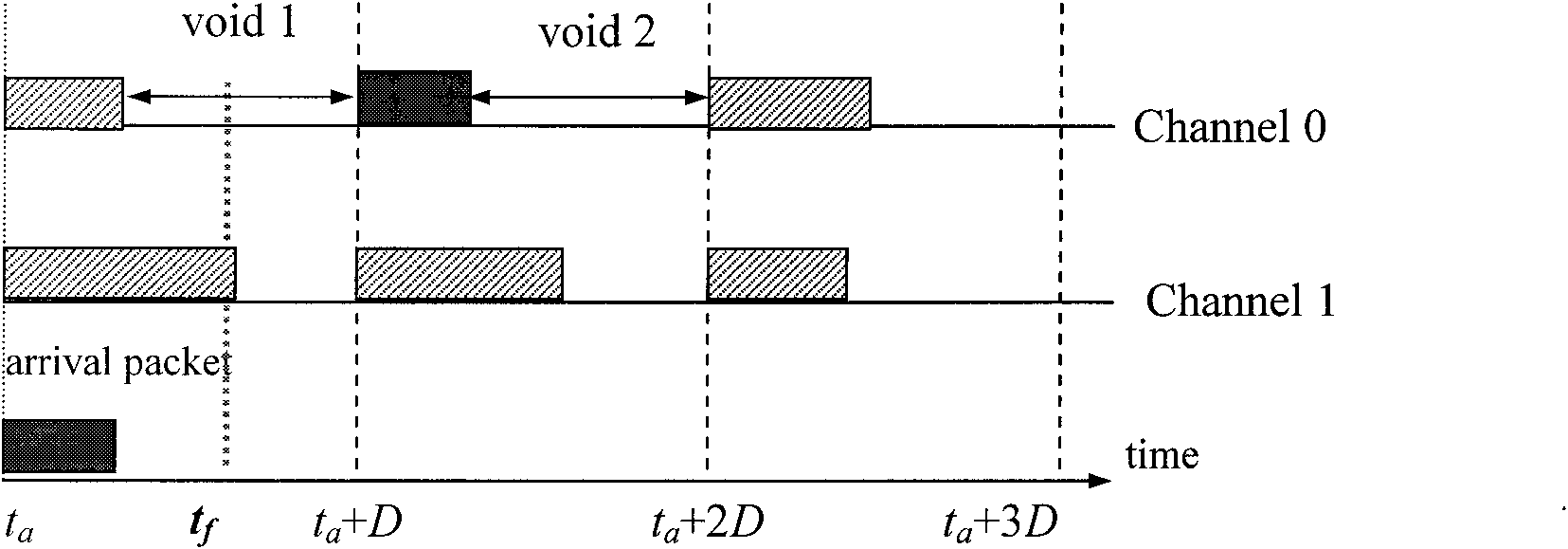Patents
Literature
73 results about "Optical IP Switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
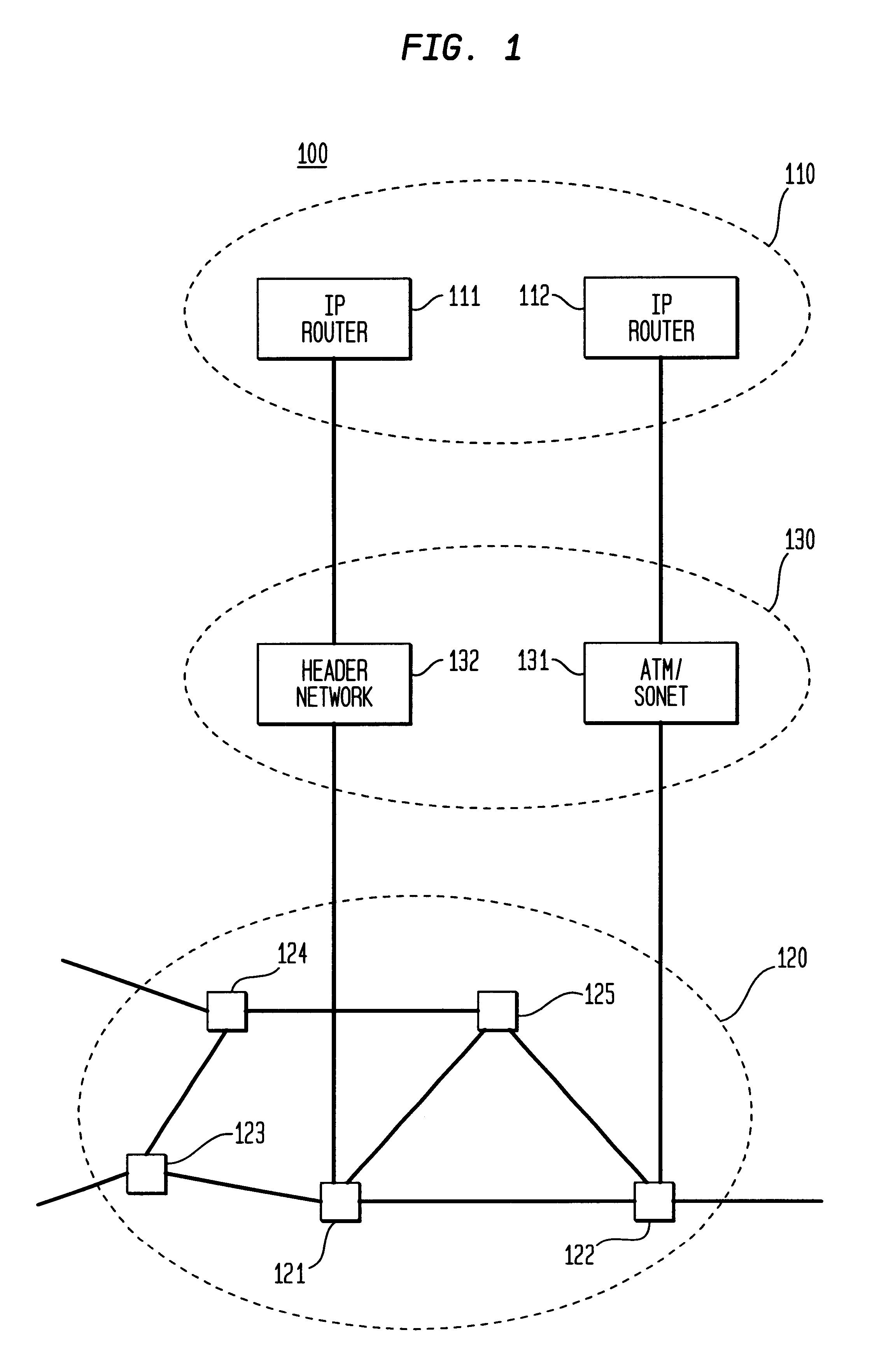
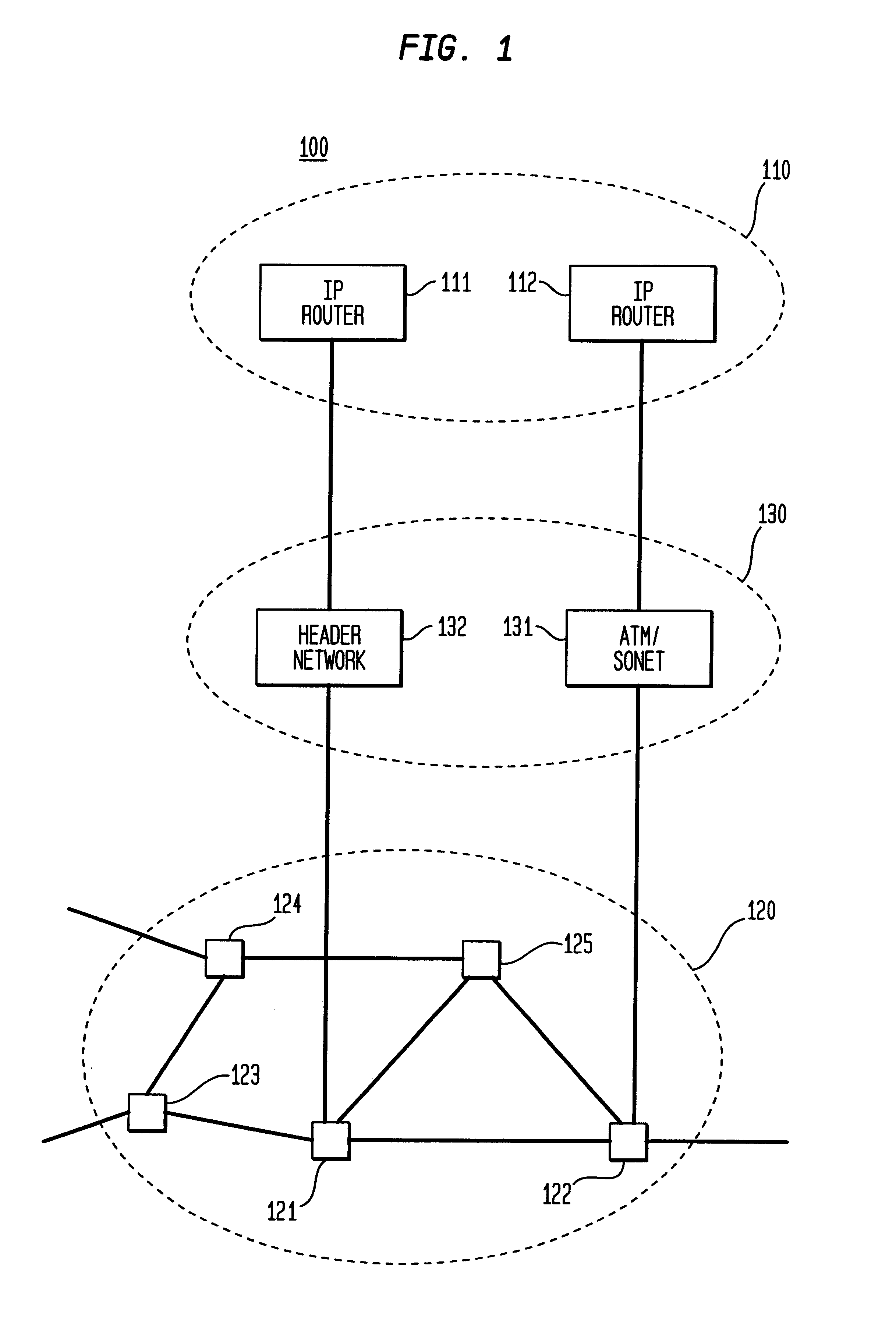
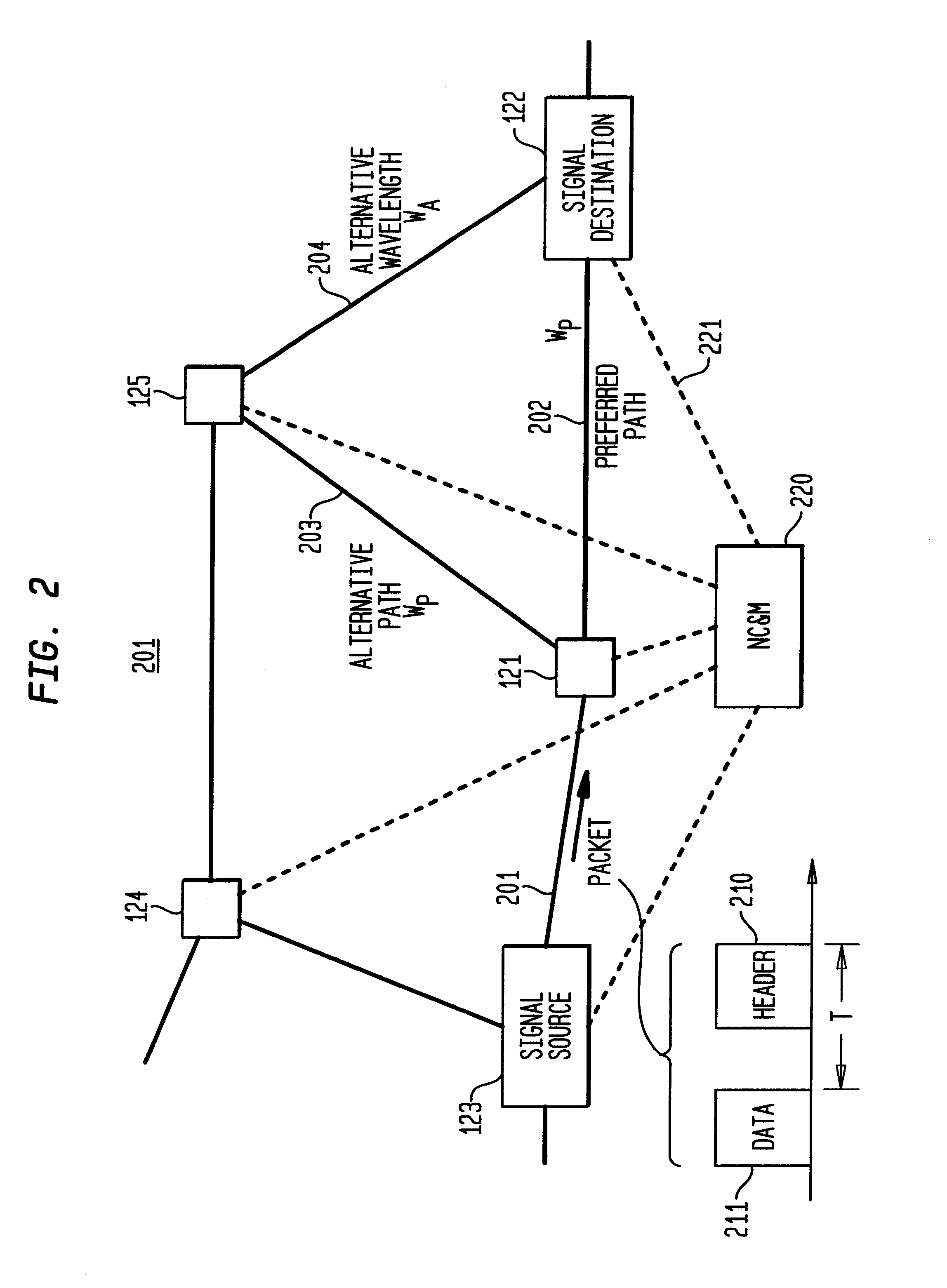
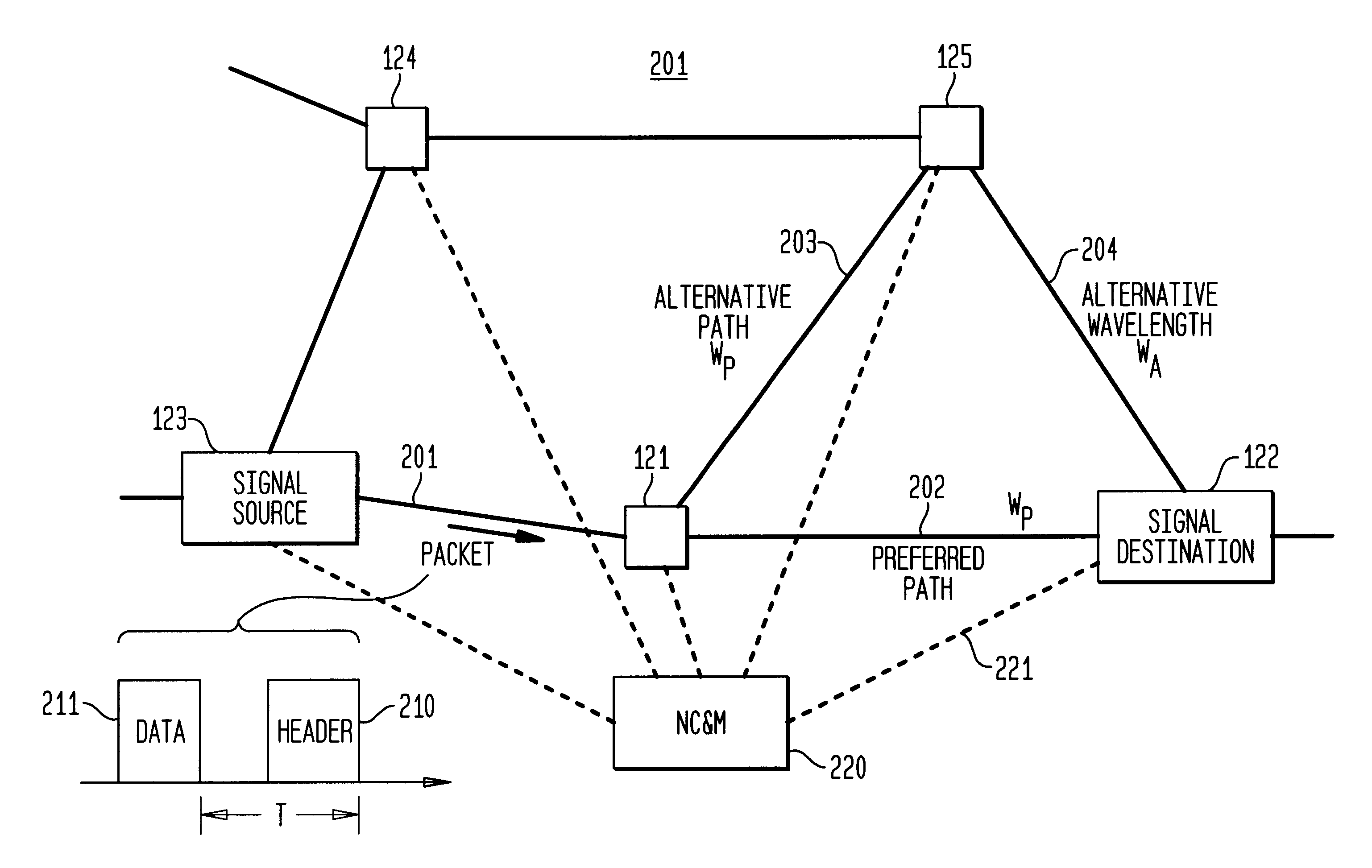
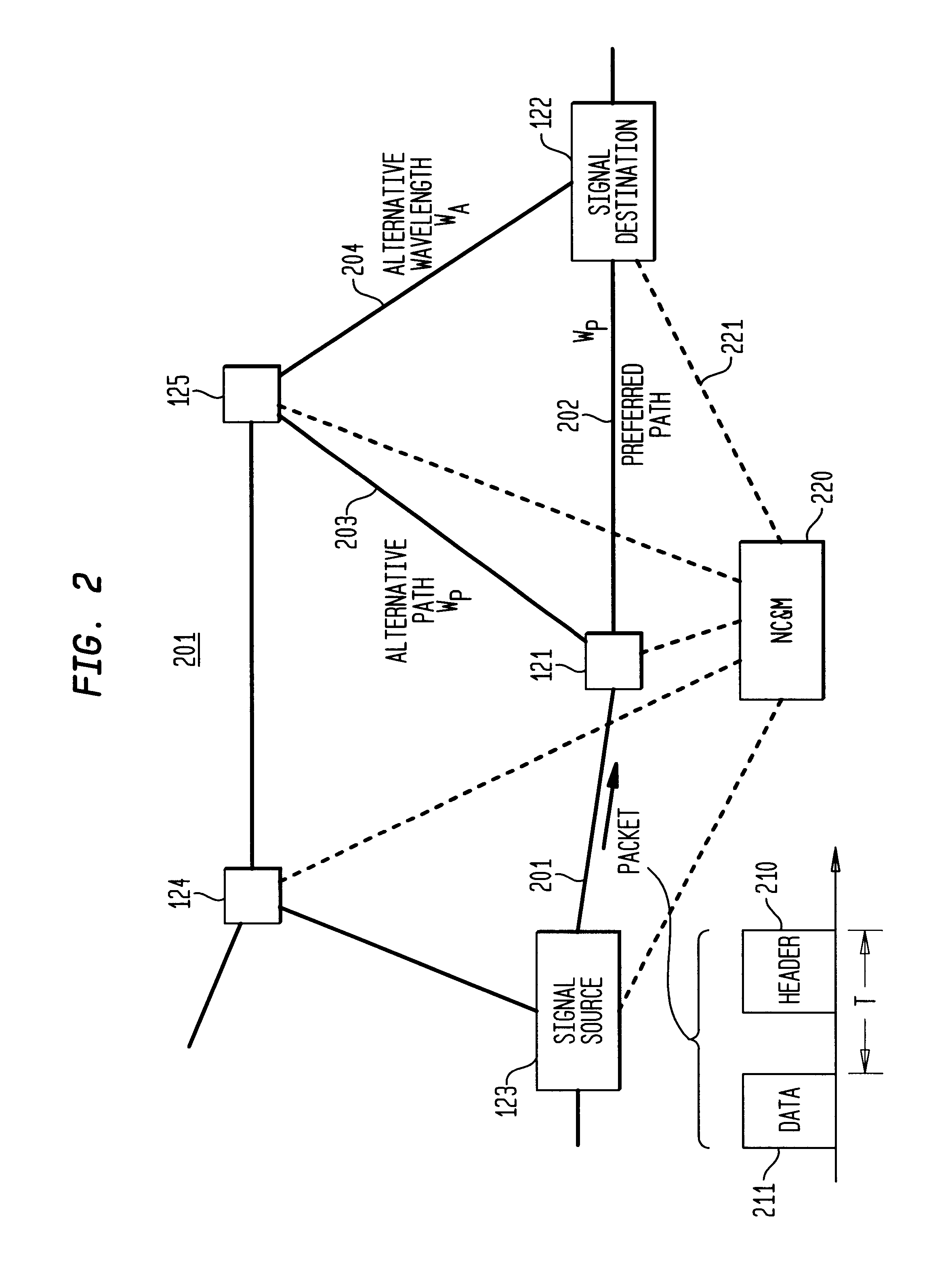
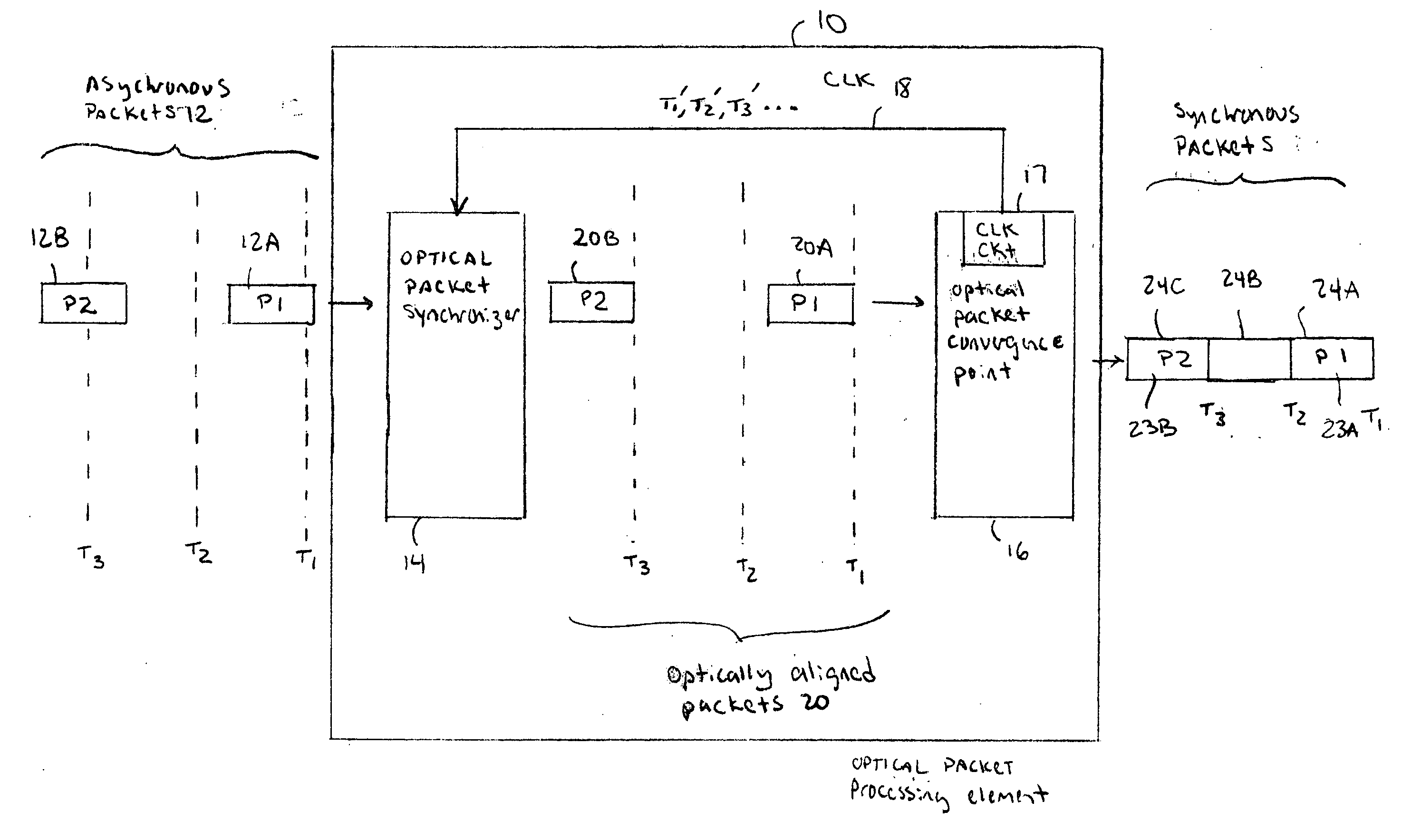
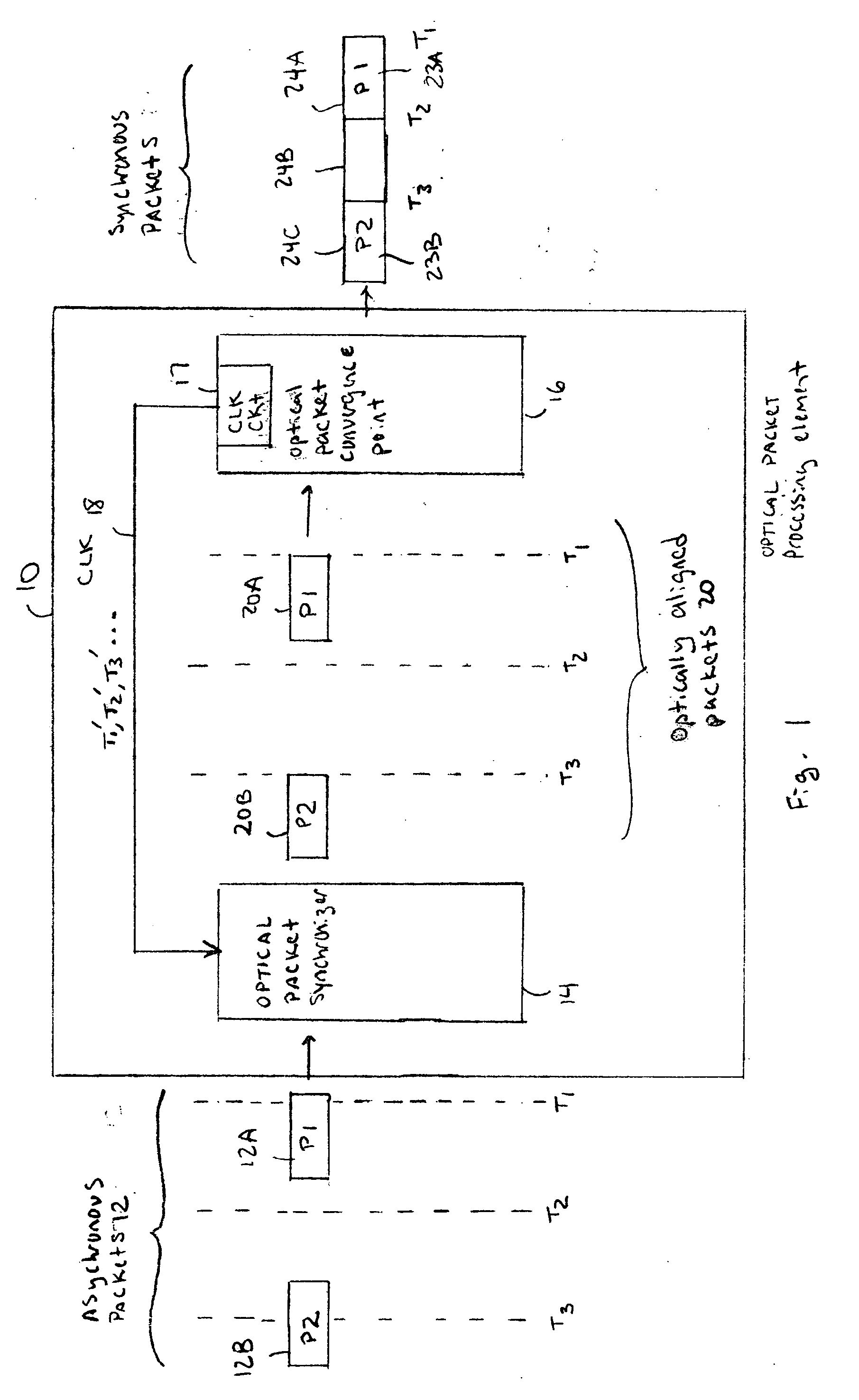
Optical IP Switching (OIS), is a novel method of creating transparent optical connections between network nodes using a flow-based approach. An IP flow is a collection of IP packets going from the same source to the same destination: the exchange of IP packets is the mechanism that allows the transport of information over the Internet.
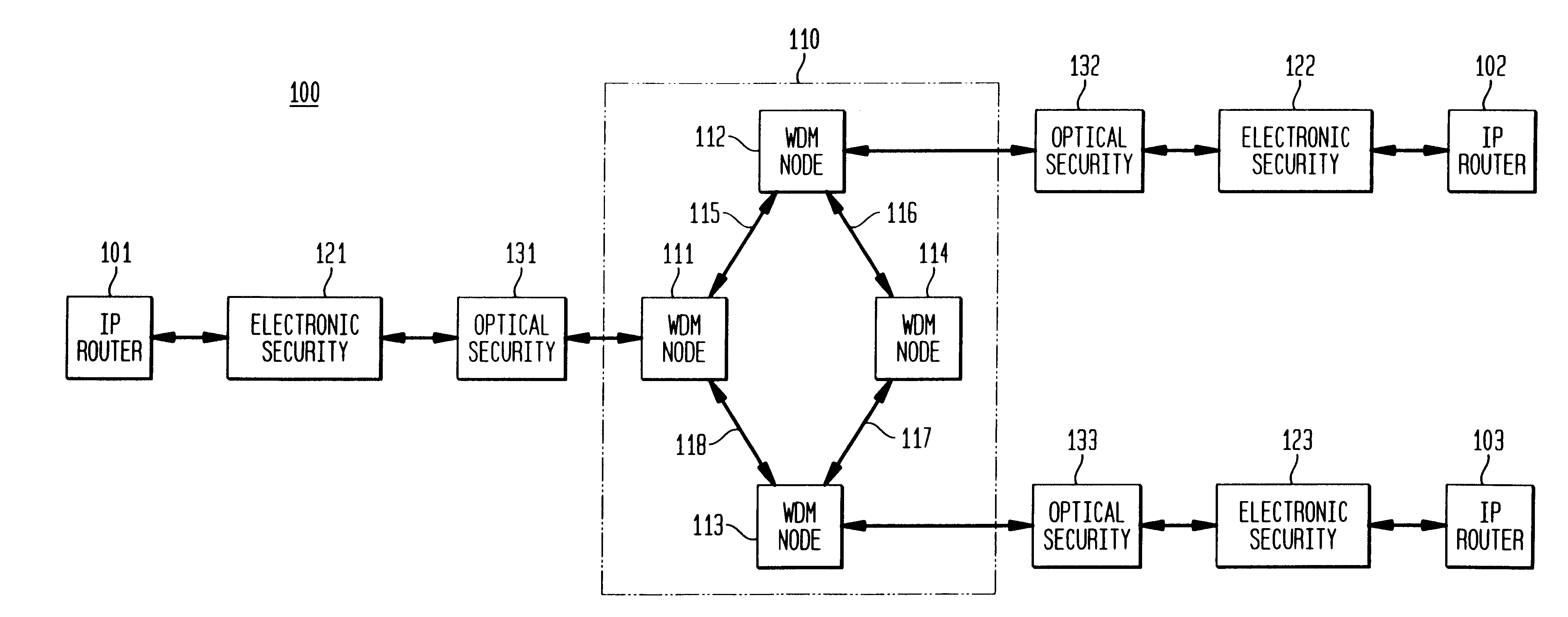
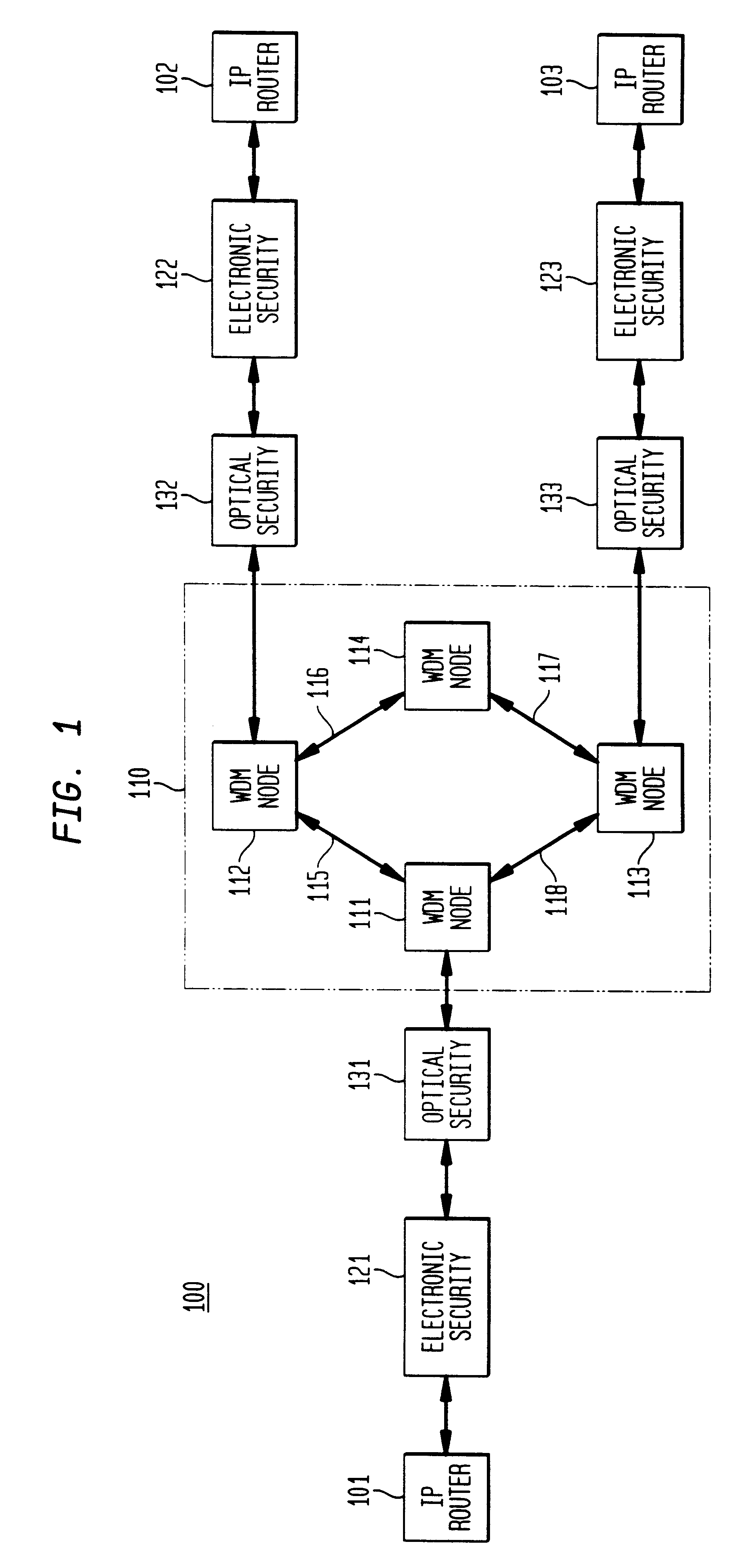
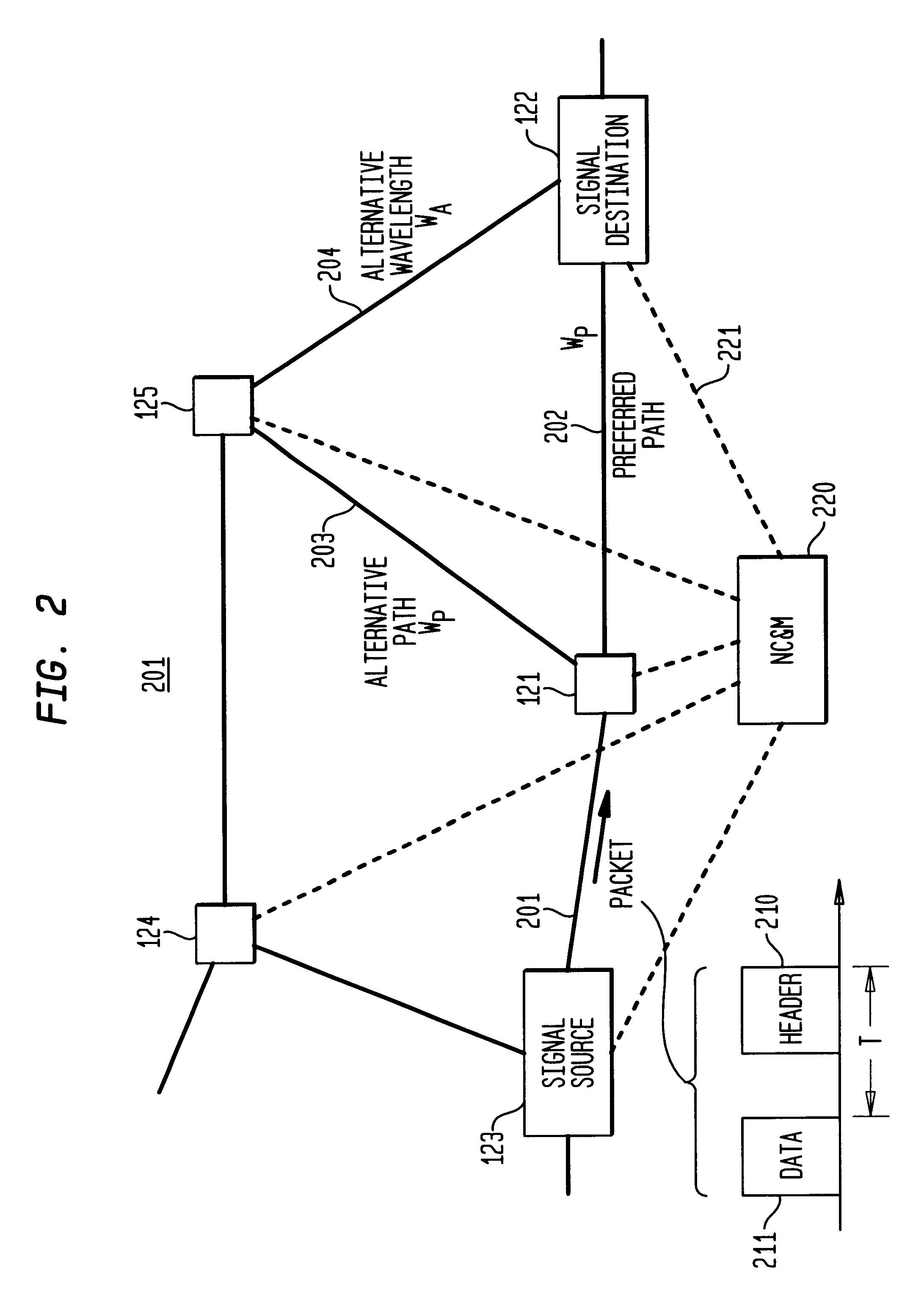
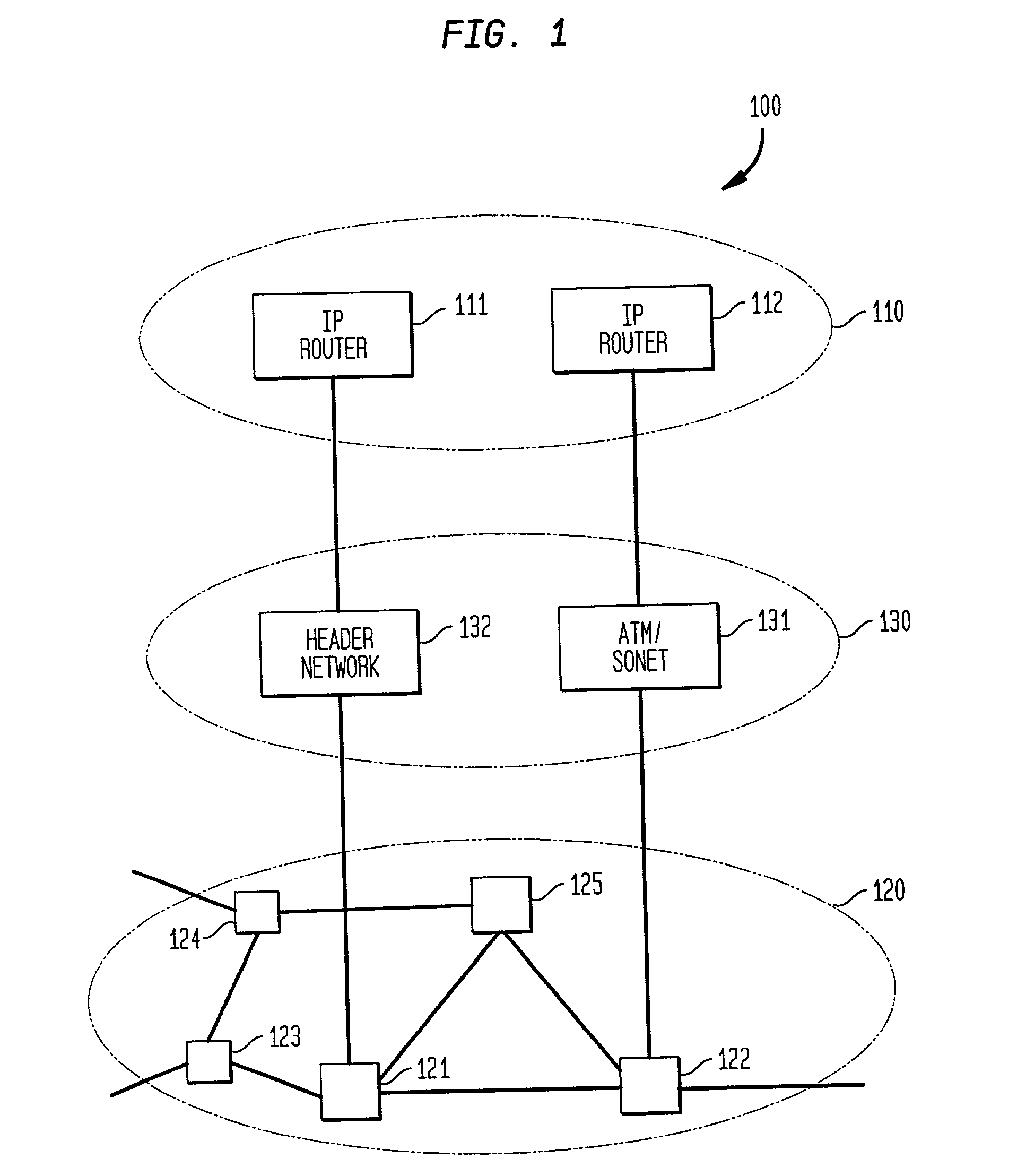
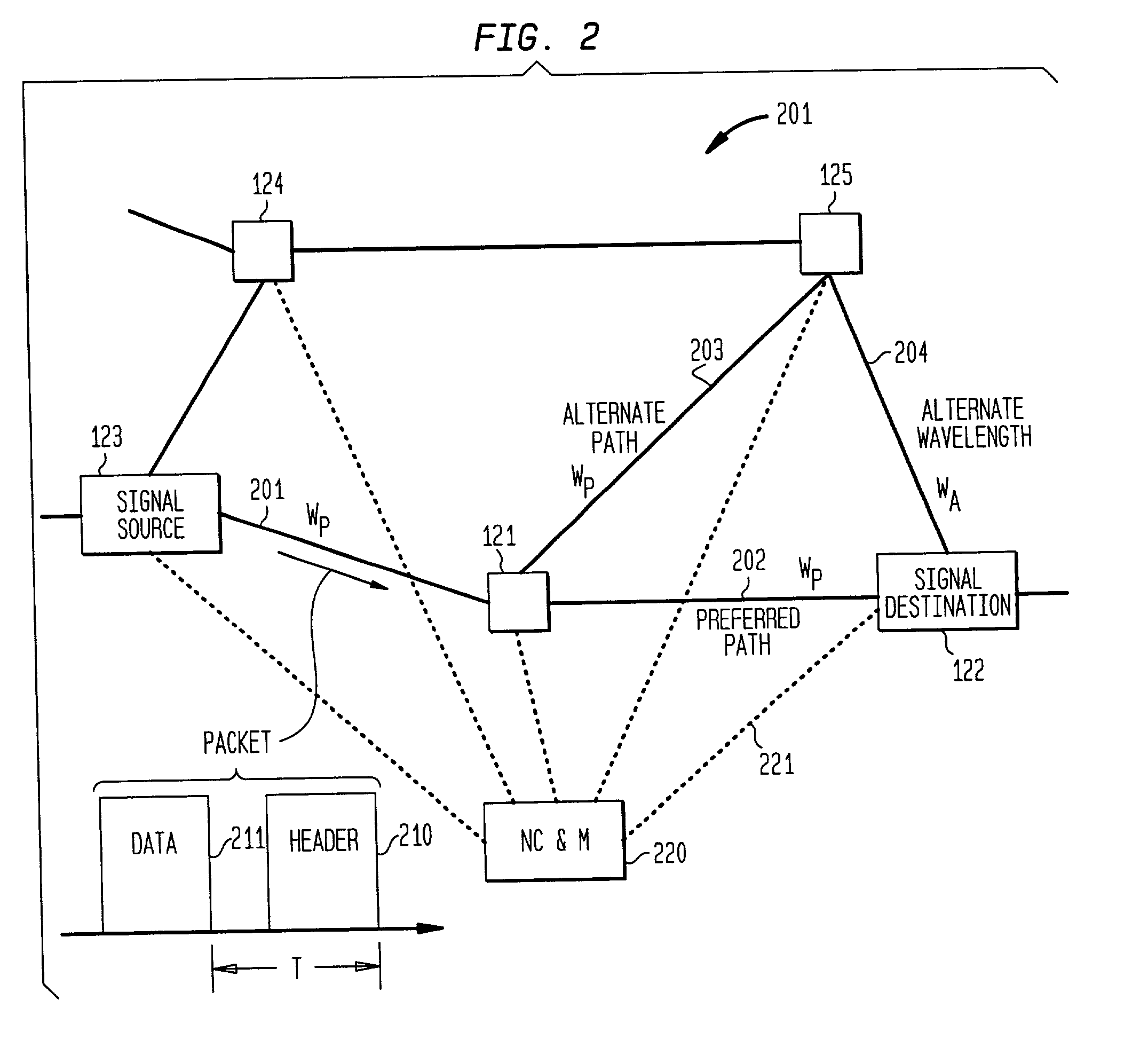
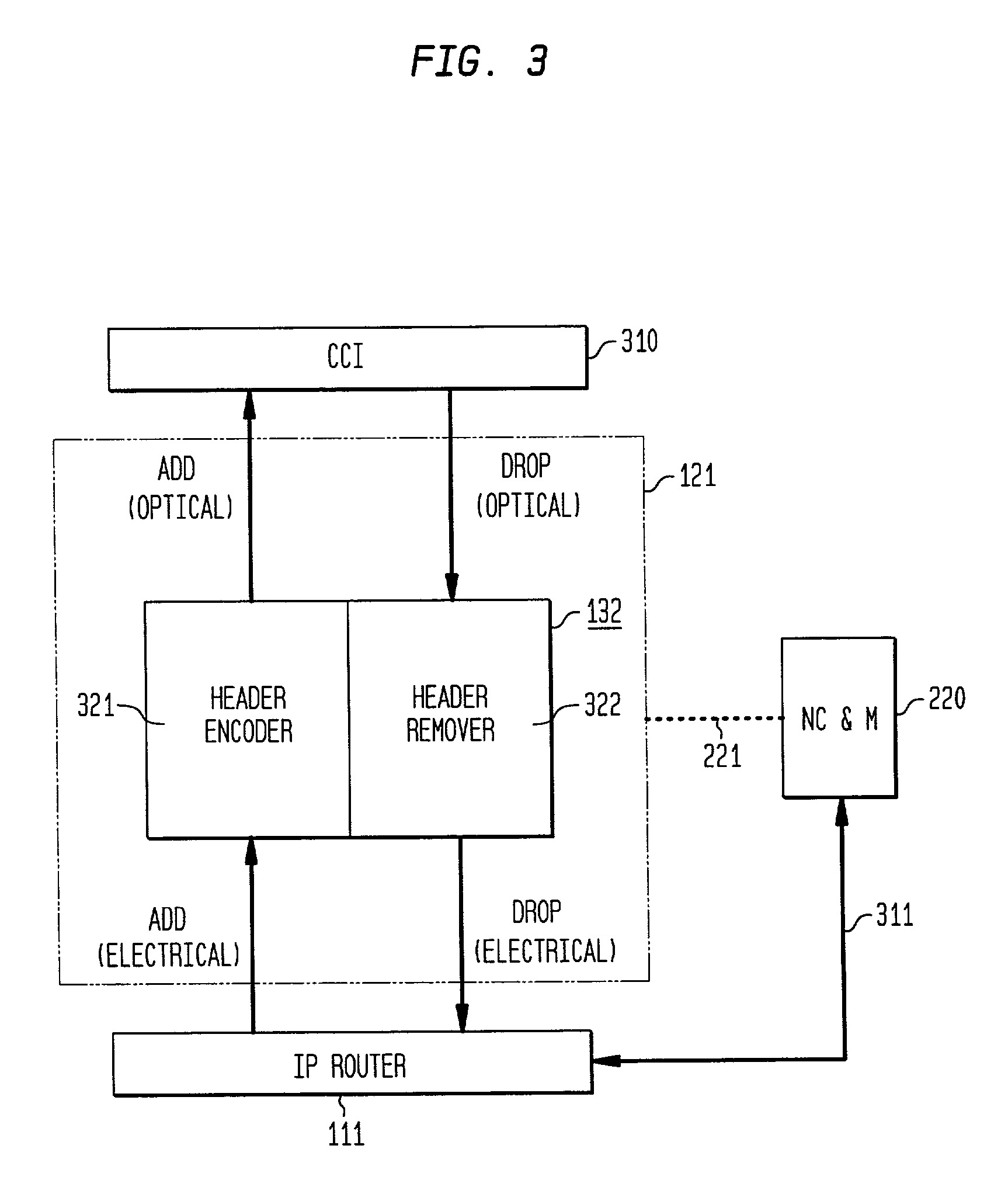
Optical layer survivability and security system using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation and detection
InactiveUS6271946B1Increase probabilityIncrease optical powerMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSurvivabilityOptical burst switching
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The technique effects survivability and security of the optical networks by encompassing conventional electronic security with an optical security layer by generating replicated versions of the input data payload at the input node, and the transmission of each of the replicated versions over a corresponding one of the plurality of links. Moreover, each of the links is composed of multiple wavelengths to propagate optical signals or optical packets, and each of the replicated versions of the data payload may be propagated over a selected one of the wavelengths in each corresponding one of the plurality of links.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
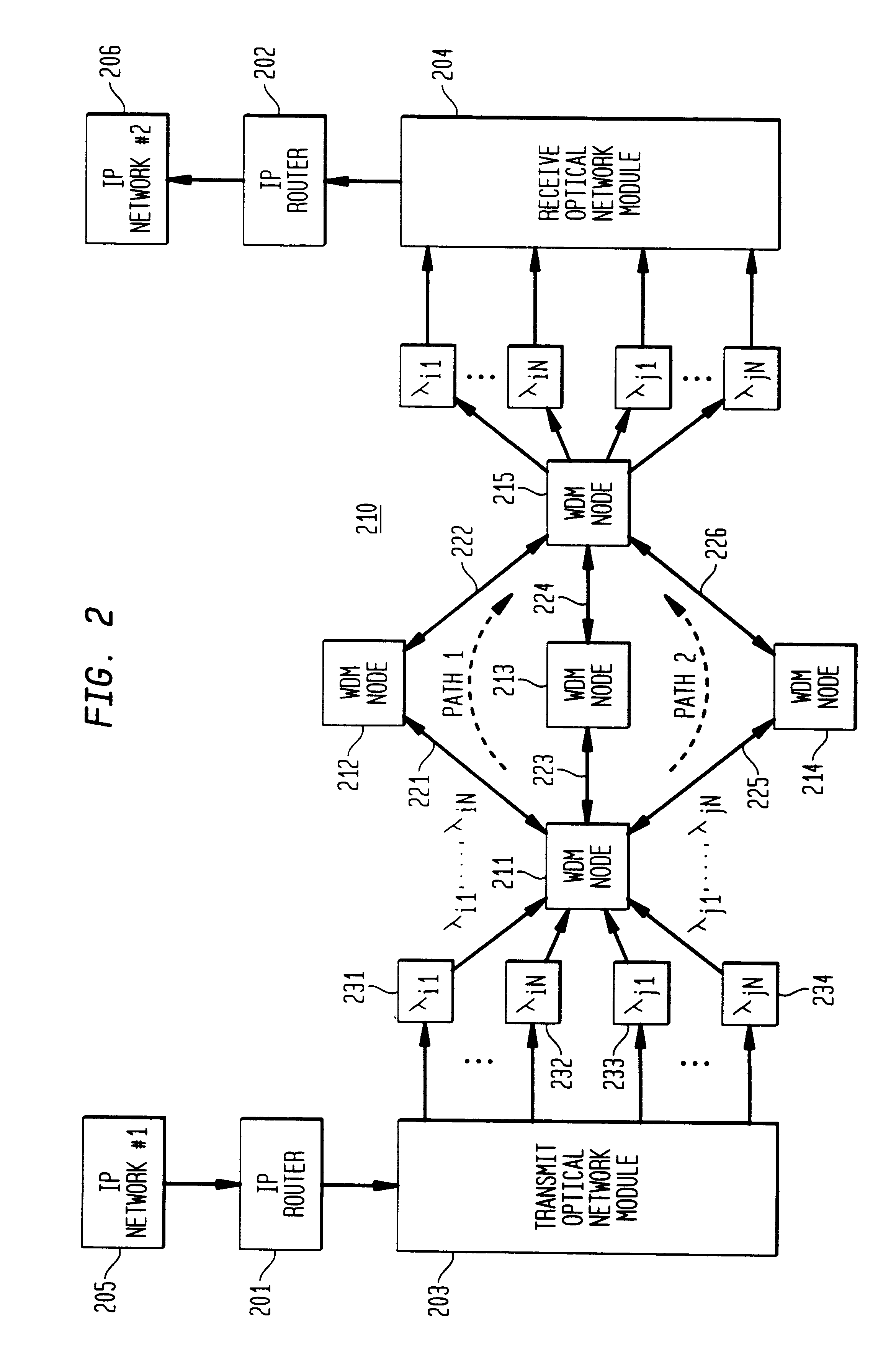
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation, detection and reinsertion
InactiveUS6545781B1Efficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer hardwareOptical IP Switching
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation, detection and reinsertion
InactiveUS6580537B1Efficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer hardwareOptical IP Switching
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation, detection and reinsertion
InactiveUS6525850B1Efficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer hardwareOptical IP Switching
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High-throughput, low-latency next generation internet networks using optical label switching and high-speed optical header generation, detection and reinsertion
InactiveUS20010017723A1Efficient comprehensive utilizationSignificant overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsComputer hardwareWavelength
An optical signaling header technique applicable to optical networks wherein packet routing information is embedded in the same channel or wavelength as the data payload so that both the single-sideband modulated header and data payload propagate through network elements with the same path and the associated delays. The header routing information has sufficiently different characteristics from the data payload so that the signaling header can be detected without being affected by the data payload, and that the signaling header can also be removed without affecting the data payload. The signal routing technique can overlaid onto the conventional network elements in a modular manner using two types of applique modules. The first type effects header encoding and decoding at the entry and exit points of the data payload into and out of the network; the second type effects header detection at each of the network elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
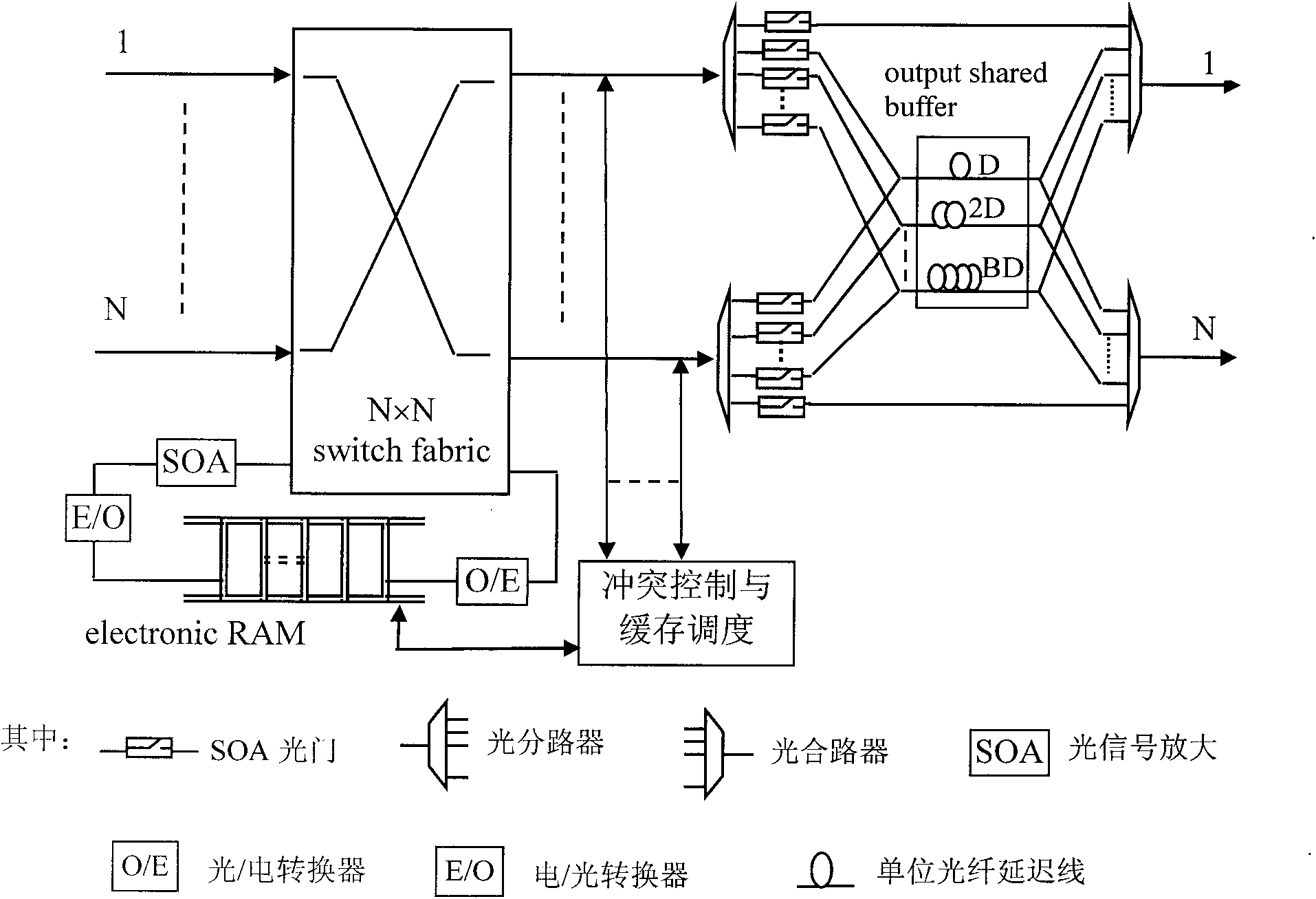
Method for resolving optical switching grouping competition and photoelectric hybrid cache device
ActiveCN101778047AImprove efficiencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksFiberPacket loss rate
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
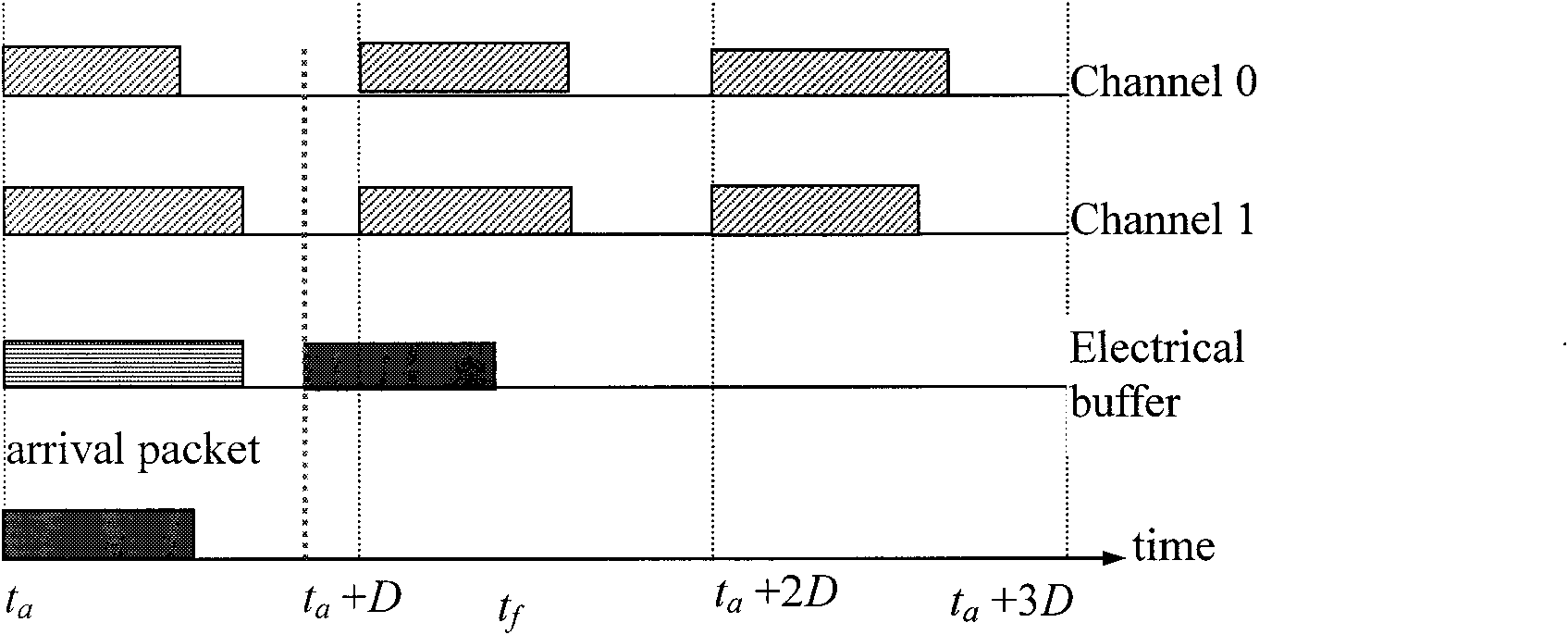
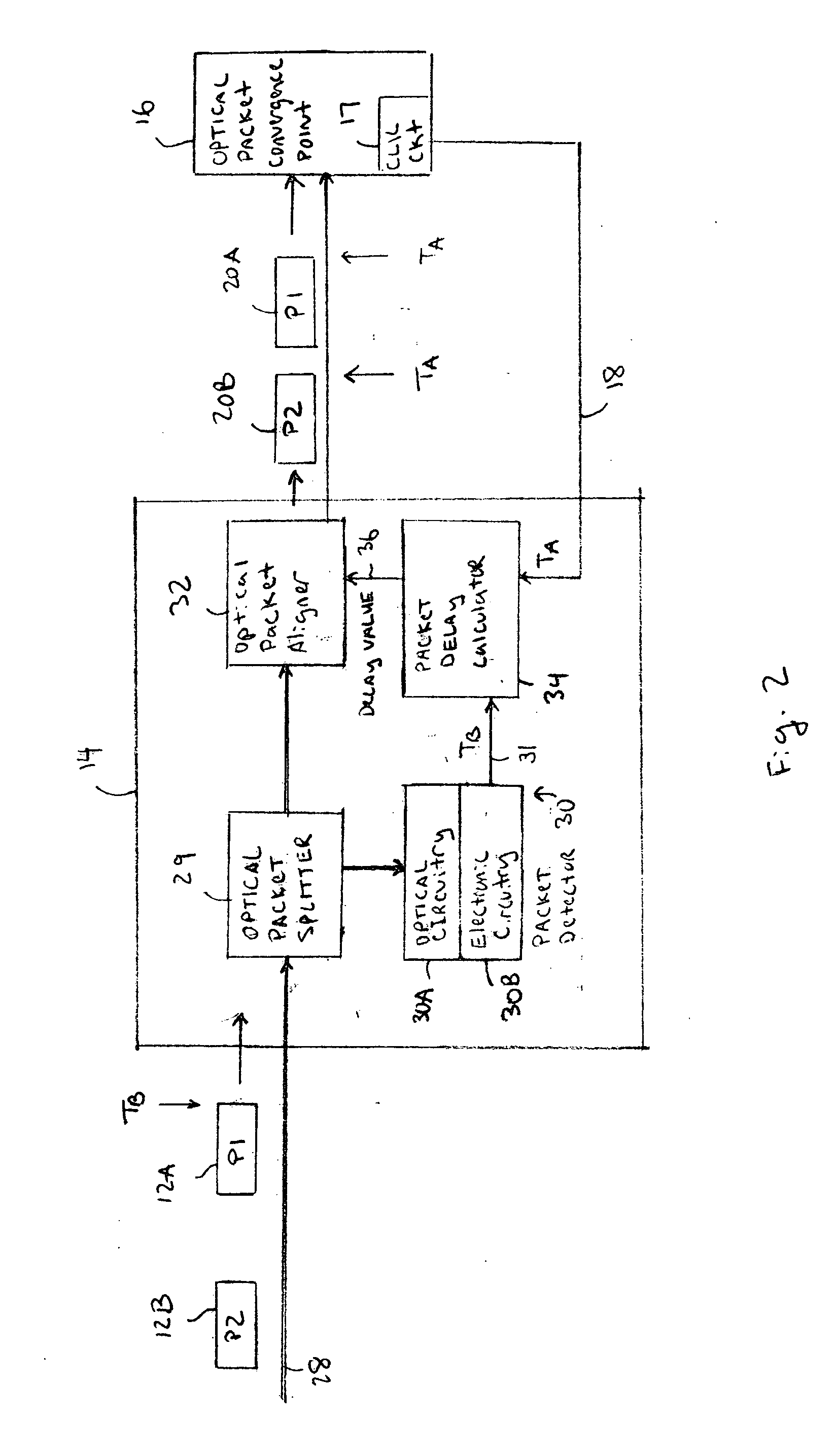
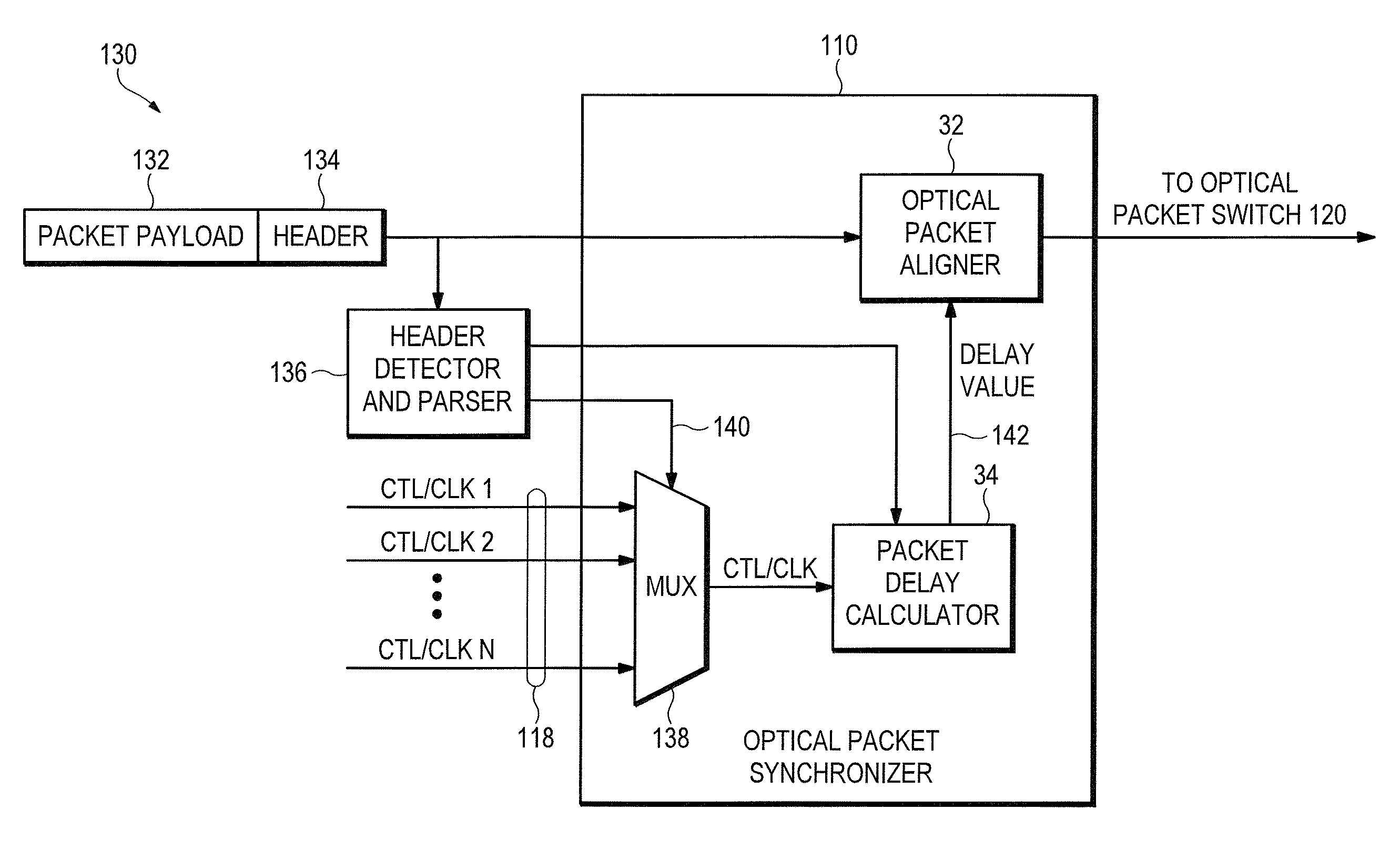
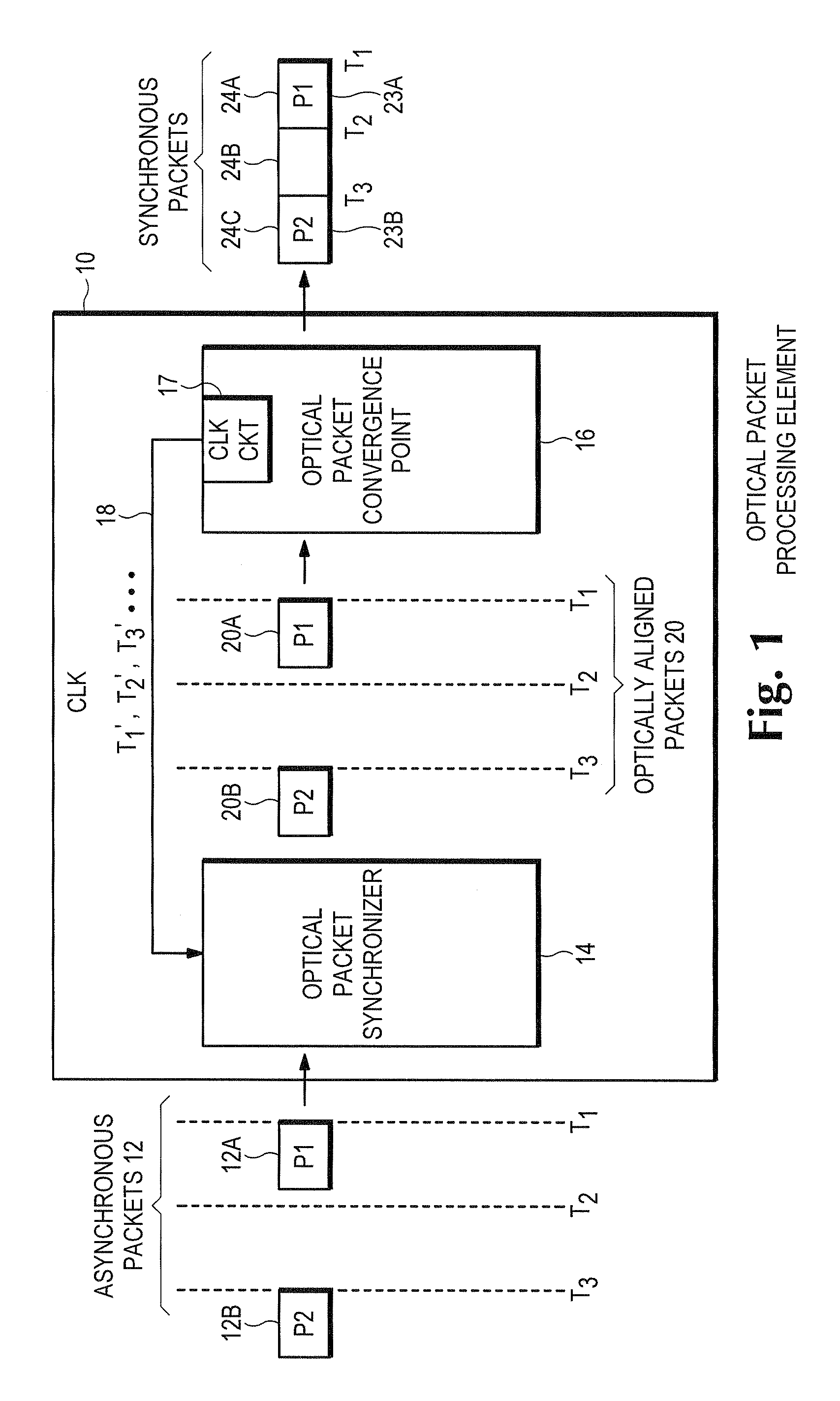
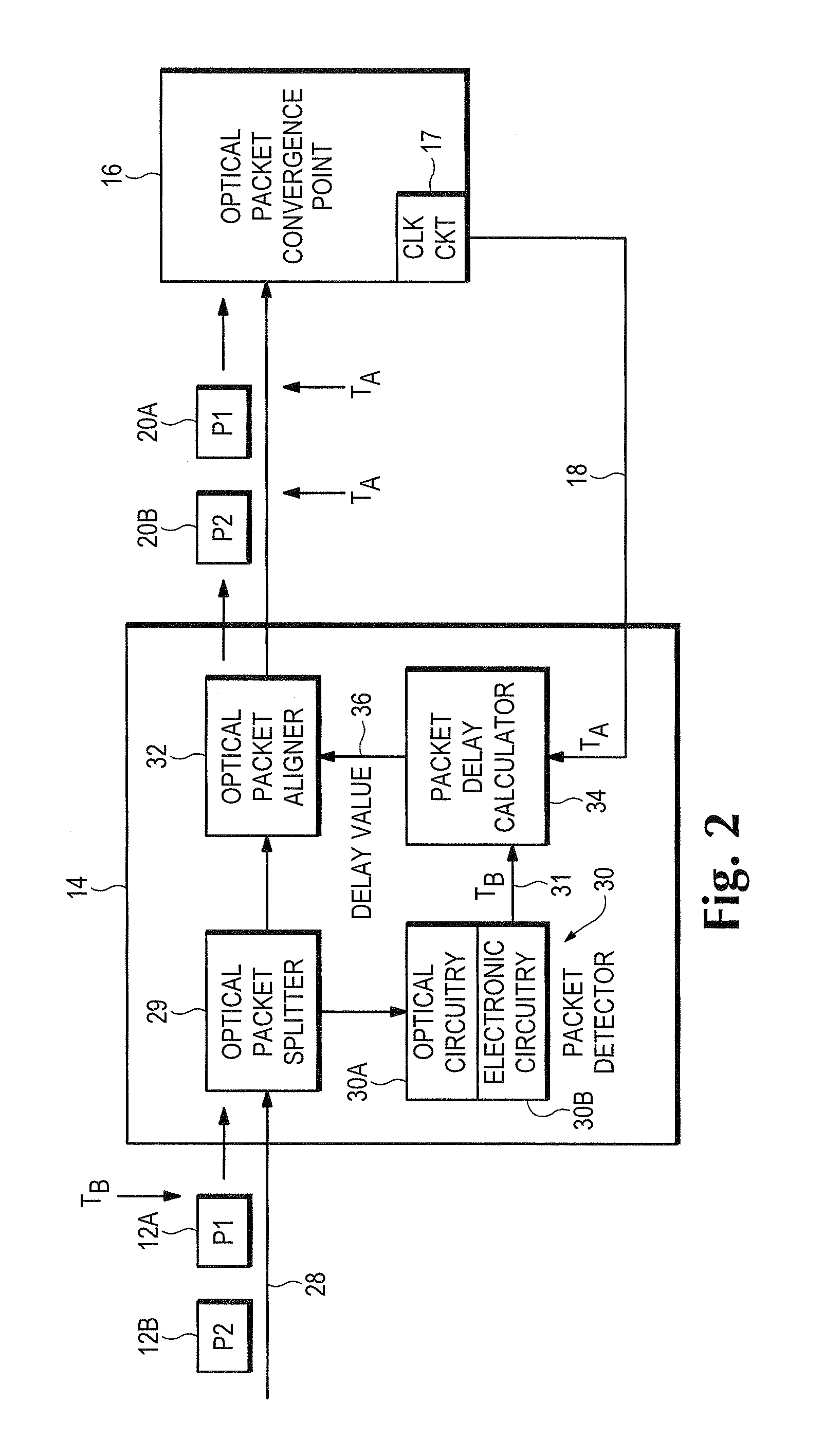
Optical data synchronization scheme
ActiveUS20070201877A1Readily apparentMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexData synchronizationOptical burst switching
Asynchronous optical data is aligned with synchronous convergence points in an optical packet switching system. The convergence points can be any place where data enters an optical packet switching element, buffer stage, switch fabric, etc. The arrival time for data approaching the convergence point is compared with a reference signal associated with the upcoming convergence point. The comparison is used to identify the amount of time-shift required to align the approaching data with the reference signal. Control information is derived according to the comparison and used to control an optical data aligner that synchronizes the data with the convergence point.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods for non-wavelength-converting multi-lane optical switching
ActiveUS8150264B2Reduce needFast and efficientMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveOptical IP Switching
A method for providing multi-wavelength switching. The method comprising receiving a plurality of signals through at least one input port, and separating the plurality of said signals into at least one wavelength signal set based on wavelengths, wherein a first wavelength signal set of said at least one wavelength signal sets corresponds to a first wavelength. The method further comprises providing a plurality of output lanes to at least one output port, and determining if two signals from said first wavelength signal set traveling on said first wavelength are scheduled output from an output port during an overlapping time period through said plurality of output lanes. The method further comprises determining if one of said plurality of output lanes is available during said overlapping time period when said two signals are schedule for said output port during the overlapping time period, wherein a first signal of said two signals is routed for output on an available lane if one of said plurality of output lanes of said output port is available.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
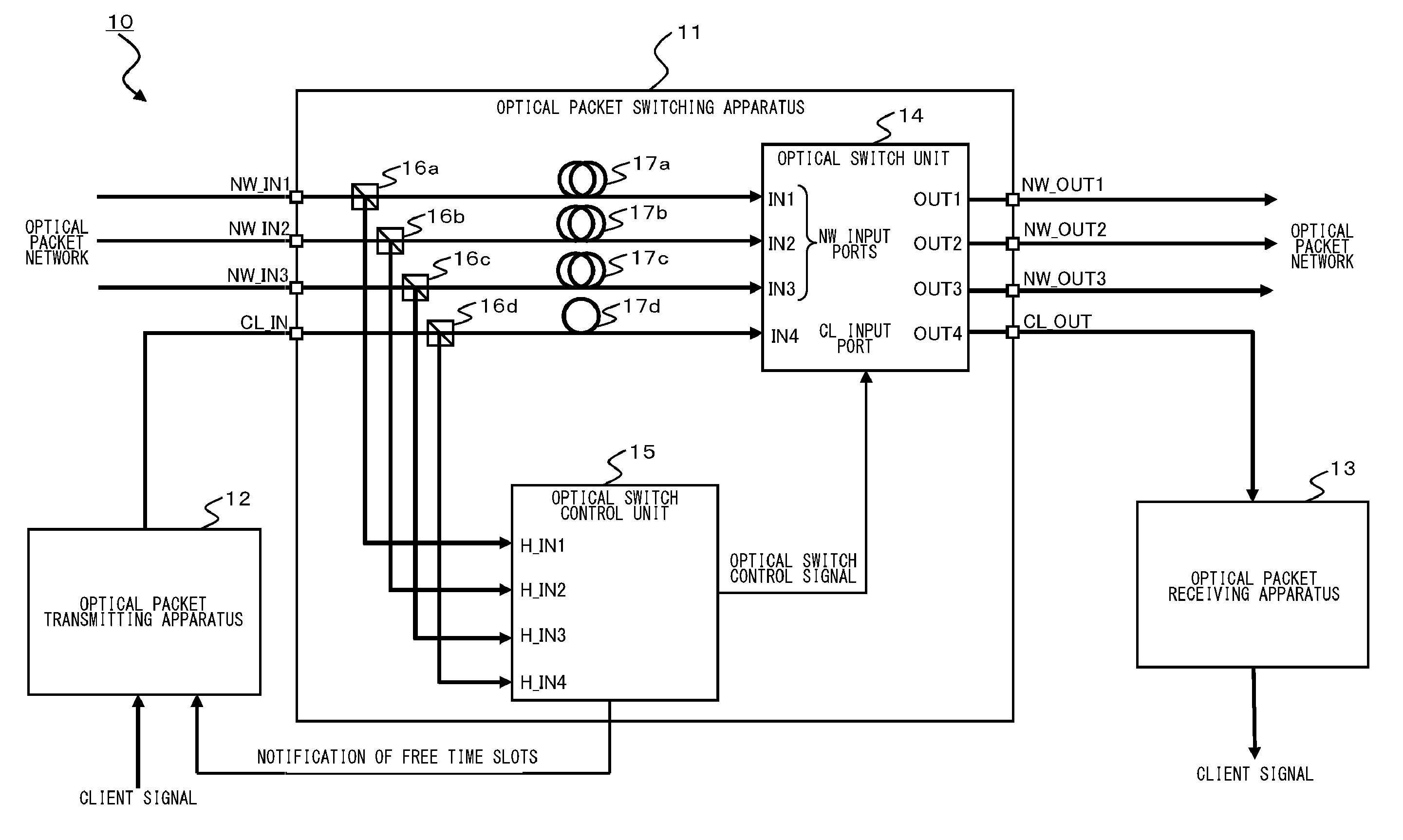
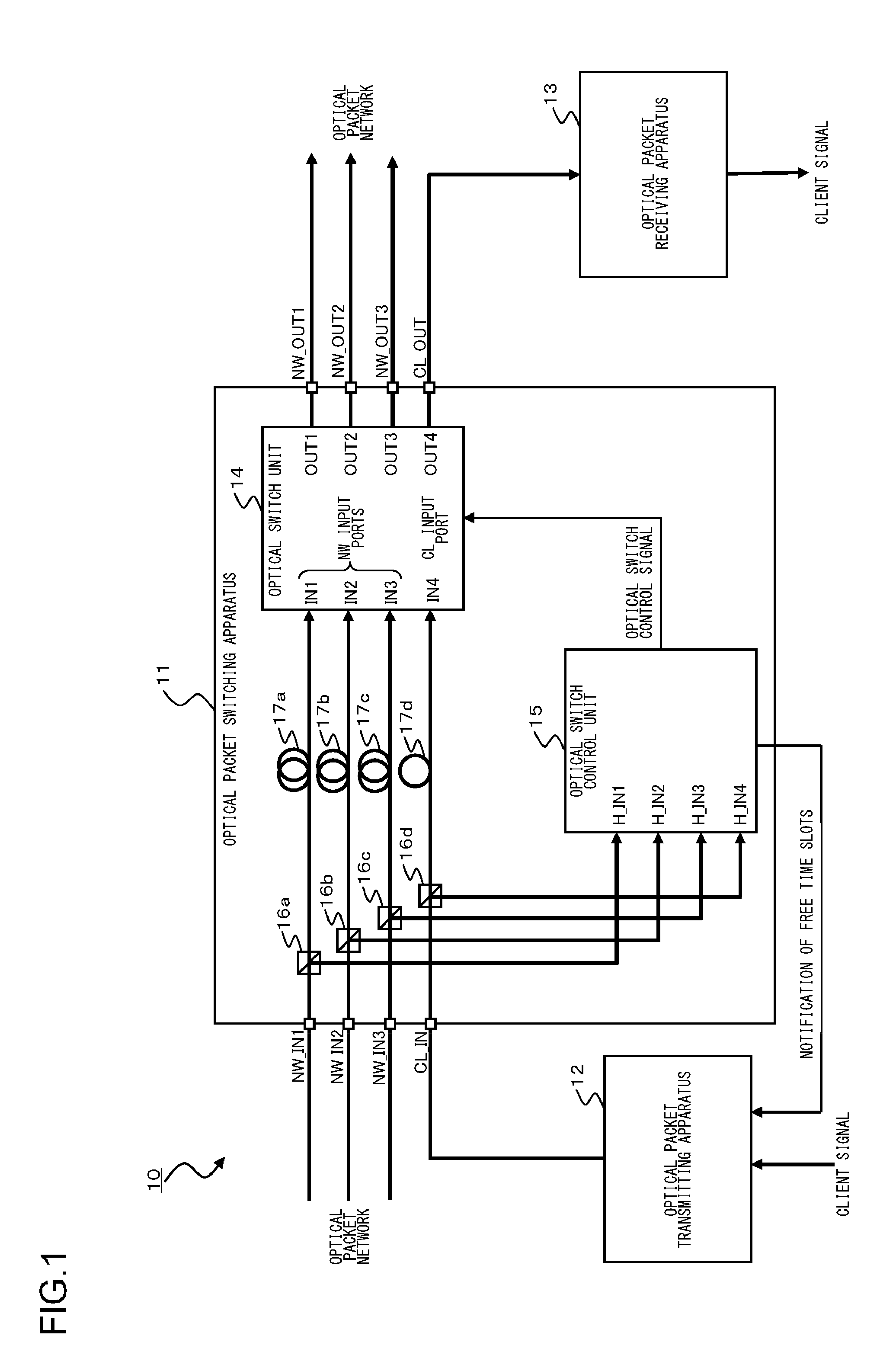
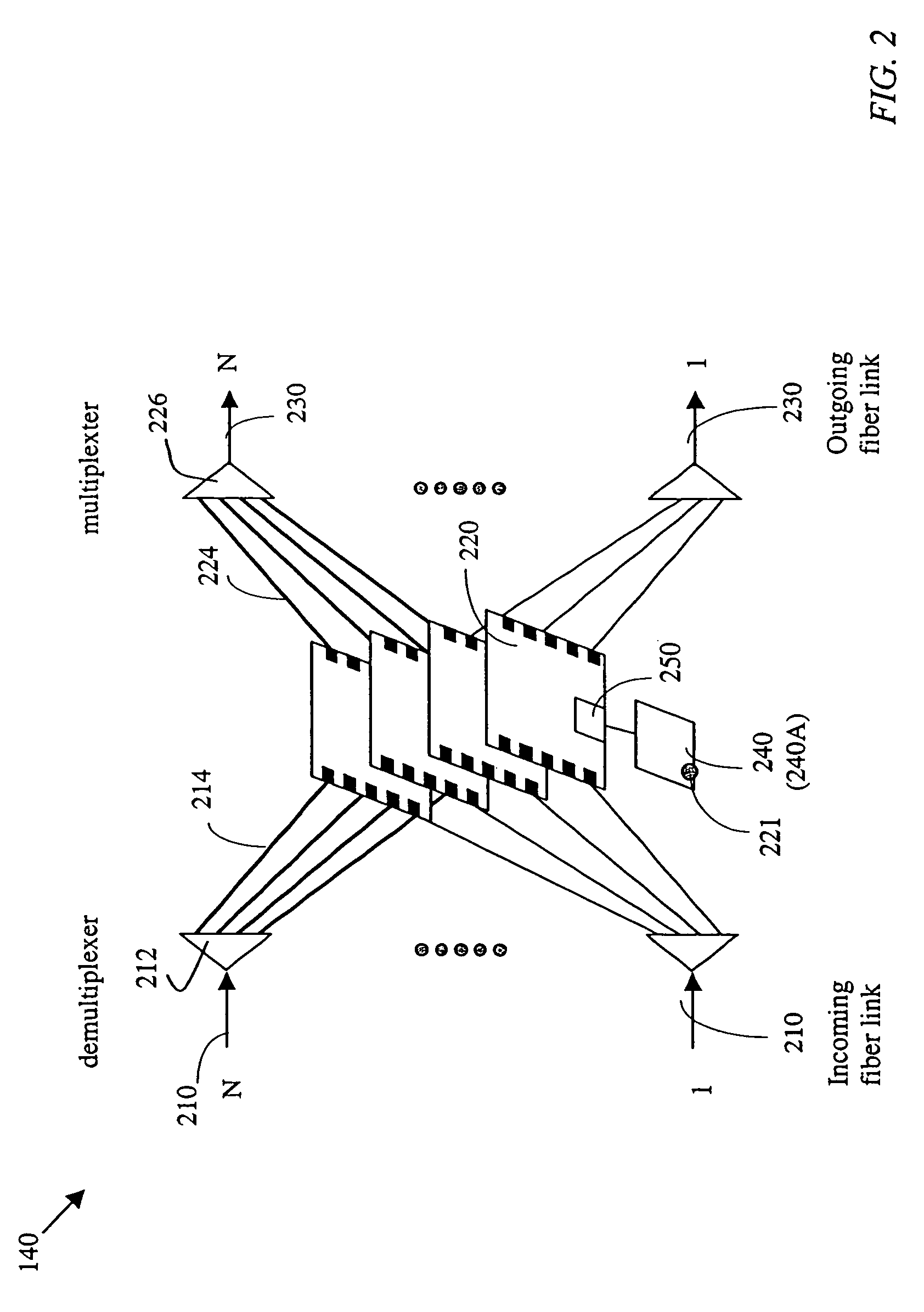
Optical packet switching system
InactiveUS20120275783A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic network arrangementsComputer hardwareElectricity
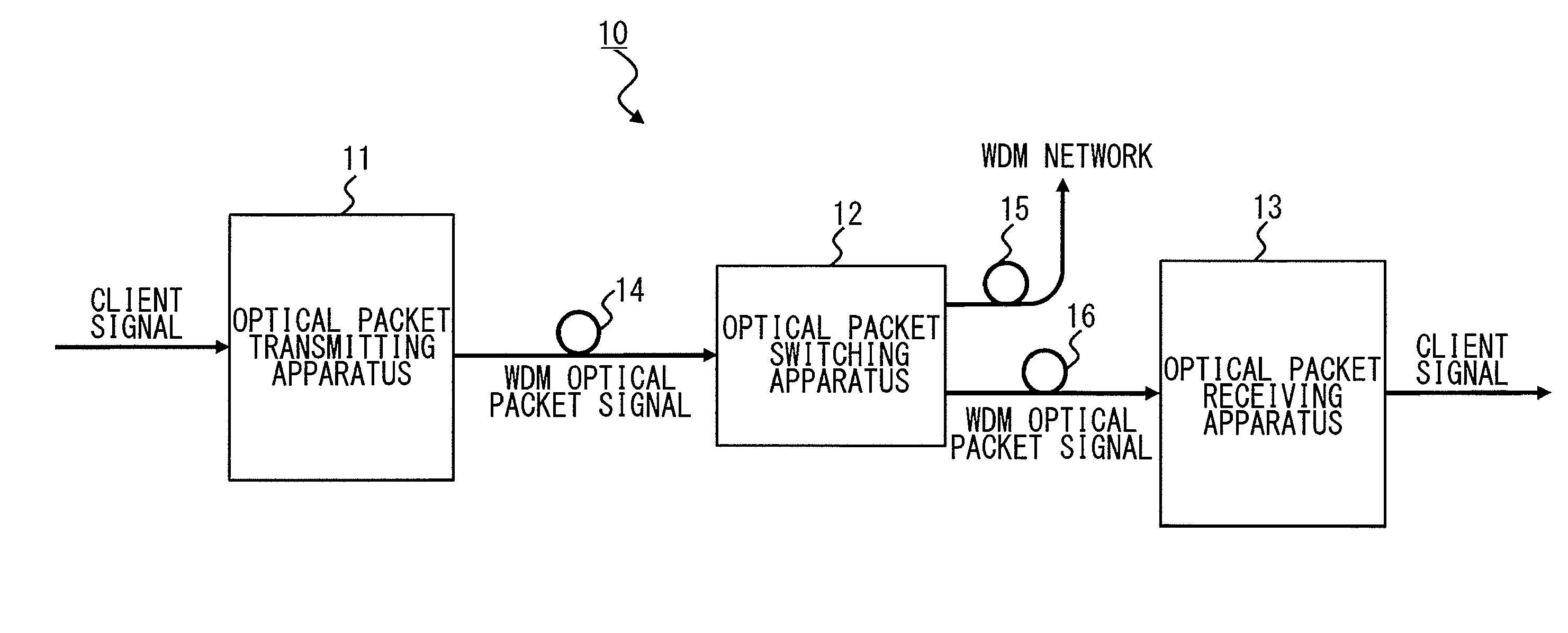
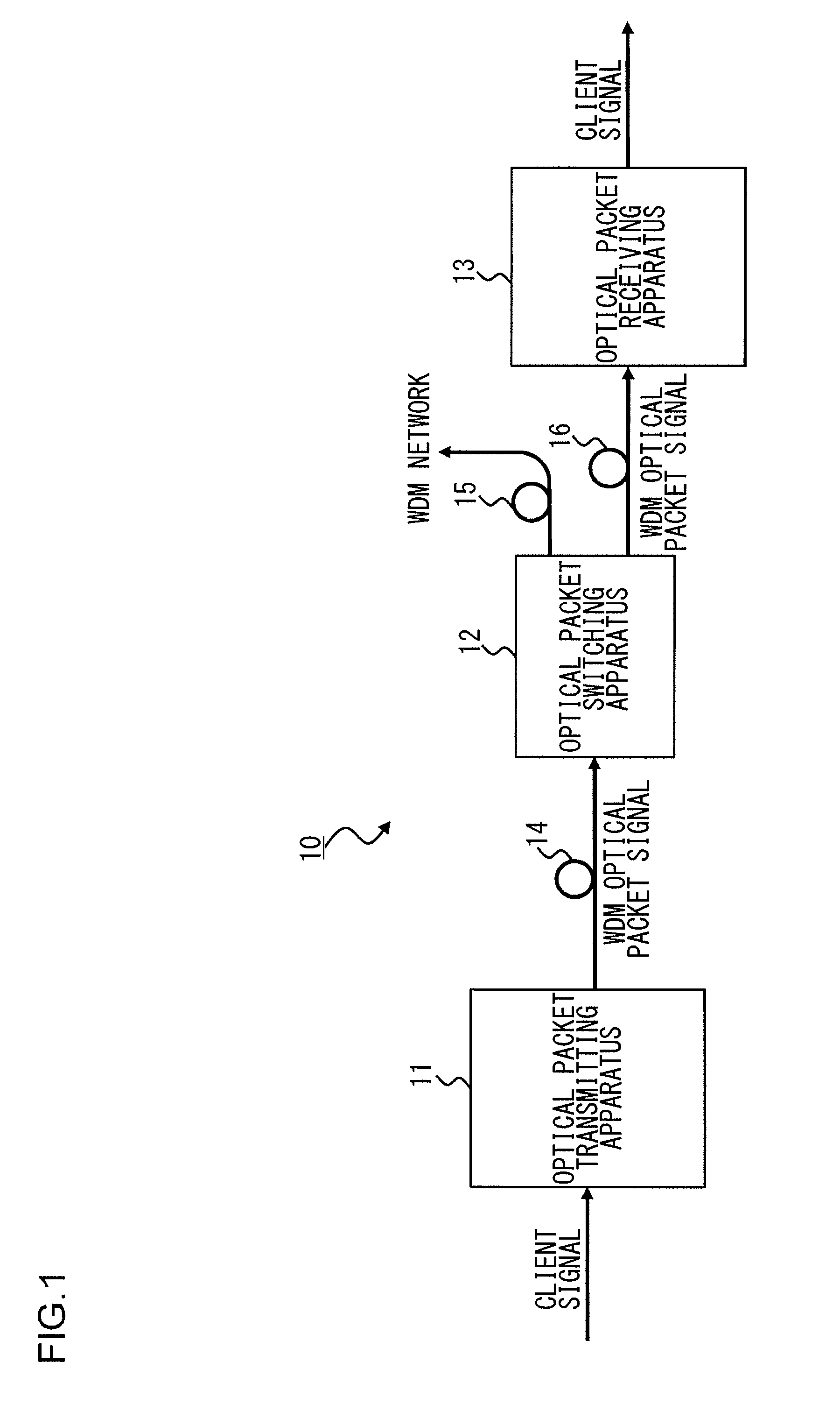
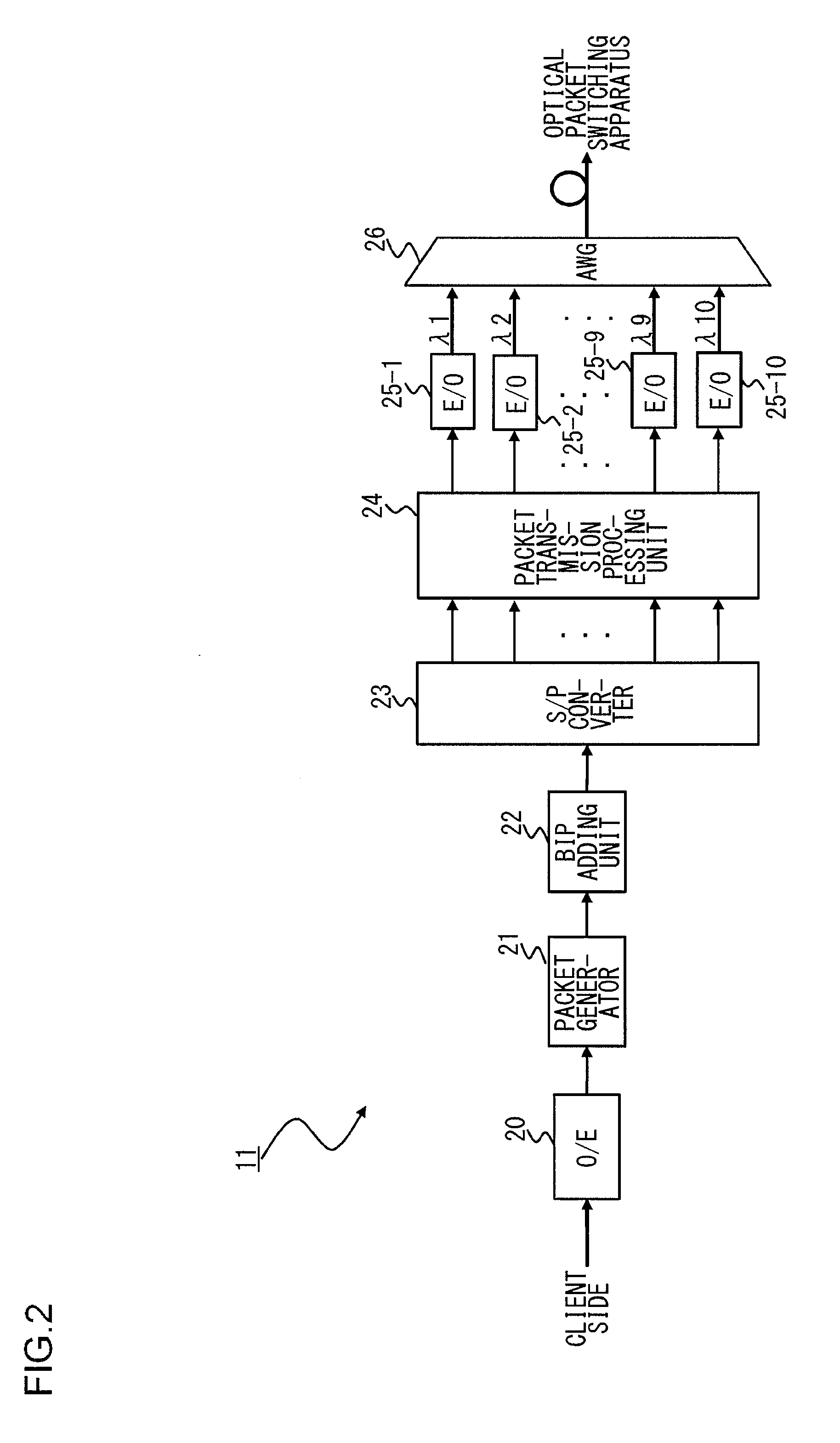
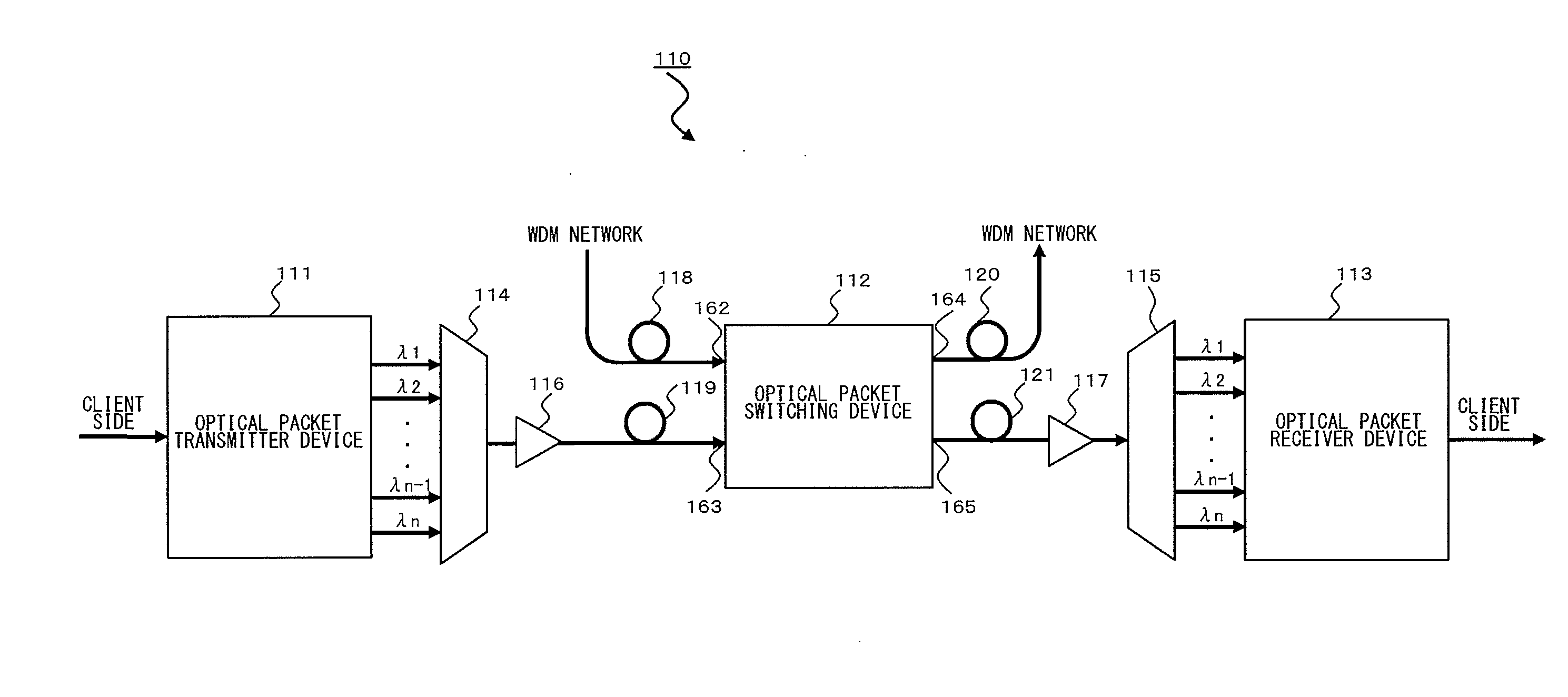
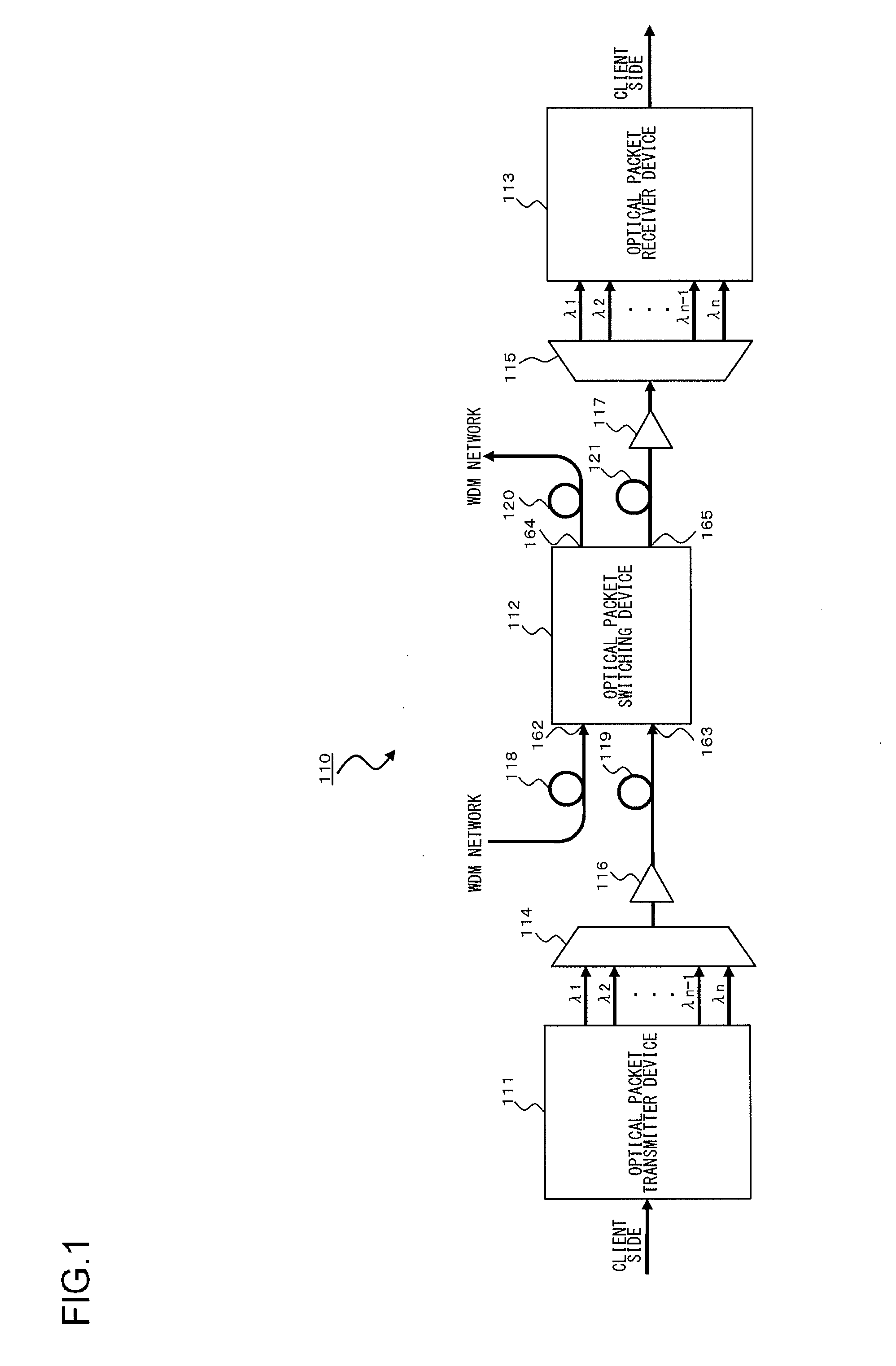
An optical packet switching apparatus includes an optical packet switching apparatus, an optical transmitting apparatus, and an optical packet receiving apparatus. The optical packet transmitting apparatus includes a packet generator for generating a packet signal by adding the routing information to a received client signal, a BIP adding unit for adding BIP to the generated packet signal, and an electrical-to-optical converter for converting the packet signal, to which the BIP has been added, into an optical packet signal so as to be sent out. The optical packet receiving apparatus includes an electrical-to-optical converter for converting the received optical packet signal into an electrical packet signal, and a BIP comparison unit for detecting the error occurrence in the packet signal, based on the BIP added to the packet signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
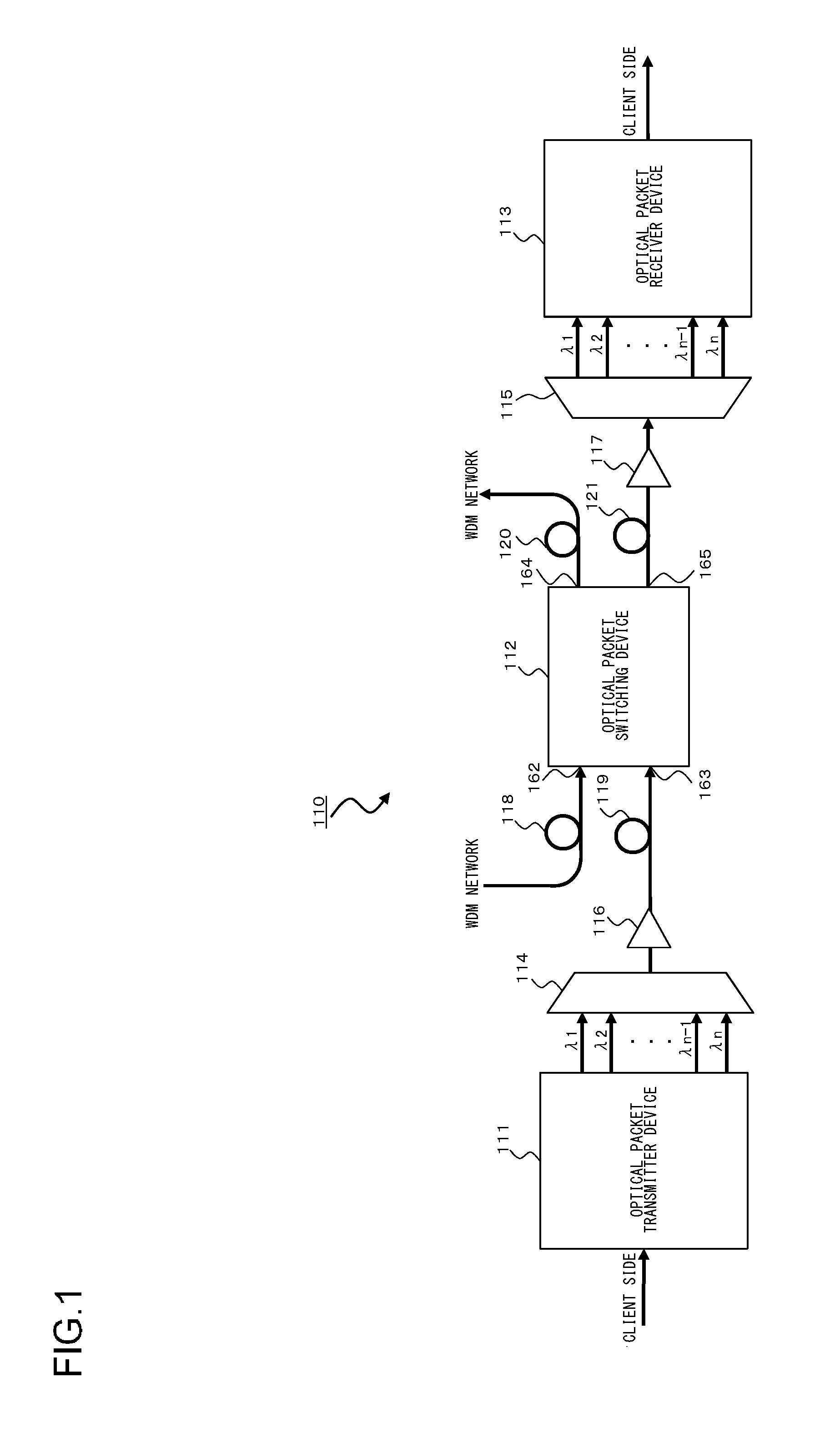
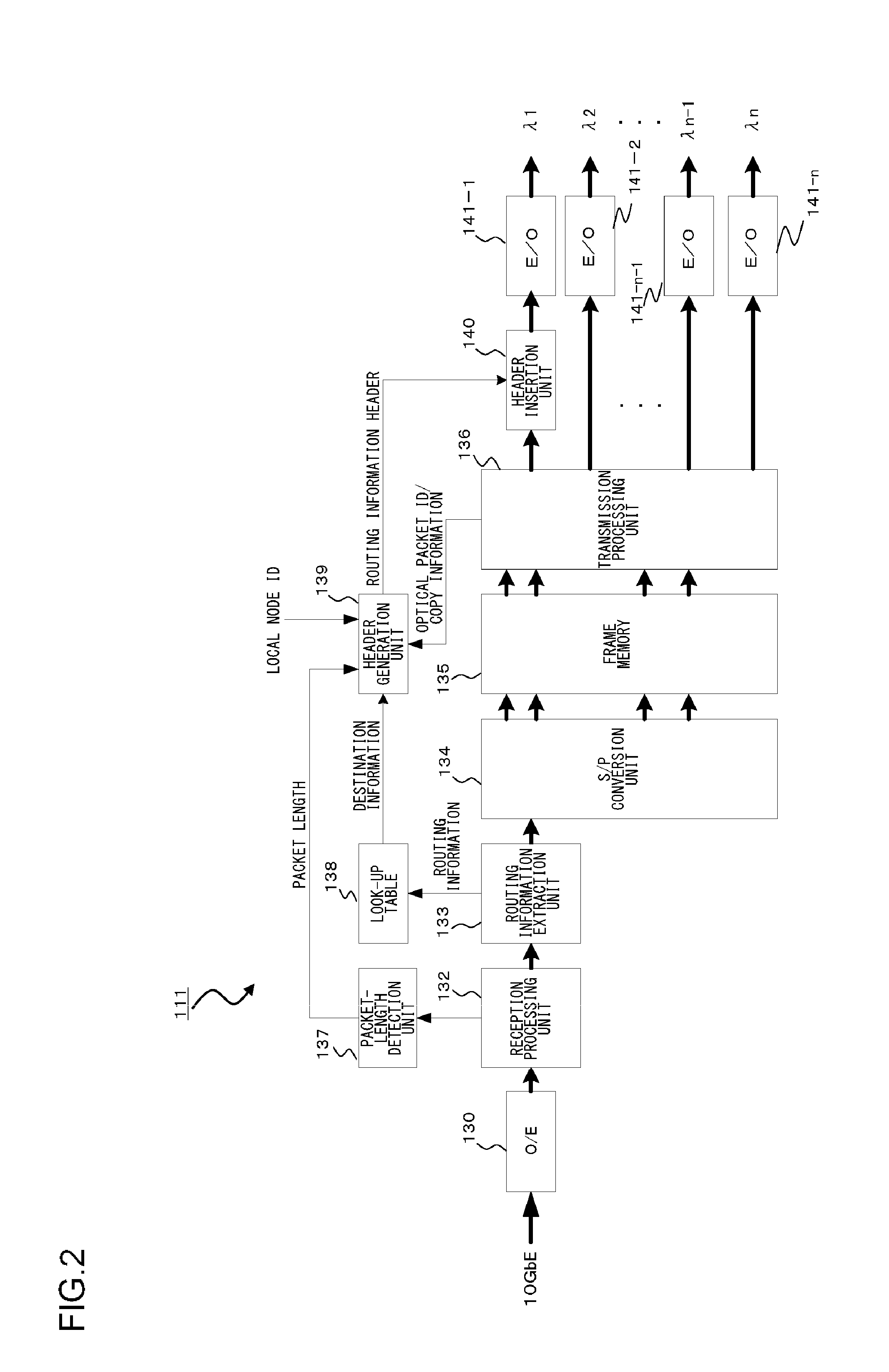
Optical packet switching system and optical packet transmitter device
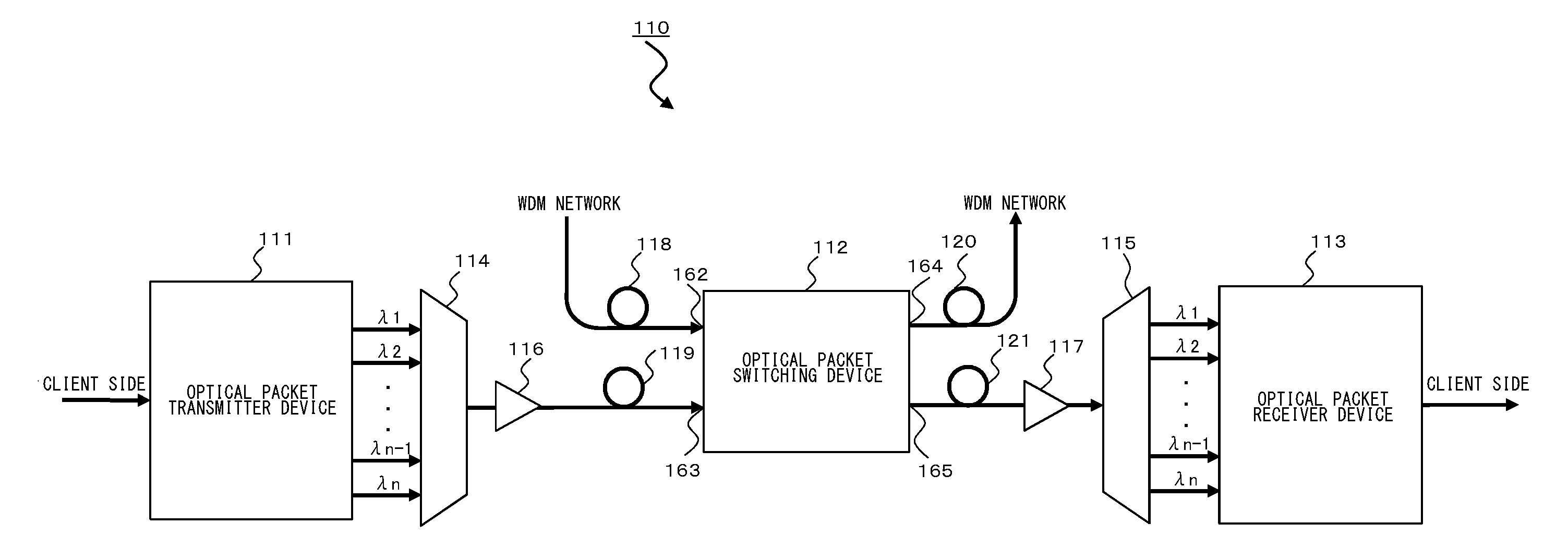
InactiveUS20120201538A1High degree of priorityIncrease speedMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsComputer hardwareElectricity
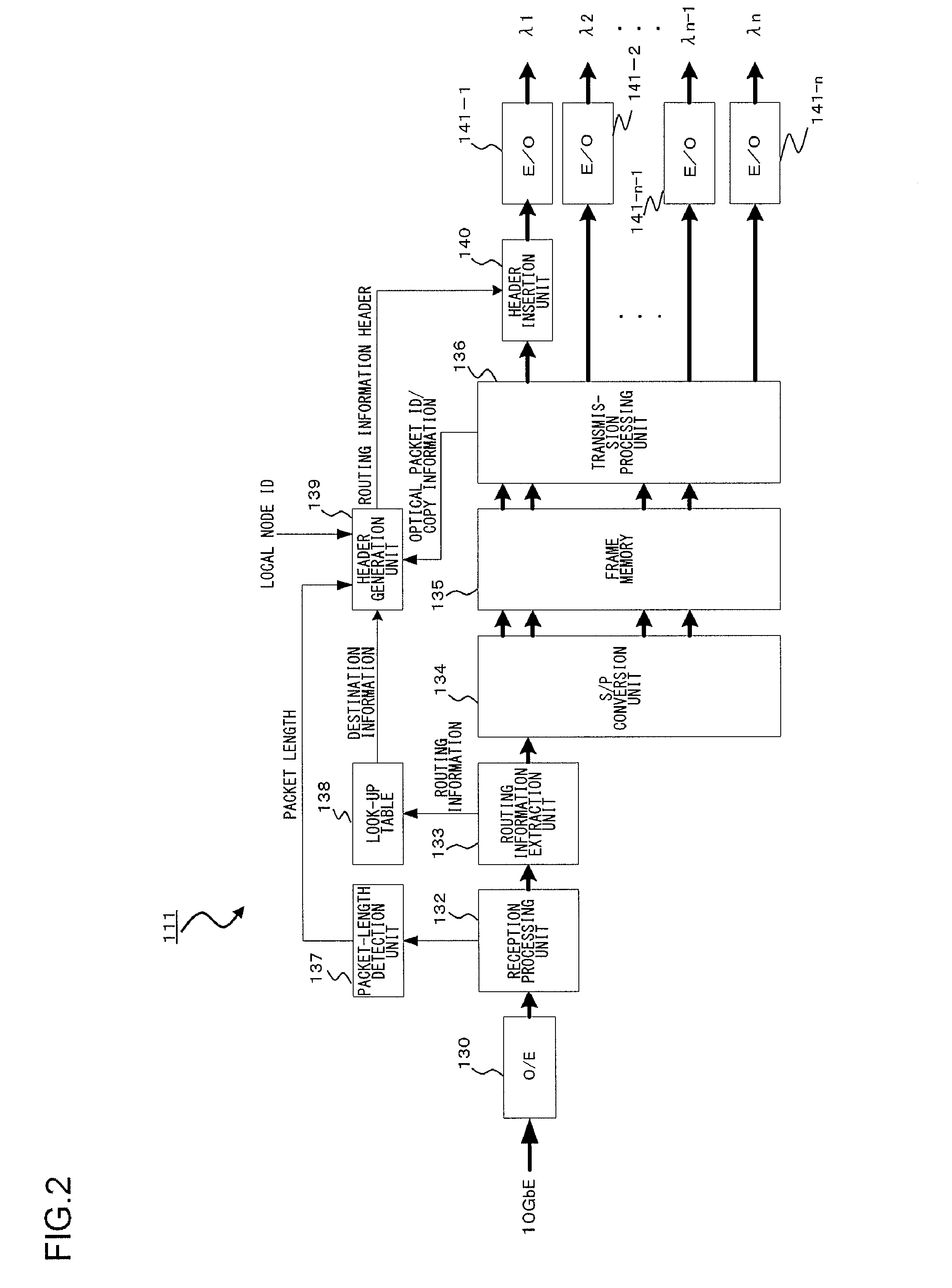
An optical packet transmitter device includes: a detection unit for detecting packet-length information and priority information from a received Ether signal; a setting unit for setting, according to the degree of priority, a division factor by which the Ether signal is divided and a wavelength used for an optical packet signal to be transmitted; a header generation unit for generating a header containing destination information, the packet-length information, the priority information, and information of wavelength in use of the Ether signal; a transmission processing unit for dividing the Ether signal according to the set division factor and generating a plurality of packet signals; a header insertion unit for inserting the generated header in at least one packet signal; and an electrical / optical converter unit for converting the plurality of packet signals into optical packet signals of a plurality of wavelengths according to the set wavelength in use.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical data synchronization scheme
ActiveUS7835649B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexData synchronizationOptical burst switching
Asynchronous optical data is aligned with synchronous convergence points in an optical packet switching system. The convergence points can be any place where data enters an optical packet switching element, buffer stage, switch fabric, etc. The arrival time for data approaching the convergence point is compared with a reference signal associated with the upcoming convergence point. The comparison is used to identify the amount of time-shift required to align the approaching data with the reference signal. Control information is derived according to the comparison and used to control an optical data aligner that synchronizes the data with the convergence point.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
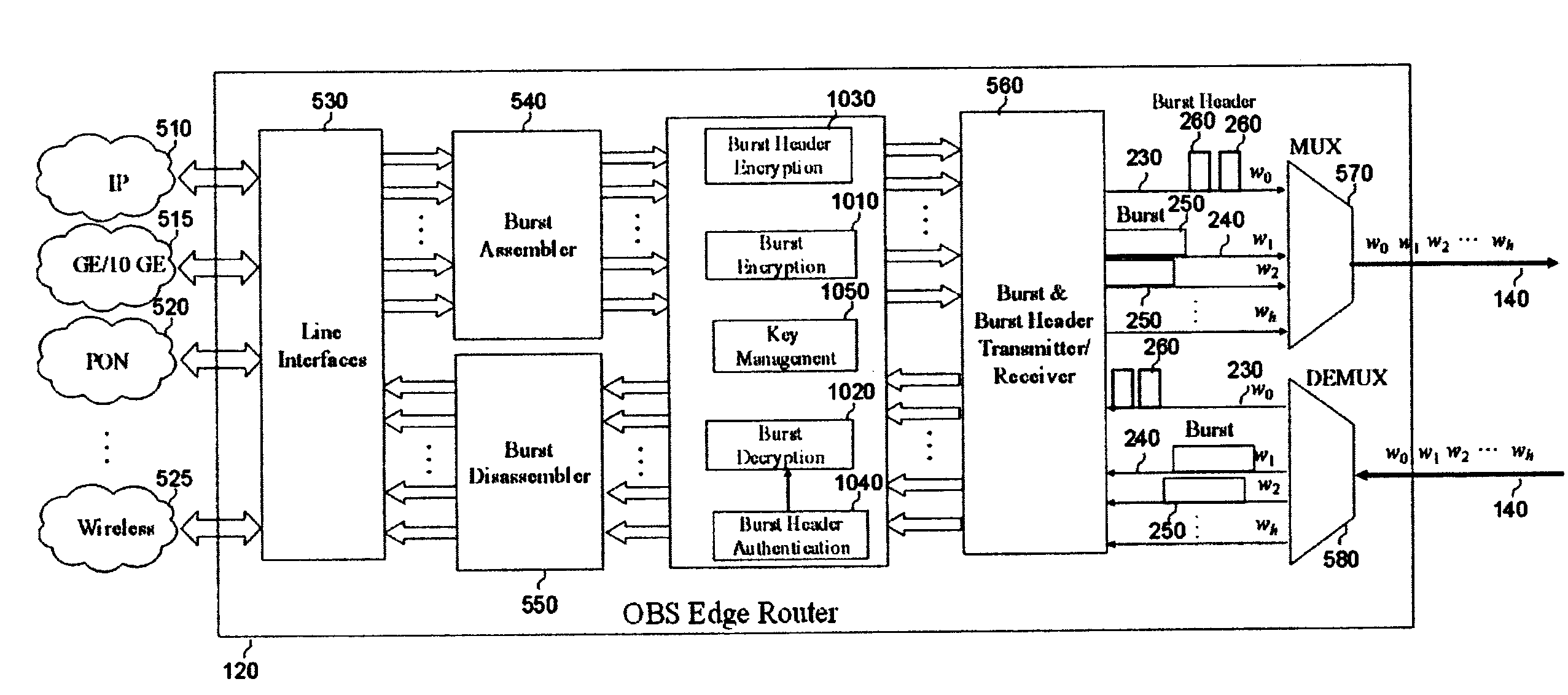
Methods and apparatus for securing optical burst switching (OBS) networks
InactiveUS20090313465A1Reduce overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsKey distribution for secure communicationTelecommunications linkOptical burst switching
An optical network, having an optical communication link and first and second routers. The first router receives and classifies data, then forms a data burst based on destination. The first router sends an encrypted header and the data burst via the optical link. The second router, at least one hop from the first router, receives, decrypts and authenticates the header. Then, the second router extracts data burst information from the header and determines whether the address of the second router is the destination address for the data burst. If so, the second router receives the data burst and sends data to an appropriate line interface. If not, the second router selects and reserves a wavelength on a second optical link for the data burst. The second router selects an encryption key for the header, encrypts and sends the header, and then routes the data burst to the selected wavelength.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA +1
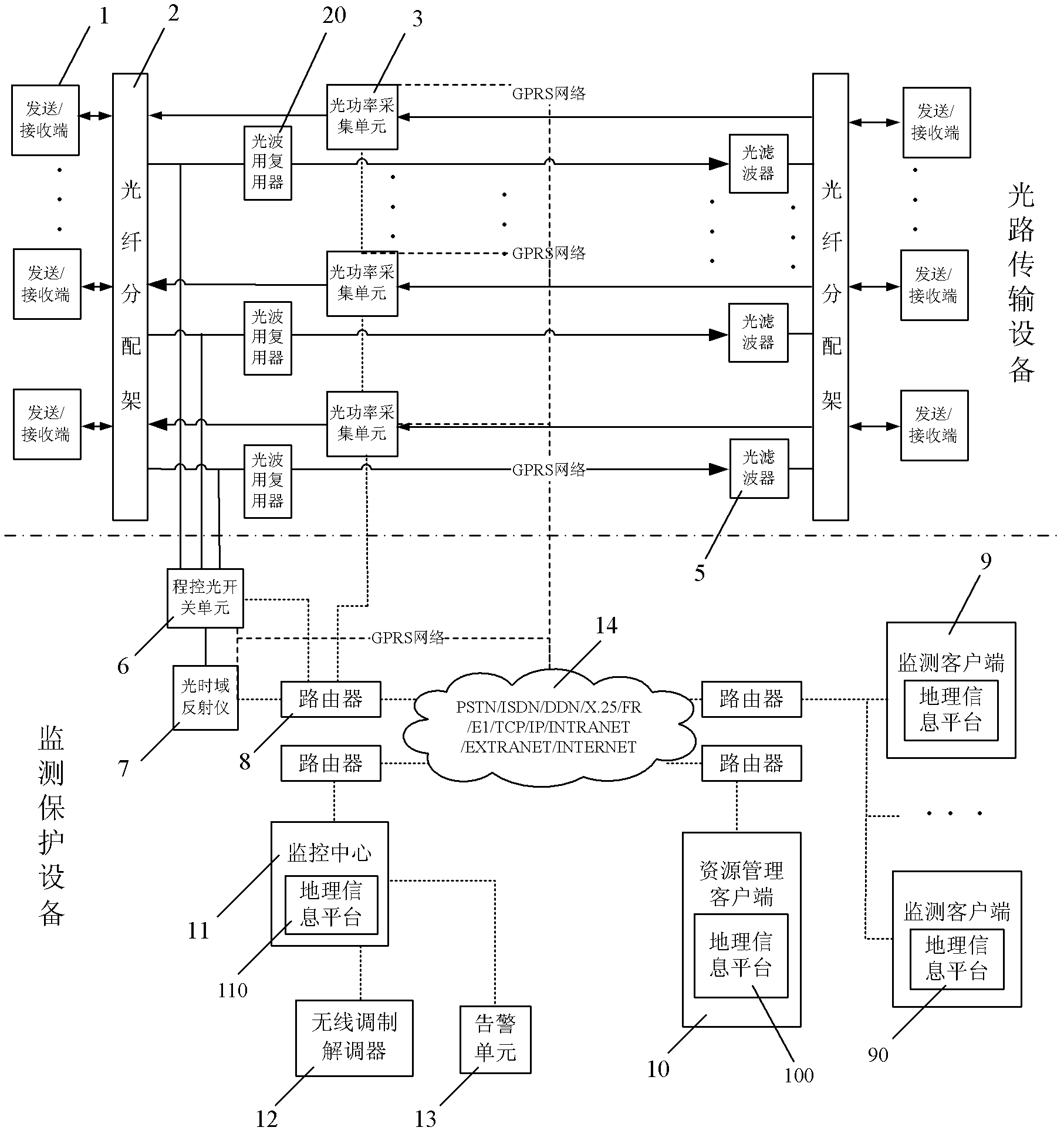
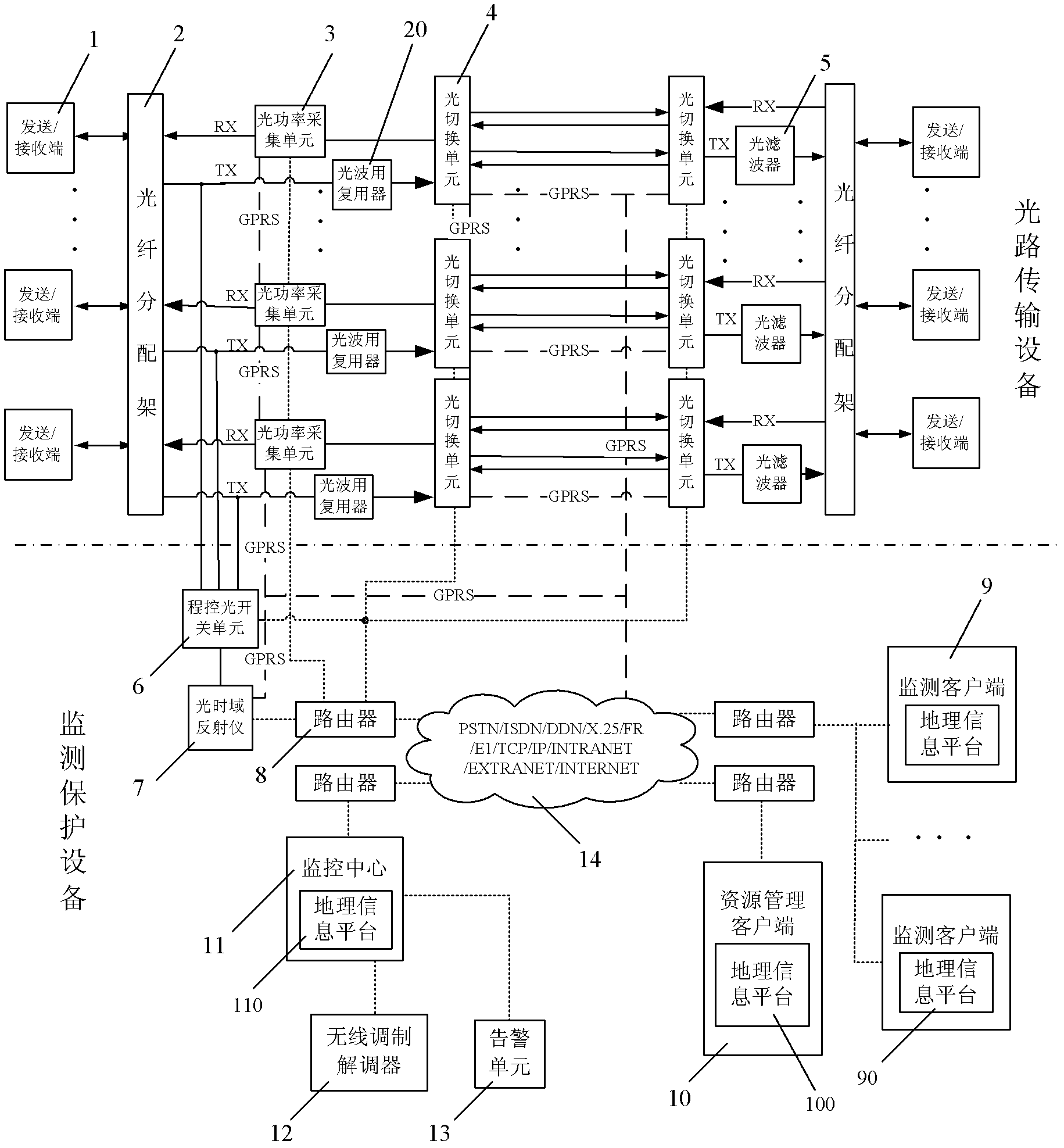
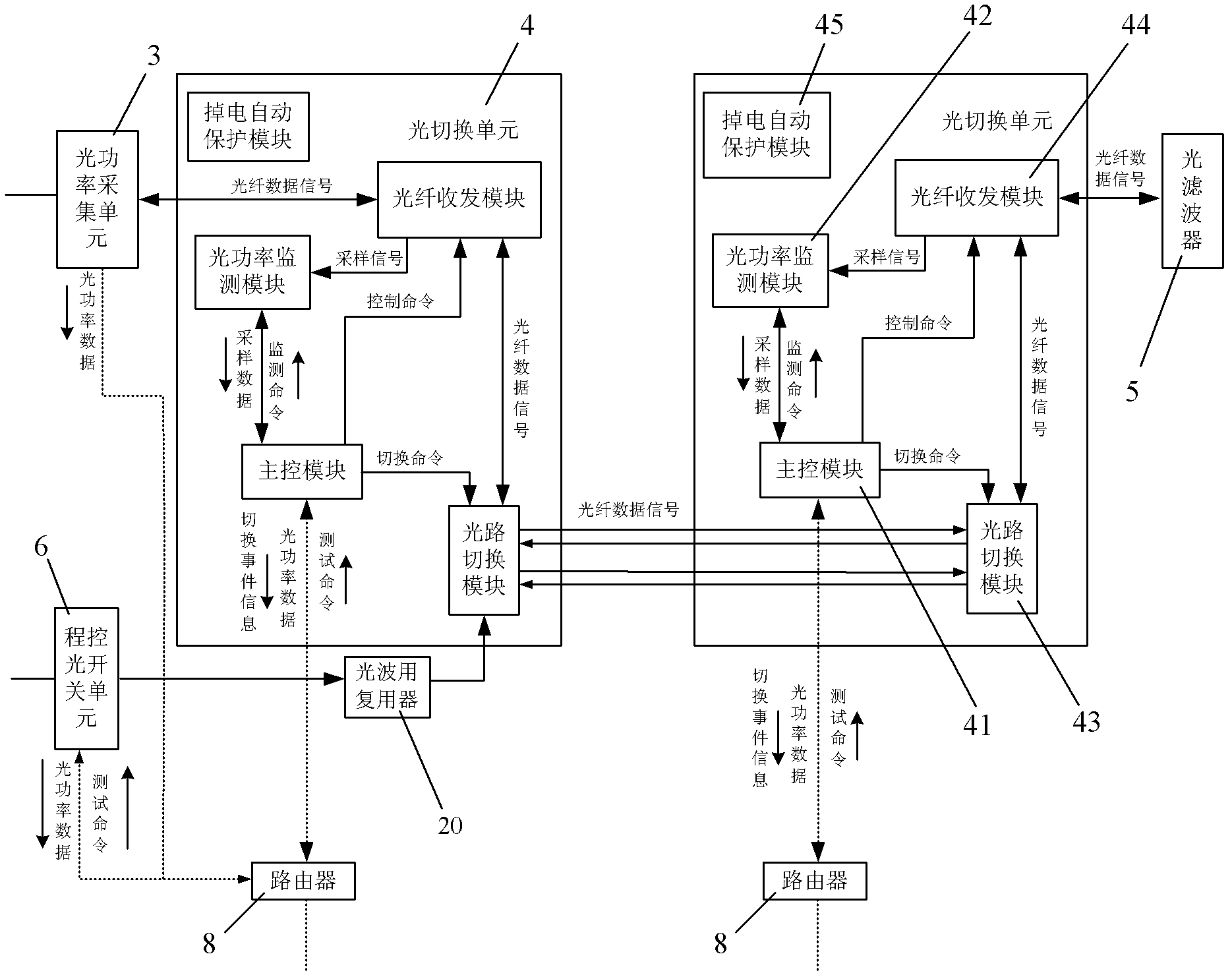
Optical fiber communication network monitoring protecting system and method thereof
InactiveCN104283607AUnaware of interruptionImprove accuracyElectromagnetic transmissionOptical powerEngineering
The invention discloses an optical fiber communication network monitoring protecting system and a method thereof. The optical fiber communication network monitoring protecting system comprises optical path transmission equipment and monitoring protecting equipment. The improvement of the optical fiber communication network monitoring protecting system is characterized in that the optical path transmission equipment comprises an optical switching unit; the optical switching unit monitors optical power data in real time, determines optical fault state and performs corresponding optical path switching; and a monitoring center receives monitoring data and information of an optical power acquiring unit and the optical switching unit and performs comprehensive analysis on the line state. The method comprises the steps of: A. performing real-time monitoring on the optical power by the optical power acquiring unit and the optical switching unit respectively, when a fault of the optical path occurs, finishing corresponding switching by the optical switching unit, and reporting the monitoring data and information to the monitoring center through a network; B. analyzing by the monitoring center for determining whether switching of the optical switching unit is correct, and then performing the following operations: B1, if switching is incorrect, transmitting an original state returning command by the monitoring center to the optical switching unit, and B2, if switching is correct, starting fault point testing for determining the geographical position of the fault point. The optical fiber communication network monitoring protecting system has high reliability and high stability.
Owner:李水进 +1
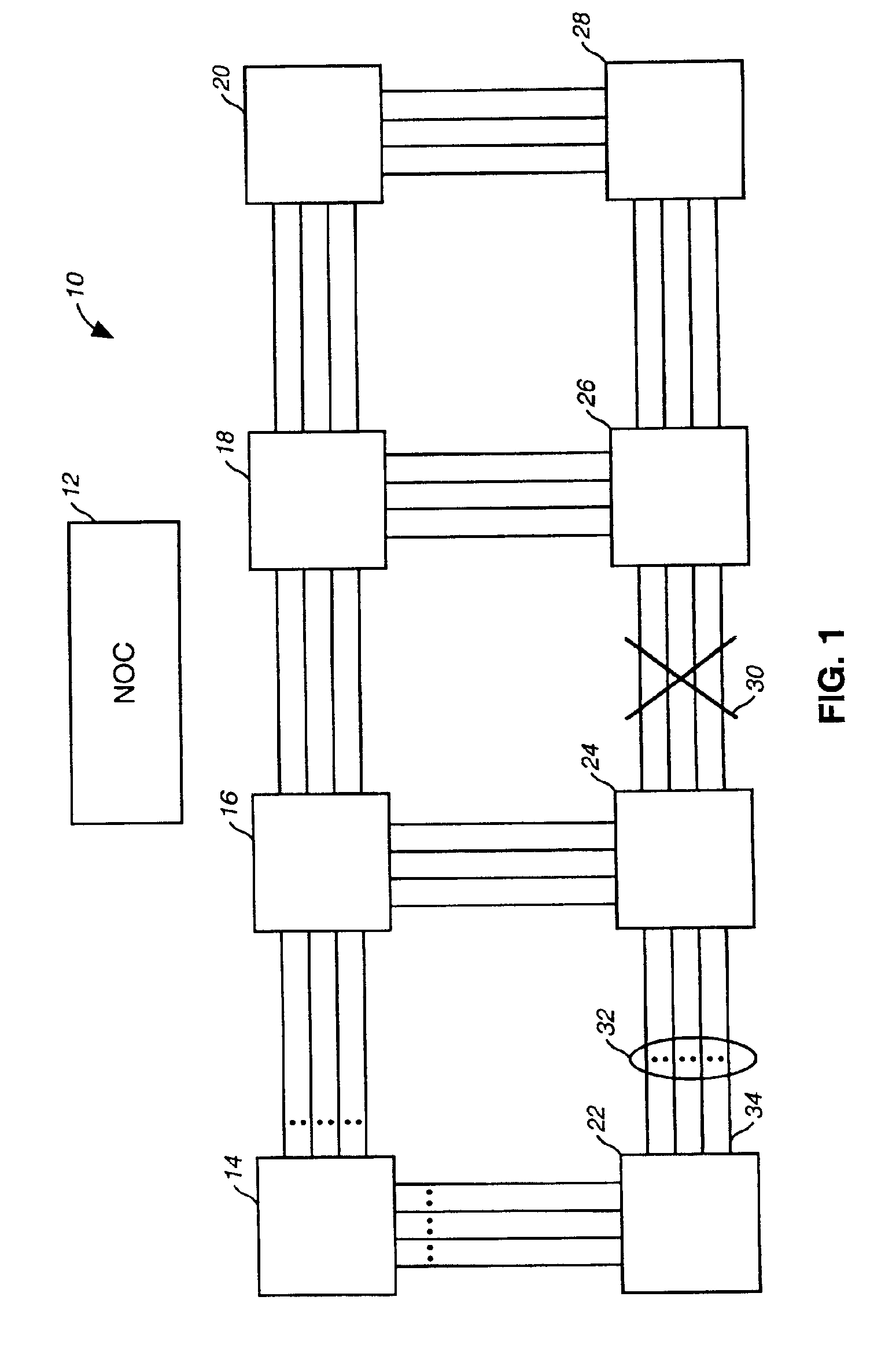
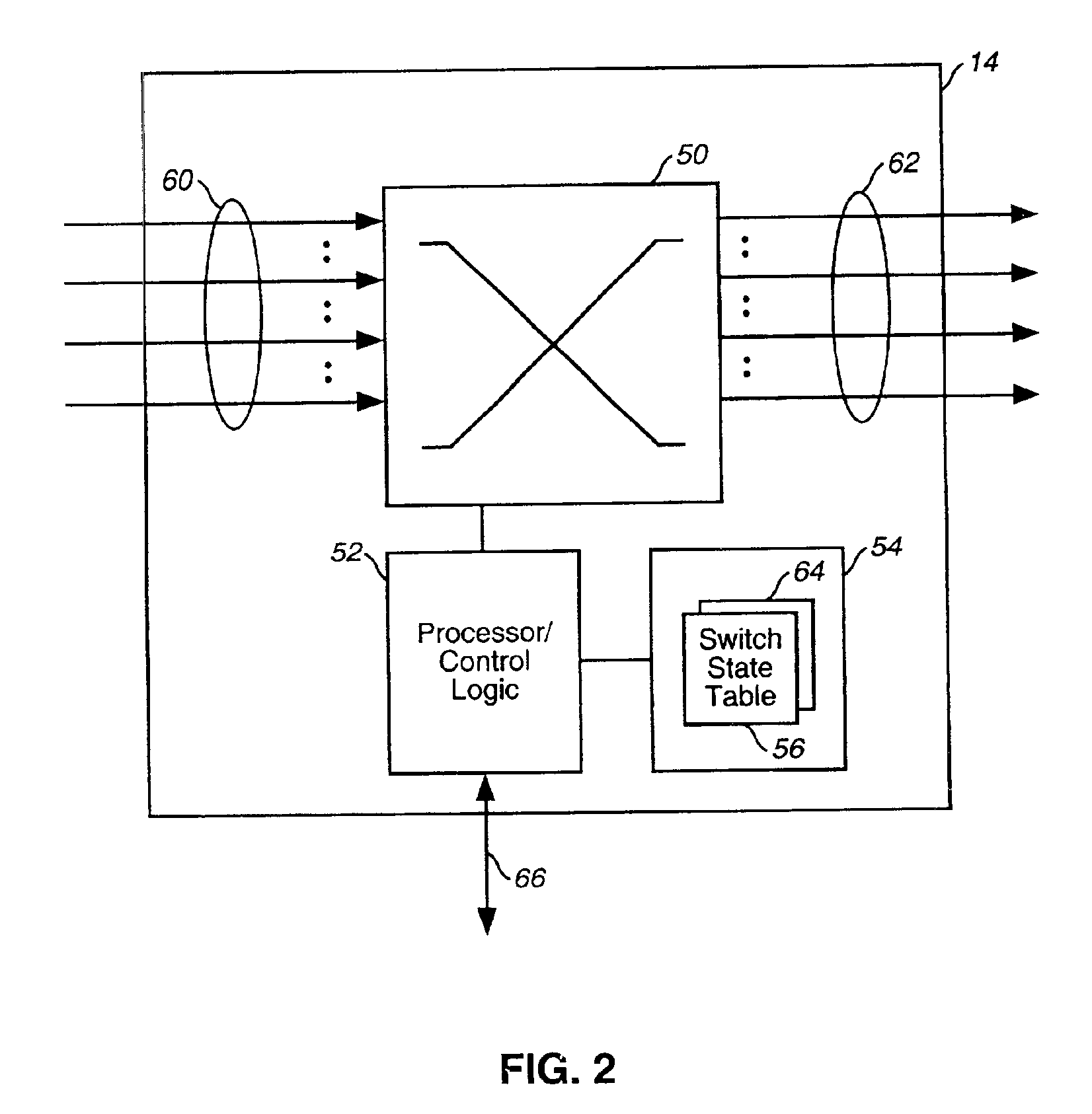
Network restoration using refreshed switch state tables
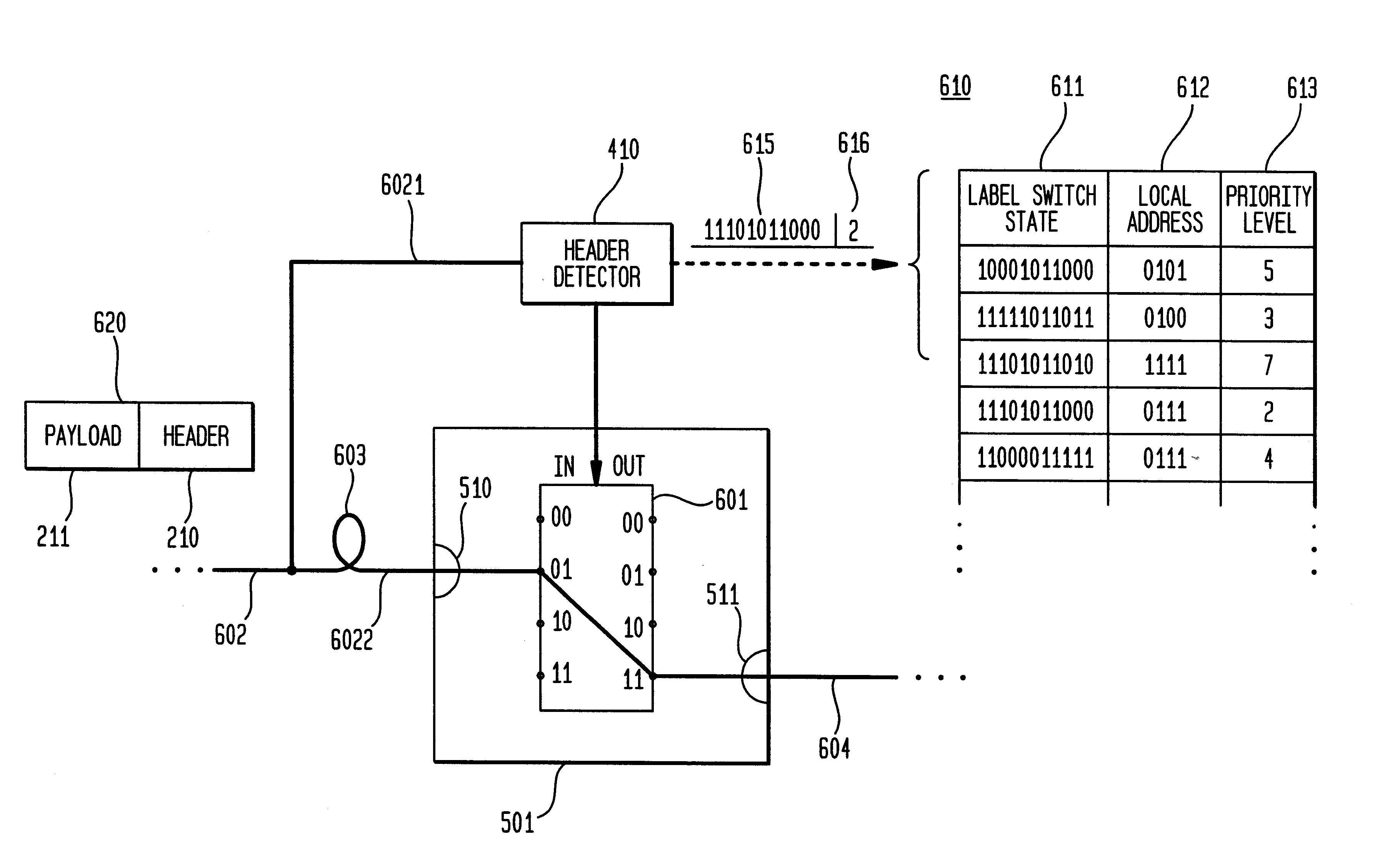
InactiveUS6963995B2Precise processPromote recoveryError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLookup tableOptical IP Switching
An exemplary method and optical network that provide optical network restoration using refreshed state tables are disclosed. The exemplary method for recovering from a failure in an optical network using refreshed switch state tables includes generating and storing connection information in switch state tables of associated optical switches that define optical link connections to be made in the event of a failure, monitoring whether a failure has occurred, and refreshing the switch state tables by continuing to generate and store connection information in the plurality of switch state tables that are associated with the plurality of optical switches of the optical network until the failure in the optical network is detected. Once the failure is detected, optical switching is automatically performed in the optical switches based on the lookup table connection information in the switch state tables that are associated with the optical switches. The exemplary method may then include determining whether any of the telecommunications traffic in the optical links of the optical network was not restored due to the optical switching that was automatically performed.
Owner:CIENA
Optical packet switching system
InactiveUS20120251109A1Reducing optical packet discarding rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsOptical packetOptical burst switching
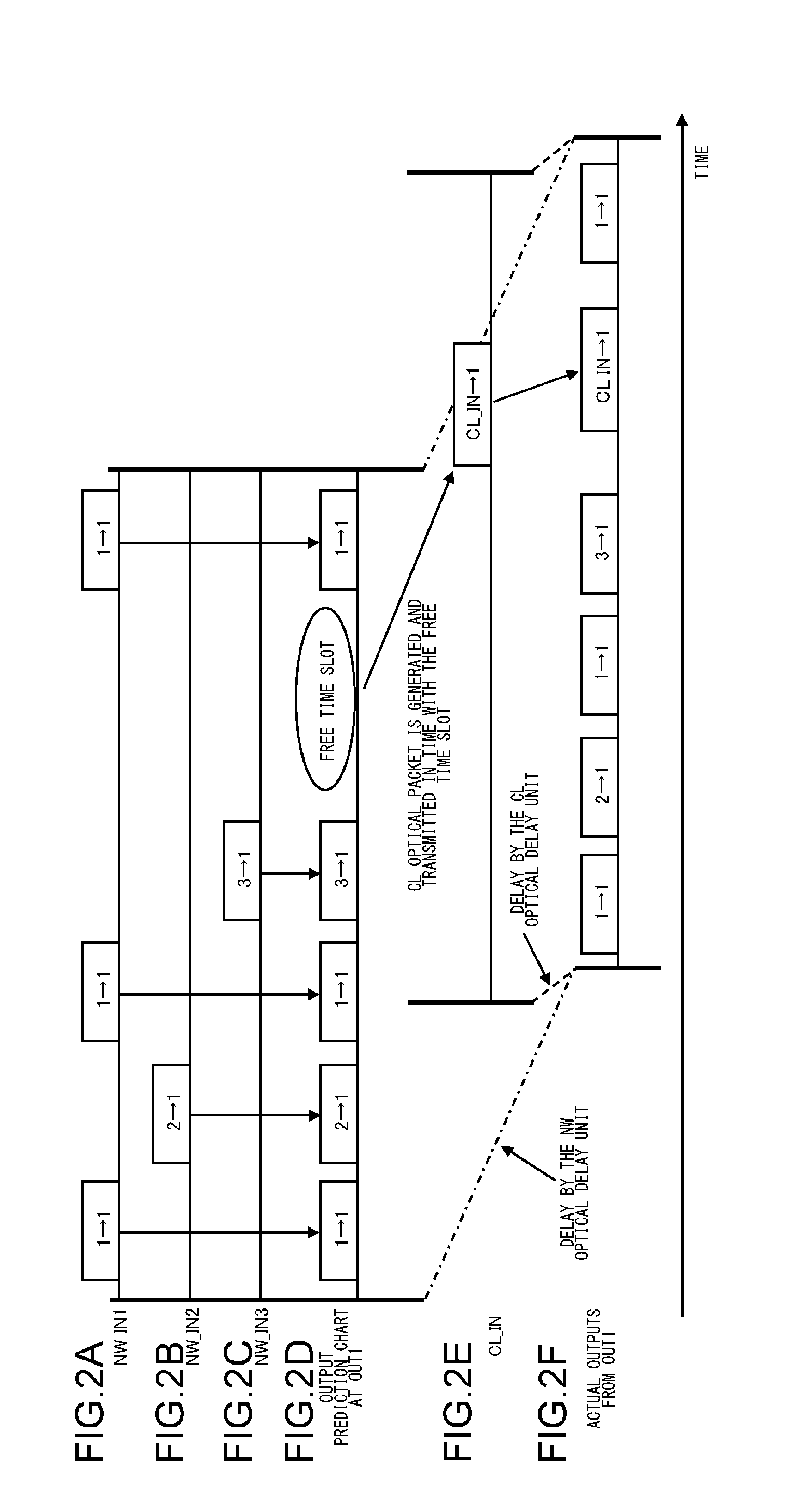
An optical packet switching system includes optical packet switching apparatus and an optical packet transmitting apparatus. The optical packet switching apparatus includes client optical delay units for delaying optical packet signals, network optical delay units for delaying one of the network optical packet signals, the network optical delay unit having a longer delay time than the client optical delay unit, an optical switch unit for switching the route of the inputted client optical packet signal so as to be sent out, an optical switch control unit for controlling the optical switch unit. The optical switch control unit is configured in such a manner as to detect a free time slot. The optical packet transmitting apparatus adjusts transmit timing, with which the client optical packet signal is sent out, in such a manner that the client optical packet signal is inserted into the free time slot.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical packet switching system and optical packet switching device
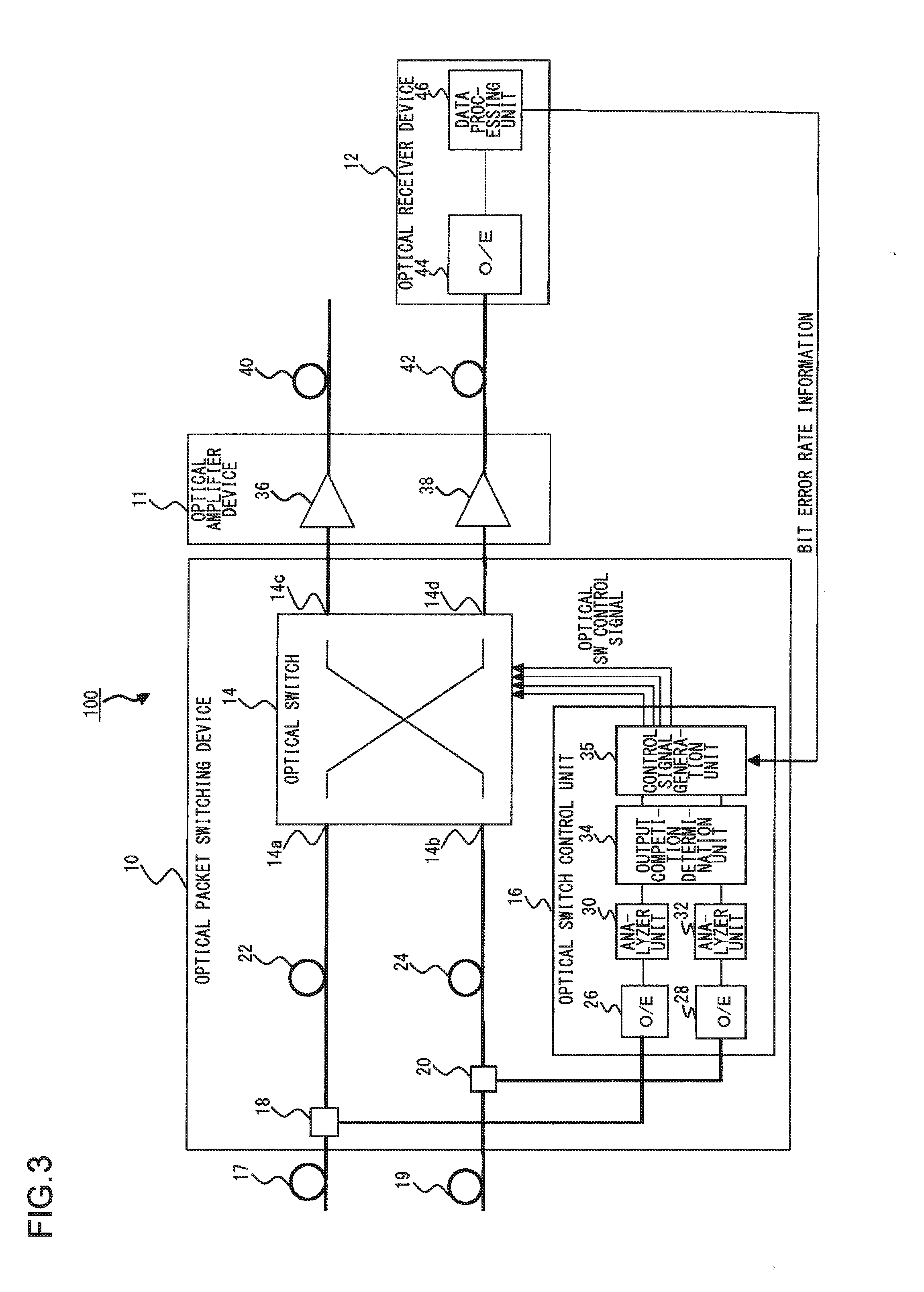
InactiveUS20120201540A1Guaranteed normal transmissionHigh degree of priorityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical packetOptical IP Switching
An optical packet switching device is provided with: a first input unit and a second input unit for receiving an optical packet signal having destination information and priority information; a first demultiplexer and a second demultiplexer for branching the optical packet signal; an optical switch unit for routing one of branched optical packet signals; a first analyzer unit and a second analyzer unit for analyzing the header of the other branched optical packet signal so as to detect the destination information and the priority information; and an output competition determination unit for checking for temporal competition of a plurality of optical packet signals based on destination information and for determining whether the optical packet signals should be transmitted or discarded based on priority information when there is competition.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical packet switching system
InactiveUS20120155869A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic network arrangementsOptical packetOptical IP Switching
An optical packet switching system includes: an optical packet switching device configured to route and output an input optical packet signal; an optical amplifier device provided in a stage subsequent to the optical packet switching device; and a dummy packet insertion device configured to insert a dummy packet in an optical packet signal prior to input to the optical amplifier device. A dummy packet includes a flag indicating that the packet is a dummy packet.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical packet switching system
InactiveUS20120155862A1Amount be controlMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsControl signalOptical packet
An optical packet switching system includes: an optical packet switching device configured to route and output an input optical packet signal; an optical amplifier device provided in a stage subsequent to the optical packet switching device; and a control signal generation unit configured to superimpose a noise component on the optical packet signal by inducing cross talk in the optical packet switch.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
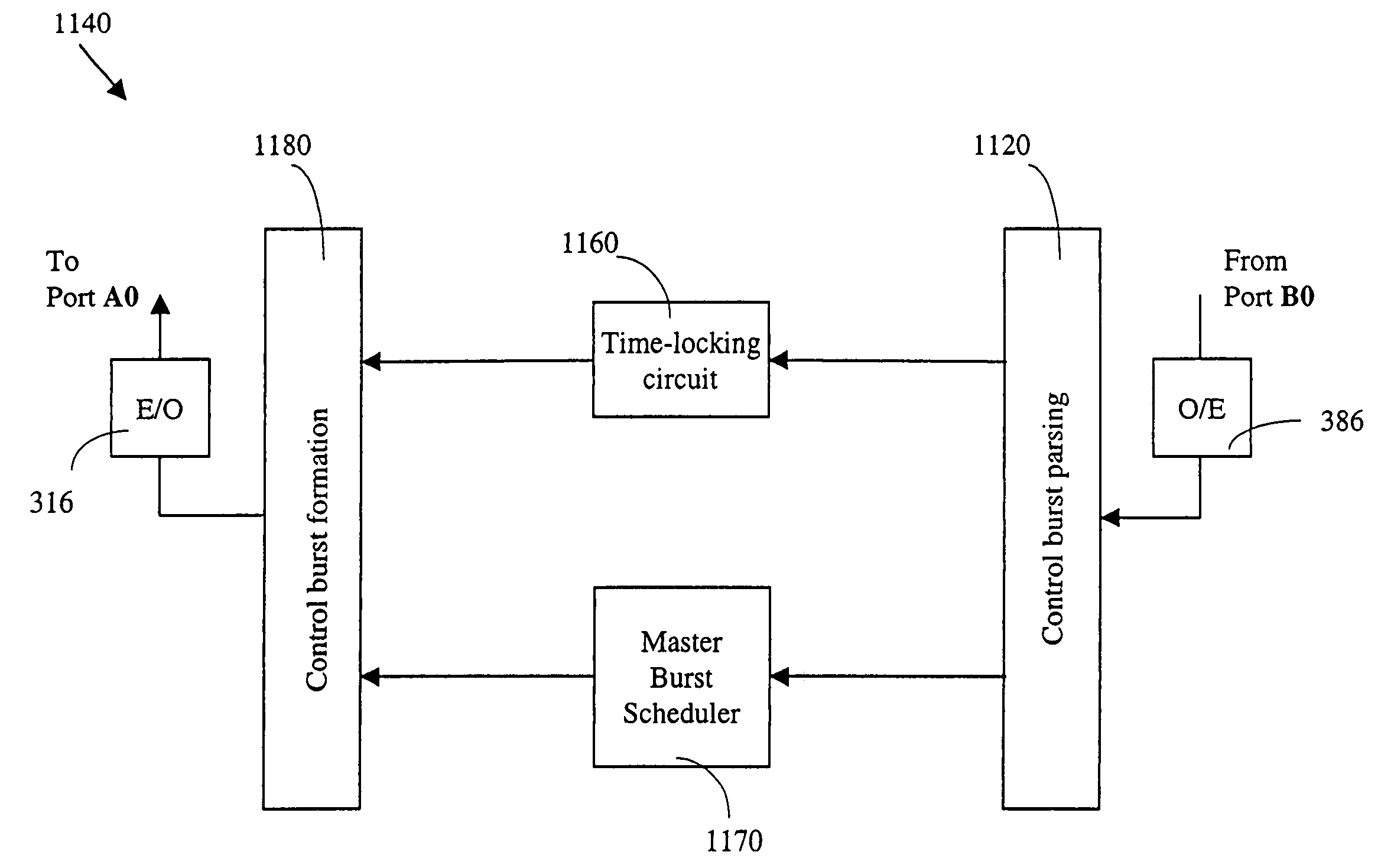
Rate-controlled optical burst switching
InactiveUS7187654B1Improve performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionOptical burst switchingEdge node
A method and apparatus are provided for low latency loss-free burst switching. Burst schedules are initiated by controllers of bufferless core nodes and distributed to respective edge nodes. In a composite-star network, the burst schedules are initiated by any of a plurality of bufferless core nodes and distributed to respective edge nodes. Burst formation takes place at source nodes and a burst size is determined according to an allocated bitrate of a burst stream to which the burst belongs. An allocated bitrate of a burst stream may be modified according to observed usage of scheduled bursts of a burst stream. A method of control-burst exchange between each of a plurality of edge nodes and each of a plurality of bufferless core nodes enables burst scheduling, time coordination, and loss-free burst switching. Both the payload bursts and control bursts are carried by optical channels connecting the edge nodes and the core nodes. A method and a circuit are provided for generating burst descriptors wherein each burst is associated with a burst stream and each burst stream is allocated a service bitrate. The generated burst descriptors are used in each master controller in each core node to create the burst schedules. In a conventional burst-scheduling process, the burst queues at a master controller of an optical switch receives burst descriptors from the source nodes and schedules the burst switching times. In a distinct departure, according to the present invention, the burst descriptors are generated by a master controller of an optical switch in a core node, the switching times of the corresponding bursts are scheduled, and the schedules are distributed to the respective edge nodes. The burst-descriptor generation is based on burst-stream bitrate-allocation defined by the source nodes.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
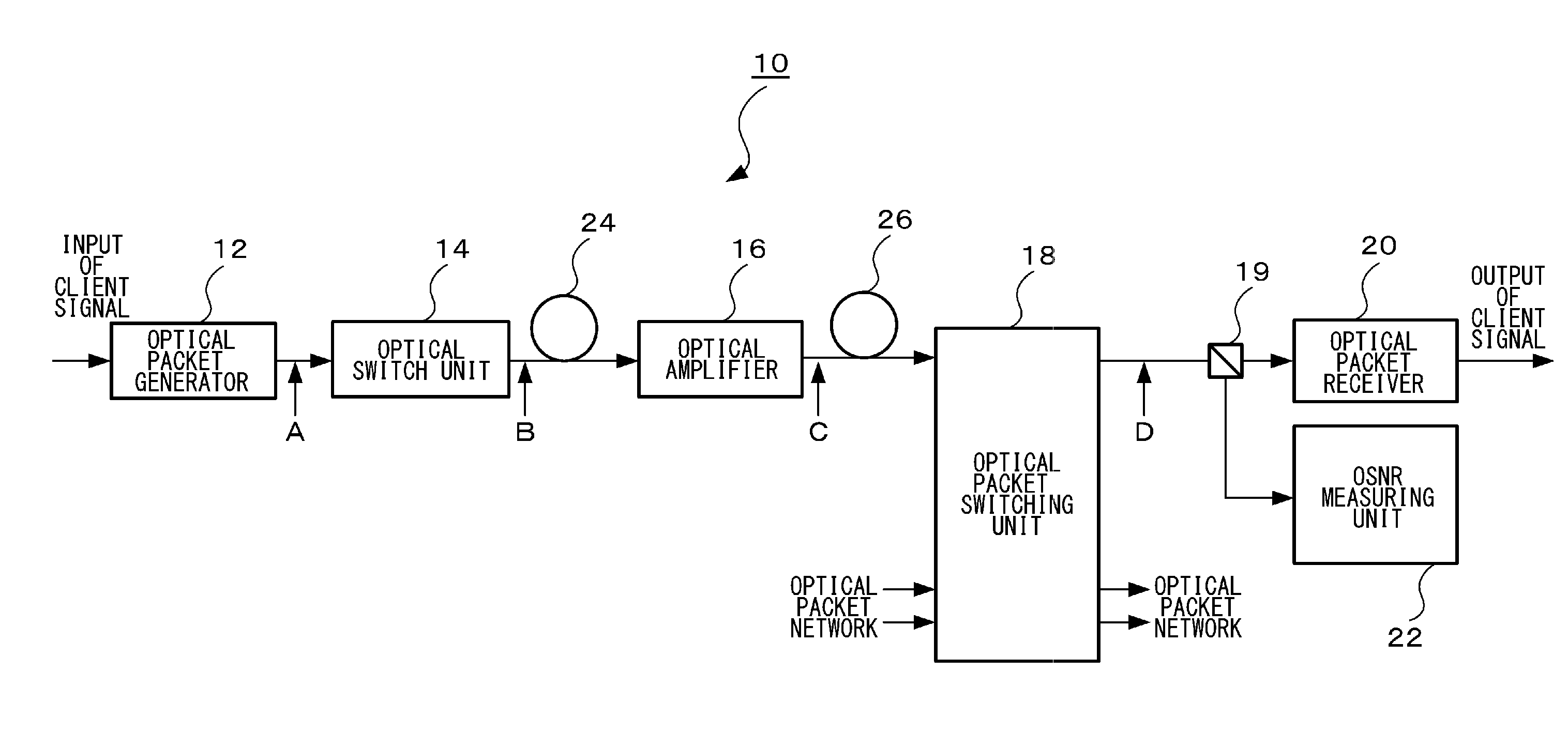
Optical packet switching system
InactiveUS20120301139A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical packetOptical power
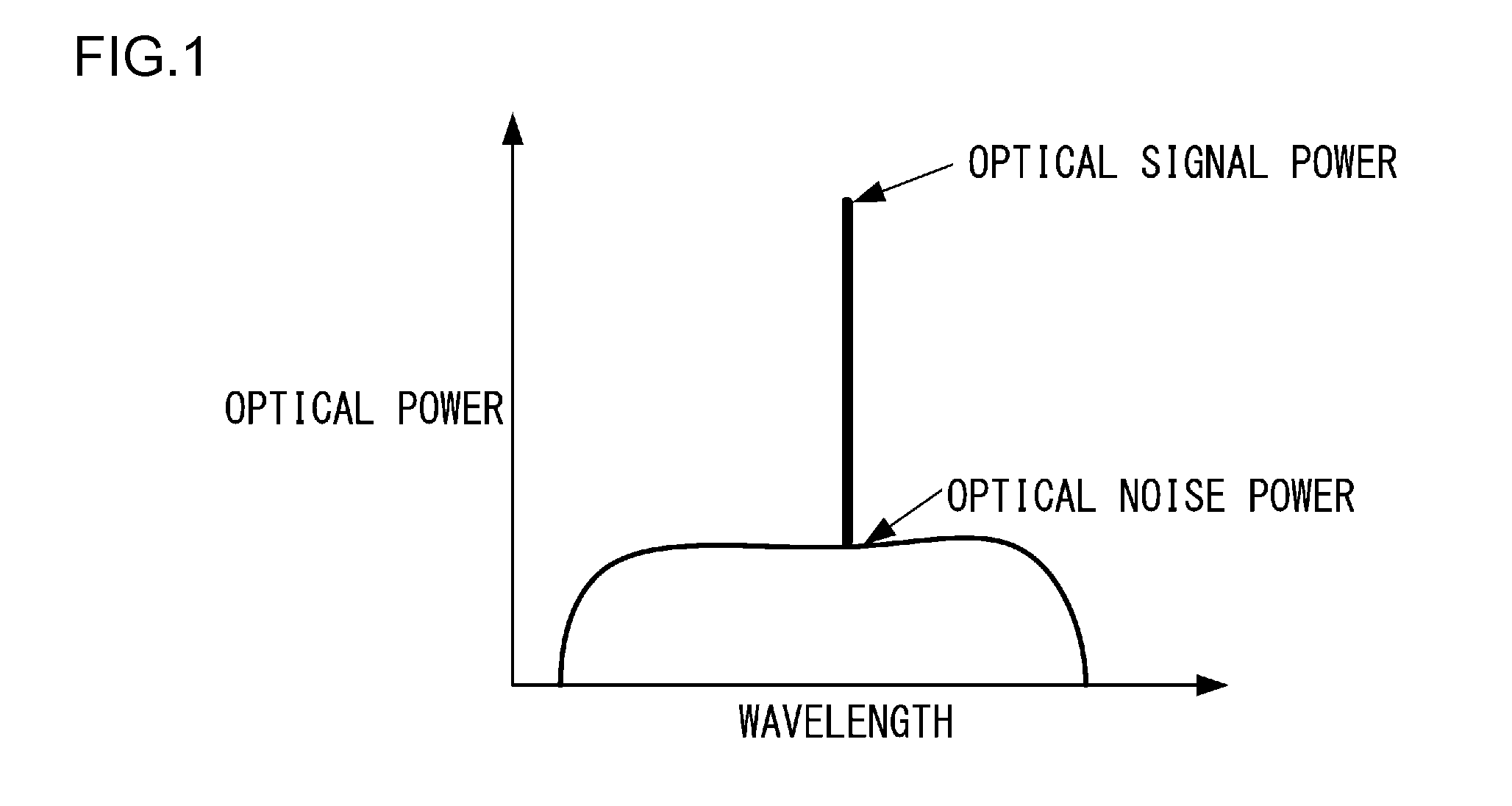
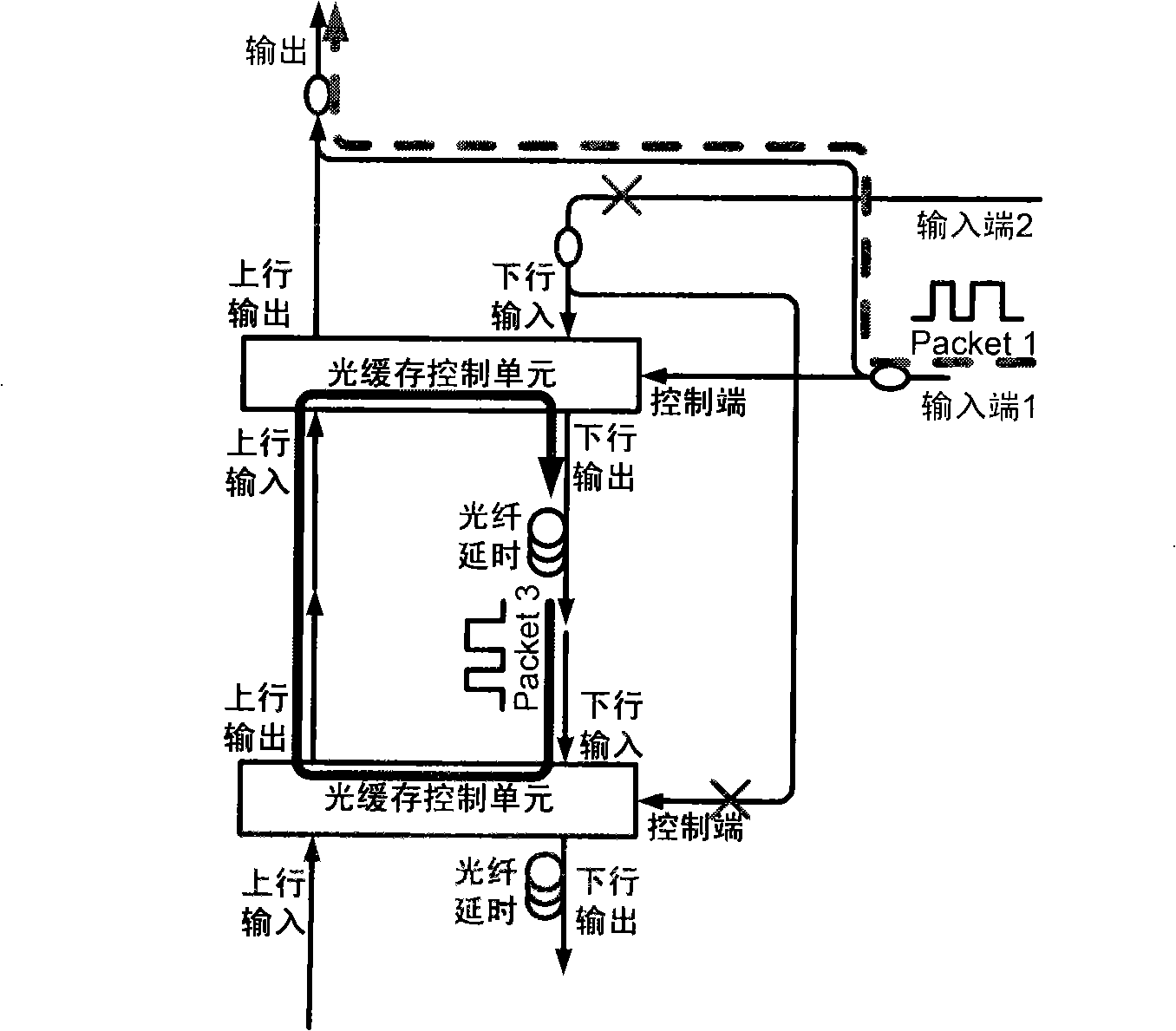
An optical packet switching system includes an optical packet generator for generating an optical packet signal, an optical packet switching unit, provided with an optical switch, for switching the route of an inputted optical packet signal by controlling on / off of the optical switch, and an optical signal-to-noise ratio measuring unit for measuring the optical signal-to-noise ratio of the optical packet signal outputted from the optical packet switching unit. When switching the route of the optical packet signal, the optical packet switching unit outputs an optical packet signal with optical noise by keeping the optical switch on longer than the time width of the packet signal. The optical signal-to-noise ratio measuring unit measures the optical signal power and the optical noise power, respectively, in the optical packet signal with optical noise and measures the optical signal-to-noise ratio by calculating the ratio between the optical signal power and the optical noise power.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
All-optical time slice switching method based on time synchronization
ActiveCN103580771AReliable all-optical switchingMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsData synchronizationData stream
The invention discloses an all-optical time slice switching method based on time synchronization. According to the method, continuous service data streams in an optical network are assembled to periodically-repeated optical time slices in a segmented mode in a time domain and are transferred in an asynchronous transfer mode. Network nodes obtain high precision synchronization time through whole network time, an optical switch is controlled to switch optical time slices reaching at precise time points periodically to a target port, and therefore full optical switching is completed. When a connection request reaches, available routes, wavelengths and occupation time slots are calculated through source nodes according to network available time slot resource information, and are reserved through a connection management module. After resource reservation is finished, the source nodes send out optical time slices of bearer service periodically at reserved time slots. Destination nodes restore received optical time slices to original service steams. Compared with an existing switching technology, the all-optical time slice switching method has the remarkable advantages that reliable and flexible sub-wavelength granularity all-optical switching can be achieved without participation of all-optical caches and all-optical logic devices.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Asynchronous multi-wavelength mesh network adaptive node system based on optical packet switching
ActiveCN102427567AAchieve sharingReduce storage pressureMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime delaysStructure of Management Information
The invention provides an asynchronous multi-wavelength mesh network adaptive node system based on optical packet switching. The system comprises N access users (U) and consists of an optical wavelength division multiplexer, an optical beam splitter, an optical wavelength division demultiplexer, an optical fiber delay line, an optical conflict resolution and switching matrix and a control processing matrix. Input user data is demultiplexed by the optical wavelength division demultiplexer and is subjected to corresponding route selection and addressing on the optical conflict resolution and switching matrix, and a data packet is transmitted to a corresponding destination port. The node has a compact structure, the switching efficiency can be improved, time delay and a blocking rate are greatly reduced, multicast and broadcast are supported simultaneously, and storage and computation pressure of a whole network consisting of the nodes can be reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Optical switching system based on arrayed waveguide grating
The invention discloses an optical switching system based on arrayed waveguide gratings, which comprises an input unit, a switching unit and an output unit, wherein the switching unit comprises two groups of arrayed waveguide gratings, the preposed first group of arrayed waveguide gratings is composed of N M*M periodic arrayed waveguide gratings, the postposed second group of arrayed waveguide gratings is composed of M N*N periodic arrayed waveguide gratings; the output port of the first grating of the first group of arrayed waveguide gratings is sequentially linked with the first input ports of various gratings of the second group of arrayed waveguide gratings respectively; the output port of the second grating of the first group of arrayed waveguide gratings is sequentially linked with the second input ports of various gratings of the second group of arrayed waveguide gratings respectively; by parity of reasoning, the output port of the N-th grating of the first group of arrayed waveguide gratings is sequentially linked with the N-th input ports of various gratings of the second group of arrayed waveguide gratings respectively. Through the switching system, large scale port numbers are realized and response speed of nanosecond level is realized at the same time, and the system has the advantages of compact structure, easiness in operation and control, flexibility in use and the like, so that the system is particularly suitable for high-speed switching of an all-optical switching system.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Wavelength division multiplexed optical channel switching
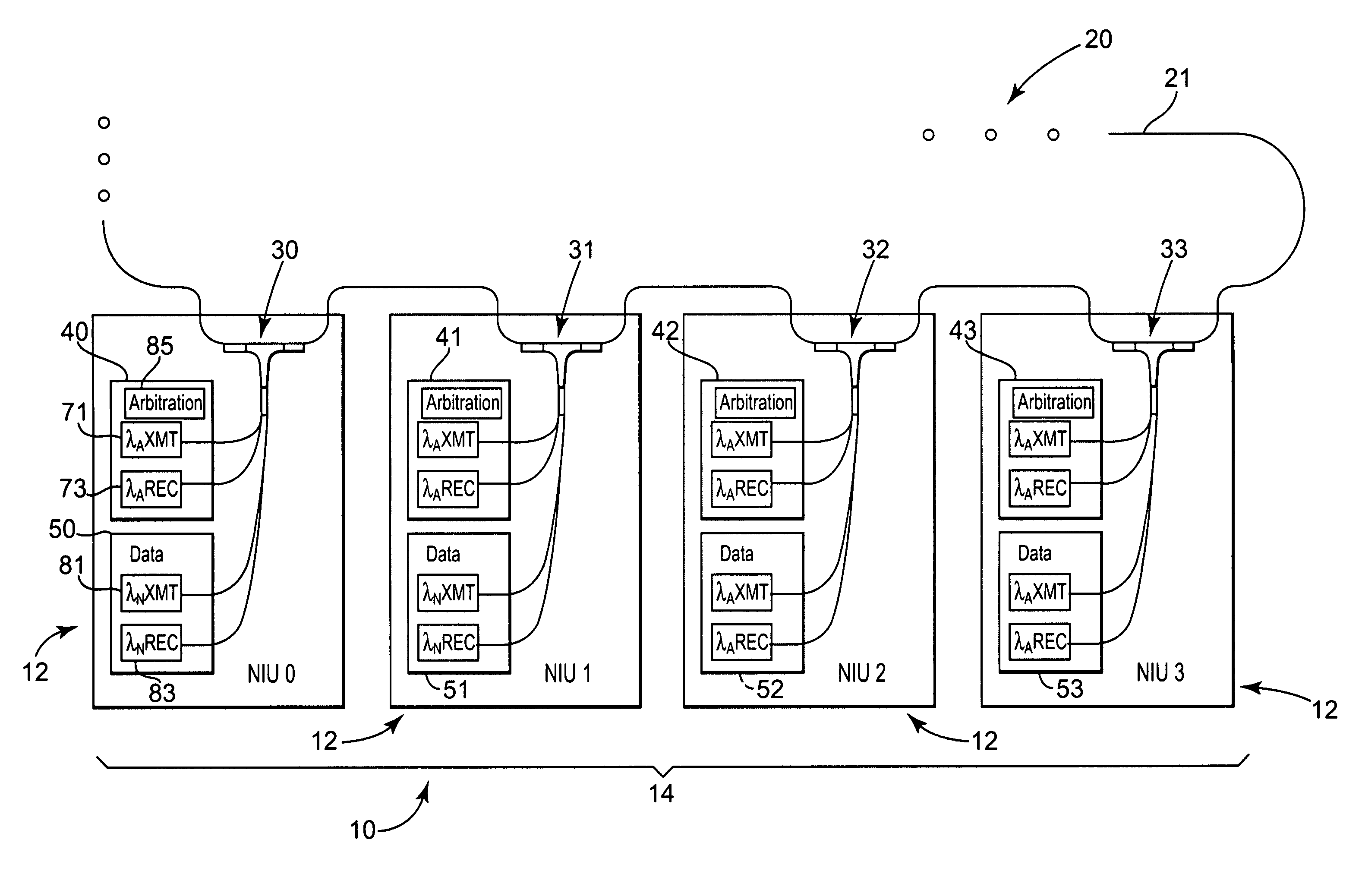
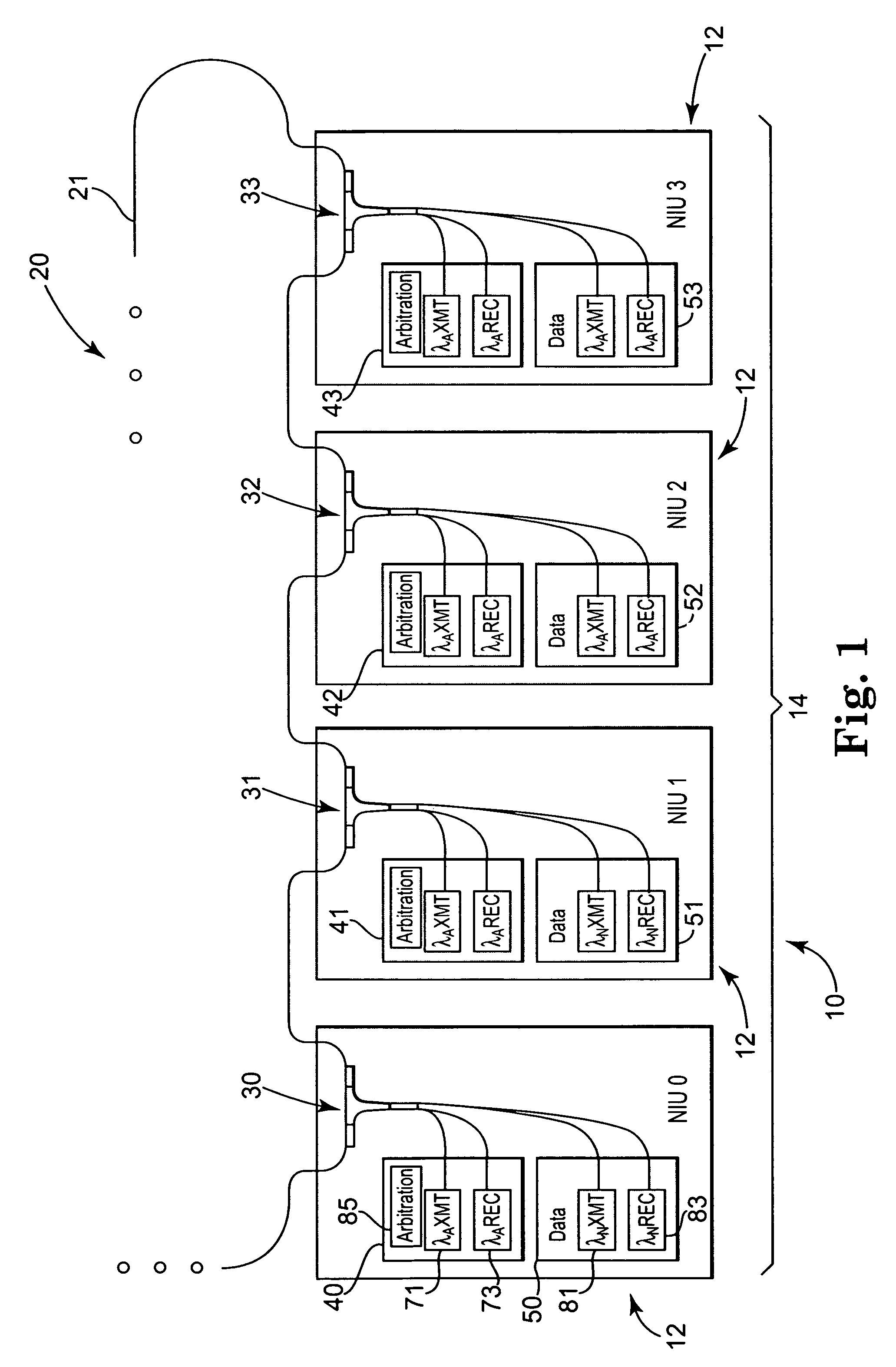
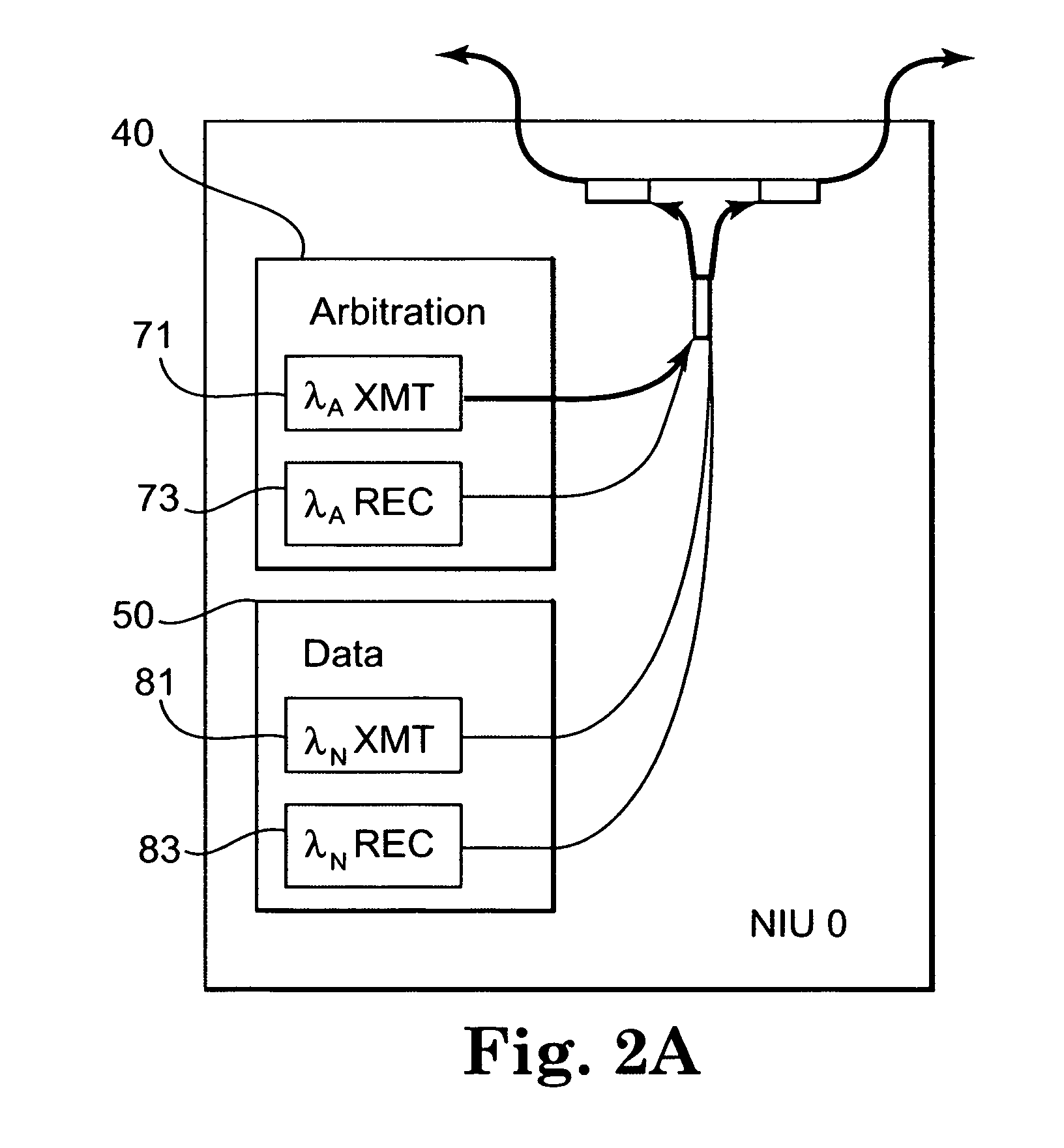
ActiveUS8014671B1Reduce weightSmall volumeBus-type electromagnetic networksOptical multiplexCommunications systemOptical communication
An optical communication system and method for use in communicating data between nodes using wavelength division multiplexing includes an optical backbone to provide an optical pathway between the nodes. Arbitration information on a dedicated arbitration wavelength transmitted during an arbitration cycle is used by the plurality of nodes to select one of a plurality of wavelengths at which to transmit data during a subsequent data cycle.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
An optical flow switching network scheduling method and an optical flow switching system
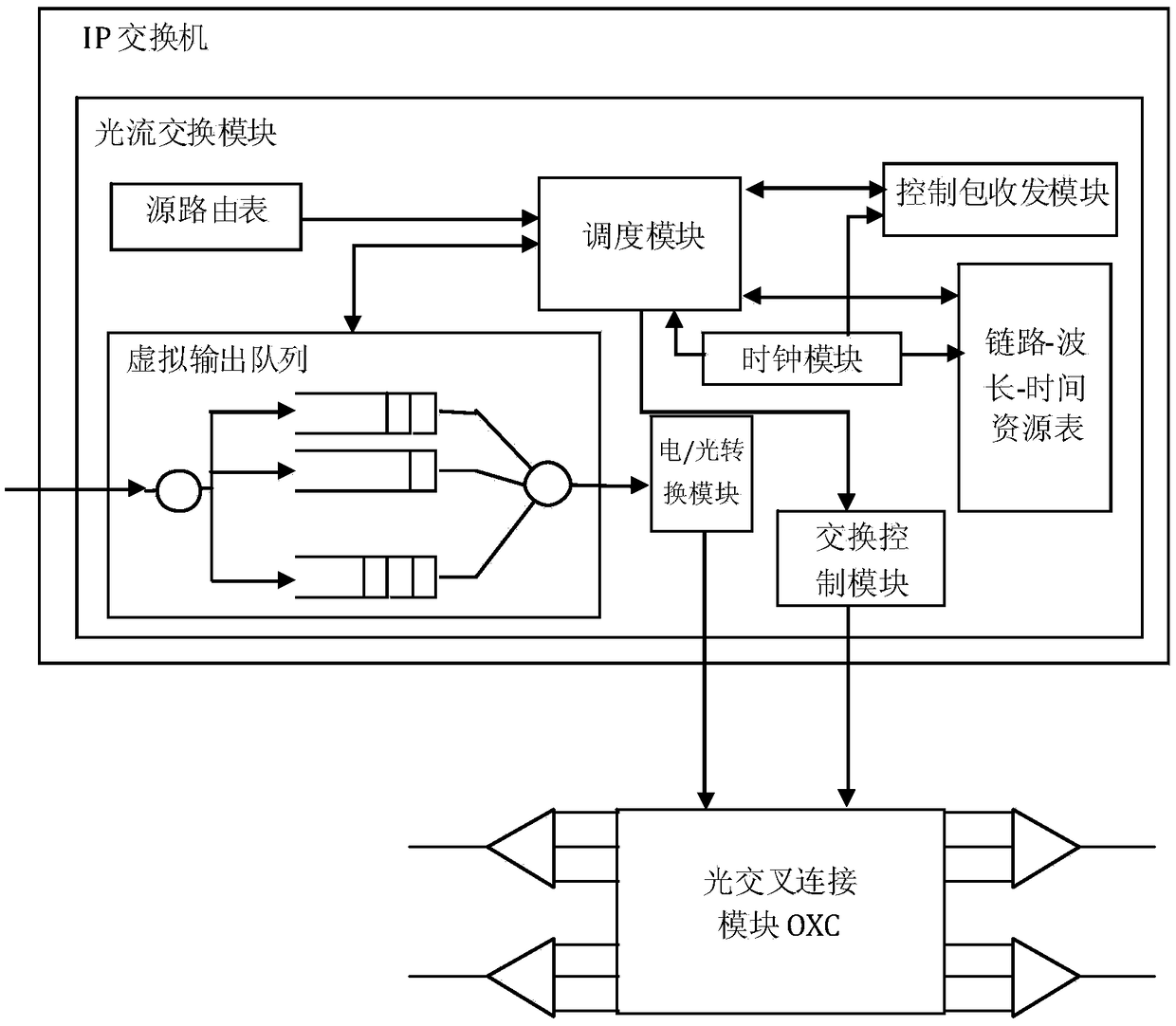
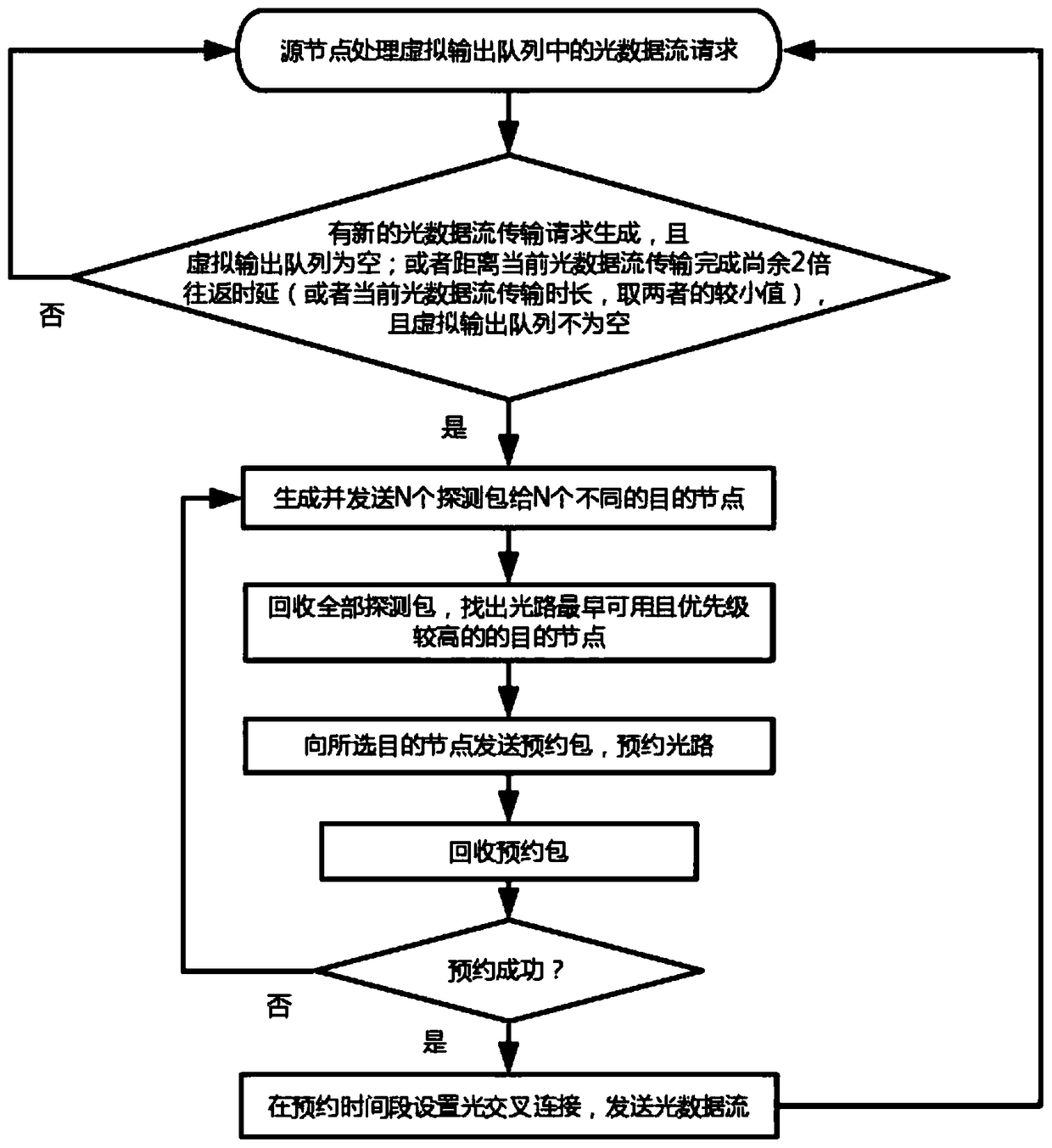
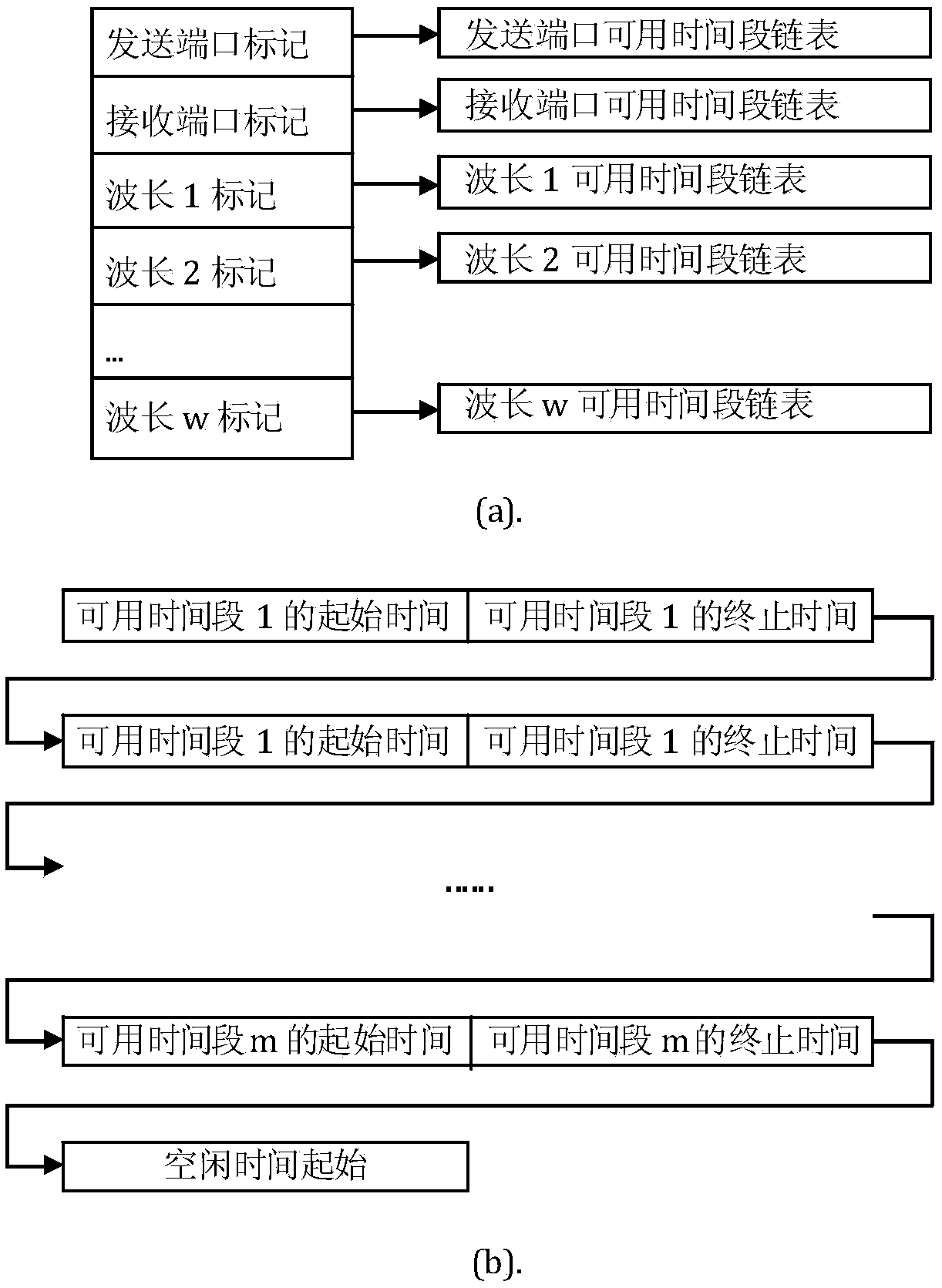
ActiveCN109168094AReduce computational complexityReduce head timeMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksCross connectionData stream
The invention discloses an optical flow switching network scheduling method and an optical flow switching system. Each node in the system is mainly composed of an IP switch and an optical cross connection module. Each IP switch is provided with an optical flow switching module. The optical flow switching module comprises a virtual output queue and a link-wavelength-time resource table, source routing table, a scheduling module, a control packet transceiver module, an electronic / optical conversion module, a switching control module and a clock module. At the same time of transmitting optical data stream, the source node requests to start optical path reservation in advance for optical data stream in virtual output queue, detects the availability of optical paths corresponding to multiple destination nodes, combines queue head request priority and optical data stream transmission time, finds out the earliest available optical paths and reserves a time period for the optical paths. The invention has the following beneficial effects: 1, centralized scheduling nodes are not needed in the network, each node executes distributed scheduling, and the computational complexity is low; 2, thatoptical path schedule calculation and the data transmission are carried out simultaneously, the head time of the data transmission is shorten, the network throughput is improved, the average waitingtime of the queue is reduced, and the bandwidth utilization ratio is optimized; 3, adding time dimension to the scheduling allocation of link wavelength resources, which can improve the performance ofthe algorithm; 4, that device can be deploy based on the exist network equipment, and the application conditions are ripe.
Owner:SUNWAVE COMM
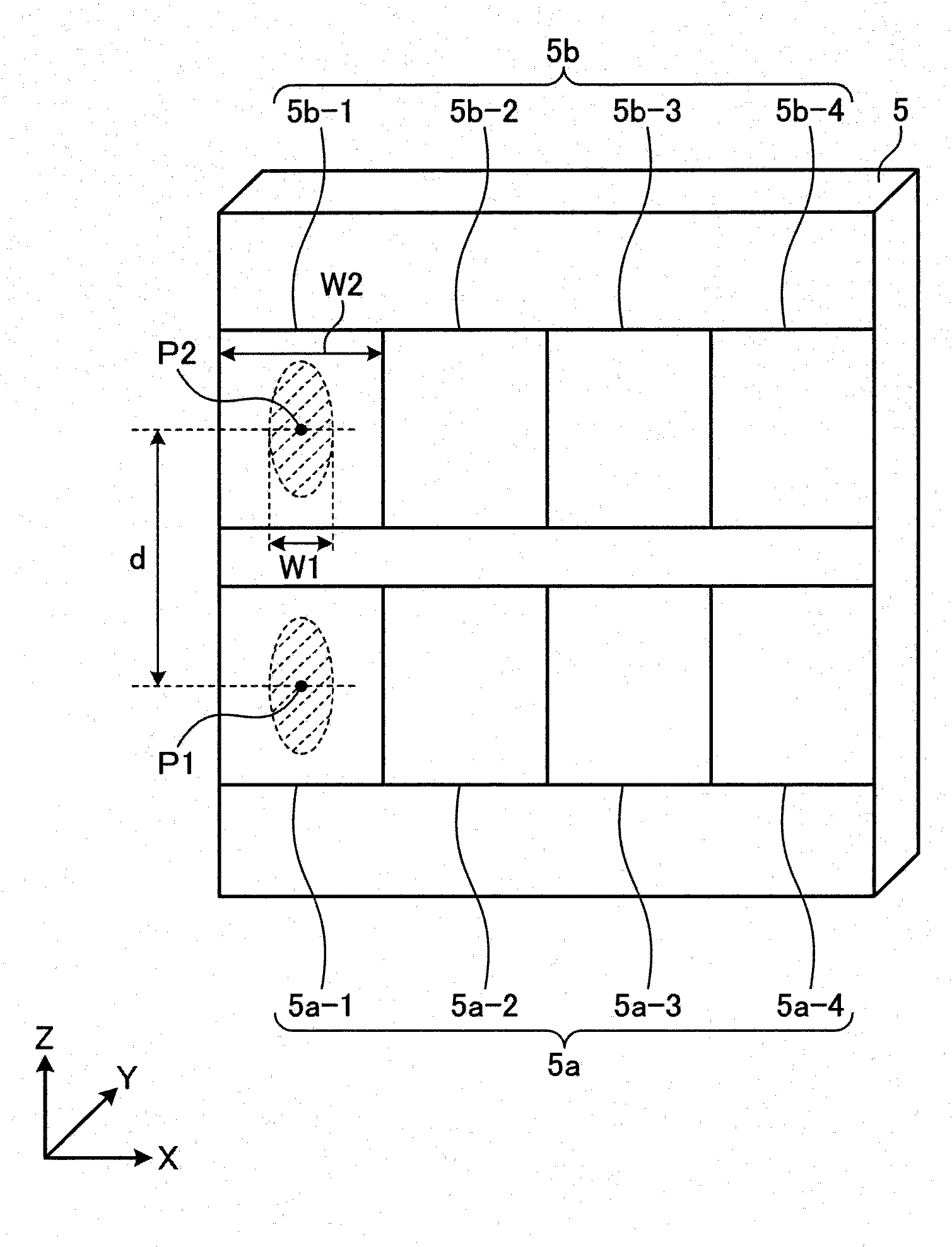
Optical Switch
InactiveCN103676009AIncrease the number of portsReduce sizeMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesEngineeringOptical IP Switching
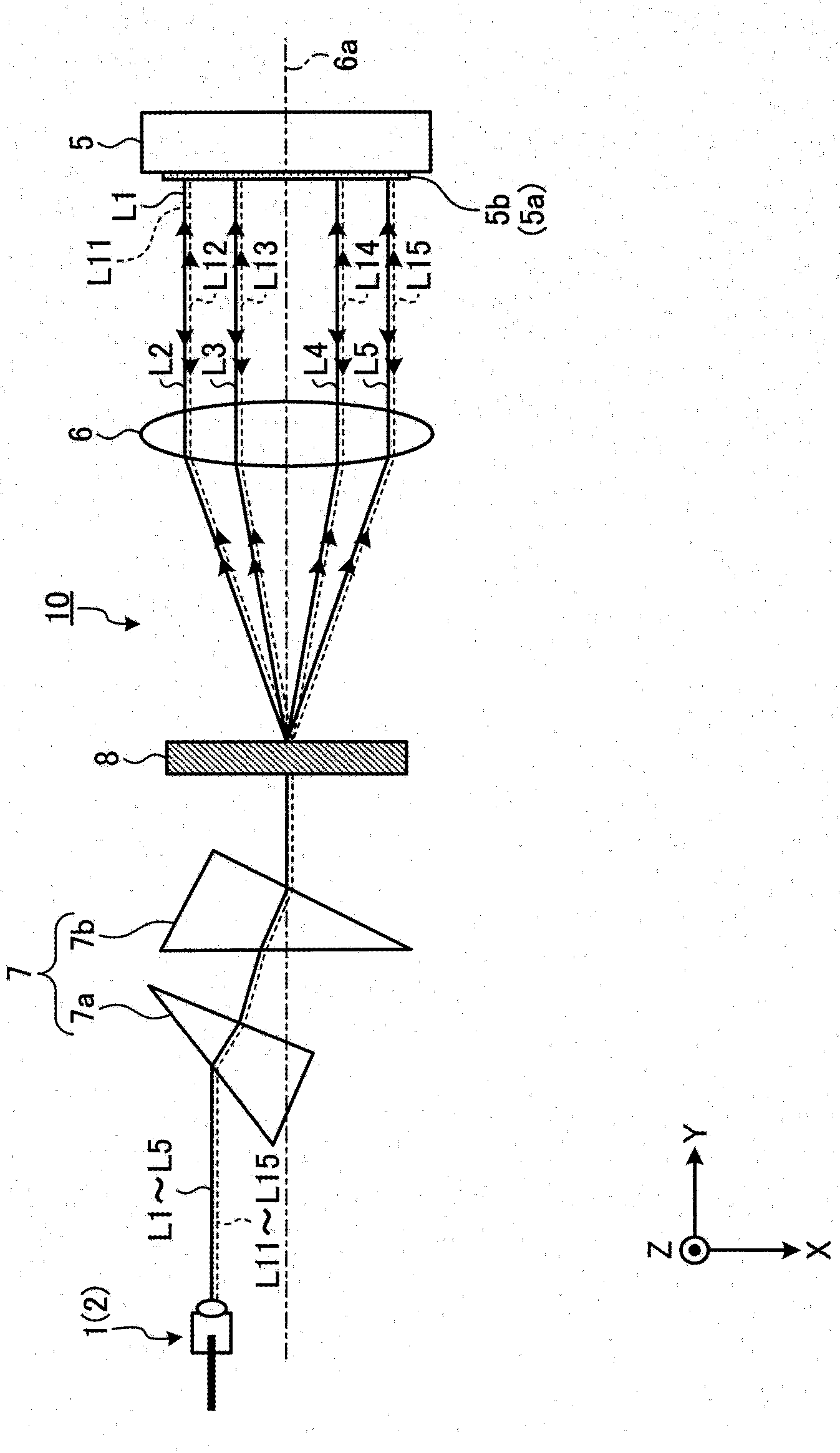
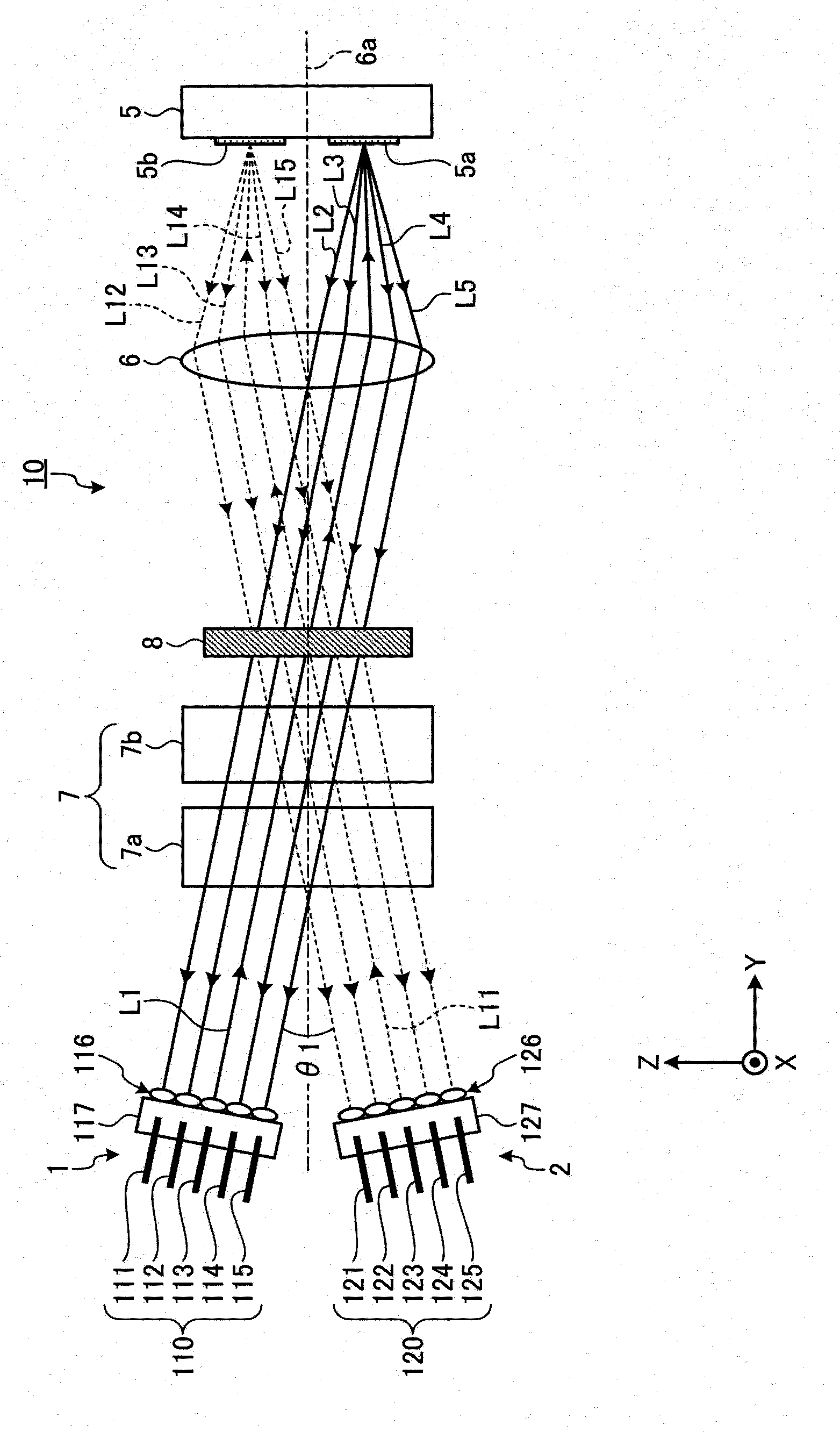
The invention provides an optical switch which is small in size, low in cost and large in number of light input / output ports. An optical switch (10) includes light input / output ports (1,2), each having a port group (110,120) of inputting / outputting a light, an optical path manipulation unit (5) having optical path switching units (5a,5b,5c) of switching an optical path of a light from an input port in the port group to an optical path toward an output port in the same port group according to each of the light input / output ports, and a condenser lens (6) condensing light from the light input / output ports on the optical path switching units corresponding to the port groups and optically-couples the light input / output ports with the optical path manipulation unit. The input / output optical paths of the light input / output ports with respect to the condenser lens are parallel to each other between the ports in the same port group and are unparallel to each other between the ports in the different port groups as seen from a direction perpendicular to a port arrangement direction.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
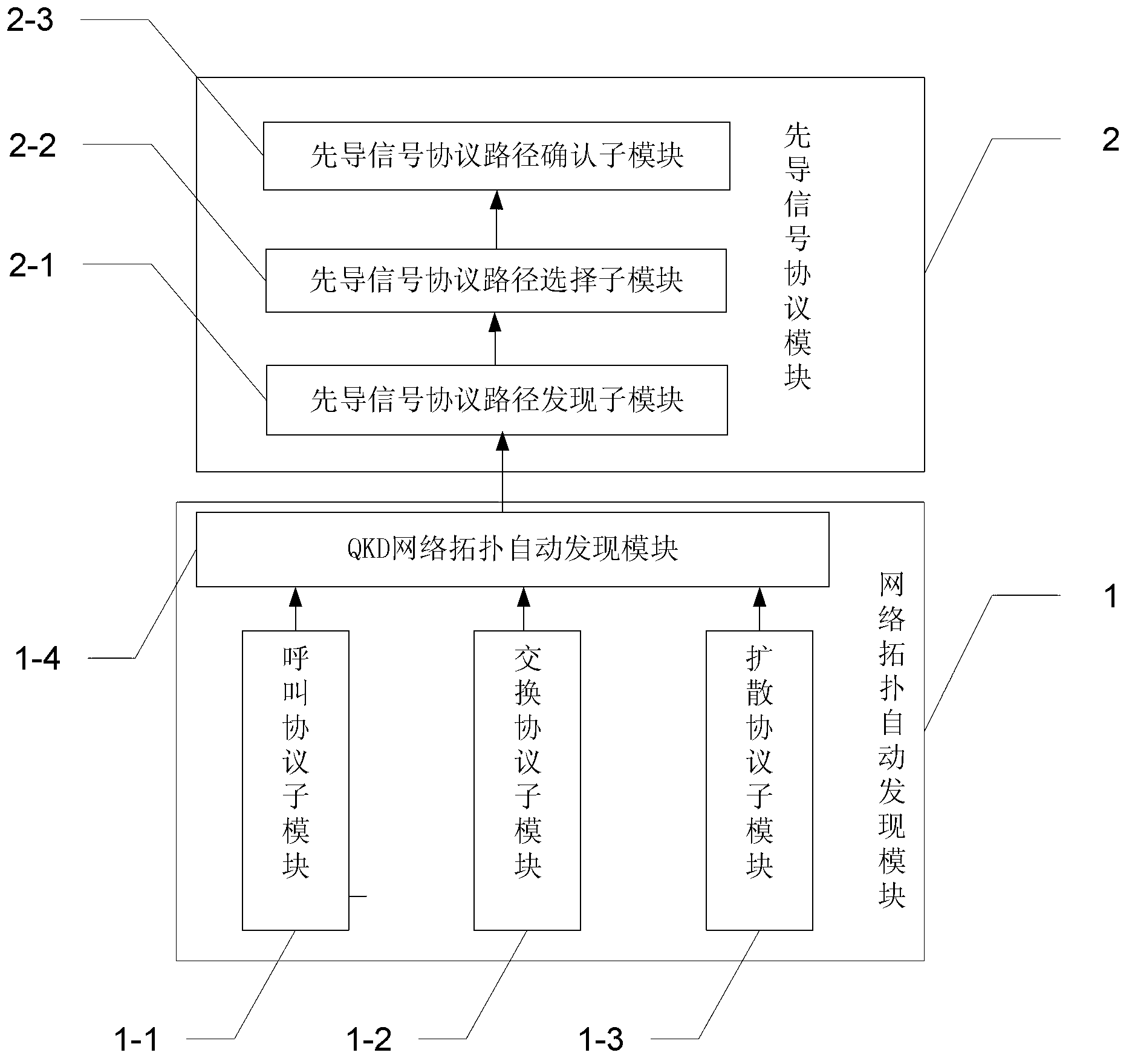
Route selection system and route selection method of quantum key distribution (QKD) network and on basis of optical path switching
ActiveCN103200105AScale upKey distribution for secure communicationFibre transmissionStructure of Management InformationSelection system
The invention belongs to the field of quantum communications and quantum key distribution (QKD) networks, particularly relates to a route selection system and a route selection method, and discloses the route selection system and the route selection method of a QKD network and on the basis of optical path switching. Through the route selection system and the route selection method of the QKD network and on the basis of the optical path switching, the problems that the route selection ability of an existing QKD network is poor, and therefore the existing QKD network is simple in topology and small in scale are solved. The route selection system of the QKD network and on the basis of the optical path switching comprises optical path switching nodes, wherein the number of the optical path switching nodes is M, a call protocol sub module of each optical path switching node can automatically find a topology structure table, sent by the module through the QKD network topology, of the QKD network and obtain a table including all feasible communication paths from a QKD communication request source node to a destination node, a pilot signal protocol path selection sub module is used for selecting an optimal communication path from the table including all the feasible communication paths, the optimal communication path is used as a current communication path, a pilot signal protocol path confirmation module is used for confirming the selected optimal communication path, and then a communication channel from the source node to the destination node is built. The route selection system and the route selection method of the QKD network and on the basis of the optical path switching are suitable for the communication field.
Owner:中数(深圳)时代科技有限公司
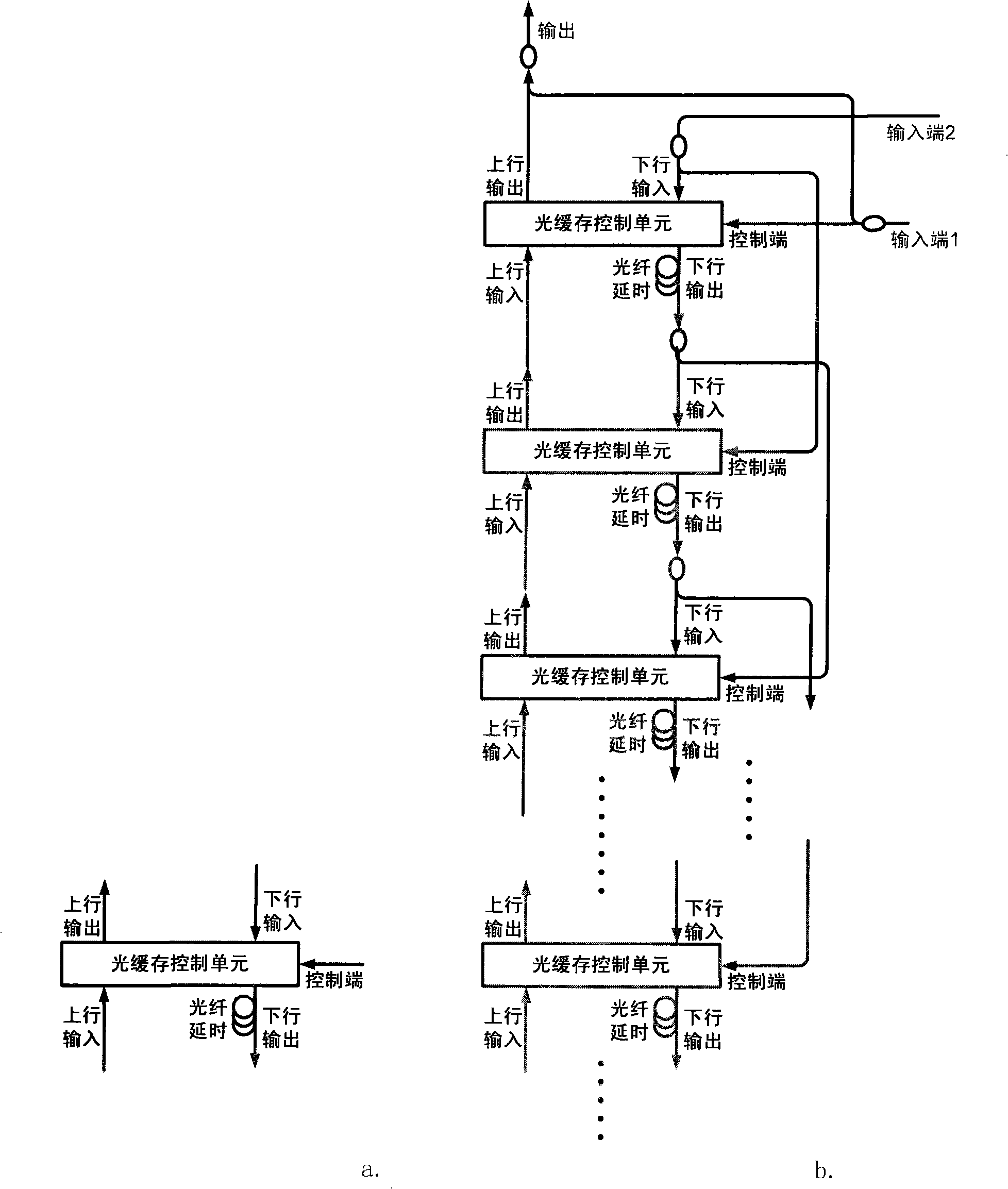
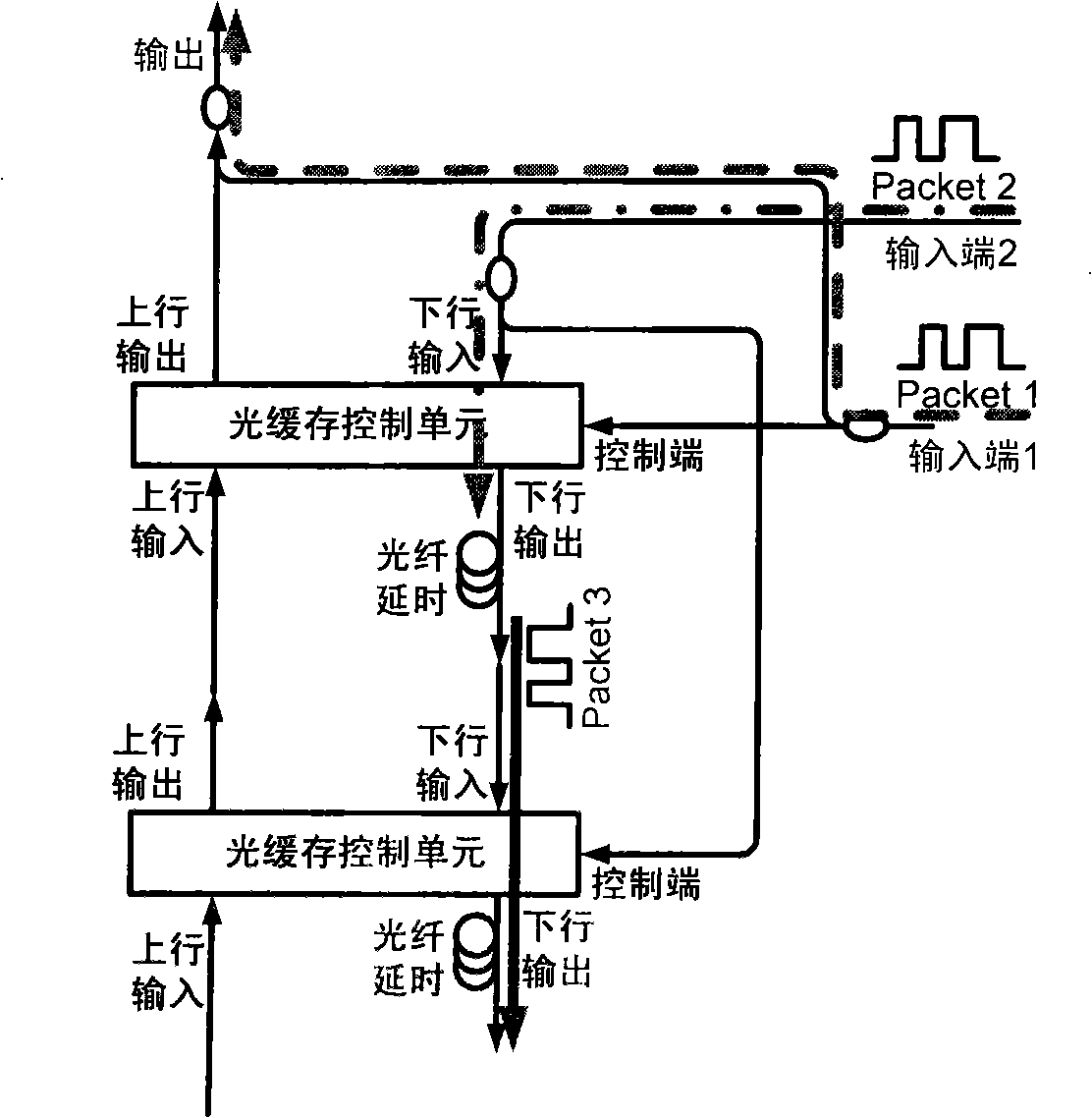
Stack type whole optical caching device
InactiveCN101350672ADecide how long to storeDecision depthMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesOriginal dataUplink transmission
The present invention relates to a stack type fully optical buffer, and belongs to the field of fully optical packet switching. The buffer is characterized by consisting of a plurality of cascading light guide units; the downlink output end of the light guide unit of each level is orderly connected with the downlink input end of lower level, so as to form a downlink channel; the uplink input end of each level is orderly connected with the uplink input end of higher level, so as to form an uplink channel. The data packet which is transmitted into the light guide unit of each level is controlled by a control end for uplink transmission or downlink transmission. The i-level downlink output end is connected with the control end of the level of i plus 2, so as to prevent the levels of i and i plus 2 from simultaneously transmitting the data to the level of i plus 1. When two data packets arrive to the buffer simultaneously, the data packet of higher priority is directly transmitted outwards, and the data packet of lower priority is stored in the buffer; and the storage depth of the original data packet in the buffer is deepened by one level. The fully optical buffer has the first-in but last-out, and last-in but first-out characteristics, the capability of simultaneously processing two data packets, and the advantages of easy expansion of the storage capacity, no requirement for additional control signals, and so on.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Optical packet switching system
InactiveUS20130039650A1Suppressing variation in signal-to-noiseMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringOptical packetOptical signal to noise ratio
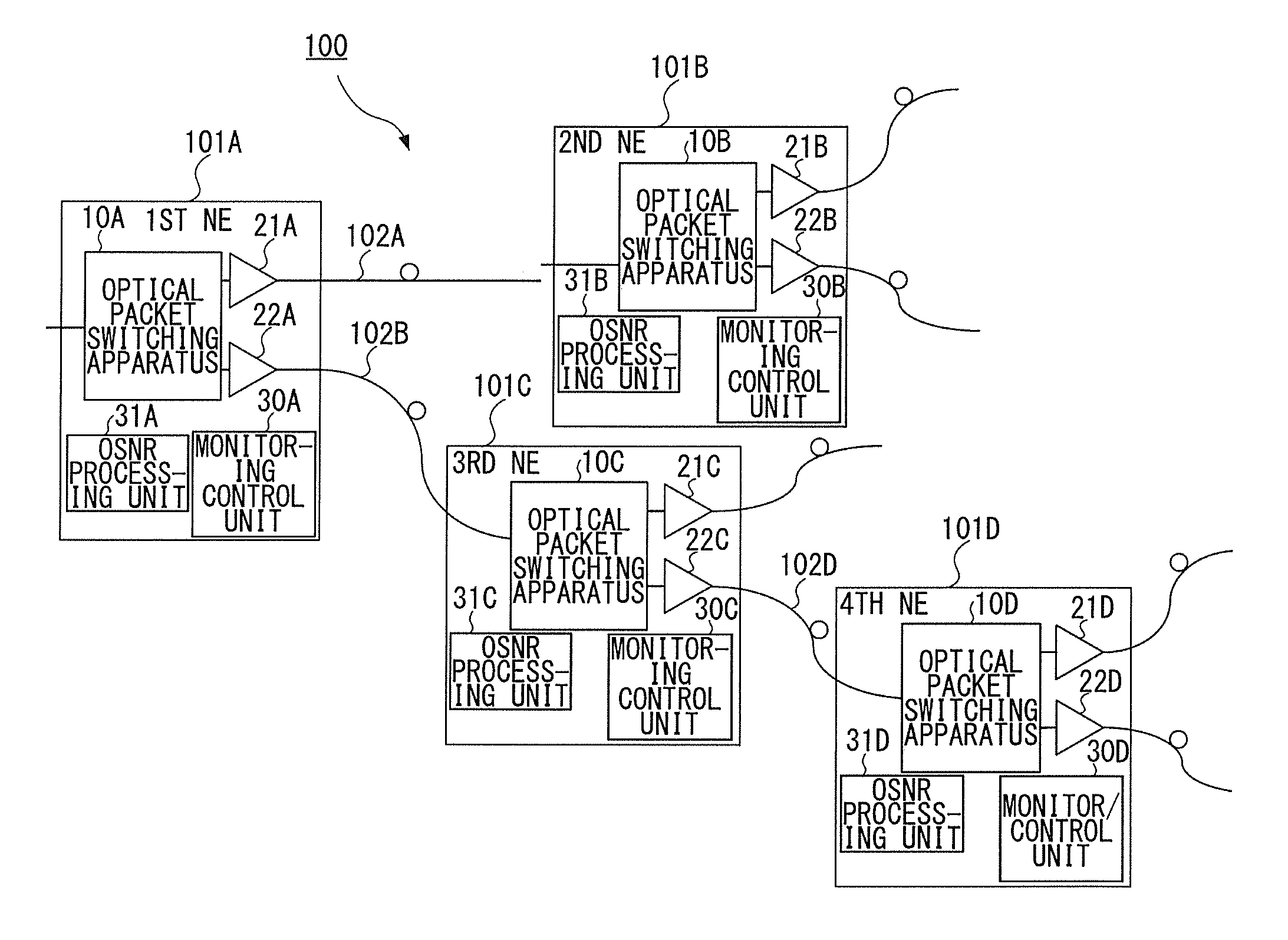
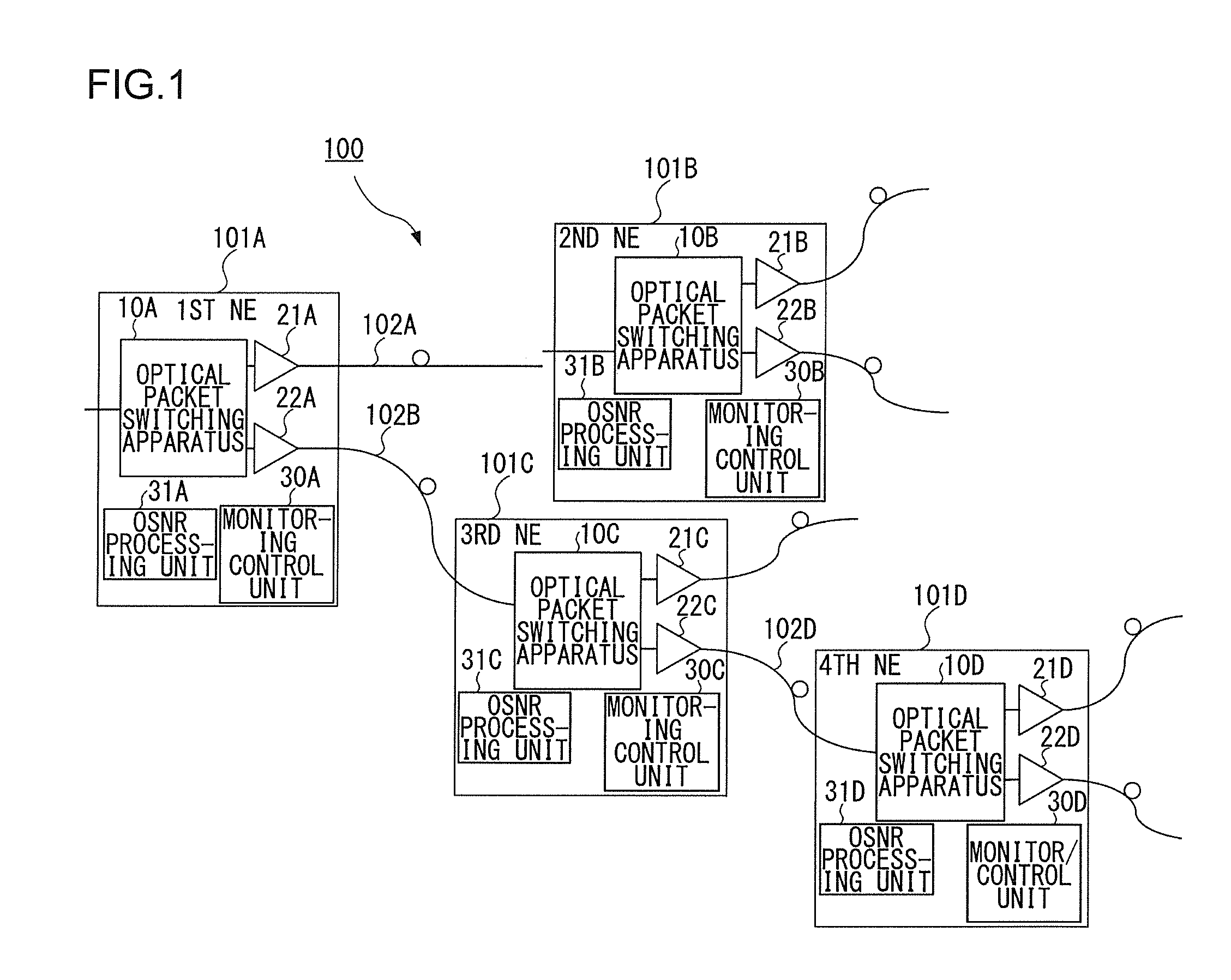
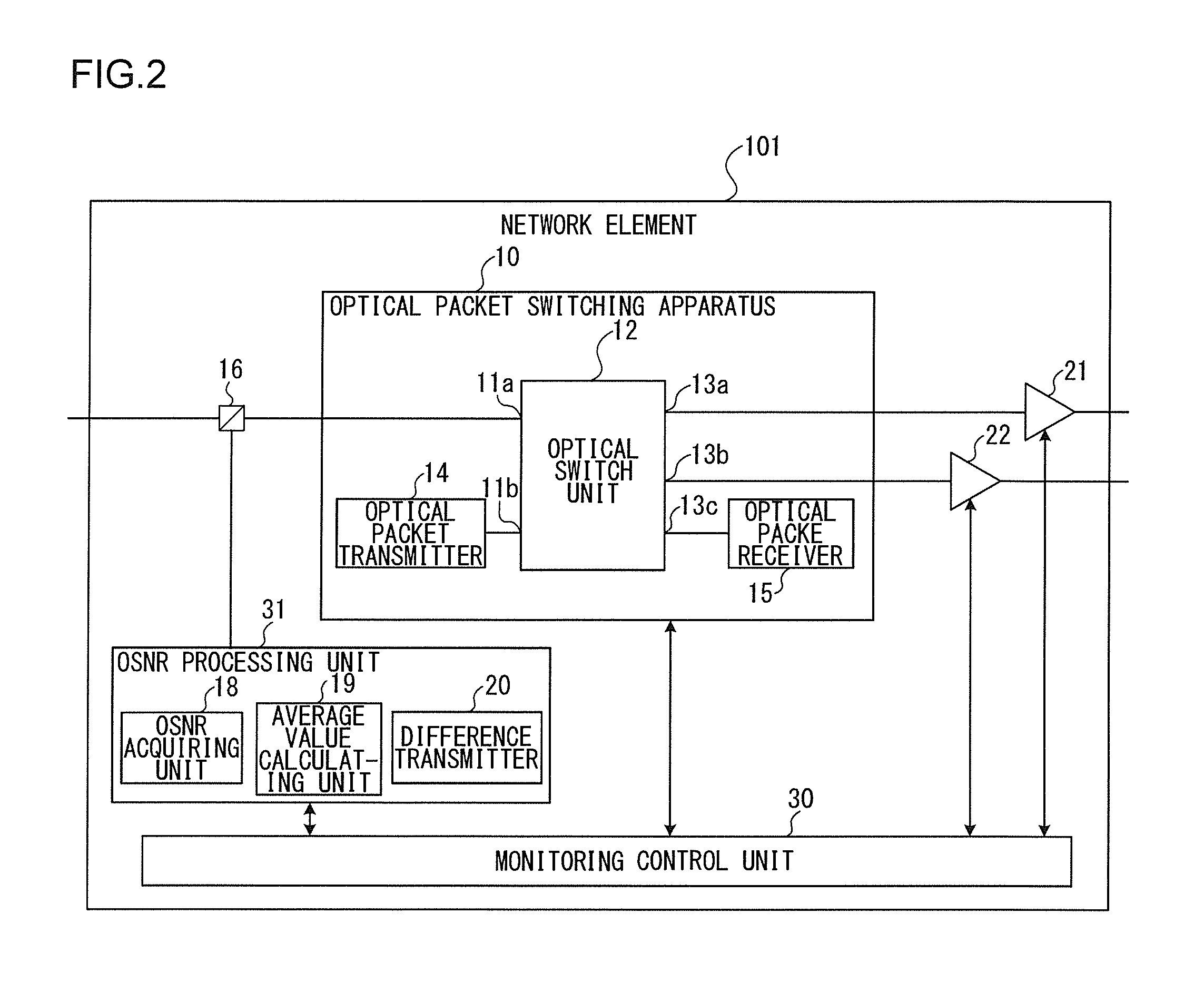
An optical packet switching system includes a plurality of network elements for transmitting and receiving optical packet signals. Each network element includes an optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) acquiring unit for acquiring the OSNR of each optical packet signal, an average value calculating unit for calculating the average value of the OSNRs of optical packet signals received within a predetermined time duration for each of the plurality of source network elements, and a difference information transmitter for calculating the difference between the calculated average value of the OSNRs and a target value of the OSNRs and then transmitting the difference to a network element corresponding to the difference. A source network element that has received the difference information adjusts the characteristics of an optical packet signal to be transmitted in a manner such that the difference is reduced.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
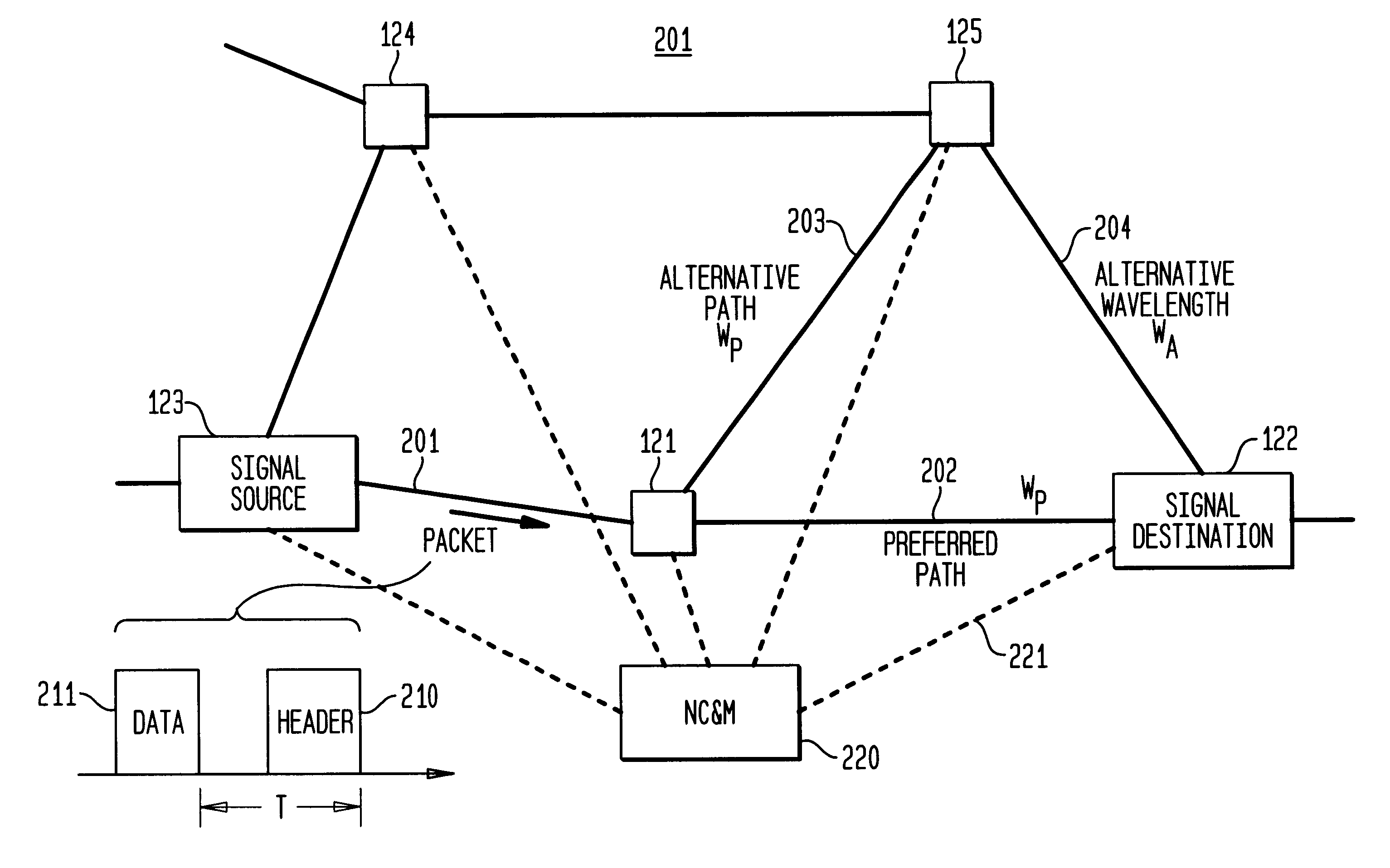
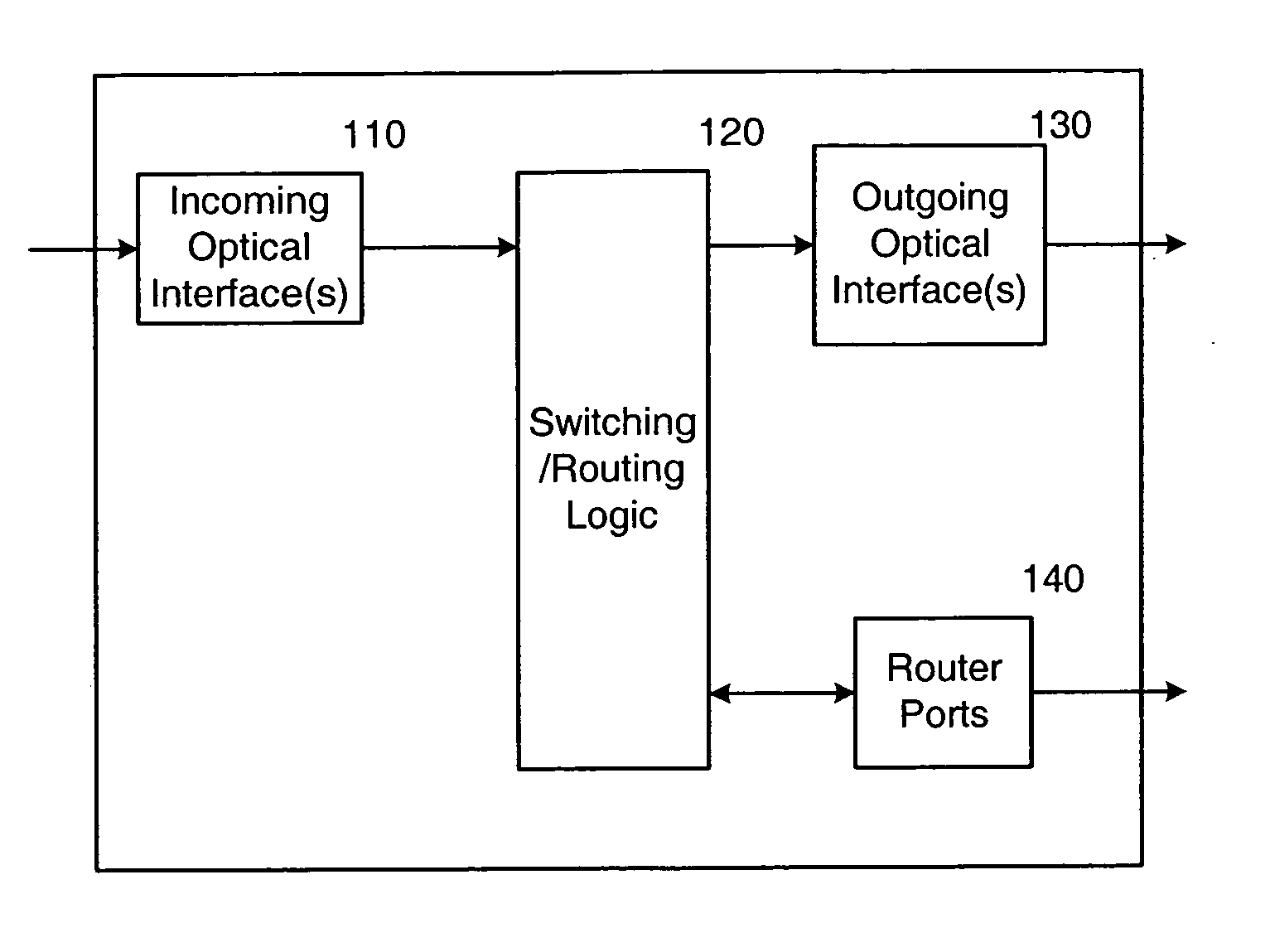
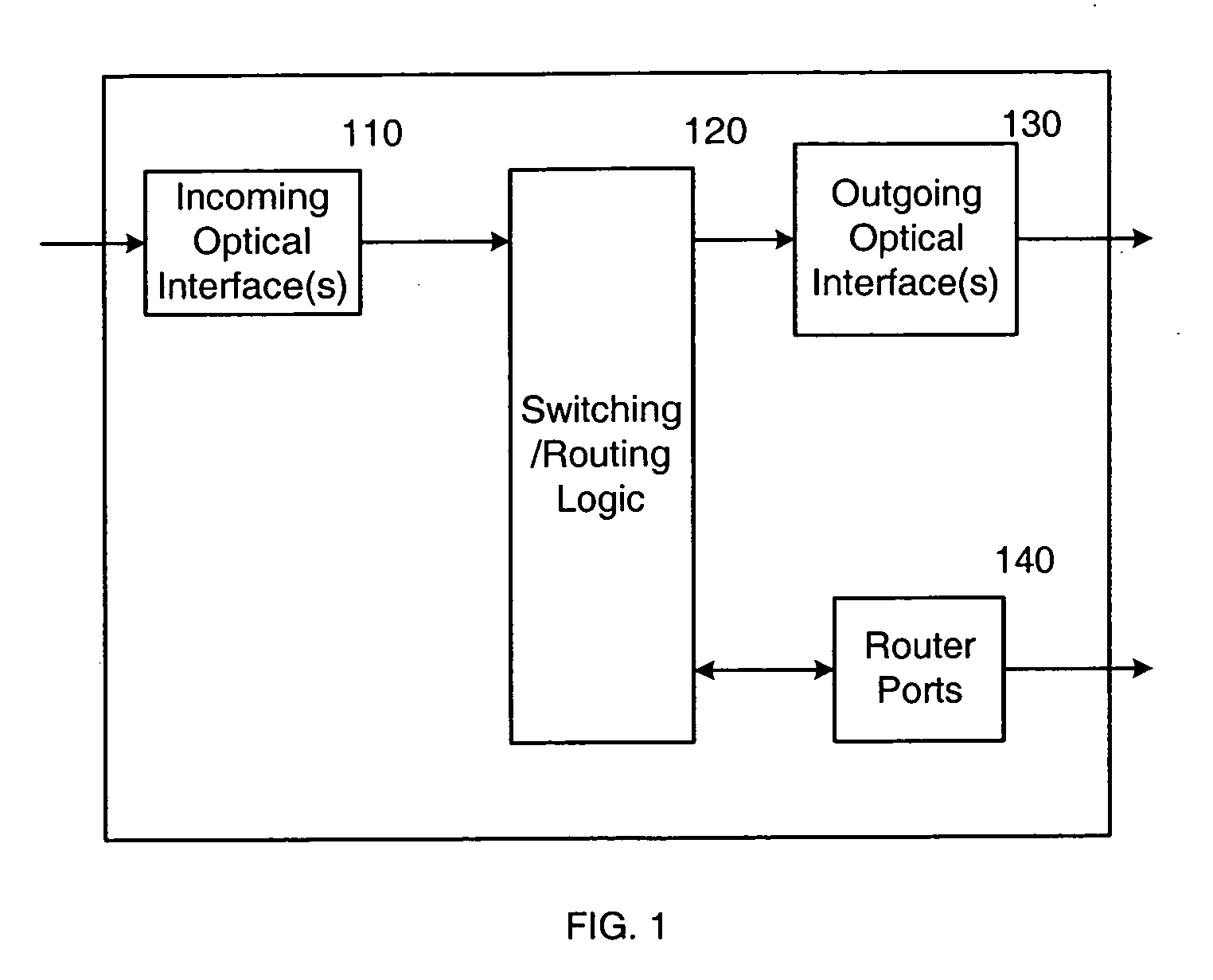
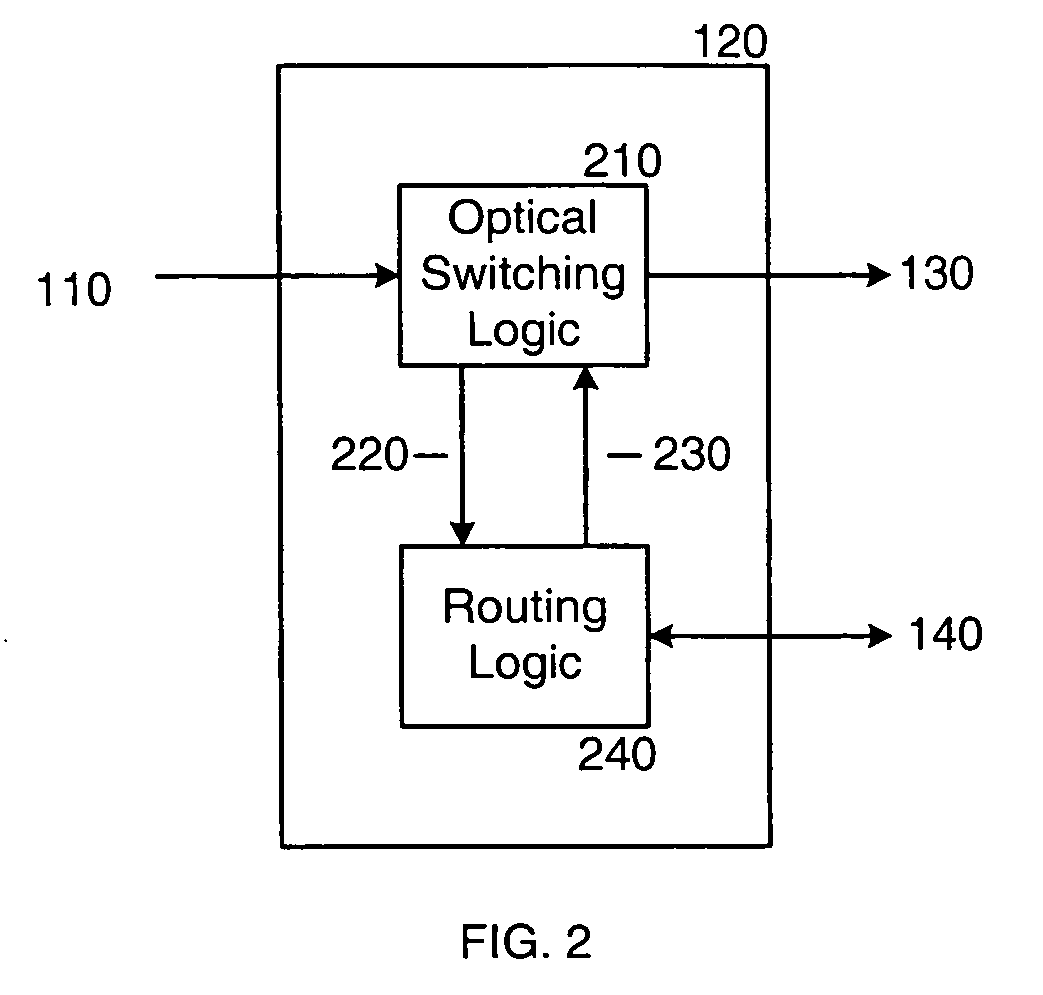
Optical switch router
InactiveUS20070025731A1Eliminate processingMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsData streamOptical communication
An optical switch router performs both optical switching and traditional routing. The optical switch router includes optical interfaces for coupling to one or more incoming optical fibers and to one or more outgoing optical fibers, and also includes a number of traditional router ports. Individual incoming optical data streams received over the incoming optical fiber(s) can be selectively passed through to one or more of the outgoing optical fibers or “dropped” from the optical communication path for traditional routing. Routed traffic, which can be received over the router ports or from the “dropped” optical data streams, can be forwarded over optical data streams that are “added” to the outgoing optical fiber(s). The “added” optical data streams may be added to the outgoing optical fiber(s) at any unused wavelengths, including, but not limited to, the wavelengths of the “dropped” optical data streams.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com