Polyethylene glycol terephthalate (PET) reconstruction method based on sparsification and Poisson model
A sparse and model technology, applied in 2D image generation, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to effectively represent images with different components, quantum noise pollution, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing impact and improving quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
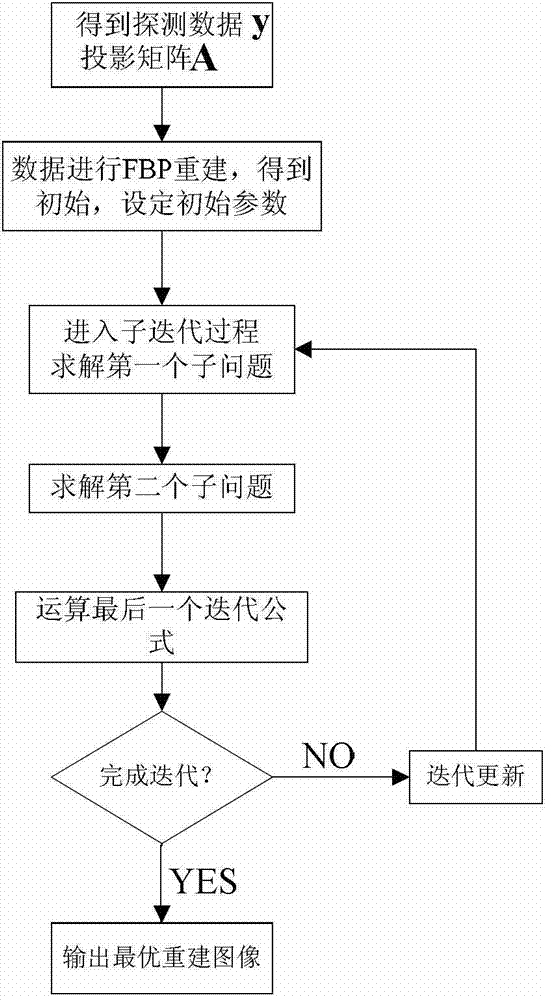
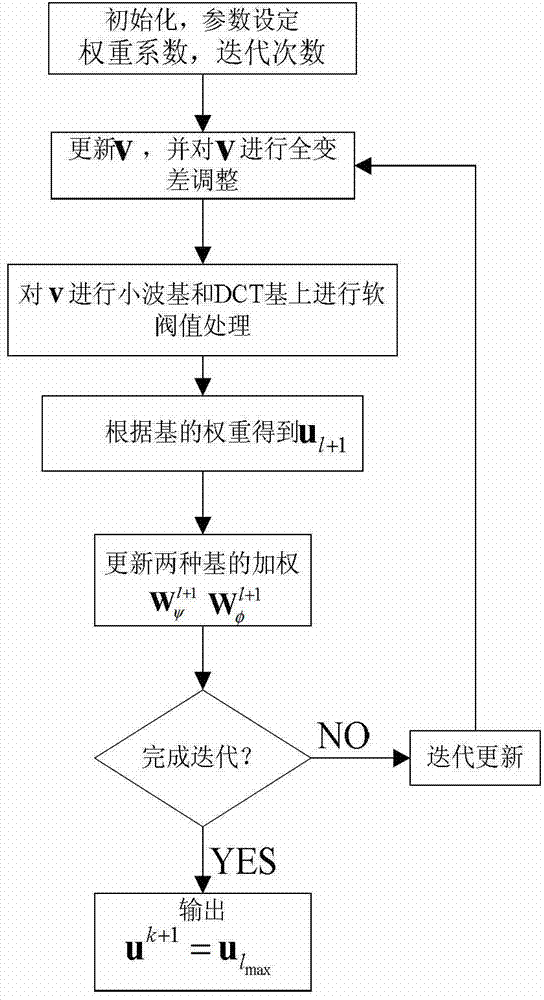
[0043] In order to improve the quality of PET imaging, reduce noise and maintain the local edge effect, we invented a PET reconstruction method based on mixed basis and weighted sparse regularization, using Poisson model to reduce noise, such as figure 1 As shown, the main algorithm steps are as follows:
[0044] (1) Obtain projection data y by PET imaging system, calculate system projection probability matrix A, y=(y 1 ,y 2 ,...,y M ) T Indicates the detected projection data, y 1 ,y 2 ,...,y M Denotes M projection data detected by PET.
[0045] (2) Perform FBP reconstruction on the data in step (1) to obtain the initial reconstructed image, and determine the gray scale range and size requirements of the image.
[0046] (3) Establish the logarithmic likelihood function as the objective function of the reconstructed recovery item:
[0047] u * = arg min u ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com