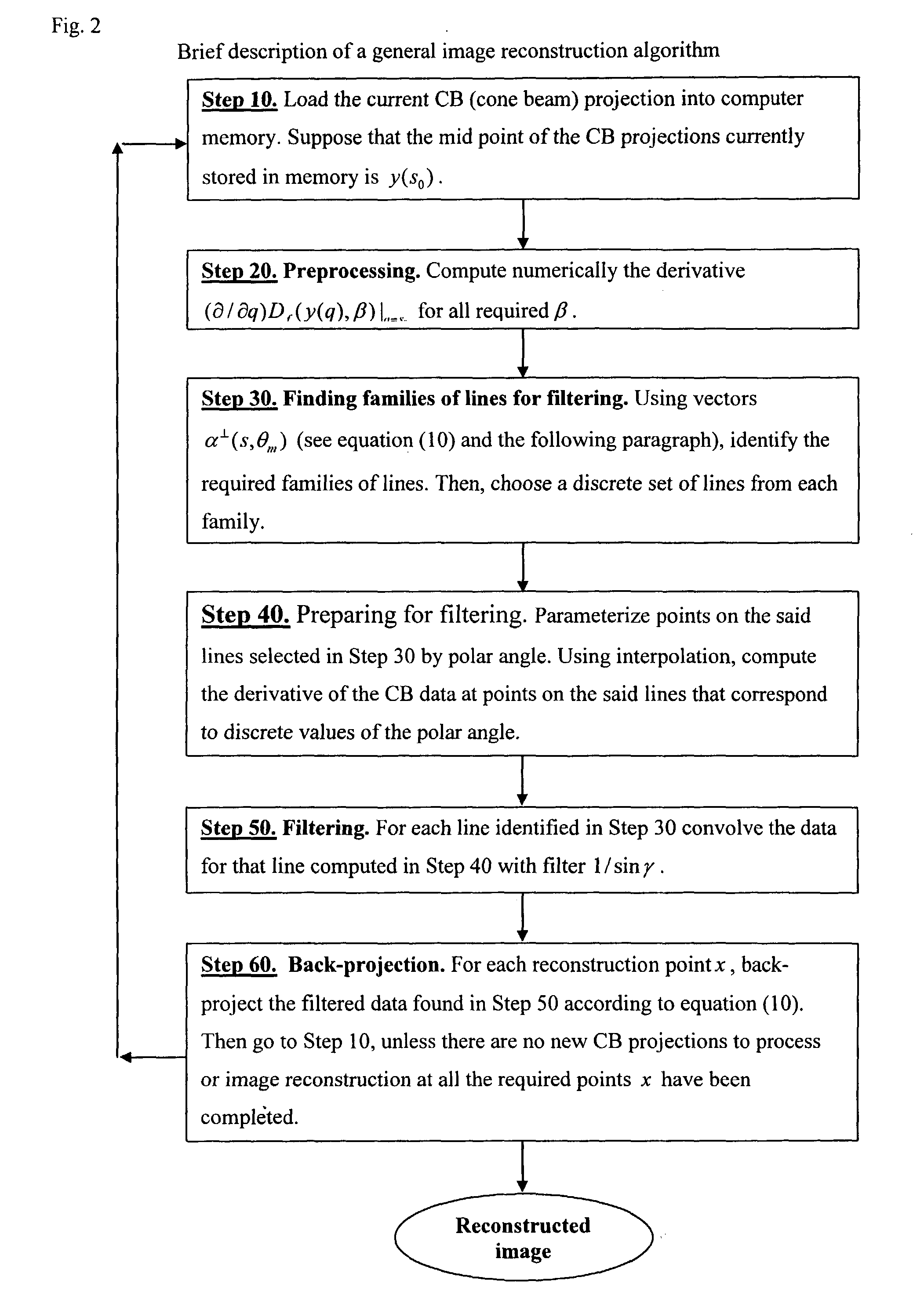
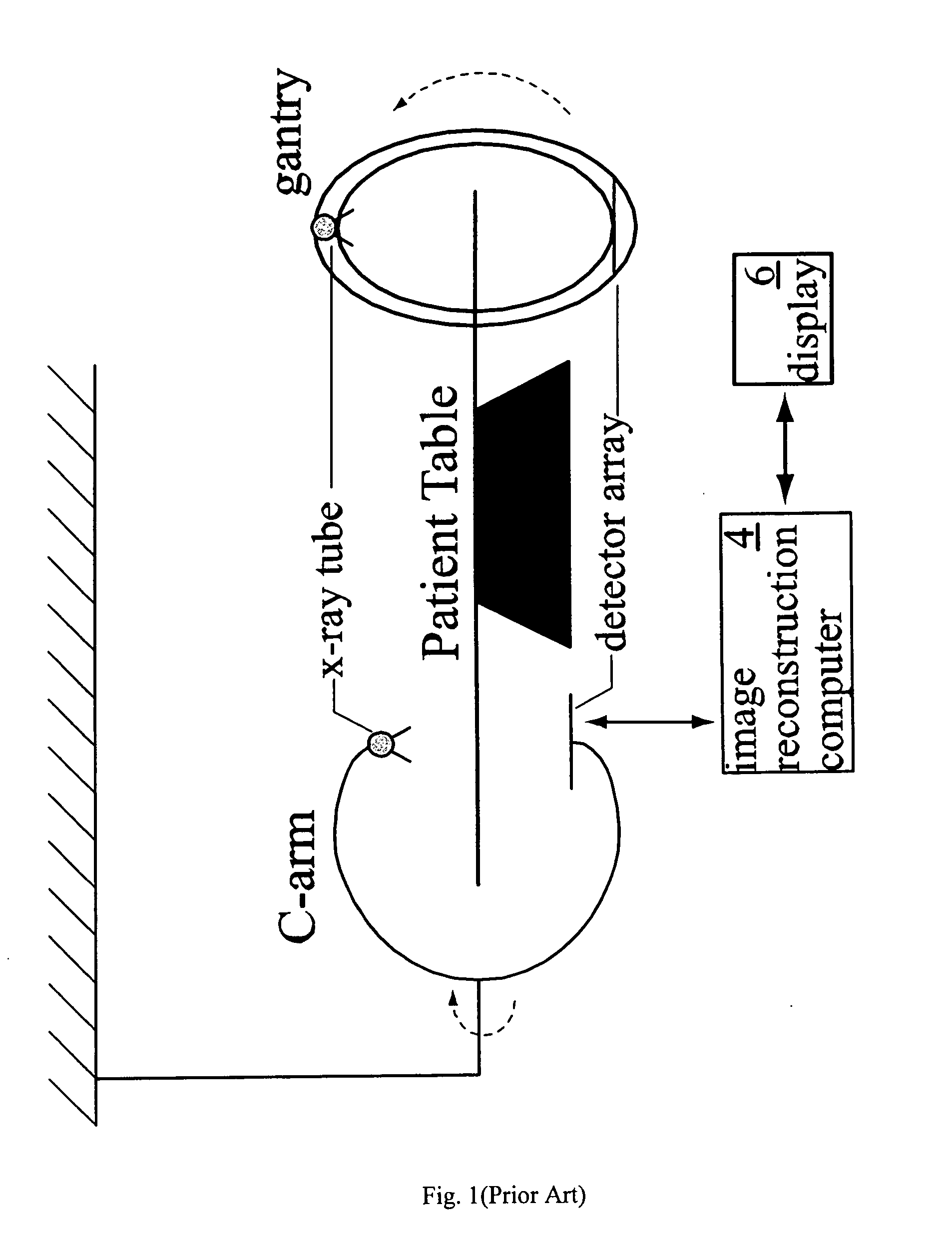
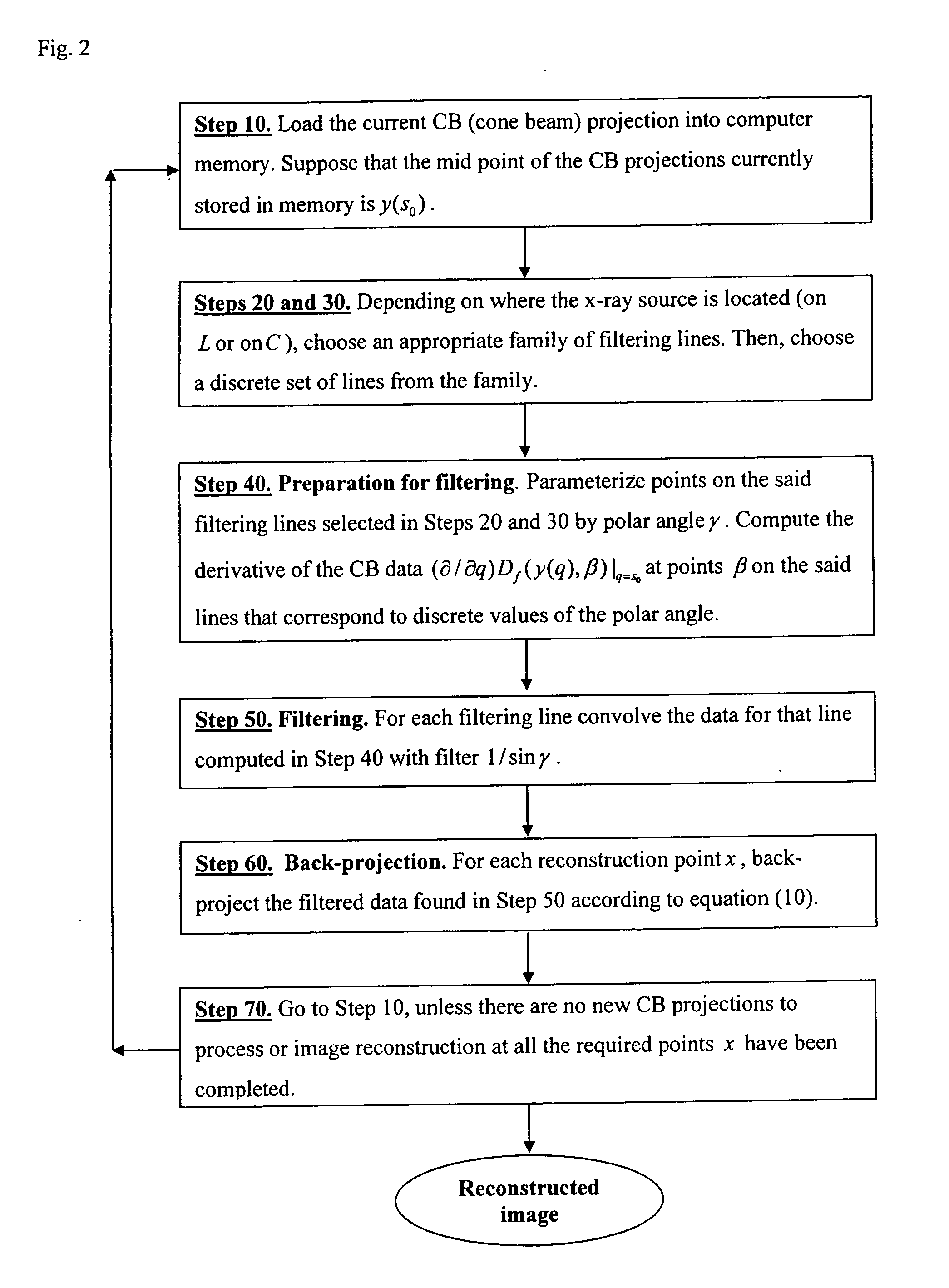
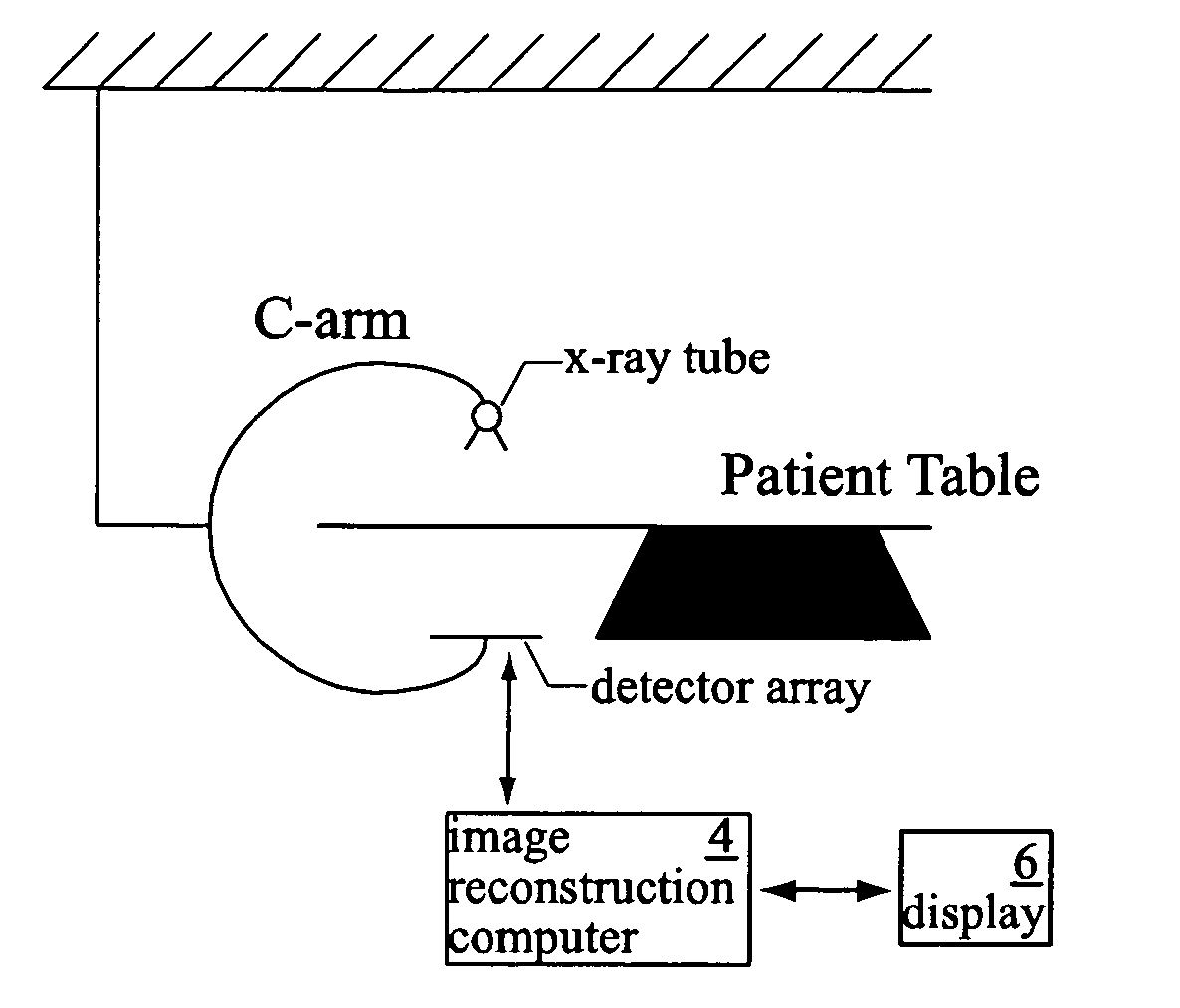
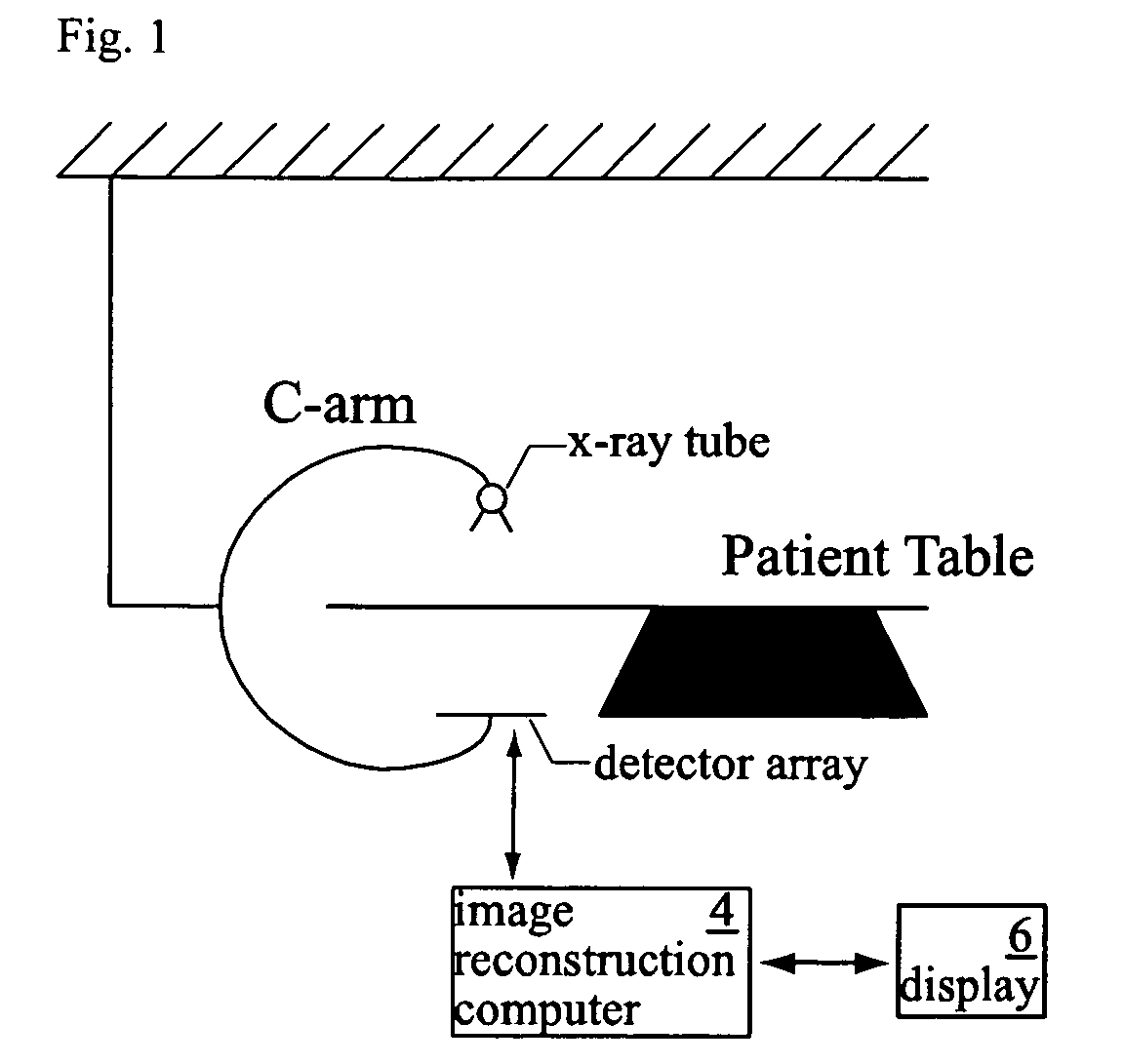
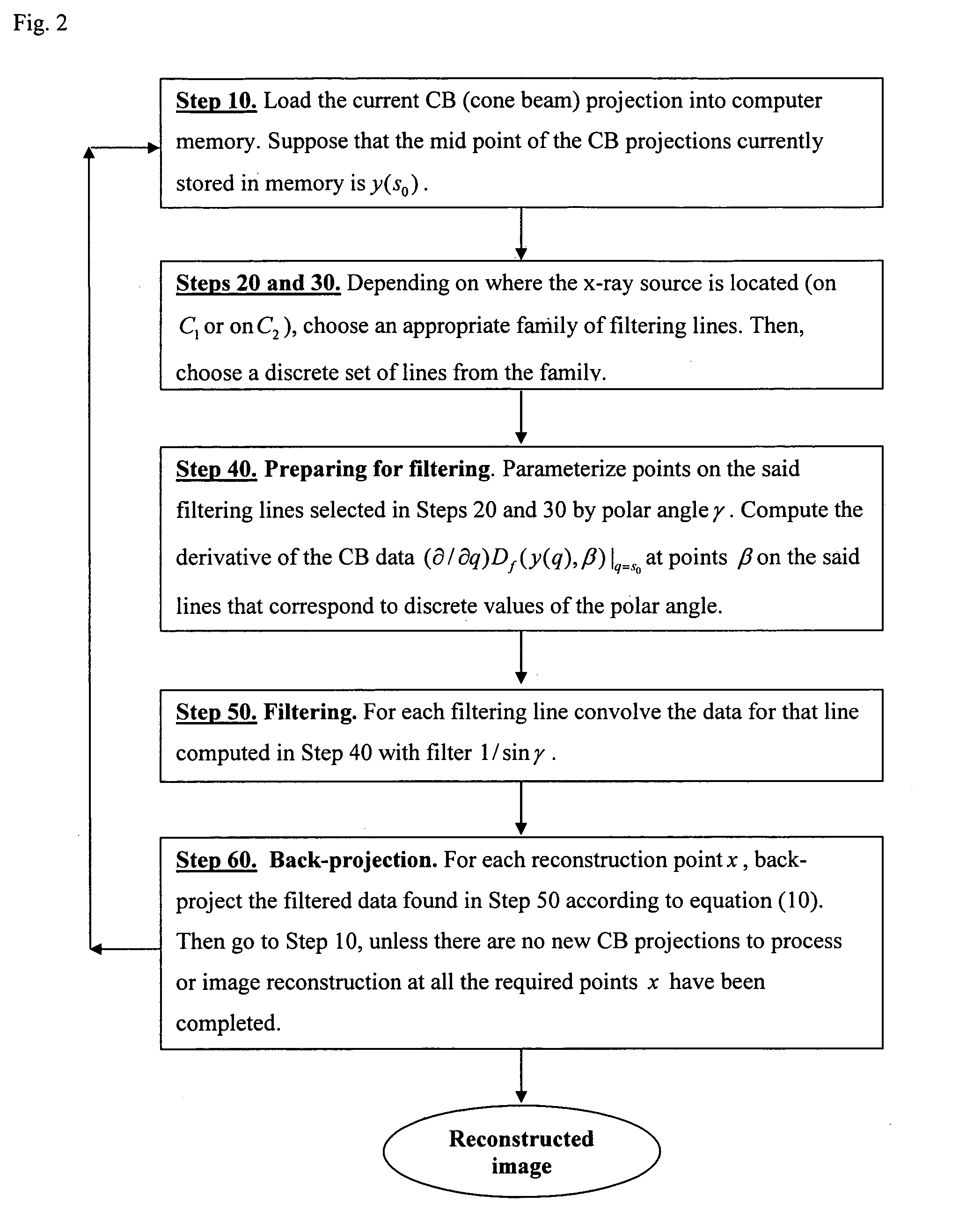
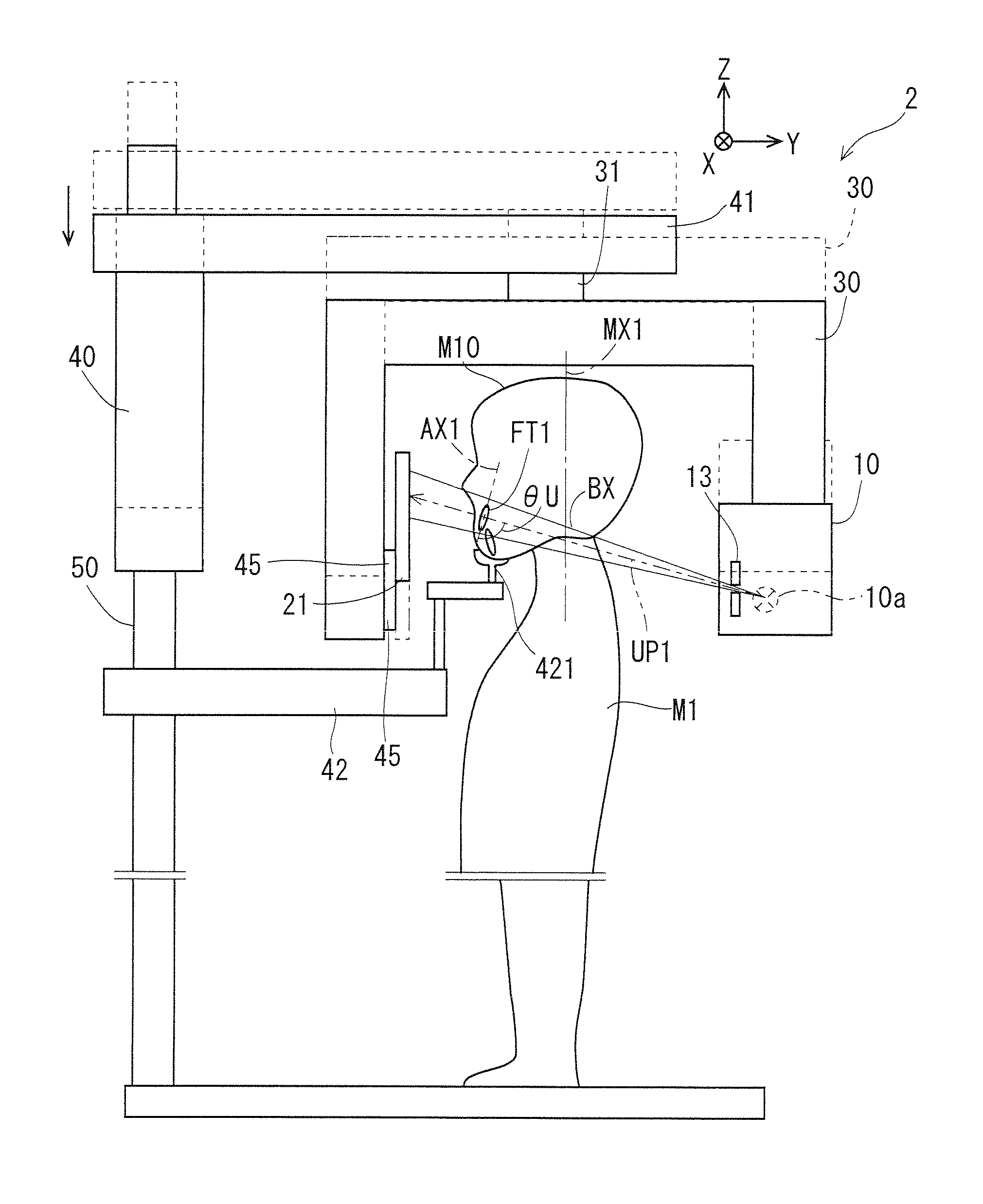
Patents
Literature
171 results about "Filter back projection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diffuse transmission measuring and correcting method of cone-beam CT system
InactiveCN101158653AIncrease contrastImprove image qualityMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation intensity measurementUltrasound attenuationHigh energy
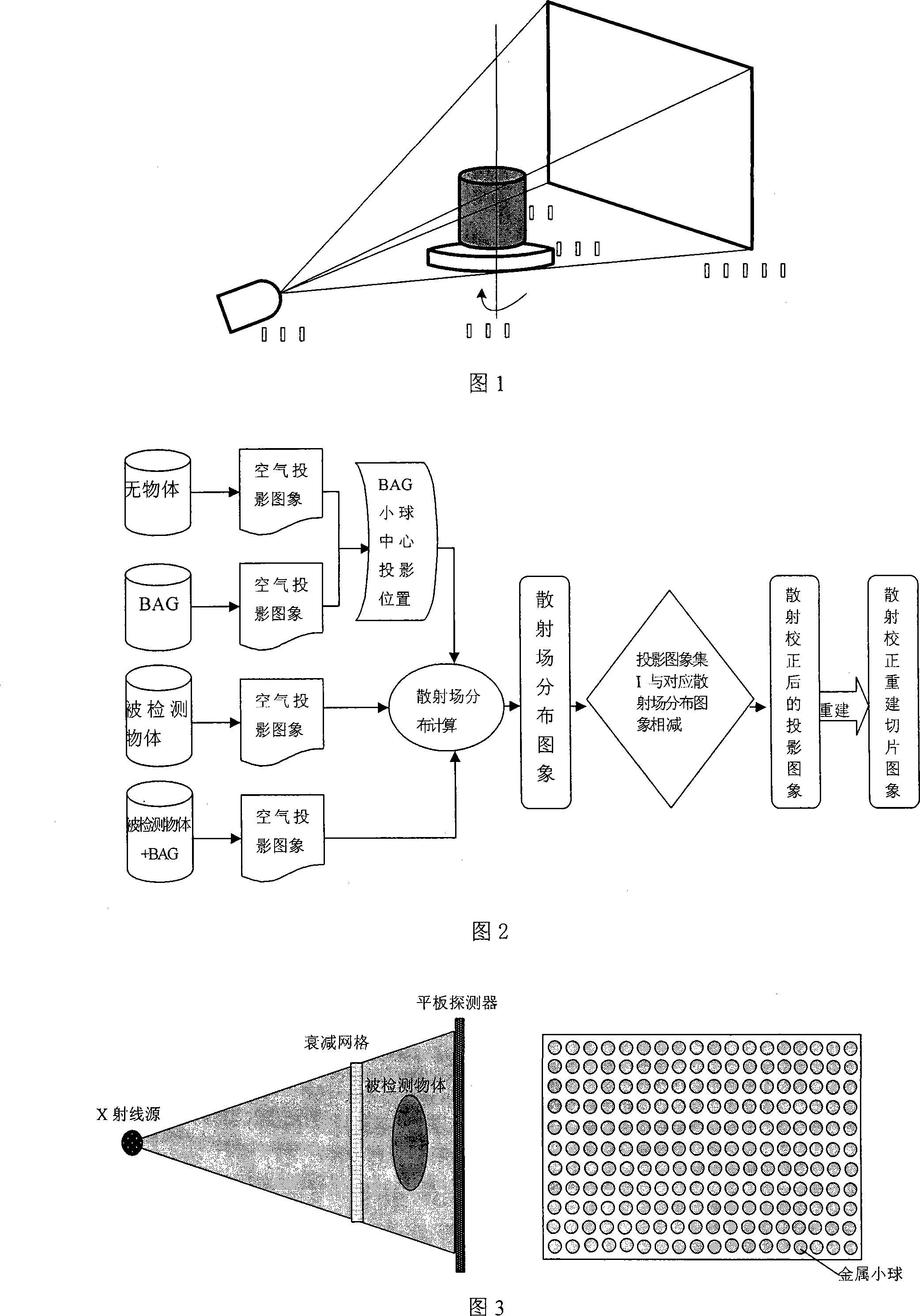
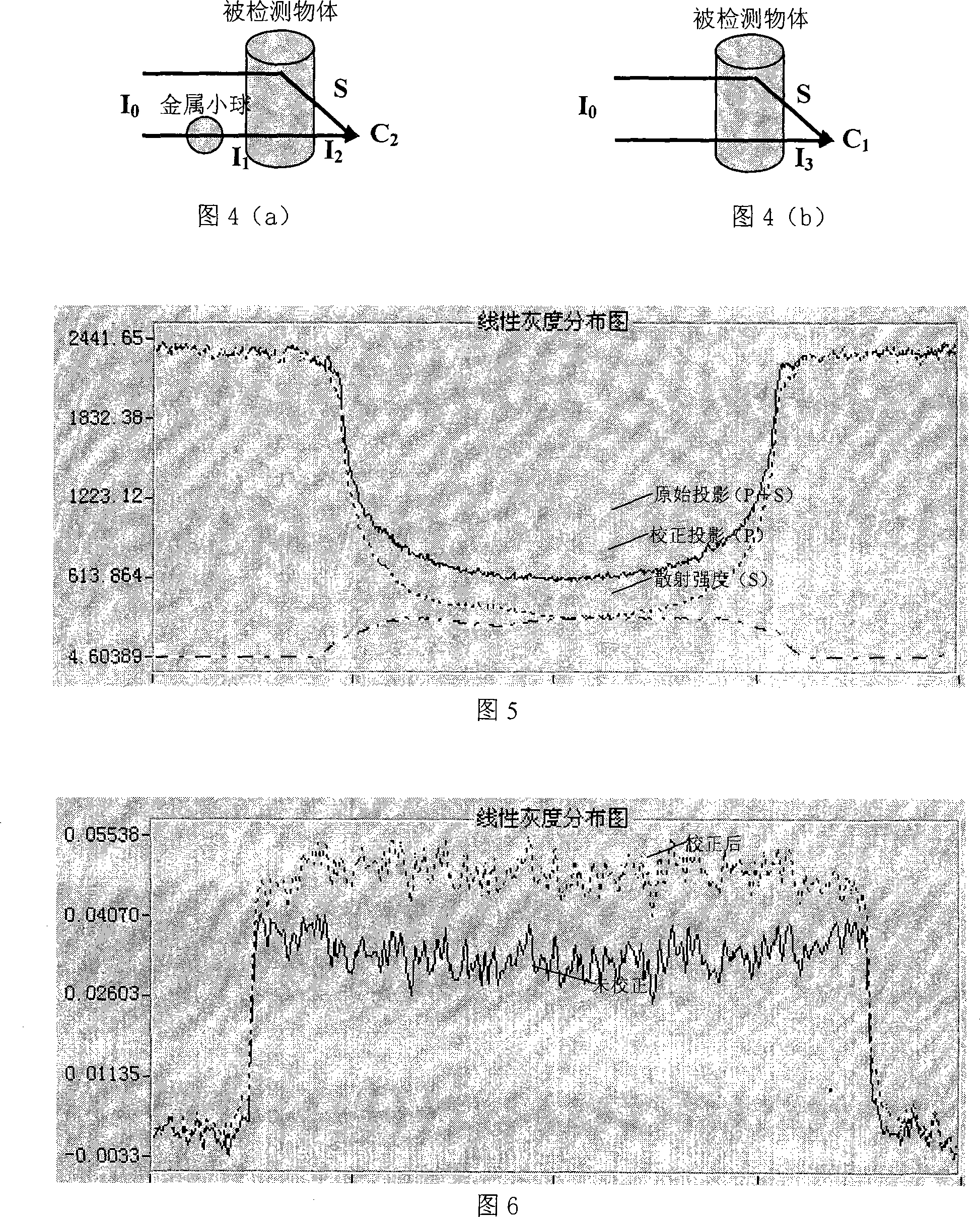
The invention discloses a scattering determination and corrector method of a taper bunch CT system. After arranging a parameter, an air projected picture and a beam attenuation grid projected picture are collected. A circular scanning is carried out on the detected object. A projected picture set I of the detected object with beam attenuation grid and a projected picture set II of the detected object are collected. The projected attitude of the center of each metal ball in the beam attenuation grid is calculated. A scattered field distributing image corresponding to the projected picture of the projected picture set I is calculated through a beam attenuation grid corrector method. A projected picture set III after scattering correction is gained through the projected picture set I subtracting the corresponding scattered field distributing image. Thereby, a sequence slice image after scattering correction is reconstructed through a filter back-projection reconstruction method. The invention can be applied to the scattering correction of the taper bunch CT system from low energy to medium or high energy. The invention is a simple and effective scattering correction method of the taper bunch CT system.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Systems, methods and apparatus for filtered back-projection reconstruction in digital tomosynthesis
ActiveUS20060204076A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomosynthesisBack projection
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and Method For Image Reconstruction
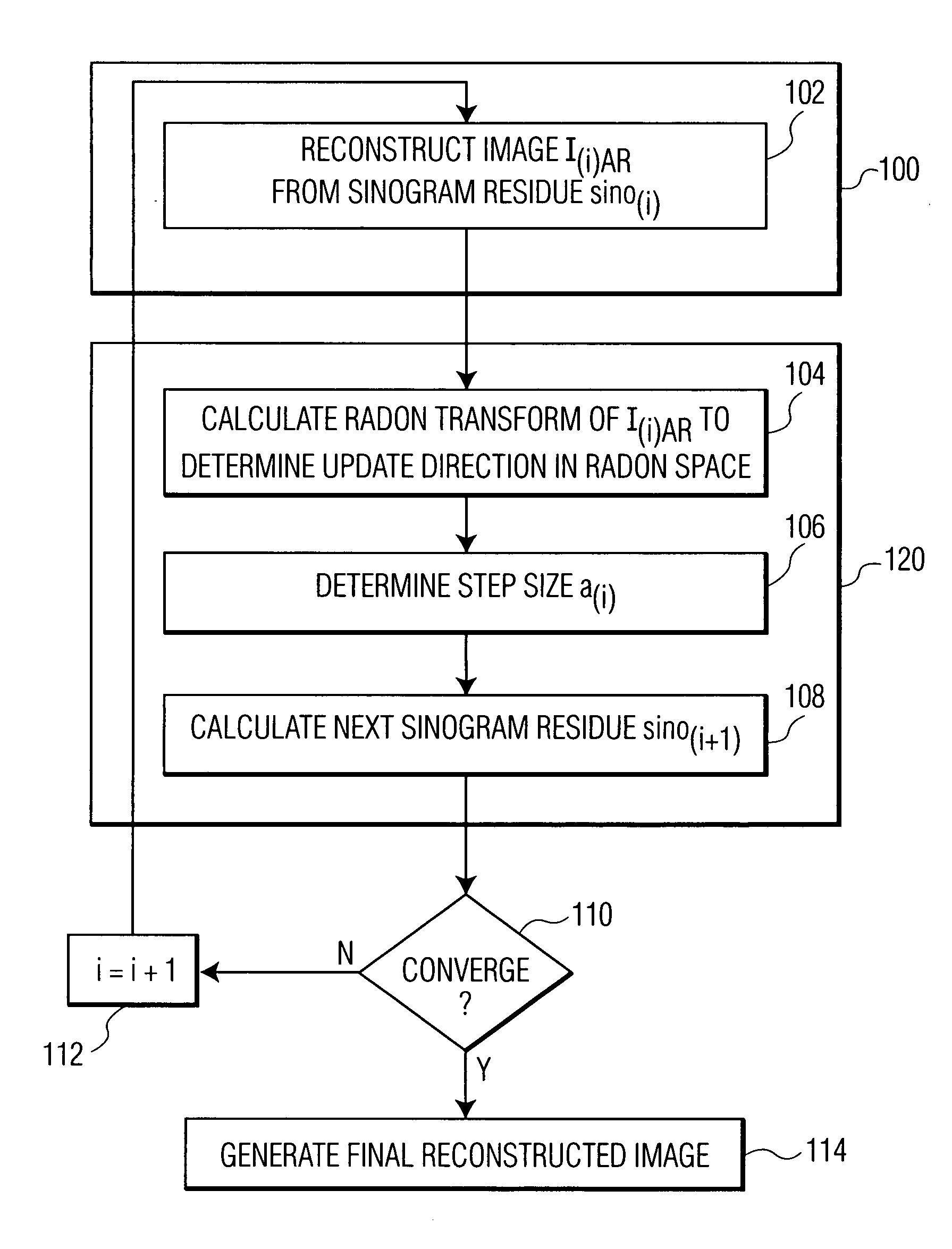
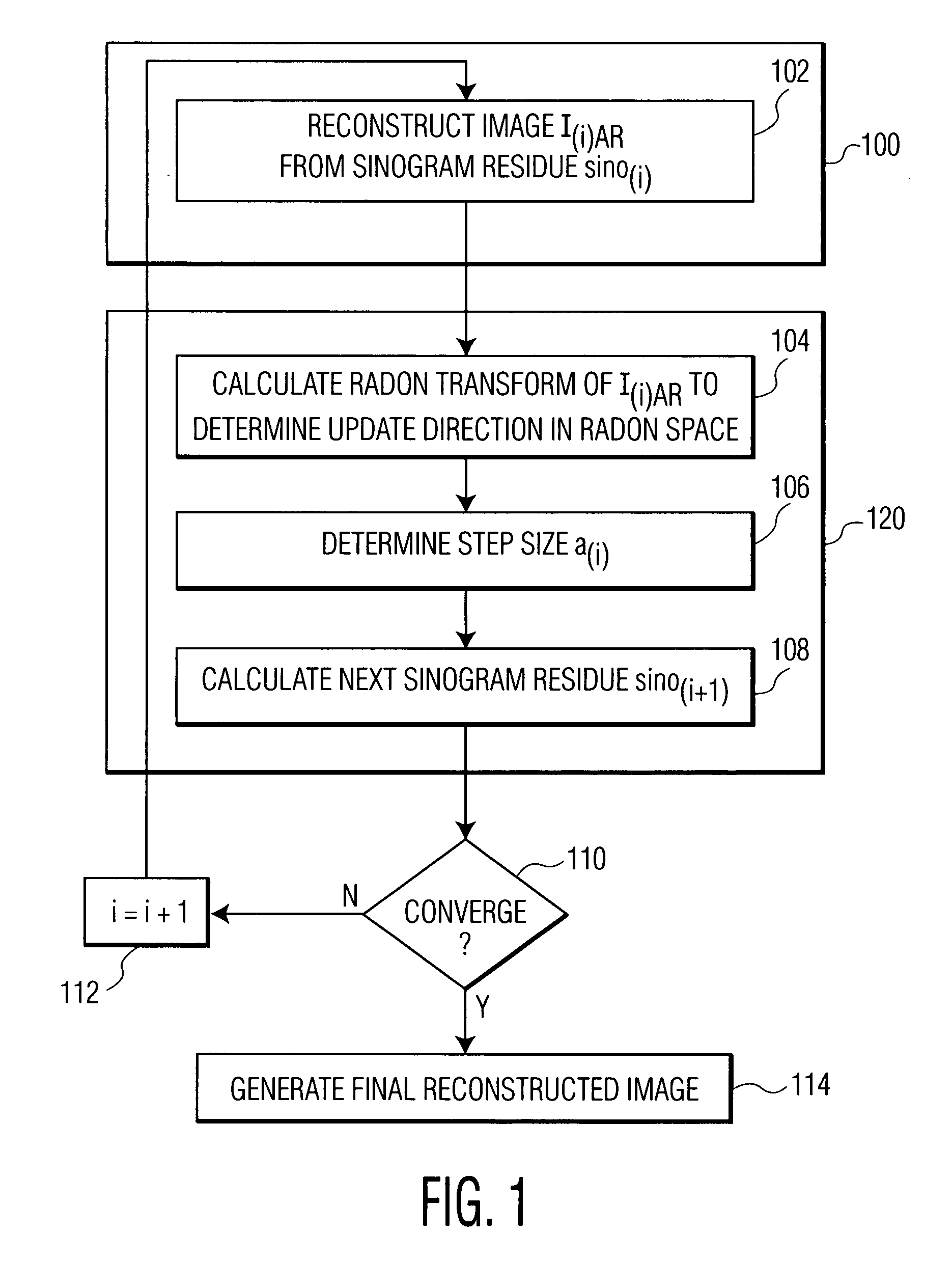
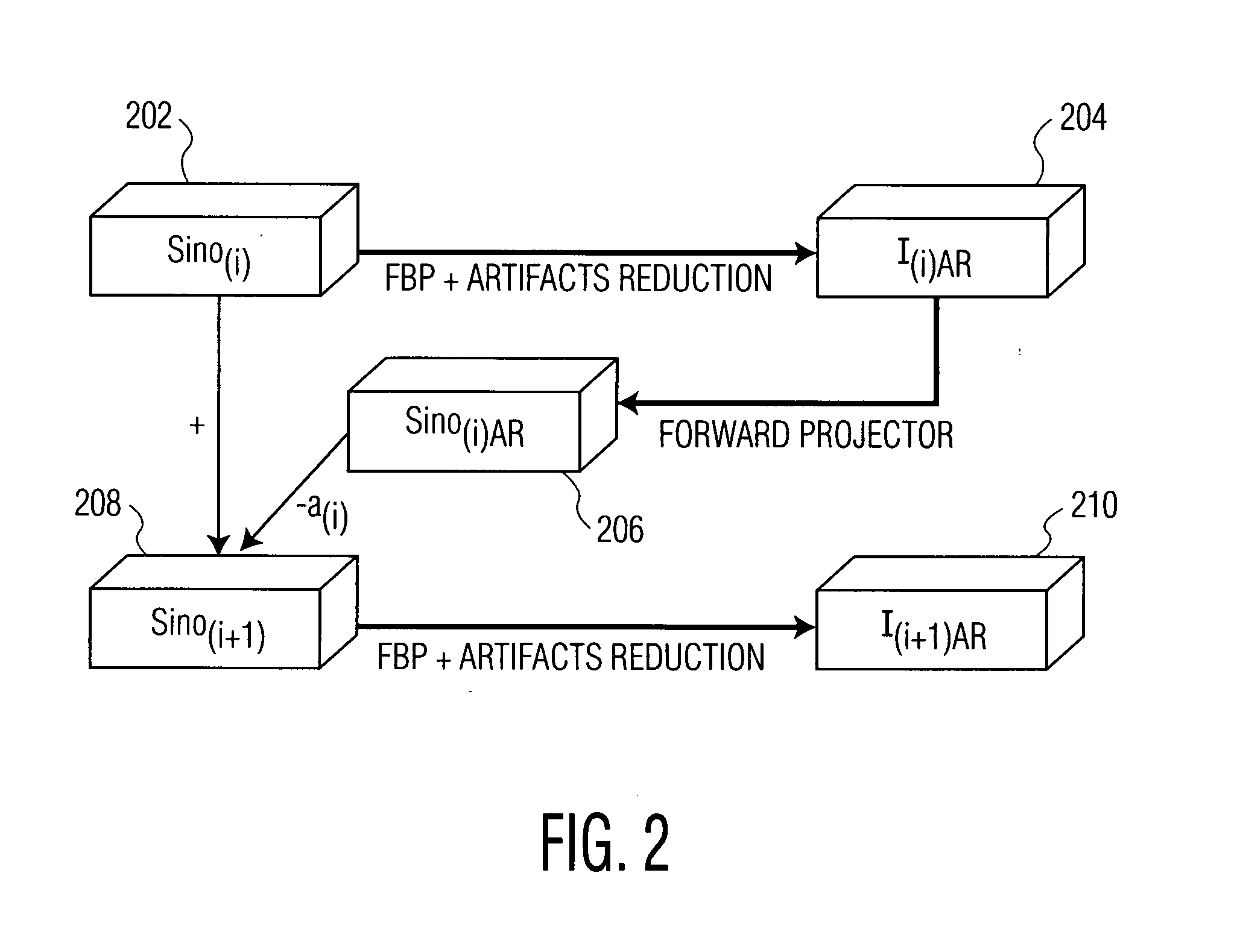
InactiveUS20070217566A1The result is accurateFast convergenceReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBack projectionFilter back projection
A system and method for image reconstruction is disclosed. The method divides iterative image reconstruction into two stages, in the image and Radon space, respectively. In the first stage, filtered back projection and adaptive filtering in the image space are combined to generate a refined reconstructed image of a sinogram residue. This reconstructed image represents an update direction in the image space. In the second stage, the update direction is transformed to the Radon space, and a step size is determined to minimize a difference between the sinogram residue and a Radon transform of the refined reconstructed image of the sinogram residue in the Radon space. These stages are repeated iteratively until the solution converges.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Polyethylene glycol terephthalate (PET) reconstruction method based on sparsification and Poisson model
InactiveCN102968762AImprove sparsityQuality improvementImage enhancement2D-image generationReconstruction methodPolyethylene glycol
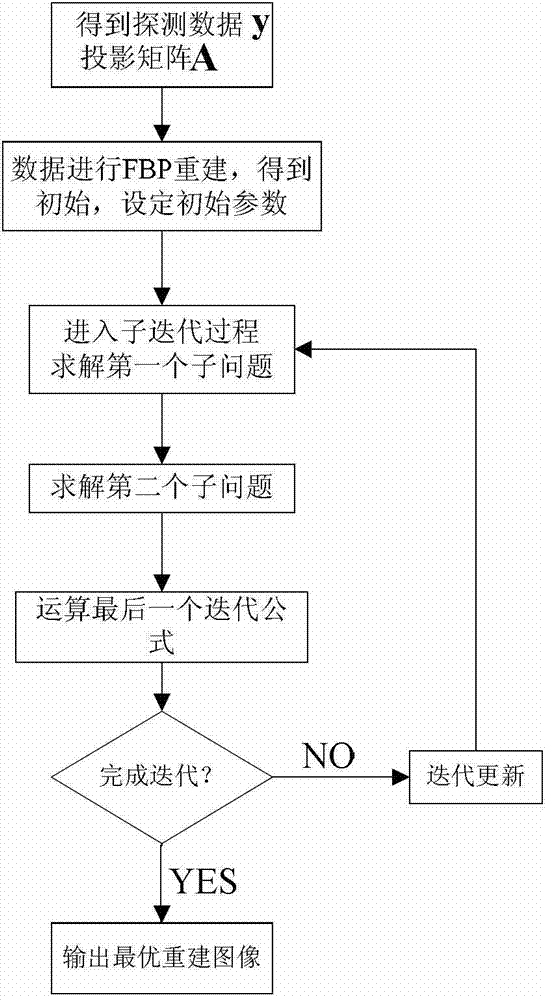
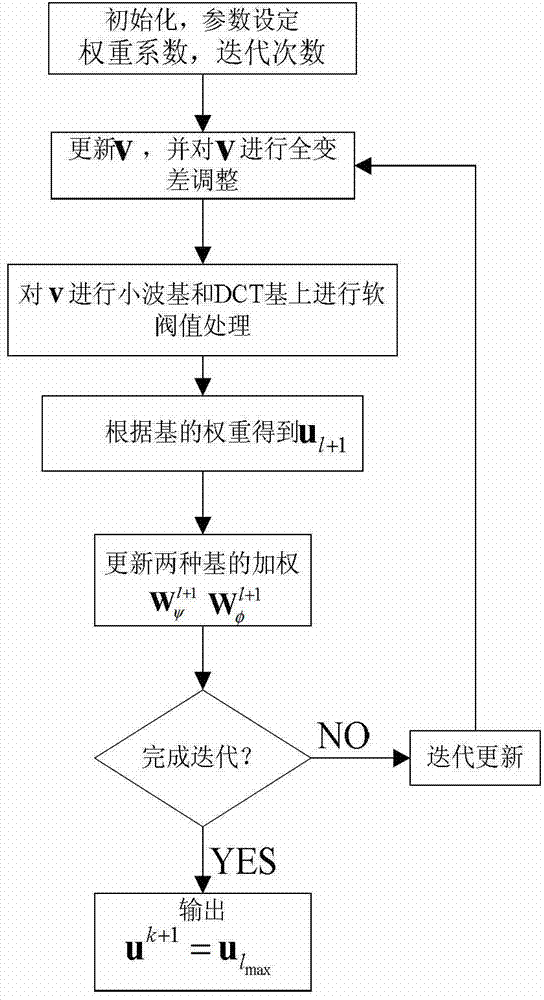
The invention discloses a polyethylene glycol terephthalate (PET) reconstruction method based on a sparsification and Poisson model. The PET reconstruction method includes: firstly, acquiring projection data, determining image size range and pixel range, and calculating a system probability matrix; obtaining an initial image through a filtered back projection (FBP) traditional algorithm, and using an obtained log-likelihood function as a reconstruction recovery item; using a wavelet transformation and discrete cosine transformation (DCT) mixed base and weighting as sparse regularization constraint, decomposing an objective function by using a split Bregman method to obtain two sub-problems, using a first sub-problem as a sparse regularization problem under a Gaussian model, and using linear Bregman interation for solving; using a second sub-problem as a Poisson denoising problem, and using a close operator method for solving; operating the last one iterative formula, completing an integrated iteration, obtaining a reconstructed image, and serving as an initial value of the next iteration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
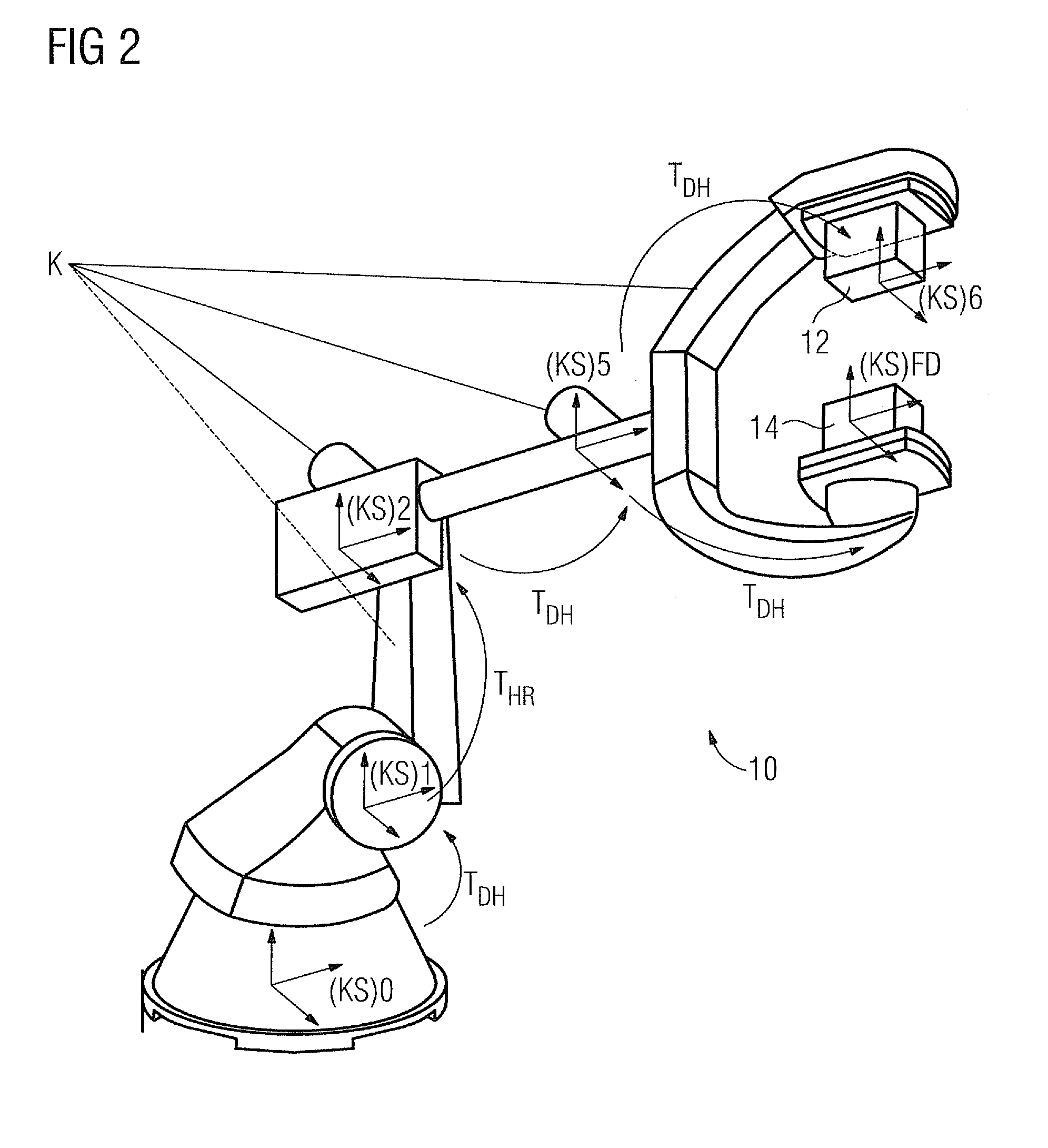
Method for generating a 3D reconstruction of a body
InactiveUS7742557B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPartition of unityBack projection
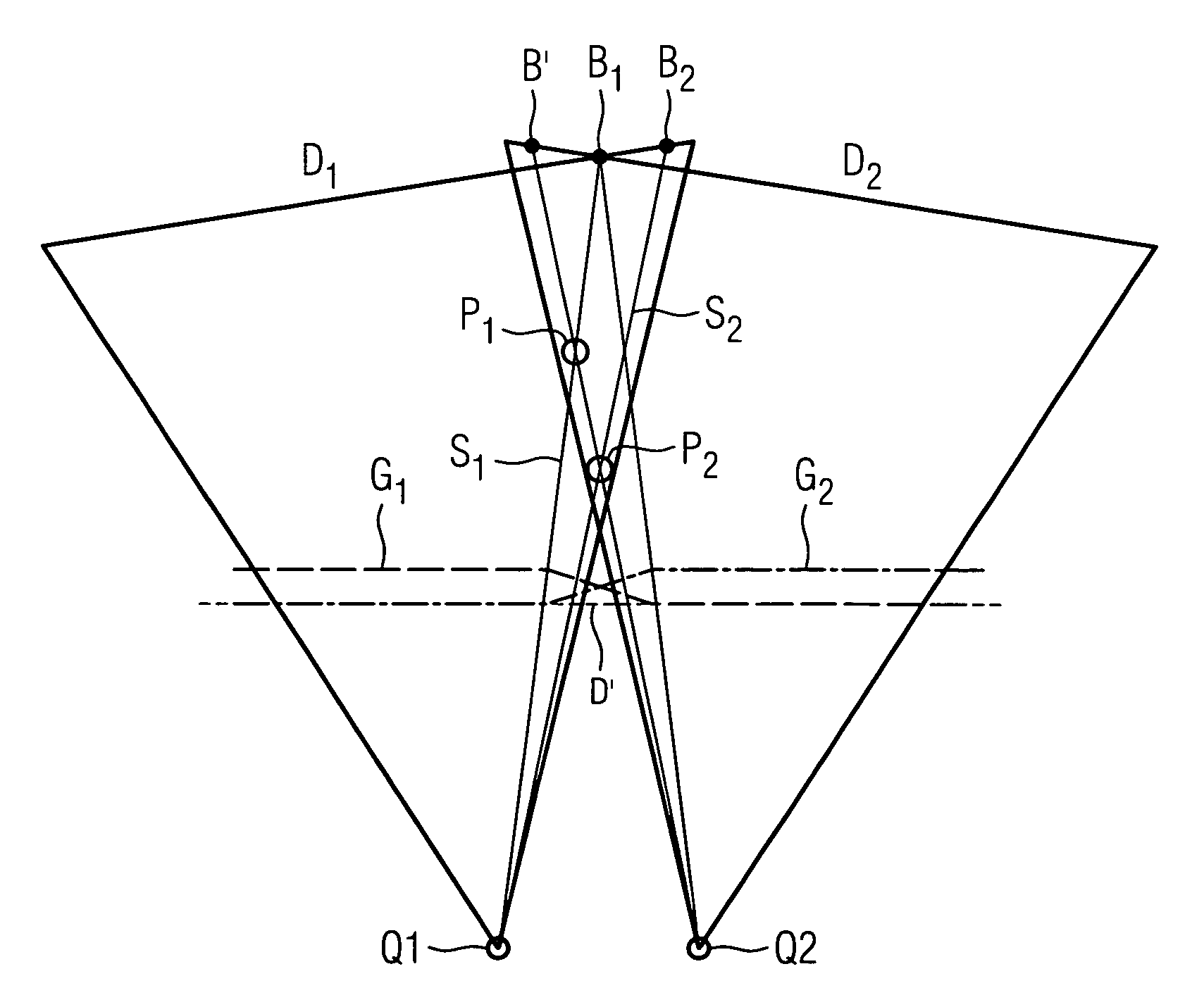
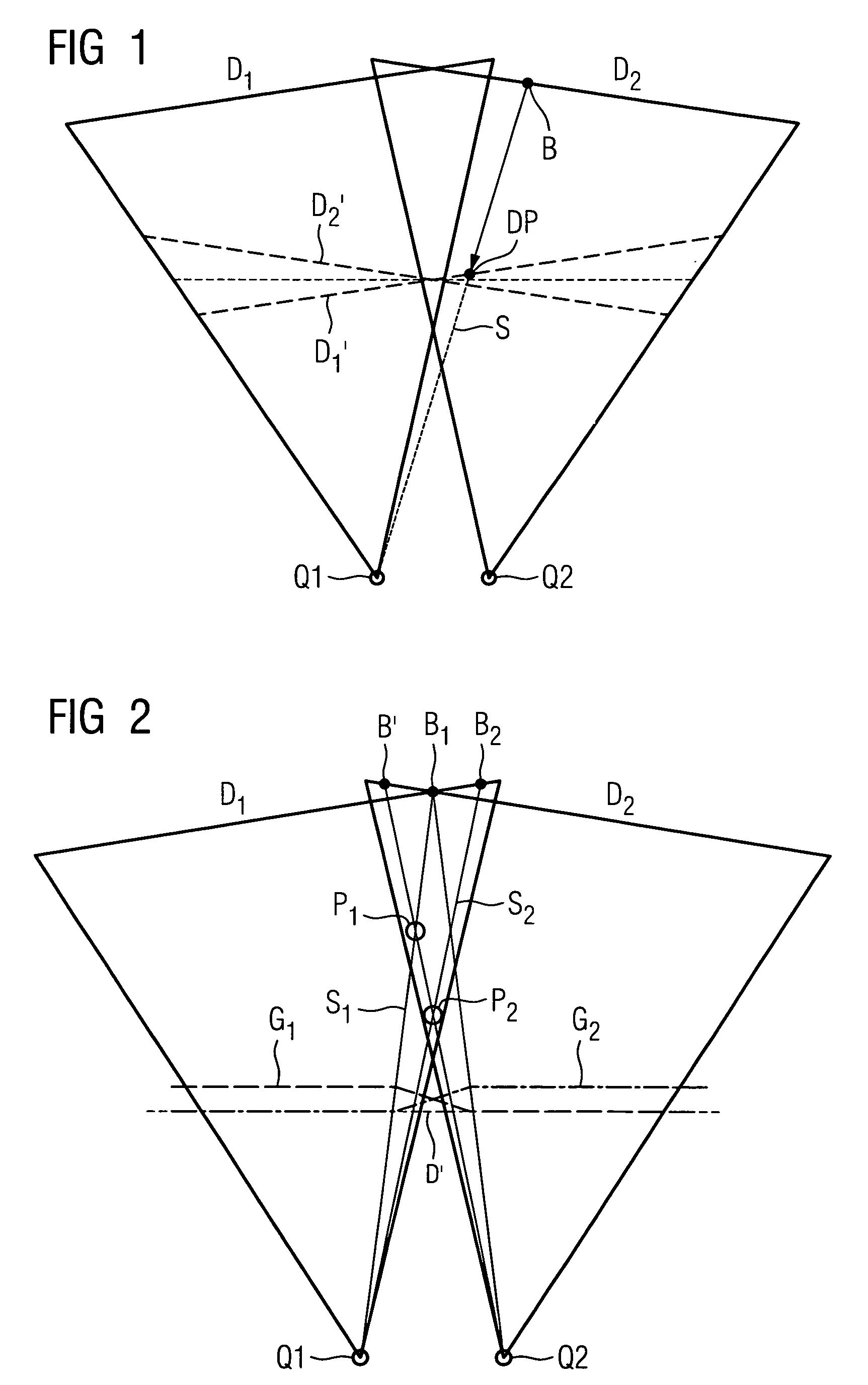
The invention relates to a method for generating a 3D reconstruction of an especially large body that cannot be captured by a single projection by capturing at least two projections, which together capture the body, at each of the positions taken up by a C-arm X-ray unit. Data from the two projections is projected onto a virtual detector and the data from the virtual detector is then used for the filtered back projection procedure. It is assumed here that the real source remains motionless and that only the detector moves. A virtual detector D1′ / D2′ is only used in order to carry out large scale filtering in the event that real sources Q1 and Q2 for the two projections do not coincide. A return is then made to two independent projections. These two independent projections are used separately in the filtered back projection procedure to generate the 3D reconstruction.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for detecting guide waves of steel storage tank bottom plate
InactiveCN101762635AEasy to detectRealize analysisAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringWavelength
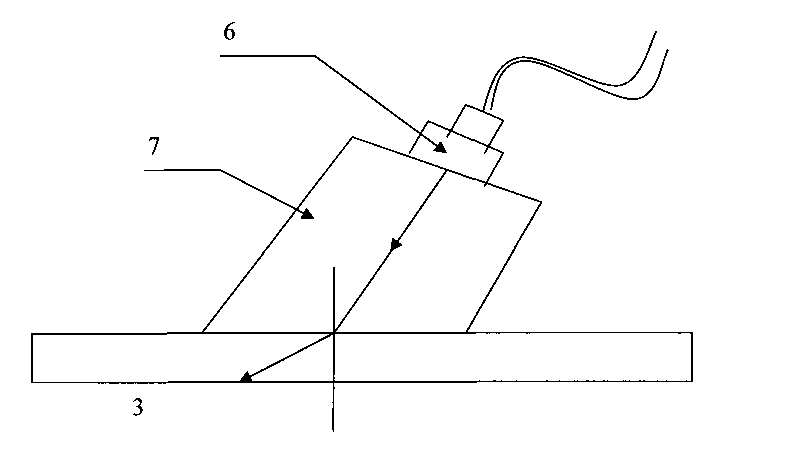
The invention relates to a method for detecting guide waves of a steel storage tank bottom plate, comprising the following steps in sequence; (1) selecting the number of ultrasonic probe arrays (5), and symmetrically distributing the ultrasonic probe arrays (5) along the steel storage tank bottom plate (3); (2) arranging two signal processing devices (4) on each ultrasound probe array (5), and arranging the ultrasound probe array (5) on the steel storage tank bottom plate (3) through a wedge block in a coupling way; (3) selecting a ultrasonic wave length which corresponds to the thickness of the steel storage tank bottom plate (3) and selecting a method for exciting Lamb waves; (4) transforming a travel time matrix with Radon algorithmic function to generate Lamb wave travel time projections of different incidence angles, which are used as the projection data for the subsequent tomography reconstruction; (5) reconstructing a tomography in the projection data with the filtered back projection algorithm; (6) analyzing the tomography to find the position of the defect and grade the defect level; and (7) if the defect existing, changing the positions of ultrasonic probes clockwise, repeating the steps (1), (2), (3), (4), (5) and (6), comparing the repeated detection and tomography reconstruction results, and eliminating the effect of noise and other factors if the position of the defect and the morphology existing.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
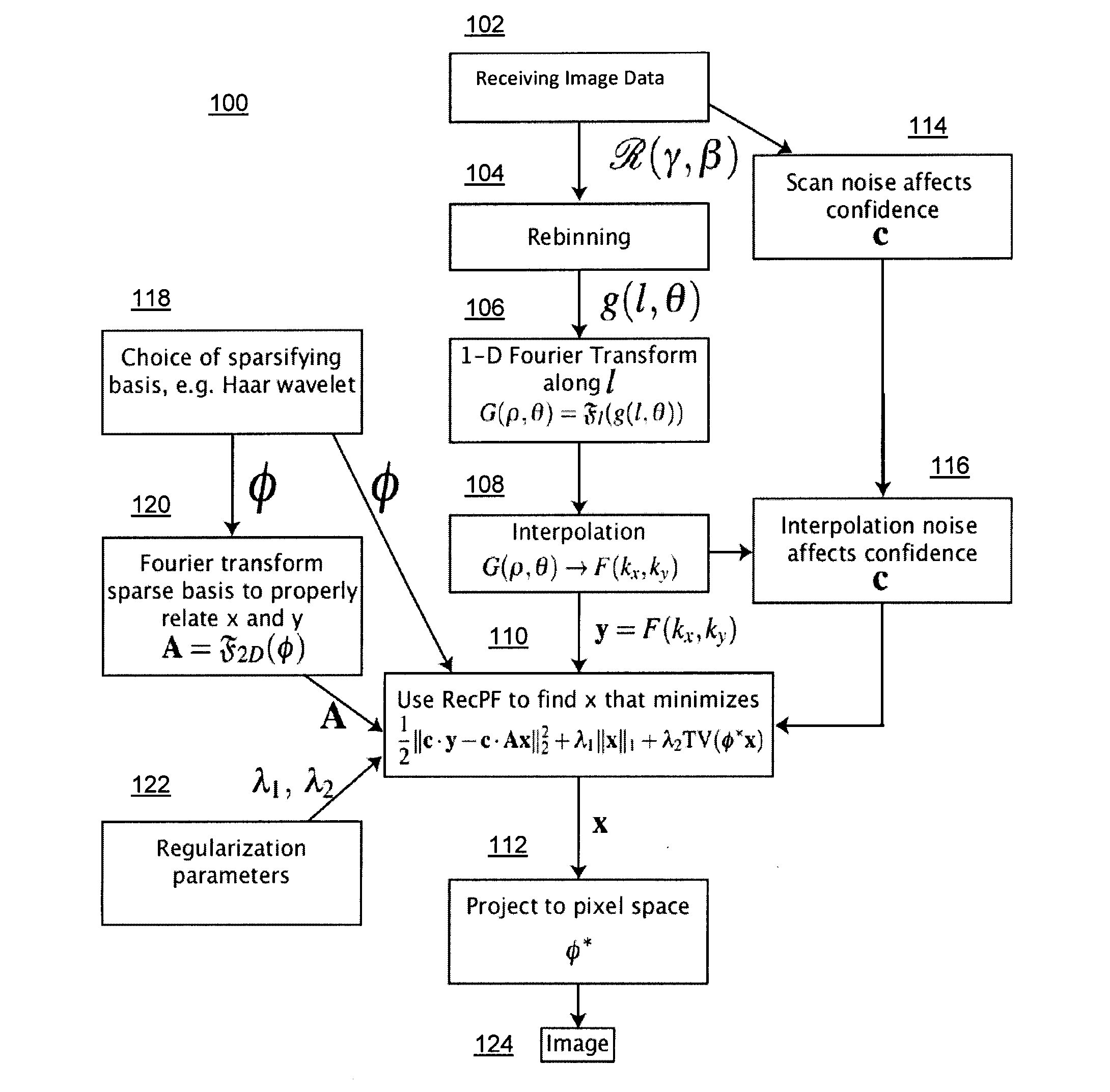
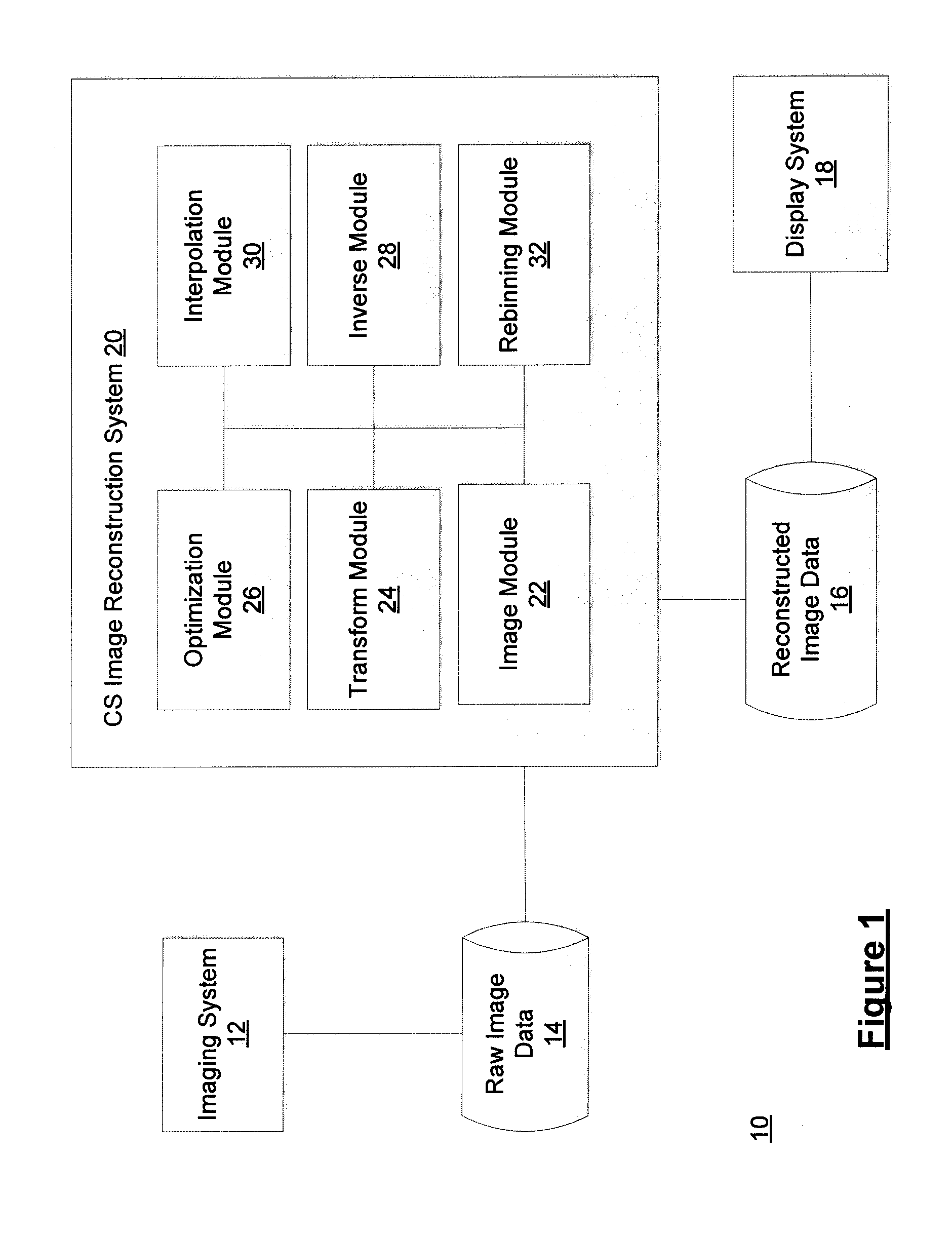
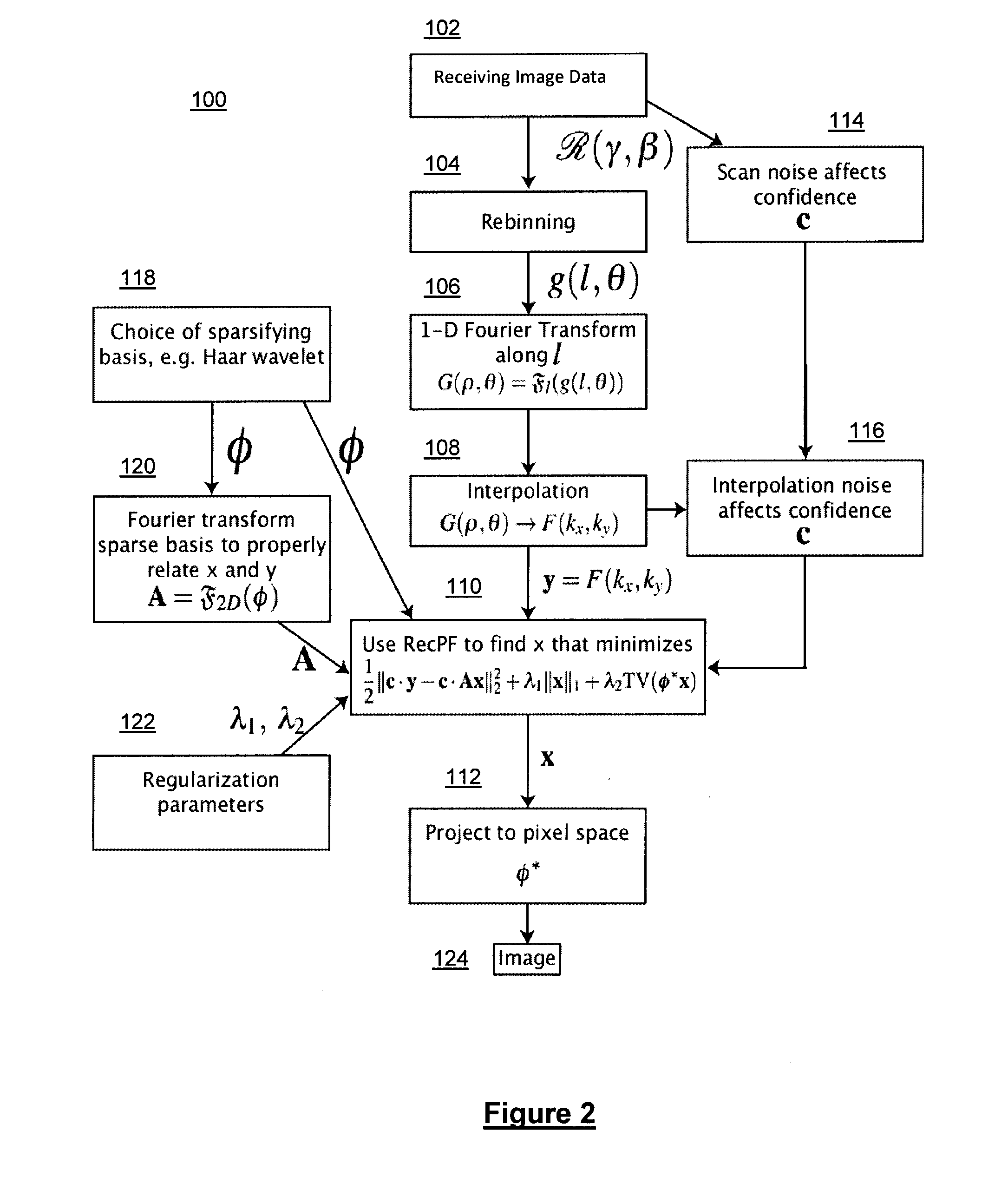
Method and system for compressed sensing image reconstruction
ActiveUS20150187052A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputation complexity
A Compressed Sensing (CS) based image reconstruction method and system is described herein which may be used to reduce the X-ray dose radiation in Computed Tomography (CT) or to decrease the scan duration in MR imaging (MRI). Methods and systems described herein may address problems that have hindered the clinical usage of CS, i.e. computation complexity and modeling problems. Using the described algorithm, high quality images may be recovered from undersampled data which may help to reduce the scan time and the exposed invasive radiations. Using the same set of data in conventional image reconstruction algorithms (e.g. Filtered Back Projection (FBP) in CT) may cause severe streak artifacts and may take significantly more time using Graphics Processing Units (GPU) and parallel clusters with the conventional CS-based methods. This method can be used other imaging modalities using Radon transform (such as C-Arm and electron tomography, for example).
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
Non-iterative algebraic reconstruction technique for tomosynthesis
InactiveUS20050058240A1Considerable computational savingImprove reconstructed image qualityReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomosynthesisAlgorithm
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Augmented lagrangian iterative reconstruction method of X-ray image and CI image
An augmented lagrangian iterative reconstruction method of an X-ray image and a CI image is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) acquiring system parameters and projecting data under a low dose scanning protocol of CI equipment; (2) carrying out one-by-one data point variance estimation on the projecting data in the step (1), and conducting filtered back projection on the projected data in the step (1) to obtain an initial pattern; (3) taking the initial pattern obtained from the step (2) as an iterative initial pattern to be subjected to iterative reconstruction, and obtaining the final reconstruction pattern through loop iteration according to the iterative formula. The invention provides an algorithm for optimizing the iterative formula. The method has the advantages of wide application range, less iterative times, and high imaging quality.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method of reconstructing images for spiral and non-spiral computer tomography
InactiveUS20030161444A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayBack projection
General scheme processes and systems for constructing algorithms for reconstructing images of objects that have been scanned in a spiral or non-spiral fashions with detectors. Application of the scheme requires finding of a weight function, which would lead to the required reconstruction algorithm. This general scheme can use a C-arm scan with the closed x-ray source trajectory and gives a new, theoretically exact and efficient (i.e., with the convolution-based FBP structure) reconstruction algorithm. The invention can also utilize the algorithms disclosed in an earlier application U.S. application Ser. No. 10 / 143,160 filed May 10, 2002, entitled: Exact Filtered Back Projection (FBP) Algorithm For Spiral Computer Tomography, which claims the benefit of U.S. Provisional Application No. 60 / 312,827 filed Aug. 16, 2001, also fit into the general scheme.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Three-dimensional digital imaging method of large view field cone-beam X-ray tilting scanning of biased detector
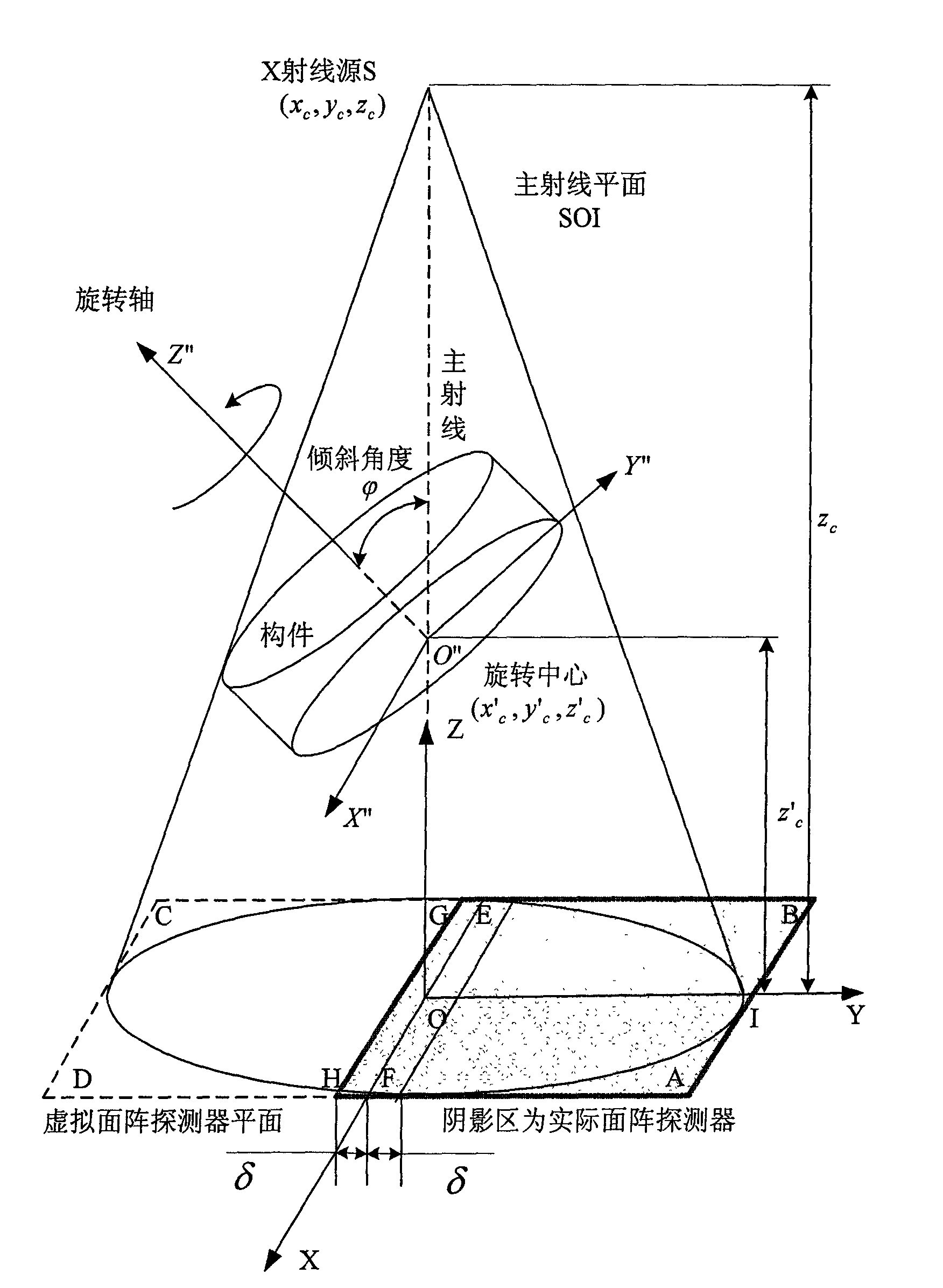
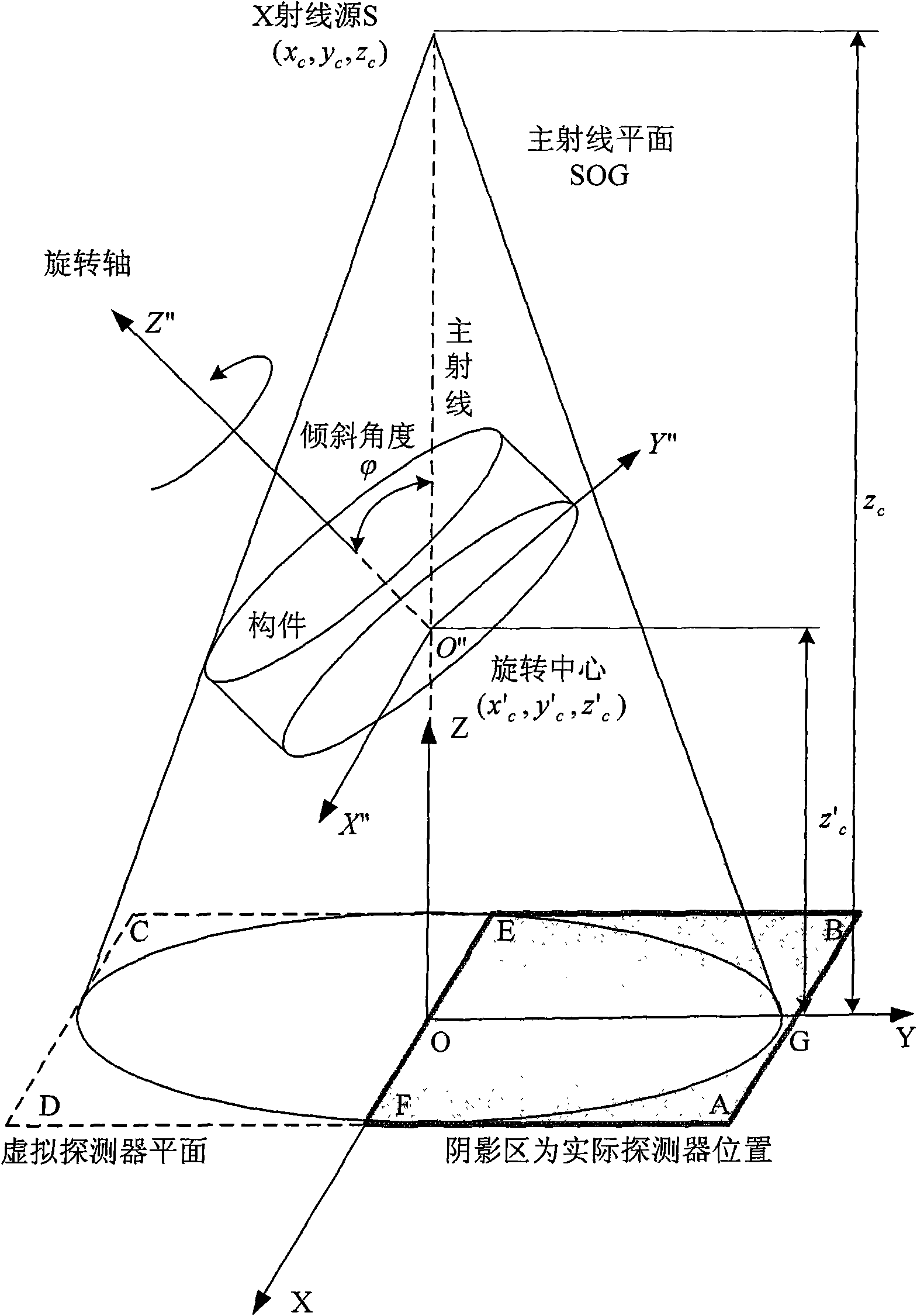
InactiveCN101634638AExpanded imaging field of viewImprove detection efficiencyComputerised tomographsTomographyDigital imagingPretreatment method
The invention relates to a three-dimensional digital imaging method of the large view field cone-beam X-ray tilting scanning of a biased detector, belonging to the technical field of X-ray computerized tomography (CT). In the three-dimensional digital imaging method, the area array detector is placed to be biased, and an X-ray source is used for generating cone-beam X-rays which irradiate a member imaging area with a certain angle in a penetrating and tilting way relative to the length and width surface of a member; in the scanning process, the X-ray source and the area array detector are static, the member rotates in an angle of 360 degrees in an equal angle and step length way surrounding a rotating shaft, and the area array detector acquires an X-ray signal modulated by the member under each rotation angle. A three-dimensional computerized tomography image of a scanning area can be reestablished and obtained by a data truncation smoothing preprocessing method and a filtering back projection reestablishing arithmetic according to data obtained by the area array detector under the scanning angle of 360 degrees. Compared with the traditional tilting scanning method, the three-dimensional digital imaging method can double the tilting scanning imaging view field without changing the system hardware and the scanning speed and has high reestablishment quality, simple process and high efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Efficient image reconstruction algorithm for the circle and line cone beam computed tomography
InactiveUS20060034417A1Create efficientlyReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBack projectionImage reconstruction algorithm
Methods, systems and processes for providing efficient, accurate and exact image reconstruction using portable and easy to use C-arm scanning devices and rotating gantries, and the like. The invention can provide exact convolution-based filtered back projection (FBP) image reconstruction by combining a curved scan of the object and a line scan of the object. The curved scan can be done before or after the line scan. The curved scan can be less than or greater than a full circle about an object being scanned.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
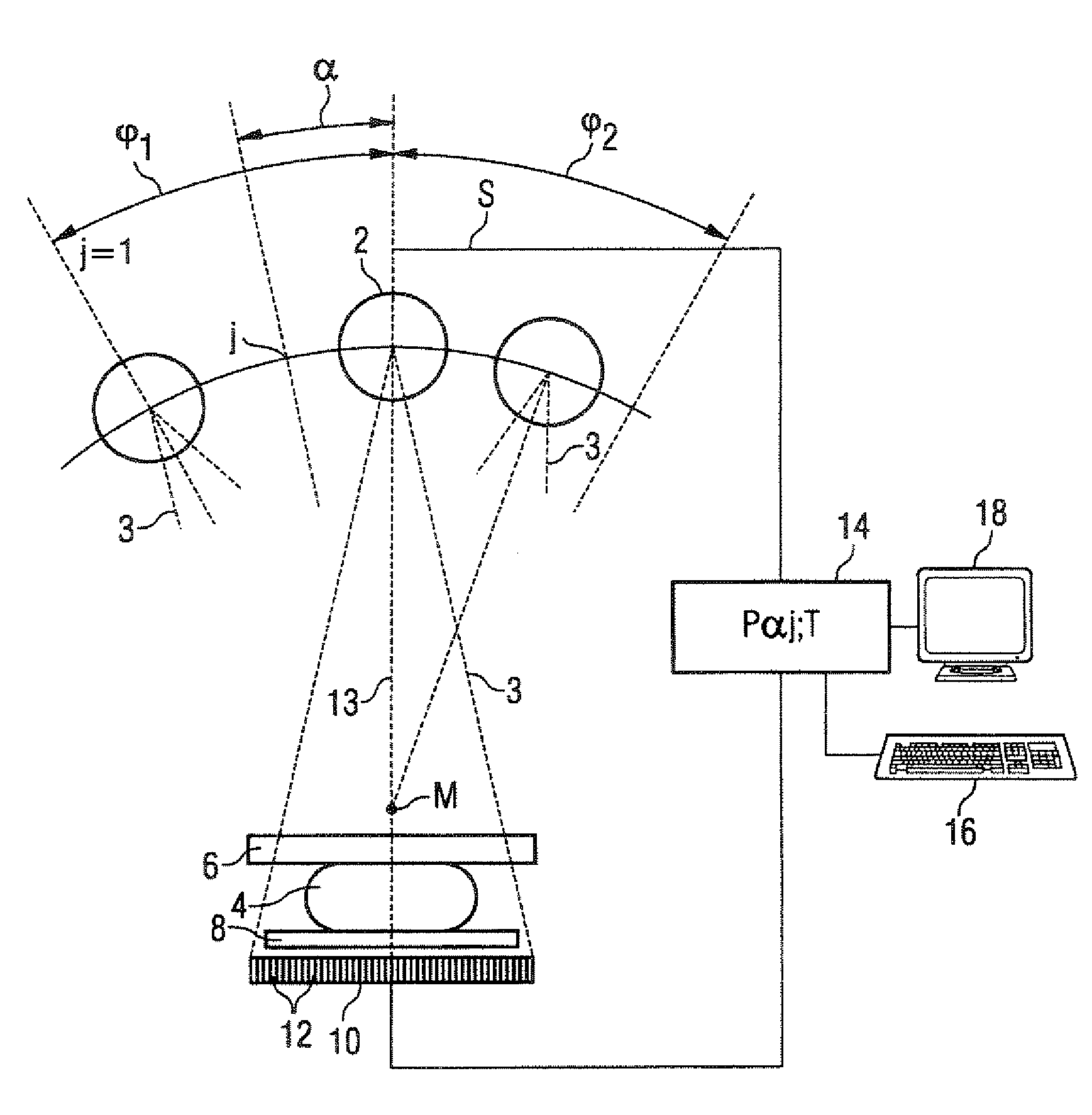
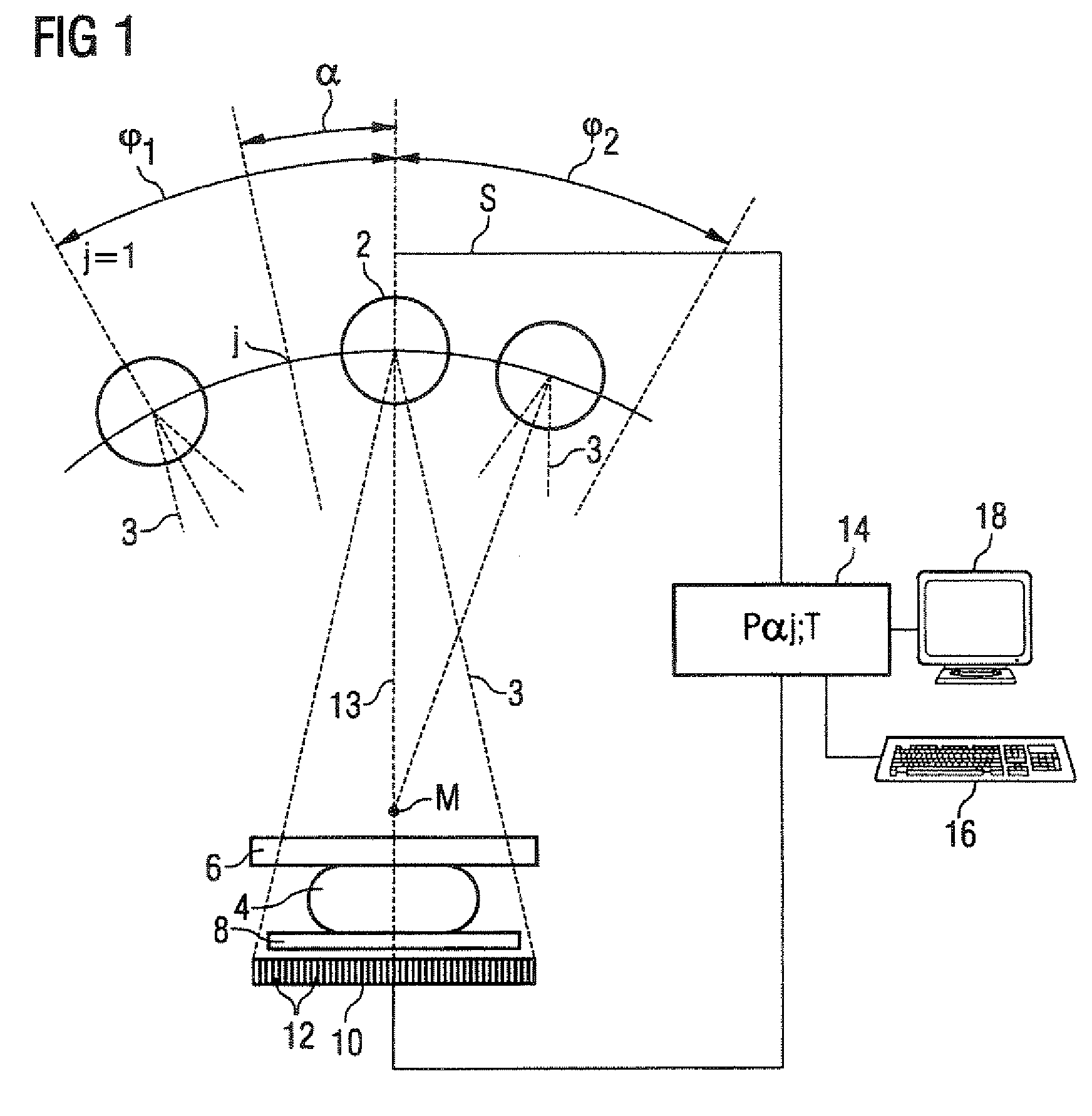
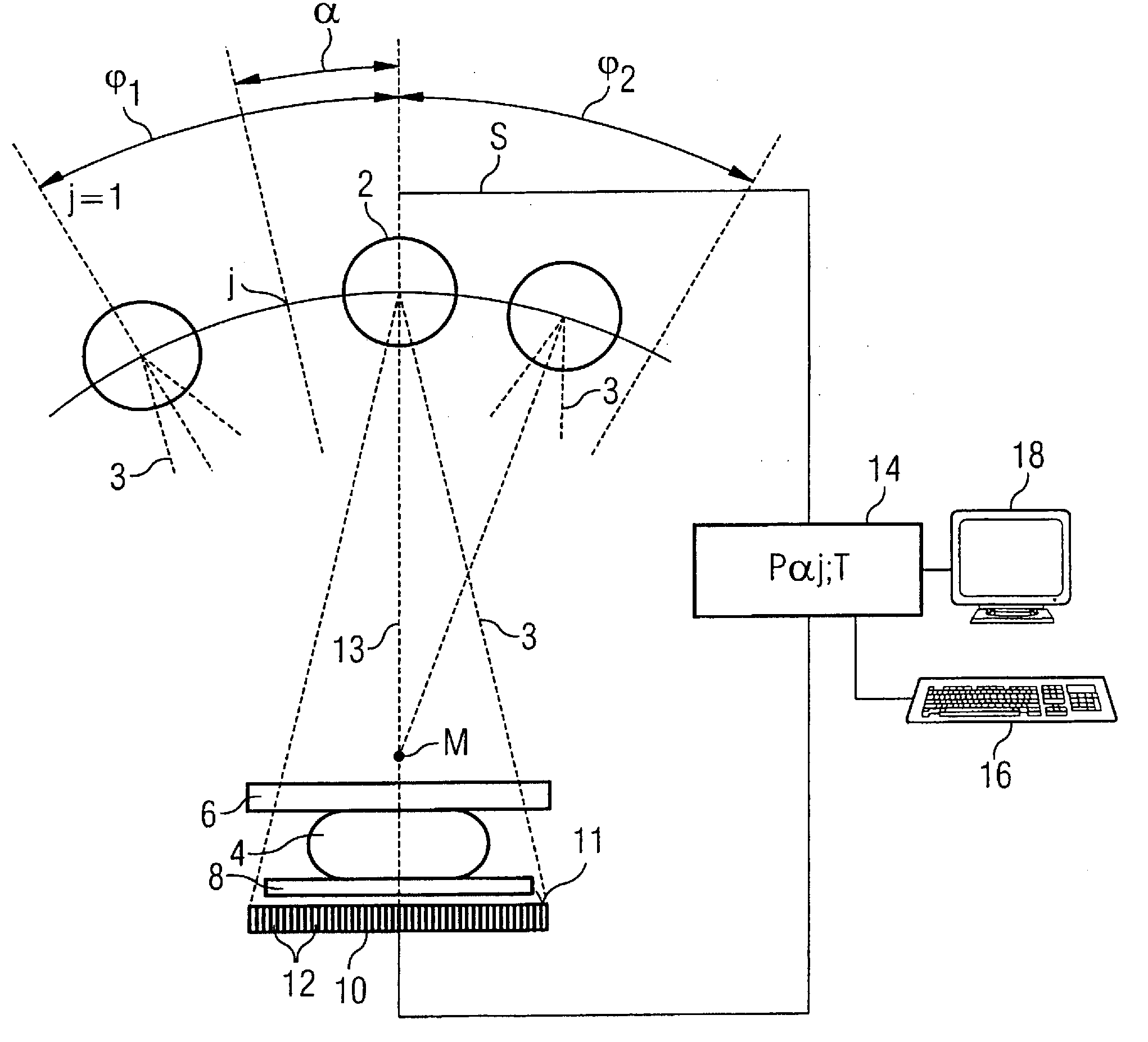
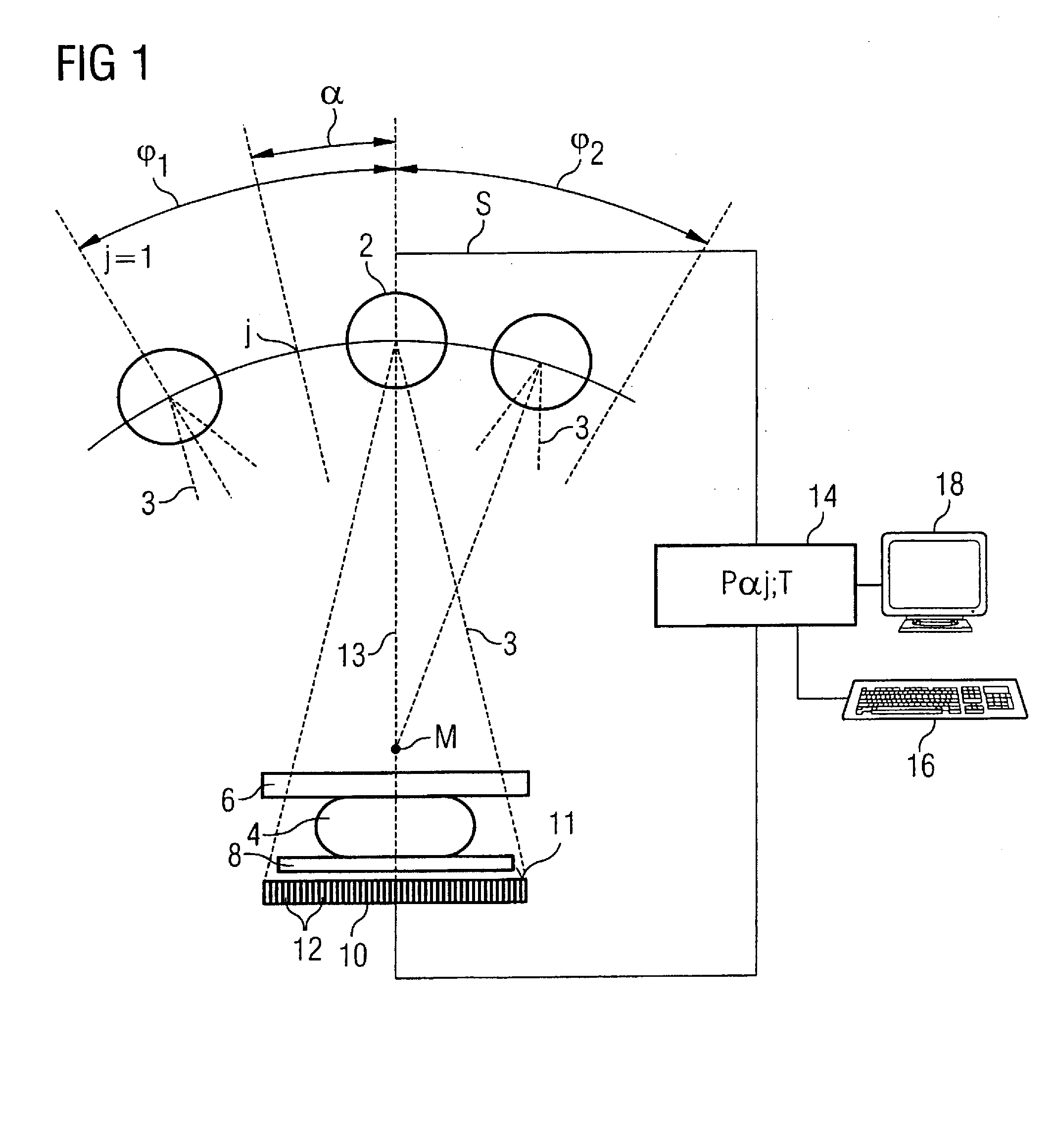
Method for obtaining a 3D image dataset of an object of interest
ActiveUS20120201352A1Quality improvementReconstruction from projectionTomographyHat matrixSoft x ray
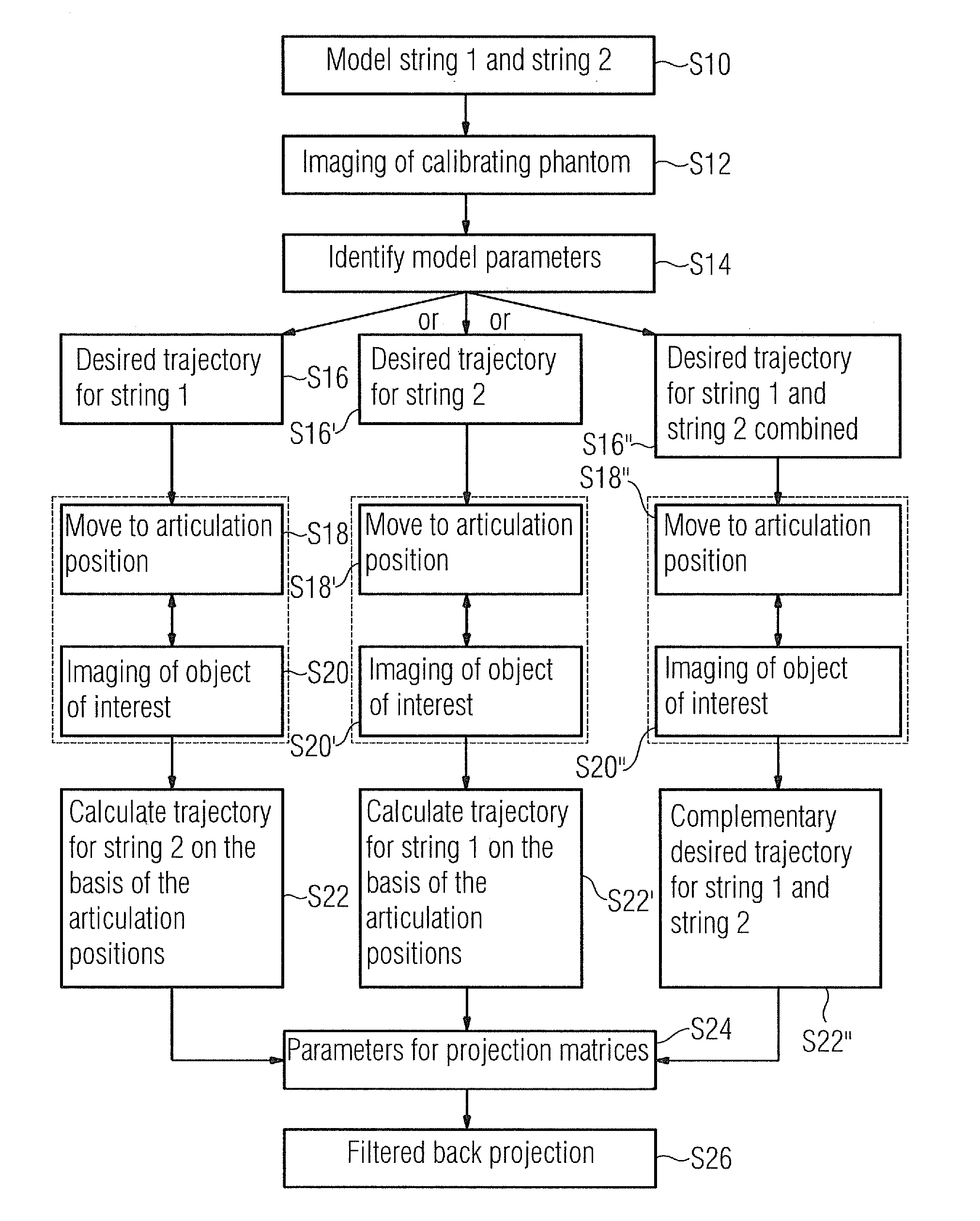
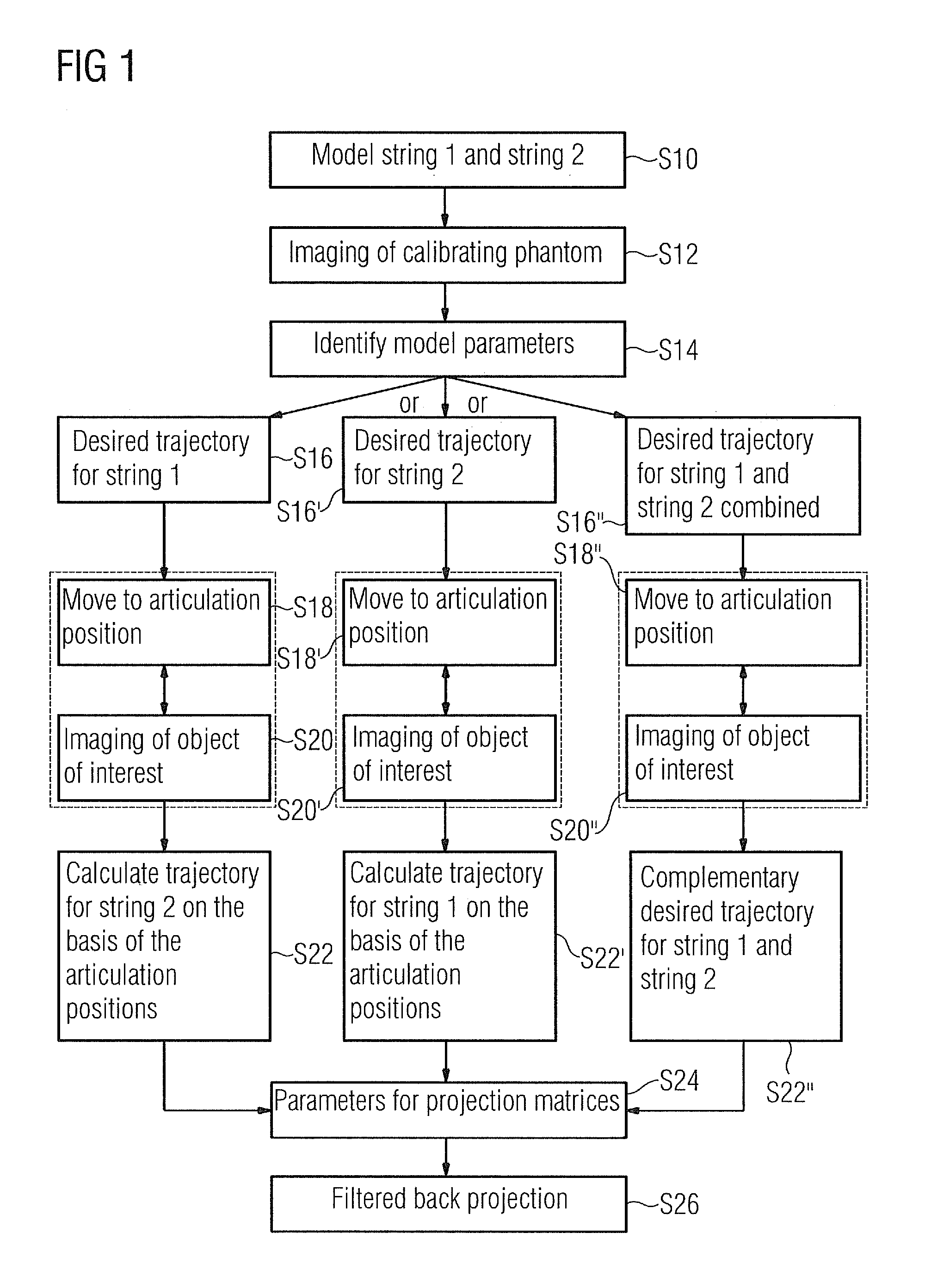
A method for obtaining a 3D image dataset of an object of interest is proposed. A plurality of 2D X-ray images are captured and a 3D reconstruction is carried out using filtered back projection. The projection parameters have been measured with the aid of a calibrating phantom, possibly using an interpolation or extrapolation of such measurements. A model of effect strings of the components in an X-ray imaging device is obtained, and the model parameters are identified based on imaging of a calibrating phantom. A projection matrix can then be calculated for any positions on any desired trajectories, without having to use imaging of a calibrating phantom at precisely that position and desired trajectory.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Tomosynthetic image reconstruction method, and diagnostic device operating according to the method
ActiveUS7558366B2Minimal processing effortEasy to operateReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomosynthesisReconstruction method
In a tomosynthetic image reconstruction method and diagnostic device operating with such a method, a tomosynthetic 3D x-ray image is reconstructed by a discrete filtered back projection from a number of individual digital projection data recorded from different project angles within a restricted angular range, in which at least one filtering is performed with a convolution kernel that, in the local area outside of its central value, corresponds to an exponential function.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method of removing metal artifact from CT image
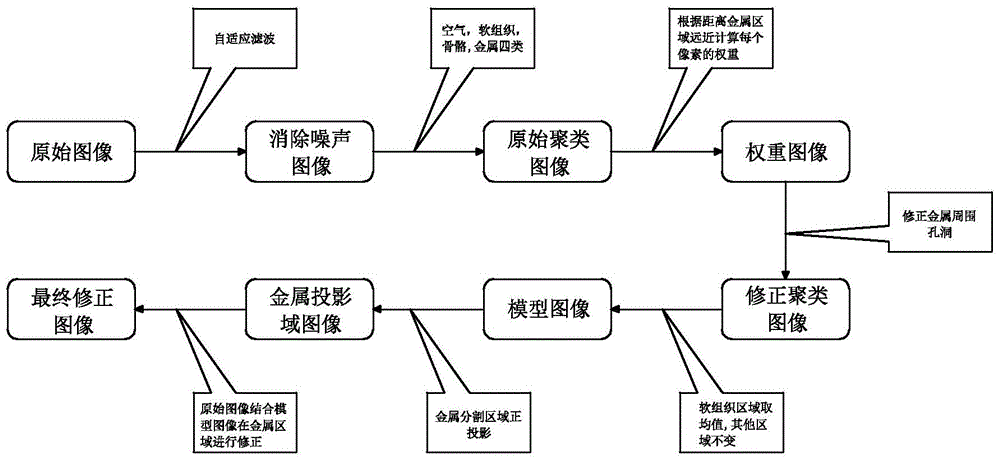
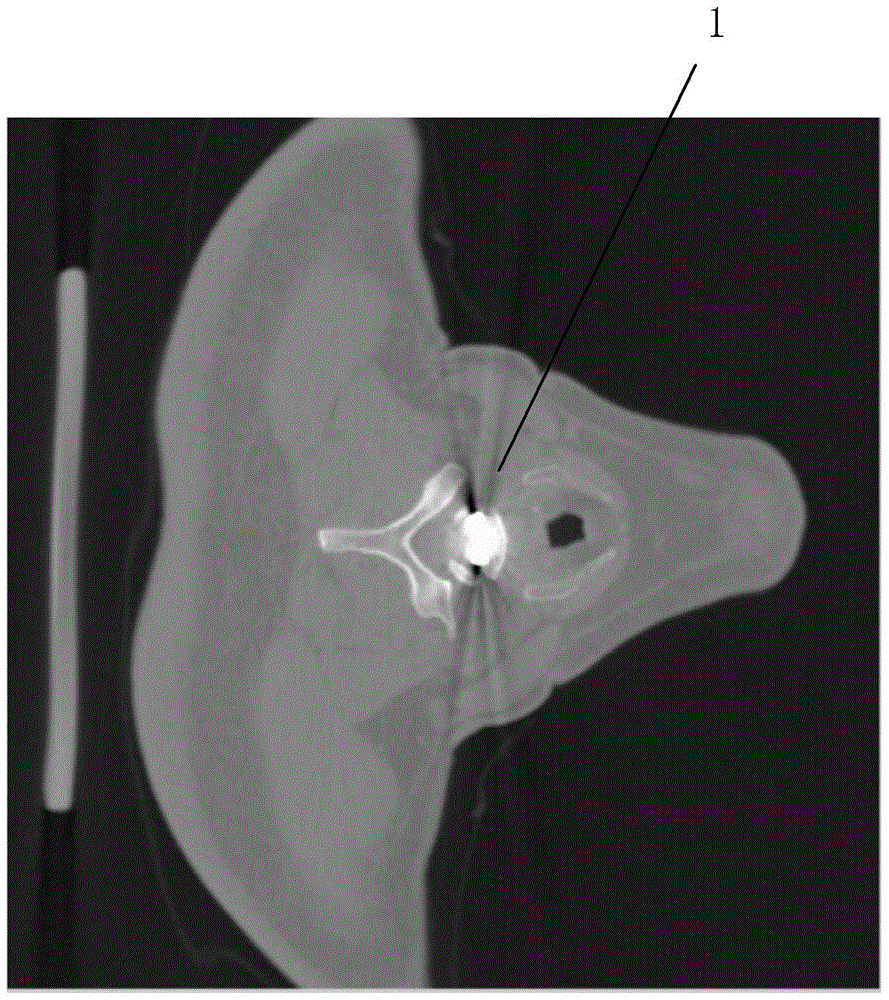
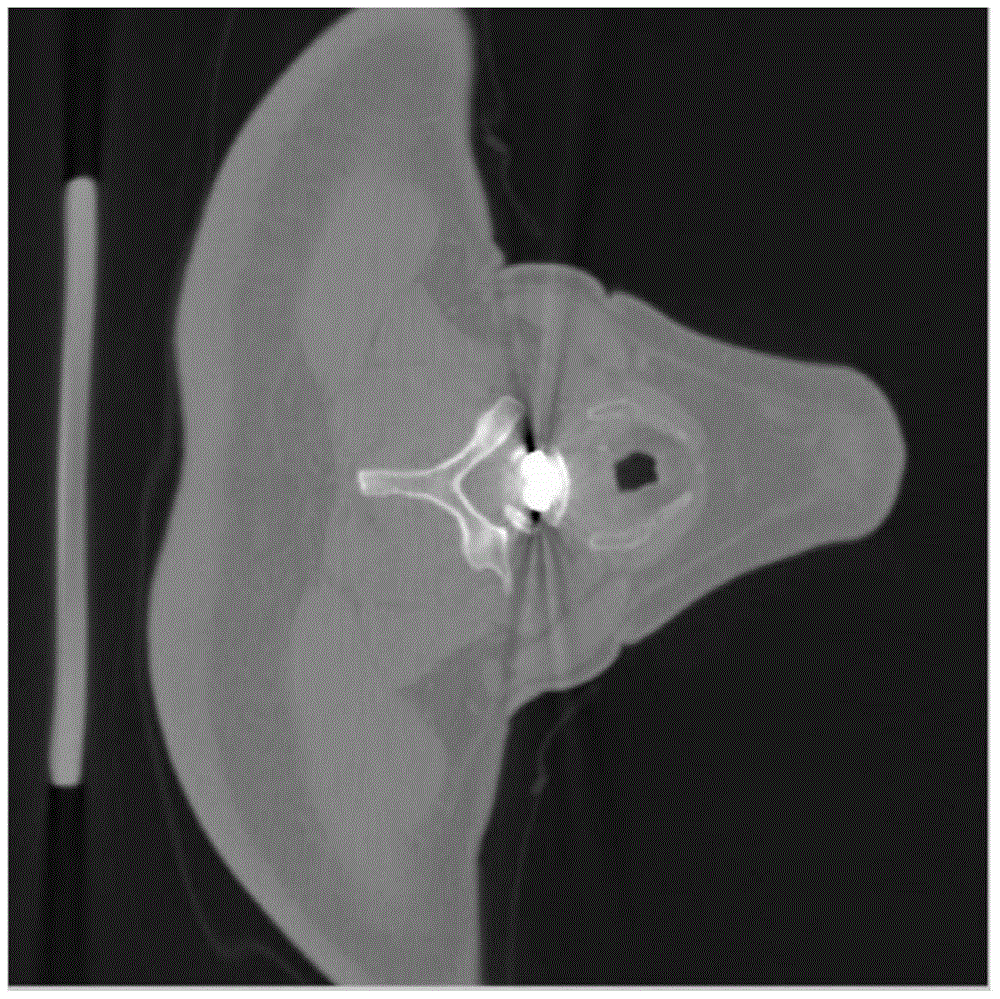
ActiveCN105701778APrecisely correct imagesEfficient removalImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMetal Artifact
The present invention relates to a method of removing metal artifact from a CT image. The method comprises the steps of firstly carrying out the pre-processing via the image adaptive filtering to obtain an original reconstruction image from which the noise and a part of streak artifact are removed; then segmenting the original reconstruction image via a clustering method to obtain the areas of different tissues, establishing a model image, at the same time, carrying out the orthographic projection on a segmented metal area to obtain the position of the metal area in a projection domain; and then carrying out the orthographic projection on the model image to obtain the projection data of the model image, and then using the projection domain data of the model image to substitute for the projection domain data of the original reconstruction image according to the previously obtained position of the metal area in the projection domain; finally carrying out the filtering back projection on the repaired projection domain data to obtain a final corrected image. The method of the present invention reduces a real image accurately, enables the metal artifact to be removed effectively, and helps doctors to judge the states of illnesses accurately.
Owner:SAINUO WEISHENG SCI & TECH BEIJING
Systems, methods and apparatus for filtered back-projection reconstruction in digital tomosynthesis
ActiveUS7522755B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomosynthesisBack projection
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
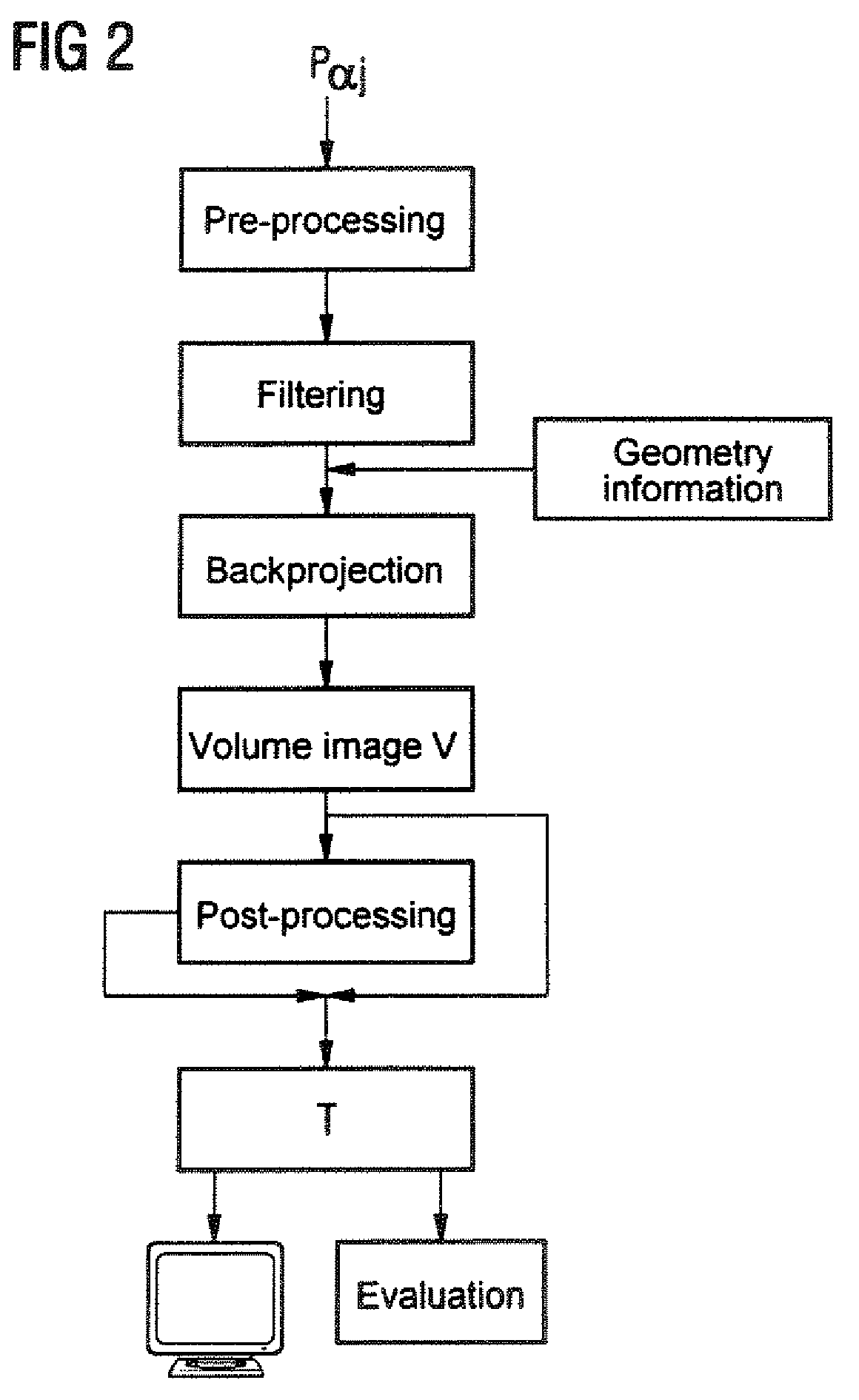
Tomographic image reconstruction method and apparatus using filtered back projection
ActiveUS20090310844A1Increase flexibilityReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionReconstruction methodBack projection
In a tomographical image reconstruction method and apparatus to generate an image of an examination subject from a number of digital projection data acquired at different projection angles, a first analytical filter kernel (formed by a first analytical function) is determined for a filtered back projection in the spatial frequency range, this first analytical filter kernel approximating, at least in a range of the spatial frequency, a discrete filter kernel iteratively determined for a model. Back projection is implemented with a second analytical filter kernel calculated from the analytical filter kernel and formed by a second analytical function.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Particle filtering-based method of reconstructing static PET (Positron Emission Tomograph) images
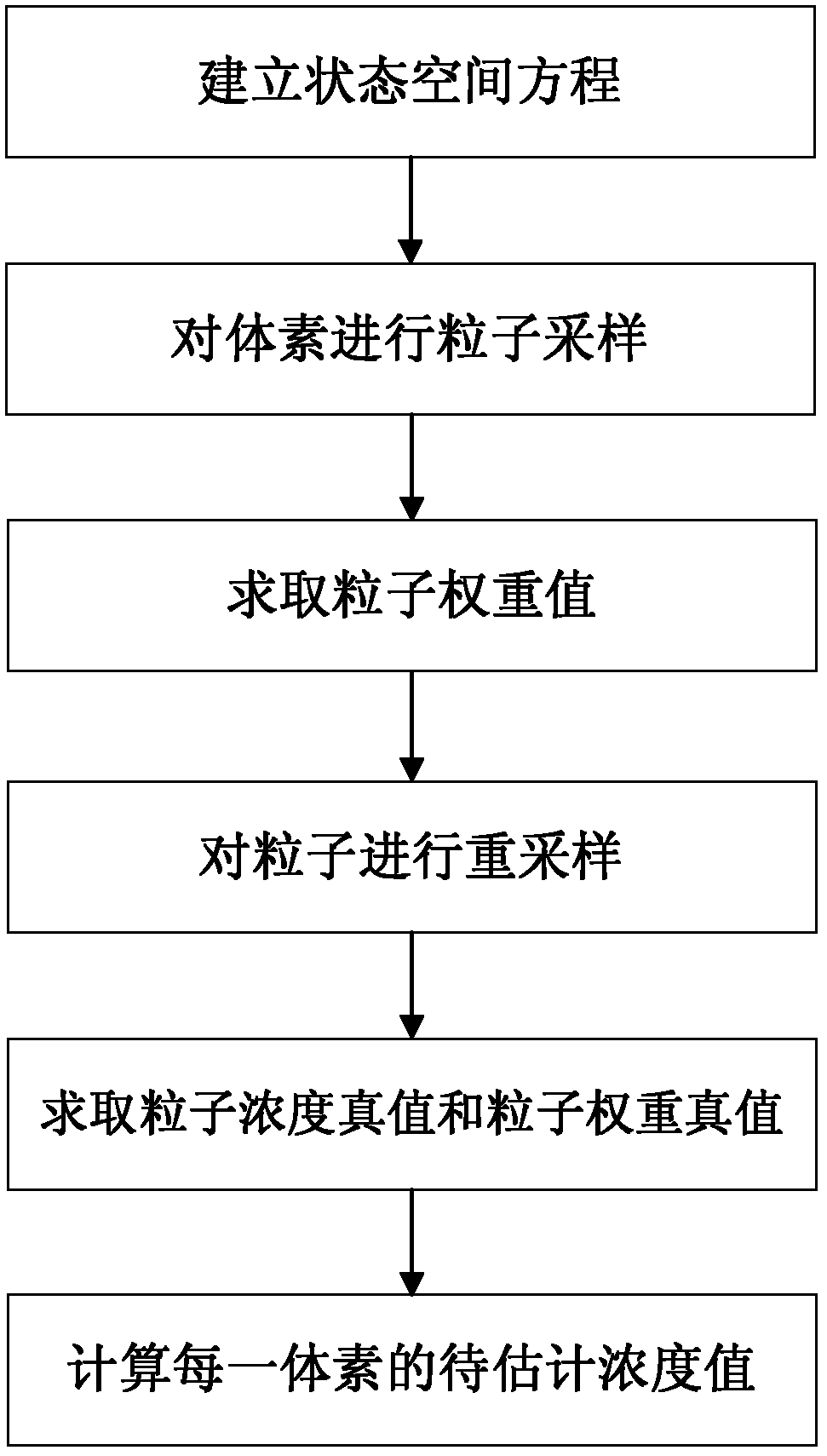
ActiveCN102184559ATrue to scanThe truth of the scan works2D-image generationVoxelReconstruction method
The invention discloses a particle filtering-based method of reconstructing static PET images, which comprises the steps of: (1) establishing a state space equation; (2) subjecting voxels to particle sampling; (3) computing a particle weight; (4) resampling the particles; (5) computing a particle concentration truth value and a particle weight truth value; and (6) computing a to-be-estimated concentration value of each voxel. By combining the particle filtering through a state space, the data statistic features and physiological property of PET are joined up to reconstruct a PET image, thereby the resolution and acutance of the image are improved, the true PET image is well restored, at the same time, a data model of noise in the PET is defined as Poisson distribution but not Gaussian distribution, which is more suitable for the actual condition of PET scanning, therefore, noises in the reconstruction process are more effectively filtered and optimized, and obtained reconstruction results are more approximate to the actual conditions of PET compared with that obtained by ML-EM (Maximum-Likelihood and Expectation-Maximization), FBP (Filtered Back Projection) and other conventional reconstruction methods, and the reconstruction effect is more excellent.
Owner:刘华锋 +1
Efficient image reconstruction algorithm for the circle and arc cone beam computer tomography
InactiveUS20050152494A1Create efficientlyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionComputer graphics (images)Algorithm
Methods, systems and processes for providing efficient, accurate and exact image reconstruction using portable and easy to use C-arm scanning devices and rotating gantries, and the like, that combines both a circle and a curve scan. The invention can provide exact convolution-based filtered back projection (FBP) image reconstruction by combining two curved scans of the object. The curved scan can be less than or greater than a full circle about an object being scanned. The invention can be done by a first curve within a first plane followed by a second curve within a second plane that is transversal to the first plane.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
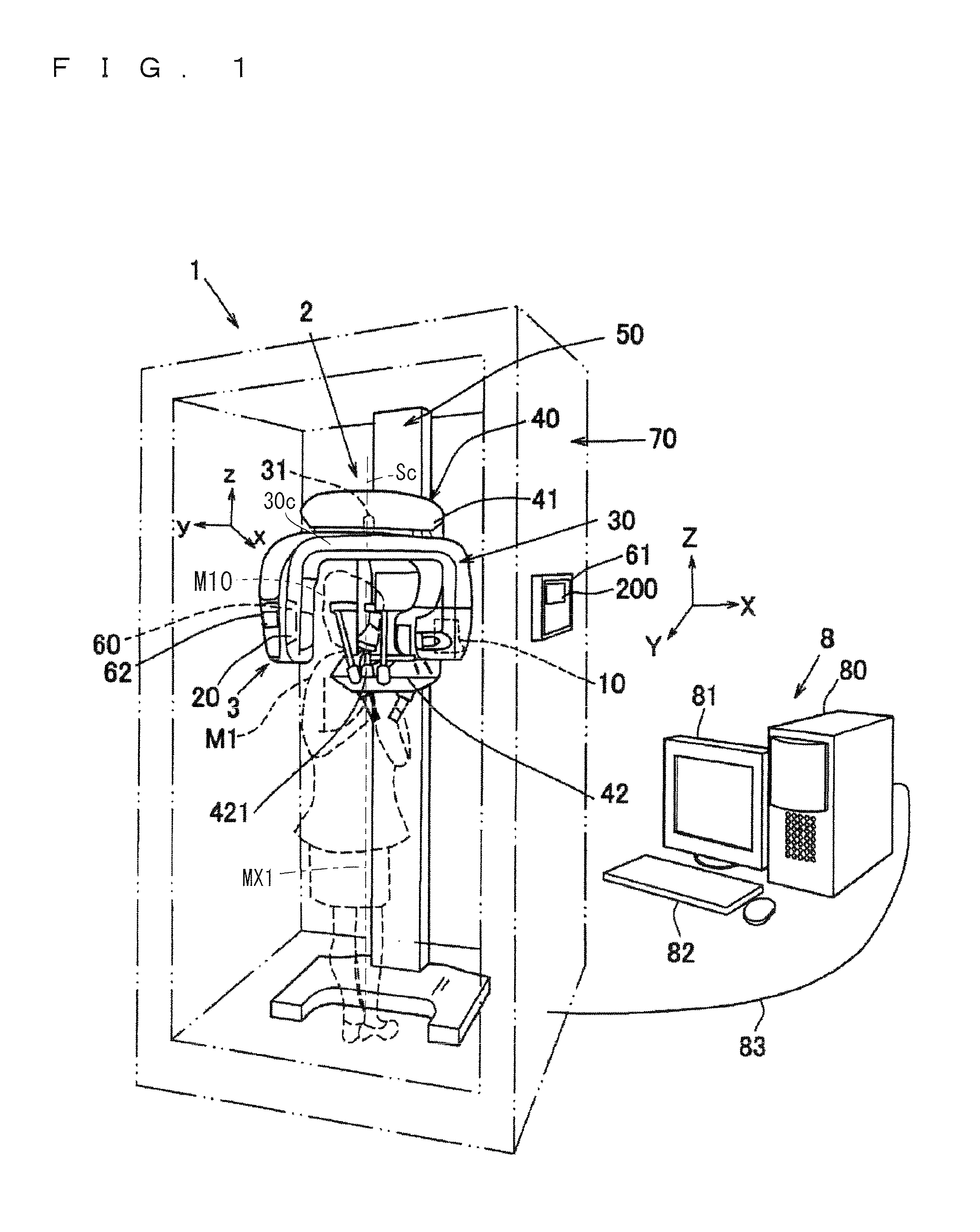
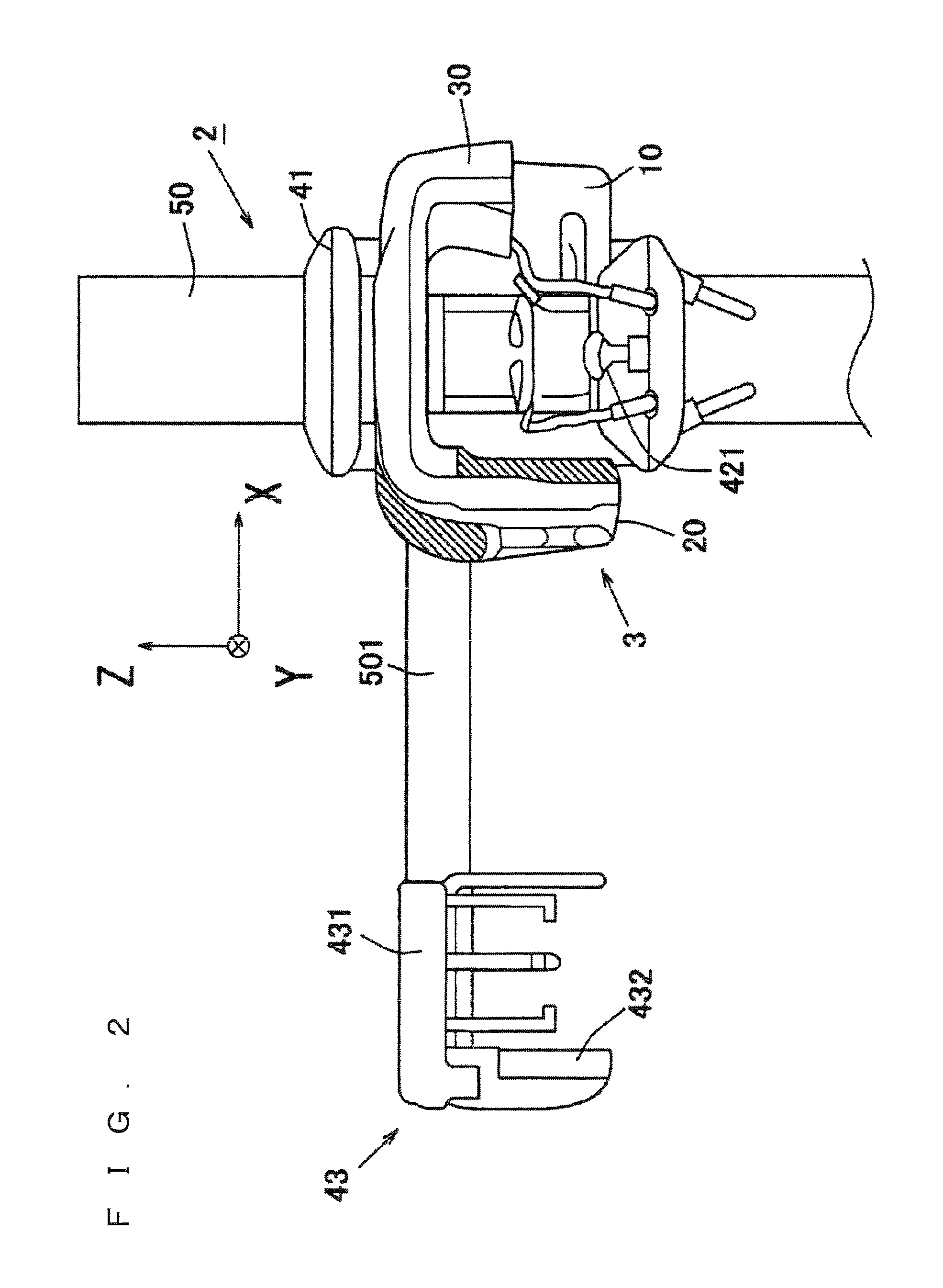
X-ray photography apparatus
ActiveUS9036776B2Sharp contrastAccurate diagnosisTomosynthesisPatient positioning for diagnosticsX ray imageTomographic image
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
Reconstruction algorithm for back projection weight cone-beam CT (Computed Tomography)
InactiveCN102521853AImprove cone artifactsIncrease rebuild rangeImage enhancement2D-image generationMissing dataFrame based
The invention relates to a reconstruction algorithm for back projection weight cone-beam CT, belonging to the field of X-ray computed tomography. The reconstruction algorithm comprises the following steps of: introducing a ray back projection weight based on a filtering back projection reconstruction frame, acting the back projection weight based on distance and continuity of conjugate rays on filtered projection data during back projection so as to reconstruct a CT image, and performing certain compensation on Radon missing data to improve the intrinsic cone-beam artifact problem of an FDK (Feldkamp-Davis-Kress) algorithm under circular track and increase the reconstruction quality. According to the reconstruction algorithm disclosed by the invention, the frame based on the filtering back projection has simple and efficient reconstruction process and is insensitive to noise.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH
C-arm tomography imaging method using semi-accurate filtered back-projection
InactiveCN102973291ACalculation speedImproved cone artifactsRadiation diagnosticsBack projectionReconstruction algorithm
The invention discloses a tomography imaging method suitable for C-arm imaging equipment. The tomography imaging method is characterized by having shift invariant features, wherein the semi-accurate reconstruction is performed on cone-beam projection data obtained by scanning a circular arc track. The circular arc track is a short scanning track, namely a scanning track of pi and a fan angle, and is also an ultra-short scanning track, namely a track smaller than the short scanning track. The method comprises the following steps: weighing of partial derivatives of projection data; one-dimensional Hilbert transform in a horizontal or non-horizontal direction; and back projection of the circular arc track. Compared with FDK type-approximate reconstruction algorithms, the C-arm tomography imaging method using semi-accurate filtered back-projection has the advantages of small reconstruction accuracy error, small discretization error and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
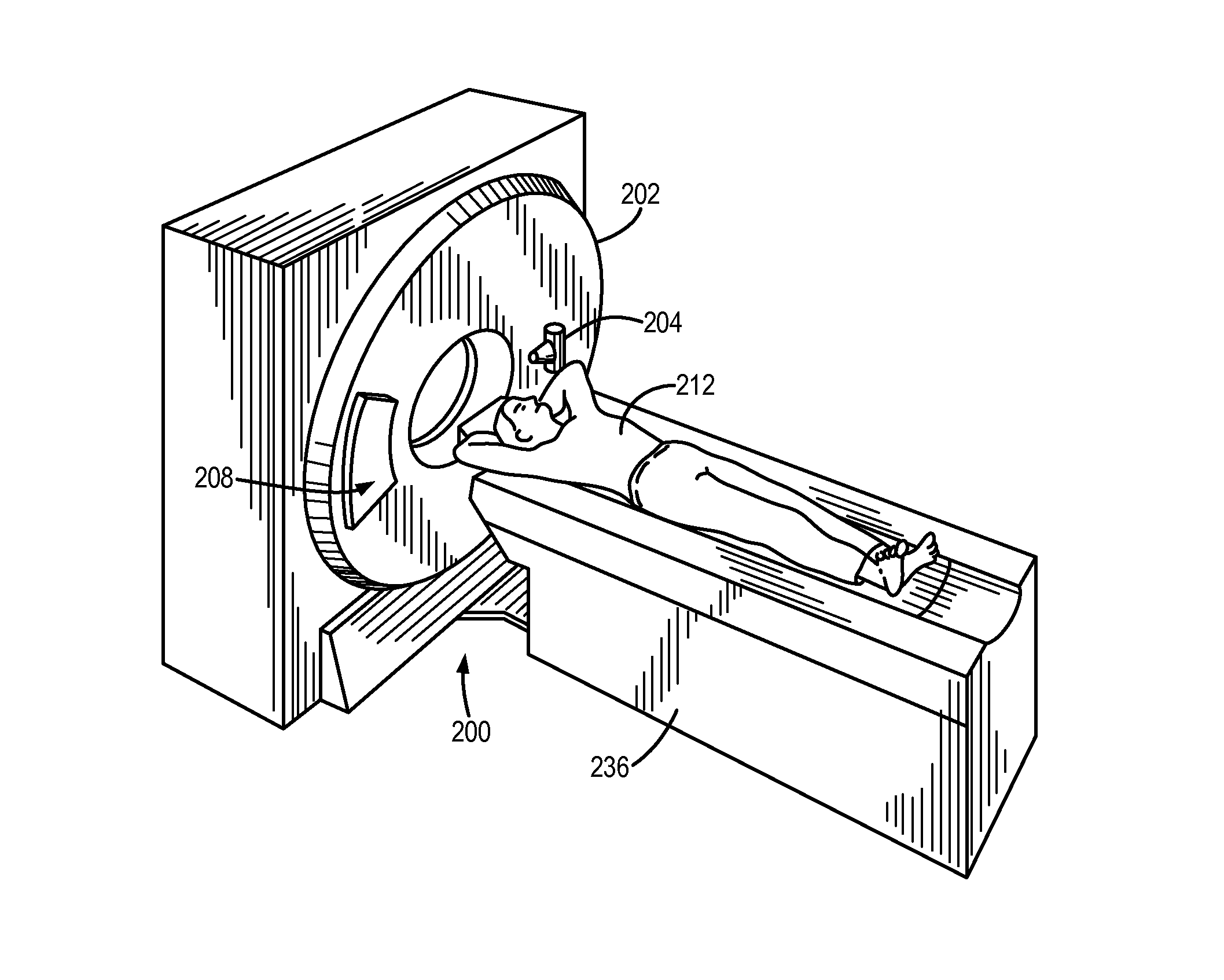
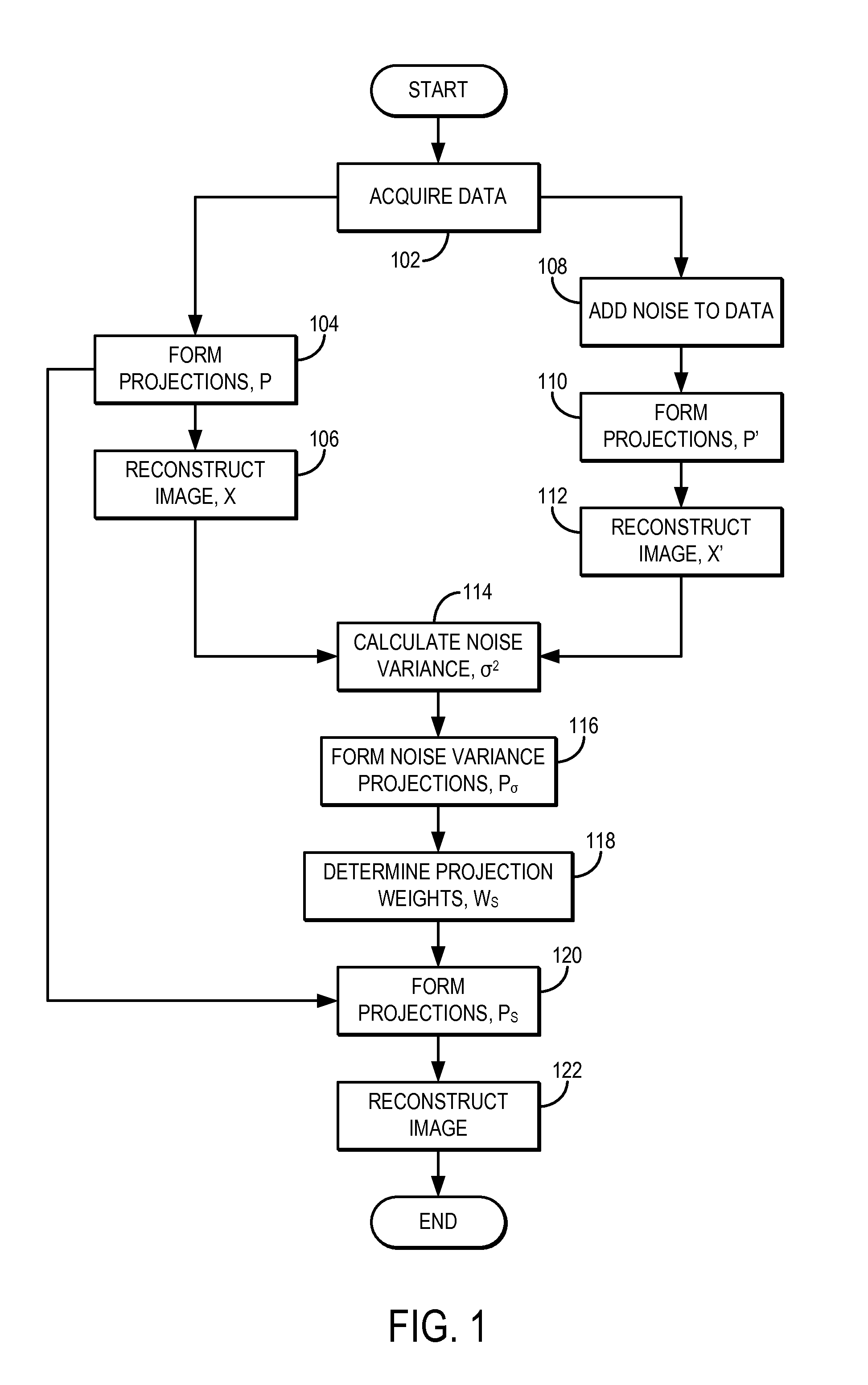
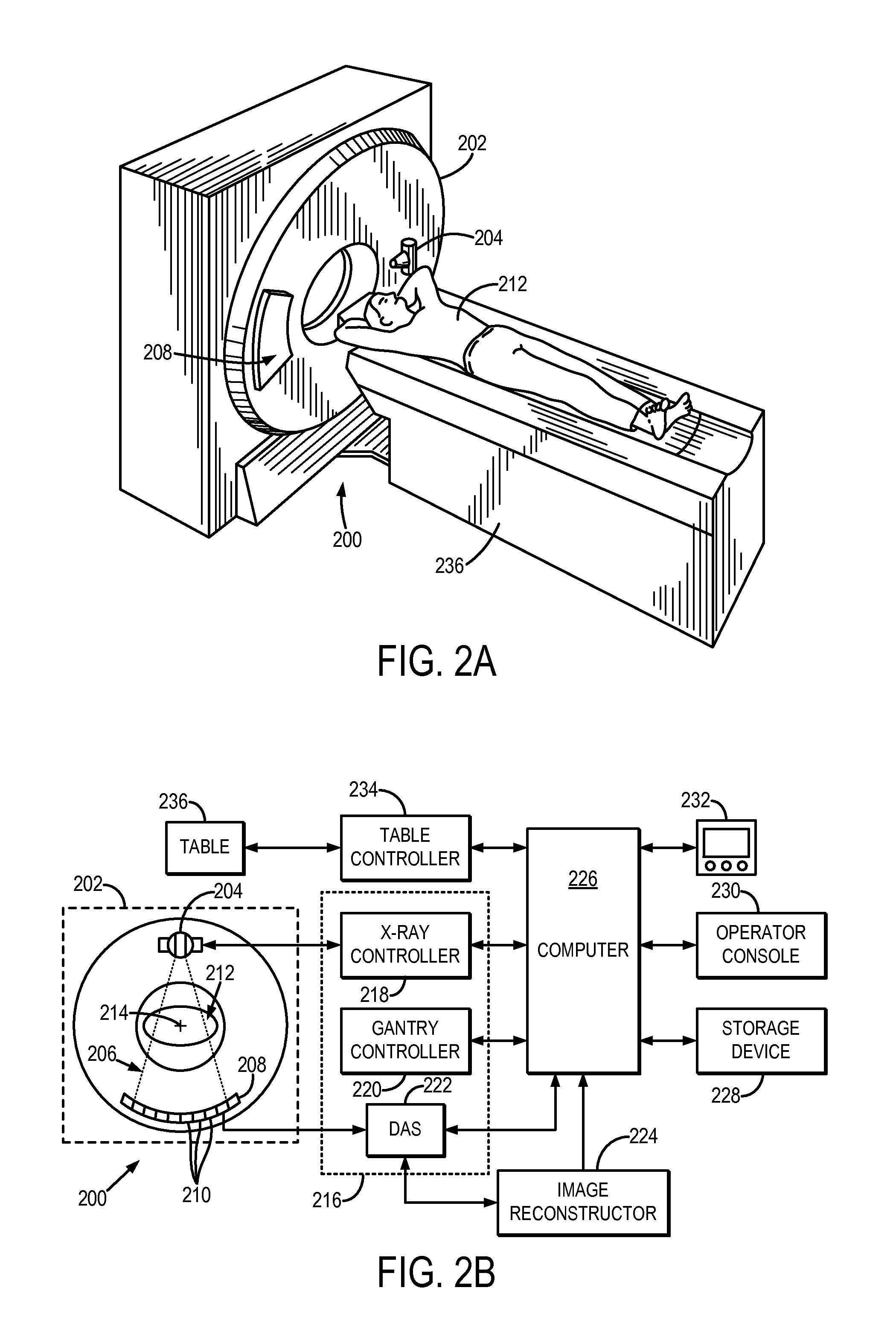
System and method for estimating a statistical noise map in x-ray imaging applications
Described here are a system and method for producing a statistical noise map that indicates the noise present in data acquired with an x-ray imaging system, such as an x-ray computed tomography system, an x-ray tomosynthesis system, a C-arm x-ray imaging system, and so on. In general, an image is reconstructed from the acquired data using, for example, any standard filtered back projection (“FBP”) image reconstruction algorithm. This image is used as a base line to estimate a noise standard distribution map. The raw projection data represents a typical measurement among many repeated measurements under the same experimental conditions; therefore, the measured projection data can be used to numerically generate an ensemble of many (e.g., twenty or more) noisy projection data sets. These noisy projection data sets are then used to reconstruct noisy images and from these noisy images and the original image, the statistical noise map can be computed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
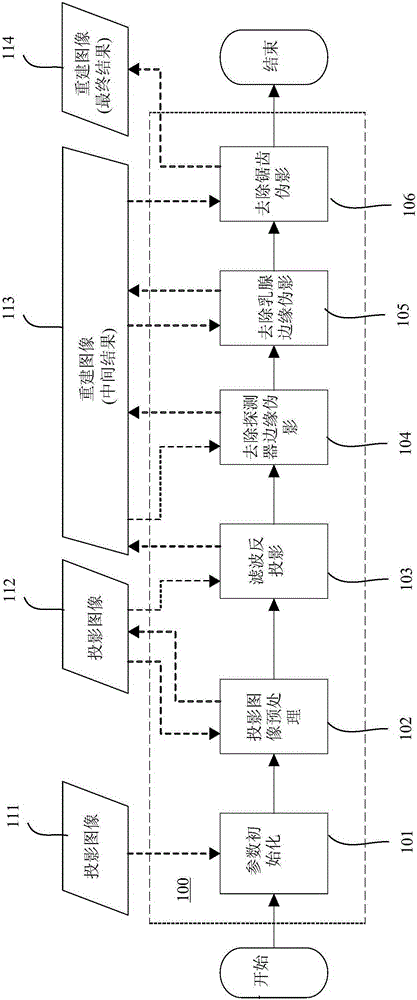
Mammary gland tomographic image reconstruction method and device
The invention provides a mammary gland tomographic image reconstruction method and a mammary gland tomographic image reconstruction device. The mammary gland tomographic image reconstruction method comprises the steps of: initializing mechanical coordinates of mammary gland tomographic equipment and image parameters of a projected image; preprocessing the projected image; carrying out filtered back-projection on the projected image after preprocessing to generate a mammary gland 3D tomographic reconstructed image; removing detector edge artifacts in the mammary gland 3D tomographic reconstructed image; removing mammary gland edge artifacts in the mammary gland 3D tomographic reconstructed image; and removing sawtooth artifacts in the mammary gland 3D tomographic reconstructed image. The mammary gland tomographic image reconstruction method and the mammary gland tomographic image reconstruction device can be adapt to the mammary gland tomographic equipment with multiple ray sources.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Cardiac computed tomography methods and systems using fast exact/quasi-exact filtered back projection algorithms
InactiveUS20120039434A1Few artifactAccurate and reliable processReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTemporal resolutionCardiac computed tomography
The present invention provides systems, methods, and devices for improved computed tomography (CT). More specifically, the present invention includes methods for improved cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) resolution using improved filtered back projection (FBP) algorithms, which can be used for cardiac tomography and across othertomographic modalities. Embodiments provide methods, systems, and devices for reconstructing an image from projection data provided by a computed tomography scanner using the algorithms disclosed herein to generate an image with improved temporal resolution.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Wide visual field cone-beam X ray oblique scanning three-dimension digital imaging method based on algebraic reconstruction algorithm
InactiveCN101672806AImprove reconstructed image qualitySmall feature aliasing between layersMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSpecific gravity measurementSoft x rayVisual field loss
The invention belongs to the technical field of X ray computerized tomography (CT), and particularly relates to a wide visual field cone-beam X ray oblique scanning three-dimension digital imaging method based on an algebraic reconstruction algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring two-dimension projection data of a scanned component in detector biasing wide visual field cone-beam X ray oblique scanning way; and rebuilding an image by the algebraic reconstruction algorithm to obtain a three-dimension computerized tomography image in a scanning area. Compared with the widevisual field cone-beam X ray oblique scanning three-dimension digital imaging method based on a filter back projection algorithm, the method can effectively inhibit structure aliasing between layers and obviously improve the quality of the rebuilt picture in the condition that the system hardware, the scanning view field and the scanning speed are not changed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
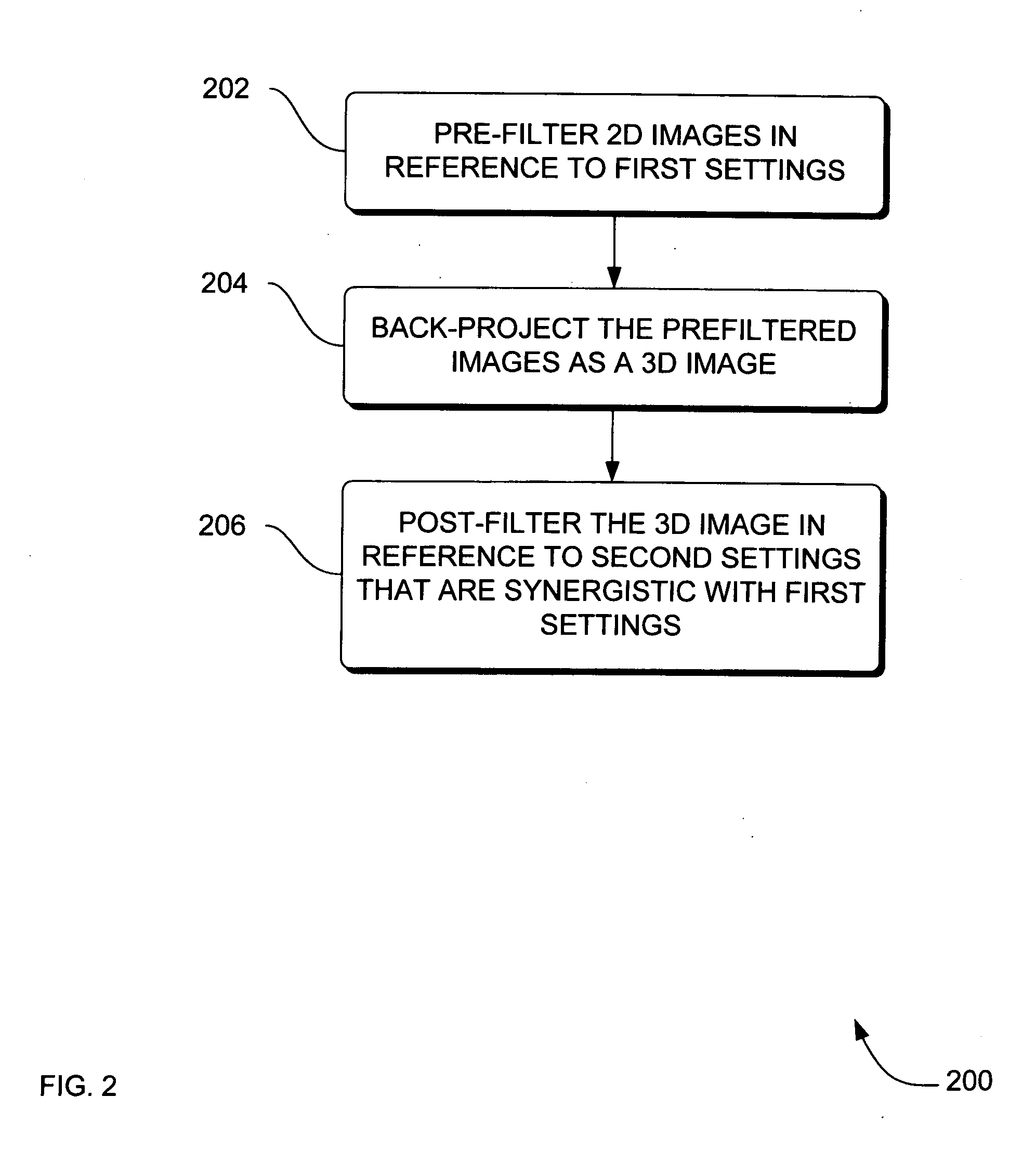
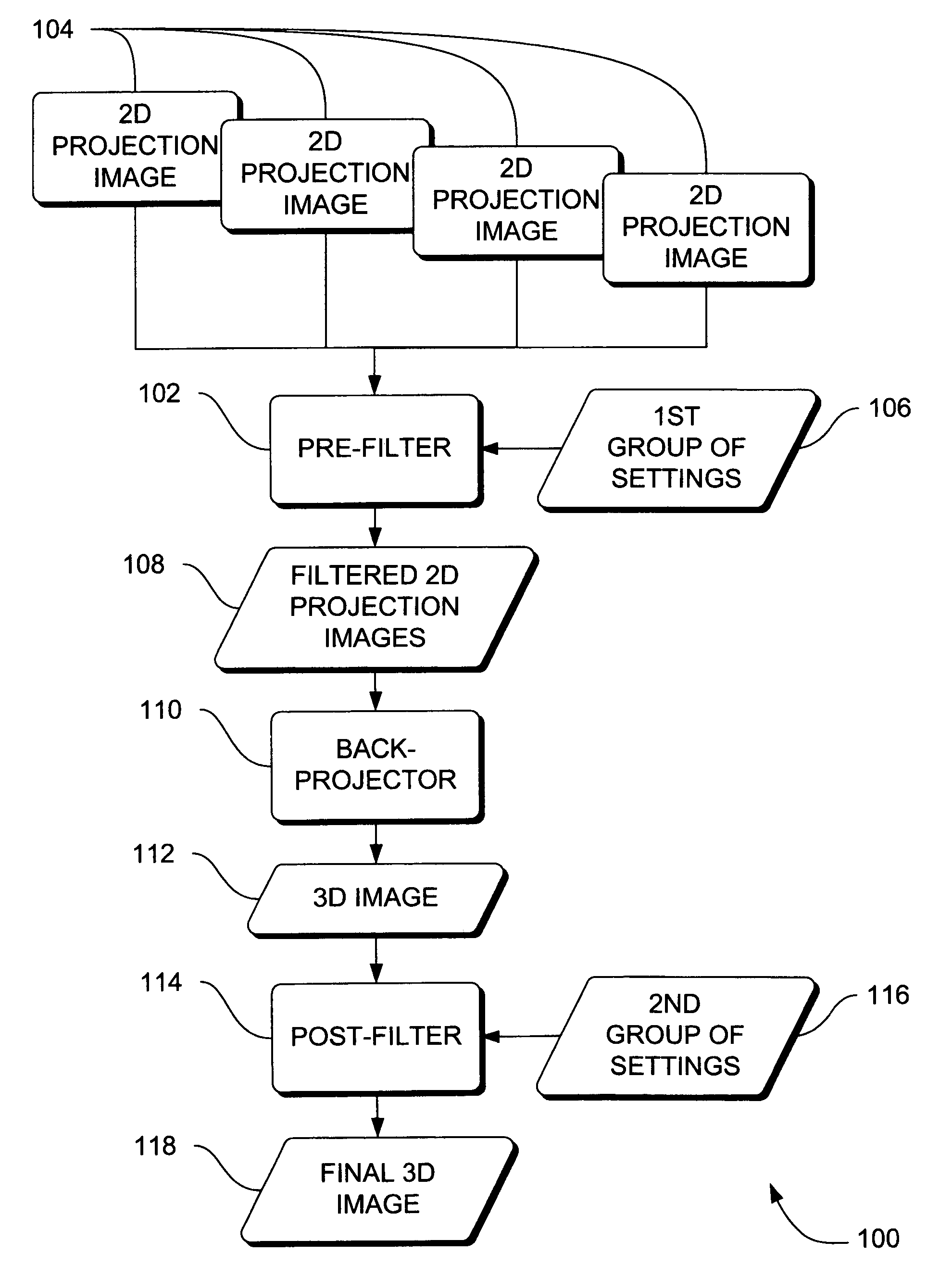
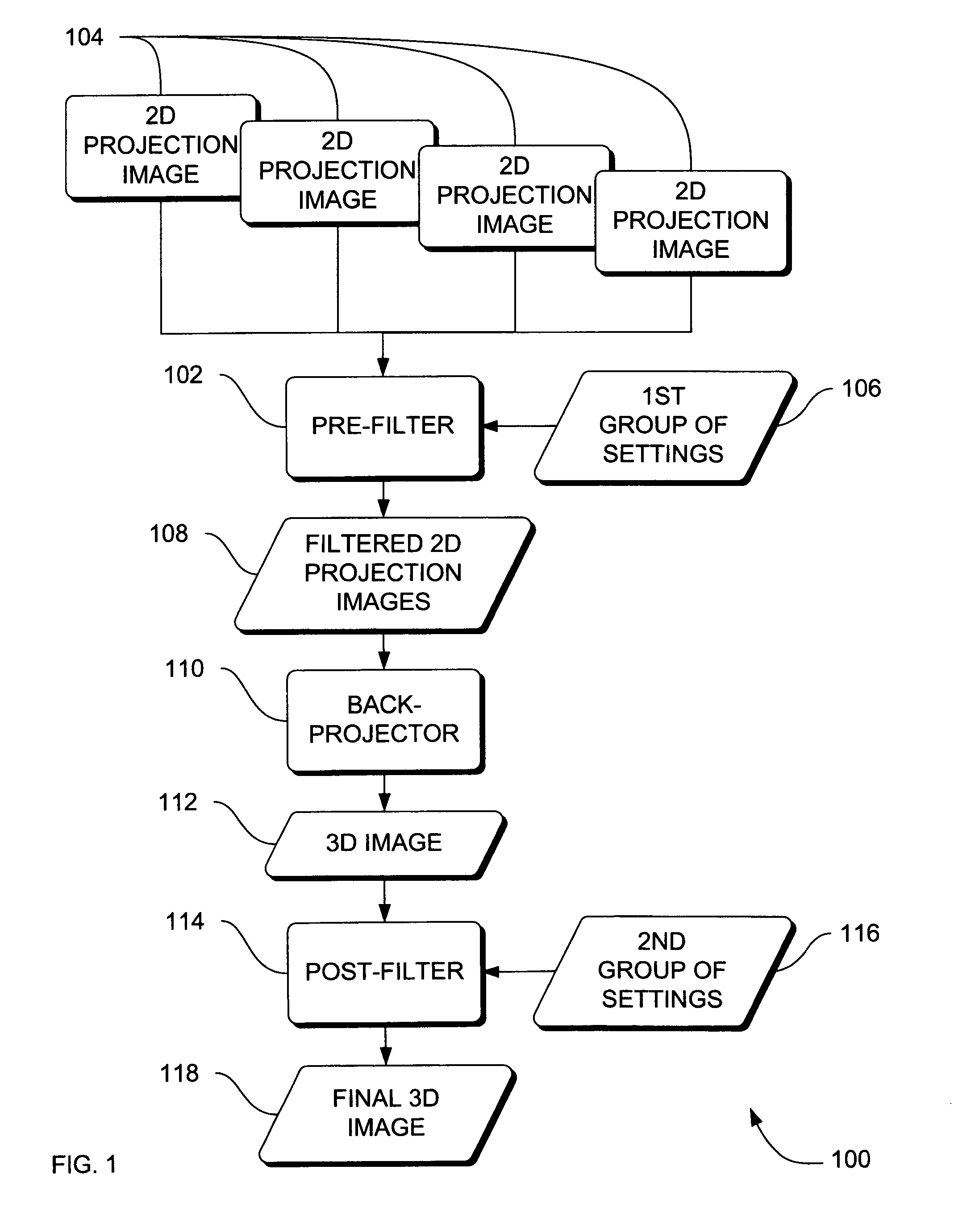
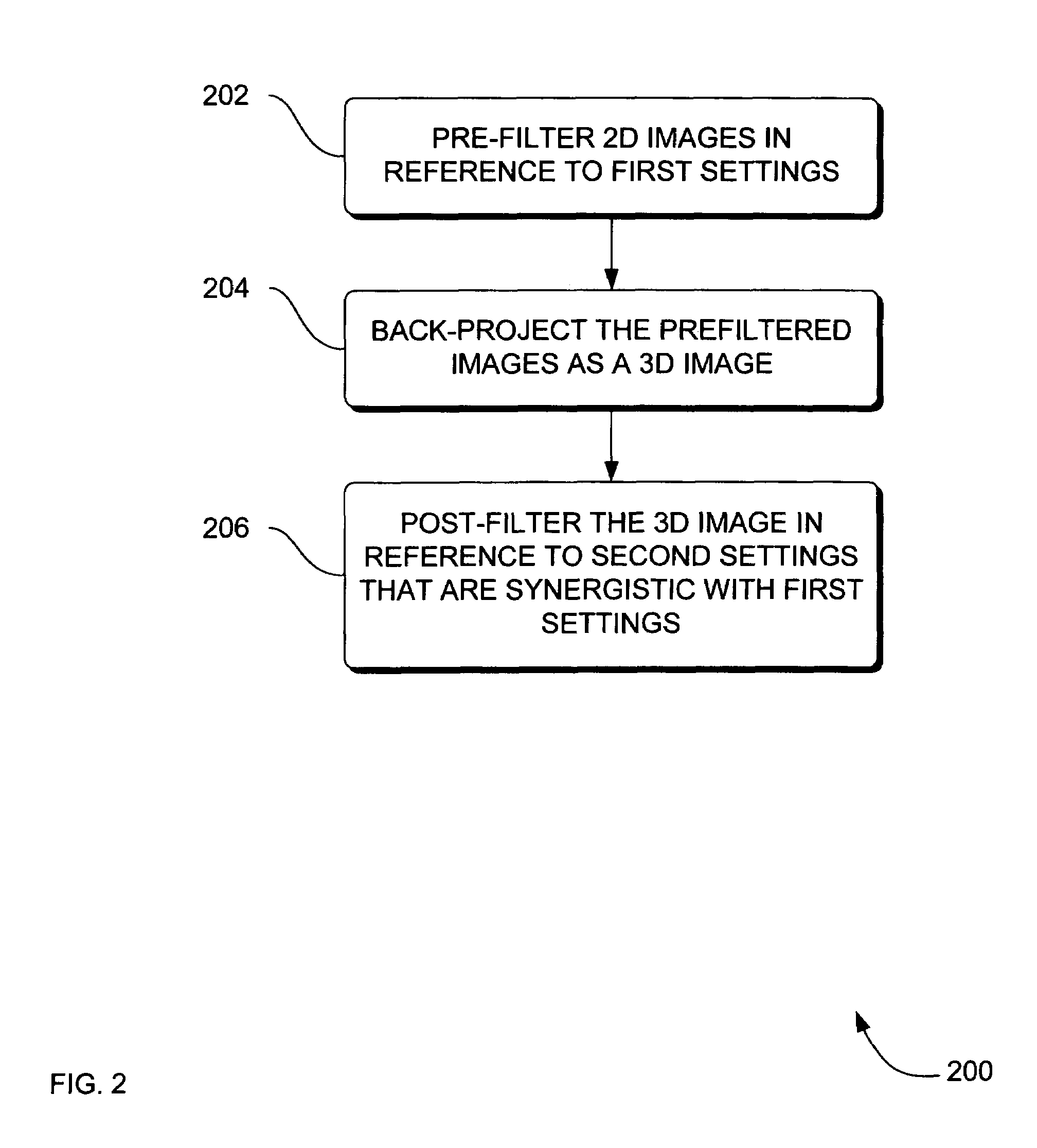
Systems, methods and apparatus for specialized filtered back-projection reconstruction for digital tomosynthesis
ActiveUS7310436B2Reduce blurReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomosynthesis3d image
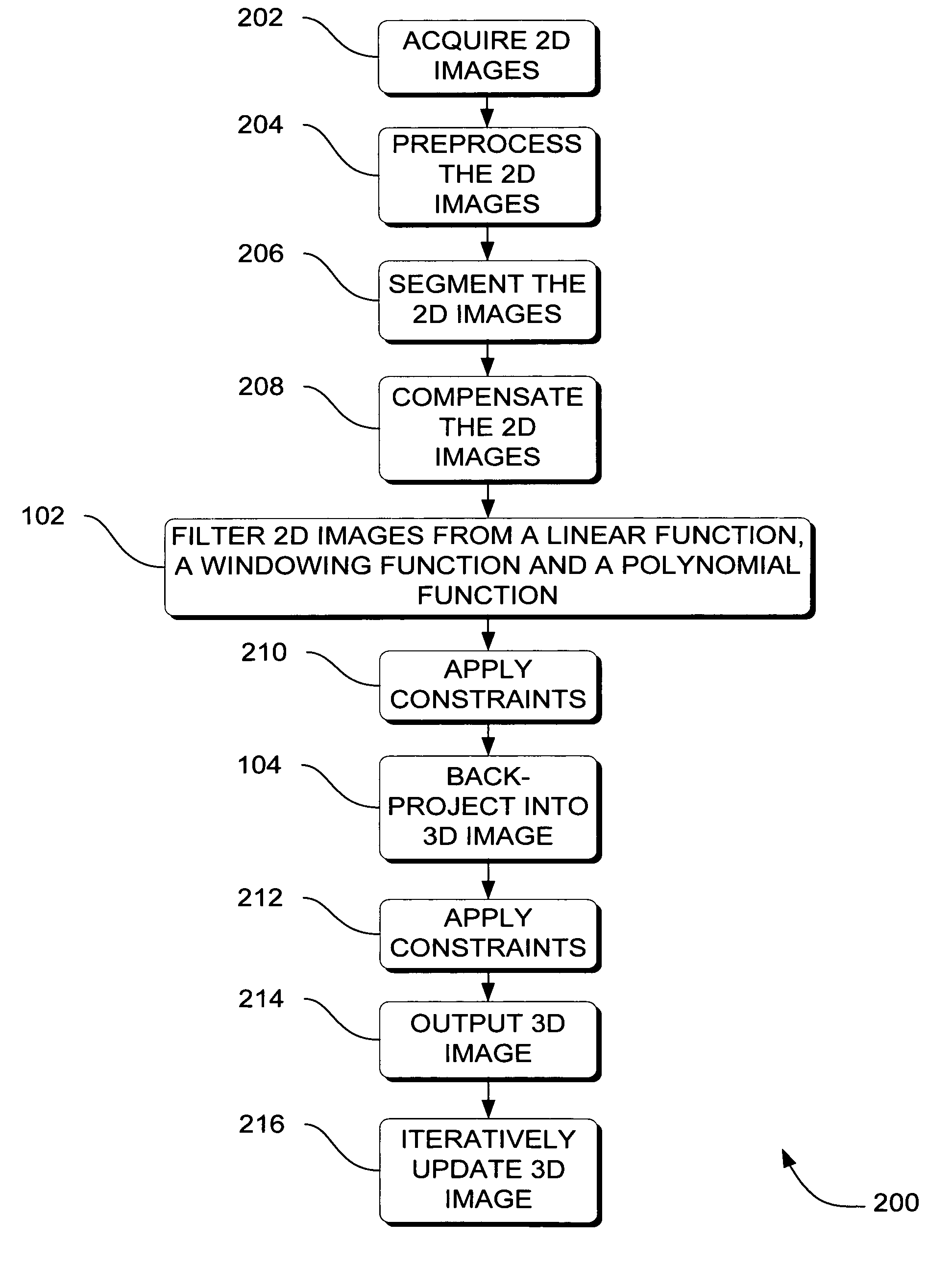
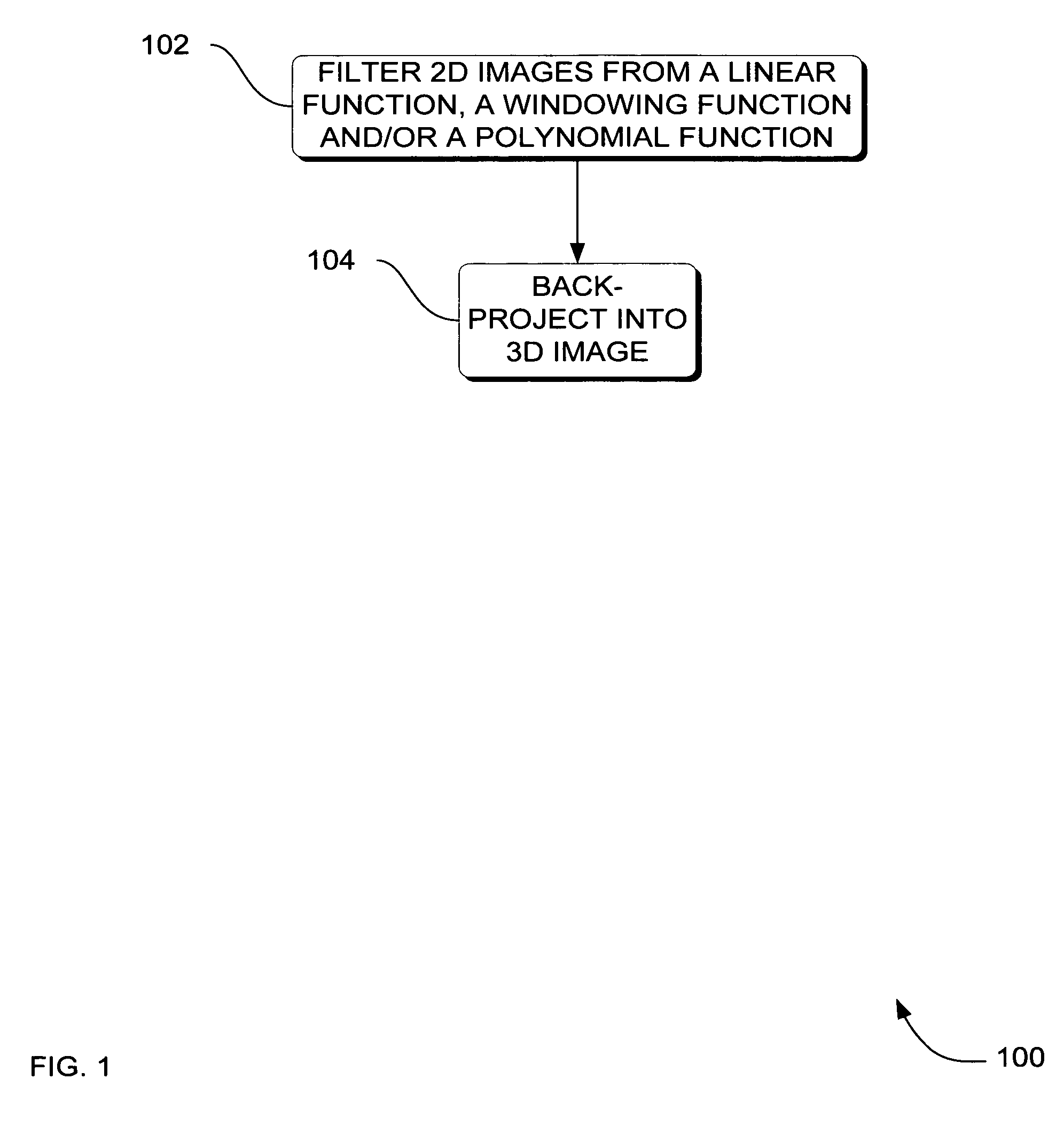
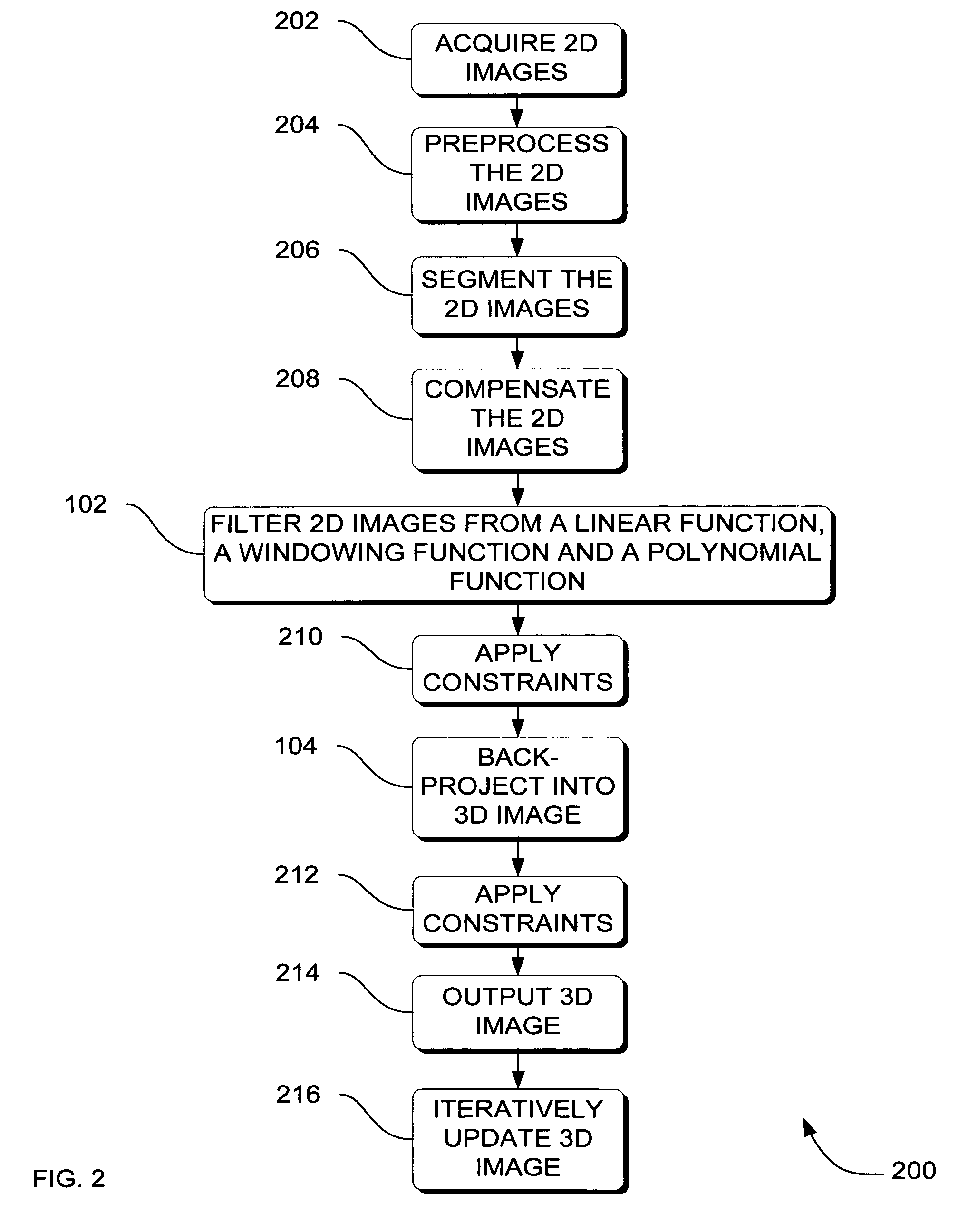
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which in one aspect, a three-dimensional (3D) image of an object is constructed from a plurality of two-dimensional (2D) images of the object using a specialized filter. The specialized filter implements a linear ramp function, a windowing function, and / or a polynomial function. The 3D image is back-projected from the filtered two-dimensional images, yielding a 3D image that has improved visual distinction of overlapping anatomic structures and reduced blurring.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Non-iterative algebraic reconstruction technique for tomosynthesis
InactiveUS6987829B2Improve image qualityConsiderable computational savingsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomosynthesisAlgorithm
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
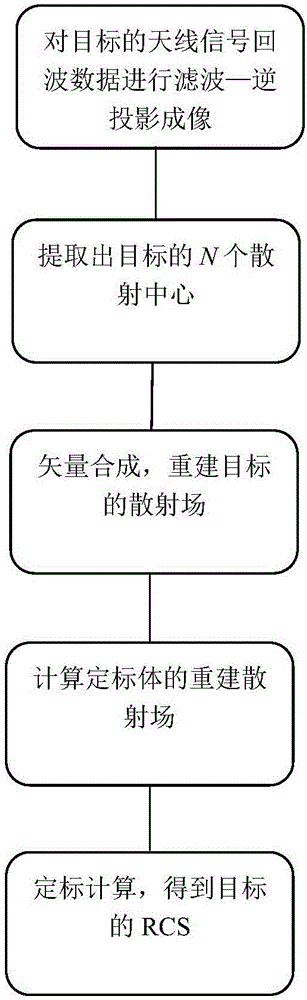
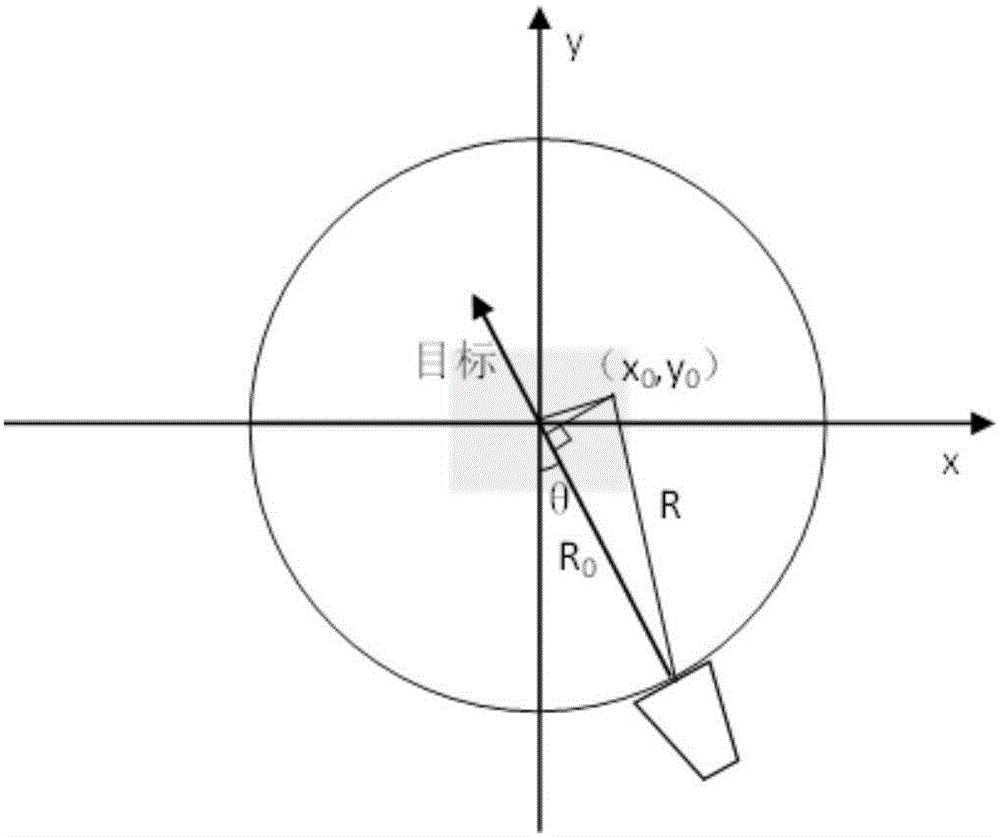
Method of acquiring target RCS by using high resolution imaging
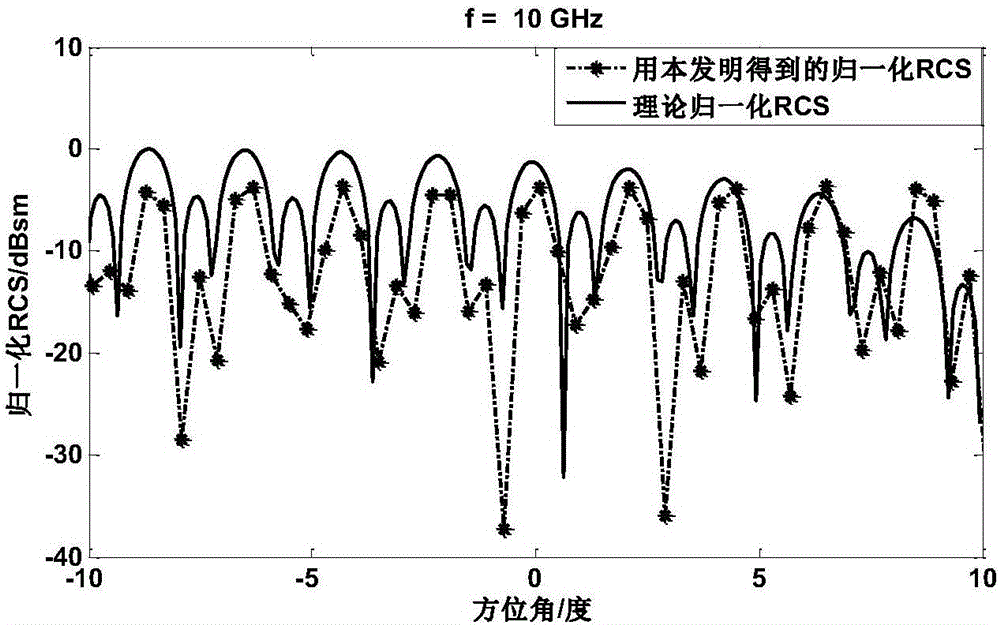
InactiveCN106569191AReflect the scattering propertiesGuaranteed calculation accuracyWave based measurement systemsHigh resolution imagingImaging processing
The invention provides a method of acquiring a target RCS by using high resolution imaging. Firstly, a filtered-back projection algorithm is adopted to carry out imaging processing on target near field echo data; then, through a CLEAN algorithm, scattering centers are extracted from a two-dimensional image sequentially from strong to weak; and finally, each scattering center serves as a discrete point scattering source for vector composition to rebuild a target scattering field, and thus, the target RCS is calculated and obtained. As the filtered-back projection algorithm is high in imaging precision, the position information and the strength value of each scattering center of the target can be accurately presented; as the rebuilt scattering field is generated by a limited number of scattering centers extracted through the CLEAN algorithm, the scattering features of the target can be restored completely, and environment noise outside the target is not introduced. As no far field testing distance problem exists for the scattering centers, the scattering features obtained through vector composition are the far field scattering features of the target, and the target RCS calculation precision is ensured.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
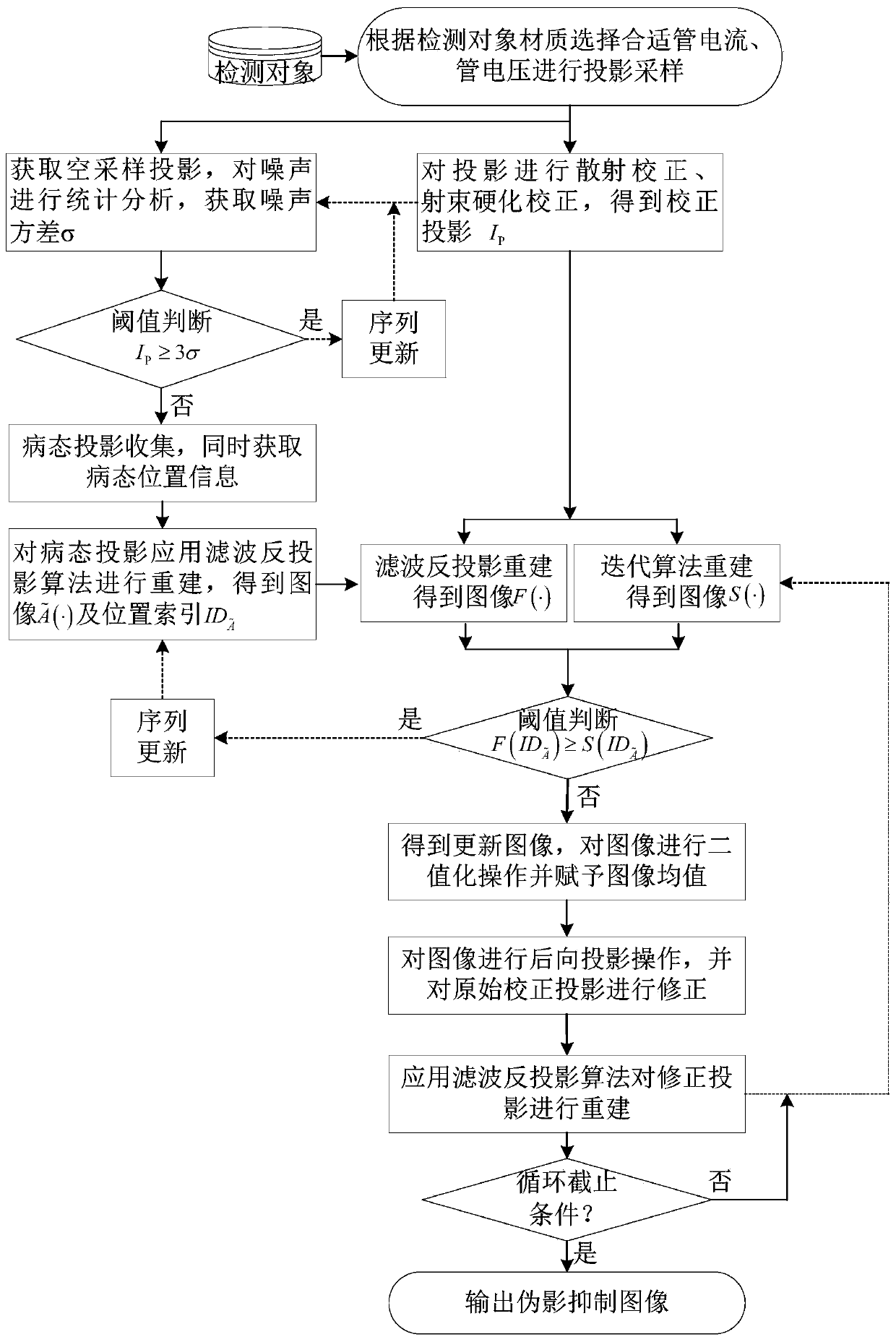
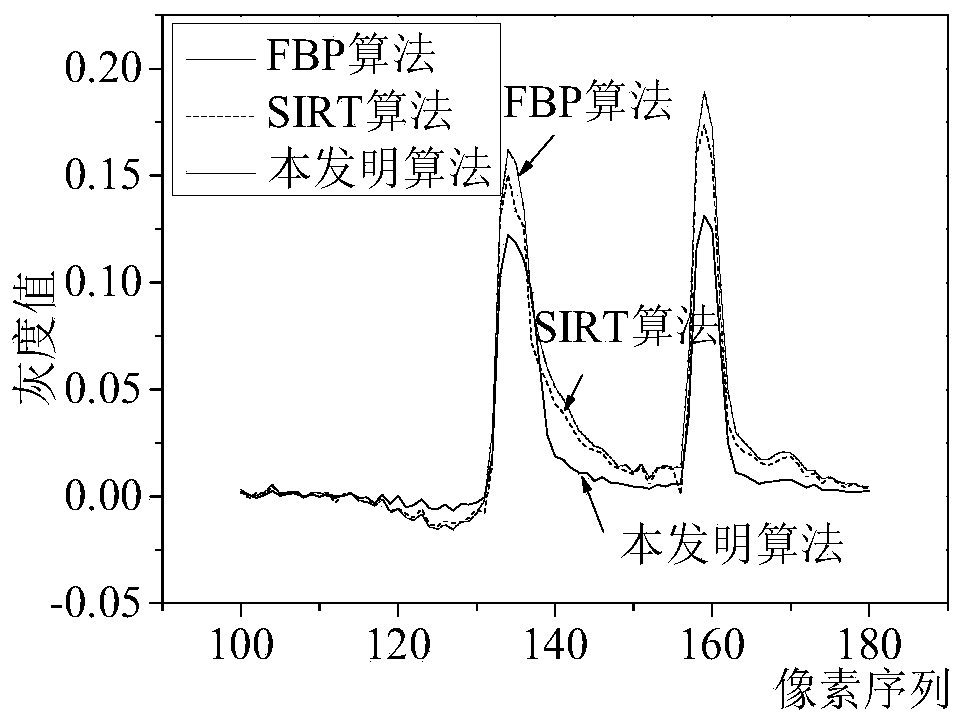
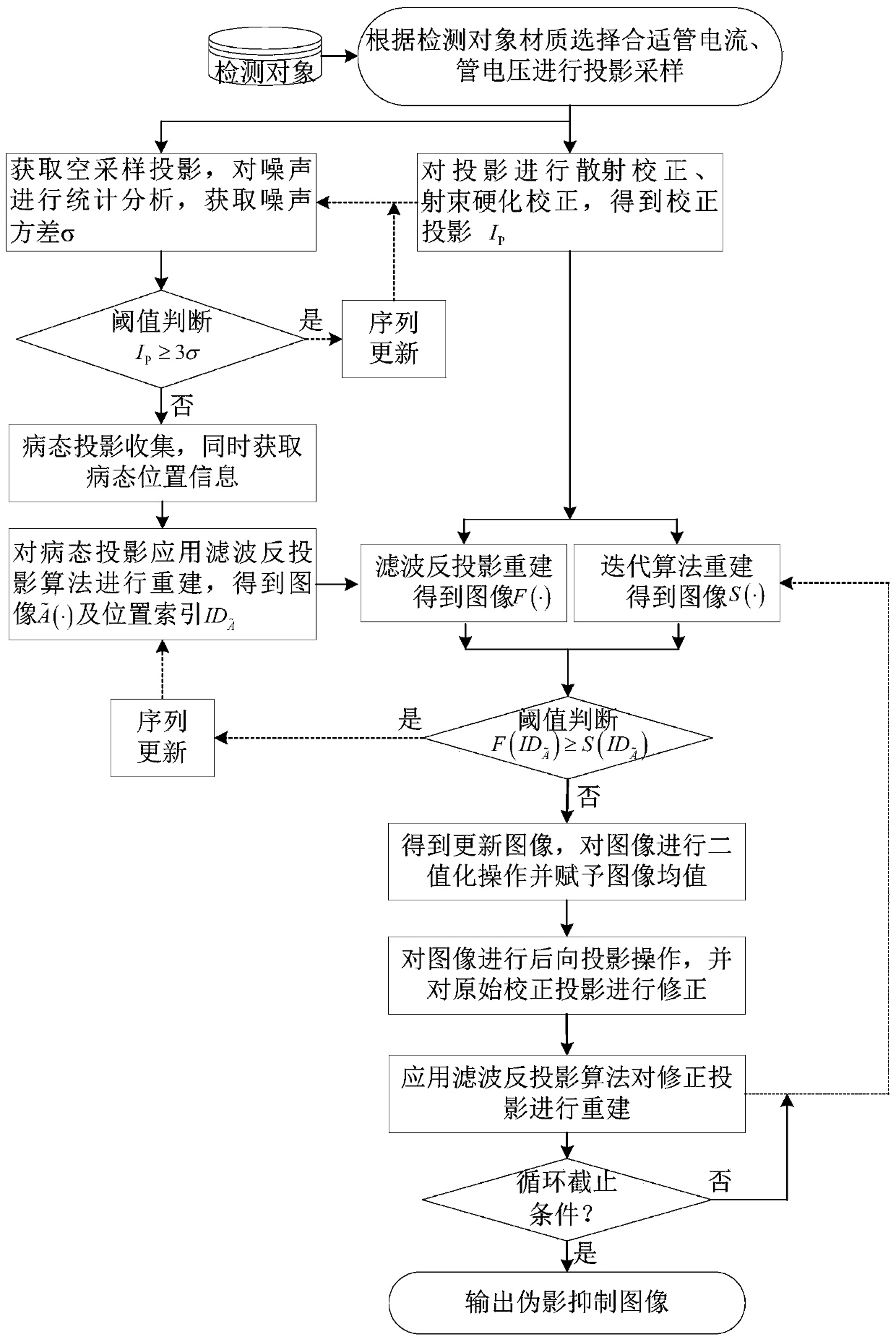
A cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact inhibition method
ActiveCN109920020AReduce distractionsReduce the impactImage enhancementImage analysisArtifact suppressionBack projection
The invention discloses a cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact inhibition method. By utilizing the accuracy of a filtering back projection algorithm and the noise suppressionadvantage of an iterative algorithm, reconstruction image fusion of an analytical algorithm and an iterative algorithm and an iterative updating method, ill-conditioned projection reconstruction artifact suppression is realized, the signal-to-noise ratio of the image is improved, and artifact interference caused by ill-conditioned projection reconstruction is prevented. The cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact inhibition method is suitable for the projection reconstruction artifact inhibition under the conditions of normal projection and less ill-condition projection angles, is good in reliability, stability and noise resistance, can reduce the interference and influence of the cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact on the image to a great extent, and obviously improves the quality of the cone beam CT image.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com