Patents
Literature
12450 results about "User needs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
User needs are requirements that add value to a product, service or environment for a user. Capturing user needs is a process of engaging users to understand their problems, processes, goals and preferences. The following are common examples of user needs.
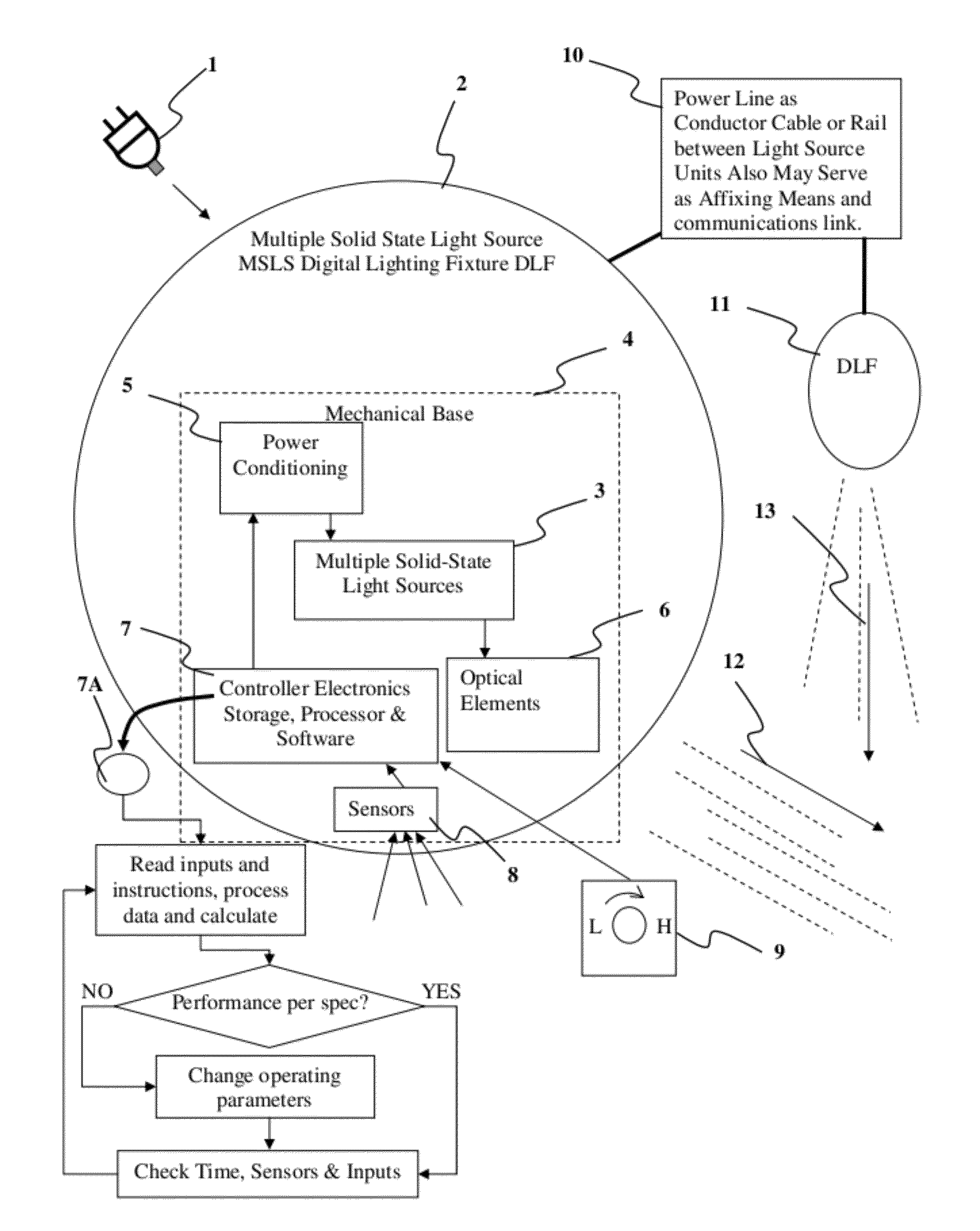
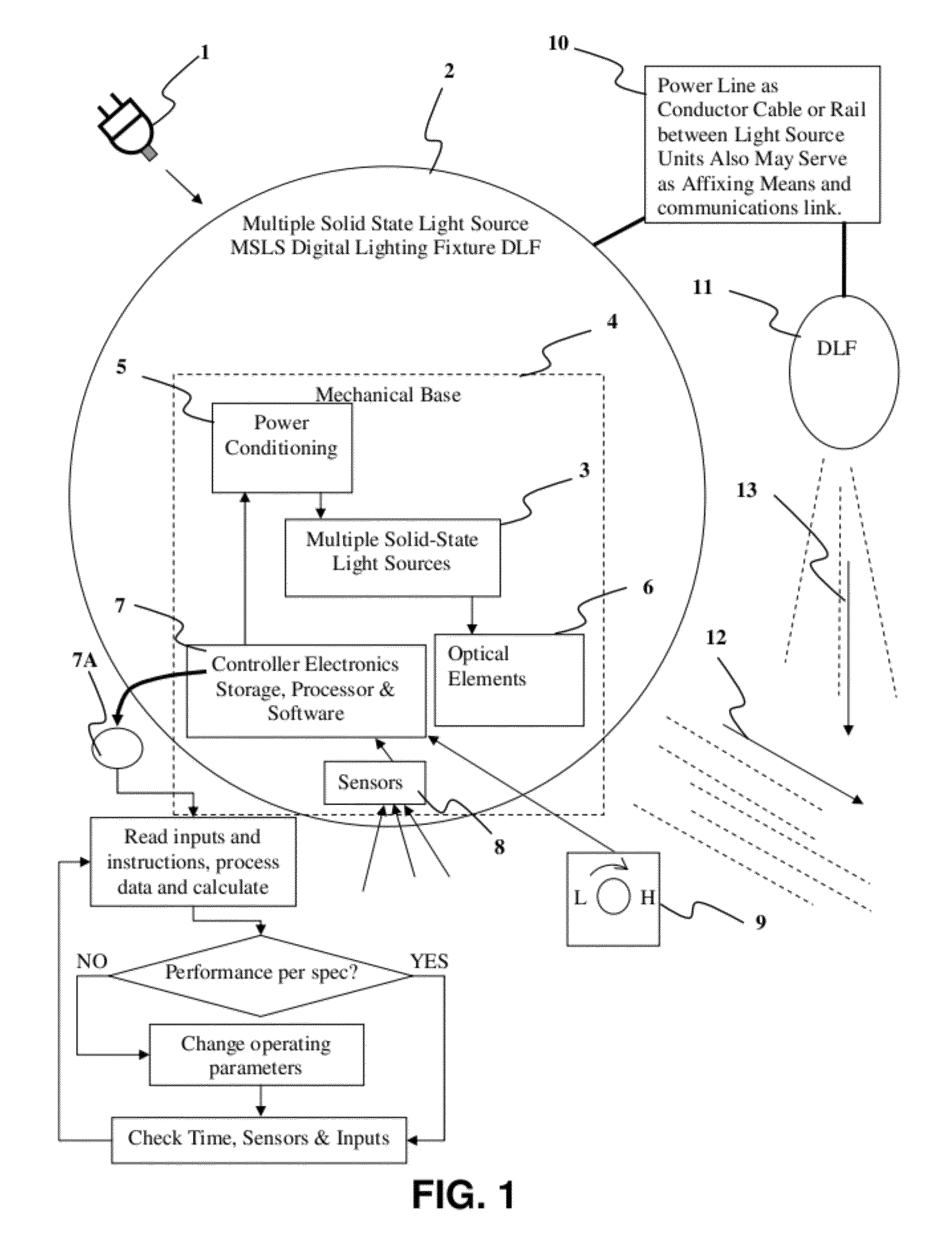
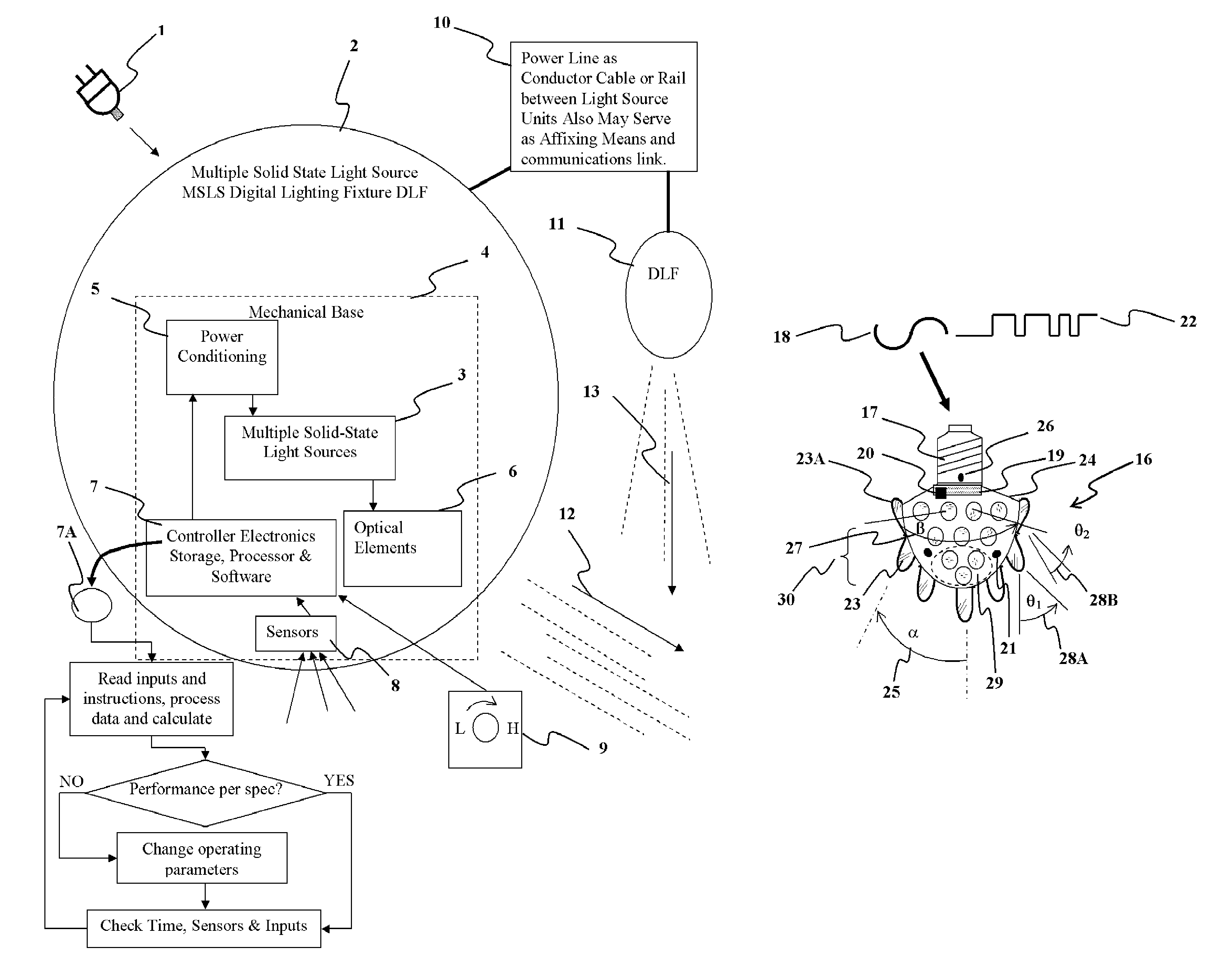
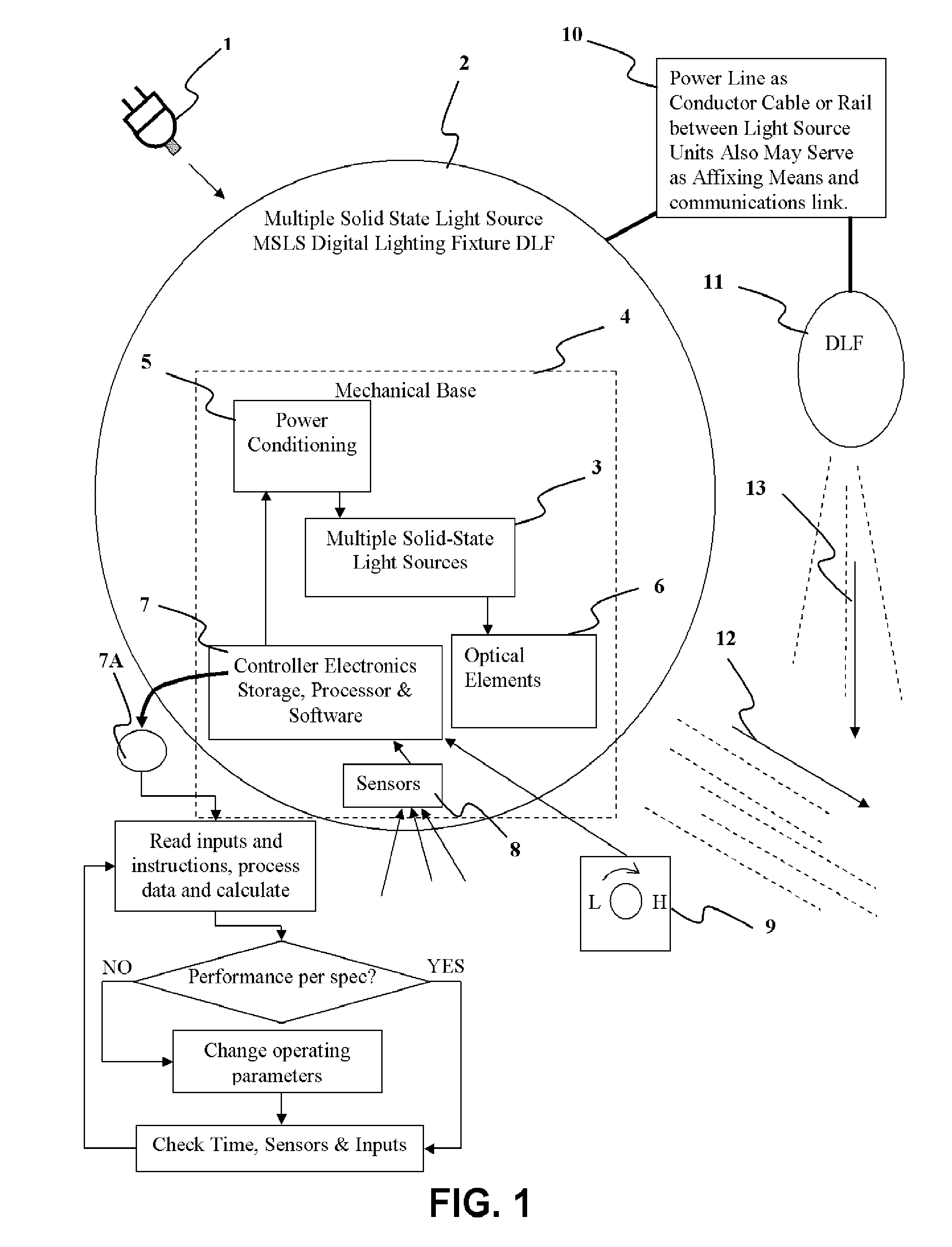
Detector Controlled Illuminating System
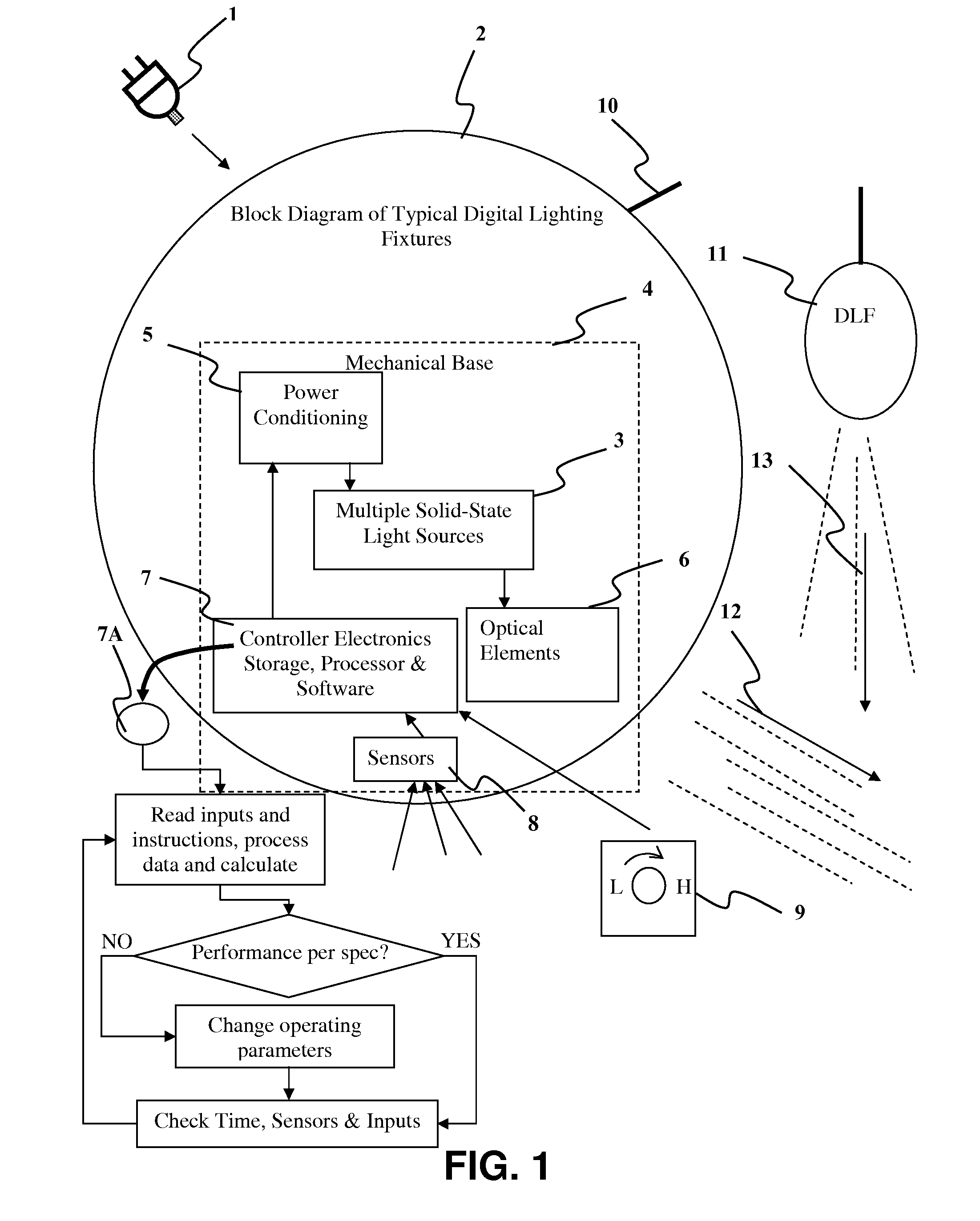
ActiveUS20120206050A1Correctly illuminateReduce electricity costsMechanical apparatusLight source combinationsUser needsCost effectiveness
An illuminating device coupled with sensors or an image acquisition device and a logical controller allows illumination intensity and spectrum to be varied according to changing user needs. The system provides illumination to areas according to the principles of correct lighting practice for the optimal performance of visual tasks in the most efficient, cost effective manner. Aspects of the invention include: lighting fixtures which adapt to ambient lighting, movement, visual tasks being performed, and environmental and personal conditions affecting illumination requirements at any given instant. Lighting fixtures having spatial distribution of spectrum and intensity, providing both “background” room lighting, and “task” lighting.
Owner:YECHEZKAL EVAN SPERO
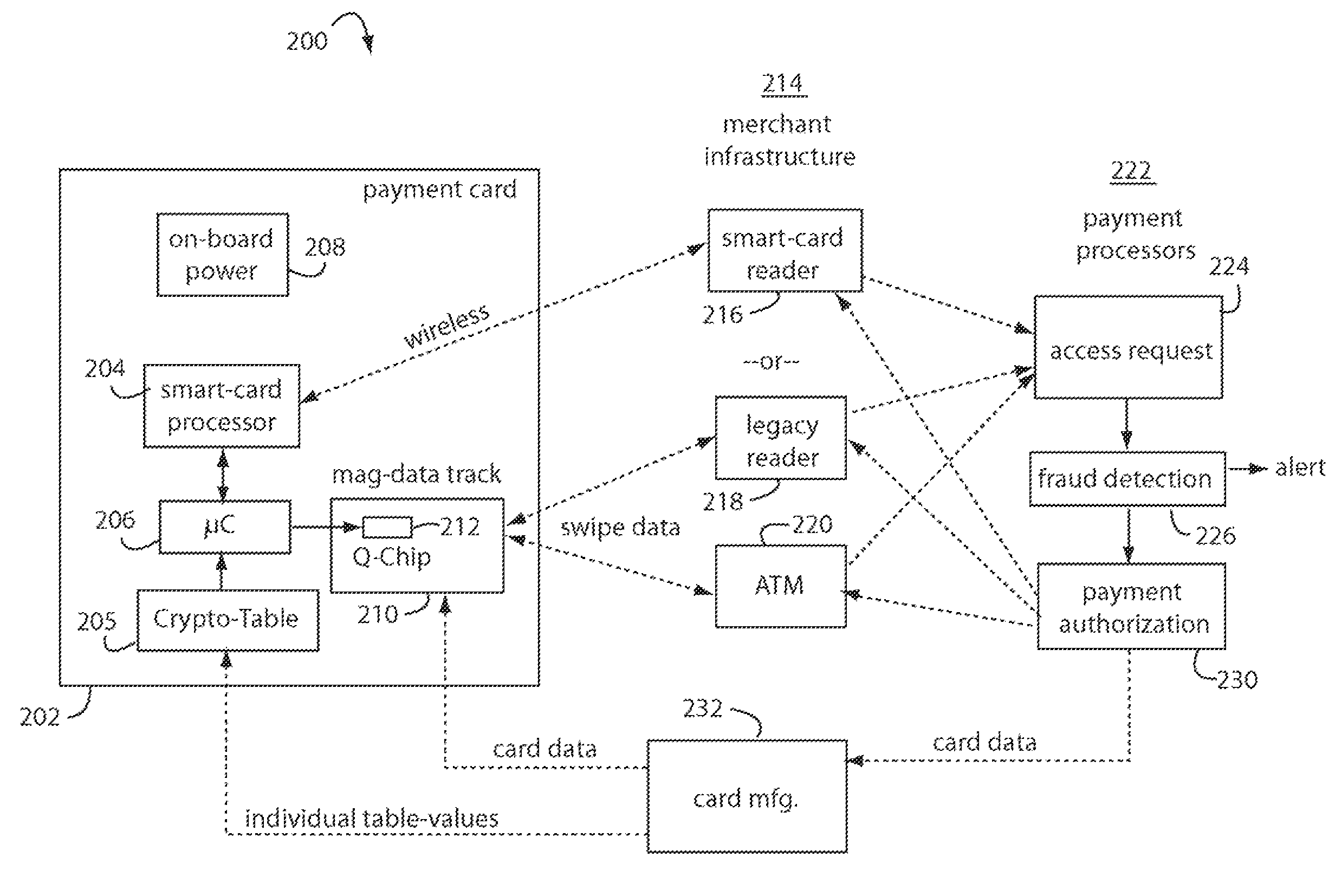
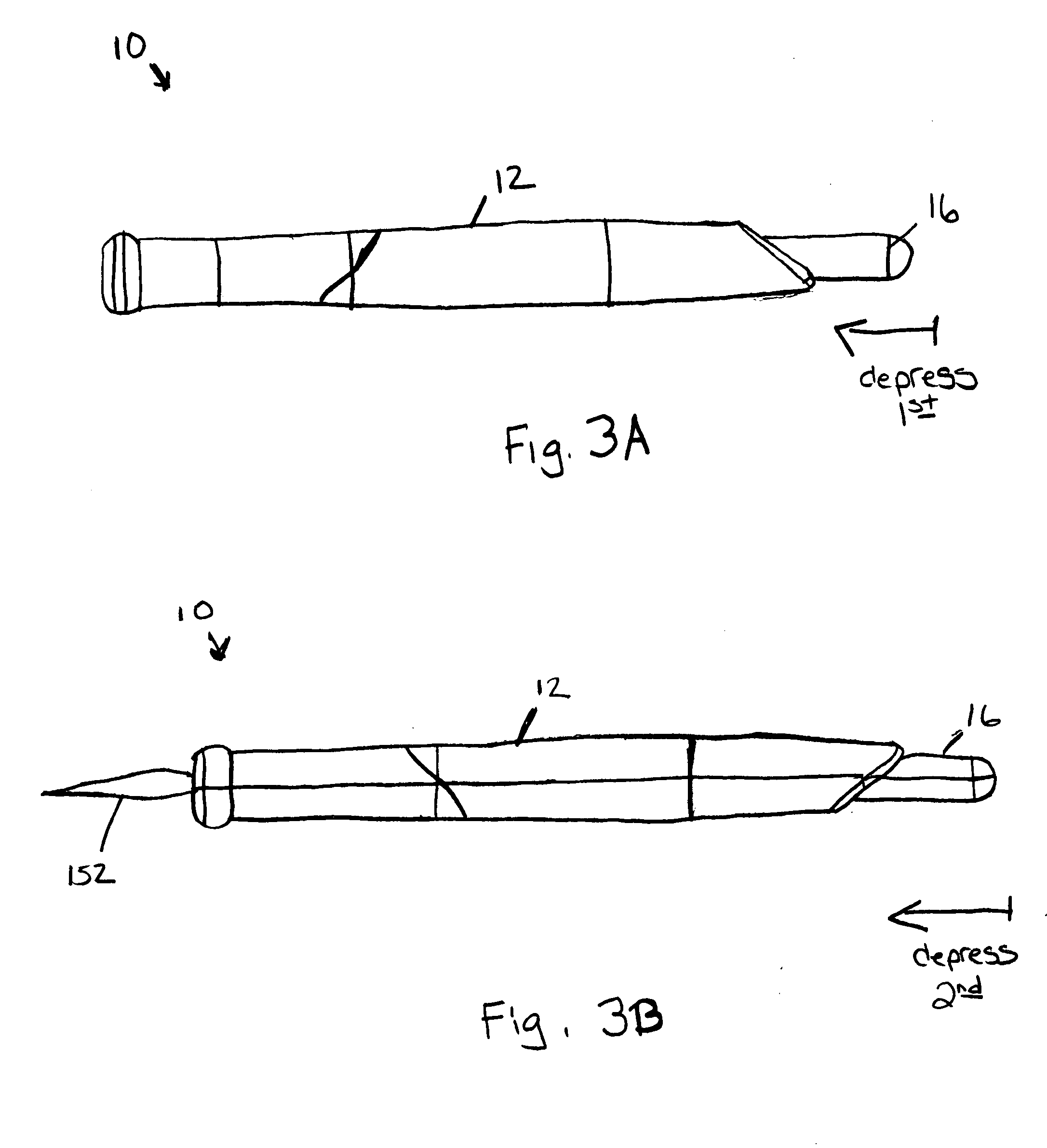
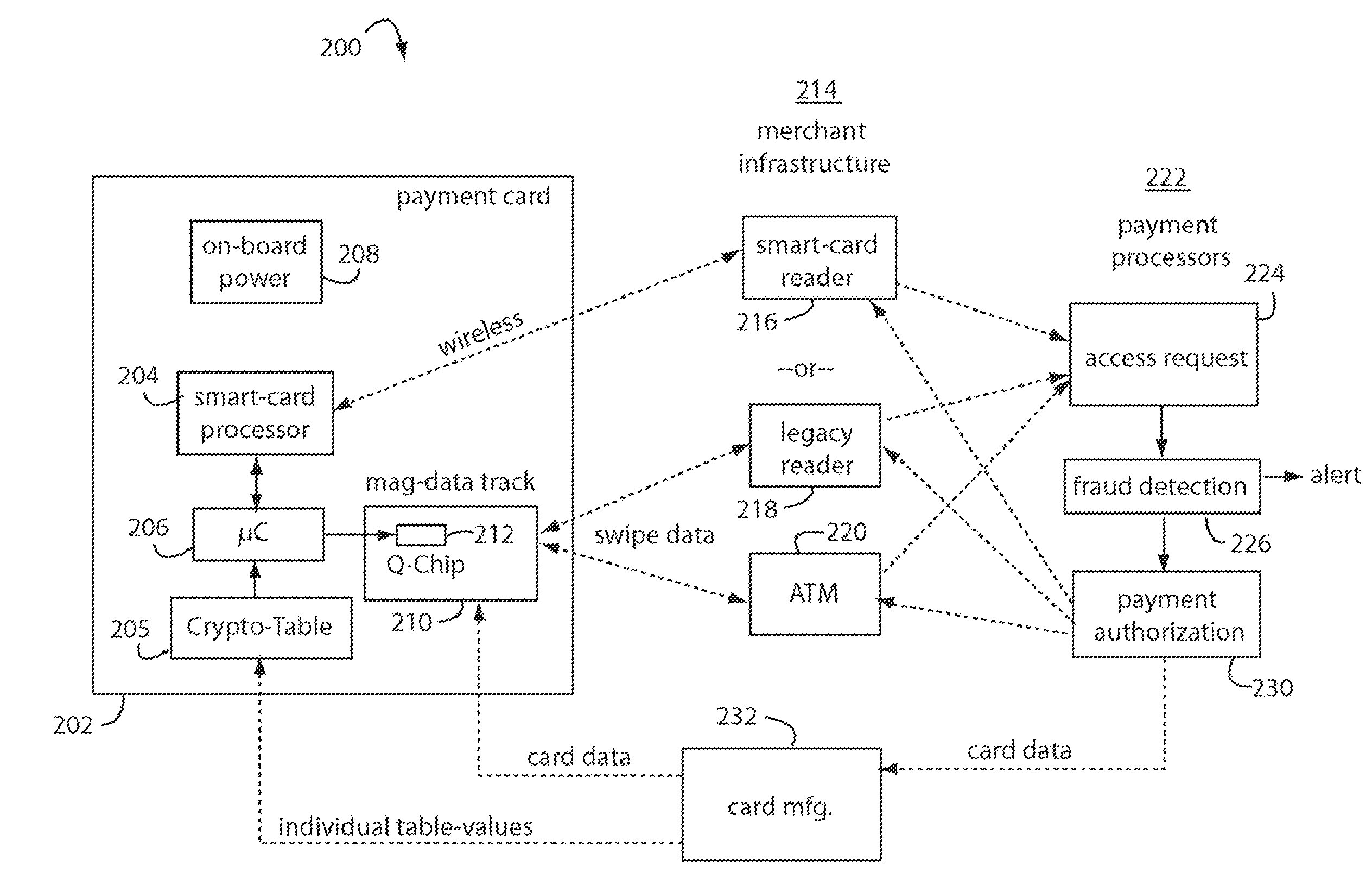
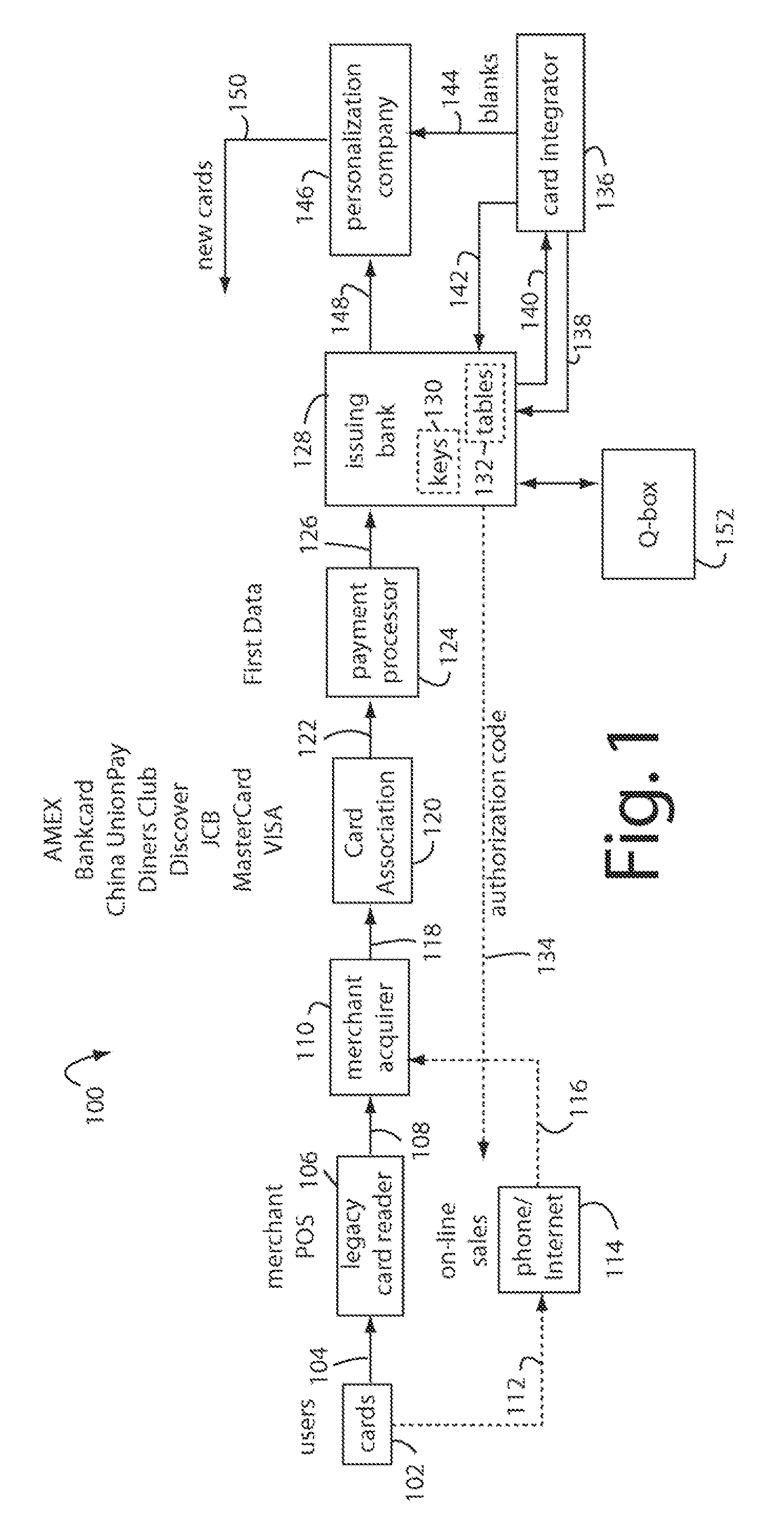
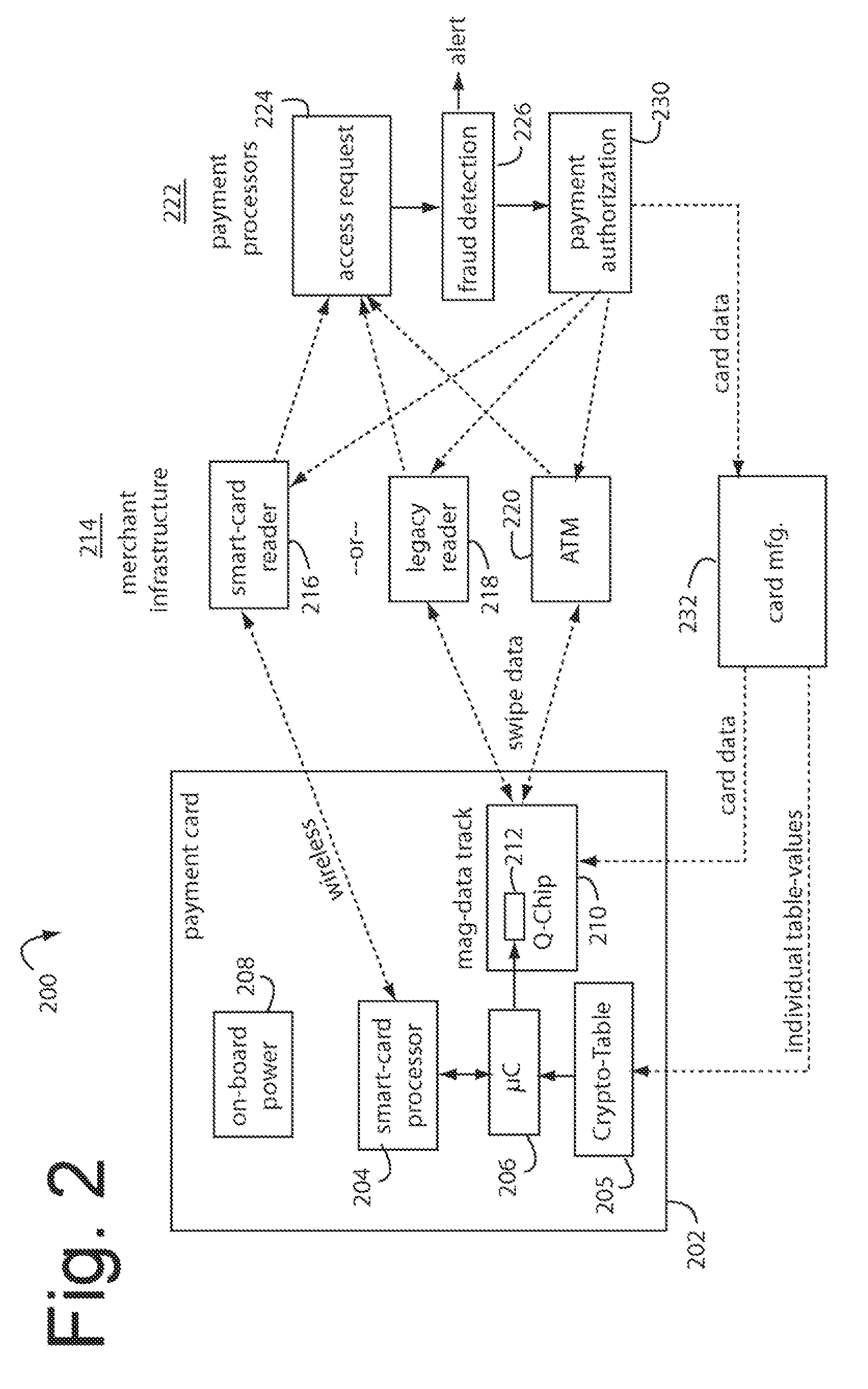
Financial transactions with dynamic card verification values
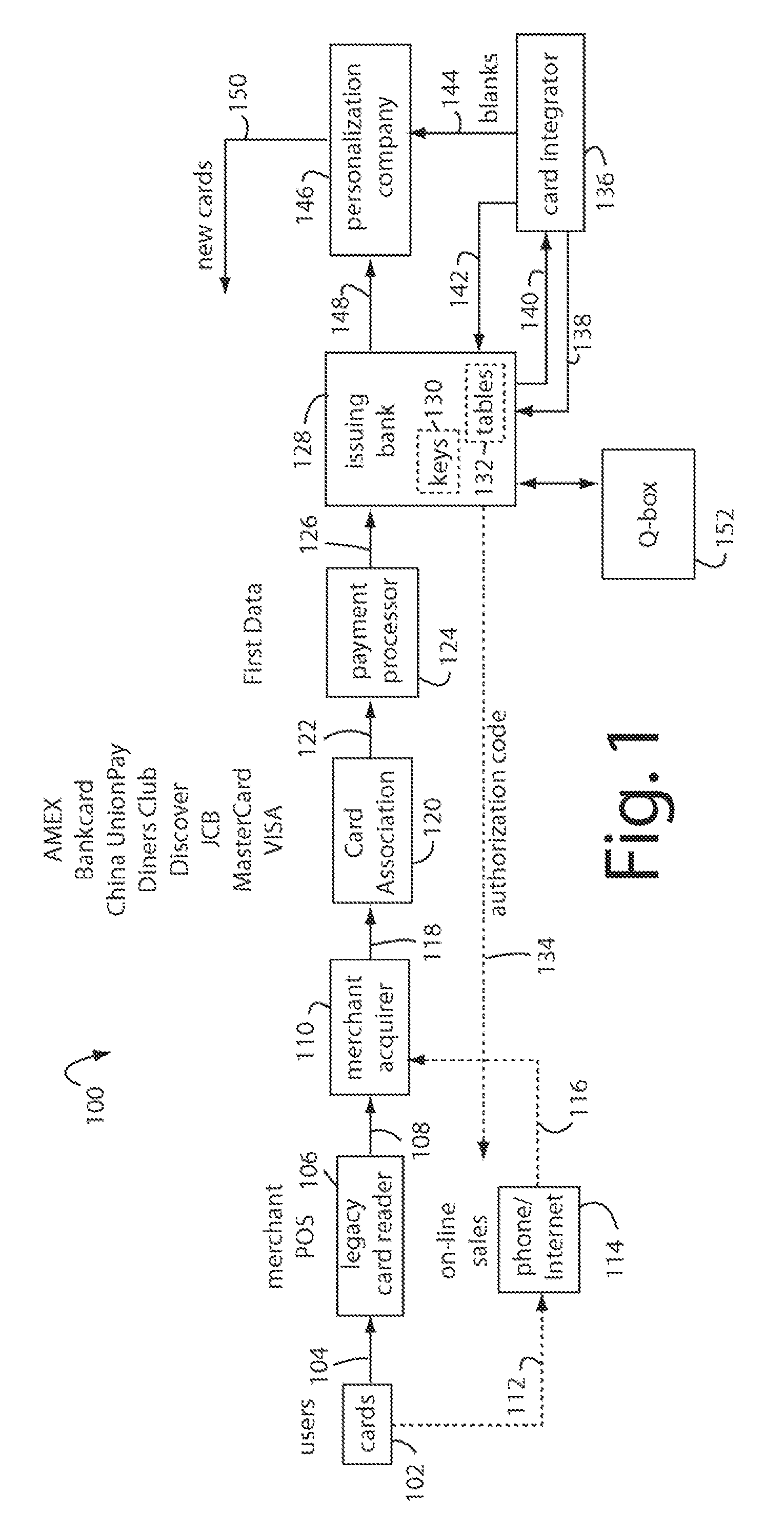
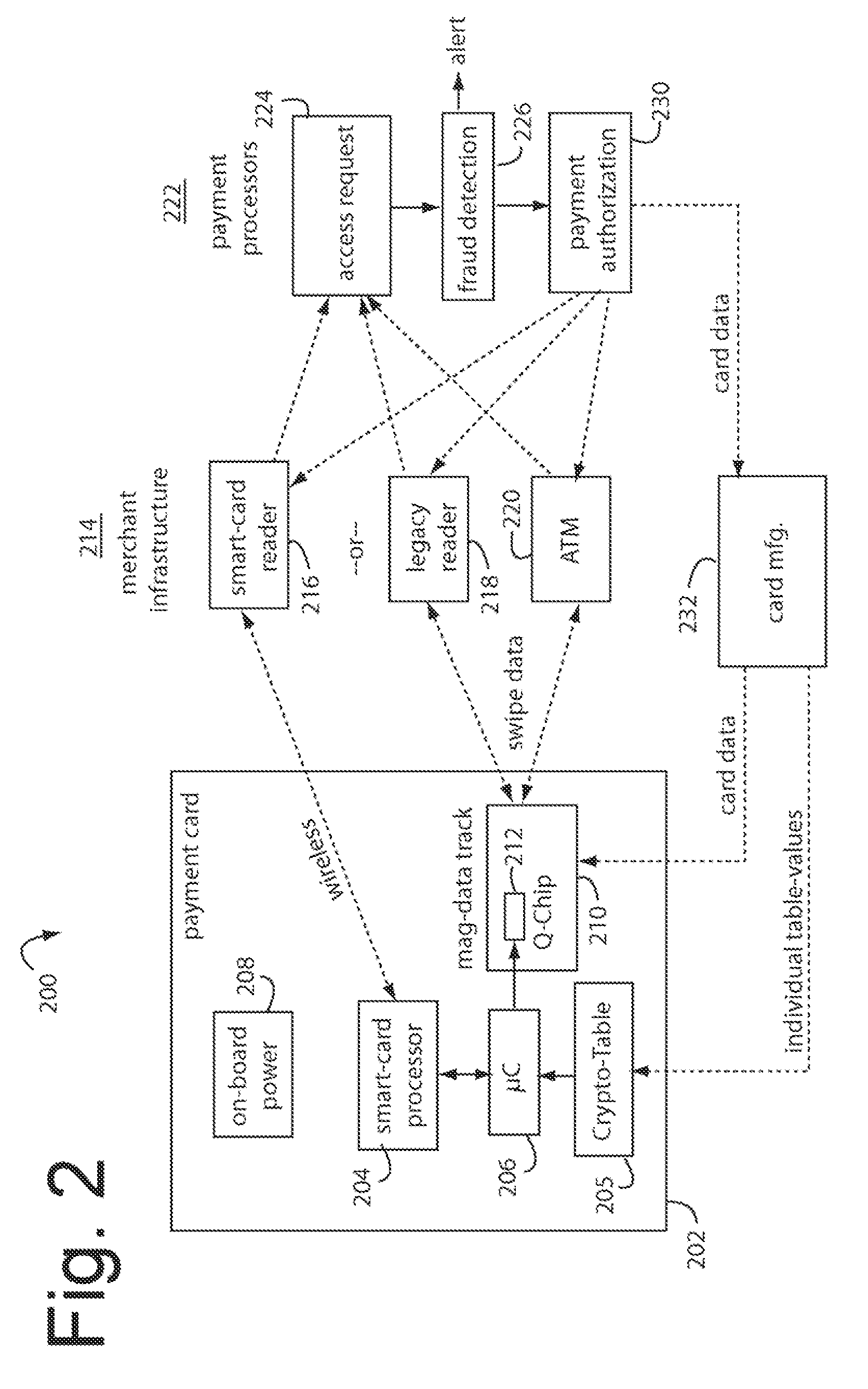
ActiveUS7584153B2Sufficient dataComputer security arrangementsPayment architectureUser needsDisplay device
A payment card comprises an internal dynamic card verification value (CVV) generator and a user display for card-not-present transactions. Card-present transactions with merchant card readers are enabled by a dynamic magnetic array internally associated with the card's magnetic stripe. The user display and a timer are triggered by the user when the user needs to see the card verification value and / or begin a new transaction. A new card verification value is provided for each new transaction according to a cryptographic process, but the timer limits how soon a next new card verification value can be generated.
Owner:FITBIT INC
Precision knife and blade dispenser for the same
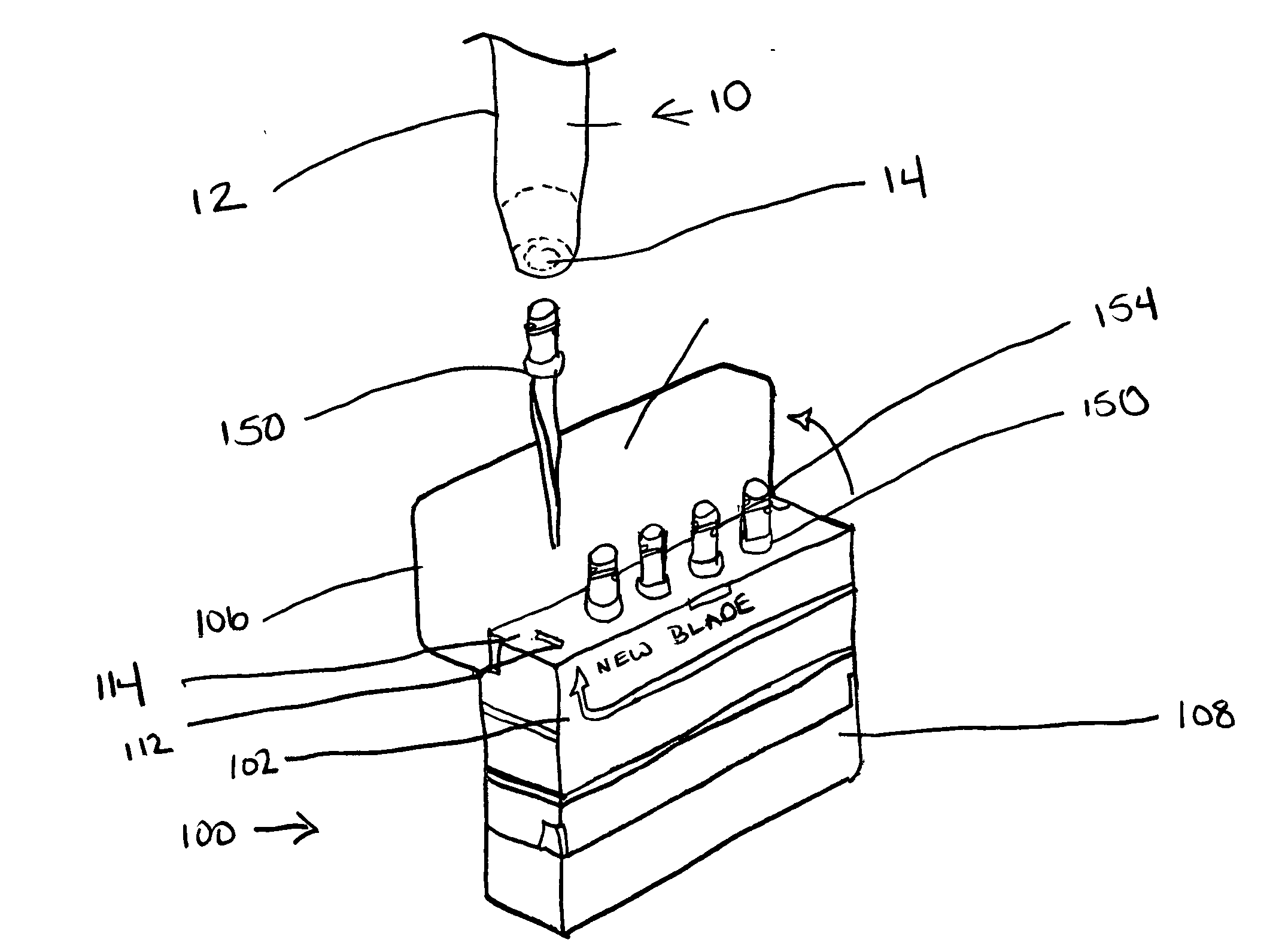
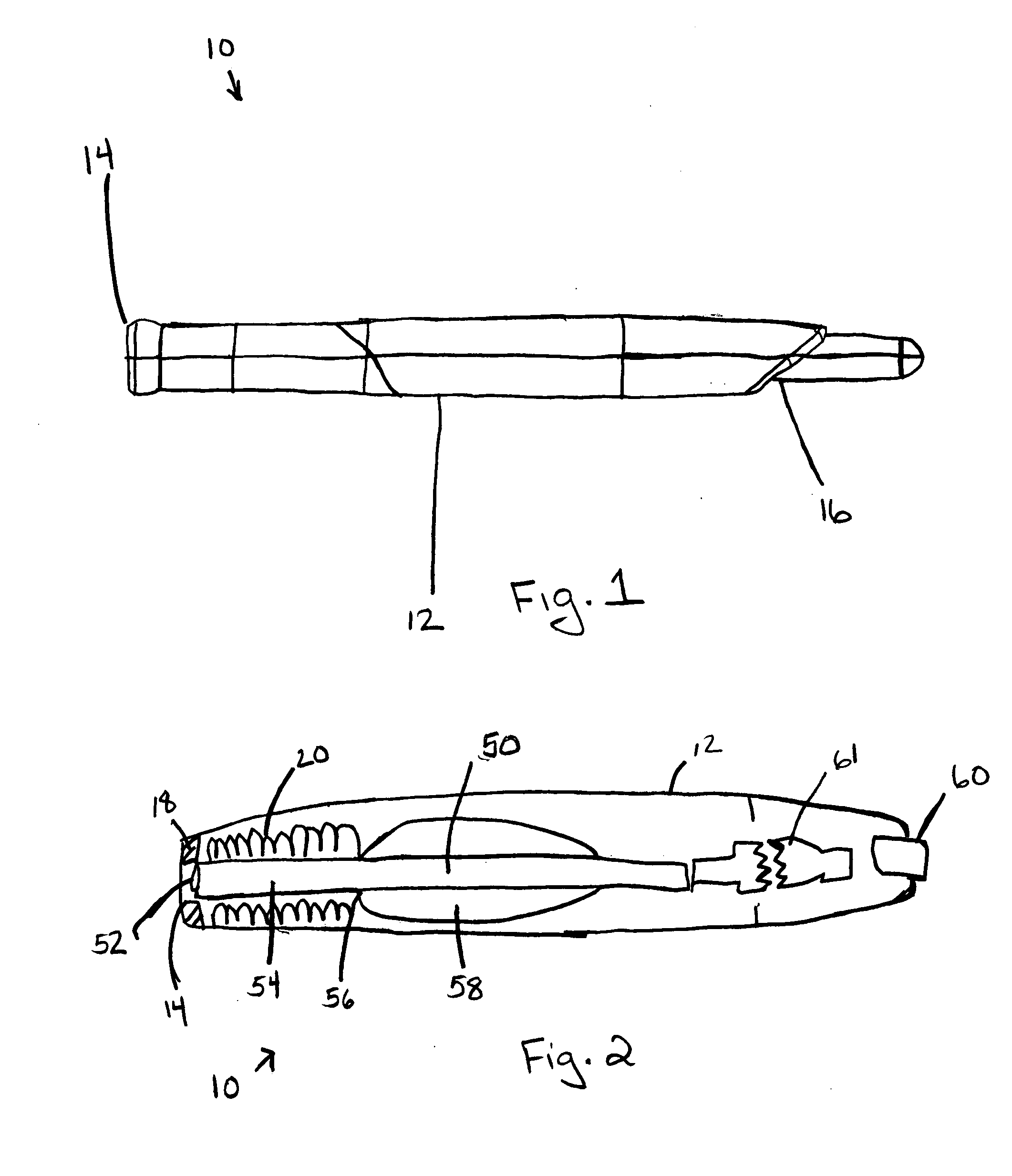
InactiveUS20080196253A1The process is simple and effectivePortable power-driven toolsMetal working apparatusUser needsKnife blades
A combination precision knife and blade dispenser having a handle portion configured to receive a blade and a dispenser. The dispenser is configured to support at least one blade in a new blade portion thereof. The dispenser further has a used blade portion configured to support at least one blade therein, where a user, manipulates the handle portion and engages a base of the at least one blade therein, and where in order to dispose of the blade, the user inserts the blade into the dispenser and disengages the base of the blade from the handle portion such that at no time does a user need to touch an edge portion of the blade.
Owner:EZRA RICHARD SIMON +1
Financial transactions with dynamic card verification values
ActiveUS20070136211A1Sufficient dataComputer security arrangementsPayment architectureUser needsPower user
A payment card comprises an internal dynamic card verification value (CVV) generator and a user display for card-not-present transactions. Card-present transactions with merchant card readers are enabled by a dynamic magnetic array internally associated with the card's magnetic stripe. The user display and a timer are triggered by the suer when the user needs to see the card verification value and / or begin a new transaction. A new card verification value is provided for each new transaction according to a cryptographic process, but the timer limits how soon a next new card verification value can be generated.
Owner:FITBIT INC
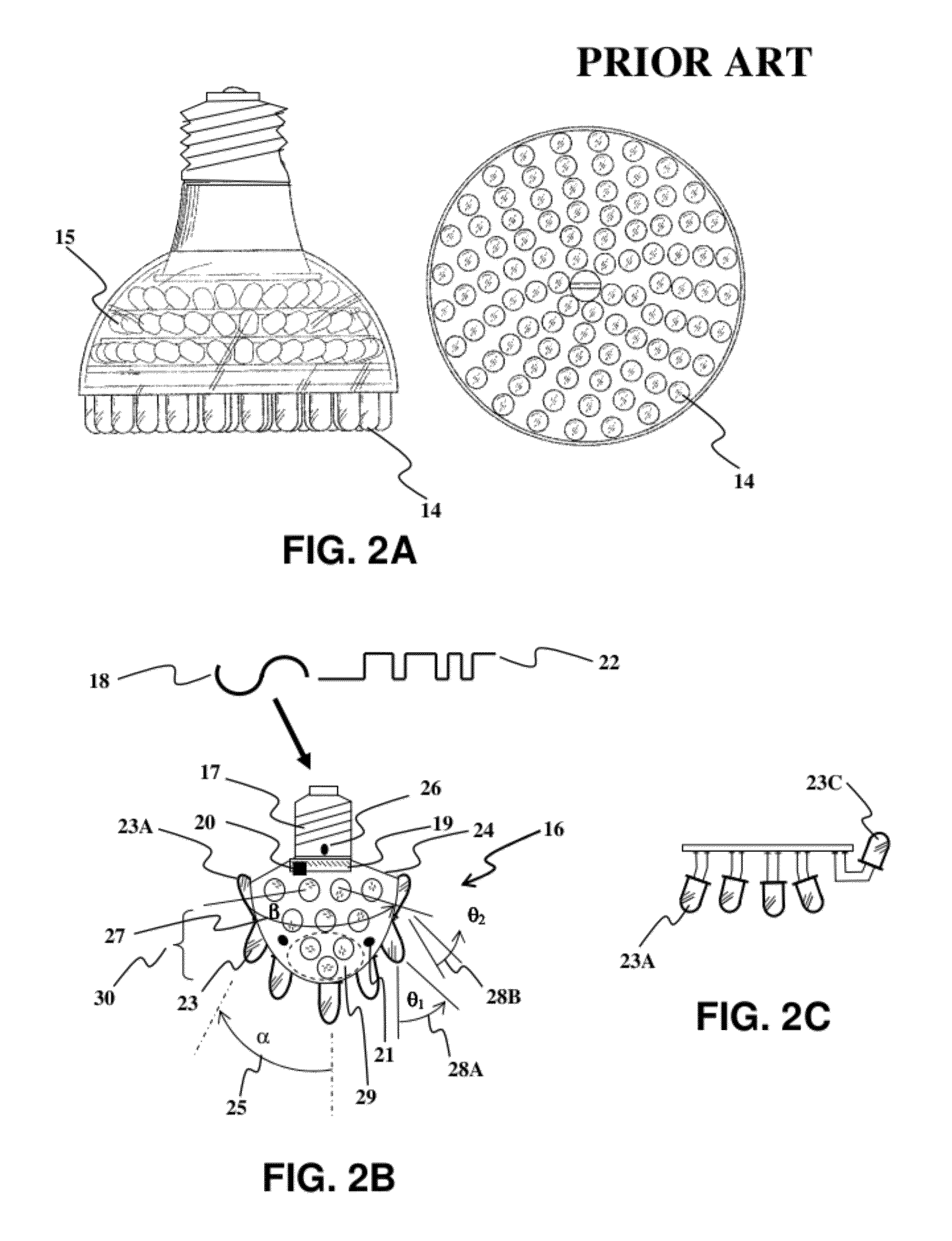
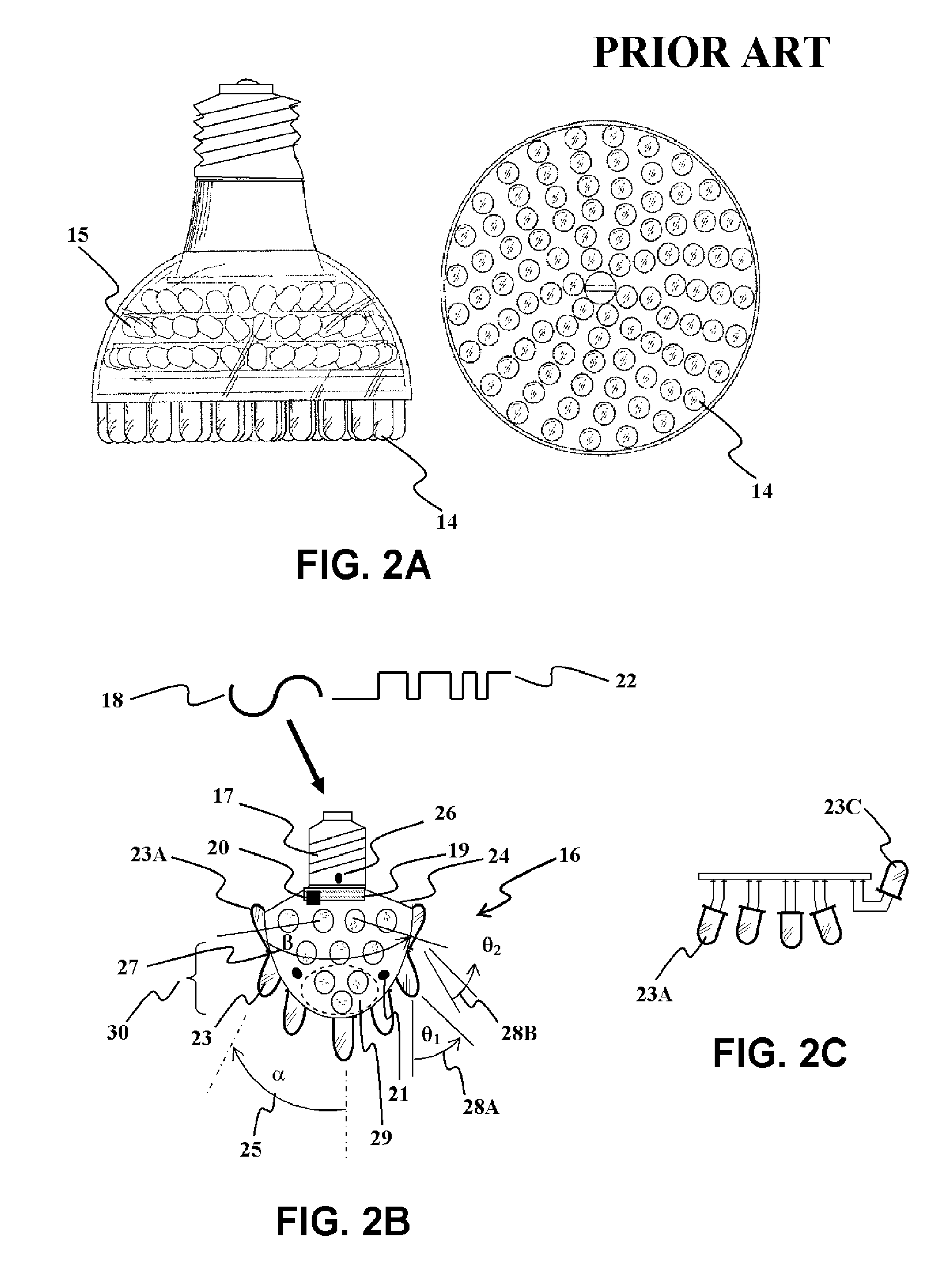
Multiple light-source illuminating system
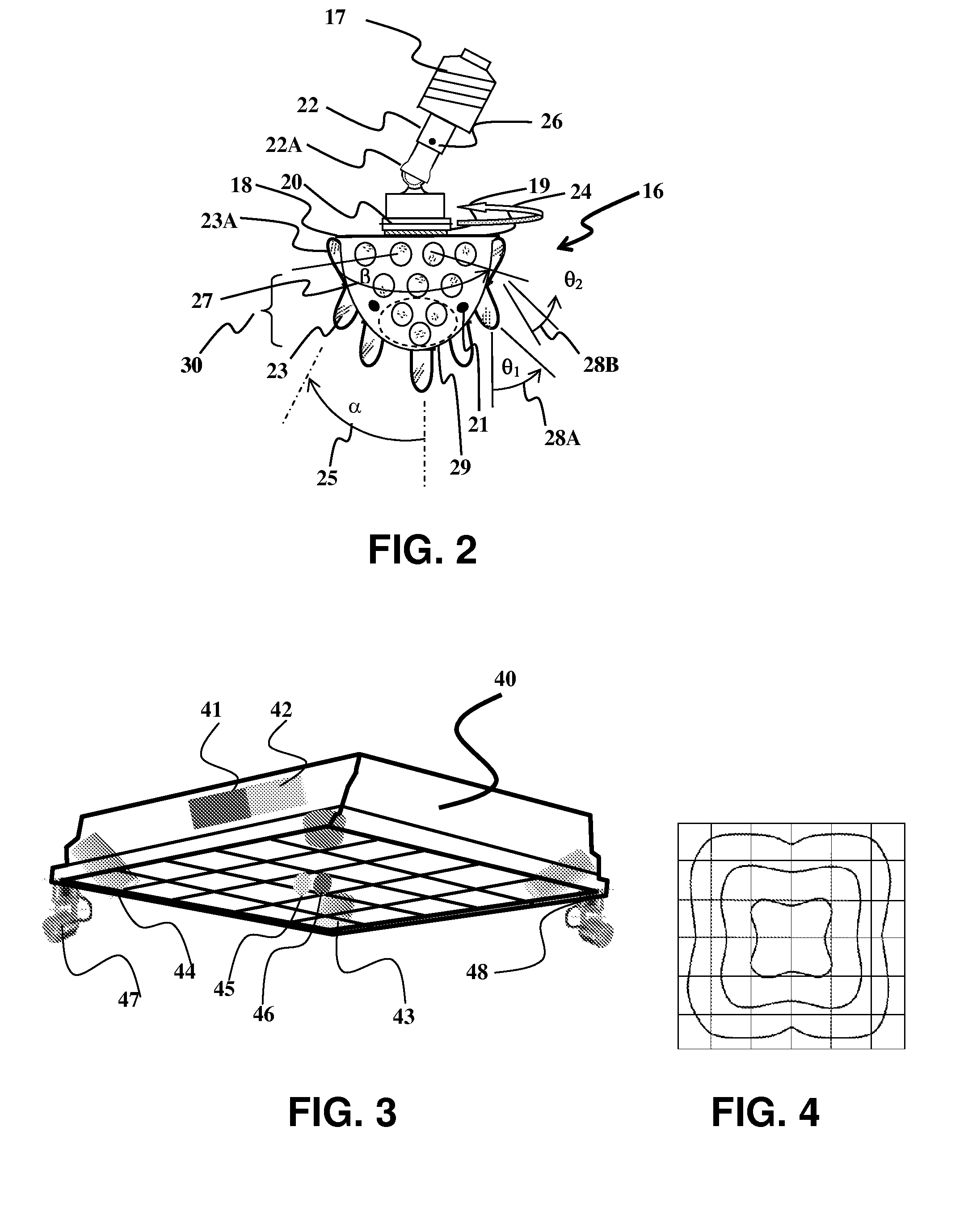
InactiveUS8100552B2OptimizationAvoid narrow scopeMechanical apparatusLight source combinationsUser needsEngineering
A method and apparatus is provided for a multiple light-source illuminating device, the design and construction of which is derived from the lighting requirements of a specific lighting application. The resulting illuminating device (16) provides illumination according to the principles of lighting practice for the optimal performance of visual tasks. Coupling with sensors (21) and logical control (20) allows illumination intensity and spectrum to be varied according to changing user needs. The illuminating device includes multiple discrete light emitting components of different spatial intensity distribution and color spectrum mounted in specific orientations such that the application oriented combined lighting effect is created. The control is provided via a differentiated power supply (19) capable of affecting the current, voltage and duty cycle determining the relative contribution of each light source effecting a different spatial intensity distribution and color spectrum.
Owner:SPERO YECHEZKAL EVAN
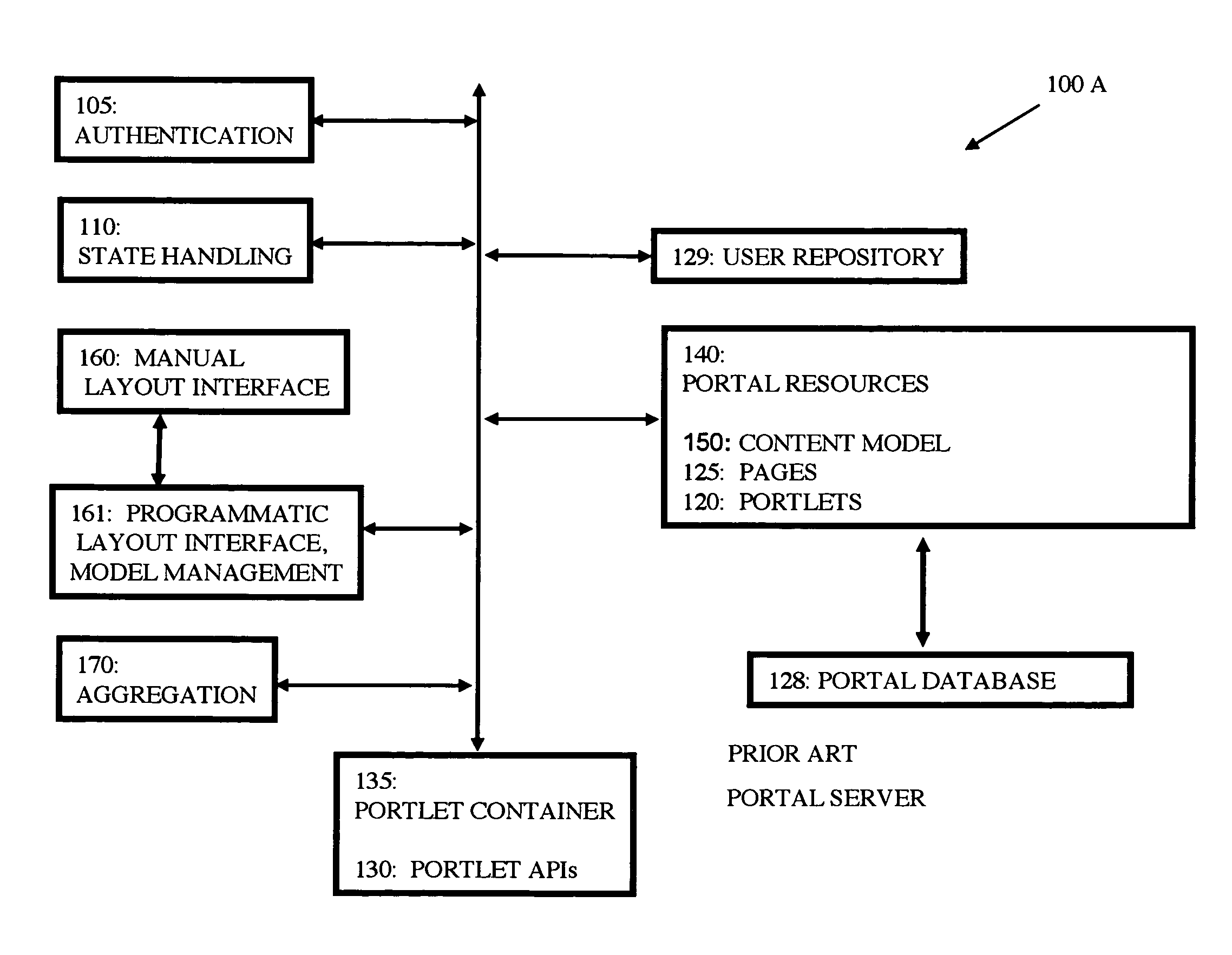
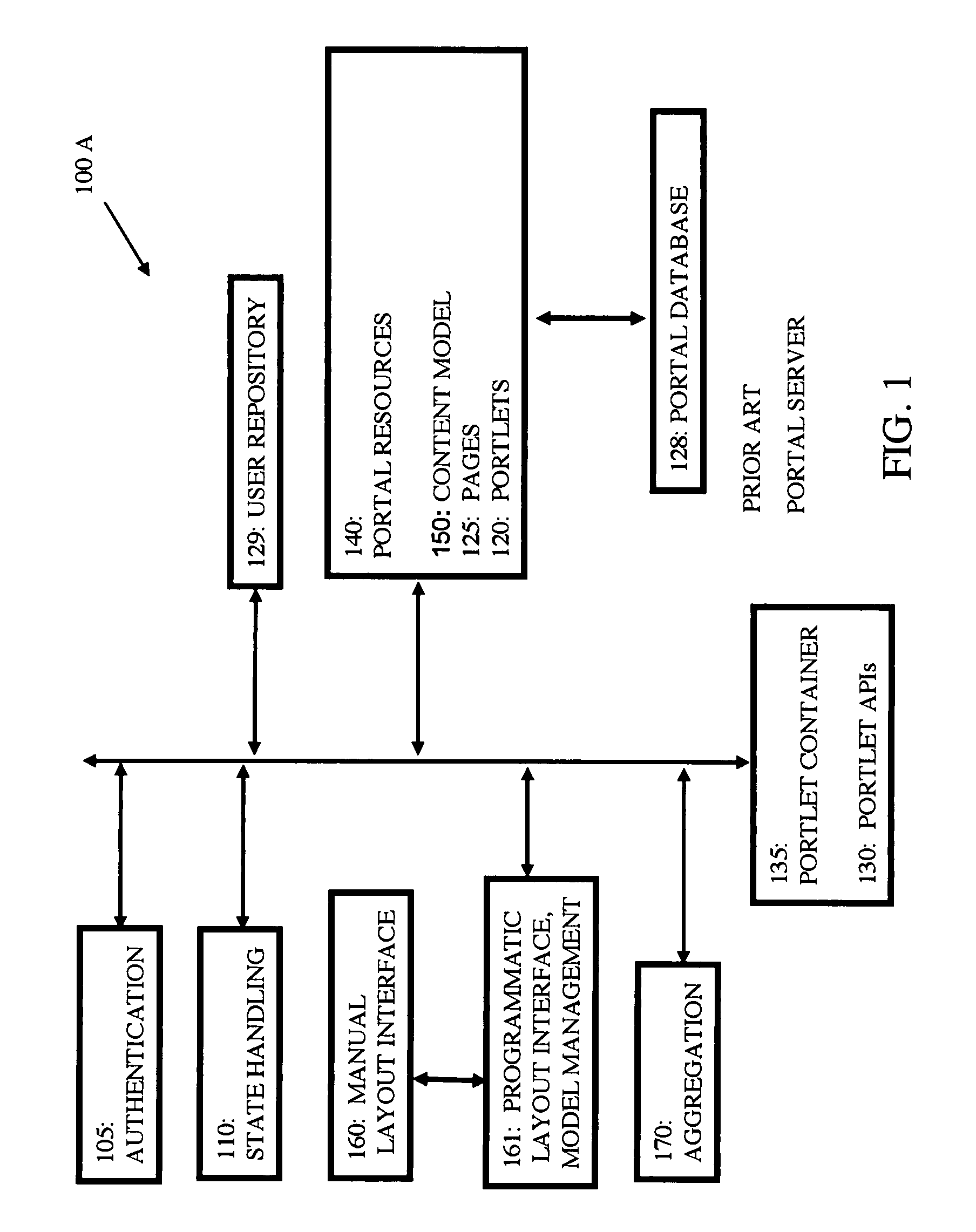
Method for learning portal content model enhancements
InactiveUS8037409B2Increase flexibilityEasily decideWebsite content managementSpecial data processing applicationsUser needsModel management
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Systems and methods for a search-based email client
InactiveUS20050144241A1Eliminating cogitationExpand the scope ofDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsUser needsRelevant information
A search-based email client may incorporate a number of useful features. A search function can default to a search of all email contexts, thereby eliminating user cogitation over which context an email message may be stored in. Furthermore, the search function can automatically search for related personal content and / or related information on the internet or other computer network, and present this useful information to the user in addition to the returned emails. The search function can be integrated into a user interface to allow for one-click searches on any likely search field. The search function can search the body of email messages by default, thereby widening the scope of default searches and eliminating potentially missed information and user need to proactively widen their search. A search function can search attachments, which also provides a wider search scope.
Owner:OATH INC
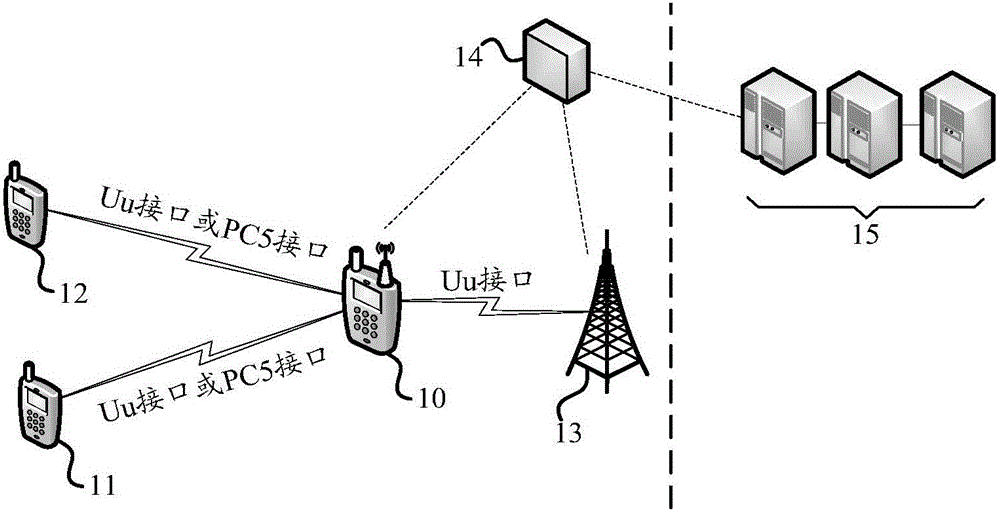
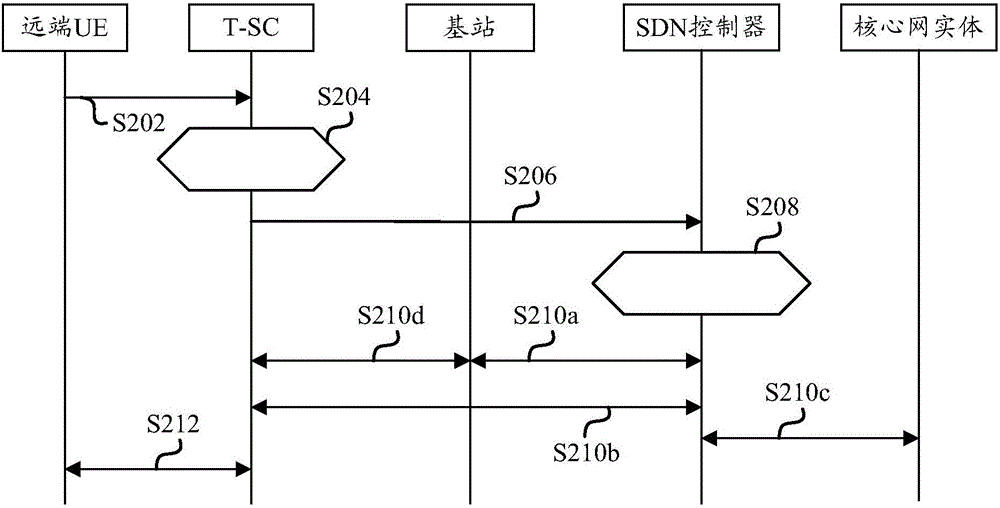
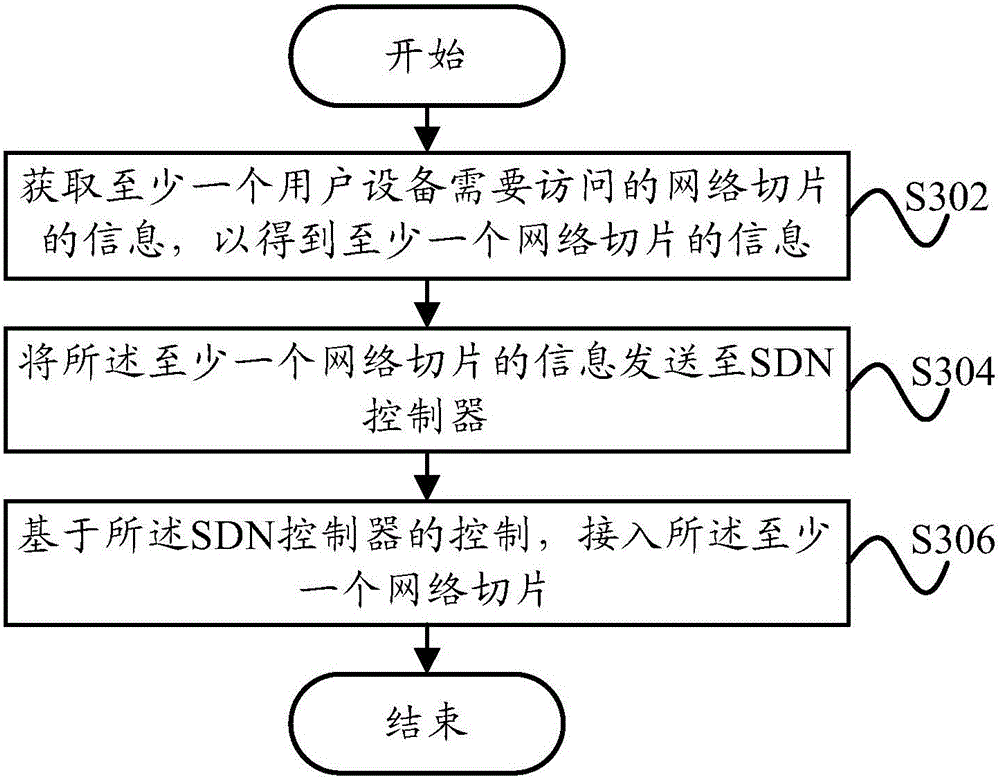
Method and apparatus for controlling access to network slicing, terminal small cell and SDN controller
ActiveCN106060900AImplementation supportAssess restrictionConnection managementUser needsTelecommunications
The invention provides a method and apparatus for controlling access to network slicing, a terminal small cell and a SDN controller. The control method which is suitable to the terminal small cell includes the following steps: acquiring information of at least one network slicing a user needs to access so as to obtain information of at least one network slicing; transmitting the information of at least one network slicing to the SDN controller; based on the control of the SDN controller, and accessing to the at least one network slicing. The technical solution of the invention enables the terminal small cell to access to a corresponding network slicing in advance so as to provide corresponding network service to a user device which is accessed to the terminal small cell, and realizes support of the terminal small cell to the network slicing.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method and system for improved viewing and navigation of content
InactiveUS20050210399A1Reduce scrollingEasy to understandDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsUser needsThumbnail Image
A system and method for small computing devices that present a thumbnail image of content such as a web page, allows a viewer to select a region, and zooms in on the selected region in a way that reduces scrolling and helps users to understand the content they are reading. The page is scaled such that a user need only scroll in one dimension to see the content, and is divided into regions. Regions may be arranged as cells of a grid, or arranged by logically-related content. A user navigates among the regions as desired, selects a region from the thumbnail view, and obtains an expanded version of that region. In the expanded view, the region is ordinarily scaled so that the user scrolls in only one dimension to view the content of the region. Browser “Back” commands are supported, as are frames.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
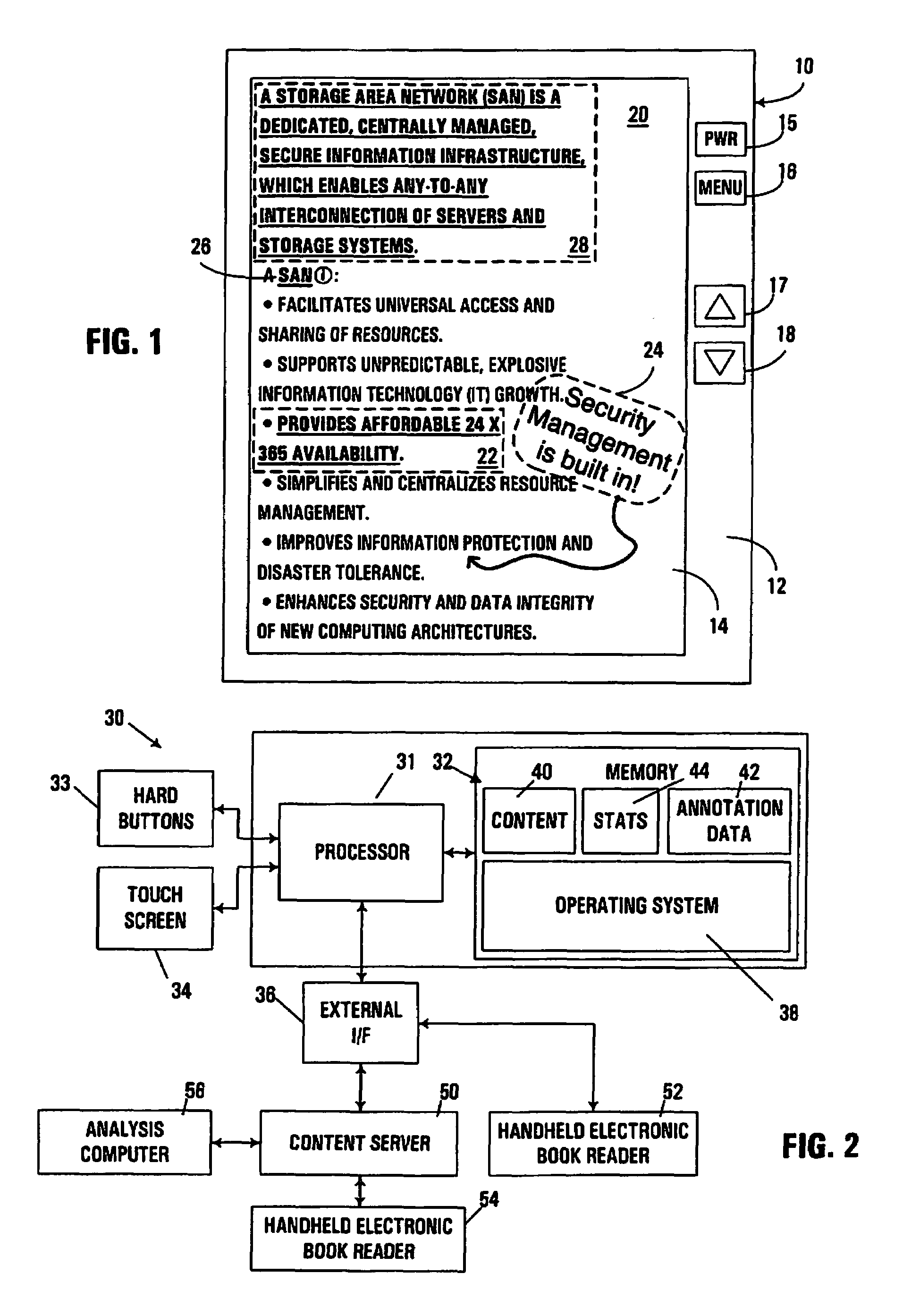
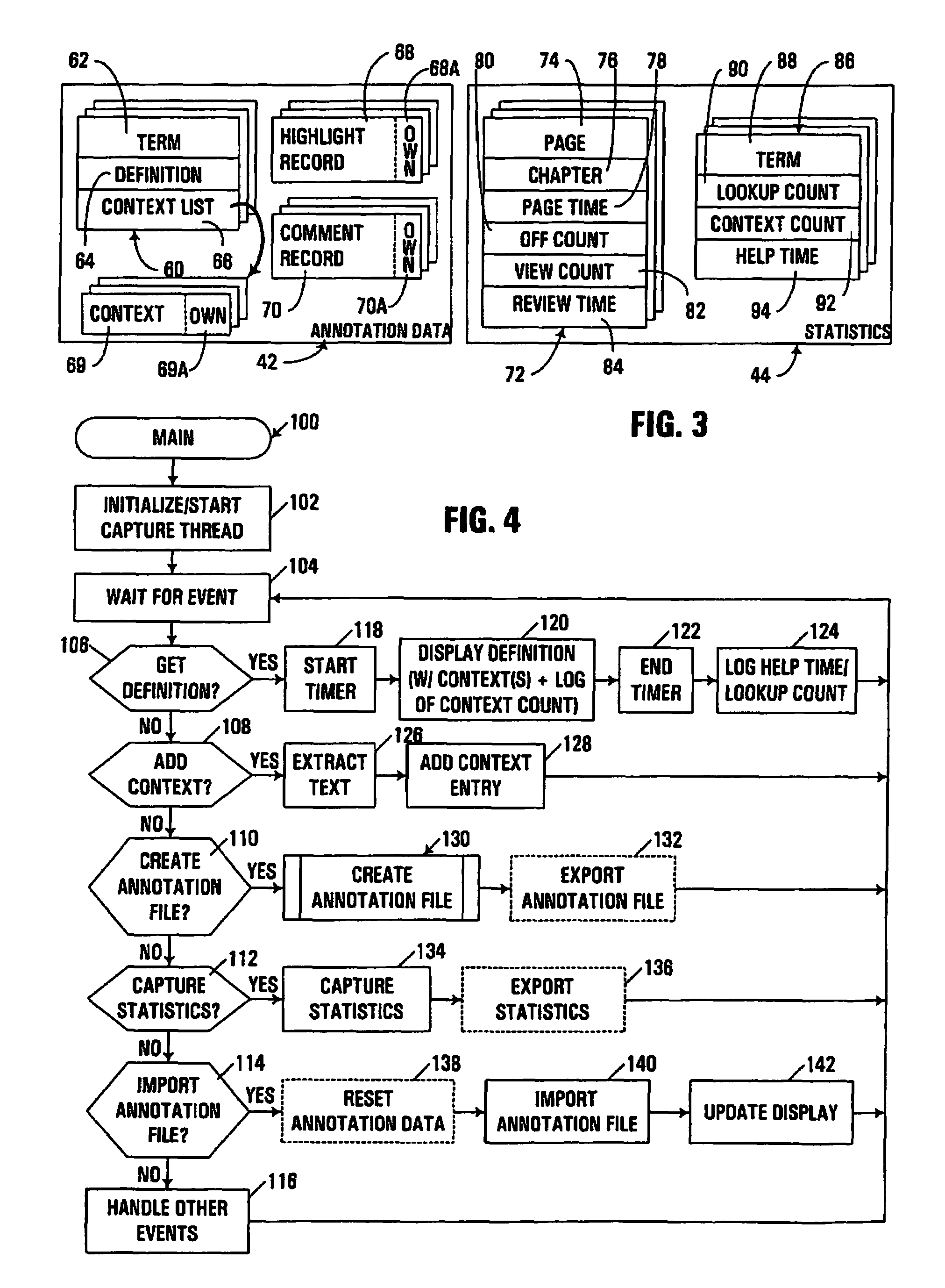
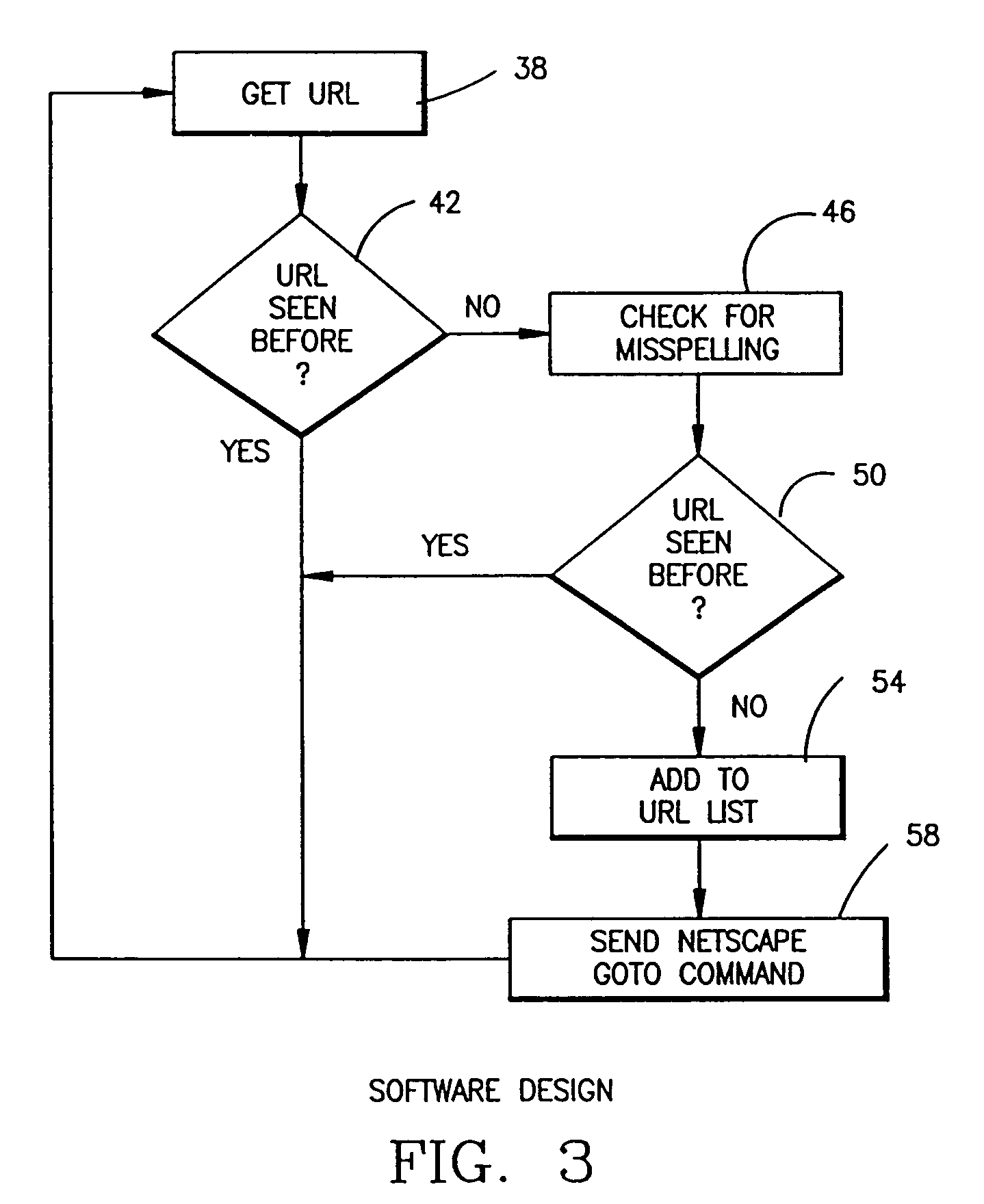
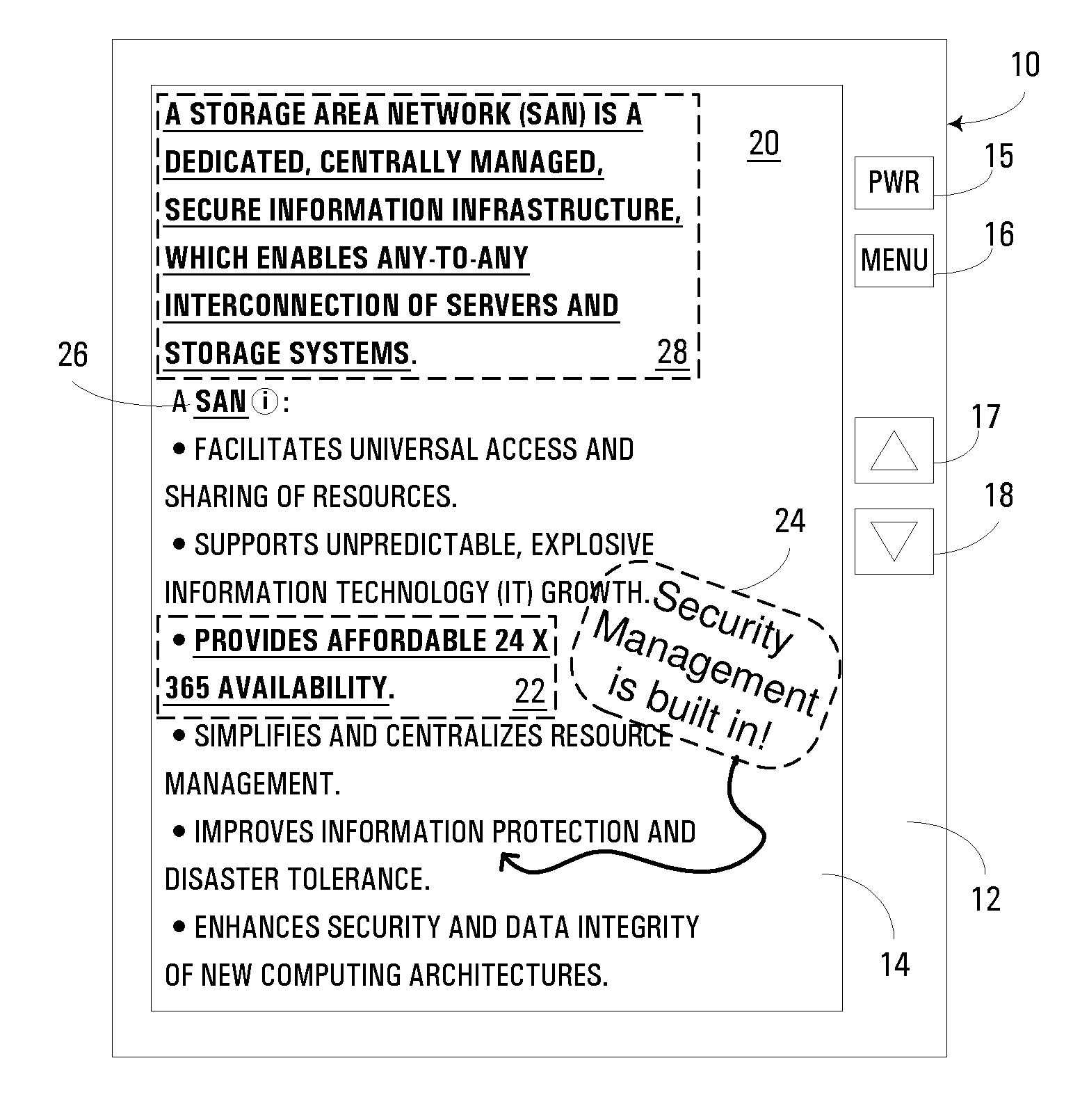
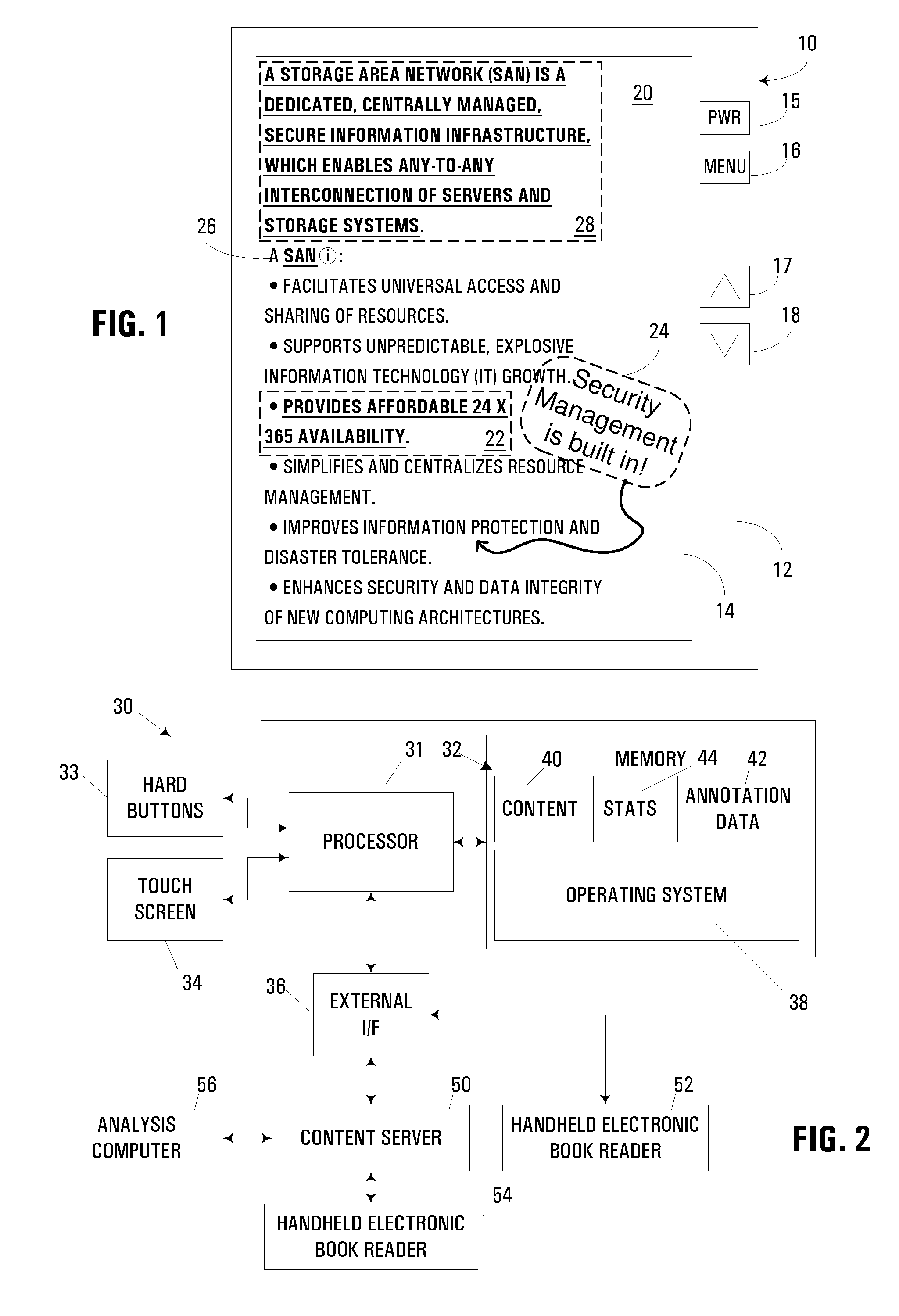
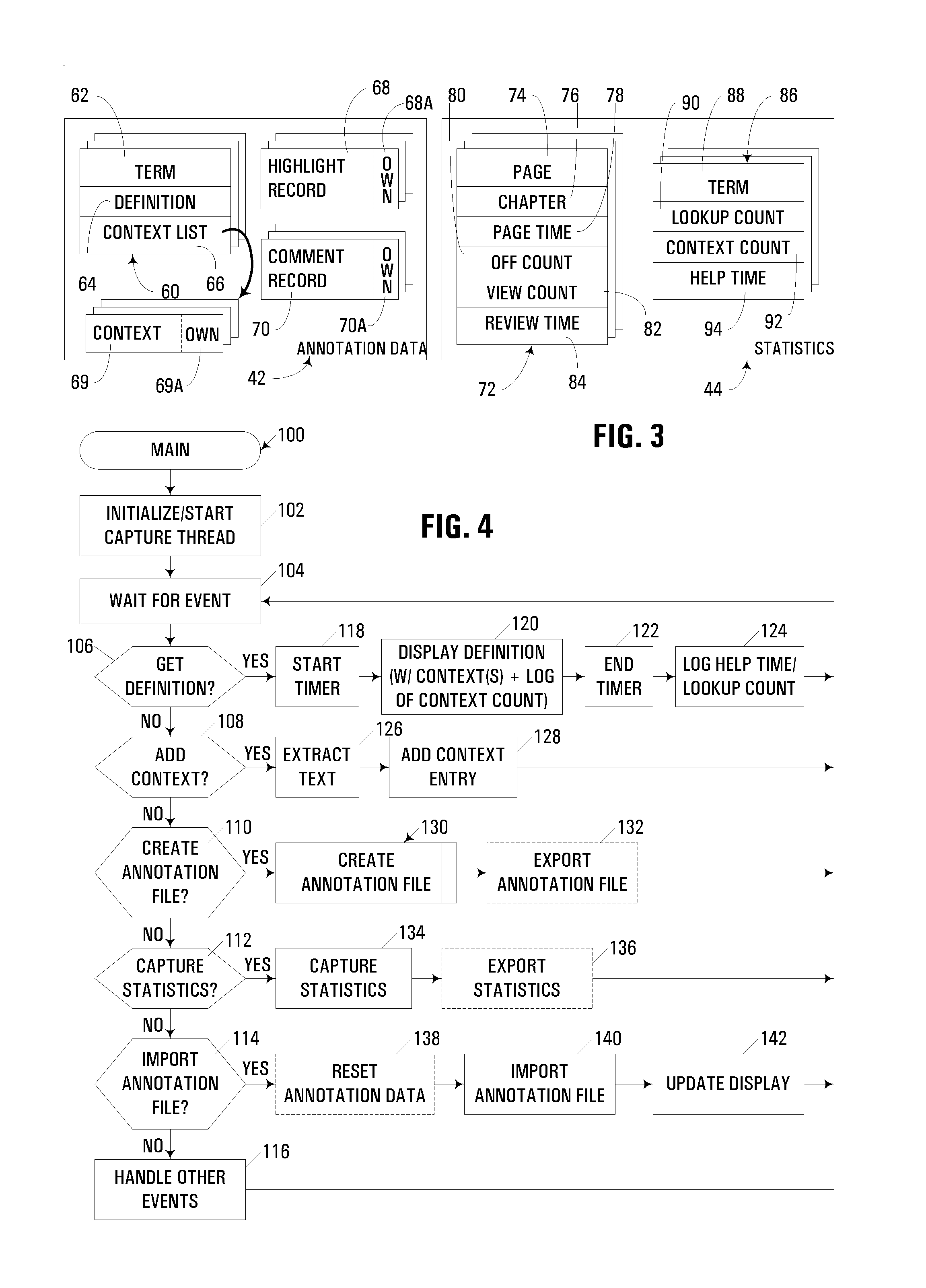
Handheld electronic book reader with annotation and usage tracking capabilities
InactiveUS7103848B2Enhanced annotationImprove rendering capabilitiesNatural language data processingProgram controlUser needsElectronic document
A handheld electronic book reader, program product, and method incorporate enhanced annotation and / or usage tracking capabilities. Support is provided for user creation of “contexts” for defined terms in an electronic document. Moreover, annotation data such as contexts, comments and highlighting may be associated with various users, and displayed in connection with the display of an electronic document so as to indicate that different annotation data has been originated by different users. In addition, from the standpoint of usage tracking, usage statistics for an electronic document displayed in a handheld electronic reader may be generated on a page-by-page basis, and / or in association with term definitions. Moreover, usage statistics for multiple users may be combined and analyzed. Through such analysis, the usage statistics may be used in the conduct of various beneficial actions such as revising an electronic document, revising a lesson plan with which an electronic document is associated, determining whether a user has read a selected portion of an electronic document, or determining whether a user needs supplemental assistance.
Owner:IBM CORP
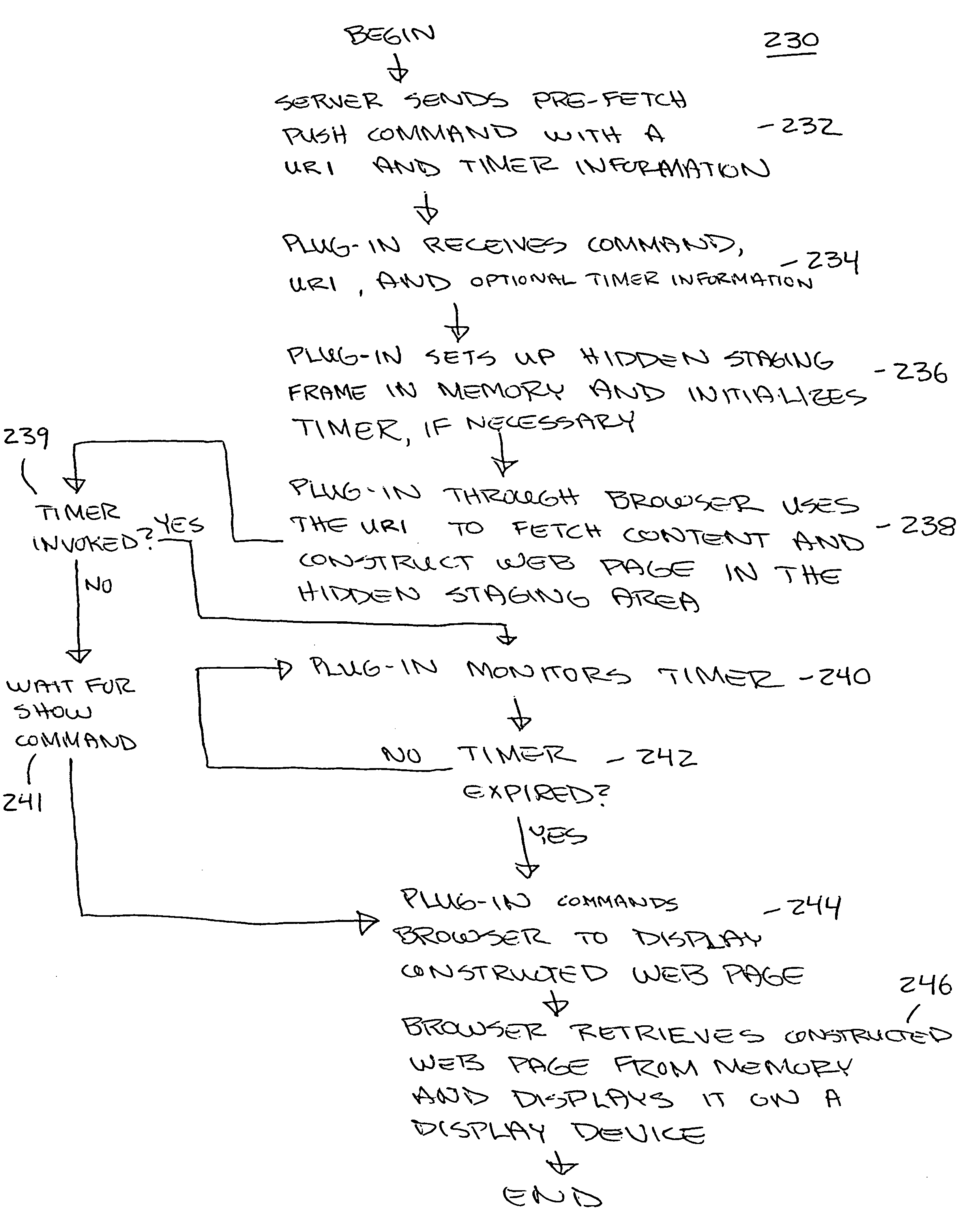
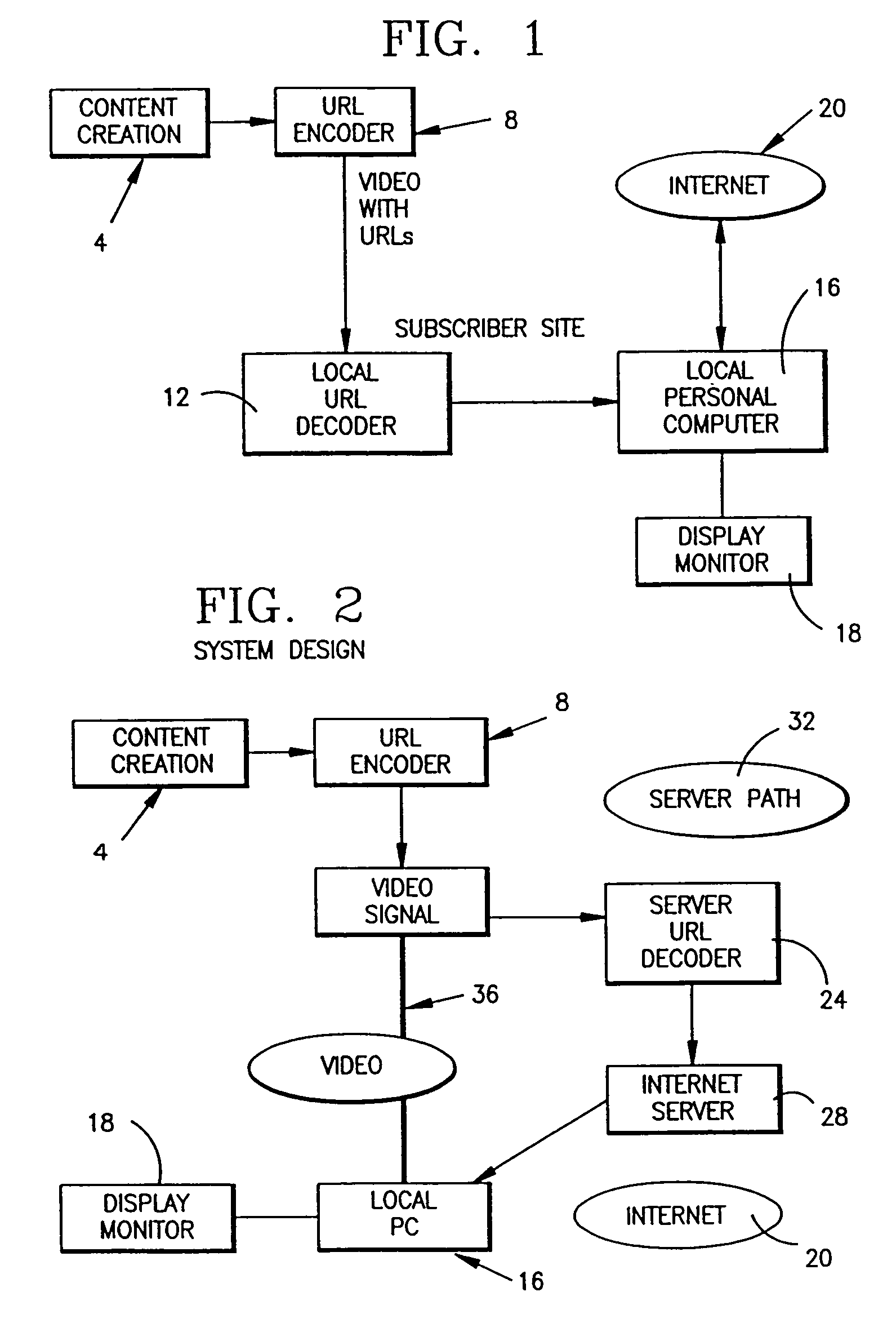
Enhanced video programming system and method utilizing a web page staging area
InactiveUS7120871B1Wide audienceLess complexDigital computer detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsUser needsThe Internet
A web page staging area for construction of web pages hidden from view of the user. Once the web page is constructed, it is displayed to the user based upon timer event information or receipt of a particular command instructing that it be displayed. Use of the staging area provides the user with a more television-like experience in viewing content from the Internet or other source in that the user need not view a web page being constructed on a display device. Use of timer event information for displaying the constructed web page permits synchronization of the web page with associated programming.
Owner:OPEN TV INC
Handheld electronic book reader with annotation and usage tracking capabilities
InactiveUS20060282778A1Enhanced annotationImprove rendering capabilitiesRecording carrier detailsRecord information storageUser needsElectronic document
A handheld electronic book reader, program product, and method incorporate enhanced annotation and / or usage tracking capabilities. Support is provided for user creation of “contexts” for defined terms in an electronic document. Moreover, annotation data such as contexts, comments and highlighting may be associated with various users, and displayed in connection with the display of an electronic document so as to indicate that different annotation data has been originated by different users. In addition, from the standpoint of usage tracking, usage statistics for an electronic document displayed in a handheld electronic reader may be generated on a page-by-page basis, and / or in association with term definitions. Moreover, usage statistics for multiple users may be combined and analyzed. Through such analysis, the usage statistics may be used in the conduct of various beneficial actions such as revising an electronic document, revising a lesson plan with which an electronic document is associated, determining whether a user has read a selected portion of an electronic document, or determining whether a user needs supplemental assistance.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic object-driven database manipulation and mapping system having a simple global interface and an optional multiple user need only caching system with disable and notify features
The present invention provides enhanced database access and performance when correlating or translating one database to another database or to an object programming application. The system and method of enhanced database access and performance of the invention provides a simplified high-level wrapper interface for global coordination of multiple software components and ease of use. Performance is also enhanced by utilizing an optional enhanced multiple user data caching system. The multiple user caching system of the invention provides a process of obtaining data from a data source, creating accessible data in the random access memory of at least one computer system the first time such data is read by a user wherein the data source corresponding to the cache is accessible to at least two users. Thus, the present invention is directed to dynamic mapping of databases to selected objects and a system and method for providing a multiple user caching system in such an environment or system.
Owner:THOUGHT
Dynamic cost network routing
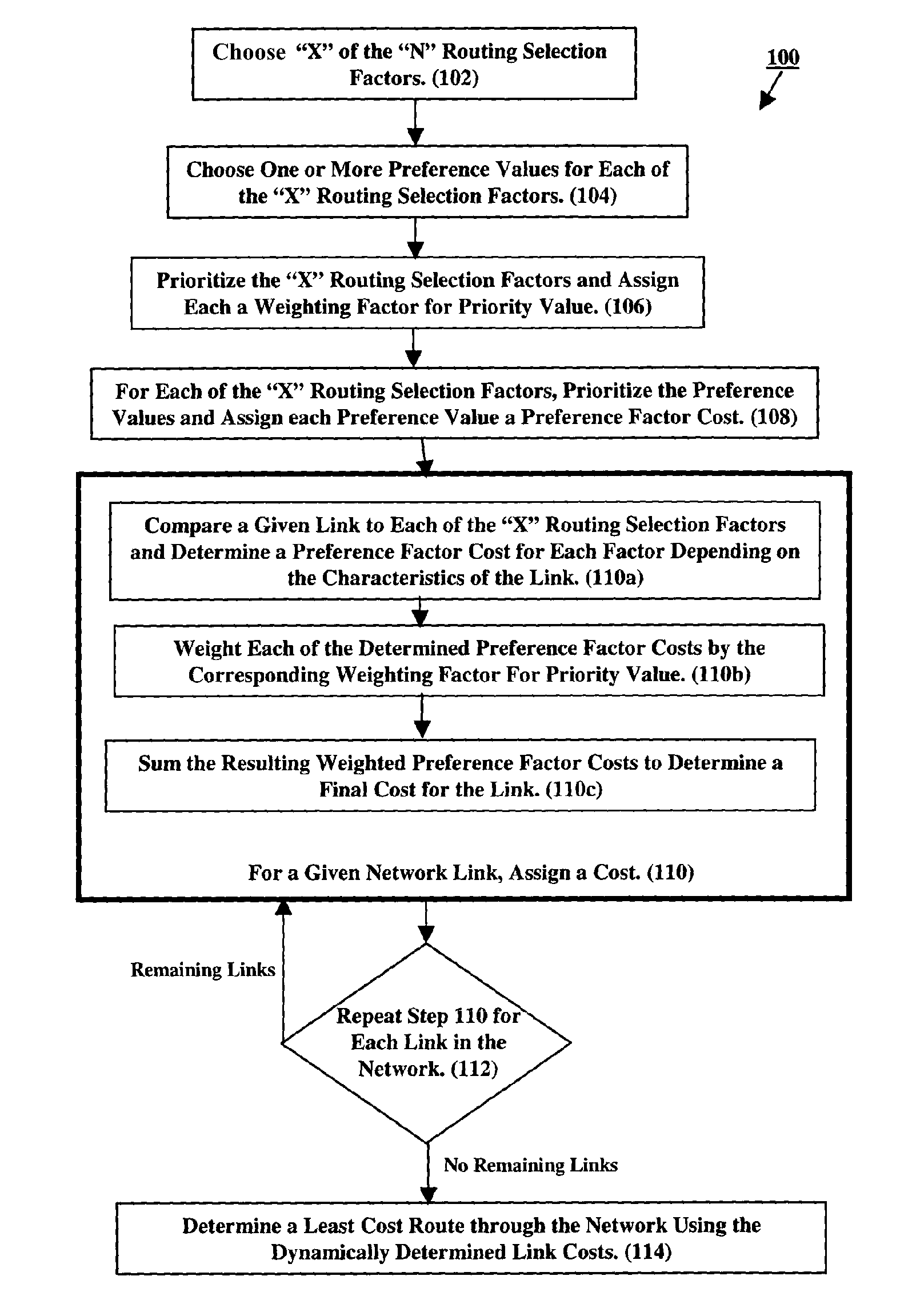
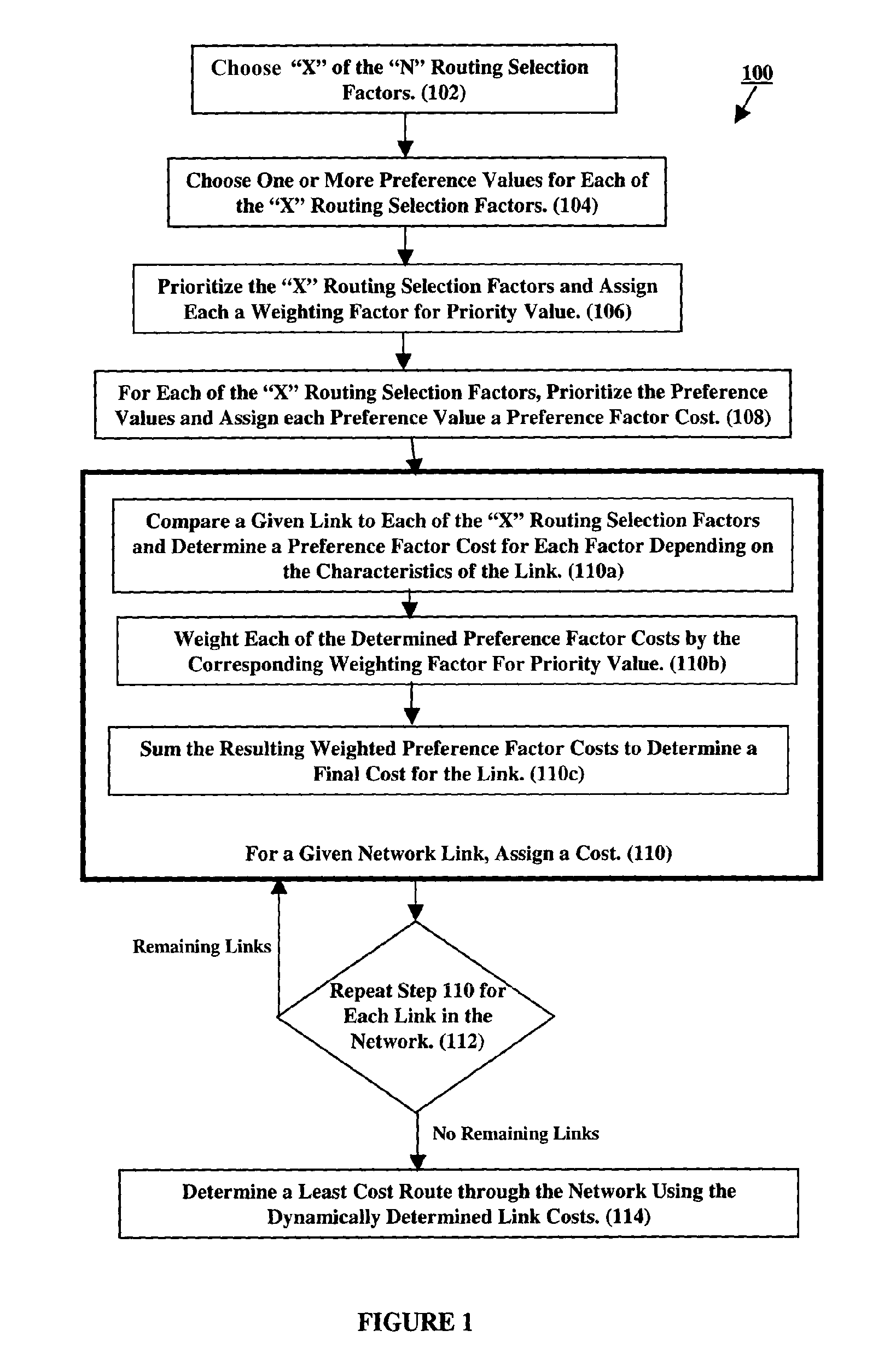
ActiveUS7779065B2Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsUser needsDistributed computing
To determine a network route corresponding to user needs, costs are dynamically defined for each link of a network. Specifically, based on link characteristics, routing factors are defined and for each factor, allowable values are defined. When determining a route, one or more routing factors and one or more allowable values for each factor are selected. Based on user prioritization of these factors and prioritization of the allowable values for each factor, weights are assigned to the factors and costs are assigned to the values. Link costs are determined by comparing a given link to each selected factor and determining for each factor which allowable value matches the link's characteristics. The cost of each matching value is then weighted by its corresponding factor. The weighted costs are summed to determine a link cost. The link costs are subsequently used to determine a route through the network.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
Detector controlled illuminating system
InactiveUS20150035440A1Save energyImprove visual effectsMechanical apparatusLight source combinationsUser needsCost effectiveness
Owner:SPERO YECHEZKAL EVAN
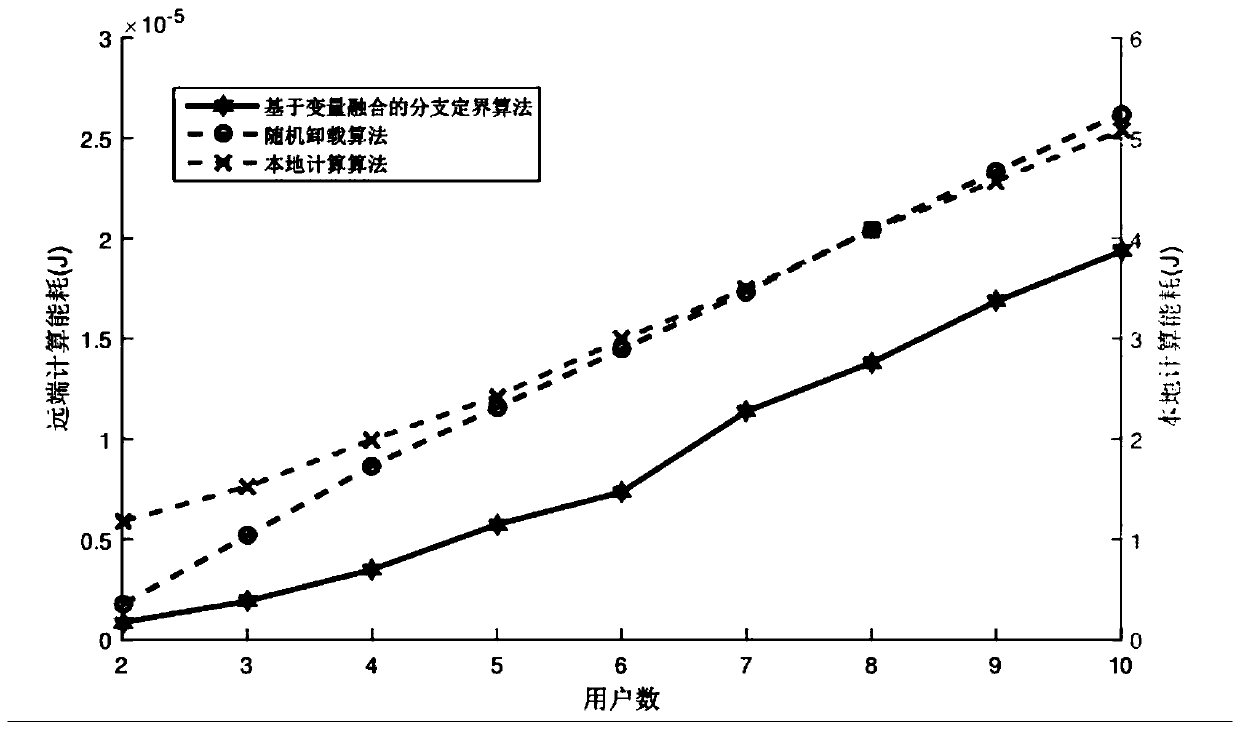
A joint optimization method for task unloading and resource allocation in a mobile edge computing network
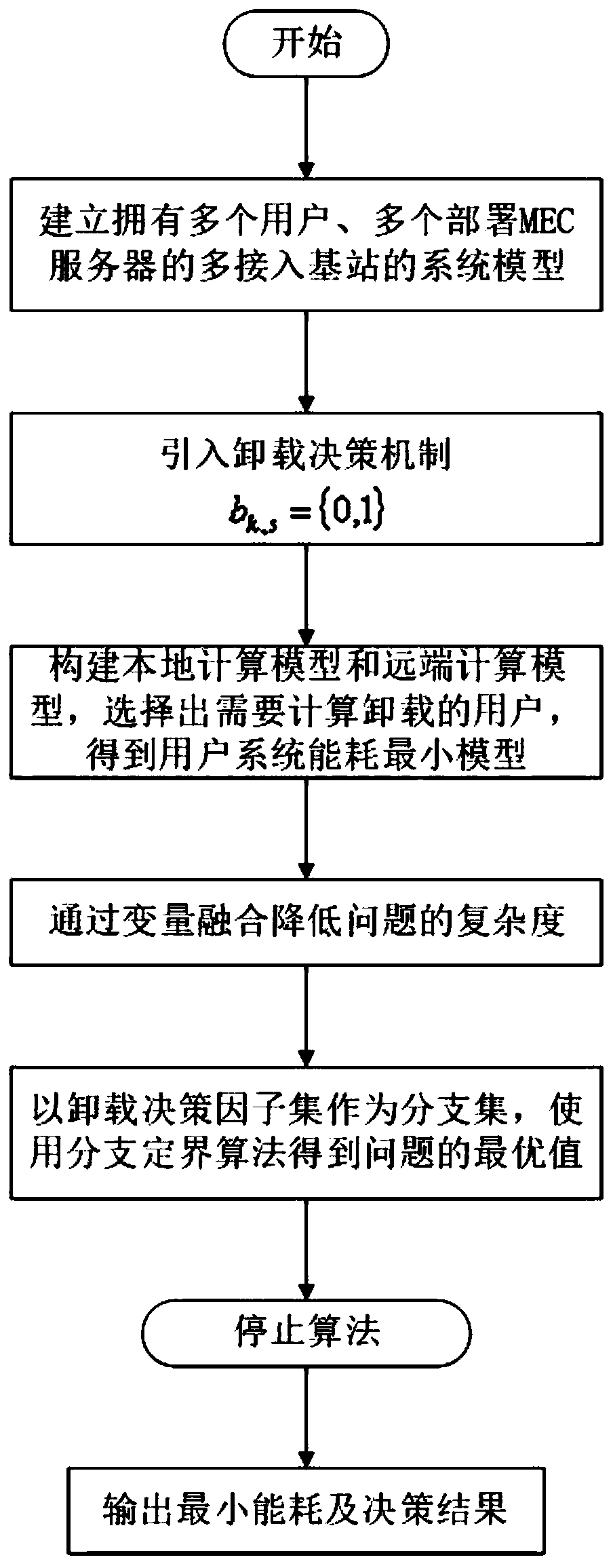
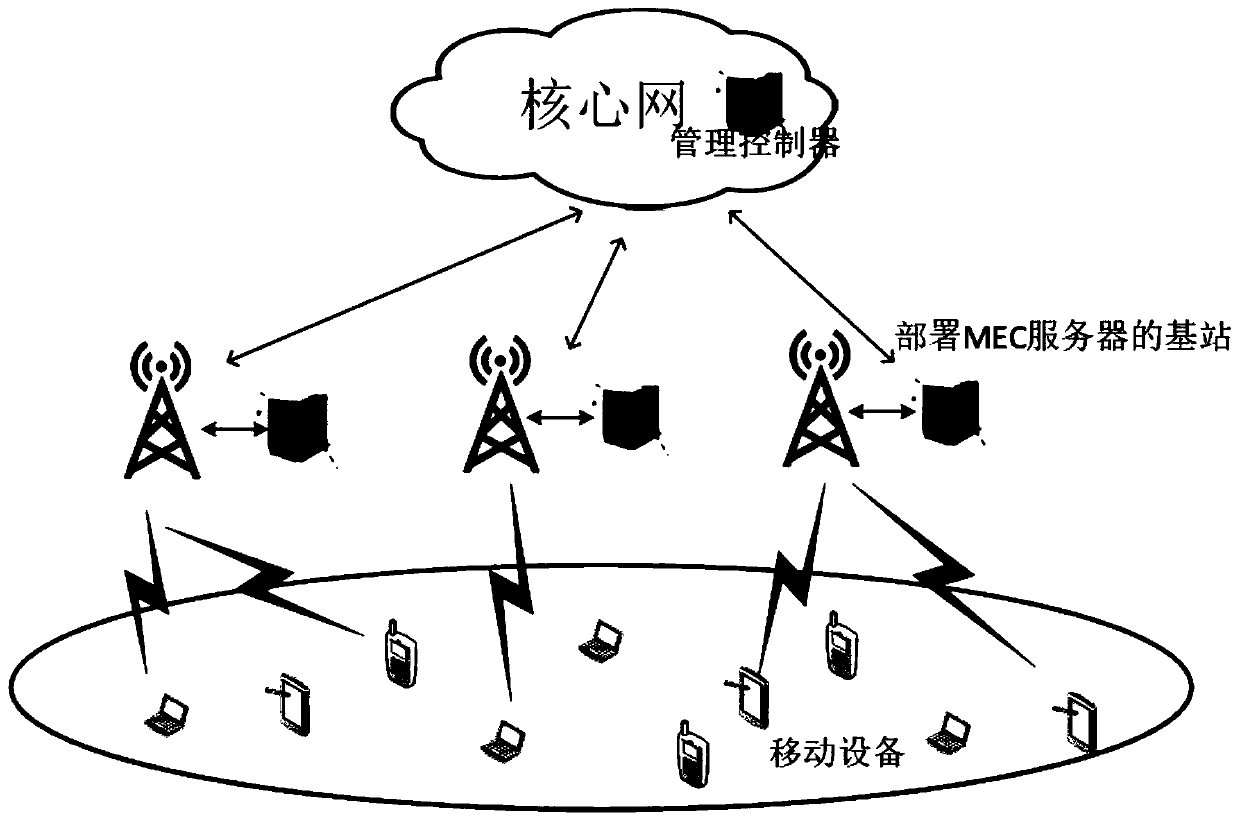
ActiveCN109814951AFull restorationUniversalService provisioningProgram loading/initiatingDecision takingWireless resource allocation
The invention discloses a joint optimization method for task unloading and resource allocation in a mobile edge computing network, which comprises the following steps of 1, establishing an OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access)-based multi-MEC (Mobile Edge Computing) base station and a multi-user scene model, wherein the MEC base station supports the multi-user access; 2, introducing an unloading decision mechanism; Meanwhile, constructing a local calculation model and a remote calculation model, selecting a user needing to perform calculation unloading, and establishing a calculation task unloading and resource allocation scheme based on minimum energy consumption under the condition of meeting the time delay constraint according to the conditions; 3, carrying out variablefusion on three mutually constrained optimization variables, namely an unloading decision variable, a wireless resource distribution variable and a computing resource distribution variable, so as to simplify the problem; and 4, obtaining an unloading decision and a resource allocation result which enable the total energy consumption of the user in the MEC system to be minimum through a branch andbound algorithm. The method has the advantage that the energy consumption of the system can be effectively reduced on the premise that strict time delay limitation is guaranteed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
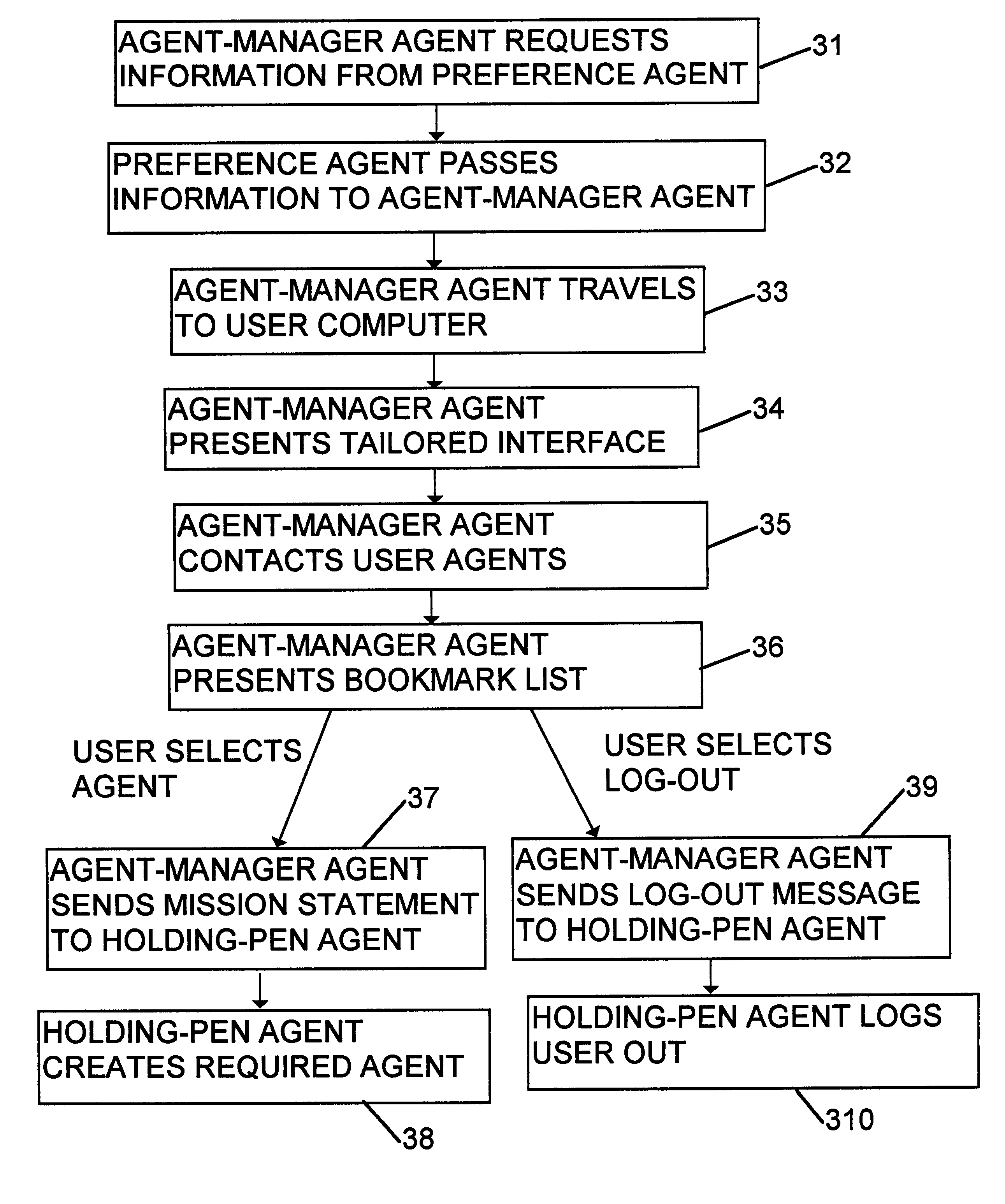
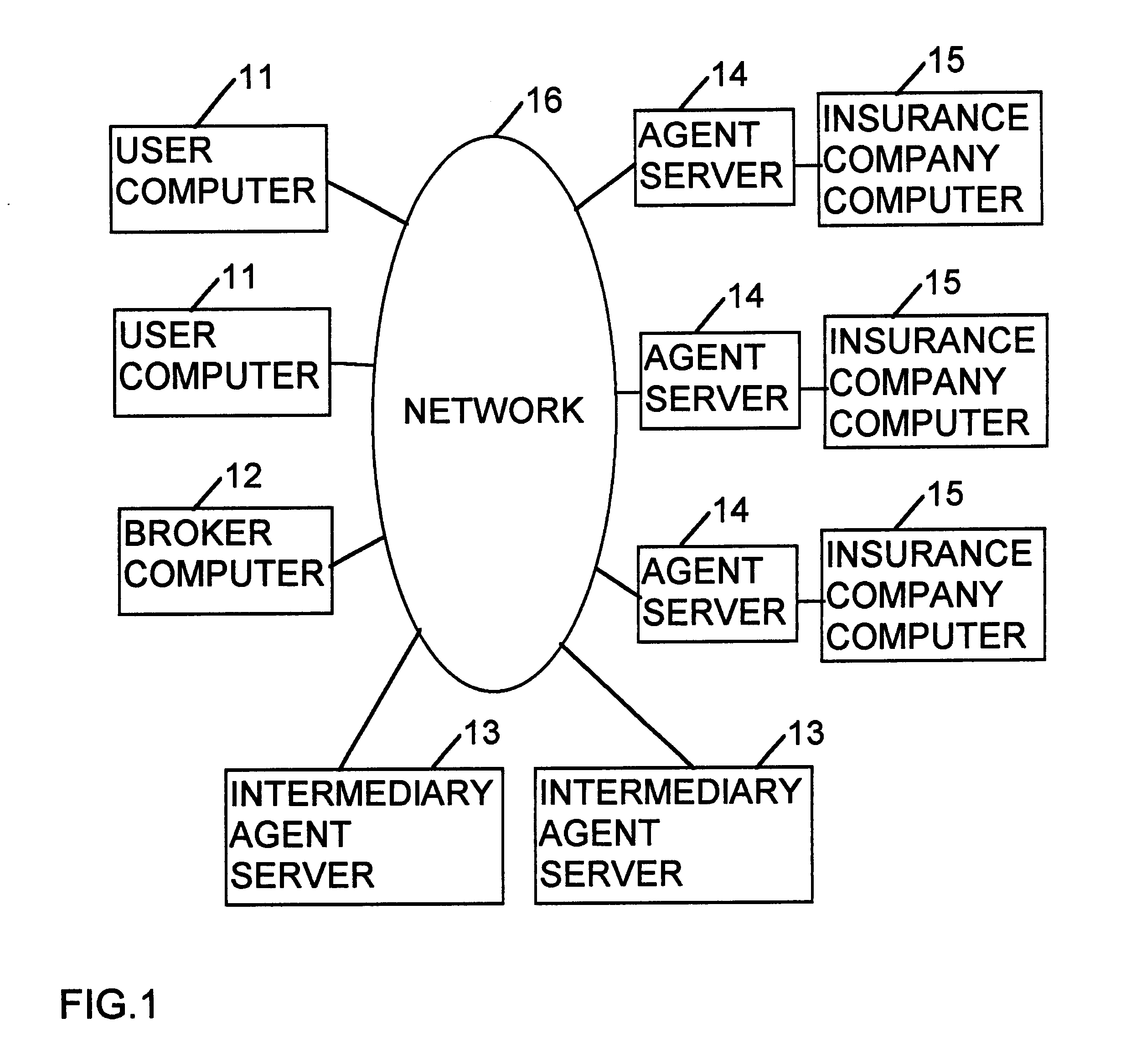
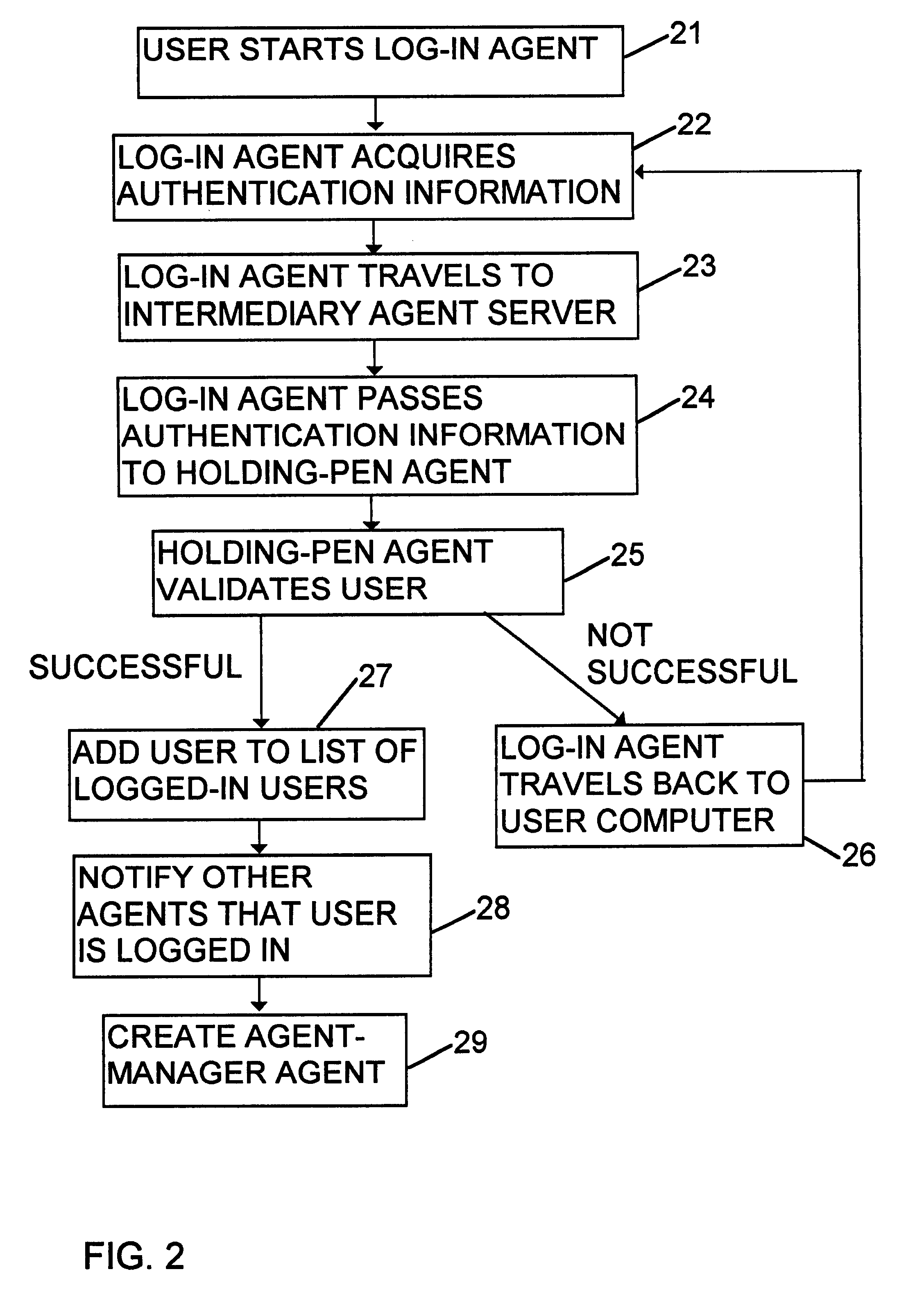
Computer method for delivery of financial services
A computer system is provided for delivery of financial services, such as banking, general insurance, life assurance, pensions and investments, loans and mortgages, and financial planning and advisory services. The system comprises a number of user computers connected to a plurality of server computers by way of a network, such as the Internet. The system creates at least one mobile agent which obtains details of a user's requirements, obtains financial information from the server computers on behalf of the user in the light of the user's requirements, and then transports itself to the user's computer to deliver the financial information to the user.
Owner:INT COMP LTD
Physically reconfigurable input and output systems and methods
InactiveUS20110234502A1Effective interactionInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsUser needsReconfigurable antenna
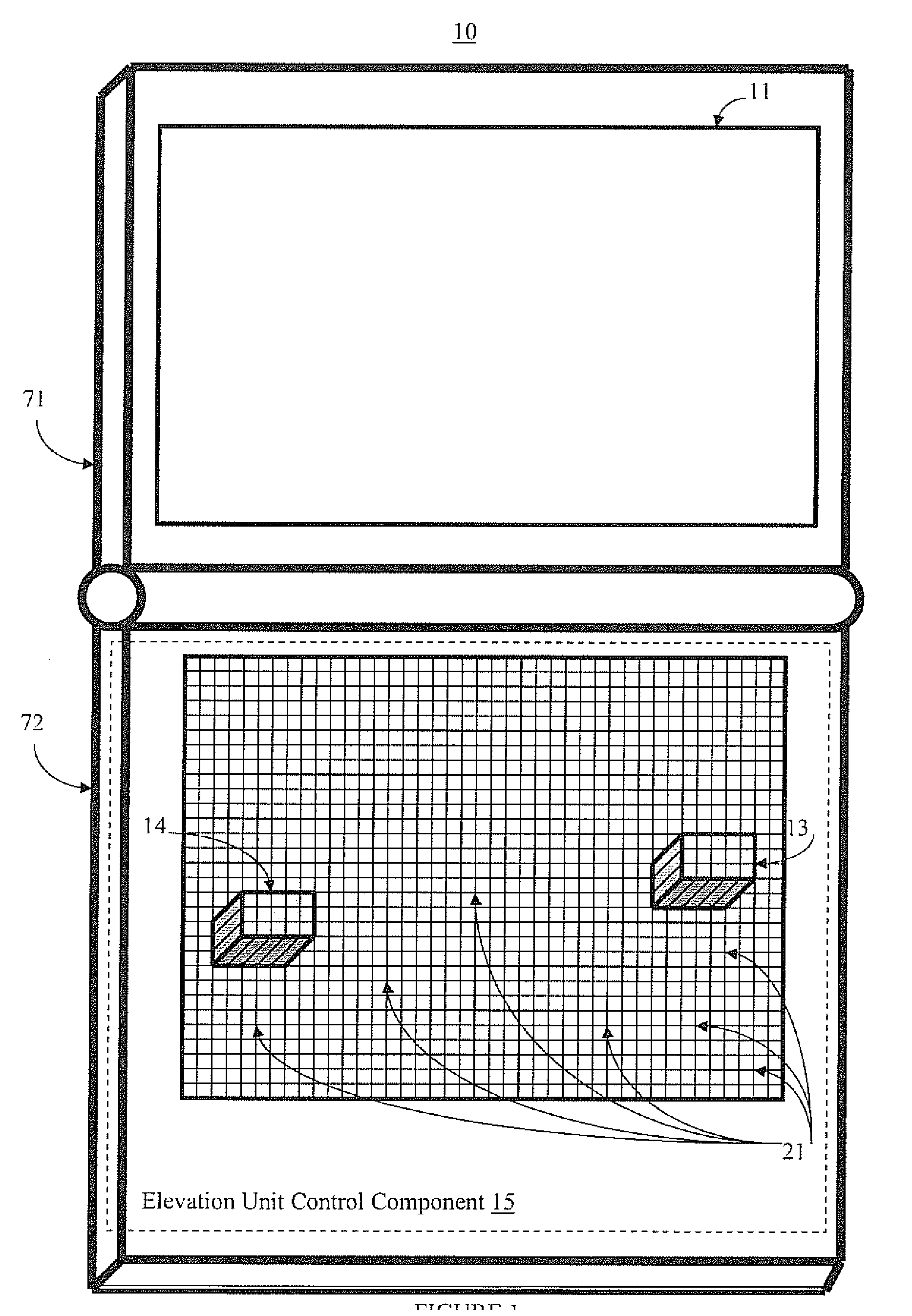
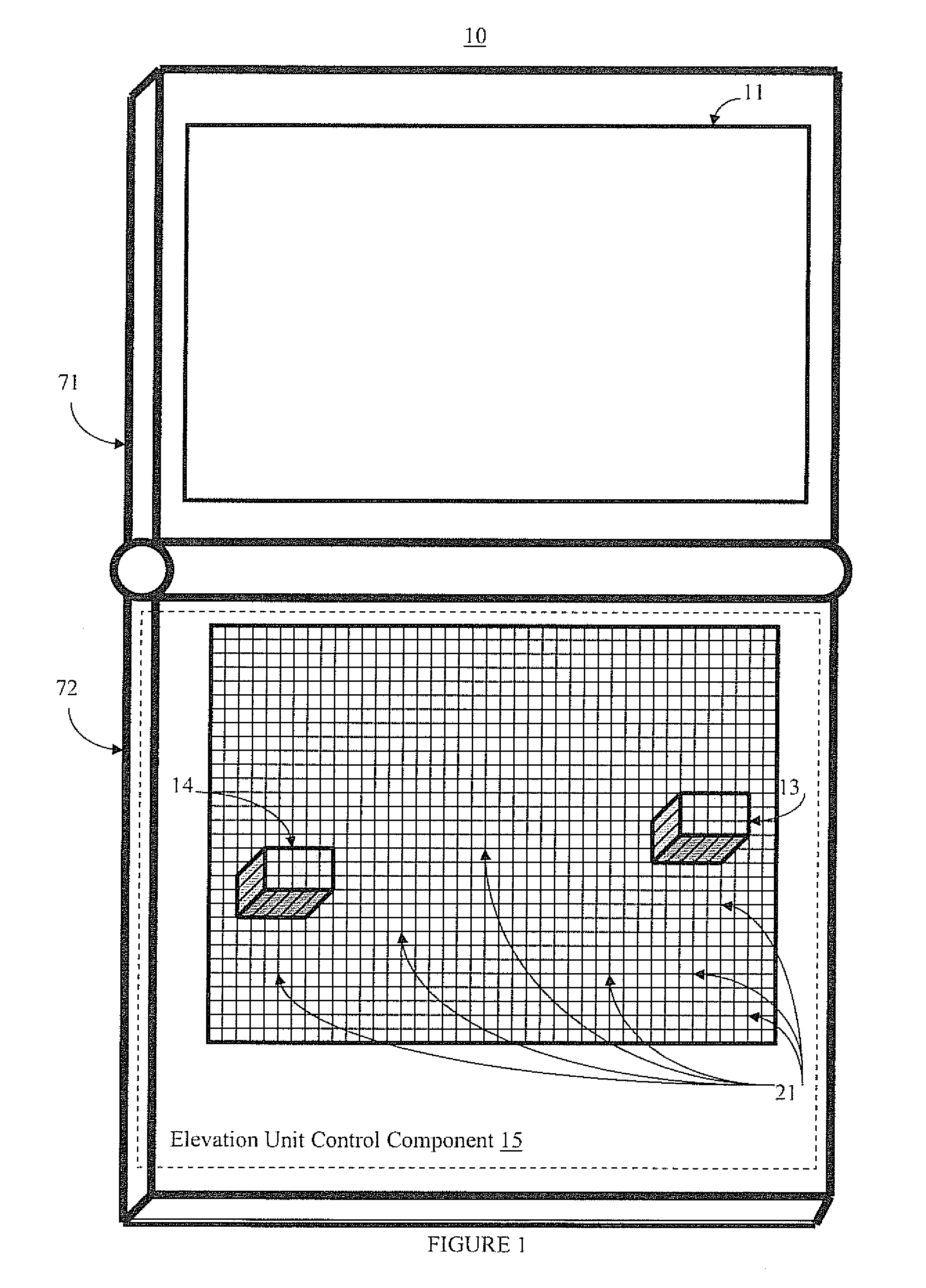
Systems and methods for altering the shape of a reconfigurable surface area are presented. The present systems and methods facilitate efficient and effective interaction with a device or system. In one embodiment, a surface reconfiguration system includes a flexible surface; an elevation unit that creates alterations in the contours of the surface; and an elevation control component that controls adjustments to the elevation unit. Thus, the surface of the device is reconfigurable based on system, application, mode, and / or user needs. Accordingly, the surface can be used to provide input and output functionality. The surface can include touch detection functionality for added input functionality.
Owner:PANASONIC OF NORTH AMERICA
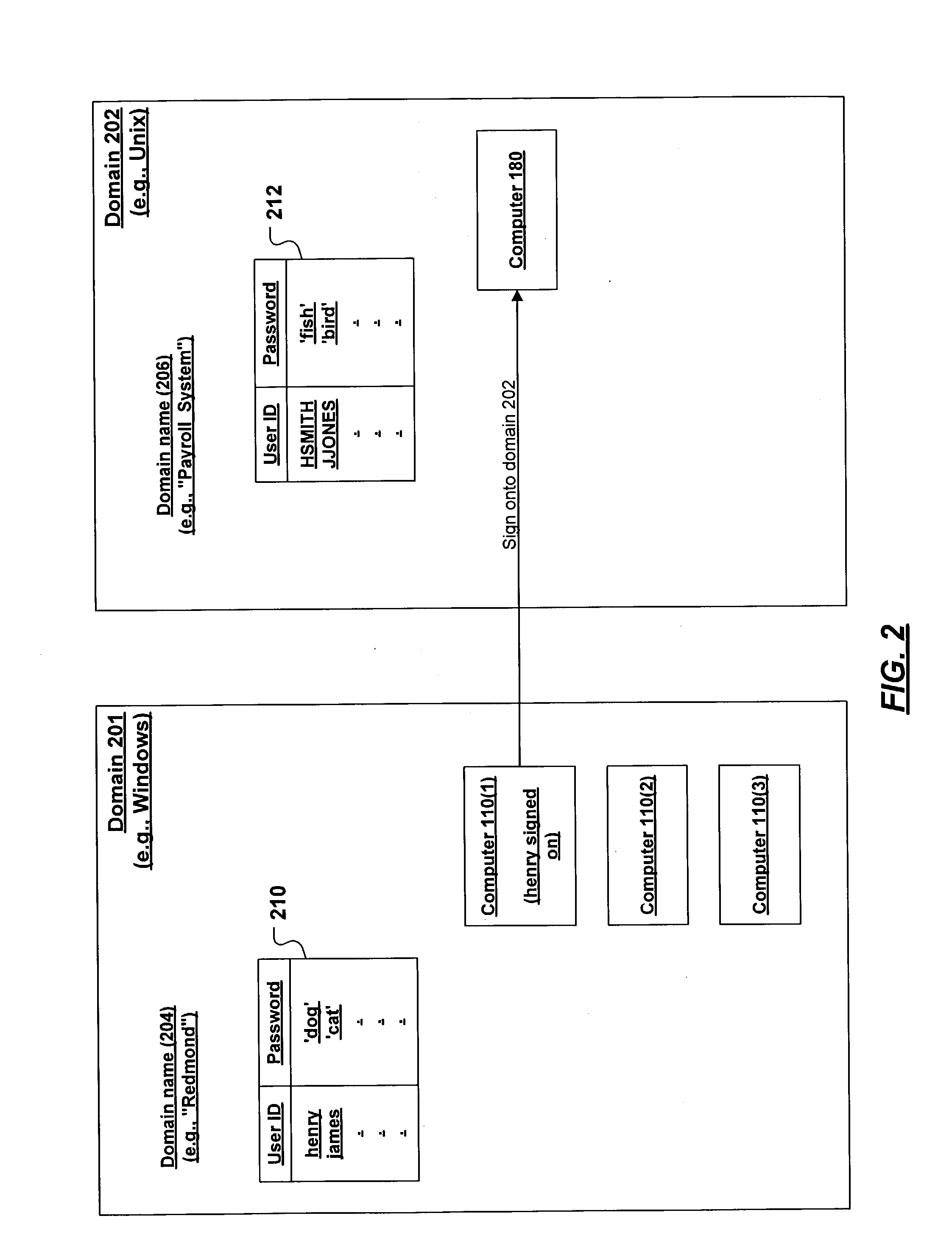
System and method for unified sign-on
InactiveUS20050005094A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUser needsPassword
A mechanism is provided for signing on a user of a first domain into an affiliate application in a second domain. When the user needs access to the affiliate application, the request for access causes a ticket to be generated. The ticket identifies the user and is passed to an adapter. The adapter, which ultimately will perform the sign on in the affiliate application, redeems the ticket for the user's credentials (e.g., a valid userID / password combination for the affiliate application), and then presents the credentials to the affiliate application. A service is provided that issues tickets, redeems tickets, manages the registration and de-registration of affiliate applications, manages the correlation between a user and the user's credentials with an affiliate application, and manages encryption of stored records.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
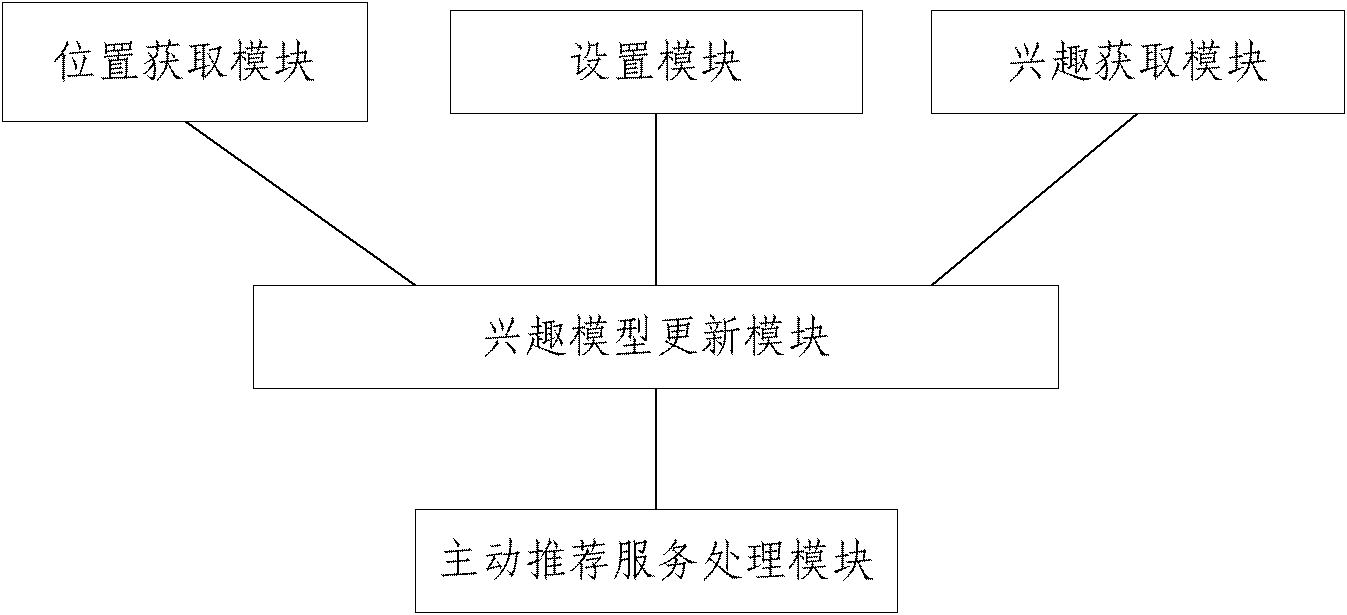
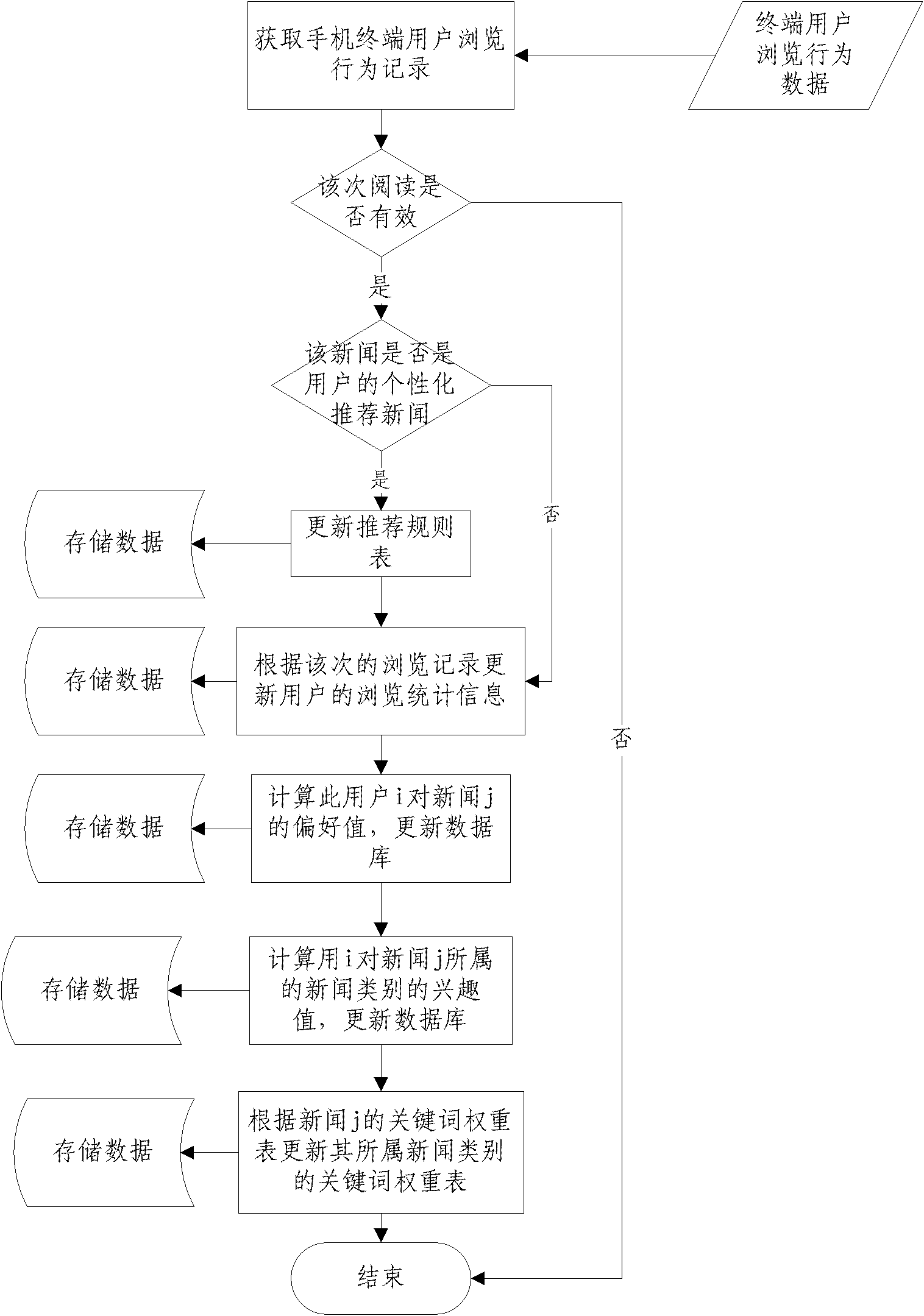
Personalized active news recommending service system and method for mobile phone user
The invention discloses a personalized active news recommending service system for a mobile phone user, which comprises an interest acquisition module, a position acquisition module, an interest model updating module and an active recommending service processing module, wherein the interest acquisition module is used for determining the preference of the user to the news; the position acquisition module is used for determining the current location of the user according to positioned information of the mobile terminal of the user; the interest model updating module is used for updating the current news preference of the user; and the active recommending service processing module is used for recommending news for the user according to set algorithm. The invention also discloses a personalized active news recommending service method for the mobile phone user. According to the invention, news information which is more suitable for the needs of the user can be recommended to the user, so that a personalized news recommending service is truly realized, and the user can obtain the news contents in which the user is most interested without turning web pages frequently.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Automated access by mobile device to automated telephone information services
InactiveUS6594484B1Automatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingSpecial service for subscribersUser needsChronological time
A method and system for automated navigation through voice menu information systems for mobile devices are disclosed. Navigation of the voice menu information systems is accomplished using a stored script (i.e., a time ordered log of the input associated with a previous interaction). A user wishing to store such a script, prior to an interaction with a voice menu system, would select this option from a menu displayed on the display screen of the wireless client device. The user is prompted to provide a label for the script. The labeled script is then created and stored by monitoring the input characters and timings thereof. After a new script has been stored, the information used to generate menu displays pertaining to available scripts for the wireless client device is updated to reflect the addition of the new script. Thereafter, for future interactions with the voice menu information system, the user need only select the appropriate script label when displayed by interacting with the wireless client device. Once a script has been launched, the script causes automated dial-in to the voice menu information system and interaction therewith in an automated fashion by way of the script. Following the processing of the script, the user can be on-line with the voice menu information system to receive the response or can have the response sent to a designated voice mailbox for later retrieval.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Methods and structure for batch processing event history processing and viewing
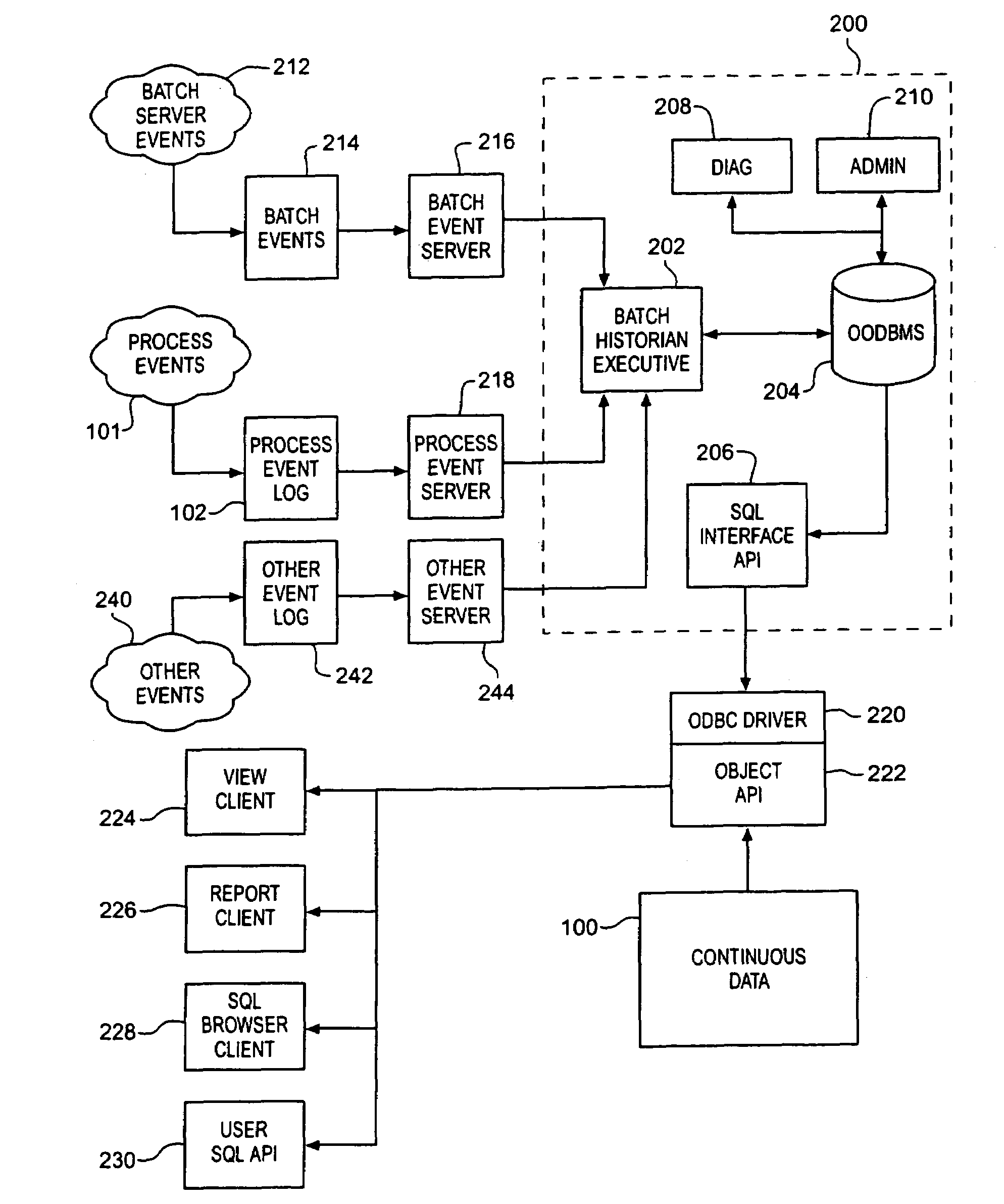
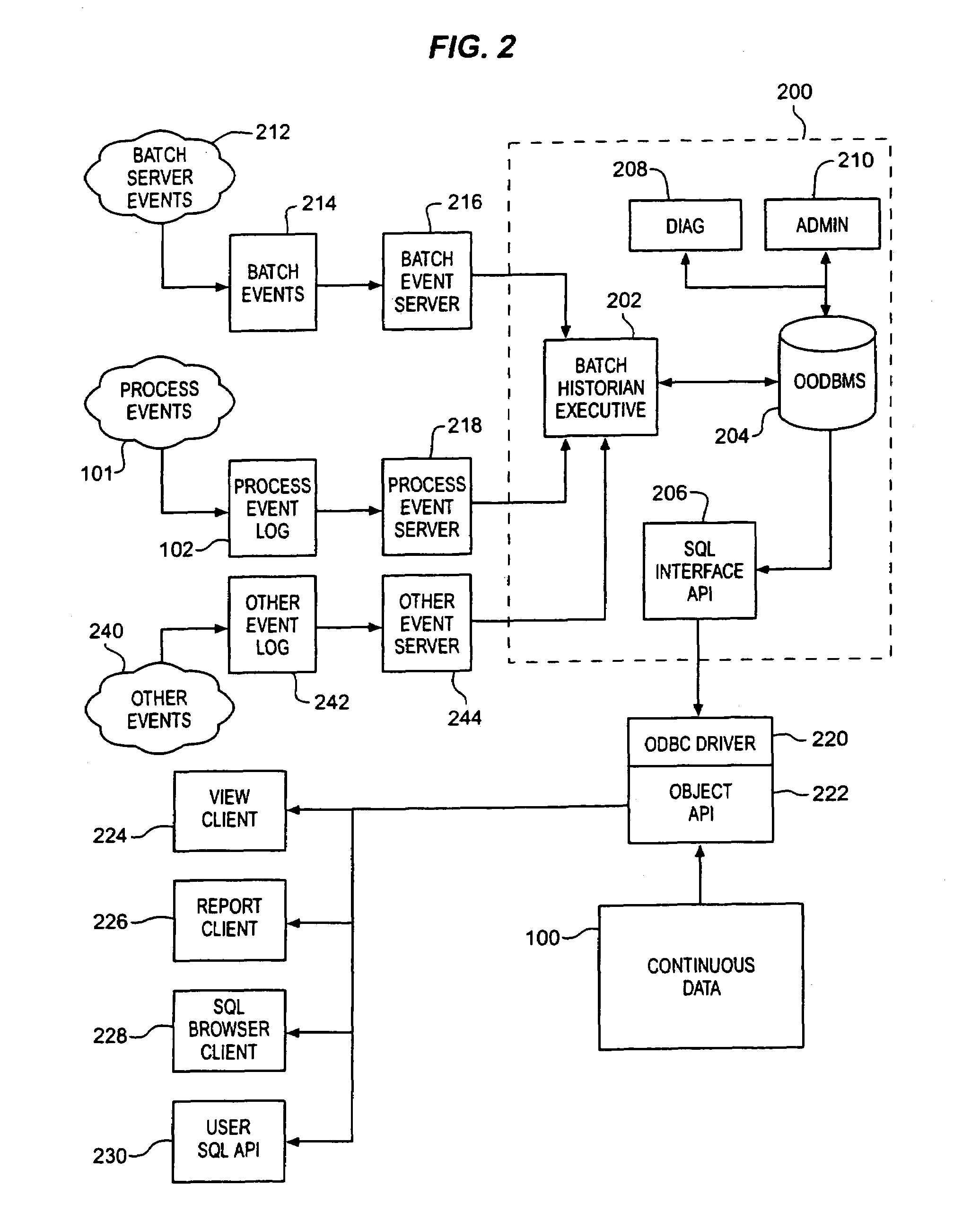
InactiveUS7249356B1Efficient captureGood conditionElectric testing/monitoringMultiprogramming arrangementsUser needsBatch processing
A batch event historian gathers, stores and presents data regarding a batch process where relationships among the various elements of data are automatically derived by an executive program. A persistent store includes structure corresponding to the relationships defined among procedural elements and equipment in accordance with batch processing industry S88.01 standards. The executive program gathers event information generated by the batch process and derives the relationships among the events in accordance with these industry standard models. Storage and corresponding retrieval and presentation of such historical data is thereby simplified for a user because the user need not manually configure the historian programs to derive the relationships. Association of any continuous data log with event information is automated thereby obviating the need for manual configuration by a user to establish such associations.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
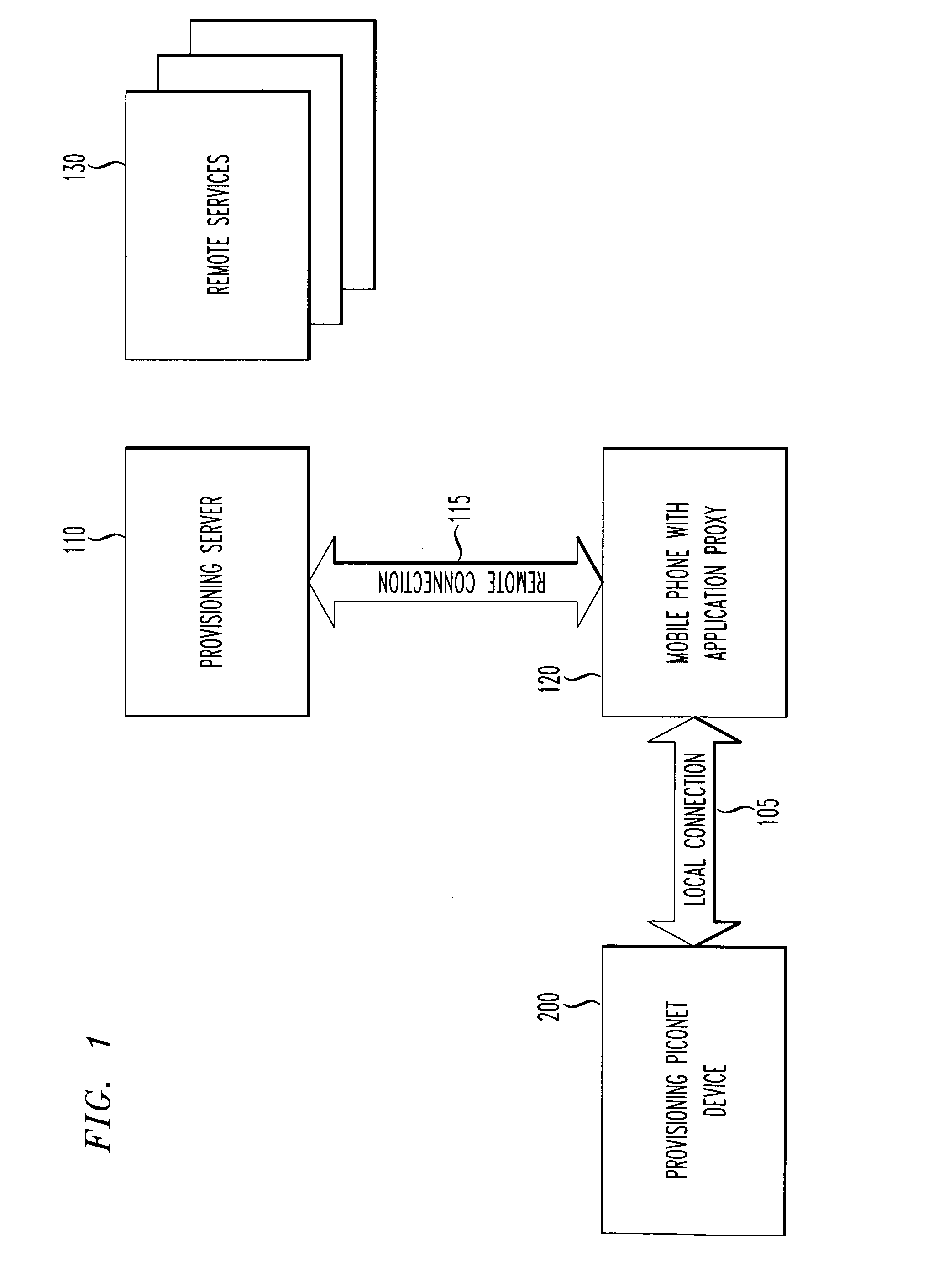
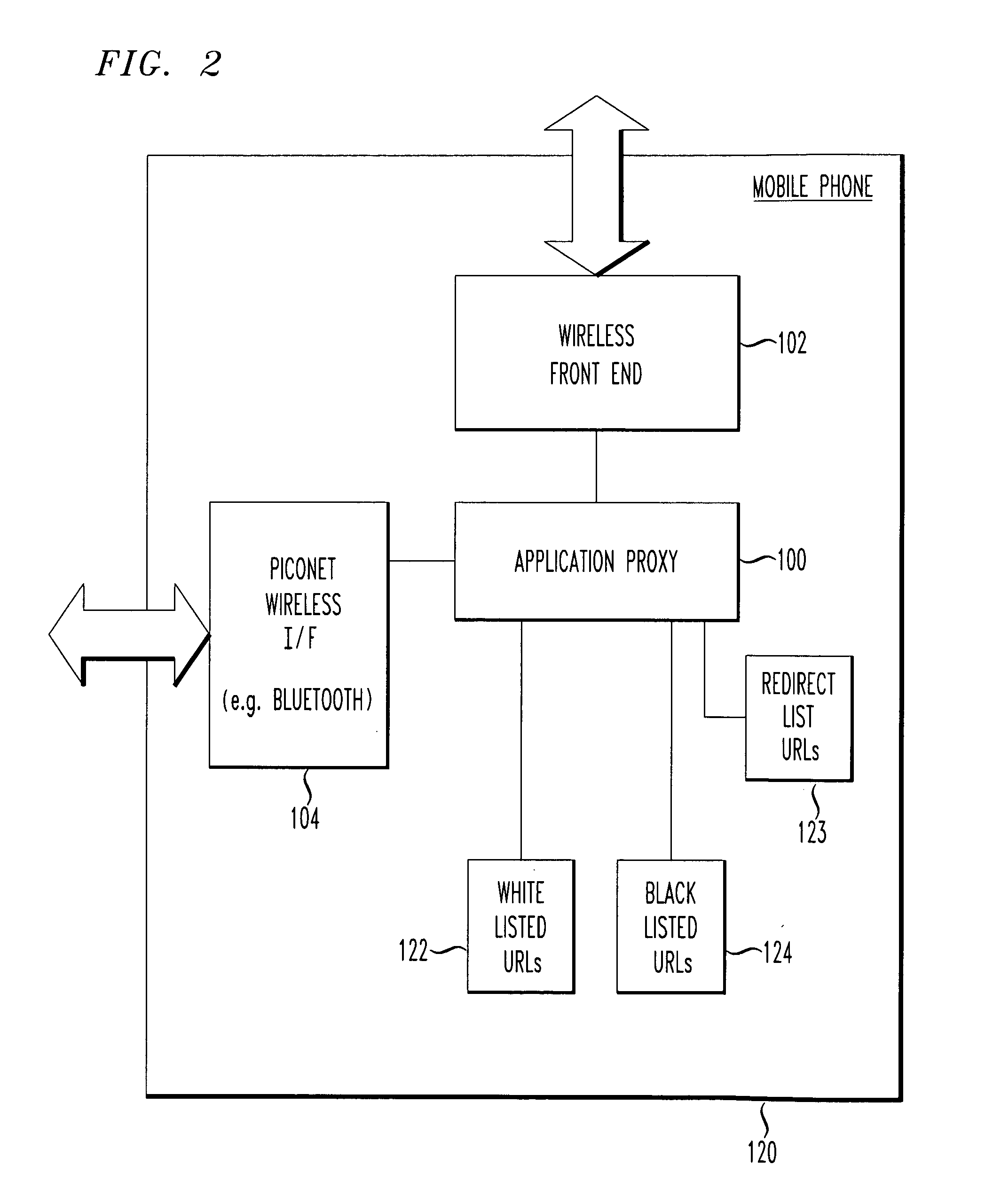
Remotely provisioned wirelessly proxy
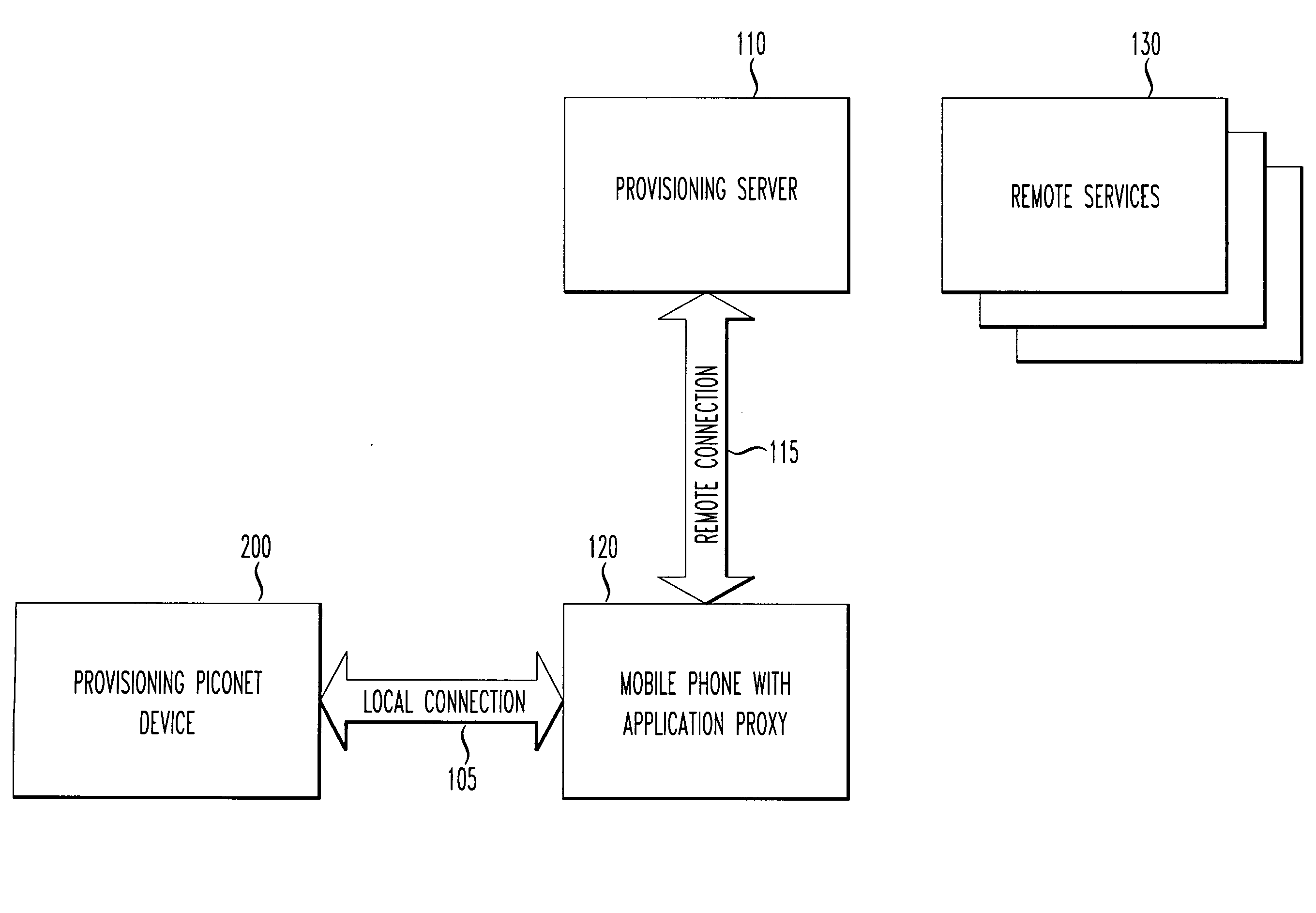
InactiveUS20100087167A1Service provisioningUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionUser needsModem device
A remotely provisioned proxy within a wireless / mobile phone that proxies a wireless communication path between a disconnected piconet (e.g., BLUETOOTH™) device and a network resource such as a universal resource locator (URL) via a mating mobile phone. Thus, an application proxy module embodied within the mobile phone provides managed access of a piconet device connected to the mating mobile phone to remote services. A disconnected piconet device uses the full data bandwidth available to a wireless phone, without the need for the disconnected piconet device to include its own separate wireless front end, or to require use of a modem within the mobile phone. Thus, using a mobile phone with application proxy, the user need not pay for the luxury of a tethered data plan.
Owner:ARTAX LLC
Dispenser for flattened articles
InactiveUS20050281706A1Reduce amountKeep the environmentAnalysis using chemical indicatorsCoin-freed apparatus detailsUser needsDiagnostic test
A substantially moisture-proof, airtight dispenser for both storing and dispensing several flattened articles such as diagnostic test strips. The inventive dispenser includes a novel pivotable housing that a user need merely grab and squeeze to eject a test strip. Independent movement of the user's fingers to push a button or turn a knob is unnecessary to dispense a strip, which makes the present invention well suited for diabetics suffering from nerve damage in their extremities and other complications resulting from the disease. The invention includes a novel flexible arm member and pusher head that engage and push an article from the dispenser as the two parts of the housing are pivoted together. The articles are dispensed through an exit that is configured with a novel flexible seal that maintains the dispenser substantially airtight. Several inventive seal embodiments and methods of making the same are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Method and apparatus for controlling communication channels using contention and polling schemes
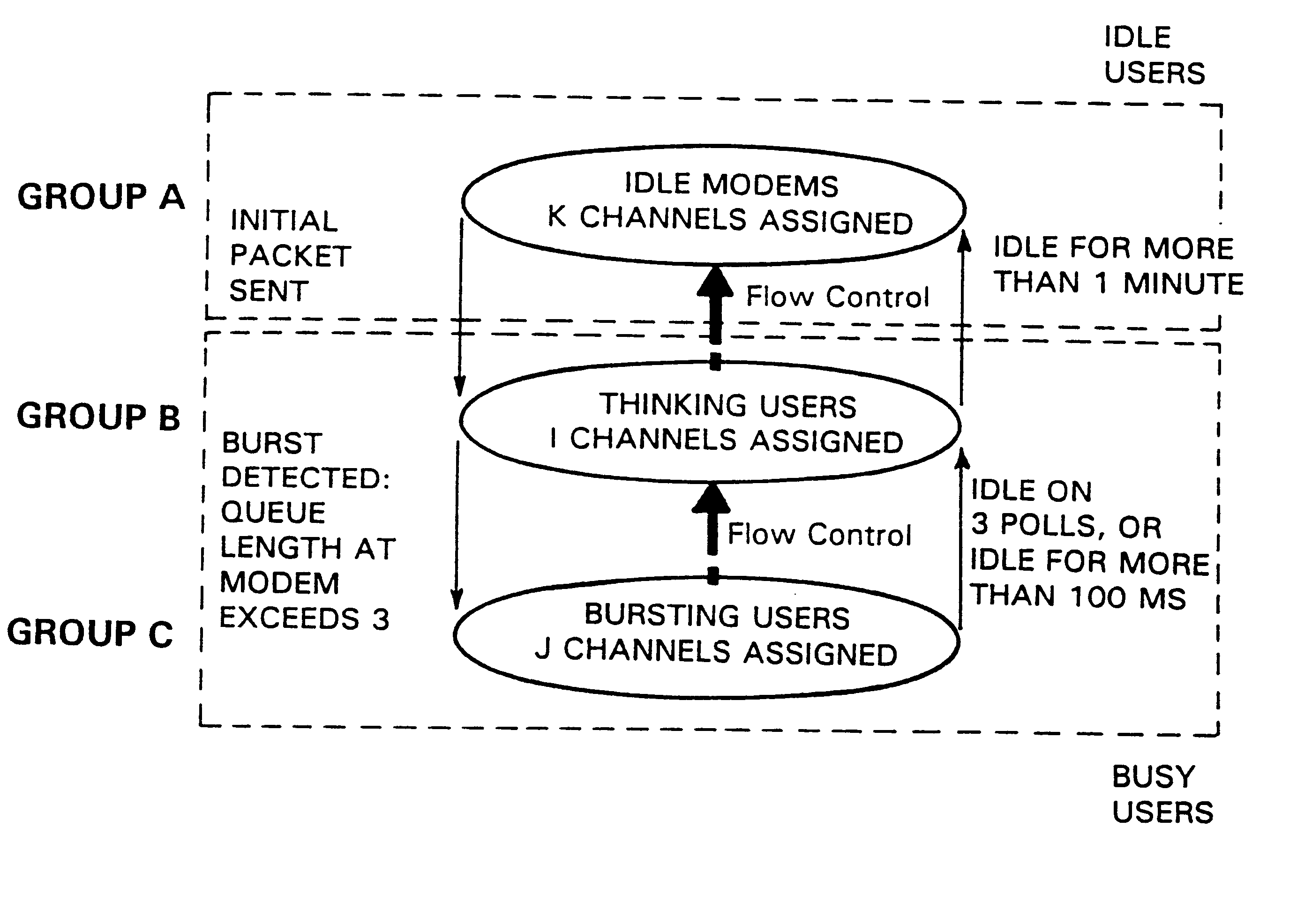
InactiveUS6275497B1Maximize throughput and reliabilityPerformance maximizationBroadband local area networksSecuring communicationModem deviceControl communications
A medium access controller for a multi-user network that assigns or changes the operating protocol of multiple upstream channels according to user loading, user status, and / or type of payload data transfers requested by the user or detected by the controller. One group of upstream channels utilizes a contention-only protocol for non-responding or off-line users, a second group utilizes a limited type polling protocol for users requiring only brief transfers of payload data, and a third group utilizes an exhaustive polling protocol user requiring large amounts of payload data transfers. Limited type polling provides low latency for quick response to accommodate multiple users, while exhaustive polling provides large data throughput at the expense of latency. Additional levels of limited or exhaustive polling may be employed to accommodate a larger variety of users needs. In addition, the channels themselves may be dynamically reclassified between and among contention and first and / or other level polling modes based on user loading and / or the nature and character of on-going data transfers in order to achieve maximum utilization of shared resources. After initiating a data transmission, the controller may also dynamically assign channels to a user based on detected changes in actual data transmissions. Thus, rules based on user activity level may be implemented to determine when a user is switched between channel groups. Essentially, the controller may effect switching of the users' upstream channels dynamically and intelligently on a packet-by-packet basis. Users may include modems and / or other terminal devices in a client-server or other data communication network.
Owner:HYBRID NETWORKS
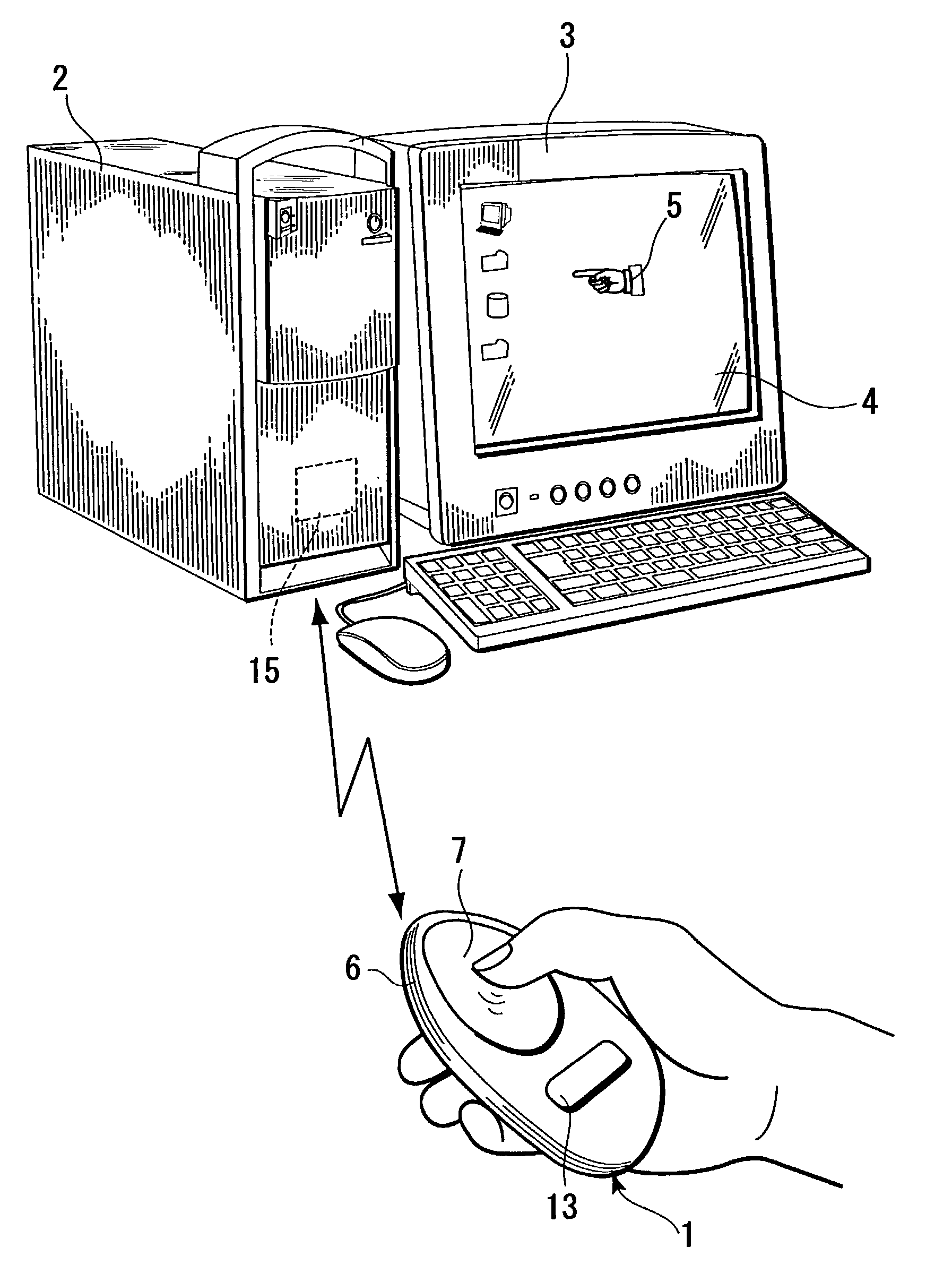
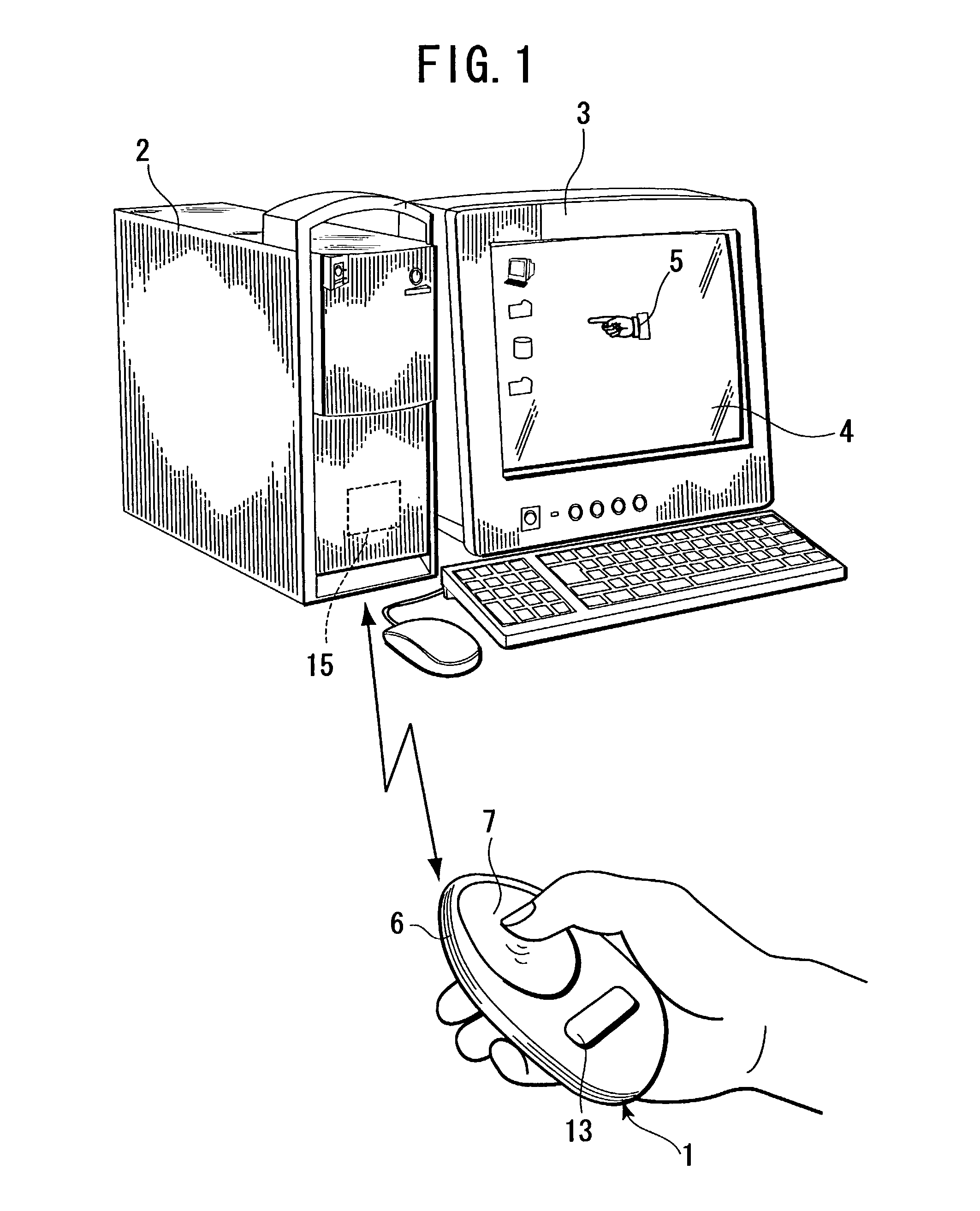
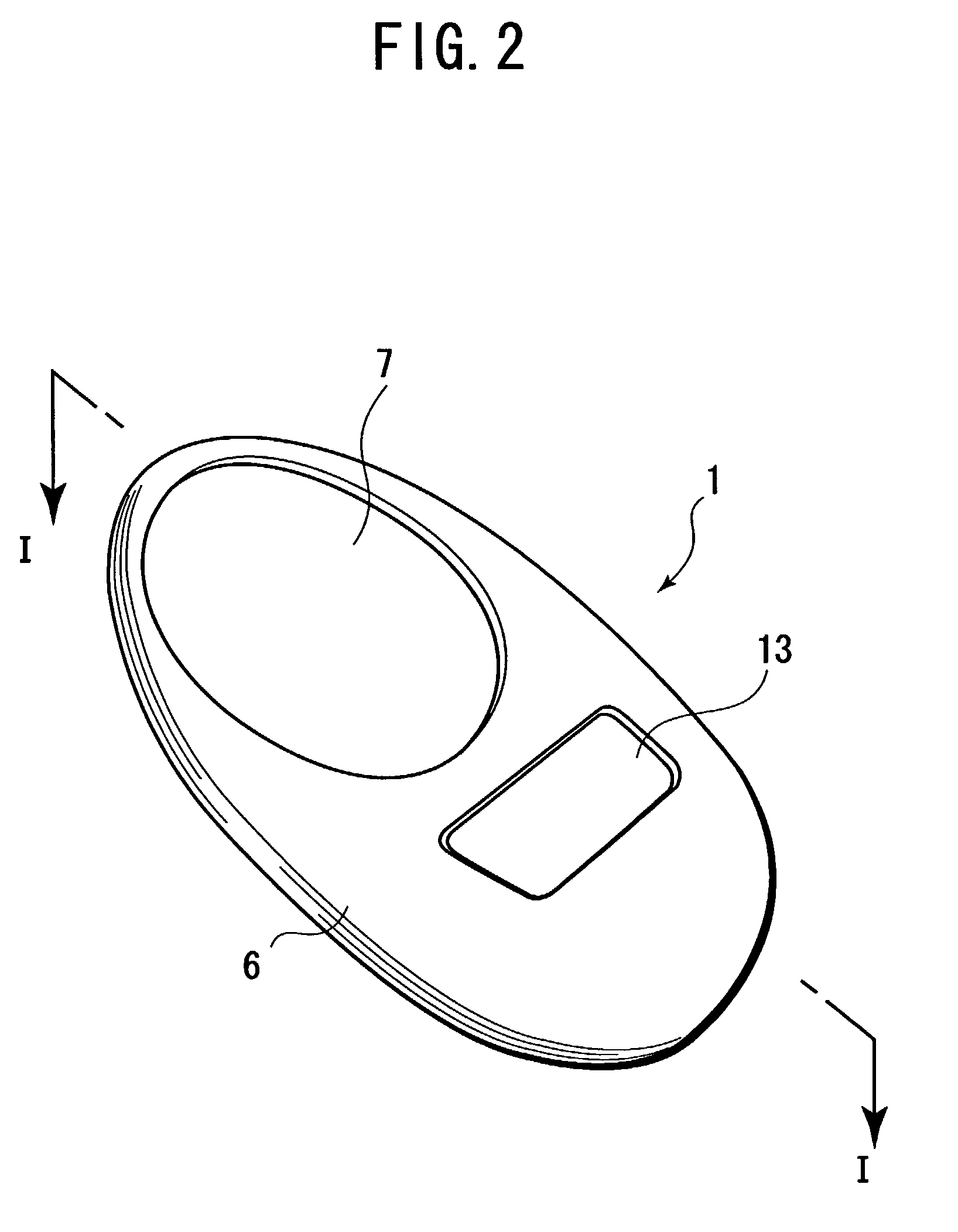
Information input device for giving input instructions to a program executing machine
ActiveUS7133026B2Improve postureFreely be designed in shapeInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsUser needsTouchpad
An information input device has a device body made of an elastically deformable material. The device body can be held in a palm and operated with one hand. The device body is provided in its face with a touchpad. A pressure sensor and an acceleration sensor are independently provided in the device body. The device body includes therein an RF module for transmitting a sensor signal from each sensor to a personal computer. By a control unit (CPU) in the device body, for example, a determination signal for determining an operation on the touchpad as input data is assigned to the pressure sensor, and a canceling signal for canceling the determination signal is assigned to the acceleration sensor. Thus, the user need not operate the device body on a desk or the like. The user can easily hold and operate the device body with one hand, without restriction of place to operate.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Needs-matching navigator system
ActiveUS20170019496A1Speed up the processLose weightBiological neural network modelsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsUser needsElectronic communication
A needs-matching navigator system and social network facilitator appurtenances including, for a large user plurality, software driven modules residing on electronic communications enabled platforms and devices. Beyond altruistically enhancing flourishing life horizons and life quality metrics, the modules facilitate (A) knowing respective user bias, profile, perspective, wellbeing orientation, and privacy preference; (B) understanding user needs description and wellbeing criteria; (C) finding answer and solutions to the needs by user biased projecting the description onto electronically stored knowledge-bases; (D) matching the user to the answers and solutions; and preferably (E) creating an instant electronic communications interactive community for the respective user, by inverse projecting large subsets of the answers and solutions back onto the large plurality of users; according to said users' profiles and needs descriptions. This navigable community may be classified into spontaneous castes; having various degrees of relevant understanding, expertise, experience, and / or curiosity about these answer and / or solution projections.
Owner:ORBACH TUVI
Power tool control system
InactiveUS20060076385A1Quality improvementWell formedStapling toolsDrilling/boring measurement devicesUser needsGraphics
A power tool control system allows a user to operate a power tool through a graphical user interface communicatively coupled with a non-contact measurement and alignment device. The graphical user interface correlates user engageable selectors with a logically related menu of power tool setting options displayed on a display screen in a high quality and easily readable format. The non-contact measurement and alignment device uses one or more lasers to determine power tool settings and establish proper alignment based on user needs. The power tool control system further enables stud detection and visual indication of stud location.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Universal hands free key and lock system
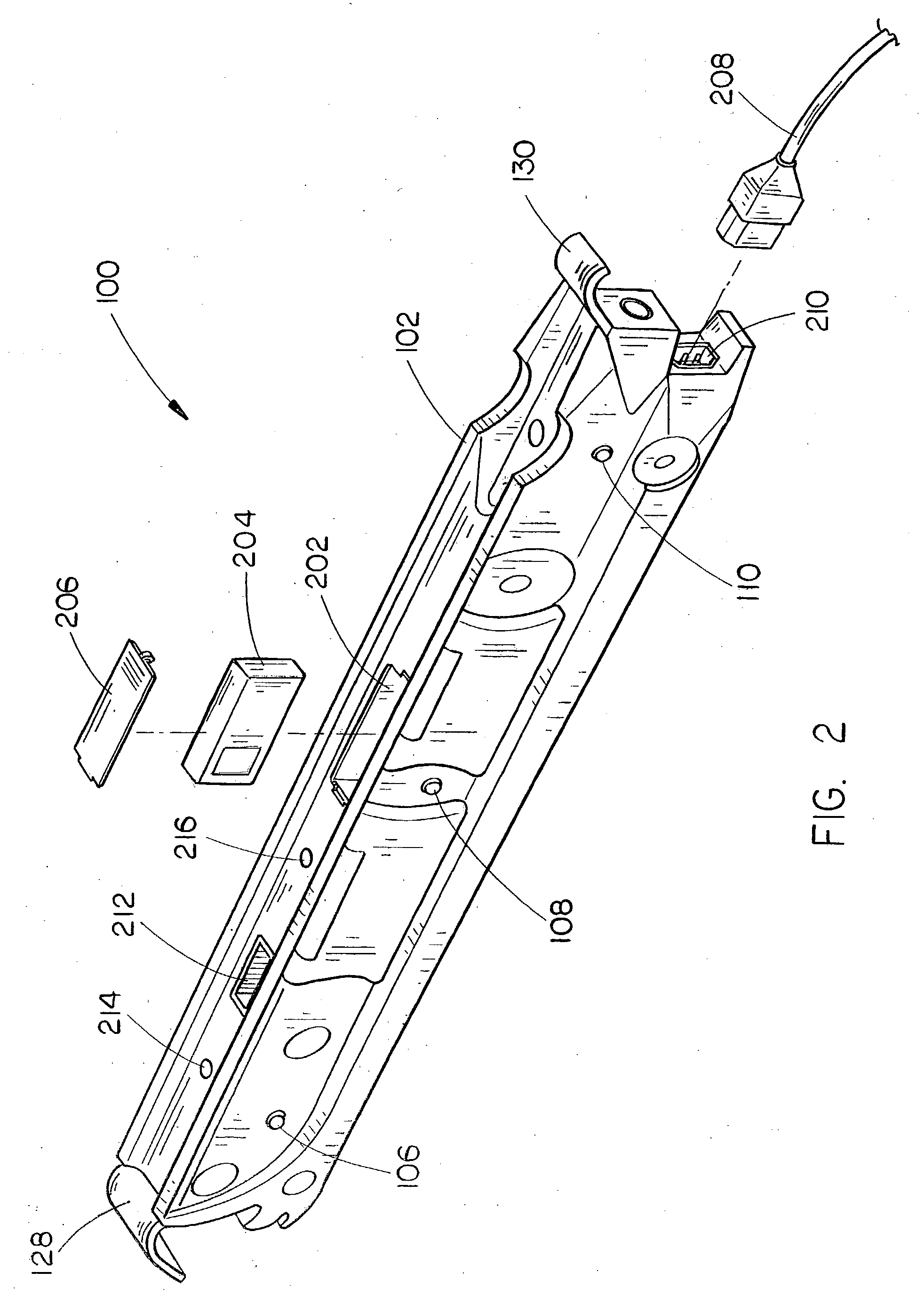
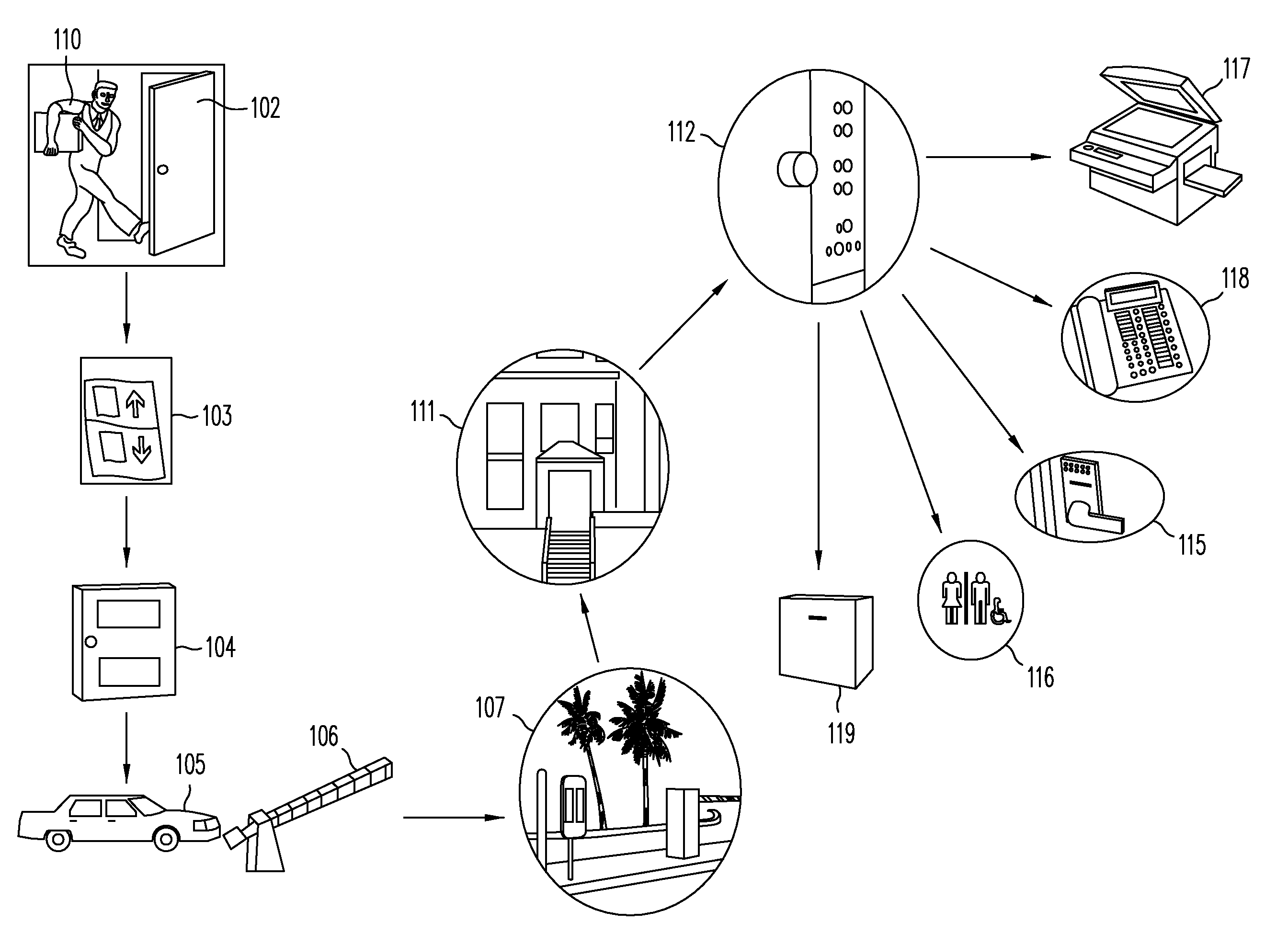
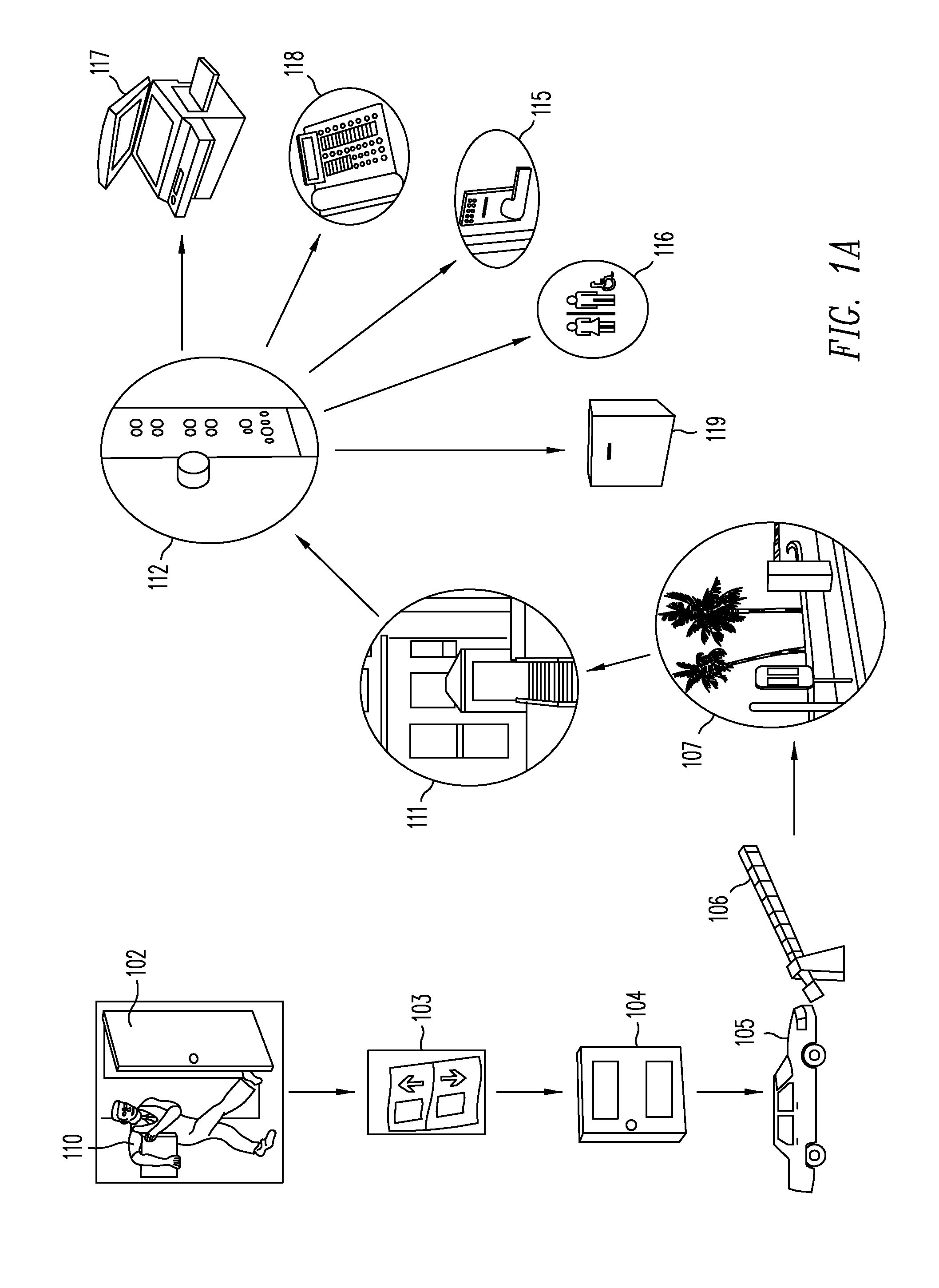
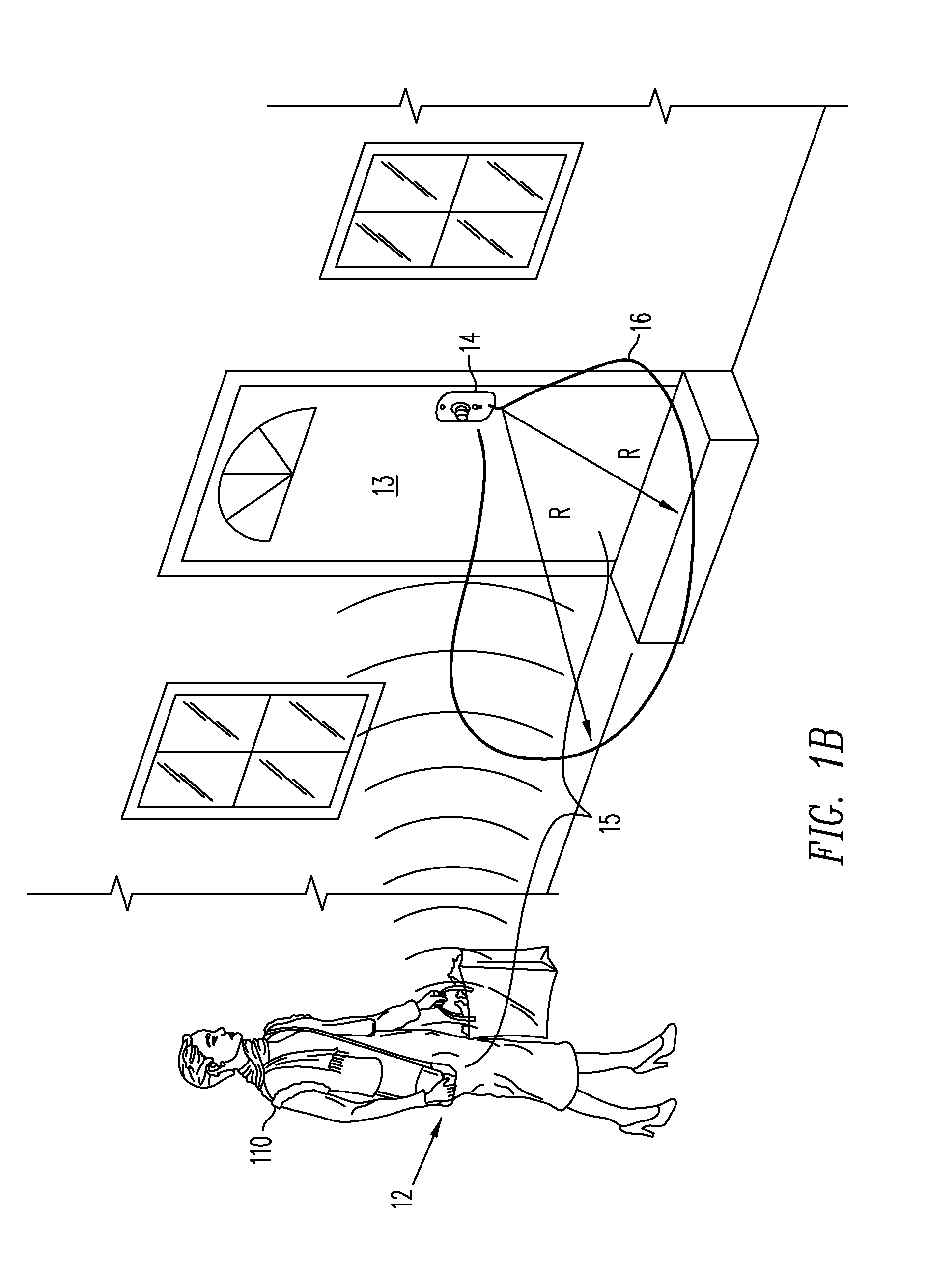
InactiveUS7446644B2Quickly and easily pass through otherwise locked doorEliminate needElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsUser needsEngineering
Methods and systems are provided for a universal key that enables a user to have access to any type of secured portal, both physical and electronic, in a wireless, hands-free, distance-independent manner without requiring contact or line of sight access between the key and the secured portal. The universal key is not distance-dependent, and each secured portal can be provided with its own prescribed activation range, if desired. Some portals may be provided with long range activation, such as 50 feet, while other portals may be provided with short range activation of a few feet or less. The type of portal being secured and the range of activation may be selected by the user and is not limited by the universal key. In addition, the universal key will provide access to the secured portals in a hands-free fashion so that the user need not push any buttons or take any other action in order to obtain access to the portal. The user need only carry the universal key somewhere on their person in order to access the portal.
Owner:SECUREALL CORP
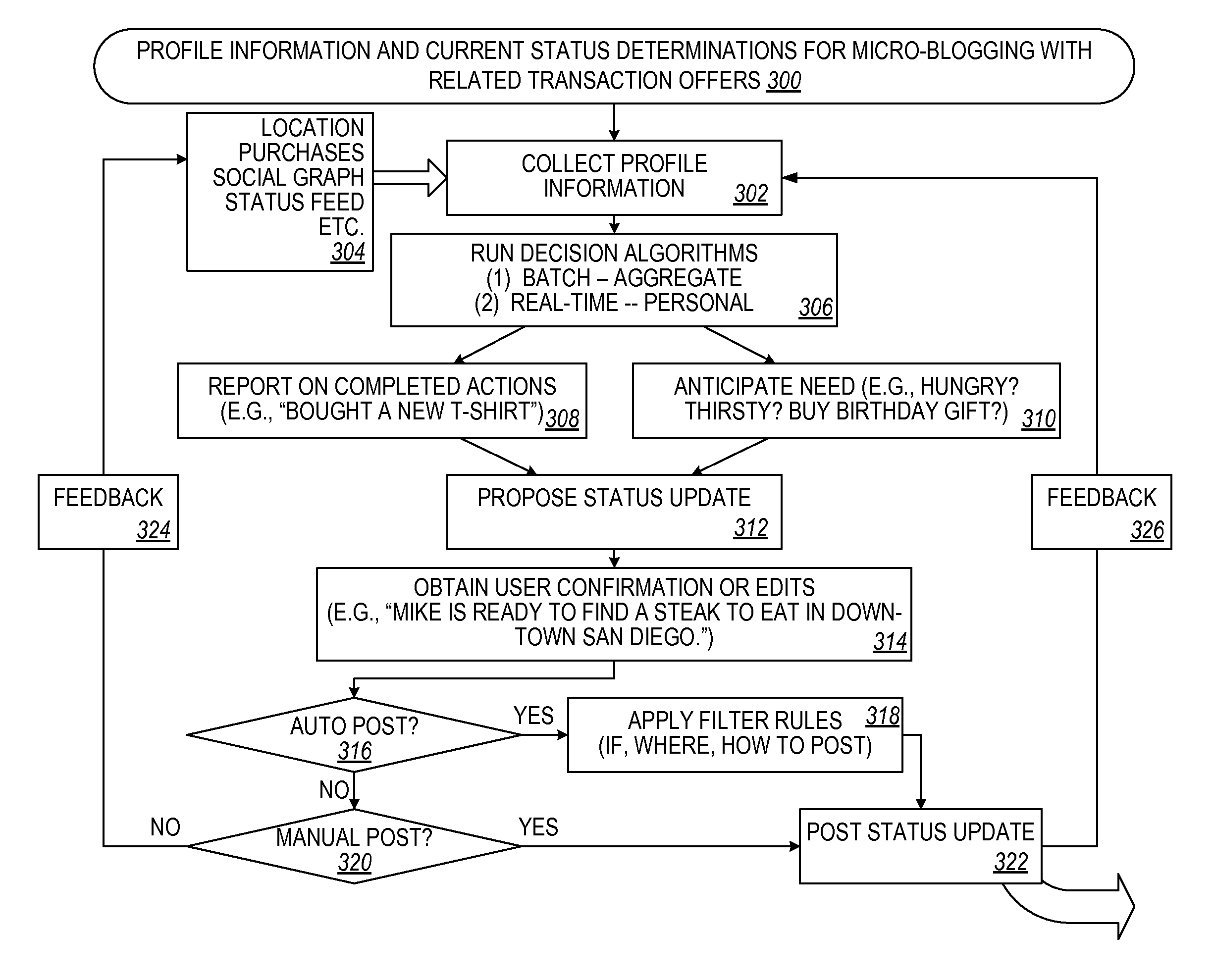
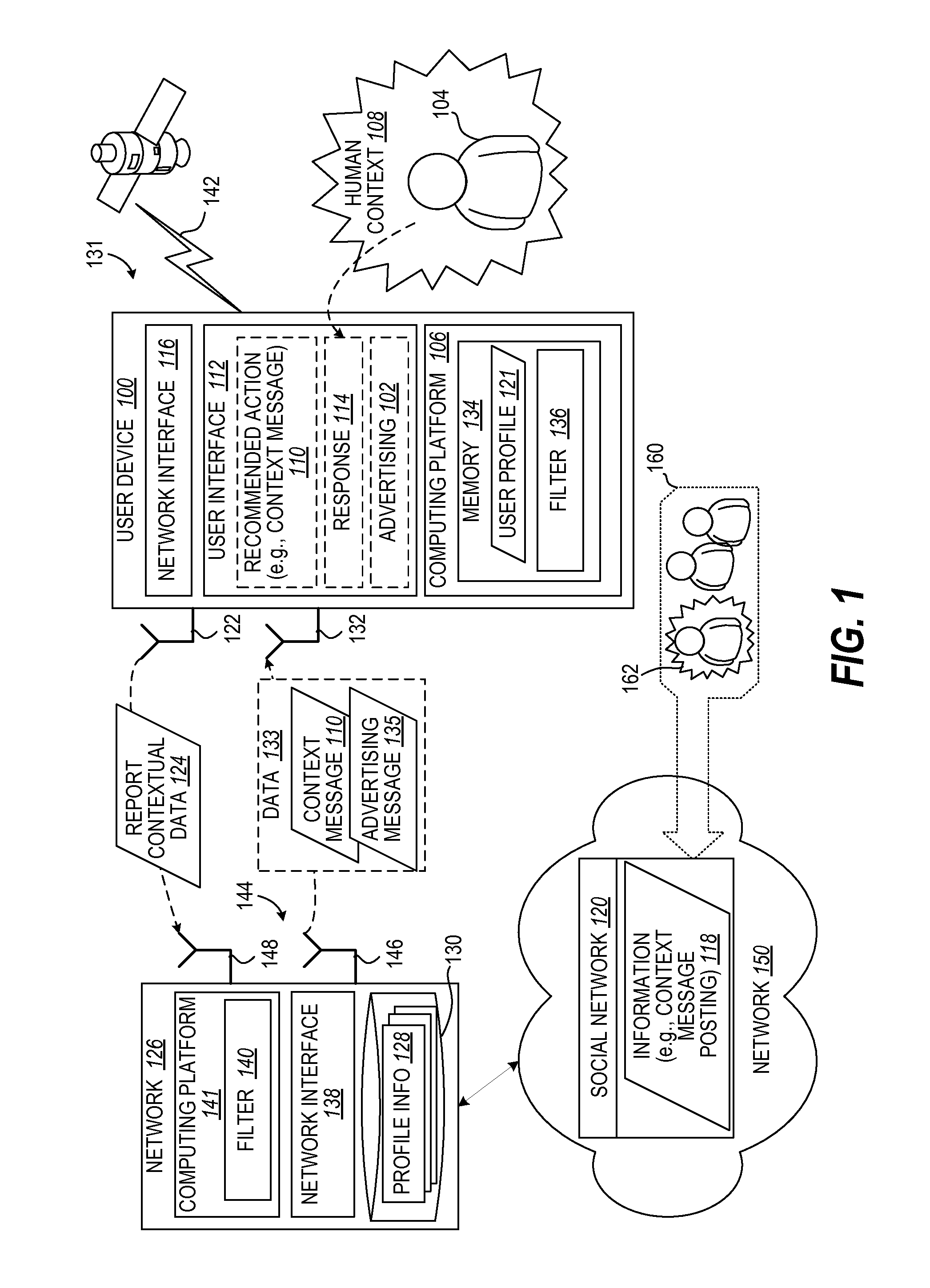
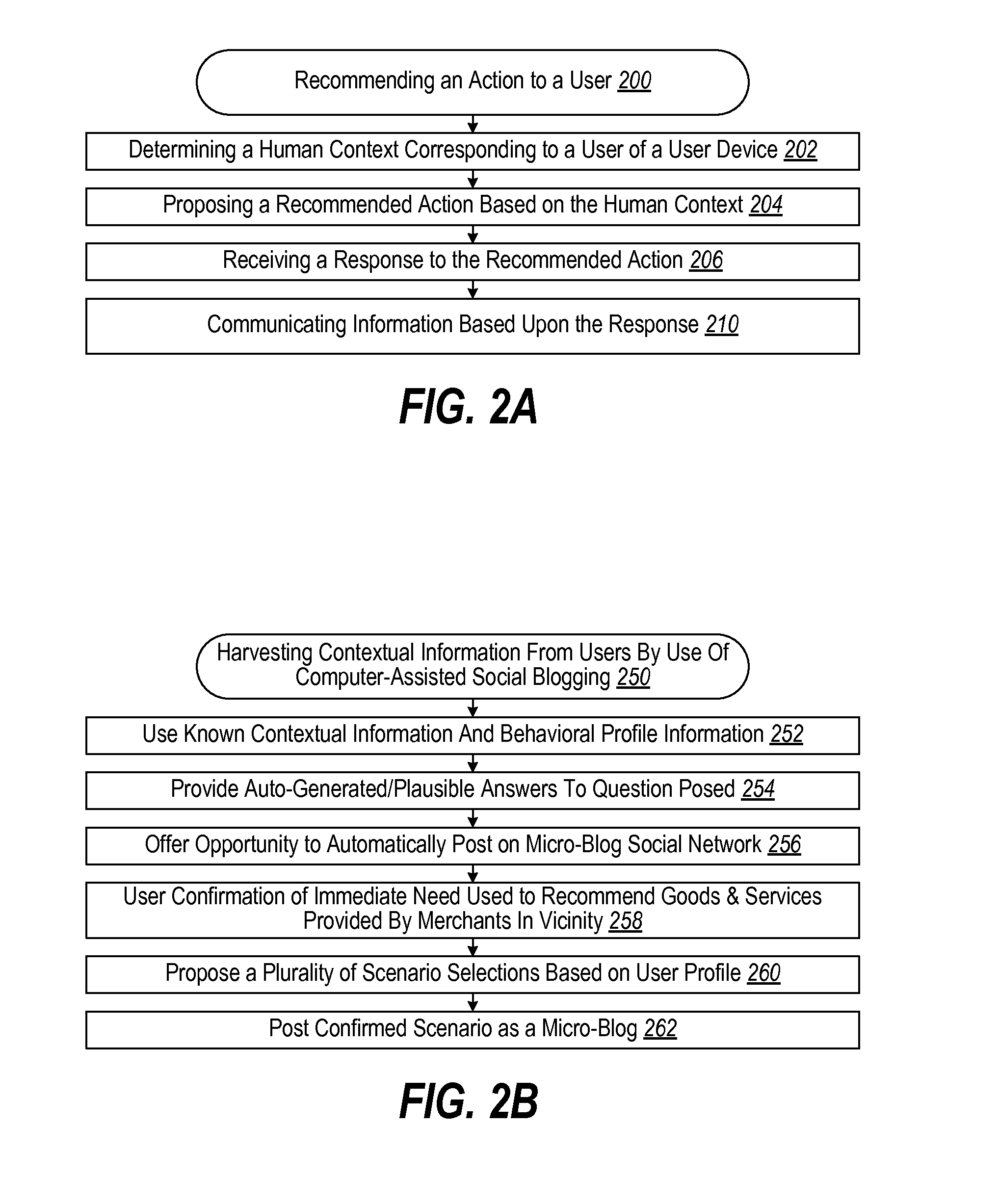
Contextual recommendations through proposed actions
InactiveUS20110264528A1Well formedServices signallingMultiple digital computer combinationsUser needsPersonalization
Knowledge of a user's profile (contextual and behavioral) can be used to predict the likely current real-time needs of the user. Confirmation of that need can be achieved by suggesting a number of personalized status updates (based on known profile information) in a form suitable for posting to micro-blogging sites. From this list, the user selects the most appropriate one to submit to a micro-blog. In doing so, valuable profile information is confirmed which allows real-time contextual recommendations to be generated to meet the recently identified need of the user. In one aspect, these recommendations comprise revenue generating opportunities.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com