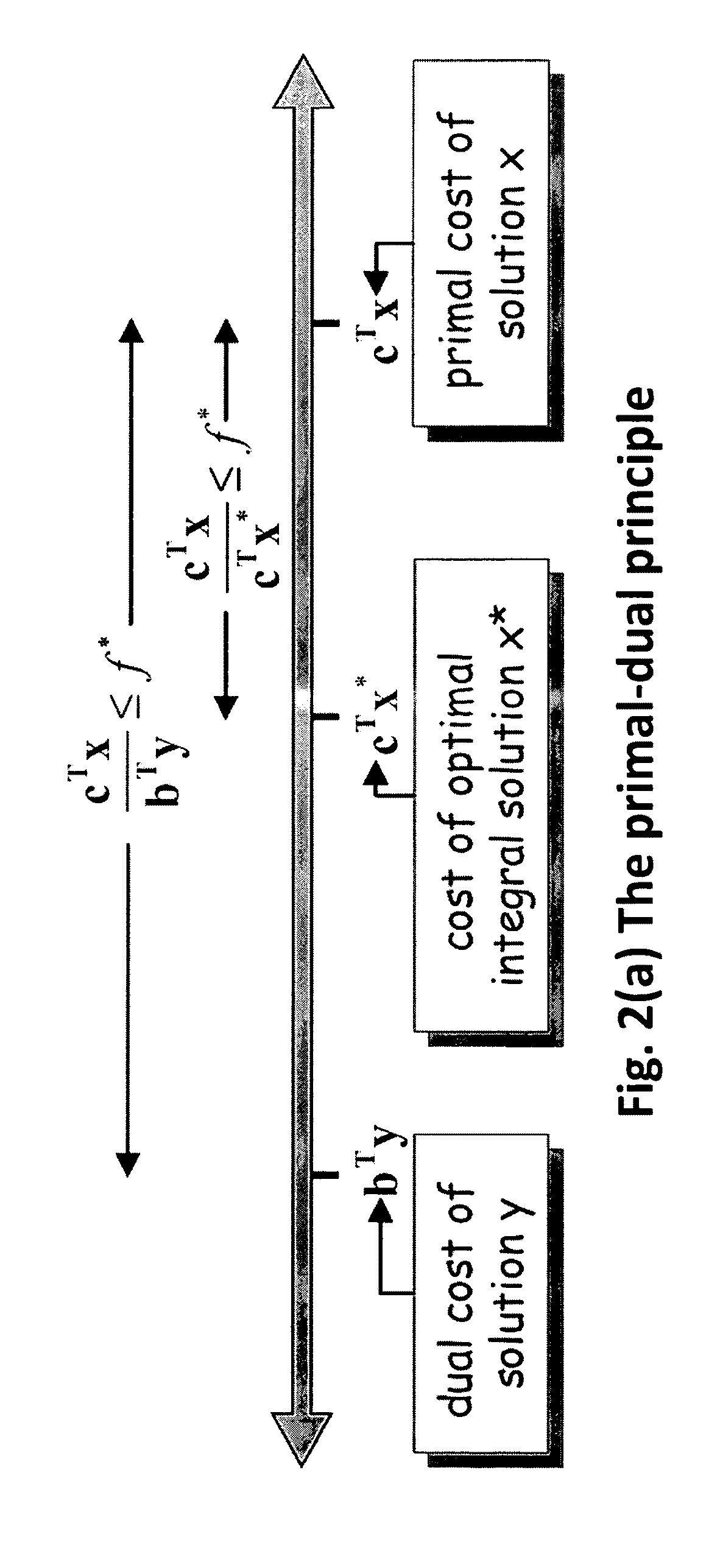
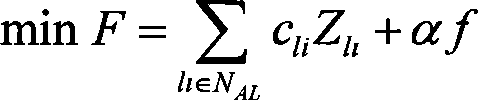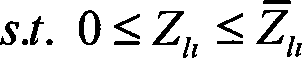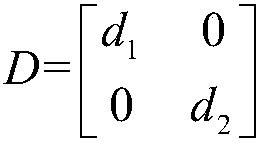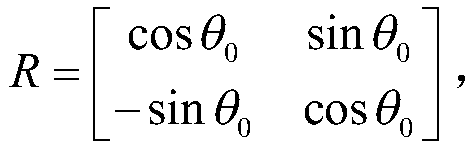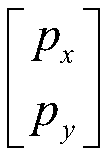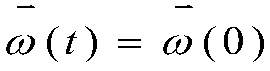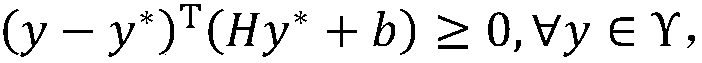Patents
Literature
101 results about "Primal dual" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
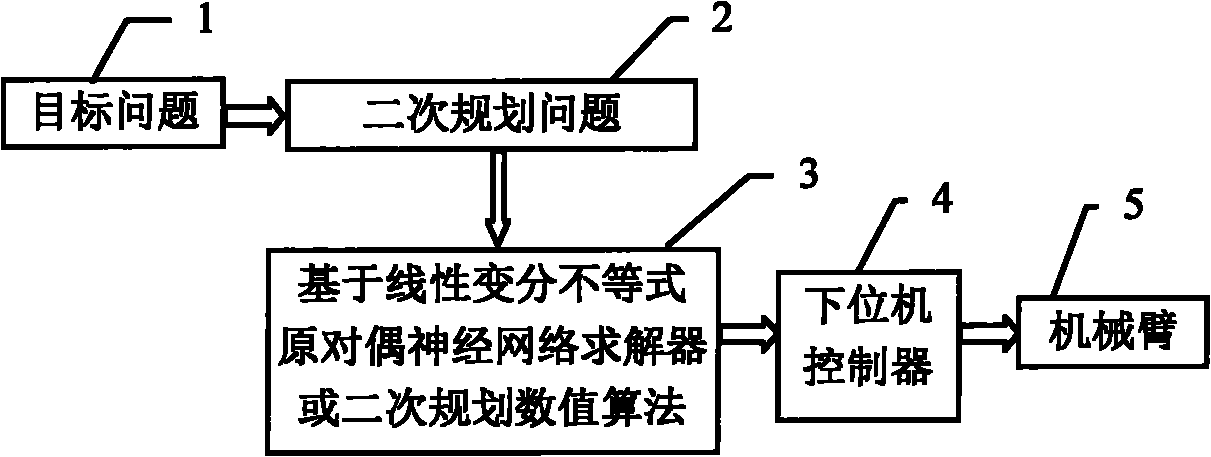
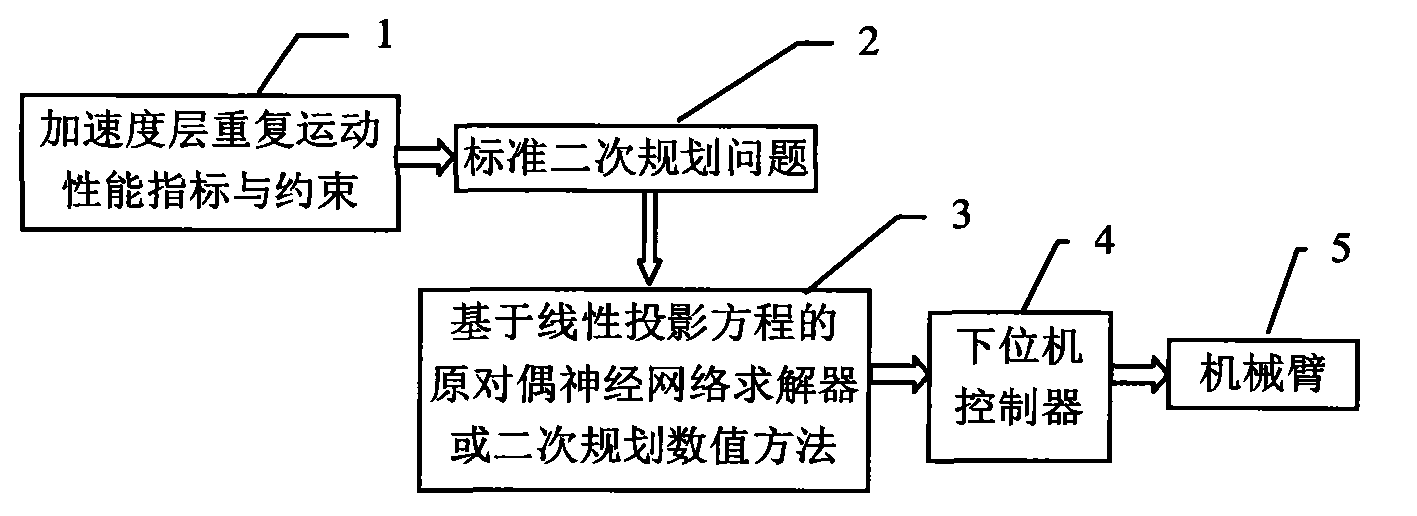
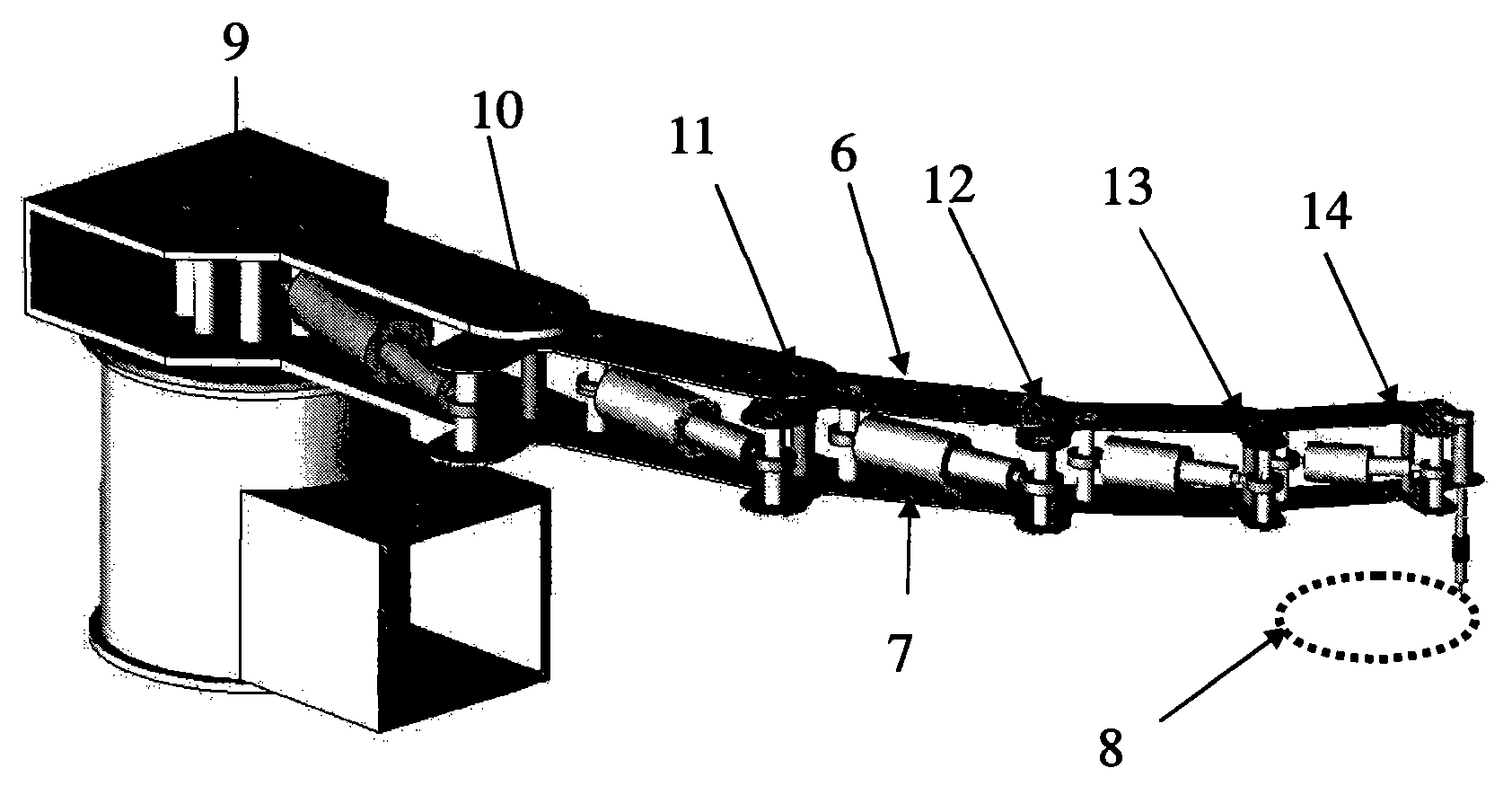
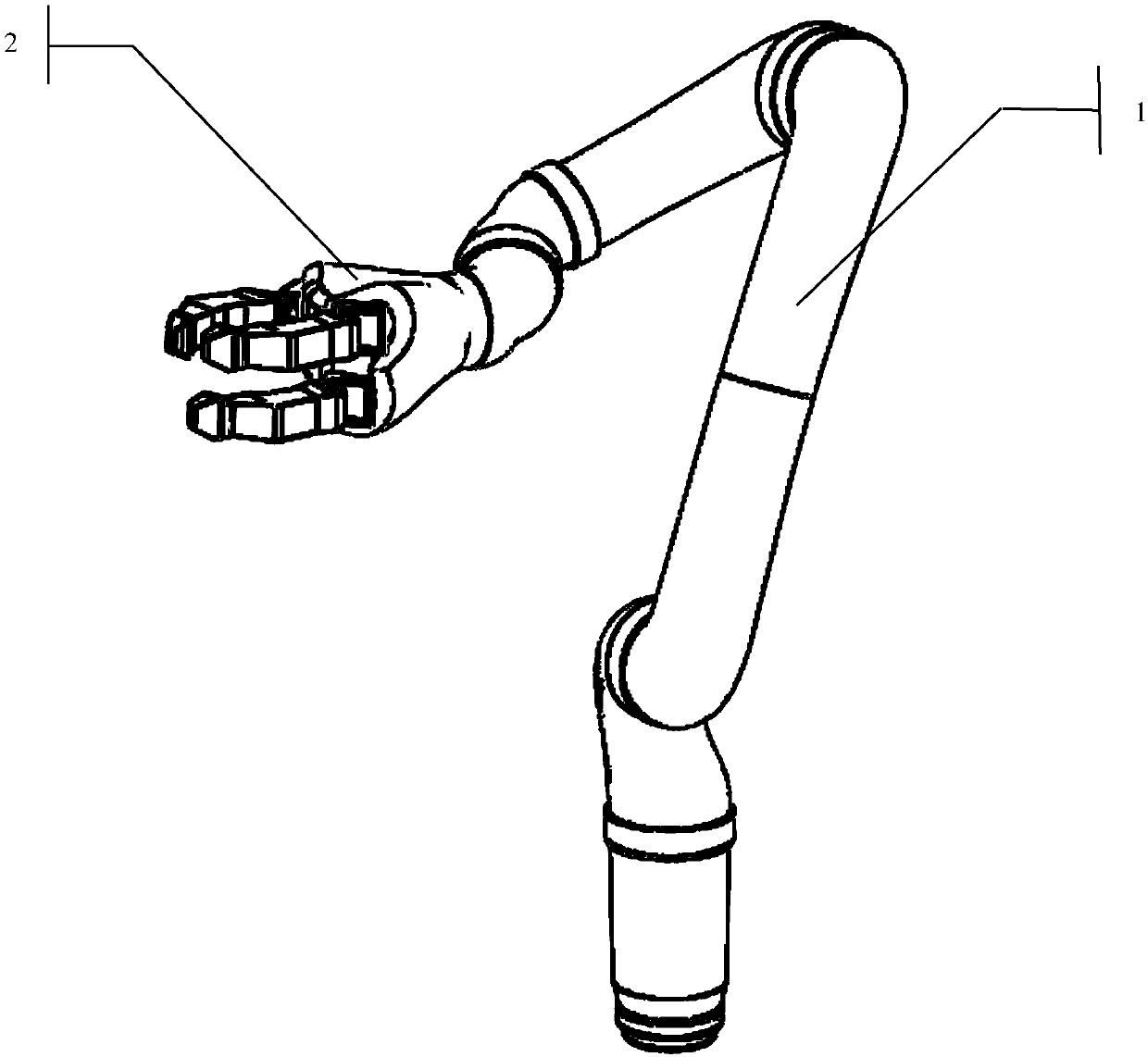
Redundant manipulator motion planning method
InactiveCN101804627AImprove computing efficiencyStrong real-timeProgramme-controlled manipulatorAngular velocityEngineering
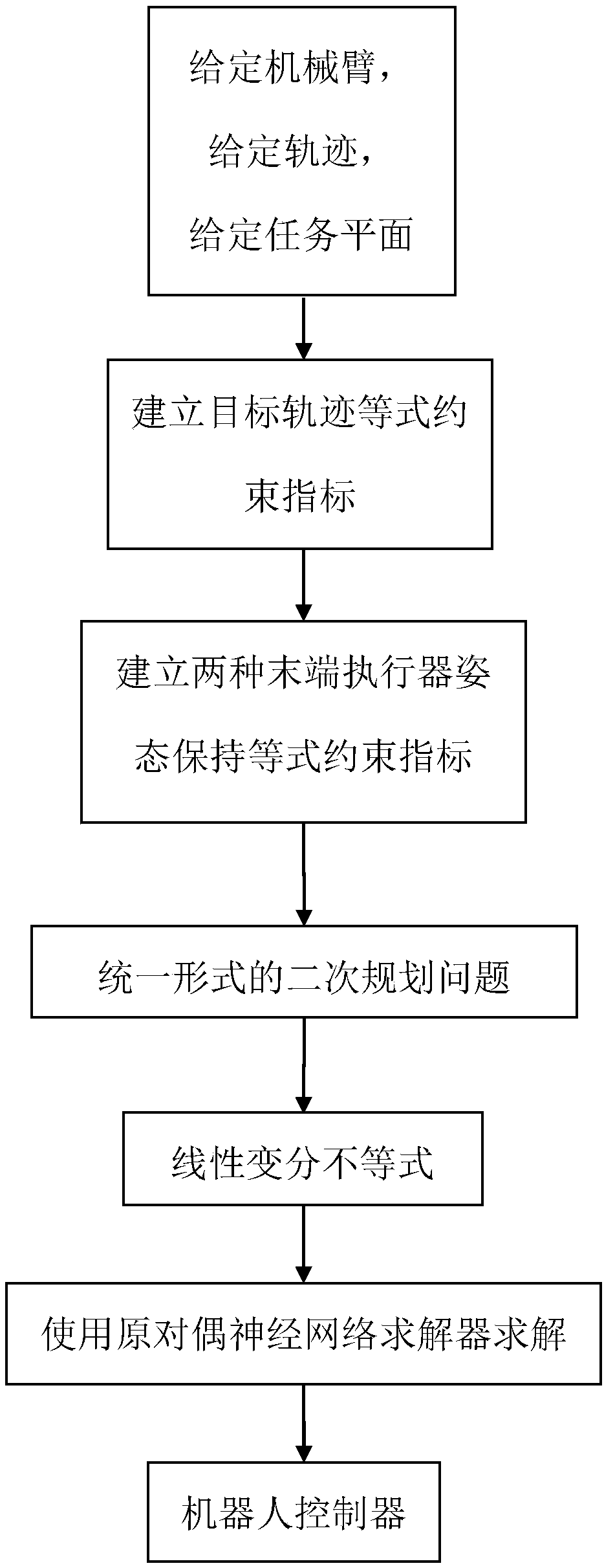
The invention provides a redundant manipulator motion planning method which comprises the following steps that: (1) an upper computer analyzes the inverse kinematics of a manipulator on a velocity layer through quadratic optimization, the designed minimum performance index can be velocity norm, repetitive motion or kinetic energy and is bound by a velocity jacobian equation, an inequation and a joint angular velocity limit, and the angular velocity limit changes with a joint angle; (2) the quadratic optimization of step (1) is optimized into a quadratic programming problem; (3) the quadratic programming problem in step (2) is calculated by a linear variational inequation primal-dual neural network solver or a numerical method; and (4) the calculation result in step (3) is transmitted to a lower computer controller to drive the manipulator to move. The redundant manipulator motion planning method is based on the primal-dual neural network of the linear variational inequation, has global exponential convergence, does not involve matrix inversion and other complicated operations, greatly improves the calculation efficiency, and simultaneously has strong real-time performance, and can adapt to the changes to the joint angular velocity limit.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
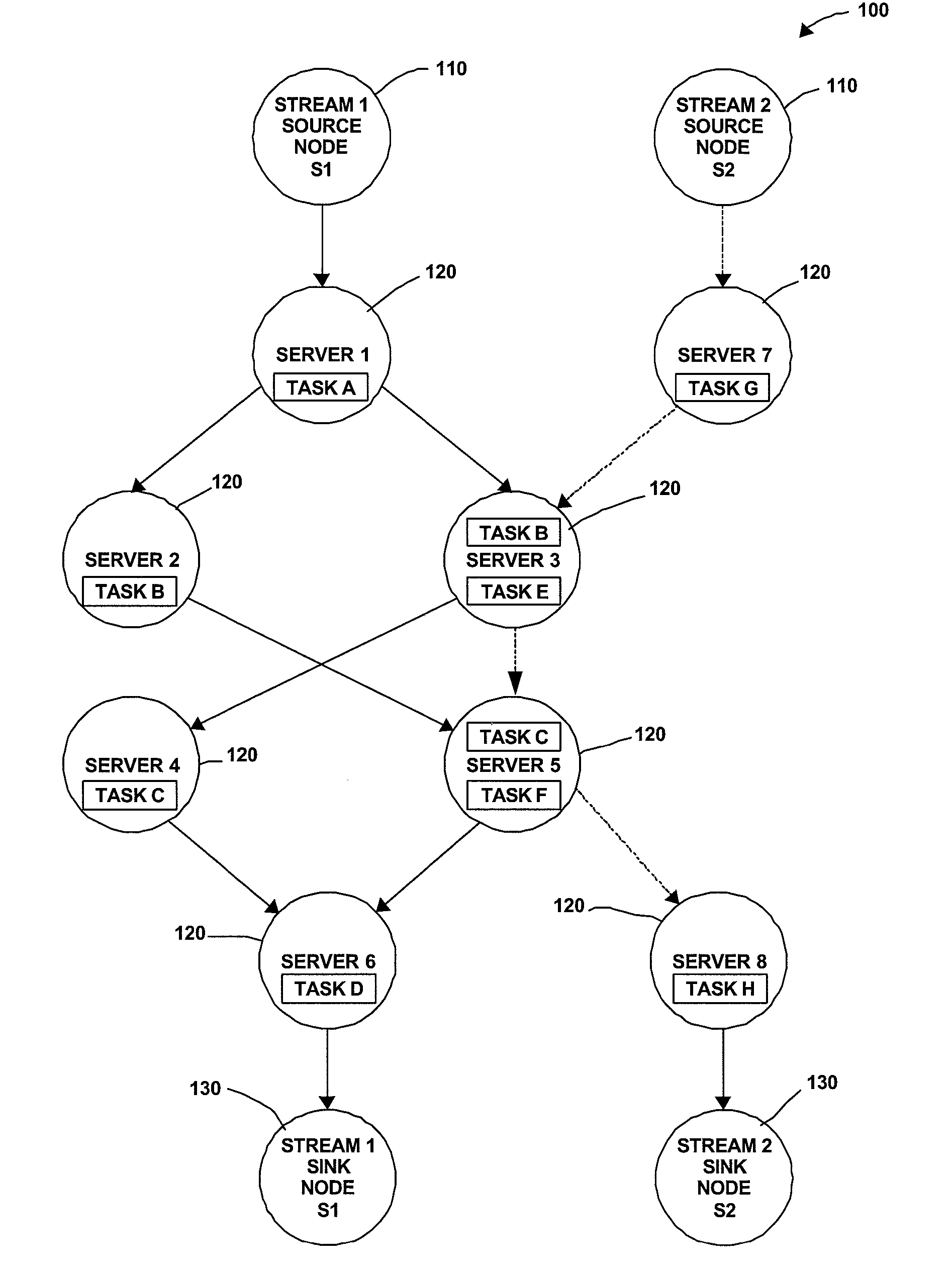
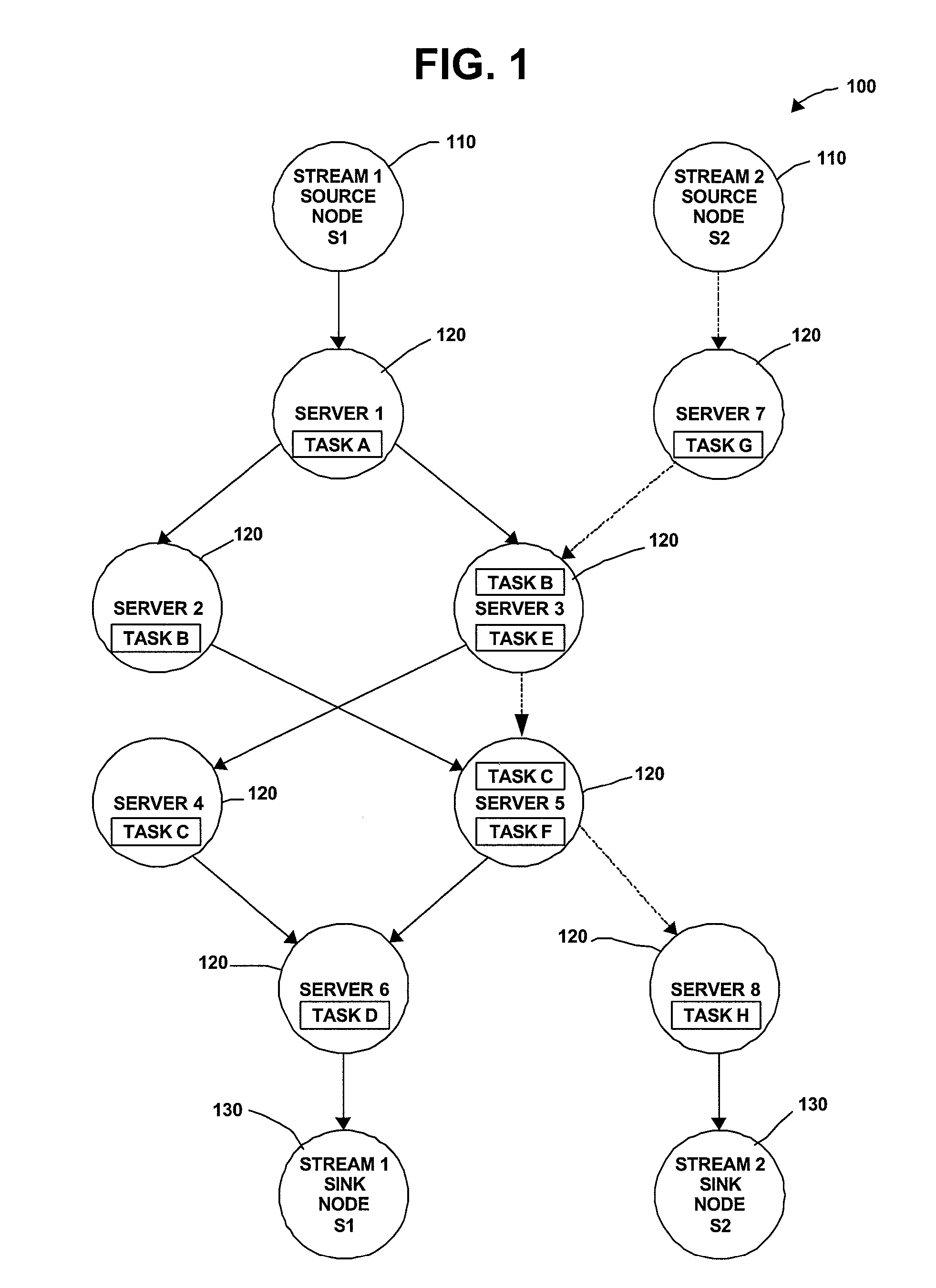
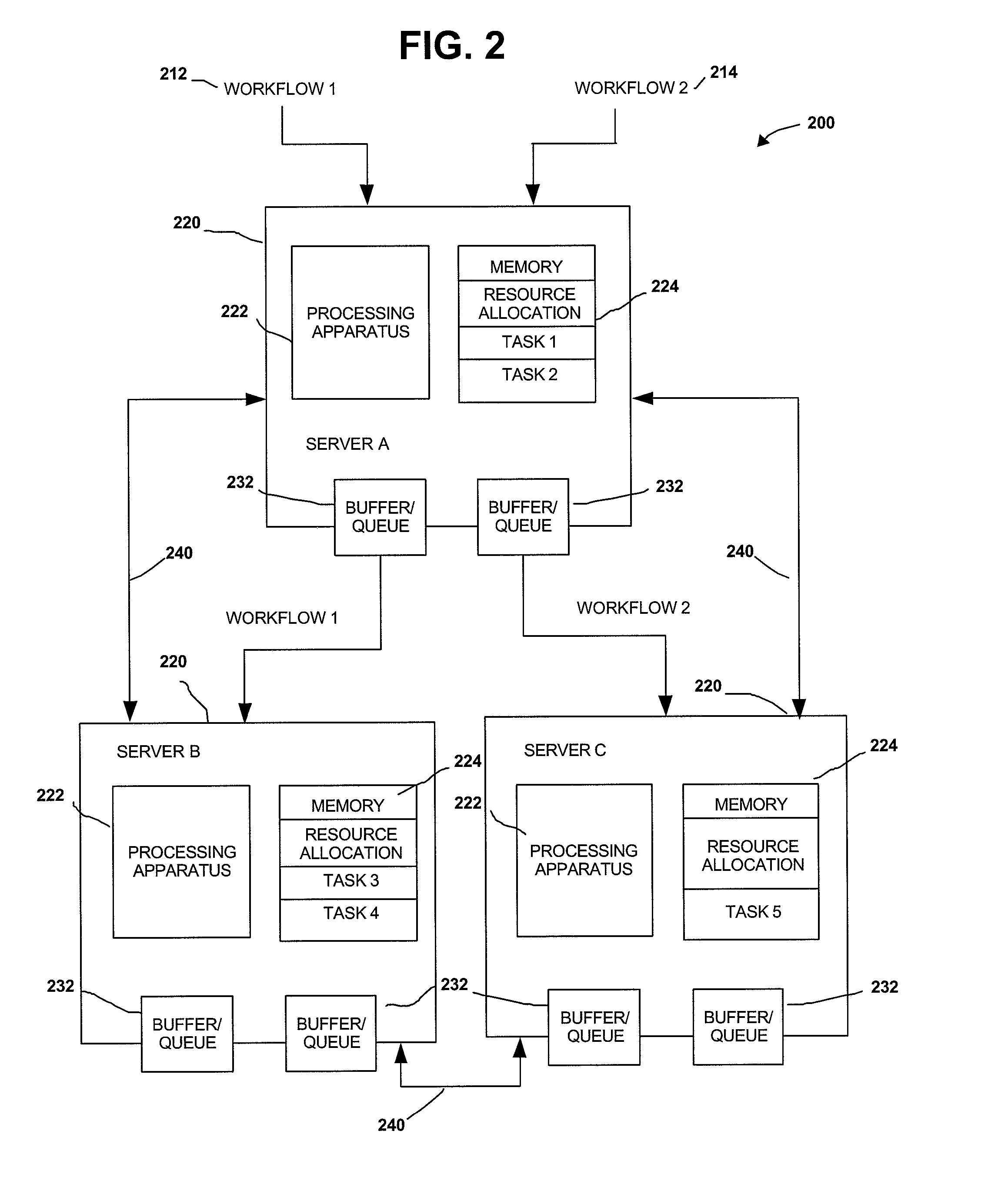
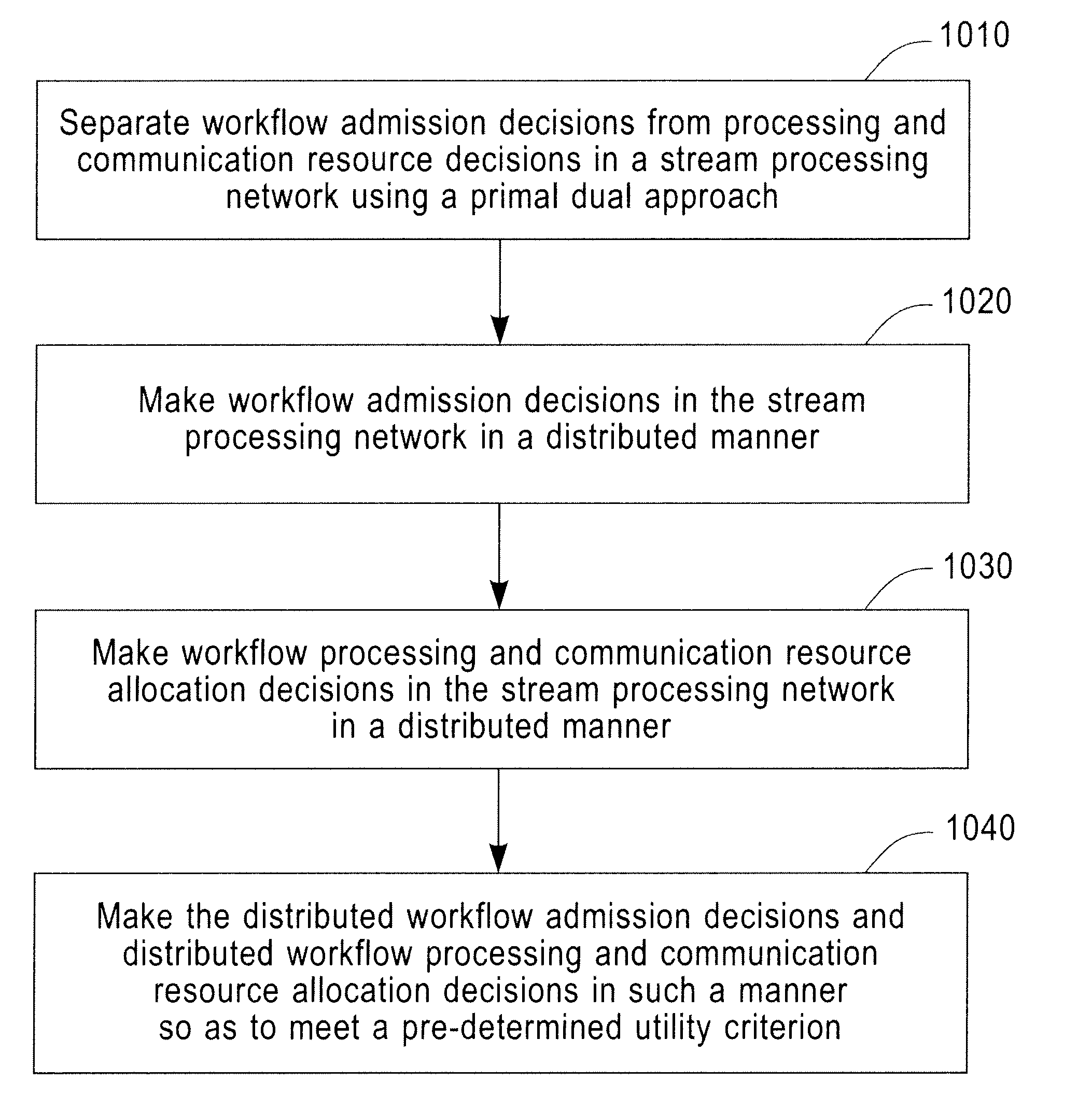
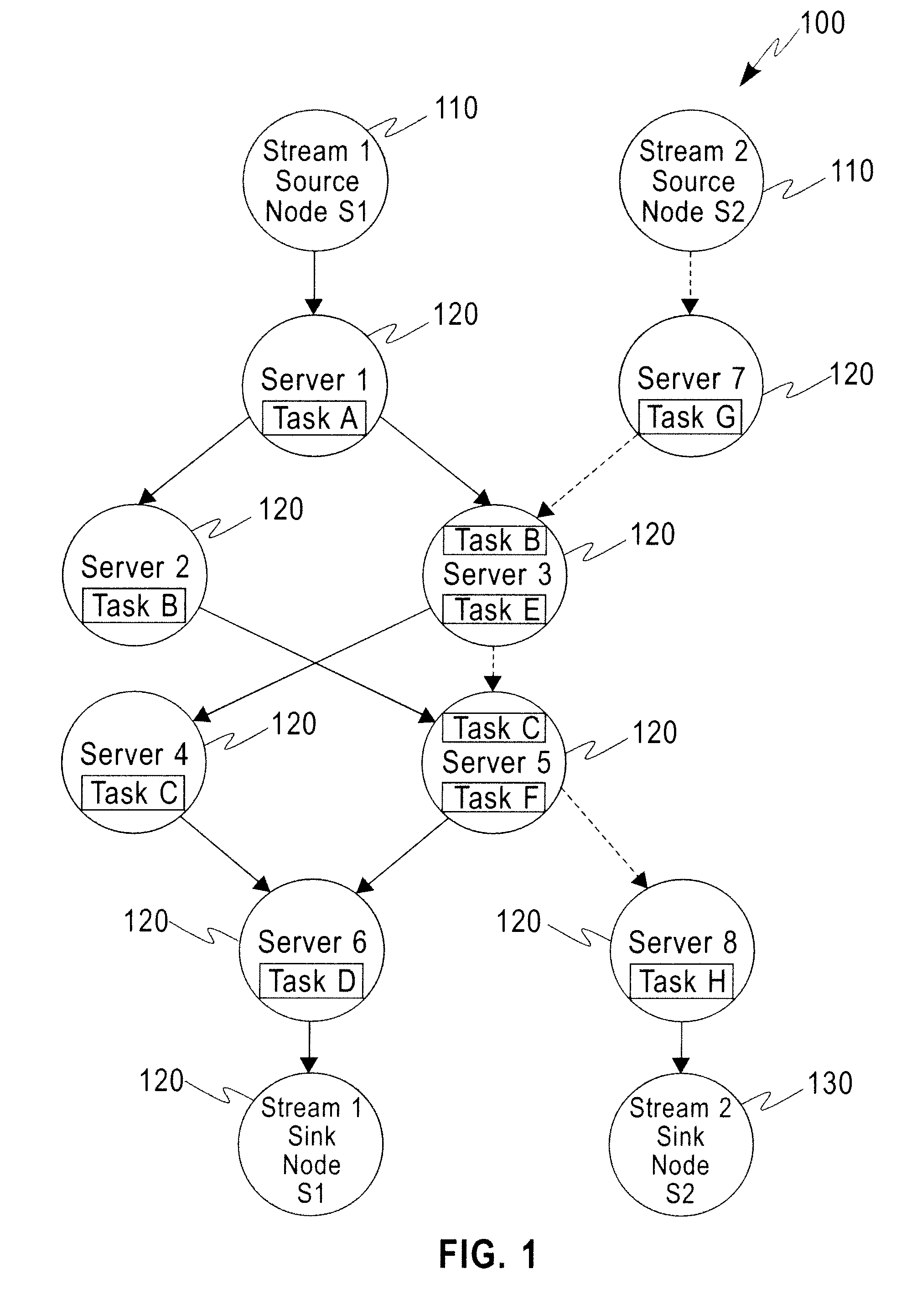
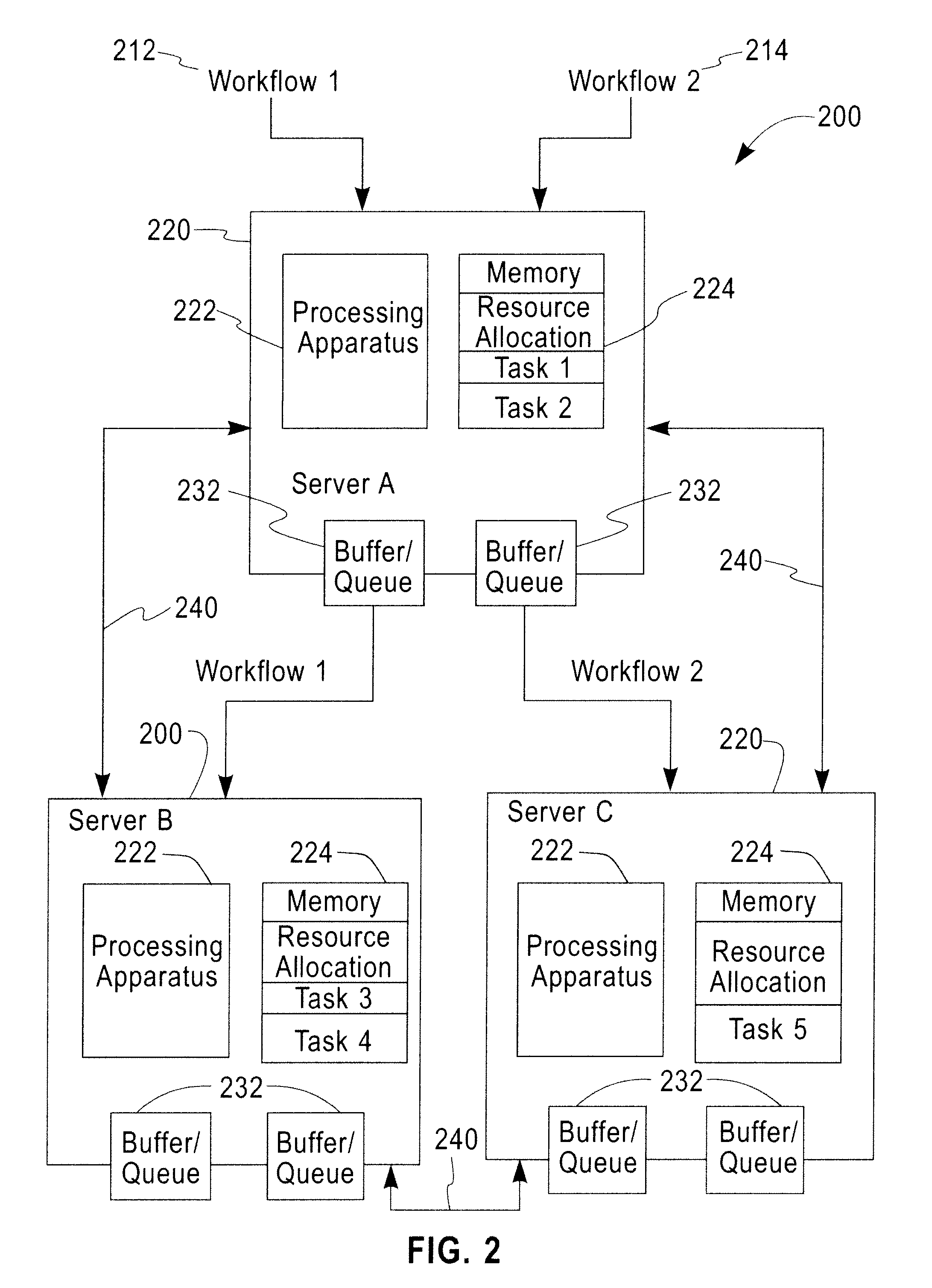
Distributed Joint Admission Control And Dynamic Resource Allocation In Stream Processing Networks
InactiveUS20080304516A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLocal congestionDynamic resource
Methods and apparatus operating in a stream processing network perform load shedding and dynamic resource allocation so as to meet a pre-determined utility criterion. Load shedding is envisioned as an admission control problem encompassing source nodes admitting workflows into the stream processing network. A primal-dual approach is used to decompose the admission control and resource allocation problems. The admission control operates as a push-and-pull process with sources pushing workflows into the stream processing network and sinks pulling processed workflows from the network. A virtual queue is maintained at each node to account for both queue backlogs and credits from sinks. Nodes of the stream processing network maintain shadow prices for each of the workflows and share congestion information with neighbor nodes. At each node, resources are devoted to the workflow with the maximum product of downstream pressure and processing rate, where the downstream pressure is defined as the backlog difference between neighbor nodes. The primal-dual controller iteratively adjusts the admission rates and resource allocation using local congestion feedback. The iterative controlling procedure further uses an interior-point method to improve the speed of convergence towards optimal admission and allocation decisions.
Owner:IBM CORP
Repetitive motion planning method for redundant manipulator
The invention provides a repetitive motion planning method for a redundant manipulator, which comprises the following steps of: 1) resolving a manipulator repetitive motion scheme on an acceleration layer by adopting quadratic model optimization through an upper computer, designing the minimum performance index as repetitive motion, and restraining by an acceleration Jacobian equation, a joint angle limit, a joint speed limit and a joint acceleration limit; 2) converting the quadratic model optimization in the step 1) into standard quadratic programming; 3) solving the standard quadratic programming in the step 2) by using a linear projection equation-based primal-dual neural-network solver or quadratic programming numerical method; and 4) transmitting a solving result in the step 3) to acontroller of a lower computer for driving the manipulator to move. The method realizes the repetitive motion of the manipulator on the acceleration layer, has good control effect on the redundant manipulator inconvenient to control, and can effectively prevent the manipulator from exceeding the limits and being physically damaged according to various joint limits.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Model and sizing information from smartphone acquired image sequences
ActiveUS9619933B2Image enhancementDetails involving processing stepsComputer graphics (images)Monocular image
Owner:OCCIPITAL INC
Determined 2-layered planning model based transmission network planning method
InactiveCN101179196AAvoid difficultiesThe solution process is clearSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemLoad SheddingPower grid
The invention relates to a method for programming a transmission network based on a determinacy two-layer programming mode. The programming mode takes a transmission network investment cost as an economy target, and takes load shedding sum of a regular operation and a single fault operation of the system as a reliability target. An underlayer target is the reliability target; an underlayer restriction is an operation restriction of the regular operation and the single fault condition of the system; an upperlayer gives priority to the economy target; the underlayer reliability target is added to the upperlayer target in a way of penalty function, and the upperlayer restriction is an awaiting frame line number restriction. An improved arithmetic mixed with a niche genetic algorithm with a primal-dual interior method together is adopted to calculate the mode; the niche genetic algorithm is used for processing a integer variable of the upperlayer programming and has a global optimization; the primal-dual interior method is adopted to have a quick calculation to improve the arithmetic speed and a convergence. The invention is able to add the reliability issue to the economy programming in a restriction way and realize an economy optimization of the programming proposal under a high reliability condition.
Owner:上海善业光电科技有限公司
Power-system economic dispatching method considering power grid topology optimization
ActiveCN104809519AImprove operating economyAlleviate transmission congestionForecastingSystems intergating technologiesPower system schedulingTopology optimization
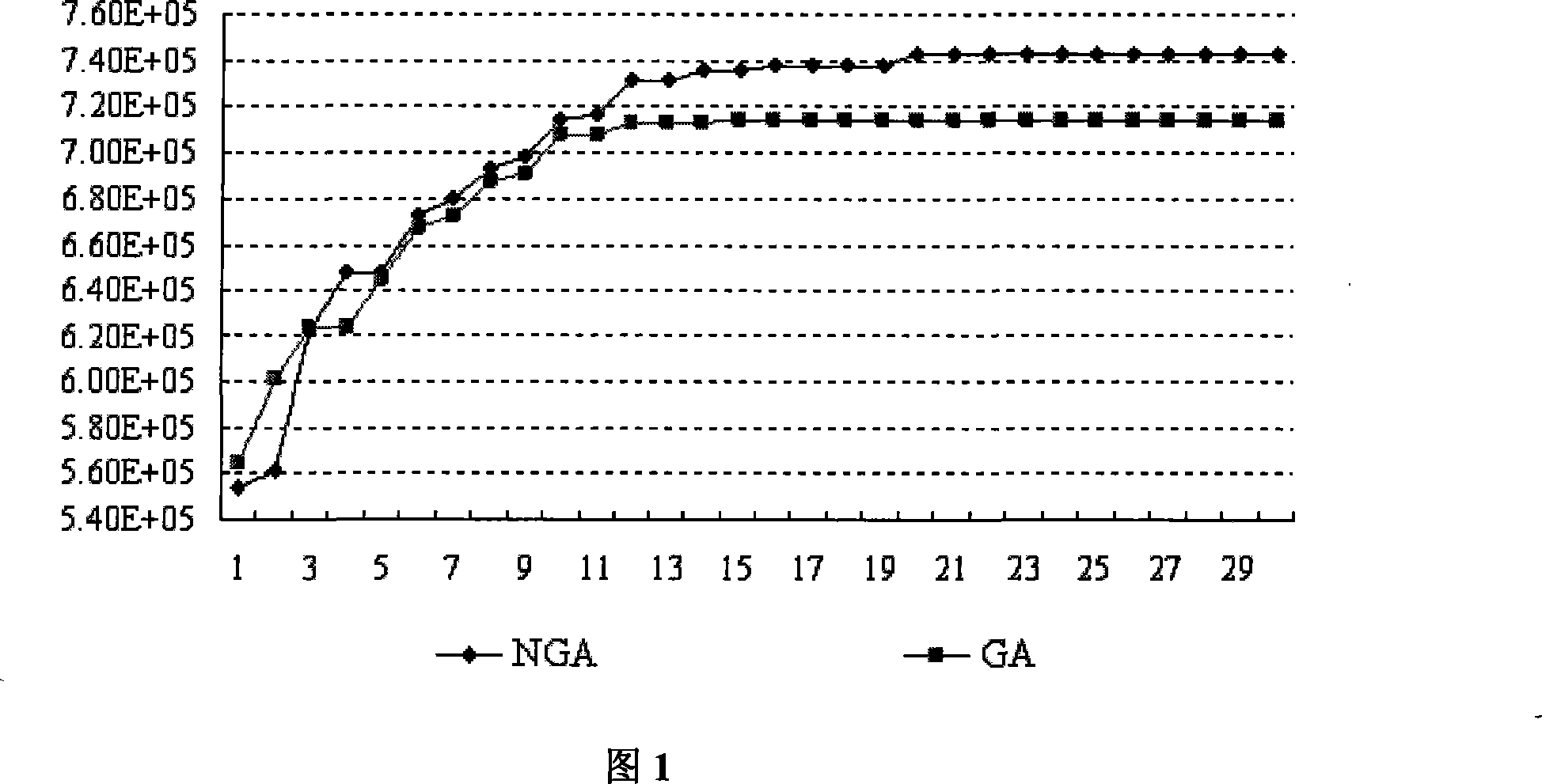
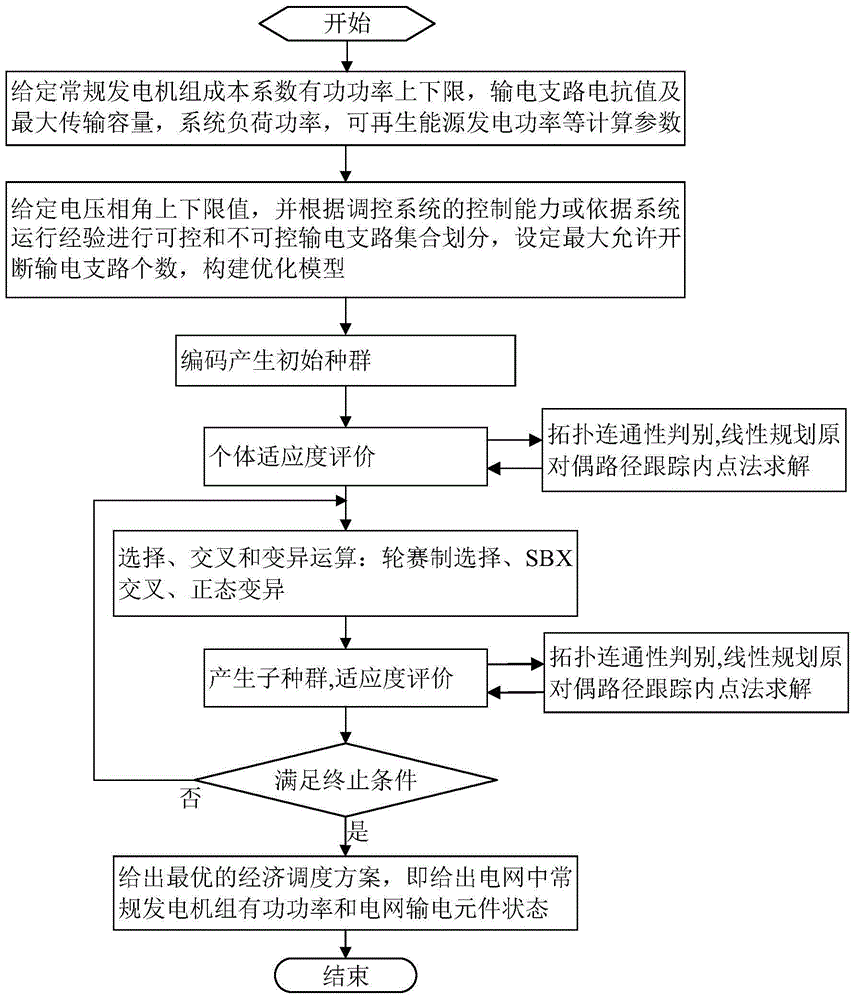
The invention discloses a power-system economic dispatching method considering power grid topology optimization. A power-system dispatching model using active power of conventional generator sets and output component states of the power grid as decision making factors is provided by incorporating the power grid topology optimization into a power-system economic dispatching model and considering the power grid topology connectivity conditions. Topological connectivity is constrained based on the minimum cutset concept in graph theory so as to judge system topological connectivity. The provided model is solved by combination of genetic algorithm and linear programming primal-dual path following interior algorithm. Conventional generator sets and power grid topology can be preset, economical efficiency of power grid operation is improved on the premise of guaranteeing safety of power grid operation, balance capacity of load power of system generation is improved, renewable energy power generation can be accepted within a larger range, abandonment of renewable energy power generation or load shedding is effectively alleviated, and technical support is provided for intelligent development for power system dispatching.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Modeling and optimized dispatching method of electrical series-parallel system on the basis of energy center
ActiveCN105046369AImprove convenienceForecastingSystems intergating technologiesSlack variableSimulation
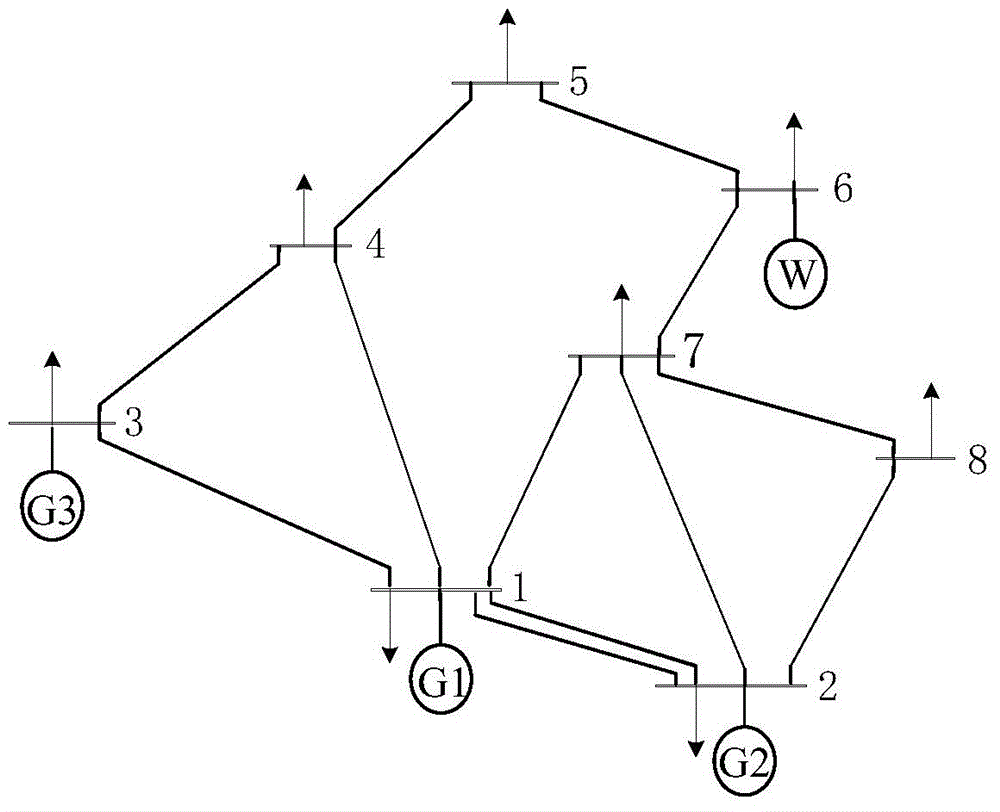
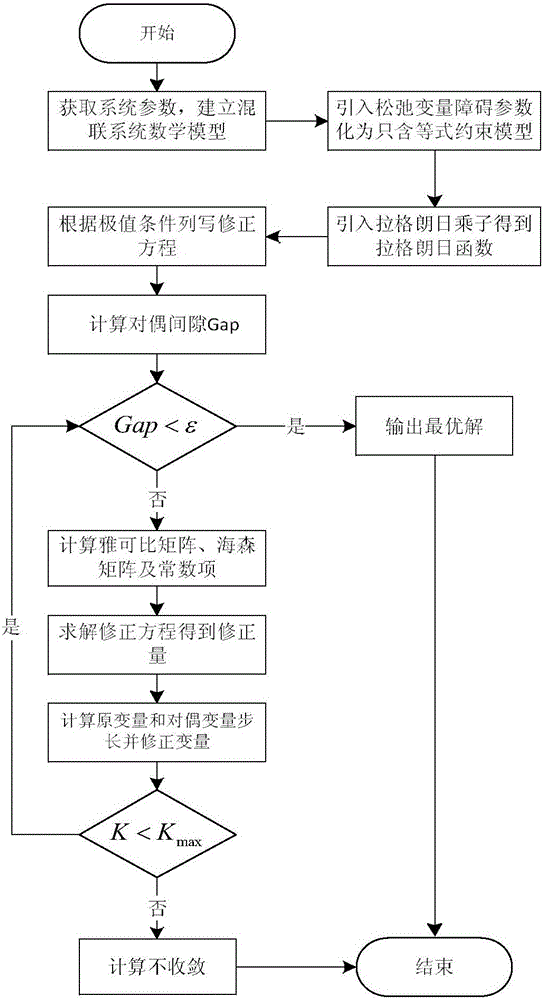
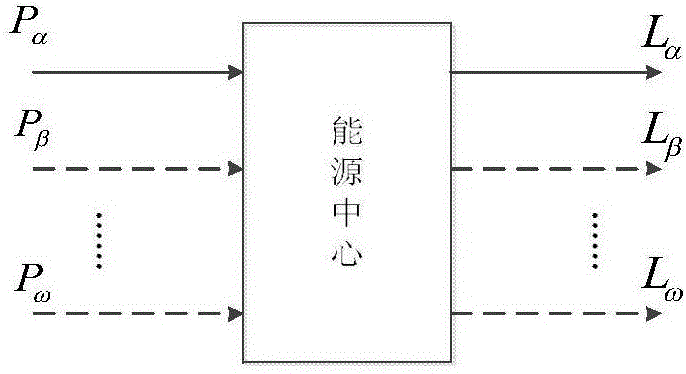
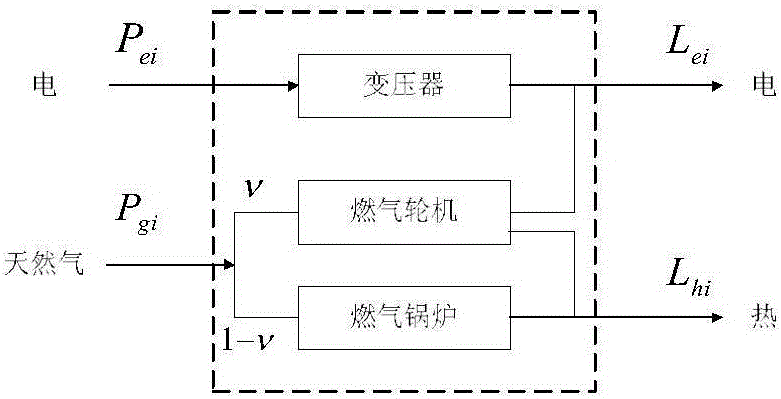
The invention discloses a modeling and optimized dispatching method of an electrical series-parallel system on the basis of an energy center. The modeling and optimized dispatching method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing an electrical network, a natural gas network and an energy hub model, and coupling the electrical network with the natural gas network through an energy hub to form the electrical series-parallel system; then, taking total energy cost as a target function, and considering various constraint conditions to establish an optimized dispatching mathematic model of the electrical series-parallel system; and carrying out solving by a primal-dual interior-point method, importing a slack variable and a barrier parameter in sequence in a solving process so as to change the model into a model which only contains an equality constraint, then, importing a Lagrange multiplier to obtain a Lagrange function, and solving a non-linear equation set formed by a KKT (Karush-Kuhn-Tucker) condition of the Lagrange function by a Newton method. A constructed example simulation result indicates that an optimization effect on the electrical series-parallel system by the modeling and optimized dispatching method is superior to an independent optimization effect.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
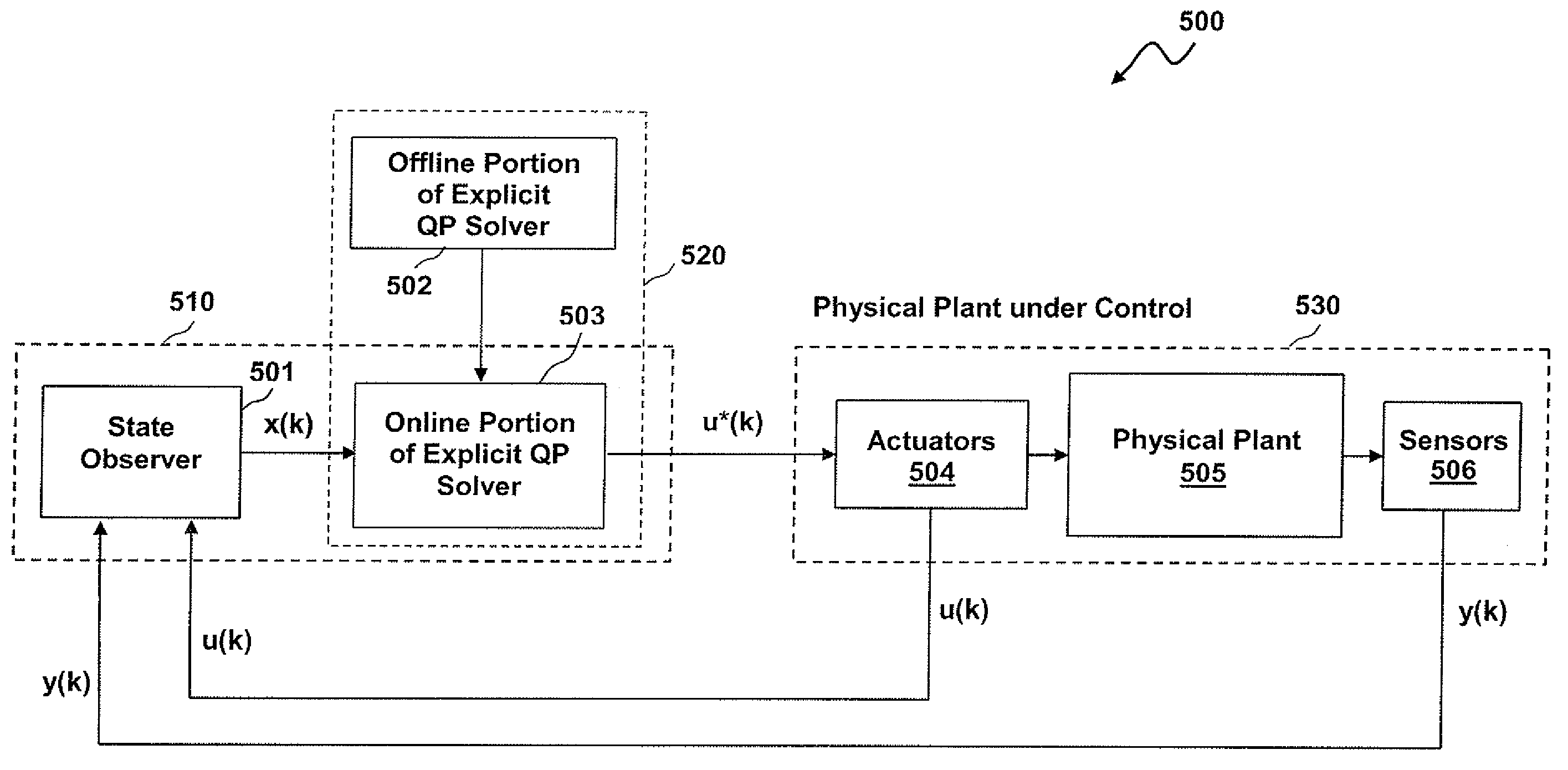
Methods and systems for the design and implementation of optimal multivariable model predictive controllers for fast-sampling constrained dynamic systems
ActiveUS20090254202A1Minimize the numberSaveMathematical modelsComputation using non-denominational number representationGraphicsDirected graph
Methods and systems for the design and implementation of optimal multivariable MPC controllers for fast-sampling constrained dynamic systems utilizing a primal-dual feasibility approach and / or a graph approach. The primal-dual feasibility approach can compute and store matrices defining constraints of quadratic programming problems in an off-line part in order to calculate vectors of Lagrange multipliers and an optimizer. Then primal-dual feasibility can be checked in an on-line part using the Lagrange multipliers and the optimizer can provide a unique optimal solution for the constrained dynamic system. The graph approach can compute and store the matrices and the vectors, and also prepare and store a structure of directed graph in off-line part. An optimizer for a given parameter vector can be determined in on-line part using the directed graph, the matrices and the vectors.
Owner:GARRETT TRANSPORATION I INC
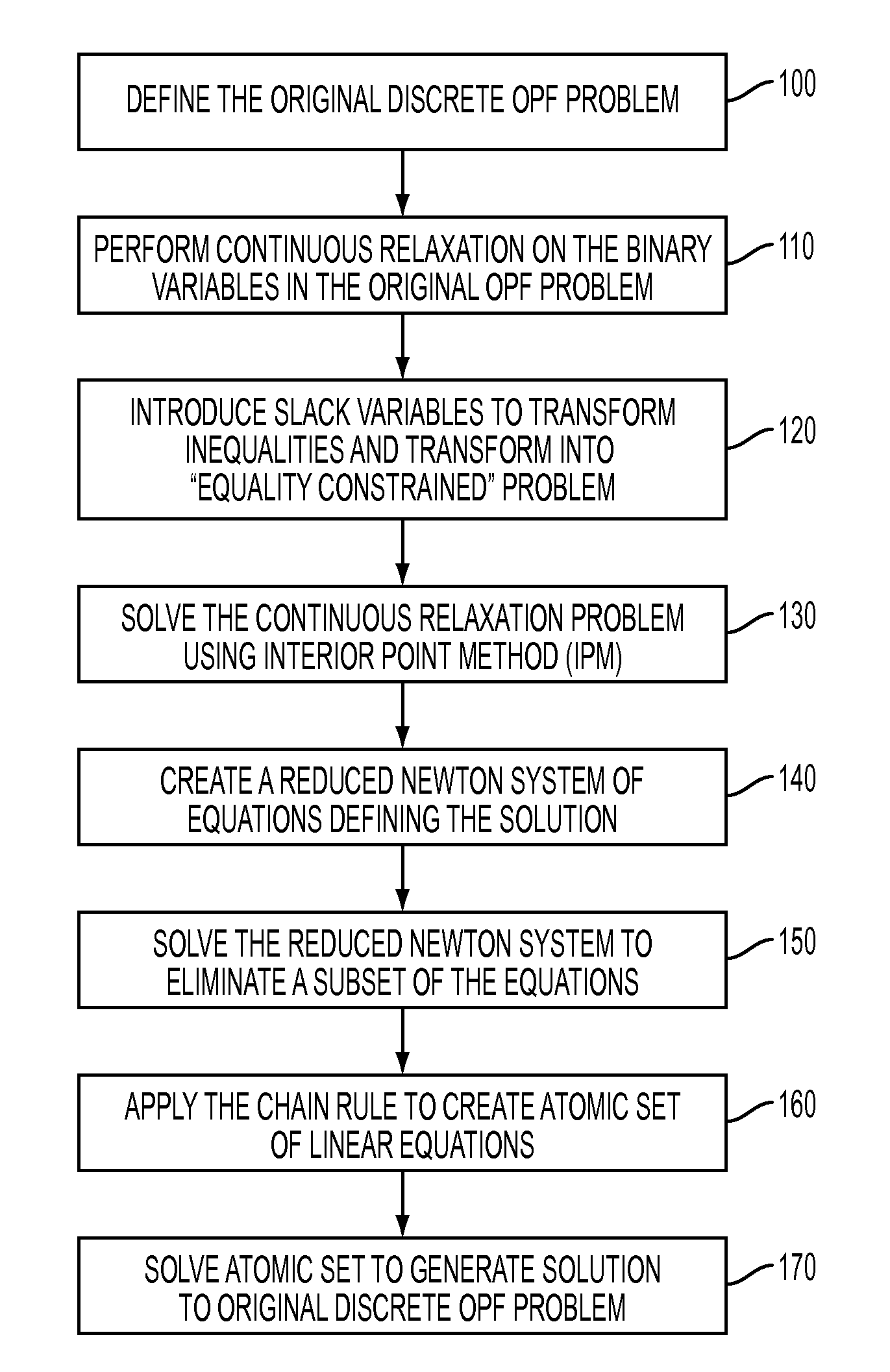
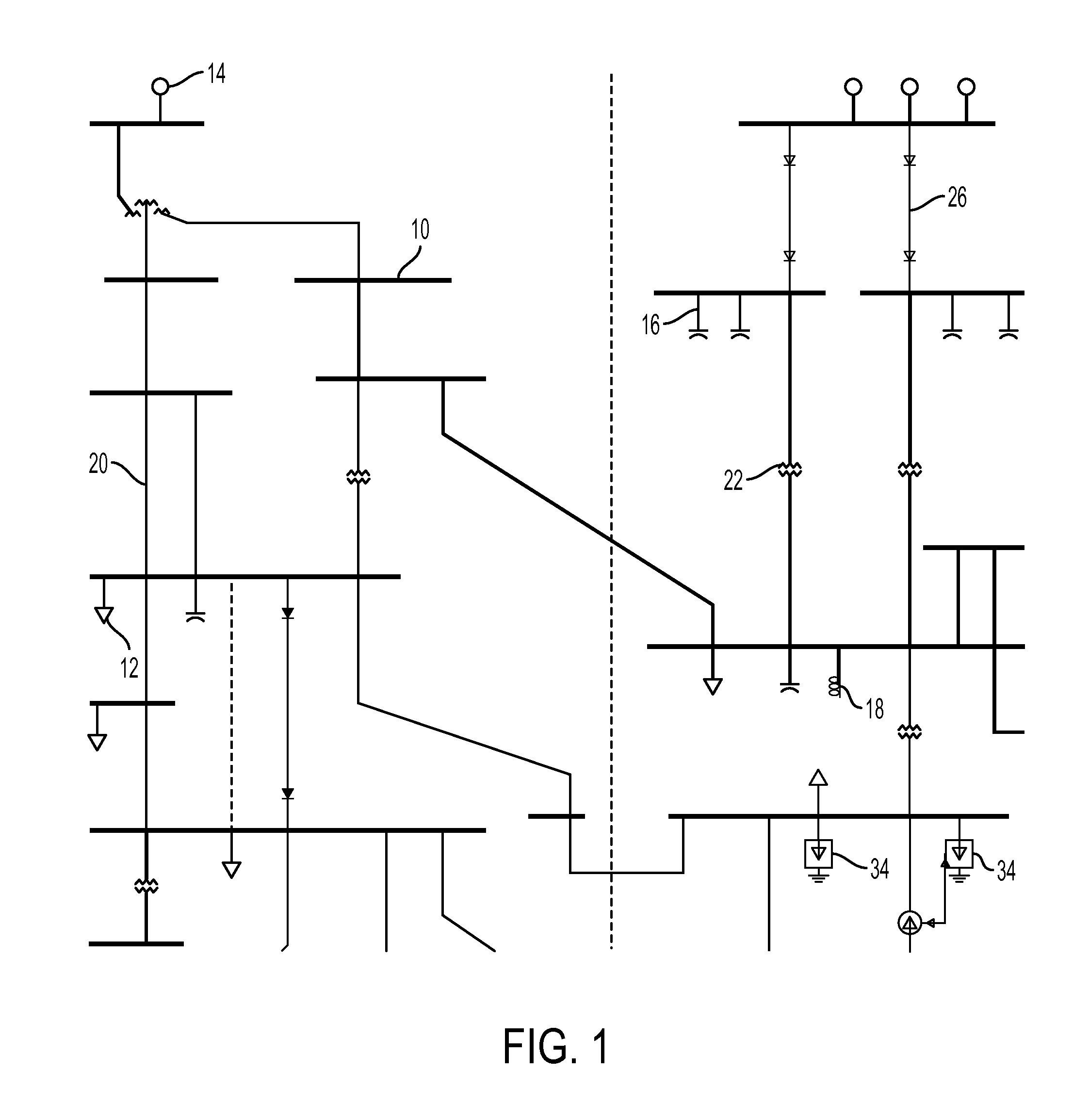
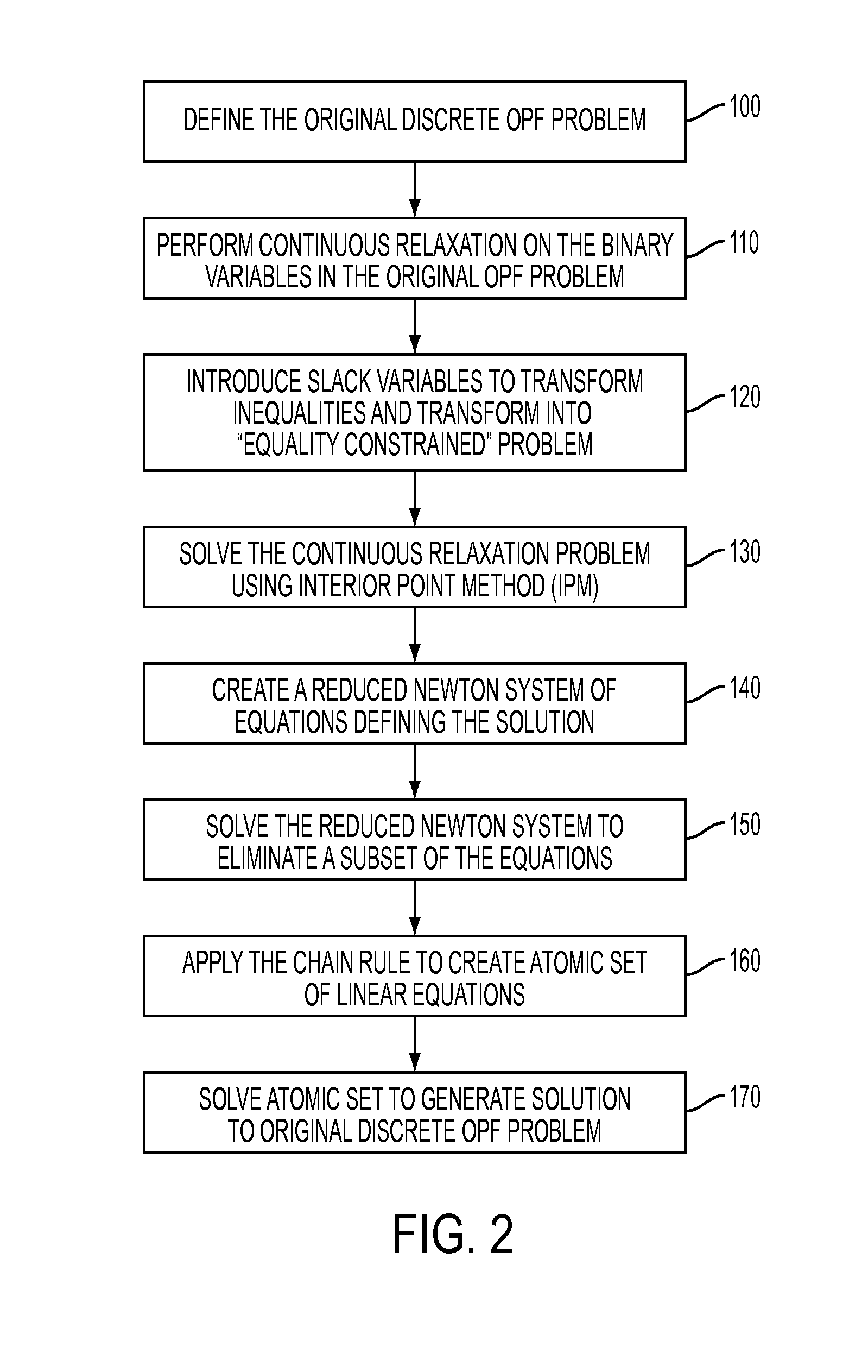
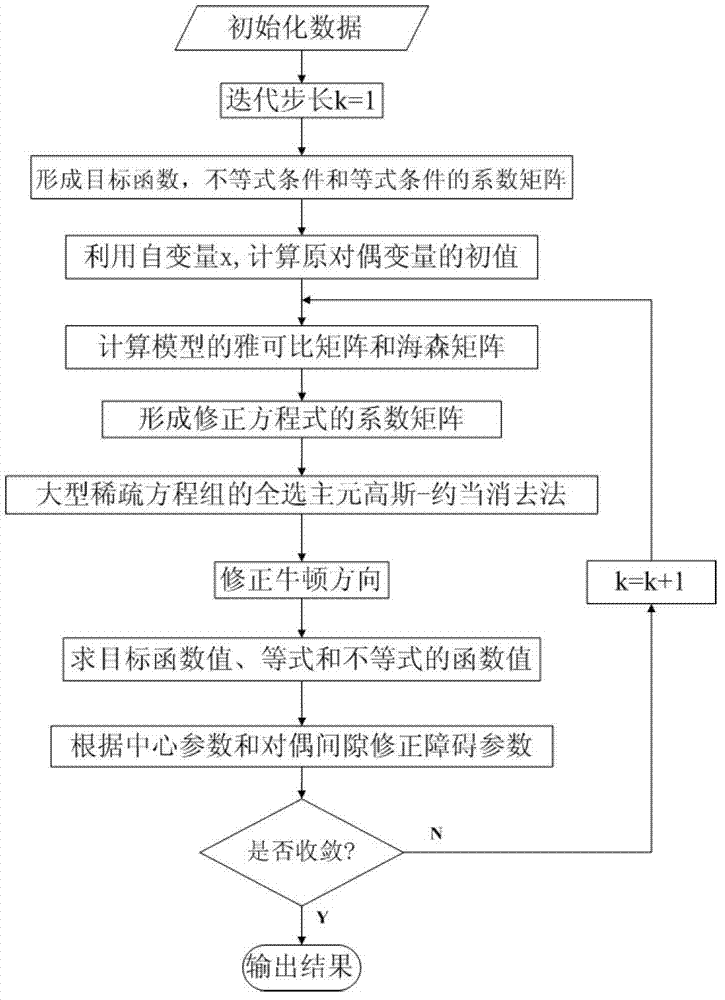
Primal-dual interior point methods for solving discrete optimal power flow problems implementing a chain rule technique for improved efficiency
ActiveUS20120150504A1Easy to analyzeSimplified resolutionPower network operation systems integrationComputation using non-denominational number representationPower flowInterior point method
A solution to the optimal power flow (OPF) problem for electrical generation and distribution systems utilizes a re-configuration of the OPF problem that allows for a simplified analysis and resolution of a network-based OPF problem in a minimal number of iterations. The standard mixed integer quadratic problem (MIQP) definition is be reconfigured, using the chain rule, to a relatively compact linear system of six equations with six unknowns (the smallest reducible (atomic) problem). Advantageously, the reduction in the complexity of the problem does not require any assumptions and yields a solution equivalent to the original problem.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
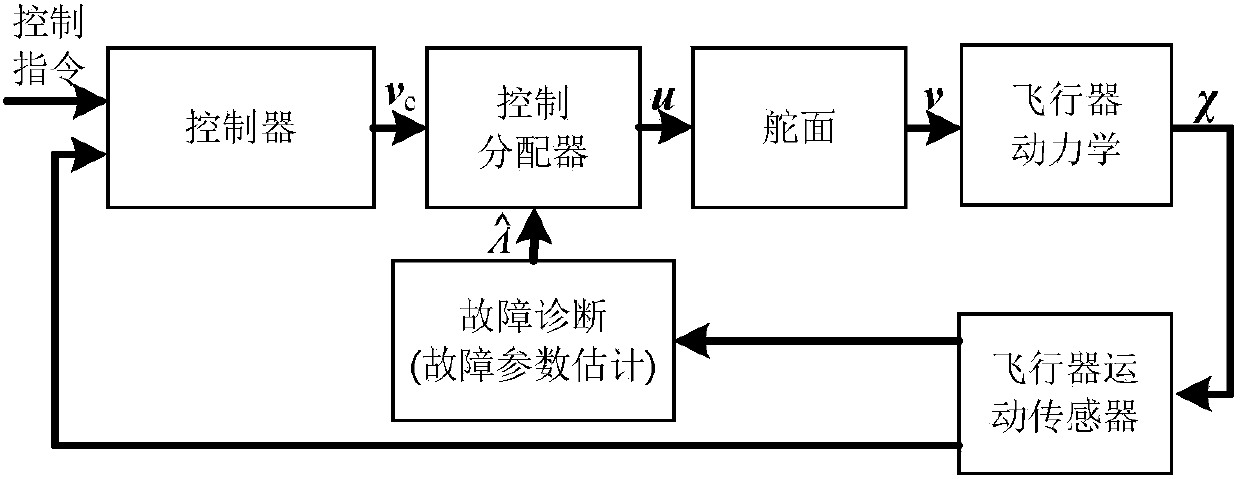
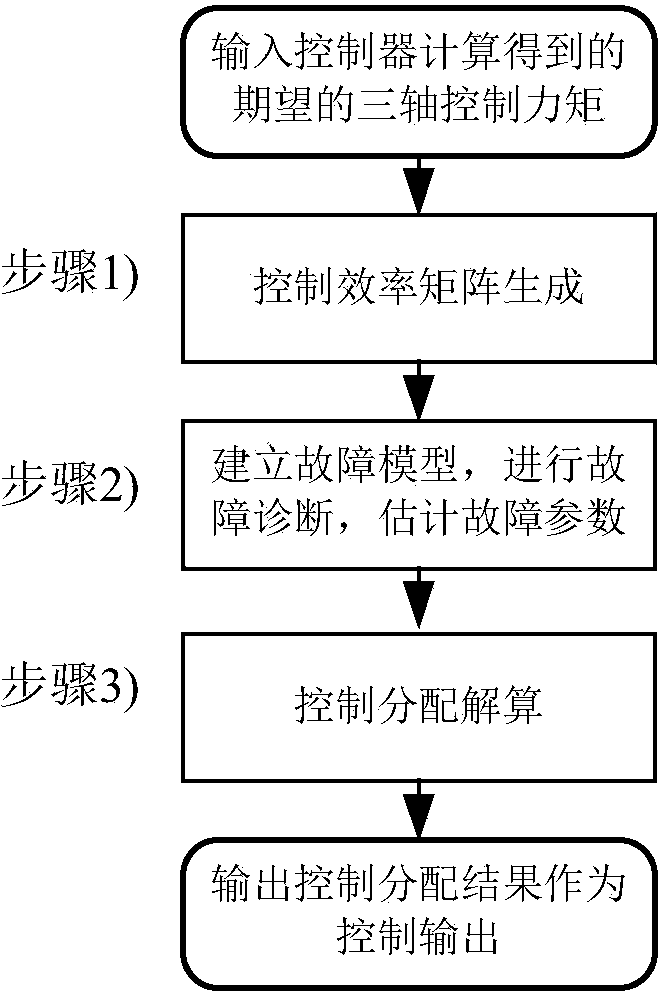
Robust control and distribution method applied to fault-tolerant flight control system
ActiveCN104238565AReduce biasImprove control distribution precisionPosition/course control in three dimensionsAdaptive controlAttitude controlSimulation
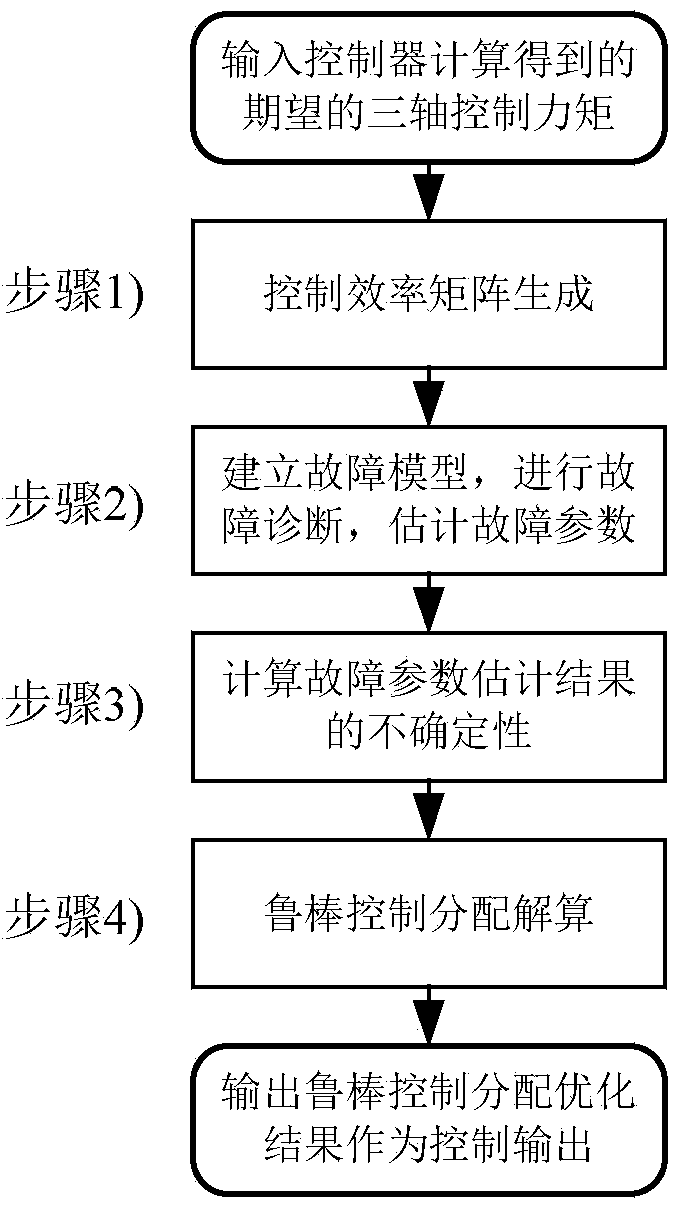
The invention relates to a robust control and distribution method applied to a fault-tolerant flight control system and belongs to the technical field of aerospace fault-tolerant flight control. The robust control and distribution method includes linearizing an aircraft model to generate a control efficiency matrix, determining efficiency coefficient of each rudder side influencing three-axis posture control of the aircraft, building a fault model, converting fault parameter estimation problems into linear regression problems so as to estimate fault parameters by a least square linear regression method, calculating uncertainties of estimated fault parameter results corresponding to each rudder side by a fault projection method and weighting and smoothing; considering difference of the uncertainties of the fault parameters corresponding to the rudder sides, solving the problem about optimization of the minimum control distribution error under the worst condition, controlling and distributing robust, equivalently converting the problem of optimization into the problem of convex optimization, and solving to obtain the robust control and distribution results by a primal dual interior point method. Robustness of control and distribution is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
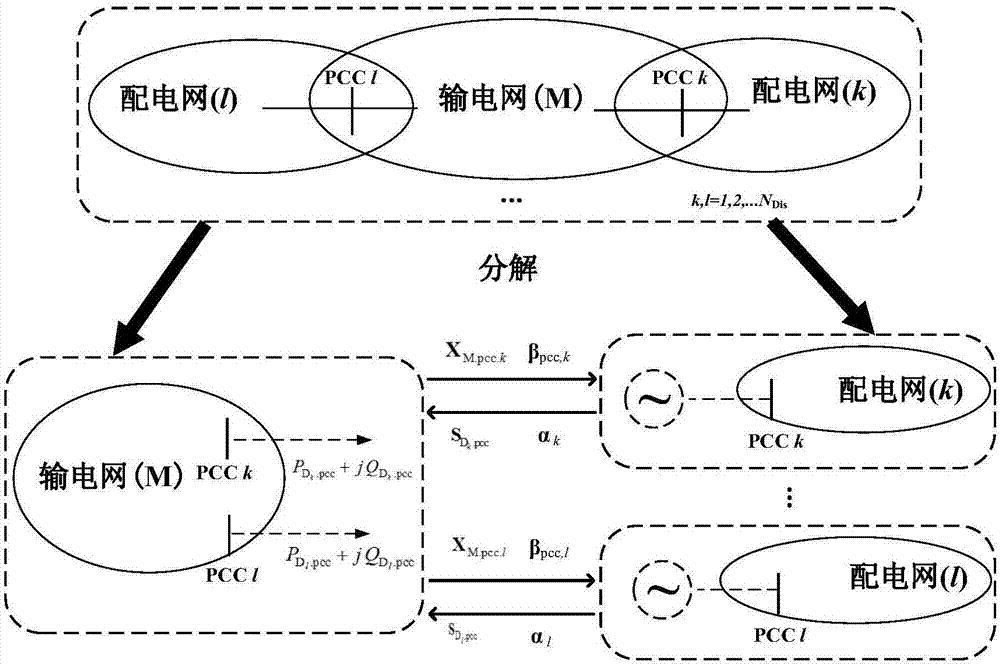
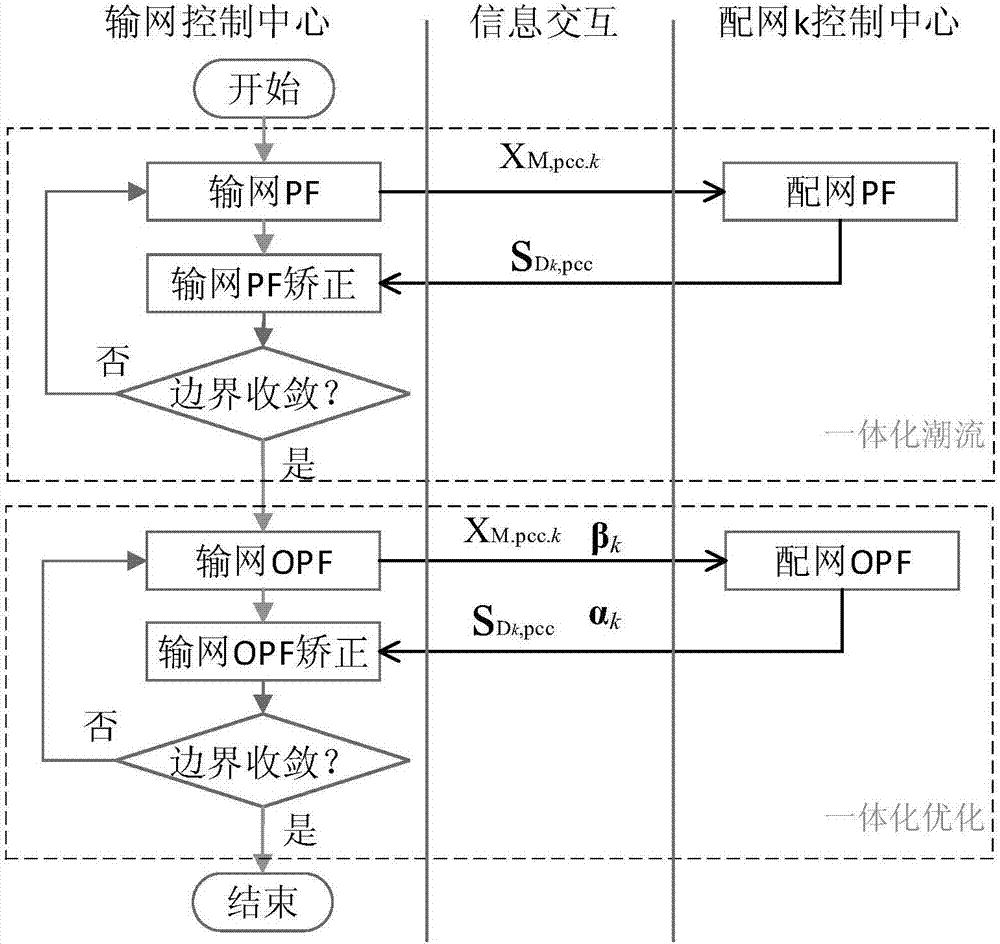
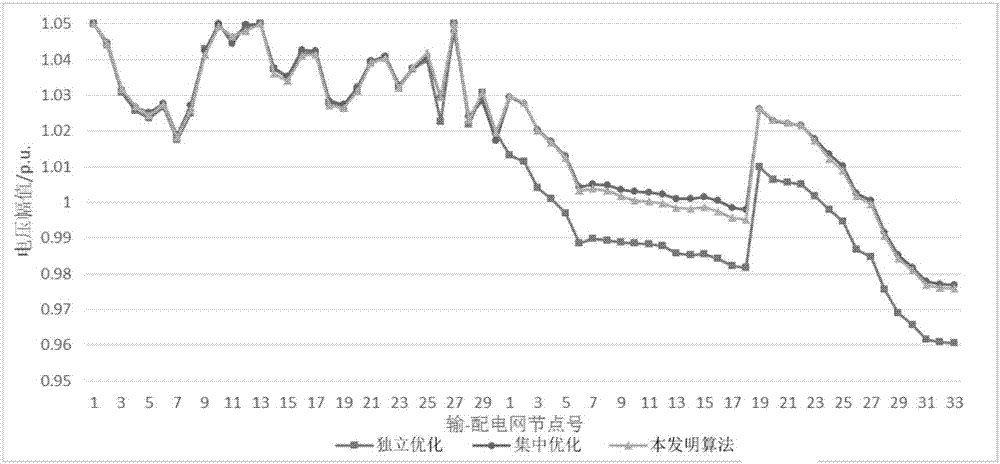
Power transmission and distribution network integrated reactive power optimization method based on distributed computation
ActiveCN107171341AEnsure consistencyGuaranteed synchronicityReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationAc networks with different sources same frequencyElectric power transmissionParallel computing
The invention discloses a power transmission and distribution network integrated reactive power optimization method based on distributed computation. A generalized master-slave method is used for decomposing a power transmission and distribution network problem to three parts, namely power transmission network reactive power optimization, power distribution network reactive power optimization and boundary information exchange. A quadratic penalty function and a primal-dual interior point method are utilized for alternately computing a power transmission reactive power optimization sub-problem and a power distribution reactive power optimization sub-problem. Through exchanging boundary influence factors (boundary connecting node voltage, equivalent power and target function boundary Lagrange multiplier information), coordination participation is realized, and furthermore distributed computation for whole network reactive power optimization is realized, wherein discrete variables which commonly exist in reactive power optimization cause high difficulty in computing the boundary multiplier. The quadratic penalty function is introduced for regulating the discrete variables so that processing of the discrete variables is realized based on a differentiable power transmission and distribution global optimization target function. According to the method of the invention, a distributed computation method is utilized for settling an integrated reactive power optimization problem of the power transmission and distribution network, thereby keeping an existing computation mode of the power transmission and distribution network and realizing relatively high computation precision.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
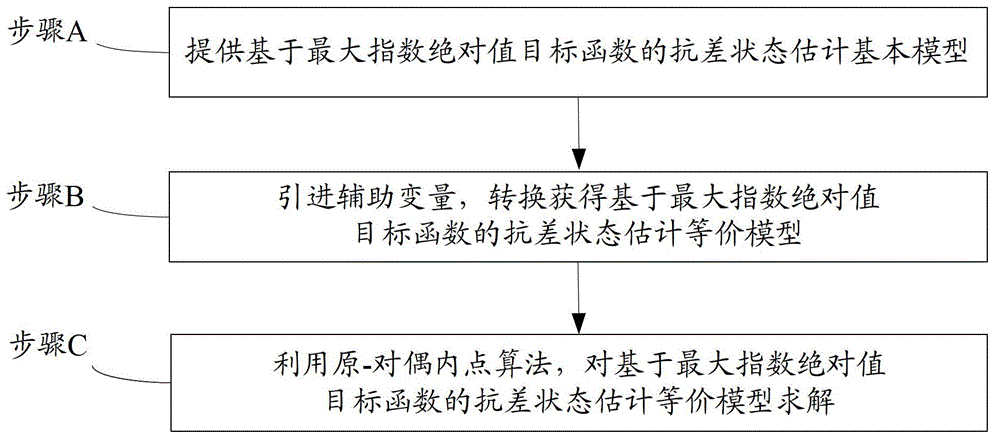
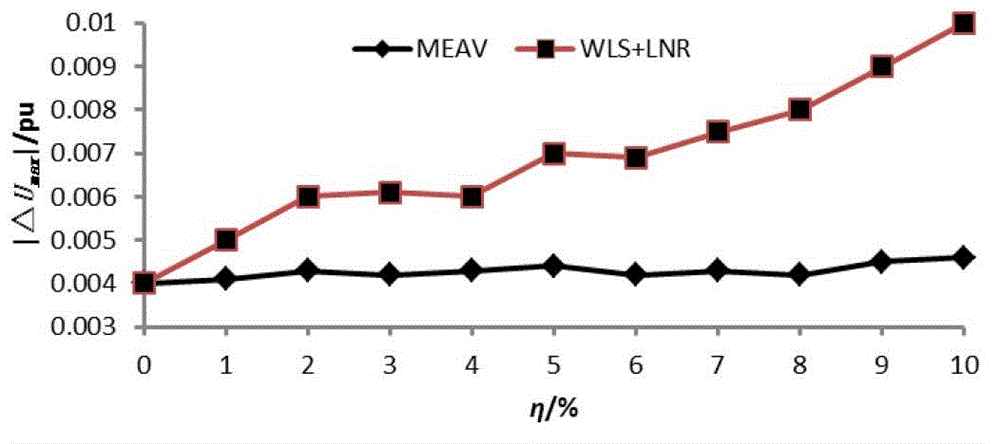
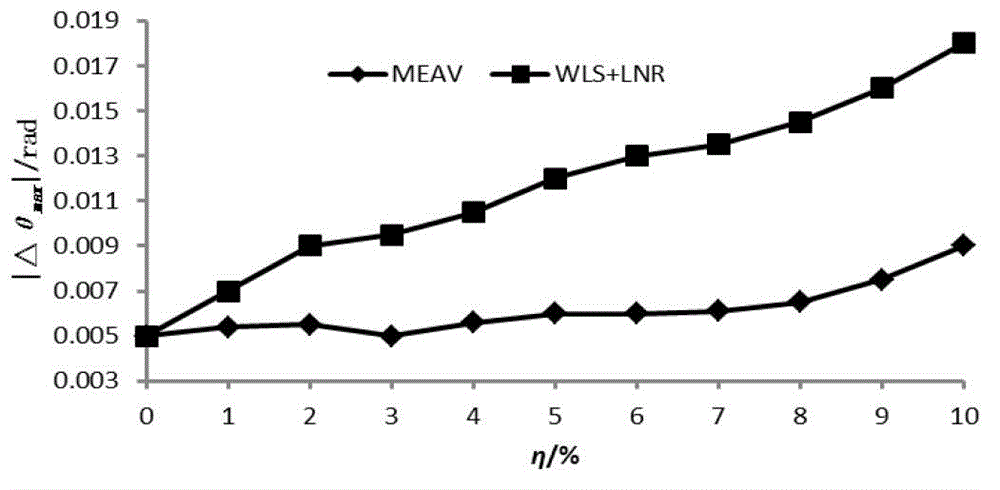
Robust estimation state estimating method based on maximum index absolute value target function
The invention provides a robust estimation state estimating method based on a maximum index absolute value target function. The robust estimation state estimating method comprises the steps of: providing a robust state estimation basic model based on the maximum index absolute value target function; introducing an auxiliary variable into the robust state estimation basic model based on the maximum index absolute value target function to obtain a robust state estimation equivalent model based on the maximum index absolute value target function; and by using a primal-dual interior point algorithm, solving the robust state estimation equivalent model based on the maximum index absolute value target function. Proved through example analysis, the robust estimation state estimating method has the advantages of strong robustness and high computing efficiency, and better engineering application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
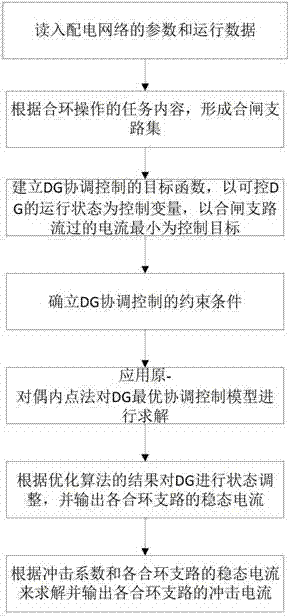
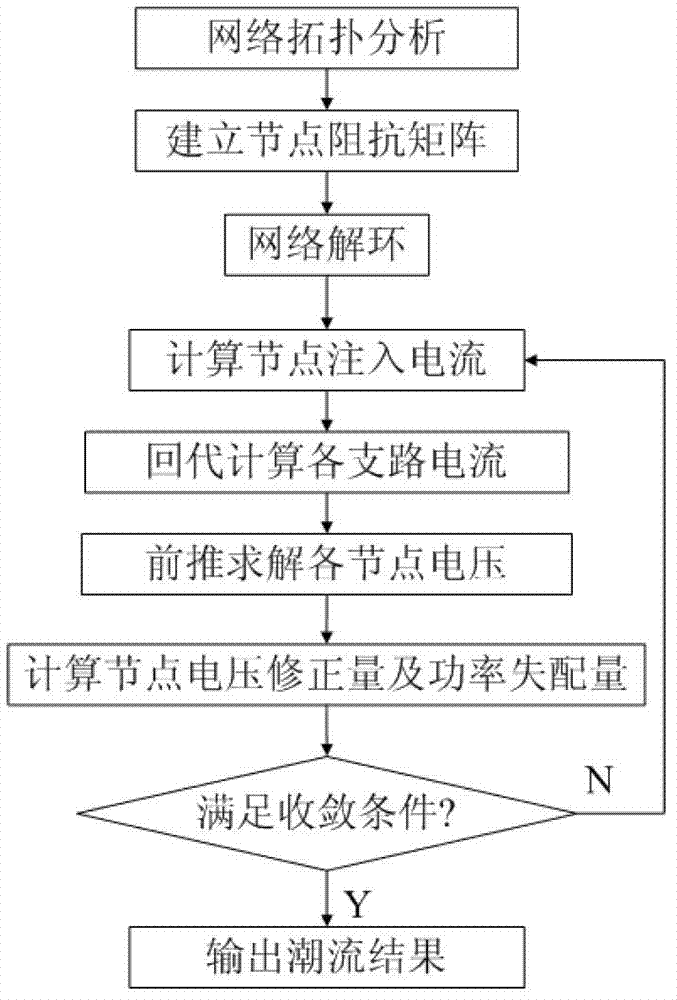
Distribution network loop closing current calculating method based on distributed power supply
InactiveCN103208818AFully play the regulatory roleReduce shockSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsLoop closingInterior point method
The invention discloses a distribution network loop closing current calculating method based on a distributed power supply. The running state of the distributed power supply is optimized and adjusted by establishing a coordinated optimization model of the distributed power supply and combining a primal-dual interior point method to reduce the loop closing operation current. Load flow distribution of a loop closing circuit is calculated by adopting a two-stage method in a weakly meshed distribution network, so that theoretical support and method reference are provided for smoothly implanting the loop closing operation and improving the power supply reliability in an intelligent power grid environment.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
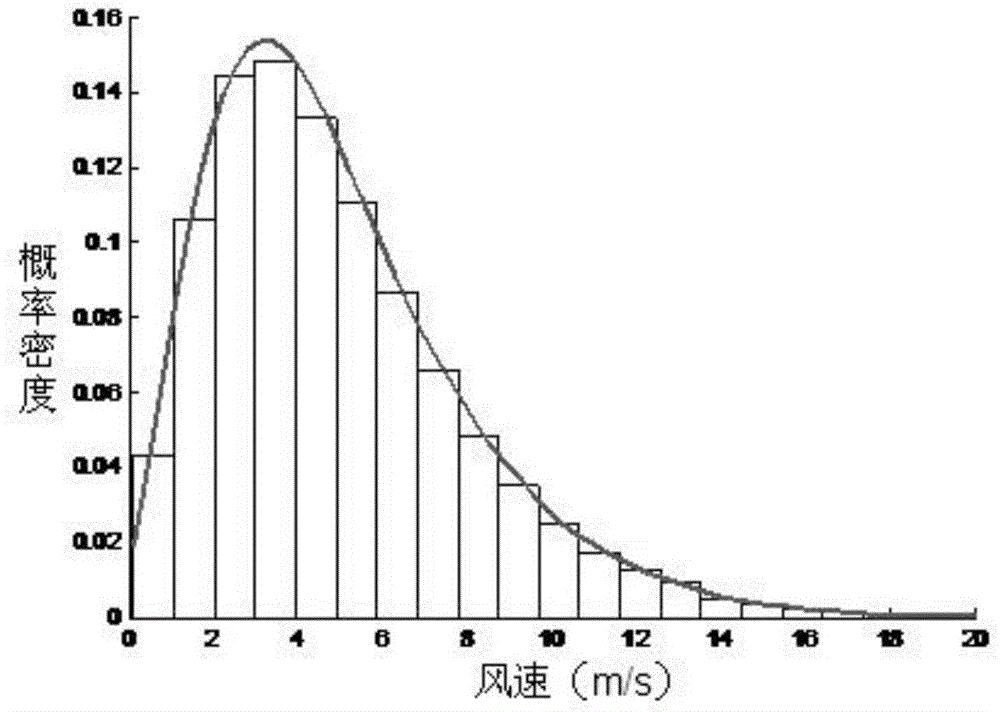
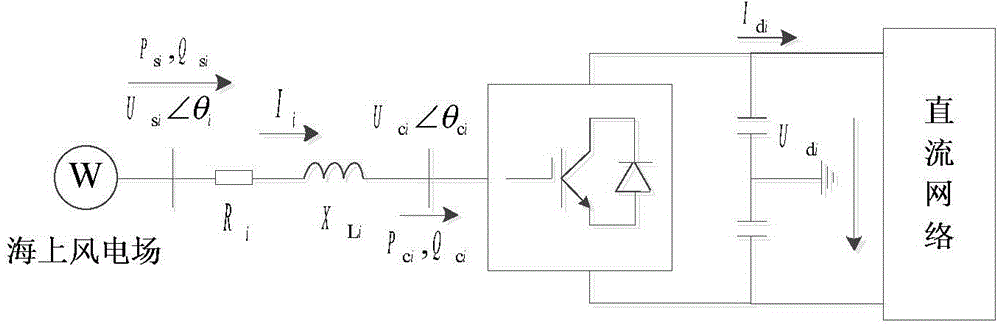
Probabilistic optimal power flow calculation method for alternating-current and direct-current systems of offshore wind power plants subjected to VSC-HVDC (voltage source converter-high voltage direct current) grid connection
InactiveCN104392135ADealing with dependenciesHigh speedSpecial data processing applicationsEqual probabilityHigh-voltage direct current
The invention discloses a probabilistic optimal power flow calculation method for alternating-current and direct-current systems of offshore wind power plants subjected to VSC-HVDC (voltage source converter-high voltage direct current) grid connection. The probabilistic optimal power flow calculation method specifically includes: firstly, fitting probability distribution of offshore wind speeds by means of nonparametric kernel density estimation, describing wind speed correlations among multiple wind power plants by a correlation coefficient matrix, and creating a probability model of output power of the wind power plants and a steady-state mode of VSC-HVDC; then, acquiring standard normal distribution samples by the Latin hypercube sampling technology, and acquiring correlated input variable samples according to the equal-probability transformation theory by the Nataf transformation technology; finally, performing deterministic optimal power flow calculation on each group of samples by the primal-dual interior-point method to acquire output variable samples, and acquiring probability distribution and numerical characteristics of output variables by the statistical method. Calculation results of the probabilistic optimal power flow calculation method can well reflect distribution conditions of state quantity and control quantity of optimal power flow of the alternating-current and direct-current systems, and the probabilistic optimal power flow calculation method has the advantages of high speed and accuracy.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
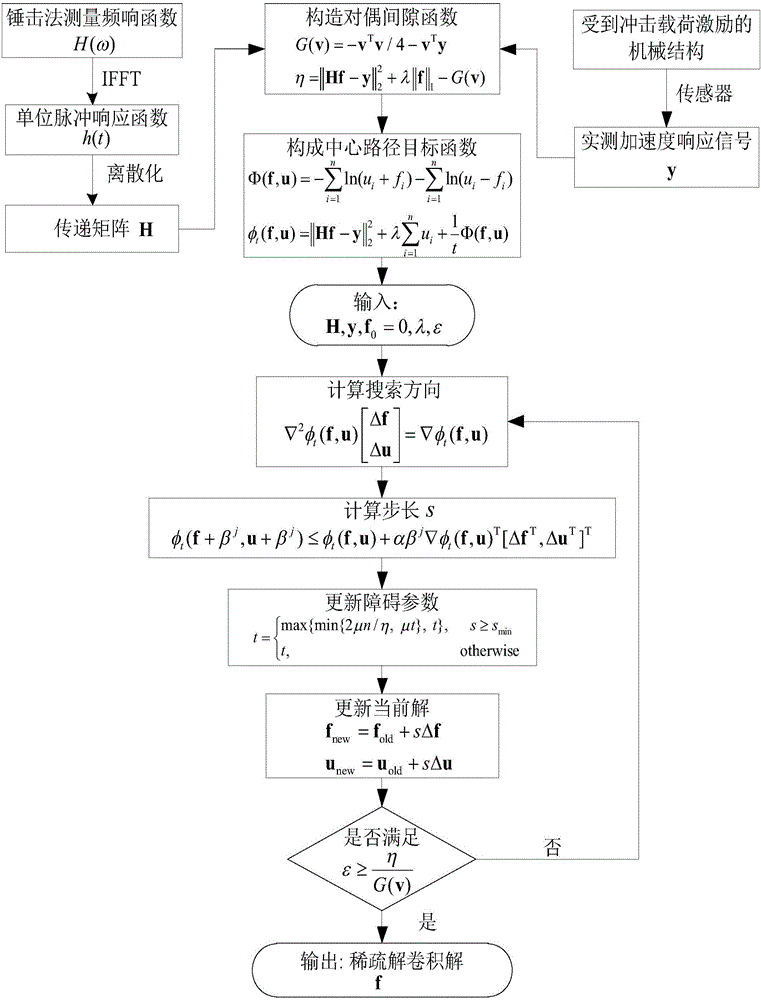
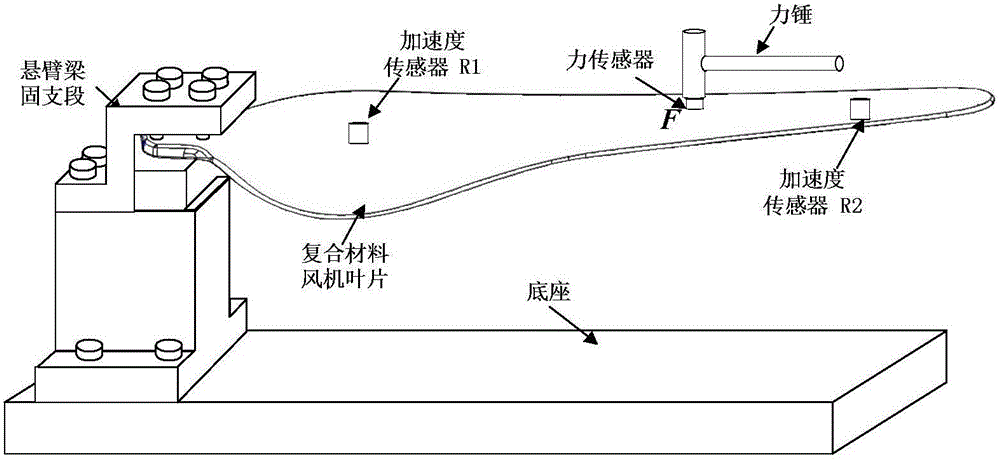
Sparse deconvolution method for impact load identification of mechanical structure
ActiveCN105843780AGrowth inhibitionImprove recognition accuracyComplex mathematical operationsMeasurement pointEngineering
The invention relates to a sparse deconvolution method for impact load identification of a mechanical structure. The method is used for solving the ill-posed nature of the impact load identification inverse problem and comprises steps as follows: 1) a frequency response function between an impact load acting point and a response measurement point of the mechanical structure is measured with a hammering method, a unit impulse response function is obtained through inverse fast fourier transform, discretization is further performed, and a transfer matrix is obtained; 2) an acceleration signal generated by impact load of the mechanical structure is measured with an acceleration sensor; 3) an L1-norm-based sparse deconvolution convex optimization model for impact load identification is established; 4) the sparse deconvolution optimization model is resolved with a primal-dual interior point method, and a sparse deconvolution solution, namely, a to-be-identified impact load, is obtained. The sparse deconvolution method is suitable for identifying the impact load acting on the mechanical structure. Compared with conventional Tikhonov regularization methods based on an L2 norm, the sparse deconvolution method has the advantages of high identification accuracy, high computation efficiency and high stability.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
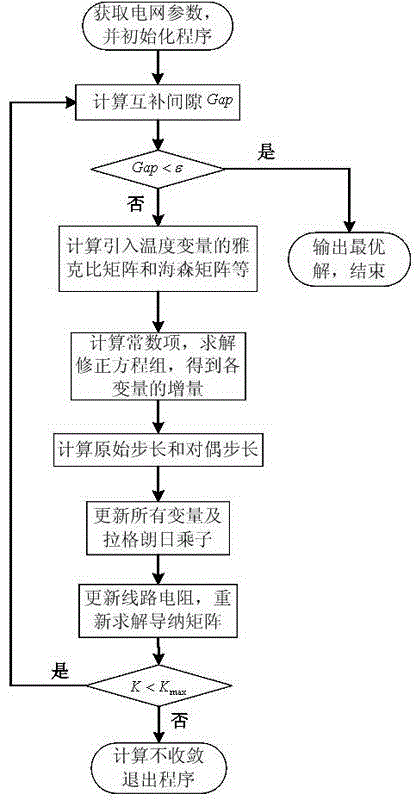
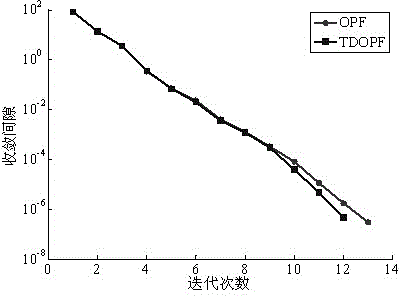
Temperature influence-considering optimal power flow algorithm of power system
InactiveCN104393592ASimplify writingGuaranteed computing speedAc network circuit arrangementsLine resistanceElectric power system
The invention discloses a temperature influence-considering optimal power flow algorithm of a power system. As the traditional optimal power flow is processed by taking power system network parameters as constants and the influence of the electric heating coupling relation of the actual power grid line is neglected, the calculation result of the traditional optimal power flow has great deviation to the scheduling operation result of the actual power grid. On the basis, the temperature influence-considering optimal power flow algorithm of the power system is characterized in that a temperature influence-considering optimal power flow model of the power system is established according to the electric heating coupling relation between line temperatures and line resistance. Besides, the problem of the temperature influence-considering optimal power flow algorithm of the power system is solved by use of a simplifying primal-dual interior point method, and generalized inequality constraints containing only upper limit constraints are formed by simplifying the inequality constraints in the optimization model, and the writing of a program can be greatly simplified. Finally, the simulation and analysis results of a plurality of examples indicate that the model and the algorithm are higher than the traditional optimal power flow in calculation accuracy and calculation efficiency and have significance to the scheduling operation of the power system.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
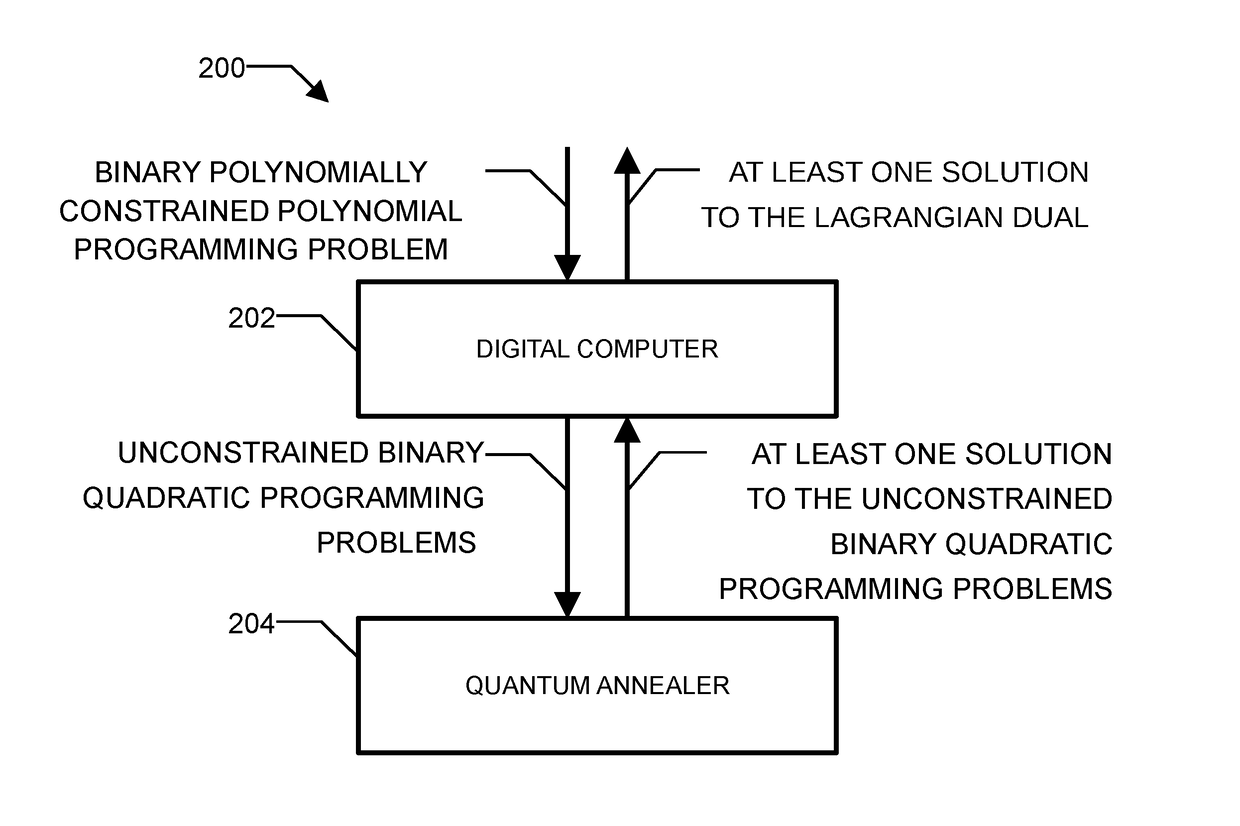
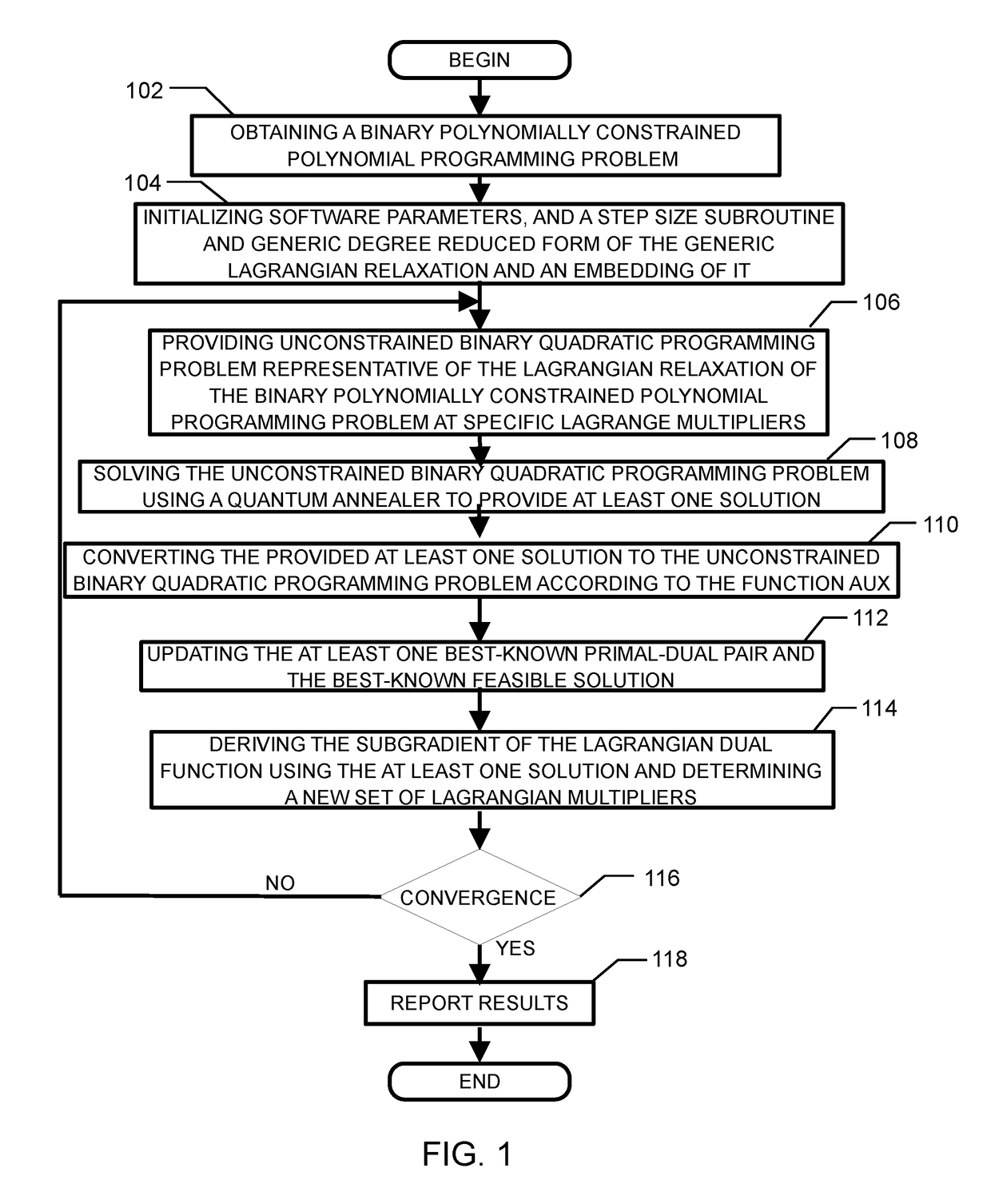
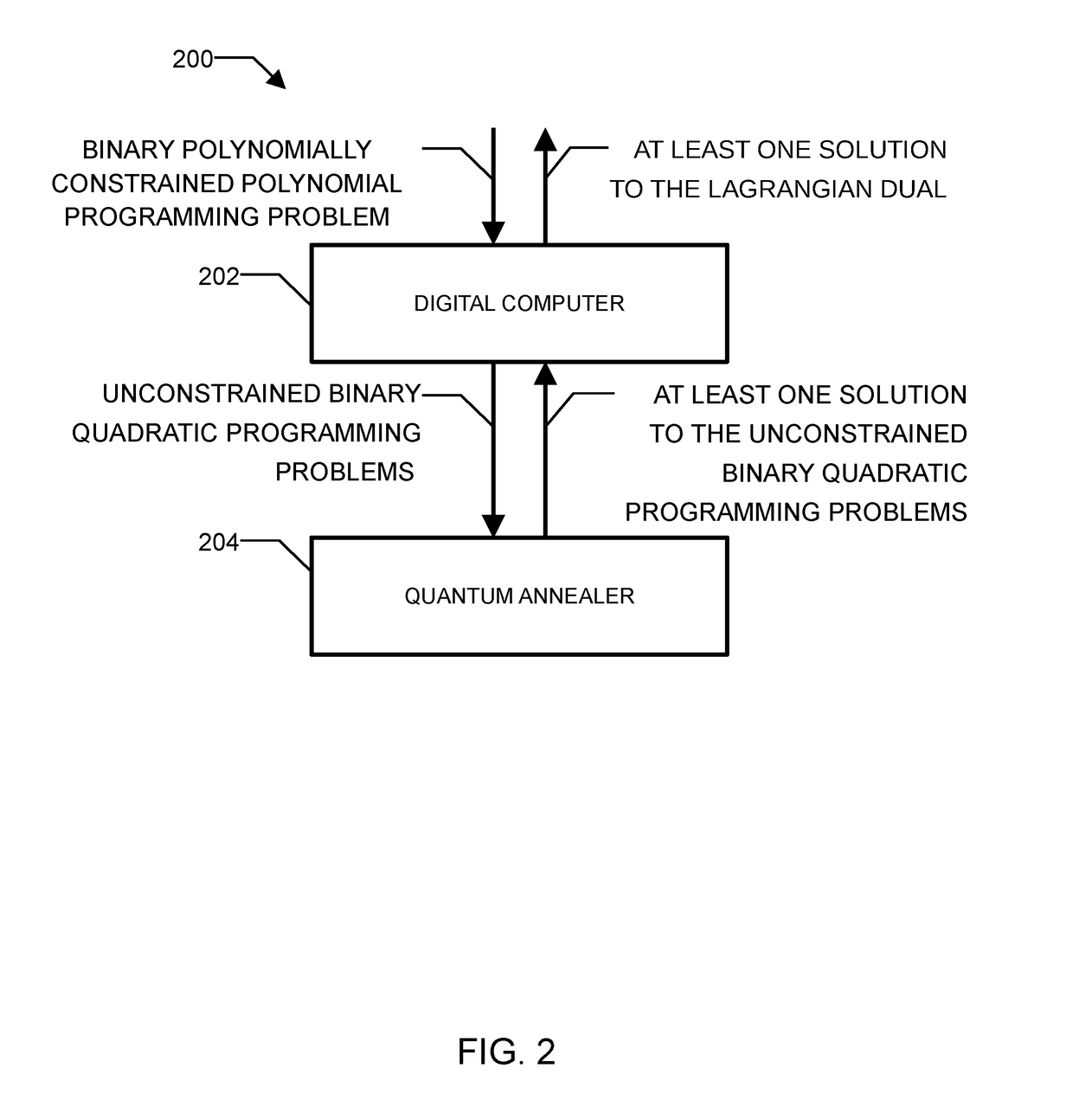
Method and system for solving the lagrangian dual of a binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem using a quantum annealer
InactiveUS20170242824A1Less sensitive to errorSpeed up the processQuantum computersComplex mathematical operationsPolynomial programmingPosynomial
A method for solving the Lagrangian dual of a binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem comprises obtaining a binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem; until a convergence is detected, iteratively, providing a set of Lagrange multipliers, providing an unconstrained binary quadratic programming problem representative of the Lagrangian relaxation of the binary polynomially constrained polynomial programming problem at these Lagrange multipliers, providing the unconstrained binary quadratic programming problem to a quantum annealer, obtaining from the quantum annealer at least one corresponding solution, using the at least one corresponding solution to generate a new set of Lagrange multipliers; and providing all corresponding best-known primal-dual pairs and best-known feasible solutions after convergence.
Owner:1QB INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES INC
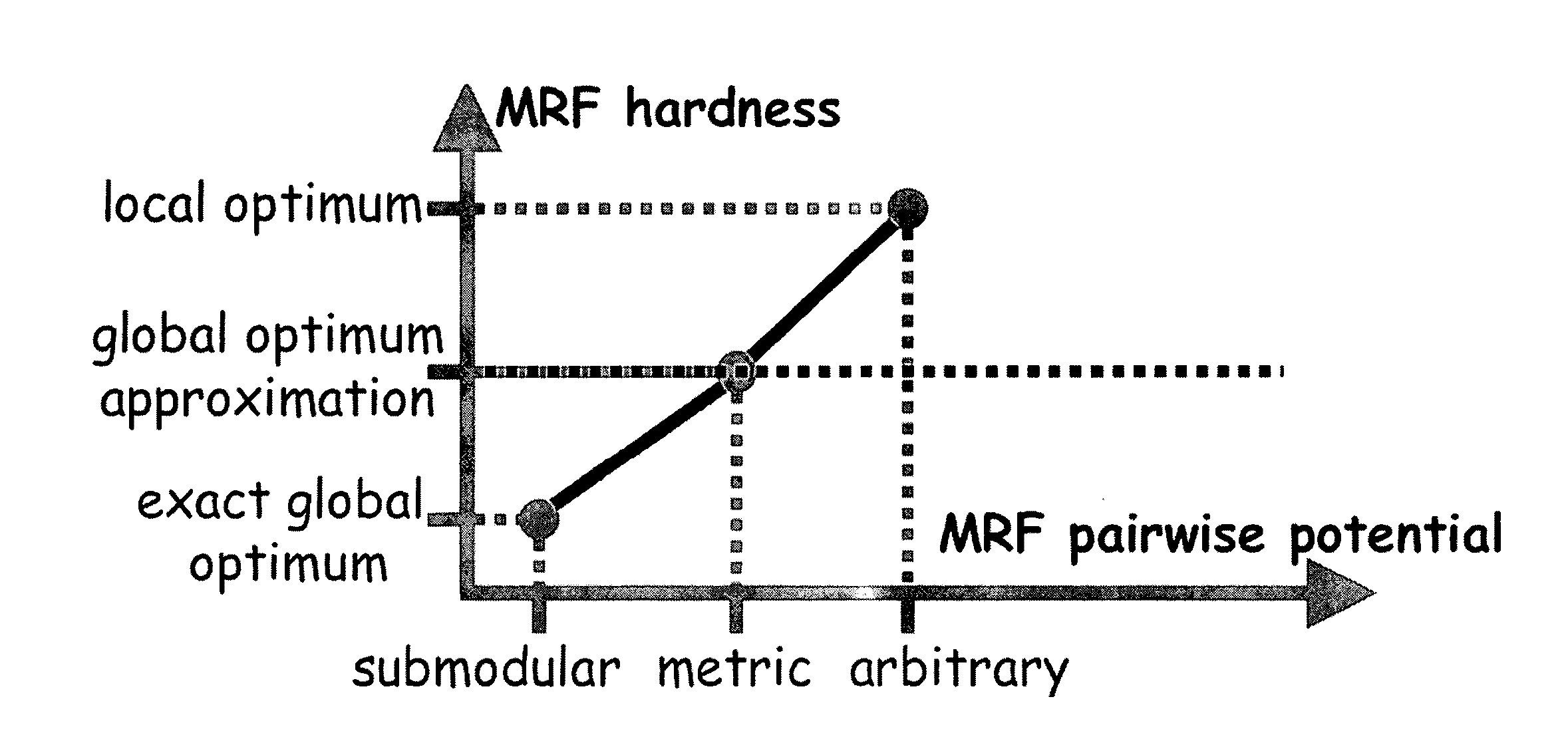
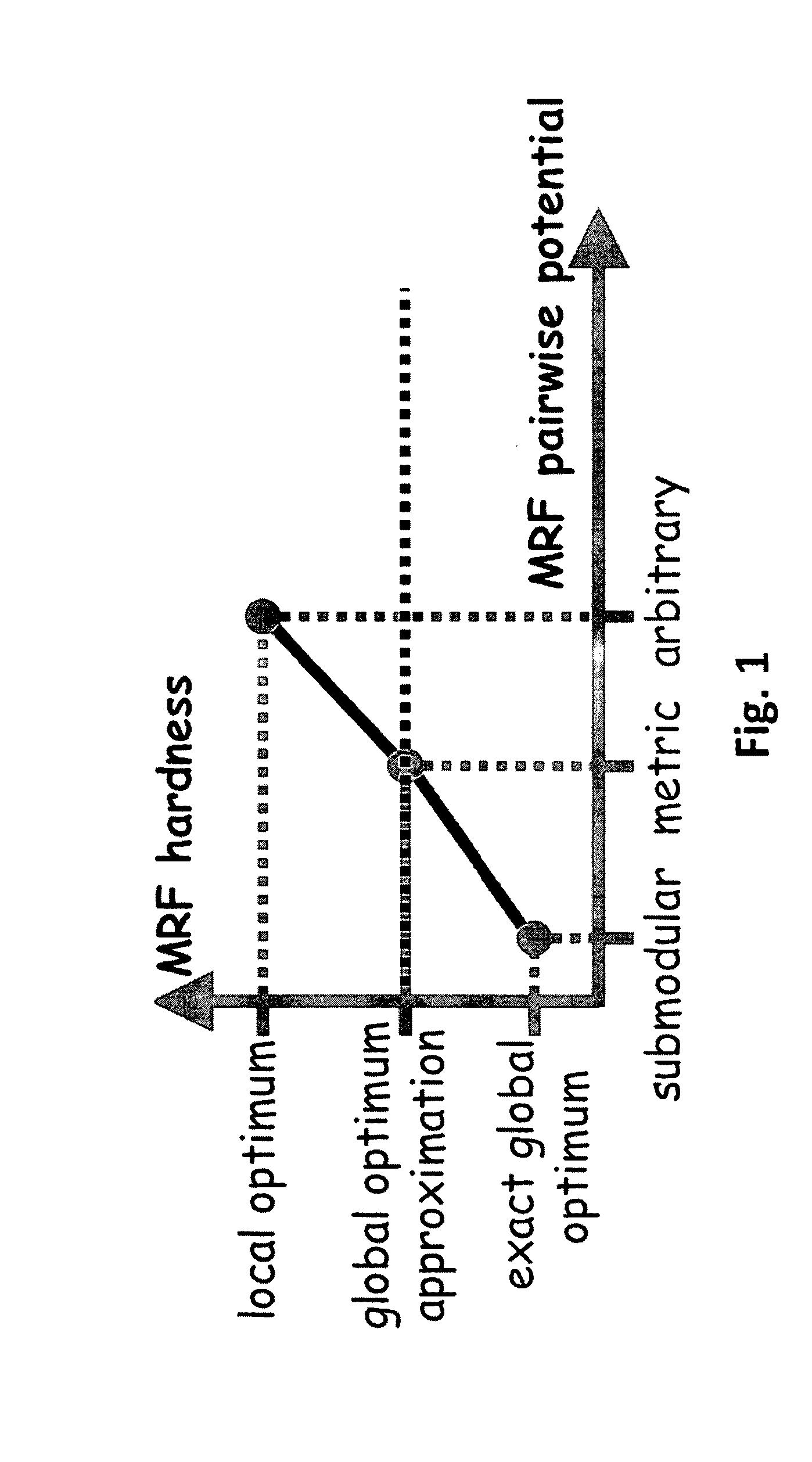
System and Method for Optimizing Single and Dynamic Markov Random Fields with Primal Dual Strategies
ActiveUS20090252416A1Not compromise efficiencyImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsAlgorithm
A method for determining an optimal labeling of pixels in computer vision includes modeling an image by a graph having interior nodes and edges where each image point p is associated with a graph node, each pair of nearest neighbor points p, q is connected by a graph edge, each graph node p is associated with a singleton potential c(p), and each graph edge is associated with a pairwise potential function d(p,q). A label is randomly assigned to each point to initialize unary variables including an indicator function that indicates which label is assigned to which point and dual variables including height variables associated with each node p and label a, and balance variables associated with each edge (p,q) and label a. For each label, a new label c is selected, a capacitated graph is constructed and solved. The label selection divides the image into disjoint regions.
Owner:CENTSUPELEC
Obstacle avoidance solution applied to redundant manipulator
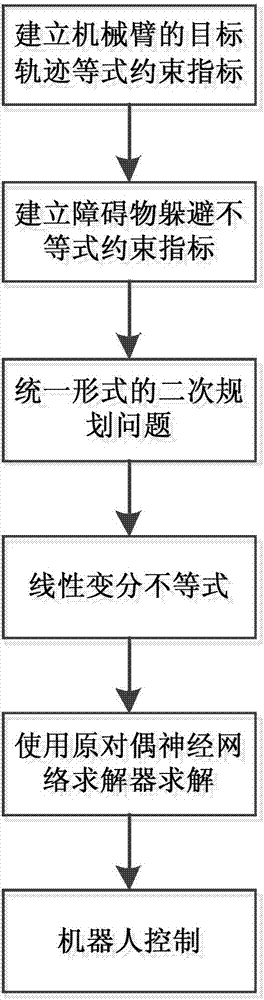
The invention discloses an obstacle avoidance solution applied to a redundant manipulator. The obstacle avoidance solution comprises the steps of: S1, acquiring a forward kinematics model of the manipulator through establishing a D-H matrix of the manipulator, and establishing a target track equality constraint index of a speed layer after performing derivation processing on the forward kinematicsmodel; S2, establishing a vector-based obstacle avoidance inequality constraint index; S3, writing the target track equality constraint index of the speed layer established in the step S1 and the vector-based obstacle avoidance inequality constraint index established in the step S2 into quadratic programming problems in the unified form; S4, transforming the quadratic programming problems in theunified form in the step S3 into a linear variational inequality; S5, solving the linear variational inequality in the step S4 by means of a primal-dual neural network solver; S6, and outputting manipulator joint angle control variables solved by means of the primal-dual neural network solver in the step S5 to the manipulator, so as to realize the effect of controlling the redundant manipulator toavoid obstacles.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Mobile robot visual servo trajectory tracking predictive control method based on primal-dual neural network
InactiveCN109213175AEasy to solveFast online calculationPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesMinimization problemPerformance index
A mobile robot visual servo trajectory tracking predictive control method based on a primal-dual neural network comprises the following steps: 1) building a mobile robot kinematical model; 2) fixing acamera on a ceiling, so that the camera can obtain global visual information, and building a visual servo mobile robot error model; 3) according to the error model, obtaining a prediction equation and defining a predictive control performance index; and 4) establishing a performance index minimization problem as a minimization problem based on the primal-dual neural network, and solving controller gain by combining a primal-dual neural network module in Matlab-Simulink, so that a trajectory tracking task is completed. The method provided by the invention transforms a problem into a multi-constrained linear quadratic programming problem and quickly finds optimal solution by utilizing a PDNN.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
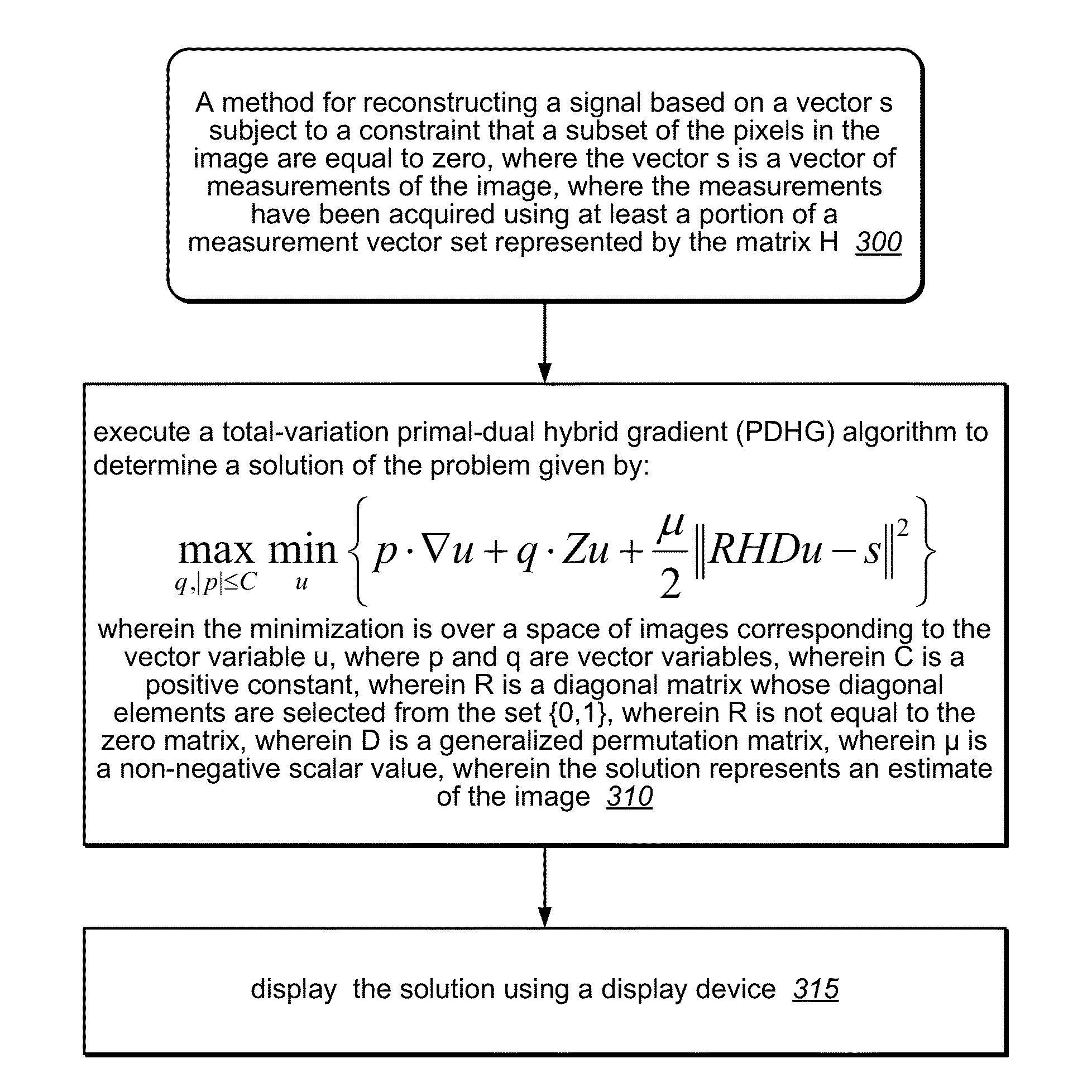
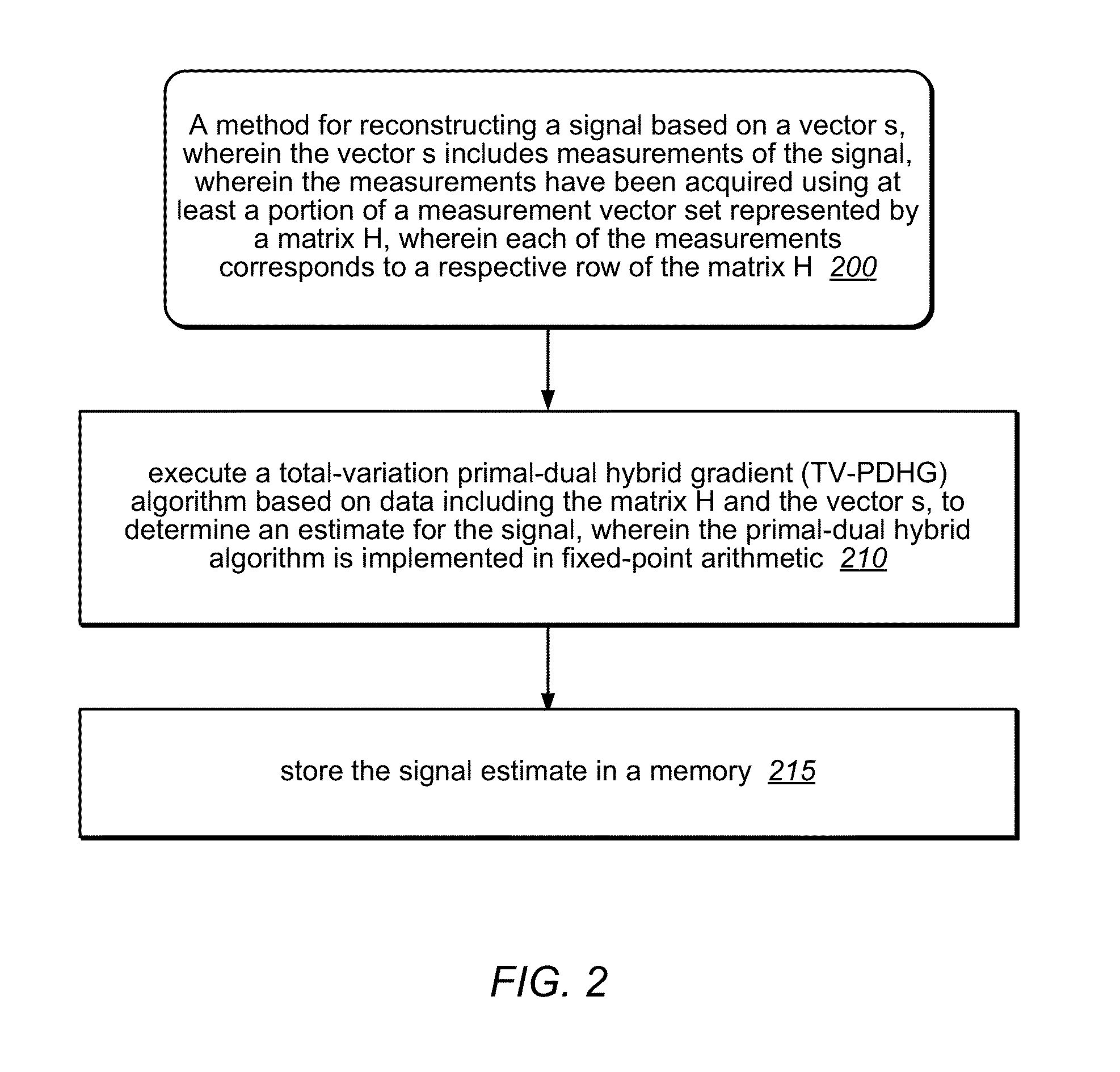
Signal reconstruction using total-variation primal-dual hybrid gradient (TV-PDHG) algorithm
A mechanism for reconstructing a signal (e.g., an image) based on a vector s, which includes measurements of the signal. The measurements have been acquired using at least a portion of a measurement vector set represented by a matrix H. Each of the measurements corresponds to a respective row of the matrix H. (For example, each of the measurements may correspond to an inner product between the signal and a respective row of the matrix product HD, wherein D is a generalized permutation matrix.) A total-variation primal-dual hybrid gradient (TV-PDHG) algorithm is executed based on data including the matrix H and the vector s, to determine an estimate for the signal. The TV-PDHG algorithm is implemented in fixed-point arithmetic.
Owner:INVIEW TECH CORP
Distributed Joint Admission Control and Dynamic Resource Allocation in Stream Processing Networks
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Power grid fast recovery method considering generator set recovery time model
InactiveCN107204631AReduce the risk of secondary accidentsPerfect black start planContigency dealing ac circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsStart upTidal current
A power grid fast recovery method considering a generator set recovery time model comprises the following steps: classifying the generators in a power grid in detail according to the start-up characteristic, and building corresponding startup time models; building a branch startup time model under the premise of considering the branch startup time; searching for the optimal startup paths of all the generators through an improved Dijkstra algorithm, sorting the generators, and determining a target generator; setting an objective function; solving the objective function through a primal-dual interior point optimal power flow algorithm; checking the transient states of the startup paths of the generators; after a generator set is started, deleting the generator set from unstarted generator sets, revising the weight value of a charged transmission line to 1 / 5 of the original value, and increasing the number of virtual branches between started generators; and finally, selecting a final startup scheme according to different optimization objectives. The problem that an unreasonable scheme is made due to an inaccurate generator time model after large-scale blackout of the system is solved.
Owner:POWER DISPATCHING CONTROL CENT OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
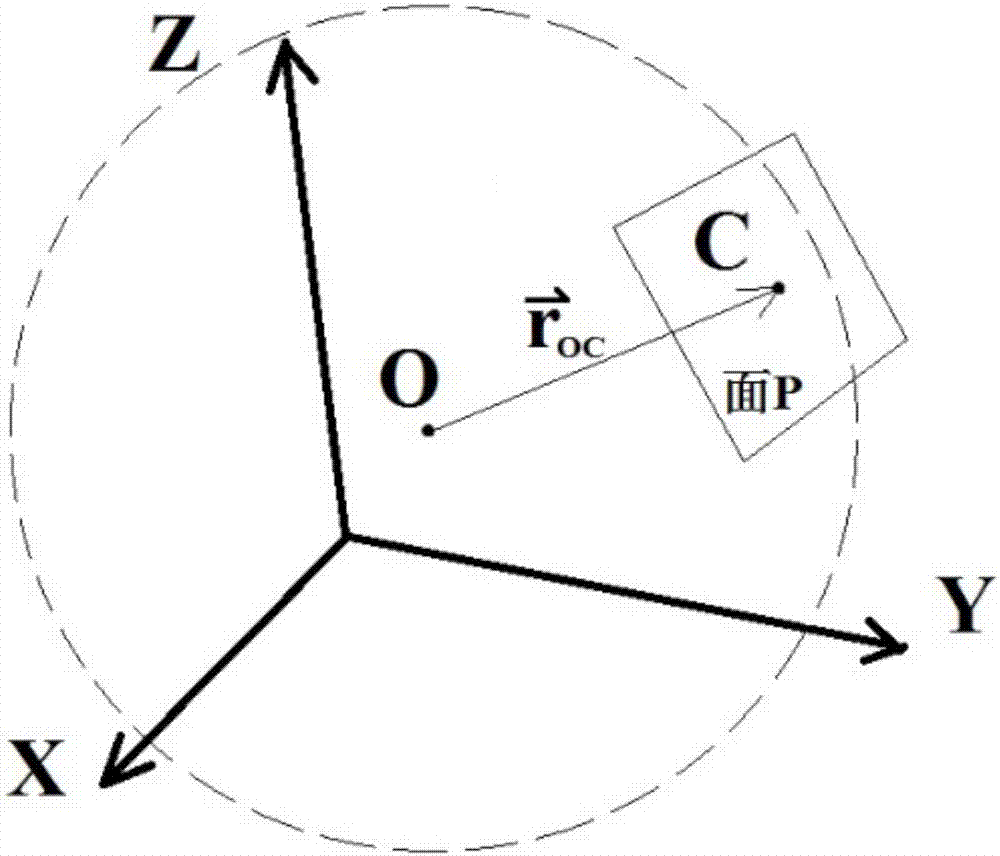
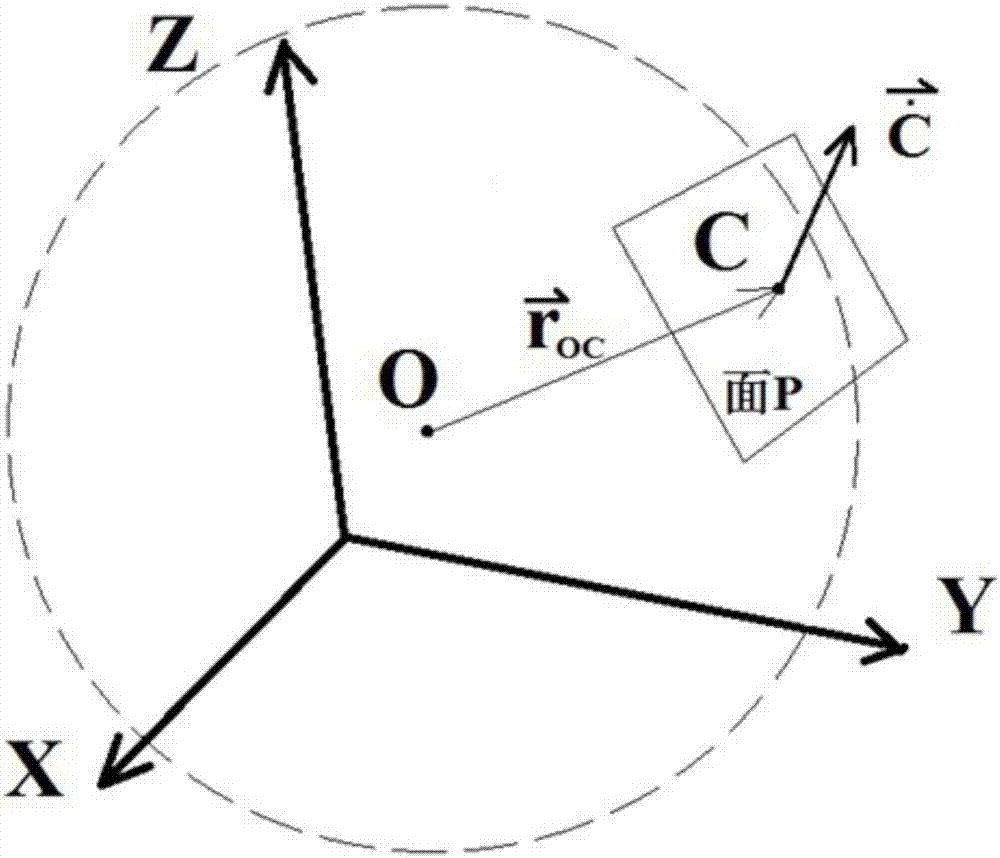
Solution to redundant mechanical arm end effector posture keeping
The invention discloses a solution to redundant mechanical arm end effector posture keeping. The solution comprises the following steps that S1, a D-H model is established for a mechanical arm to obtain a forward kinematic model, derivation is carried out on the forward kinematic model, velocity layer conversion is conducted, and target trajectory equality constraint indexes are set up; S2, numerical values of a normal vector of a mechanical arm task surface in a mechanical arm base coordinate system are measured; S3, two end effector posture keeping equality constraint indexes are built through the established D-H model and the normal vector; S4, the established target trajectory equality constraint indexes and the two end effector posture keeping equality constraint indexes are written into quadratic programming problems of a unified form; S5, the quadratic programming problems are converted into a linear variational inequality; S6, a primal-dual neural network is utilized to solve the linear variational inequality; and S7, a mechanical arm joint angle control quantity solved by the primal-dual neural network is output to a machine to achieve control over the redundant mechanical arm.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
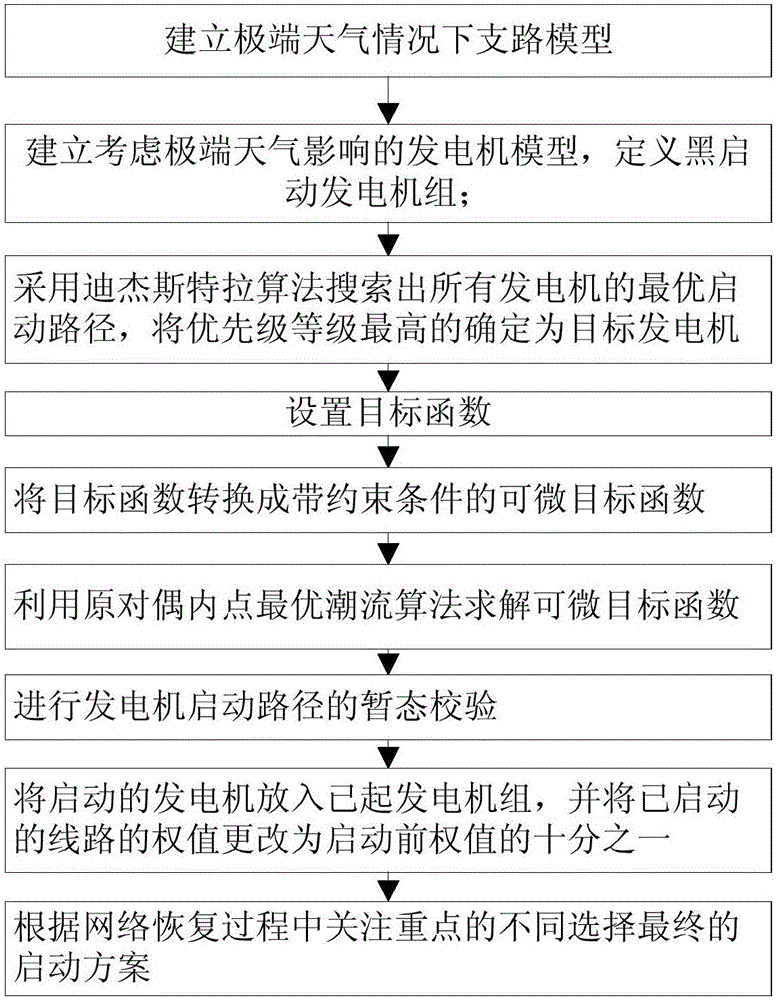
Power grid quick recovery method adapted to extreme weather condition
InactiveCN106786530AReduce the risk of secondary accidentsForecastingInformation technology support systemRecovery methodSelf-healing
The invention belongs to the technical field of power system operating and control, and particularly relates to a power grid quick recovery method adapted to an extreme weather condition. The power grid quick recovery method comprises the steps of establishing a branch model in the extreme weather condition; establishing a generator model considering extreme weather influence; searching optimal starting paths of all generators by adopting a dijkstra algorithm; determining the generator with the highest priority as the target generator; setting a target function, and converting the target function into a differentiable target function with a constraint condition; solving the differentiable target function by adopting a primal-dual interior point optimal power flow algorithm; performing transient state verification on the starting paths of the generators; and putting the started generators into a started generator group, changing the weight values of the started circuits into 1 / 10 of the weight values before starting, and selecting the final starting scheme according to different emphasis points in a network recovery process. By adoption of the power grid quick recovery method, correct decision-making analysis of an operating planner can be assisted; and meanwhile, risk of secondary accidents in the self-healing process can be lowered.
Owner:POWER DISPATCHING CONTROL CENT OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Day-ahead reactive power optimization method based on branch-bound method and primal-dual interior point method
ActiveCN104701867ASatisfy the coupling constraintsSmall amount of calculationReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationReactive power compensationInterior point methodElectric power system
The invention discloses a day-ahead reactive power optimization method based on a branch-bound method and a primal-dual interior point method and belongs to the reactive power optimization technology field of a power system. The method is characterized in that constraints of discrete variables in each period, adjusting gears in adjacent period and whole-day operation times are considered, and primary problems are branched and combined with branched branch-cutting strategies according to the periods, so that all discrete variables gradually approach to discrete values and meet the coupling constraints among the period; the primary problems are decomposed into a series of single-period reactive power optimization sub-problems only containing continuous variables after being branched according to the periods, the sub-problems are solved by adopting the primal-dual interior point method, and the calculated amount is reduced. The day-ahead reactive power optimization method is excellent in convergence, high in reliability and steady in calculation result.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
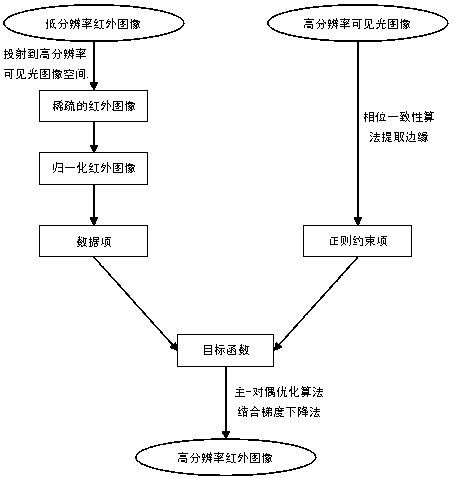
Total generalized variation-based infrared image multi-sensor super-resolution reconstruction method
InactiveCN104252704AImprove performanceQuality improvementImage enhancementReconstruction methodEqualization algorithm
The invention discloses a total generalized variation-based infrared image multi-sensor super-resolution reconstruction method. The total generalized variation-based infrared image multi-sensor super-resolution reconstruction method mainly comprises the steps of projecting a low-resolution infrared image into the coordinate space of a high-resolution visible image, obtaining a sparse infrared image and solving a data item weighting coefficient according to the sparse infrared image; performing normalization processing on the sparse infrared image and obtaining a normalization infrared image; solving the marginal information of the high-resolution visible image through a phase equalization algorithm; constructing a data item by the data item weighting coefficient and the normalization infrared image; weighting a TGV regular term improved by a first-order gradient operator through the marginal information of the visible image and constructing a regular bound term; adding the data item and the regular bound term to construct an objective function, solving the objective function in an iterative mode through a primal-dual optimization algorithm with the normalization infrared image serving as an initial value and obtaining a reconstructed high-resolution infrared image. Experiments show that the quality of the image reconstructed by the total generalized variation-based infrared image multi-sensor super-resolution reconstruction method is high and the image is close to an original high-resolution infrared image.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
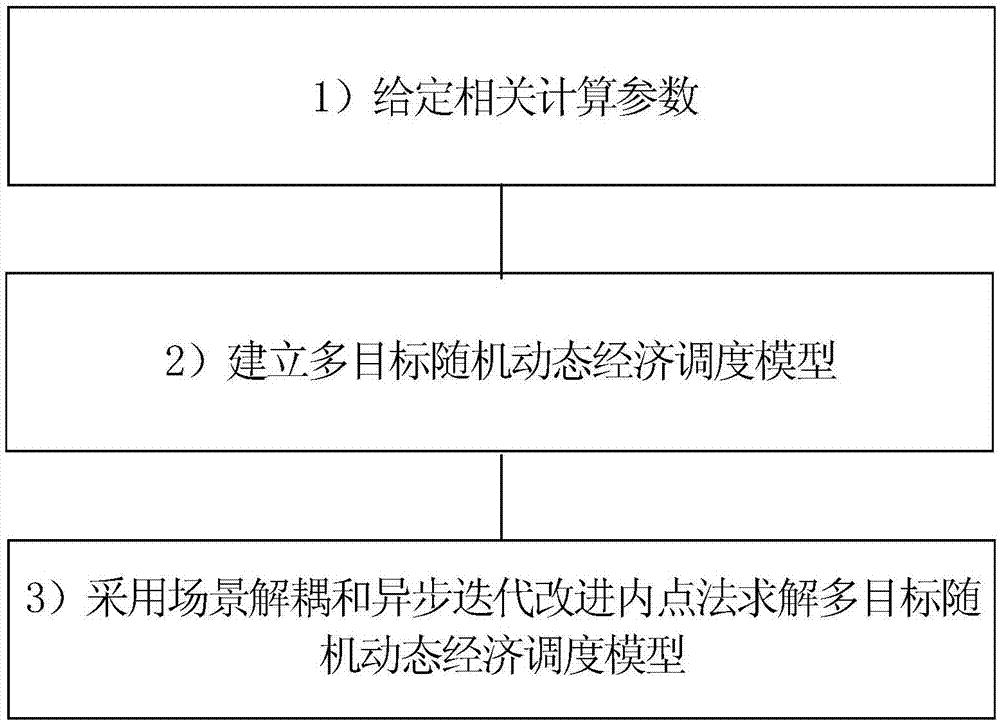
Multi-target random dynamic economic dispatch method based on scenario decoupling and asynchronous iteration
InactiveCN107171365AAvoid sparsityAvoid it happening againSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAsynchronous iterationInterior point method
The invention discloses a multi-target random dynamic economic dispatch method based on scenario decoupling and asynchronous iteration. The method herein includes the following steps: 1. assigning relevant computing parameters; 2. establishing a multi-target random dynamic economic dispatch model; 3. using scenario decoupling and asynchronous iteration to improve the interior point method to resolve the multi-target random dynamic economic dispatch model. According to the invention, the method uses the scenario method translates the problem of multi-target random dynamic economic dispatch to the problem of large-scale multi-target deterministic dynamic economic dispatch, translates the problem of large-scale multi-target deterministic dynamic economic dispatch to the problem of a series of large-scale single object non-linear planning by means of the normal boundary cross method, conducts resolution by using the nonlinear primal-dual interior point algorithm, and avoids the generation of dense matrix, such that the matrix in the entire computing process is sparse, is better compatible with economy and environmental protection in operating a power grid, and therefore is a dispatch plan with higher operation benefits.
Owner:RES INST OF ECONOMICS & TECH STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
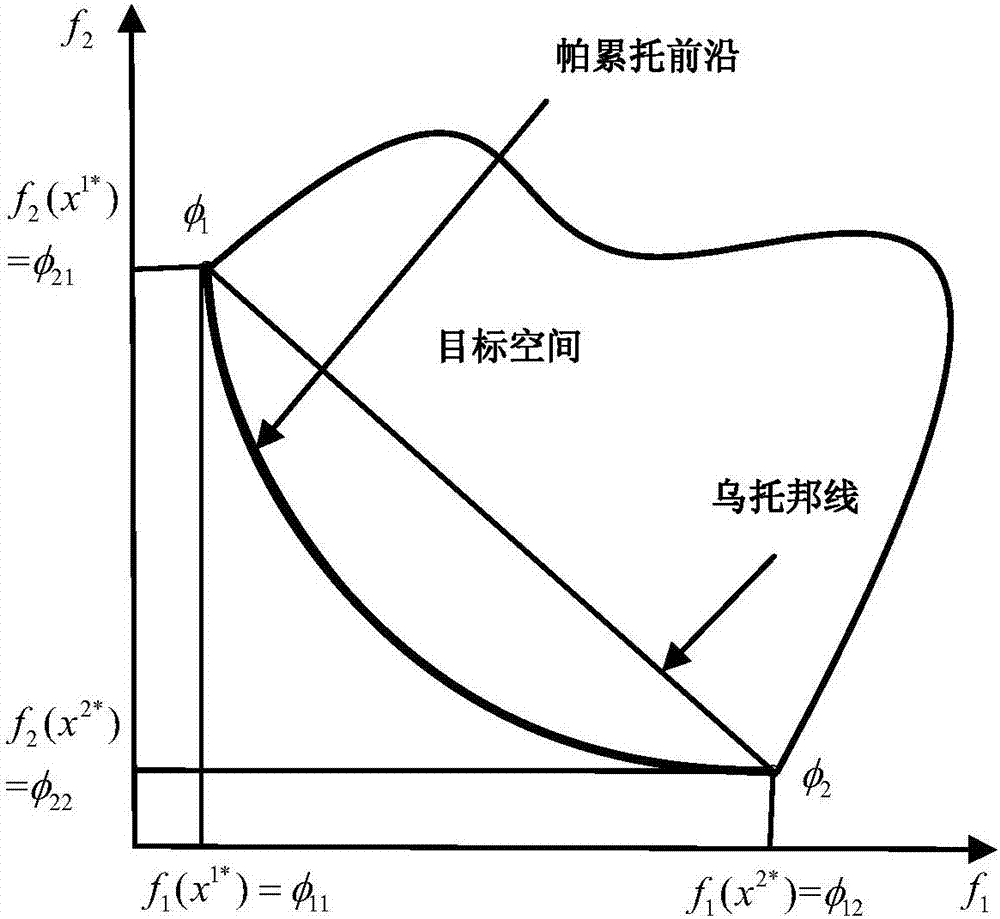
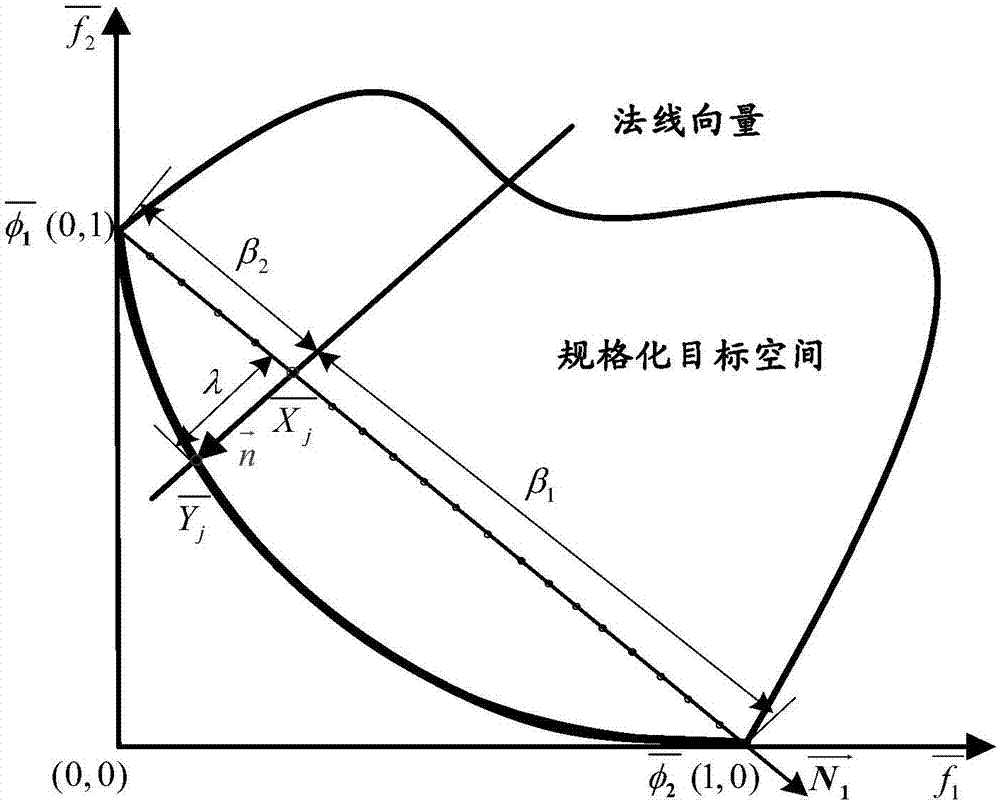
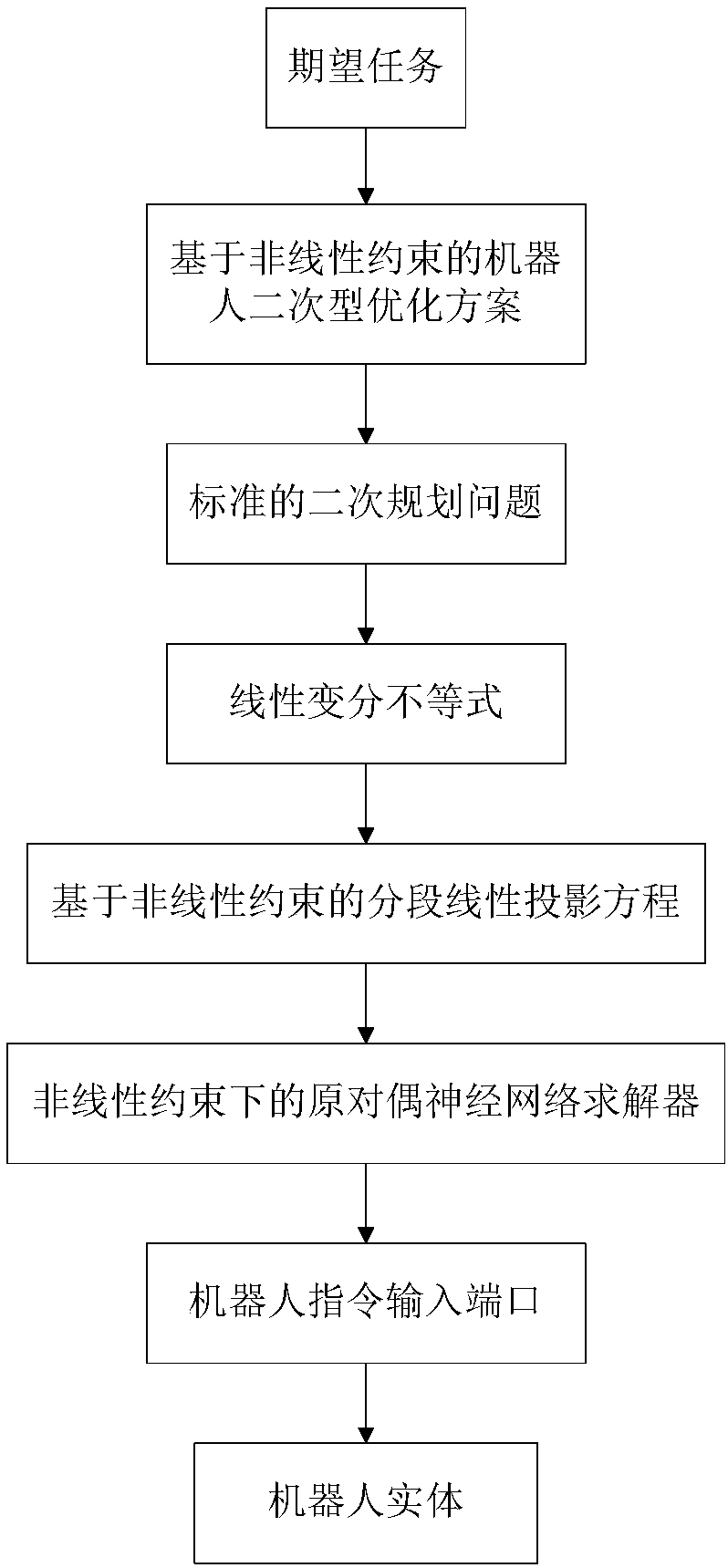
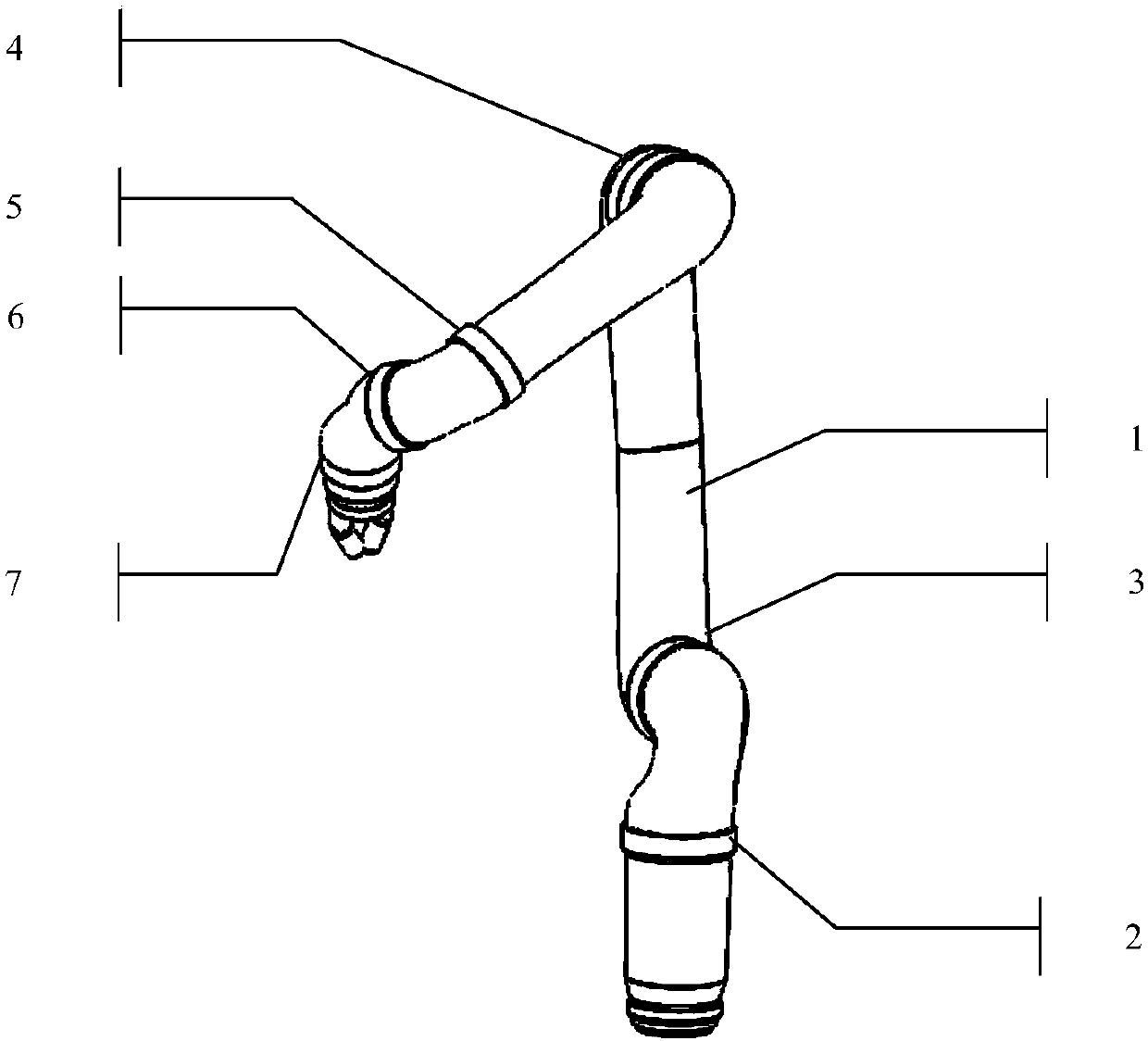
Nonlinear constrained primal-dual neural network robot action planning method
ActiveCN108015766AEliminate the initial error problemOvercome the problem of error accumulationProgramme-controlled manipulatorNerve networkStandard form
The invention discloses a nonlinear constrained primal-dual neural network robot action planning method, which comprises the steps of acquiring a current state of a robot, and adopting a quadratic optimization scheme for carrying out inverse kinematics analysis on a robot track on a speed layer; converting the quadratic optimization scheme to a standard form of a quadratic planning problem; enabling a quadratic planning optimization problem to be equivalent to a linear variational inequality problem; converting the linear variational inequality problem to a solution of a piecewise linearity projection equation based on nonlinear equality constraint; utilizing a nonlinear constrained primal-dual neural network solver for solving the piecewise linearity projection equation; and transferringa solved instruction to a robot instruction input port, and driving a robot to carry out path follow. According to the nonlinear constrained primal-dual neural network robot action planning method provided by the invention, convex set constraint and non-convex set constraint can be compatible, a preliminary test error problem occurred in robot control is eliminated, and an error accumulation problem during a robot control process is solved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
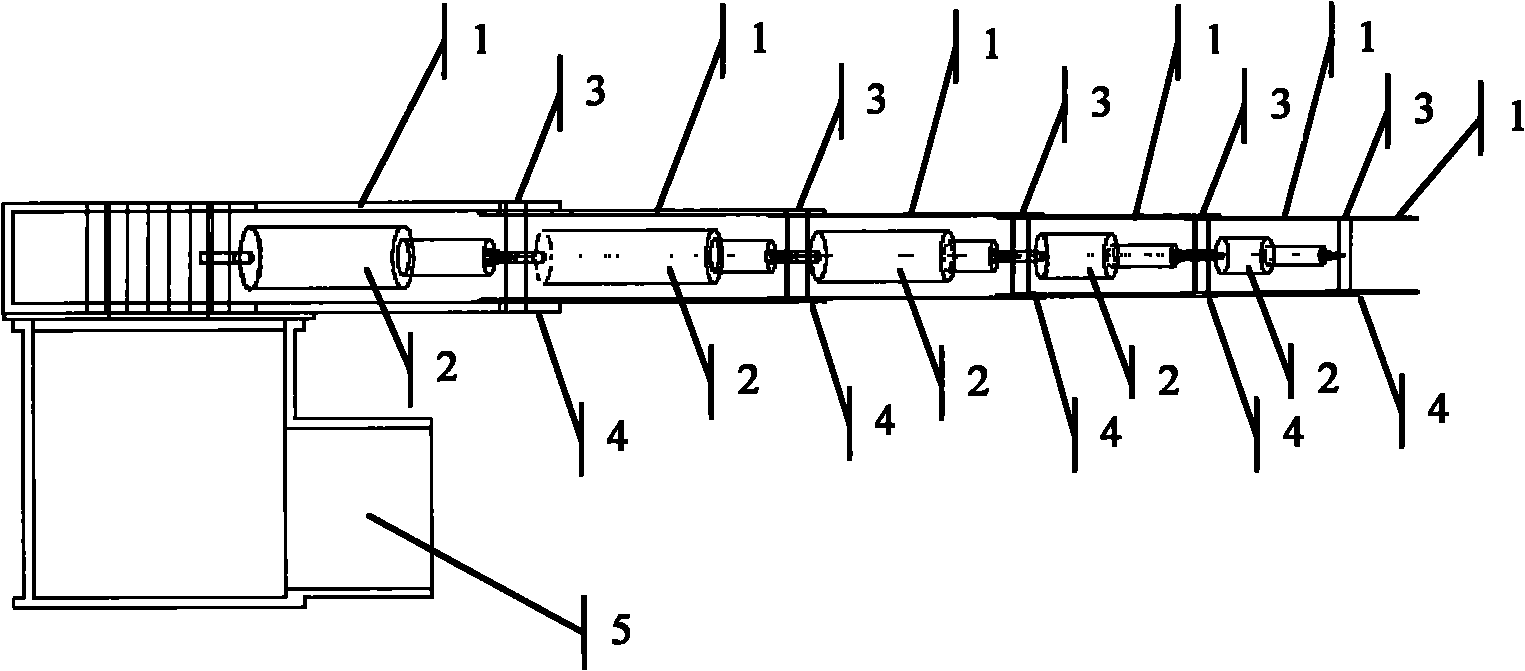
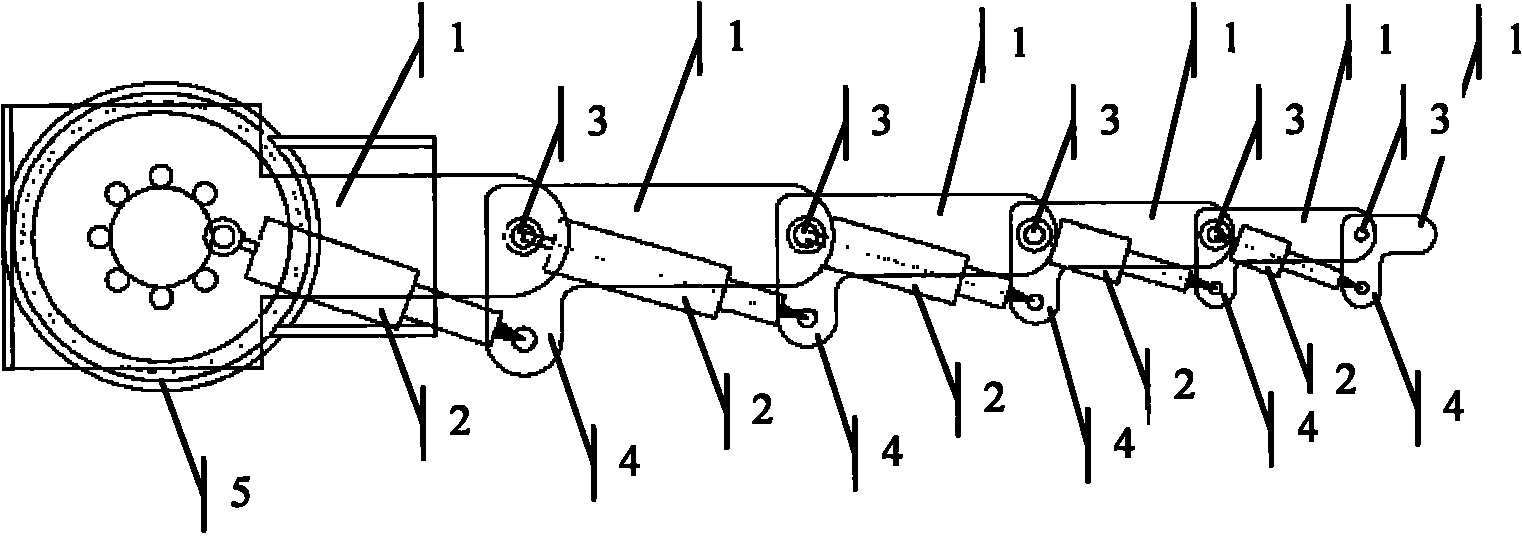
Design method of lower computer of redundancy mechanical arm of flying operation robot
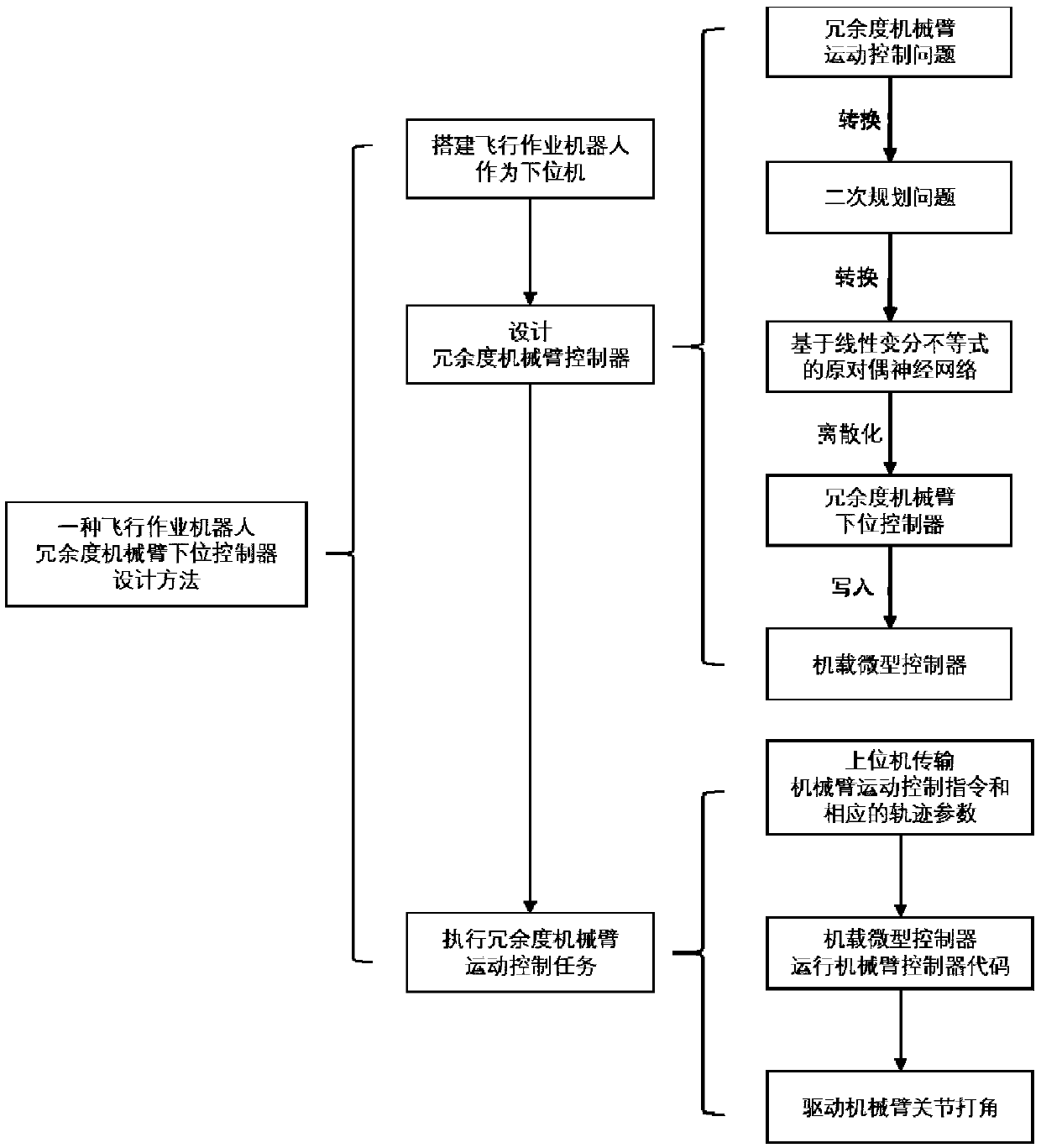
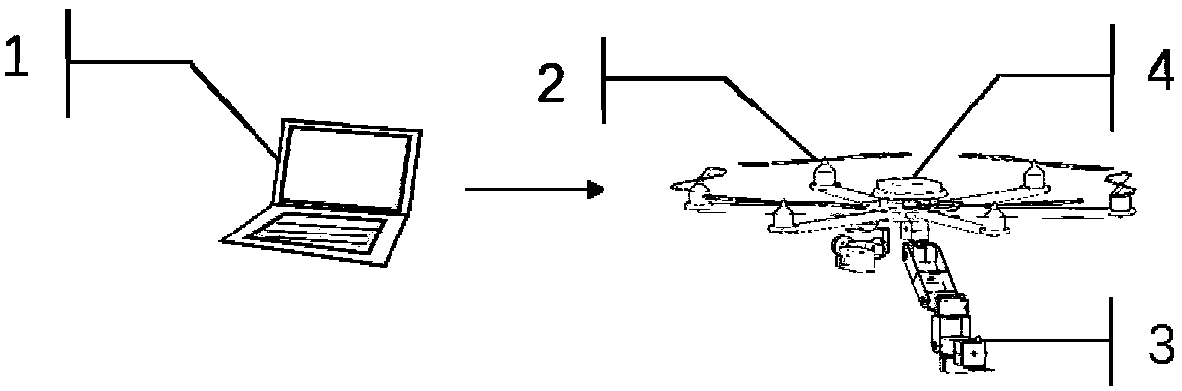
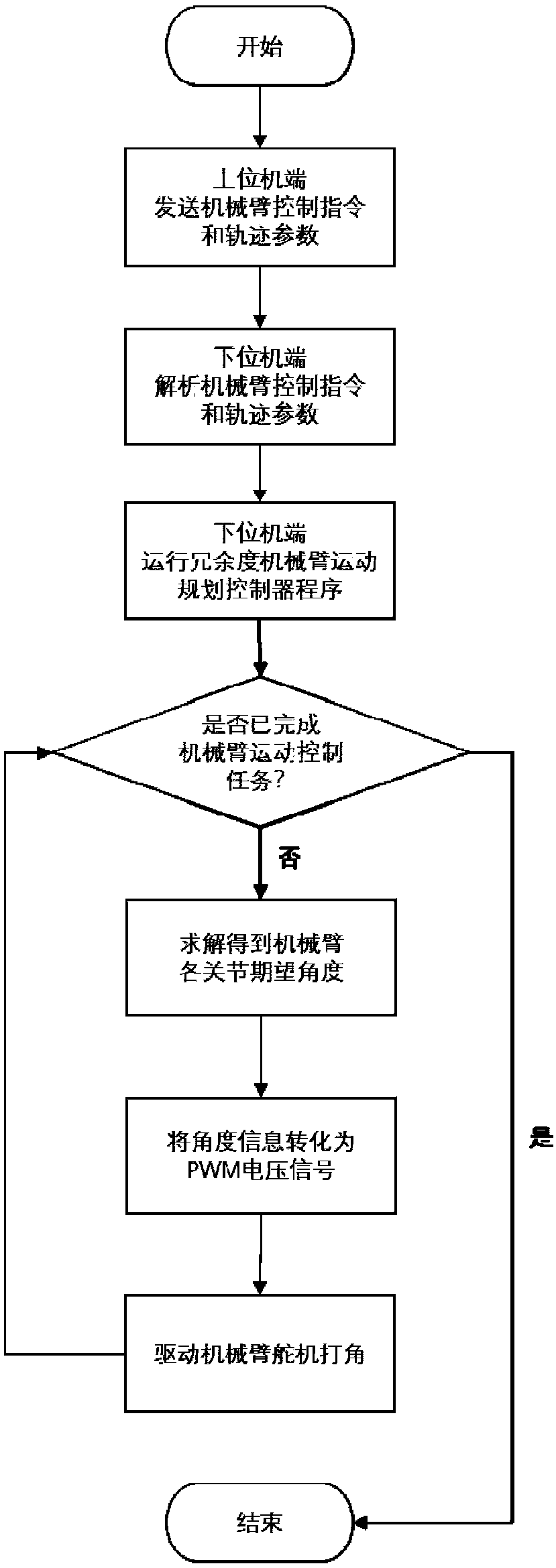
ActiveCN108381555AImprove real-time performanceIncrease flexibilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorMicrocontrollerData needs
The invention discloses a design method of a lower computer of a redundancy mechanical arm of a flying operation robot. The design method includes the specific steps that (1), the flying operation robot is built as the lower computer; (2), a movement control problem of the redundancy mechanical arm is converted into a controlled time-varying convex quadratic programming problem; (3), solving of aquadric form optimal solution is converted into solving of a primal-dual neural network based on a linear variational inequality; (4), the primal-dual neural network is discreted into a redundancy mechanical arm lower controller and written in an onboard microcontroller; (5), according to the designed controller, when a control instruction and track parameters are received, the lower computer solves expected angles of all joints of the mechanical arm and converts the expected angles into PWM voltage signals, a steering engine is driven to steer, and a control task is completed. The problems that a large amount of data needs to be transmitted after calculation on the upper computer side is completed, a large amount of time is consumed, and transmission errors are generated can be effectively solved, the real-time control effect and the flexibility of the redundancy mechanical arm are improved, and practical significance is achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com