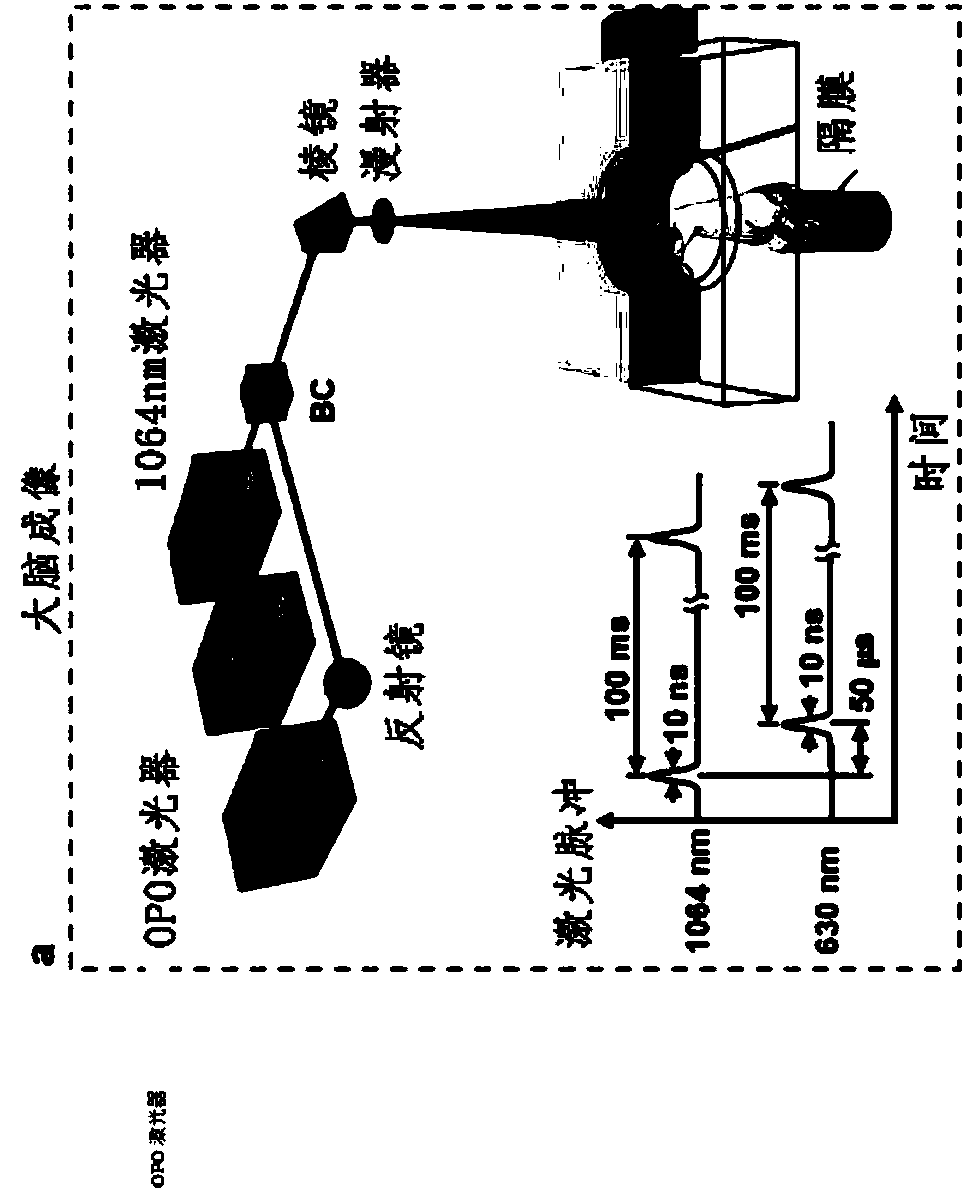
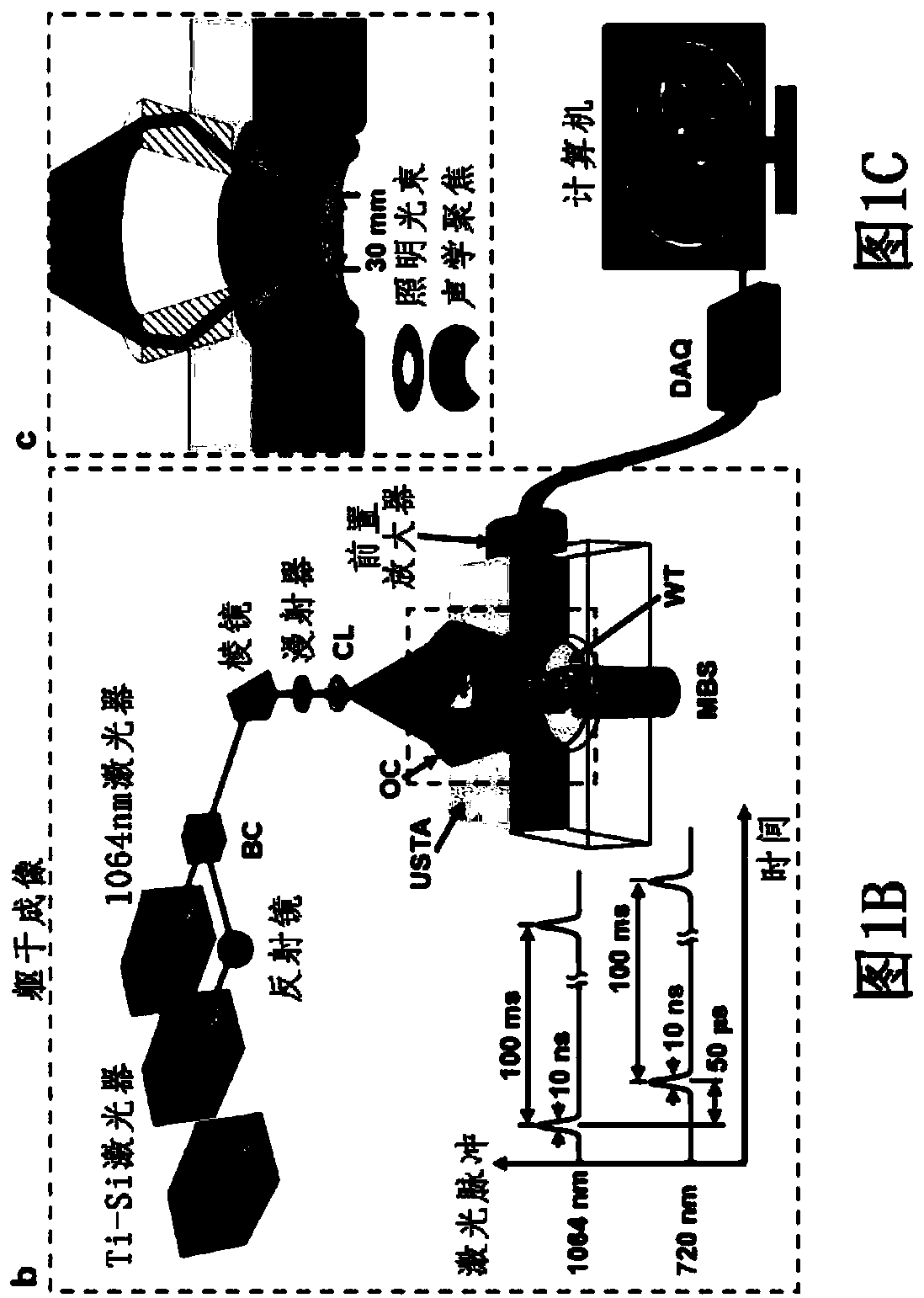
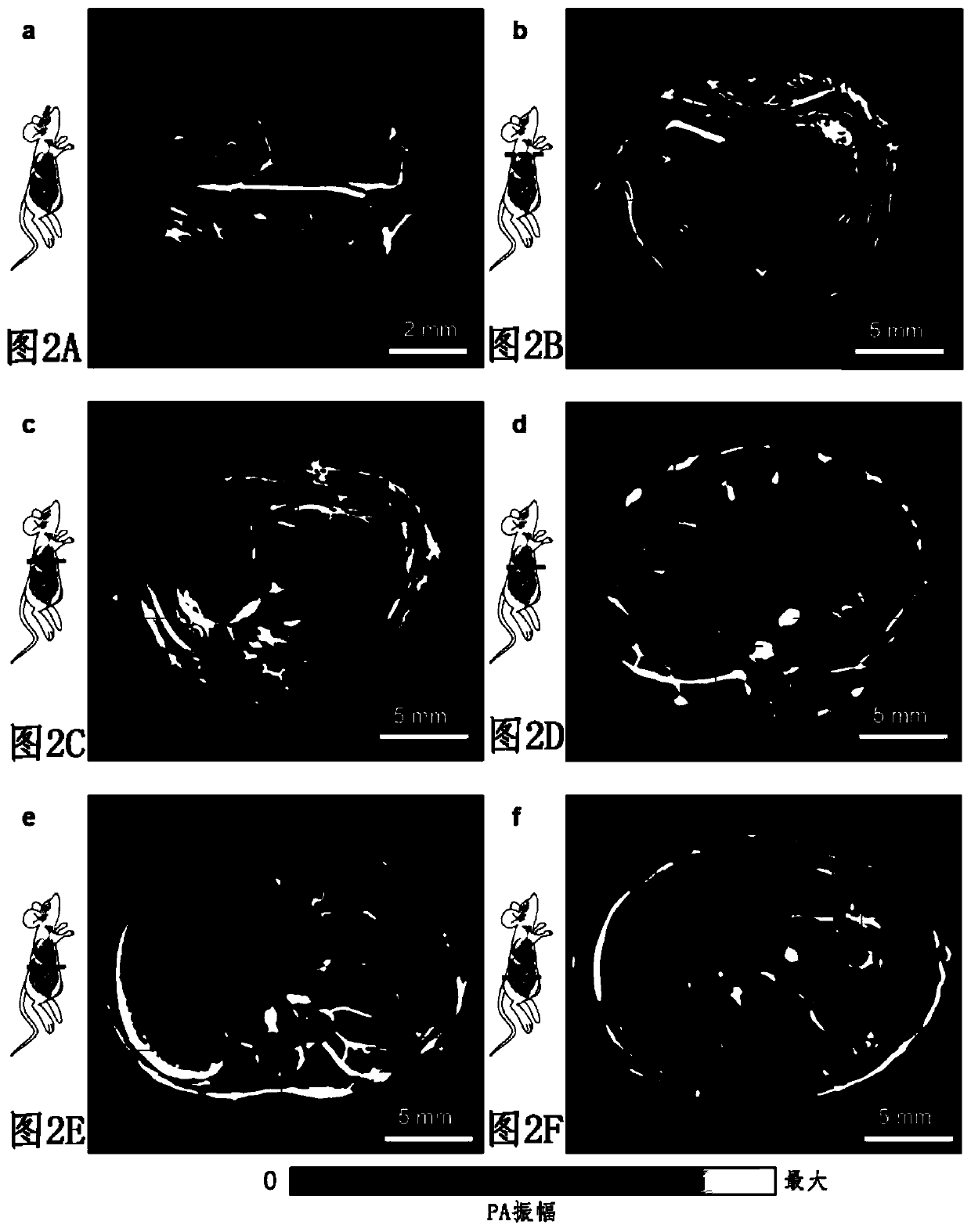
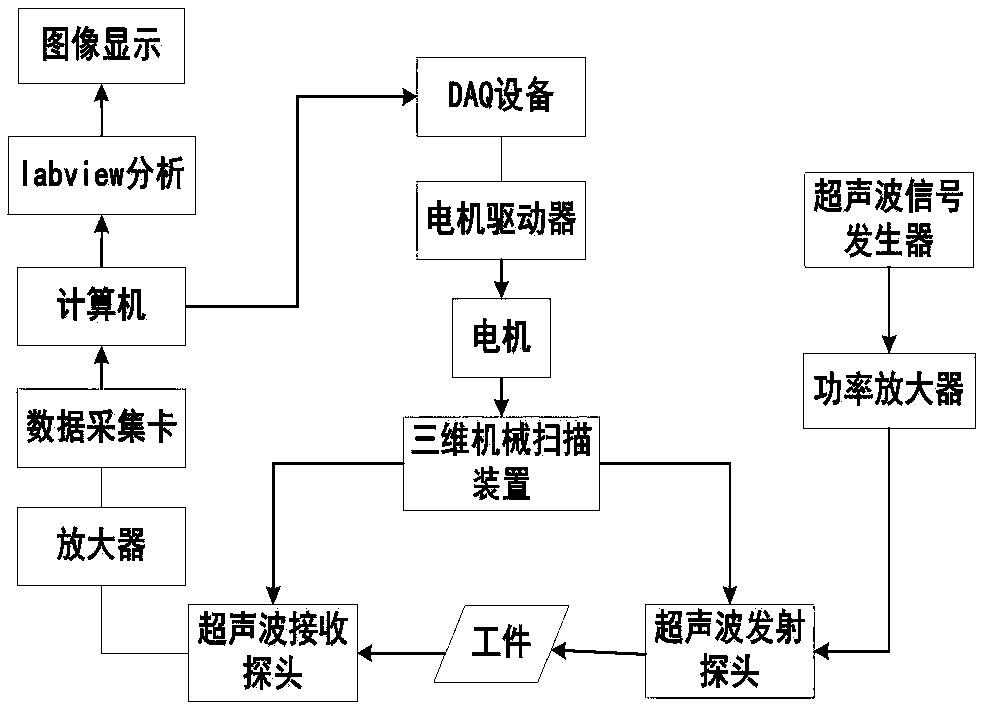
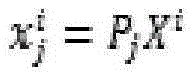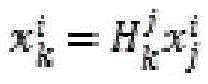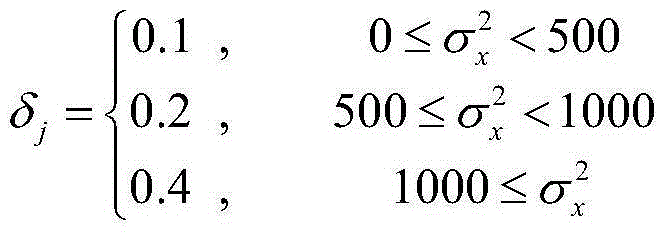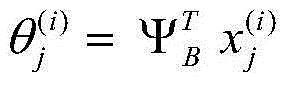Patents
Literature
85 results about "Projection reconstruction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
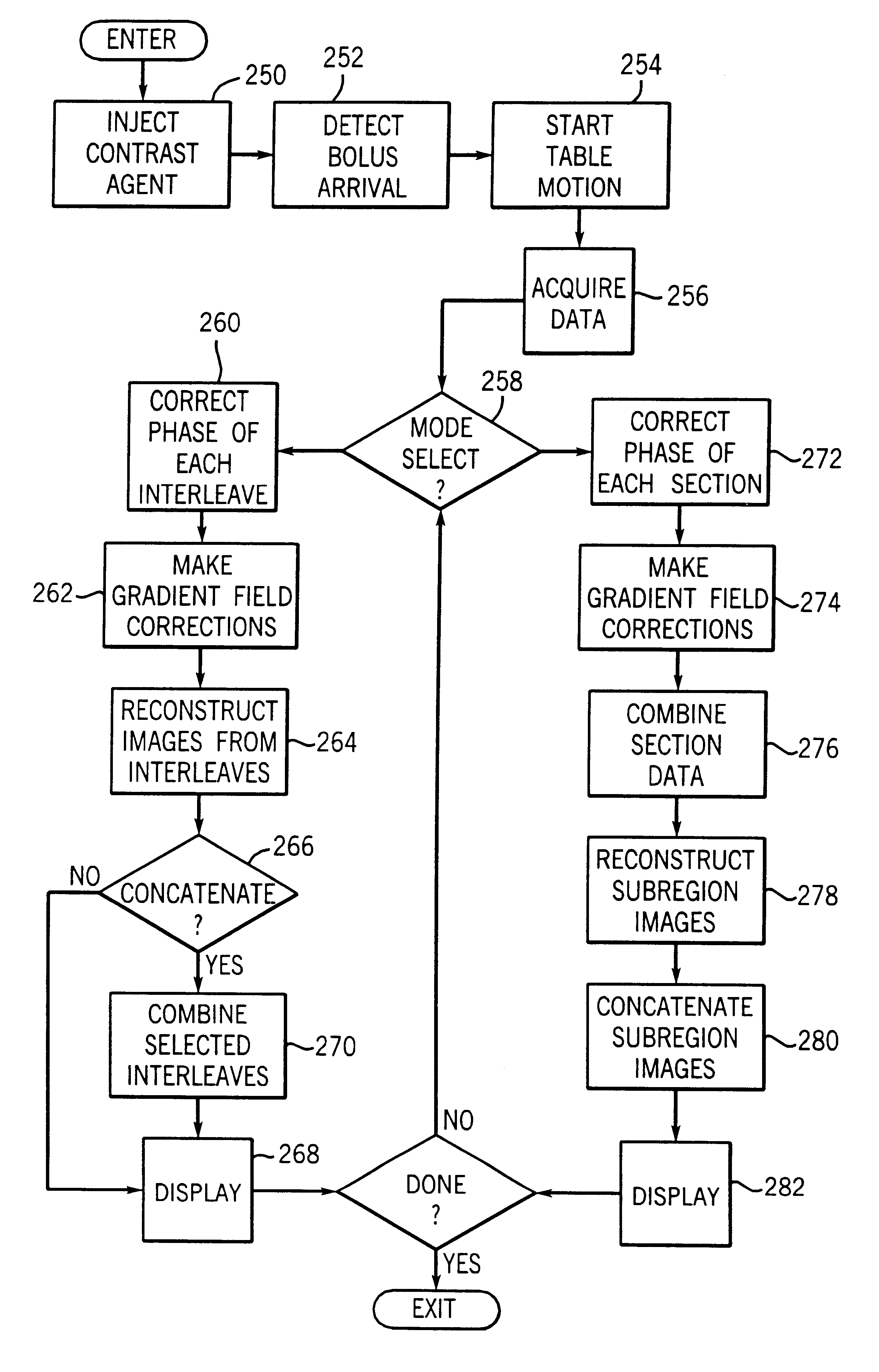
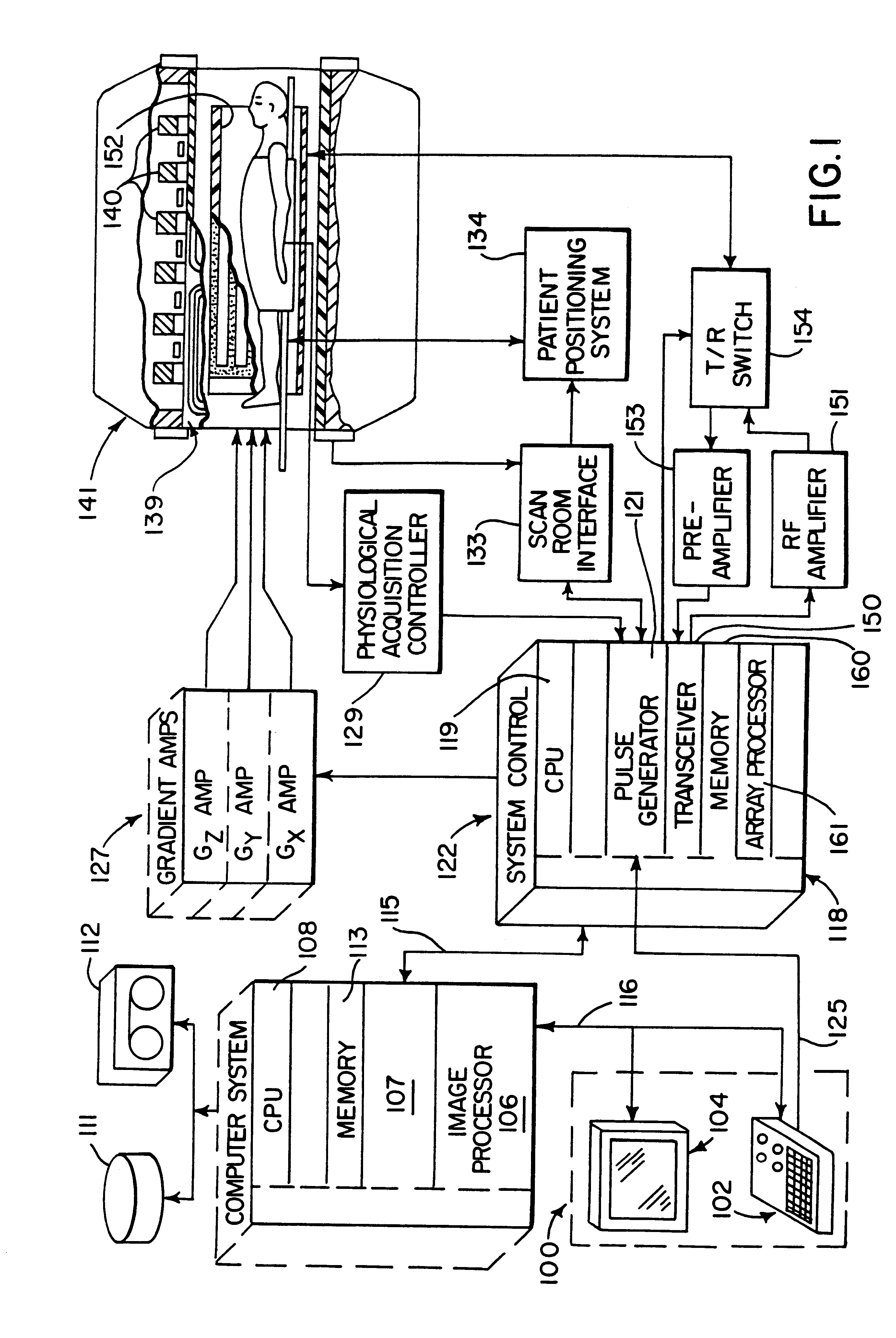
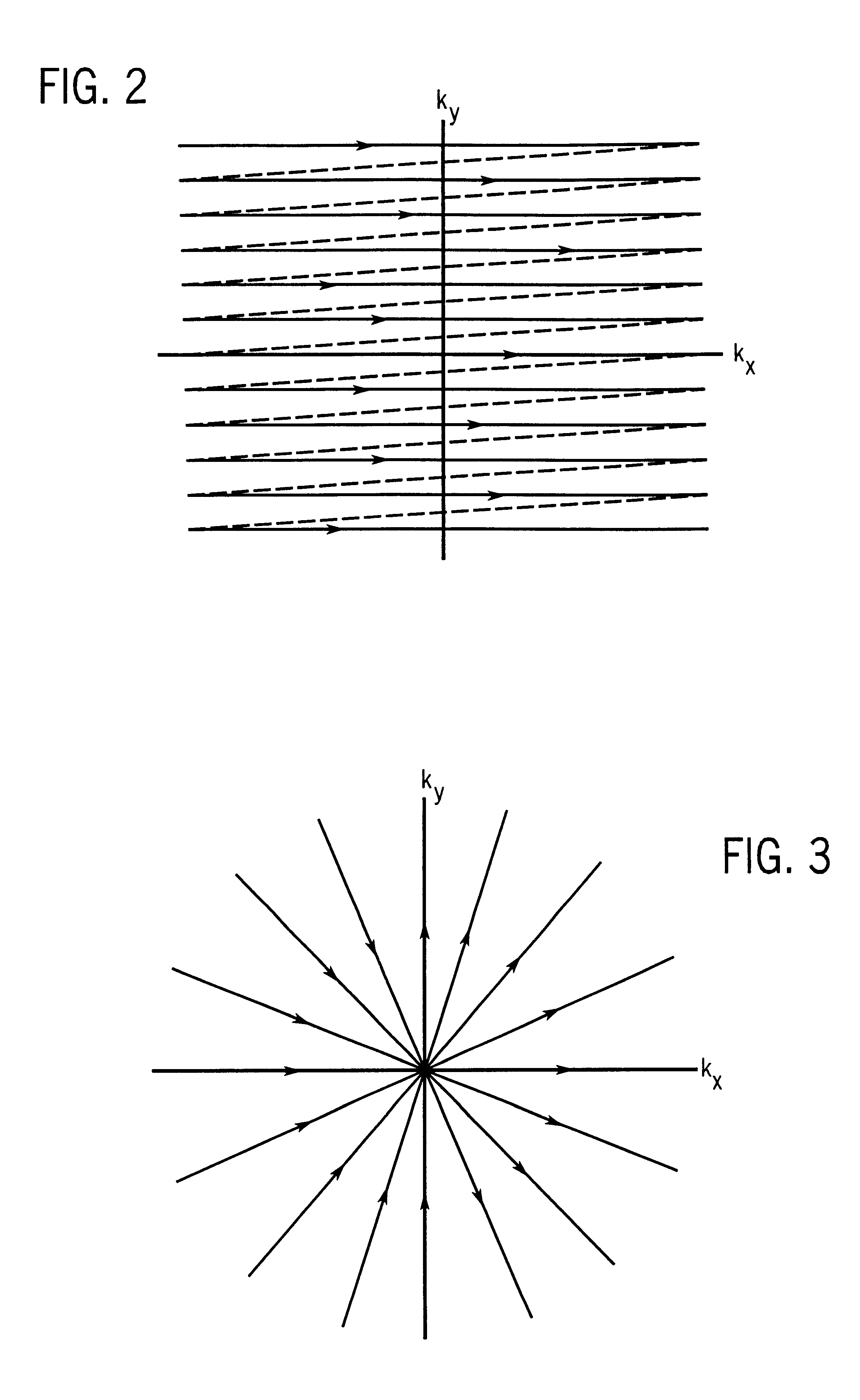
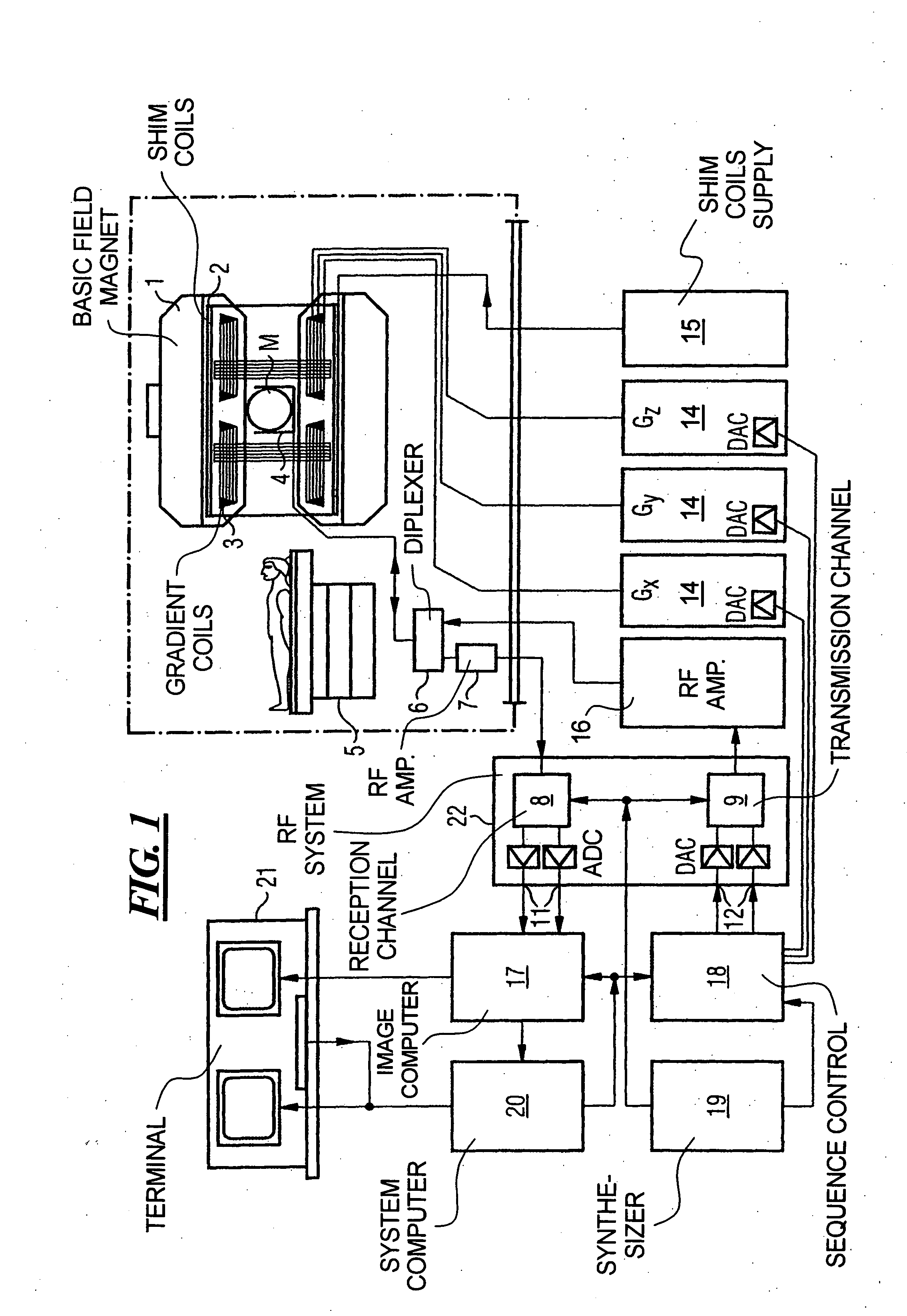
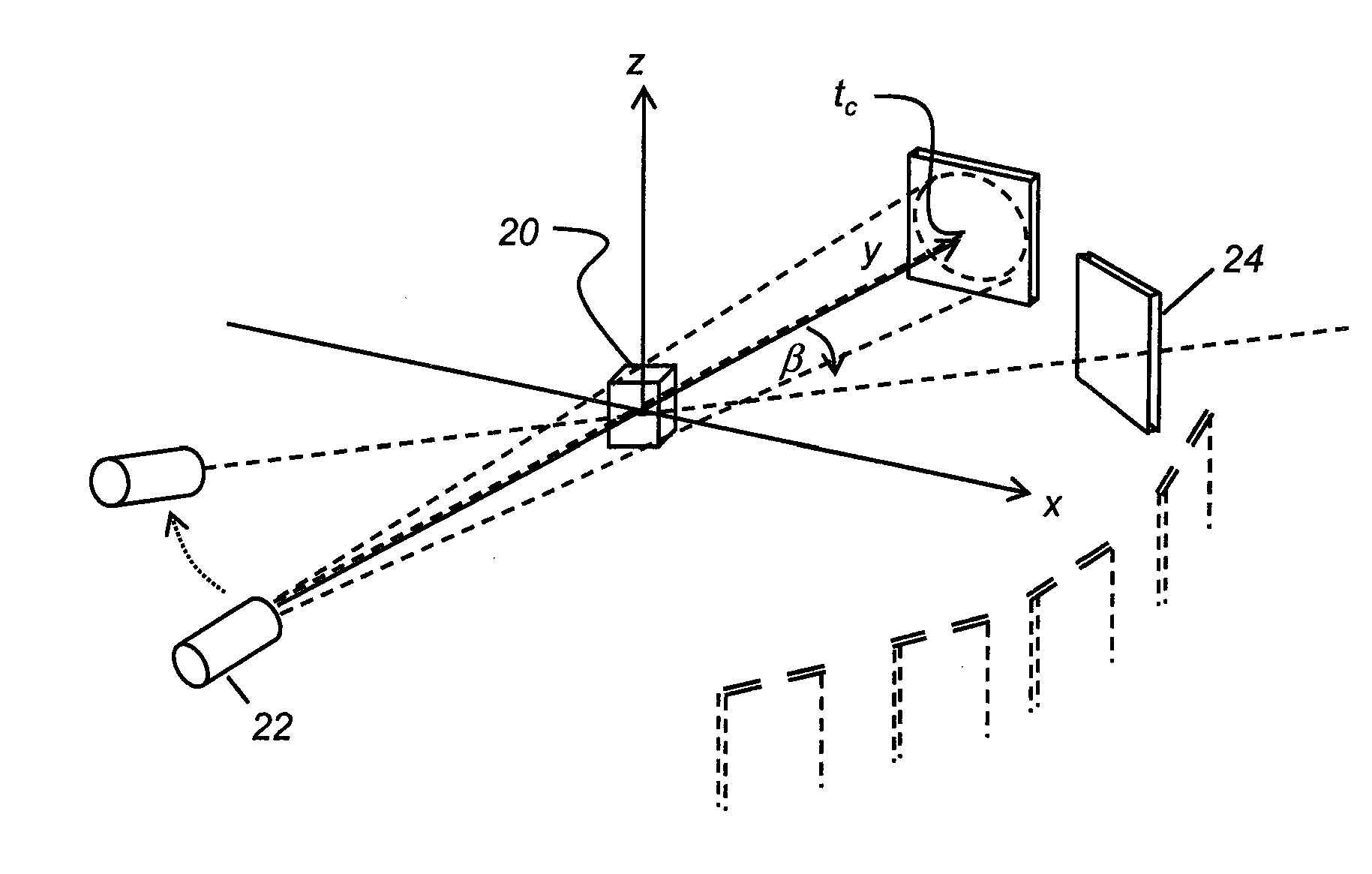
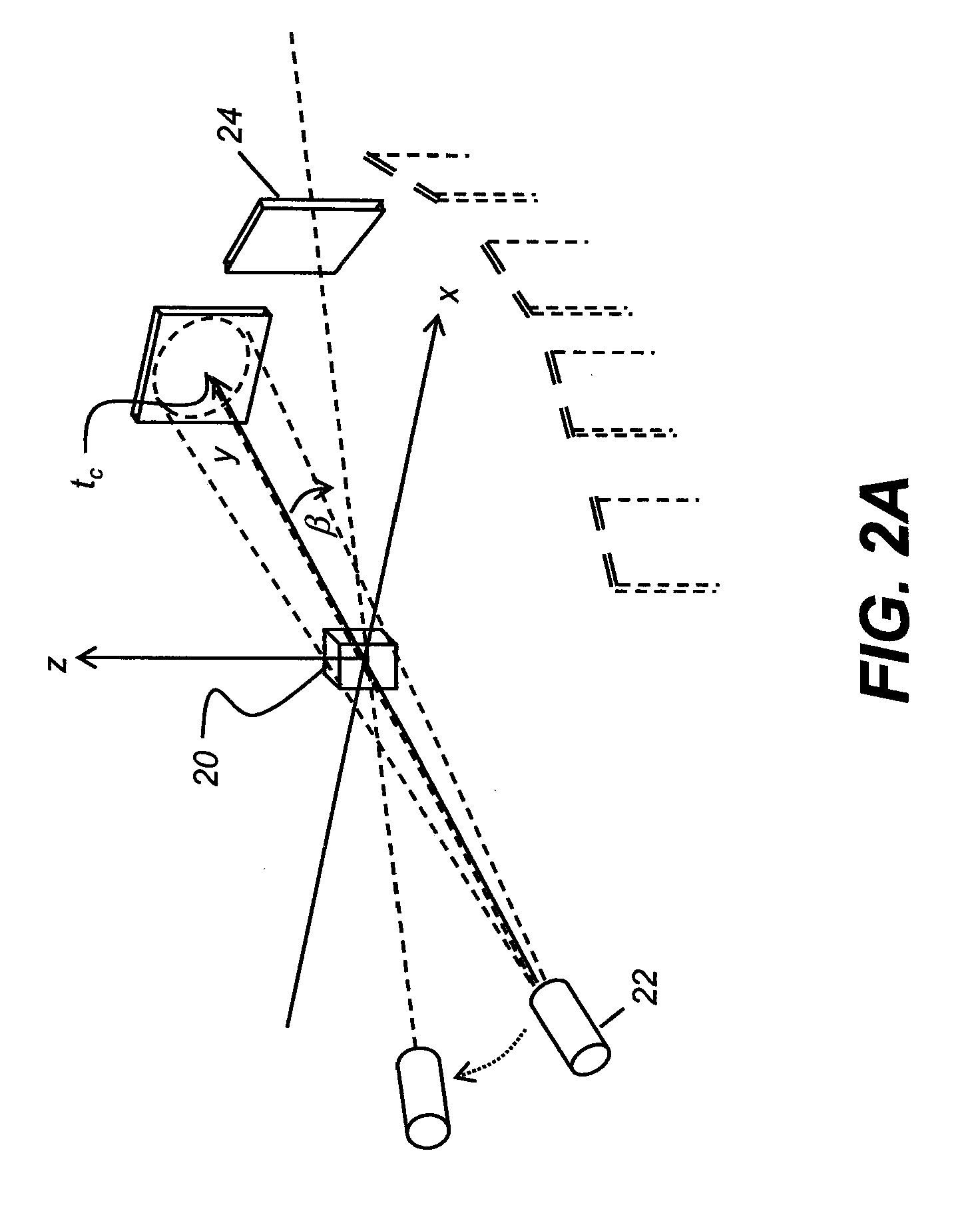
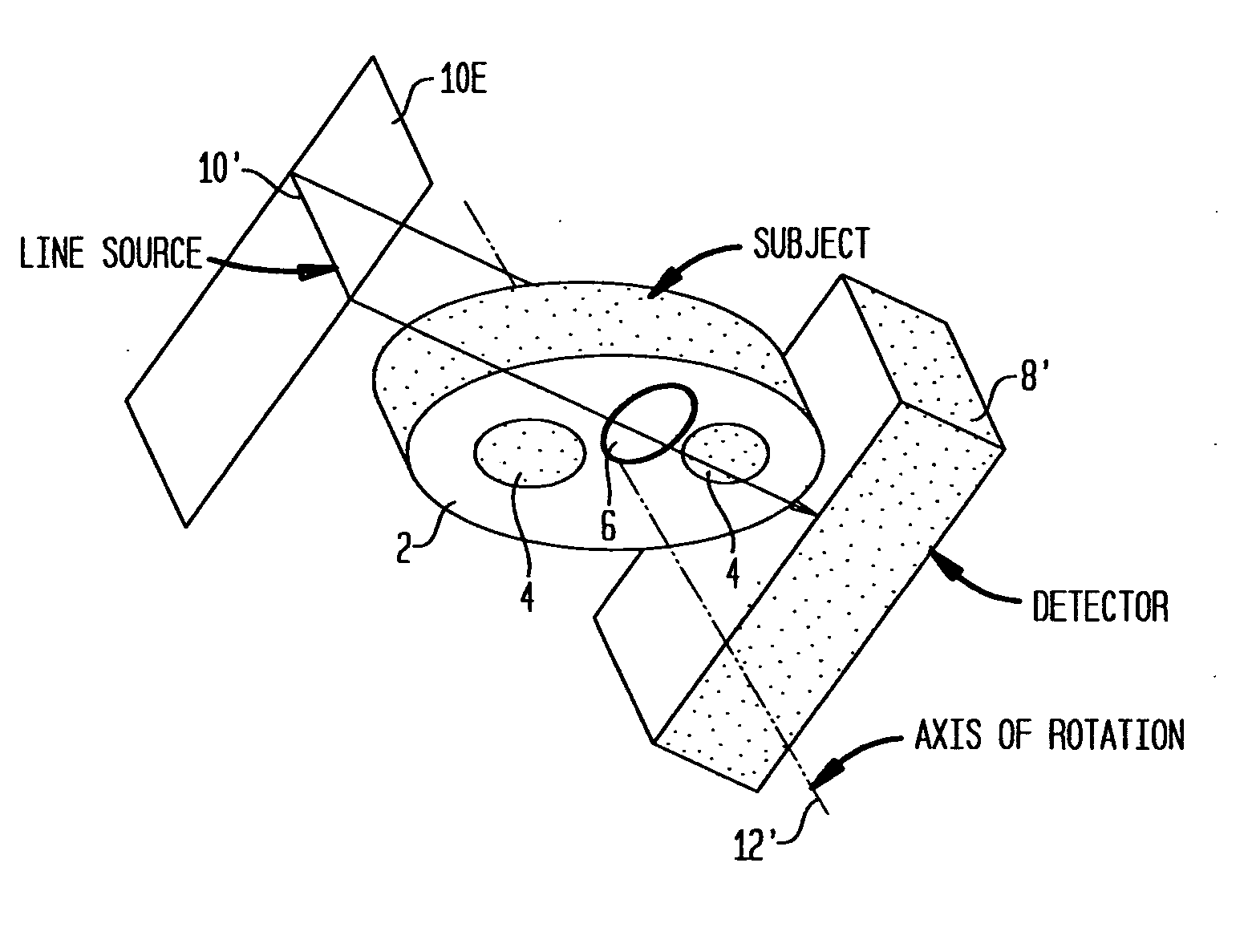
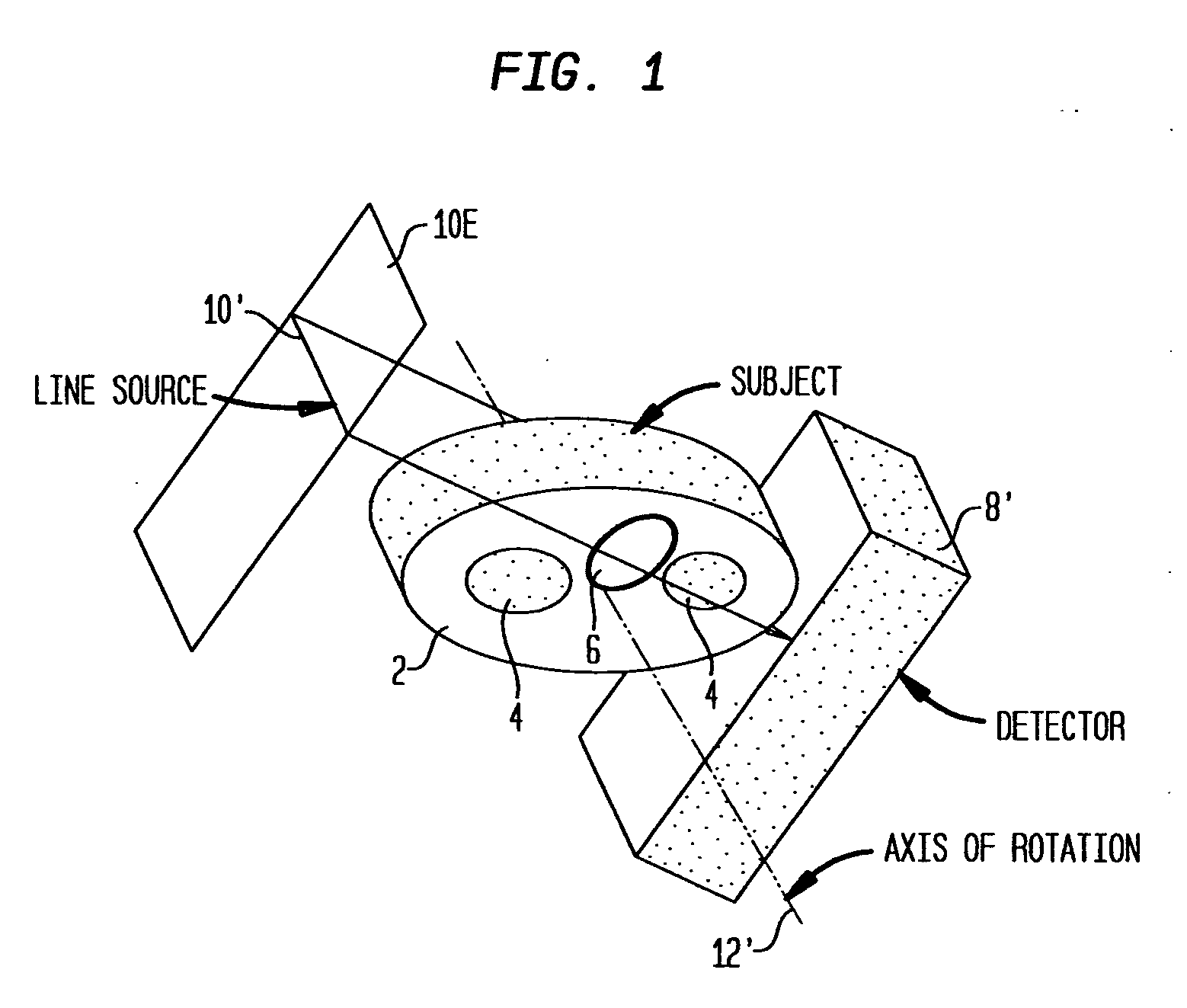
Magnetic resonance angiography using floating table projection imaging
InactiveUS6671536B2Quality improvementOptimal contrast enhancementSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionPhase correctionSingle image
A 3D projection reconstruction pulse sequence is employed to acquire CEMRA data as the subject is continuously moved through the field of view of the MRI system. The acquired k-space data is phase corrected to offset the table motion and the corrected data is used to reconstruct an image over a field of view that far exceeds the size of the MRI system field of view. In one embodiment the image is formed as a set of anatomic subregion images which are concatenated to form a single image and in another embodiment a series of images of each anatomic subregion are produced to depict the dynamic inflow of contrast agent.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
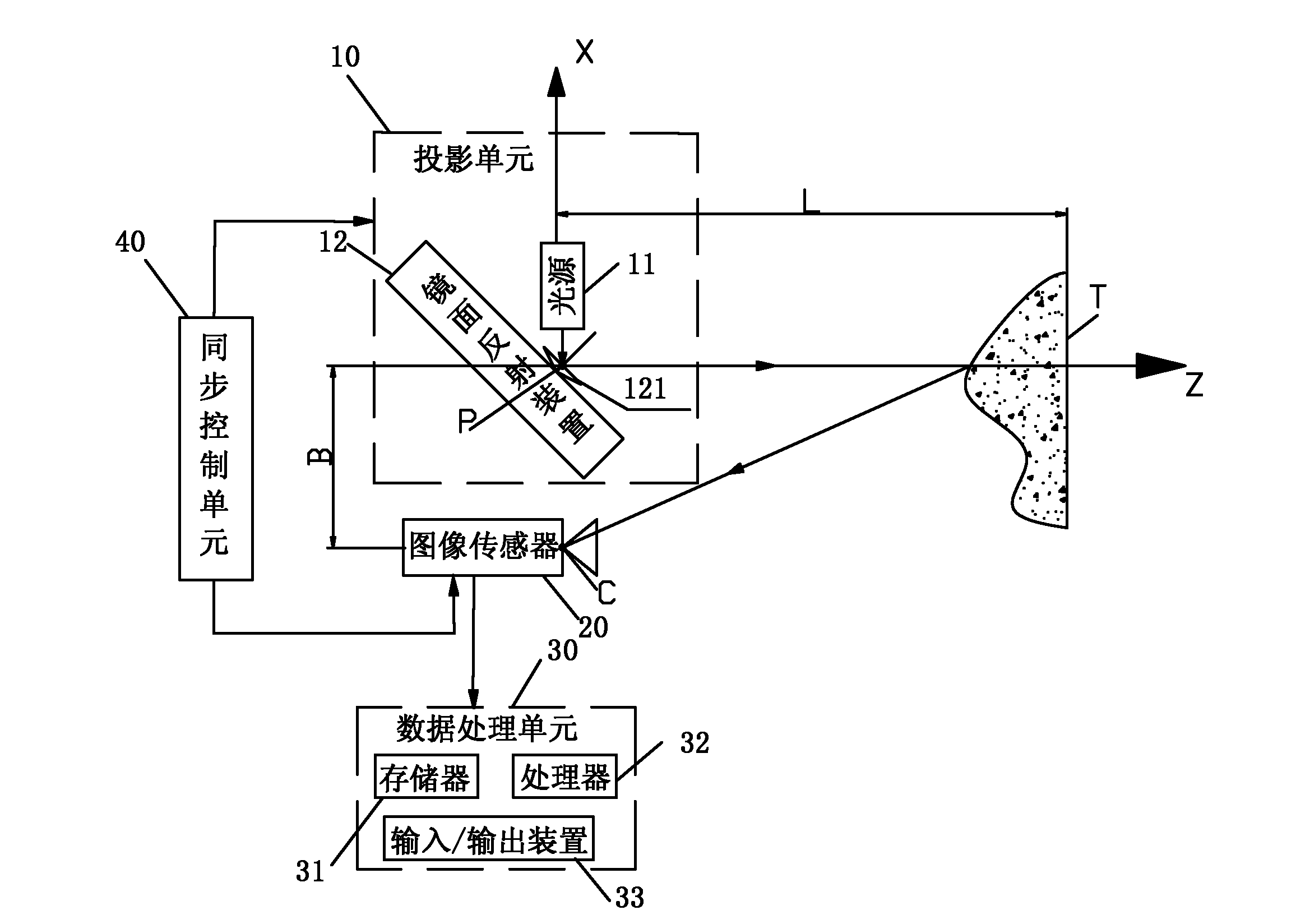
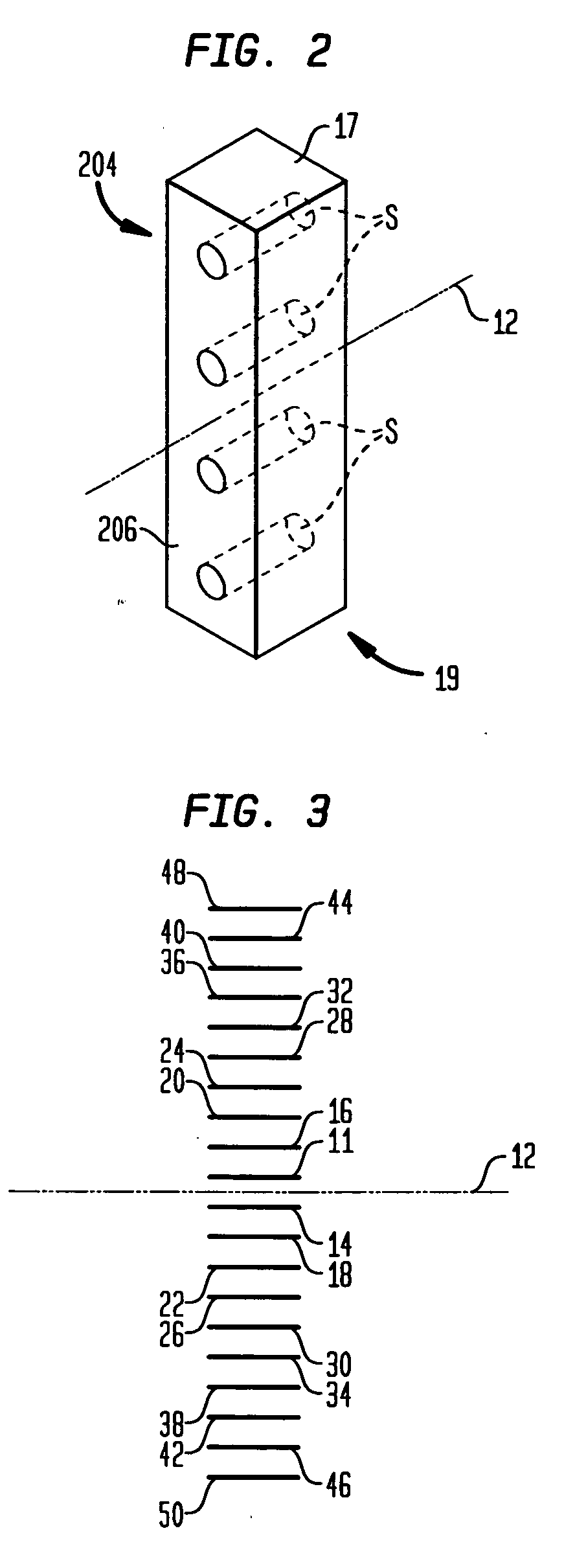
System and method for projection reconstruction
The invention relates to a system and a method for projection reconstruction. The system comprises a projection unit, an image sensor, a synchronous control unit and a data processing unit, wherein the projection unit comprises a light source and a specular reflection device and is used for forming a preset structured light pattern in a target region, and the image sensor is used for carrying outgradual exposure to shoot a projection image of the structured light pattern in at least part of the region; the synchronous control unit is used for controlling the image sensor to realize that at least part of an exposure region of a continuous two-small-frame image is overlapped, and the overlapped part and the projection region of structured light reflected by the specular reflection device synchronize; and the data processing unit receives multi-small-frame image in real time and carried out differential processing of the multi-small-frame image in the projection image and then obtains aprojection image without background light, and calculates three-dimensional (3D) point cloud data. According to needs, the preset structured light pattern can be projected in the target region, and the image sensor is controlled to carry out offset exposure so as to remove the background light to improve accuracy, and thus the three-dimensional depth data of an object in the target region to achieve the projection reconstruction.
Owner:SHENZHEN TAISHAN SPORTS TECH CO LTD
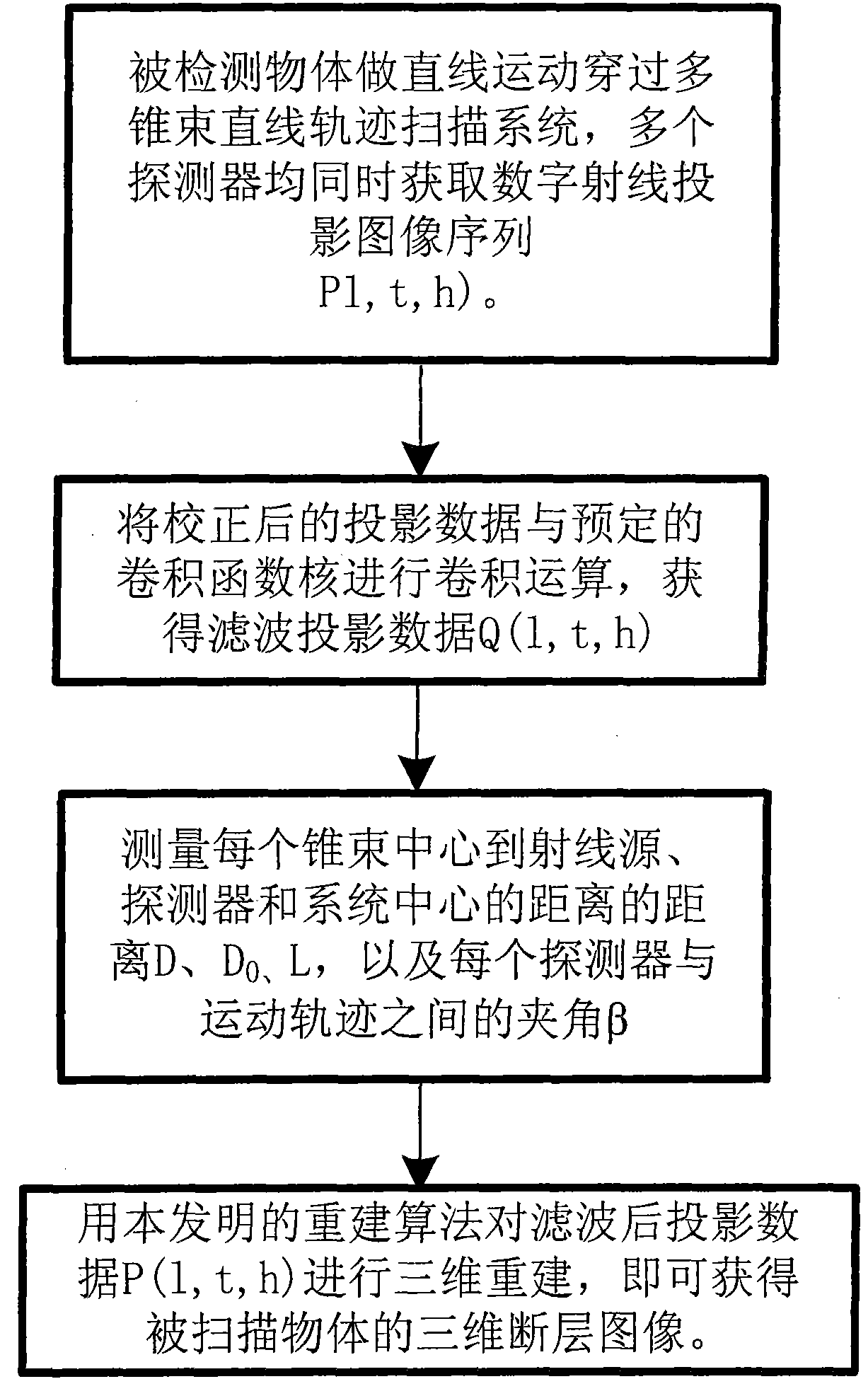
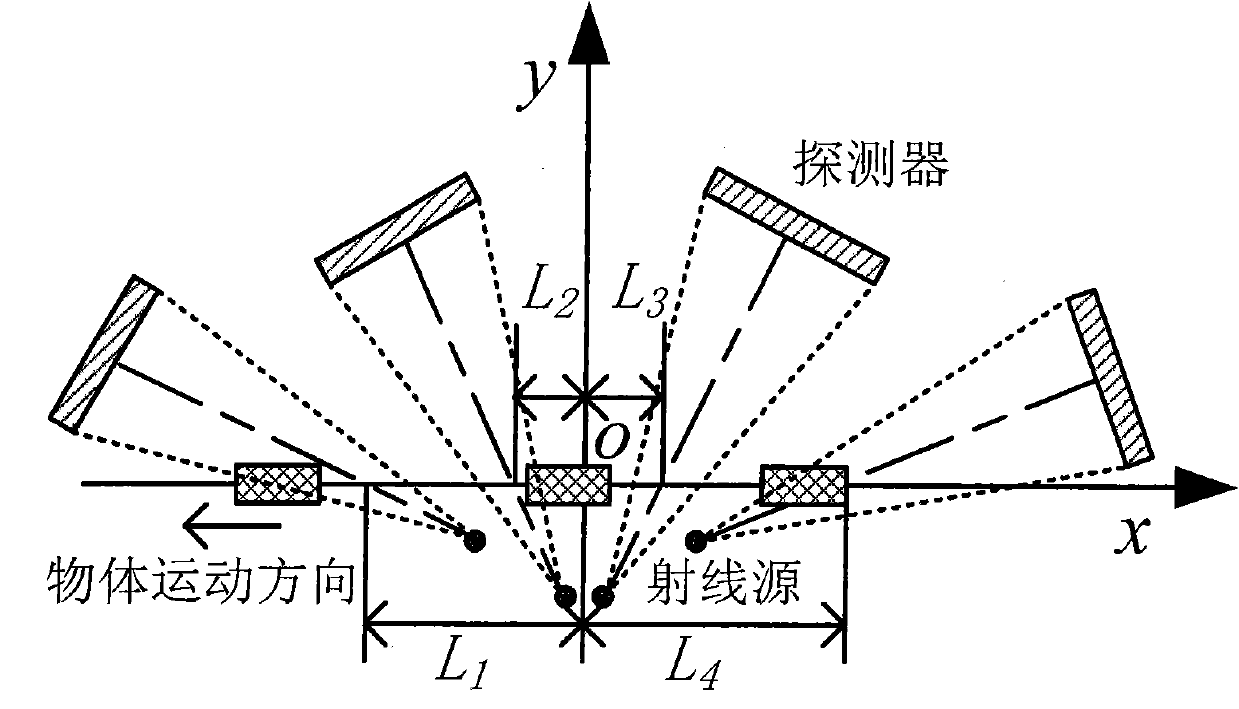
CT imaging method using tilted multi-cone-beam linear track
InactiveCN102004111AScan structure is simpleDetection speedMaterial analysis by transmitting radiation3D modellingLinear motionDigital Ray
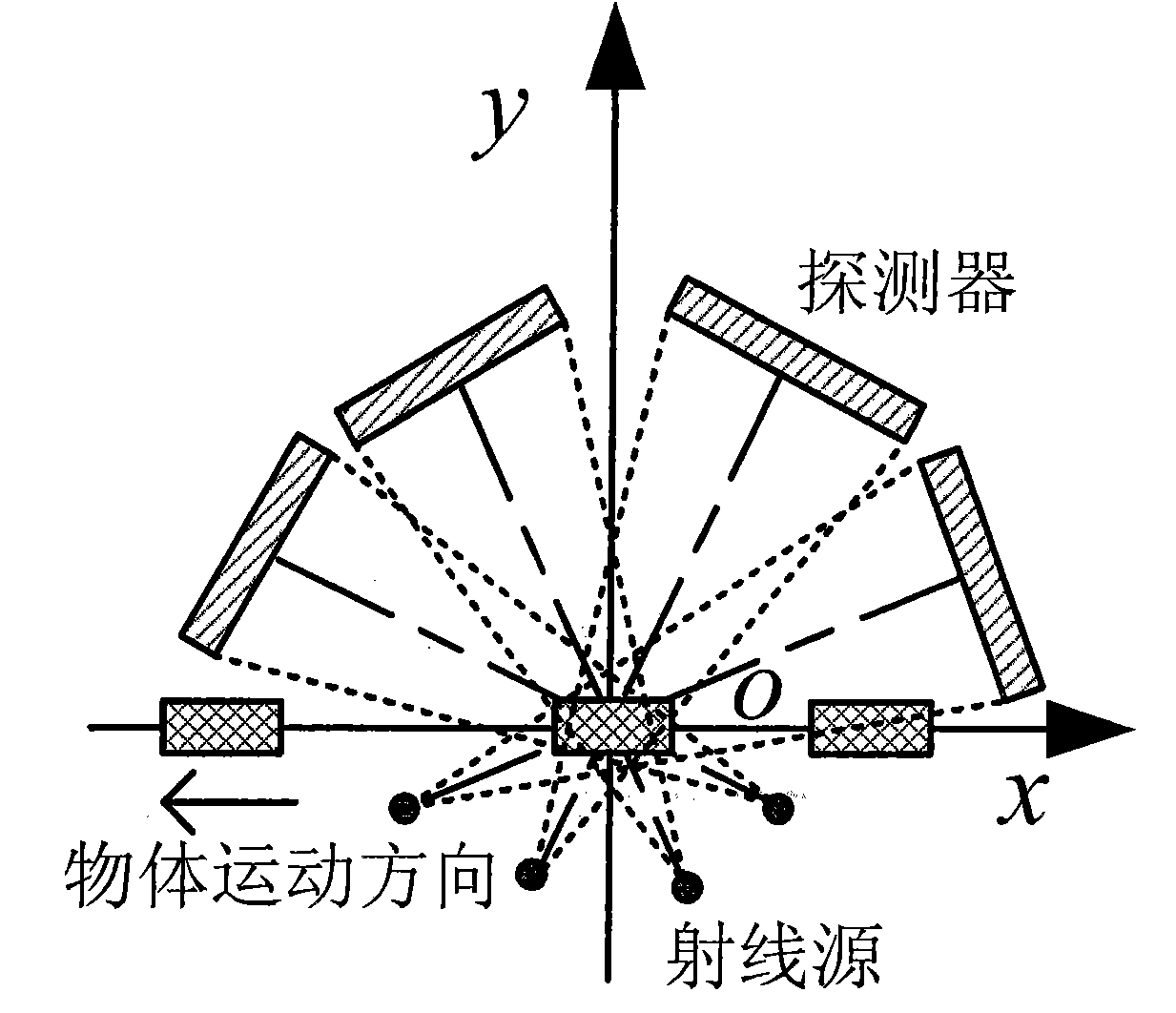
The invention relates to the technical field of X-ray CT imaging testing, which discloses a CT imaging method using a tilted multi-cone-beam linear track. The imaging method comprises the steps of: projection acquisition, wave filtering and back-projection reconstruction, wherein during the projection acquisition, a detector receives rays from a ray source so as to obtain the sequence of digital ray projective images; during the wave filtering, specified filter function and ray projection are subjected to convolution operation to obtain the data of the filtered projection; and during back-projection reconstruction, the weighted back-projection reconstruction of the data of the filtered projection is conducted according to the system parameters. In the method of the invention, a scanning mode using the tilted multi-cone-beam linear track is adopted, multiple cone beams are aslant installed in different places, an object to be tested passes through all the cone beams in linear motion, the detector collects the rays which pass through the object in different directions, and thus the scanning process is simple, and the scanning rate is high; because of the back-projection reconstruction method, the reconstruction rate is high, and the problems of low detecting rate and large object volume are solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Combination method of two-dimensional stitching and three-dimensional surface reconstruction of image
InactiveCN105303615AReduce cumulative errorStitching Angle AdjustmentImage enhancementGeometric image transformationThree-dimensional spaceGlobal optimization
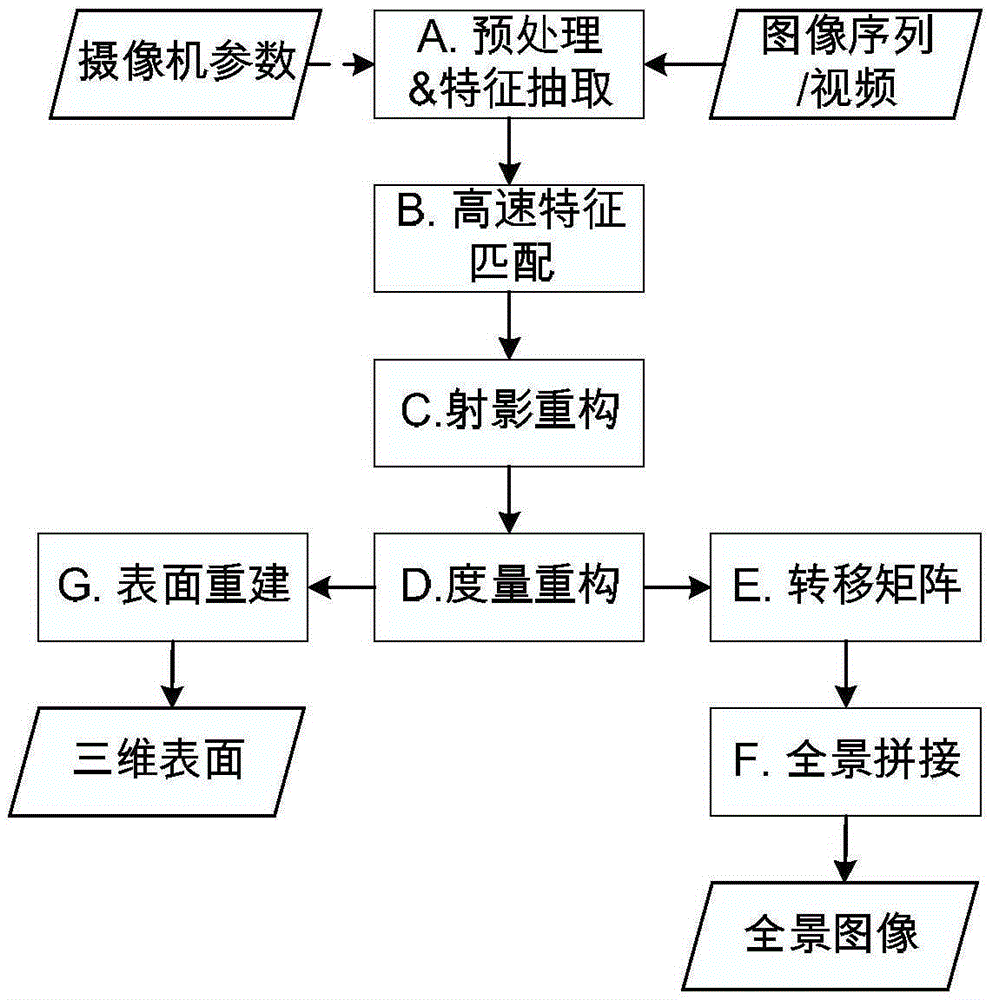
The invention discloses a combination method of the two-dimensional stitching and the three-dimensional surface reconstruction of an image. The combination method comprises the following steps: preprocessing an input image, and extracting feature points; carrying out feature point matching, and screening point sets which succeed in pairing to obtain a multiple-view geometrical corresponding relationship of the feature points; according to the corresponding relationship of the feature points, calculating a projection reconstruction relationship of a scene, and obtaining the relative position and the relative posture of a camera in a three-dimensional space; carrying out metric reconstruction and global optimization; according to the relative position relationship of the camera in the three-dimensional space, selecting a proper visual angle and observation plane, establishing the projection relationships of all images on the observation plane; and carrying out the image stitching and the three-dimensional surface reconstruction. The combination method fully considers the common points and the different points of the two-dimensional stitching and the three-dimensional surface reconstruction technology of the image, extracts common steps in the implementation processes of the two-dimensional stitching and the three-dimensional surface reconstruction, and can simultaneously obtain the panoramic image and the three-dimensional surface of the scene in relatively short time.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Rapid 3-dimensional bilateral breast MR imaging
ActiveUS8135452B2Quick identificationFast samplingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringHigh frame rateParallel imaging
Provided is a method for rapid, 3D, dynamic, projection reconstruction bilateral breast imaging using simultaneous multi-slab volume excitation and radial acquisition of a contrast enhanced bilateral image, in conjunction with SENSE processing, using k-Space Weighted Image Contrast (“KWIC”) filtering and multi-coil arrays for signal separation in an interleaved bilateral MR bilateral breast scan that uses conventional Cartesian sampling without parallel imaging. Software was developed for the reconstruction, modeling contrast kinetics using a heuristic model, display by parametric mapping and viewer / analysis of the multidimensional, high frame-rate bilateral breast images.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
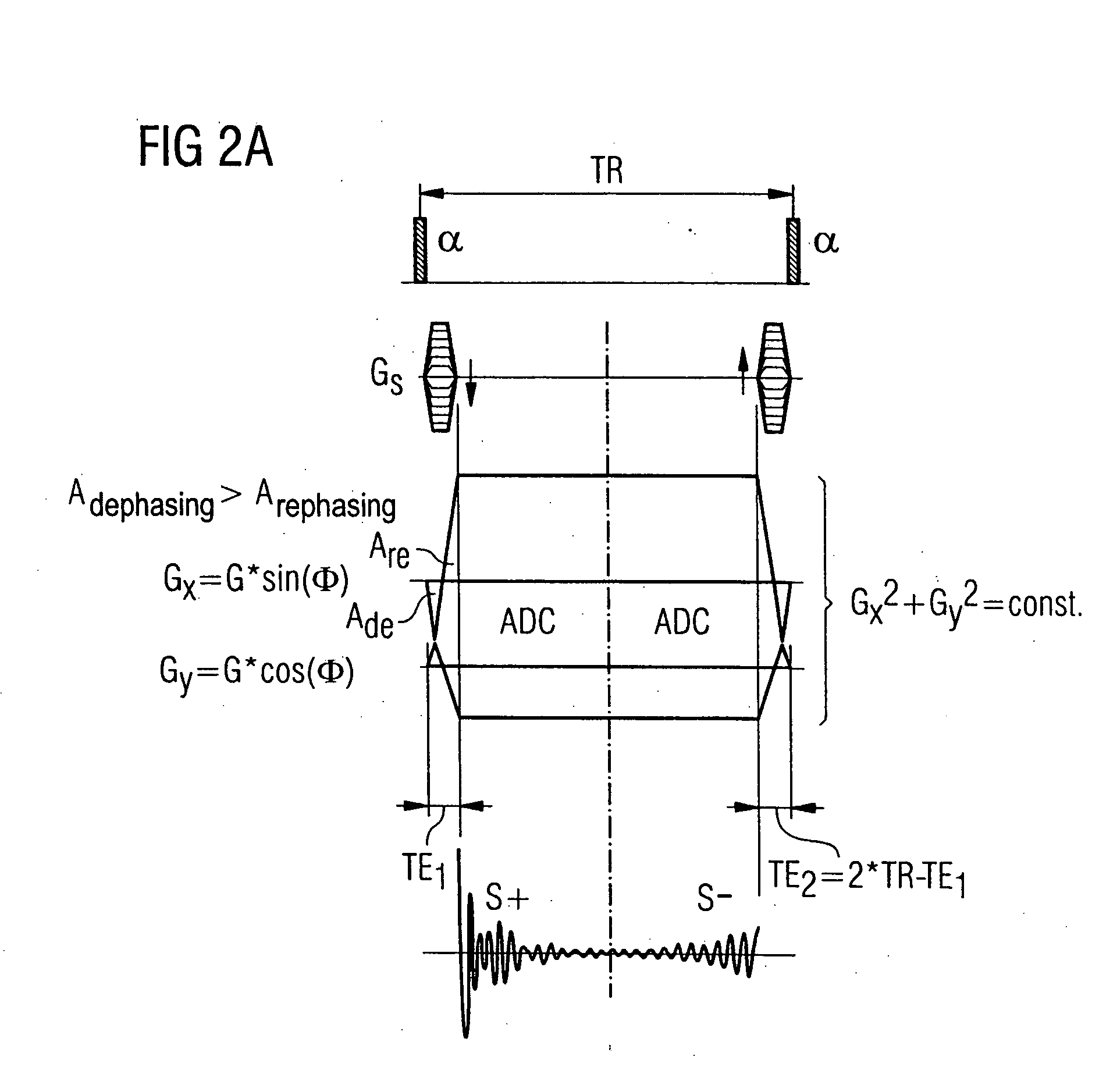
Magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and method for representation of tissue with very short T2 relaxation time
InactiveUS20060036154A1Short T relaxation timeIncrease contrastMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceT2 weighted
In a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and method for determination of T2-weighted images of tissue with short T2 time, in the framework of a steady-state free precession sequence with non-slice-selective RF excitation pulses and projection-reconstruction methods, in each sequence repetition a first steady-state is read out in the form of a half echo and a second steady-state signal is read out in the form of a further half echo with very short echo times TE1 and TE2=2TR−TE1, and are combined by weighted addition such that an MRT image of tissue with very short T2 time is obtained with the sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
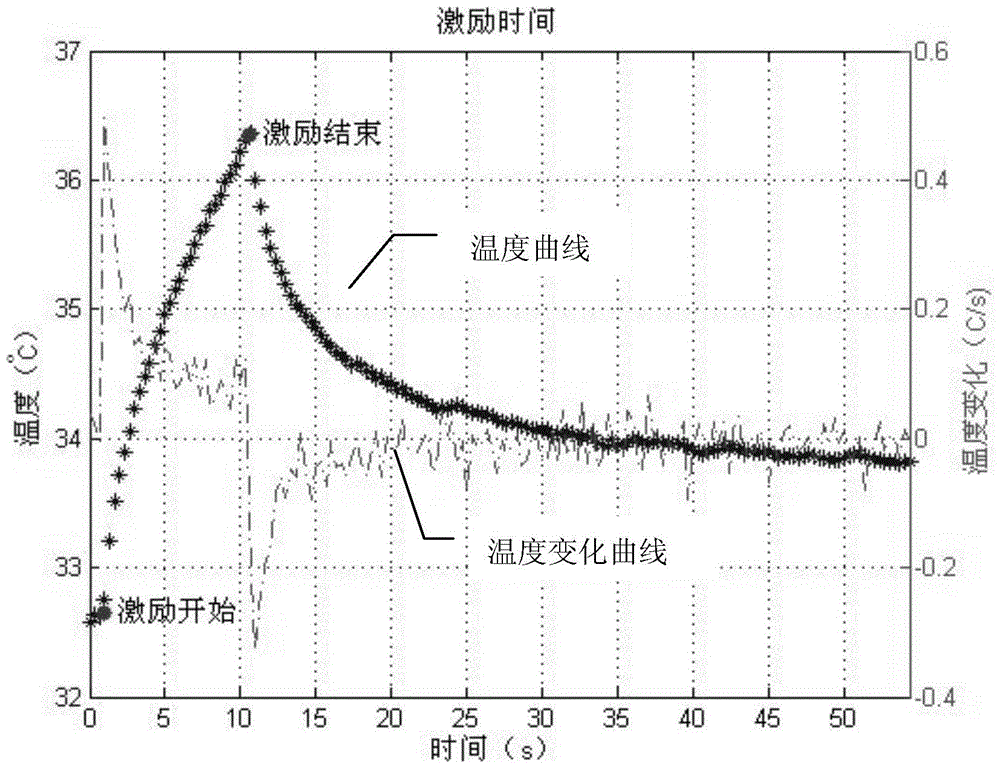
Method for detecting flaw through infrared thermography
InactiveCN105717163AImprove extraction accuracyQuality improvementMaterial flaws investigationStart timeThermodynamics
The invention provides a method for detecting a flaw through infrared thermography. The method comprises the following steps that thermal excitation is performed on a detected test piece, time sequence detection thermal images of the surface of the detected test piece in a period of time before, in and after excitation are acquired through a thermal infrared imager; temperature fitting is performed on the temperature rising stage and the temperature lowering stage; the average temperature is derived to take a maximum value to determine an excitation starting time point and an excitation finishing time point in detection to build time references for analyzing a relationship between the flaw and the time; second derivatives of the average temperature are solved to take an extreme value to determine the precise time when a temperature difference occurs; after excitation is finished, the area size of the flaw is detected, and a threshold value coefficient in a half maximum contrast width method is determined to range from 0.5 to 0.7; a contour surface is constructed in time sequence according to a same image grey value, and a three-dimensional flaw reconstruction result is acquired by adopting a projection method. According to the method, high-precision flaw projection reconstruction can be achieved.
Owner:COMAC +1
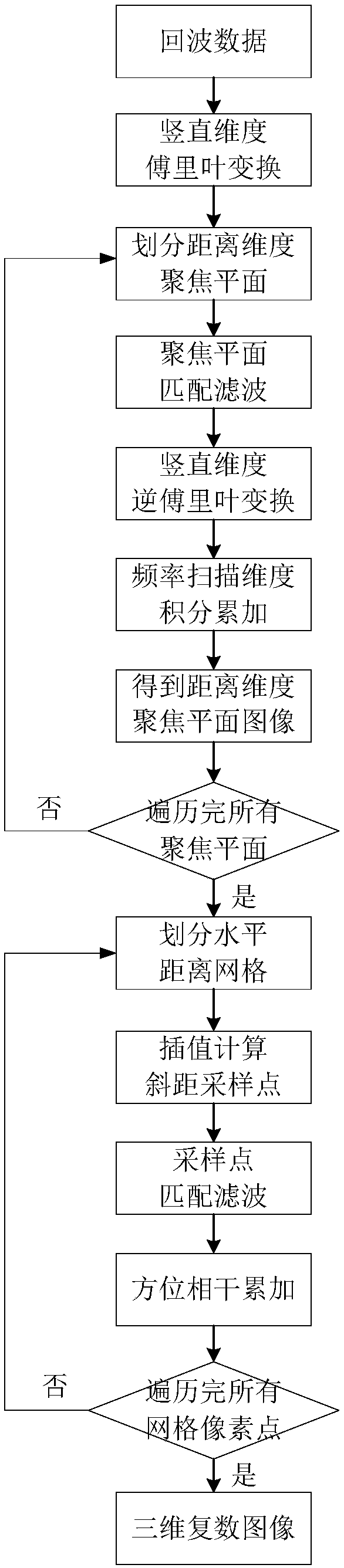
Microwave millimeter wave three-dimensional holographic imaging system signal processing and imaging method
ActiveCN109471193AShorten the development cycleFacilitates motion compensationGeological detection using milimetre wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHolographic imagingReconstruction algorithm
The invention discloses a microwave millimeter wave three-dimensional holographic imaging system signal processing and imaging method. Echo signals are obtained in the microwave millimeter wave antenna array scanning process, and image focusing is carried out on a (y,k) dimension through a phase displacement migration algorithm; image focusing is carried out on the x-dimension by adopting a backward projection reconstruction method; finally, a three-dimensional complex image of an imaging target is obtained. The method integrates the characteristics of a time domain imaging algorithm and a frequency domain imaging algorithm, decoupling and imaging focusing are carried out on a vertical array dimension and a distance dimension through the phase displacement migration algorithm, the backwardprojection reconstruction algorithm is used for imaging focusing of a planar or cylindrical motion scanning dimension, and the advantages that the backward projection reconstruction algorithm is suitable for any antenna scanning rack and capable of facilitating motion compensation are used, so that the method is suitable for a microwave millimeter wave planar scanning imaging system and a microwave millimeter wave cylindrical scanning imaging system, the aim of being applicable to the two kinds of imaging systems though one-time algorithm development can be achieved, clear imaging can be achieved, and the calculation efficiency is higher.
Owner:博微太赫兹信息科技有限公司
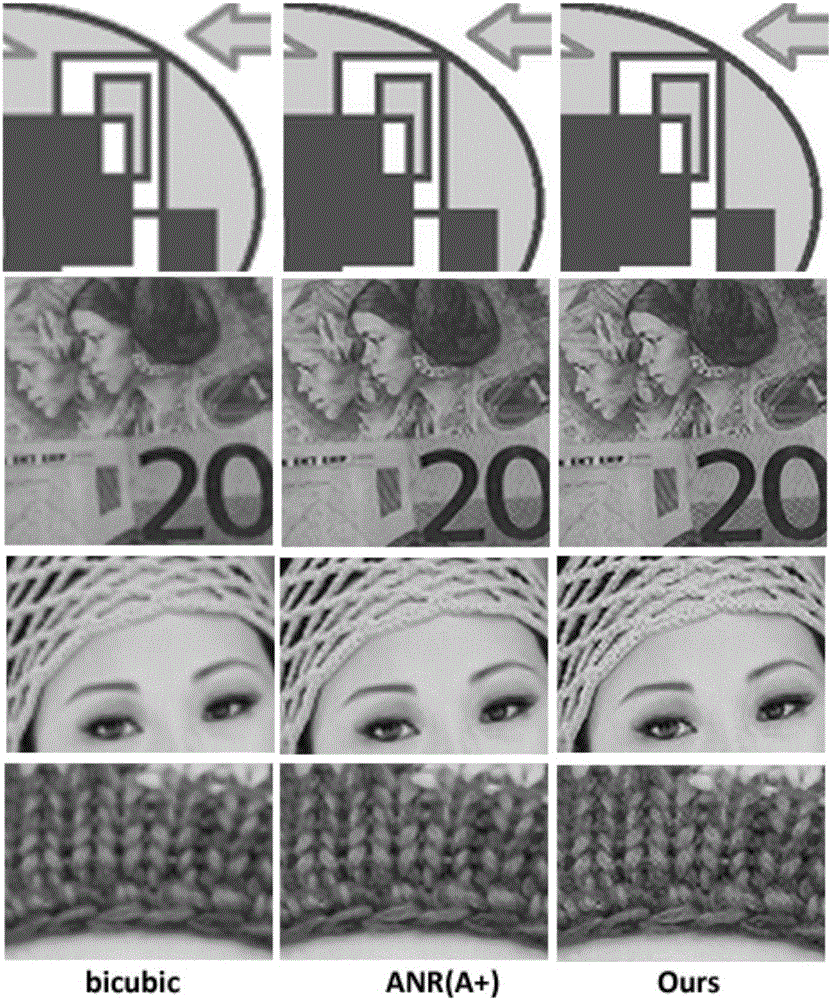
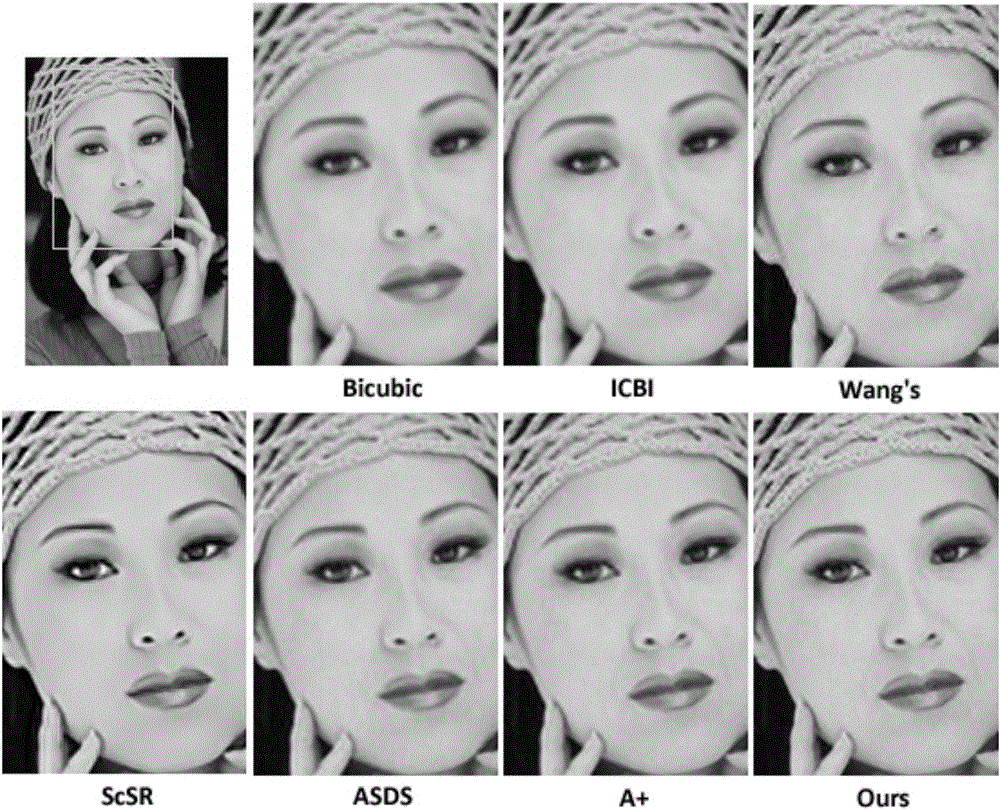
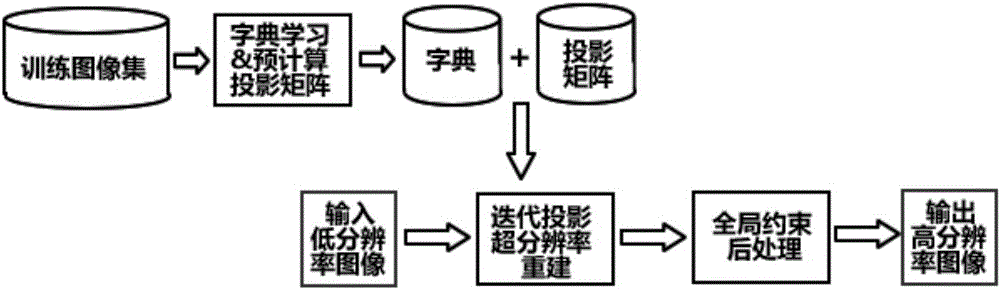
Dictionary-type image super-resolution system and method based on iteration projection reconstruction
ActiveCN105023240ACalculation speedEliminate unnatural effectsGeometric image transformationHat matrixDictionary learning
The invention provides a dictionary-type image super-resolution system and method based on iteration projection reconstruction. The system comprises a dictionary training and pre-calculation matrix prediction module, an iteration projection super-resolution reconstruction module based on a projection matrix and a post-processing module based on global restriction. The method comprises steps: firstly, dictionary learning and projection matrix calculation are carried out; secondly, iteration projection super-resolution reconstruction based on a projection matrix is carried out, namely, y is inputted into a low-resolution image block, an atom most similar to y is searched in a dictionary, y is subjected to super-resolution reconstruction by utilization f the projection matrix of the atom, the generated residual vector is subjected to projection reconstruction, high-resolution reconstruction of the residual vector is obtained, iteration reconstruction is carried out in the above way, finally all the reconstruction components are subjected to weighing addition and the sum is employed as the reconstruction result; thirdly, the reconstruction image is subjected to global restriction to eliminate the unnatural effect. The calculation speed of the dictionary-type method can be raised effectively and image high-frequency detail information can be recovered.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Noise suppression in cone beam ct projection data
InactiveUS20110150307A1Degrade image reconstructionSuppress noiseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionData setRadiology
A method for suppressing noise in a diagnostic 3-D image, executed at least in part on a logic processor, captures, at each of a number of projection angles, 2-D image projection data, wherein each 2-D image projection has a central pixel and arranges the 2-D image projection data to form a 3-D data set. Each of the 2-D image projections is processed by performing a diffusion filtering process that obtains a homogeneity value for the 3-D data set, generates a diffusion conductance function according to an intensity gradient between adjacent digital image elements, and applies the diffusion filtering process to digital image elements according to the obtained homogeneity value, the generated diffusion conductance function, and a weighting value that relates to the distance of each pixel in the projection from the central pixel. The diagnostic 3-D image is reconstructed from the processed 2-D image projections.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
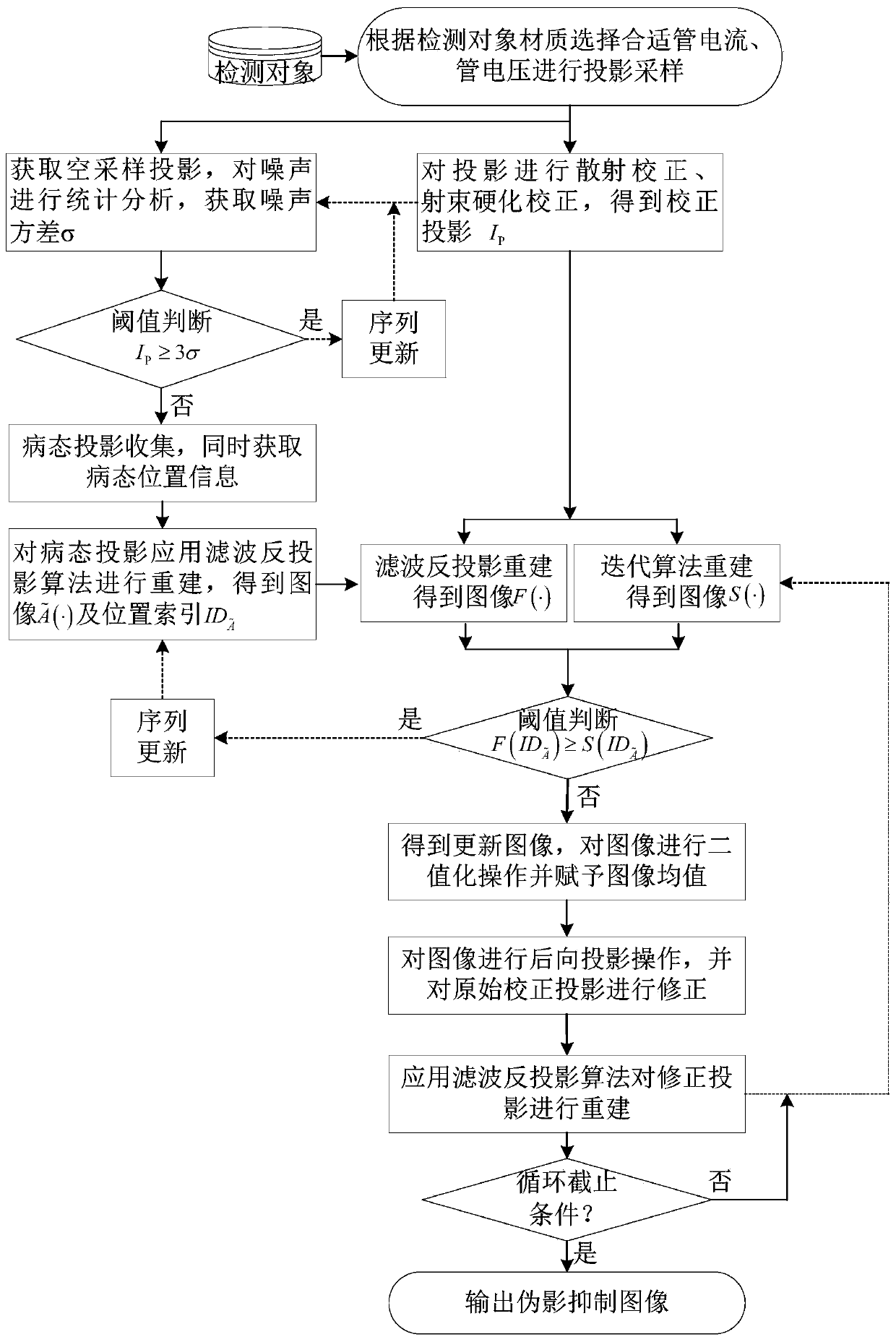
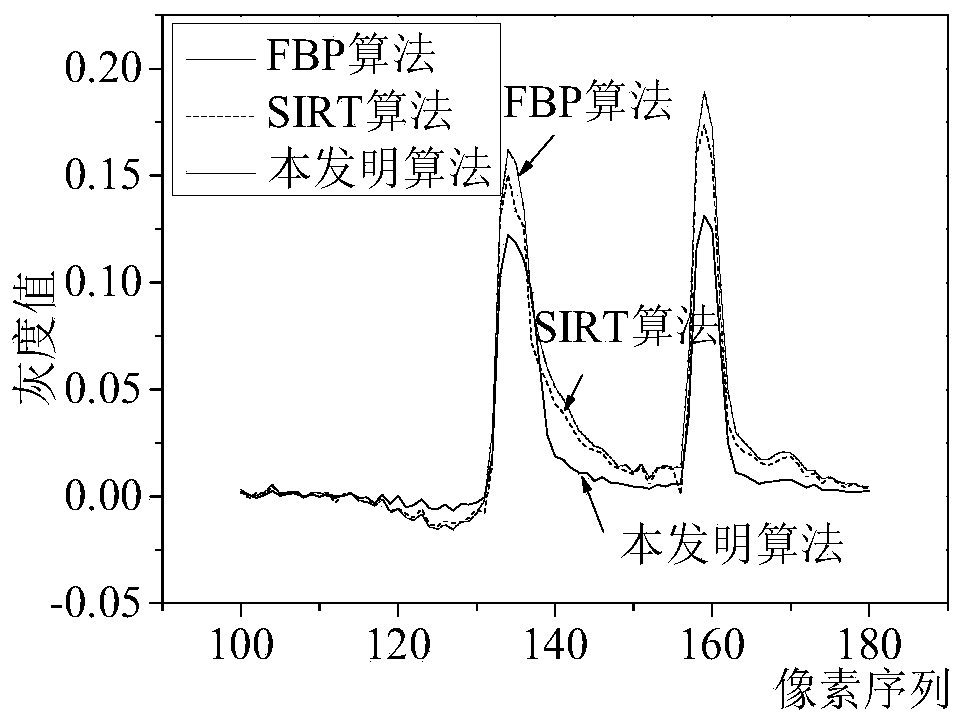
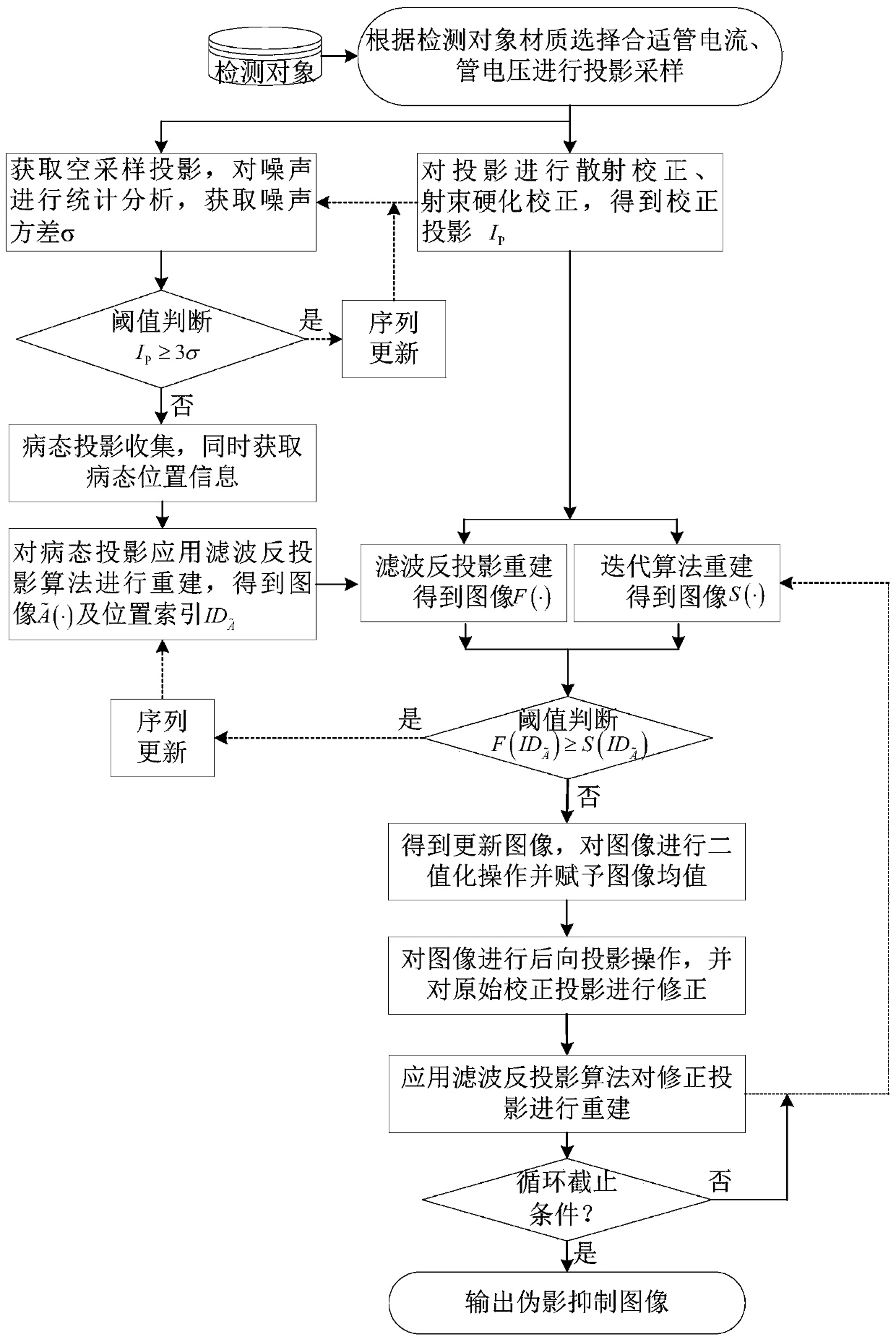
A cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact inhibition method
ActiveCN109920020AReduce distractionsReduce the impactImage enhancementImage analysisArtifact suppressionBack projection
The invention discloses a cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact inhibition method. By utilizing the accuracy of a filtering back projection algorithm and the noise suppressionadvantage of an iterative algorithm, reconstruction image fusion of an analytical algorithm and an iterative algorithm and an iterative updating method, ill-conditioned projection reconstruction artifact suppression is realized, the signal-to-noise ratio of the image is improved, and artifact interference caused by ill-conditioned projection reconstruction is prevented. The cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact inhibition method is suitable for the projection reconstruction artifact inhibition under the conditions of normal projection and less ill-condition projection angles, is good in reliability, stability and noise resistance, can reduce the interference and influence of the cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact on the image to a great extent, and obviously improves the quality of the cone beam CT image.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
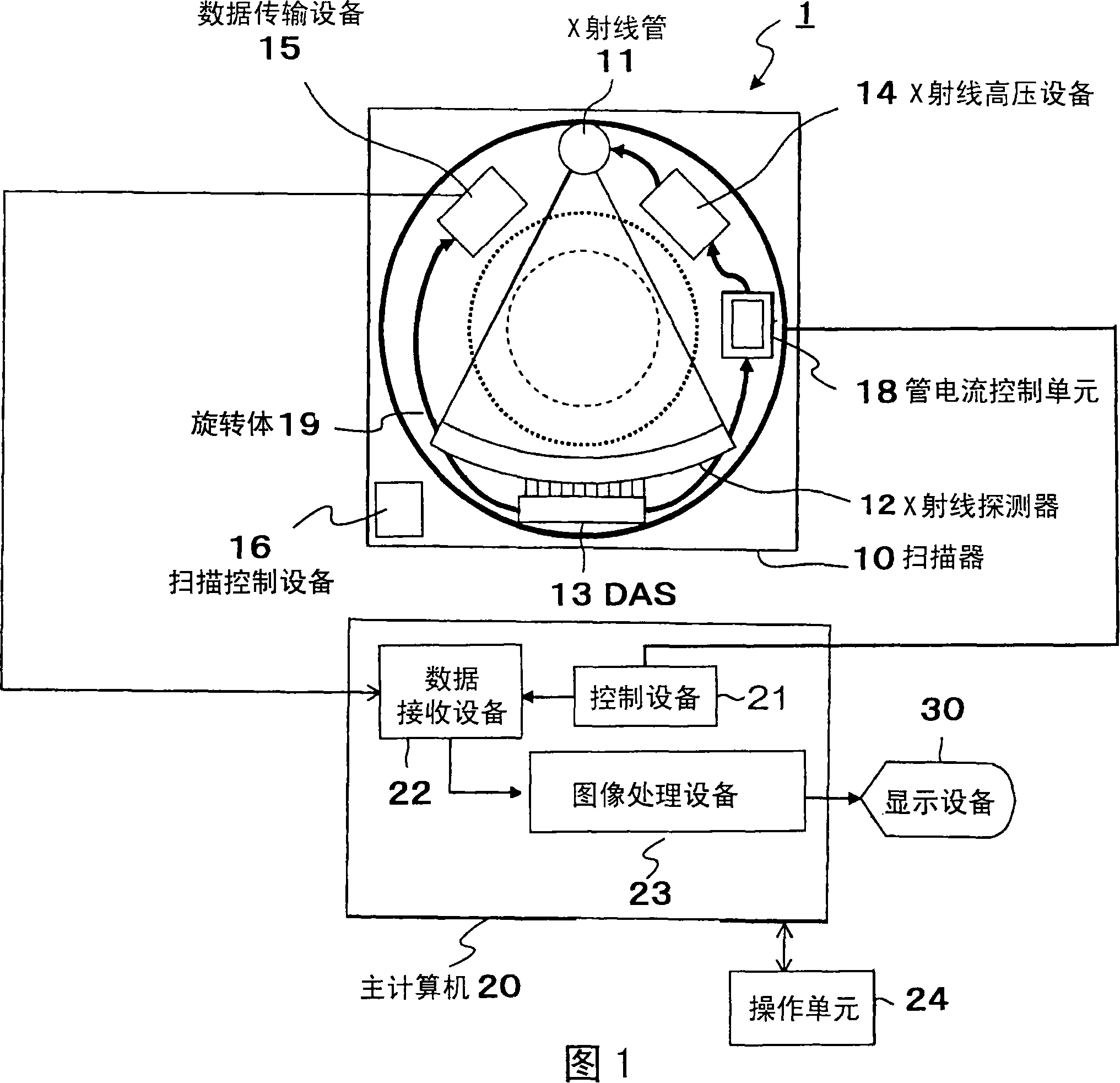
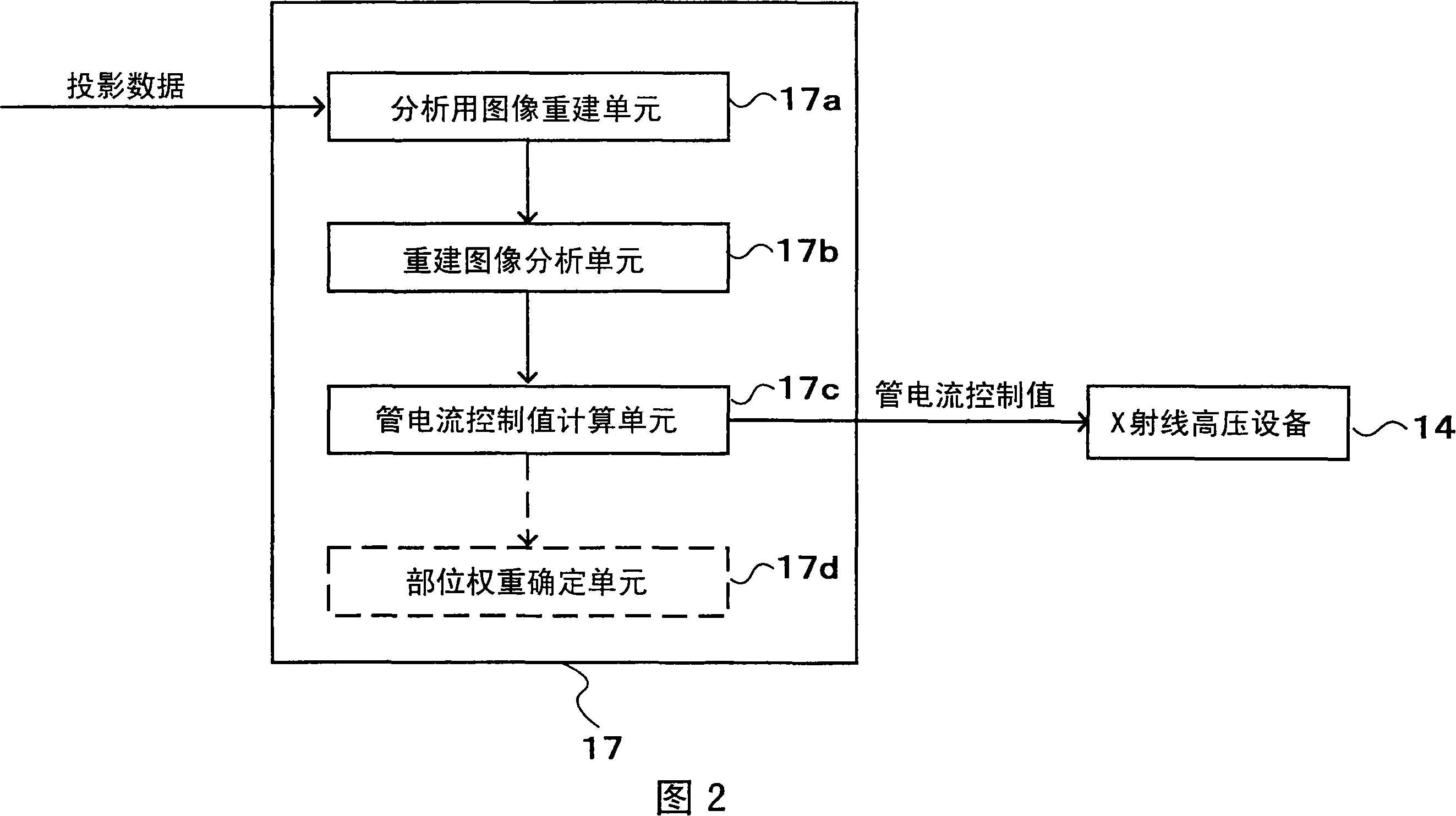
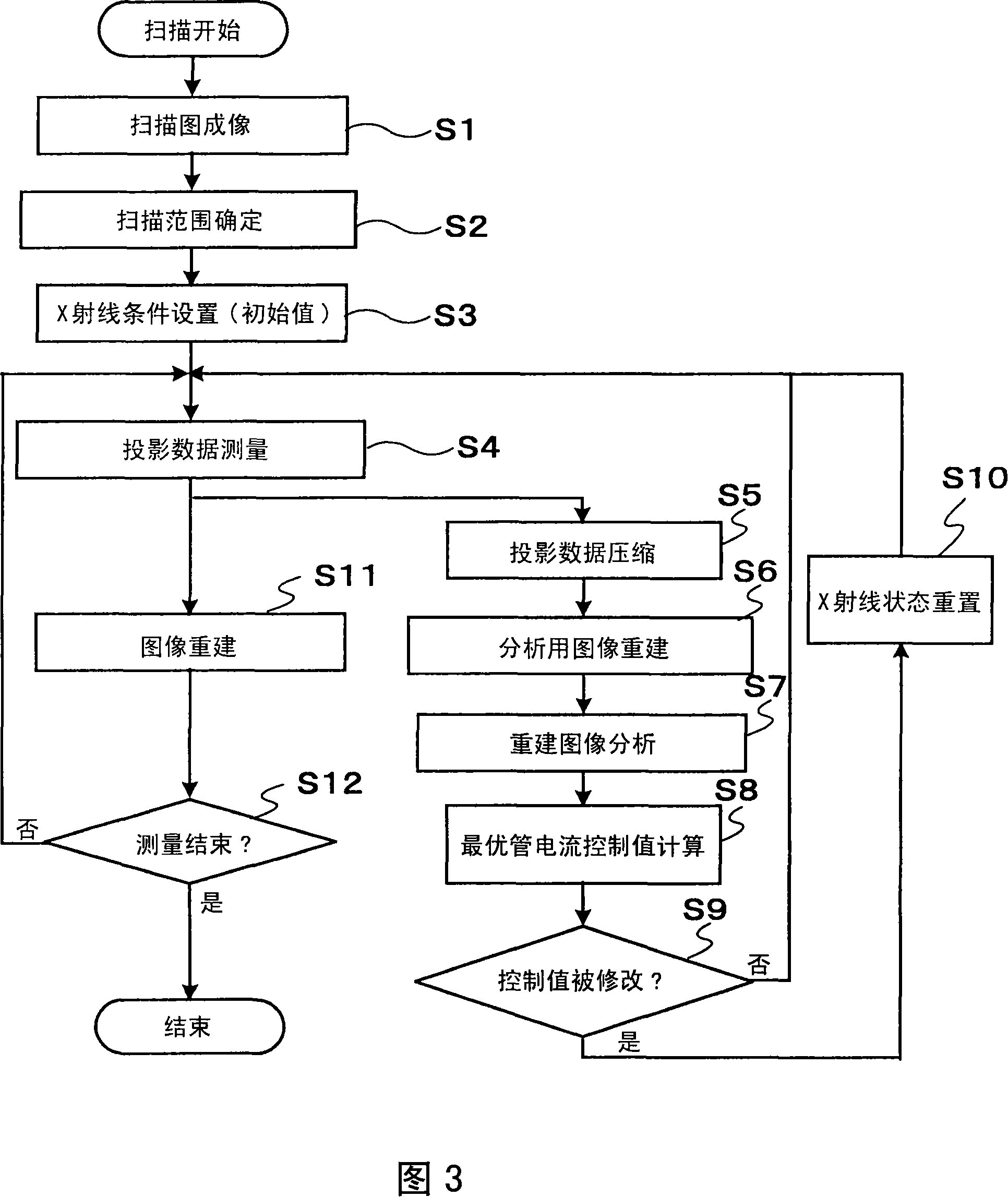
X-ray ct apparatus
InactiveCN101128153AQuality improvementComputerised tomographsTomographyX-rayProjection reconstruction
An X-ray CT device, comprising: an X-ray source for irradiating X-rays to a subject; an X-ray detector placed opposite to the X-ray source so that the subject is located between the X-ray detector and the X-ray source , and is used to detect X-rays transmitted through the subject as projection data; the rotating device rotates the X-ray source and the X-ray detector; the control device rotates the X-ray tube and the X-ray detector from the rotating device The obtained projection data is collected in multiple angle directions, the collected projection data is reconstructed and calculated to generate a tomogram of the subject, and the X-ray source and the rotating device are controlled; and a display device is used to display the generated tomogram. The X-ray CT apparatus further includes: a projection data analysis device for reconstructing a tomogram of an imaging site for analysis of the subject from the projection data, and generating a control curve by re-projecting the reconstructed tomographic image; a tube current control device, The value of the current fed into the X-ray tube is controlled according to the generated control curve.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
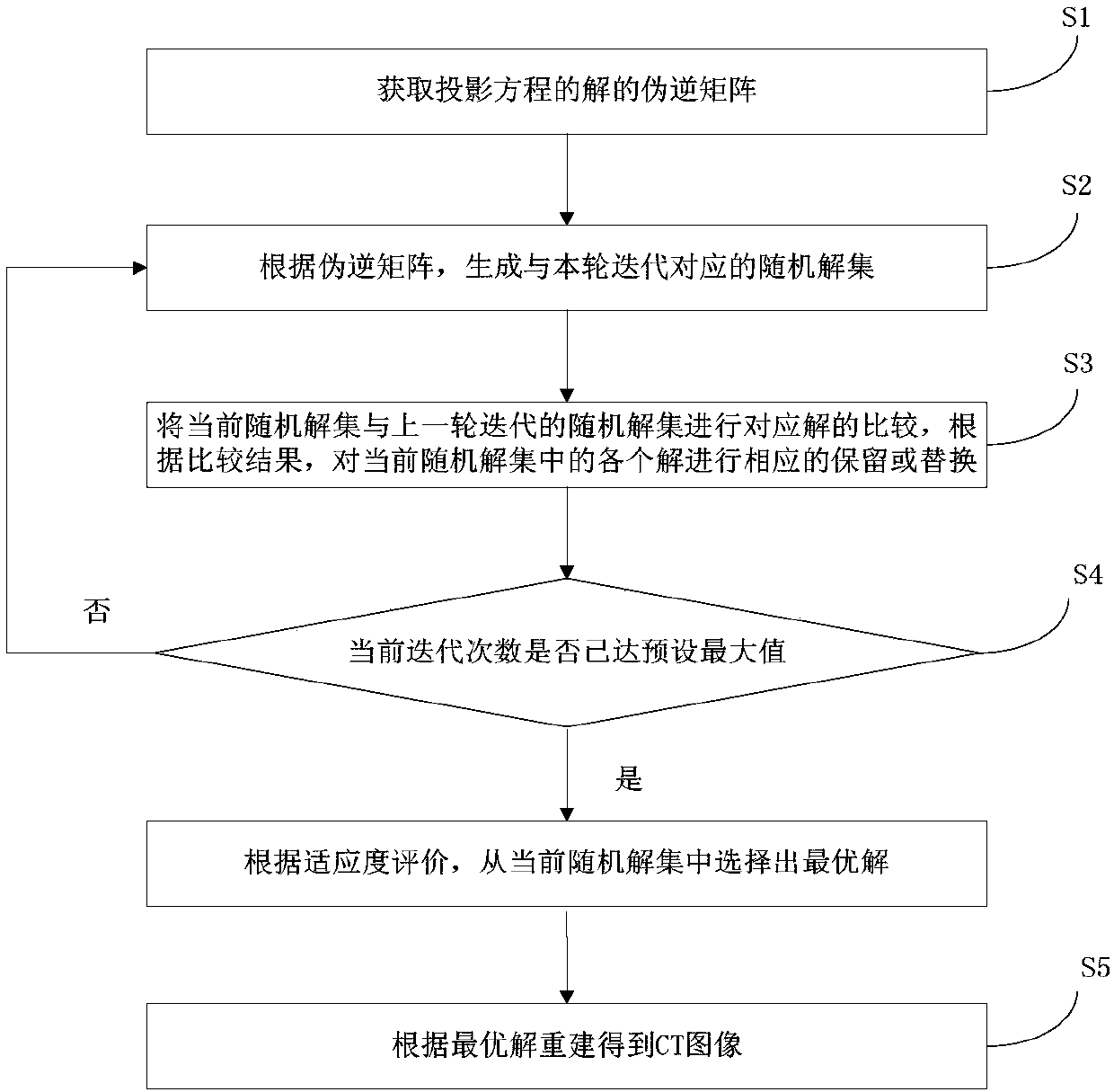
CT sparse projection image reconstruction method and CT sparse projection image reconstruction device at limited sampling angle
ActiveCN108280859AQuality assuranceDiversity guaranteedReconstruction from projectionImage generationImaging processingProjection image
The invention discloses a CT sparse projection image reconstruction method and a CT sparse projection image reconstruction device at a limited sampling angle. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a pseudo-inverse matrix of a projection equation according to projection data, generating a random solution set according to the pseudo-inverse matrix, reserving or replacing each solution in the current random solution set correspondingly, selecting an optimal solution from the current random solution set when the number of iterations reaches a preset maximum value, and adopting the selected optimal solution as a to-be-obtained reconstruction result. The device comprises a memory for storing at least one program and a processor for loading at least one program to execute the method of theinvention. According to the method, the pseudo-inverse of a discretized projection reconstruction equation is used as an initial solution of the algorithm, so that the quality of the initial solutionis guaranteed. A set of solutions are generated through random walk, and then the iterative optimization is carried out respectively. The diversity of optimization paths is guaranteed. Troubles causedby the defects of an initial solution and an iteration path of a traditional reconstruction method can be overcome. The method and the device are applied to the technical field of image processing.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Three-dimensional x-ray imaging
ActiveUS20150036905A1Reconstruction from projectionX-ray/infra-red processesIntermediate imageComputer graphics (images)
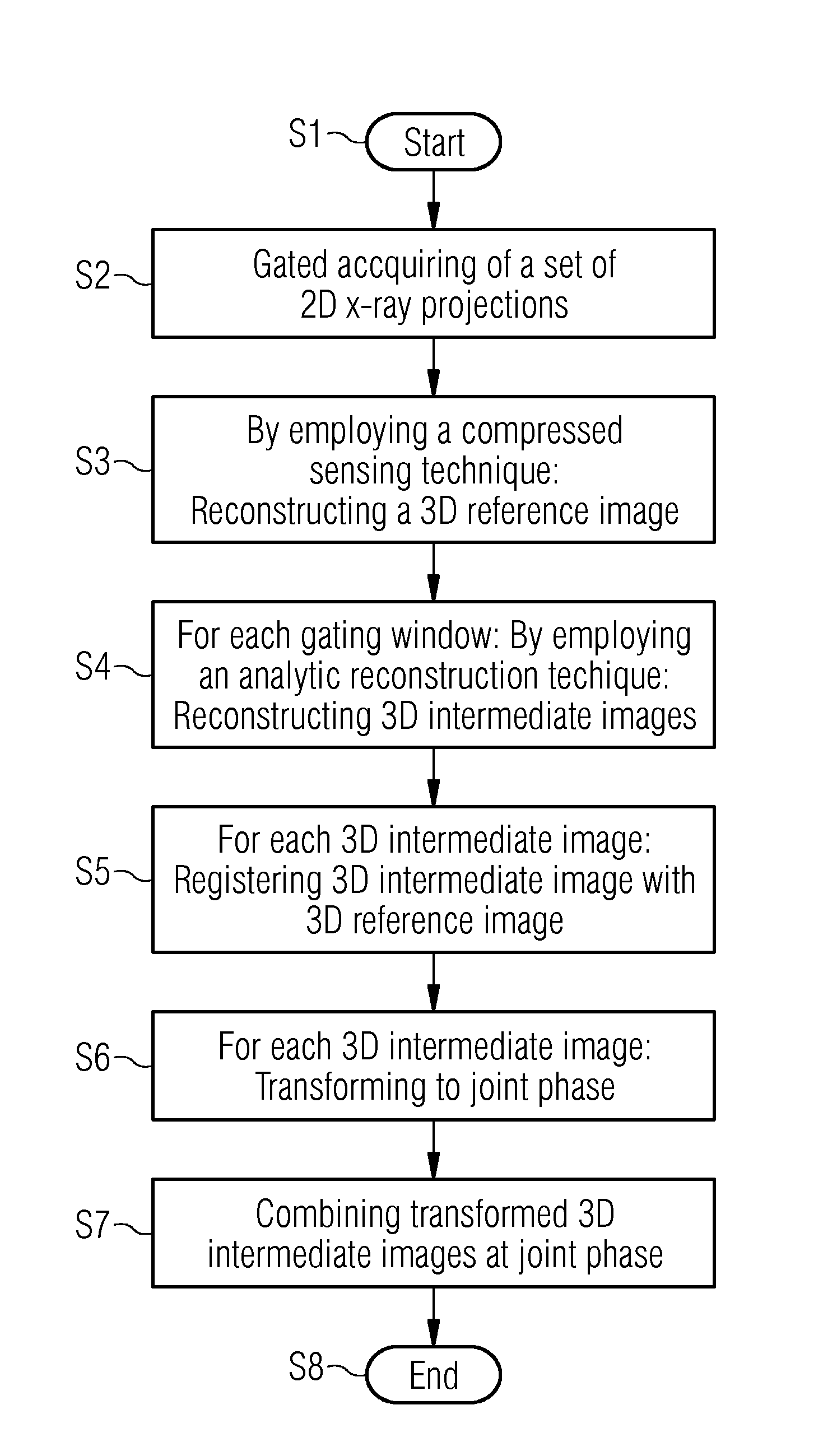
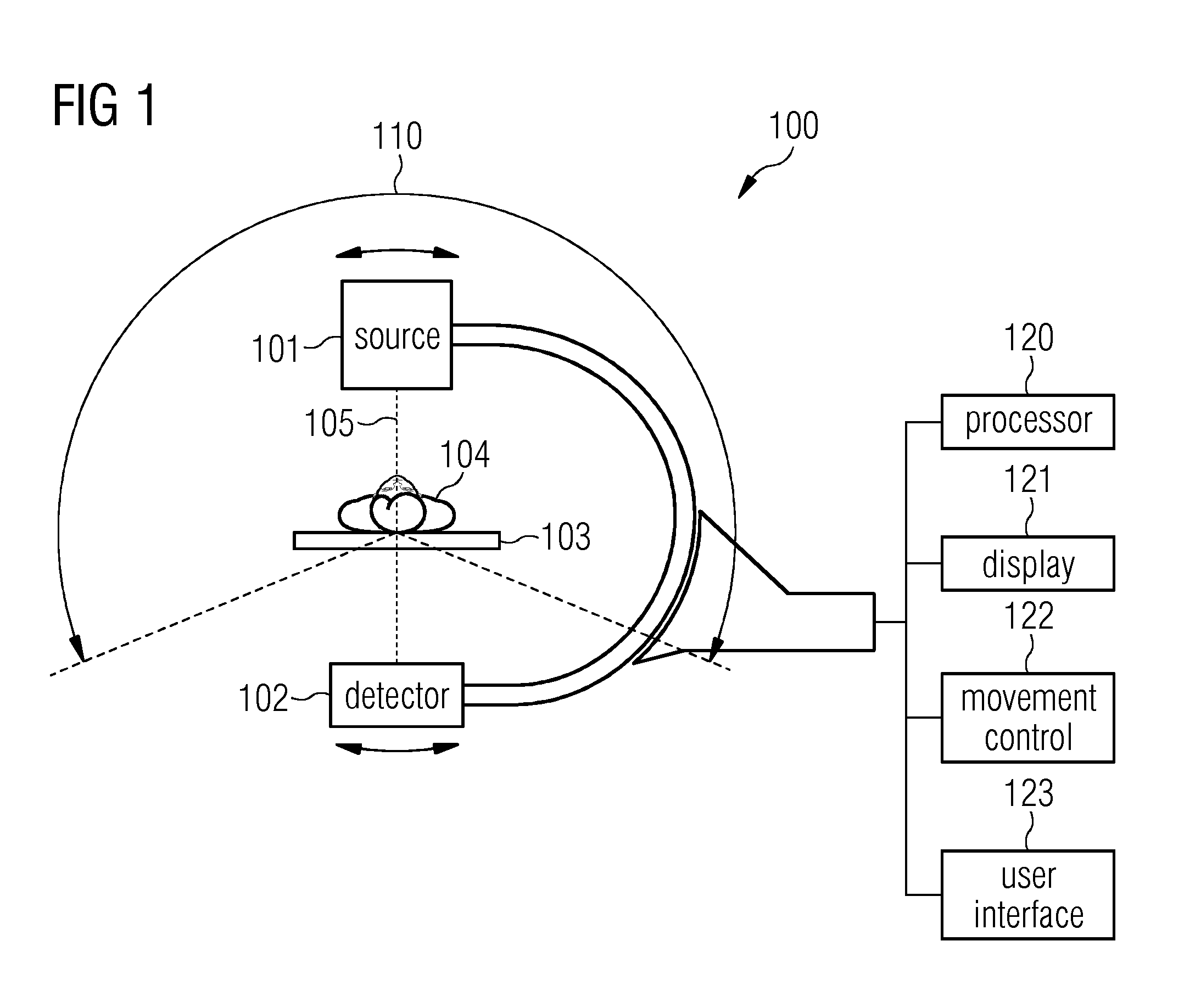
A 3D result image of an object is reconstructed from a set of X-ray two-dimensional projections of the object. A 3D reference image of the object is reconstructed by employing a compressed sensing technique based on at least some of the 2D projections at a reference motion state of the object. By employing an algebraic and / or analytic reconstruction technique, 3D intermediate images are reconstructed for various motion states of the object. The 3D intermediate images are registered with the 3D reference image to obtain spatial transformations for the various motion states of the object. Based on the spatial transformations, the 3D intermediate images are transformed to a joint phase and combined to obtain the 3D result image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
A finite angle projection reconstruction method based on L0 norm and singular value threshold decomposition for double-regular-term optimization
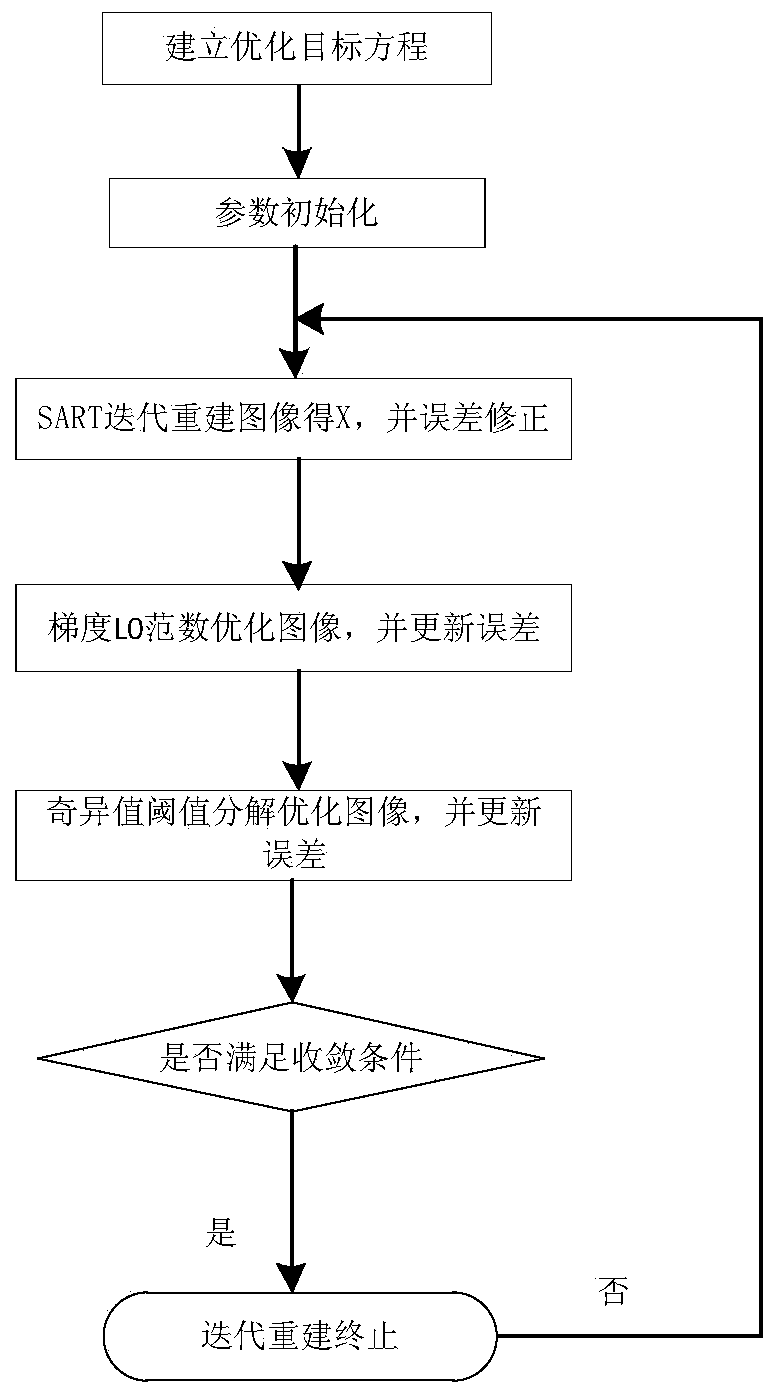
ActiveCN109697691AReduce artifactsEstore contourGeometric image transformationSingular value decompositionData set
The invention relates to a finite angle projection reconstruction method based on double regular item optimization of L0 norm and singular value threshold decomposition, and belongs to the field of image processing. The method specifically comprises the following steps: S1, establishing an optimization problem target equation according to a CT imaging principle, a regularization framework and a projection data set P; S2, initializing parameters; S3, performing iteration by adopting a SART algorithm to obtain an image X, and correcting the X through error feedback; S4, performing gradient L0 norm optimization on the corrected image X to obtain an image XL0, and updating an error d1; S5, performing singular value decomposition on the image optimized in the step S4, adding a soft threshold constraint to optimize the image to obtain an XSVT, and updating an error d2; and S6, carrying out next round of iteration on the image obtained in the step S5 according to the step S3 until an iteration termination condition is met. According to the method, the CT image contour can be effectively recovered, finite angle artifacts are reduced, and therefore the finite angle CT imaging quality and applicability are improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Attenuation correction in nuclear medicine studies by simultaneous transmission and emission data measurement and estimation of emission-to-transmission crosstalk
ActiveUS20060091315A1Increase sampleEliminate gapsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltrasound attenuationLight beam
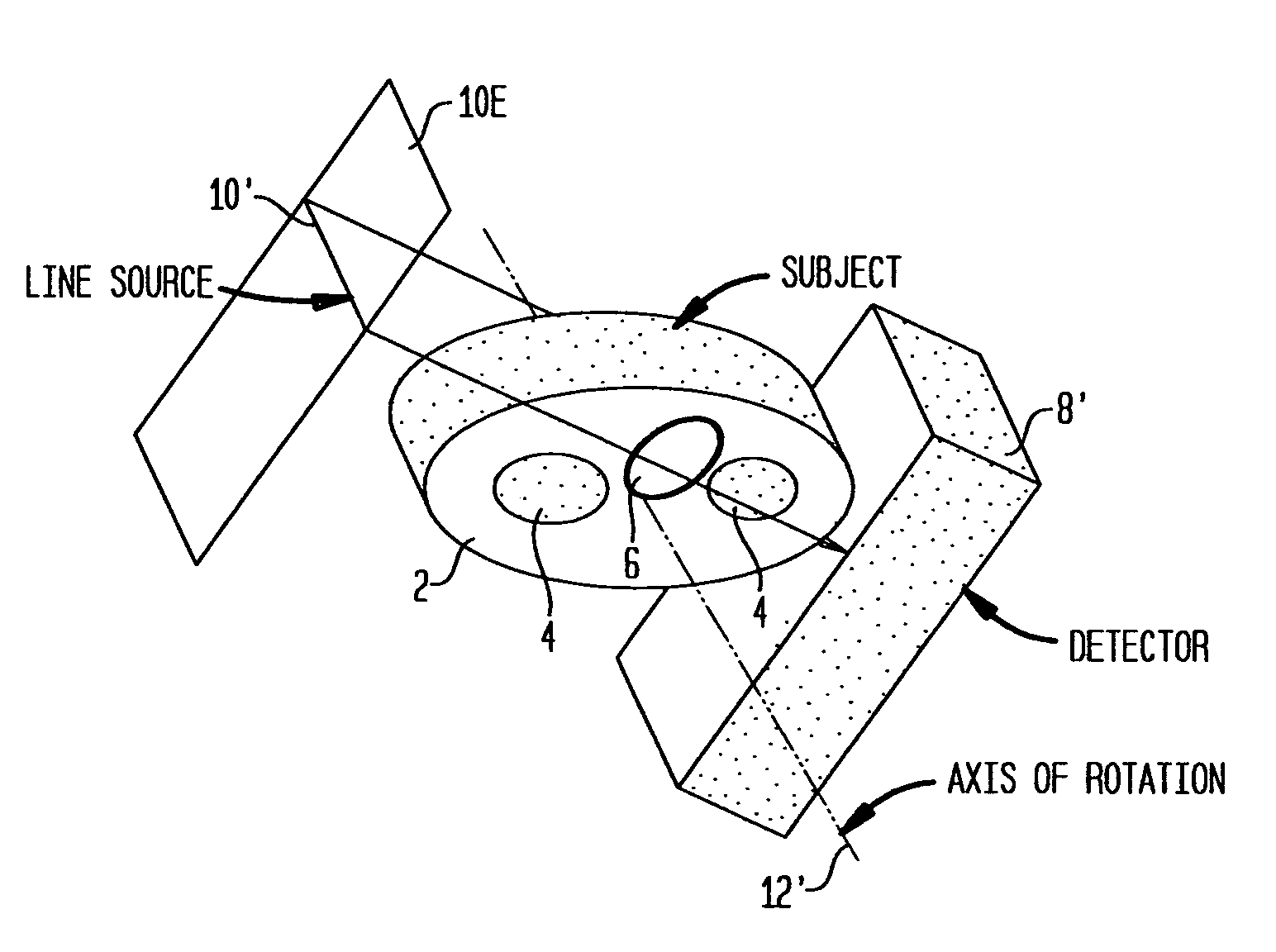
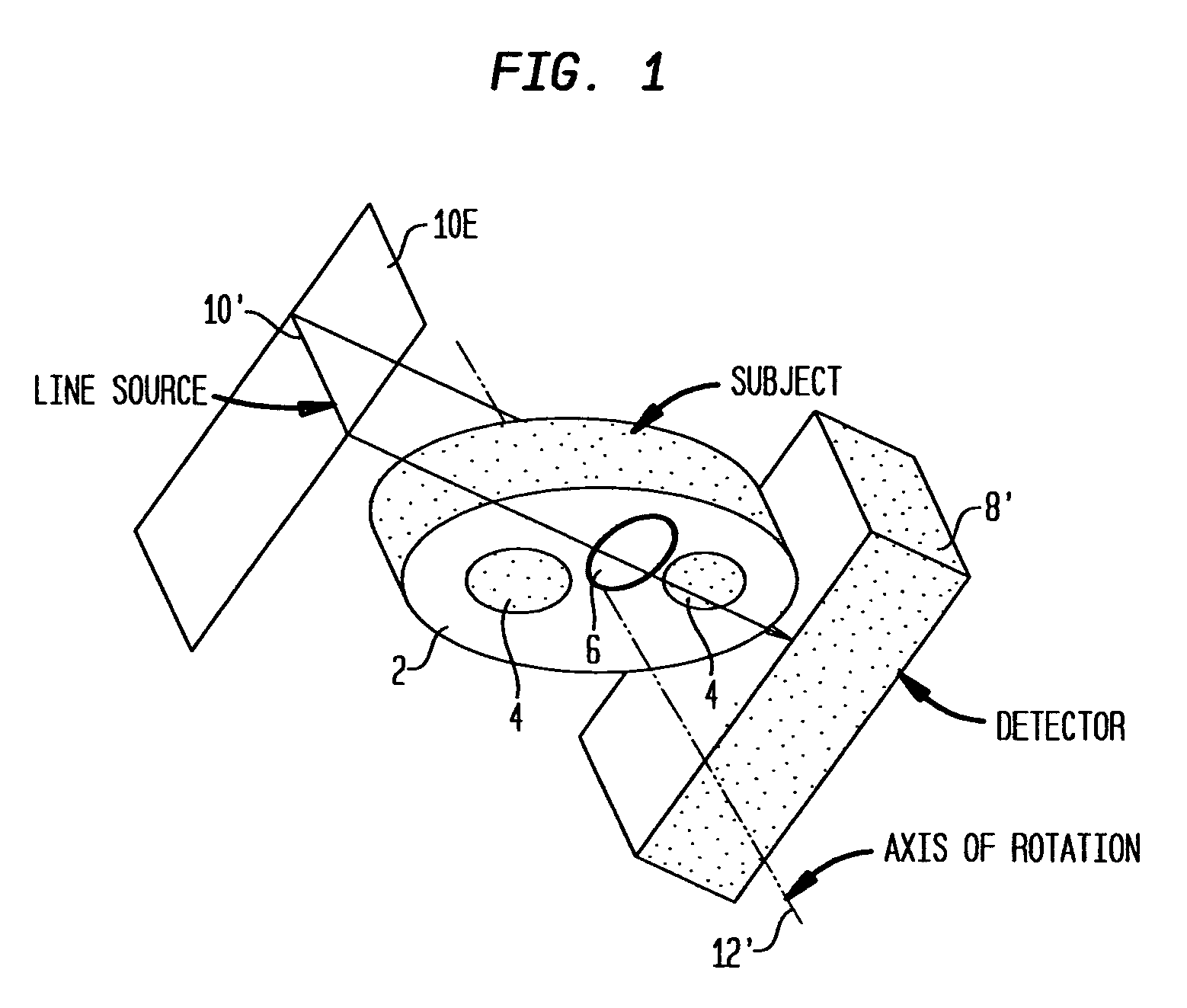
Attenuation correction in SPECT studies such as cardiac function imaging is carried out using an iterative statistically-based transmission projection reconstruction algorithm that is capable of modeling overlapping transmission beams from a line source array of radiation emitters. Downscatter between emission and transmission photons is additively corrected for in the algorithm. Optimal line source spacing techniques and source collimation angle selection are derived to improve performance and reduce cost.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
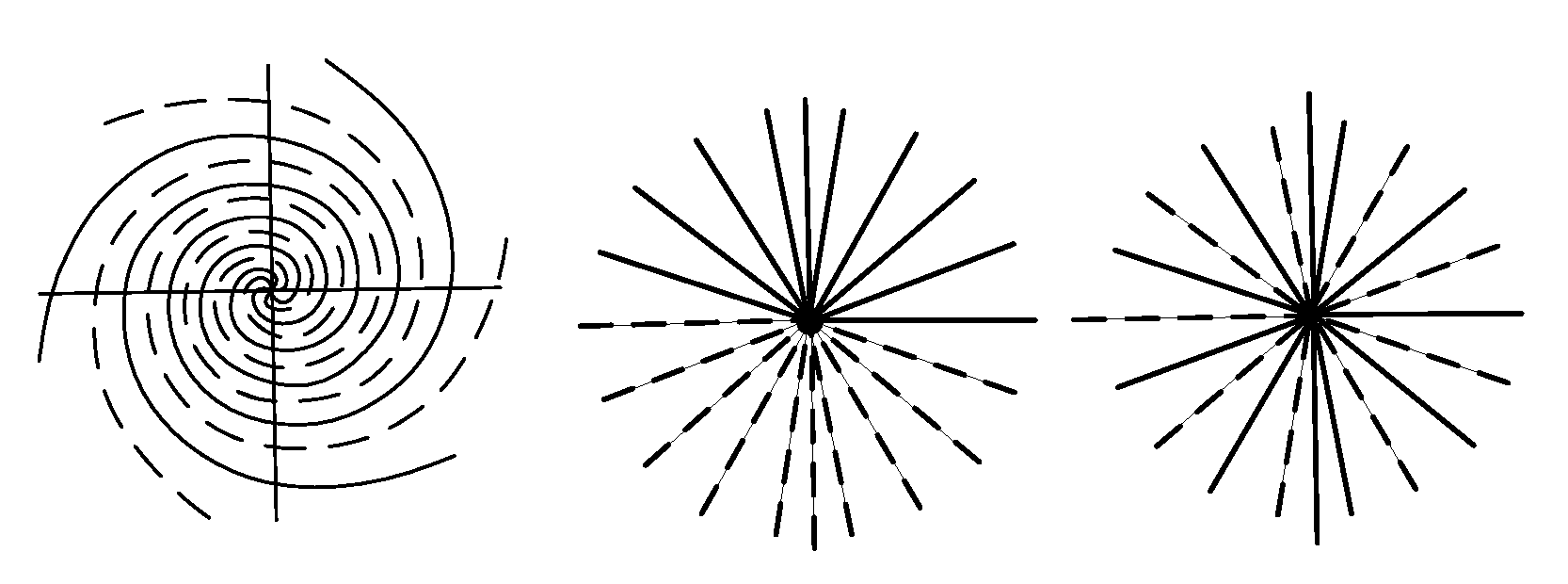
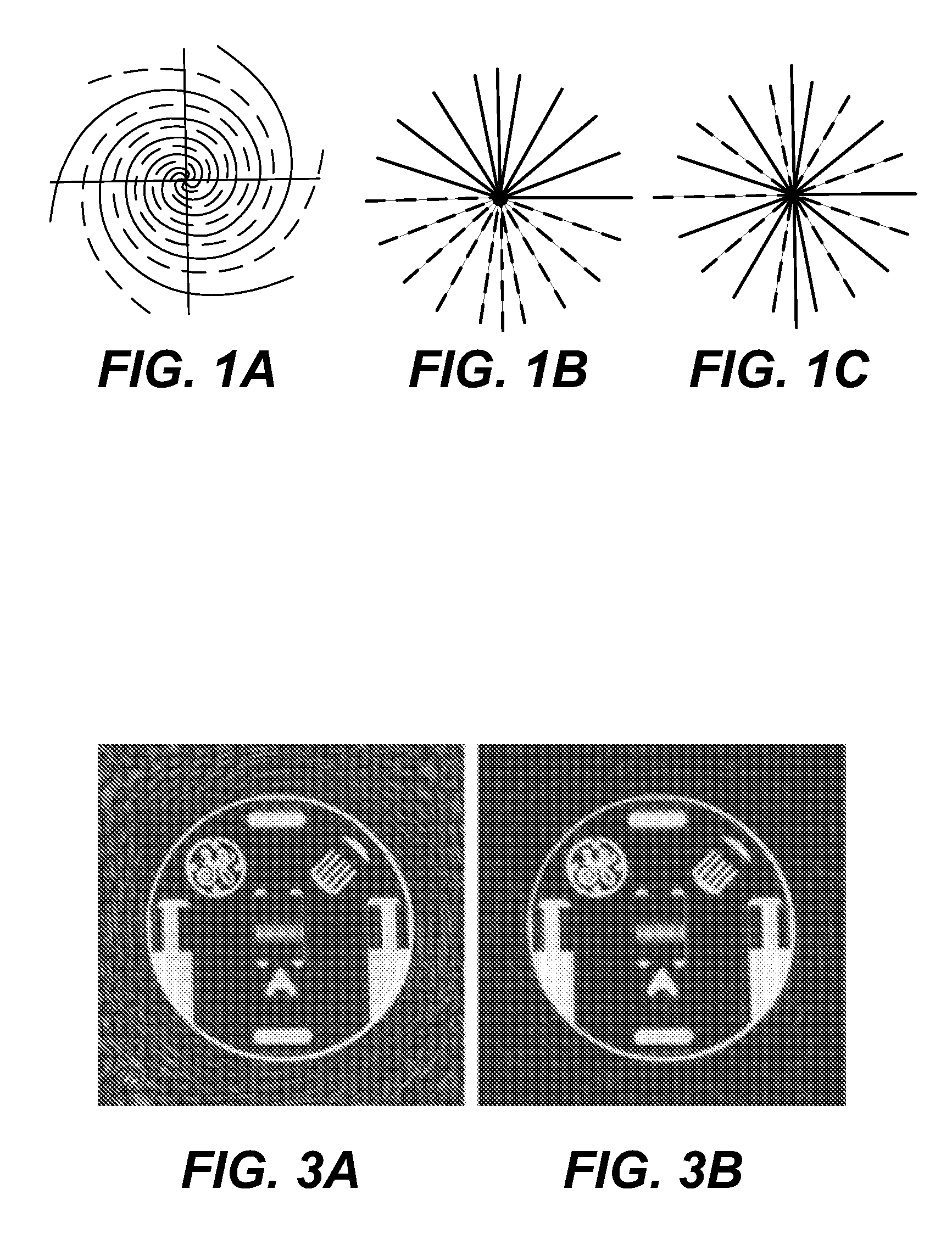
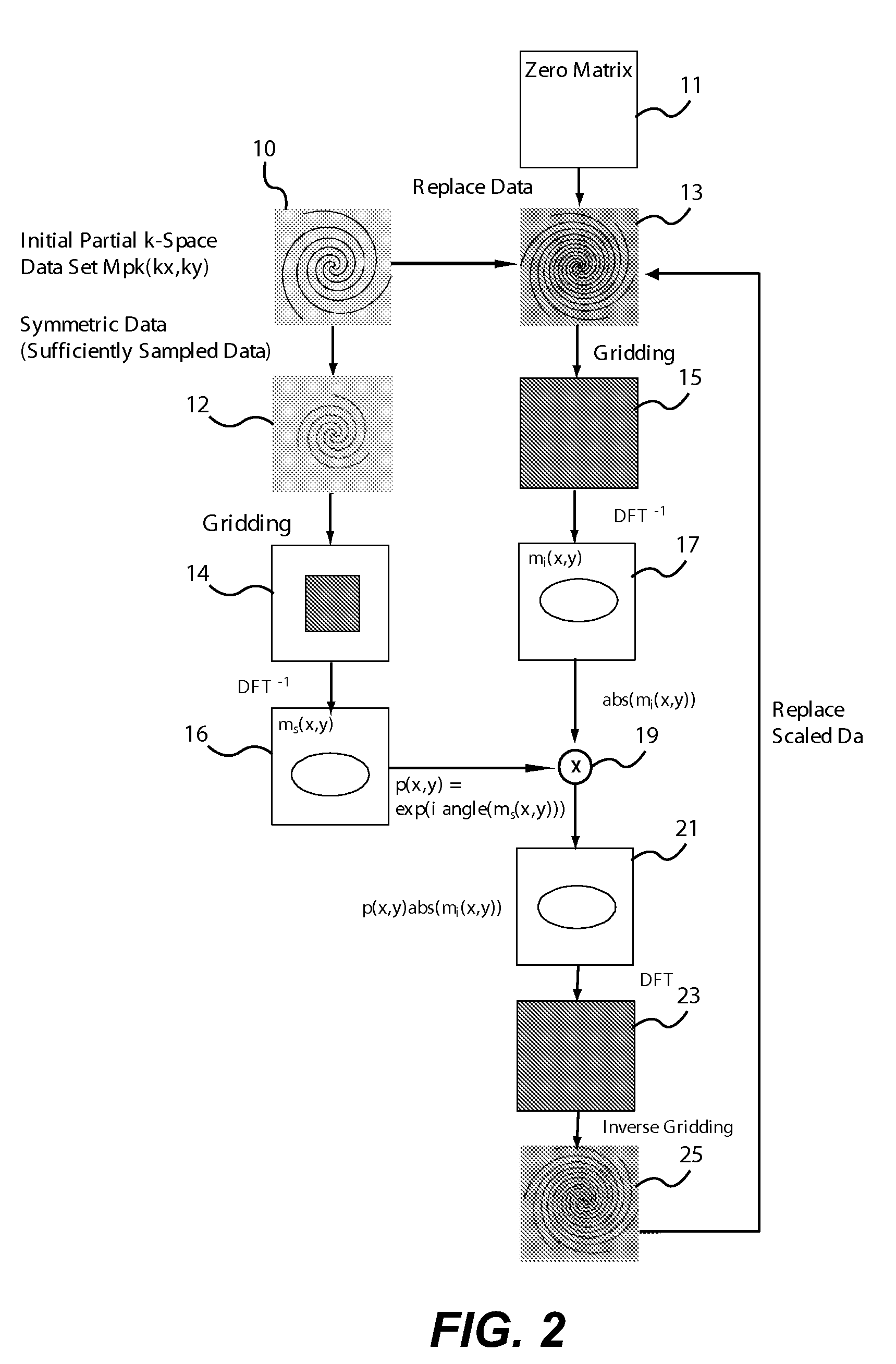
Partial k-space reconstruction for radial k-space trajectories in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7277597B2Minimal aliasing artifactAccurate compensationMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmK space trajectory
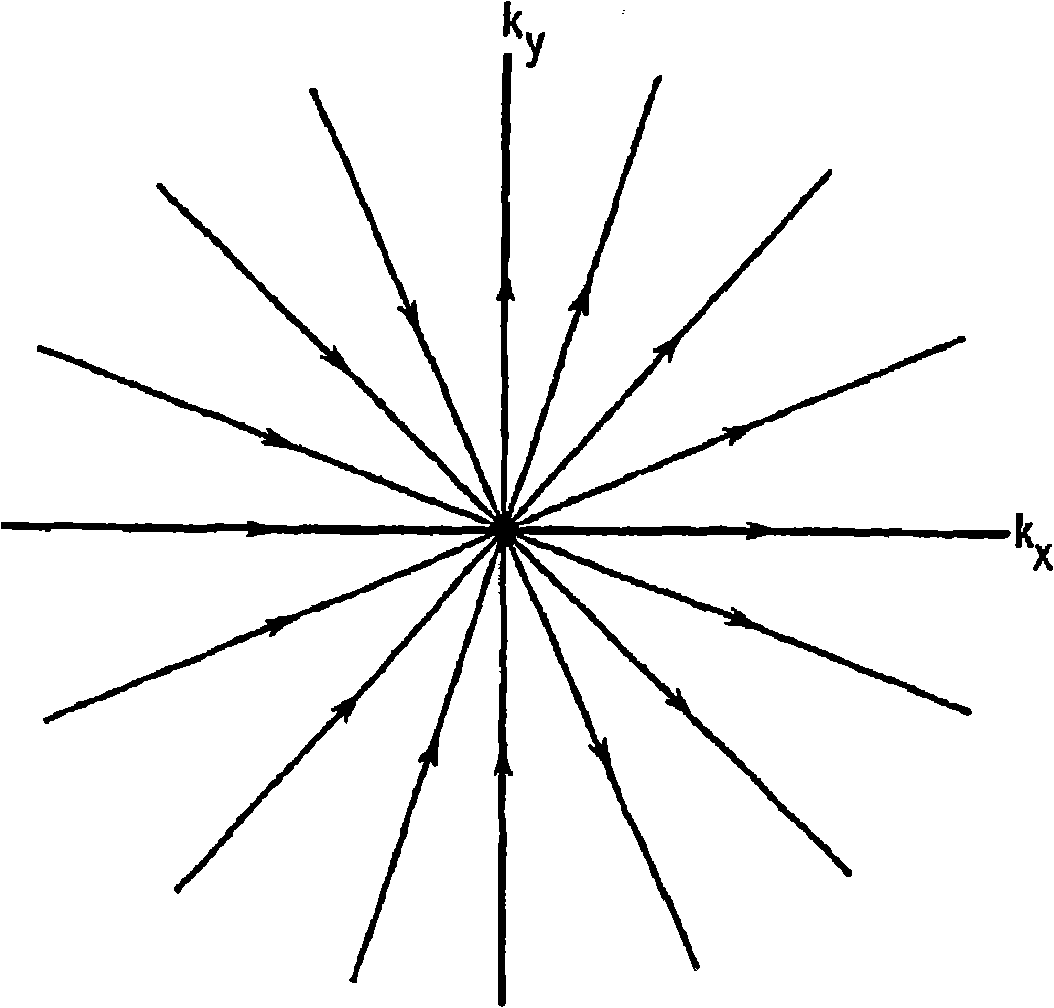
A modified projection on convex sets (POCS) algorithm and method for partial k-space reconstruction using low resolution phase maps for scaling full sets of reconstructed k-space data. The algorithm can be used with partial k-space trajectories in which the trajectories share a common point such as the origin of k-space, including variable-density spiral trajectories, projection reconstruction trajectories with a semicircle region acquisition, and projection reconstruction trajectories with every other spike acquired.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Image rendering model training method and device and image rendering method and device
PendingCN113888689AAccelerated trainingImprove efficiencyNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsPattern recognitionVoxel
The invention provides an image rendering model training method and device and an image rendering method and device, and the model training method comprises the steps: inputting a multi-angle target scene graph into a volume rendering model, and obtaining a volume rendering image outputted by the volume rendering model; based on the volume rendering image and the multi-angle target scene graph, training the initialized neural radiation field with implicit scene expression ability to obtain an image rendering model, wherein the volume rendering model is obtained based on multi-angle sample scene graph training; enabling the volume rendering model to firstly carry out projection reconstruction on the multi-angle target scene graph to obtain an explicit density distribution matrix used for representing 3D scene density of a target scene, and after sampling points in the projection direction are determined based on the density distribution matrix, generating a volume rendering image based on voxel features including density and color values in the sampling points. According to the method and device, the sampling points can be quickly and directly determined based on the explicit density distribution matrix, and the training and reasoning efficiency of the image rendering model is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIREN TECH CO LTD
Attenuation correction in nuclear medicine studies by simultaneous transmission and emission data measurement and estimation of emission-to-transmission crosstalk
ActiveUS7323689B2Increase sampleEliminate gapsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltrasound attenuationProjection reconstruction
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Highly constrained backprojection reconstruction in diffusion weighted mri
Highly undersampled diffusion weighted image data sets are acquired for a plurality of different directions using a projection reconstruction pulse sequence. The acquired projection views are interleaved and are combined to form a more highly sampled data set that is used to reconstruct a composite image. A DWI image is reconstructed from each undersampled data set for each direction using a highly constrained backprojected method that employs the composite image. Diffusion tensor values are calculated from the DWI images.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Single-impulse panoramic photoacoustic computed tomography (sip-pact)
ActiveCN110291390AReconstruction from projectionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProjection reconstructionAcoustics
A single-impulse panoramic photoacoustic computed tomography (SIP-PACT) system for small-animal whole-body imaging is disclosed. In addition, a dual-speed of sound image universal back-projection reconstruction method is disclosed. Further, a PACT system for imaging a breast of a subject is disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Method for detecting defect of light ceramic-based porous composite material based on ultrasonic principle
InactiveCN109283253AIdeal defect detectionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial defectReciprocating motion
The invention discloses a method for detecting defect of the light ceramic-based porous composite material based on the ultrasonic principle, comprising the following steps of: immersing an ultrasonictransmitter probe and an ultrasonic receiver probe in water at the same time, wherein the ultrasonic transmitter probe and the ultrasonic receiver probe are perpendicular to both sides of the light porous ceramic-based composite material to be detected; the ultrasonic transmitter probe and the ultrasonic receiver probe reciprocating in the x-y direction of the both sides of the light porous ceramic-based composite material to be detected to scan the light porous ceramic-based composite material to be detected, a data acquisition card collecting the ultrasonic signal received by the ultrasonicreceiver probe and transmitting the ultrasonic signal to the computer on which the LabVIEW program is installed; and the LabVIEW performing a maximum projection reconstruction on the obtained data toobtain an ultrasonic C-scan image, which can identify a defect area and complete a material defect detection experiment. Compared to the prior art, the method for detecting defect of light ceramic-based porous composite material based on ultrasonic principle can realize the detection of dangerous defects such as holes, inclusions and debonding in the ceramic-based composite material.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
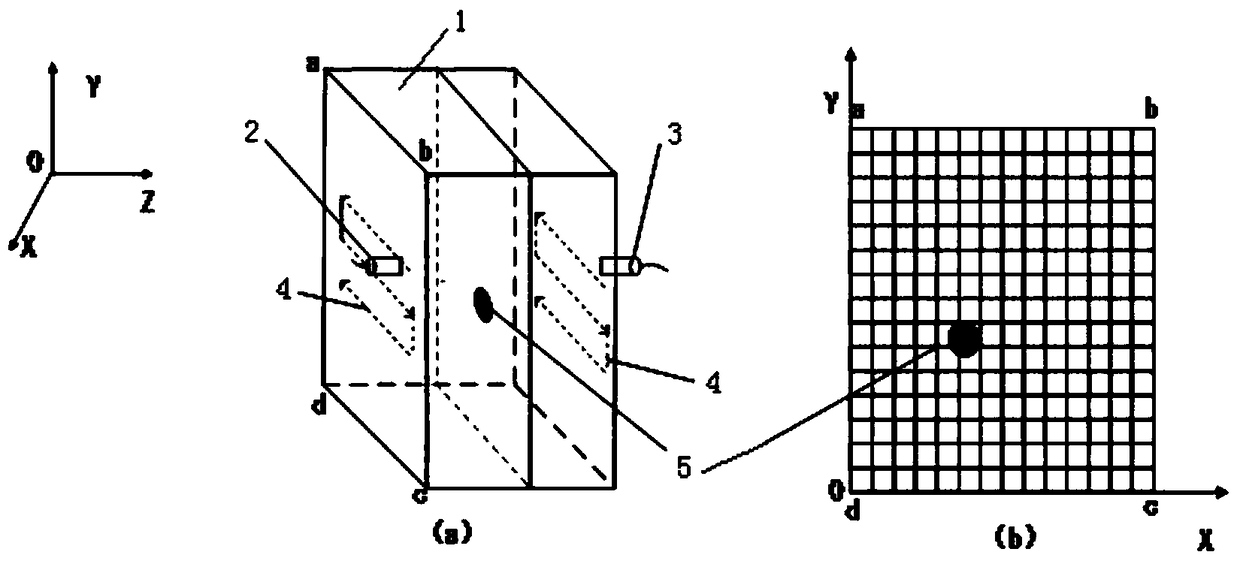
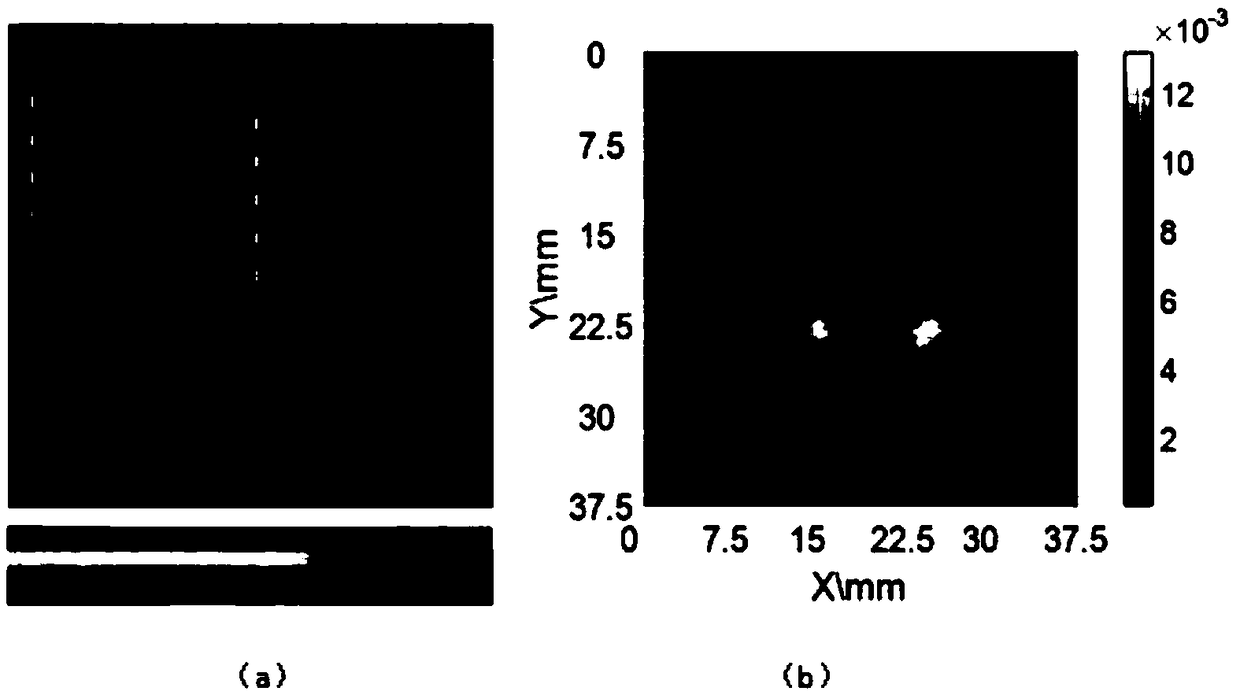
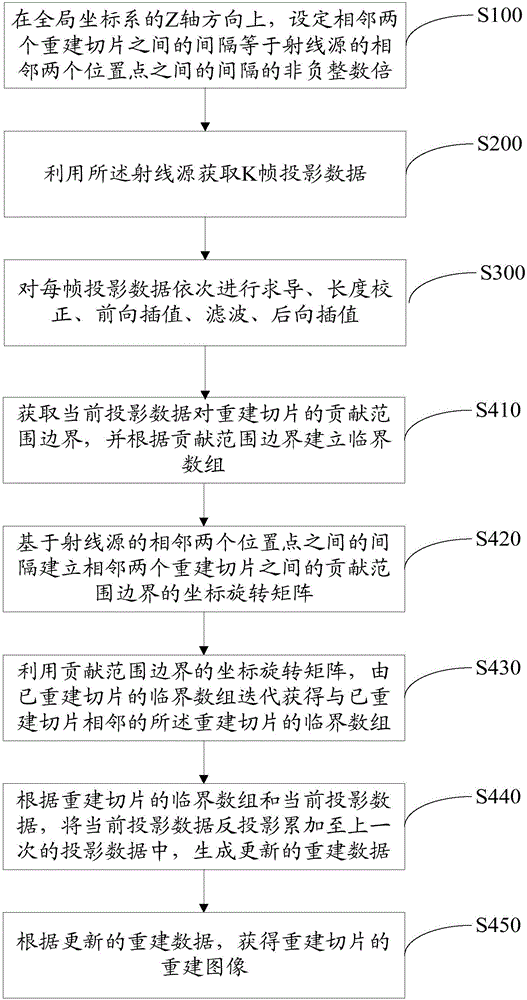
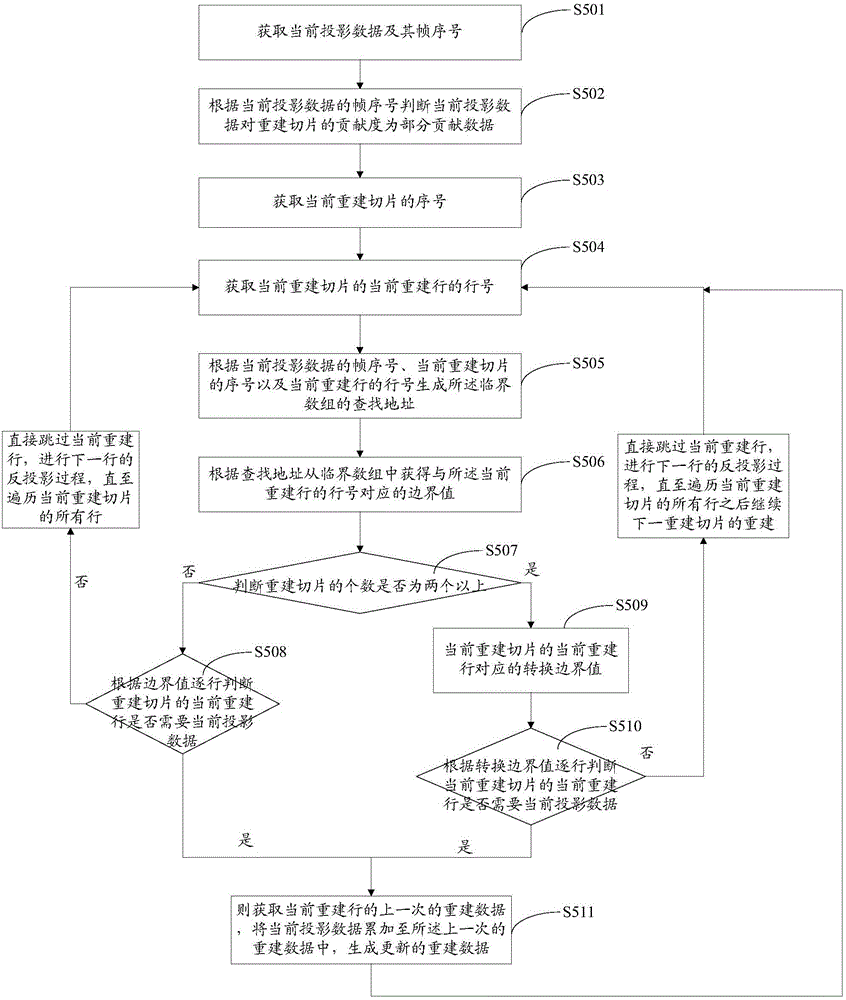
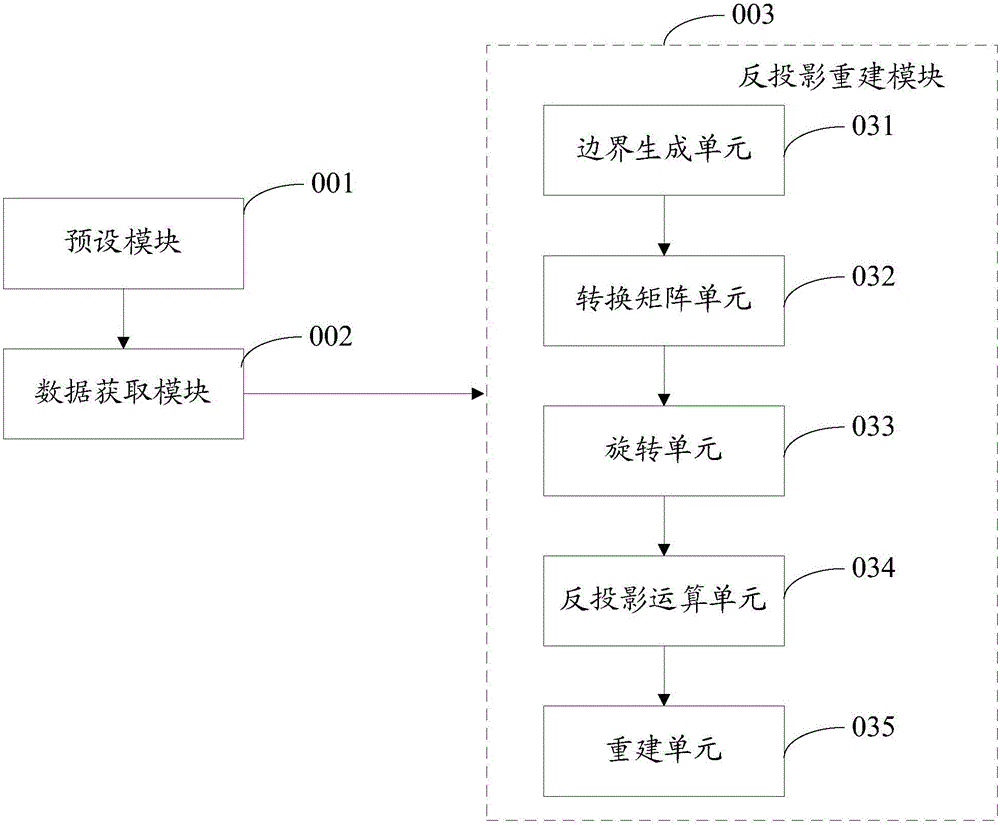
CBCT (cone beam computed tomography) reconstruction method and system
InactiveCN105809723AEasy to implementSimple calculationReconstruction from projectionArray data structureFpga implementations
The invention provides a CBCT (cone beam computed tomography) reconstruction method. The CBCT reconstruction method includes the following steps that: on the Z-axis direction of a global coordinate system, the interval between two adjacent reconstruction slices is set to equal to M times of the interval between two adjacent position points of a ray source, wherein M is a non-negative integer; the ray source is utilized to obtain k frames of projection data; and if the projection data are a part of contribution for a current reconstruction slice, a critical array is established for the boundary of the reconstruction range of the current reconstruction slice according to current projection data, and back projection operation is performed on each frame of projection data according to the critical array and the current projection data. The invention also provides a CBCT reconstruction system. The CBCT reconstruction system comprises a presetting module, a data acquisition module and a back projection reconstruction module. The invention further provides a CBCT system. The CBCT system comprises a radiation source, a detector, an upper computer and an FPGA accelerating circuit. With the CBCT reconstruction method and system of the invention adopted, the calculation amount of the system is simplified, and the efficiency of the back projection operation can be improved, the complexity of the system can be reduced, and FPGA implementation can be achieved with easiness.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
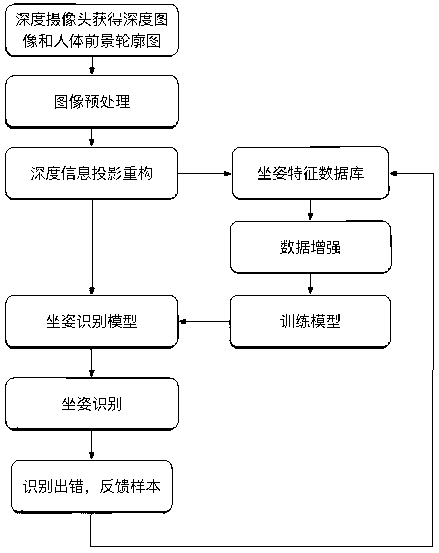
Sitting posture recognition method based on projection reconstruction and multiple-input-multiple-output neural network
ActiveCN111325166AImprove recognition accuracyEliminate distractionsCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesMulti inputHuman body
The invention relates to a sitting posture recognition method based on projection reconstruction and a MIMO-CNN. The sitting posture recognition method comprises the following steps: acquiring a humanbody upper body depth image and a human body foreground contour map; performing pretreatment; projecting the depth information of the sitting posture contour, and reconstructing to obtain a three-view depth map; designing an MIMO-CNN network for sitting posture recognition and learning model parameters; sitting posture recognition; model self-learning. The method has the advantages that the preprocessed depth image is combined with the human body contour map, and interference of surrounding backgrounds on sitting posture recognition is eliminated. A three-view depth map is obtained by using aprojection reconstruction method, so that sitting posture information is richer. The invention discloses a designed MIMO-CNN structure. The method is especially suitable for projecting and reconstructing feature information and integrating an attention mechanism at the same time, hot spot areas of different sitting postures can be better concerned, so that the recognition precision is improved, meanwhile, model self-learning is adopted, the requirements for real-time performance and accuracy are well balanced, and the method has high anti-interference capacity for visual angle changes and complex environment backgrounds.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
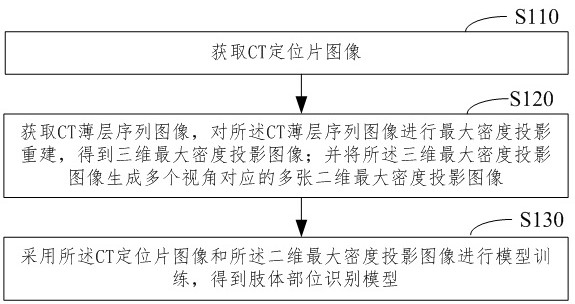
Method and system for training limb part recognition model in CT (Computed Tomography) image
ActiveCN113989407AAvoid the problem of poor recognition accuracyReduce in quantityReconstruction from projectionNeural architecturesComputed tomographyProjection image
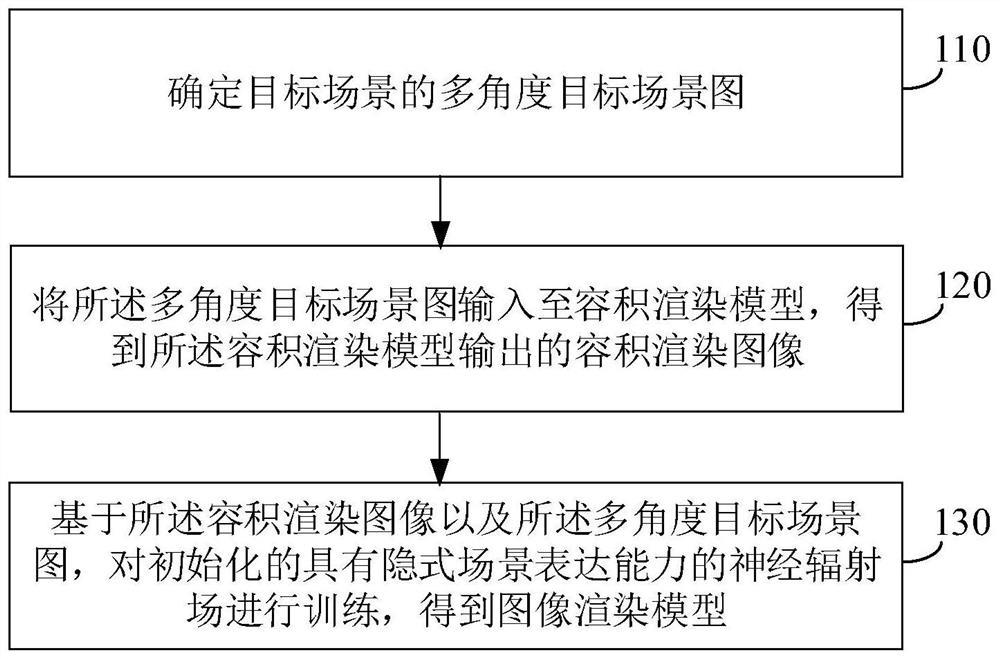
The invention relates to the technical field of medical image recognition, and provides a method and a system for training a limb part recognition model in a CT (Computed Tomography) image. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a CT positioning sheet image; acquiring a CT thin-layer sequence image, and performing maximum density projection reconstruction on the CT thin-layer sequence image to obtain a three-dimensional maximum density projection image; generating a plurality of two-dimensional maximum density projection images corresponding to a plurality of visual angles from the three-dimensional maximum density projection image; and carrying out model training by adopting the CT positioning sheet image and the two-dimensional maximum density projection image to obtain a limb part identification model. The system comprises a first acquisition module, a second acquisition module and a model training module. According to the invention, training samples are supplemented through a maximum-density projection image, so that the problem of insufficient training samples is solved.
Owner:青岛美迪康数字工程有限公司
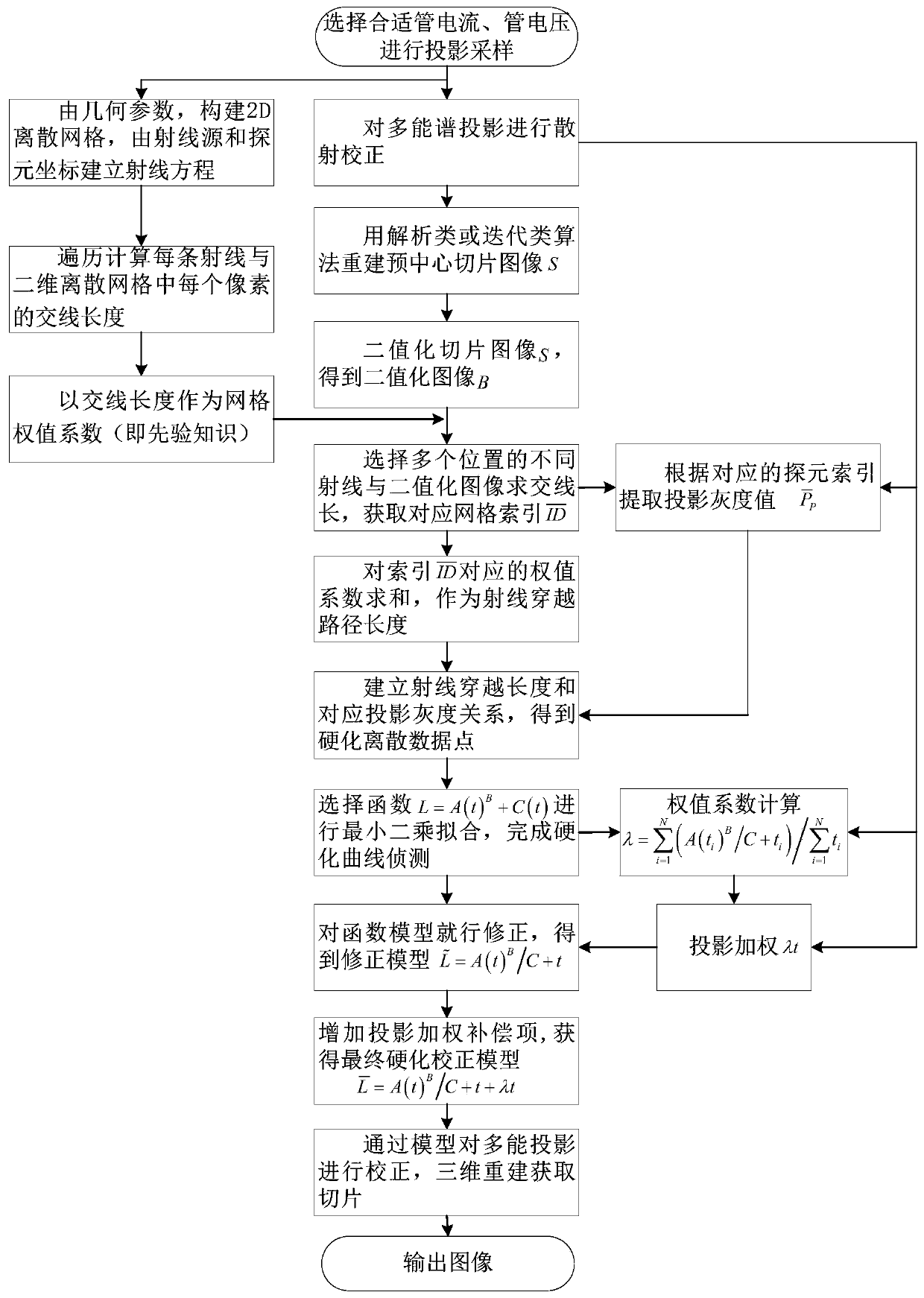
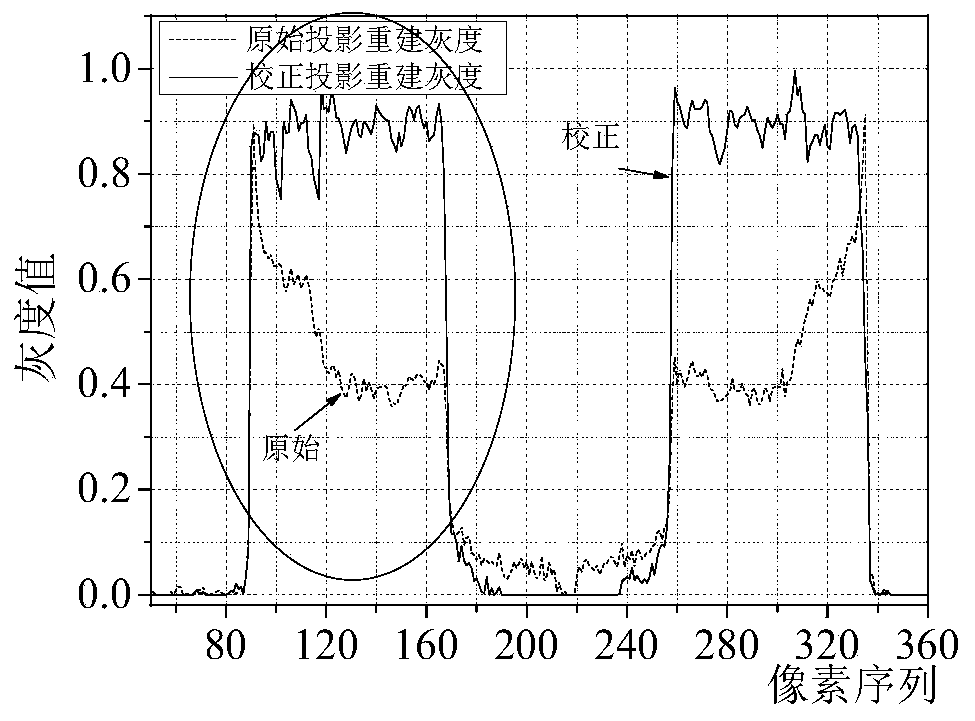
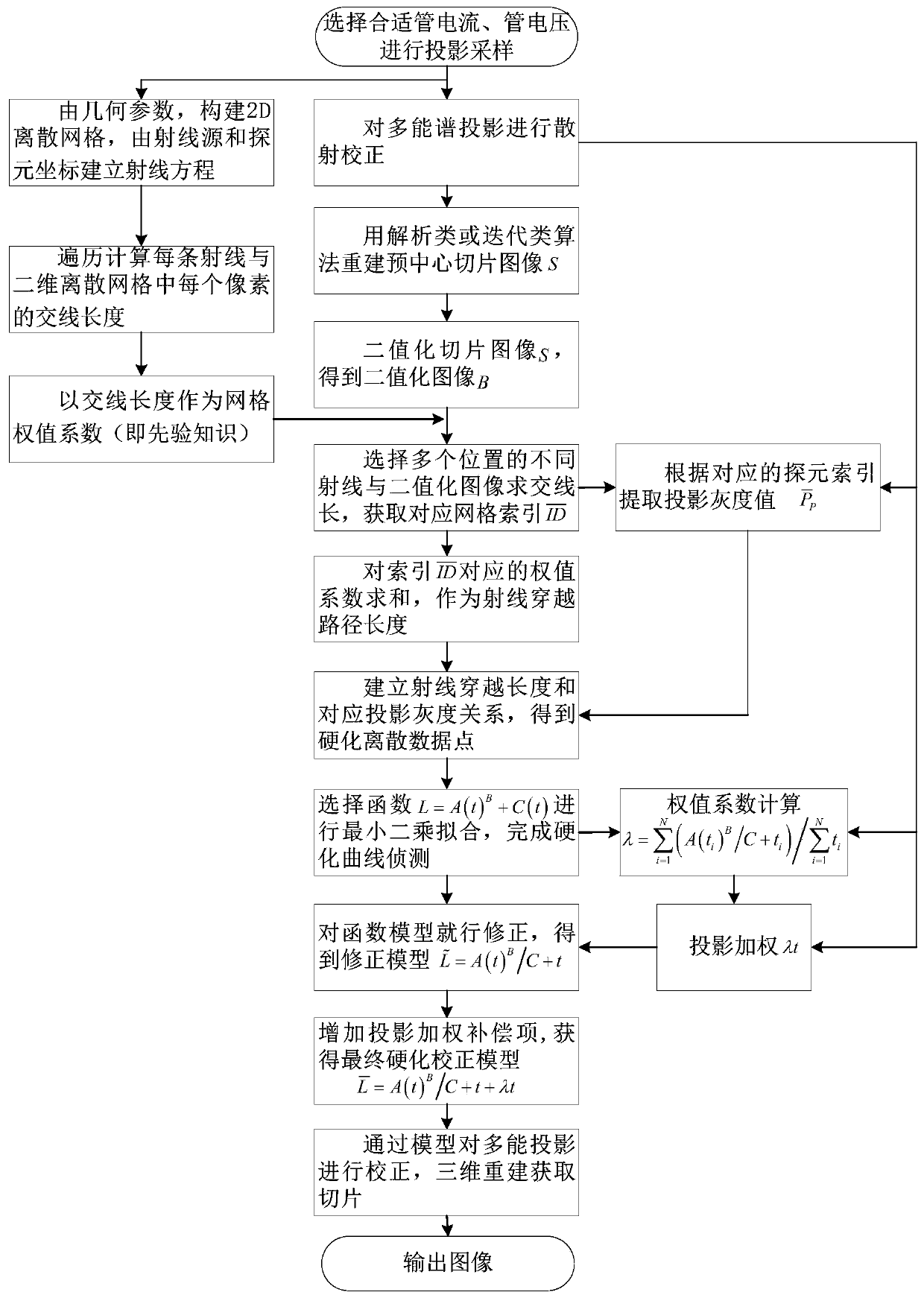
A cone beam CT beam hardening curve detection and projection weighting correction method
ActiveCN109919868AImprove image qualityQuality improvementImage enhancementImaging qualityBeam hardening
The invention discloses a cone beam CT (computed tomography) beam hardening curve detection and projection weighting correction method, which comprises the following steps of: solving an intersectionline length by using ray sampling matrix information priori knowledge and a pre-reconstructed slice image and by using rays and a binary image, and performingdetecting to obtain a beam hardening curve; By performing projection weighting correction on the fitting function, hardening correction of multi-energy projection is realized, cup-shaped artifacts caused by multi-energy projection reconstruction can be prevented, and the image quality is improved. The cone beam CT beam hardening curve detection and projection weighting correction method is suitable for hardening curve detection and cup-shaped artifact correction of a measured object with any complexity, the method is good in reliability, stability and noise resistance, interference and influence of cone beam CT hardening projection cup-shaped artifacts on an image can be reduced to a great extent, and the quality of the cone beam CT image is obviously improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
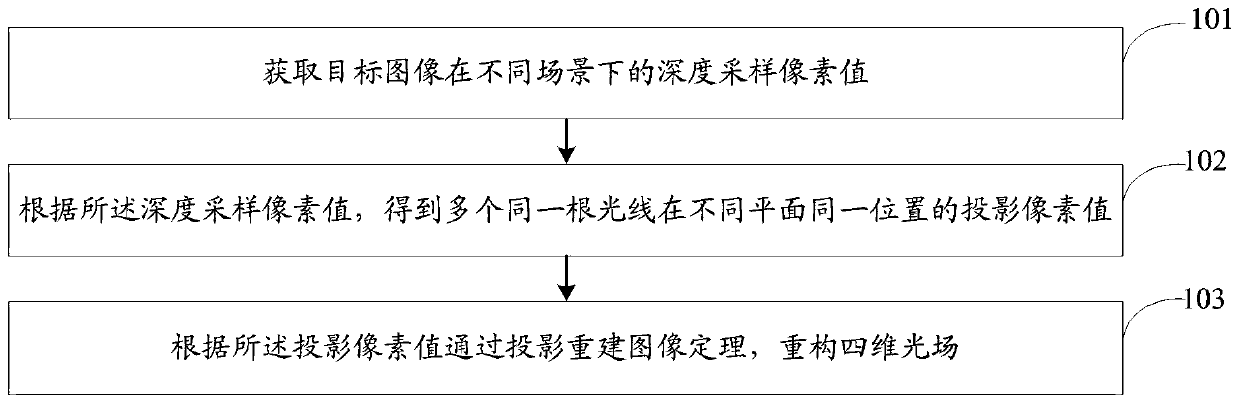
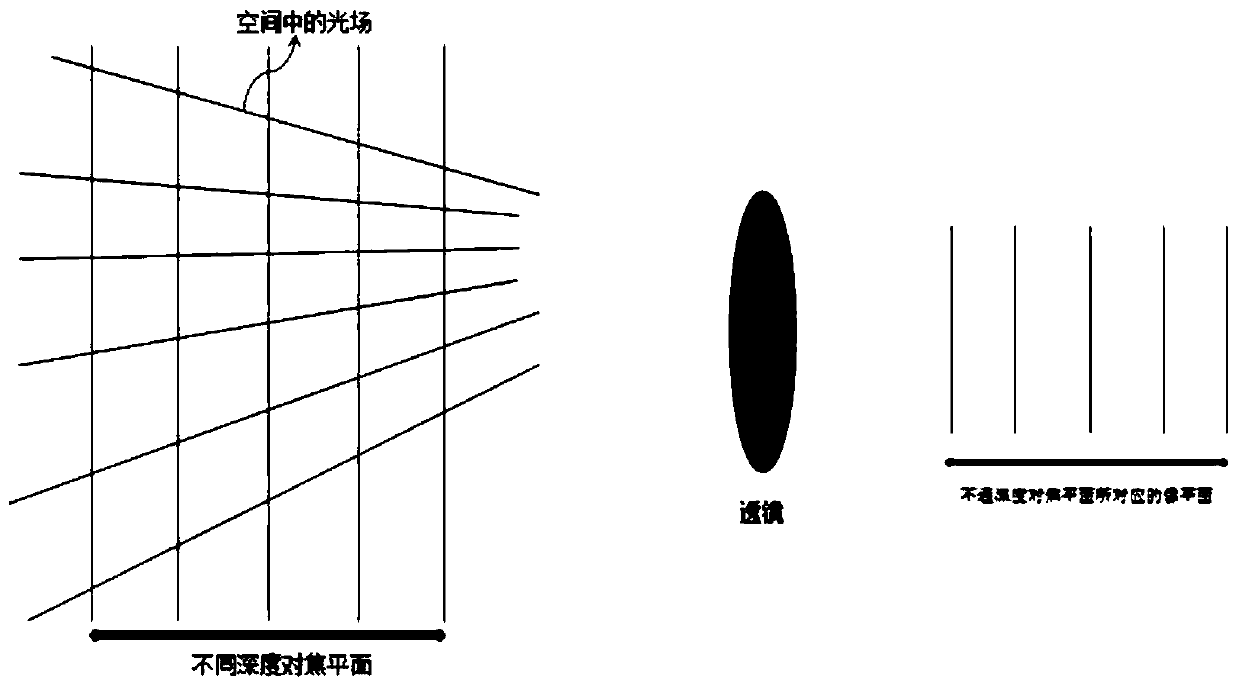
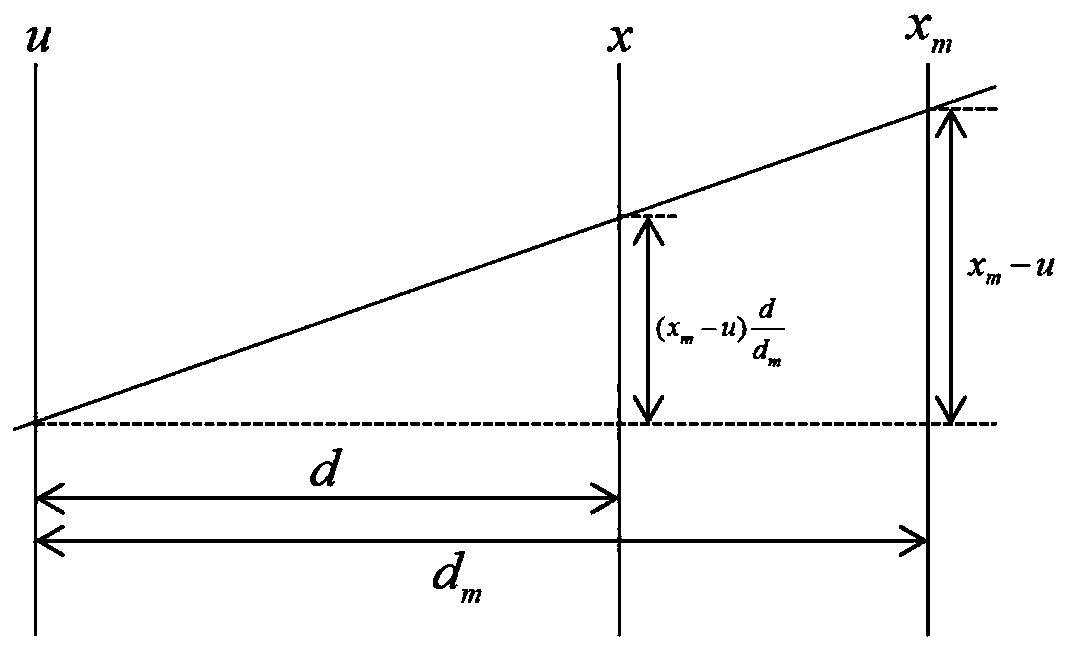
Method and system for reconstructing light field by applying depth sampling
The invention relates to a method and a system for reconstructing a light field by applying depth sampling. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring depth sampling pixel values of a targetimage in different scenes; according to the depth sampling pixel values, obtaining projection pixel values of the same light ray at the same position in different planes; and reconstructing a four-dimensional light field through a projection reconstruction image theorem according to the projection pixel value. By adopting the method or the system provided by the invention, light field reconstruction can be quickly carried out, and the spatial resolution of imaging can be improved.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
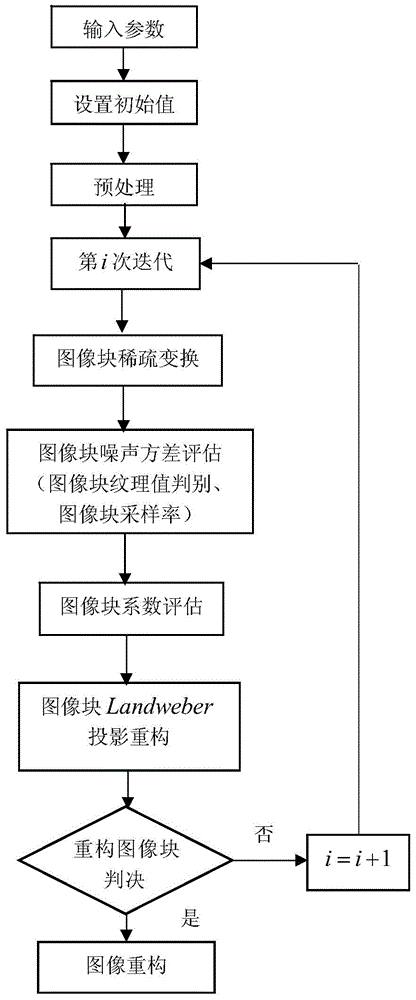
Image reconstruction design method improving noise variance estimation
ActiveCN105184832AQuality improvementImprove accuracyImage enhancement2D-image generationProjection reconstructionCompressed sensing
The invention discloses an image reconstruction design method improving noise variance estimation. The method comprises the following steps of step1, using a sparse matrix psi B to convert an image block xj; step2, carrying out noise variance estimation; step3, carrying out image coefficient estimation; step4, carrying out Lanweber continuous projection on each block image so as to reconstruct the image; step5, determining whether the projection reconstruction block image satisfies a termination criterion. In the method, during a compression perception reconstruction image process, an image block texture characteristic, a sparse conversion type and an image sampling rate are used to improve the noise variance estimation; the estimated noise variance is substituted into a bivariate threshold projection reconstruction algorithm so as to reconstruct a compressed image and quality of the reconstruction image is increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
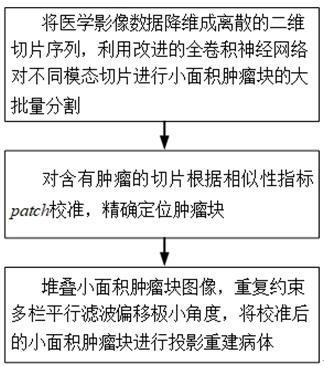
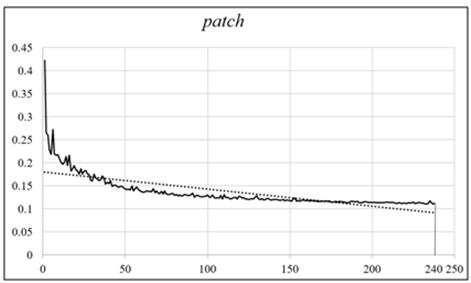
Stacked projection reconstruction method for segmented small-area tumor blocks
ActiveCN113256754AAvoid non-applicable problemsOvercome volume effectImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMinimal invasive surgeryMedical imaging data
The invention provides a stacked projection reconstruction method for small-area tumor blocks after segmentation. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, carrying out dimensionality reduction on medical image data to form a discrete two-dimensional slice sequence, and carrying out large-scale segmentation of small-area tumor blocks on different modal slices by utilizing an improved full convolutional neural network; step 2, calibrating the slices containing the tumor according to a similarity index patch, and accurately positioning a tumor block; and step 3, stacking small-area tumor block images, repeatedly constraining multi-column parallel filtering to shift a minimum angle, and projecting the calibrated small-area tumor blocks to reconstruct a sick body. The objective of the method is to realize rapid segmentation, accurate positioning and reverse reconstruction of a sick body so as to display multi-dimensional structure information, display the distribution condition and the relative position of tumor tissues independently or in a combined manner, and promote the development of emerging medical schemes such as image navigation minimally invasive surgery and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Image rendering model training method and device and image rendering method and device
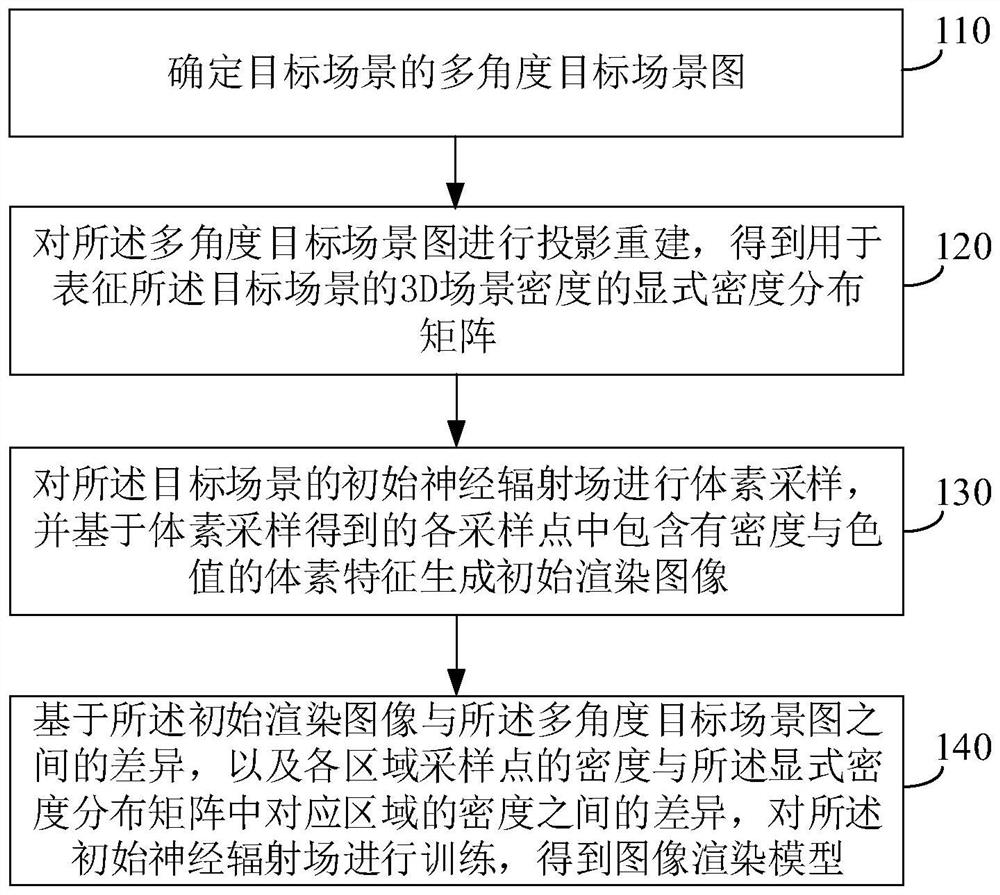
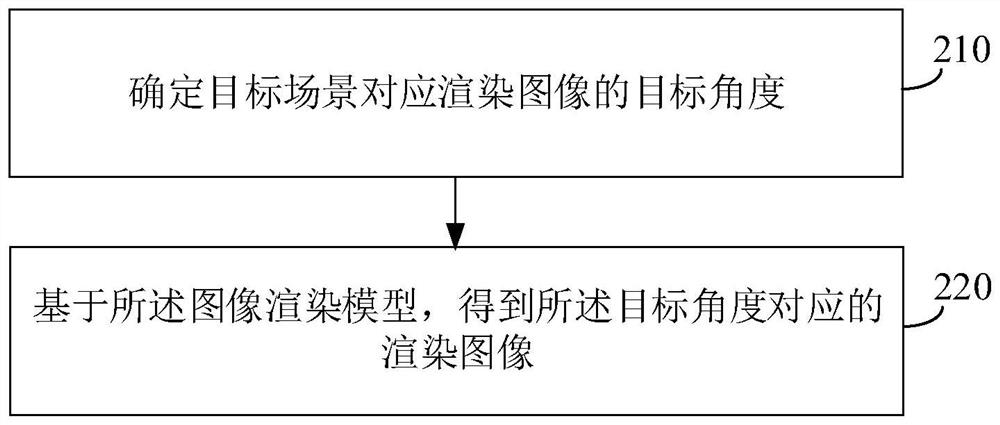
PendingCN114493995AIncrease training speedFast convergenceGeometric image transformationNeural learning methodsVoxelRadiology
The invention provides an image rendering model training method and device and an image rendering method and device. The model training method comprises the steps of determining a multi-angle target scene graph of a target scene; performing projection reconstruction on the multi-angle target scene graph to obtain an explicit density distribution matrix for representing the 3D scene density of the target scene; voxel sampling is carried out on the initial neural radiation field of the target scene, and an initial rendering image is generated based on voxel features containing density and color values in sampling points obtained through voxel sampling; and training the initial neural radiation field based on the difference between the initial rendering image and the multi-angle target scene graph and the difference between the density of the sampling points in each region and the density of the corresponding region in the explicit density distribution matrix to obtain an image rendering model. On the basis of not increasing additional forward operation, convergence of the loss function is accelerated, and the training speed of the model is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIREN TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com