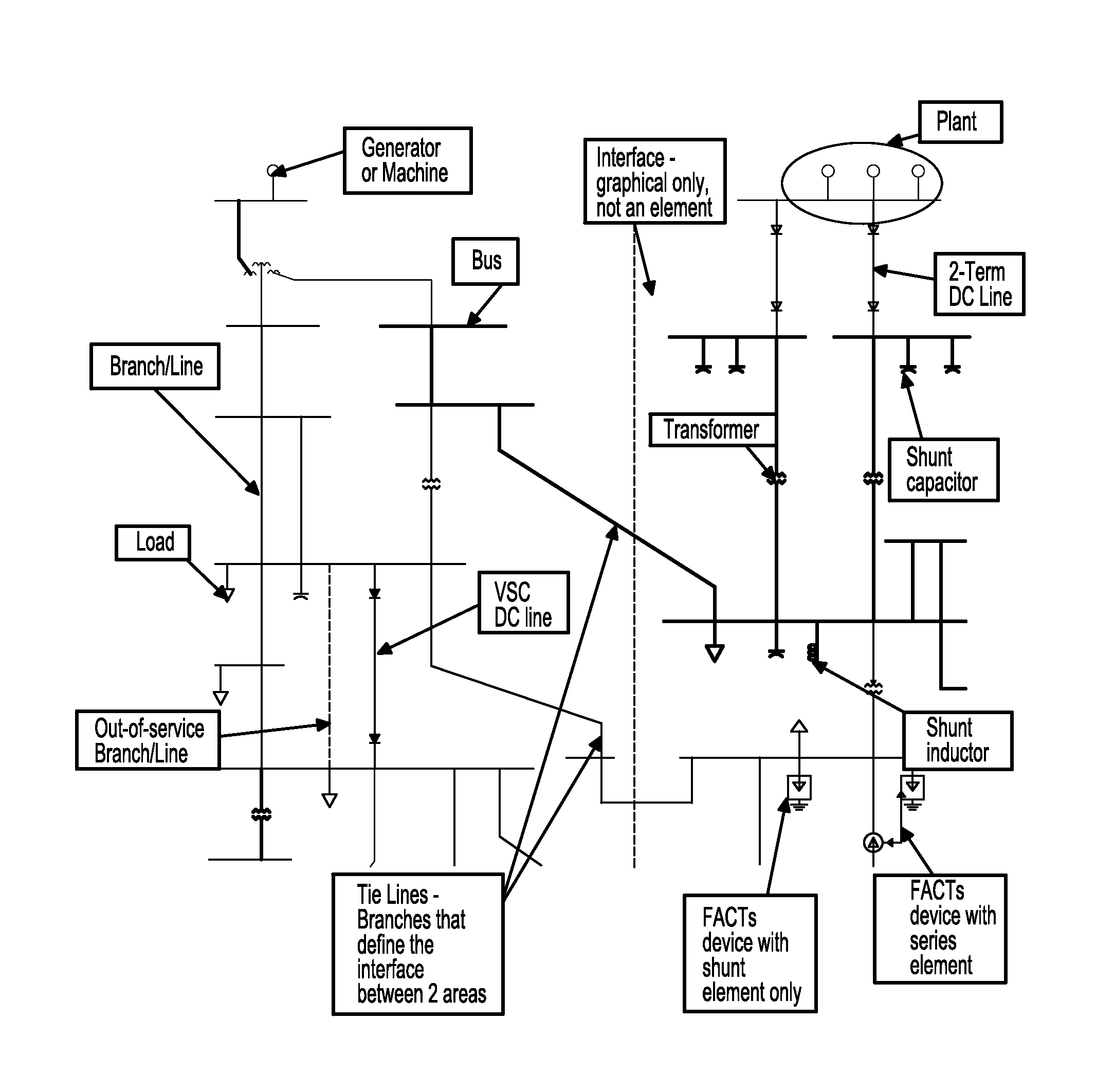
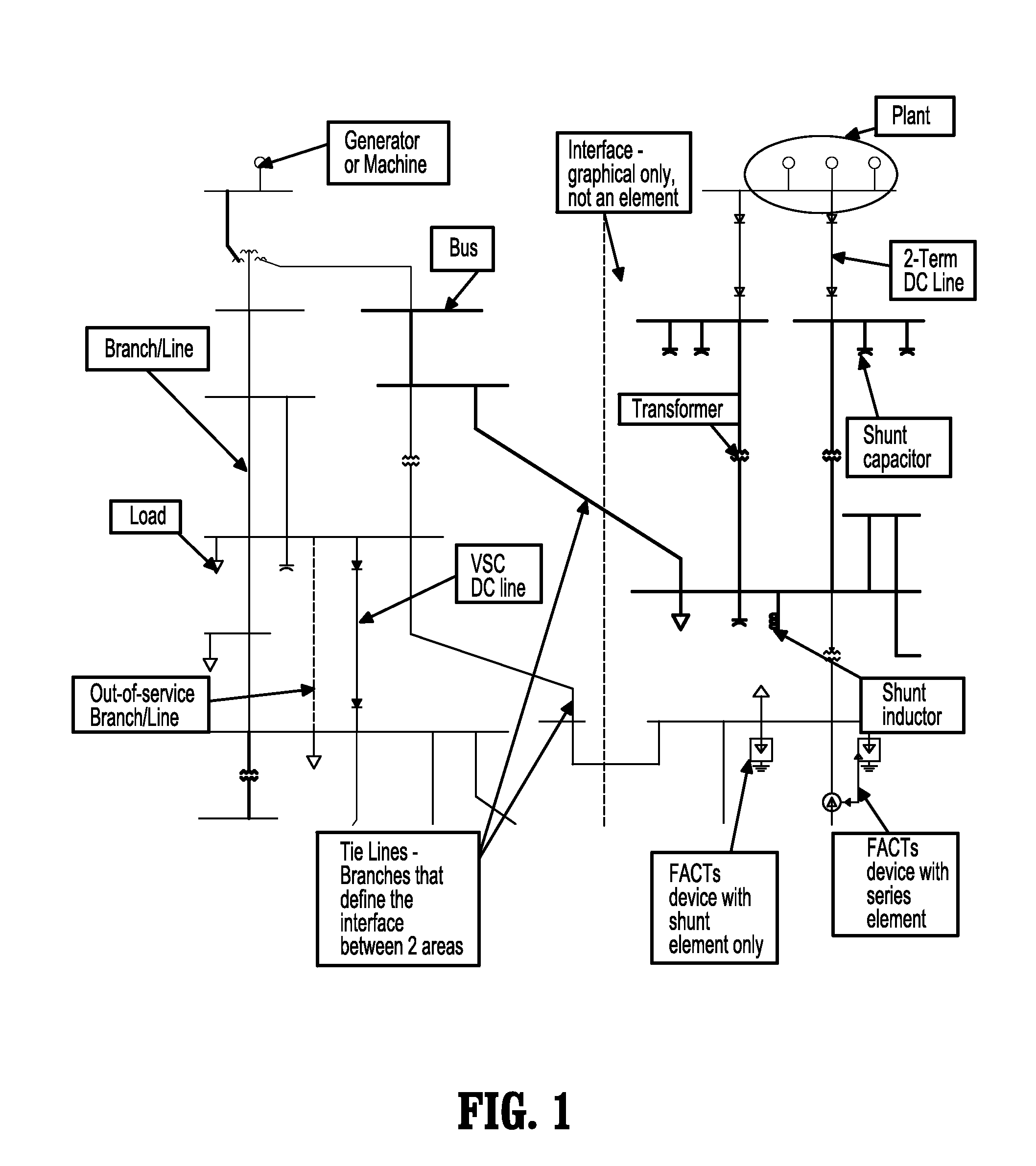
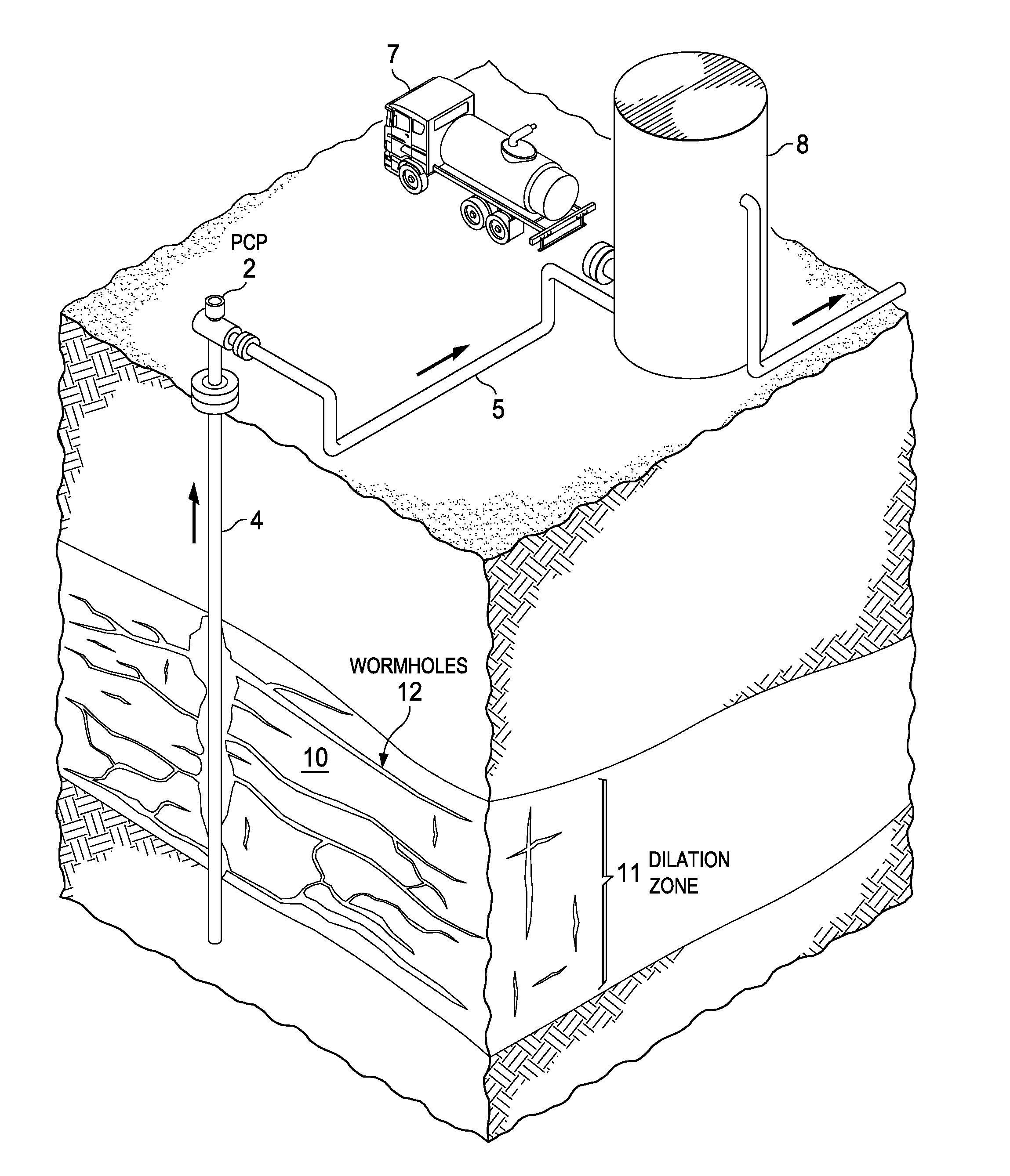
Patents
Literature
367 results about "Interior point method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interior-point methods (also referred to as barrier methods or IPMs) are a certain class of algorithms that solve linear and nonlinear convex optimization problems. John von Neumann suggested an interior-point method of linear programming, which was neither a polynomial-time method nor an efficient method in practice. In fact, it turned out to be slower than the commonly used simplex method. In 1984, Narendra Karmarkar developed a method for linear programming called Karmarkar's algorithm, which runs in provably polynomial time and is also very efficient in practice. It enabled solutions of linear programming problems that were beyond the capabilities of the simplex method. Contrary to the simplex method, it reaches a best solution by traversing the interior of the feasible region. The method can be generalized to convex programming based on a self-concordant barrier function used to encode the convex set.
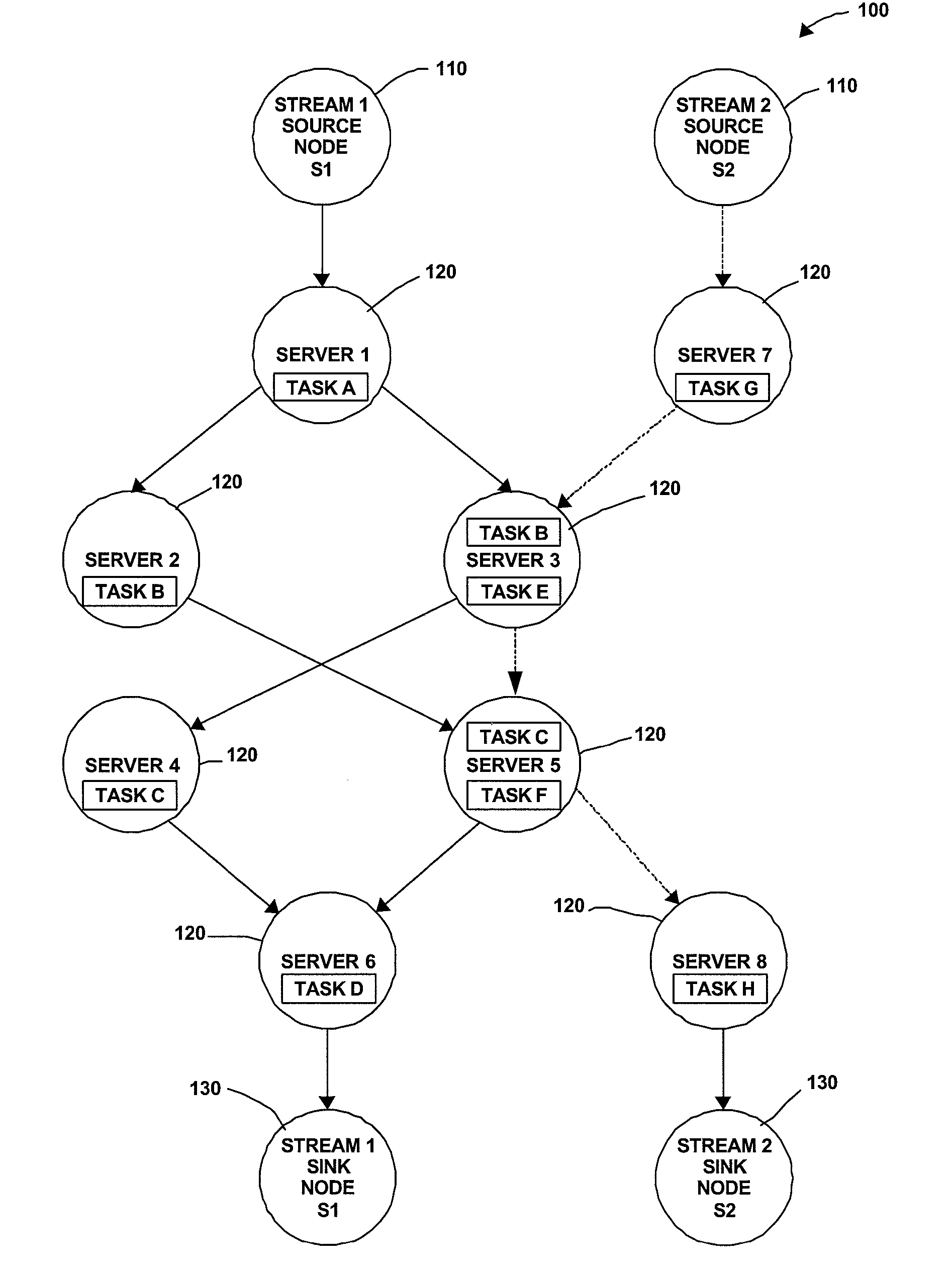
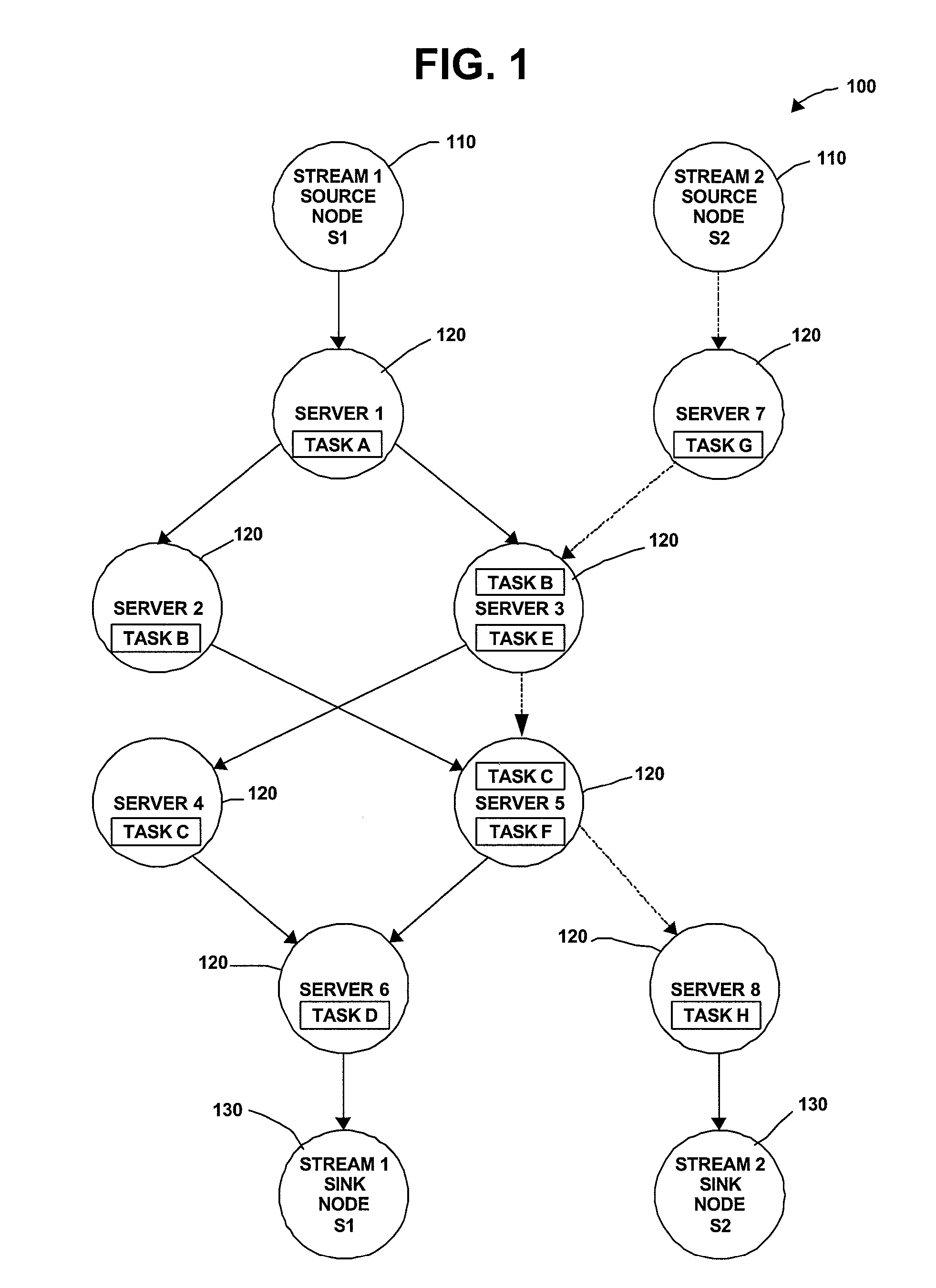
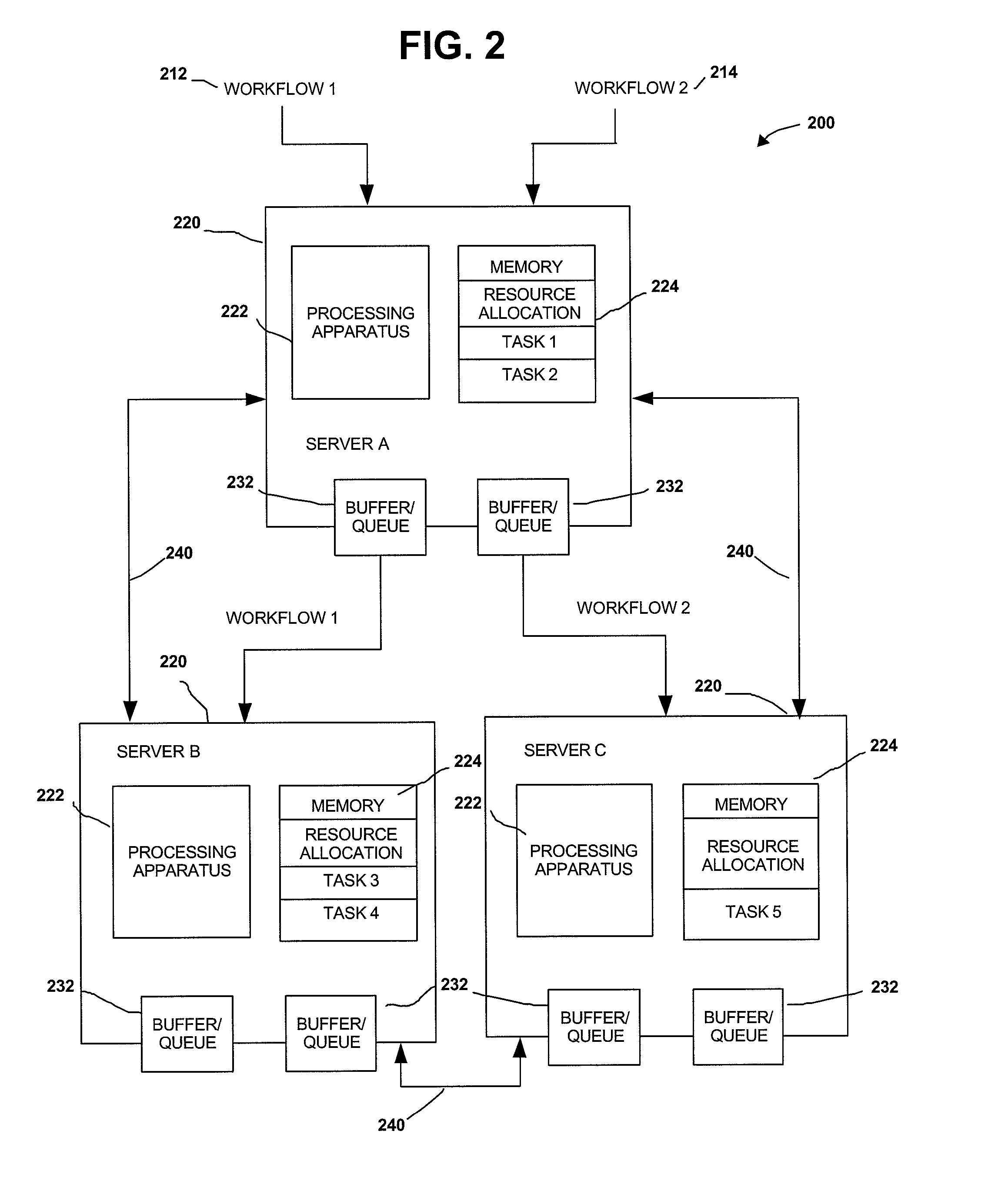
Distributed Joint Admission Control And Dynamic Resource Allocation In Stream Processing Networks
InactiveUS20080304516A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLocal congestionDynamic resource
Methods and apparatus operating in a stream processing network perform load shedding and dynamic resource allocation so as to meet a pre-determined utility criterion. Load shedding is envisioned as an admission control problem encompassing source nodes admitting workflows into the stream processing network. A primal-dual approach is used to decompose the admission control and resource allocation problems. The admission control operates as a push-and-pull process with sources pushing workflows into the stream processing network and sinks pulling processed workflows from the network. A virtual queue is maintained at each node to account for both queue backlogs and credits from sinks. Nodes of the stream processing network maintain shadow prices for each of the workflows and share congestion information with neighbor nodes. At each node, resources are devoted to the workflow with the maximum product of downstream pressure and processing rate, where the downstream pressure is defined as the backlog difference between neighbor nodes. The primal-dual controller iteratively adjusts the admission rates and resource allocation using local congestion feedback. The iterative controlling procedure further uses an interior-point method to improve the speed of convergence towards optimal admission and allocation decisions.
Owner:IBM CORP
UAV-assisted WSN, as well as method for designing node scheduling, route planning and power distribution of same
InactiveCN108566670APower managementInternal combustion piston enginesTransmitted powerNon convex optimization
The invention discloses a UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)-assisted WSN (Wireless Sensor Network), as well as a method for designing node scheduling, route planning and power distribution of the same, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication and IOT (Internet Of Things). The UAV-assisted WSN consists of a UAV aerial base station and K single-antenna ground terminal nodes. The method of the invention is characterized by aiming at minimizing system power consumption, considering constraint conditions such as a data transmission rate of the terminal node, a flight speed of the UAV and a transmitting power of the UAV, building a mathematical optimization model by taking a scheduling variable of the terminal node, a flying route of the UAV and a transmitting power variable of the UAV as parameters, respectively converting two sub-problems decomposed from a non-convex optimization problem of mixed integer variables into upper bound convex problems corresponding to the two sub-problems, alternately iterating sub-optimization problems through a block coordinate descent method and an interior point method, and obtaining a suboptimal parameter solution for scheduling of theterminal node, the flying route and the power distribution of the UAV.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF AERONAUTICS
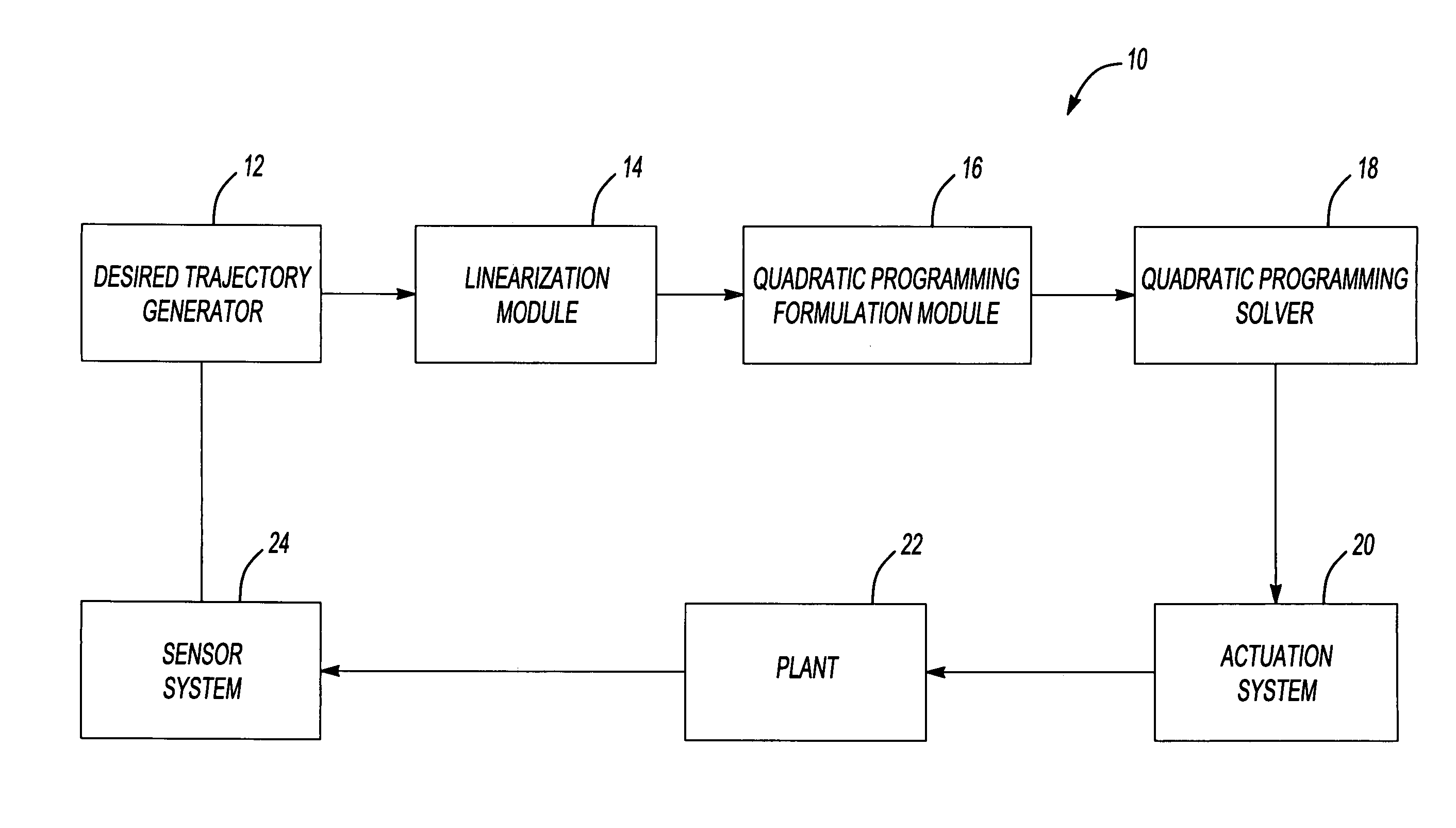
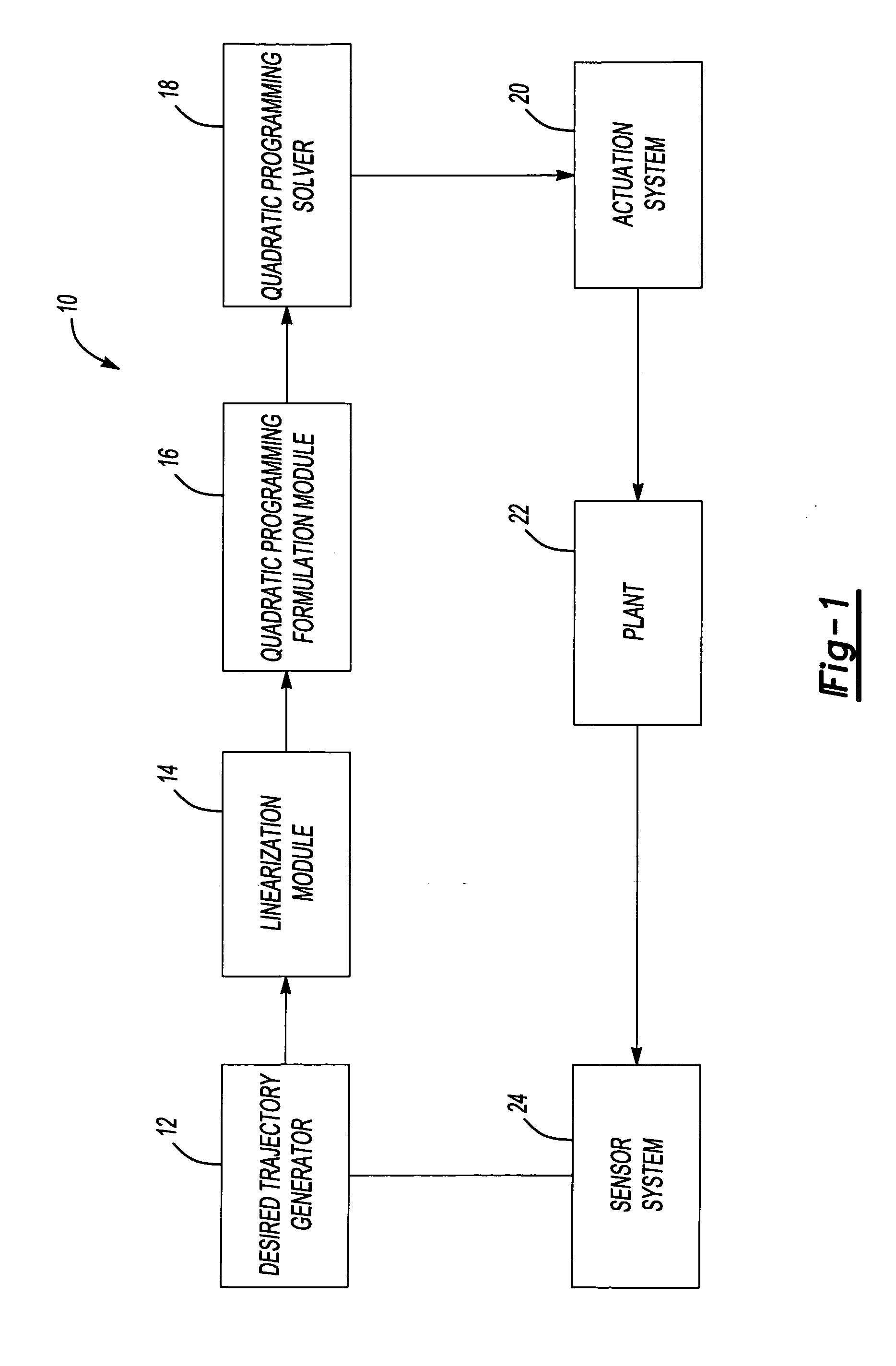
System and method of applying interior point method for online model predictive control of gas turbine engines
A Model Predictive Control System, particularly useful in controlling gas turbine engines, formulates a problem of controlling the engine to achieve a desired dynamic response as a solution to a quadratic programming problem. The Model Predictive Control System also includes a quadratic programming problem solver solving the quadratic programming problem in real time using an interior point algorithm that searches for an optimal solution.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
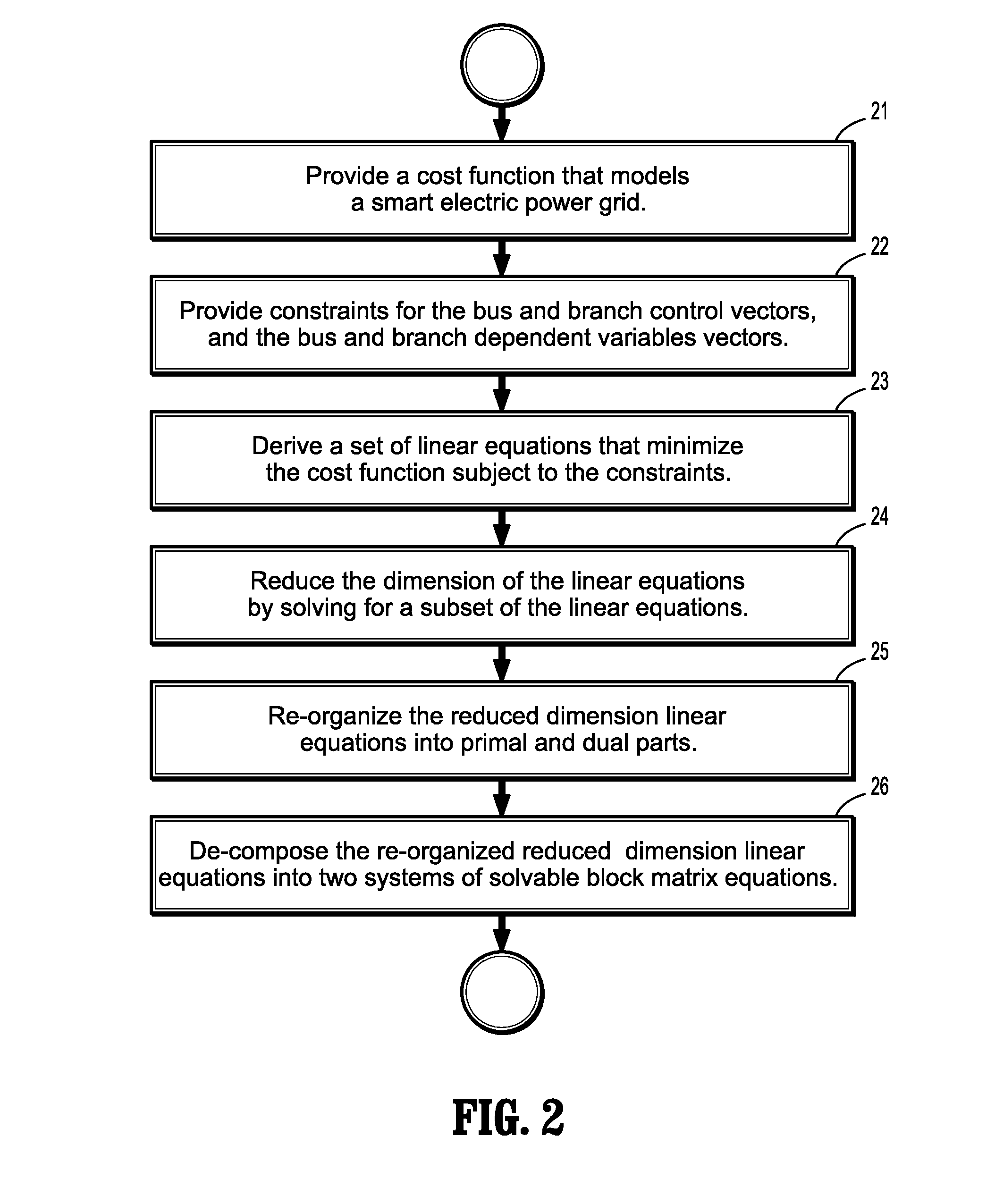
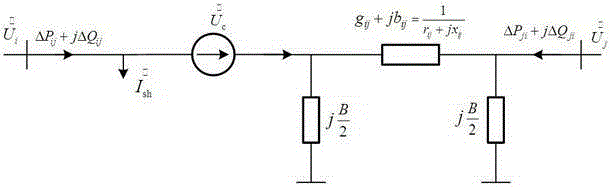
Interior point method for reformulated optimal power flow model
A method for approximating an optimal power flow of a smart electric power grid includes providing a cost function that models a smart electric power grid having buses connected by branches, deriving a set of linear equations that minimize the cost function subject to constraints from an expression of an extremum of the cost function with respect to all arguments, reducing a dimension of the linear equations by solving for a subset of the linear equations, re-organizing the reduced dimension linear equations into primal and dual parts, and decomposing the re-organized reduced dimensional linear equations into two systems of block matrix equations which can be solved by a series of back substitutions. A solution of the two systems of block matrix equations yields conditions for a lowest cost per kilowatthour delivered through the smart electric power grid.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
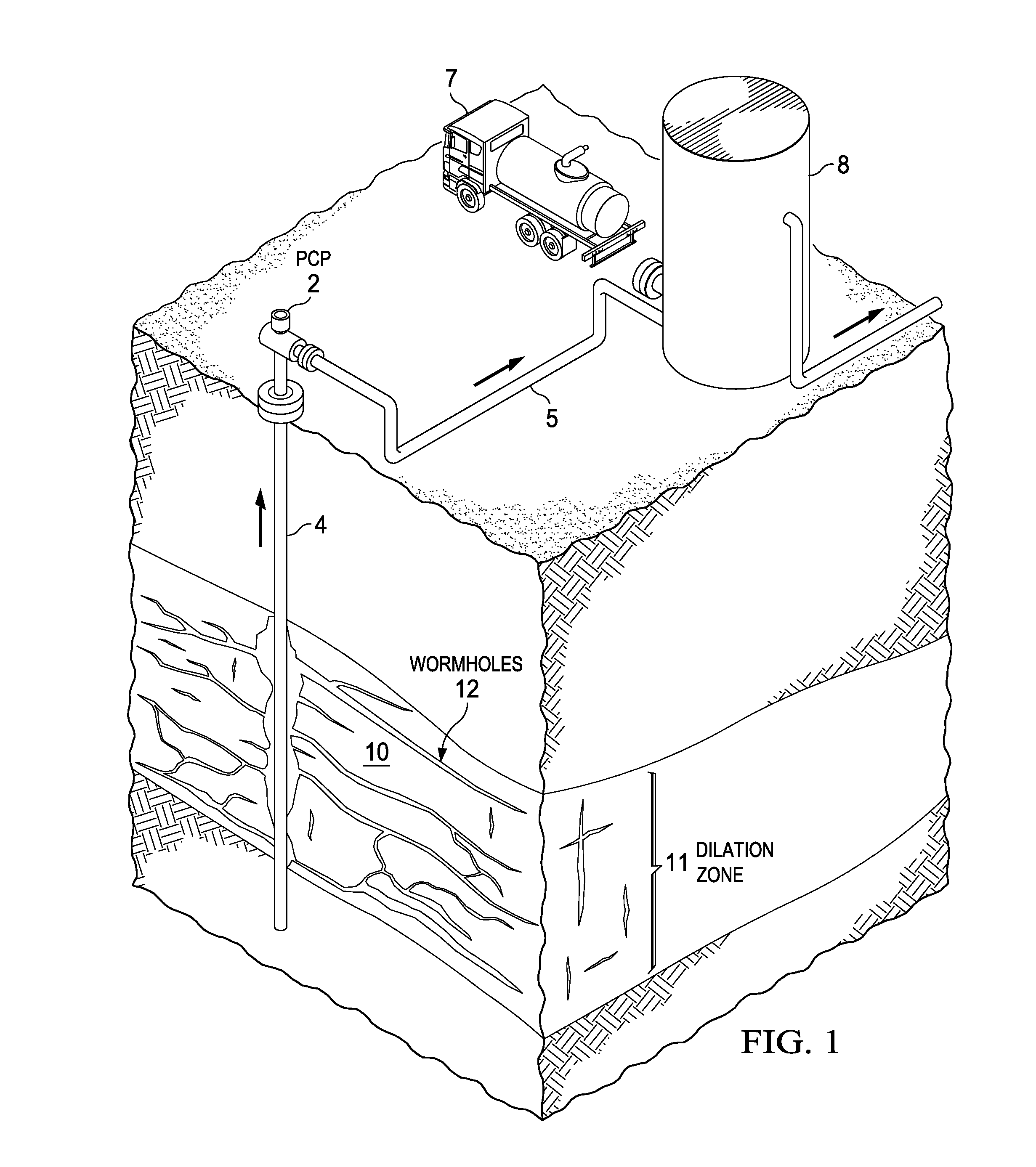
Material point method modeling in oil and gas reservoirs
InactiveUS20130096890A1Accurate modelingSimulation is accurateFluid removalSeismologyLaws of thermodynamicsEquation of state
A computer system and method of simulating the behavior of an oil and gas reservoir including changes in the margins of frangible solids. A system of equations including state equations such as momentum, and conservation laws such as mass conservation and volume fraction continuity, are defined and discretized for at least two phases in a modeled volume, one of which corresponds to frangible material. A material point model technique for numerically solving the system of discretized equations, to derive fluid flow at each of a plurality of mesh nodes in the modeled volume, and the velocity of at each of a plurality of particles representing the frangible material in the modeled volume. A time-splitting technique improves the computational efficiency of the simulation while maintaining accuracy on the deformation scale. The method can be applied to derive accurate upscaled model equations for larger volume scale simulations.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC +1
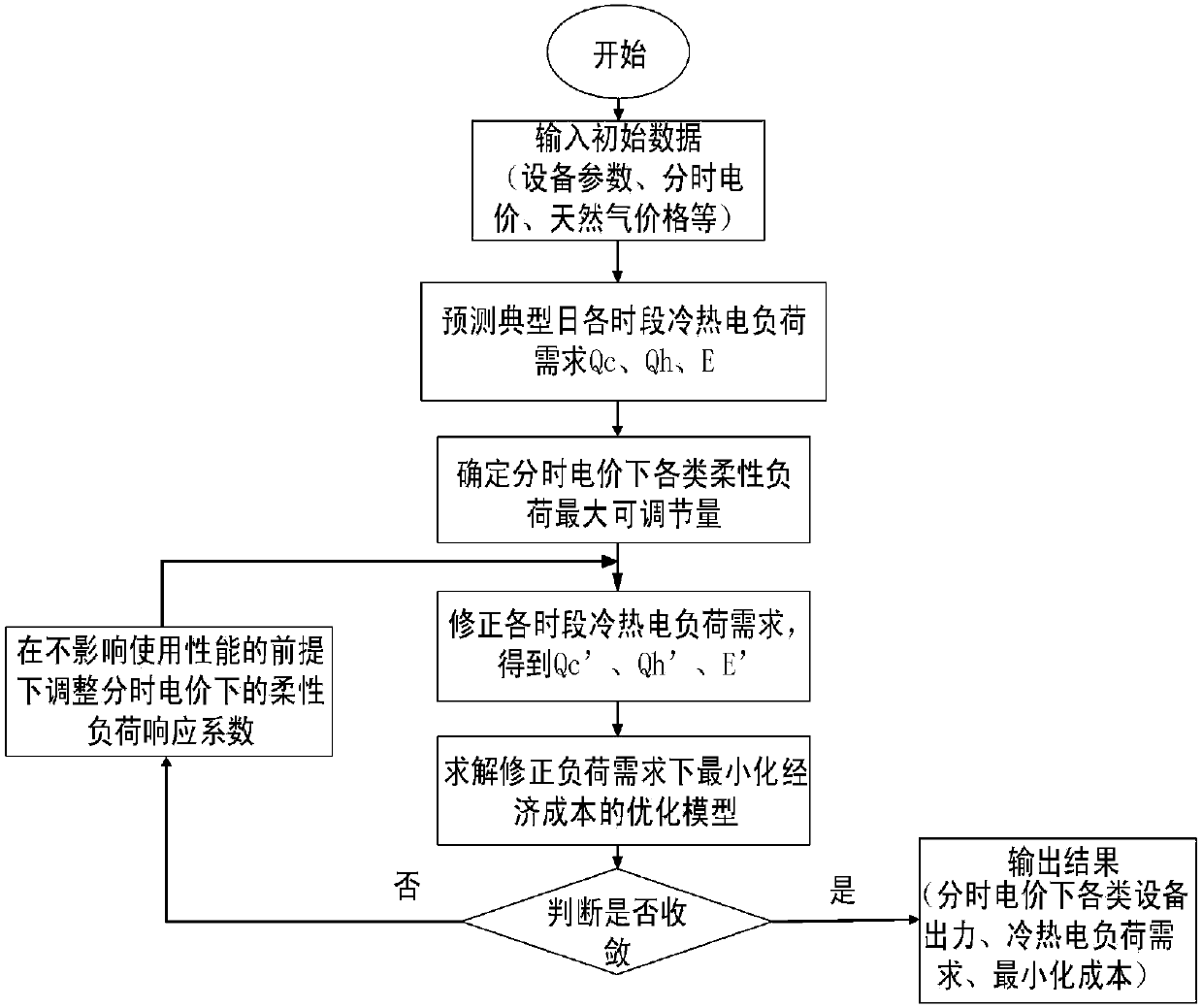
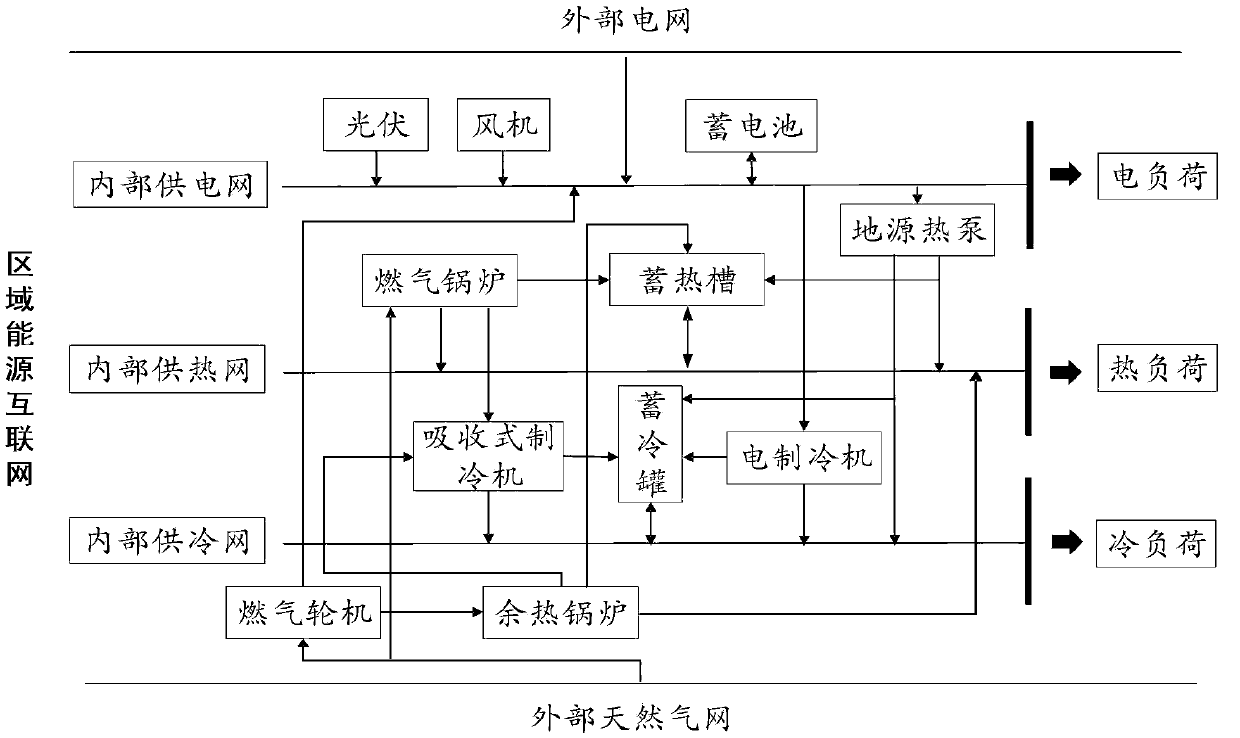
Regional energy internet multi-source coordinated optimization operation strategy considering time-of-use power price
InactiveCN107807523AImprove consumption levelRealize the safe operation of the economyAdaptive controlElectricity priceInterior point method
The invention relates to a regional energy internet multi-source coordinated optimization operation strategy considering time-of-use power price. The strategy is technically characterized by comprising the following steps that step 1, the initial data parameter of a regional energy internet system is inputted; step 2, cold / heat / electric flexible load response under the time-of-use power price is analyzed, and two classes of response models of cold / heat / electric flexible load are constructed; step 3, a regional energy internet system optimization scheduling model of the minimal economic cost and the operation constraint conditions thereof are constructed; and step 4, the regional energy internet system optimization scheduling model of the minimal economic cost is solved by using a Hessian interior point method. The regional energy internet renewable energy consumption level can be enhanced, and the strategy is also significant for realizing economic and safe operation of the system.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCI & RES INST OF STATE GRID TIANJIN ELECTRIC POWER CO +2
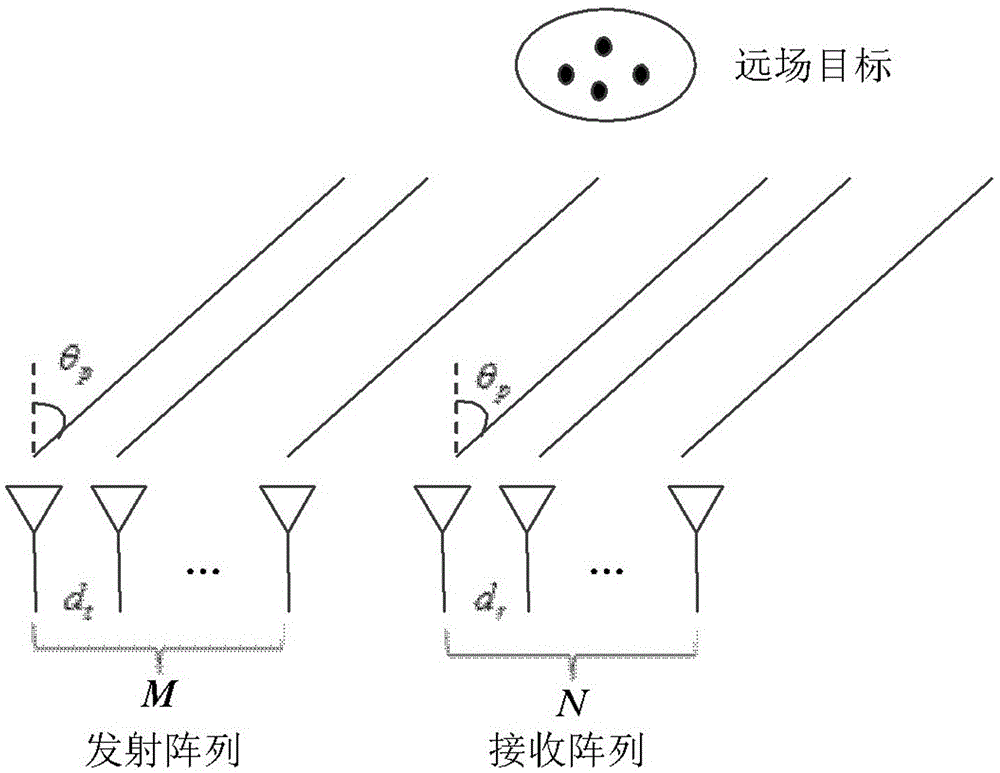
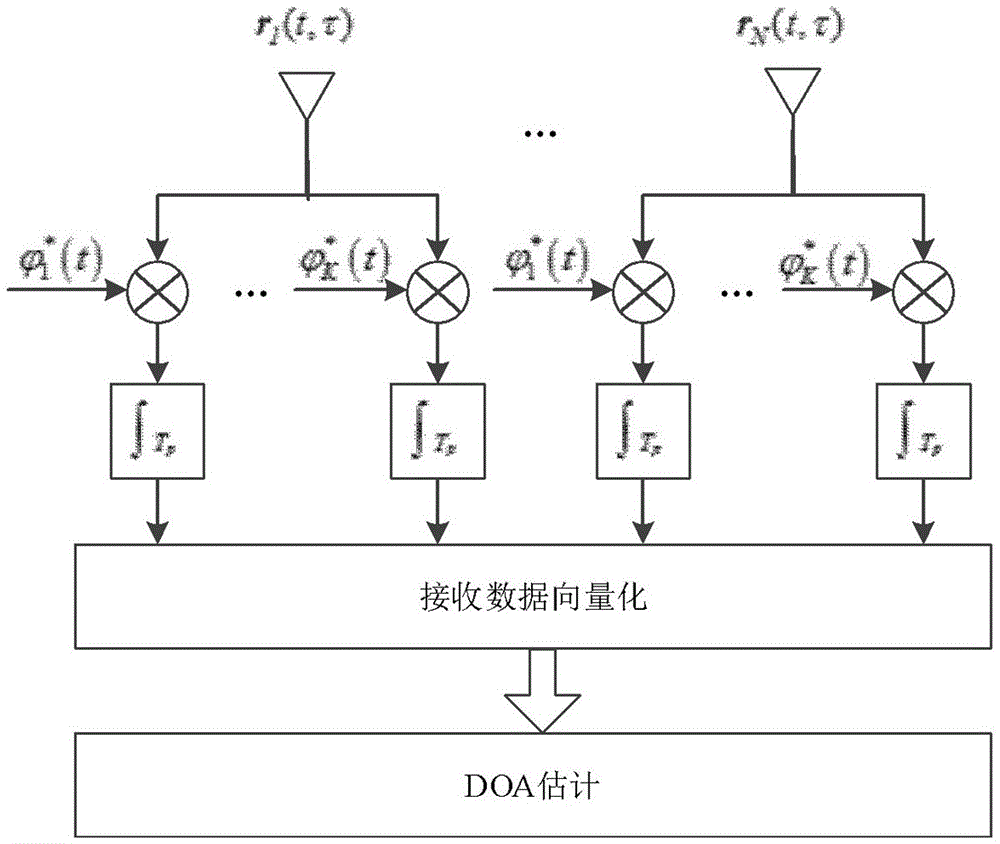
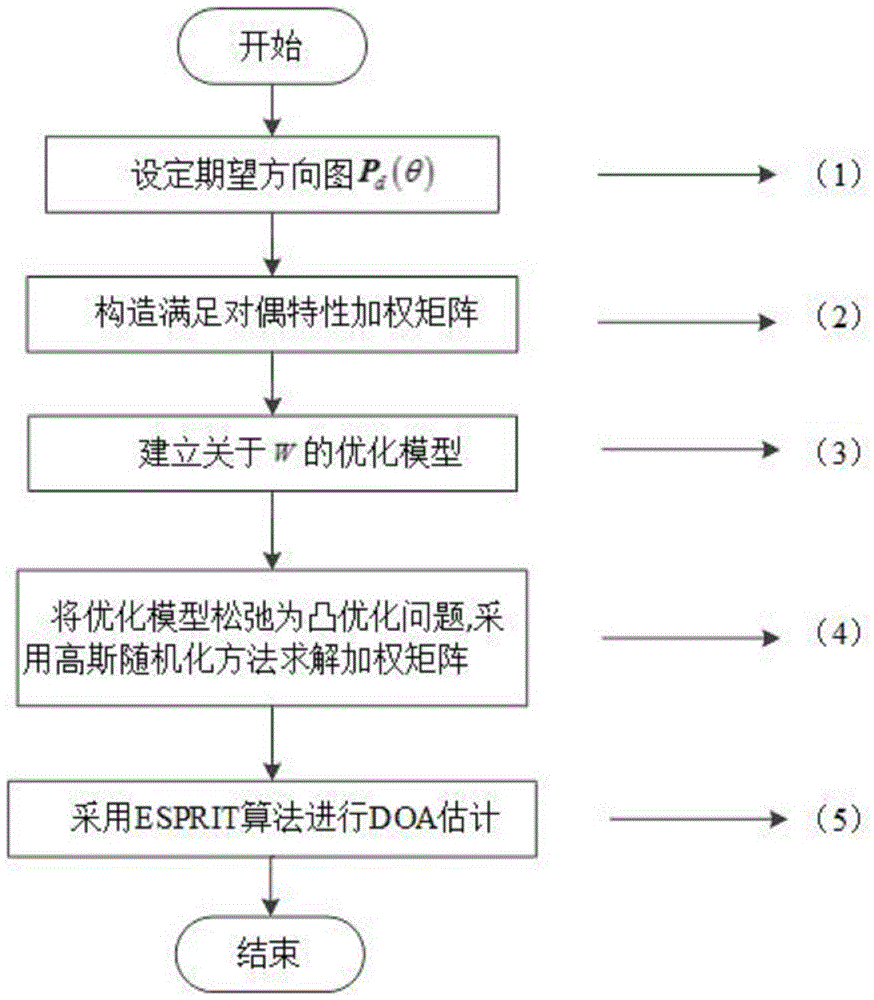
A low-sidelobe emission directional diagram design method improving DOA estimated performance of a MIMO radar
ActiveCN105467365AVector number reductionGuaranteed approximationWave based measurement systemsEngineeringRandomization
The invention relates to a low-sidelobe emission directional diagram design method improving DOA estimated performance of a MIMO radar. The method comprises the following steps: setting an interesting area; ensuring column vectors of a beam space weighting matrix to satisfy pairing characteristics; ensuring signals at a receiving end to satisfy rotation invariance; constructing an optimized model of a beam space weighting matrix with directional diagram coupling characteristics, rotation invariance of the signals and equality of various array element emission powers as constraint conditions; introducing an auxiliary variable and relaxing a rank-1 constraint to be a positive semidefinite constraint through utilization of the semidefinite relaxing technology; and through utilization of an interior point method, obtaining an optimal solution of the relaxing problem; through a Gaussian randomization method, the beam space weighting matrix is solved; and DOA estimation is carried out on a target at the receiving end through the ESPRIT algorithm. The MIMO radar waveform design technology which is good in performance in the invention can raise the signal to noise ratio at the receiving end, provide an important theoretical basis and a specific realization method for raising the precision of MIMO radar angle estimation.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Method and device for robust interval wind power scheduling based on consideration on wind power field current collecting line fault
InactiveCN104242356AImprove absorption capacityReduce operational riskSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationElectricityInterior point method
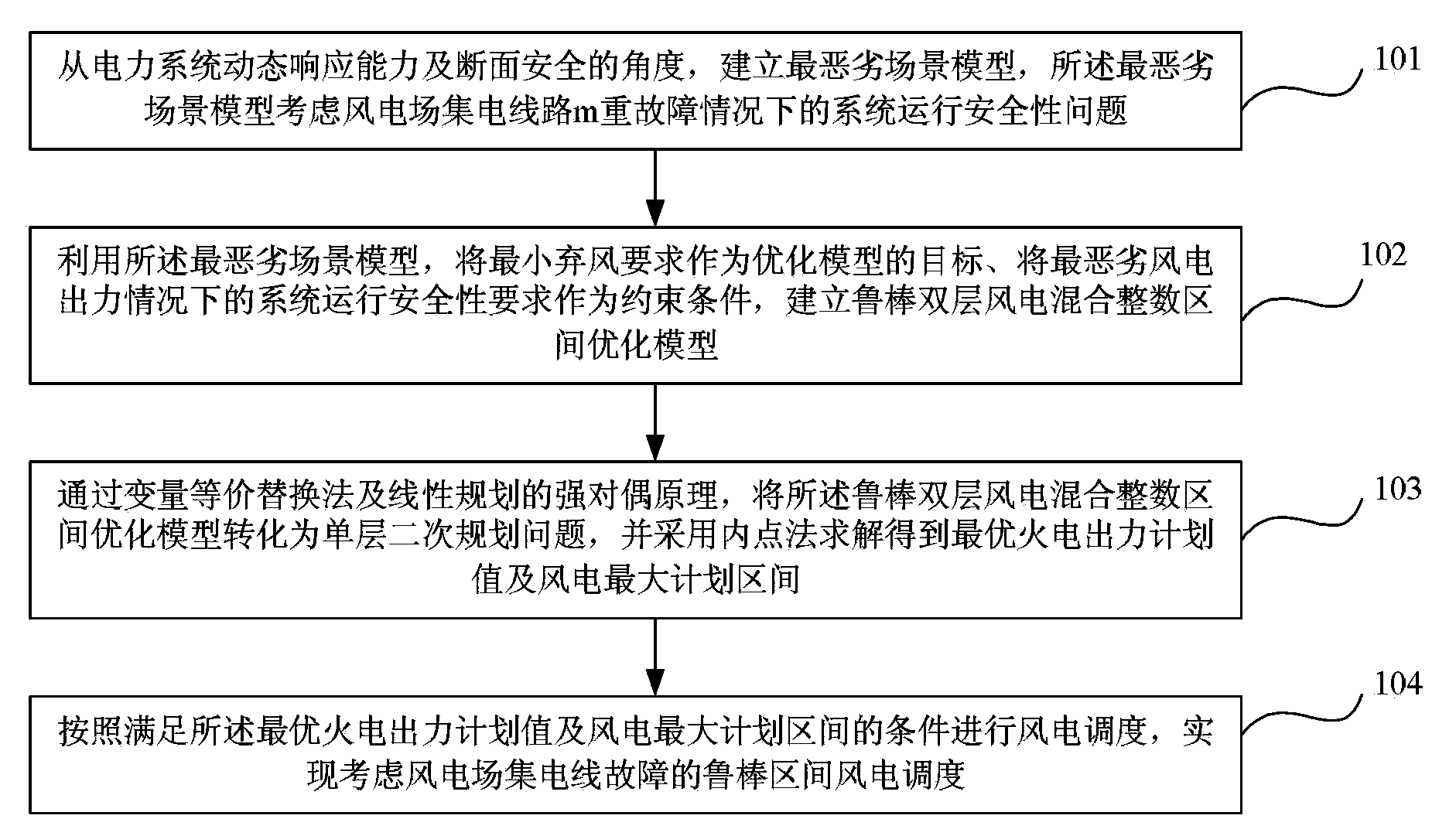
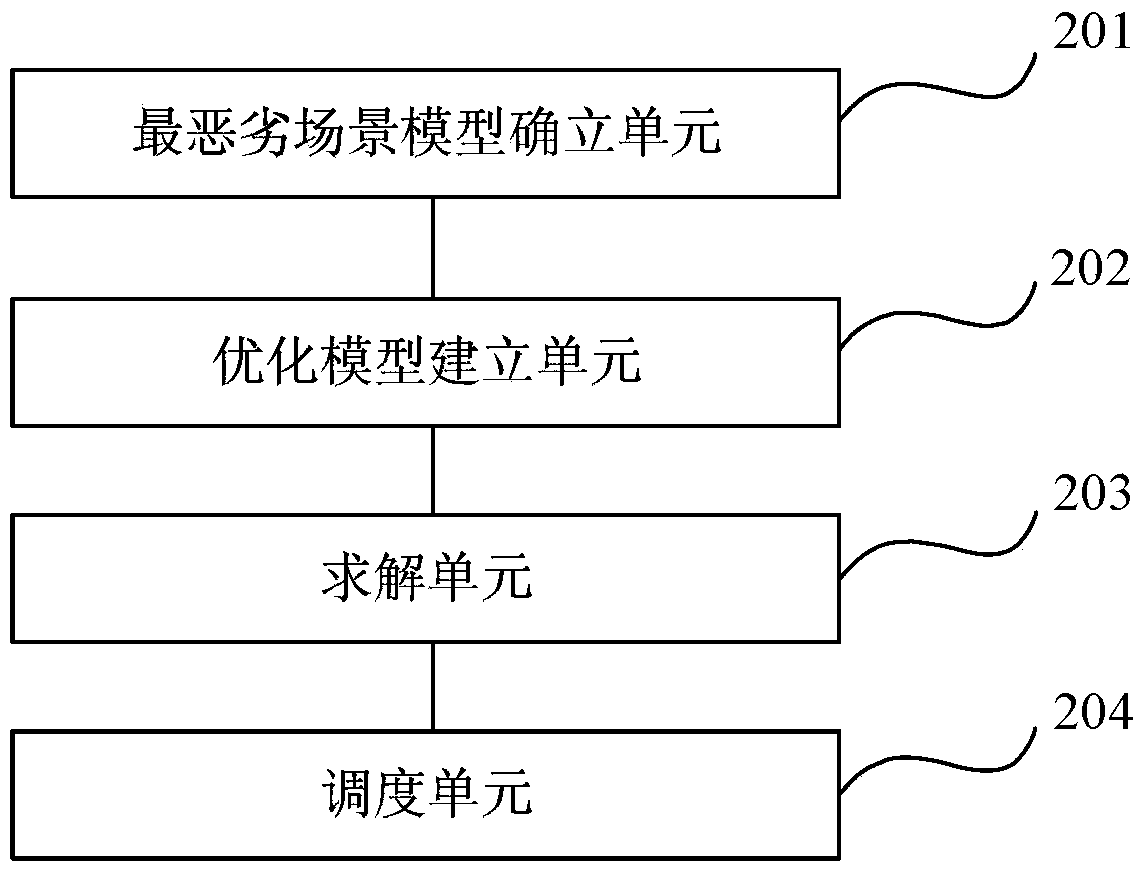
The invention relates to a method and a device for robust interval wind power scheduling based on consideration on wind power field current collecting line fault. The method includes, from the points of power system dynamic response capacity and section safety, building a worst scene model with consideration on system running safety on the circumstance of wind power field current collecting line m faults; according to the worst scene model, taking the minimum wind curtailment demand as the target to optimize the model and taking the system running safety requirement on the circumstance of the worst wind power output as a constraint condition to build a robust dual-layer wind power mixed integer interval optimization model; according to a variable equivalent substitution method and a strong dual principle of linear programming, transforming the robust dual-layer wind power mixed integer interval optimization model into the problem about single-layer secondary programming, and utilizing an interior point method to solve the optimal thermal power output planned value and the maximum wind power planned interval; and finally performing wind power scheduling according to the optimal thermal power output planned value and the maximum wind power planned interval so as to achieve the robust interval wind power scheduling.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
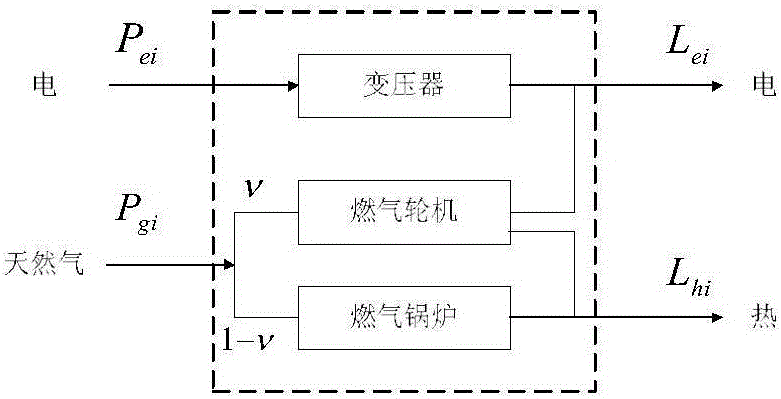
Modeling and optimized dispatching method of electrical series-parallel system on the basis of energy center
ActiveCN105046369AImprove convenienceForecastingSystems intergating technologiesSlack variableSimulation
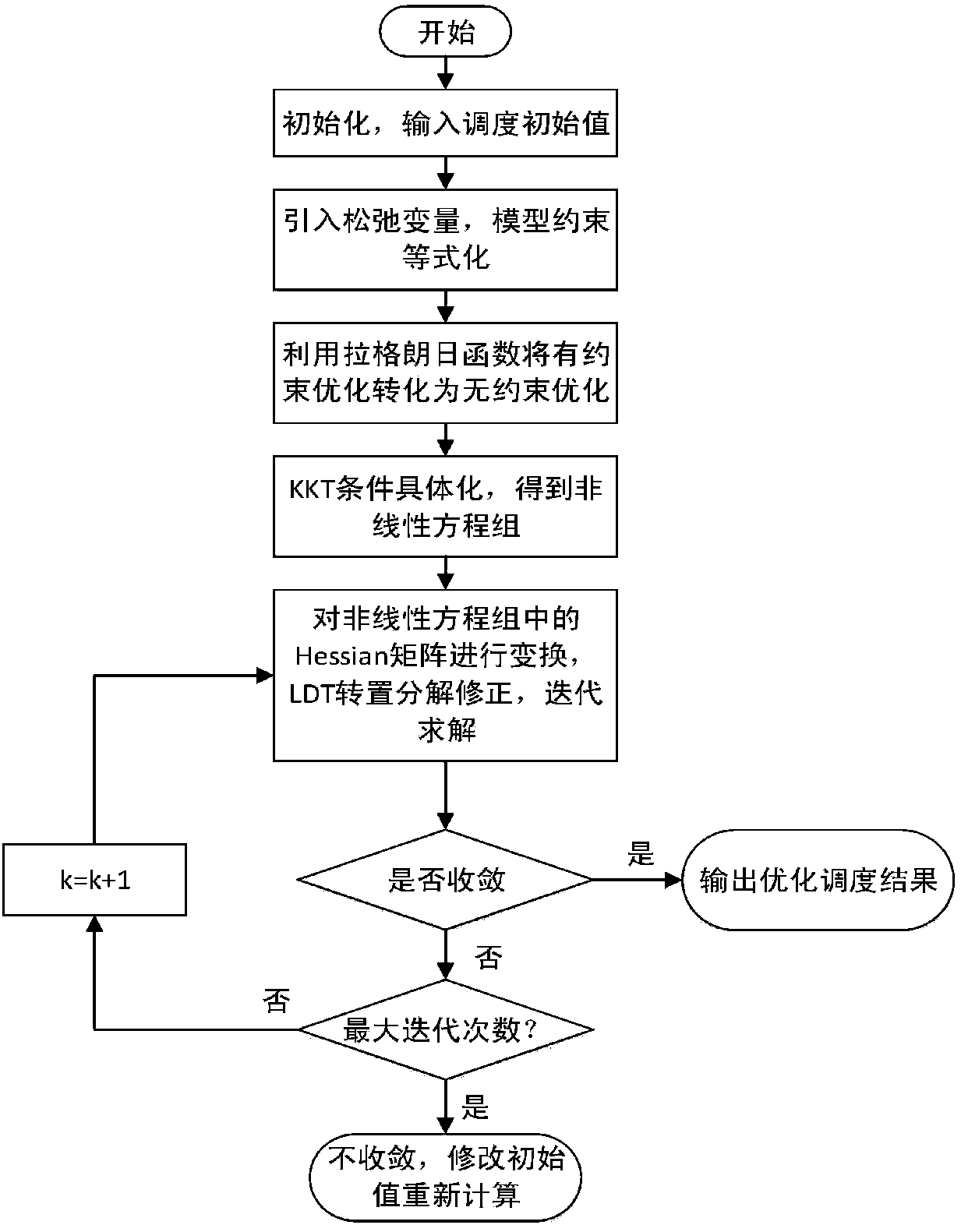
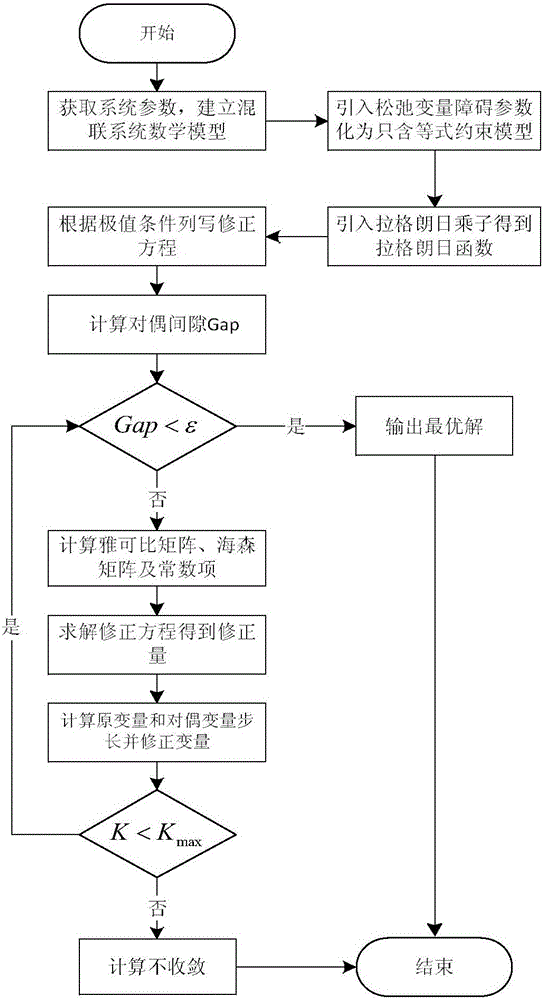
The invention discloses a modeling and optimized dispatching method of an electrical series-parallel system on the basis of an energy center. The modeling and optimized dispatching method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing an electrical network, a natural gas network and an energy hub model, and coupling the electrical network with the natural gas network through an energy hub to form the electrical series-parallel system; then, taking total energy cost as a target function, and considering various constraint conditions to establish an optimized dispatching mathematic model of the electrical series-parallel system; and carrying out solving by a primal-dual interior-point method, importing a slack variable and a barrier parameter in sequence in a solving process so as to change the model into a model which only contains an equality constraint, then, importing a Lagrange multiplier to obtain a Lagrange function, and solving a non-linear equation set formed by a KKT (Karush-Kuhn-Tucker) condition of the Lagrange function by a Newton method. A constructed example simulation result indicates that an optimization effect on the electrical series-parallel system by the modeling and optimized dispatching method is superior to an independent optimization effect.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
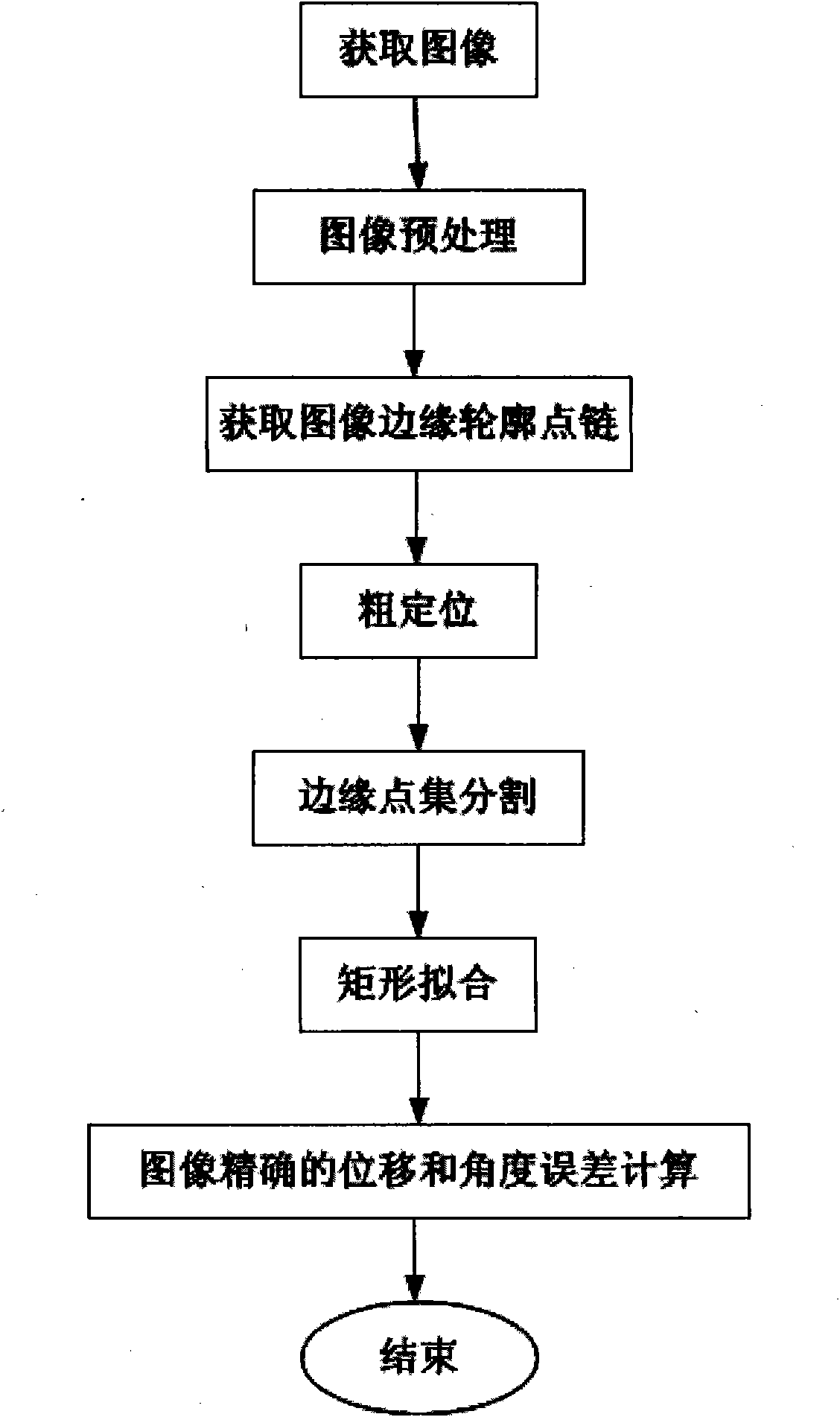
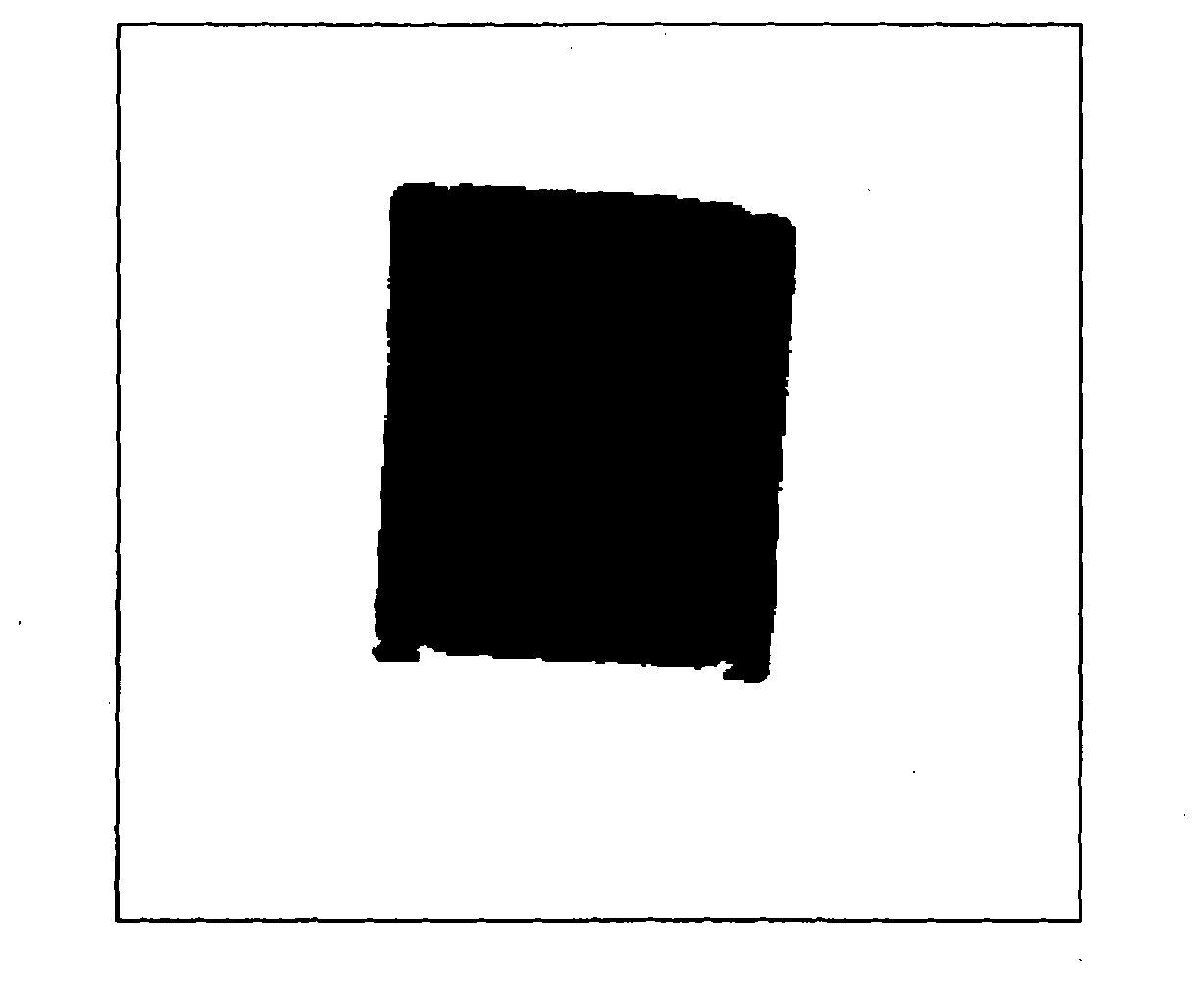
Visual inspection method for chip electronic component position error based on edge fitting
InactiveCN101839690ACalculation speedImage analysisUsing optical meansBoundary contourGravity center
The invention discloses a visual inspection method for chip electronic component position error based on edge fitting. The method is that a boundary contour point set of an entire image is obtained by adopting boundary following to generate the edge point chain structure of the image; the image center a chip electronic component is preliminarily calculated by adopting a contour gravity center method, a corner is roughly calculated by adopting a closest-to-center point method, two lines which pass through the image center and are perpendicular to each other are established, the two lines divides the image contour into four areas containing corner points, four corner points are obtained in each area respectively according to the distance from a point to the center and four line sides are formed, and the corresponding edge point set is extracted by using the four line sides to partition an edge; and the edge fitting is conducted to each edge point set by adopting an edge point set rectangle least square method to obtain the fitting rectangle of the edge, and the center coordinates of the fitting rectangle and the corner relative to a horizontal direction are calculated. The invention has the advantages that the center position and the corner of the chip surface mounting component can be accurately inspected and the calculation speed is fast.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Wind, water and fire united dispatching method based on power grid dispatching side demand
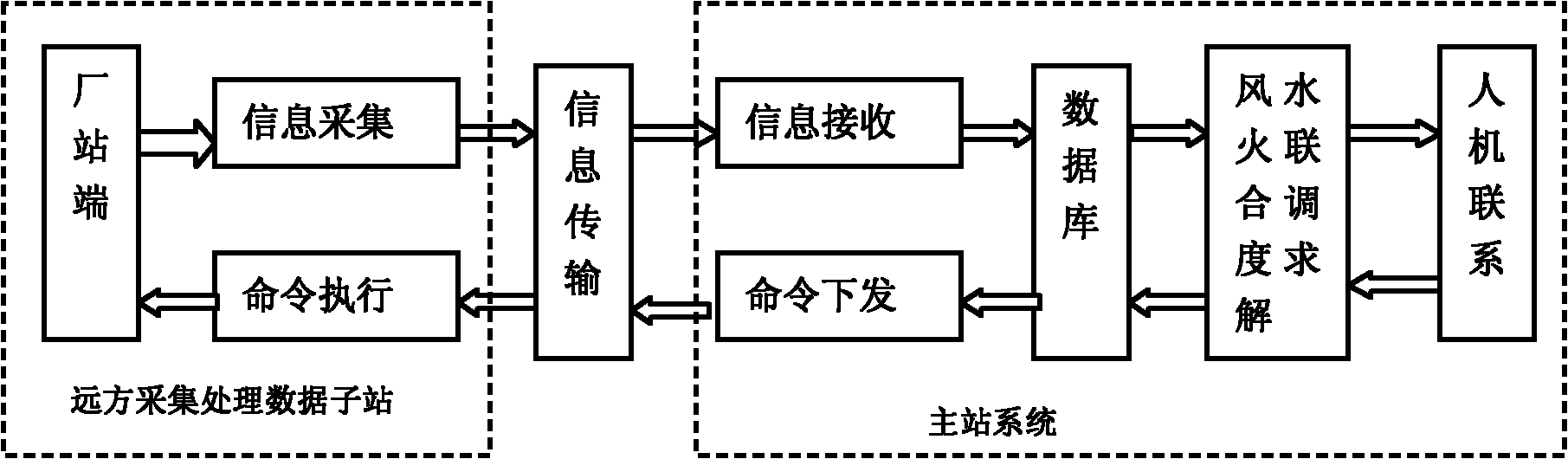
InactiveCN102184472AMeet scheduling needsSolve the impact caused by safe and stable operationData processing applicationsPrimary stationInterior point method
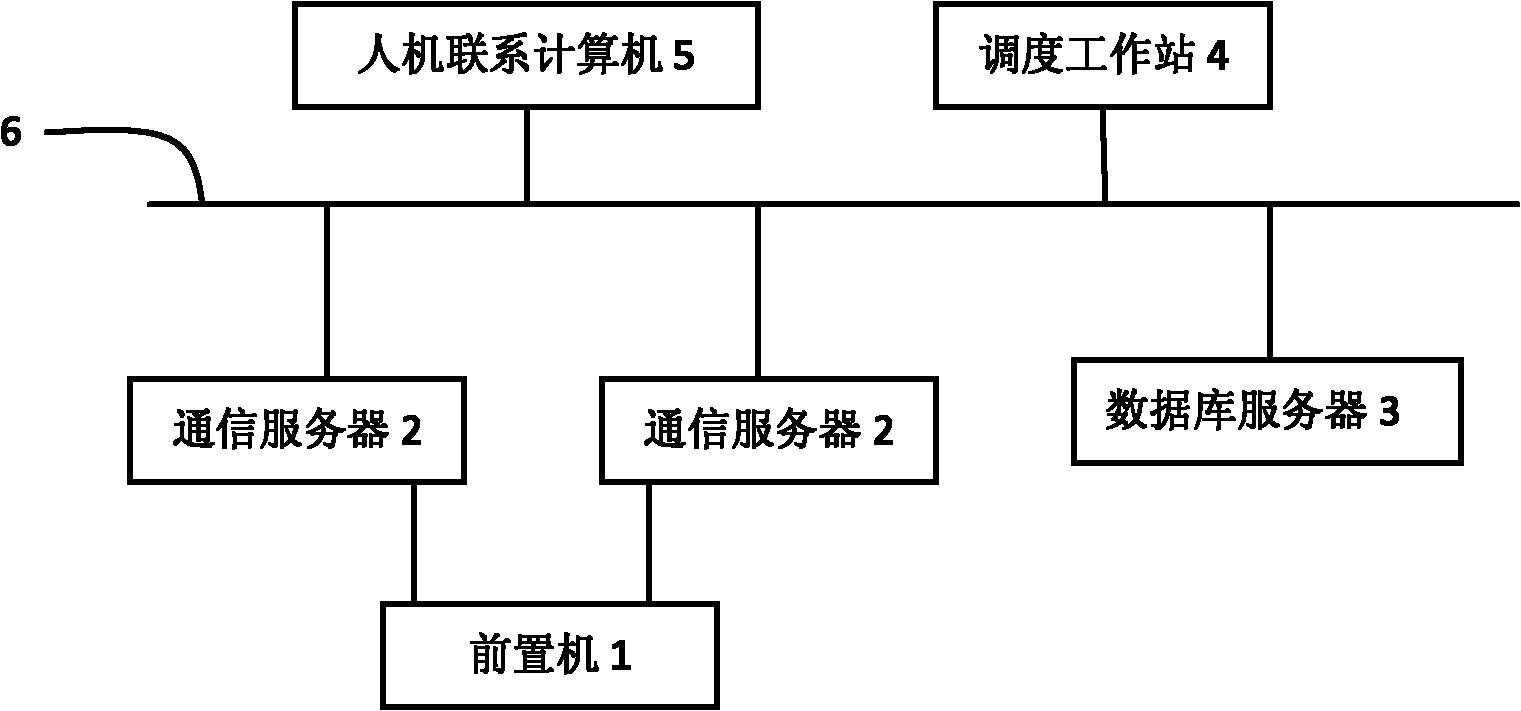
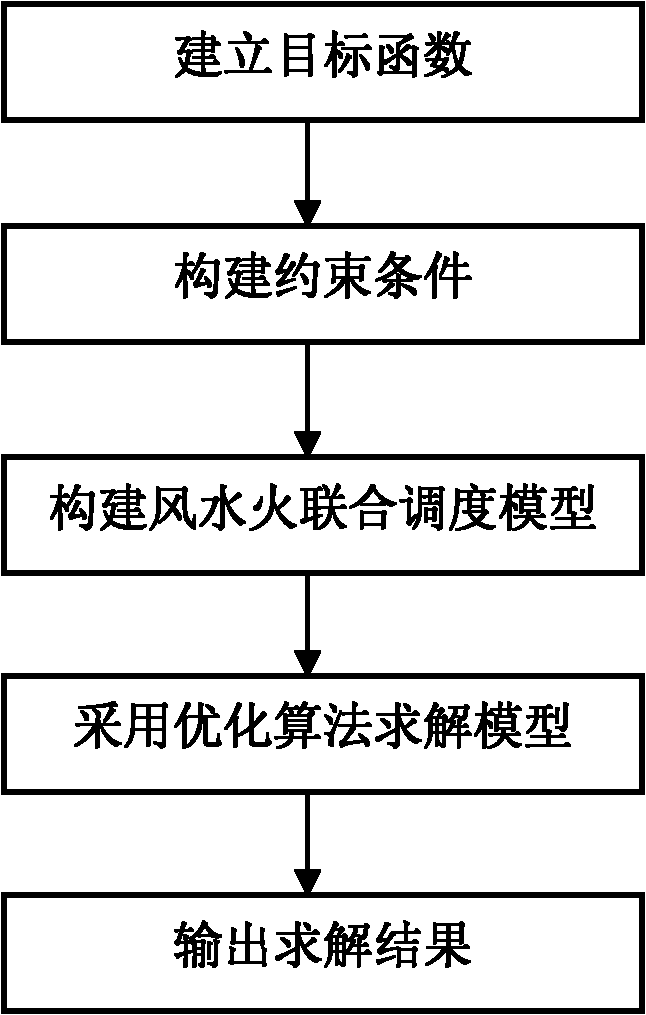
The invention relates to a wind, water and fire united dispatching method based on power grid dispatching side demand. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring basic data, predicted and planned data and historical data from the database of a power grid scheduling automatic main station system; 2, constructing a wind, water and fire united dispatching model which comprises the target function and the constraint conditions of the model; 3, inputting the basic data, the predicted and planned data and the historical data which are acquired in the step 1 into the wind, water and fire united dispatching model which is constructed in the step 2, and solving by using optimized algorithms such as a simplex method, an interior point method and the like; and 4, providing a solving result which is acquired in the step 3 for a dispatcher through a human-machine contacting computer in the main station system, making a dispatching command by the dispatcher in reference to the solving result, controlling to transmit the dispatching command through the human-machine contacting computer, and executing the transmitted dispatching command by using a plant station.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Addressing and capacity configuration method used for unified power flow controller (UPFC)
ActiveCN105226668ASolve the problem of site selectionEasy to operateFlexible AC transmissionReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationTransient stateInterior point method
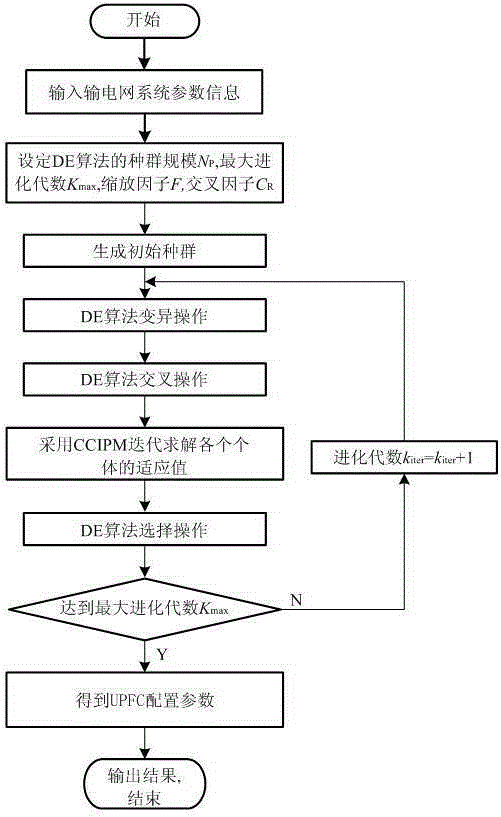
The invention discloses an addressing and capacity configuration method used for a UPFC. A UPFC addressing and capacity configuration model with transient stability constraints is established, a difference evolution algorithm serves as a framework, and the installation position and the capacity of the UPFC are optimized; in addition, a centrality correction interior point method is adopted for carrying out optimization and fitness assessment on continuous variables of each difference evolution unit. The difference evolution algorithm is simple in operation, high in searching capability, fewer in adjusting parameters and suitable for mixed optimization, and the interior point method is good in convergence and strong in robustness, so that the provided mixed algorithm can well solve the problems of UPFC addressing and capacity configuration, the method is highly efficient and convenient, and the application prospect is good.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
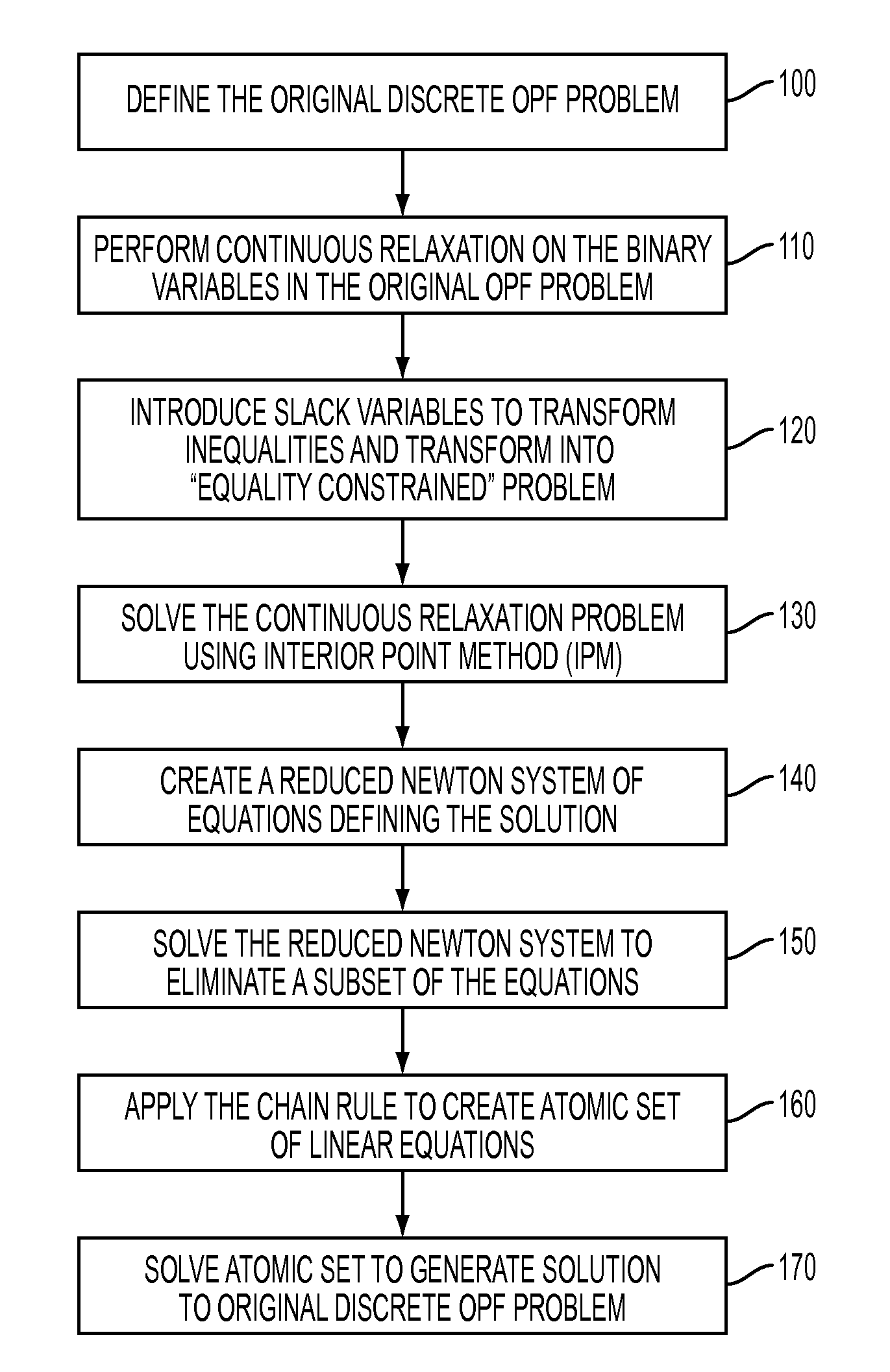
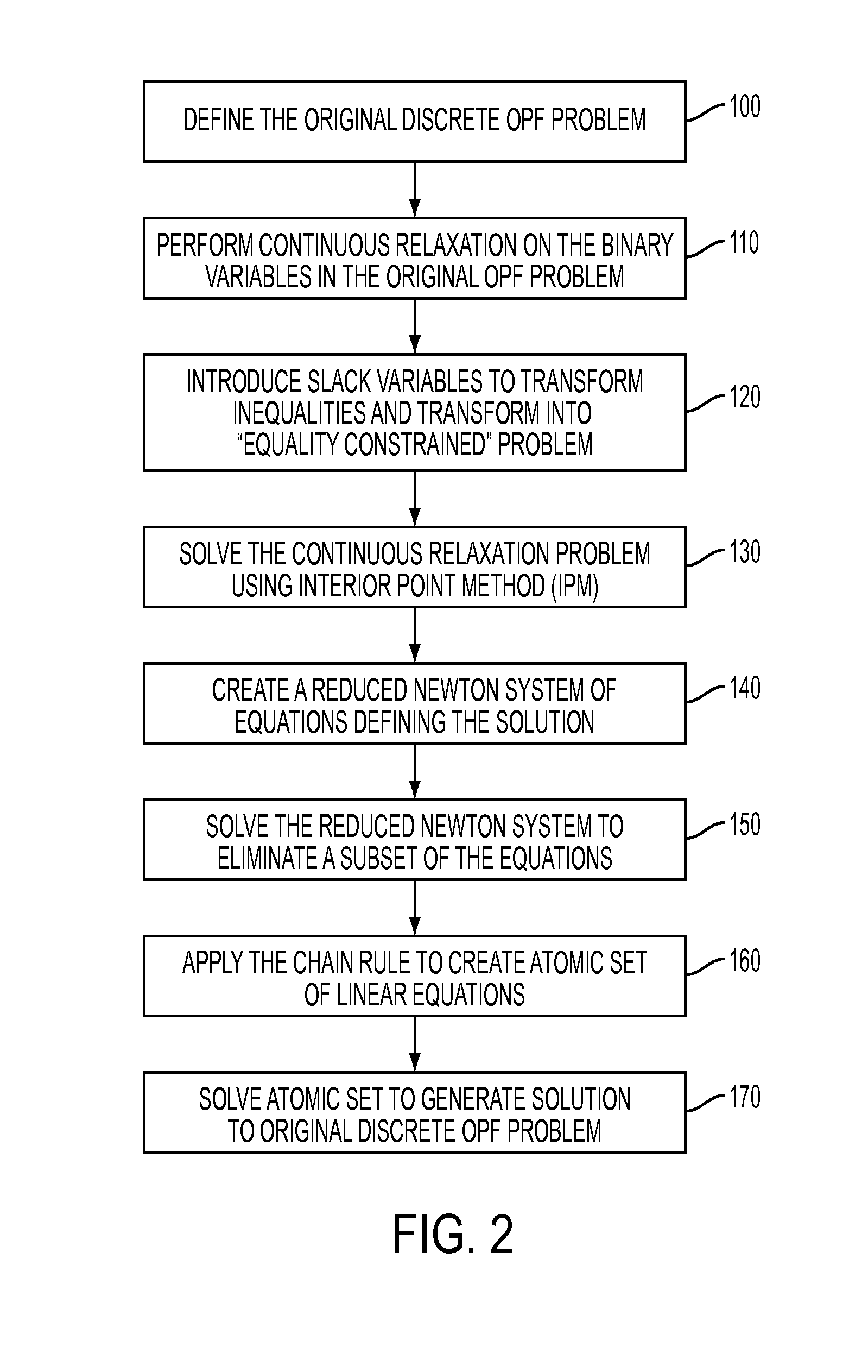
Primal-dual interior point methods for solving discrete optimal power flow problems implementing a chain rule technique for improved efficiency
ActiveUS20120150504A1Easy to analyzeSimplified resolutionPower network operation systems integrationComputation using non-denominational number representationPower flowInterior point method
A solution to the optimal power flow (OPF) problem for electrical generation and distribution systems utilizes a re-configuration of the OPF problem that allows for a simplified analysis and resolution of a network-based OPF problem in a minimal number of iterations. The standard mixed integer quadratic problem (MIQP) definition is be reconfigured, using the chain rule, to a relatively compact linear system of six equations with six unknowns (the smallest reducible (atomic) problem). Advantageously, the reduction in the complexity of the problem does not require any assumptions and yields a solution equivalent to the original problem.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
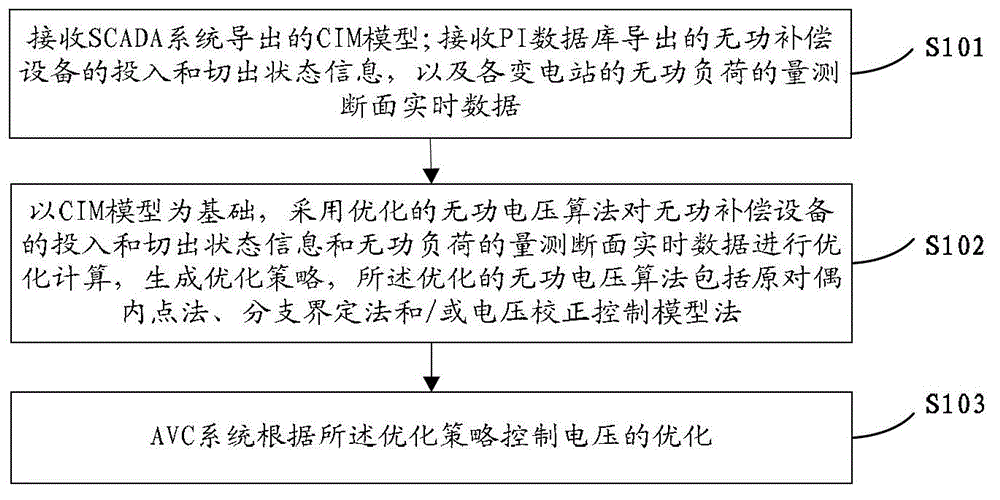
AVC (automatic voltage control) system-based reactive voltage optimization method and device
ActiveCN103151784AIncrease profitBig amount of dataAc network voltage adjustmentReactive power compensationAutomatic controlData acquisition
The embodiment of the application discloses an AVC (Automatic Voltage Control) system-based reactive voltage optimization method. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving a CIM (Common Information Model) which is derived through an SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) system; receiving input and switching out status information of reactive-load compensation equipment which is derived through a PI (Plant Information System), and reactive-load measurement section real-time data of transformer substations; on the basis of the CIM, optimally calculating the input and switching out status information of the reactive-load compensation equipment and the reactive-load measurement section real-time data through an optimized reactive voltage algorithm, and generating an optimized strategy, wherein the optimized reactive voltage algorithm comprises a primary dual interior point method, a branch-and-bound method and / or a voltage correcting control model method; and the AVC system controls optimization of the voltage according to the optimized strategy. The embodiment of the application further discloses an AVC system-based reactive voltage optimization device. Utilization efficiency of electrical energy can be improved through the embodiment of the application.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
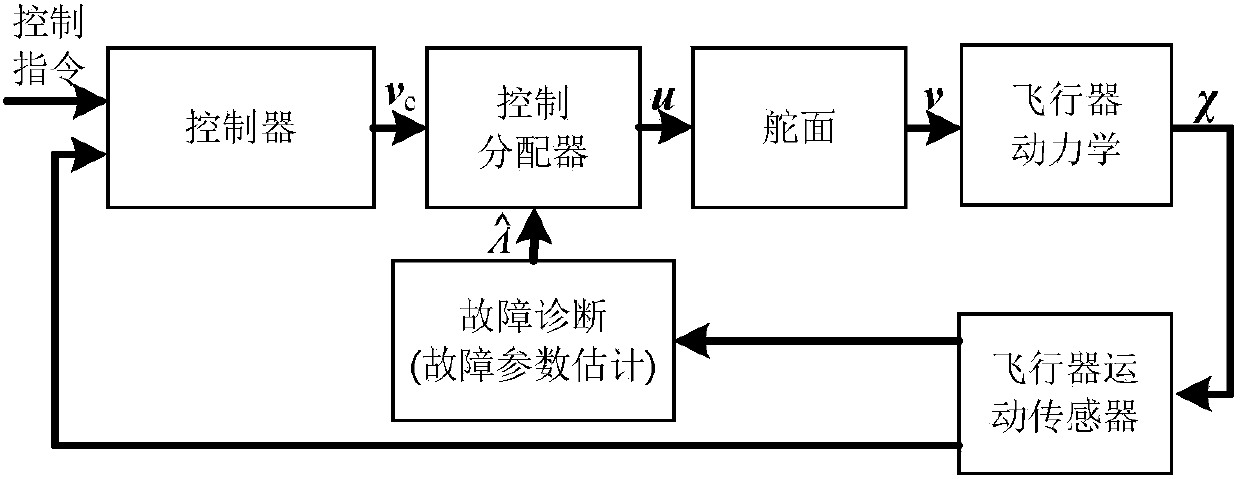
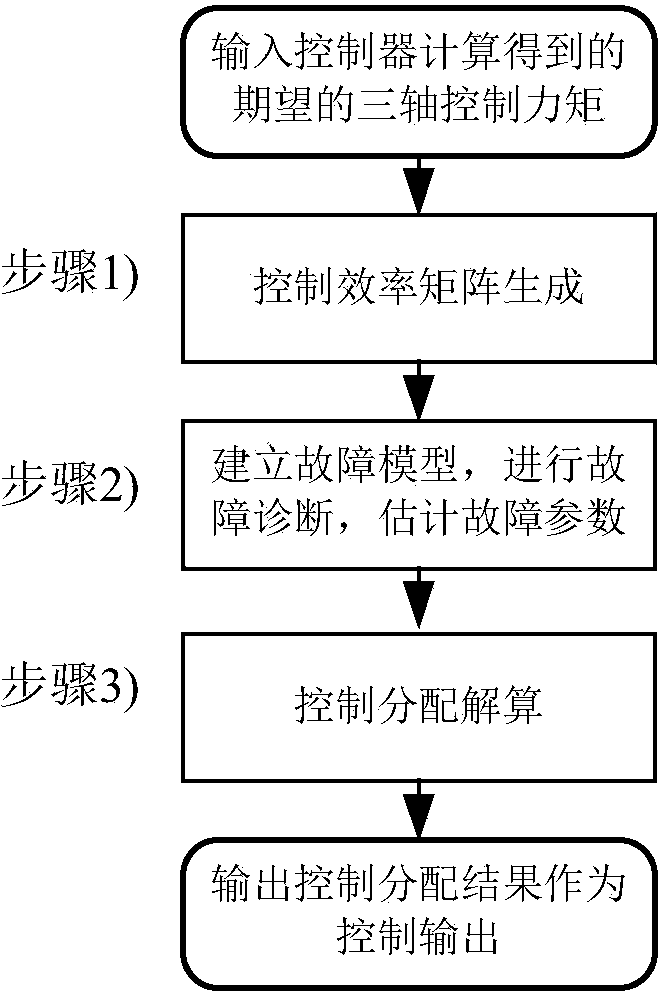
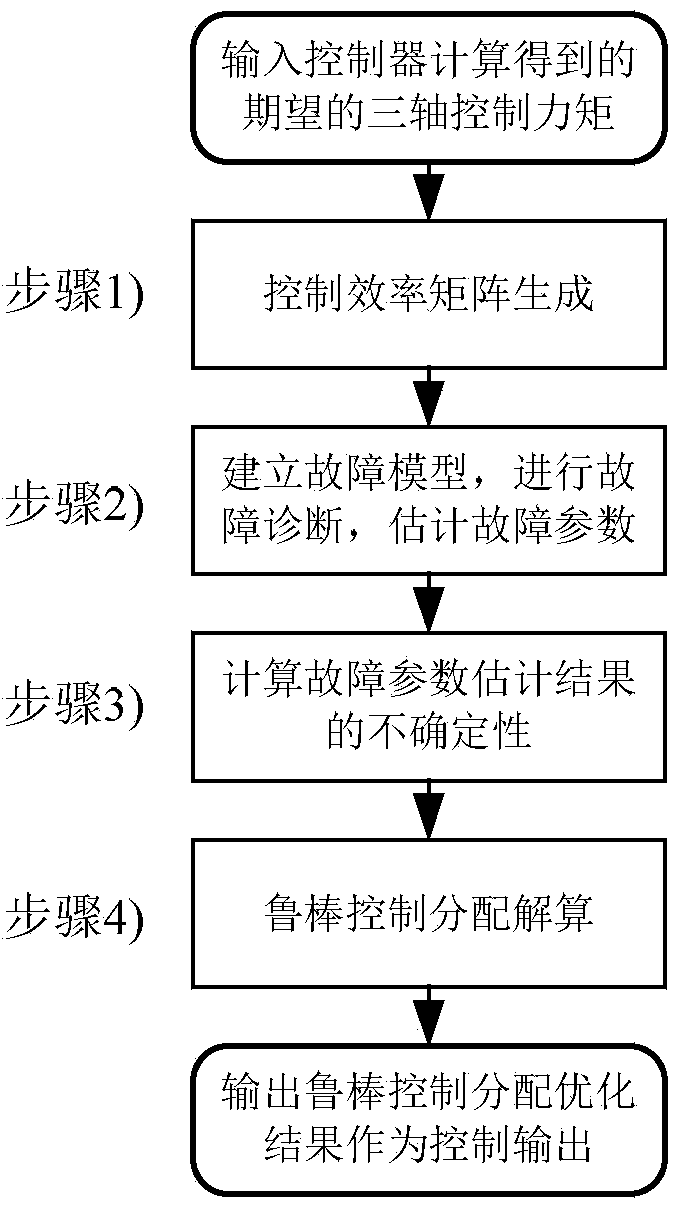
Robust control and distribution method applied to fault-tolerant flight control system
ActiveCN104238565AReduce biasImprove control distribution precisionPosition/course control in three dimensionsAdaptive controlAttitude controlSimulation
The invention relates to a robust control and distribution method applied to a fault-tolerant flight control system and belongs to the technical field of aerospace fault-tolerant flight control. The robust control and distribution method includes linearizing an aircraft model to generate a control efficiency matrix, determining efficiency coefficient of each rudder side influencing three-axis posture control of the aircraft, building a fault model, converting fault parameter estimation problems into linear regression problems so as to estimate fault parameters by a least square linear regression method, calculating uncertainties of estimated fault parameter results corresponding to each rudder side by a fault projection method and weighting and smoothing; considering difference of the uncertainties of the fault parameters corresponding to the rudder sides, solving the problem about optimization of the minimum control distribution error under the worst condition, controlling and distributing robust, equivalently converting the problem of optimization into the problem of convex optimization, and solving to obtain the robust control and distribution results by a primal dual interior point method. Robustness of control and distribution is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
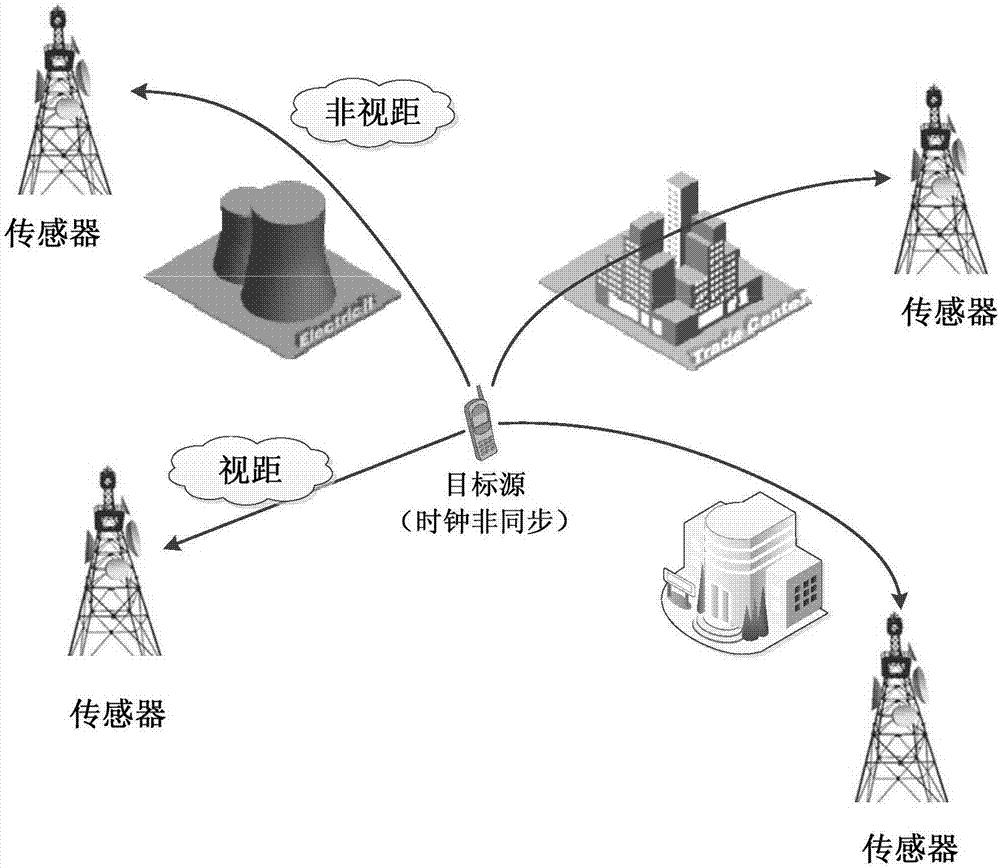
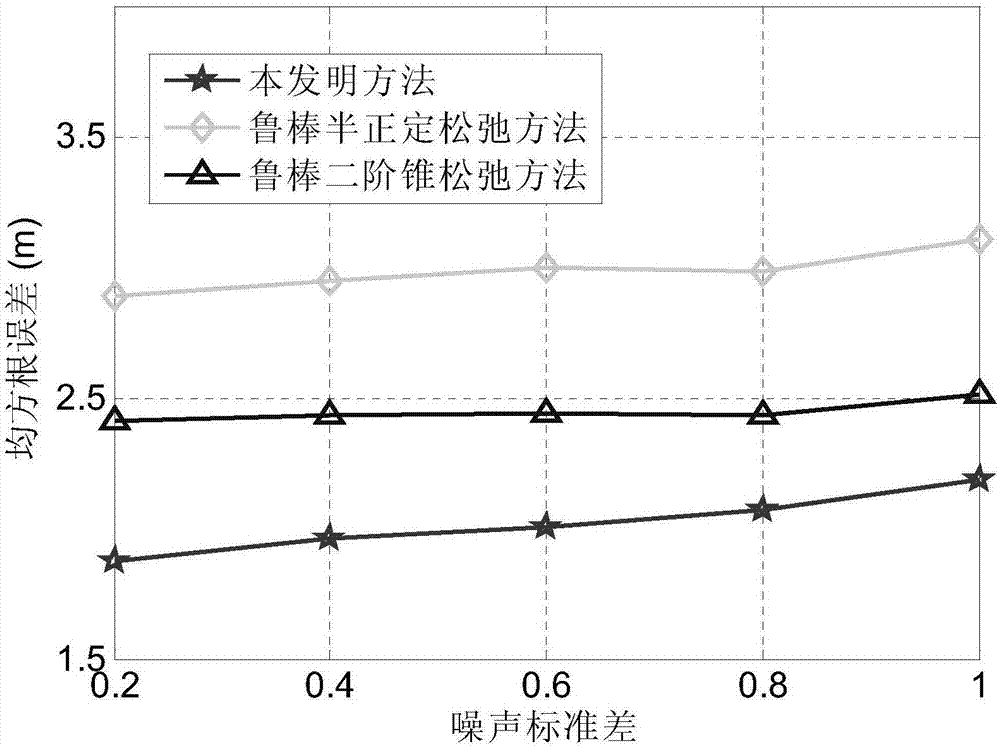
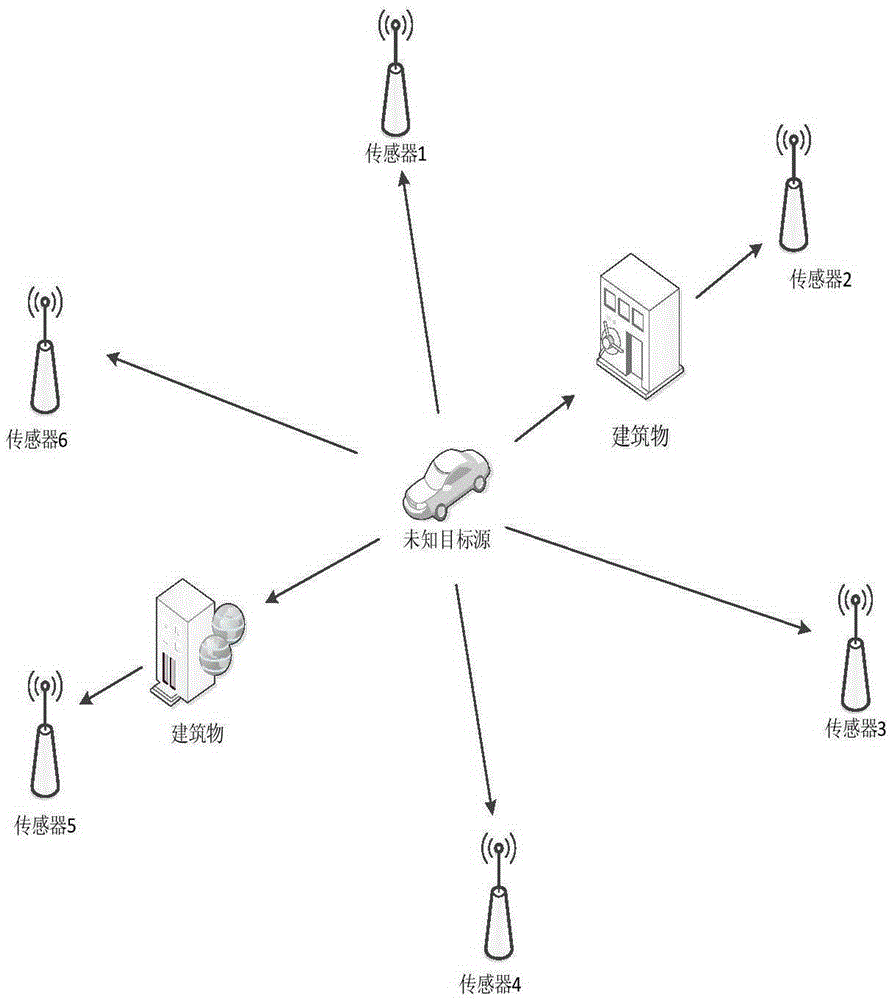
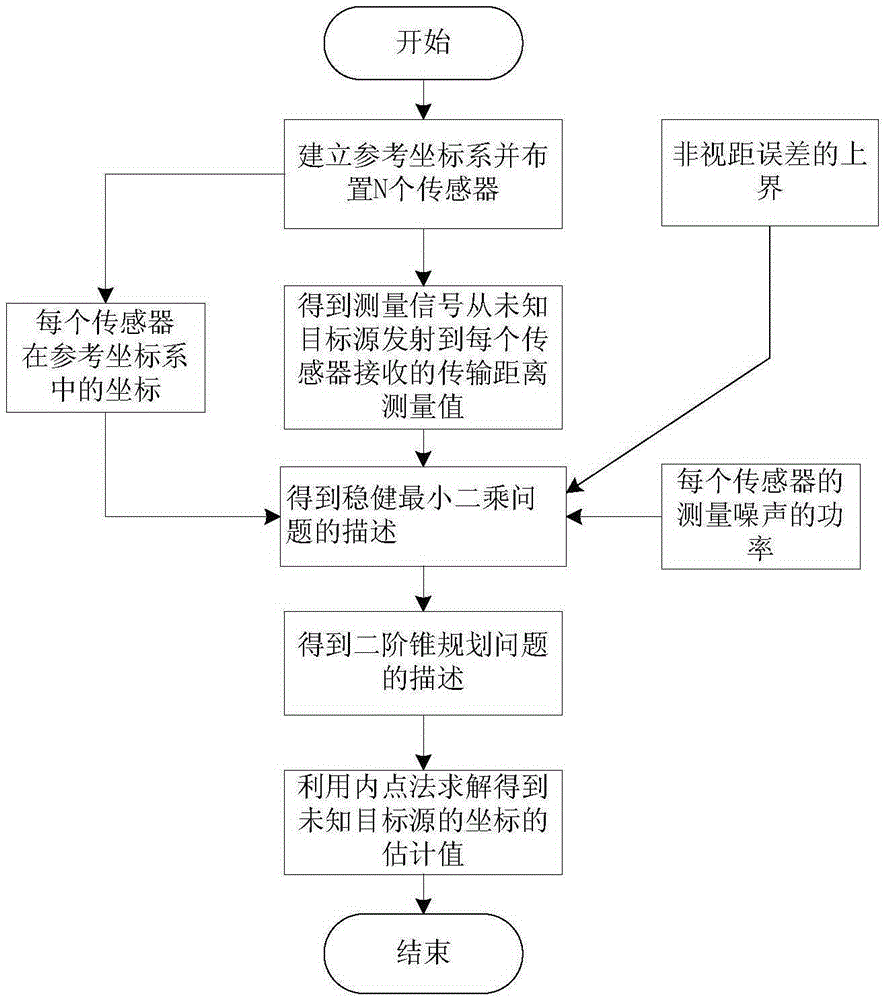
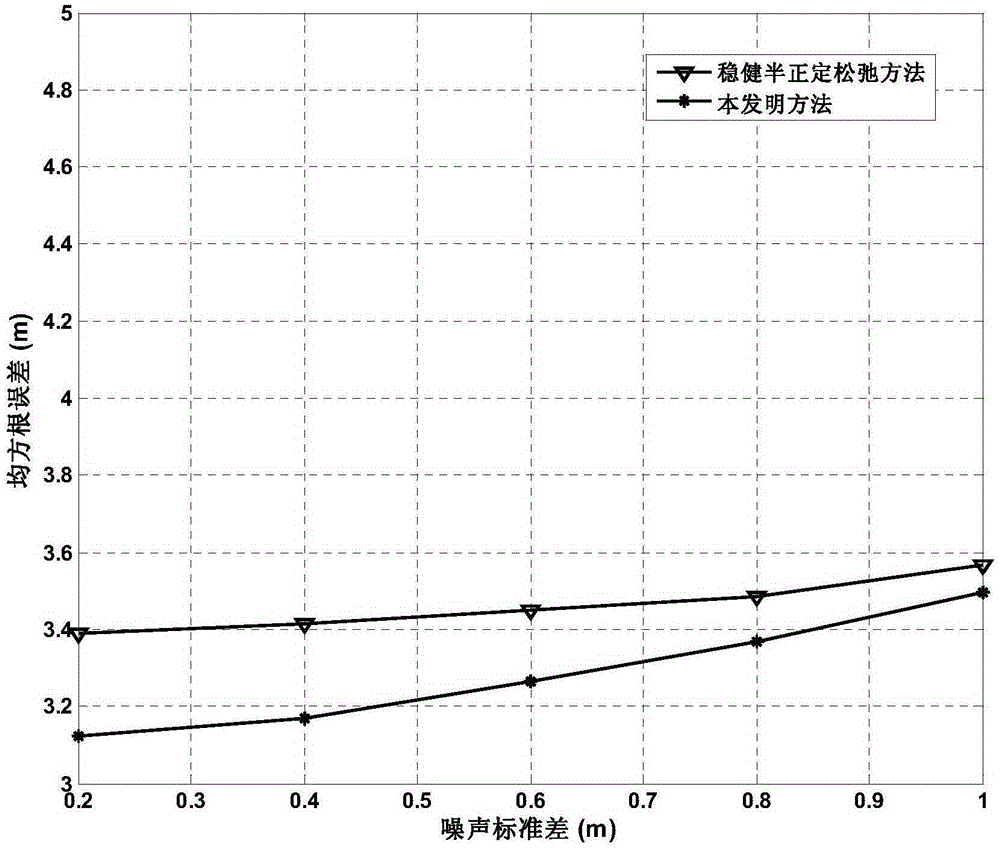
Positioning method based on arrival time of unknown starting time in non-line-of-sight environment
ActiveCN107271956APrecise positioningAdequate performance advantagePosition fixationStart timeInterior point method
The invention discloses a positioning method based on arrival time of unknown starting time in the non-line-of-sight environment. The method comprises steps of firstly establishing a model of a signal transmission distance between a target source and each sensor; obtaining a description of the measurement noise based on the model; according to the description of the measurement noise, using the robust weighted least squares method under the worst case to obtain the positioning problem in the environment of unknown signal transmission start time and non-line-of-sight errors, and converting the positioning problem into a non-convex positioning problem; by introducing auxiliary variables and using the second-order cone relaxation method, obtaining a second-order cone programming problem; and finally, using the interior point method to solve the second-order cone programming problem to get the final estimation value of the coordinate position of the target source in the reference coordinate system. The method has the advantages of being capable of simultaneously solving the problems of the unknown signal transmission start time and the non-line-of-sight errors so as to improve the positioning accuracy.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Co-generation type micro-grid economy coordination and optimization dispatching method
InactiveCN104537443AIncrease profitabilityImprove economic indicatorsForecastingInterior point methodMicro gas turbine
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Real-time electric vehicle and wind power collaborative dispatching and optimizing method
ActiveCN103296681AReduce capacity requirementsReduce consumptionInternal combustion piston enginesSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectricityInterior point method
The invention discloses a real-time electric vehicle and wind power collaborative dispatching and optimizing method. The method includes: charging and loading a wind power generator and an electric vehicle accessing into the power grid, absorbing wind power fluctuation by dispatching charging and loading of the electric vehicle, and for an optimizing and dispatching model for charging and loading of the electric vehicle, solving the optimizing and dispatching model by minimizing the sum of output adjustment amounts of all conventional generators in the power grid as a target function and utilizing a quadratic programming method or an interior point method under constraint condition of safe and stable operating of the power grid. In the real-time electric vehicle and wind power collaborative dispatching and optimizing method, the used target function is simple, computing load is reduced, computing time is shortened, and requirement for real-time dispatching can be met.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Acquiring method for dynamic random optimal power flow of power system for wind-containing power field
InactiveCN104638644ASolve the acquisition problemEngineering practicabilityAc network circuit arrangementsSpatial correlationPower flow
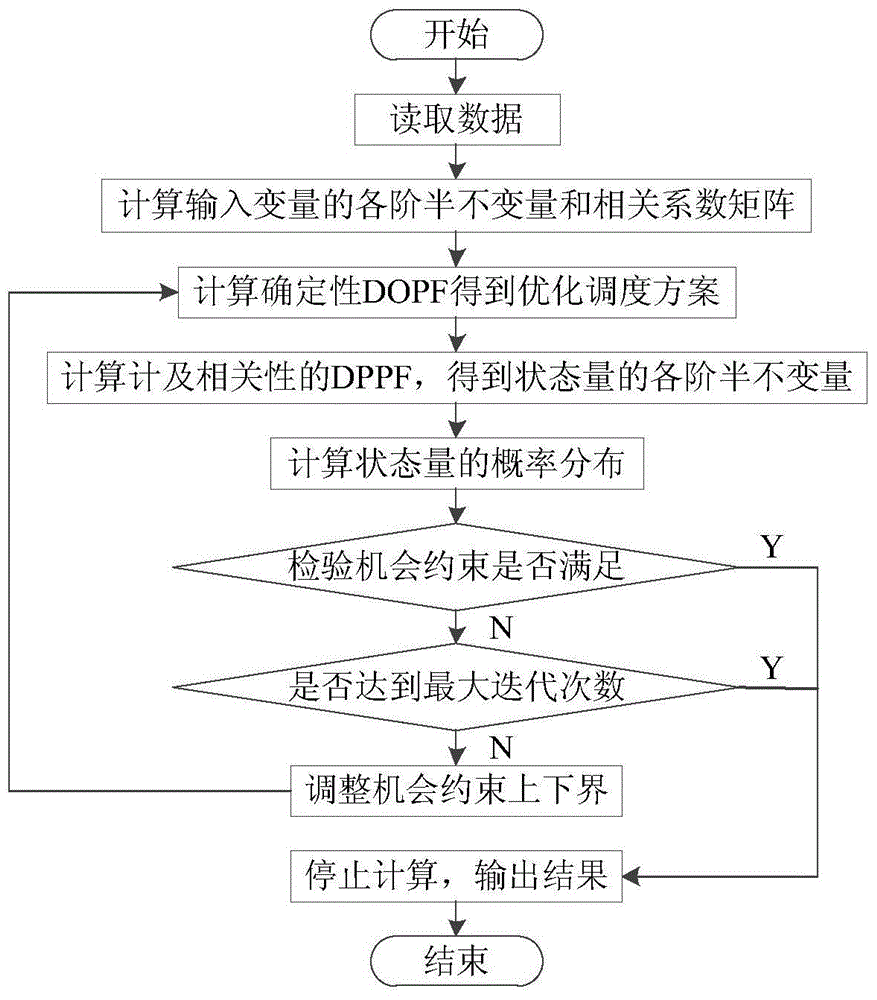
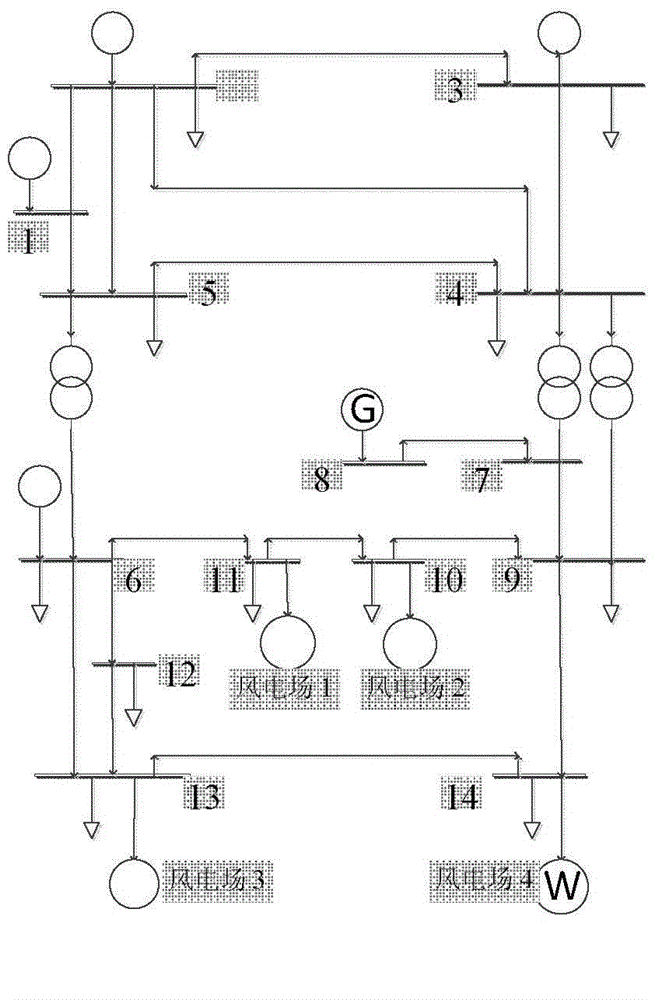
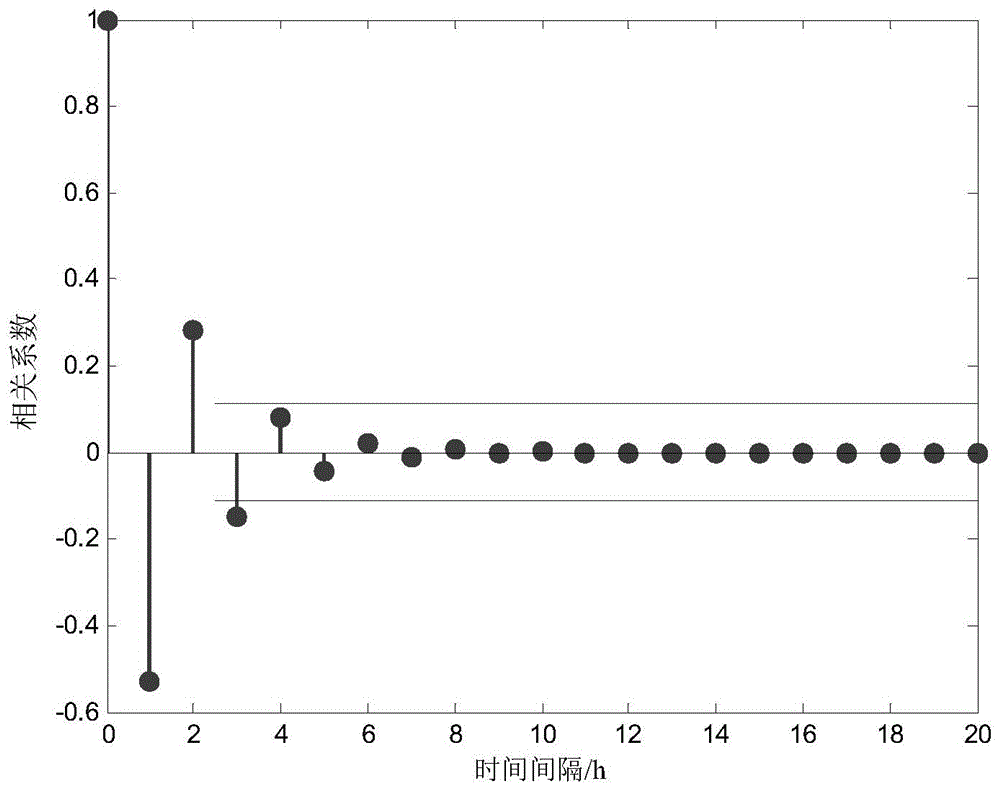
The invention discloses an acquiring method for a dynamic random optimal power flow of a power system for a wind-containing power field. According to the acquiring method, the dynamic random optimal power flow of the power system under the influence of the randomness of wind speed and load as well as temporal and spatial correlation is realized. The acquiring method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a dynamic probability model of wind speed, and analyzing the temporal and spatial correlation of the wind speed; secondly, calculating by adopting a deterministic dynamic optimal power flow based on an original dual and decoupling interior point method to obtain an optimal dispatching scheme; secondly, under the guidance of the dispatching scheme, solving the dynamic random optimal power flow considering the correlation based on a cumulants method to obtain probability distribution of a state variable, and adjusting the upper and lower bound of chance constraint according to the probability distribution; finally, performing iterative computation to solve a group of optimal dispatching schemes meeting all the chance constraints. According to the acquiring method disclosed by the invention, the optimal power flow of the power system under the random influence of an input variable can be effectively processed. The acquiring method has the advantages of accurate result and convenience for realization. The obtained result has certain guiding significance for dispatching persons.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
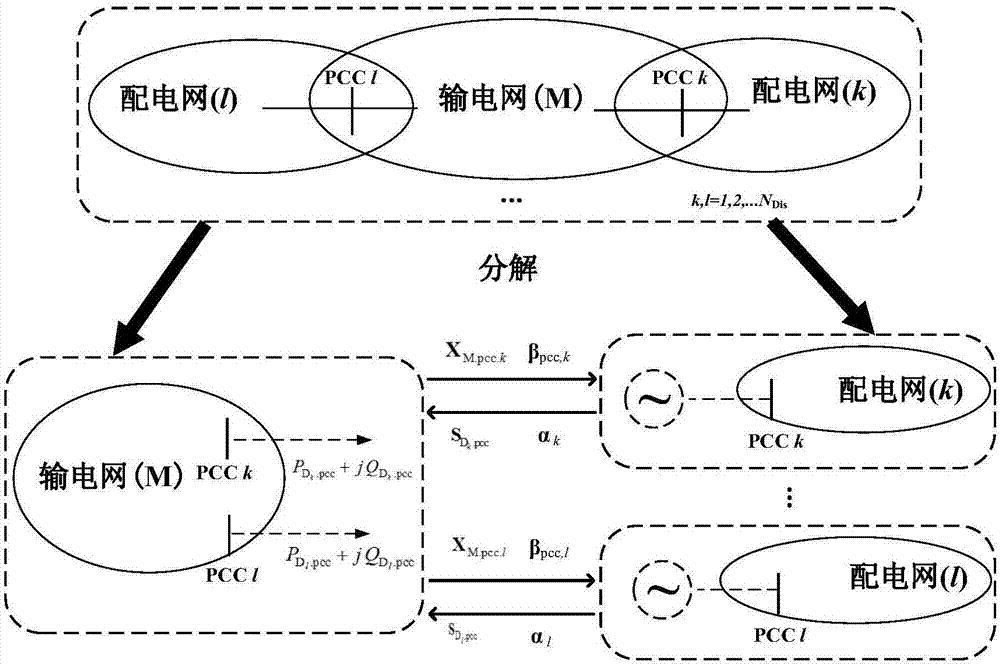
Power transmission and distribution network integrated reactive power optimization method based on distributed computation
ActiveCN107171341AEnsure consistencyGuaranteed synchronicityReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationAc networks with different sources same frequencyElectric power transmissionParallel computing
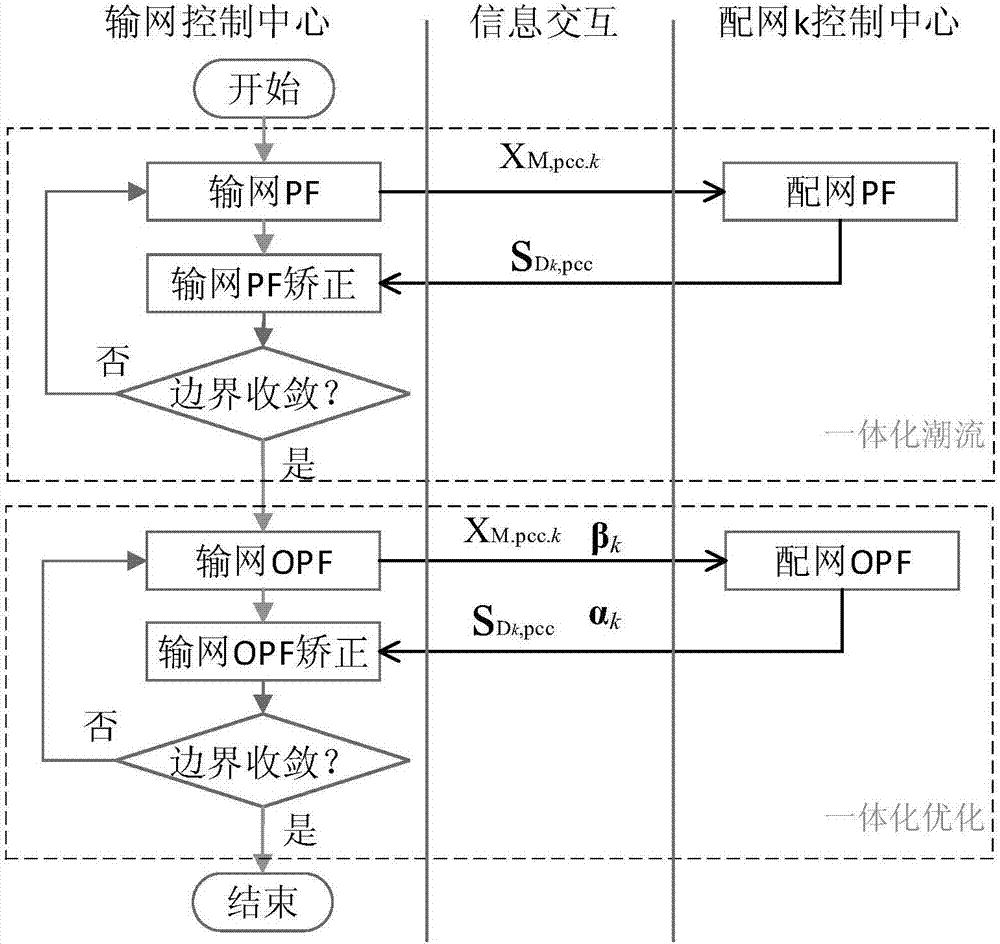
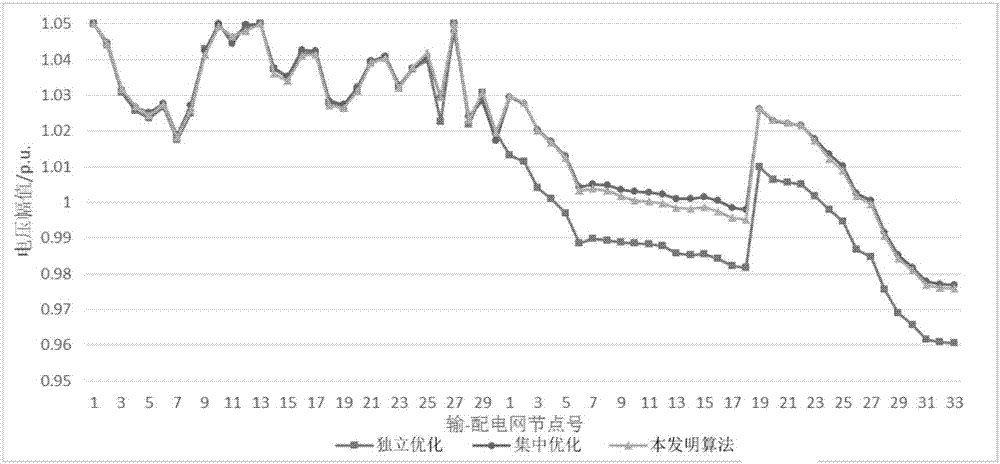
The invention discloses a power transmission and distribution network integrated reactive power optimization method based on distributed computation. A generalized master-slave method is used for decomposing a power transmission and distribution network problem to three parts, namely power transmission network reactive power optimization, power distribution network reactive power optimization and boundary information exchange. A quadratic penalty function and a primal-dual interior point method are utilized for alternately computing a power transmission reactive power optimization sub-problem and a power distribution reactive power optimization sub-problem. Through exchanging boundary influence factors (boundary connecting node voltage, equivalent power and target function boundary Lagrange multiplier information), coordination participation is realized, and furthermore distributed computation for whole network reactive power optimization is realized, wherein discrete variables which commonly exist in reactive power optimization cause high difficulty in computing the boundary multiplier. The quadratic penalty function is introduced for regulating the discrete variables so that processing of the discrete variables is realized based on a differentiable power transmission and distribution global optimization target function. According to the method of the invention, a distributed computation method is utilized for settling an integrated reactive power optimization problem of the power transmission and distribution network, thereby keeping an existing computation mode of the power transmission and distribution network and realizing relatively high computation precision.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Power distribution network reconstruction and island division method containing distributed power supply
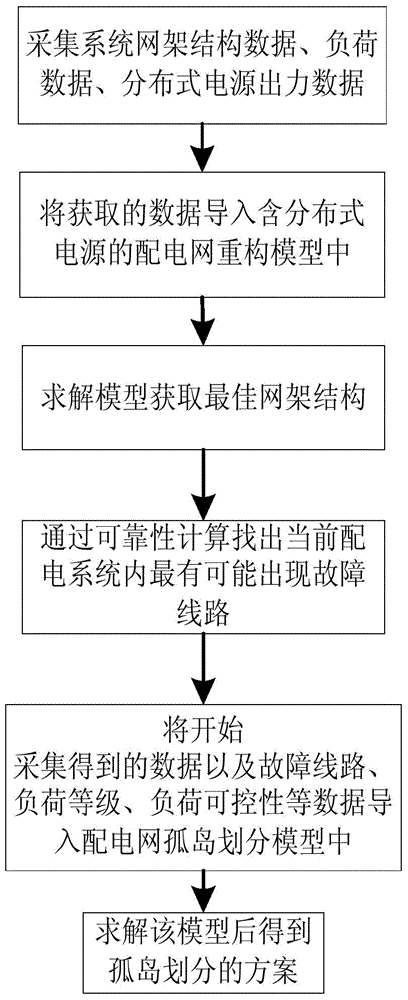
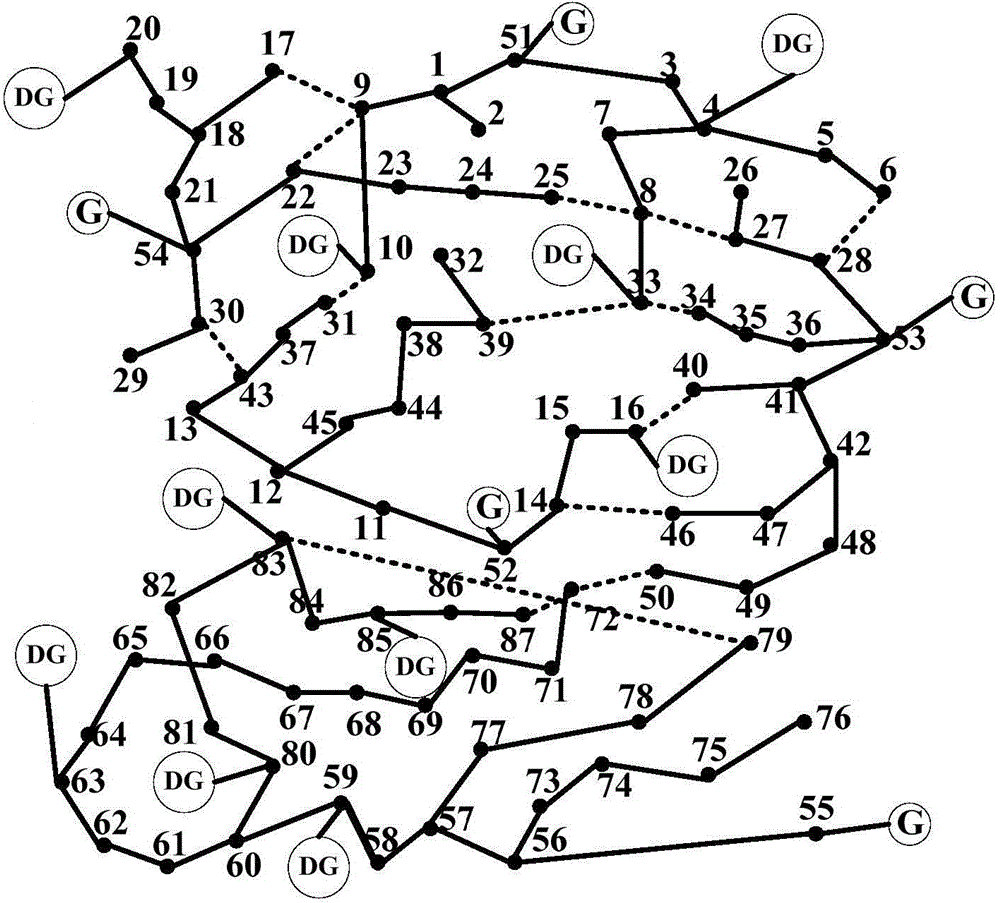
ActiveCN104934964AGuaranteed cost-effective operationImprove reliabilityForecastingSystems intergating technologiesIslandingInterior point method
The present invention provides a power distribution network reconstruction and island division method containing a distributed power supply. The method comprises the following content of introducing a complementarity constraint condition in a power distribution network reconstruction model containing the distributed power supply, and carrying out the model solution by utilizing a modern interior point method of fast speed and strong robustness; for the distributed power supply which can be in the flexible grid connection or island operation, according to a power supply characteristic of the distributed power supply and a power distribution network island operation characteristic, establishing a power distribution network island division model considering the load priority, the controllability / uncontrollability and the power balance constraint. Compared with a conventional island division scheme obtained by a searching method, the model of the present invention adopts a mathematical optimization techniques to solve, the obtained island scheme does not need the additional verification and correction, the power supply of the important loads can be recovered rapidly and reasonably, the operation electric energy loss of a power distribution system is reduced, and the economy and reliability of the power distribution network operation are improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Distribution network loop closing current calculating method based on distributed power supply
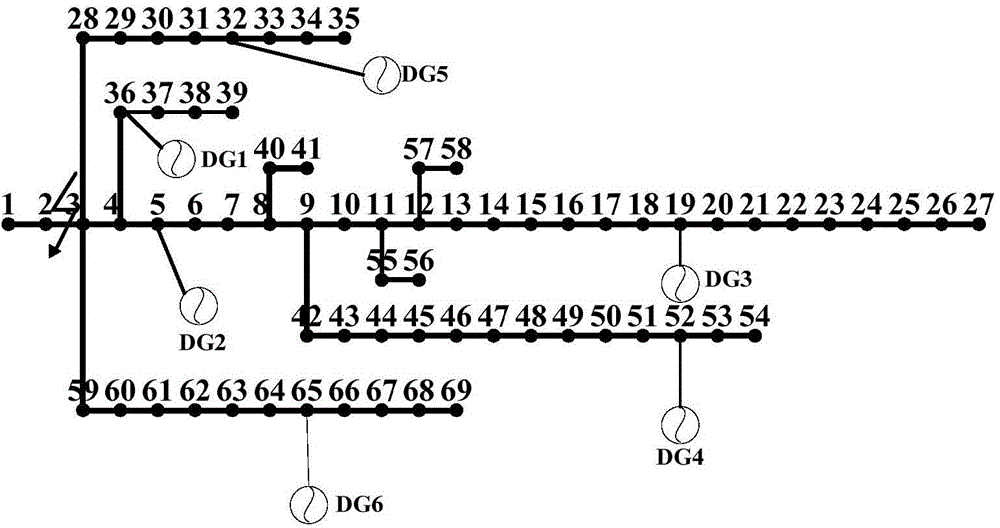
InactiveCN103208818AFully play the regulatory roleReduce shockSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsLoop closingInterior point method
The invention discloses a distribution network loop closing current calculating method based on a distributed power supply. The running state of the distributed power supply is optimized and adjusted by establishing a coordinated optimization model of the distributed power supply and combining a primal-dual interior point method to reduce the loop closing operation current. Load flow distribution of a loop closing circuit is calculated by adopting a two-stage method in a weakly meshed distribution network, so that theoretical support and method reference are provided for smoothly implanting the loop closing operation and improving the power supply reliability in an intelligent power grid environment.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Random task queuing unloading optimization method based on edge computing
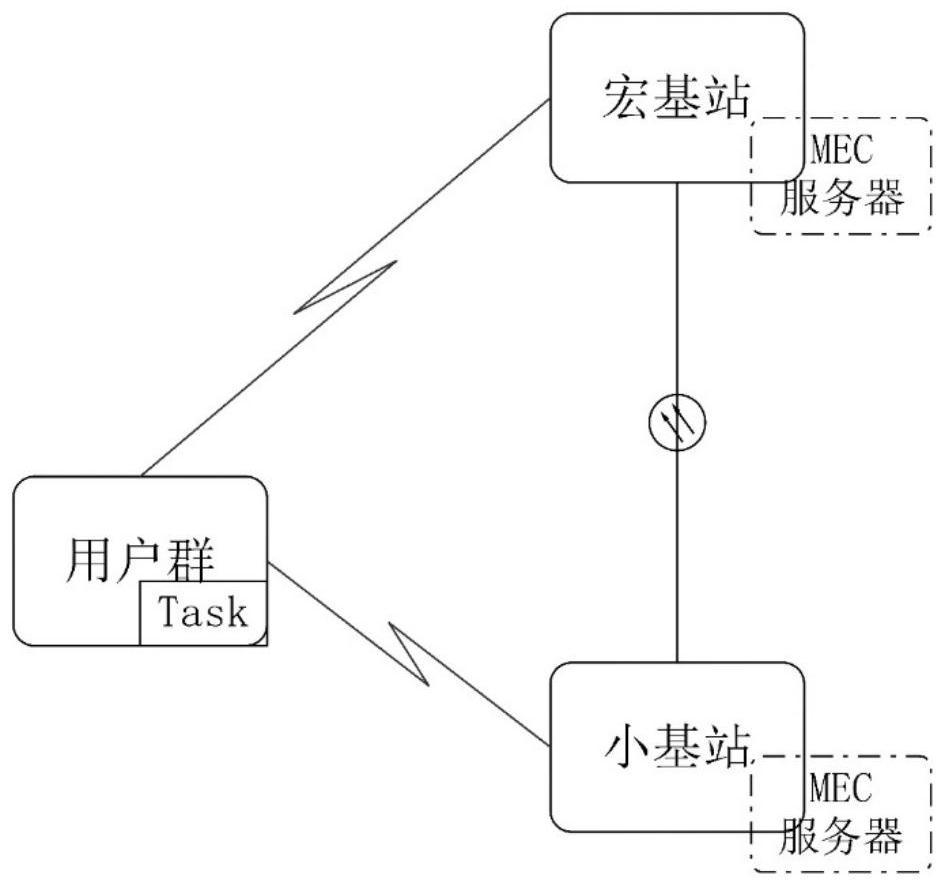
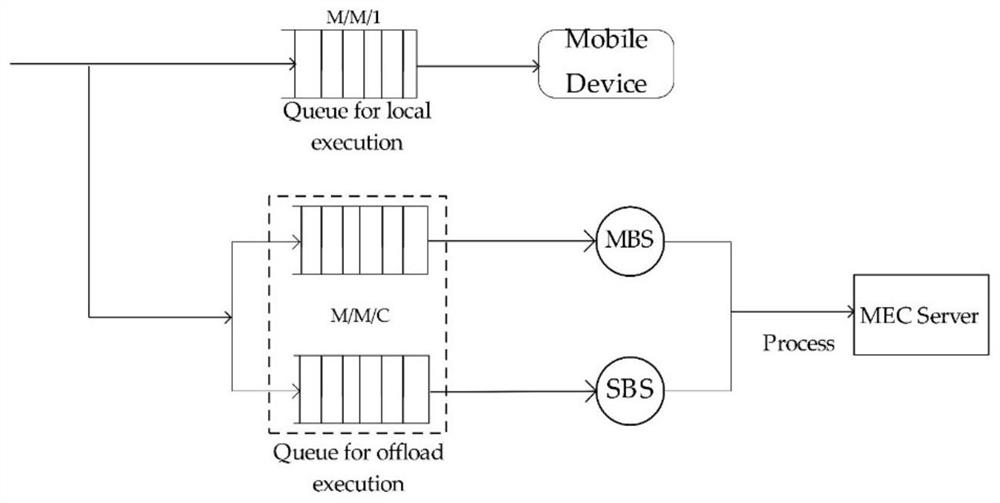
ActiveCN111930436AIncrease flexibilityMeet diverse optimization needsResource allocationProgram loading/initiatingEnergy consumption minimizationPathPing
The invention provides a random task queuing unloading optimization method based on edge computing and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the probability that a task generated by a user MDi is locally executed as the probability that the MDi unloads the task is represented through a macro base station and the probability that the task is unloaded through a small base station respectively, wherein the queuing model of the tasks processed locally is an M / M / 1 queue, and the queuing model of the tasks unloaded to the serverfor processing is an M / M / c queue. Secondly, a user-centered time delay and energy consumption minimization optimization target is established, and the decision probability is utilized to reflect the intention of the user to select different paths to execute tasks; the objective of the invention is to solve the problems of time delay and energy consumption minimization. A task allocation algorithmbased on a quasi-Newton interior point method is provided, the optimal solution of a target variable is regarded as a combination, the inverse of a target function Hessian matrix is replaced with an approximate matrix Dk by using a quasi-Newton condition, the Dk matrix is continuously updated through an iterative formula, the optimal search direction and the search step length are updated, and finally the optimal solution is approximated.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Probabilistic optimal power flow calculation method for alternating-current and direct-current systems of offshore wind power plants subjected to VSC-HVDC (voltage source converter-high voltage direct current) grid connection
InactiveCN104392135ADealing with dependenciesHigh speedSpecial data processing applicationsEqual probabilityHigh-voltage direct current
The invention discloses a probabilistic optimal power flow calculation method for alternating-current and direct-current systems of offshore wind power plants subjected to VSC-HVDC (voltage source converter-high voltage direct current) grid connection. The probabilistic optimal power flow calculation method specifically includes: firstly, fitting probability distribution of offshore wind speeds by means of nonparametric kernel density estimation, describing wind speed correlations among multiple wind power plants by a correlation coefficient matrix, and creating a probability model of output power of the wind power plants and a steady-state mode of VSC-HVDC; then, acquiring standard normal distribution samples by the Latin hypercube sampling technology, and acquiring correlated input variable samples according to the equal-probability transformation theory by the Nataf transformation technology; finally, performing deterministic optimal power flow calculation on each group of samples by the primal-dual interior-point method to acquire output variable samples, and acquiring probability distribution and numerical characteristics of output variables by the statistical method. Calculation results of the probabilistic optimal power flow calculation method can well reflect distribution conditions of state quantity and control quantity of optimal power flow of the alternating-current and direct-current systems, and the probabilistic optimal power flow calculation method has the advantages of high speed and accuracy.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
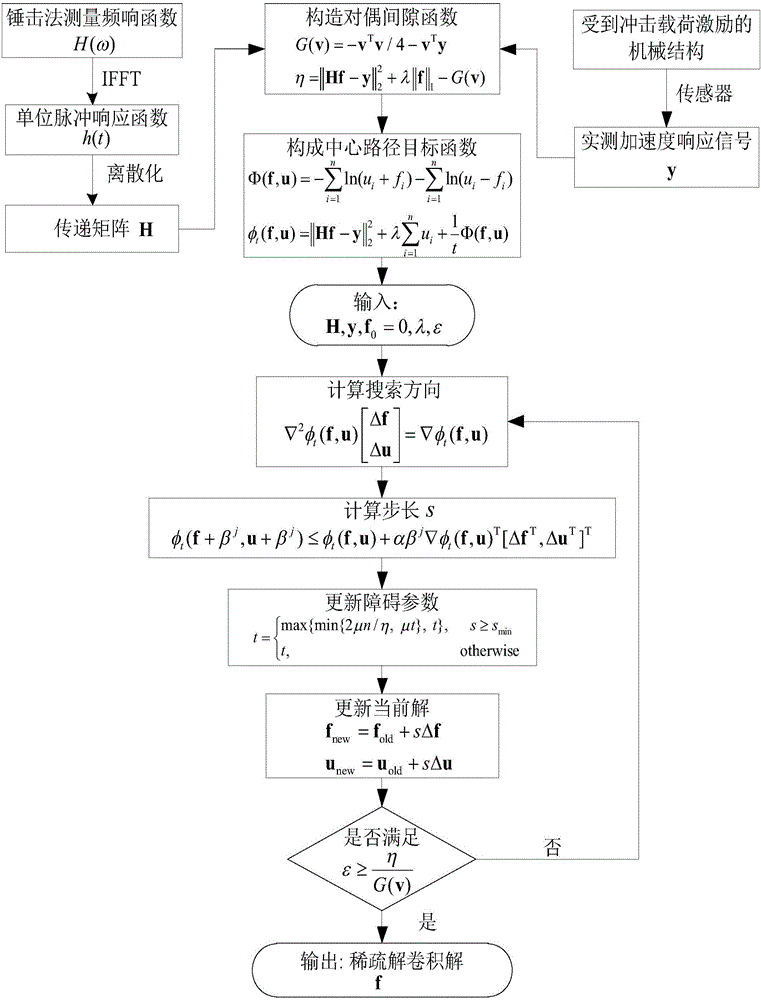
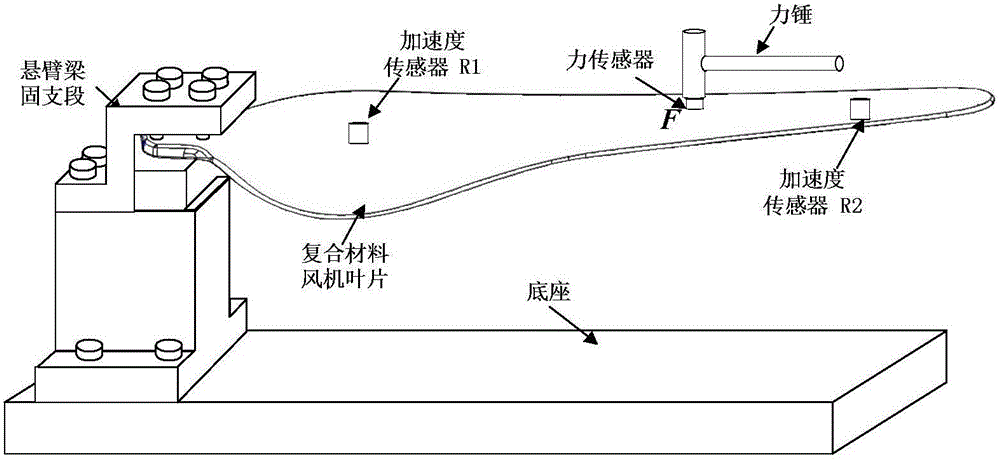
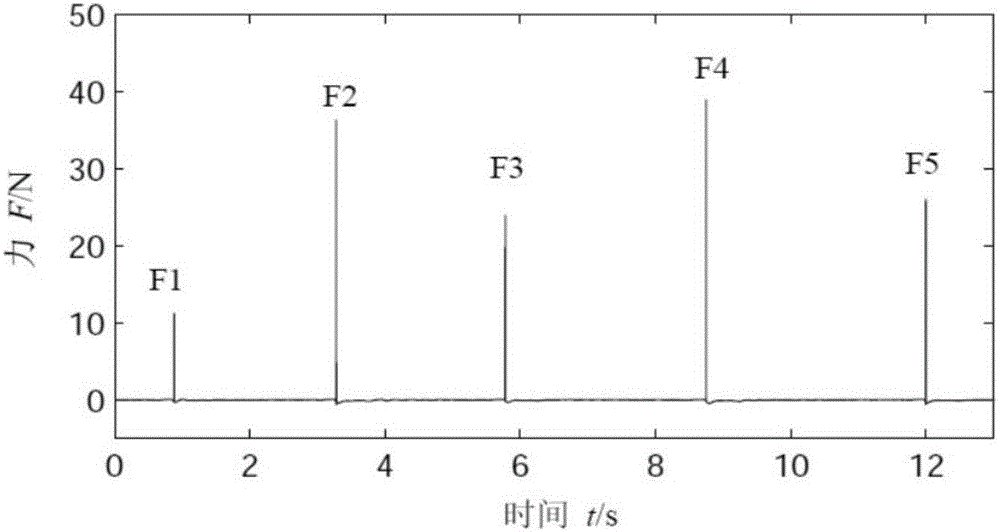
Sparse deconvolution method for impact load identification of mechanical structure
ActiveCN105843780AGrowth inhibitionImprove recognition accuracyComplex mathematical operationsMeasurement pointEngineering
The invention relates to a sparse deconvolution method for impact load identification of a mechanical structure. The method is used for solving the ill-posed nature of the impact load identification inverse problem and comprises steps as follows: 1) a frequency response function between an impact load acting point and a response measurement point of the mechanical structure is measured with a hammering method, a unit impulse response function is obtained through inverse fast fourier transform, discretization is further performed, and a transfer matrix is obtained; 2) an acceleration signal generated by impact load of the mechanical structure is measured with an acceleration sensor; 3) an L1-norm-based sparse deconvolution convex optimization model for impact load identification is established; 4) the sparse deconvolution optimization model is resolved with a primal-dual interior point method, and a sparse deconvolution solution, namely, a to-be-identified impact load, is obtained. The sparse deconvolution method is suitable for identifying the impact load acting on the mechanical structure. Compared with conventional Tikhonov regularization methods based on an L2 norm, the sparse deconvolution method has the advantages of high identification accuracy, high computation efficiency and high stability.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Non-line-of-sight stable positioning method based on signal arrival time in wireless network
ActiveCN105334495ANot affected by local convergenceHigh positioning accuracyPosition fixationComputation complexityWireless mesh network
The invention discloses a non-line-of-sight stable positioning method based on signal arrival time in a wireless network. The method comprises the following steps: transmission distance measured values from the time when measuring signals are emitted from an unknown target source to the time when each sensor receives the measuring signals is measured; then re-describing is performed on a distance measurement model corresponding to each sensor; next, according to the re-described distance measurement model, an initial stable least square problem is established; afterwards, an epigraph is obtained according to the stable least square problem; then a second-order cone planning problem is obtained by use of a second-order cone relaxation technology relaxation constraint condition; and finally, the second-order cone planning problem is solved by use of an interior point method technology to obtain an estimated value of the position of the unknown target source. The method provided by the invention has the following advantages: a description of the second-order cone planning problem is obtained through relaxing the description of the stable least square problem by use of the second-order cone relaxation technology, it can be ensured that a global optimal solution is obtained without being affected by local convergence, and the positioning precision is high; and since the number of solved unknown optimization variables is small, and thus the calculation complexity is quite low.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
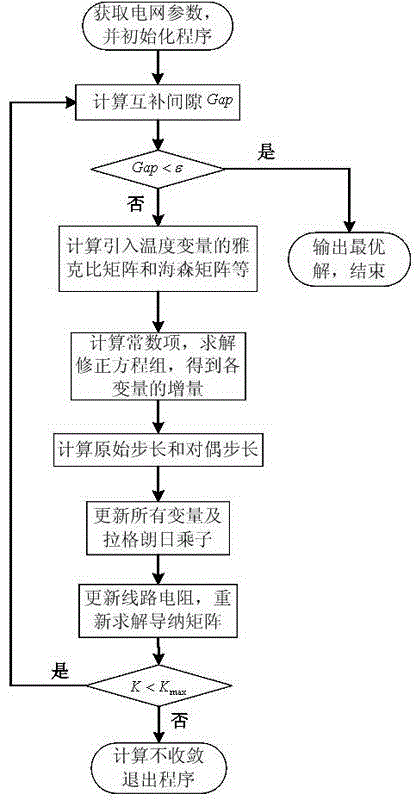
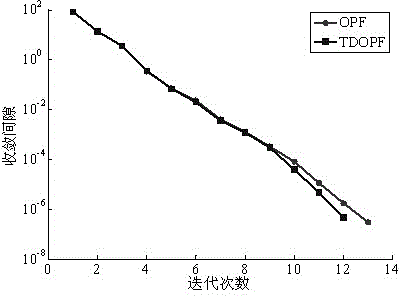
Temperature influence-considering optimal power flow algorithm of power system
InactiveCN104393592ASimplify writingGuaranteed computing speedAc network circuit arrangementsLine resistanceElectric power system
The invention discloses a temperature influence-considering optimal power flow algorithm of a power system. As the traditional optimal power flow is processed by taking power system network parameters as constants and the influence of the electric heating coupling relation of the actual power grid line is neglected, the calculation result of the traditional optimal power flow has great deviation to the scheduling operation result of the actual power grid. On the basis, the temperature influence-considering optimal power flow algorithm of the power system is characterized in that a temperature influence-considering optimal power flow model of the power system is established according to the electric heating coupling relation between line temperatures and line resistance. Besides, the problem of the temperature influence-considering optimal power flow algorithm of the power system is solved by use of a simplifying primal-dual interior point method, and generalized inequality constraints containing only upper limit constraints are formed by simplifying the inequality constraints in the optimization model, and the writing of a program can be greatly simplified. Finally, the simulation and analysis results of a plurality of examples indicate that the model and the algorithm are higher than the traditional optimal power flow in calculation accuracy and calculation efficiency and have significance to the scheduling operation of the power system.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
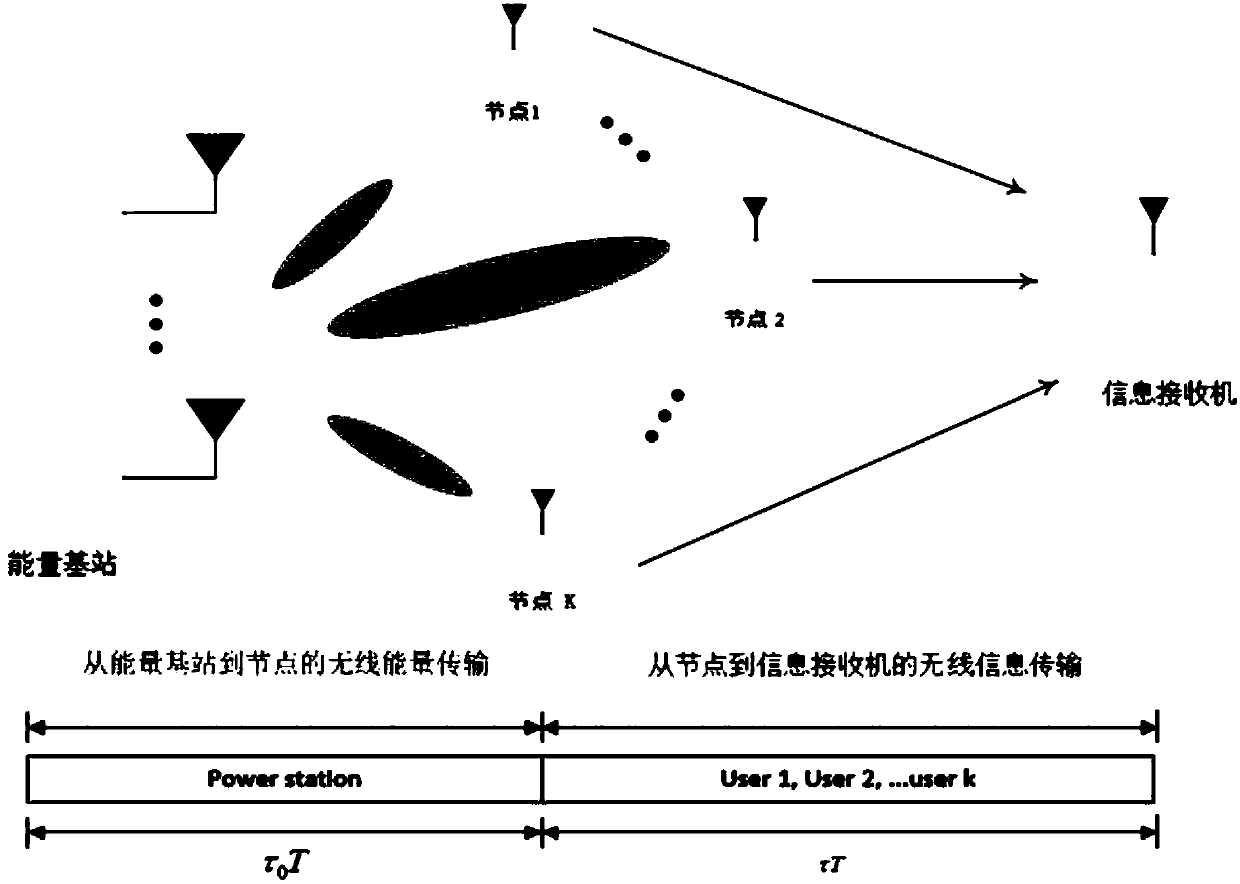
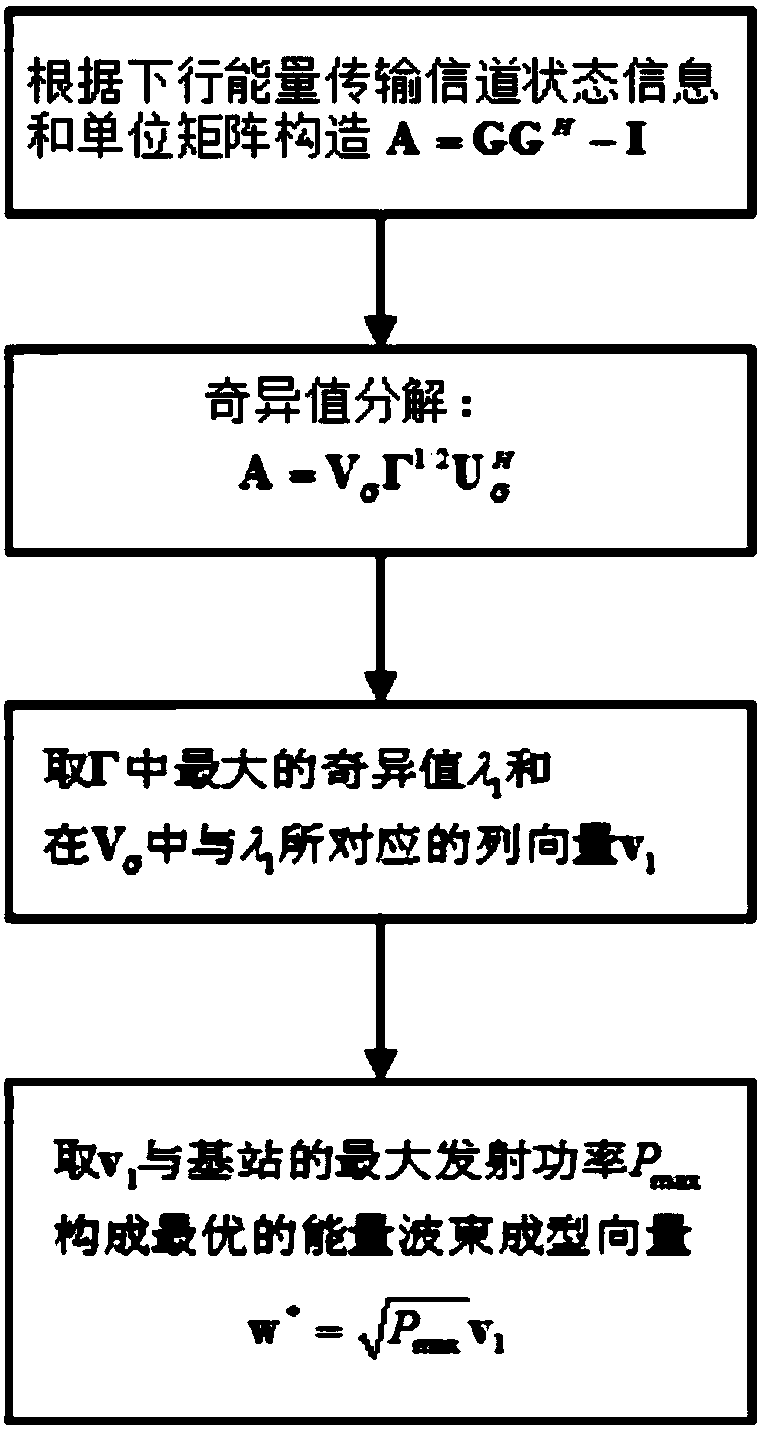
Wireless sensor networks resource allocation method based on wireless energy transmission
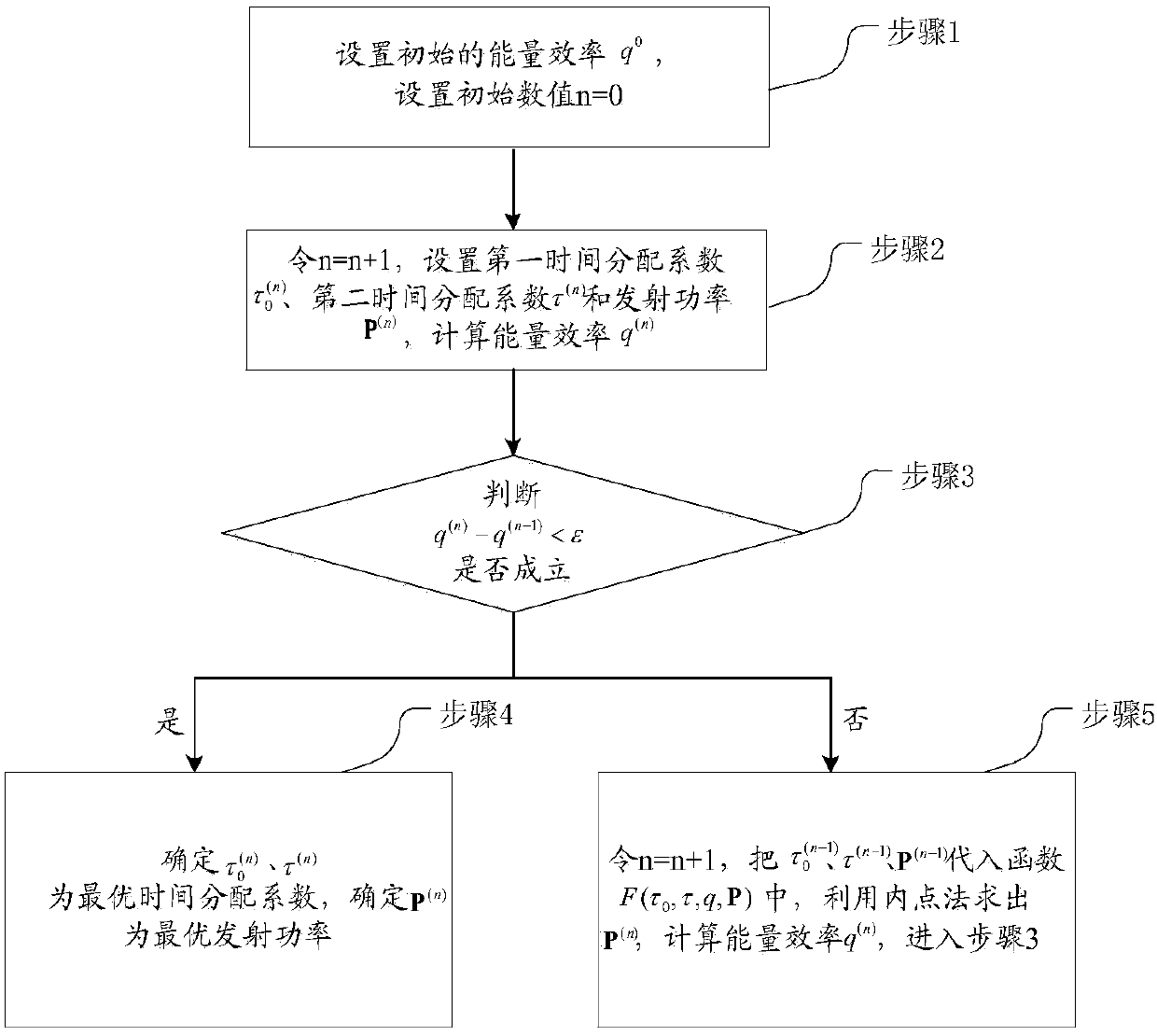
ActiveCN107613567ATake advantage ofImprove energy efficiencyWireless communicationCommunications systemInterior point method
The invention discloses a wireless sensor networks resource allocation method based on wireless energy transmission. The method is applied to a wireless energy carried transmission non-orthogonal multiple access communication system. The method comprises the steps of S1, setting initial energy efficiency q<0> and setting an initial numerical value n=0; S2, assuming that n is equal to n+1, settinga first time allocation coefficient tau<0><(n)>, a second time allocation coefficient tau<(n)> and a transmitting power p<(n)>, and calculating energy efficiency q<(n)>; S3, judging whether q<(n)>-q<(n-1)> is smaller than epsilon or not, if the q<(n)>-q<(n-1)> is smaller than the epsilon, entering a S4, otherwise, entering a S5, wherein the epsilon is an error threshold value; S4, determining thetau<0><(n)> and tau<(n)> as the optimum time allocation coefficients and determining the p<(n)> as the optimum transmitting power; and S5, assuming that the n is equal to n+1, substituting tau<0><(n-1)>, tau<(n-1)> and P<(n-1)> into a function F(tau<0>, tau, q, P), calculating the P<(n)> through utilization of an interior point method, calculating the energy efficient q<(n)>, and entering the S3.According to the method, the energy utilization efficiency is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Spectral clustering method for automatically determining number of clusters based on neighboring point method
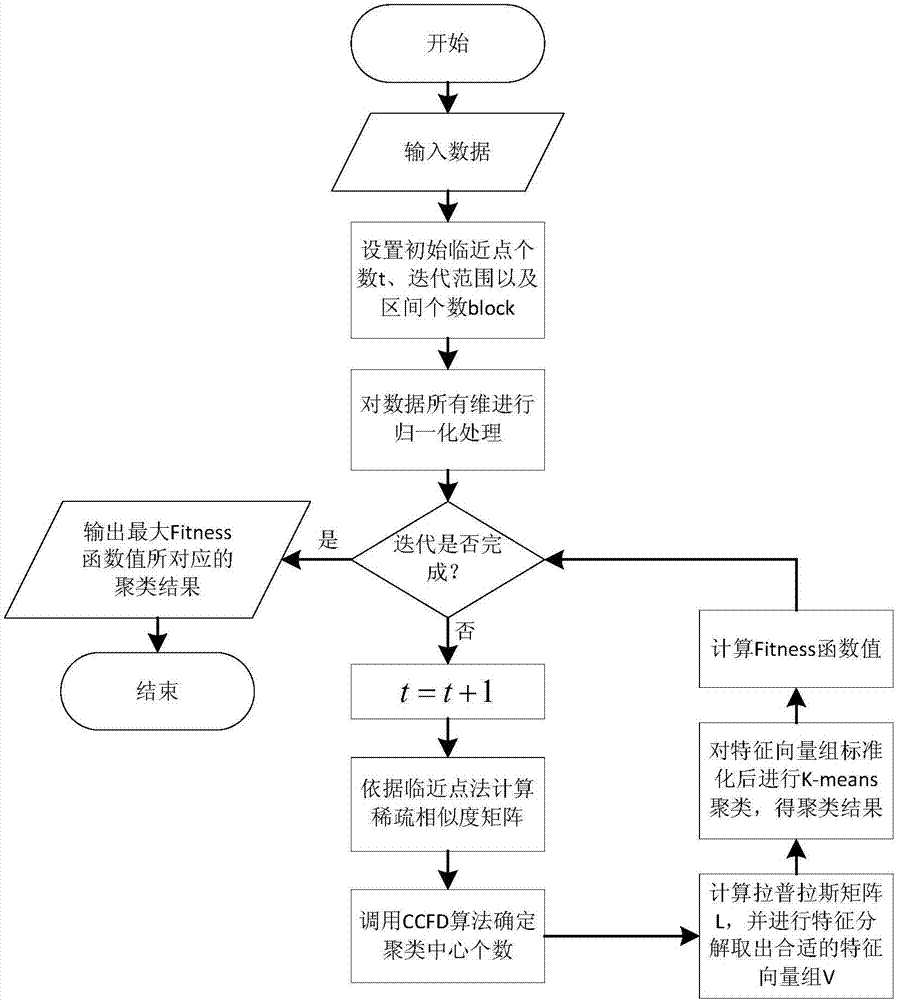
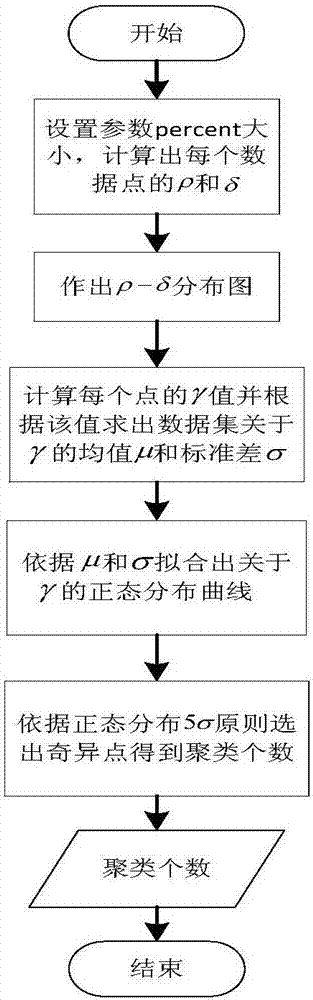
InactiveCN106991430AAchieve adaptiveQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionData setLocal scale
A spectral clustering method for automatically determining the number of clusters based on a neighboring point method comprises the steps of 1) normalizing all dimensions of a data set; 2) calculating an interval sparse distance matrix by a neighboring point method and defining the matrix as local scale parameters of distance mean values of the neighboring points to obtain a whole sparse similarity matrix; 3) determining the local density of each data point and the minimum distance to other points with a higher local density by calling a CCFD method, and obtaining the number of singular points generated by the fitting outside a confidence interval; 4) calculating a degree matrix D and a Laplacian matrix L according to a formula and extracting an eigenvector group by eigen decomposition of L; 5) outputting clustering results; and 6) selecting and outputting the clustering result with the optimal number of neighboring points corresponding to the maximum Fitness function value. According to the invention, the local scale parameter of each data point can be estimated according to data distribution, the number of clustering centers is automatically determined, and the parameter adaptation of the number of neighboring points is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Global reactive voltage optimization method for power transmission and distribution network
ActiveCN104319780ASolve power problemsImprove calculation accuracyAc network voltage adjustmentReactive power compensationElectric power transmissionInterior point method
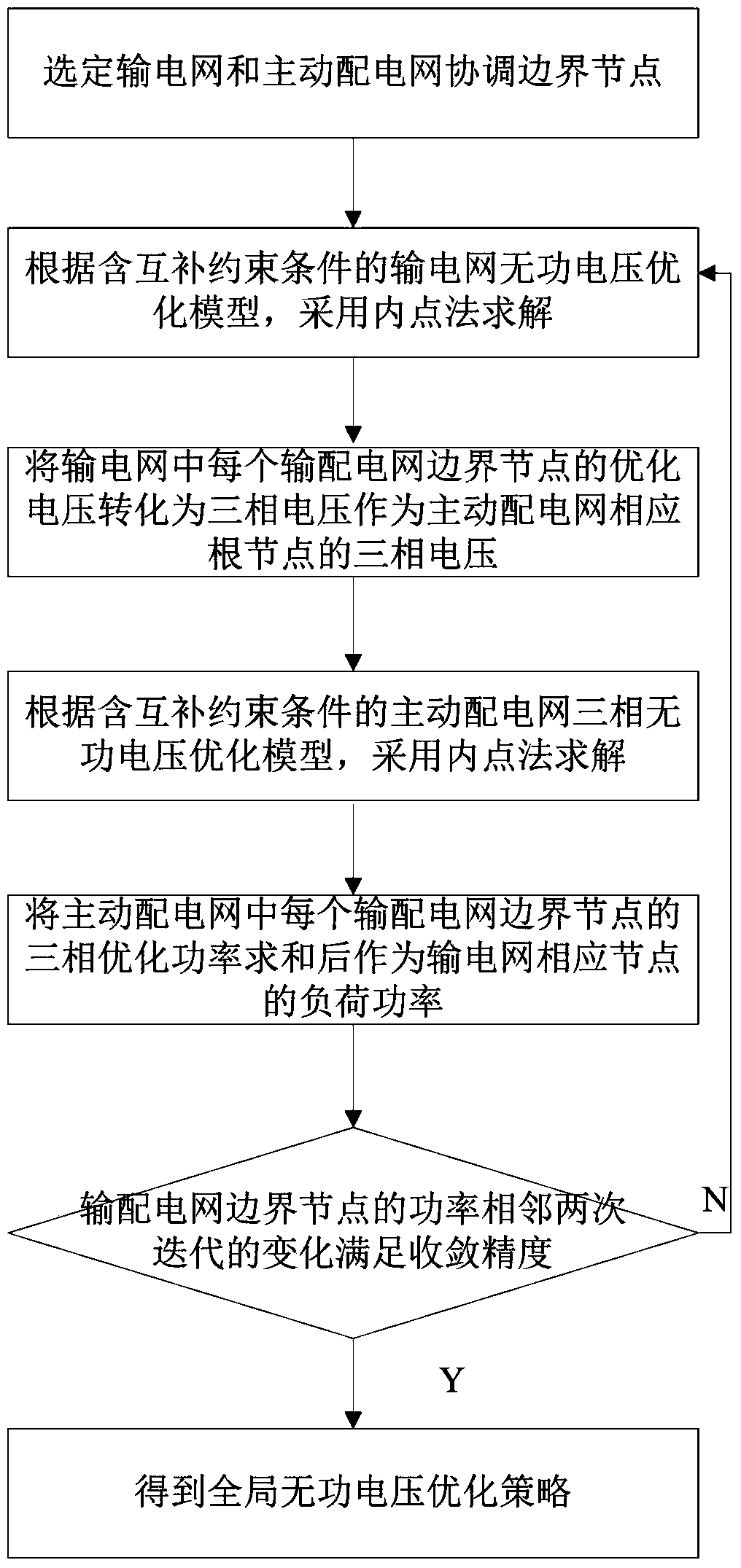
The invention relates to a global reactive voltage optimization method for a power transmission and distribution network. The method includes the steps that coordinate boundary points of a power transmission network and an active power distribution network are selected; a power transmission network reactive voltage optimization model including complementary constraints is established, and an interior point method is used for solving; the optimization voltage of the power transmission network is converted into a three-phase voltage which is used as the three-phase voltage of an active power distribution network root node; a three-phase reactive voltage optimization model including complementary constraints of the active power distribution network is established, and the interior point method is used for solving; the three-phase optimization power of the active power distribution network is summated and then is used as the corresponding load power of the power transmission network; reactive voltage optimization of the power transmission network and reactive voltage optimization of the active power distribution network are in alternate iteration, when every two adjacent iteration changes of the boundary point power of the power transmission and distribution network meet convergence precision, the global reactive voltage of the power transmission and distribution network is subjected to optimizing convergence, and accordingly a global reactive voltage optimizing strategy is obtained. The problem that the reactive voltage optimization results of the power transmission and distribution network are inconsistent at the boundary points of the power transmission and distribution network can be solved, voltage and power mismatching at the boundary points is eliminated, and reactive resources of the two stages of networks are optimized.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com