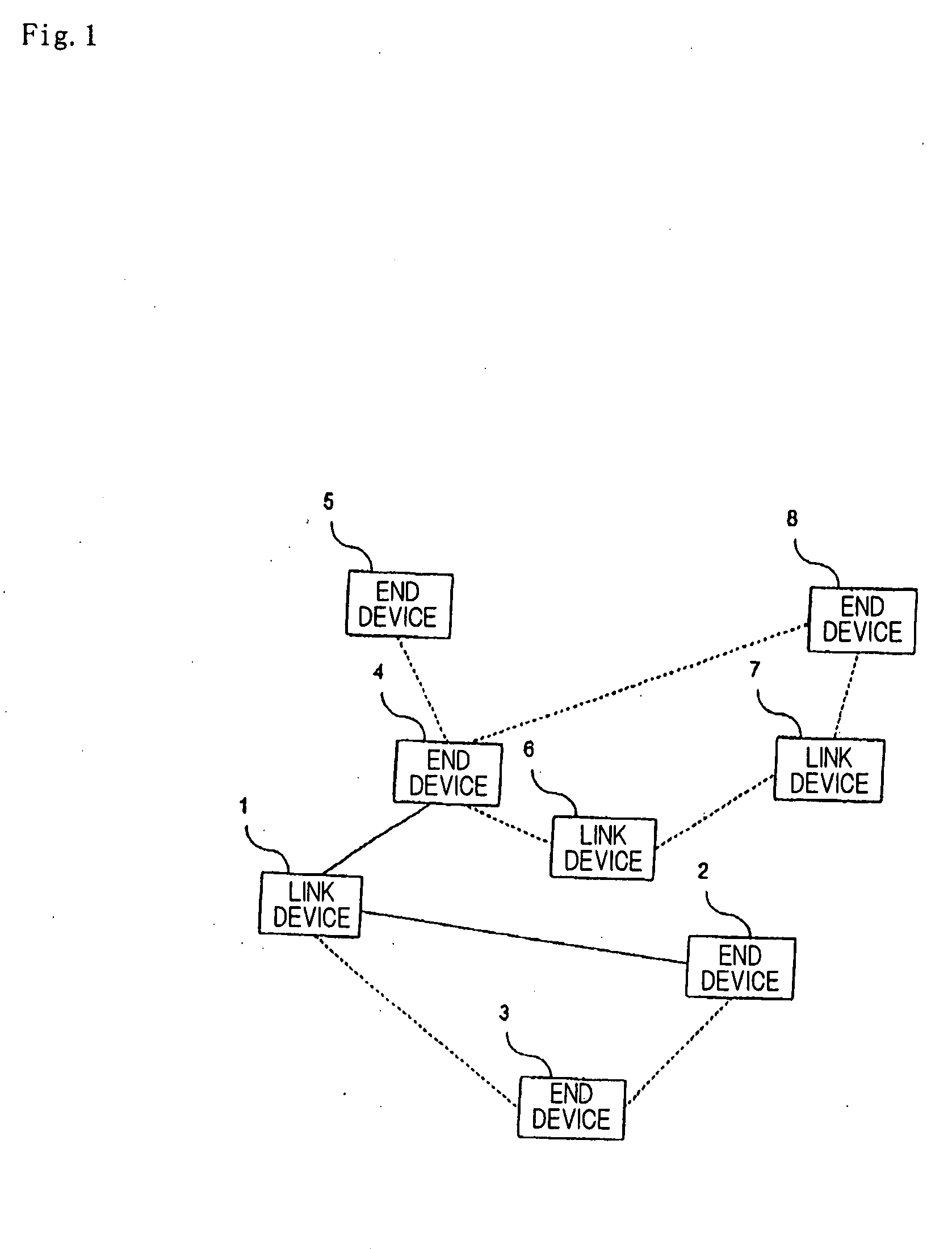
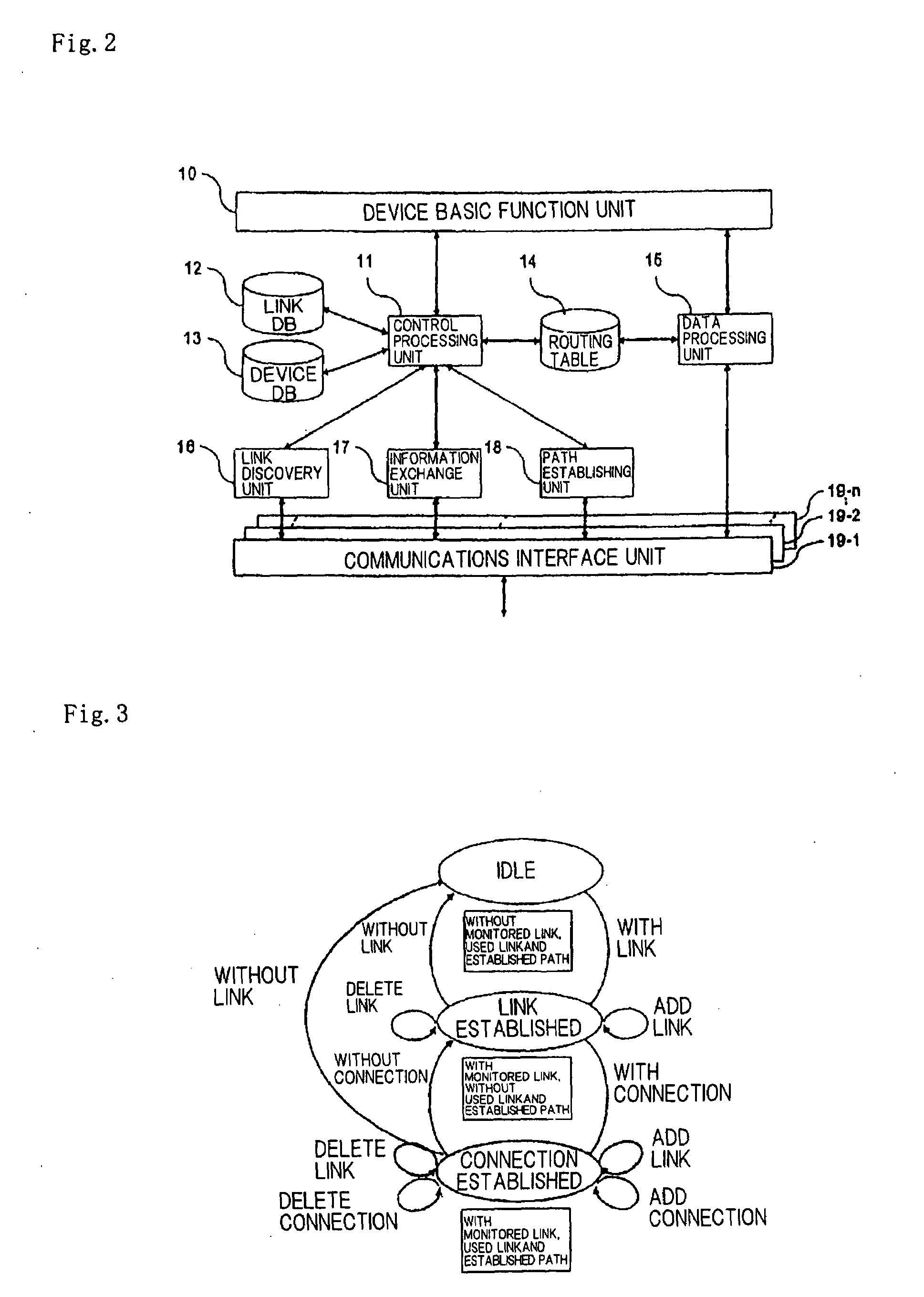
Patents
Literature
1677 results about "Path switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
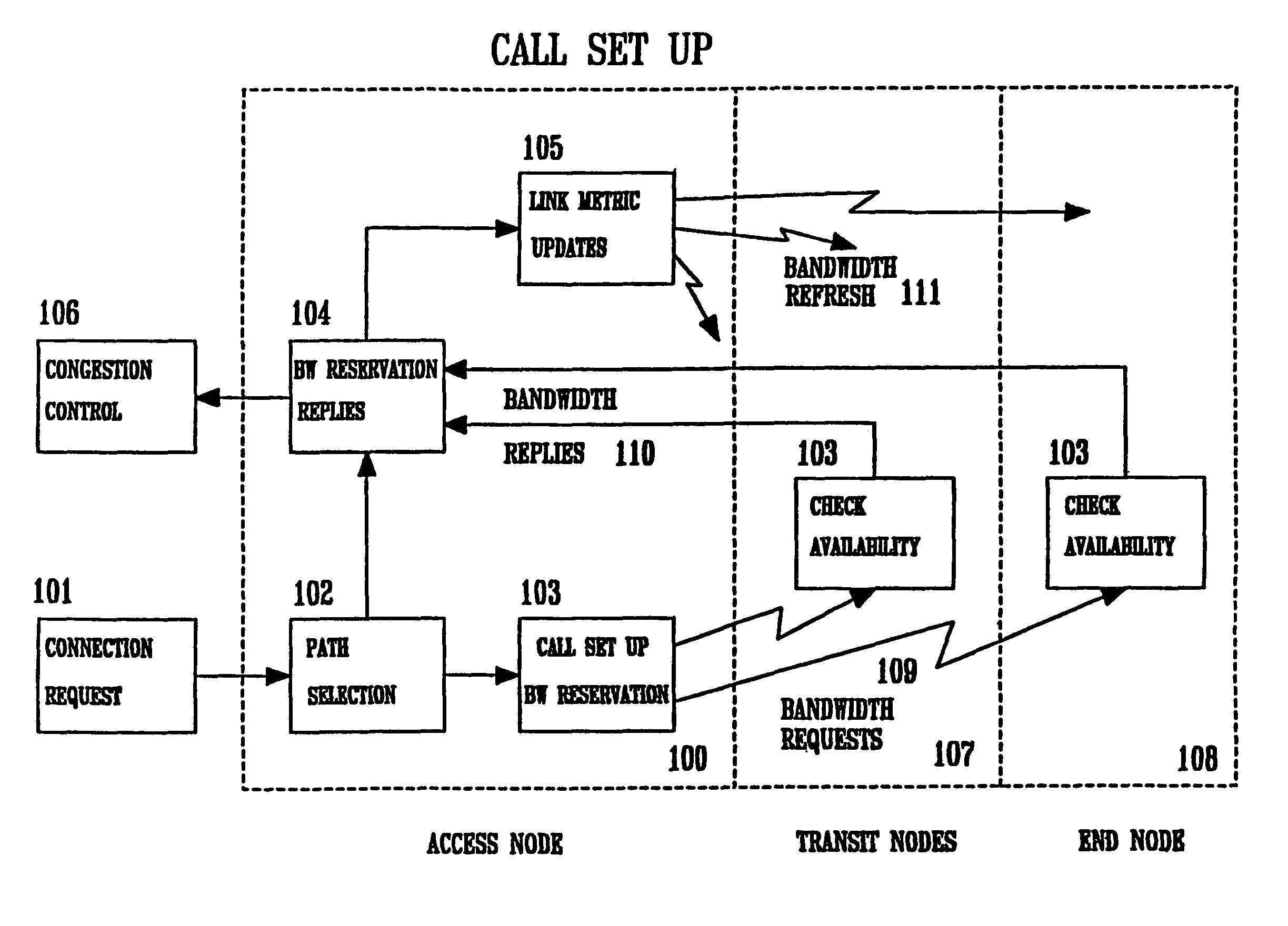
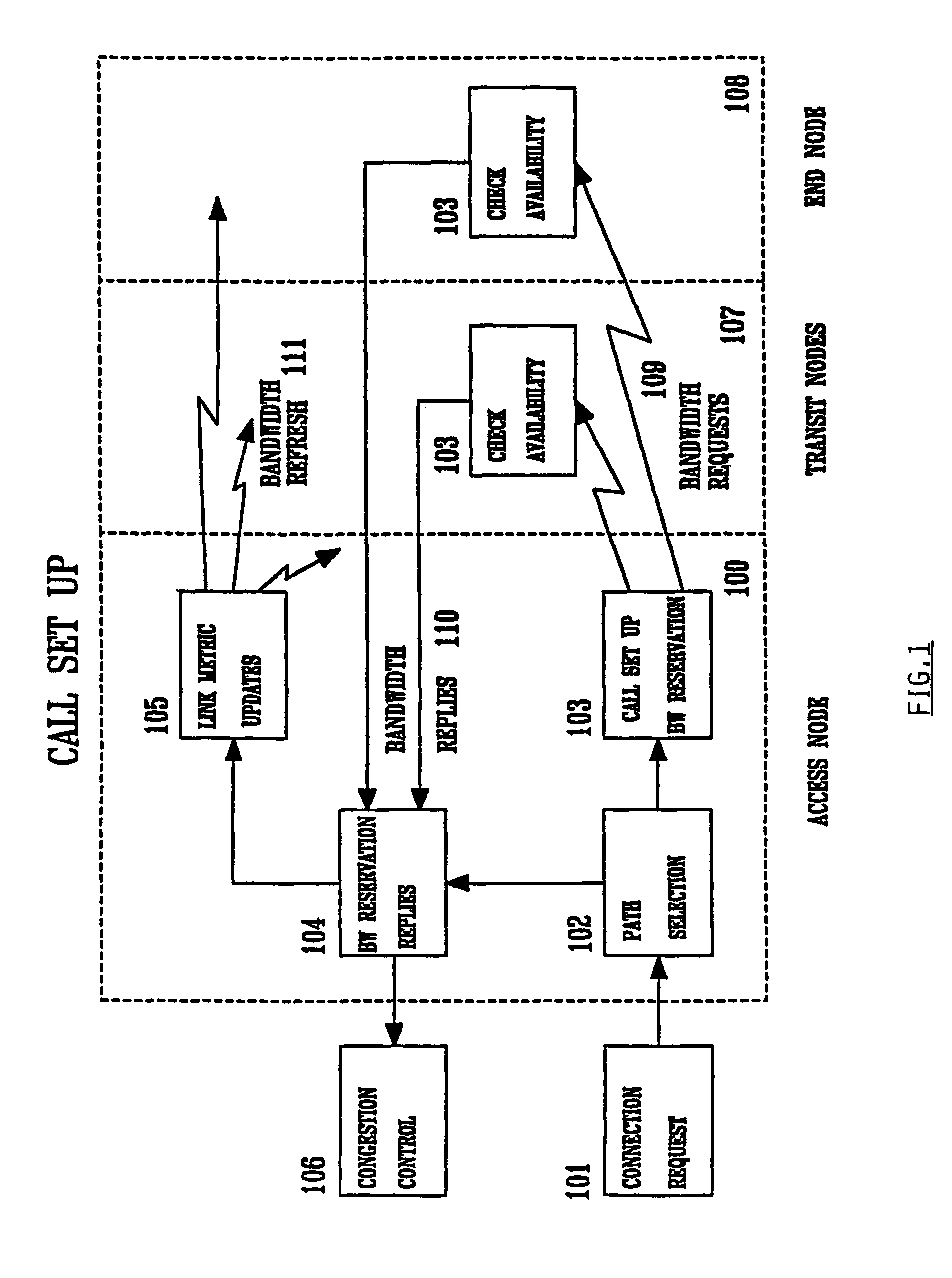
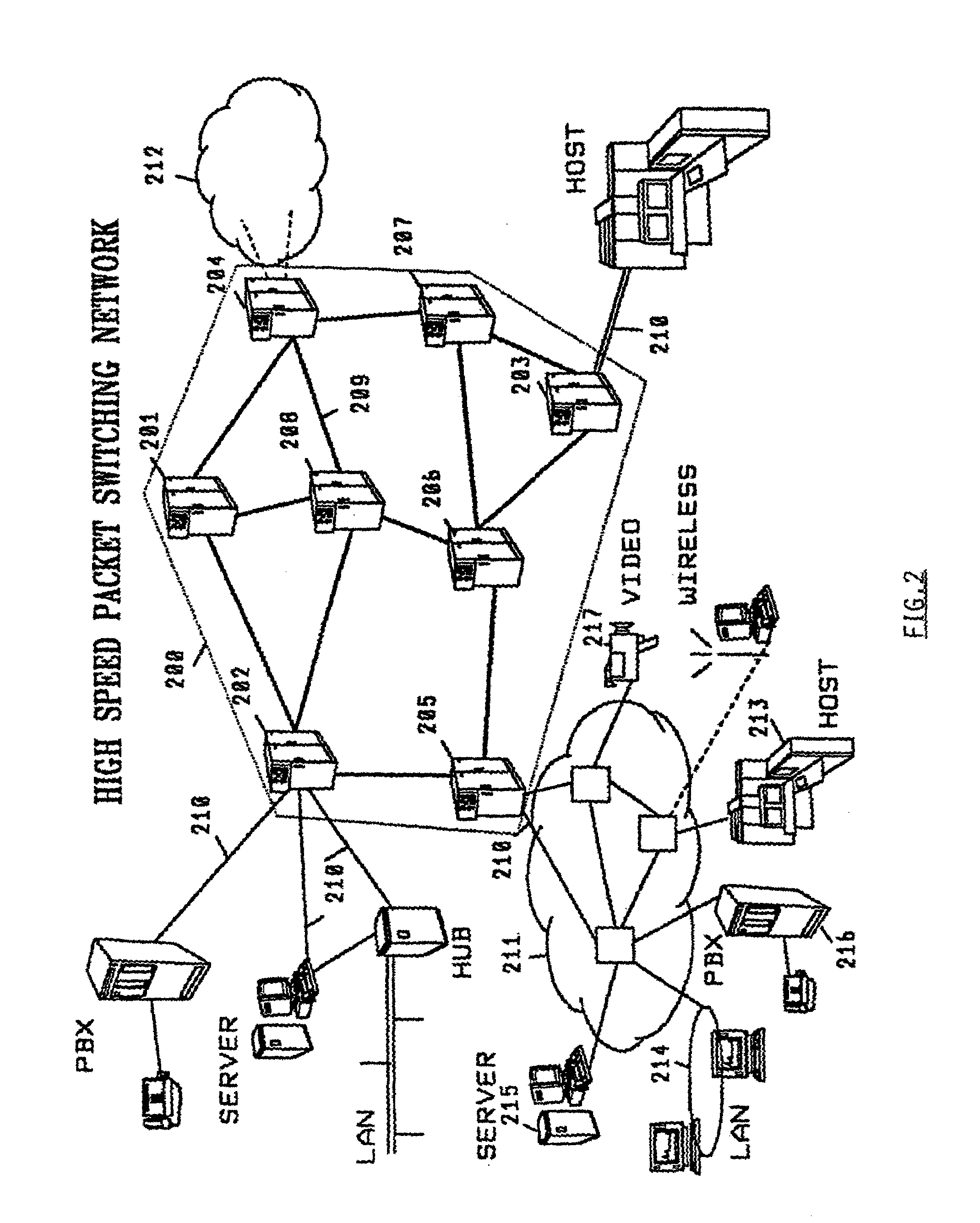
Method and system for minimizing the connection set up time in high speed packet switching networks
InactiveUS6934249B1Minimize delayMinimize in in to selectError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPacket switched
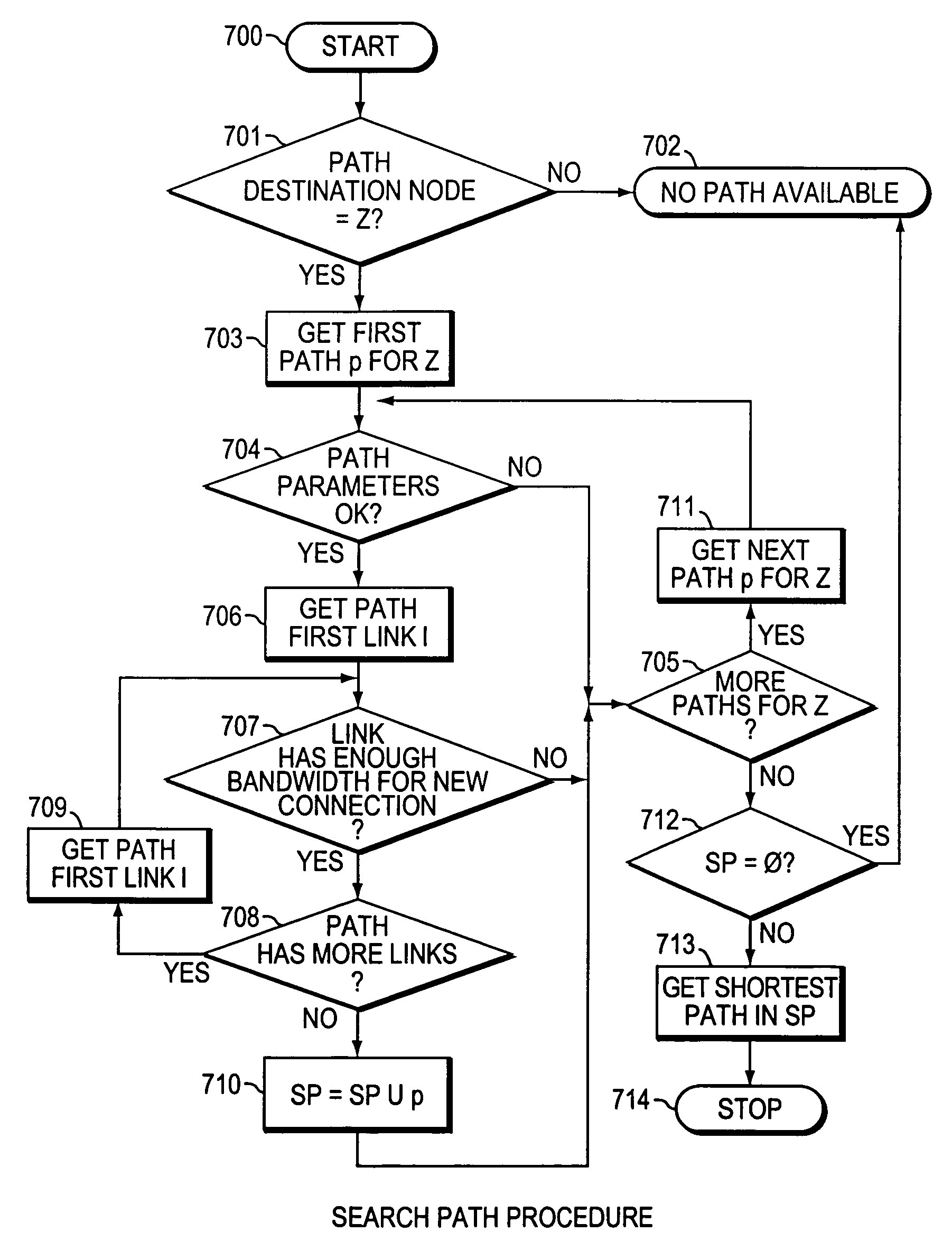
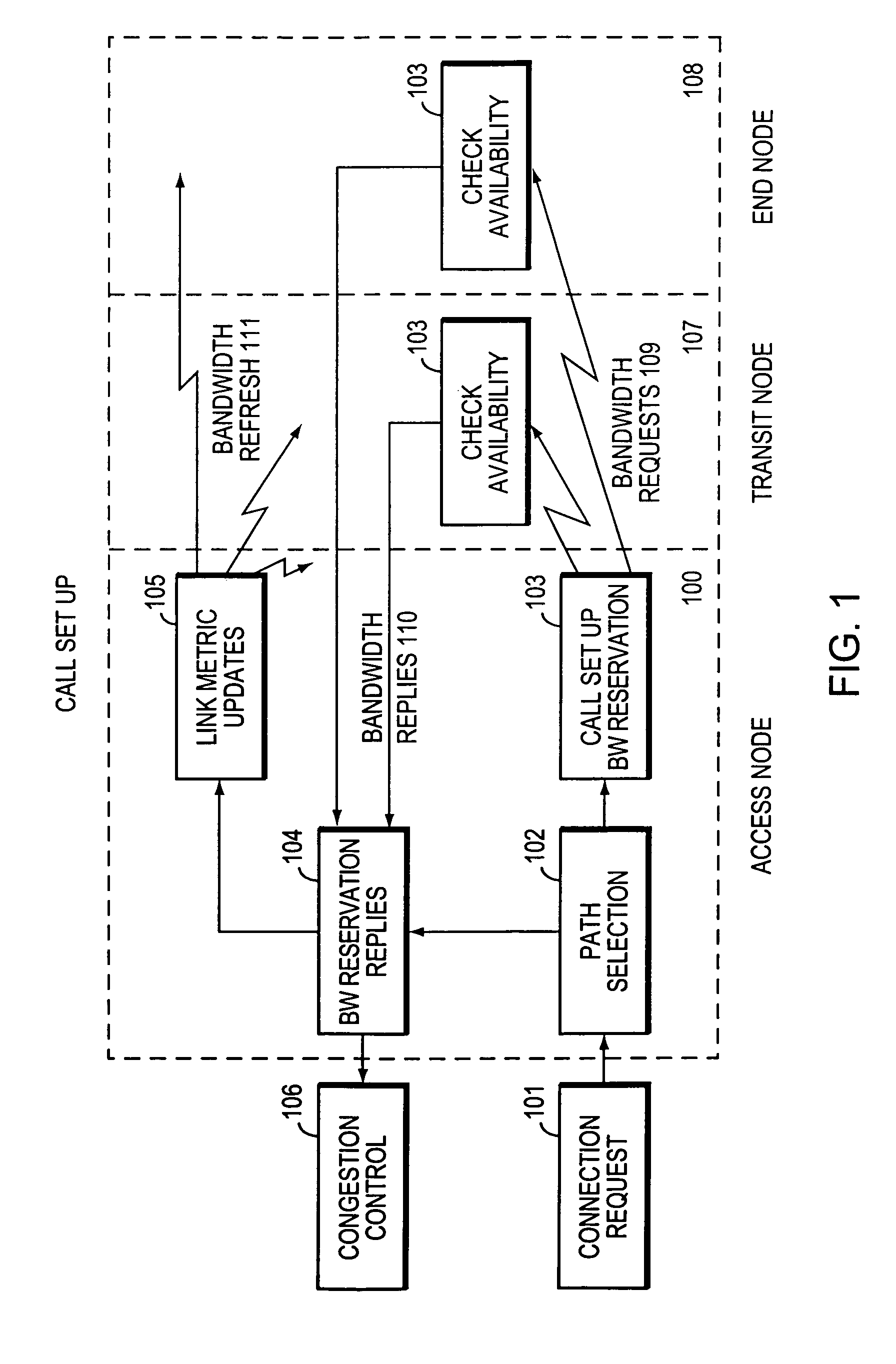
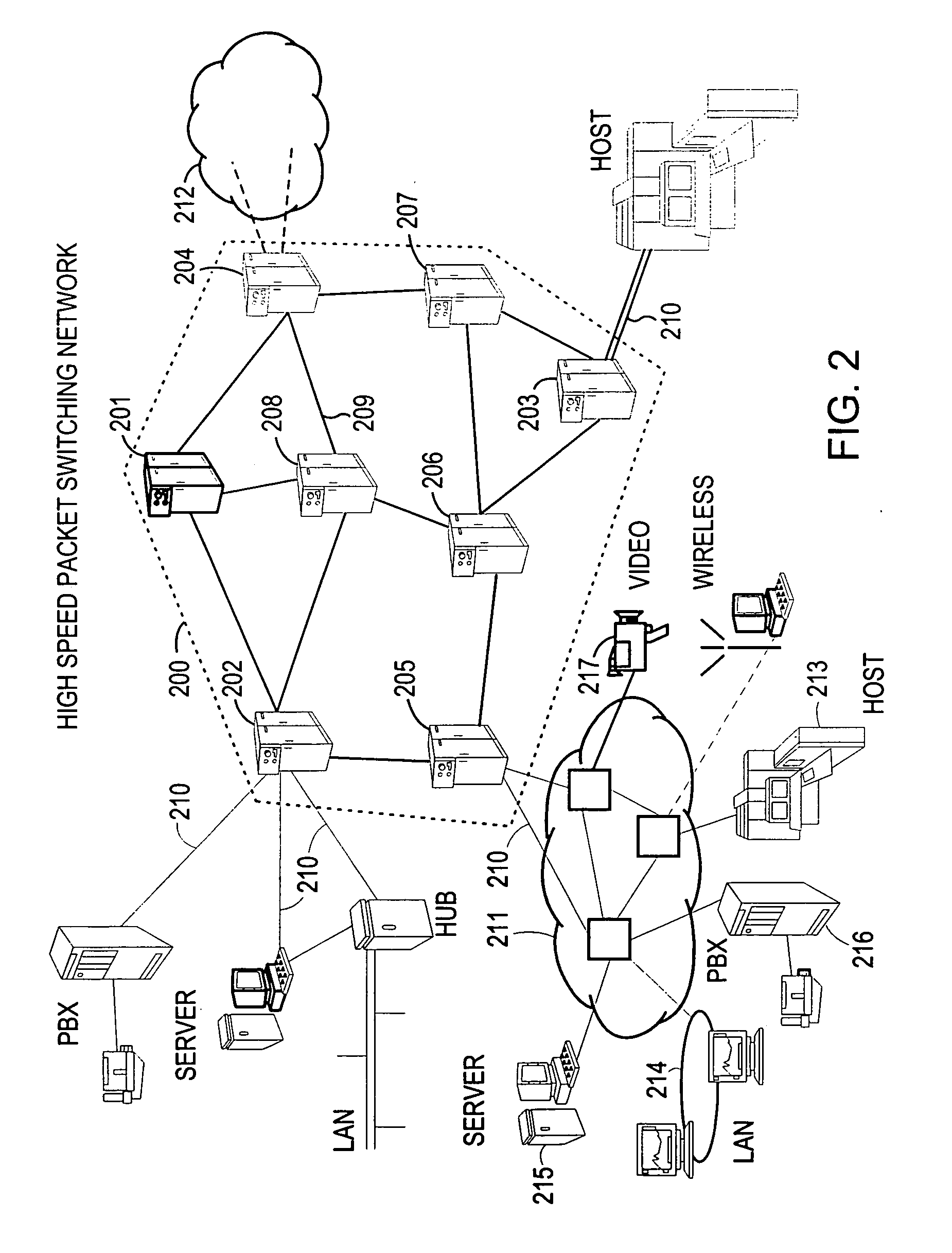
The present invention is directed to a high speed packet switching network and, in particular to a method and system for minimizing the time to establish a connection between an origin and a destination node. Due to high dynamicity of the traffic on transmission links, it is important to select a routing path according to a fully up-to-date information on all network resources. The simpler approach is to calculate a new path for each new connection request. This solution may be very time consuming because there are as many path selection operations as connection set up operations. On another hand, the calculation of paths based on an exhaustive exploration of the network topology, is a complex operation which may also take an inordinate amount of resources in large networks. Many of connections originated from a network node flow to the same destination network node. It is therefore possible to take a serious benefit in reusing the same already calculated paths for several connections towards the same node. The path calculated at the time the connection is requested is recorded in a Routing Database and updated each time a modification occurs in the network. Furthermore, alternate paths for supporting non-disruptive path switch on failure or preemption, and new paths towards potential destination nodes can be calculated and stored when the connection set up process is idle. These last operations are executed in background with a low processing priority and in absence of connection request.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
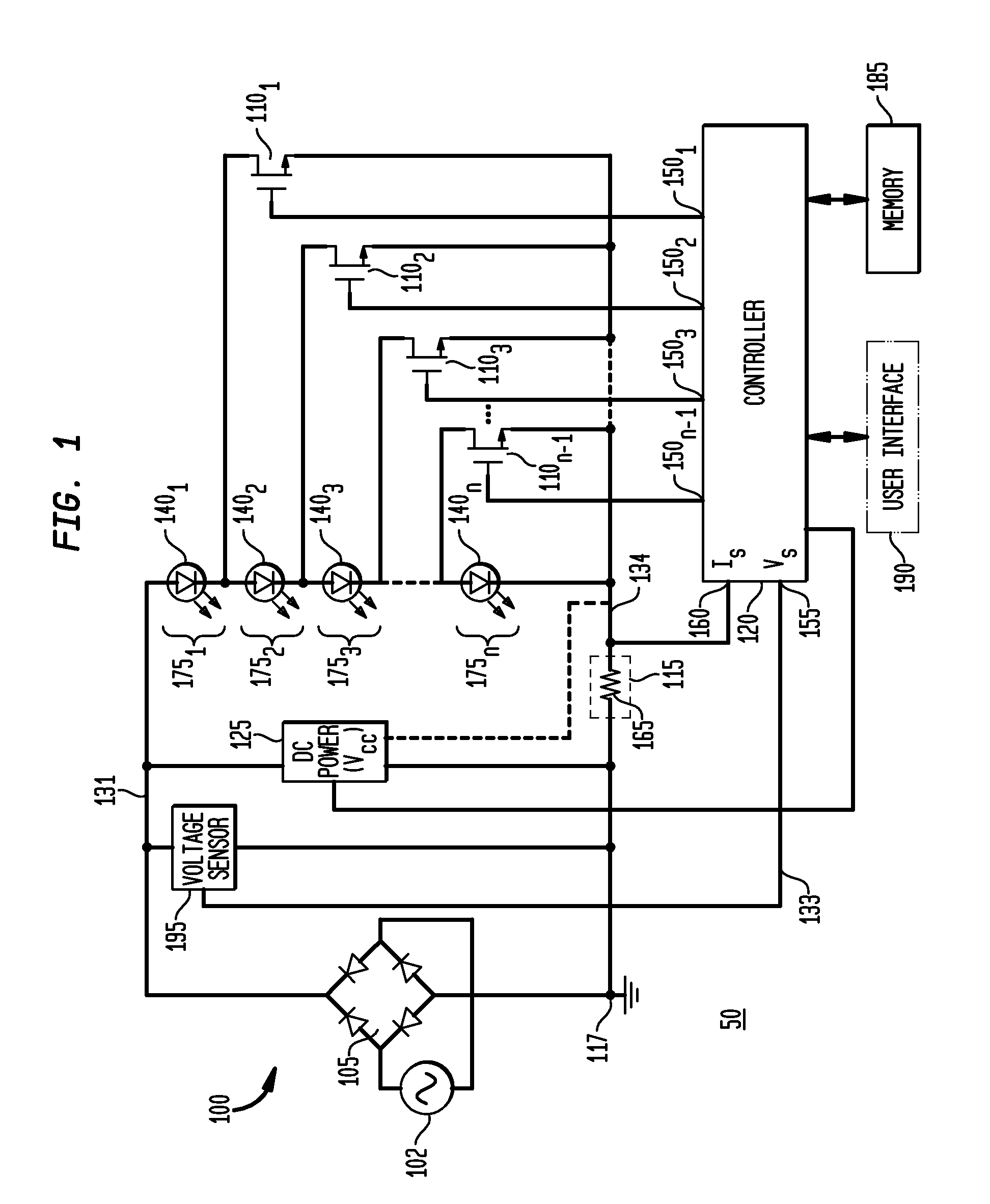
Apparatus, Method and System for Providing AC Line Power to Lighting Devices
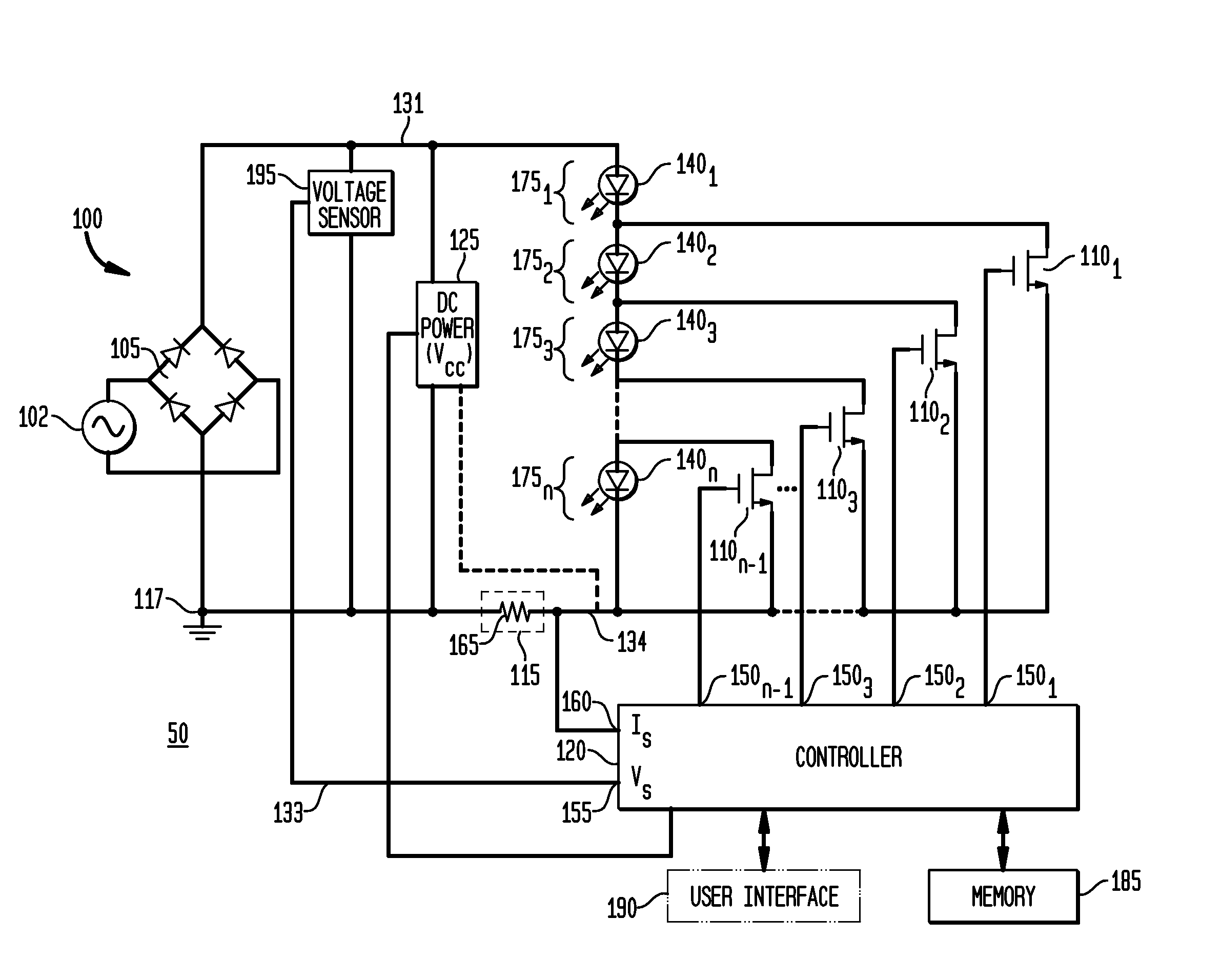
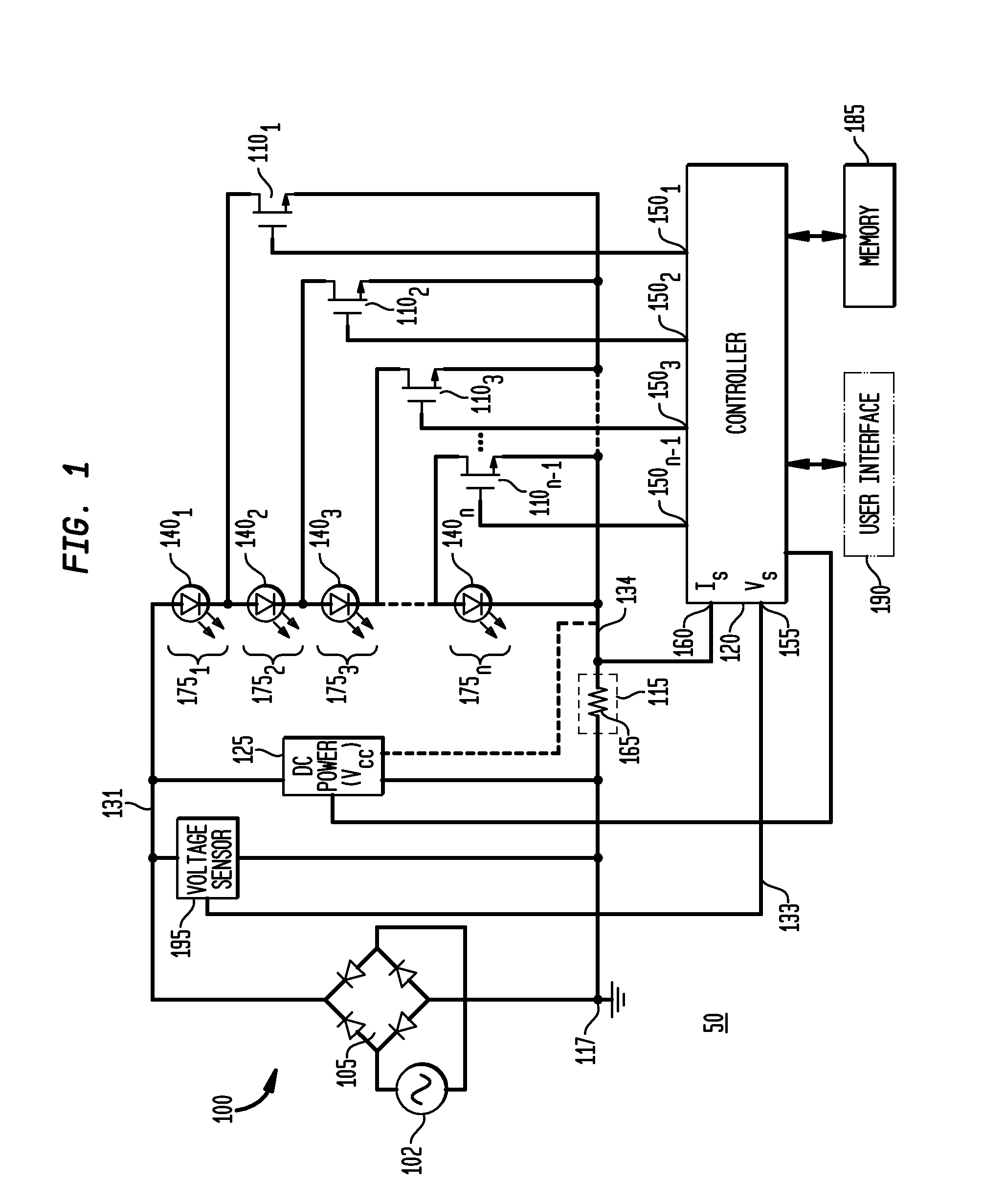
ActiveUS20100308739A1Reduction in size and costImprove Utilization and EfficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentControl signal
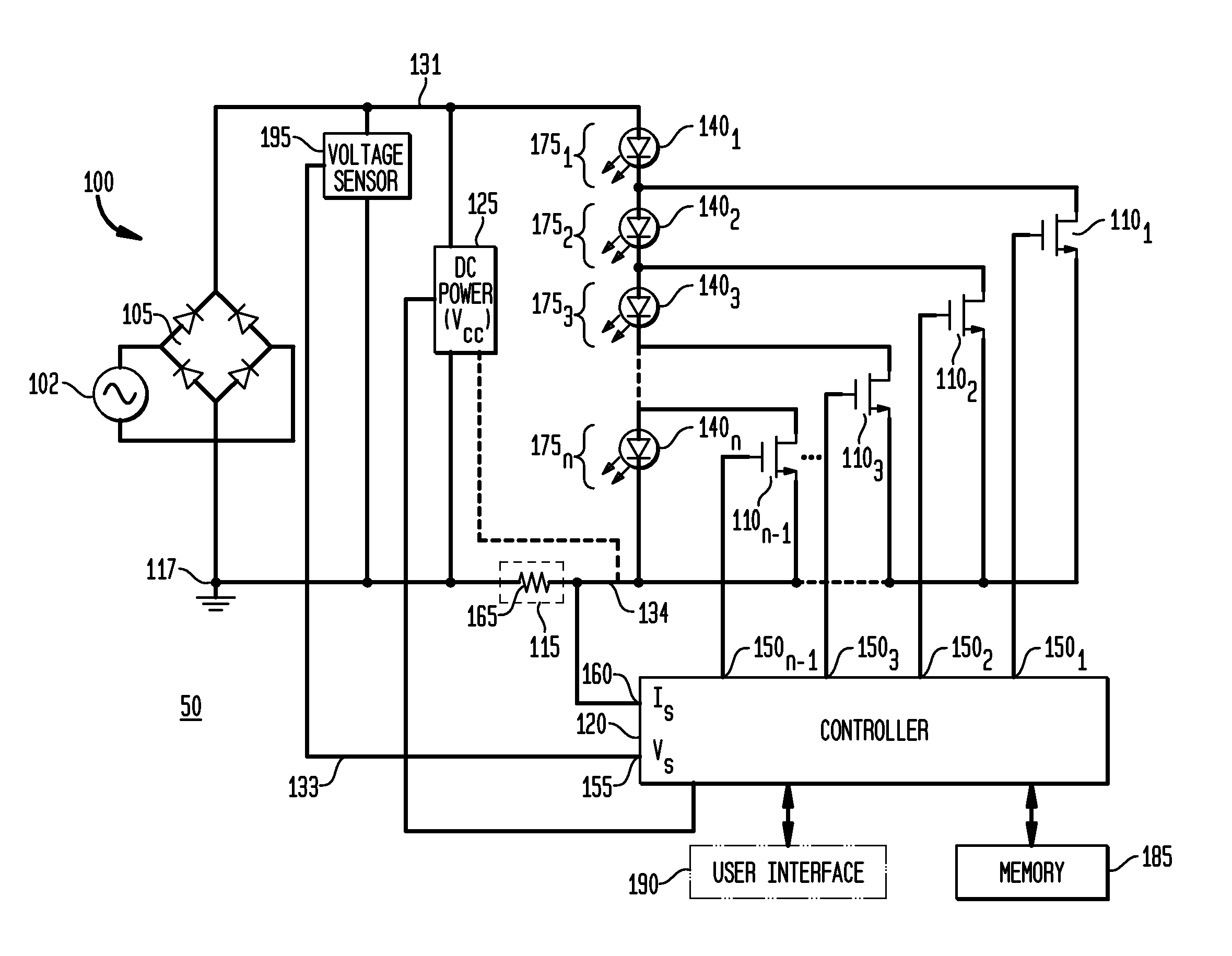
An apparatus, method and system are disclosed for providing AC line power to lighting devices such as light emitting diodes (“LEDs”). An exemplary apparatus comprises: a plurality of LEDs coupled in series to form a first plurality of segments of LEDs; a plurality of switches coupled to the plurality of segments of LEDs to switch a selected segment into or out of a series LED current path in response to a control signal; a memory; and a controller which, in response to a first parameter and during a first part of an AC voltage interval, determines and stores in the memory a value of a second parameter and generates a first control signal to switch a corresponding segment of LEDs into the series LED current path; and during a second part of the AC voltage interval, when a current value of the second parameter is substantially equal to the stored value, generates a second control signal to switch a corresponding segment of LEDs out of the first series LED current path.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
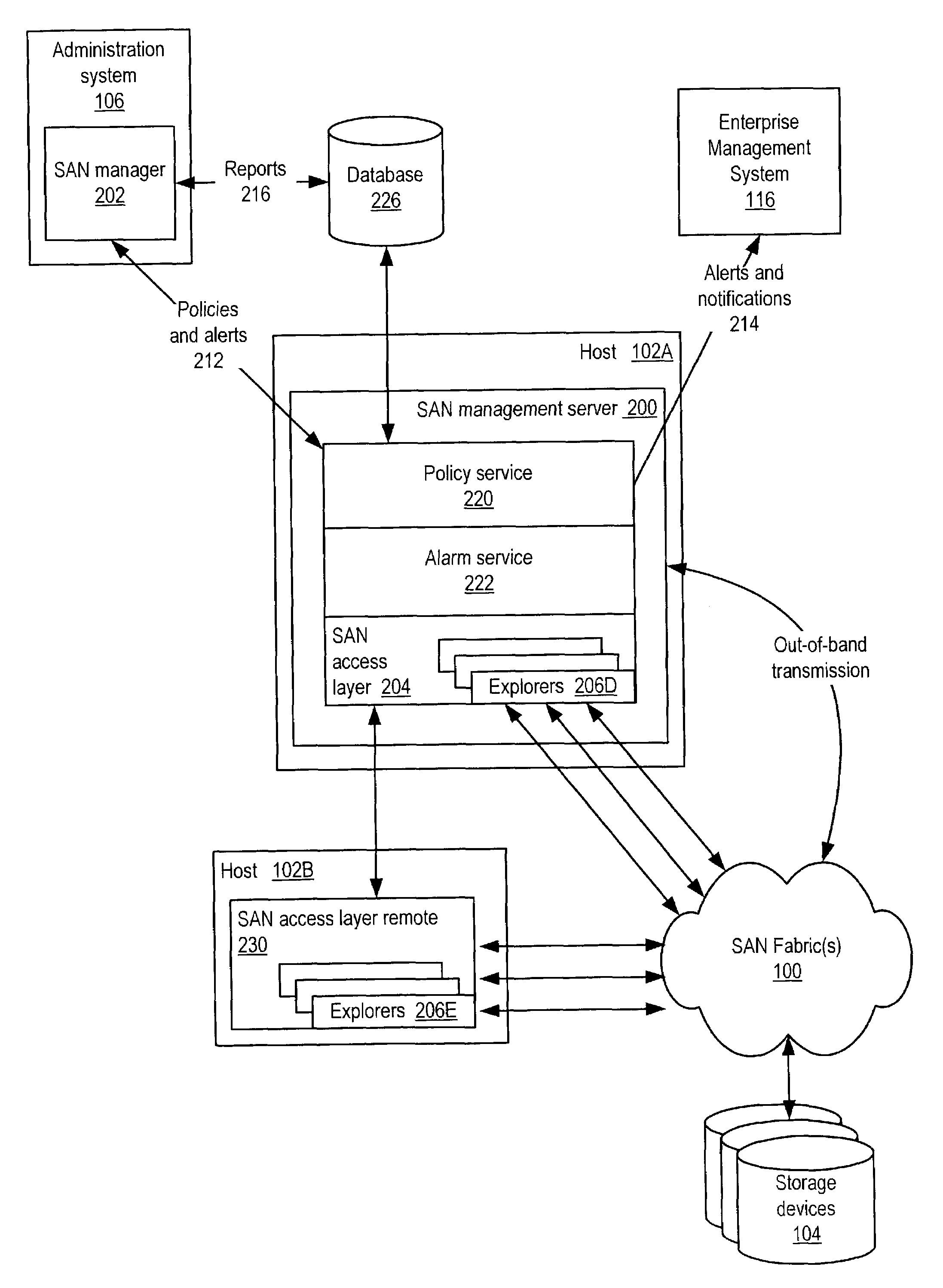
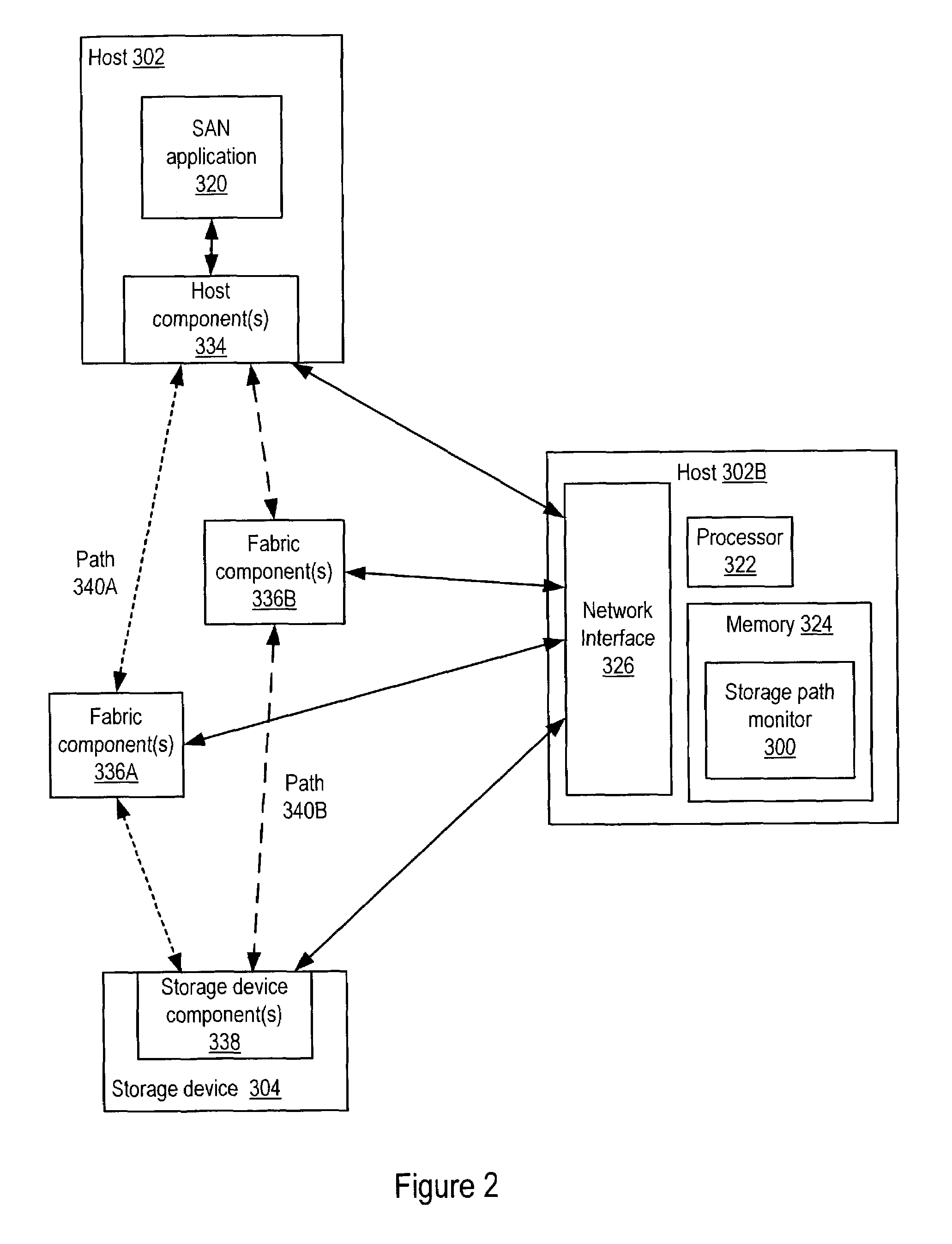
Storage path optimization for SANs
Embodiments of a system and method for rule-based proactive storage path optimization for SANs. Embodiments may evaluate paths between an application and its storage on a SAN based on current and / or historical path quality of service. Performance of alternative paths may be monitored to determine if a better path than a path currently in use is available. If a better path is determined, then the path may be switched to the better path. In one embodiment, one or more zones may be reconfigured to migrate to a different path. Path migration may be performed automatically without user intervention. Alternatively, a user may be given the option to manually migrate to a new path. Embodiments may proactively change paths between an application and its storage before path performance becomes a problem. Embodiments may be integrated with a SAN management system or, alternatively, may be standalone mechanisms.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
Apparatus, Method and System for Providing AC Line Power to Lighting Devices
ActiveUS20100308738A1Small sizeLow costElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentControl signal
An apparatus, method and system are disclosed for providing AC line power to lighting devices such as light emitting diodes (“LEDs”). An exemplary apparatus comprises: a plurality of LEDs coupled in series to form a first plurality of segments of LEDs; a plurality of switches coupled to the plurality of segments of LEDs to switch a selected segment into or out of a series LED current path in response to a control signal; a current sensor; and a controller which, in response to a first parameter and during a first part of an AC voltage interval, generates a first control signal to switch a corresponding segment of LEDs into the series LED current path; and during a second part of the AC voltage interval, generates a second control signal to switch a corresponding segment of LEDs out of the first series LED current path.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
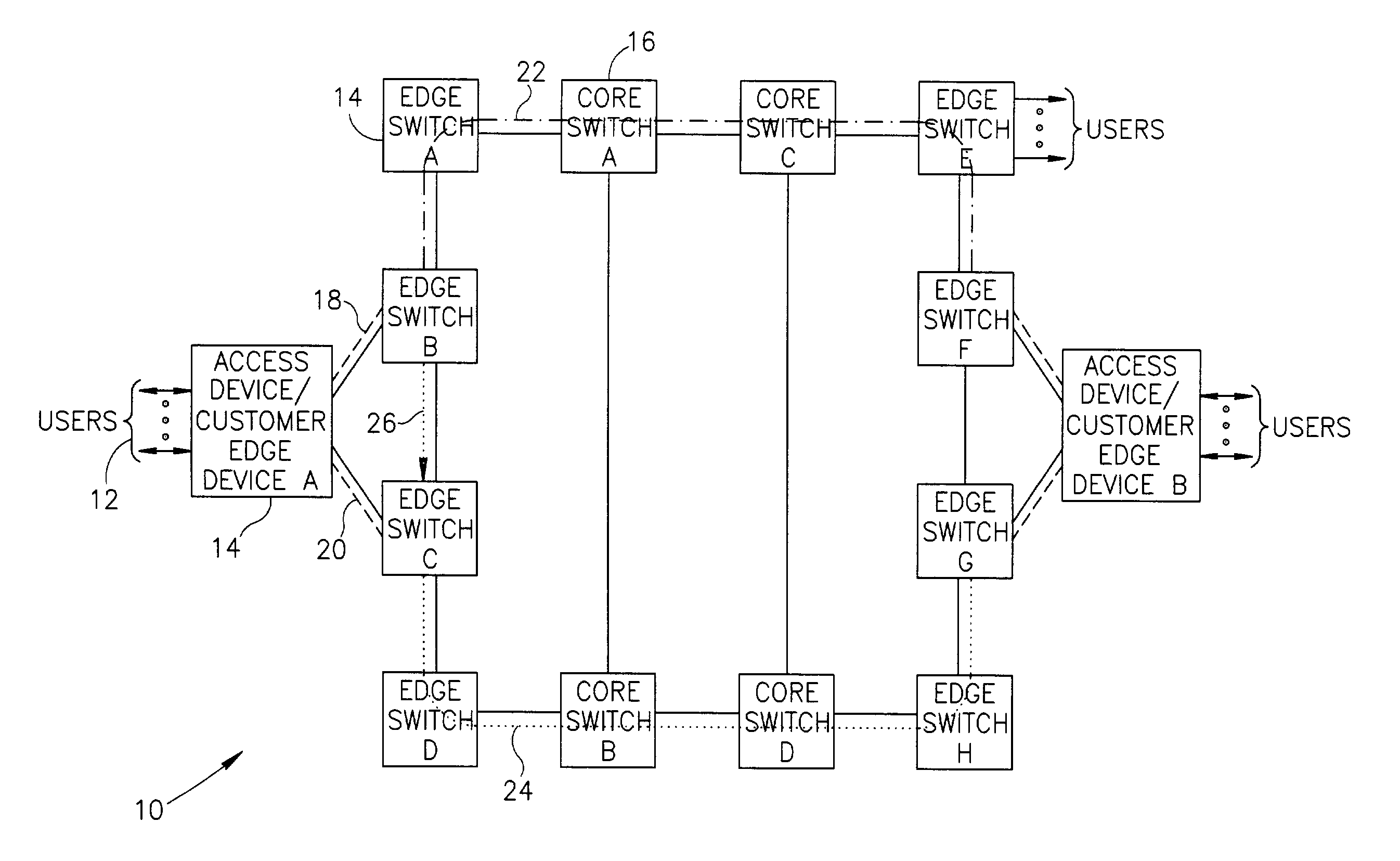
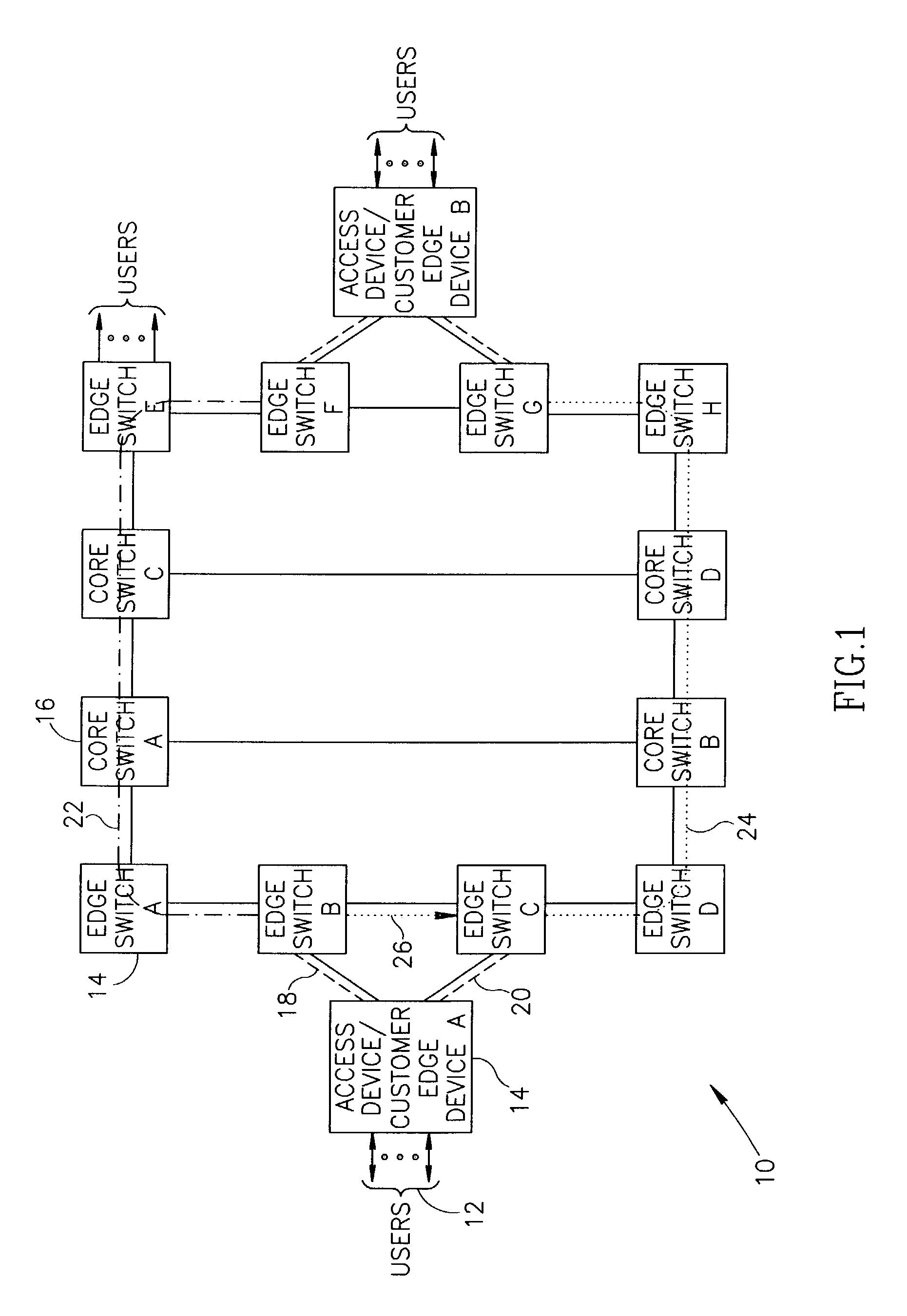
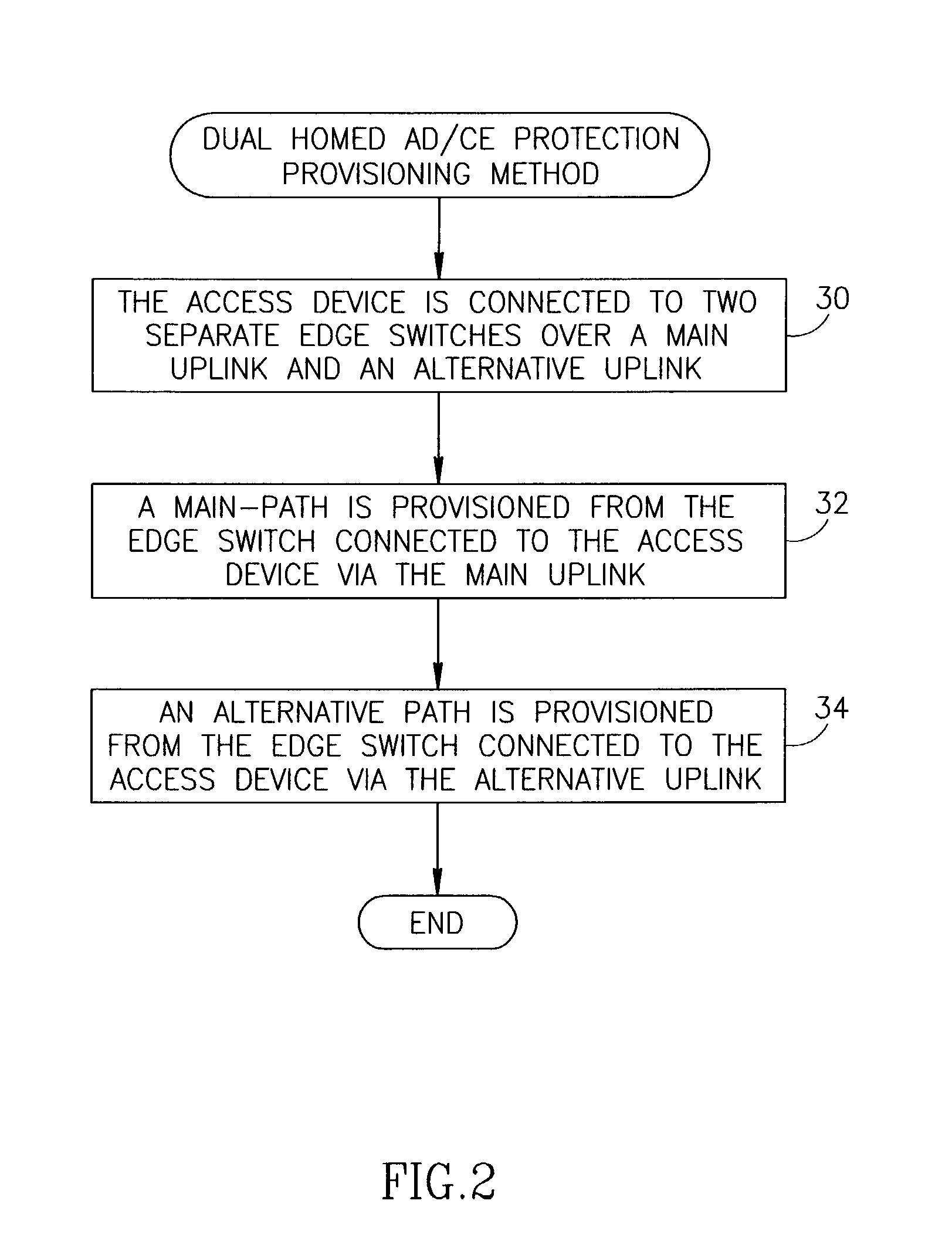
Connection protection mechanism for dual homed access, aggregation and customer edge devices
InactiveUS7345991B1Quick protectionImprove reliabilityEnergy efficient ICTError preventionOff the shelfProtection mechanism
A protection mechanism capable of providing both local and end-to-end connection protection for dual homed access / aggregation devices or customer-edge devices in a network. The protection mechanism provides end-to-end and fast local protection for off the shelf access devices that do not have any built in per-connection protection capabilities. The access device is connected via two separate physical uplinks to two edge switches of the network. For each connection to be protected, a main path is provisioned from one edge switch and an alternative path is provisioned from the other edge switch. The edge switches are adapted to comprise means for switching traffic from the main path to the alternative path in the event a failure along the main path is detected. Failures both in the stack portion, the core portion and in the access device uplinks are protected against.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS ETHERNET SOLUTIONS
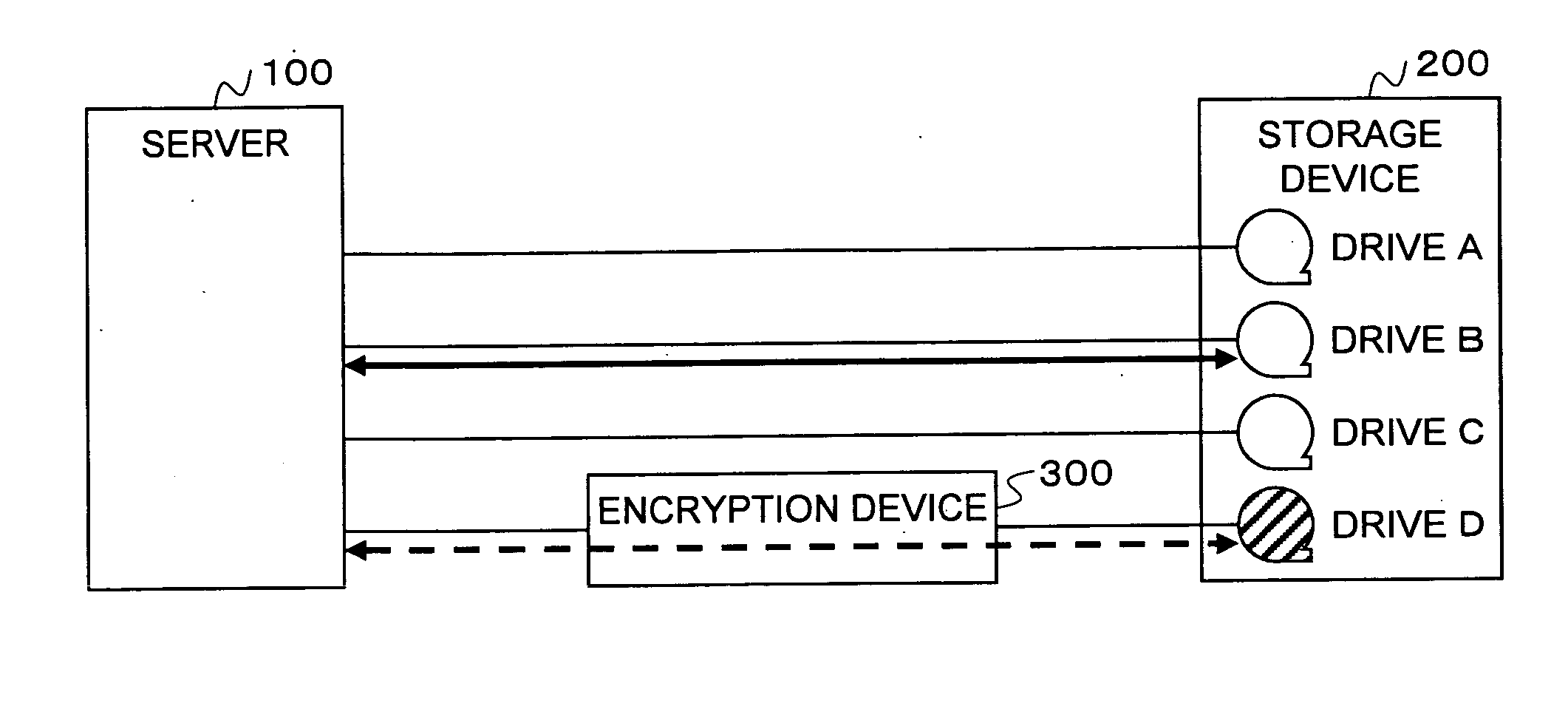
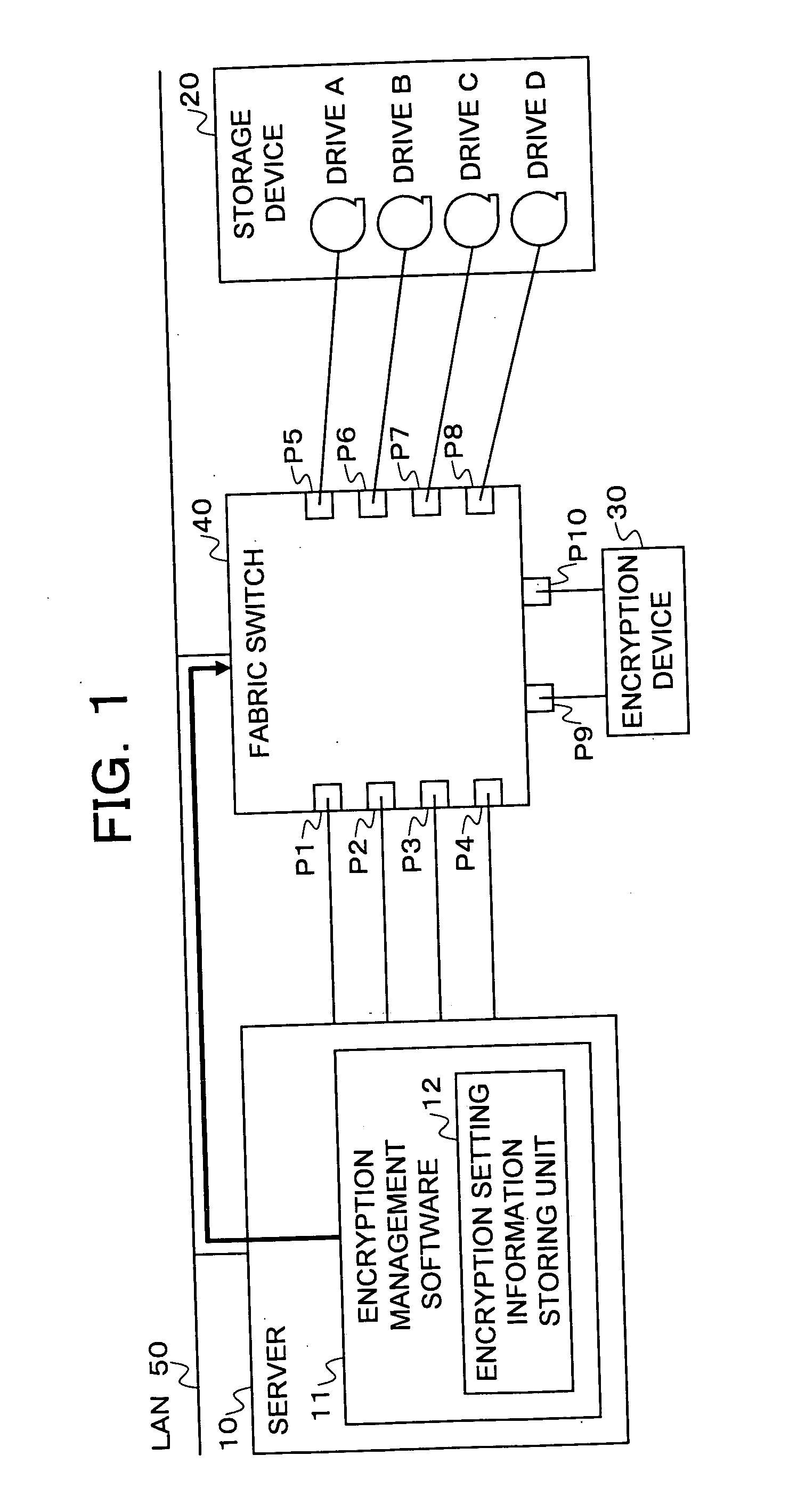
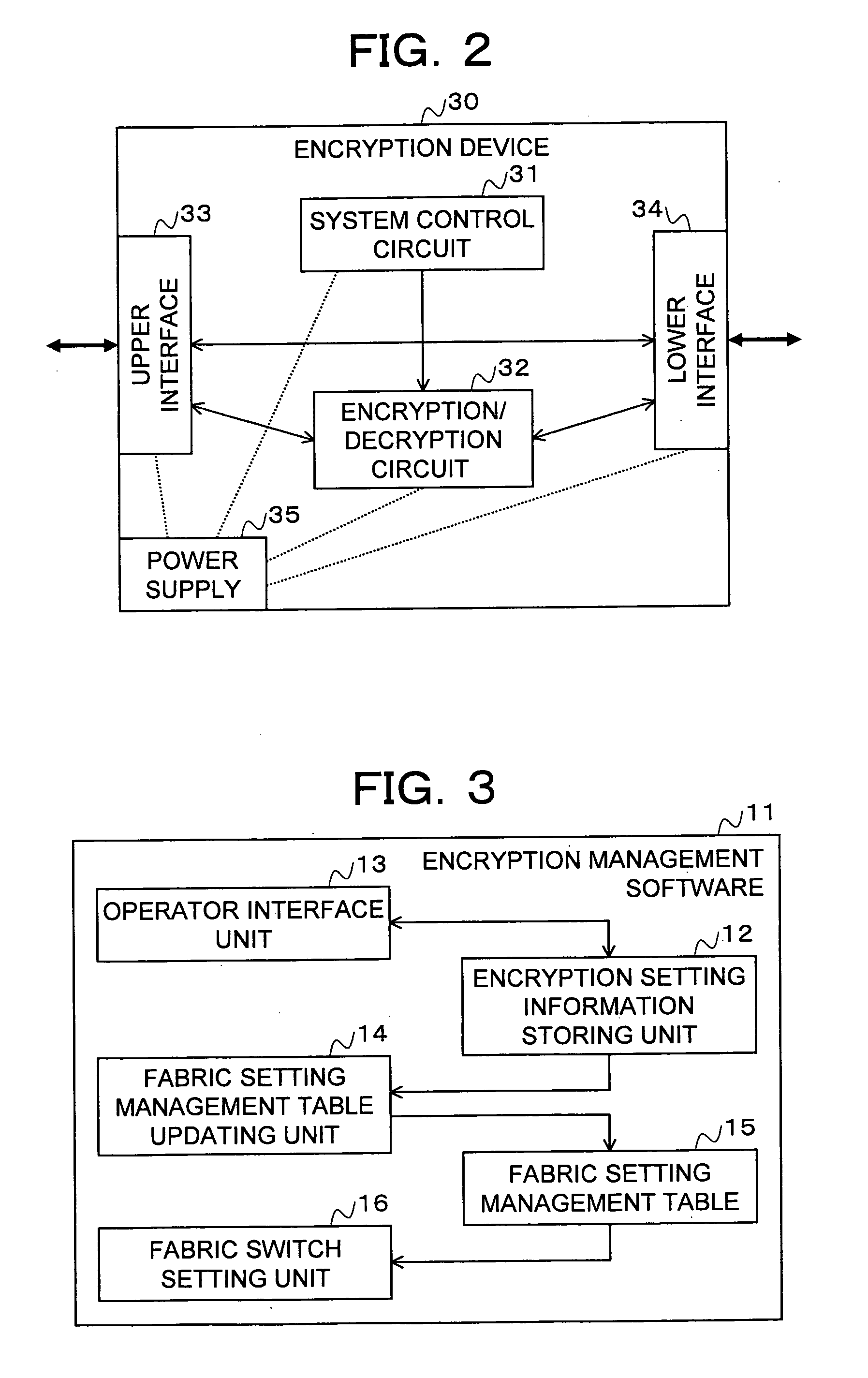
Storage system, encryption path switching system, encryption path switching program, and recording medium thereof
InactiveUS20070192629A1Easy to changeAvoid performance degradationFurniture joining partsWriting connectorsComputer hardwarePath switching
In a storage system, a server, a storage device, and an encryption device are connected to ports of a fabric switch. Encryption management software of the server performs, on the basis of encryption setting information inputted to an encryption setting information storing unit from the outside and stored in the encryption setting information storing unit, connection setting for the ports of the fabric switch such that a path from the server to the storage on which encryption is performed passes through the encryption device and such that a path on which encryption is not performed does not pass through the encryption device. It is possible to freely switch a path on which encryption is performed simply by changing encryption setting information.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
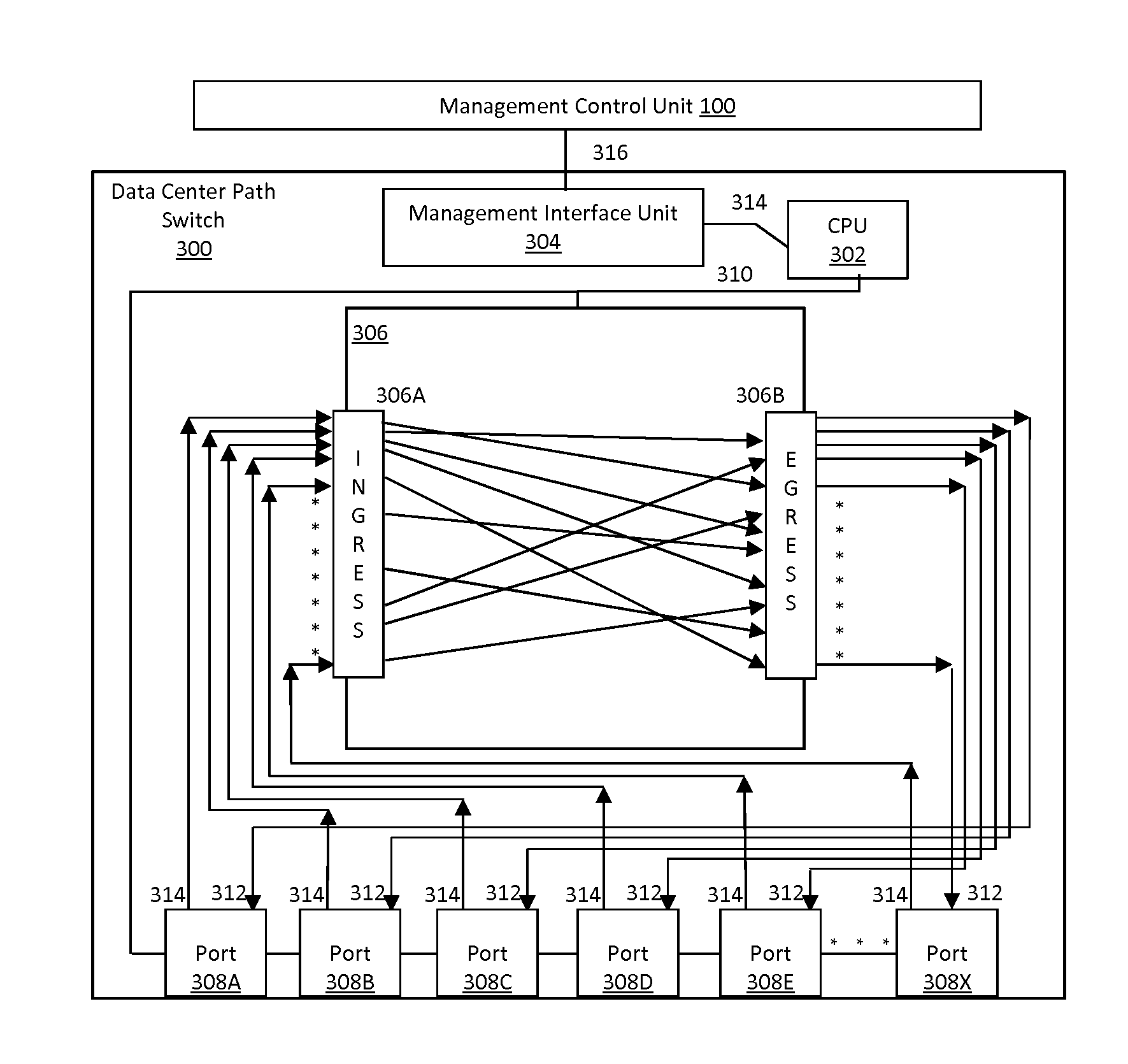
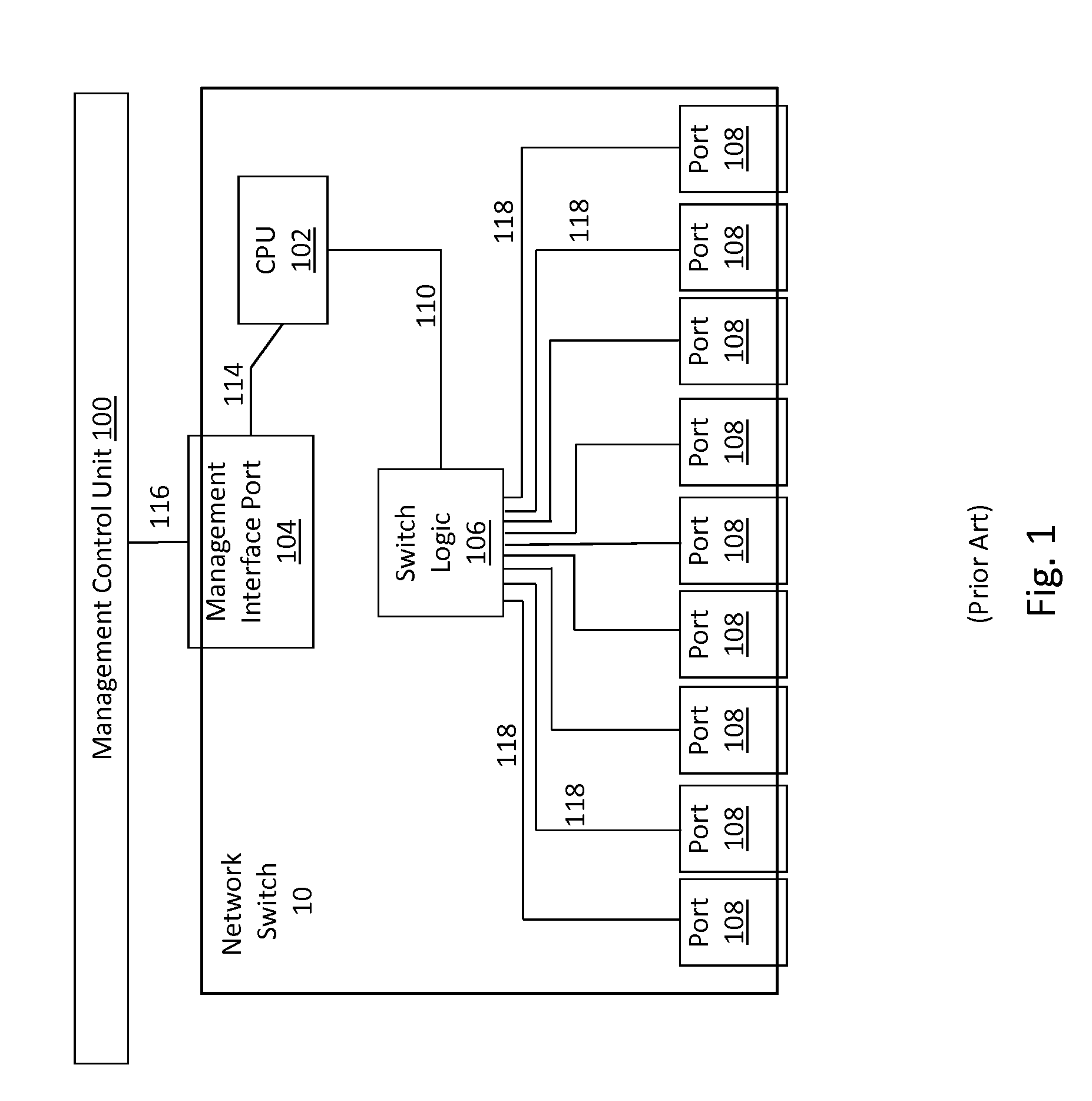
Data center path switch with improved path interconnection architecture
ActiveUS20160007102A1Easy to controlSimplifying interconnectionMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexData centerSwitching signal
A data center path switch architecture permits path switching of the signal path of incoming signals to one or more output paths in real time without the need for manual intervention, and without delays associated with current data center network switches. In this architecture, a switching core capable of switching signals directly from the ingress of the switching core to alternate destination ports in real time, either under software or hardware control.
Owner:FIBER MOUNTAIN INC
Communication system, node device, communication method in the communication system, and program
InactiveUS8908502B2Number of hop is usedIncrease speedError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemPath switching
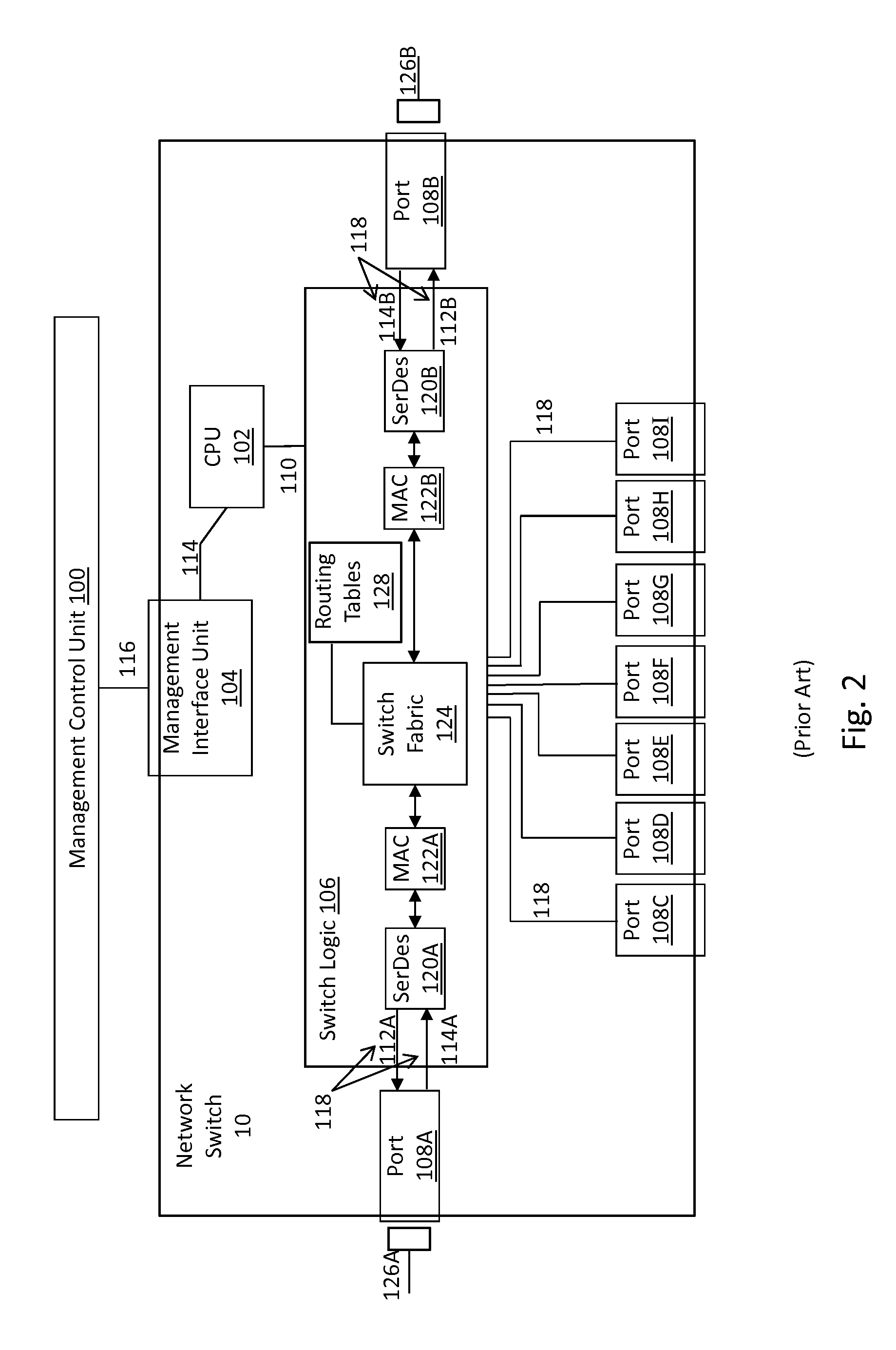
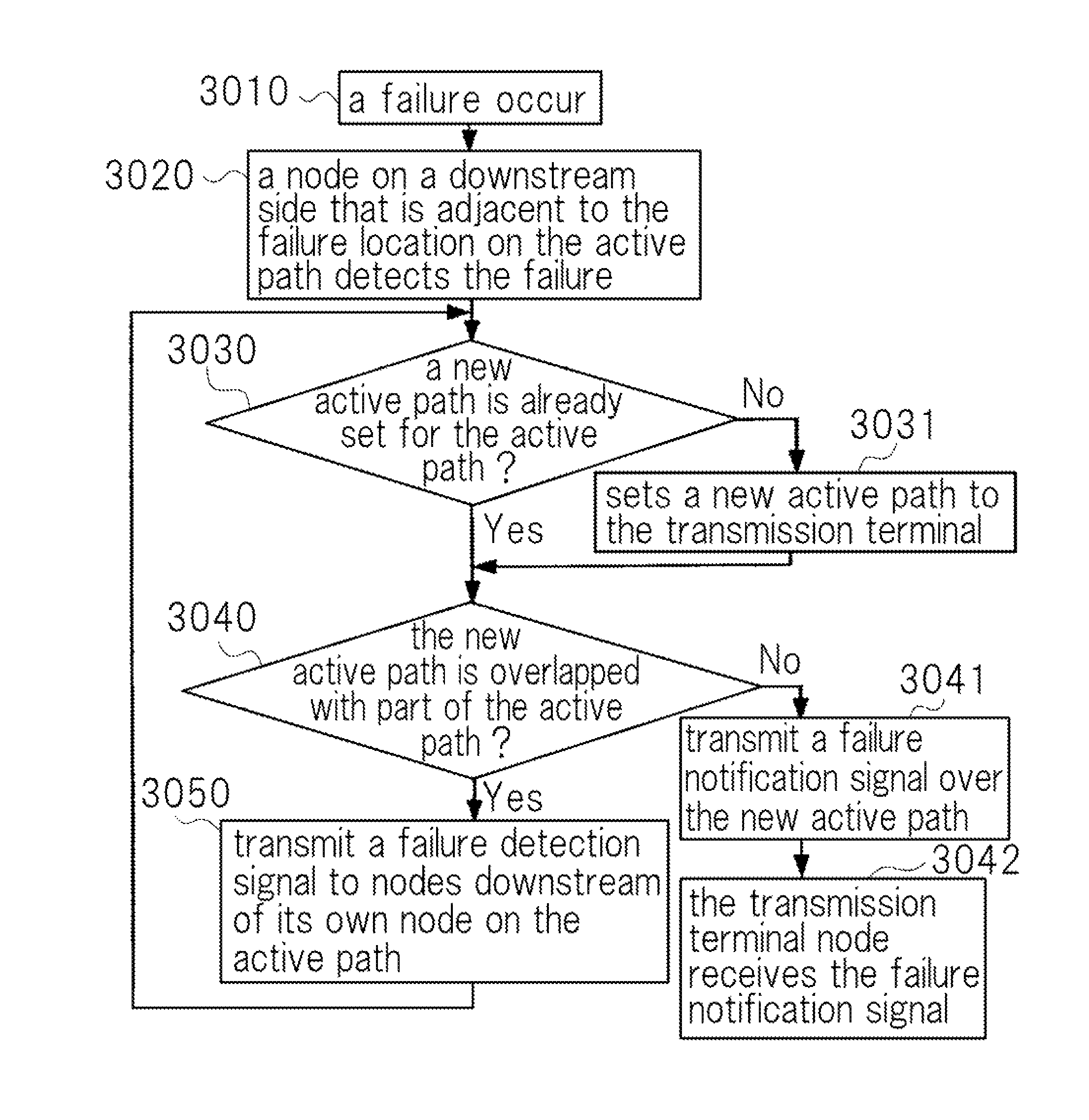
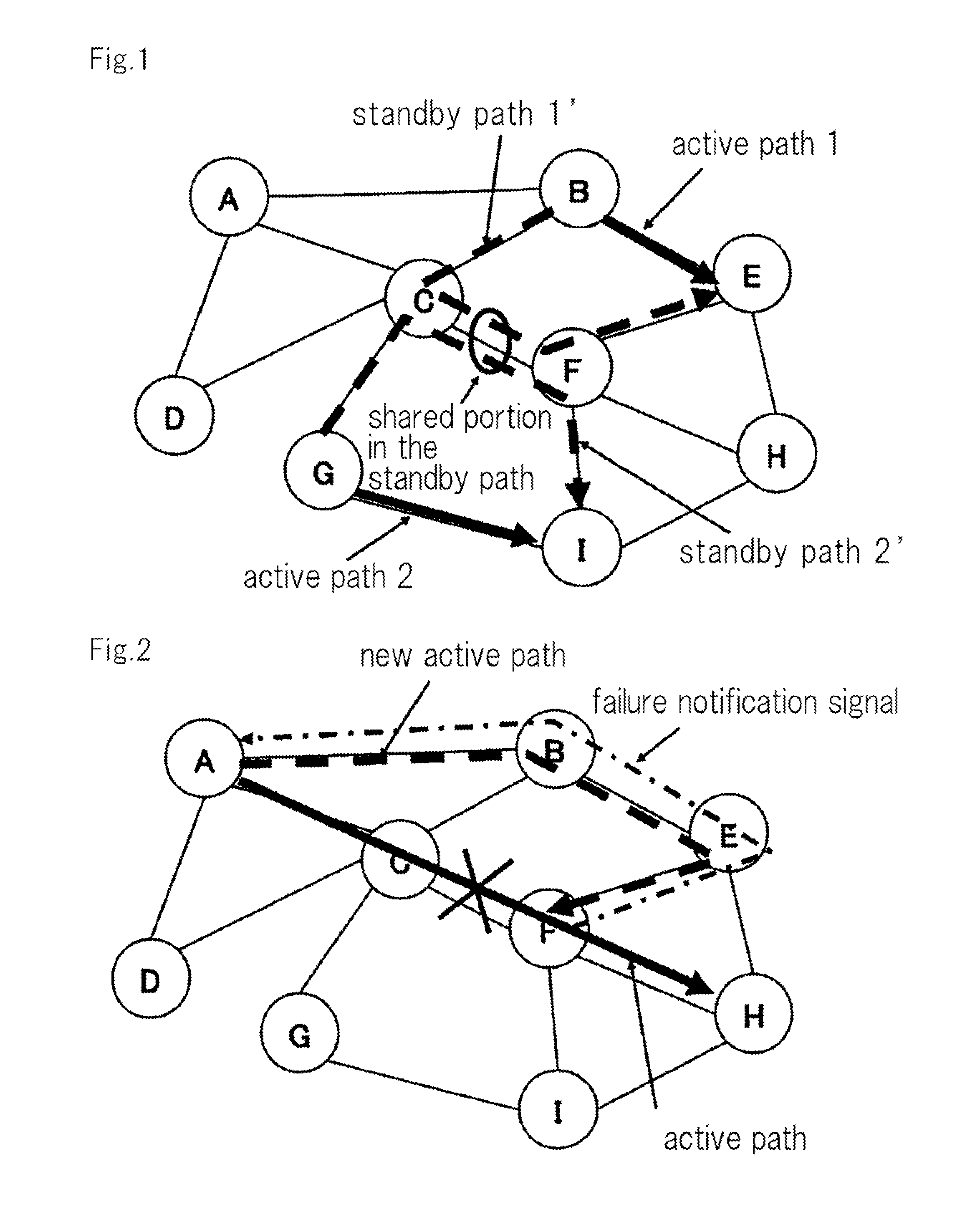
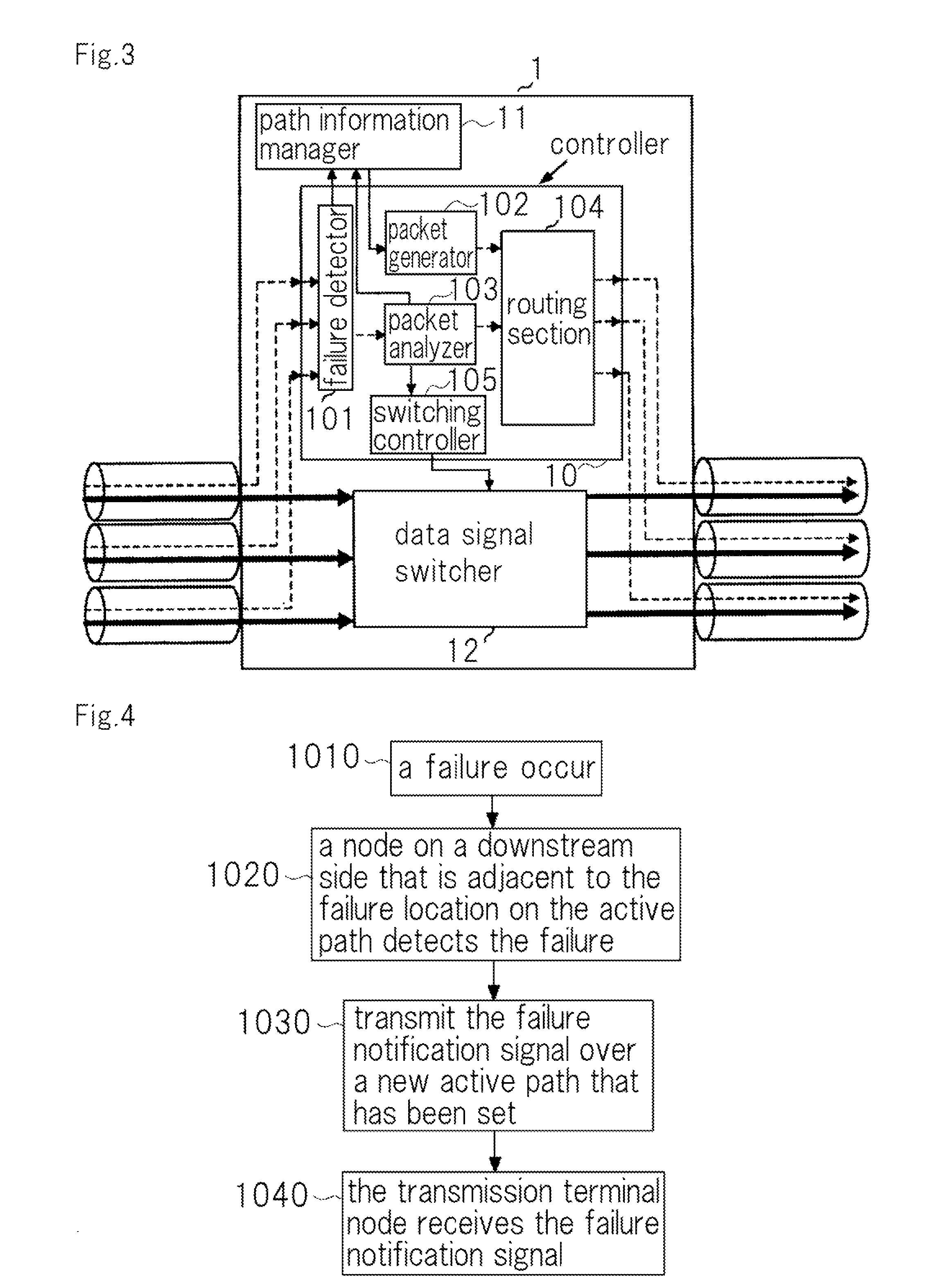
A communication system comprises: failure detection means that detects a failure on a first transmission path over which data transmission is being performed; transmission path setting means that, when the failure exists in a link or a node that is located immediately before its own node, sets a second transmission path as far as a transmission terminal node, the second transmission path that excludes a path from the transmission terminal node to a node that has detected the failure within the first transmission path; first failure notification means that transmits a failure notification signal as far as the transmission terminal node over the second transmission path; new path switching means that, upon receipt of the failure notification signal, switches a switch for data transmission so that a path for new data transmission is the same path as a transmission path for the failure notification signal; and data transmission means that, upon the transmission terminal node receiving the failure notification signal, switches the switch to the second transmission path and performs a new data transmission over the second transmission path.
Owner:NEC CORP
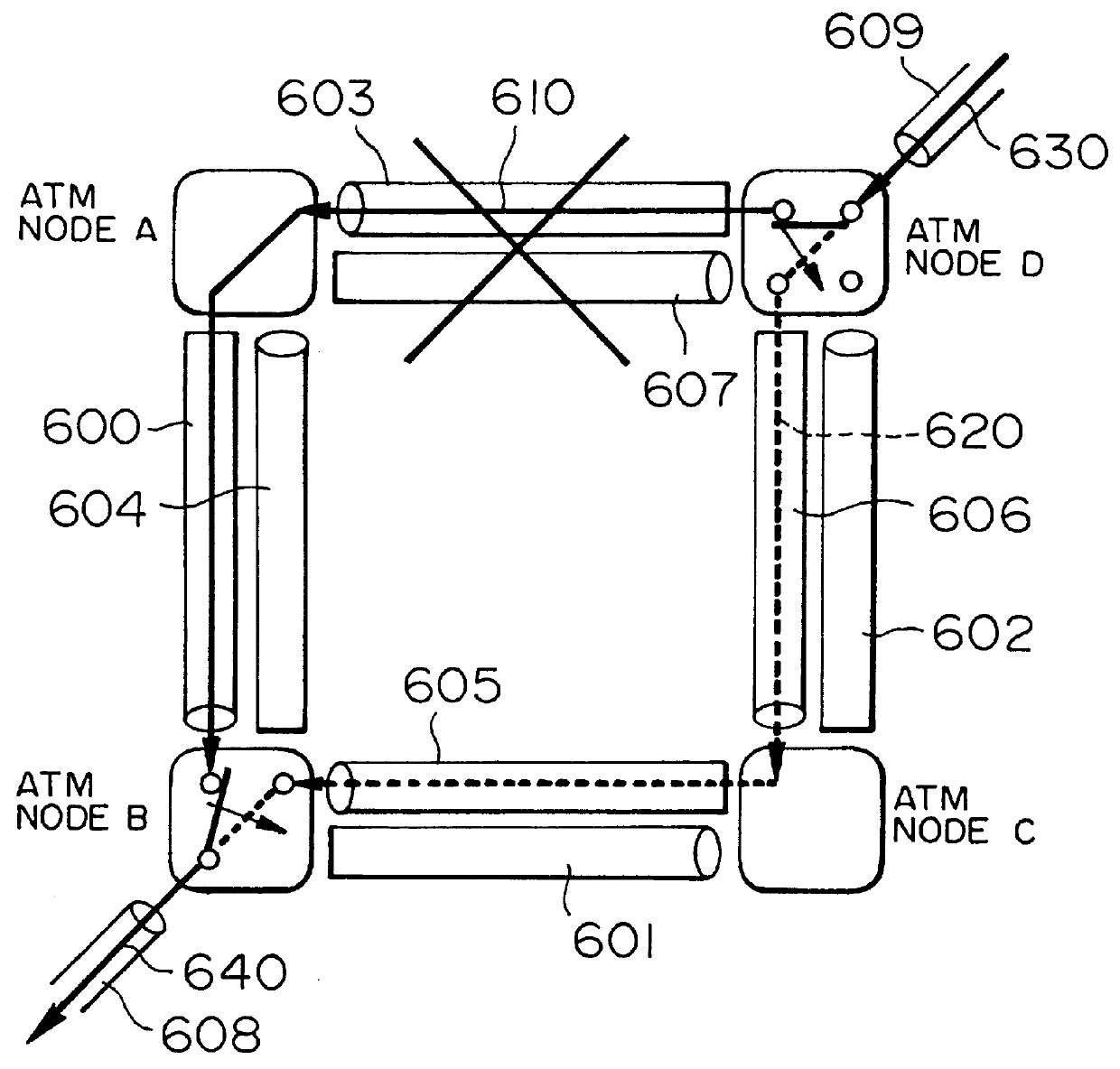
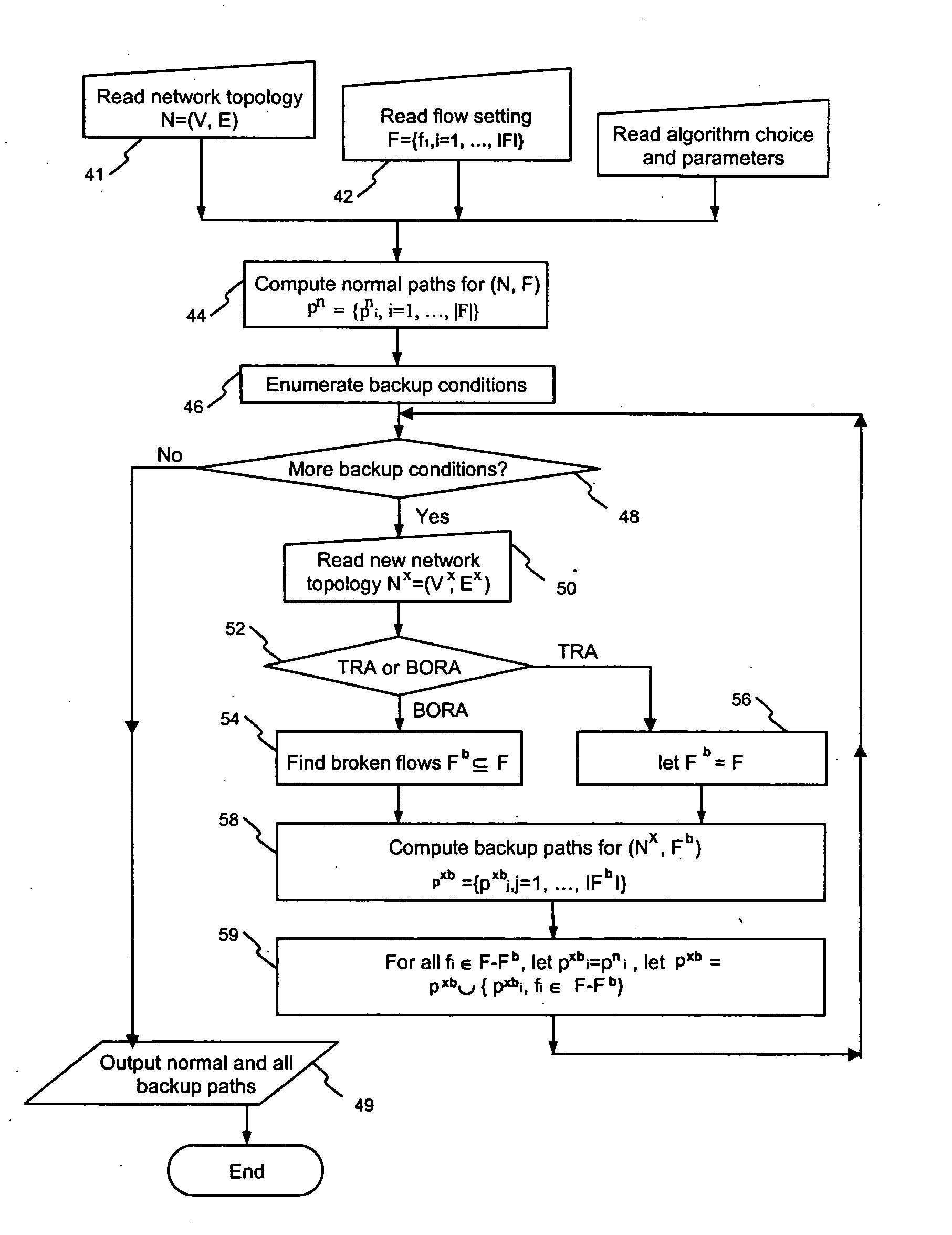
Method and system for a local and fast non-disruptive path switching in high speed packet switching networks
InactiveUS7593321B2Increase the number ofError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityExchange network
A method for operating a node in a computer network is disclosed, where the network is made up of nodes connected by links. The method has the steps: determining an alternate path for one or more links; reserving resources for the alternate path; and rerouting traffic on the alternate path in case of a link failure. The alternate path may be periodically updated. A plurality of alternate paths may be maintained. The alternate paths may not have any links in common. User traffic may be rerouted substantially simultaneously to each link of the alternate path in the event of failure of a primary path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
ATM virtual path switching node
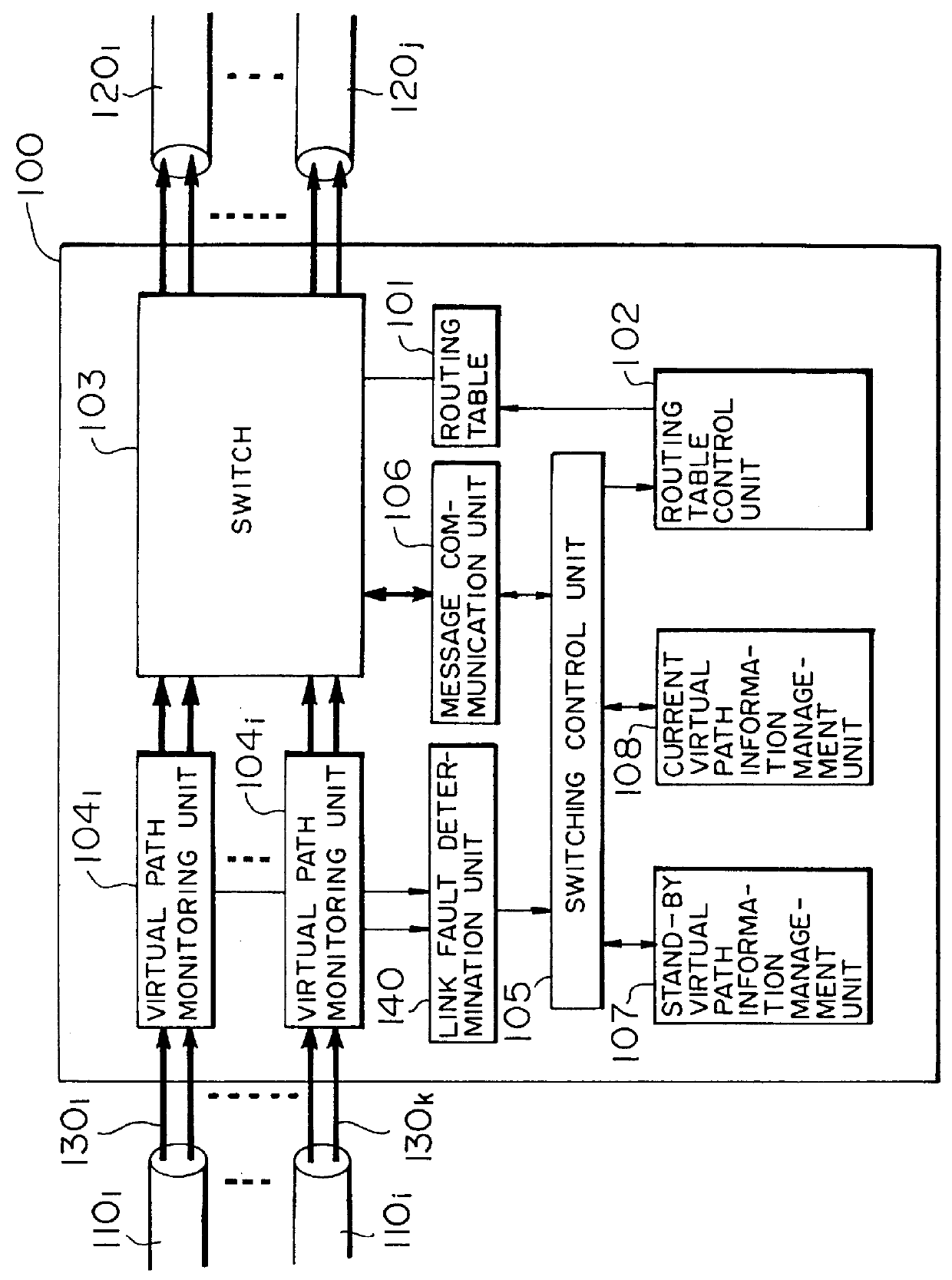
InactiveUS6041037AReduce processing loadShort timeError preventionTransmission systemsCommunication unitControl signal
In an ATM virtual path switching node, upon being notified of a current virtual path by a virtual path monitoring unit, a link fault determination unit compares the number of faulty current virtual paths with a predetermined threshold value. When the number of faulty current virtual paths is equal to or larger than the threshold value, a link fault is determined, and a message communication unit transmits / receives a link fault notification signal to / from another ATM virtual path switching node. When the number of faulty current virtual paths is smaller than the threshold value, a current virtual path fault is determined, and the message communication unit transmits / receives a virtual path fault notification signal to / from another ATM virtual path switching node. The message communication unit transmits a switching control signal for designating switching from the current virtual path to a stand-by virtual path. A current virtual path information management unit manages correspondence between the current virtual path having, as one switching terminal, a self ATM virtual path switching node and a plurality of links in an ATM network.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Cross-connect method and cross-connect apparatus
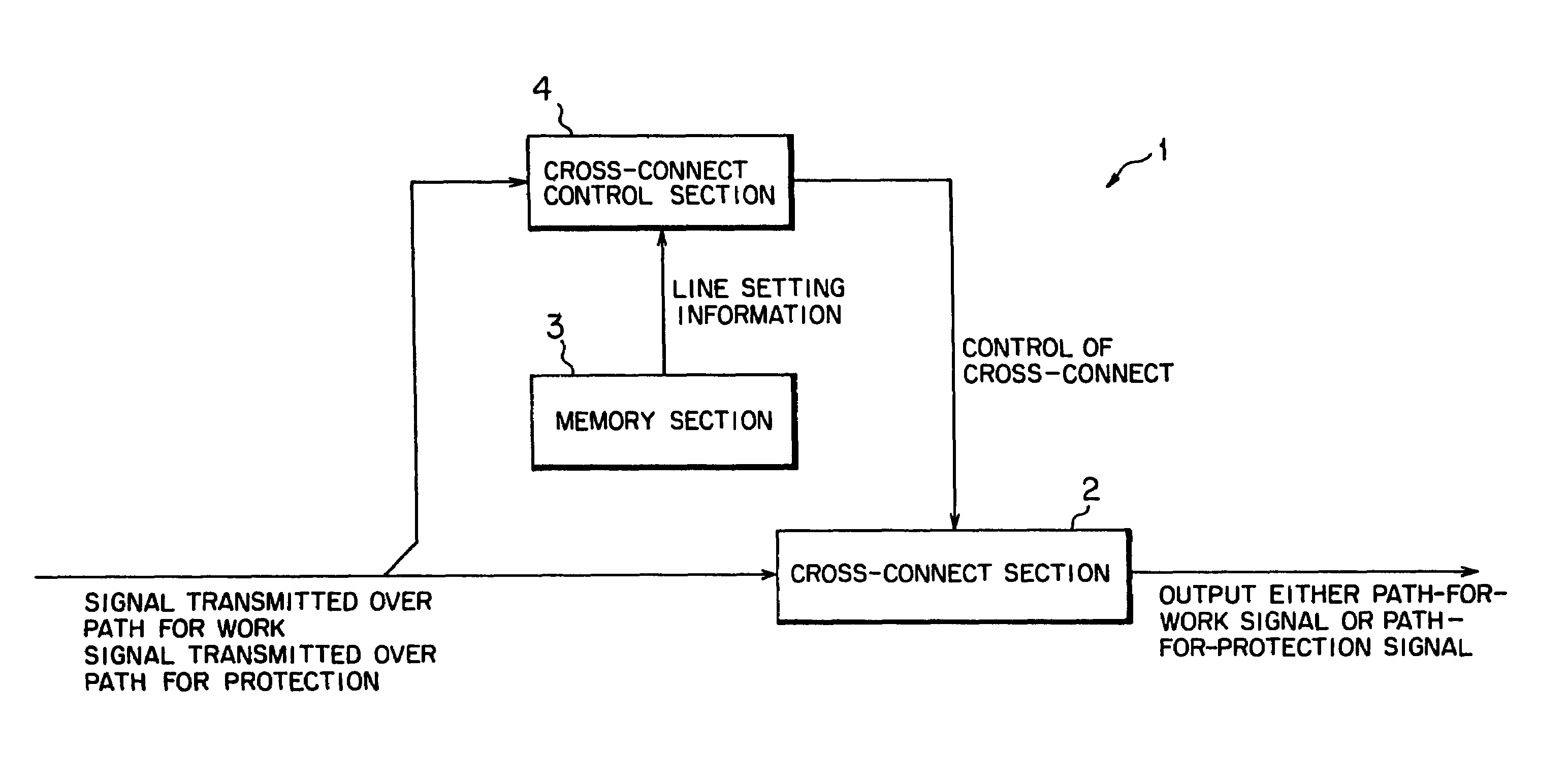
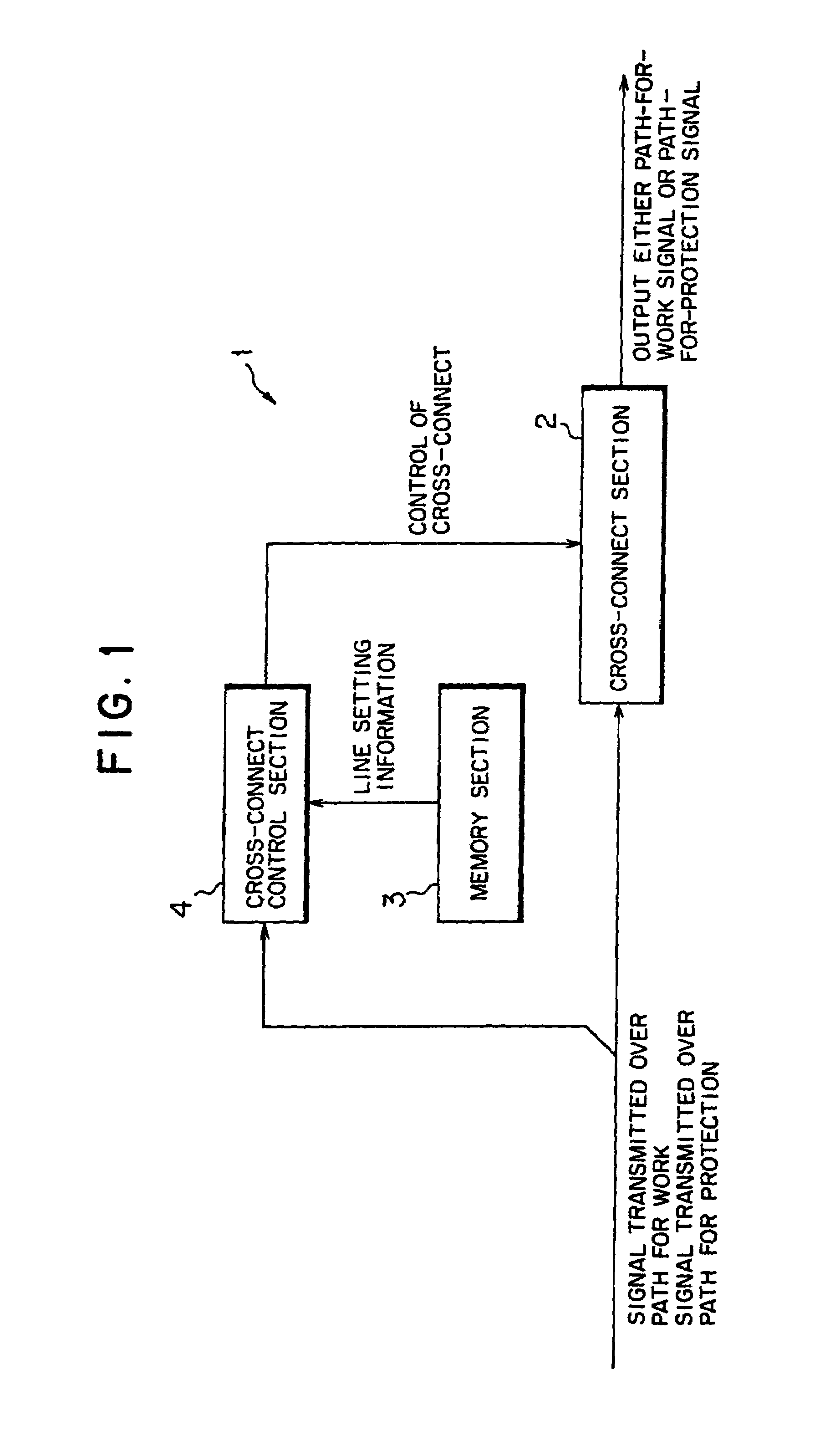
InactiveUS6977889B1Reduce power consumptionAvoid redundant configurationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCross connectionService selection
There is described a cross-connect apparatus which can apply a cross-connect operation in place of a function of a hard switch that has conventionally been used for a purpose other than a cross-connect operation, by selection of line setting information used for path switching and service selection operations, and by performing a cross-connect operation based on the information, thereby preventing redundant configuration of the cross-connect apparatus and diminishing power consumption.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
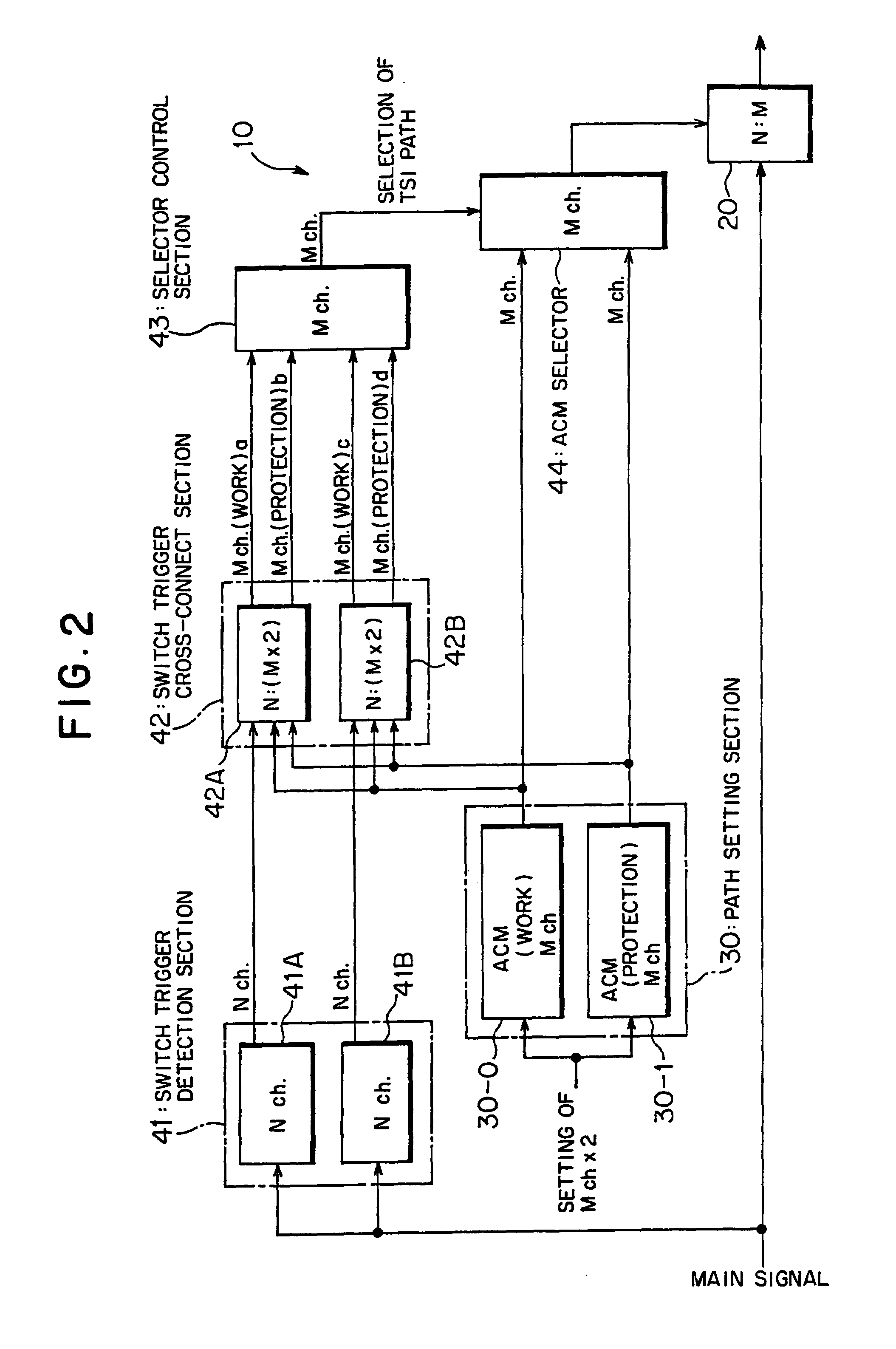
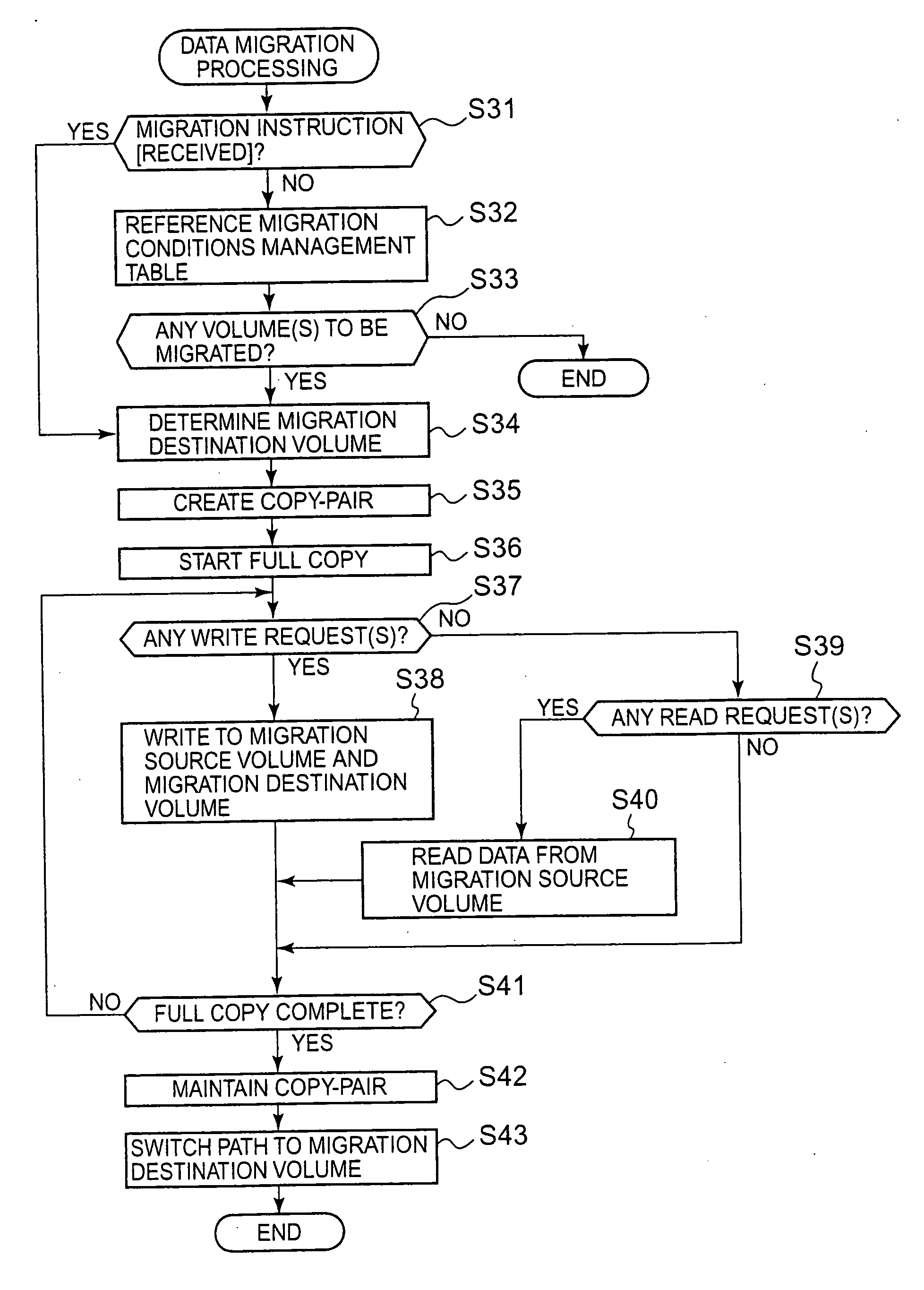
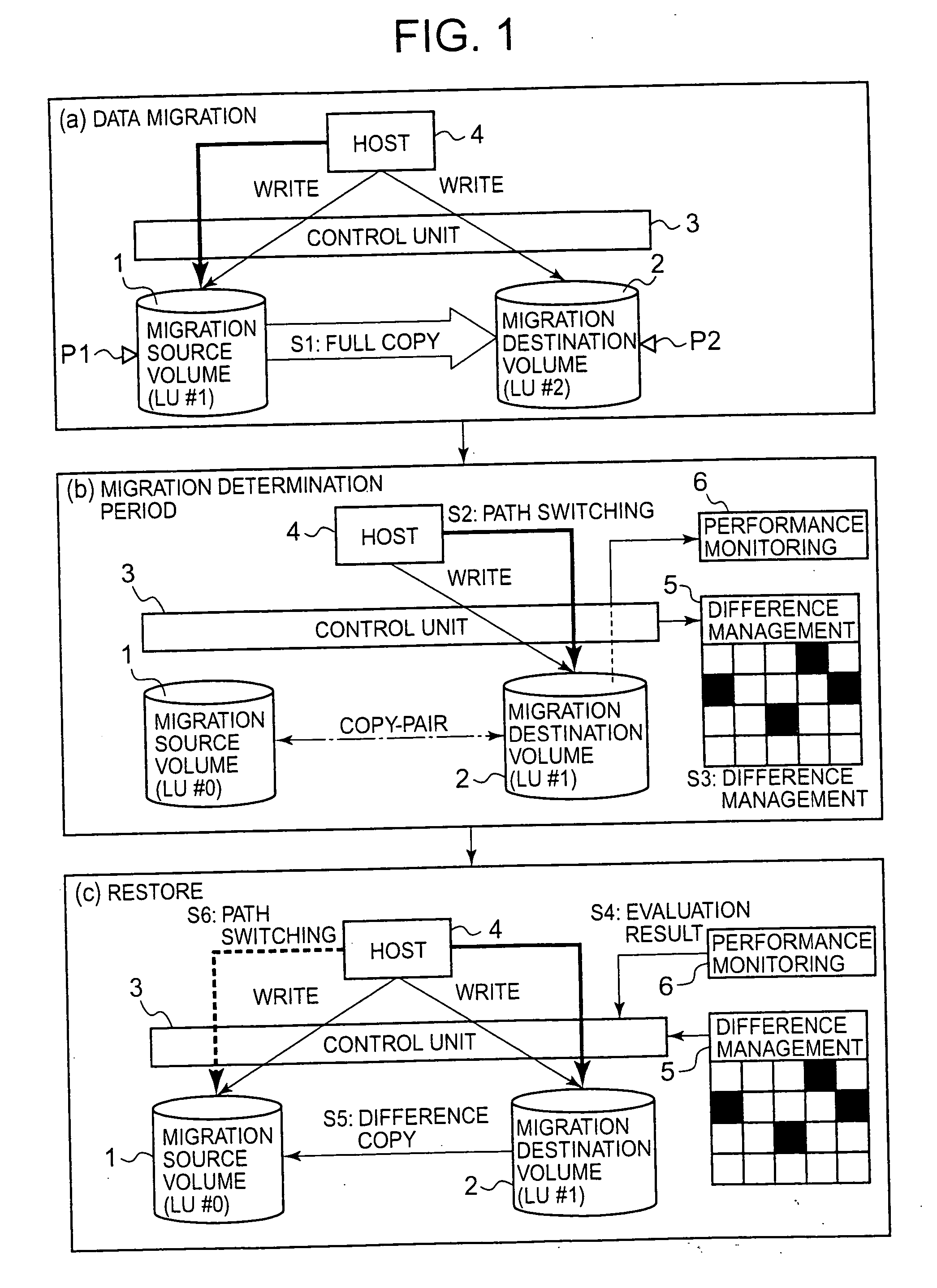
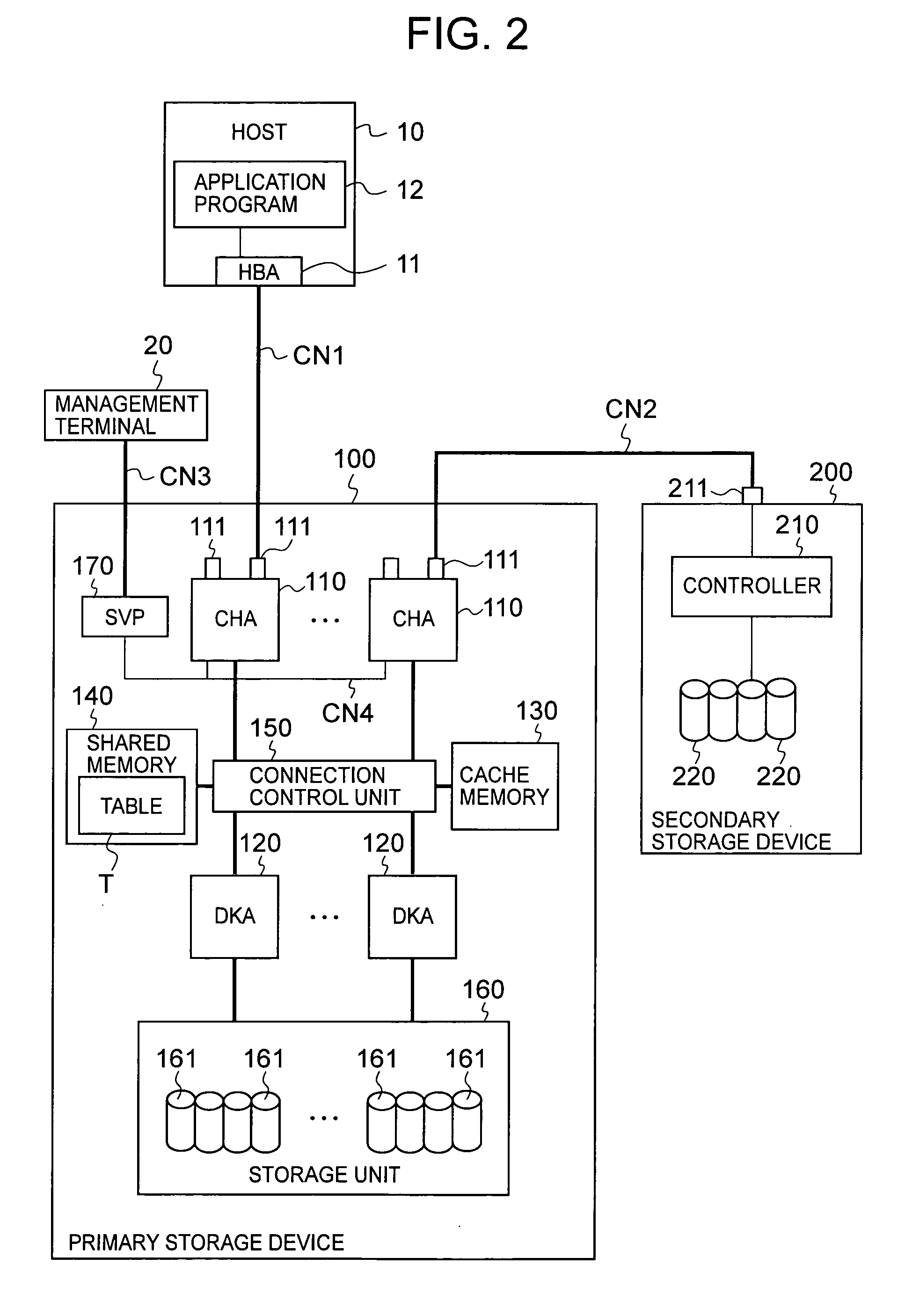
Storage system and storage system data migration method
The present invention suitably monitors the performance of a migration destination volume and conducts data migration all over again over a short time. When conducting data migration, all data is copied from the migration source volume to the migration destination volume, and when the full copy is completed, the host access path is switched to the migration destination volume 2. The copy-pair between the volumes is maintained following completion of the full copy, and difference data created in the migration destination volume is managed. A performance monitoring unit monitors performance of the migration destination volume based on indices according to migration source volume type. When, as a result of monitoring, restoration to the status prior to data migration is decided, difference data is copied from the migration destination volume to the migration source volume, and the host access path of the host is switched to the migration source volume.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System and method for controlling network traffic
Owner:CHO CHANG HWAN +1
Method and system for looping back traffic in qiq ethernet rings and 1:1 protected PBT trunks
InactiveUS20080095047A1Reduce delaysError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCross connectionPath switching
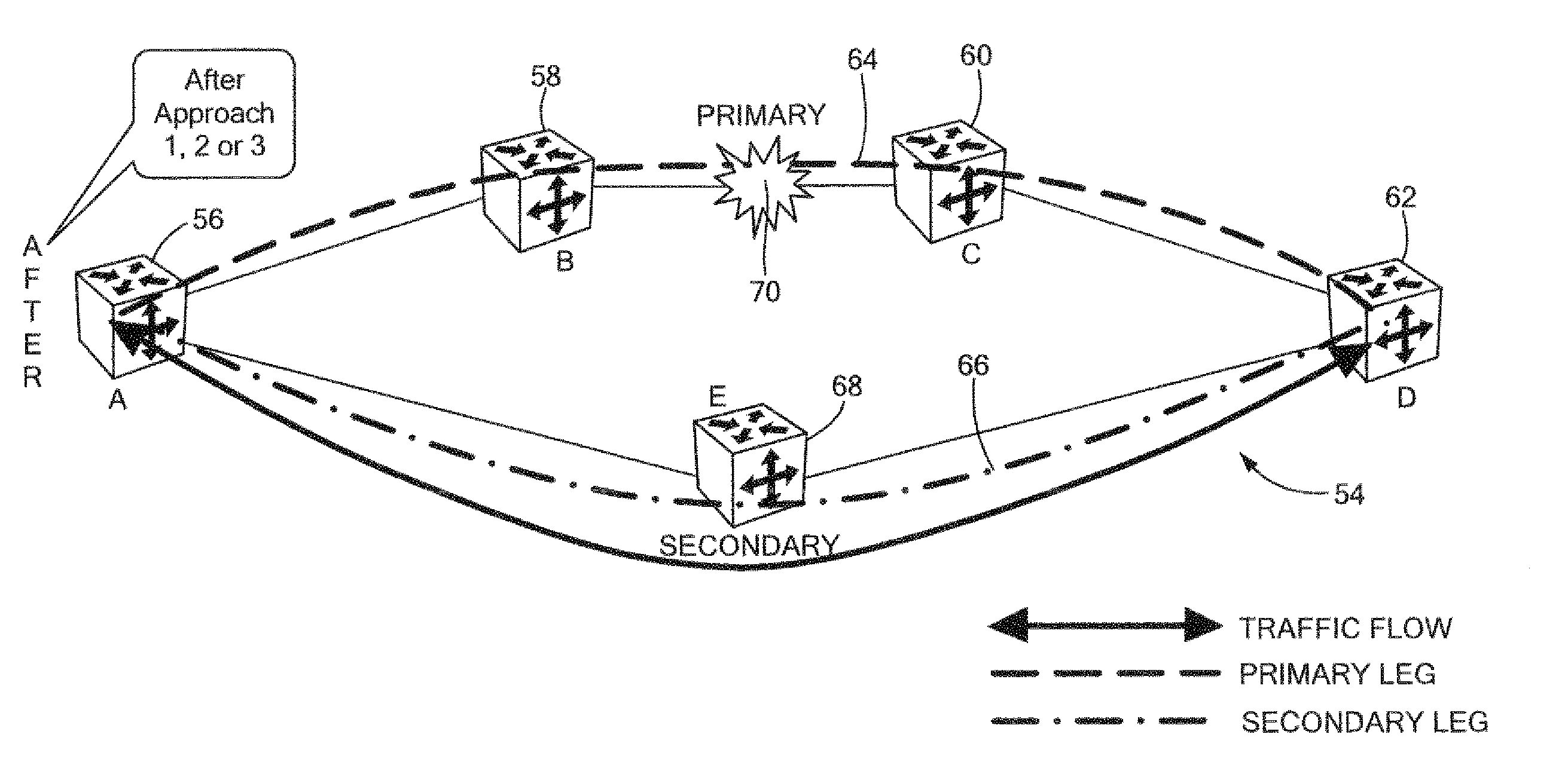
A resilient virtual Ethernet ring has nodes interconnected by working and protection paths. If a span fails, the two nodes immediately on either side of the failure are cross-connected to fold the ring. Working-path traffic is cross-connected onto the protection path at the first of the two nodes and is then cross-connected back onto the working path at the second of the two nodes so that traffic always ingresses and egresses the ring from the working path. A traffic originating node, upon determining that transmitted packets are being looped back due to a fault on a primary path, is adapted to switch transmission of data packets from the primary path to a secondary path.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
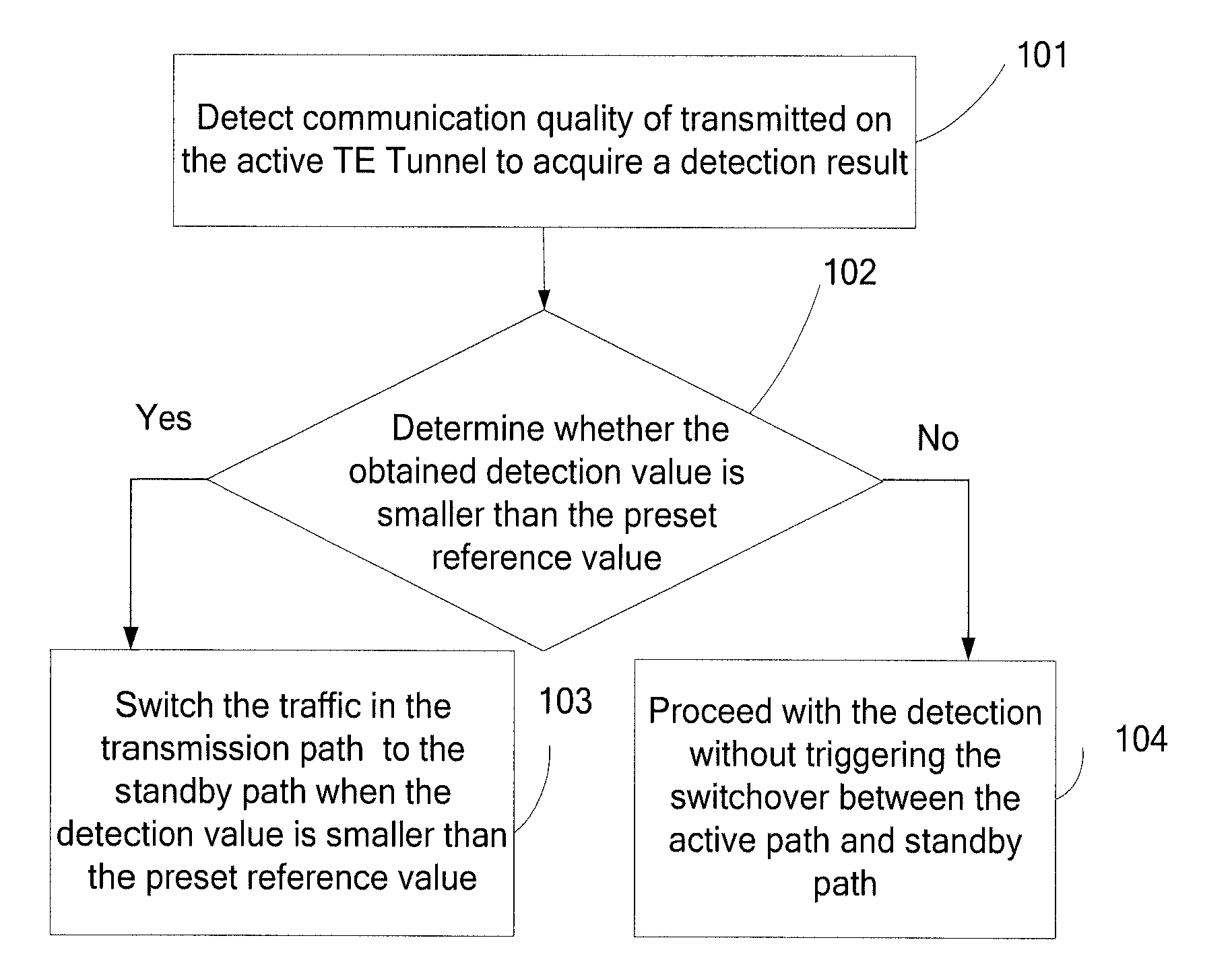
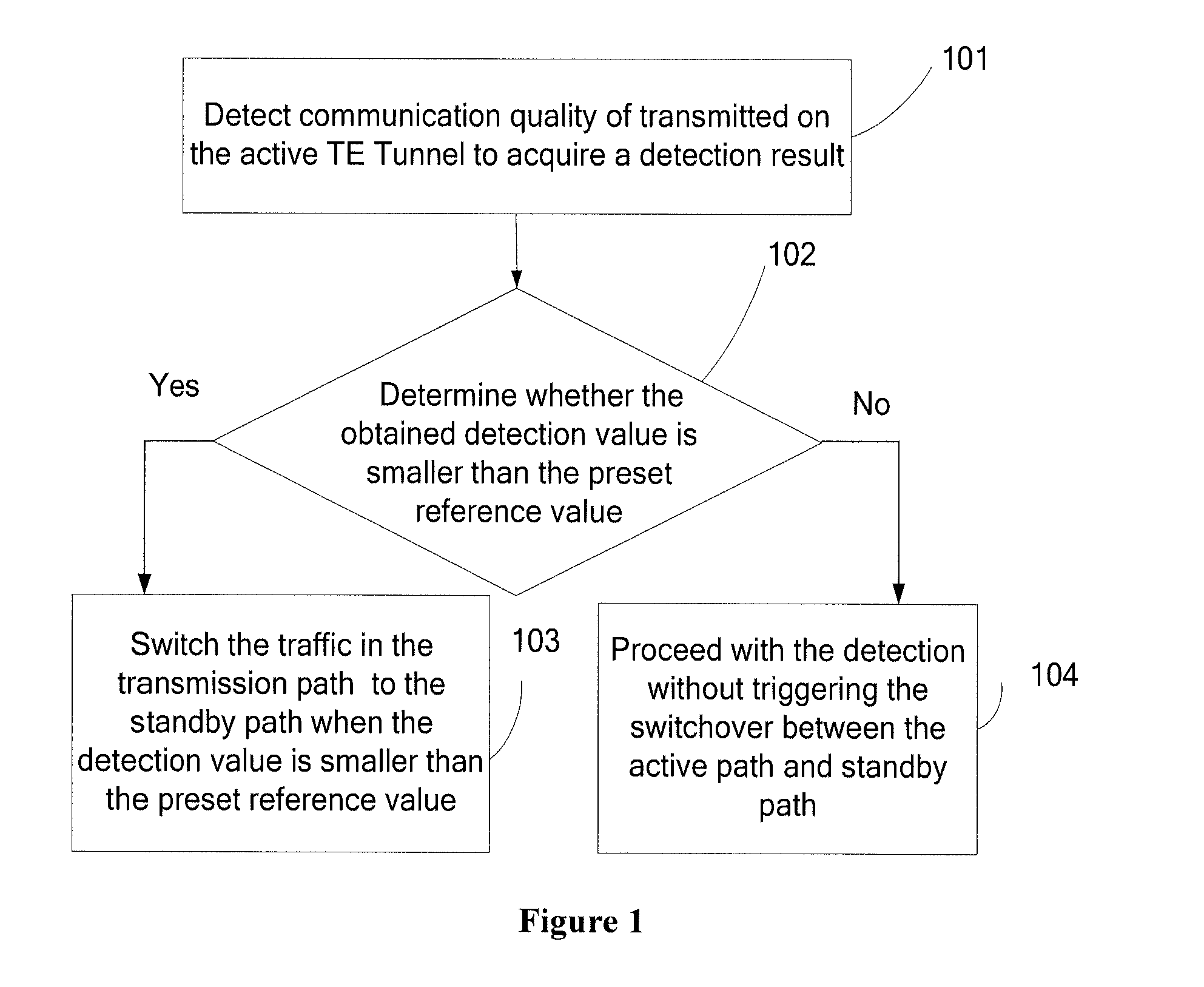
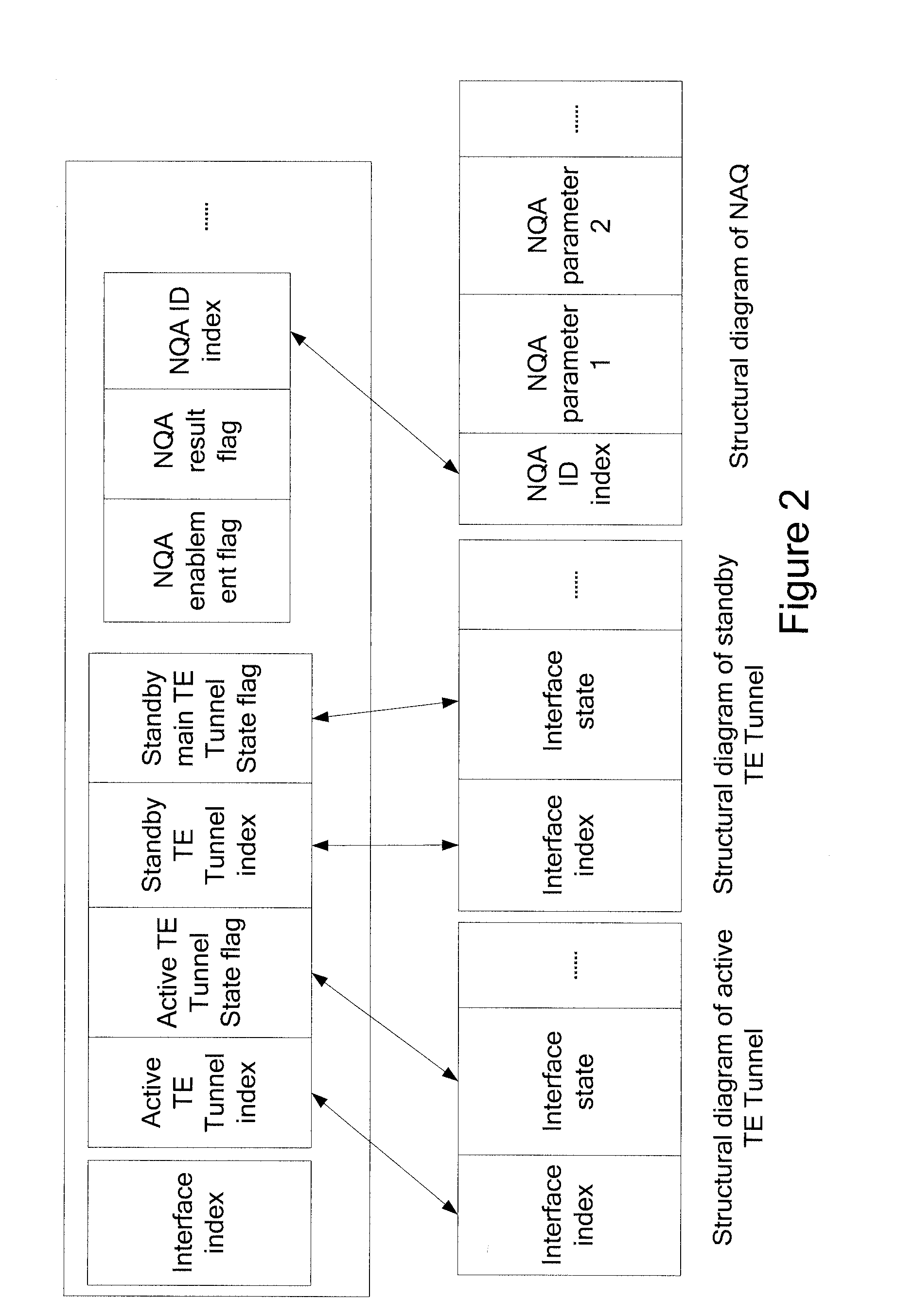
Method and device for path switchover
ActiveUS20110007652A1Reduce complaintsImprove satisfactionError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityFast path
A method and device for path switchover in communications field are provided. The method includes: detecting communication quality of traffic transmitted on an active path and obtaining a detection value of the communication quality; determining whether the detection value meets a switching condition; if yes, switching the traffic transmitted on the active path to a standby path. The device includes a detecting module, an obtaining module, a determining module and a switching module. The embodiment of the present disclosure integrates the NQA technology for detecting the path communication quality and the TE FRR fast path switching technology, and the NQA detection result may trigger the TE FRR path to switch quickly. Therefore, when the signal quality of the path degrades, making the QoS requirement of the SLA hard to meet, the traffic may be switched to standby path to meet the requirement of the SLA agreed originally between the carrier and the user, so as to improve the user experience and the satisfactory degree on the service provided by the carriers.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
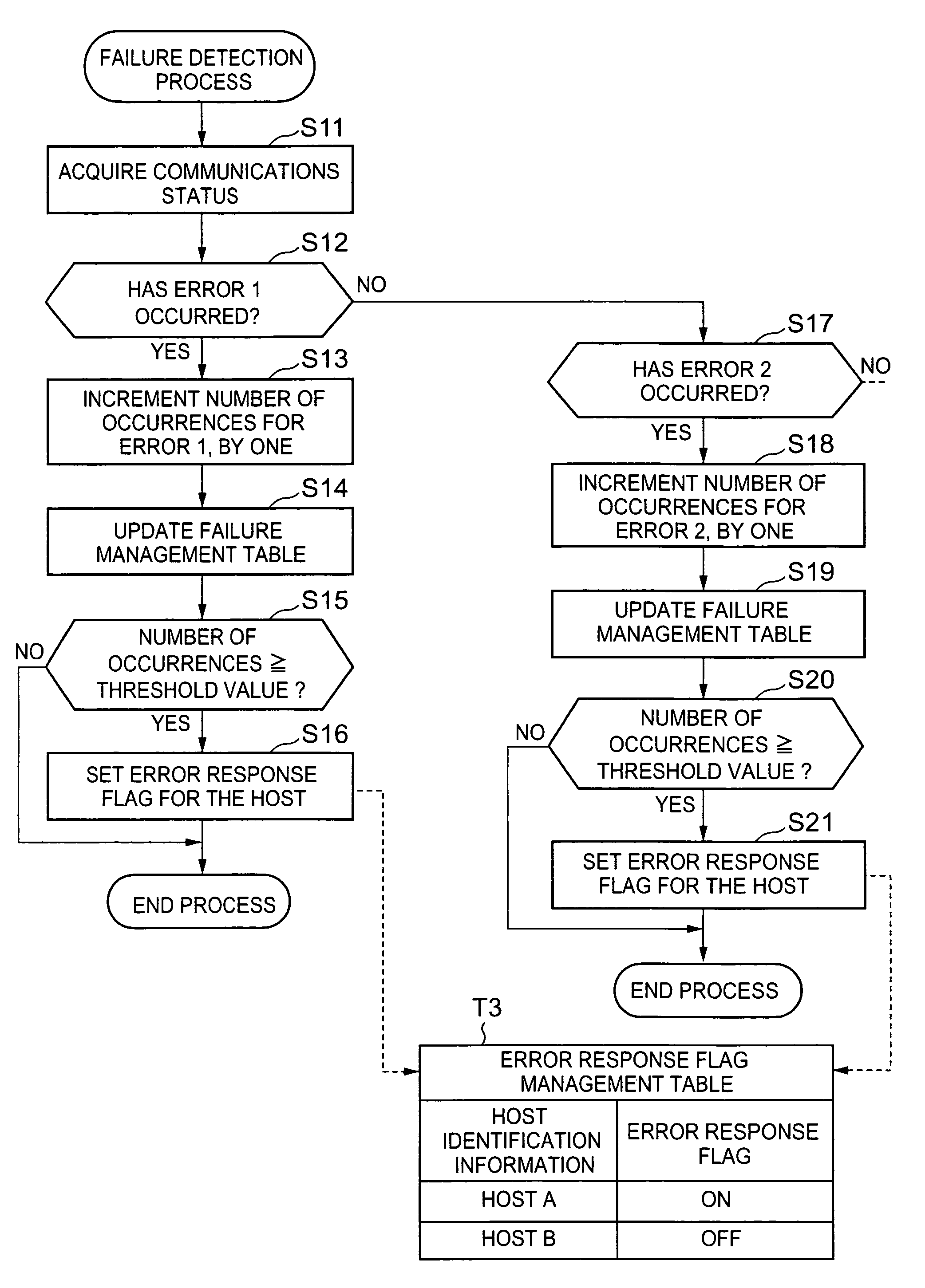
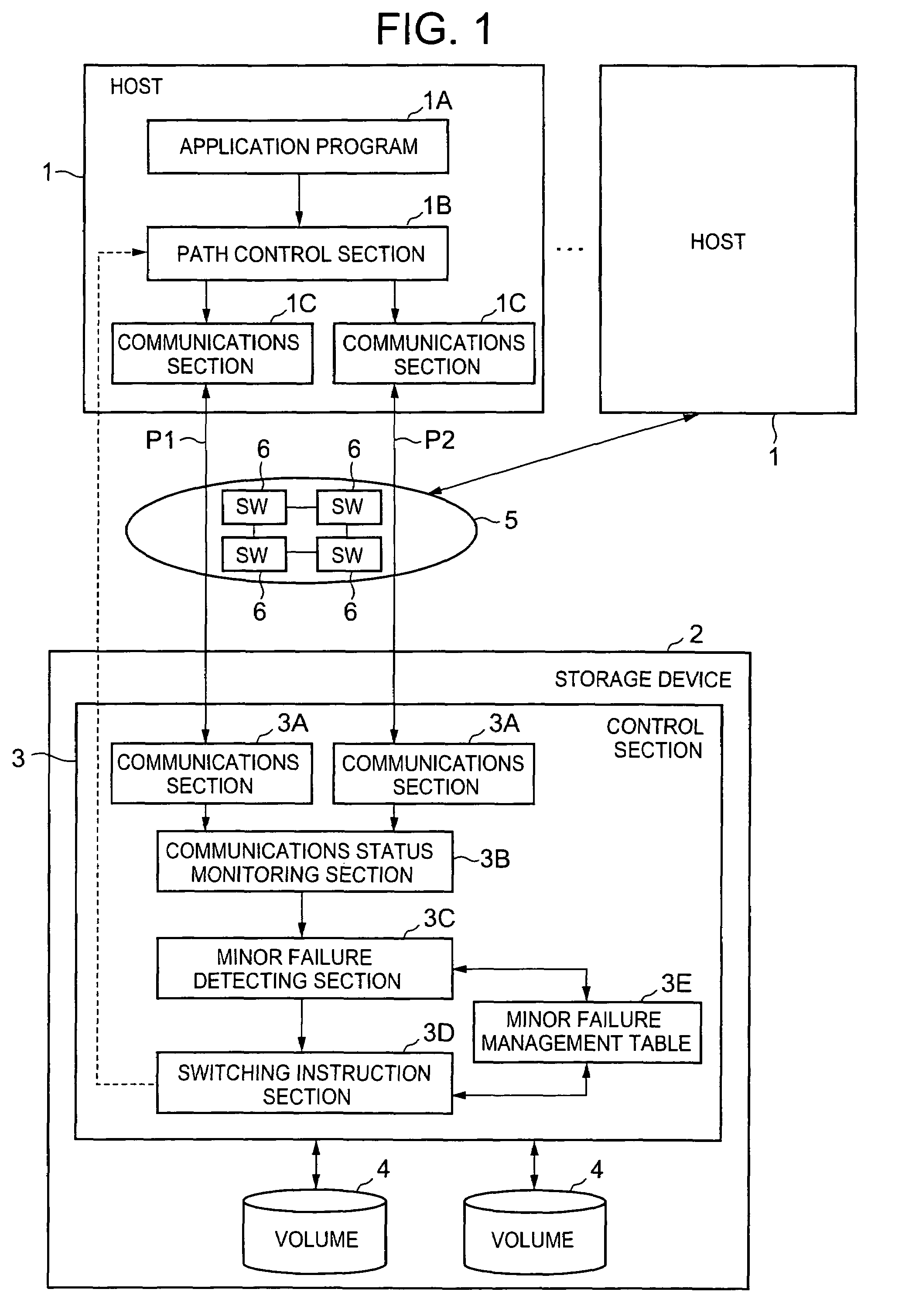
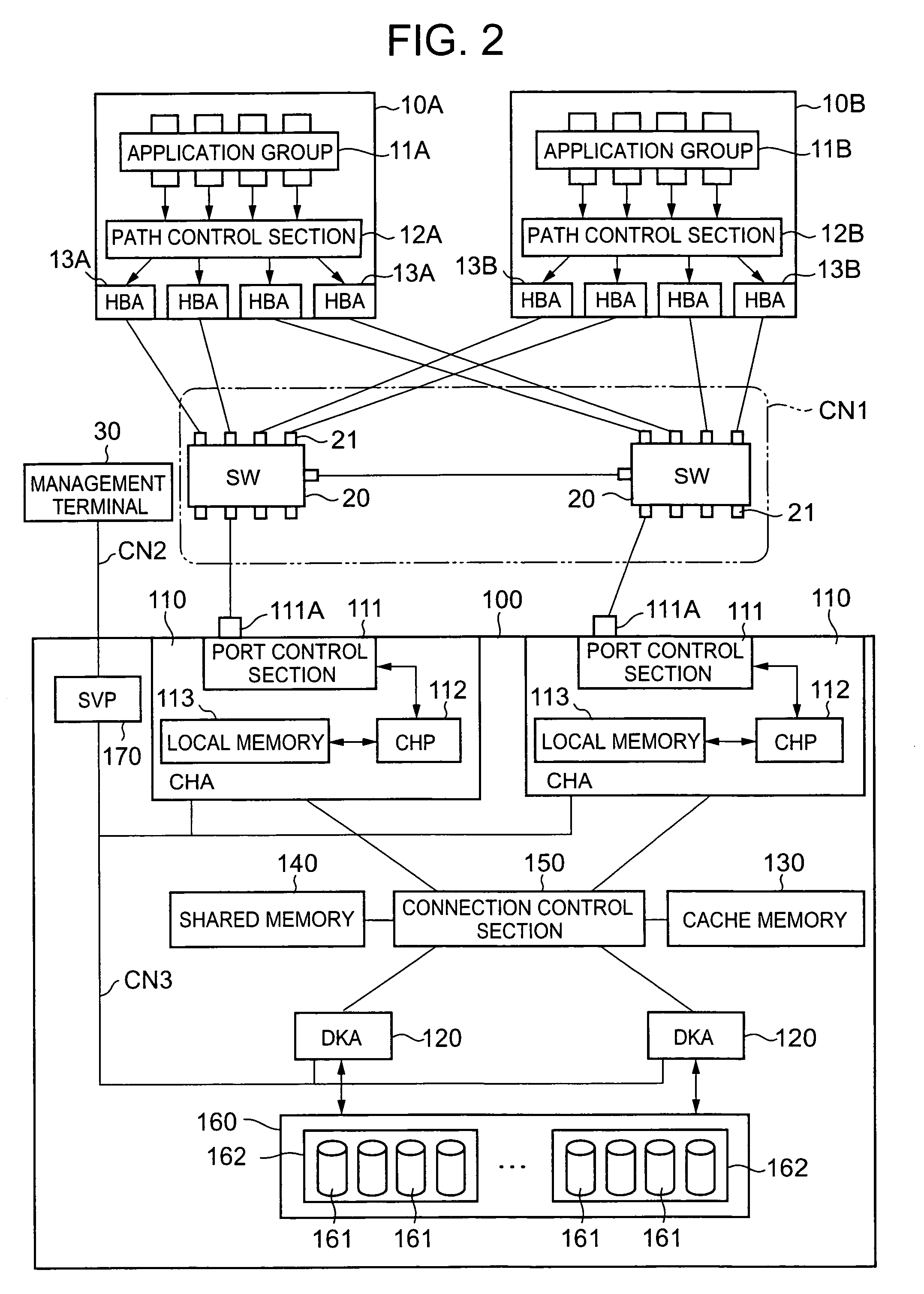
Storage system and communications path control method for storage system
A method for controlling communications paths in a storage system provided between a storage device and a plurality of host devices. The method includes: respectively monitoring communications statuses between each of the host devices and the storage device; detecting whether a prescribed temporary failure, which can be corrected without switching communications paths, has occurred, based upon the detected communications statuses; a switching instruction step of not outputting a switching request signal for requesting switching from a failed communications path to a to-be-used communications path, before a number of occurrence of the prescribed temporary failure thus detected reaches a threshold value which is equal to or larger than 2, and outputting the switching request signal only when the number of occurrence of the prescribed temporary failure reaches the threshold value; and selecting the to-be-used communications path, from among the plurality of communications paths, on the basis of the switching request signal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Fast multicast path switching
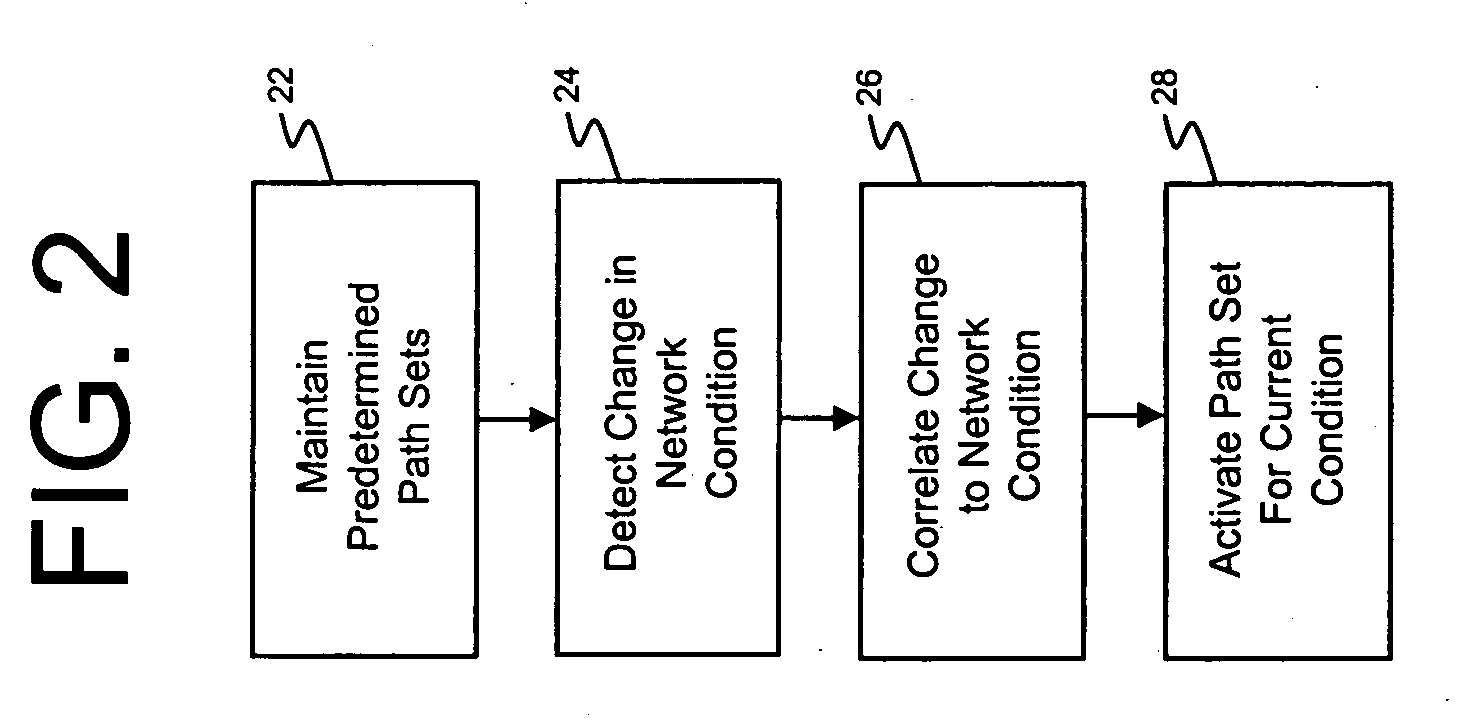
InactiveUS20060182033A1Simple methodError preventionTransmission systemsNetwork conditionsPath switching
An improved method is provided for switching paths at a network routing device residing in a multicast distribution environment. The method includes: maintaining a plurality of predetermined path sets in a data store associated with the network routing device, where each path set corresponds to a given network condition and defines a path for each data transmission session; receiving a message indicative of a current network condition at the network routing device; selecting a path set from the plurality of predetermined path sets, where the selected path set correlates to the current network condition; and configuring the network routing device in accordance with the selected path set.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for dual mode communication
ActiveUS20110286343A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPathPingCommunications system
Wi-Fi setup application and path switching applications are provided to allow commands received from native applications of the UE to be redirected to a Wi-Fi engine. The Wi-Fi engine supports circuit switched and packet switched services over a Wi-Fi connection, thus allowing commands received from native applications on a UE to connect the user to either a wireless unlicensed communication system or a wireless licensed communication system.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
Apparatus and methods for ion beam implantation using ribbon and spot beams
ActiveUS7326941B2Difficult to controlIncrease throughputMagnetsMaterial analysis by optical meansBand shapeIon beam
This invention discloses an ion implantation apparatus with multiple operating modes. It has an ion source and an ion extraction means for extracting a ribbon-shaped ion beam therefrom. The ion implantation apparatus includes a magnetic analyzer for selecting ions with specific mass-to-charge ratio to pass through a mass slit to project onto a substrate. Multipole lenses are provided to control beam uniformity and collimation. The invention further discloses a two-path beamline in which a second path incorporates a deceleration system incorporating energy filtering. The invention discloses methods of ion implantation in which the mode of implantation may be switched from one-dimensional scanning of the target to two-dimensional scanning, and from a simple path to an s-shaped path with deceleration.
Owner:ADVANCED ION BEAM TECHNOLOGY INC
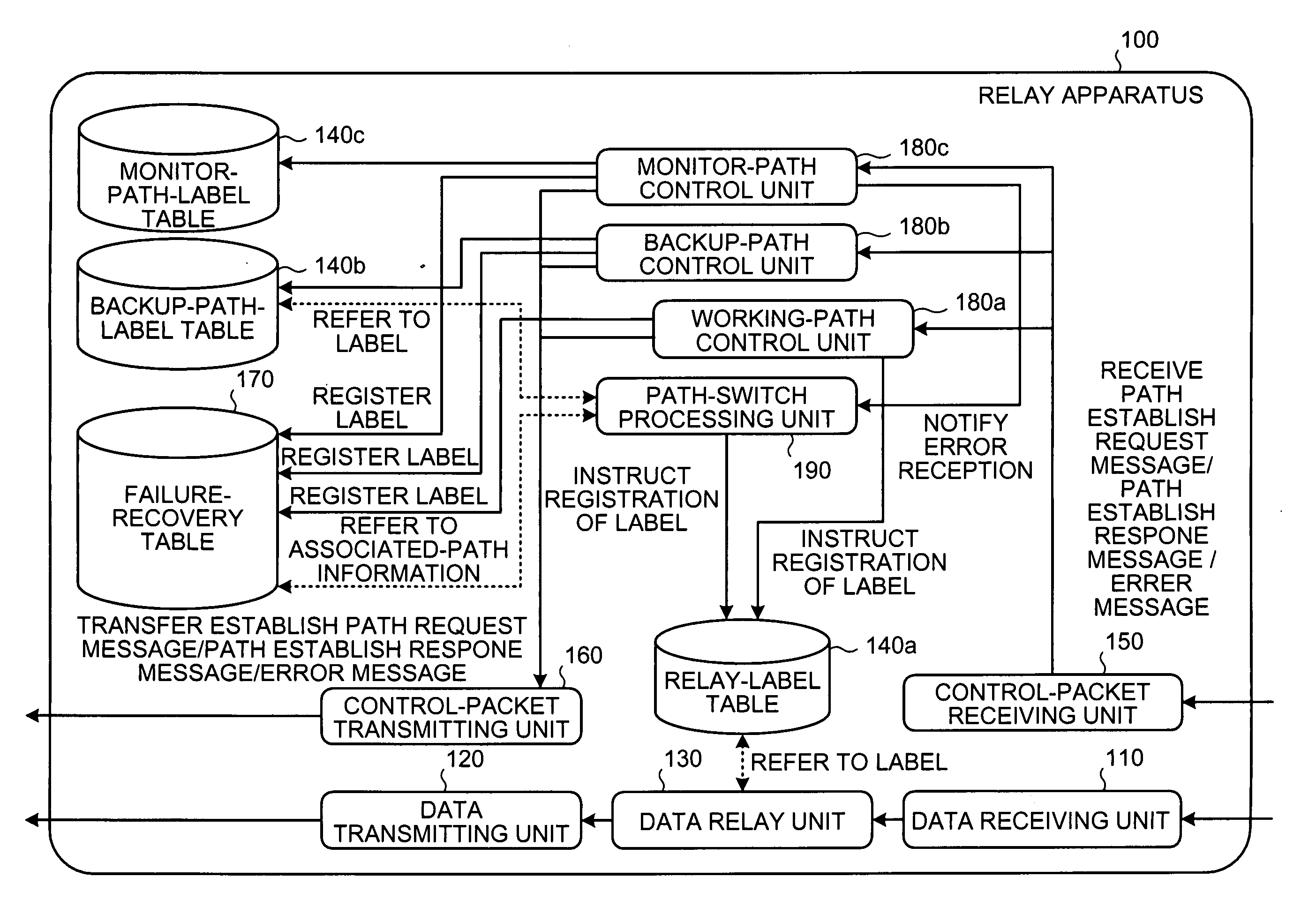
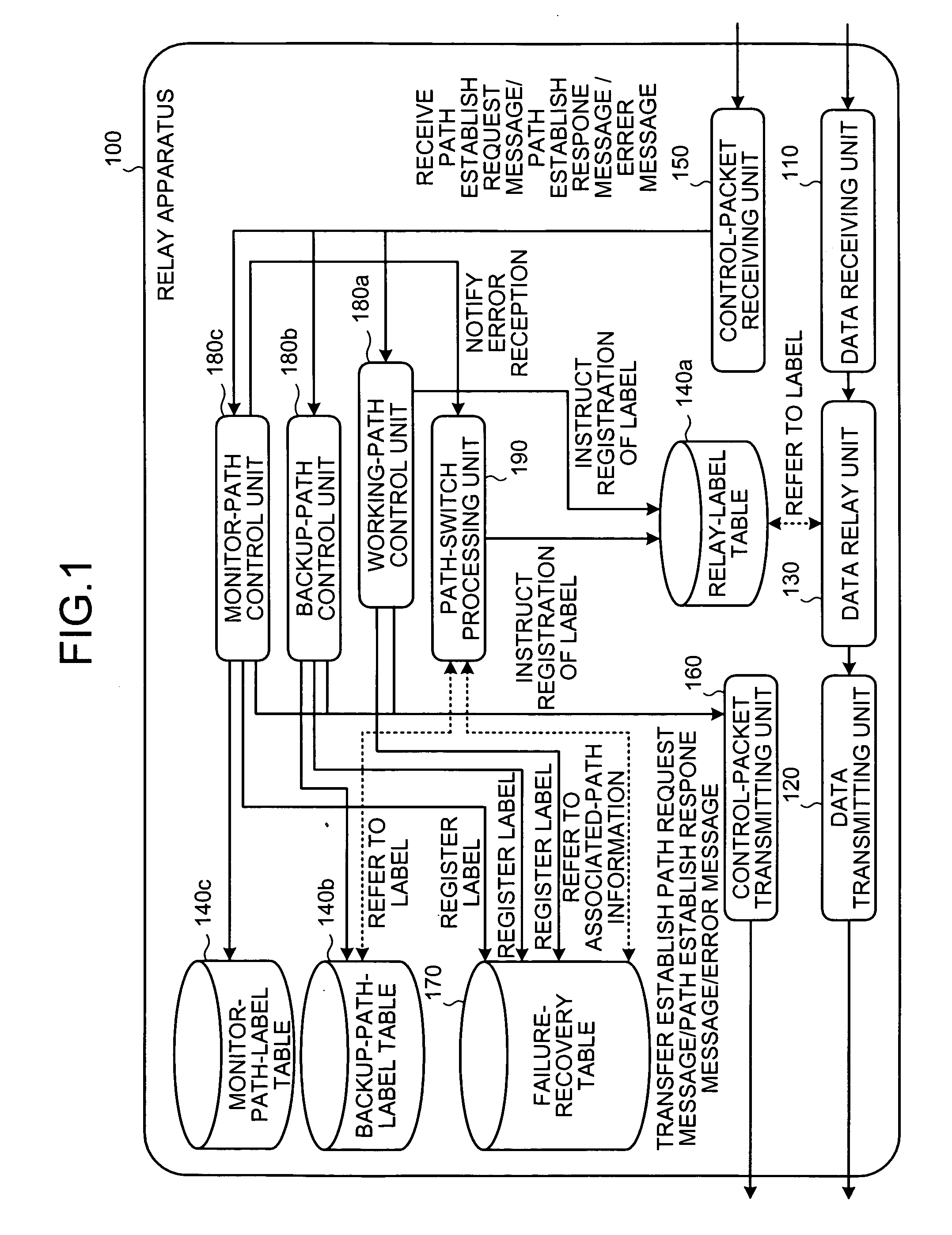
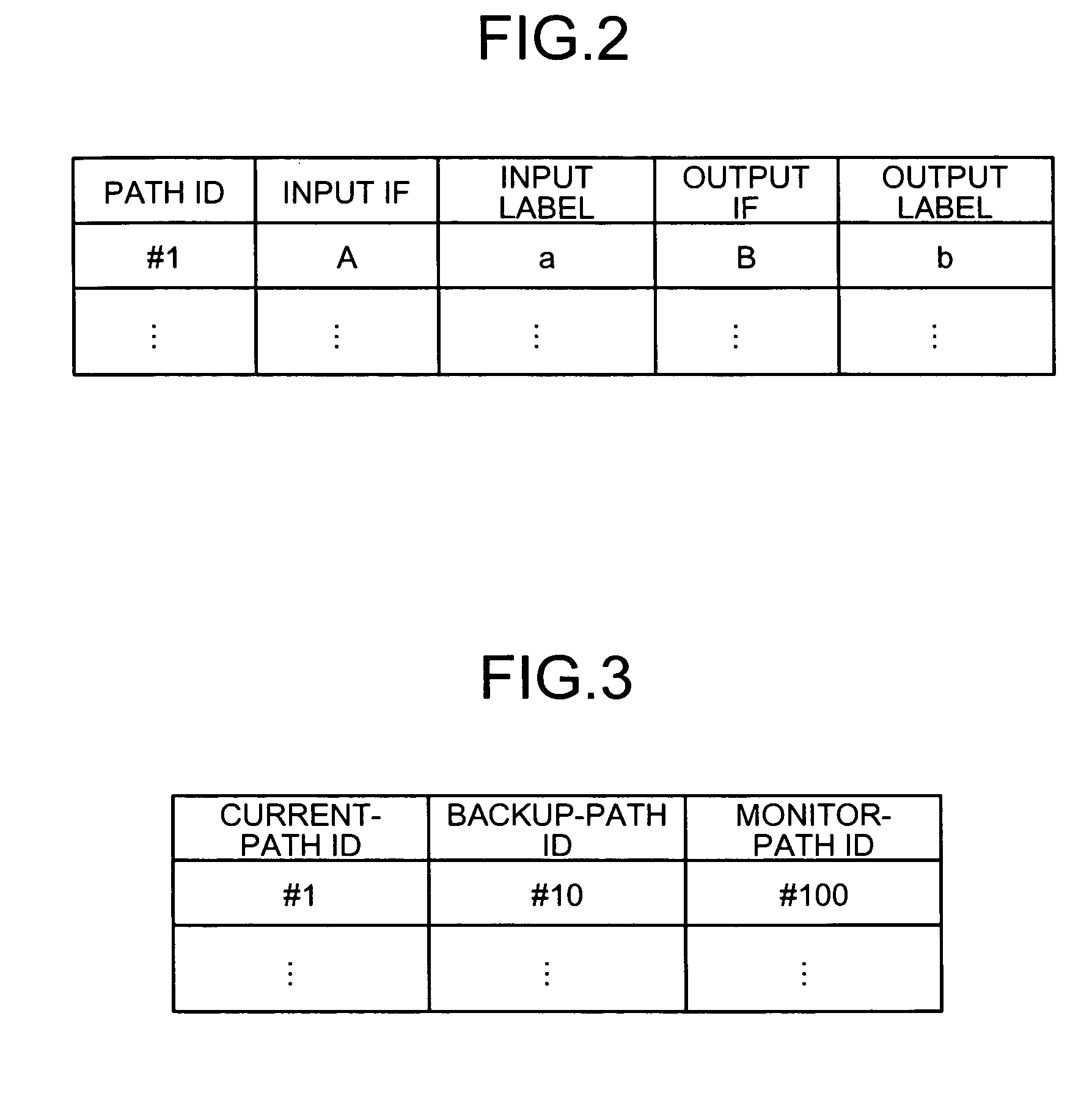
Data relay apparatus and data relay method
A failure-recovery-information storing unit stores failure-recovery information in which a working path is associated with a backup path. A failure-occurrence-notification receiving unit receives a failure-occurrence notification indicating that a failure has occurred in the working path. A backup-path searching unit searches for a backup path corresponding to the working path on which the failure has occurred, based on the failure-recovery information. A path-switch processing unit carries out a path-switch process, in such a manner that the data to be transferred using the working path in which the failure has occurred is transferred using the backup path.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Controlled switchover of unicast and multicast data flows in a packet based switching system
ActiveUS7058010B2Special service provision for substationError preventionTraffic capacityData stream
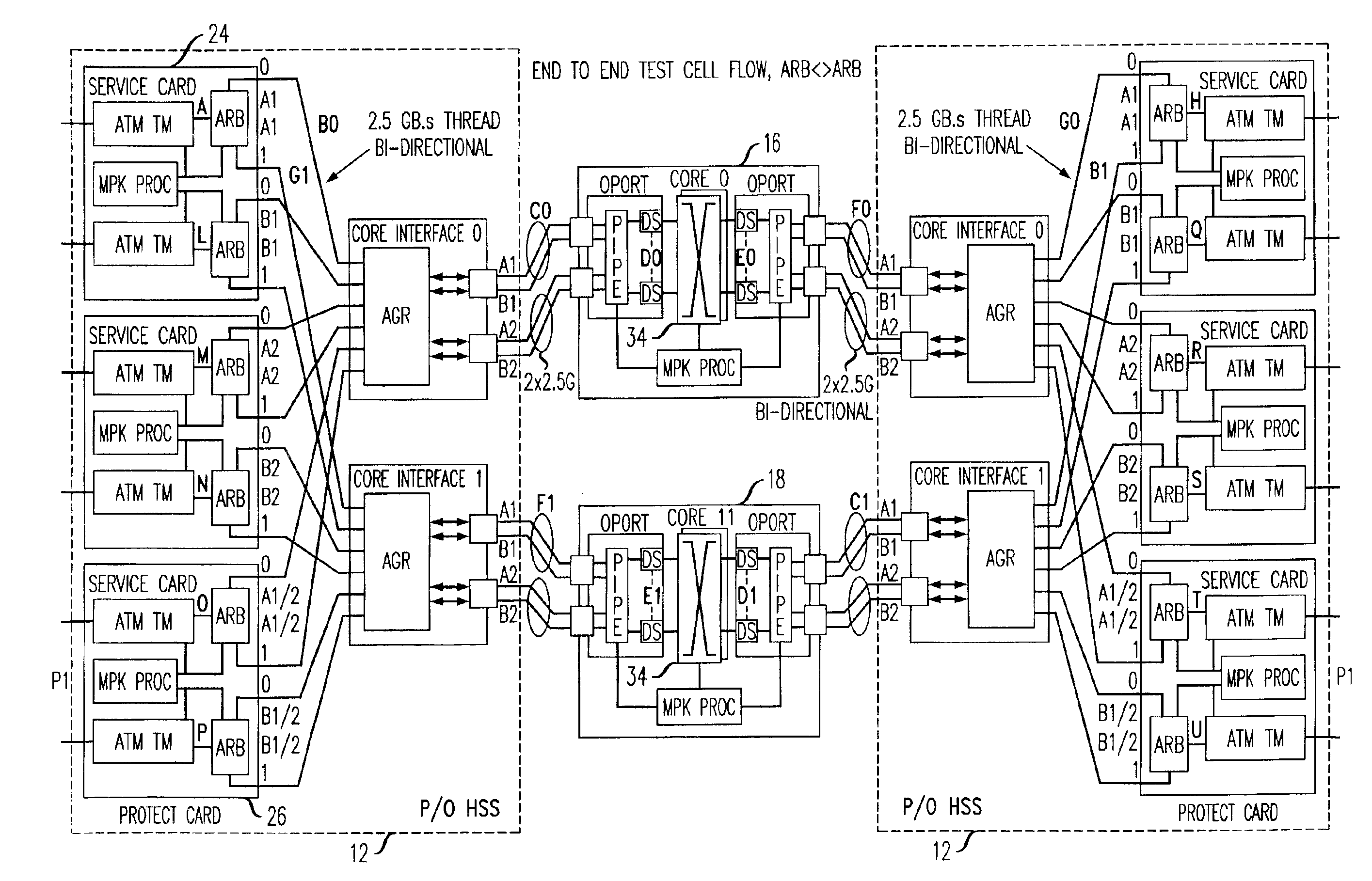
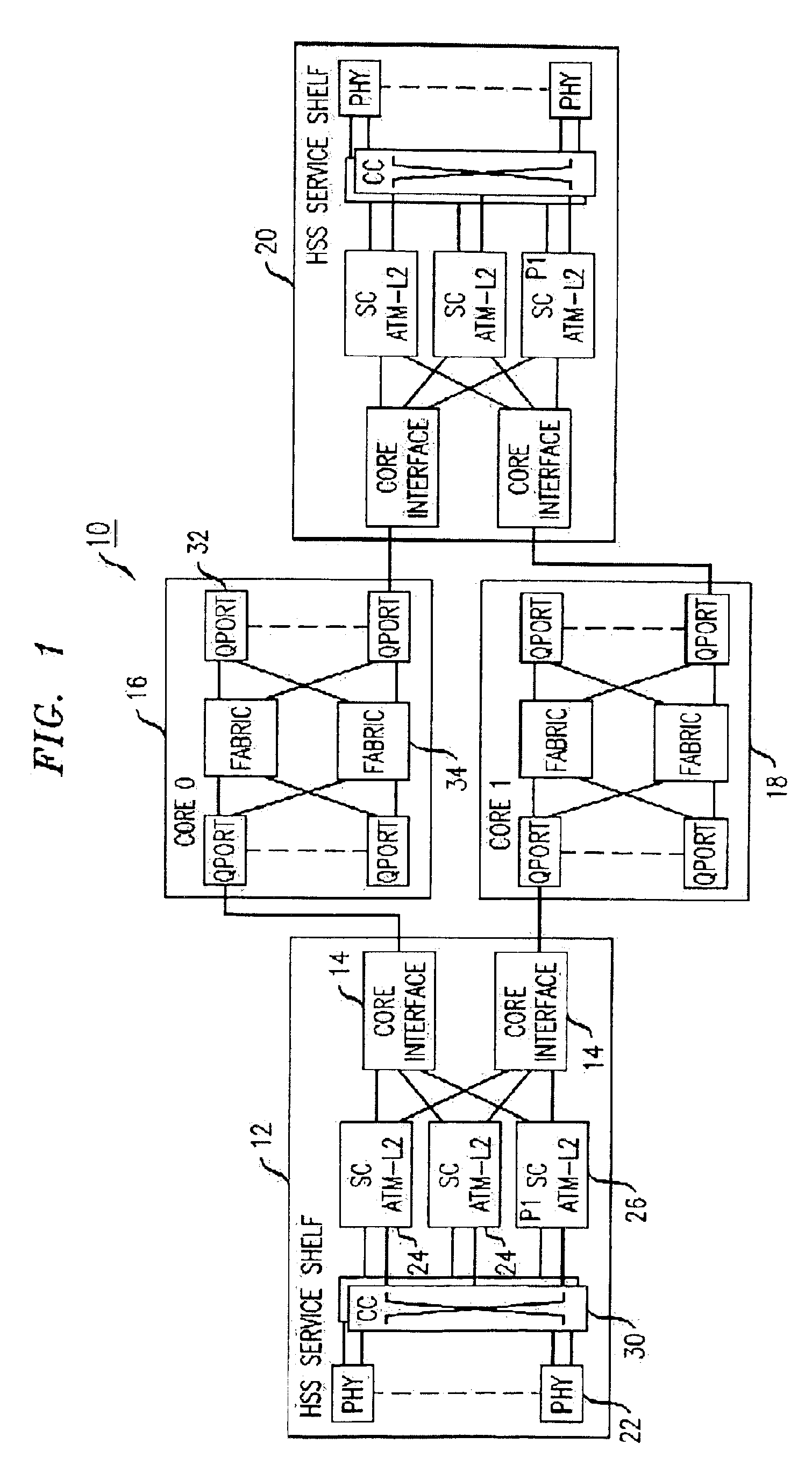
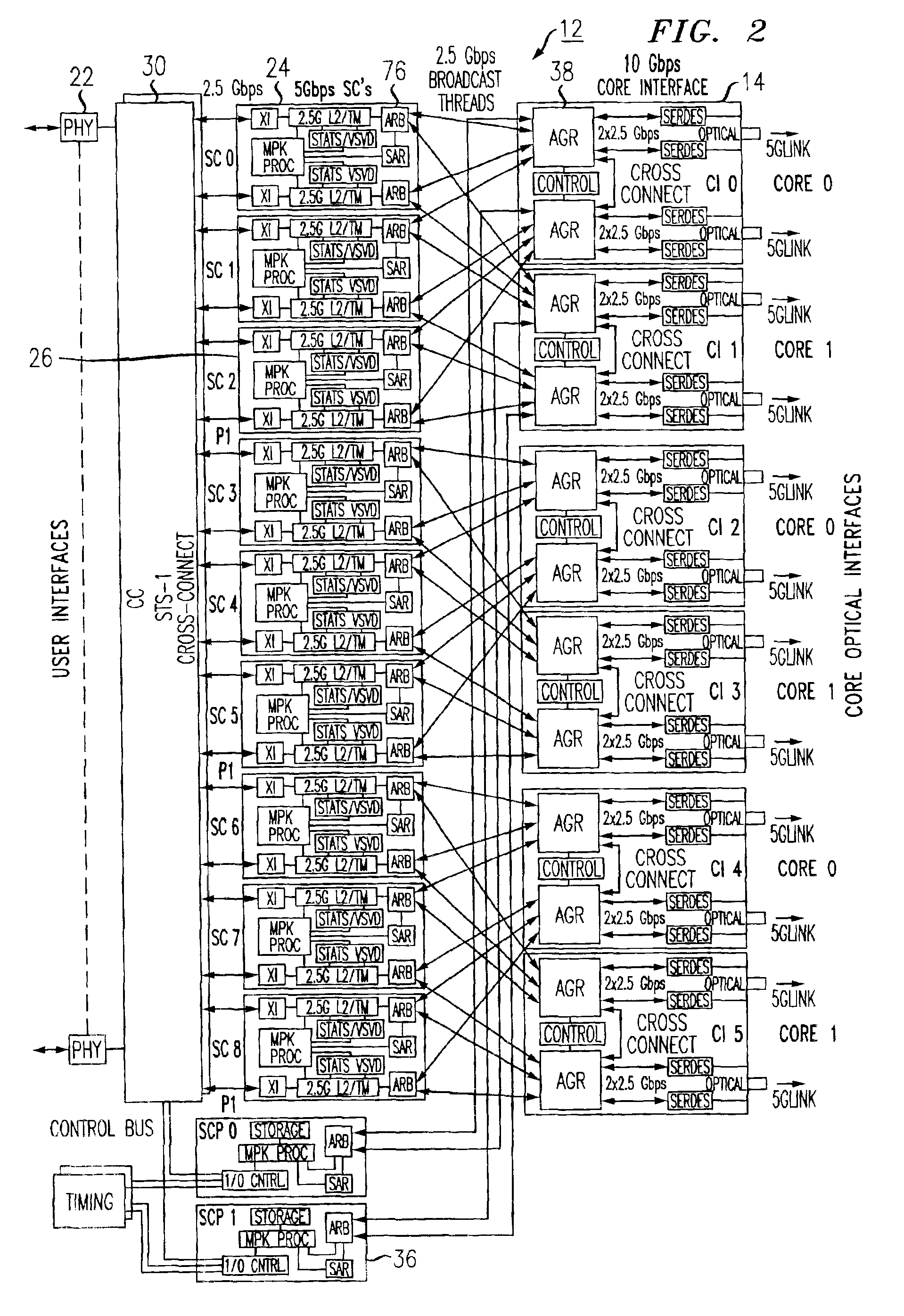
The present invention is a methodology for controlled switchover of unicast and multicast data flows in packet based switching system. In some cases it is advantageous to purposefully support switchover of flows from one path to the other without causing loss of data. This is termed a “controlled” or “hitless” switchover. In accordance with the present invention switchover methodology, given that an ingress arbiter device is transmitting to both cores simultaneously, it is required that the flows to both switching cores be synchronized at an aggregator level and that an egress arbiter be given time to cease receiving packets from one Core then switch over to the other Core, and continue receiving packets.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
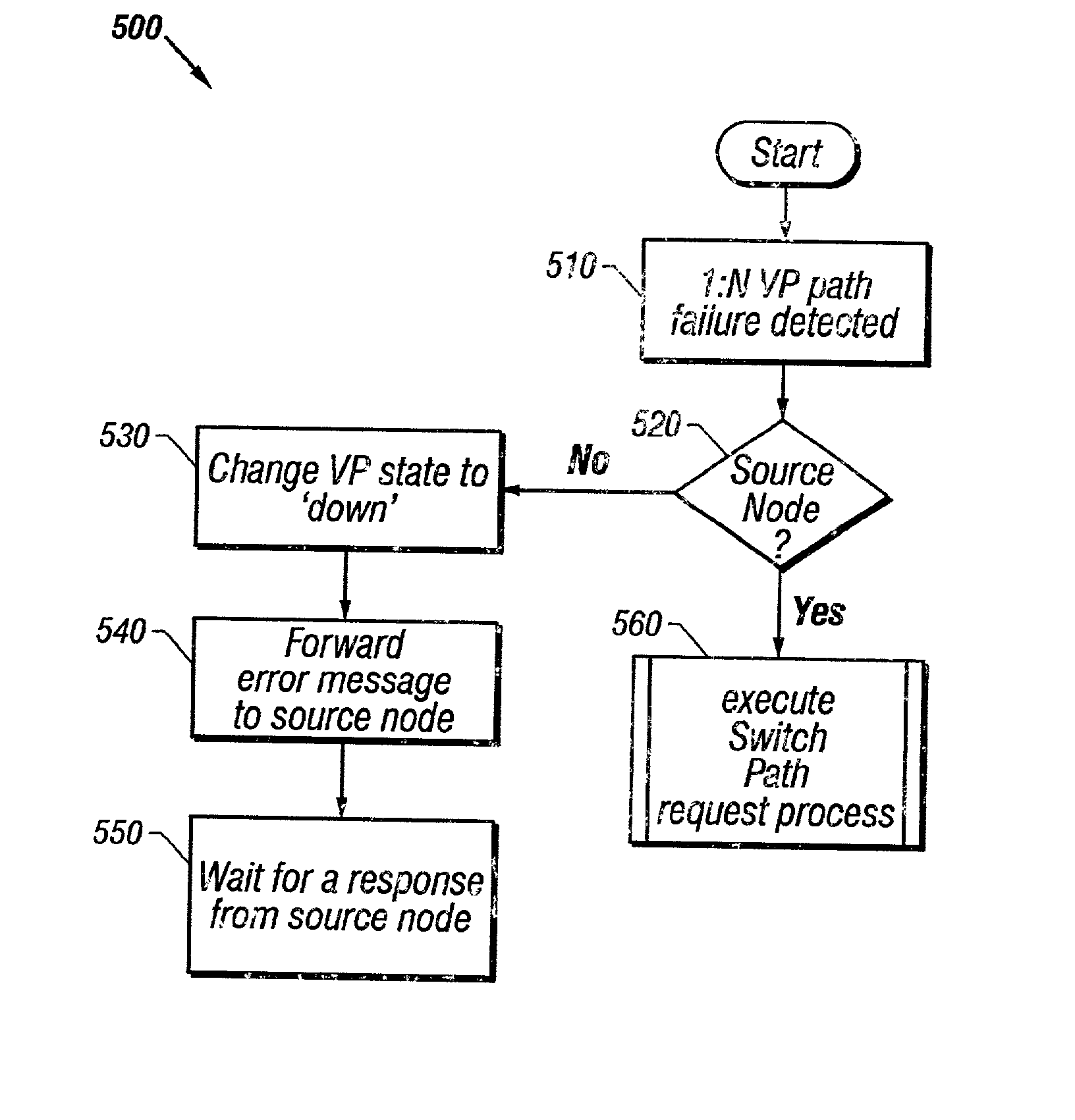
Method for restoring a virtual path in an optical network using 1:N protection
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
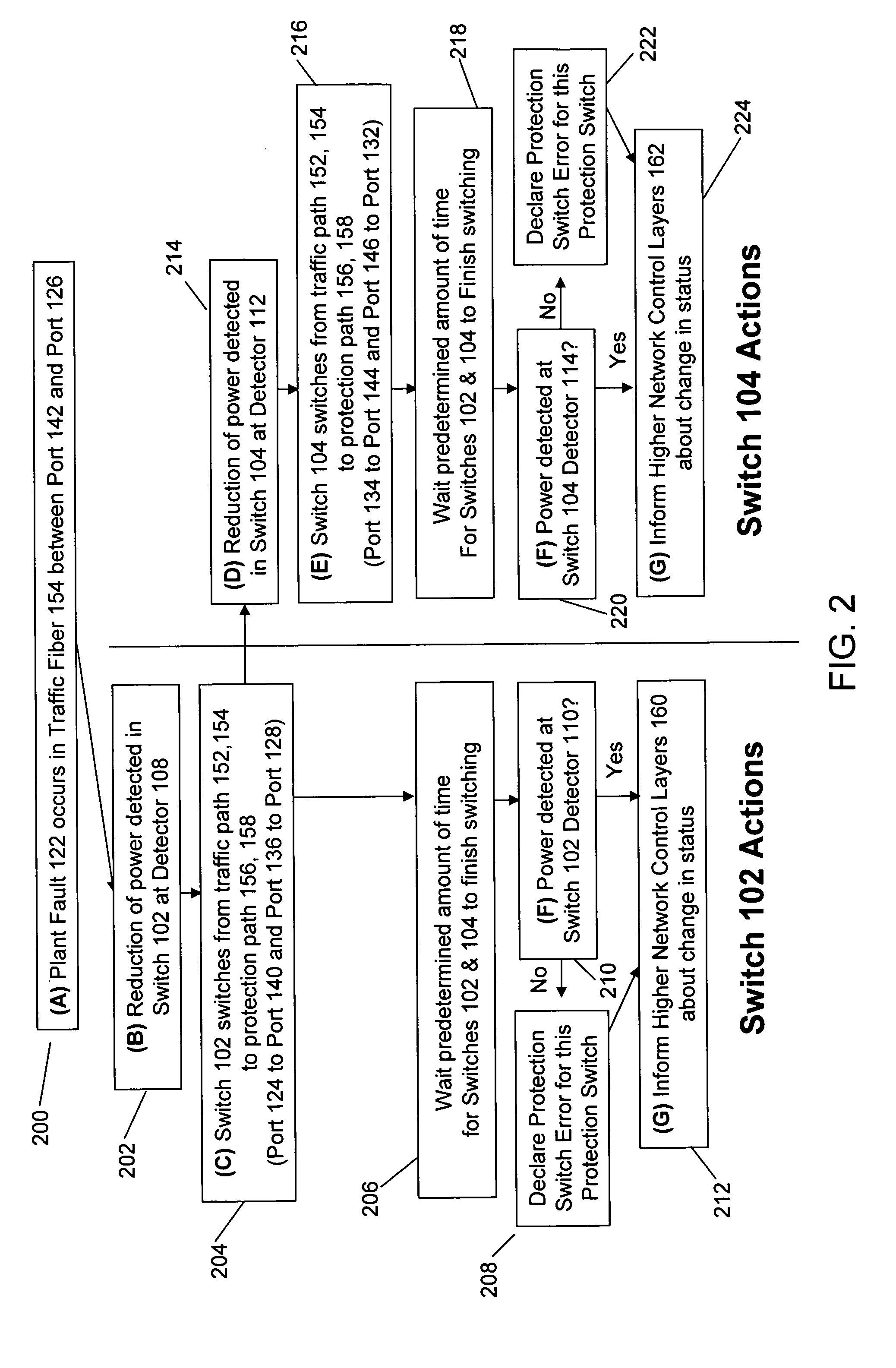
Method and apparatus for network fault detection and protection switching using optical switches with integrated power detectors
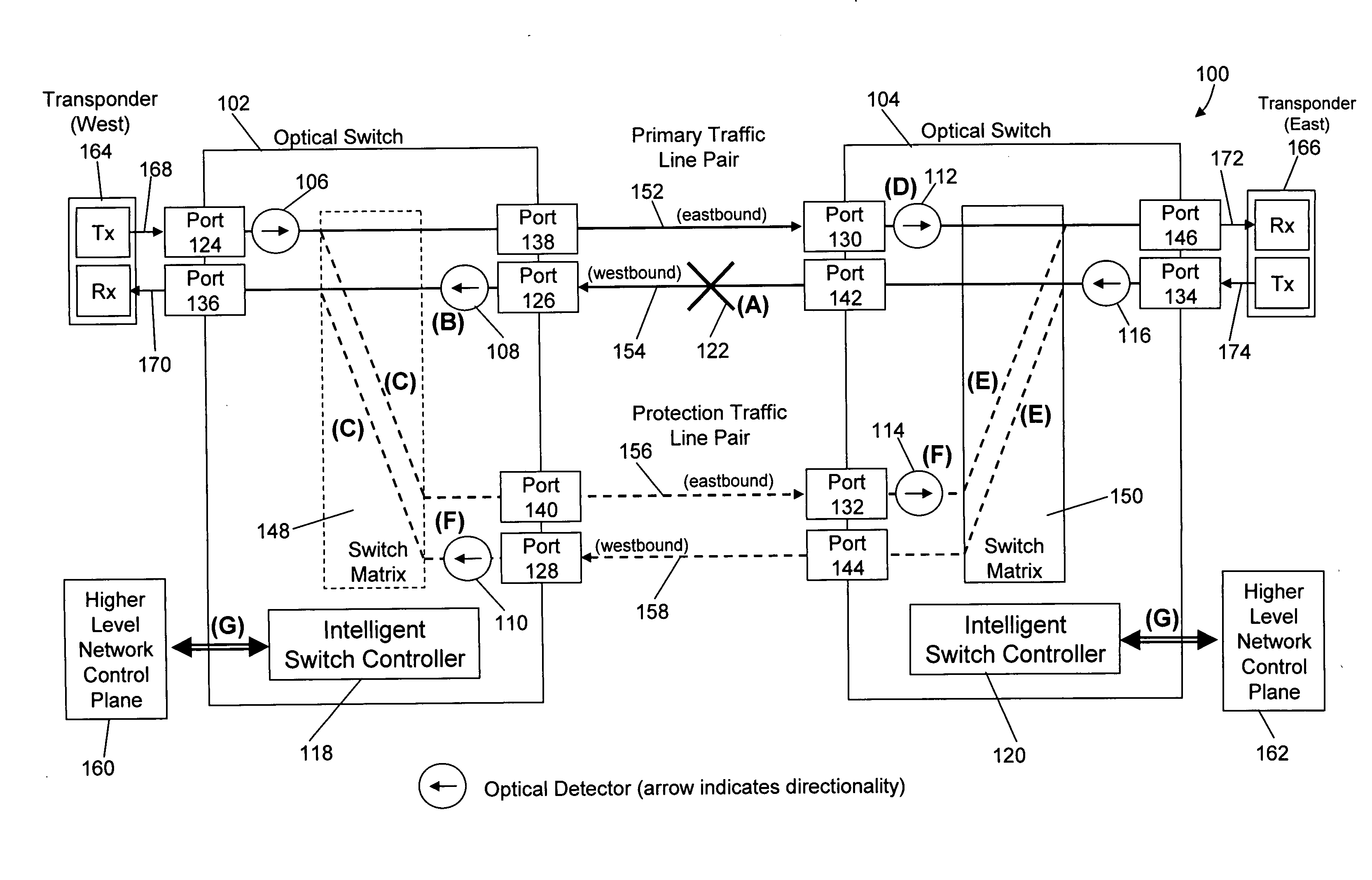
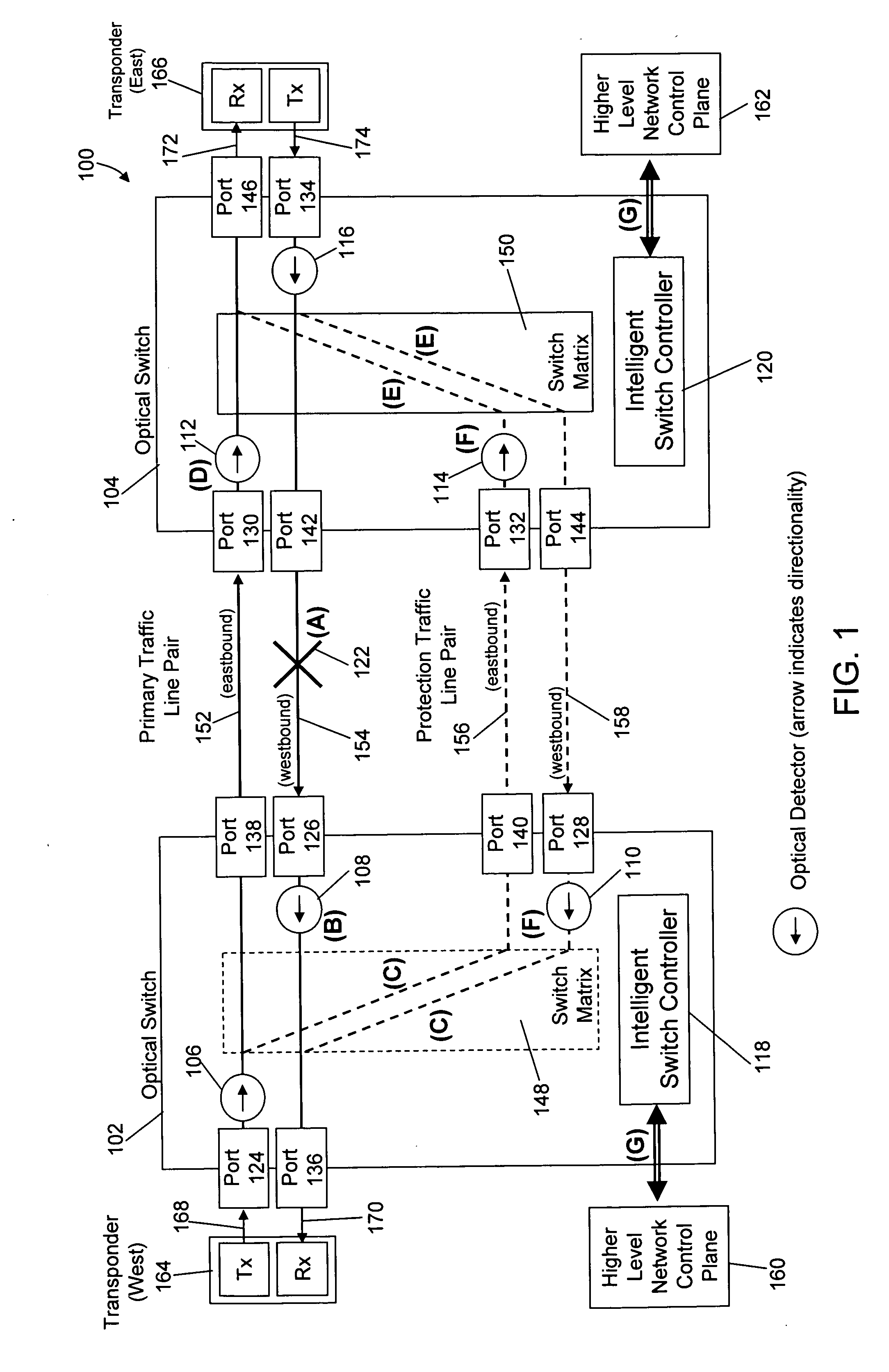
ActiveUS20080175587A1Reduced network fault recovery timeShorten recovery timeMultiplex system selection arrangementsLaser detailsPower detectorPhysical layer
Current network switching architectures require communication with a higher level network control plane, which can be slow to reroute communications, resulting in unacceptable losses of communications for customers. Examples embodiments of the present invention reroute communications faster detecting optical power of an optical signal at optical switches coupled via optical communication paths, and causing at least one optical communication path between a first optical switch and second optical switch to switch to an alternative optical communication path, in part, through physical layer triggering in an event optical power at at least one of the first or second optical switches falls below a threshold level. Switching in response to physical layer triggering may result in reduced switching times and, consequently, faster restoration of communications to customers after a network fault interruption.
Owner:POLATIS PHOTONICS INC
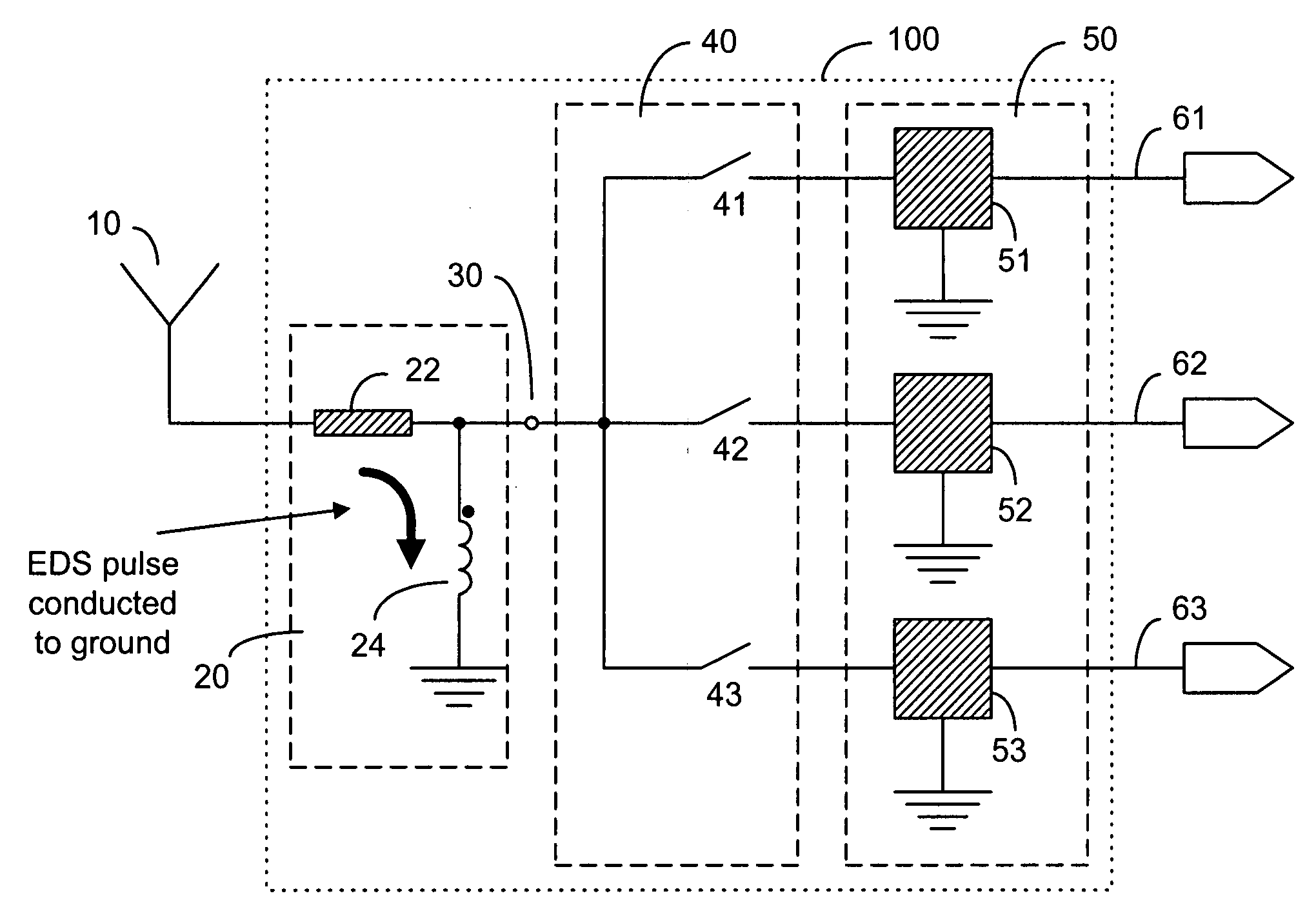
RF front-end architecture for a separate non-50 ohm antenna system
InactiveUS20070085754A1Multiple-port networksAntennas earthing switches associationTransceiverRF front end
A transceiver system having an RF front-end operatively connected to two separate non-50 ohm antennas for separately providing transmission / reception paths for 1 GHz band and for 2 GHz band. A switching module is operatively connected to each antenna for mode and frequency-range selection within each band. Each switching module has a plurality of switching elements connected to a plurality of signal paths. Matching is separately and independently provided for each signal path. The matching can be achieved by using distributed elements or lumped elements arranged in shunt or series in order to widen the bandwidth. An electrostatic discharge protection circuit is provided between the antenna feed point and the switching module. The protective circuit can also be used as a discrete matching network that can be optimized depending on the phone mechanics and dimensions.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
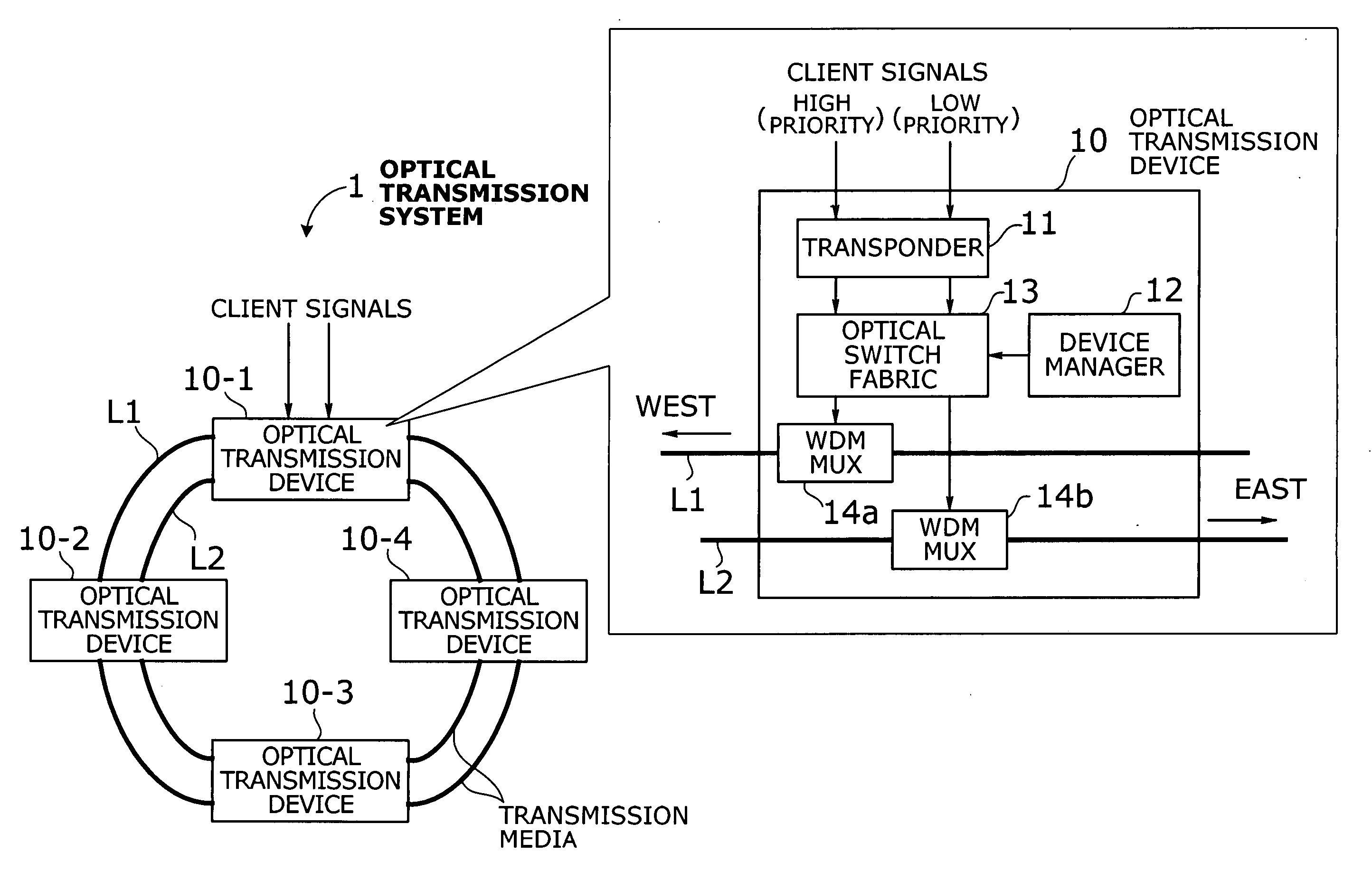
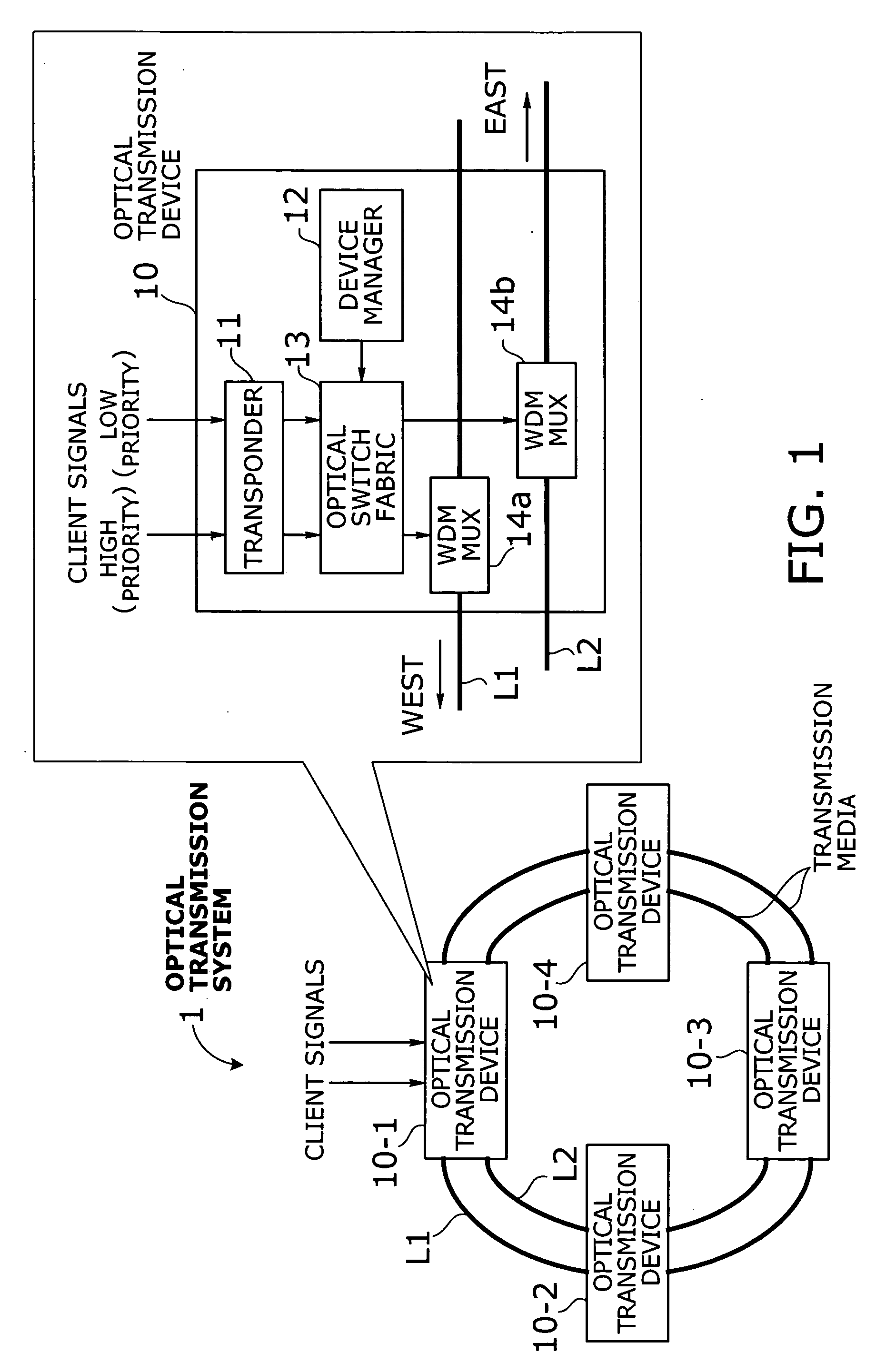
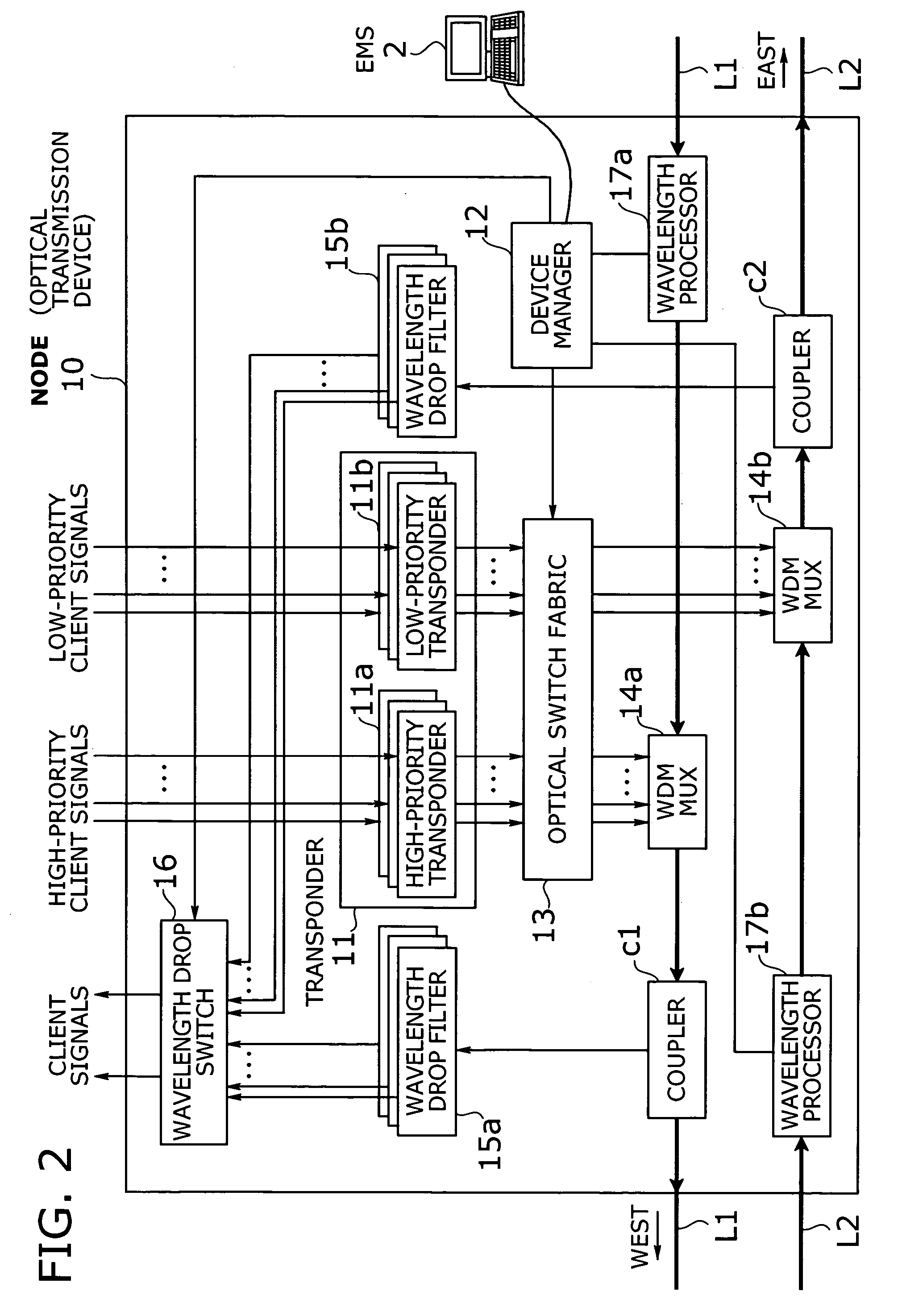
Optical transmission system with two-mode ring protection mechanism for prioritized client signals
InactiveUS20060013584A1Efficient use of bandwidthImprove fault toleranceRing-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsFault toleranceSurvivability
An optical transmission system that offers more efficient bandwidth usage in normal operation, as well as enhanced fault tolerance for higher service availability. A transponder converts high-priority and low-priority client signals into high-priority and low-priority wavelength signals to be added to network traffic. An optical switch fabric normally delivers high-priority and low-priority wavelength signals to high-priority and low-priority paths, respectively, where the two paths run in opposite directions. Such signals and paths are prioritized in terms of survivability against network failure. In case of a network failure, the optical switch fabric performs protection switching in either duplicate switching mode or path switchover mode depending on network failure information and drop wavelengths of each optical transmission device. In duplicate switching mode, high-priority wavelength signals are directed to both the high-priority and low-priority paths. In path switchover mode, they are routed to the low-priority path, instead of the high-priority path.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
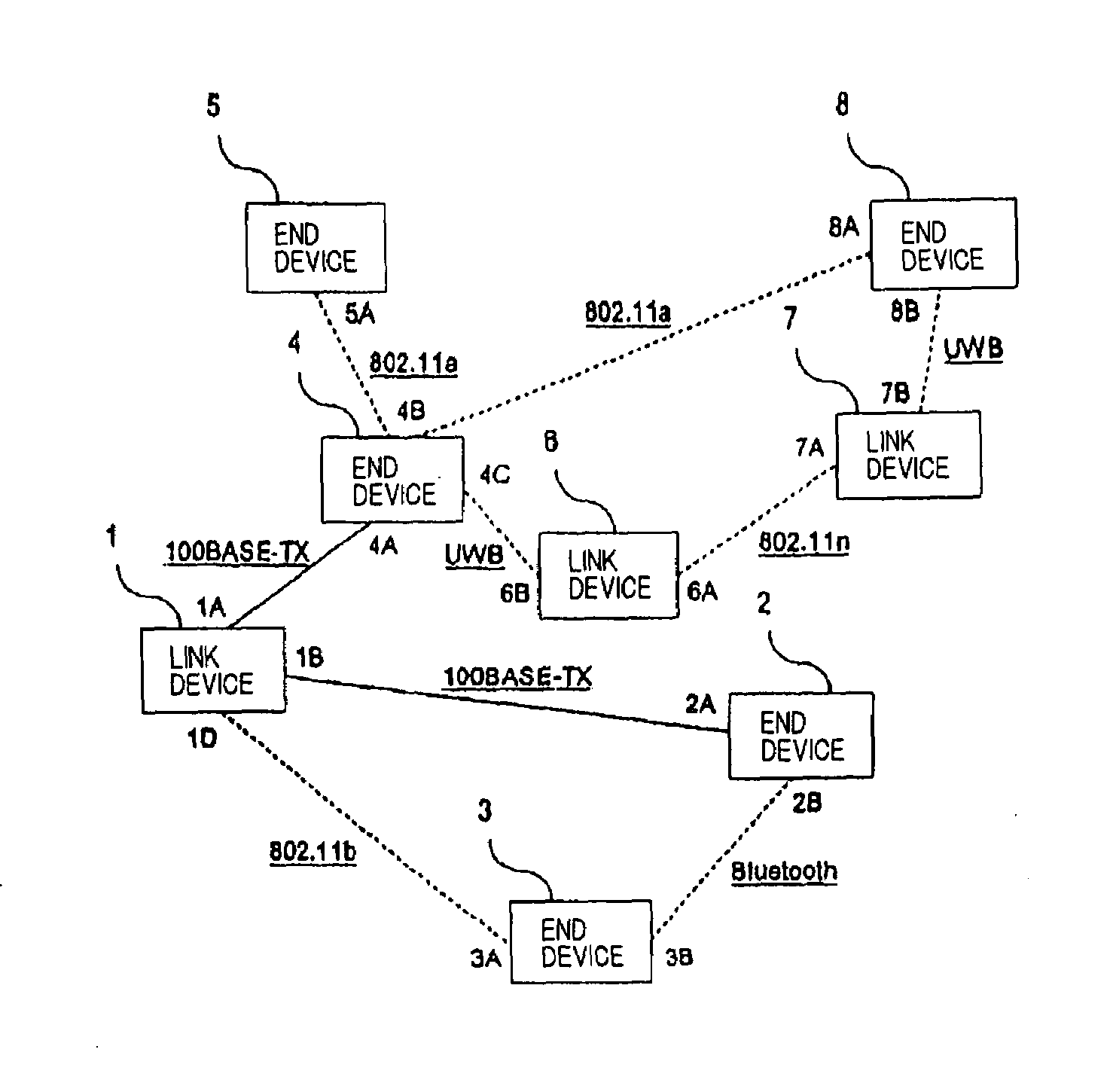
Communications apparatus, communications system, and communication method
InactiveUS20070195715A1Network topologiesConnection managementCommunications systemTelecommunications link
In a network made up of a plurality of devices each capable of a multi-hop communication that conforms to at least one of the wired communication standards or wireless communication standards, each device monitors a communication situation on communication links and path established between the device and a destination device. When the communication situation changes, the device switches the communication path for use in a communication with the destination device to another communication path which can be established between the device and destination device.
Owner:NEC CORP
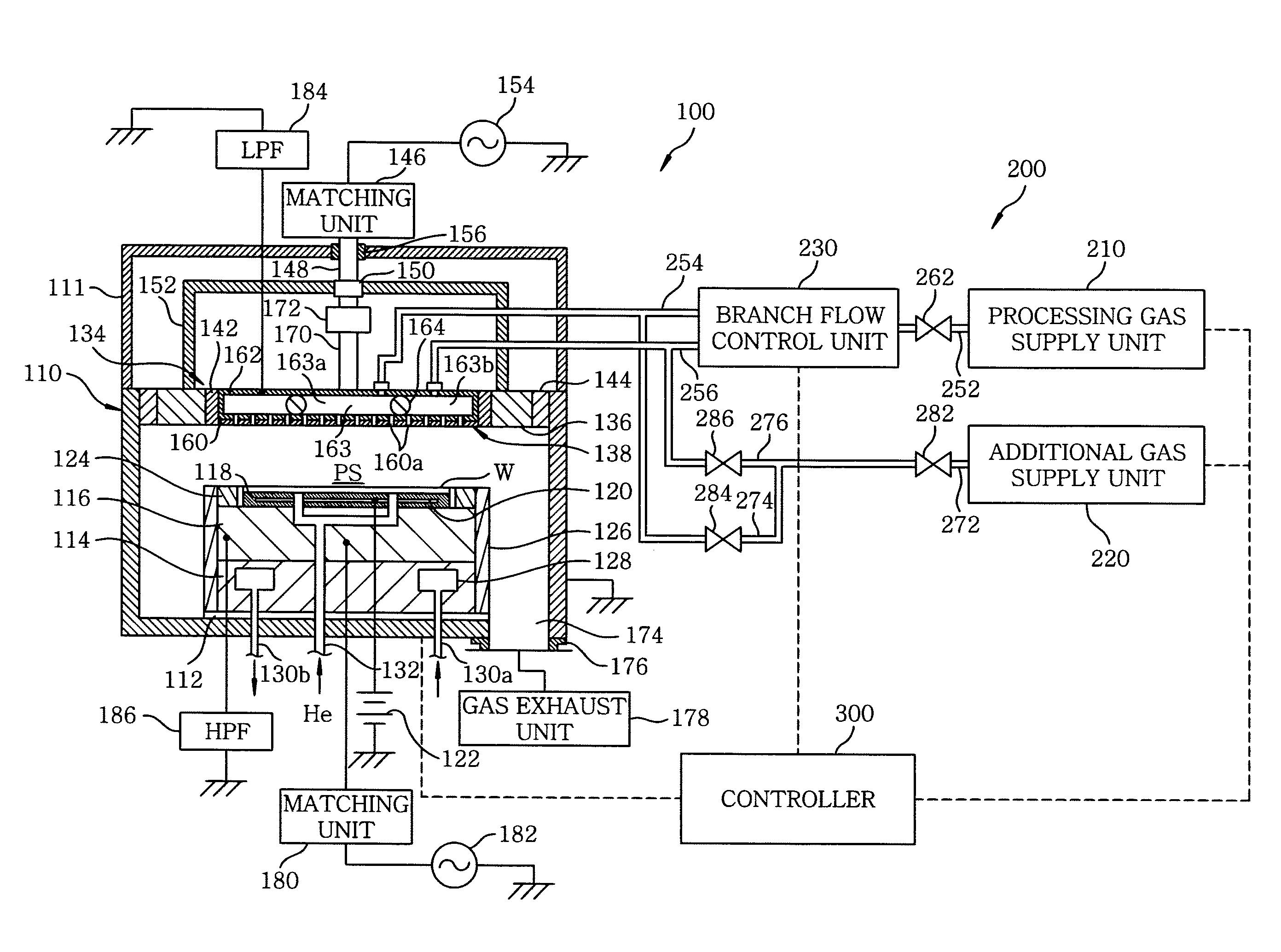
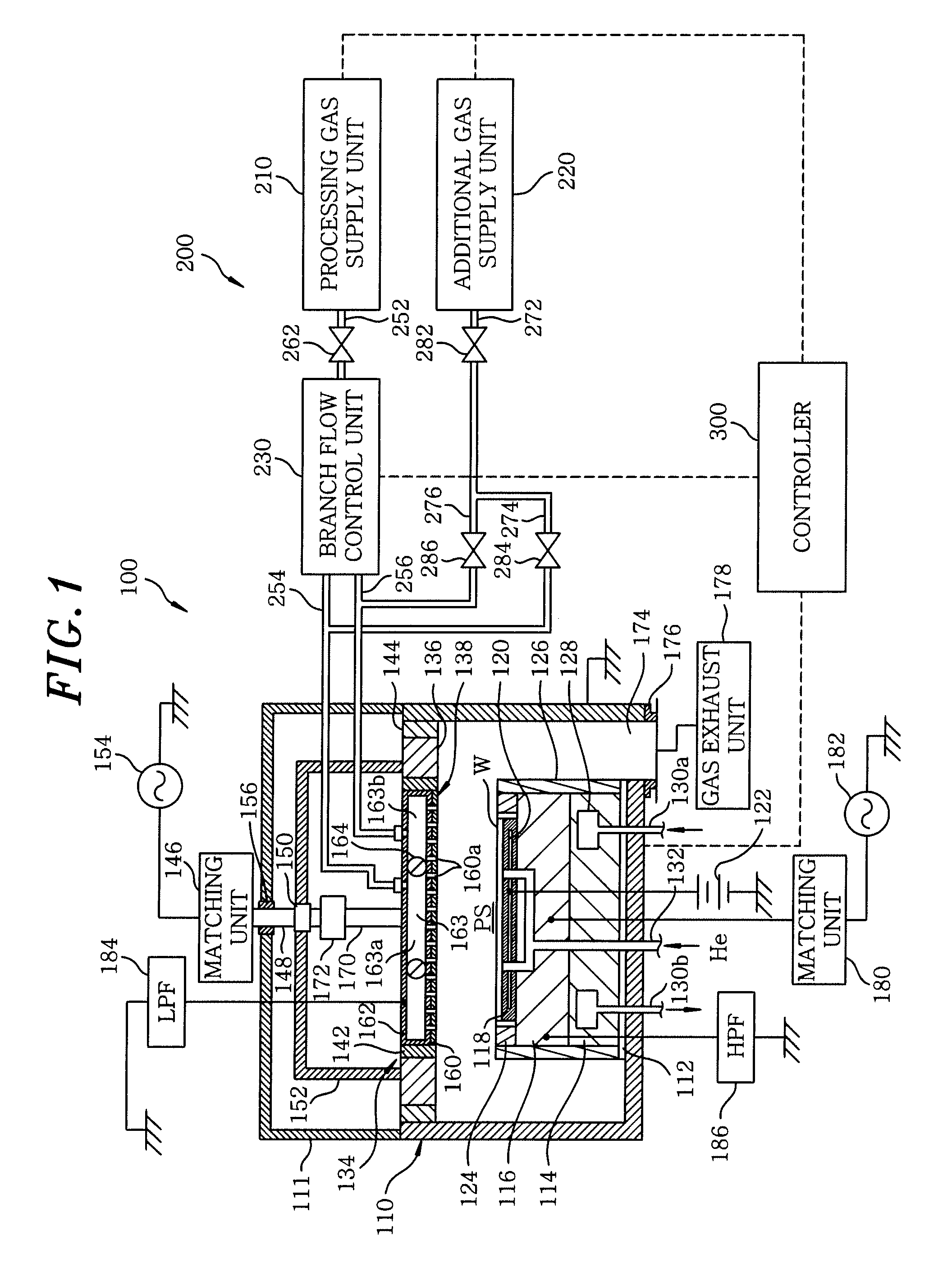
Gas supply system, substrate processing apparatus and gas supply method
InactiveUS20070175391A1Desired in-surface uniformityEasy to operate and controlLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInternal pressureProcess engineering
A gas supply system for supplying a gas into a processing chamber for processing a substrate to be processed includes: a processing gas supply unit; a processing gas supply line; a first and a second processing gas branch line; a branch flow control unit; an additional gas supply unit; an additional gas supply line; a first and a second additional gas branch line; a flow path switching unit; and a control unit. Before processing the substrate to be processed, the control unit performs a pressure ratio control on the branch flow control unit while the processing gas supply unit supplies the processing gas. After the inner pressures of the first and the second processing gas branch line become stable, the control unit switches the pressure ratio control to a fixed pressure control, and then the additional gas supply unit supplies the additional gas.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Electric optical distance wavelength meter
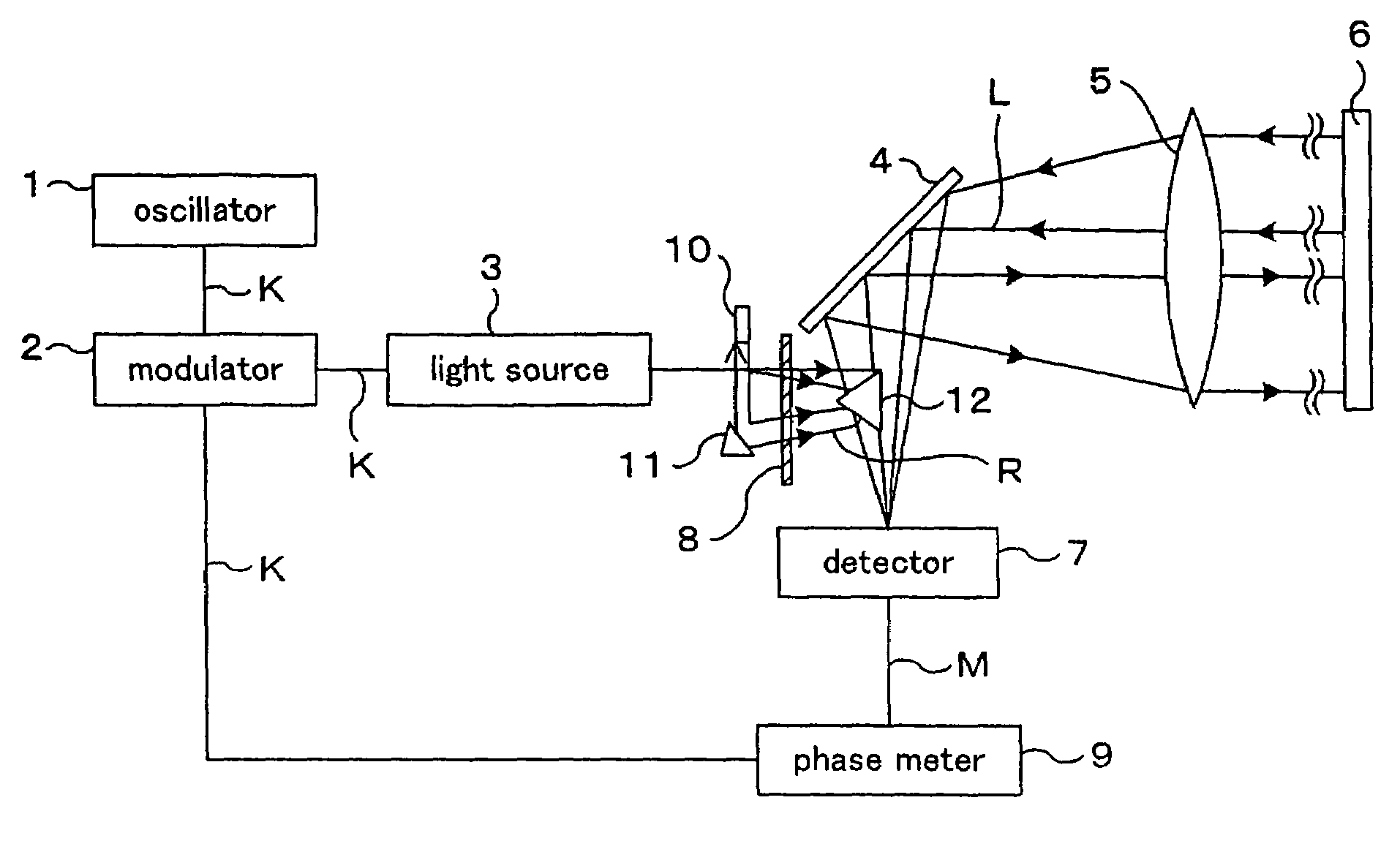
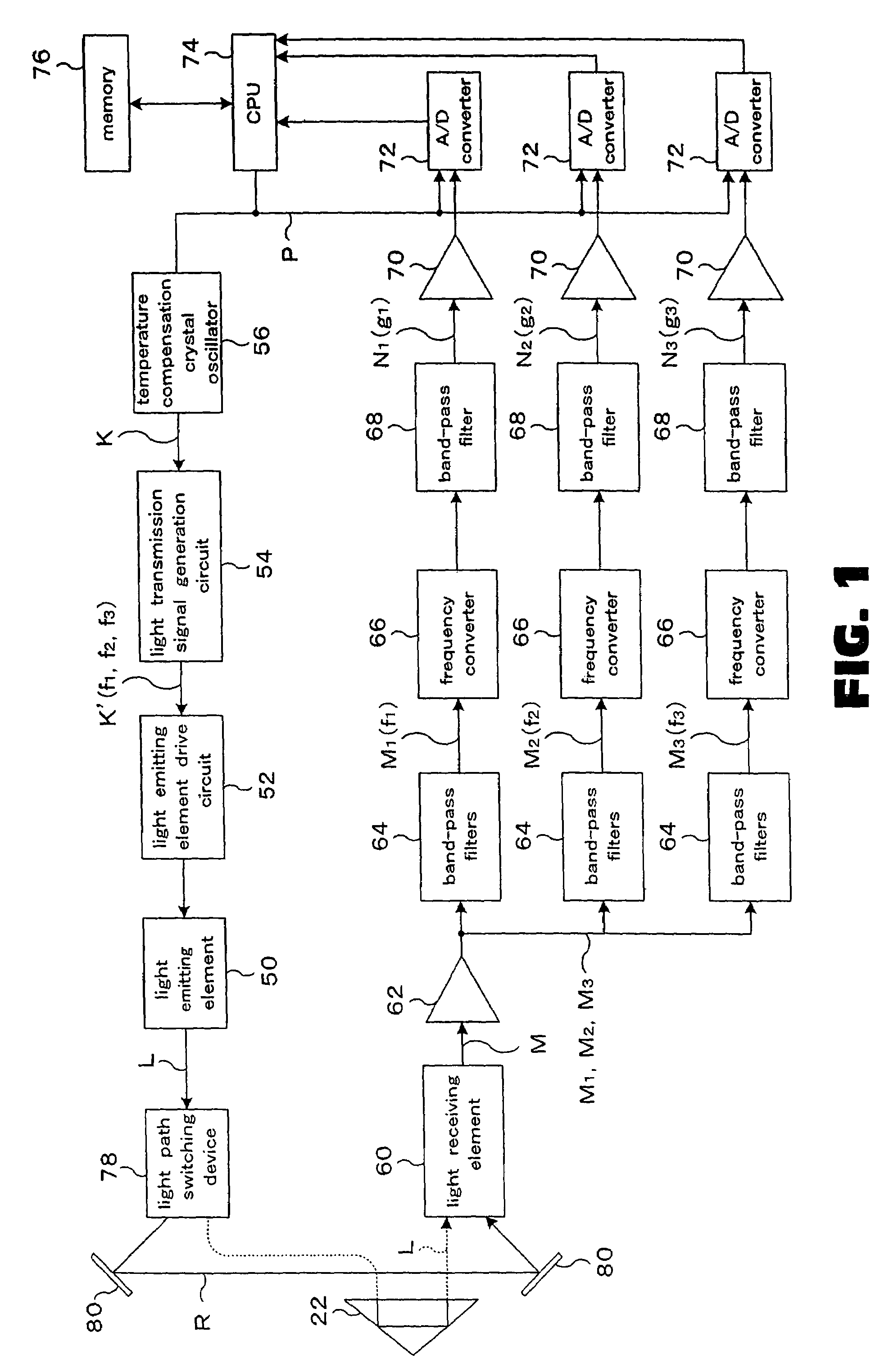
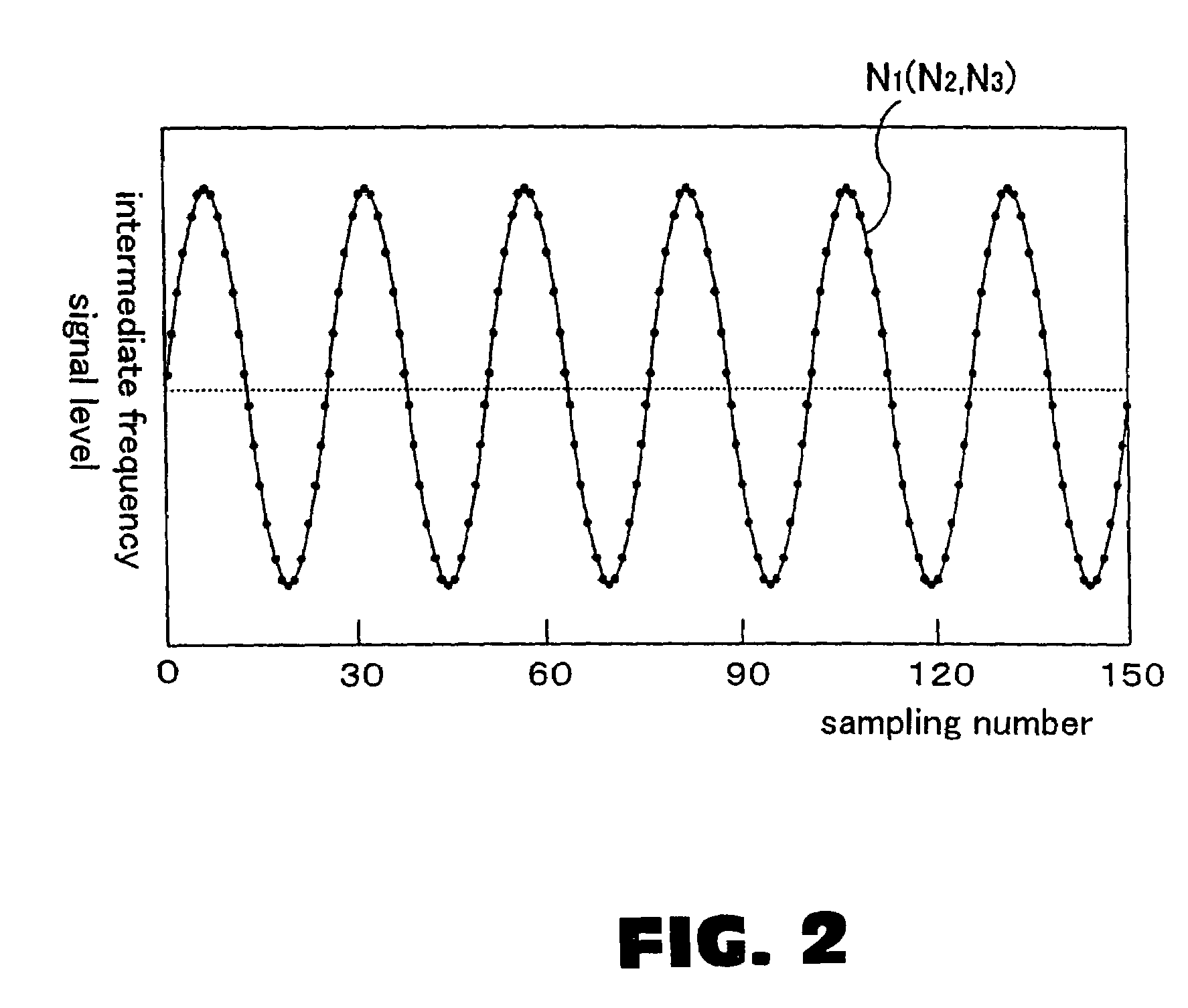
InactiveUS7339655B2Shorten the timeAccurate measurementOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationElectricityObject based
Owner:SOKKOIA COMPANY LIMITED
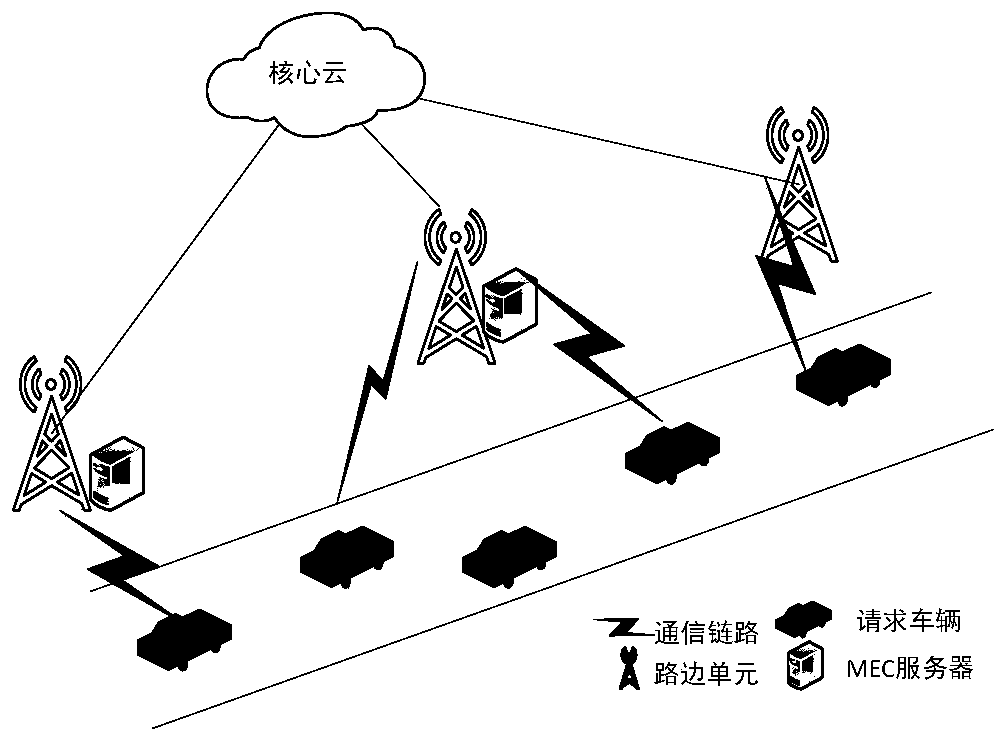
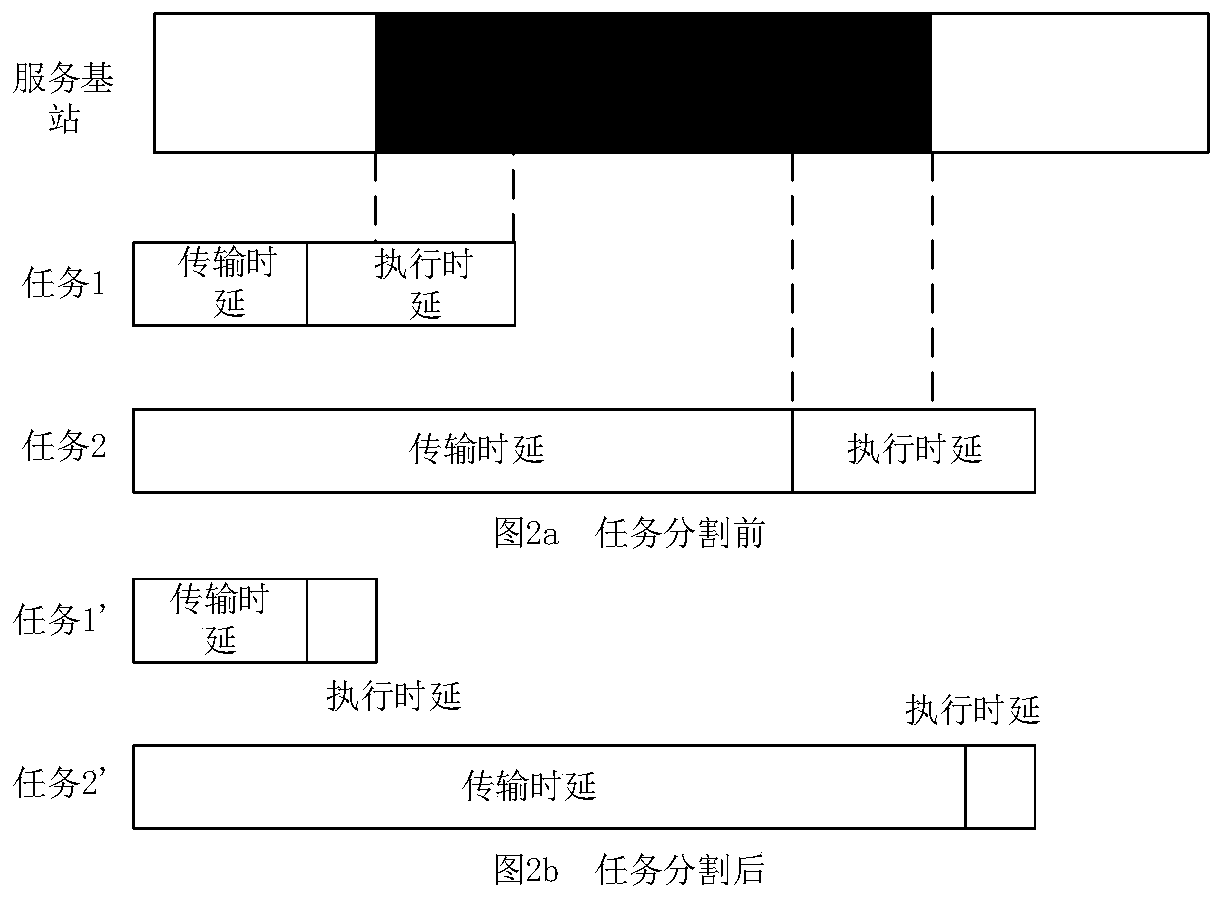
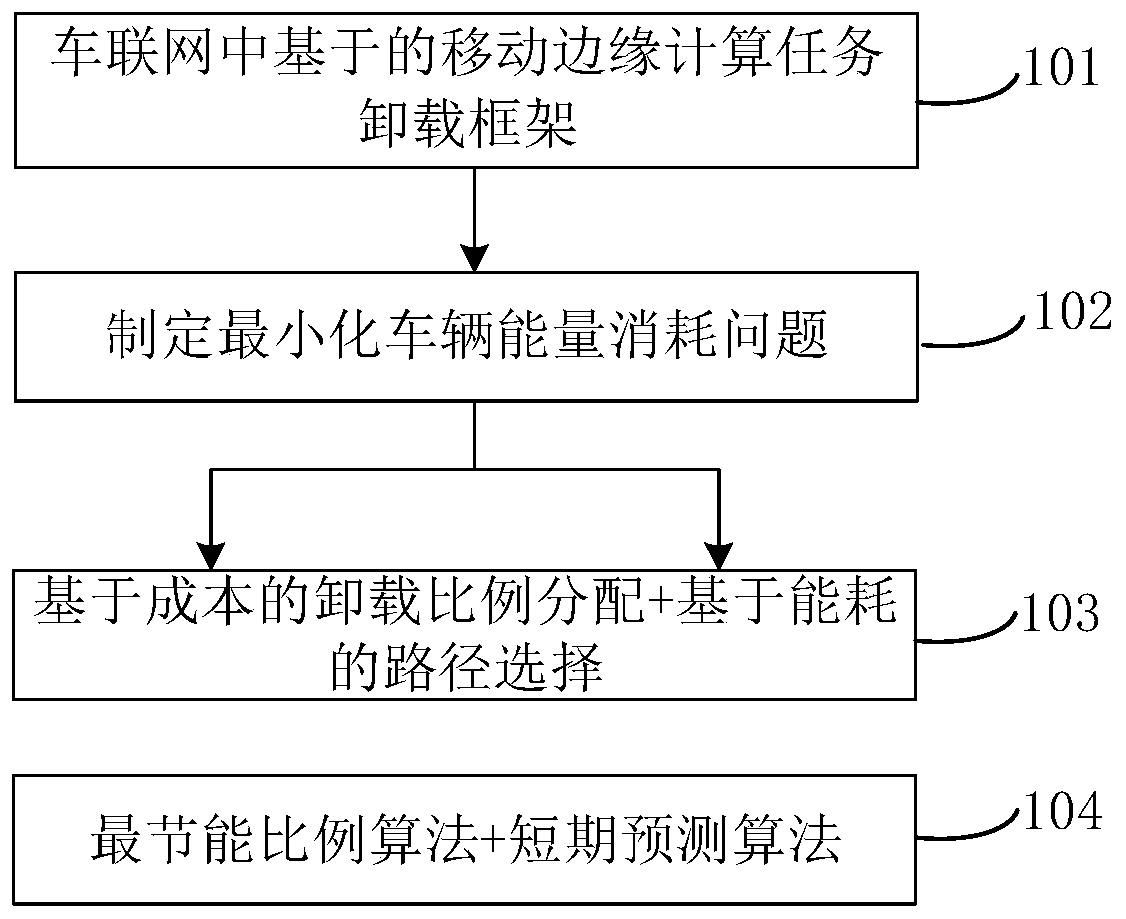
Minimized vehicle energy consumption task unloading scheme based on mobile edge calculation
ActiveCN109951821AParticular environment based servicesLocation information based servicePrediction algorithmsThe Internet
The mobile edge calculates close attention of researchers caused by communication advantages brought by the fact that the mobile edge is close to a user, and the communication quality of vehicles canbe effectively improved by combining the mobile edge with the Internet of Vehicles technology. Task offloading problems based on vehicle mobility management are studied herein. In consideration of real-time switching of a communication area passing through a base station and real-time connection and disconnection of a communication line when a vehicle moves, the task unloading problem is decomposed into a resource-based unloading proportion distribution sub-problem and a prediction-based path switching sub-problem. And a maximum energy-saving selection algorithm and a short-term path prediction algorithm are formulated to meet the time delay constraint and minimize the task unloading energy consumption at the same time.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
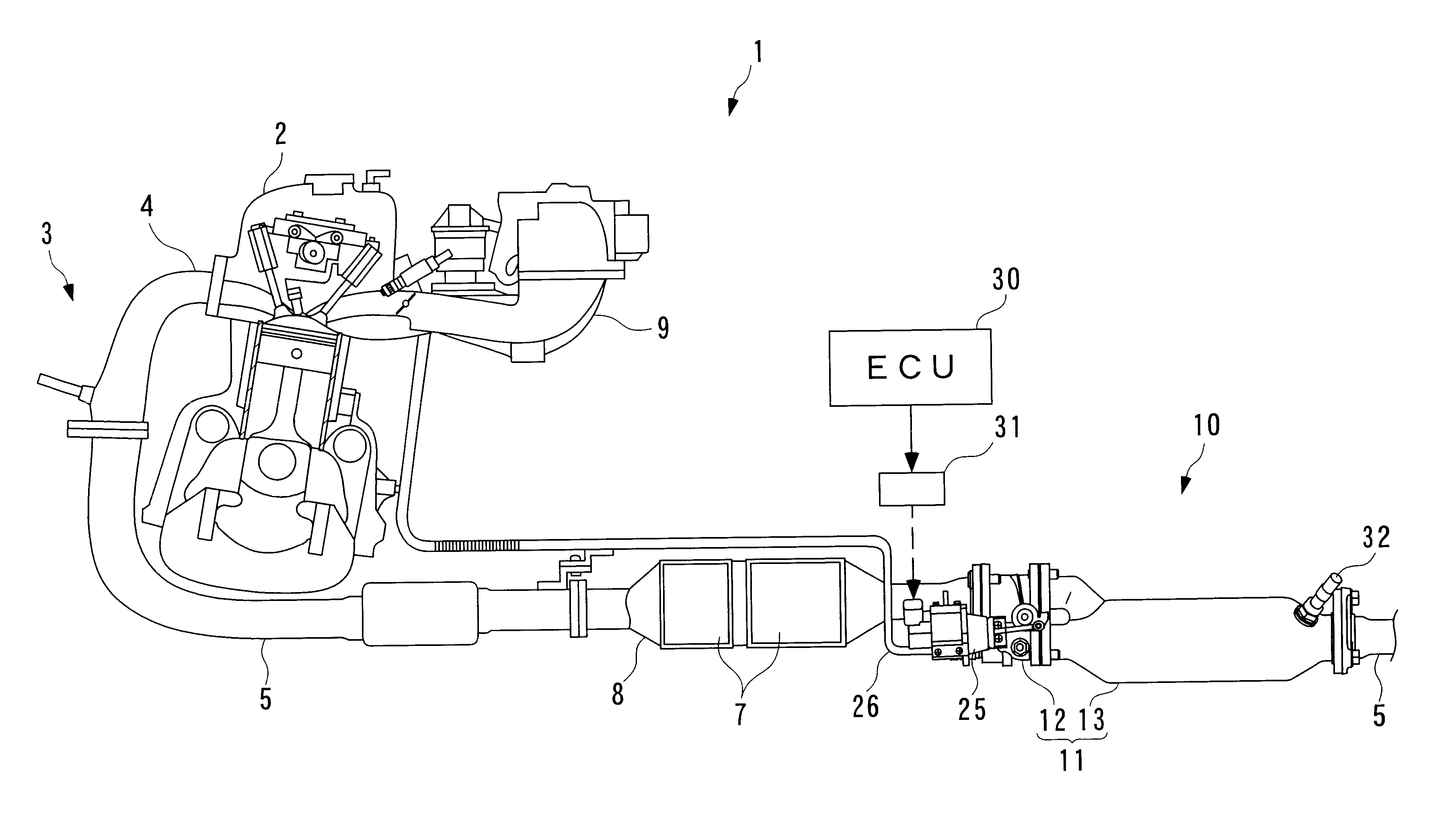
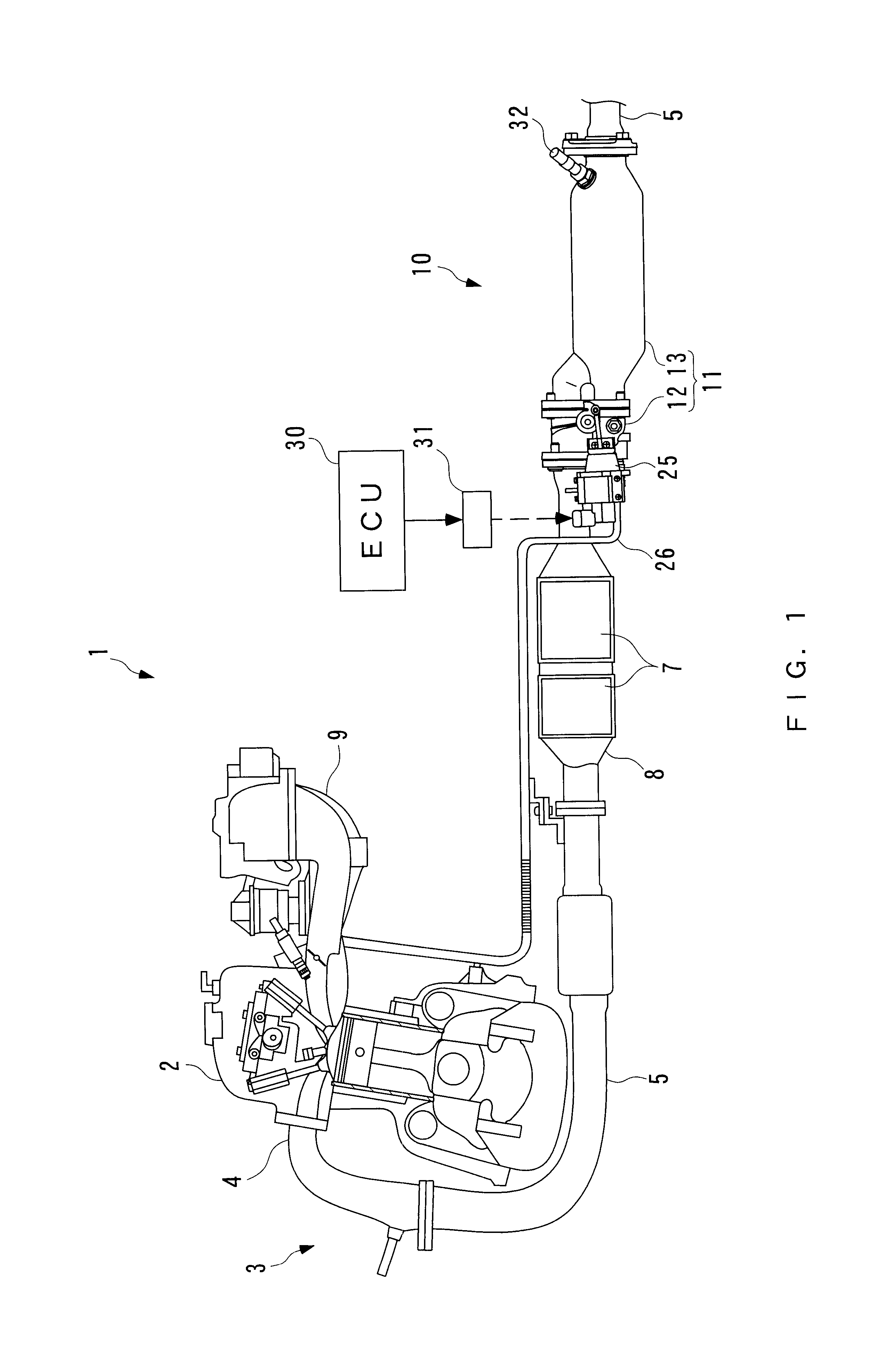
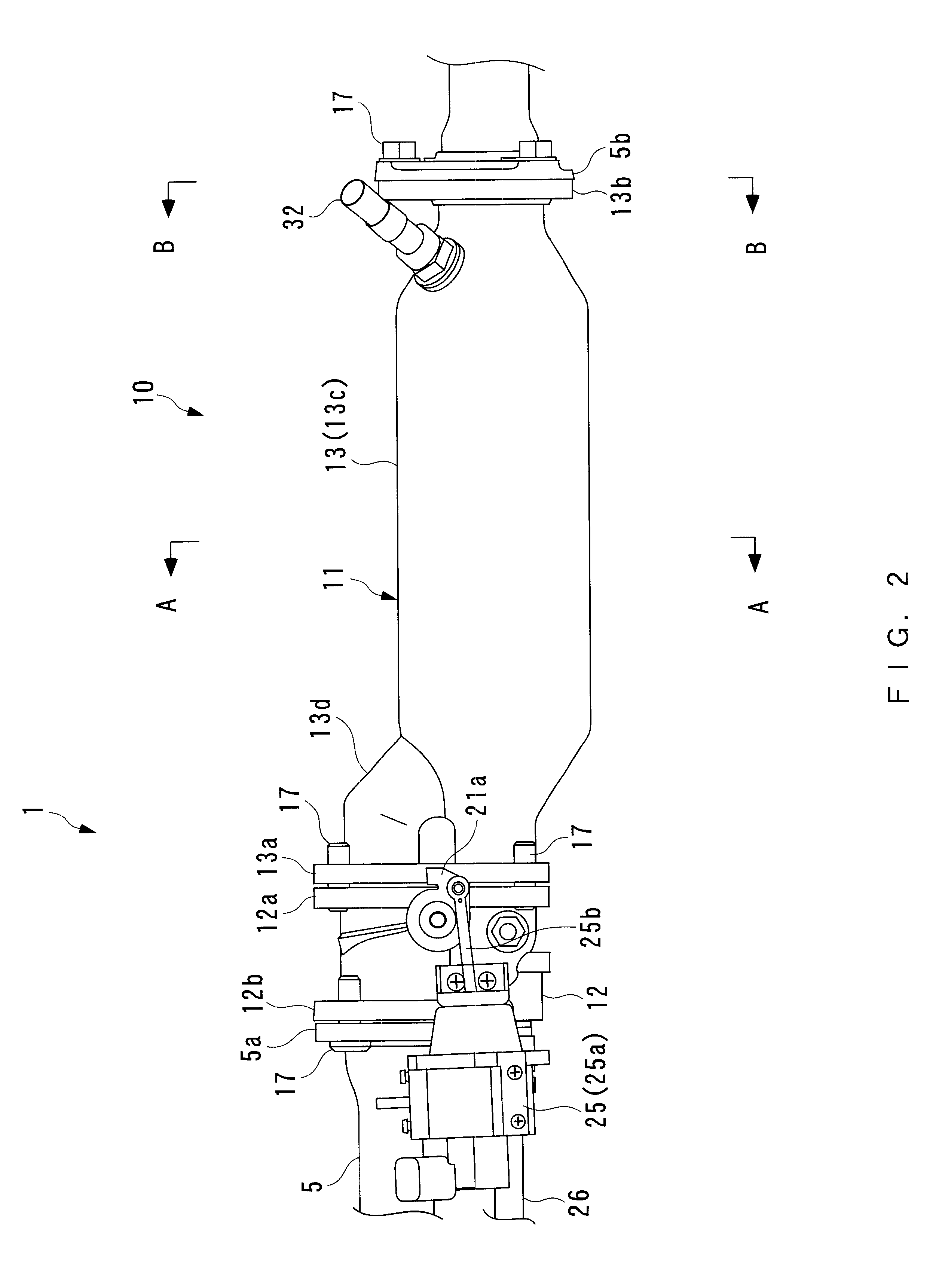
Exhaust gas purifying apparatus for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS6422006B2Full recoveryIncrease exhaust resistanceInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusDesorptionExternal combustion engine
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com