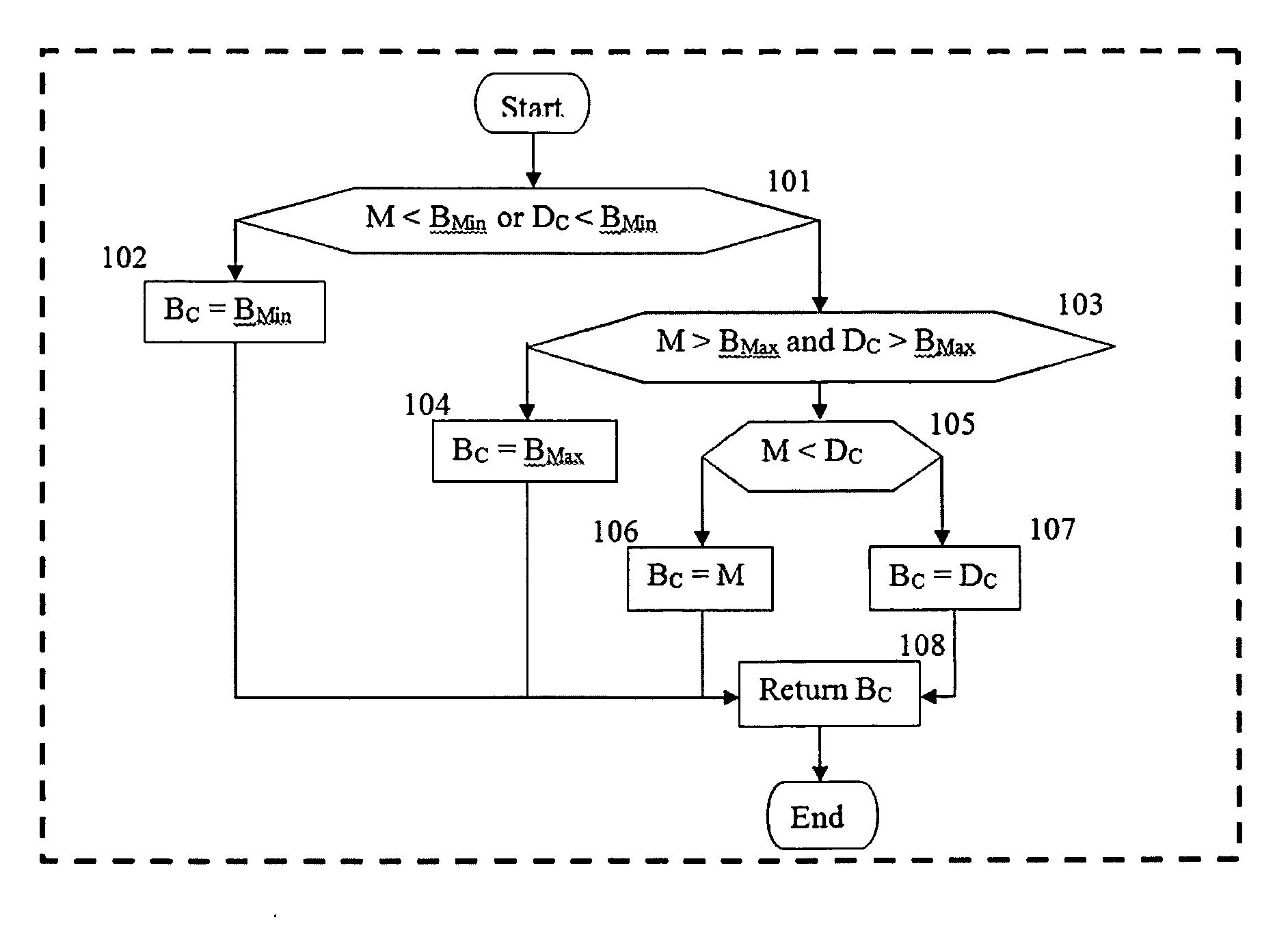
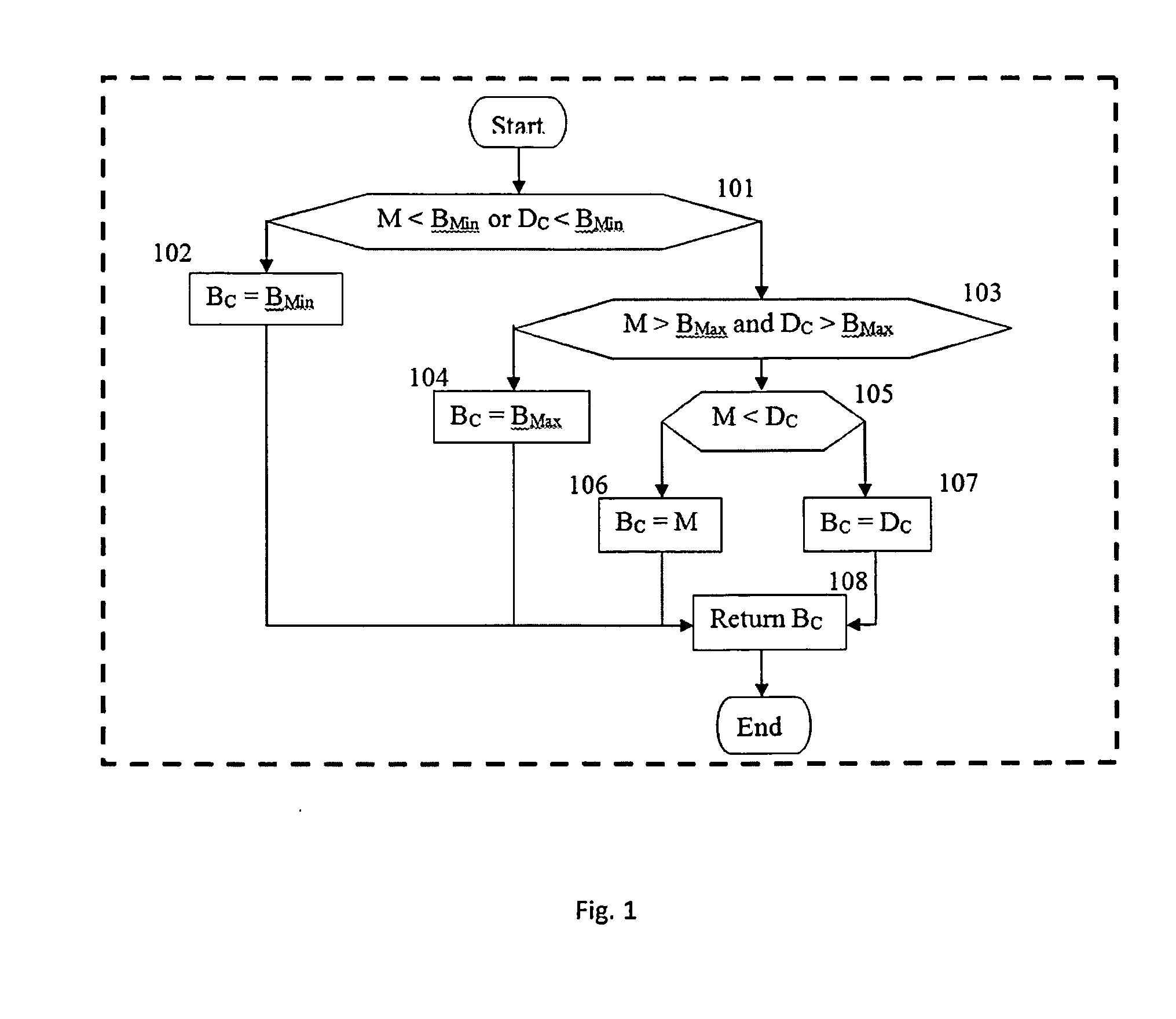
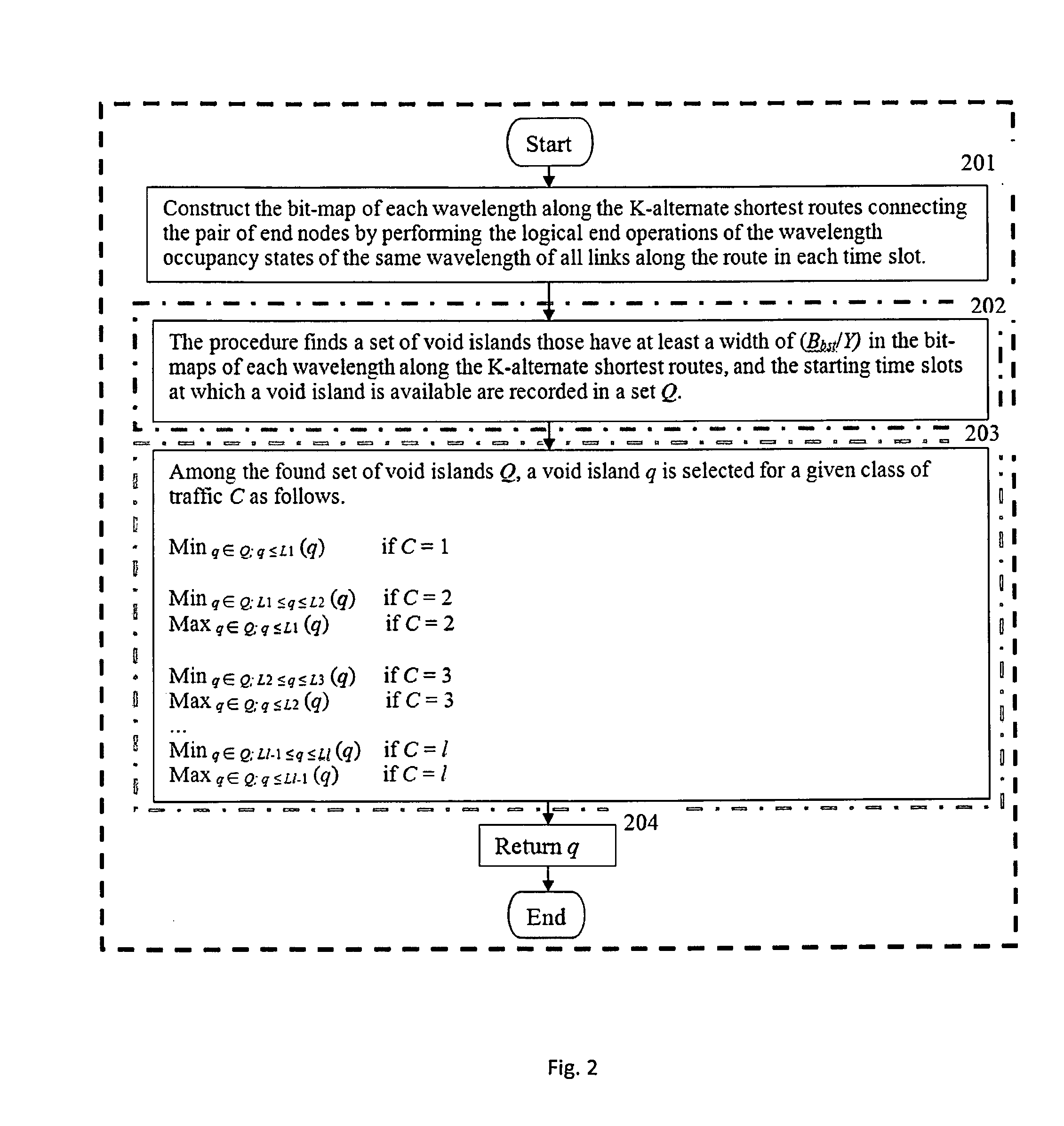
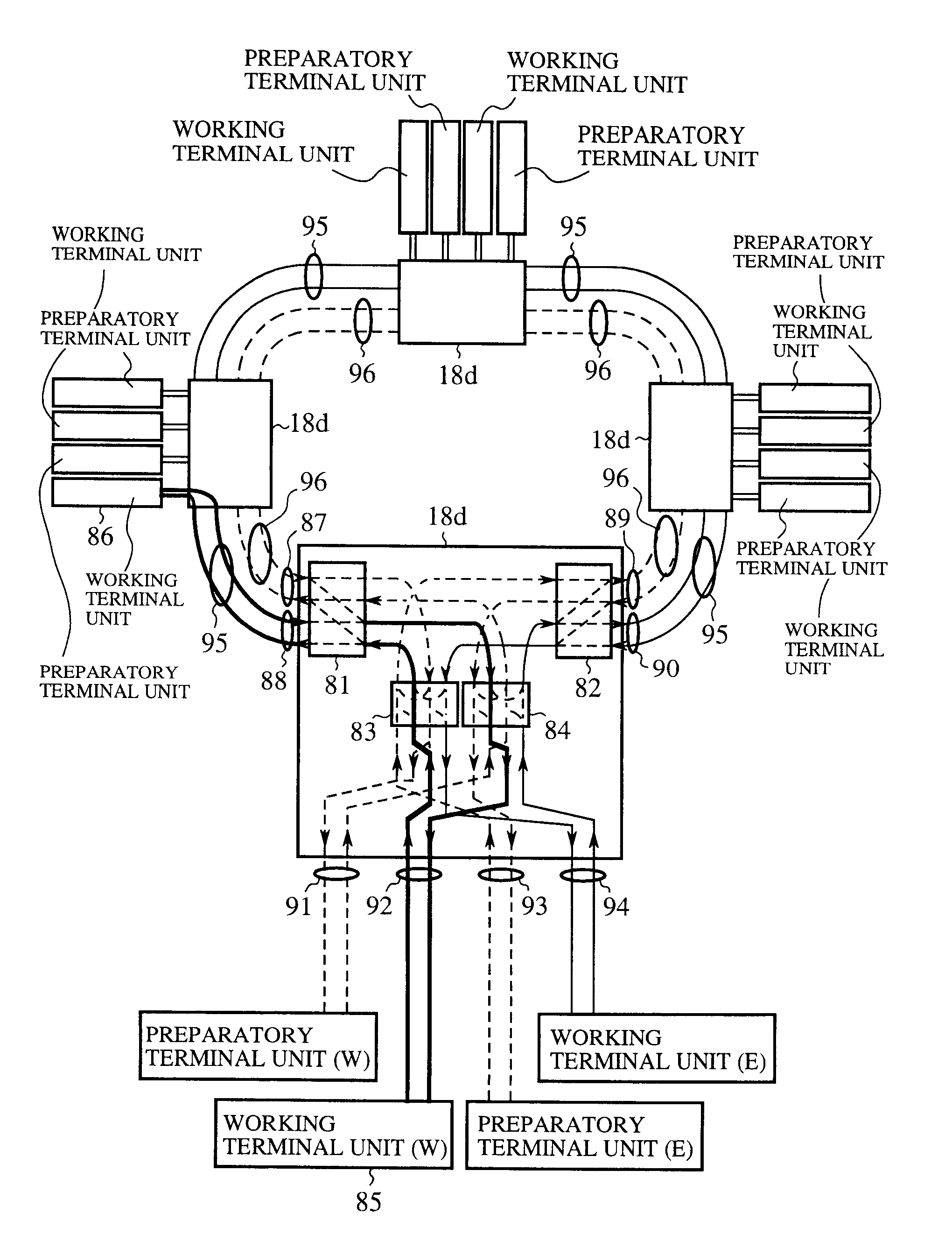
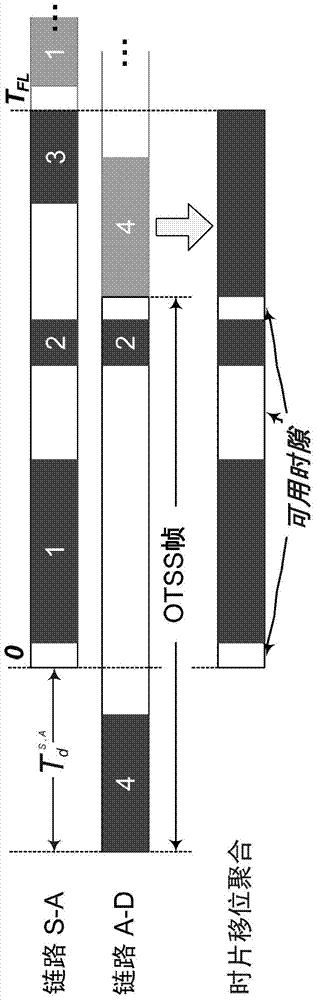
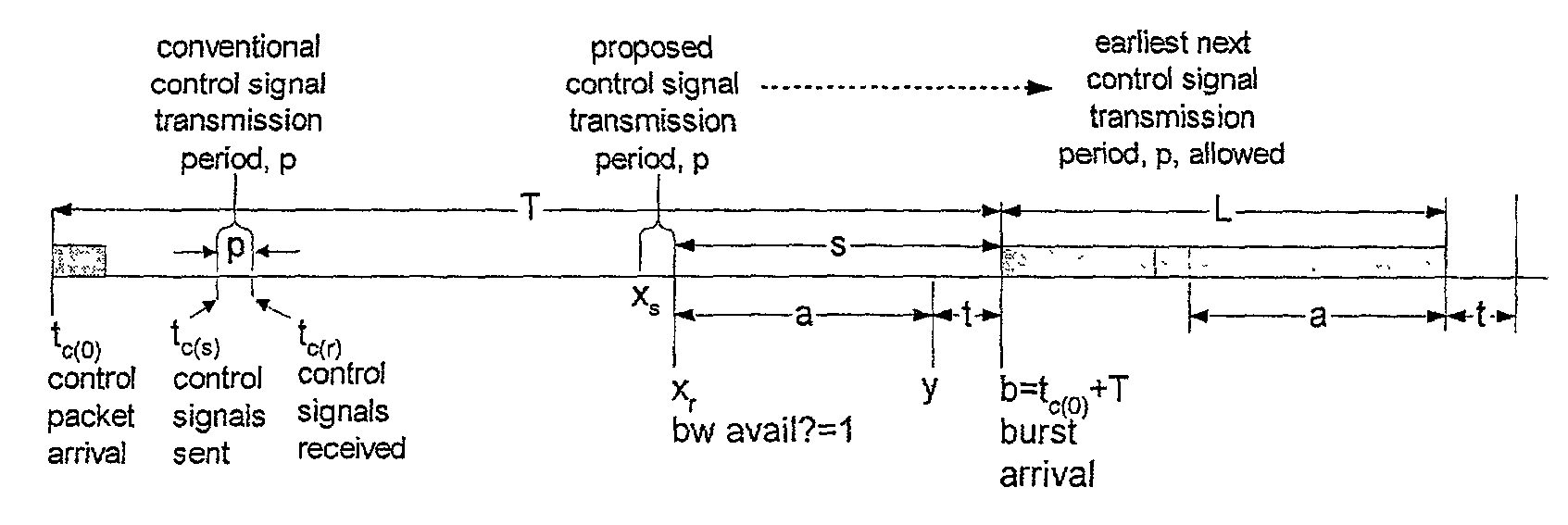
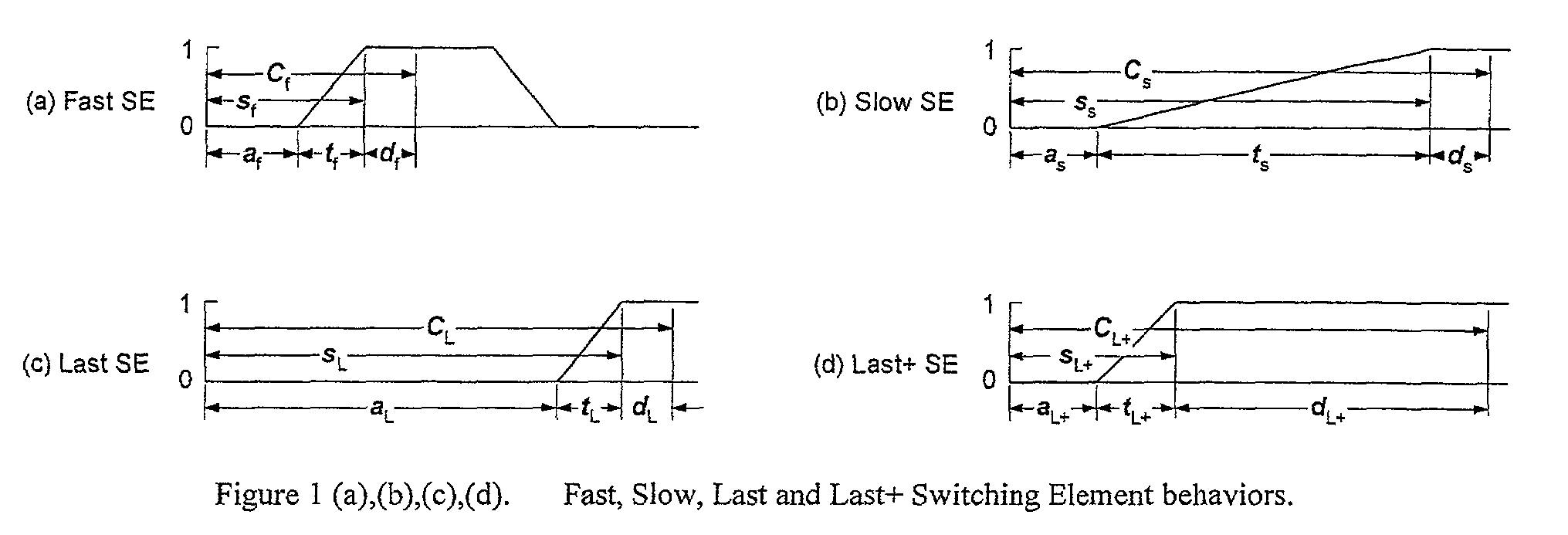
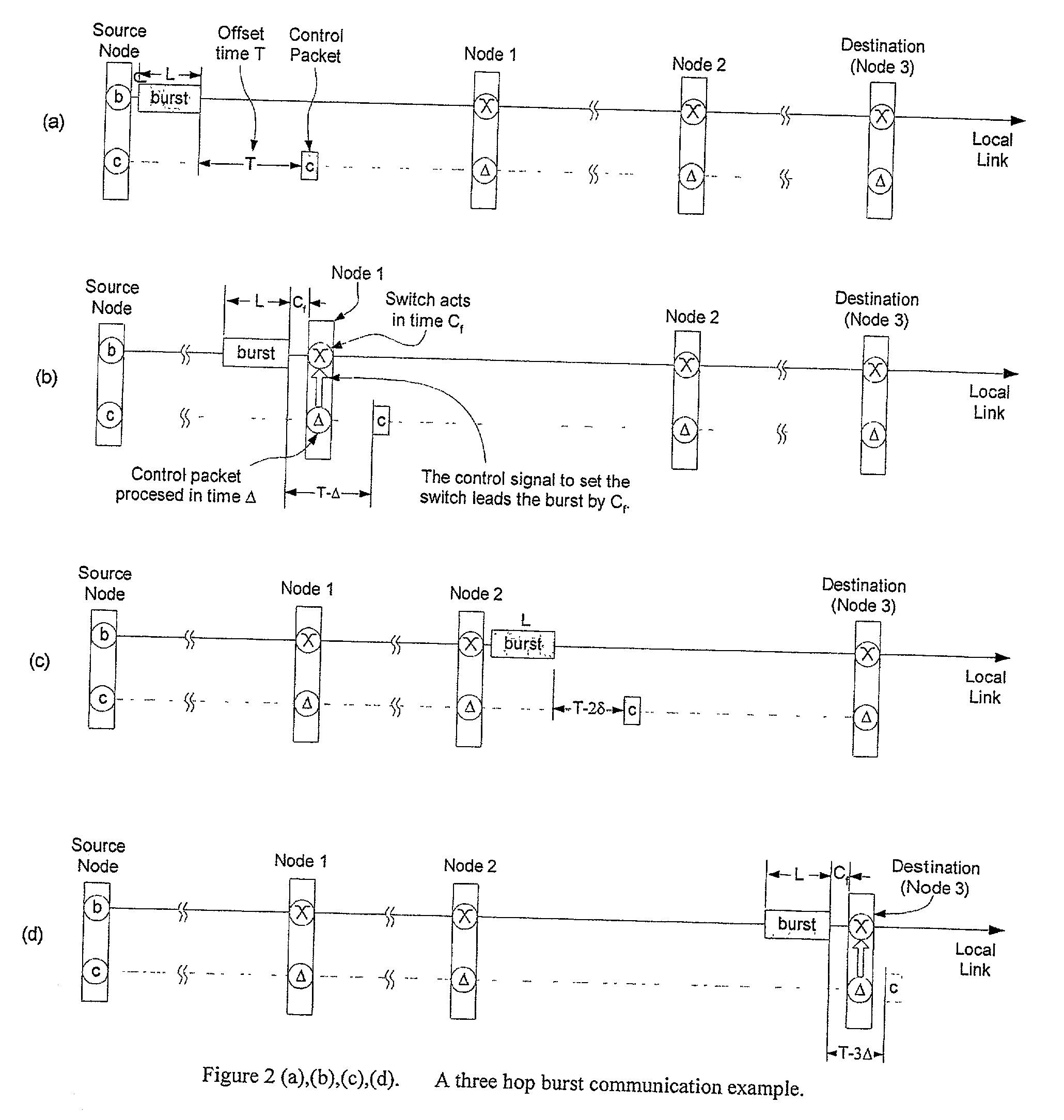
Patents
Literature
127 results about "Optical burst switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
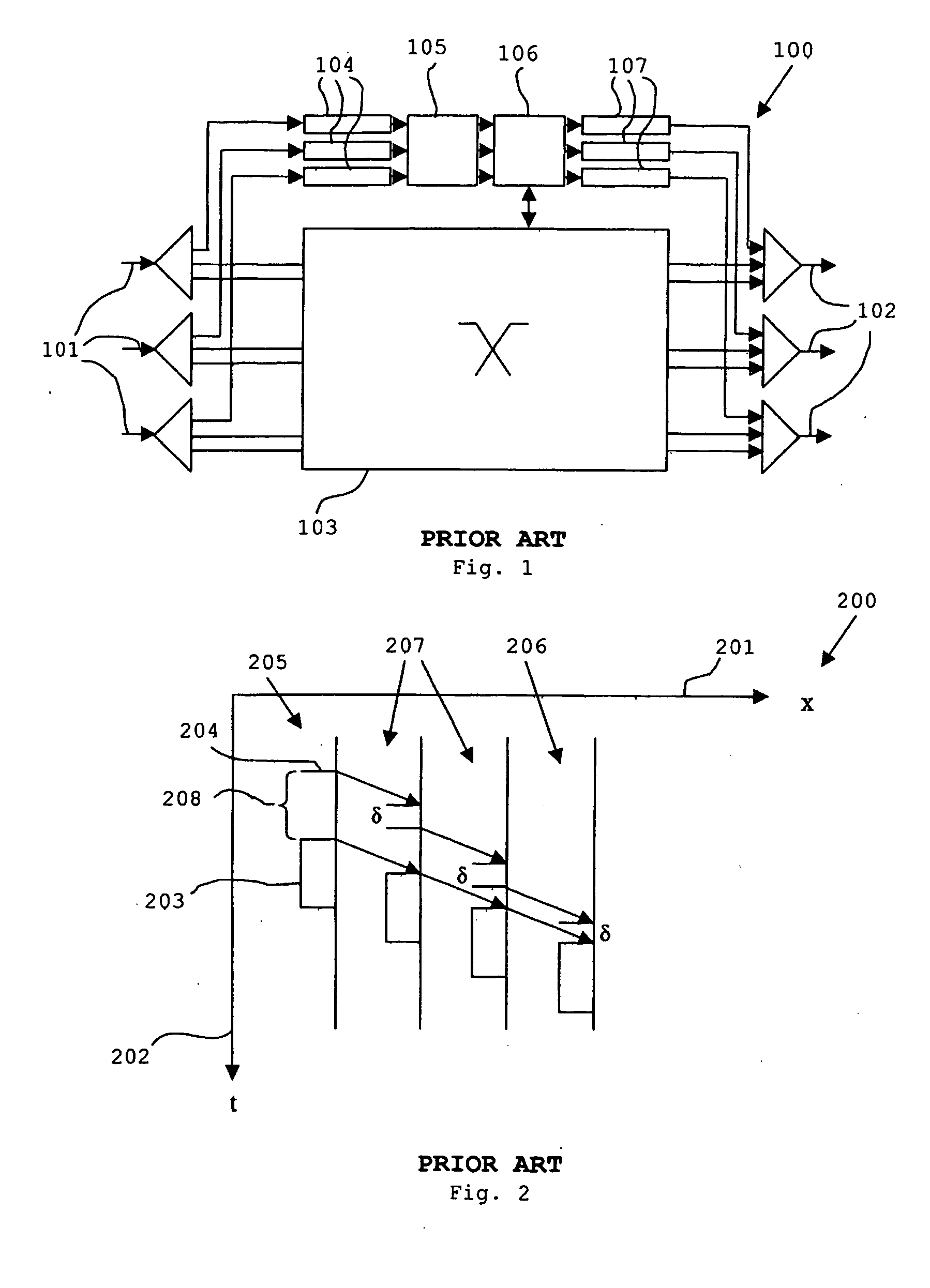
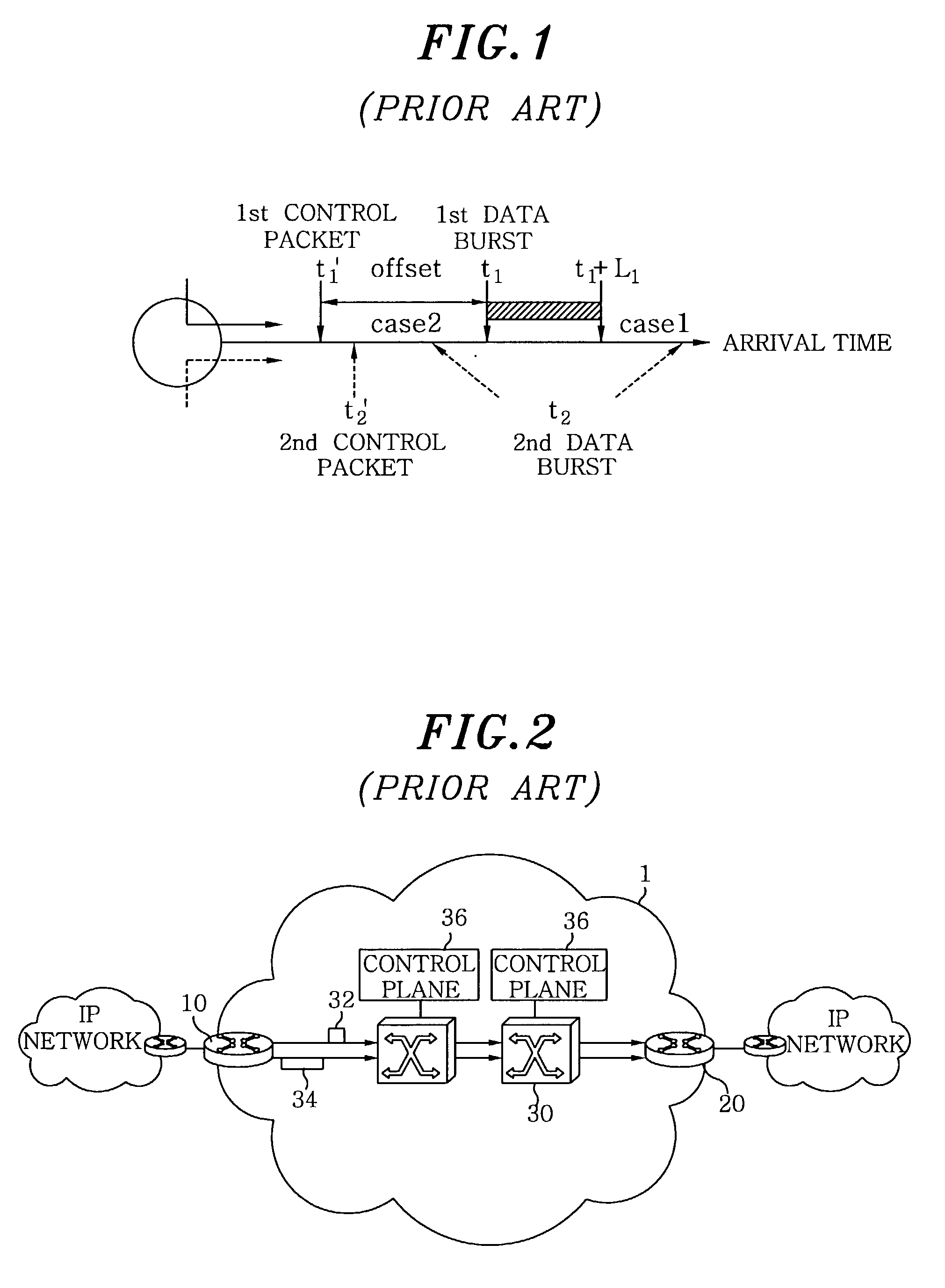
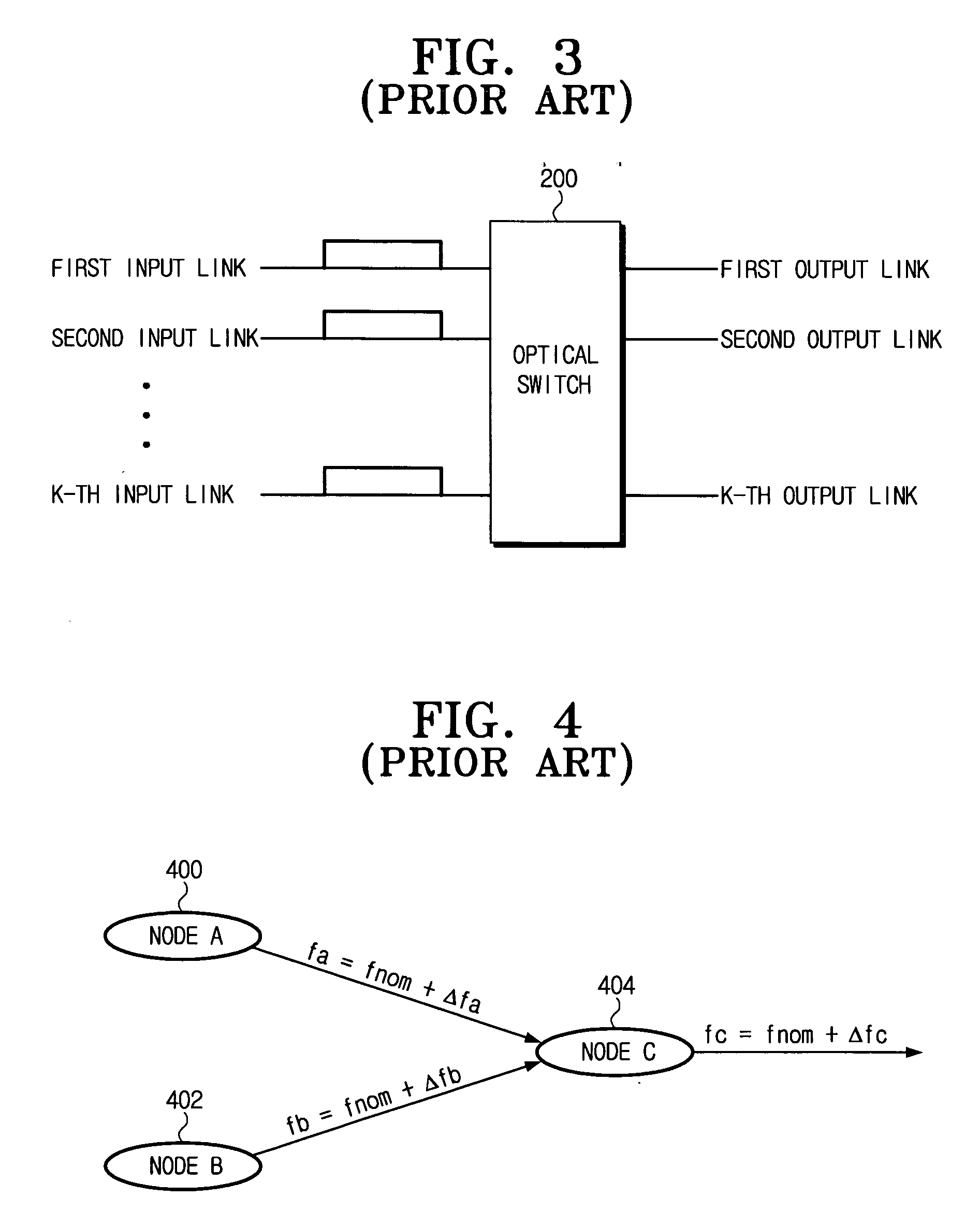
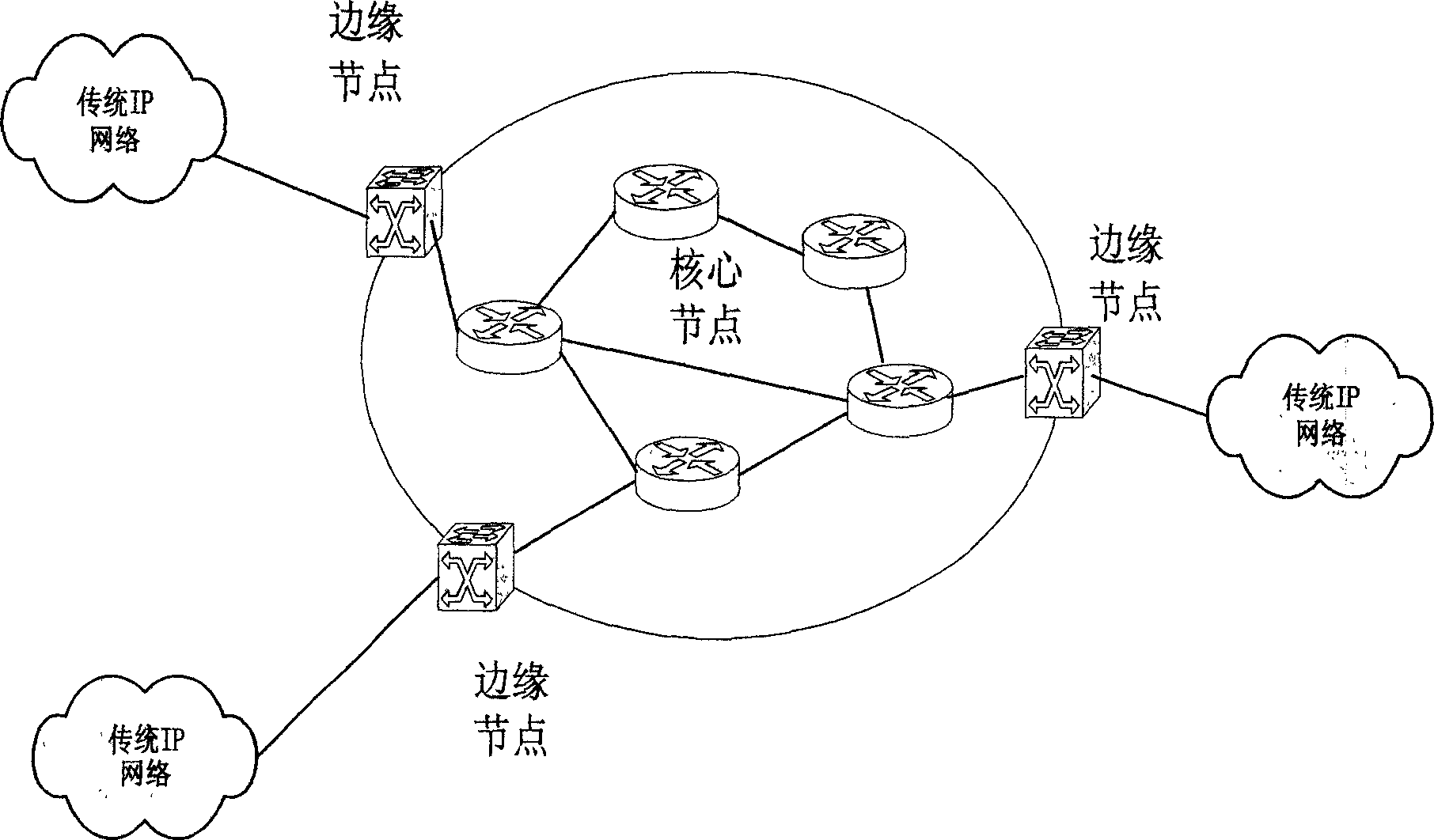
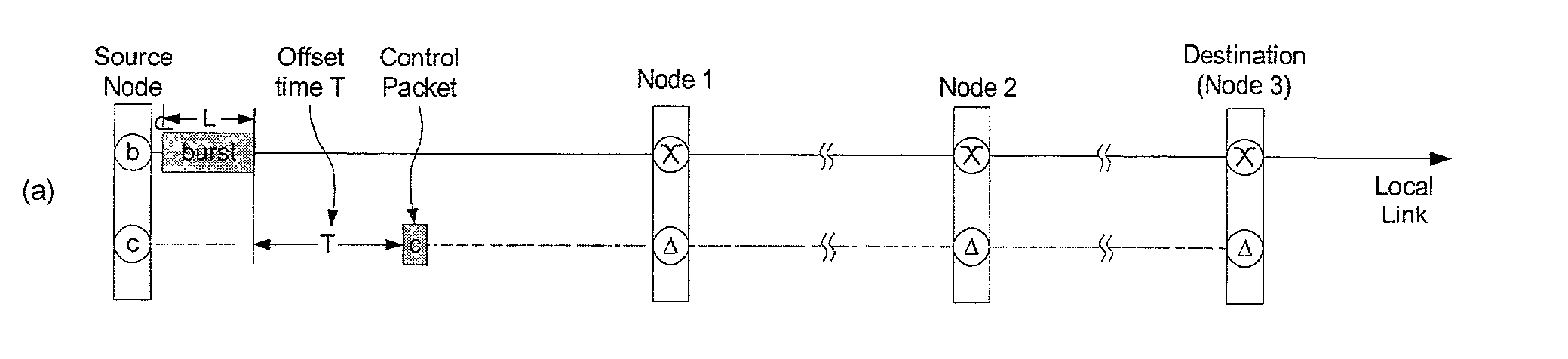
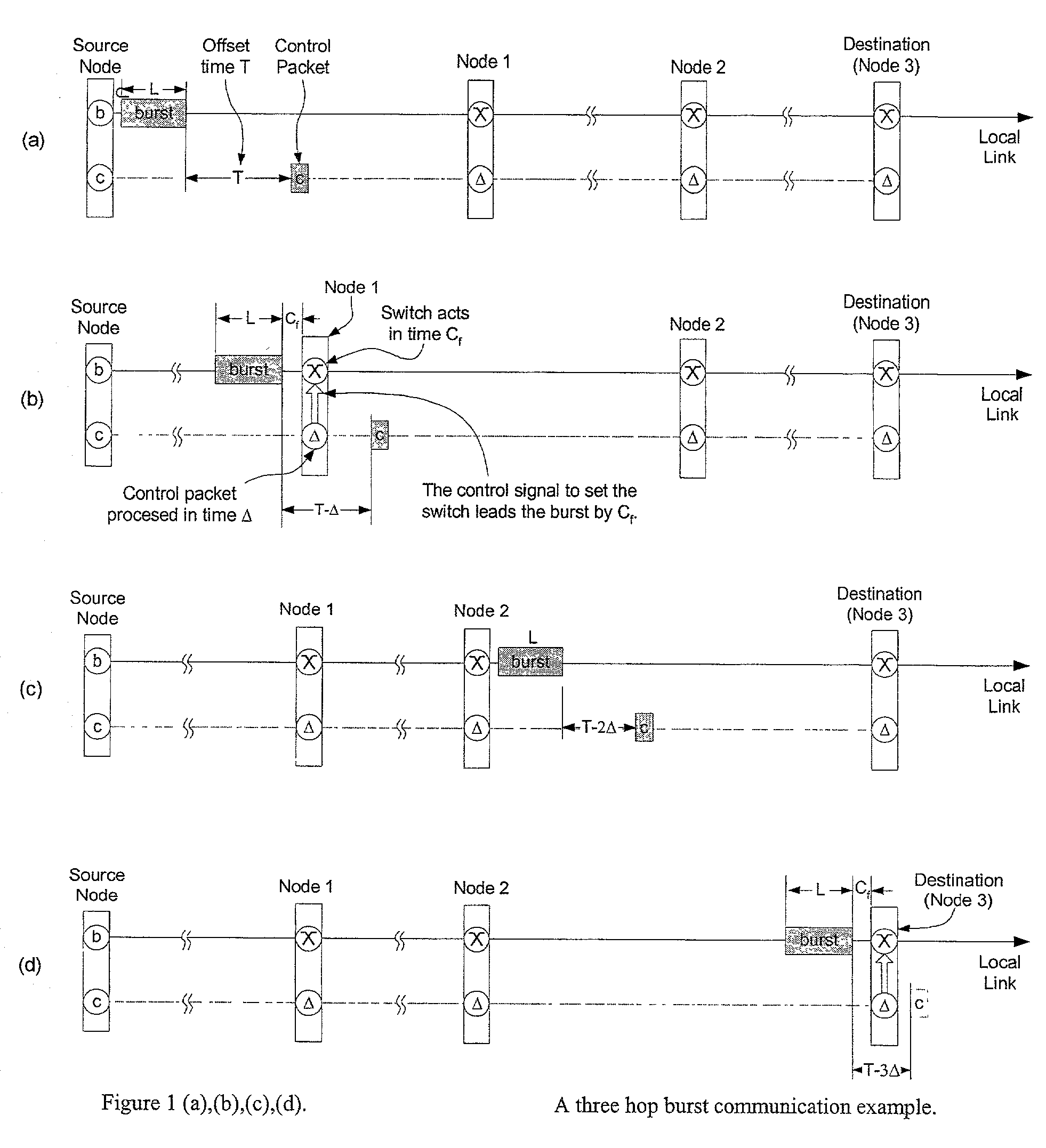
Optical burst switching (OBS) is an optical networking technique that allows dynamic sub-wavelength switching of data. OBS is viewed as a compromise between the yet unfeasible full optical packet switching (OPS) and the mostly static optical circuit switching (OCS). It differs from these paradigms because OBS control information is sent separately in a reserved optical channel and in advance of the data payload. These control signals can then be processed electronically to allow the timely setup of an optical light path to transport the soon-to-arrive payload. This is known as delayed reservation.
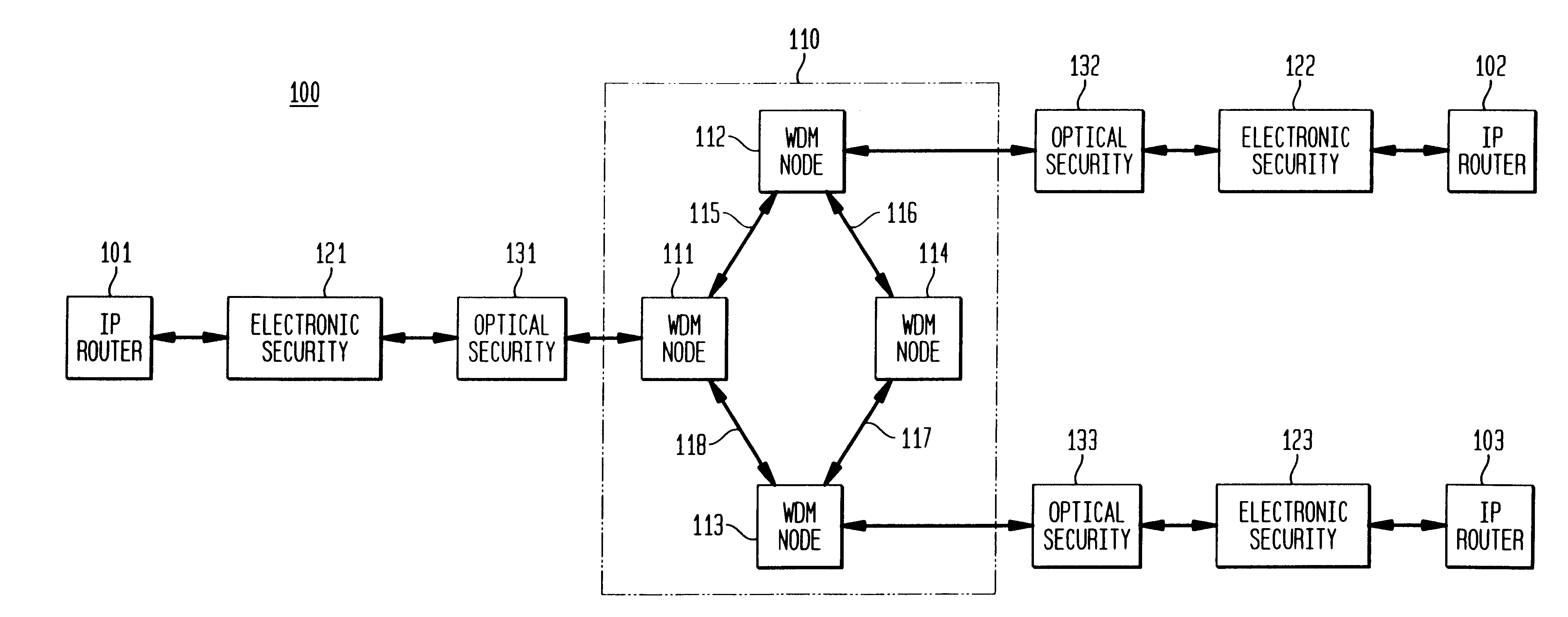
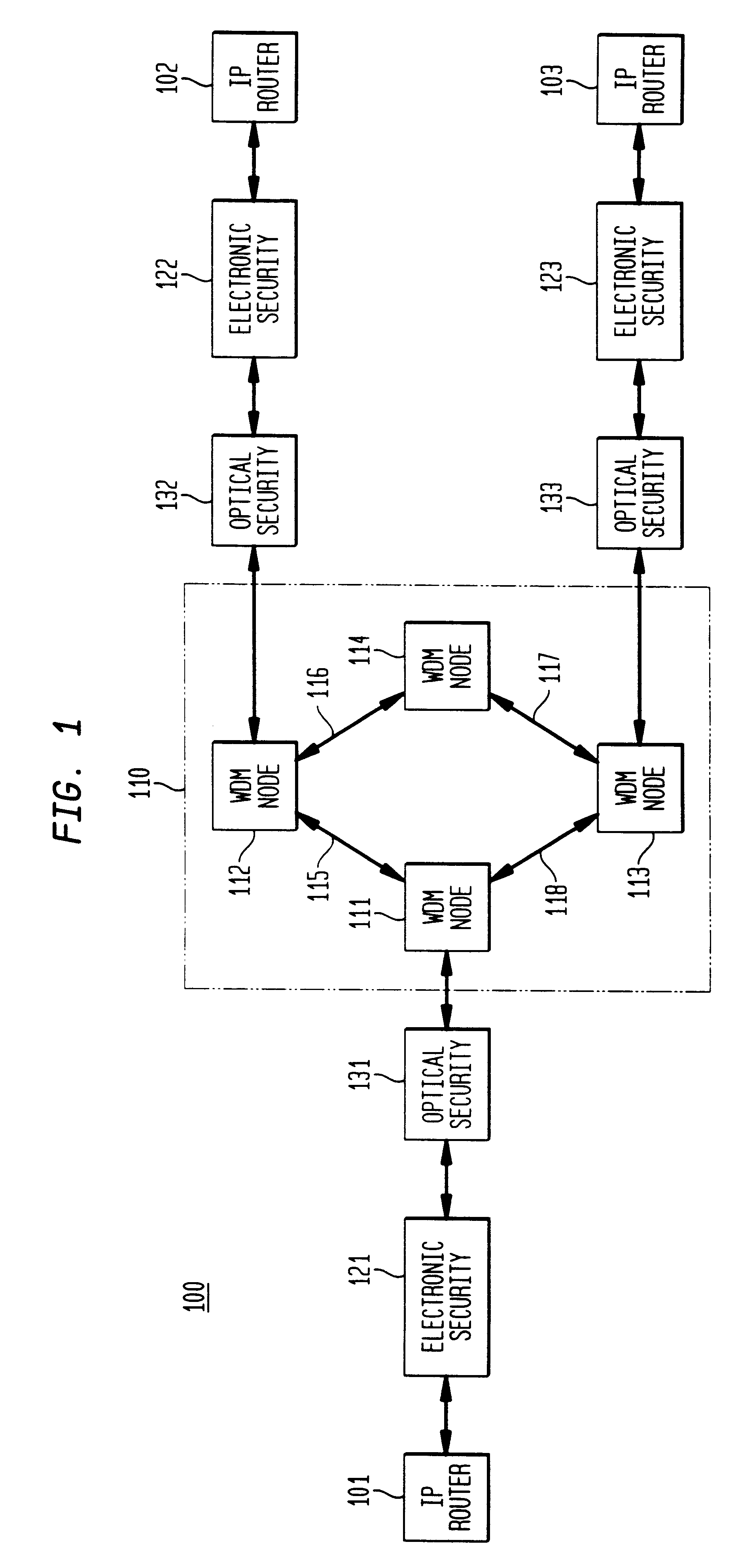
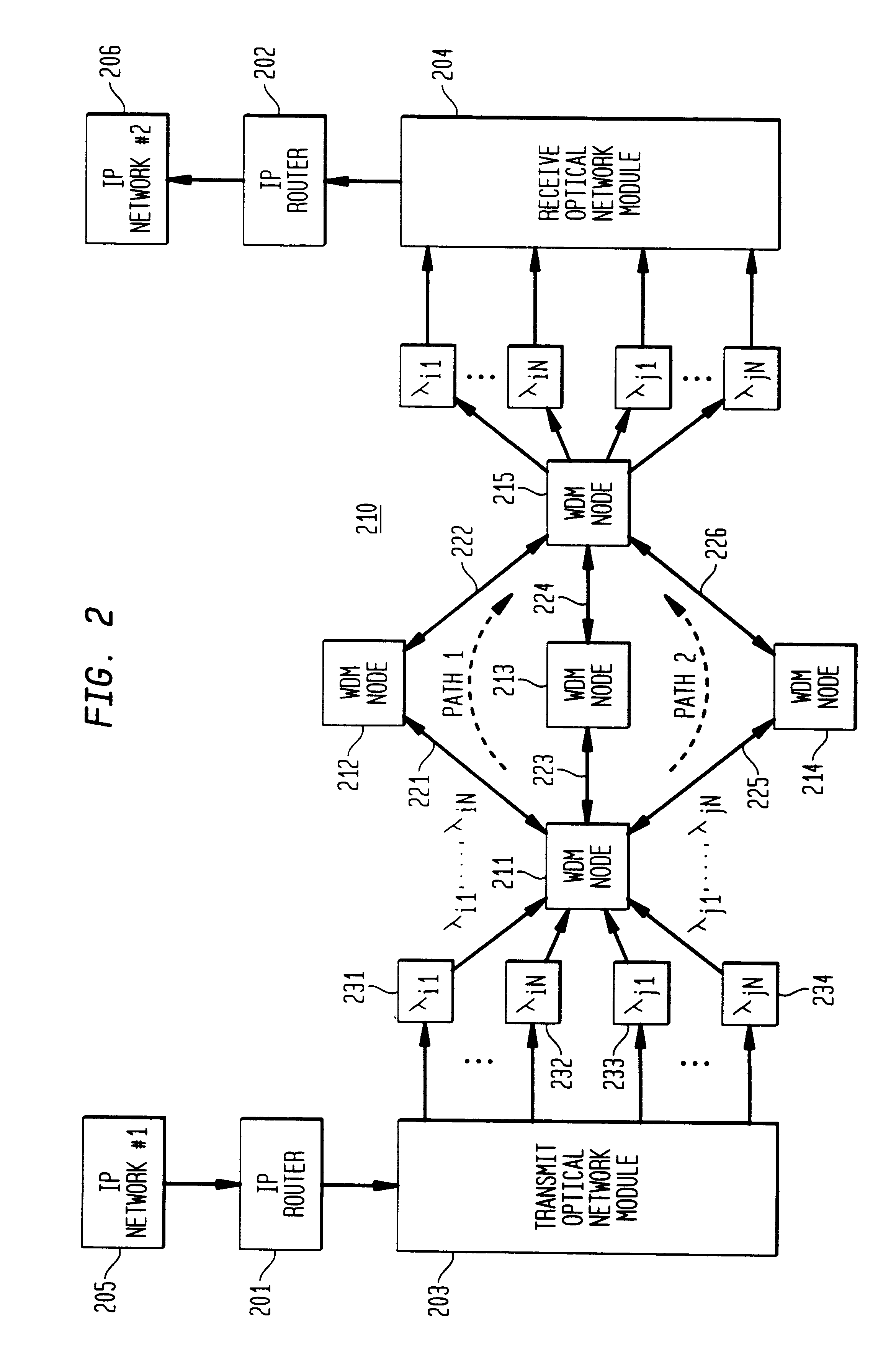
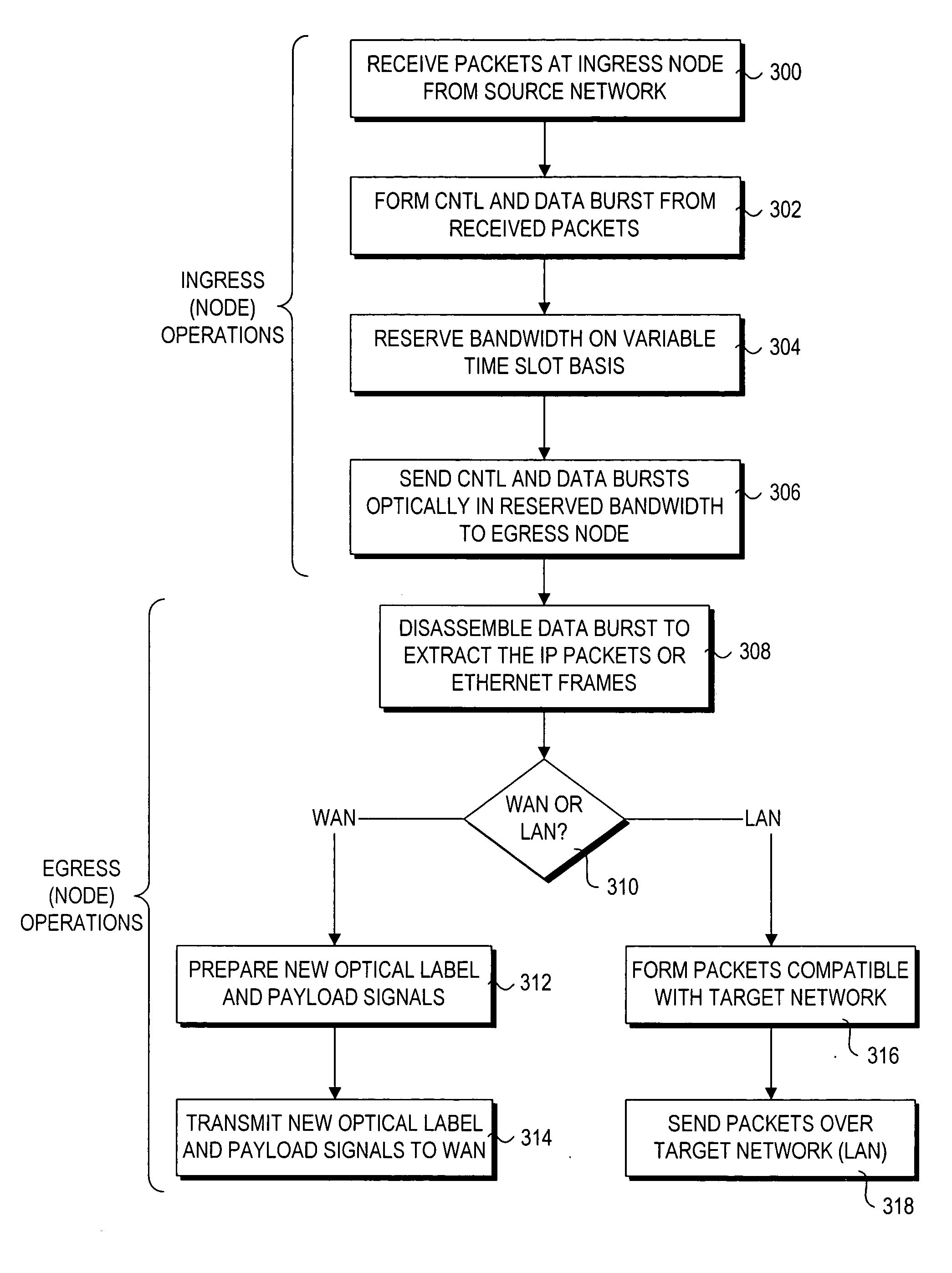
Optical layer survivability and security system using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation and detection
InactiveUS6271946B1Increase probabilityIncrease optical powerMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSurvivabilityOptical burst switching
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The technique effects survivability and security of the optical networks by encompassing conventional electronic security with an optical security layer by generating replicated versions of the input data payload at the input node, and the transmission of each of the replicated versions over a corresponding one of the plurality of links. Moreover, each of the links is composed of multiple wavelengths to propagate optical signals or optical packets, and each of the replicated versions of the data payload may be propagated over a selected one of the wavelengths in each corresponding one of the plurality of links.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
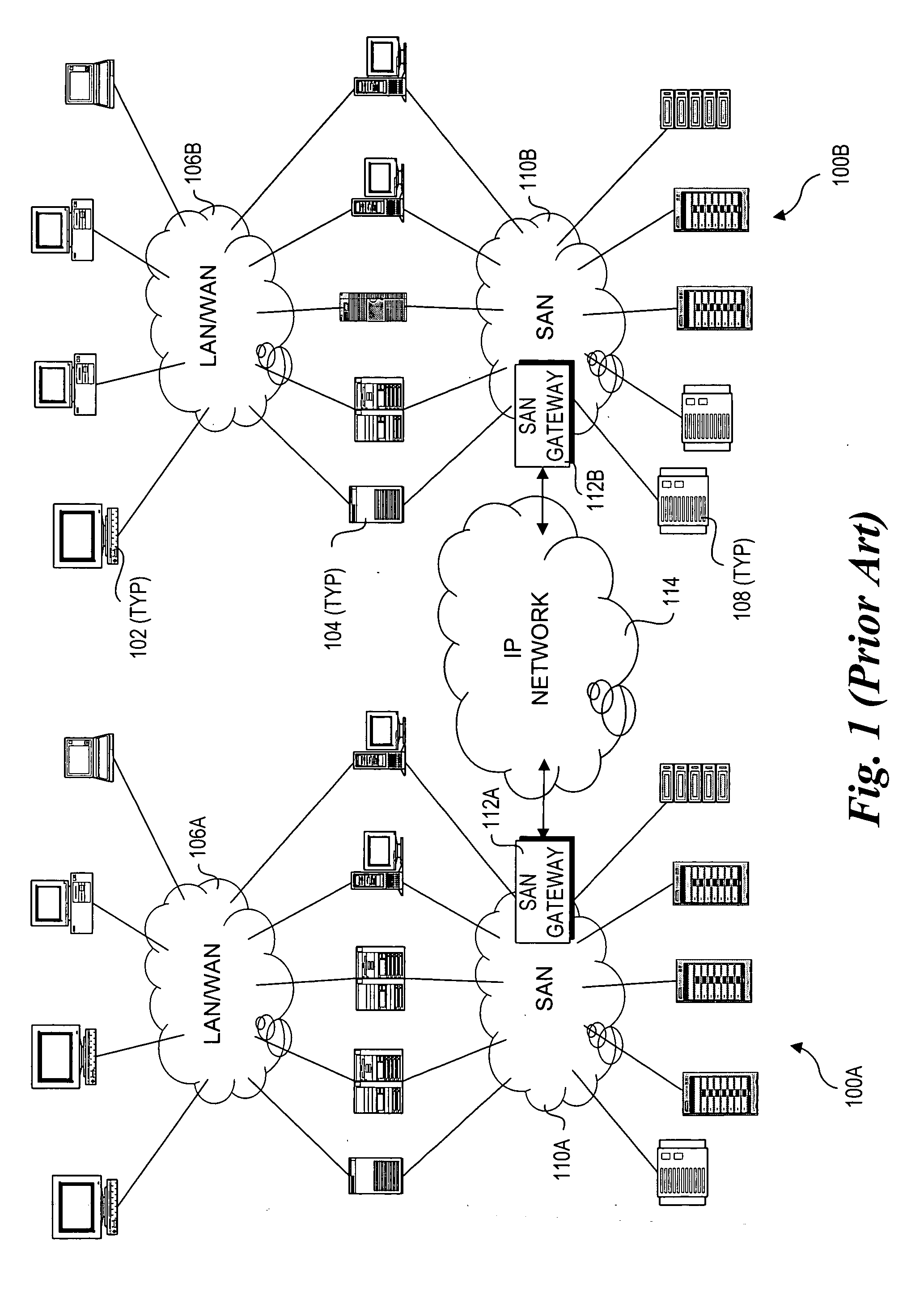
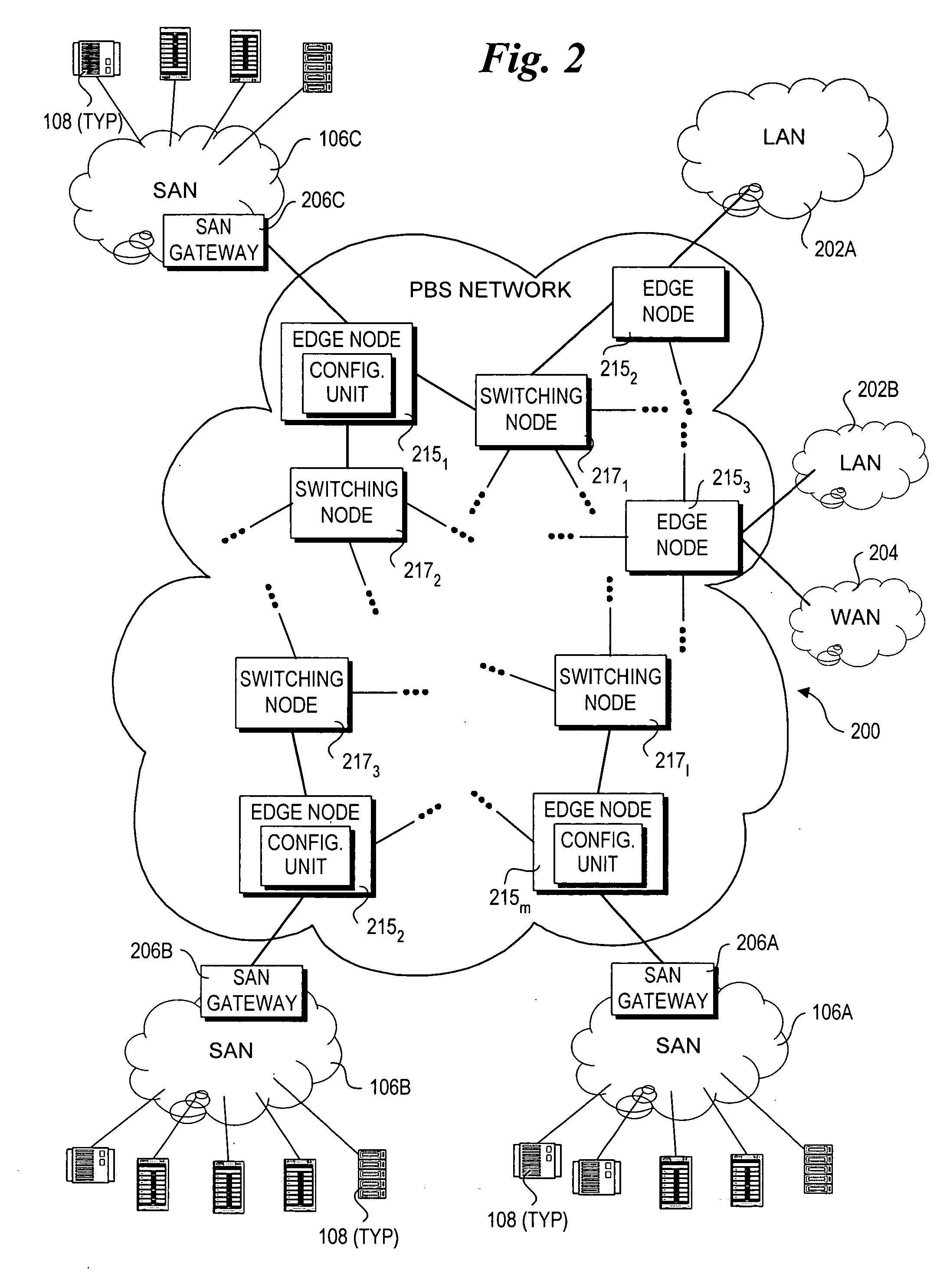
Method and architecture for optical networking between server and storage area networks
InactiveUS20050175341A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsArea networkStorage area network
A method and system for routing high-speed data to and from SANs (Storage Area Networks and Server Area Networks) via optical burst-switched (OBS) networks. OBS network components, including edge nodes and switching nodes, are coupled between SAN islands. In one embodiment, the OBS network comprises a photonic burst-switched (PBS) network. Under one scheme, a PBS edge node and SAN gateway are co-located at the interface to the SAN, while a plurality of PBS switching nodes are deployed between the PBS edge nodes. Under another scheme, PBS switching / edge nodes are co-located at respective SANs. This scheme employs an external gateway protocol (EGP) for routing data via selected route segments. Data going to and received from a SAN is packaged as Fibre Channel Frames. Data transmitted via the PBS network is converted into PBS frames having encapsulated Fibre Channel Frames. The schemes also support interfaces with legacy networks, such as LANs and WANs.
Owner:INTEL CORP
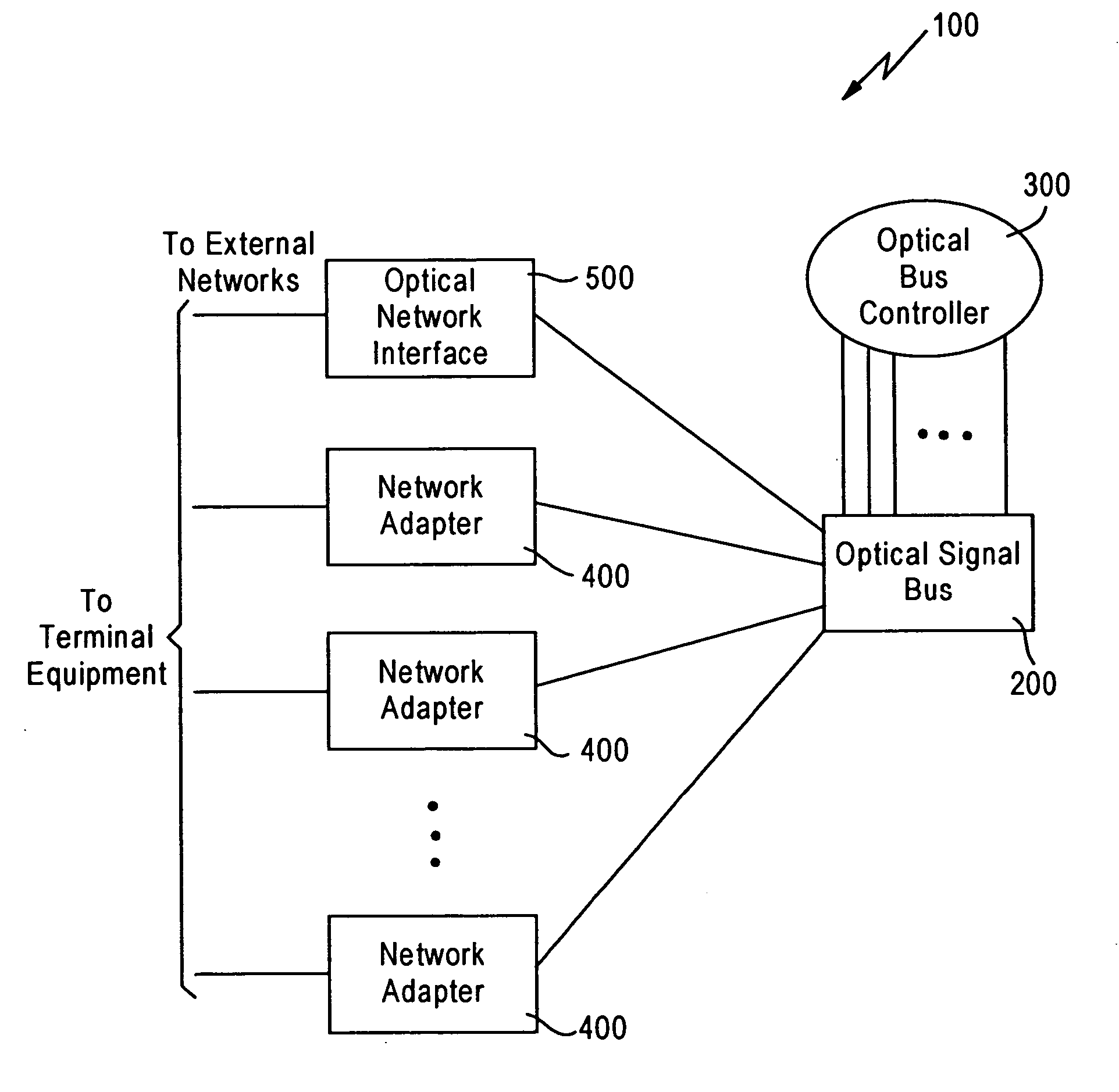
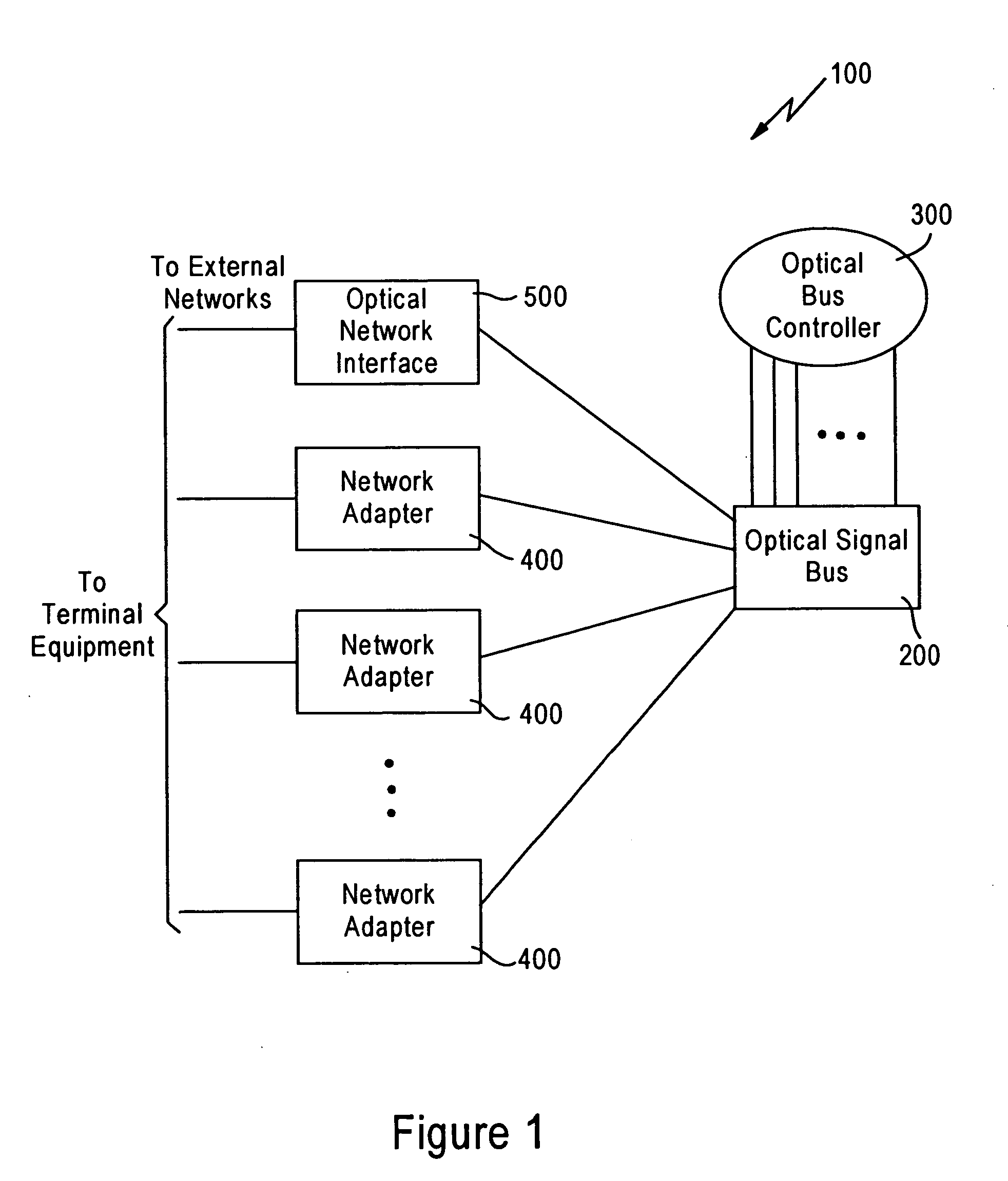
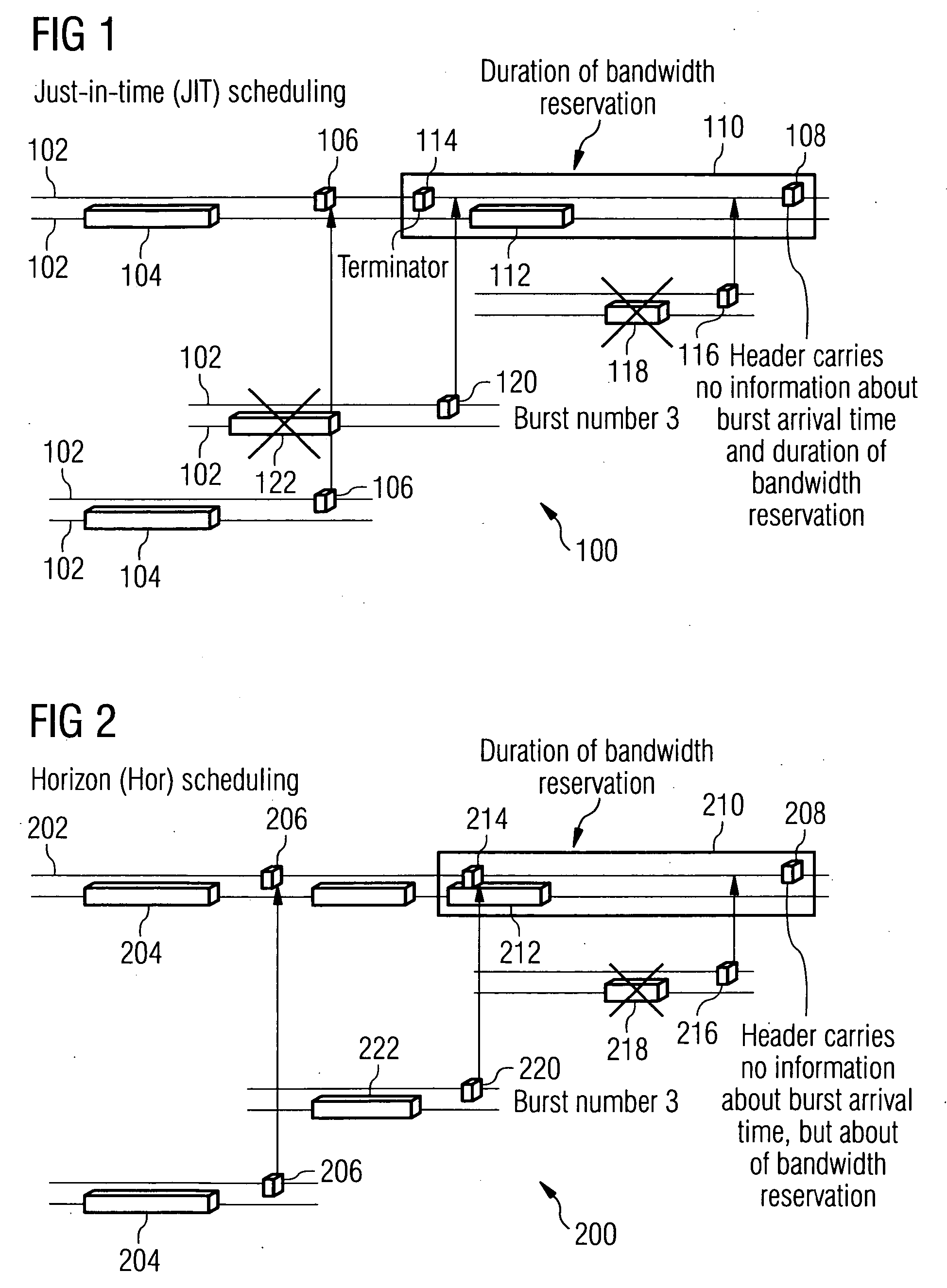
Optical burst switch network system and method with just-in-time signaling
InactiveUS20050013613A1Lower latencyRich varietyMultiplex system selection arrangementsFibre transmissionNetwork terminationOptical burst switching
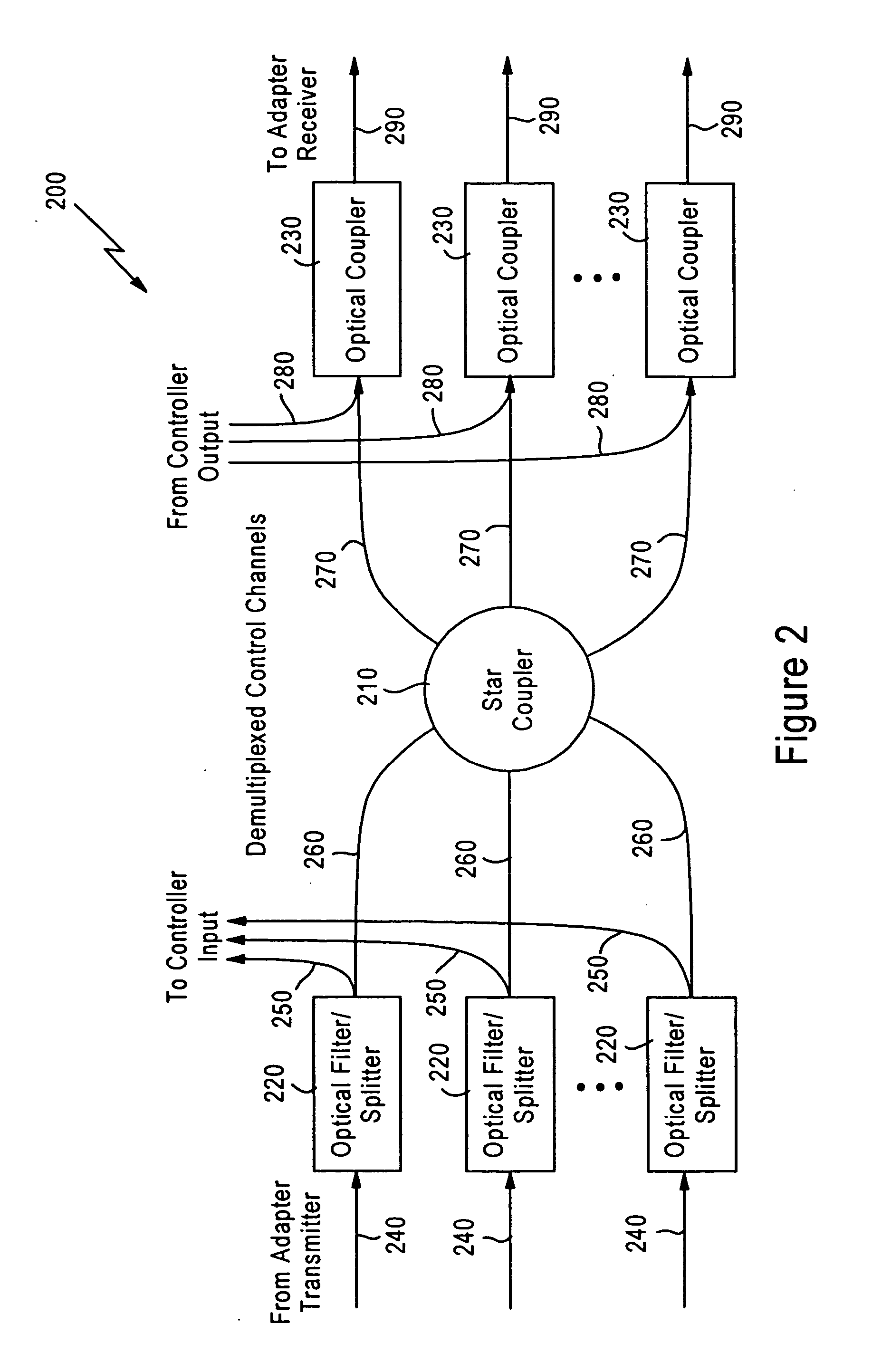
Optical burst switch network system and method with Just-in-Time (JIT) signaling and advanced data transmission and memory access and management. The system and method allow concurrent data transmission having arbitrary signal types, such as analog and digital signal types, in which the JIT signaling allows for subsequent simultaneous transmission of optical signals that do not require electro-optical conversion. The system includes an optical signal bus having a passive star coupler. A plurality of network adapters that are in optical communication with the optical signal bus and in network communication with network terminal devices are provided. The network adapters include receivers, transmitters and control logic that allows for bi-directional movement of data signals as bursts between the terminal equipment and the network system. The transmitter and receiver may be fixed or tunable. The system further includes an optical bus controller in optical communication with the optical signal bus that processes signals from the optical signal bus to connect a requested network adapter to a requesting network adapter in accordance with the user-to-network protocol. The network system implements a just-in-time signaling protocol to signal nodes in the network that burst communications are forthcoming. Optionally, the system allows comprehensive memory access in a Local Area Network (LAN). The nodes in the network are capable of seamlessly addressing memories of all other nodes that comprise the network.
Owner:RES TRIANGLE INST
Method and apparatus for synchronized slotted optical burst switching
InactiveUS6963564B1Efficient and flexibleMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsFiberOptical burst switching
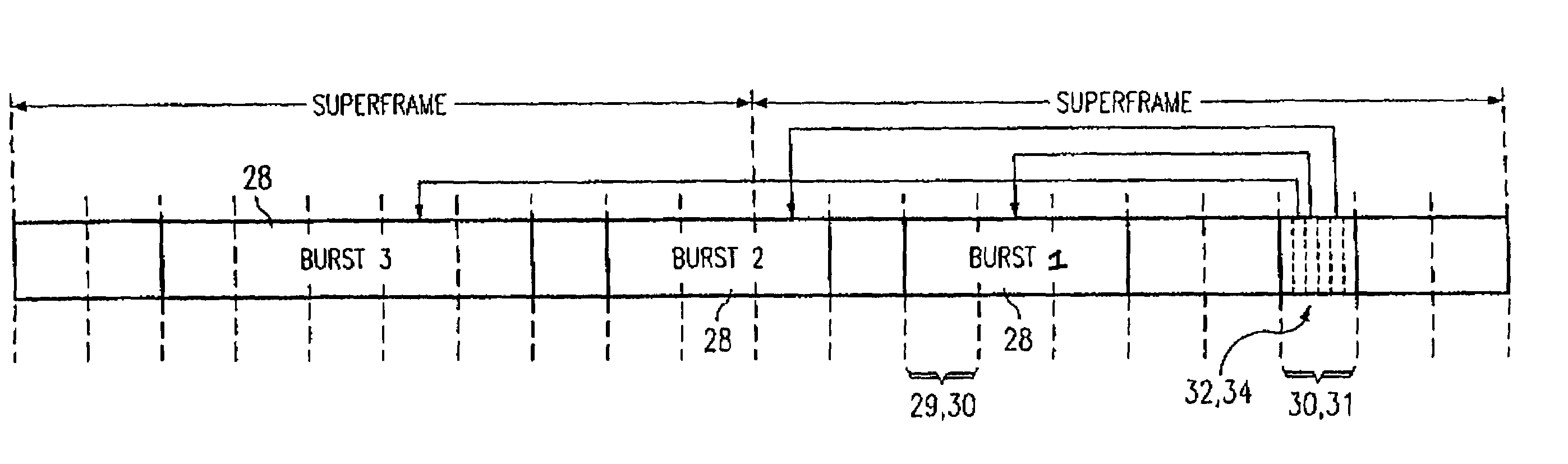
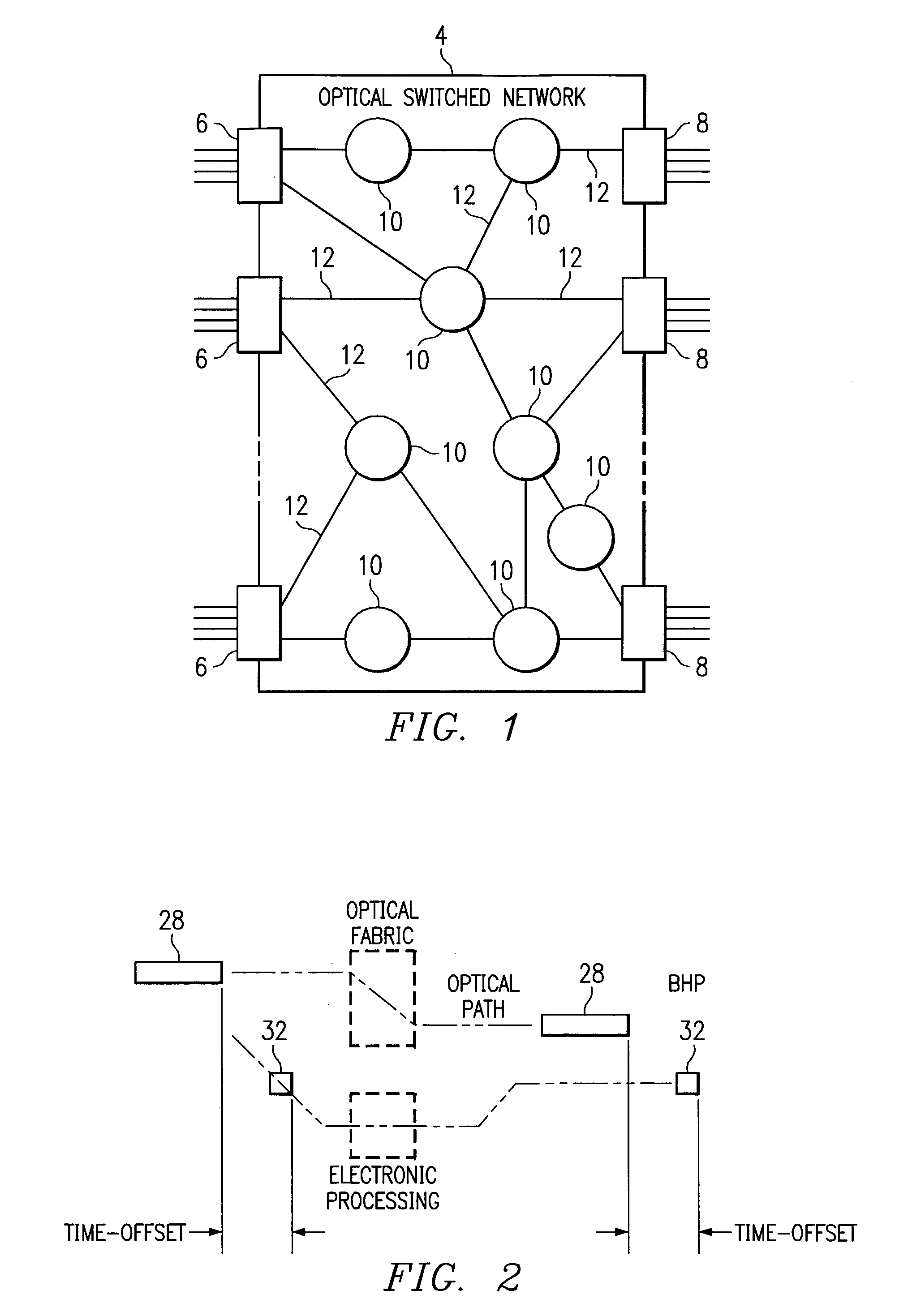
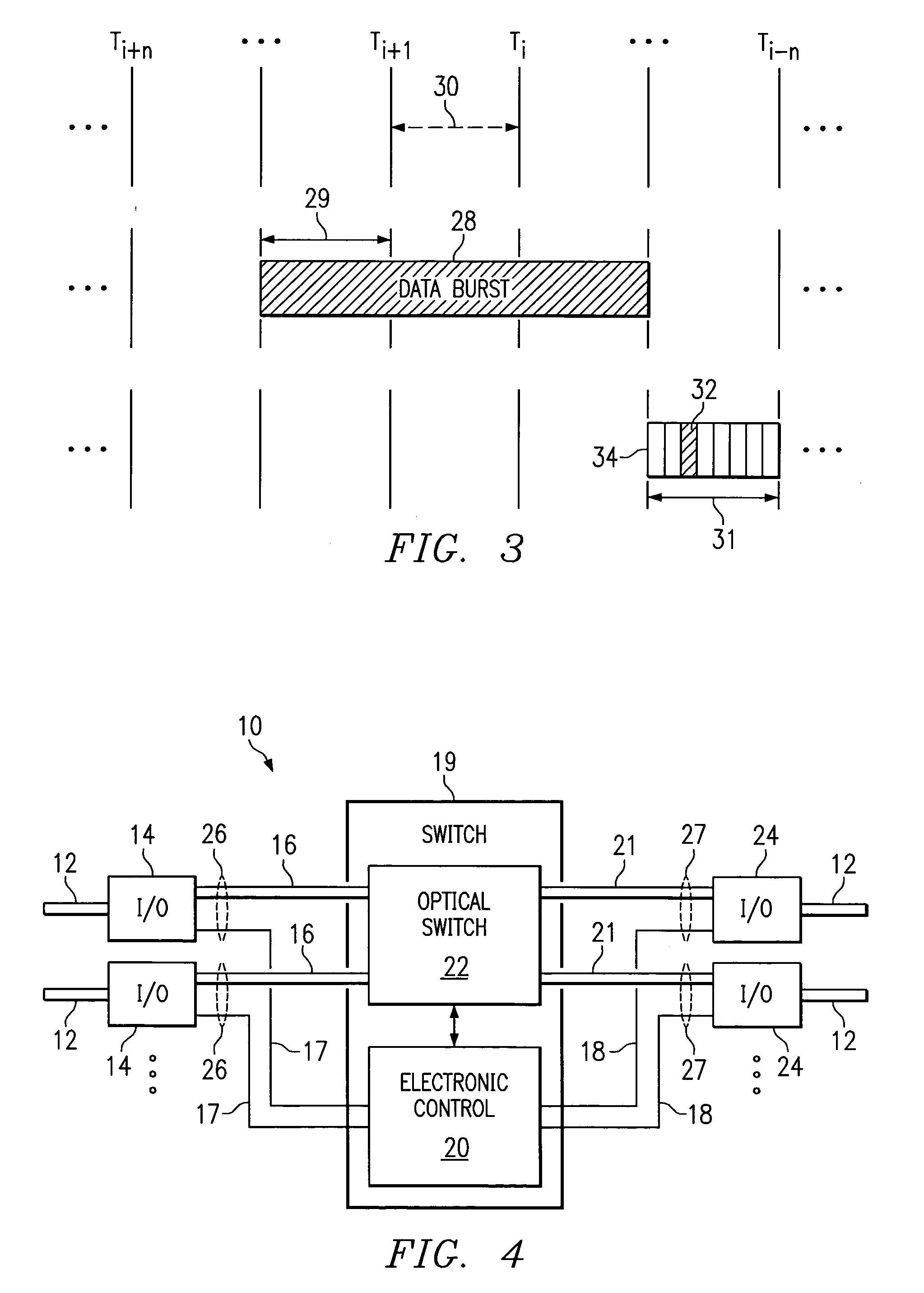
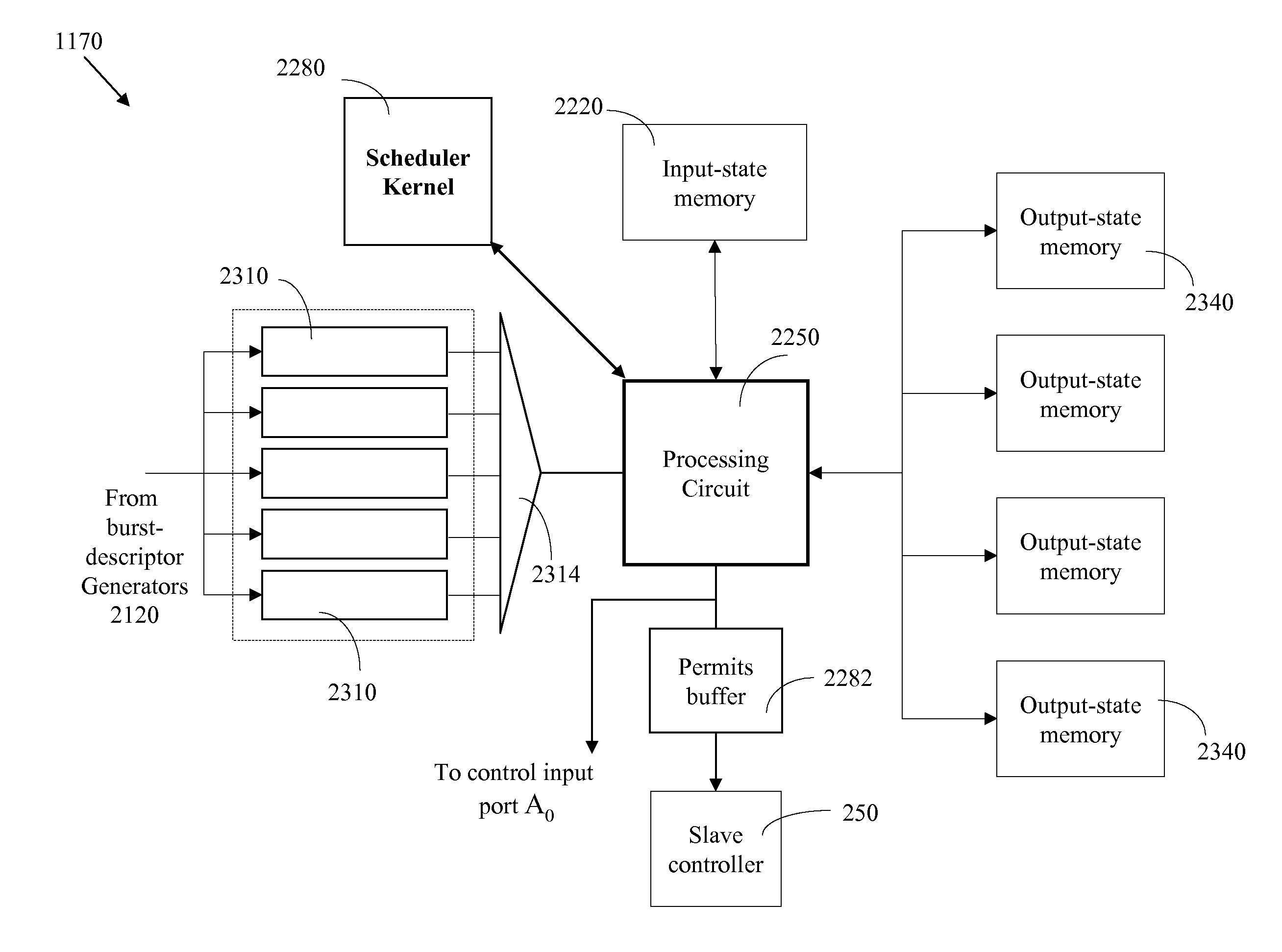
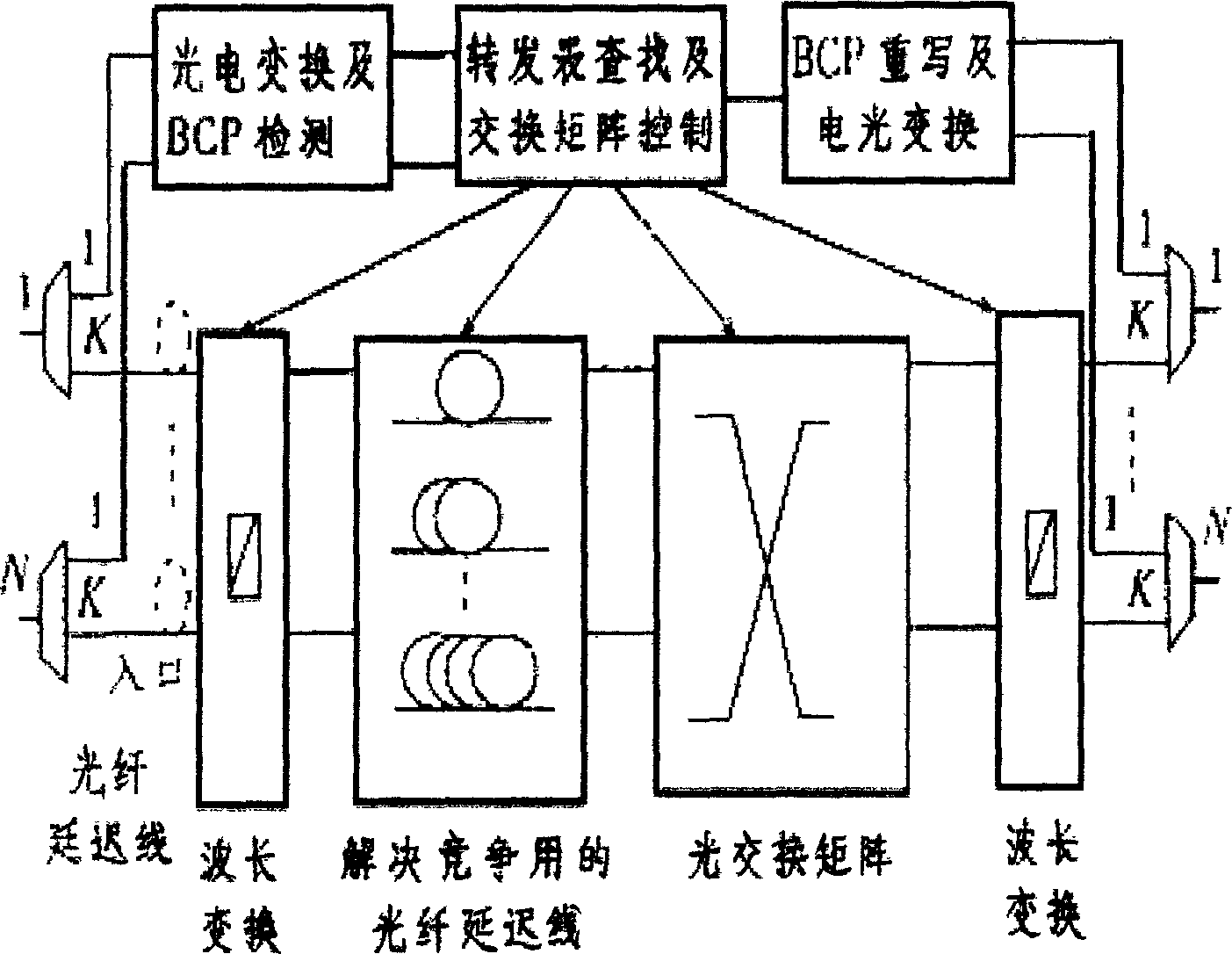
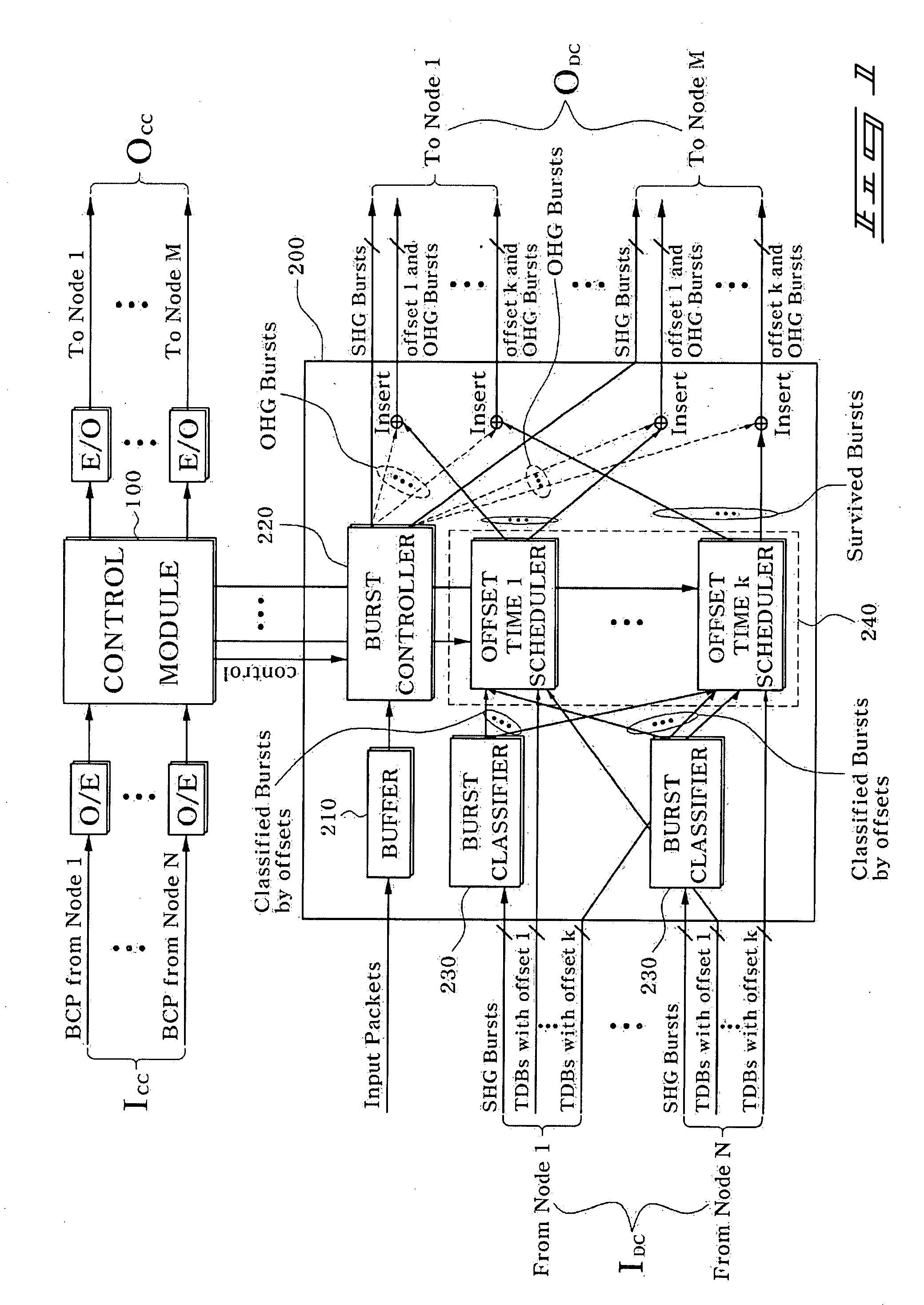
A network (4) includes optical routers (19), which route information in fibers (10). Each fiber carries a plurality of data channels (16), carrying data in data bursts (28) and a control channel, carrying control information in burst header packets (32). A burst header packet includes routing information for an associated data burst (28) and precedes its associated data burst. Information on the data channels and control channel is organized in synchronized slots. Multiple burst header packets occupy portions of a slot, referred to as micro-slots. When the burst header packets are received, an egress processor (52) schedules the routing of their associated bursts. The egress processor (52) determines a time at which a data burst can be scheduled for passing through an optical matrix (40) to the desired output channel group (the burst can be delayed via fiber delay lines (46) if necessary).
Owner:RPX CORP
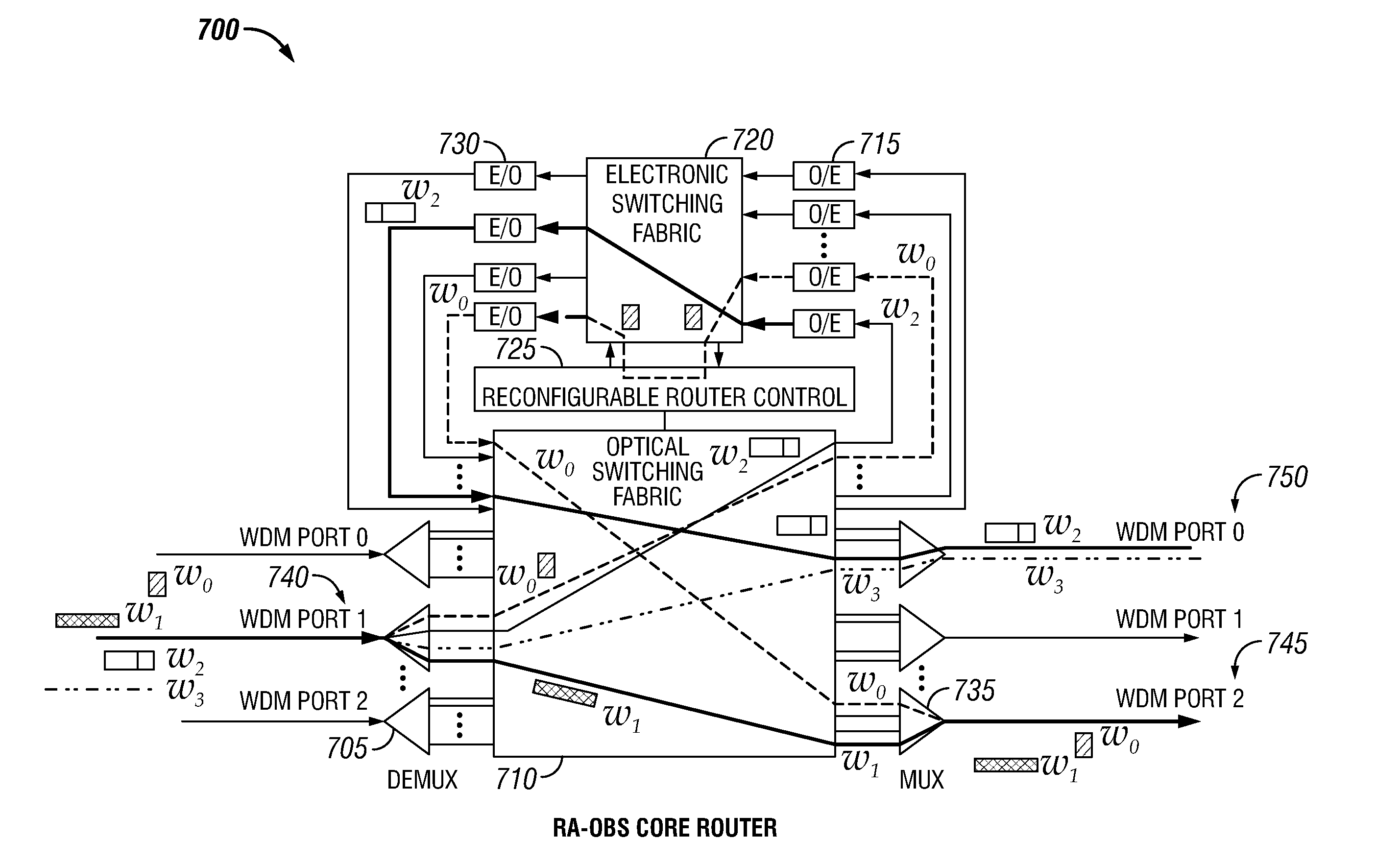
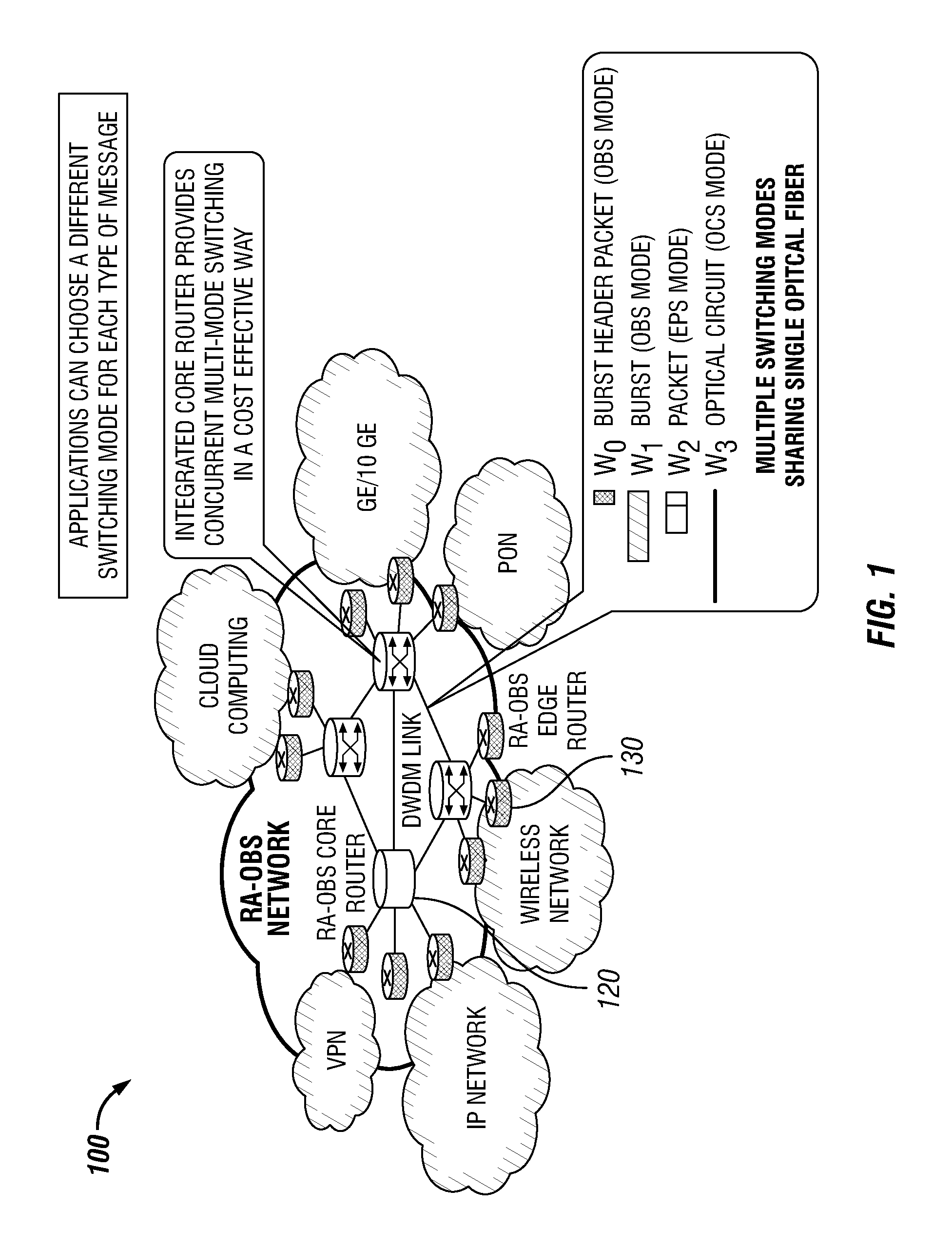
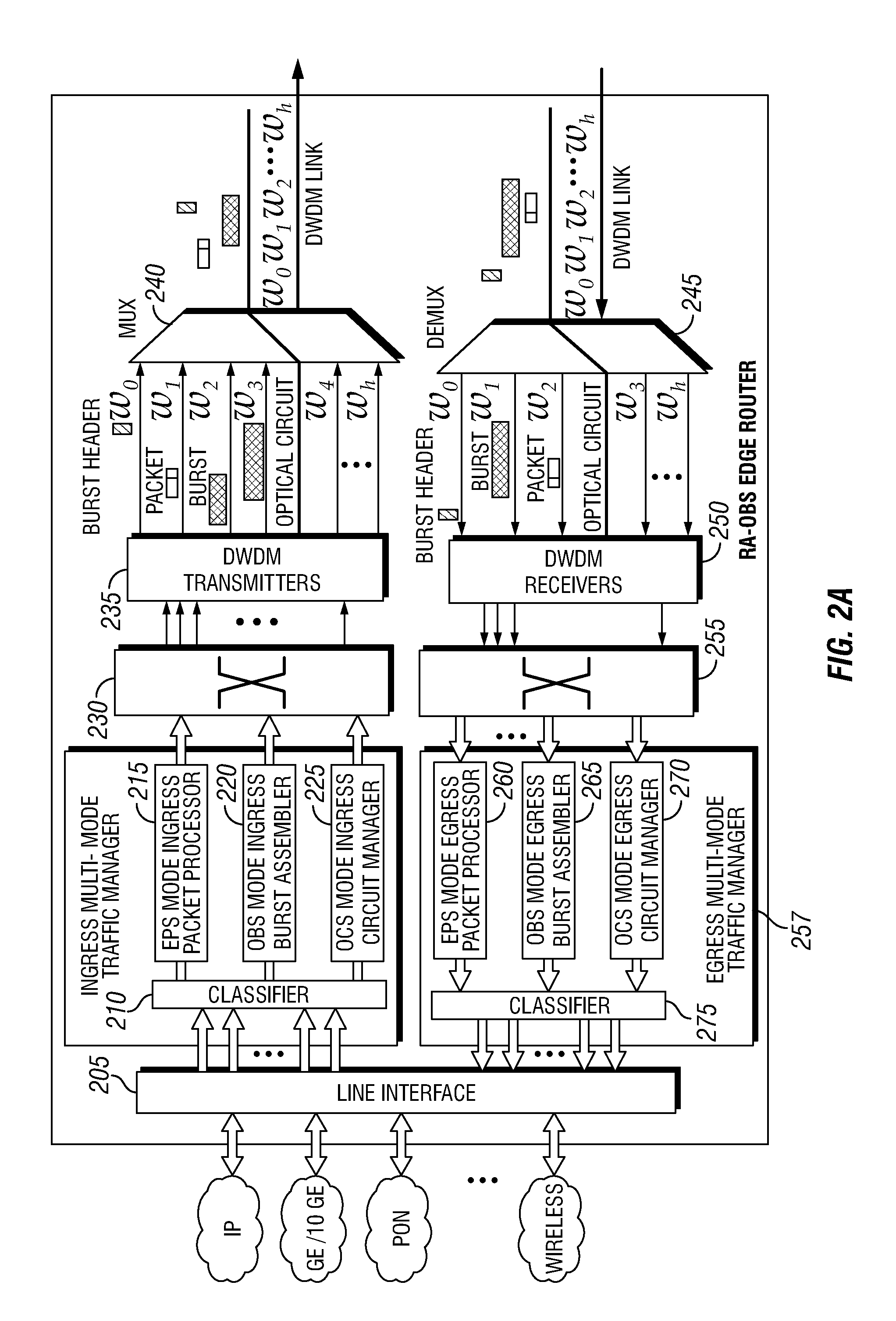
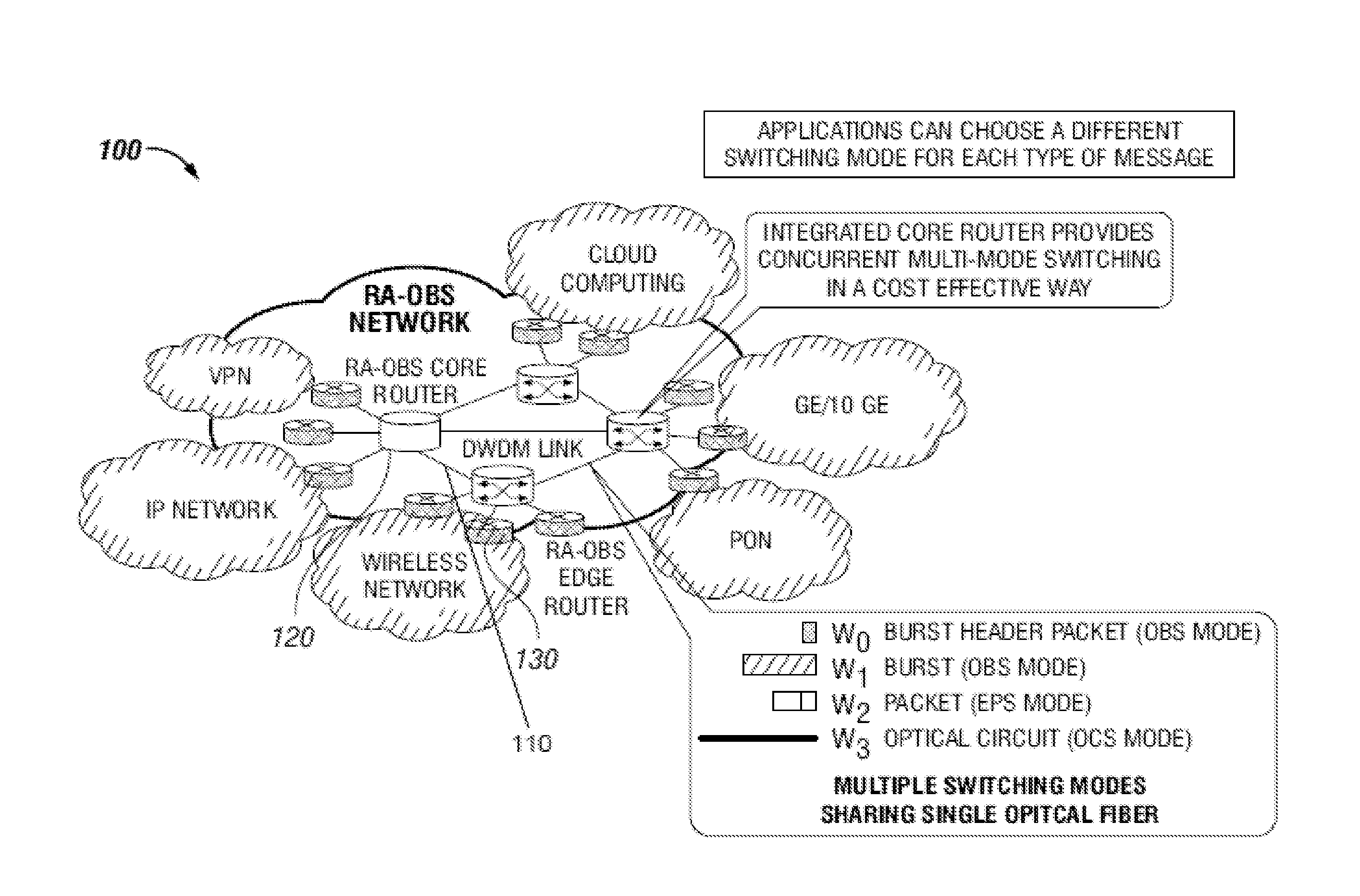
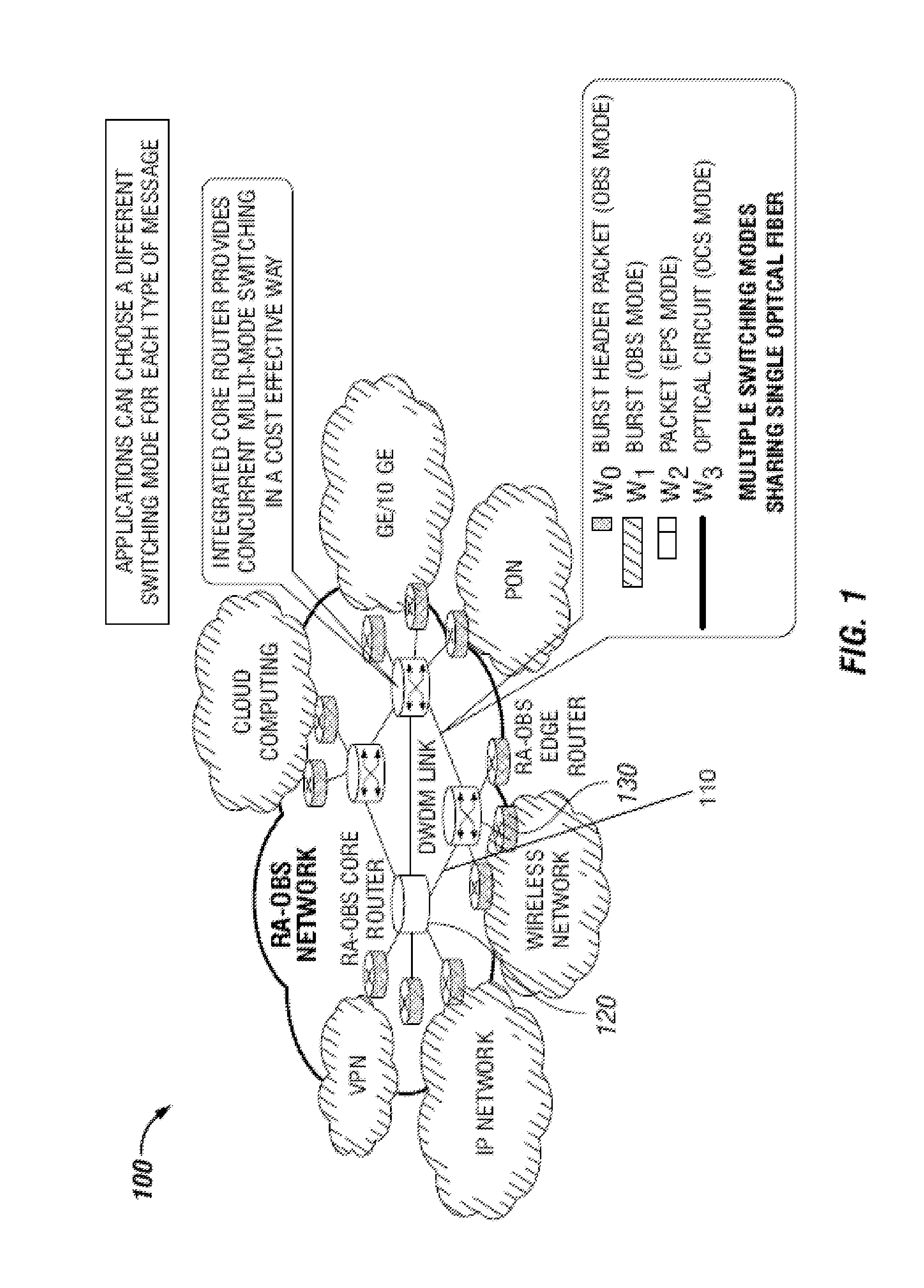
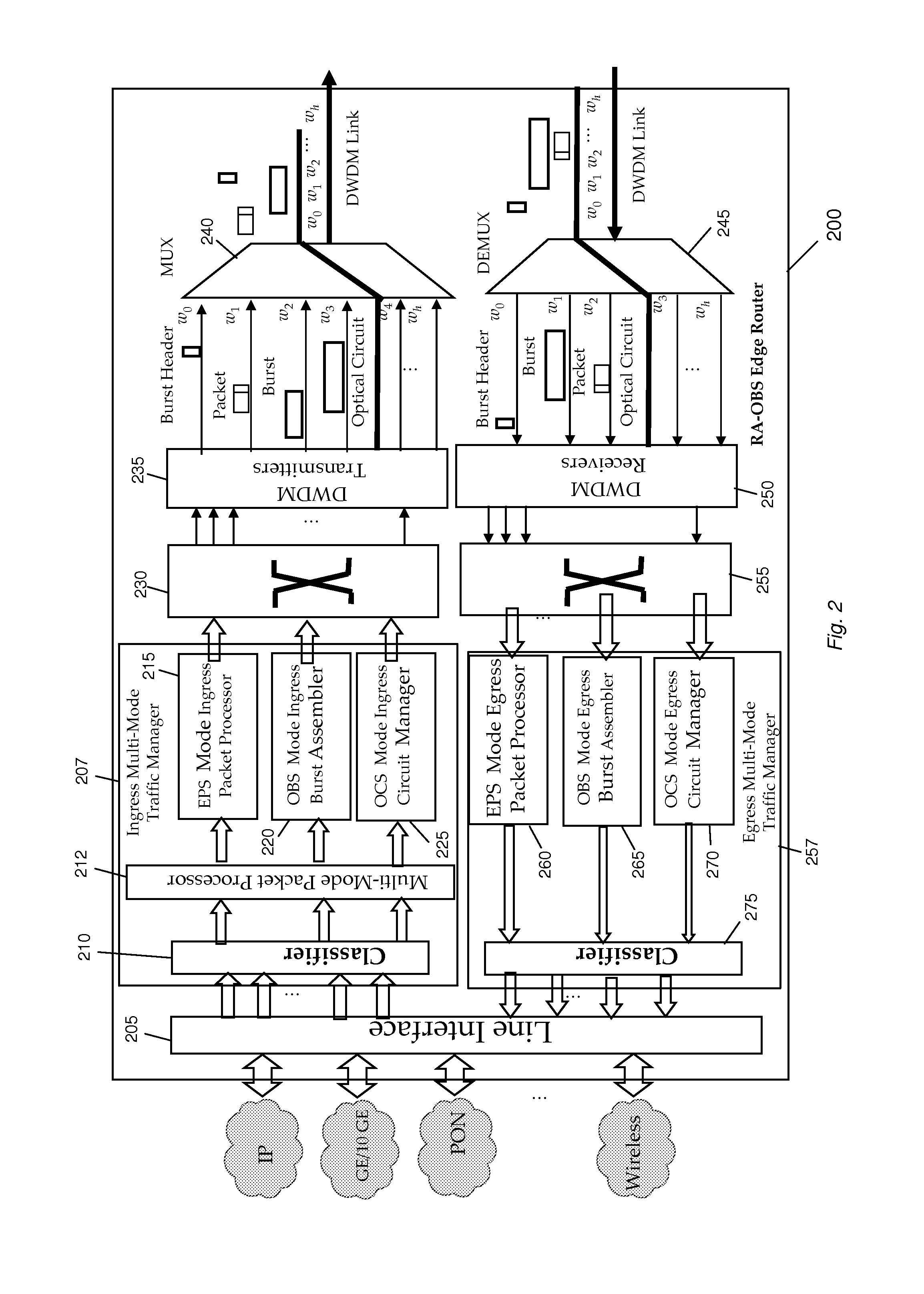
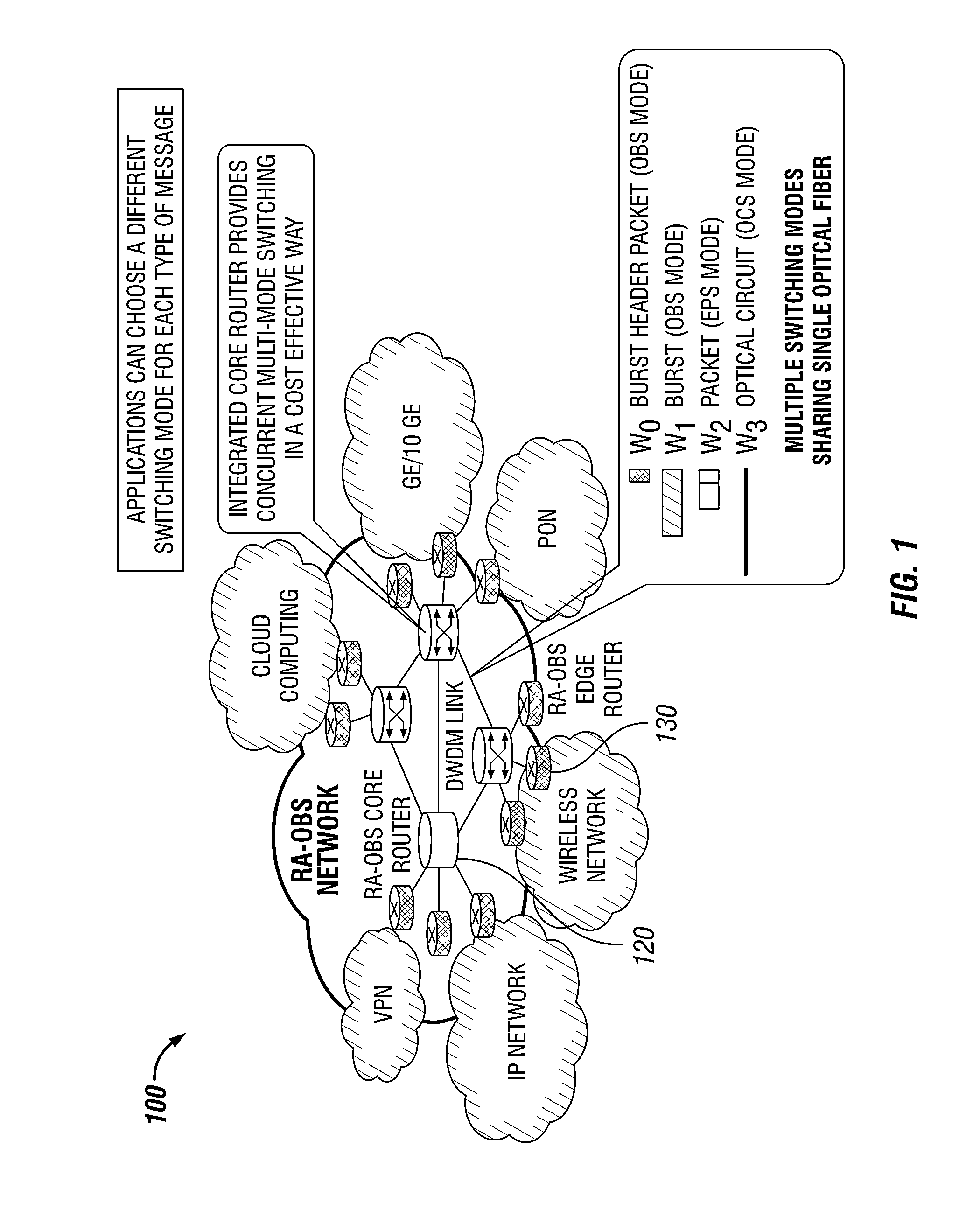
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Multi-Mode Switching Systems and Methods for Concurrent and Dynamic Reconfiguration with Different Switching Modes
ActiveUS20120148242A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmissionOptical burst switchingCore router
A Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) multi-mode switching system and method and method provides concurrent switching in various switching modes. For example, WDM links may communicate data in various switching modes including, but not limited to, an electronic packet switching (EPS) mode, optical circuit switching (OCS) mode, and optical burst switching (OBS) mode. Edge routers and core routers in the WDM multi-mode switching systems and methods provide switching and processing necessary to handle data provided in the various switching modes. Further, the WDM multi-mode switching systems and methods can also provide dynamic reconfiguration between the various switching modes.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
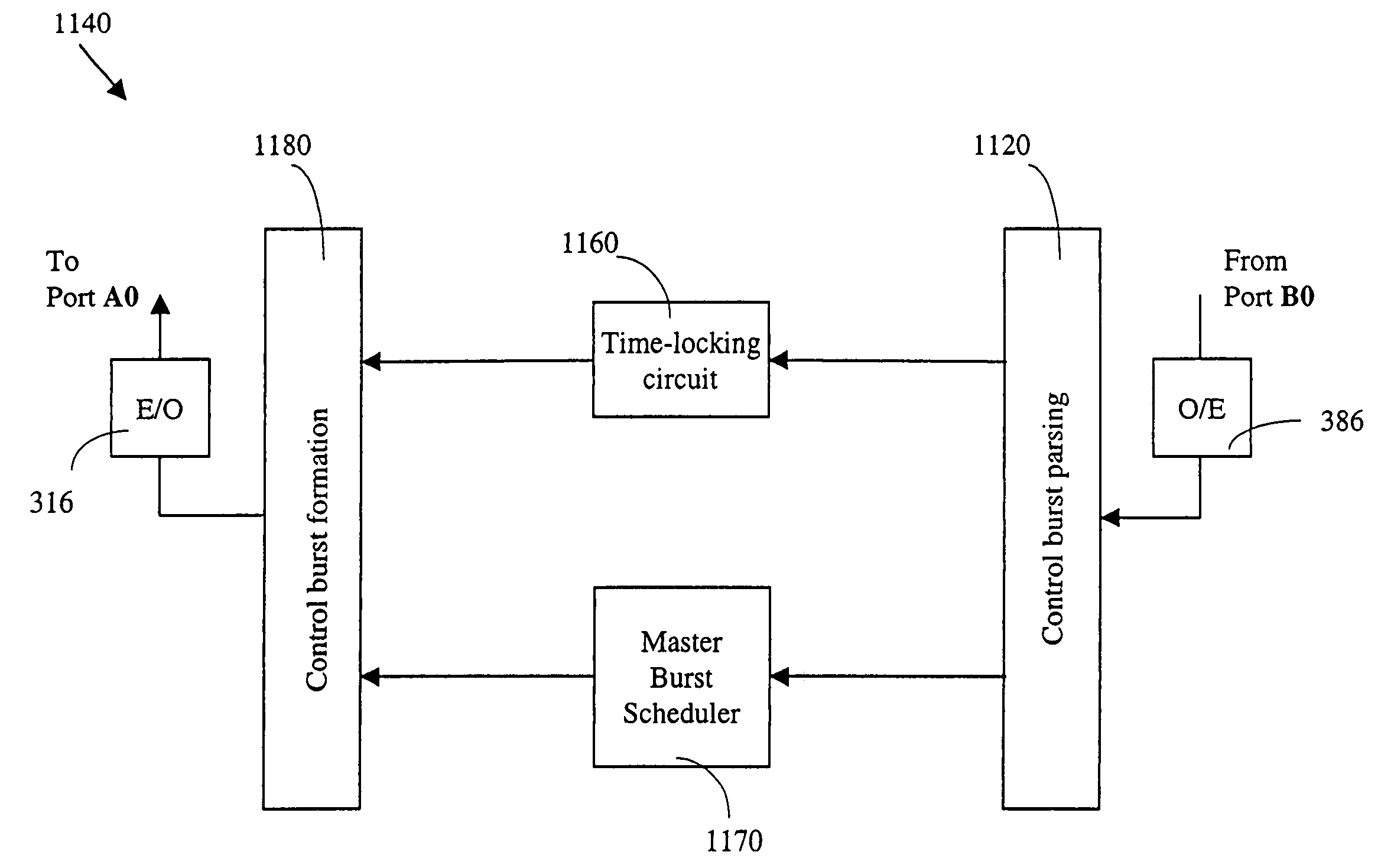
Control device and a method for controlling an optical data transmission, and a shared storage network system
InactiveUS20090142055A1Improve performanceQuality improvementHybrid switching systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsBurst transmissionOptical data transmission
A control device for controlling the optical data transmission in an optical burst switching mode between a source computer and a destination computer, the control device being connected to the source computer and to the destination computer and being adapted such that in case of a burst to be transmitted from the source computer to the destination computer, the length of the burst is determined based on a parameter indicating an available buffer size of the destination computer, and a predetermined timeout value parameter indicating a time after which improper burst transmission is assumed to have been occurred. After the burst length is determined and the traffic starts to be accumulated, a proposed burst reservation and transmission scheme, namely random burst eligibility time method, is used to deliver the burst.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Optical packet switching system
InactiveUS7317873B2Easy to controlQuality improvementMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic network arrangementsSystems managementLine card
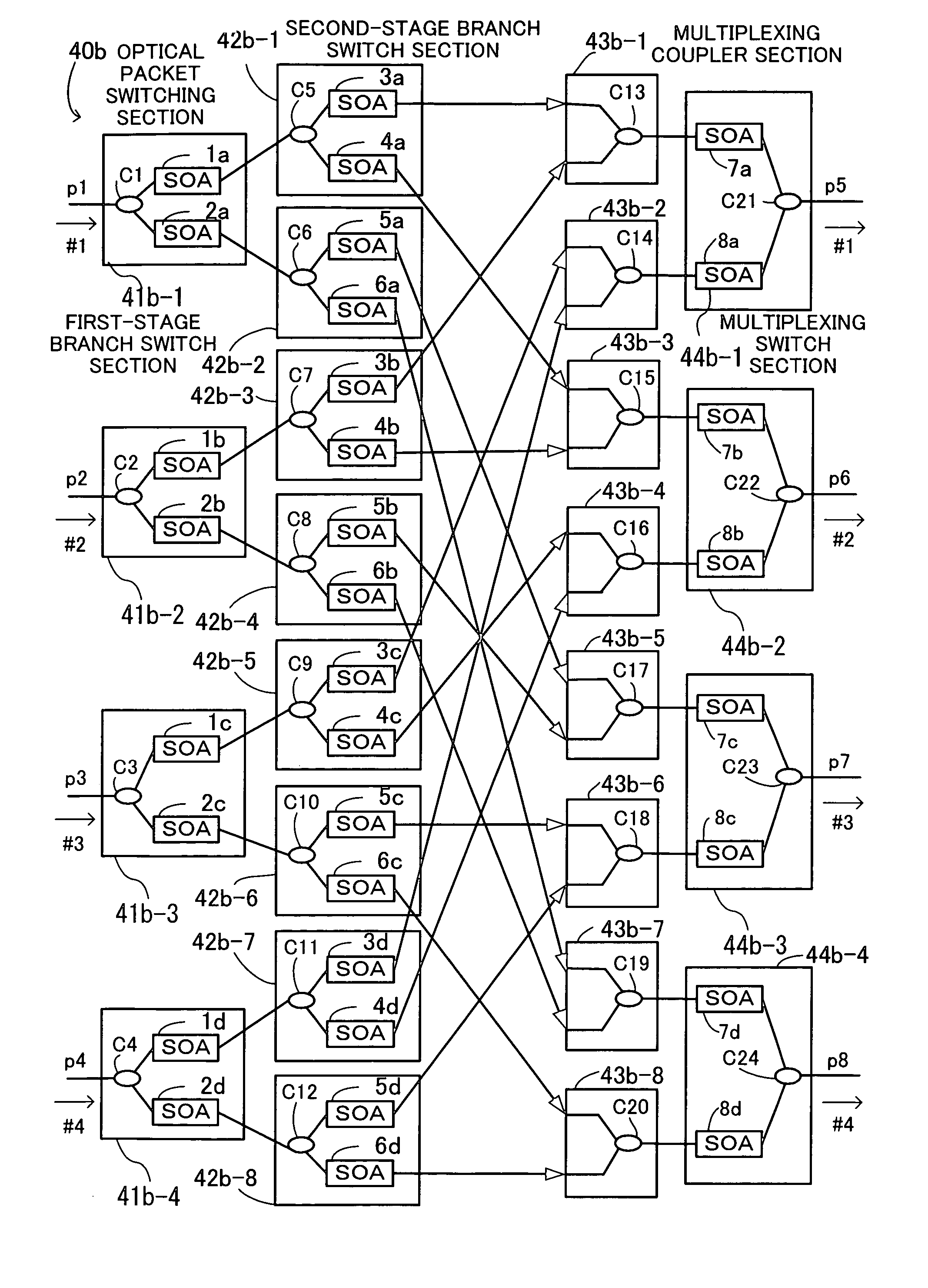
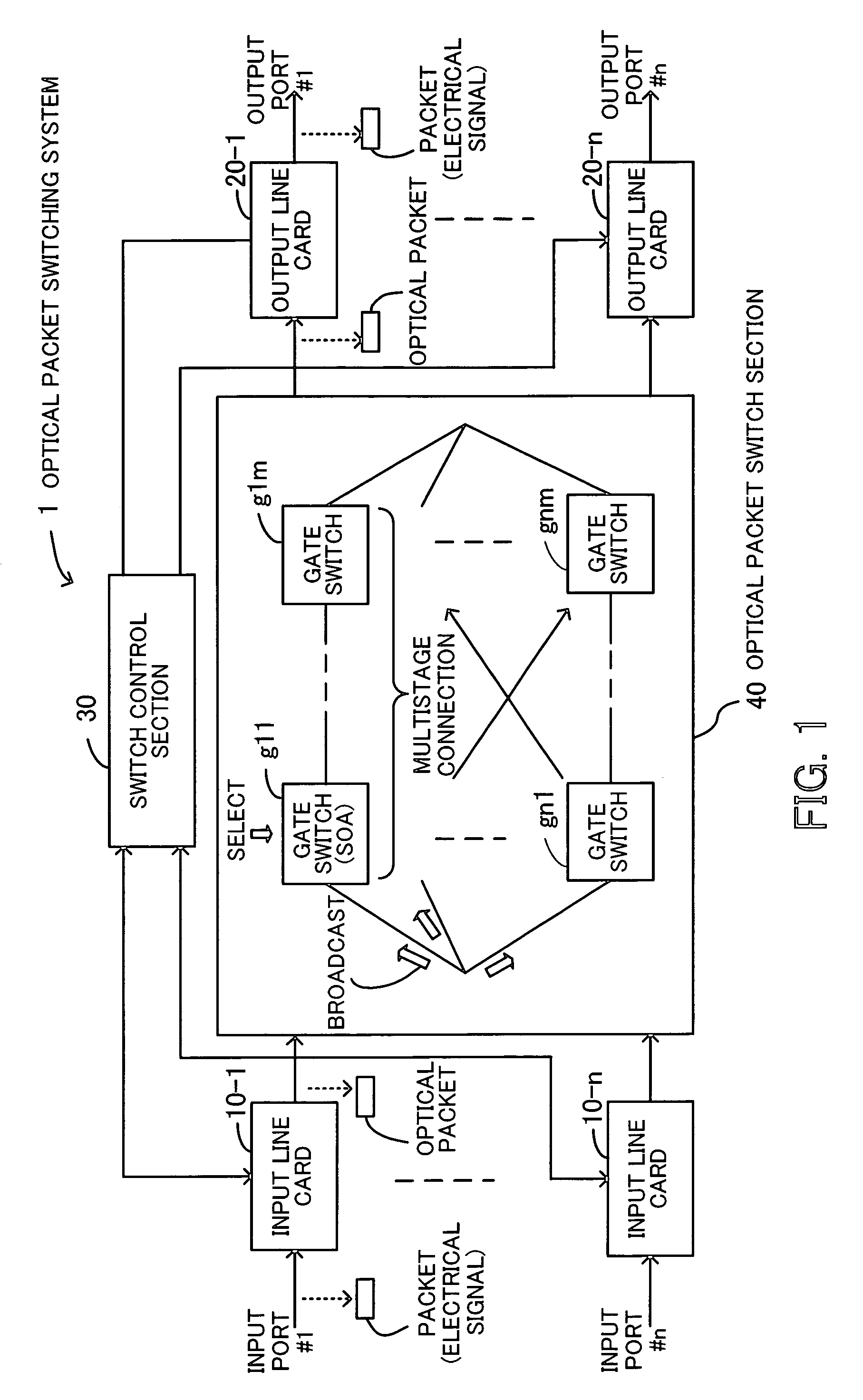
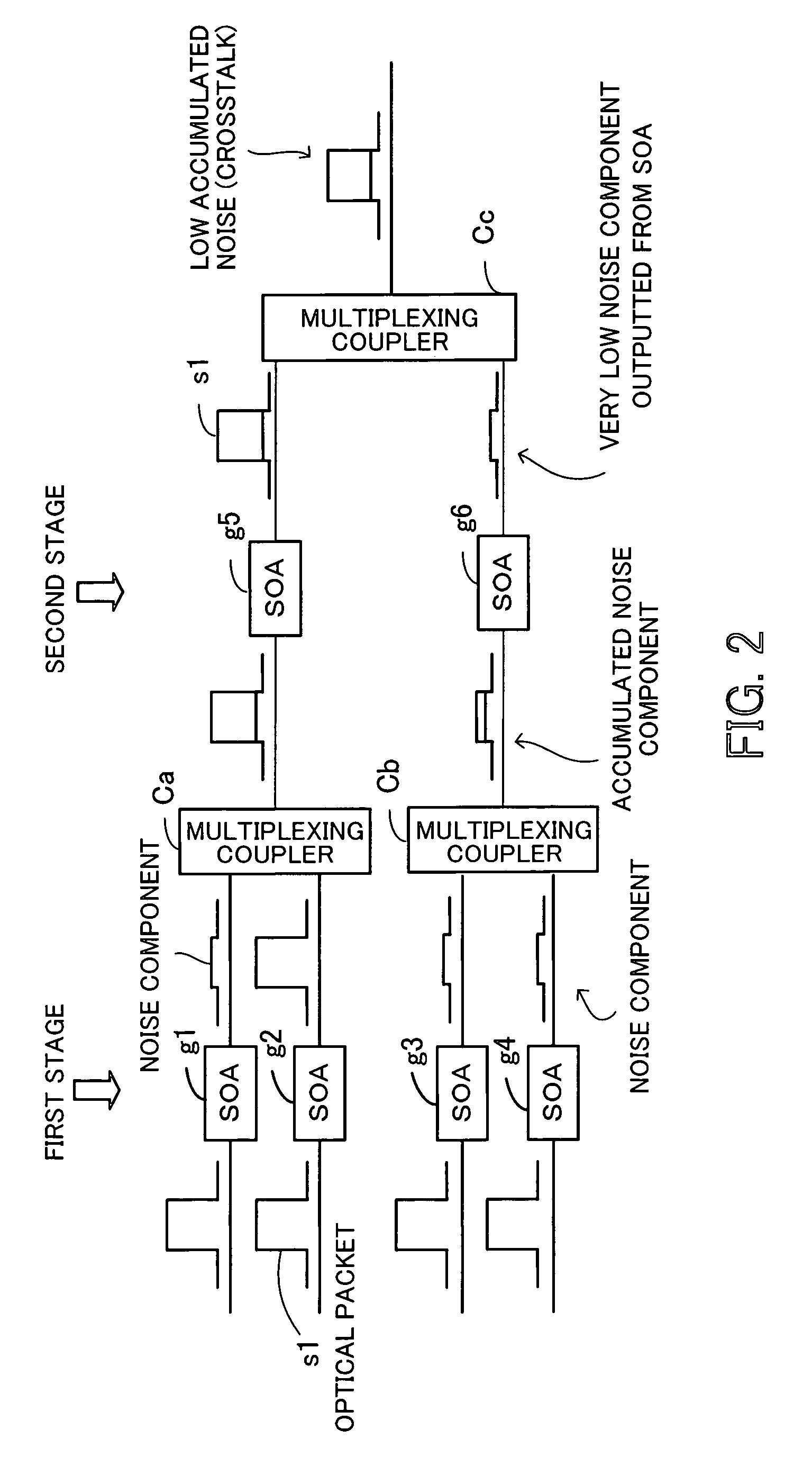
An optical packet switching system in which transmission quality, reliability, and system management in optical packet switching control are improved. An optical packet switch section includes semiconductor optical amplifiers as gate switches multistage-connected on paths along which optical packets sent from a plurality of input line cards are transmitted and performs optical packet switching by broadcasting the optical packets to a plurality of gate switches, by selecting the optical packets by ON / OFF gating operation of the gate switches, and by absorbing noise signals which flow along non-selected paths by putting gate switches at a final stage into the OFF state. A switch control section exercises ON / OFF drive control over the gate switches in the optical packet switch section on the basis of port connection requests from the plurality of input line cards so as to generate requested paths.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
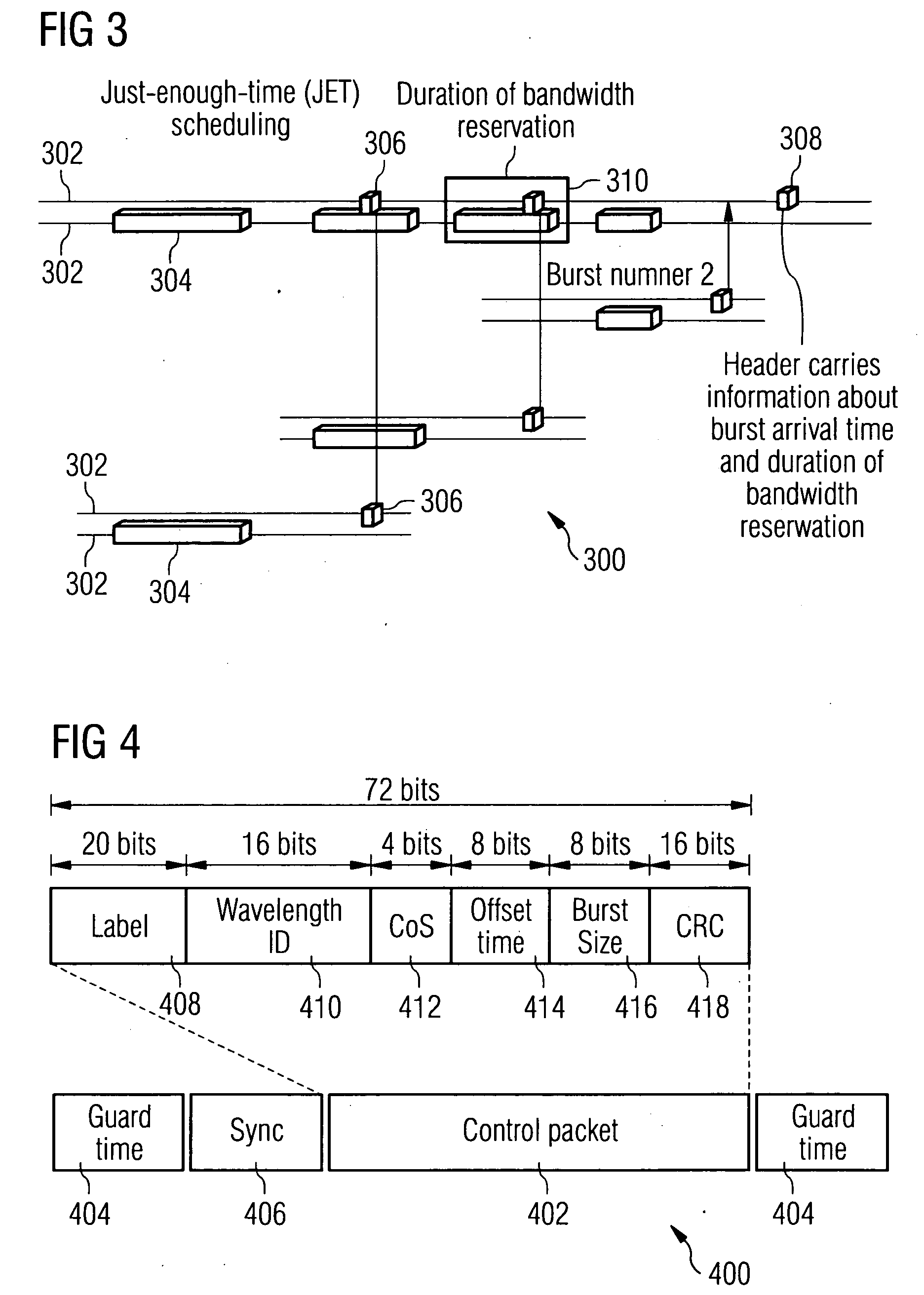
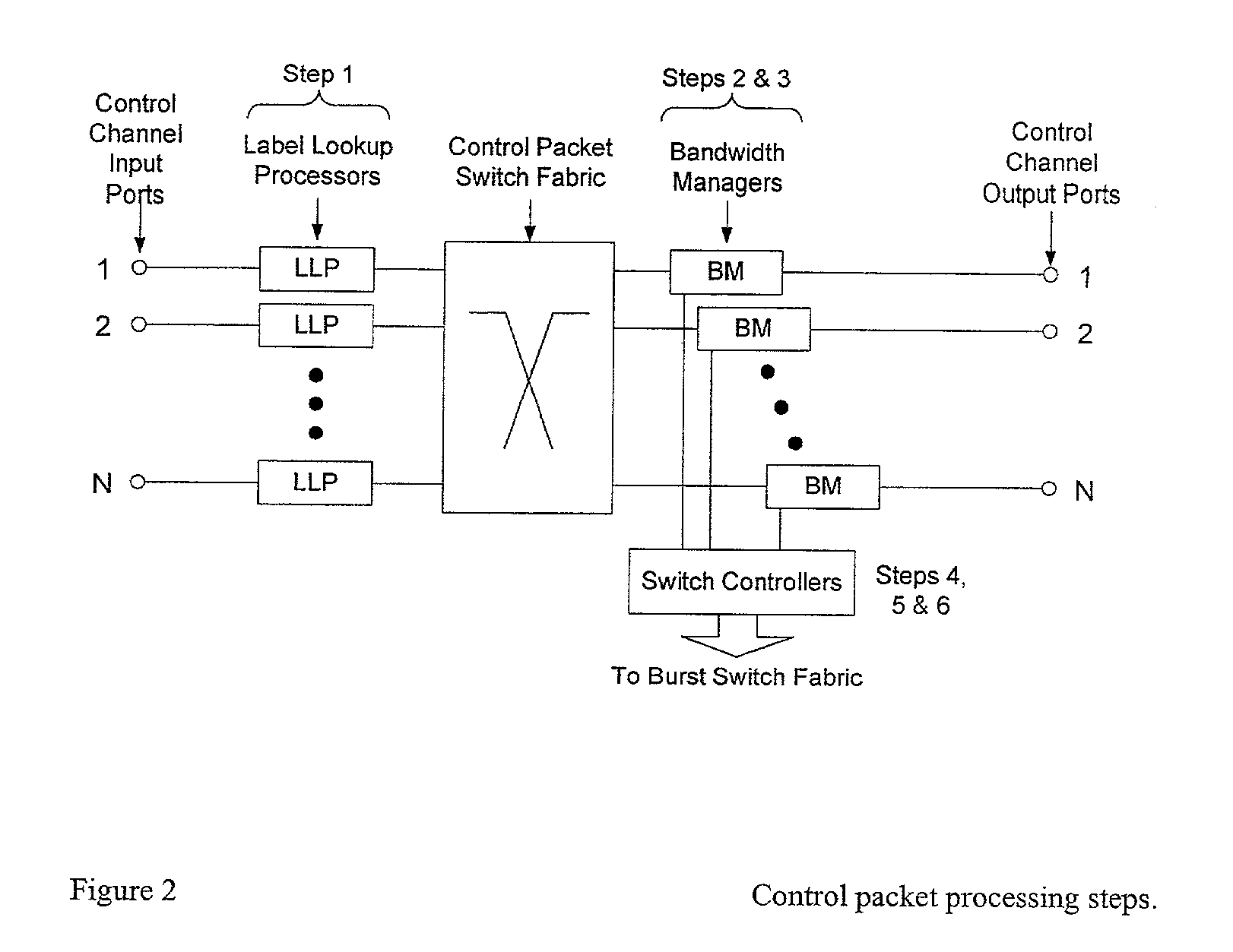
Control packet structure and method for generating a data burst in optical burst switching networks
ActiveUS7280478B2Reduces continuous blocking problemHigh average data burst utilizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionOptical burst switchingEdge node
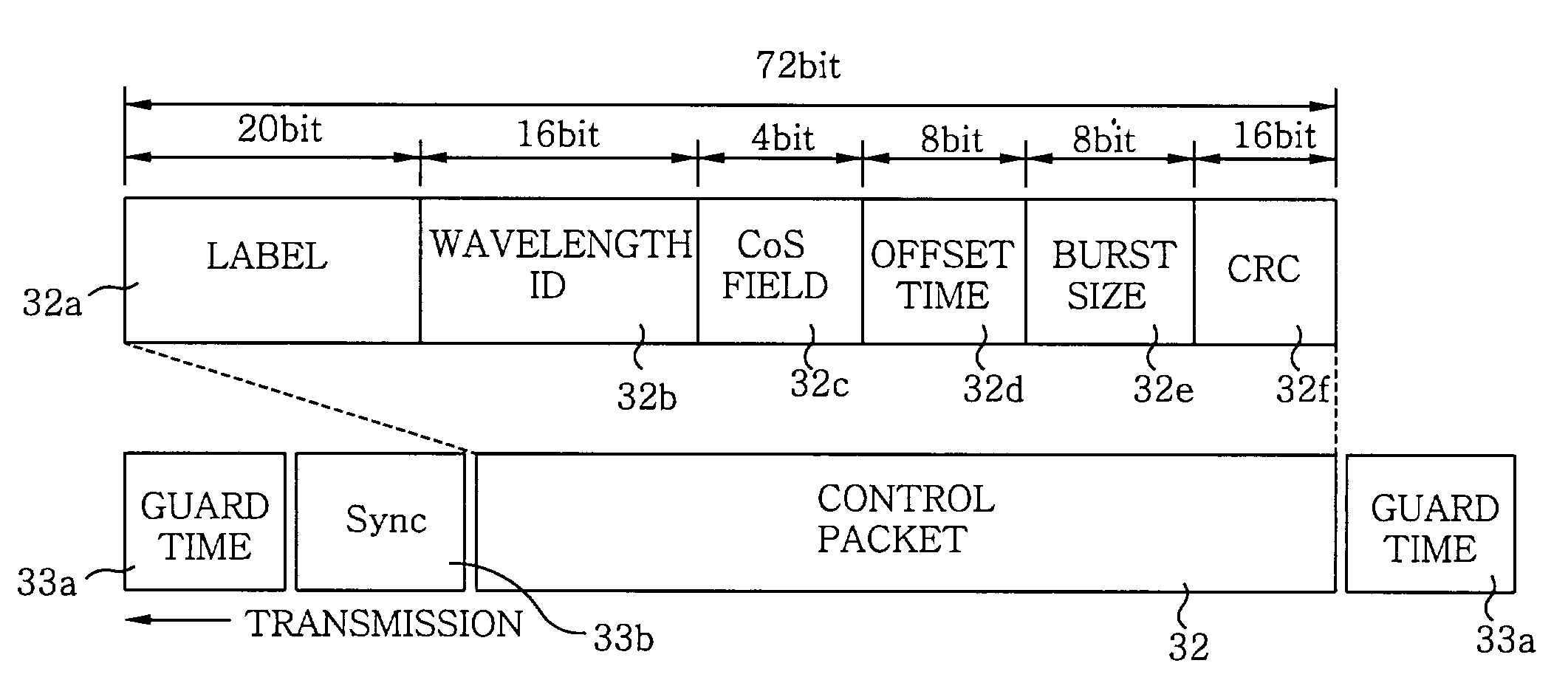
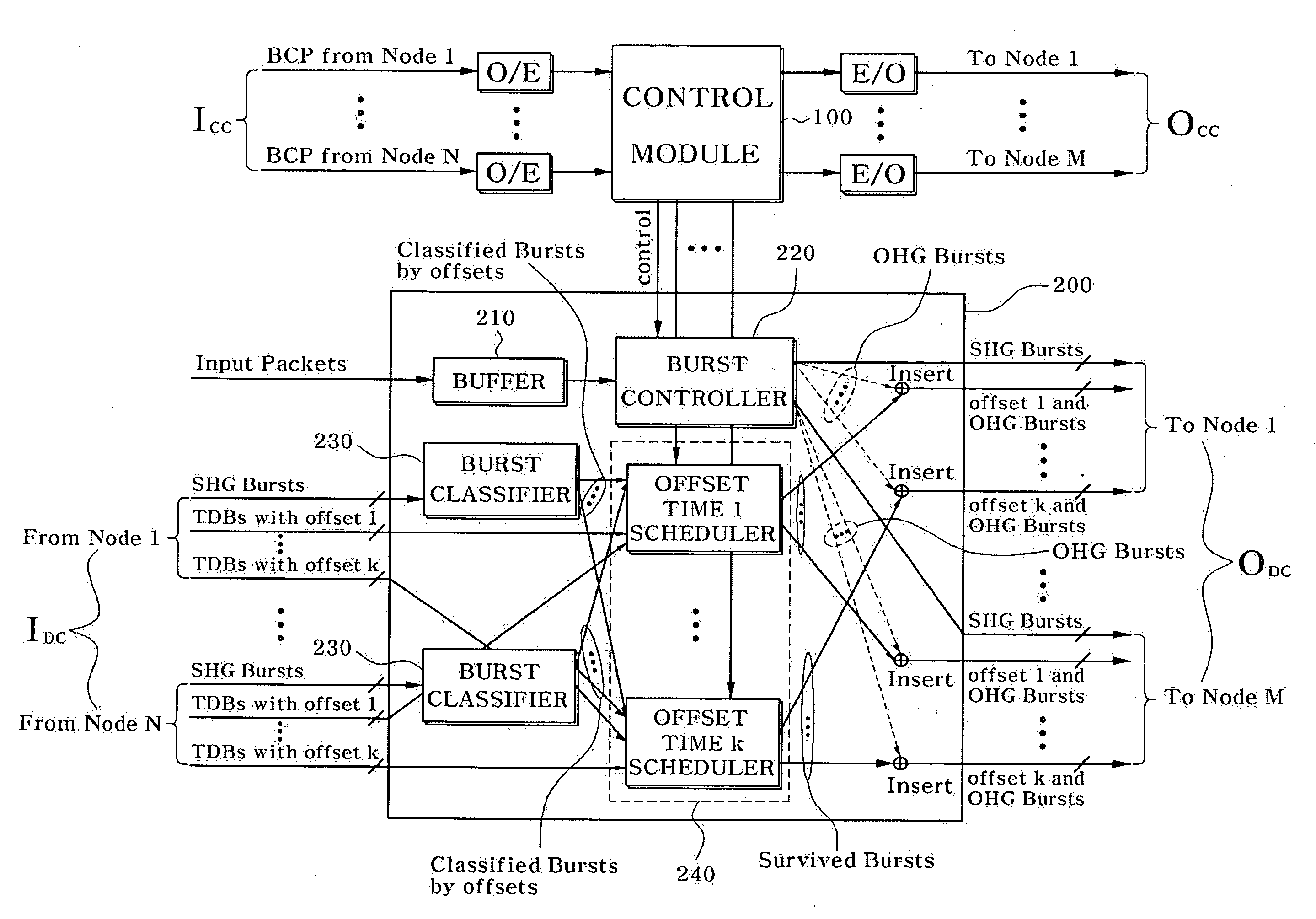
A control packet of an OBS network comprises a label which is switched for fast transmitting each packet from a source host to a corresponding destination host, a wavelength ID for distinction of channel and switching, a CoS field providing different type of CoS, an offset time indicating the difference between an arrival time of the control packet and an arrival time of the data burst, a data burst size and a CRC for error detecting. A data burst generation algorithm uses hysterisis characteristics in the queueing model for an ingress edge node in an optical burst switching network. This algorithm adaptively changes the data burst size according to the offered load and offers high average data burst utilization with a lower timer operation.
Owner:INFORMATION & COMM UNIV EDUCATIONAL FOUND
QoS-aware united control protocol for optical burst switching in software defined optical netoworks
ActiveUS20140178066A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic network arrangementsComputer hardwareOptical burst switching
The present invention is directed to a QoS-aware unified protocol that is applicable in the control plane of software defined networks, which can bring following benefits and includes optical burst switching protocol mainly requires four key operations; burst assembling, burst routing, burst scheduling, and control packet signaling protocols.
Owner:NEC CORP
Optical switching system
InactiveUS6434288B1Ring-type electromagnetic networksError preventionOptical spaceOptical burst switching
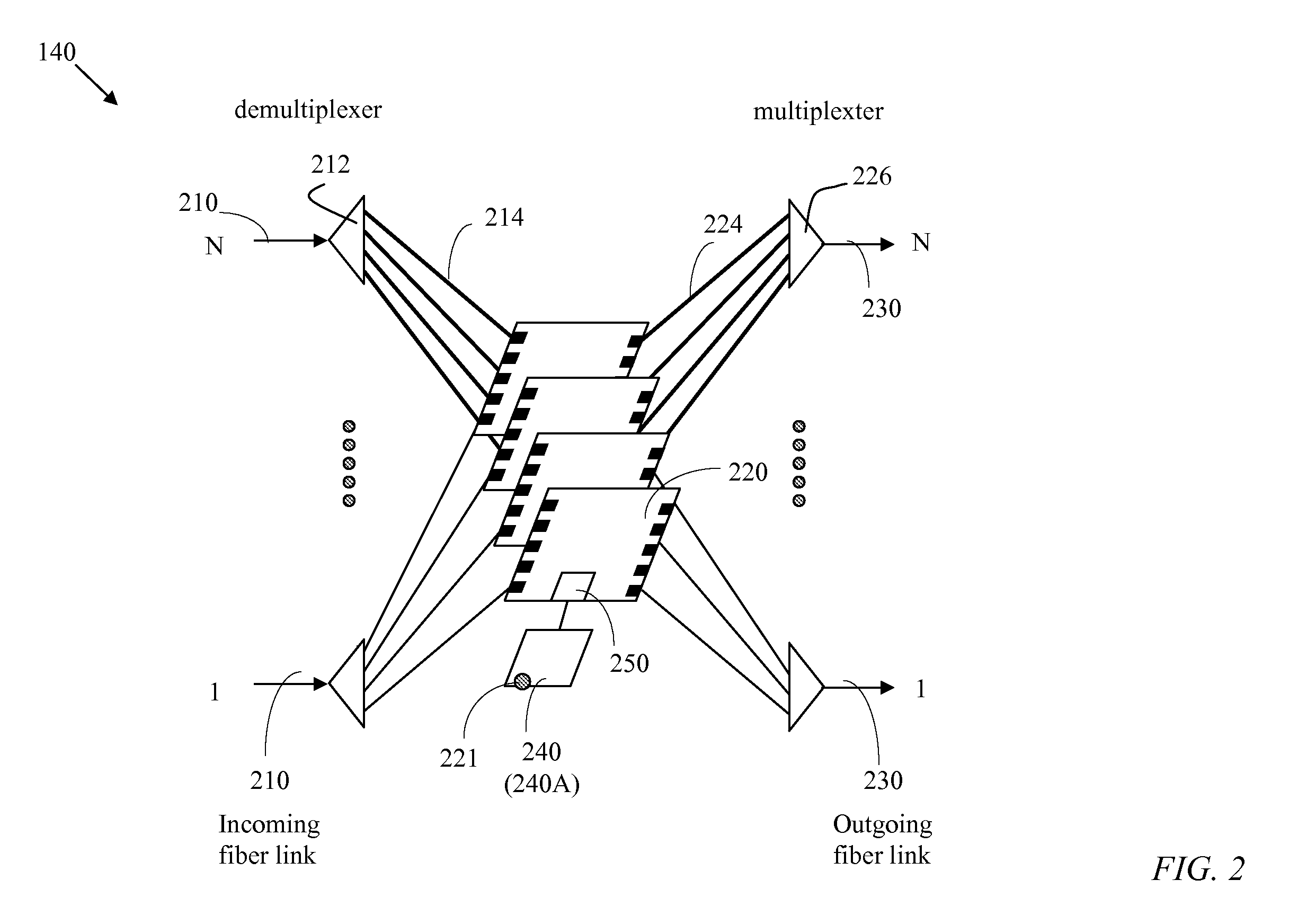
An optical switching system is implemented by providing a transmitting section with a preparatory transmitted optical signal selector and a working transmitted optical signal splitter, which are each implemented by a 1x2 optical space switch, and by providing a receiving section with a receiving optical switch which is implemented by a 2x2 optical space switch, and with a preparatory receiving optical gate which is implemented by a 1x2 optical space switch. This makes it possible to switch between the working system and preparatory system without employing any 4x4 optical space switch, thereby implementing a practical optical switching system without causing such problems as communication interruption during maintenance or impairment of transmission path working efficiency.
Owner:KDD CORP
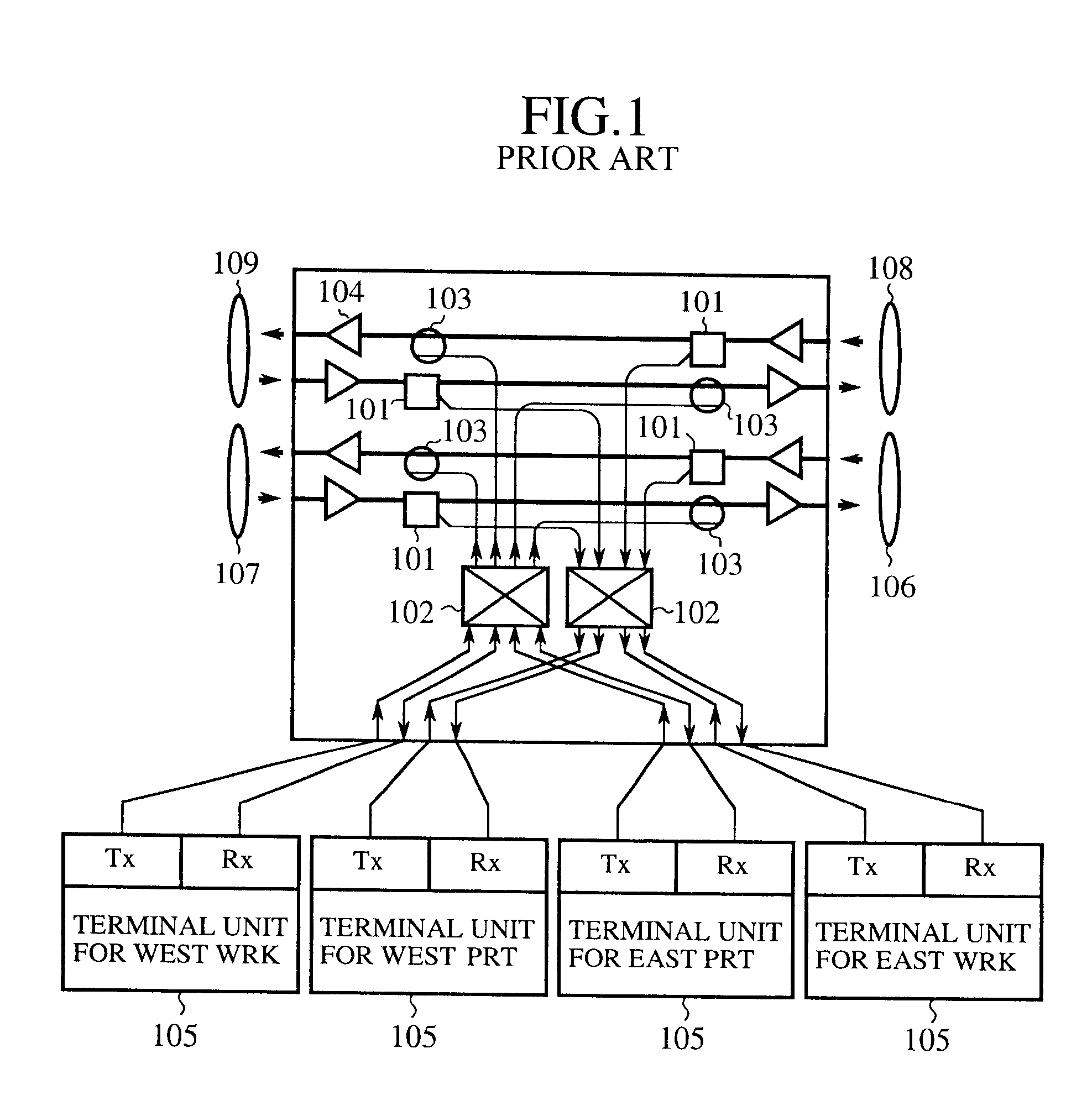
Apparatus for adjusting receiving time point of burst data in optical burst switching network and method thereof
InactiveUS20060146888A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsSynchronous controlOptical burst switching
An apparatus and method for adjusting a receiving time point of burst data in an optical burst switching network is provided. The method includes comparing a reference time point of a node with a time slot boundary of the burst data; and adjusting the time slot boundary of the burst data in accordance with the reference time point. The apparatus includes a sync detection section which is configured to detect a difference between a time slot boundary of the burst data and a reference time point; and a sync control section which is configured to control shifting and re-aligning the received burst data with the reference time point according to the difference detected by the sync detection section.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
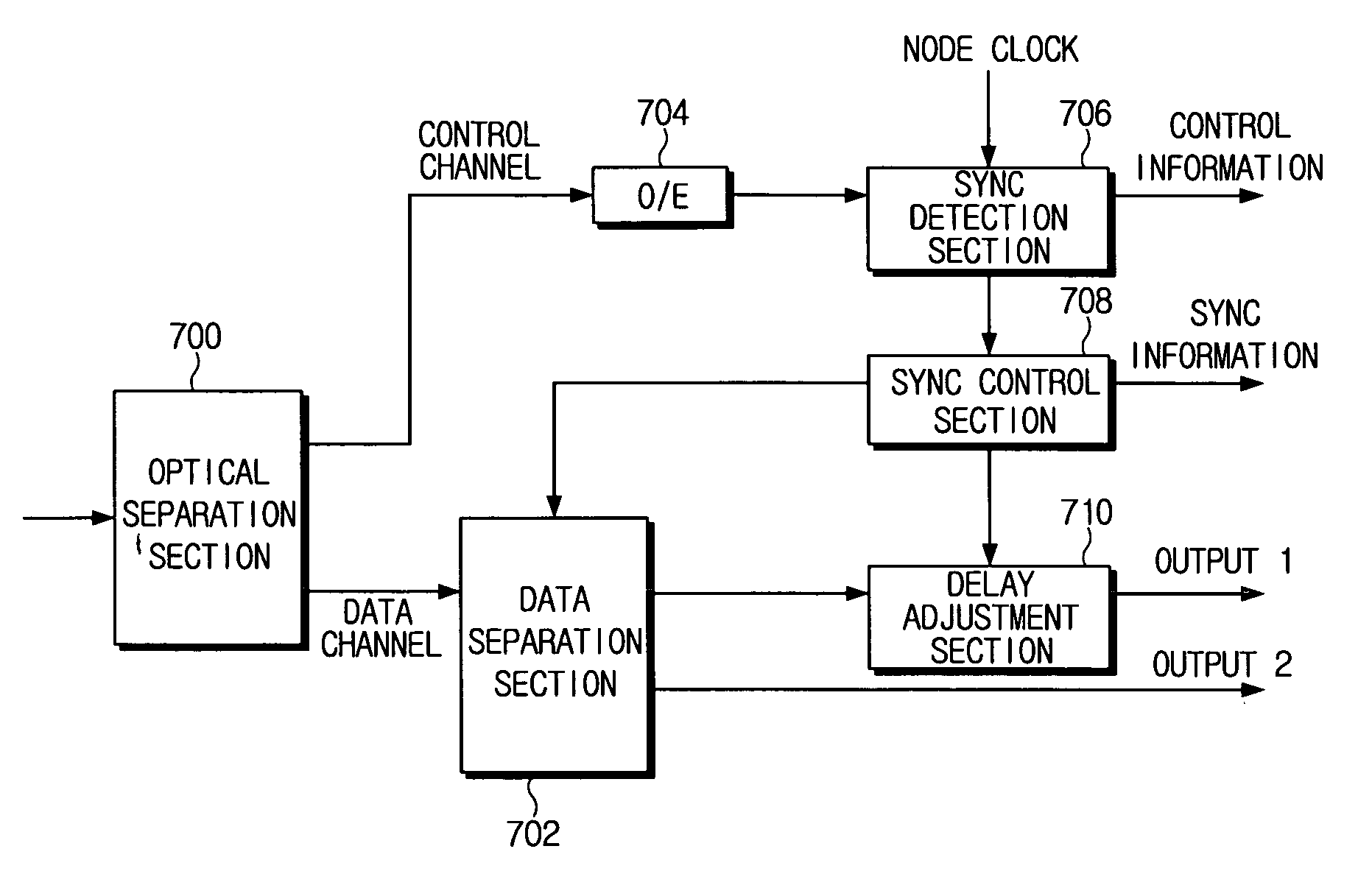
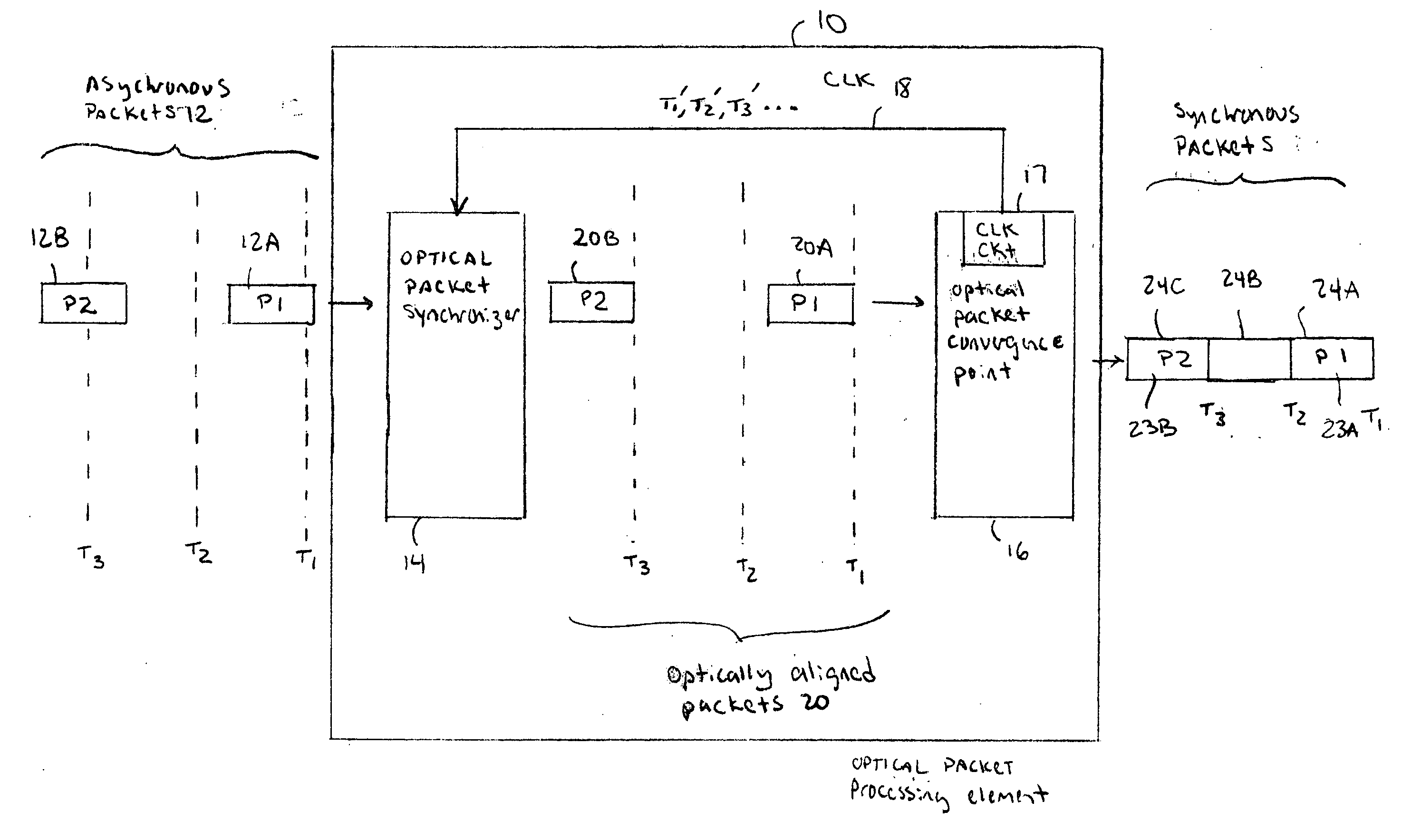
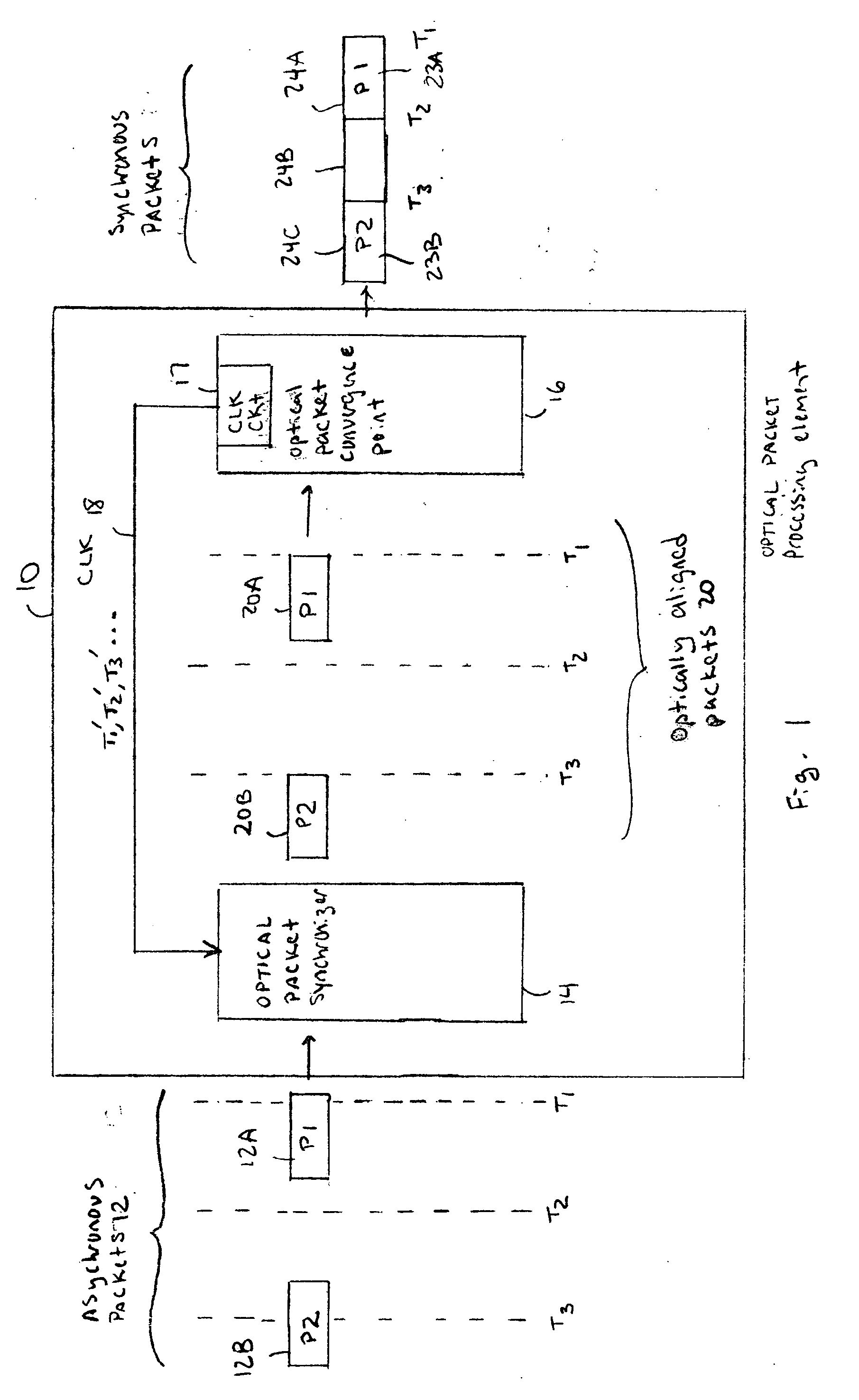
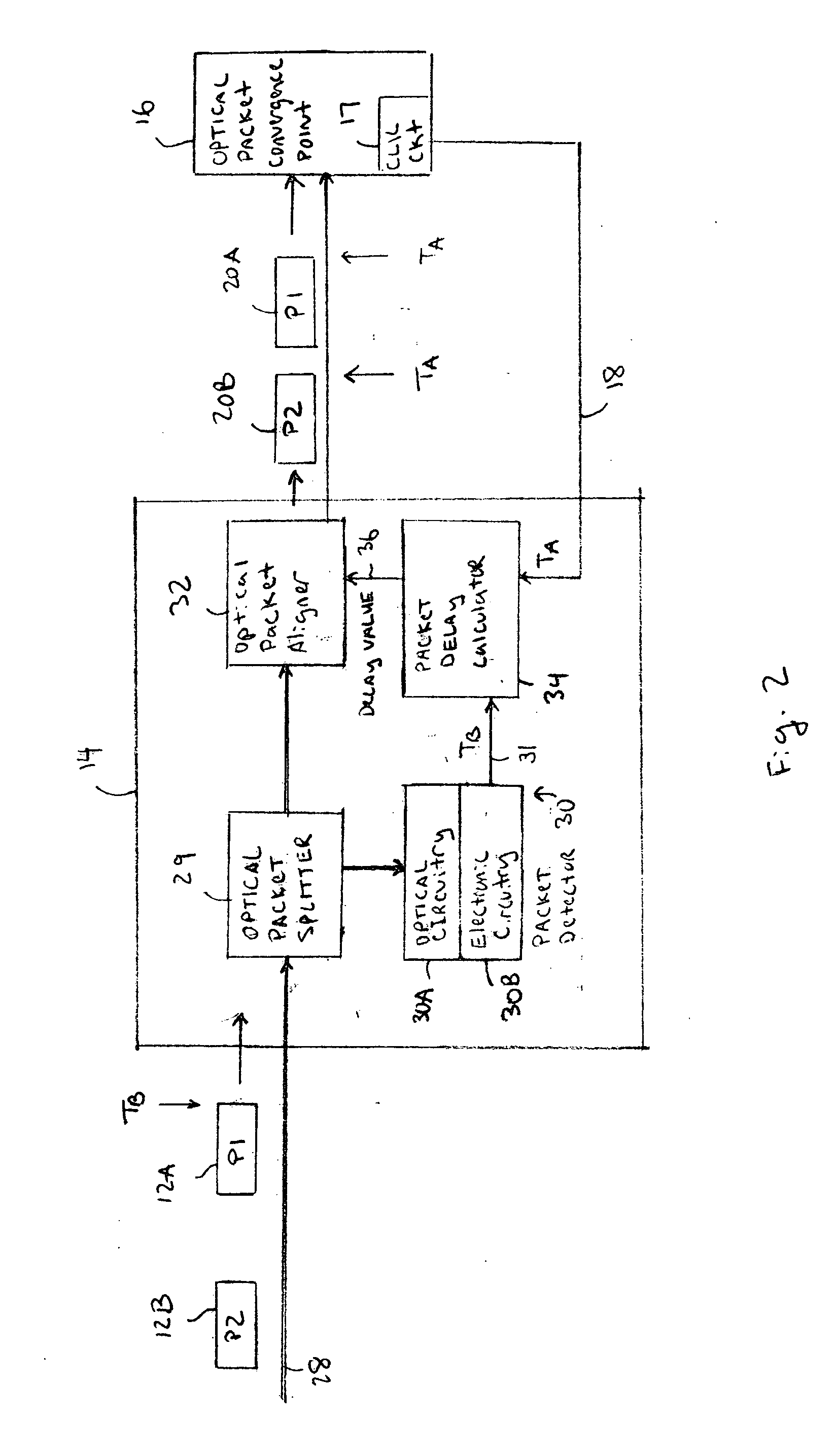
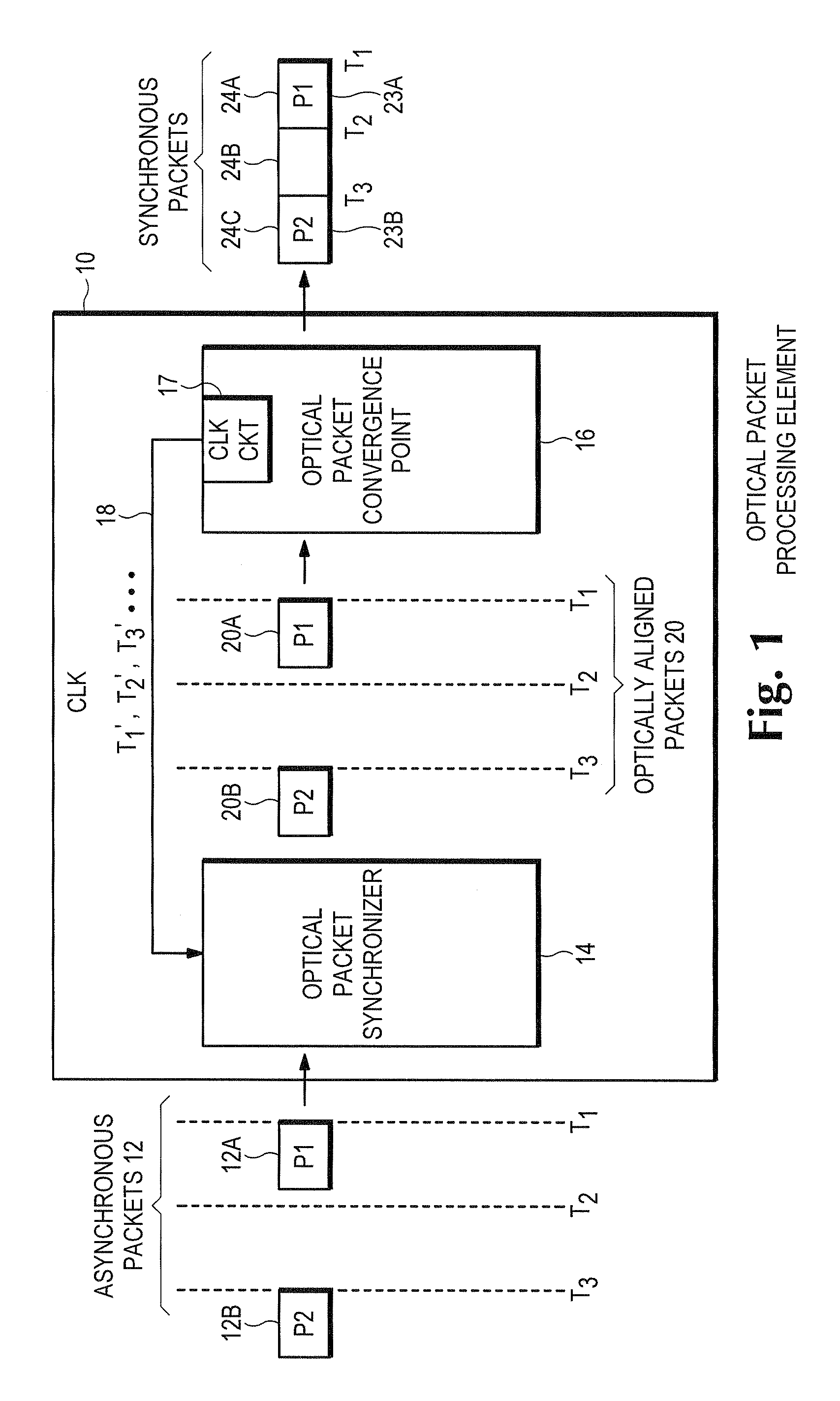
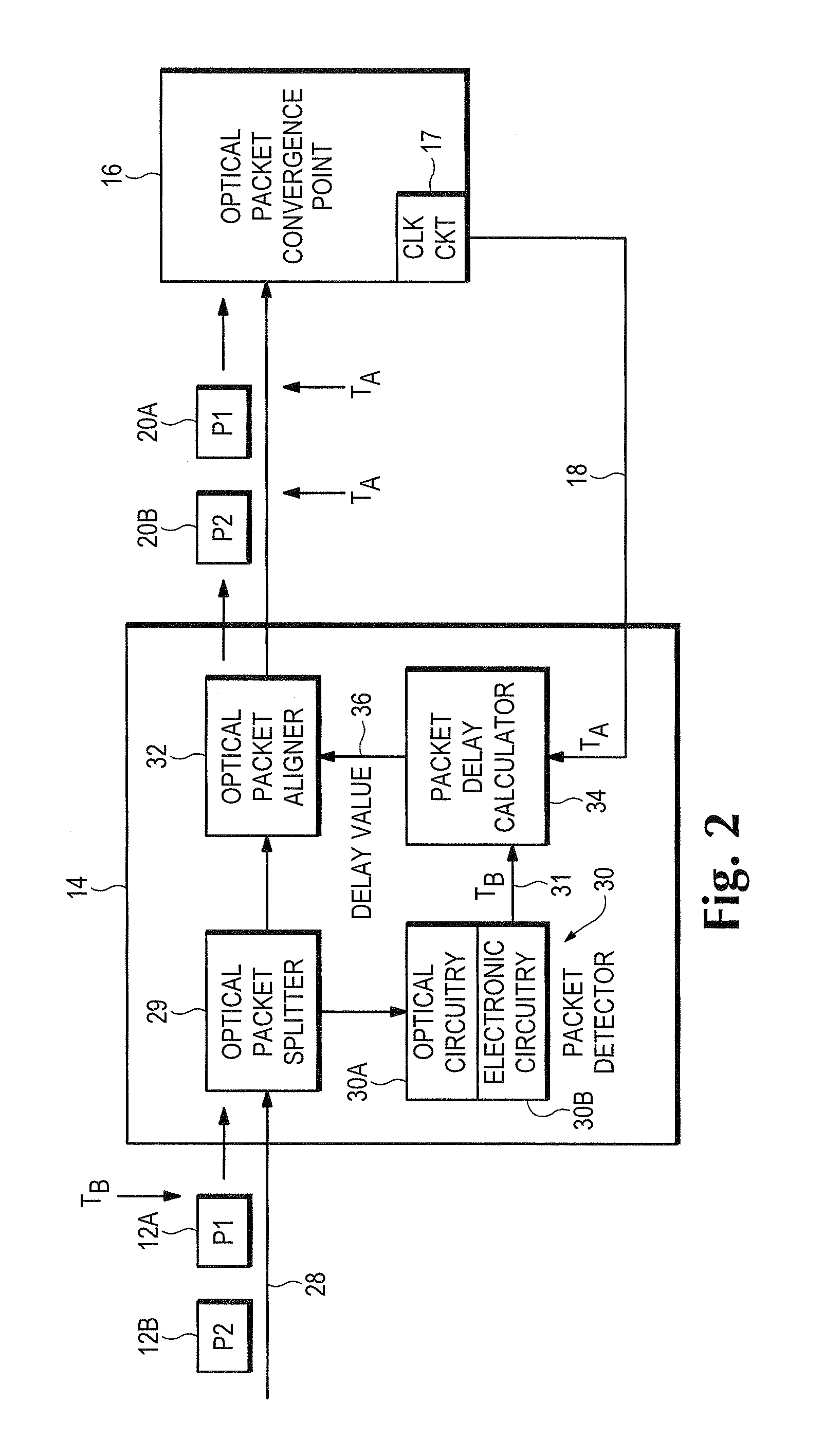
Optical data synchronization scheme
ActiveUS20070201877A1Readily apparentMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexData synchronizationOptical burst switching
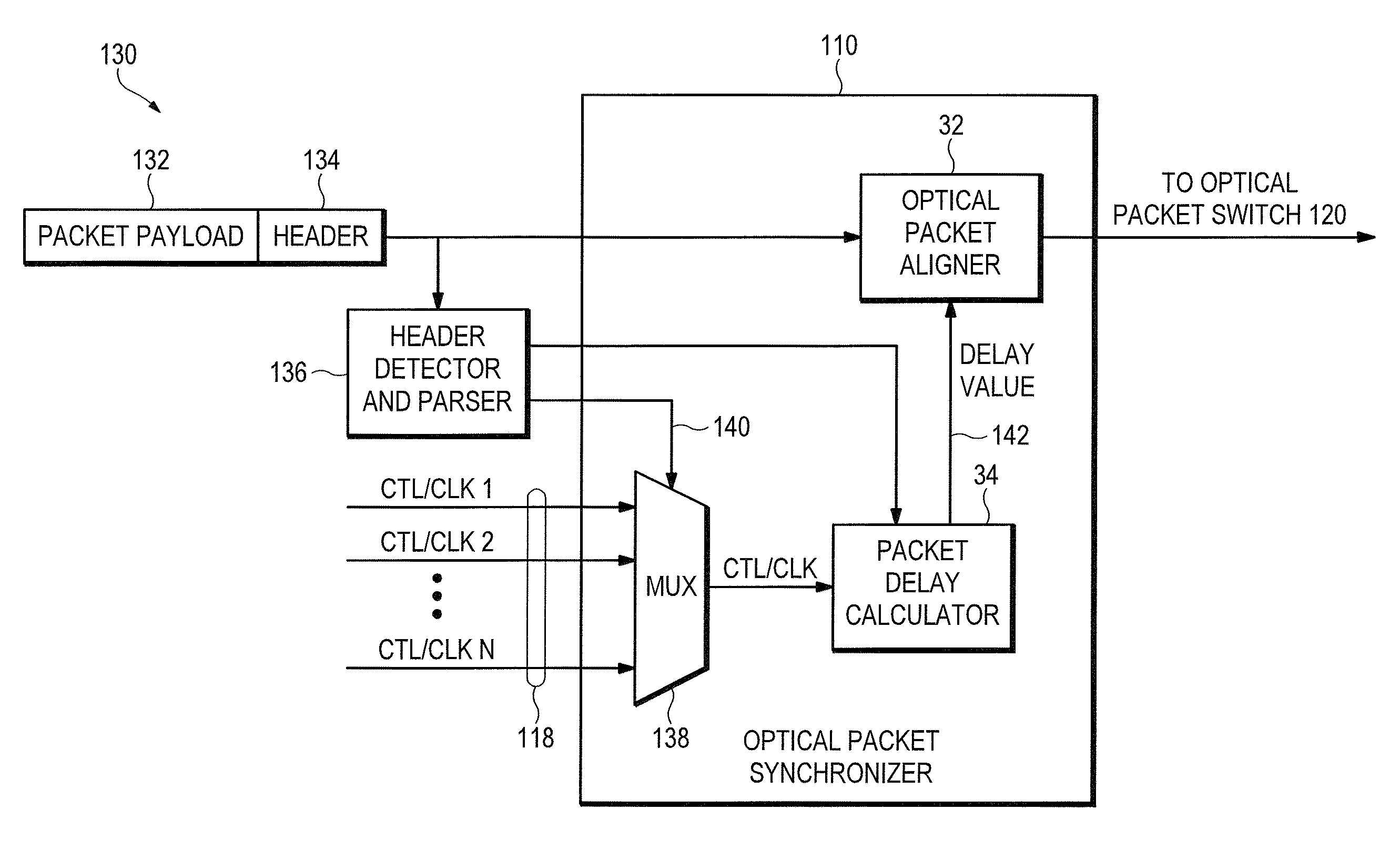
Asynchronous optical data is aligned with synchronous convergence points in an optical packet switching system. The convergence points can be any place where data enters an optical packet switching element, buffer stage, switch fabric, etc. The arrival time for data approaching the convergence point is compared with a reference signal associated with the upcoming convergence point. The comparison is used to identify the amount of time-shift required to align the approaching data with the reference signal. Control information is derived according to the comparison and used to control an optical data aligner that synchronizes the data with the convergence point.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Rate-Controlled Optical Burst Switching
InactiveUS20070115956A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementOptical burst switchingEdge node
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Optical data synchronization scheme
ActiveUS7835649B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexData synchronizationOptical burst switching
Asynchronous optical data is aligned with synchronous convergence points in an optical packet switching system. The convergence points can be any place where data enters an optical packet switching element, buffer stage, switch fabric, etc. The arrival time for data approaching the convergence point is compared with a reference signal associated with the upcoming convergence point. The comparison is used to identify the amount of time-shift required to align the approaching data with the reference signal. Control information is derived according to the comparison and used to control an optical data aligner that synchronizes the data with the convergence point.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
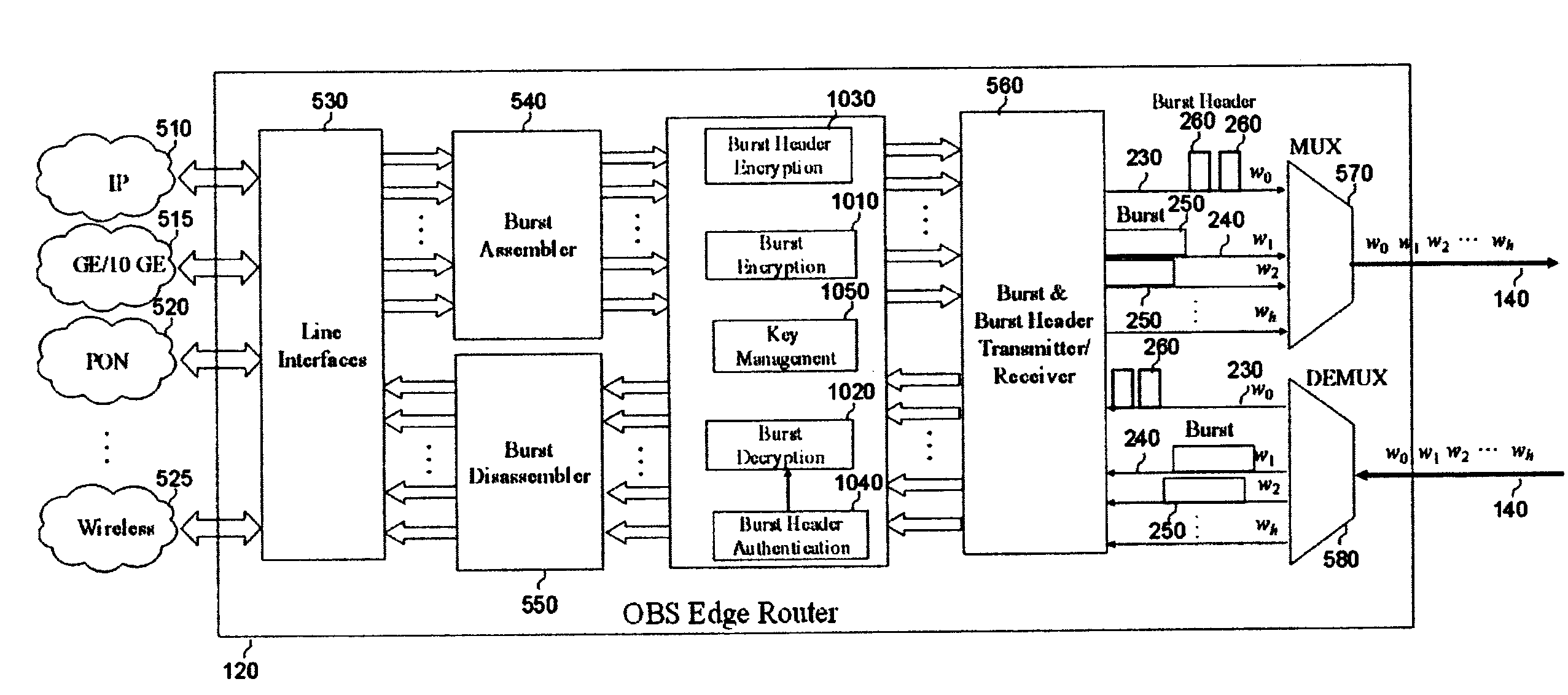
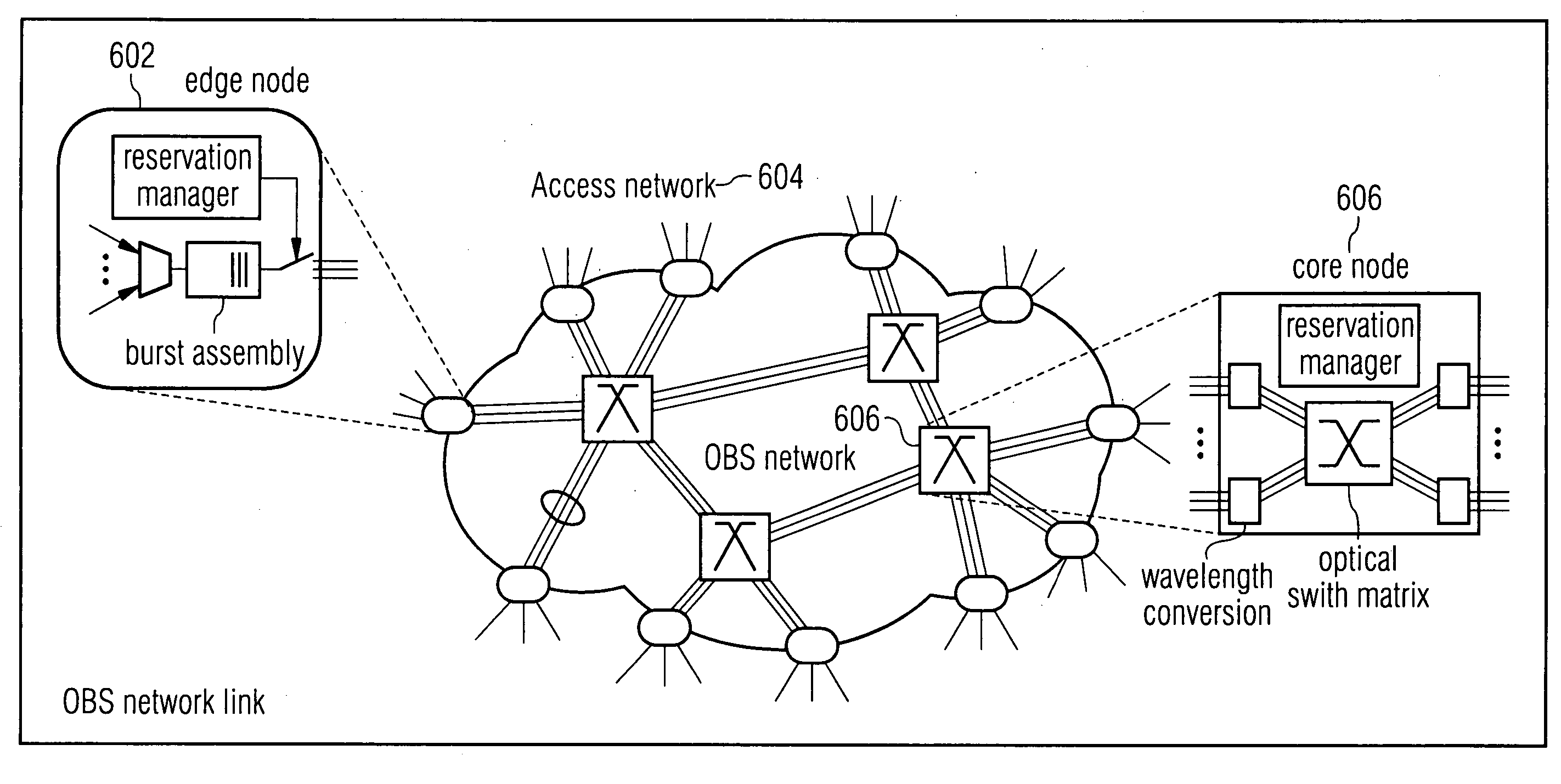
Methods and apparatus for securing optical burst switching (OBS) networks
InactiveUS20090313465A1Reduce overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsKey distribution for secure communicationTelecommunications linkOptical burst switching
An optical network, having an optical communication link and first and second routers. The first router receives and classifies data, then forms a data burst based on destination. The first router sends an encrypted header and the data burst via the optical link. The second router, at least one hop from the first router, receives, decrypts and authenticates the header. Then, the second router extracts data burst information from the header and determines whether the address of the second router is the destination address for the data burst. If so, the second router receives the data burst and sends data to an appropriate line interface. If not, the second router selects and reserves a wavelength on a second optical link for the data burst. The second router selects an encryption key for the header, encrypts and sends the header, and then routes the data burst to the selected wavelength.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA +1
Optical packet switching system
InactiveUS20120251109A1Reducing optical packet discarding rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical packetOptical burst switching
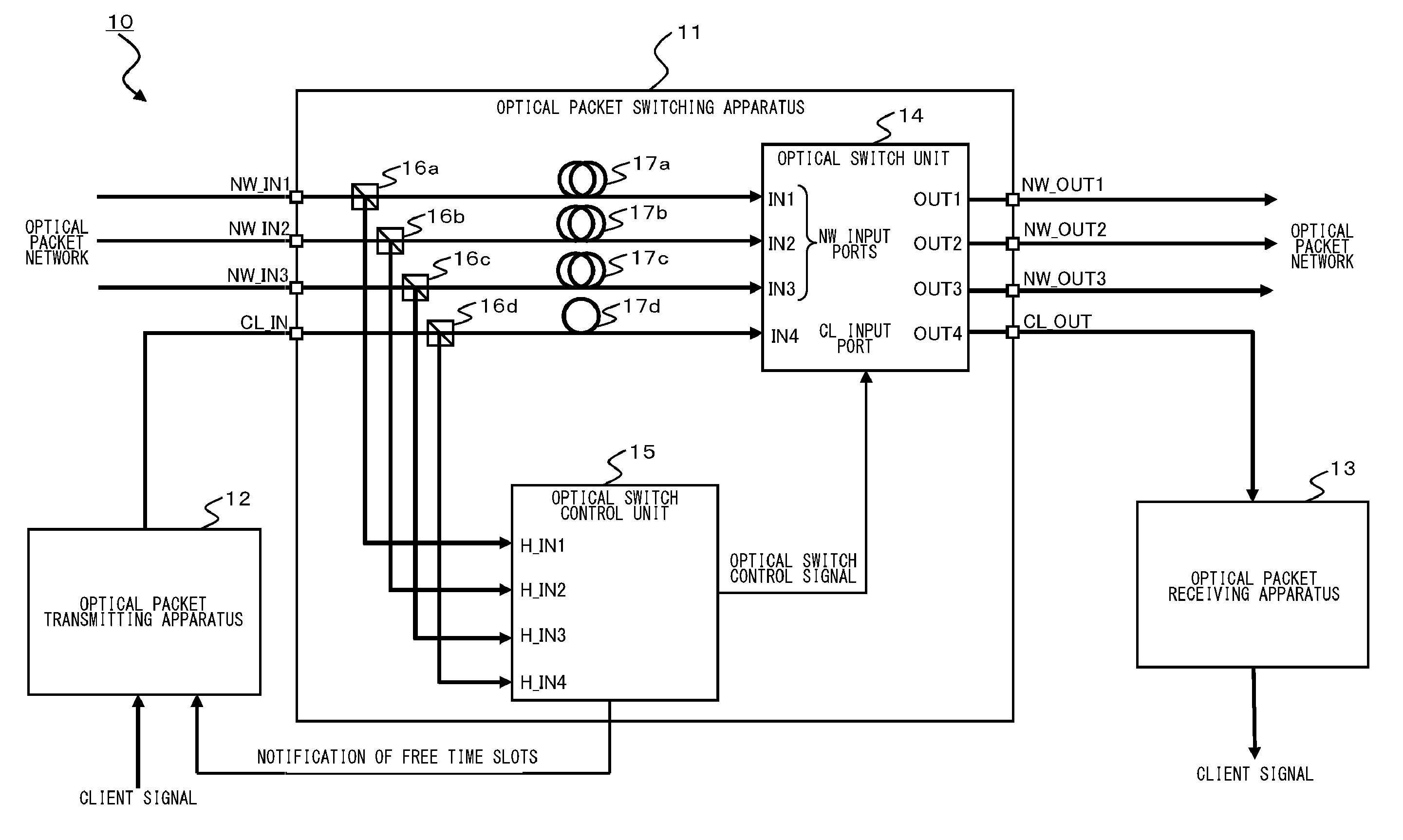
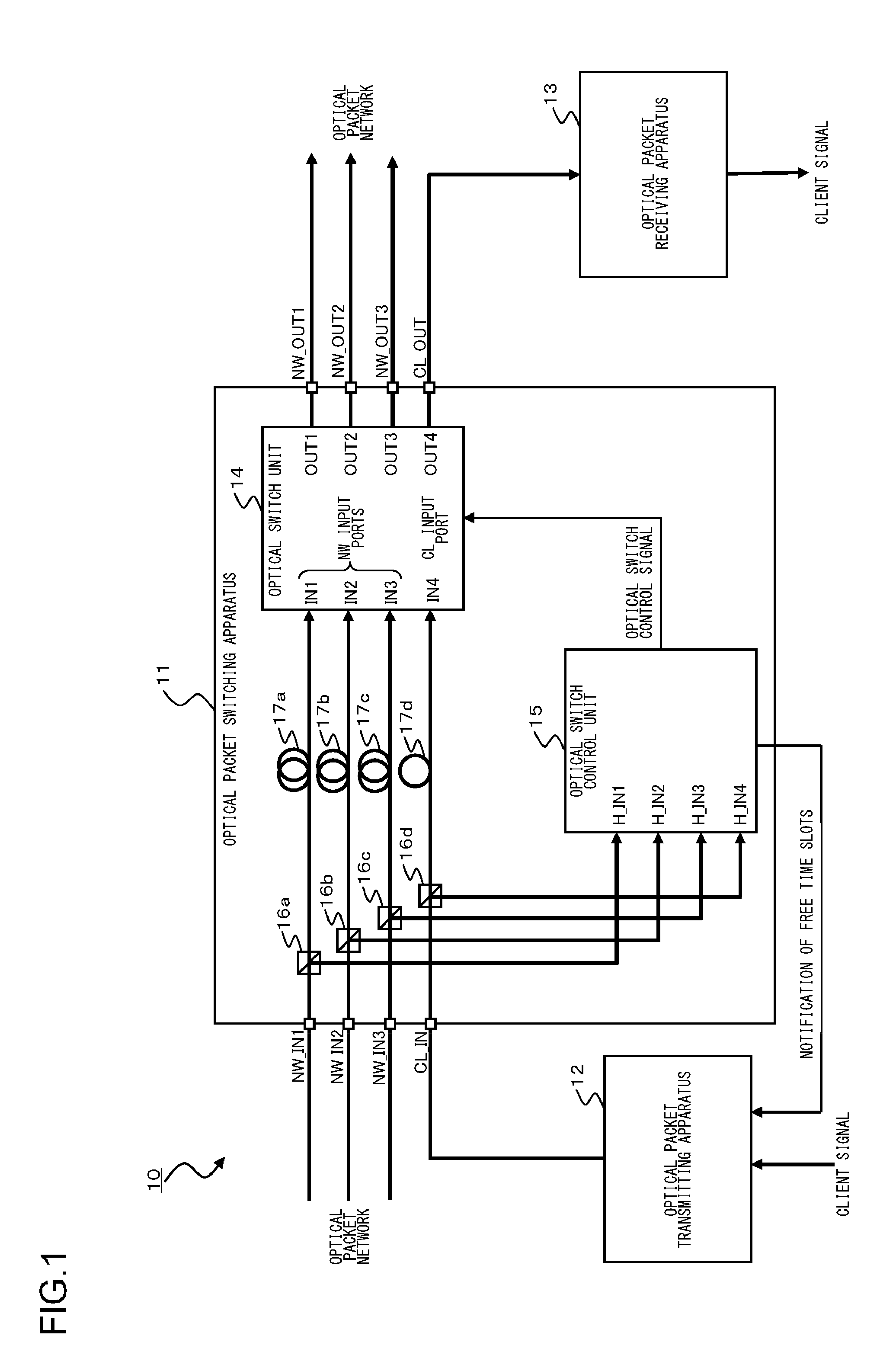
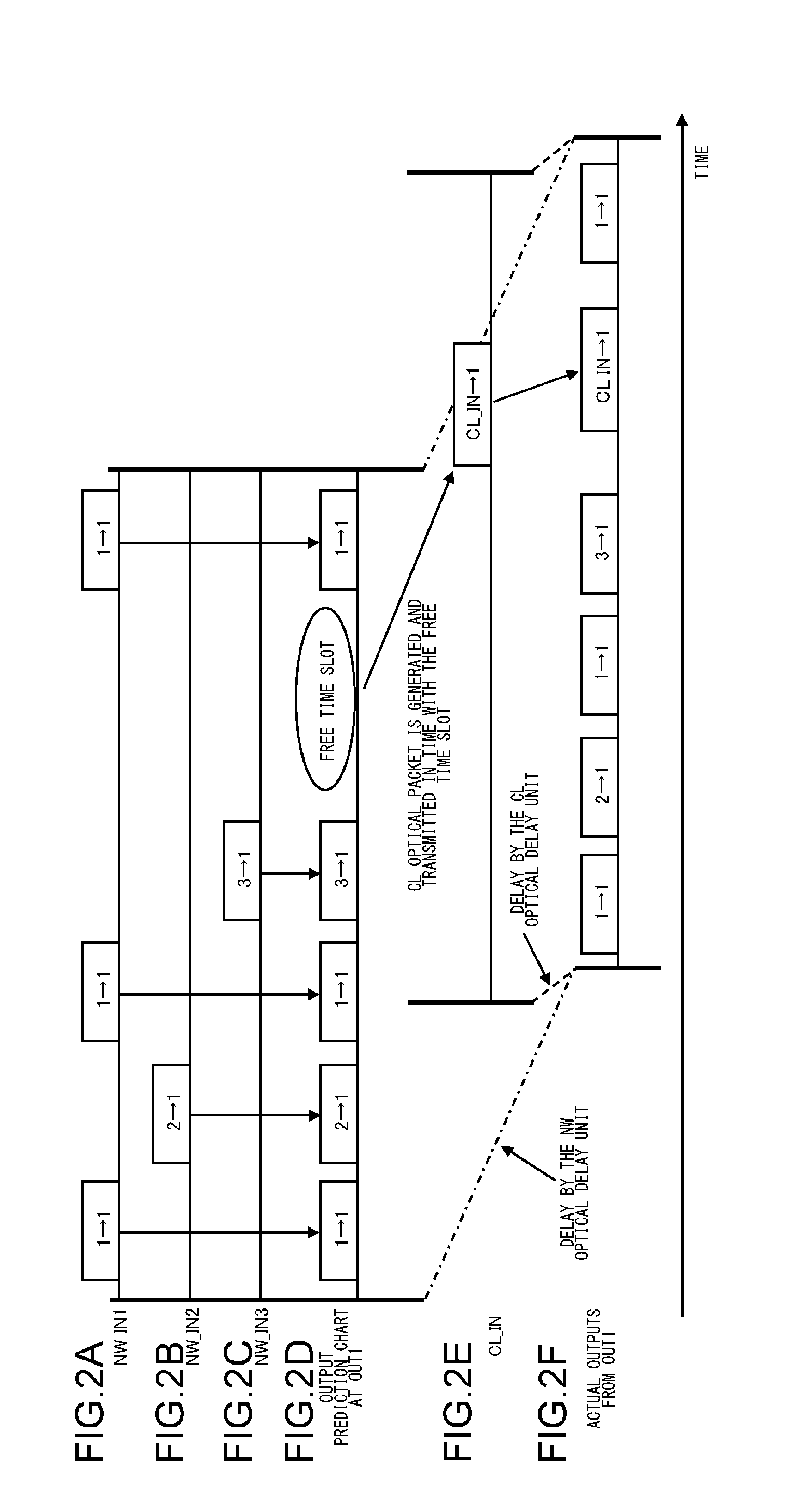
An optical packet switching system includes optical packet switching apparatus and an optical packet transmitting apparatus. The optical packet switching apparatus includes client optical delay units for delaying optical packet signals, network optical delay units for delaying one of the network optical packet signals, the network optical delay unit having a longer delay time than the client optical delay unit, an optical switch unit for switching the route of the inputted client optical packet signal so as to be sent out, an optical switch control unit for controlling the optical switch unit. The optical switch control unit is configured in such a manner as to detect a free time slot. The optical packet transmitting apparatus adjusts transmit timing, with which the client optical packet signal is sent out, in such a manner that the client optical packet signal is inserted into the free time slot.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
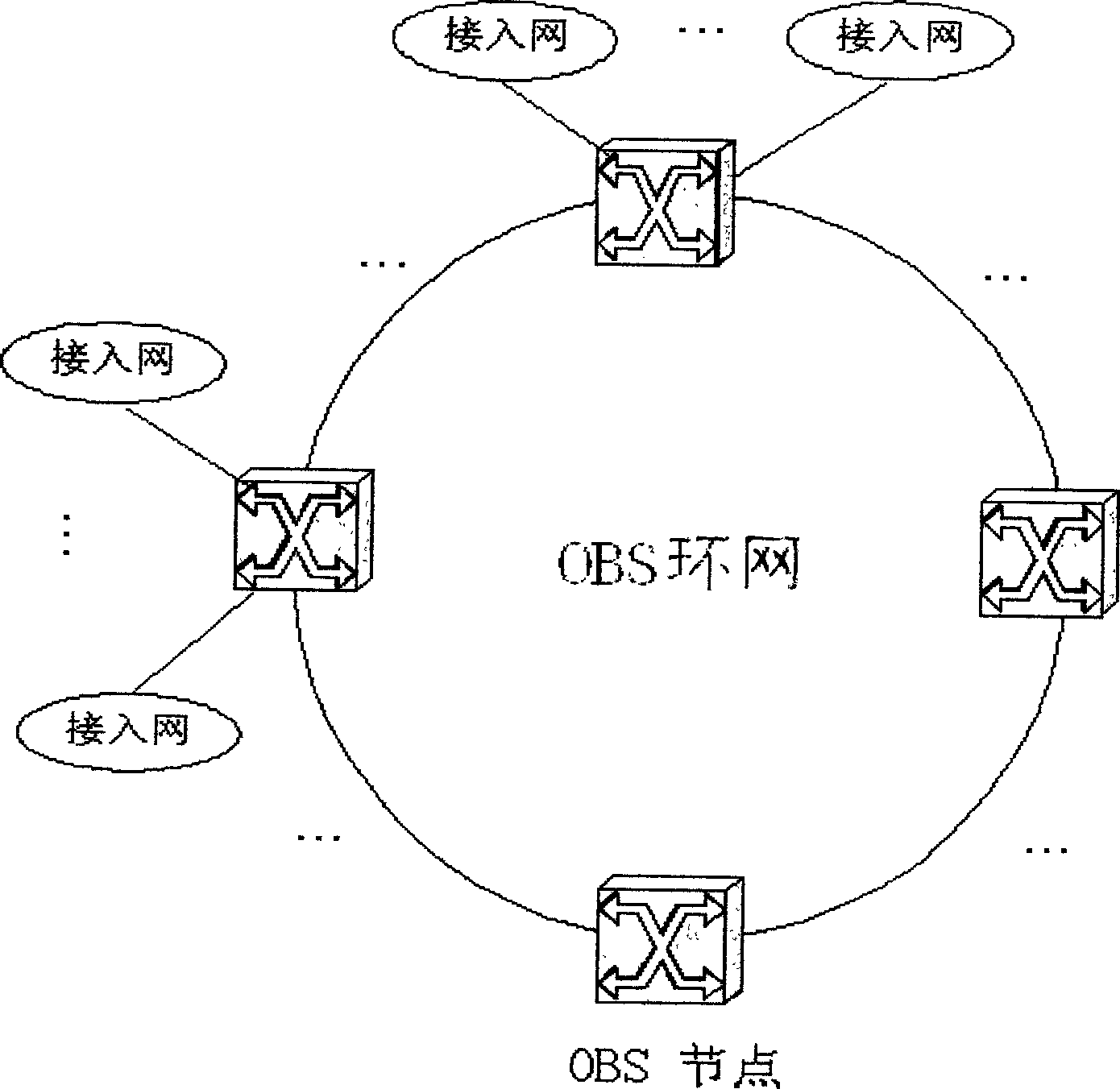
Polling persisting multicast protocol based on retransmission acknowledgement mechanism in optical burst switching ring network
InactiveCN1595909AFair treatmentEqual treatmentRing-type electromagnetic networksLoop networksExtensibilityNetwork packet
The invention discloses a poll continuous multicast protocol based on repeating confirmation mechanism in light mutation exchange rig net. It supports reliable service, acquires the reliability through retransmitting and confirmation mechanism; the dispatcher processes the multicast queue with poll mode; when there has several data packet reaches the target joint, the target joint selects one to receive from the several data packet; if the joint can not receive the mutation packet to be signed, one or several joints in the multicast addresses does not receive the data packet transmitted from the source joint, the source joint retransmits the data packet, guarantees all the joints received the data. The method decreases the complexity of protocol, and the protocol is simplified through the smallest control.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Burst scheduling methods in Optical Burst Switching system
InactiveUS20080285975A1Improve system performanceRaise priorityTime-division optical multiplex systemsTransmissionOptical burst switchingDistributed computing
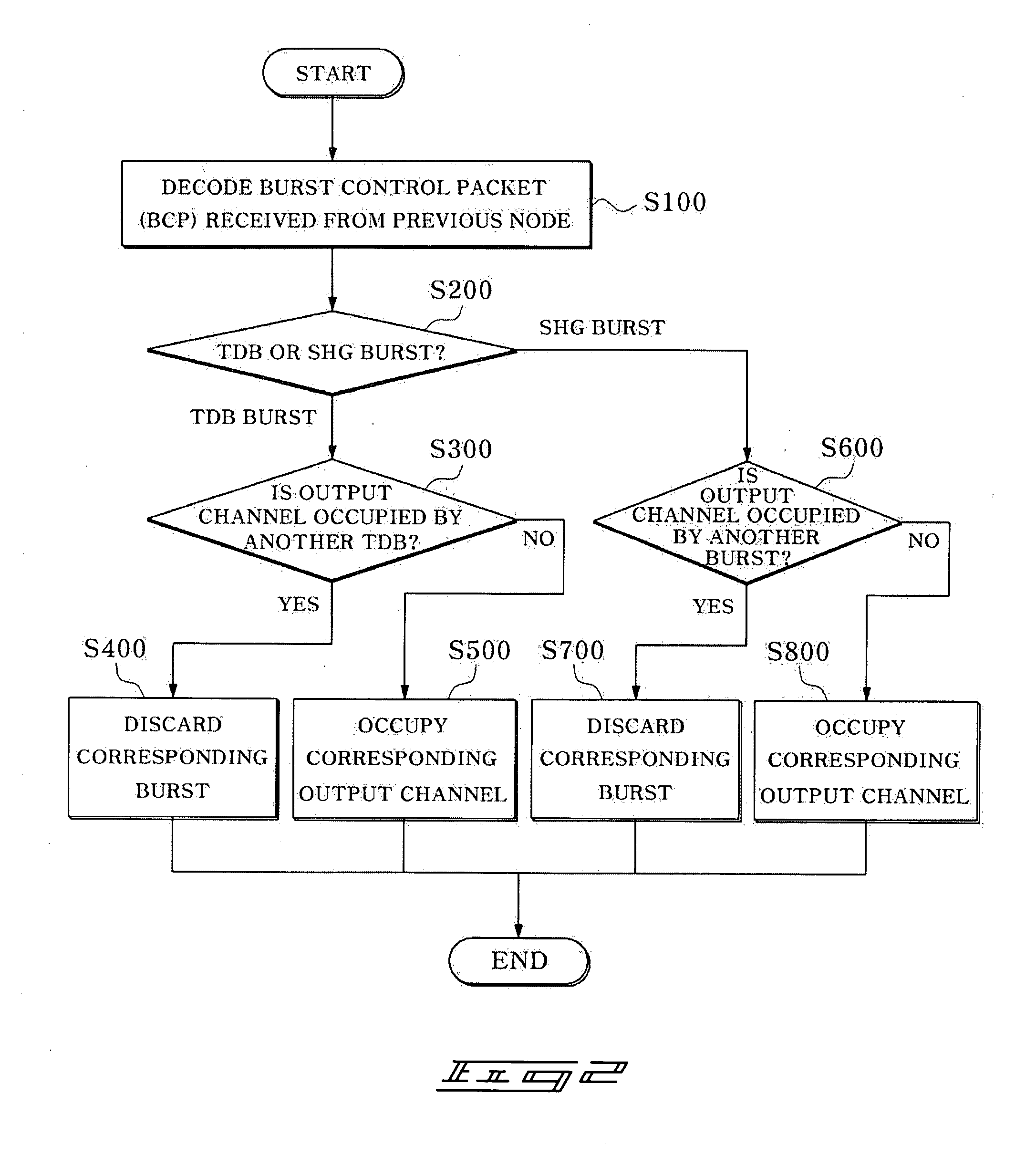
Provided is a burst scheduling method in an Optical Burst Switching (OBS) system in which a plurality of nodes are connected through a mesh-type network. When a TDB which has used many network resources via a plurality of nodes and an SHG burst generated in a previous node, among bursts including BCPs transmitted from the previous node, compete in a current node so as to occupy a specific output channel, scheduling is performed to cause the TDB to have a higher priority than the SHG burst such that the corresponding output channel is occupied. Therefore, it is possible to minimize a burst loss in a network node, thereby enhancing the overall system performance.
Owner:ICU RES & INDAL COOPERATION GROUP
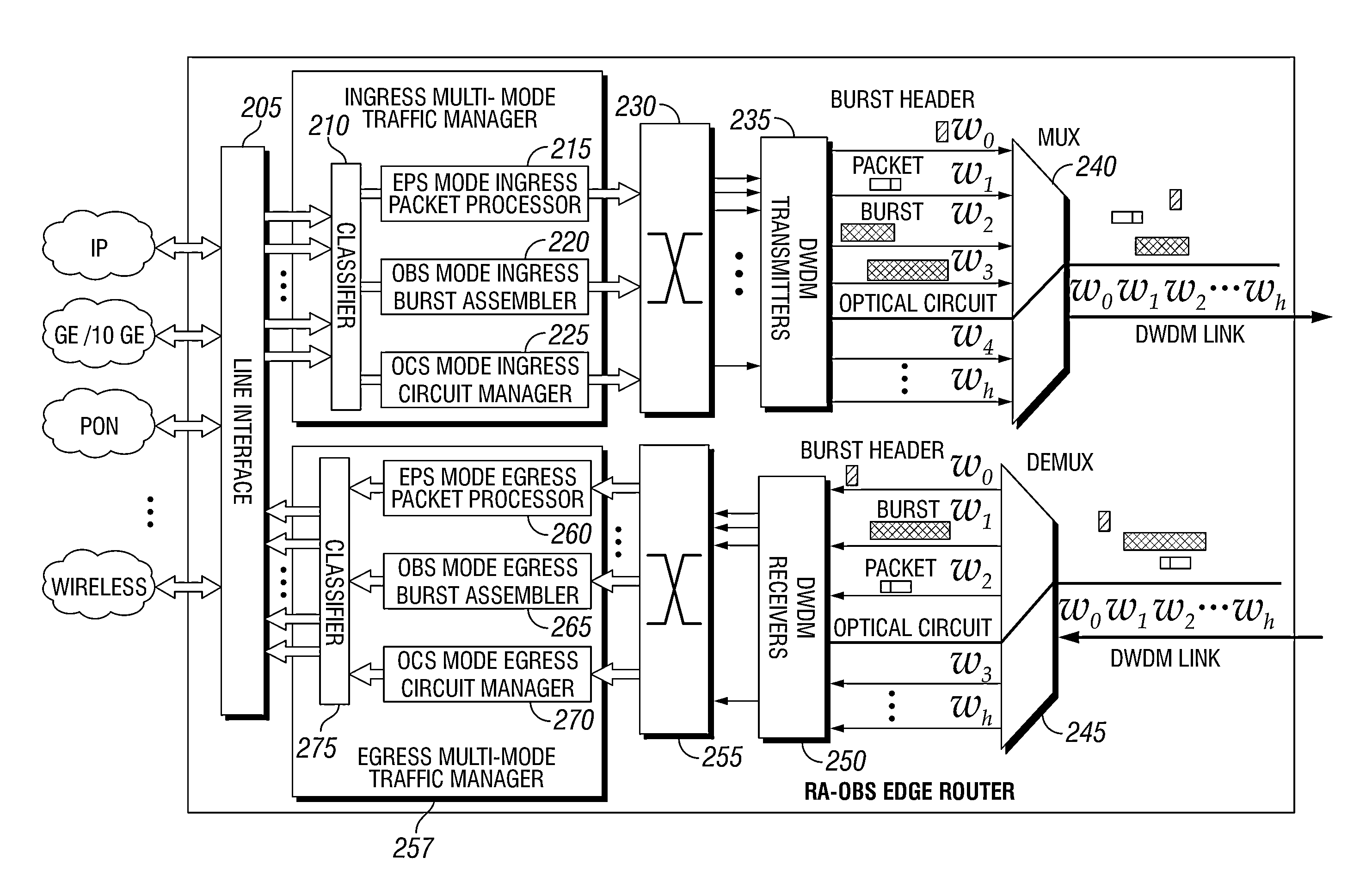
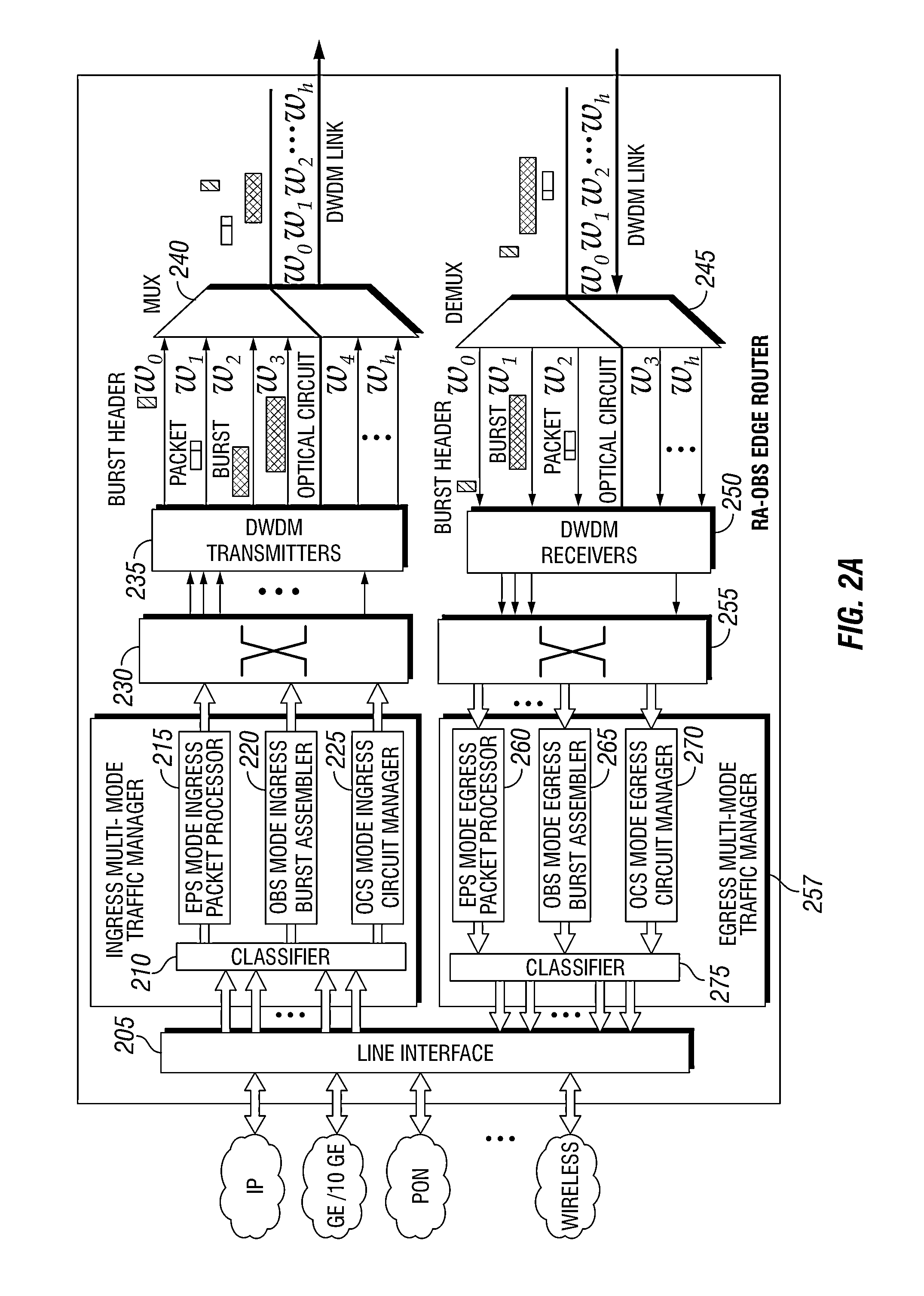
Methods and apparatus for traffic management in multi-mode switching dwdm networks
ActiveUS20130094856A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmissionOptical burst switchingOptical circuit switching
A Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) multi-mode switching system and method and method provides concurrent switching in various switching modes including, but not limited to, an electronic packet switching (EPS) mode, optical circuit switching (OCS) mode, and optical burst switching (OBS) mode. Edge routers in the WDM multi-mode switching systems may provide a traffic management module that processes incoming data and routes the data for transmission in an electronic packet switching (EPS), optical burst switching (OBS), or optical circuit switching (OCS) modes via a WDM link.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Method and apparatus for transmitting an optical signal in an optical burst switching network using arrival time
InactiveUS20060165079A1Reduce blocking rateSatisfactory degree of deflection routingData switching by path configurationOptical multiplexData processing systemOptical burst switching
A method and a system for entering data in a data processing system is provided. In this case, the data is entered in a number of steps, with a view being displayed at a step in a display region of a display means, with the entering and / or display taking place in subsequent steps at least partially as a function of the data entered in one or a number of preceding steps. To design the step-by-step entering of data in a more user friendly manner, it is proposed to simultaneously display the views of a number of consecutive steps in the display region.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Optical burst switching node with internal speedup
InactiveUS20050152351A1High bandwidthImprove efficiencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical burst switchingEngineering
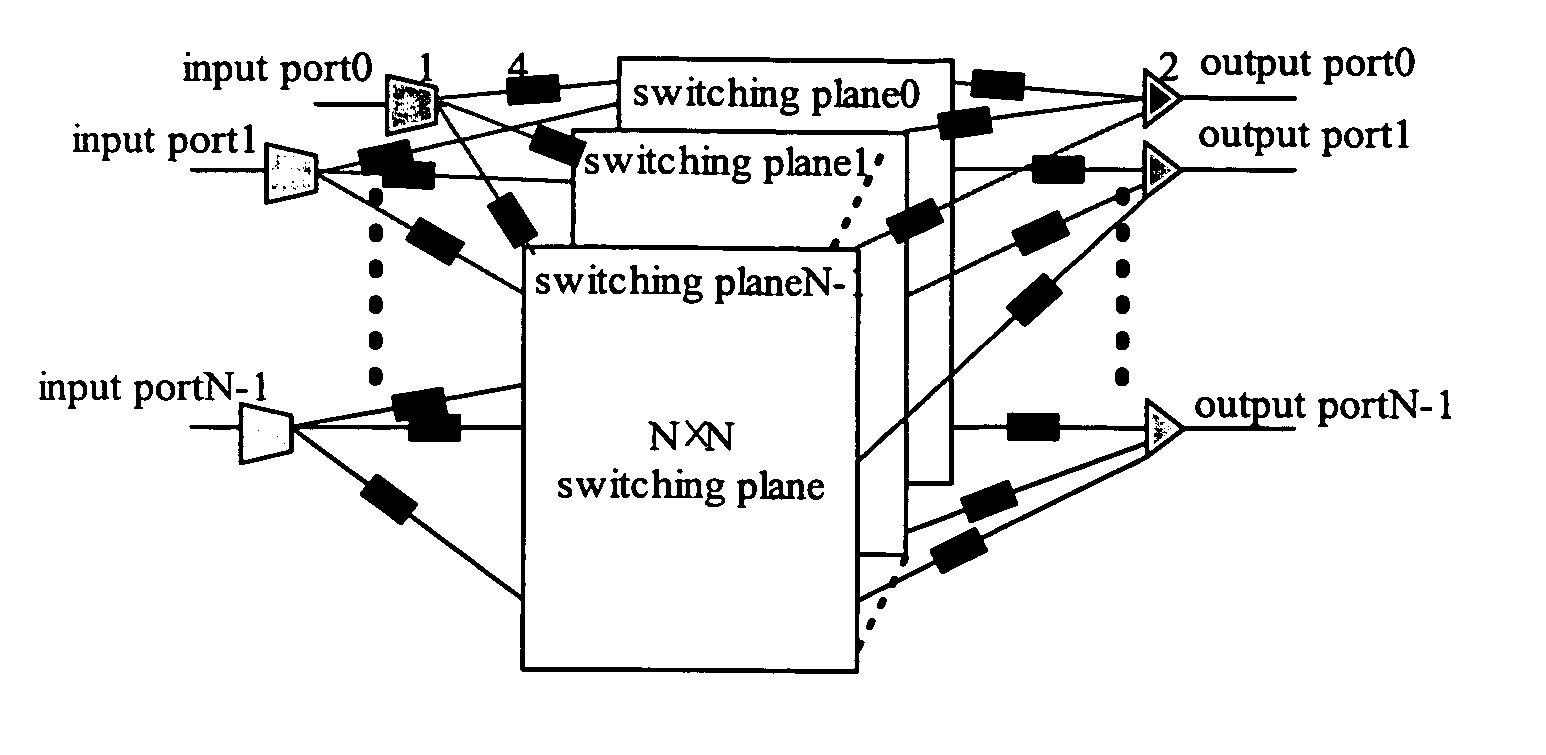
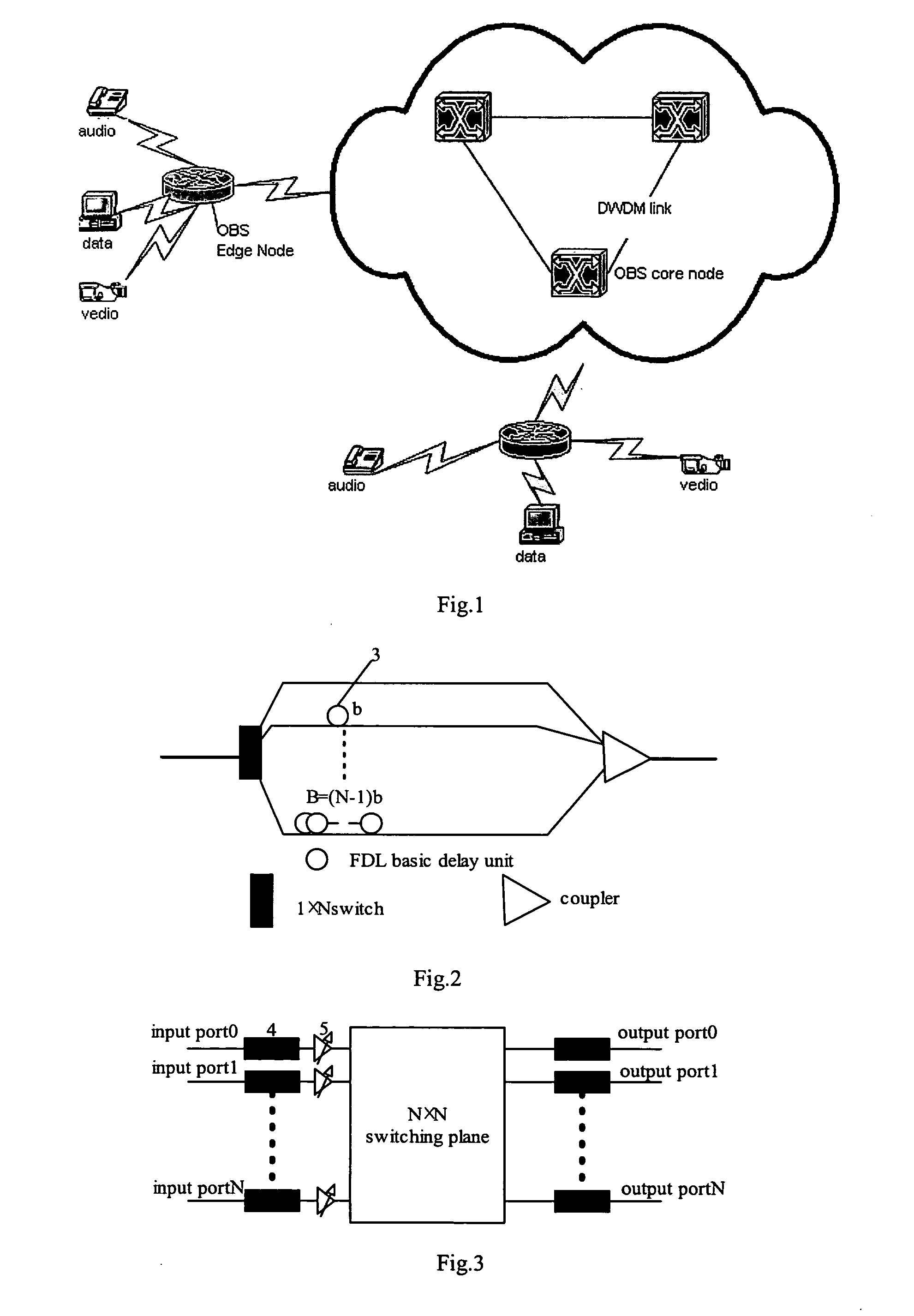
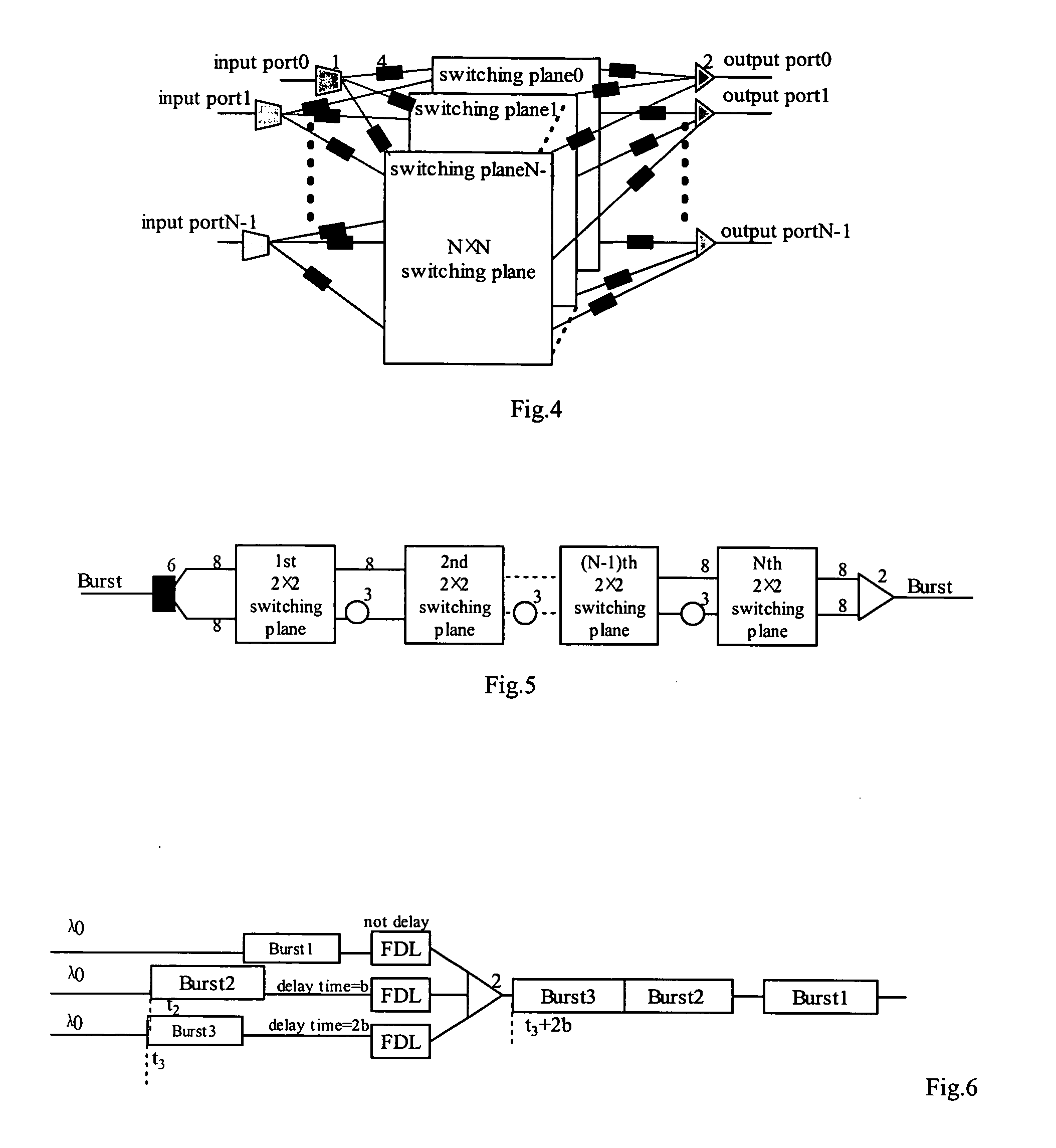
A multiple-plane OBS node comprises N input ports, N 1×N switches, N switching planes, N2 FDLs, N optical couplers, and N output ports, each input port is connected with the input of a corresponding 1×N switches, the N outputs of each 1×N switch are connected with a corresponding input of each switching plane respectively, a corresponding output of each switching plane is connected with the input of the same corresponding optical coupler via a respective FDL, and each output port is connected with the output of a corresponding optical coupler, wherein N is an integer.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Switch processor matched with core node of hybrid optical switching network
InactiveCN101621719AFlexible automatic deploymentConvenient automatic provisioningMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic network arrangementsLow speedExchange network
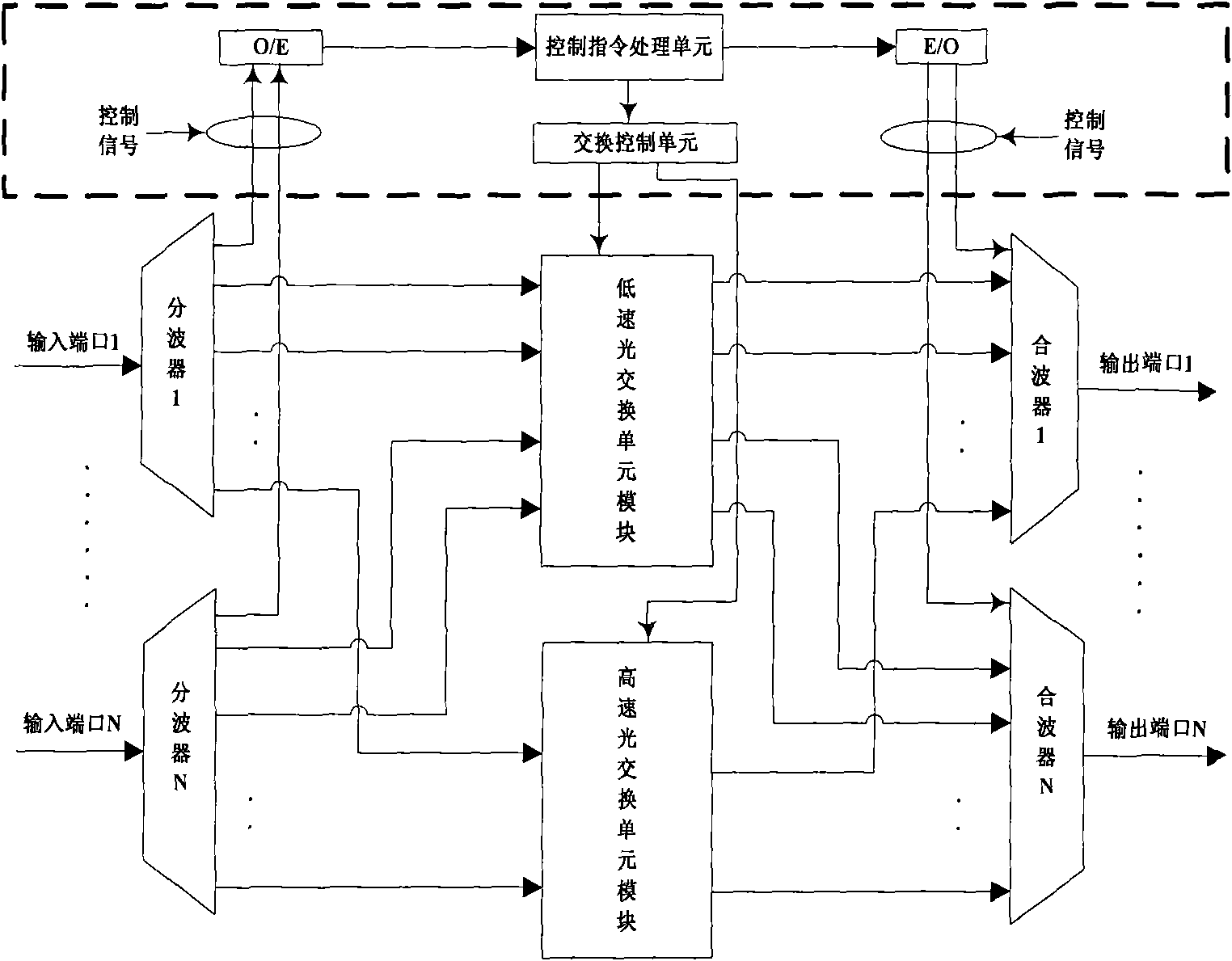
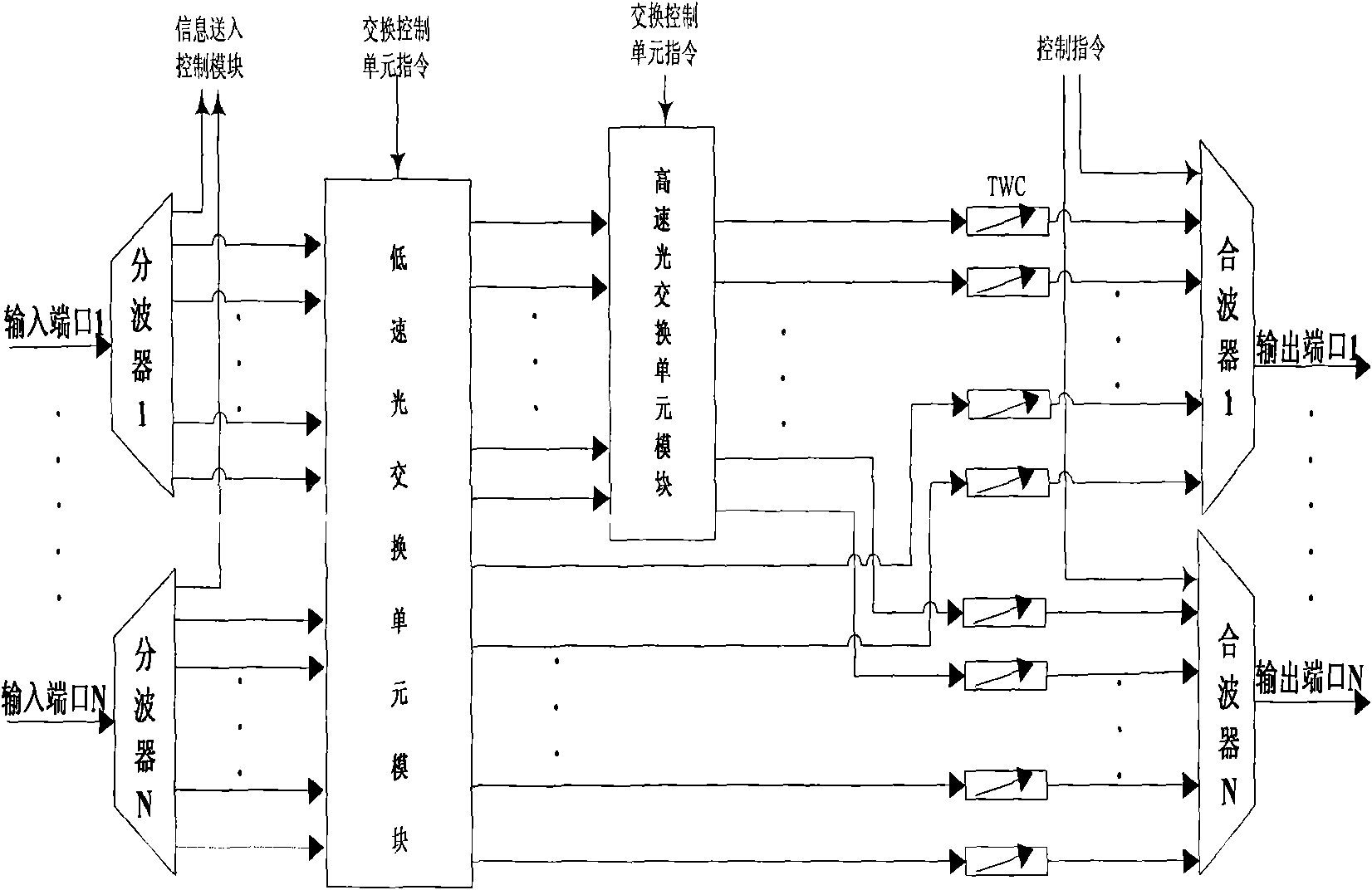
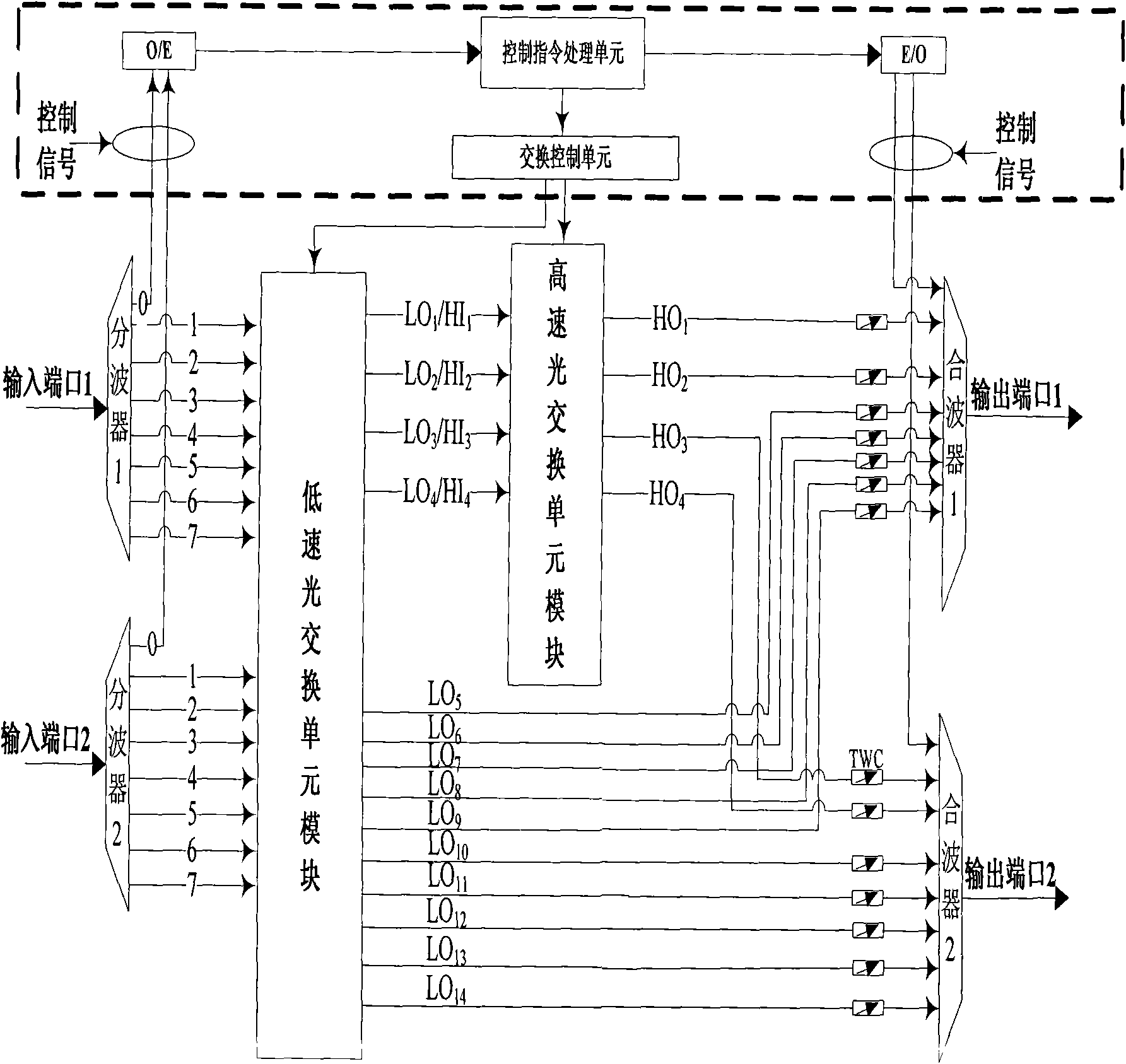
The invention relates to a switch processor matched with a core node of a hybrid optical switching network in an optical network communication technology. The switch processor comprises a wave separator set, a wave combiner set, a low-speed optical switch unit module, a high-speed optical switch unit module and tunable wavelength converters, wherein the wave separator set and the wave combiner set are provided with an input port and an output port; the low-speed optical switch unit module and the high-speed optical switch unit module are sequentially arranged between the wave separator set and the wave combiner set in series and respectively provided with an interface connected with a switching control unit in a node; and the tunable wavelength converters are arranged between a high-speed optical switch unit module output port and wave combiners and a low-speed optical switch unit module output port and the wave combiners. The low-speed optical switch unit module in the switch processor is used for supporting optical circuit switching, and the high-speed optical switch unit module simultaneously supports optical burst switching and the optical circuit switching; therefore the switch processor has the characteristics of flexibly, conveniently, reliably and automatically deploying hybrid optical switching modes, improving the flexibility of the optical burst switching / the optical circuit switching, the utilization rate of wavelength resources, the bearing capacity of the optical circuit switching in a network, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Methods to process and forward control packets in OBS/LOBS and other burst switched networks
InactiveUS20020141398A1Improve business performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsData packOptical burst switching
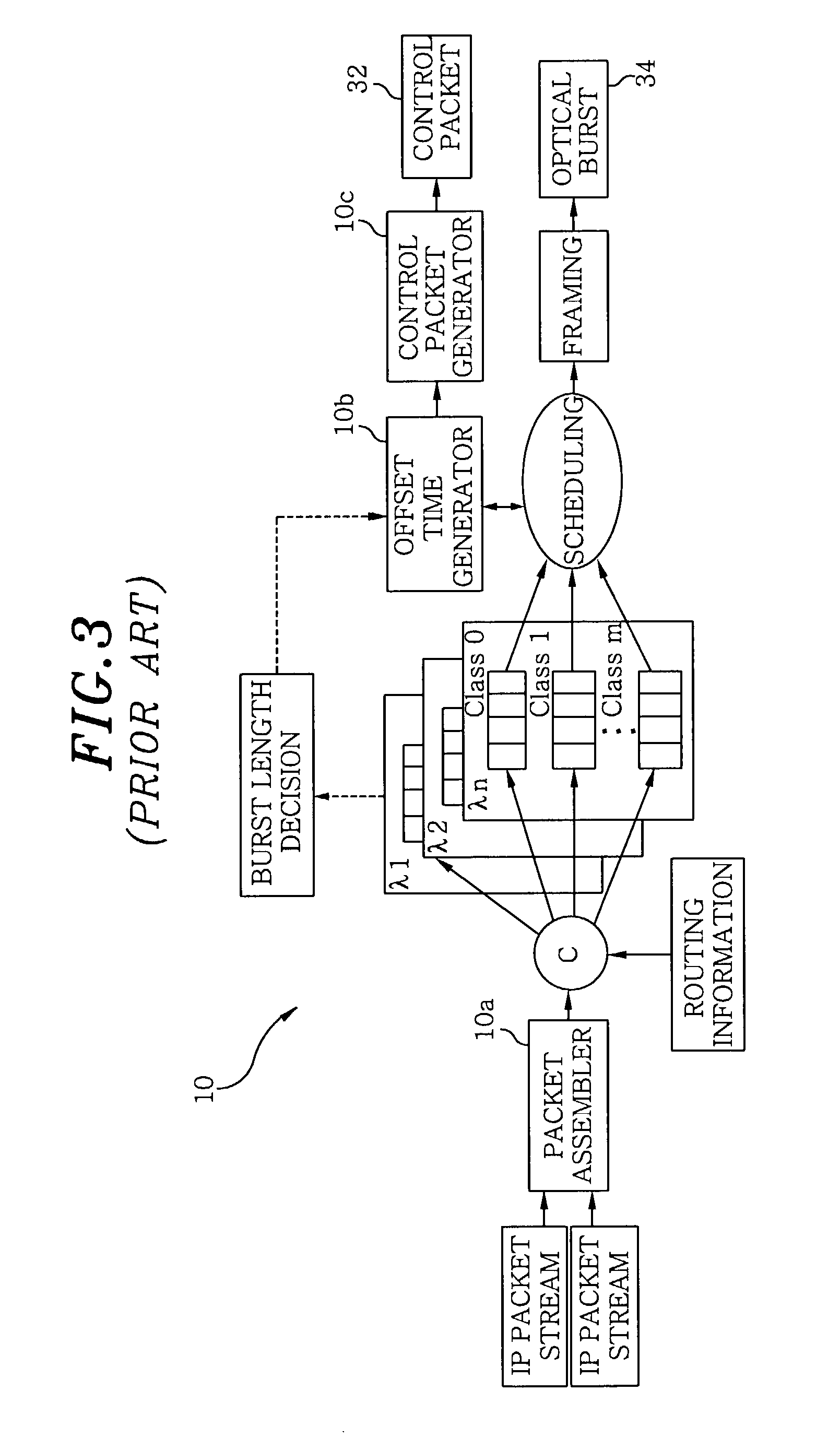
The invention provides a novel method to reduce the minimum offset time and pre-transmission delay for each data burst in Optical Burst Switching or Labeled Optical Burst Switching or other packet or burst switched systems. Under this method, the control packet is relayed as soon as it is determined if bandwidth for the data burst at the data burst output port(s) can be reserved successfully, greatly speeding up the setup and configuration of the Switching Element.
Owner:BRILLIANT OPTICAL NETWORKS
Rate-controlled optical burst switching
InactiveUS7187654B1Improve performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionOptical burst switchingEdge node
A method and apparatus are provided for low latency loss-free burst switching. Burst schedules are initiated by controllers of bufferless core nodes and distributed to respective edge nodes. In a composite-star network, the burst schedules are initiated by any of a plurality of bufferless core nodes and distributed to respective edge nodes. Burst formation takes place at source nodes and a burst size is determined according to an allocated bitrate of a burst stream to which the burst belongs. An allocated bitrate of a burst stream may be modified according to observed usage of scheduled bursts of a burst stream. A method of control-burst exchange between each of a plurality of edge nodes and each of a plurality of bufferless core nodes enables burst scheduling, time coordination, and loss-free burst switching. Both the payload bursts and control bursts are carried by optical channels connecting the edge nodes and the core nodes. A method and a circuit are provided for generating burst descriptors wherein each burst is associated with a burst stream and each burst stream is allocated a service bitrate. The generated burst descriptors are used in each master controller in each core node to create the burst schedules. In a conventional burst-scheduling process, the burst queues at a master controller of an optical switch receives burst descriptors from the source nodes and schedules the burst switching times. In a distinct departure, according to the present invention, the burst descriptors are generated by a master controller of an optical switch in a core node, the switching times of the corresponding bursts are scheduled, and the schedules are distributed to the respective edge nodes. The burst-descriptor generation is based on burst-stream bitrate-allocation defined by the source nodes.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
System and method of time-slotted optical burst switching
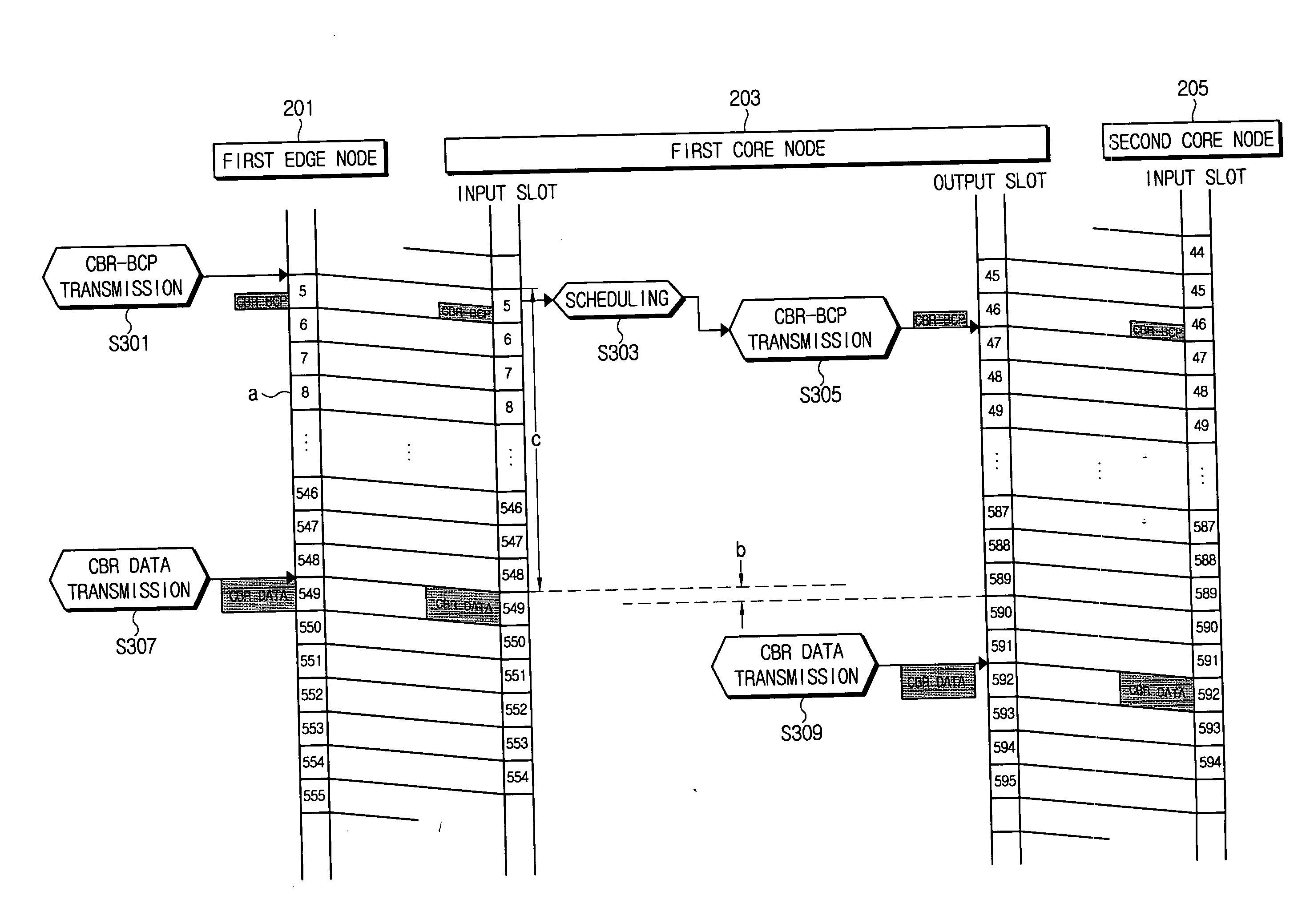
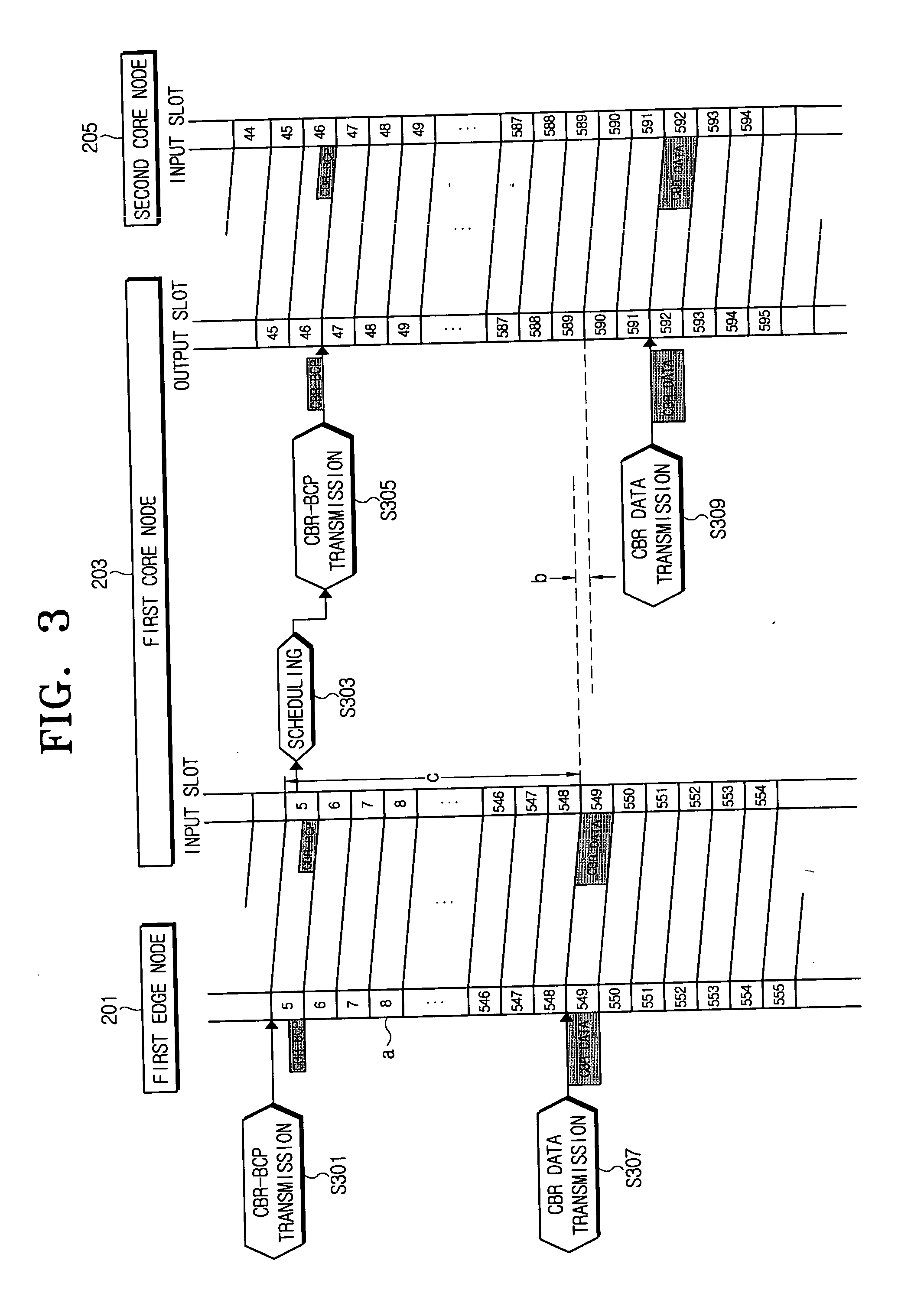
InactiveUS20060147207A1Minimizes data delayMinimize delayMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical burst switchingEdge node
A time-slotted optical burst switching system and method therefor can support data transmissions for a constant bit rate (CBR) and at a variable bit rate (VBR) and improves a data transmission method at an edge node and a core node. Accordingly, it is possible to perform a data service for the constant bit rate and for a variable bit rate and to substantially prevent a delay due to a scheduling for a slot assignment at the core node by transmitting a burst control packet before the data burst to be transmitted at the edge node is generated in case of transmitting the data burst at the constant bit rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dense wavelength division multiplexing multi-mode switching systems and methods for concurrent and dynamic reconfiguration with different switching modes
A Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) multi-mode switching system and method and method provides concurrent switching in various switching modes. For example, WDM links may communicate data in various switching modes including, but not limited to, an electronic packet switching (EPS) mode, optical circuit switching (OCS) mode, and optical burst switching (OBS) mode. Edge routers and core routers in the WDM multi-mode switching systems and methods provide switching and processing necessary to handle data provided in the various switching modes. Further, the WDM multi-mode switching systems and methods can also provide dynamic reconfiguration between the various switching modes.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Space laser communication forwarding system based on passive optical switch
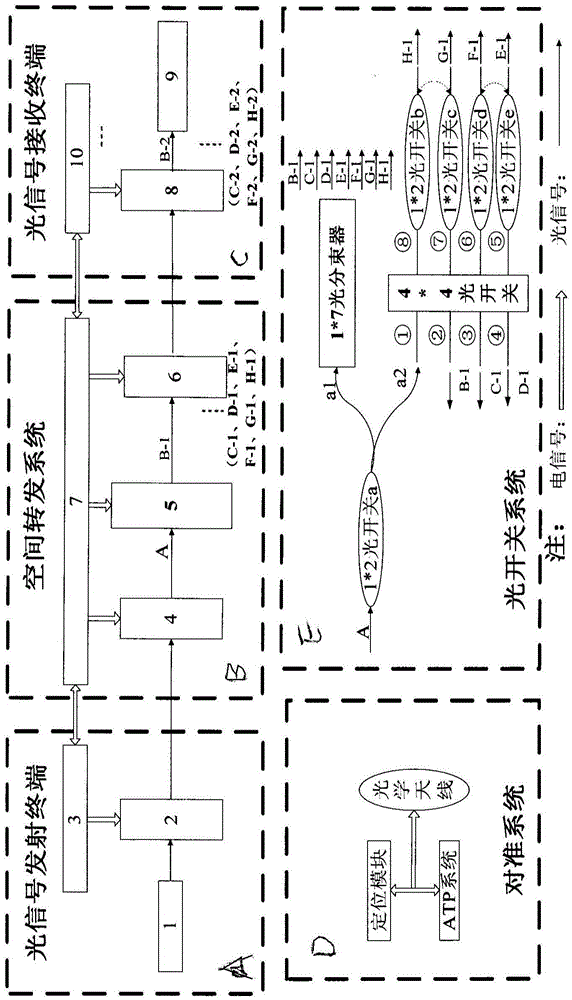
ActiveCN105490727ASolve the speed bottleneckTo achieve high-speed transmission requirementsRadio transmissionElectromagnetic transmittersOptical burst switchingBroadcasting
The invention discloses a space laser communication forwarding system based on a passive optical switch. The system consists of a ground optical signal transmitting terminal, a space forwarding system and a ground optical signal receiving terminal. A transmitting end and a receiving end for space optical communications are placed on the ground, and the space forwarding system is carried by an aircraft and only forwards optical signals without processing such as amplification, modulation, demodulation and the like, so that the complexity of a space system is lowered greatly, and the sizes, weights and power consumption of space loads are lowered. Moreover, point-to-point or broadcasting-mode forwarding of the optical signals is realized through an optical switching system. The signals are modulated on the transmitting end, and demodulated on the receiving end, so that ground-space-ground forwarding communications are realized.
Owner:山东中科际联光电集成技术研究院有限公司
Data transmission method for integrated mixed optical network based on burst exchange
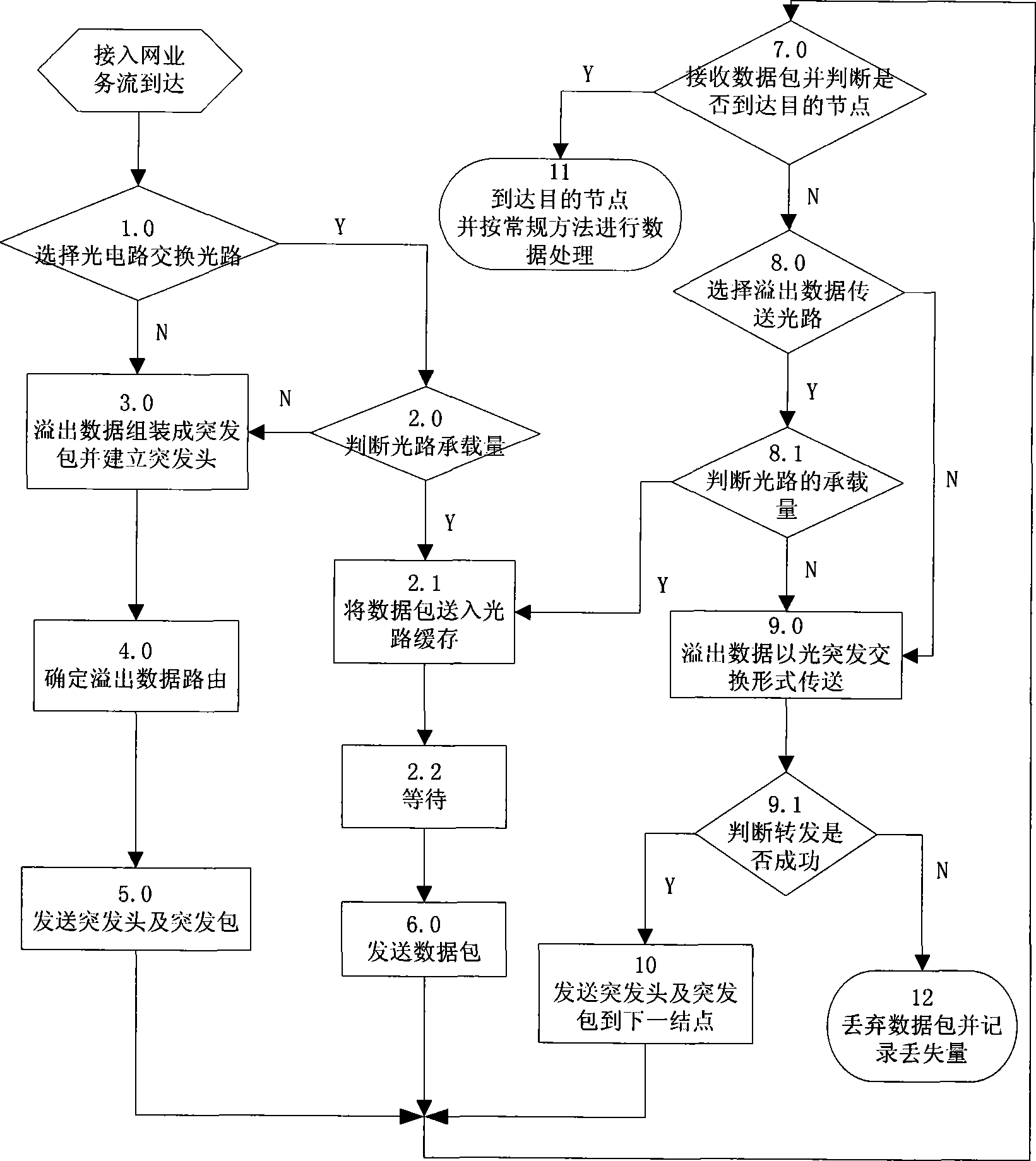
InactiveCN101426152ASpeed up deliveryImprove reliabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksData streamOptical burst switching
The invention pertains to a data transmission method in the optical network communication technology. The invention organically combines optical circuit switching (OCS) and optical burst switching (OBS) based on the original physical topological network, reserves wavelength in each physical link to establish an overflow transmission light path, transmits the discarded data packets of the original OBS due to booking collision into the light path to transmit continuously, accordingly resolving the problem of packet loss due to one time booking collision; most of the data packets in the network operation adopts an OCS mode transmission, and adopts an OBS mode overflow transmission light path to transmit the data packets to destination nodes when the data conveying capacity has a high a burst performance; and can switch back to the OCS mode transmission when the OCS light path is smooth, accordingly can flexibly adjust the transmission modes according to the current state of network and significantly reduce the packet loss rate. The present invention thus not only has high efficiency of OCS but also has flexibility of OBS, and has features of strong transmission capability and adaptability to burst data streams, rapid network transmission, high reliability, no additional optical devices and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
All-optical time slice switching method based on time synchronization
ActiveCN103580771AReliable all-optical switchingMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsData synchronizationData stream
The invention discloses an all-optical time slice switching method based on time synchronization. According to the method, continuous service data streams in an optical network are assembled to periodically-repeated optical time slices in a segmented mode in a time domain and are transferred in an asynchronous transfer mode. Network nodes obtain high precision synchronization time through whole network time, an optical switch is controlled to switch optical time slices reaching at precise time points periodically to a target port, and therefore full optical switching is completed. When a connection request reaches, available routes, wavelengths and occupation time slots are calculated through source nodes according to network available time slot resource information, and are reserved through a connection management module. After resource reservation is finished, the source nodes send out optical time slices of bearer service periodically at reserved time slots. Destination nodes restore received optical time slices to original service steams. Compared with an existing switching technology, the all-optical time slice switching method has the remarkable advantages that reliable and flexible sub-wavelength granularity all-optical switching can be achieved without participation of all-optical caches and all-optical logic devices.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method to control a special class of OBS/LOBS and other burst switched network devices
InactiveUS7042906B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTelecommunicationsOptical burst switching
The invention is an unique control method that maintains the bandwidth efficiency of Optical Burst Switched, Labeled Optical Burst Switched, and other burst or packet switched networks. The invention also combines in a novel manner the delayed Reserve-a-Fixed-Duration (RFD) class of switching techniques and special classes of slow Switching Elements.
Owner:BRILLIANT OPTICAL NETWORKS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com