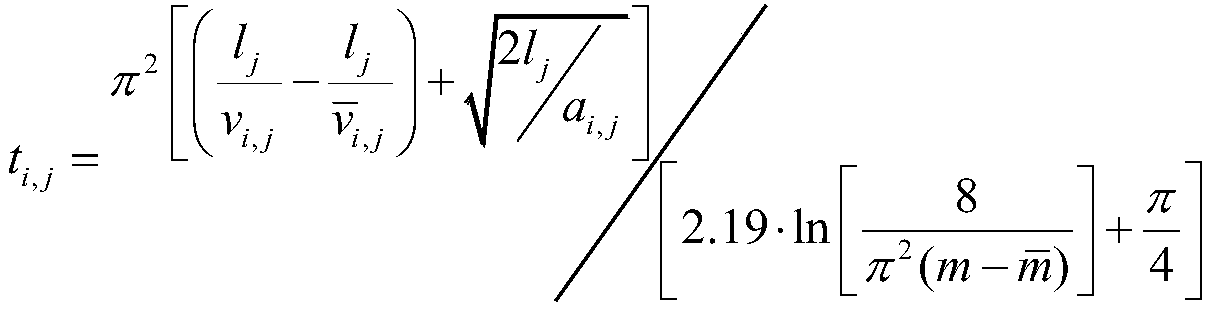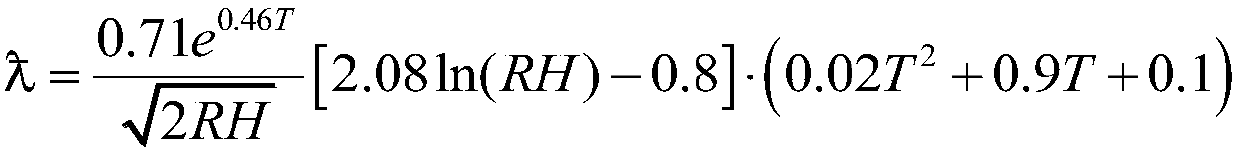Patents
Literature
68 results about "Local congestion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Unordered multi-path routing in a pcie express fabric environment
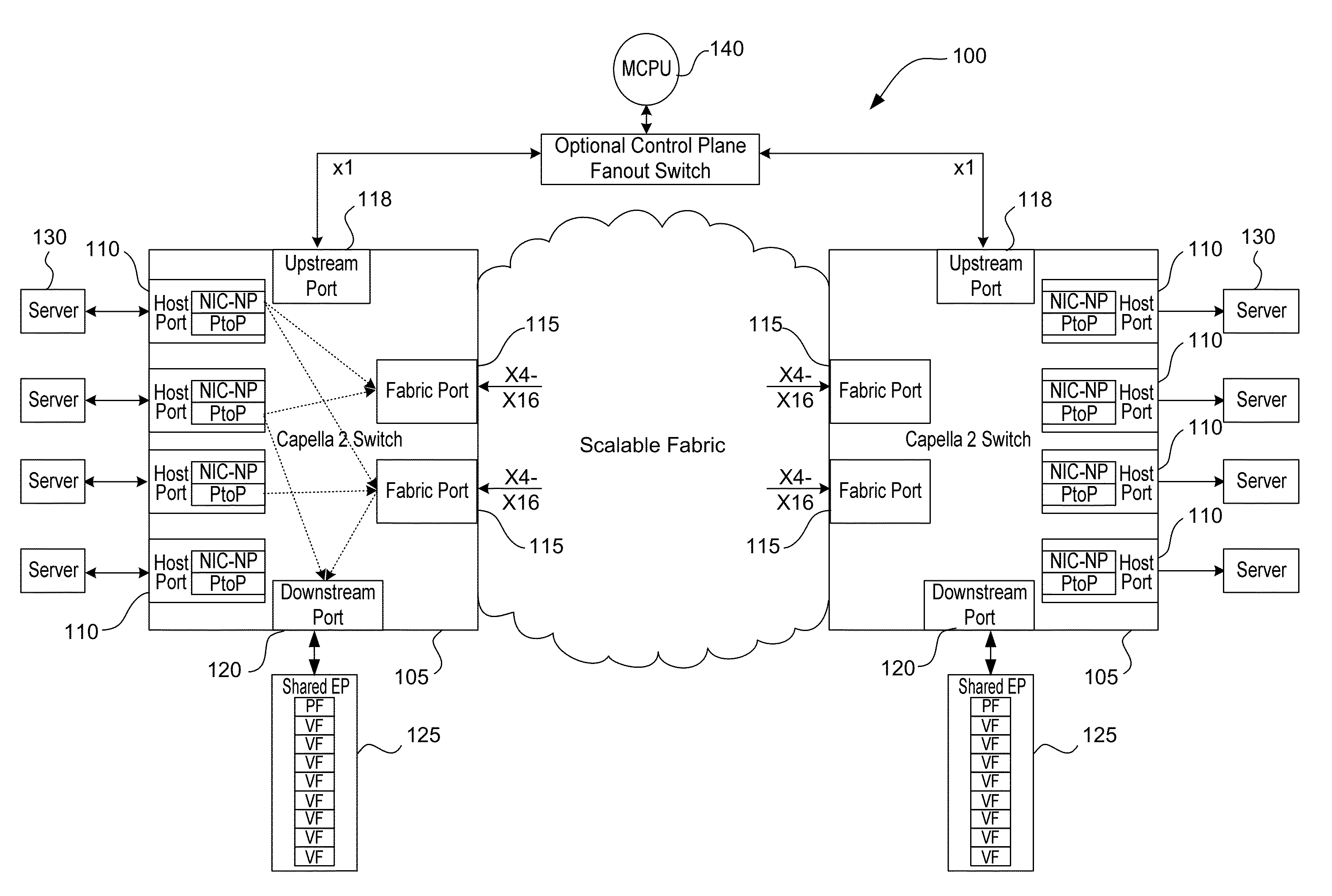
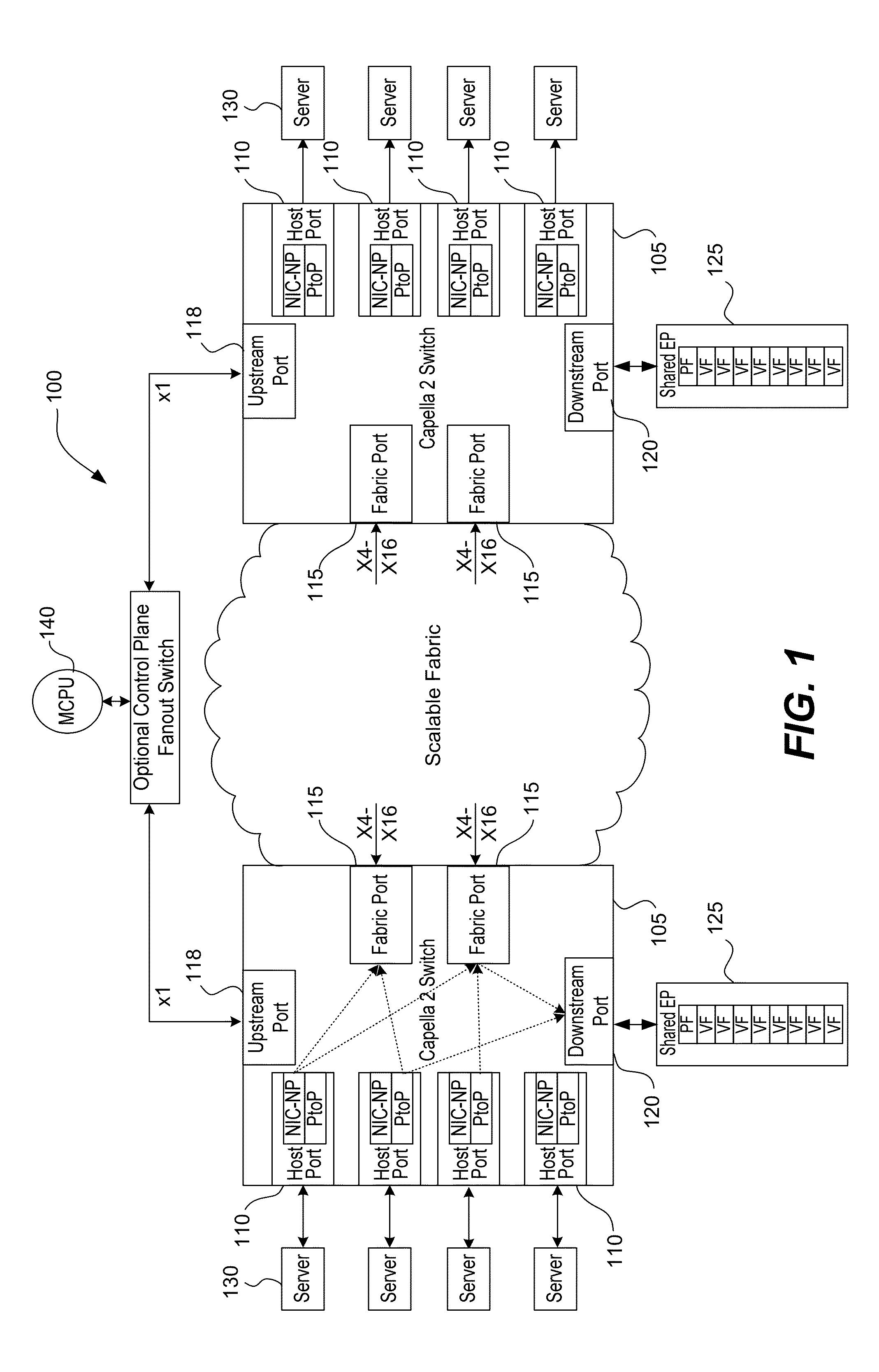
A method of providing unordered packet routing in a multi-path PCIe switch fabric is provided. Fabric egress port congestion is measured and distributed to all ports within a switch and to neighboring switches. An unordered route choice vector is generated by table lookup. The local congestion mask vector identifies which of these choices has local congestion. A next hop masked choice vector generated by table lookup is gated with the next hop congestion mask vectors, received from neighboring switches, to identify the choices that have next hop congestion. Congested choices are excluded by masking. If multiple choices remain at the conclusion of the masking process, then a selection is made by round-robin among the surviving choices. If no choices remain, the selection is made by round robin among the original choices. The final selection is mapped to an egress port on the switch by table lookup.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
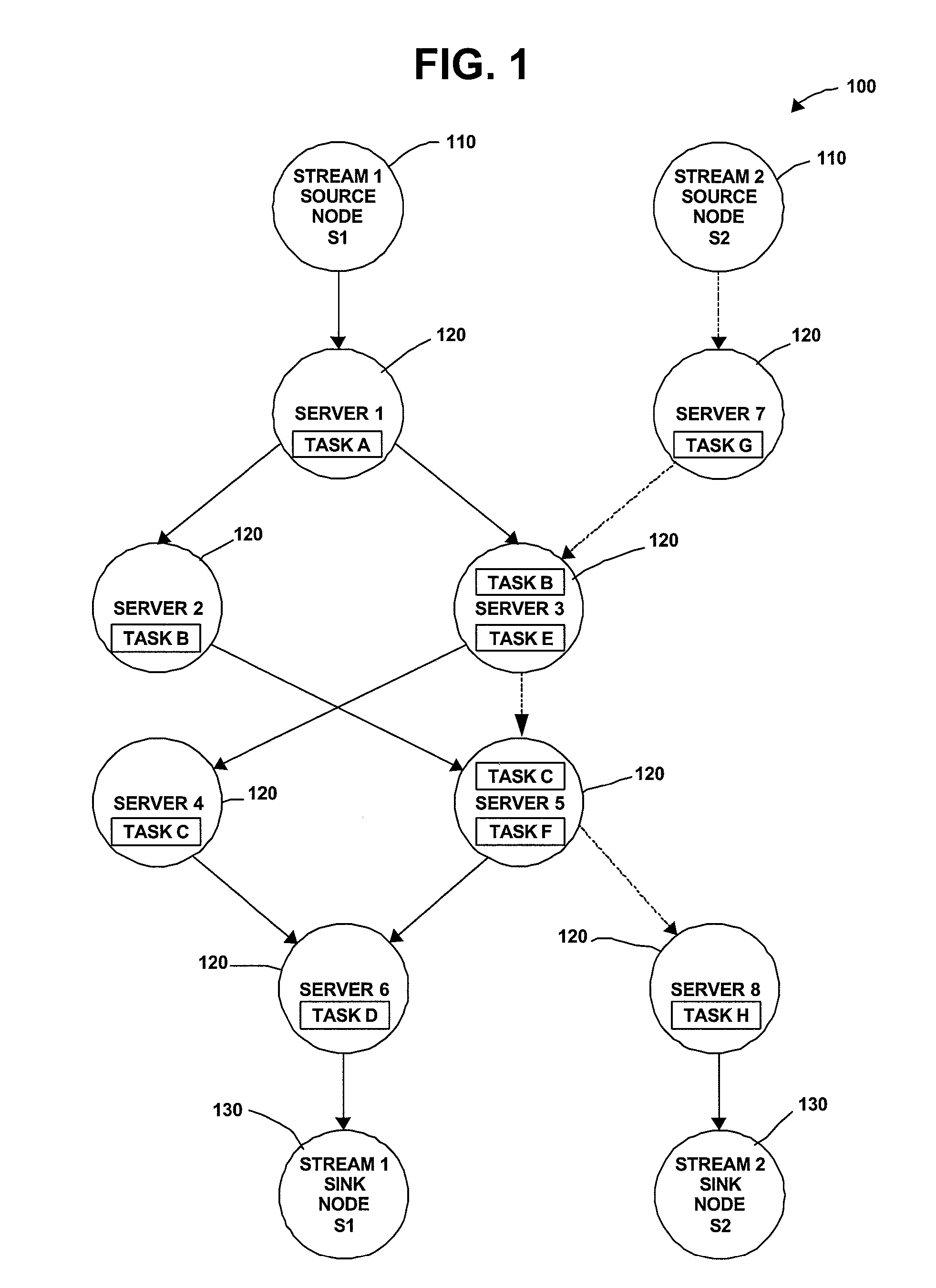
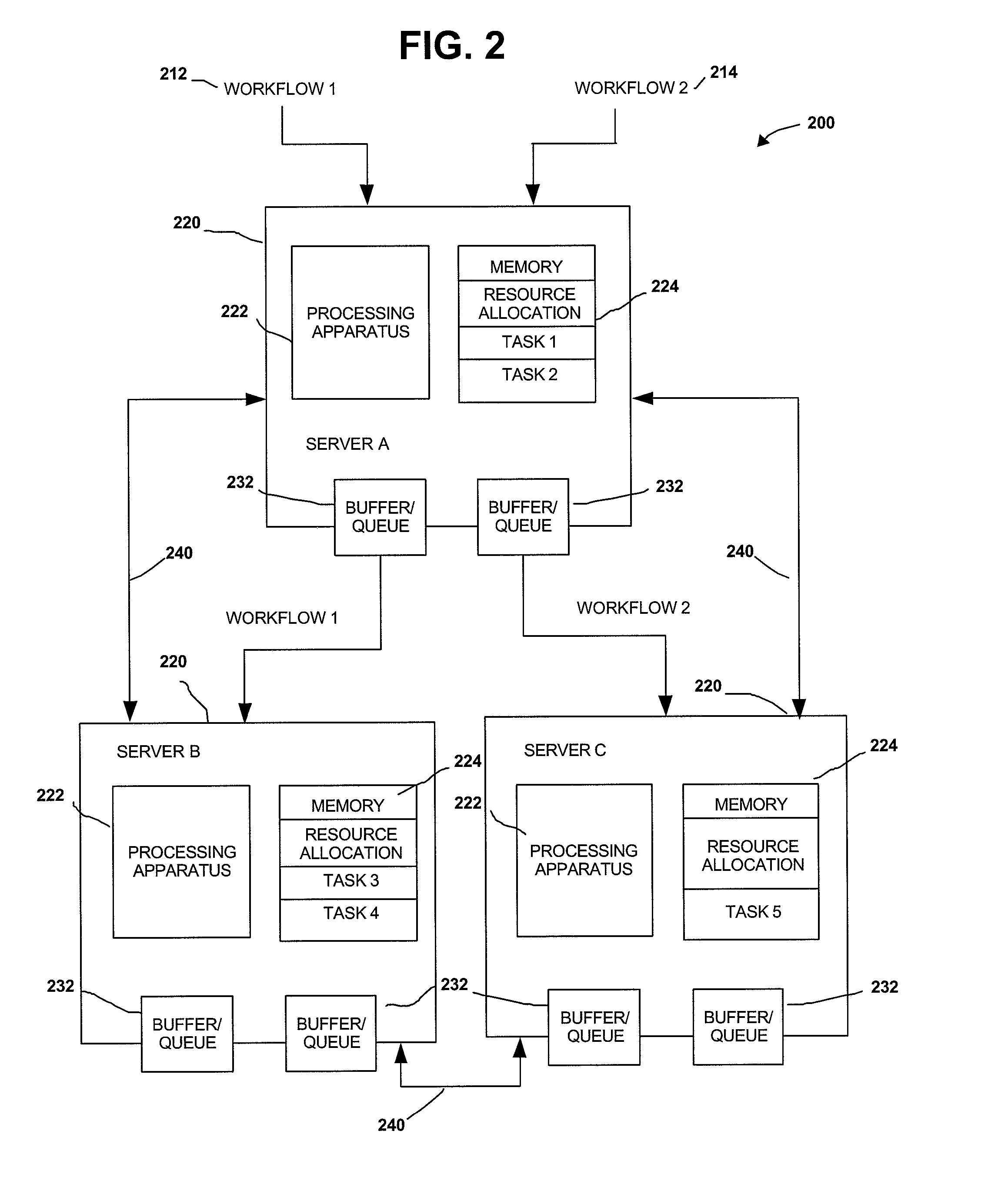
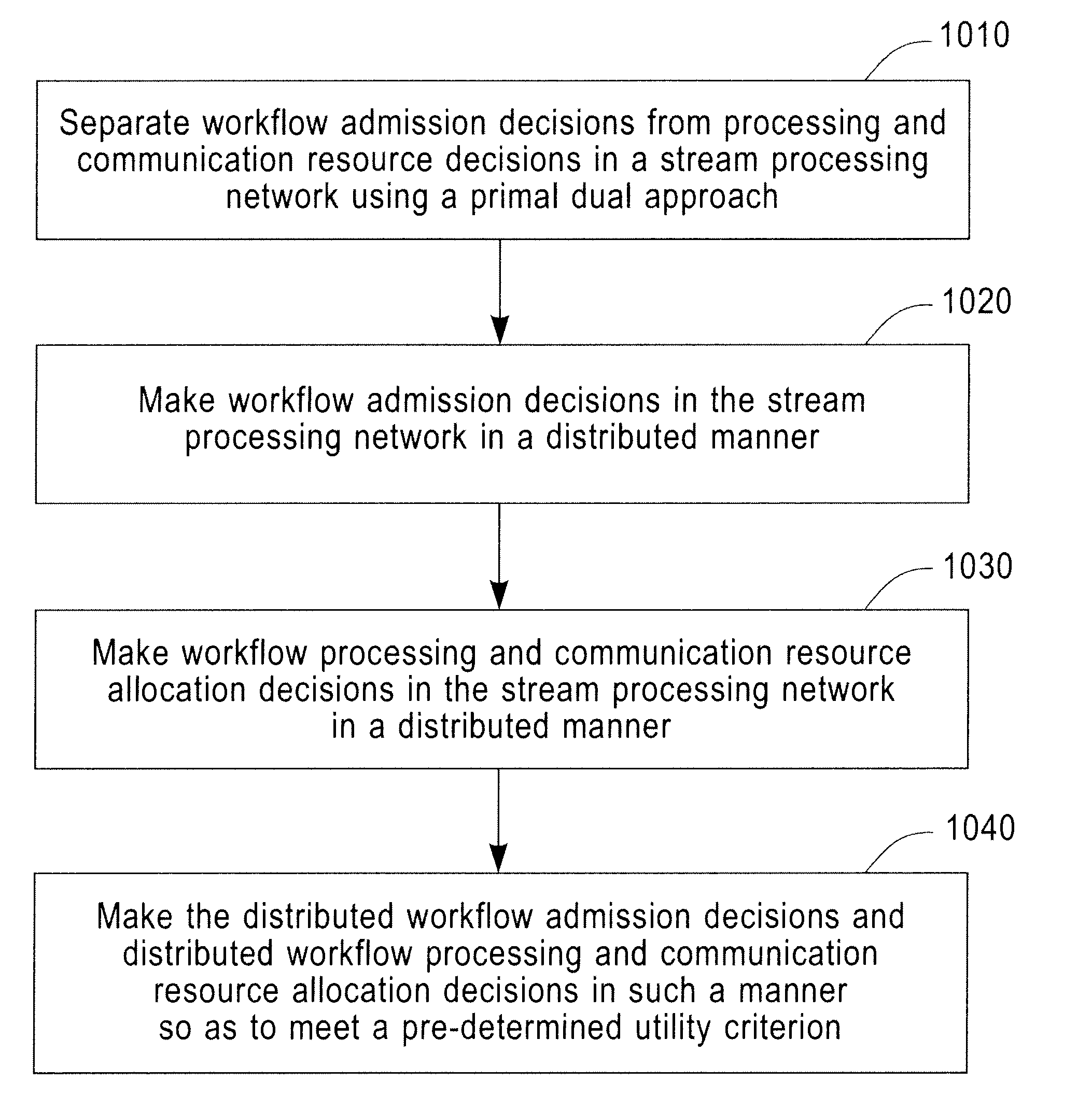
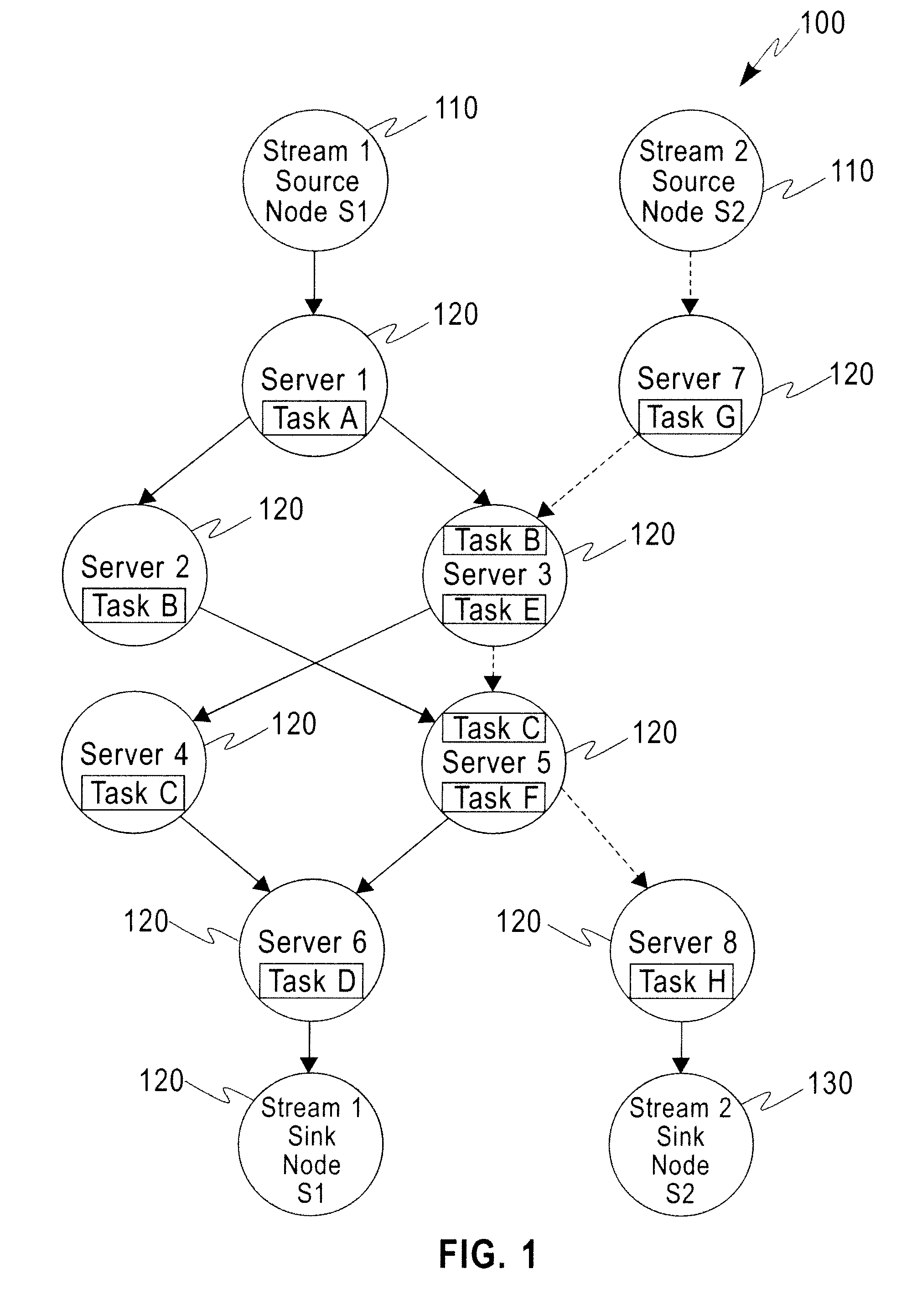
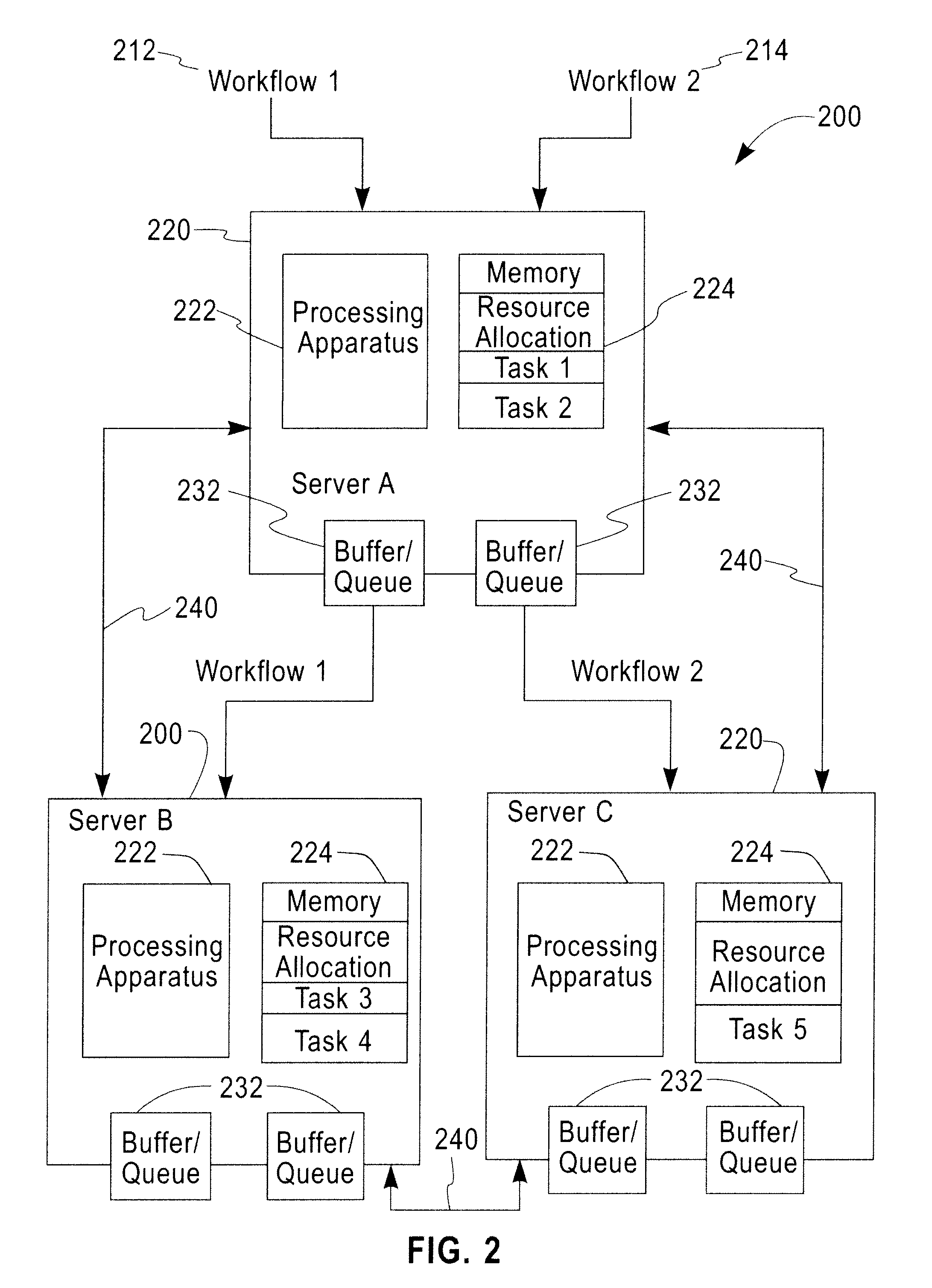
Distributed Joint Admission Control And Dynamic Resource Allocation In Stream Processing Networks
InactiveUS20080304516A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLocal congestionDynamic resource
Methods and apparatus operating in a stream processing network perform load shedding and dynamic resource allocation so as to meet a pre-determined utility criterion. Load shedding is envisioned as an admission control problem encompassing source nodes admitting workflows into the stream processing network. A primal-dual approach is used to decompose the admission control and resource allocation problems. The admission control operates as a push-and-pull process with sources pushing workflows into the stream processing network and sinks pulling processed workflows from the network. A virtual queue is maintained at each node to account for both queue backlogs and credits from sinks. Nodes of the stream processing network maintain shadow prices for each of the workflows and share congestion information with neighbor nodes. At each node, resources are devoted to the workflow with the maximum product of downstream pressure and processing rate, where the downstream pressure is defined as the backlog difference between neighbor nodes. The primal-dual controller iteratively adjusts the admission rates and resource allocation using local congestion feedback. The iterative controlling procedure further uses an interior-point method to improve the speed of convergence towards optimal admission and allocation decisions.
Owner:IBM CORP
Congestion control and QOS in noc by regulating the injection traffic
Systems and methods described herein are directed to solutions for NoC interconnects that provide congestion avoidance and end-to-end uniform and weighted-fair allocation of resource bandwidths among various contenders in a mesh or torus interconnect. The example implementations are fully distributed and involve using explicit congestion notification messages or local congestion identification for congestion detection. Based on the congestion level detected, the injection rates of traffic at various agents are regulated that avoids congestion and also provides end-to-end QoS. Alternative example implementations may also utilize end-to-end credit based flow control between communicating agents for resource and bandwidth allocation of the destination between the contending sources. The resource allocation is performed so that both the weighted and strict bandwidth allocation QoS policies are satisfied.
Owner:INTEL CORP
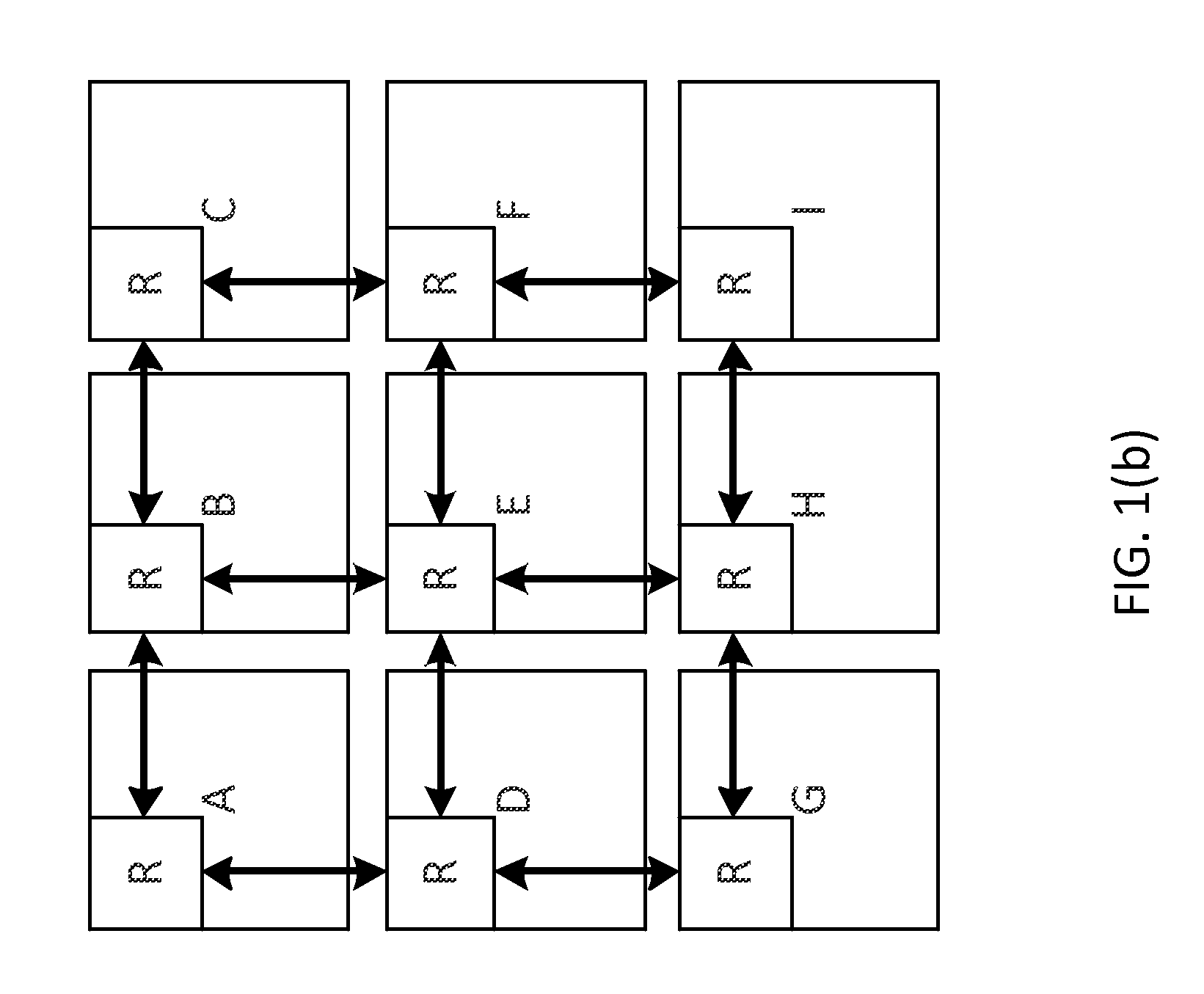
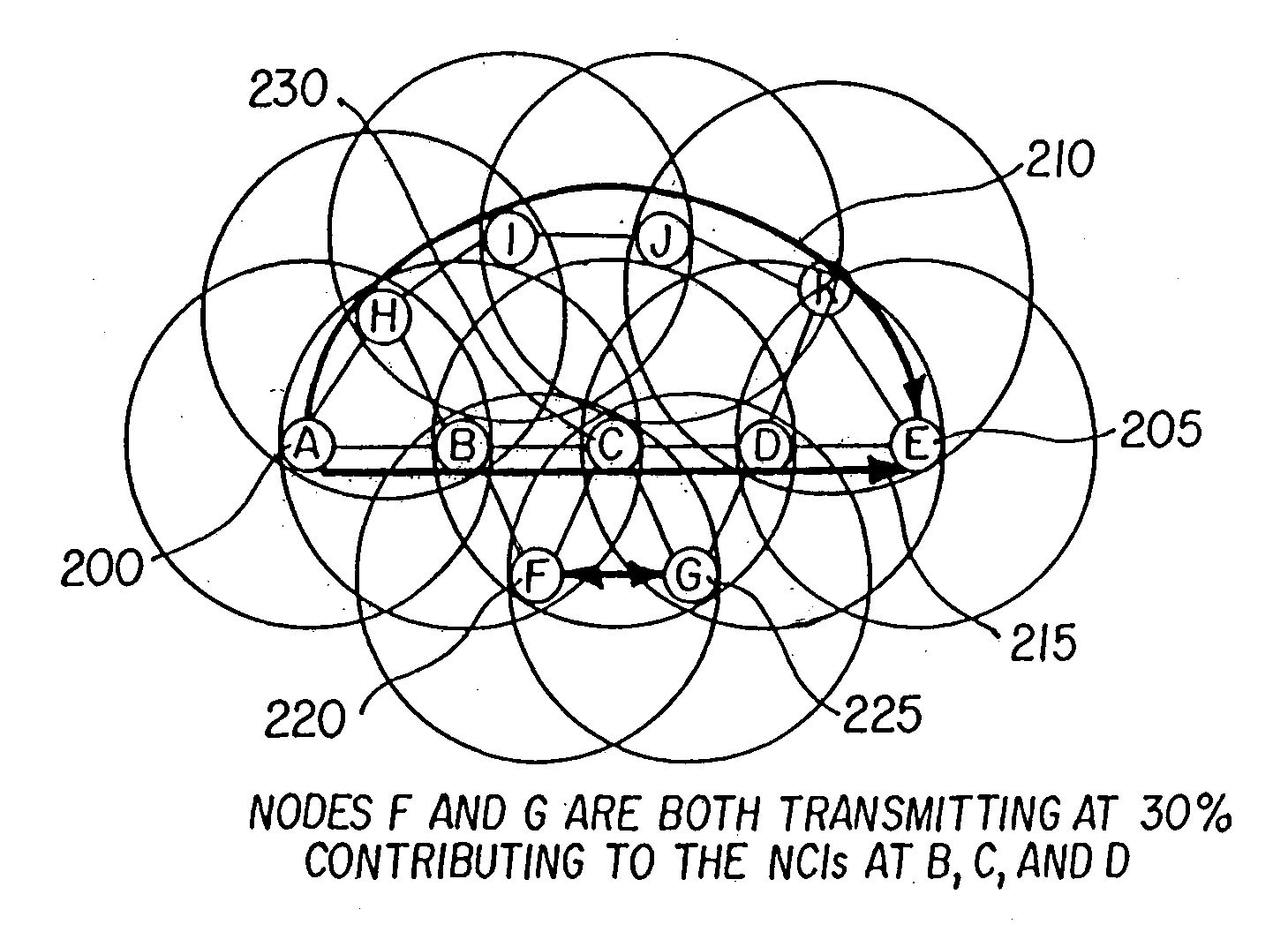
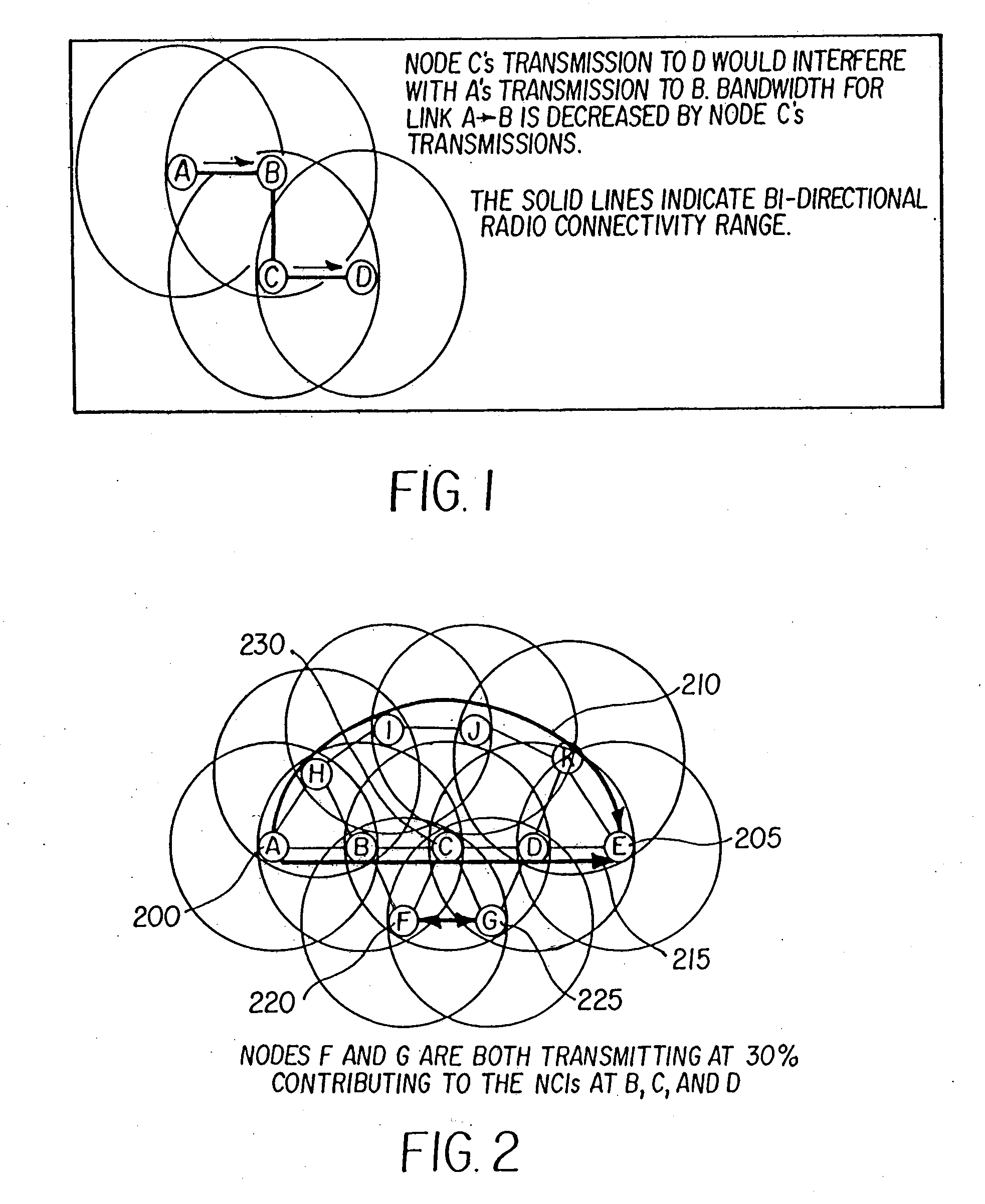
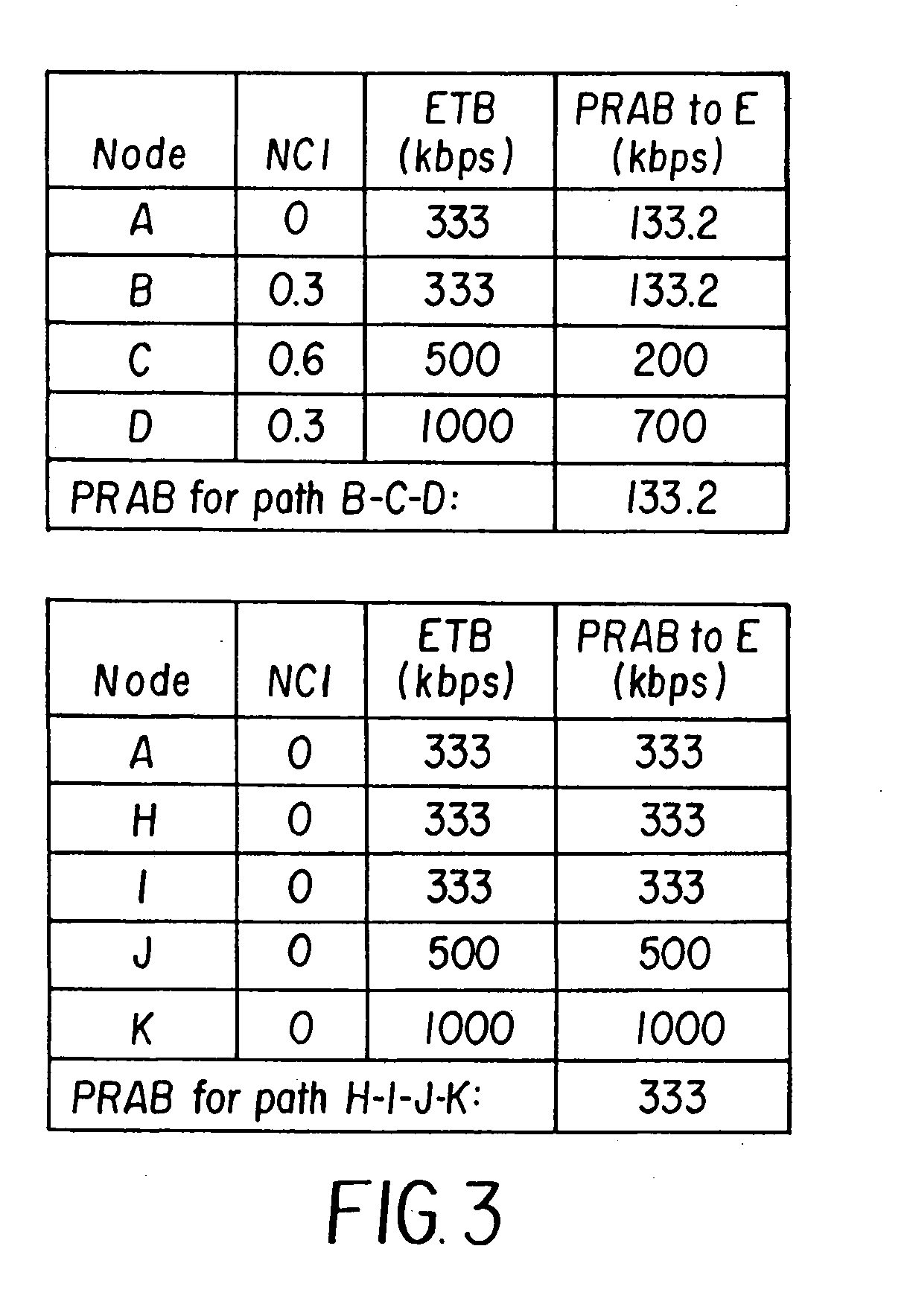
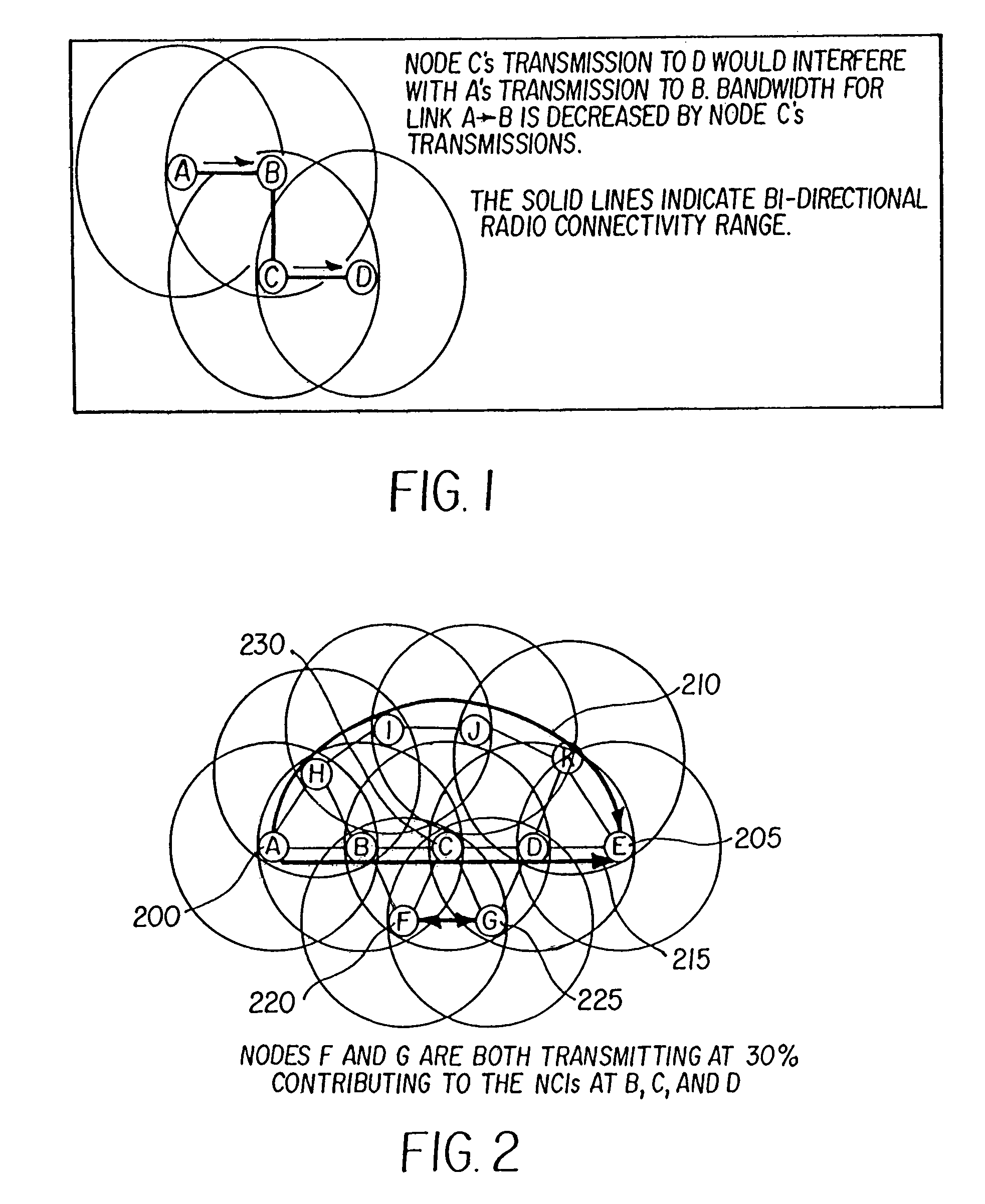
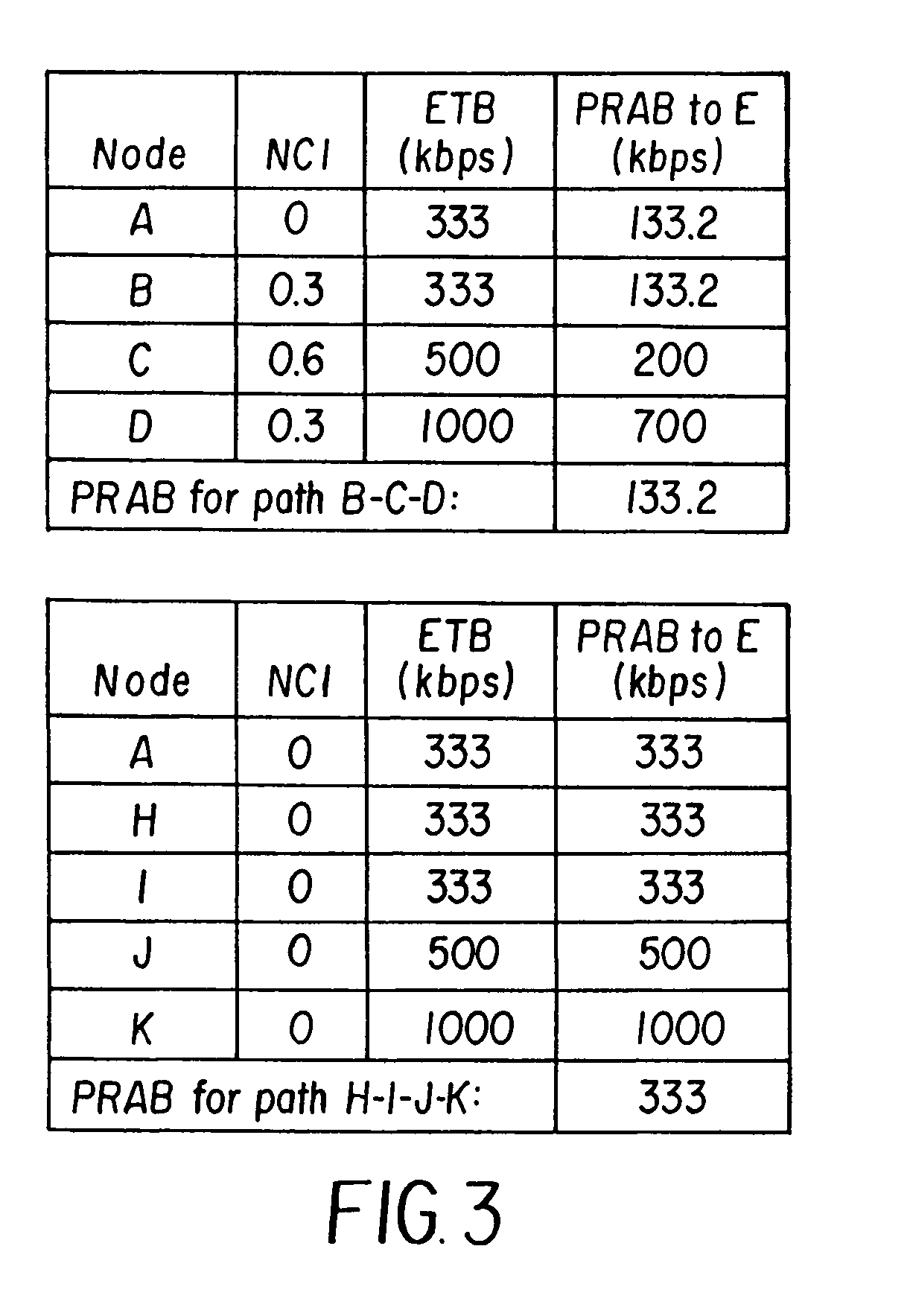
INTEGRATING LOCAL CONGESTION AND PATH INTERFERENCE INTO QoS ROUTING FOR WIRELESS MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
A method and apparatus is provided for using a distributed multi-path QoS-aware routing scheme that considers basic MANET characteristics to meet transport service requirements of real-time applications and makes use of multiple discovered paths to calculate a next-hop decision. The QoS Routing scheme superimposes distributed neighborhood congestion, neighborhood density, and link stability and delay information over the multiple discovered paths when the next-hop decision is calculated.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
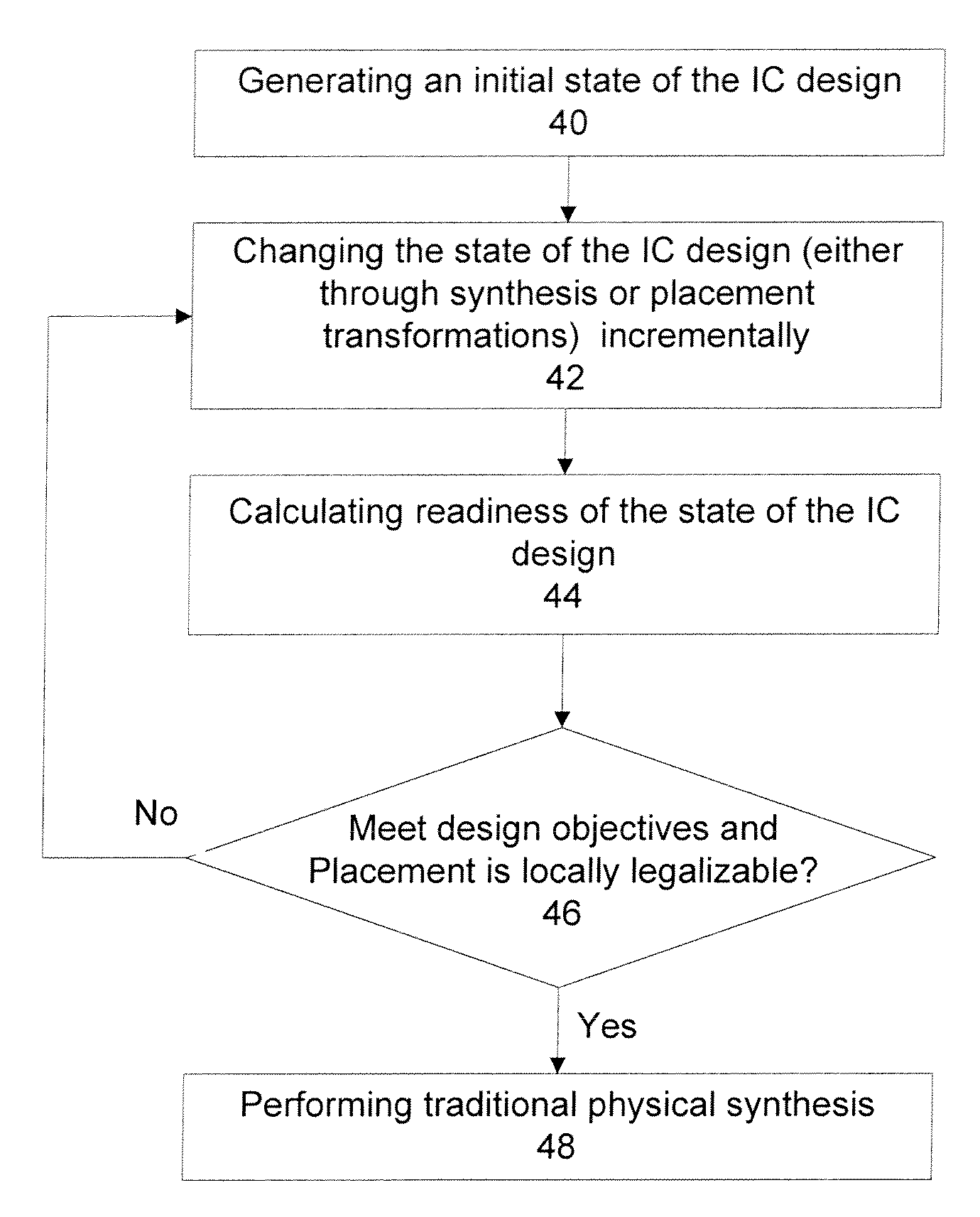
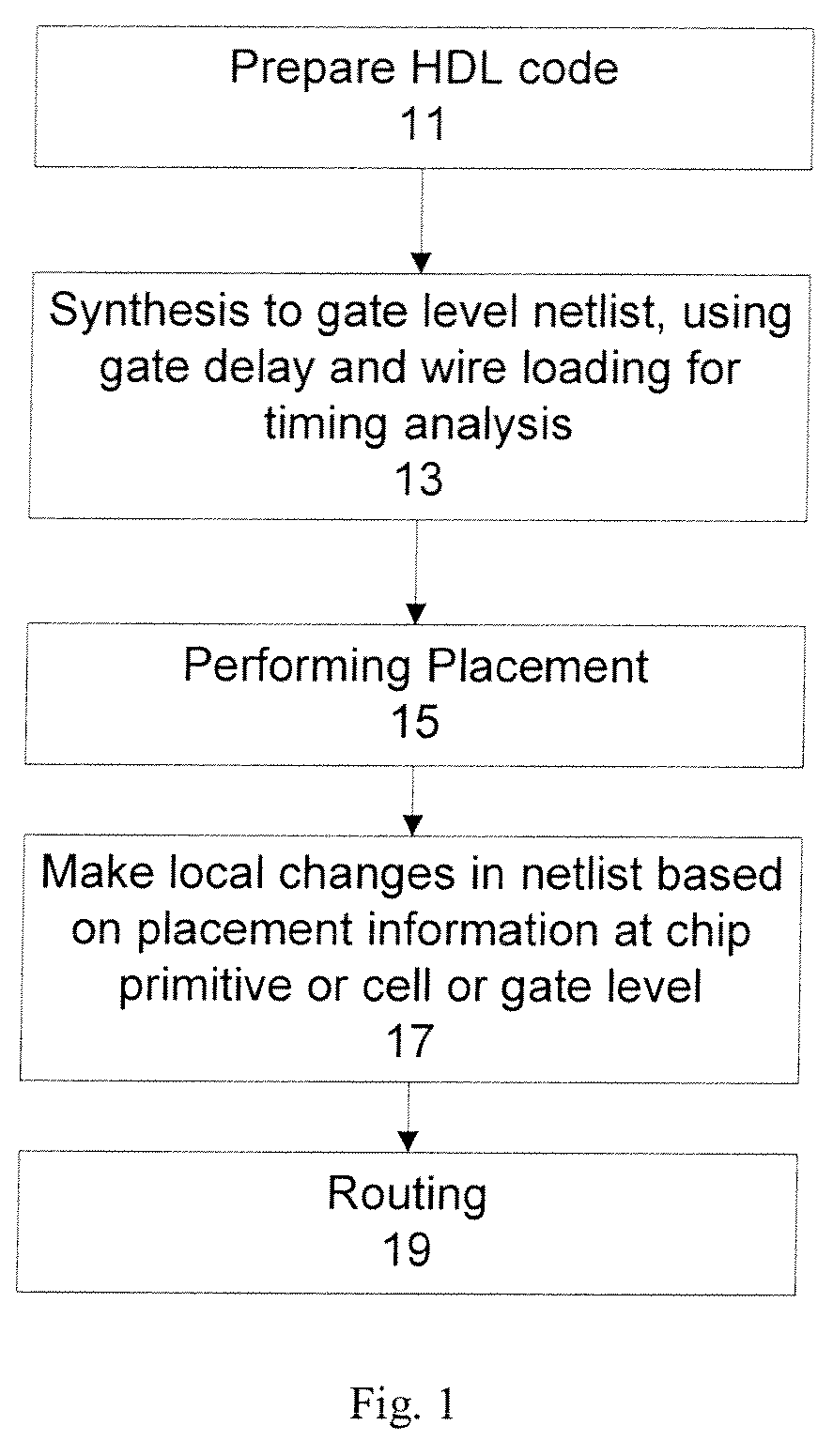
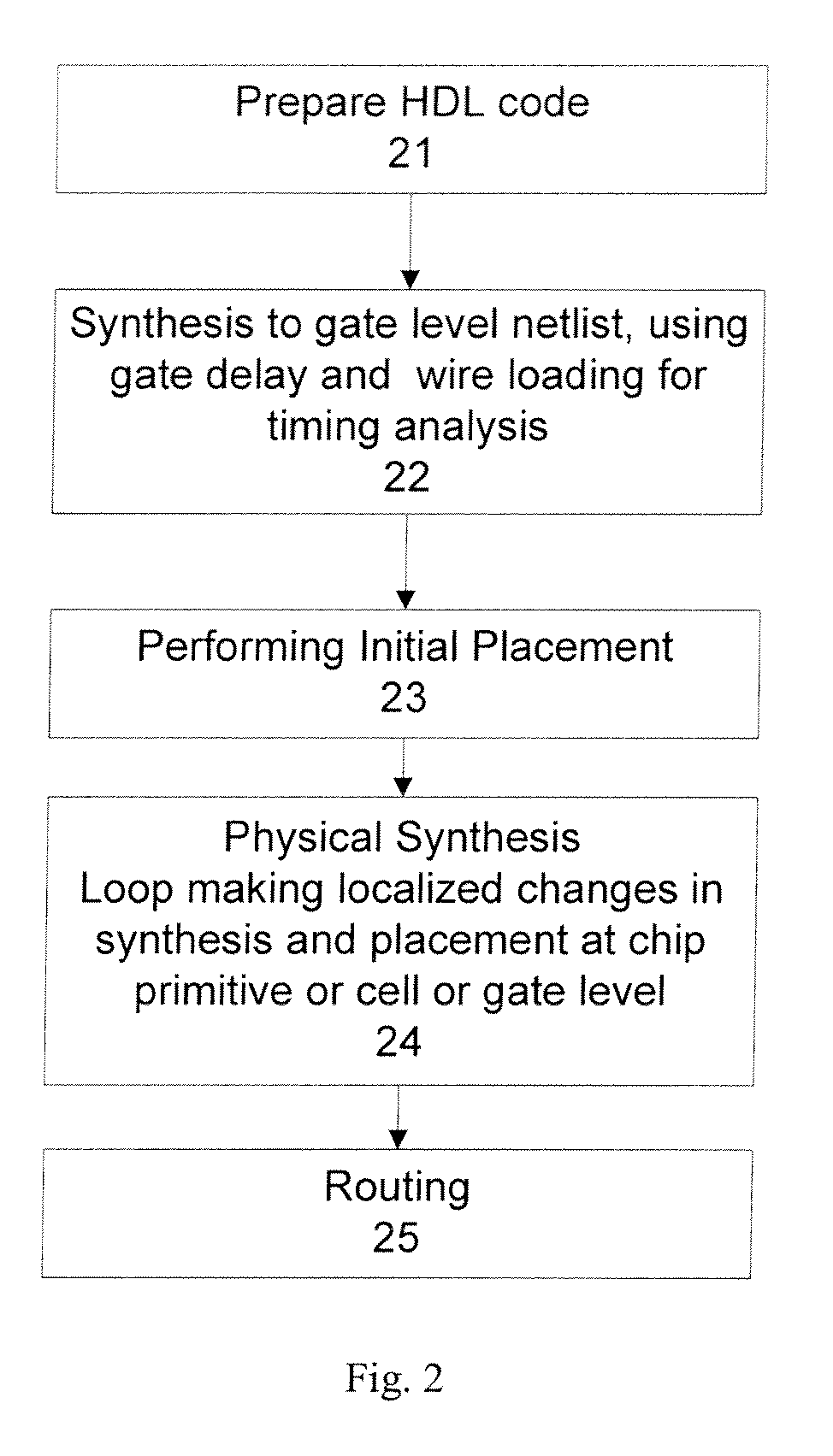
Architectural physical synthesis
ActiveUS20090031278A1Quality improvementEasy to placeComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsLocal congestionResource utilization
The present invention discloses methods and apparatuses to design an integrated circuit. According to one aspect, the present invention circuit design discloses an iterative process of synthesis and placement where each iteration provides incremental changes on the design of the integrated circuit. The incrementally iterative approach of the present invention provides a continuous advancement from synthesis to placement and vice versa, with the incremental improvements on synthesis made with knowledge of current instance placement, and the incremental improvements on placement made with knowledge of current circuit logic. According to another aspect, the present invention circuit design discloses incremental force directed placement transforms utilizing resource layers to address the heterogeneous resource distribution problem, where the force on an instance can be a weighted average of the forces from its resource layers based on the local congestion of those resources. In addition, incremental area removal method can be utilized to address resource utilization problem through a quality metric based on force directed placement transforms, such as a resource demand topological mapping.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Integrating local congestion and path interference into QoS routing for wireless mobile AD HOC networks
A method and apparatus is provided for using a distributed multi-path QoS-aware routing scheme that considers basic MANET characteristics to meet transport service requirements of real-time applications and makes use of multiple discovered paths to calculate a next-hop decision. The QoS Routing scheme superimposes distributed neighborhood congestion, neighborhood density, and link stability and delay information over the multiple discovered paths when the next-hop decision is calculated.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Congestion control and QoS in NoC by regulating the injection traffic
Systems and methods described herein are directed to solutions for NoC interconnects that provide congestion avoidance and end-to-end uniform and weighted-fair allocation of resource bandwidths among various contenders in a mesh or torus interconnect. The example implementations are fully distributed and involve using explicit congestion notification messages or local congestion identification for congestion detection. Based on the congestion level detected, the injection rates of traffic at various agents are regulated that avoids congestion and also provides end-to-end QoS. Alternative example implementations may also utilize end-to-end credit based flow control between communicating agents for resource and bandwidth allocation of the destination between the contending sources. The resource allocation is performed so that both the weighted and strict bandwidth allocation QoS policies are satisfied.
Owner:INTEL CORP
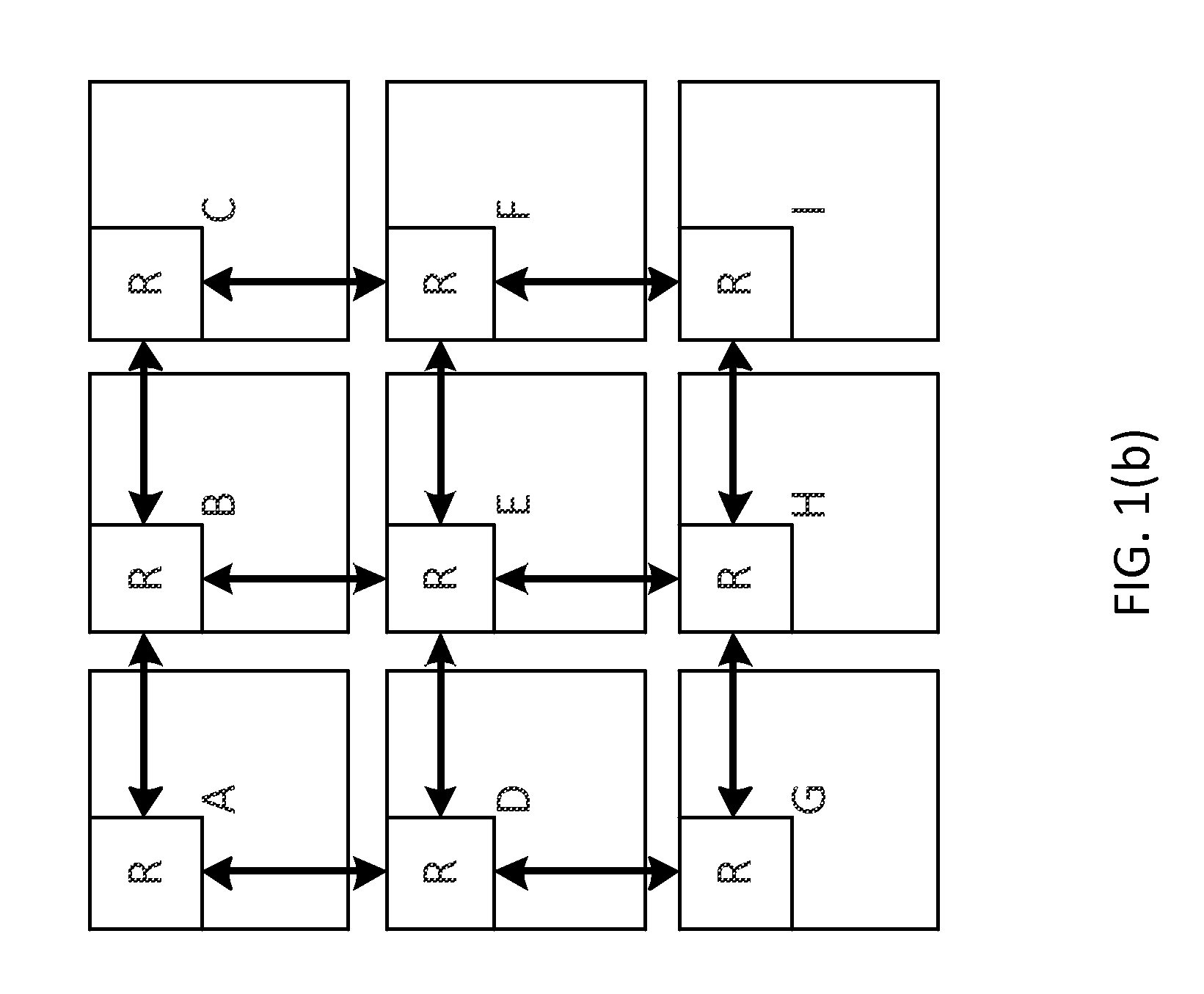
Local congestion-avoidance method in wireless personal area network
InactiveUS20070129081A1Avoid congestionNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsLocal congestion
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Programmed controllable infant jaundice treatment bed
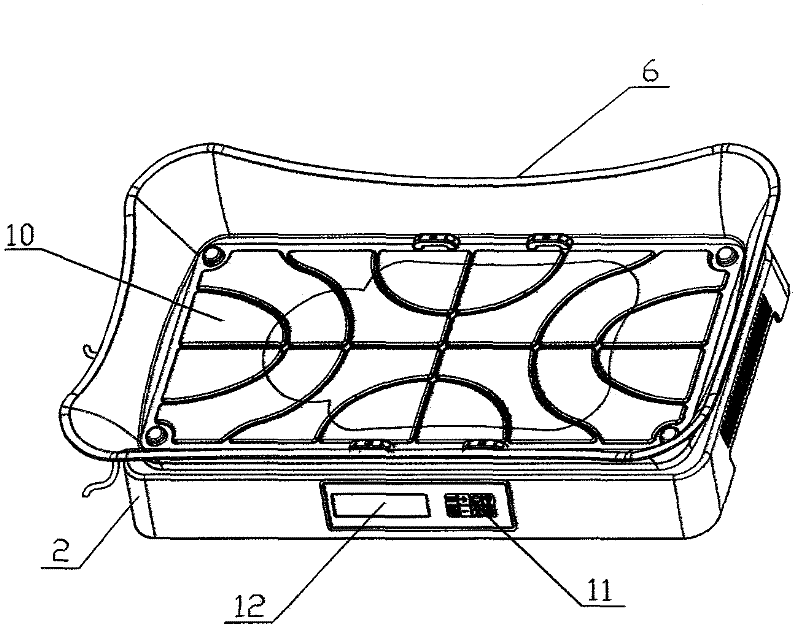
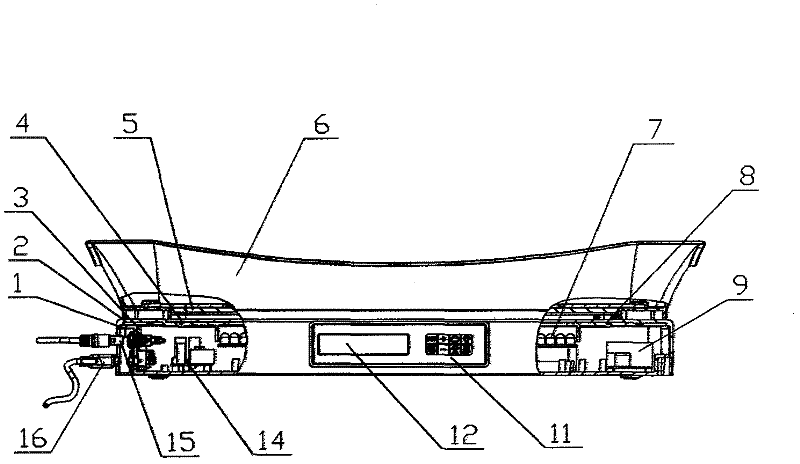
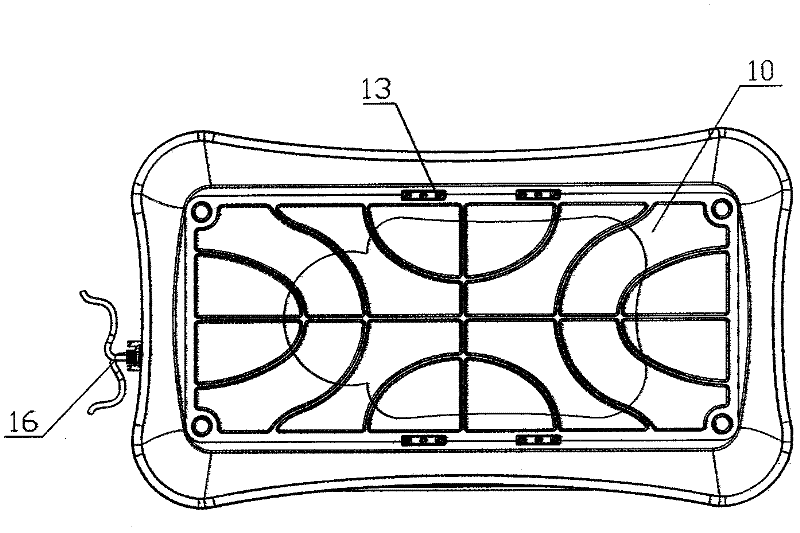
ActiveCN102327671ACompact structureSimple structureNursing bedsLight therapyTreatment effectSide effect
The invention discloses a programmed controllable infant jaundice treatment bed which comprises an infant tray having a basin-shaped structure and an LED (light-emitting diode) luminescent plate arranged below the infant tray, wherein the LED luminescent plate comprises a plurality of blue light LEDs which are distributed according to subregions of the orthographic projection shape of an infant body under a prone position state, and the working states of the blue light LEDs are controlled by an intelligent module; light emitted by the LED luminescent plate is projected to the bottom surface of the infant tray having a transparent structure so as to form an irradiation treatment surface; and the intelligent module is respectively connected with a display unit and an operation panel. The programmed controllable infant jaundice treatment bed has a simple and beautiful structure, and is convenient to operate and maintain; the blue light irradiation intensity can be subjected to step control; and by combining light irradiation region and intensity and timing control and being matched with a visual man-machine interaction interface, the programmed controllable infant jaundice treatment bed can realize programmable control and create multiple treatment modes, thereby achieving a good treatment effect. Meanwhile, a high molecular elastic transparent cushion can provide a comfortable sprawl posture for an infant and relieve local congestion and pressing pain and other side effects.
Owner:SUZHOU BEING MEDICAL DEVICES
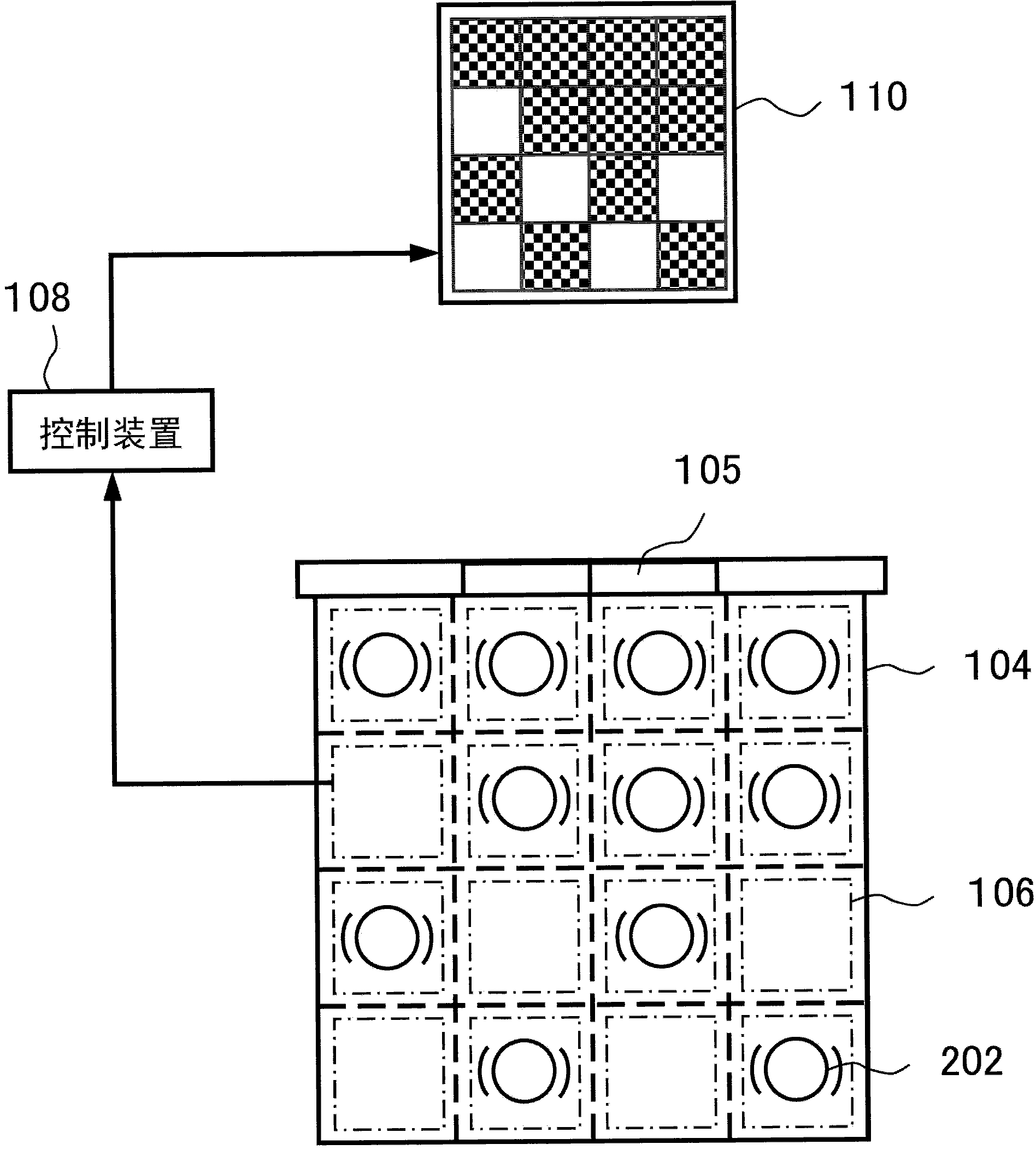
Elevator device
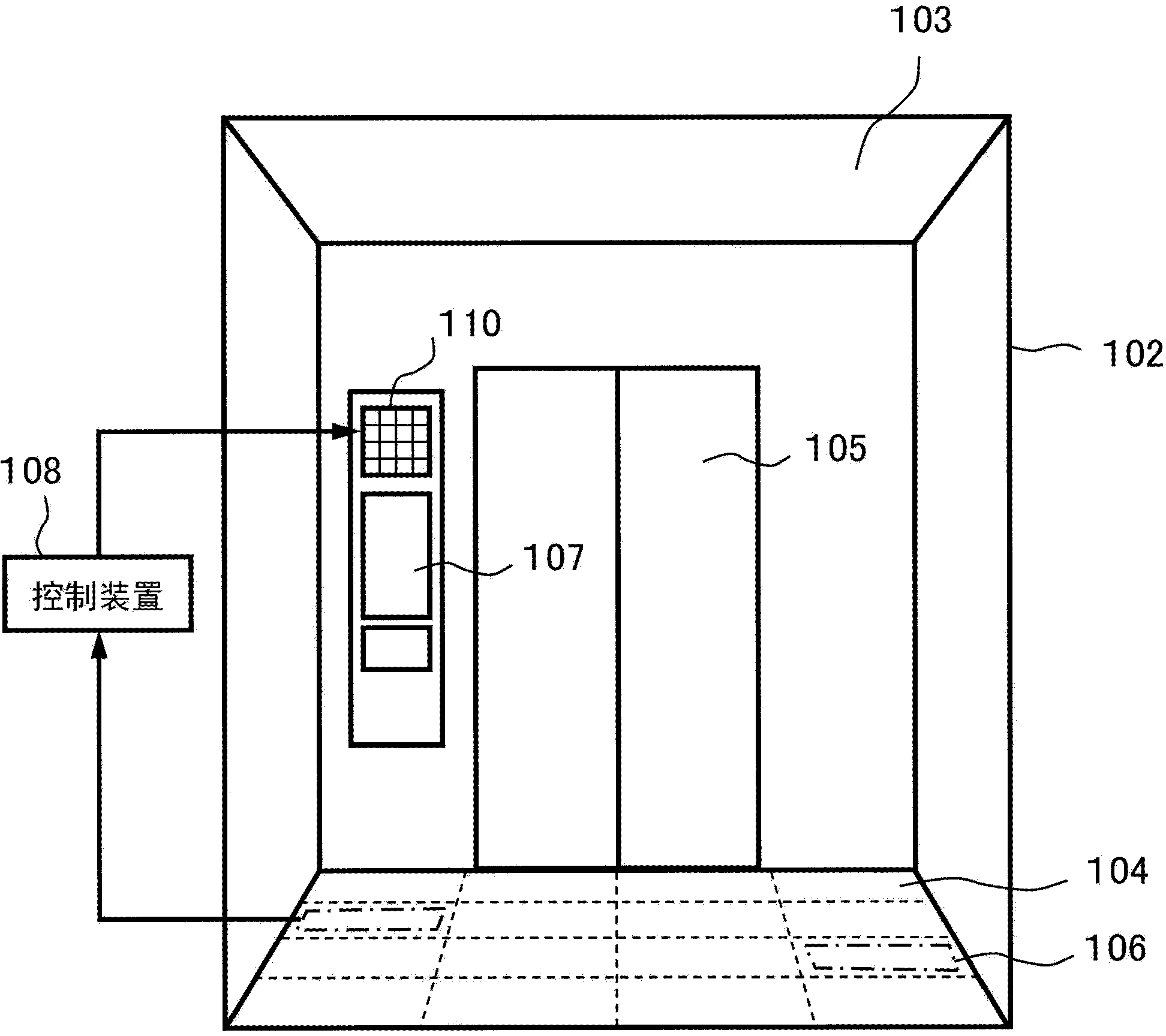
InactiveCN104276468AImprove the situation of congregation at the entrance of the carImprove delivery efficiencyElevatorsLocal congestionDisplay device
The invention relates to an elevator device. The elevator device comprises a lift car (102) for carrying passengers, a control device (108), position detecting devices (106) and an available position displaying device (110). The control device (108) is used for controlling all components of the elevator device. The position detecting devices are used for detecting the positions of the passengers inside the lift car, and the control device judges the available position inside the lift car based on detecting results of the position detecting devices. The available position displaying device is used for displaying the available position inside the lift car based on an instruction of the control device. Because the elevator device can display the available position inside the lift car for the passengers and guide the passengers to move to the available position, the condition that the passengers gather at an entrance of the lift car can be improved, more passengers can take the elevator, the carrying efficiency of the elevator is improved, the local congestion condition inside the lift car can be improved, and the passengers take the elevator comfortably.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Distributed Joint Admission Control and Dynamic Resource Allocation in Stream Processing Networks
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
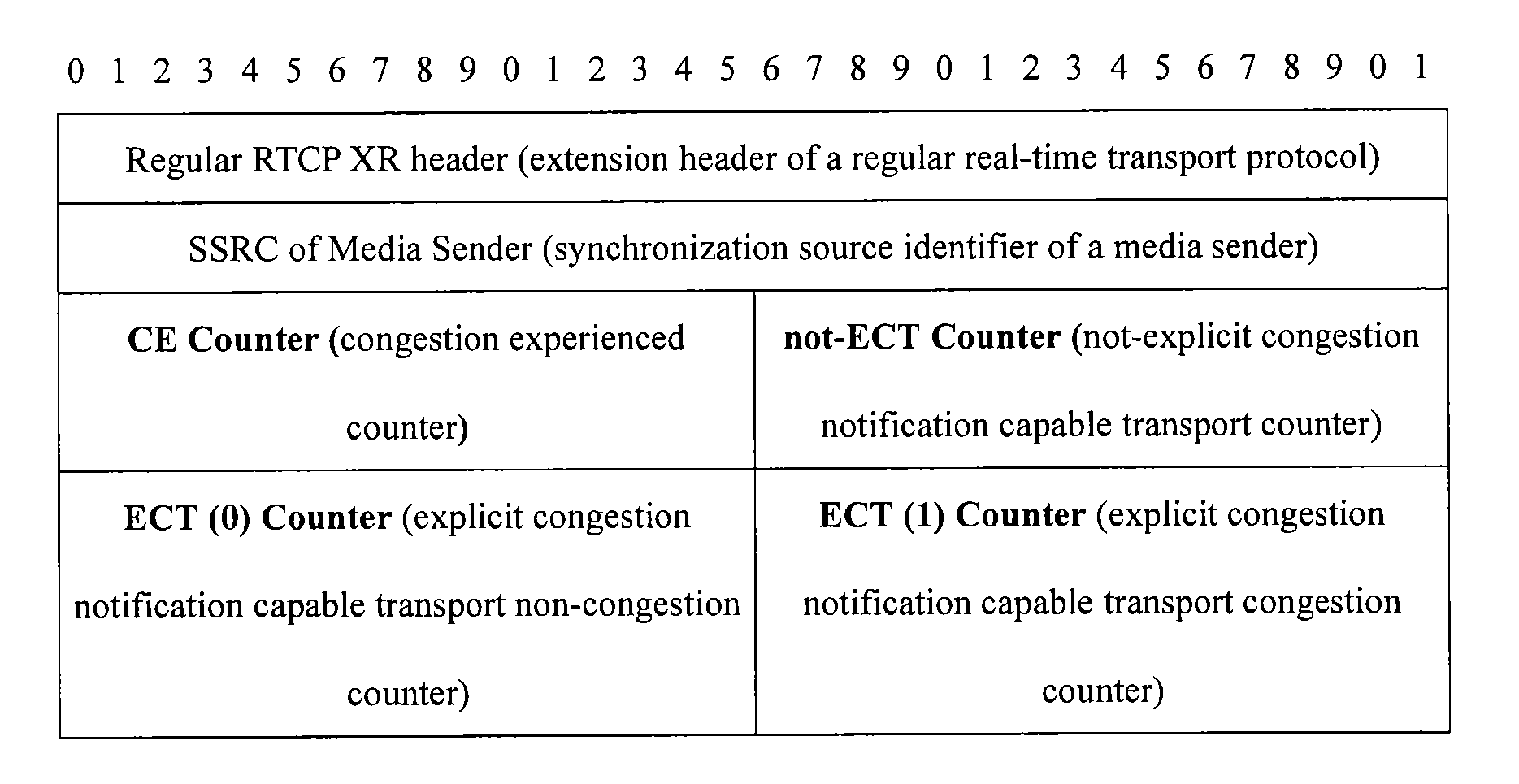
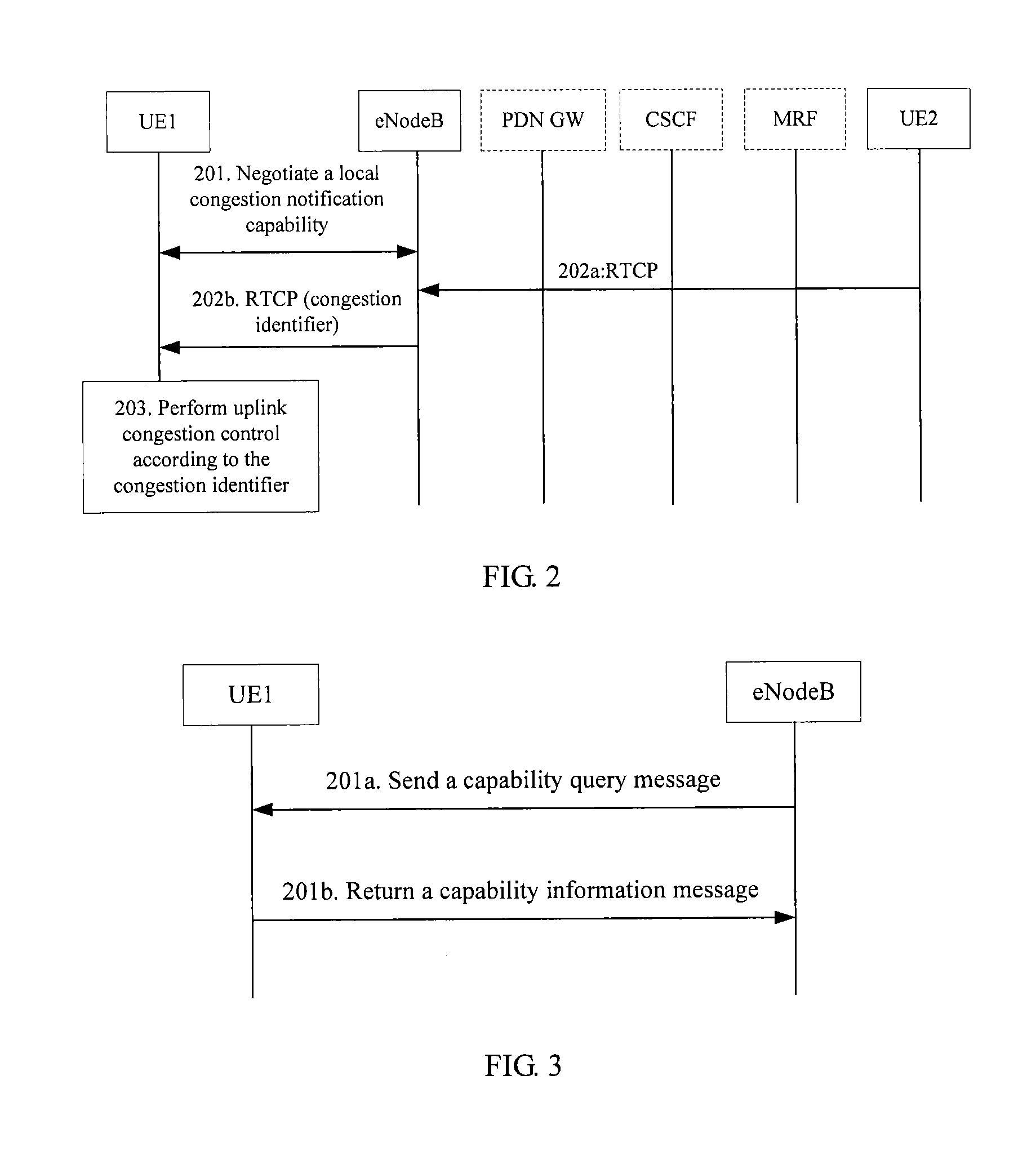
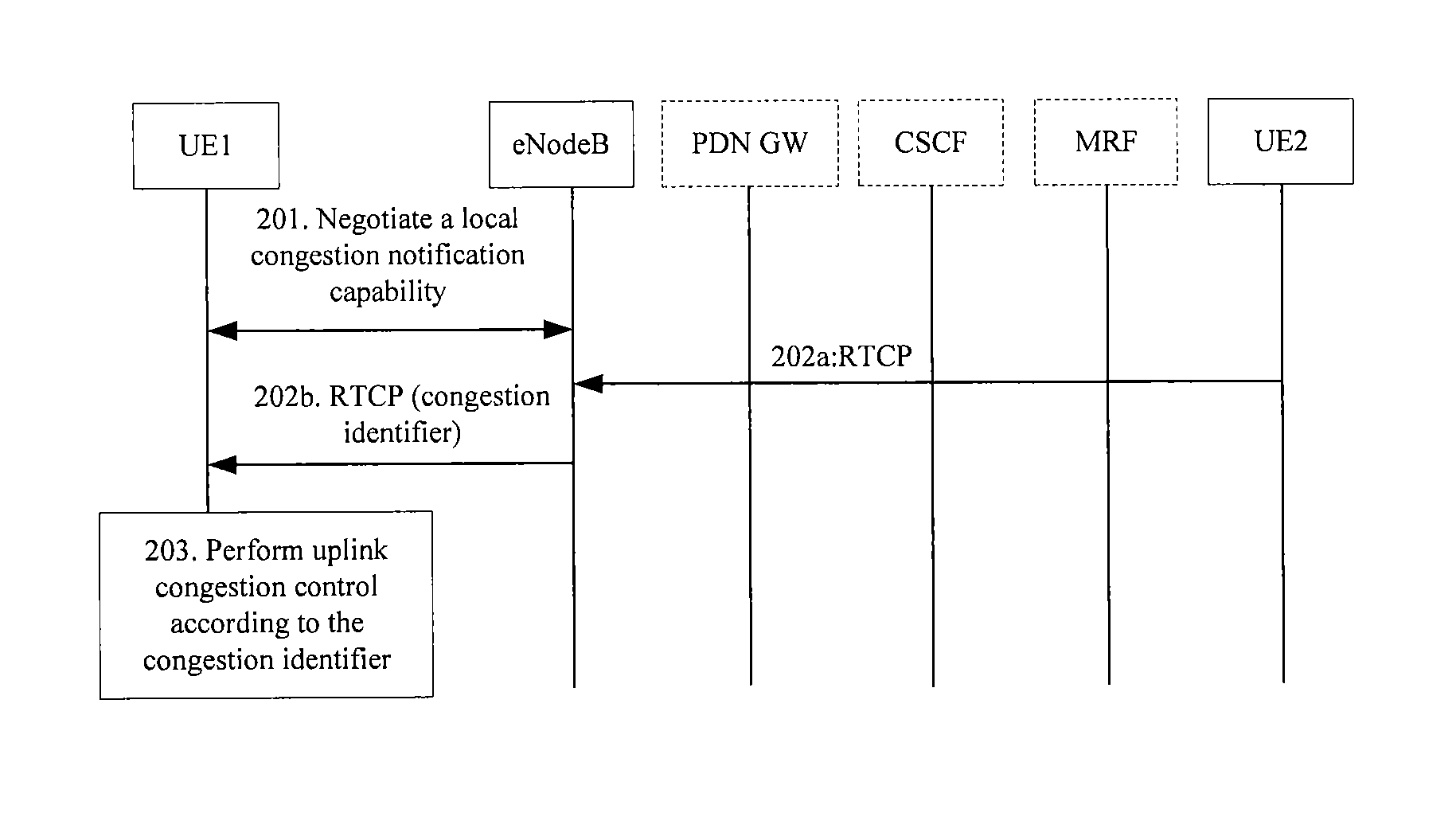
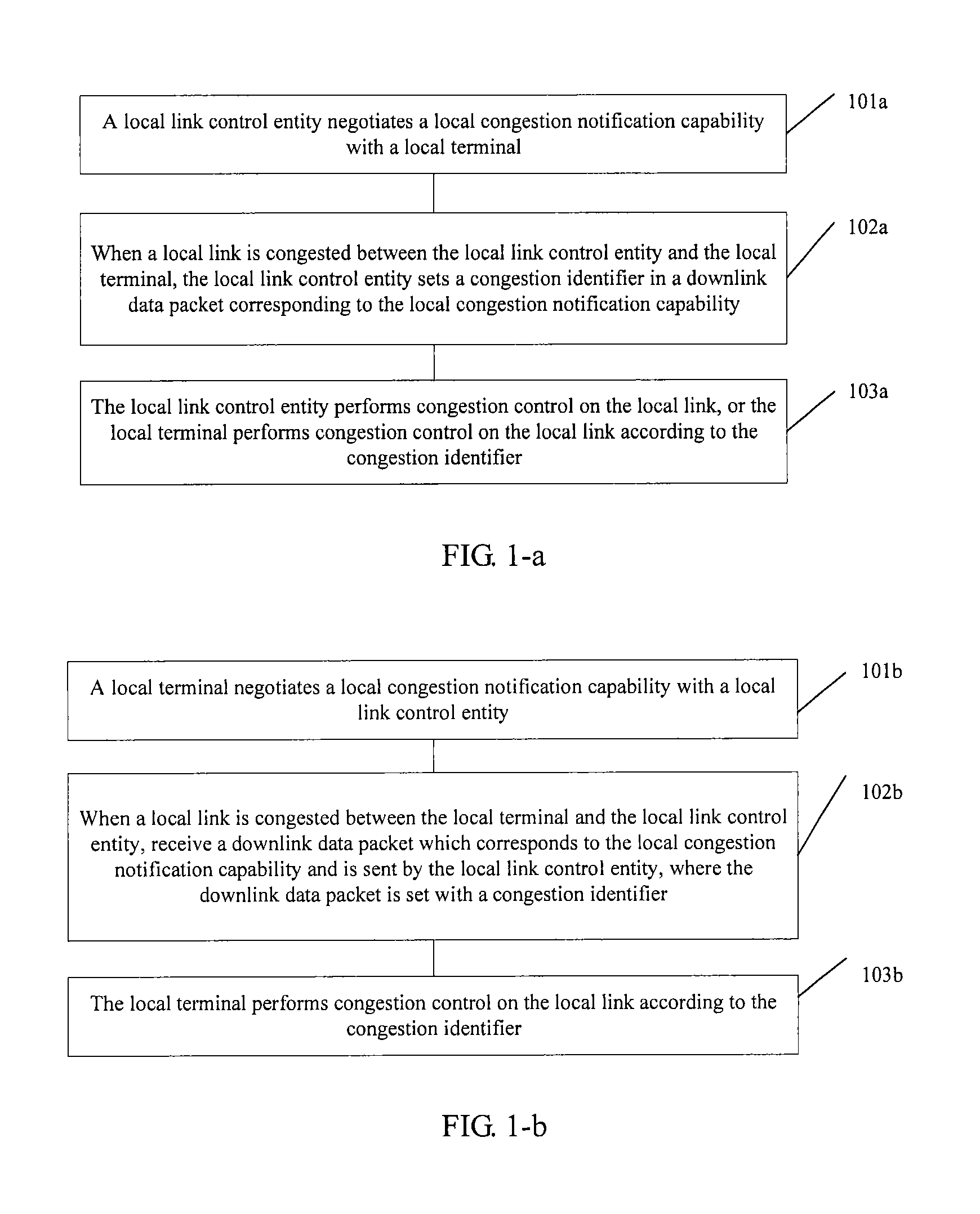
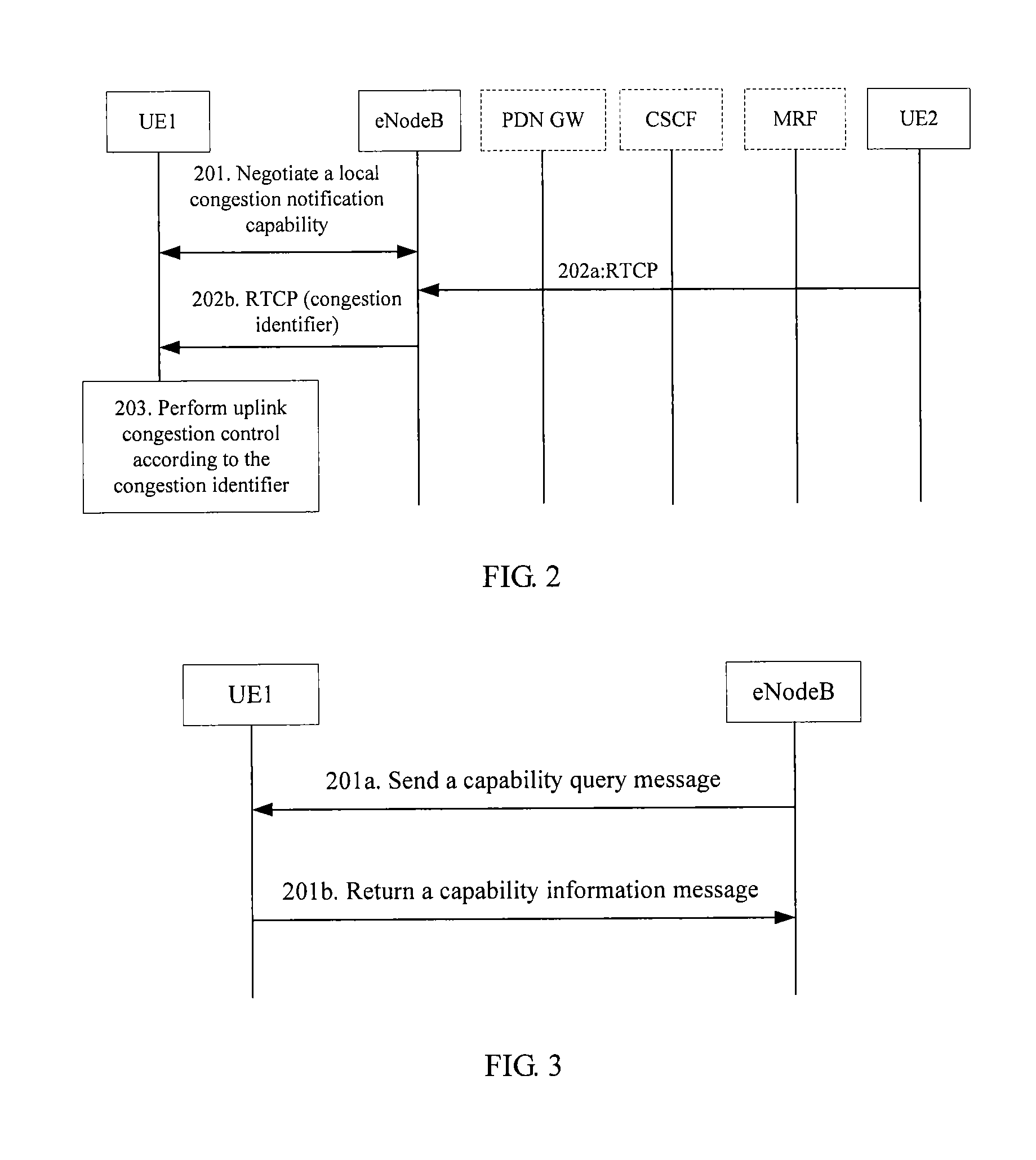
Method for handling local link congestion and apparatus
ActiveUS20120307634A1Solve the real problemError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLocal congestionTerminal equipment
The present invention relates to the field of congestion control, and discloses a method for handling local link congestion and an apparatus. The method includes: negotiating, by a local link control entity, a local congestion notification capability with a local terminal; setting, by the local link control entity, a congestion identifier in a downlink data packet corresponding to the local congestion notification capability when a local link is congested between the local link control entity and the local terminal; and performing, by the local link control entity, congestion control on the local link, or performing, by the local terminal, congestion control on the local link according to the congestion identifier. The apparatus includes a local link control entity and a terminal device.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
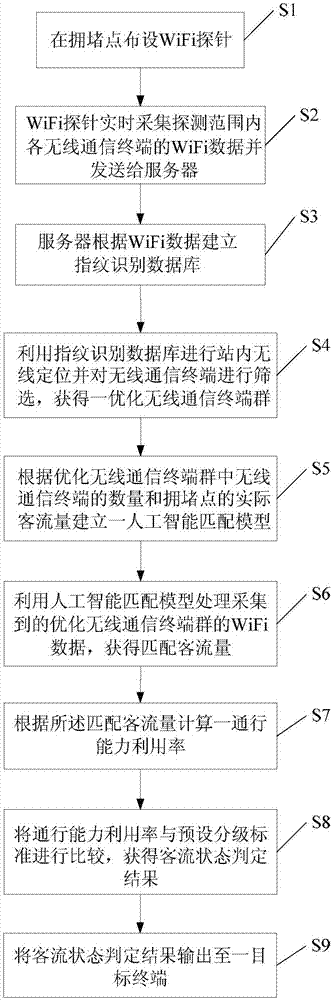
Method for determining state of passenger flow at local congestion points at transit station
InactiveCN107360590AImprove judgment accuracyImprove accuracyNetwork topologiesIndividual entry/exit registersTraffic capacityLocal congestion
The invention provides a method for determining the state of passenger flow at local congestion points at a transit station. The method includes the following steps: deploying WiFi probes at congestion points at a transit station; real-time acquiring the WiFi data of respective wireless communication terminals within a detection range and transmitting the WiFi data to a server; establishing a fingerprint identifying database; using the fingerprint identifying database to perform wireless inter-station positioning and screening the wireless communication terminals, acquiring a wireless optimized communication group; establishing an artificial intelligence matching model; processing the acquired WiFi data of the wireless optimized communication terminal group by using the artificial intelligence matching model, acquiring matched passenger flow; on the basis of the matched passenger flow, computing the traffic capacity utilization rate; comparing the traffic capacity utilization rate and a preset grade standard, acquiring the result of determining the state of passenger flow; and outputting the result of determining the state of passenger flow to an objective terminal. According to the invention, the method herein has the advantages of high accuracy and strong effectiveness.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
Equipment and method for detaching waste television
ActiveCN103990642ARealize resource reuseTo achieve the purpose of harmless dismantlingSolid waste disposalDirt cleaningLogistics managementLocal congestion
The invention relates to equipment and a method for detaching a waste television. The structure of the equipment comprises a cargo conveying device, a detaching operation platform, a television picture tube screen cone cutting separating machine and a matched industrial dust-collection processing device. The equipment and the method have the advantages that (1) an optimized layout that a complete machine and parts are detached and then intensively conveyed is realized, the logistics efficiency is increased, the labor intensity is reduced, meanwhile, purposes of harmlessly detaching electronic products of various types and standards are achieved, the safety is high, and the comprehensive resource reutilization of various materials of the waste television with a picture tube is further realized; (2) the field operation is ordered, and the potential safety hazards are eliminated; (3) by utilizing a dust hood arranged at each station, the dust generated in the detaching process of the television can be effectively processed; (4) the problems of local congestion, even full-line production stop and the like are avoided; (5) the drifting of fluorescent powder in an adsorption process is reduced; (6) the equipment is convenient to mount and implement and easy to maintain and is low in cost.
Owner:NANJING KAIYAN ELECTRONICS
Domain based congestion management
The Domain-based Congestion Management method and apparatus detects and regulates congestion in a Diff-serv network. It uses an improvRED method for congestion detection at the core routers and token bucket filters for traffic regulation at the ingress nodes. In addition, improvRED also provides feedback control. ImprovRED uses three thresholds for detecting congestion: a minth, a maxth and a FeedbackThreshold, which takes a value between the minth and the maxth thresholds. Whenever the average queue size is greater than minth and less than Feedback-Threshold, all outgoing packets are marked appropriately to indicate a potential onset of a congestion period. When the average queue size is greater than FeedbackThreshold (but less than maxth) packets are dropped probabilistically and all the outgoing packets are marked appropriately to denote the dropping phase. When the average queue size is greater than the maximum threshold, all incoming packets are dropped. Feedback, in the form of a Local Congestion Notification (LCN) message, is used to notify the ingress nodes of a likely onset of congestion. Ingress nodes immediately respond to the congestion notification by appropriately regulating their respective traffic rates (i.e., the amount of packets they inject into the Diff-serv network). The amount of traffic (or data packets) injected into the core of the Diff-serv domain is controlled by a token bucket filter at each of the ingress nodes.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Implementation method for retransmitting and controlling congestion control in separating system
InactiveCN103051560AImprove QoS performanceProspects for widespread practical useData switching networksQuality of serviceData pack
The invention discloses an implementation method for retransmitting and controlling congestion control in a separating system. The implementation method comprises the following steps of: 1.calculating whether the occupying ratio of a total buffer-area queue exceeds a preset threshold value or not by a control element according to a dispatcher in a transmission mapping layer; 2. if judging that a message in the queue is in a local congestion state, redistributing the residual service time of the round by the dispatcher to meet the requirement of the queue to the greatest degree; 3. managing a module through the control element by a transmission-mapping layer module and notifying a protocol-layer module in the mode of a callback function; and constructing a congestion feedback message by the protocol-layer module and sending the congestion feedback message to the opposite end of the transmission mapping layer through the transmission-mapping layer module; and 4. delivering the congestion feedback message to the protocol-layer module through the module at the opposite end of the transmission mapping layer, and actively adjusting the sending rate of a data packet by the protocol-layer module in the modes of additive increase and multiplicative decrease. The implementation method is applied to an existing ForCES prototype system, so that the overall QoS (Quality of Service) performance of the system is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
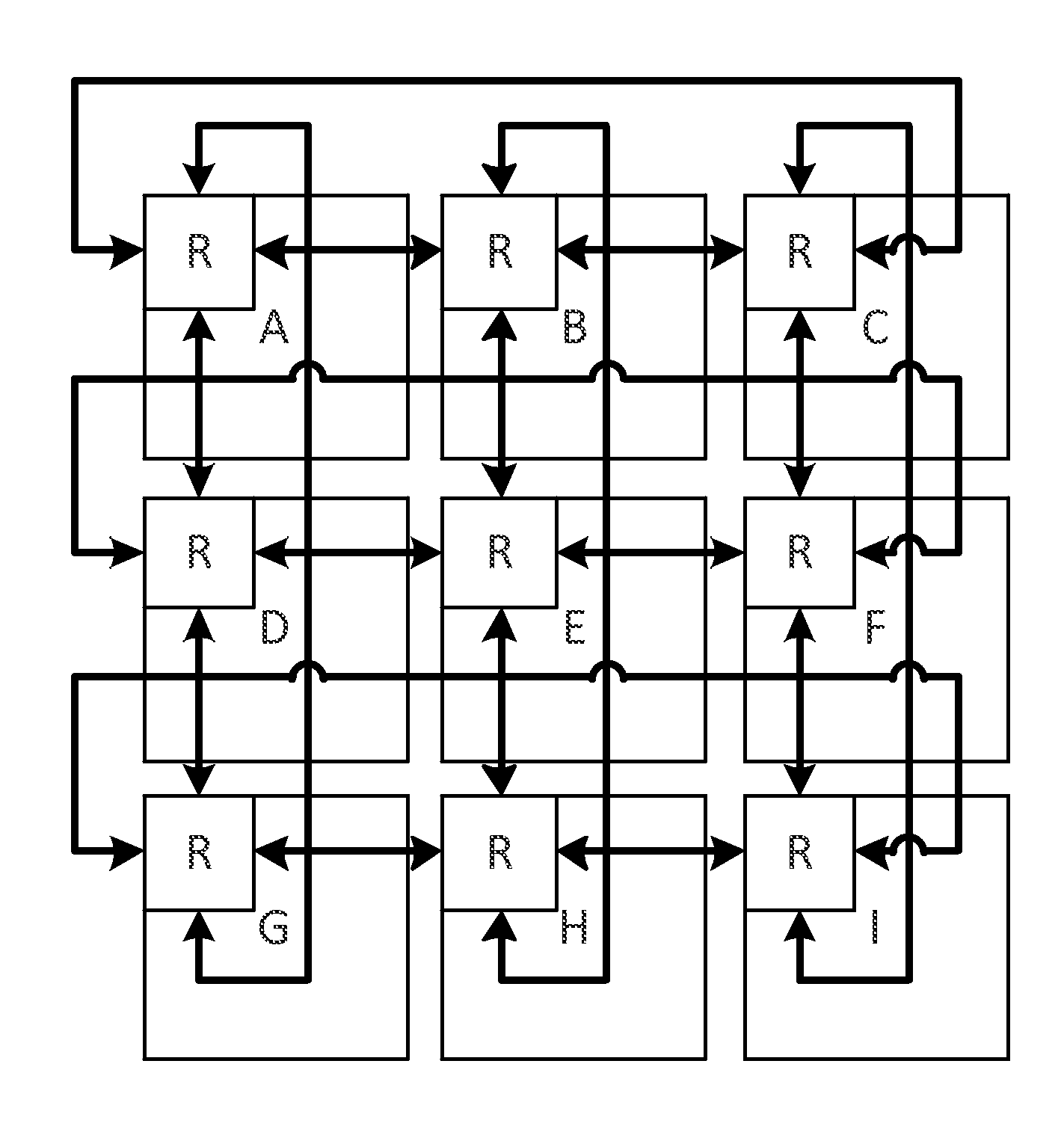
Router structure capable of sharing and self-configuring cache
InactiveCN104022950AImprove throughputMonitoring statusDigital computer detailsData switching networksChannel state informationLocal congestion
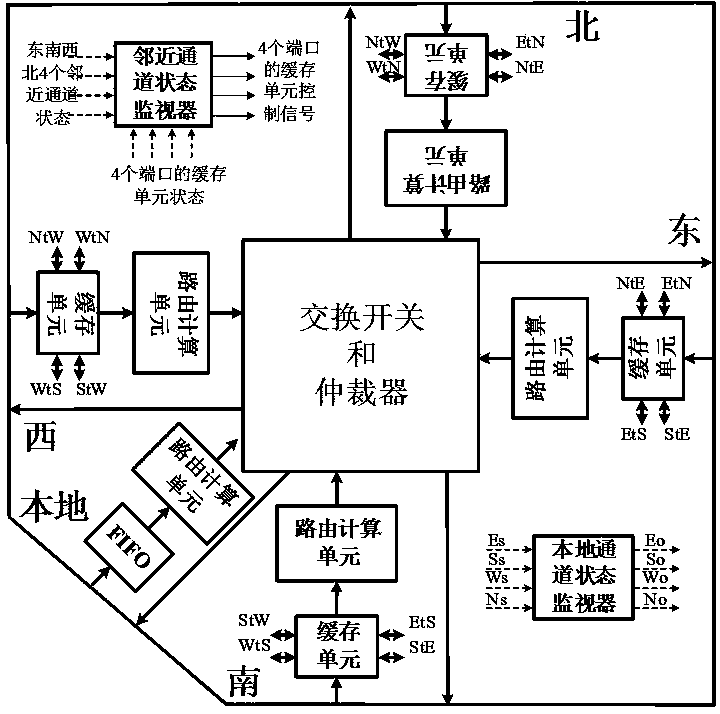
The invention belongs to the field of reliability on-chip network design, in particular to a router structure capable of sharing and self-configuring a cache applied to an on-chip network. The router structure comprises cache units, routing computation units, a data exchange switch, an arbiter, an adjacent channel status monitor and a local channel status monitor. According to the router structure, the adjacent channel status monitor and the local channel status monitor are added in the conventional router structure, so that the status of a router channel in the local on-chip network can be effectively monitored, and the routing computation unit is capable of figuring out a more reasonable routing path according to the real-time channel status information, thus the local congestion probability of the on-chip network is reduced, the throughput rate of the on-chip network is improved, and a delay to reach a target node of data of the on-chip network is reduced. Each of cache units of an eastern port, a southern port, a western port and a northern port contains a cache formed by three first input-first output queues, and two virtual data channels are formed, so that sharing of the caches is implemented in a self-configuration manner, and self-adaptability of data routing is effectively increased.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Time sequence estimation method for FPGA (field programmable gate array) post-mapping net list
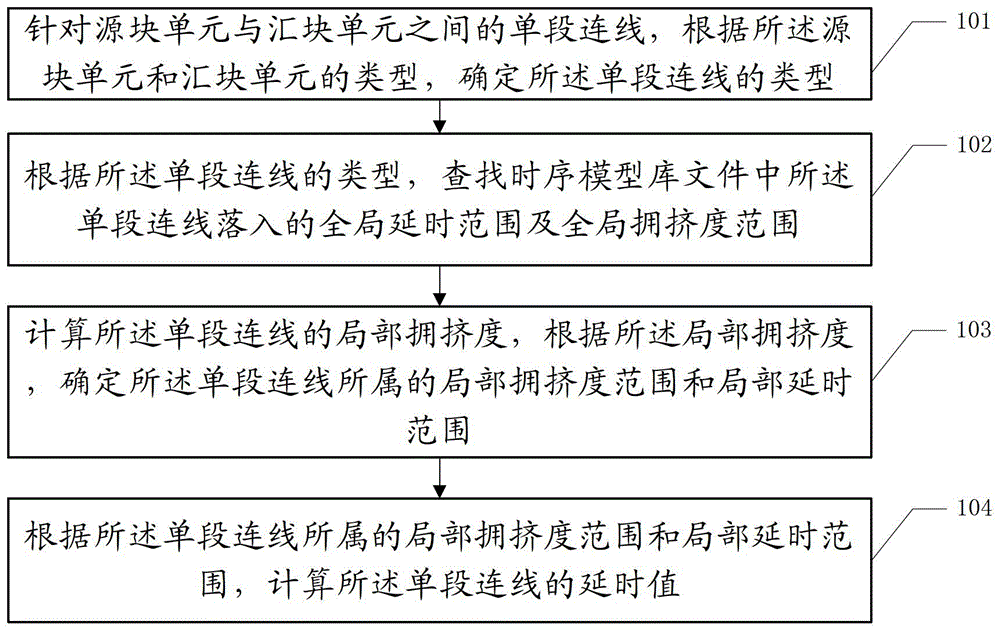
The invention discloses a time sequence estimation method for an FPGA (field programmable gate array) post-mapping net list. The method includes the steps: determining the type of a single connecting wire between a source block unit and a collecting block unit according to types of the source block unit and the collecting block unit; searching the global delay range and the global congestion range of the single connecting wire in a timing model library file according to the type of the single connecting wire; calculating local congestion of the single connecting wire and determining the local congestion range and the local delay range of the single connecting wire according to the local congestion; calculating the delay value of the single connecting wire according to the local congestion range and the local delay range of the single connecting wire. Therefore, the highest working frequency of an FPGA before placement and routing can be estimated, a clock constraint file is generated and replaces clock constraint set by a user to serve as input of a placement and routing tool, and the better highest frequency can be obtained by fewer iteration times.
Owner:CAPITAL MICROELECTRONICS
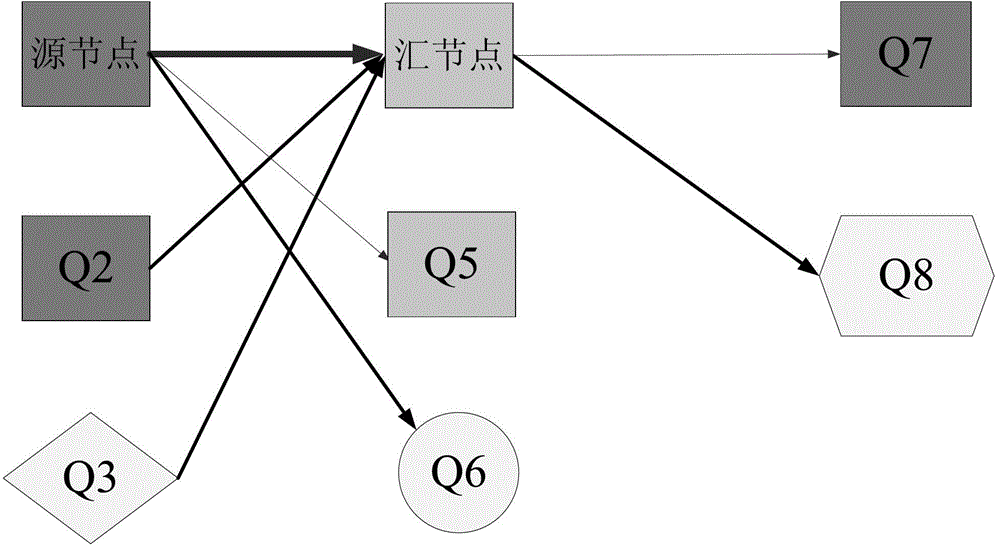
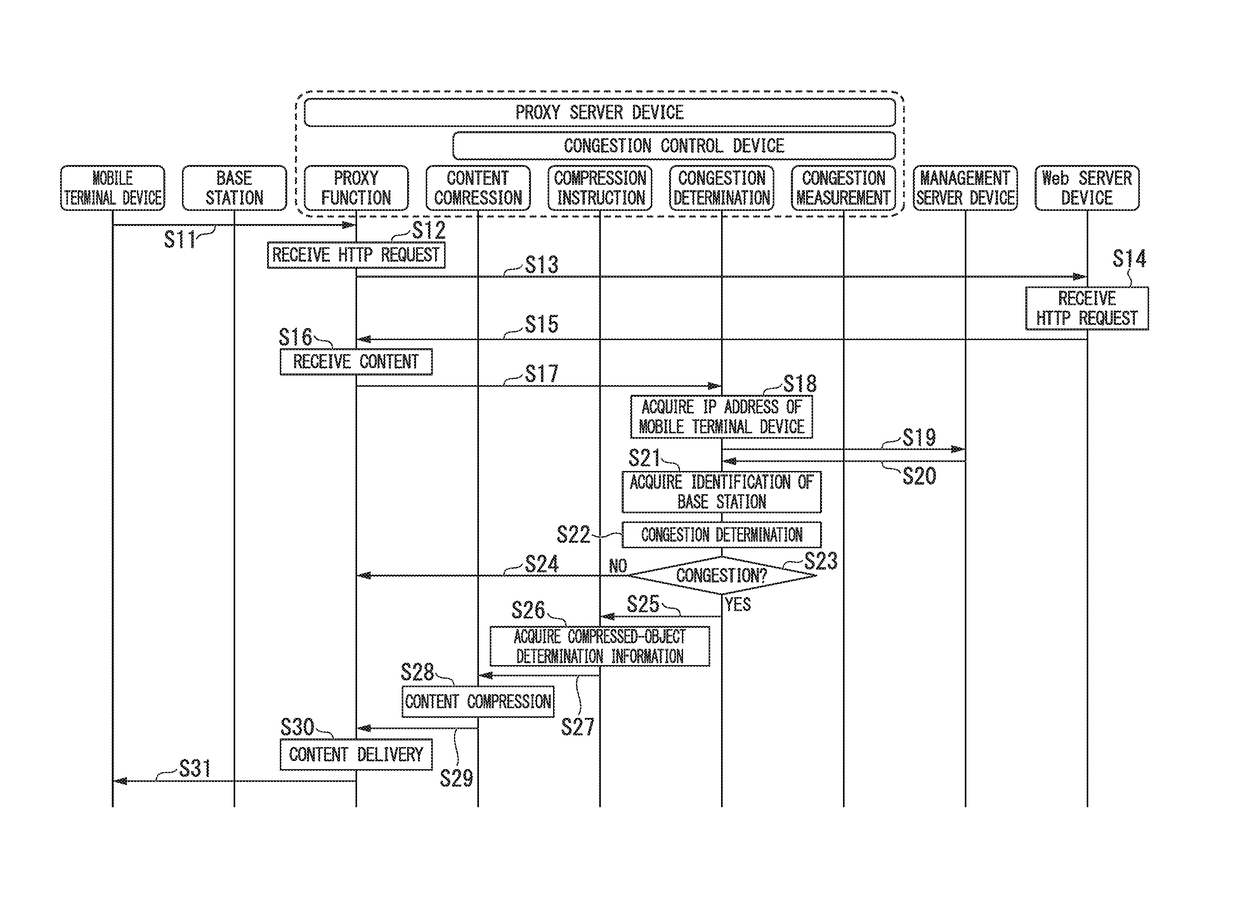
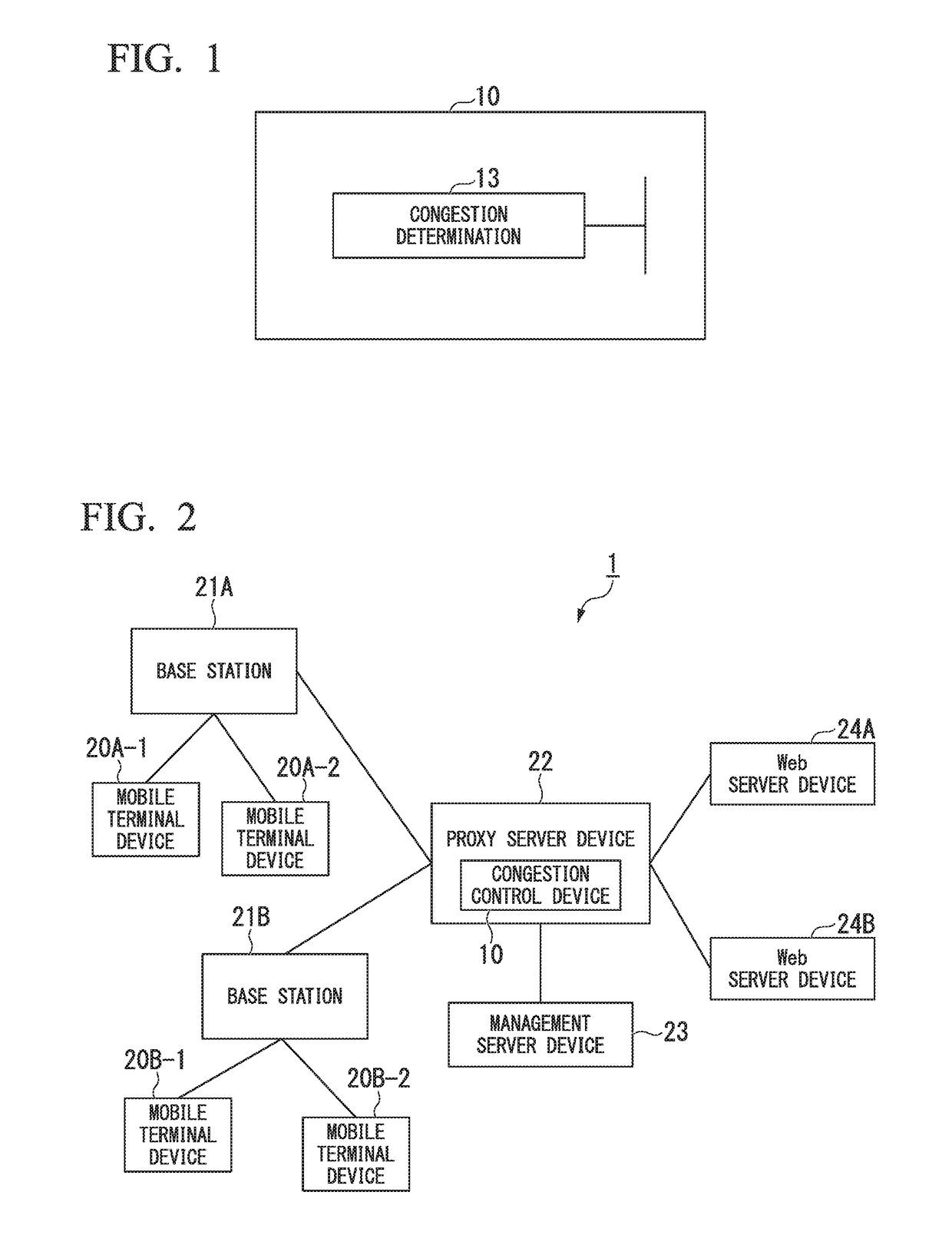
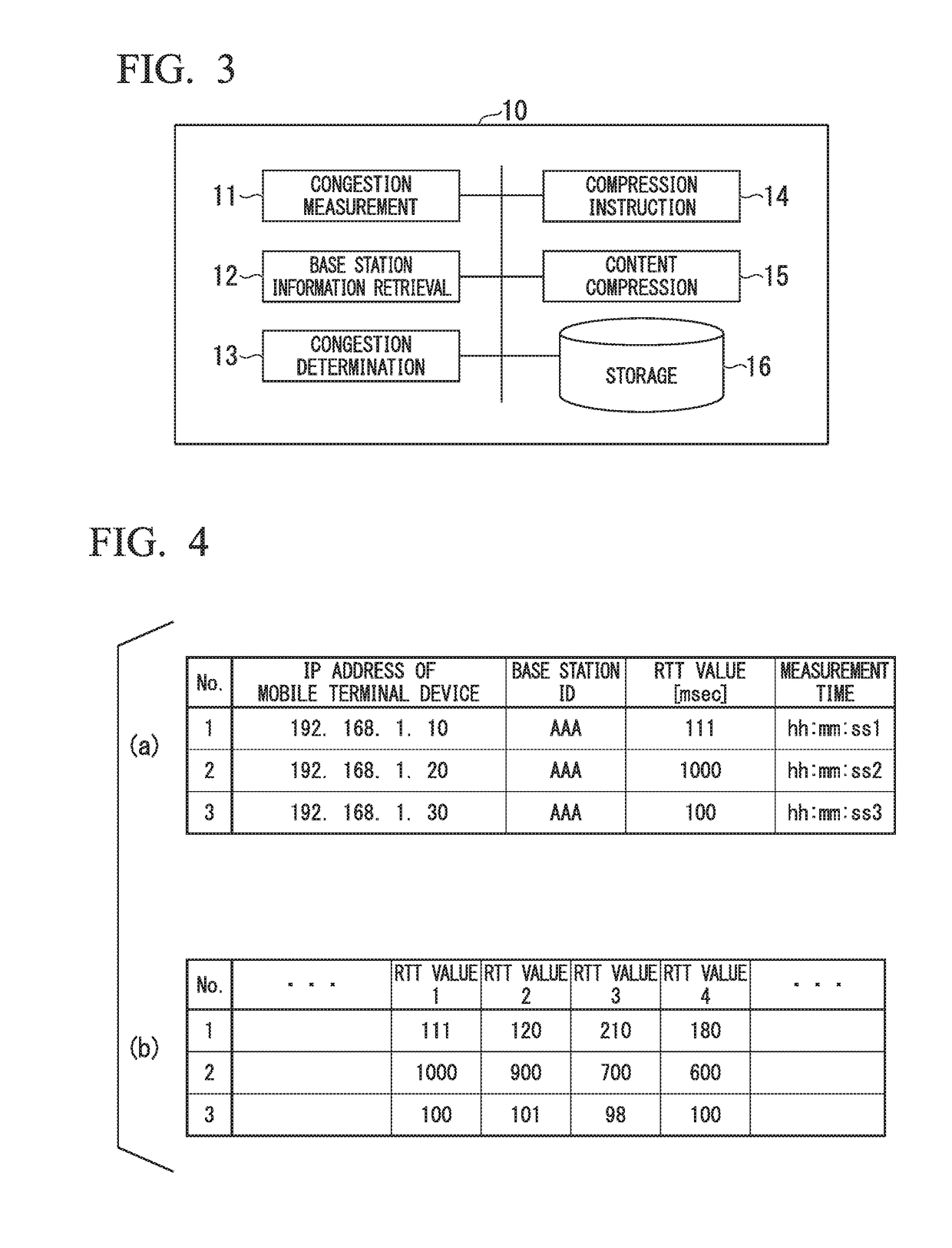
Local congestion determination method and congestion control device for mobile communication
InactiveUS20180139642A1Sure easyCongestion may have clearedNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksLocal congestionTerminal equipment
A congestion control device determines whether congestion occurs in a base station when a mobile terminal device connected to a mobile communication network communicates with a content delivery device through the base station. The congestion control device is installed in a proxy server device relaying communications between the base station and the content delivery device. The congestion control device includes a congestion condition table for registering congestion condition information, representing measurement results of communication received or transmitted by the mobile communication terminal through the base station. Upon acquiring the identification of the base station communicating with the mobile terminal device, the congestion control device reads the congestion condition information correlated to the identification of the base station from the congestion condition table, thus determining whether congestion occurs in the base station.
Owner:NEC CORP
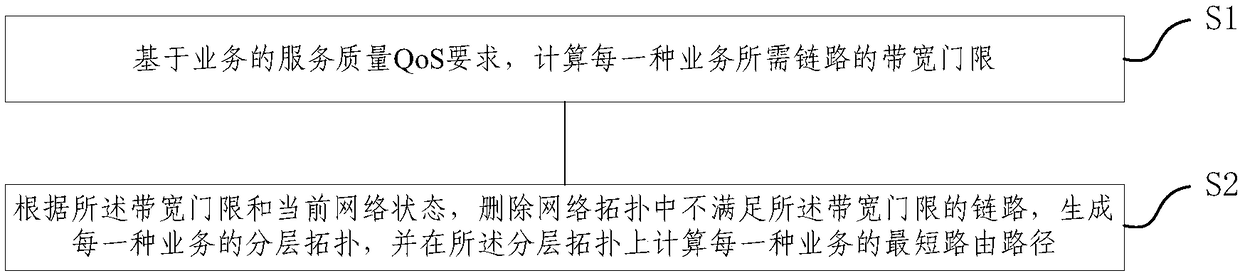
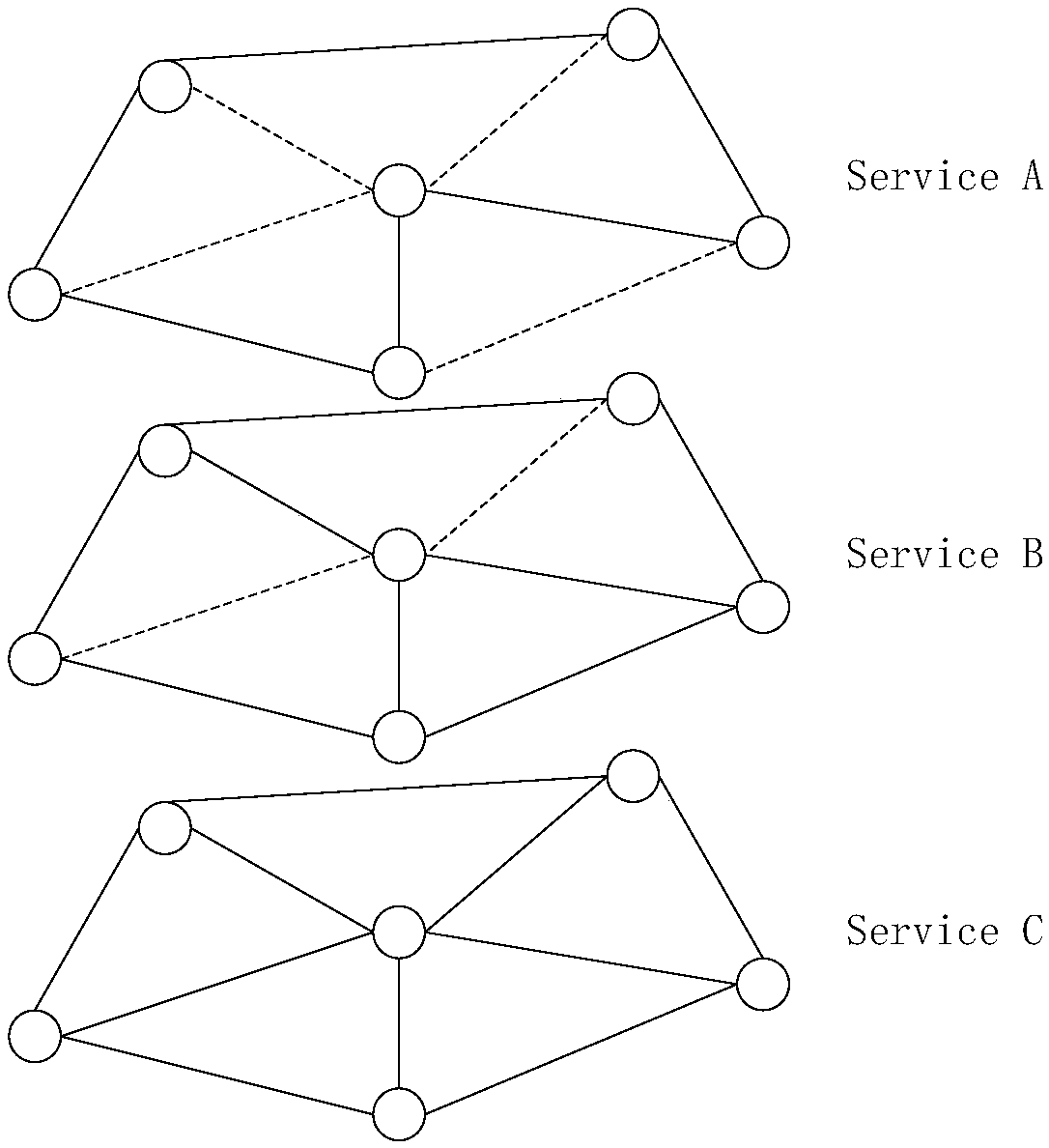
Differentiated QoS based multi-service hierarchical topology routing method and system
ActiveCN108173766AMeet QoS requirementsReduce congestionData switching networksService flowLocal congestion
The invention provides a differentiated QoS based multi-service hierarchical topology routing method and system. The method includes the following steps: S1, based on the quality of service (QoS) requirements of services, calculating a link bandwidth threshold required for each type of service; and S2, according to the bandwidth threshold and the current network state, deleting links that do not satisfy the bandwidth threshold in the network topology, generating a hierarchical topology for each type of service, and calculating the shortest routing path of each type of service on the hierarchical topology. The corresponding logical hierarchical topology is generated for each type of service, the QoS requirements of the services and the load balancing of the network are comprehensively considered, the load balancing level of the network can be effectively improved, the interaction effect between service flows can be reduced, the network load balancing can be maximally optimized in the routing process of distinguishing the services, and thus each link can have the maximum residual bandwidth, the local congestion of the network can be reduced, and the interaction effect between the service flows can be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +2
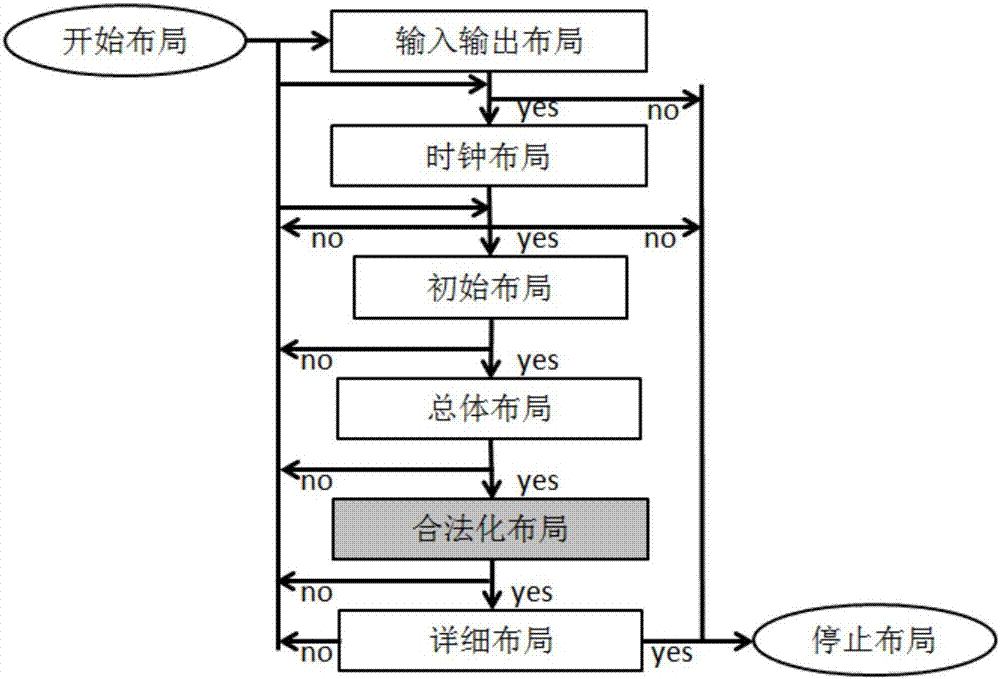
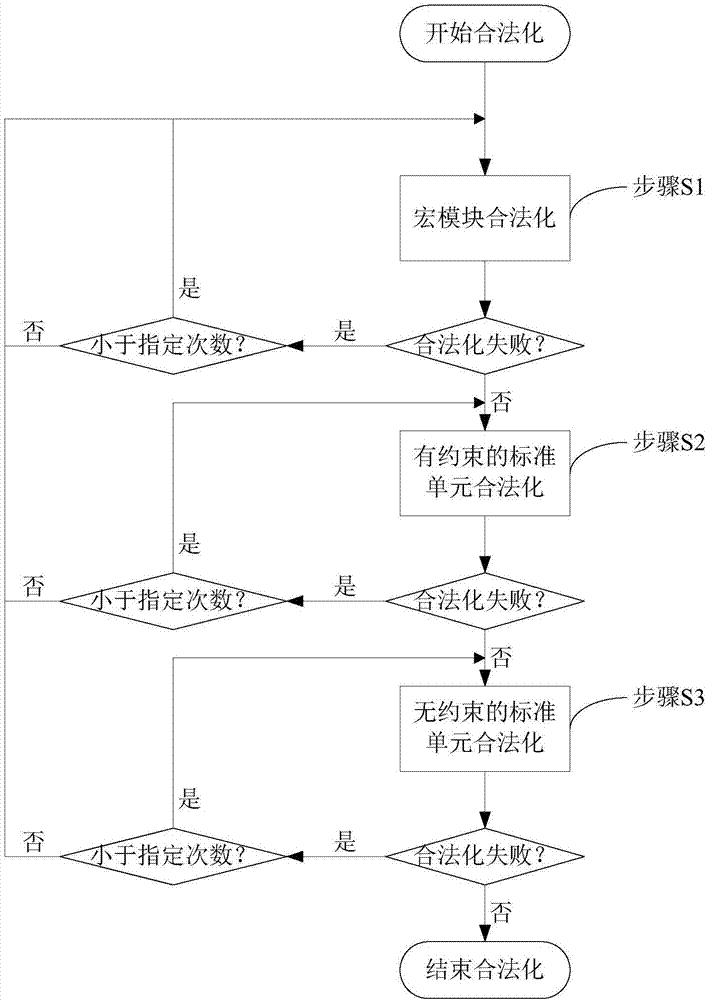
Method for legalizing overall layout of FPGA
ActiveCN107967372AAvoid damageReduce local congestionSpecial data processing applicationsLocal congestionComputer science
A method for legalizing the overall layout of an FPGA comprises the steps that firstly, an integer programming mode and a network flow mode are used for legalization of a macroblock; secondly, a constrained standard unit is legalized in a graded integer programming mode; finally, an unconstrained standard unit is legalized in a graded network flow mode. According to the method, by processing legalization of different types of unit modules with different constraints, legalization operation is conducted through small-range unit moving under the condition that an overall layout result is damagedas little as possible, and the effectiveness of the overall layout is guaranteed; the local congestion degree is reduced, so that damage of legalization to the overall layout is reduced; a legalized frame is very easy to expand through a graded mode, and the layout legalization efficiency is obviously improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI FUDAN MICROELECTRONICS GROUP
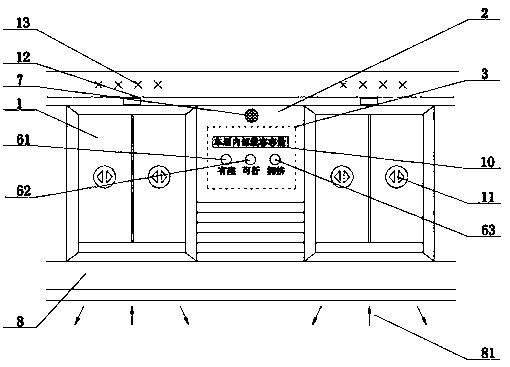
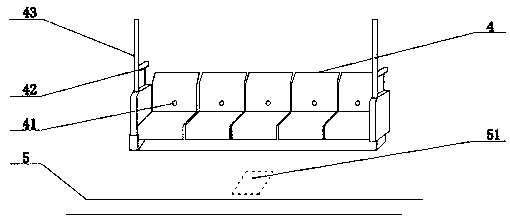
Shunting device for selecting a train compartment when riding a subway
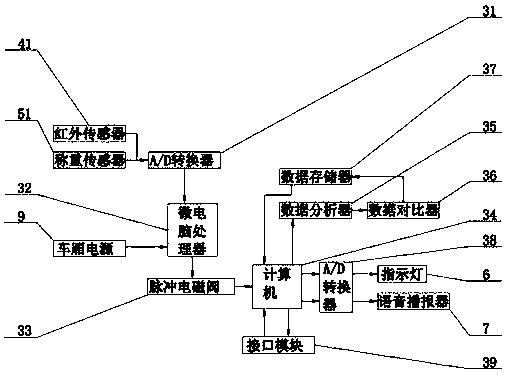
The utility model relates to a shunting device for selecting a train compartment when riding a subway, which relates to the field of shunting in the subway. The shunting device contains subway doors,glass doors, integrated circuit boards, seats, car bottom panels, indicator lights, voice announcers, waiting areas, car power, passenger capacity identification, infrared sensors, weighing sensors. The invention has the following beneficial effects: let the indicator light of the corresponding car display one of the colors of red, yellow and green before the subway arrives at the station, Passengers are guided to choose the best carriage to wait in queue, so as to play the role of diversion when boarding the train, and to maximize the use of subway interior compartment space, to avoid the same high-speed rail local congestion and local idle state coexistence of the situation.
Owner:JINLING INST OF TECH
Goods sorting method and device of sorting center and goods sorting system
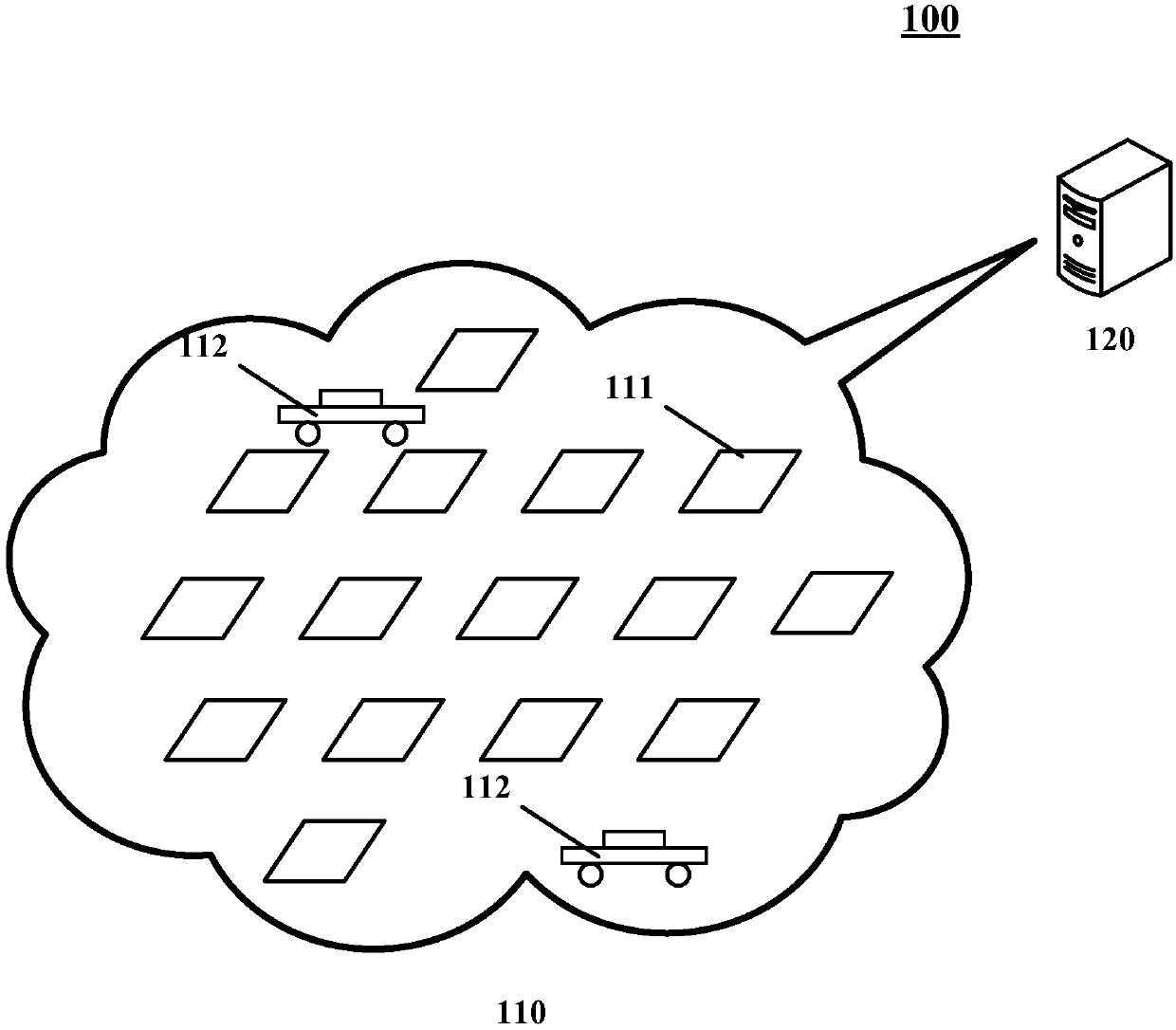
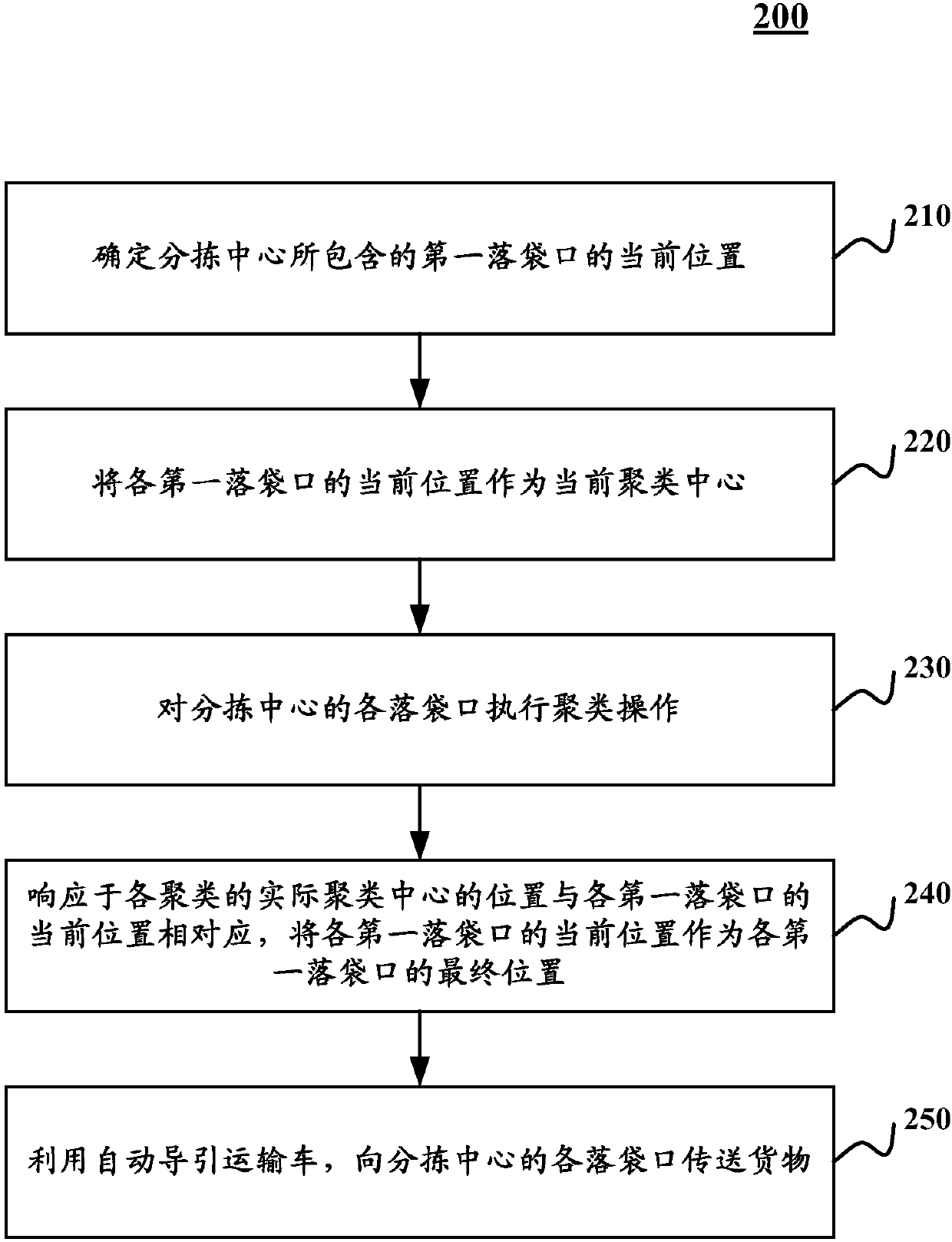
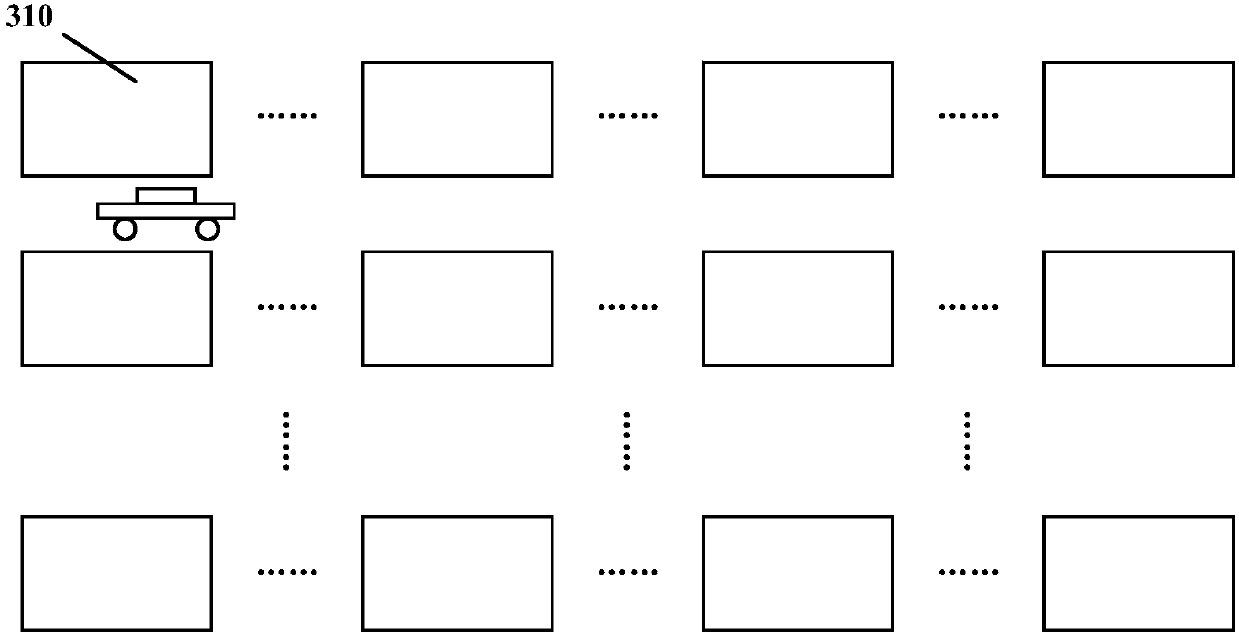
ActiveCN109919167ARealize decentralized arrangementReduce congestionCharacter and pattern recognitionLogisticsLocal congestionEngineering
The embodiment of the invention discloses a cargo sorting method and device of a sorting center and a cargo sorting system. One specific implementation mode of the method comprises the steps that determining the current position of each first bag falling opening contained in a sorting center, and the first bag falling openings are bag falling openings with the sorting quantity exceeding the presetsorting quantity in the sorting center in unit time; taking the current position of each first bag falling opening as a current clustering center; performing clustering operation on each bag fallingopening of the sorting center; responding to the position of the actual clustering center of each cluster corresponding to the current position of each first bag falling opening, and taking the current position of each first bag falling opening as the final position of each first bag falling opening; and conveying the goods to each bag falling opening of the sorting center by utilizing the automatic guide transport vehicle. According to the embodiment, the AGV local congestion can be relieved, and the sorting efficiency can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING JINGDONG QIANSHITECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Distributing method for VOIP service band width
InactiveCN1901505AReduce congestionPoor solutionData switching networksLocal congestionDistribution method
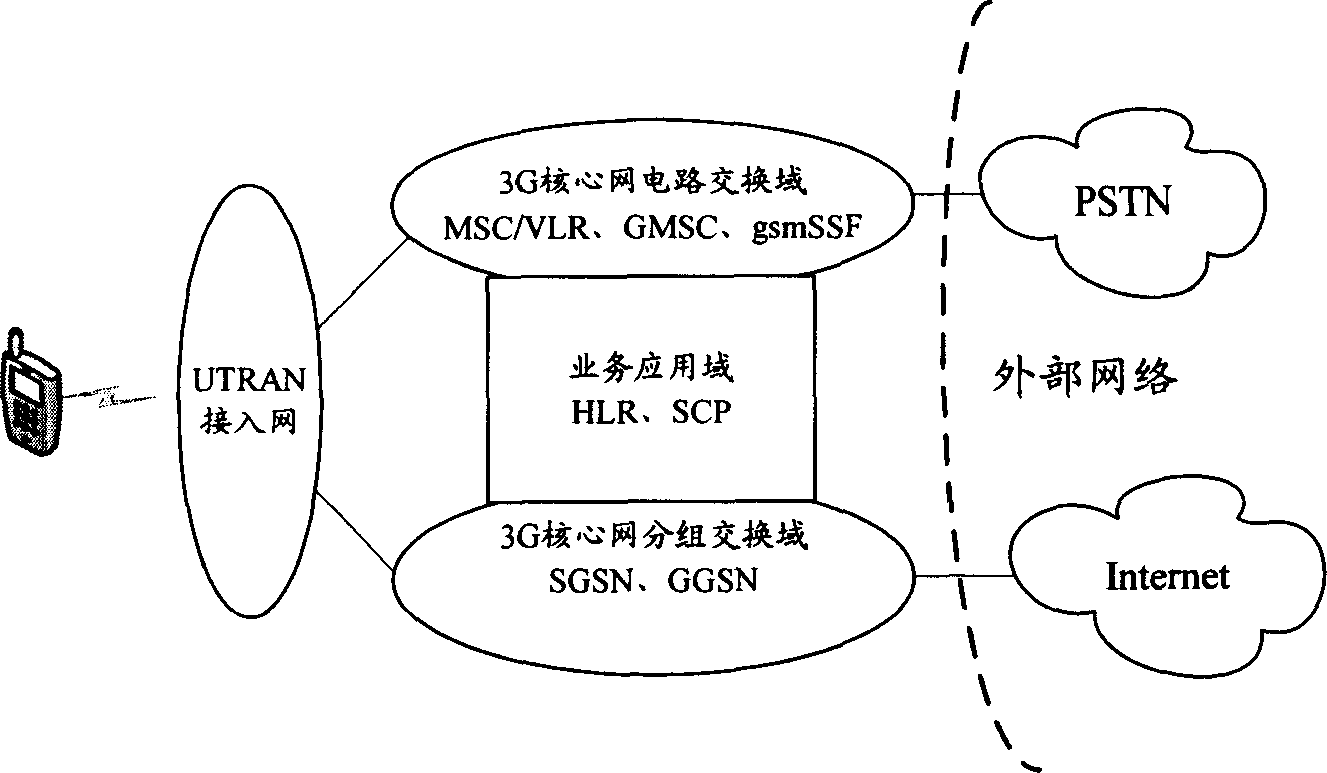
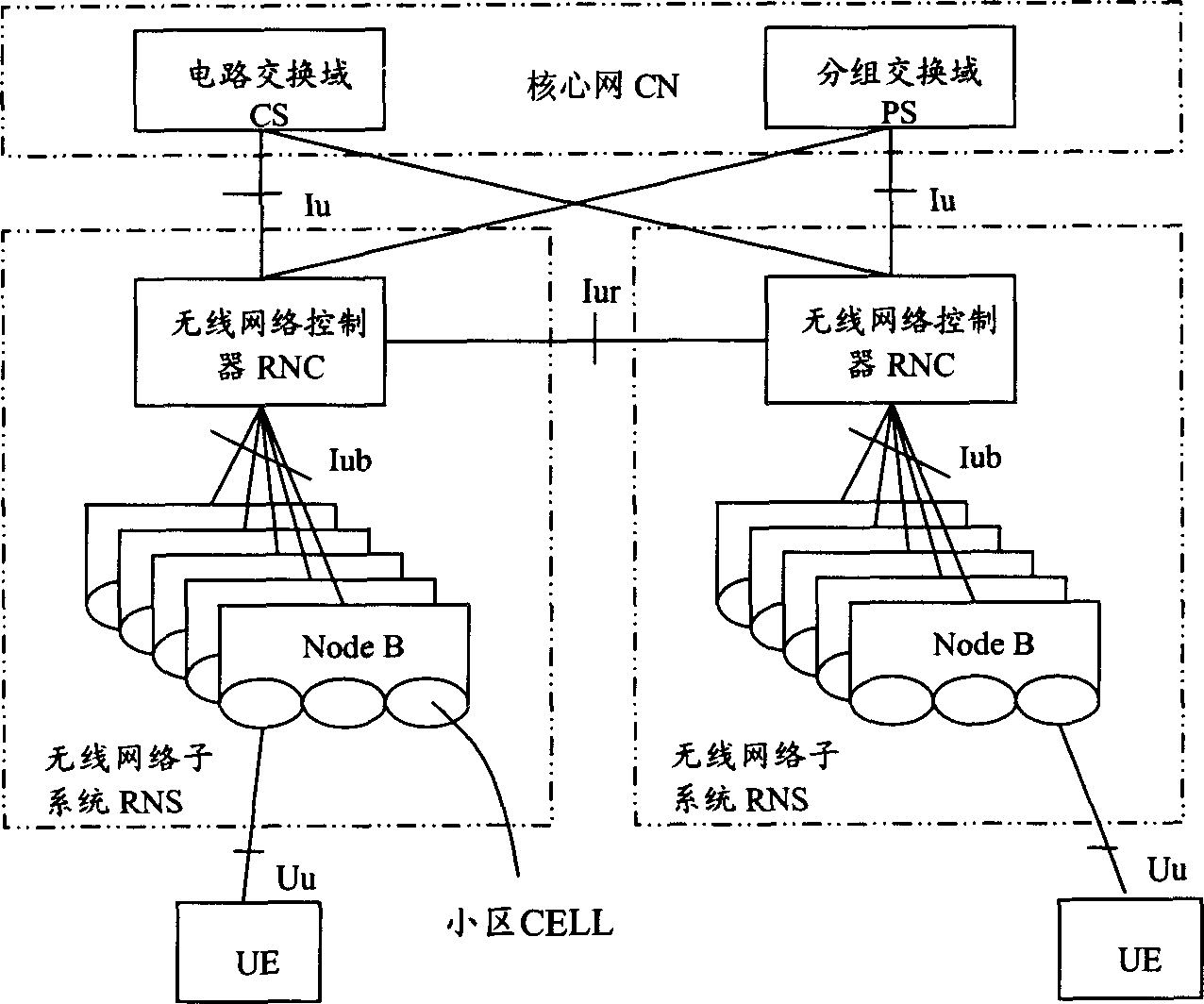
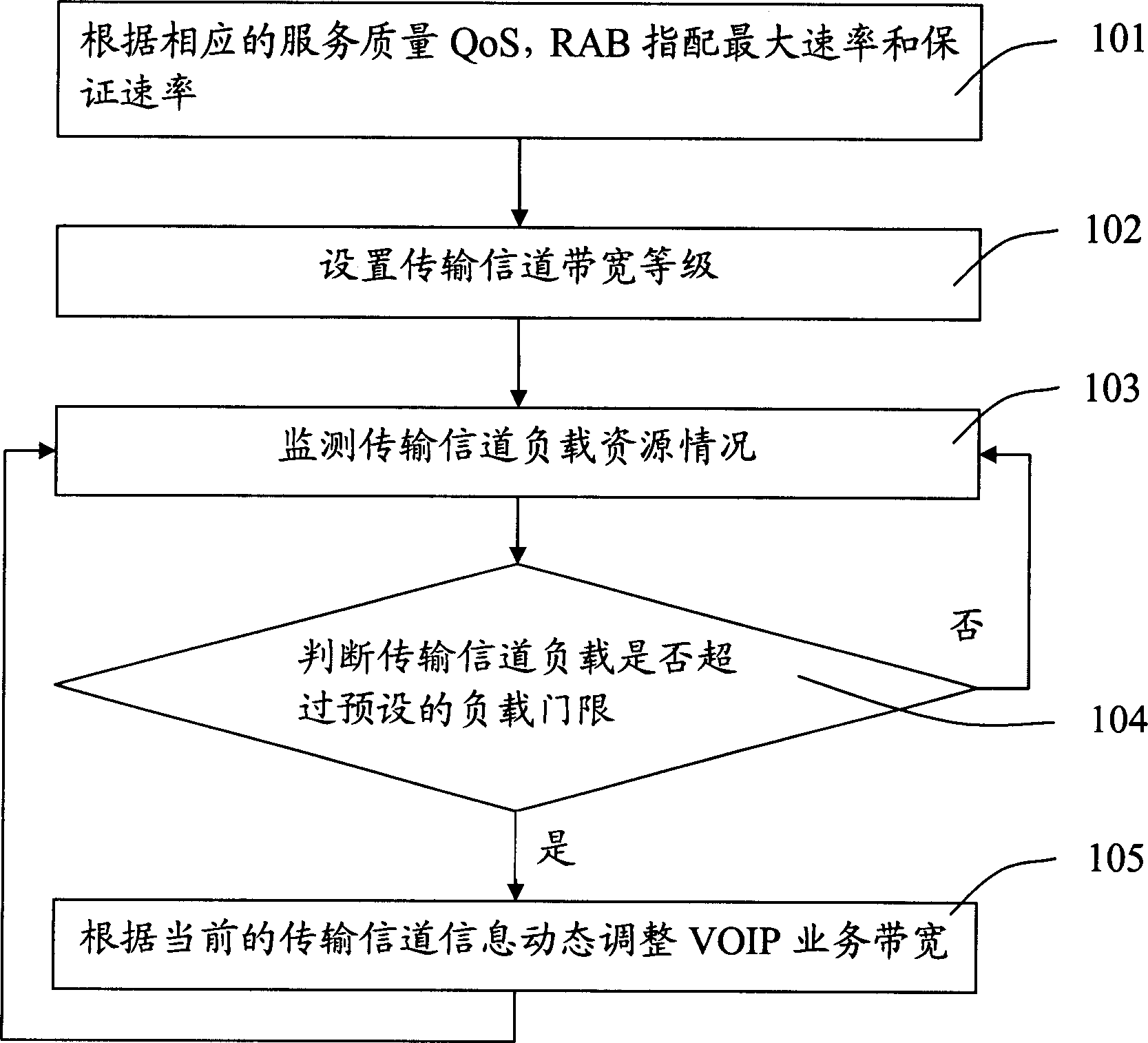
Thisinvention relates to a distribution method for VOIP service bandwidth including: setting bandwidth classes of tansmission channels according to the maximum rate and ensured rate of the VOIP service assigned by RAB, dynamically adjusting the clases of the VOIP service bandwidth by monitoring the load resource of the transmission channels to distribute a large bandwidth when the local resource is normal to secure the high phone quality and distribute the bandwidth based on the ensuring rate when the local resource is congested to reduce the local congestion so as to increase the usability of the bandwidth of the transmission channels and ensure the QoS of other services of users as well.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Link control method and device
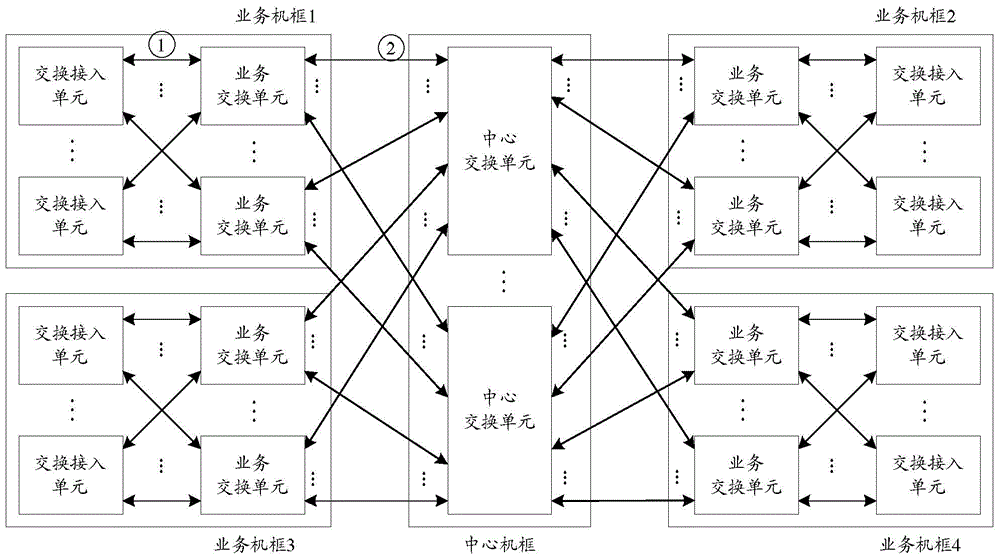
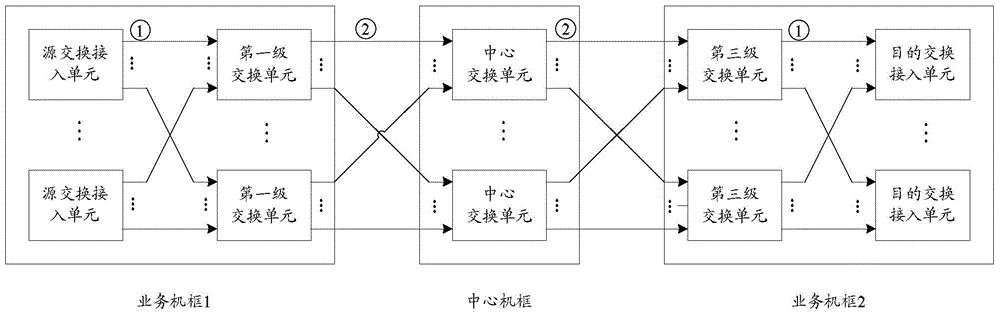
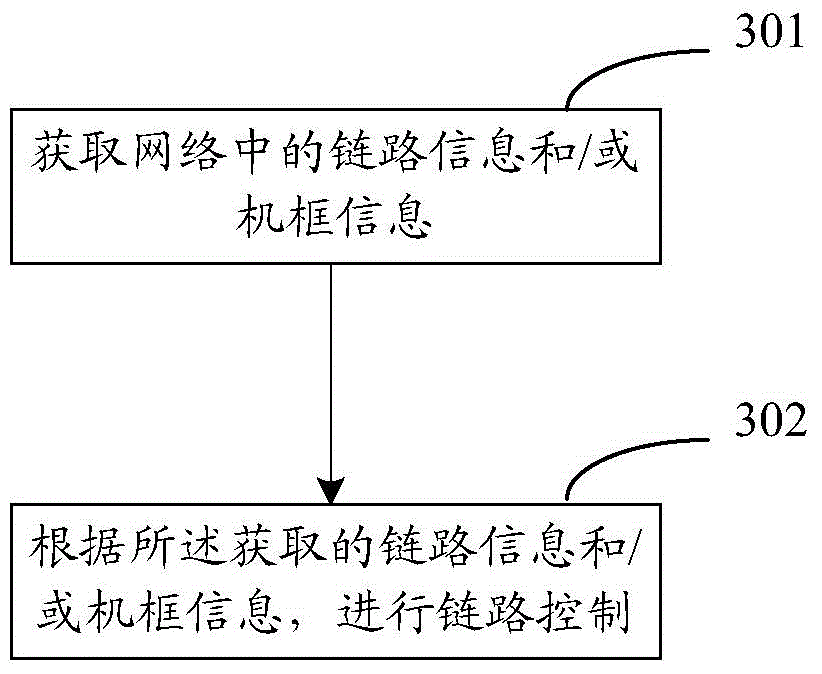
ActiveCN105577575ASolve local congestionSolve packet lossData switching networksThree levelPacket loss
The invention discloses a link control method and device. The method comprises that link information and / or machine frame information in a system is obtained; and link control is implemented according to the obtained link information and / or machine frame information. According to the technical schemes of the invention, the problems of local congestion and packet loss in the three-level asymmetric exchange system can be effectively solved, the flow level of the system is ensured, and the system performance is improved.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
City region road classification inducing method
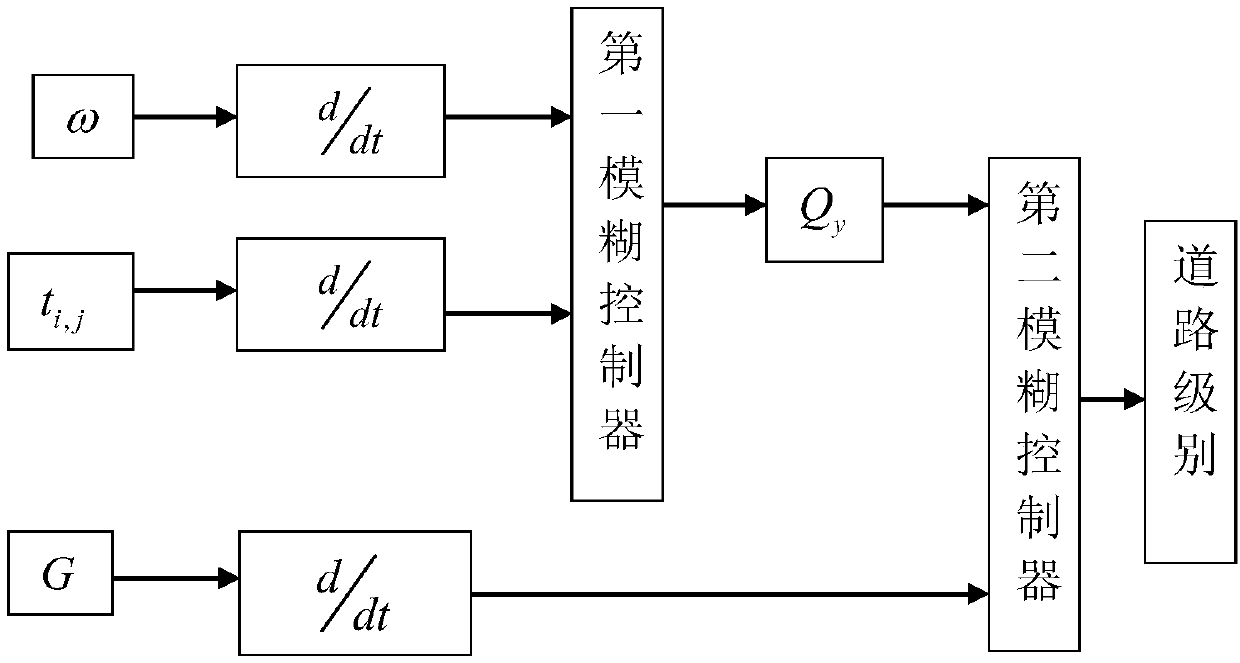
InactiveCN108665706AEase traffic pressureDetection of traffic movementLocal congestionDriver/operator
The invention discloses a city region road classification inducing method. The method comprises the steps that a bicycle delaying time change rate signal and a traffic flow change rate signal are input in a first fuzzy controller, and the traffic flow congestion grade is output; the road surface temperature and air humidity are detected, and rod surface width is combined to obtain a city road condition evaluation index; the traffic flow congestion grade and a road condition evaluation index change rate signal are input in a second fuzzy controller, the rod passage grade is output, a driver isprompted to make a detour or pass according to the road passage grade, city region roads are effectively utilized, and partial congestion is avoided.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Network local congestion processing method based on OSPF protocol
ActiveCN108259342ASolve the local congestion problemReduce complexityData switching networksLower limitLocal congestion
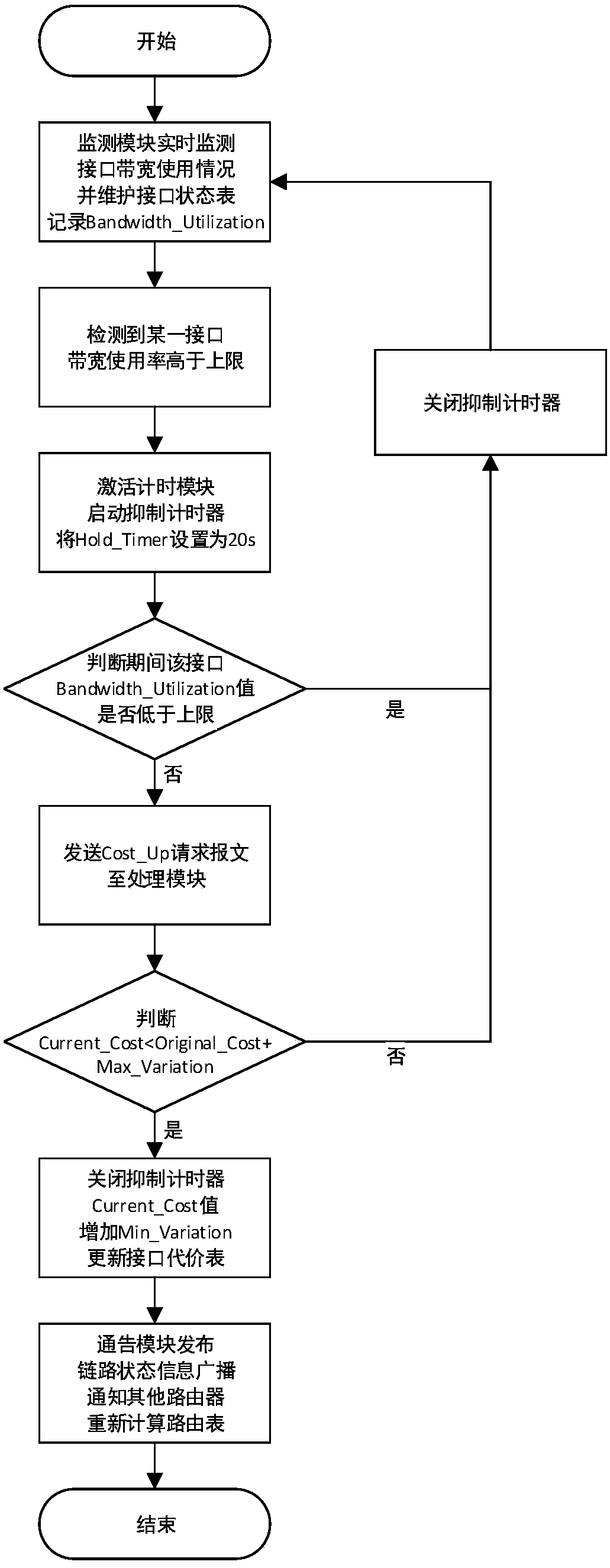
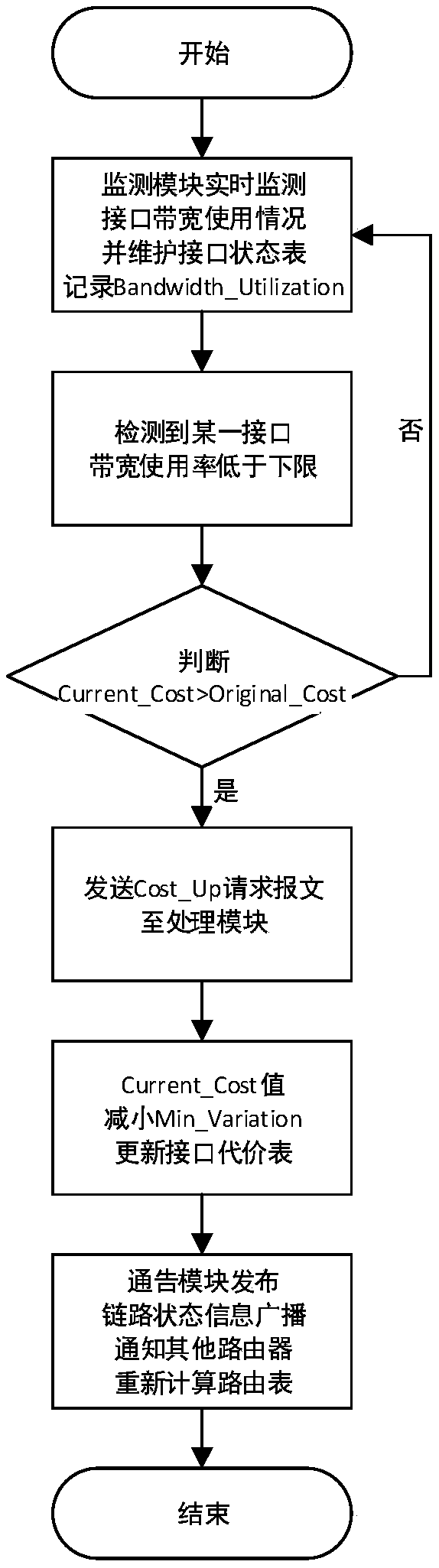
The invention discloses a network local congestion processing method based on an OSPF protocol and relates to the technical field of network local congestion processing. In the method, four parts of amonitoring module, a timing module, a processing module and an announcing module are composed. Firstly, in the process that a router operates the OSPF protocol, the monitoring module monitors the bandwidth utilization rate of a router interface in real time; and when the value is higher than an upper limit or lower than a lower limit, different processing schemes are adopted; secondly, the stateof the interface is judged; when the interface is in an idle state, a Cost-Down request message is sent to the processing module; when the interface is in a saturated state, a Hold-Timer is started; the state of the interface is monitored during the timing period of the Hold-Timer; if the interface is always in the saturated state, a Cost-Up request message is sent to the processing module; otherwise, the timer is shut down; then, when receiving the request message, the processing module modifies the cost value of the interface; finally, the announcing module broadcasts the link state information LSA, so that the router recalculates an optimal route.
Owner:HUAYANG COMM TECH CO LTD
Method for handling local link congestion and apparatus
ActiveUS9013987B2Solve the real problemError preventionTransmission systemsLocal congestionTerminal equipment
The present invention relates to the field of congestion control, and discloses a method for handling local link congestion and an apparatus. The method includes: negotiating, by a local link control entity, a local congestion notification capability with a local terminal; setting, by the local link control entity, a congestion identifier in a downlink data packet corresponding to the local congestion notification capability when a local link is congested between the local link control entity and the local terminal; and performing, by the local link control entity, congestion control on the local link, or performing, by the local terminal, congestion control on the local link according to the congestion identifier. The apparatus includes a local link control entity and a terminal device.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
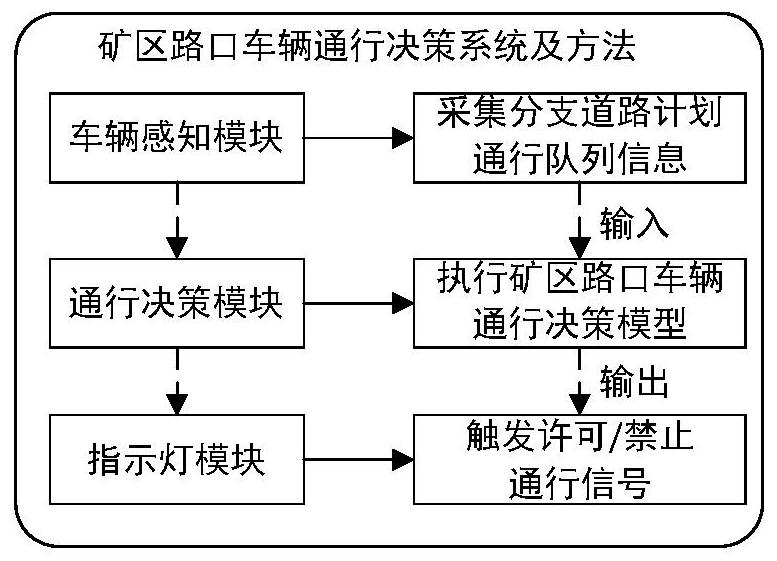
Mining area intersection vehicle passing decision-making system and mining area intersection vehicle passing decision-making method
ActiveCN113781811AImprove transportation efficiencyReduce travel timePlatooningLocal congestionDecision system
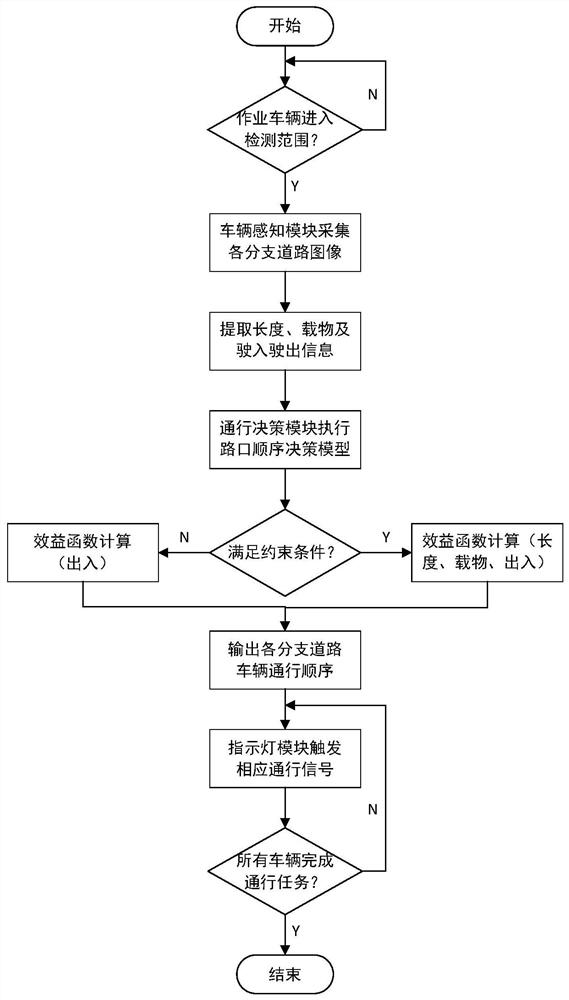
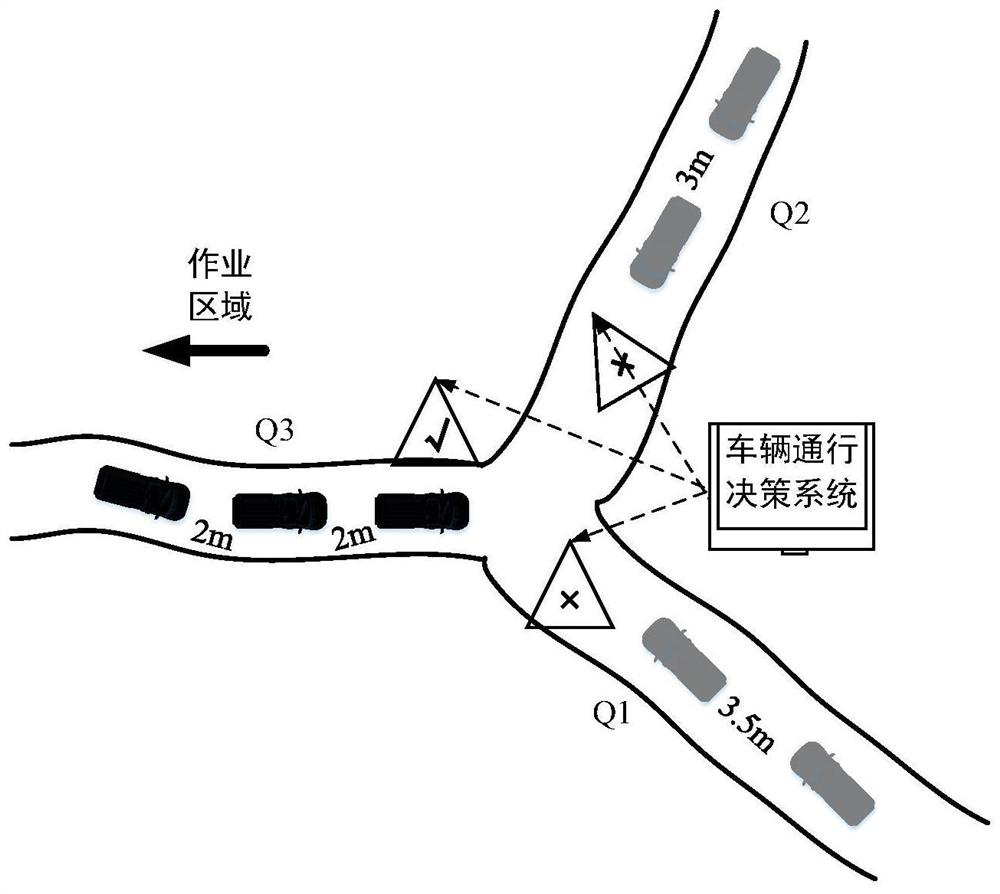
The invention discloses a mining area intersection vehicle passing decision-making system and method. The mining area intersection vehicle passing decision-making system comprises a vehicle sensing module, a passing decision-making module and an indicating lamp module. The system is arranged at an intersection of a mining area and provides passing indication information for passing vehicles on all branches. The mining area intersection vehicle passing decision-making method comprises the steps that the vehicle sensing module is used for calculating the number and length of vehicles waiting for passing, detecting whether the vehicles carry objects or not and judging the driving-in and driving-out states of the vehicles; the passage decision-making module can access perception information as input and execute a vehicle passage sequence decision model; and the indicating lamp module receives the output result of the model and sends indicating lamp signals for allowing / forbidding passing to different queues of vehicles. According to the method, local congestion of the mining area under the unstructured road condition can be improved, the passing efficiency and the transportation level of vehicles can be improved, and the working efficiency of the vehicles in the mining area is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Real-time control system and method for improving traffic capacity of directional lane
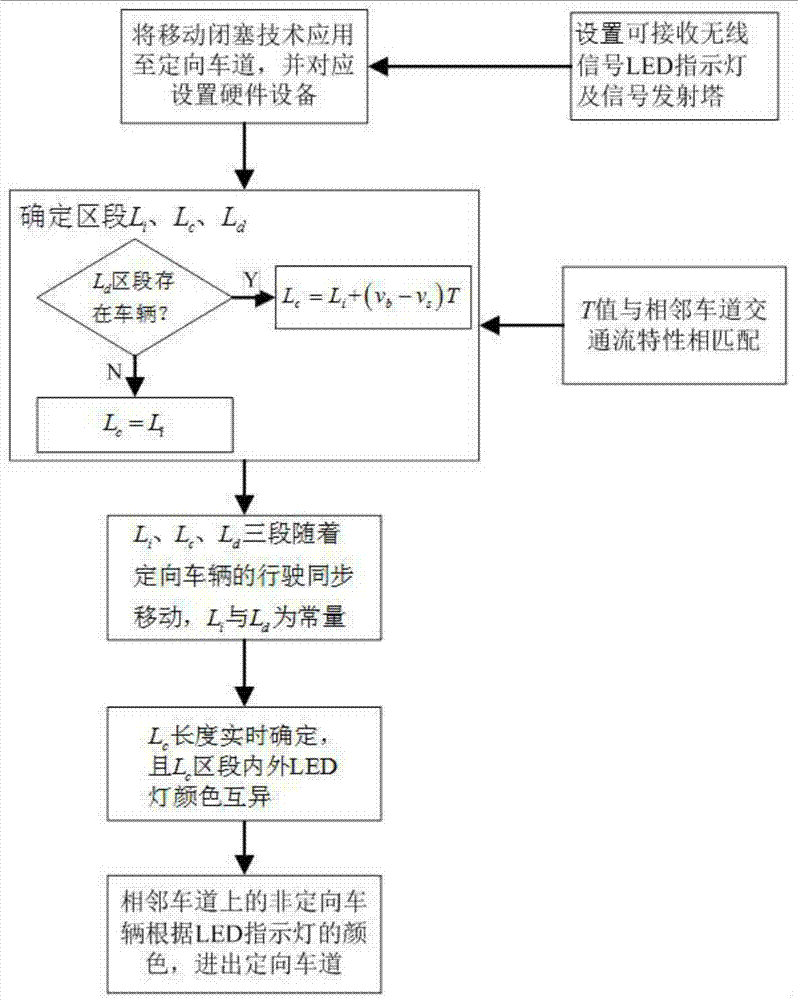
InactiveCN107958600ASolve the problem of insufficient utilization of remaining traffic capacityEnable mixed useArrangements for variable traffic instructionsReal-time Control SystemTraffic capacity
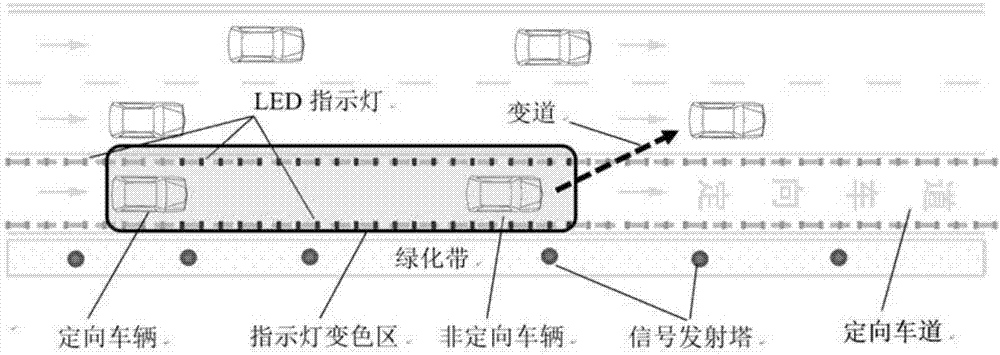
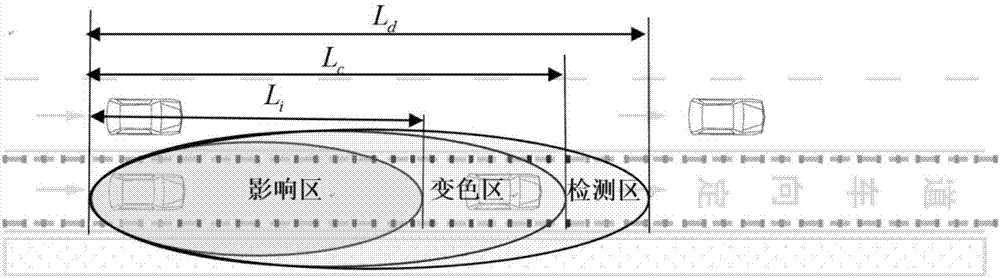
The invention belongs to the intelligent signal control technological field and discloses a real-time control system and method for improving the traffic capacity of a directional lane. The system includes signal transmission towers and LED indication lamps; the signal transmission tower includes a non-directional vehicle identification device, a vehicle information acquisition device, a section control device and a wireless signal transmission device; and the LED indication lamp comprises a wireless signal receiving device. The method includes the following steps that: the signal transmissiontowers identify non-directional vehicles in the directional lane, obtain the positions and speeds of all vehicles in the directional lane, obtain color changing area length information, send the color changing area length information to the LED indication lamps; and the LED indication lamps receive the color changing area length information, maintain or change colors. With the real-time control system and method of the invention adopted, the problem of the insufficient utilization of the remaining traffic capacity of the directional lane in the prior art can be solved, the traffic resources of the directional lane can be utilized to the greatest extent, traffic vehicle distribution can be balanced, and the local congestion of urban roads can be alleviated.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com