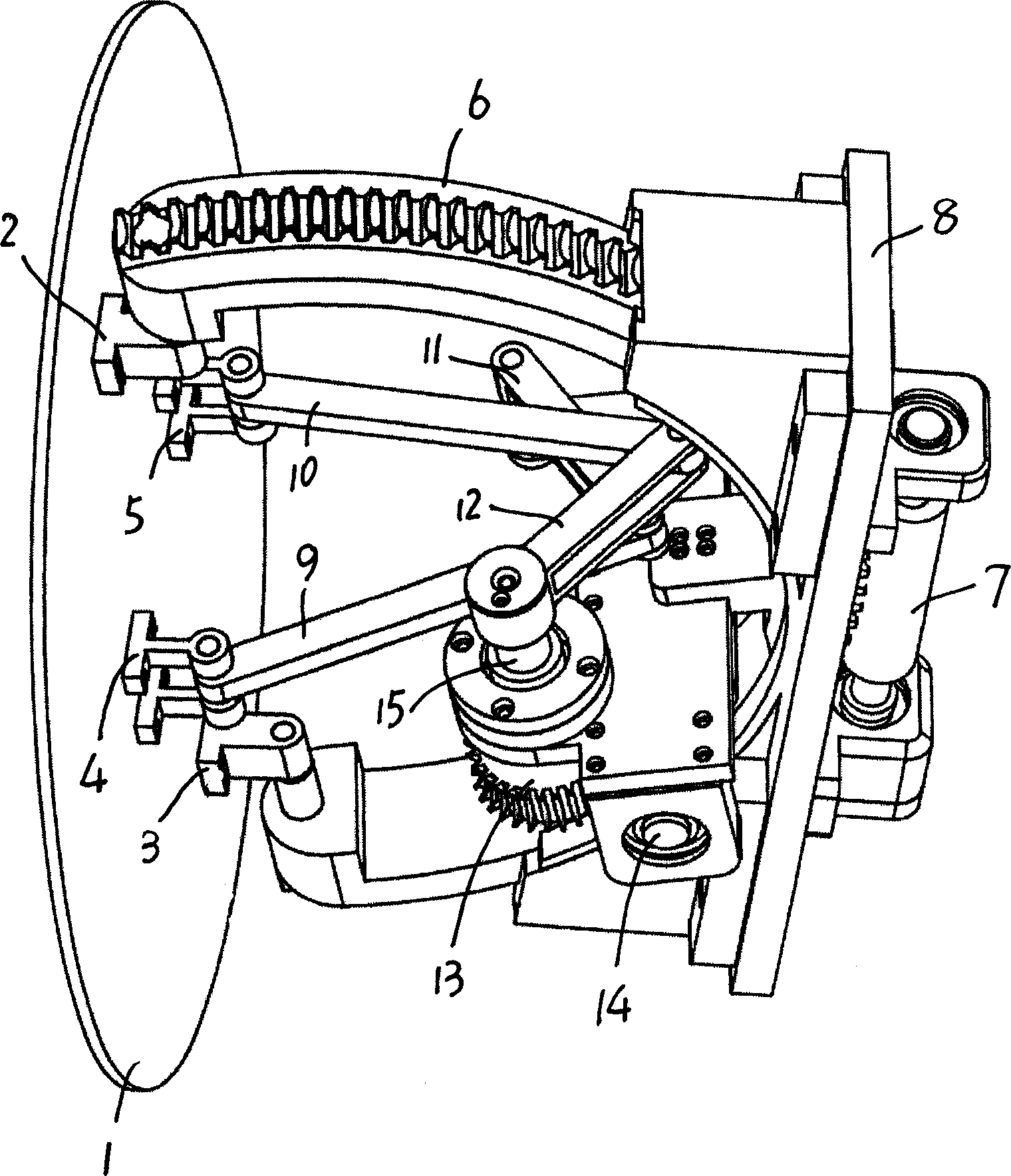
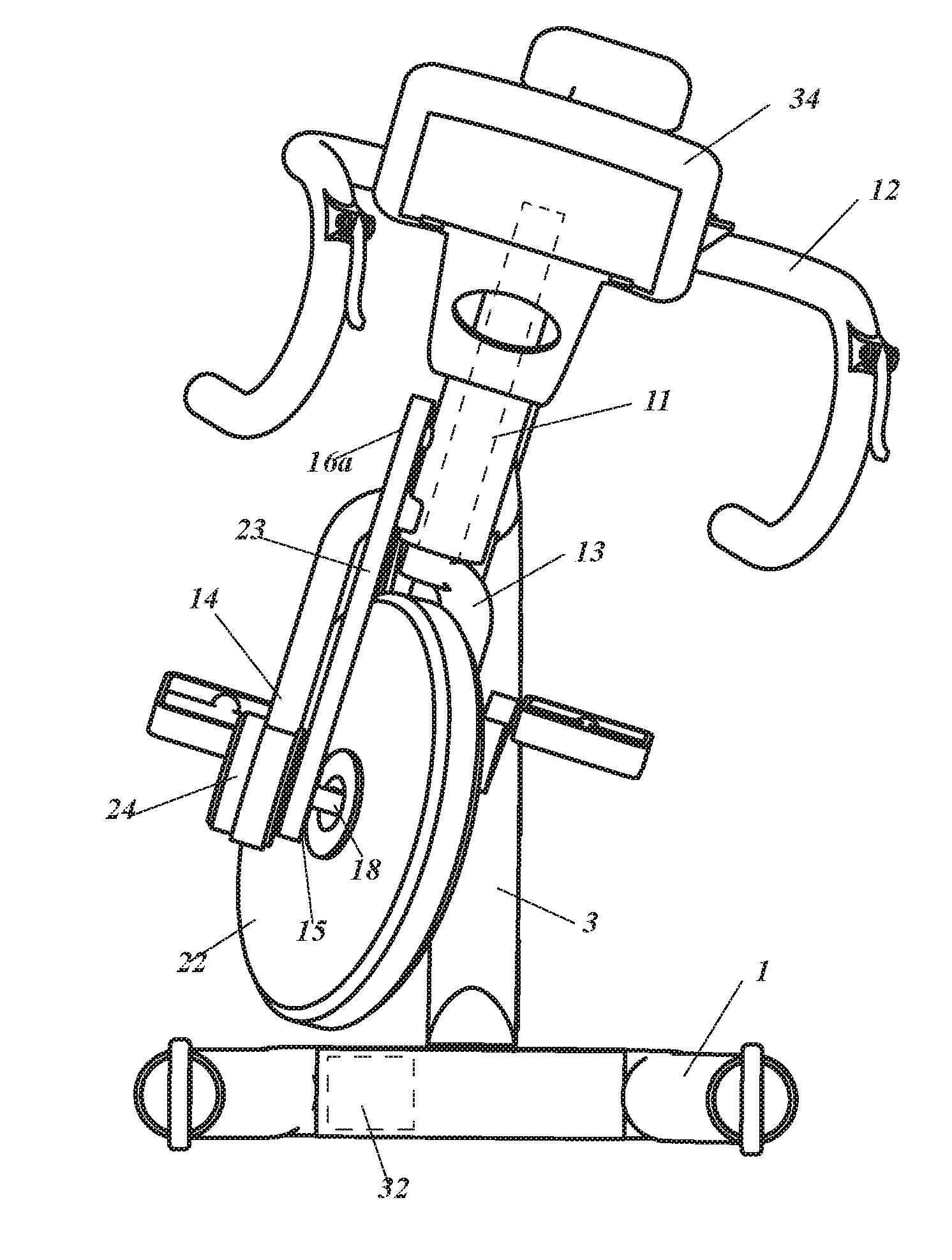
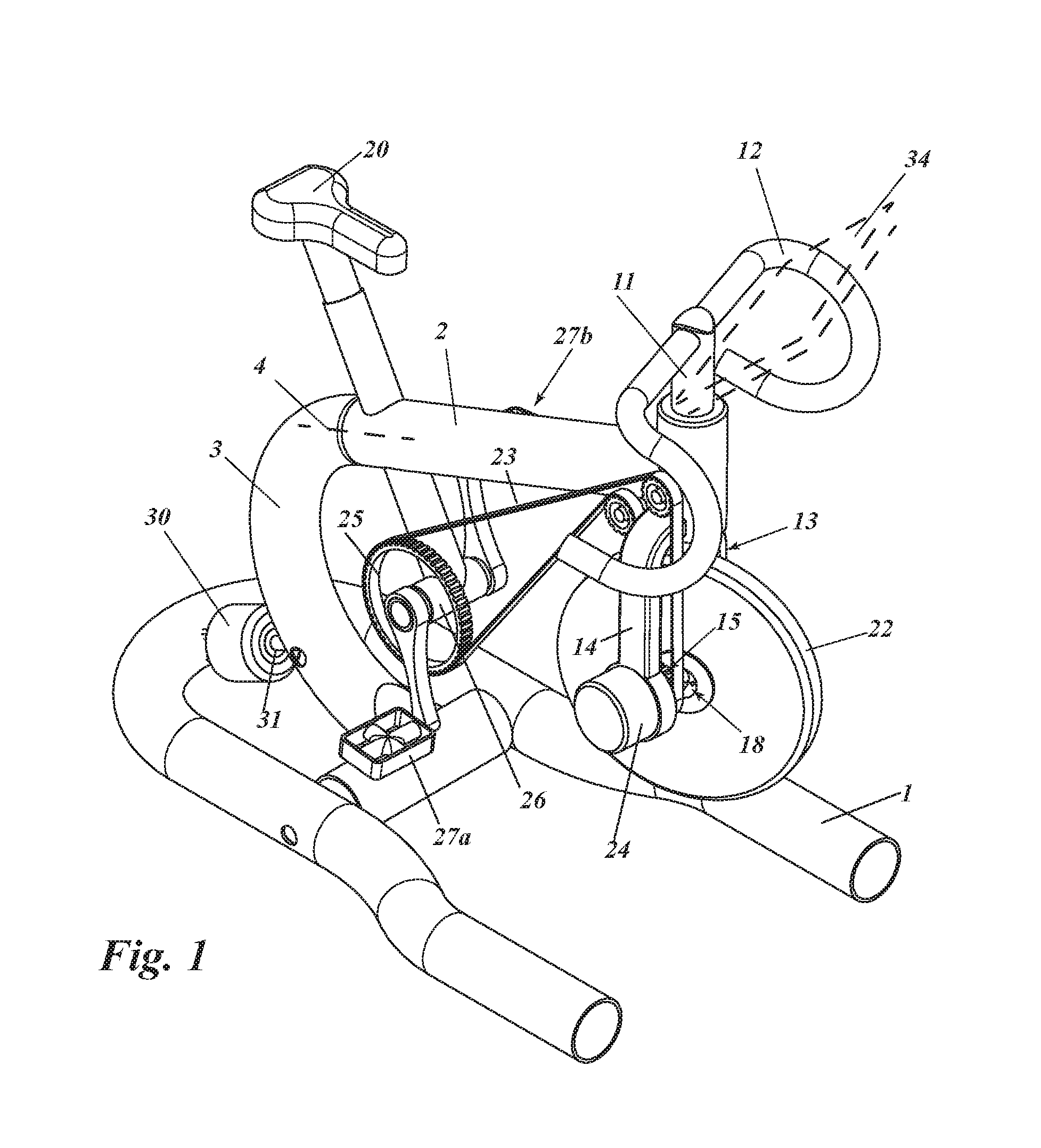
Exercising bicycle
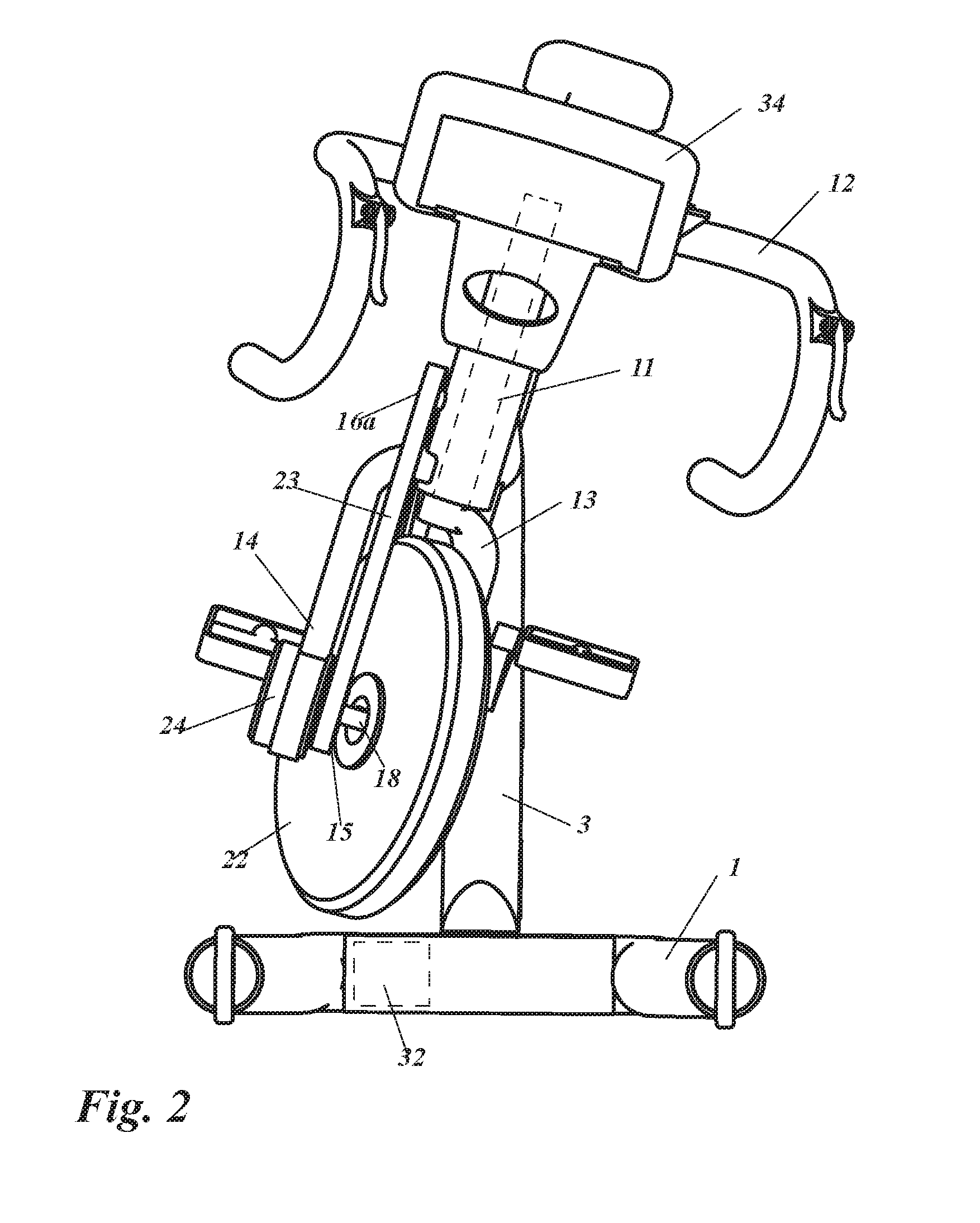
InactiveUS20150290490A1Entertaining and usefulAccelerated trainingMuscle exercising devicesMovement coordination devicesEngineeringFlywheel
A training bicycle, including a first frame (1, 36) configured to be supported on a floor, a second frame (2, 37) connected to the first frame, the second frame including an axle (4) allowing the second frame to tilt relative to the first frame along an axis in the longitudinal direction of the training apparatus, a handlebar (12, 35, 77, 90) connected to the upper end of a steering shaft (11, 76), the steering shaft being rotationally connected to the second frame, a crank (26, 110) connected to the second frame, and a first flywheel (22, 41, 56, 167, 193) rotationally connected to the lower end of said steering shaft with means for transferring movement from the crank to the first flywheel.
Owner:ACTIVETAINMENT
Method and apparatus for simultaneously monitoring computer user screen and telephone activity from a remote location
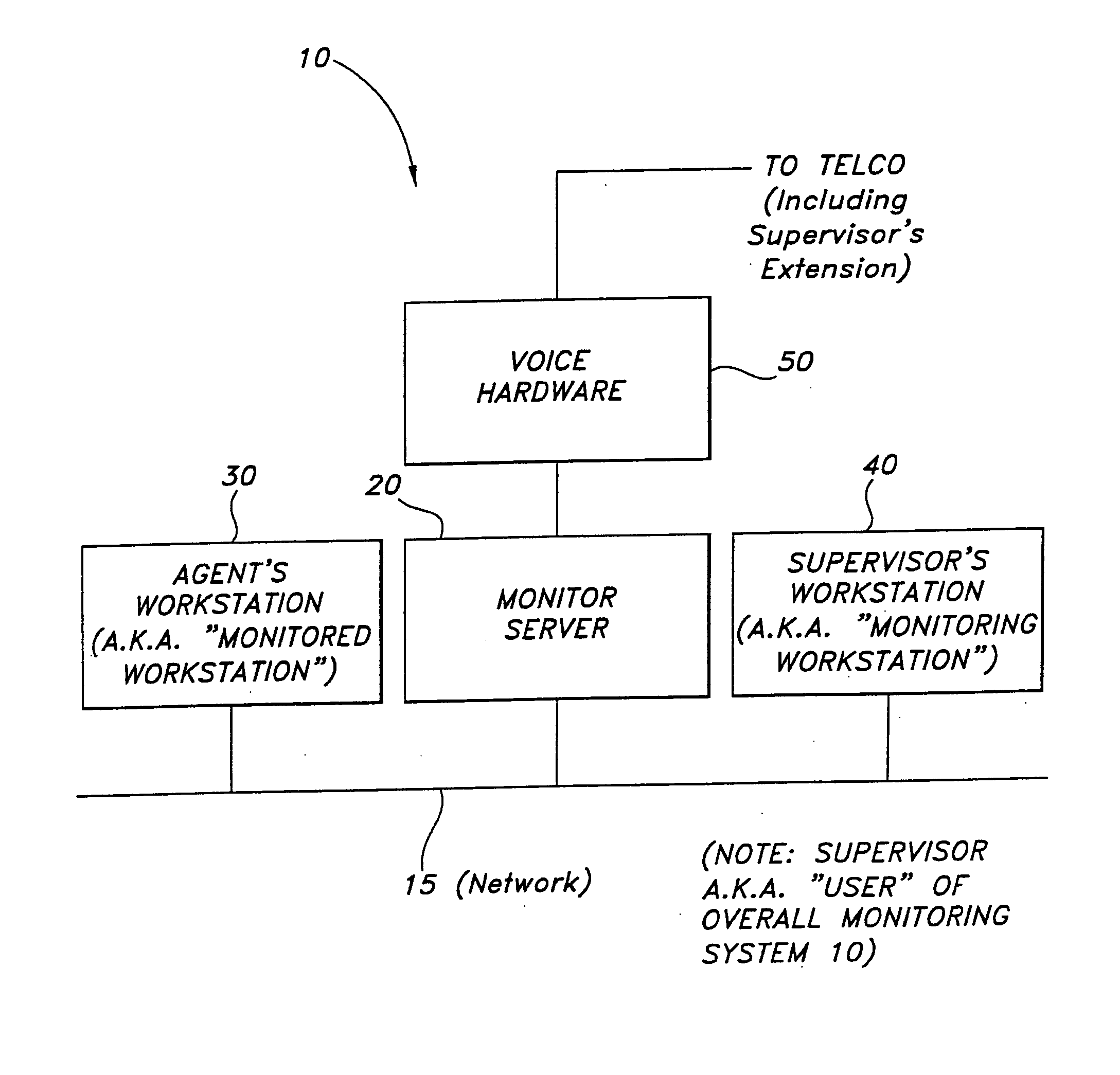
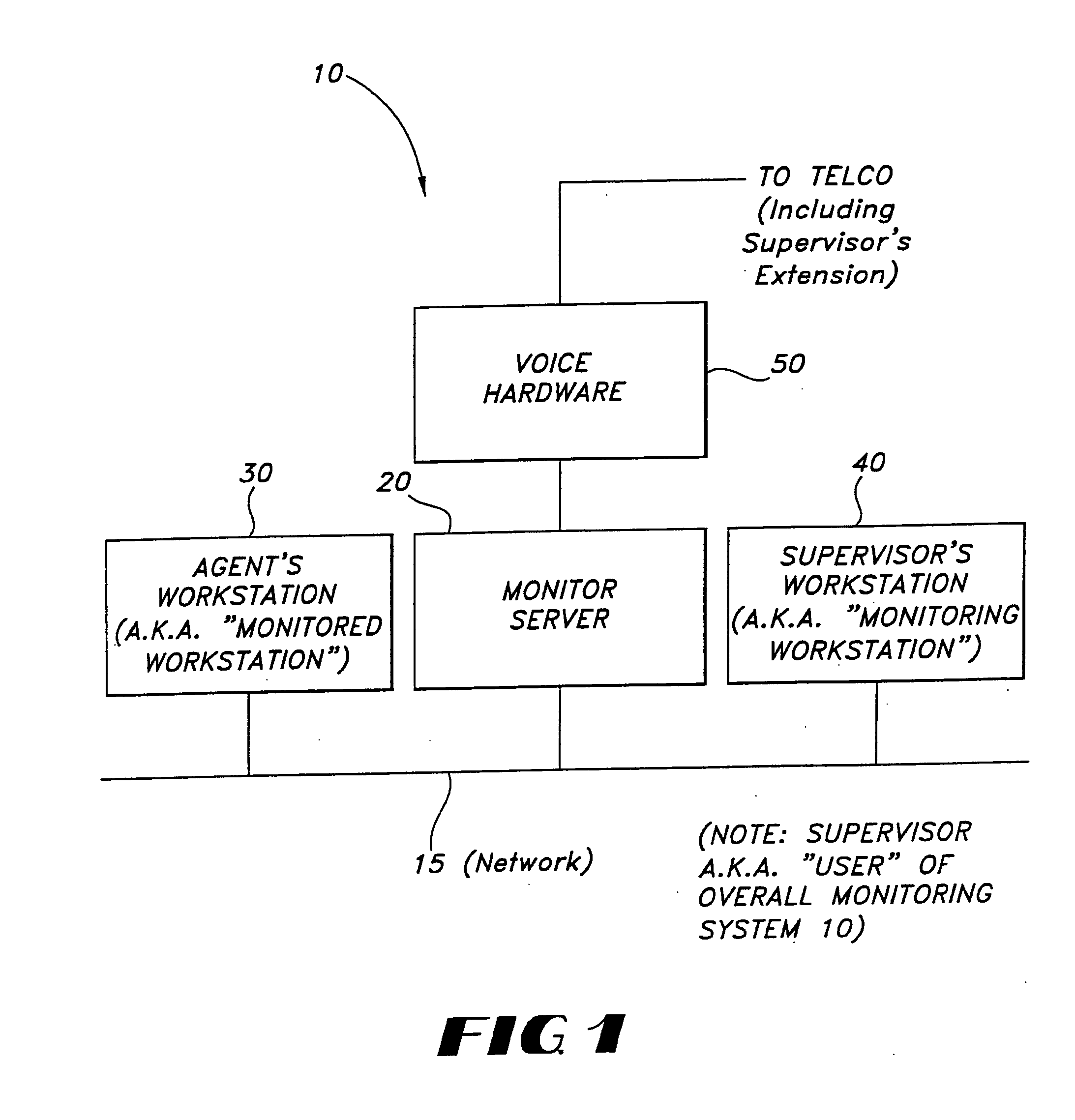
InactiveUS20060126817A1Accelerating transactionValuable and accurate feedback regarding that employee'sManual exchangesAutomatic exchangesComputer usersWorkstation
Systems and methods for monitoring computer user screen an telephone activity from a remote location are provided. The method includes the steps of recording data corresponding to two actual sequential screen changes at the monitored workstation and storing the screen change-related data; recording data corresponding to audio telephone conversation occurring at the monitored workstation during the sequential screen changes and storing the audio telephone conversion-related data; subsequent to steps “a” and “b”, playing back, with the use of the screen change-related data and the audio telephone conversation-related data, the audio telephone conversation with the sequential screen changes as they both happened in real time at the monitored workstation, to allow a monitoring workstation to view and hear on-screen and telephone activities as they occurred at the monitored workstation; and, providing training to an agent at the monitored workstation based upon the played back audio and sequential screen changes.
Owner:CREDIT SUISSE AS ADMINISTATIVE AGENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com