Patents
Literature
1045 results about "Networks on chip" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
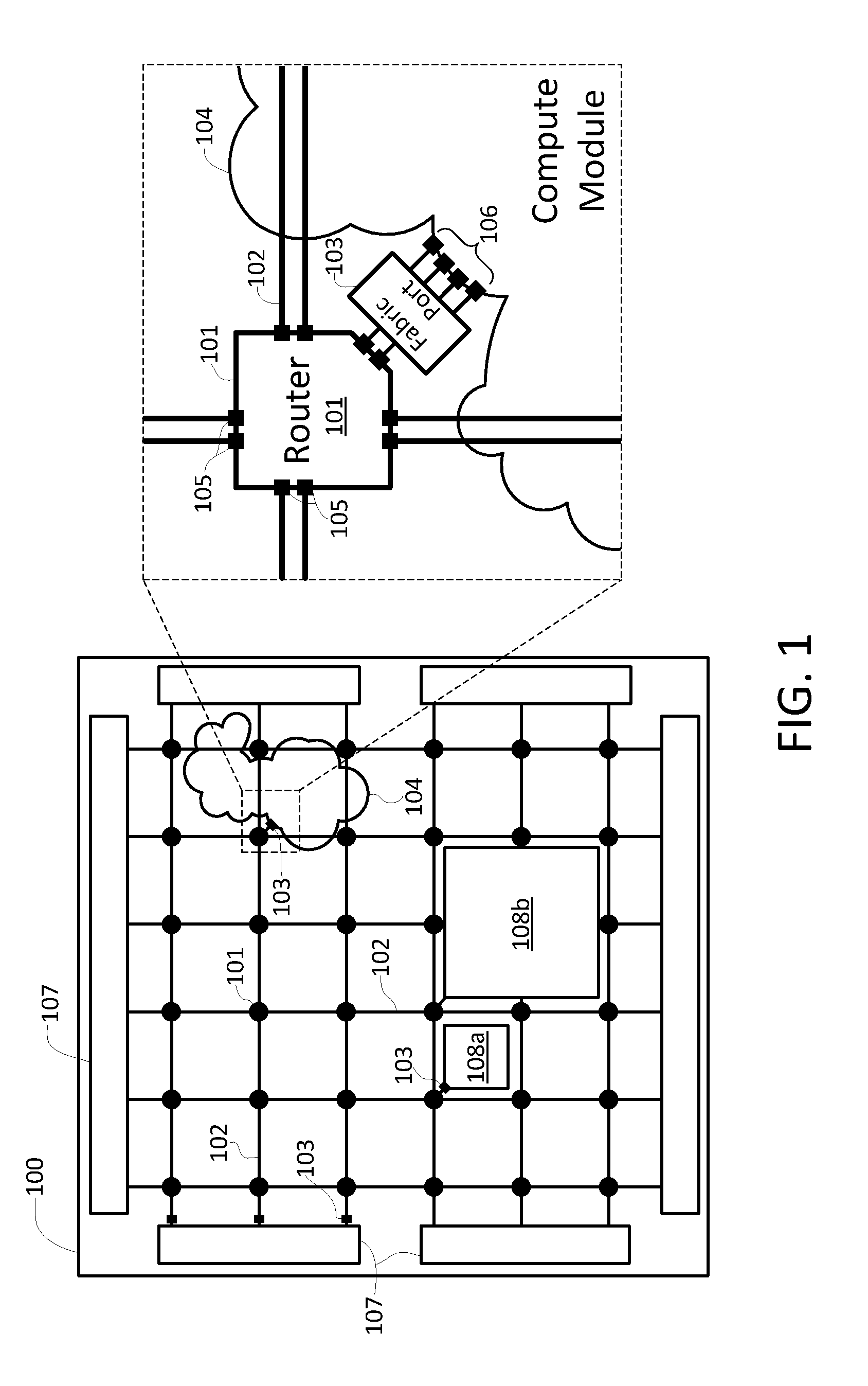
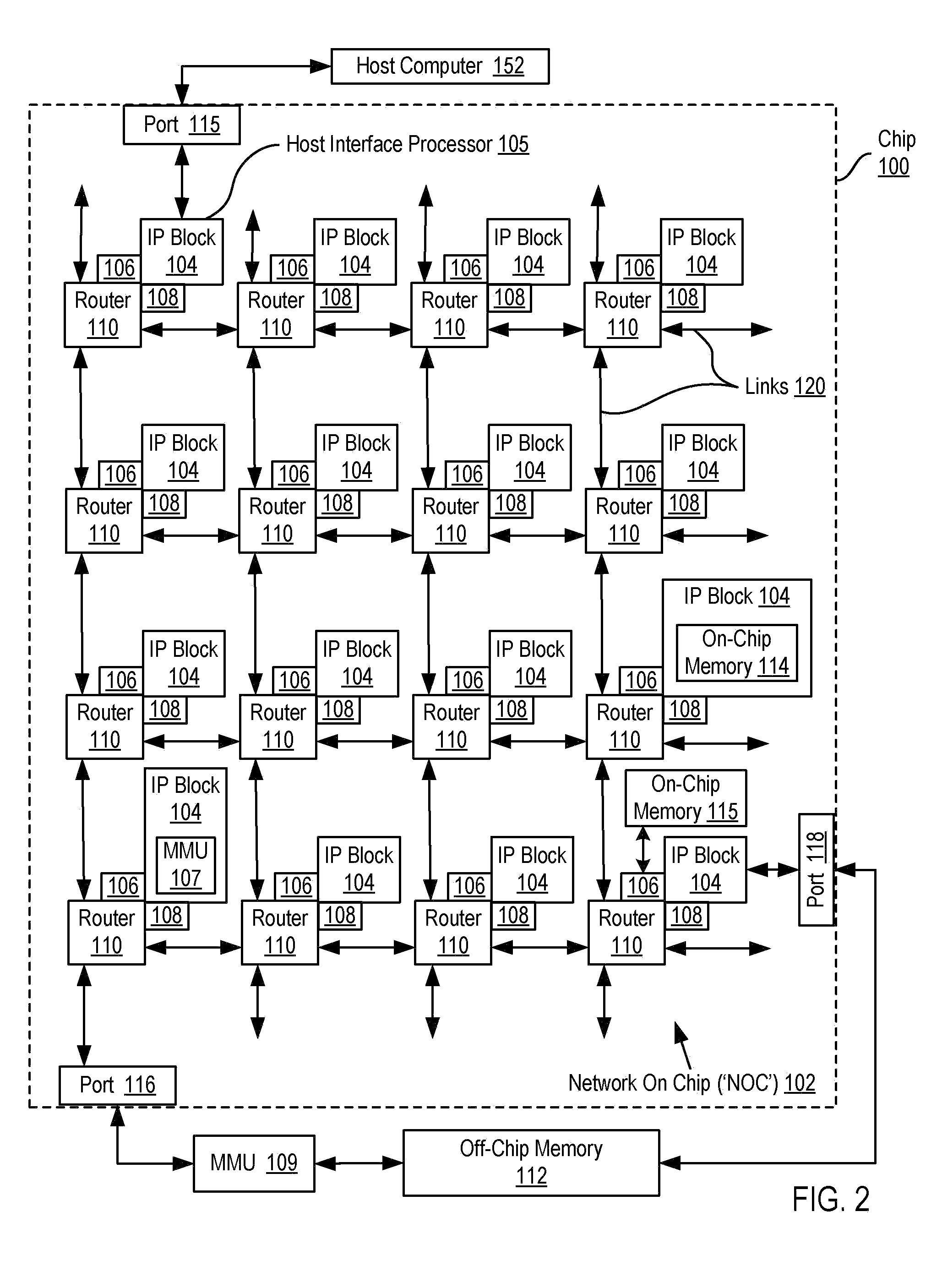
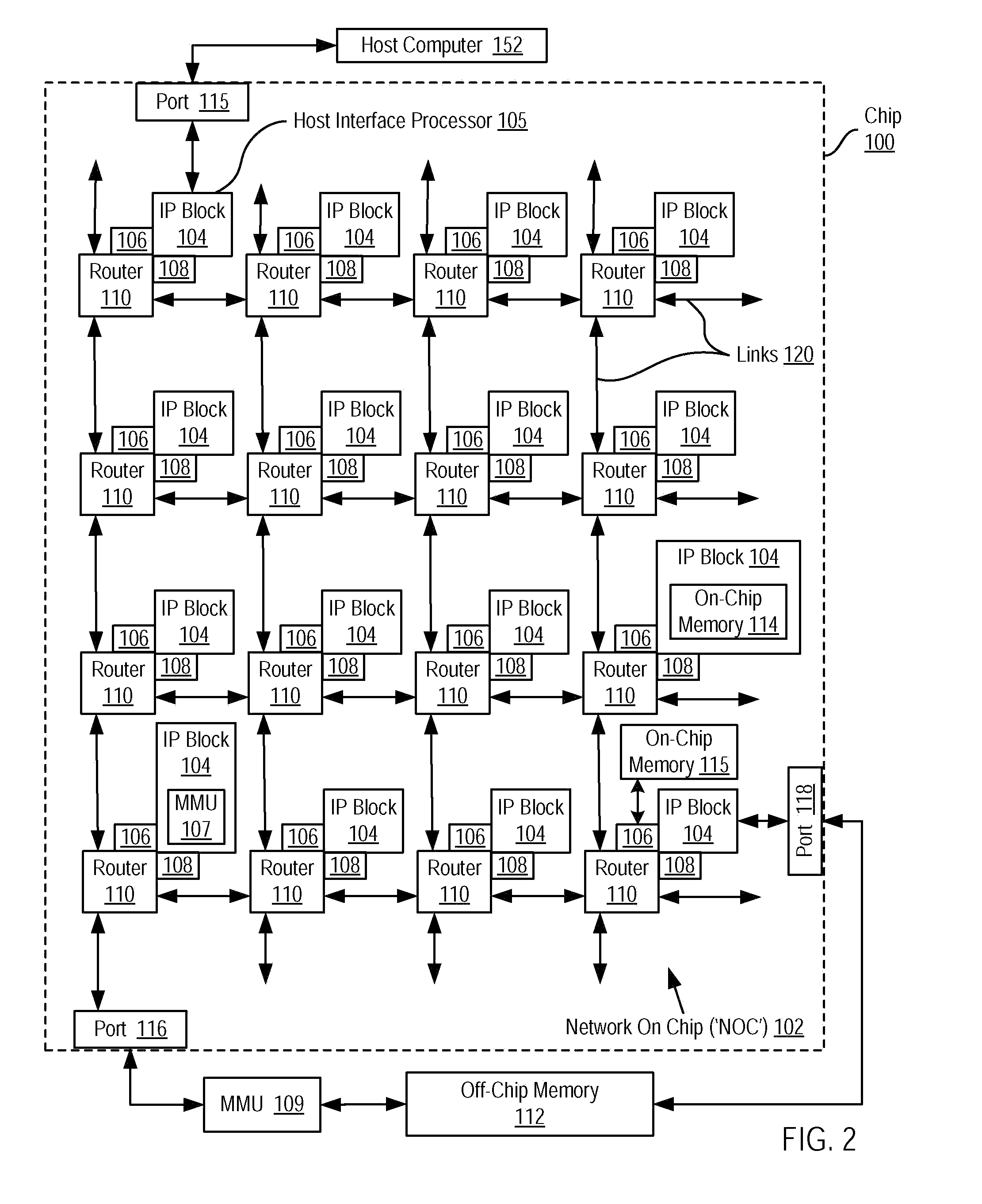
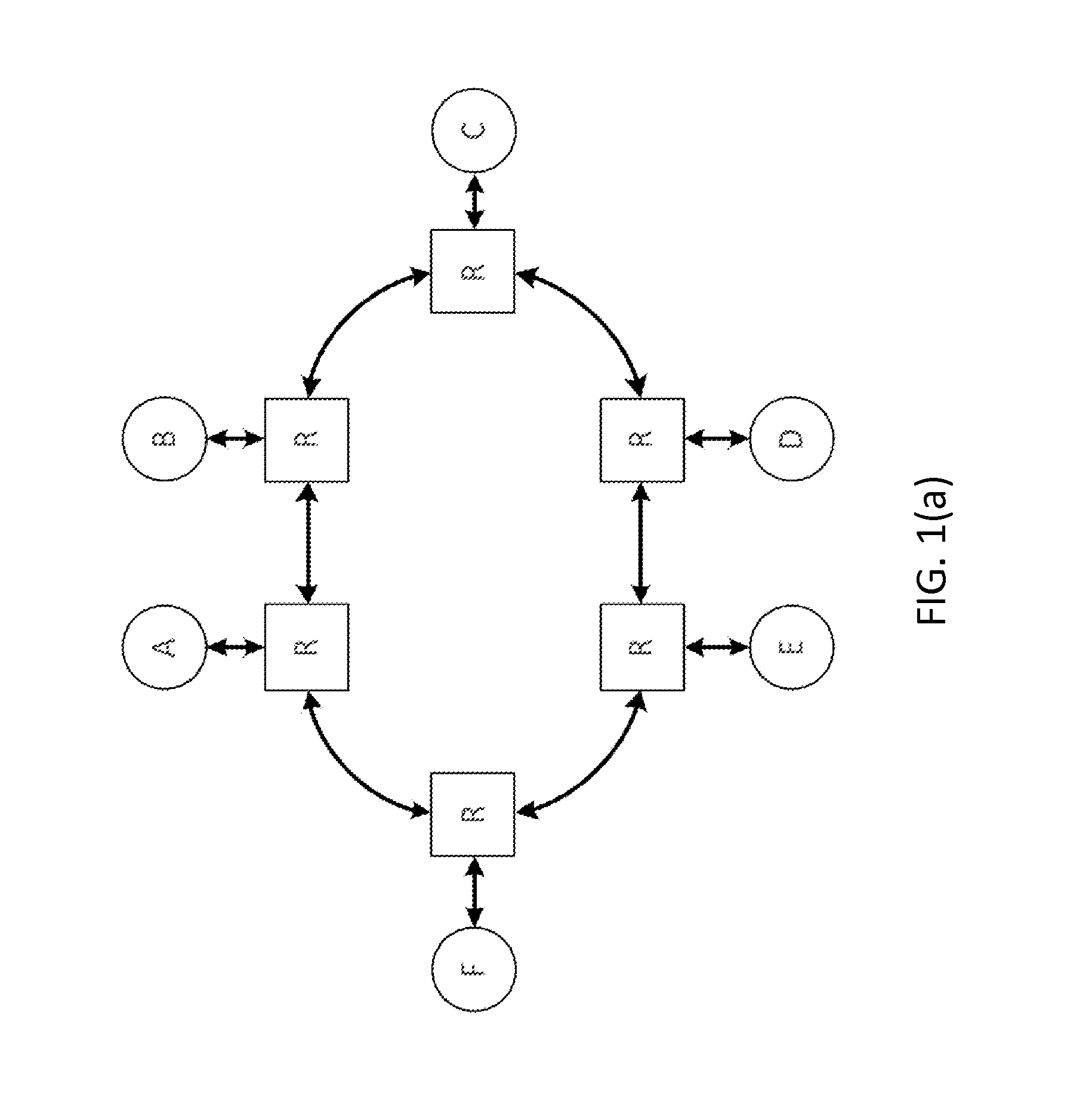
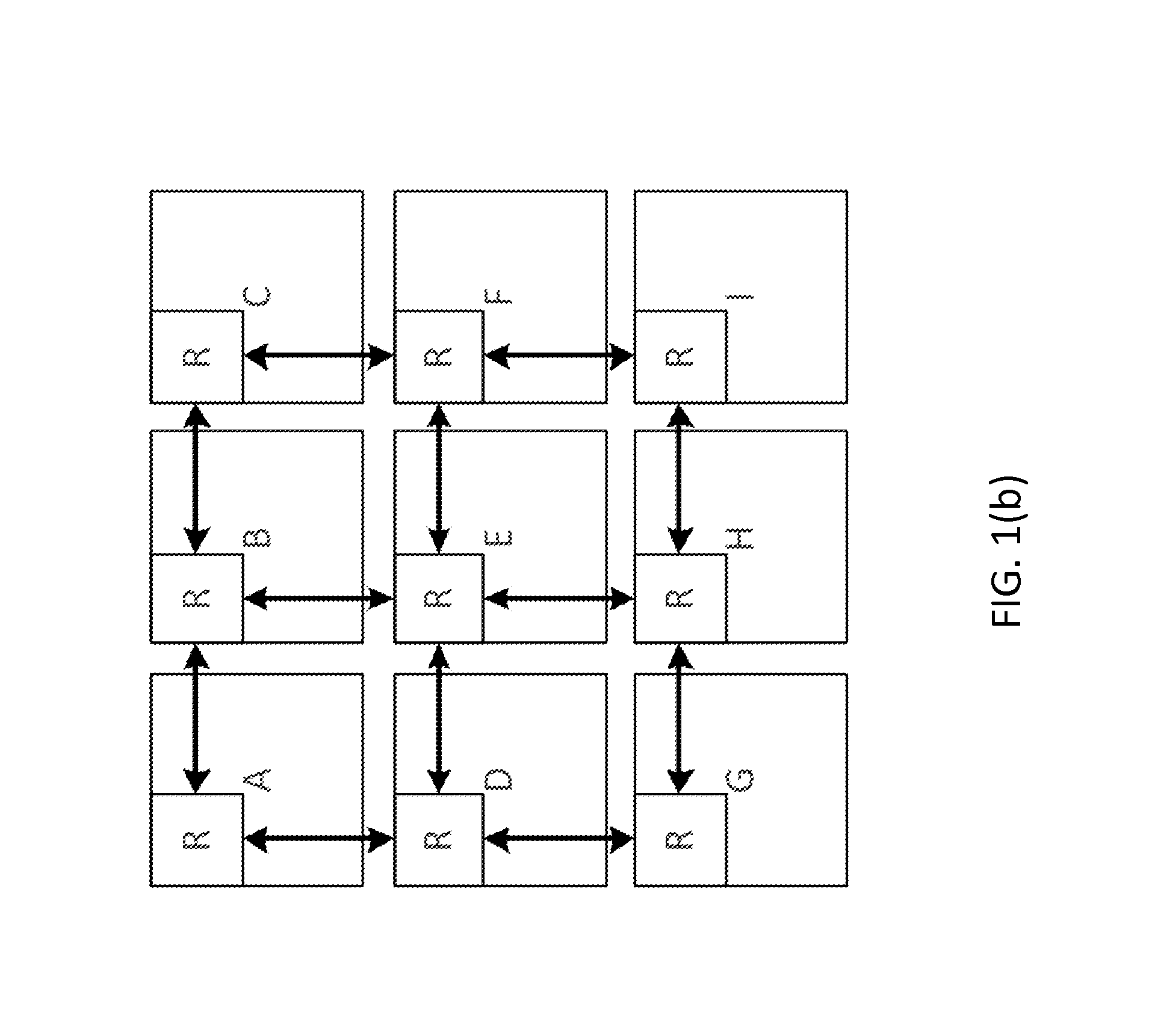
A network on a chip or network-on-chip ( NoC /ˌɛnˌoʊˈsiː/ en-oh-SEE or /nɒk/ knock) is a network -based communications subsystem on an integrated circuit ("microchip"), most typically between modules in a system on a chip (SoC). The modules on the IC are typically semiconductor IP cores schematizing various...
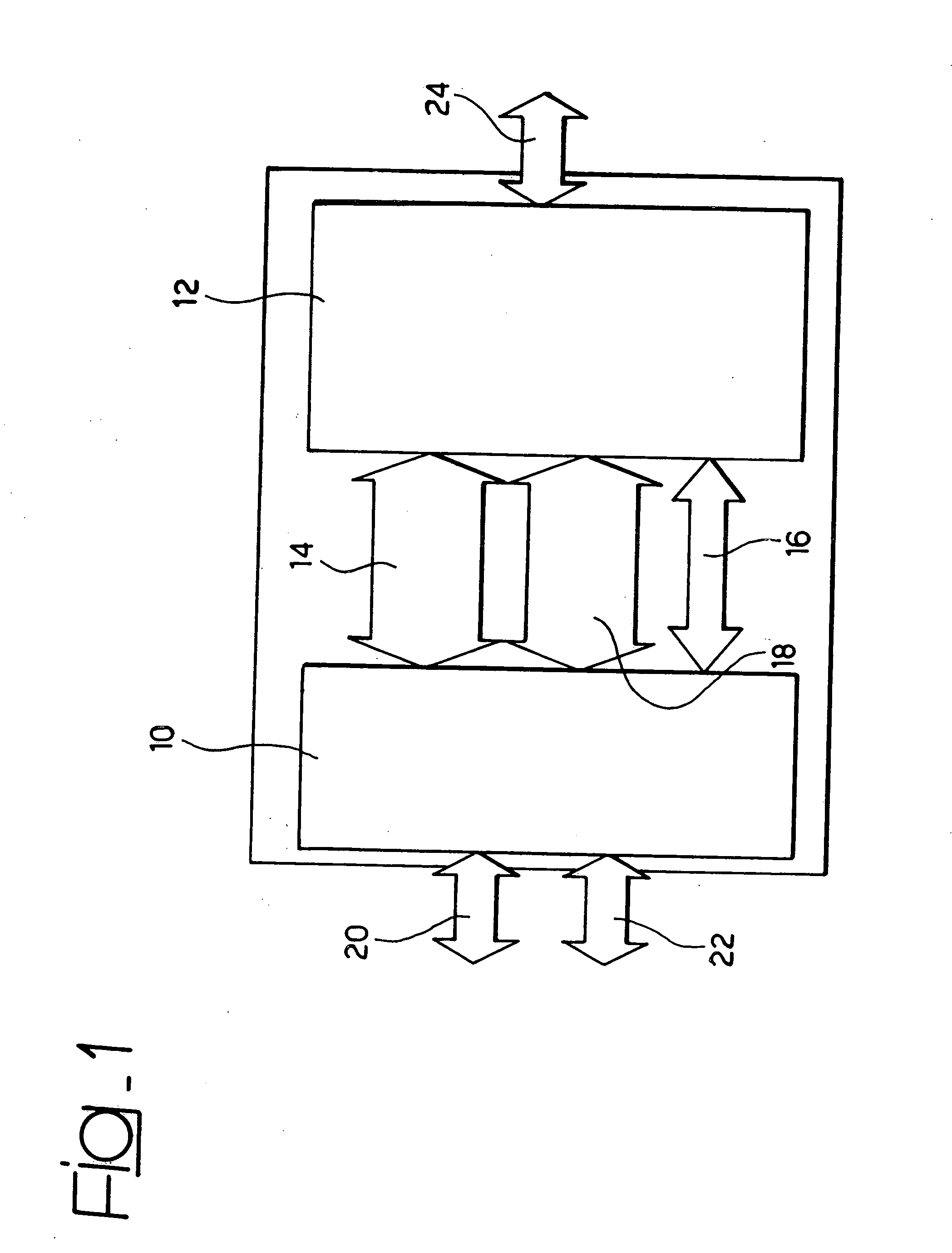
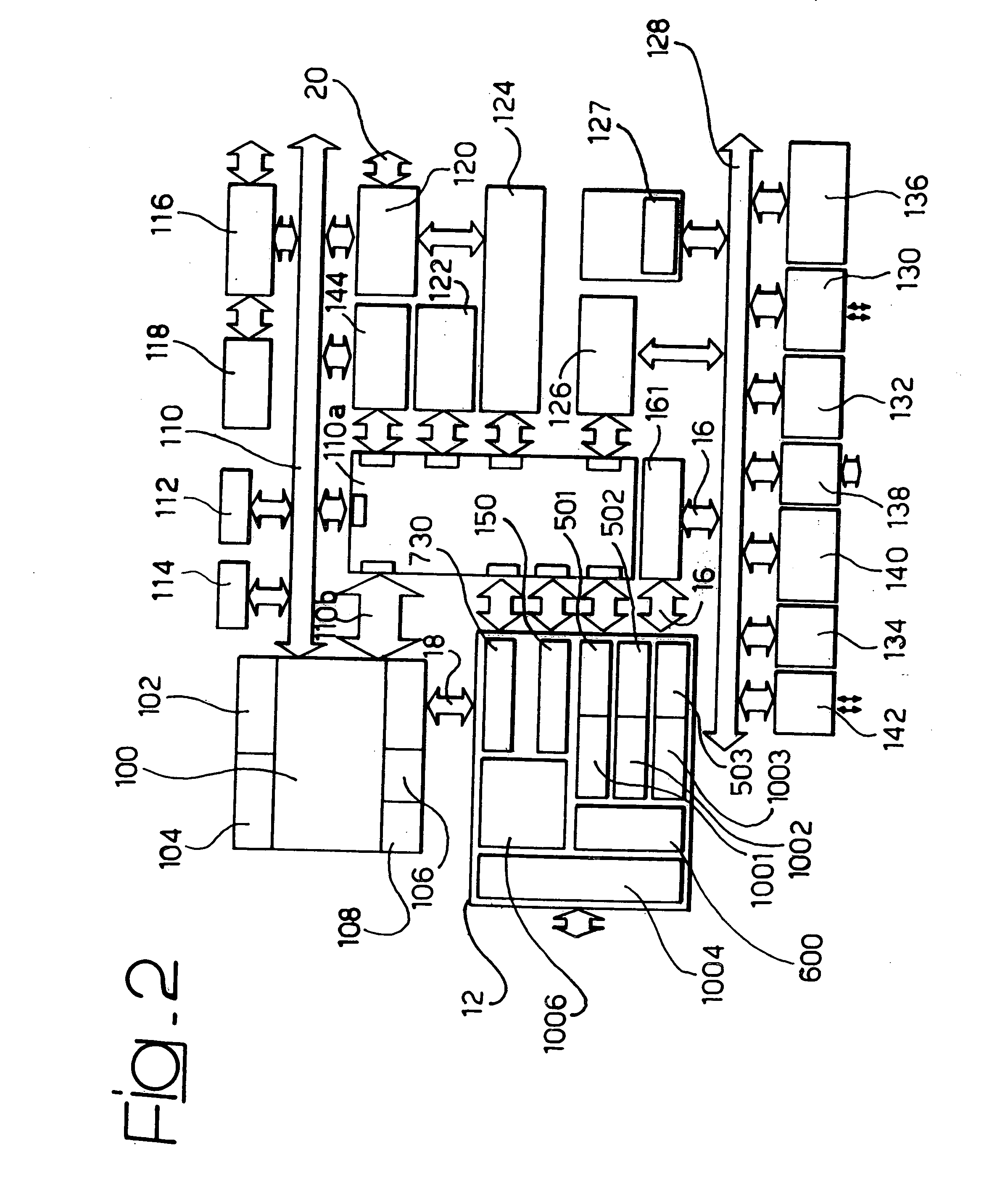
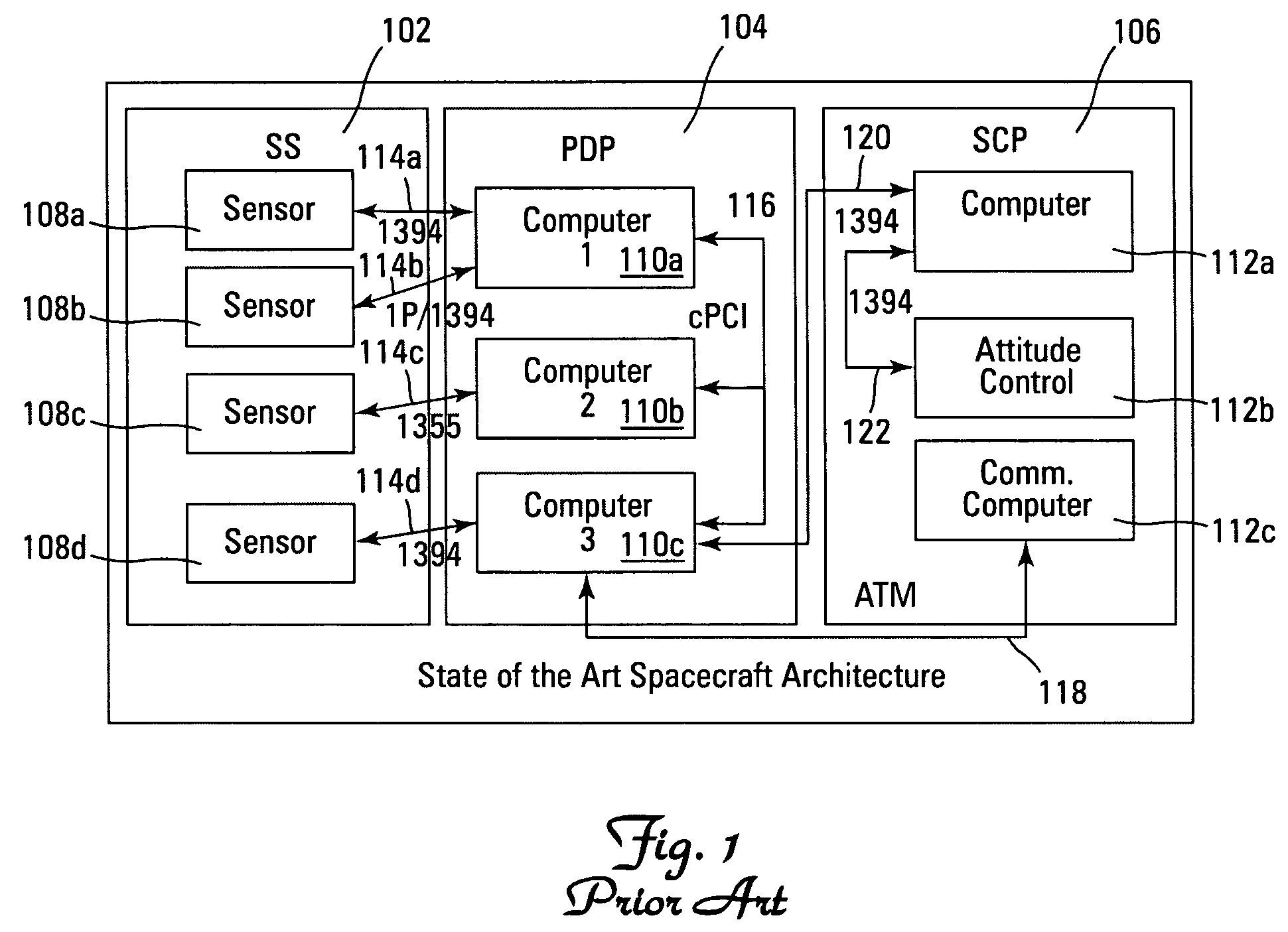
Globally asynchronous communication architecture for system on chip
InactiveUS7957381B2Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsAsynchronous communicationNetworks on chip
This invention relates to the domain of Networks on Chips (NoC) and relates to a method of transferring data in a network on chip, particularly using an asynchronous “send / accept” type protocol.The invention also relates to a network on chip used to implement this method.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Directional two-dimensional router and interconnection network for field programmable gate arrays, and other circuits and applications of the router and network
ActiveUS20160344629A1Reduce switching delayLower latencyData switching networksNetwork sizeFpga implementations
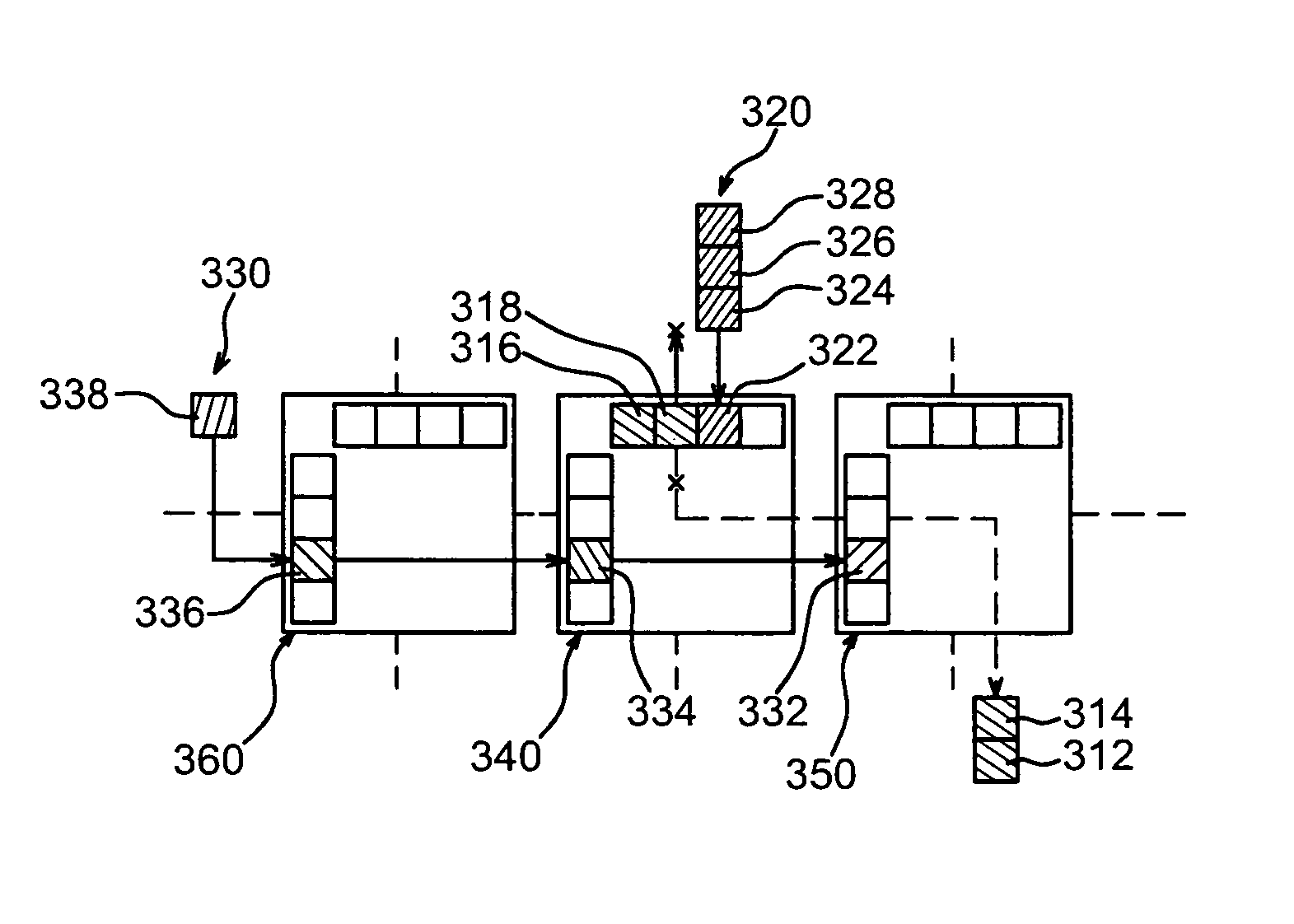
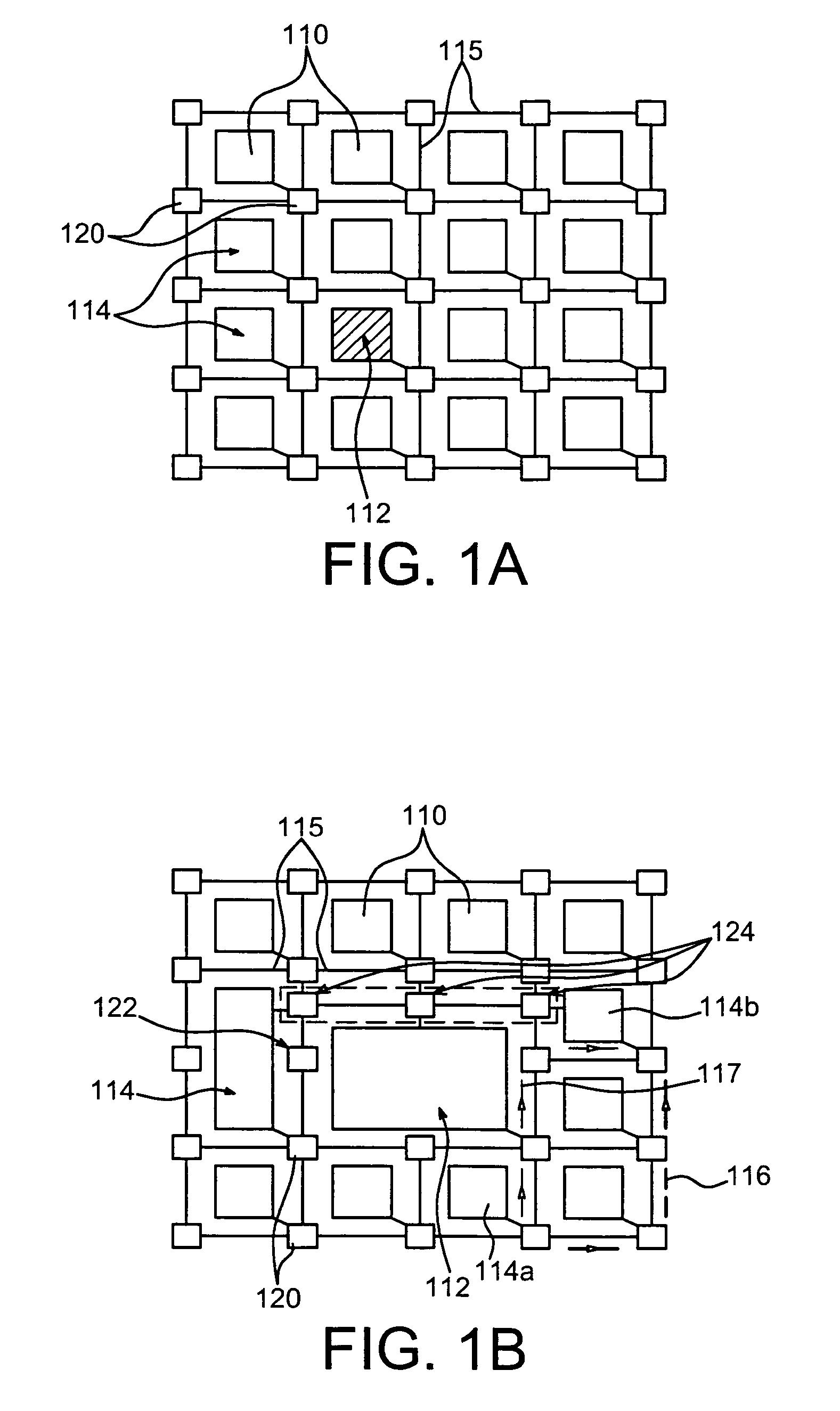
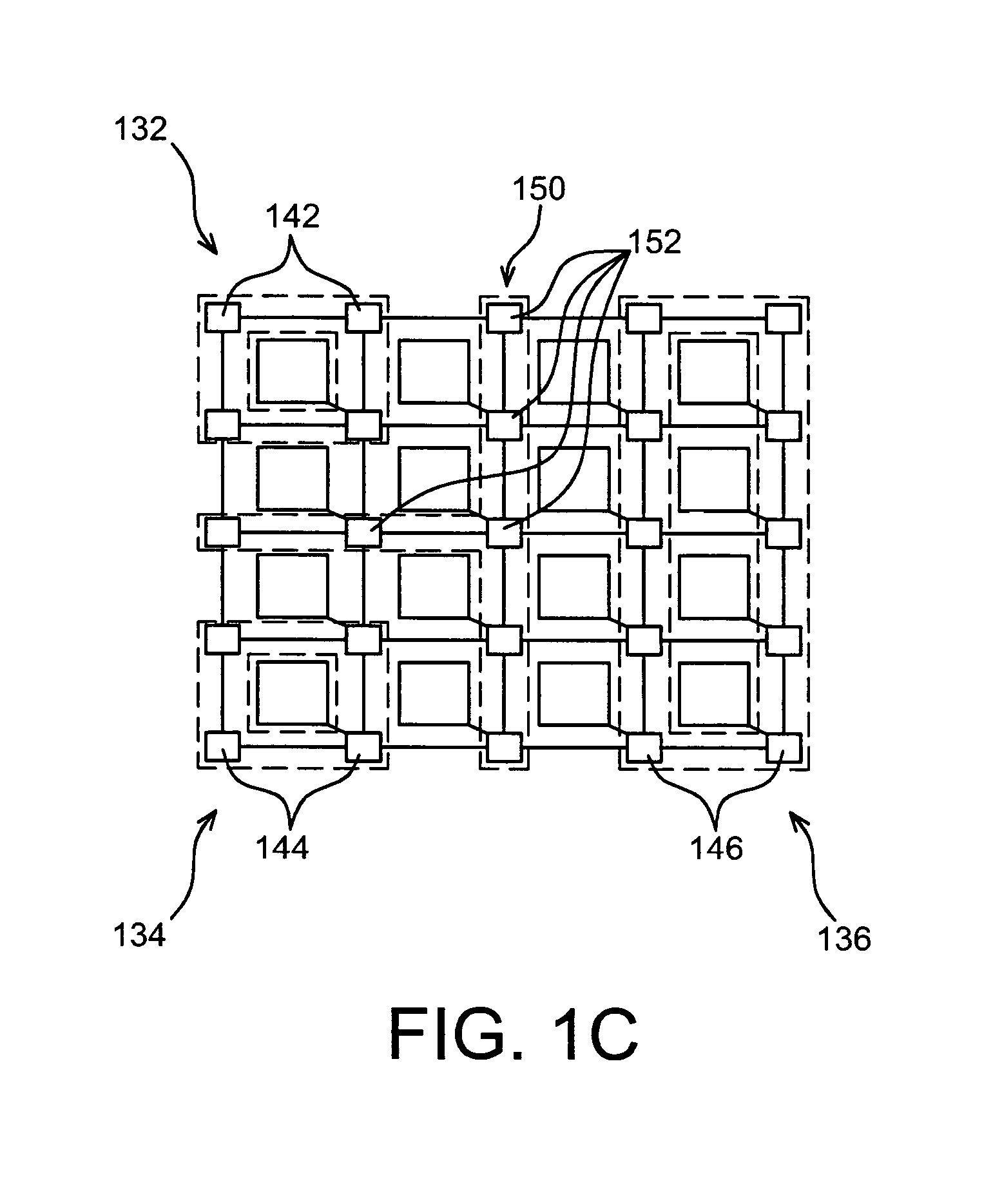
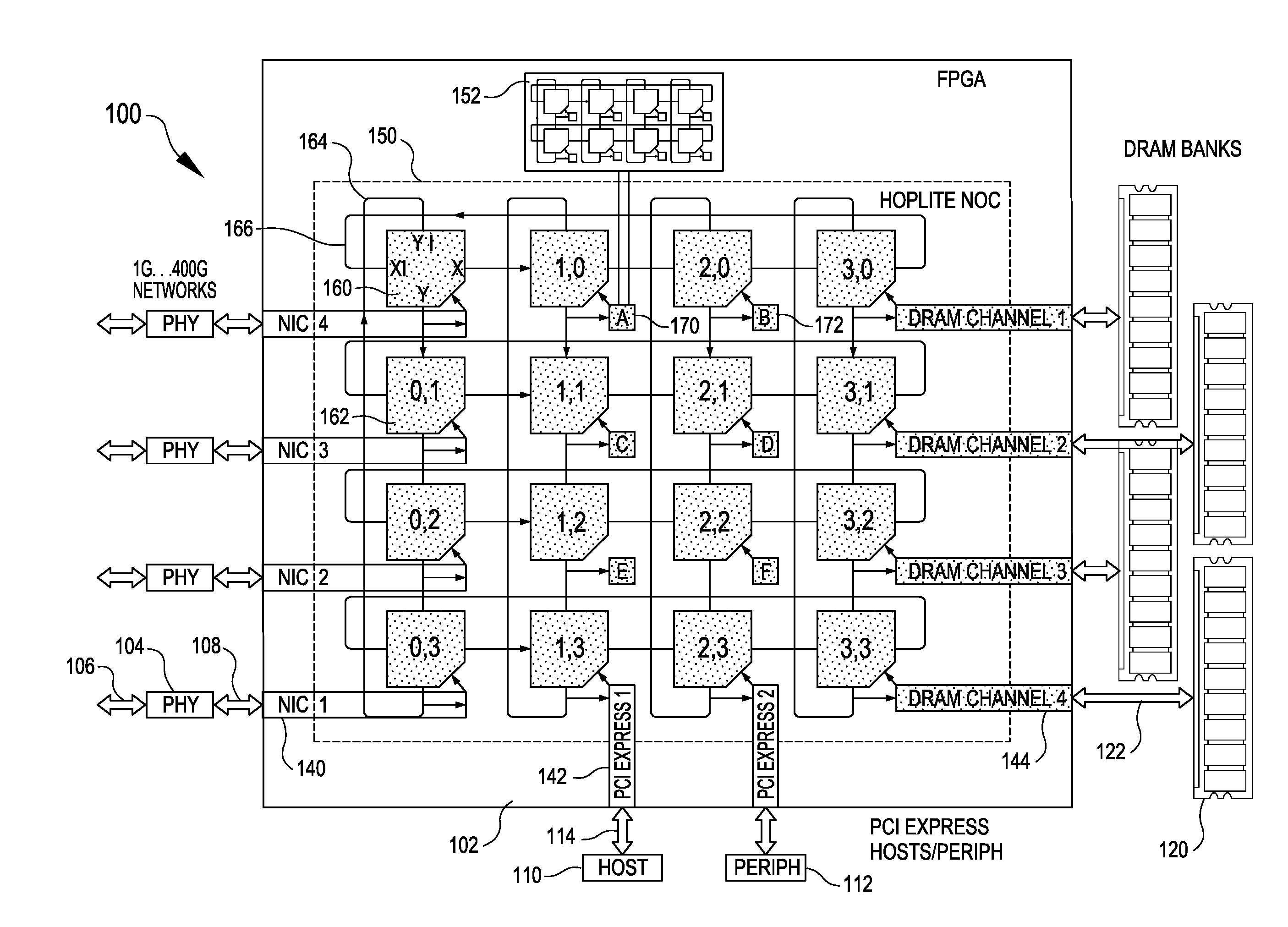
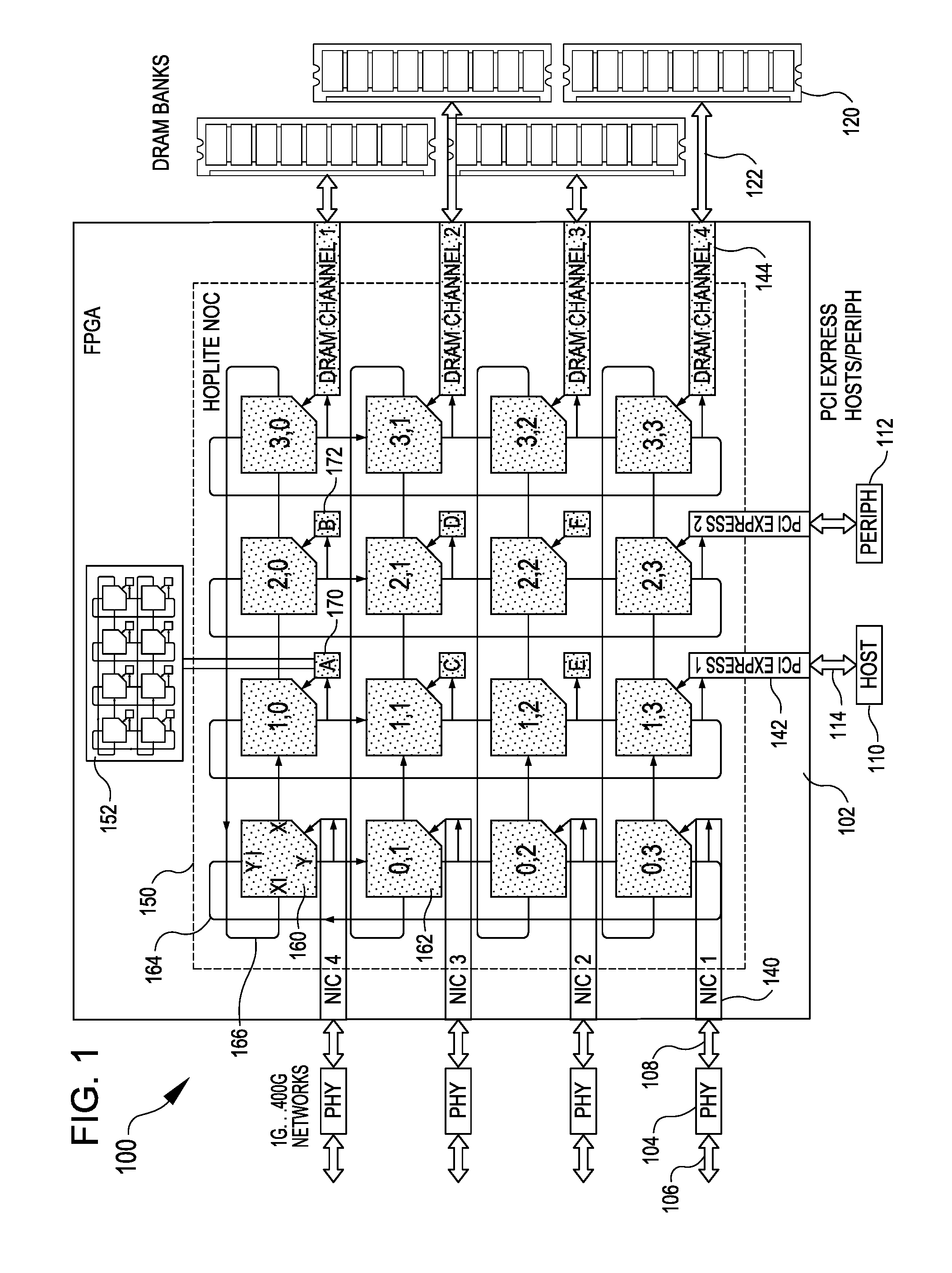
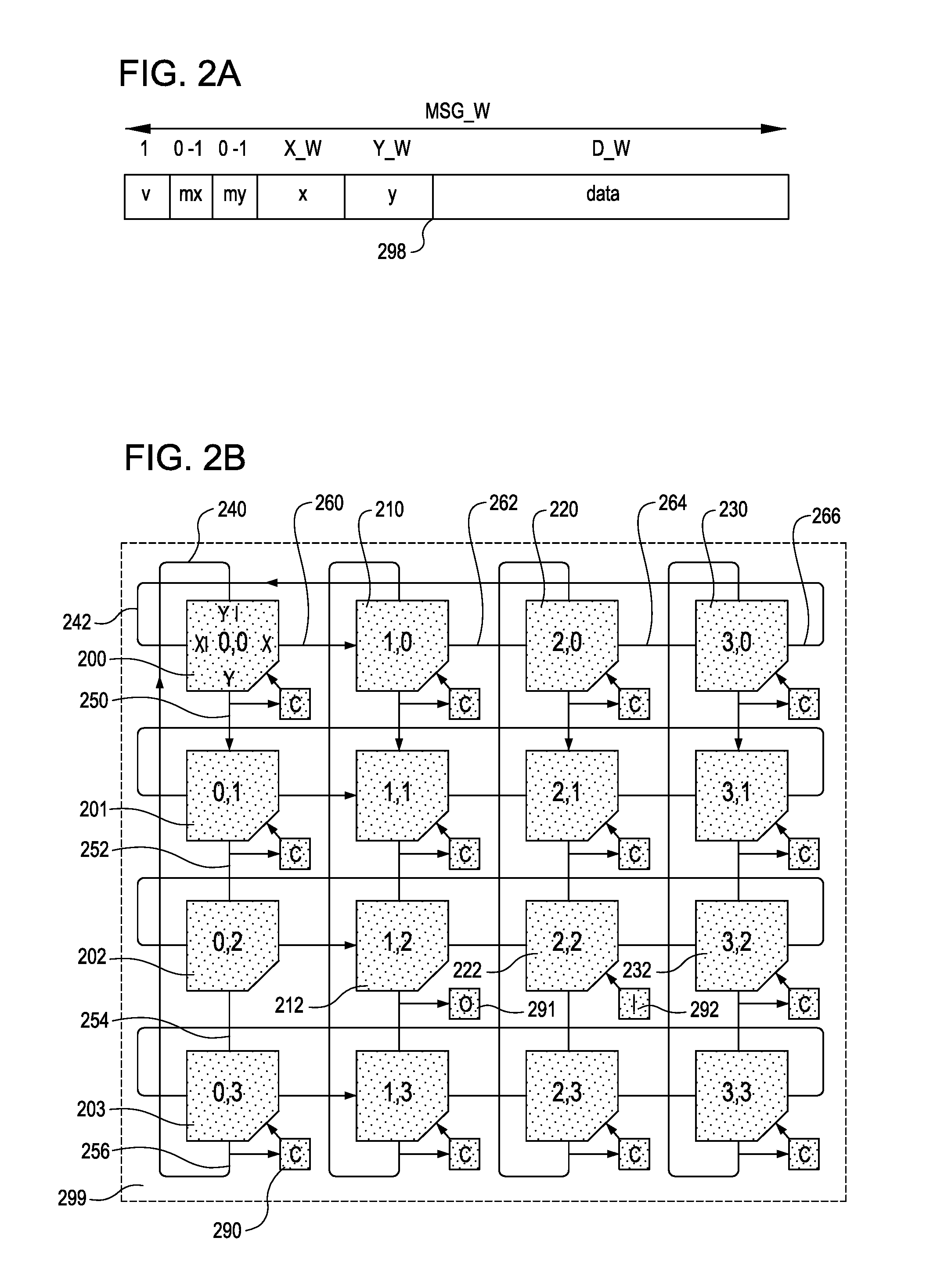
A configurable directional 2D router for Networks on Chips (NOCs) is disclosed. The router, which may be bufferless, is designed for implementation in programmable logic in FPGAs, and achieves theoretical lower bounds on FPGA resource consumption for various applications. The router employs an FPGA router switch design that consumes only one 6-LUT or 8-input ALM logic cell per router per bit of router link width. A NOC comprising a plurality of routers may be configured as a directional 2D torus, or in diverse ways, network sizes and topologies, data widths, routing functions, performance-energy tradeoffs, and other options. System on chip designs may employ a plurality of NOCs with different configuration parameters to customize the system to the application or workload characteristics. A great diversity of NOC client cores, for communication amongst various external interfaces and devices, and on-chip interfaces and resources, may be coupled to a router in order to efficiently communicate with other NOC client cores. The router and NOC enable feasible FPGA implementation of large integrated systems on chips, interconnecting hundreds of client cores over high bandwidth links, including compute and accelerator cores, industry standard IP cores, DRAM / HBM / HMC channels, PCI Express channels, and 10G / 25G / 40G / 100G / 400G networks.
Owner:GRAY RES LLC
Globally asynchronous communication architecture for system on chip
InactiveUS20060209846A1Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsAsynchronous communicationNetworks on chip
This invention relates to the domain of Networks on Chips (NoC) and relates to a method of transferring data in a network on chip, particularly using an asynchronous “send / accept” type protocol. The invention also relates to a network on chip used to implement this method.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Field Programmable Gate-Array with Embedded Network-on-Chip Hardware and Design Flow
InactiveUS20150109024A1Raise the level of abstractionDesign integration of large systems simpler and more automatedProgrammable logic circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesComputer moduleNetworks on chip
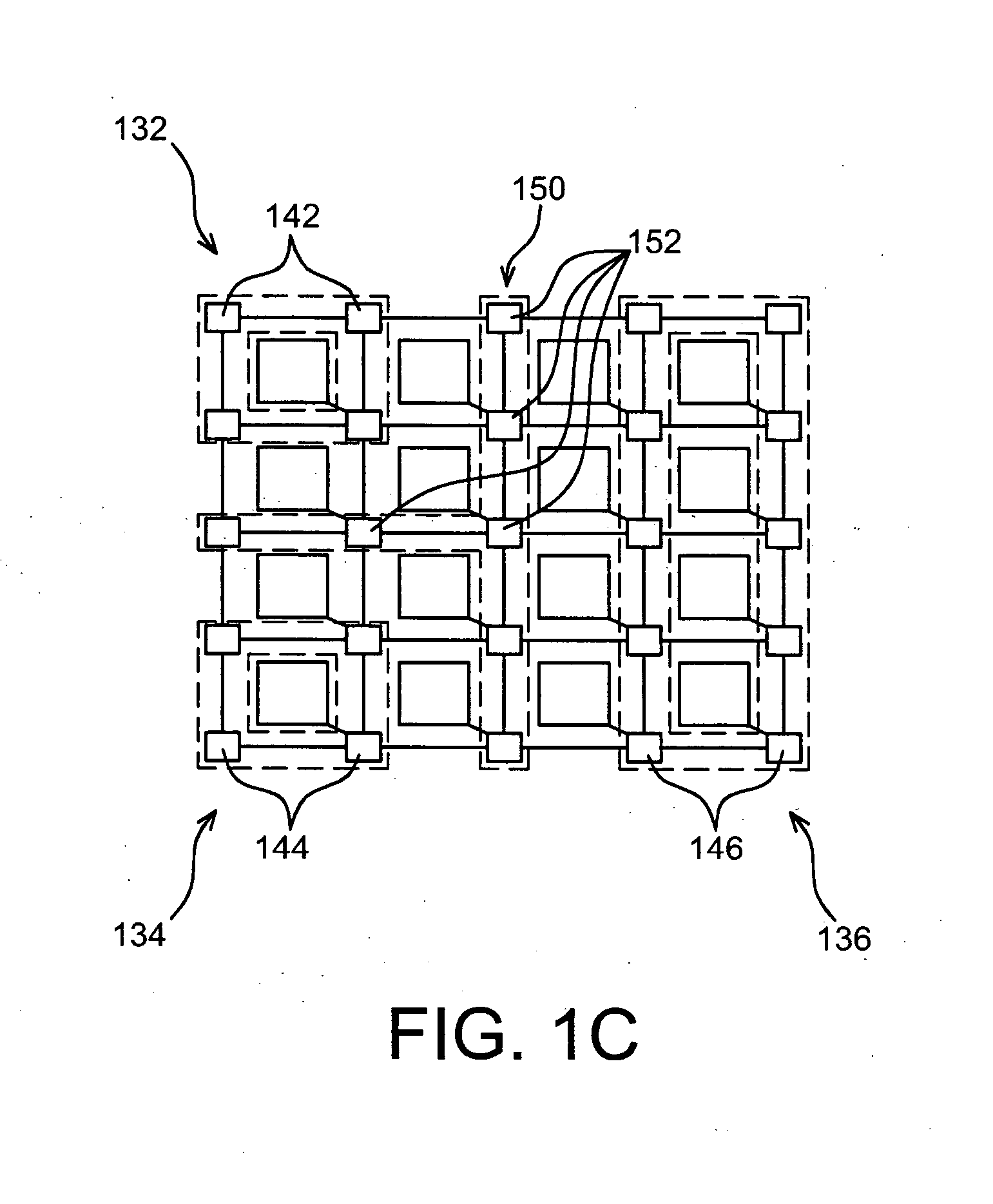
An enhanced field programmable gate-array (FPGA) incorporates one or more programmable networks-on-chip (NoCs) or NoC components integrated within the FPGA fabric. This NoC interconnect augments the existing FPGA interconnect. In one embodiment, the NoC is used as system-level interconnect to connect compute and communication modules to one another and integrate large systems on the FPGA. The NoC components include a “fabric port”, which is a configurable interface that bridges both data width and frequency between the embedded NoC routers and the FPGA fabric components such as logic blocks, block memory, multipliers, processors or I / Os. Finally, the FPGA design flow is modified to target the embedded NoC components either manually through designer intervention, or automatically.
Owner:VAUGHN TIMOTHY BETZ +1
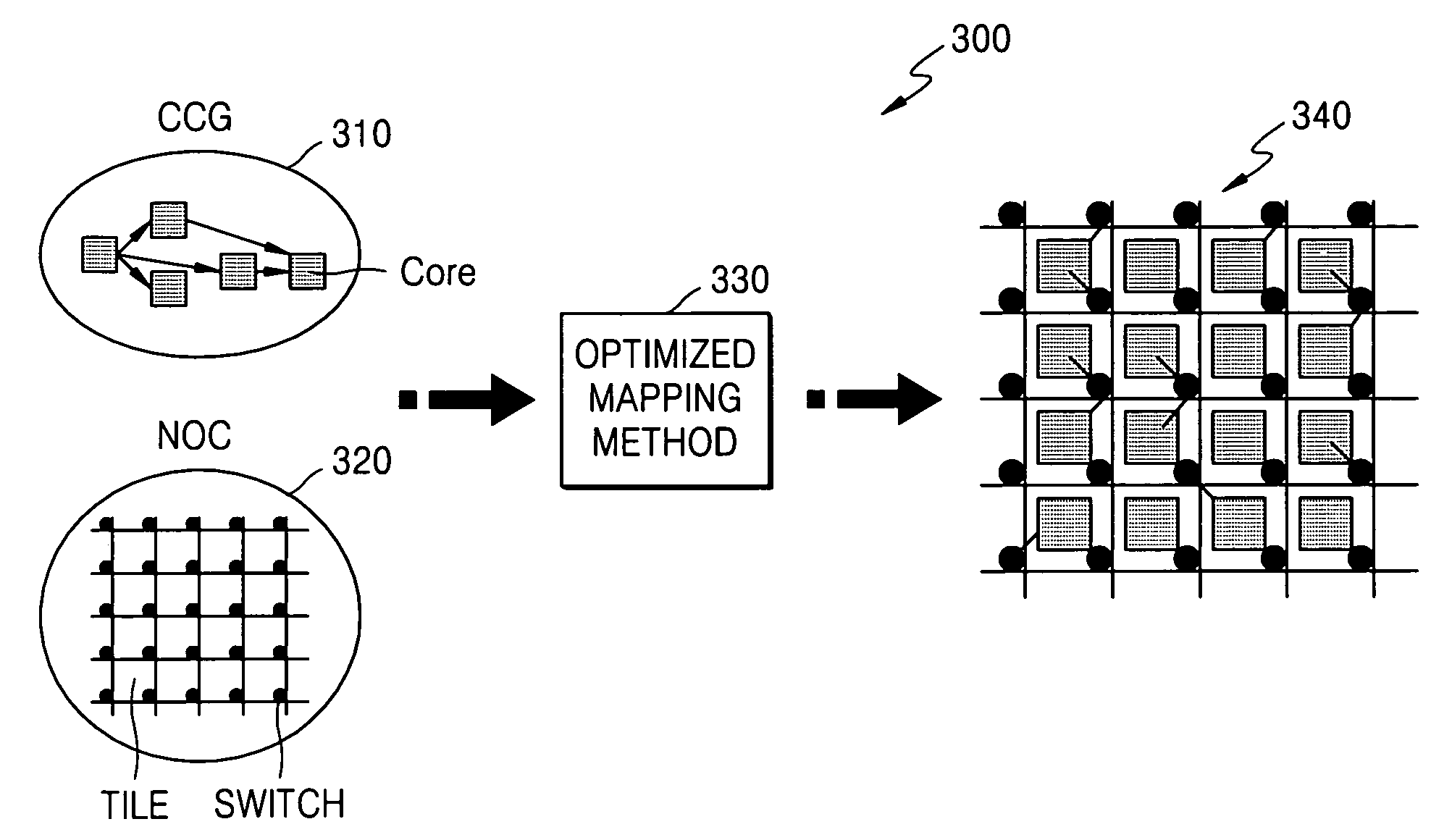
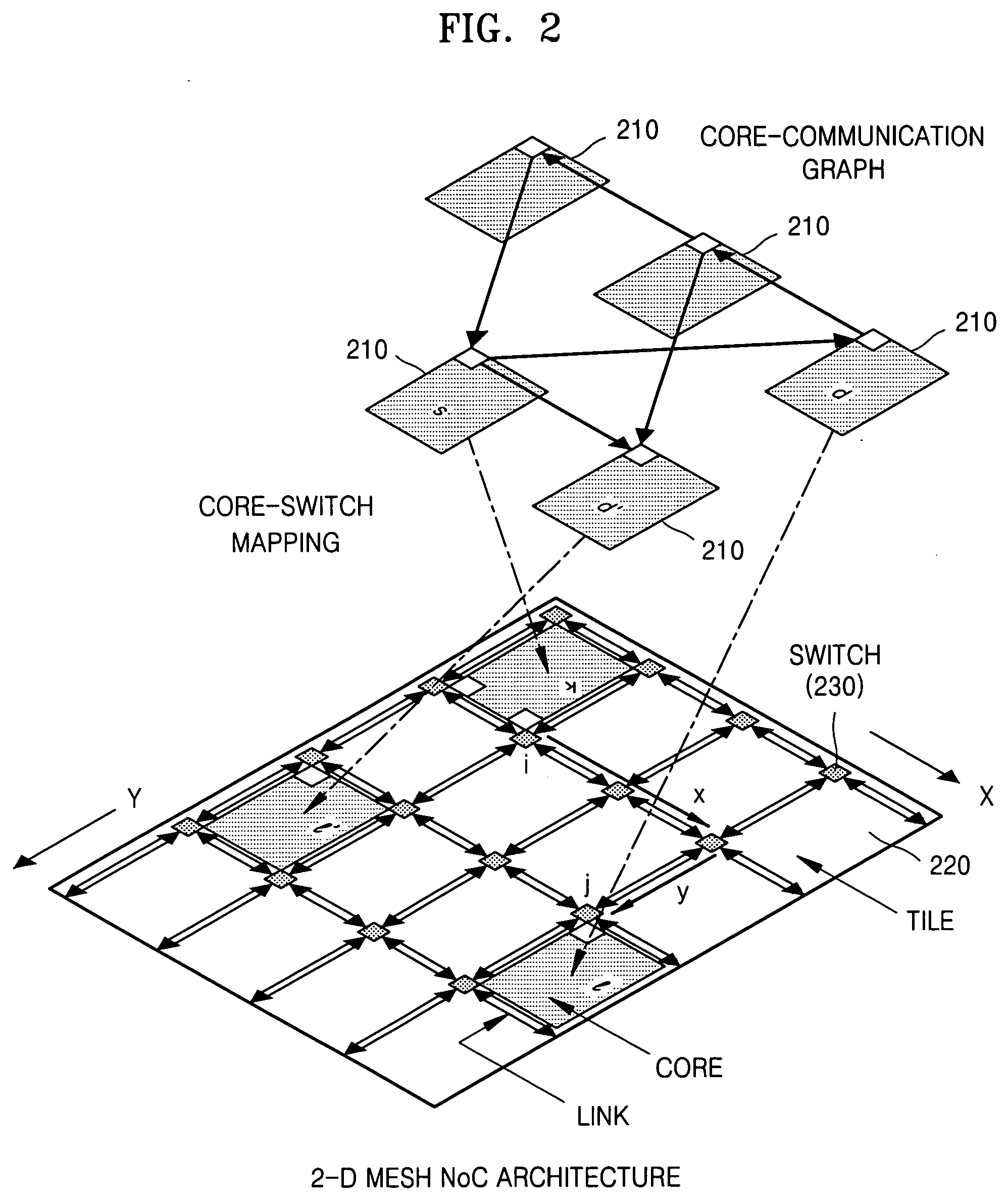
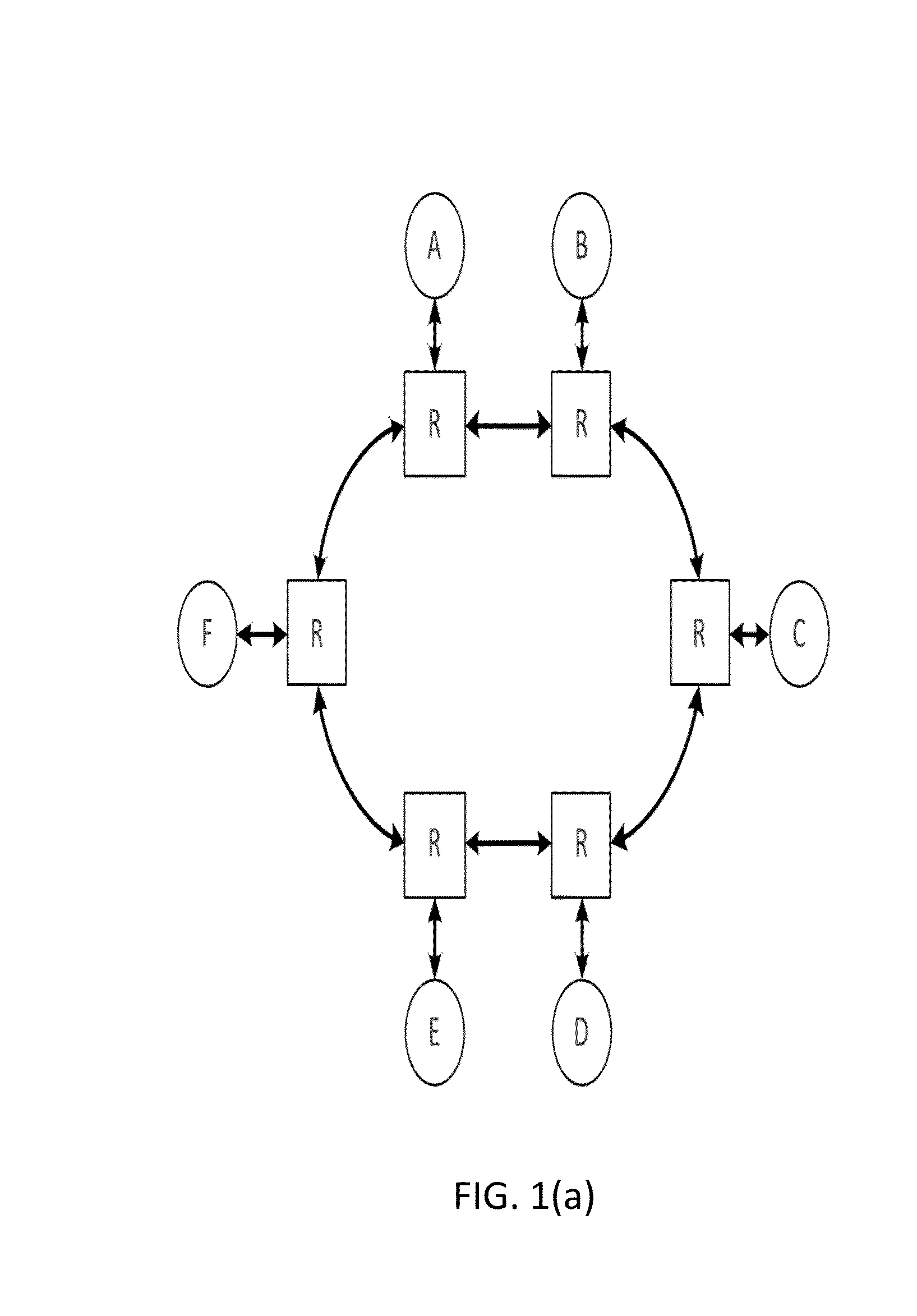
Method of creating core-tile-switch mapping architecture in on-chip bus and computer-readable medium for recording the method
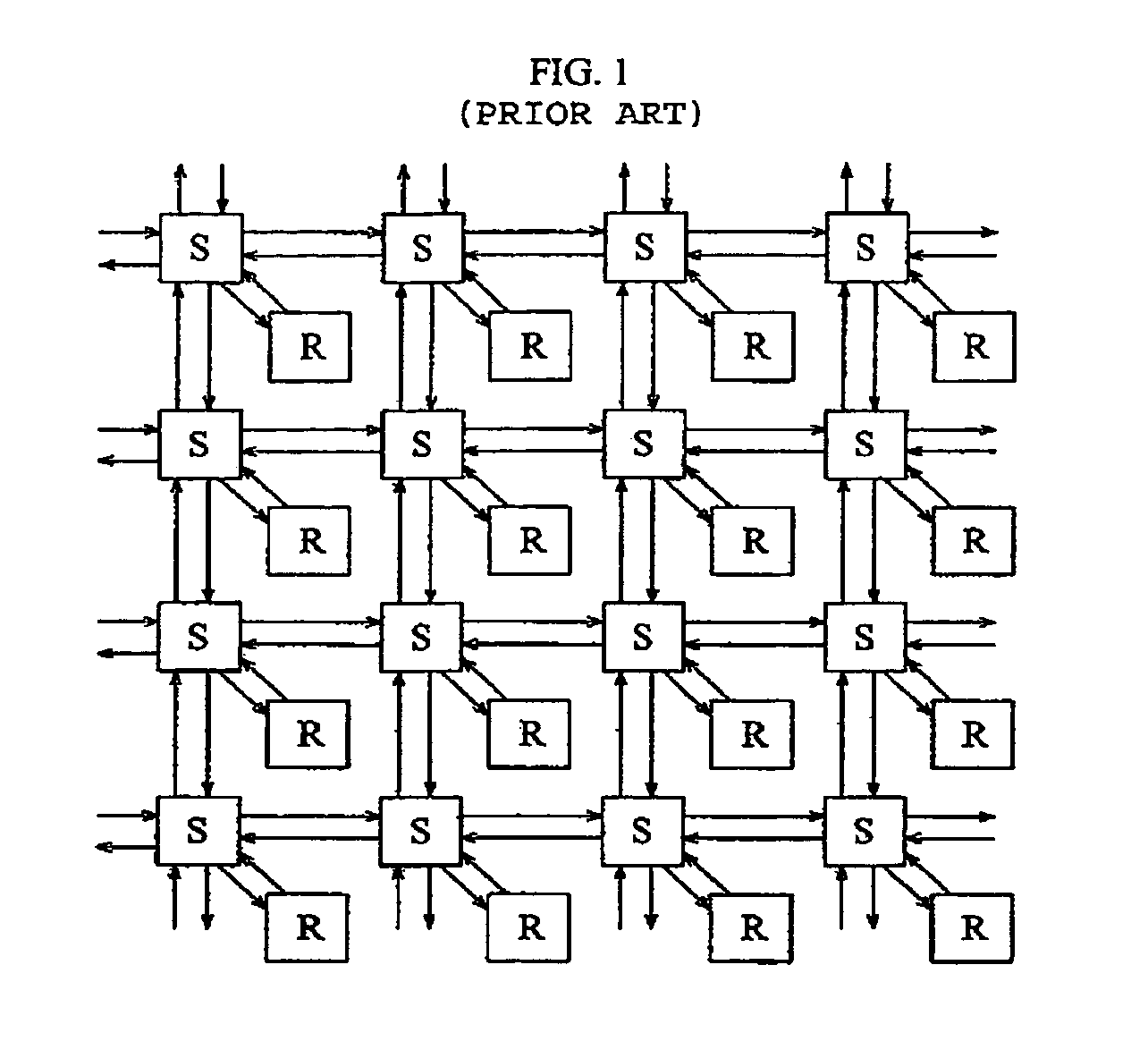
There are provided a method of creating an optimized core-tile-switch mapping architecture in an on-chip bus and a computer-readable recording medium for recording the method. The core-tile-switch mapping architecture creating method includes: creating a core communication graph representing the connection relationship between arbitrary cores; creating a Network-on-chip (NOC) architecture including a plurality of switches, a plurality of tiles, and a plurality of links interconnecting the plurality of switches; and mapping the cores to the tiles using a predetermined optimized mapping method to thereby create the optimized core-tile-switch mapping architecture. The optimized mapping method includes first, second, and third calculating steps. According to the optimized core-tile-switch mapping architecture creating method and the computer-readable recording medium for recording the method, since the hop distance between cores is minimized, it is possible to minimize energy consumption and communication delay time in an on-chip bus. Furthermore, the optimized mapping architecture presents a standard for comparing the optimization of other mapping architectures.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method to design network-on-chip (NOC) - based communication systems
ActiveUS20090313592A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemEngineering
A method to design a Networks on Chips (NoCs)-based communication system for connecting on-chip components in a multicore system, said system comprising several elements communicating through the communication system, said communication system comprising at least switches, said method comprising the steps of modelling the applications running on the multicore system, establishing the number and configuration of switches to connect the elements, establishing physical connectivity between the elements and the switches, for each two pairs of communicating elements: (a) a defining a communication path, (b) calculating metrics as affected by the need to render said path into physical connectivity, taking into account any previously defined physical connectivity, (c) iterating the steps a and b for a plurality of possible paths, (d) choosing the path having the optimal metrics, and (e) establishing any missing physical connectivity between the switches so that the selected optimal path occurs across physically connected switches.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
On chip network
InactiveUS20040017820A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationExchange networkProcessing element
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Network On Chip With Partitions
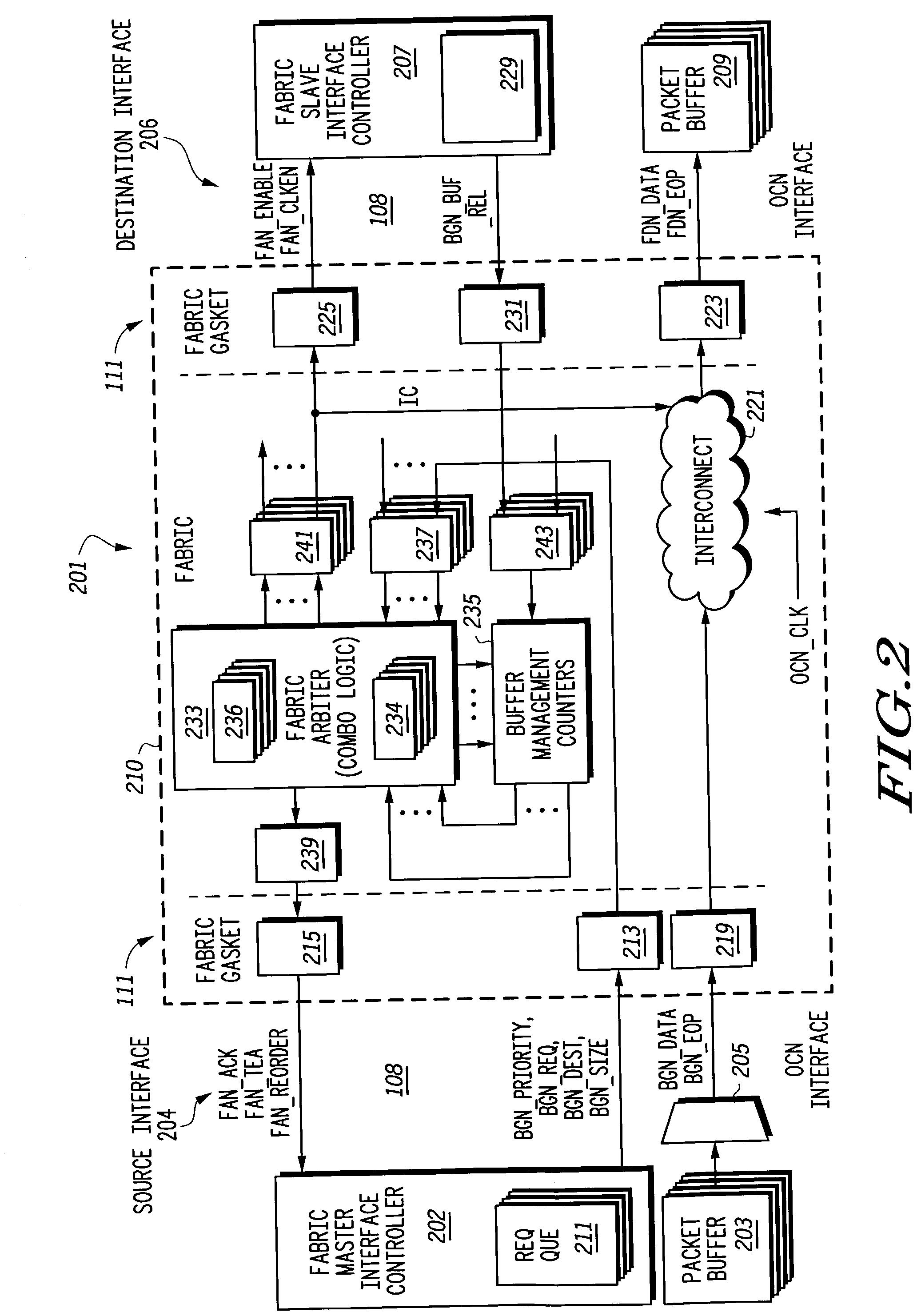
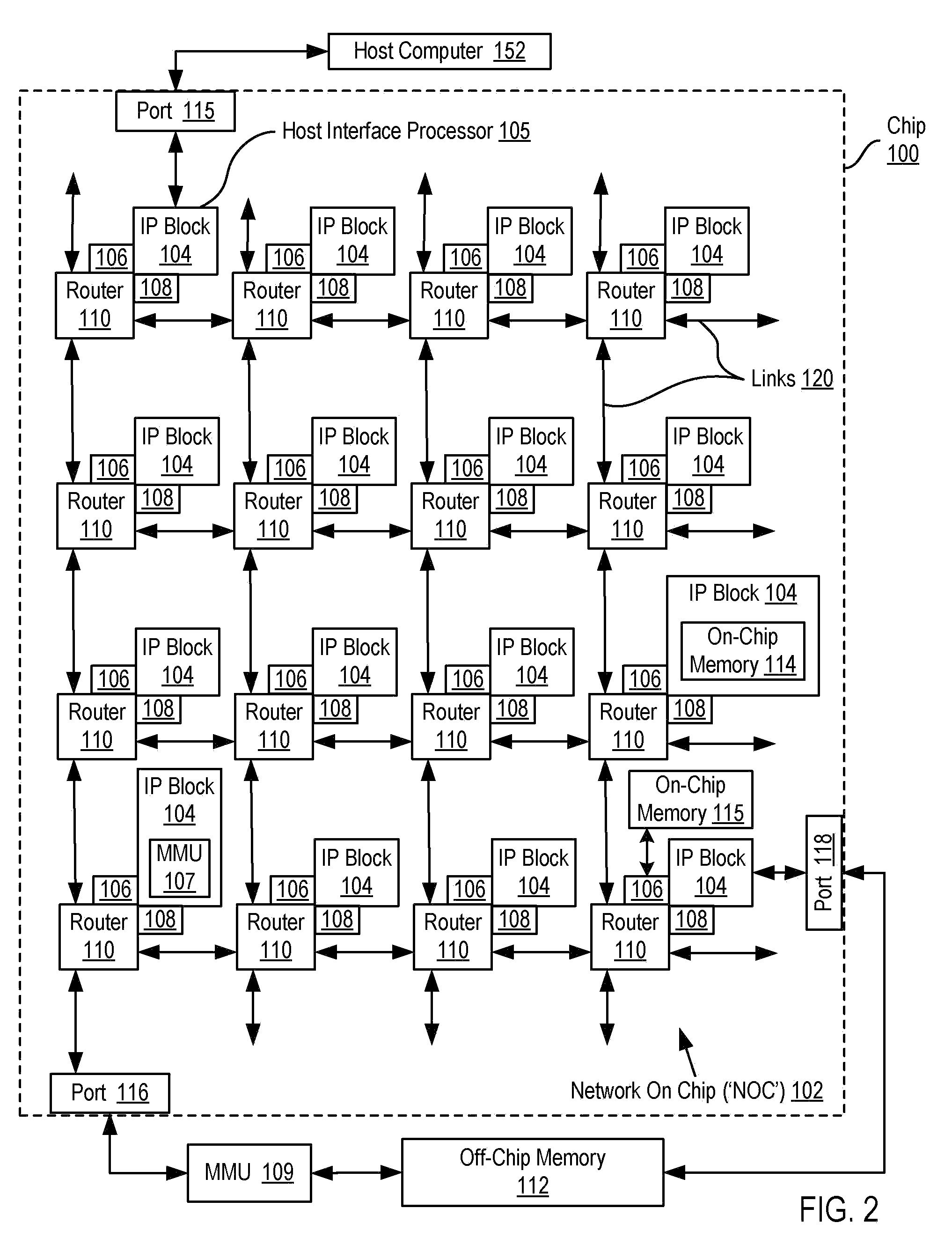
InactiveUS20090135739A1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationMemory addressParallel computing
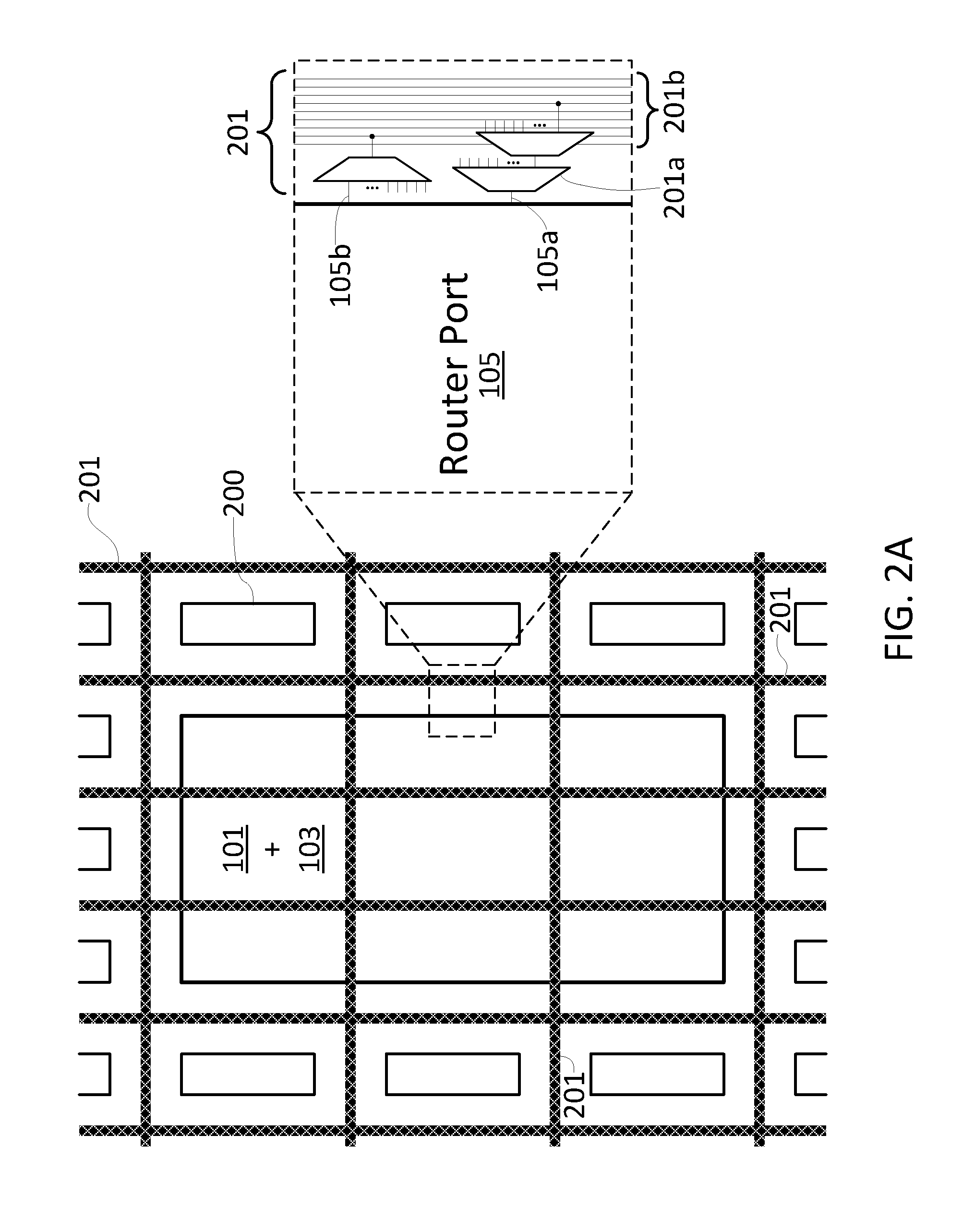
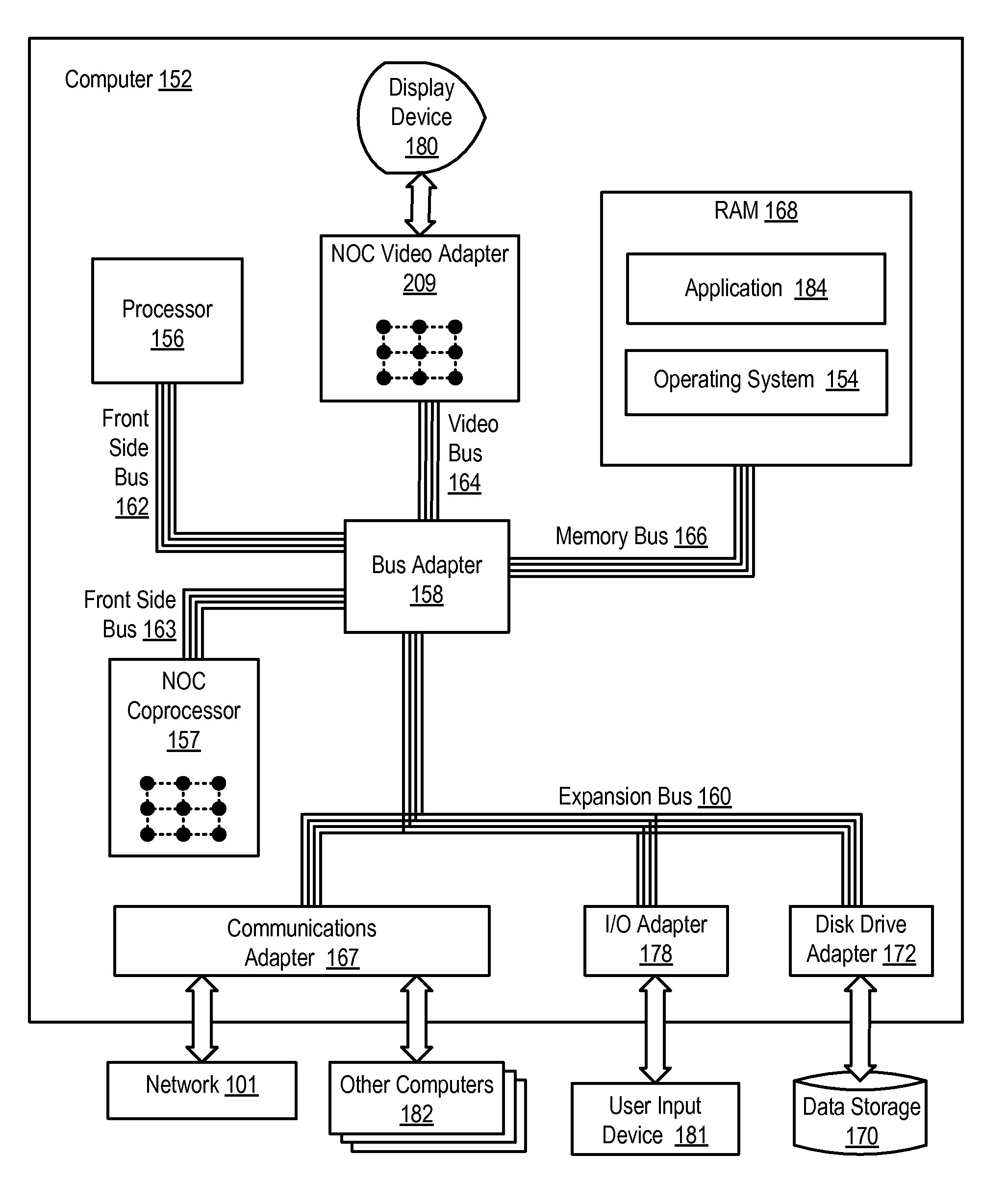
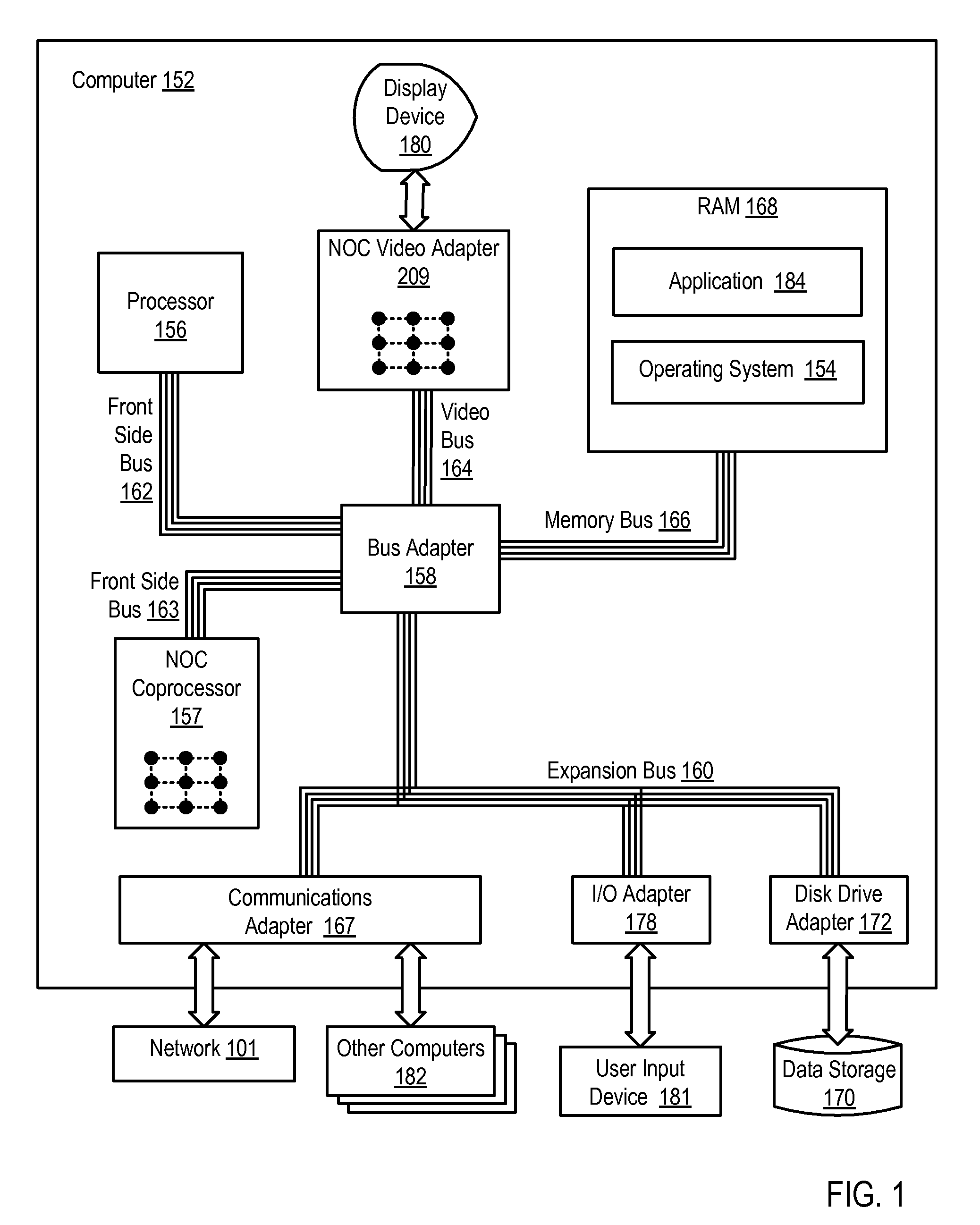
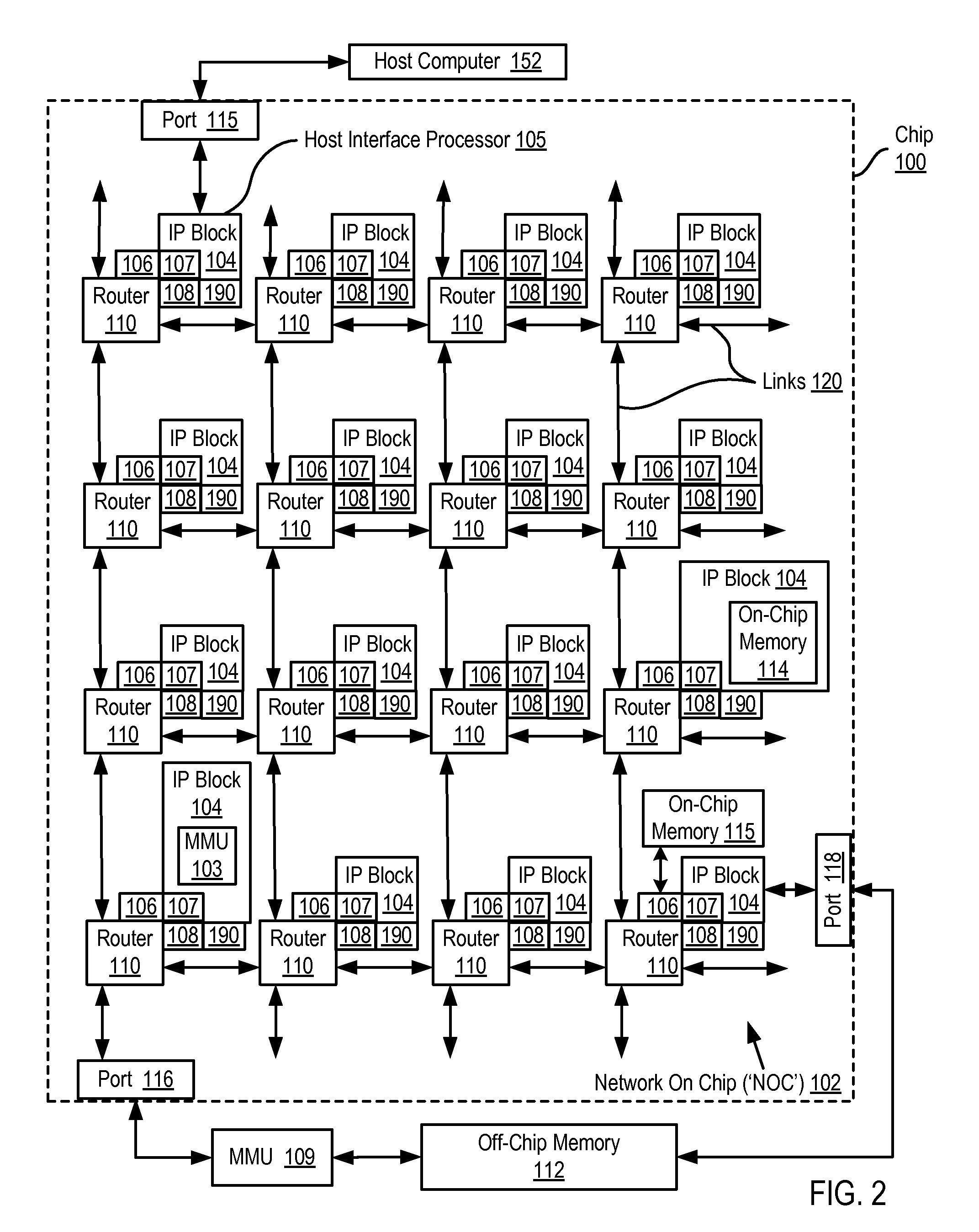
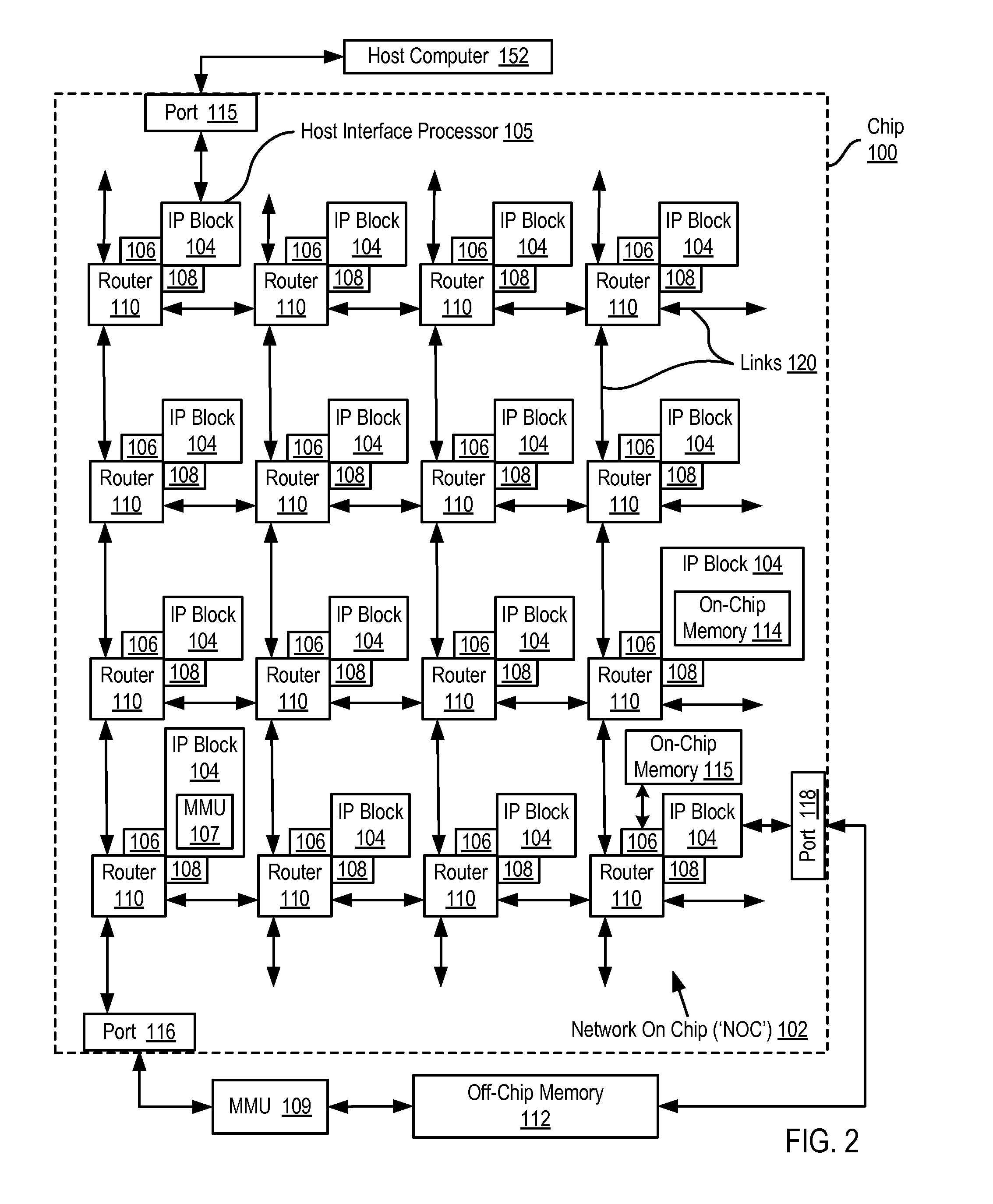
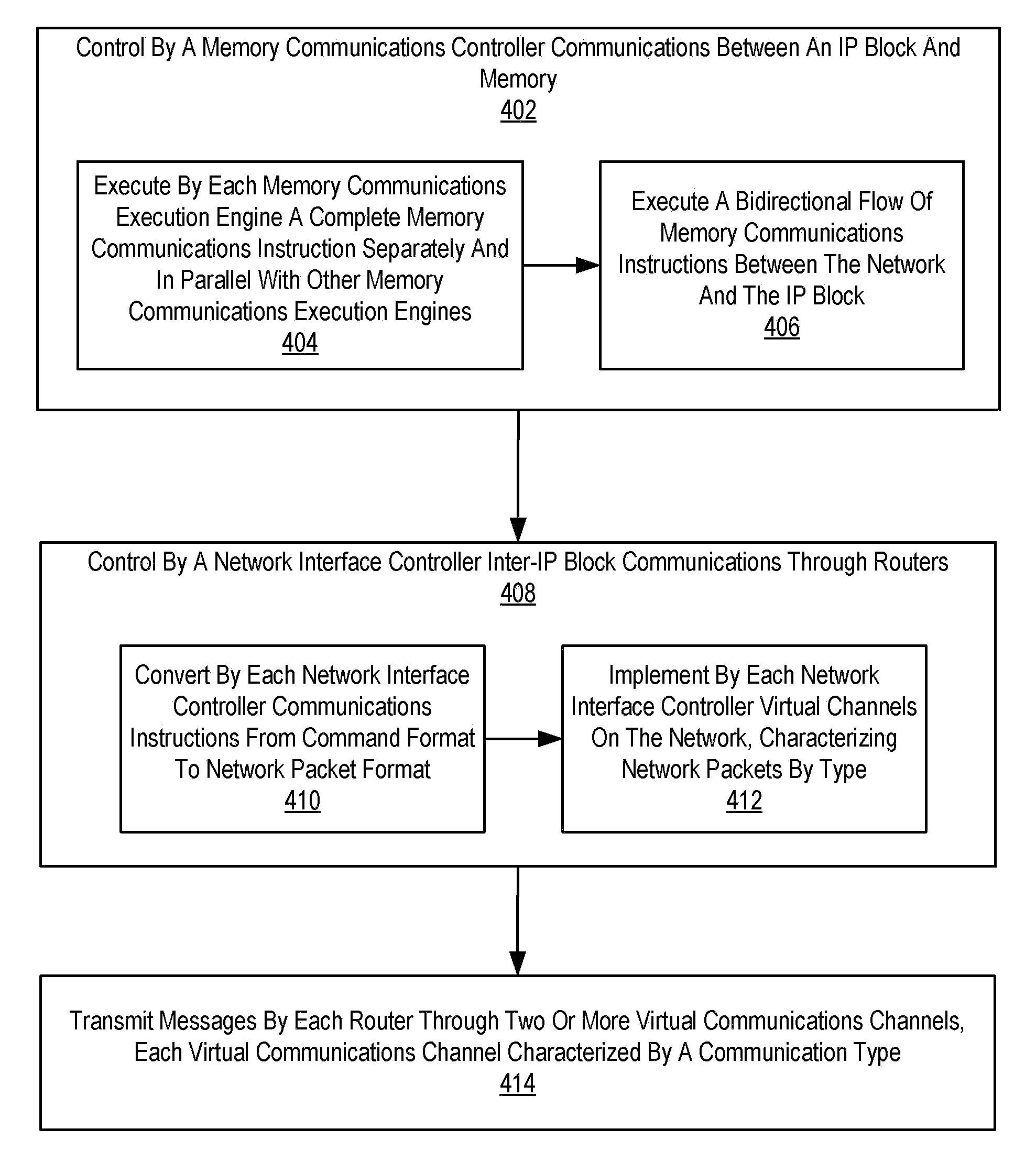
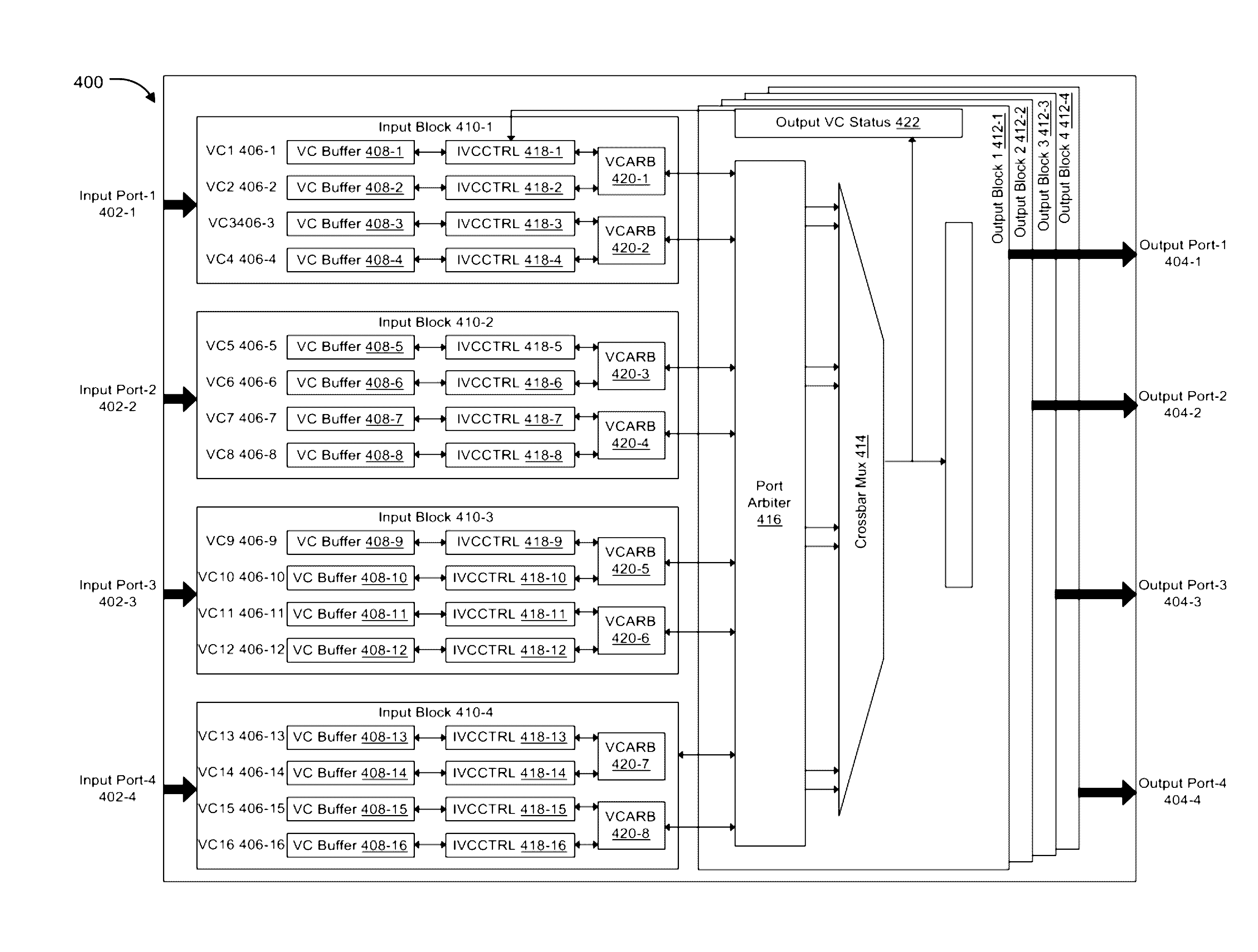
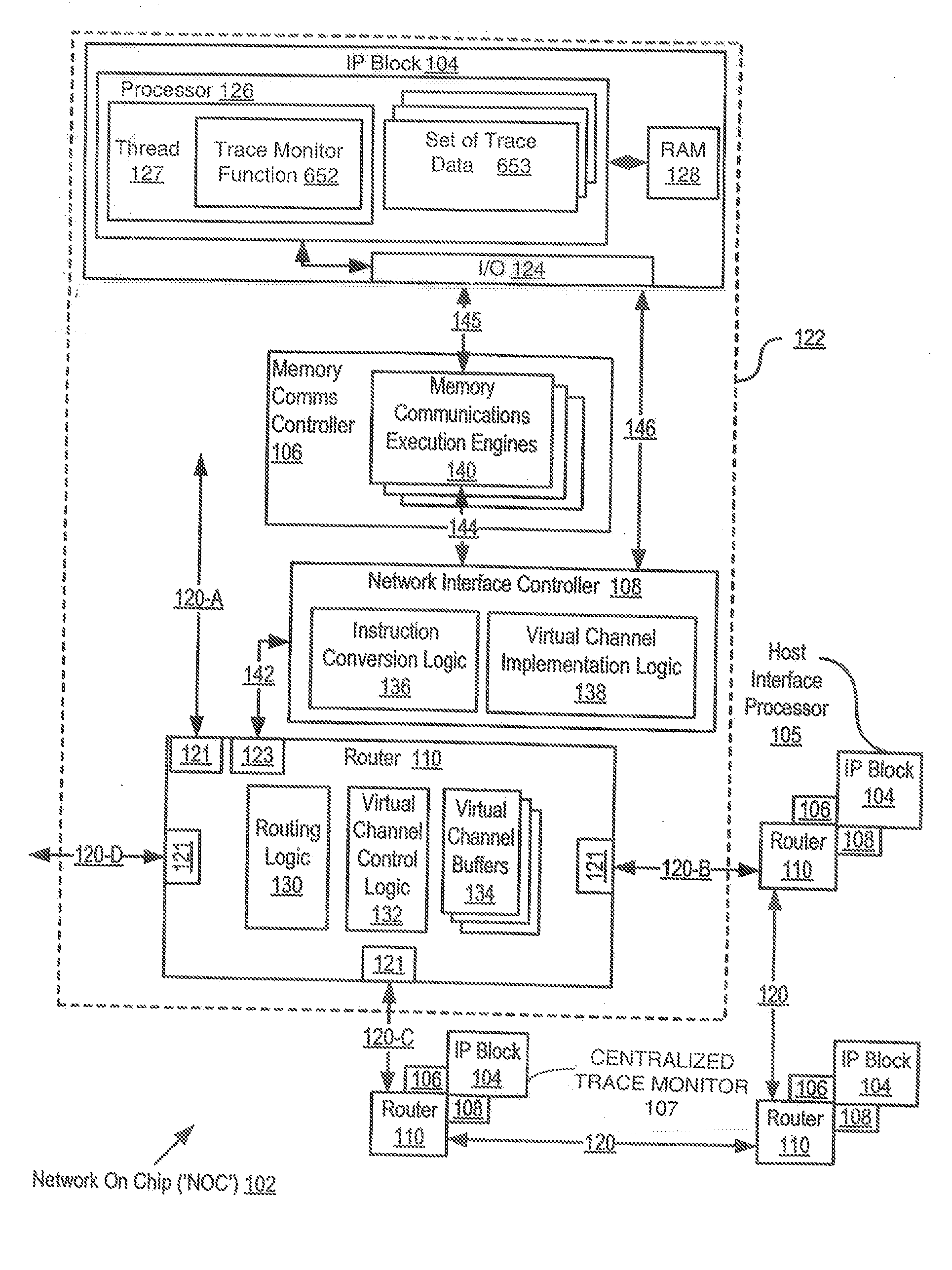
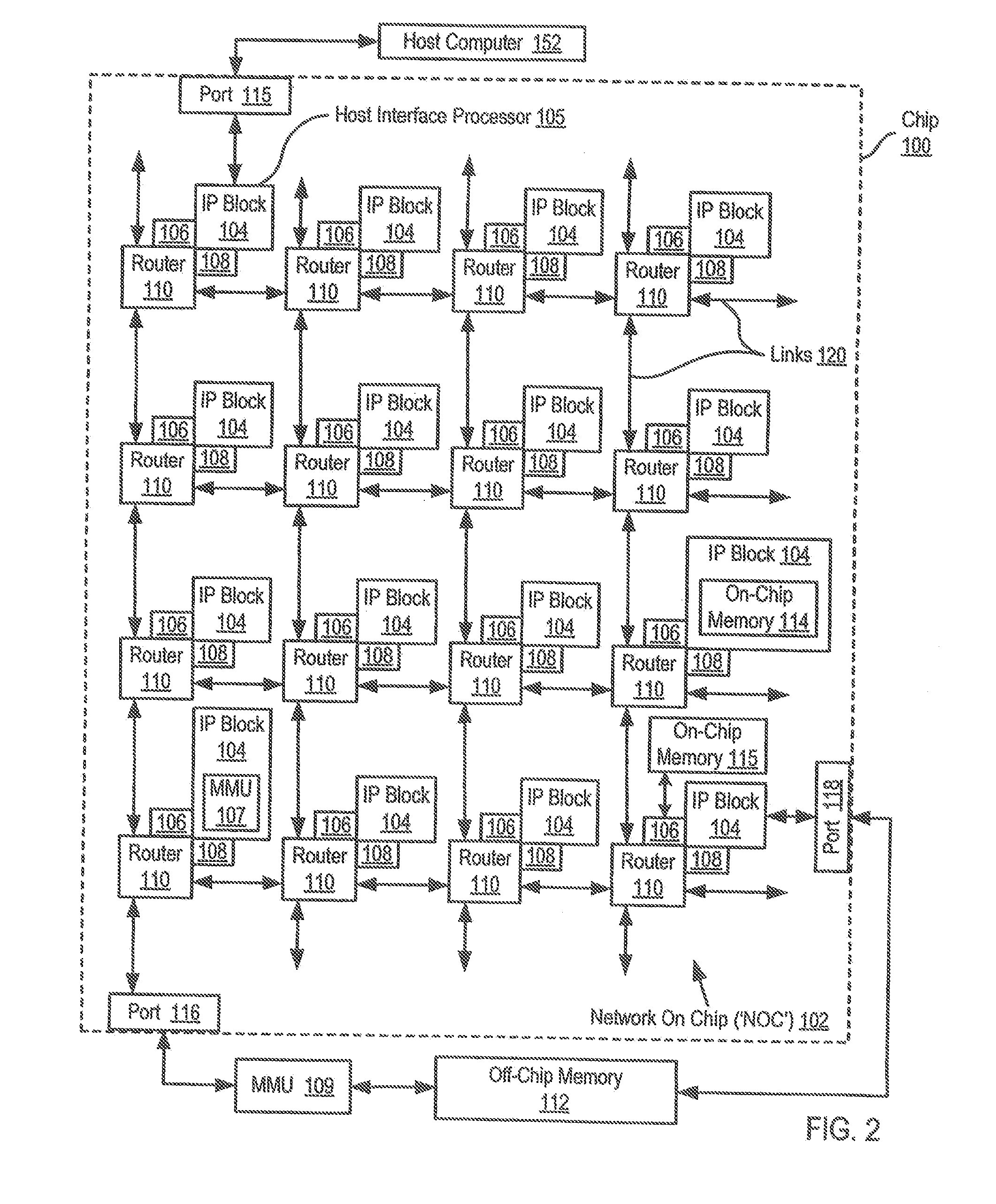
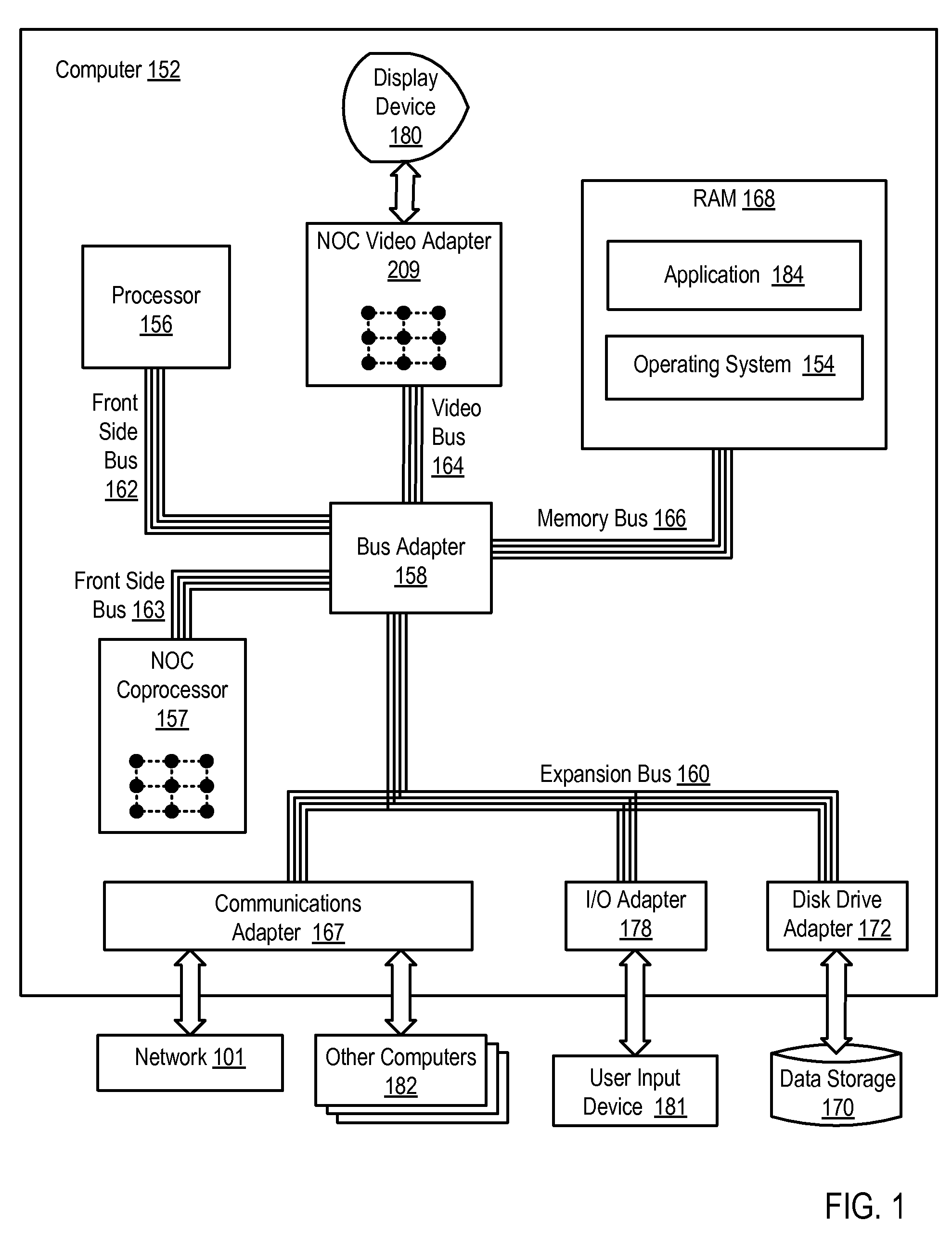
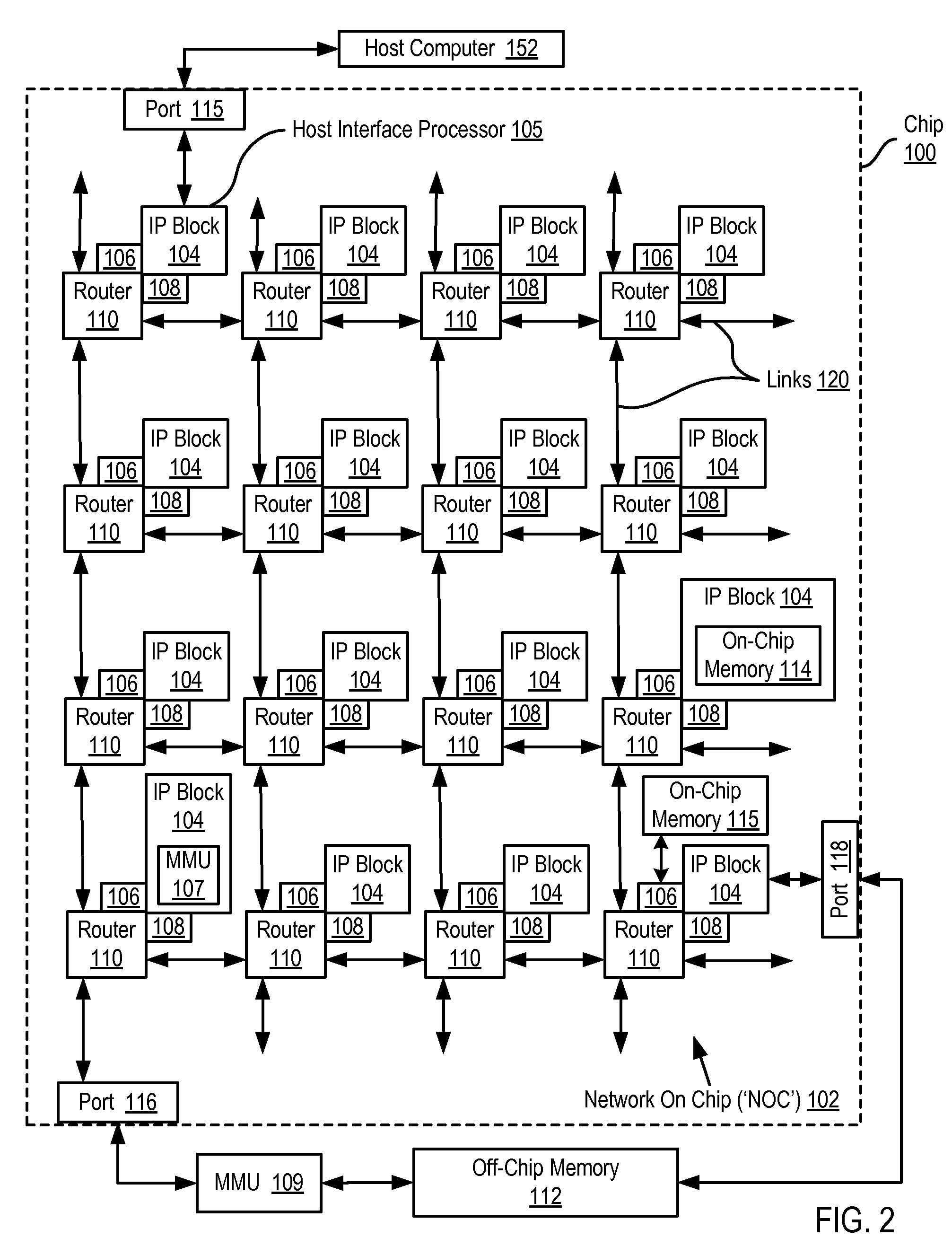
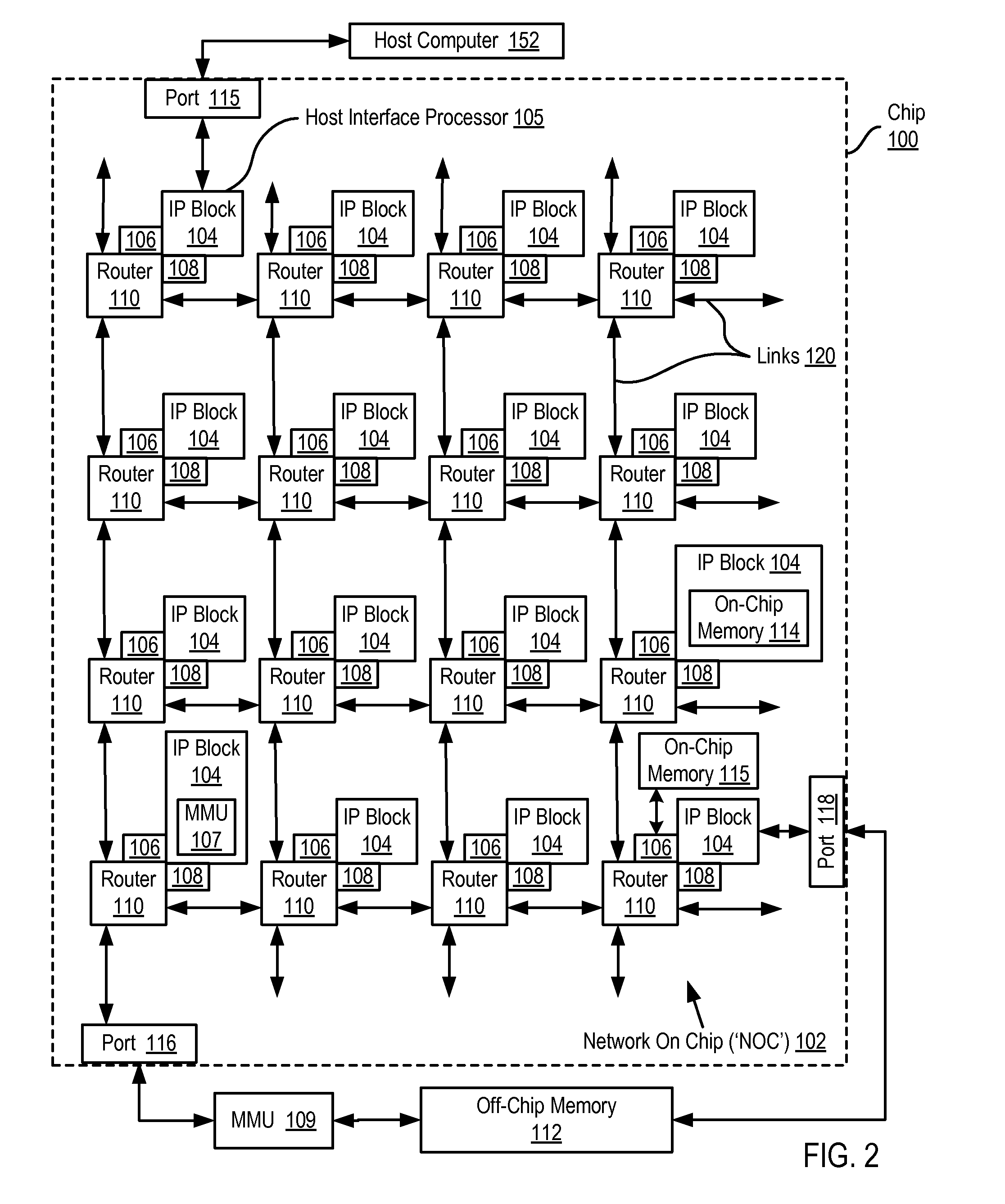
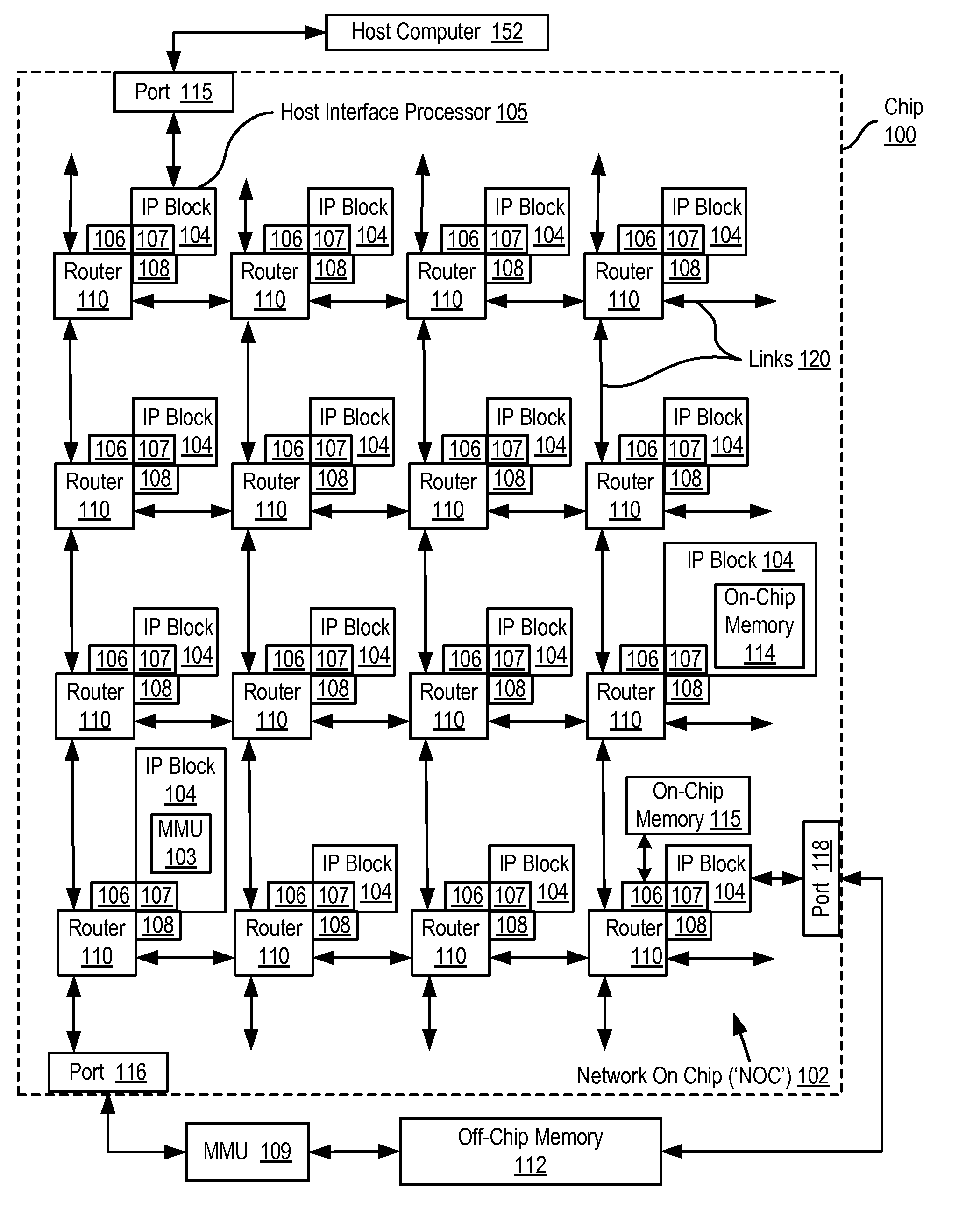
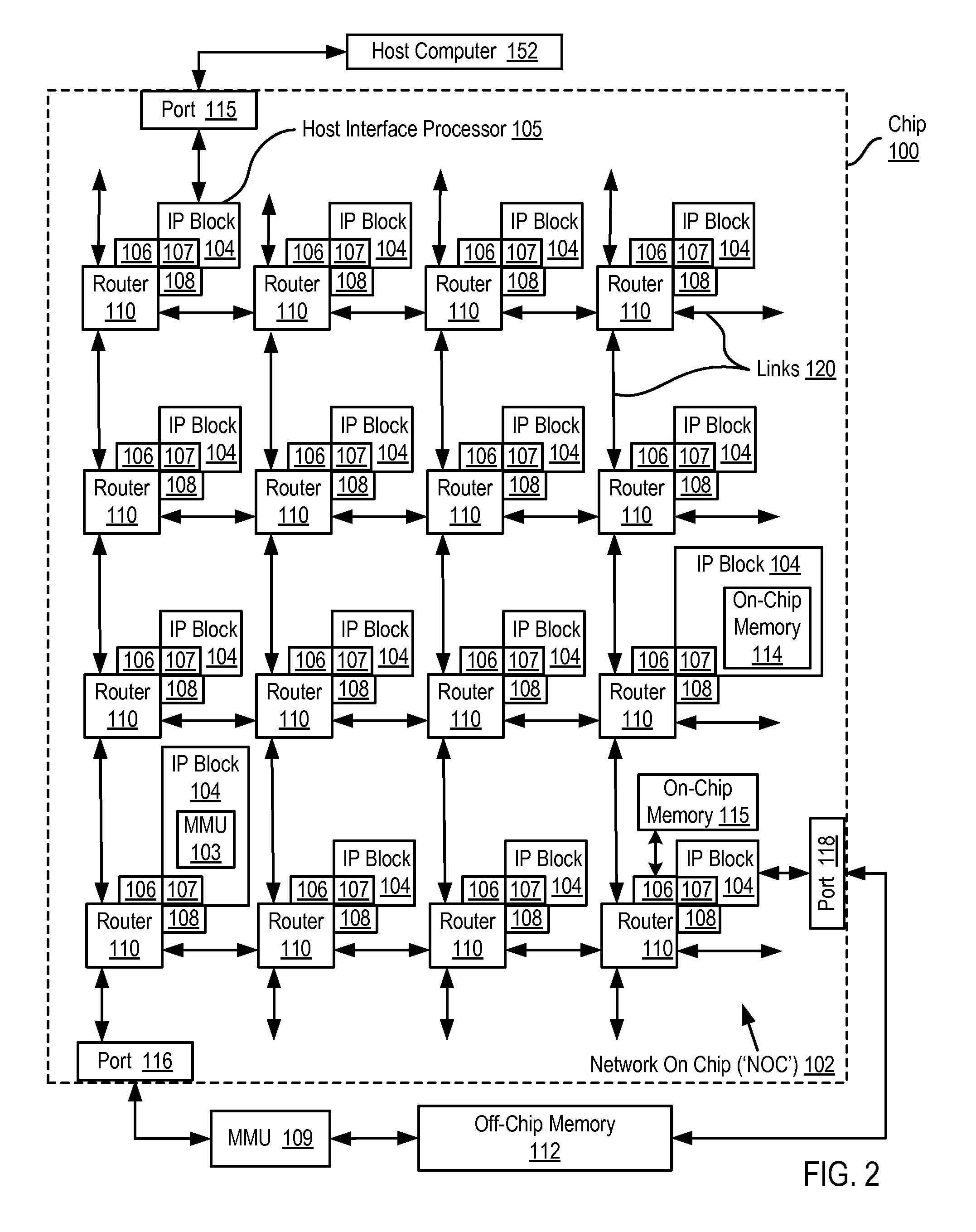
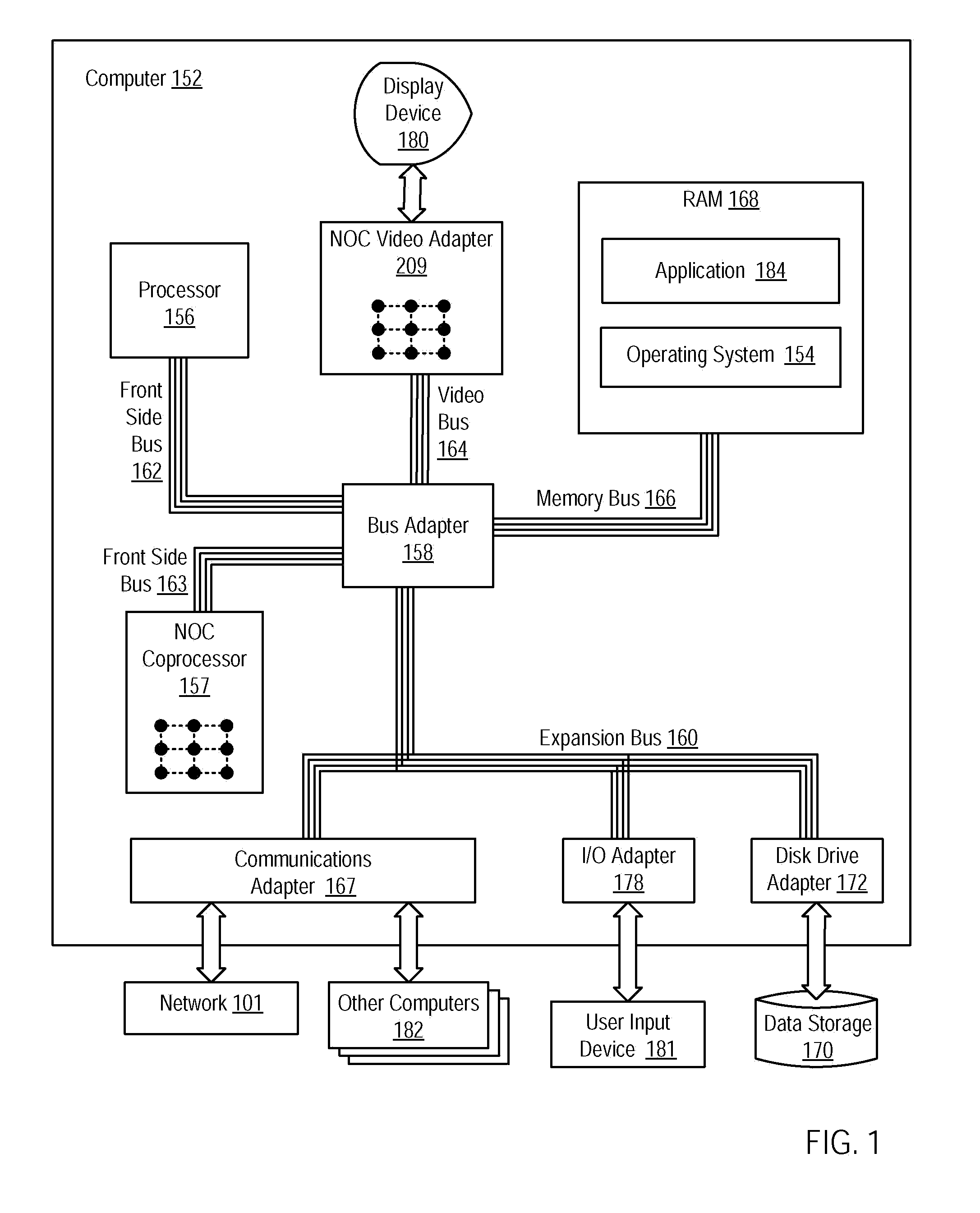
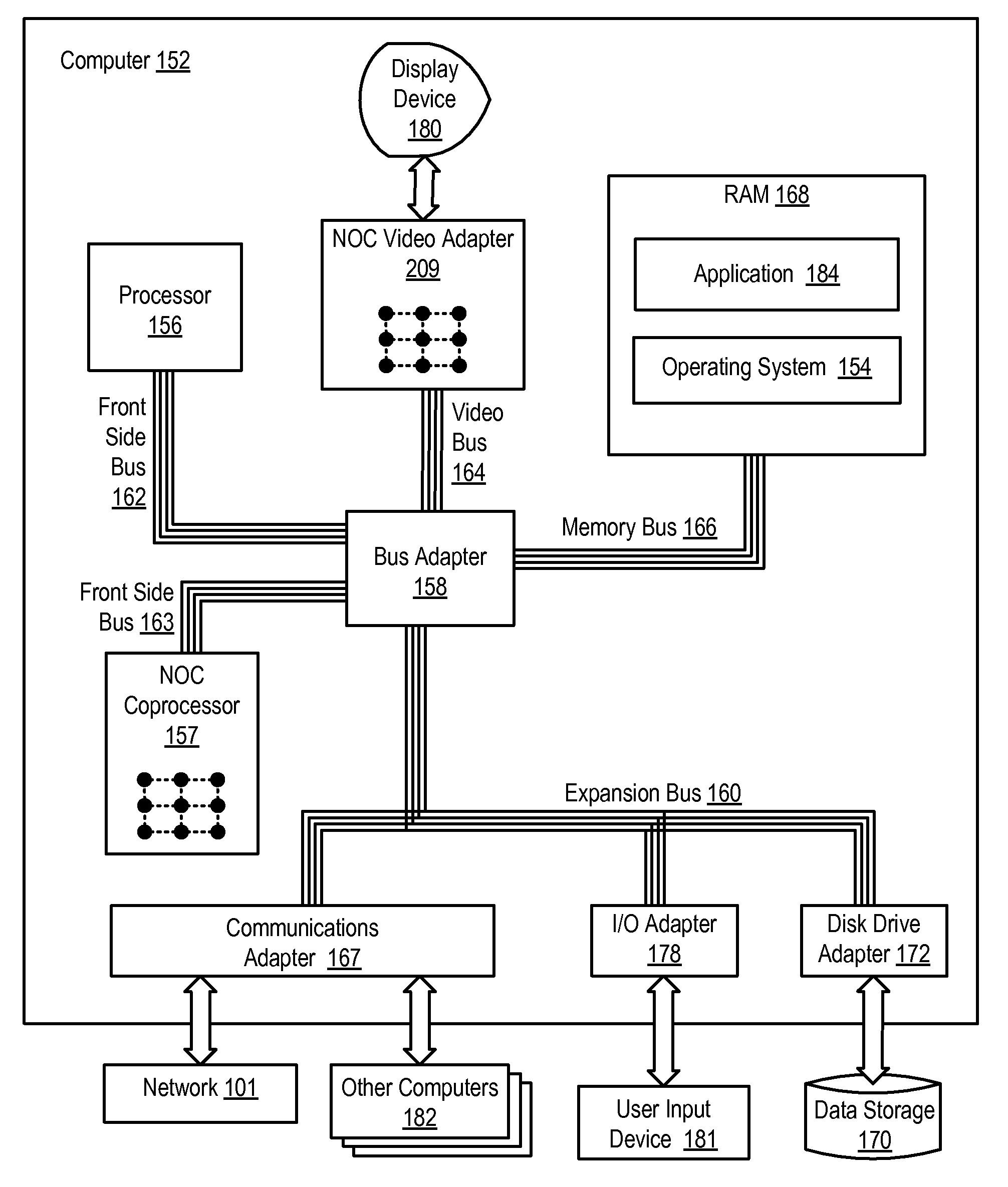
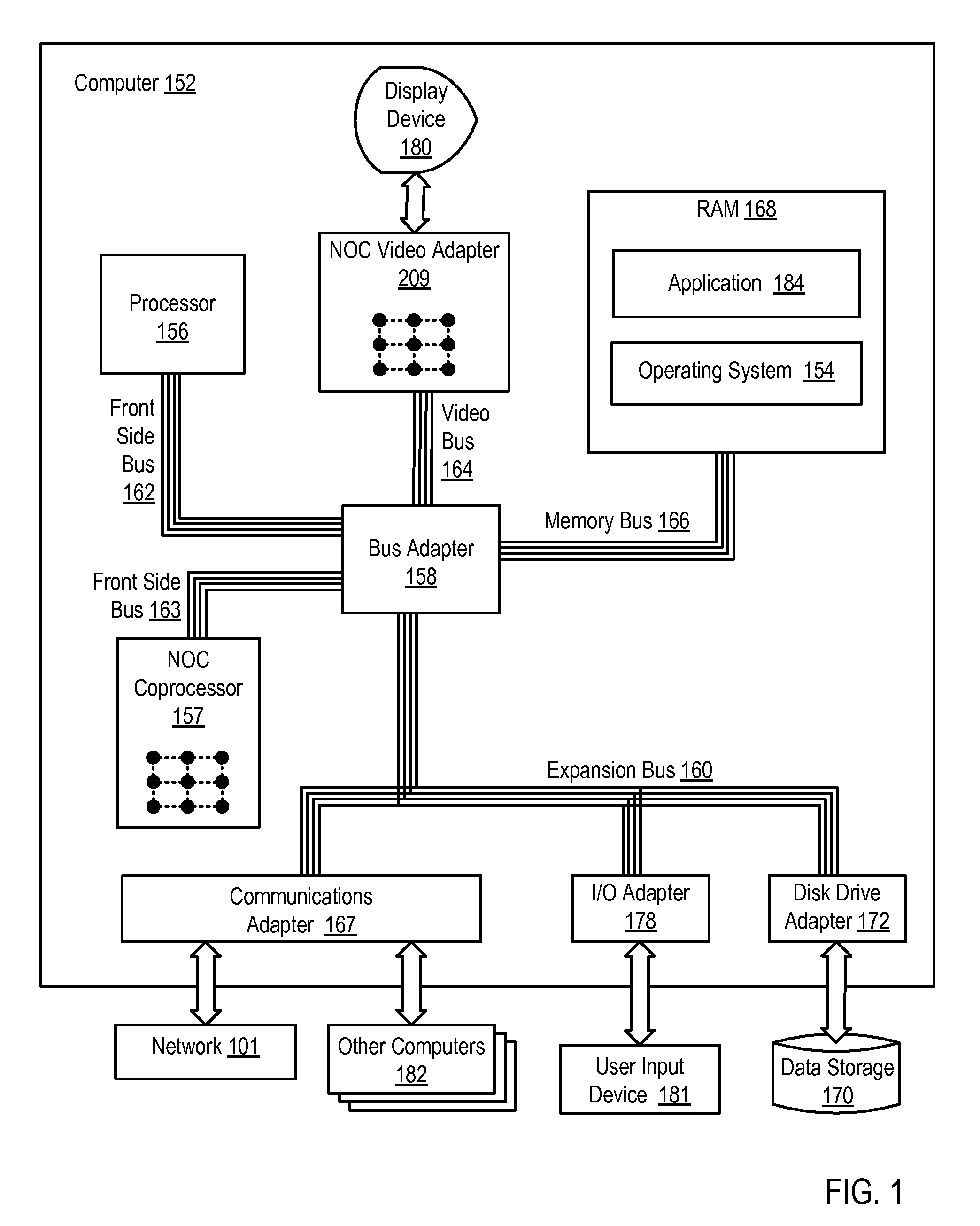
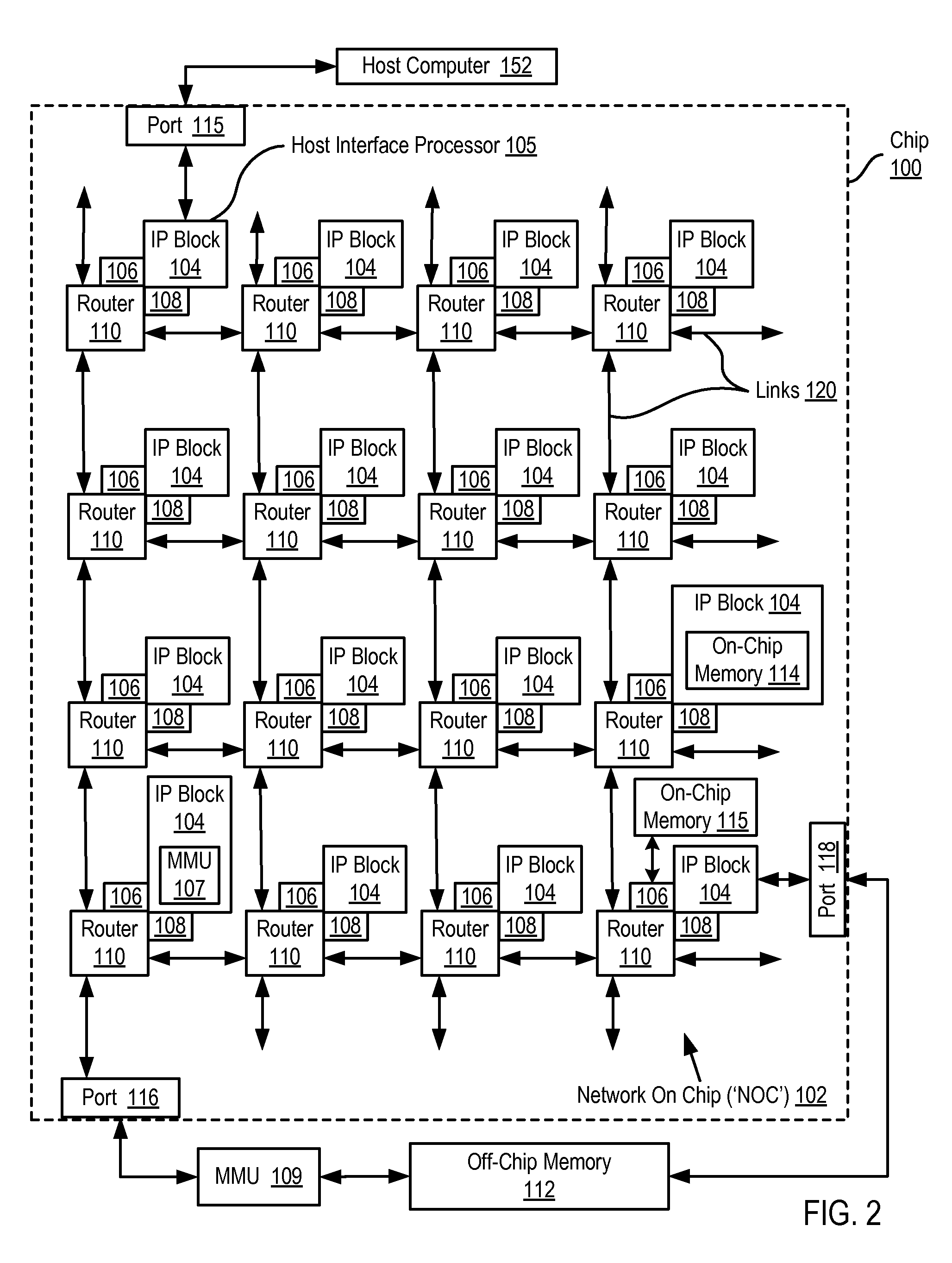
A network on chip (‘NOC’) that includes integrated processor (‘IP’) blocks, routers, memory communications controllers, and network interface controllers, with each IP block adapted to a router through a memory communications controller and a network interface controller, where each memory communications controller controlling communications between an IP block and memory, and each network interface controller controlling inter-IP block communications through routers, with the network organized into partitions, each partition including at least one IP block, each partition assigned exclusive access to a separate physical memory address space and one or more applications executing on one or more of the partitions.
Owner:IBM CORP
Ordered And Unordered Network-Addressed Message Control With Embedded DMA Commands For A Network On Chip
InactiveUS20090282419A1Lower latencyHigh bandwidthInterprogram communicationTransmissionHigh bandwidthLatency (engineering)
Data processing on a network on chip (‘NOC’) that includes integrated processor (‘IP’) blocks, routers, memory communications controllers, network interface controllers, and network-addressed message controllers, with each IP block adapted to a router through a memory communications controller, a network-addressed message controller, and a network interface controller, where each memory communications controller controlling communications between an IP block and memory, each network interface controller controlling inter-IP block communications through routers, with each IP block also adapted to the network by a low latency, high bandwidth application messaging interconnect comprising an inbox and an outbox.
Owner:IBM CORP
Automatic construction of deadlock free interconnects
Systems and methods for automatically building a deadlock free inter-communication network in a multi-core system are described. The example embodiments described herein involve deadlock detection during the mapping of user specified communication pattern amongst blocks of the system. Detected deadlocks are then avoided by re-allocation of channel resources. An example embodiment of the deadlock avoidance scheme is presented on Network-on-chip interconnects for large scale multi-core system-on-chips.
Owner:INTEL CORP
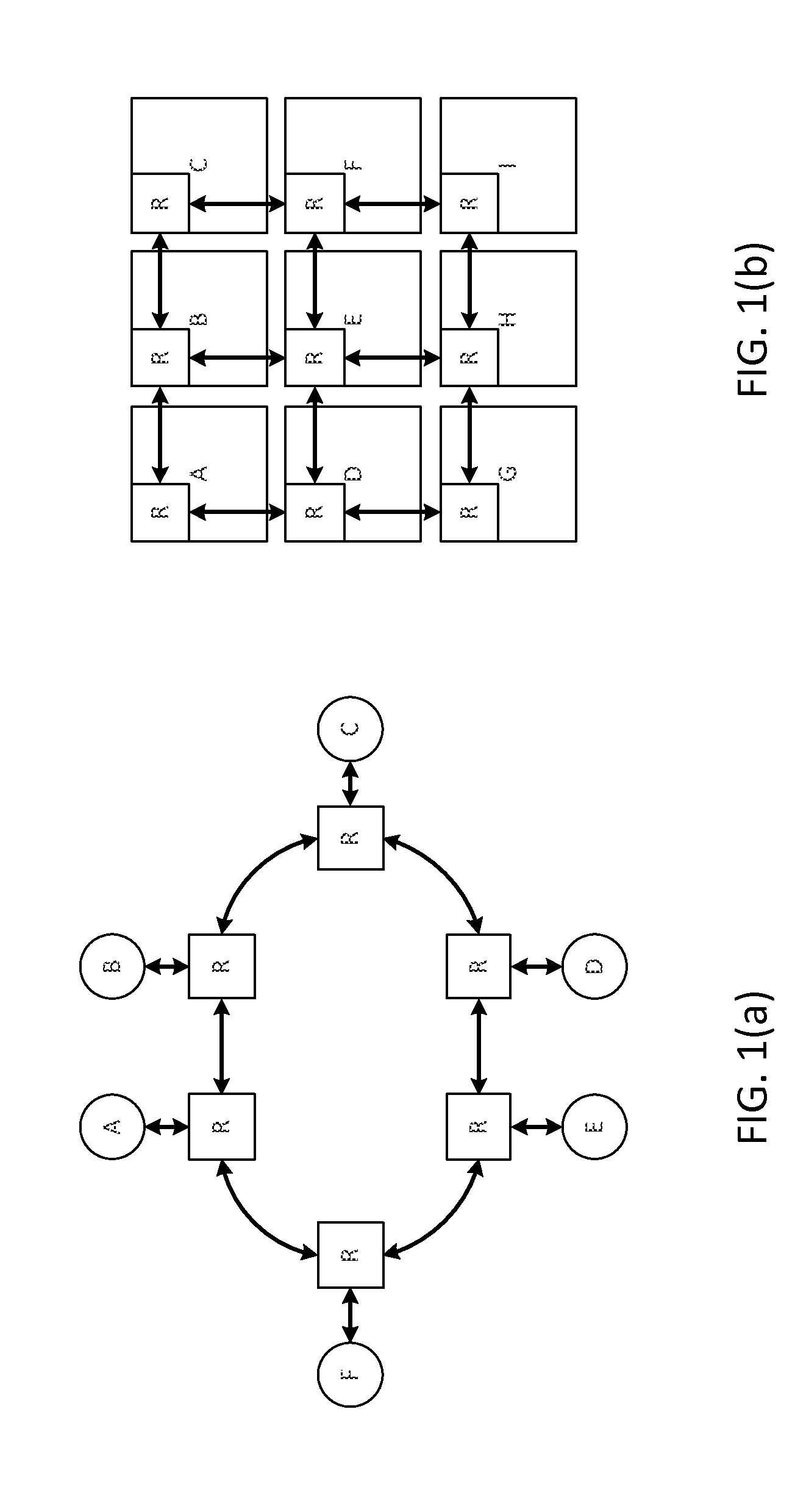
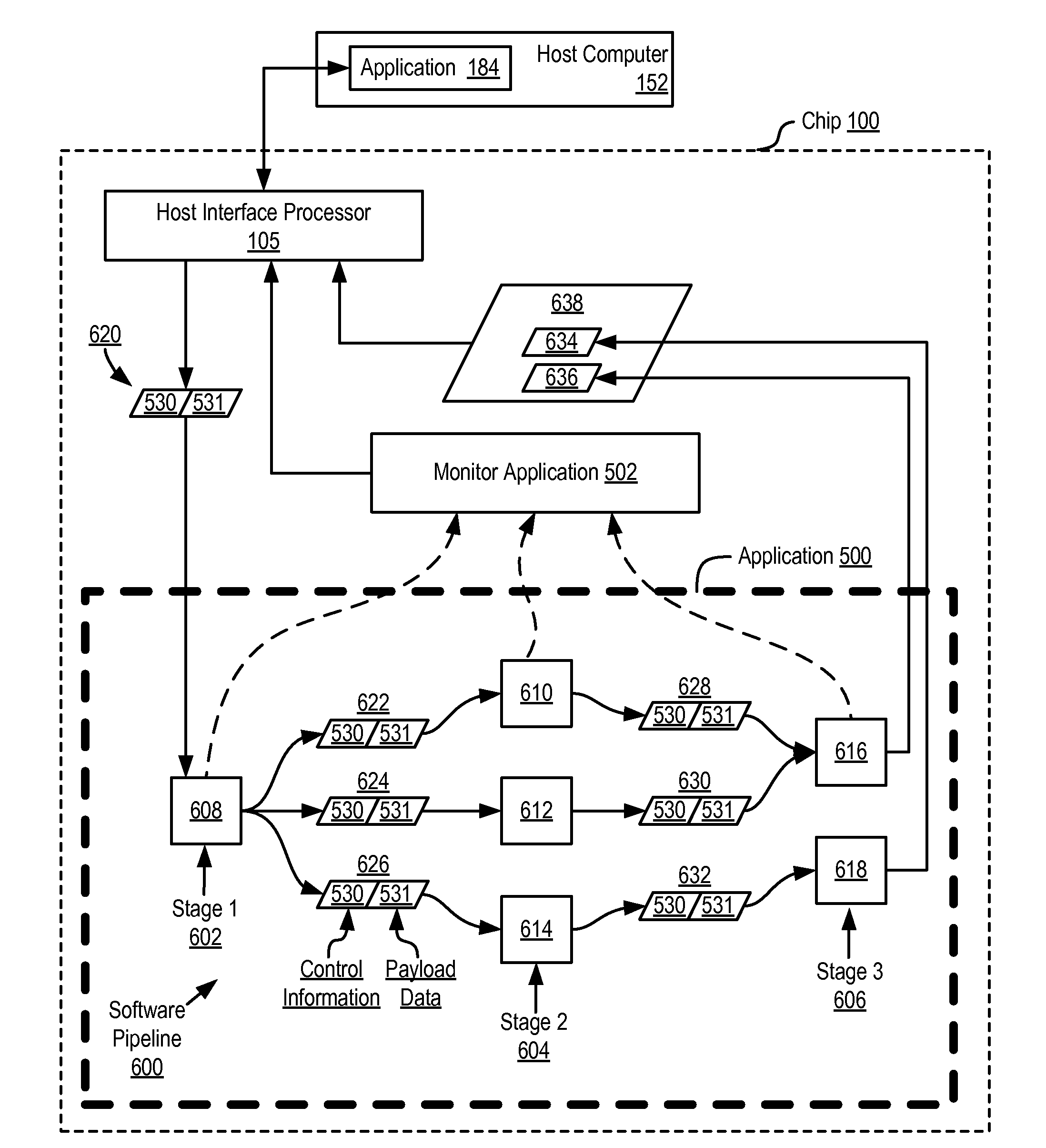
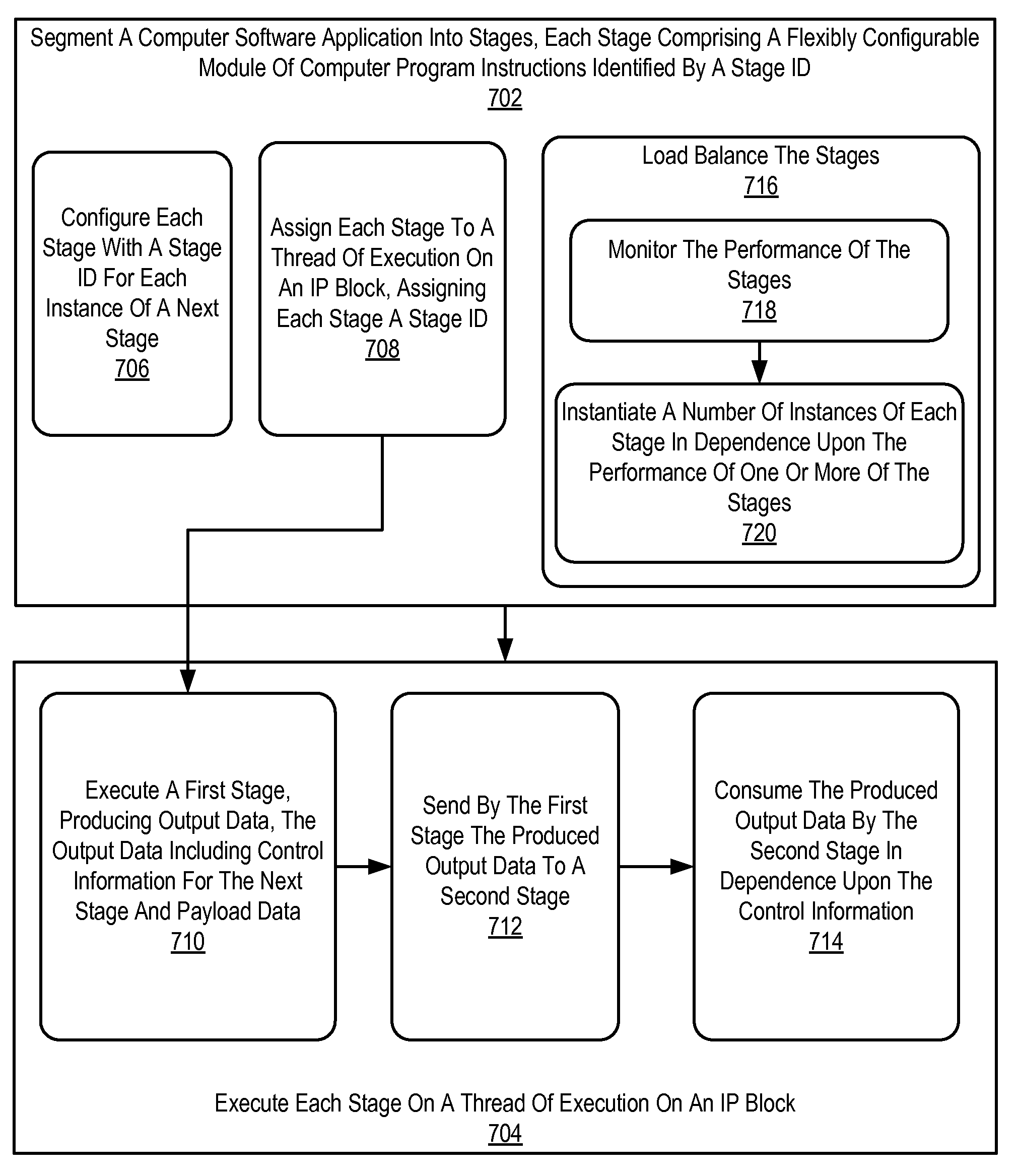
Dynamic Virtual Software Pipelining On A Network On Chip
InactiveUS20090282222A1General purpose stored program computerMultiprogramming arrangementsParallel computingSoftware pipelining
A NOC for dynamic virtual software pipelining including IP blocks, routers, memory communications controllers, and network interface controllers, each IP block adapted to a router through a memory communications controller and a network interface controller, the NOC also including: a computer software application segmented into stages, each stage comprising a flexibly configurable module of computer program instructions identified by a stage ID, each stage assigned to a thread of execution on an IP block; and each stage executing on a thread of execution on an IP block, including a first stage executing on an IP block, producing output data and sending by the first stage the produced output data to a second stage, the output data including control information for the next stage and payload data; and the second stage consuming the produced output data in dependence upon the control information.
Owner:IBM CORP
Reconfigurable noc for customizing traffic and optimizing performance after noc synthesis
Systems and methods described herein are directed to solutions for Network on Chip (NoC) interconnects that supports reconfigurability to support a variety of different traffic profiles each having different sets of traffic flows after the NoC is designed and deployed in a SoC. Reconfiguration of the NoC to map and load a new traffic profile or change the currently mapped traffic profile is performed by an external optimization module which maps various transactions of a given traffic profile to the NoC and reconfigure the NoC hardware by loading the computed mapping information. As part of the mapping process, load balancing between NoC layers may be performed by automatically assigning the transactions in the traffic profile to be routed over certain NoC layers and channels, automatically determining the routes based on the bandwidth requirements of the transaction. The deadlock avoidance and isolation properties of various transactions are maintained during the mapping.
Owner:INTEL CORP
High bandwidth reconfigurable on-chip network for reconfigurable systems
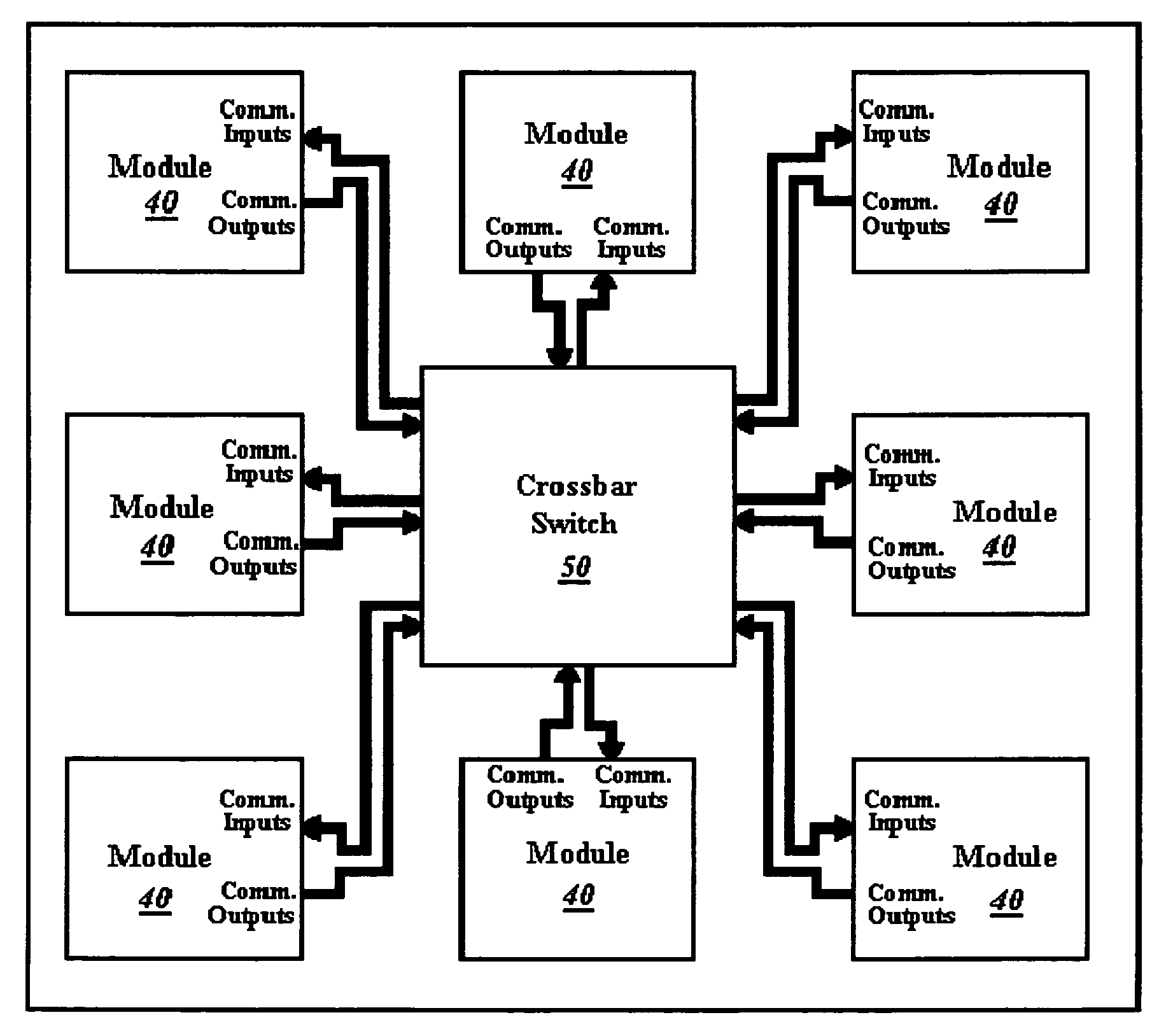
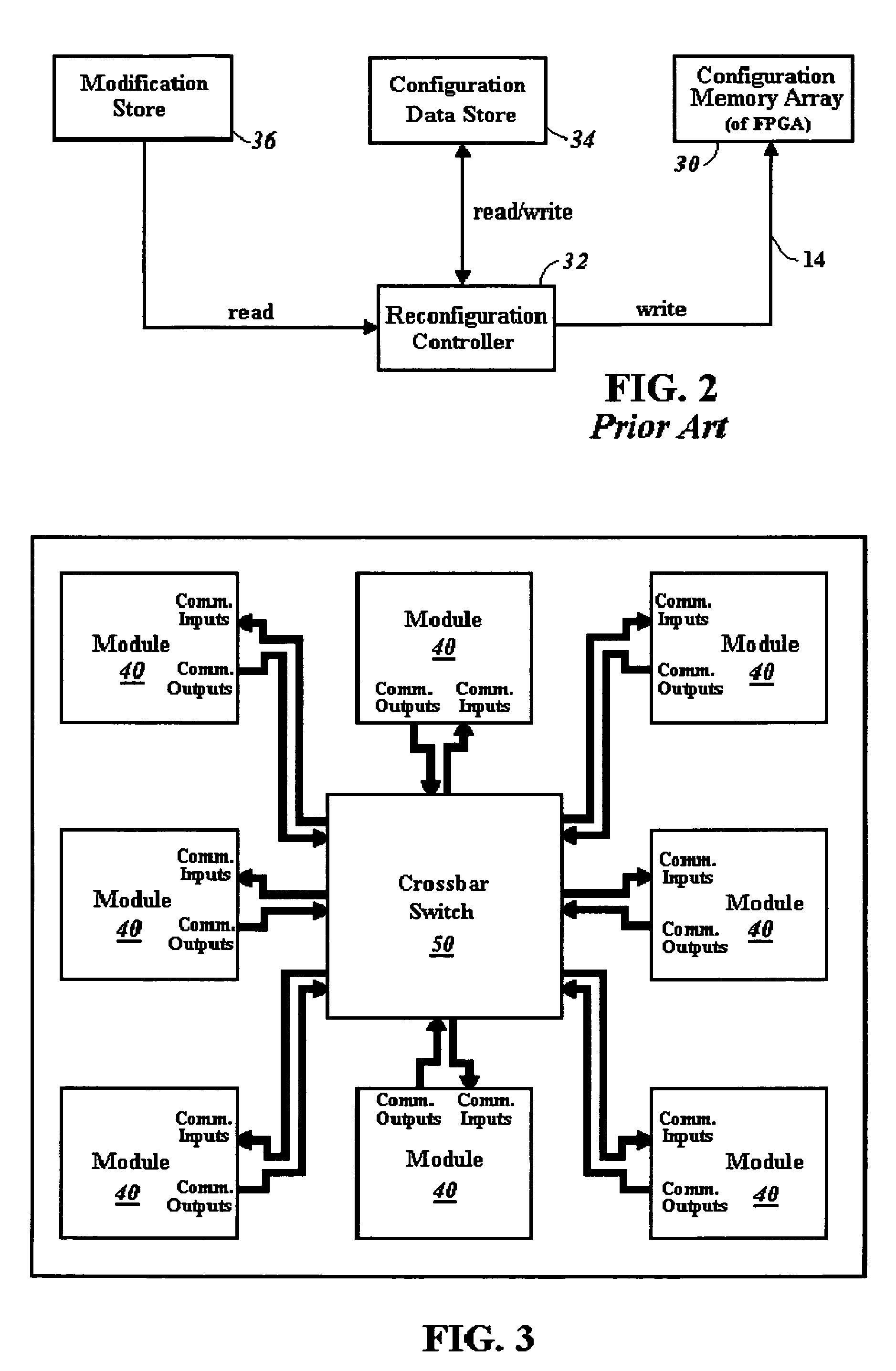
ActiveUS7224184B1Quickly reconfiguredReduce necessarySolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsCrossbar switchAsynchronous communication
A crossbar switch (50) is implemented in a reconfigurable circuit, such as a FPGA, instantiated with a number of modules (40), the crossbar switch (50) providing communication links between the modules (40). The modules (40) and crossbar switch (50) can be easily updated in a partial reconfiguration process changing only portions of modules (40) and the crossbar switch (50) while other portions remain active. The crossbar switch (50) uses individual wiring to independently connect module outputs and inputs so that asynchronous communications can be used. The crossbar switch (50) can be implemented in different embodiments including a Clos crossbar switch, and a crossbar switch connecting each module output only to a corresponding module input, allowing for a reduction in the amount of FPGA resources required to create the crossbar switches.
Owner:XILINX INC
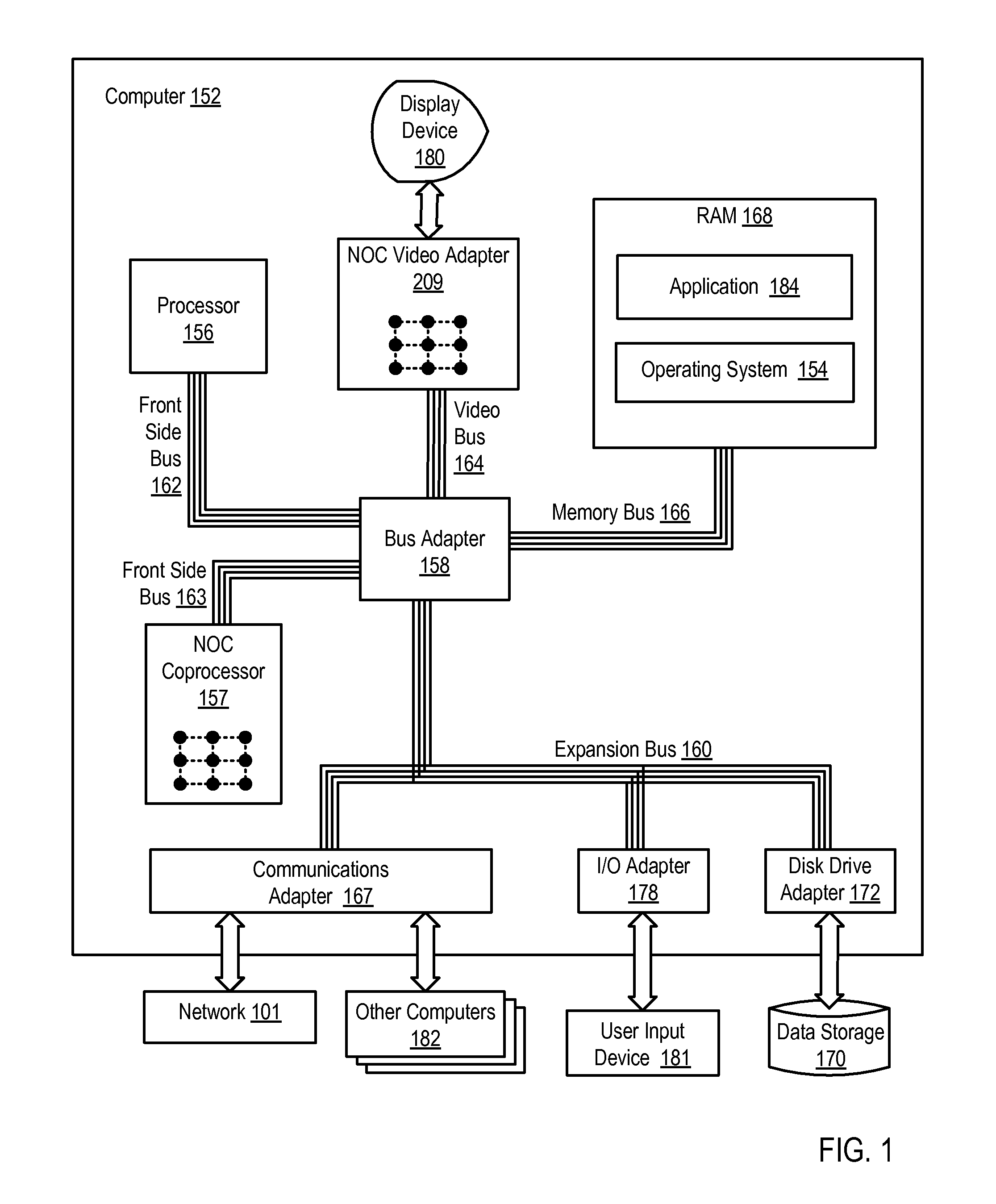
Architecture for dynamically reconfigurable system-on-chip arrangements, related methods and computer program product
ActiveUS20070088537A1Increase flexibilitySave energyDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsMicrocontrollerExtensibility
A system-on-chip arrangement having, in possible combination with a processor, a plurality of reconfigurable gate array devices, and a configurable Network-on-Chip connecting the gate array devices to render the arrangement scalable. The arrangement lends itself to be operated by mapping in one device of the gate array a set of processing modules, and configuring another device of the plurality of gate array devices as a microcontroller having stored therein software code portions for controlling inter-operation of the processing modules stored in the one device of the plurality. The arrangement is thus adapted, e.g., to handle different computational granularity levels.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
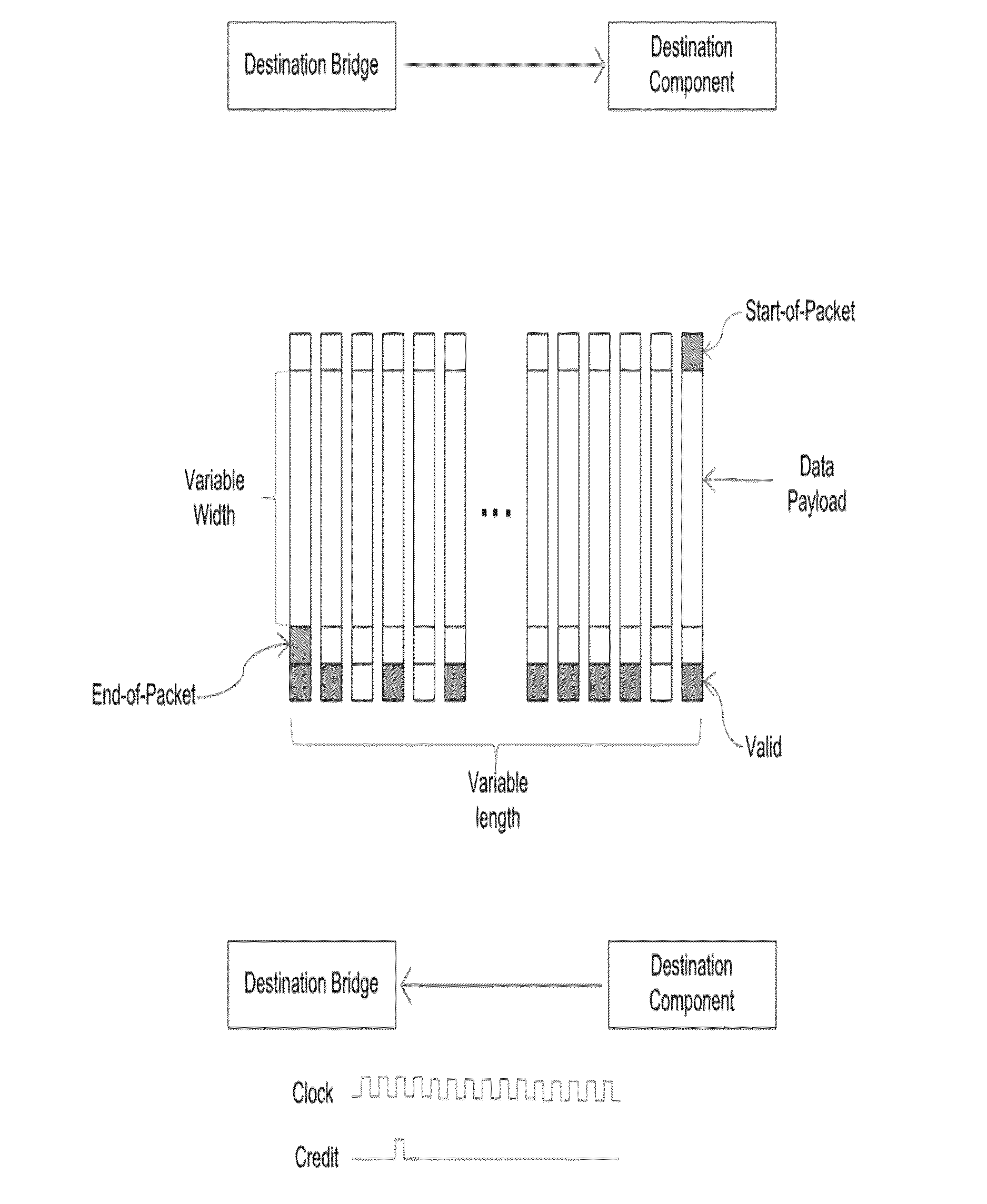
Noc interface protocol adaptive to varied host interface protocols
InactiveUS20150103822A1Hinder propertyDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationData setTransport layer
Systems and methods described herein are directed to solutions for Network on Chip (NoC) interconnects that support a variety of different component protocols each having different sets of data and / or metadata even after the NoC is designed and finalized. Example implementations include, automatically changing format of packets received from an originating SoC component by an originating bridge based on a NoC interface protocol and then transmitting the packet across the NoC interconnect to a destination bridge. The format may again be changed based on the protocol of the destination SoC component. The proposed protocol can be configured to map various transactions presented to it, be they packets belonging to the physical, data link layer, network layer or transport layer. As part of the mapping process, virtual channels for latency or deadlock avoidance may be created and may be maintained for the entire life of the packet within the NoC.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Software Pipelining on a Network on Chip
InactiveUS20090125706A1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionParallel computingCommunication control
A network on chip (‘NOC’) that includes integrated processor (‘IP’) blocks, routers, memory communications controllers, and network interface controllers, with each IP block adapted to a router through a memory communications controller and a network interface controller, where each memory communications controller controlling communications between an IP block and memory, and each network interface controller controlling inter-IP block communications through routers, the NOC also including a computer software application segmented into stages, each stage comprising a flexibly configurable module of computer program instructions identified by a stage ID with each stage executing on a thread of execution on an IP block.
Owner:IBM CORP
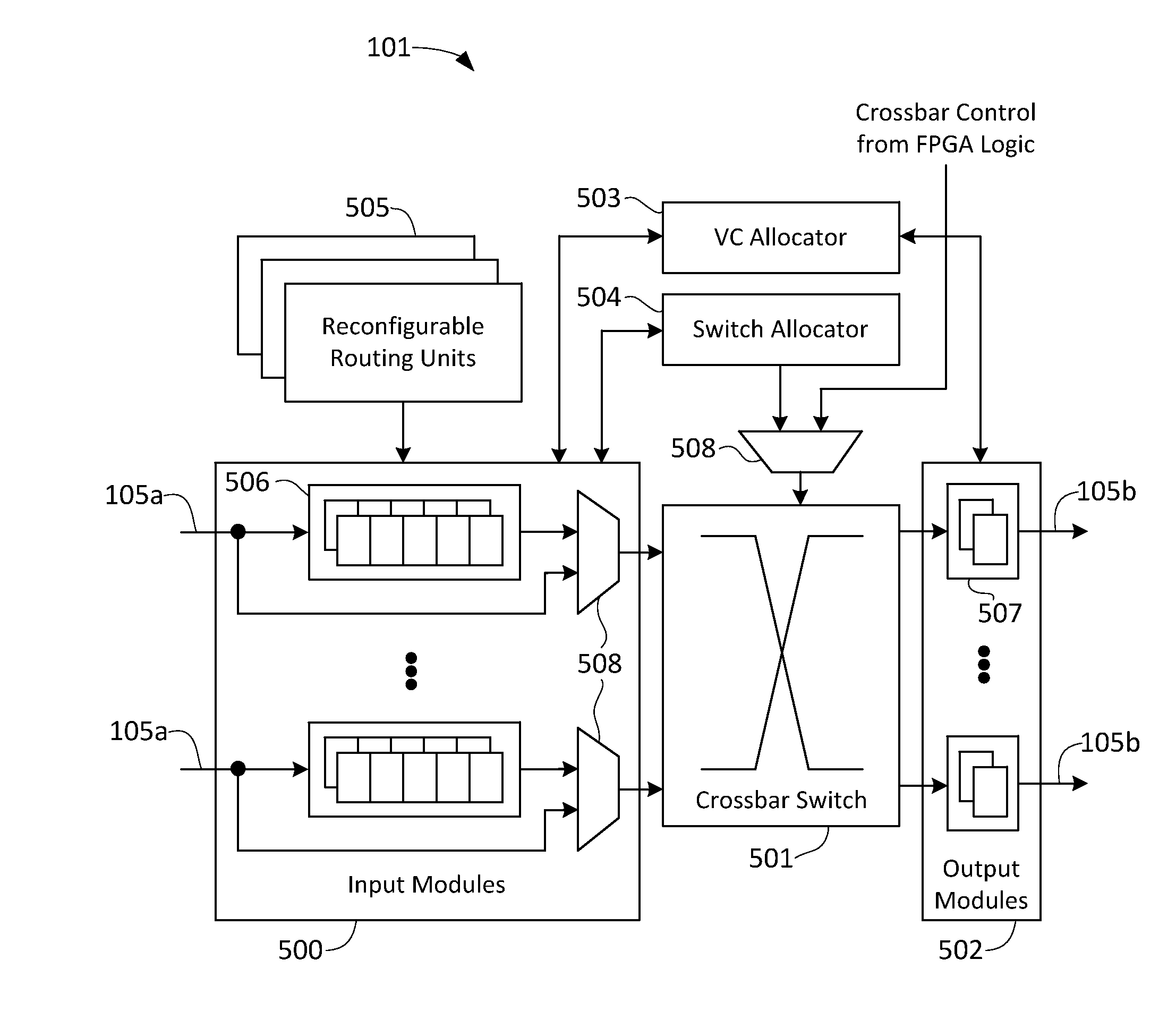
Configurable router for a network on chip (NOC)
Example implementations described herein are directed to a configurable building block, such as a router, for implementation of a Network on Chip (NoC). The router is parameterized by a software layer, which can include the number of virtual channels for a port, the number of ports, the membership information of the virtual channels, clock domain, and so forth. The router may further be configured to implement arbitration techniques and flit processing techniques based on the parameters specified by the software layer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Noc-centric system exploration platform and parallel application communication mechanism description format used by the same
InactiveUS20110191774A1Fast simulationSimplifies some non-critical detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsTransmissionDescription formatComputer architecture
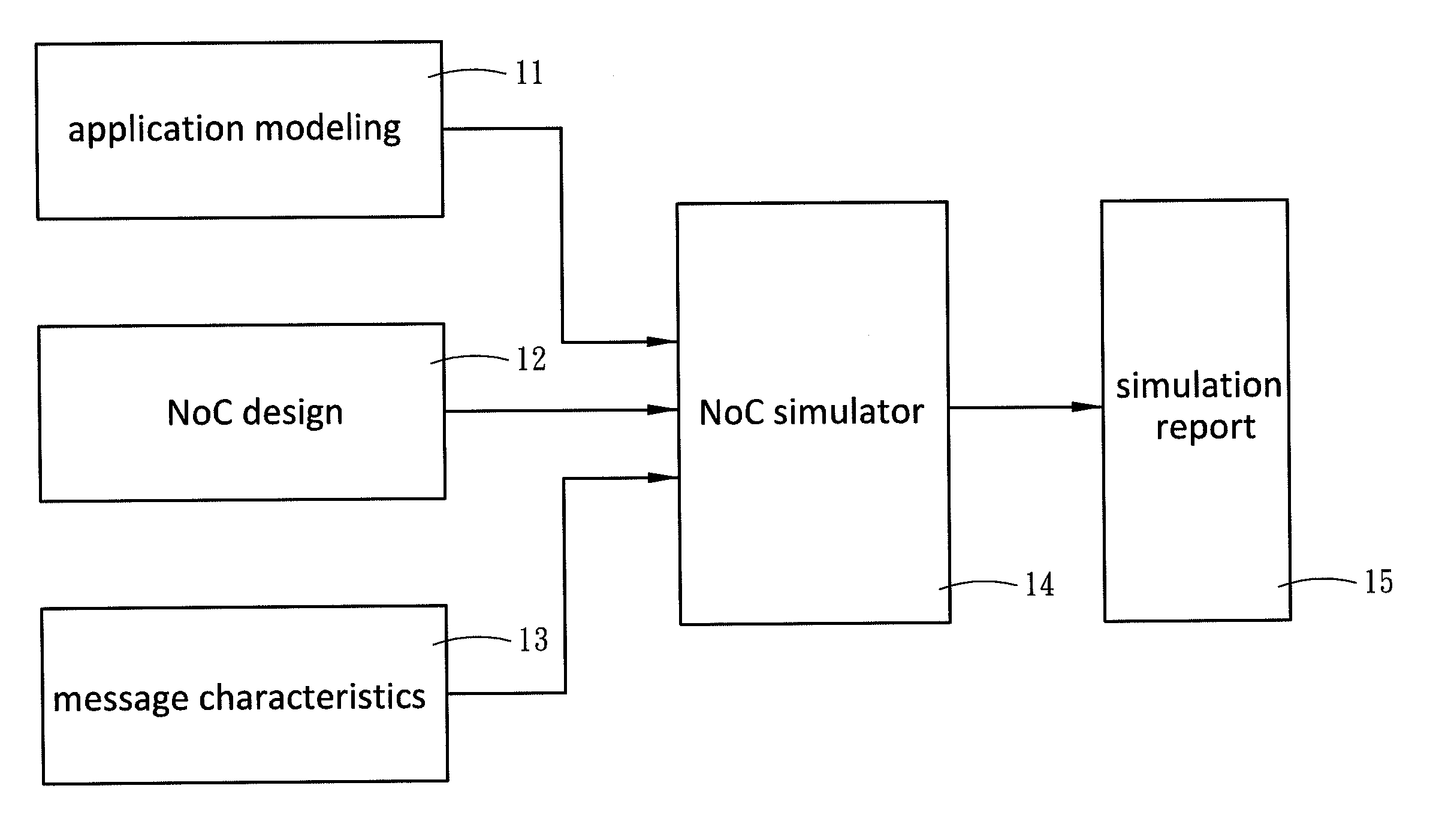
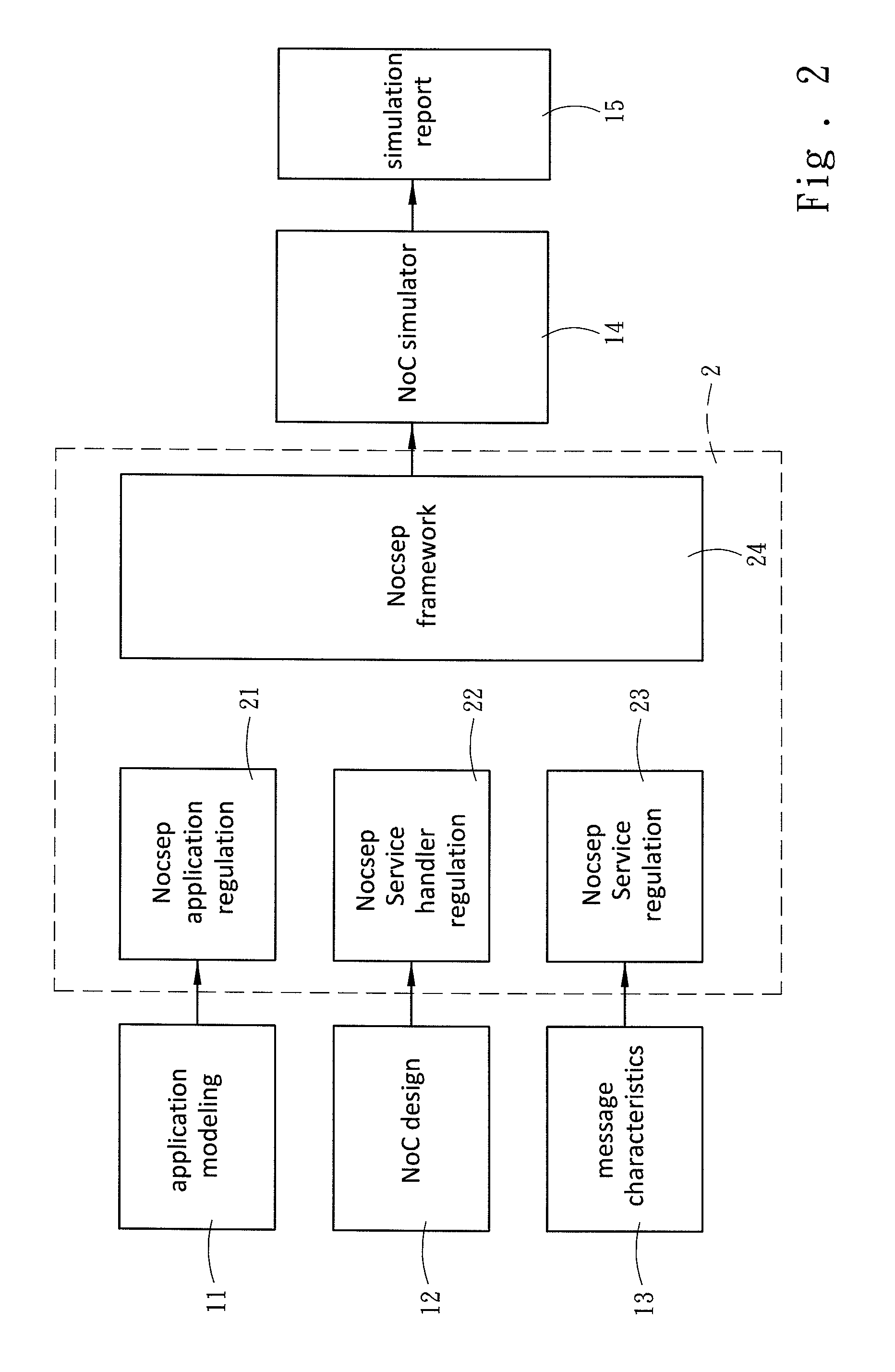
Network-on-Chip (NoC) is to solve the performance bottleneck of communication in System-on-Chip, and the performance of the NoC significantly depends on the application traffic. The present invention establishes a system framework across multiple layers, and defines the interface function behaviors and the traffic patterns of layers. The present invention provides an application modeling in which the task-graph of parallel applications is described in a text method, called Parallel Application Communication Mechanism Description Format. The present invention further provides a system level NoC simulation framework, called NoC-centric System Exploration Platform, which defines the service spaces of layers in order to separate the traffic patterns and enable the independent designs of layers. Accordingly, the present invention can simulate a new design without modifying the framework of simulator or interface designs. Therefore, the present invention increases the design spaces of NoC simulators, and provides a modeling to evaluate the performance of NoC.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Programmable logic device with integrated network-on-chip
ActiveUS20140126572A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsDigital computer detailsProgrammable logic deviceNetworks on chip
Systems and methods for providing a Network-On-Chip (NoC) structure on an integrated circuit for high-speed data passing. In some aspects, the NoC structure includes multiple NoC stations with a hard-IP interface having a bidirectional connection to local components of the integrated circuit. In some aspects, the NoC stations have a soft-IP interface that supports the hard-IP interface of the NoC station.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Reconfigurable network on a chip
ActiveUS7382154B2Easy programmingIncrease flexibilitySolid-state devicesDigital computer detailsSemiconductor chipProgrammable logic array
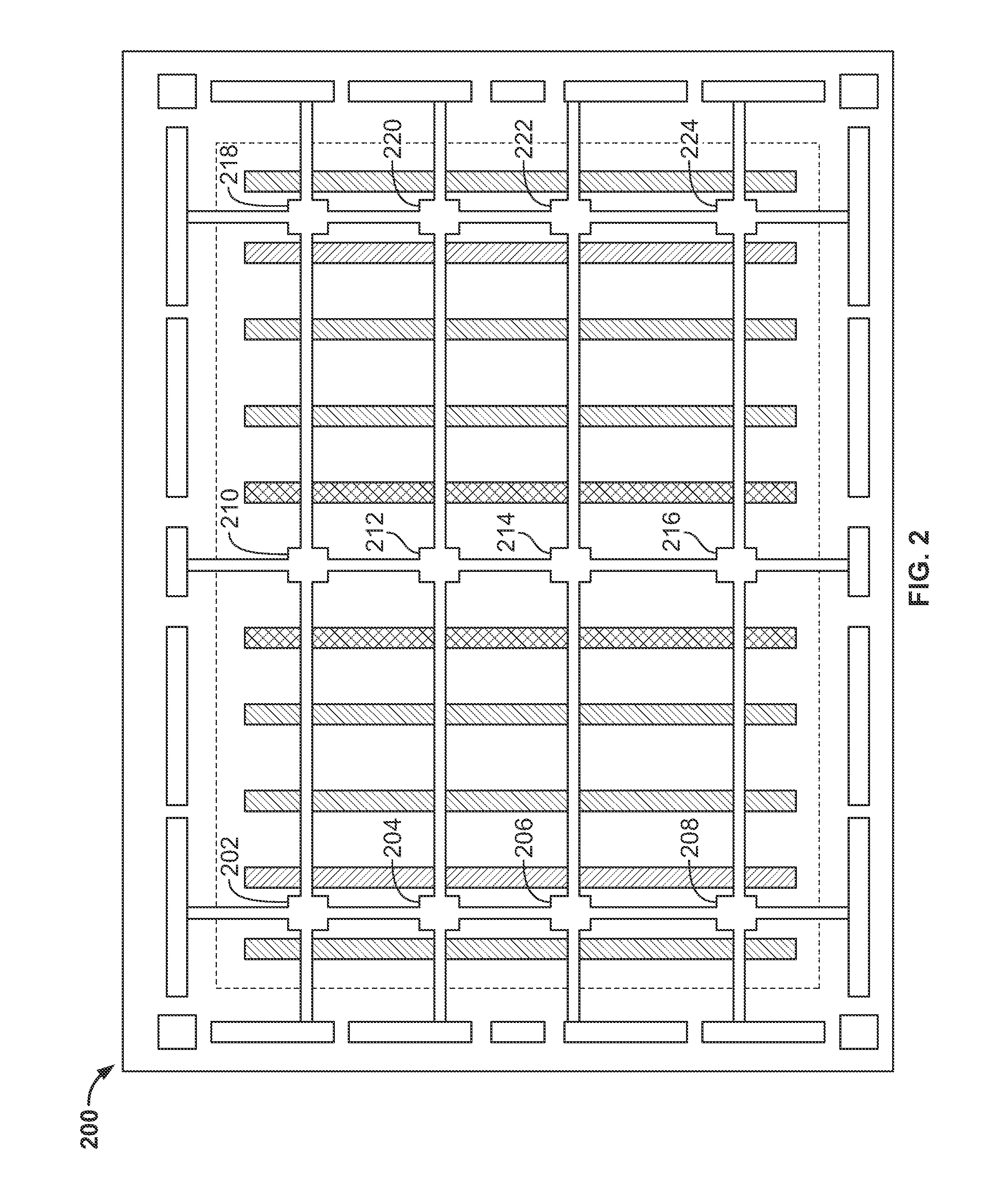
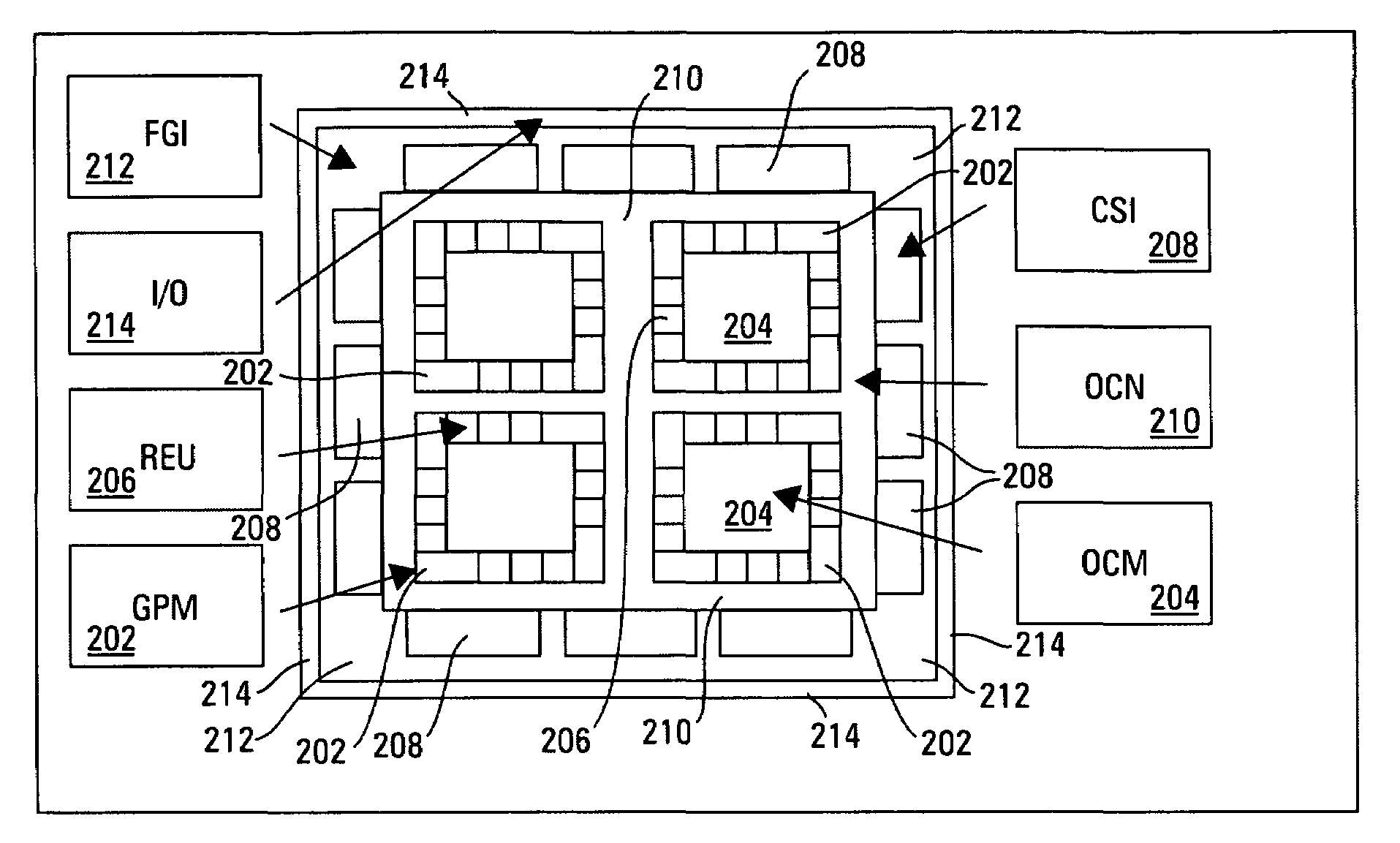
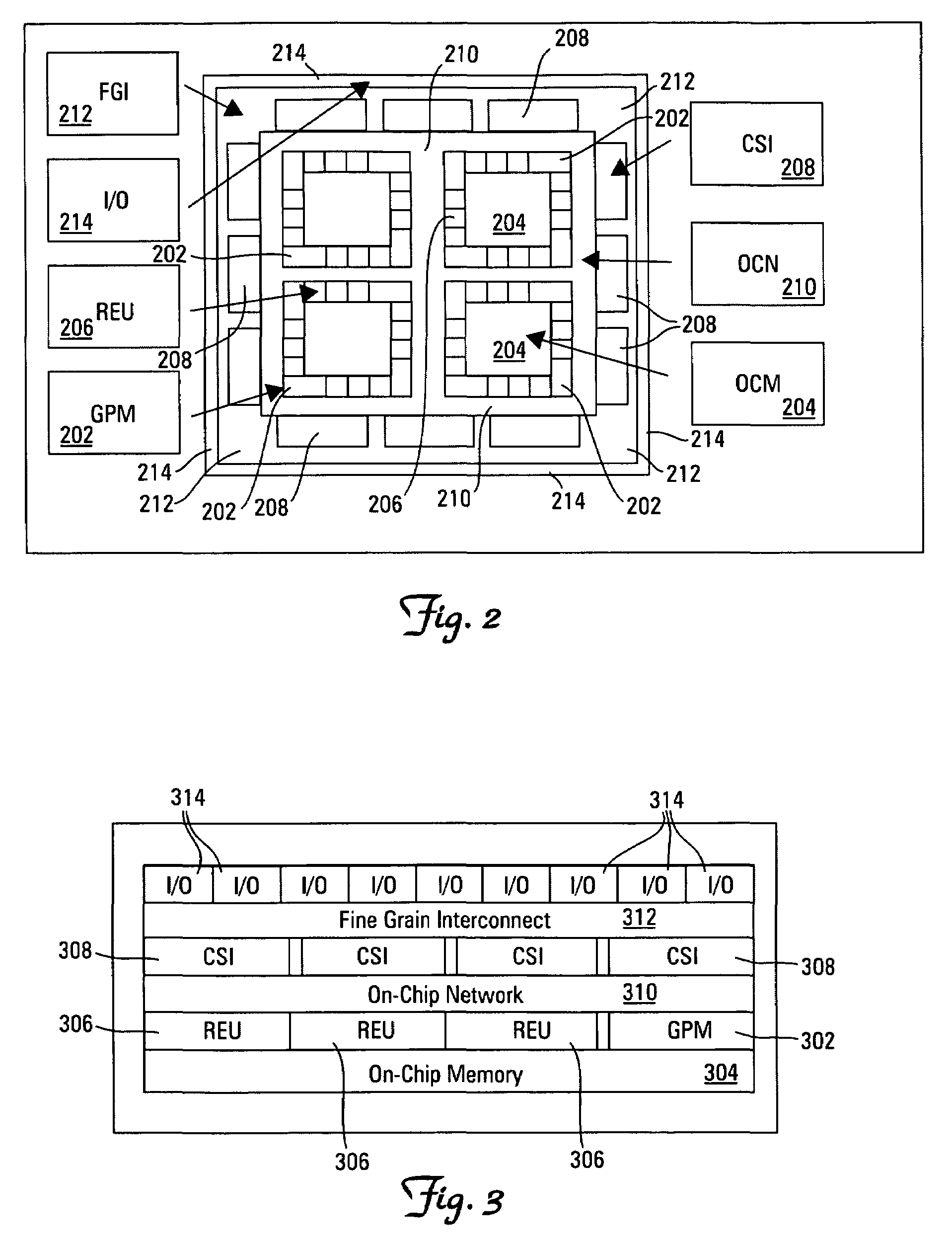
An architecture for a reconfigurable network that can be implemented on a semiconductor chip is disclosed, which includes a hierarchical organization of network components and functions that are readily programmable and highly flexible. Essentially, a reconfigurable network on a chip is disclosed, which includes aspects of reconfigurable computing, system on a chip, and network on a chip designs. More precisely, a reconfigurable network on a chip includes a general purpose microprocessor for implementing software tasks, a plurality of on-chip memories for facilitating the processing of large data structures as well as processor collaboration, a plurality of reconfigurable execution units including self-contained, individually reconfigurable programmable logic arrays, a plurality of configurable system interface units that provide interconnections between on-chip memories, networks or buses, an on-chip network including a network interconnection interface that enables communication between all reconfigurable execution units, configurable system interface units and general purpose microprocessors, a fine grain interconnect unit that gathers associated input / output signals for a particular interface and attaches them to a designated system interface resource, and a plurality of input / output blocks that supply the link between an on-chip interface resource and a particular external network or device interface. Advantageously, the network minimizes the configuration latency of the reconfigurable execution units and also enables reconfiguration on-the-fly.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Software Trace Collection and Analysis Utilizing Direct Interthread Communication On A Network On Chip
InactiveUS20110289485A1Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsParallel computingCommunication control
Collecting and analyzing trace data while in a software debug mode through direct interthread communication (‘DITC’) on a network on chip (‘NOC’), the NOC including integrated processor (‘IP’) blocks, routers, memory communications controllers, and network interface controllers, with each IP block adapted to a router through a memory communications controller and a network interface controller, where each memory communications controller controlling communications between an IP block and memory, and each network interface controller controlling inter-IP block communications through routers, including enabling the collection of software debug information in a selected set of IP blocks distributed through the NOC, each IP block within the selected set of IP blocks having a set of trace data; collecting software debugging information via the set of trace data; communicating the set of trace data to a destination repository; and analyzing the set of trace data at the destination repository.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic virtual software pipelining on a network on chip
InactiveUS8020168B2General purpose stored program computerMultiprogramming arrangementsParallel computingCommunication control
A NOC for dynamic virtual software pipelining including IP blocks, routers, memory communications controllers, and network interface controllers, each IP block adapted to a router through a memory communications controller and a network interface controller, the NOC also including: a computer software application segmented into stages, each stage comprising a flexibly configurable module of computer program instructions identified by a stage ID, each stage assigned to a thread of execution on an IP block; and each stage executing on a thread of execution on an IP block, including a first stage executing on an IP block, producing output data and sending by the first stage the produced output data to a second stage, the output data including control information for the next stage and payload data; and the second stage consuming the produced output data in dependence upon the control information.
Owner:IBM CORP
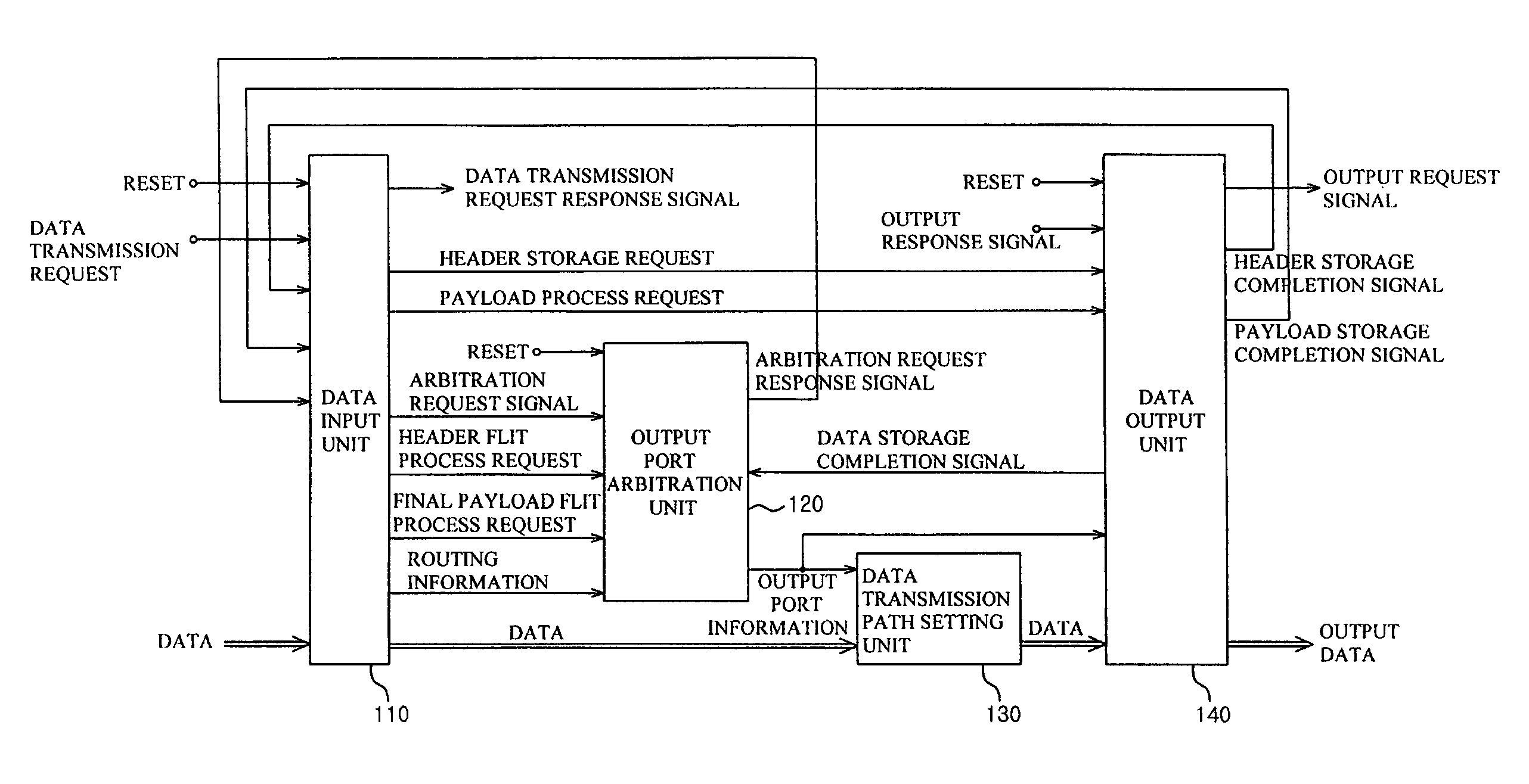
Asynchronous switch based on butterfly fat-tree for network on chip application
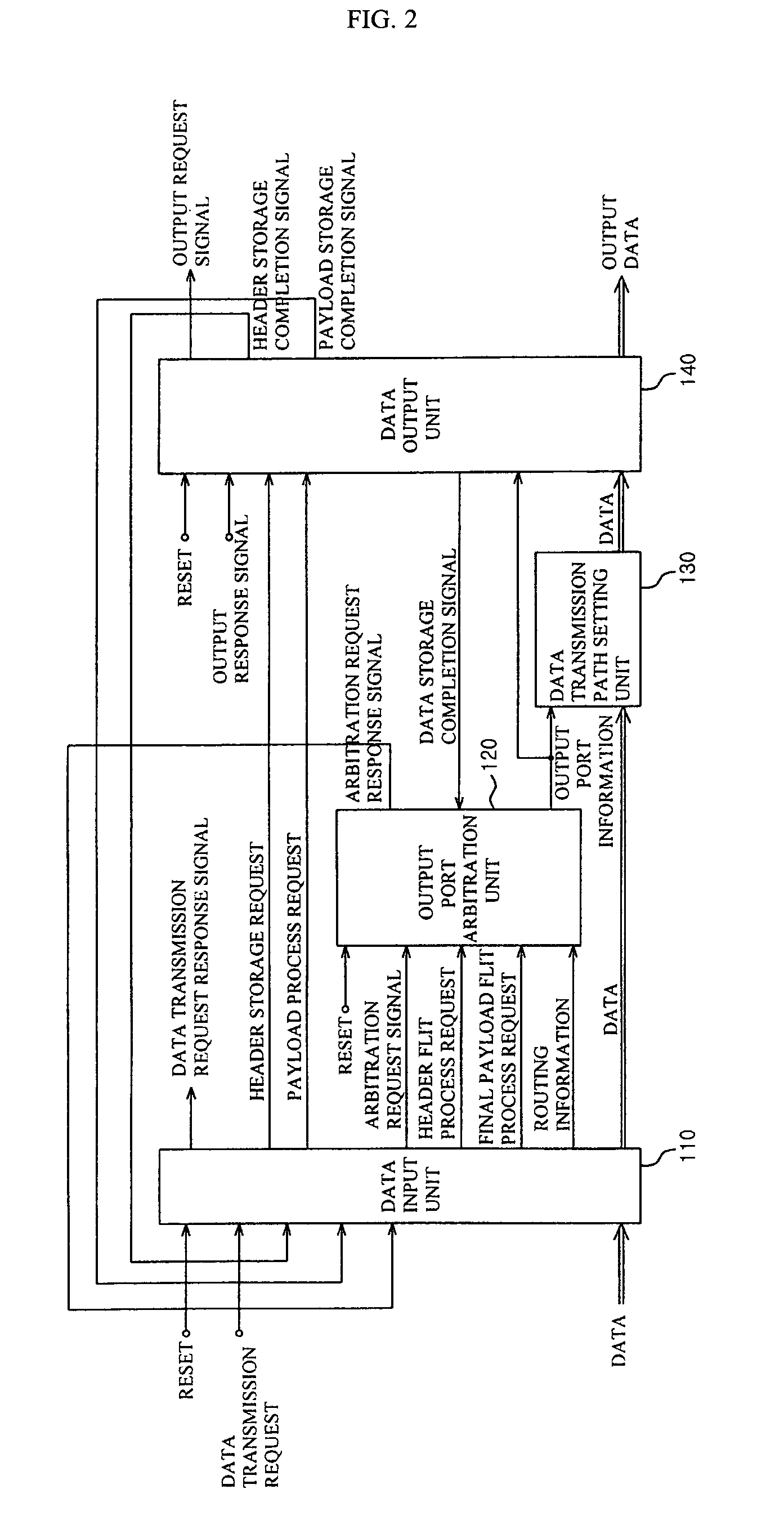
InactiveUS7467358B2Performance maximizationSimple control logicData switching by path configurationProgram controlComputer hardwareIntellectual property
The present invention disclosed herein is an asynchronous switch for an network on chip application making possible between IP (Intellectual Property) communication among various IPs in the network on chip. The asynchronous switch according to the present invention in which comprises a data input unit for receiving and storing a plurality of data flits, and confirming whether a kind of each data flit is a header flit or a payload flit according to a transmission request signal; an output port arbitration unit for outputting an output port selection signal showing a output priority of the data by receiving a header flit request signal, final payload flit process request signal, routing information of the header flit, and the a arbitration request signal from the data input unit; and a data output unit for receiving a header storage request signal and a payload storage request signal from the data input unit, temporarily storing the data flit inputted from the data transmission path setting unit, transferring header and payload storage completion signals indicating that the data flit is stored to the data input unit, and outputting the temporarily stored data flit to a designated port according to a pre-set order.
Owner:GWANGJU INST OF SCI & TECH
Network on chip with an I/O accelerator
InactiveUS20090307714A1Lower latencyHigh bandwidthInterprogram communicationDigital computer detailsHigh bandwidthLatency (engineering)
Data processing on a network on chip (‘NOC’) that includes IP blocks, routers, memory communications controllers, and network interface controllers; each IP block adapted to a router through a memory communications controller and a network interface controller; each memory communications controller controlling communication between an IP block and memory; each network interface controller controlling inter-IP block communications through routers; each IP block adapted to the network by a low latency, high bandwidth application messaging interconnect comprising an inbox and an outbox; a computer software application segmented into stages, each stage comprising a flexibly configurable module of computer program instructions identified by a stage ID with each stage executing on a thread of execution on an IP block; and at least one of the IP blocks comprising an input / output (‘I / O’) accelerator that administers at least some data communications traffic to and from the at least one IP block.
Owner:IBM CORP
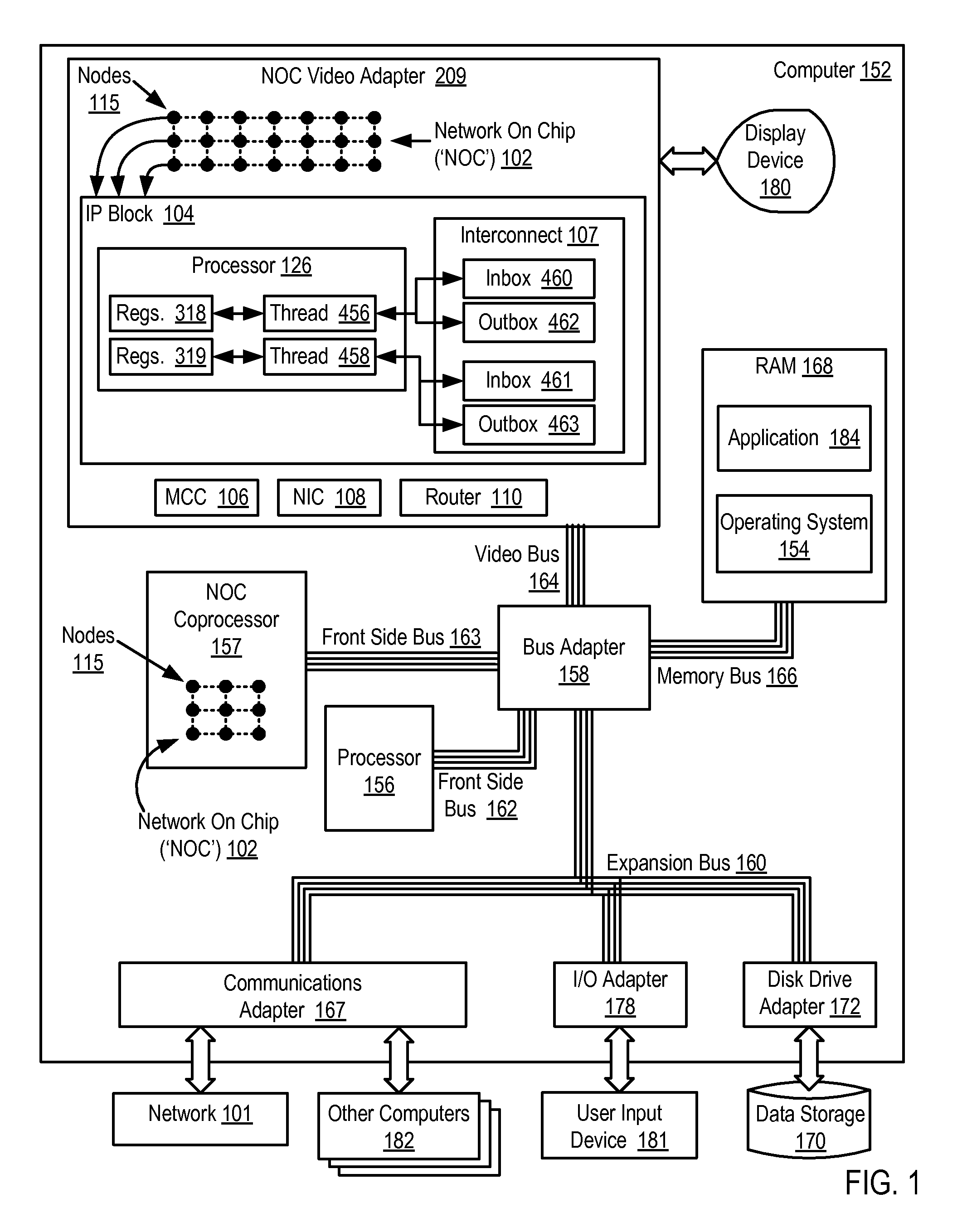
Network on chip with low latency, high bandwidth application messaging interconnects that abstract hardware inter-thread data communications into an architected state of a processor
ActiveUS7991978B2General purpose stored program computerConcurrent instruction executionHardware threadHigh bandwidth
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
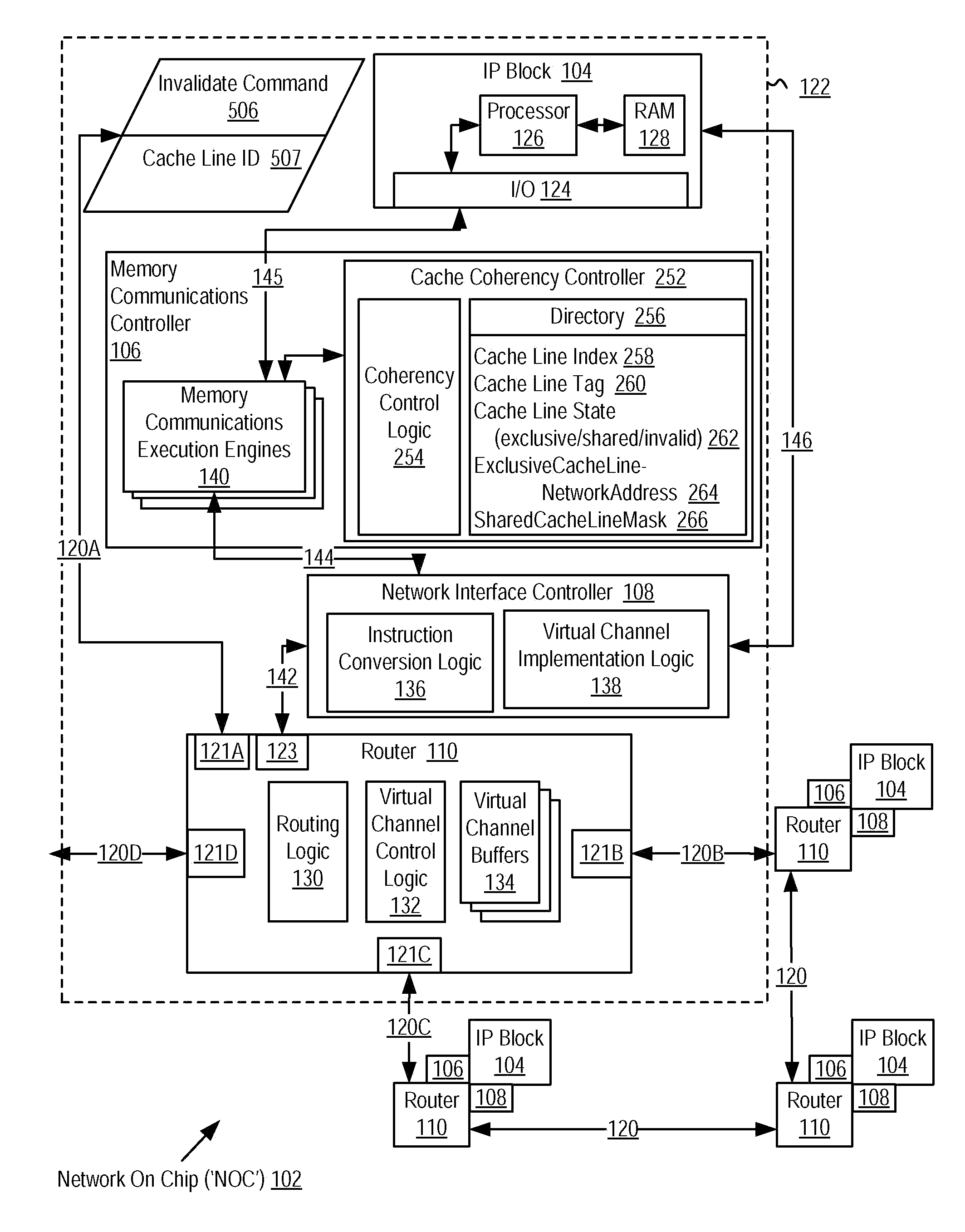
Network On Chip that Maintains Cache Coherency with Invalidate Commands
A network on chip (‘NOC’) that maintains cache coherency, the NOC including integrated processor (‘IP’) blocks, routers, memory communications controllers, and network interface controller, each IP block adapted to a router through a memory communications controller and a network interface controller, at least one memory communications controller further comprising a cache coherency controller each memory communications controller controlling communication between an IP block and memory, and each network interface controller controlling inter-IP block communications through routers, wherein the memory communications controller configured to execute a memory access instruction and configured to determine a state of a cache line addressed by the memory access instruction, the state of the cache line being one of shared, exclusive, or invalid; the memory communications controller configured to broadcast an invalidate command to a plurality of IP blocks of the NOC if the state of the cache line is shared; and the memory communications controller configured to transmit an invalidate command only to an IP block that controls a cache where the cache line is stored if the state of the cache line is exclusive.
Owner:IBM CORP
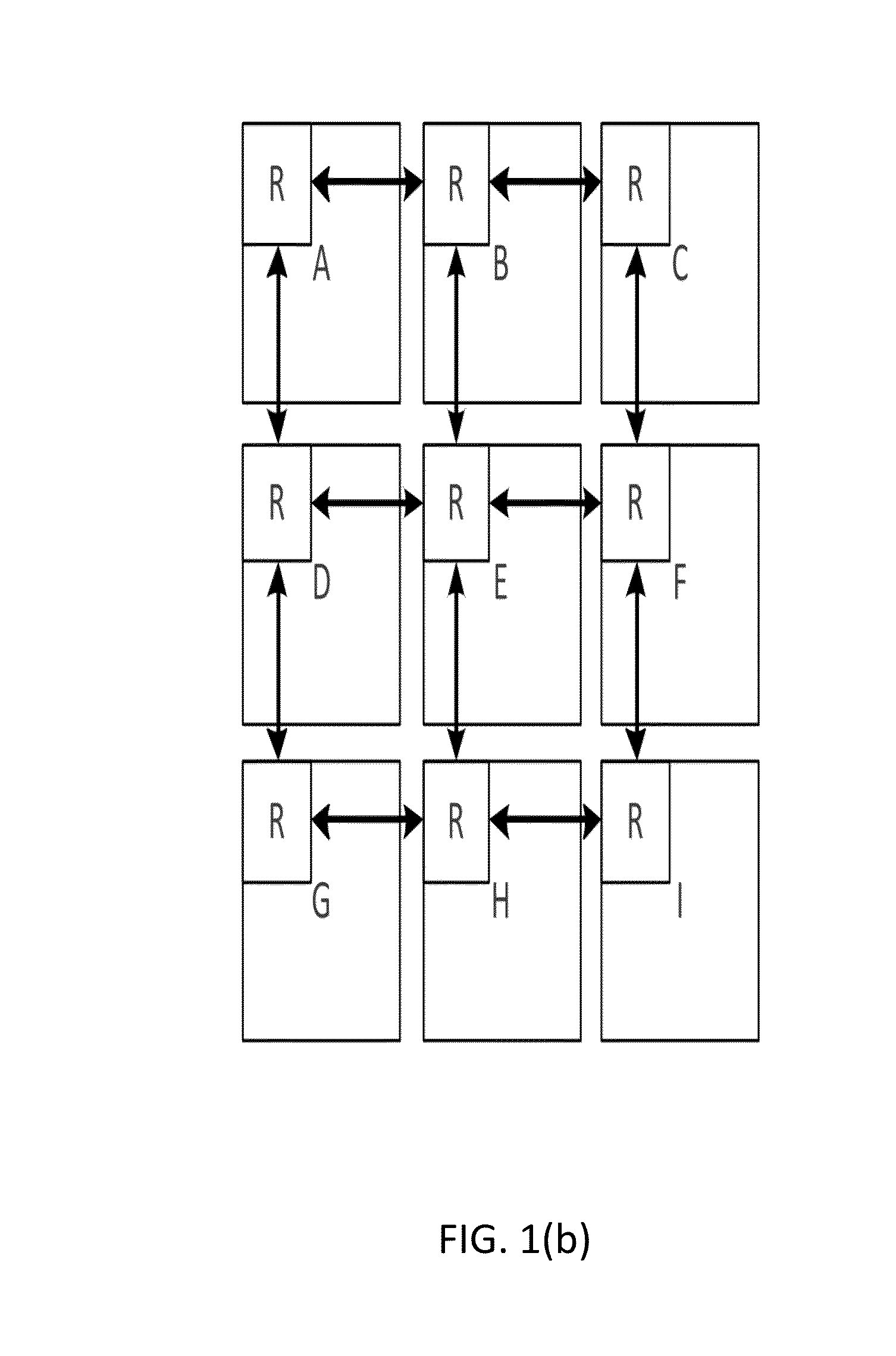
Network On Chip With Minimum Guaranteed Bandwidth For Virtual Communications Channels
InactiveUS20090285222A1Minimum bandwidthError preventionTransmission systemsData transmissionNetworks on chip
A network on chip (‘NOC’) with guaranteed minimum bandwidth for virtual communications channels, the NOC including: integrated processor (‘IP’) blocks, routers, memory communications controllers, and network interface controllers, each IP block adapted to a router through a memory communications controller and a network interface controller, each memory communications controller controlling communications between an IP block and memory, each network interface controller controlling inter-IP block communications through routers, each router coupled for data communications with at least one other router through at least one link, each link including a wire bus wide enough to accommodate simultaneously, for transmission in one direction on the link, all or part of a data switching packet, each router implementing two or more virtual communications channels, each virtual communications channel characterized by a communication type, each virtual communications channel guaranteed at least a minimum bandwidth for data transmissions over a link between routers.
Owner:IBM CORP
Weight factor based allocation of time slot to use link in connection path in network on chip IC
ActiveUS7564865B2Reduce chanceMore freedomGeneral purpose stored program computerLoop networksLink weightCoupling
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
Methods and apparatus for multi-core processing with dedicated thread management
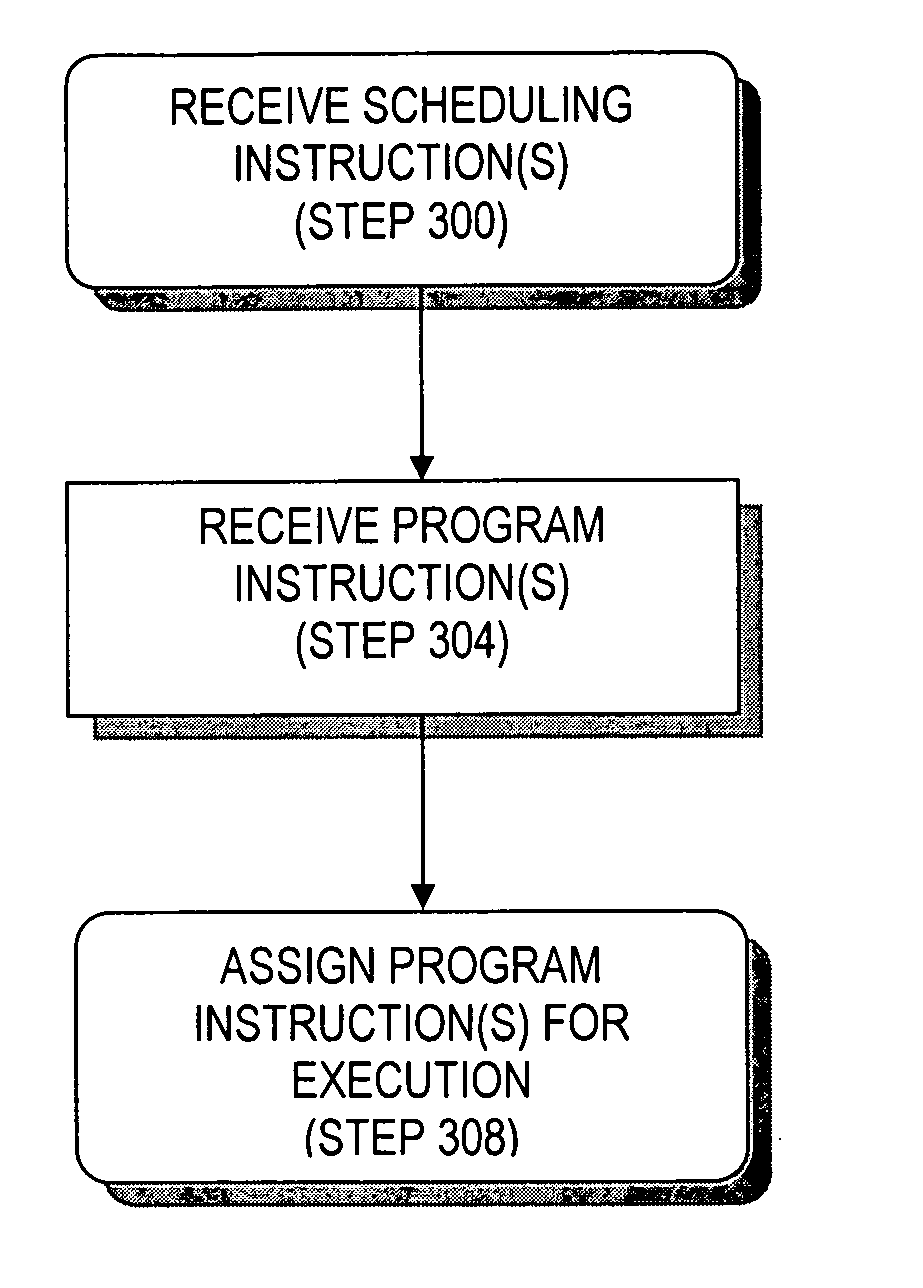
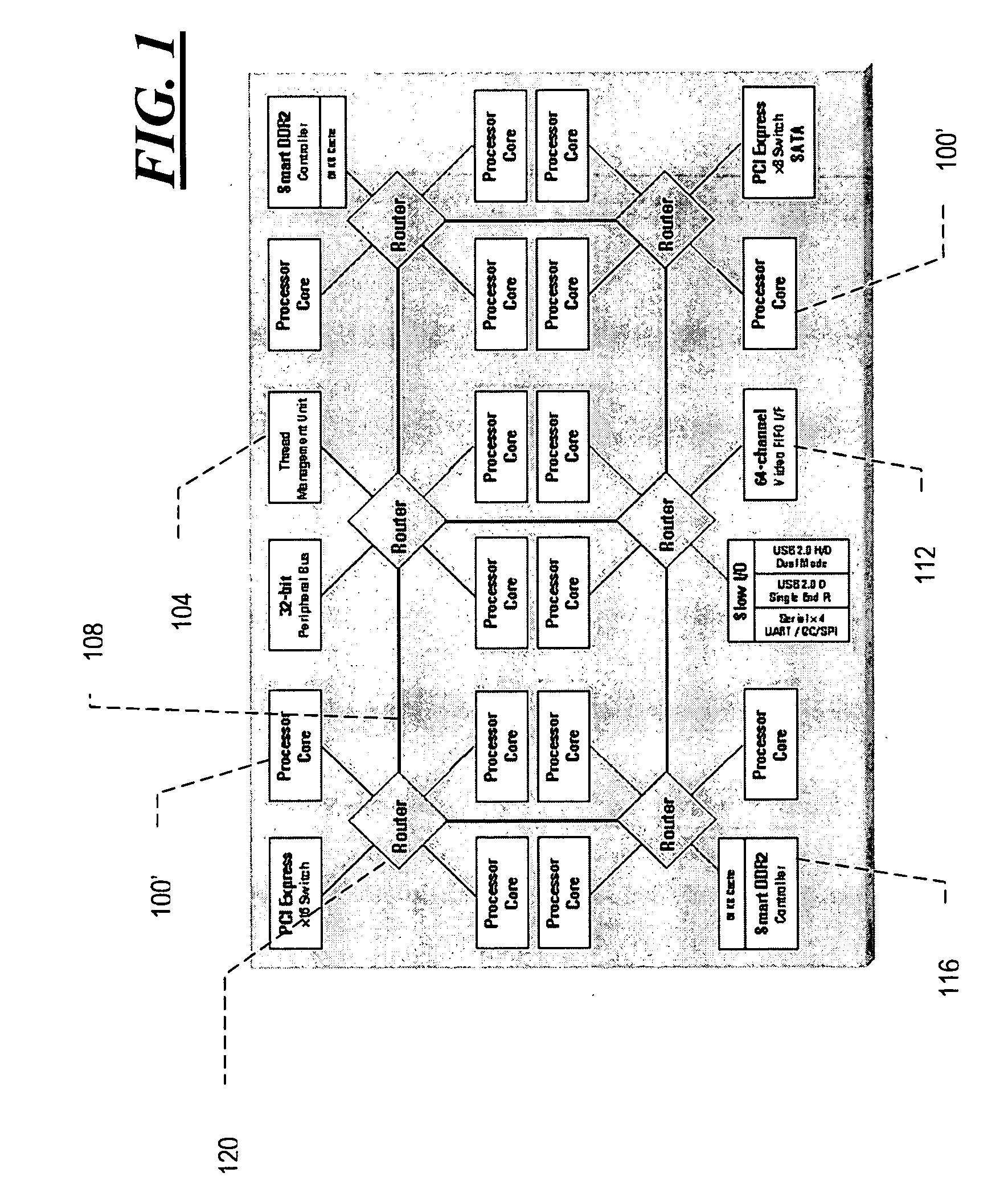
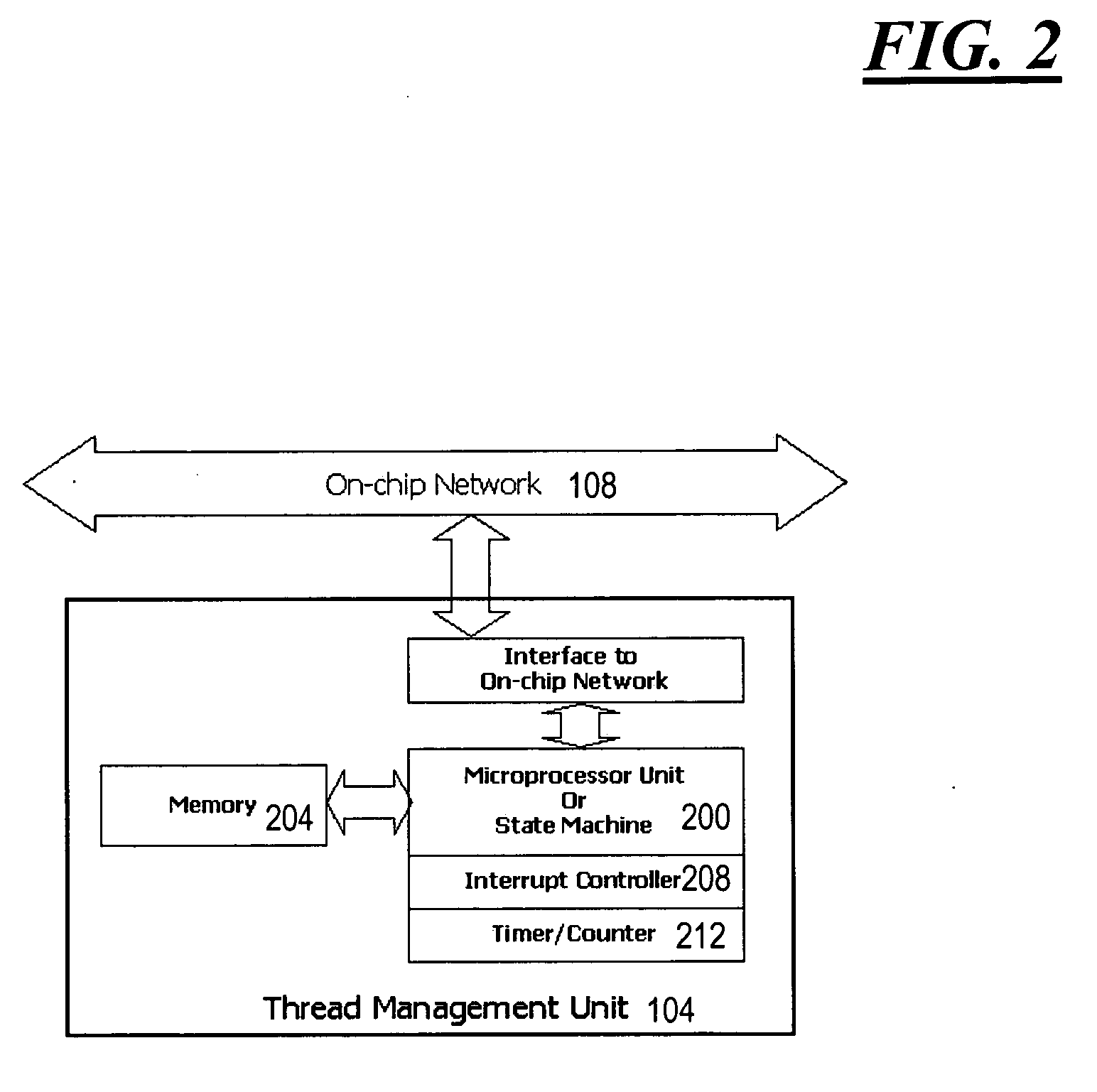
InactiveUS20070150895A1Fast, low-latency switching of threads without incurring the overheadEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringLatency (engineering)Networks on chip
Methods and apparatus for dedicated thread management in a CMP having processing units, interface blocks, and function blocks interconnected by an on-chip network. In various embodiments, thread management occurs out-of-band allowing for fast, low-latency switching of threads without incurring the overhead associated with a software-based thread-management thread.
Owner:BOSTON CIRCUITS
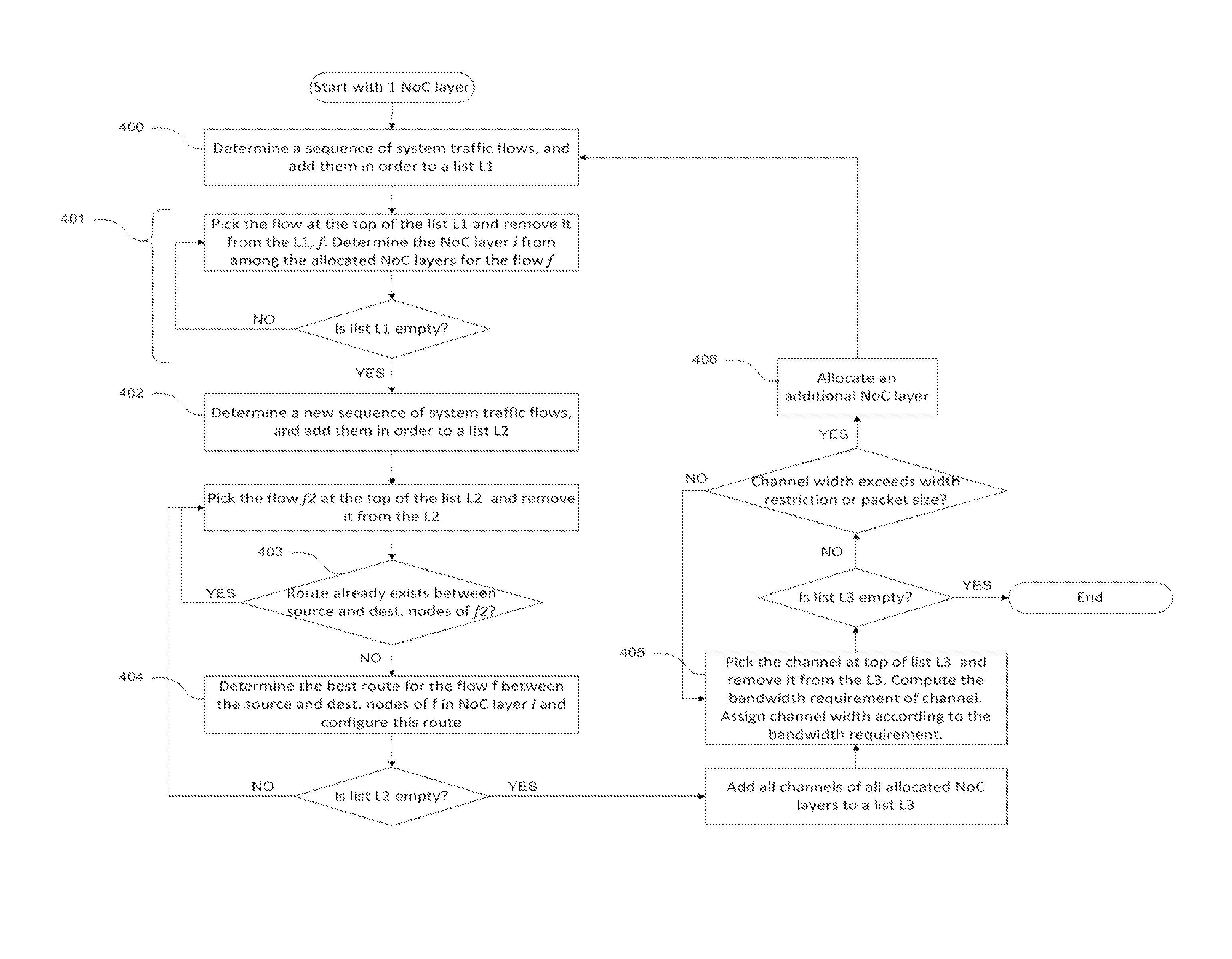
Creating multiple noc layers for isolation or avoiding noc traffic congestion
Systems and methods described herein are directed to solutions for Network on Chip (NoC) interconnects that automatically and dynamically determines the number of layers needed in a NoC interconnect system based on the bandwidth requirements of the system traffic flows. The number of layers is dynamically allocated and minimized by performing load balancing of the traffic flows between the channels and routes of different NoC layers as they are mapped. Additional layers may be allocated to provide the additional virtual channels that may be needed for deadlock avoidance and to maintain the isolation properties between various system flows. Layer allocation for additional bandwidth and additional virtual channels (VCs) may be performed in tandem.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com