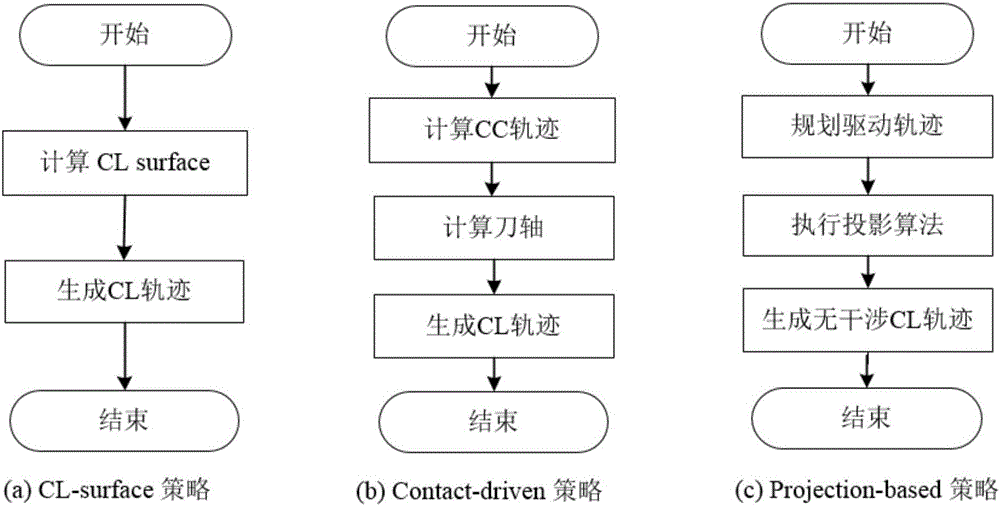
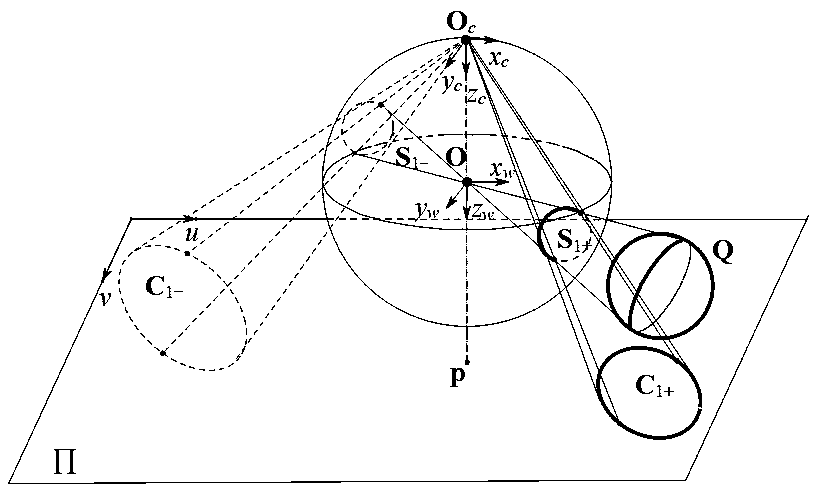
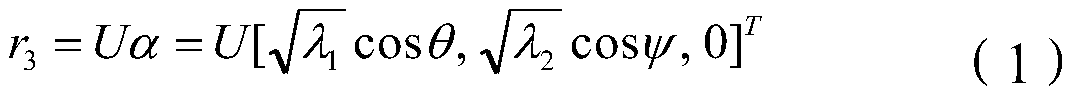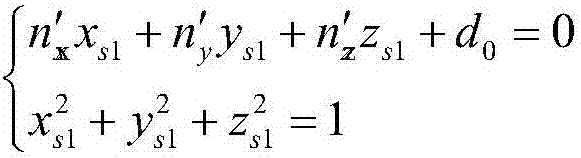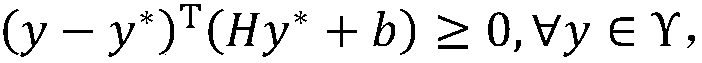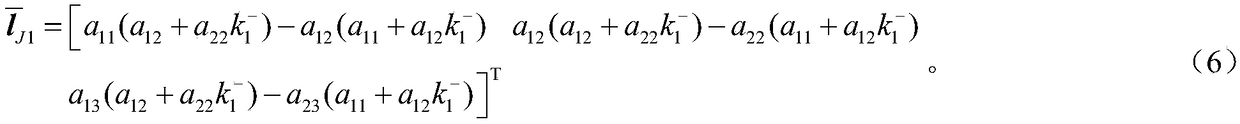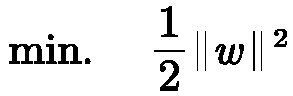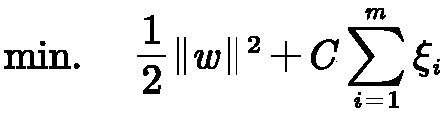Patents
Literature
58 results about "Projection equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Simple Equation for Population Equation. A simple equation for population projection can be expressed as: Nt=Pe rt. In this equation, (Nt) is the number of people at a future date, and (P) is equal to the present population.
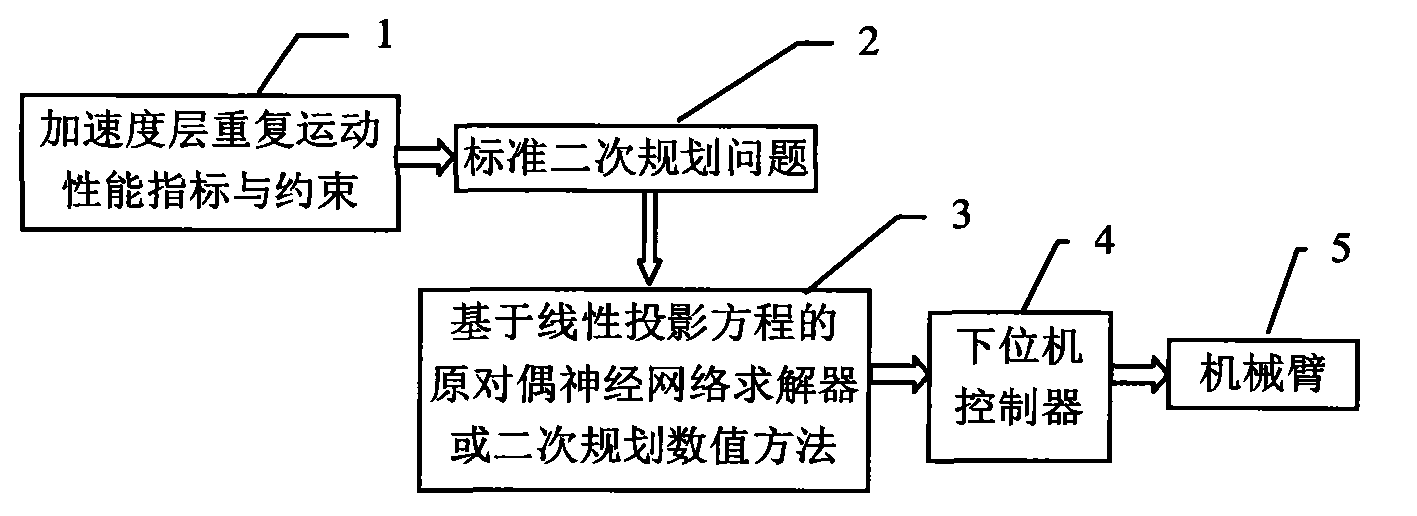
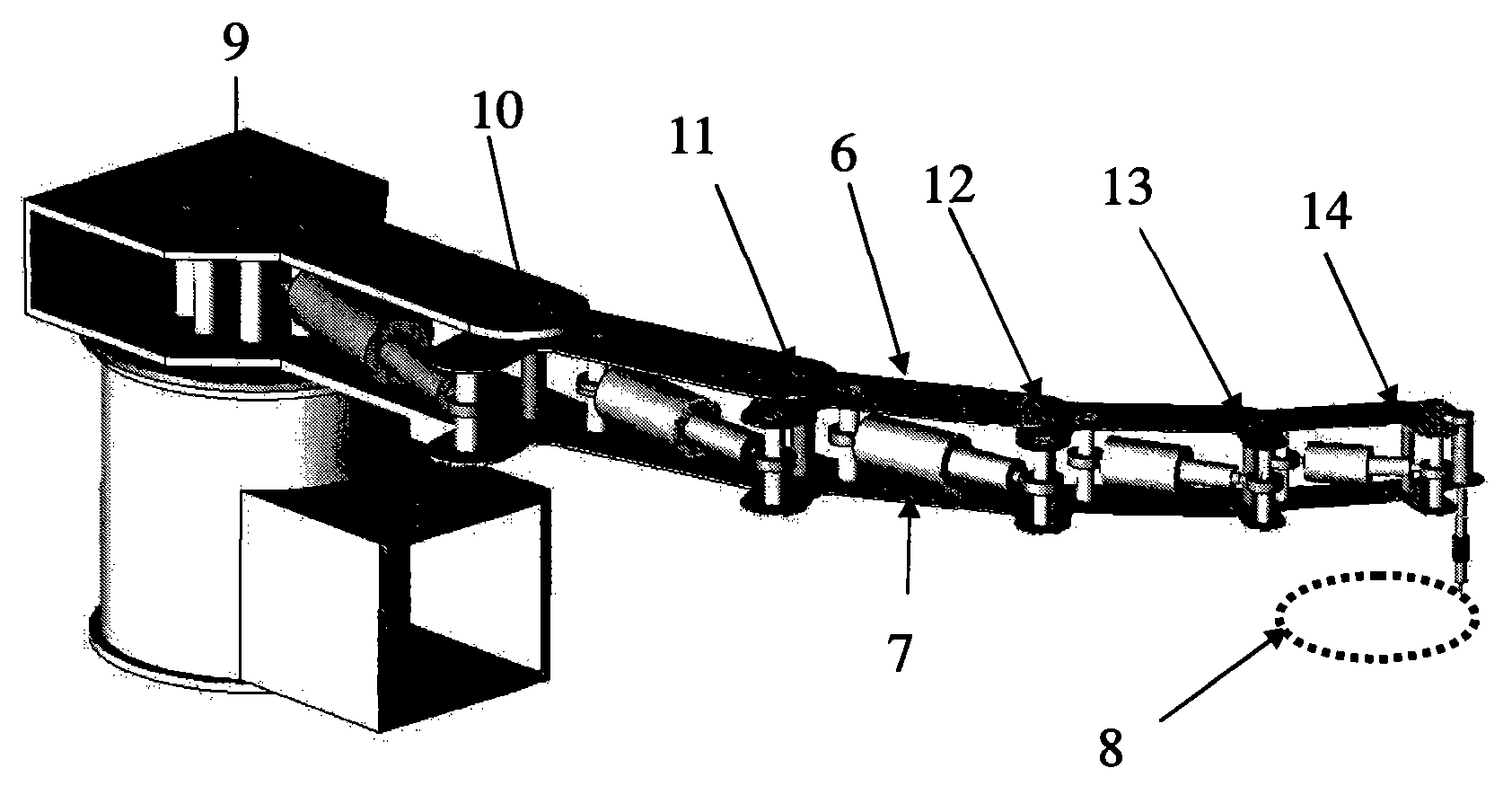
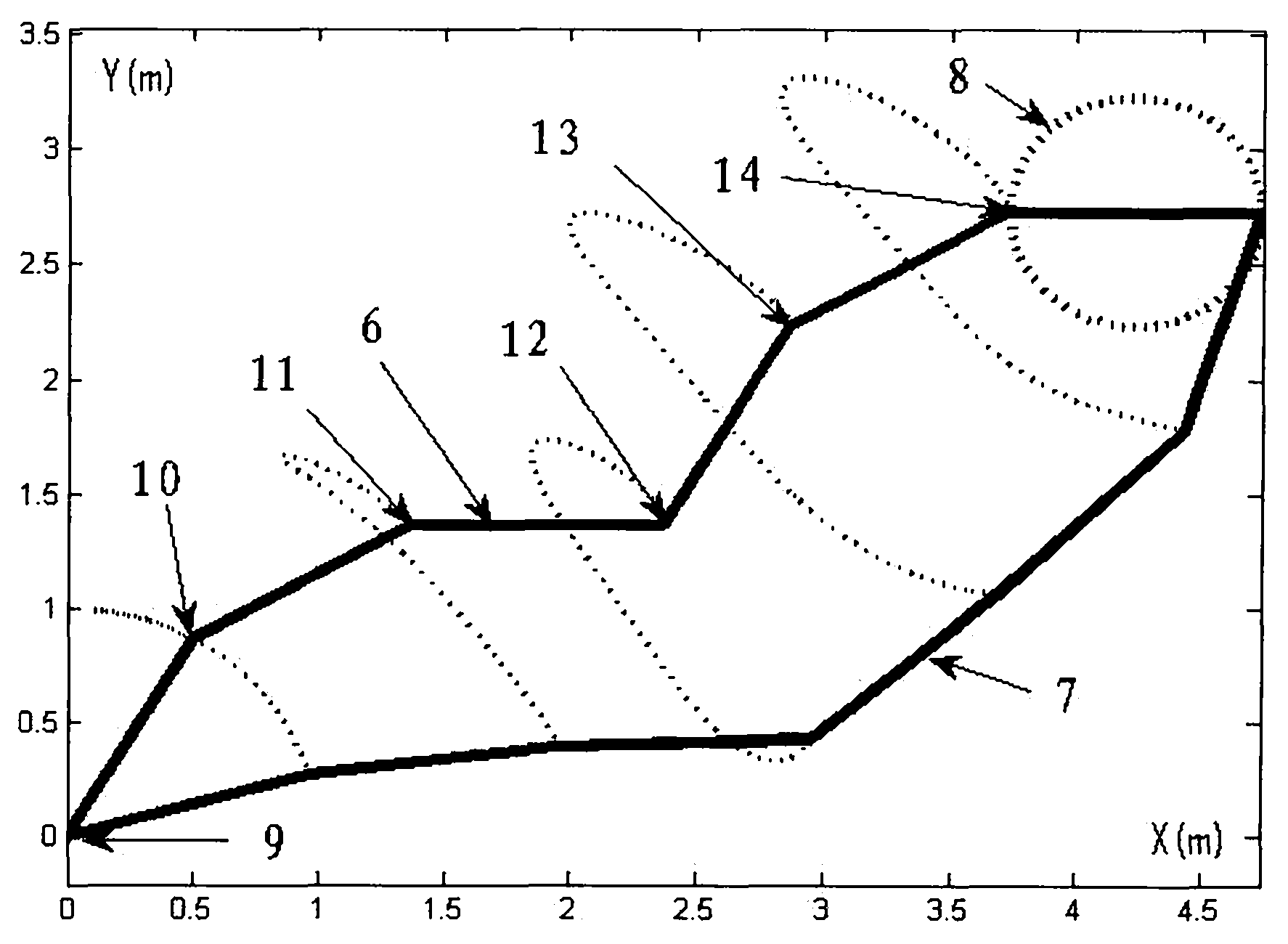
Repetitive motion planning method for redundant manipulator
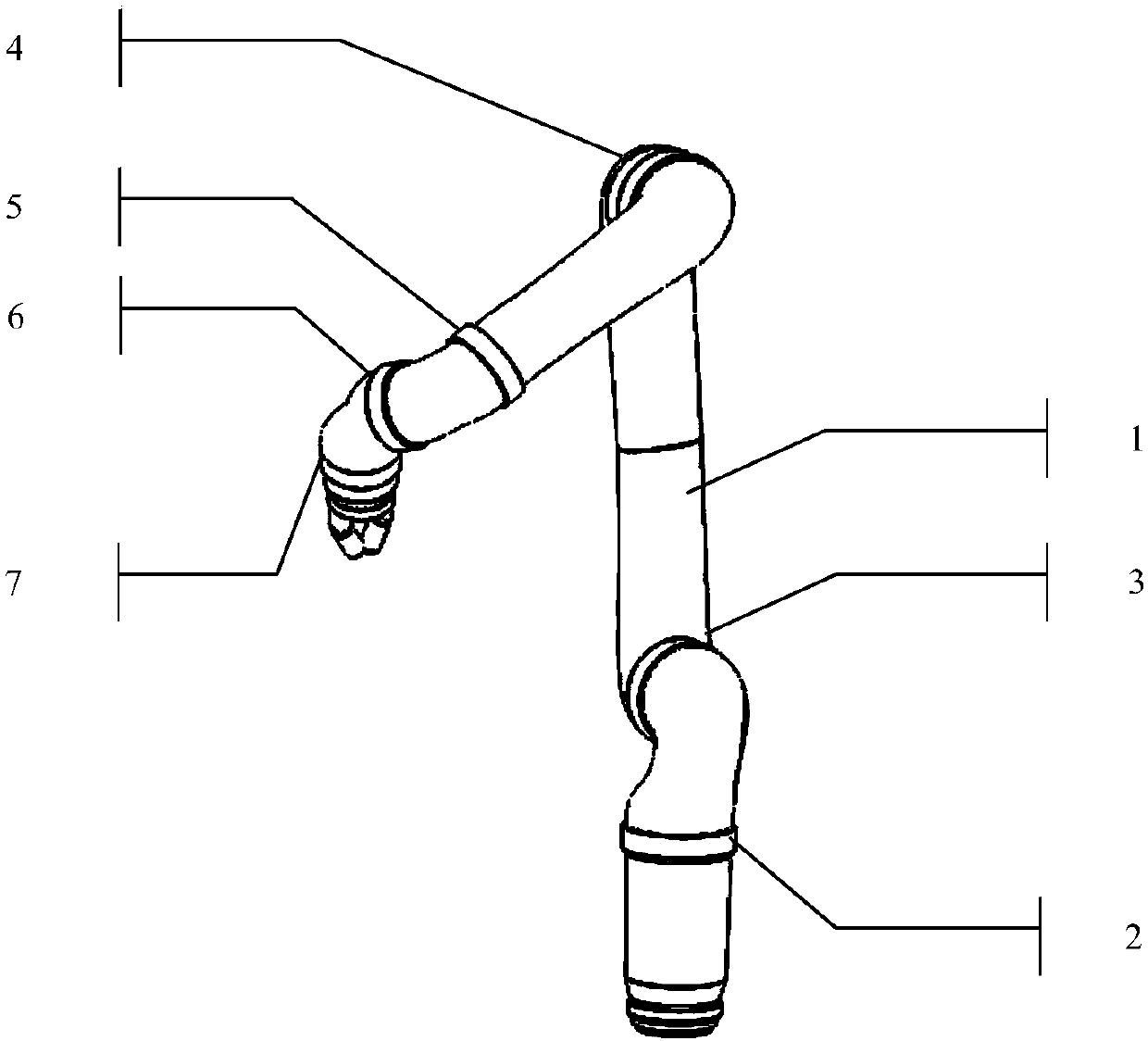
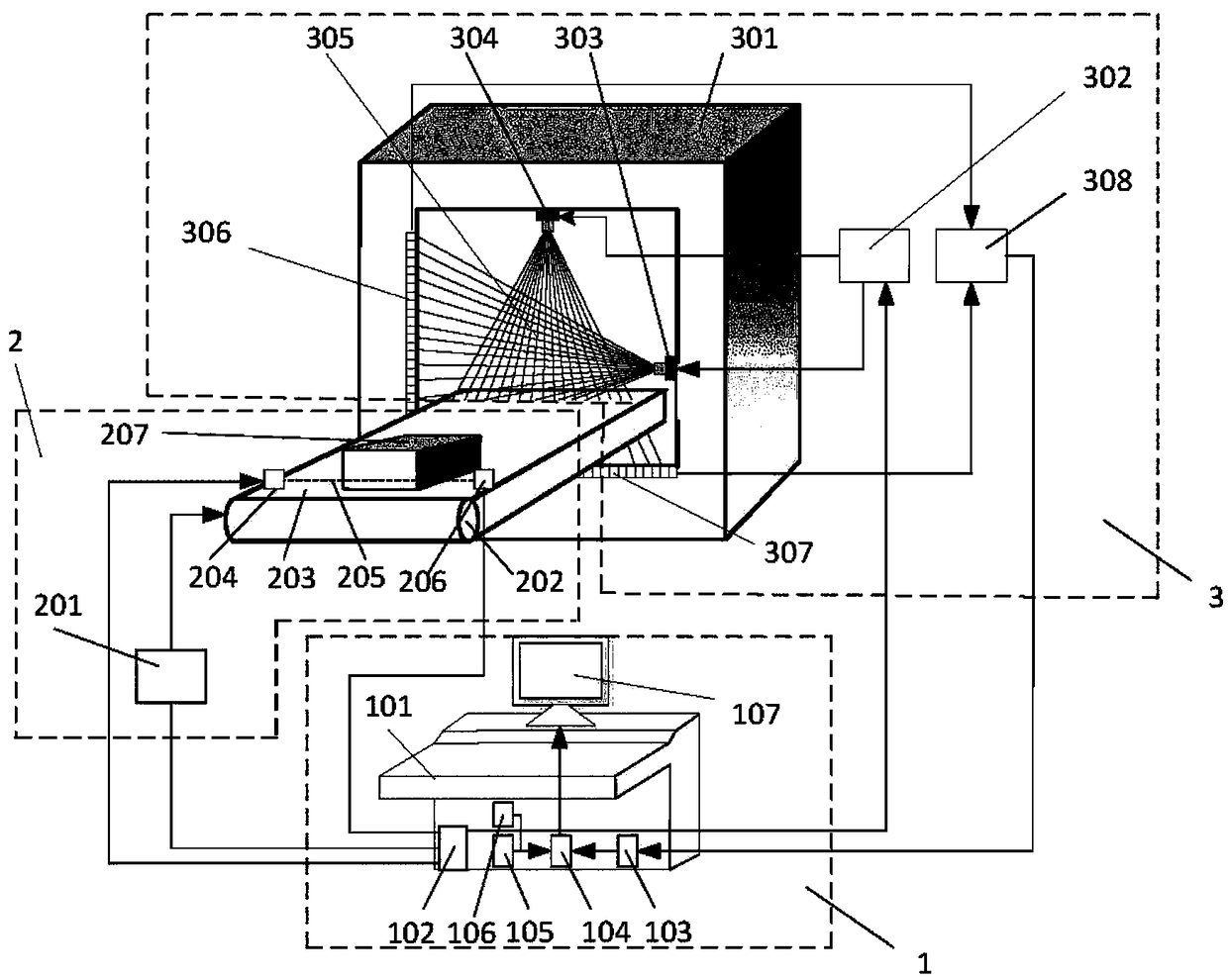
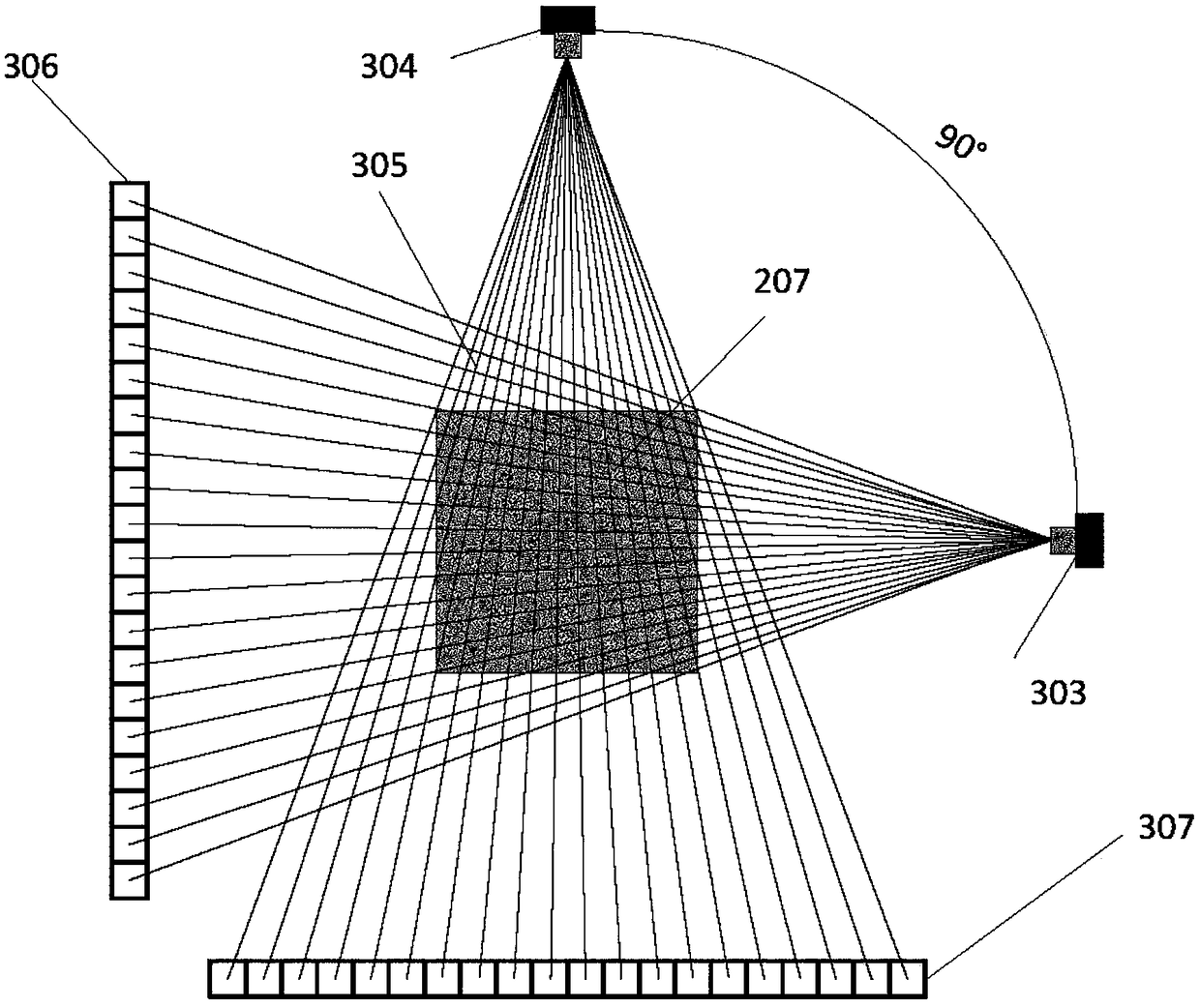
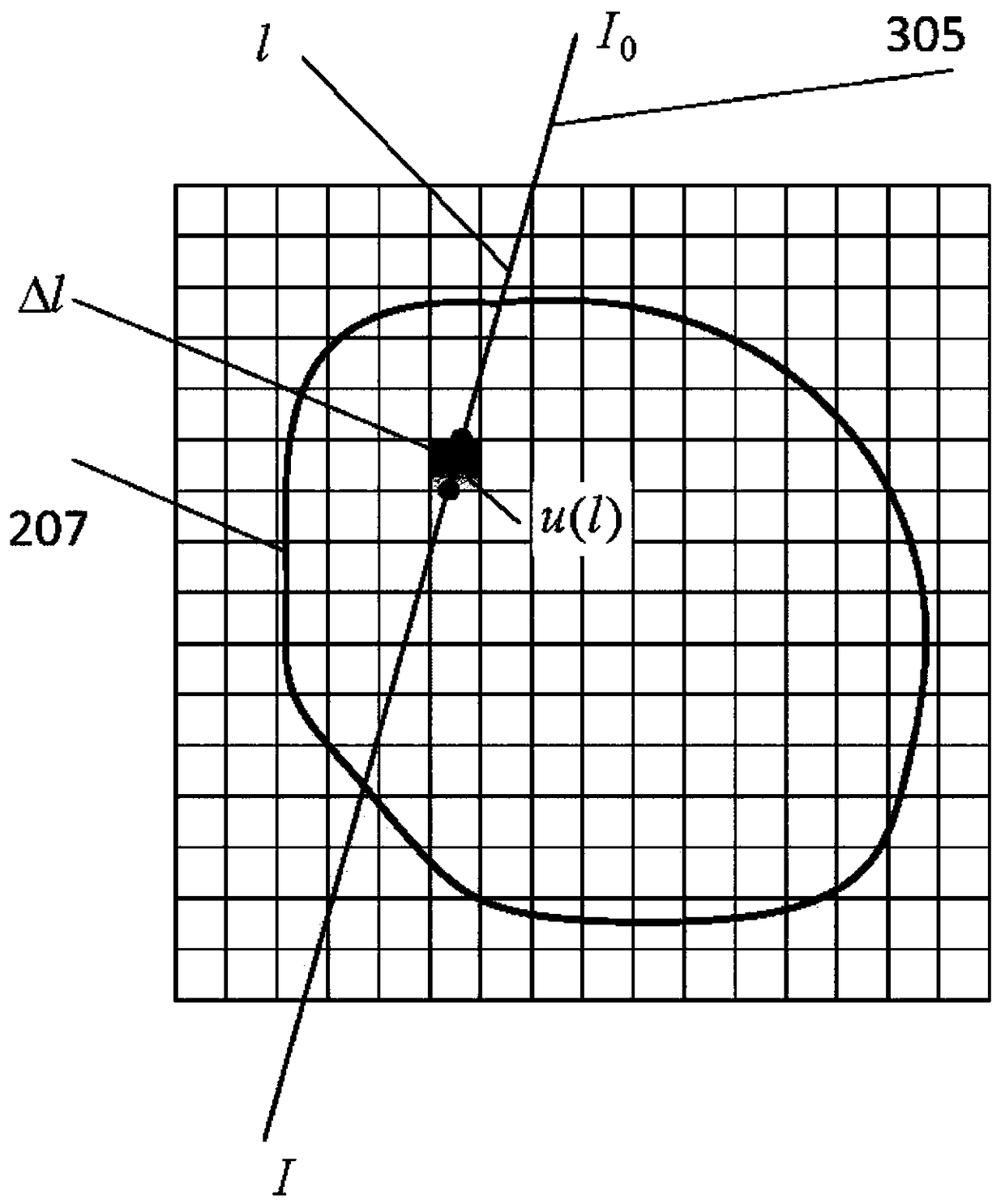
The invention provides a repetitive motion planning method for a redundant manipulator, which comprises the following steps of: 1) resolving a manipulator repetitive motion scheme on an acceleration layer by adopting quadratic model optimization through an upper computer, designing the minimum performance index as repetitive motion, and restraining by an acceleration Jacobian equation, a joint angle limit, a joint speed limit and a joint acceleration limit; 2) converting the quadratic model optimization in the step 1) into standard quadratic programming; 3) solving the standard quadratic programming in the step 2) by using a linear projection equation-based primal-dual neural-network solver or quadratic programming numerical method; and 4) transmitting a solving result in the step 3) to acontroller of a lower computer for driving the manipulator to move. The method realizes the repetitive motion of the manipulator on the acceleration layer, has good control effect on the redundant manipulator inconvenient to control, and can effectively prevent the manipulator from exceeding the limits and being physically damaged according to various joint limits.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
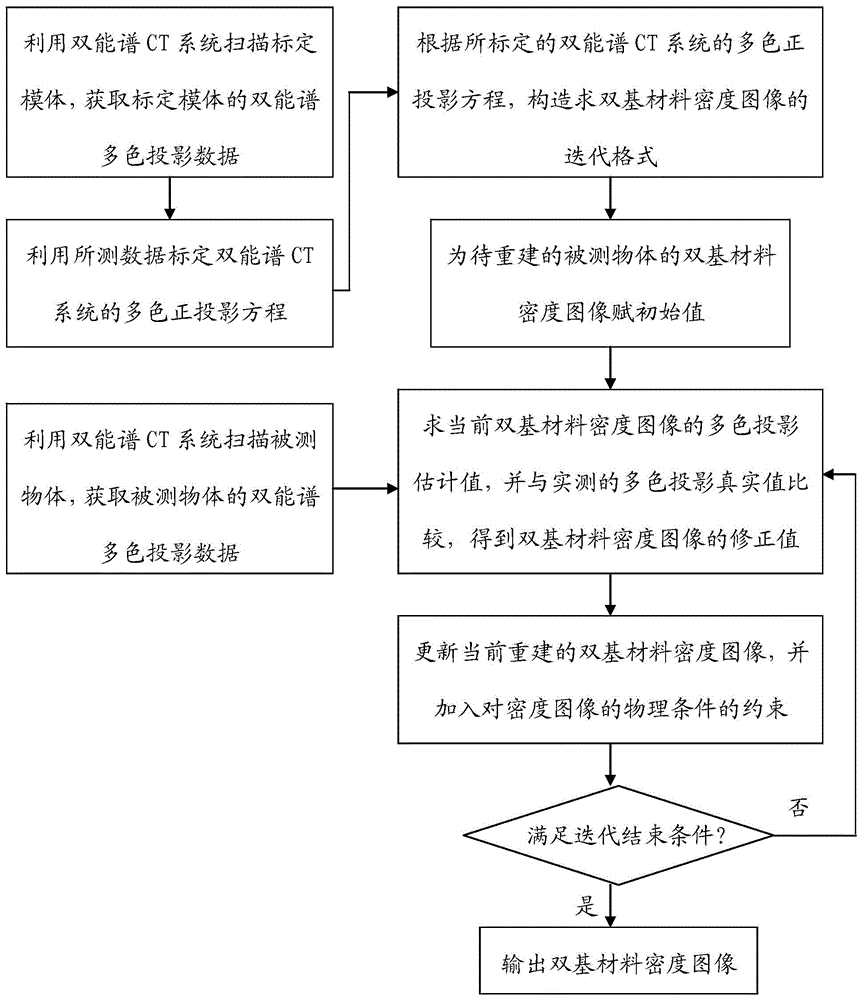
Method for iterating and reconstructing double-energy-spectrum CT image
InactiveCN103559729ALow energy spectrumImprove applicabilityImage enhancement2D-image generationAttenuation coefficientHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for iterating and reconstructing a double-energy-spectrum CT image. The method is used for reconstructing a base material density image of a measured object and comprises the following steps of (1) selecting a calibration model body containing tow types of different base materials according to the size of a material of the measured object; measuring the model body through a double-energy-spectrum CT system, and calibrating a double-energy-spectrum multi-color orthographic projection equation presenting a curvilinear relationship between a multi-color projection value and base material thickness combination; (2) collecting double-energy-spectrum multi-color projection data of the measured object by utilizing the double-energy-spectrum CT system; (3) constructing a iterative scheme according to the calibrated multi-color orthographic projection equation, and iterating and reconstructing the double-base-material density image of the measured object through comparison with the practically measured multi-color projection data and addition of a physical constraint condition. Compared with the existing method, the method for iterating and reconstructing the double-energy-spectrum CT image has the advantages that the high energy spectrum and the low energy spectrum of the double-energy-spectrum CT system and an attenuation coefficient of the base materials do not need to be detected in advance, and meanwhile the method is applied to the situation that the high energy spectrum and the low energy spectrum are matched with each other or not in geometry.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Self-calibration for a catadioptric camera
InactiveUS6870563B1Easy to useAccurate CalibrationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionView camera
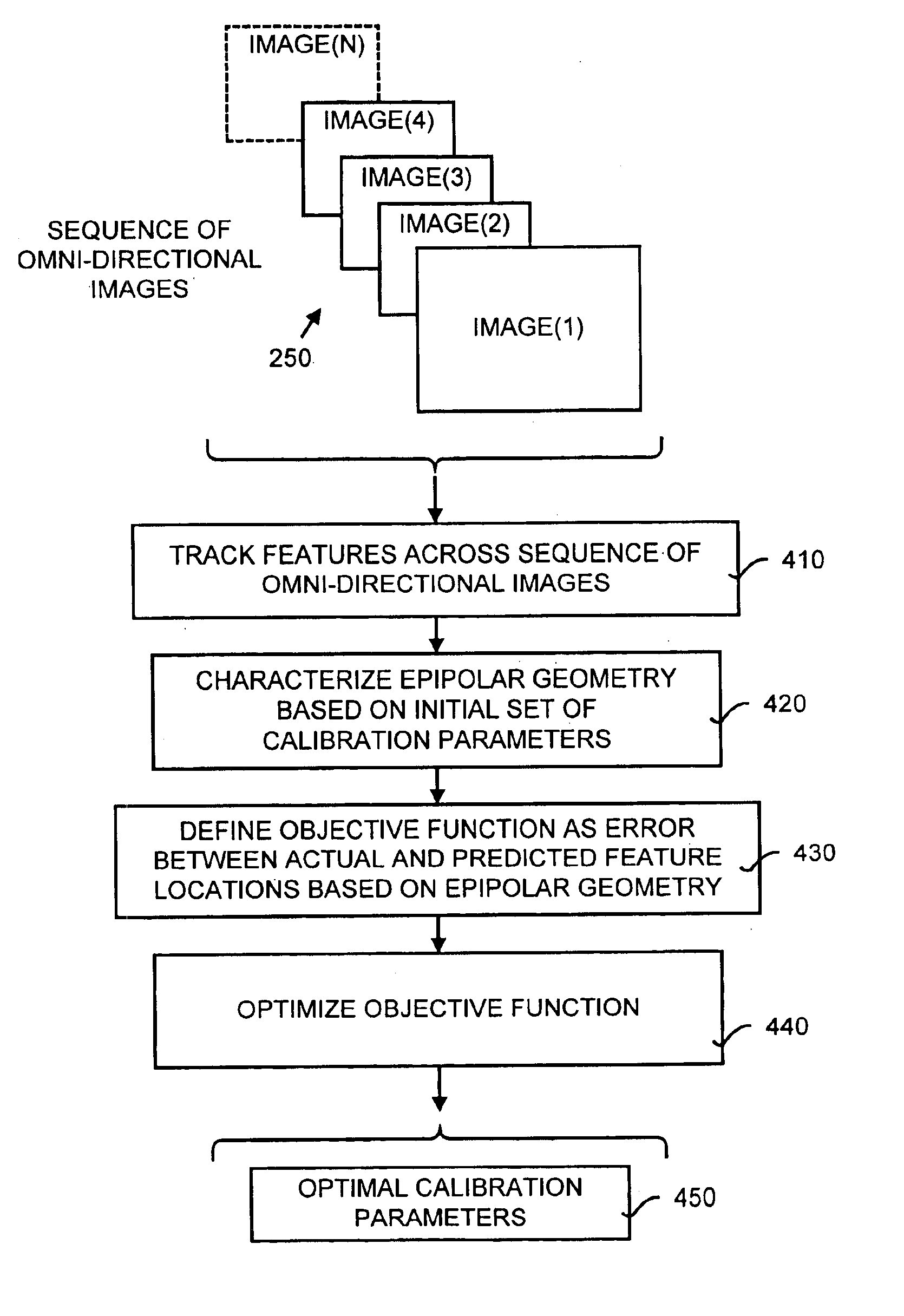
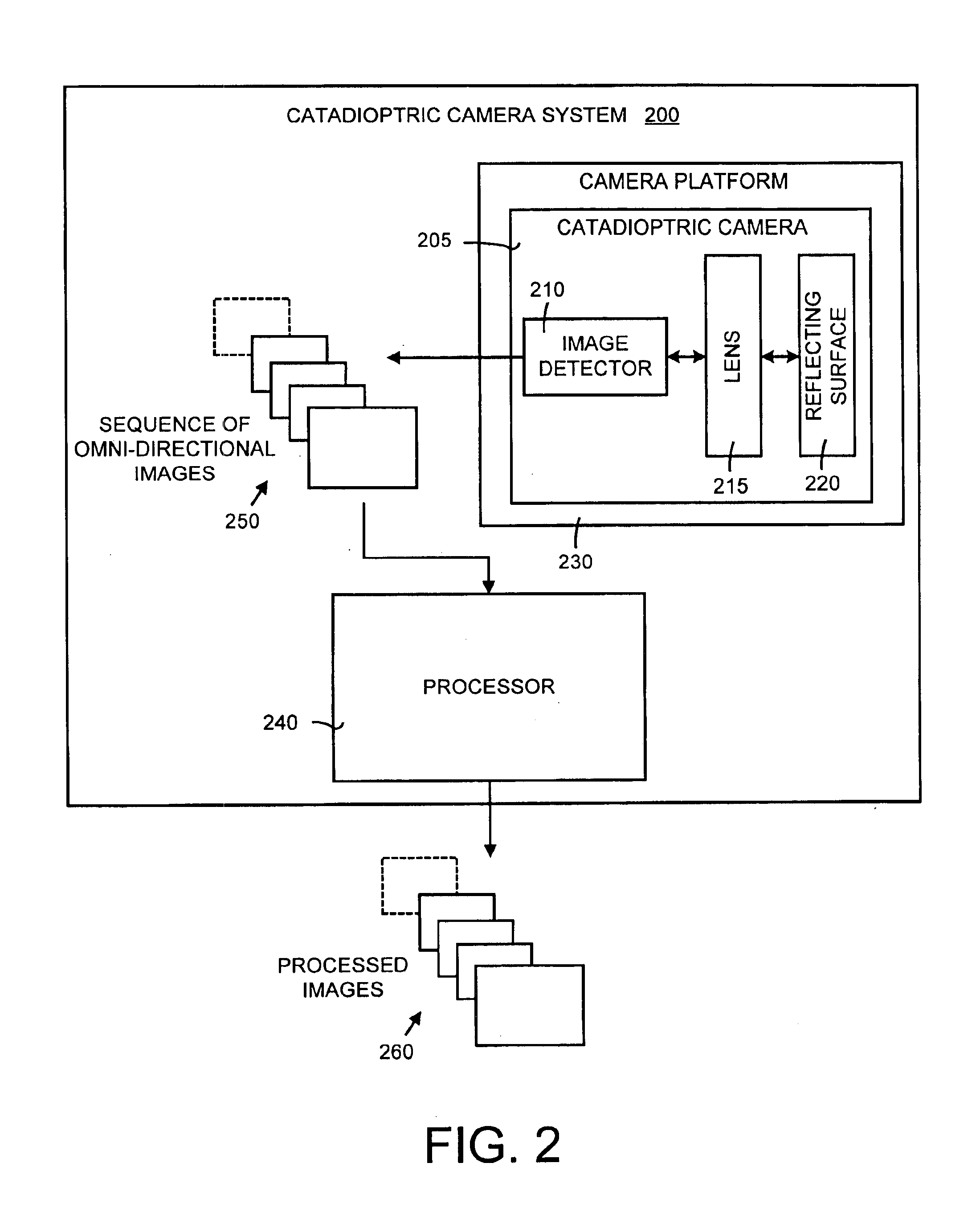
A method and a system for self-calibrating a wide field-of-view camera (such as a catadioptric camera) using a sequence of omni-directional images of a scene obtained from the camera. The present invention uses the consistency of pairwise features tracked across at least a portion of the image collection and uses these tracked features to determine unknown calibration parameters based on the characteristics of catadioptric imaging. More specifically, the self-calibration method of the present invention generates a sequence of omni-directional images representing a scene and tracks features across the image sequence. An objective function is defined in terms of the tracked features and an error metric (an image-based error metric in a preferred embodiment). The catadioptric imaging characteristics are defined by calibration parameters, and determination of optimal calibration parameters is accomplished by minimizing the objective function using an optimizing technique. Moreover, the present invention also includes a technique for reformulating a projection equation such that the projection equation is equivalent to that of a rectilinear perspective camera. This technique allows analyses (such as structure from motion) to be applied (subsequent to calibration of the catadioptric camera) in the same direct manner as for rectilinear image sequences.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
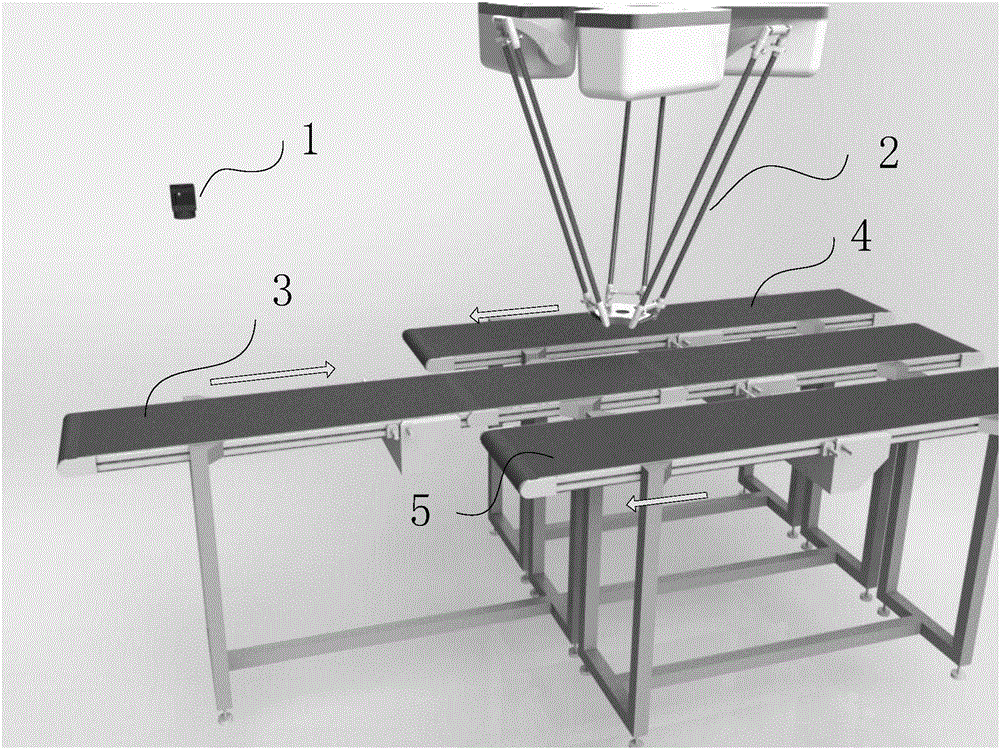
Delta robot control method and system for sorting multiclass workpieces
ActiveCN106737664AMeet processing needsLow costImage enhancementProgramme-controlled manipulatorInformation processingAcquisition time
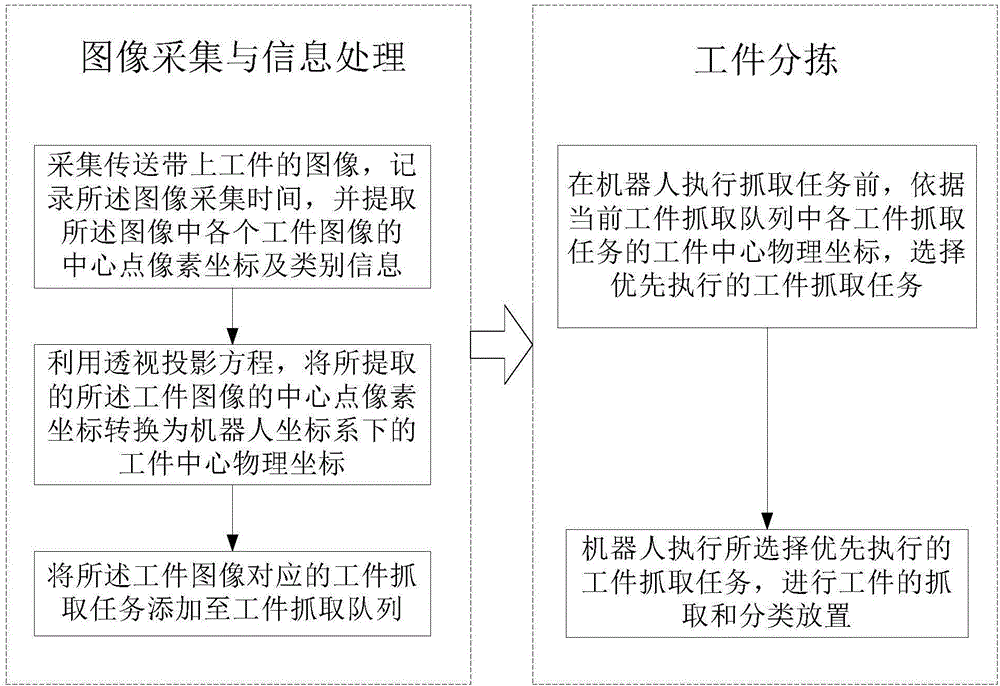
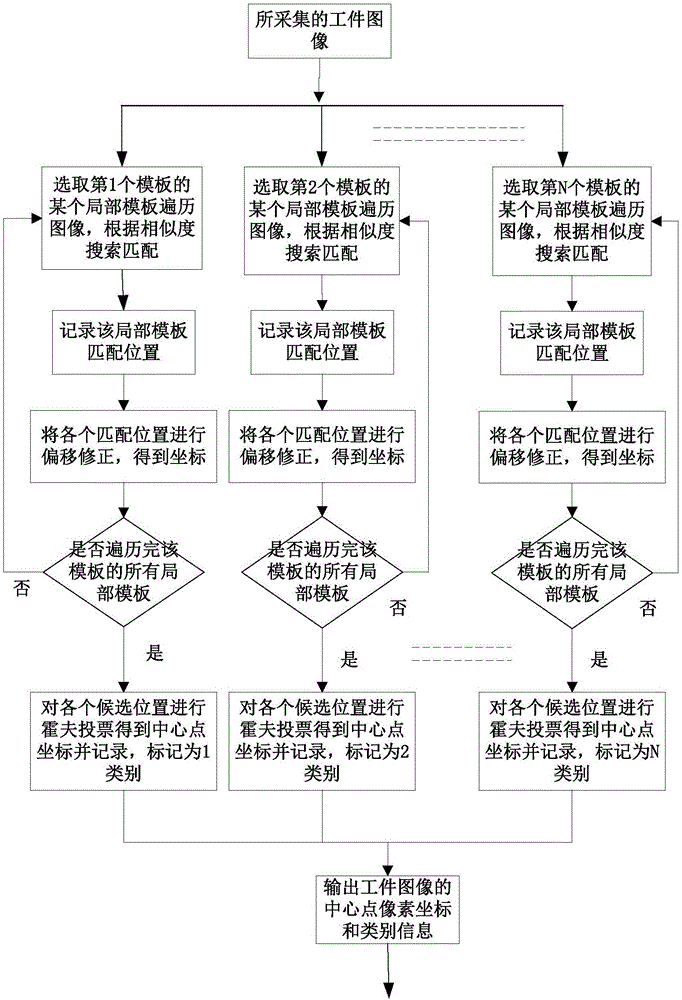
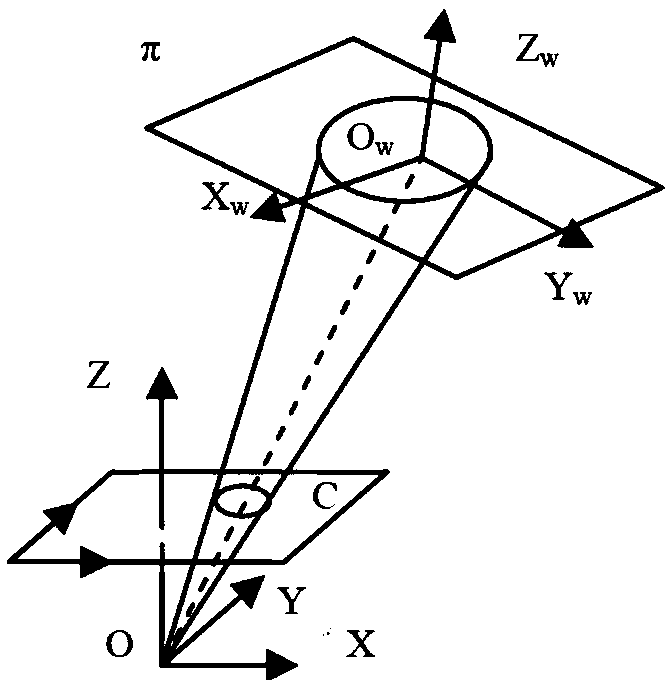
The invention relates to a delta robot control method for sorting multiclass workpieces. The delta robot control method for sorting multiclass workpieces comprises the step of image acquisition and information processing, specifically images of the workpieces on a conveyor belt are collected, the acquisition time is recorded and a center point pixel coordinate and class information of each workpiece image in the images are extracted, workpiece center point physical coordinates are obtained through a perspective projection equation, workpiece grasp tasks corresponding to the workpiece images are added to the workpiece grasp queue; and the step of workpiece sorting, specifically, before implementing the grasp task, according to the workpiece center point physical coordinates of each workpiece grasp task in current workpiece grasp queue, the workpiece grasp task has the priority to be implemented is selected; and based on the Ferrari's dynamic grasp algorithm, workpiece grasping and a calculation of sorting placement coordinates are conducted and the grasp task is implemented. The invention further provides a delta robot control system for sorting multiclass workpieces based on the method. The delta robot control method and system for sorting multiclass workpieces saves costs and spaces by grasping and sorting multi-class workpieces through a Delta robot.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
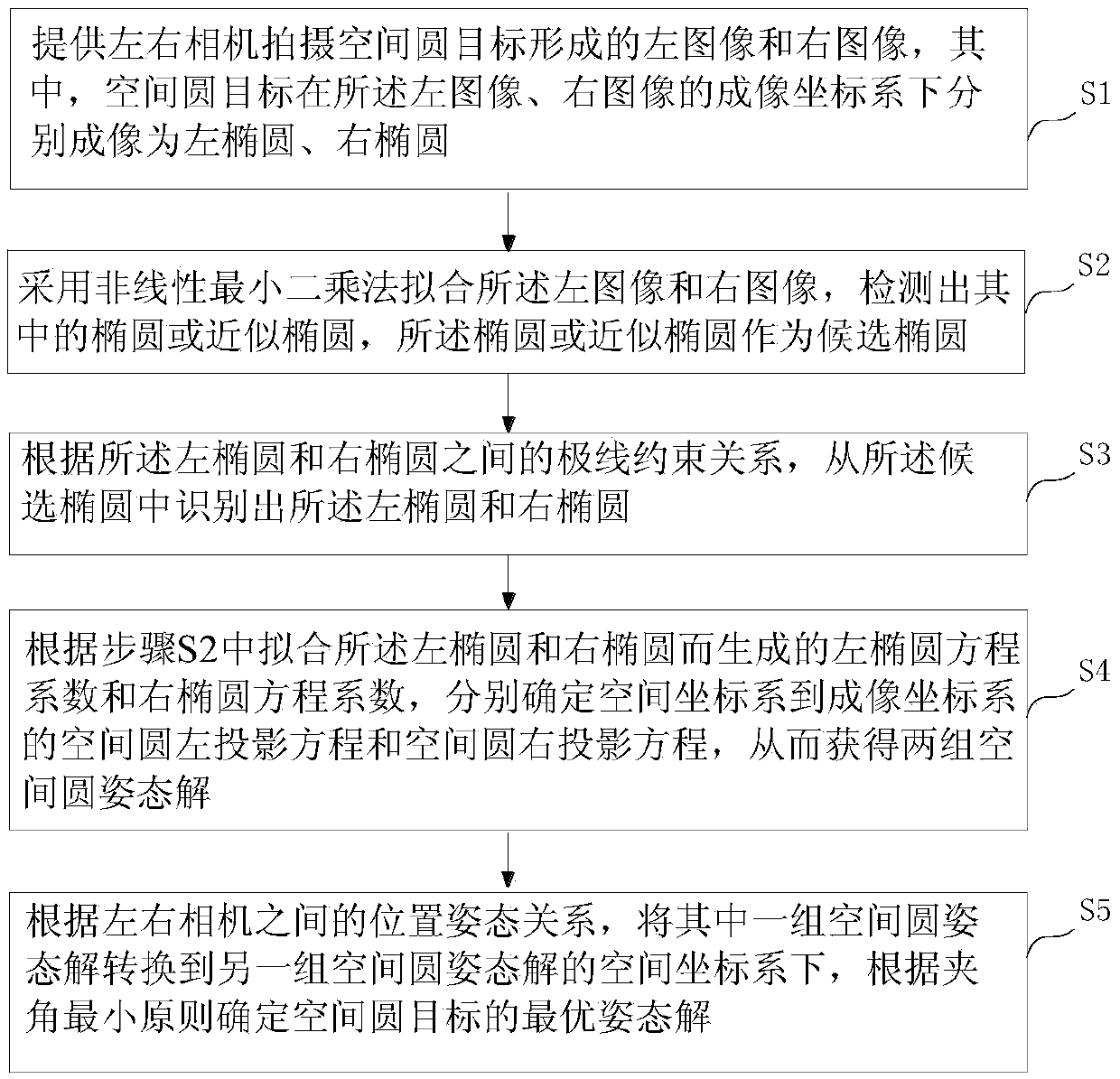
Measuring method for relative pose of non-cooperative spatial circular object
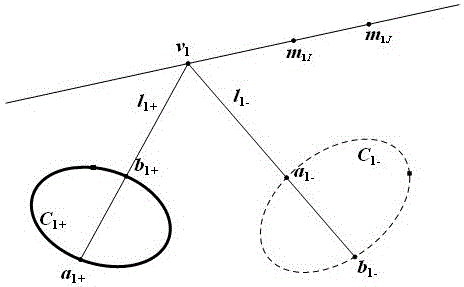
ActiveCN105509733ARealize position calculationNo ambiguityNavigation instrumentsPicture interpretationEllipseAmbiguity
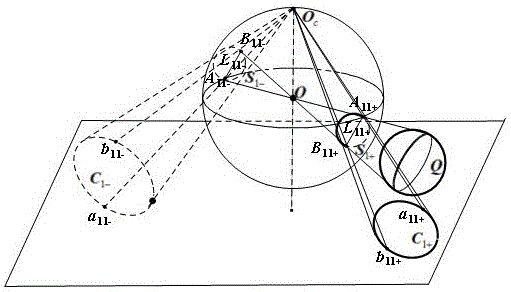
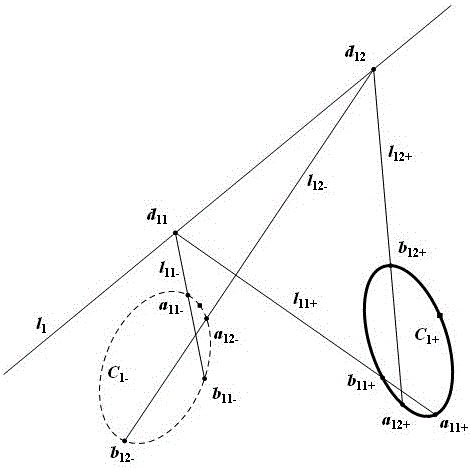
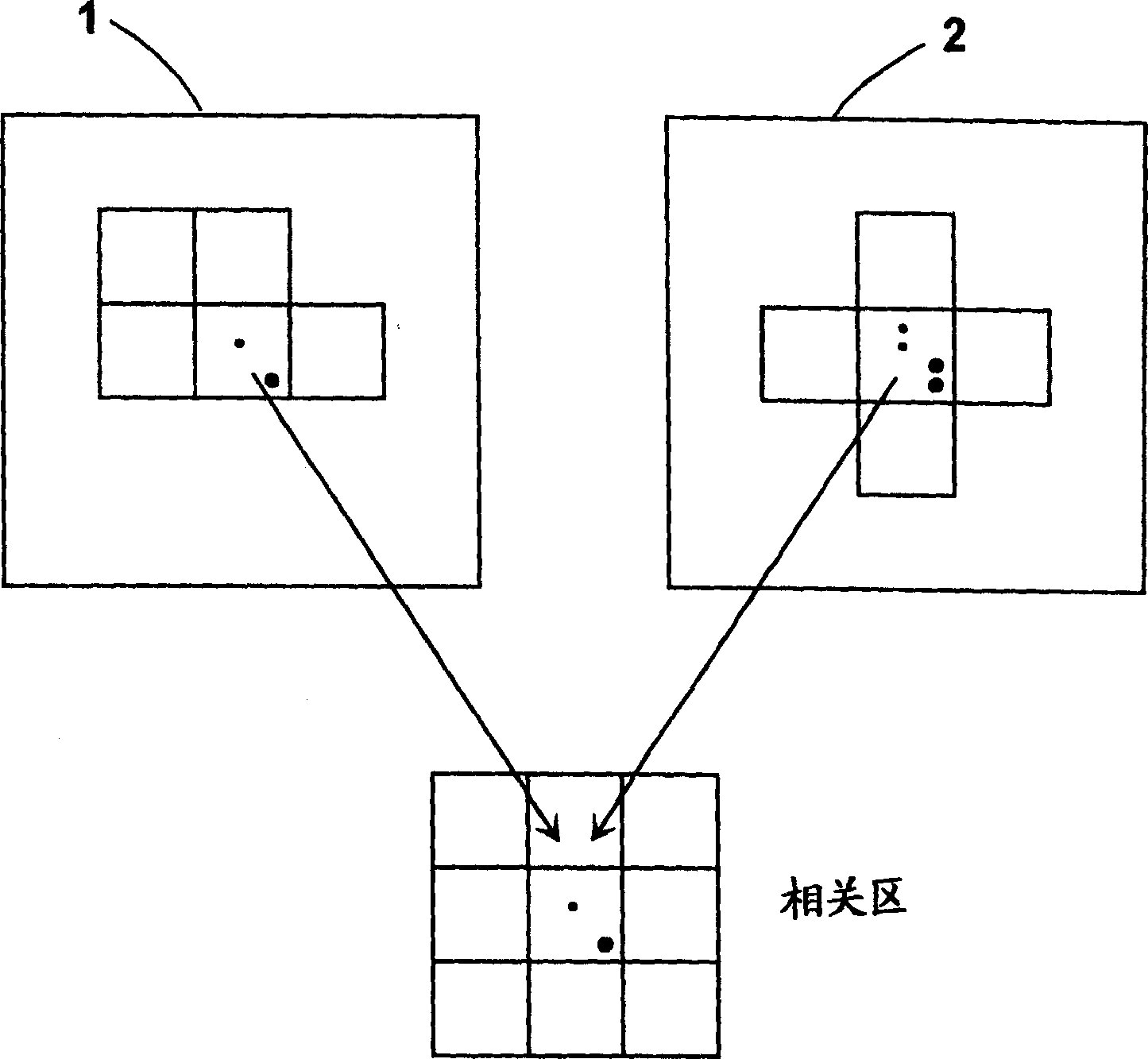
The invention provides a measuring method for the relative pose of a non-cooperative spatial circular object. The method comprises the following steps: providing left and right cameras to shoot left and right images formed by the spatial circular object, wherein images of the spatial circular object comprise a left ellipse and a right ellipse; carrying out non-linear least square fitting to detect ellipses or approximate ellipses and using the detected ellipses or approximate ellipses as candidate ellipses; recognizing the left ellipse and the right ellipse from the candidate ellipses according to epipolar constraint relationship between the left ellipse and the right ellipse; respectively determining a left projection equation of a spatial circle and a right projection equation of the spatial circle according to an equation coefficient of the left ellipse and the equation coefficient of the right ellipse generated by fitting the left ellipse and the right ellipse so as to obtain two sets of pose solutions of the spatial circle; and converting one of the two sets of pose solutions of the spatial circle to the spatial coordinate system of the other set according to the positional and attitude relationship between the left and right cameras and determining the optimal pose solutions of the spatial circular object according to the principle that an included angle is the smallest. The measuring method provided by the invention can overcome the problem of ambiguity in the process of pose resolution.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
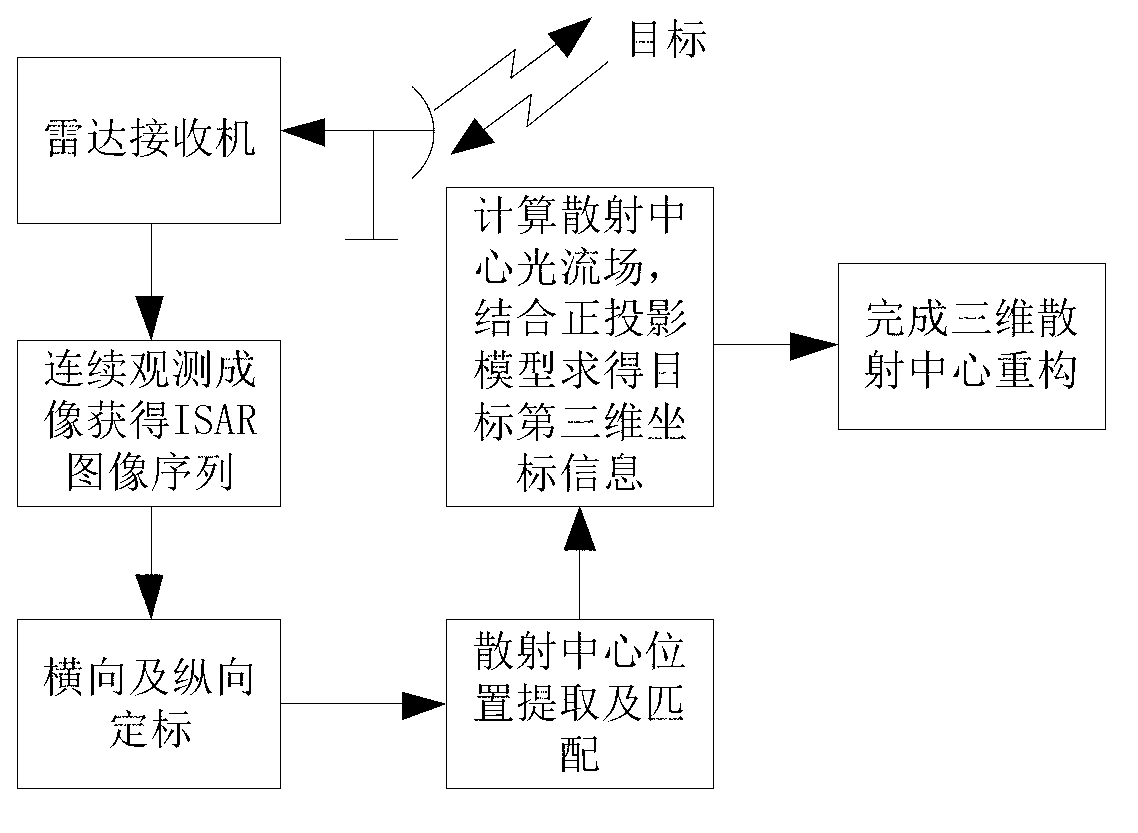
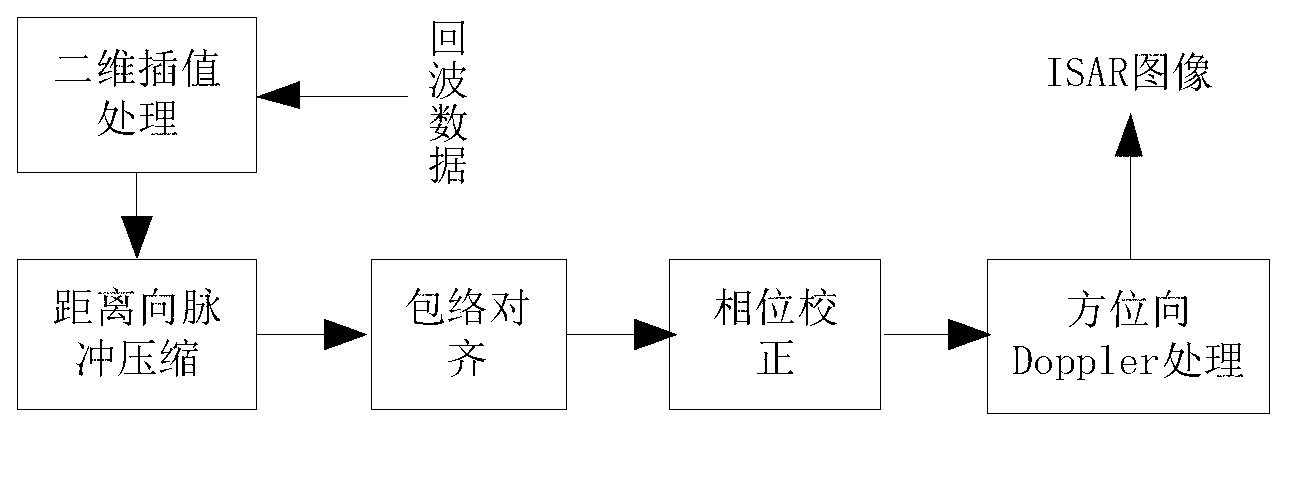
Method for reconstructing target three-dimensional scattering center of inverse synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN103217674AResolve mismatchSmall amount of calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
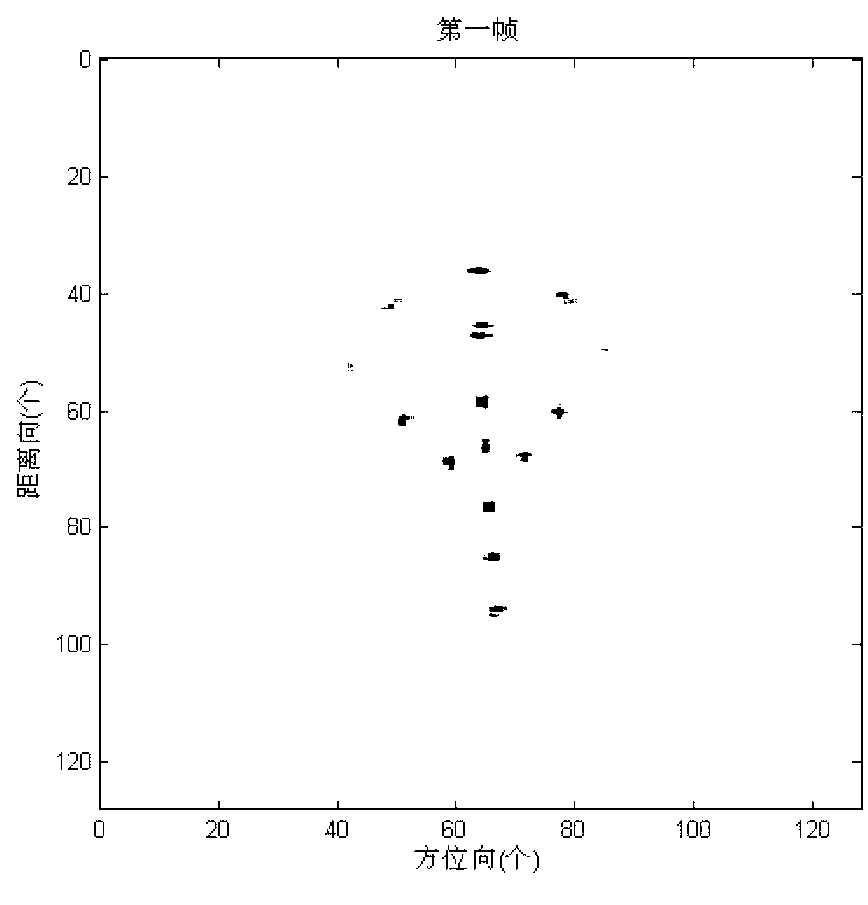
The invention provides a method for reconstructing target three-dimensional scattering center inverse synthetic aperture radar. The method for reconstructing the target three-dimensional scattering center of the inverse synthetic aperture radar comprises the following steps: conducting continuous image formation on echo data after motion compensation so as to obtain an ISAR two-dimensional image sequence; respectively conducting horizontal scaling and vertical scaling on the information storage and retrieval (ISAR) two-dimensional image sequence so as to obtain a position coordinate of the scattering center; and respectively extracting a position coordinate of the scattering center in an ISAR two-dimensional image of each frame, calculating a displacement velocity field of every two adjacent frames of the scattering center of the ISAR two-dimensional image, combining projection equation and target motion equation of an orthographic projection model so as to obtain estimated values of a third dimension coordinate by combining a projection equation and a target motion equation of an orthographic projection model, and averaging multiple estimated values to obtain the final third dimension coordinate. Therefore, reconstruction of the target three-dimensional scattering center is completed directly. The method for reconstructing the target three-dimensional scattering center of the inverse synthetic aperture radar does not need cost of extra system hardware, can distinguish scattering centers with different heights in the same distance and position resolution unit, does not need to utilize prior information such as observation perspective of the radar, and has relatively small calculating amount.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for object tracking
ActiveUS8055020B2Reduce effortSave computing powerTelevision system detailsImage analysisImaging processingField of view
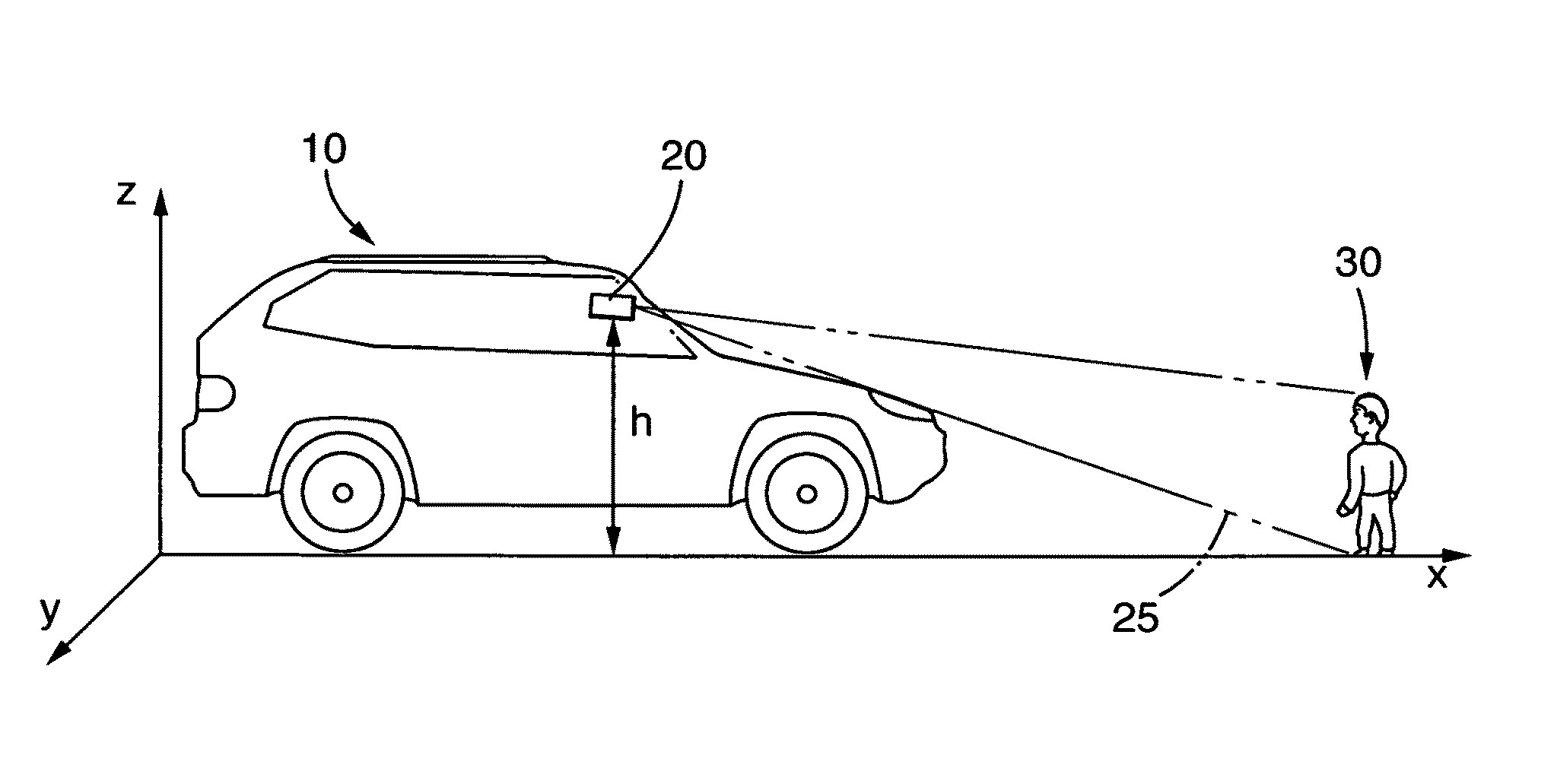
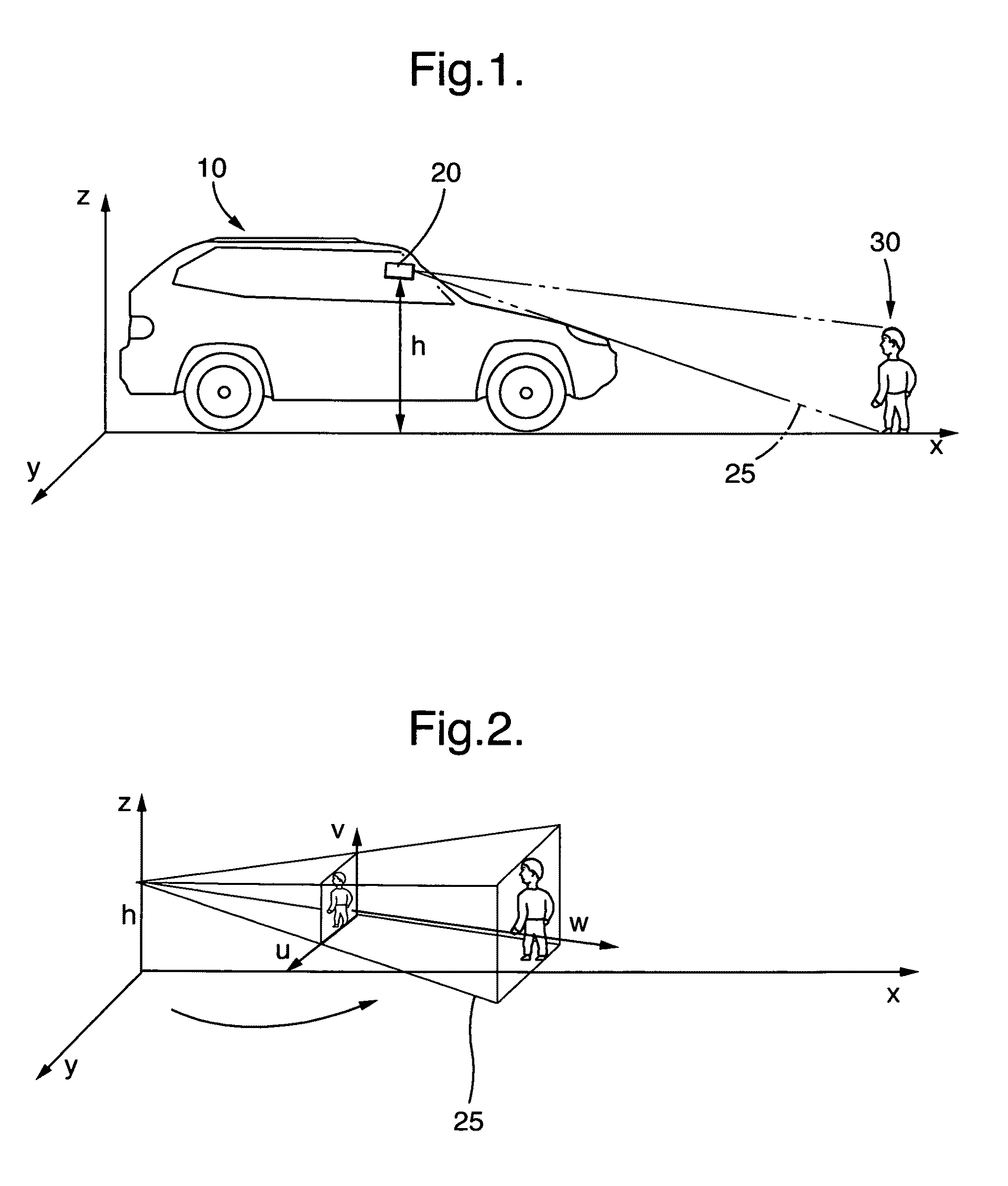
The present invention relates to a method for the recognition and tracking of a moving object, in particular of a pedestrian, from a motor vehicle, at which a camera device is arranged. An image of the environment including picture elements is taken in the range of view of the camera device (20) by means of the camera device at regular time intervals and those picture elements are identified with the help of an image processing system which correspond to moving objects to be tracked. A picture element is extracted for each of these objects which represents a projection in image coordinates of that spatial point at which the object contacts a road plane The movement of the corresponding spatial point in the road plane is tracked by means of a state estimator which uses an at least four-dimensional state vector whose components are a position of the spatial point in the road plane and an associated speed in the road plane, wherein the tracking of the movement by the state estimator includes the steps that a prediction is generated for the state vector, this prediction is converted into image coordinates via suitable projection equations, an error to be expected for this prediction is calculated in image coordinates by means of a covariance matrix, and this prediction is compared with the picture element extracted in a later image and is updated.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Three-dimensional flight track planning method for electric transmission line inspection unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN106403948AImprove track planning efficiencyReduce 3D trajectory planning timeNavigational calculation instrumentsSequence planningPlanning approach
The present invention relates to a three-dimensional flight track planning method for an electric transmission line inspection unmanned aerial vehicle. The three-dimensional flight track planning method comprises: 1, establishing the models of obstacles, setting cylindrical models for wrapping each obstacle in the map of an unmanned aerial vehicle onboard computer, and obtaining the plane projection equation of the smallest cylinder capable of wrapping the obstacle; and 2, according to the detected flight environment information, carrying out unmanned aerial vehicle overall-situation flight track planning by using a BP neural network algorithm, and obtaining a reference flight track. According to the present invention, the electric transmission line inspection unmanned aerial vehicle flight track planning method is researched, and the reference flight track is planned by using the BP neural network algorithm based on the sequence planning idea, such that the flight track planning efficiency is improved, and the three-dimensional flight track planning time of the electric transmission line inspection of the unmanned aerial vehicle is reduced.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Method of calibrating paracatadioptric camera using image of single sphere and circular points
InactiveCN106327504AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisVanishing lineSurface contour
The present invention relates to a method for calibrating a paracatadioptric camera using the images of a single sphere and circular points. According to the method, two different points are selected from the image of the sphere, so that two vanishing points are obtained; a straight line where the two vanishing points are located is a vanishing line, the images of the vanishing line and the image of the sphere intersect with the images of the circular points, and three images can provide the images of three circular points; and the inner parameters of the camera are solved through using the constraint of the images of the circular points for an absolute conic curve image. The method specifically includes the following steps of: fitting a mirror surface contour projection equation and a target projection equation; estimating an antipodal sphere image; determining the images of the circular points; and solving the inner parameters of the paracatadioptric camera. In a process of solving the inner parameters of the paracatadioptric camera, five inner parameters of the paracatadioptric camera are solved by using three images of a target shoot by the paracatadioptric camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Pose measuring method based on coaxial circle characteristics of target
ActiveCN104517291AImprove fitting accuracySimplify the measurement stepsImage analysisPicture interpretationEllipsePoint projection
The invention relates to a pose measuring method based on coaxial circle characteristics of a target and belongs to the technical field of computer vision measurement. The pose measuring method is characterized in that the target is provided with coaxial circle characteristics, curve extraction and ellipse fitting technologies are combined to obtain two coaxial circular projection equations in an image, and circular point projection coordinates and vanishing line equation of a target plane are obtained by means of relation of absolute conic, vanishing line and circular points in projection geometry of the circle characteristics; by means of the polar line-pole theorem, circular center projection coordinates of two coaxial circles are obtained by the vanishing line equation of the plane, and pose and position information of the target is solved by taking the actual distance of the coaxial circles as prior condition and combining the projection of the circular points and the projection coordinates of the circular centers. The pose measuring method based on the coaxial circle characteristics of the target has the advantages that measuring of target pose is completed by means of a single target image of coaxial circle characteristics, so that the pose measuring method is simple to operate and applicable to measurement in real time. Meanwhile, without manual intervention, high-precision measurement is realized.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for calibration of parabolic catadioptric camera by employing ball image and common self-polar triangles
The present invention relates to a method for calibration of a parabolic catadioptric camera by employing a ball image and common self-polar triangles. A ball in a space is employed as a calibration object to fit a mirror surface contour projection equation and a ball image equation under a parabolic catadioptric camera and calculate an antipodal ball image equation and an equation of an image ofa great circle having a center of a circle being coincided with a center of a circle of a unit virtual ball and being parallel with a projection small circle of the ball on a unit visual ball model, two common poles, corresponding to two common self-polar triangles formed by the ball image and the antipodal ball image, of the image of the great circle are connected with two common poles to solve avanishing line, a relation of the projection of the circle and the vanishing line is employed to solve the images of circular ring points, and three images are shot to obtain images of the three circular ring points, and the images of the circular ring points and the constraint of the internal parameter matrix of the camera are employed to complete calibration of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Semi-analysis modeling method of contact area between ball-end milling cutter and guide vane
ActiveCN106502202AGuaranteed accuracyHigh precisionNumerical controlRectangular coordinatesMilling cutter
The invention belongs to the five-axis numerical control machine tool machining field, and provides a semi-analysis modeling method of a contact area between a ball-end milling cutter and a guide vane. The semi-analysis modeling method of a contact area between a ball-end milling cutter and a guide vane includes the following steps: performing cutter path programming, and setting numerical control machining parameters; establishing a workpiece coordinate system, and acquiring the parameter equations of the design surface and the machining surface of the vane, and the movement track equation of the ball center of the milling cutter; determining the cutter contact point and the cutter location point during the machining process, taking the cutter contact point and the cutter location point as the origin to respectively establish a three dimensional rectangular coordinate system; converting solving problems of No.1-No.4 boundary curves of the contact area into projection equation solving problems of the curves in an XL-YL two dimensional coordinate system, and respectively solving the projection equations of the No.1-No.4 boundary curves; and obtaining the intersection points of the No.1-No.4 boundary curves, by mutually making a simultaneous system of equations, and obtaining the projection of the contact area. The semi-analysis modeling method of a contact area between a ball-end milling cutter and a guide vane can solve the problem of performing analysis modeling of the contact area during the process of processing a straight-vane-body vane molded in a vane grid by means of a ball-end milling cutter on a five-axis numerical control machine tool.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and device for determining height and pitch angle of stereo camera
ActiveCN105469386ALow environmental requirementsEasy to implementImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxOptical axis
The invention discloses a method and a device for determining the height and pitch angle of a stereo camera. The method comprises the steps of: using internal and external parameters, which are obtained by pre-calibration, of the stereo camera to carry out epipolar correction on a first image and a second image in an image pair shot by the stereo camera; determining a corresponding relation between parallax and vertical coordinates of an image coordinate system; according to the corresponding relation between the parallax and the vertical coordinates of the image coordinate system and a triangle method three-dimensional reconstruction principle, determining projection equations of camera optical axes on a reference surface; and according to the projection equations of the camera optical axes on the reference surface and triangle relations among the camera optical axes, determining the height and the pitch angle of the stereo camera relative to the reference surface. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that auxiliary tools such as a calibration board and a calibration block are not needed, the requirements on environment are low, the method is easy to realize, and the universality is high; in addition, there is no need to move a calibration object to obtain a plurality of groups of images, the height and the pitch angle of the stereo camera relative to the reference surface can be determined by only one group of image pair, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DAHUA TECH CO LTD
Method for calibrating camera by utilizing concentric circles
InactiveCN101783018AEasy and accurate calibrationRealize CalibrationImage analysisAutonomous Navigation SystemImaging processing
The invention discloses a method for calibrating camera by utilizing concentric circles, and belongs to the technical field of image processing, which comprises the following steps: pasting white paper on a horizontally even panel to prepare a calibration object; acquiring three initial images; fitting according to an elliptical point set to obtain an elliptical image matrix; and obtaining a projection equation of a circle by adopting projective transformation, calculating circle center projection of two concentric circles according to a correlation of a projection equation of the concentric circles, and obtaining a symmetrical matrix according to the circle center projection so as to obtain an internal parameter matrix of the camera and complete the internal parameter calibration of the camera. The method avoids an error caused by a mode that the internal parameters of the camera are determined by calculating imaginary circular points, and a linear method is adopted to simply, conveniently and accurately calibrate all the internal parameters of the camera (including a principal point position, an aspect ratio and an obliquity factor). The method is suitable for vision-based autonomous navigation system and non-contact industrial detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
X-ray CT multi-phase current inspection based on hereditary algorithm
InactiveCN1745713AReduced completeness requirementsQuick collectionComputerised tomographsTomographyObservational errorGram
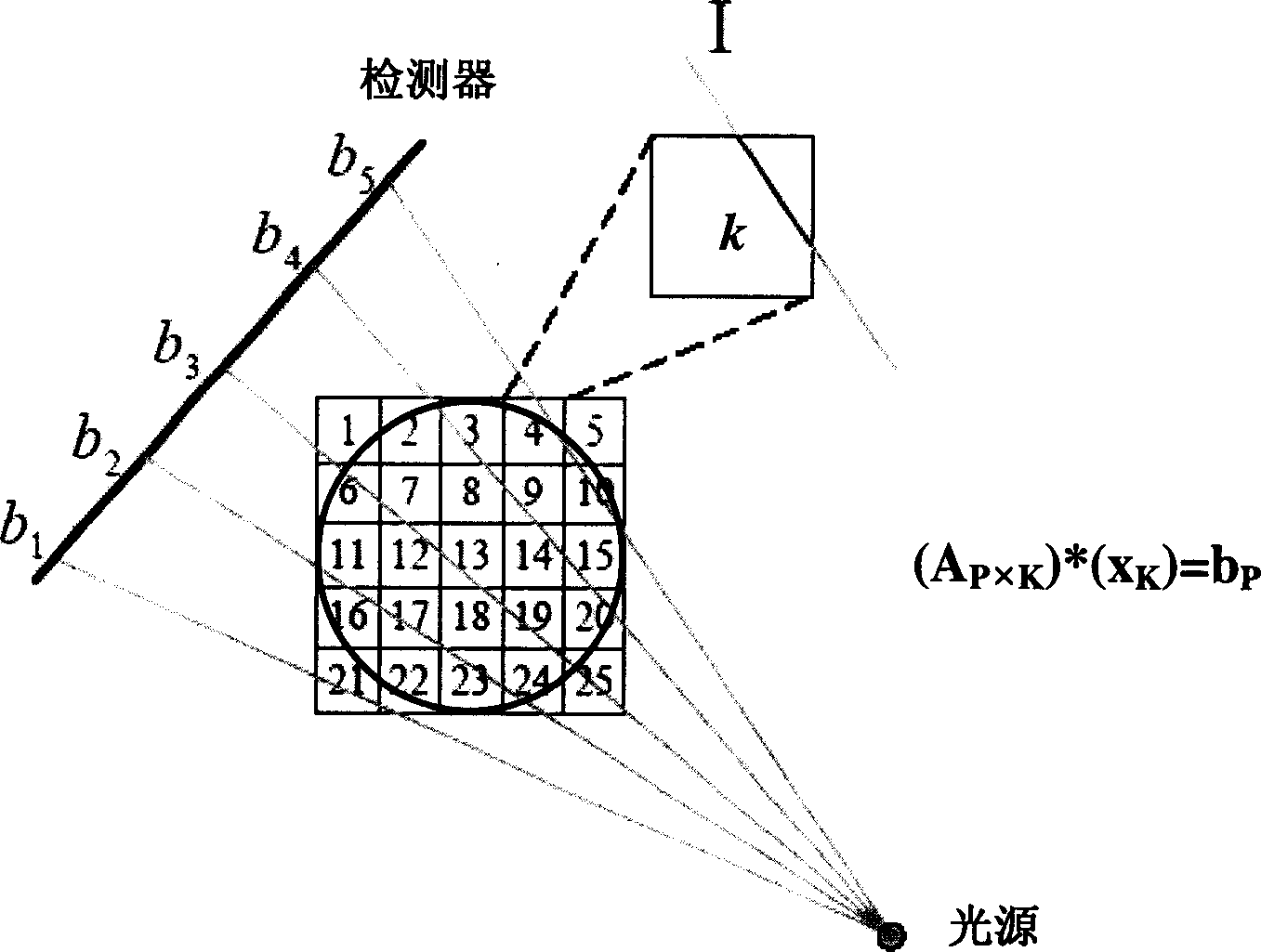
A method based on genetic algorithm for detecting the multi-phase flow of computerized X-ray tomography includes such steps as simplifying the system to be detected, geometrically splitting the region to be detected, acquiring the X-ray projection data, discrelizing the X-ray projection equation set, creating actual genetic algorithm for reconstructing image, and converting the numerical solution to the phase / medium distribution gram of the region to be detected. Its advantages are high anti-interference power and high reconstruction fidelity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
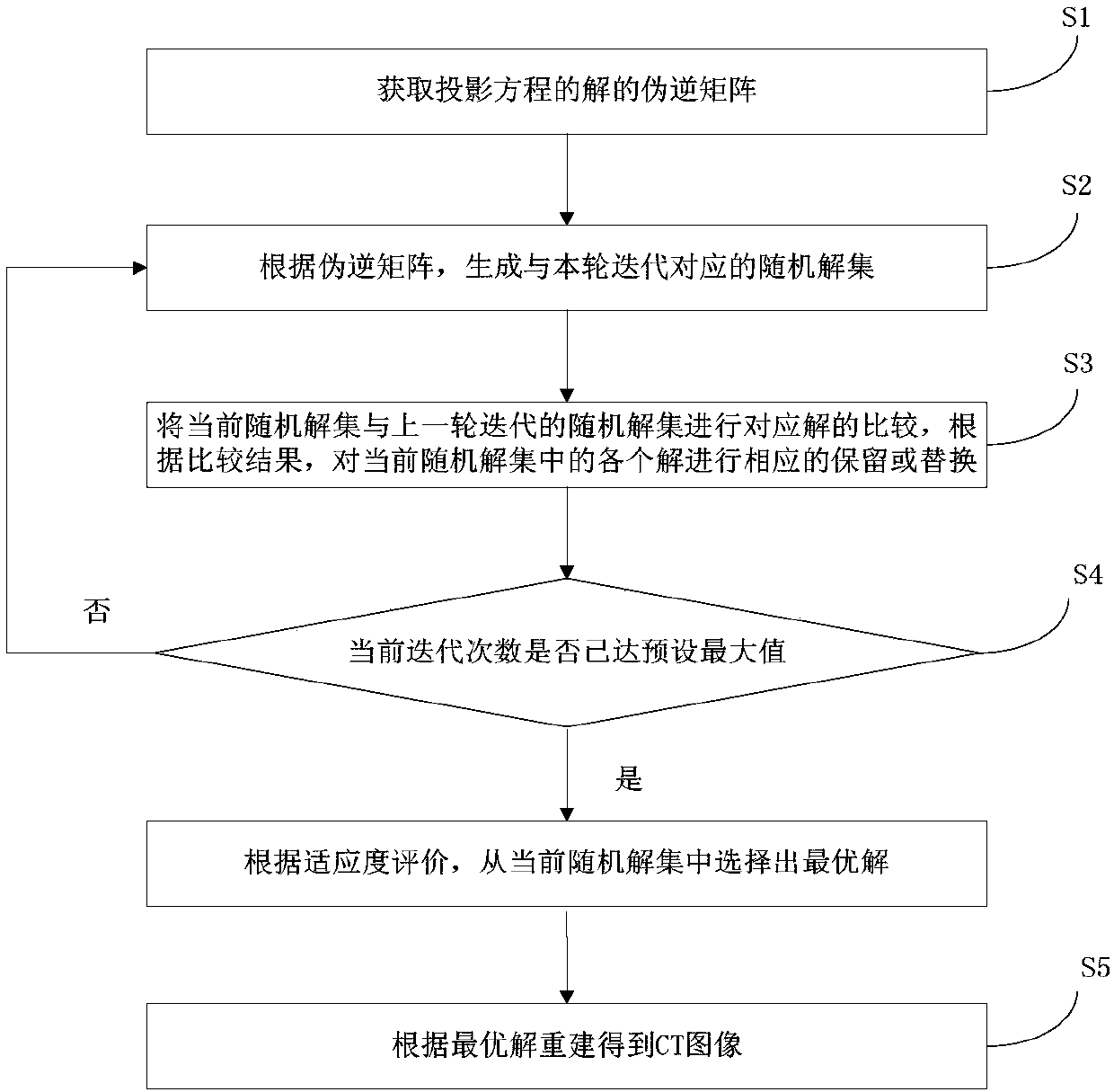
CT sparse projection image reconstruction method and CT sparse projection image reconstruction device at limited sampling angle
ActiveCN108280859AQuality assuranceDiversity guaranteedReconstruction from projectionImage generationImaging processingProjection image
The invention discloses a CT sparse projection image reconstruction method and a CT sparse projection image reconstruction device at a limited sampling angle. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a pseudo-inverse matrix of a projection equation according to projection data, generating a random solution set according to the pseudo-inverse matrix, reserving or replacing each solution in the current random solution set correspondingly, selecting an optimal solution from the current random solution set when the number of iterations reaches a preset maximum value, and adopting the selected optimal solution as a to-be-obtained reconstruction result. The device comprises a memory for storing at least one program and a processor for loading at least one program to execute the method of theinvention. According to the method, the pseudo-inverse of a discretized projection reconstruction equation is used as an initial solution of the algorithm, so that the quality of the initial solutionis guaranteed. A set of solutions are generated through random walk, and then the iterative optimization is carried out respectively. The diversity of optimization paths is guaranteed. Troubles causedby the defects of an initial solution and an iteration path of a traditional reconstruction method can be overcome. The method and the device are applied to the technical field of image processing.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for calibrating parabolic refraction and reflection camera via single ball and parallel circle properties
InactiveCN106651956AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisIntersection of a polyhedron with a lineImage plane
A method for calibrating a parabolic refraction and reflection camera via single ball and parallel circle properties is disclosed. In a parabolic refraction and reflection system, two small parallel circles are formed when a ball is projected onto a unit visual ball for a first time. The two parallel circles in a space have two pairs of conjugated virtual intersection points, and two conjugated virtual intersection points that are collinear with a point at infinity on a plane where space circles are positioned are circular ring points. An image of the circular ring points is obtained on an image plane according to colinearity of the image of the circular ring points and a vanishing point; three images provide images of three groups of circular ring points. Intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved via constraints posed on an absolute conic image by the images of the circular ring points. The method specifically comprises the following steps: a mirror surface contour projection equation and a target projection equation are fitted, an antipodal sphere image of a sphere image is estimated, the images of the circular ring points are determined, and the intrinsic parameters of the parabolic refraction and reflection camera are solved.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Method of determining a three-dimensional velocity field in a volume
ActiveUS20050062954A1Add depthAccurately determinedAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesImage analysisVoxelImage capture
A method of determining a three-dimensional velocity field in a volume, the particles within the volume being excited to radiate by illuminating said volume, a) at least two cameras simultaneously image capturing the observation volume at two different instants of time (t1, t2) at least, b) the observation volume being divided into small volume elements (voxels), c) each voxel being projected at the location x, y, z onto the image points (xn, yn) of the at least two cameras using a projection equation, d) the intensity of all the voxels being reconstructed from the measured intensity of the respective ones of the associated image points (xn, yn), e) a plurality of voxels being combined to form an interrogation volume, f) the displacement vector (dx, dy, dz) being determined at the times (t1, t2) at the same location by a three-dimensional cross correlation of the two interrogation volumes.
Owner:LAVISION
Self-calibrating projection equation method for implementing stereo PIV method
A method for determining a conjugate distance equation for automatic calibration in the execution of stereo-PIV(Particle Image Velocimetry) is provided to execute calibration of stereo-PIV even in a closed space or micro-channel. A method for determining a conjugate distance equation includes ate least two cameras and a single light slit. The cameras observe a region of the light slit in different directions, and point-to-point correspondence between the cameras is determined by moving and measuring each interrogation field in camera images according to optical correlation. The conjugate equation is decided using an approximation method according to internal and external camera parameters.
Owner:LAVISION
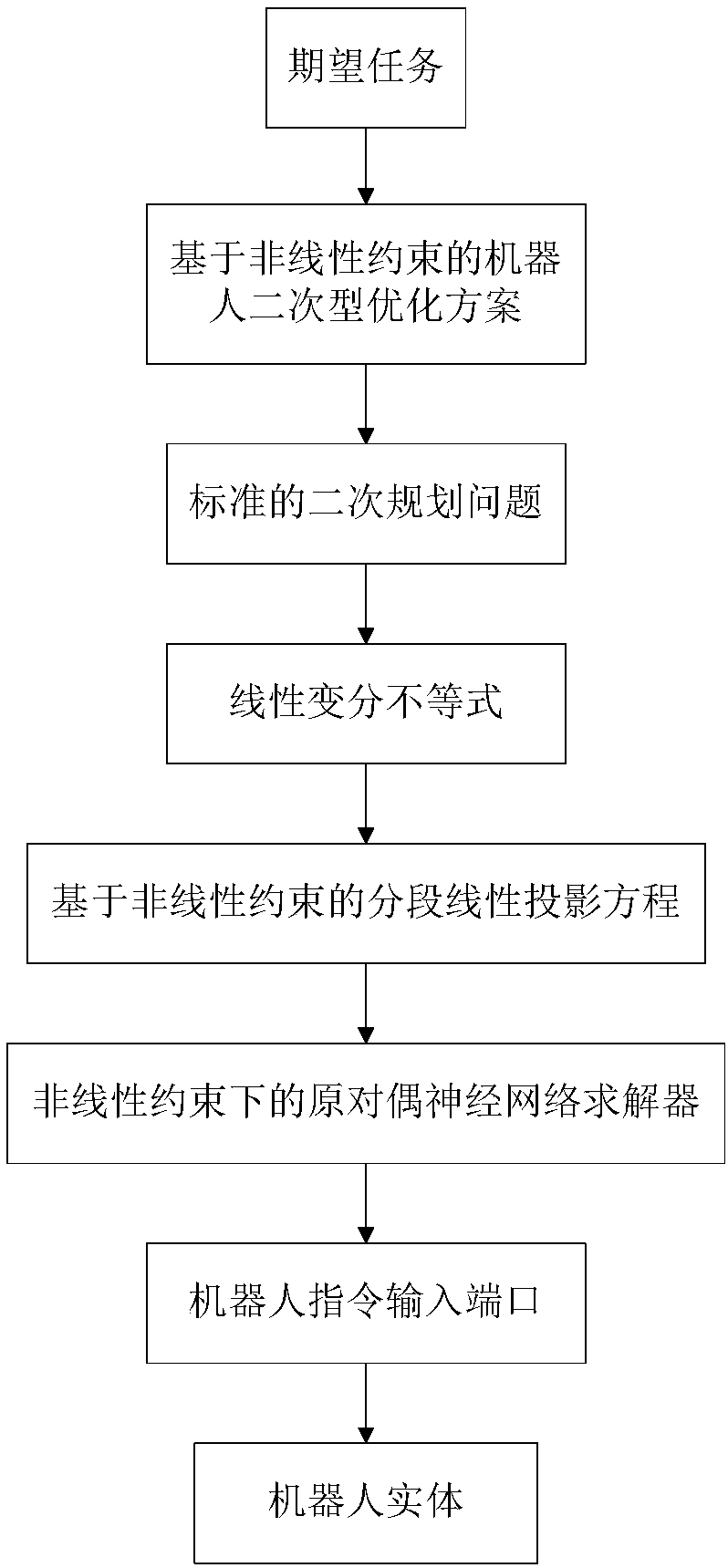
Nonlinear constrained primal-dual neural network robot action planning method
ActiveCN108015766AEliminate the initial error problemOvercome the problem of error accumulationProgramme-controlled manipulatorNerve networkStandard form
The invention discloses a nonlinear constrained primal-dual neural network robot action planning method, which comprises the steps of acquiring a current state of a robot, and adopting a quadratic optimization scheme for carrying out inverse kinematics analysis on a robot track on a speed layer; converting the quadratic optimization scheme to a standard form of a quadratic planning problem; enabling a quadratic planning optimization problem to be equivalent to a linear variational inequality problem; converting the linear variational inequality problem to a solution of a piecewise linearity projection equation based on nonlinear equality constraint; utilizing a nonlinear constrained primal-dual neural network solver for solving the piecewise linearity projection equation; and transferringa solved instruction to a robot instruction input port, and driving a robot to carry out path follow. According to the nonlinear constrained primal-dual neural network robot action planning method provided by the invention, convex set constraint and non-convex set constraint can be compatible, a preliminary test error problem occurred in robot control is eliminated, and an error accumulation problem during a robot control process is solved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
One-dimensional range profile recognition method based on self-adaptive locality sparsity preserving projection
ActiveCN107194329AImprove recognition accuracyTo achieve the purpose of dimensionality reductionCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixSupport vector machine
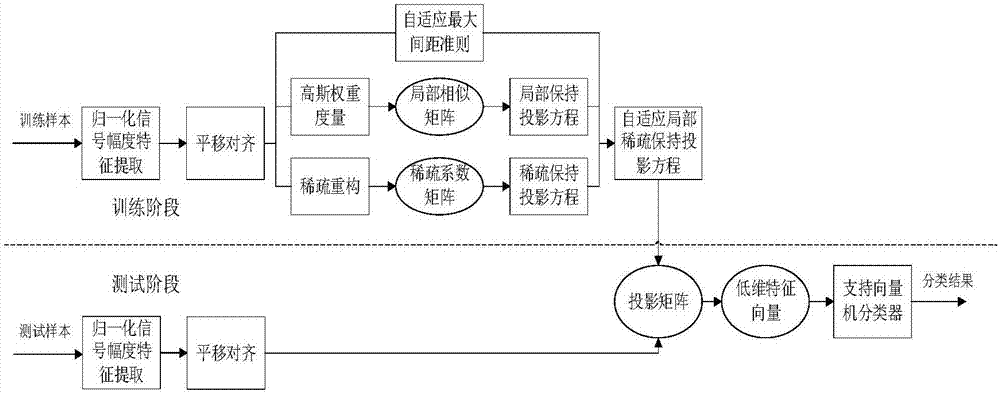
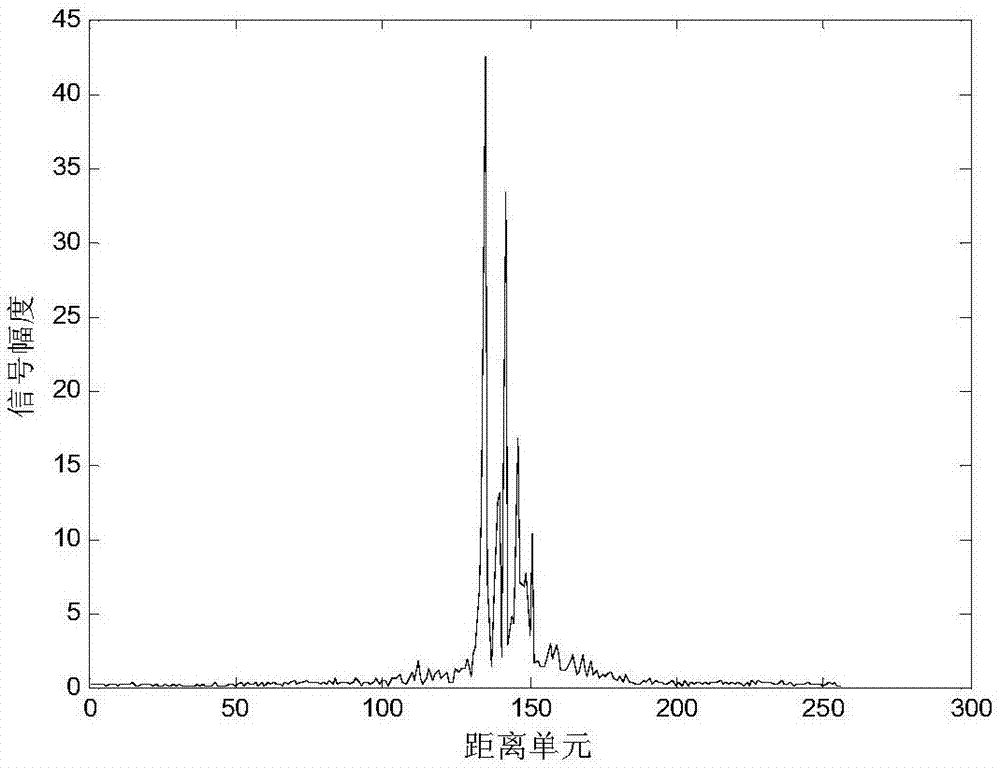
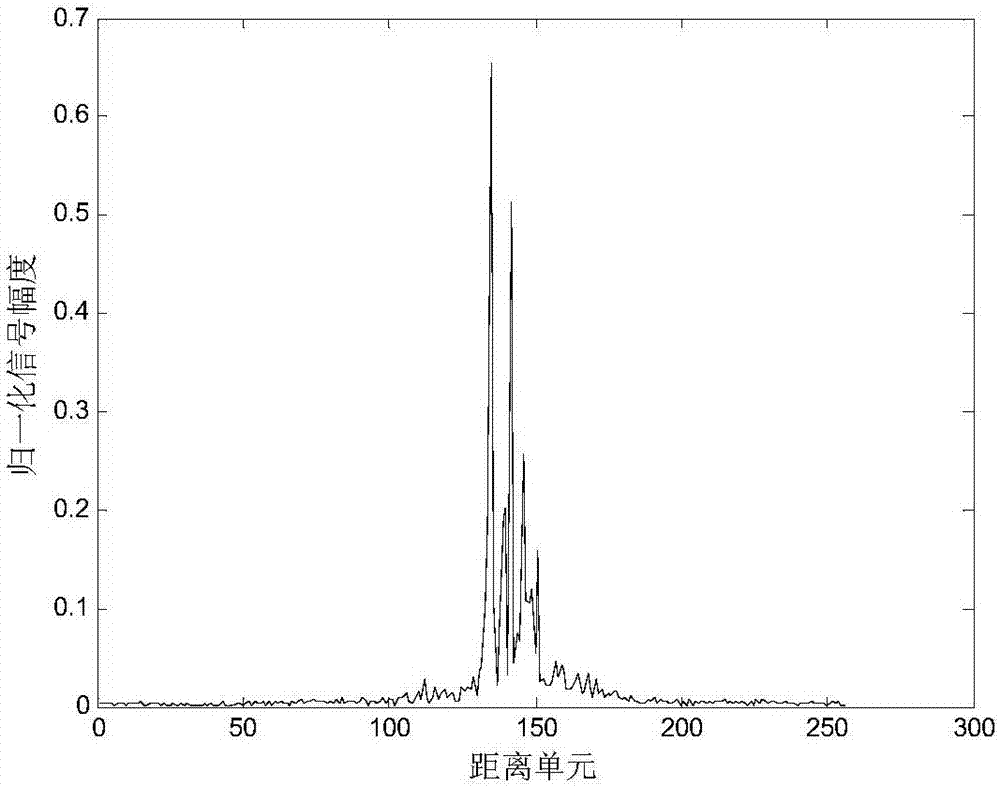
The invention discloses a one-dimensional range profile recognition method based on self-adaptive locality sparsity preserving projection. According to the method, actually measured one-dimensional range profile signal samples are preprocessed; a sparsity coefficient matrix is obtained through sparsity preserving projection (SPP), and a locality similarity matrix is obtained by locality preserving projection (LPP); sparsity preserving projection equations, locality preserving projection equations and a self-adaptive maximum margin criterion are fused, a joint constraint equation set is established, and a self-adaptive locality sparsity preserving projection matrix is obtained; and training samples and test samples are projected into lower-dimensional space through the projection matrix, and a support vector machine is used to carry out training and classification thereof. Based on the sparsity preserving projection, the locality preserving projection and the self-adaptive maximum margin criterion, the method makes full use of sparse reconstruction of the samples and recognition information contained in neighbor relations and combines with the self-adaptive maximum margin criterion to extract lower-dimensional features of the samples, the recognition accuracy of one-dimensional range profile signals is improved, the feature dimensionality is reduced, and the noise immunity is enhanced.
Owner:南京御达电信息技术有限公司
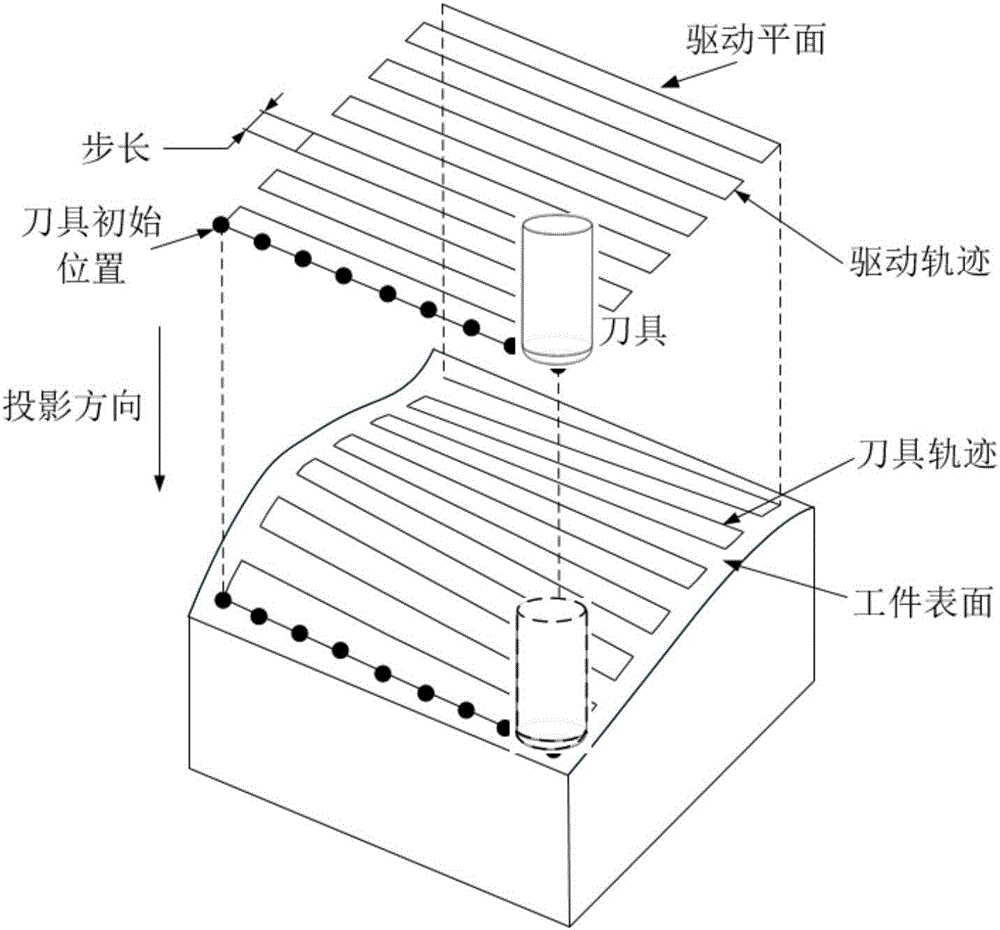
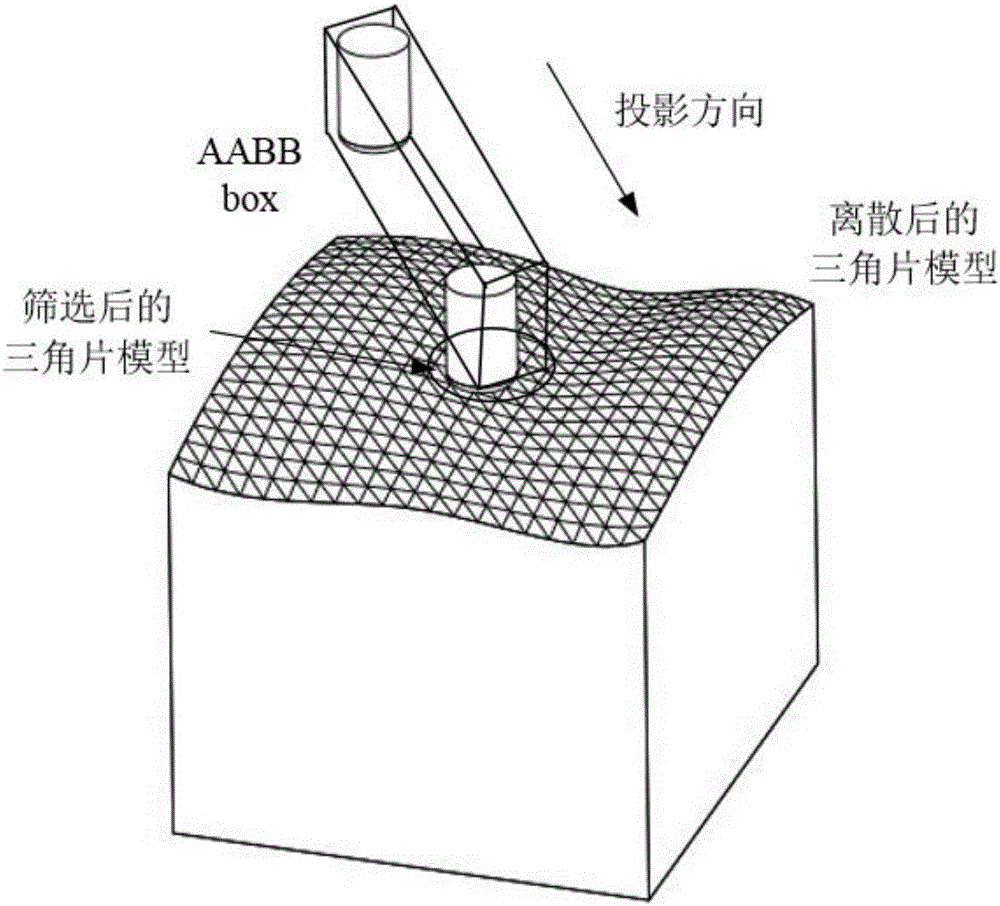
Projection algorithm for generating interference-free five-axis machining paths
InactiveCN106774145AGuaranteed uniformityGuaranteed RegularityNumerical controlAlgorithmProjection algorithms
The invention belongs to the field of related technologies for milling, and discloses a projection algorithm for generating interference-free five-axis machining paths. The projection algorithm includes steps of (1), discretizing the surfaces of workpieces to obtain triangle models; (2), building an AABB box for tools along projection directions; (3), screening the triangle models; (4), projecting each tool to a single triangle, to be more specific, acquiring projection equations according to constraint conditions, and concentrating calculation for tool contacts in tool coordinate systems; deriving a quartic equation with one unknown quantity according to the projection equations when rings of the tools are projected towards the edges of the triangles and projection directions are directions along tool shafts, and solving analytical solutions; deriving an eight-degree equation with one unknown quantity according to the projection equations when the projection directions are optional directions and subdividing intervals on the basis of Bezier cut-off processes to solve projection points; (5), outputting the projection points corresponding to the shortest projection distances. The projection algorithm has the advantage that the tools can be particularly projected to the triangles along the optional directions by the aid of the projection algorithm.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
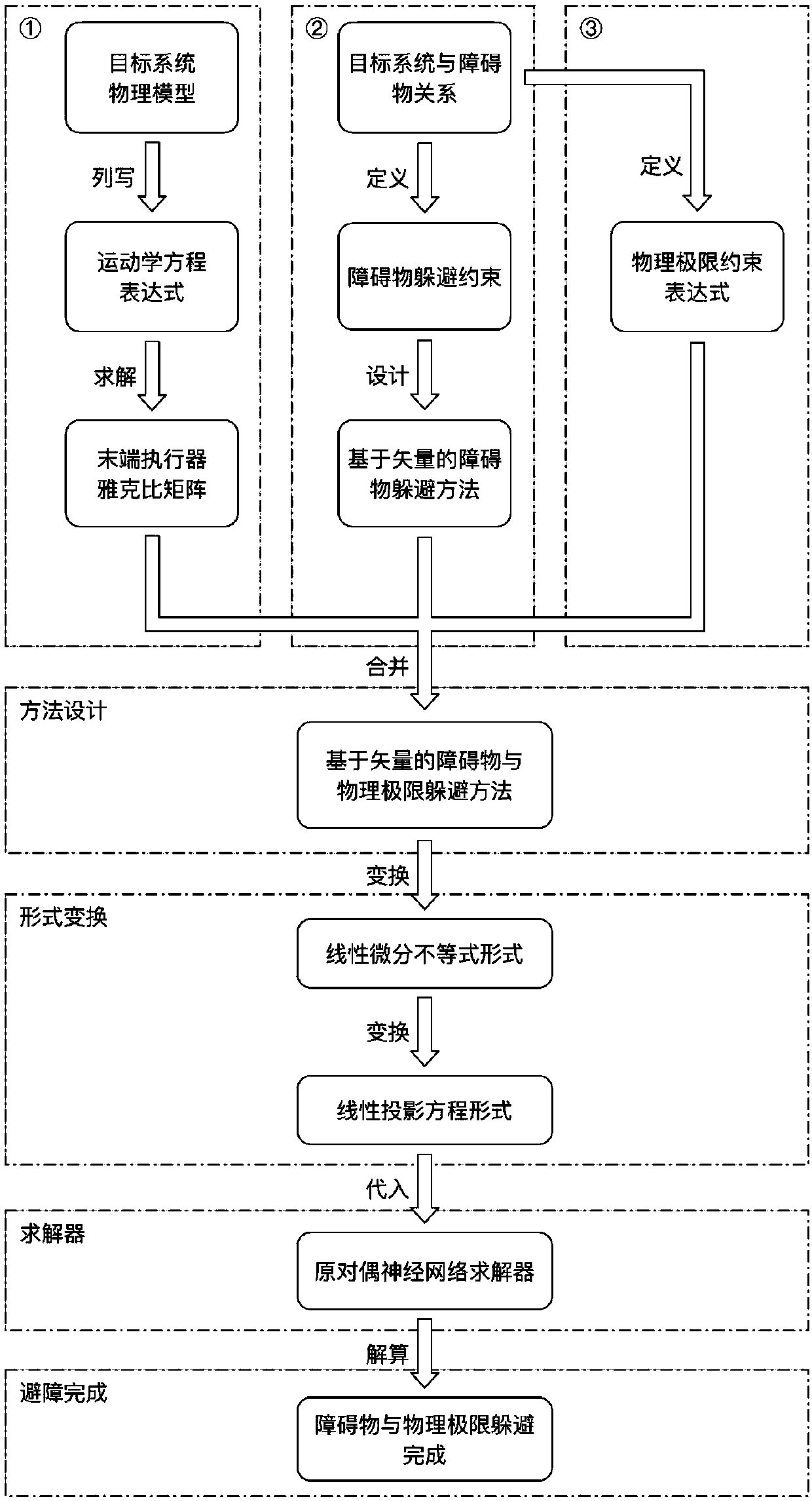
Avoidance method for obstacles and physical limits
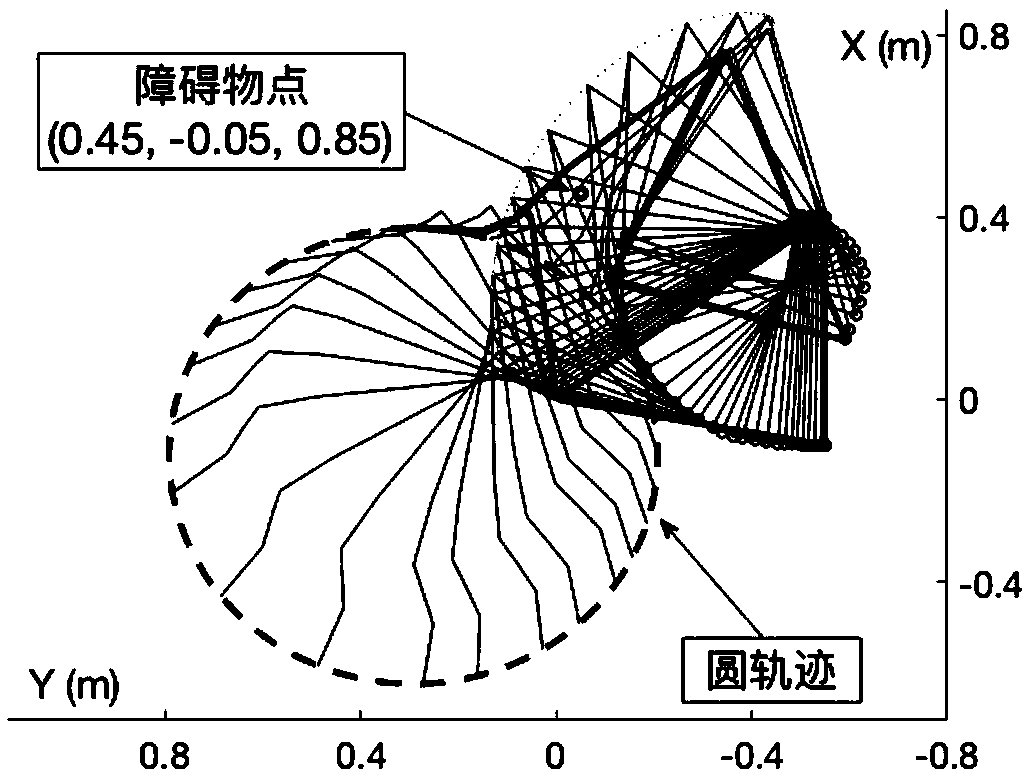
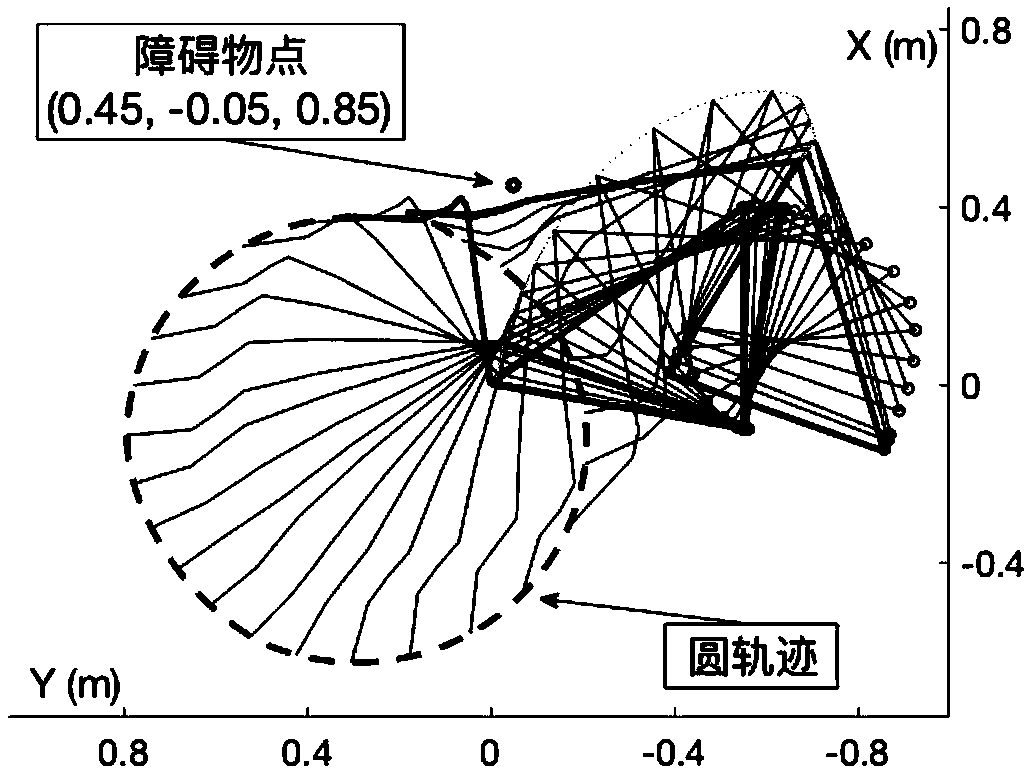
ActiveCN108772835ADodge guaranteeGuaranteed to workProgramme-controlled manipulatorKinematicsKinematics equations
The invention discloses an avoidance method for obstacles and physical limits. The method includes the following steps: writing a kinematical equation expression according to a physical model of a target system; solving a Jacobian matrix of an end effector of the target system; defining an obstacle avoidance constraint according to a relationship between the target system and the obstacles; optimizing the obstacle avoidance constraint, and designing a vector-based obstacle avoidance method; setting a physical limit constraint expression according to the physical model of the target system; merging the vector-based obstacle avoidance method with the physical limit constraint expression, and designing a vector-based obstacle and physical limit avoidance method of the target system combiningthe Jacobian matrix of the end effector; performing transformation to obtain an equivalent linear differential inequation; performing transformation to obtain an equivalent linear projection equation;and substituting the linear projection equation ton an original dual neural network solver to performing solution, and avoidance of the obstacles and physical limits by the target system can be completed.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method of determining a three-dimensional velocity field in a volume
A method of determining a three-dimensional velocity field in a volume, the particles within the volume being excited to radiate by illuminating said volume, a) at least two cameras simultaneously image capturing the observation volume at two different instants of time (t1, t2) at least, b) the observation volume being divided into small volume elements (voxels), c) each voxel being projected at the location x, y, z onto the image points (xn, yn) of the at least two cameras using a projection equation, d) the intensity of all the voxels being reconstructed from the measured intensity of the respective ones of the associated image points (xn, yn), e) a plurality of voxels being combined to form an interrogation volume, f) the displacement vector (dx, dy, dz) being determined at the times (t1, t2) at the same location by a three-dimensional cross correlation of the two interrogation volumes.
Owner:LAVISION
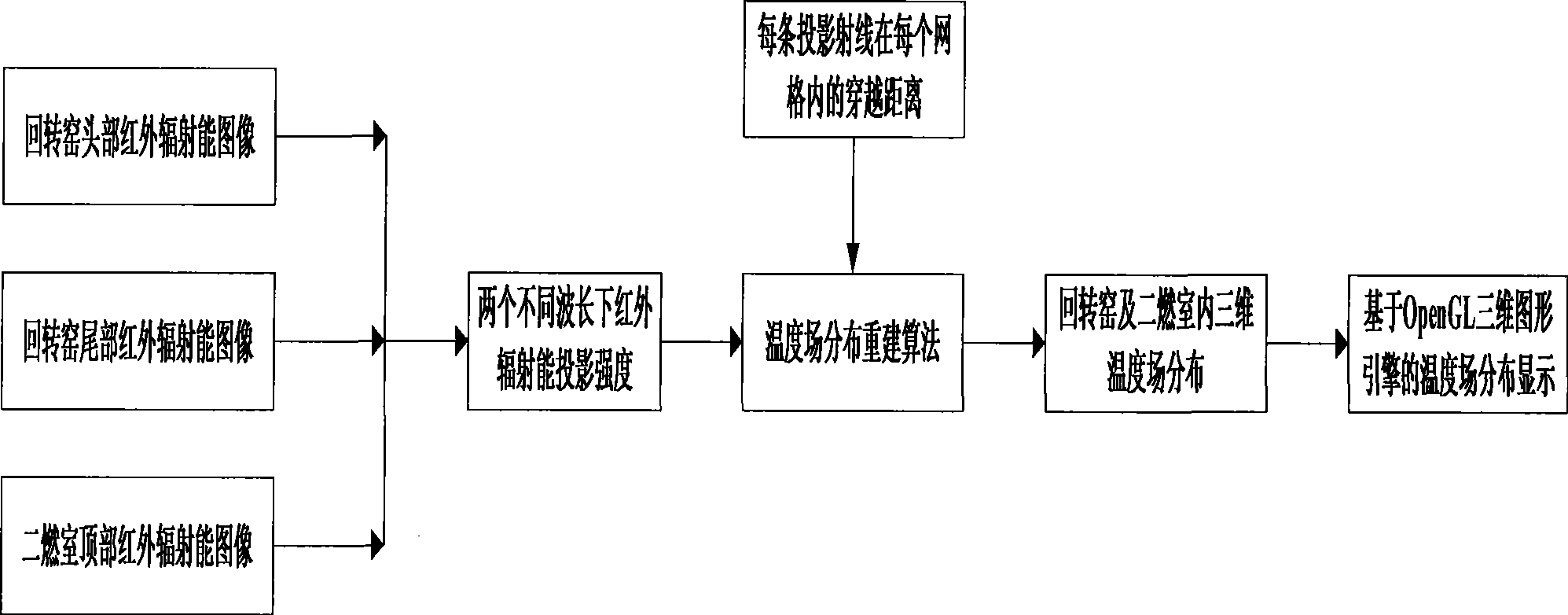
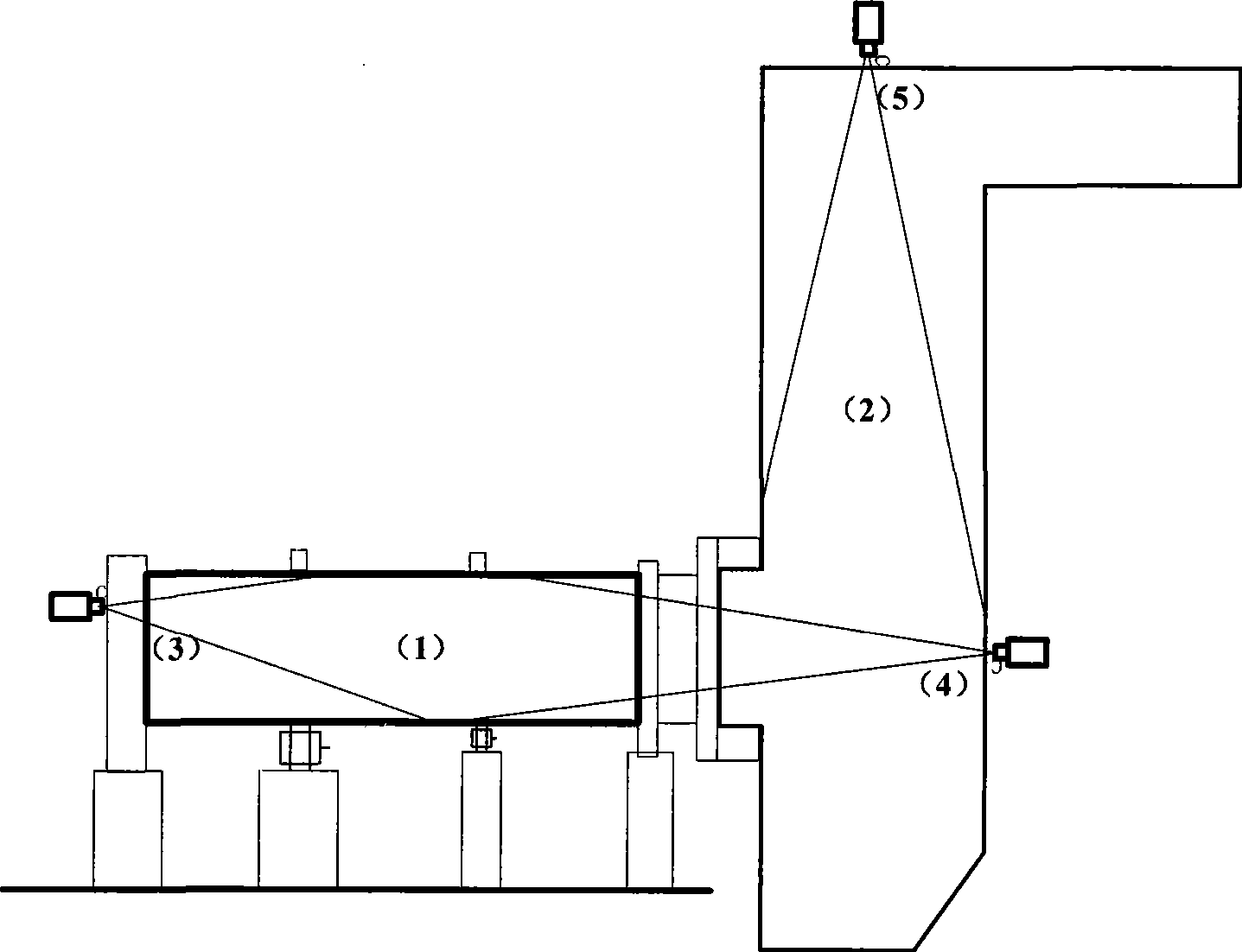
Temperature field distribution non-contact measuring method in danger wastes thermal decomposition incineration furnace
The invention discloses a non-contact measuring method of temperature field distribution in an incinerator for thermal decomposition of hazardous wastes. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, 3D grid division is carried out on an incineration system by infrared thermal radiation characteristics of high-temperature smoke in the incinerator, and a radiation projection equation is established; then an infrared radiation projection picture is obtained by equipping infrared radiant energy sensors at different positions, and radiation projection values of different wavelengths are extracted from an infrared radiant energy picture; finally, temperature distribution data of a rotary kiln and a secondary incineration chamber in a hazardous waste incineration system are computed by combining a reconstruction algorithm of 3D temperature distribution in the incineration system. The temperature field distribution reconstruction method based on the infrared radiant energy picture is a non-contact online temperature measurement method for reconstructing the 3D temperature distribution in the incineration system in an online manner based on the infrared radiation transfer characteristic of the high-temperature smoke in the hazardous waste incineration system and by the acquired infrared radiant energy picture.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
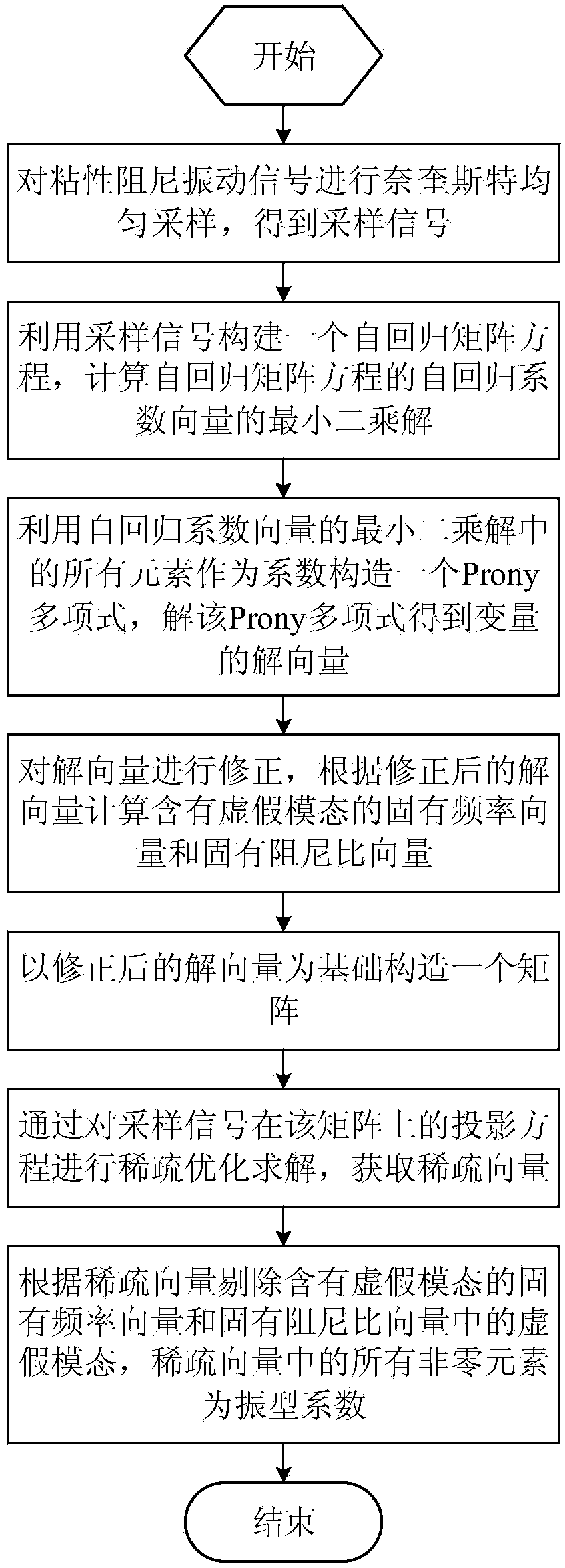
Method for extracting modal parameter from viscous damping vibration signals
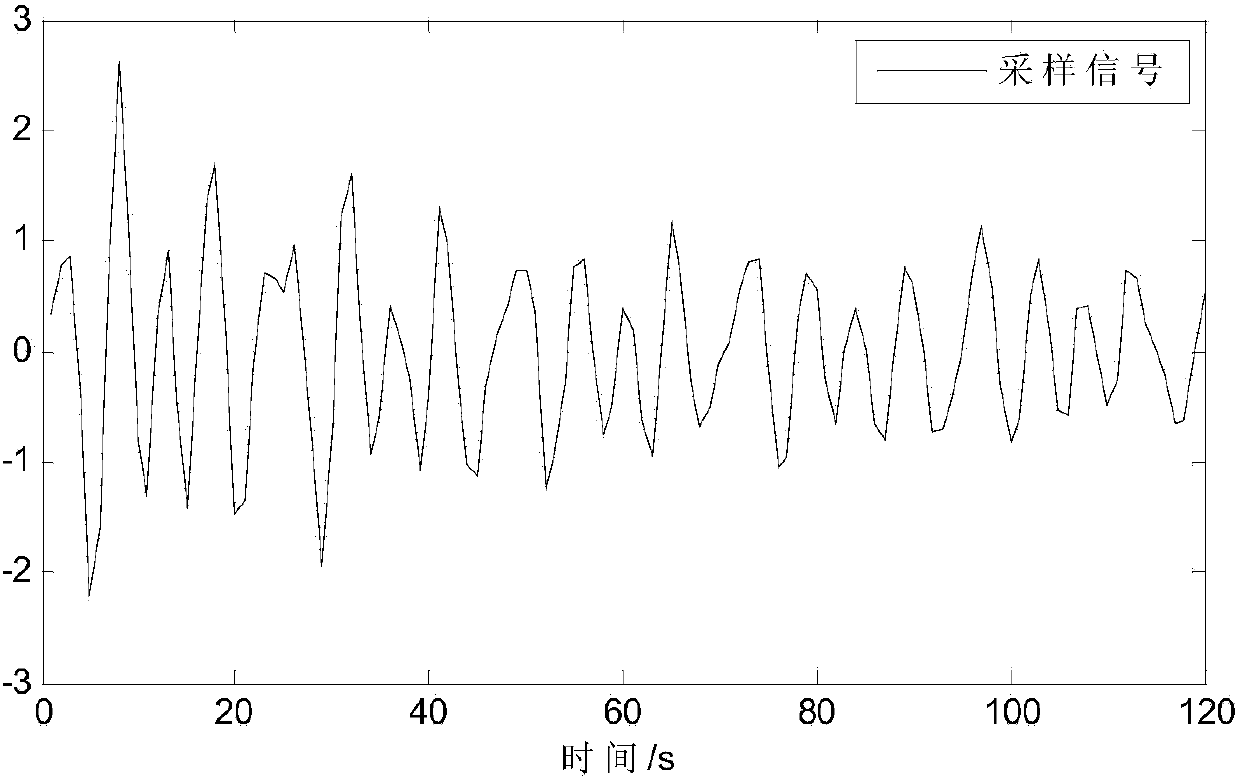
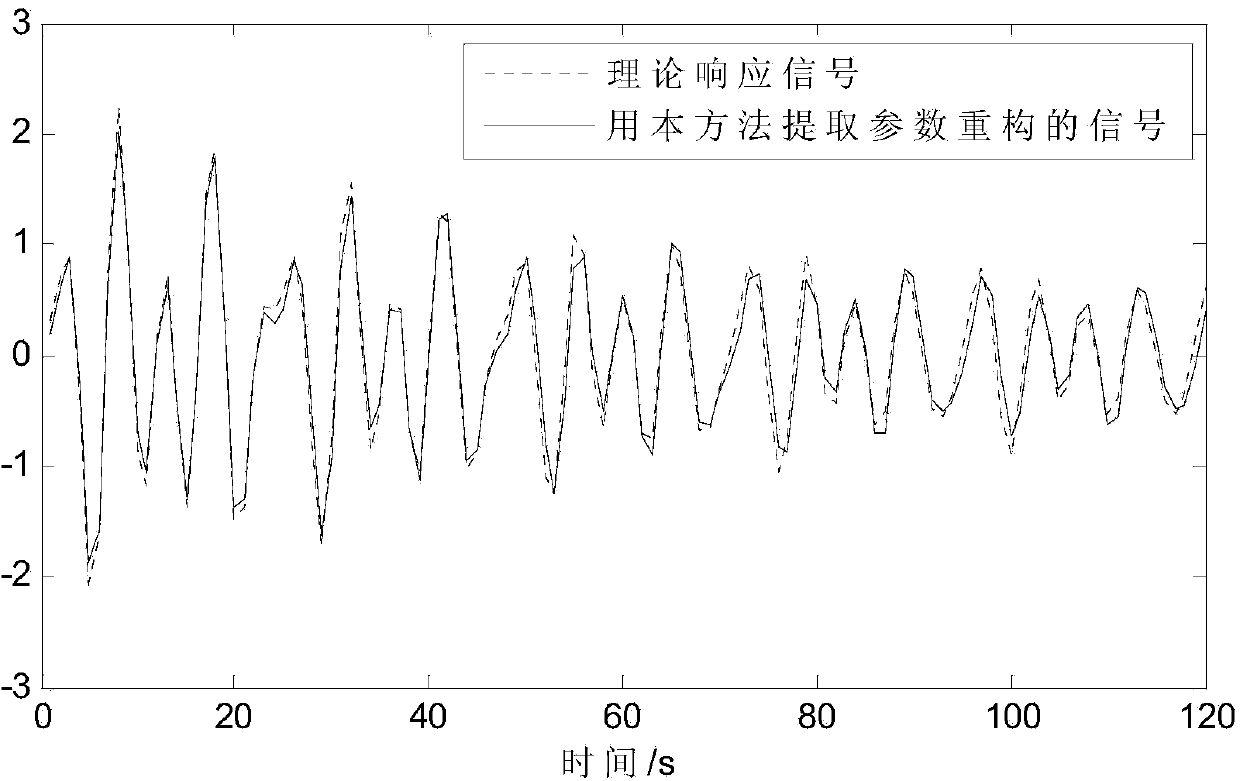
ActiveCN104200002AKeep the original informationHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency vectorViscous damping
The invention discloses a method for extracting a modal parameter from viscous damping vibration signals. The method for extracting the modal parameter from the viscous damping vibration signals comprises the steps that firstly, Nyquist uniform sampling is conducted on the vibration signals; secondly, an autoregression matrix equation is established through sampled signals, the least square solution of the autoregression coefficient vector of the autoregression matrix equation is worked out, a Prony polynomial is established with all the elements of the least square solution as coefficients, and the polynomial is solved so that the solution vector of variables can be obtained; thirdly, the solution vector is corrected, and an inherent frequency vector containing a false modality and an inhehrent damping ratio vector are worked out according to the corrected solution vector; fourthly, a matrix is established with the corrected solution vector as the basis, sparse optimization solution is conducted on the projection equation on the matrix through the sampled signals, and then a sparse vector is obtained; finally, the false modality is removed through the sparse vector, wherein all the nonzero elements in the sparse vector are vibration mode coefficients. The method for extracting the modal parameter from the viscous damping vibration signals has the advantages that the noise immunity is high, and the extracted modal parameter is high in precision and high in stability.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for qualitatively calibrating pinhole camera by utilizing single ball and asymptotic line
ActiveCN108921904AEasy to makePhysical scale is not requiredImage analysisPinhole cameraPinhole camera model
The invention relates to a method for qualitatively calibrating a pinhole camera by utilizing a single ball and an asymptotic line, characterized in that a ball element is utilized only. Firstly, pixel coordinates of target image edge points are extracted from three images and a ball image equation is obtained by adopting least square fitting. On the basis of the obtained ball image equation, an asymptotic line of a ball image is solved. The asymptotic line of the ball image is namely a polar line of an image of a circular point about the ball image, thus an image of a circle center is determined according to a polarity principle, orthogonal end points can be obtained by virtue of the image of the circle center, and the three images provide six groups of orthogonal end points. Finally, intrinsic parameters of the camera are solved by utilizing constraints of the orthogonal end points on an absolute conic image. The method comprises the following specific steps: fitting a target projection equation, estimating the asymptotic line of the ball image, determining the orthogonal end points, and solving the intrinsic parameters of the pinhole camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
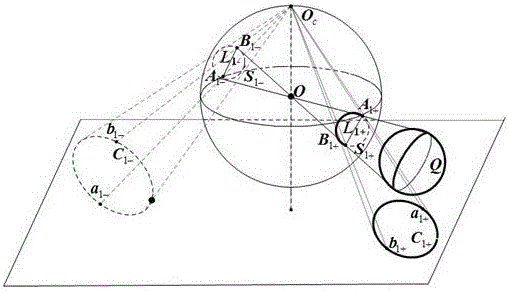
A method for homography estimation by using a common autopolar triangle of a spherical image
The invention relates to a method for homography estimation by using a public autopolar triangle of a spherical image, which comprises the following steps of: taking a sphere in space as a target, shooting two images of the sphere in the space from different positions under a parabolic catadioptric system, and fitting a mirror surface contour projection equation, a target projection equation and an antipodal sphere image equation; Secondly, respectively calculating a characteristic value and a characteristic vector of a matrix formed by the spherical image and the antipodal spherical image inthe two images; then, by matching characteristic values, three pairs of line correspondence are obtained, and the three pairs of line correspondence are three pairs of corresponding edges of the public self-polar triangle; then, connecting the intersection points of the public self-polar triangle and the quadratic curve to obtain a fourth pair of line correspondence which is correspondingly positioned in the public self-polar triangle; and finally, the four pairs of lines are correspondingly subjected to SVD decomposition to obtain a homography matrix.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Neural network reconstruction tomography method of dual-viewing angle X-ray security check system
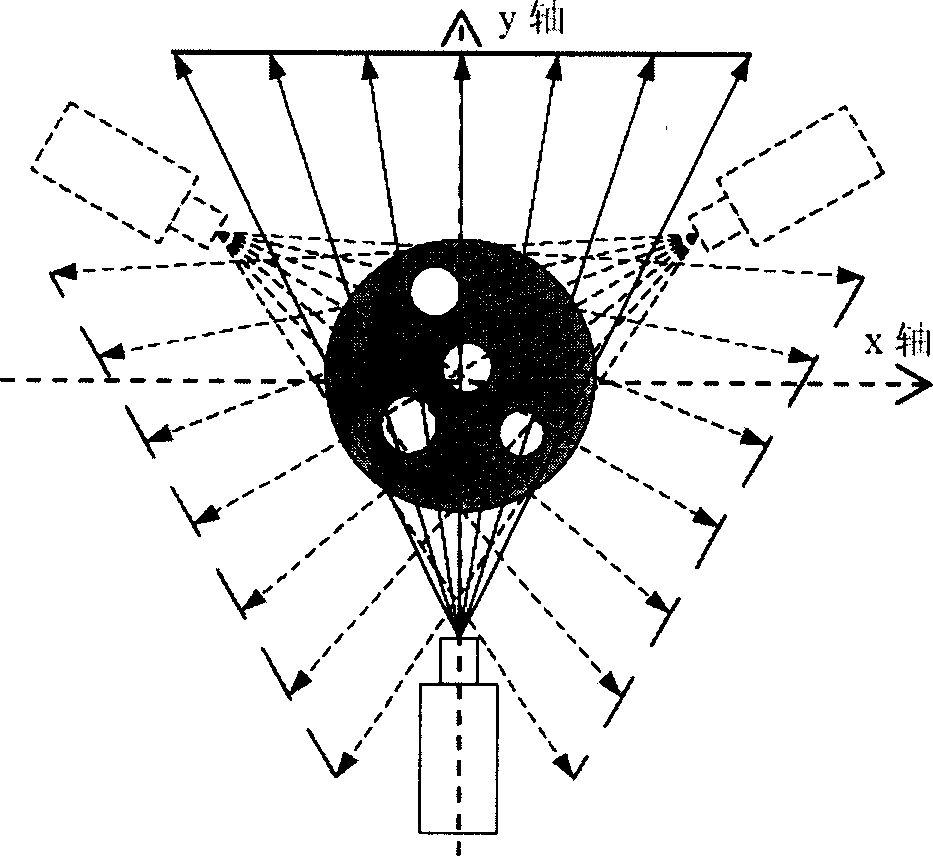
The invention provides a neural network reconstruction tomography method of a dual-viewing angle X-ray security check system. The neural network reconstruction tomography method is characterized in that in the security check system, X-ray devices placed vertically with each other are used for transmitting and detecting X-ray signals, and acquired signals are transmitted into a computer system; ina computer, a reconstructed image is meshed, and the total-variation square root operation of reconstructed meshes is rewritten as the matrix operation, so that the coefficients of the reconstructed meshes have strictly positive matrix representation. Through calculation of the projection weight value of each reconstructed mesh on the propagation path of each X ray, establish a linear projection equation set from a ray source to a detector is established, so that a reconstruction problem is transformed into optimization meeting convex quadratic programming, and finally optimization solution isperformed by a neural network algorithm. By the neural network reconstruction tomography method, the problem of mutual overlapping of perspective images is avoided and the advantages of relatively clear reconstruction of a three-dimensional image of an object and the like are achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A soft-interval support vector machine classification method based on neurodynamics
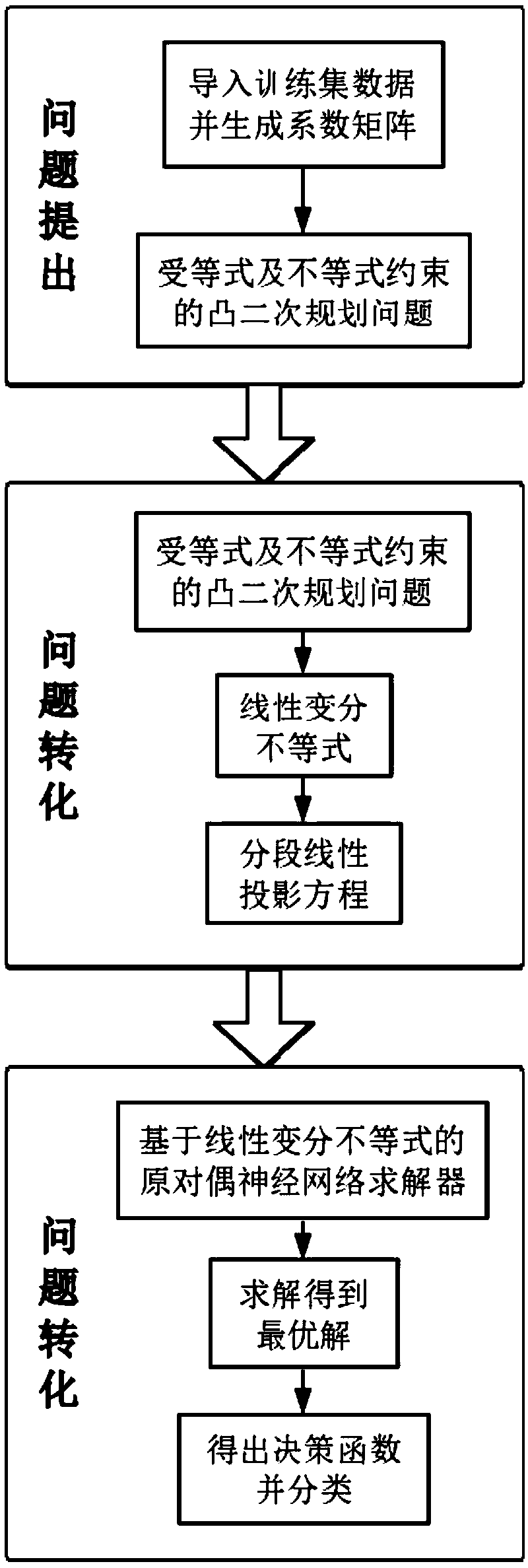
InactiveCN109508735AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmClassification methods
The invention discloses a soft-interval support vector machine classification method based on neurodynamics, which comprises the following steps: 1) introducing a training set and generating a soft-interval support vector machine coefficient matrix; 2) designing a convex quadratic programming problem constrained by equality and inequality by using the coefficient matrix in step 1); 3) equivalentlyconverting the convex quadratic programming problem constrained by equality and inequality in the step 2) into a linear variational inequality; 4) equivalently converting the linear variational inequality in the step 3) into a piecewise linear projection equation; 5) obtaining an optimal solution of the piecewise linear projection equation in the step 4) by using a neurodynamic method, and obtaining a decision function of a soft-interval support vector machine; 6), import that test set and use the decision function in step 5) to classify. The invention adopts the neurodynamic solver to solve,and has the advantages of high sensitivity, better specificity, stronger real-time performance and higher accuracy.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com