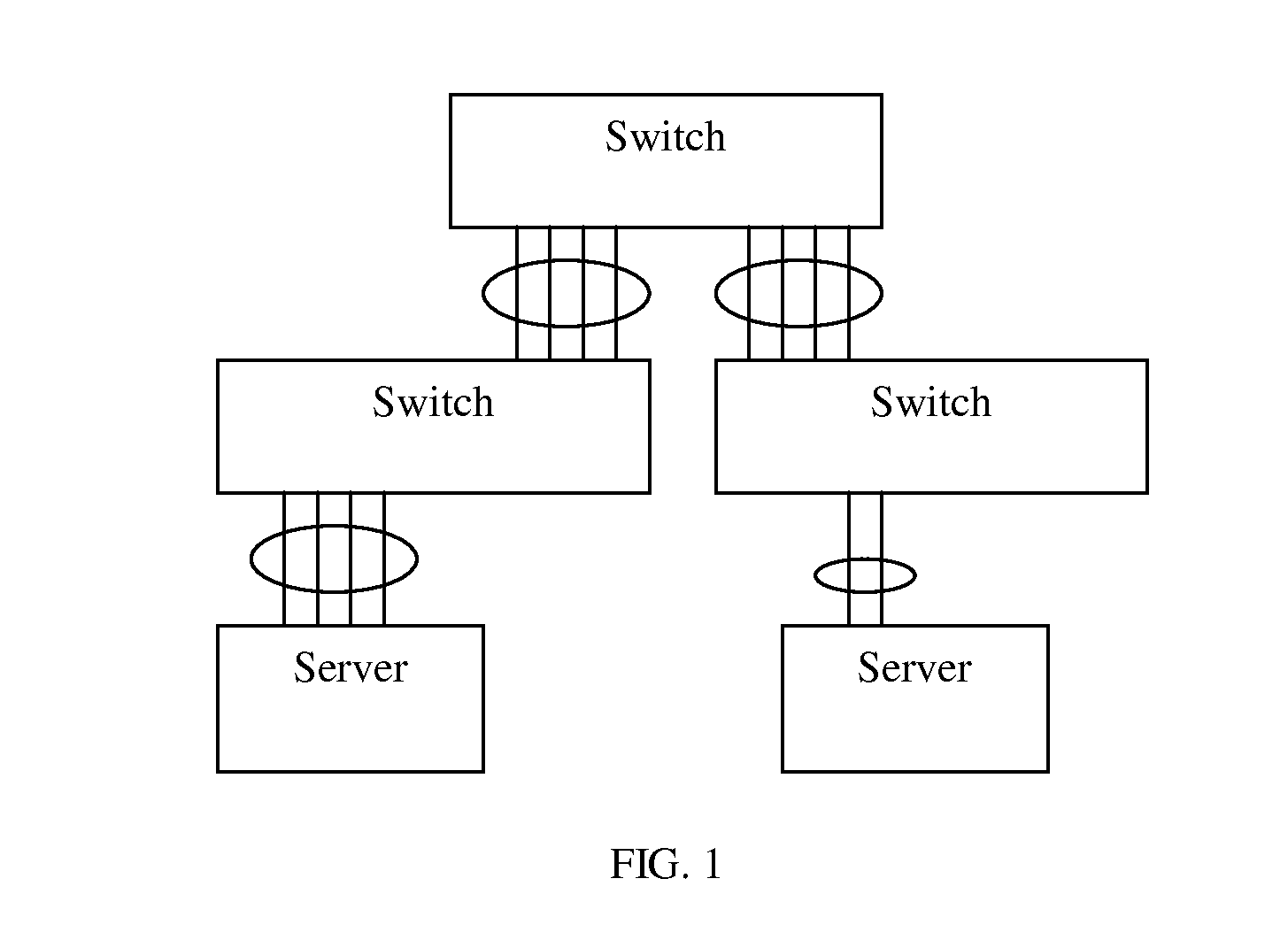
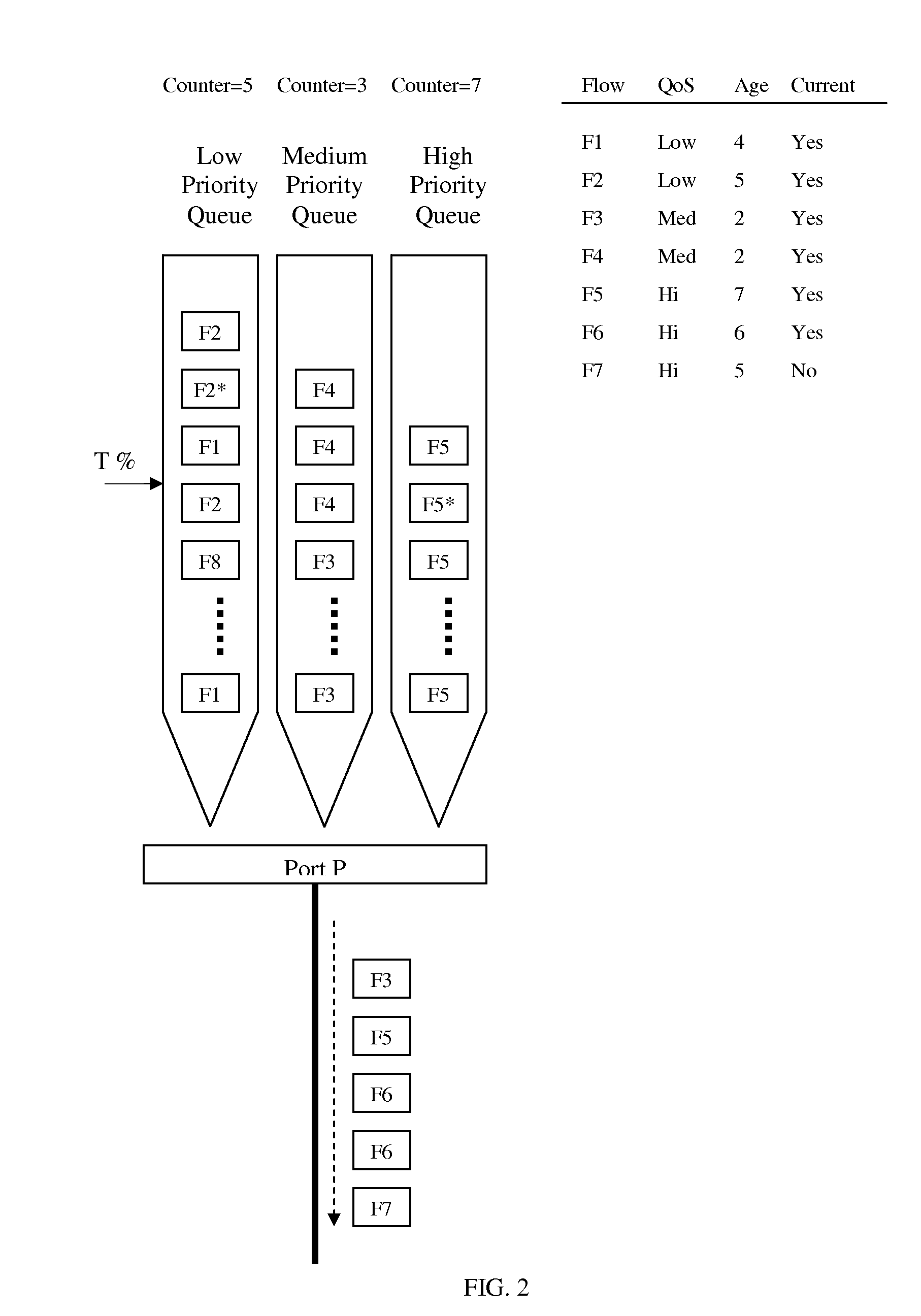
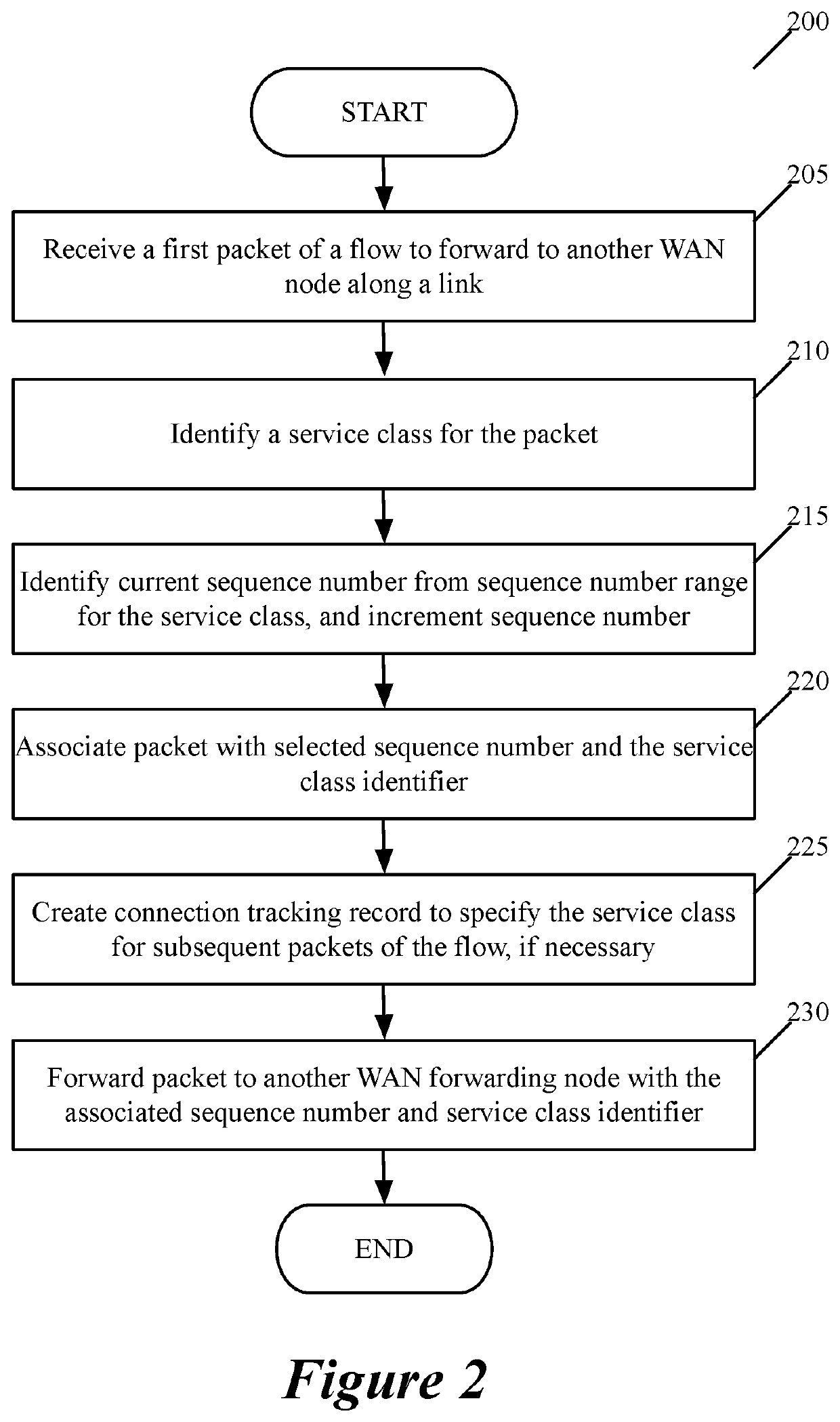
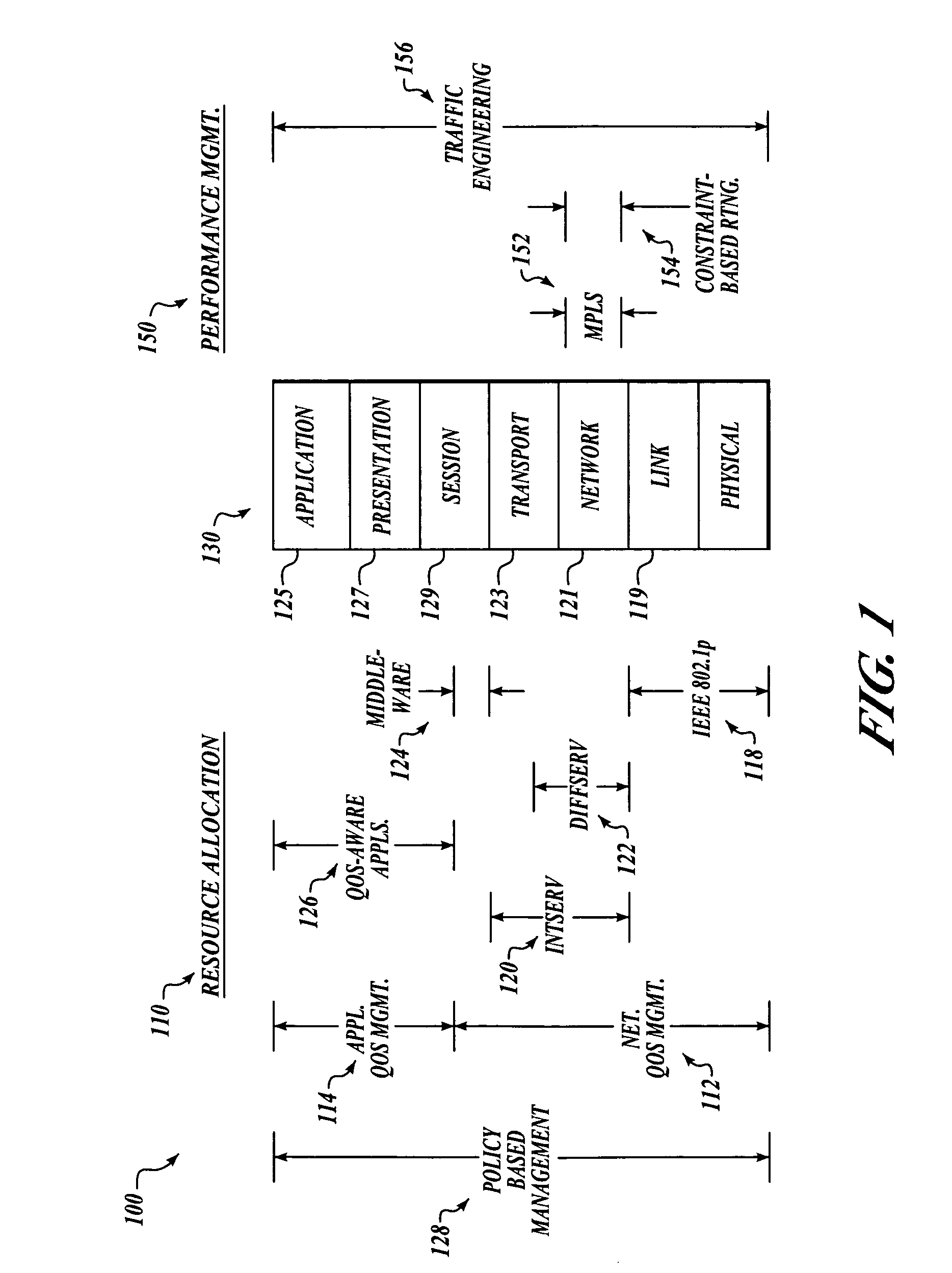
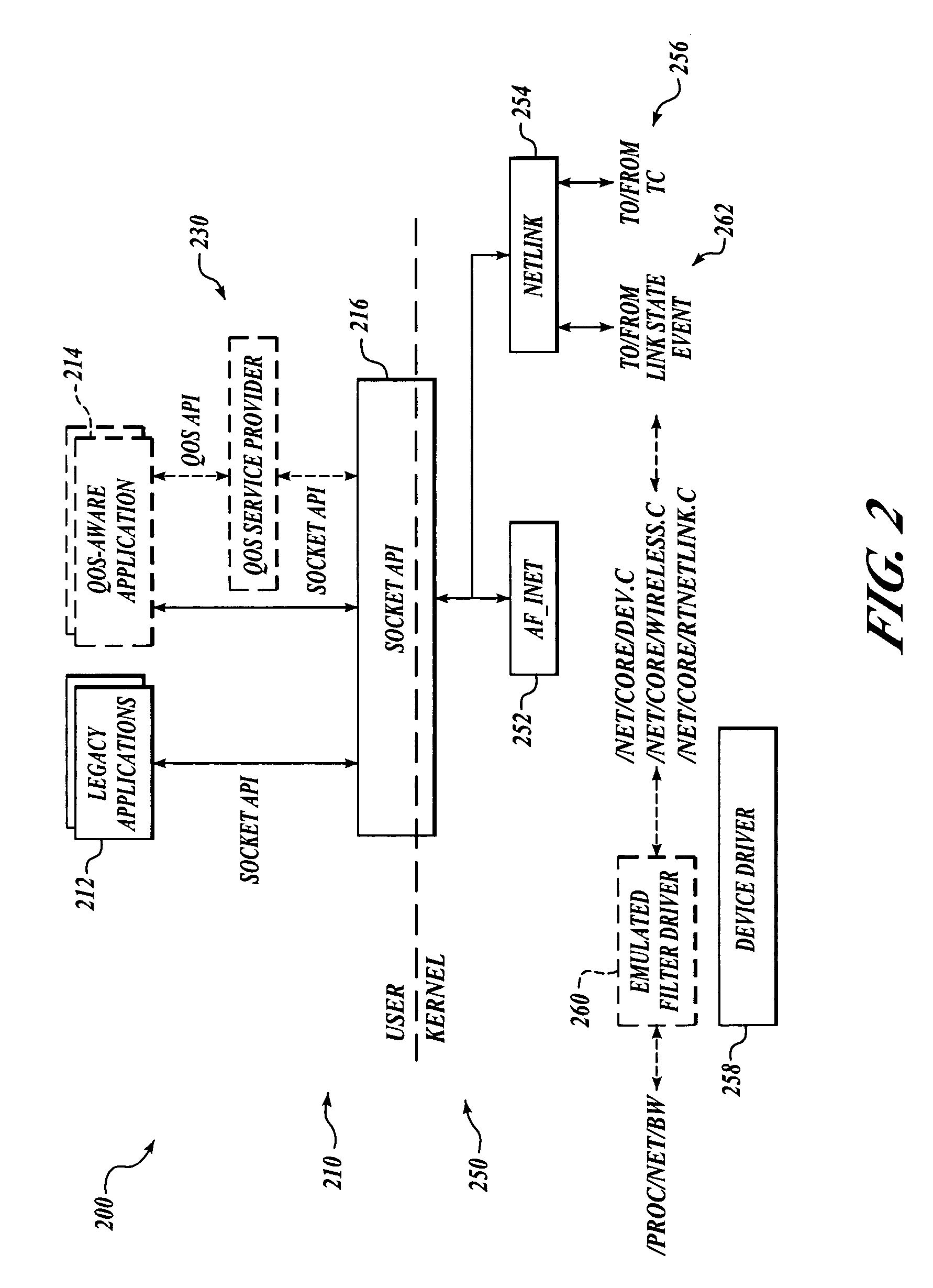
Patents
Literature
50 results about "Qos aware" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
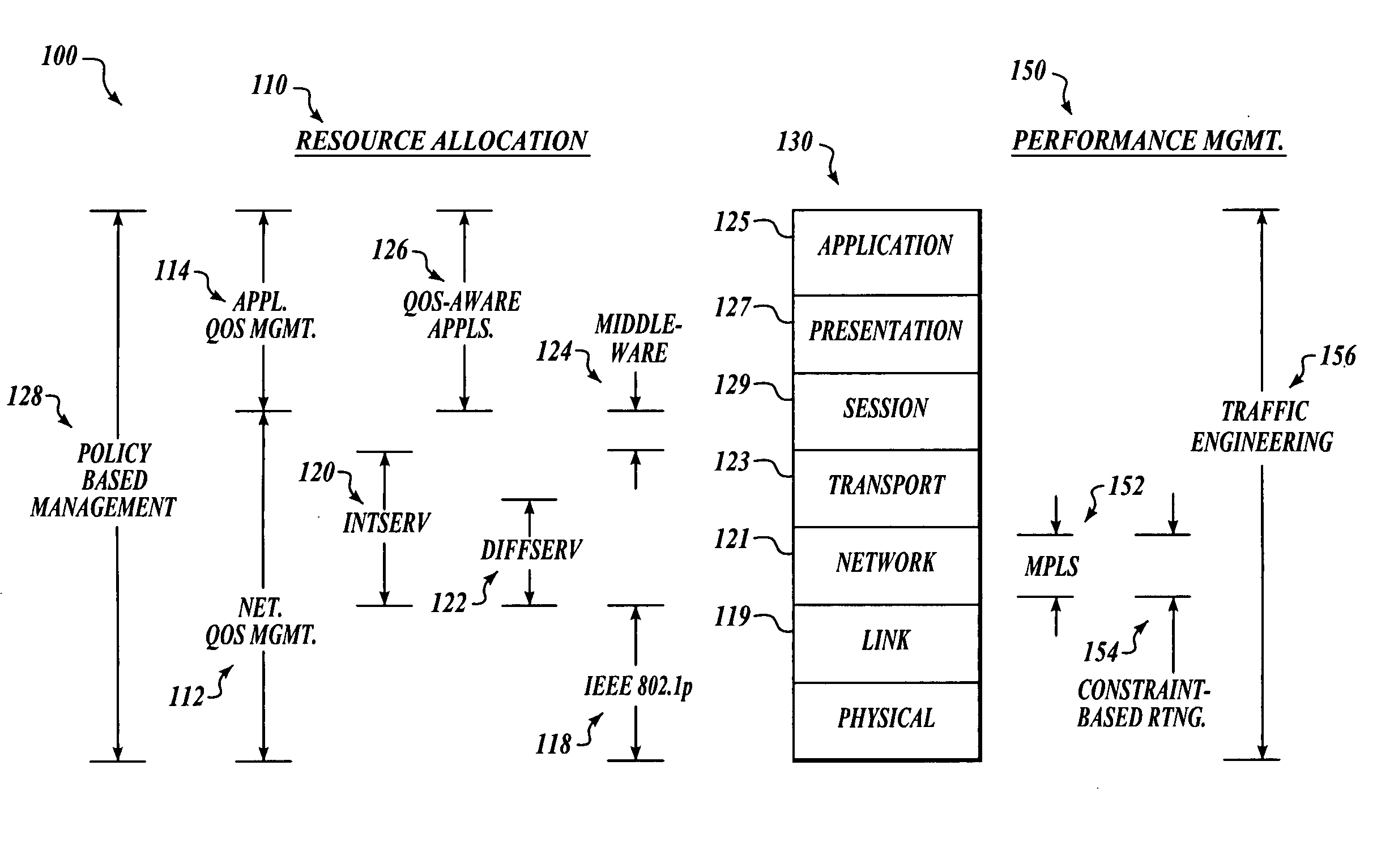
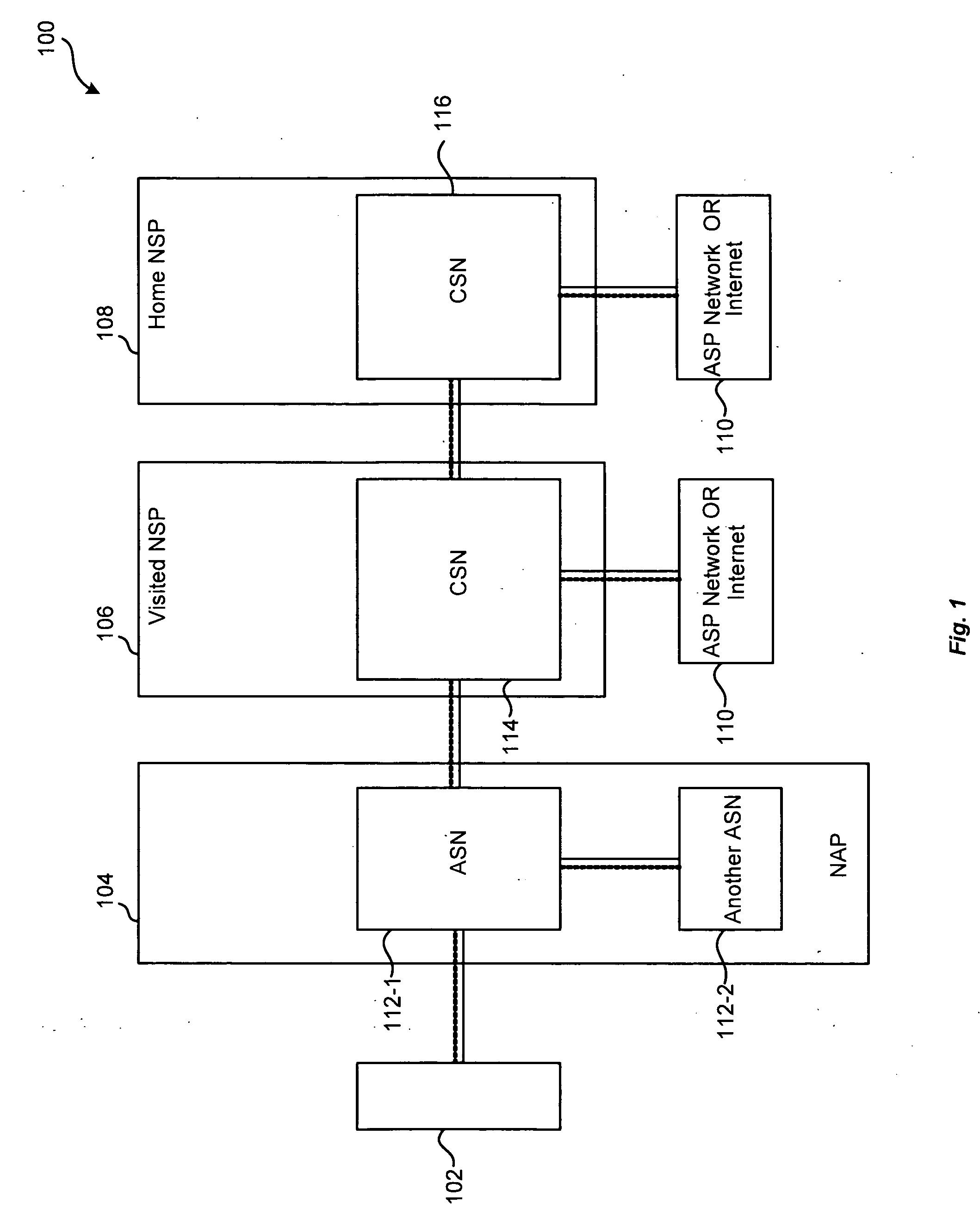
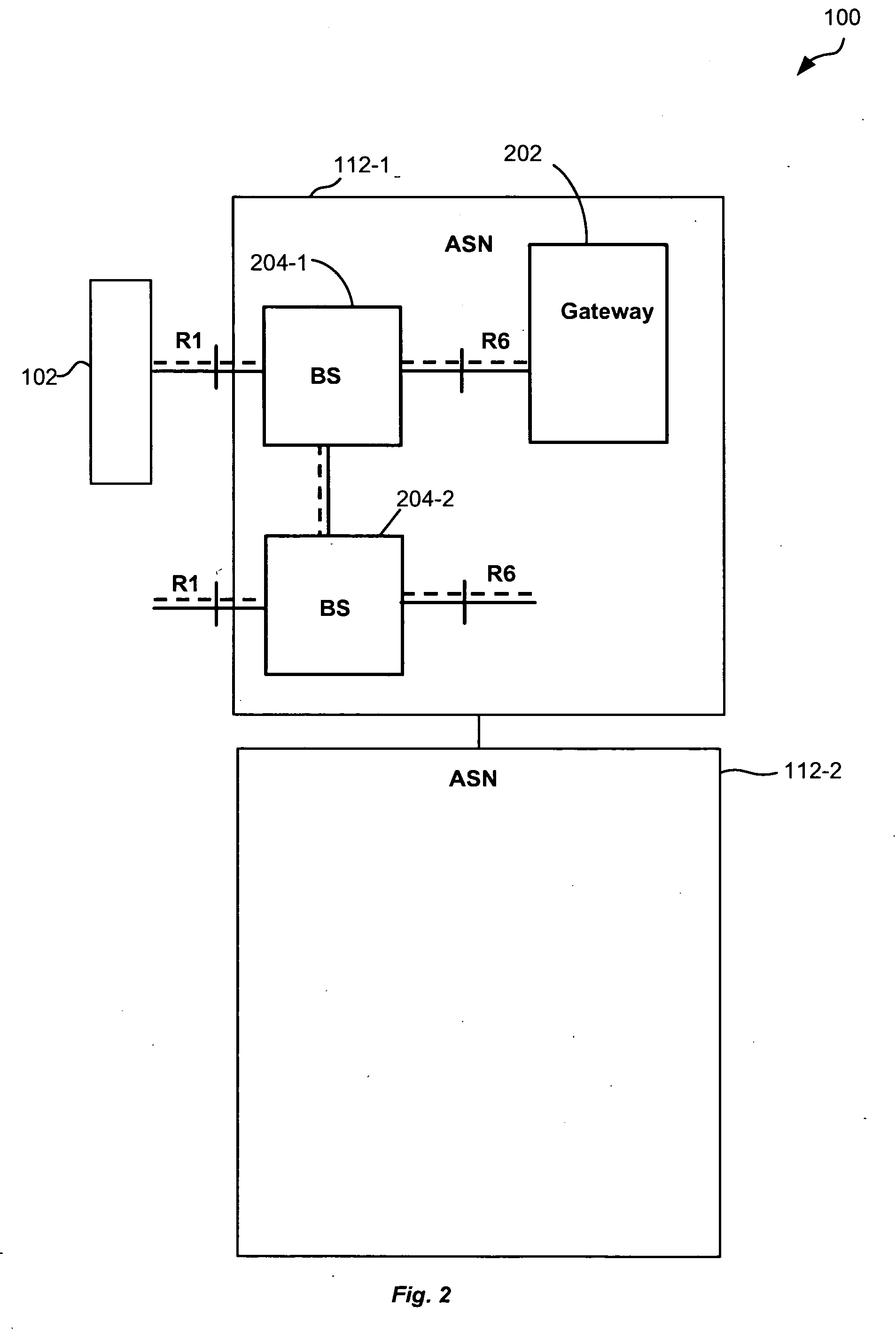
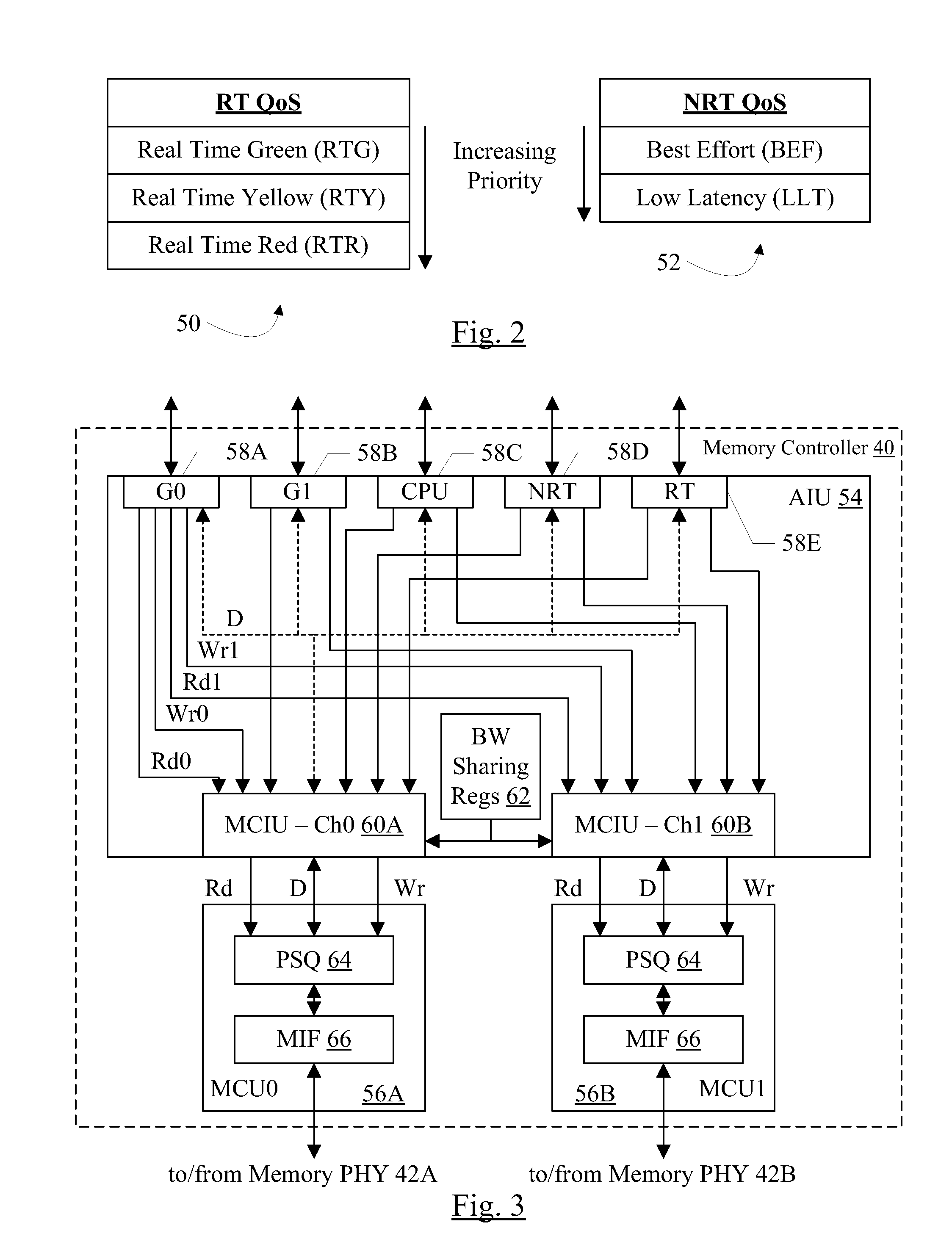
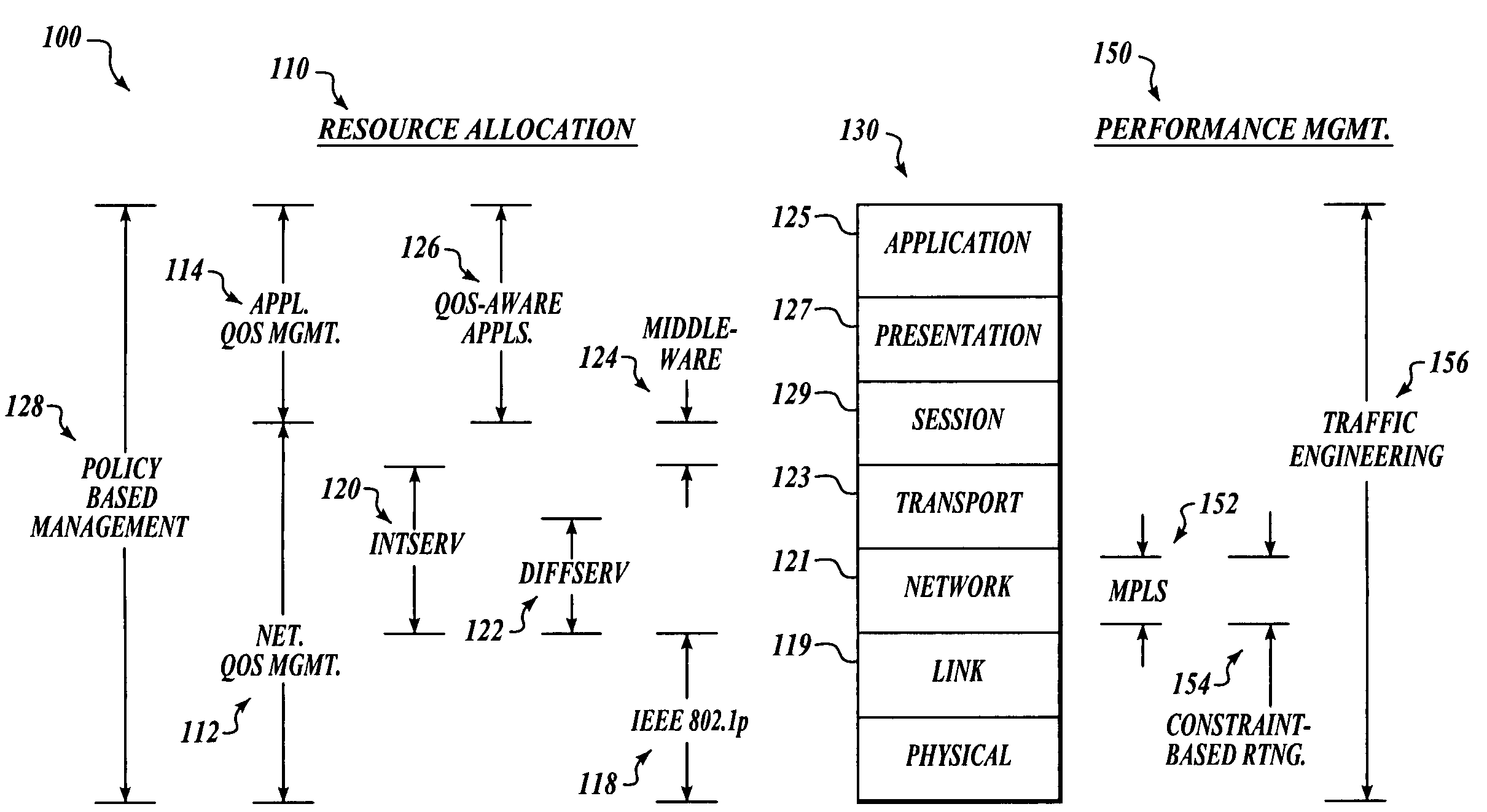
Network centric quality of service using active network technology
InactiveUS20060126504A1Improving network centric qualityError preventionTransmission systemsDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
Systems and methods for improving network centric quality of service using active network technology are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method includes controlling how a packet is passed over at least one of the interfaces using a differentiated services portion of a network management architecture, monitoring a request for a Quality of Service (QoS) level from at least one QoS-aware application, and adjusting at least one service rate of packet travel controlled by the differentiated services portion based on at least one of the requested QoS level and an available bandwidth. In an alternate embodiment, the controlling of how a packet is passed over at least one of the interfaces includes using at least one of a queuing discipline, a class, and a filter.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
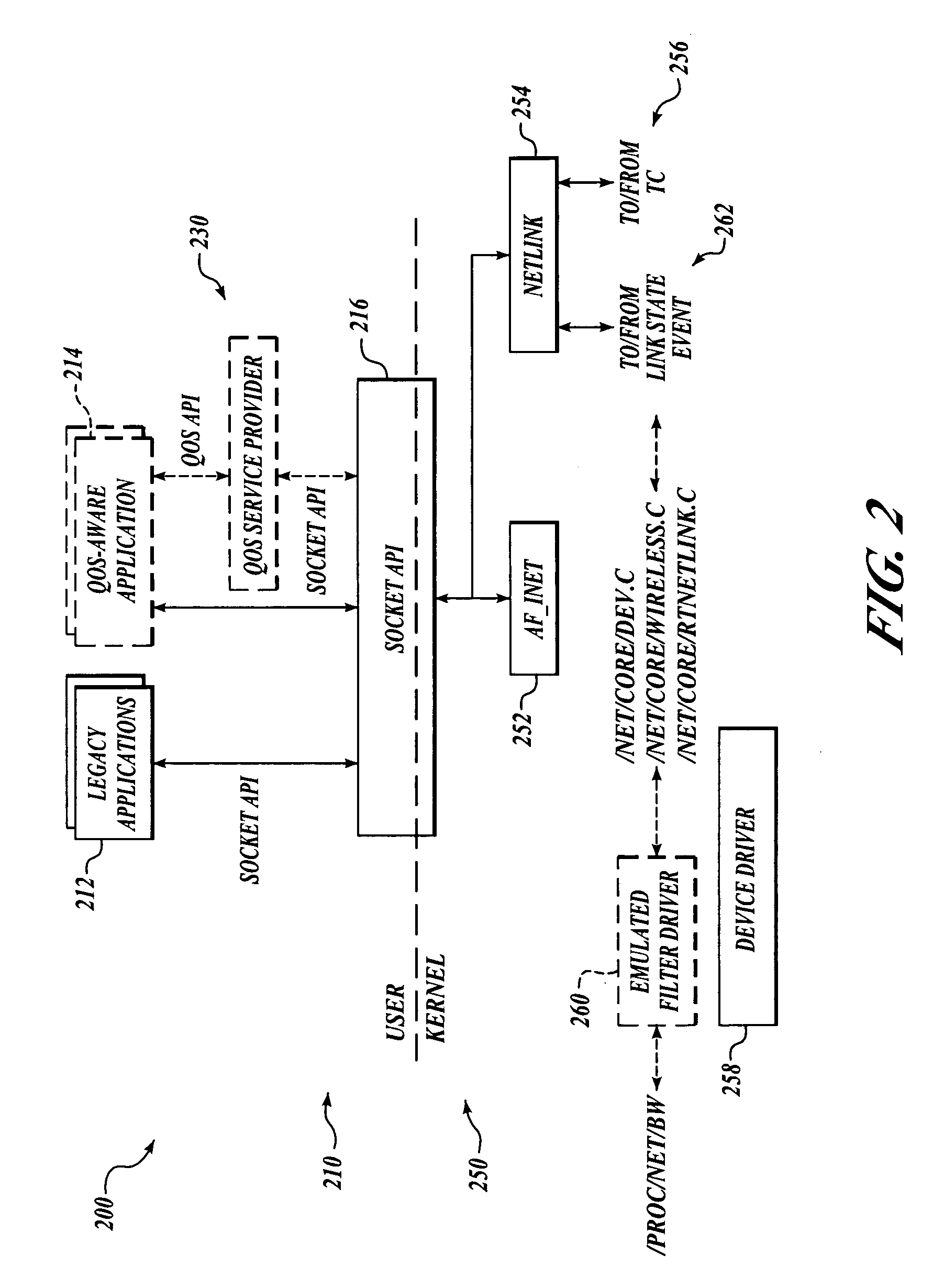
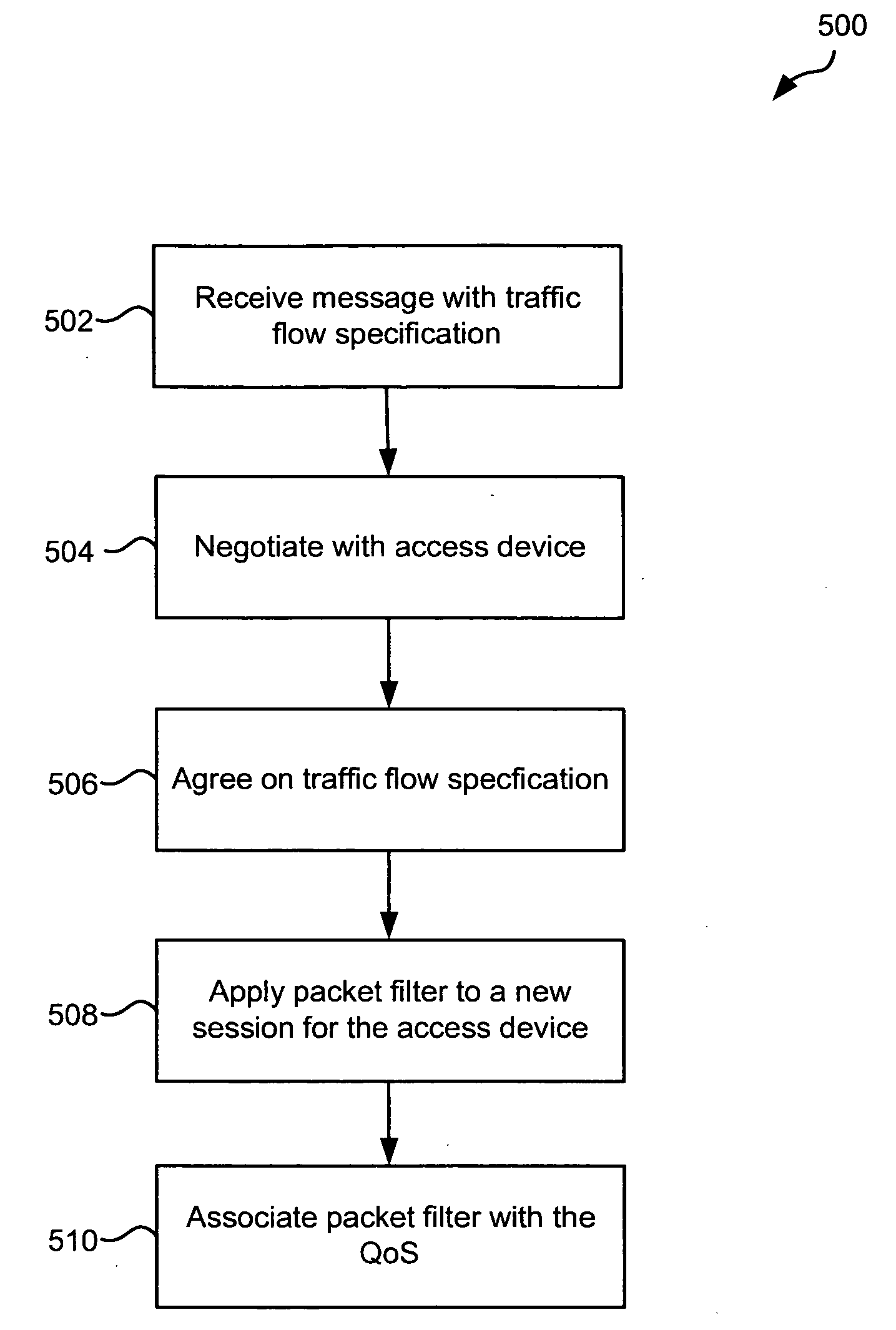
QoS-aware service flow mapping in mobile wireless all IP networks
In one embodiment, techniques provide QoS-aware service flow mapping in an access network. A message is received from an access device at a gateway in the access network. The message includes a traffic flow specification. The traffic flow specification may include packet filter information, which is used to install a packet filter to route traffic to the access device. The gateway creates a session and associates the packet filter with it. When an incoming packet is received at the network device, the packet is matched to the packet filter. The incoming packet is then sent to the access device for the session. The traffic flow specification may also specify QoS parameters that are desired. The QoS parameters may then be applied to the packet sent to the access device. The gateway and access device may negotiate to determine a QoS to apply.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
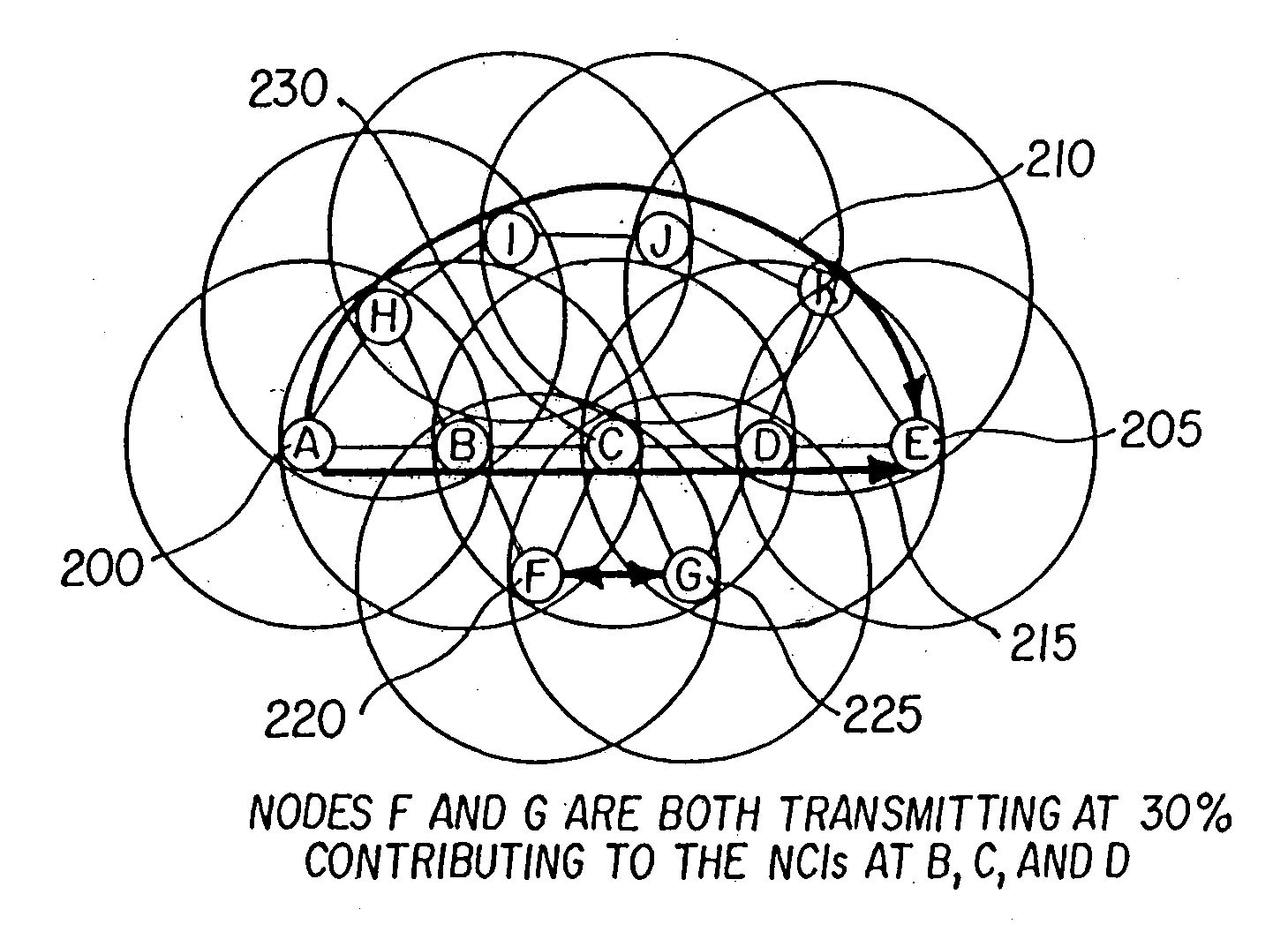
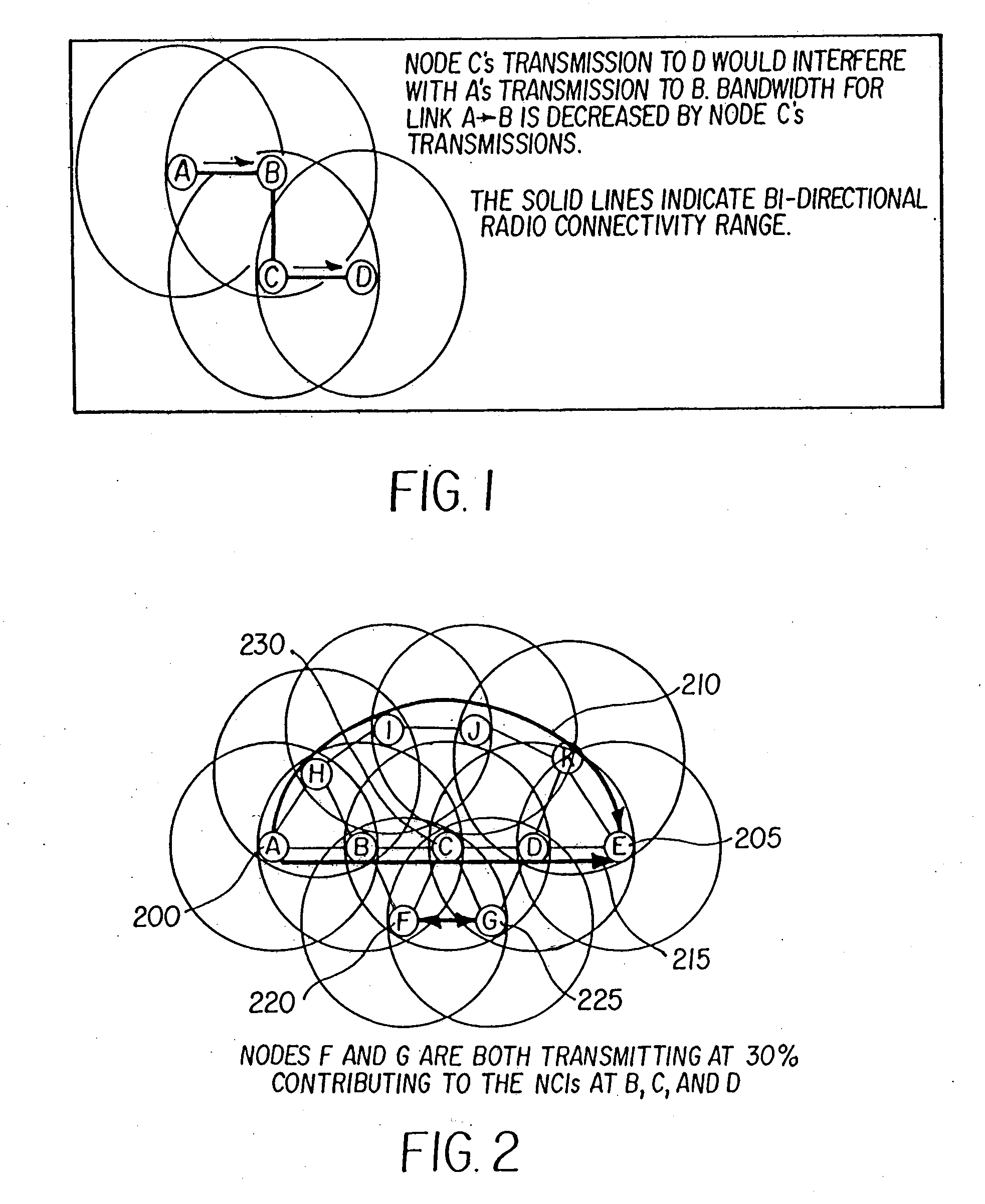
INTEGRATING LOCAL CONGESTION AND PATH INTERFERENCE INTO QoS ROUTING FOR WIRELESS MOBILE AD HOC NETWORKS
A method and apparatus is provided for using a distributed multi-path QoS-aware routing scheme that considers basic MANET characteristics to meet transport service requirements of real-time applications and makes use of multiple discovered paths to calculate a next-hop decision. The QoS Routing scheme superimposes distributed neighborhood congestion, neighborhood density, and link stability and delay information over the multiple discovered paths when the next-hop decision is calculated.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
QoS-aware paging in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20070171850A1Increased latencyShorten the timeError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsService flowCommunications system
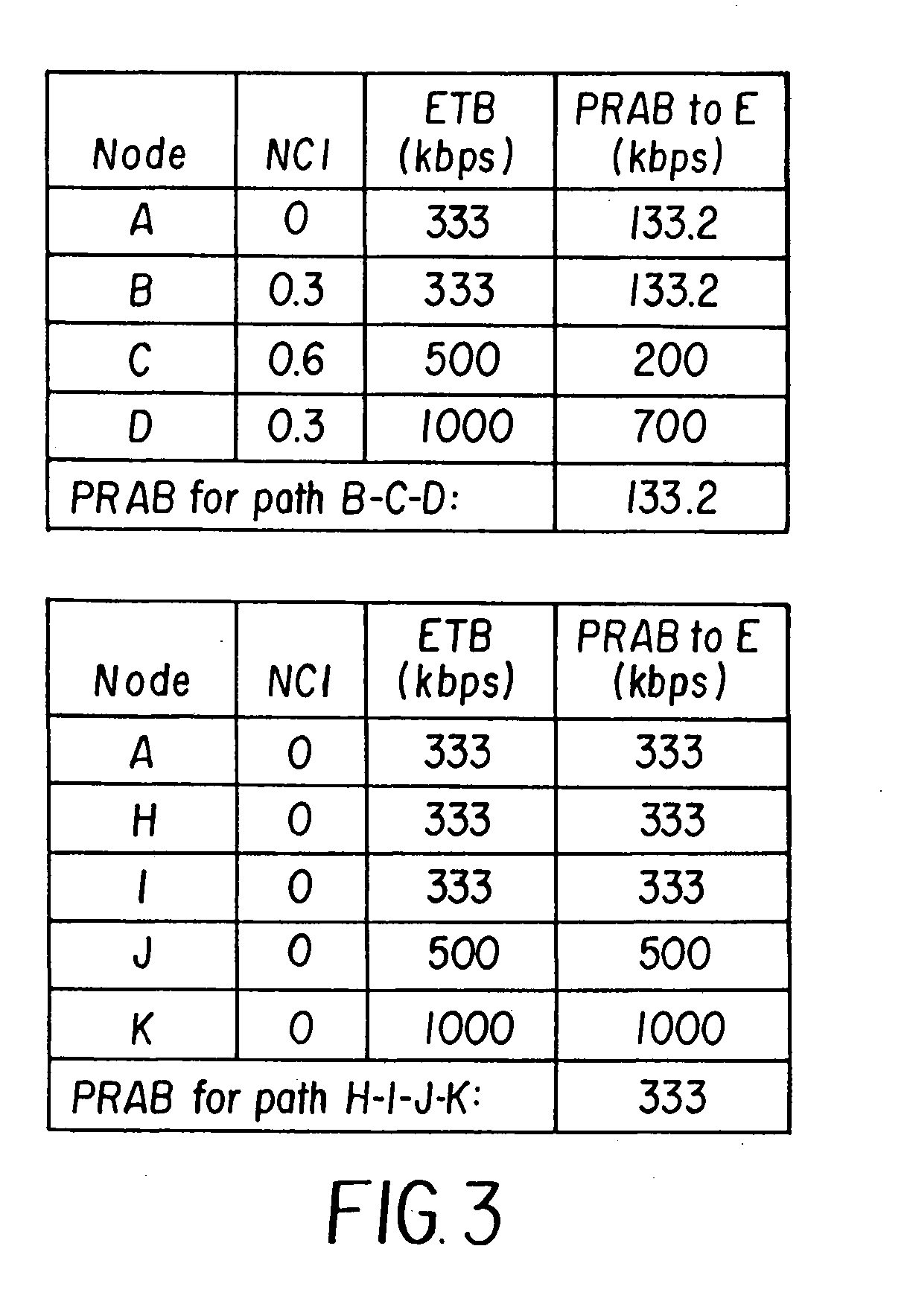
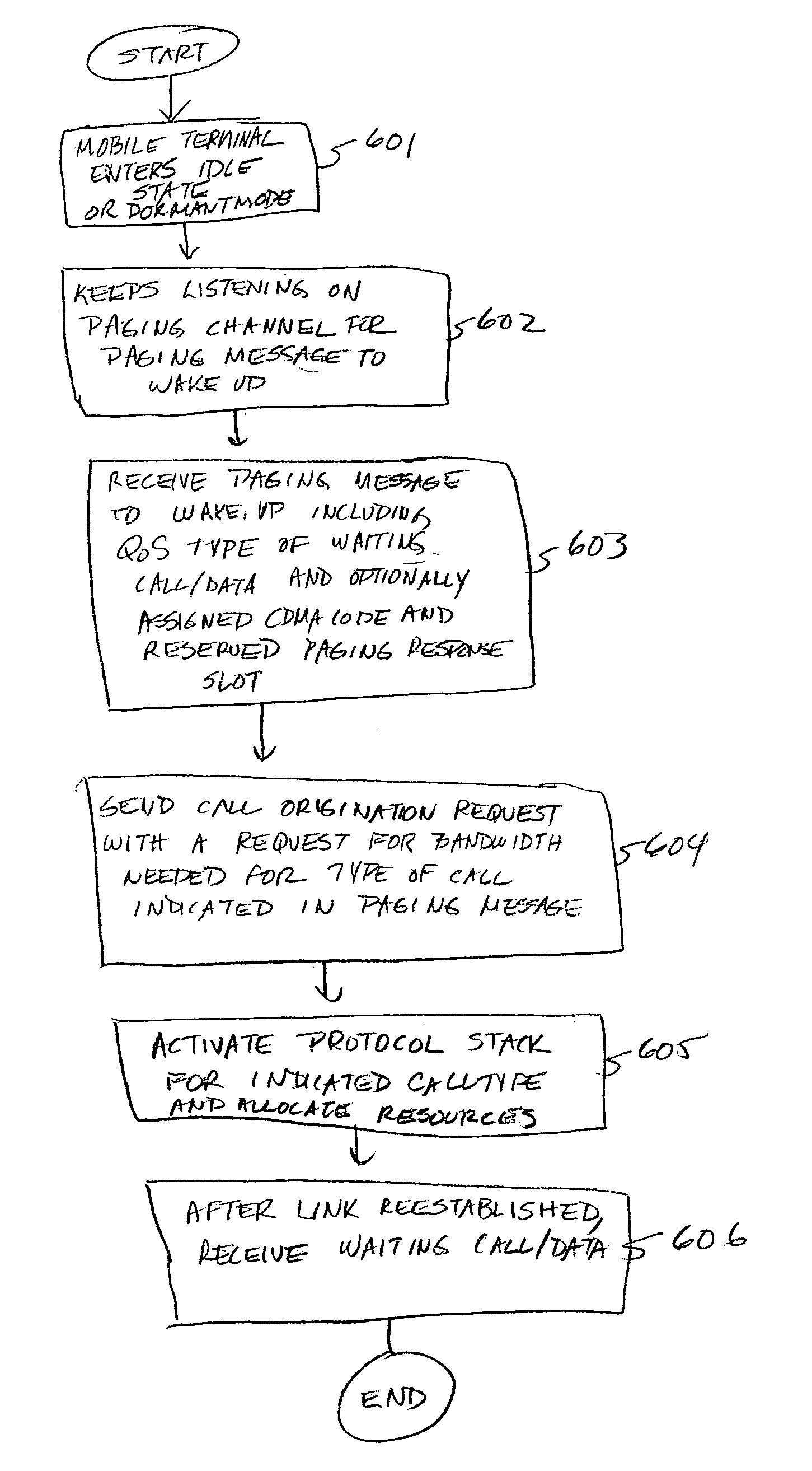
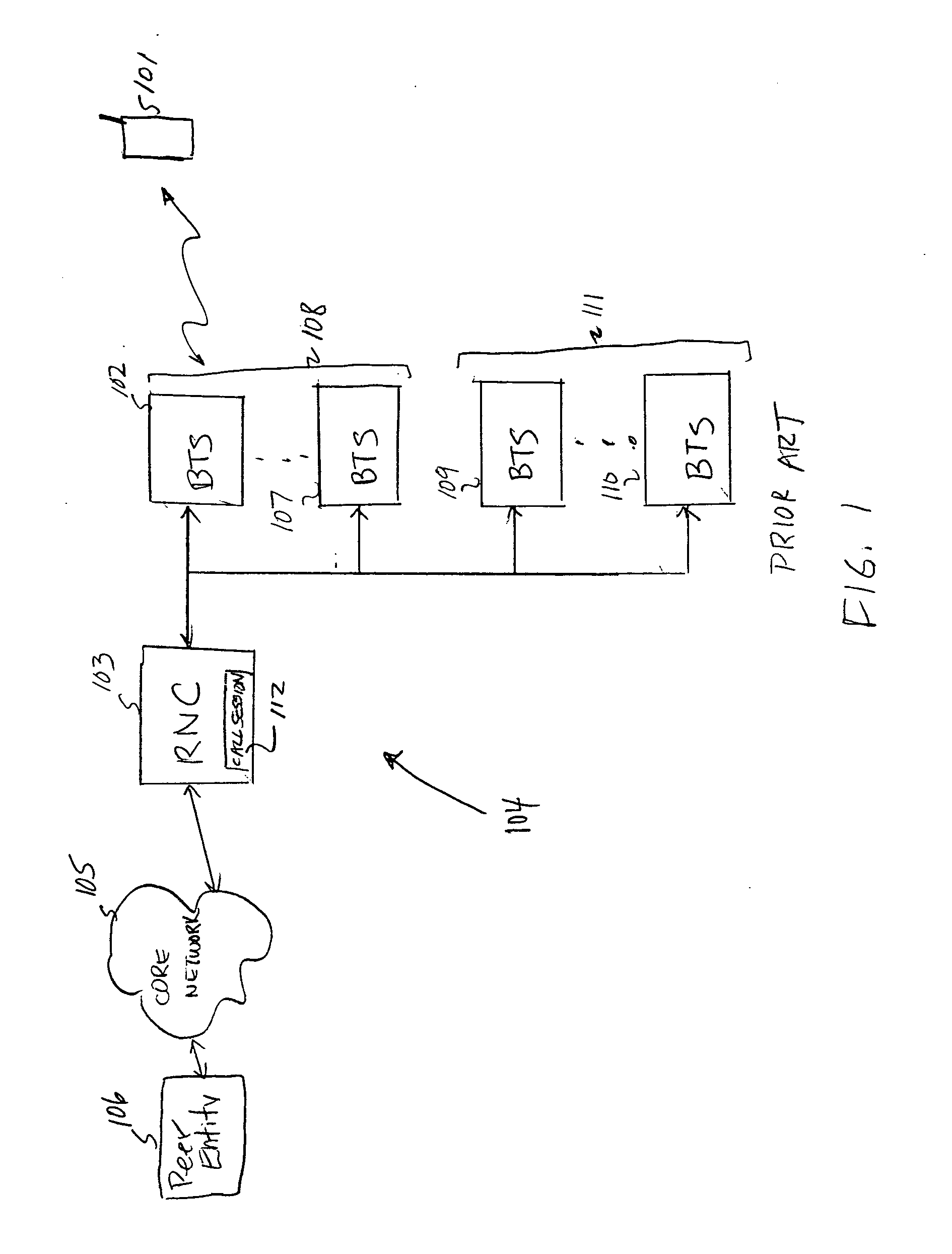
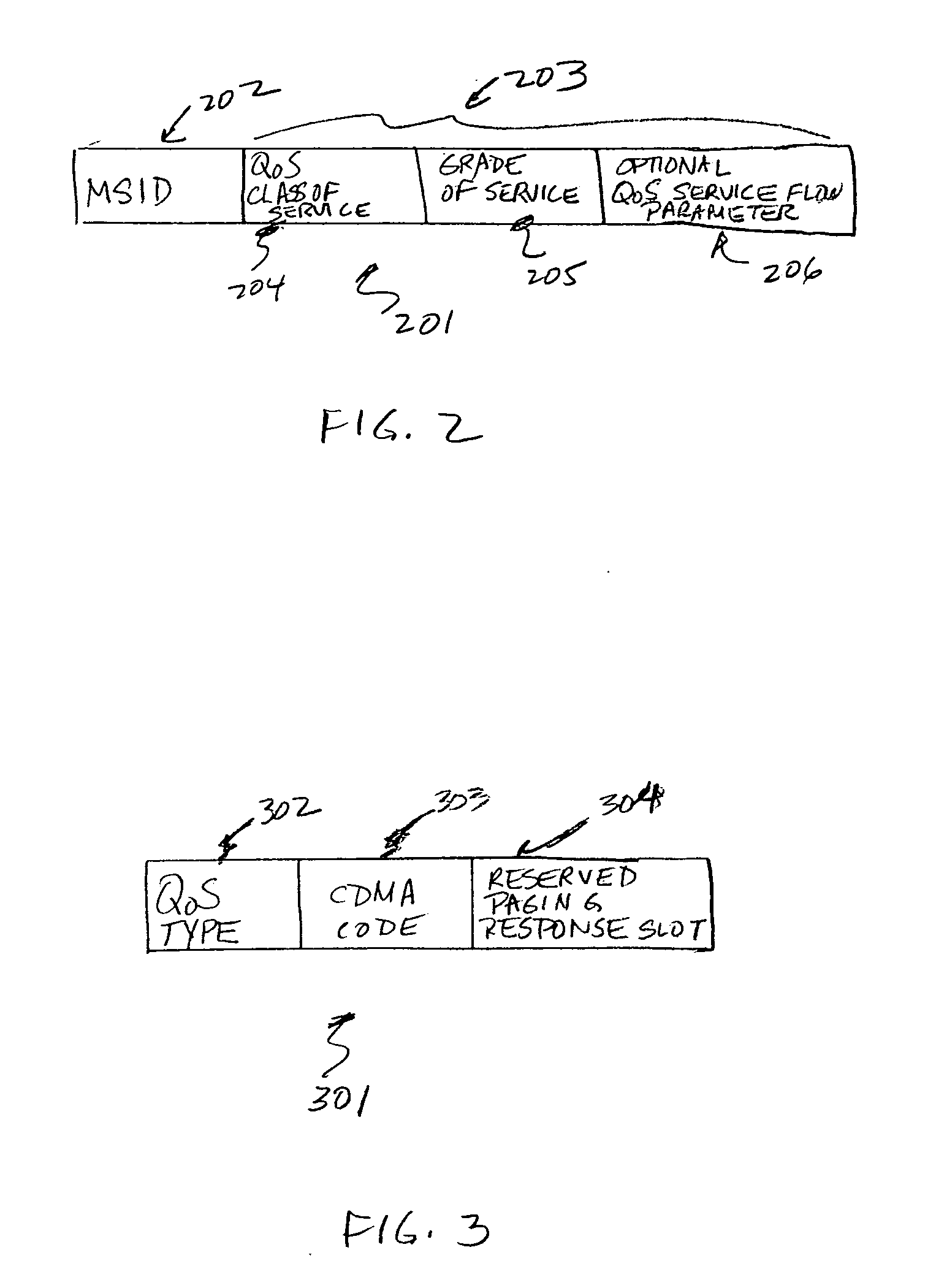
Paging messages are transmitted by a wireless communications network to mobile terminals, which have been in an idle state or dormant mode and which have waiting calls / data from their associated peer entities, in accordance with the qualities of service (QoS) associated with the waiting calls / data, where the QoS associated each waiting call / data includes a type of the call / data. To make paging of mobile terminal QoS aware, a QoS field is included in the Paging Announce requests sent from an RNC to another RNC, or from an RNC to a BTS. The QoS field includes: a QoS class of service of the waiting call / data indicating the type of the waiting call; a grade of service of the waiting call / data to which the mobile terminal is subscribed; and, optionally, other QoS service flow parameters whose presence depends on the type of wireless technology being used in the network.
Owner:RPX CORP
Using heart beats to monitor operational state of service classes of a QOS aware network link
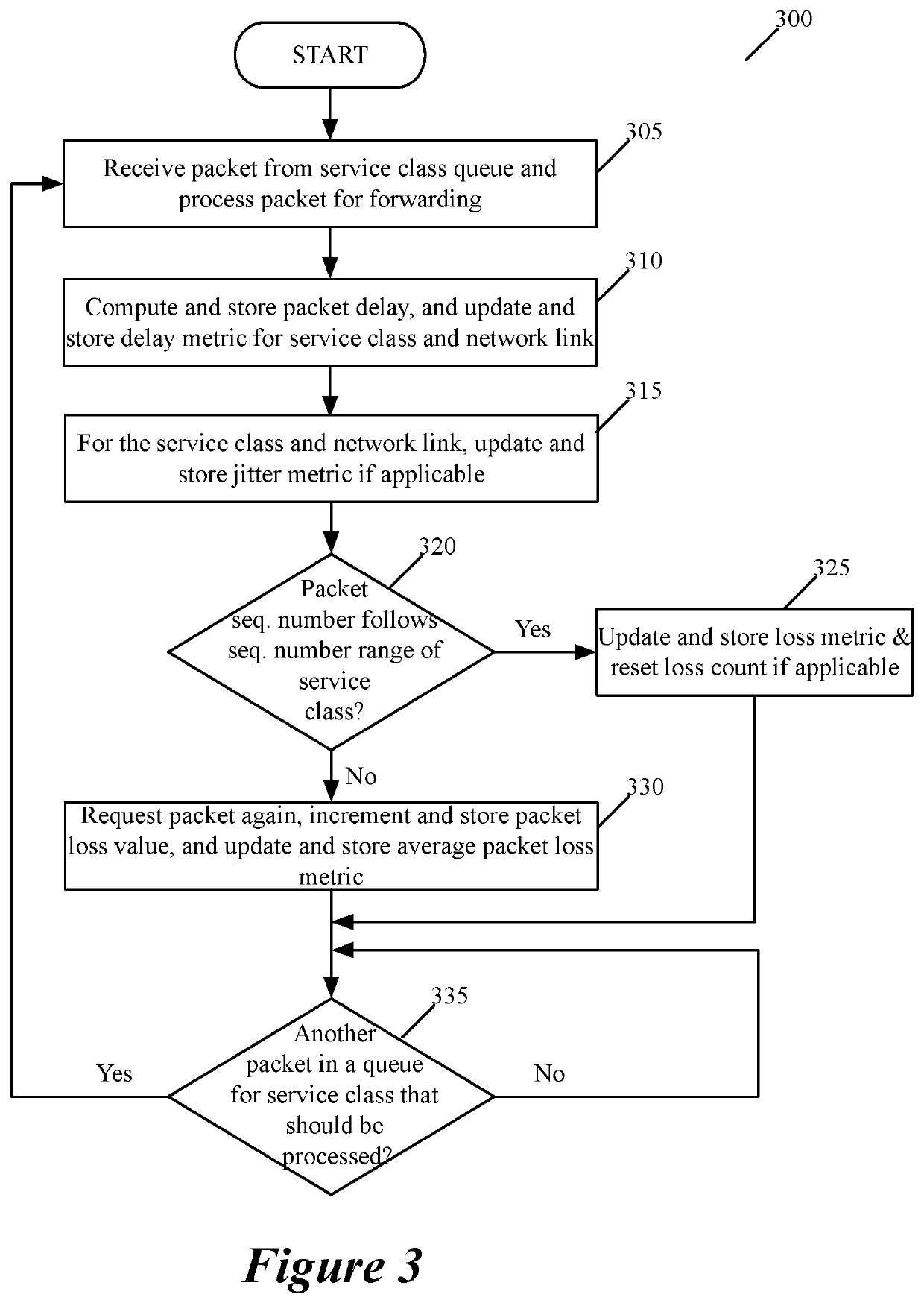
ActiveUS20210234786A1Increases egress rateIncrease ratingsNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksQos quality of serviceNetwork link
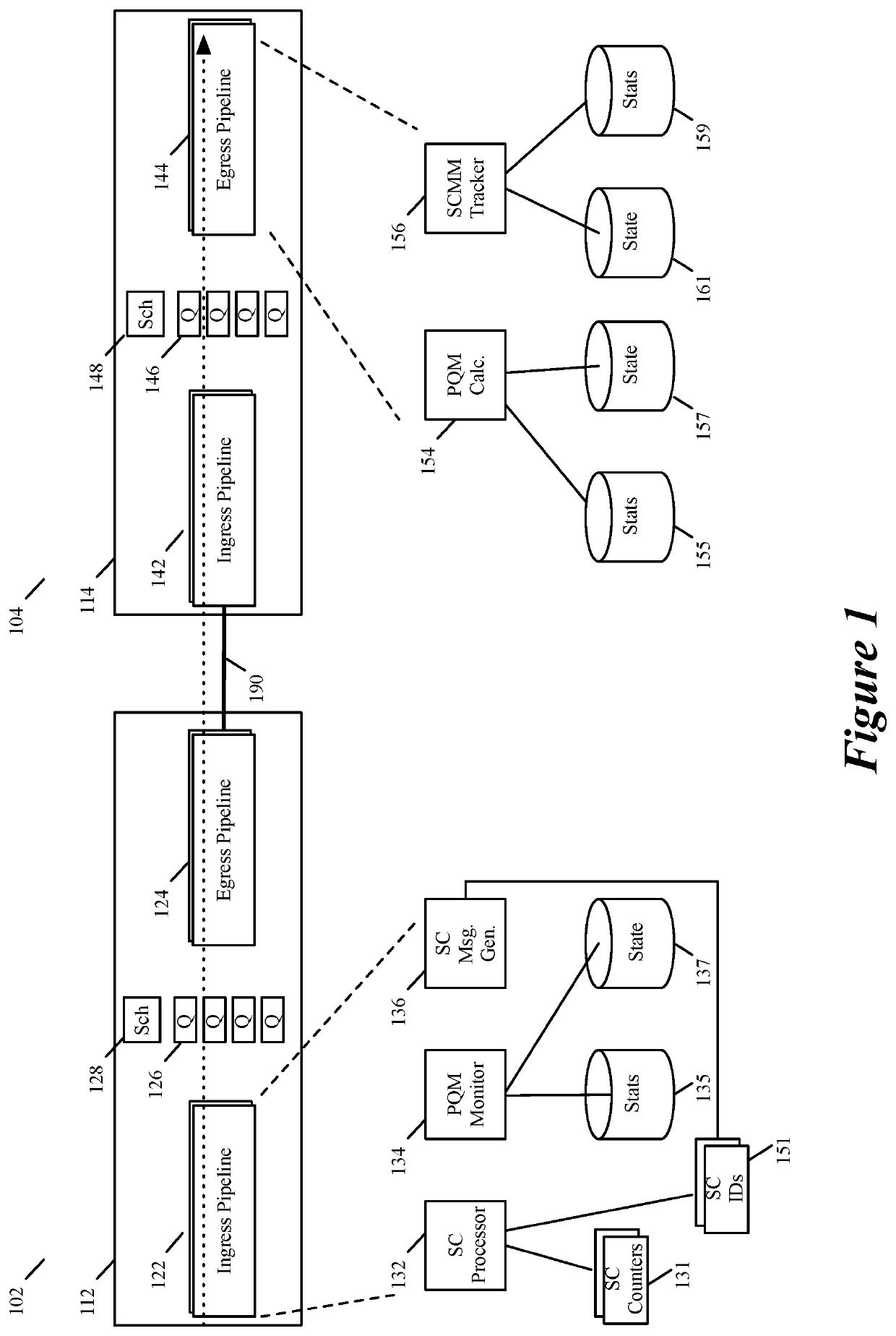
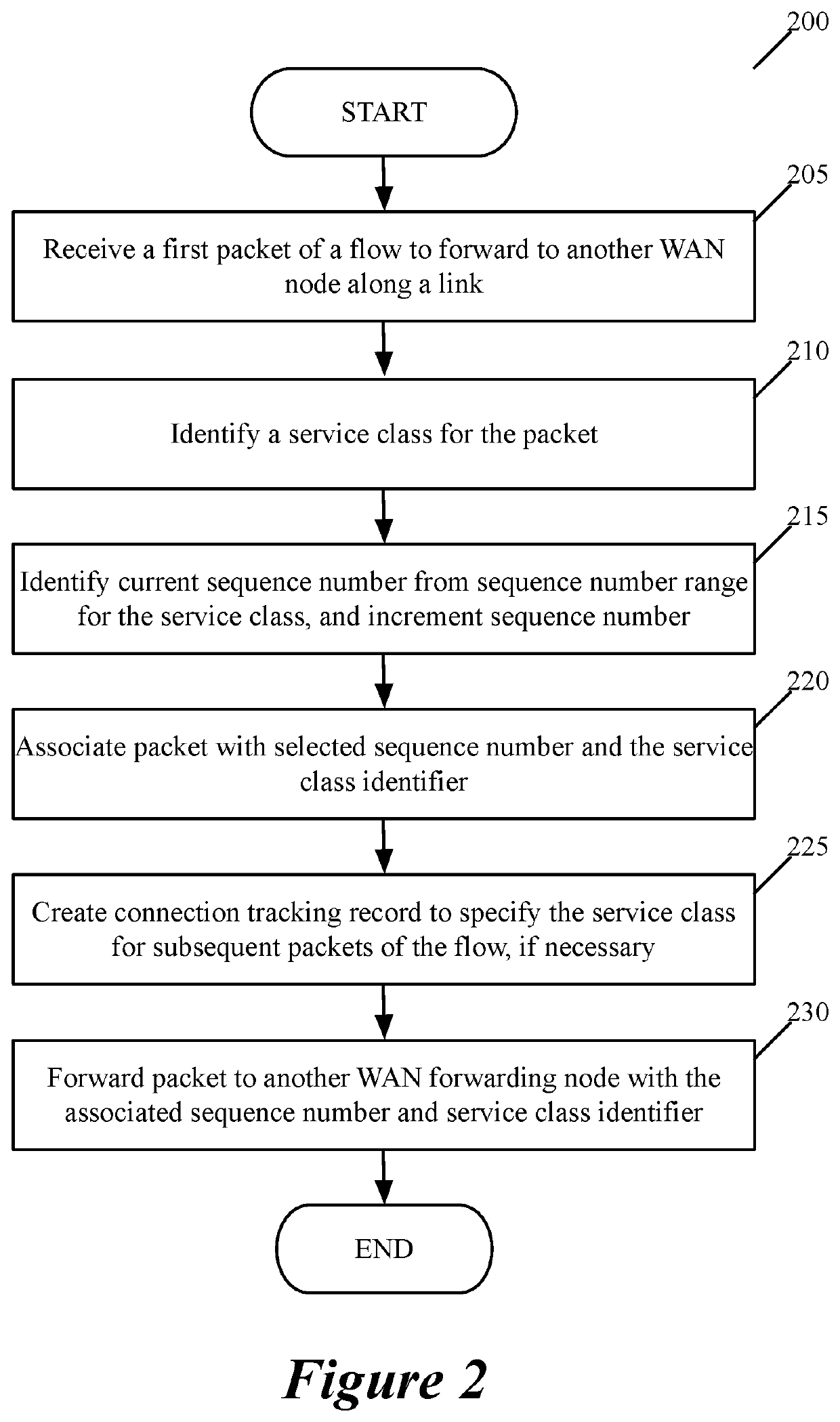
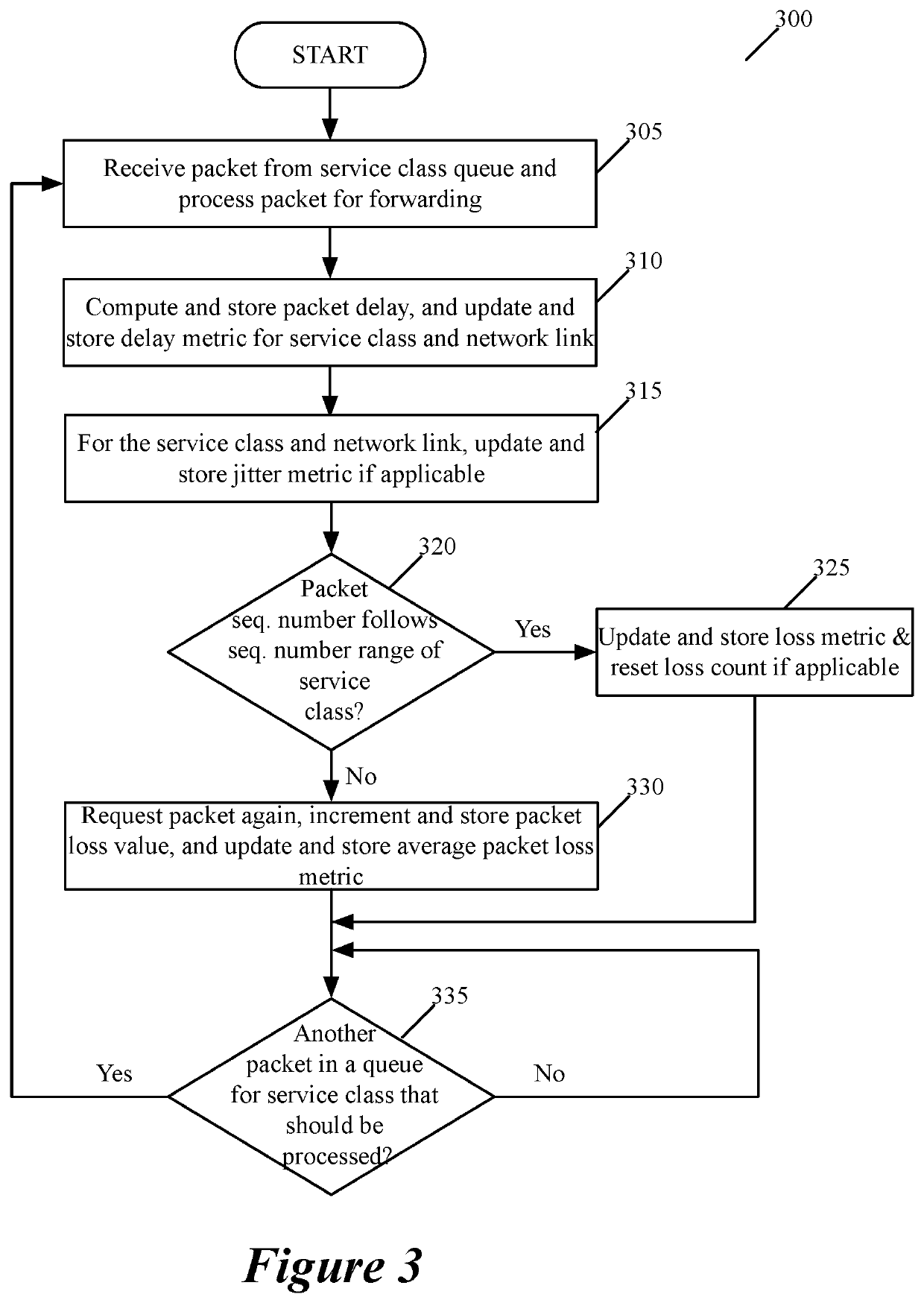
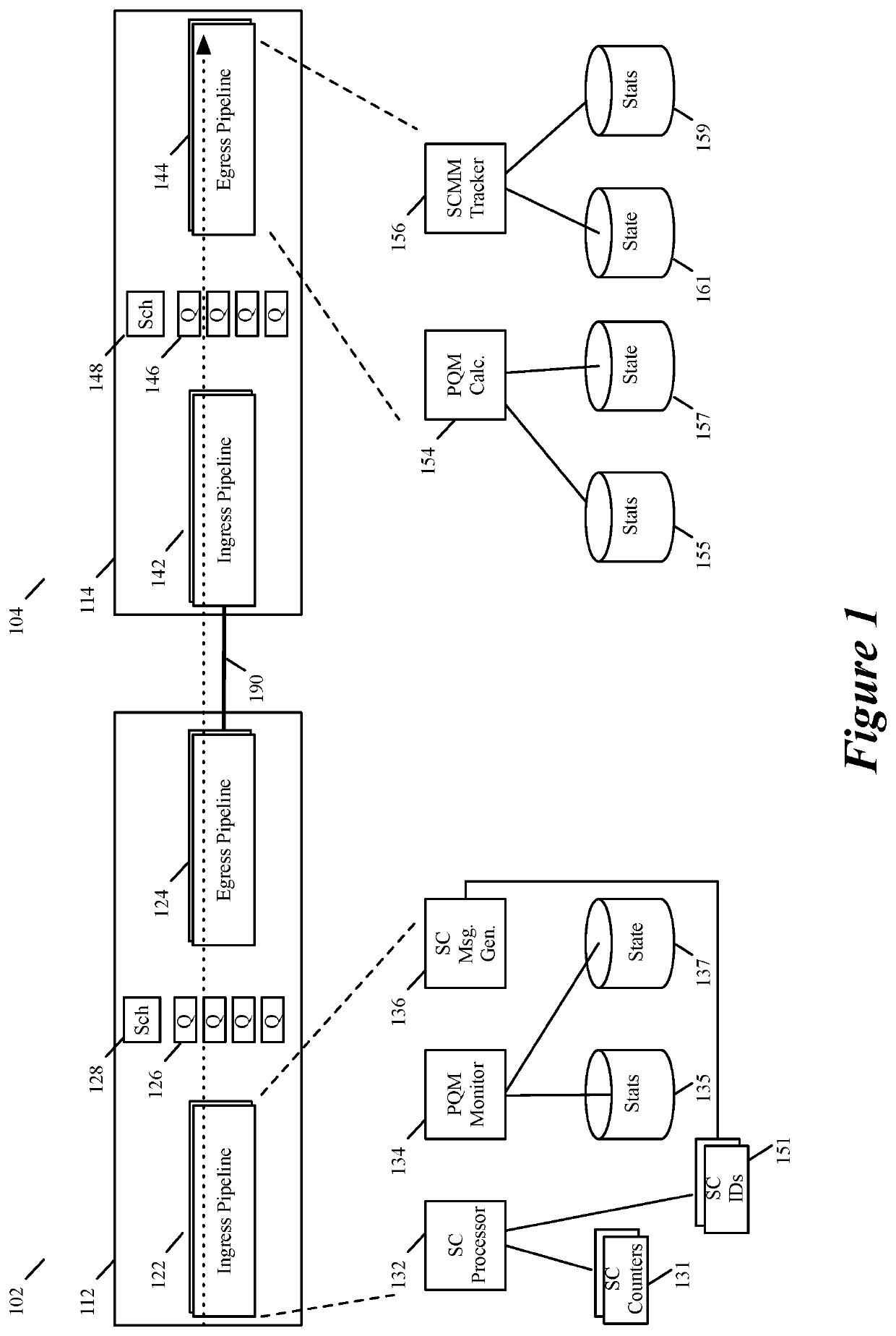
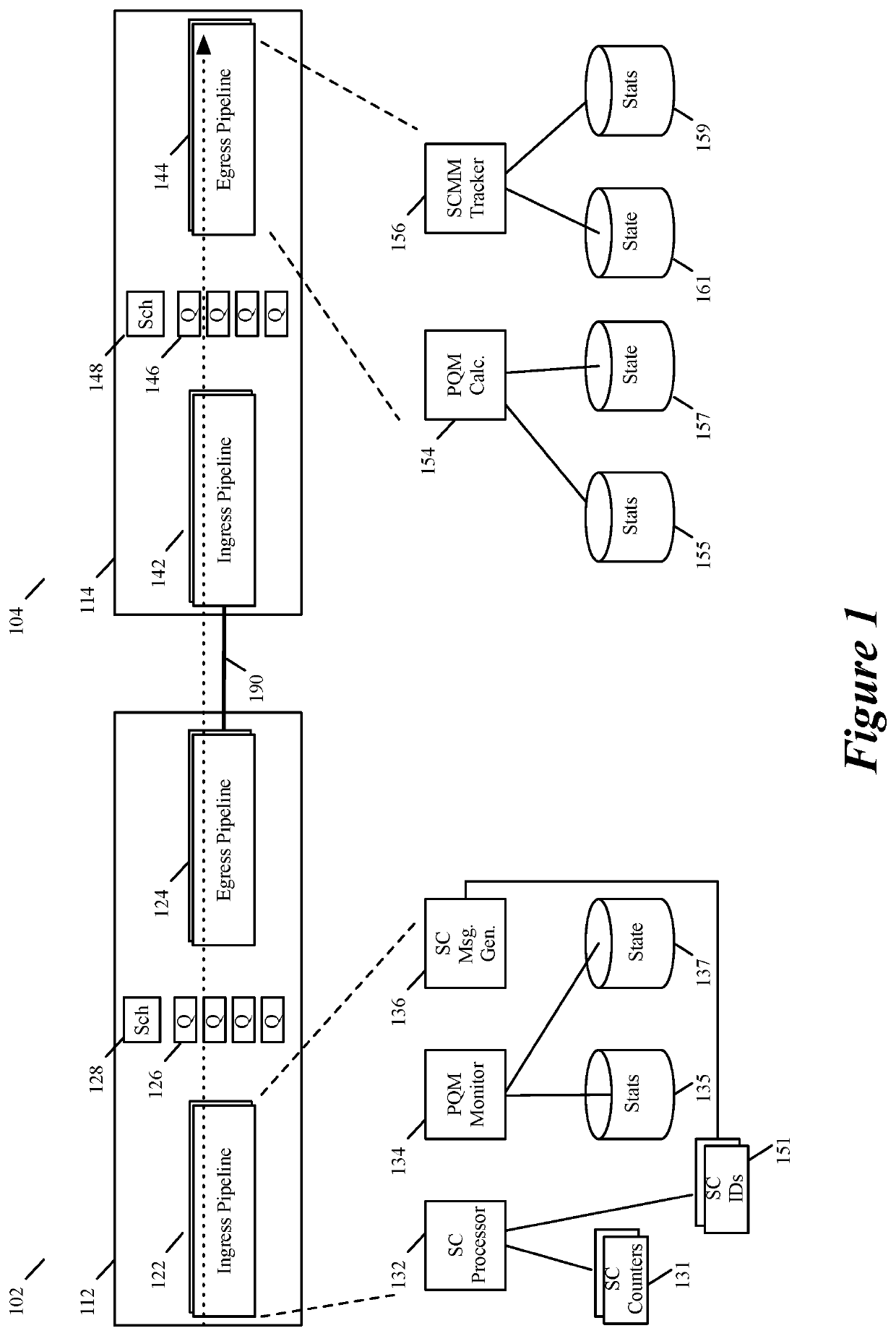
Some embodiments provide a method for quantifying quality of several service classes provided by a link between first and second forwarding nodes in a wide area network (WAN). At a first forwarding node, the method computes and stores first and second path quality metric (PQM) values based on packets sent from the second forwarding node for the first and second service classes. The different service classes in some embodiments are associated with different quality of service (QoS) guarantees that the WAN offers to the packets. In some embodiments, the computed PQM value for each service class quantifies the QoS provided to packets processed through the service class. In some embodiments, the first forwarding node adjusts the first and second PQM values as it processes more packets associated with the first and second service classes. The first forwarding node also periodically forwards to the second forwarding node the first and second PQM values that it maintains for the first and second service classes. In some embodiments, the second forwarding node performs a similar set of operations to compute first and second PQM values for packets sent from the first forwarding node for the first and second service classes, and to provide these PQM values to the first forwarding node periodically.
Owner:VMWARE INC
QoS-aware flow-based dynamic load balancing for link aggregation
InactiveUS8238250B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityDynamic load balancing
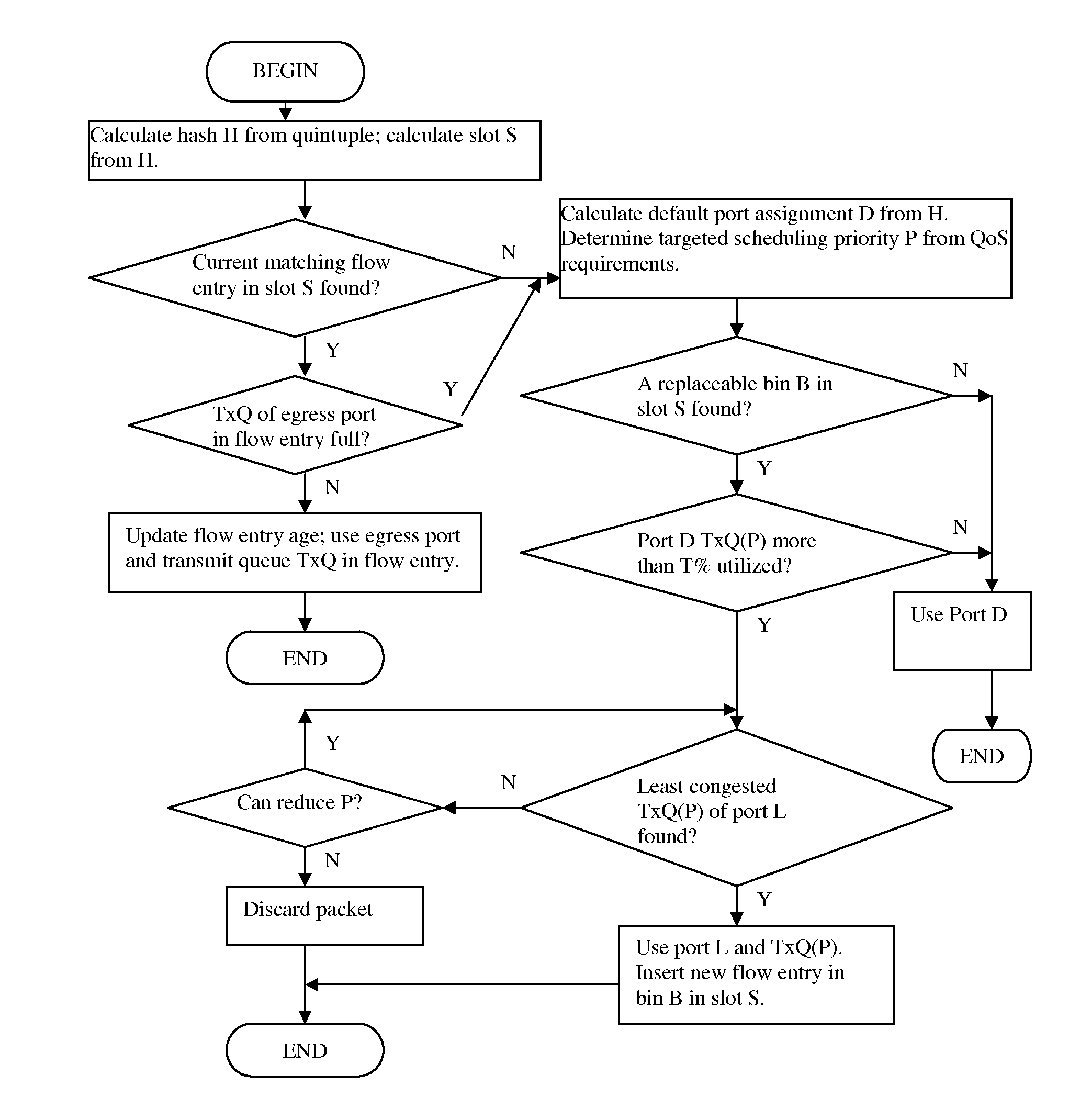
A method for dynamic load balancing of packet flows on link aggregation provides dynamic assignment of individual packet flow to egress port that is least congested. The degree of congestion is measured by the utilization of the transmit queues. The dynamic assignments are maintained in a flow table. They are timed out by tracking packet tags in the transmit queues of corresponding scheduling priorities. The load balancing method is aware of quality of service requirements of the traffic and also capable of preserving packet order.
Owner:LUXAR TECH INC
Dynamically assigning service classes for a QOS aware network link
ActiveUS20210235312A1Increases egress rateIncrease ratingsNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksQos quality of servicePathPing
Some embodiments provide a method for quantifying quality of several service classes provided by a link between first and second forwarding nodes in a wide area network (WAN). At a first forwarding node, the method computes and stores first and second path quality metric (PQM) values based on packets sent from the second forwarding node for the first and second service classes. The different service classes in some embodiments are associated with different quality of service (QoS) guarantees that the WAN offers to the packets. In some embodiments, the computed PQM value for each service class quantifies the QoS provided to packets processed through the service class. In some embodiments, the first forwarding node adjusts the first and second PQM values as it processes more packets associated with the first and second service classes. The first forwarding node also periodically forwards to the second forwarding node the first and second PQM values that it maintains for the first and second service classes. In some embodiments, the second forwarding node performs a similar set of operations to compute first and second PQM values for packets sent from the first forwarding node for the first and second service classes, and to provide these PQM values to the first forwarding node periodically.
Owner:VMWARE INC
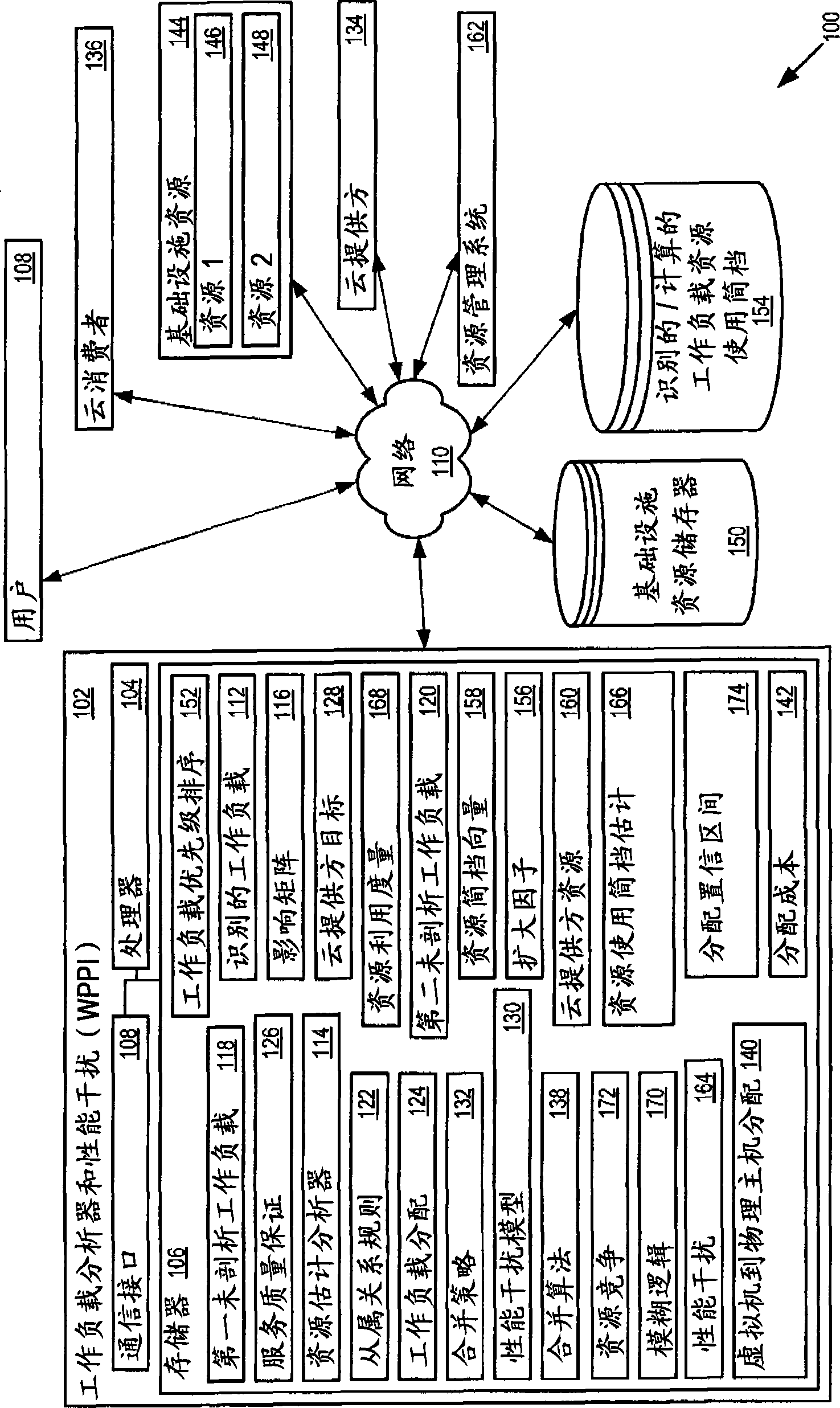
Performance interference model for managing consolidated workloads in qos-aware clouds
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
GATEWAY WITH IMPROVED QoS AWARENESS
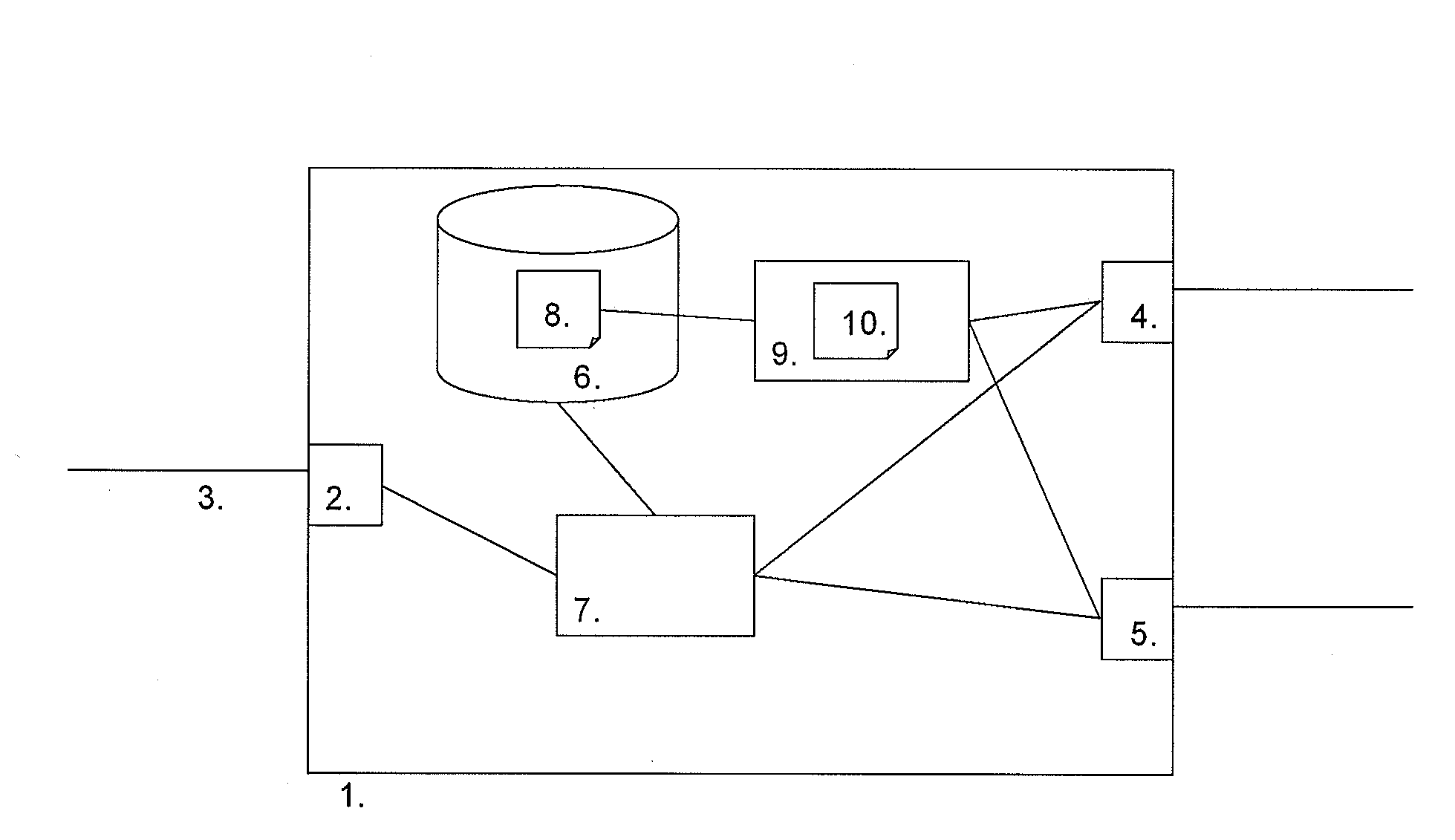
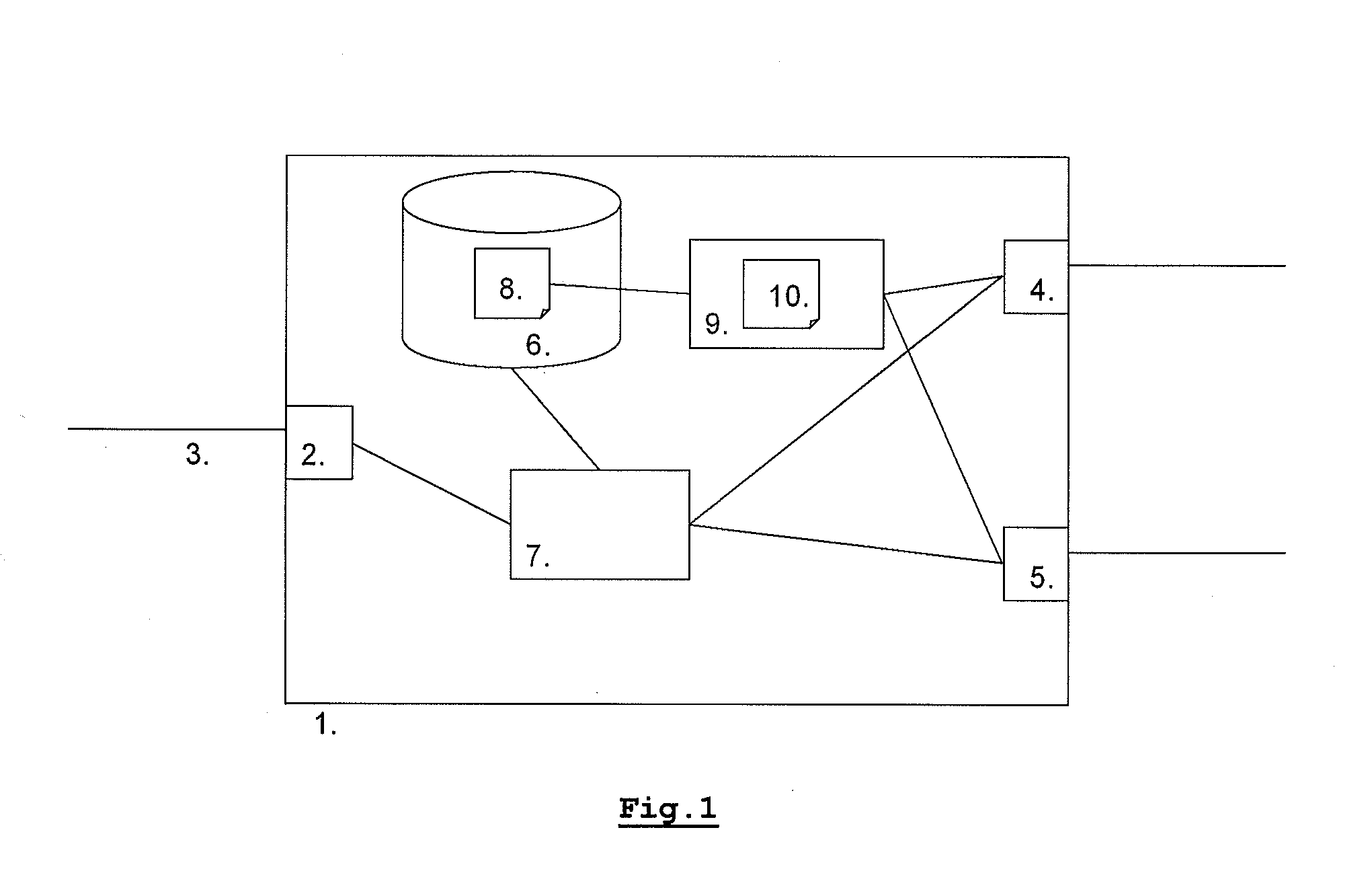
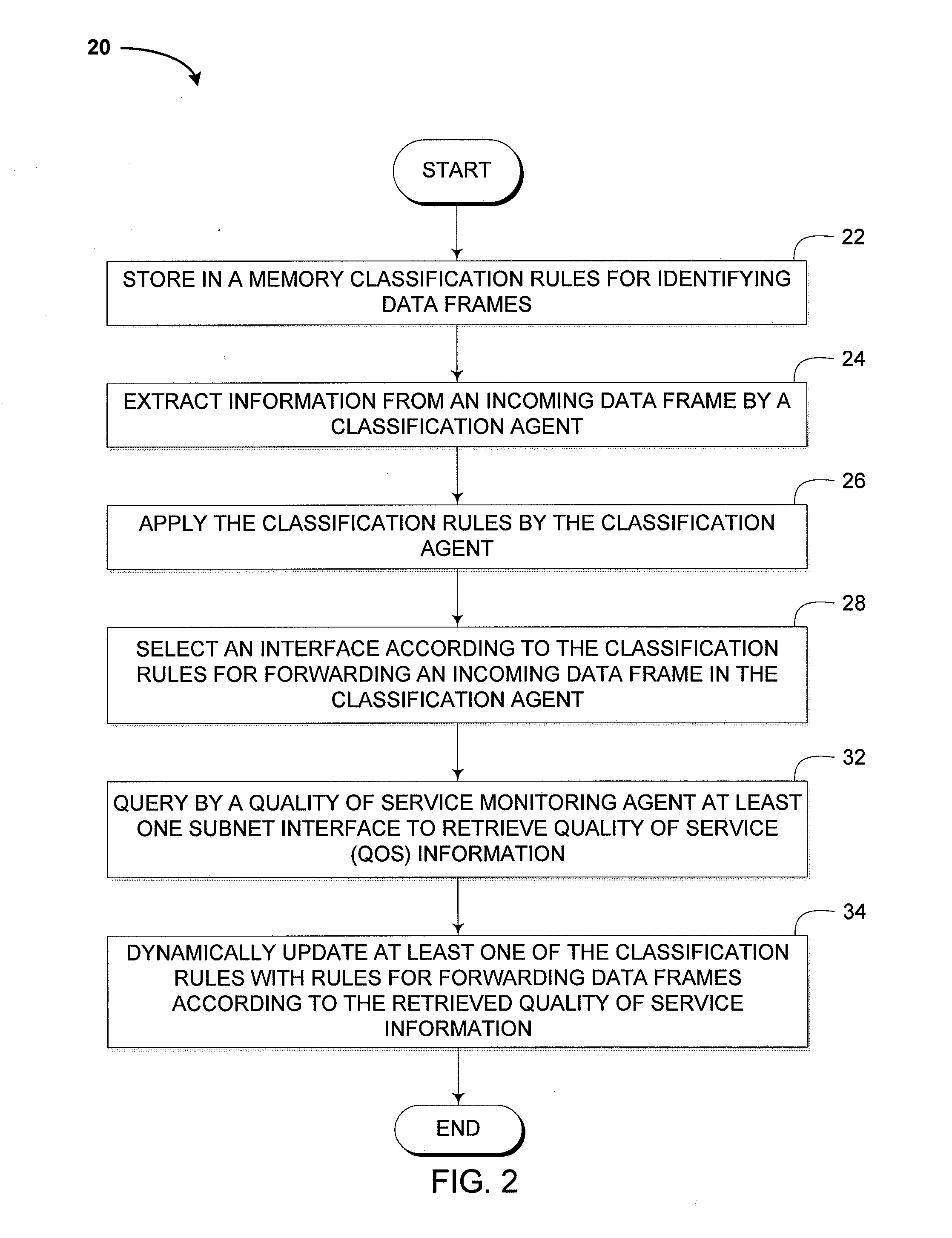
ActiveUS20080267087A1Available bandwidthImprove quality experienceError preventionTransmission systemsAccess networkClassification rule
A device and method for exchanging data frames are disclosed. In one aspect, the device exchanges data between a WAN and one or more LAN segments in an optimized way leading to a better quality of experience for the user. The device comprises an interface exchanging data frames over an access network, at least a first and second subnet interface exchanging data frames and arranged for being coupled to a network, a memory storing classification rules, a classification agent extracting information from an incoming data frame and applying the rules to the extracted information to determine the interface via which the incoming data frame is to be forwarded, and a Quality of Service monitoring agent for retrieving Quality of Service information from the subnet interfaces and dynamically updating the classification rules according to the QoS information.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
QoS in a system with end-to-end flow control and QoS aware buffer allocation
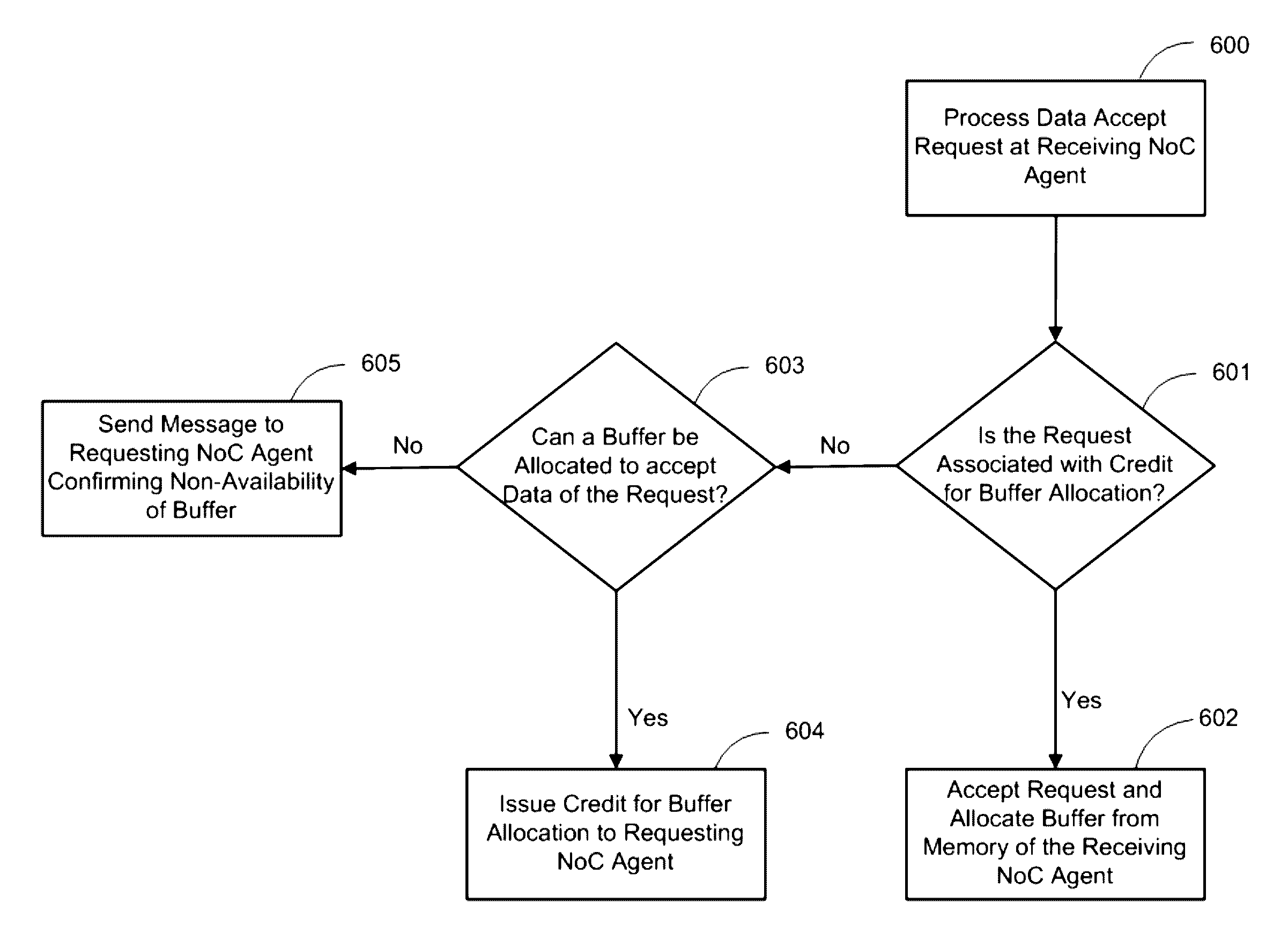
ActiveUS9473415B2Reliability increasing modificationsData switching networksDynamic bandwidth allocationProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
The present disclosure is directed to Quality of Service (QoS) and handshake protocols to facilitate endpoint bandwidth allocation among one or more agents in a Network on Chip (NoC) for an endpoint agent. The QoS policy and handshake protocols may involve the use of credits for buffer allocation which are sent to agents in the NoC to compel the acceptance of data and the allocation of an appropriate buffer. Messages sent to the agent may also have a priority associated with the message, wherein higher priority messages have automatic bandwidth allocation and lower priority messages are processed using a handshake protocol.
Owner:INTEL CORP
QoS-aware united control protocol for optical burst switching in software defined optical netoworks
ActiveUS20140178066A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic network arrangementsComputer hardwareOptical burst switching
The present invention is directed to a QoS-aware unified protocol that is applicable in the control plane of software defined networks, which can bring following benefits and includes optical burst switching protocol mainly requires four key operations; burst assembling, burst routing, burst scheduling, and control packet signaling protocols.
Owner:NEC CORP
Integrating local congestion and path interference into QoS routing for wireless mobile AD HOC networks
A method and apparatus is provided for using a distributed multi-path QoS-aware routing scheme that considers basic MANET characteristics to meet transport service requirements of real-time applications and makes use of multiple discovered paths to calculate a next-hop decision. The QoS Routing scheme superimposes distributed neighborhood congestion, neighborhood density, and link stability and delay information over the multiple discovered paths when the next-hop decision is calculated.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
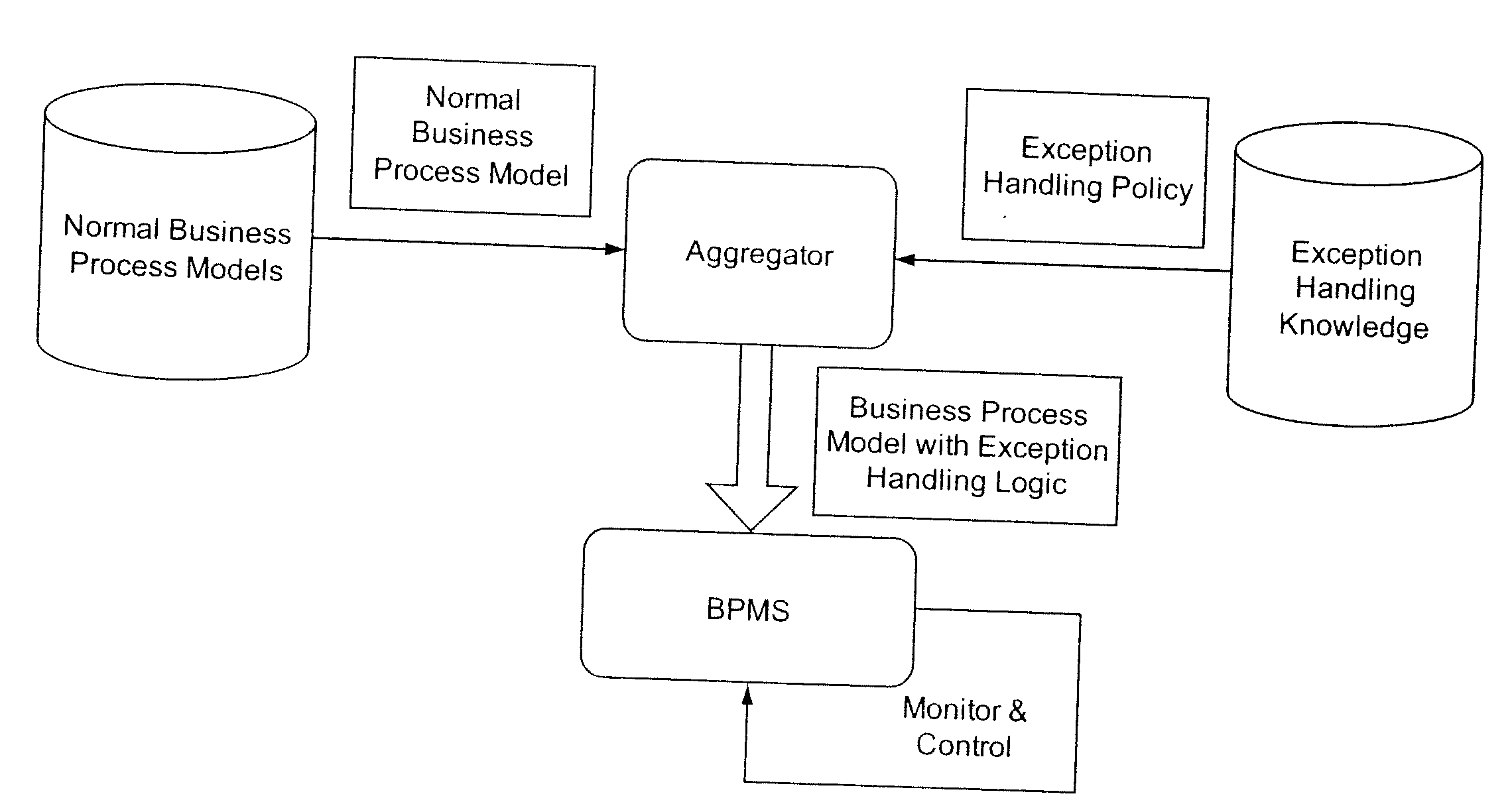
Apparatus and method for policy-driven business process exception handling
InactiveUS20050267765A1Simplify the development processShorten development timeOffice automationResourcesService compositionProcess schema
A model-driven and QoS-aware infrastructure facilitates the scalable composition of Web services in highly dynamic environments. An exception management framework supports two modes of exception management for business processes, providing a novel policy-driven approach to exception management implemented in the system infrastructure. Exception management is implemented in the system infrastructure, with exception handling policies supplied by individual business processes. Using the exception management framework, developers define exception policies in a declarative manner. Before a business process is executed, the service composition middleware integrates the exception policies with normal business logic to generate a complete process schema. This policy driven-approach can significantly reduce the development time of business processes through its separation of the development of the business logic and the exception handling policies.
Owner:IBM CORP
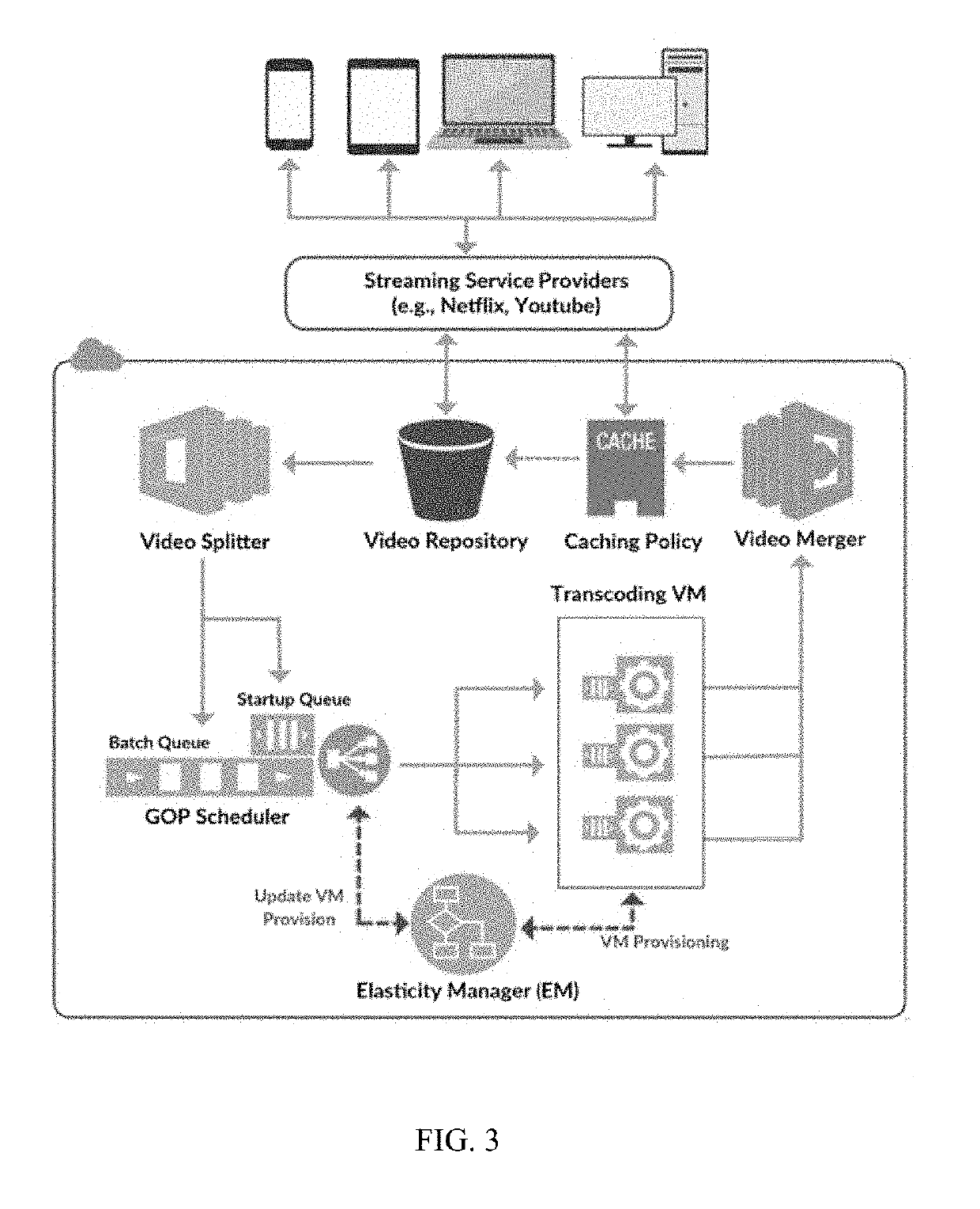
Architecture and method for high performance on demand video transcoding
ActiveUS20180131979A1Decrease deadline miss rateReduce start-up delayResource allocationDigital video signal modificationCloud baseService provision
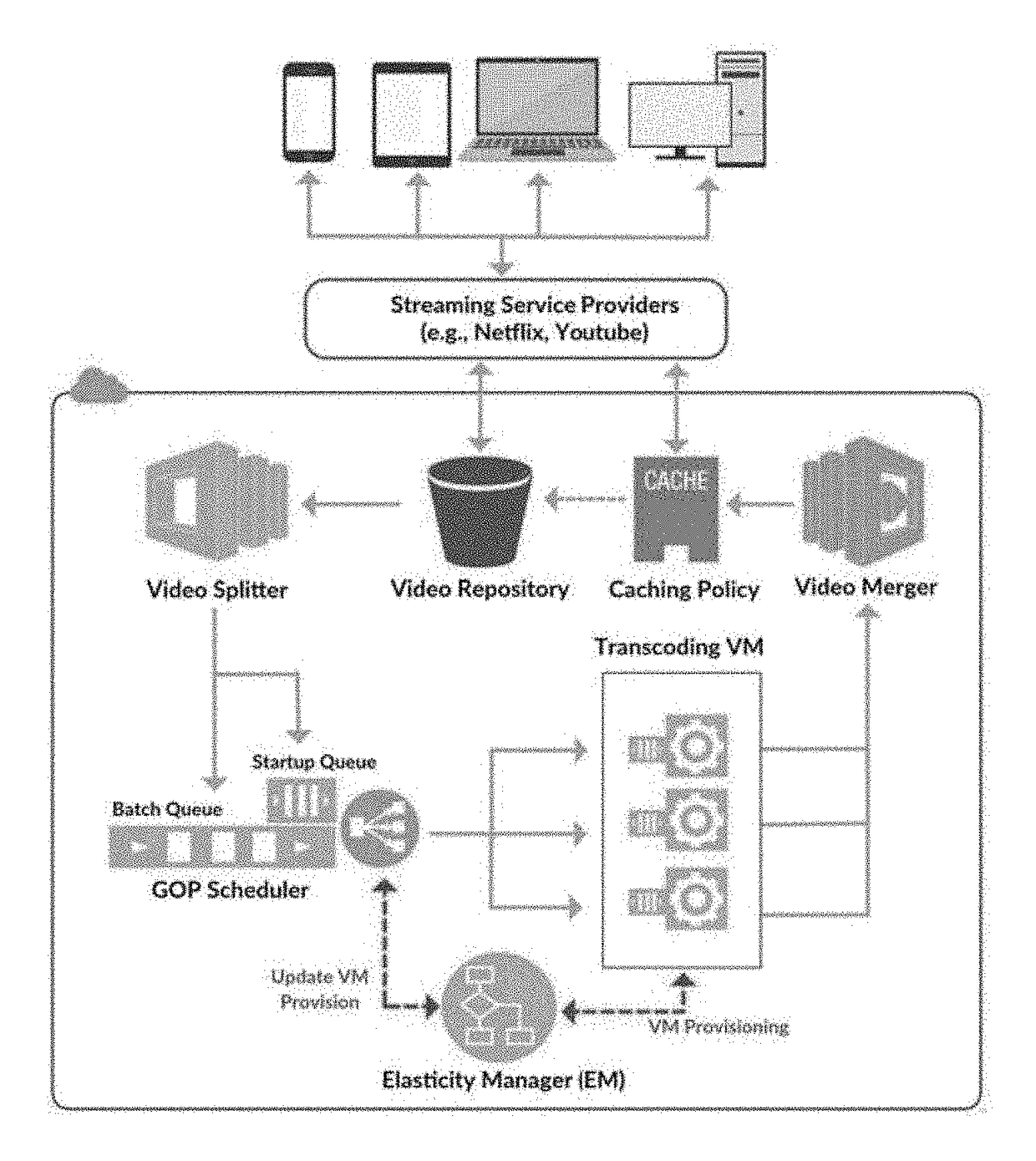
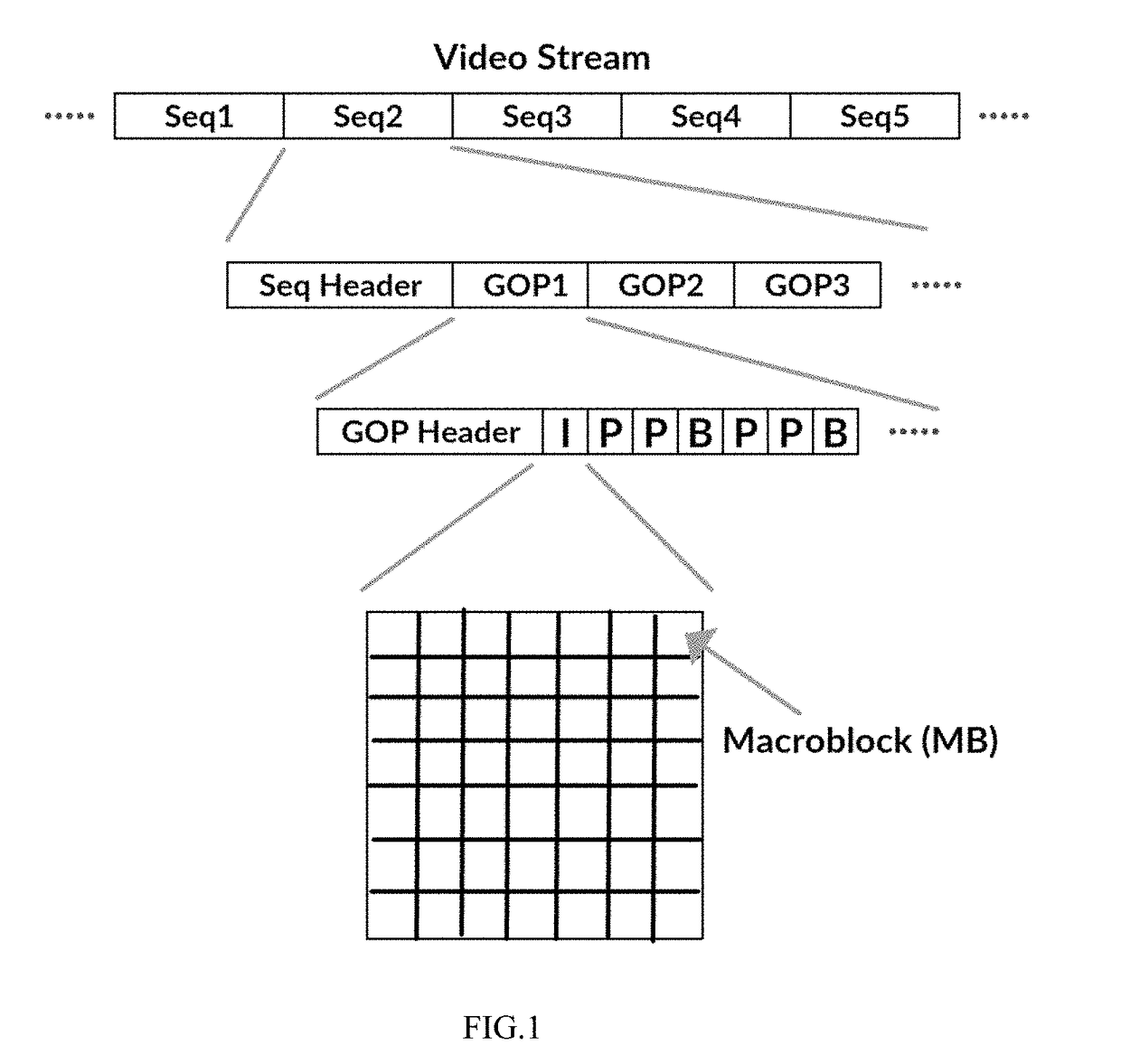
Video streams, either in form of on-demand streaming or live streaming, usually have to be transcoded based on the characteristics of clients' devices. Transcoding is a computationally expensive and time-consuming operation; therefore, streaming service providers currently store numerous transcoded versions of the same video to serve different types of client devices. Due to the expense of maintaining and upgrading storage and computing infrastructures, many streaming service providers recently are becoming reliant on cloud services. However, the challenge in utilizing cloud services for video transcoding is how to deploy cloud resources in a cost-efficient manner without any major impact on the quality of video streams. To address this challenge, in this paper, the Cloud-based Video Streaming Service (CVSS) architecture is disclosed to transcode video streams in an on-demand manner. The architecture provides a platform for streaming service providers to utilize cloud resources in a cost-efficient manner and with respect to the Quality of Service (QoS) demands of video streams. In particular, the architecture includes a QoS-aware scheduling method to efficiently map video streams to cloud resources, and a cost-aware dynamic (i.e., elastic) resource provisioning policy that adapts the resource acquisition with respect to the video streaming QoS demands. Simulation results based on realistic cloud traces and with various workload conditions, demonstrate that the CVSS architecture can satisfy video streaming QoS demands and reduces the incurred cost of stream providers up to 70%.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LOUISIANA AT LAFAYETTE
Using heart beats to monitor operational state of service classes of a QoS aware network link
ActiveUS11418997B2Increase ratingsNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmissionQos quality of serviceNetwork link
Some embodiments provide a method for quantifying quality of several service classes provided by a link between first and second forwarding nodes in a wide area network (WAN). At a first forwarding node, the method computes and stores first and second path quality metric (PQM) values based on packets sent from the second forwarding node for the first and second service classes. The different service classes in some embodiments are associated with different quality of service (QoS) guarantees that the WAN offers to the packets. In some embodiments, the computed PQM value for each service class quantifies the QoS provided to packets processed through the service class. In some embodiments, the first forwarding node adjusts the first and second PQM values as it processes more packets associated with the first and second service classes. The first forwarding node also periodically forwards to the second forwarding node the first and second PQM values that it maintains for the first and second service classes. In some embodiments, the second forwarding node performs a similar set of operations to compute first and second PQM values for packets sent from the first forwarding node for the first and second service classes, and to provide these PQM values to the first forwarding node periodically.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Quality of service (QoS) aware self-adaptive bandwidth distribution system for wireless-optical broadband access networks (WOBAN) and self-adaptive bandwidth distribution method
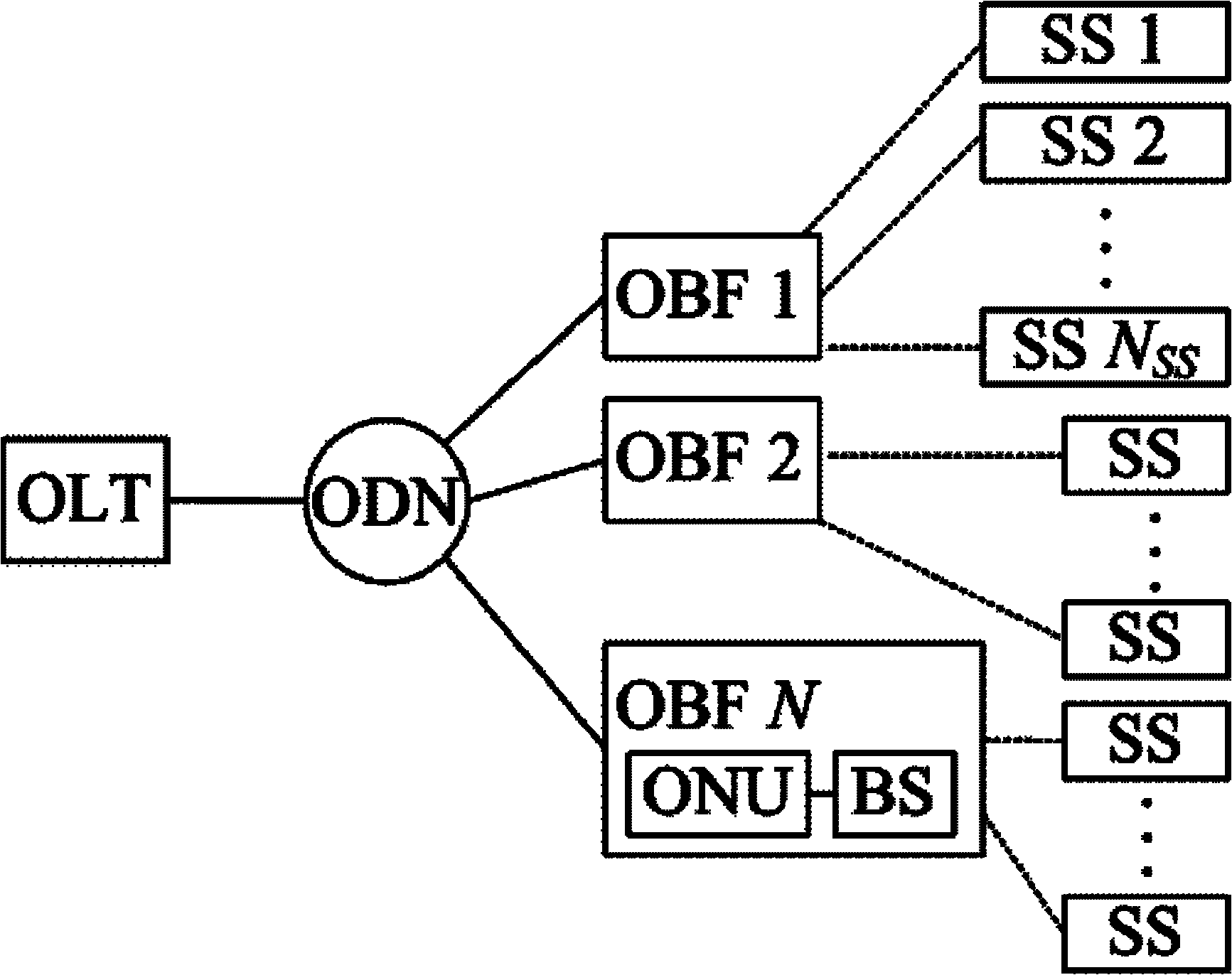
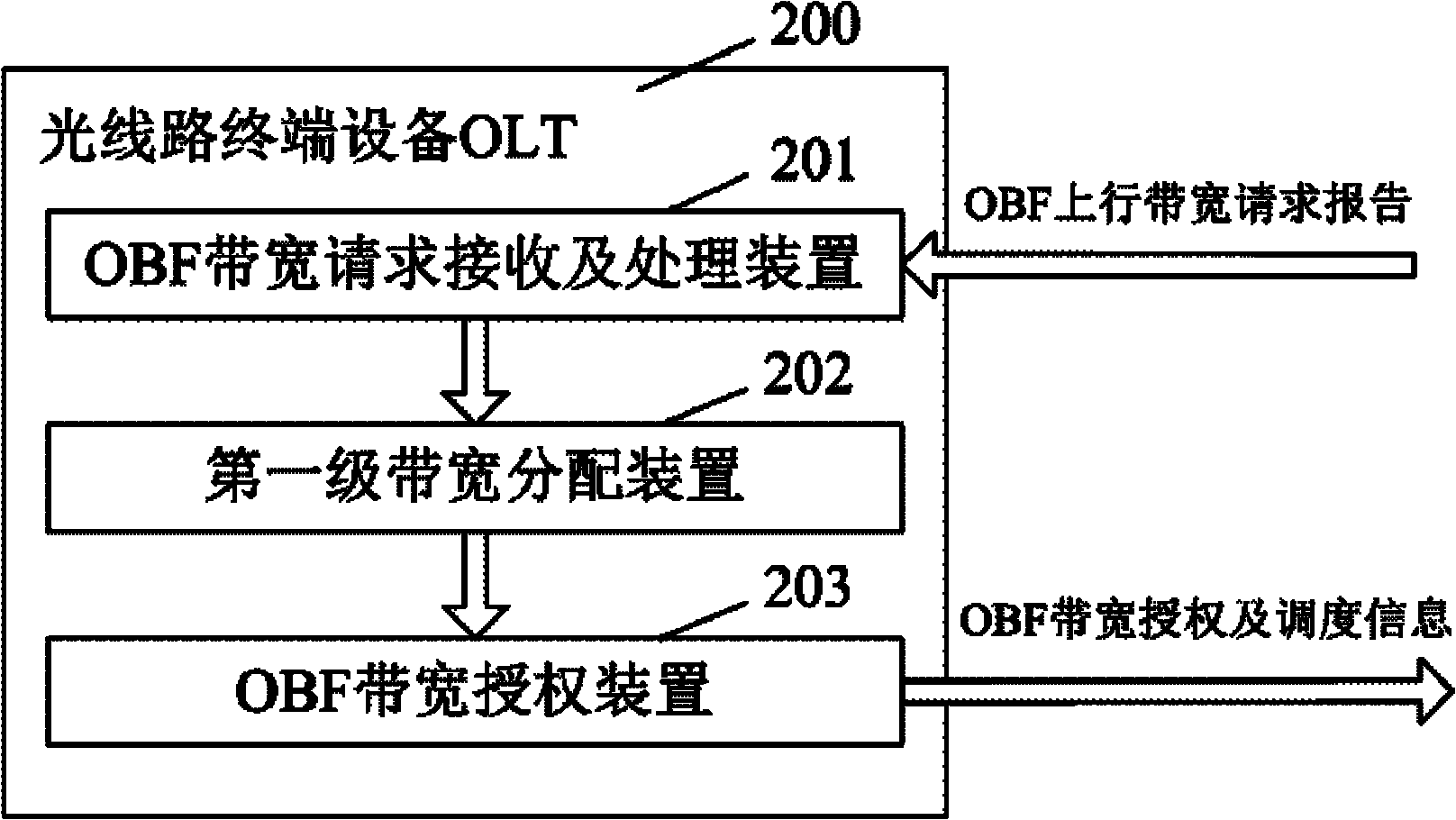
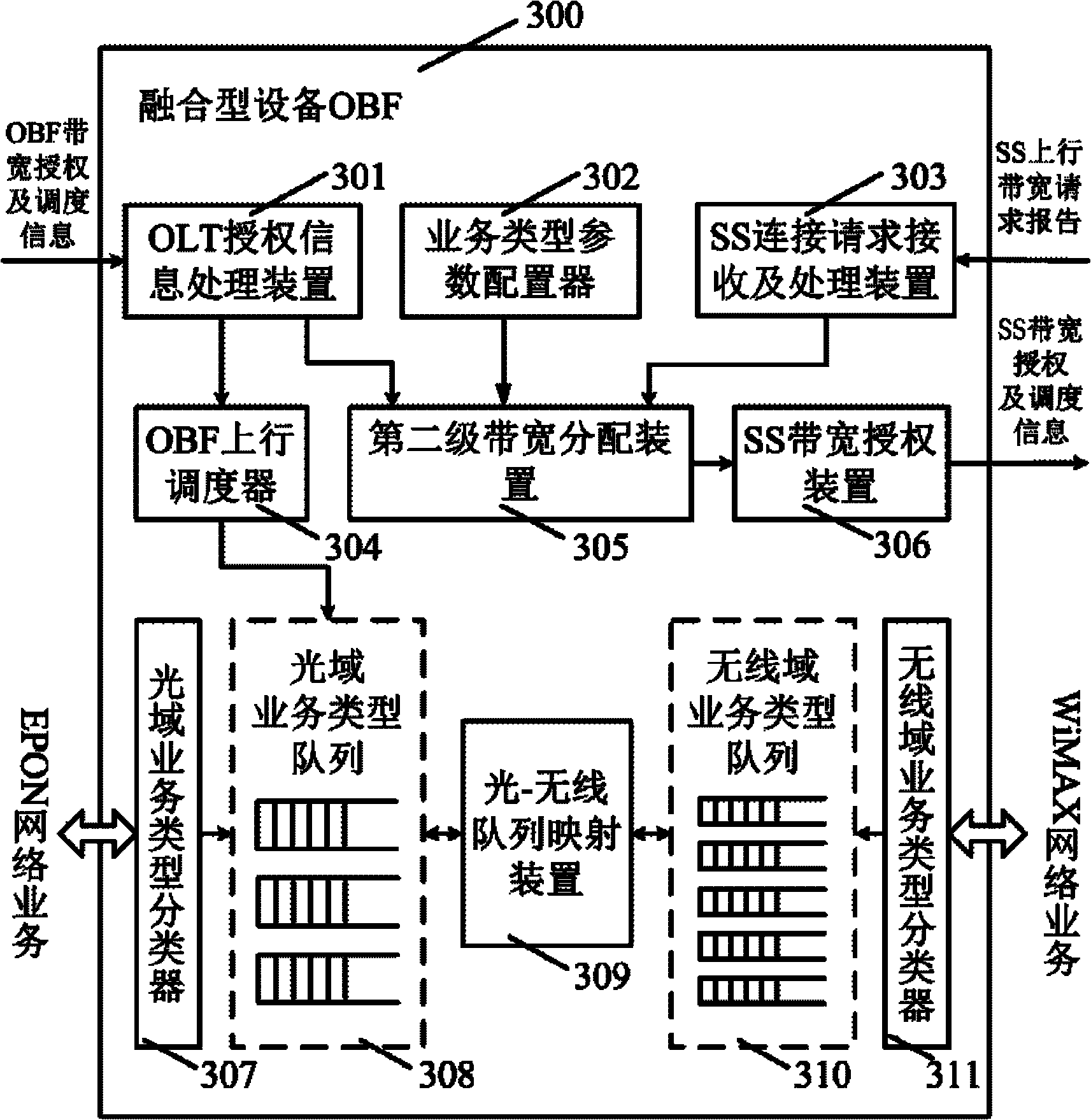
InactiveCN102571583ARealize seamless transmissionGood web service performanceData switching networksWireless communicationWireless networkBandwidth distribution
A quality of service (QoS) aware self-adaptive bandwidth distribution system for wireless-optical broadband access networks (WOBAN) comprises optical line terminal devices, optical network unit, function integrating devices of wireless stations (BSs) and user terminals. The optical line terminal devices are respectively connected with a plurality of the function integrating devices through a light distribution network, and the plurality of the function integrating devices are covered at a plurality of user terminals within a governance range through a wireless network. The optical line terminal devices are used for distributing bandwidths to optical branching filters (OBFs) and wireless sub-networks governed by the OBFs. The function integrating devices are used for distributing bandwidths to user terminals governed by the OBFs according to business types at different priority levels and achieve smooth transition and transmission of data or business between optical fiber domains and wireless domains. A self-adaptive bandwidth distribution method is provided. The QoS aware self-adaptive bandwidth distribution system for the WOBAN and the self-adaptive bandwidth distribution method reasonably distribute and dispatch bandwidth resources according to bandwidth request information of users and server priority levels of different request business.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
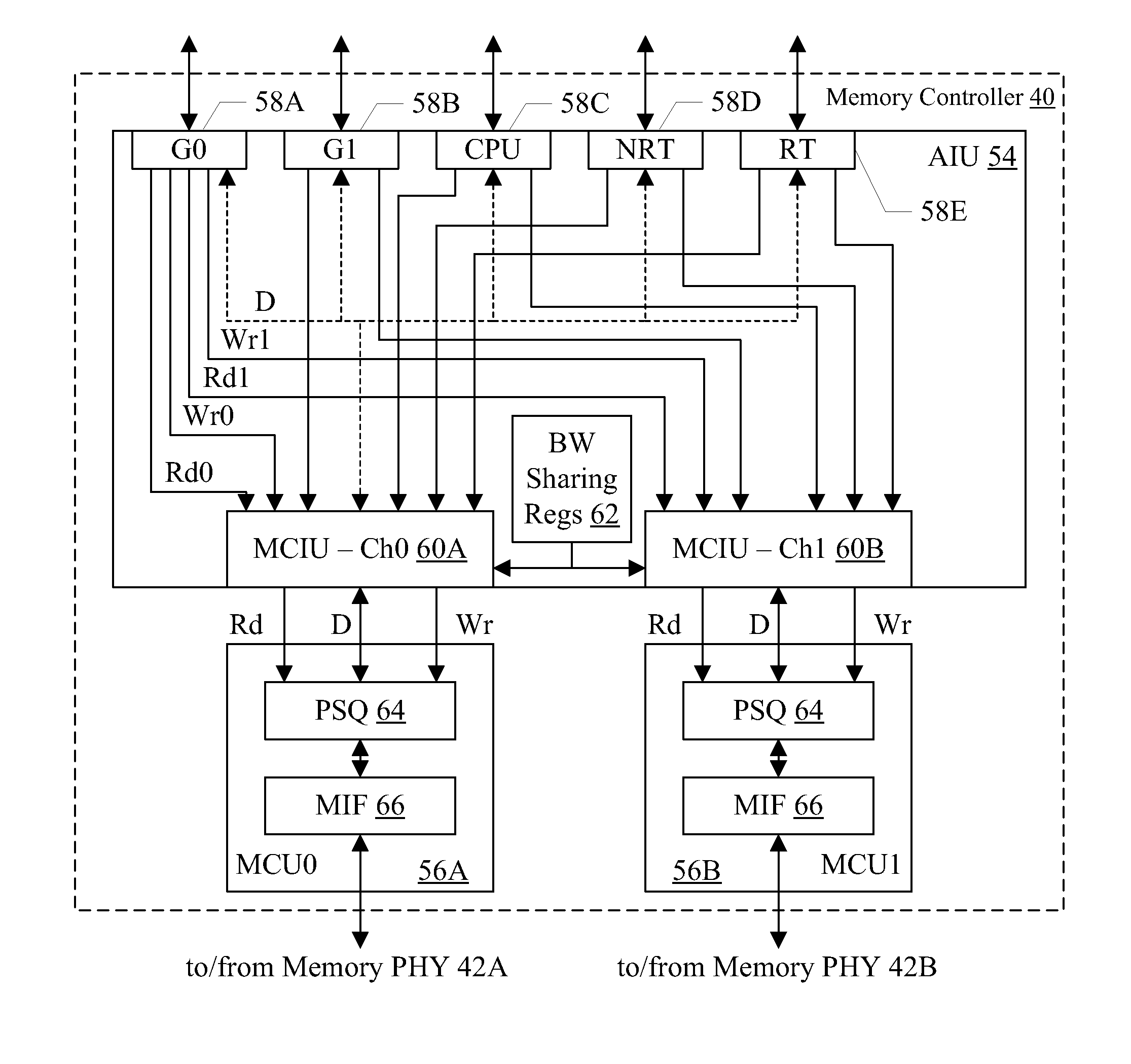
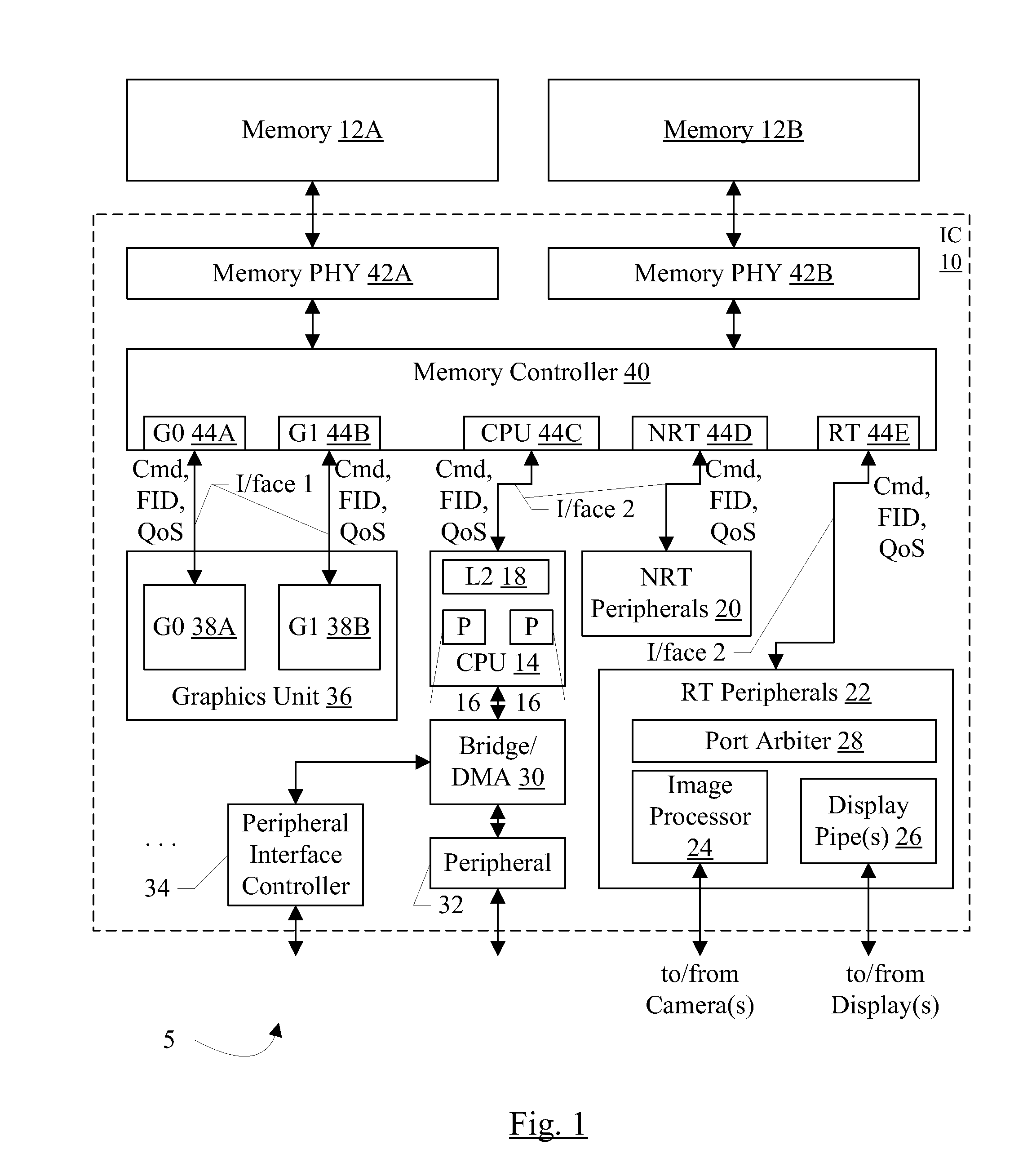
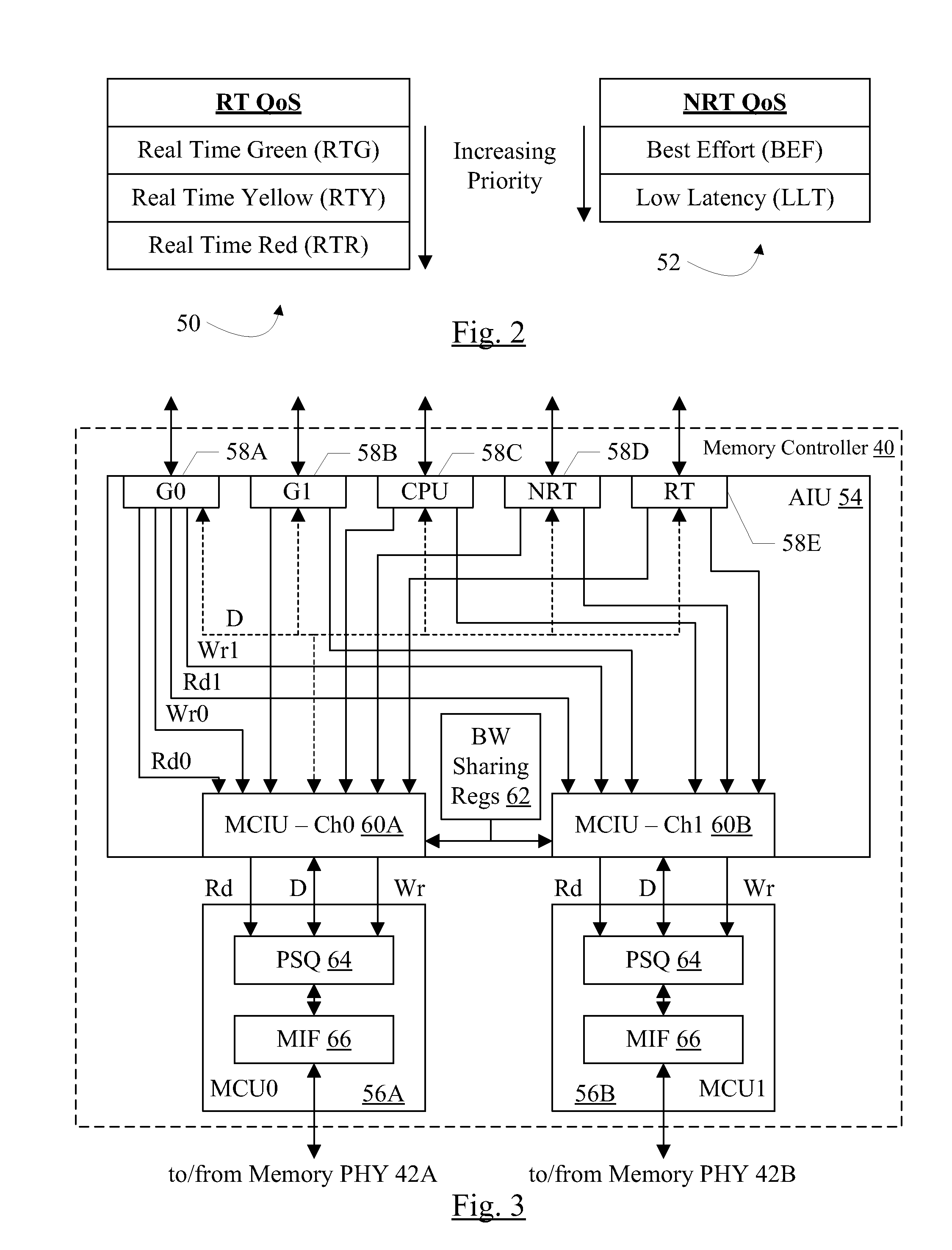
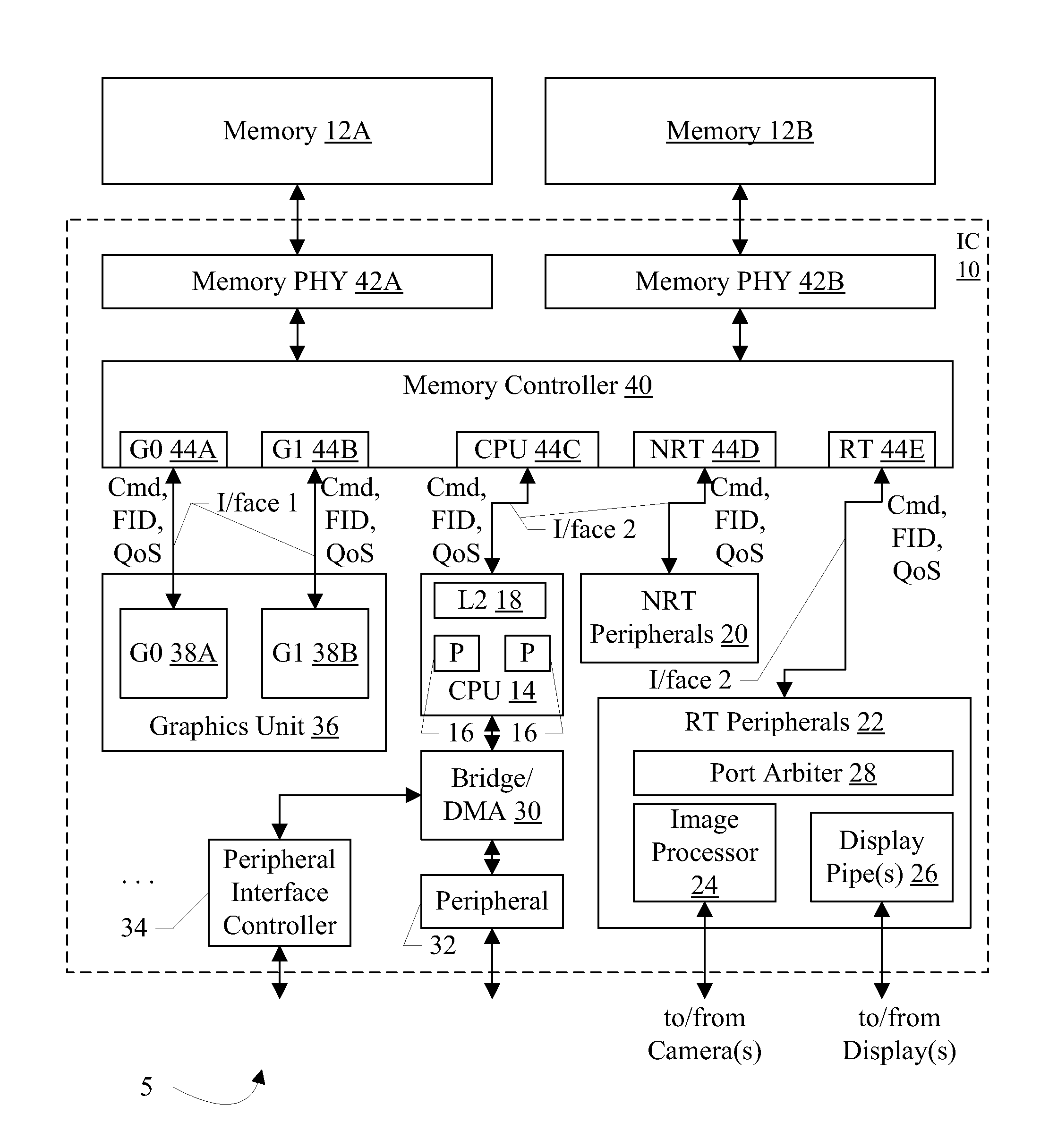
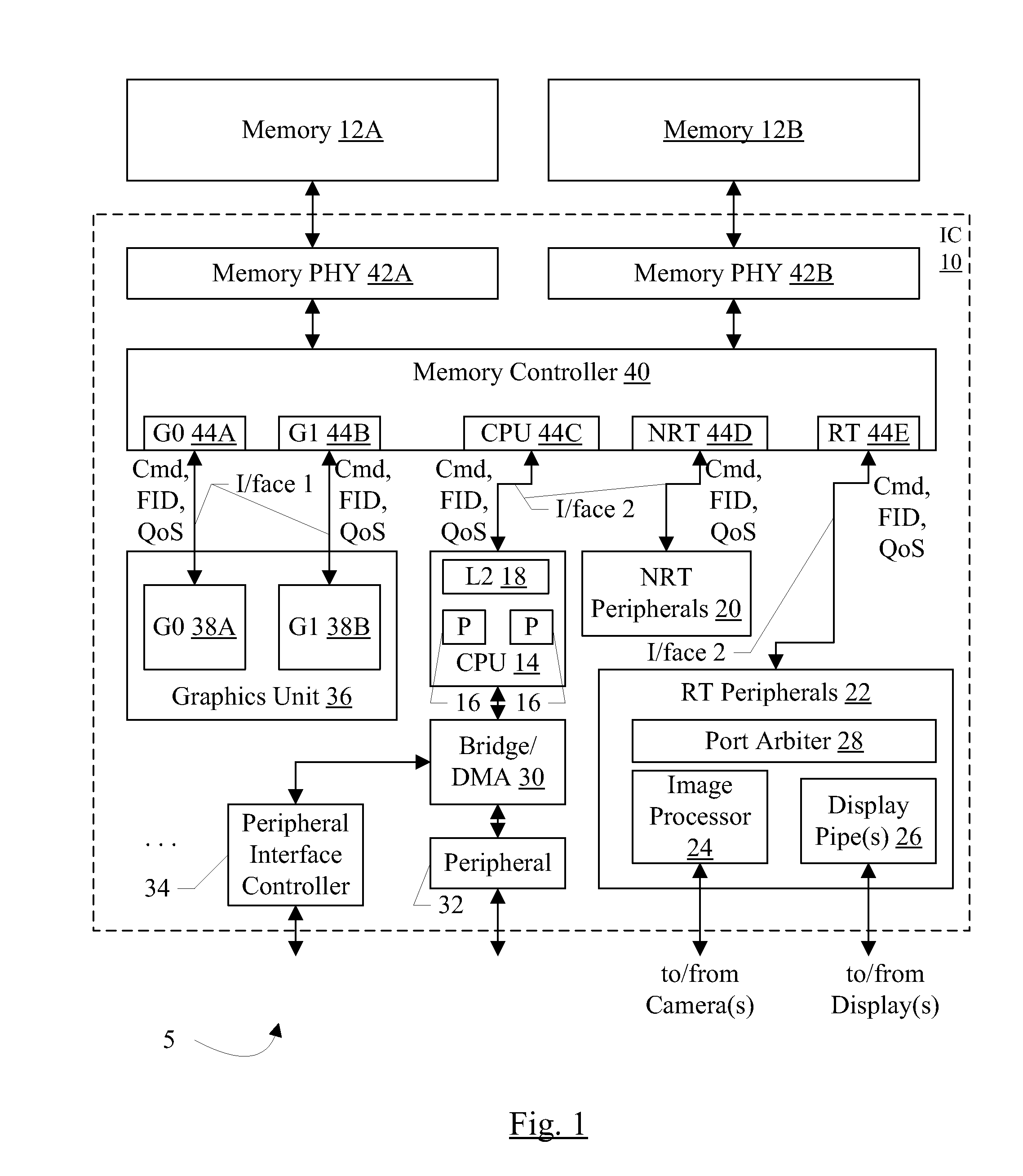
Memory controller with QoS-aware scheduling
ActiveUS8314807B2Improve performanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsProgram controlTraffic capacityMemory controller
In an embodiment, a memory controller includes multiple ports. Each port may be dedicated to a different type of traffic. In an embodiment, quality of service (QoS) parameters may be defined for the traffic types, and different traffic types may have different QoS parameter definitions. The memory controller may be configured to schedule operations received on the different ports based on the QoS parameters. In an embodiment, the memory controller may support upgrade of the QoS parameters when subsequent operations are received that have higher QoS parameters, via sideband request, and / or via aging of operations. In an embodiment, the memory controller is configured to reduce emphasis on QoS parameters and increase emphasis on memory bandwidth optimization as operations flow through the memory controller pipeline.
Owner:APPLE INC
QoS-aware scheduling
ActiveUS20120069034A1Improve performanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsProgram controlTraffic capacitySideband
In an embodiment, a memory controller includes multiple ports. Each port may be dedicated to a different type of traffic. In an embodiment, quality of service (QoS) parameters may be defined for the traffic types, and different traffic types may have different QoS parameter definitions. The memory controller may be configured to scheduled operations received on the different ports based on the QoS parameters. In an embodiment, the memory controller may support upgrade of the QoS parameters when subsequent operations are received that have higher QoS parameters, via sideband request, and / or via aging of operations. In an embodiment, the memory controller is configured to reduce emphasis on QoS parameters and increase emphasis on memory bandwidth optimization as operations flow through the memory controller pipeline.
Owner:APPLE INC
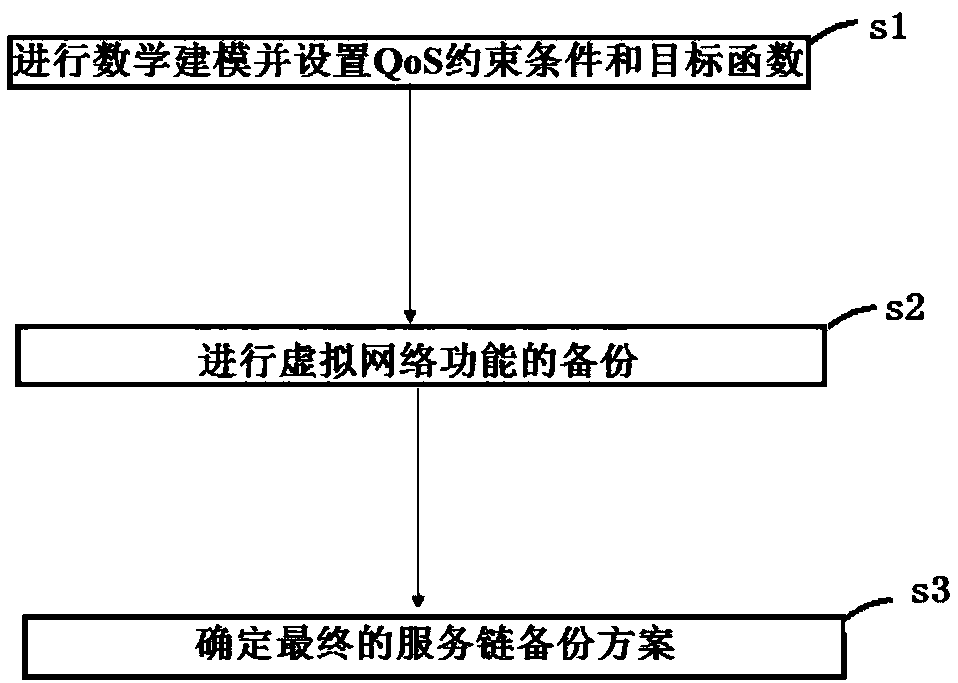
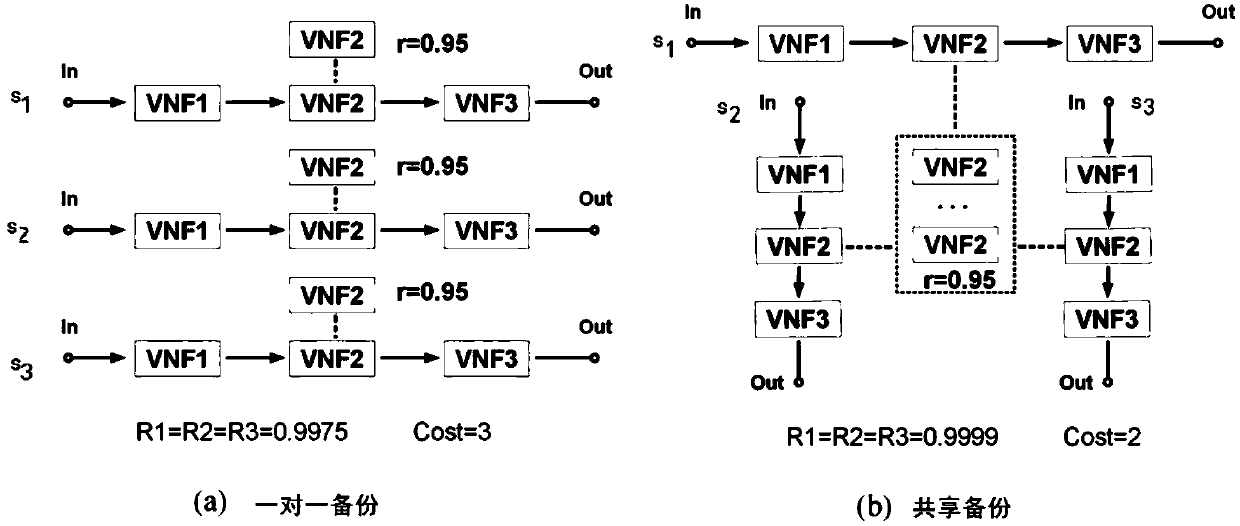
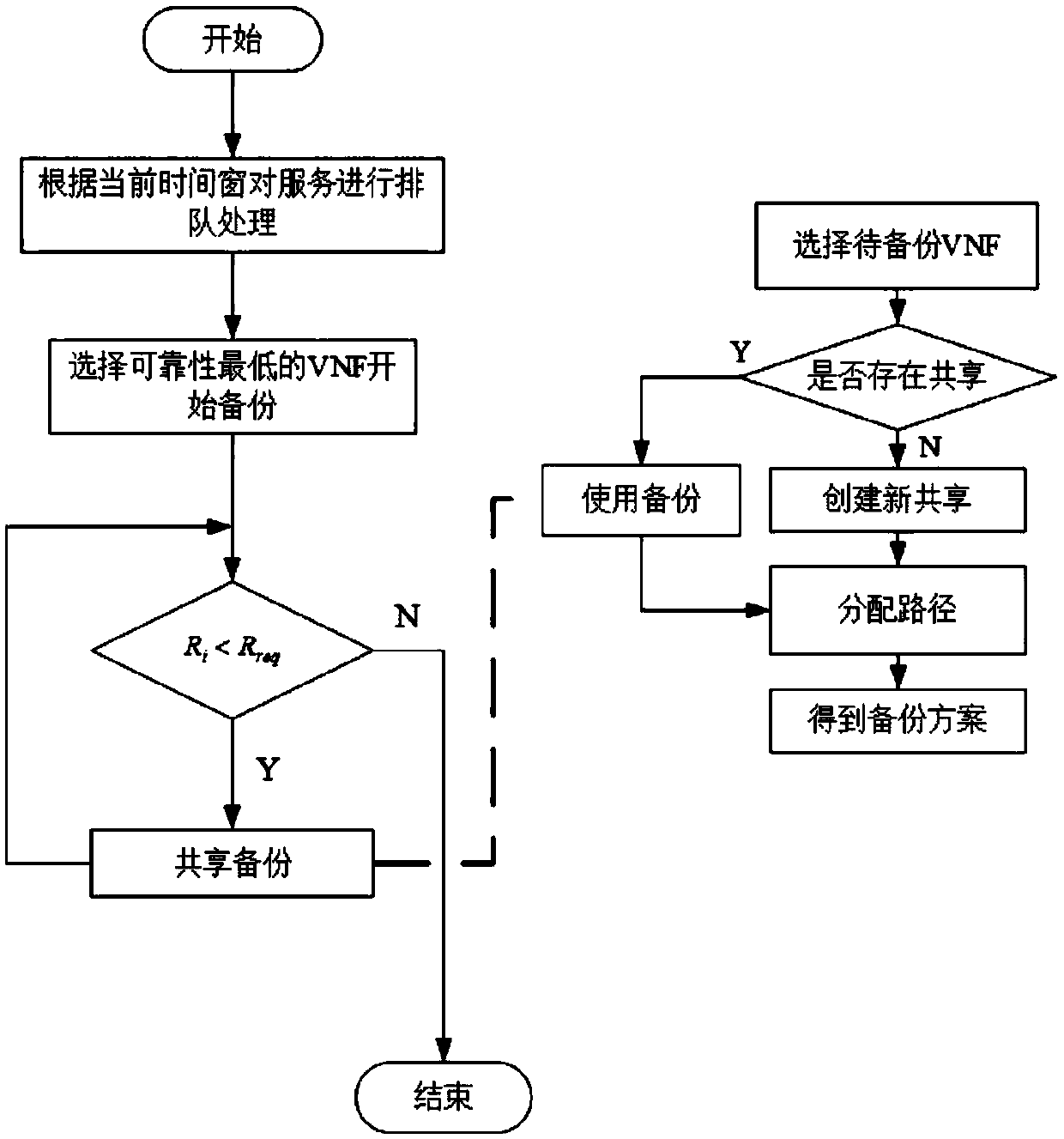
QoS-aware service chain backup method and system
ActiveCN108965014AImprove resource utilization efficiencyLoad balancingData switching networksResource utilizationDependability
The invention discloses a QoS-aware service chain backup method and system. The service chain backup method comprises the following steps: a QoS-aware service chain backup problem is subjected to mathematical modeling, and QoS constraint conditions and a target function of the service chain backup problem are set; a service chain with the reliability lower than a reliability threshold is subjectedto backup of a virtual network function according to the QoS constraint conditions of the service chain backup problem, if the to-be-backed up virtual network function exists, an existing backup virtual network function is preferentially selected to serve as a shared backup, and if the to-be-backed up virtual network function does not exist, a new backup is created; and a final service chain backup scheme is determined according to the QoS constraint conditions and the target function of the service chain backup problem. According to the QoS-aware service chain backup method and system, the QoS requirement is combined with the backup process, the sharability of the backup network function is considered, therefore, excessive backup of the VNF is reduced, and the resource utilization efficiency and reliability of the service chain are improved.
Owner:BEIJING SMARTCHIP MICROELECTRONICS TECH COMPANY +4
Scalable and QoS aware flow control
InactiveUS7522624B2Improve scalabilityImprove transmittanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityAnticipatory scheduling
The present invention relates to a switching unit with a scalable and QoS aware flow control. The actual schedule rate of an egress queue, wherein the outgoing traffic belonging to a particular class of service is backlogged, is measured and compared to its expected schedule rate. If the egress queue is scheduled below expectation, then the bandwidth of every virtual ingress-to-egress pipe connecting an ingress queue, wherein the incoming traffic belonging to the same class of service is backlogged before transmission through the switch core fabric, to that egress queue is increased, thereby feeding that egress queue with more data units.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
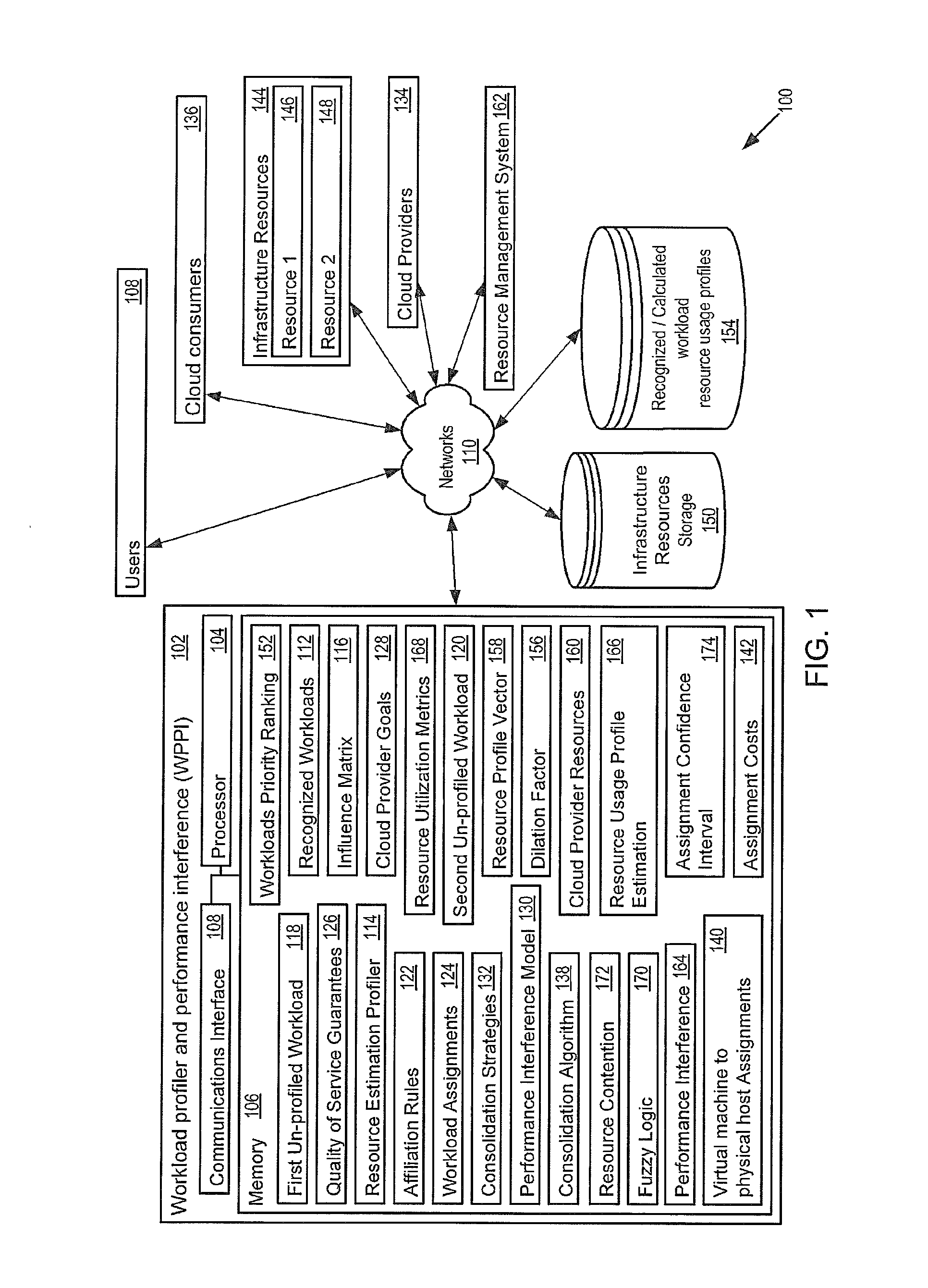
Performance interference model for managing consolidated workloads in QoS-aware clouds
The workload profiler and performance interference (WPPI) system uses a test suite of recognized workloads, a resource estimation profiler and influence matrix to characterize un-profiled workloads, and affiliation rules to identify optimal and sub-optimal workload assignments to achieve consumer Quality of Service (QoS) guarantees and / or provider revenue goals. The WPPI system uses a performance interference model to forecast the performance impact to workloads of various consolidation schemes usable to achieve cloud provider and / or cloud consumer goals, and uses the test suite of recognized workloads, the resource estimation profiler and influence matrix, affiliation rules, and performance interference model to perform modeling to determine the initial assignment selections and consolidation strategy to use to deploy the workloads. The WPPI system uses an online consolidation algorithm, the offline models, and online monitoring to determine virtual machine to physical host assignments responsive to real-time conditions to meet cloud provider and / or cloud consumer goals.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
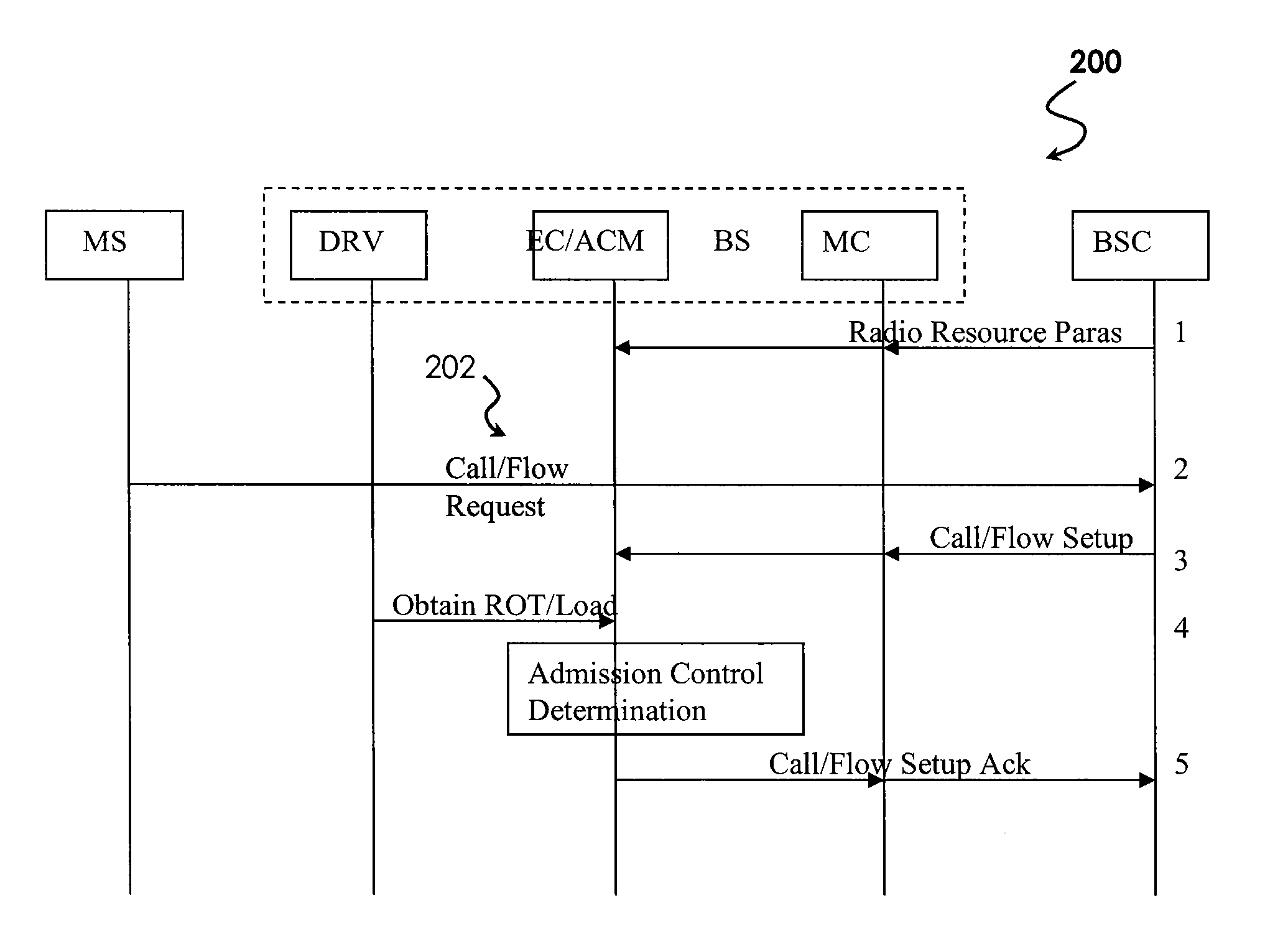
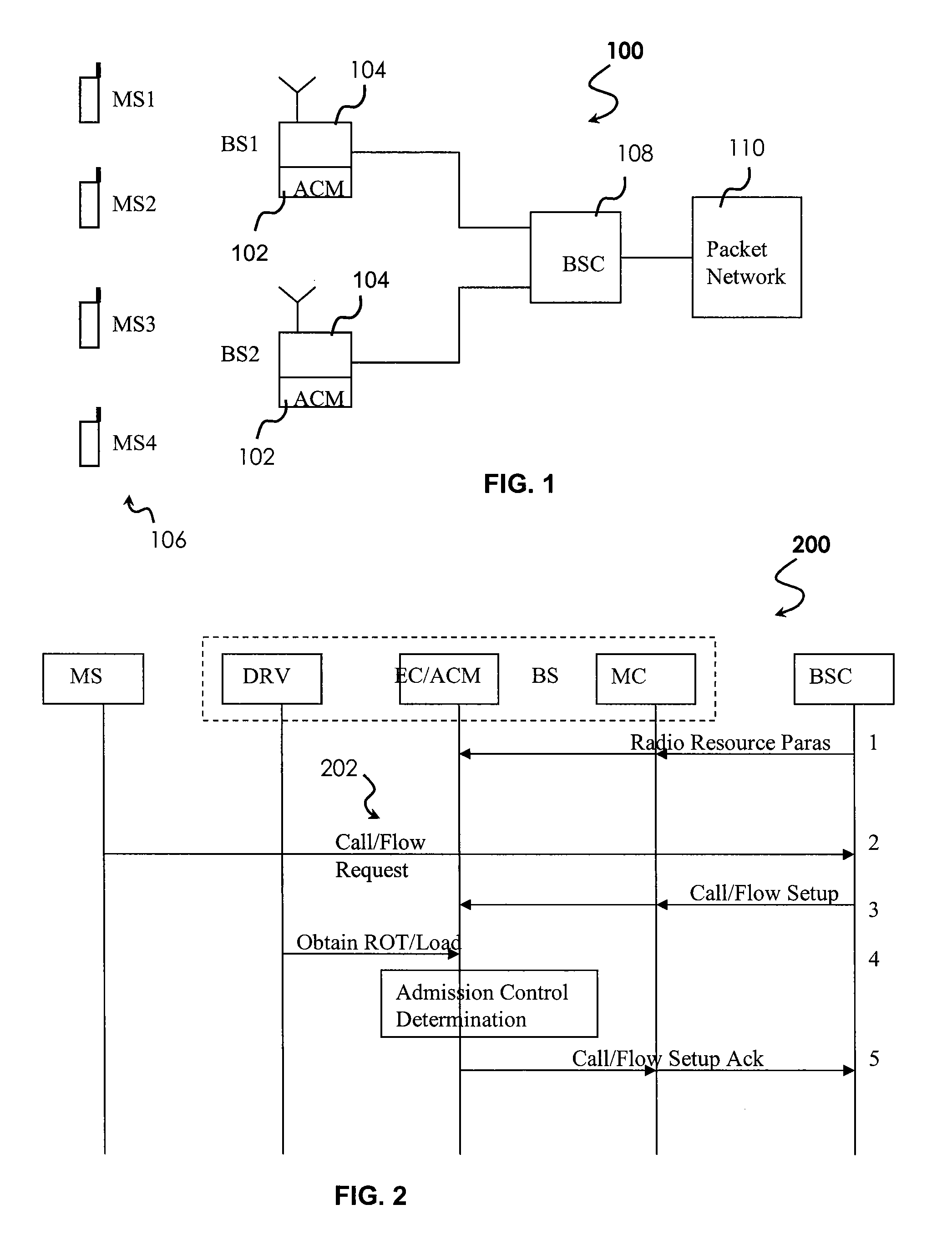
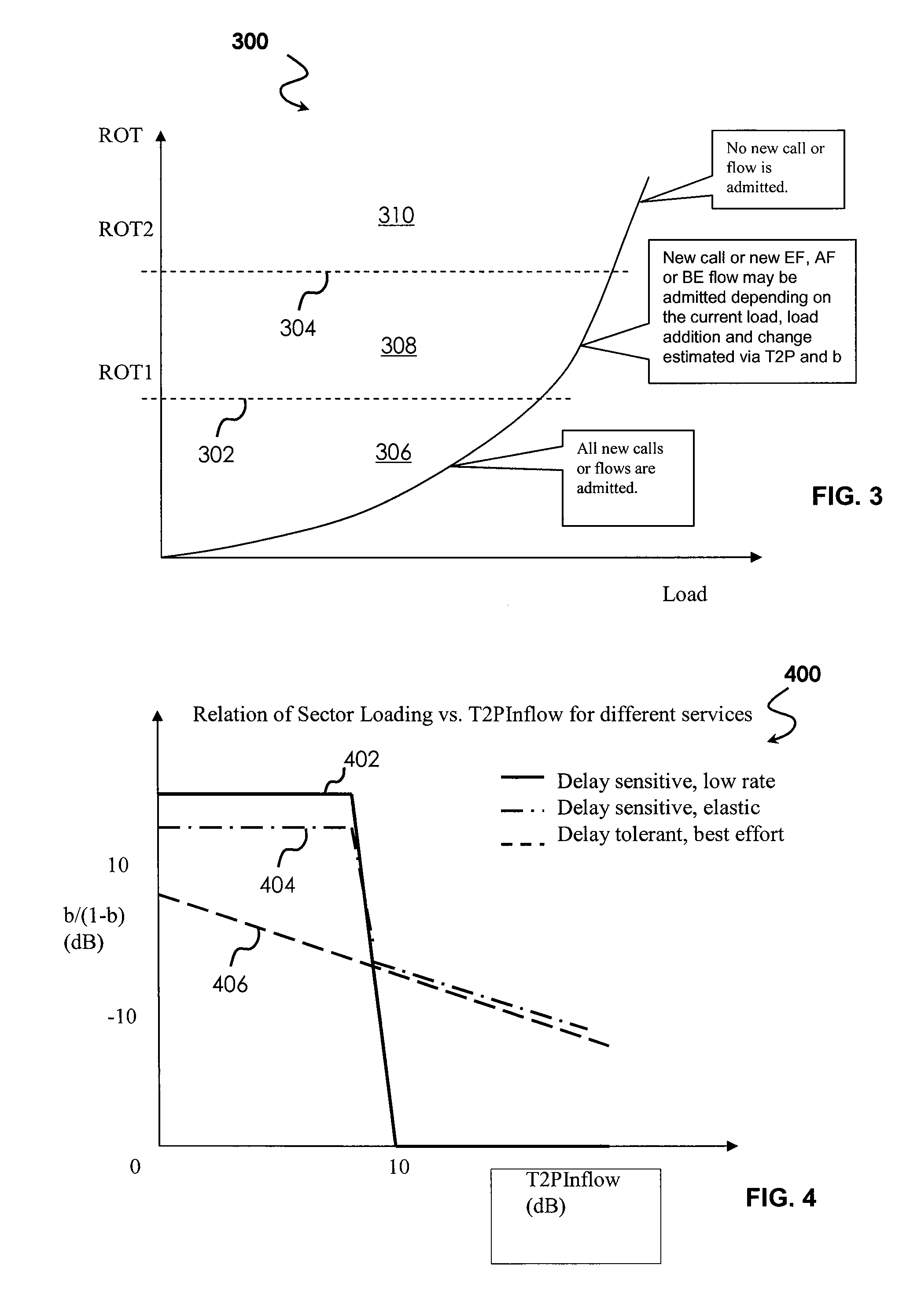
System For QOS Aware Reverse Link Admission Control In Wireless Communication Systems
ActiveUS20090054072A1Improve performanceImprove stabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemQos aware
A system, comprising various methods and apparatus, for Reverse Link Admission Control (RLAC) with QoS differentiation in wireless communication systems is disclosed. With the present invention, wireless systems may admit new calls or transmission flows based upon sector loading conditions QoS requirements or characteristics of an incoming transmission—providing optimal system performance and stability while addressing QoS needs.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Apparatus and method for policy-driven business process exception handling
ActiveUS20080189534A1Simplify the development processShorten development timeDigital computer detailsOffice automationService compositionProcess schema
A model-driven and QoS-aware infrastructure facilitates the scalable composition of Web services in highly dynamic environments. An exception management framework supports two modes of exception management for business processes, providing a novel policy-driven approach to exception management implemented in the system infrastructure. Exception management is implemented in the system infrastructure, with exception handling policies supplied by individual business processes. Using the exception management framework, developers define exception policies in a declarative manner. Before a business process is executed, the service composition middleware integrates the exception policies with normal business logic to generate a complete process schema. This policy driven-approach can significantly reduce the development time of business processes through its separation of the development of the business logic and the exception handling policies.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Network centric quality of service using active network technology
InactiveUS7561521B2Error preventionTransmission systemsDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
Systems and methods for improving network centric quality of service using active network technology are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method includes controlling how a packet is passed over at least one of the interfaces using a differentiated services portion of a network management architecture, monitoring a request for a Quality of Service (QoS) level from at least one QoS-aware application, and adjusting at least one service rate of packet travel controlled by the differentiated services portion based on at least one of the requested QoS level and an available bandwidth. In an alternate embodiment, the controlling of how a packet is passed over at least one of the interfaces includes using at least one of a queuing discipline, a class, and a filter.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
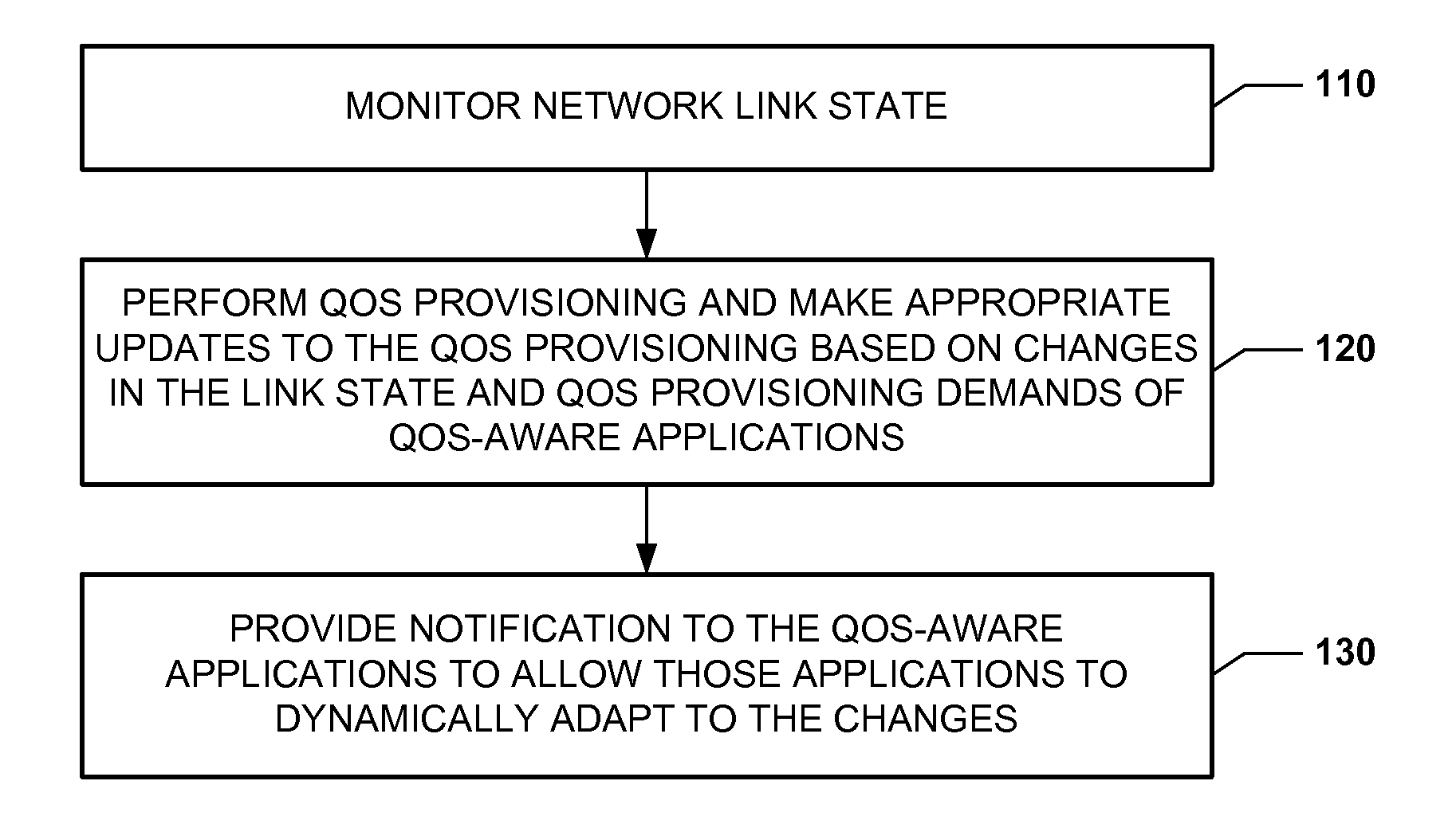
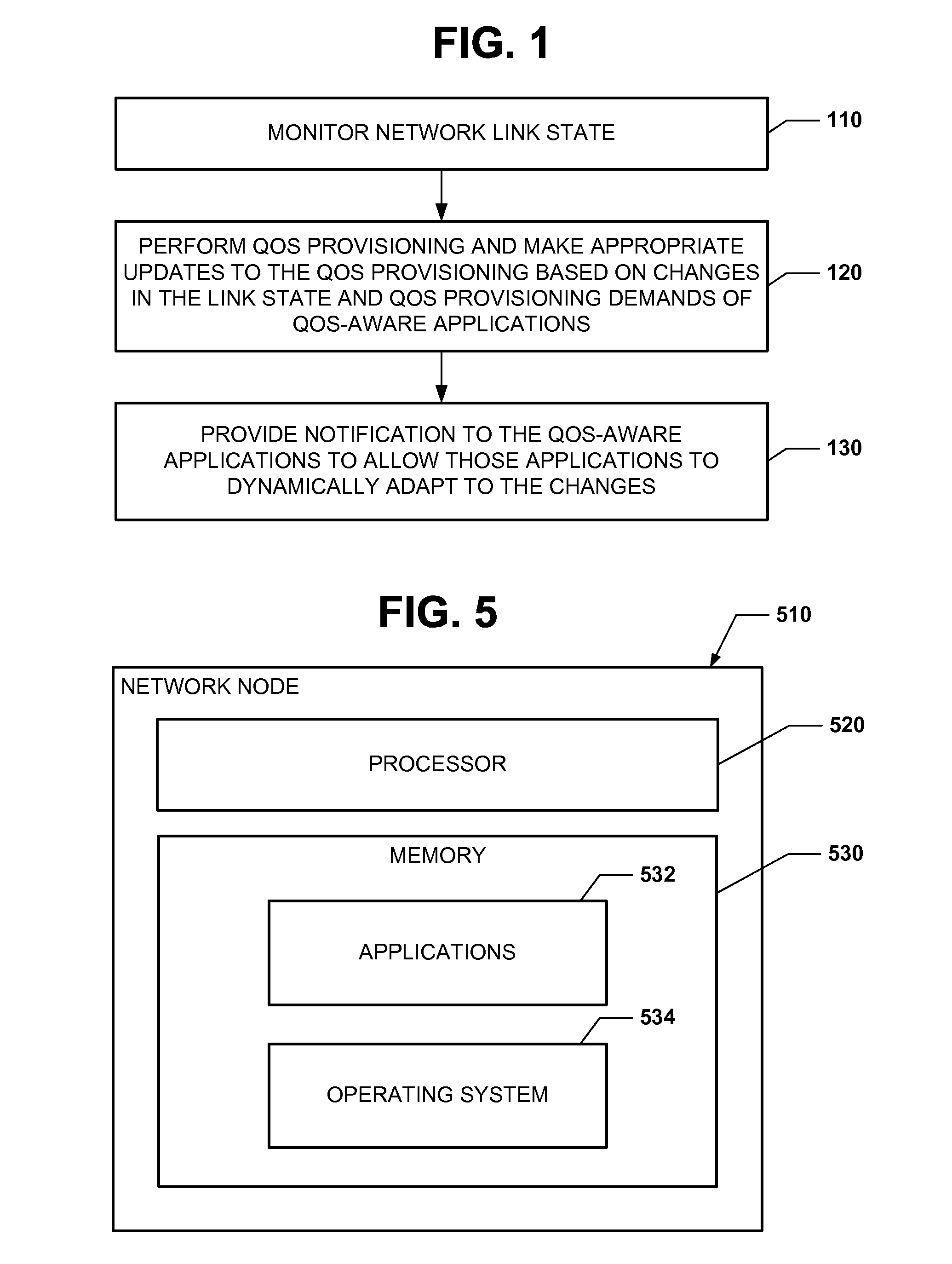
QOS provisioning in a network having dynamic link states
A network node for a network having dynamic link states includes a processing unit and computer-readable memory for causing the processing unit to monitor a link state of the network; perform QoS provisioning and make appropriate updates to the QoS provisioning based on changes in the link state and QoS provisioning demands of QoS-aware applications; and provide notification to the QoS-aware applications to allow those applications to dynamically adapt to the link state changes.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
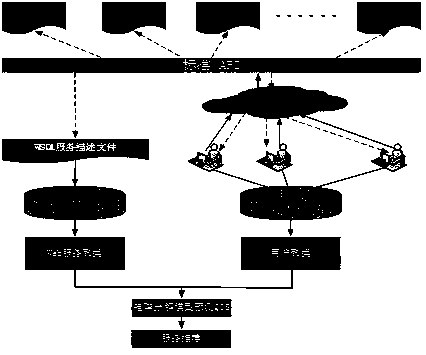
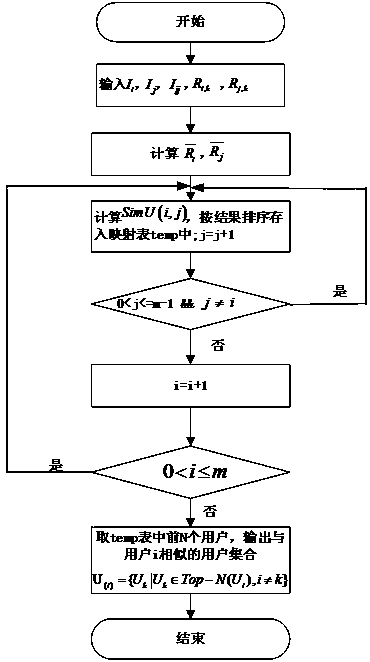
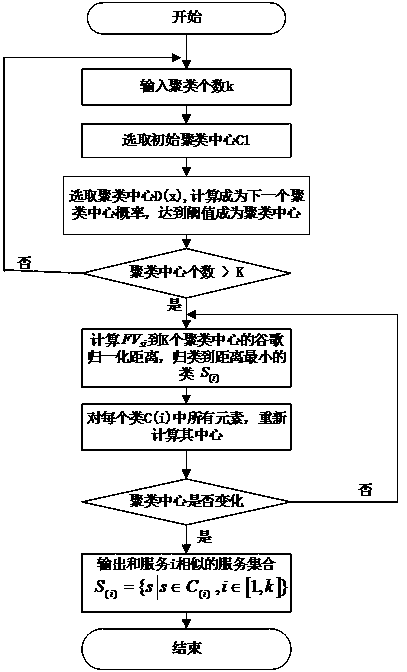
A QoS-aware Web service recommendation method based on user and service clustering
ActiveCN109471982AGet efficientlyDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsCosine similarityData set
The invention provides a Web service recommendation method based on QoS perception of user and service clustering, which clusters users with similar service preference by using cosine similarity calculation based on QoS record of user calling service. Then the WSDL file, which is the description document of the service itself, is extracted and normalized. Means + + algorithm clusters services withsimilar functional characteristics; Finally, the similar user set and the similar service set are integrated into the collaborative filtering algorithm to calculate the missing QoS value of the service invocation matrix and generate recommendations. By using the data set provided by the WSDream Open Source Project, the simulation results show that the proposed Web service recommendation method based on user and service clustering has better results on two mainstream evaluation indexes, namely mean absolute error and root mean square error, compared with the existing technology.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR QoS AWARE GTP-U TRANSPORT IN MOBILE NETWORKS
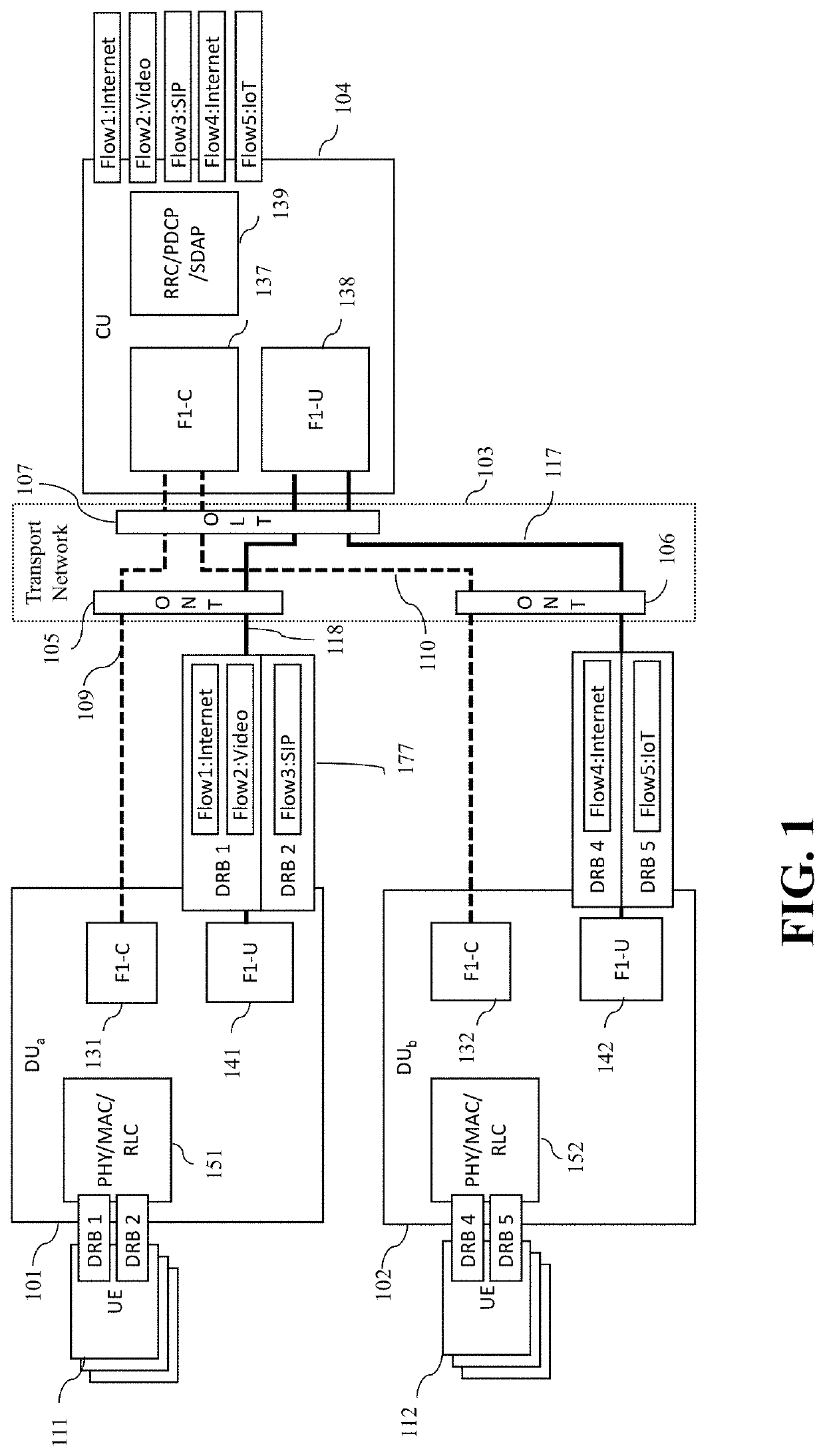
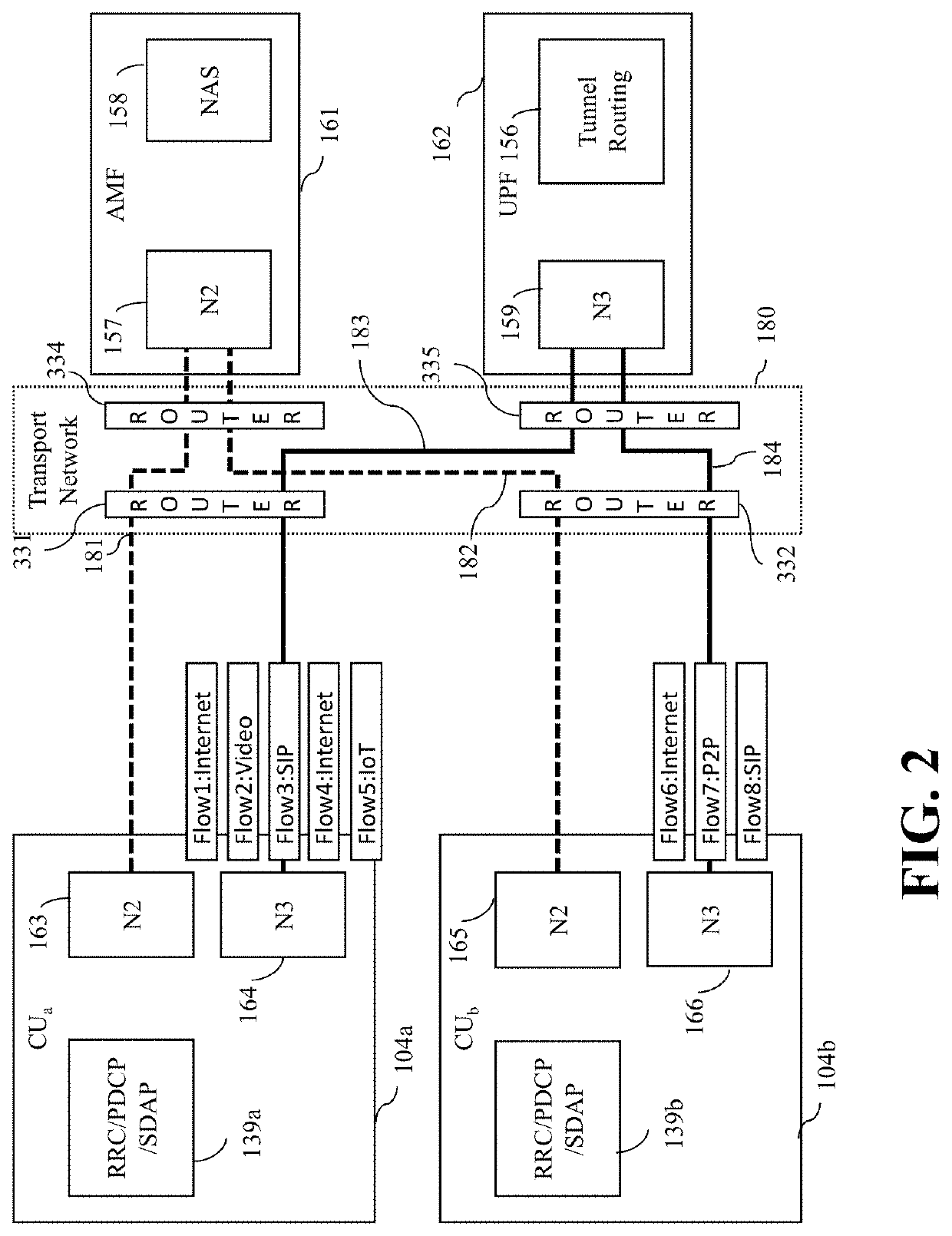
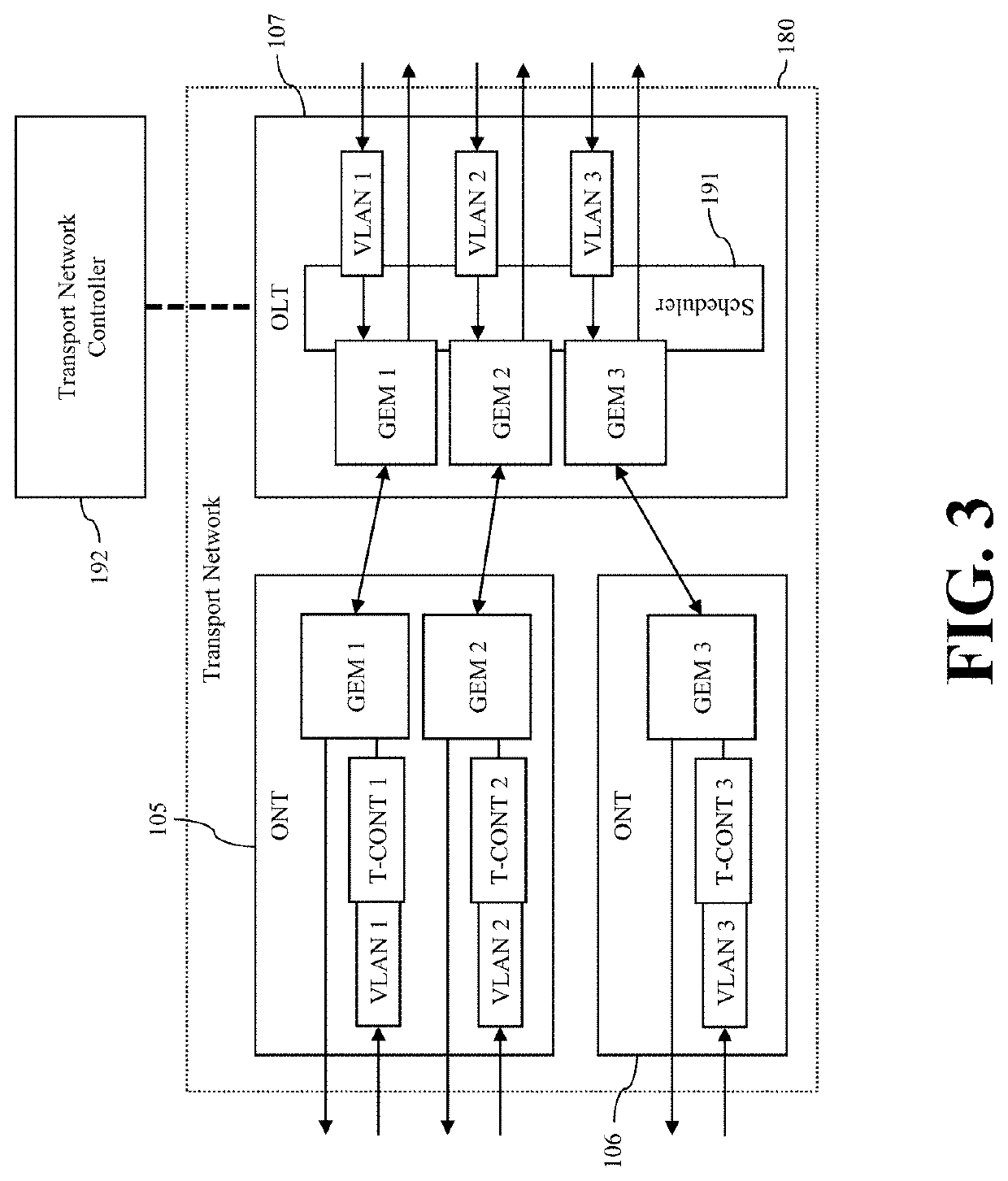
ActiveUS20210160768A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionEngineeringTransport network
The embodiments in this invention extend distributed unit (DU), central unit (CU) and control plane of F1 (F1-C) capabilities so that differentiated DRBs of F1-U are placed on differentiated transport network components of equivalent QoS. This is achieved by a transport-aware DU and CU that can map each F1-U DRB into appropriate OSI layer 2-4 headers and can, subsequently, store such mappings. The F1-C interface is extended to distribute the layer 2-4 headers acquired from the transport network controller to the DUs and CU. A new control interface TN-C is defined between transport network controller and CU / DU. Furthermore, a trivial mapping of those embodiments is applicable for the N3 interface as well, which solves the same problem on the backhaul transport network.
Owner:NETSIA INC
QOS in a system with end-to-end flow control and QOS aware buffer allocation
ActiveUS20150236963A1Improve service qualityEnhanced interactionData switching networksDynamic bandwidth allocationNetworks on chip
The present disclosure is directed to Quality of Service (QoS) and handshake protocols to facilitate endpoint bandwidth allocation among one or more agents in a Network on Chip (NoC) for an endpoint agent. The QoS policy and handshake protocols may involve the use of credits for buffer allocation which are sent to agents in the NoC to compel the acceptance of data and the allocation of an appropriate buffer. Messages sent to the agent may also have a priority associated with the message, wherein higher priority messages have automatic bandwidth allocation and lower priority messages are processed using a handshake protocol.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System for high performance on-demand video transcoding
ActiveUS20190335214A1Decrease deadline miss rate and startup delayMinimize incurred costResource allocationDigital video signal modificationCloud baseService provision
Video streams, either in form of on-demand streaming or live streaming, usually have to be transcoded based on the characteristics of clients' devices. Transcoding is a computationally expensive and time-consuming operation; therefore, streaming service providers currently store numerous transcoded versions of the same video to serve different types of client devices. Due to the expense of maintaining and upgrading storage and computing infrastructures, many streaming service providers recently are becoming reliant on cloud services. However, the challenge in utilizing cloud services for video transcoding is how to deploy cloud resources in a cost-efficient manner without any major impact on the quality of video streams. To address this challenge, in this paper, the Cloud-based Video Streaming Service (CVSS) architecture is disclosed to transcode video streams in an on-demand manner. The architecture provides a platform for streaming service providers to utilize cloud resources in a cost-efficient manner and with respect to the Quality of Service (QoS) demands of video streams. In particular, the architecture includes a QoS-aware scheduling method to efficiently map video streams to cloud resources, and a cost-aware dynamic (i.e., elastic) resource provisioning policy that adapts the resource acquisition with respect to the video streaming QoS demands. Simulation results based on realistic cloud traces and with various workload conditions, demonstrate that the CVSS architecture can satisfy video streaming QoS demands and reduces the incurred cost of stream providers up to 70%.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LOUISIANA AT LAFAYETTE
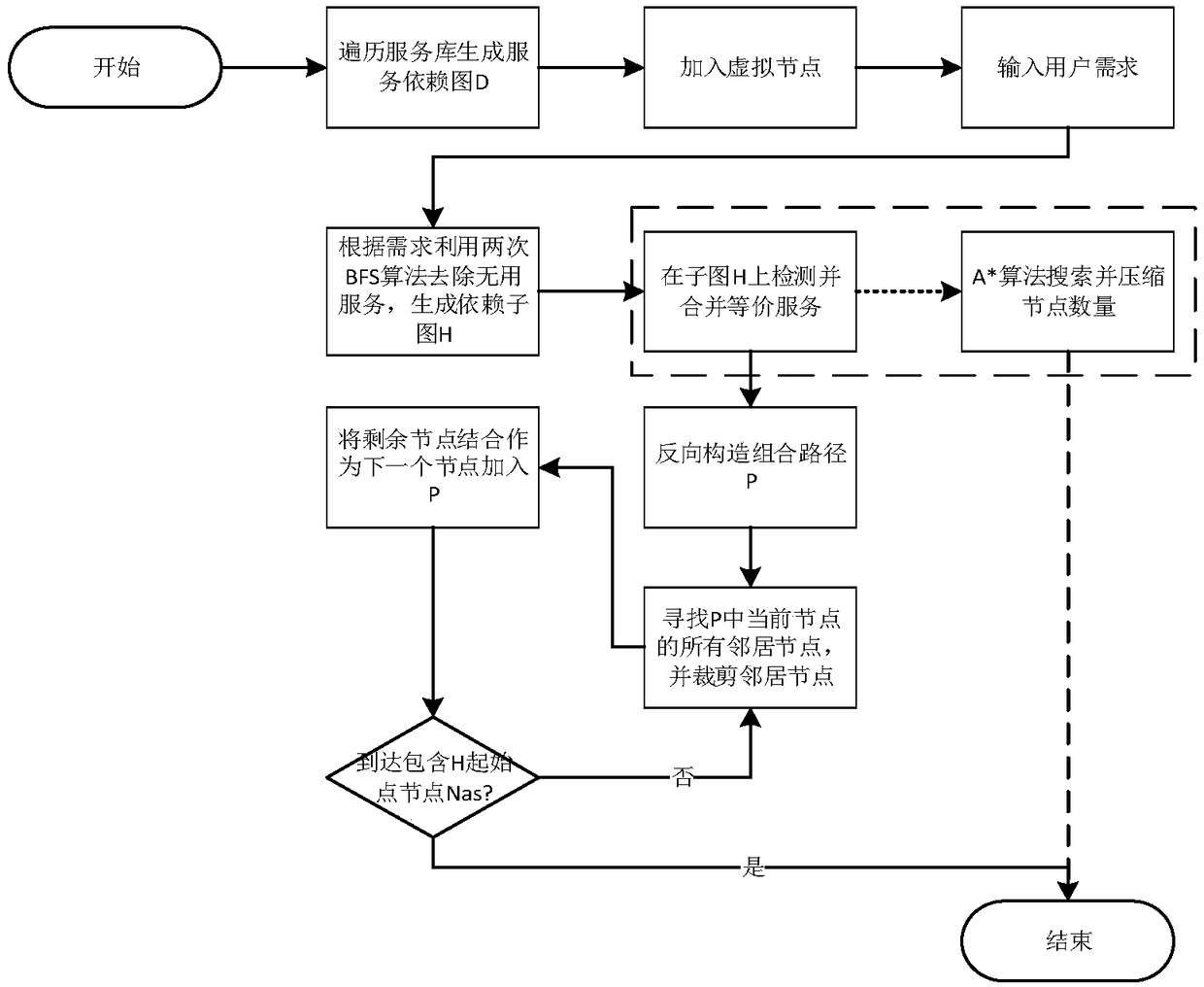
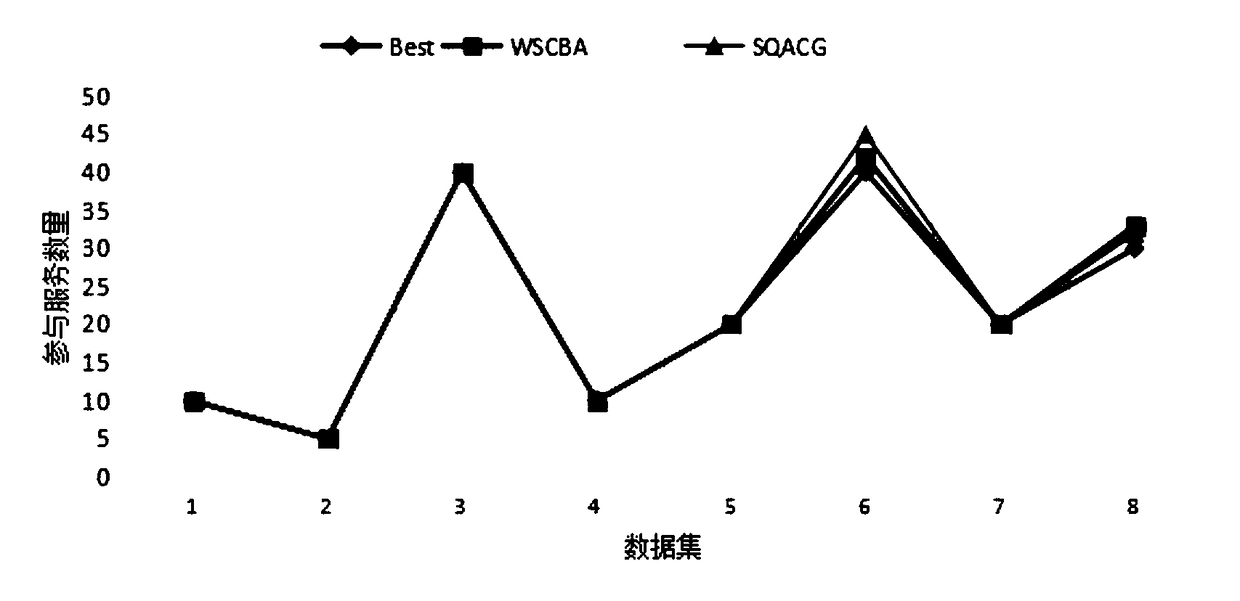
A graph-based scalable QoS perceptual combination method
The invention discloses a graph-based extensible QoS perceptual composition method, belonging to the Web service composition technology in the Web service field. Based on the WSCBA algorithm, a graph-based scalable QoS aware service composition (SQACG) method is proposed. The SQACG method scales nodes according to user needs when constructing a solution, regardless of the optimality of the final service composition solution, but tradeoffs between computational speed and QoS optimality for composite services, A QoS paramete of a non-functional attribute is considered, Moreover, the algorithm ofgenerating service dependency graph is improved, which sacrifices the optimality of the final result for the performance of space and time, and has good scalability, which enables users to adjust thesolution between the execution speed and the quality of service according to the needs, which reflects the good scalability of the algorithm.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com